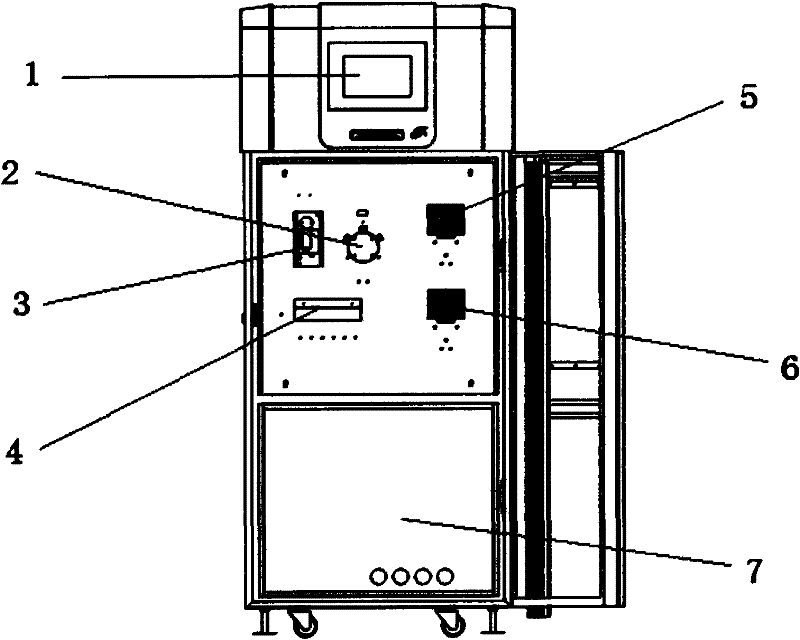
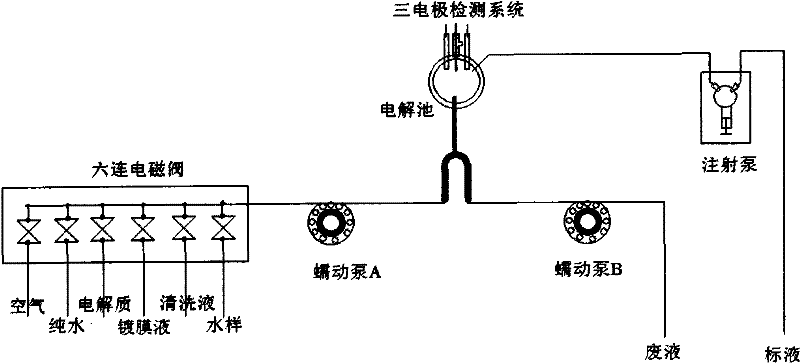
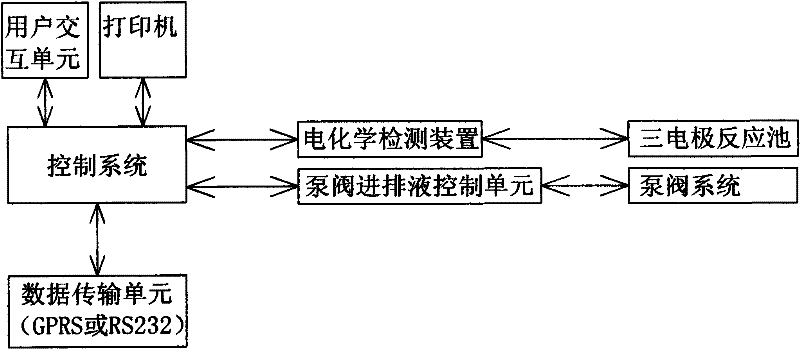
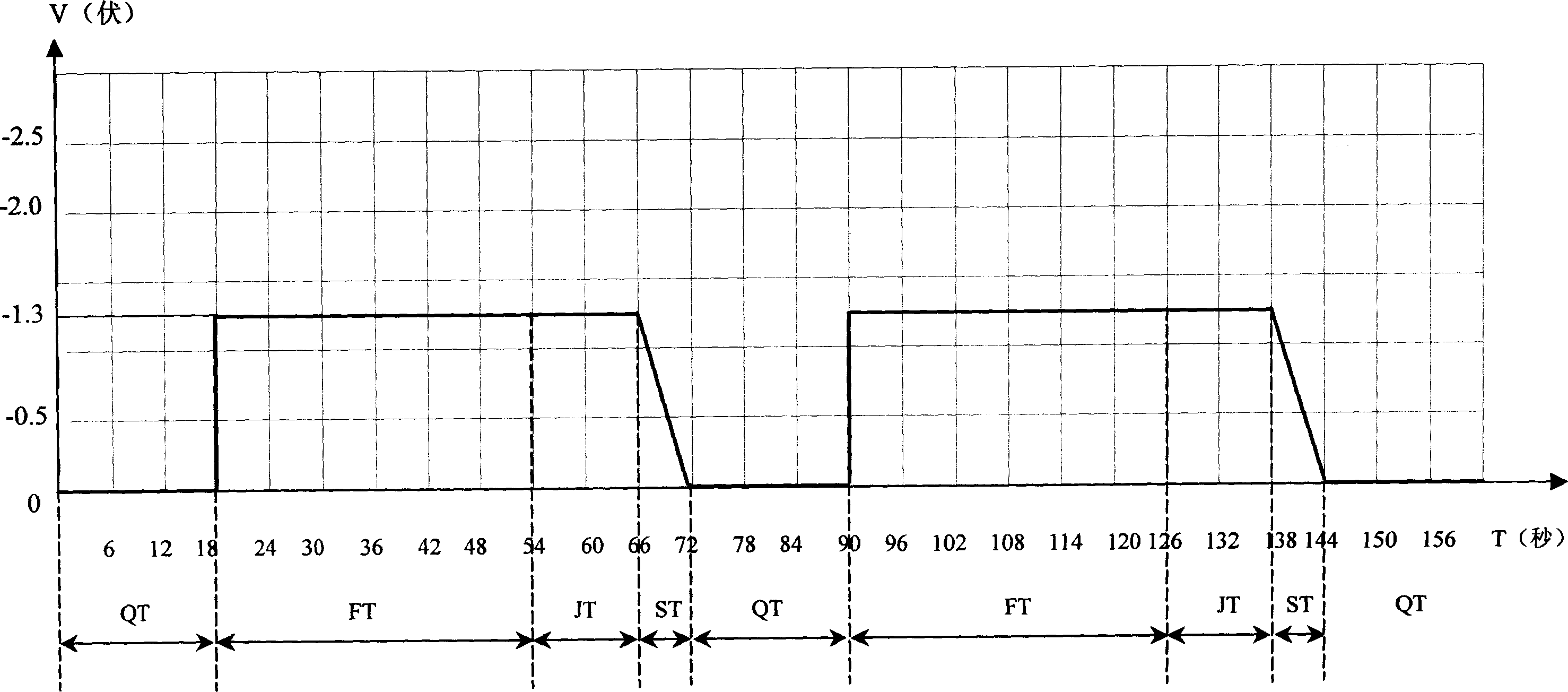
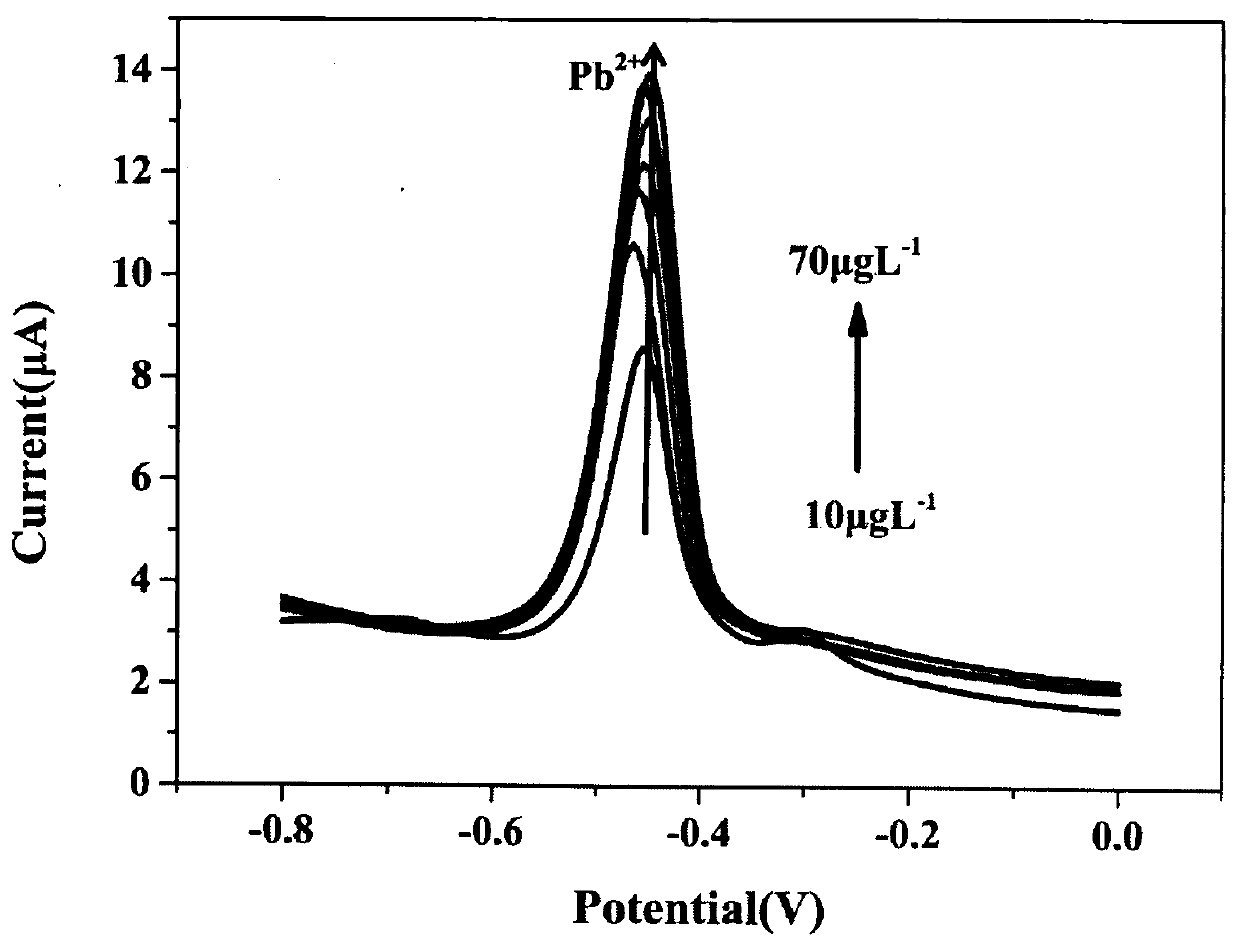
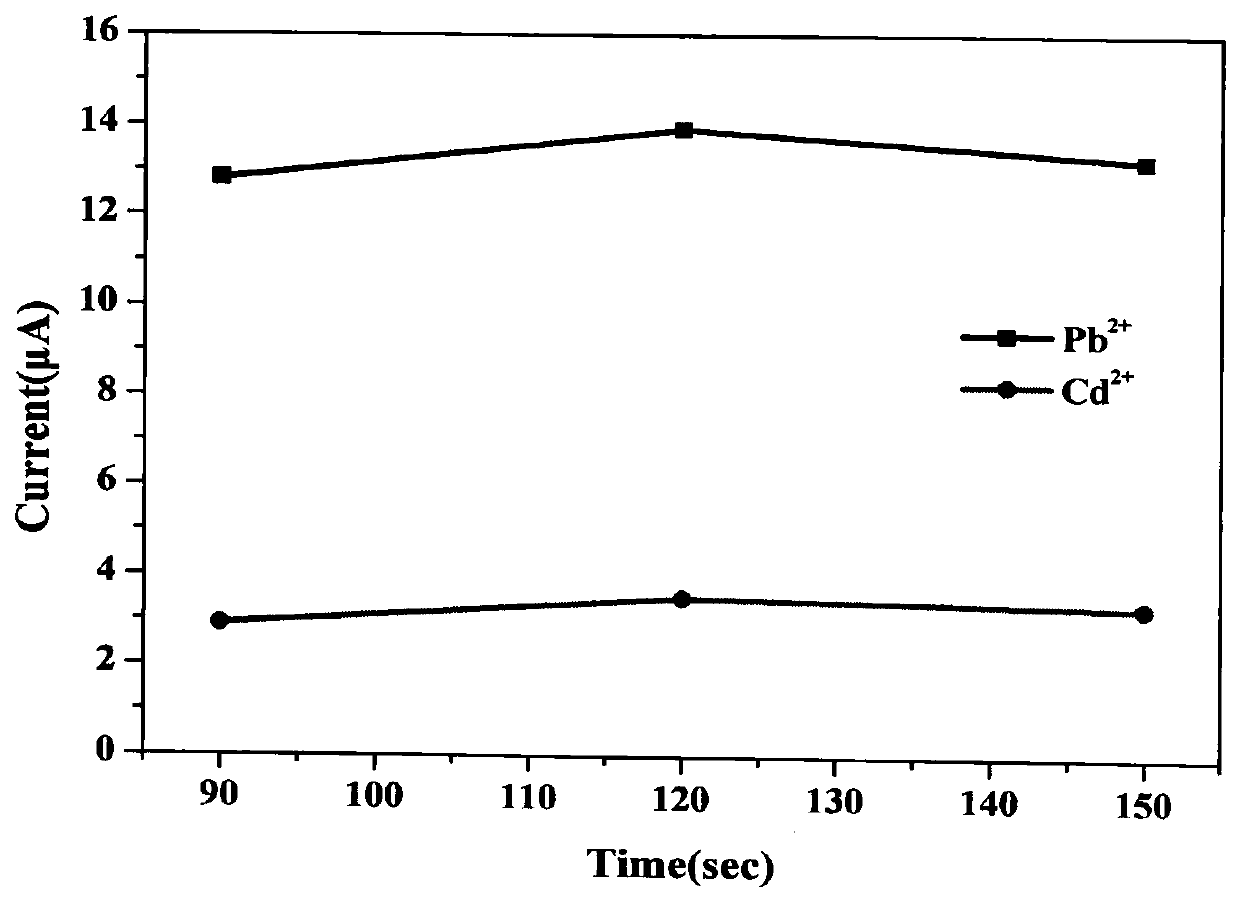
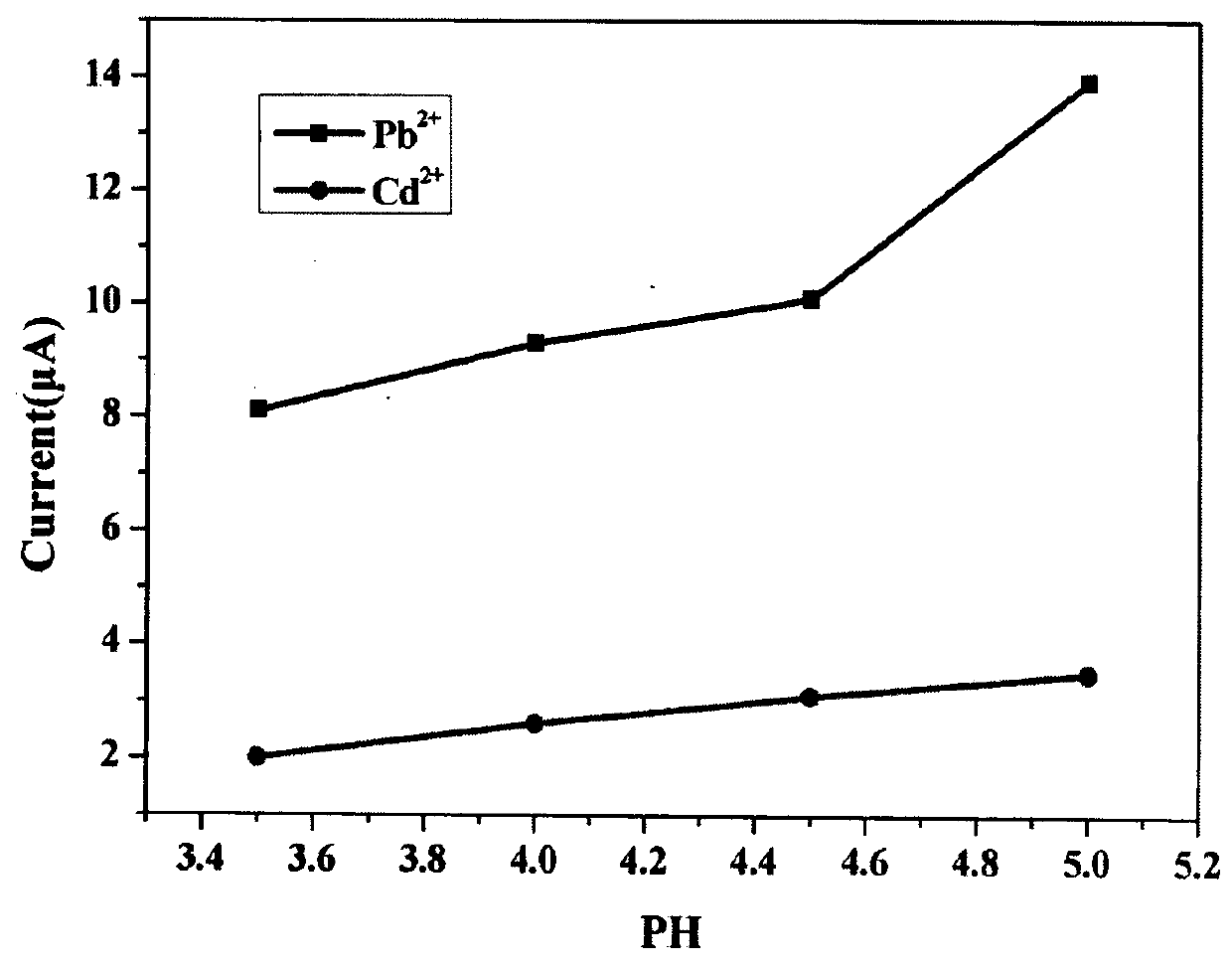
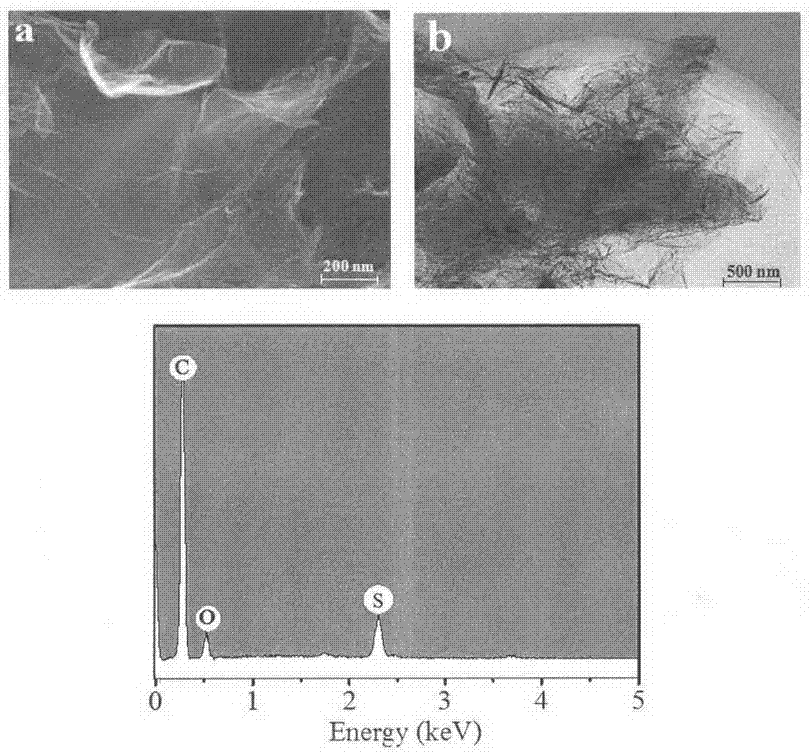
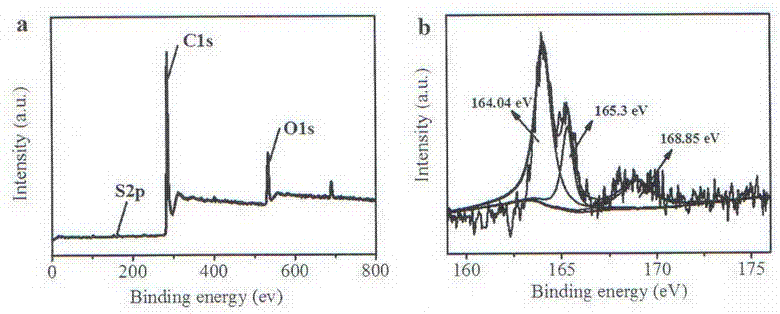
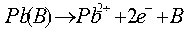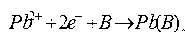Patents
Literature
95 results about "Anodic stripping voltammetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electrochemical stripping analysis is a set of analytical chemistry methods based on voltammetry or potentiometry that are used for quantitative determination of ions in solution. Stripping voltammetry (anodic, cathodic and adsorptive) have been employed for analysis of organic molecules as well as metal ions. Carbon paste, glassy carbon paste, and glassy carbon electrodes when modified are termed as chemically modified electrodes and have been employed for the analysis of organic and inorganic compounds.
