Patents
Literature
45 results about "Soil lead" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
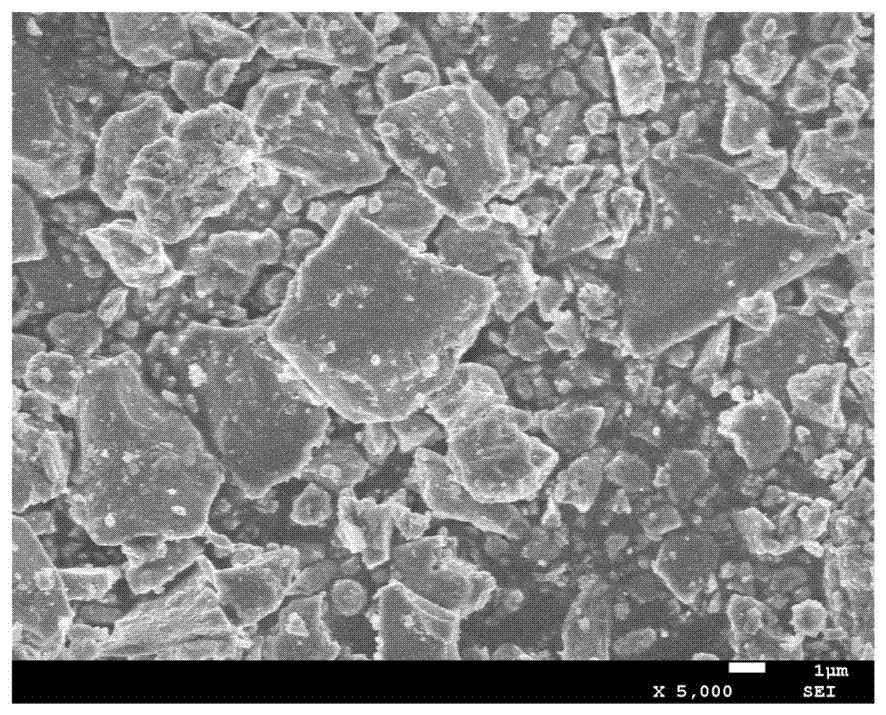
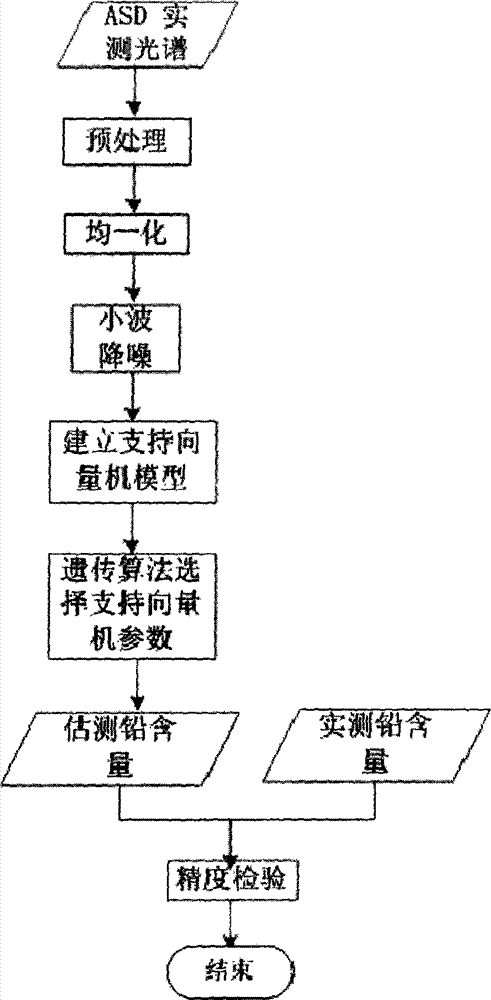
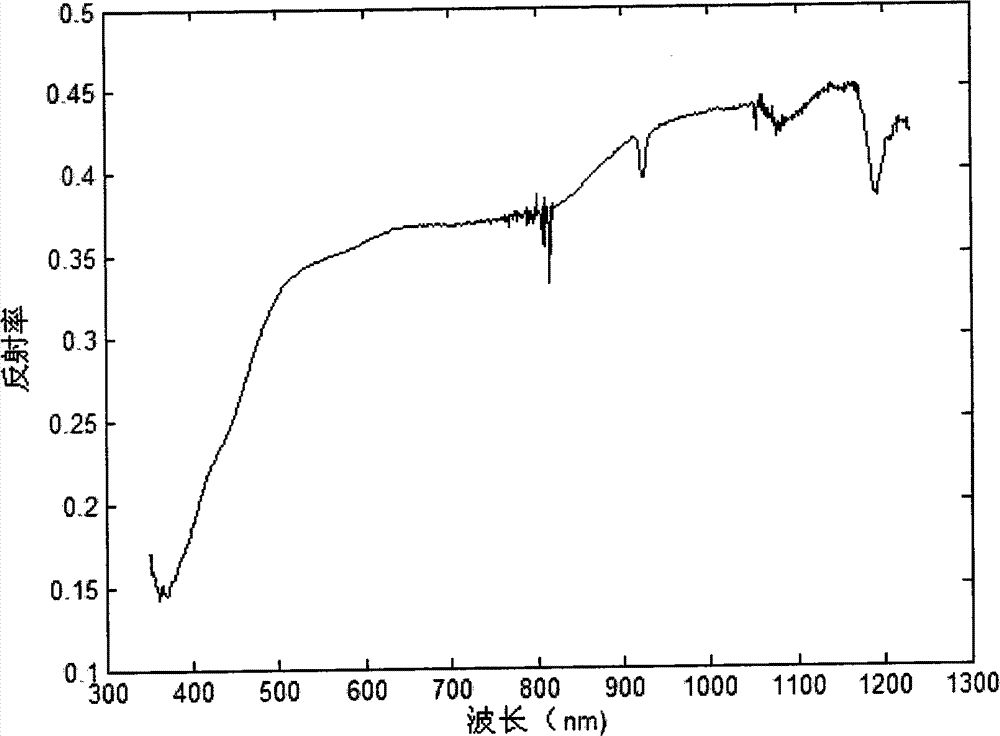
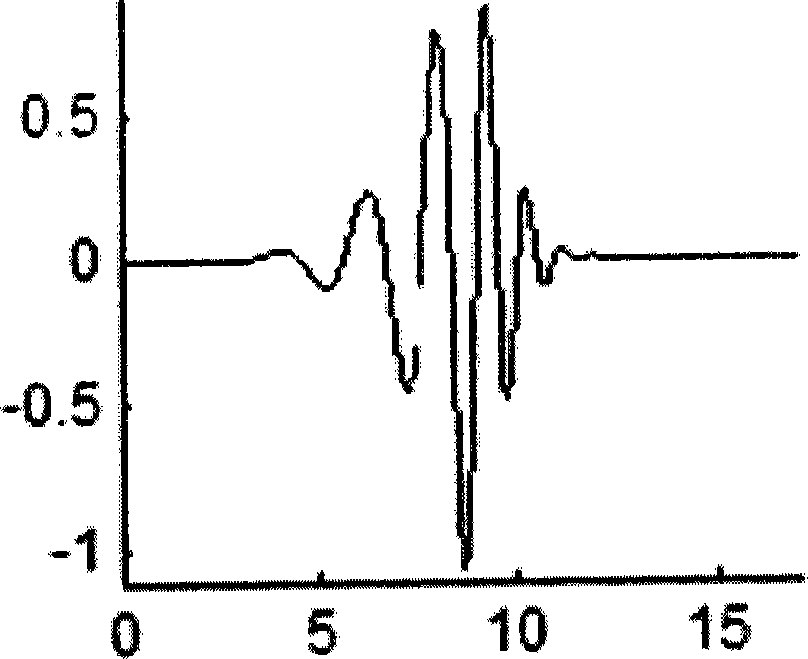
Soil lead content measurement method using visible and near-infrared spectroscopy technology
InactiveCN104502288ACalculation method is simpleReduce running timeColor/spectral properties measurementsSpectroscopyChlorophyllin
The invention discloses a soil lead content measurement method using a visible and near-infrared spectroscopy technology. According to the soil lead content measurement method disclosed by the invention, quantitative estimation for the content of soil lead in a tailing area is realized by virtue of spectrum data, the measurement does not require direct contact with a sample and is complete nondestructive measurement, and moreover, an operation process and a calculation method of the content of the soil lead are simple; the method disclosed by the invention is based on a support vector machine, the computer program running time of the measurement time is less than 10 minutes, and the measurement speed is greatly increased compared with that, which needs at least one hour of cumbersome detection operation process, in a traditional chlorophyll content detection method; the soil lead content measurement method disclosed by the invention is free of environment pollution.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
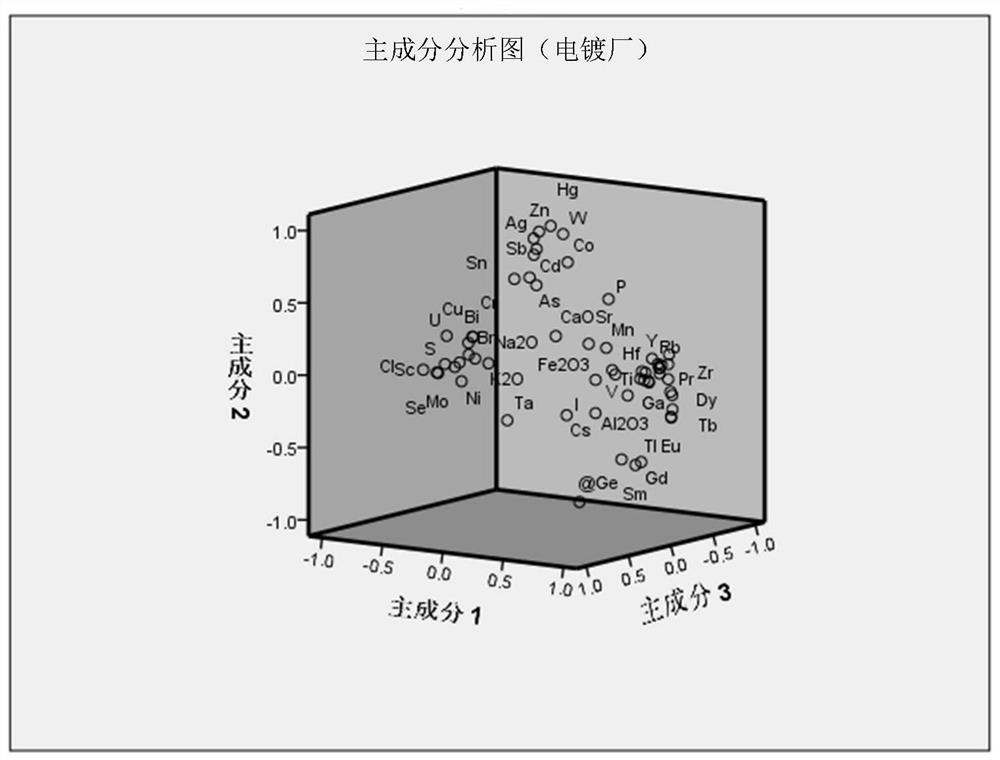
Soil lead pollution source identification method based on stable isotope and multi-element characteristic analysis
ActiveCN112179974AOvercoming the defects that have no practical guiding significanceFast trackMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCharacter and pattern recognitionSoil scienceMultivariate statistics
The invention relates to the technical field of environmental detection, and discloses a soil lead pollution source identification method based on stable isotope and multi-element characteristic analysis. The method comprises the steps of 1) determining an investigation area of a lead pollution source; 2) carrying out environment investigation on the determined lead pollution source investigationarea; 3) according to an environmental survey result, arranging sampling points according to different conditions, and collecting a risk source sample; 4) analyzing and determining the lead isotope ratio and the contents of various mineral elements in the lead-polluted soil and the risk source sample; and 5) identifying the lead pollution source based on stable isotope and multi-element characteristic fingerprint in combination with principal component clustering analysis. Based on a lead pollution source identification technology combining lead stable isotope, multi-element characteristics and multivariate statistics, a soil heavy metal lead pollution source can be accurately discriminated and identified, and a scientific basis is provided for soil lead pollution prevention and control work.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for remediation of lead pollution on beach soil
ActiveCN102764756ANo secondary hazardsReduce consumptionContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a method for remediation of lead pollution on beach soil. The method disclosed by the invention comprises the following steps of: carrying out alternate drying and wetting treatment on the beach soil, regulating and controlling soil oxidation-reduction potential, thus oxidizable and reducible lead in the beach soil is released and is changed into soluble or exchangeable lead; and carrying out complexing, strengthening and analyzing on the released lead by utilizing chloride ion in sea water, soaking and washing the soil, and washing the lead away from soil body at a surface layer, thus the lead pollution on the soil at the surface layer is remediated. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that removal rate of pollutant is high, no chemical agent is required to be added and no secondary harm can be caused to the soil and also has the advantage that beach inning and pollution remediation can be carried out at the same time.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Method for restoring lead polluted soil by rinsing
InactiveCN103639192APromote degradationEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationSoil sciencePolyaspartic acid
The invention relates to a method for restoring lead polluted soil by rinsing, which has the advantages of higher biodegradability and higher rinsing efficiency. The method comprises the following steps: taking a PVC (polyvinyl chloride) rinsing column of which the internal diameter is 5cm and the height is 15cm, making pinholes in the bottom of the rinsing column, fixing filter paper to the bottom, accurately weighing 100.00g of lead polluted soil, filling the lead polluted soil into the column, and adding a 1-24 mol / L PASP (polyaspartic acid) solution to the upper end of the soil column at one time in a soil-to-liquid ratio of 1:1-1:5; and after finishing rinsing, determining the content of the heavy metal lead in the rinsing liquid.2-16 pinholes are uniformly made in the bottom of the rinsing column. The filter paper fixed to the bottom is composed of two layers. The lead concentration of the polluted soil is 1000-4020 mg.kg<-1>. By using the PASP for reinforced restoration of the lead polluted soil, the method has the characteristics of high restoration efficiency, high operability, low environmental risk and the like.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND CHEMICAL TECHNOLOGY
