Patents
Literature
327results about How to "Reduce light absorption" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
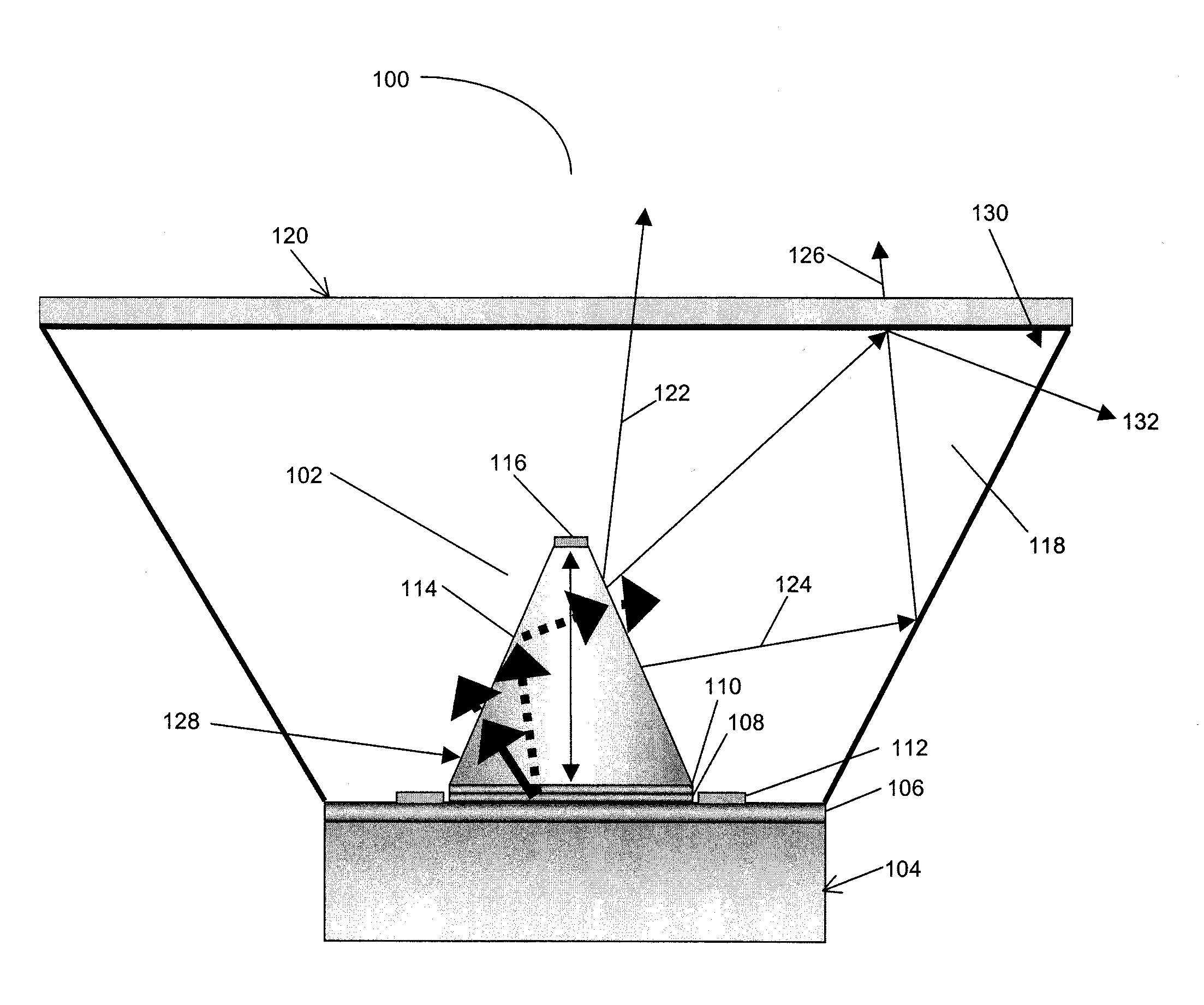
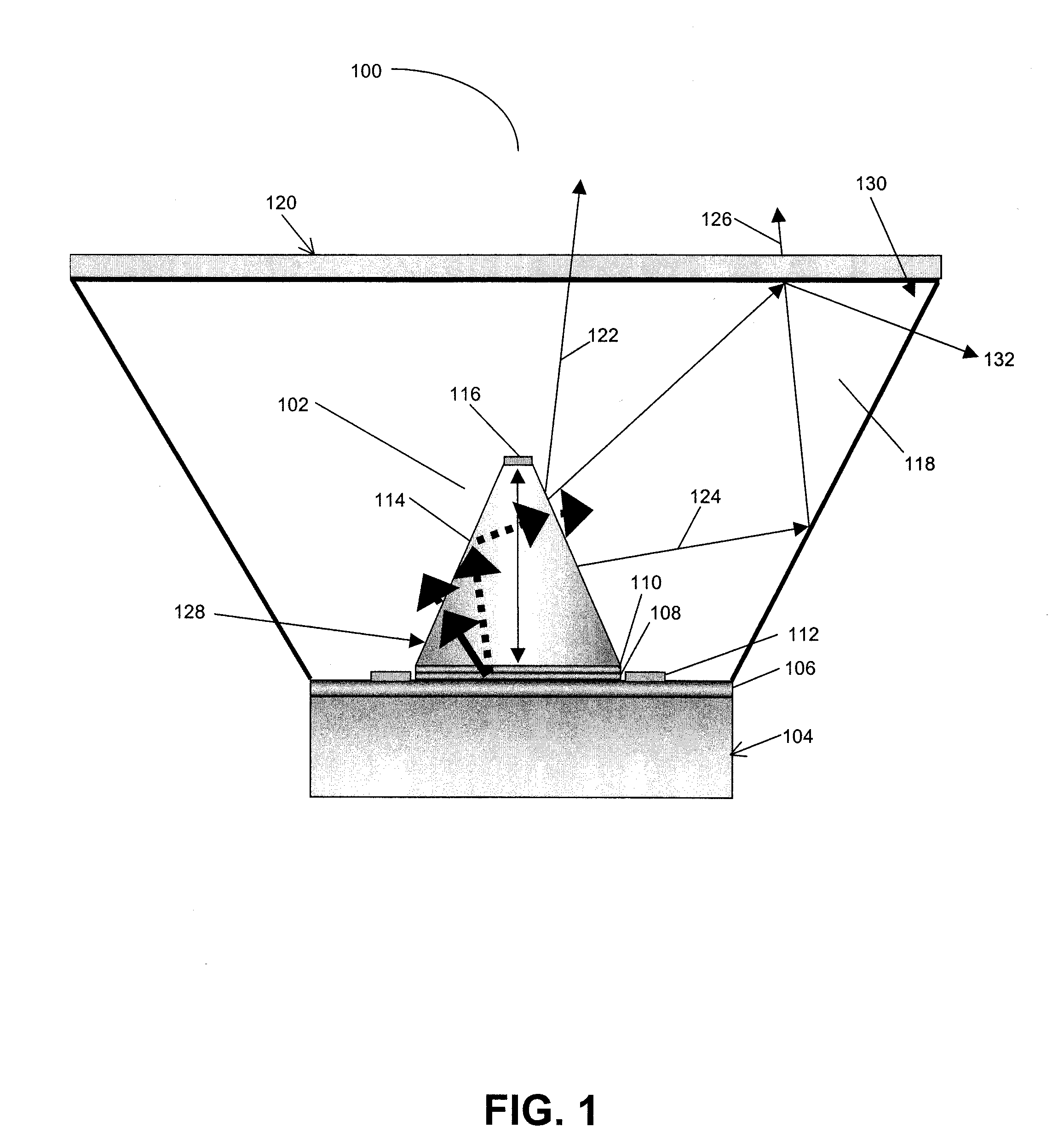
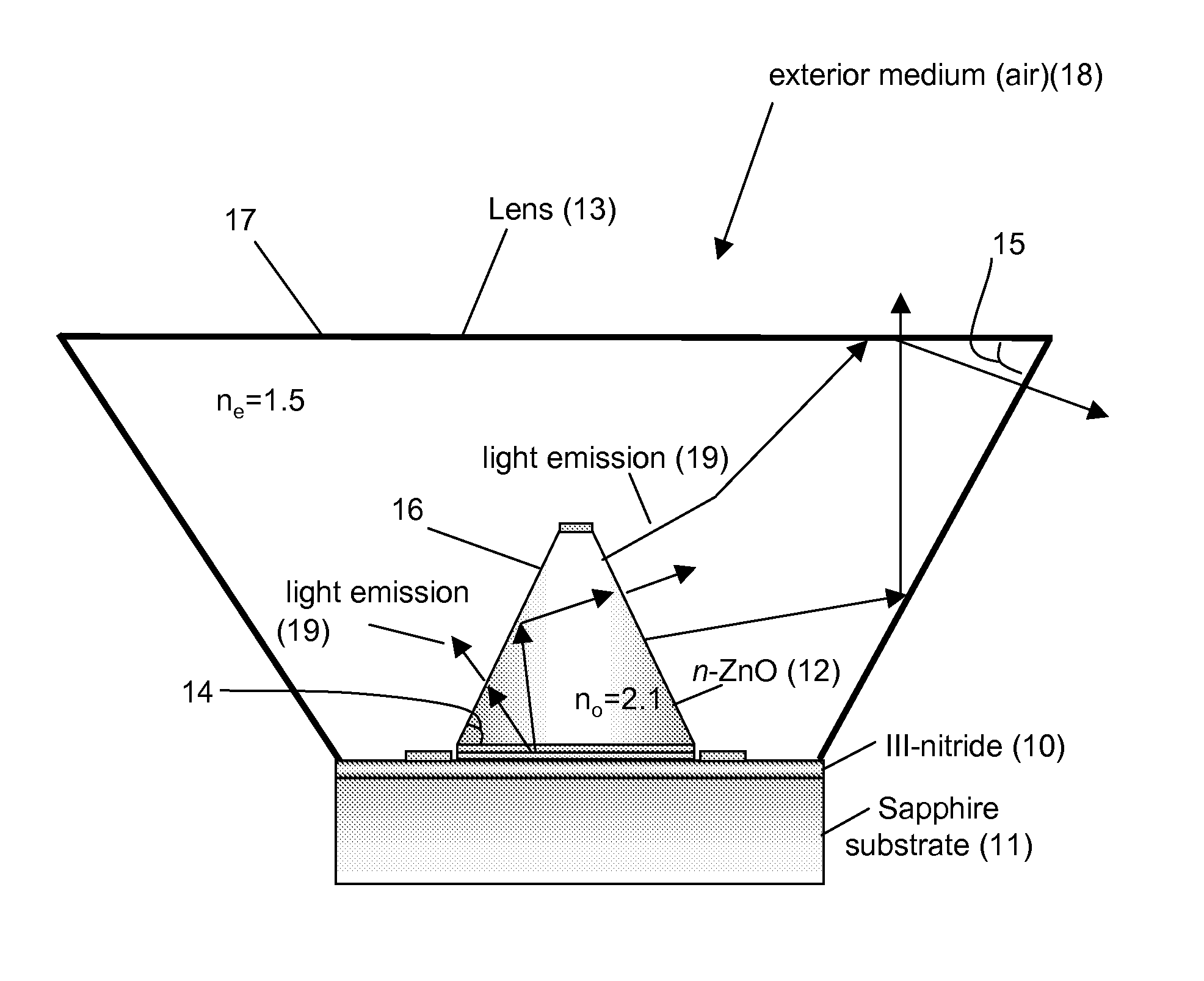
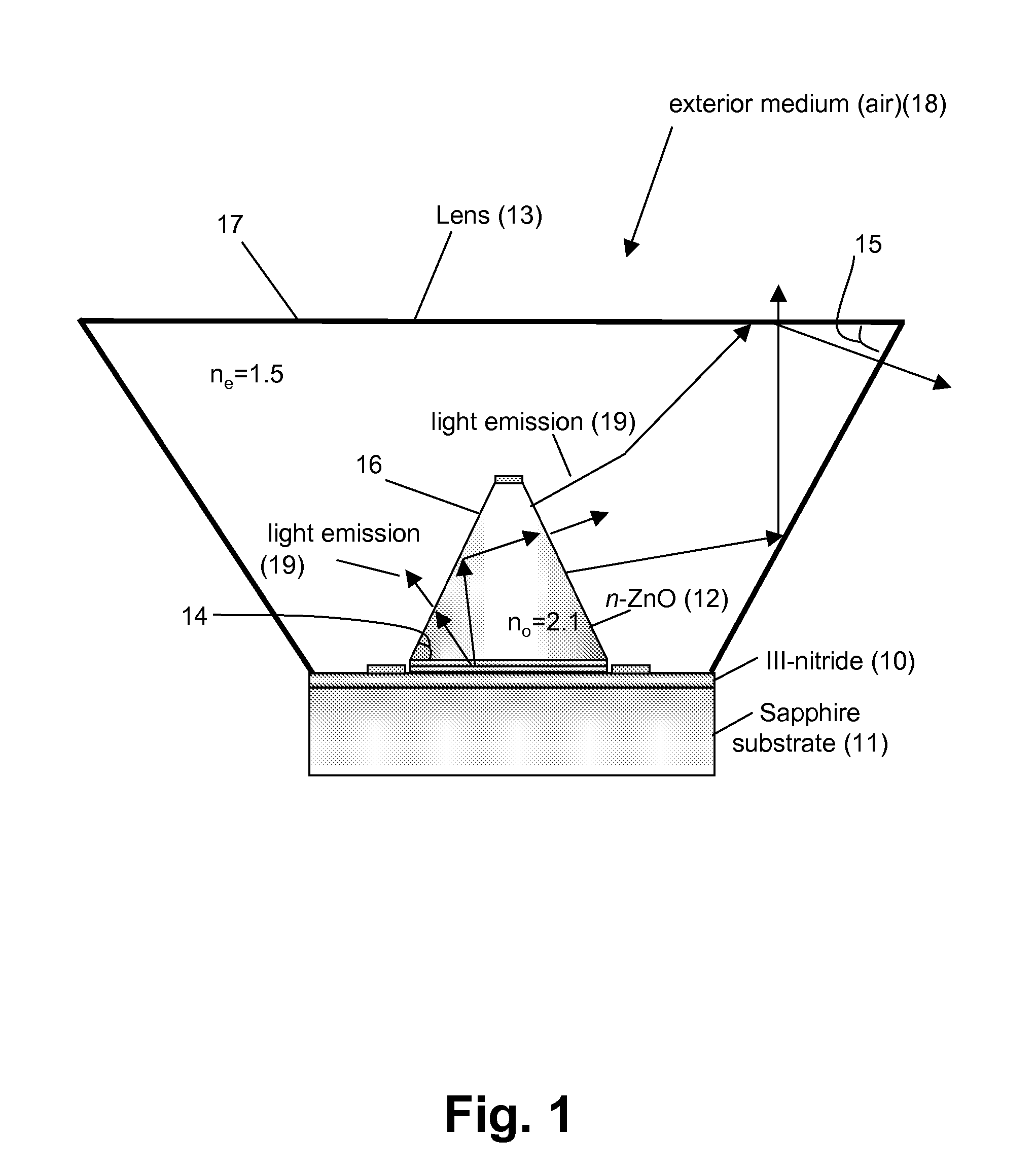
High light extraction efficiency light emitting diode (LED)
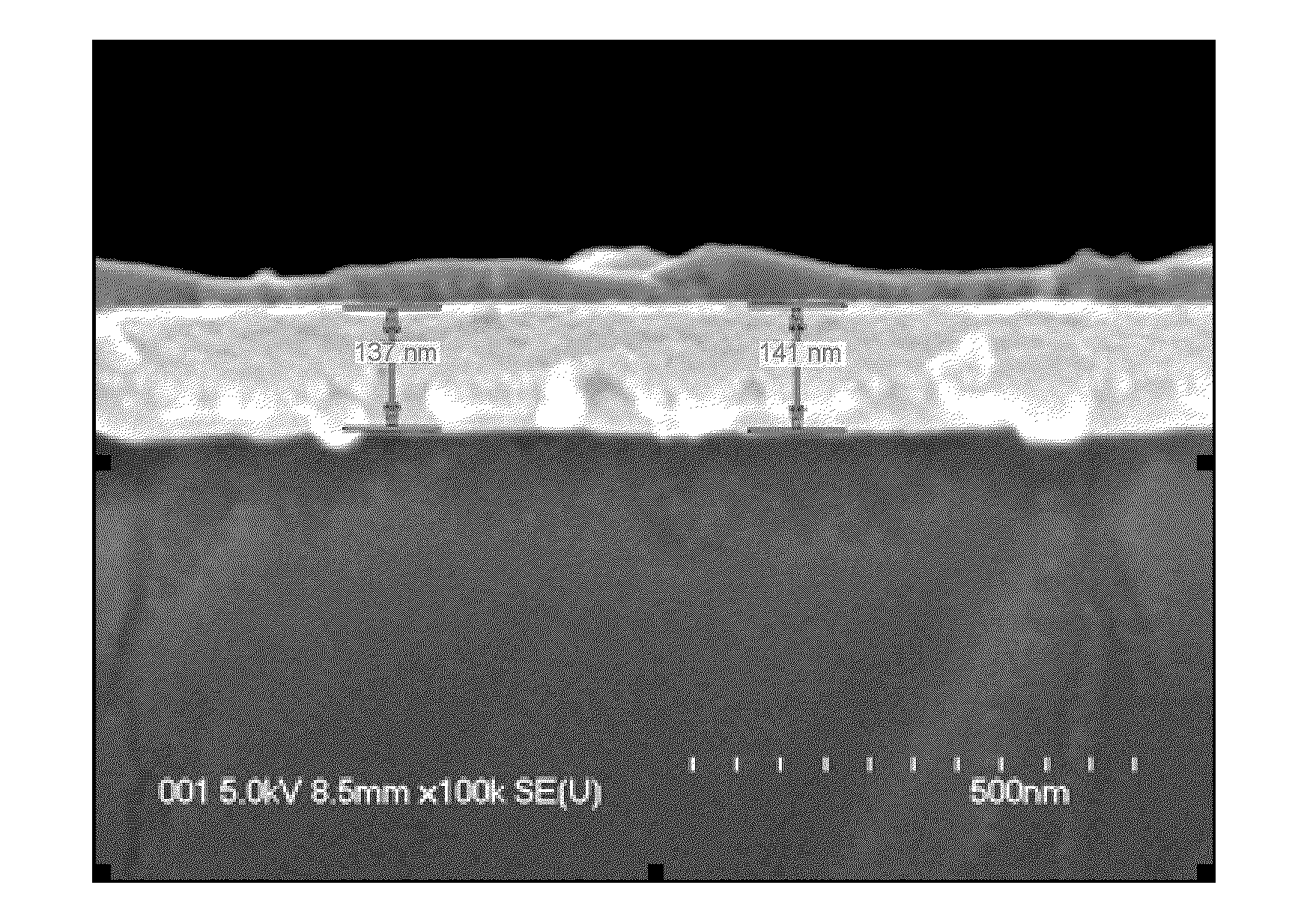
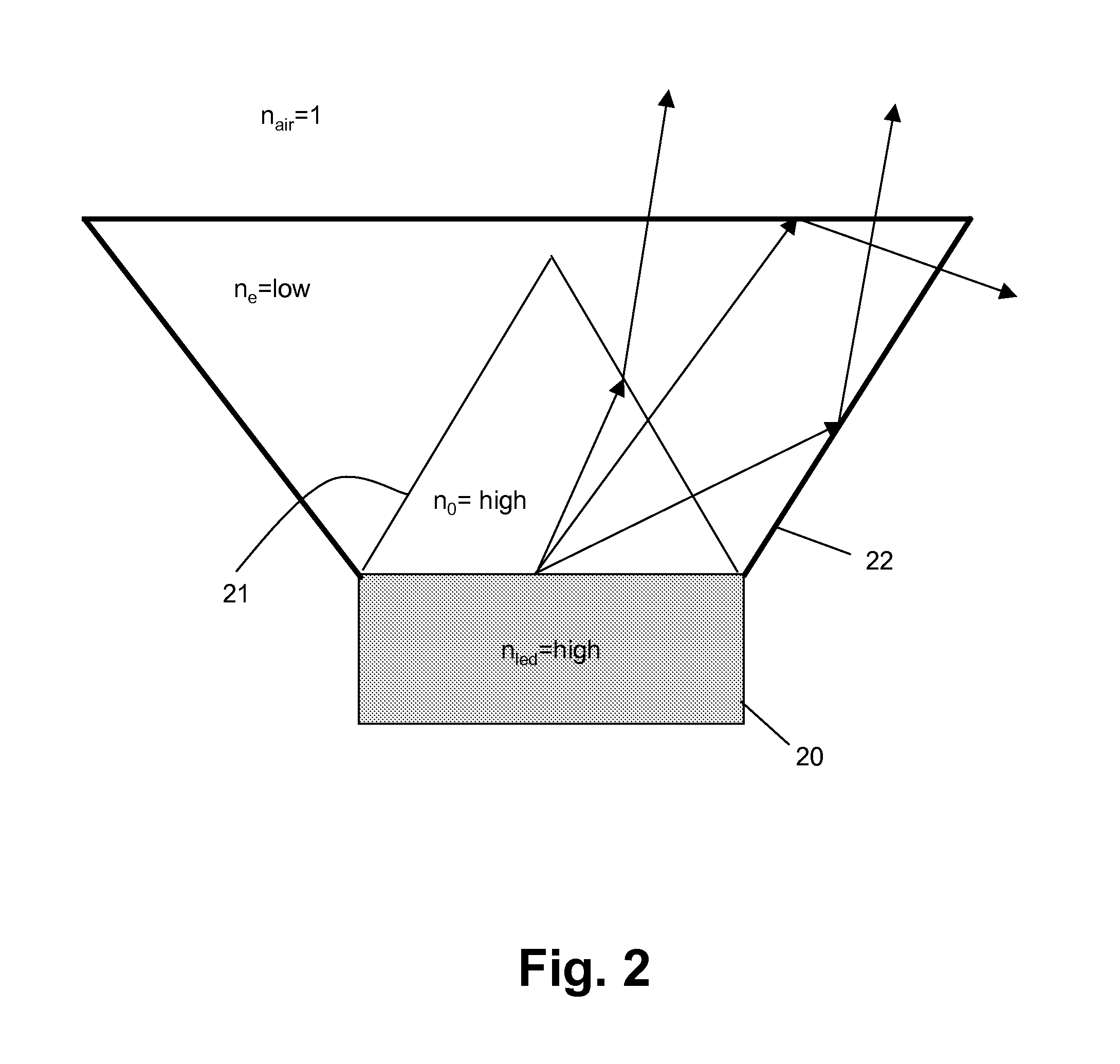
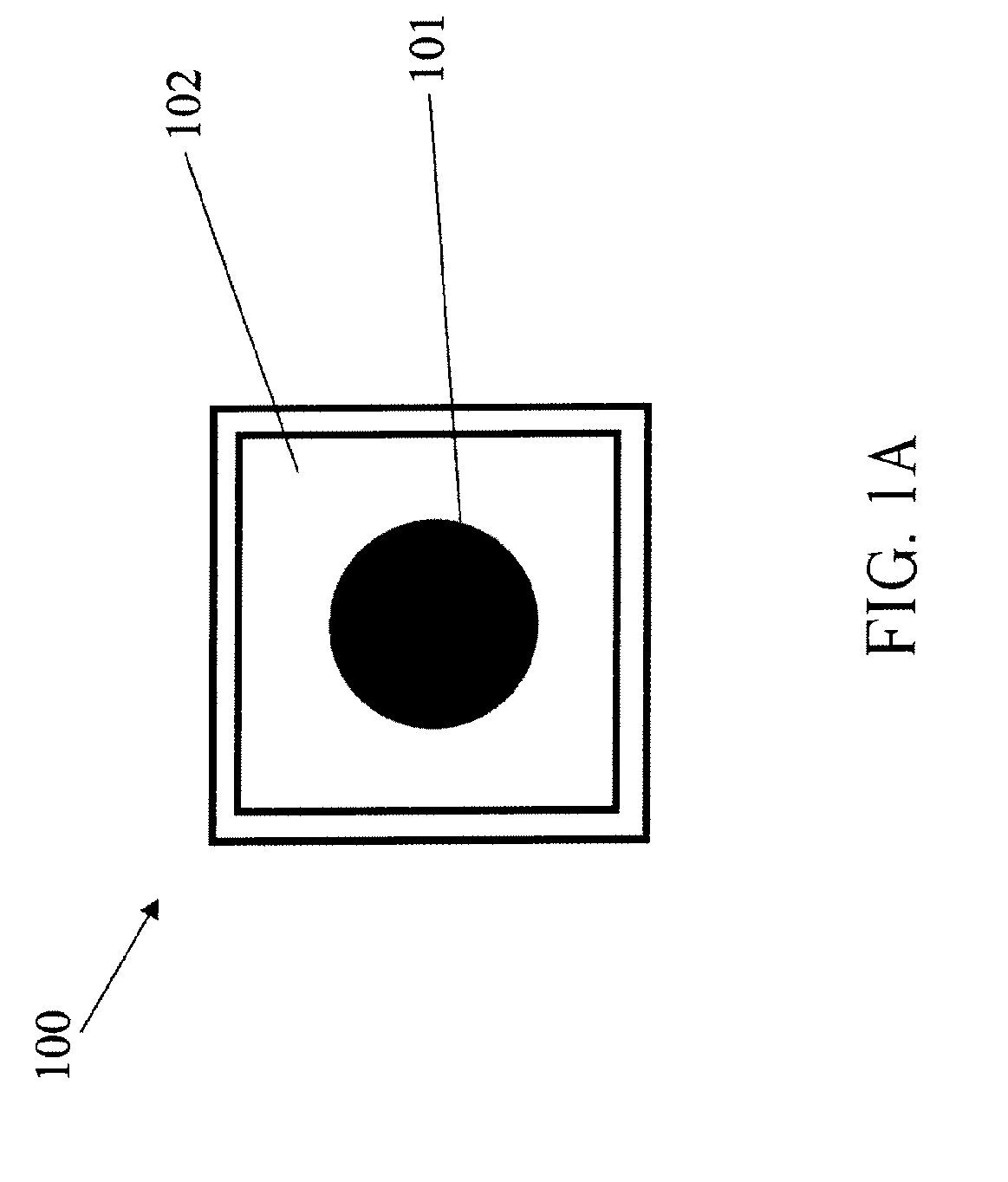
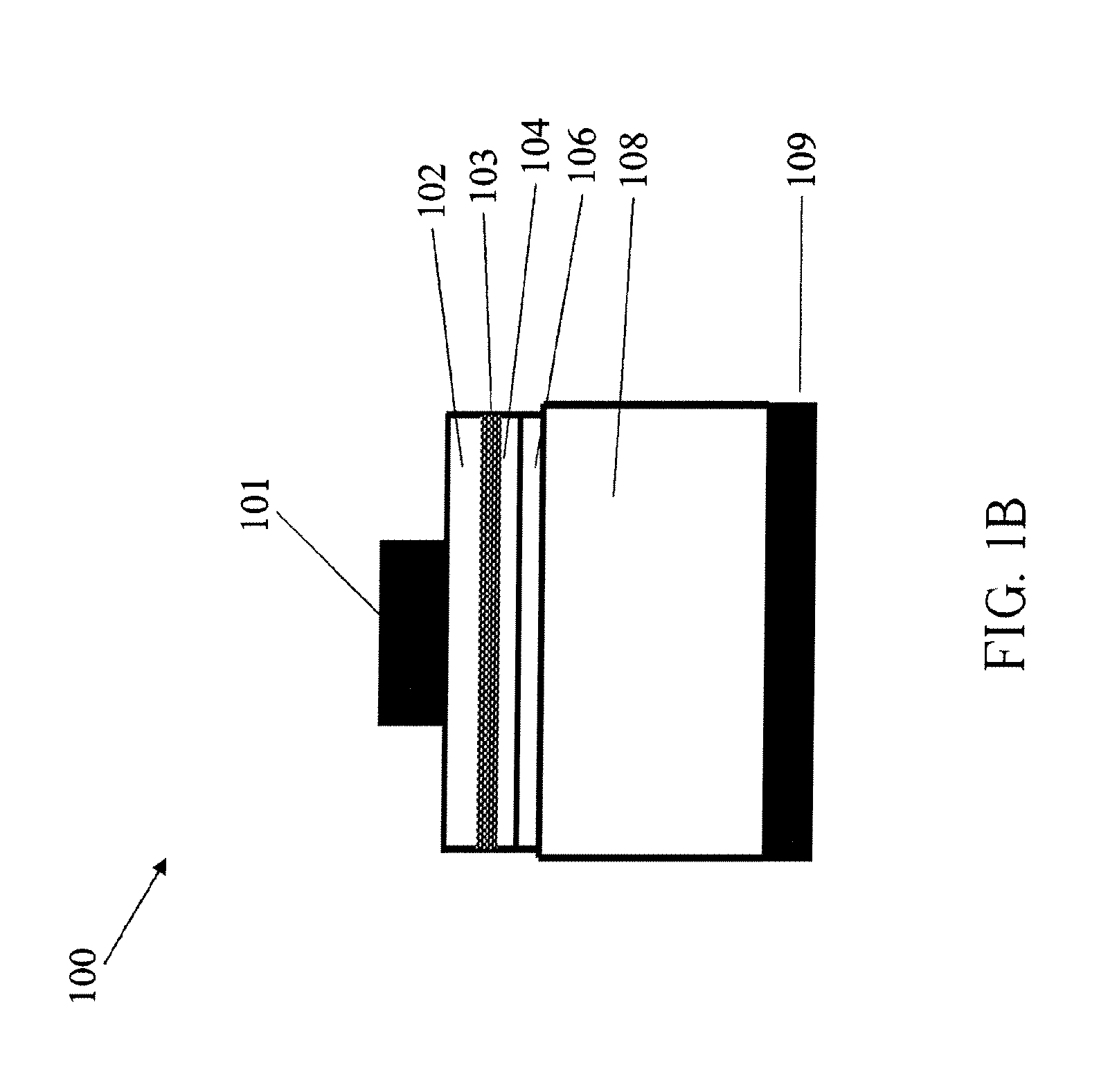
InactiveUS20070102721A1Maximize refraction of lightHigh extraction efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractorsPhysicsRefractive index
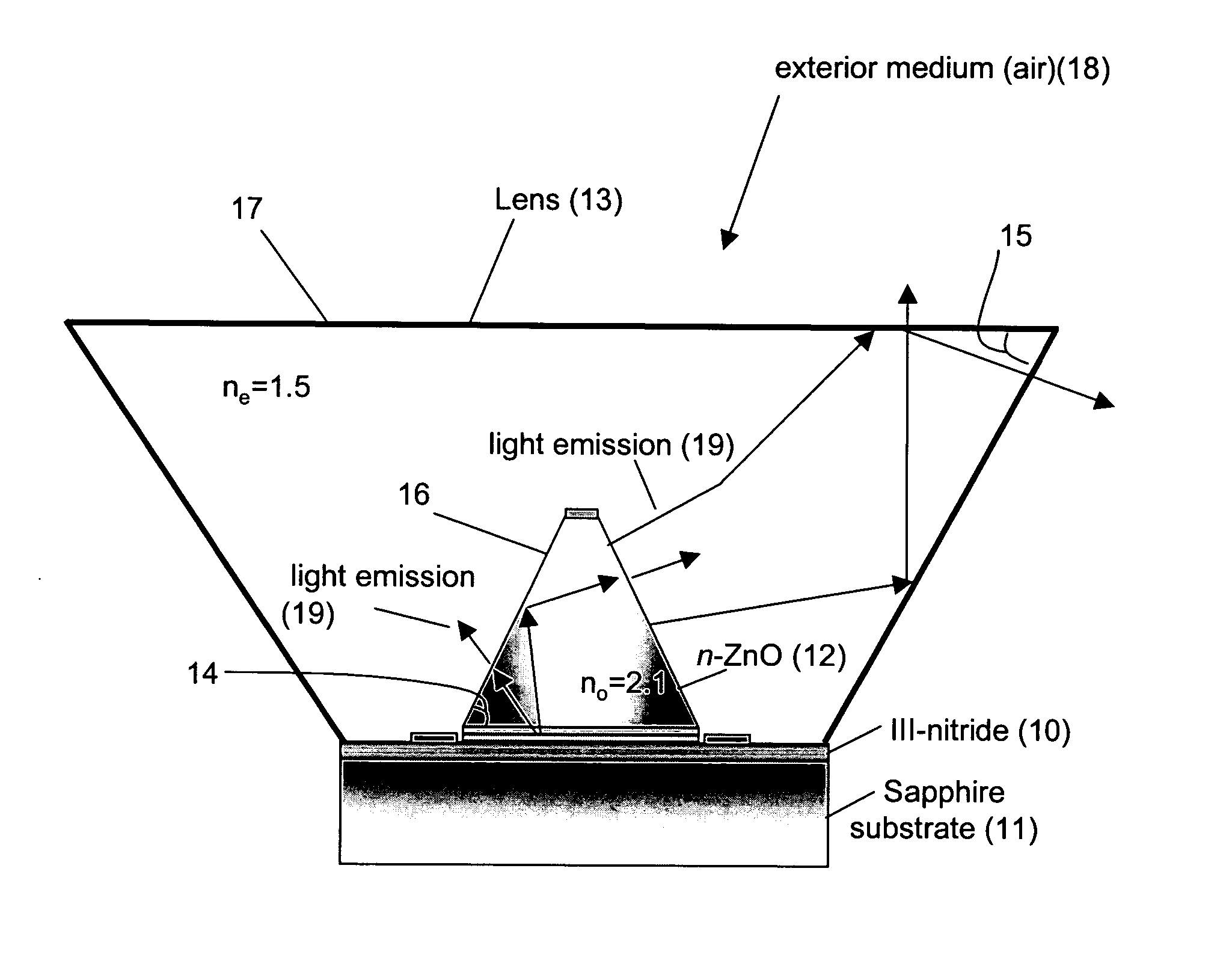
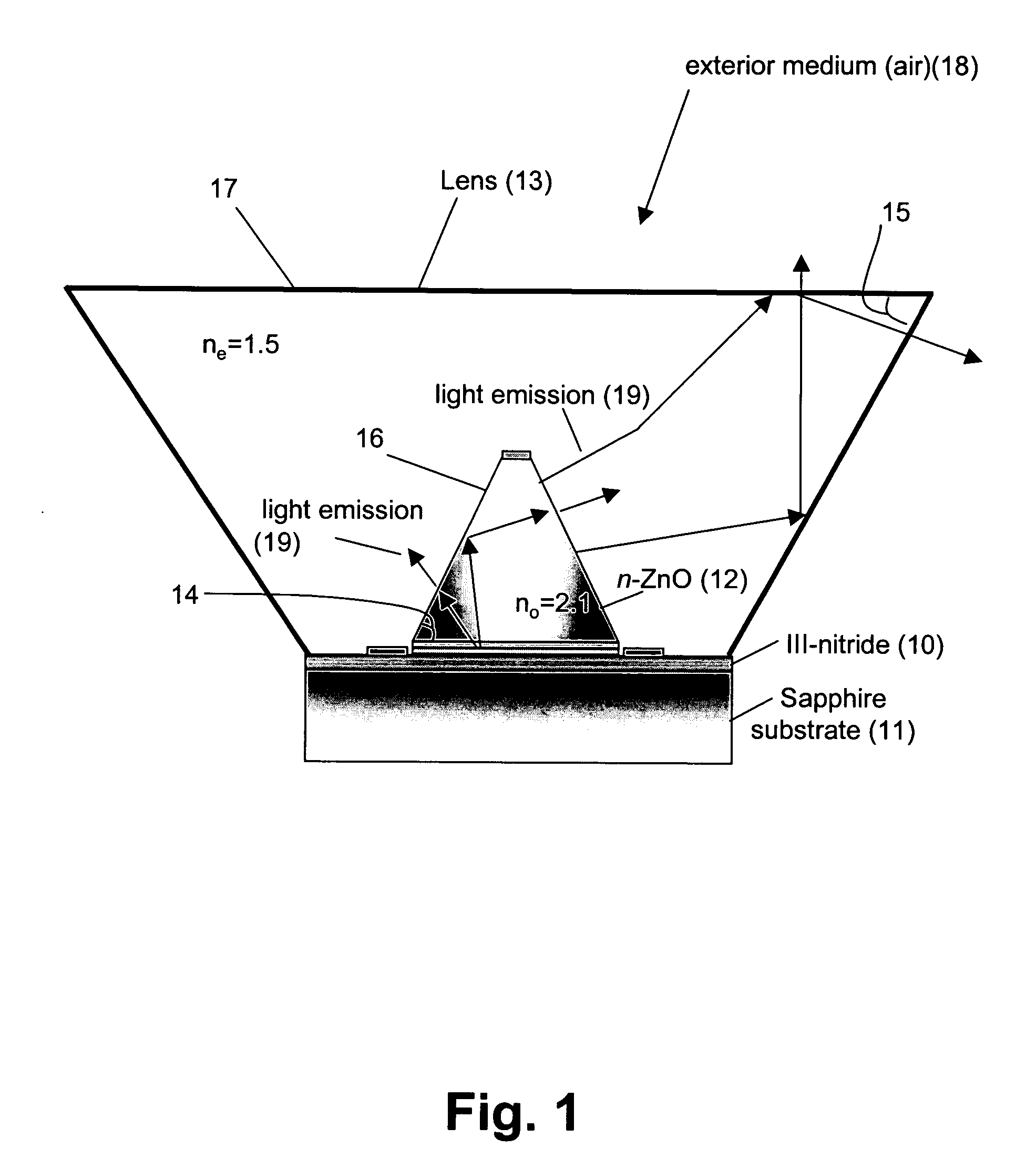
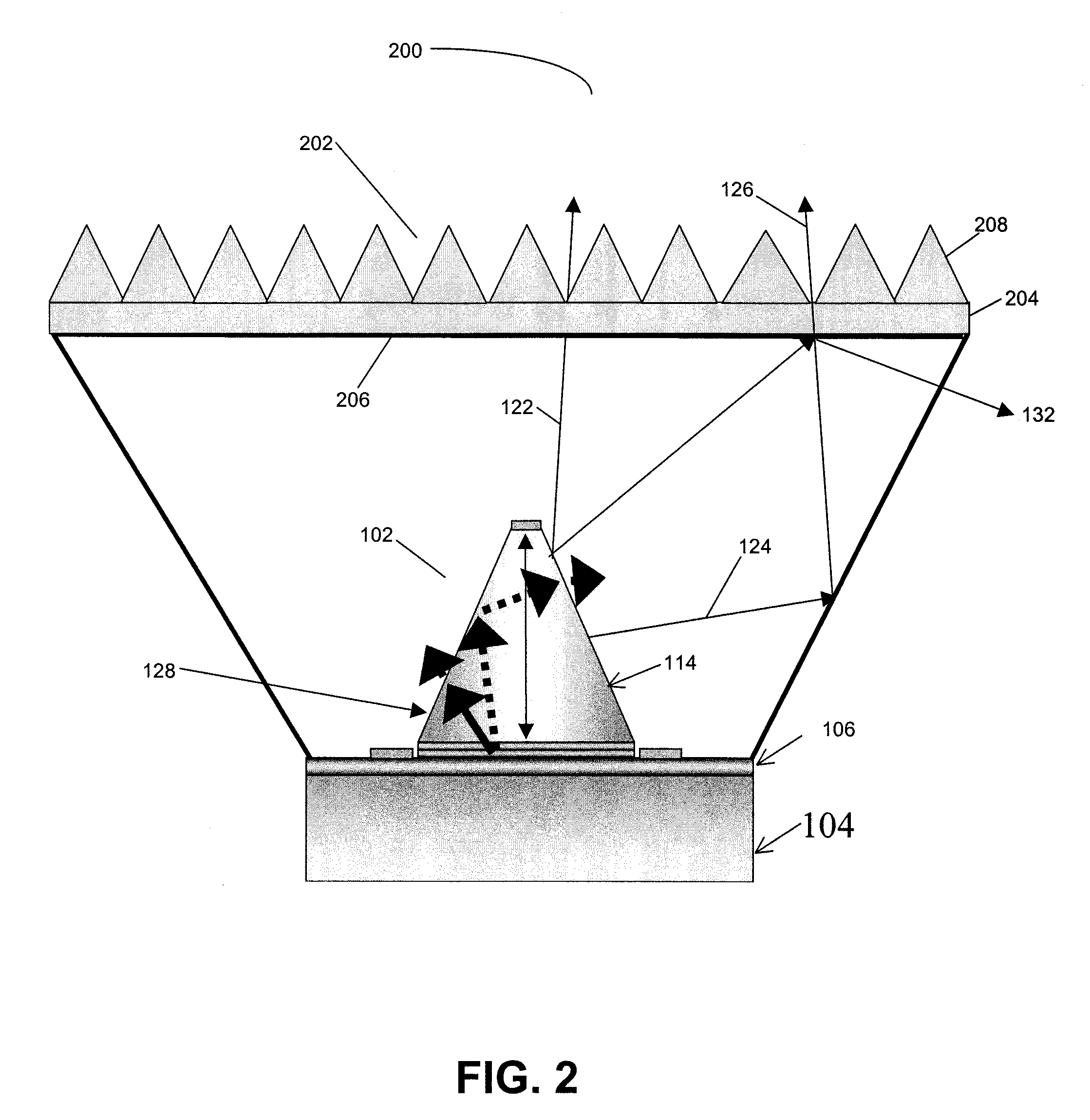
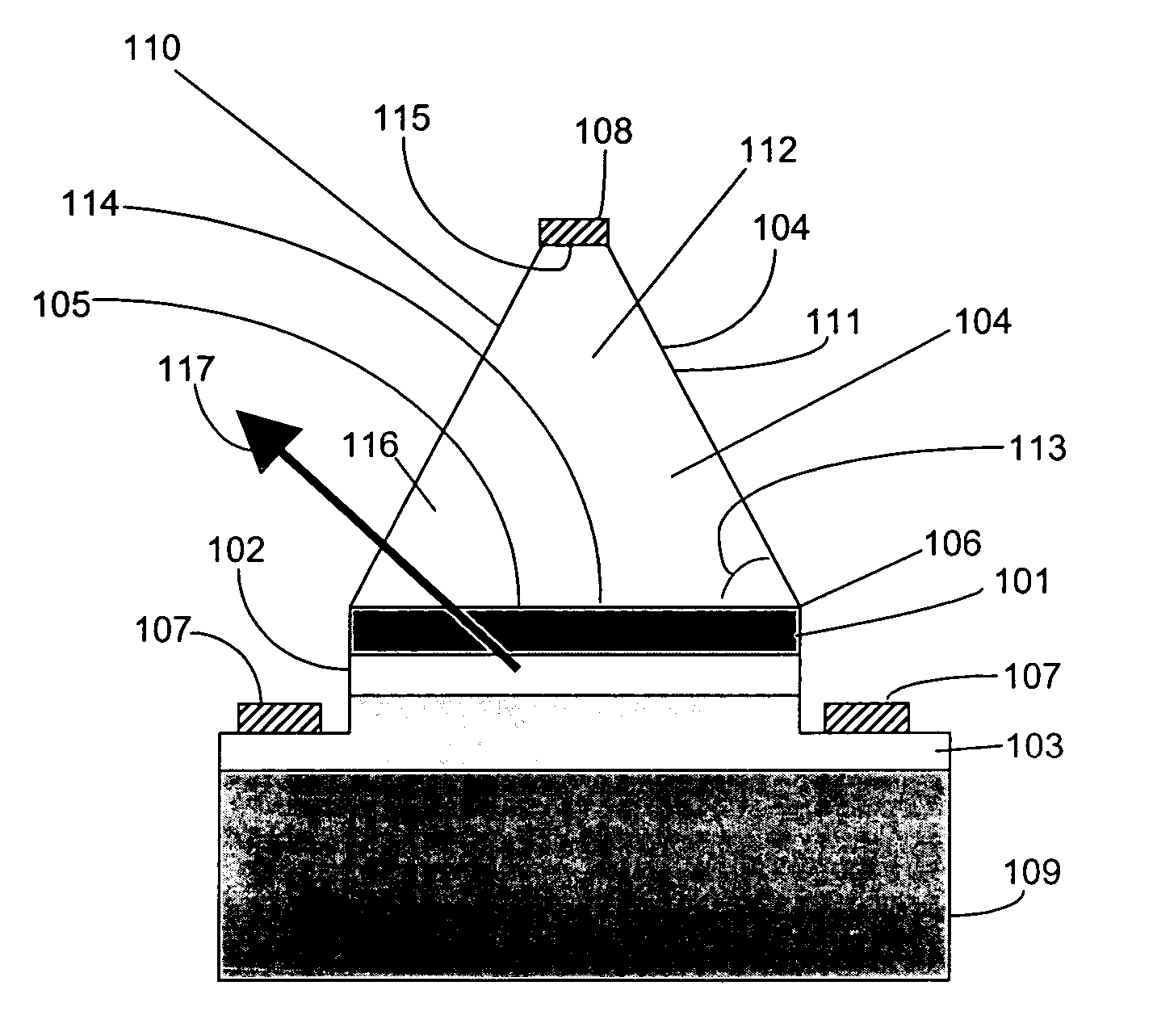
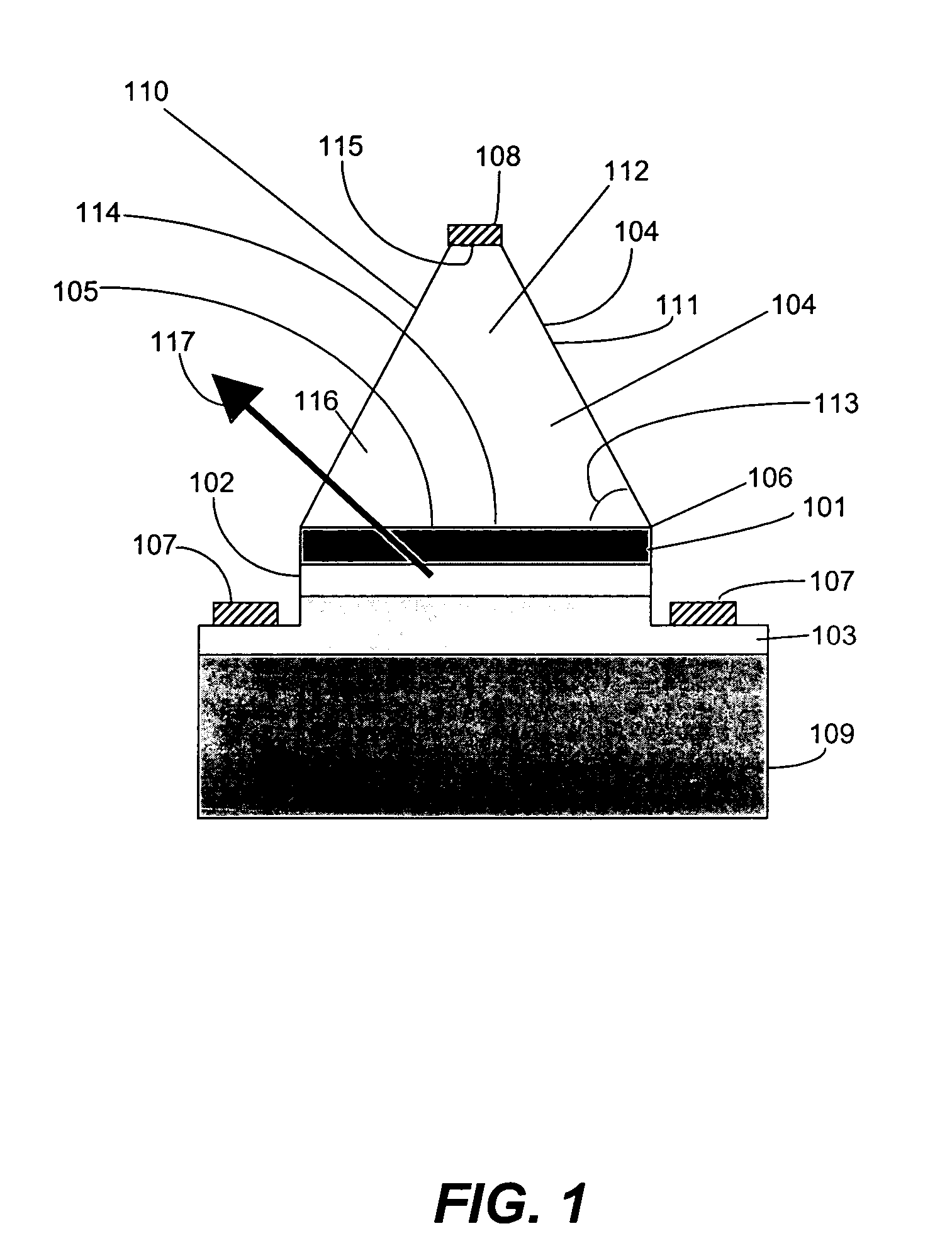
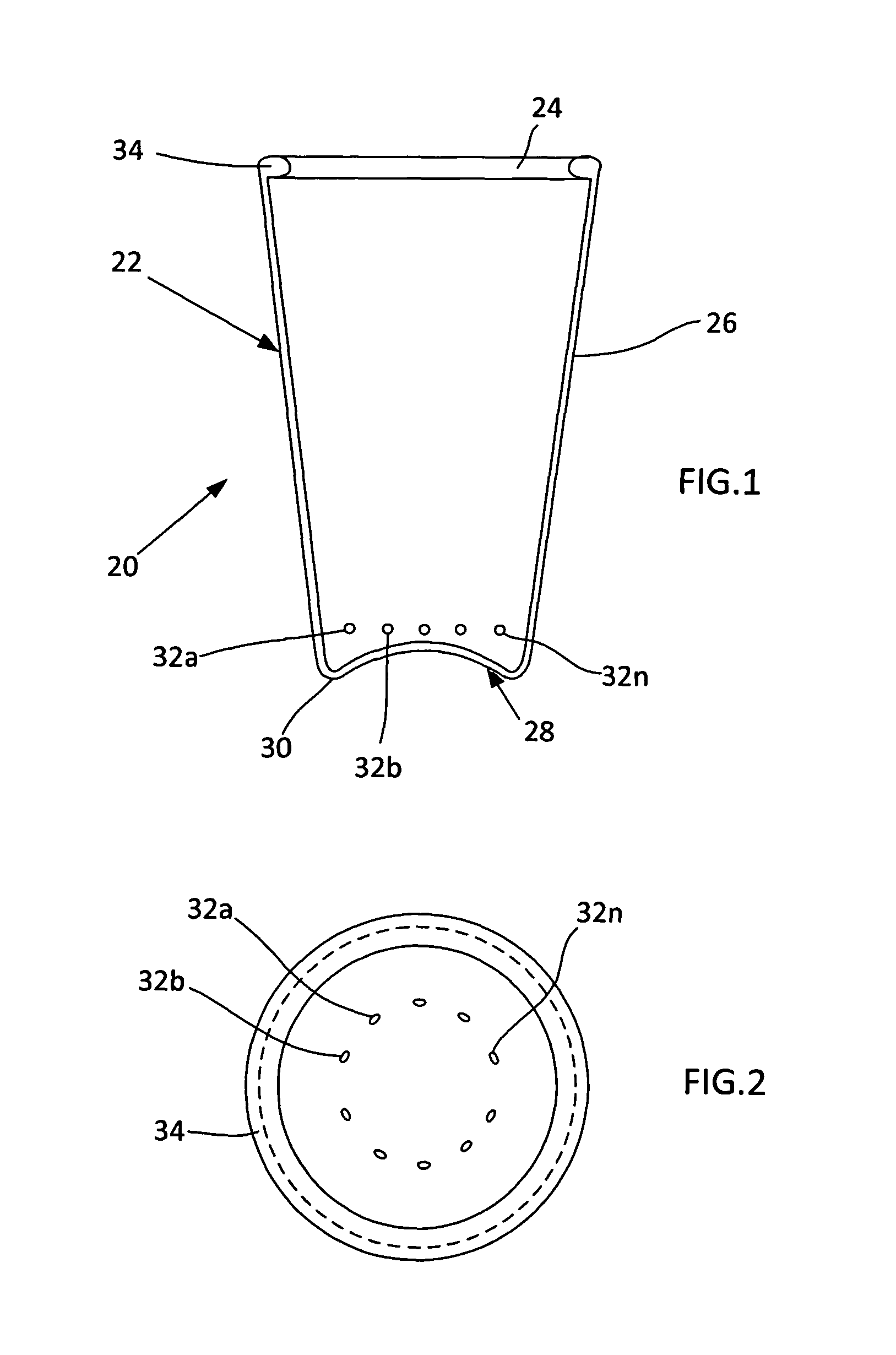
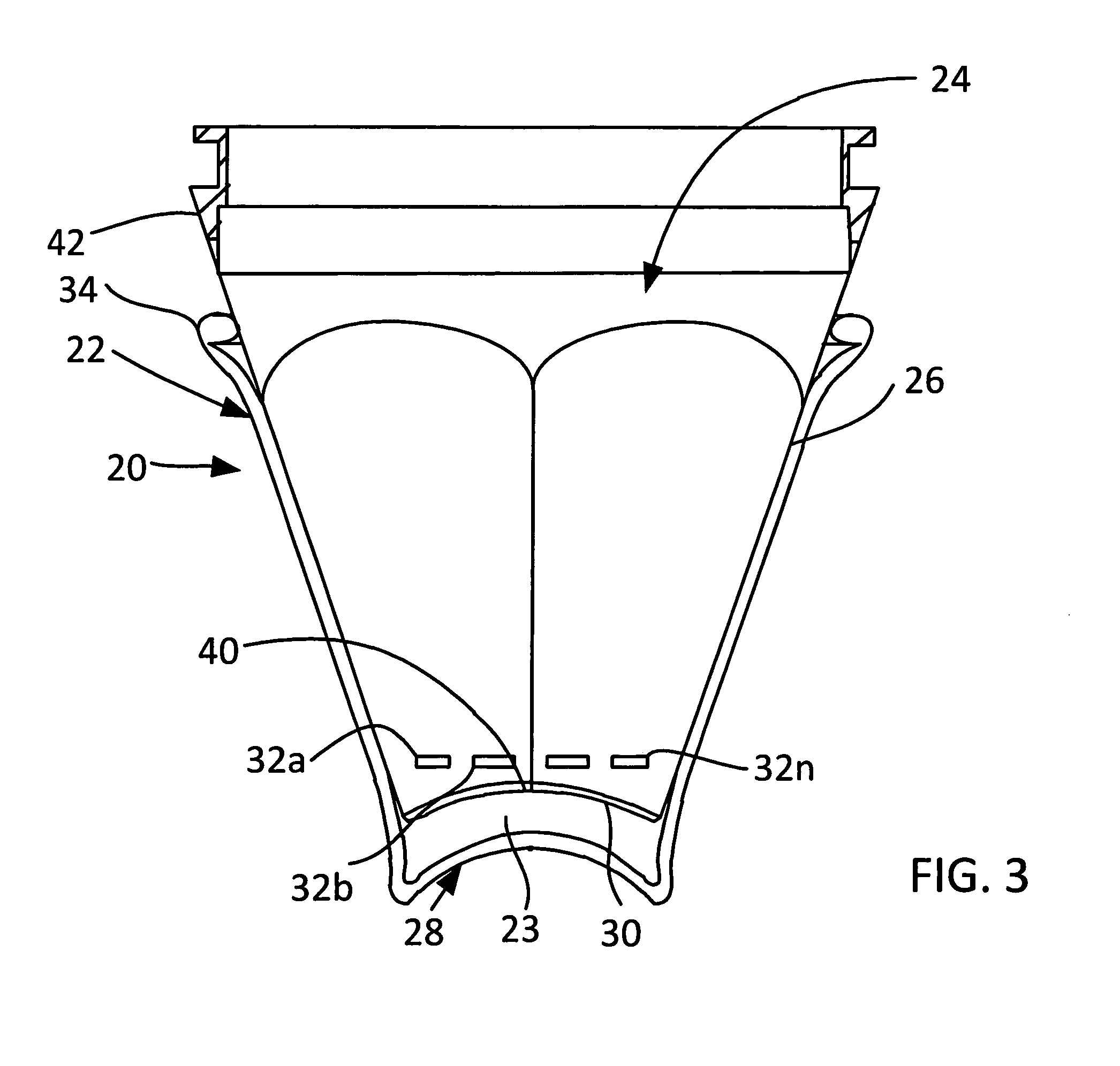
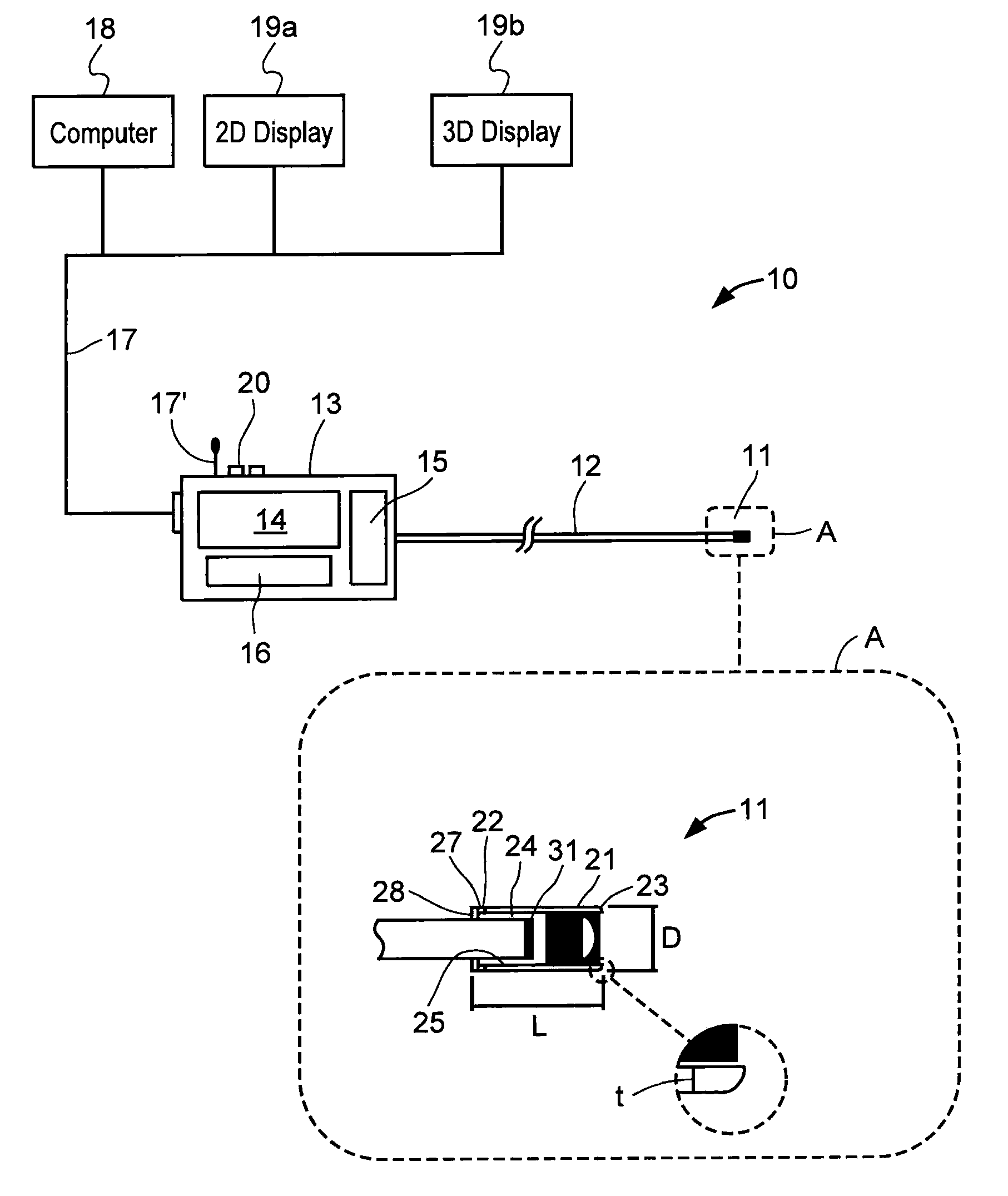
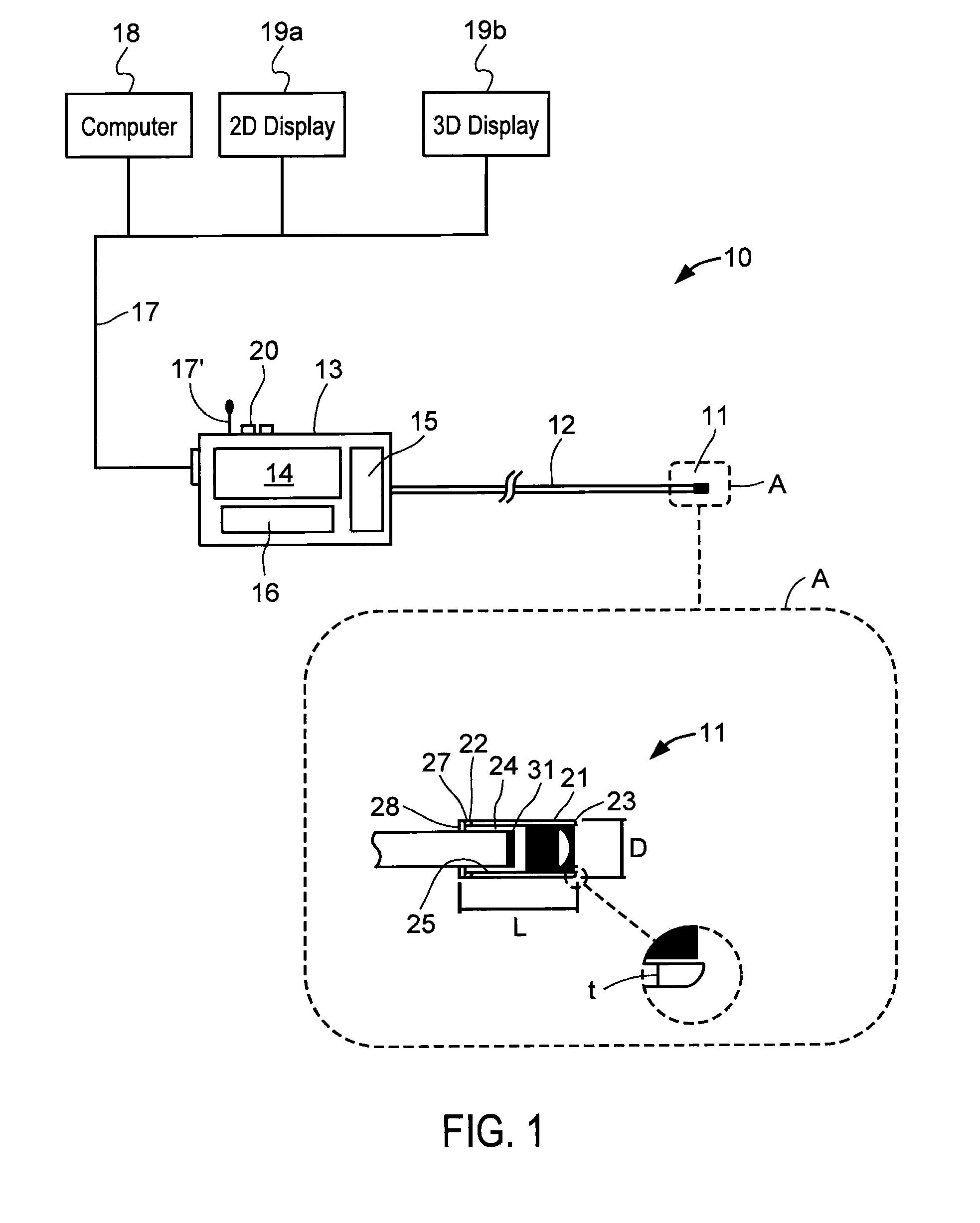
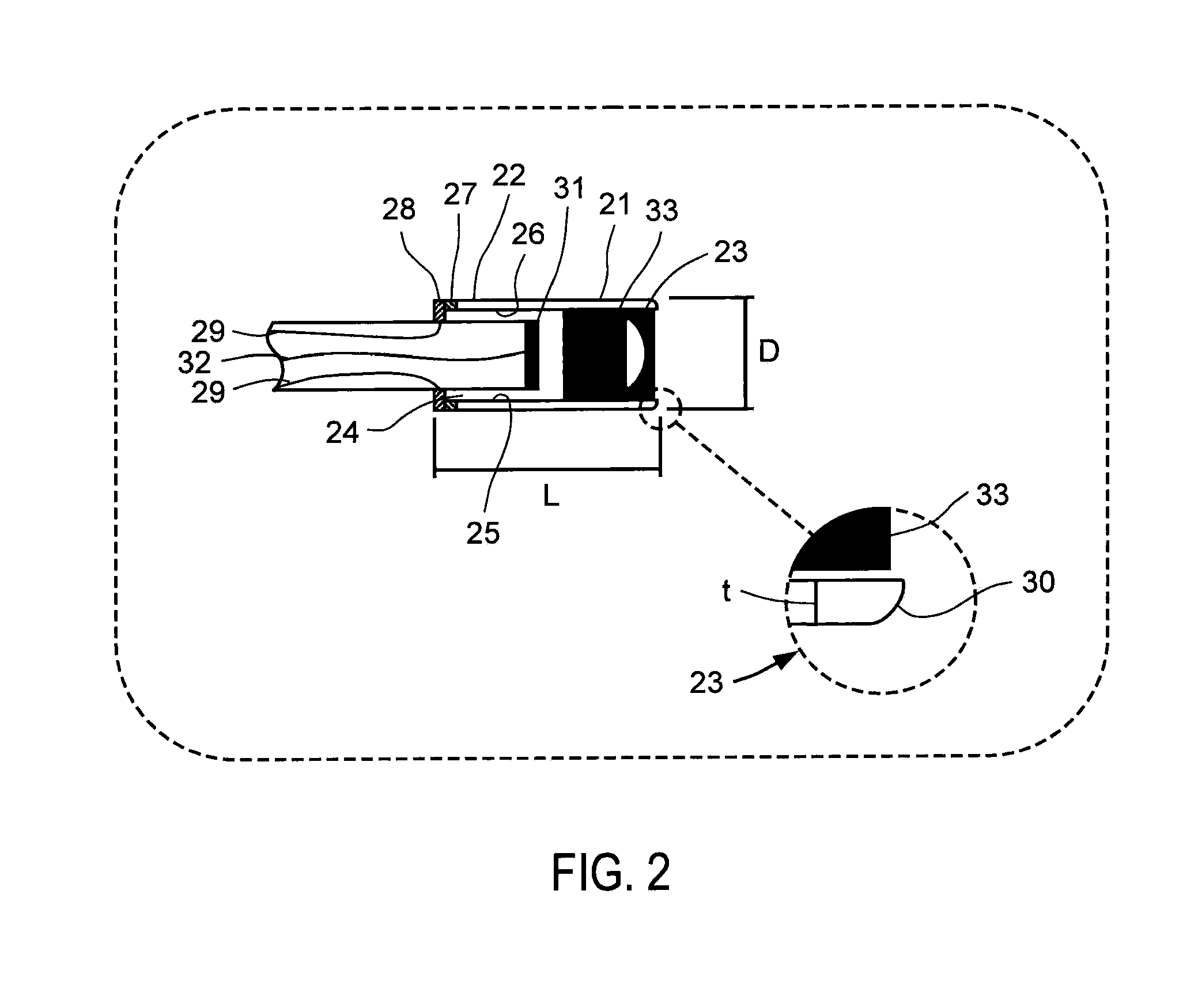
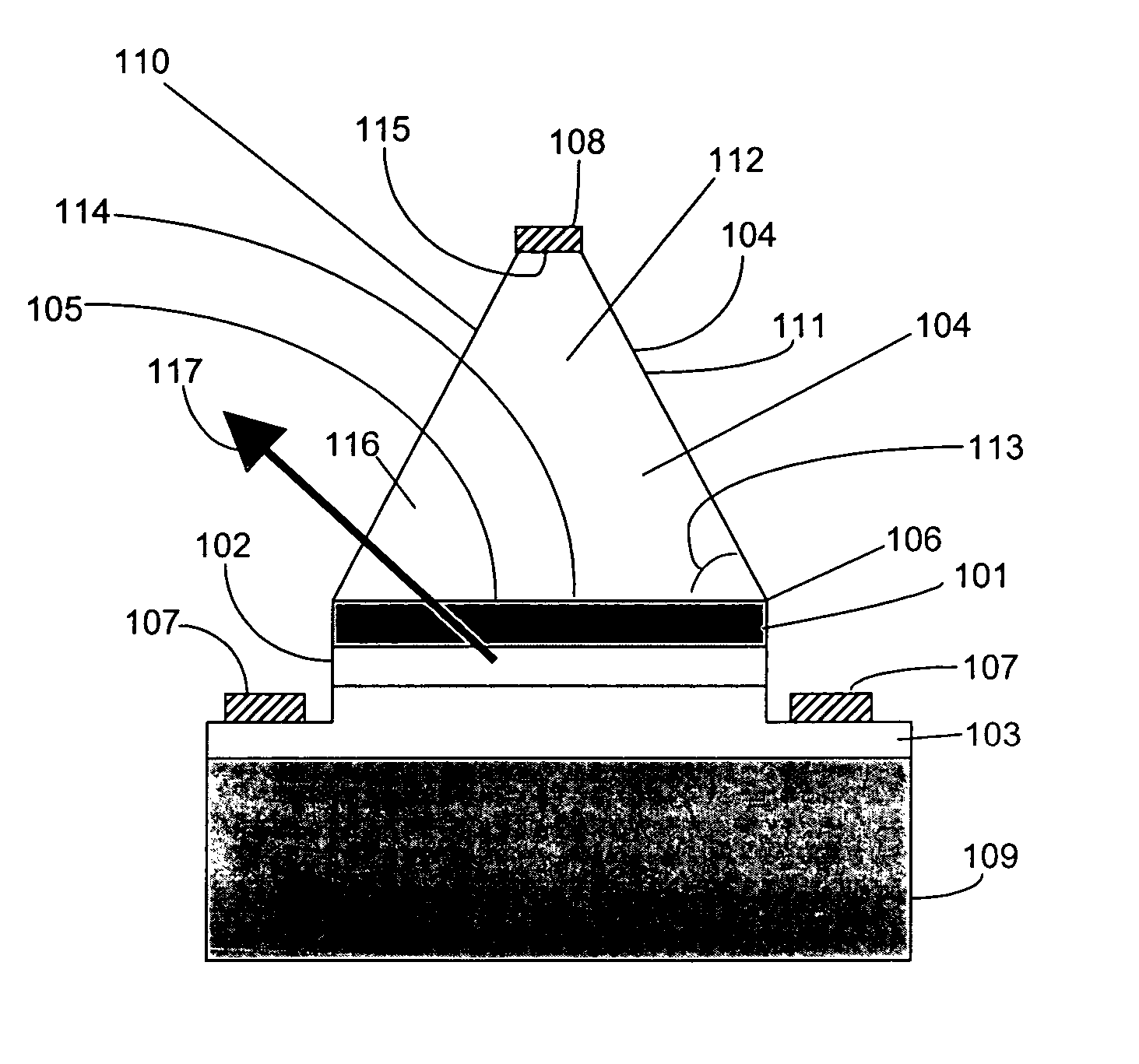
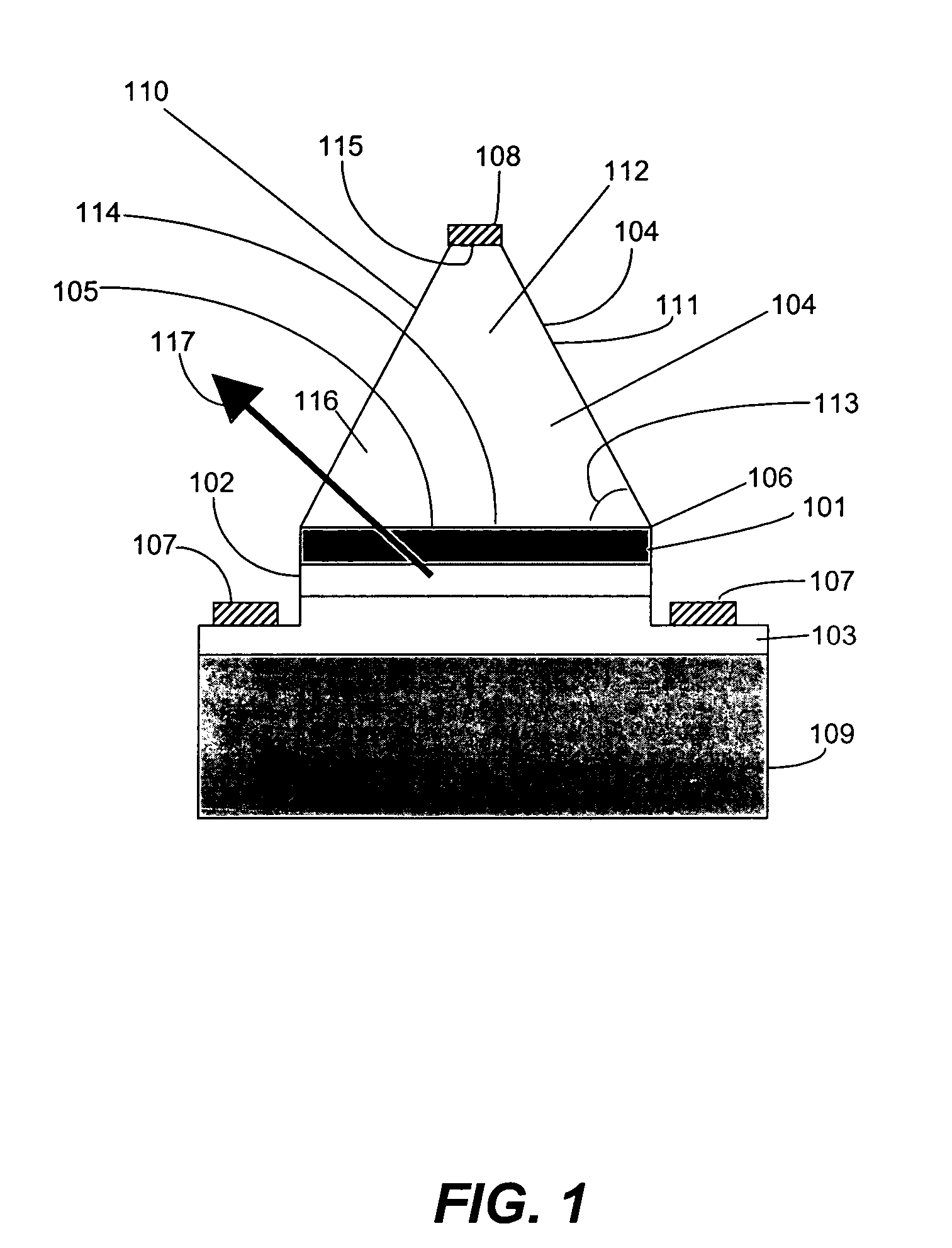
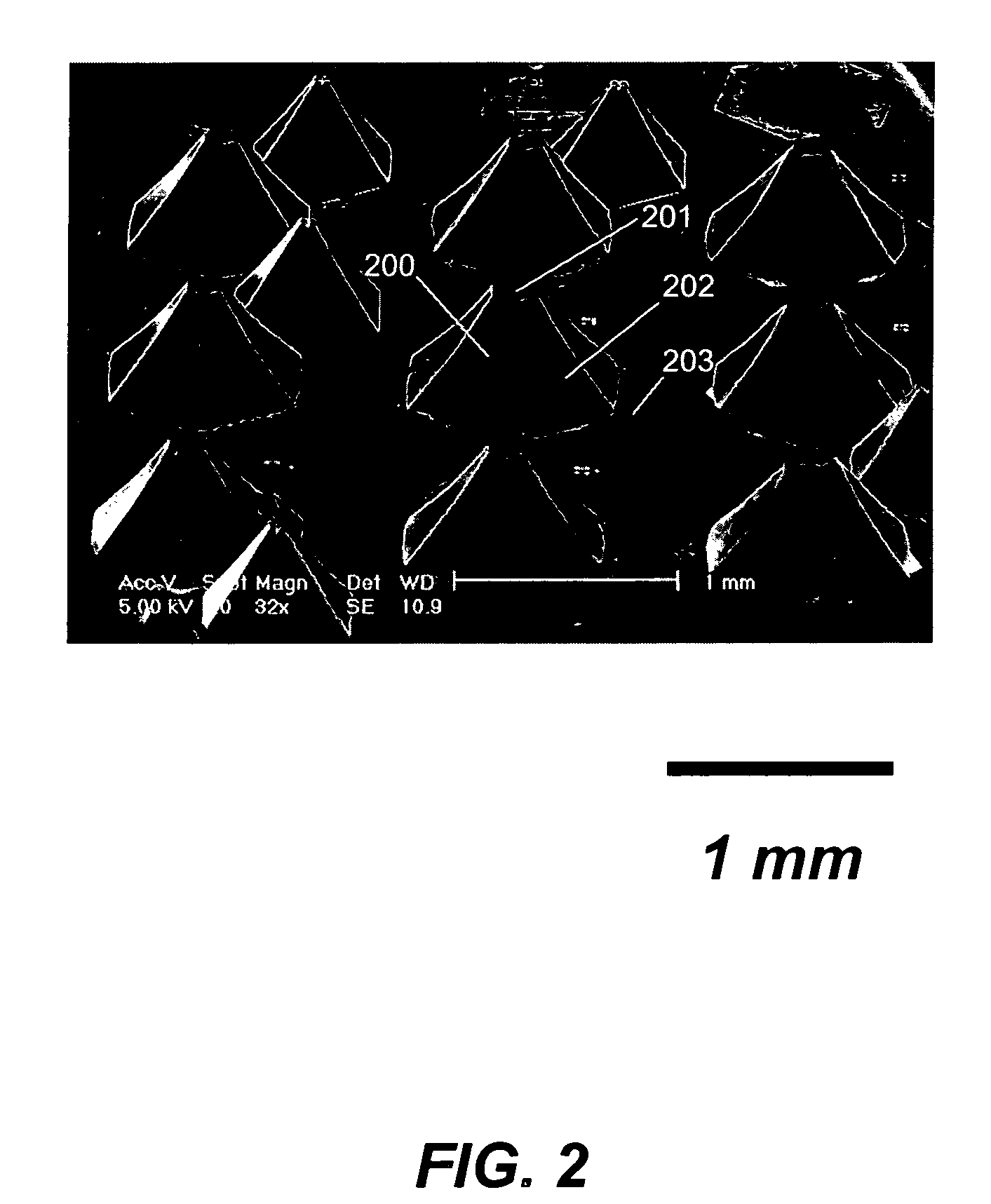
An (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO direct wafer bonded light emitting diode (LED) combined with a shaped plastic optical element, in which the directional light from the ZnO cone, or from any high refractive index material in contact with the LED surface, entering the shaped plastic optical element is extracted to air.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
