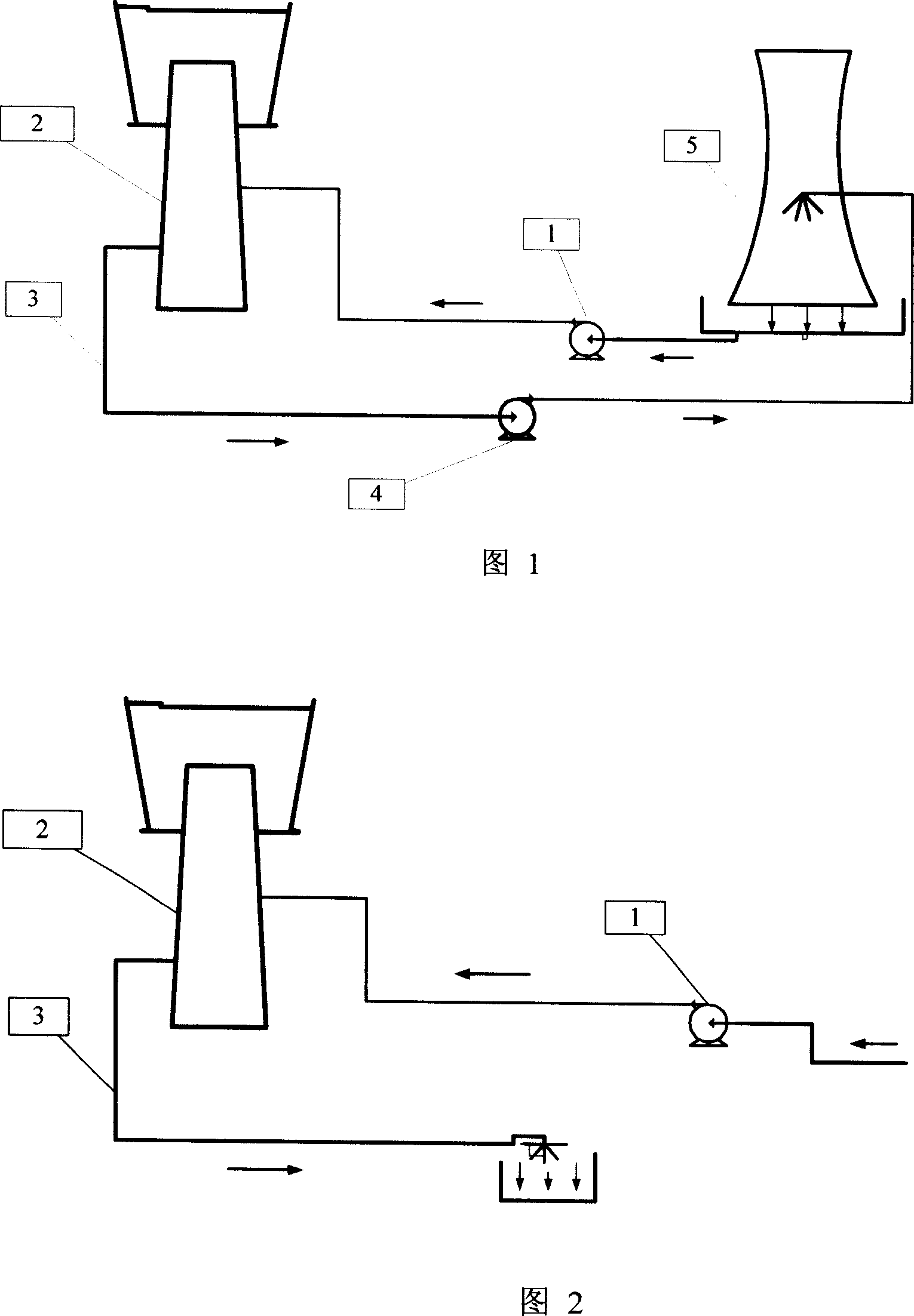
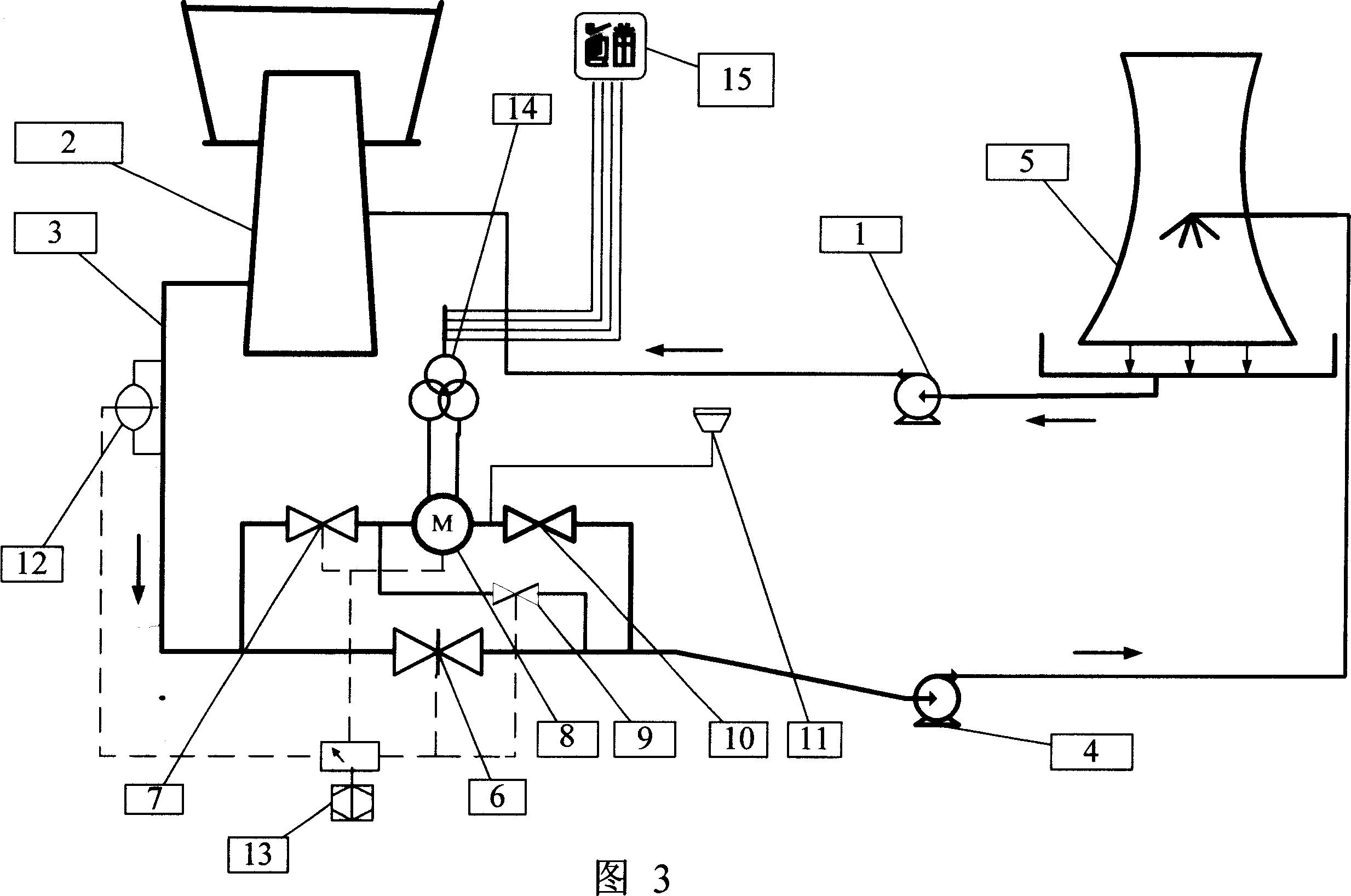
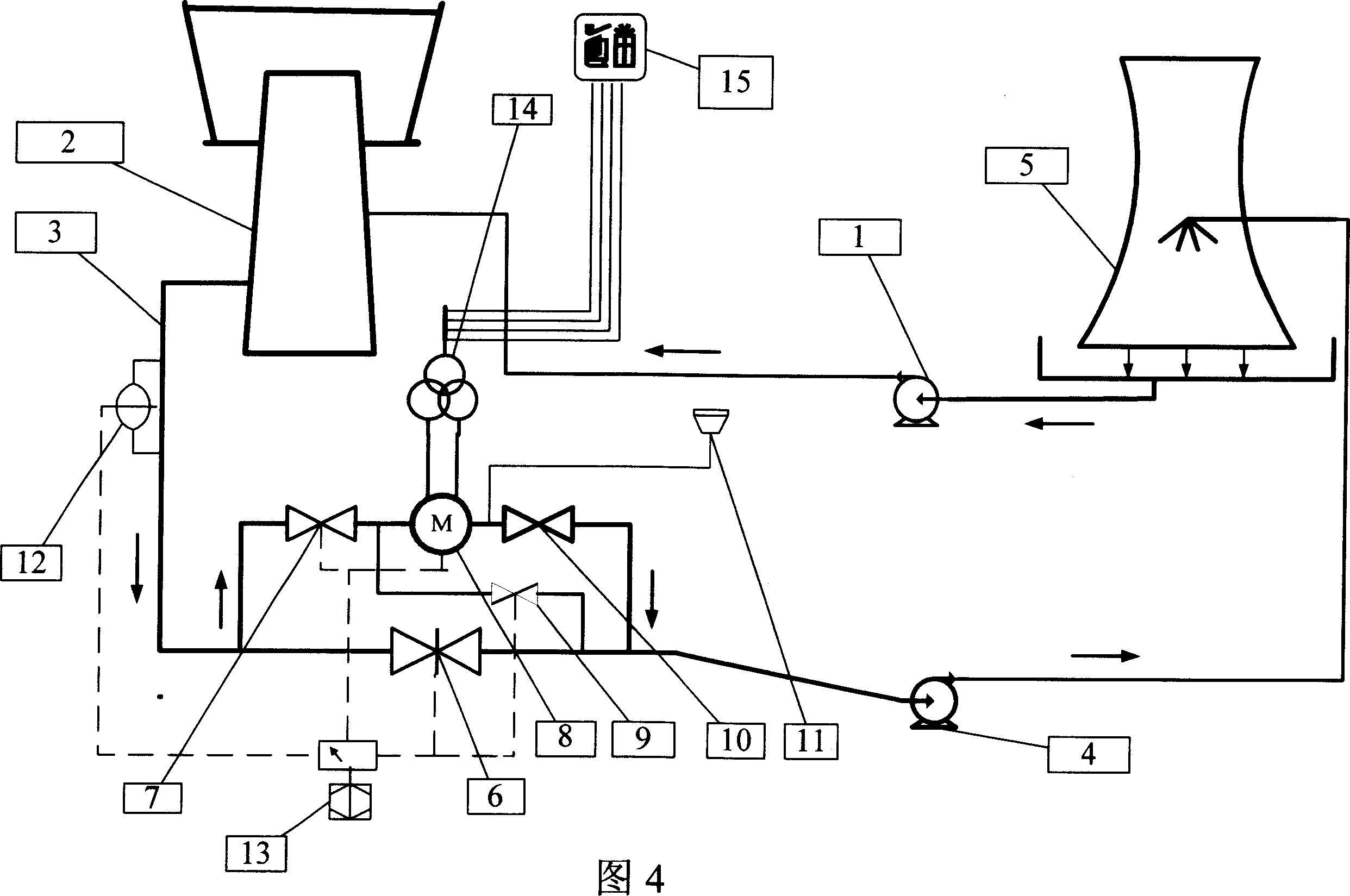
Patents
Literature
896results about "Cooling devices" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
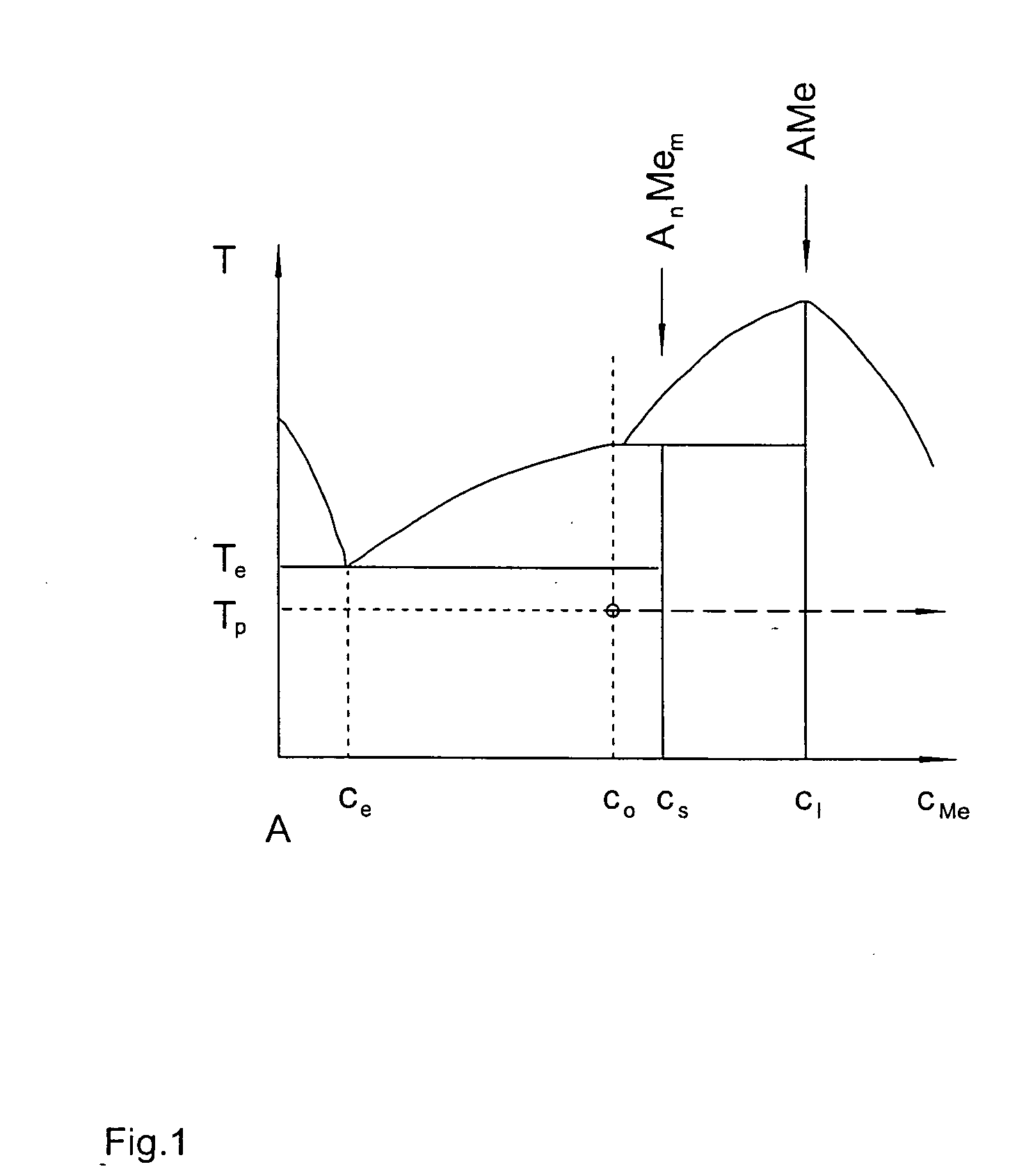
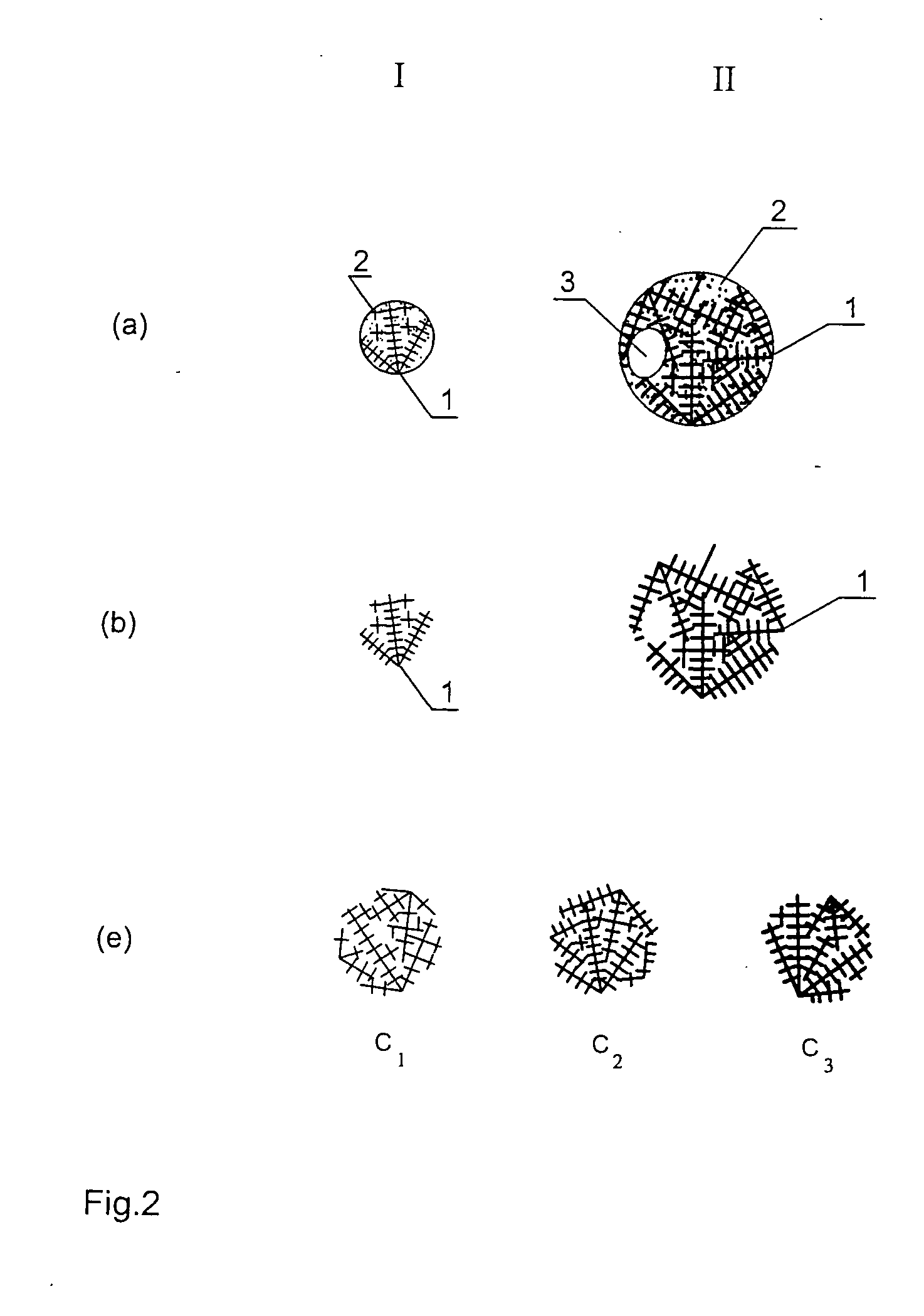
Iron production method of operation in a rotary hearth furnace and improved furnace apparatus
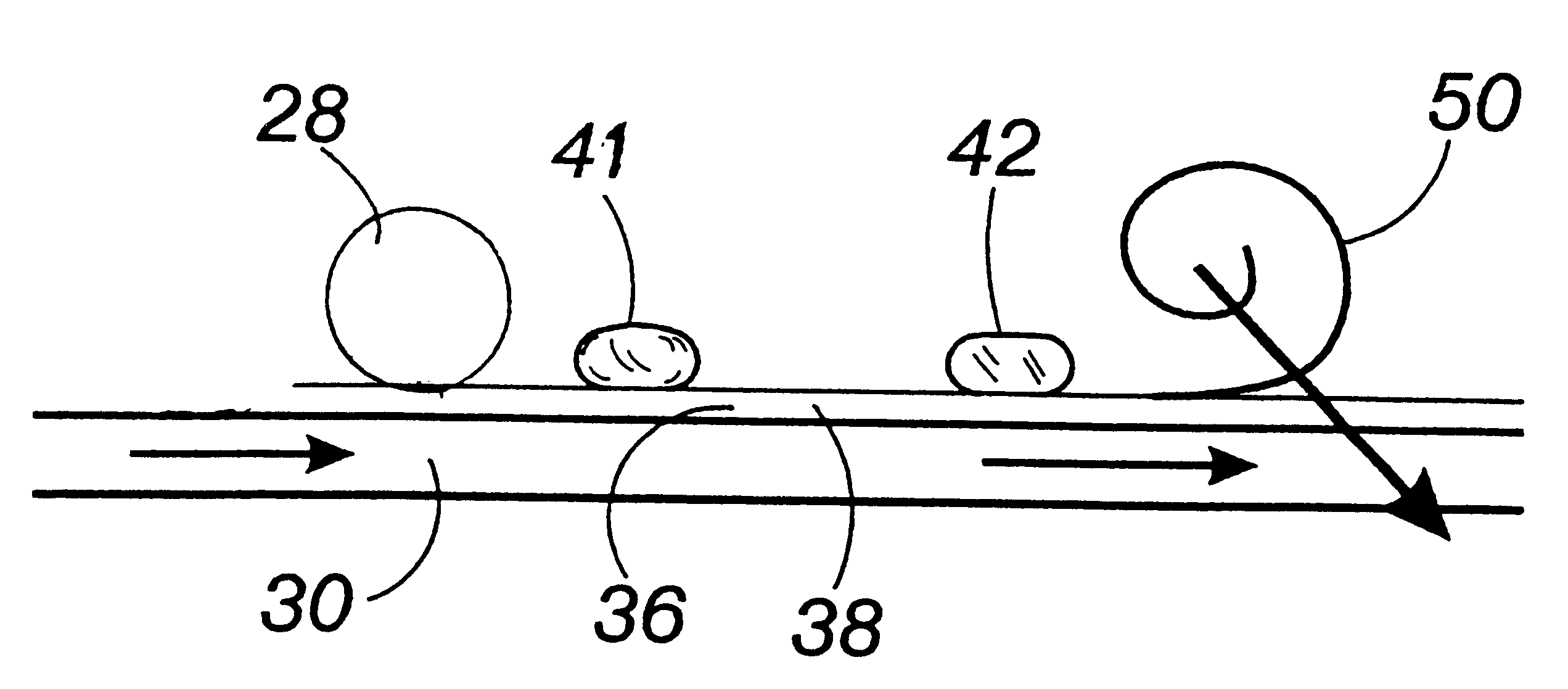
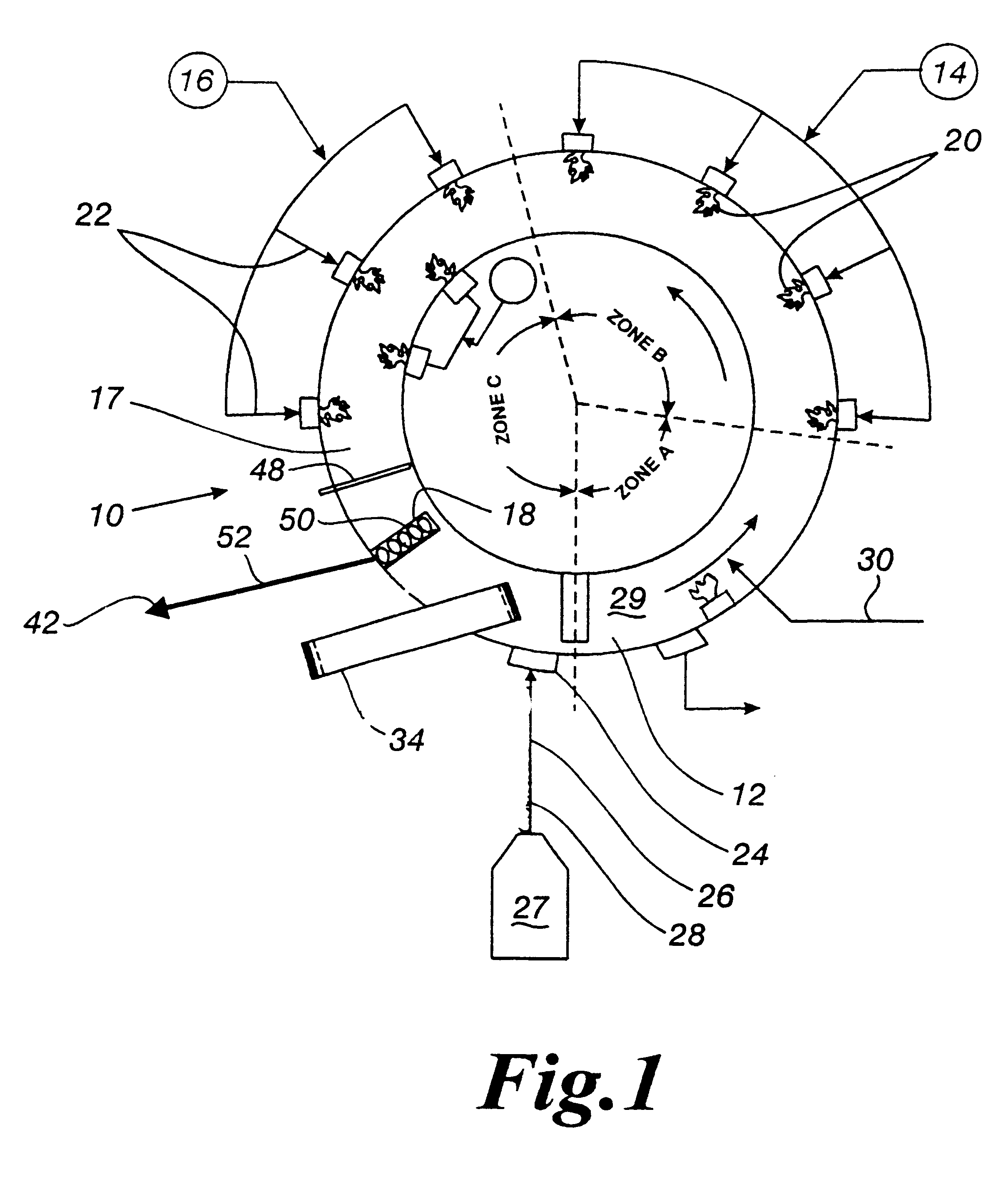
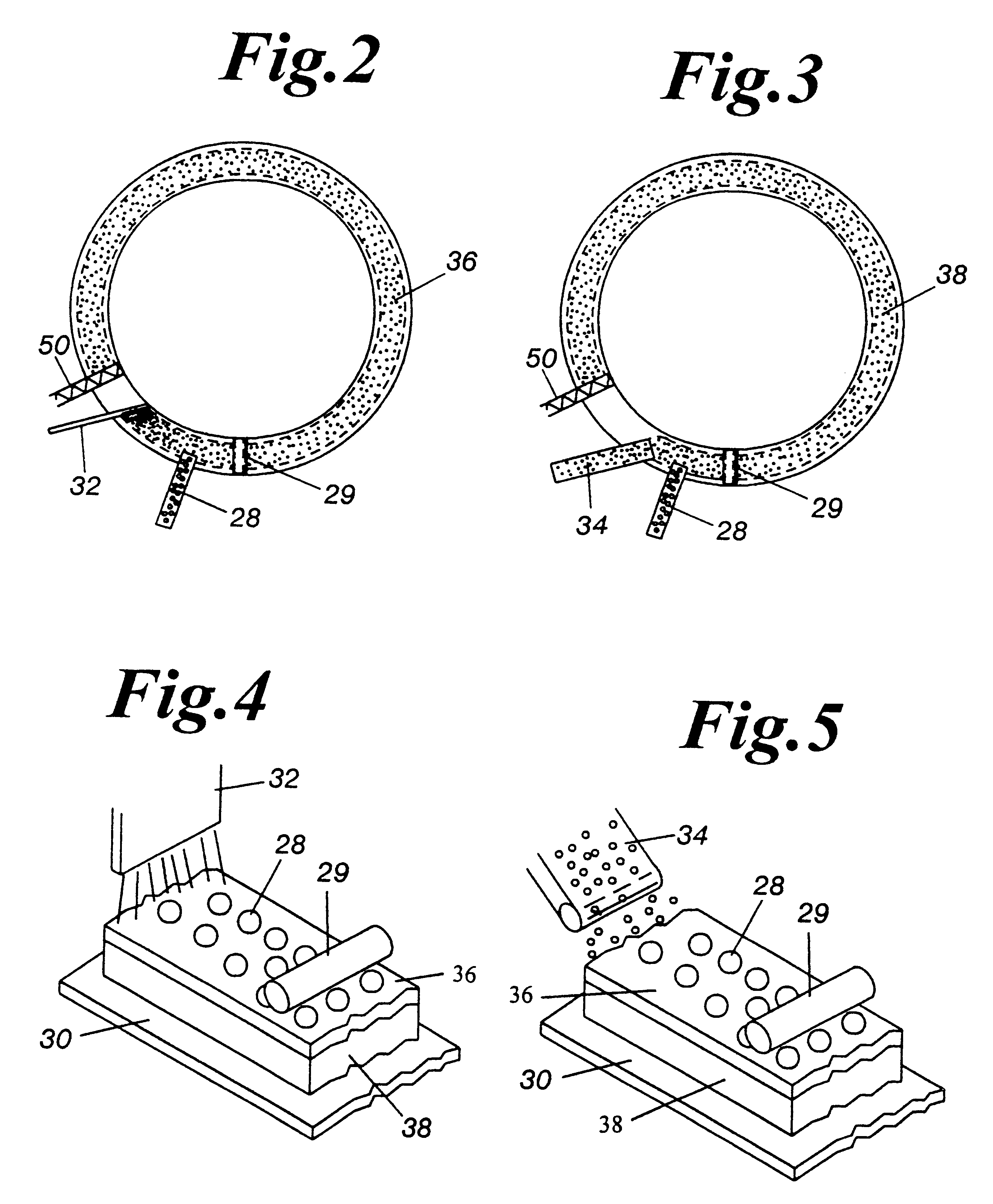
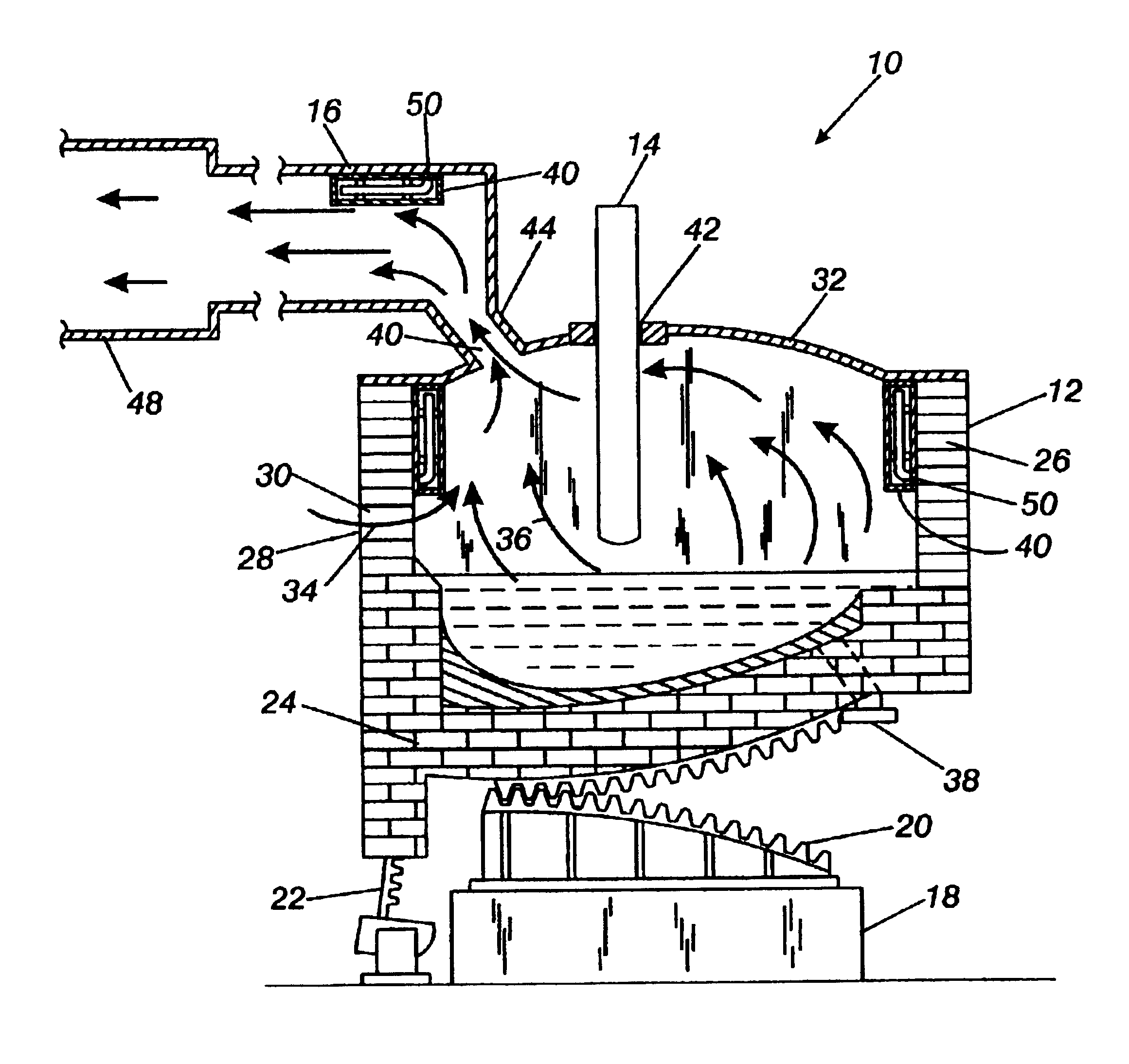
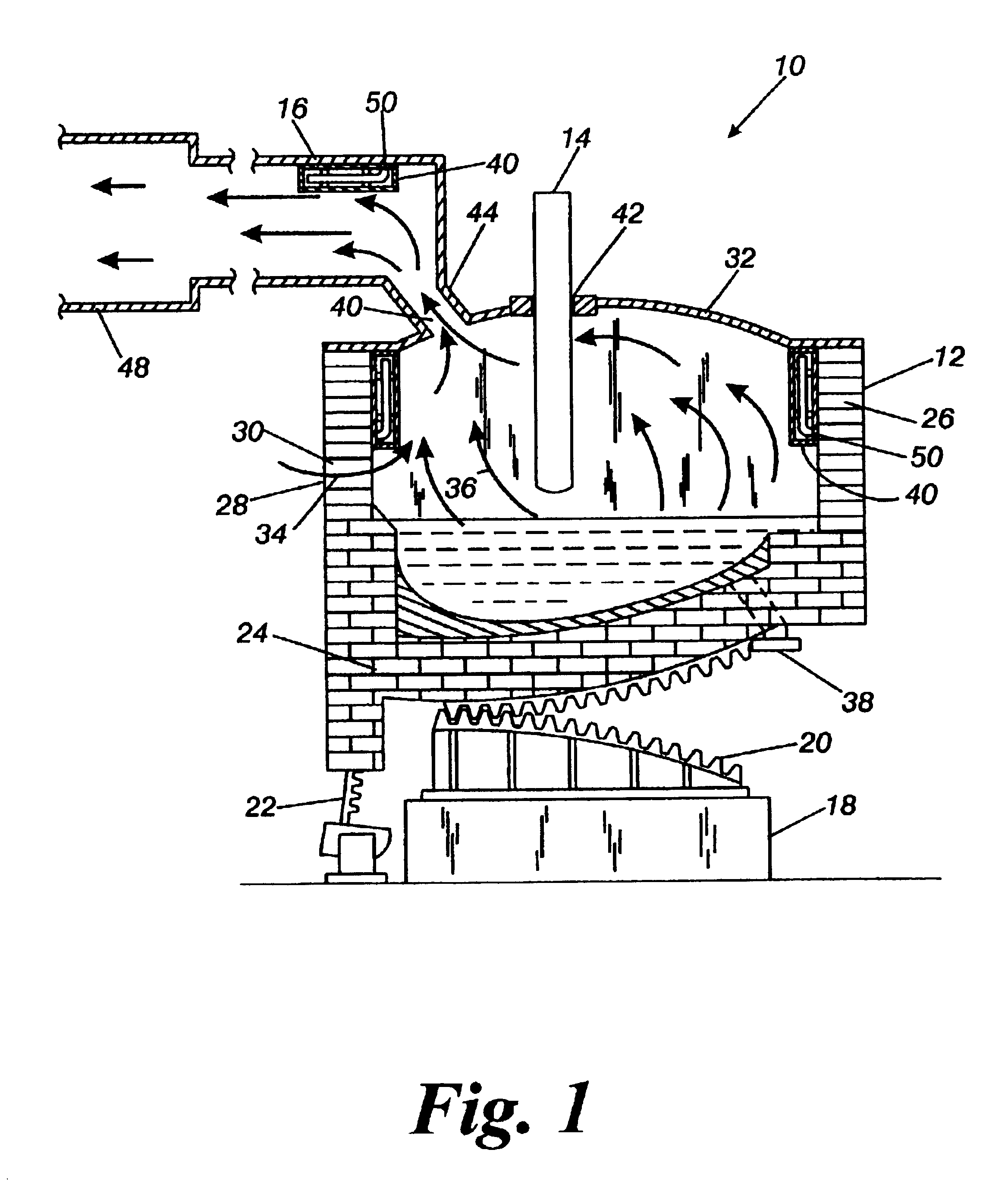
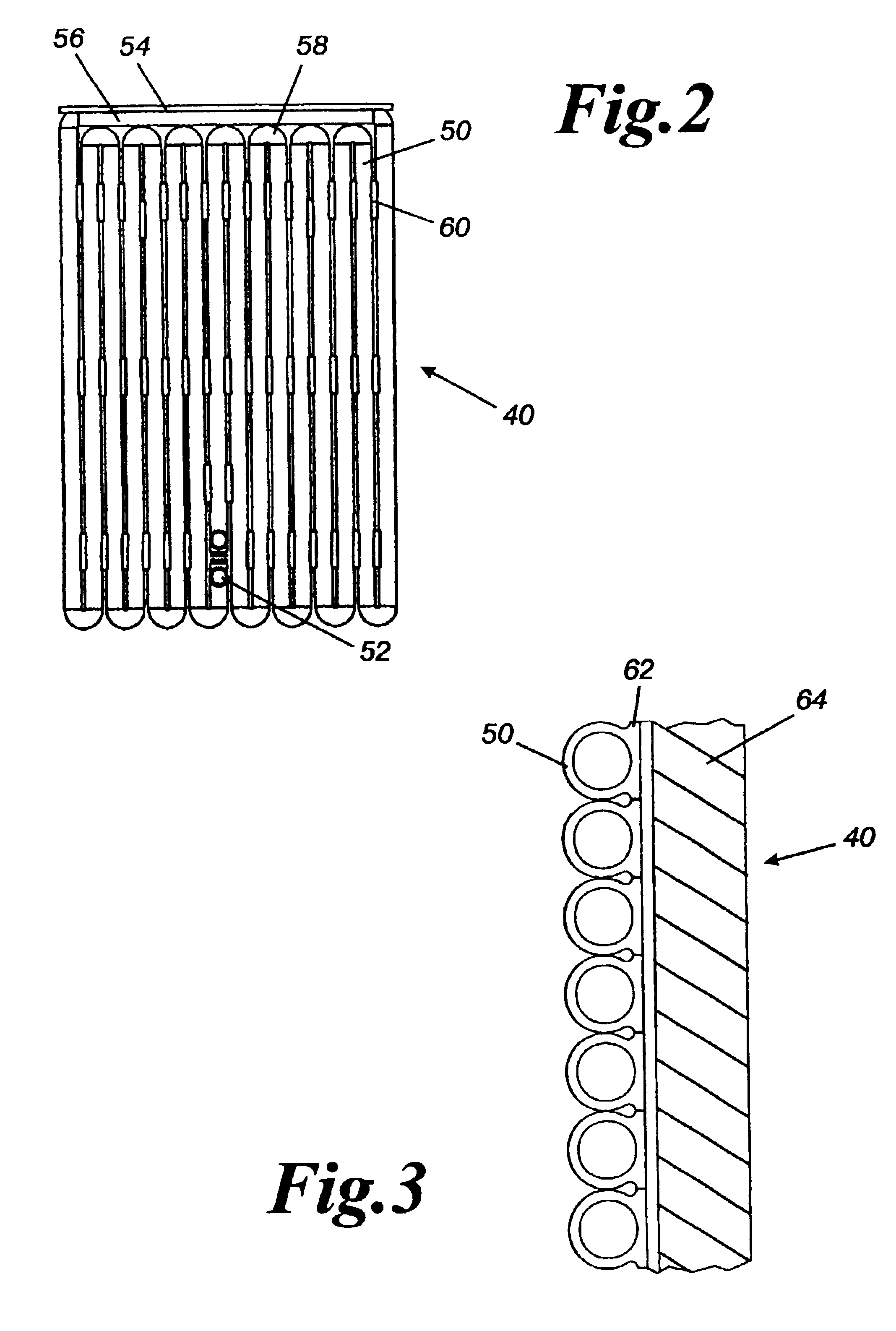
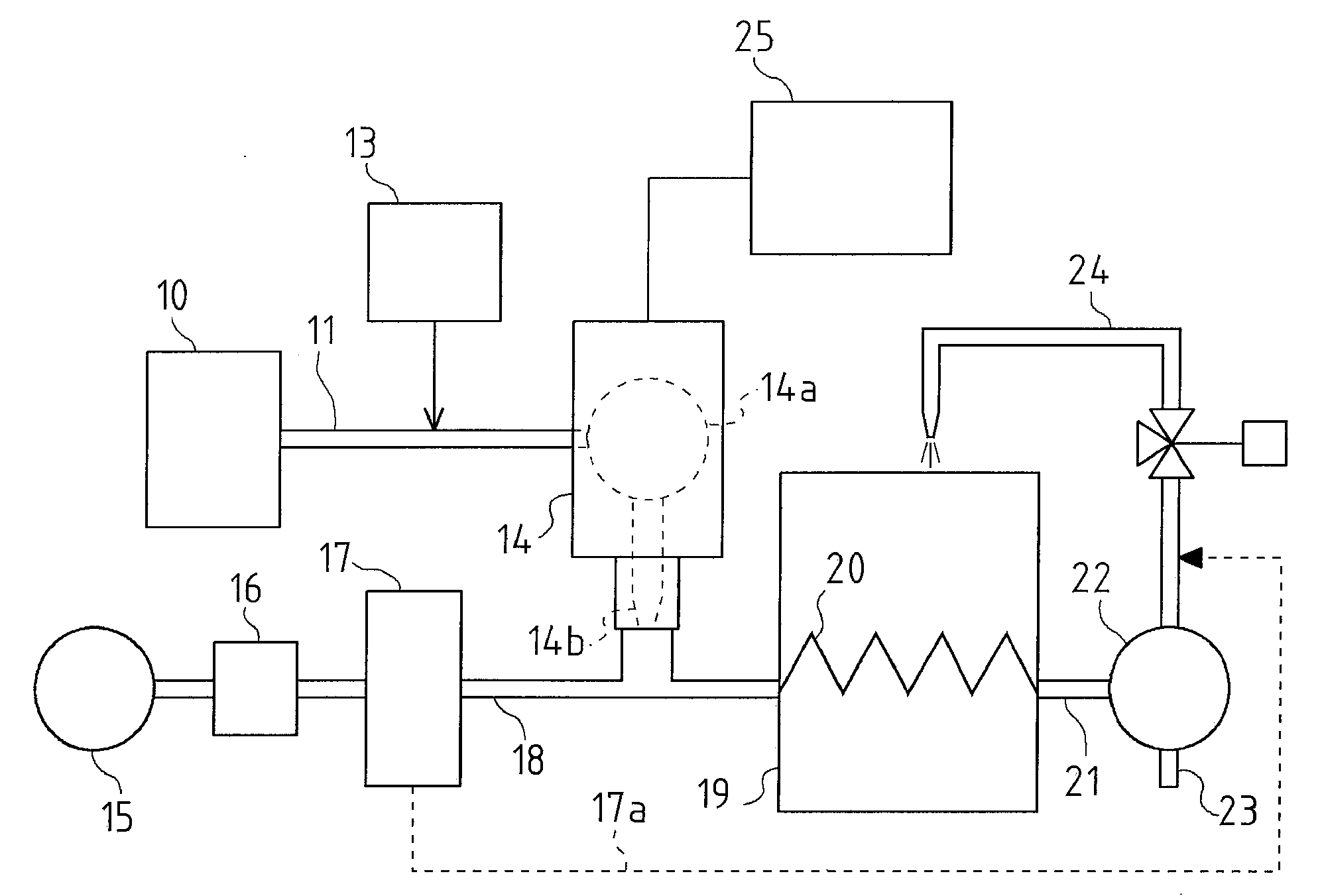
The present invention is an apparatus and method for the direct reduction of iron oxide utilizing a rotary hearth furnace to form a high purity carbon-containing iron metal button. The hearth layer may be a refractory or a vitreous hearth layer of iron oxide, carbon, and silica compounds. Additionally, coating materials may be introduced onto the refractory or vitreous hearth layer before iron oxide ore and carbon materials are added, with the coating materials preventing attack of the molten iron on the hearth layer. The coating materials may include compounds of carbon, iron oxide, silicon oxide, magnesium oxide, and / or aluminum oxide. The coating materials may be placed as a solid or a slurry on the hearth layer and heated, which provides a protective layer onto which the iron oxide ores and carbon materials are placed. The iron oxide is reduced and forms molten globules of high purity iron and residual carbon, which remain separate from the hearth layer. An improved apparatus includes a cooling plate that is placed in close proximity with the refractory or vitreous hearth layer, cooling the molten globules to form iron metal buttons that are removed from the hearth layer. The improvements due to the present apparatus and method of operation provide high purity iron and carbon solid buttons, which are separate from slag particulates, and discharged without significant loss of iron product to the interior surfaces of the furnace.