Soil lead pollution in-situ bioremediation method
InactiveCN107971336AEasy to fixStrong toleranceContaminated soil reclamationLiquid ratioSoil remediation
The invention discloses a soil lead pollution in-situ bioremediation method and belongs to the technical field of soil remediation. The remediation method comprises the steps that (1) soil and sulfatereducing bacteria liquid are mixed at the solid-to-liquid ratio of 100g:(2-10)ml and are subjected to anaerobic culturing at 25-37 DEG C for 2-10 d; and (2) thiobacillus denitrificans liquid is sprinkled onto the surface of the soil treated in the step (1) at the solid-to-liquid ratio of 100g:(1-10)ml to conduct culturing for 1-15 d. According to the soil lead pollution in-situ bioremediation method, comprehensive treatment on the polluted soil is achieved through regulation and control over the sulfur valence state through different bacteria, so that the efficiency is high, additional devices are not needed, the cost is low, and secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Soil remediation fertilizer
InactiveCN106748483AFull of nutritionGood restorativeAnimal corpse fertilisersAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserSlagMonopotassium phosphate
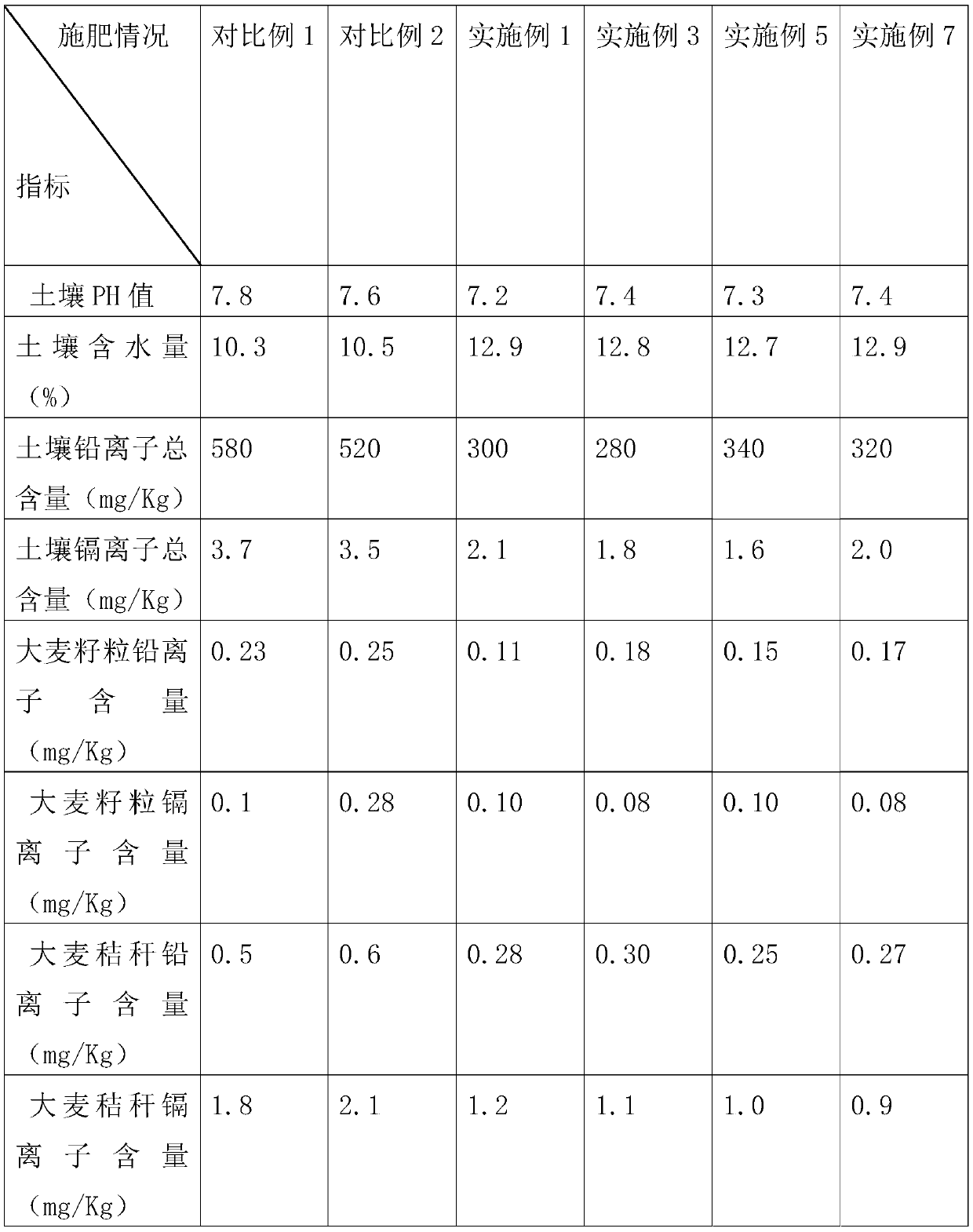
The invention relates to the technical field of fertilizer, in particular to a soil remediation fertilizer. The soil remediation fertilizer is prepared from, by weight, 30-50 parts of urea, 25-30 parts of sodium nitrate, 20-25 parts of ammonium sulfate, 25-30 parts of urea phosphate, 10-15 parts of calcium phosphate, 20-30 parts of monopotassium phosphate, 15-20 parts of potassium sulfate, 8-12 parts of clay, 10-13 parts of siderite slag, 10-13 parts of limonite slag, 15-20 parts of bagasse, 10-18 parts of edible fungus residues, 12-16 parts of shell powder, 25-30 parts of modified red clay, 15-20 parts of modified kaolin and 15-25 parts of plant extract. The fertilizer is rich in nutrition and contains multiple macroelements and micronutrient elements necessary for crops, and the total nutrient content of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium is larger than or equal to 69.7%; with the effective state-ineffective state conversion rate as the evaluation index of soil remediation, the conversion rate of the soil remediation fertilizer on soil cadmium metal reaches 99.84% or above, the conversion rate of the soil remediation fertilizer on soil copper metal reaches 91.48% or above, and the conversion rate of the soil remediation fertilizer on soil lead metal reaches 90.8% or above; taking peanuts as an example, the yield can be increased by 11-13.7%; the double benefits of obtaining a high yield and remediating soil with heavy metal are realized.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
Soil remediation agent for lead and benzopyrene combined pollution and application thereof
InactiveCN108586122AShort repair cycleShort cycleCalcareous fertilisersAgriculture tools and machinesPoultry manureTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a soil remediation agent for lead and benzopyrene combined pollution and an application thereof. The soil remediation agent is applied through the following steps: mixing diatomite, carboxymethyl cellulose, zeolite powder, composite shell powder, quick lime, humic acid and derivatives thereof, a compound inoculum, livestock and poultry manure, waste tea residue, urea, calcium superphosphate, polymeric aluminum ferric sulphate, ferrous chloride, calcium oxide, urea phosphate, potassium sulfate and diammonium phosphate so as to constitute a mixture, placing the mixture into contaminated soil, and carrying out standing and curing so as to complete remediation. The method provided by the invention can quickly and effectively degrade lead and benzopyrene combined pollution to soil, shortens the remediation period of the contaminated soil, has low remediation cost, does not cause secondary pollution, is simple and practicable, can improve the fertility of the soil in acontaminated site, and is applicable to remediation of lead and benzopyrene contaminated sites in various scales. The soil remediation agent provided by the invention has the following advantages: pollution of the soil remediation agent to the environment is reduced; meanwhile, the cost of the soil remediation agent is decreased; and by combining precipitation action and biological action, the soil remediation agent has good treatment effect on lead and benzopyrene combined pollution to the soil.