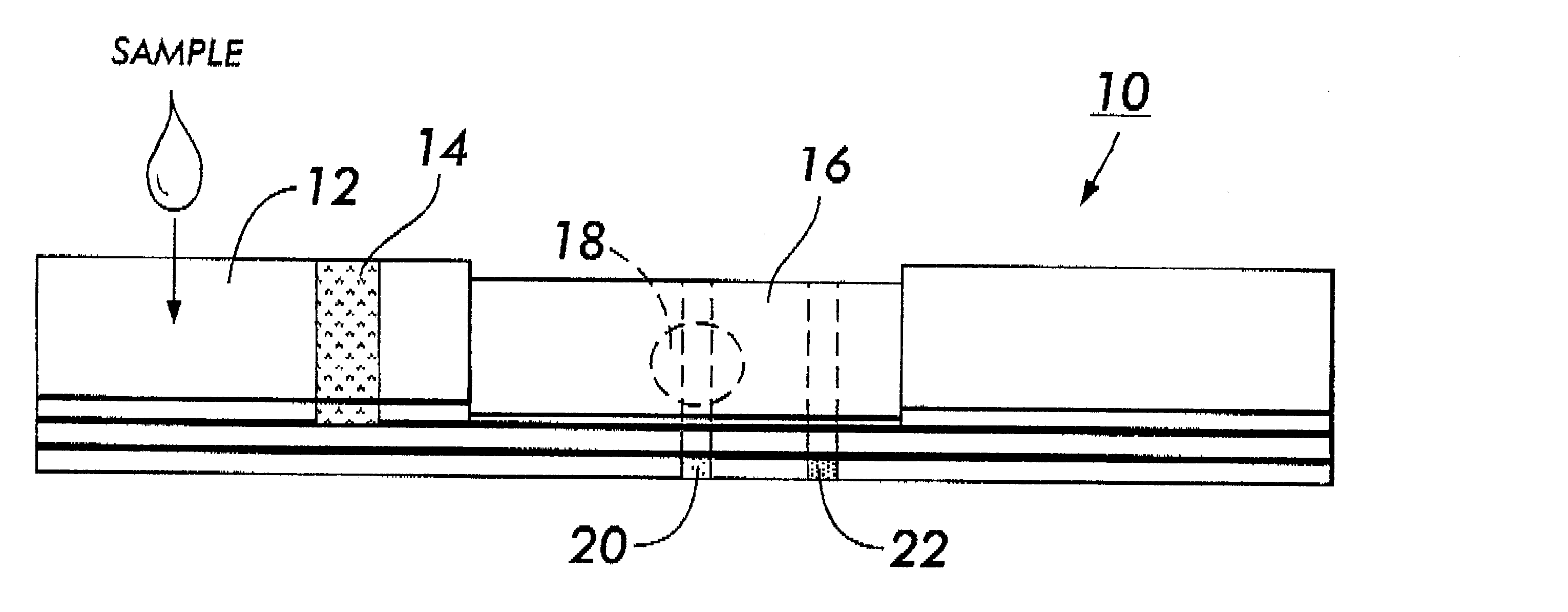
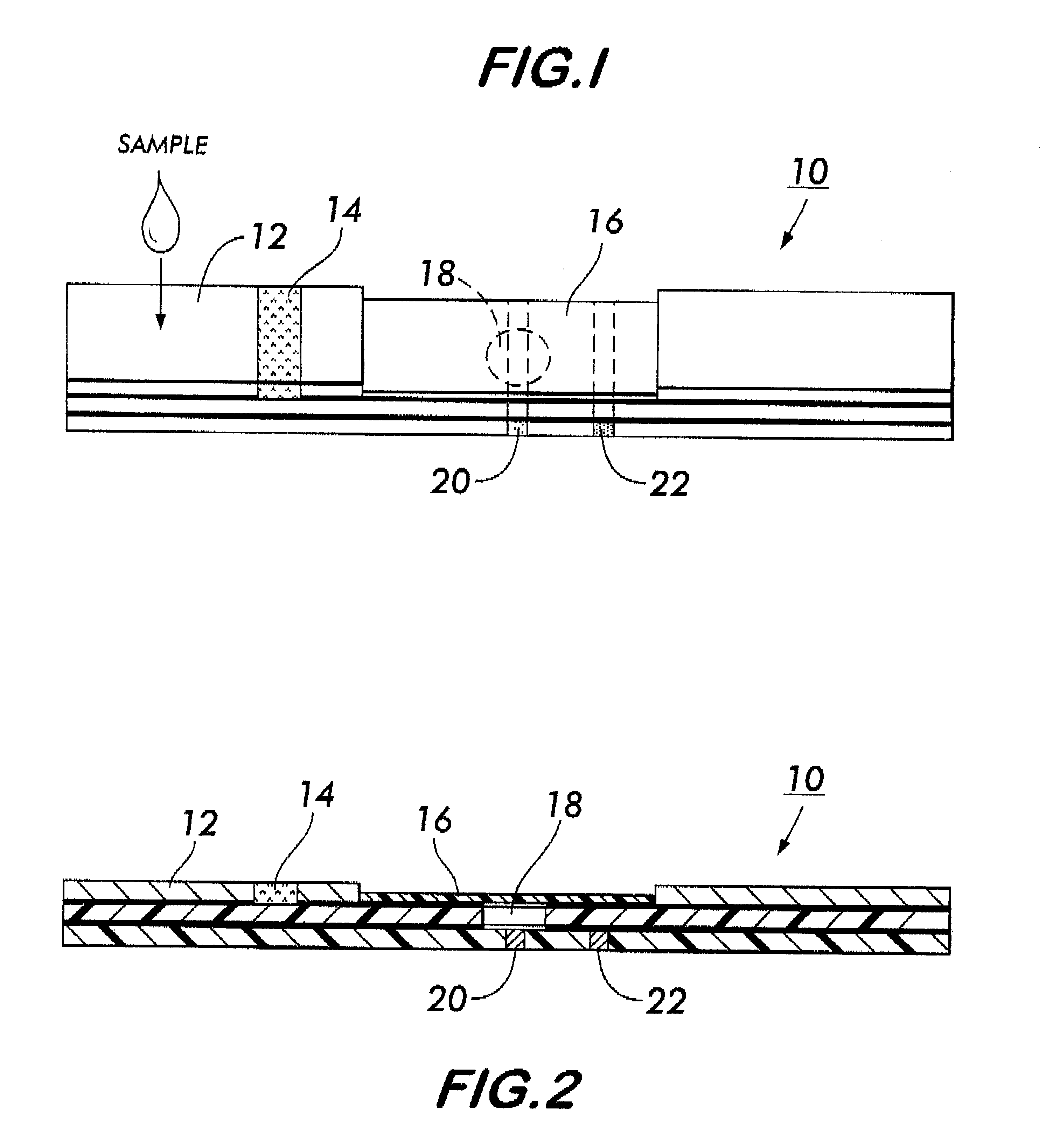
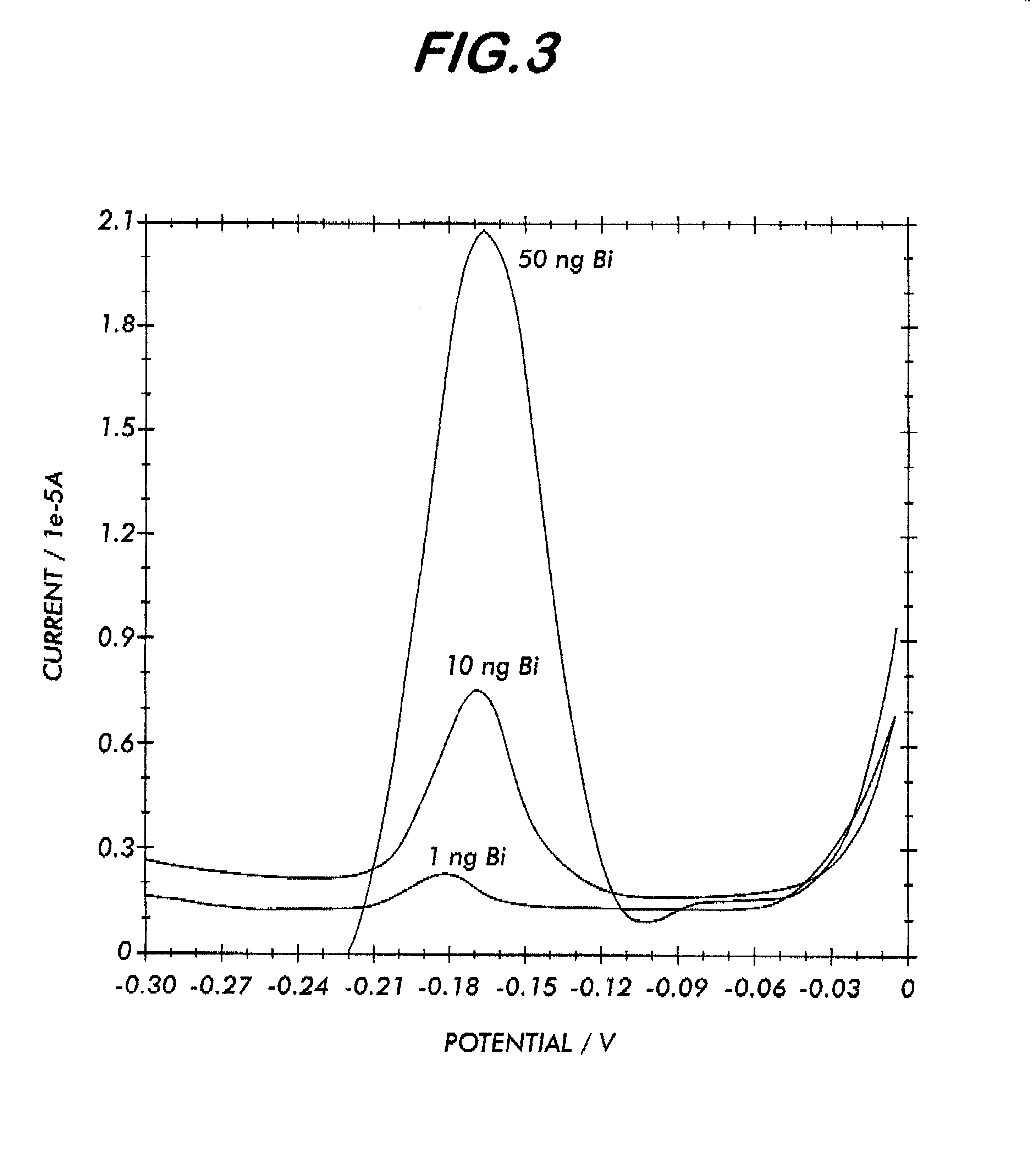
System for electrochemical quantitative analysis of analytes within a solid phase and affinity chromatographic test strip
InactiveUS6485983B1High sensitivityWide linear rangeVolume/mass flow measurementFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsProstate cancerTime-Consuming
System, method, and test strip for solid phase, electrochemical, quantitative analysis of analytes contained in biological fluid samples. Preliminary to analysis, a test sample solution can be applied to a sample collection pad associated with the solid phase test environment of the test strip. The test sample solution and a test kit reagent are thereby initially contacted, under assay conditions, within this solid phase test environment, and caused to migrate along a fluid pathway therein. Irrespective of the assay format (competitive assay, sandwich assay, etc.), a test kit reagent (e.g. labeled substance) and the analyte of interest (e.g. proteins, hormones or enzymes, small molecules, polysaccharides, antibodies, nucleic acids, drugs, toxins, viruses or virus particles, portions of a cell wall and other compounds which have specific or characteristic markers that permit their identification), either interact with one another to form a complex, or, alternatively, compete with one another for interaction with another test kit reagent, resulting in the concentration of an indicator substance within a delimited area of the solid phase. Thereafter, the delimited area of the test strip is subjected to electrochemical analysis and the results determined by monitoring an electrochemical transition in the form of an indicator, or derivative of the indicator (e.g. indicator species), by potentiostatic or potentiometric quantitative analysis (e.g. anodic stripping voltammetry). This electrochemical transition of the indicator has a characteristic electrical fingerprint that can be measured and which, when compared to a standard, can be correlated with the concentration of the analyte in the sample. This method is suitable for the determination / monitoring of therapeutic range of drugs (anti-convulsants drugs), determination of critical and potentially dangerous levels of endogenous materials which are indicative of disease states (prostate cancer), and numerous other applications presently requiring elaborate and time-consuming clinical laboratory analysis.