Owner:MIDREX INT B V ROTTERDAM
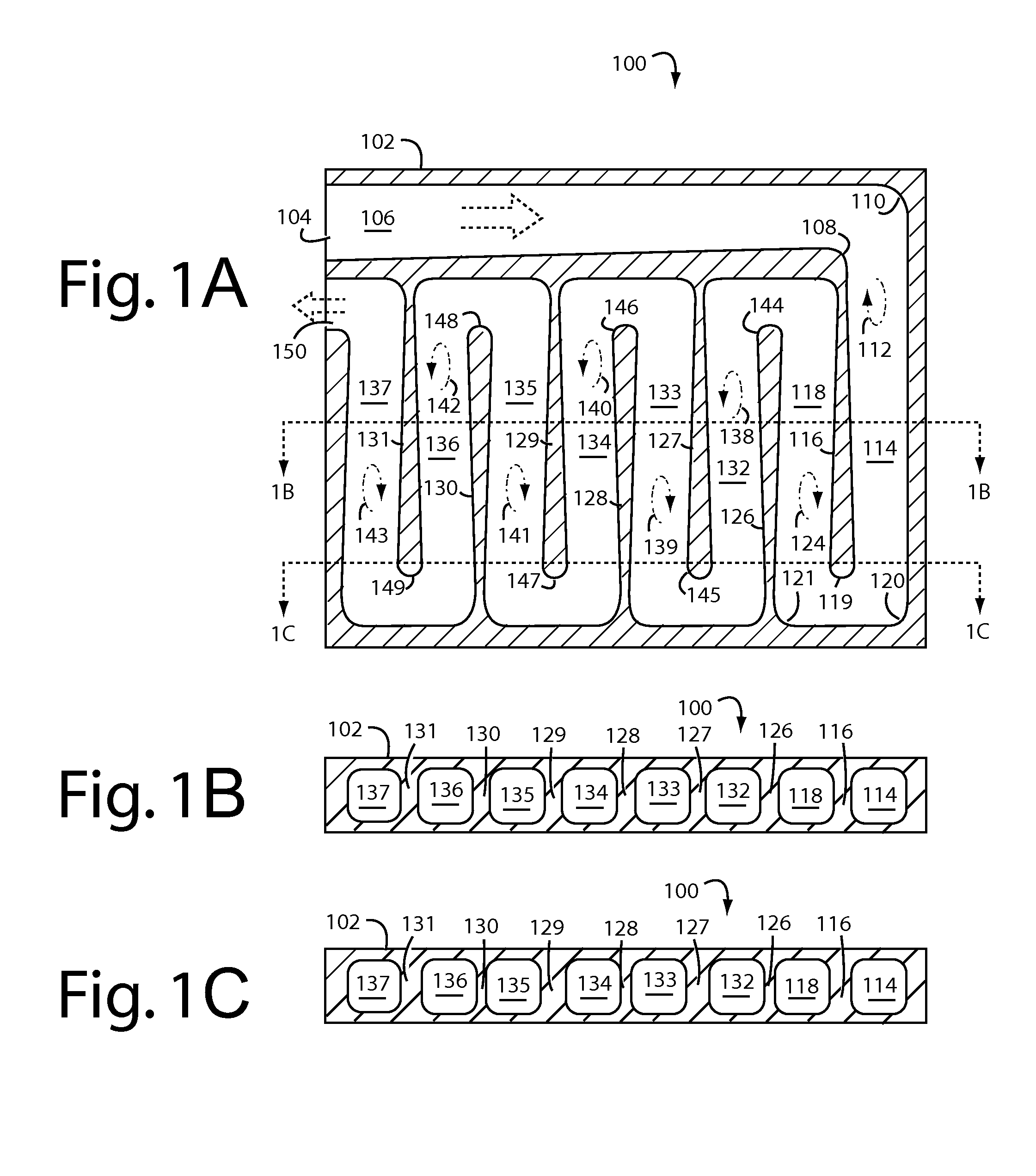
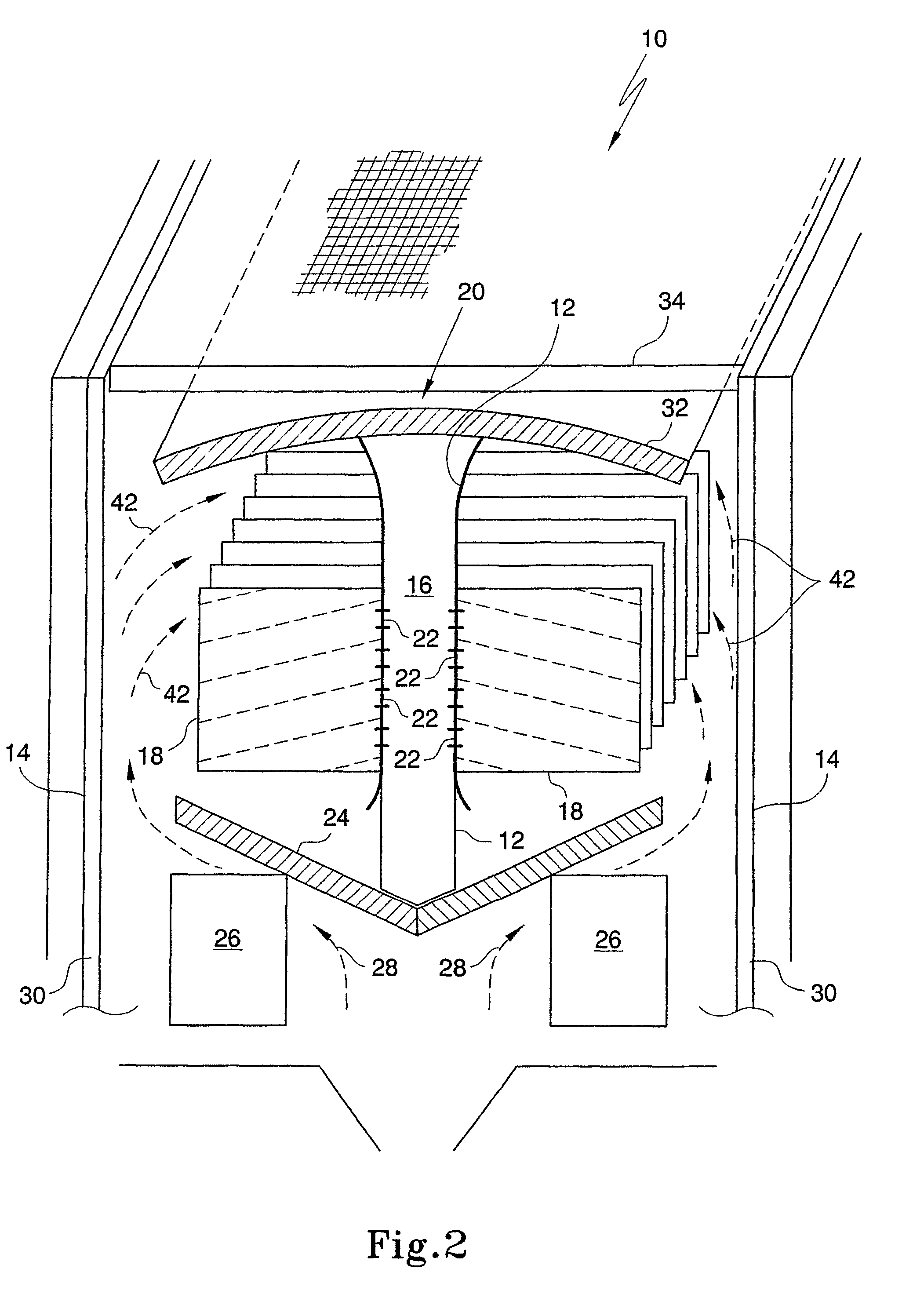
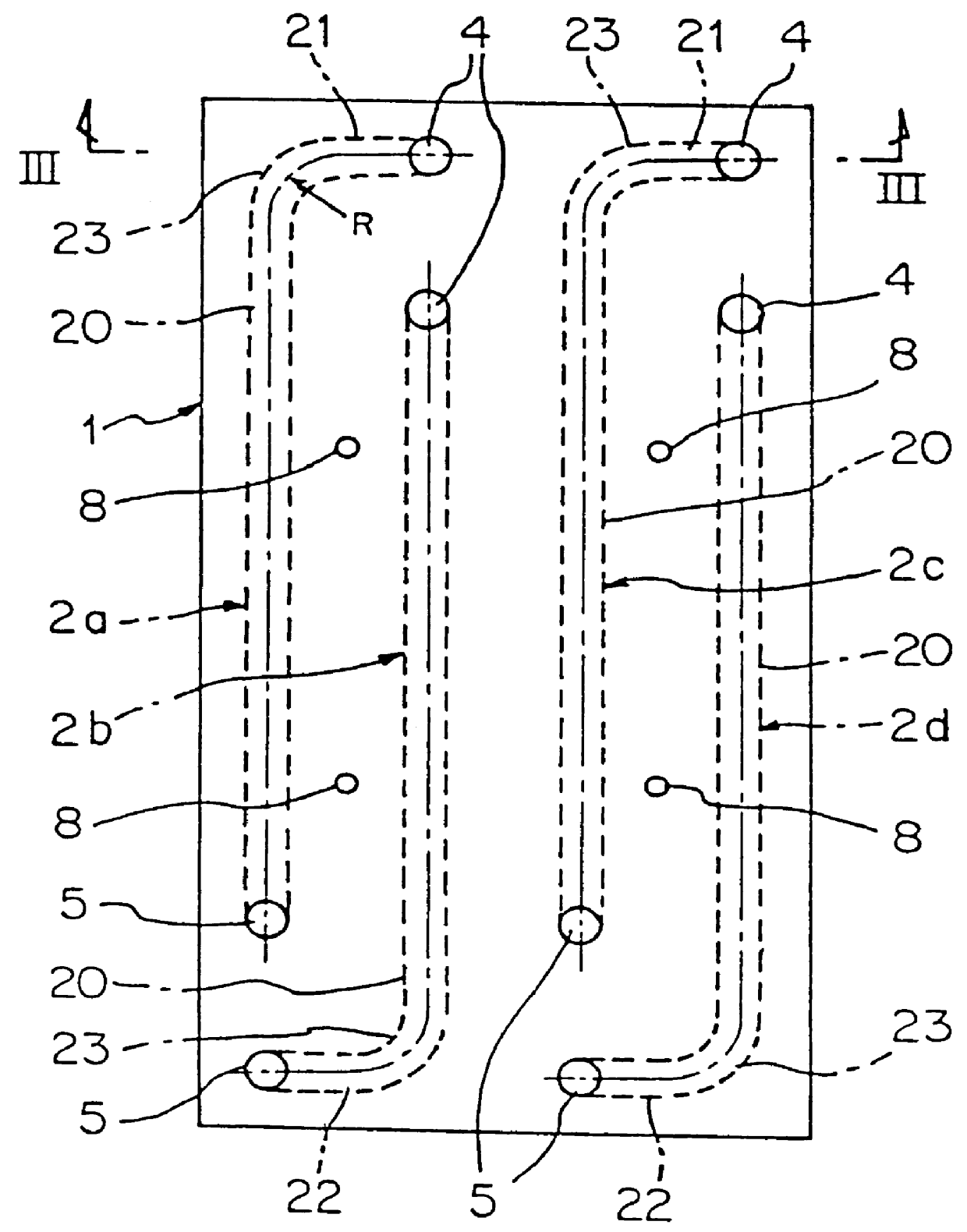
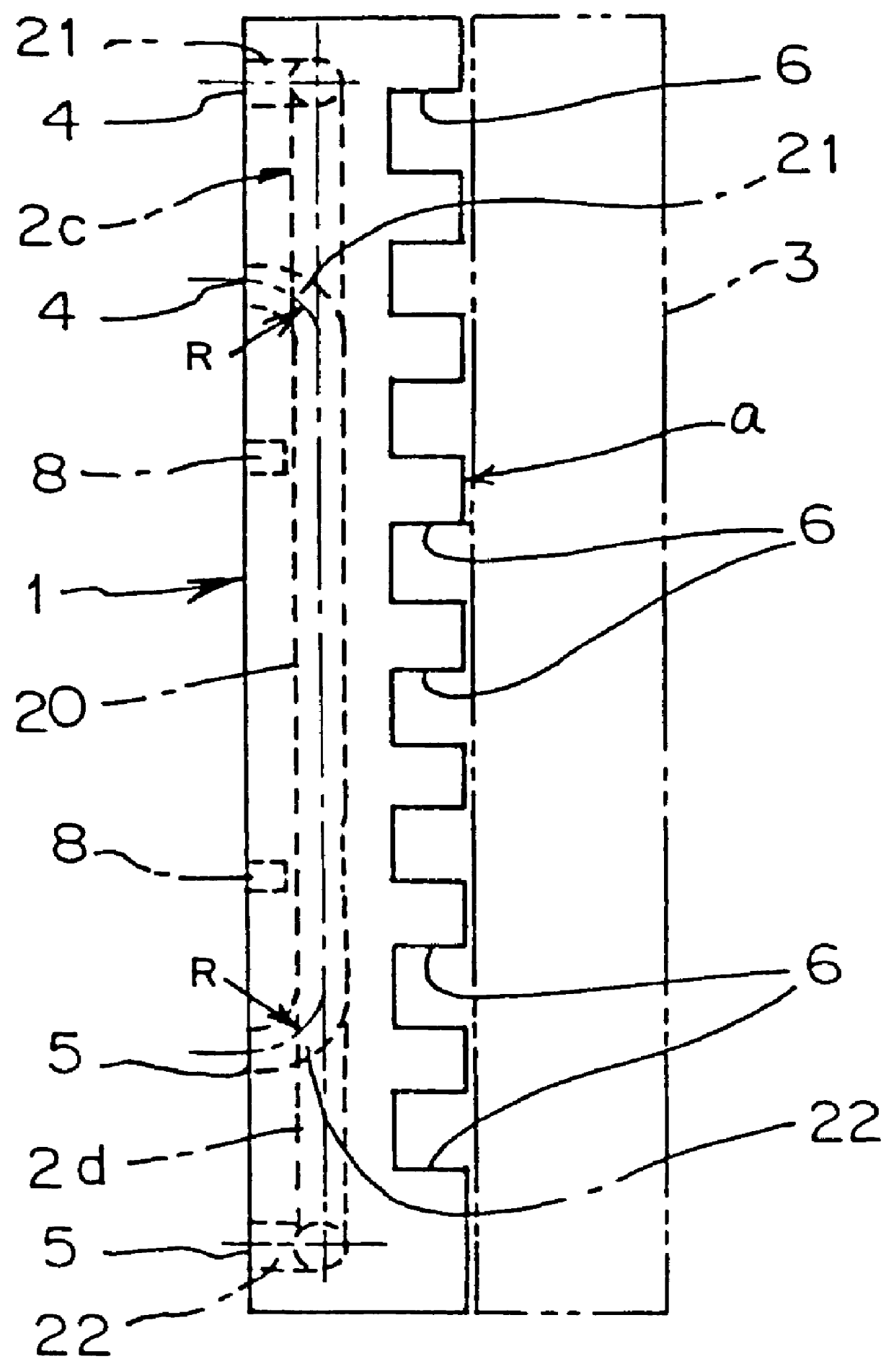
Eddy-free high velocity cooler
A cooling system comprises serpentine cooling fluid passages cast into a work piece with carefully controlled turning radii and profiles. Individual interdigitated baffles are contoured in the plane of coolant flow to have walls that thicken and then round off at their distal ends. The outside radii at these turns is similarly rounded and controlled such that the coolant flow will not be swirled into eddies.
Owner:MACRAE ALLAN J
Heat exchanger
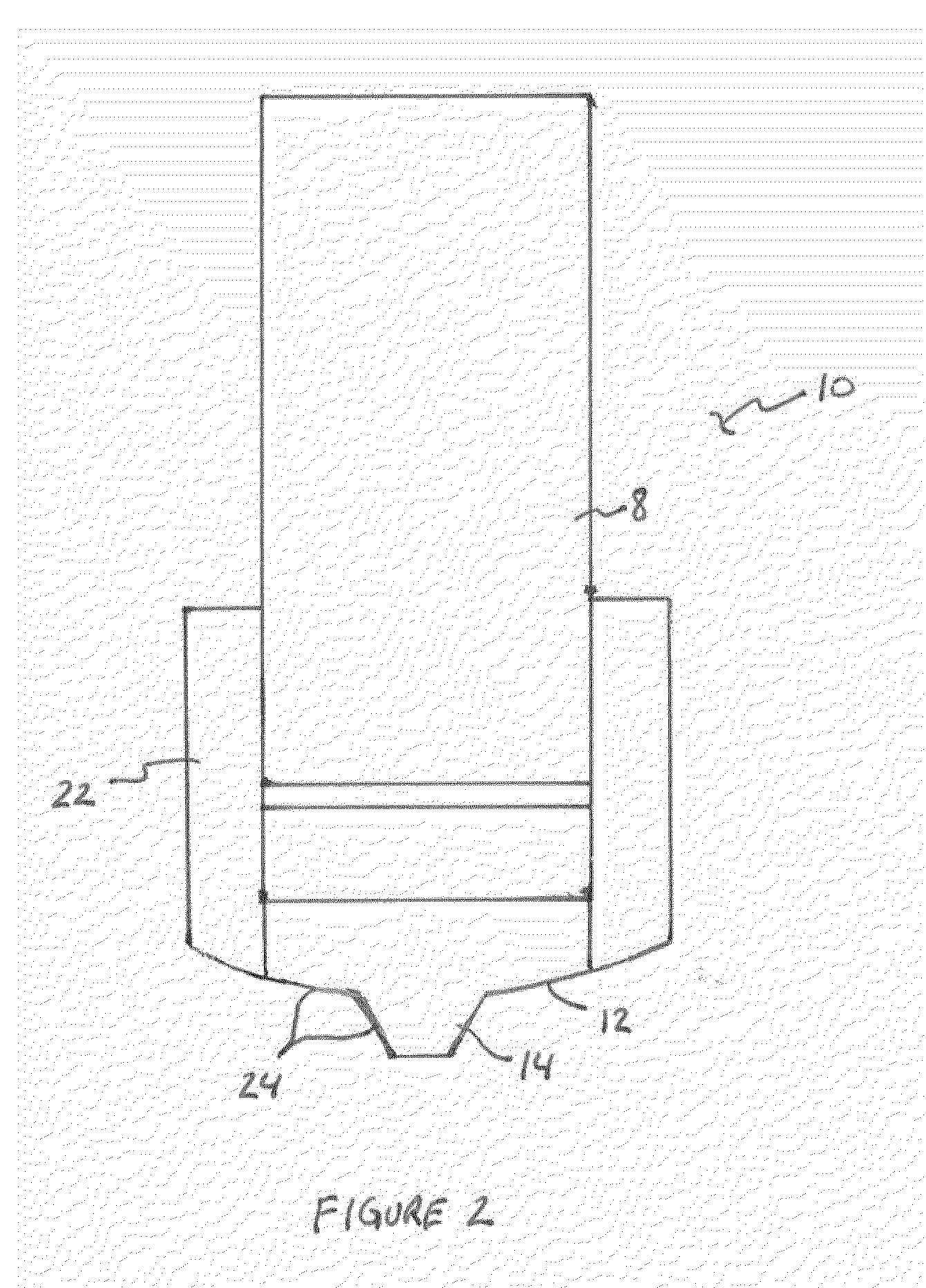
ActiveUS7901617B2Lower overall pressure dropImprove heat transfer performanceBlast furnace detailsManufacturing convertersEngineeringCooling fluid
A heat exchanger 10 includes a conduit 12 for conveying cooling fluid relative to a body to be cooled. A heat transfer arrangement 62 is arranged in communication with an interior of the conduit 12, the heat transfer arrangement 62 and the conduit 12 together defining an assembly that is mountable adjacent the body to be cooled, convective heat exchange occurring, in use, due to movement of the cooling fluid relative to the body and the heat transfer arrangement 62 of the assembly and radiant heat exchange occurring between the body and at least part of the heat transfer arrangement 62 of the assembly.
Owner:ENPOT HLDG LTD
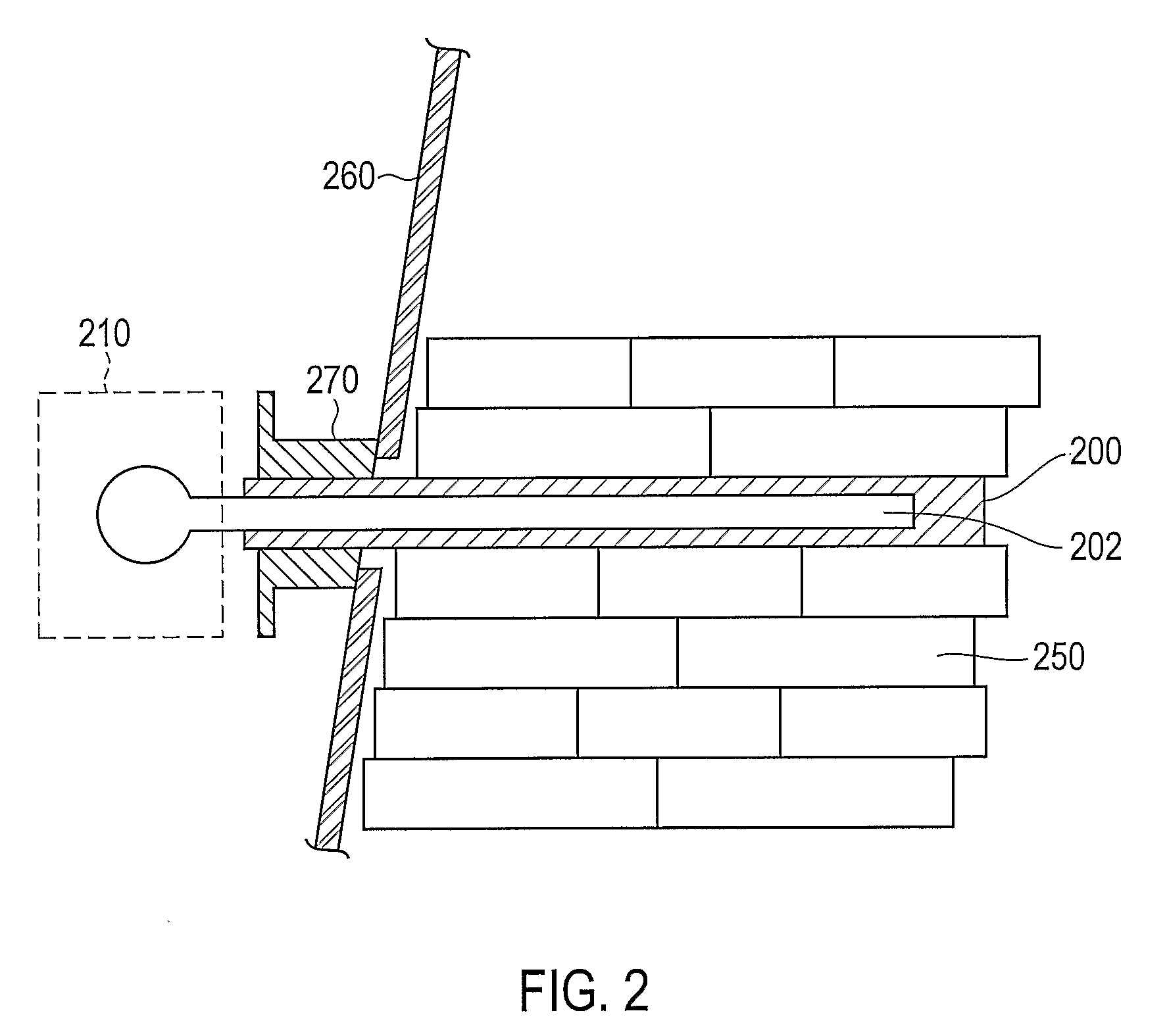
Systems and Methods of Cooling Blast Furnaces
InactiveUS20080111287A1Complicates designIncrease costBlast furnace detailsFurnace cooling arrangementsNuclear engineeringHeat pipe
Systems and methods provide a cooling device for a blast furnace that may prevent an excessive amount of coolant from entering the blat furnace and may be easily installed in a conventional blast furnace. Systems and methods may provide a cooling device for a blast furnace that may prevent an excessive amount of coolant from entering the blast furnace and may be simple and cost effective to manufacture. The end of a heat pipe (202) that is outside of the furnace may be configured to interact with a heat sink (210). The heat sink (210) may be for example, a separate amount of coolant that is circulated outside of the furnace, an evaporative cooling system, and / or any other system or method of cooling the heat pipe (202) that transfers heat from the heat pipe (202) to the heat sink (210). Because the coolant within the heat pipe (202) is sealed within the heat pipe (202), only the small, fixed amount of coolant that. is within the heat pipe (202) will enter the furnace should the cooling plate (200) rupture. Thus, substantial damage to the furnace, extensive repairs, and / or long periods of non-production may be avoided.
