Patents
Literature
295 results about "Lens effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
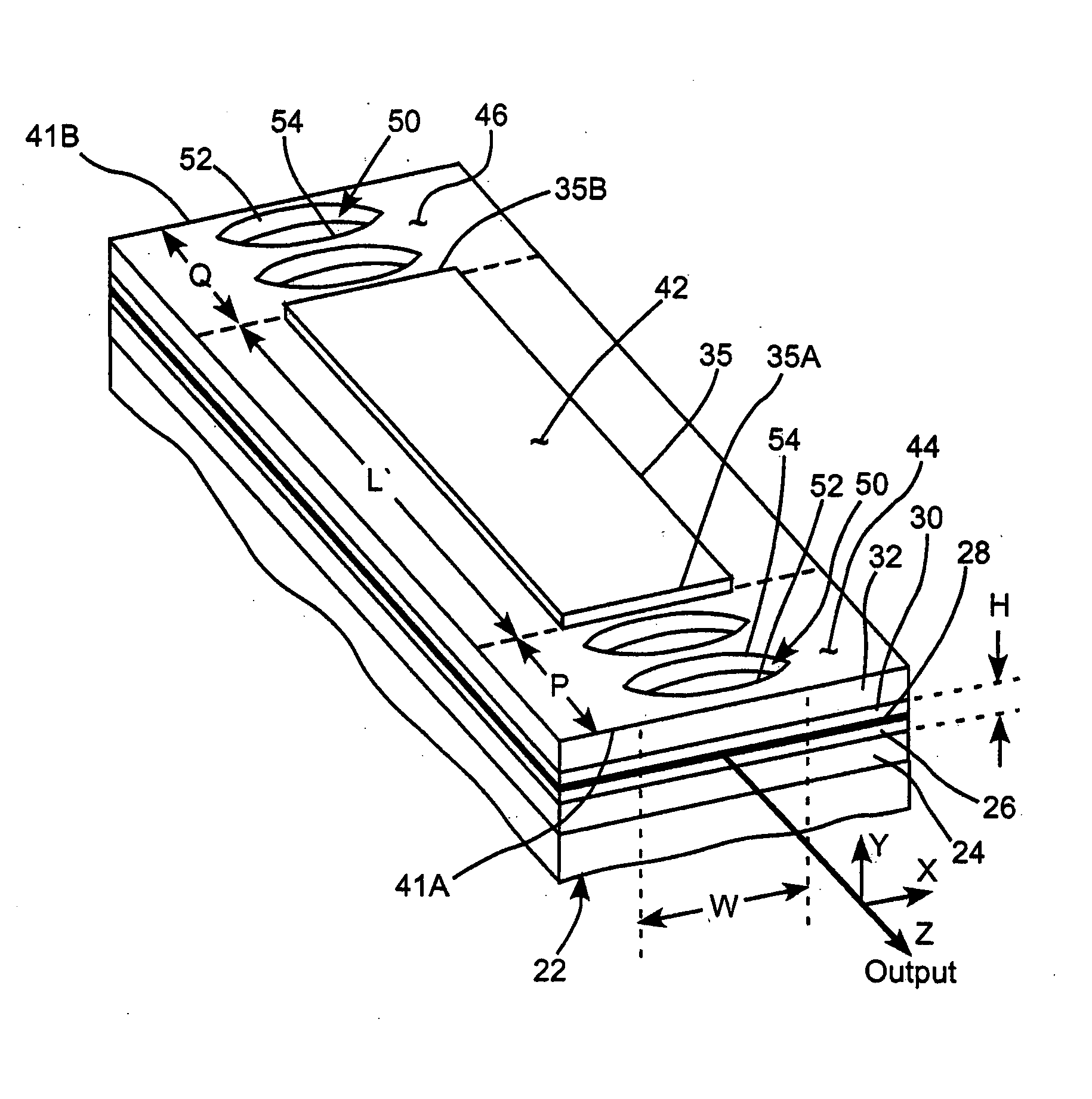
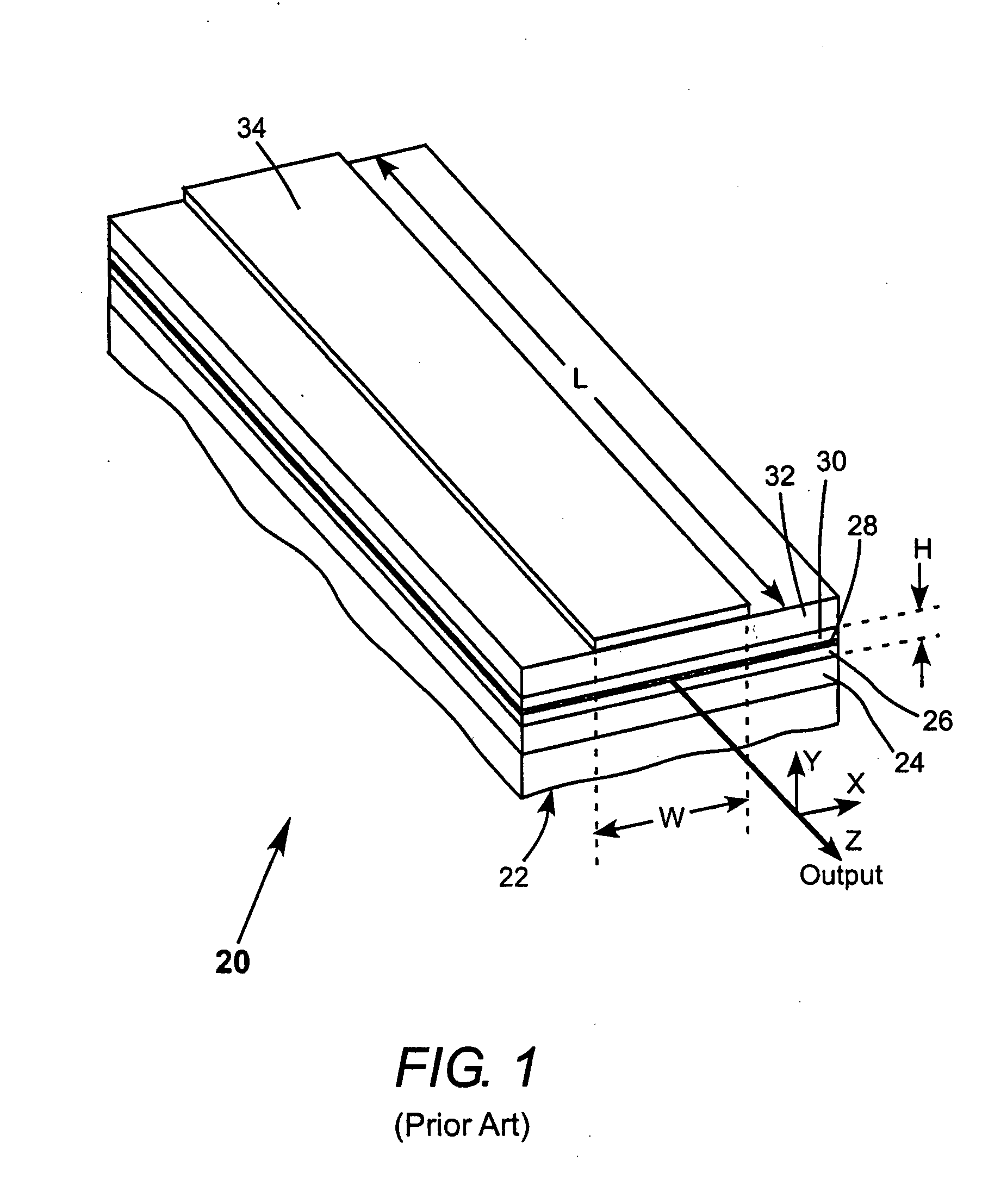
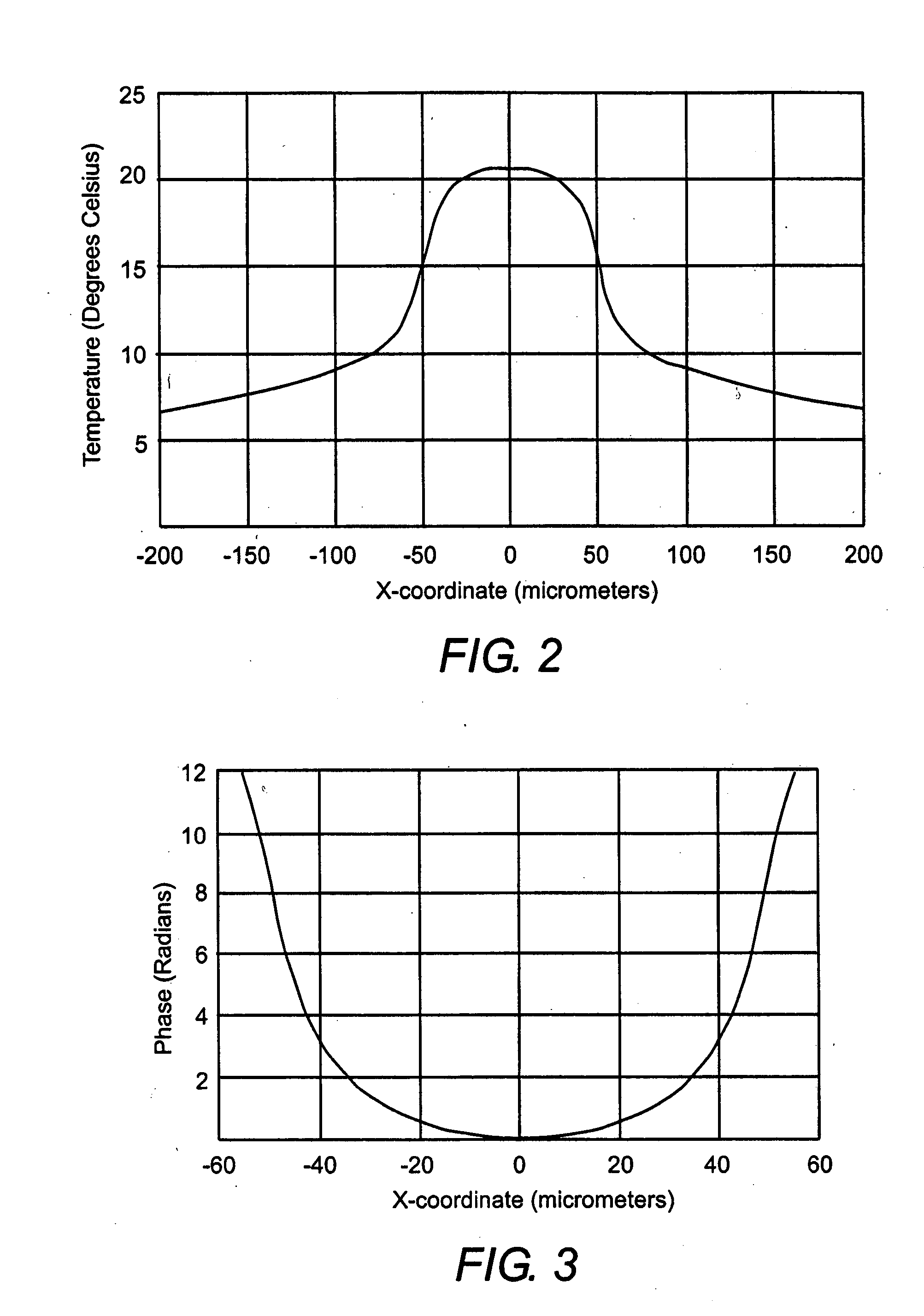