Owner:INTEC SCI INC
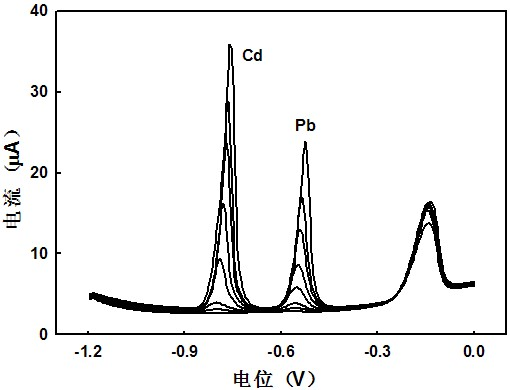
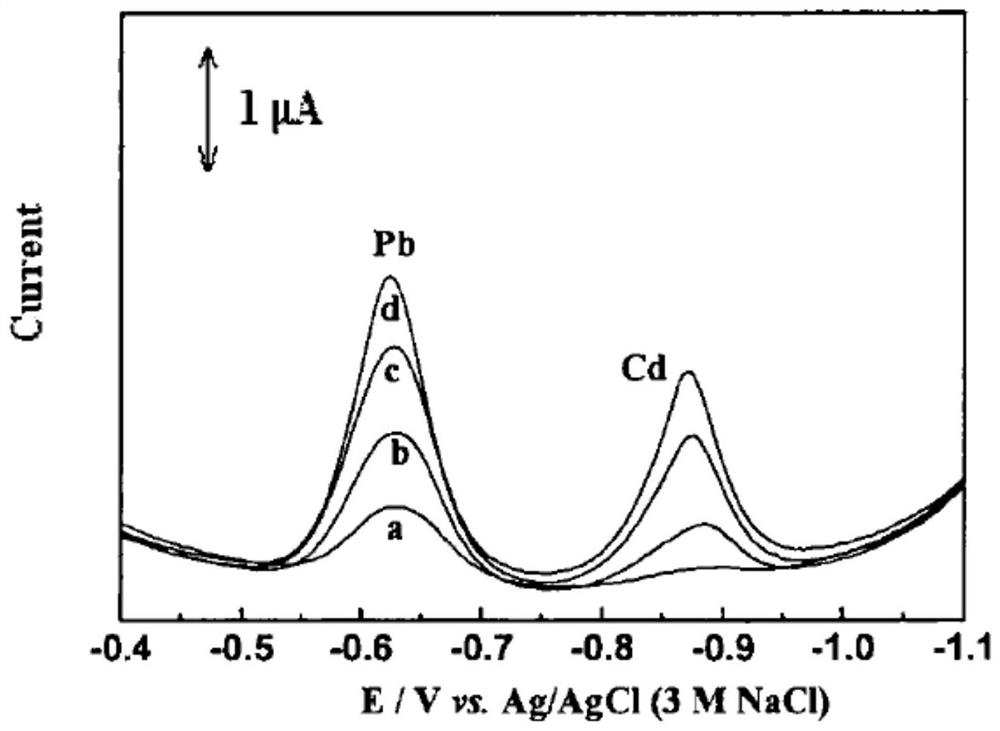
Method for quickly detecting lead and cadmium by adopting scanning anodic stripping voltammetry
InactiveCN103592356AImprove stabilityGuaranteed stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesRelative standard deviationMercury pollution
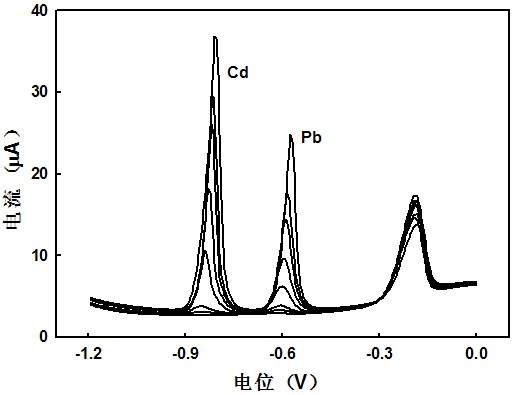
The invention discloses a method for quickly detecting lead and cadmium by adopting scanning anodic stripping voltammetry. The method comprises the following steps: a sample to be tested is prepared; lead or cadmium standard liquid is prepared; a three-electrode system consisting of glassy carbon electrodes plated with mercury films, platinum wire counter electrodes and Ag / AgCl reference electrodes is assembled; parameters are set and the scanning anodic stripping voltammetry is adopted to respectively implement parallel determination for current values between working electrodes and reference electrodes of each standard liquid solution until the relative standard deviation of readings is not more than 5%; lead and cadmium heavy metals of the sample are measured through detecting the current values between the working electrodes and the reference electrodes; a working station automatically calculates to obtain detecting results through automatically searching peaks to determine each curve peak area. The detecting method has the advantages of high sensitivity, good accuracy, reduction of mercury pollution, high electrode stability and good reproducibility, and can be applied to the detection of the heavy metals of lead and cadmium with conventional trace and ultratrace.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Multiparameter water quality heavy metal automatic online monitor based on anodic stripping voltammetry
InactiveCN102445488ASimultaneous measurementAchieve qualitativeMaterial electrochemical variablesPeristaltic pumpSolenoid valve
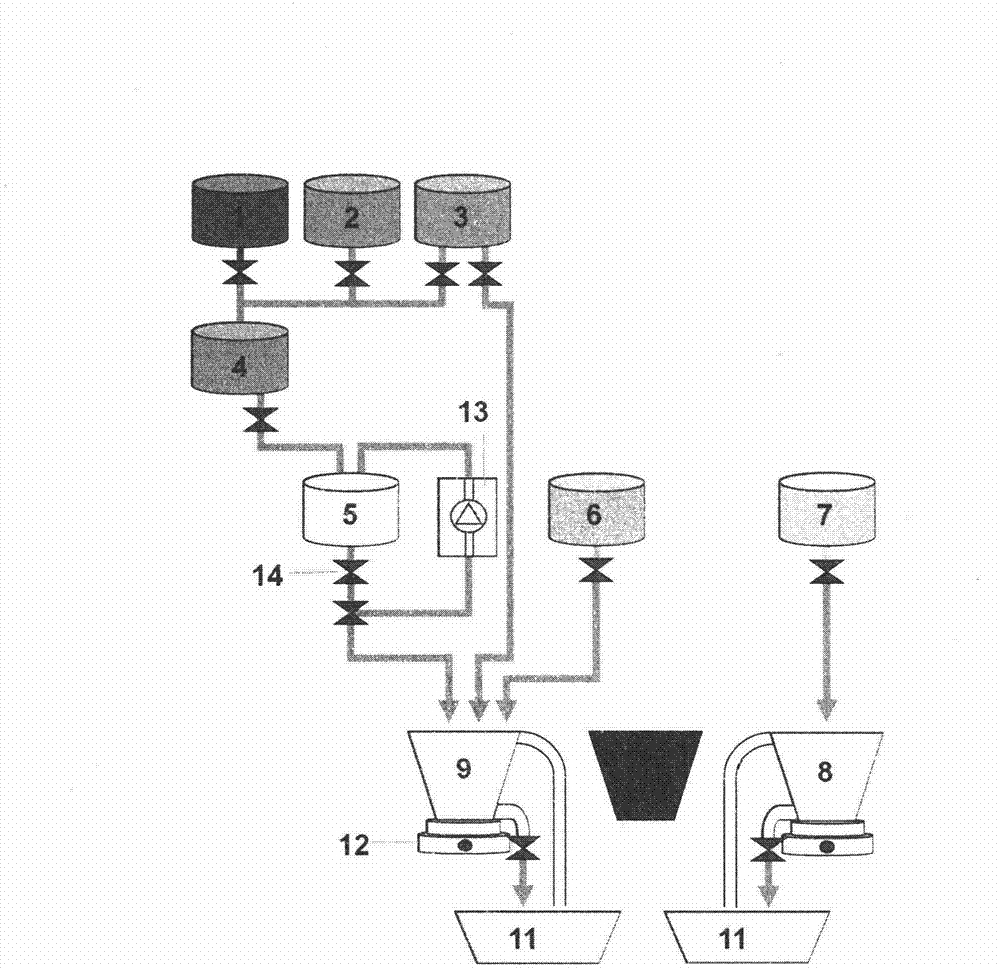
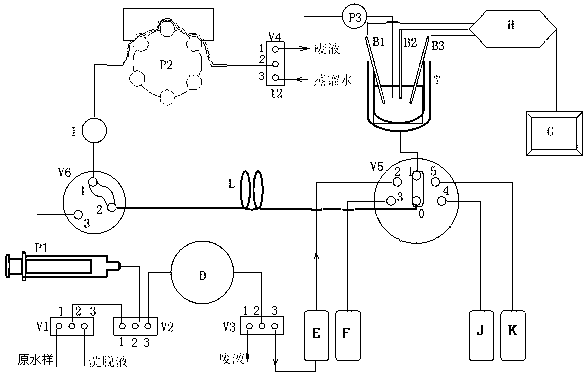
The invention relates to a multiparameter water quality heavy metal automatic online monitor based on the anodic stripping voltammetry. The monitor is characterized in that: the monitor comprises an electrochemical detection device, a control system, and a liquid charging device, a reaction device and a liquid discharging device which are respectively connected with the control system; the liquid charging device and the liquid discharging device, which jointly comprise peristaltic pumps, a precise syringe pump and six connection solenoid valves, are connected with the reaction device through pipelines to send a solution to the reaction device or discharge the solution from the reaction device; and the reaction device which is formed by inserted electrodes and an electrolytic cell with a stir bar provided therein is connected with the electrochemical detection device and can timely obtain effective data. By adopting the anodic stripping voltammetry in the invention, the simultaneous determination of multiple parameters can be realized, the reagent consumption is less, the apparatus is simple, the determination lower limit can be reduced by 2-3 orders of magnitude, and the chroma and the turbidity have no influences on the monitor, so the monitor can be used for the analysis of surface water and purified water.
Owner:QINGDAO JIAMING MEASUREMENT & CONTROL TECH
Anode digestion votammetry
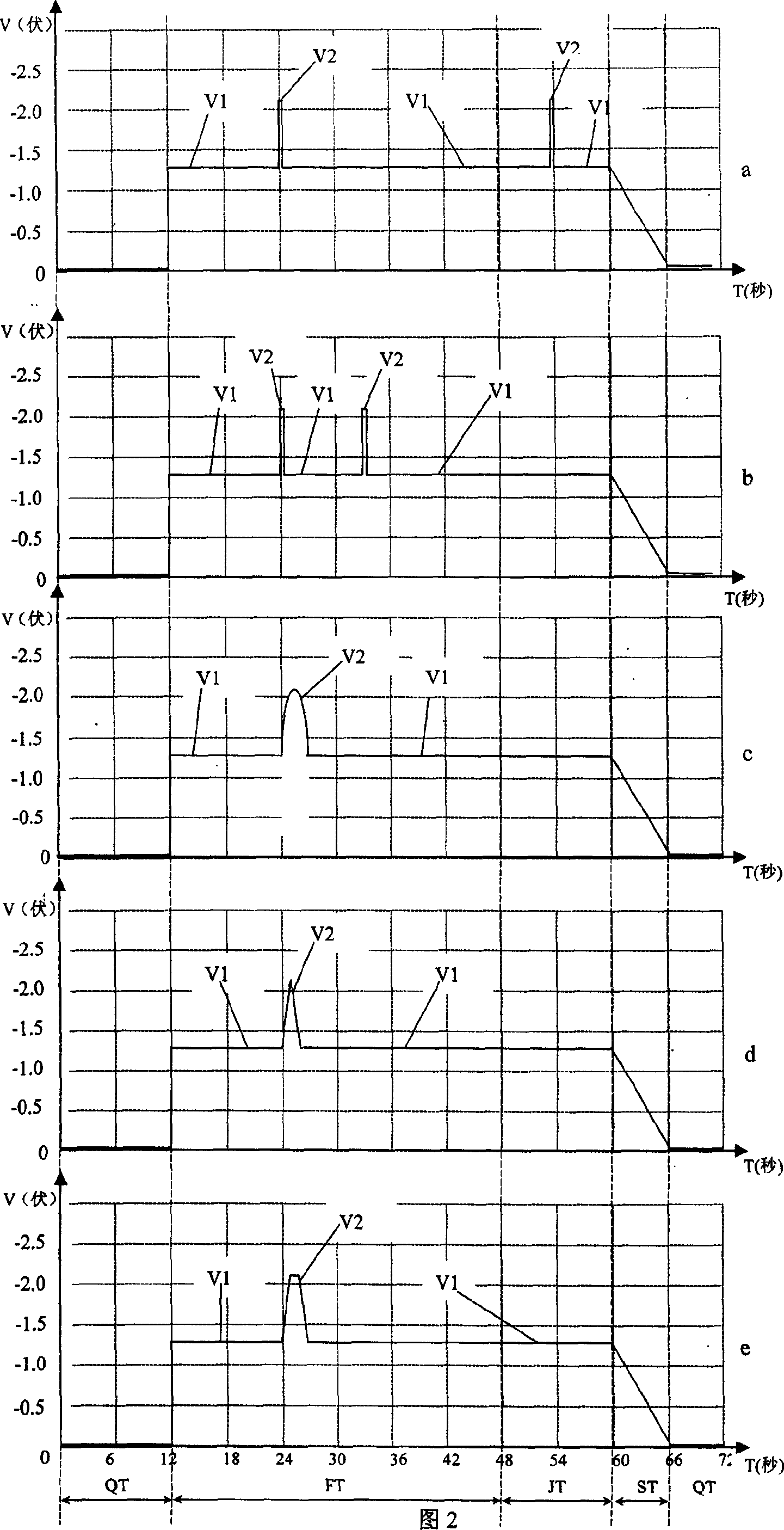
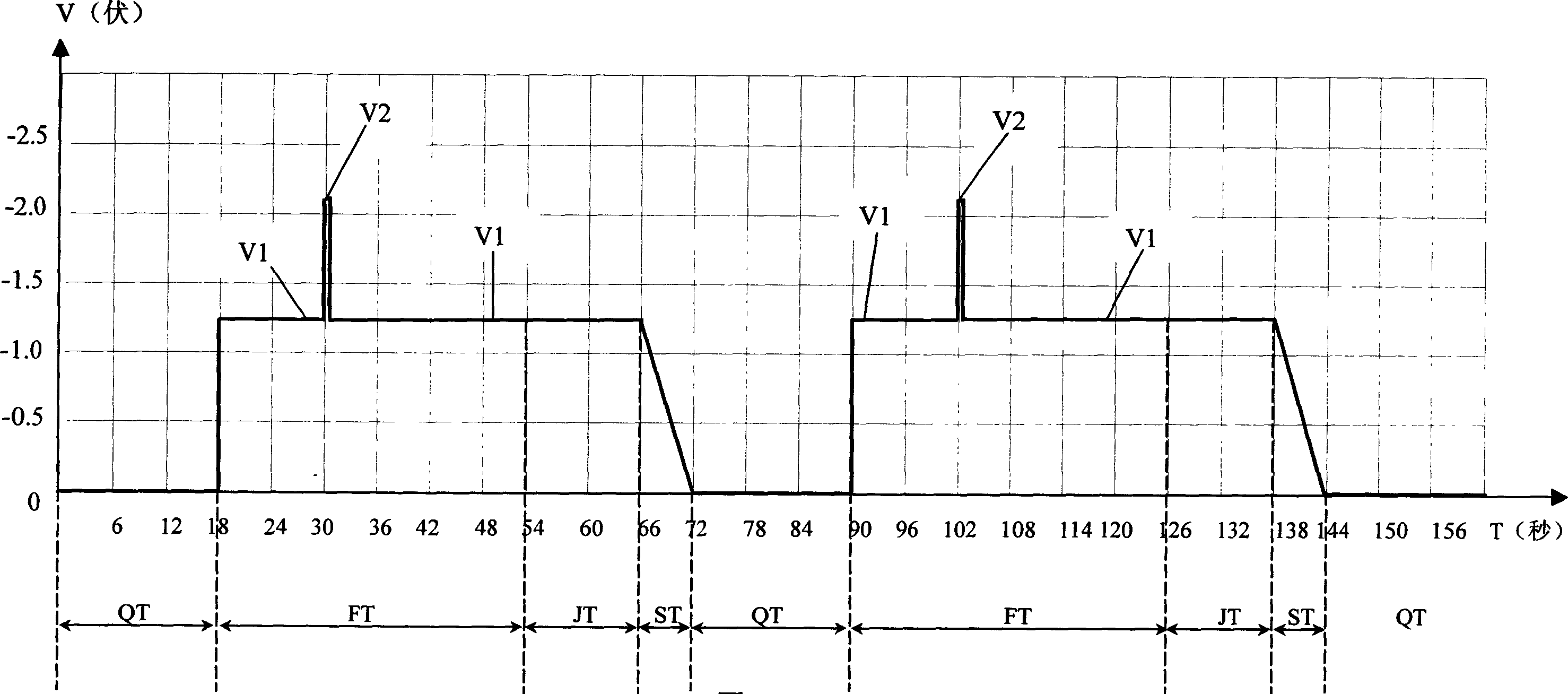
A polarography of anode dissolving out includes four steps of washing concentrating , stewing and scanning in each test cycle as at least one voltage of concentration voltage in concentrating step and stewing voltage in stewing step is less than minus 1.7 V in one period or several periods of time . The present invention can activate operating electrode processed by Hg for raising sensitivity of polarography.
Owner:刘文涛
Electrochemical sensor for detecting heavy metals and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103983681AHigh sensitivityEasy to detectMaterial electrochemical variablesPollutionSurface modification
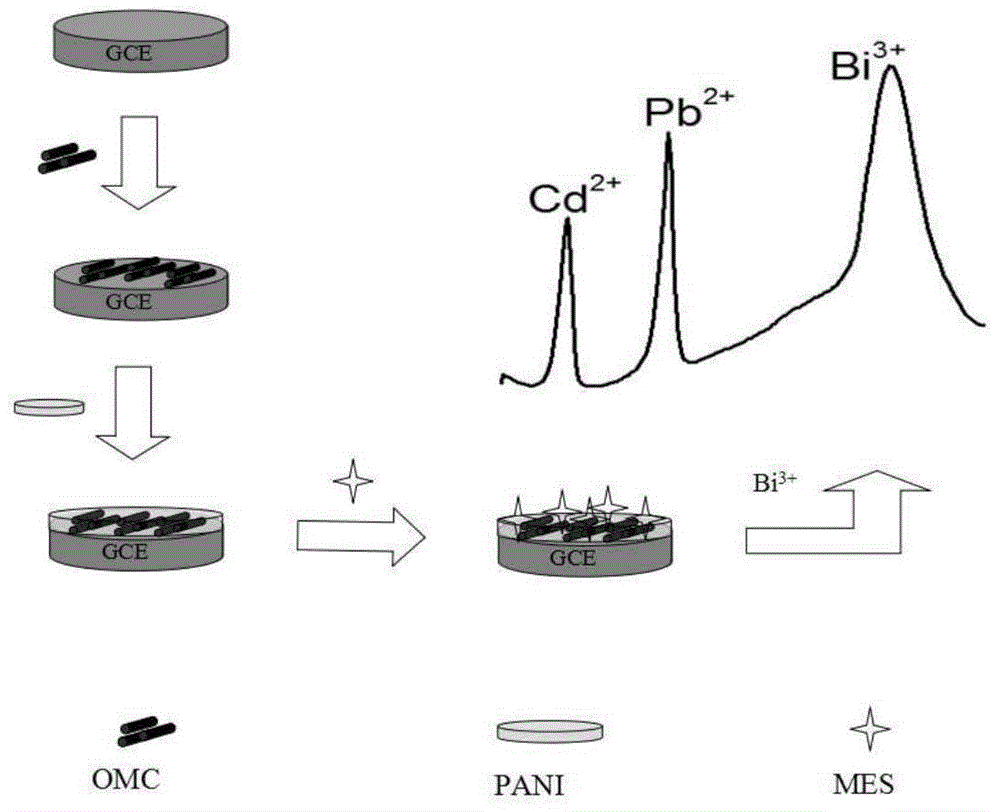
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensor for detecting heavy metals. The sensor comprises a glassy carbon electrode serving as a working electrode in a three-electrode system, wherein ordered mesoporous carbon is modified on the surface of the detection end of the glassy carbon electrode; polyaniline and 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate are deposited on the ordered mesoporous carbon. A preparation method comprises the following steps of dispersing the mesoporous carbon into an organic solvent to obtain a mixture, then dispensing the mixture onto the surface of the glassy carbon electrode, and depositing polyaniline and 2-mercaptoethanesulfonate on the surface by an electrochemical cyclic voltammetry to prepare the electrochemical sensor. An application step comprises the following steps: putting the reaction end of the glassy carbon electrode of the electrochemical sensor into a solution to be measured, then connecting to an electrolytic basin of the three-electrode system, and implementing the detection on the concentration of heavy metal ions by a differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. The electrochemical sensor for detecting the heavy metals is low in cost, easy to manufacture, high in sensitivity, low in detection lower limit, high in interference resistance, easy to apply and operate and safe and pollution-free to the environment.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Anodic stripping voltammetric mechanism-based online automatic monitoring system for heavy metal ions in water
InactiveCN103076381AAvoid cross contaminationAchieving processing powerMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansWater qualityAnodic stripping voltammetry
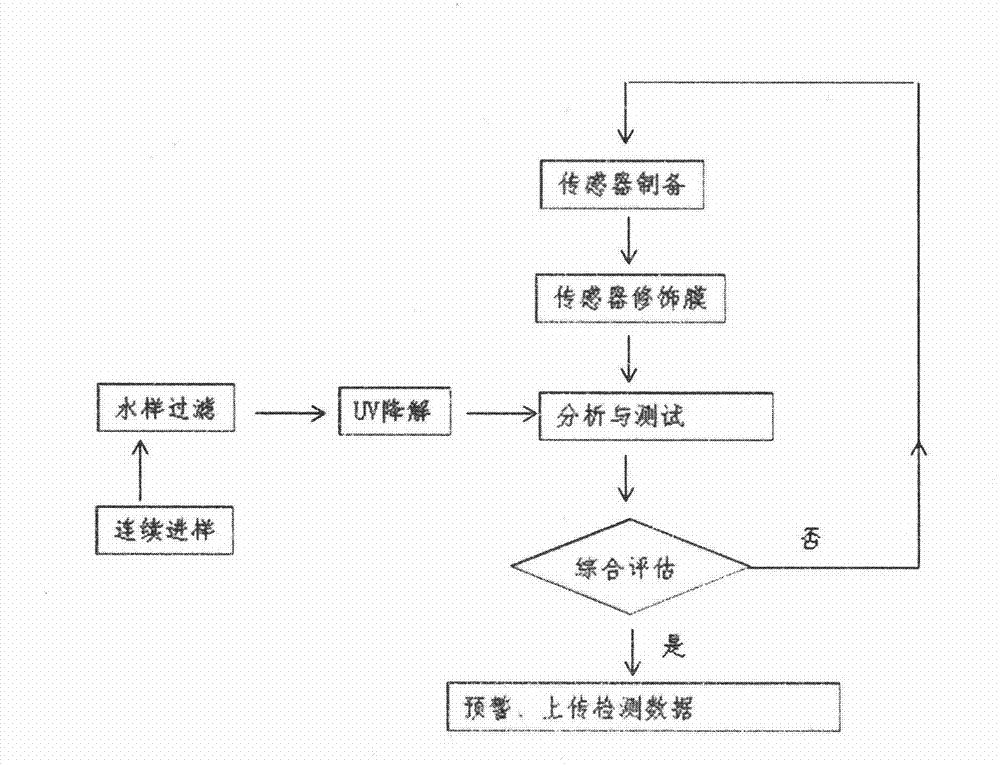
An anodic stripping voltammetric mechanism-based online automatic monitoring system for heavy metal ions in water takes electrochemical anodic stripping square wave method as a detecting mechanism and mainly comprises a system control molecule, a water sample filtering molecule, a water sample pretreating molecule, a sensor molecule and an analyzing molecule. The online automatic monitoring system for the heavy metal ions in water can continuously monitor multiple heavy metal ions in water on the spot in real time and perform pre-warning process according to whether the heavy metal content exceeds a standard or not. The online automatic monitoring system for the heavy metal ions in water is relatively low in cost, convenient to carry and easy to operate, can achieve remote control and data networking, and has a wide application prospect in routine water quality detection, real-time monitoring, pre-warning and prevention and emergency processing.