Owner:ANDCO METAL IND PROD
Iron production method of operation in a rotary hearth furnace and improved furnace apparatus
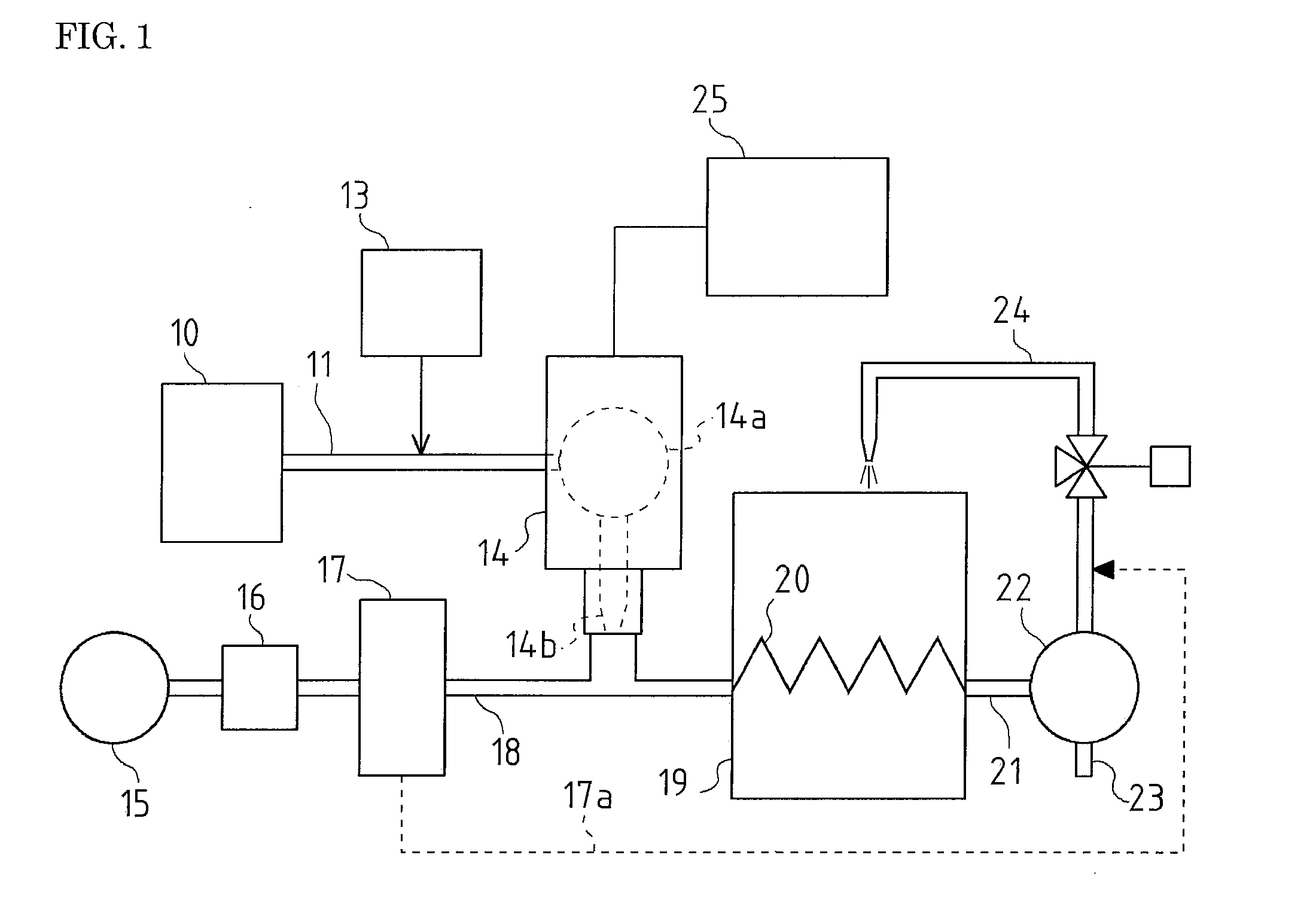
The present invention is an apparatus and method for the direct reduction of iron oxide utilizing a rotary hearth furnace to form a high purity carbon-containing iron metal button. The hearth layer may be a refractory or a vitreous hearth layer of iron oxide, carbon, and silica compounds. Additionally, coating materials may be introduced onto the refractory or vitreous hearth layer before iron oxide ore and carbon materials are added, with the coating materials preventing attack of the molten iron on the hearth layer. The coating materials may include compounds of carbon, iron oxide, silicon oxide, magnesium oxide, and / or aluminum oxide. The coating materials may be placed as a solid or a slurry on the hearth layer and heated, which provides a protective layer onto which the iron oxide ores and carbon materials are placed. The iron oxide is reduced and forms molten globules of high purity iron and residual carbon, which remain separate from the hearth layer. An improved apparatus includes a cooling plate that is placed in close proximity with the refractory or vitreous hearth layer, cooling the molten globules to form iron metal buttons that are removed from the hearth layer. The improvements due to the present apparatus and method of operation provide high purity iron and carbon solid buttons, which are separate from slag particulates, and discharged without significant loss of iron product to the interior surfaces of the furnace.
Owner:MIDREX INT B V ROTTERDAM
Construction method for internal cooling wall and furnace liner of blast furnace
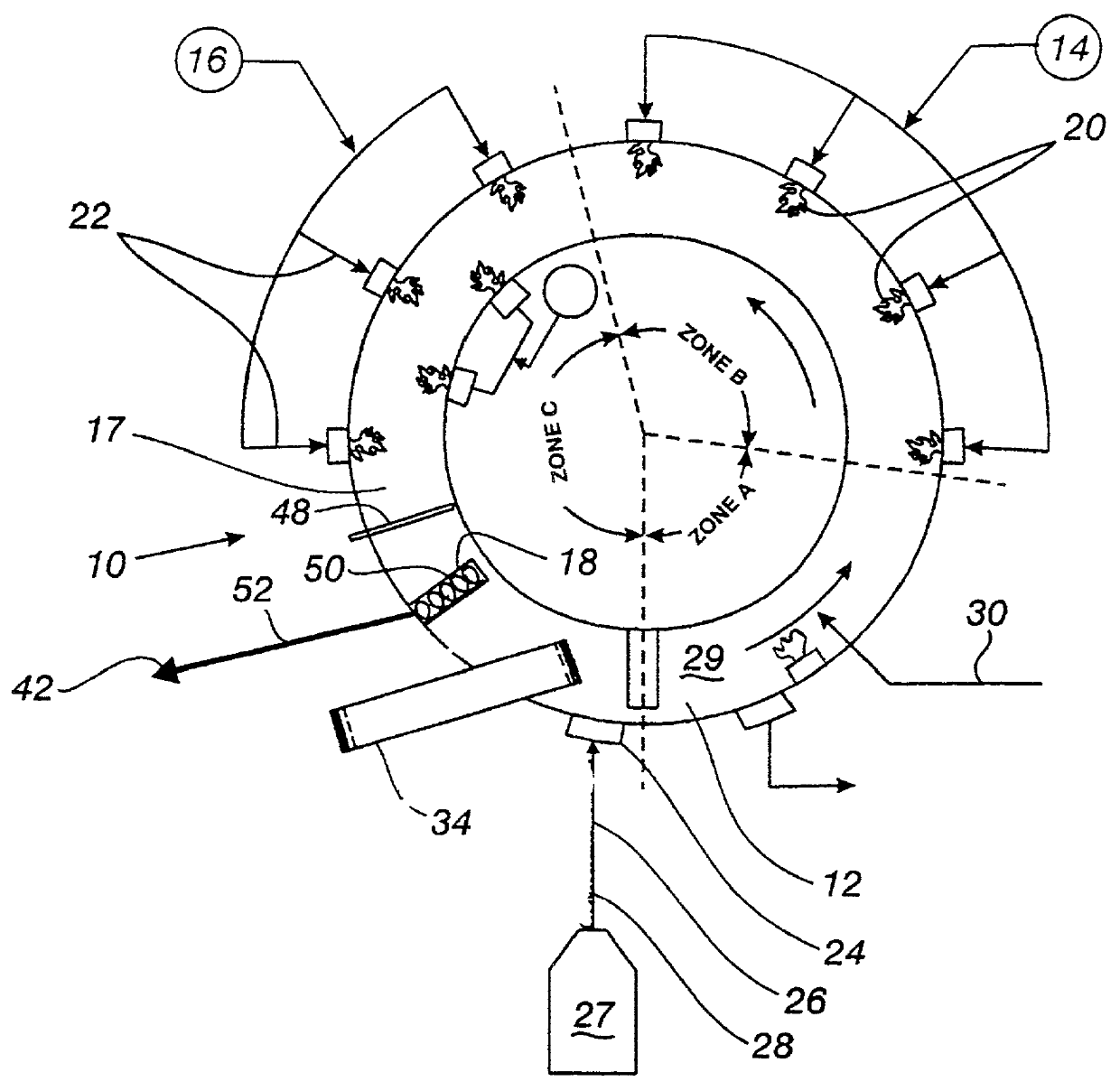
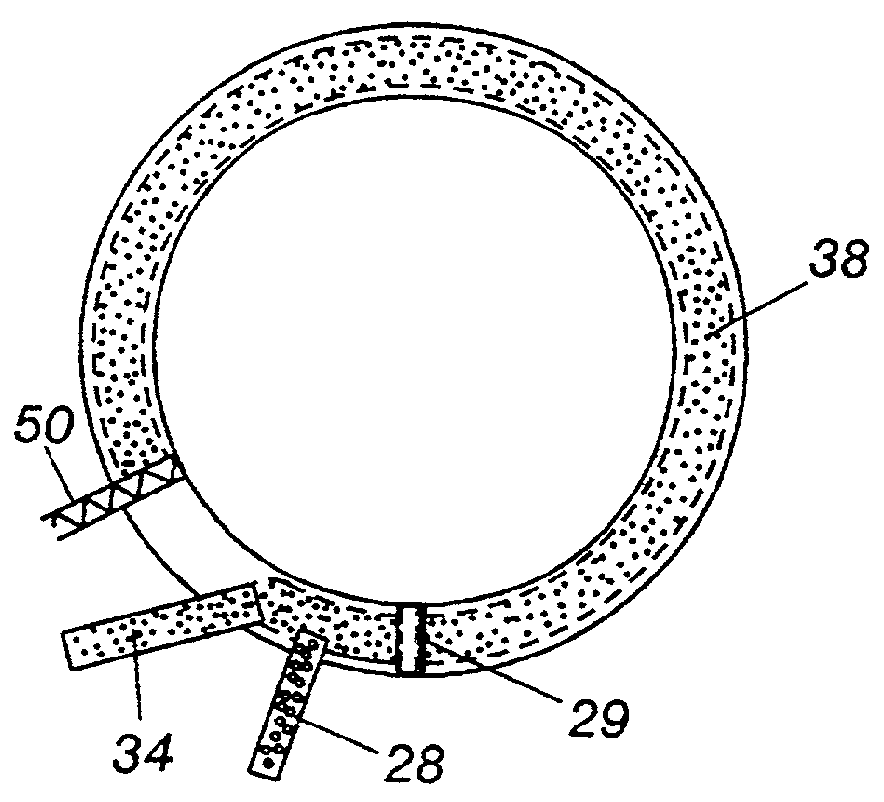
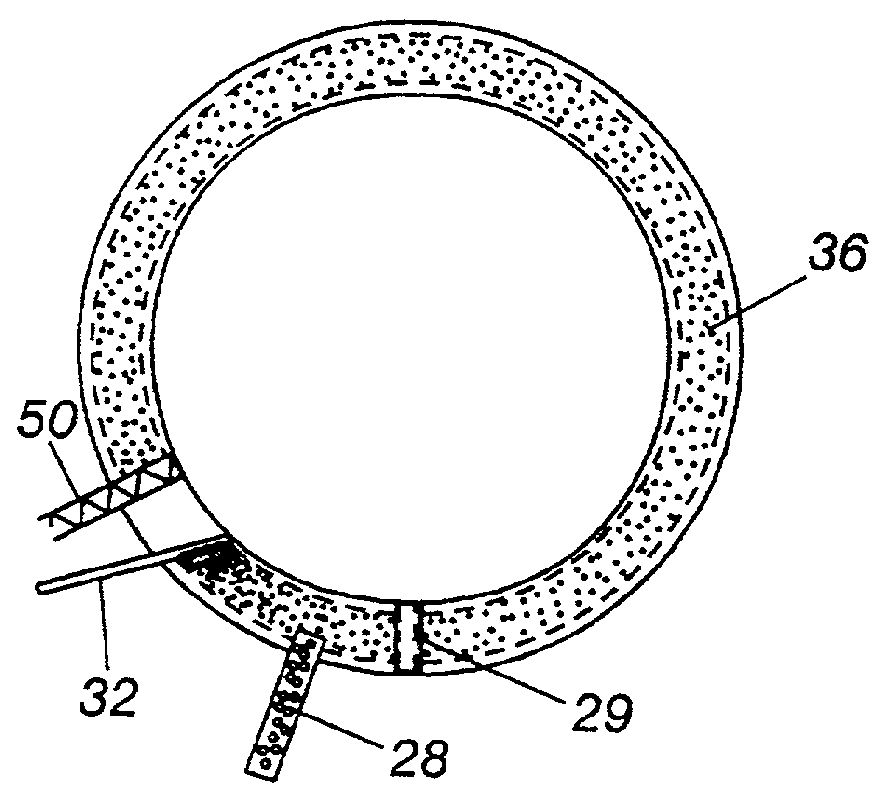
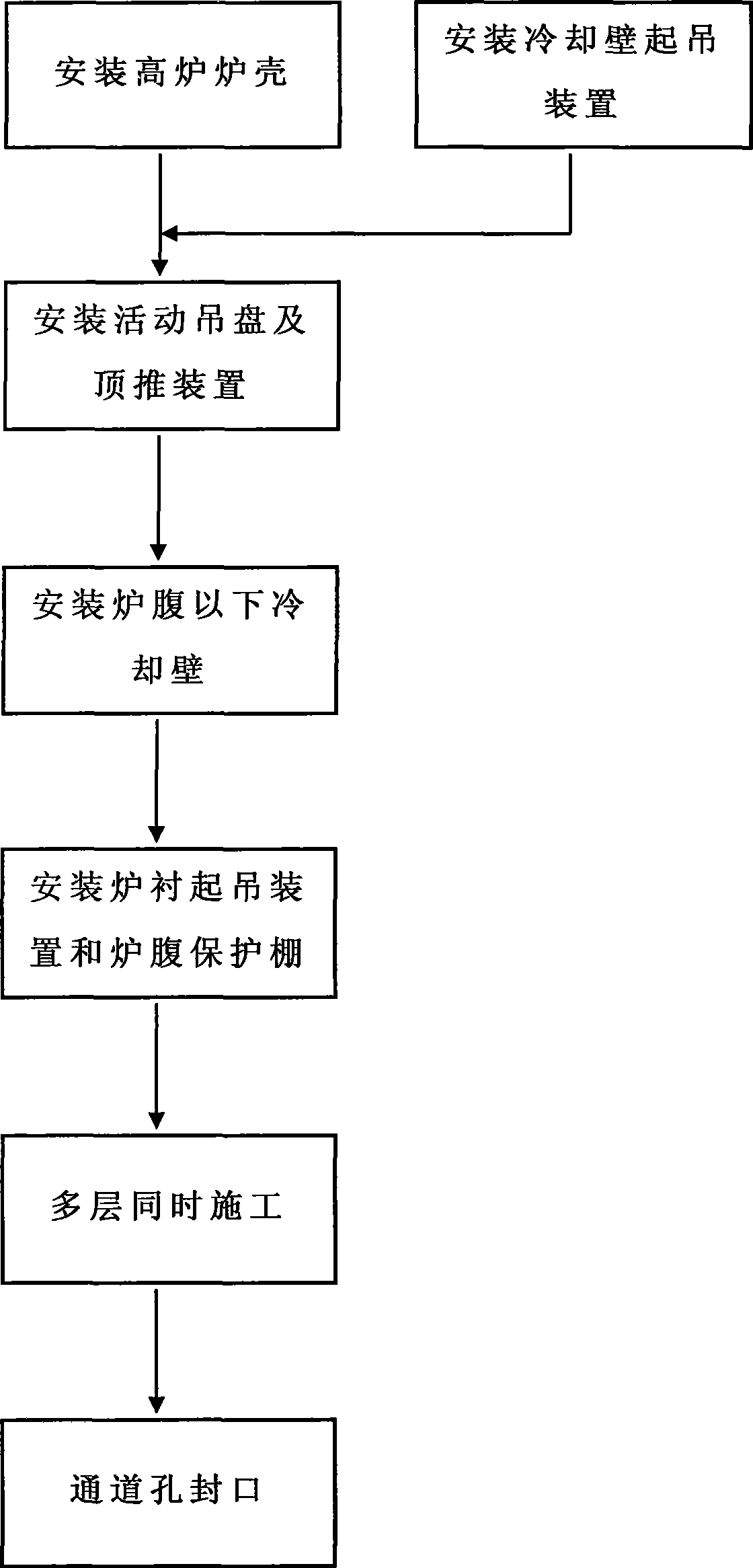
InactiveCN101509049AReduce workloadSave the use of shift feesCooling devicesInternal formsEngineeringBlast furnace
The invention discloses a construction method for blast furnace internal cooling wall and furnace lining. Firstly, an access opening through which the blast furnace internal cooling wall enters into an internal furnace is arranged on the furnace mantle above a blast-furnace tuyere; the cooling wall under a furnace bosh is firstly arranged by ways that a cooling wall lifting appliance arranged at the furnace throat of the internal furnace and a lifting movable swinging tray swinged in the internal furnace firstly, and a furnace bosh protection shed and a furnace lining lifting appliance are arranged at the furnace bosh secondly. Then, and the cooling wall is arranged at the top part of the furnace bosh by the cooling wall lifting appliance and the movable swinging tray, meanwhile the furnace lining construction is carried out at the lower part of the furnace bosh by a furnace lining lifting appliance and the cooling wall except for the access opening is sealed so as to complete the construction of the cooling wall of the access opening. The construction method has the advantages of low cost, convenient operation, short construction period and high construction efficiency, etc.
Owner:五矿二十三冶建设集团有限公司
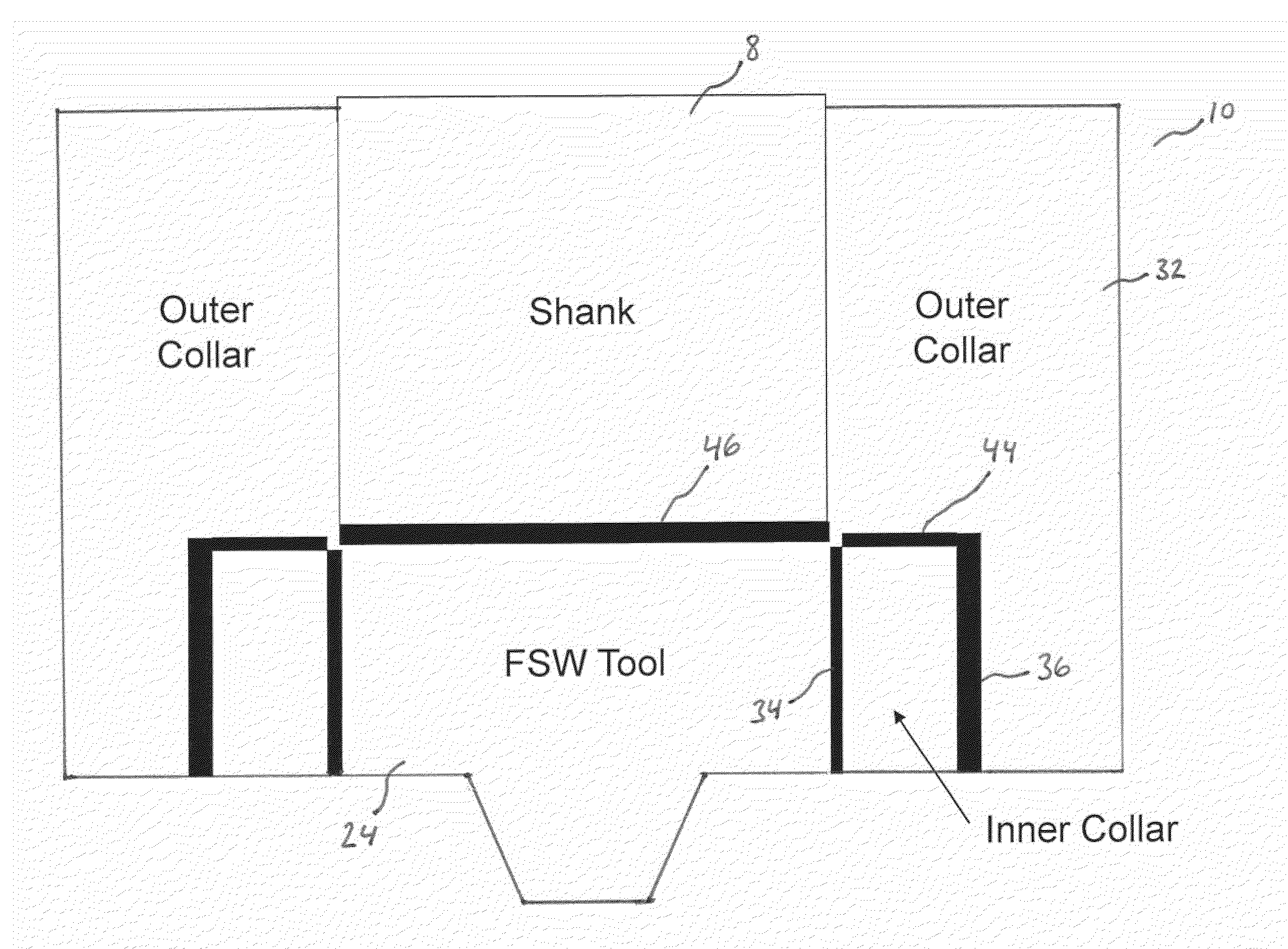
Rotary holding device for gripping tool material at elevated temperatures through multiple collar assembly
ActiveUS20100038832A1Improve stressImprove gripWelding/cutting auxillary devicesBlast furnace detailsEngineeringFriction stir processing
A tool is provided that is capable of friction stir processing, friction stir mixing, and friction stir welding of high melting temperature and low melting temperature materials, wherein the collar is now divided into at least an inner and an outer collar coupled to the shank and the FSW tip, wherein new thermal barriers enable expansion of the inner collar to be directed inward to thereby create compression on the FSW tip instead of allowing the FSW tip to become loose in the tool at elevated temperatures.
Owner:MAZAK CORP
Casting method of metal substrate cooling wall
InactiveCN1513622AEnhanced feedingImprove feeding capacityFoundry mouldsCooling devicesIron powderChemical reaction
A technology for casting the steel-based cooling wall features that the cooling medium which is the mixture of corundum powder, iron powder and electrode powder is filled in its cooling pipeline. Said cooling medium features strong cooling action, low thermal expansibility, not adhering to pipe wall, and easy removing it.
Owner:MAANSHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
System and method for steel making
InactiveUS6890479B2Improve conductivityHigh hardnessTuyeresBlast furnace detailsProduction rateAlloy
A metallurgical furnace, which includes a furnace shell, an exhaust system, and a gas cleaning system, further includes a plurality of improved pipes and fume ducts throughout to increase operational life and productivity. The pipes and fumes ducts are comprised of an aluminum-bronze alloy which provides enhanced properties over prior art materials including thermal conductivity, modulous of elasticity and hardness. The use of the alloy also minimizes maintenance requirements of the pipes and fume ducts, thereby extending their operational life. In operation, gases formed from smelting or refining are evacuated from the furnace shell through the exhaust system into the gas cleaning system. The gases, as well as the system, are water cooled by way of the plurality of pipes displaced throughout.