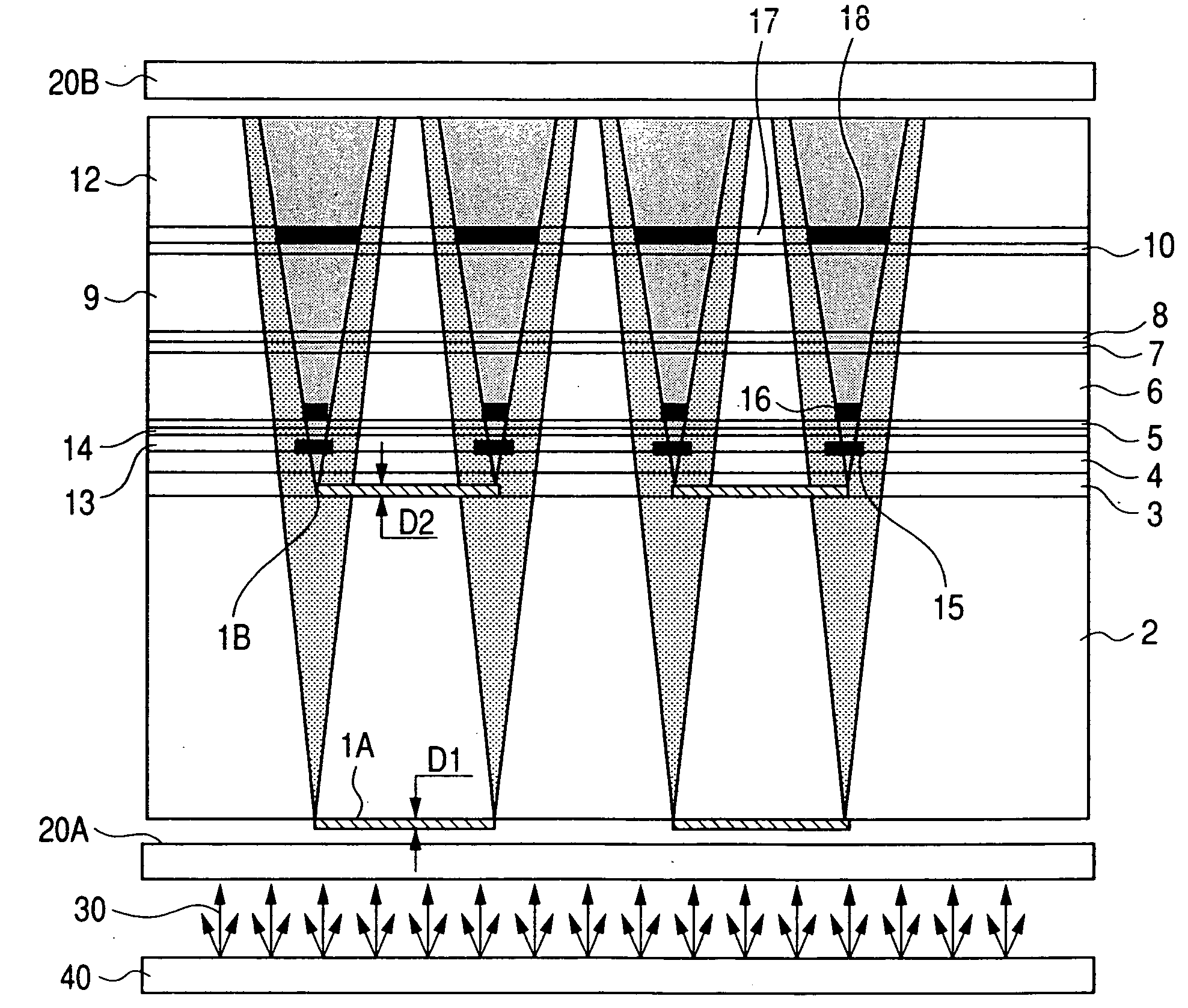
Lens Effects is a render effect plug-in that simulates real-world camera lens effects such as bloom and glare. The Lens Effects plug-in uses a fast multi-threaded technique to compute the result.
