Device and method for in-situ remediation of cadmium and lead polluted farmland soil by microbial electrochemically driven sulfate reduction system
An in-situ remediation and sulfate technology, applied in the field of lead-contaminated farmland soil, sulfate reduction system in-situ remediation of cadmium, to achieve the effect of reducing production costs and the output of pollutants such as sludge
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
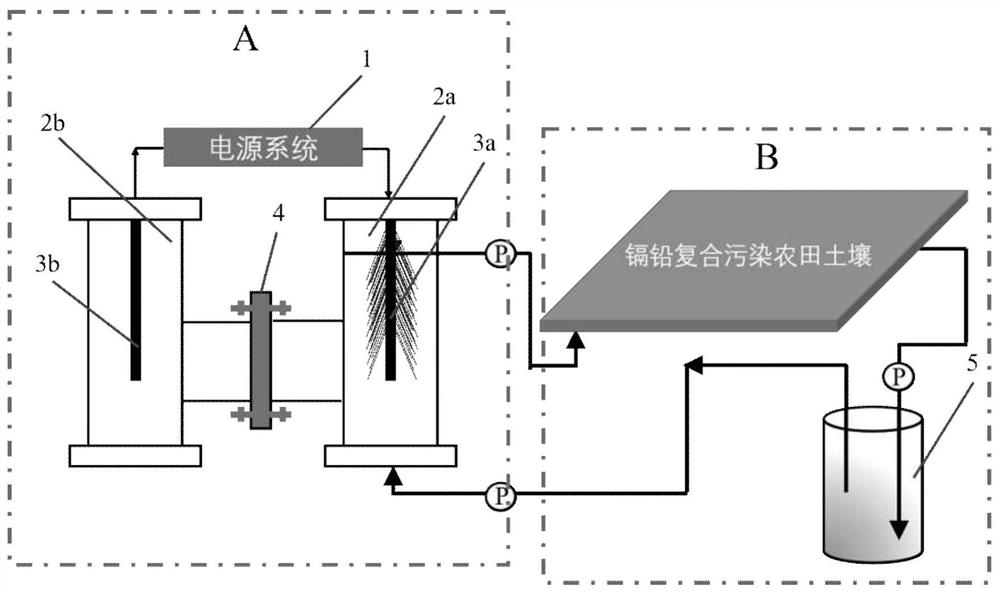
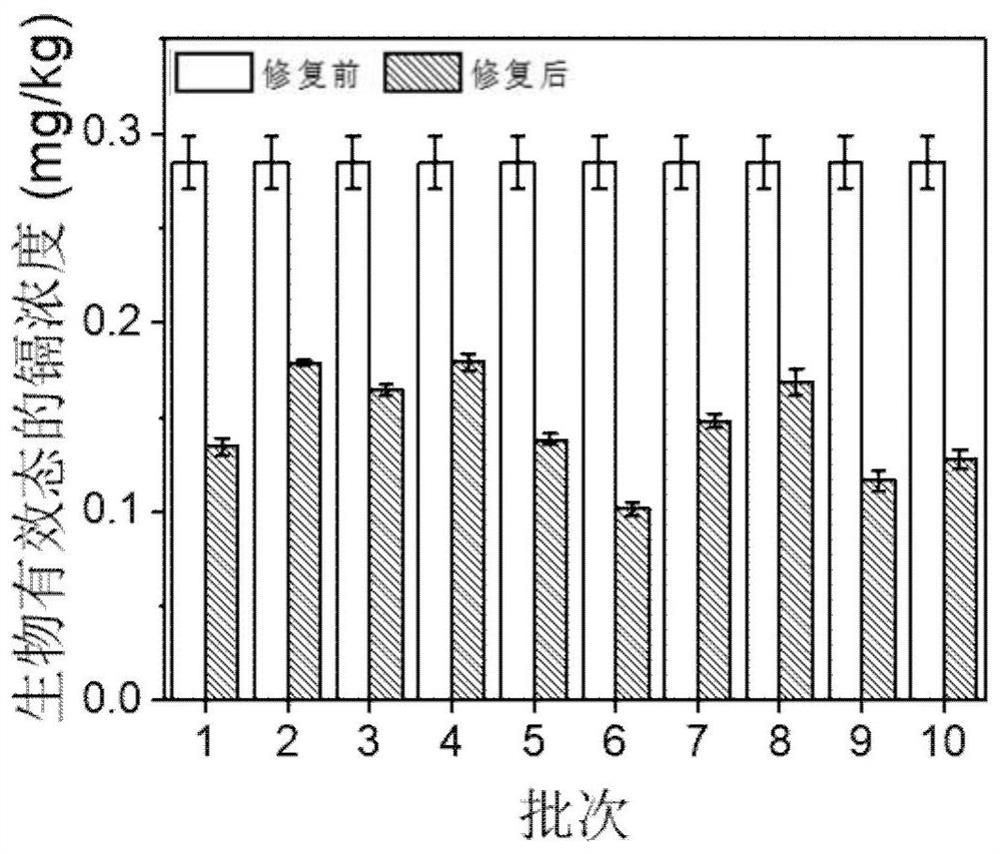
[0034] Remediation of cadmium and lead compound polluted farmland soil from Shangyu, Zhejiang. Bacterial culture solution includes sodium bicarbonate 1g / L, sodium sulfate 0.3g / L, potassium chloride 0.07g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.1g / L, ammonium chloride 