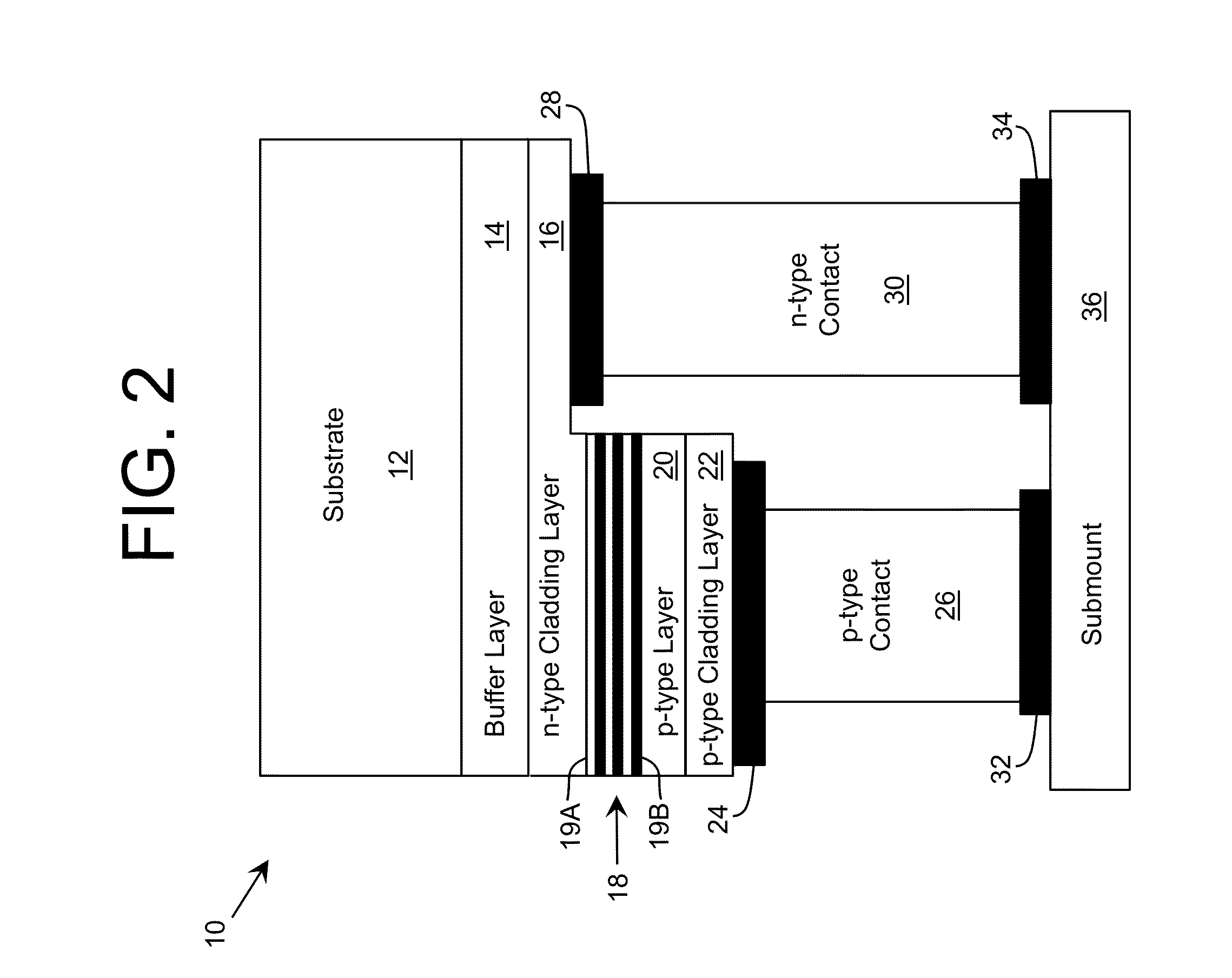
Semiconductor light-emitting device
InactiveUS20050001227A1Improve external quantum efficiencyImprove efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyCrystallographic defect
Owner:NICHIA CORP
Substrates comprising a photocatalytic TiO2 layer
InactiveUS20050191505A1Effective photocatalytic layerReduce light absorptionMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentCompound (substance)Concentration gradient
Substrates comprising a photocatalytic layer containing TiO2 are produced using TiO2 particles which may optionally be doped with metallic or non-metallic elements or compounds. The photocatalytic layer exhibits a concentration gradient of the TiO2 particles. An organically modified inorganic hybrid layer may be provided between the substrate and the photocatalytic layer.
Owner:INST FUR NEUE MATERIALIEN GEMEINNUTZIGE GMBH
High efficiency light emitting diode (LED)
InactiveUS20070145397A1Improve efficiencyReduce light absorptionPlanar/plate-like light guidesLight sourcesLight-emitting diodeDiode
An (Al, Ga, In)N light emitting diode (LED), wherein light extraction from chip and / or phosphor conversion layer is optimized. By novel shaping of LED and package optics, a high efficiency light emitting diode is achieved.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