Owner:AMERIFAB INC
Process for producing reduced matal and agglomerate with carbonaceous material incorporated therein
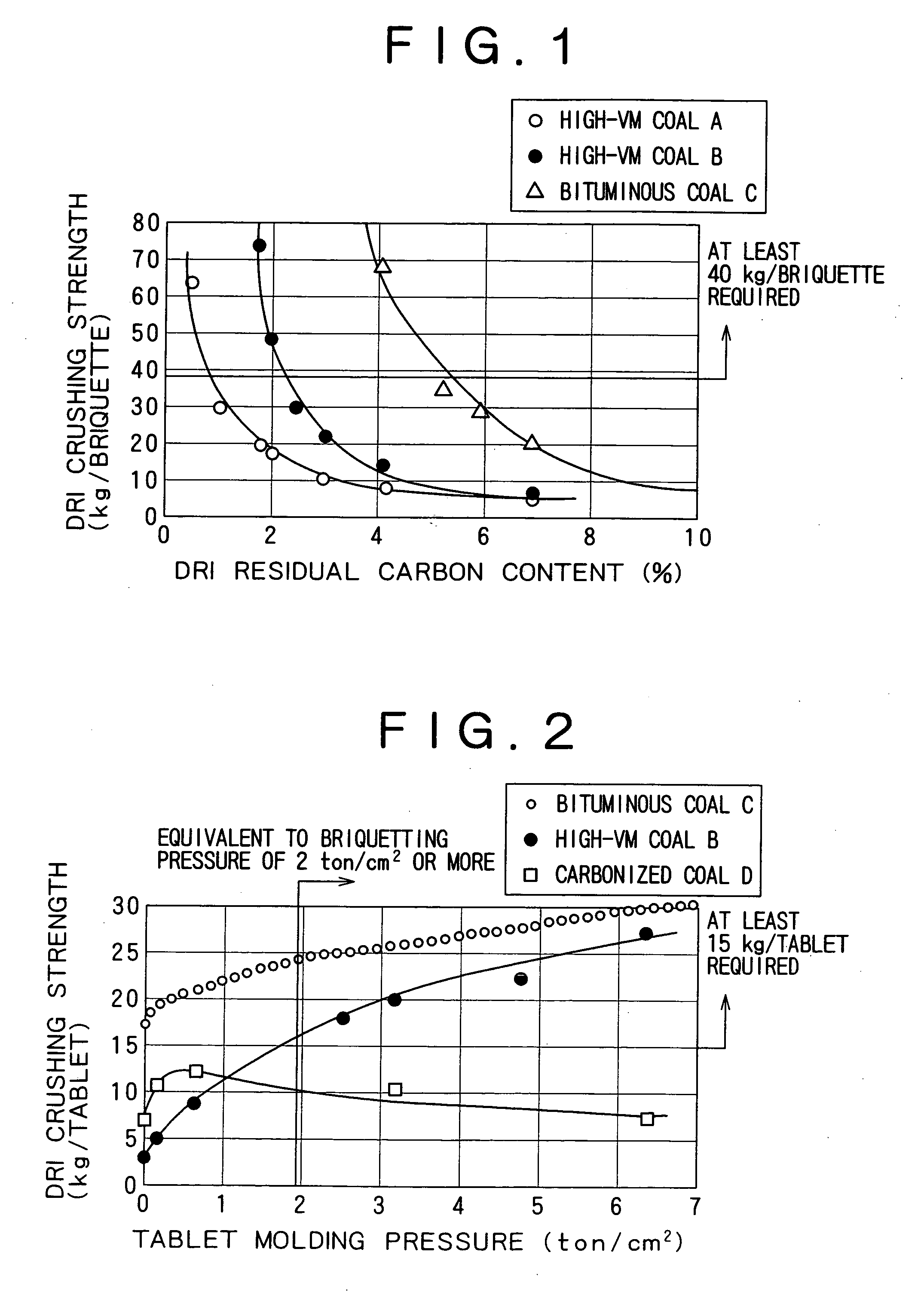
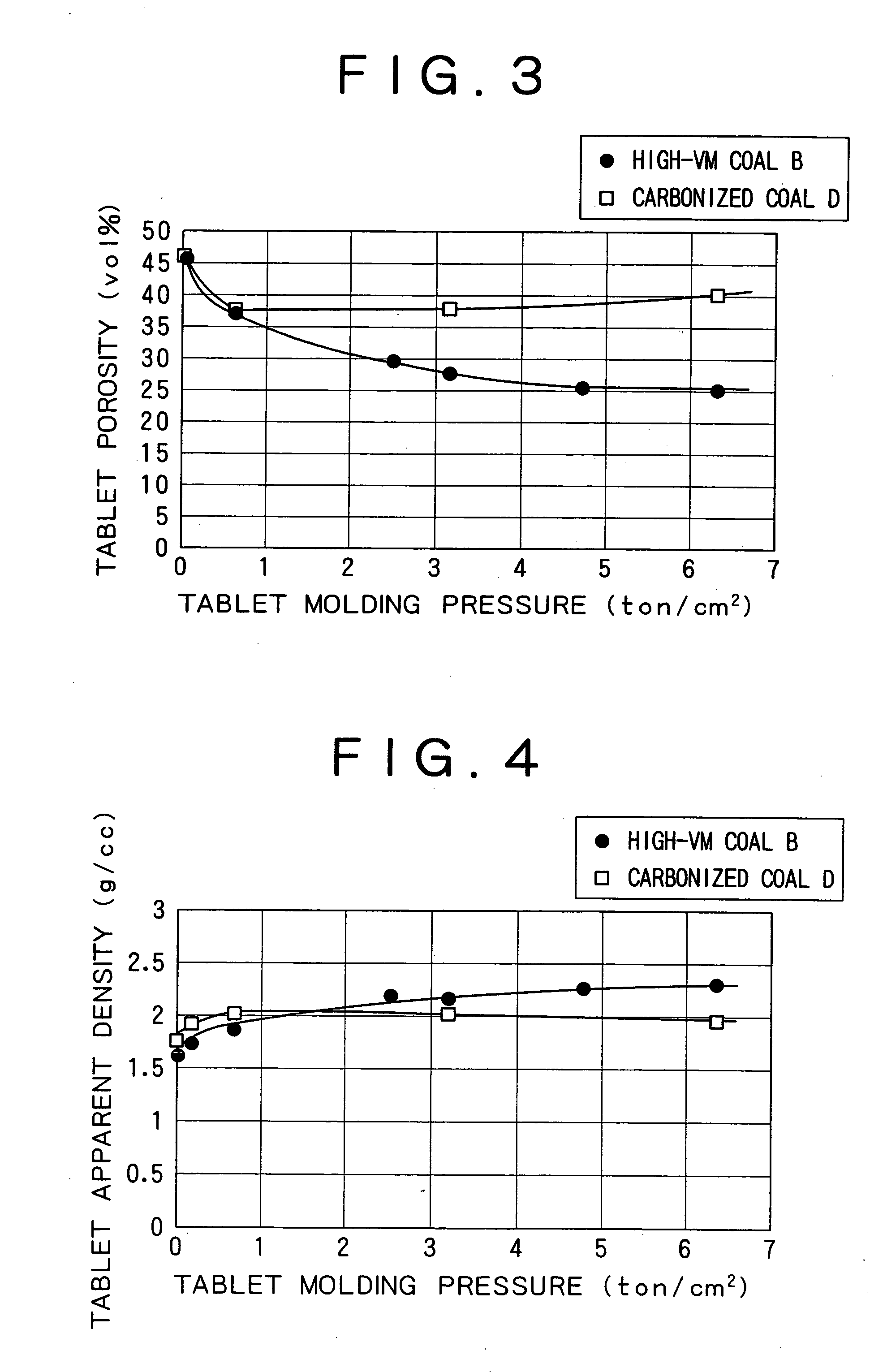
InactiveUS20060278040A1Reduce porosityHigh compressive strengthRotary drum furnacesBlast furnace detailsPorosityCoal
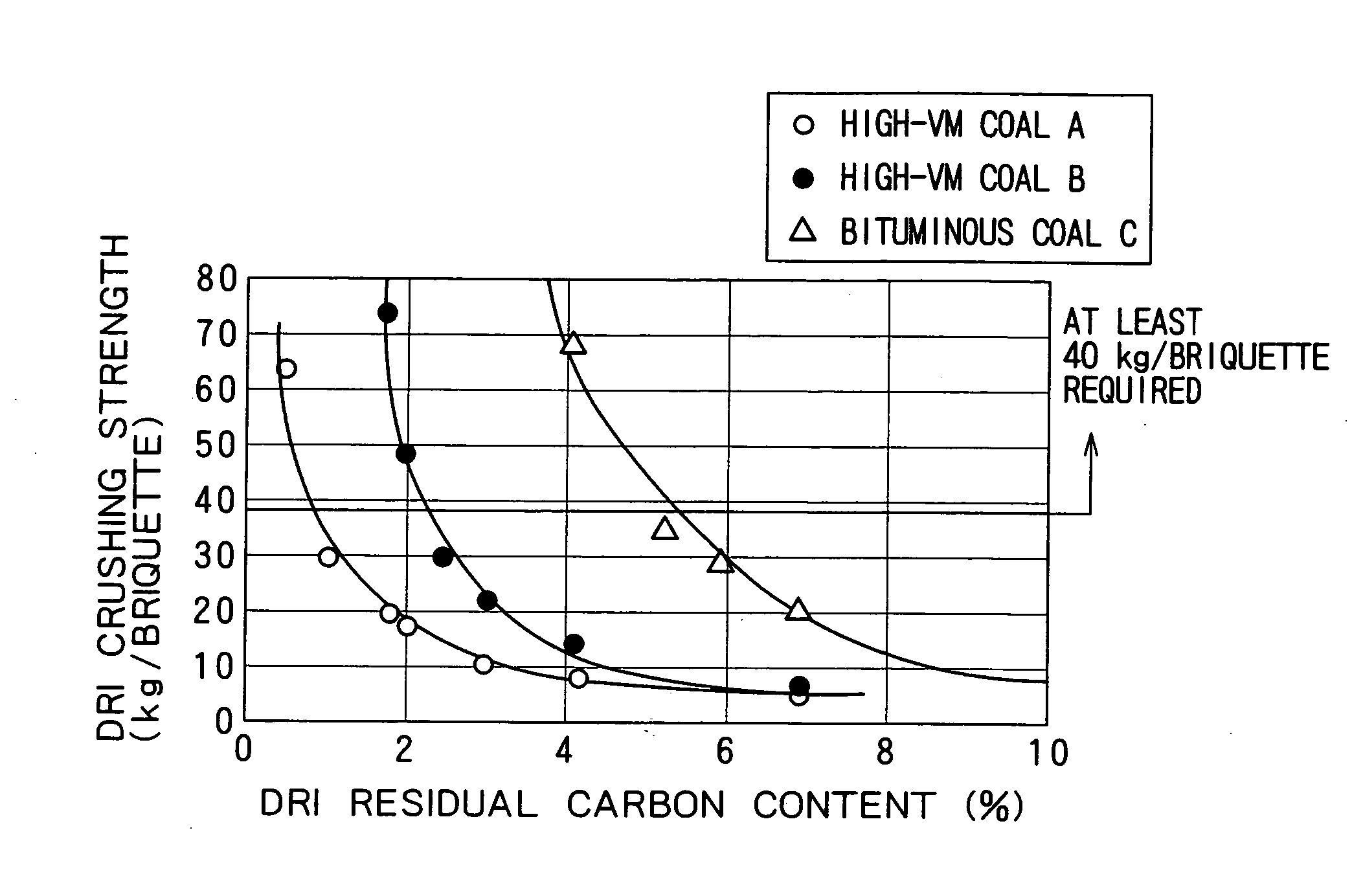
Agglomerates with a carbonaceous material incorporated therein and a process for producing reduced metal using the agglomerates are provided. The agglomerates are prepared with high-VM coal, which is widely and abundantly produced and is less expensive, and they provide high strength after reduction without the need for finer metal oxide particles. The agglomerates are made of a carbonaceous material and a raw material to be reduced that contains a metal oxide, such as iron ore. The carbonaceous material used is a high-VM coal containing 35% or more by mass of volatile matter. The agglomerates are formed at a pressure of at least 2 t / cm2 so that the porosity thereof is reduced to 35% or less. The reduction in porosity is effective in promoting heat transfer inside the agglomerates in a rotary hearth furnace in a high-temperature reduction step so that the sintering of reduced metal proceeds efficiently in the overall regions of the agglomerates to produce a reduced metal having high crushing strength.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
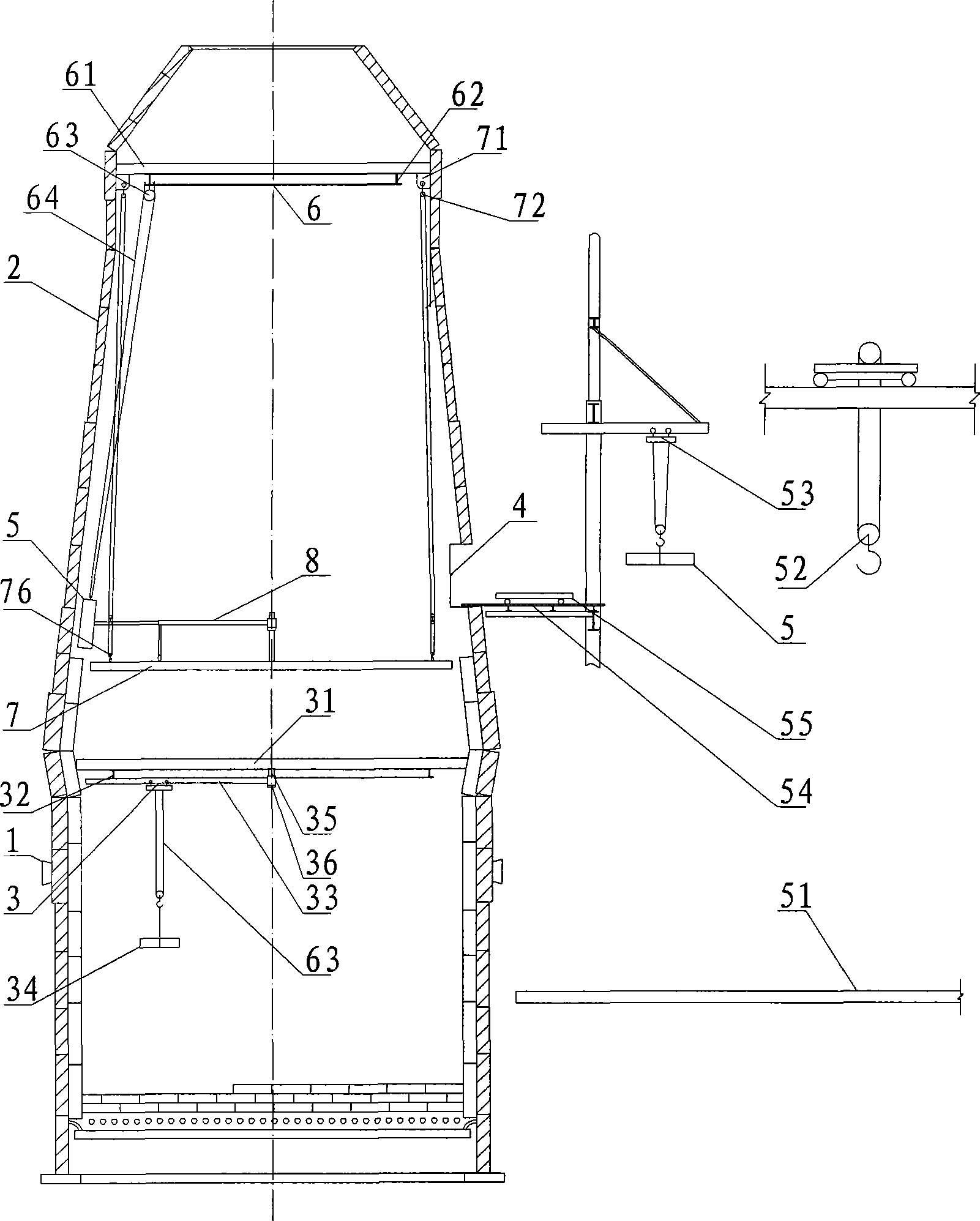
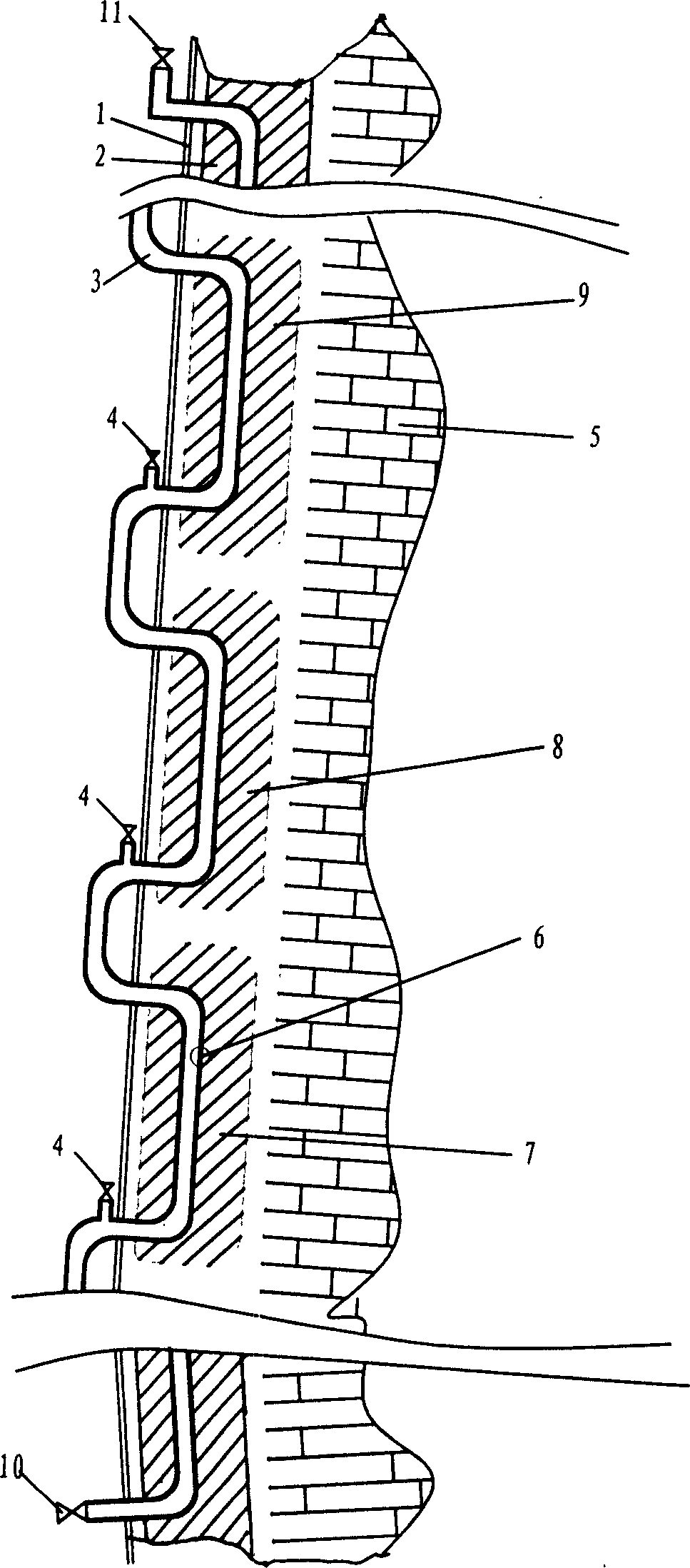
Method for preparing water cooling system of blast furnace cooling wall
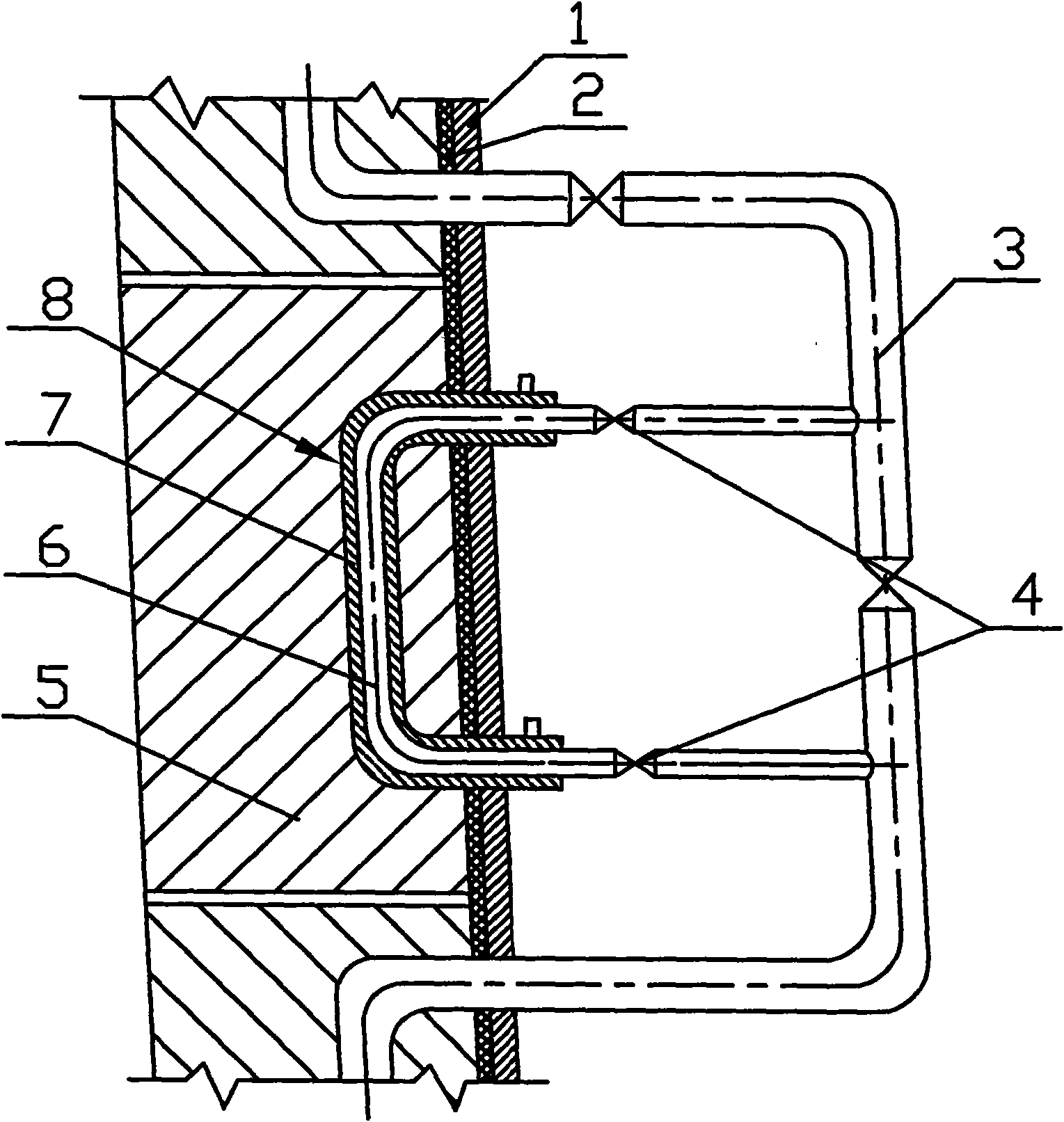
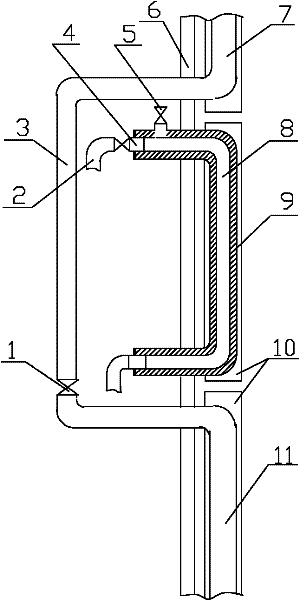
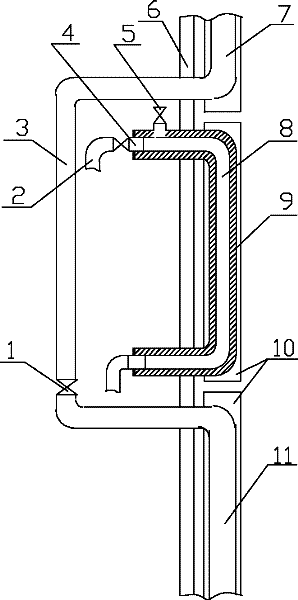
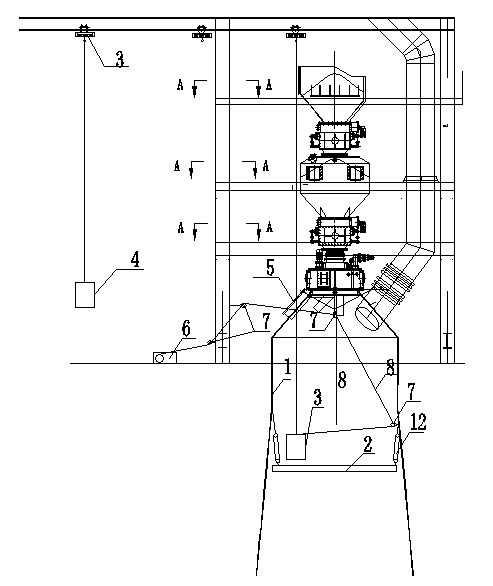
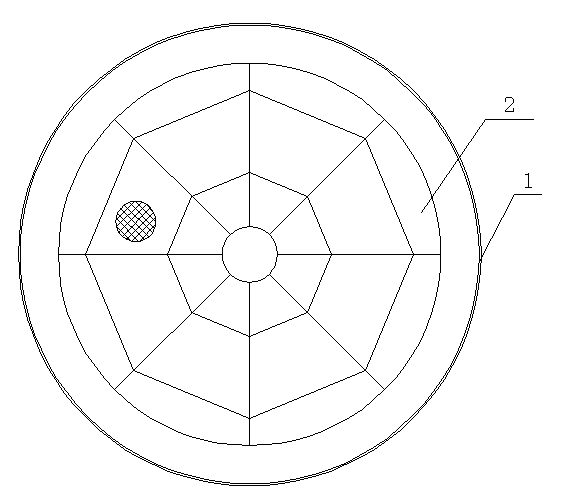
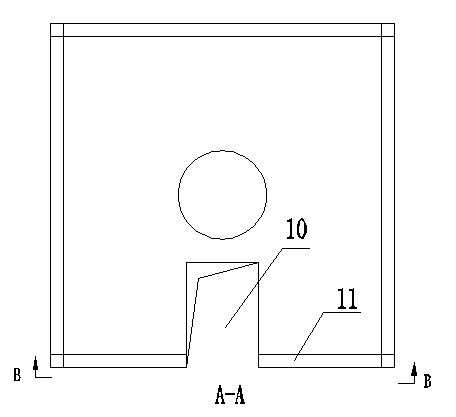
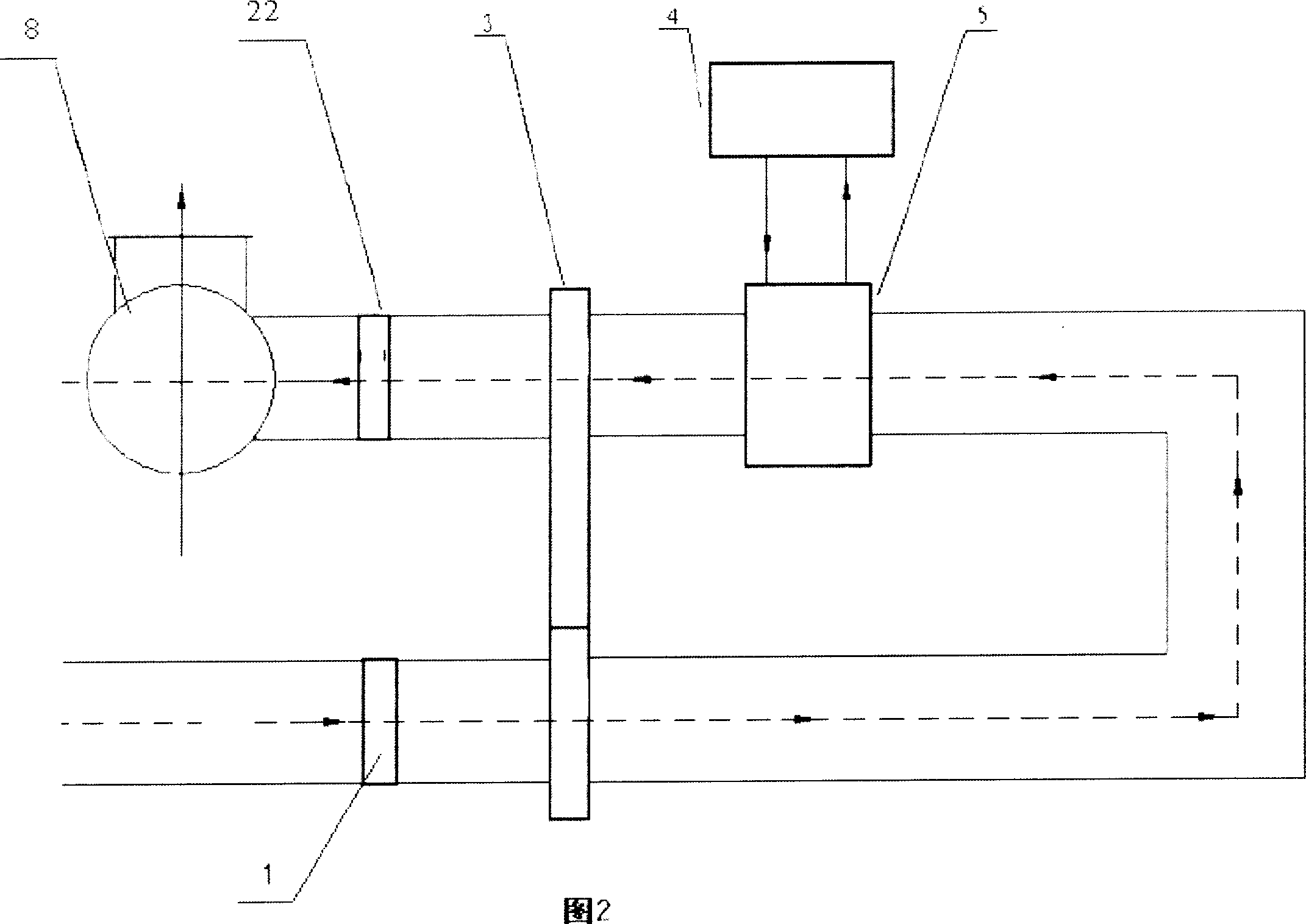
The present invention relates to a method for preparing water cooling system of blast furnace cooling wall. A technical scheme is that: the cooling system includes a cooling water pipe (8) and an outer water pipe (3), the cooling water pipe (8) communicates with the outer water pipe (3), the cooling water pipe (8) is beset on the blast furnace cooling wall (5) passing through a furnace shell (1) and a filling agent layer (2). When the cooling water pipe (8) is broke and water leakage in the blast furnace cooling wall (5), the cooling water pipe (8) disconnects with the outer water pipe (3) on the furnace shell (1), then a metal flexible pipe (6) passes through the cooling water pipe (8), and two ends of the metal flexible pipe (6) communicates with the disconnected out water pipe (3). The metal flexible pipe (6) located on the furnace shell outside is equipped with a valve for controlling, grouting material (7) is filled between the metal flexible pipe (6) and the furnace shell (1). The method has characteristics of convenient operation, safety, low cost and superior integrality which can be widely used for preparing the water pipe with water leakage in the blast furnace cooling wall system.
