Semiconductor laser light output stabilizing circuit and light transmitting module
A technology for stabilizing circuits and lasers, used in semiconductor lasers, lasers, laser parts, etc., and can solve the problems of reduced receiving sensitivity, increased extinction ratio, and deterioration of dispersion compensation characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
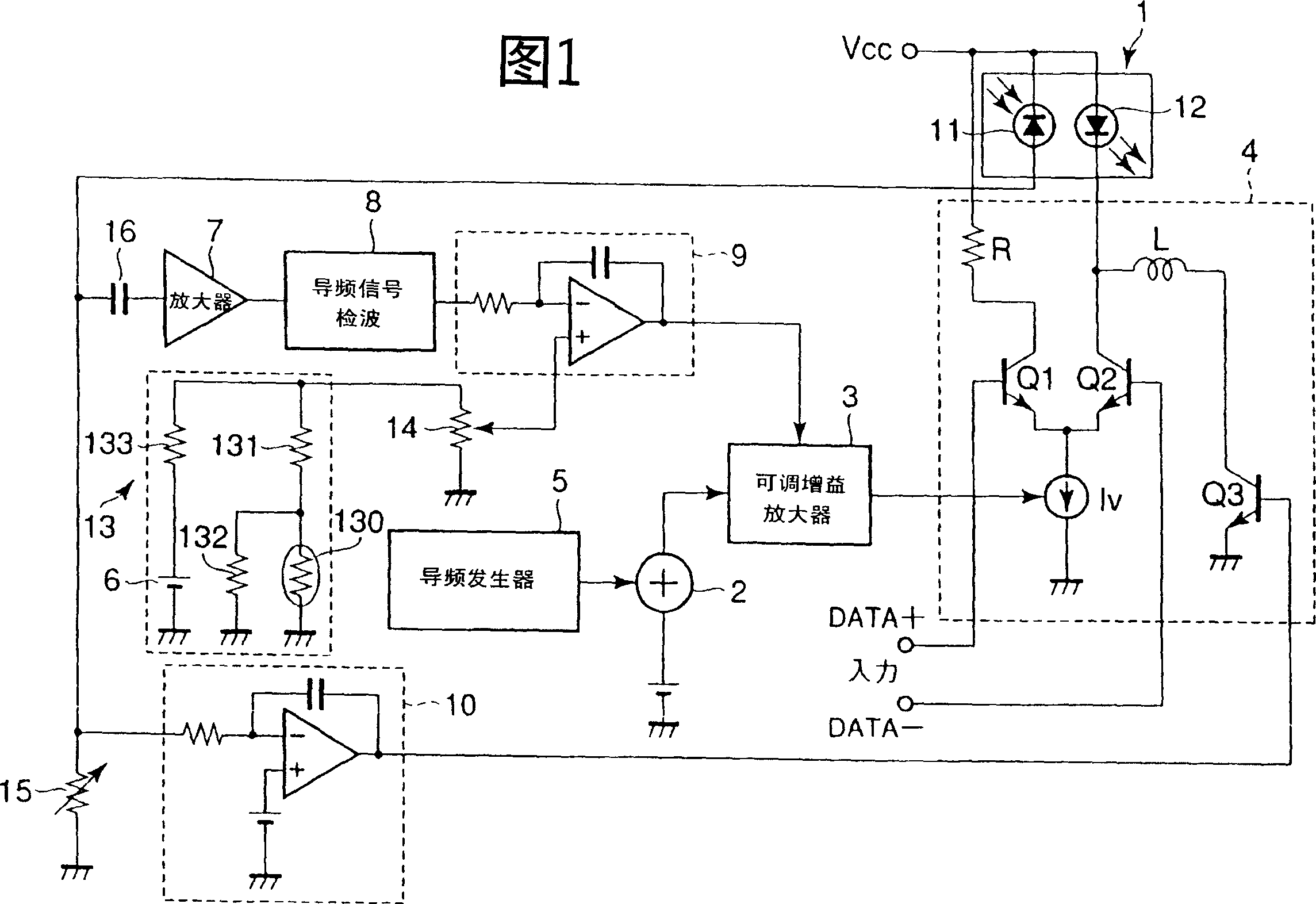
[0059] FIG. 1 is an explanatory diagram showing the configuration of an optical transmission module employing an optical output stabilization circuit according to a first embodiment of the present invention.
[0060] The optical transmission module shown in Figure 1, compared with the optical transmission module shown in Figure 6, is different in that the standard voltage of the first error amplifier 9 is temperature compensated (the higher the temperature, the lower the standard voltage) The temperature compensation circuit 13 reduces the variation of the extinction ratio of the laser output light during high temperature operation, and the others are the same, so the same symbols as those in FIG. 6 are marked.