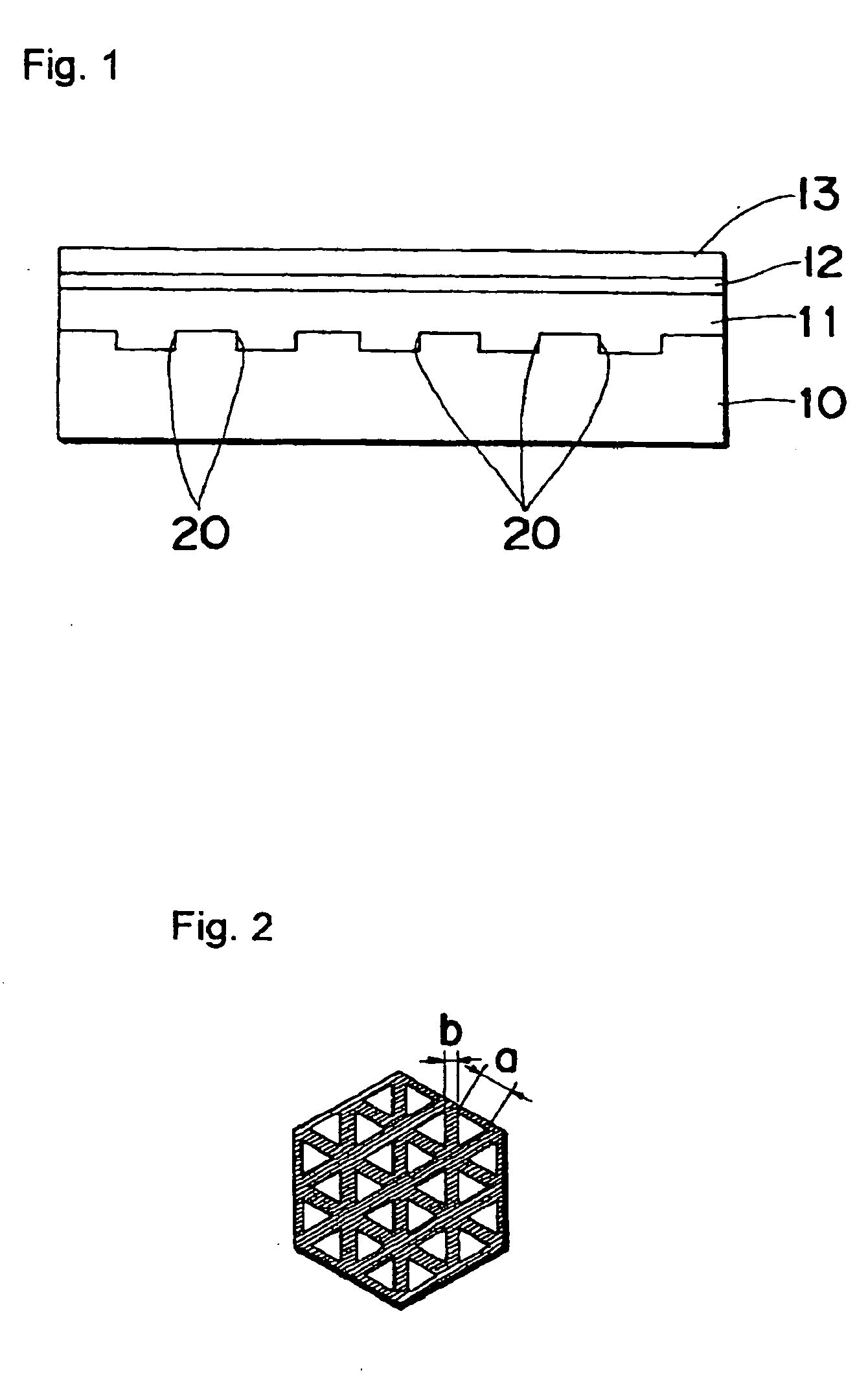
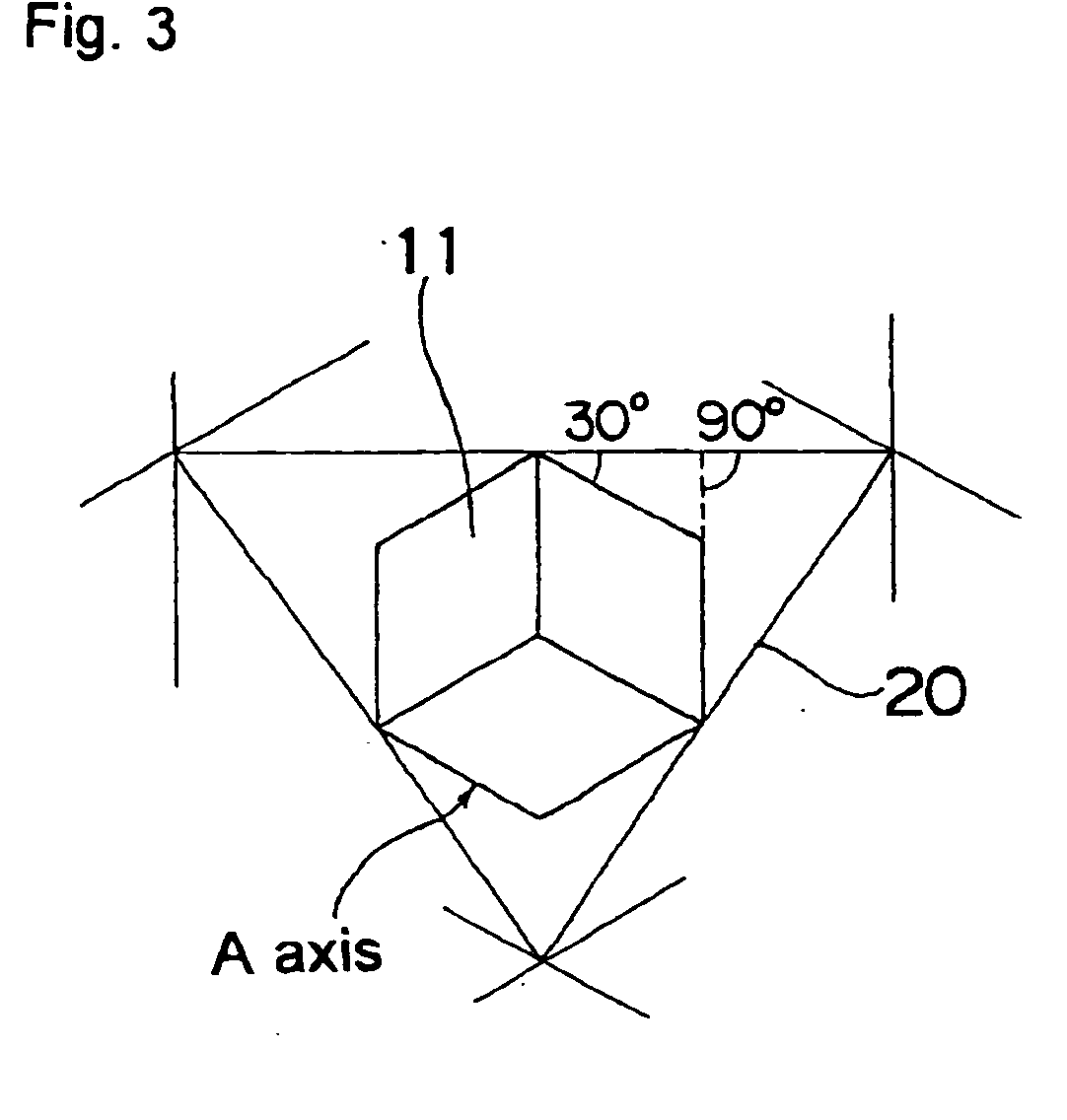
(Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO direct wafer bonded structure for optoelectronic applications, and its fabrication method
InactiveUS20070001186A1Improve conductivityStrong wafer bonded interfaceIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensElectrically conductiveNitrogen gas
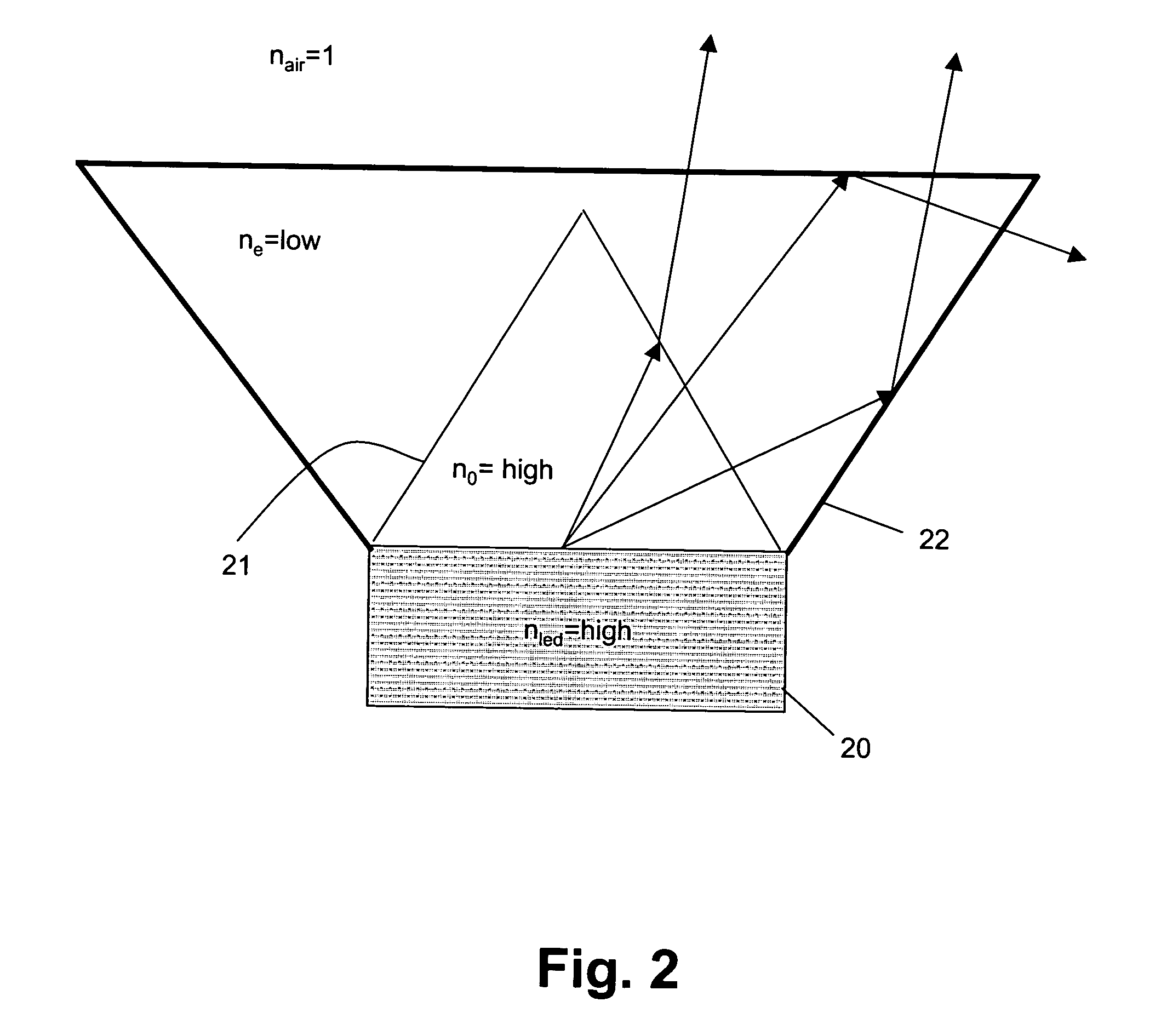
An (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO direct wafer bonded light emitting diode (LED), wherein light passes through electrically conductive ZnO. Flat and clean surfaces are prepared for both the (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO wafers. A wafer bonding process is then performed between the (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO wafers, wherein the (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO wafers are joined together and then wafer bonded in a nitrogen ambient under uniaxial pressure at a set temperature for a set duration. After the wafer bonding process, ZnO is shaped for increasing light extraction from inside of LED.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Light emitting diode and method of fabricating the same
ActiveUS20140175465A1Increase the number ofReduce the numberSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesInsulation layerInterconnection
