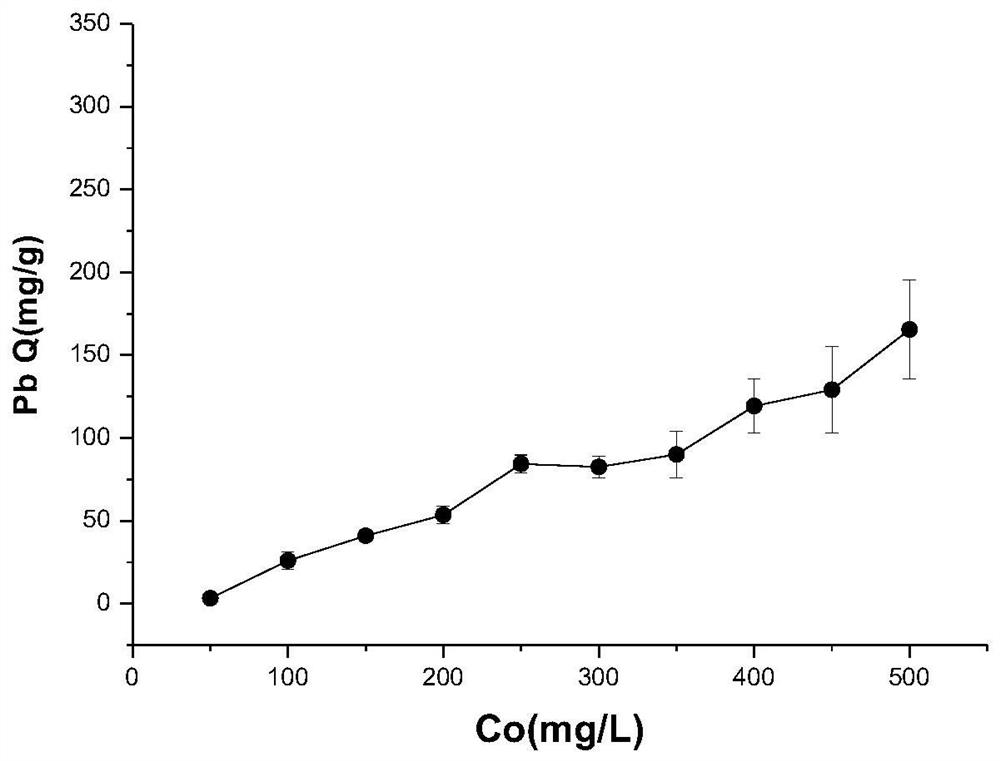
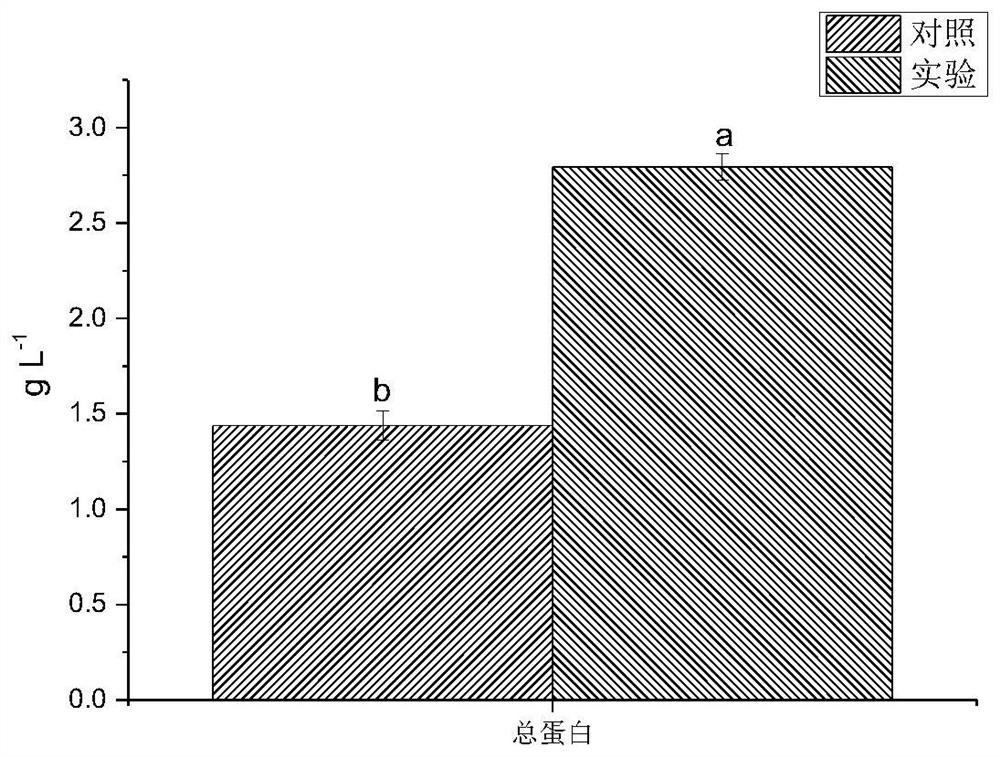
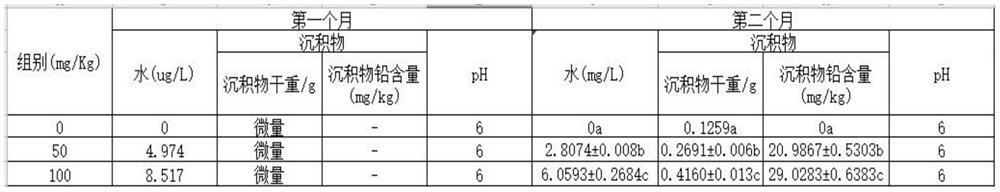
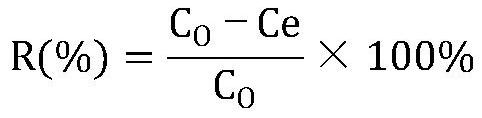Patents
Literature
36 results about "Pb contamination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Application and method of utilizing enriching plant in repairing lead polluted soil
InactiveCN1887457AReduce energy consumptionLow costContaminated soil reclamationContaminated soilsRoot system
The present invention relates to botanical repairing technology of polluted environment, and is especially the method of utilizing super enriching plant in repairing heavy metal contaminated soil. The method includes planting castor in lead contaminated soil for the root system of castor to absorb lead from soil and removing the castor in blooming stage or maturing stage from the contaminated soil. The said method can eliminate lead from the contaminated soil to repair lead contaminated soil without affecting the physical and chemical properties, and has low power consumption, low cost, easy operation, no secondary pollution and other advantages.
Owner:云南省环境科学研究院(中国昆明高原湖泊国际研究中心)
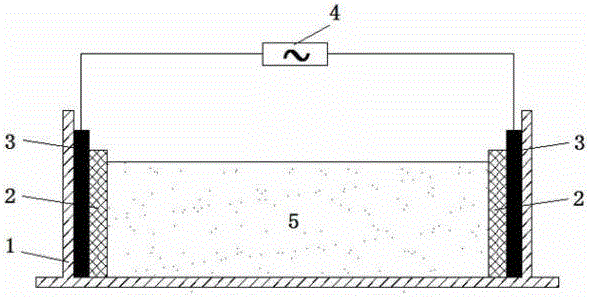
Repair method of cadmium and lead polluted soil and electric-microorganism united permeable reaction wall repair device
InactiveCN105880276AShort repair cycleLow costContaminated soil reclamationMicroorganismSoil remediation
The invention discloses a repair method of cadmium and lead polluted soil and an electric-microorganism united permeable reaction wall repair device. The device comprises a reaction tank, an electrode, a power supply and permeable reaction walls, space between the two permeable reaction walls is filled with to-be-treated cadmium and lead polluted soil added with microorganisms, pollutants which are migrated to an electrode from the soil are adsorbed by the permeable reaction walls, and therefore, heavy metals including cadmium and lead are removed from the to-be-treated soil. The soil is repaired by uniting the microorganisms, an ecological adsorption material and electrodynamics, a plurality of methods are used, a plurality of systems are used in an integrated manner, the pollutants which are transferred to two poles are adsorbed and fixed through PRB, so that the heavy metals are removed from the soil, by use of the permeable reaction walls and an electric method, an electric pollutant extracting system is omitted, the repair method is close to reality, and the repair performance of an electrokinetic system is optimized. By the method, soil repair period is short, cost is low, efficiency of repair to the cadmium and lead polluted soil is high, and secondary pollution is not caused easily.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
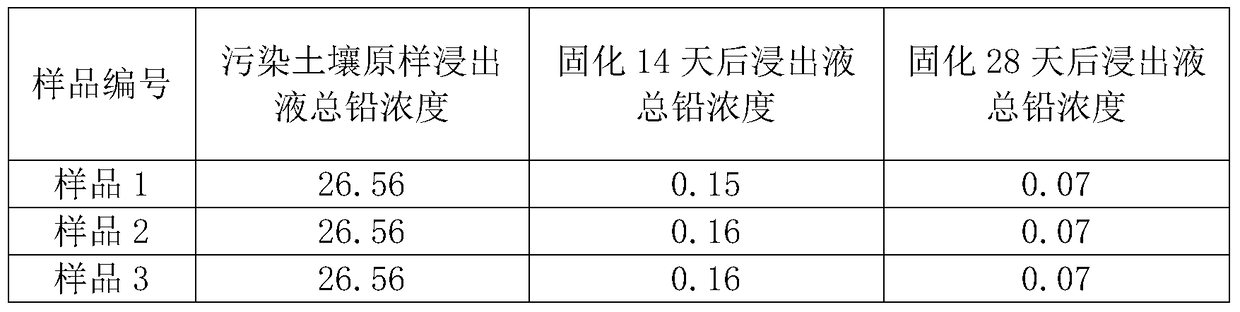
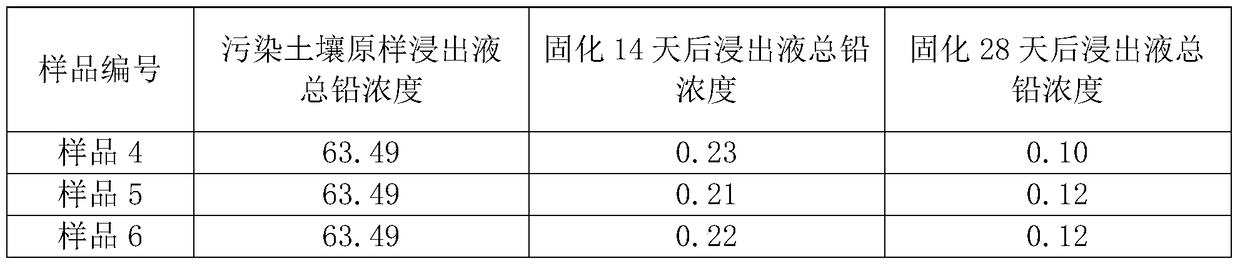
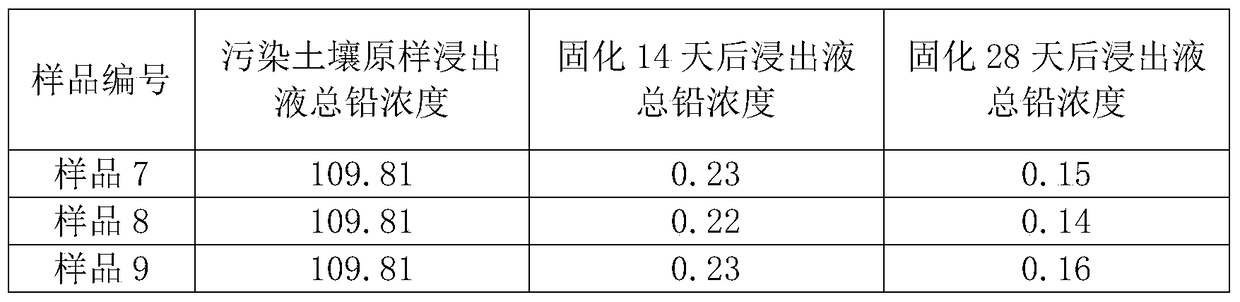
Remediation method of stabilization/solidification of lead-polluted soil
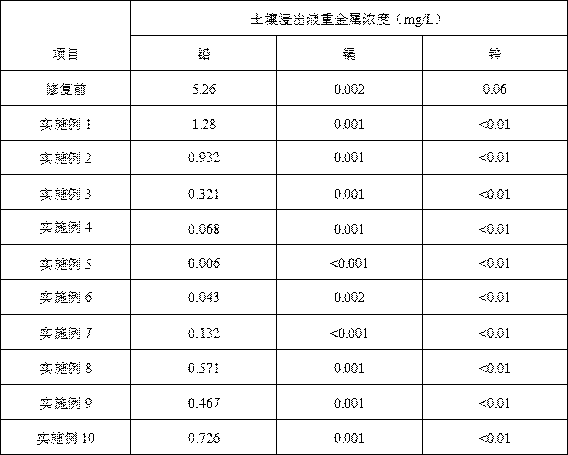
The invention discloses a remediation method of stabilization / solidification of lead-polluted soil. According to the method, a FeSO4 solution is added to the heavy metal lead-polluted soil, so that H+is generated through oxidization of the Fe2+, thus reducing pH value of soil, and promoting the conversion of instable lead in the soil into an effective state; then biochar and phosphate are added to the heavy metal lead-polluted soil, so that through adsorption, complexness, kation exchange, precipitation and the like between the biochar and phosphate and lead ions, the lead of effective stateis further converted into a lead compound in a stable residue state, thereby reducing the bio-availability of the heavy metal, reducing the content of the heavy metal in effective state in soil, and achieving adsorption and stabilization treatment of lead. The remediation method can reduce the leaching concentration of a leachate from the lead-polluted soil to lower than type III water quality standard (0.01 mg / L) according to the Quality Standard for Ground Water GBT 14848-2017.