Owner:LIAONING UNIVERSITY
Method for repairing phenanthrene-polluted soil by using potentilla
InactiveCN101444787AExtended growing seasonStrong resistance to diseases and insect pestsContaminated soil reclamationDiseaseChemical treatment
A method for repairing phenanthrene-polluted soil by using potentilla relates to a method for repairing phenanthrene-polluted soil and solves the following problems: physical and chemical treatments of phenanthrene in the soil have the problems of high cost, secondary pollution and unsuitability for large-scale application; micro-organism treatment of the phenanthrene in the soil leads to soil ecological risk; and phenanthrene degradation by using field crops or ryegrass has the problems of small biomass, weakness in pest and disease resistance and long growing period. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, basic fertilizer is applied in the phenanthrene-polluted soil, and the potentilla is planted; and secondly, when the potentilla grows to the anthesis or maturation phase, overground parts of potentilla plants are harvested, so that the repair of the phenanthrene-polluted soil is finished. In the invention, the potentilla has long growing period, strong capability in pest and disease resistance and great overground biomass; the method has the advantages of low cost and simple and convenient operation, does not damage polluted-site soil structure and river ecological conditions or cause secondary pollution and is suitable for large scale use in the phenanthrene-polluted soil.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Applying watered honeycomb briquette ash to stabilize lead in lead contaminated soil
InactiveCN102240668AGuaranteed moisture contentKeep from freezingSolid waste disposalContaminated soil reclamationHoneycombElectro conductivity
The invention belongs to soil lead contamination repairing and solid waste utilization, and relates to a method for stabilizing lead in lead contaminated soil and a method for utilizing honeycomb briquette combustible solid waste, in particular to a method for applying watered honeycomb briquette ash to stabilize lead in lead contaminated soil. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is as follows: the lead in the lead contaminated soil has higher effectiveness and mobility; because the honeycomb briquette ash is applied in the soil, pH and conductivity of the soil are increased; the method comprises the following steps of: grinding or crushing the honeycomb briquette ash; screening at 2 mm; uniformly mixing; and then mixing the ash and water according to a ratio of 1:3 (weight ratio); filtering after stirring or oscillating; drying the ash; and finally, mixing the ash with the lead contaminated soil according to a proportion of 1:50; adjusting water content by 15% to 25%; and culturing for above 60 d.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
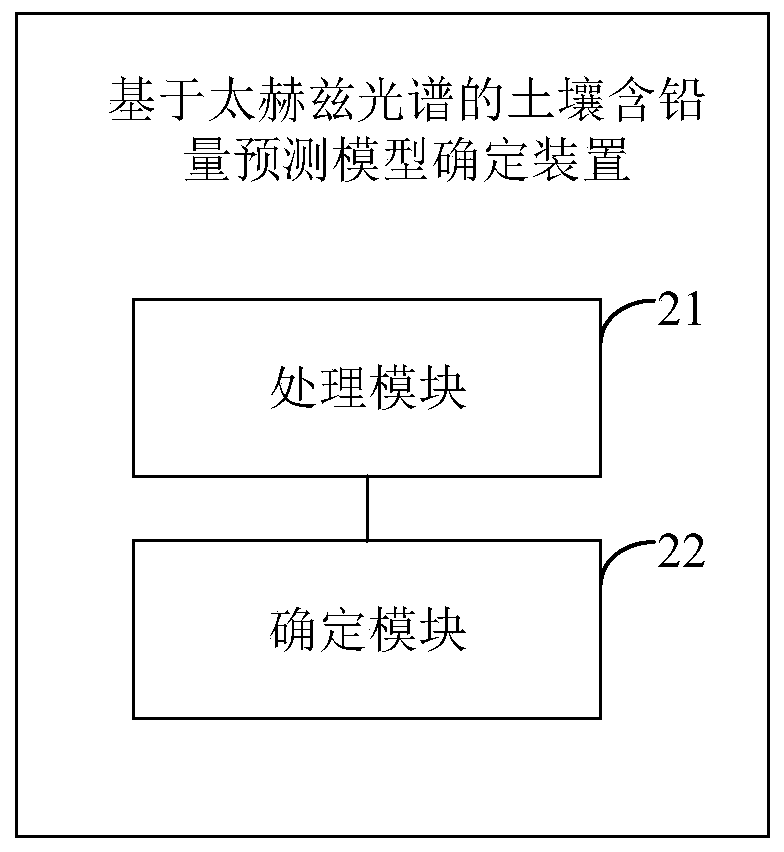
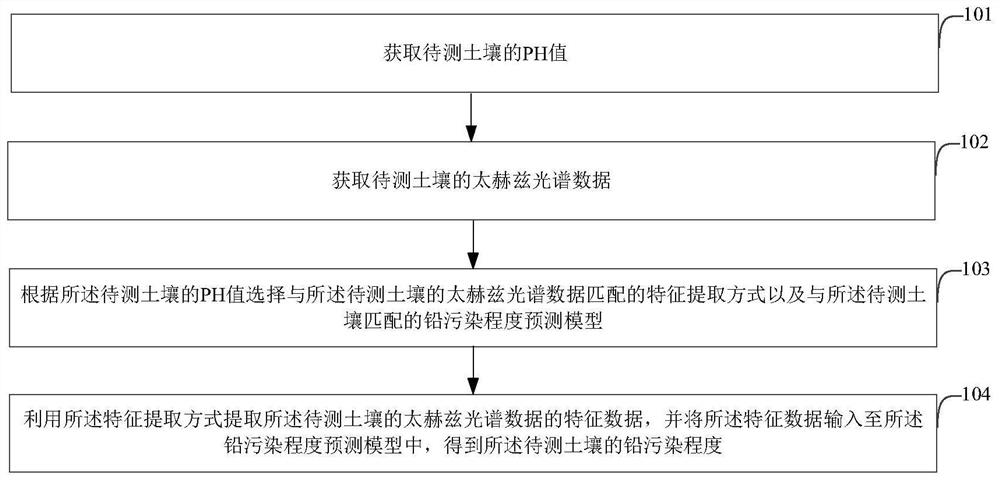
Method and device for determining soil lead content prediction model based on terahertz spectrum
ActiveCN110867221AImprove accuracyPrediction is accurateMaterial analysis by optical meansChemical machine learningSoil scienceFeature extraction
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and device for determining a soil lead content prediction model based on a terahertz spectrum. The method comprises the steps of: respectively carrying out feature extraction on terahertz spectrum data of sample soil in each pH value interval by adopting different feature extraction modes; inputting feature extraction results obtained by adoptingdifferent feature extraction modes into different soil lead content prediction models to obtain a plurality of lead content prediction results under various combinations of the different feature extraction modes and the different soil lead content prediction models; and determining an optimal feature extraction mode and an optimal soil lead content prediction model combination corresponding to thesoil in each pH value interval according to the plurality of lead content prediction results respectively corresponding to the sample soils in the pH value intervals. According to the embodiment of the invention, the combination of an optimal feature extraction mode and an optimal soil lead content prediction model suitable for soil in different pH value intervals can be determined.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
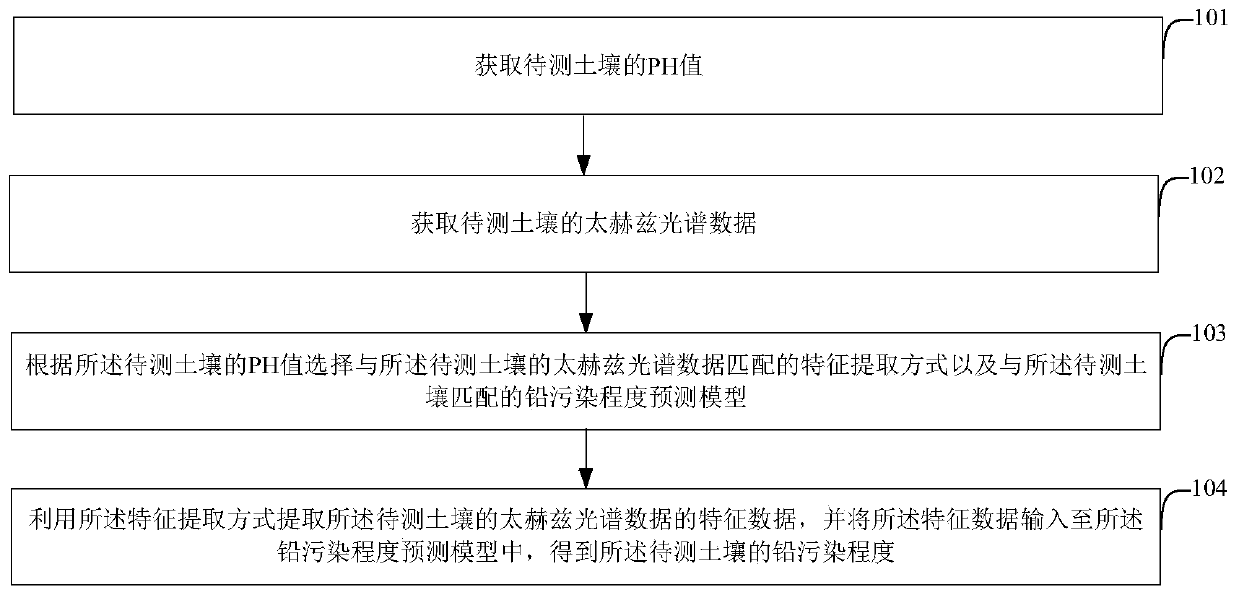
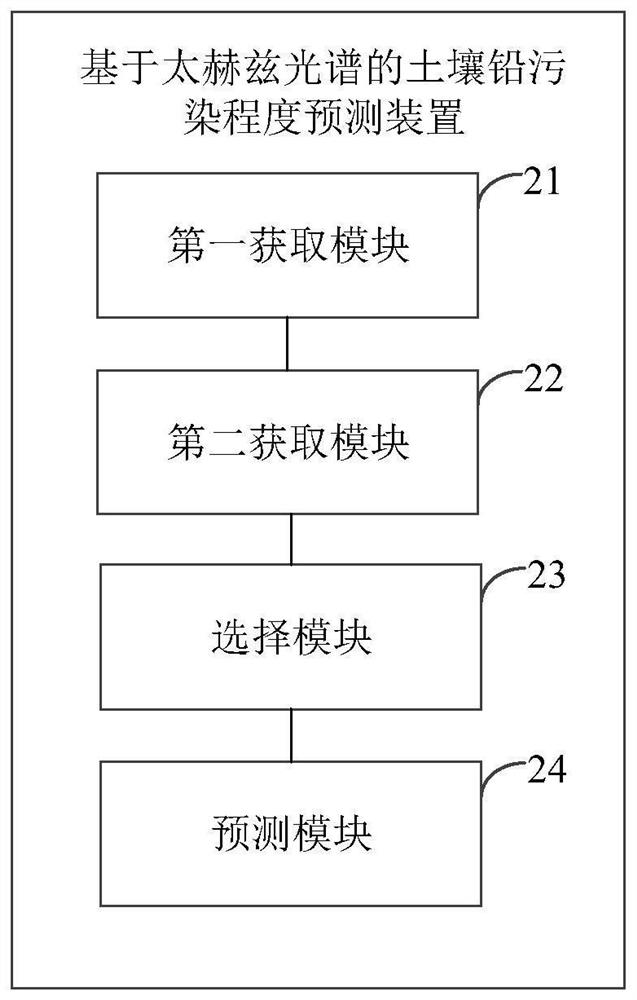
Soil lead pollution degree prediction method and device based on a terahertz spectrum
ActiveCN110987853AImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansEarth material testingSoil scienceFeature extraction
The embodiment of the invention discloses a soil lead pollution degree prediction method and device based on a terahertz spectrum, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining the pH value of to-be-detected soil; acquiring terahertz spectrum data of the soil to be detected; according to the pH value of the to-be-detected soil, selecting a feature extraction mode matched with the terahertz spectral data of the to-be-detected soil and a lead pollution degree prediction model matched with the to-be-detected soil; and extracting characteristic data of the terahertz spectral data of the soil to bedetected by using the characteristic extraction mode, and inputting the characteristic data into the lead pollution degree prediction model to obtain the lead pollution degree of the soil to be detected. According to the embodiment of the invention, an accurate soil lead pollution degree prediction result can be obtained.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Phosphorus slag-based repairing material for lead polluted soil
ActiveCN107384417AA large drop in concentrationLarge declineContaminated soil reclamationOrganic fertilisersSlagPhosphate
The invention provides a phosphorus slag-based repairing material for lead polluted soil. The phosphorus slag-based repairing material mainly comprises phosphorus slag, boiled slag, petroleum coke desulfurized ash, cement kiln ash and an additive. The phosphorus slag-based repairing material provided by the invention is applied to the lead polluted soil according to the following steps: adopting a rotary cultivator for rotary cultivating till reaching the bottom layer in appointed depth of the polluted soil, and then regulating the moisture content of the polluted soil to 4% by tedding or watering; uniformly spraying the phosphorus slag-based repairing material to the polluted soil according to the minimal dosage 2% of the repairing material for lead polluted soil containing; after 1 day, adopting a land leveler for leveling and then adopting a rubber-wheel road roller for rolling for 2-4 times, coating a membrane and maintaining under the moisture-maintaining and temperature-maintaining state; and accumulatively maintaining for more than 7 days, and then adopting the rotary cultivator for rotary cultivating, breaking and recovering the fluffy structure of the soil, thereby completing the repairing for the lead polluted soil. Compared with the application of the cement and phosphate materials, the application of the phosphorus slag-based repairing material for lead polluted soil according to the technical scheme of the invention has the advantages that the soil lead concentration is greatly reduced, the time is short and the continuous repairing can be realized.