Owner:WUHAN WINNING TECH
Gas sorbents on the basis of intermetallic compounds and a method for producing the same
InactiveUS20060225817A1Large specific surface areaDispersed particle separationBlast furnace detailsSorbentPositive pressure
The present invention relates to new gas sorbents on the basis of intermetallic compounds and a method for producing the same. The method comprises the following steps: mixing and melting of initial metals and homogenization of the melt under negative pressure of inert gas, manufacturing of cast shot by quenching of melted droplets under positive pressure, obtaining of skeleton-type granules by evaporation of the excess of the component A from cast shot under vacuum.
Owner:NANOSHELL MATERIALS RES & DEV
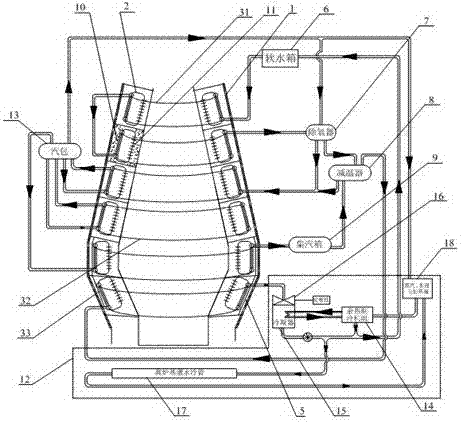
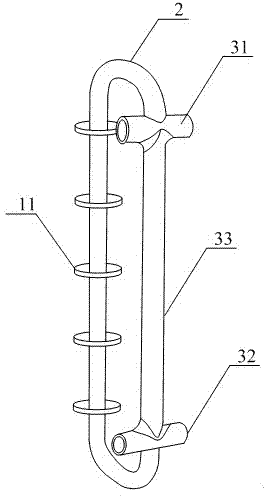
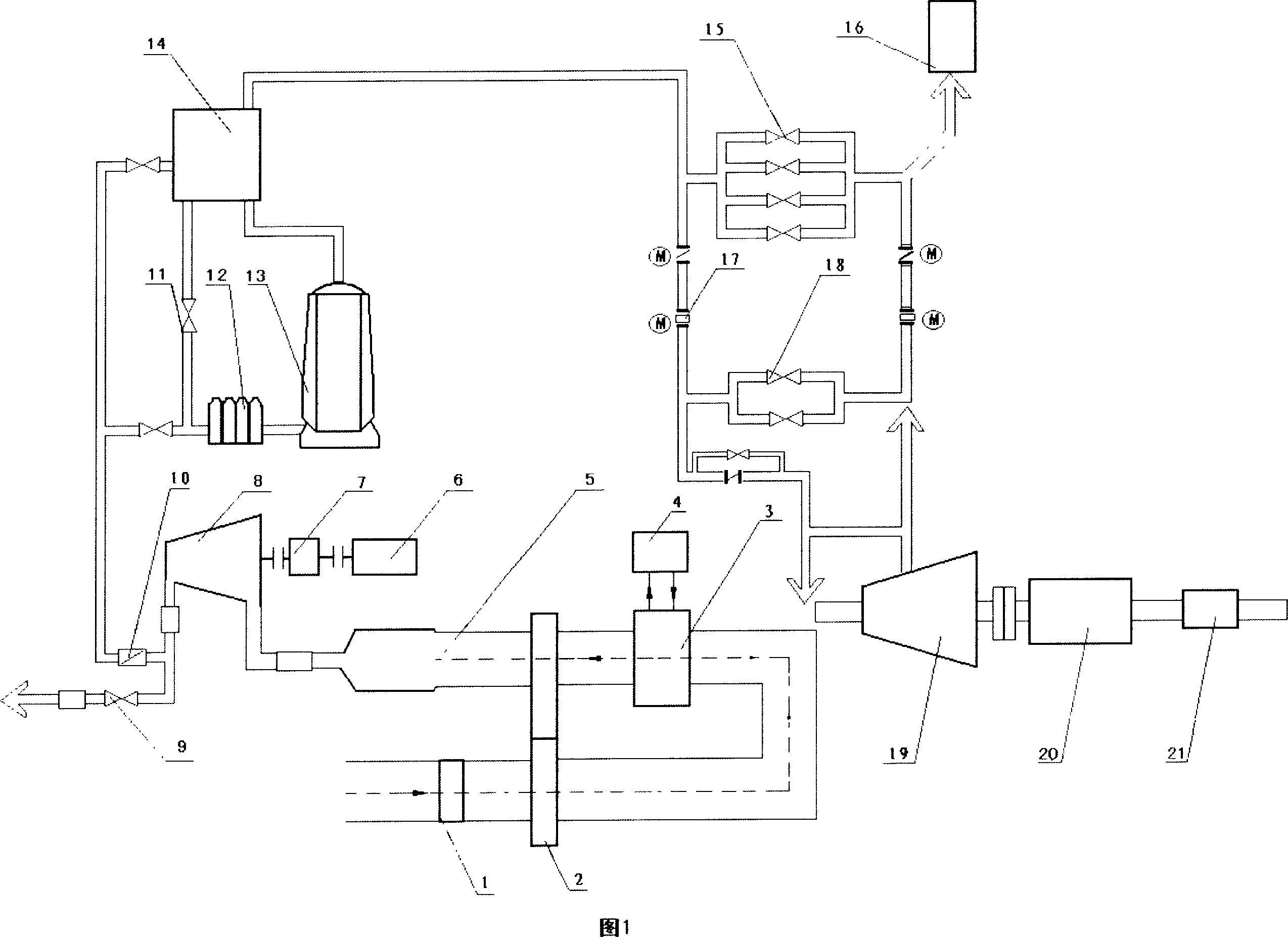
Blast furnace superconducting cooling and waste heat power generation system
InactiveCN102382914AReduce dosageReasonable designBlast furnace detailsCooling devicesRefractoryEngineering
The invention discloses a blast furnace superconducting cooling and waste heat power generation system. The system is composed of a blast furnace body (1), a power generation system (12) and a steam utilization device. The system is characterized in that more than one superconducting ring type heat exchange ring (2) is arranged along the side wall of the blast furnace body (1) in a layering and surrounding mode; each superconducting ring type heat exchange ring (2) is provided with a pouring solidification body (10) formed by using wear-resisting thermal-shock-resisting carburizing-resisting elastic castable refractory; each superconducting ring type heat exchange ring (2) is embedded in the inner lining of the side wall of the blast furnace body (1) through the pouring solidification body (10); and the like. According to the invention, hot water subjected to heat exchange is intently led out through the superconducting ring type heat exchange ring and an annular pipeline system corresponding to the superconducting ring type heat exchange ring, thus heat exchange intensity is enlarged, and heat exchange efficiency and cooling efficiency are improved; and the traditional cooling water temperature is improved to 250 DEG C from 40 DEG C, and then the cooling water is overheated to 400 DEG C through applying the superconducting ring type heat exchange ring twice, so that cooling waste heat can be utilized for power generation.
Owner:CHENGDU SINOMETALLURGY ENERGY CONSERVATION ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG CO LTD
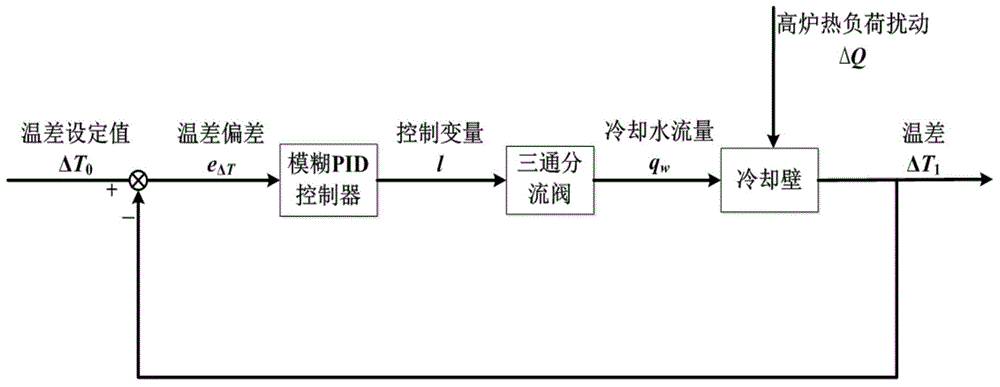
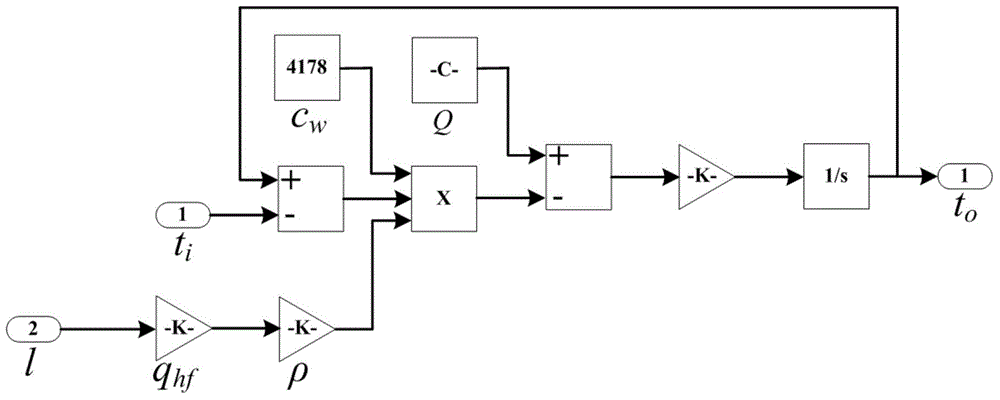
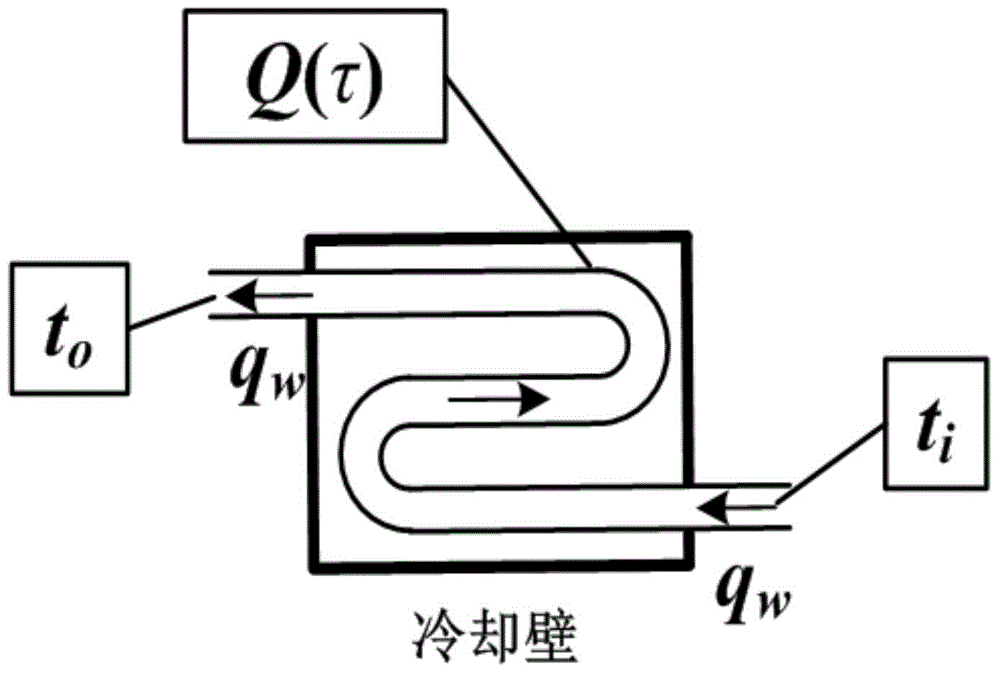
Furnace cooling intensity control method based on vague PID control
ActiveCN104898433ARealize automatic controlReduce volatilityCooling devicesAdaptive controlClosed loopSoft water
The present invention discloses a furnace cooling intensity control method based on vague PID control, and belongs to the technical field of furnace cooling control. The control method is based on the heat transfer theory and the engineering thermodynamics. A novel furnace water supply cooling method is provided; a diverging three-way valve serves as an executing mechanism; advantages of conventional PID control and vague control are combined; according to nonlinearity, obsoleteness and possible uncertain factors of a furnace cooling intensity control method and operating characteristics of a furnace closed-loop soft water circulating cooling system, PID parameter self-tuning inference rules are established, and opening of the diverging three-way valve is adjusted, thereby controlling cooling wall cooling intensity; in comparison with those in the prior art, real-time control of the cooling intensity is realized, control accuracy and stability are also raised, and manpower consumption is reduced.
Owner:马鞍山市安工大智能装备技术研究院有限公司
Cooling system for forming mold and method of cooling forming mold
InactiveUS20090315231A1Increase back pressureImprove cooling effectMelt-holding vesselsFoundry mouldsEvaporationEngineering
In a forming mold equipped with a cooling channel for circulation of a refrigerant composed of a cooling gas and a atomized cooling liquid, any increase of back pressure attributed to evaporation of the refrigerant fed to the cooling channel is inhibited to thereby attain cooling acceleration, and further any occurrence of rust or scale by the refrigerant circulated through the cooling channel is prevented. Accordingly, a channel for supply of the refrigerant to the cooling channel of the forming mold is provided with air pressure source for trapping of air in the supply channel and pressure feeding of the same; oxygen separation means for separation removal of oxygen from the pressure fed air to thereby lower the oxygen concentration of the air; and atomizing means for spraying of the cooling liquid into the air with oxygen concentration lowered. The oxygen separated from the air by the oxygen separation means is returned to the refrigerant forcedly emitted from the cooling channel by means of forced exhaust means.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Replacement method for cooling water pipe of cooling wall of blast furnace
InactiveCN102534078AThe replacement method is simple and easyEasy to operateCooling devicesFurnace temperatureWater leakage
The invention provides a replacement method for a cooling water pipe of a cooling wall of a blast furnace. A broken cooling water pipe is disconnected with a front cooling water pipe and a rear cooling water pipe; and the front cooling water pipe and the rear cooling water pipe are connected through an external water pipe, so that cooling water is directly circulated across the broken cooling water pipe. Meanwhile, a metal hose is penetrated in the broken cooling water pipe and is connected to a replaced cooling water pipe, which is communicated with an external water source, through seamless steel pipes at the two ends, so that cooling water in the metal hose independently forms a passage to continuously realize a cooling function. By using the method, quick replacement of the broken cooling water pipe is realized without affecting normal water supply cooling of other cooling water pipes, the water leakage phenomenon in the blast furnace is eliminated, the problem of increased coke ratio caused by reduced furnace temperature is prevented, the cooling function of the broken cooling water pipe is restored, the cooling effect of the cooling wall is guaranteed, and the service life of the cooling wall can be prolonged.
Owner:ANGANG STEEL CO LTD
Hoisting method for replacing cooling wall in overhauling of blast furnace
ActiveCN103266192AAvoid situations that cannot be hoistedReduce replacement timeCooling devicesEngineeringWindlass
The invention discloses a hoisting method for replacing a cooling wall in overhauling of a blast furnace. The hoisting method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1, making a special pallet for installing the cooling wall in the blast furnace; 2, unchoking a special channel for hoisting the cooling wall; 3, installing a windlass and fixed pulleys on a platform at the top of the furnace; and 4, hoisting the cooling wall by a furnace top overhauling hoist. The hoisting method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of reasonable installation, safety and reliability, the time of replacing the cooling wall is saved, and the overhauling cost is reduced.
Owner:CHINA MCC17 GRP
Efficient economical dust collecting method and dust collector for iron-smelting blast furnace
InactiveCN101074453AImprove the efficiency of waste heat recovery and utilizationIncrease temperatureBlast furnace detailsCooling devicesCombustionHeat transfer efficiency
An efficient energy-saving dust-collecting method and its apparatus for iron-smelting blast furnace are disclosed. The procedure is carried out by pre-cooling wet air before entering them into air blower, re-cooling, lowering temperature below saturated temperature, coagulating while precipitating for water content in wet air, re-cooling, delivering into blast furnace by air blower, discharging smoke from blast furnace, heat-exchanging, recovering partial tailed heat, lowering temperature, bagged collecting dust, storing or generating. It's cheap and simple, has higher heat-transfer rate, long utilizing life, less apparatus, full combustion and recovery and better high-temperature resistance for bagged dust collector.
Owner:童裳慧
Replacing method of blast furnace shell and water wall
ActiveCN101570802AQuick changeEasy to feedCooling devicesInternal formsWater coolingMaterials science
The invention discloses a rapid and efficient replacing method of a blast furnace shell and a water wall, which comprises the following steps: 1) installing support frames around the furnace body to prevent the furnace shell from sinking or slanting; 2) cutting the furnace shell which needs to be replaced, integratively removing the cut-out furnace shell and the water wall connected with the furnace shell; 3) installing a new furnace shell on the furnace body; and 4) after replacing the furnace shell, opening an inlet hole on the furnace shell, introducing the new water wall into the furnace body through the inlet hole and installing the new water wall on the inner wall of the furnace shell. The method directly and integratively removes the furnace shell and the water wall connected together and introduces the new water wall rapidly and conveniently into the furnace body, thus greatly shortening the repair and construction time, saving the use of mechanical devices and labor cost, and realizing rapid and efficient replacement of the blast furnace shell and water wall. The construction method of the invention in particular applies to small-sized blast furnaces with the volume of no more than 1000 cubic meters.
Owner:CHINA 19TH METALLURGICAL CORP
Repairing method for cooling staveleakage
InactiveCN101333569AFix cooling functionRestoring coolingLiquid surface applicatorsArc welding apparatusLeaking waterSlag
The invention belongs to a repairing method of iron-making blast furnace equipment, which relates to a cooling wall leakage repairing method. The method mainly solves the technical problems that grouting can stop leakage but can not repair big gaps and the conduction cooling capacity is reduced after grouting. The repairing method of cooling wall leakage is characterized in that the method comprises the following steps of: a. shell opening: including opening holes with apertures of 150 to 250mm on the furnace shell around water pipes on a cooling wall; b. root grooving: including opening grooves at the root part of the cooling wall around the leaking water pipes and sheaths for eliminating cracks as well as molding sand, slag inclusion and loosening on the surface of the cooling wall; c. surface pretreatment: comprising eliminating the grooving parts and residual oxidative metal and oxide films on the surface around the grooves for exposing the metallic luster; d. leakage repairing: the leakage repairing method includes one process of a welding process and a high-molecular polymeric metal bonding process or a composite process combining the two processes; and e. hydrostatic test: after the repairing work, water is supplied for testing the pressure for 30min so as to check the leakage condition. The method is mainly used for repairing cooling wall leakage of blast furnaces.