Owner:BEIJING GEOENVIRON ENG & TECH
Method for restoring lead polluted soil with amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP)
InactiveCN103639190APromote degradationEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationEnvironmental engineeringPb contamination
The invention discloses a method for restoring lead polluted soil with amino trimethylene phosphonic acid (ATMP), which has the advantages of higher biodegradability and higher rinsing efficiency. The method comprises the following steps: accurately weighing 1.00g of lead polluted soil sample, adding a 10-70% ATMP solution in a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:25, oscillating at room temperature, standing, centrifugating and filtering to complete the rinsing process, wherein the oscillation time is 12 hours, the standing time is 12 hours, the centrifugating speed is 4000 r / min, and the centrifugating time is 20 minutes. The lead concentration of the polluted soil is 1000-4020 mg.kg<-1>. By using the ATMP for reinforced restoration of the lead polluted soil, the method has the characteristics of high restoration efficiency, high operability, low environmental risk and the like.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
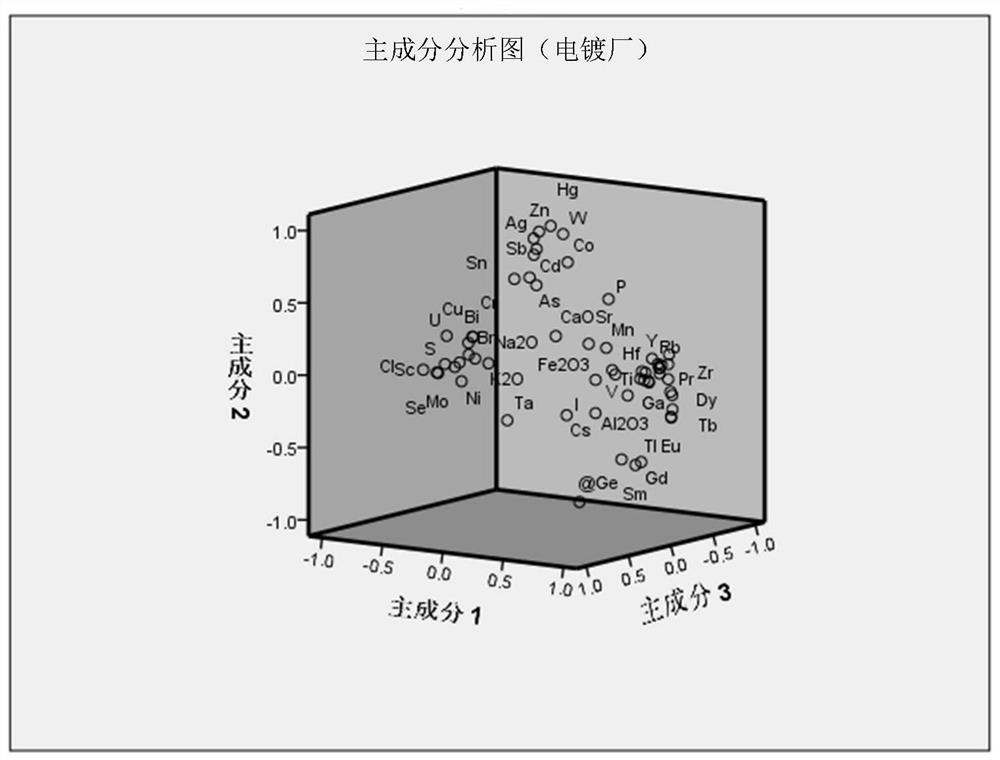
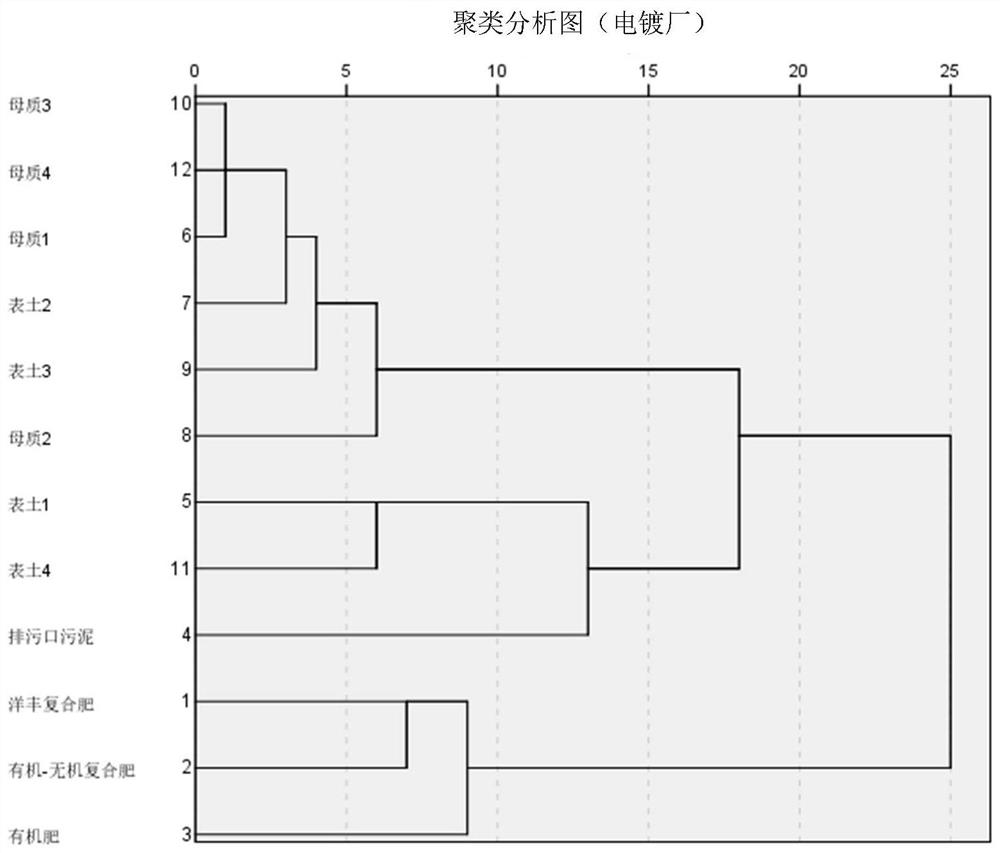
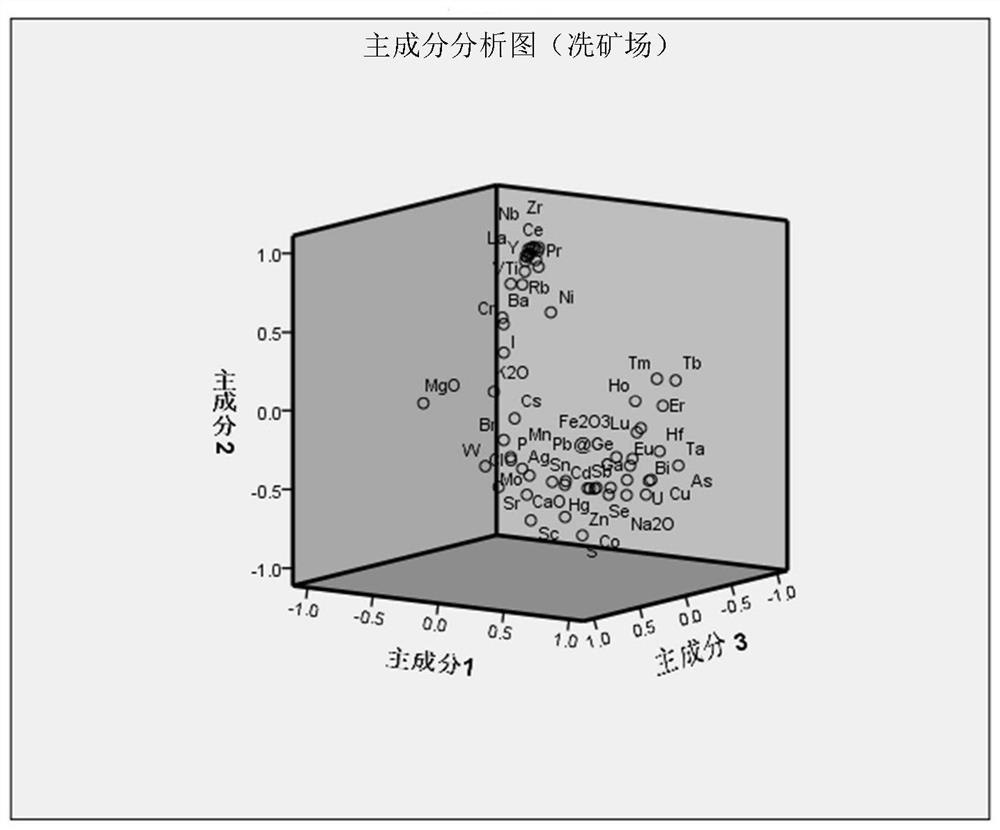
Soil lead pollution source identification method based on stable isotope and multi-element characteristic analysis
ActiveCN112179974AOvercoming the defects that have no practical guiding significanceFast trackMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil scienceMultivariate statistics
The invention relates to the technical field of environmental detection, and discloses a soil lead pollution source identification method based on stable isotope and multi-element characteristic analysis. The method comprises the steps of 1) determining an investigation area of a lead pollution source; 2) carrying out environment investigation on the determined lead pollution source investigationarea; 3) according to an environmental survey result, arranging sampling points according to different conditions, and collecting a risk source sample; 4) analyzing and determining the lead isotope ratio and the contents of various mineral elements in the lead-polluted soil and the risk source sample; and 5) identifying the lead pollution source based on stable isotope and multi-element characteristic fingerprint in combination with principal component clustering analysis. Based on a lead pollution source identification technology combining lead stable isotope, multi-element characteristics and multivariate statistics, a soil heavy metal lead pollution source can be accurately discriminated and identified, and a scientific basis is provided for soil lead pollution prevention and control work.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
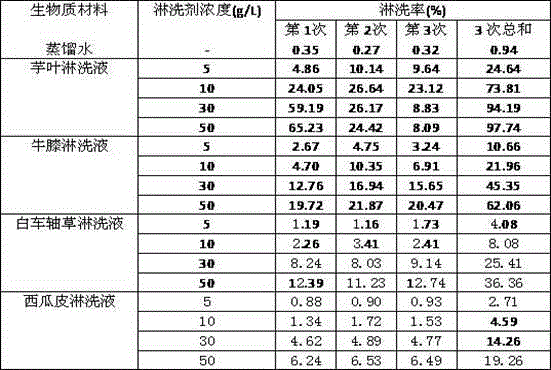
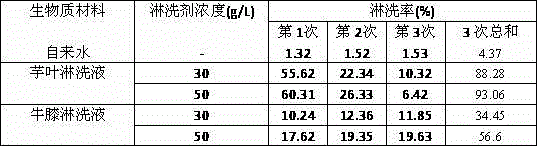
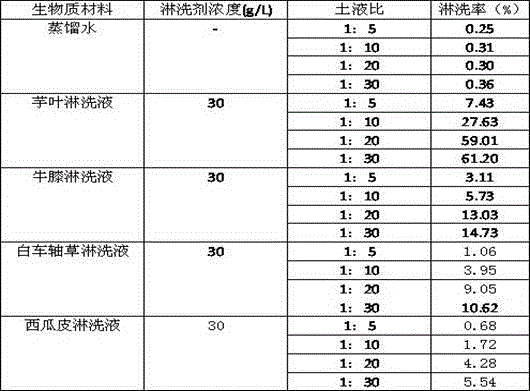
Method for removing lead from contaminated soil by virtue of taro leaf or achyranthes bidentata leaching
InactiveCN104550224AGood rinse effectEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceBiology