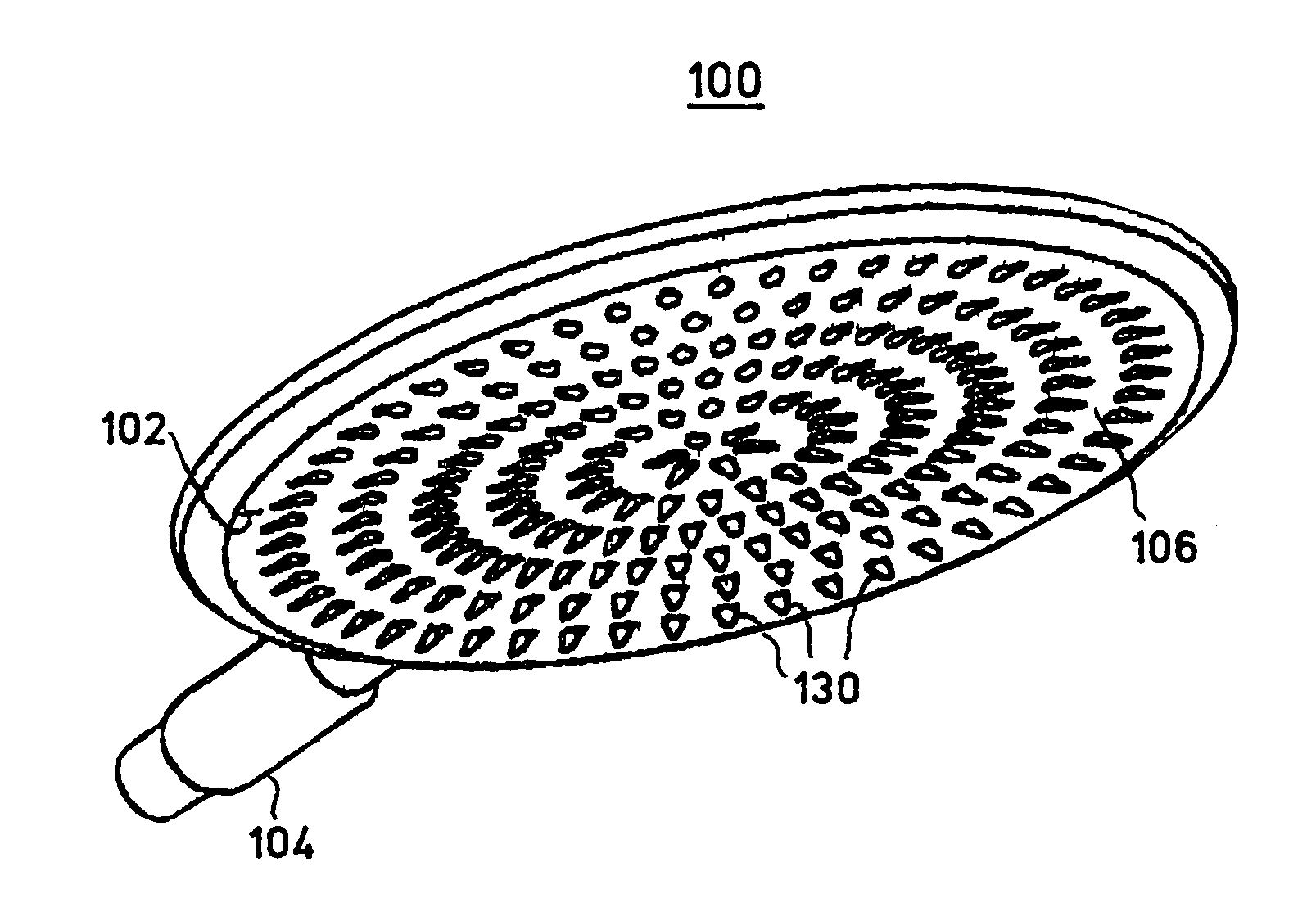
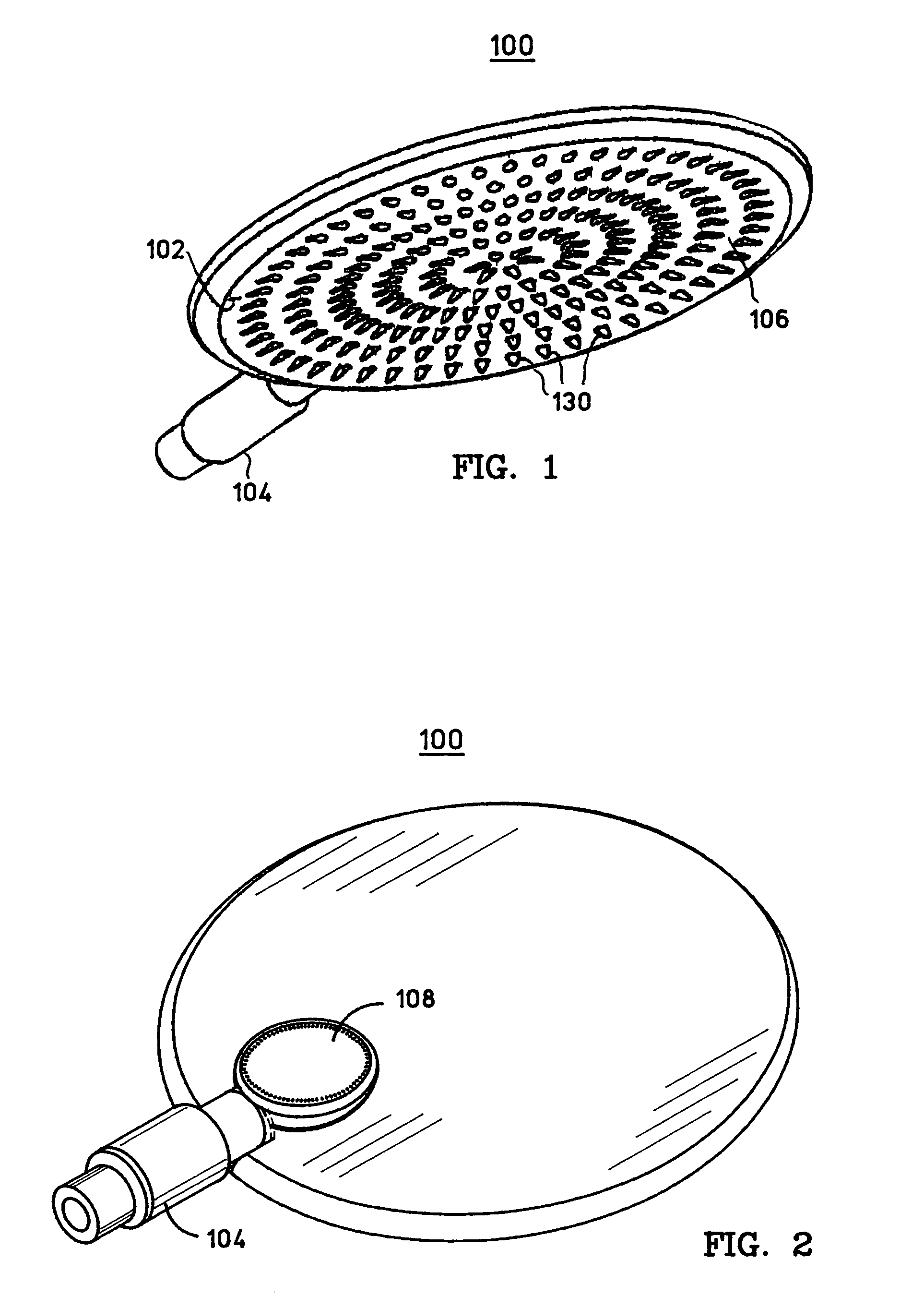
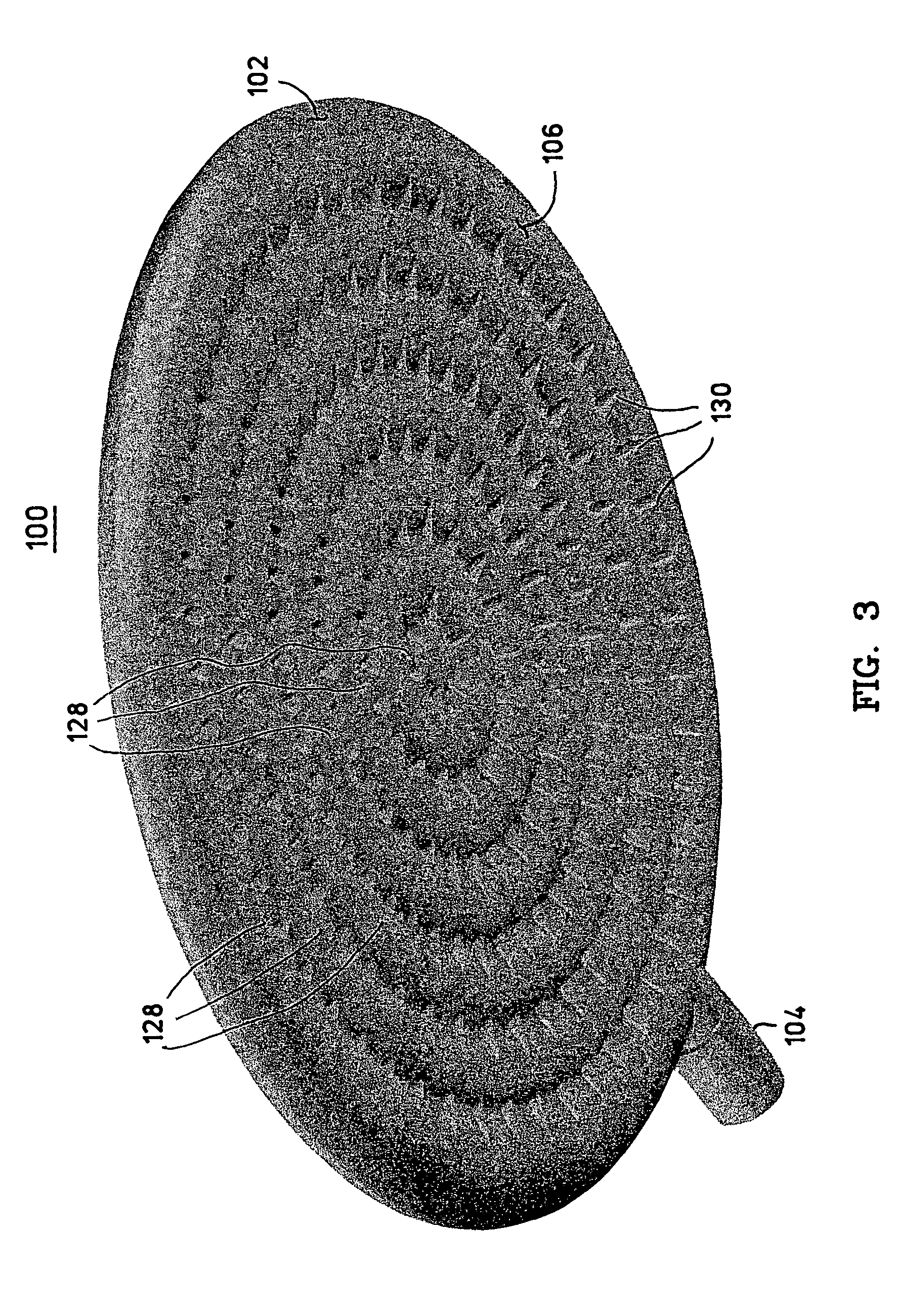
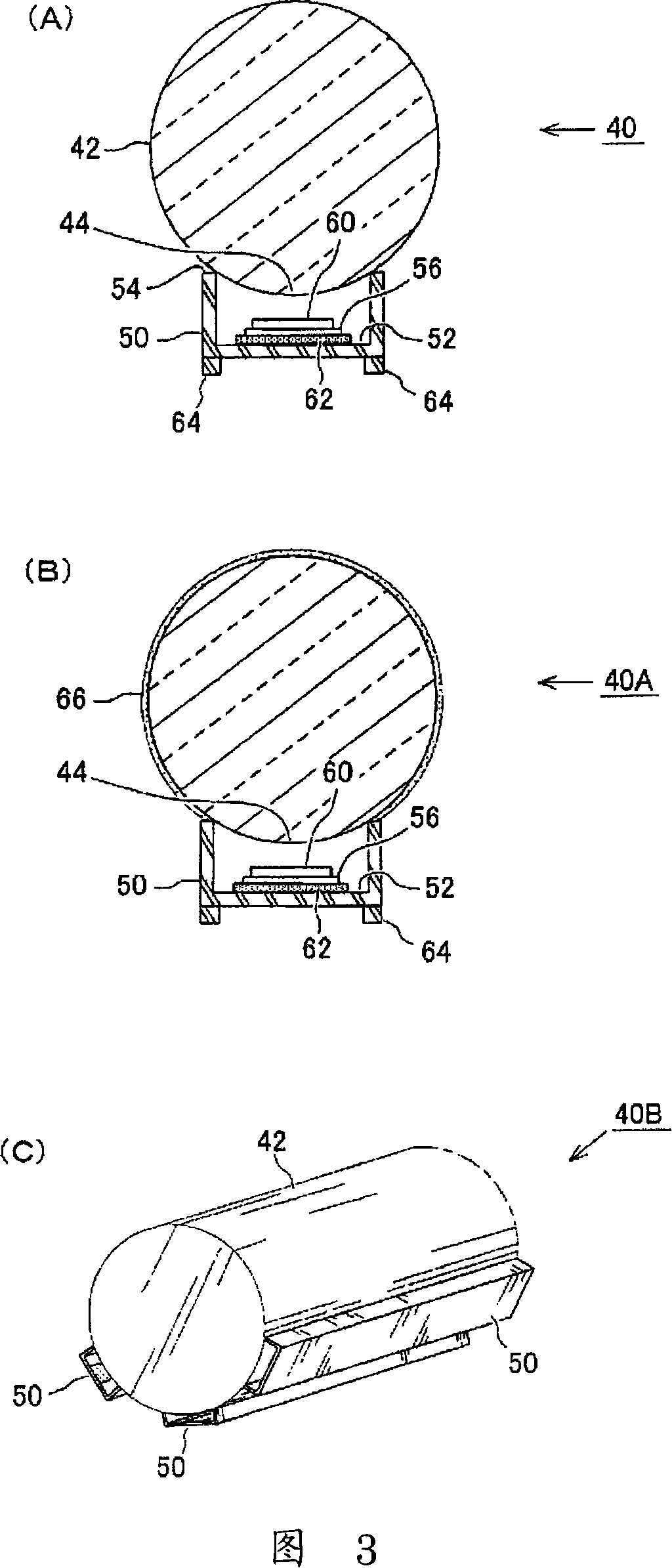
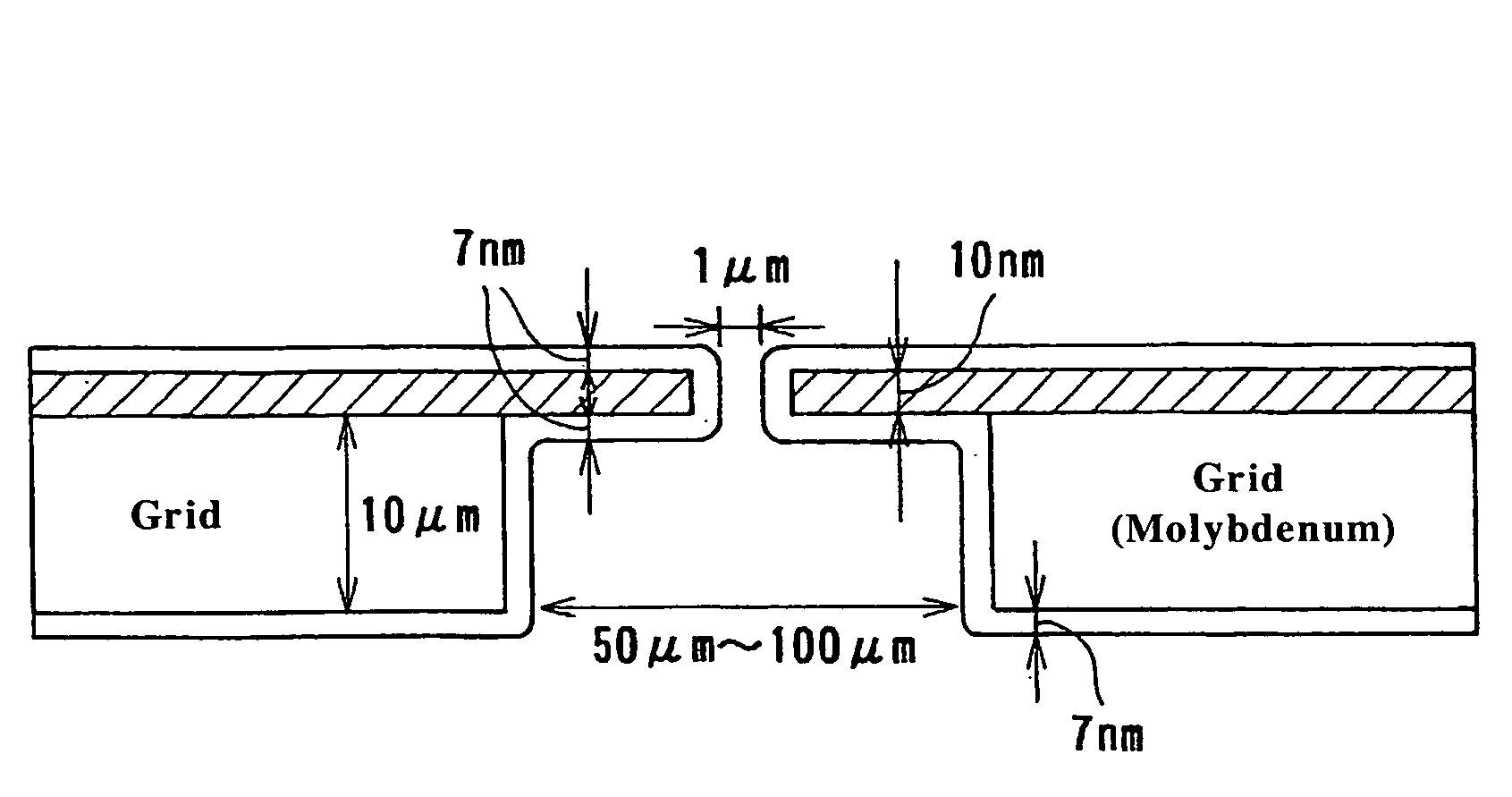
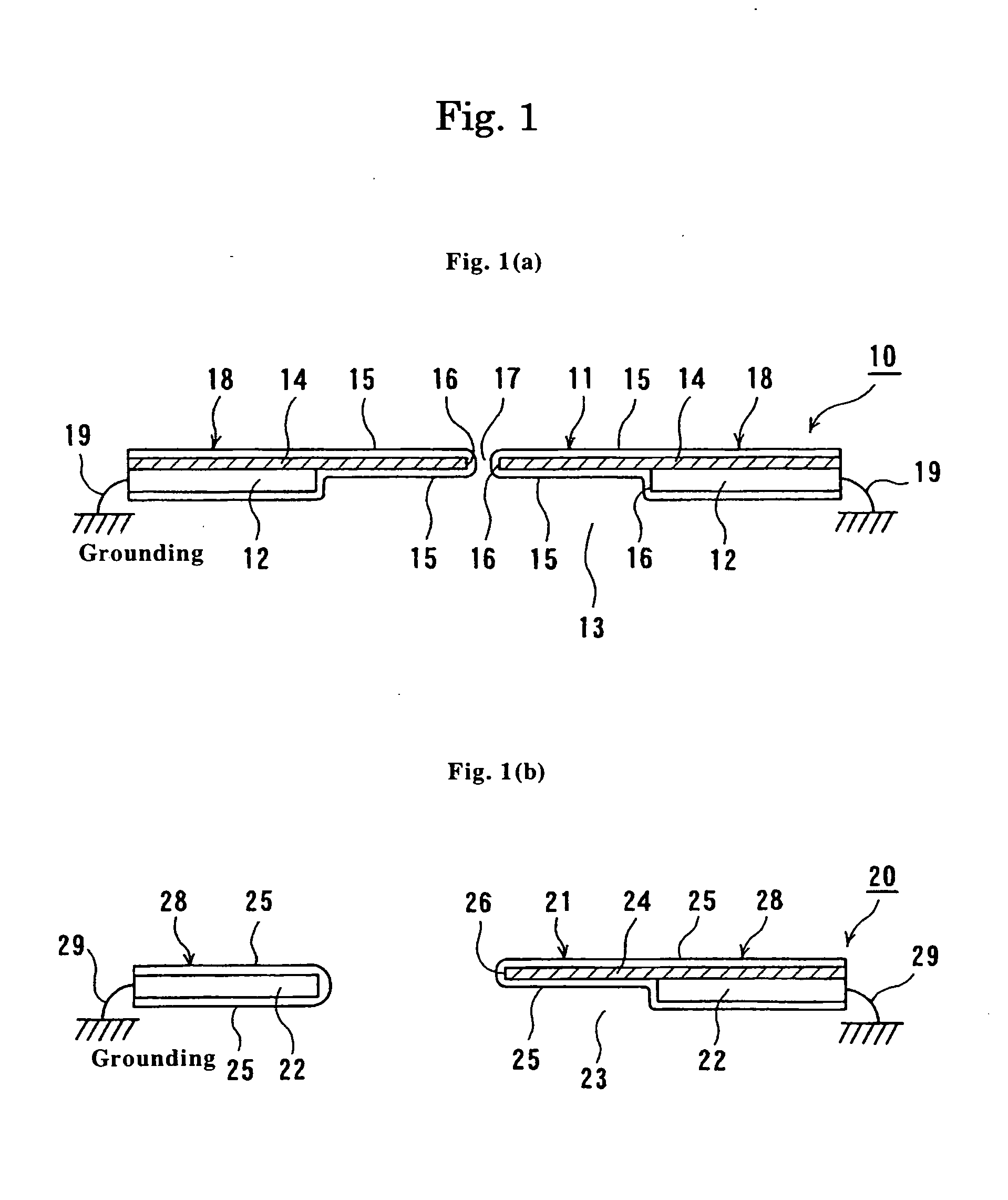
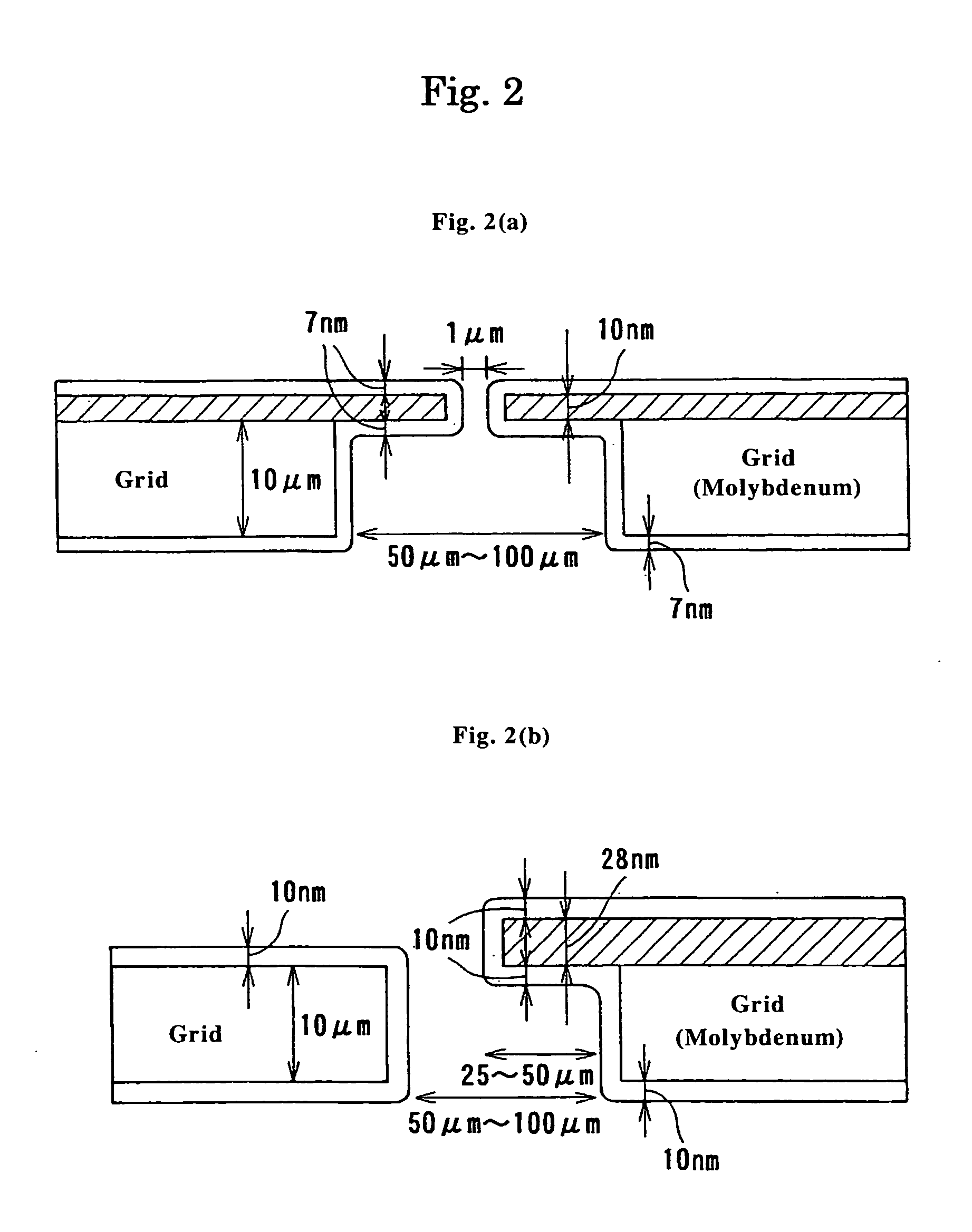
Showerhead with grooved water release ducts
InactiveUS7048210B2Efficient and effective shower of waterConserve waterDust removalFire preventionEngineeringLens effect
A showerhead as described herein includes a translucent hollow body having a fluid chamber, and a fluid distribution element configured to release fluid contained in the fluid chamber. The fluid distribution element includes a plurality of raised concentric rings having peaks that serve as the fluid release points. The fluid distribution element contains a number of fluid ducts that are specifically shaped to transport the fluid from the fluid chamber toward the fluid release points. The translucent nature of the showerhead creates an optical lens effect that illuminates the showerhead and the water droplets formed by the showerhead. The illumination of the water droplets creates a pleasant showering experience for the user.