Owner:湖北冉擎建设工程有限公司
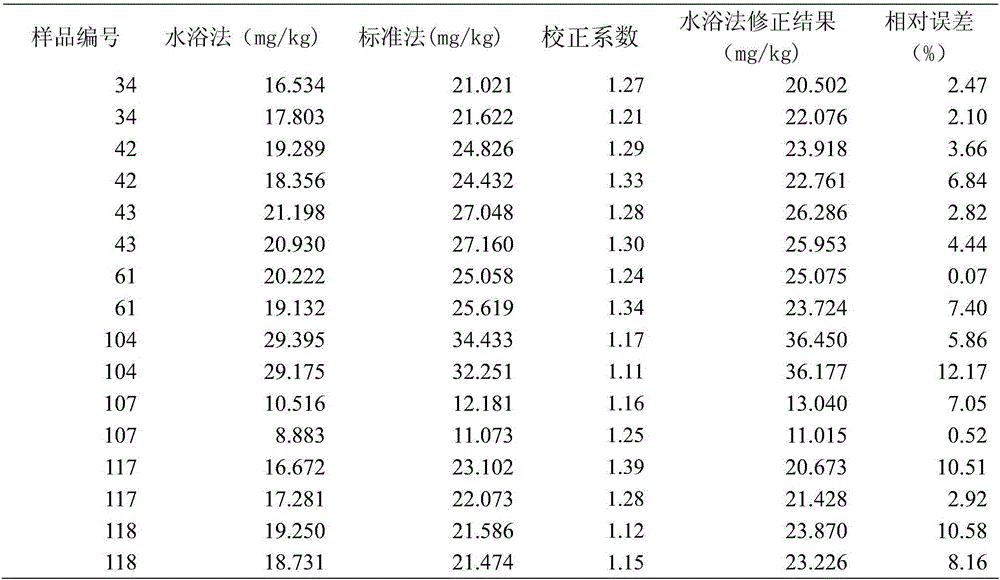
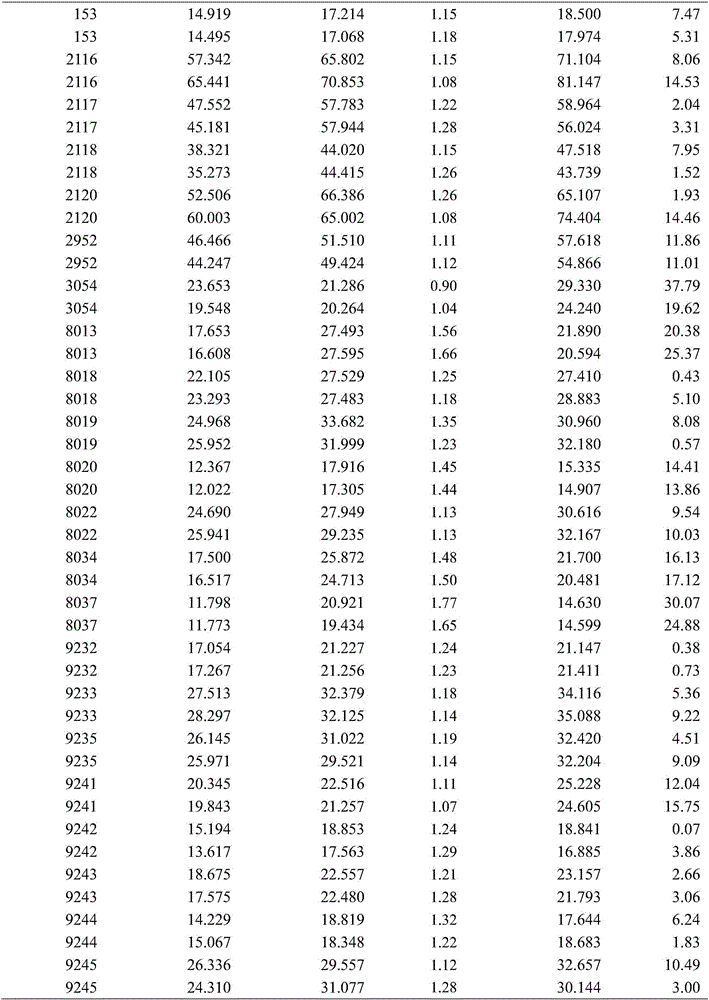
Method for determining lead content of red soil in Guizhou province and correcting factor thereof
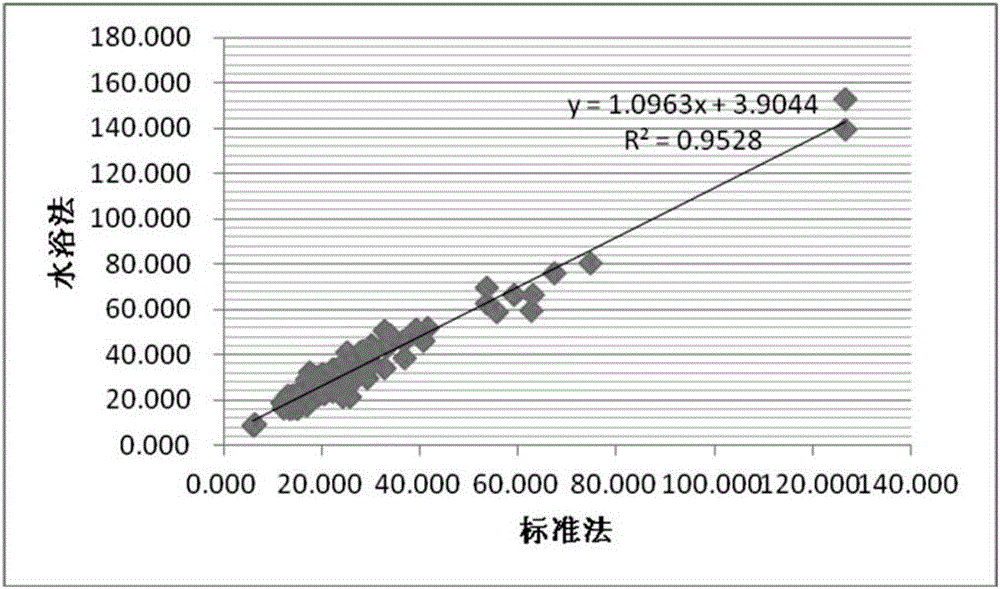
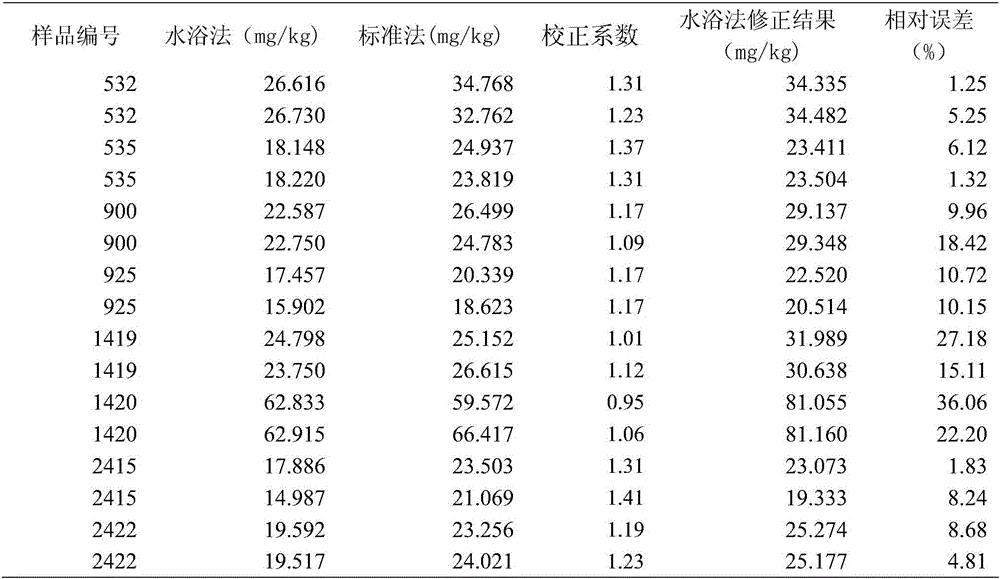
InactiveCN106680461AMeet application needsDetection value correctionPreparing sample for investigationEarth material testingAcid waterScreening method
The invention discloses a method for determining lead content of red soil in Guizhou province and a correcting factor thereof. The method comprises the following steps of: taking a ratio of a determining value of the lead content in a soil sample acquired on the basis of the flame atomic absorption spectrometry to the determining value acquired on the basis of a 1:1 chloroazotic acid water-bath digestion-ICP-MS preliminary screening method as a correcting coefficient; taking an average value of the correcting coefficients of all the samples as the correcting factor; utilizing the correcting factor to quickly determine the lead content of the red soil in Guizhou province according to the 1:1 chloroazotic acid water-bath digestion-ICP-MS preliminary screening method. Through the method and the correcting factor, the determining time can be greatly shortened. The 1:1 chloroazotic acid water-bath digestion-ICP-MS preliminary screening method is adopted for correcting the determining value of the lead element in the soil, so that the application requirement in the practical work can be met.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF SOIL & FERTILIZER
Preparation method of fluorescent probe test paper for detecting lead content of soil
InactiveCN111220586AEasy to makeEasy to operateOrganic chemistryEarth material testingFluoProbesSoil science
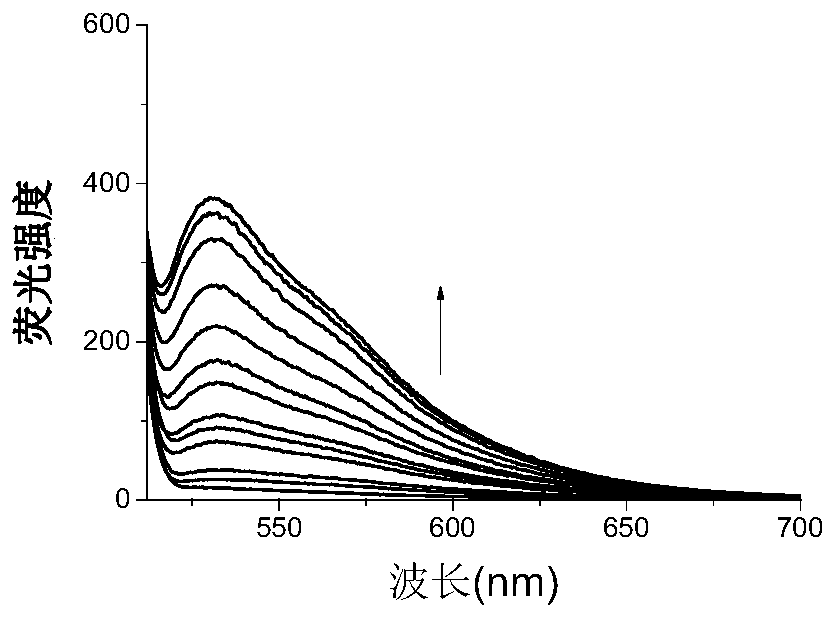
The invention relates to a preparation method of fluorescent probe test paper for detecting the lead content of soil, and the fluorescent probe test paper provided by the invention comprises an organic small molecular fluorescent material as shown in a formula (I), the fluorescent probe test paper disclosed by the invention is obviously distinguished under different concentrations of heavy metal lead ions, can be used for semi-quantitatively detecting the lead ions in sewage, cosmetics, foods and the like, and has substantive significance; the fluorescent probe test paper for detecting the heavy metal lead ions has the advantages of simple preparation, low detection limit, sensitive reaction, high efficiency and the like.