0.9g / L, vitamin 5ml / L, minerals 10ml / L. The hydraulic retention time of the cathode chamber of the sulfate reduction reactor was 20 hours. The current is controlled at 20mA. Soil remediation time is 21.5 hours. After the soil was replaced, the next repair was carried out, and a total of ten batches of soil were repaired.
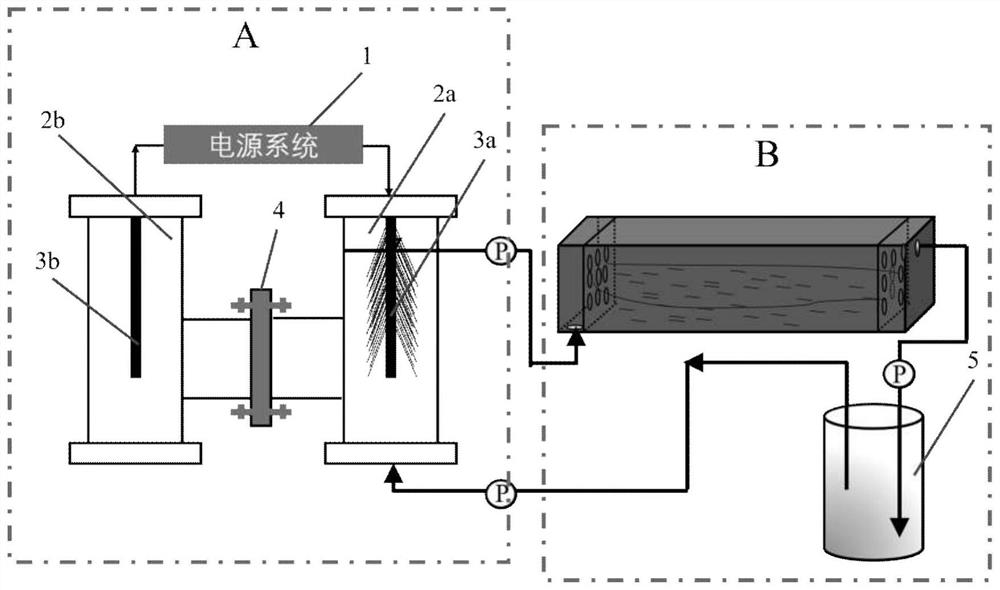
[0035] For the actual experimental setup, see figure 2 .
[0036] Under the condition of 20mA current, the sulfate reduction reactor will convert 60mg / L of S-SO 4 2- Solution reduced to 30mg / L S-S 2- solution, remaining 30mg / L of S-SO 4 2- solution. The conversion rate was 50%.
[0037] The average curing efficiency of bioavailable cadmium was 48.98% (±9.36%), and the average curing eff...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com