[0061] In this module, a semiconductor laser module 1 incorporates an LD 12 and a monitoring photoelectric element (for example, a photodiode PD) 11 for detecting the optical output power of the LD 12 .
[0062] In the above optical output stabilization circuit, 2 is ...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
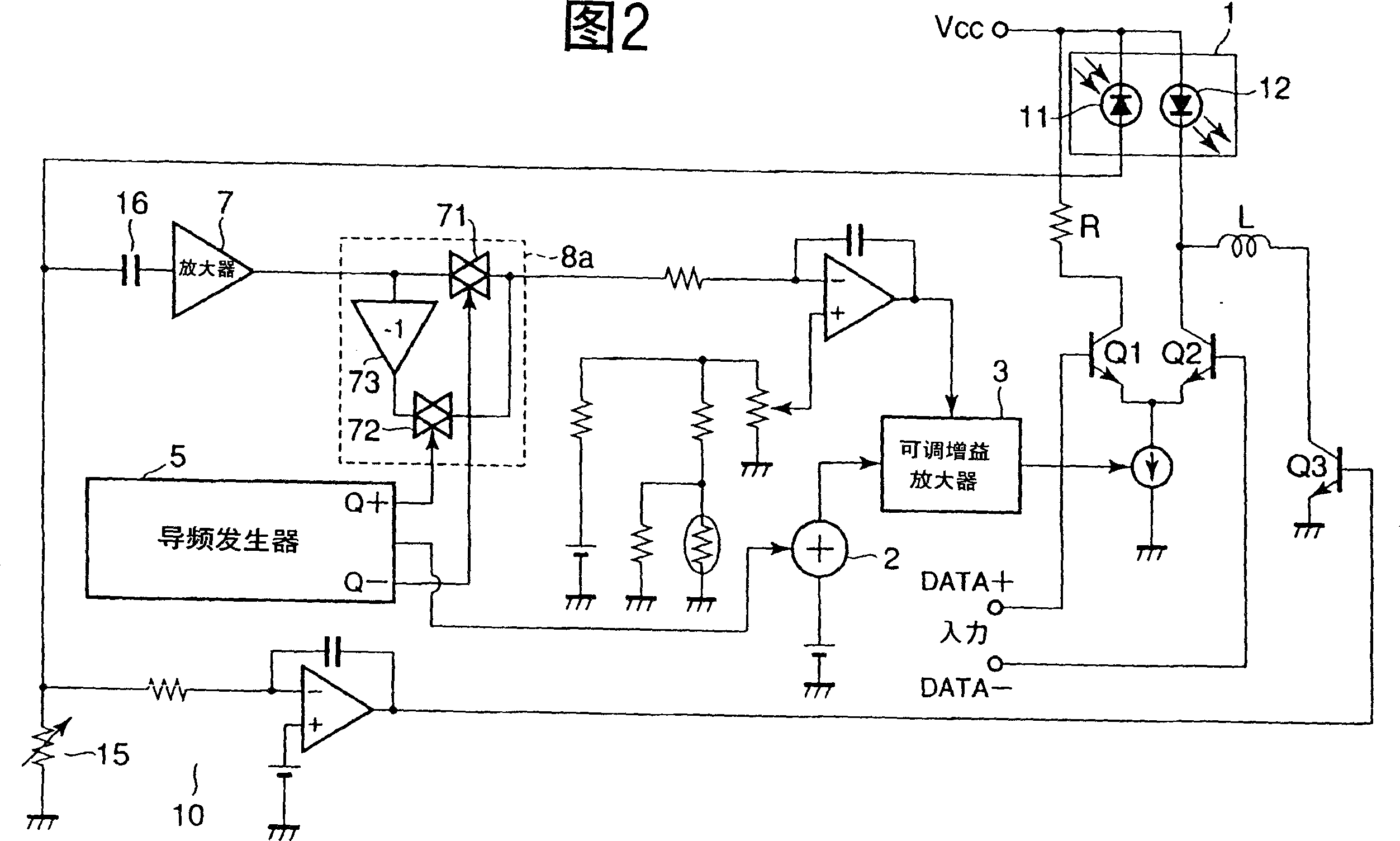
[0080] FIG. 2 is an explanatory diagram showing the configuration of an optical transmission module employing an optical output stabilization circuit according to a second embodiment of the present invention.
[0081] Compared with the optical transmission module shown in FIG. 1 , the optical transmission module shown in FIG. 2 is different in that a synchronous pilot signal detection circuit 8 a is used as the pilot signal detector 8 , and the others are the same.
[0082] The above-mentioned synchronous pilot signal detection circuit 8a can be realized with a simple structure by using a full-wave rectifier, including: using a clock signal synchronized with the pilot signal supplied by the pilot signal generator 5 to perform complementary ON / OFF operation A pair of analog switches 71, 72, and an inverting amplifier 73 for inverting one input of the analog switches 71, 72.