Owner:SUZHOU WENHAO MICROFLUIDIC TECH CO LTD
In-situ anode dissolving-out volt-ampere analytical method based on metal marking and biology affinity
ActiveCN103472123AThickness minimizationHigh outputMaterial electrochemical variablesMaterials scienceAnodic stripping voltammetry
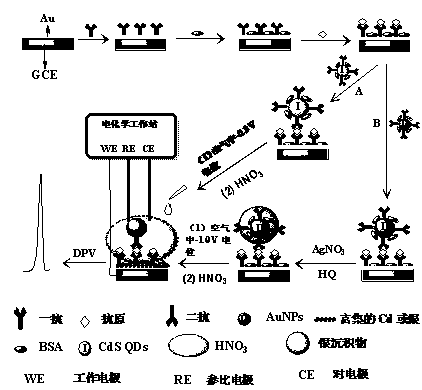
An in-situ anode dissolving-out volt-ampere analytical method based on metal marking and biology affinity comprises the following steps that (1) an immune electrode or a nucleic acid aptamer electrode is used as a working electrode, an electrochemistry instrument is connected in air, cathode potential which can achieve metal marker metal ion electro-deposition is exerted in advance, then a small-size releasing agent is added to the surface of the working electrode, an electrolytic tank is connected, so that a metal marker is dissolved, metal ions are released and are continuously and electrically reduced to atom state metal, and accordingly a metal layer is formed in the surface of the working electrode in a gathering mode; (2) anode dissolving-out current signals of the metal layer gathered on the surface of the working electrode are directly obtained on the surface of an original working electrode, and accordingly quantitative analysis on target analyte in a sample is achieved indirectly. The in-situ anode dissolving-out volt-ampere analytical method can be used for single-target analyte detecting and multi-target analyte multi-channel detecting based on metal marking and biology affinity.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical removal method for heavy metals in breeding circulating seawater
ActiveCN102642955AHigh degree of automationImprove controllabilityWater contaminantsMultistage water/sewage treatmentSeawaterSodium hydroxide
The invention discloses an electrochemical removal method for heavy metals in breeding circulating seawater, belonging to the technical field of water treatment. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, adjusting the pH value of seawater to be treated to 1.0-2.4, and removing heavy metals in the seawater by utilizing a three-electrode system in an electrochemical mode; testing the concentration of the surplus heavy metals in the treated seawater by utilizing the three-electrode system in an anodic stripping voltammetry mode; representing the removal effect; and finally, adjusting the pH value of the seawater which is completely treated by adding sodium hydroxide, and adjusting the pH value by adding fresh water to the salinity required for actual breeding. The method is high in application current efficiency and low in material consumption and running cost, and is simple to operate and easy to learn without special training; and moreover, work electrodes are less vulnerable to poisoning, namely, the work electrodes are not be polluted. Five kinds of heavy metals in the seawater can be simultaneously removed efficiency and rapidly. The heavy metal removal effects of the method can be represented by only one piece of equipment without any other auxiliary materials or conditions.
Owner:YELLOW SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERIES SCI
Double-face nanometer band electrode array integration sensor capable of being cut and method for manufacturing same
InactiveCN101358941AReduce distractionsQuick measurementDecorative surface effectsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrode arraySurface modification
The present invention discloses an electrode array integrated sensor which can cut two-sided nanobelts, and a preparation method thereof. Silicon or glass is selected as a base; the MEMS technology is adopted to deposit two different electrode materials onto the positive plane and the negative plane of the base; the lithography is used for forming a comb-shaped working electrode array and a reference electrode array, which are vertically symmetrical; the PECVD method is used for depositing a silicon nitride insulating layer respectively on two sides; the lithography extends out of the pad; the insulating layers on the two sides are provided with a plurality of cutting lines which are etched vertical to the electrodes. The sensor is used for regularly cutting and polishing, and can be repeatedly used so as to prolong the service life of the device and to enhance and maintain the consistency and stability of the electrodes. The sensor is fixed in the Teflon cavity, and adopts the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry to collect the impedance of the tested solution and complete the oxidation-reduction of current signals. The integrated sensor can be used for direct quantitative detection of the concentration of anions and cations in the solution in such fields as rivers and lakes, biomedicine, industrial wastewater and waste gas, and so on, and can be used for qualitative detection of biological molecules after completing the surface modification.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
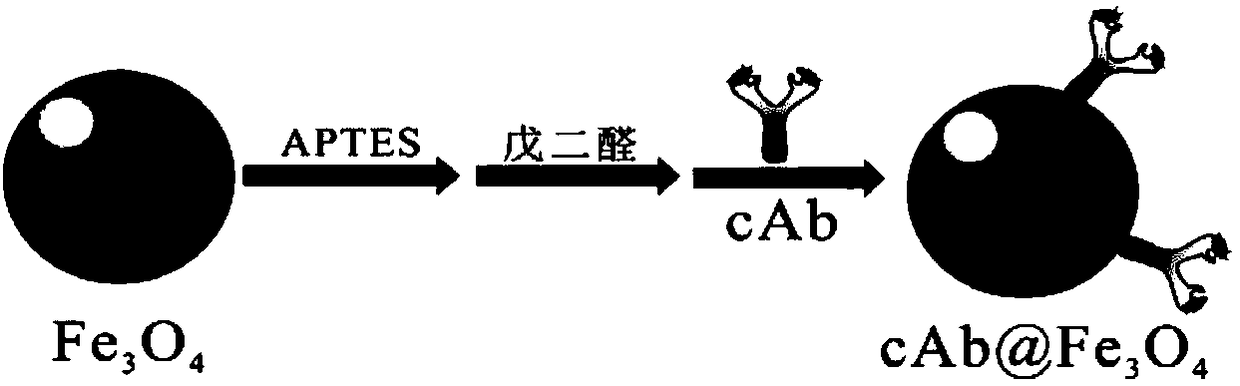
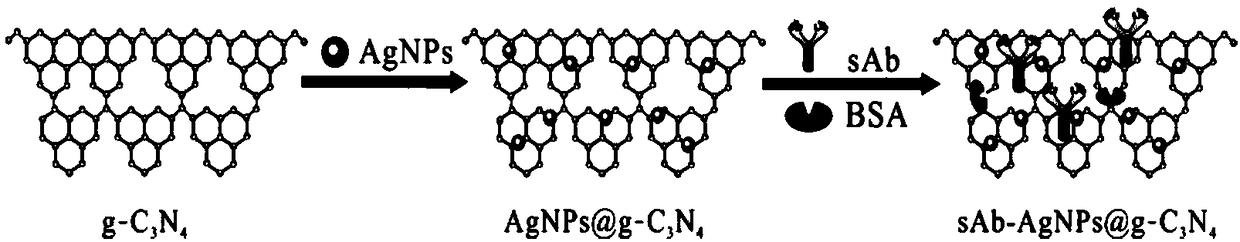
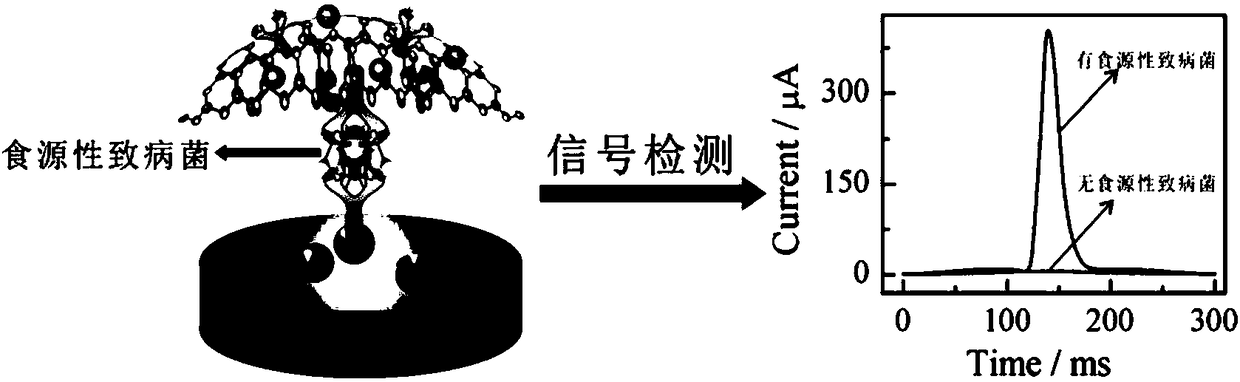
Method for preparing electrochemical immunosensors for detecting food-borne pathogens on basis of quick scanning anodic stripping voltammetry technologies and application of electrochemical immunosensors
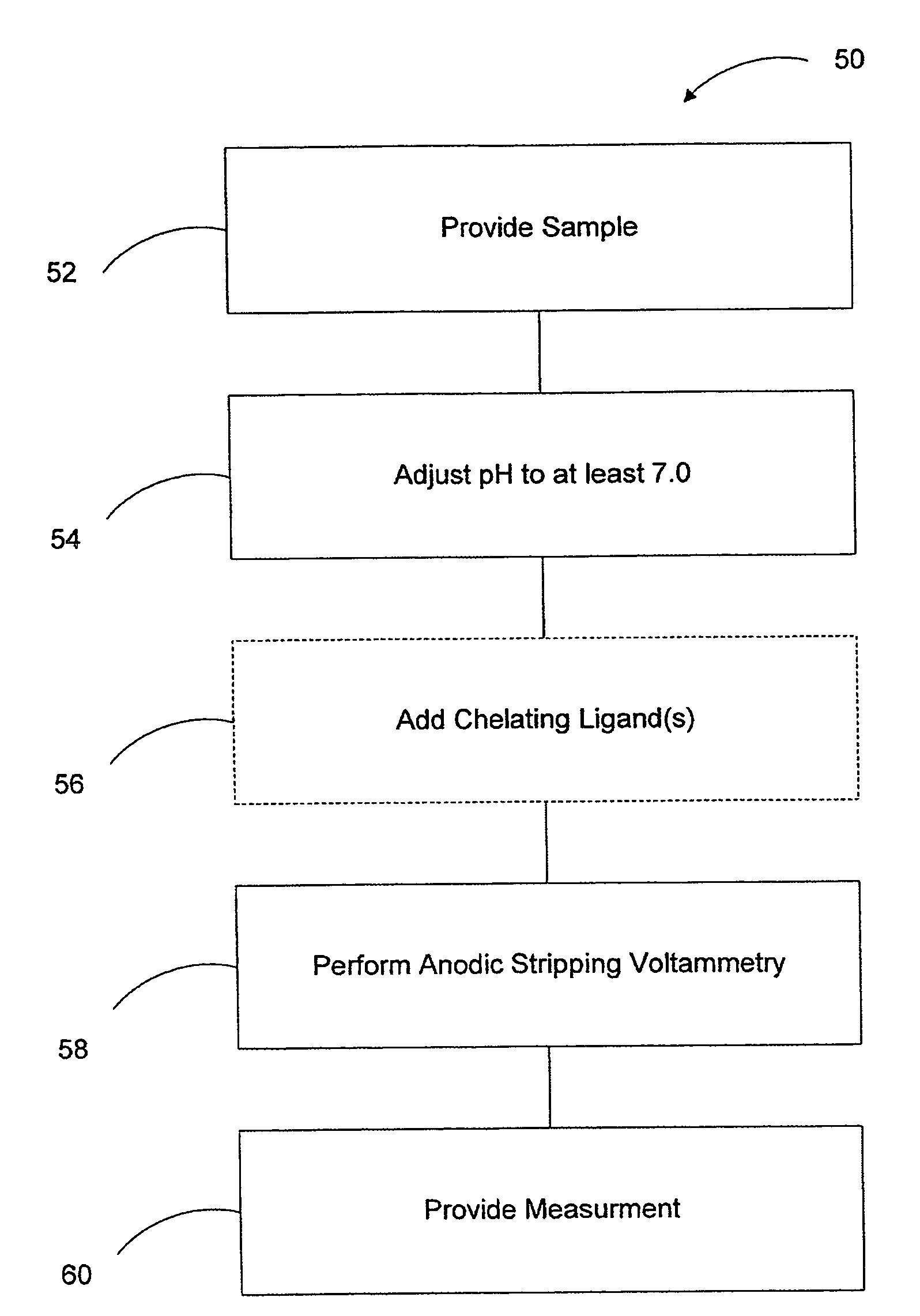
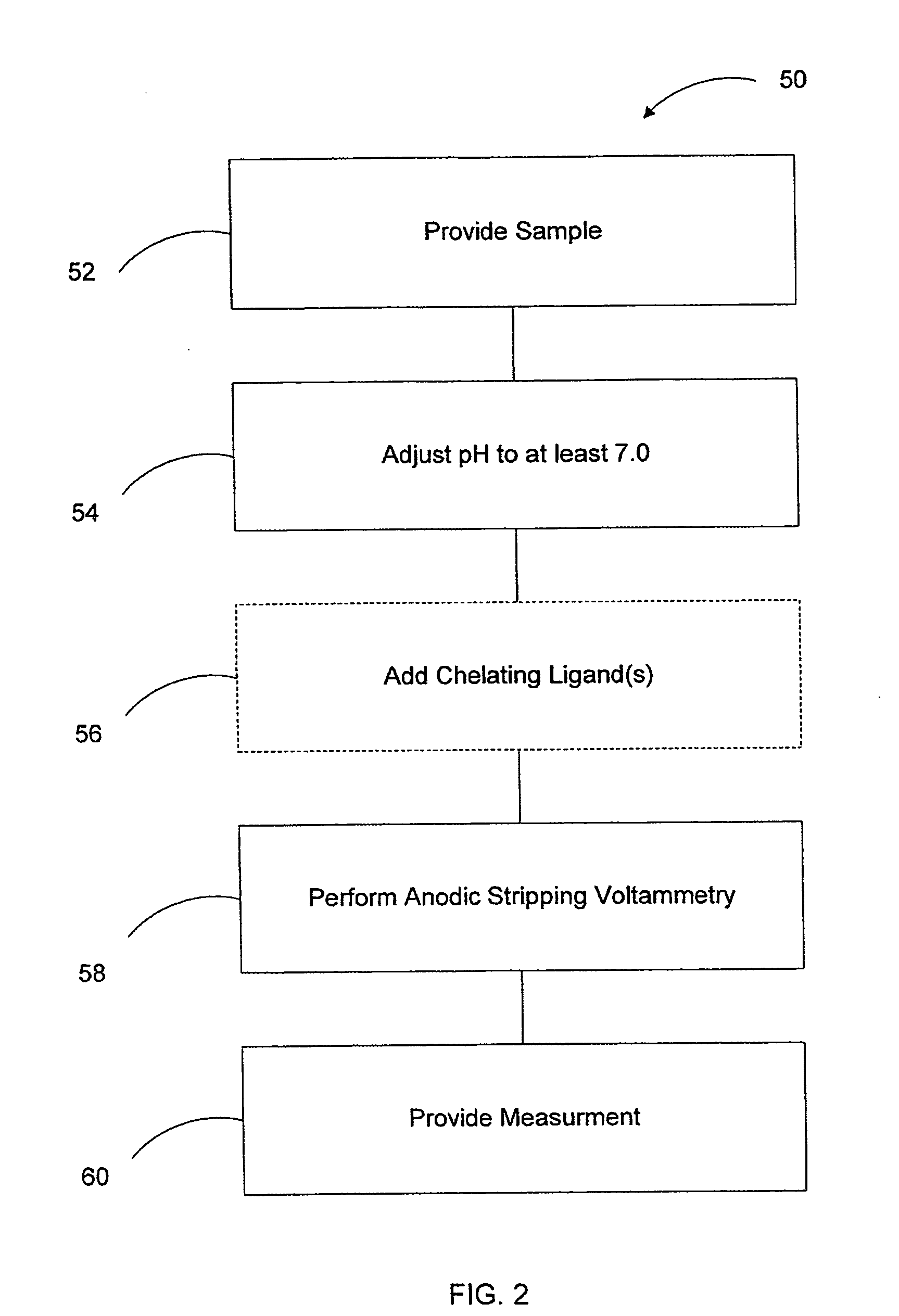
InactiveCN108375623ASecondary amplification is realizedImprove thermal stabilityMaterial electrochemical variablesFood borneAnodic stripping voltammetry
The invention discloses a method for preparing electrochemical immunosensors for detecting food-borne pathogens on the basis of quick scanning anodic stripping voltammetry technologies and applicationof the electrochemical immunosensors. The method is characterized by comprising steps of (1), adding Fe3O4 amide nano-particle solution into glutaraldehyde solution, carrying out reaction, magnetically separating and cleaning first reaction products, then adding food-borne pathogen capture antibodies into the first reaction products, carrying out reaction, and magnetically separating and cleaningsecond reaction products to obtain capture unit solution; (2), binding a composite nano-material AgNPs@g-C3N4 with food-borne pathogen antibodies to obtain signal units; (3), sequentially dropwise adding capture units, food-borne pathogen sample solution and the signal units to the surfaces of magnetic glassy carbon electrodes to obtain the electrochemical immunosensors. The application of the electrochemical immunosensors includes measuring the concentration of the food-borne pathogens in unknown samples according to quantitative relationships between anodic stripping peak currents ip and the concentration of the food-borne pathogens. The method and the application have the advantages of high sensitivity, specificity and detection speeds, reliable detection results and simple steps.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Monodispersive bimetal Au/Pt nano-particle modified electrode for detecting mercury in water and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101750442ALow detection limitHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesFiberAnodic stripping voltammetry
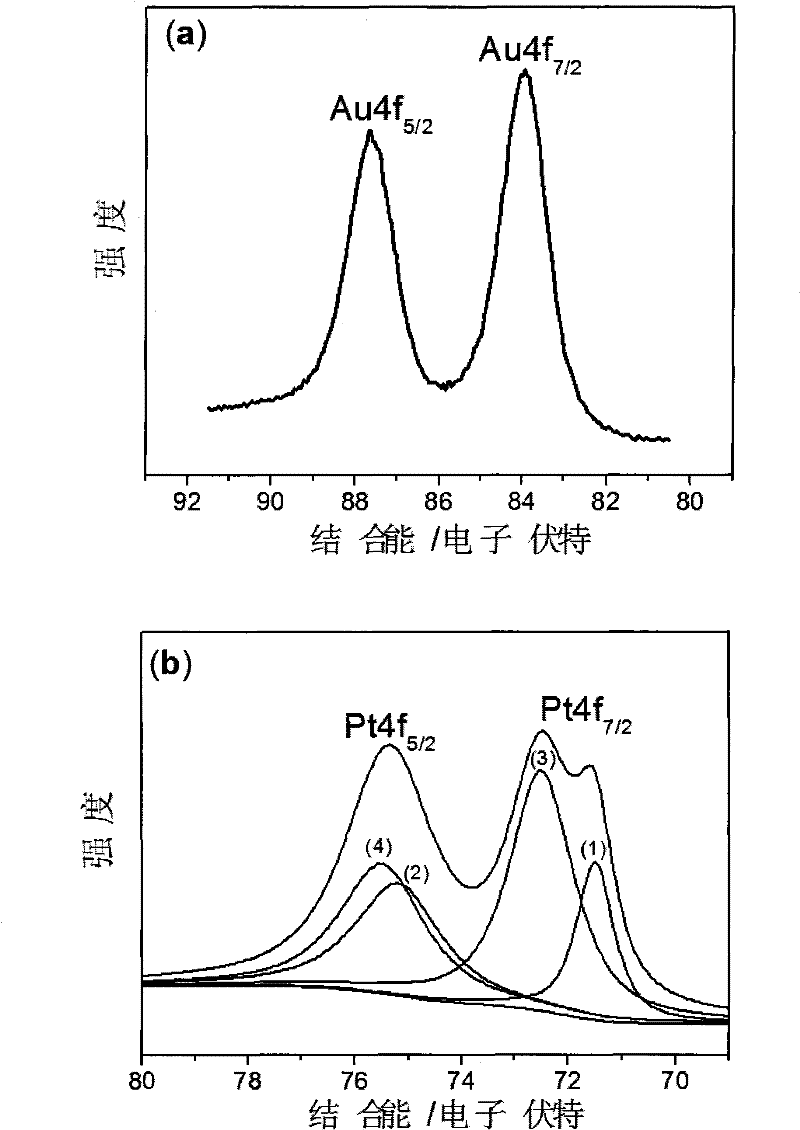
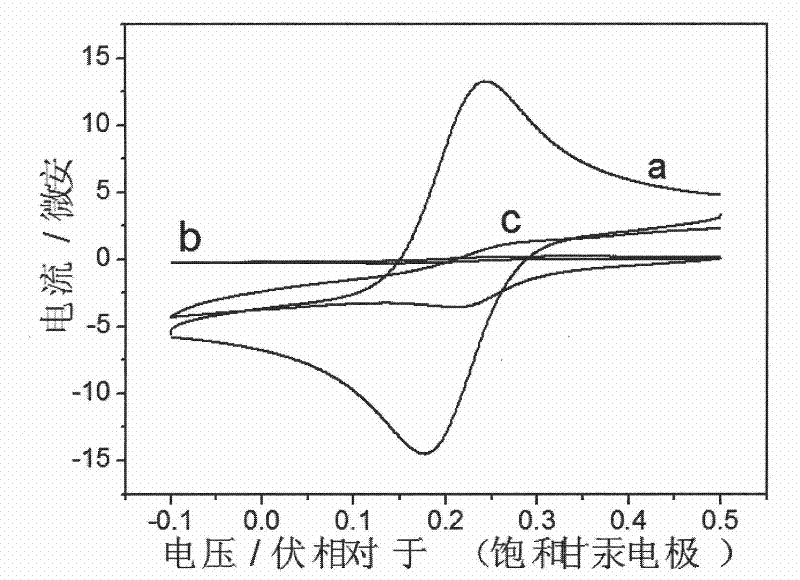