Owner:CLARK
Lens array device and image display
InactiveUS20100157181A1Not easy to degradeImprove powerStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsCamera lensElectricity
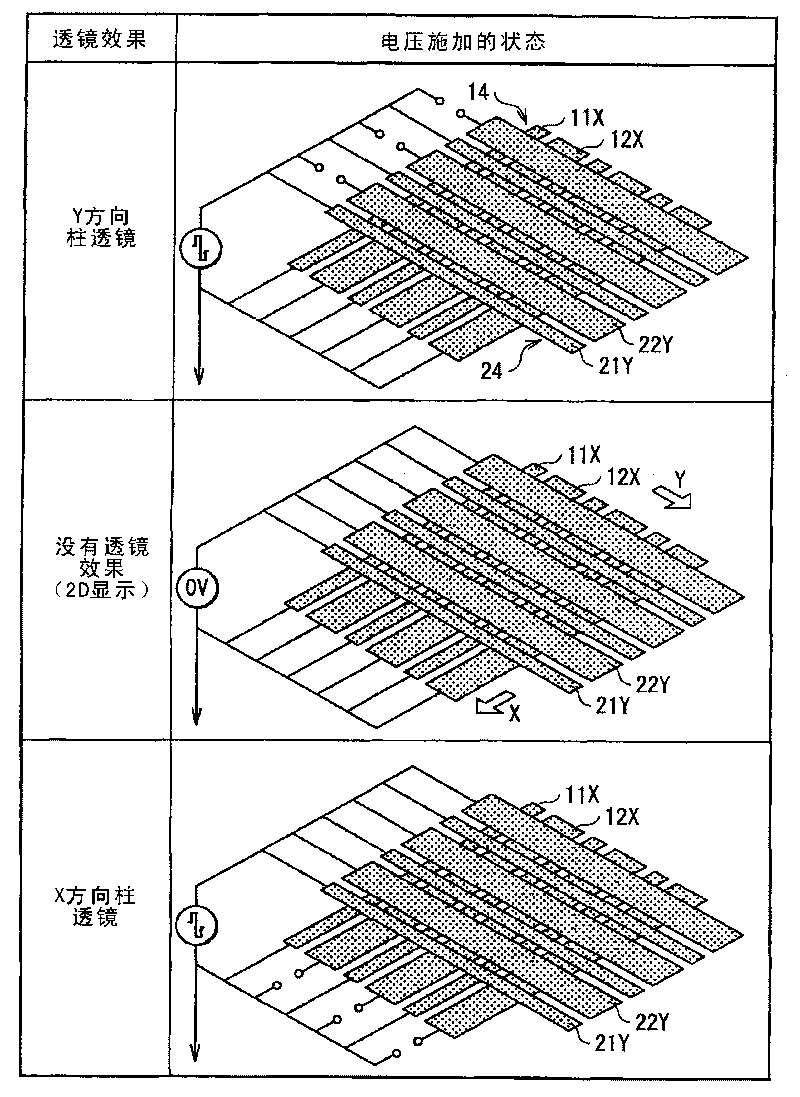
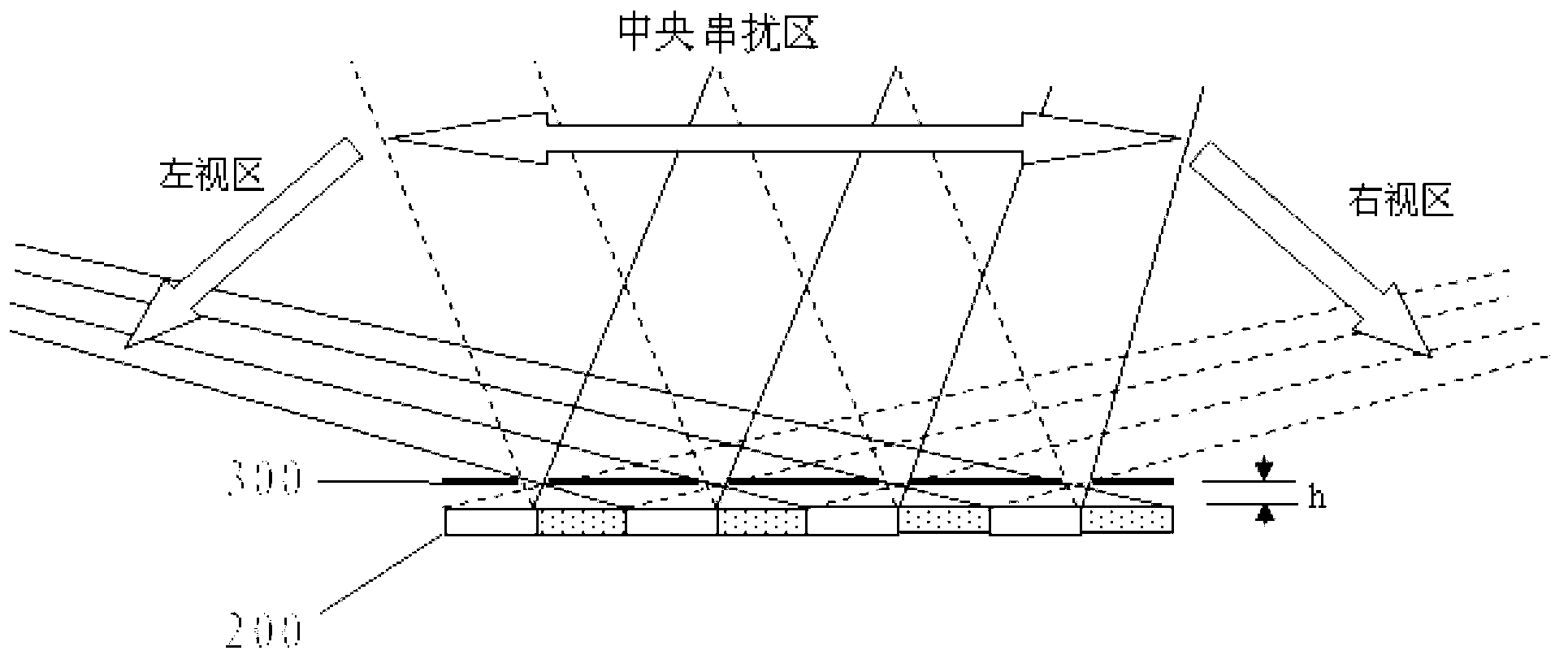
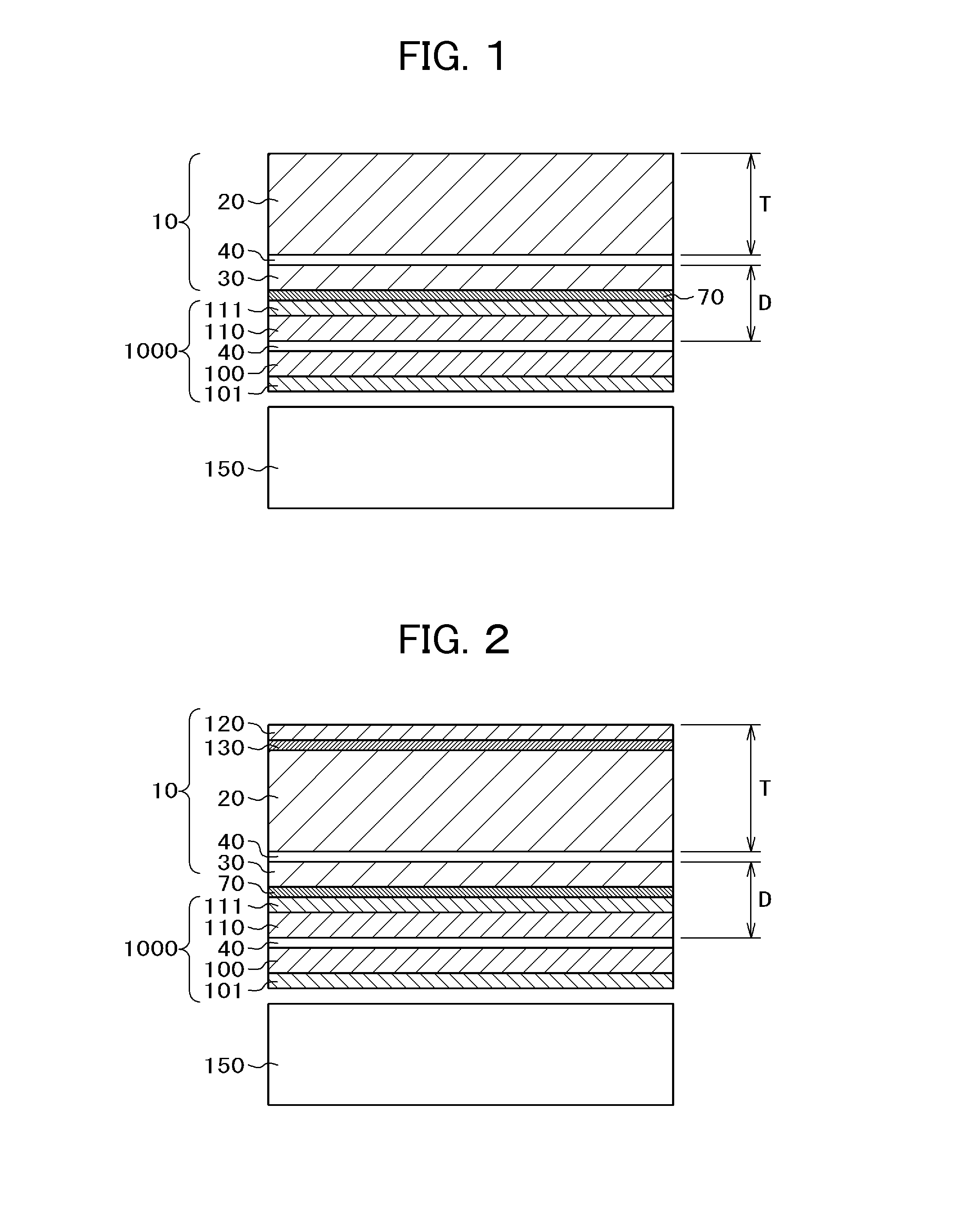
The lens array device includes: first and second substrates; a first electrode group formed on the first substrate to include transparent electrodes extending in a first direction; a second electrode group formed on the second substrate to include transparent electrodes extending in a second direction; and a liquid crystal layer with refractive index anisotropy arranged between the first and second substrates to produce a lens effect by changing the liquid crystal molecule alignment. The liquid crystal layer electrically changes into one of three states according to voltages applied to the first and second electrode groups. The three states include a state with no lens effect, a first lens state where a lens effect of a first cylindrical lens extending in the first direction is produced, and a second lens state where a lens effect of a second cylindrical lens extending in the second direction is produced.