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
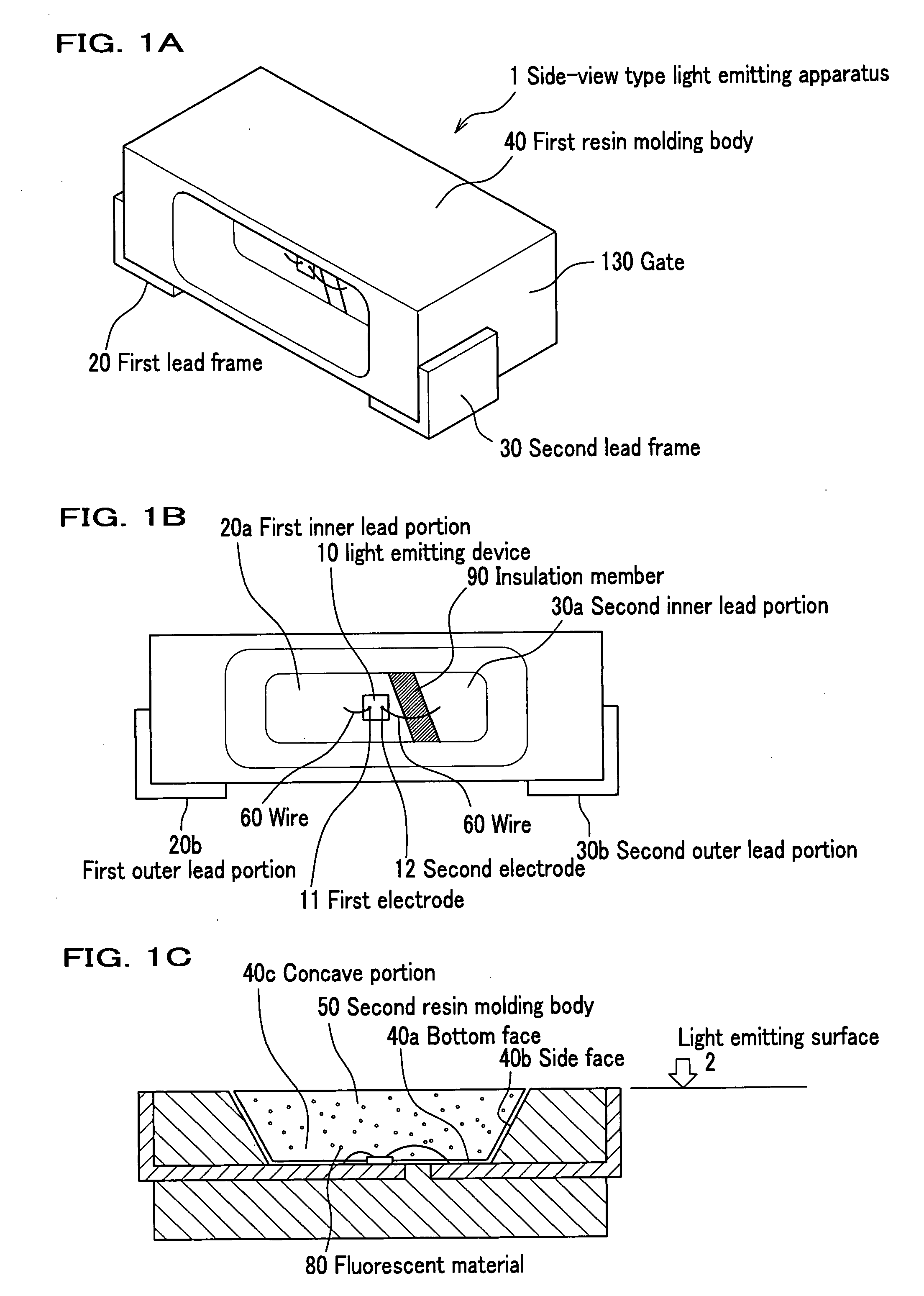
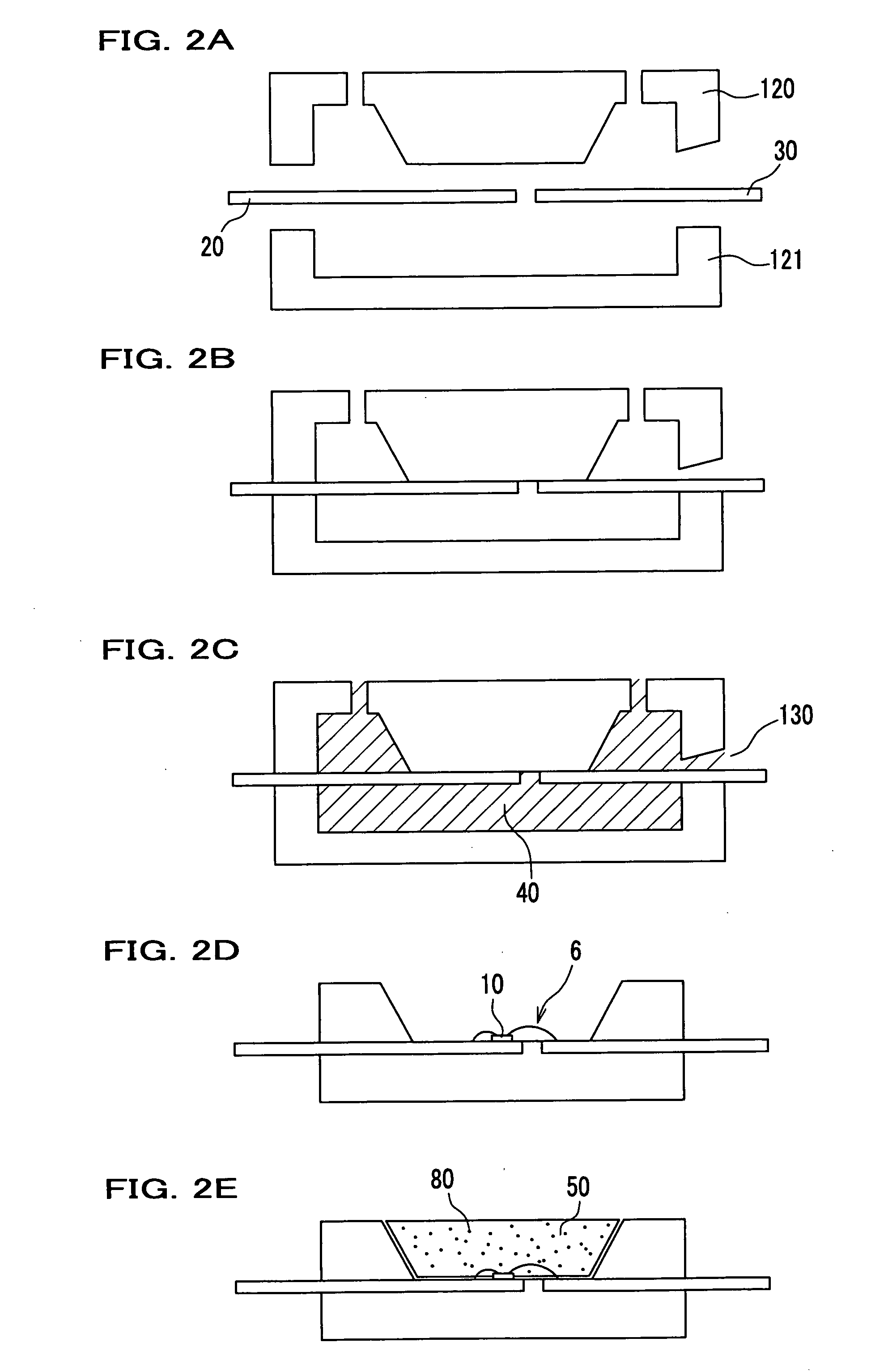
Surface mount lateral light emitting apparatus and fabrication method thereof
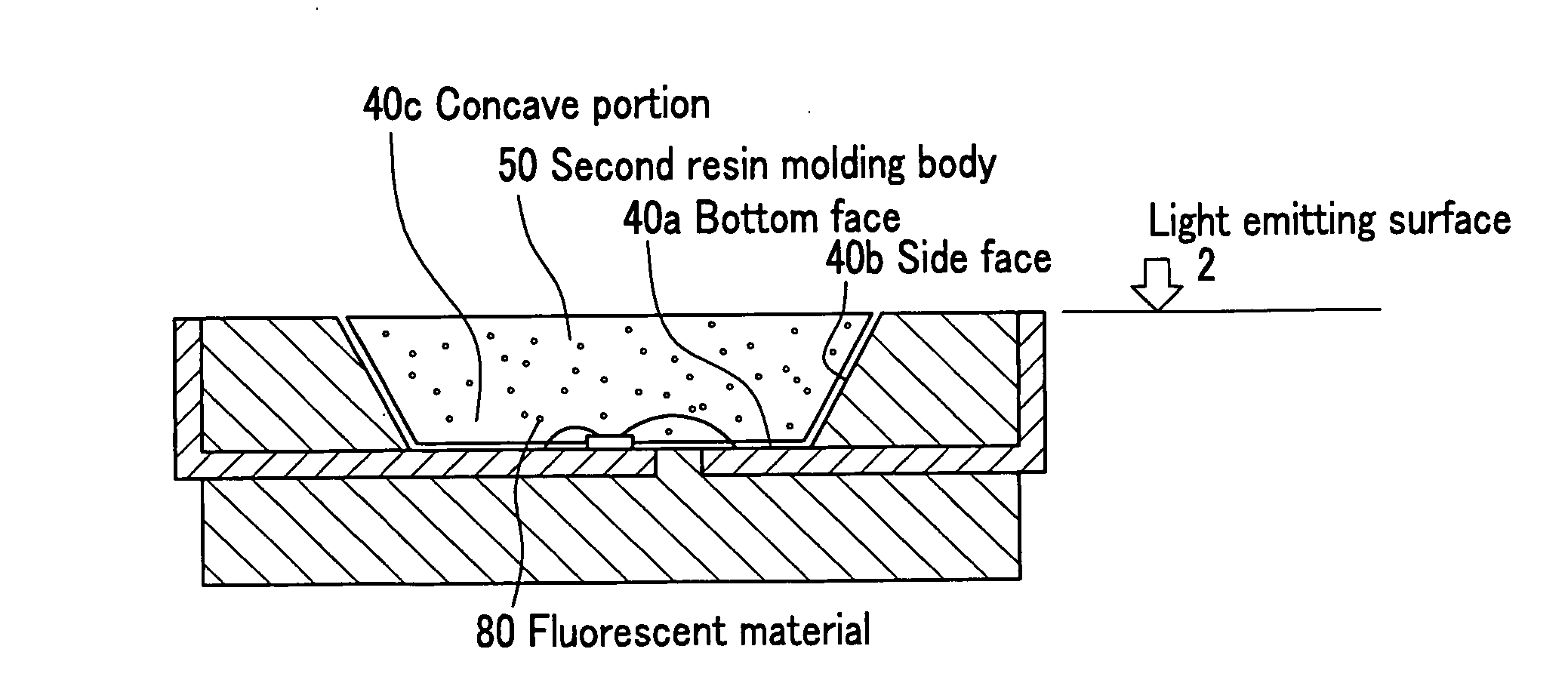
ActiveUS20080157113A1Good resin flowSmall sizeSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSurface mountingLead frame
A surface mount lateral light emitting apparatus, which includes a light emitting device; a first lead frame connected to the light emitting device; a second lead frame connected to the light emitting device; a first resin molding body in which a concave portion for mounting the light emitting device is formed and the first lead frame and the second lead frame are fixed; and a second resin molding body which covers the light emitting device to form a light emitting surface in the concave portion of the first resin molding body, wherein the first resin molding body contains a filler or a light diffusion agent; wherein in a periphery of the concave portion, a width of at least one side of the first resin molding body is not more than 0.2 mm; and wherein the first resin molding body and the second resin molding body are formed with a thermosetting resin.
Owner:NICHIA CORP
High light extraction efficiency light emitting diode (LED)
InactiveUS7994527B2Reduce light absorptionImprove light extractionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingRefractorsRefractive indexWafer bonding