The invention relates to a monodispersive bimetal Au / Pt nano-particle modified electrode for detecting mercury in water and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the electrode comprises the following steps of: adding chloroplatinic acid to 3,3',5,5'-tetramethylbenzidine to obtain a purple precipitate, i.e. a Pt(II) doped organic nano fiber material; modifying the organic nano fiber material containing Pt(II) onto the surface of a glassy carbon electrode and then putting the modified glassy carbon electrode in a chloroauric acid solution; and carrying out electrochemical reduction by adopting cyclic voltammetry, wherein in the reduction process, the chloroauric acid is reduced into simple substance Au, and partial Pt(II) doped in the organic nano fiber material is also reduced into simple substance Pt, thereby forming a glassy carbon electrode which is adhered with Au-Pt bimetal nano particles on the surface and modified by a three-dimensional porous composite membrane with a network-shaped structure by using organic fibrous nano material as a supporting skeleton. The electrode can be used for detecting the content of mercury by adopting anodic stripping voltammetry, and has low detection limit to 0.008ppb, high sensitivity, strong selectivity and convenient and quick operation.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
Method and device for sequentially injecting lead in online detection of water quality
InactiveCN102998358AAccurate detectionEliminate distractionsPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesWater sourceDose delivery
The invention relates to a method for sequentially injecting lead in online detection of water quality, wherein each step for detecting lead in stripping voltammetry and quantitative dose delivery of required solvent or solution are finished in sequence with sequential injection method; the method comprises the following steps: plating mercury on the surface of a working electrode by using mercury plating liquid HgSO4 solution or Hg(NO3)2 solution; absorbing lead ions in a raw water sample by using polystyrene-dithizone nanofiber; then eluting and condensing into sample water for detection; respectively injecting the sample water and carrier liquid in a electrolytic bath at fixed quantities, wherein the deposition potential is -1.0 to -1.2V, the deposition time is 140-160s, the cleaning potential is -0.3V, and the time is 15s; carrying out anode stripping voltammetry detection on the sample water so as to obtain a sample water stripping voltammetry curve, wherein the stripping peak area is combined with the stripping peak area of a guide sample; and calculating to obtain the lead concentration of sample water. The invention provides a special detection device, which is accurate in fixed quantity and high in sensitivity and can realize online and quick detection of lead content in various water sources.
Owner:DELIN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Electrochemical method of detecting trace heavy metal by using walnut shell-based carbon material modified glassy carbon electrode
ActiveCN109884147ALow costWide variety of sourcesMaterial electrochemical variablesPorous carbonCarbonization
The invention discloses an electrochemical method of detecting trace heavy metal by using walnut shell-based carbon material modified glassy carbon electrode. The method comprises steps of preparing biomass porous carbon with walnut shell as a raw material through high temperature carbonization and activation by an activator, modifying the walnut shell-based carbon material on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode, and performing trace detection on heavy metal ions like Cu<2+>, Hg<2+>, Pb<2+> and Cd<2+> by using an electrochemical differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry method. The biomass porous carbon prepared by the method has advantages of large specific surface area, rich pores, and more surface defects. The method can highly selectively detect heavy metal ions like Cu<2+>, Hg<2+>, Pb<2+> and Cd<2+>, and has advantages of high detection flexibility, high stability, high anti-interference, and wide detection linear range, thereby meeting actual industrial requirements.
Owner:SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical method for detecting microscale and trace arsenic and heavy metals by carbon material modified working electrode
PendingCN107121480AEasy to makeRich sourcesMaterial electrochemical variablesAnodic stripping voltammetryActive carbon
The invention relates to an electrochemical method for detecting microscale and trace arsenic and heavy metals by a carbon material modified working electrode and belongs to the fields of food, health, environmental monitoring and the like. According to the invention, a working electrode is modified mainly by the utilization of a common carbon material such as graphite, carbon black, active carbon and the like, and microscale and trace arsenic and heavy metals undergo quantitative analytical determination by anodic stripping voltammetry. The working electrode only needs to be coated with the carbon material for direct testing. By adding microscale nafion or adding a proper amount of bismuth ions into a solution to be tested, sensitivity of the working electrode can be greatly raised. The electrode modification material is cheap and easily available. The modification process is simple and fast, and one or more microscale and trace arsenic and heavy metals can be rapidly detected at the same time. Sensitivity is high; performance is stable; and detection limit is low. The method has a very good promotion and application prospect. The carbon material is the first choice as an actual working electrode coating material for the electrochemical method for rapidly detecting microscale and trace arsenic and heavy metals.
Owner:BAISE UNIV
Method and apparatus for measuring cadmium in food
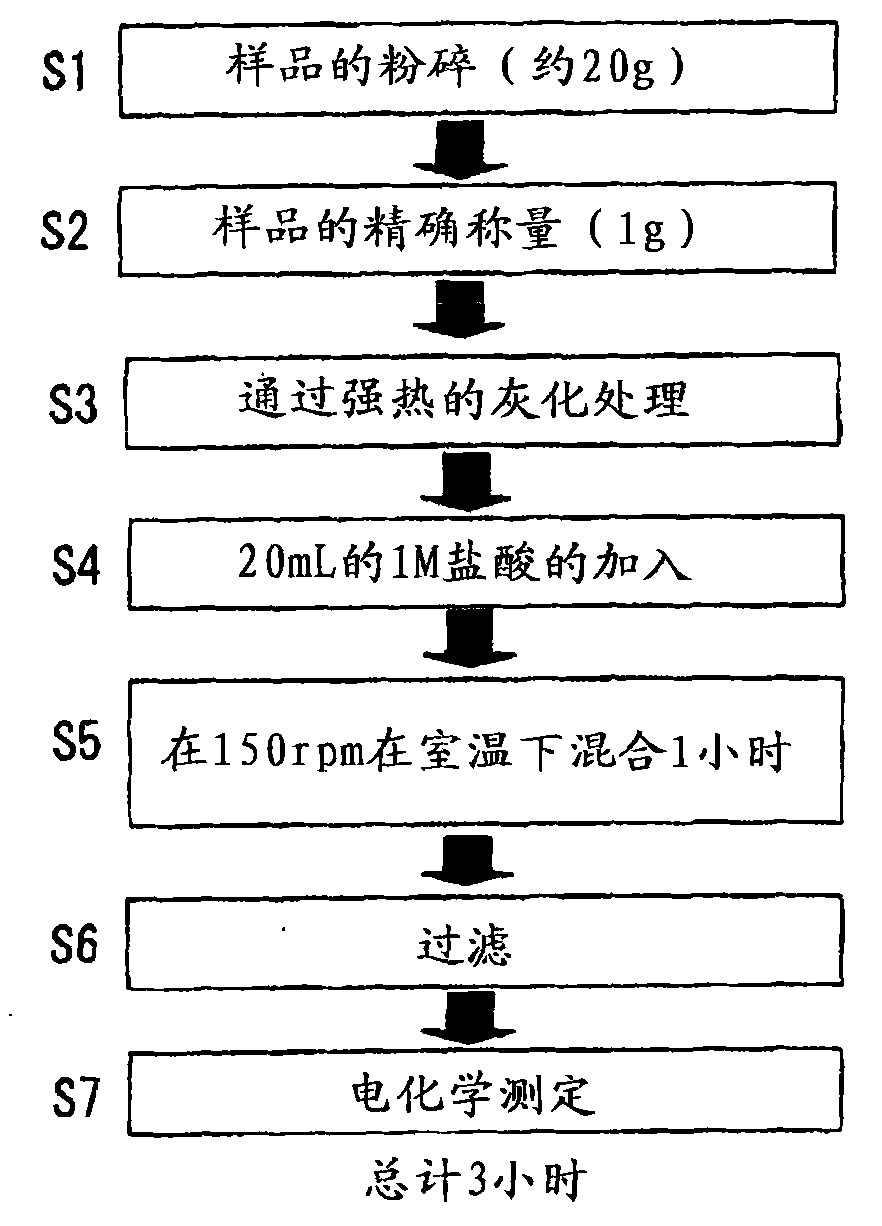
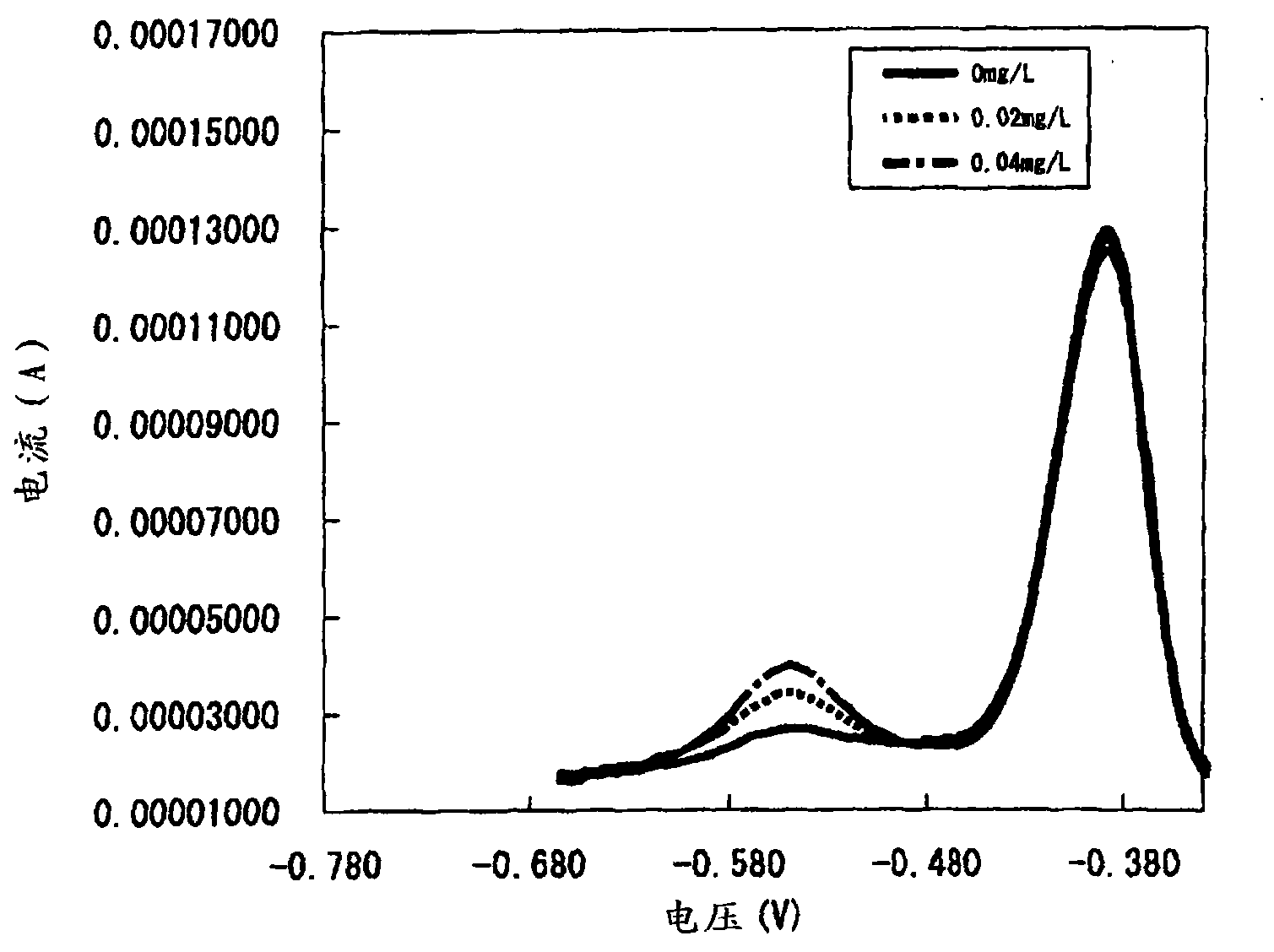
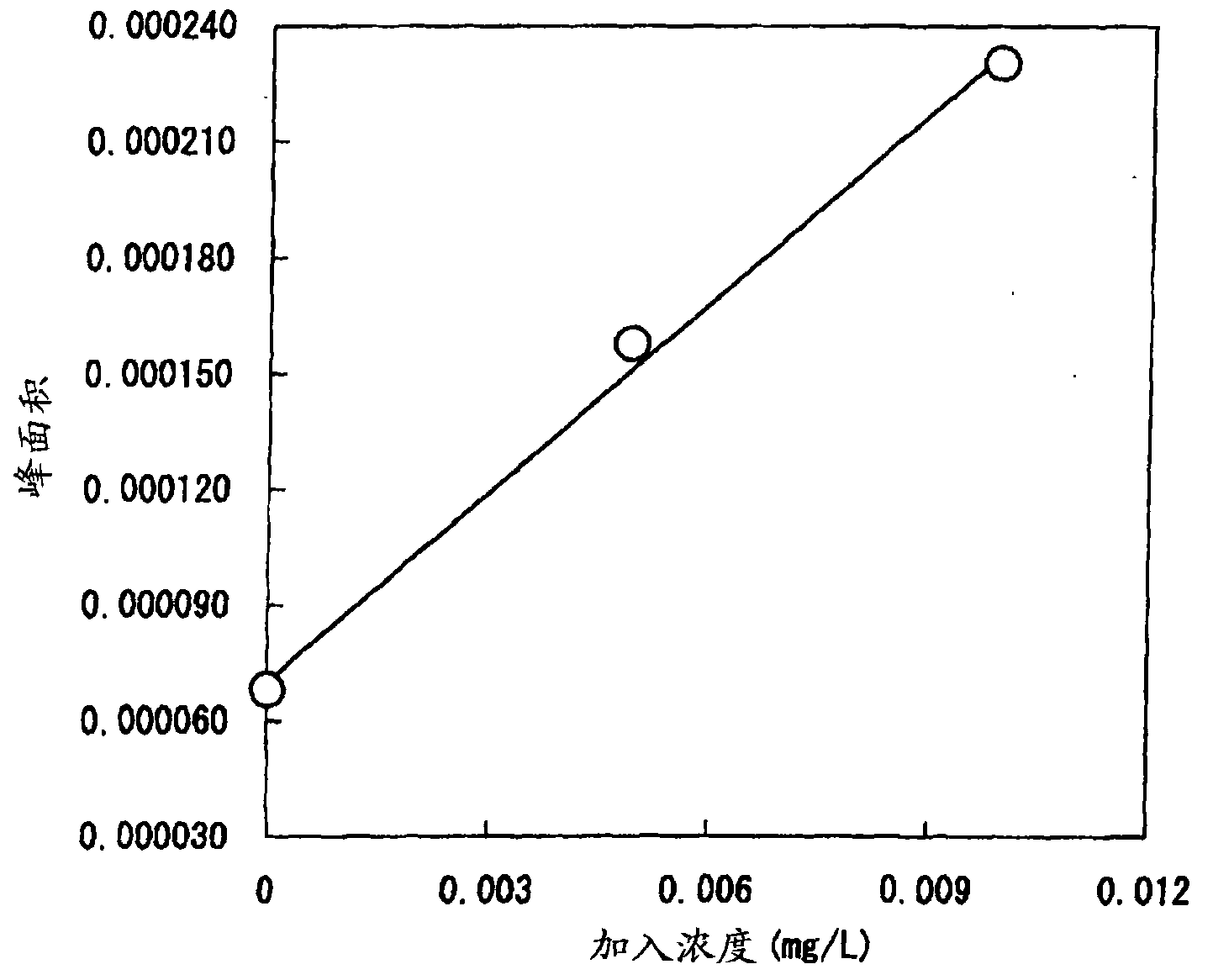
The purpose is to measure the concentration of cadmium in a food with high accuracy in a simple manner. A food which is to be measured on the cadmium concentration is weighed precisely and pulverized. The pulverized sample is subjected to an ashing treatment by strong heating. The resultant sample is mixed with an acid and the mixed solution is shaken. A residue is removed from the mixed solution to produce a solution, and the solution is subjected to an electrochemical measurement. The method for the electrochemical measurement to be employed is an anodic stripping voltammetry or the like. The working electrode to be used in the electrochemical measurement is a copper electrode or the like. The temperature to be employed for the ashing treatment by strong heating is equal to or higher than the melting point of zinc and equal to or lower than the boiling point of cadmium, and the solution to be subjected to the measurement is adjusted to pH 3.5 to 5.5.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD
Method for improving detection accuracy of electrochemical active metal ions
InactiveCN101957336AFast analysisReduce lossMaterial electrochemical variablesInternal standardReaction system
The invention relates to the improvement of a cathodic stripping voltammetric method, in particular to a method for normatively adding another kind of internal standard metal ions with electrical activity into a reaction system to eliminate the influence on a detection result due to factors such as the non-uniformity of charges on the surface of a screen electrode, and the like and correct data obtained for detecting the concentration of metal ions by a voltammetric detection method so as to improve the accuracy of a detection result of an anodic stripping voltammetric method.