Owner:SHANGHAI MEISHAN IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Cooling panel for a furnace for producing iron or steel
InactiveUS7549463B1Pressure loss becomes excessiveReduce total pressure lossMetal-working apparatusCooling devicesSteelmakingCopper
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
Device and method for cooling hot strip
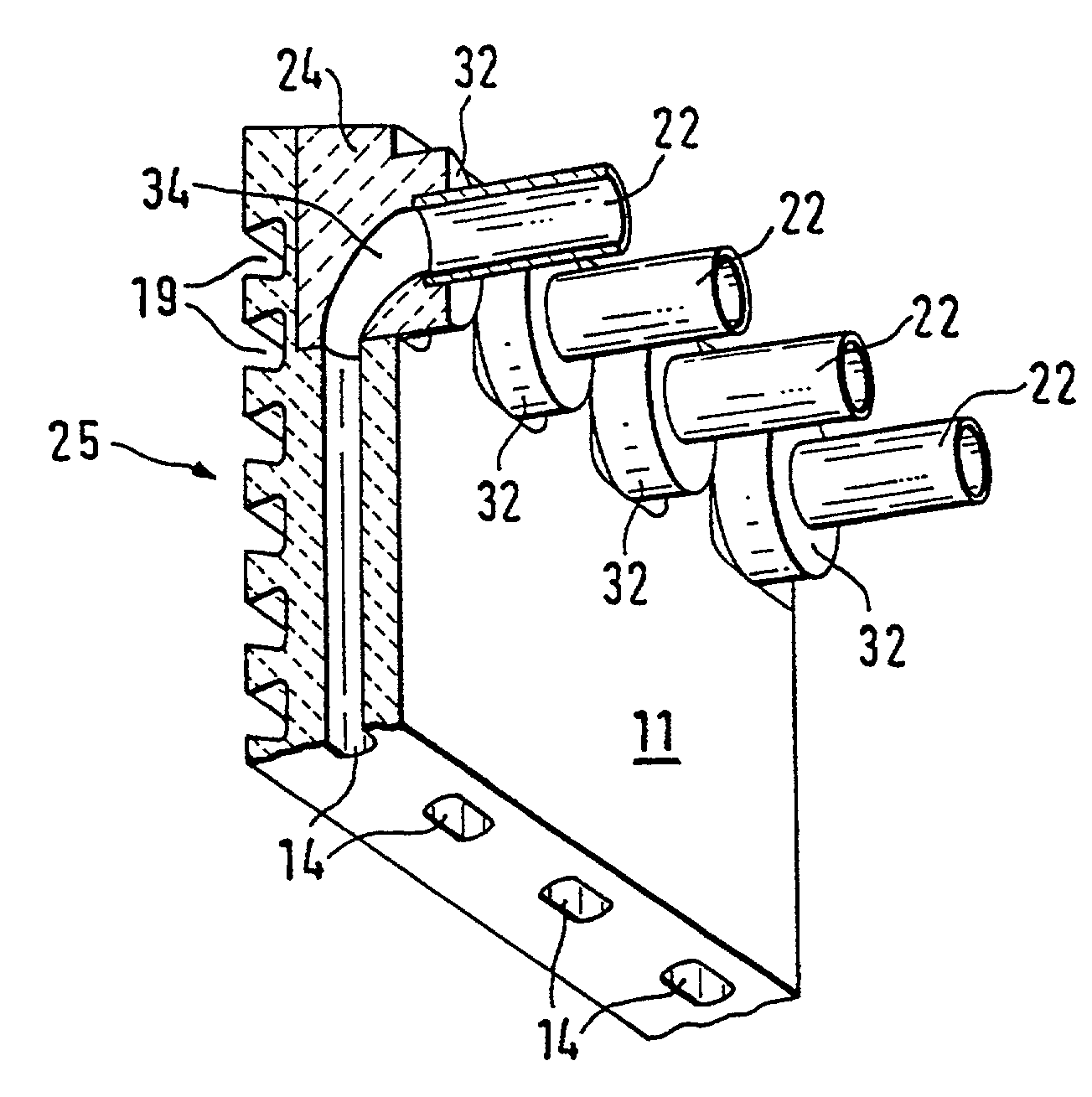
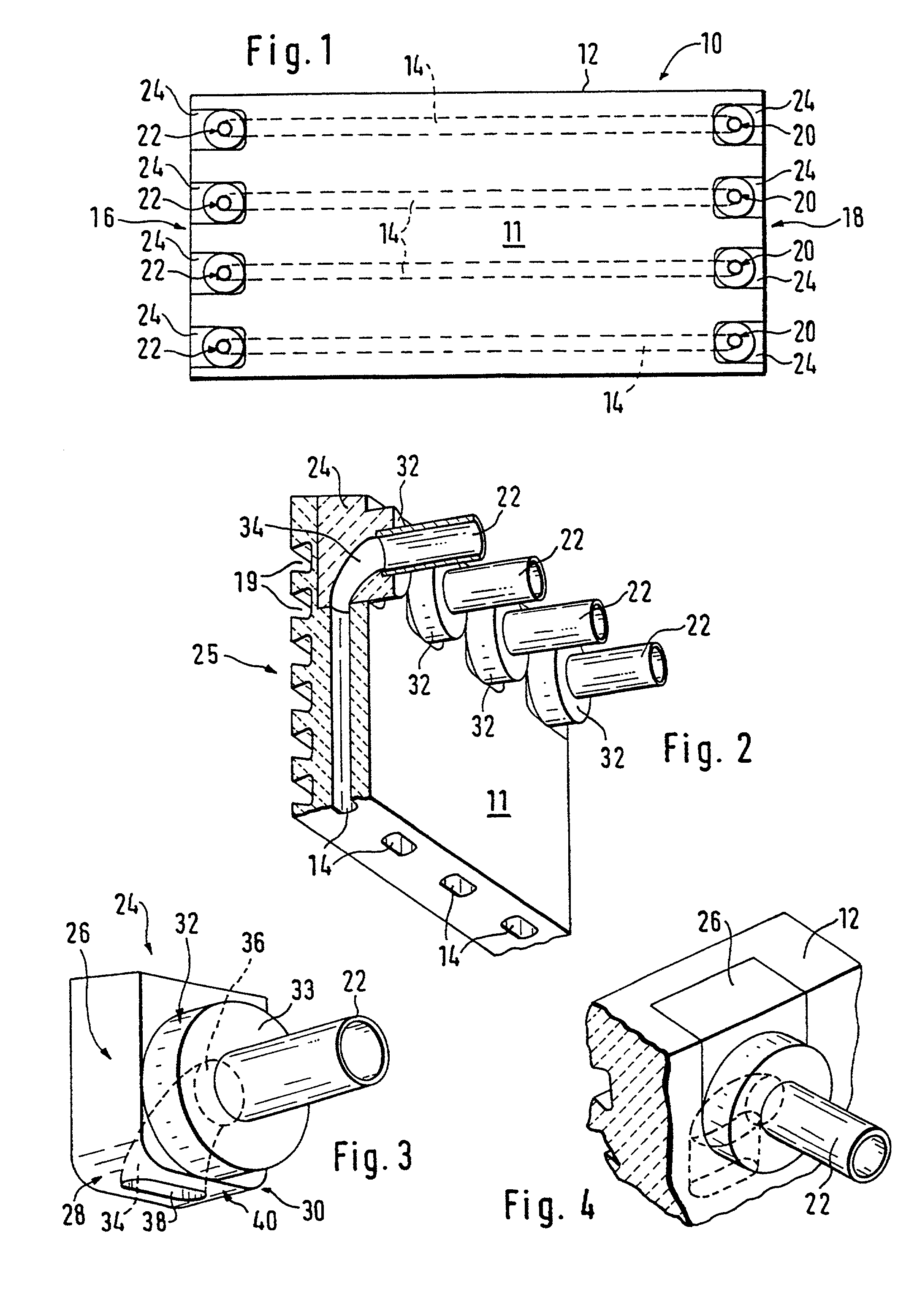
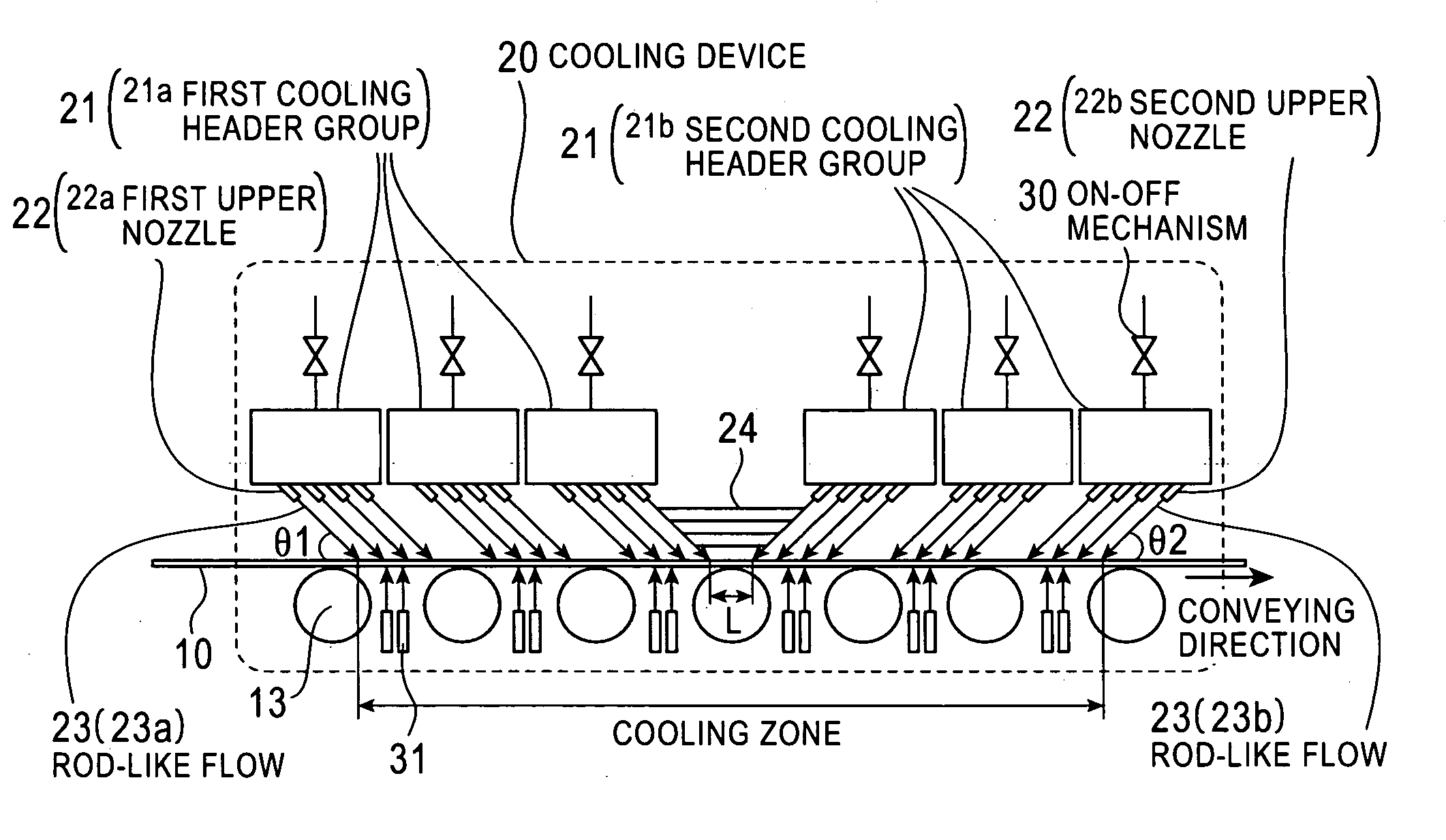
ActiveUS20100024505A1Suppressing material unevennessReduce yield lossTemperature control deviceBlast furnace detailsEngineeringCoolant
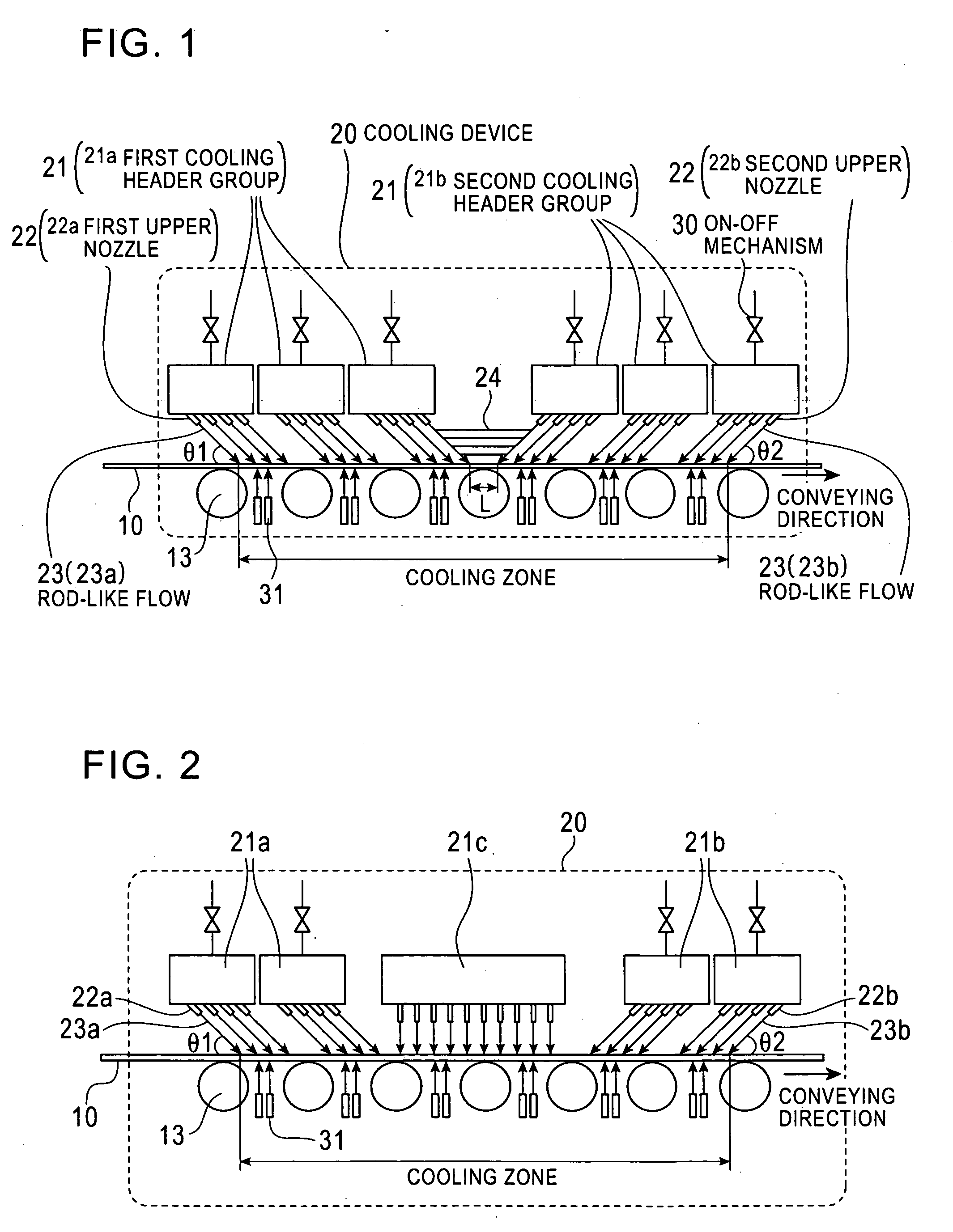
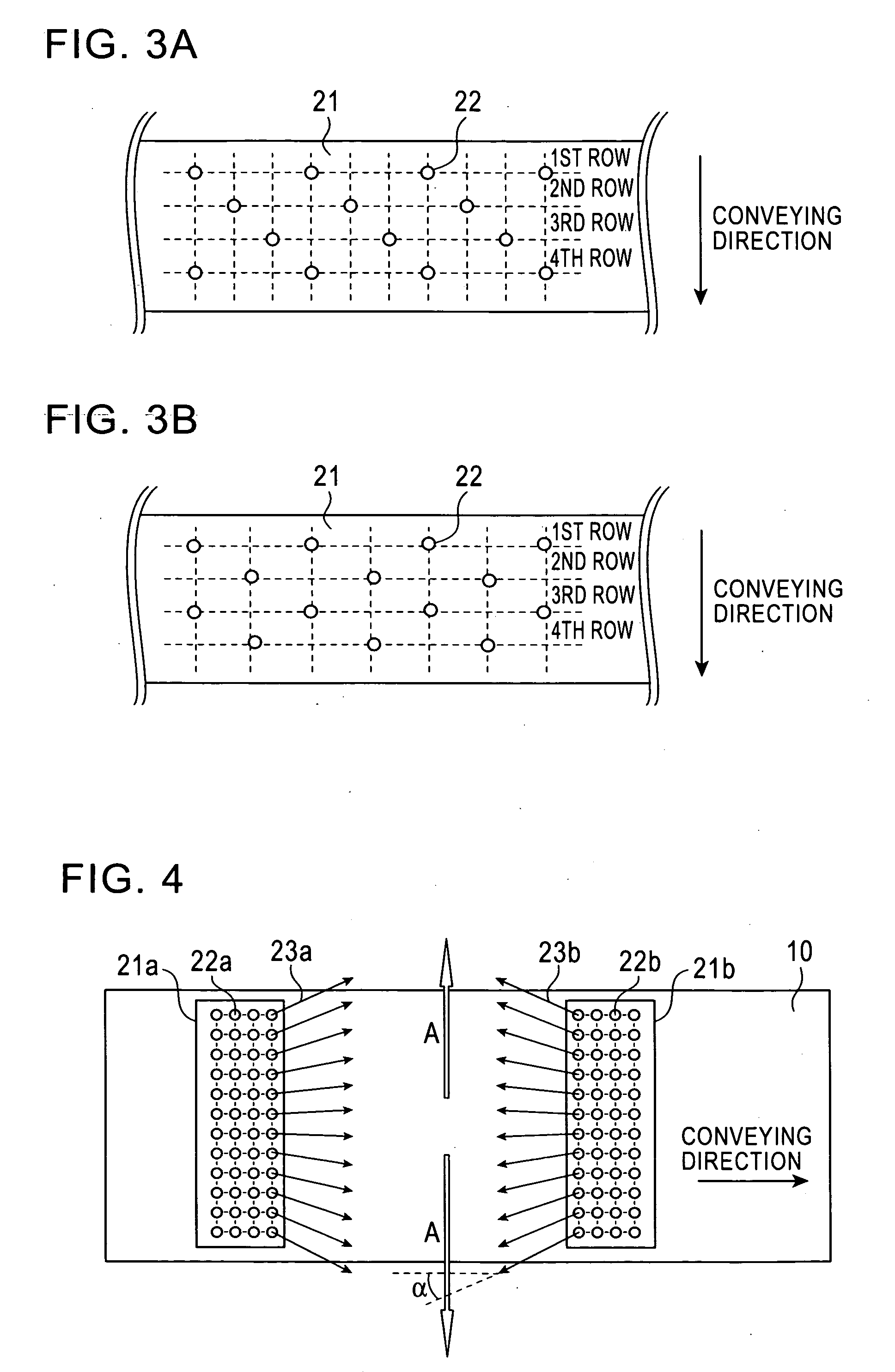
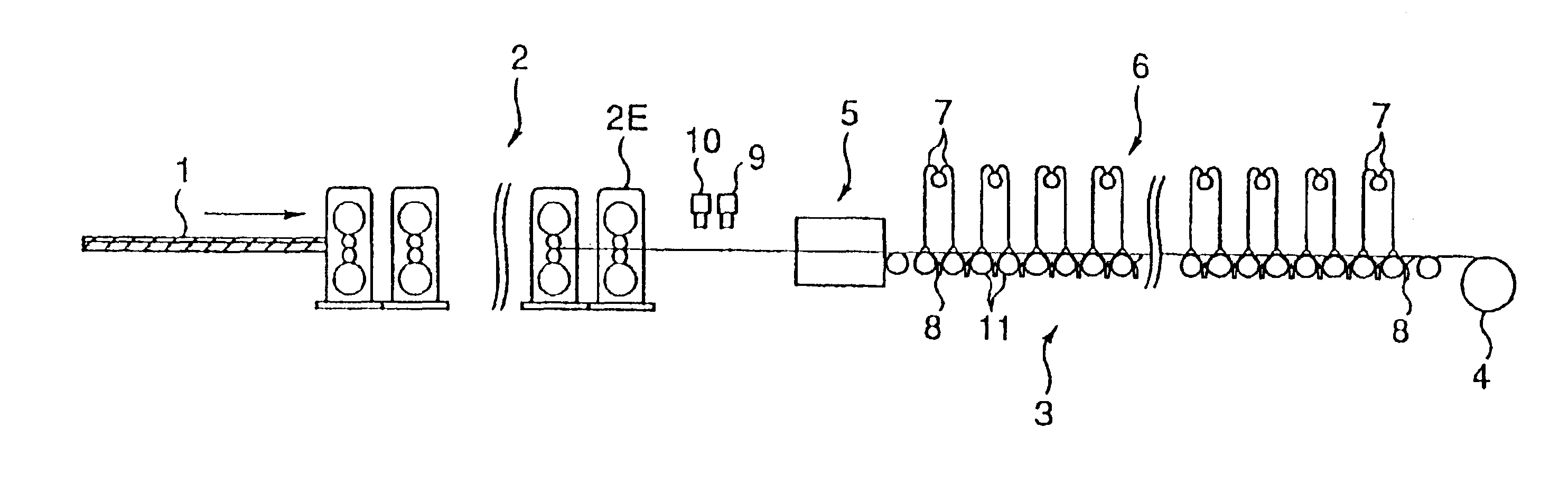
A cooling device and a cooling method for a hot strip allow uniform and stable cooling of the strip at a high cooling rate when supplying the coolant to the upper surface of the hot strip. The cooling device includes an upper header unit 21 for supplying a rod-like flow to the upper surface of the strip 10. The upper header unit 21 is formed of the first upper header group including plural first upper headers 21a arranged in a conveying direction and a second upper header group including plural second upper headers 21b arranged in the conveying direction. The cooling device is provided with an ON-OFF mechanism 30 to allow each of the upper headers 21a and 21b of the first and the second upper header groups to independently execute the ON-OFF control (start / end injection control) of an injection (feeding) of the rod-like flow.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
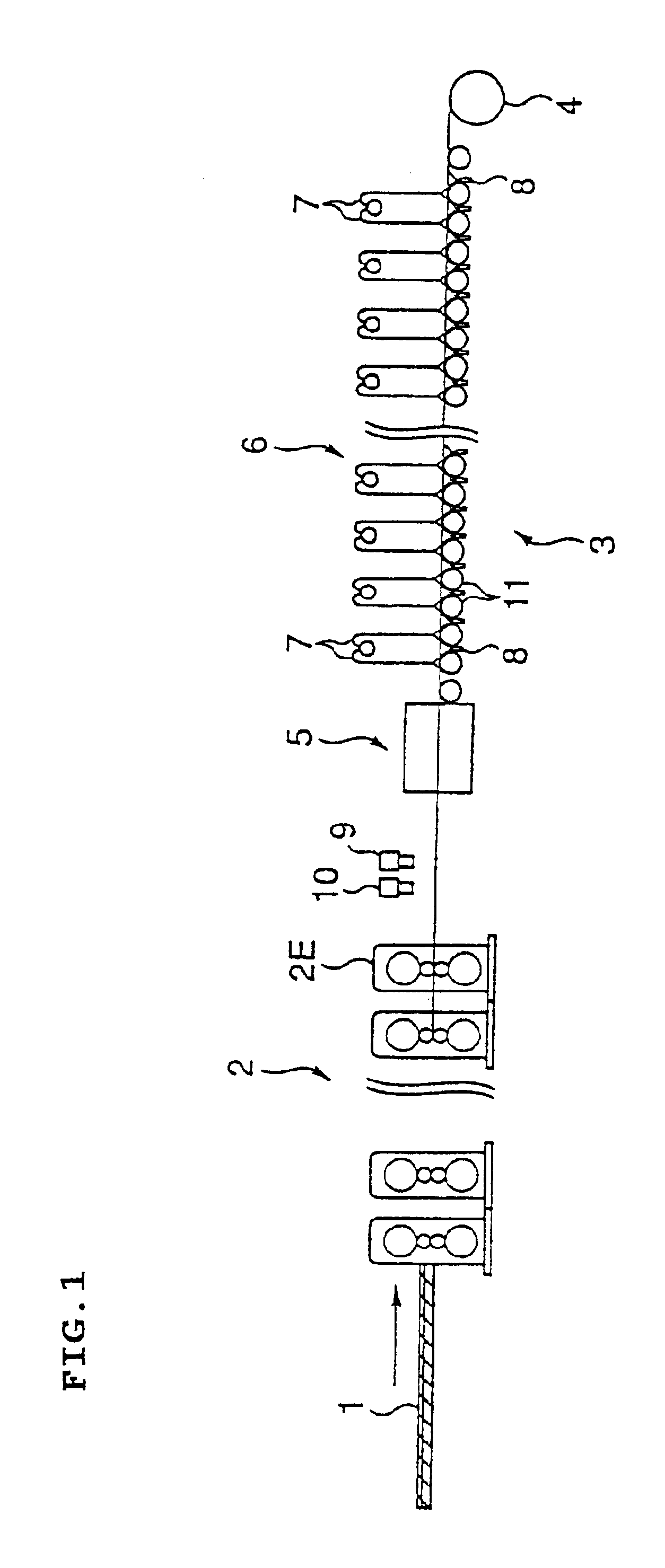
Method and apparatus for cooling hot rolled steel strip, and method for manufacturing hot rolled steel strip
InactiveUS6733720B2Efficient dischargeFine granularityBlast furnace detailsCooling devicesSurface coolingSteel belt
A lower surface cooling box 12 is arranged between transfer rolls 11 on a runout table 3 and an upper cooling box 14 moving freely is arranged at a position corresponding to the cooling box 12 to eject cooling water to the steel strip symmetrically in the vertical direction. The steel strip passes the center of converge of cooling water from upper and lower surfaces of the steel strip. A water breaking roll 16 is provided elevating freely at least at the outlet side rotating at the same peripheral speed as the transfer rolls and is rotated to lower concurrently with passing of the steel strip top at the cooling apparatus. The upper cooling box is also lowered concurrently to cool the steel strip.