An (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO direct wafer bonded light emitting diode (LED) combined with a shaped plastic optical element, in which the directional light from the ZnO cone, or from any high refractive index material in contact with the LED surface, entering the shaped plastic optical element is extracted to air.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
Wavelength converting element comprising ceramic capsule
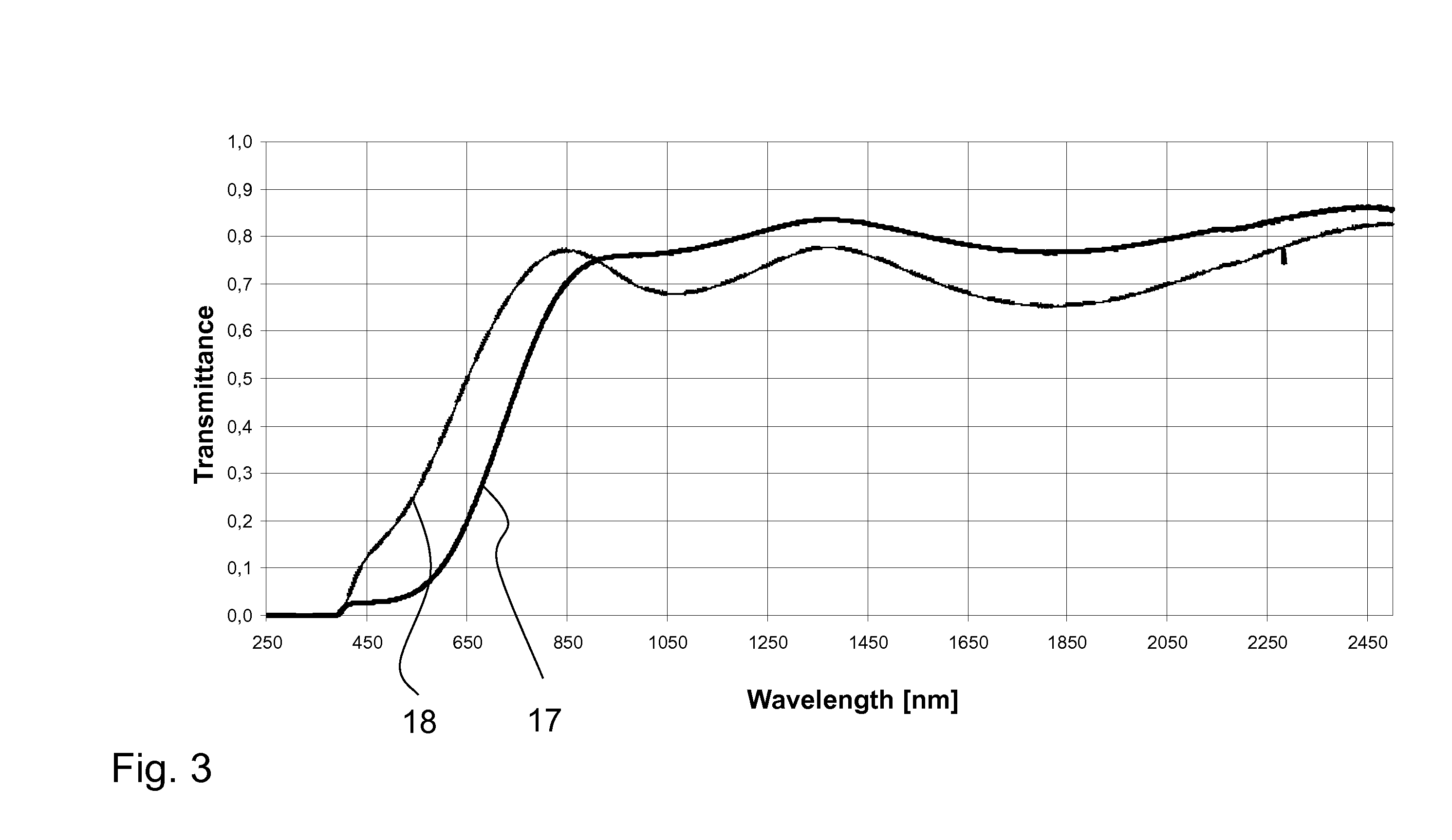
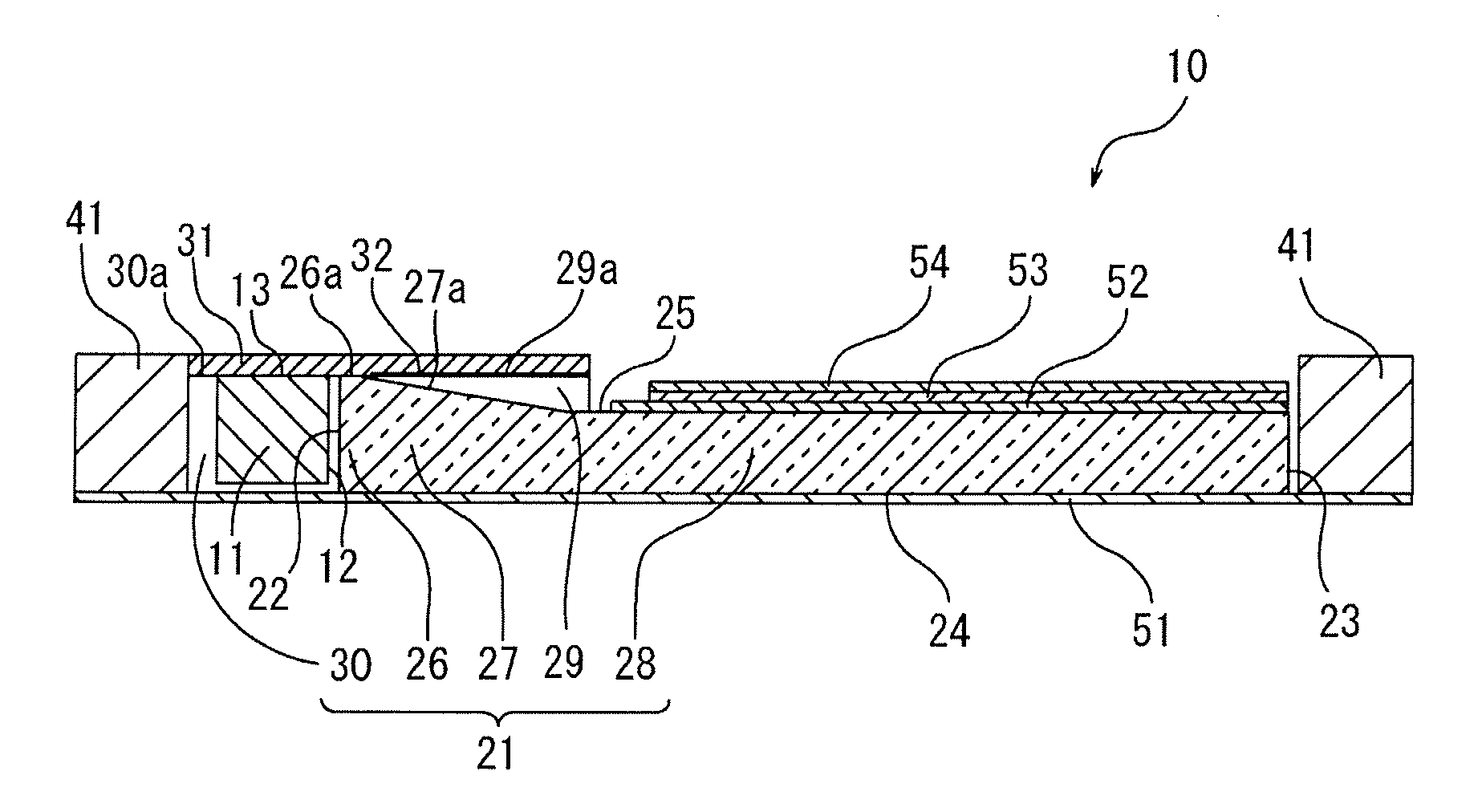
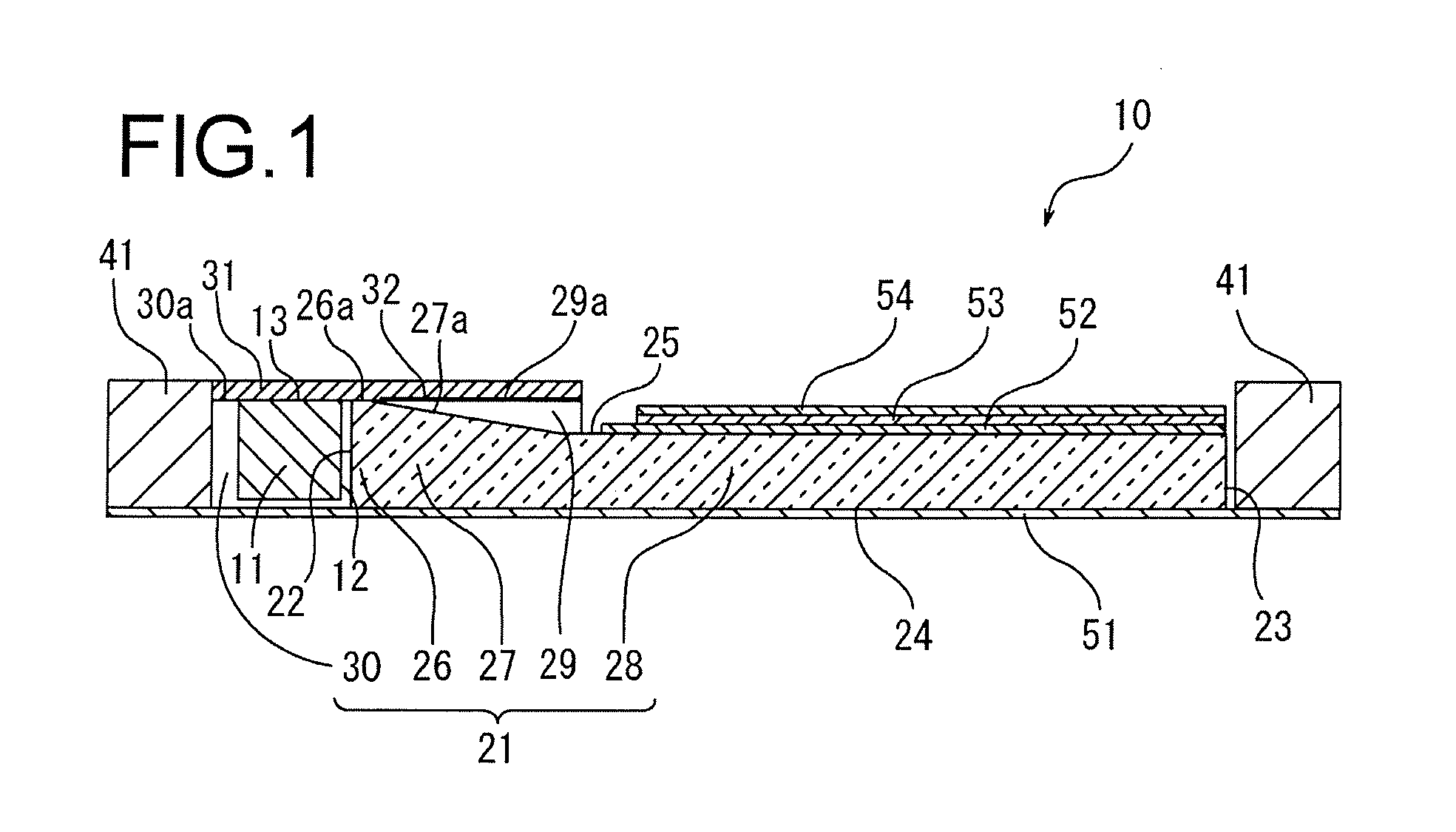
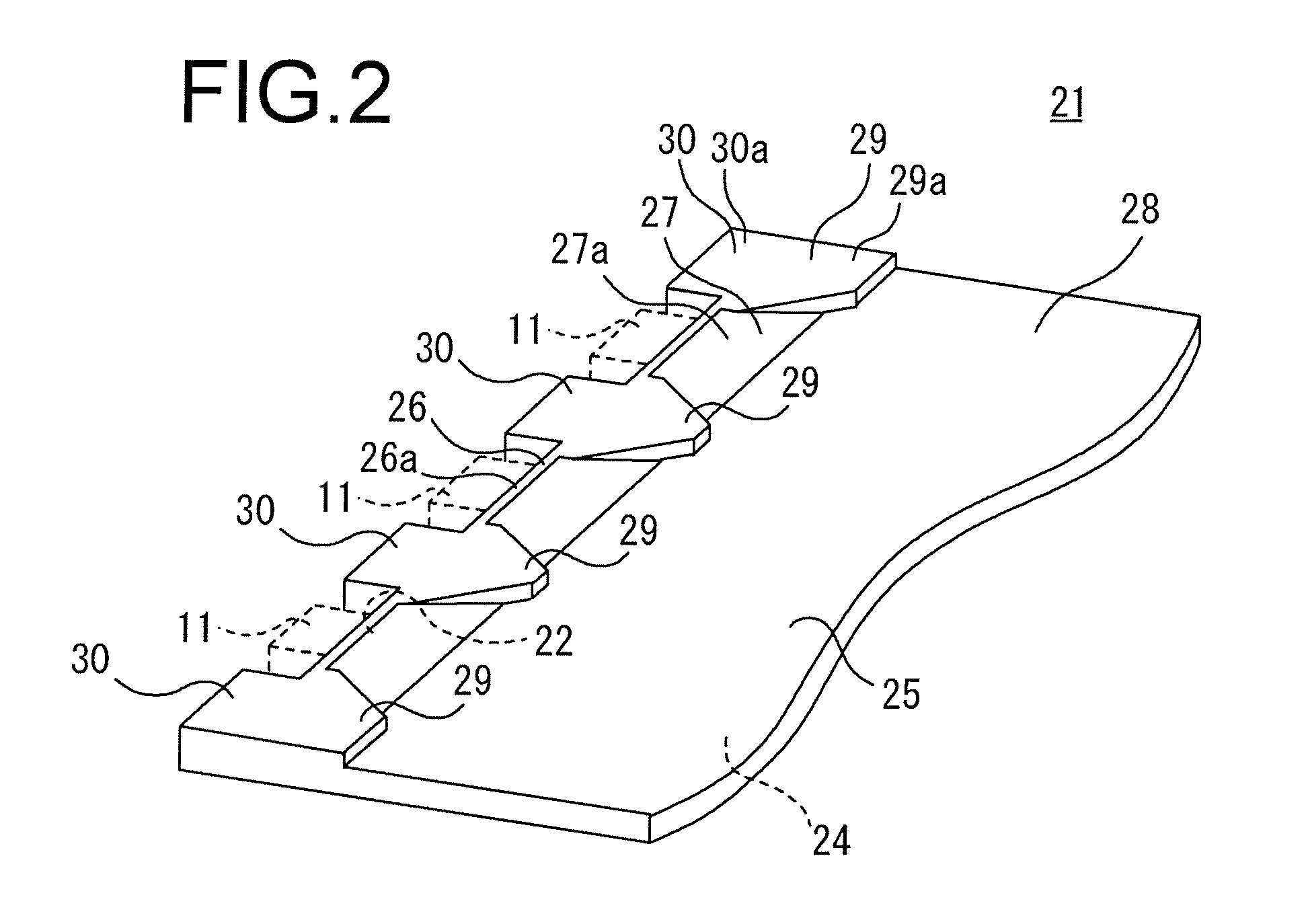
ActiveUS20150261076A1Prevent degradationConvenient lightingPoint-like light sourceProjectorsTransmittanceOxygen
A wavelength converting member is provided, comprising a sealed capsule at least partly made of sintered polycrystalline ceramic, for example sintered polycrystalline alumina, said capsule defining at least one sealed cavity; and—a wavelength converting material contained within said sealed cavity. The wavelength converting member has high total forward transmission of light, high thermal conductivity, high strength and provides excellent protection for the wavelength converting member against oxygen and water. The wavelength converting member can advantageously be applied in a light emitting arrangement or as a color wheel for a digital image projector.