Owner:广州市尚信净化工程有限公司
Method for repairing lead-chromium composite contaminated soil by combining humic acid and sudangrass
PendingCN110877048ASolve pollutionSolving activityContaminated soil reclamationChromium contaminationSoil science
The invention relates to a method for repairing lead-chromium composite contaminated soil by combining humic acid and sudangrass. The method effectively solves the problem that humic acid reduces thebiological availability of heavy metals lead and chromium, relieves the poisons of the heavy metals lead and chromium to the sudangrass, creates conditions for the growth of sudangrass in moderately and severely contaminated areas, and improves the remediation efficiency of the sudangrass on the lead-chromium composite contaminated soil. Humic acid is uniformly scattered on the surface layer, withthe chromium content of 275.4 mg / kg or above and the lead content of 989.7 mg / kg or above, of the lead-chromium contaminated soil, the soil is plowed, raked and ridged, sudangrass seeds are sowed, watering is conducted once every 3-7 days in the plant growth process, management is conducted according to the normal growth requirement of the sudangrass, the sudangrass grows for 30 days, soil samples are collected and measured, the lead content of soil is smaller than or equal to 218 mg / kg, and the chromium content of soil is smaller than or equal to 95 mg / kg, so the national environmental standard requirements are met, and remediation of the lead-chromium contaminated soil is achieved. The method is simple, can effectively solve the problems of heavy metal combined pollution, difficult survival of plants and the like, and also has the advantages of soil improvement, fertility enhancement, crop growth promotion, low cost and environmental friendliness.
Owner:HENAN ACAD OF SCI INST OF BIOLOGY LIABILITY
Correction factor and method for determining lead content of purple soil in Guizhou province
InactiveCN106769935ADetection value correctionShorten detection timePreparing sample for investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsWater bathsScreening method
The invention discloses a corrector factor and a method for determining lead content of purple soil in Guizhou province. The method includes: taking a ratio of a measured value, obtained according to a flame atomic adsorption spectrophotometry method, of the lead content of each soil sample to a measured value obtained according to a 1:1 aqua regia water bath digestion-ICP-MS preliminary screening method as a correction coefficient; taking an average value of correction coefficients of all samples as a correction factor; adopting the correction factor for quickly determining the lead content of purple soil in Guizhou province according to the 1:1 aqua regia water bath digestion-ICP-MS preliminary screening method. By the correction factor and the method, detection time can be greatly shortened, correction of soil chromium detection values is realized according to the 1:1 aqua regia water bath digestion-ICP-MS preliminary screening method, and accordingly application demands in practical operation are met.
Owner:GUIZHOU INST OF SOIL & FERTILIZER
Method for promoting lead-zinc ore plant recovery by using organic and inorganic composite modifier
InactiveCN111687200APromote recoveryImprove physical and chemical propertiesContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceWoody plant
The invention discloses a method for promoting lead-zinc ore plant recovery by using an organic and inorganic composite modifier, which comprises the following steps: 1) selecting mushroom residues and calcium carbonate, grinding and crushing; 2) uniformly mixing and stirring the mushroom residues and calcium carbonate according to a mass ratio of 2: 1-1: 2 to obtain a composite modifier; 3) adding the composite modifier into the heavy metal contaminated soil, repeatedly and uniformly plowing, and fully mixing the heavy metal contaminated soil to obtain mixed heavy metal contaminated soil; and4) selecting fast-growing woody plants resistant to heavy metals, planting the fast-growing woody plants in the mixed heavy metal contaminated soil, and ploughing the soil regularly. By adding the organic and inorganic composite improver, the physicochemical properties of lead-zinc mining area soil are effectively improved, mining area lead-zinc ore and mining area water and soil are fixed, the growth of heavy metal resistant woody plant seedlings is promoted, water and soil loss and dust raising are prevented, and the mining area environment is improved; the growth of woody plants realizes the transfer of the lead-zinc ore to the plants, and reduces the content of the lead-zinc ore in the soil.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Ricefield eel mucus-containing biofertilizer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105967945APromote moisture penetrationImprove water retentionBio-organic fraction processingAnimal corpse fertilisersFiberRhodobacter azotoformans
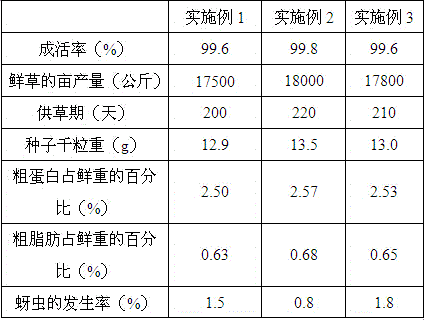
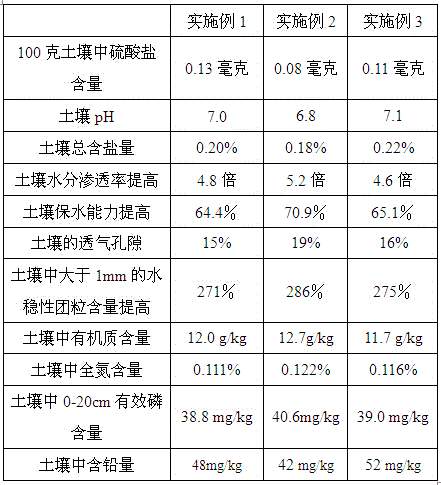
The invention provides a ricefield eel mucus-containing biofertilizer. The ricefield eel mucus-containing biofertilizer comprises fulvic acid potassium salt, peat, chlorogenic acid, ricefield eel mucus, vegetable leaves, cotton hulls, coriolus versicolor polysaccharide, secoiridoid, cellulose nitrate powder, fertile land radish plant, perlite, sweet potato meal fibers, rhodobacter azotoformans and halophilic methanogens. The invention also provides a preparation method of the ricefield eel mucus-containing biofertilizer. The ricefield eel mucus-containing biofertilizer is applied for sulfate-form lead-polluted saline-alkali soil, reduces soil sulfate content and soil pH and total salt content, improves soil water permeability and a water retaining capacity, improves soil gas permeability, increases content of water-stability soil granules with the size greater than 1mm in soil, increases soil nutrients and reduces soil lead content. The ricefield eel mucus-containing biofertilizer is used for Gaodan grass, improves a survival rate and a yield, prolongs a grass supply period and improves a Gaodan grass seed yield. The ricefield eel mucus-containing biofertilizer is used for Gaodan grass plantation, has the effect of resisting Gaodan grass aphids and reduces an aphid incidence rate.