Owner:JFE STEEL CORP
Detecting method for air flow distribution of blast furnace
ActiveCN104212924AExtended service lifeLower fuel ratioBlast furnace detailsCooling devicesDistribution systemEngineering
The invention provides a detecting method for air flow distribution of a blast furnace. The heat exchange between an air flow and a solid material bed is considered; the distribution of a material layer structure in the radial direction of the blast furnace influences the air permeability of the blast furnace in the radial direction so as to influence the form of the air flow distribution; and the material layer structure in the radial direction of the blast furnace and the air flow distribution are calculated by combining a cross-shaped temperature measuring gun and other main operation parameters of the blast furnace. According to the detecting method provided by the invention, a blast furnace operator can timely and accurately speculate the material layer structure in the radial direction of the furnace throat part and the change direction of the air flow distribution according to the variation of the radial air flow temperature distribution at present, so that the direction is provided for the adjustment of the distribution system, the stable and smooth operation of the blast furnace is guaranteed, the service life is prolonged, the fuel ratio is reduced, and other expensive detecting instruments are not needed.
Owner:INST OF RES OF IRON & STEEL JIANGSU PROVINCE
Carbonaceous refractory and method for preparing same
InactiveCN1366515AEasily wets molten ironImprove corrosion resistanceBlast furnace detailsCooling devicesTitanium nitrideCoke
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP +1
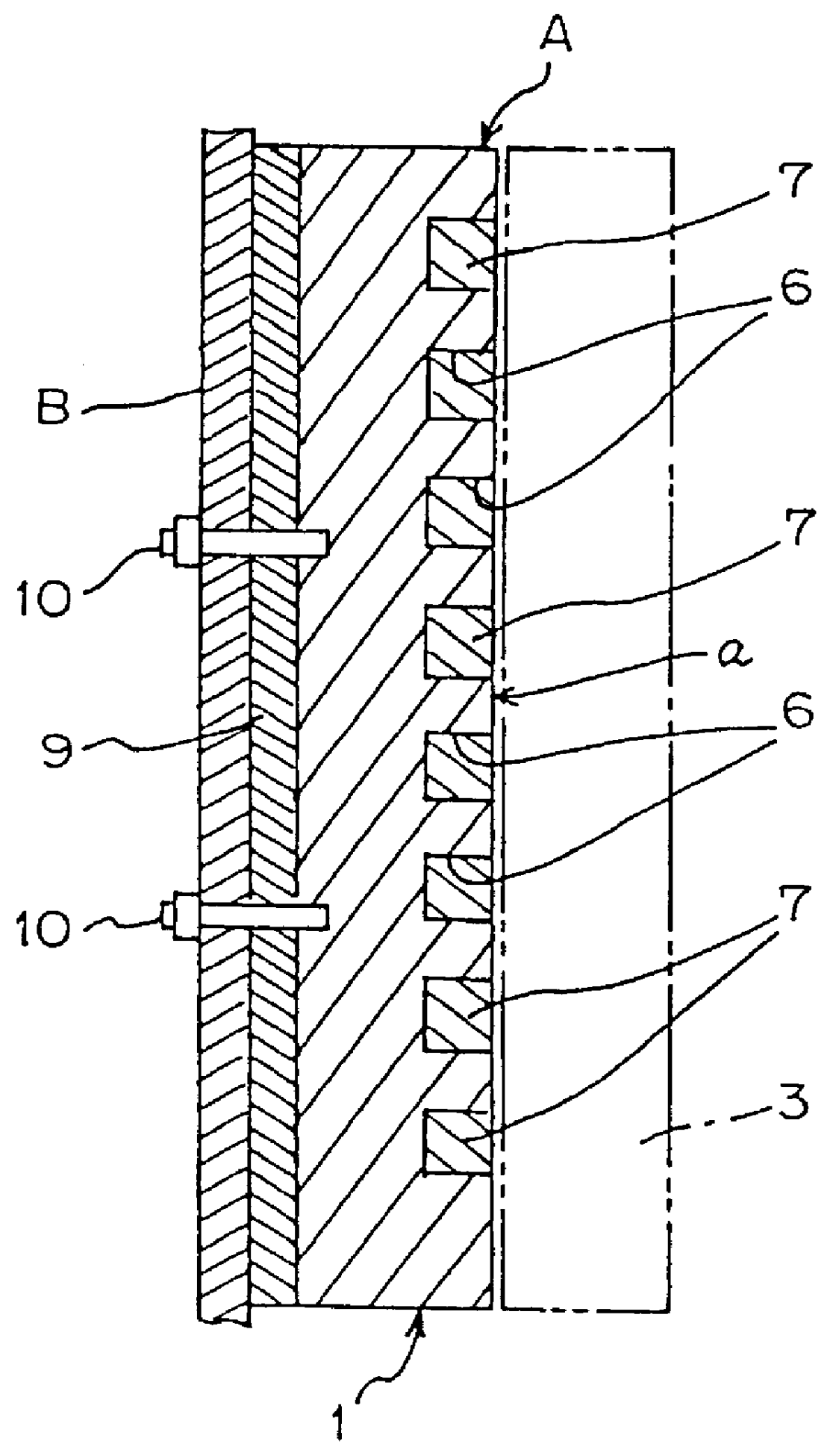
Cooled furnace wall
InactiveUS20060208400A1Save a lot of timeEliminate needBlast furnace detailsManufacturing convertersEngineeringTube bending
A cooled furnace wall comprises a furnace shell with an inner and an outer side and cooling plates lining the inner side of the furnace shell. Each of the cooling plates has a plate body and protruding connection pieces for supplying the cooling plate with a coolant. The furnace shell has connection openings therein for interconnecting the connection pieces of adjacent connection plates from the outer side of the furnace shell. At least one of the connection pieces is formed by a tube bend that protrudes from an edge face of the plate body and that has a connection end to extending through one of the connection openings in the furnace shell.
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
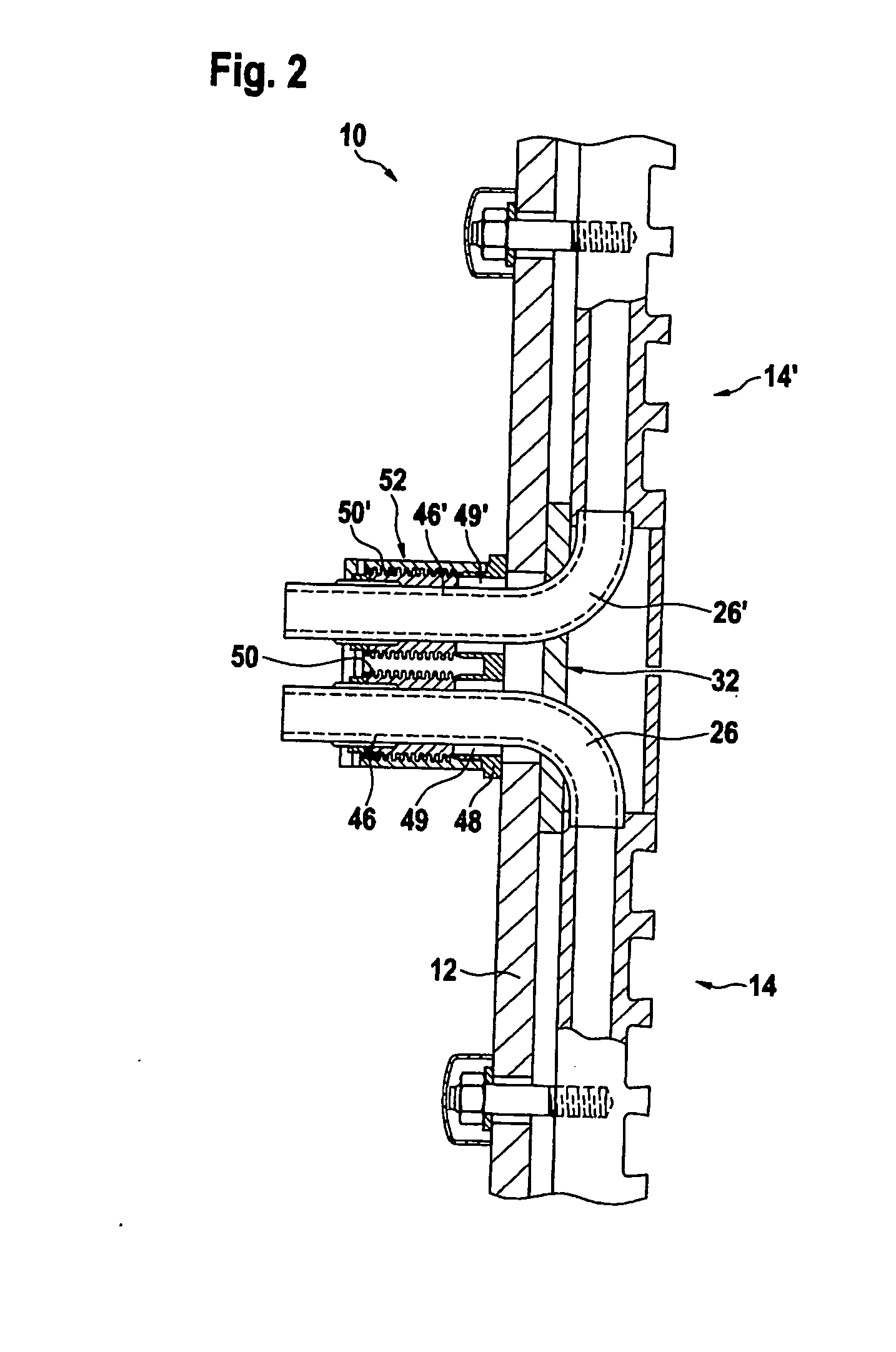
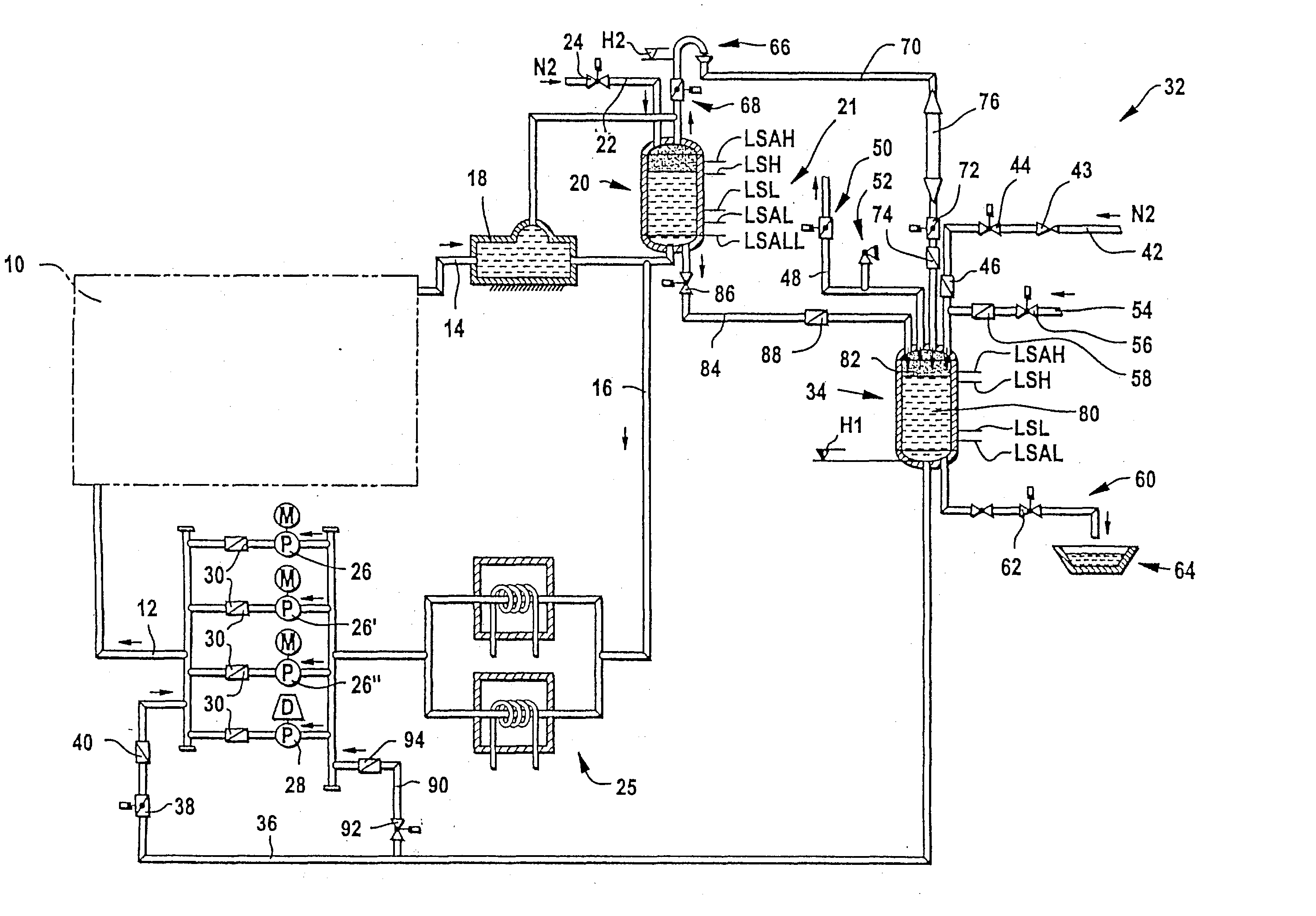
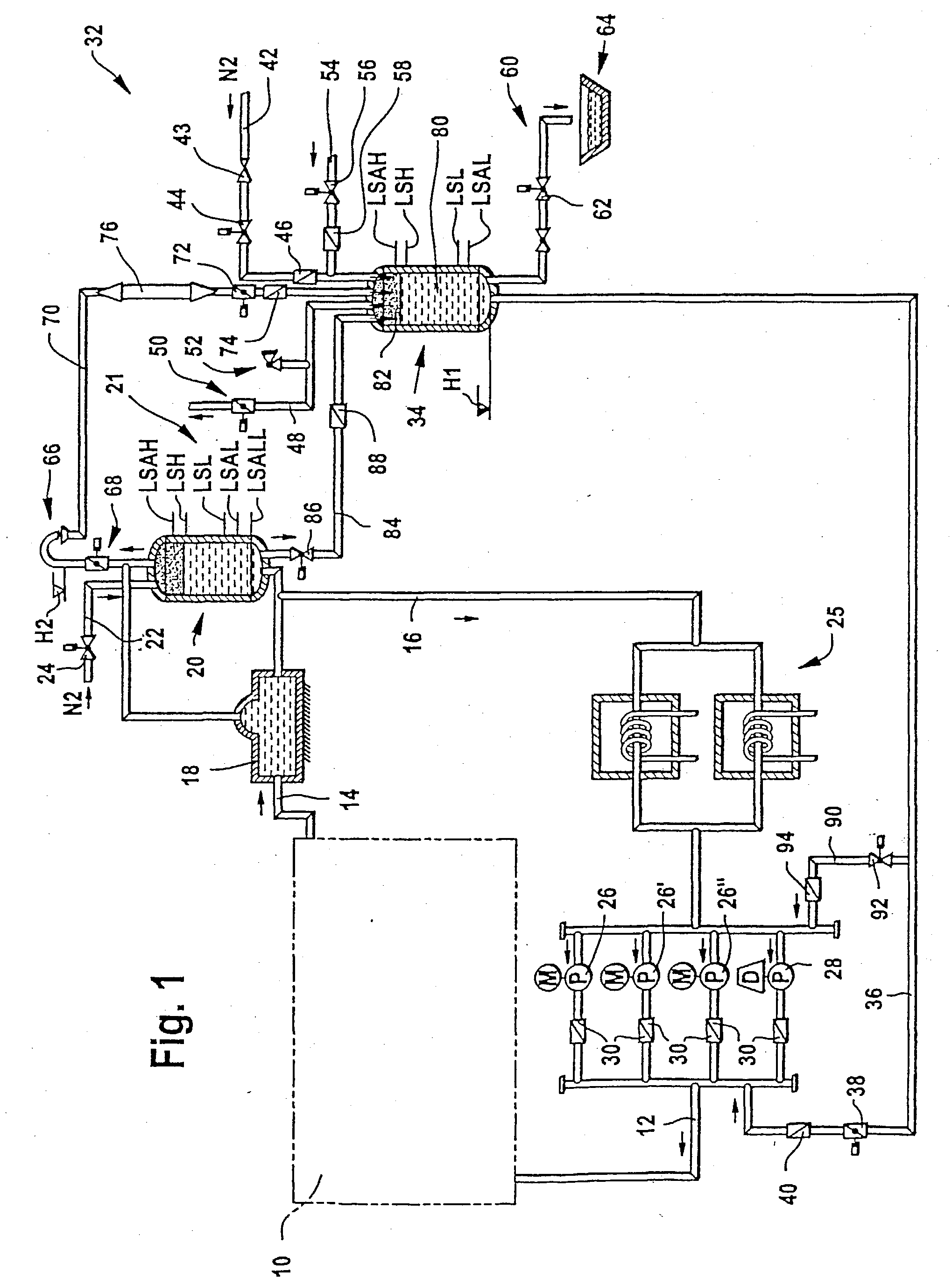
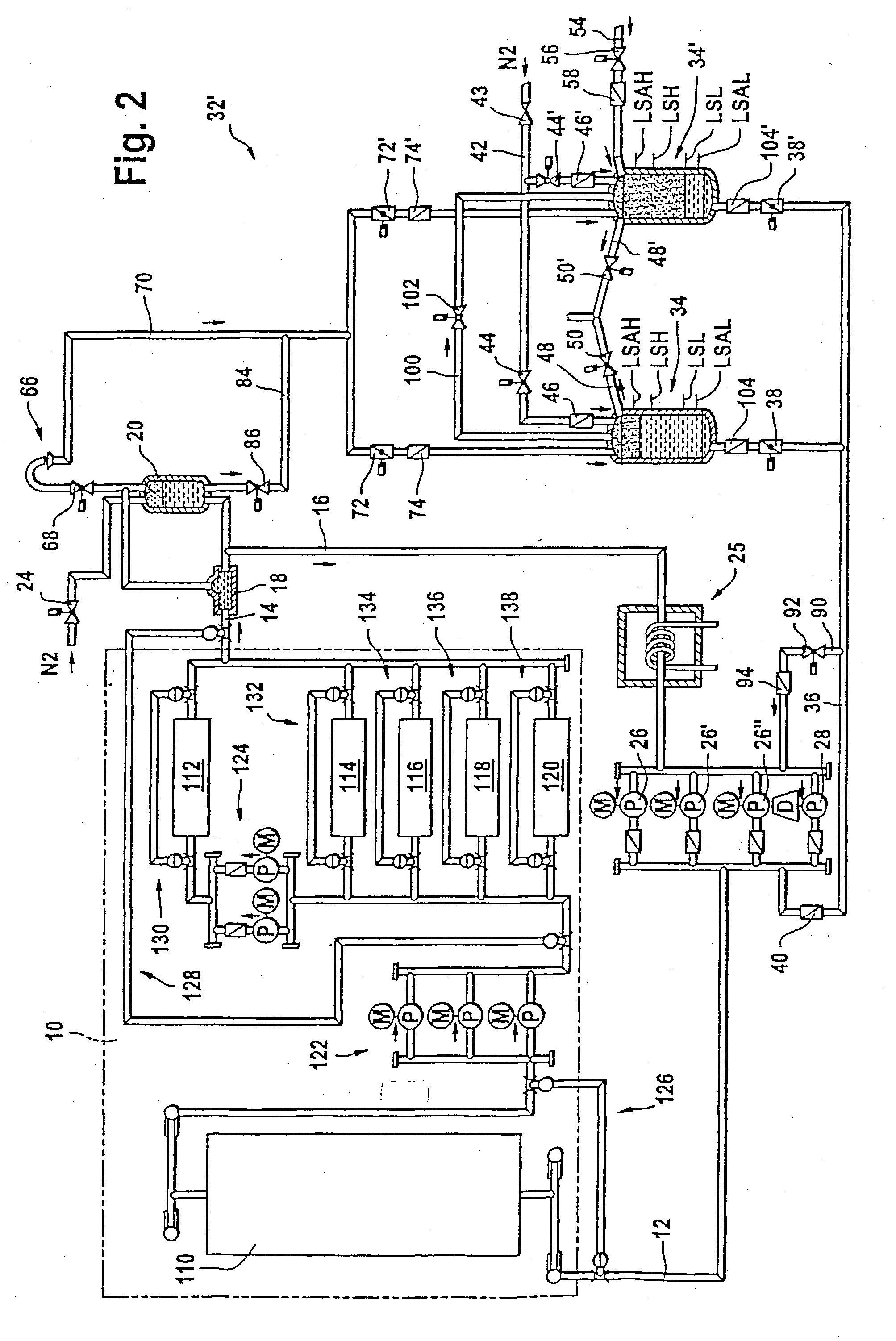
Cooling system for a metallurgical furnace
InactiveUS20030106673A1Positive repercussionShorten the timeCooling devicesStationary conduit assembliesWater flowAtmospheric pressure discharge
A cooling system for a blast furnace includes a cooling circuit (10) closed by a return line (16) and at least one circulation pump (26, 26', 26'') for circulating cooling water through the closed cooling circuit. An emergency feed line (36) with an emergency feed valve (38), which opens in case of a power failure, is connected to the cooling circuit (10). An emergency overflow valve (68) is located at the highest point of the closed cooling circuit (10). This emergency overflow valve (68) opens in case of a power failure, so that the closed cooling circuit (10) becomes an open cooling circuit (10) with an atmospheric pressure discharge at its highest point. A pressure vessel (34), which is connected to the emergency feed line (36), contains a certain volume of emergency water which is pressurised by a gas, so that, in case of a power failure, an emergency water flow establishes through the open cooling circuit (10).
Owner:PAUL WURTH SA
Leakage-checking spacing method of blast furnace
InactiveCN1818594AGuarantee normal productionReduce or avoid anomaliesDetection of fluid at leakage pointMeasurement of fluid loss/gain rateEngineeringOpen air
A method for detecting out leakage and its position on cooling wall of blast furnace includes confirming line existed by damaged cooling wall, blocking water supply of said line, supplying air on water supply tube and opening air vent valve at top section of cooling wall, leading compressed air with pressure greater than pressure in furnace in water supply tube on said cooling wall, opening air vent valve on adjacent cooling wall to see whether there is water being led out or not then opening said valve on cooling wall of the line in sequence till water is led out at one of valves ,confirming that section above water-out valve is damaged .
Owner:HEBEI IRON AND STEEL
Blast furnace cooling water backwater top pressure power generation
InactiveCN101021197AImprove power generation efficiencyStable flowHydro energy generationCooling devicesExhaust valveControl system
The present invention relates to a power generation method by utilizing iron-smelting blast furnace cooling water backwater residual pressure (water head). It is characterized by that said invention utilizes the principle of small runoff type hydroelectric generation in the blast furnace cooling backwater system, and utilizes the blast furnace cooling water backwater and makes the blast furnace cooling water backwater be flowed into cooling water pump or be freely discharged to form a height difference with about 9 m and produce a stable water resource with stable water head and stable water quantity, and utilizes the stable water resource to implement power generation. Besides, said invention also provides a technical scheme for implementing the invented power generation method.
Owner:王岗
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com