Owner:LUMILEDS
High-brightness light emitting diode having reflective layer
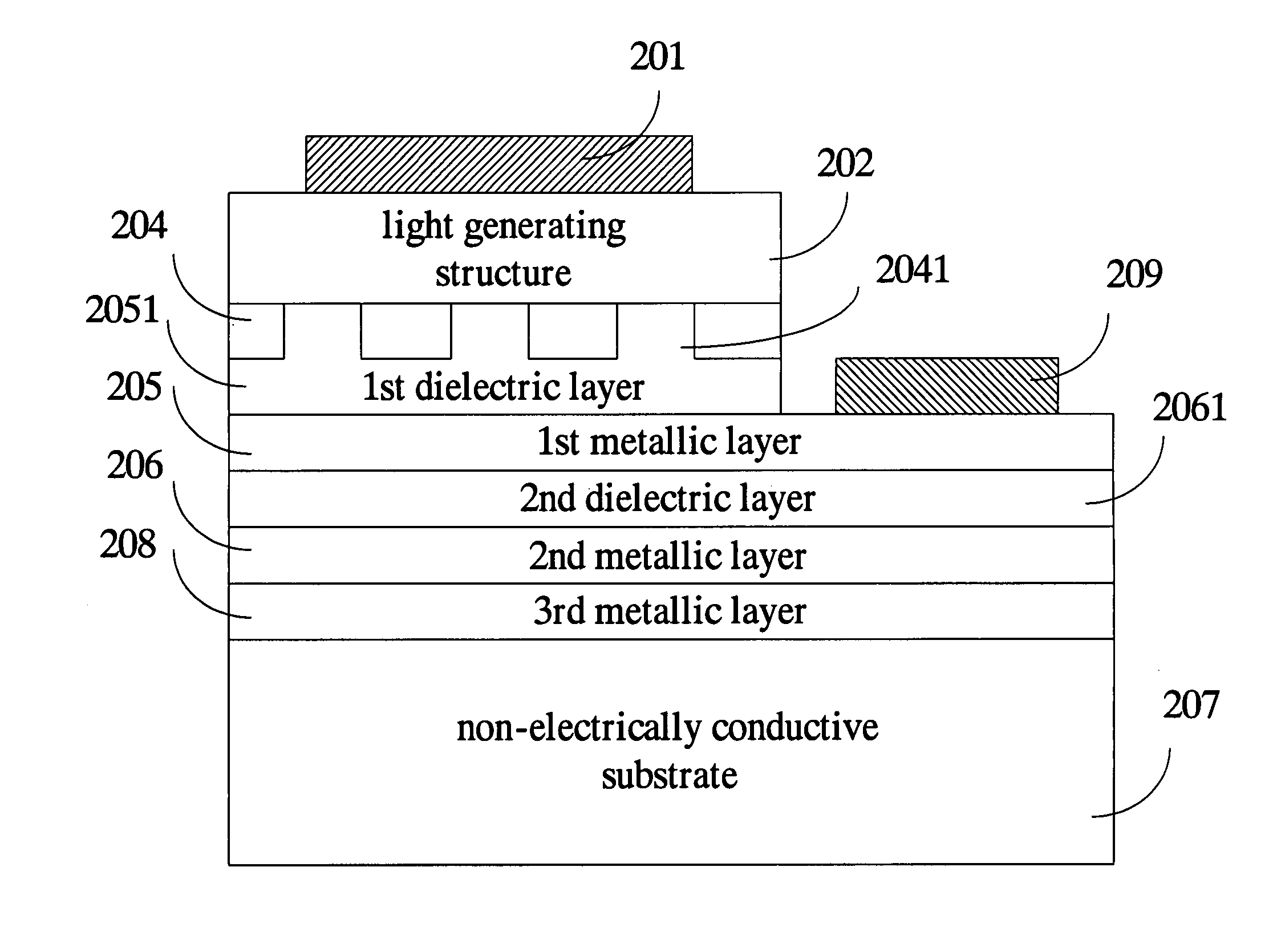
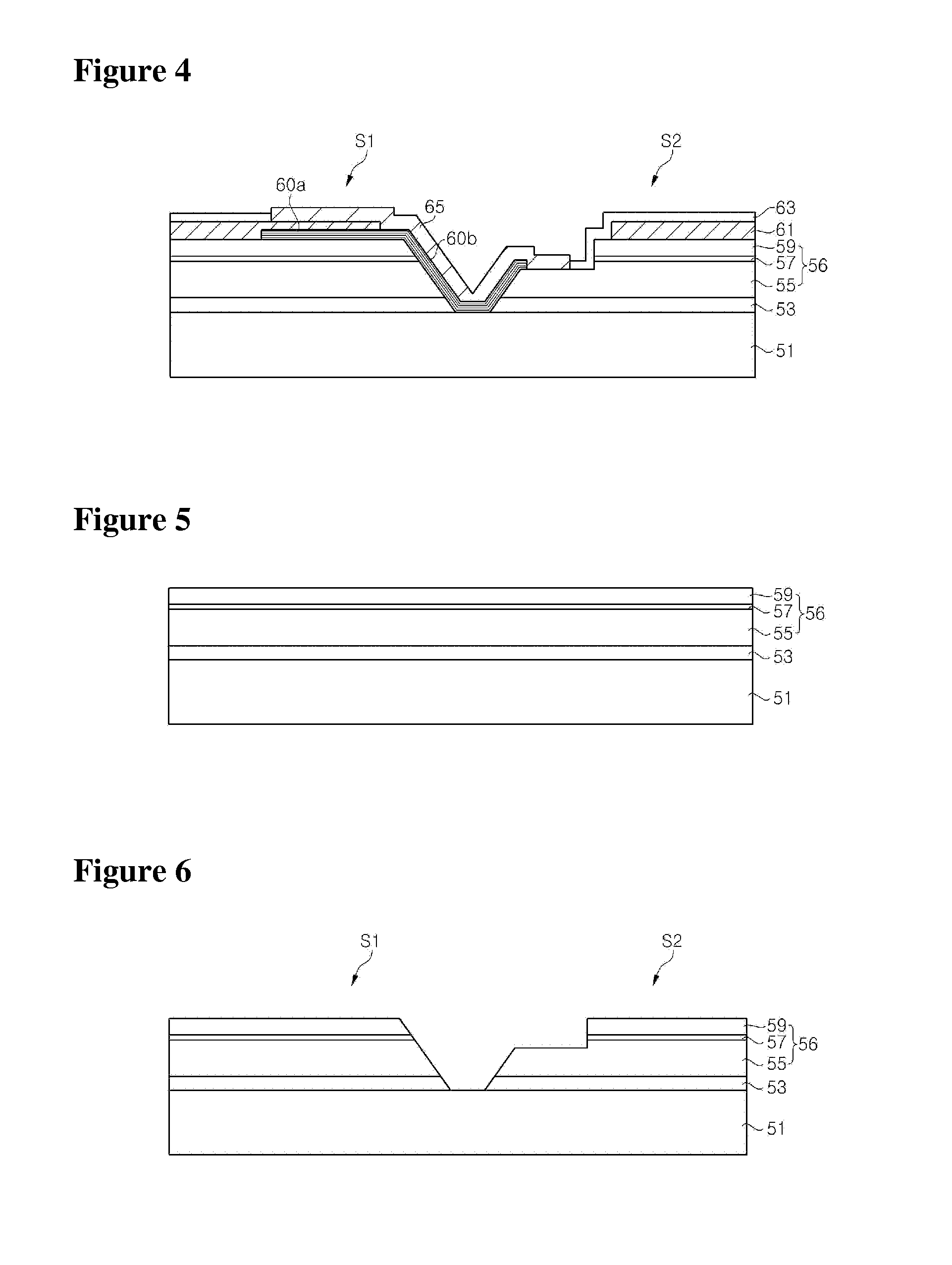
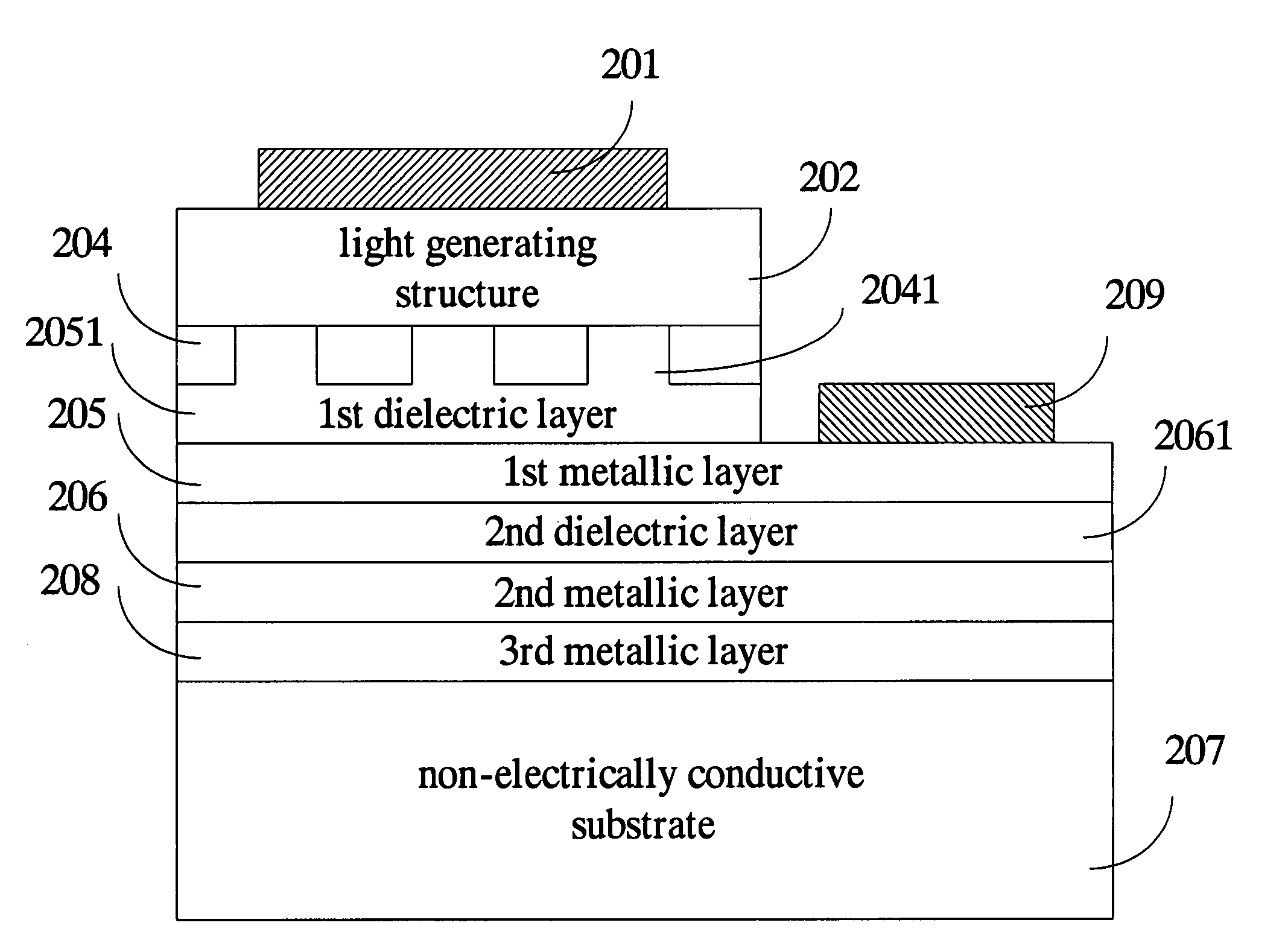
ActiveUS20070012937A1Increase brightnessImprove insulation performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactAlloy
An LED structure is disclosed herein, which comprises, sequentially arranged in the following order, a light generating structure, a non-alloy ohmic contact layer, a metallic layer, and a substrate. As a reflecting mirror, the metallic layer is made of a pure metal or a metal nitride for achieving superior reflectivity. The non-alloy ohmic contact layer is interposed between the metallic layer and the light generating structure so as to achieve the required ohmic contact. To prevent the metallic layer from intermixing with the non-alloy ohmic contact layer and to maintain the flatness of the reflective surface of the first metallic layer, an optional dielectric layer is interposed between the metallic layer and the non-alloy ohmic contact layer.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Disposable sterile protective cover for optical devices used in ophthalmology
InactiveUS8011504B1High refractive indexDiagnosing glaucomaDispensing apparatusSurgical needlesTotal internal reflectionSoft materials
The device of the invention comprises a protective cover for an optical device such as a gonioscope, capsulatomy lens, wide-angle lens, or any other lens having an eye-contacting surface. The cover is made sterile and disposable for allowing multiple use of the protected optical device. The cover is made from a soft material biologically acceptable for contact with a human eye. According to one aspect, the gonioscope protective cover is used merely for physically protecting the eye-contacting surface from direct contact with the eye. According to another aspect, the gonioscope protective cover combines the protective function with an optical function that changes the direction of light so that it becomes possible to observe the light emitted from the pupil at angles that are close to the angle of full internal reflection from the pupil medium.
Owner:FARBEROV ARKADIY
Semiconductor light-emitting element
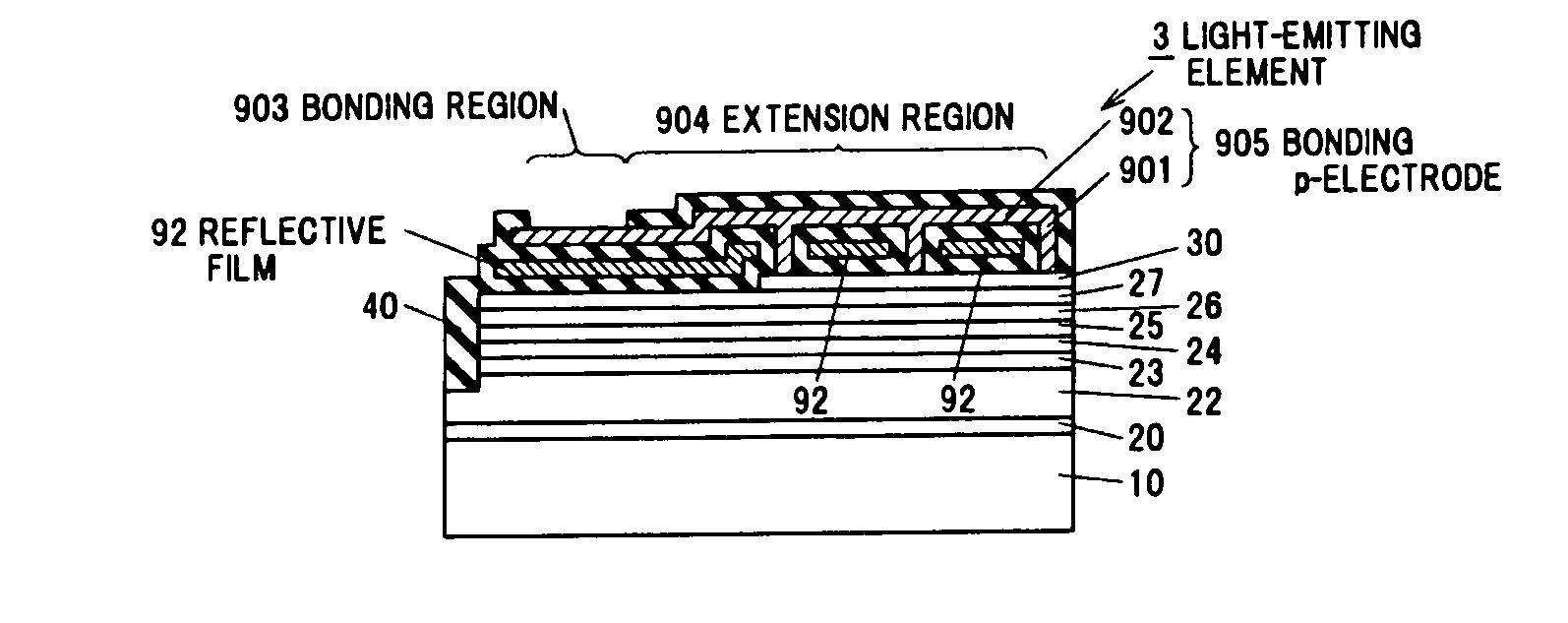
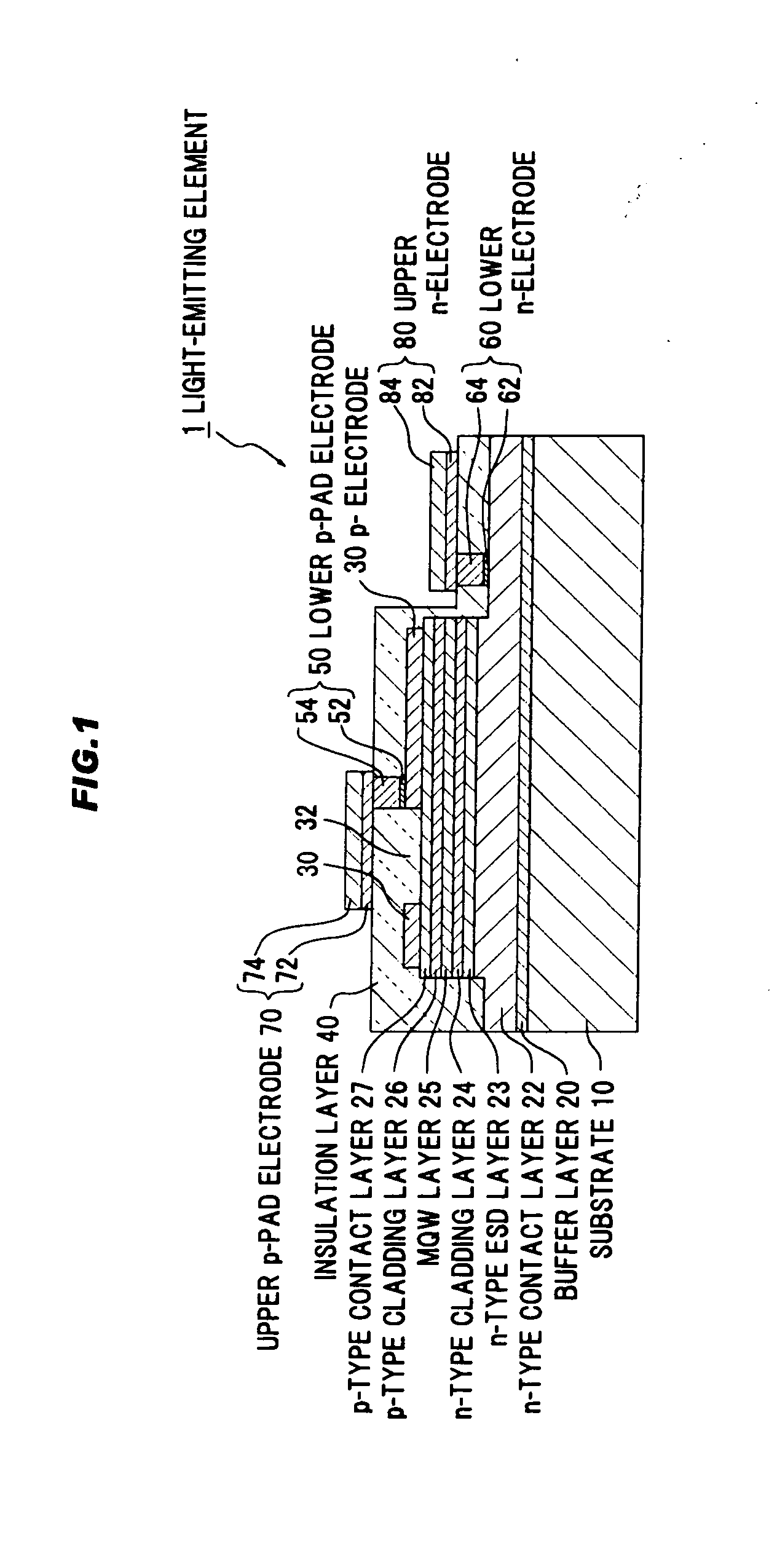
ActiveUS20110198641A1Light extraction efficiencyReduce light absorptionSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesInsulation layerOhmic contact
A semiconductor light-emitting element includes a semiconductor laminated structure including a light-emitting layer sandwiched between first and second conductivity type layers for extracting an emitted light from the light-emitting layer on a side of the second conductivity type layer, a transparent electrode in ohmic contact with the second conductivity type layer, an insulation layer formed on the transparent electrode, an upper electrode for wire bonding formed on the insulation layer, a lower electrode that penetrates the insulation layer, is in ohmic contact with the transparent electrode and the electrode for wire bonding, and has an area smaller than that of the upper electrode in top view, and a reflective portion for reflecting at least a portion of light transmitted through a region of the transparent electrode not in contact with the lower electrode.