The invention relates to the technical field of remediation of contaminated soil in the environment, and particularly relates to a method for removing lead from contaminated soil by virtue of taro leaf or achyranthes bidentata leaching. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing biomass leachate: washing a biomass material taro leaves with tap water, rinsing the taro leaves with distilled water, air-drying the taro leaves at a naturally-ventilated place, grinding the taro leaves by virtue of a crusher, sieving the taro leaves with a 2mm sieve, adding a proper amount of distilled water, performing oscillatory extraction on the mixed liquor for 12h, and performing filtration to obtain the leachate; (2) leaching the contaminated soil: adding the leachate obtained in step (1) into the lead-contaminated soil, regulating the pH value of the mixed solution to 4.4 to 5.0 by virtue of diluted hydrochloric acid and a sodium hydroxide solution, and performing oscillatory leaching. Achyranthes bidentata can be used instead of the biomass material taro leaves. The method is convenient and simple, an obvious leaching effect on the lead-contaminated soil is played, and secondary contamination to the environment is avoided.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
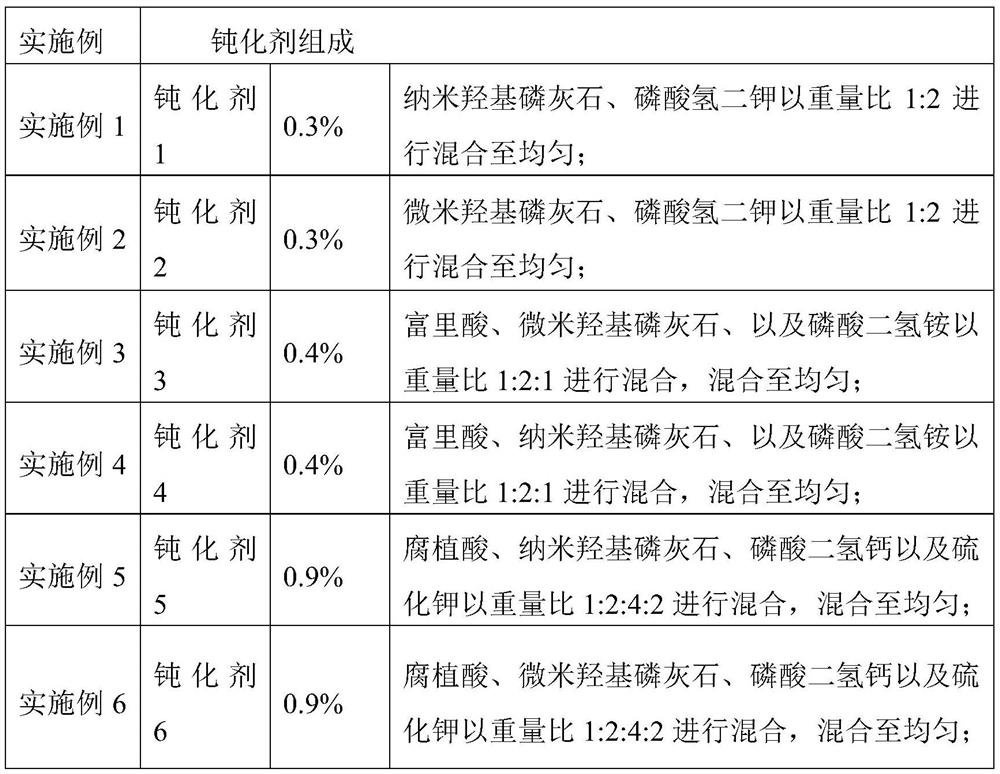
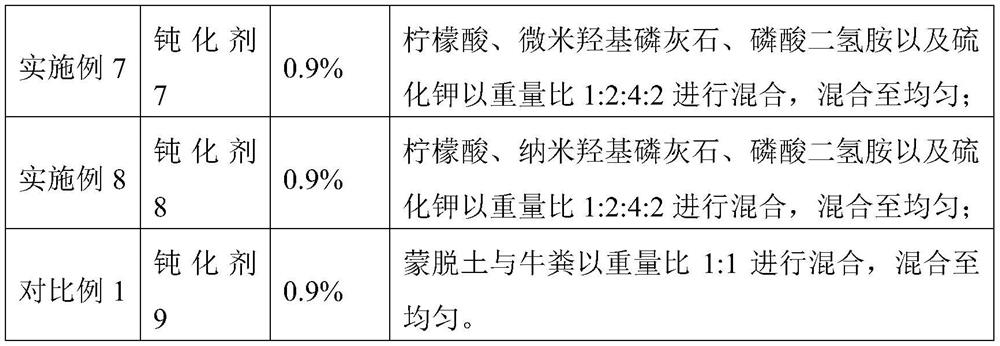
Heavy metal passivator and application thereof
InactiveCN113046088AFriendlyNo secondary pollutionAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersEngineeringSulfide
The invention discloses a heavy metal passivator. The heavy metal passivator comprises hydroxyapatite and a phosphorus-containing material, and further comprises acidic substances and sulfides. The invention also discloses application of the heavy metal passivator in repairing soil polluted by heavy metal cadmium and / or lead. The heavy metal passivator is wide in raw material source and simple in formula, all the components are mixed according to the corresponding proportion, the heavy metal passivator is applied to the heavy metal cadmium contaminated soil during application, use is convenient, new negative effects are avoided, and secondary pollution is avoided; and the heavy metal passivator has high soil environment friendliness and has good application and popularization value.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
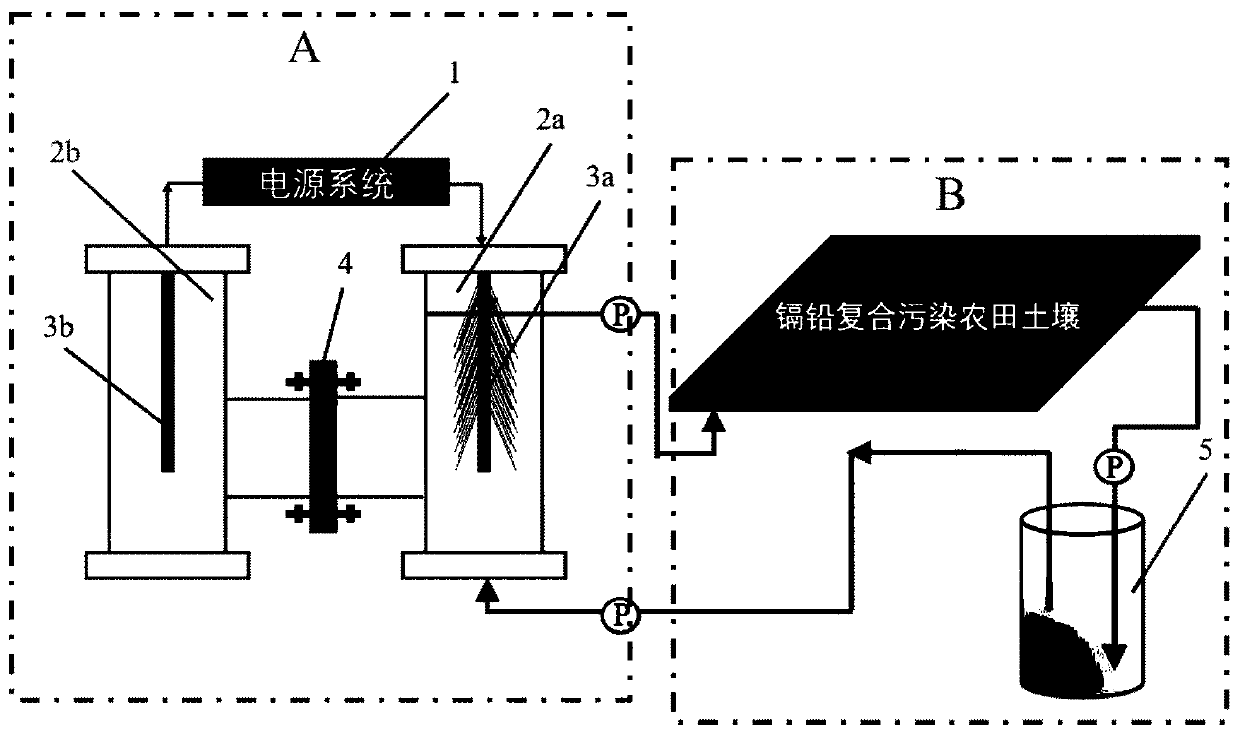
Device for in-situ remediation of cadmium and lead contaminated farmland soil through sulfate reduction system driven by microorganism electrochemistry and method thereof
ActiveCN111054740AReduce lead toxicityWill not cause significant changes in physical and chemical propertiesContaminated soil reclamationElectrolysisEdaphic
The invention discloses a device for in-situ remediation of cadmium and lead contaminated farmland soil by microbial electrochemical enhanced sulfate reduction and a method thereof. According to the method, a sulfate reduction reactor is used for generating the sulfur-containing (S<2->) water system passivator, the passivator can be used for in-situ remediation of cadmium and lead polluted farmland soil, and cadmium and lead are converted into forms which are difficult to absorb by crops. A double-chamber sulfate reduction reactor is constructed, current is applied to promote hydrogen production reaction of a cathode chamber, and autotrophic sulfate reducing bacteria in the cathode chamber can reduce sulfate into S <2-> by utilizing hydrogen and an inorganic carbon source generated by water electrolysis of an electrode. After the passivator containing S<2-> is mixed with soil, the toxicity of cadmium and lead in farmland soil can be reduced. The liquid passivator is used for restoringthe cadmium and lead polluted farmland soil, the physicochemical property of the soil cannot be obviously changed, and the device and the method have obvious advantages compared with the mode of restoring the heavy metal polluted soil through quick lime, biochar and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and activating agent for restoring cadmium and/or lead contaminated soil through Hylotelephium erythrostictum and application