Owner:INTEC PROD INC
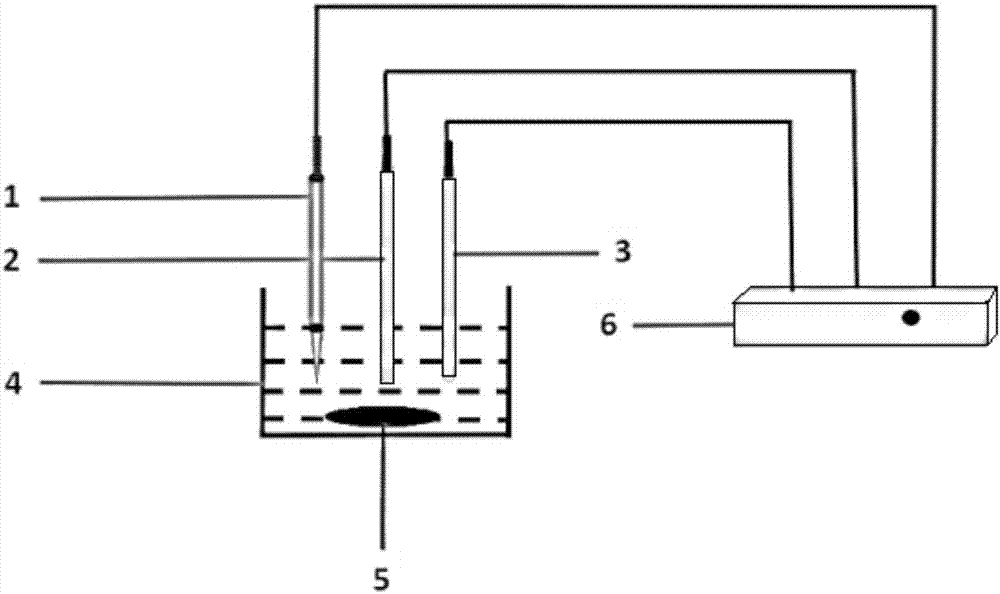
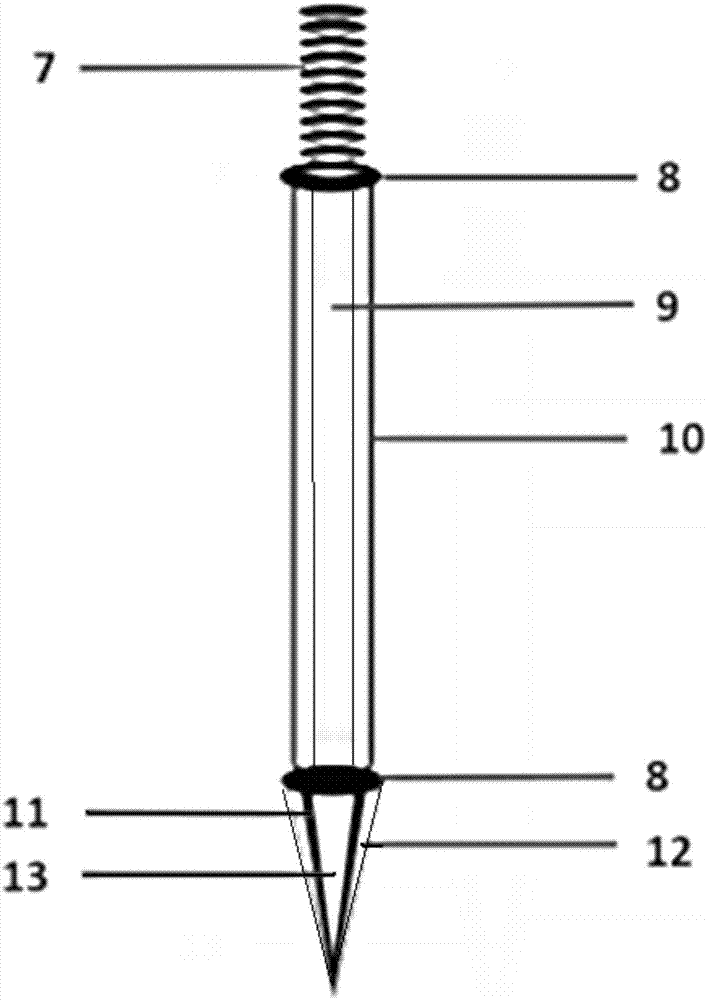
Acupuncture needle-based working electrode electrochemical sensor for detecting trace heavy metals
ActiveCN107576716AEasy to makeLow costMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical gas sensorPolyvinyl chloride
The invention relates to the field of electrochemical sensors, in particular to an acupuncture needle-based working electrode electrochemical sensor for detecting trace heavy metals. The acupuncture needle-based working electrode electrochemical sensor comprises an acupuncture needle-based working electrode, a reference electrode and an auxiliary electrode. The working electrode consists of a stainless steel acupuncture needle. A polyvinyl chloride tube is used to insulate the needle bar part of the acupuncture needle. The joint part of the polyvinyl chloride tube and the needle bar is sealedwith silicone rubber, the needle tip of the acupuncture needle is used as a sensing surface, the needle tip surface is covered with metal nanoparticles and cation exchange membranes on the surfaces ofthe metal nanoparticles. The detection method is that inserting the acupuncture needle-based working electrode into a sample to be tested along with the reference electrode and the auxiliary electrode, and detecting the concentration of heavy metal ions in the sample to be tested by anodic stripping voltammetry. The acupuncture needle-based working electrode electrochemical sensor prepared by themethod has the advantages of simple process, low cost, high sensitivity, good selectivity and stability and can be widely used for detecting trace heavy metals.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
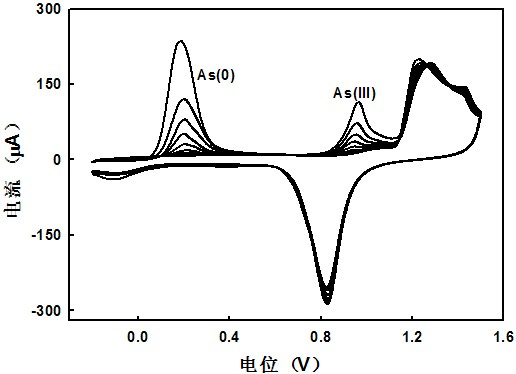
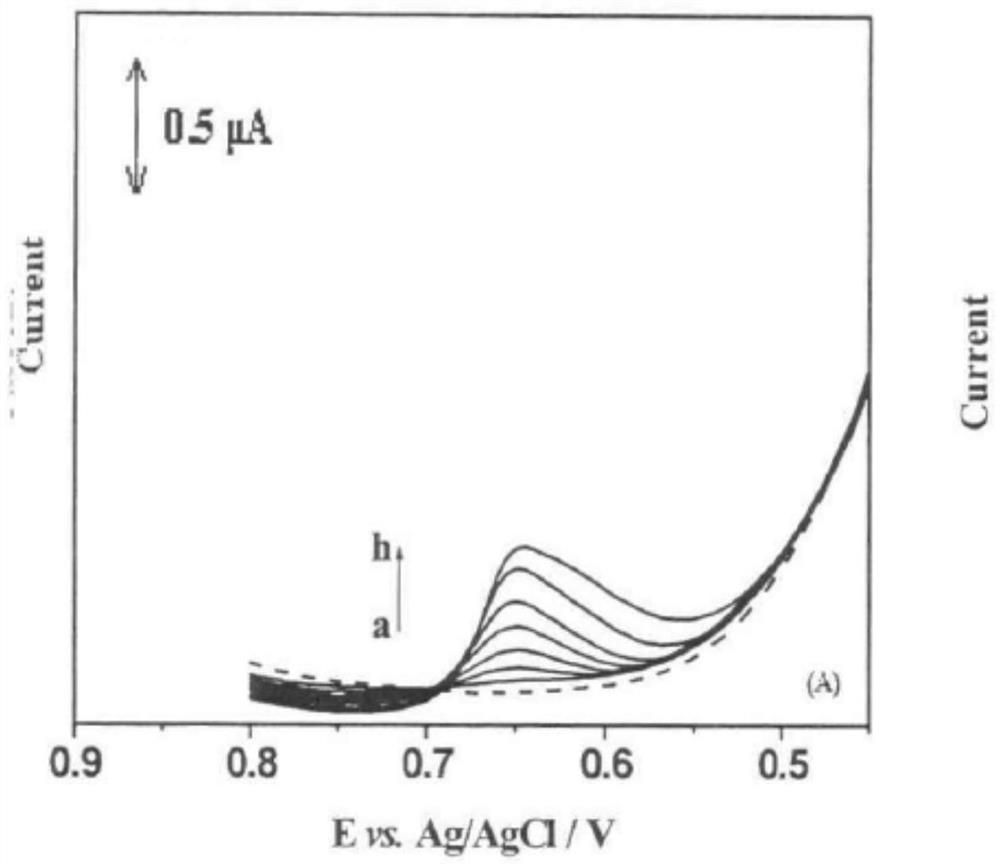
Method for detecting trace trivalent arsenic through two-signal anodic stripping voltammetry
InactiveCN102565173AImprove detection flexibilityEasy to detectMaterial electrochemical variablesSupporting electrolytePhosphate
The invention relates to a method for detecting trace trivalent arsenic through two-signal anodic stripping voltammetry, wherein a working electrode is a gold electrode, a reference electrode is a saturated calomel electrode (SCE) or a silver / silver chloride electrode; and a counter electrode is a platinum, carbon or gold inert electrode; supporting electrolyte solution includes neutral phosphate buffer solution, B-R buffer solution with pH 1.81 to 8.95, or sulphuric acid solution with 0.1 to 0.5 mol.L-1; under the negative potential (-1.1 to -0.1 VvsSCE), test solution is mixed for enrichment for 300 to 600s, so that As (III) is reduced to As (0) to be enriched to the surface of the working electrode; the solution is on standing for 10 to 20s; when forward scanning reaches a certain electric potential point between 1 to 1.6 VvsSCE, the enriched As (0) is electro-oxidized and stripped into the As (III), and the As (III) is further electro-oxidized into As (V); and the trivalent arsenic in the test solution is calculated by the prior art according to the oxidation current double-response signals generated through detection. The method has more accurate detection result, high sensitivity, better property for resisting interference of materials as copper ion, obtains satisfactory result by being applied to the sample detection, is simple and quick, and can be widely applied in fields as environmental monitoring, food safety and bioelectrochemistry.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Arsenic measurement using anodic stripping voltammetry
InactiveUS20070158211A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementAqueous solutionArsenic measurement
Measurement of arsenic in an aqueous solution is provided. The pH of the aqueous solution is adjusted to a pH of about 7.0 or higher. The pH adjusted aqueous solution is then analyzed using anodic stripping voltammetry to obtain an indication of a quantity of arsenic in the solution. In one aspect, the pH is adjusted using a phosphate buffer.