Owner:SHANDONG SUNWAY LANDSCAPE TECH
Method for reducing lead content in rice grains by using NPK fertilizer together
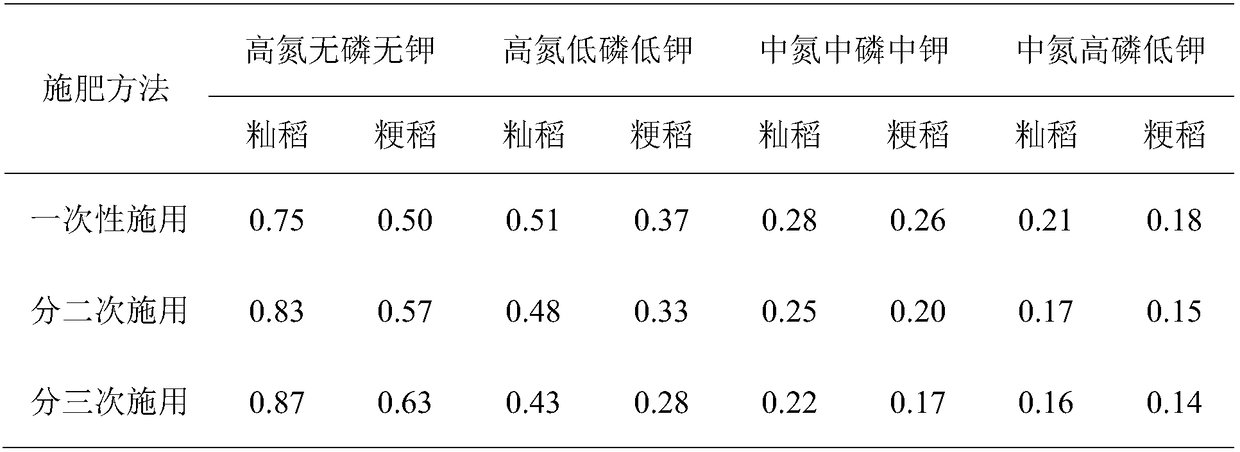
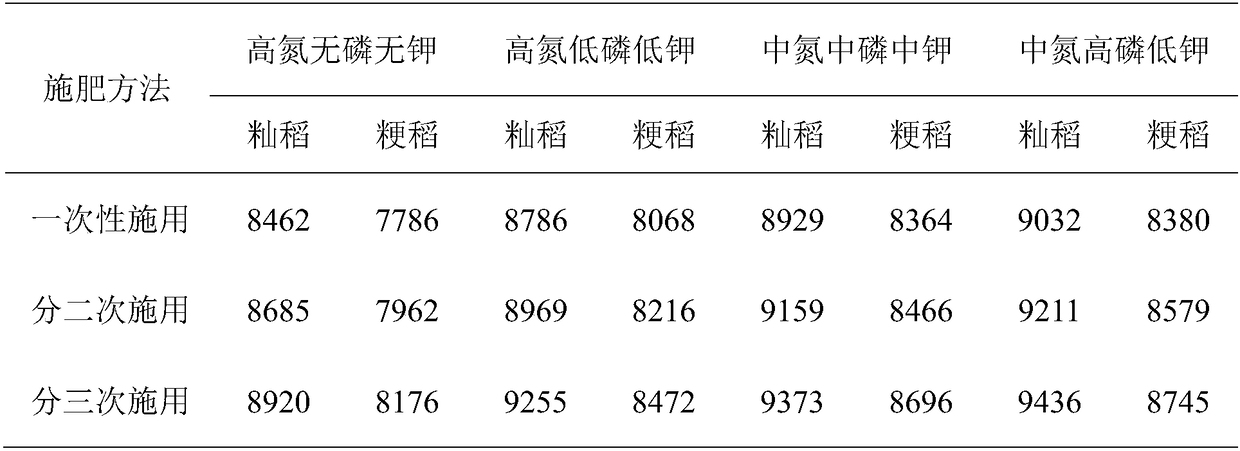
InactiveCN109275527AReduce contentEliminate health threatsFertilising methodsRice cultivationNitrogenPotassium
The invention relates to a method for reducing the lead content in rice grains by using NPK fertilizer together. The method has the characteristics that in the lead-contaminated soil with severe leadcontamination of a soil lead content of 300 mg / kg which is three times or above that of the limit of the soil lead content of edible agricultural product producing areas in China, the total amount ofapplied nitrogen is 225 kg / hm<2> which is medium-level nitrogen application based on pure nitrogen, the total amount of applied phosphorus is 150 kg / hm<2> which is high-level phosphorus application based on the content of an active ingredient P2O5, and the total amount of applied potassium is 100 kg / hm<2> which is low-level potassium application based on an active ingredient K2O; application is completed in three times, and one third of the total fertilization amount is separately applied 3 days before rice planting, 25 days after rice planting and 5 days before heading. When the application effect of the method is compared with that of conventional fertilization methods for rice production, the yield of Indica rice is increased by 5.99%, the yield of japonica rice is increased by 6.96%, the lead content of grains of Indica rice is decreased by 81.61%, and the lead content of grains of japonica rice is decreased by 77.68%.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
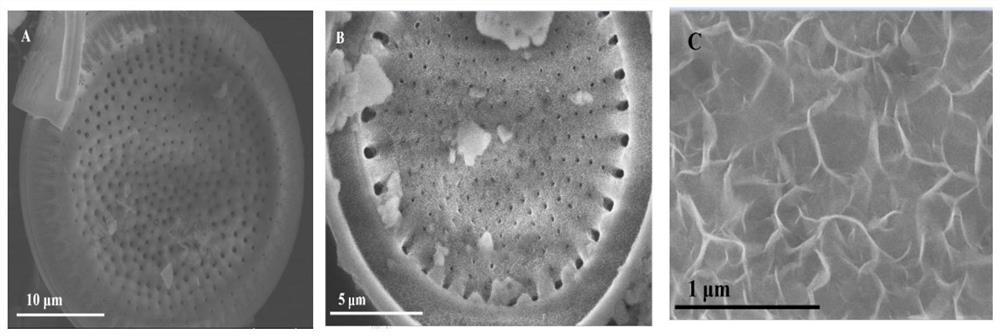
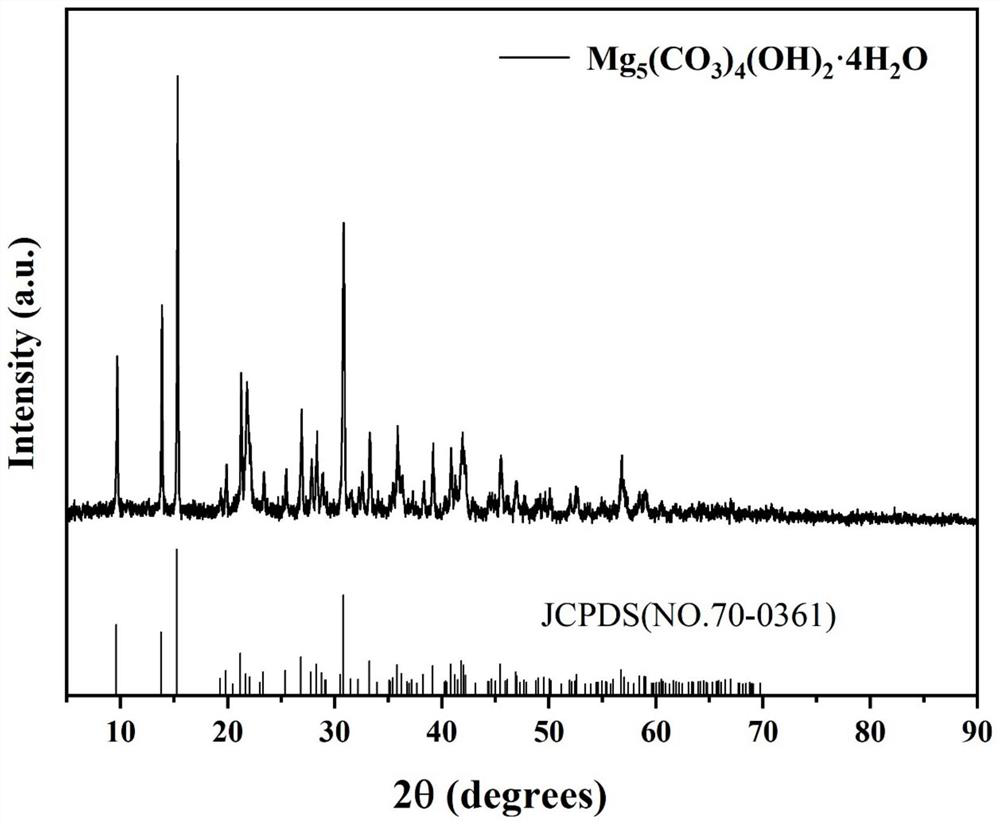
Composite material formed by loading basic magnesium carbonate on surface of diatomite, and method for fixing lead in soil
ActiveCN113174261AEffectively fixedEasy to operateContaminated soil reclamationAnalysis by thermal excitationSoil scienceFluid phase
The invention discloses a composite material formed by loading basic magnesium carbonate on the surface of diatomite, and a method for fixing lead in soil, belonging to the field of functional and environmental protection materials. According to the invention, diatomite is used as a carrier and has certain water binding capacity; basic magnesium carbonate is modified on the surface of the diatomite, so a spontaneous ion replacement route with solubility difference as driving force can be established, and metal cations in soil can be driven from a liquid phase to a solid phase of an adsorption material in a humid environment; and therefore, the basic magnesium carbonate-based diatomite composite material can realize efficient synergy of the two materials, and further provides a new thought for development of an adsorption and fixation material for heavy metal lead ions in soil. In addition, the invention provides a reliable and rapid screening method for evaluating a heavy metal passivator for soil, and the method has very high practical application value.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Soil lead pollution passivating agent
InactiveCN109880633ARealize resource utilizationLower synthesis costAgriculture tools and machinesContaminated soil reclamationResource utilizationPeat
The invention provides a soil lead pollution passivating agent, and particularly provides wood peat carried nano iron prepared from a waste tobacco leaf extract. By uniformly mixing the soil lead pollution passivating agent and soil, the transformation of lead in soil into a residual state can be promoted, and the aim of lowering the bioavailability of the lead in soil is fulfilled. The preparation of the wood peat carried nano iron does not need any toxic reagent, and can be finished with conventional instruments at room temperature and under normal pressure, so that resource utilization of tobacco leaves can be realized, and the preparation cost of the nano iron is lowered. The soil lead pollution passivating agent is environmentally friendly, can increase the organic matter content of soil while restoring soil lead pollution, improves the yield of crops, and belongs to the technical field of heavy metal pollution remediation.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for promoting lead-zinc ore plant recovery by using organic and inorganic composite modifier
InactiveCN111687198APromote recoveryImprove physical and chemical propertiesContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceWoody plant
The invention discloses a method for promoting lead-zinc ore plant recovery by using an organic and inorganic composite modifier, which comprises the following steps: 1) selecting peat soil and calcium carbonate, grinding and crushing; 2) uniformly mixing and stirring peat soil and calcium carbonate according to a mass ratio of 2: 1-1: 2 to obtain a composite modifier; 3) adding the composite modifier into the heavy metal contaminated soil, repeatedly and uniformly plowing, and fully mixing the heavy metal contaminated soil to obtain mixed heavy metal contaminated soil; and 4) selecting fast-growing woody plants resistant to heavy metals, planting the fast-growing woody plants in the mixed heavy metal contaminated soil, and ploughing the soil regularly. By adding the organic and inorganiccomposite improver, the physicochemical properties of lead-zinc mining area soil are effectively improved, mining area lead-zinc ore and mining area water and soil are fixed, the growth of heavy metalresistant woody plant seedlings is promoted, water and soil loss and dust raising are prevented, and the mining area environment is improved; the growth of woody plants realizes the transfer of the lead-zinc ore to the plants, and reduces the content of the lead-zinc ore in the soil.
Owner:CENTRAL SOUTH UNIVERSITY OF FORESTRY AND TECHNOLOGY
Saline-alkali soil lead and cadmium heavy metal ion remover and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN111500290AAdjust salinityAdjust alkalinityAgriculture tools and machinesOther chemical processesSoil scienceAlkali soil
The invention discloses a saline-alkali soil lead and cadmium heavy metal ion remover and a preparation method thereof. The remover comprises the following raw material components in parts by weight:25 to 35 parts of mineral source humus ultrafine powder; 20 to 35 parts of mesoporous silica; 25-30 parts of shale, 10-15 parts of citric acid, and 4-8 parts of cyanobacteria liquid; the citric acid in the soil desalting agent can improve the alkaline environment of soil; the mesoporous silica is matched with mineral source humus ultrafine powder, so various heavy metal ions can be strongly adsorbed in a short time, and the landform of saline-alkali soil is improved; the cyanobacteria can effectively treat the heavy metal ions in the soil for a long time, and the heavy metal ions in the soil are continuously and efficiently removed through the matching effect of the mesoporous silica and the cyanobacteria.