PendingCN107876551AEasy to degradeImprove adsorption capacityContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersHylotelephium erythrostictumEngineering
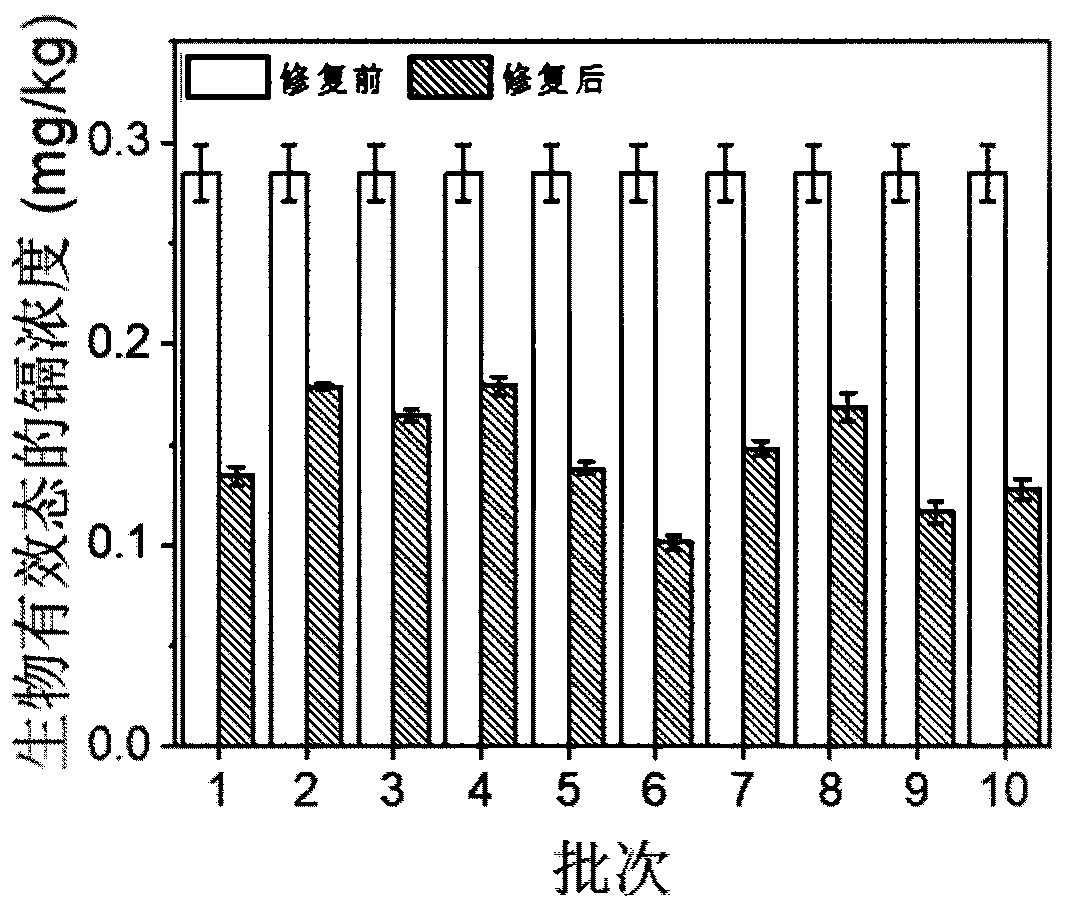
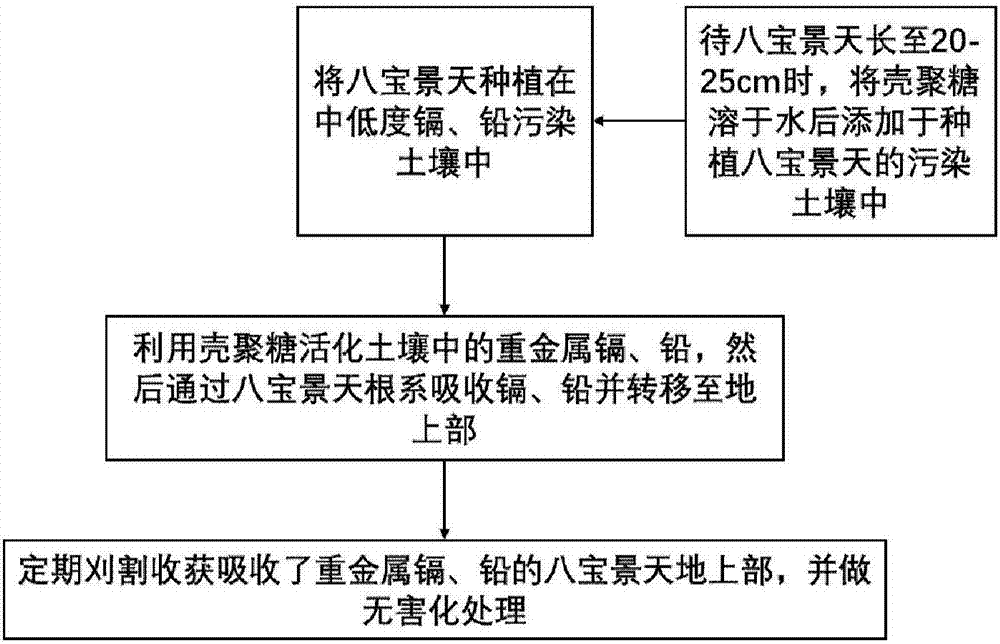
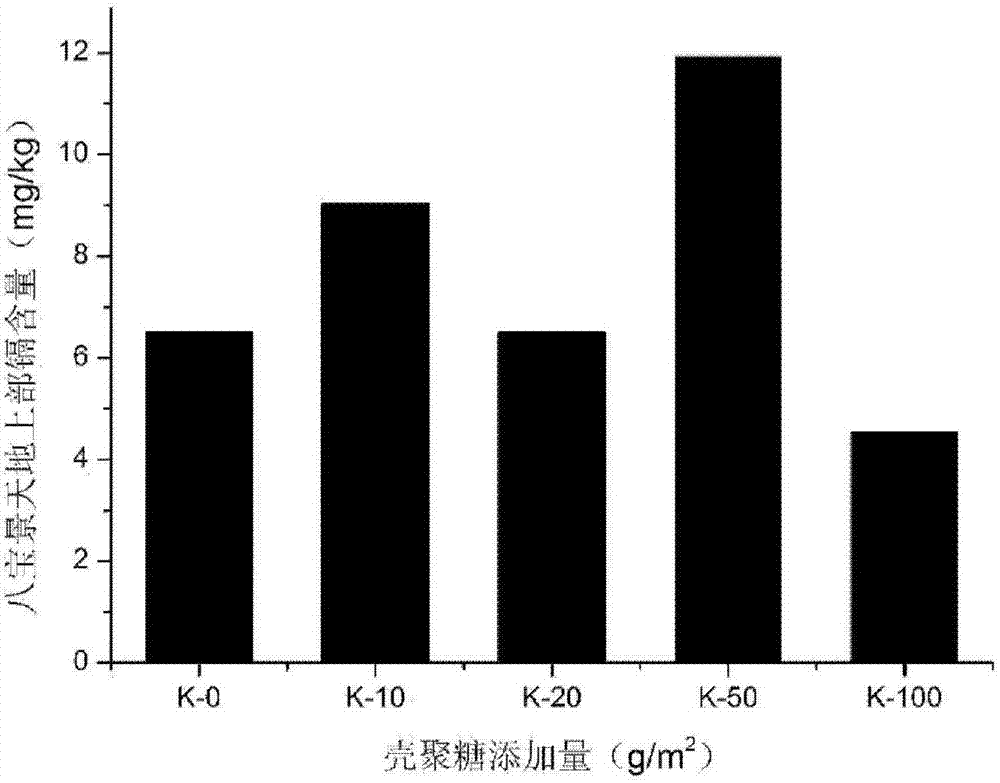
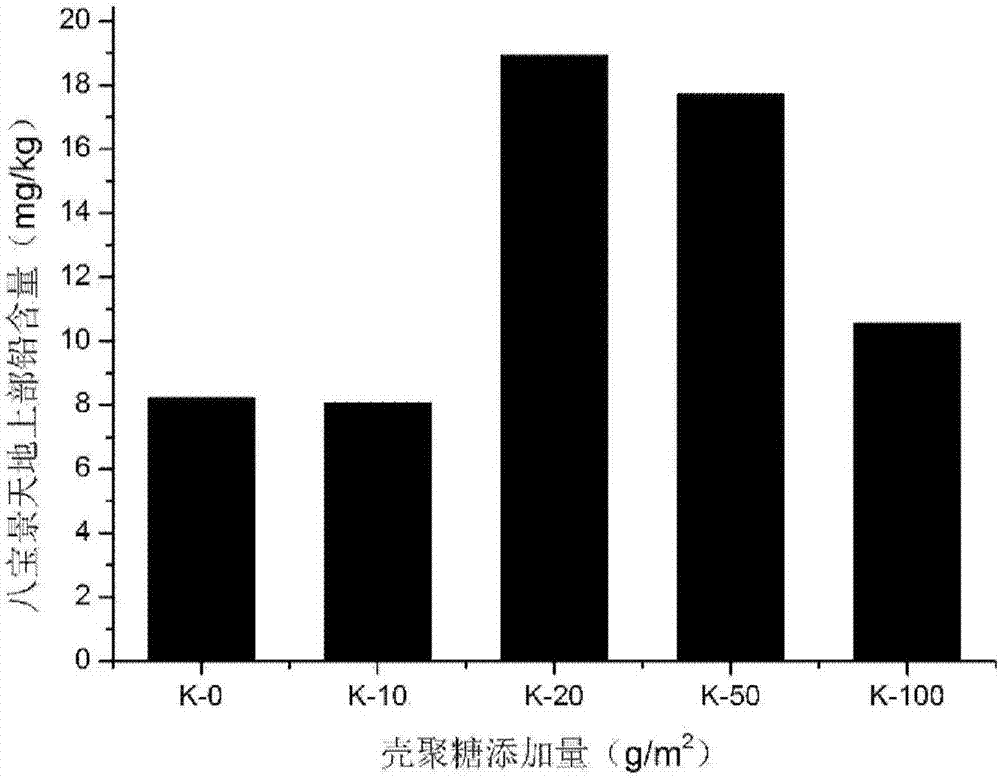
The invention discloses a method and activating agent for restoring cadmium and / or lead contaminated soil through Hylotelephium erythrostictum and application of the activating agent. According to themethod, the Hylotelephium erythrostictum is planted on the cadmium and / or lead contaminated soil, and water-soluble carboxyethyl chitosan is applied into the contaminated soil to activate heavy metalcadmium and / or lead; and the Hylotelephium erythrostictum survives and grows, the overground part, absorbing the heavy metal cadmium and / or lead, of the Hylotelephium erythrostictum is reaped regularly, the heavy metal cadmium and lead in the soil can be effectively removed, and thus the restoring efficiency of the Hylotelephium erythrostictum to the cadmium and / or lead contaminated soil is greatly improved, wherein the activating agent is the water-soluble carboxyethyl chitosan. The method and the activating agent have the advantages that the restoring efficiency of the Hylotelephium erythrostictum is improved, the cost is low, operation is easy and convenient, biodegradability is achieved, and secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:INST OF GEOGRAPHICAL SCI & NATURAL RESOURCE RES CAS
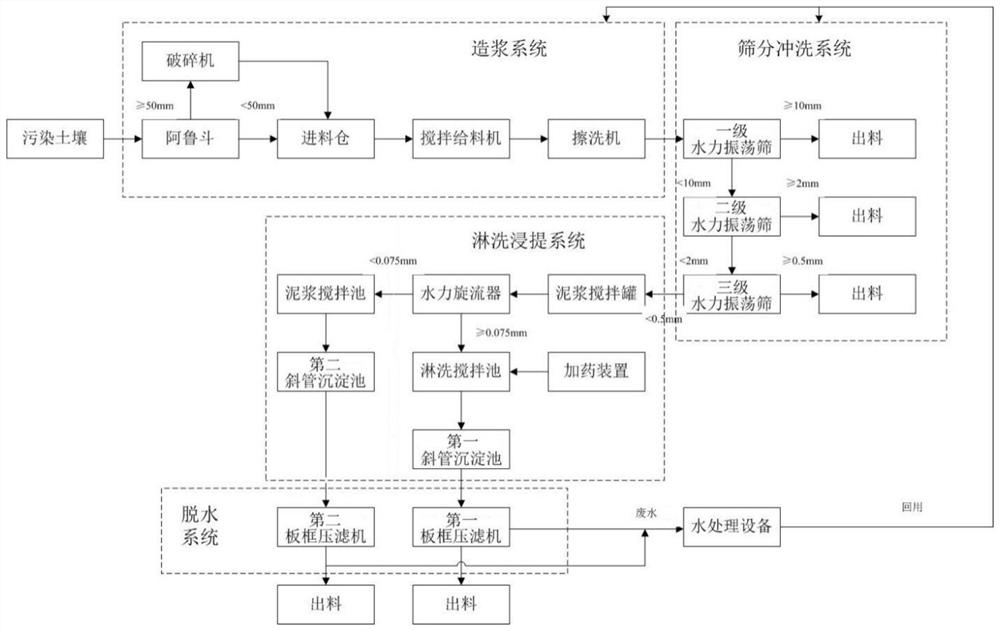
Engineered remediation equipment and remediation method for heavy metal arsenic and lead contaminated soil
The invention discloses engineered remediation equipment and remediation method for heavy metal arsenic and lead contaminated soil. The remediation equipment comprises a slurry making system, a screening and washing system, a leaching and leaching system and a dehydration system which are connected in sequence. The remediation method comprises the steps: (1) preparing slurry; (2) screening and washing; (3) leaching and extracting; and (4) dehydrating. Key parameters such as a slurry-making water-soil ratio, a screening and washing water-soil ratio and an agent leaching liquid-solid ratio are improved, meanwhile, according to the nature of south and north soil, south clay soil is more beneficial to attachment of arsenic, lead and other heavy metals, and the particle size grading limit of screening and washing and agent leaching in the remediation process is defined; economic cost accounting is carried out on the process, the engineered remediation equipment and remediation method for the heavy metal arsenic and lead contaminated soil are provided, and the remediation efficiency of the soil can be economically and effectively improved.
Owner:ZHONGKE DINGSHI ENVIRONMENTAL ENG CO LTD
Application of florists cineraria in repairing lead polluted soil
InactiveCN104475435AReduce erosionNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationOperabilityAeolian processes