Owner:ROSEMOUNT ANALYTICAL
Method for judging limit exceeding of heavy metals in water
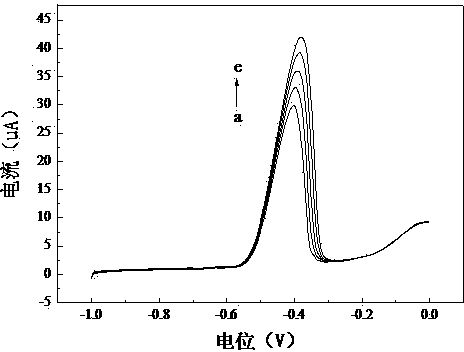
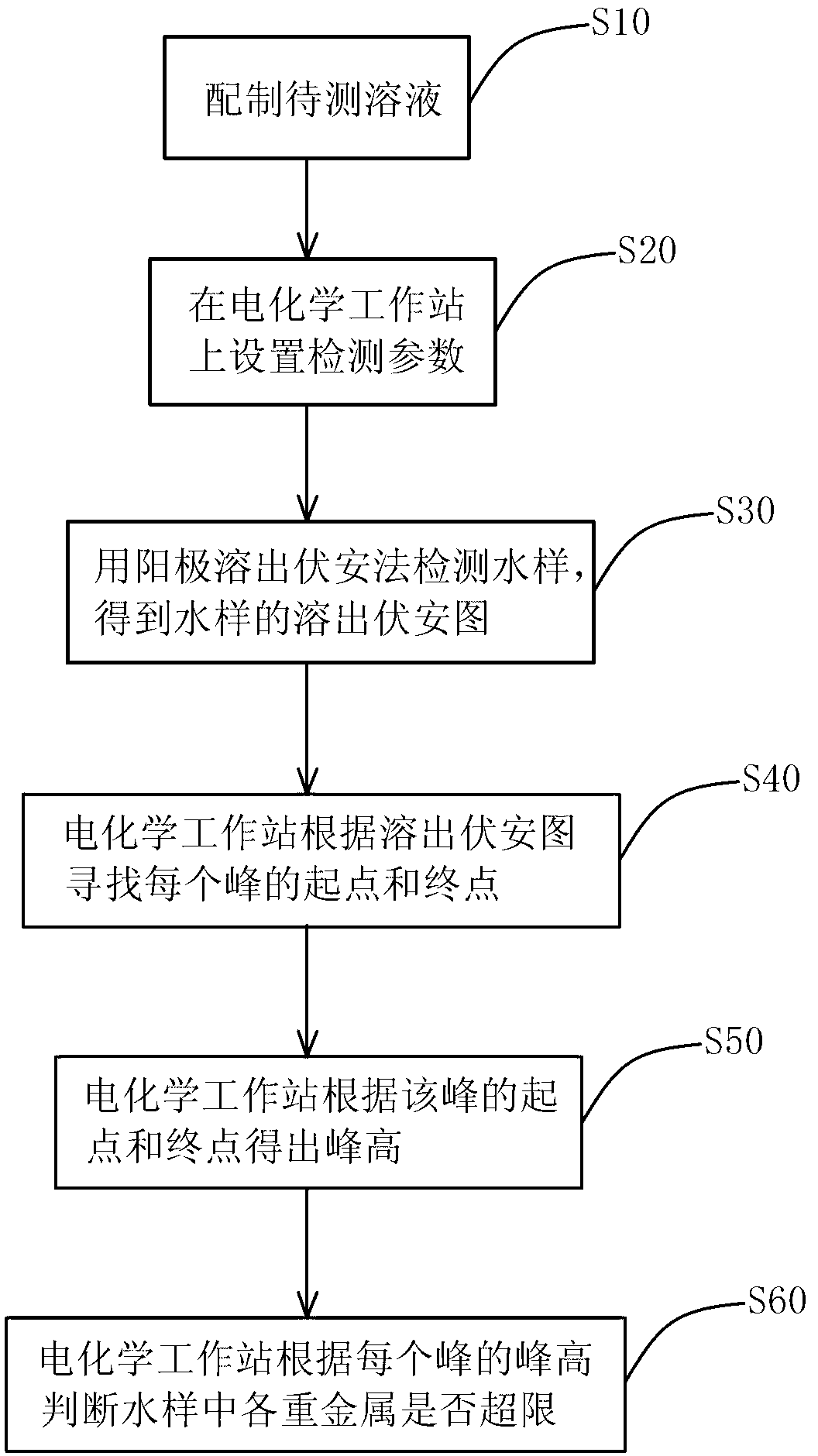
ActiveCN103105428AImprove accuracyAvoid missing peaksMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityPower flow
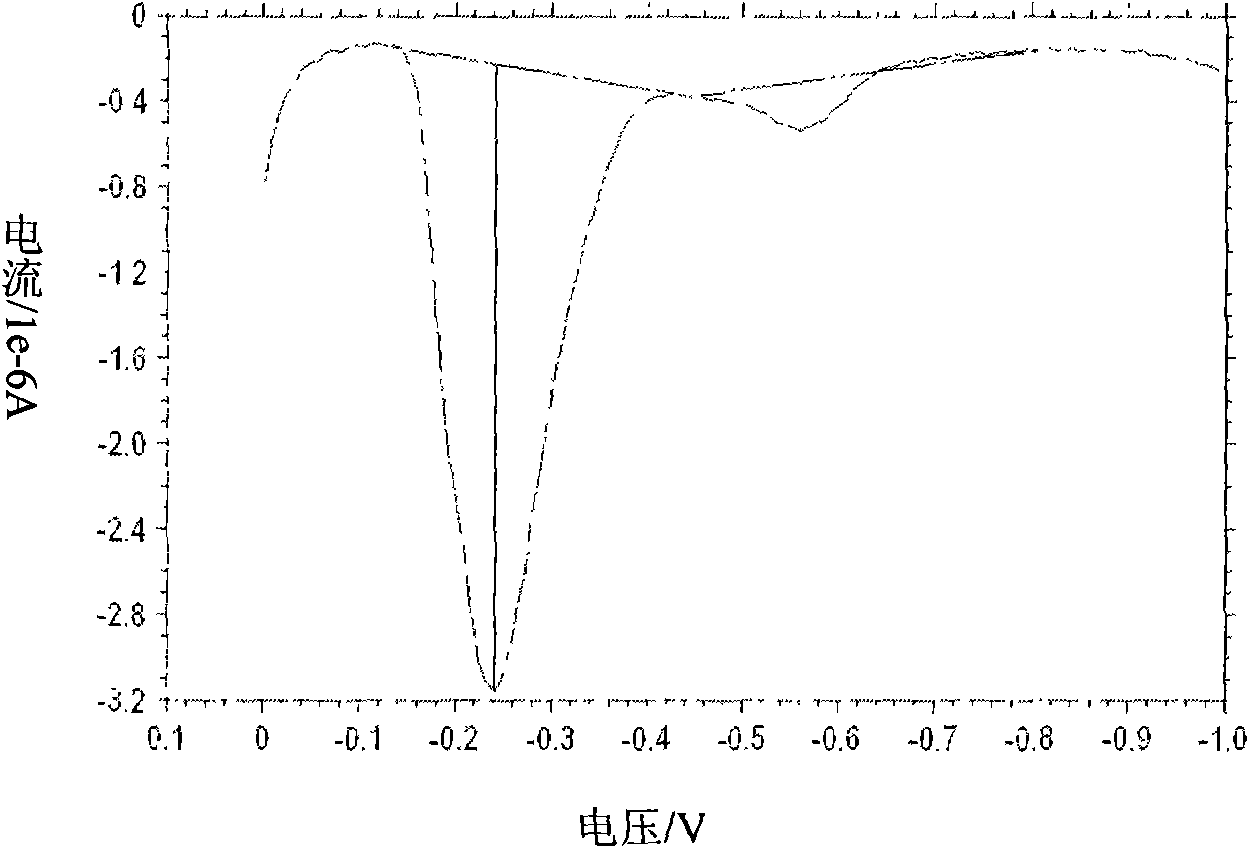
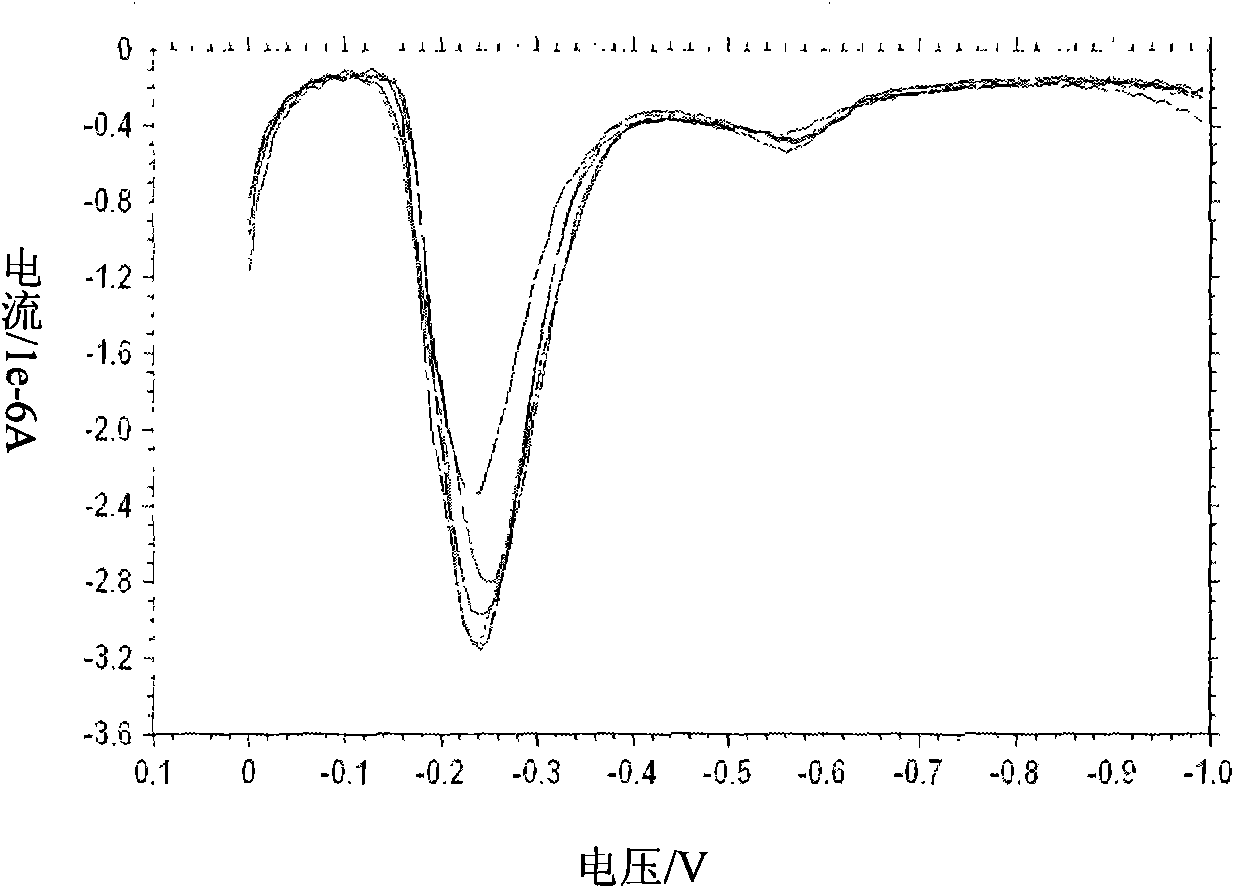
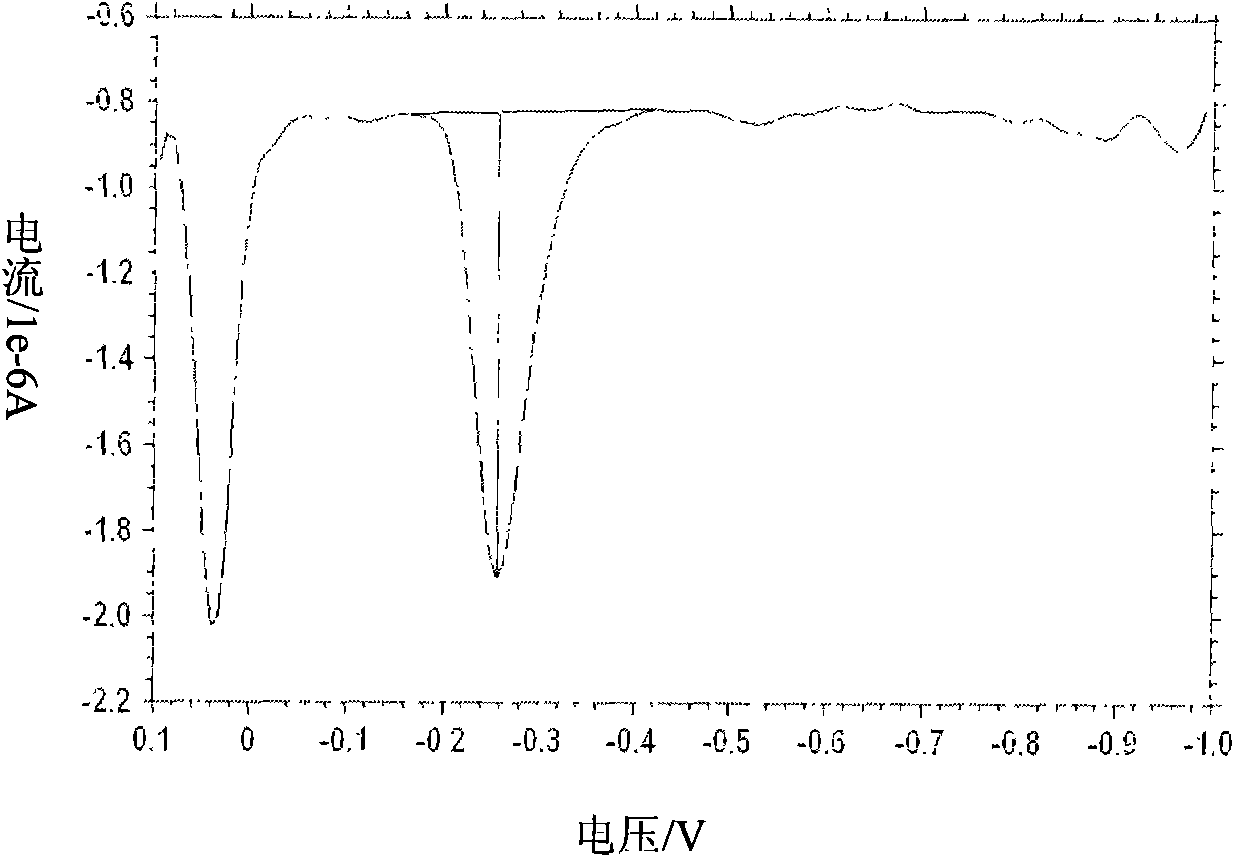
The invention discloses a method for judging whether heavy metals in water exceed the limit. The method comprises the following steps of: S10, preparing a solution to be tested; S20, setting detection parameters at an electrochemical work station; S30, detecting a water sample by an anodic stripping voltammetry method so as to obtain a stripping voltammetry diagram of the water sample, wherein an X-axis is taken as a voltage axis, and a Y-axis is taken as a current axis; S40, searching the starting point and the final point of each peak according to the stripping voltammetry diagram in the electrochemical work station; S50, calculating the peak height according to the starting point and the final point of the peak in the electrochemical work station; and S60, judging whether the heavy metals in the water sample exceed the concentration limited by the national standard GB5749-2006 according to the peak height of each peak in the electrochemical work station. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of less possibility of peak omission, high accuracy and simplicity in detection process.
Owner:SHENZHEN SINSCHE TECH
Application of filter paper adsorbent to direct electrochemical detection of lead in water sample
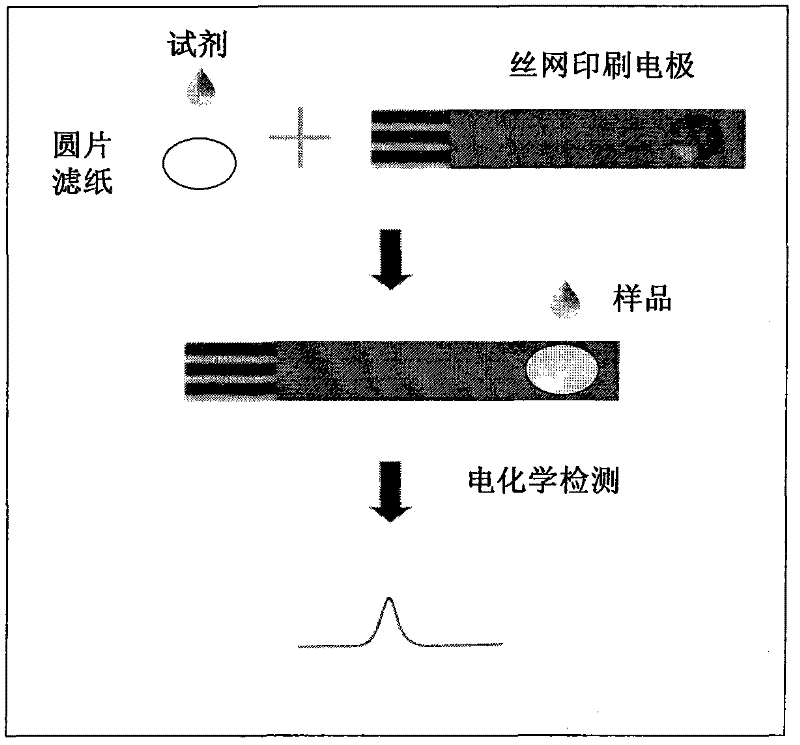
The invention discloses application of a filter paper adsorbent to direct electrochemical detection of lead in a water sample. The application is realized by adopting the steps of: punching Waterman No.1 filter paper to obtain a round paper sheet with the diameter of about 7mm through a puncher, then dripping 10 microlitre of an acetic acid buffer solution (with the pH value of 4.5) to the filer paper, drying at room temperature, then adding 10 microlitre of 500ppb bismuth nitrate solution, and drying at room temperature; before measurement, covering the filter paper on the surface of a screen printing electrode (Gwent group, Torfaen, United Kingdom), dripping 10 microlitre of water sample on the filter paper, and measuring with the frequency of 20Hz and the potential amplitude of 5mV according to an electrochemical anodic stripping voltammetry; depositing for 120s under -1.40V in an electrochemical way, and balancing for 30s; and carrying out anodic scanning from -1.40V to -0.40V, wherein before each measurement, stopping for 60s under +0.50V to clean the electrode. The method is used for determining the lead below 100ppb and has the errors within 6%.
Owner:YANCHENG INST OF TECH
Electrochemical method for detecting micro-arsenic and trace arsenic and heavy metal by composite material modified working electrode
InactiveCN107121481ARich sourcesMeet the test requirementsMaterial electrochemical variablesDirect testMaterials science
The invention relates to an electrochemical method for detecting micro-arsenic, trace-arsenic and heavy metal by a composite material modified working electrode and belongs to the fields of food, health, environmental monitoring and the like. According to the invention, a working electrode is modified mainly by the utilization of a composite material formed by a common carbon material and g-C3N4, and micro and trace arsenic and heavy metal ions undergo quantitative analytical determination by anodic stripping voltammetry. The working electrode only needs to be coated with a graphene / g-C3N4 composite material for directly testing. Microscale nafion is added or bismuth ion is added into a solution to be tested. Then, detection limit of arsenic and heavy metal ions can be obviously raised. The electrode modification process is simple and fast; sensitivity is high; performance is stable; and microscale and trace arsenic and heavy metal ions can be detected rapidly. The method of the invention has a great promotion and application prospect.