Owner:WEIFANG YOURONG IND
A kind of soil optimization method of Chinese radish planting land
The invention discloses a soil optimization method of a petasites japonicus planting field. The method comprises the steps that pioneering crops are planted to lower soil lead content, by soil modification treatment, petasites japonicus growing can be well achieved, and the yield and the quality of petasites japonicus are improved. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that by planting the pioneering crops, lead in soil is removed, accordingly, the lead content of the petasites japonicus planted in the later period is lowered below the standard, product quality and safety are guaranteed, by soil modification treating, soil permeability is improved, fertility is sufficient and durable, the probability of plant diseases and insect pests of petasites japonicus is lowered, presetting soil is prepared through agricultural production waste, and environment protection and economy are achieved.
Owner:GUANGDE ZHIYUN BAMBOO SHOOT
A method for repairing heavy metal polluted soil by pressure filtration and leaching
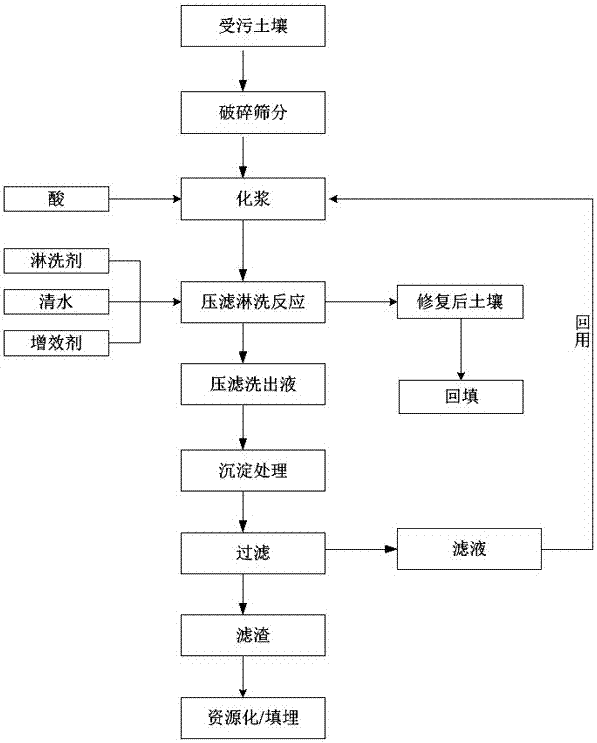
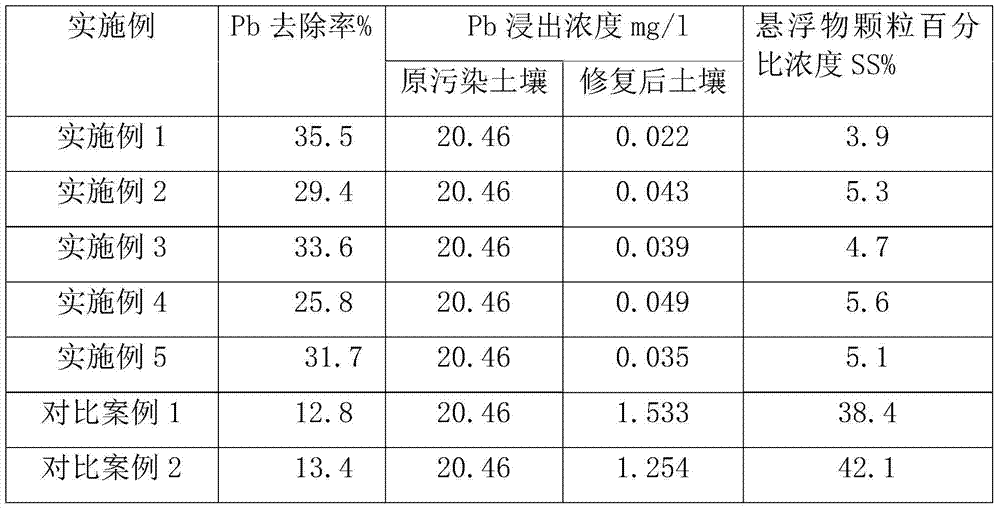
InactiveCN104984992BReduce the amount requiredReduce the solid-to-liquid ratioContaminated soil reclamationSlurryFilter press
The invention discloses a method for repairing heavy metal polluted soil by pressure filtration and leaching. The restoration method includes the following steps: S1, crushing and screening the heavy metal-contaminated soil; S2, pulping the crushed and screened soil, and adding acid to fully react with acid-soluble heavy metals in the soil; S3 The above-mentioned fully reacted slurry is subjected to pressure filtration, and the residual acid solution in the capillary pores of the soil filter cake is replaced and diluted by clear water; Heavy metals are fully reacted; S5 puts synergists into the filter press reactor to stabilize the free heavy metals remaining in the soil, and at the same time migrates the tiny heavy metal particles formed during the stabilization process out of the soil, and the filter cake is passed through clean water Rinse, so that the heavy metal ions or compounds or complexes remaining in the filter cake can be further fully washed out with the water flow, and the repaired soil can be obtained. The invention solves the problem in the prior art that the leaching solution remains in the soil during the leaching process and the index of toxic heavy metals leached from the soil exceeds the standard.
Owner:HUNAN MUKUN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION
Rapid detection system for lead in soil
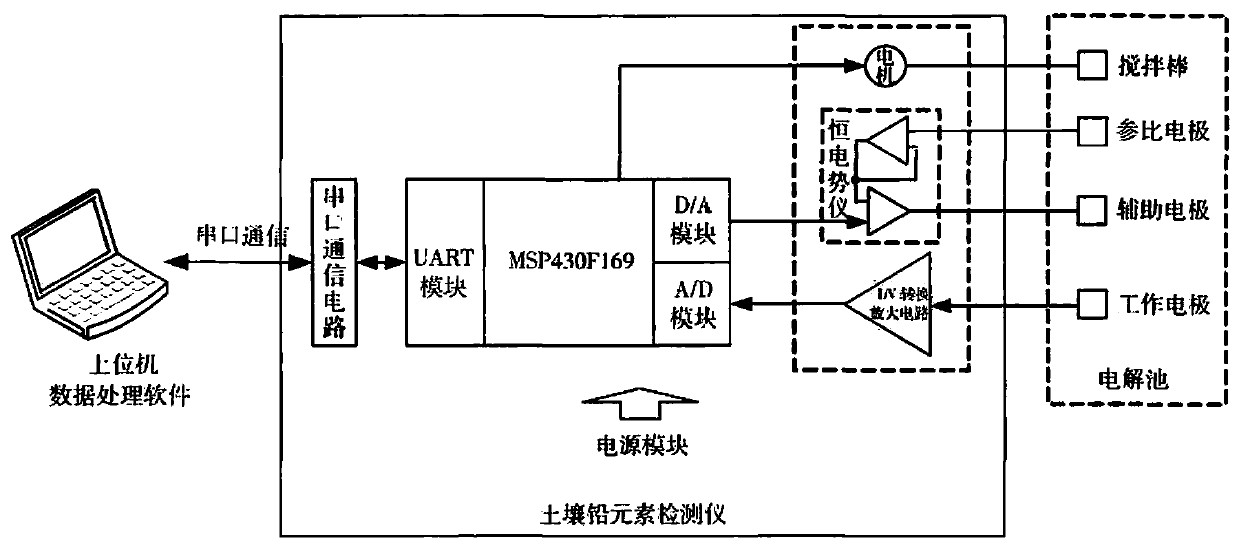
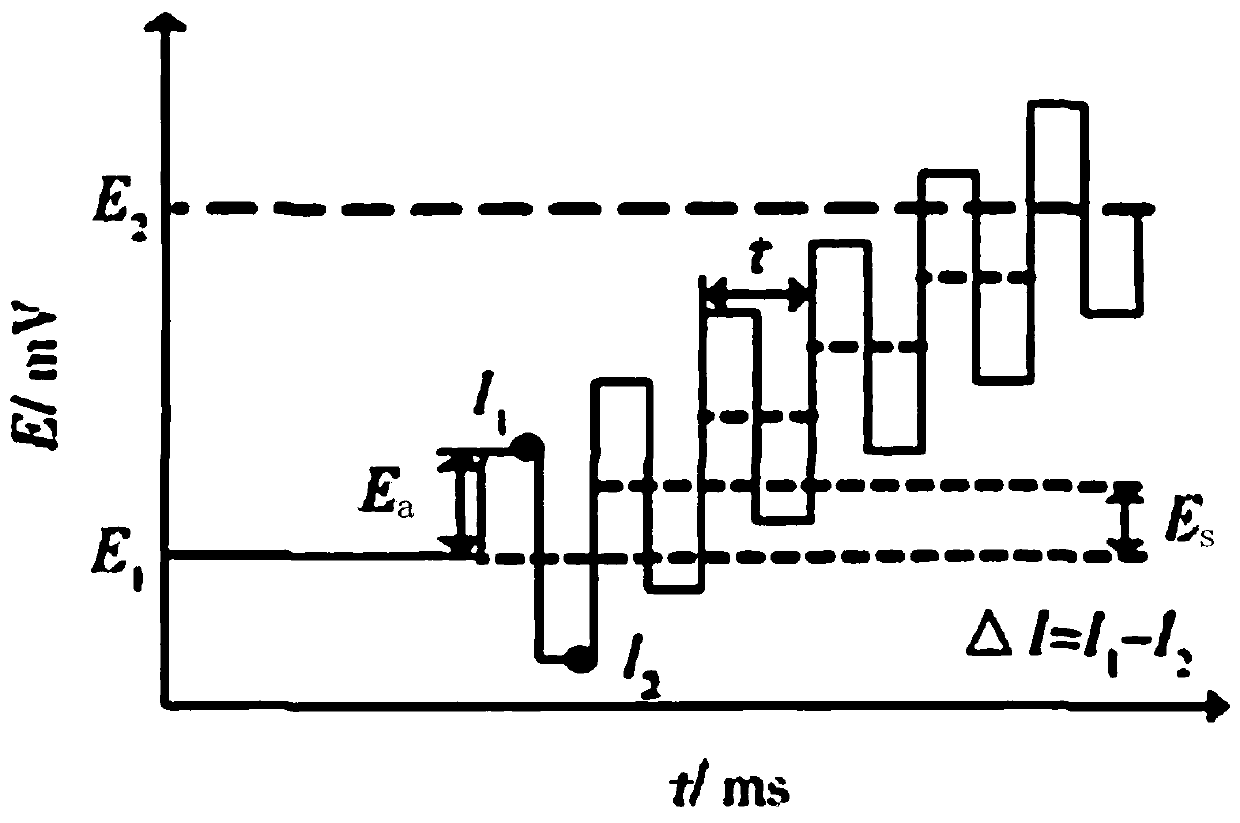
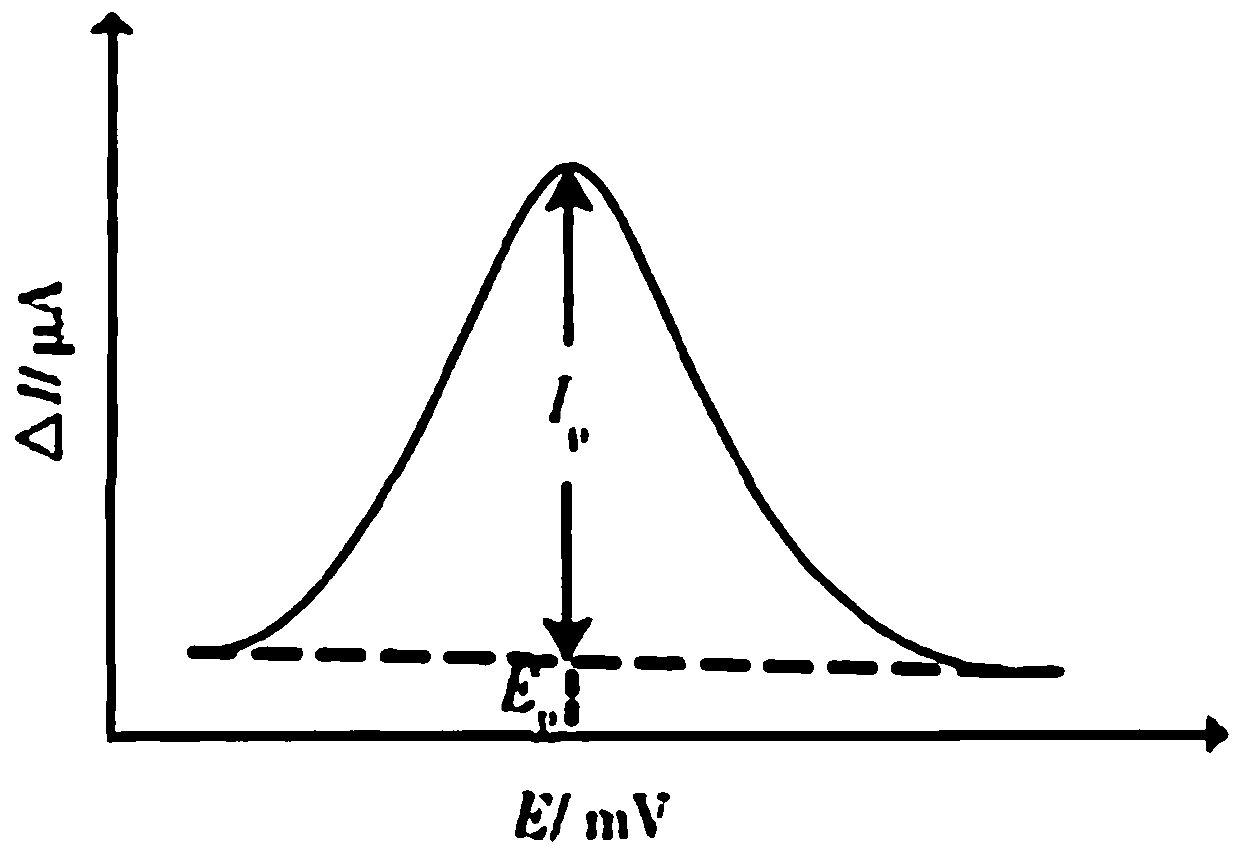
InactiveCN107643336AReduce power consumptionReduce volumeMaterial electrochemical variablesDissolutionPeak current
In order to rapidly obtain the lead content in soil at low cost, the invention provides a rapid detection system for lead in soil. According to the present invention, the rapid detection system is designed based on an anodic stripping voltammetry detection principle, and comprises a soil lead detector and a master computer data processing software, wherein the soil lead detector is designed basedon an anodic stripping voltammetry detection principle, uses a MSP430 mixed signal processor as a control core, integrates a potentiostatic apparatus, a current-voltage conversion amplification circuit and a power module, and is connected to a master computer through RS232 serial communication protocol. According to the present invention, the dissolution peak current detected by the rapid detection system and the lead ion concentration have good linearity, wherein the correlation coefficient was R2 is 0.9951, the relative error between the detection result of the rapid detection system of thepresent invention and the detection result of the atomic absorption spectrometry method is less than 8%, and the repeatability is good; and with the rapid detection system, the lead in farmland soil can be rapidly detected.
Owner:张桂春
A method for accurate detection of lead pollution in soil based on Agrimonia persicae
InactiveCN106771057BIncreased sensitivityLow evolutionEarth material testingMoss cultivationAtrichum undulatumBiology