The invention relates to a plant reparation technique of lead polluted soil, and particularly relates to an application of florists cineraria in repairing lead polluted soil. Florists cineraria is planted on soil containing pollutant lead; the root system of florists cineraria absorbs a large amount of lead in the polluted soil, and the lead is transferred to organs of the overground part; and when the plant grows to the overground part, and biomass is maximal, organs of the overground part of the plant are removed from the polluted soil, thereby achieving the aim of removing pollutant lead in the soil. According to the invention, an abundant plant, namely florists cineraria, is utilized for treating lead polluted soil, and the plant reparation technique has the advantages of low expense, high operability, no harm to the physical and chemical properties of soil, no secondary pollution, good effects of preventing wind erosion and water erosion of the polluted soil and the like.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
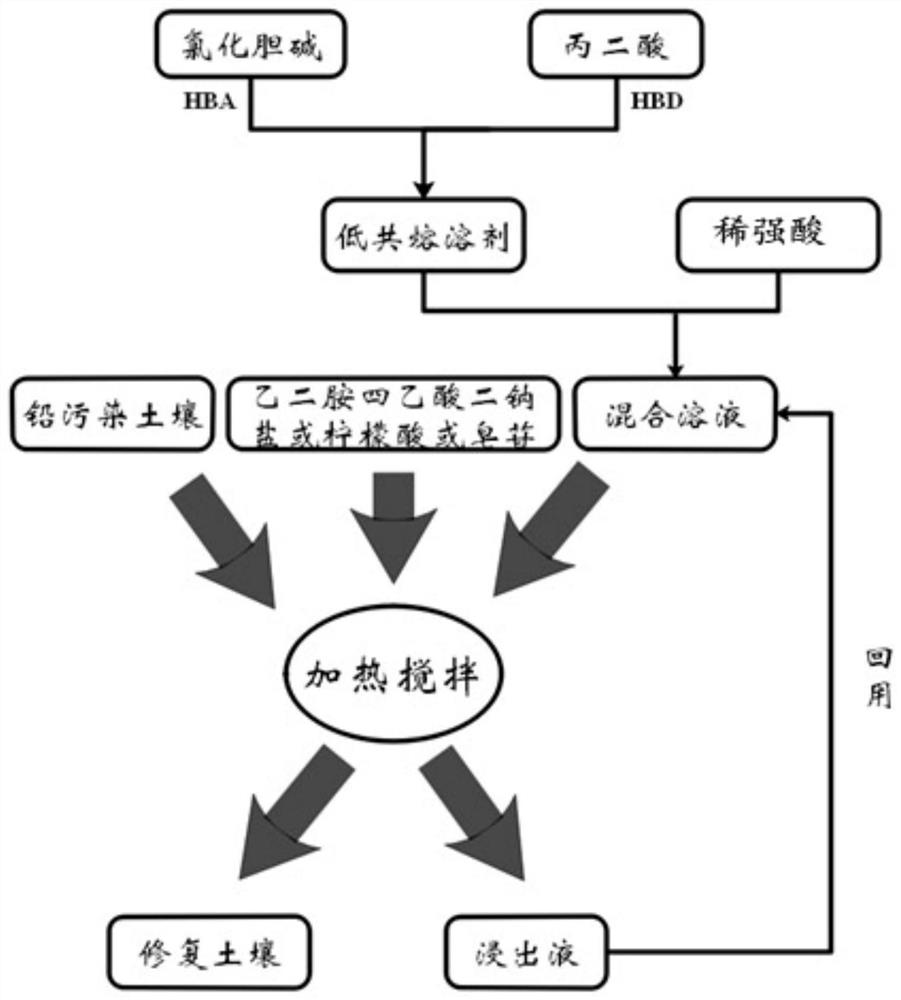
Heavy metal lead contaminated soil remediation method based on deep eutectic solvent synthesized from choline chloride and malonic acid
PendingCN112222181AEfficient Governance RepairLow costContaminated soil reclamationSoil treatmentWater chlorination
The invention belongs to the technical field of heavy metal contaminated soil treatment, and particularly relates to a heavy metal lead contaminated soil remediation method based on a deep eutectic solvent synthesized from choline chloride and malonic acid. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, grinding and sieving naturally air-dried heavy metal lead contaminated soil, then adding sieved contaminated soil particles, a synthesized choline chloride malonic acid solvent, nitric acid and a soil chelating agent into a conical flask in proportion, and putting the conical flask into a magnetic stirrer for stirring, heating and leaching reaction. The lead-containing compounds which are insoluble in water in the soil are eluted through heating leaching of the stirrer, and effective leaching remediation of the lead-contaminated soil is achieved. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of simplicity, high efficiency and no secondary pollution, and is a lead-contaminated soil remediation method with a good prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI SECOND POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Remediation agent suitable for lead-contaminated soil and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110791292AOther chemical processesOrganic fertilisersSoil scienceEnvironmental engineering
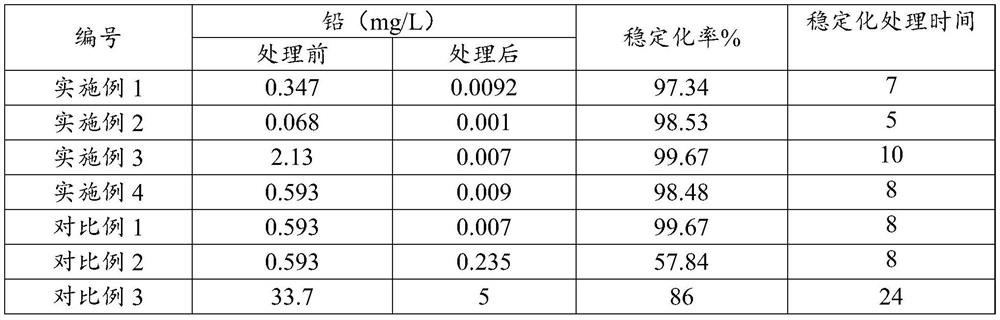
The invention discloses a remediation agent suitable for lead-contaminated soil and a preparation method thereof. The remediation agent suitable for lead-contaminated soil is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 20-60 parts of sepiolite, 10-50 parts of sodium sulfide, 5-35 parts of calcium dihydrogen phosphate and 5-20 parts of calcium carbonate. The average particle size of the materials is 200 meshes. The preparation method of the sepiolite-based remediation agent for lead-contaminated soil includes the steps of: grinding sepiolite ore to 200 meshes, and carrying out microwave modification treatment; mixing the modified sepiolite with sodium sulfide, calcium dihydrogen phosphate and calcium carbonate, and performing packaging to obtain the sepiolite-based remediation agent for lead-contaminated soil. The sepiolite-based remediation agent prepared according to the invention is used for remediation of lead-contaminated soil, can significantly reduce the concentration oflead in soil leachate, and has a stabilization rate up to 99.5% or more. The sepiolite-based remediation agent prepared according to the invention has the advantages of environmental friendliness, low remediation cost and strong operability, and has good economic benefits and wide social benefits.