Owner:BAISE UNIV
Double-channel anodic stripping voltammetry
InactiveCN102621215AGuaranteed flexibilityIncreased sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesSupporting electrolyteEngineering
The invention relates to double-channel anodic stripping voltammetry, which comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing a standard solution and a supporting electrolyte solution; (2) detecting a channel 1 and a channel 2 by using a three-electrode system; (3) adjusting the potential of a working electrode of the channel 1 to be -1.4 to -1.0 V vs saturated calomel electrode (SCE), adjusting the potential of a working electrode of the channel 2 to be -0.8 to -0.1V vs SCE, enriching at the stirring rate of 350 to 450rpm for 290 to 590s, stopping stirring, and standing for 10 to 30s; and scanning the potential of the channel 1 forwards until the potential is -0.3 to 0V vs SCE, scanning the potential of the channel 2 forwards until the potential is 1.3 to 1.6V vs SCE, and thus acquiring oxidation current response signals; and (4) adding a solution to be detected, and detecting by a standard addition method. By the double-channel anodic stripping voltammetry, trace lead, cadmium and trivalent arsenic can be detected simultaneously, and a detection effect is good.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
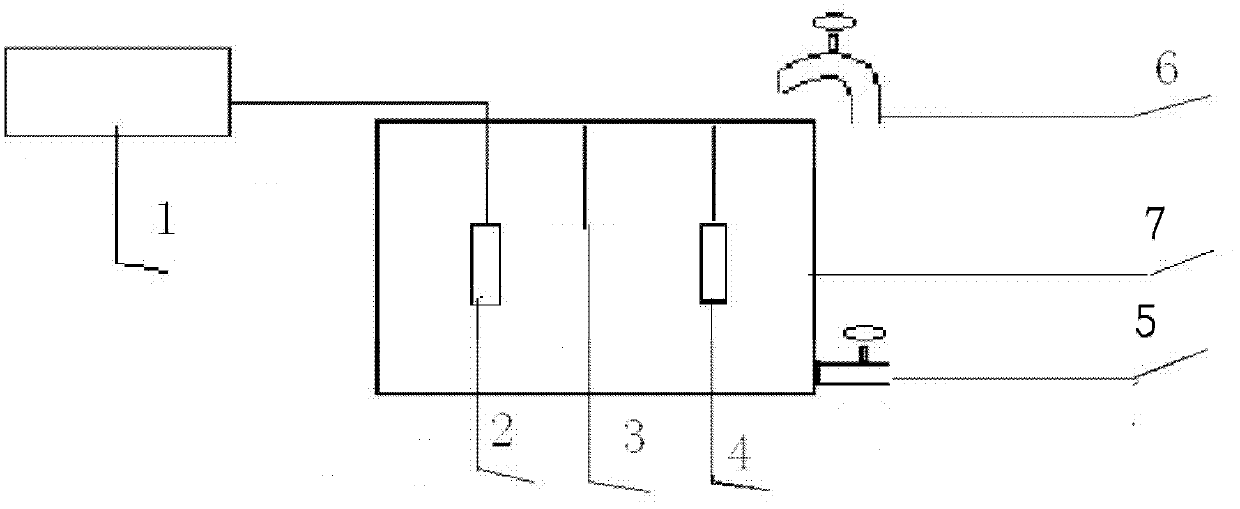
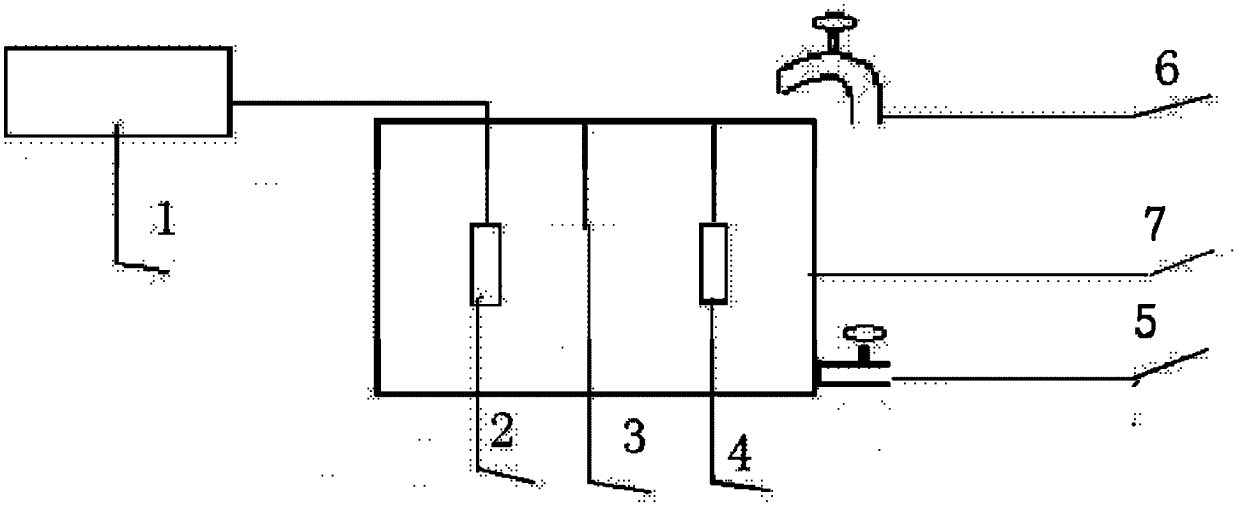
Automated smart water quality monitor and analyzer and associated methods
A fluid testing system can be used to measure the levels of contaminants in a fluid system. The system can utilize anodic stripping voltammetry or some other chemical, electrical, or electrochemical process to measure the contaminant levels. Wire electrodes may be used to facilitate the tests. Unused portions of the electrode wires can be fed into the test chambers between tests to ensure clean and reliable electrodes for subsequent testing.
Owner:KETOS INC
Preparation method of electrochemical sensor for trace lead ion detection
ActiveCN108982641AImprove adsorption capacityUniform microporous structureMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical gas sensorPeak current
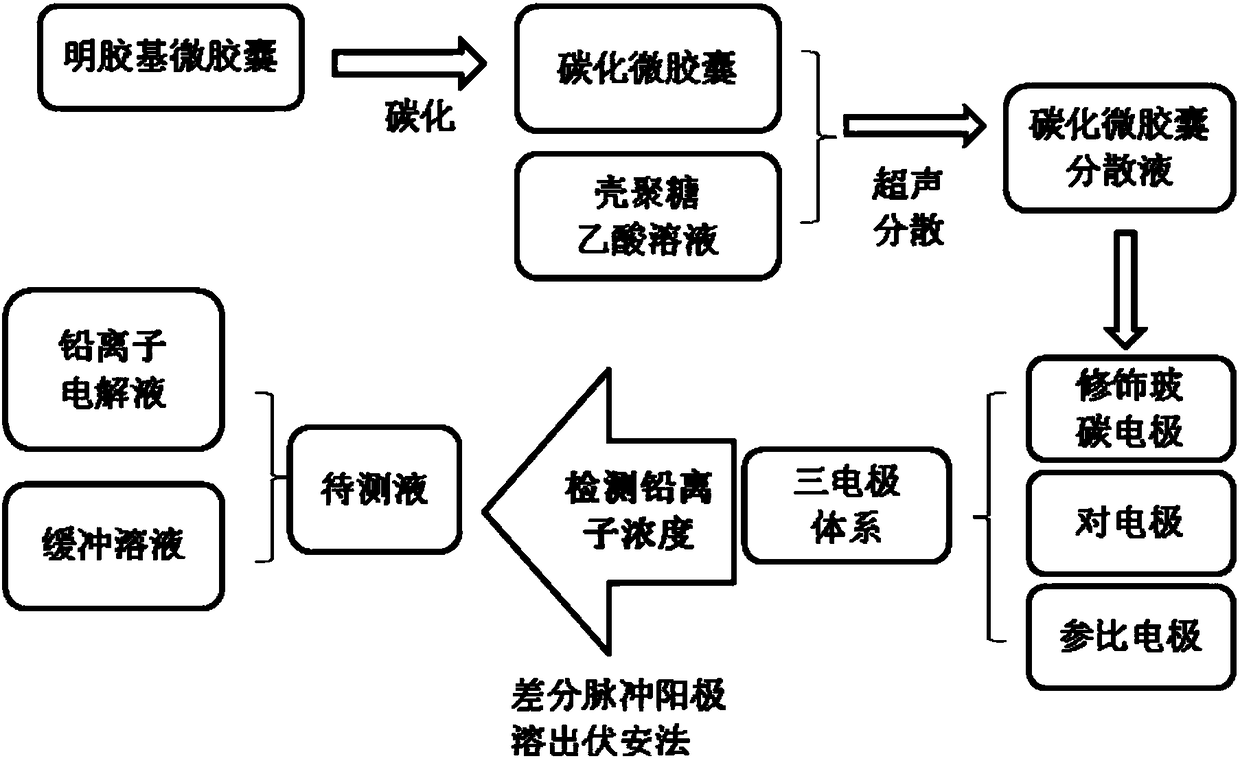
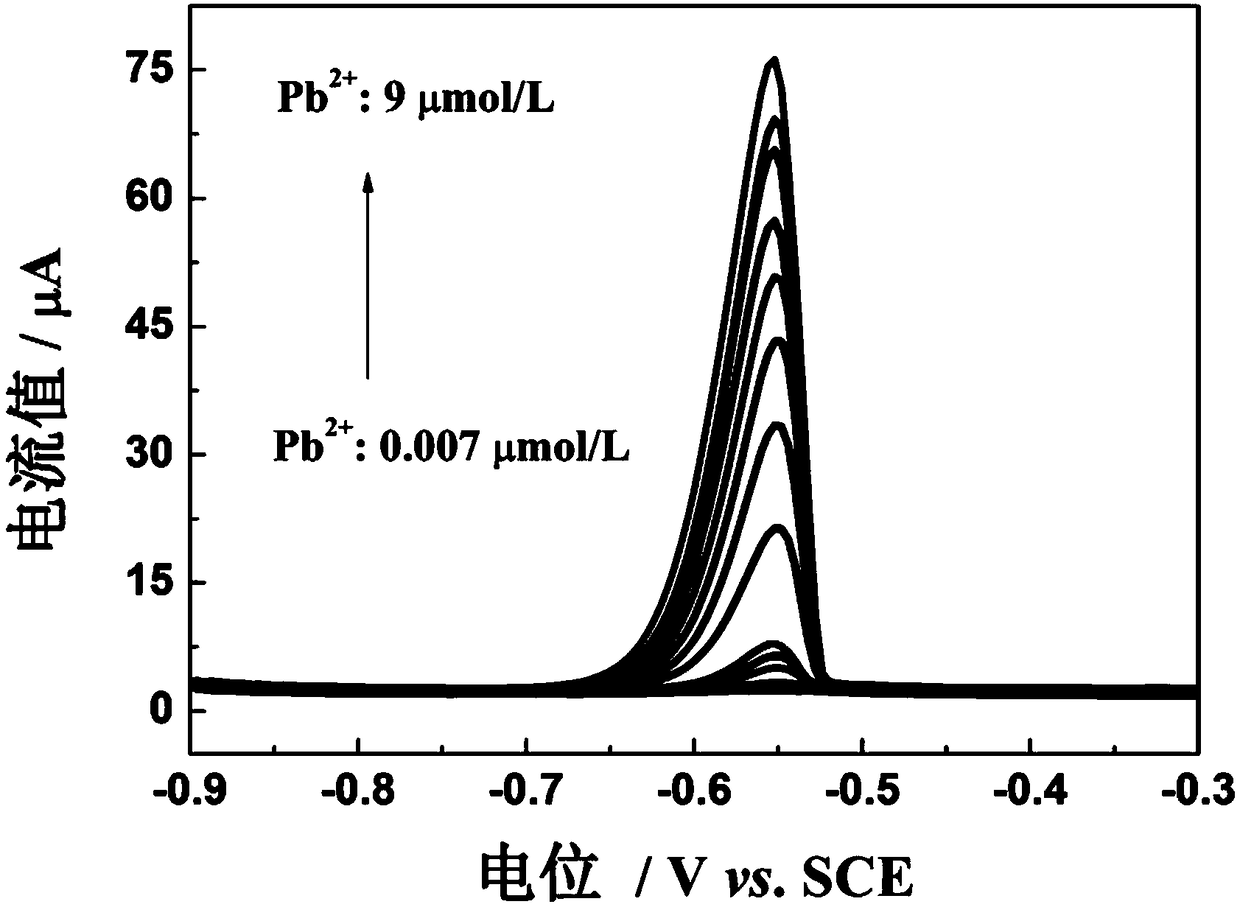
The invention discloses a preparation method of an electrochemical sensor for trace lead ion detection, belonging to the technical field of environmental detection and analysis. The method comprises the following steps: step 1: enabling gelatin-based microcapsules, which are prepared through a complex coacervation method, to be frozen and dried, and enabling carbonized microcapsule powder to be ultrasonically dispersed in a chitosan acetic acid solution; step 2: taking 5 mu L of carbonized microcapsule dispersion liquid, which is prepared in step 1, to serve as an electrode material so as to modify the surface of a glassy carbon electrode to act as a working electrode; step 3: adding different concentrations of lead ion electrolyte into a buffer solution to form 5 mL of a to-be-tested solution, inserting an electrode system in step 2 into the lead ion electrolyte, and enriching lead ions in the electrolyte at constant voltage; step 4: obtaining the standard curves of peak current values and lead ion concentrations by adopting a differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry; and step 5: detecting lead ion concentrations in to-be-tested samples. The working electrode modification material prepared by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation, low cost, controllable structure, good repeatability and the like.
Owner:普瑞丰环保科技(武汉)有限公司
Micro-pore board fixing and nano lead sulfide marking electrochemistry detecting method for transgene soybean
InactiveCN101260441AMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial electrochemical variablesWater bathsLoop-mediated isothermal amplification
The invention relates to a method for microplate fixing and nanometer lead sulfide marker electrochemical detecting genetically modified soybeans, which is characterized in that: the method comprises the following steps that: an amplification reactant namely a double-strand target sequence of an exogenous gene CP4 EPSPS to be detected is obtained through loop-mediated isothermal amplification, the reactant amplimer strain is exogenous gene CP4E PSPS of GTS 40-3-2 genetically modified soybeans, the double-strand target sequence is pyrolyzed to single-strand target sequences in water bath to fix on a microplate, and nanometer lead sulfide is led to marking a probe sequence from the exogenous gene CP4E PSPS to obtain a marked probe sequence, the marked probe sequence and the target sequence fixed on the microplate are performed molecular hybridization, and performed electrochemical detection with coordinate mercury plating anodic stripping voltammetry, aiming to electrochemically detect the exogenous gene (CP4 EPSPS) of the detected genetically modified soybeans. The method for microplate fixing and nanometer lead sulfide marker electrochemical detecting genetically modified soybeans has the advantages of rapidness, strong specificity, high sensitivity and convenient use.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cadmium lead electrochemical detection method based on sulfur-doped graphene
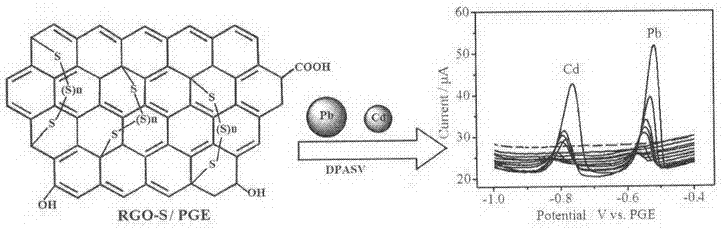
The invention discloses a cadmium lead electrochemical detection method based on sulfur-doped graphene. An electrochemical sensor involved in the method is composed of a polysulfide / graphene-Nafion modified working electrode, an Ag / AgCl reference electrode, a Pt wire counter electrode, an electrolytic tank and an electrochemical workstation. The adopted electrochemical technology is differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry. The sensor has a cadmium ion detection range of 2.0-300microgL<-1>, a lead ion detection range of 1.0-300microgL<-1>, and the detection limits are 0.67microgL<-1> and 0.17microgL<-1> respectively, and are both 4.5 times and 59 times lower than standard drinking water values given by WHO. At the same time, the sensor shows good reproducibility, stability and anti-interference performance. In detection of the content of lead and cadmium ions in tap water, the sensor shows good sensitivity and reproducibility. The sensor can accurately, quickly and simultaneously detect the content of cadmium and lead ions on site, and therefore has good practical application prospect.
Owner:XINJIANG TECHN INST OF PHYSICS & CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for electrochemical automatic monitoring of COD combined with water heavy metal ions
ActiveCN104062335AImprove applicabilityLow detection limitMaterial electrochemical variablesChemical oxygen demandMembrane electrode assembly
The invention introduces a method and a device for automatic monitoring of water chemical oxygen demand (COD) combined with heavy metal ion concentration. The method is based on a three-electrode system with boron-doped diamond (BDD) membrane electrodes, tests COD of a water sample by an electrochemical anodic oxidation method, and tests heavy metal ion concentration of the water sample by anodic stripping voltammetry (ASV). The BDD electrodes are used both as an anode for testing water sample COD and as a working electrode for testing water sample heavy metal ion concentration, which realizes combined testing of COD and heavy metal ion concentration. With an integrated electrolytic bath, ultrasonic wave and constant temperature measures, the method and the device of the invention are economic and practical, are reliable in testing results, and are good in stability.
Owner:SICHUAN BELAM TECH
Method for detecting heavy metals in aquatic product dried food
PendingCN111638260ANo secondary pollutionReduce manufacturing costPreparing sample for investigationMaterial electrochemical variablesDigestionDried food
The invention relates to the technical field of food detection, in particular to a method for detecting heavy metals in dried aquatic food. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a graphene / Bi / Nafion composite material by using an electrochemical deposition method, and using the graphene / Bi / Nafion composite material as a working electrode for detecting trace amounts of heavy metals Pband Cd in a digestion solution; and preparing an Au / graphene composite material by using a microwave radiation method, and using the Au / graphene composite material as a working electrode to detect the trace amount of heavy metal Hg in the digestion solution. The trace amount of the heavy metal in the dried aquatic product is determined by using the anodic stripping voltammetry, and compared witha traditional mercury electrode, the electrode designed by the invention is an environment-friendly electrode and does not cause secondary pollution to the environment; compared with a traditional spectrum detection method, the detection method designed by the invention has the characteristics of simple operation, short analysis time and low instrument preparation cost, so that the detection method has a good application prospect in detection of heavy metals in dried aquatic products.
Owner:曹峰
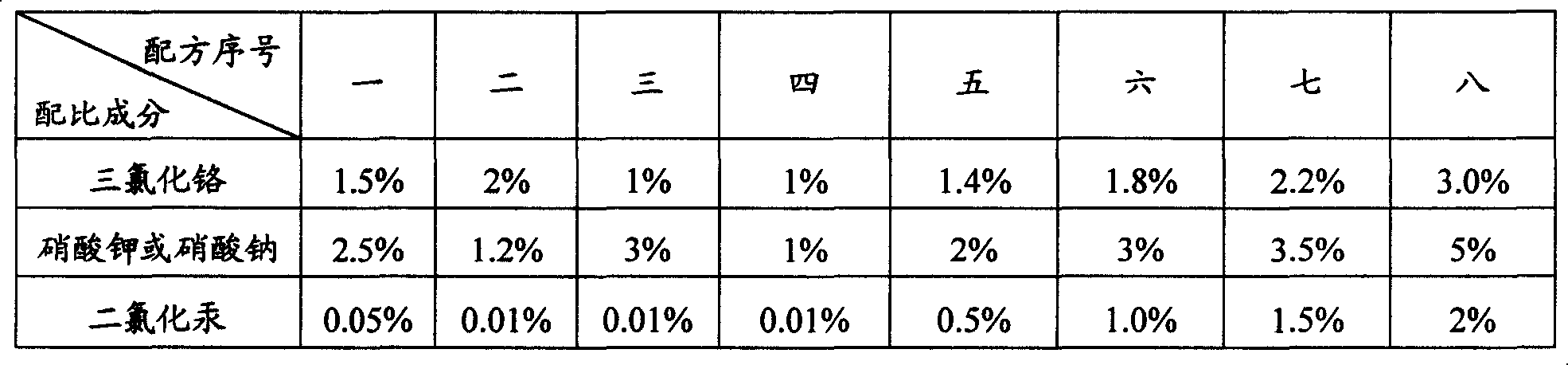
Determination reagent for trace content of heavy metal
InactiveCN1570619AGood reproducibilityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesChromate saltOrganic solvent
It is a reagent for measuring the marked heavy metal component, which substitute the containing heavy metal ion in the sample before using the method of anodic stripping voltammetry for measuring. The reagent comprises one to three percent of soluble chromate salt, one to five percent of potassium salt or sodium salt, 0.01 to 0.2 percent of soluble mercury salt for guarding electrode, and a organic solvent with one to three ph value to increase dispersibility and eliminate foams. The said reagent is combined with electrochemical measuring device and is characterized by quickness, convenience, high accuracy and reproduction ability.
Owner:北京艾联联合科技发展有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com