Owner:TOYODA GOSEI CO LTD
Highly reflective microcrystalline/amorphous materials, and methods for making and using the same
ActiveUS20140271440A1Increase in albedoMitigate the urban heat island effectCalcium/strontium/barium carbonatesPigmenting treatmentAlbedoCarbonate
Compositions comprising highly reflective microcrystalline / amorphous materials are provided. In some instances, the highly reflective materials are microcrystalline or amorphous carbonate materials, which may include calcium and / or magnesium carbonate. In some instances, the materials are CO2 sequestering materials. Also provided are methods of making and using the compositions, e.g., to increase the albedo of a surface, to mitigate urban heat island effects, etc.
Owner:BLUE PLANET SYST CORP
Endoscope having disposable illumination and camera module
InactiveUS8928746B1Low illuminationUniform illuminationTelevision system detailsSurgeryEllipseSingle use
An endoscope having a single-use disposable illumination and camera module is provided in which an imaging element is disposed within an annular tube of optically transparent material having proximal and distal ends, wherein the proximal end is configured to engage a plurality of LEDS and the distal end has a cross-section in the form of an arc of a circle or ellipse, so that the annular tube serves as a light mixer and diffuser, providing uniform illumination within the field of view of the imaging element. Methods of analyzing and displaying the output of the endoscope also are provided.
Owner:STEVRIN & PARTNERS
Optoelectronic Component
ActiveUS20130140580A1Avoid absorption lossReduce absorption lossSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor chipElectromagnetic radiation
An optoelectronic component can be used for mixing electromagnetic radiation having different wavelengths, in particular in the far field. The optoelectronic component includes a carrier. A first semiconductor chip has a first radiation exit surface for emitting electromagnetic radiation in a first spectral range is provided on the carrier and a second semiconductor chip as a second radiation exit surface for emitting electromagnetic radiation in a second spectral range is provided on the carrier. A diffusing layer is provided on the radiation exit surfaces of the semiconductor chips which face away from the carrier.
Owner:OSRAM OLED
Light emitting diode and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20140353692A1Increase the number ofReduce the numberSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorInterconnection
A light emitting diode includes light emitting cells disposed on a substrate and interconnections connecting the light emitting cells to each other. Each of the light emitting cells includes a first semiconductor layer, a second semiconductor layer, an active layer disposed between the first semiconductor layer and the second semiconductor layer, and a transparent electrode layer disposed on the second semiconductor layer, wherein the first and second semiconductor layers have different conductivity types. The interconnections include a common cathode commonly connecting first and second light emitting cells of the light emitting cells, the first and second light emitting cells share the first semiconductor layer, the transparent electrode layer is continuously disposed between the first and second light emitting cells, and the common cathode is electrically connected to the first and second light emitting cells through the transparent electrode layer.
Owner:SEOUL VIOSYS CO LTD
High-brightness light emitting diode having reflective layer
ActiveUS7335924B2Increase brightnessImprove insulation performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactAlloy
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Conductive oxide film, display device, and method for forming conductive oxide film
ActiveUS20140063368A1High conductivityHigh transmittanceConductive layers on insulating-supportsZinc oxides/hydroxidesHigh transmittanceOptoelectronics
One embodiment of the present invention provides a conductive oxide film having high conductivity and high transmittance of visible light. The conductive oxide film having high conductivity and high transmittance of visible light can be obtained by forming a conductive oxide film at a high substrate temperature in the film formation and subjecting the conductive oxide film to nitrogen annealing treatment. The conductive oxide film has a crystal structure in which c-axes are aligned in a direction perpendicular to a surface of the film.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Light emitting diode device
ActiveUS20110114966A1Increase brightnessImprove efficiencySemiconductor devicesEvaporationChemical vapor deposition
A high-brightness vertical light emitting diode (LED) device having an outwardly located metal electrode. The LED device is formed by: forming the metal electrode on an edge of a surface of a LED epitaxy structure using a deposition method, such as physical vapor deposition (PVD), chemical vapor deposition (CVD), evaporation, electro-plating, or any combination thereof; and then performing a packaging process. The composition of the LED may be a nitride, a phosphide or an arsenide. The LED of the invention has the following advantages: improving current spreading performance, reducing light-absorption of the metal electrode, increasing brightness, increasing efficiency, and thereby improving energy efficiency. The metal electrode is located on the edge of the device and on the light emitting side. The metal electrode has two side walls, among which one side wall can receive more emission light from the device in comparison with the other one.
Owner:SEMILEDS OPTOELECTRONICS CO LTD
Manufacture method of array type high-voltage LED device
InactiveCN102867837AReduce light absorptionIncrease light emitting areaSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesSulfurPhosphoric acid
The invention discloses a manufacture method of an array type high-voltage LED device, which comprises the steps of: manufacturing a mask on a P type gallium nitride layer with an epitaxial structure, selectively etching the epitaxial structure to form an N type step structure; manufacturing a mask on the surface of an N type gallium nitride layer with an epitaxial structure, forming isolated deep trench; carrying out high-temperature sulfur phosphoric acid corrosion; depositing an insulation dielectric layer on the surface of the etched epitaxial structure; corroding the insulation dielectric layer outside the side wall of the deep trench; manufacturing a transparent conductive layer between adjacent N type step structures; partially corroding the transparent conductive layer on the surface of the P type gallium nitride layer on the N type step structure on the outermost side; and manufacturing a P metal electrode and an N metal electrode on the transparent conductive layer. According to the invention, electrode light absorption can be reduced, the light outlet area on the epitaxial side surface and the bottom of the chip is increased, the manufacture method is mutually matched with a post process, and thus the light emitting efficiency of a high-voltage LED chip can be increased.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Anti-Reflective and Anti-Soiling Coatings with Self-Cleaning Properties
InactiveUS20100275815A1Augment anti-reflection benefitImprove efficiencyAnti-reflective coatingsSolventPolymer
The embodiments of the invention are directed to organosilane-based coating compositions having anti-reflective, anti-soiling, and self-cleaning properties; methods of forming of the coatings; and articles of manufacture that utilize the coatings. In some embodiments, the coating compositions comprise an organosilane or mixture of organosilanes, a solvent, optionally an acid catalyst, and optionally a low molecular weight polymer.
Owner:DAVE BAKUL CHAMPAKLAL
Laser ignition apparatus
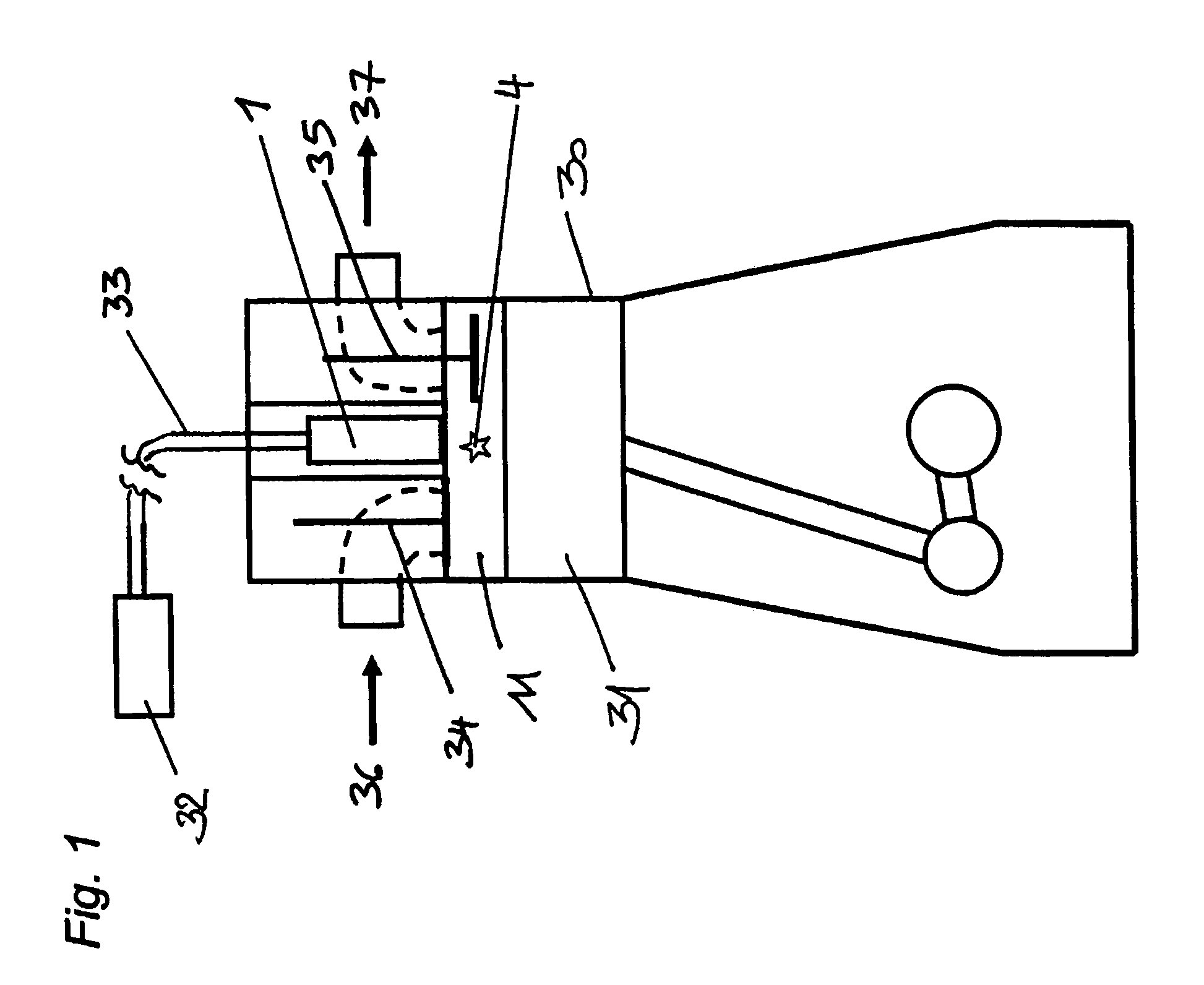
InactiveUS7806094B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce depositionLaser detailsIncandescent ignitionCombustion chamberInlet valve
An apparatus is provided for the ignition of a fuel / air mixture in the combustion chamber of a combustion machine, wherein the combustion chamber has at least one inlet valve and at least one outlet valve. There are further provided a laser light generating device for giving off laser light and a combustion chamber window for coupling the laser light into a combustion chamber of the combustion machine. There is provided at least one fluid feed means which is separate from the inlet valve or valves and with which a fluid can be caused to flow at least on to regions of the surface of the combustion chamber window or between the combustion chamber window and the focal point of the laser light.
Owner:GE JENBACHER
Fabrication Method of GaN Power LEDs with Electrodes Formed by Composite Optical Coatings
ActiveUS20090029495A1High densityPrevent leakageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOptical coatingEvaporation
Fabrication method of GaN power LED with electrodes formed by composite optical coatings, comprising epitaxially growing N—GaN, active, and P—GaN layers successively on a substrate; depositing a mask layer thereon; coating the mask layer with photoresist; etching the mask layer into an N—GaN electrode pattern; etching through that electrode pattern to form an N—GaN electrode region; removing the mask layer and cleaning; forming a transparent, electrically conductive film simultaneously on the P—GaN and N—GaN layers; forming P—GaN and N—GaN transparent, electrically conductive electrodes by lift-off; forming bonding pad pattern for the P—GaN and N—GaN electrodes by photolithography process; simultaneously forming thereon bonding pad regions for the P—GaN and N—GaN electrodes by stepped electron beam evaporation; forming an antireflection film pattern by photolithography process; forming an antireflection film; thinning and polishing the backside of the substrate, then forming a reflector thereon; and completing the process after scribing, packaging and testing.
Owner:INST OF SEMICONDUCTORS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
(Al,Ga,In)N and ZnO direct wafer bonded structure for optoelectronic applications, and its fabrication method
InactiveUS7719020B2Reduce light absorptionLight evenlyIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensWaferingNitrogen
An (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO direct wafer bonded light emitting diode (LED), wherein light passes through electrically conductive ZnO. Flat and clean surfaces are prepared for both the (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO wafers. A wafer bonding process is then performed between the (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO wafers, wherein the (Al, Ga, In)N and ZnO wafers are joined together and then wafer bonded in a nitrogen ambient under uniaxial pressure at a set temperature for a set duration. After the wafer bonding process, ZnO is shaped for increasing light extraction from inside of LED.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP
Wire gating polaroid, manufacturing method of wire gating polaroid, display panel and display device
InactiveCN104459863AControl shotAvoid peripheral light leakageSolid-state devicesPolarising elementsContinuous lightDisplay device
The invention belongs to the display technical field, and particularly relates to a wire gating polaroid, a manufacturing method of the wire gating polaroid, a display panel and a display device. The wire gating polaroid comprises a substrate, wire gating structures which are arranged in an array mode are arranged in the substrate at intervals, and due to the wire gating structures, light can penetrate from the gating distances. A continuous light-proof structure is arranged in the other area, except the wire gating structures, of the substrate. The wire gating polaroid is provided with the wire gating structures which are arranged at intervals in the array mode, hence, a local light transmitting area can be formed, and light emergence can be controlled more flexibly. By means of the display panel using the wire gating polaroid, the light absorption rate can be effectively lowered, peripheral light leakage in a non-subpixel area can further be avoided, and the pixel light leakage can be prevented; correspondingly, due to the display device using the display panel, the light utilization rate is improved, and a good display effect is achieved.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
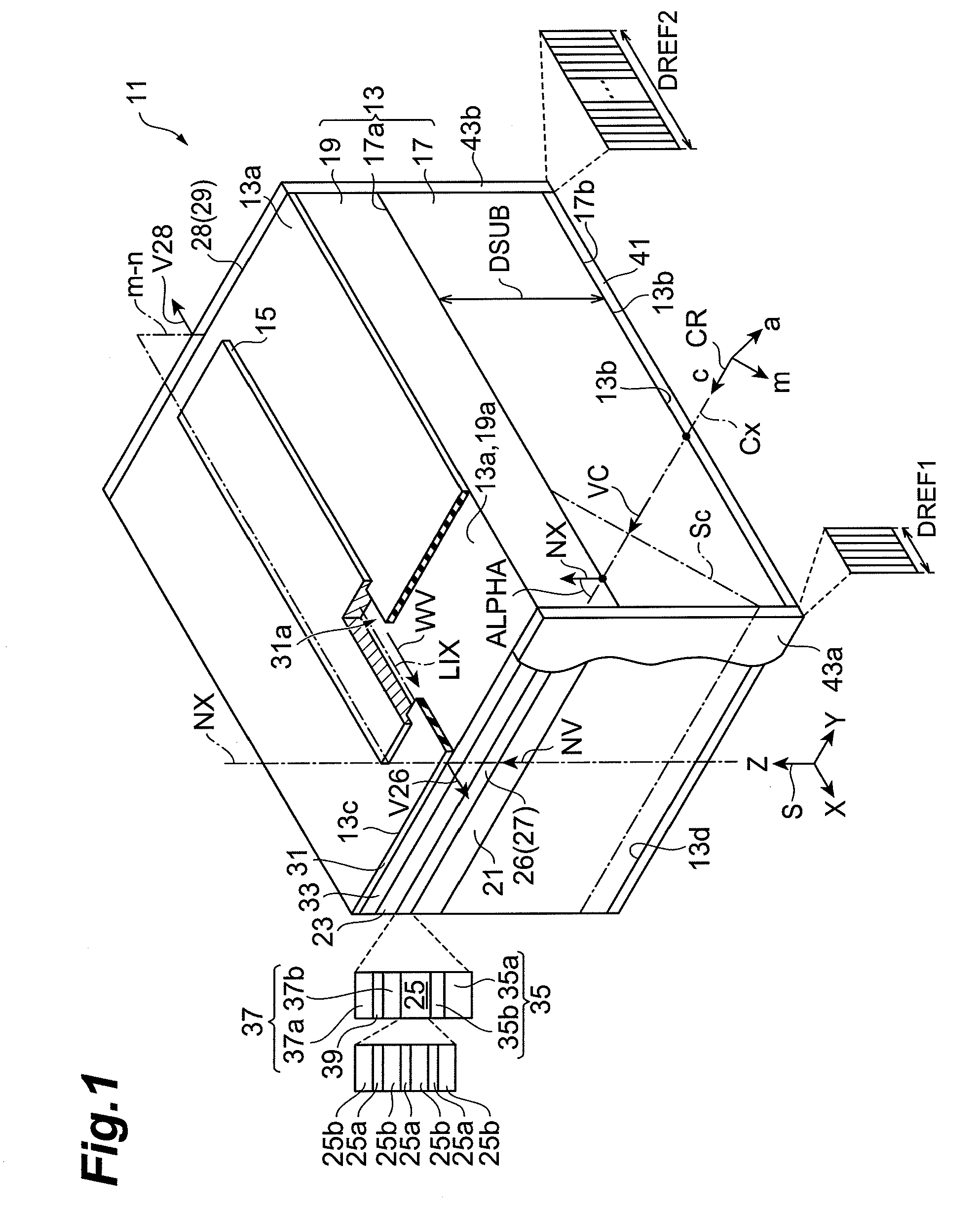
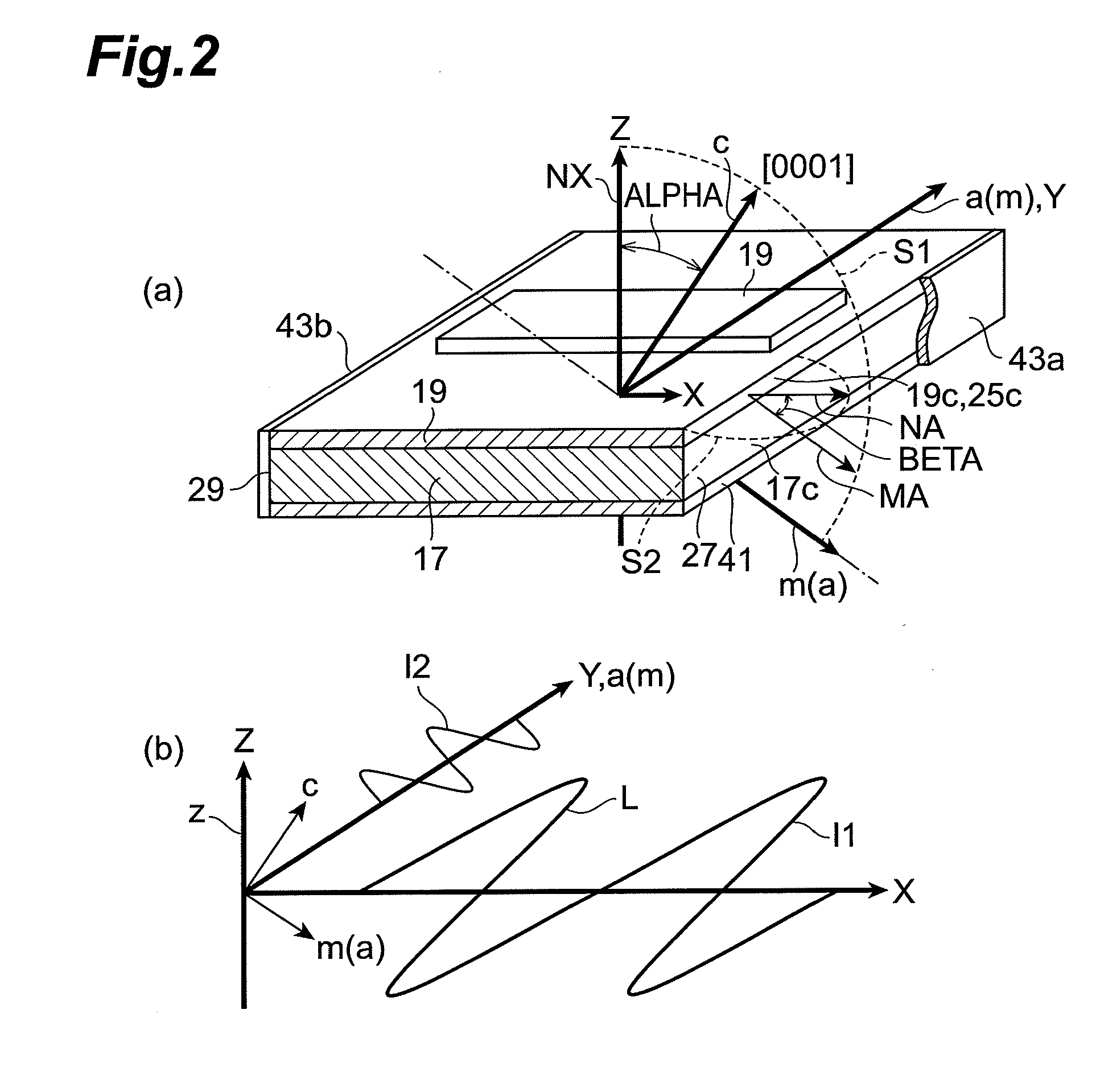
Iii-intride semiconductor laser device, and method of fabricating the iii-nitride semiconductor laser device
InactiveUS20110075695A1Reduce light absorptionImprovement in COD levelLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionDielectricOptical cavity
In a III-nitride semiconductor laser device, a laser structure includes a support base with a semipolar primary surface comprised of a III-nitride semiconductor, and a semiconductor region provided on the semipolar primary surface of the support base. First and second dielectric multilayer films for an optical cavity of the nitride semiconductor laser device are provided on first and second end faces of the semiconductor region, respectively. The semiconductor region includes a first cladding layer of a first conductivity type gallium nitride-based semiconductor, a second cladding layer of a second conductivity type gallium nitride-based semiconductor, and an active layer provided between the first cladding layer and the second cladding layer. The first cladding layer, the second cladding layer, and the active layer are arranged in an axis normal to the semipolar primary surface. A c+ axis vector indicating a direction of the <0001> axis of the III-nitride semiconductor of the support base is inclined at an angle in the range of not less than 45 degrees and not more than 80 degrees or in the range of not less than 100 degrees and not more than 135 degrees toward a direction of any one crystal axis of the m- and a-axes of the III-nitride semiconductor with respect to a normal vector indicating a direction of the normal axis. The first and second end faces intersect with a reference plane defined by the normal axis and the one crystal axis of the hexagonal III-nitride semiconductor. The c+ axis vector makes an acute angle with a waveguide vector indicating a direction from the second end face to the first end face. A thickness of the first dielectric multilayer film is smaller than a thickness of the second dielectric multilayer film.