Owner:湘潭海泡石科技有限公司
Lead-contaminated soil stabilizing agent and lead-contaminated soil stabilizing remediation method
InactiveCN112143501AContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersPhosphateEnvironmental engineering
Owner:SHOUGANG ENVIRONMENTAL IND
Lead-resistant bacterium and application thereof
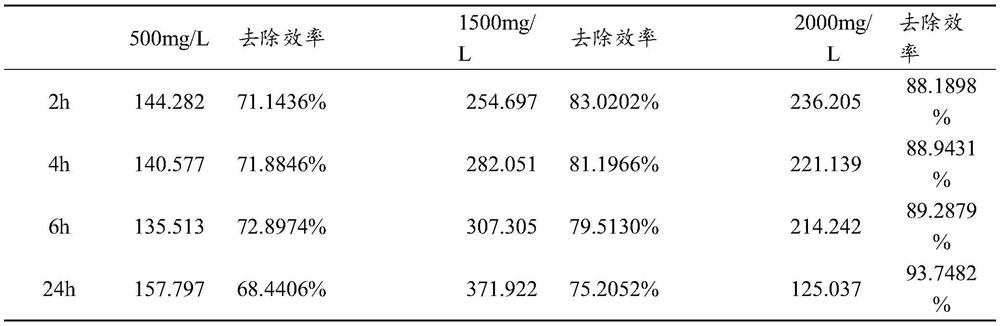
The invention discloses a lead-resistant bacterium and application thereof, the lead-resistant bacterium is citrobacter freundii, the lead-resistant bacterium is preserved in Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection Center (GDMCC), and the preservation number is GDMCC No: 61961. The invention further provides application of the lead-resistant bacterium in treatment of lead-polluted water or soil. The high-lead-resistant bacterial strain MPEB0002917 can survive in a high-concentration lead environment and has an extremely strong adsorption effect on lead, the 24-hour removal efficiency can reach up to 93.75% when the concentration is 2000mg / L, and the high-lead-resistant bacterial strain MPEB0002917 can be used for removing lead elements in polluted soil. The high-lead-resistant bacterial strain MPEB0002917 is prepared into a lead adsorbent, and the lead adsorbent can be applied to removal of heavy metal contaminated soil on a large scale.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI +1
Application of mesembrianthemum to repairing of lead polluted soil
InactiveCN104438304AReduce erosionNo secondary pollutionContaminated soil reclamationOperabilityAeolian processes
The invention relates to a plant repairing technology of lead polluted soil and particularly relates to application of mesembrianthemum to repairing of the lead polluted soil. Mesembrianthemum is planted on the soil containing pollutant lead and a lot of the lead in the polluted soil is absorbed by a mesembrianthemum root system and is transferred to organs of an over-ground part; and when the plant grows until the biomass of the over-ground part is maximum, the organs of the over-ground part of the plant are removed from the polluted soil so that the aim of removing the pollutant lead in the soil is realized. According to the application, the lead polluted soil is managed by enriching the plant mesembrianthemum; and the application has the advantages that the cost is low, the operability is high, the physicochemical property of the soil is not damaged, the secondary pollution is not caused, and the effects for preventing soil wind erosion and water erosion are good.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Method for applying humic acid to soil remediation
PendingCN111906137AReduced available lead contentReduce use costContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSoil scienceSoil remediation
The invention discloses a method for applying humic acid to soil remediation, and particularly relates to the technical field of soil remediation, which comprises the following steps: 1, selecting lead-contaminated soil, and detecting the content of available lead in the soil; 2, uniformly spreading the humic acid repairing agent on the surface of the soil according to the dosage of 0.5-1.0 Kg ofhumic acid repairing agent to each square meter of the selected soil area; 3, after deep ploughing is conducted on the soil, covering the soil with a plastic film, and after 15 days, detecting the content of available lead in the soil again; and 4, comparing the two detection results, and stopping using the humic acid repairing agent when the effective state content reduction rate of the soil is greater than 20% to enter a soil tillage stopping and renovating period. According to the humic acid soil remediation agent and the formula composition thereof, the content of available lead in soil can be remarkably reduced, meanwhile, the content of organic matter is increased, the effect of several times of application of a common soil remediation agent can be achieved by adding a small amount of humic acid soil remediation agent, the use cost can be reduced, and large-scale application is facilitated.
Owner:JINING UNIV
A method for in-situ stabilization and remediation of lead-contaminated sediment with iron-based materials and microorganisms
ActiveCN110436728BStabilized reagent repair is efficient and sustainableEfficient and sustainable repairWater contaminantsFixation/solidifcation sludge treatmentOXALIC ACID DIHYDRATEMicroorganism
The invention discloses a novel method and a reagent for in-situ stabilizing repairing of lead polluted sediment by using an iron-based material synergistic microbes. The reagent comprises the iron-based material and a sulfate-reducing bacterium solution, and the iron-based material is prepared by reacting an iron-containing silicate mineral with oxalic acid in an aqueous medium at 55-120 DEG C. The reagent is added to the lead-polluted sediment, so the lead immobilization efficiency is 97% or above, the repairing is carried out in situ without an additional device, and the reagent and the method have the advantages of high lead stabilizing efficiency, low cost and no secondary pollution.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
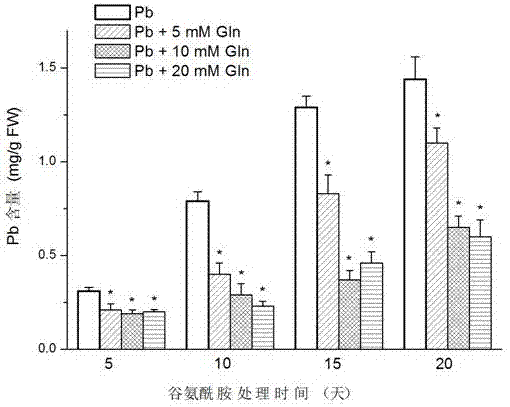
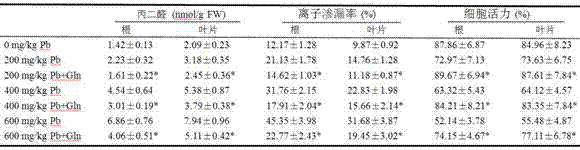
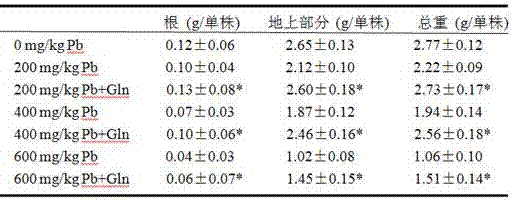
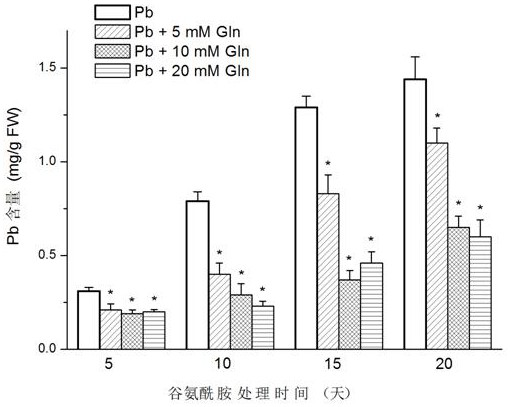
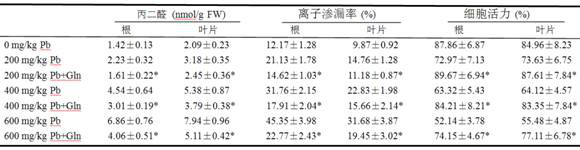
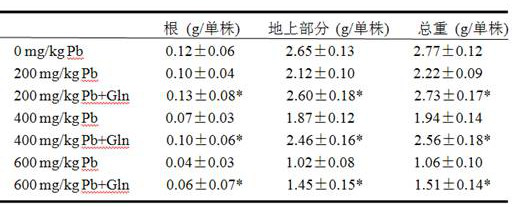
Method of using glutamine to inhibit Pb absorption of Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis and increase ability to resist Pb contamination
ActiveCN107306952AAvoid absorptionReduce accumulationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsBrassica rapaBirdsrape Mustard
The invention discloses application and method of glutamine to inhibit heavy metal Pb absorption of plants to relieve vegetable heavy metal contamination and reduce vegetable damage by Pb and growth inhibition by Pb. Soil Pb absorption by plants is inhibited via glutamine treatment herein; by applying 10 mmol / L of glutamine to Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis and other vegetables grown in soil with different Pb contamination levels, it is possible to effectively inhibit soil Pb absorption by Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis, reduce Pb accumulation in roots and stem leaves of Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis, and relieve Pb contamination of Brassica rapa subsp. Chinensis.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A strain of Trichoderma aculeatus and its application in remediation of lead-contaminated soil
ActiveCN108277166BImprove toleranceImprove adsorption capacityPlant growth regulatorsBiocideTrichoderma asperellumEdaphic