The invention relates to a method for accurately detecting pollution degree of lead in soil based on atrichum undulatum. The method comprises a plant material cultivation and acquisition method and a double-layer isolated type pollution absorption and dust prevention detection method, wherein the plant material cultivation and acquisition method comprises the following steps: preparation of spore suspension; preparation of culture mediums; setting of culture conditions; in the double-layer isolated type pollution absorption and dust prevention detection method, a double-layer isolated type pollution absorption and dust prevention device is adopted for covering a plant used for pollution detection of lead in the soil. An atrichum undulatum artificial culture and propagation technology provided by the invention and a 'double-layer pollution absorption and dust prevention cover' capable of effectively isolating and excluding the influence of lead pollutants contained in atmosphere are applied to an implementation process of detecting the pollution of lead in the soil based on atrichum undulatum, so that the pollution of lead in the soil can be detected with high accuracy based on atrichum undulatum.
Owner:HUNAN CITY UNIV
A base fertilizer additive for controlling lead pollution in cotton field soil, base fertilizer and its preparation method and application
ActiveCN109534895BReduce contentReached contentAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserAmmonium orthophosphate fertilisersPotassium nitrateSoil science
The invention provides a base fertilizer additive for controlling lead pollution in cotton field soil, a base fertilizer and a preparation method and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of soil improvement. The base fertilizer additive provided by the present invention comprises the following components in parts by weight: 280-320 parts of cotton straw decomposition liquid, 12-17 parts of potassium nitrate, 2-4 parts of polyethyleneimine, and 80-120 parts of trichodermacidin dispersion liquid and 8-12 parts of active potassium silicate mixed solution; the pH value of the base fertilizer additive is 7.0-8.0. The base fertilizer adjuvant provided by the invention reduces the dose of heavy metals in the soil, so as to ensure normal field cotton planting and effectively resist the accumulation of heavy metals in planted crops to achieve normal harmlessness, thereby achieving governance and purpose of repair.
Owner:INST OF COTTON RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
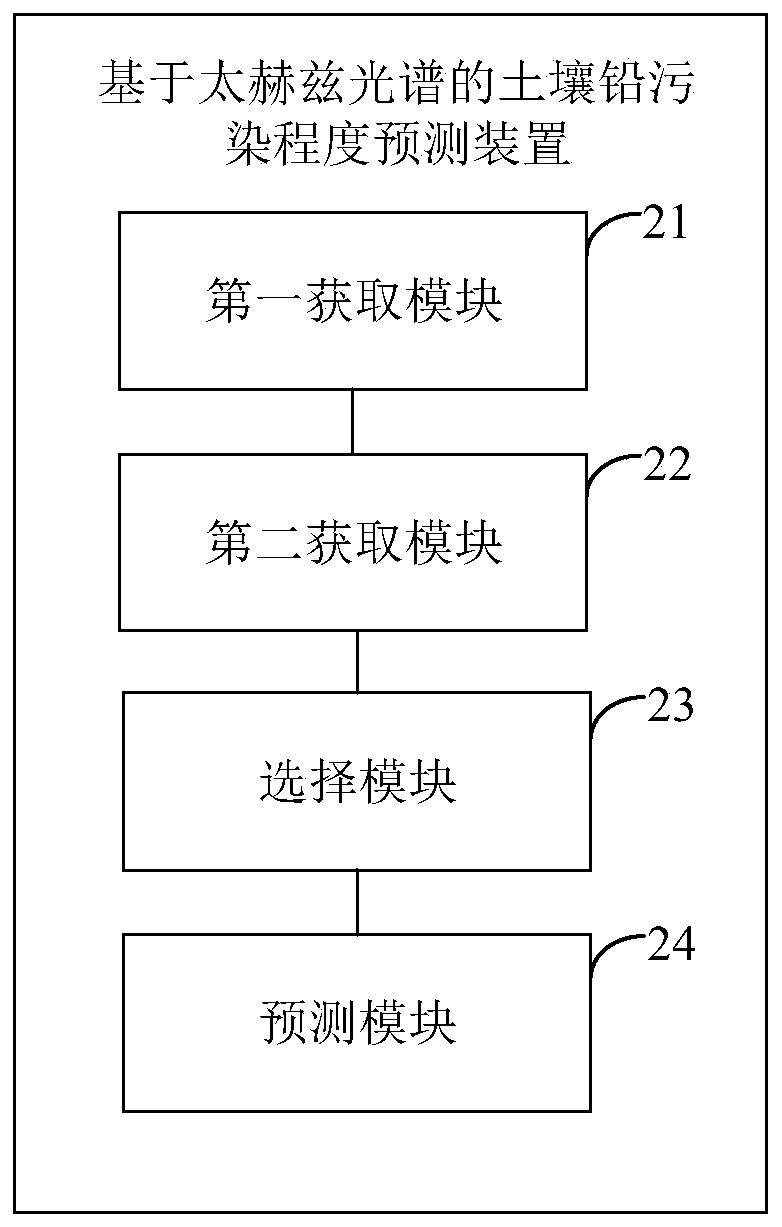
Method and device for predicting soil lead pollution degree based on terahertz spectroscopy
ActiveCN110987853BImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansEarth material testingSoil scienceFeature extraction
The embodiment of the present invention discloses a method and device for predicting soil lead pollution degree based on terahertz spectrum. The method for predicting soil lead pollution degree based on terahertz spectrum includes: obtaining the pH value of the soil to be tested; obtaining the soil to be tested terahertz spectral data; according to the pH value of the soil to be tested, select a feature extraction method that matches the terahertz spectral data of the soil to be tested and a lead pollution degree prediction model that matches the soil to be tested; use the The feature extraction method extracts the feature data of the terahertz spectral data of the soil to be tested, and inputs the feature data into the lead pollution degree prediction model to obtain the lead pollution degree of the soil to be tested. The embodiment of the present invention can obtain more accurate prediction results of soil lead pollution degree.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment
InactiveCN110756576AReduce contentLow costContaminated soil reclamationSoil scienceEnvironmental engineering
The invention discloses a borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment. The borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment is characterized in that surfacesoil of polluted soil is excavated, borrowed soil is added, adsorption plants are planted in the borrowed soil, the non-polluted soil is added, filter ponds are excavated around a polluted area, and the eichhornia crassipes is used to remove lead. The borrowed soil lead removal method for soil lead pollution treatment can effectively reduce the content of the lead in the soil; the plants having agood adsorption effect on heavy metals such as lead can be used to adsorb the lead in the subsequently added borrowed soil to reduce the content of the lead transmitted into the borrowed soil from thebottom polluted soil, at the same time, the excavated polluted soil can be placed in the filter ponds, the aquatic plant eichhornia crassipes is used to adsorb the lead in the soil for purifying thesoil, and polluted water in the filter ponds is used as irrigation water to irrigate the adsorption plants, so that the problem of secondary pollution existing in a traditional borrowed soil deep ploughing method is improved, and the purification method has low costs, thereby being easy to promote and use.
Owner:金晨辉
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com