Owner:SUMITOMO ELECTRIC IND LTD
Method for producing a glass ceramic with a predefined transmittance
A method of manufacturing glass ceramic articles such as glass ceramic plates for cooktops or fireplace windows is provided. The method facilitates the adjustment of a specific hue or a specific absorptivity of the glass ceramic in the visible spectral range. The method is based on the finding that the absorption of light by coloring agents which are appropriate for or present in glass ceramics can be attenuated during the ceramization process by adding substances that have a decoloring effect.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Spread illuminating apparatus
ActiveUS20110103091A1Improve brightness uniformityReduce light absorptionPlanar/plate-like light guidesReflectorsLight guideFlexible electronics
There is provided a spread illuminating apparatus including an LED, a light guide plate and a flexible printed circuit board on which the LED is mounted, wherein the light guide plate includes: a light entrance end surface at which the light source is disposed; a light emitting portion from which light emitted from the light source and introduced into the light guide plate exits out in a spread manner; a slope portion which is disposed between the light entrance end surface and the light emitting portion and which has a thickness decreasing toward the light emitting portion; and a seat block disposed at the slope portion and configured to fixedly receive the flexible printed circuit board. In the spread illuminating apparatus, the length of the slope portion is substantially 1.78 times as large as the largest thickness of the slope portion.
Owner:MINEBEAMITSUMI INC
P-Type Semiconductor Material and Semiconductor Device
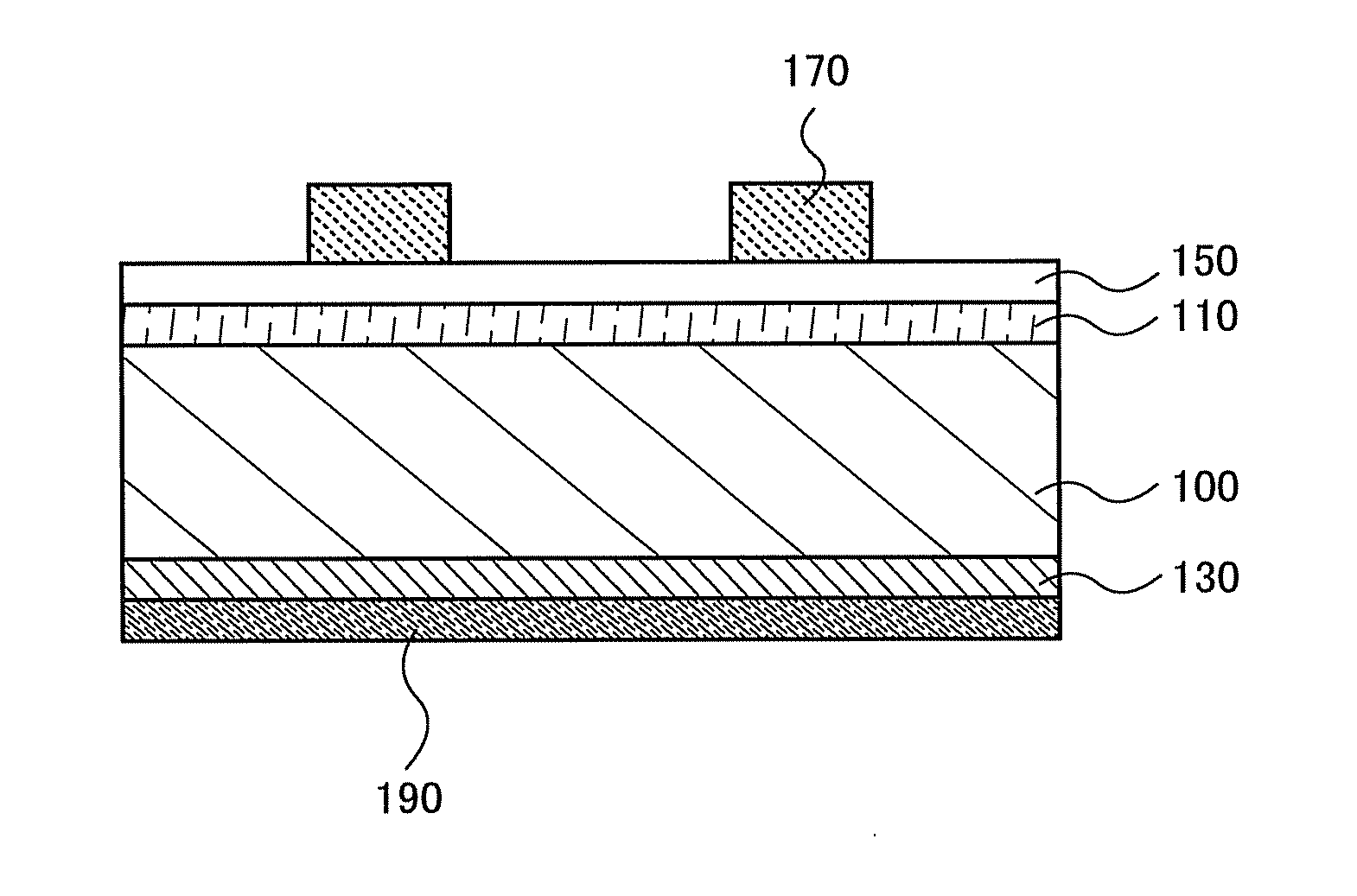
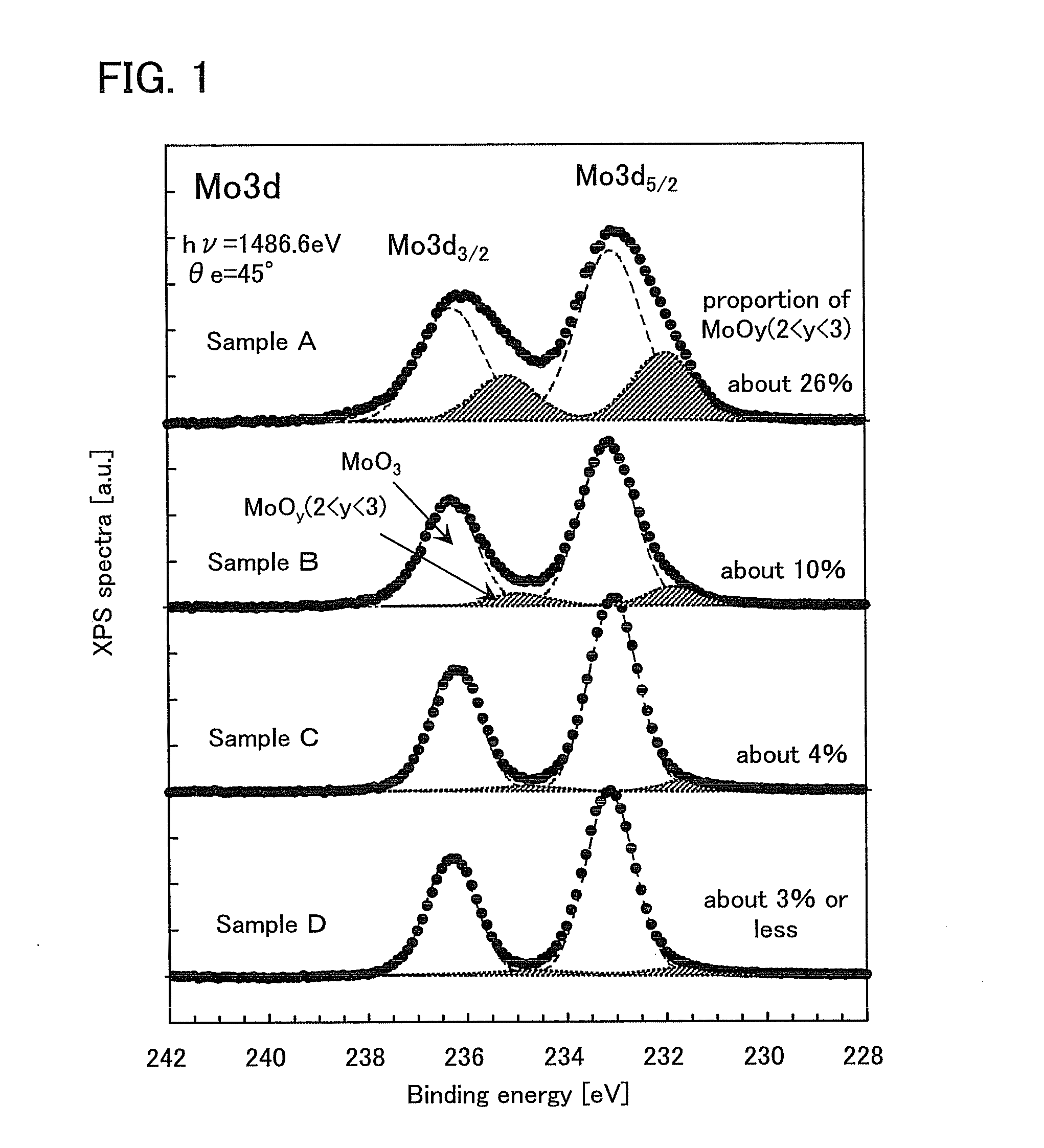
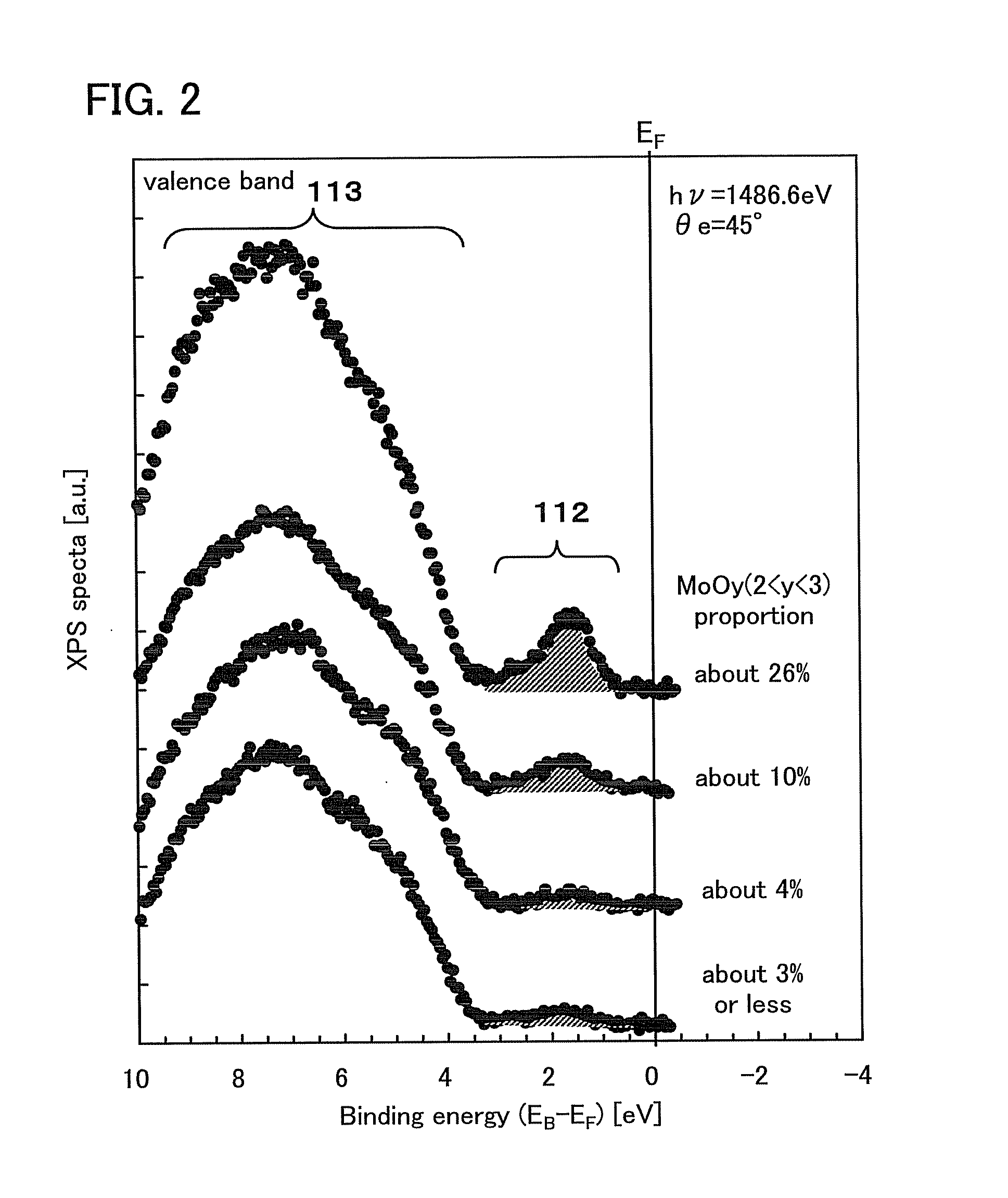
InactiveUS20130214271A1Reduce light absorption lossFavorable carrier extractionPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsIntermediate composition
An oxide semiconductor material having p-type conductivity and a semiconductor device using the oxide semiconductor material are provided. The oxide semiconductor material having p-type conductivity can be provided using a molybdenum oxide material containing molybdenum oxide (MoOy (2<y<3)) having an intermediate composition between molybdenum dioxide and molybdenum trioxide. For example, a semiconductor device is formed using a molybdenum oxide material containing molybdenum trioxide (MoO3) as its main component and MoOy (2<y<3) at 4% or more.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
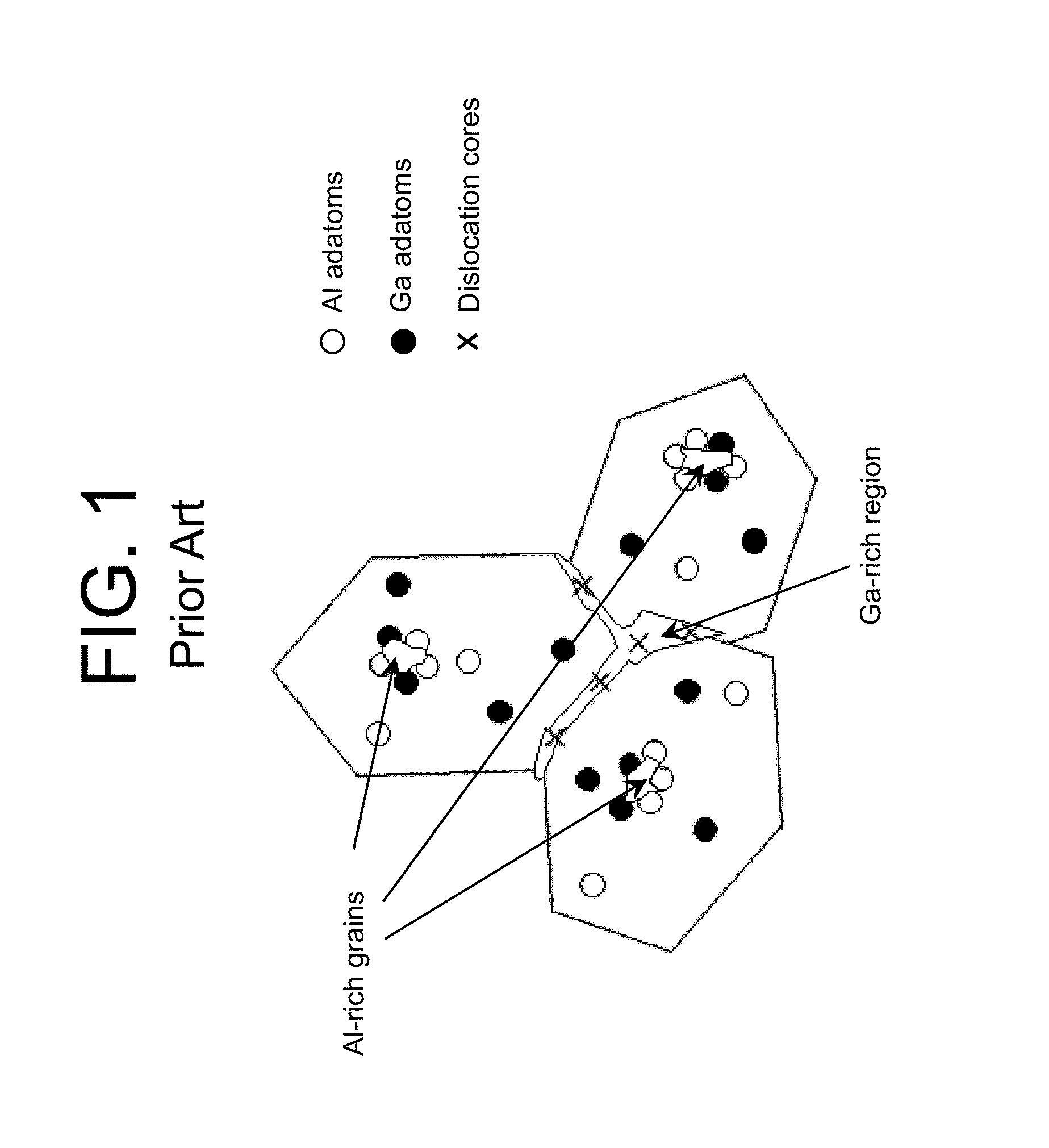
Emitting Device with Compositional and Doping Inhomogeneities in Semiconductor Layers
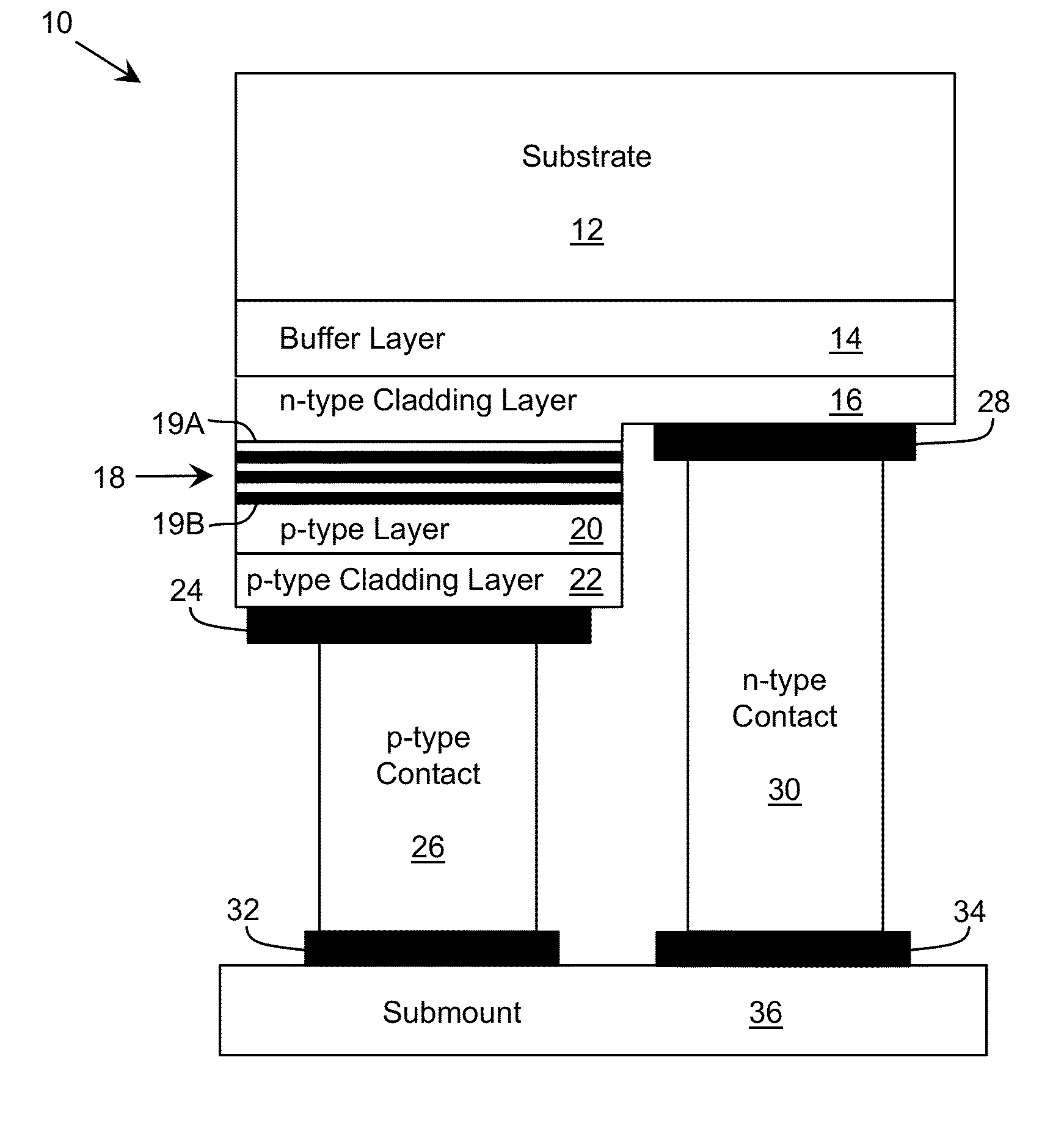
ActiveUS20140064314A1Improvement factorReduce light absorptionLaser detailsLaser active region structureLateral regionVoltage drop
A device including one or more layers with lateral regions configured to facilitate the transmission of radiation through the layer and lateral regions configured to facilitate current flow through the layer is provided. The layer can comprise a short period superlattice, which includes barriers alternating with wells. In this case, the barriers can include both transparent regions, which are configured to reduce an amount of radiation that is absorbed in the layer, and higher conductive regions, which are configured to keep the voltage drop across the layer within a desired range.
Owner:SENSOR ELECTRONICS TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com