The invention discloses a strain of Trichoderma asperellum. The strain has been preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee on January 22, 2018, and its biological preservation number is: CGMCC NO.15266. The trichoderma asperellum (Trichoderma asperellum) screened and isolated by the present invention has excellent tolerance and adsorption capacity to various heavy metals, especially lead, and is easy to colonize in soil polluted by heavy metals, especially in soil polluted by lead. Survival, suitable for microbial remediation of soil.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
A method for remediating lead-contaminated soil by using A. philodendron
ActiveCN111672901BStrong growth and survival abilityShorten the growth cycleContaminated soil reclamationBiotechnologyEngineering
The invention relates to a method for repairing the lead-containing bottom mud of an electroplating factory by utilizing the physiological integrity and the chemical precipitation method of philodendron philodendron. The specific steps are as follows: firstly, plant Azalea philodendron on the bottom mud of the electroplating factory, and build a reservoir 5cm beside the bottom mud pool, artificially control the growth direction of Azalea philodendron, so that it extends toward the reservoir, due to physiological integration Sexual effect, philodendron philodendron will transfer to the water body and release lead ions, after a certain period of cultivation, put Na in the water body of the reservoir 3 PO 4 Carry out precipitation recovery. The invention mainly uses the Physiologically Integrated transfer of lead ions by the Physiophthora philodendron to repair the bottom mud of the electroplating plant, and the method is simple in operation and strong in feasibility.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Regulation and control method for promoting excessive absorption and accumulation of lead by Arabis alpina Linn. var. parviflora Franch. through mediation of sulfur
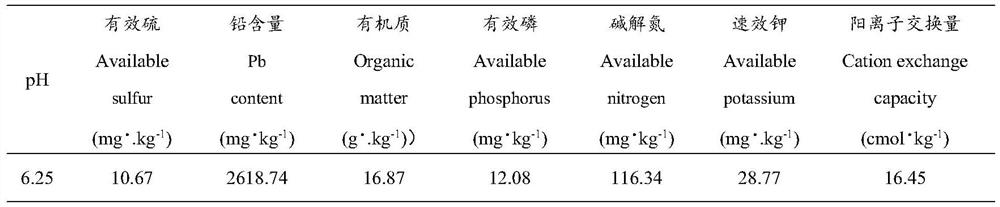
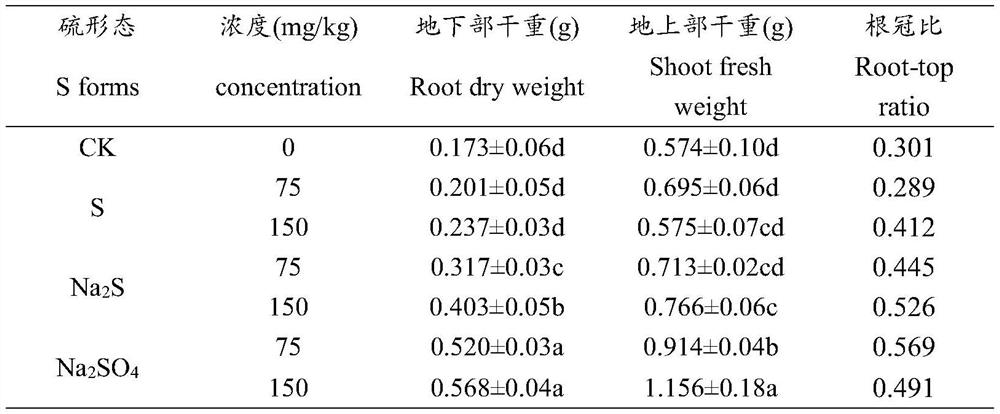
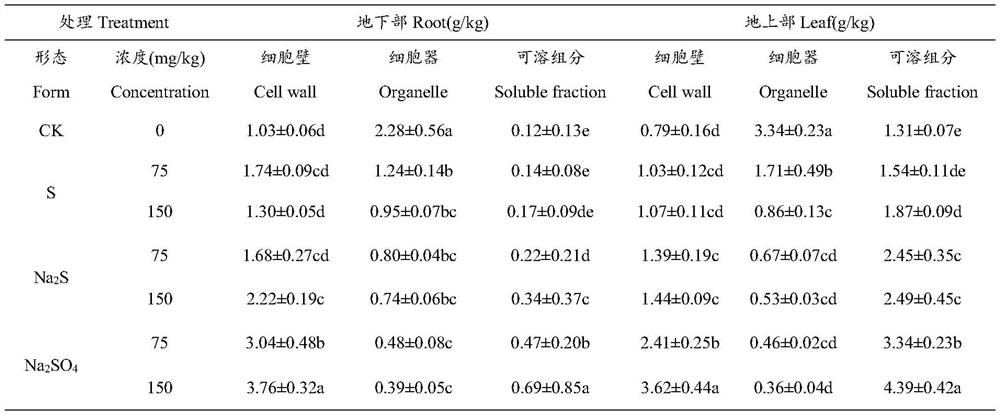
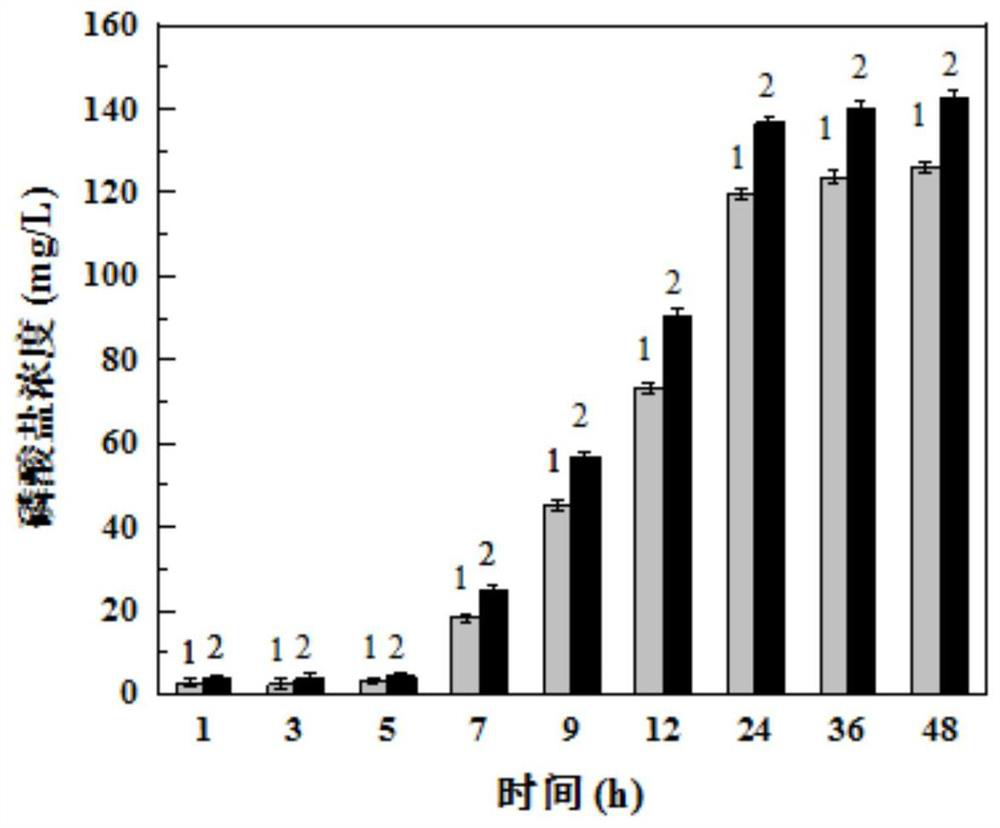
The invention discloses a regulation and control method for promoting excessive absorption and accumulation of lead by Arabis alpina Linn. var. parviflora Franch. through mediation of sulfur. The regulation and control method comprises the following steps of: soil selection, plant planting, sulfur element solution preparation, sulfur element treatment, biomass determination, determination of sulfur and lead in subcells, determination of lead content, data statistics and analysis and the like. According to the method of the invention, the biomass of the overground part and the underground part of the Arabis alpina Linn. var. parviflora Franch. under the treatment of sulfur with different valence states and concentrations, theoretical and technical method guidance is provided for the enrichment characteristic of lead and the distribution of lead in subcellular components, the research of the coping mechanism of the Arabis alpina Linn. var. parviflora Franch. to lead stress under the action of sulfur, the action mechanism of lead enrichment of the Arabis alpina Linn. var. parviflora Franch. on the subcellular level and the promotion of the restoration of lead-polluted soil by the hyperaccumulatedArabis alpina Linn. var. parviflora Franch.through sulfur regulation and control.
Owner:YUNNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of bone black/CMC (carboxy methylated cellulose) stabilized FeS composite material loaded phosphate solubilizing bacteria functionalized microbial agent
PendingCN113502283AToxic reductionHigh activityBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationMicrobial agentBioremediation
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a bone black / CMC stabilized FeS composite material loaded phosphate solubilizing bacteria functionalized microbial agent, and relates to the technical field of soil remediation. The invention aims to solve the problem of low passivation efficiency caused by serious inhibition of biological activity of phosphate solubilizing bacteria (PSB) by high-concentration lead when lead pollution is repaired by adopting a bioremediation method. The method comprises the following steps: placing phosphate solubilizing bacteria in an LB culture medium, and carrying out shake culture for 7-9 hours to obtain a phosphate solubilizing bacteria suspension; and mixing the bone black / CMC stabilized FeS composite material with a phosphate solubilizing bacteria suspension, carrying out shake culture for 5-8 hours, centrifuging, washing, and freeze-drying to obtain the bone black / CMC stabilized FeS composite material loaded phosphate solubilizing bacteria functionalized microbial agent. The invention discloses a preparation method and application of the bone black / CMC stabilized FeS composite material loaded phosphate solubilizing bacteria functional microbial agent.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Comprehensive technique for reducing pollutions to amaranths by heavy metals of cadmium and lead in soil
InactiveCN101715685BReduce the risk of harming human healthReduce accumulationContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceSoil heavy metals
The invention relates to a method for reducing pollutions to amaranths by heavy metals of cadmium and lead in soil, which comprises the following steps: firstly, screening an amaranth pollution strategy variety (Cd+Pb-PSC) with low accumulation of the cadmium and the lead; and secondly, planting the amaranth pollution strategy variety (Cd+Pb-PSC) with the low accumulation of the cadmium and the lead, and cooperatively employing a special soil conditioner for inhibiting the amaranth pollution strategy variety (Cd+Pb-PSC) with the low accumulation of the cadmium and the lead from absorbing the cadmium and the lead in the planting process. The method of the invention effectively reduces the absorption of Cd and Pb by the amaranths and reduces the pollutions to the amaranths by the heavy metals of the cadmium and the lead in the soil by screening the amaranth pollution strategy variety (Cd+Pb-PSC) with the low accumulation of the cadmium and the lead and employing the special soil conditioner for inhibiting the amaranth pollution strategy variety (Cd+Pb-PSC) with the low accumulation of the cadmium and the lead from absorbing the cadmium and the lead.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
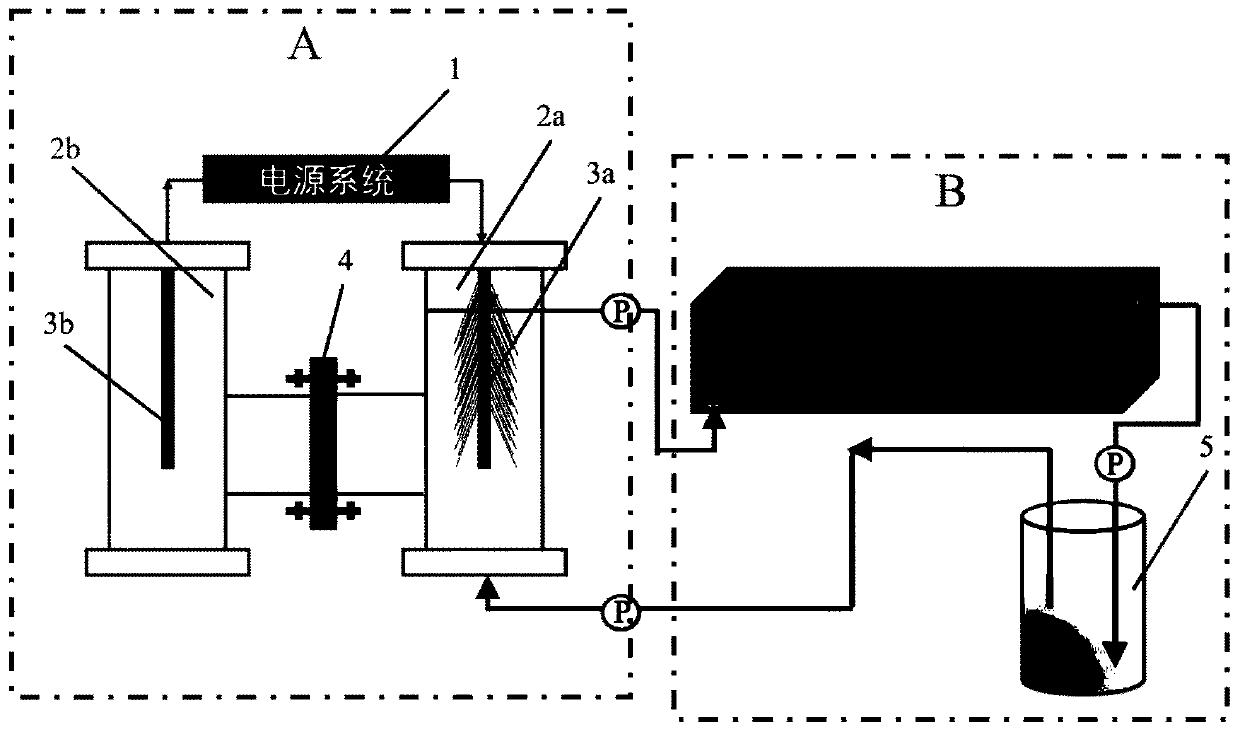
Device and method for in-situ remediation of cadmium and lead polluted farmland soil by microbial electrochemically driven sulfate reduction system
ActiveCN111054740BReduce lead toxicityWill not cause significant changes in physical and chemical propertiesContaminated soil reclamationEdaphicElectrolysis of water