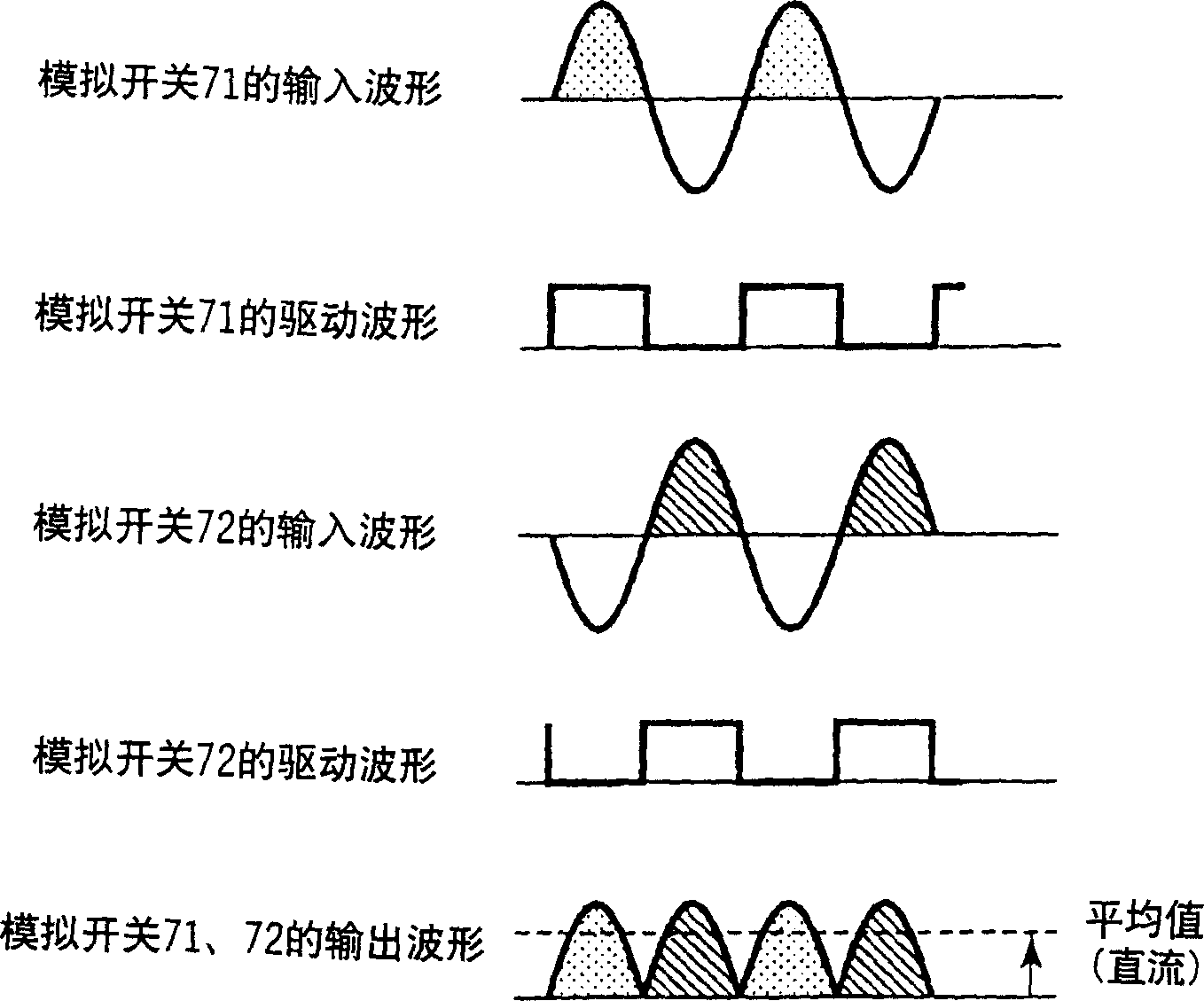
[0083] image 3 Operation waveforms of the synchronous pilot signal detection circuit in FIG. 2 are sh...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0087] In the third embodiment, a modified example of the control device for the laser driving pulse current of the pilot signal of the optical output stabilization circuit in the above-mentioned first and second embodiments will be described.
[0088] FIG. 4 shows the configuration of an optical transmission module using an optical output stabilization circuit according to a third embodiment of the present invention.
[0089] Compared with the optical transmission module shown in FIG. 1, the optical transmission module shown in FIG. 4 replaces the combination of the analog addition circuit 2 and the adjustable gain amplifier 3, and adopts such a laser driving pulse current control circuit 80, that is, It includes: inputting the output signal of the first error amplifier 9, an analog switch 81 for on / off operation by using a clock signal synchronized with the pilot signal supplied from the above-mentioned pilot signal generator 5, and inputting the output of the analog switch 8...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com