The invention discloses a device and method for in-situ restoration of cadmium and lead polluted farmland soil by microbial electrochemically enhanced sulfate reduction. The present invention utilizes sulfate reduction reactor to produce sulfur-containing (S 2‑ ) Water-based passivation agent, which can repair cadmium and lead-contaminated farmland soil in situ, and convert cadmium and lead into forms that are difficult to be absorbed by crops. By constructing a double-chamber sulfate reduction reactor, the application of electric current promotes the hydrogen production reaction in the cathode chamber, and the autotrophic sulfate-reducing bacteria in the cathode chamber can use the hydrogen generated by the electrode electrolysis of water and the inorganic carbon source to reduce sulfate. for S 2‑ . The containing S 2‑ The passivator mixed with soil can reduce the toxicity of cadmium and lead in farmland soil. The invention uses the liquid passivating agent to remediate the cadmium- and lead-contaminated farmland soil without causing obvious changes in the physical and chemical properties of the soil, and has obvious advantages compared with the remediation of the heavy metal-contaminated soil by using quicklime, biochar and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
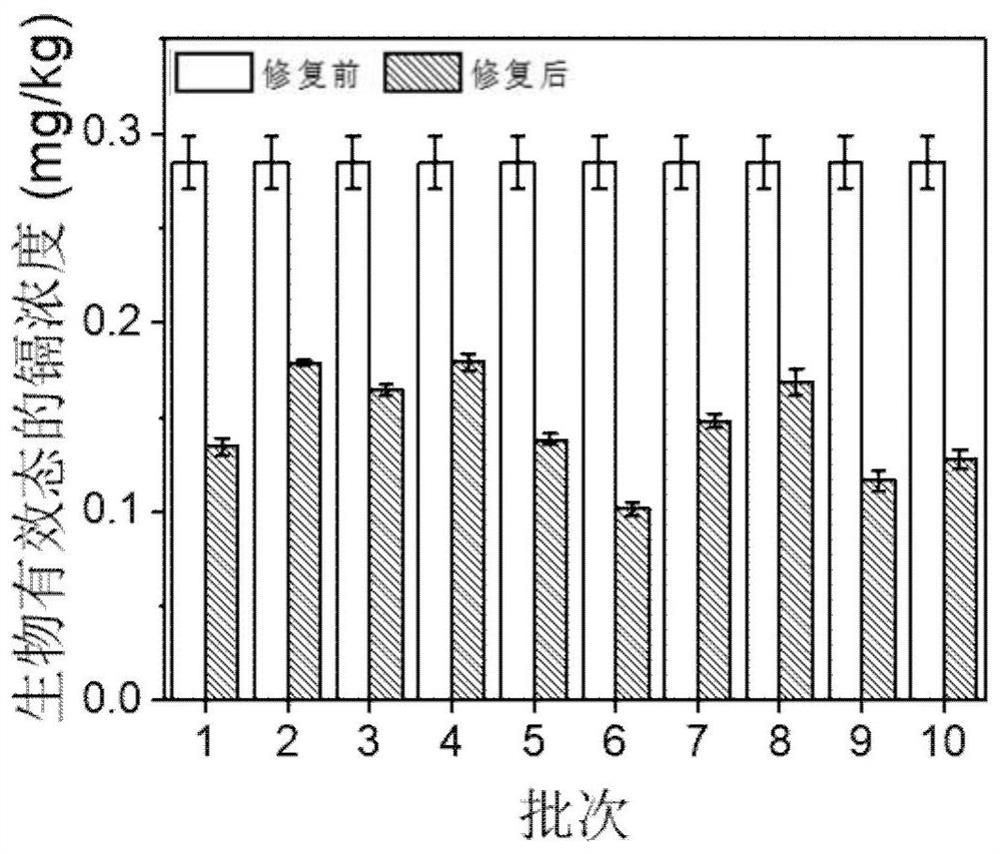
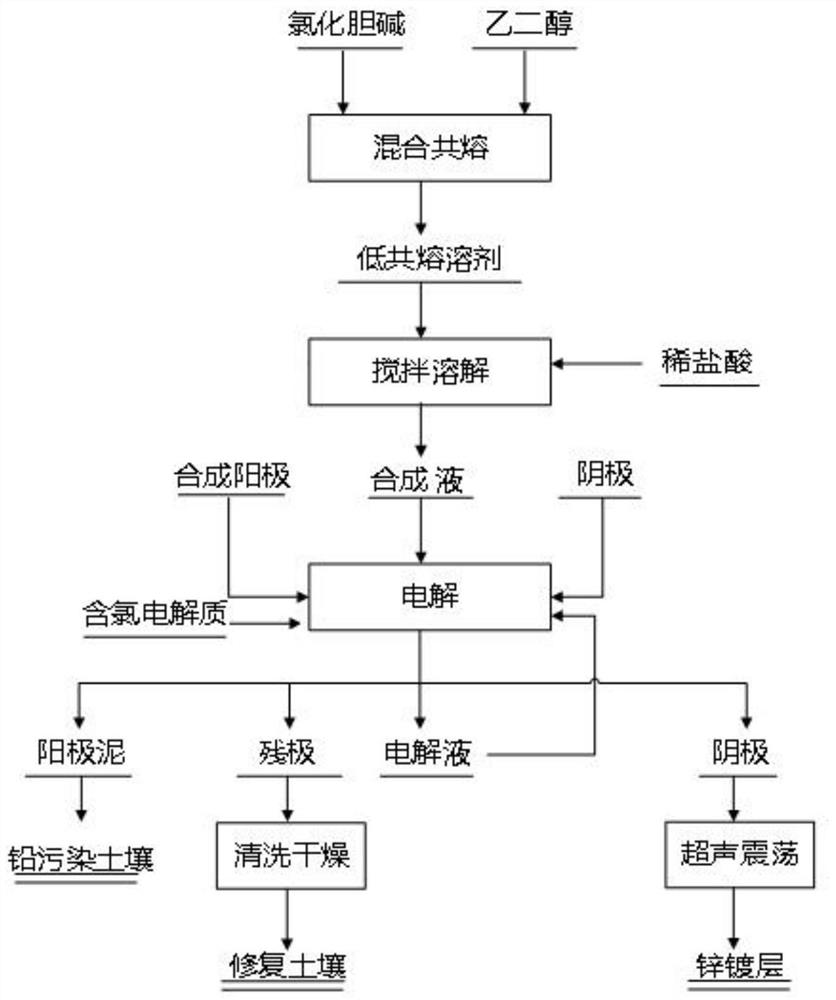
Electrochemical remediation method for lead-zinc combined polluted soil based on deep-eutectic solvent
PendingCN113798318ARaw materials are cheap and easy to getLow steam pressureContaminated soil reclamationElectrolytic agentWater chlorination
The invention relates to an electrochemical remediation method for lead-zinc combined contaminated soil based on a deep-eutectic solvent, and belongs to the technical field of heavy metal contaminated soil remediation. The method comprises the following specific steps: firstly, mixing choline chloride and ethylene glycol according to a molar ratio of 1: 2, heating, stirring and co-melting at 70 DEG C to synthesize a choline chloride-ethylene glycol deep-eutectic solvent; adding diluted hydrochloric acid into the deep-eutectic solvent, stirring and dissolving uniformly to prepare a synthetic solution, and injecting into an electrolytic cell; and preparing a contaminated soil anode from graphite, contaminated soil and a pore-forming agent, arranging a cation exchange membrane on one side close to the cathode, adding a chlorine-containing electrolyte into an anode chamber, performing electrolysis, and after electrolysis is finished, taking anode mud as lead contaminated soil, anode scrap as repaired soil and cathode sediment as recycled metal. The method is simple, the electric energy utilization rate is high, the deep-eutectic solvent is non-toxic and degradable, the electrolyte can be recycled, secondary pollution is avoided, and the method is an economical and efficient lead-zinc combined contaminated soil remediation method.
Owner:云南省生态环境科学研究院
Enterobacter agglomerans with phosphate-solubilizing capacity, and application thereof
InactiveCN102690763BGuaranteed stabilityHigh phosphorus dissolving capacityBacteriaSeed and root treatmentBiotechnologyPhosphate
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment
InactiveCN110756576AReduce contentLow costContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment. The borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment is characterized in that surfacesoil of polluted soil is excavated, borrowed soil is added, adsorption plants are planted in the borrowed soil, the non-polluted soil is added, filter ponds are excavated around a polluted area, and the eichhornia crassipes is used to remove lead. The borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment can effectively reduce the content of the lead in the soil; the plants having agood adsorption effect on heavy metals such as lead can be used to adsorb the lead in the subsequently added borrowed soil to reduce the content of the lead transmitted into the borrowed soil from thebottom polluted soil, at the same time, the excavated polluted soil can be placed in the filter ponds, the aquatic plant eichhornia crassipes is used to adsorb the lead in the soil for purifying thesoil, and polluted water in the filter ponds is used as irrigation water to irrigate the adsorption plants, so that the problem of secondary pollution existing in a traditional borrowed soil deep ploughing method is improved, and the purification method has low costs, thereby being easy to promote and use.
Owner:金晨辉
Glutamine inhibits the absorption of Pb in Chinese cabbage and improves the ability to resist Pb pollution
ActiveCN107306952BAvoid absorptionReduce accumulationBiocidePlant growth regulatorsPb contaminated soilGrowth inhibitory
The invention discloses an application and method for using glutamine treatment to inhibit the absorption of heavy metal Pb by plants, reduce the heavy metal pollution of vegetables, and reduce the damage and growth inhibition of vegetables by Pb. The present invention utilizes glutamine treatment to inhibit plants from absorbing Pb in the soil, and by applying 10 mmol / L glutamine to vegetables such as pakchoi grown in different Pb-contaminated soils, it can effectively inhibit the absorption of Pb from the soil by pakchoi and reduce Pb Accumulate in the roots, stems and leaves of Chinese cabbage to reduce Pb pollution in Chinese cabbage.
Owner:HANGZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
A method for in-situ remediation of the surface of lead-contaminated soil, a passivator and a preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104861984BImprove curing effectReduce leaching concentrationContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersIn situ remediationSlag
The present invention relates to a soil in situ passivating agent, and in particular to a surface in situ remediation method of lead-contaminated soil, a passivating agent and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of environmental engineering. The passivating agent comprises 50-80% of slag, 10-16% of cement clinker and 10-34 % of rice hull ash; and the raw materials are mixed and milled, and the specific surface area of the milled powder is controlled at higher than 800m<2> / kg, so as to obtain the passivating agent. The passivating agent in the present invention mainly uses silicate hydrated gel phase for passivation consolidation on lead; the passivating agent has obvious curing effect on heavy metal lead in soil, can reduce the leaching concentration in early curing stage, carry out sustainable curing reaction in the middle and long term, can keep the leaching concentration in a decreasing trend; the raw materials are all from the typical industrial solid wastes, so as to utilize waste, treat pollution and help to reduce costs; therefore, the invention has significant economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:湖北省地质调查院 +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com