Owner:SONY CORP
Stereoscopic display
InactiveUS20100259697A1Good stereo visionReduce brightness unevennessSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsComputer scienceLens effect
A stereoscopic display includes: a display panel configured to display an image in either one of two or more arrangement states including a first arrangement state and a second arrangement state which are switchable with each other; and a lens array device arranged to face a display surface of the display panel. The lens array device produces a lens effect in a direction, the direction of effect being changed between in the first arrangement state and in the second arrangement state. The display panel includes an array of a plurality of sub-pixels, and a combination of sub-pixels used as a unit pixel is changed between in the first arrangement state and in the second arrangement state.
Owner:SONY CORP
Adaptive phase contrast microscope
InactiveUS20120257040A1Region can be greatEnhance the imageColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsMicro platePhase image
An optical microscope is provided with an adjustable optical phase ring. The adjustable ring provides a way to compensate for distortion in the visible phase ring before the light reaches the sample. In an inverted microscope, when observing transparent cells under a liquid, the visible light phase ring is distorted. By the use of a Liquid Crystal Display (LCD) in place of a fixed ring, the projected ring is adjusted to realign the light and produce phase. In a typical micro plate, the meniscus formed produces a lens effect that is realigned by providing changes in the position and pattern, to allow phase imaging over a wider portion of the well. The realignment of the ring can be manual or automated and can be dynamically adjusted based upon an observed image of the sample.
Owner:KAIROS INSTR
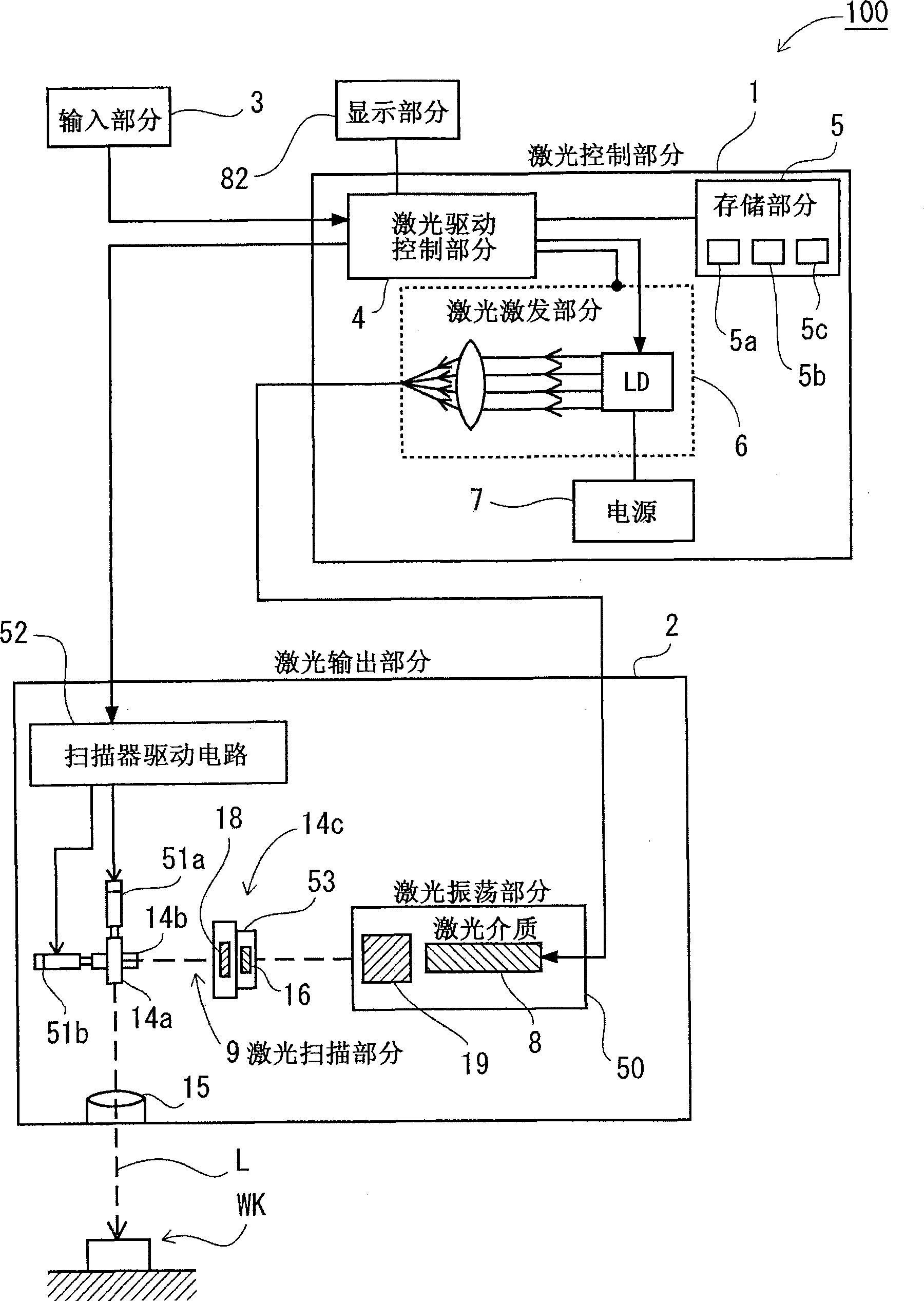
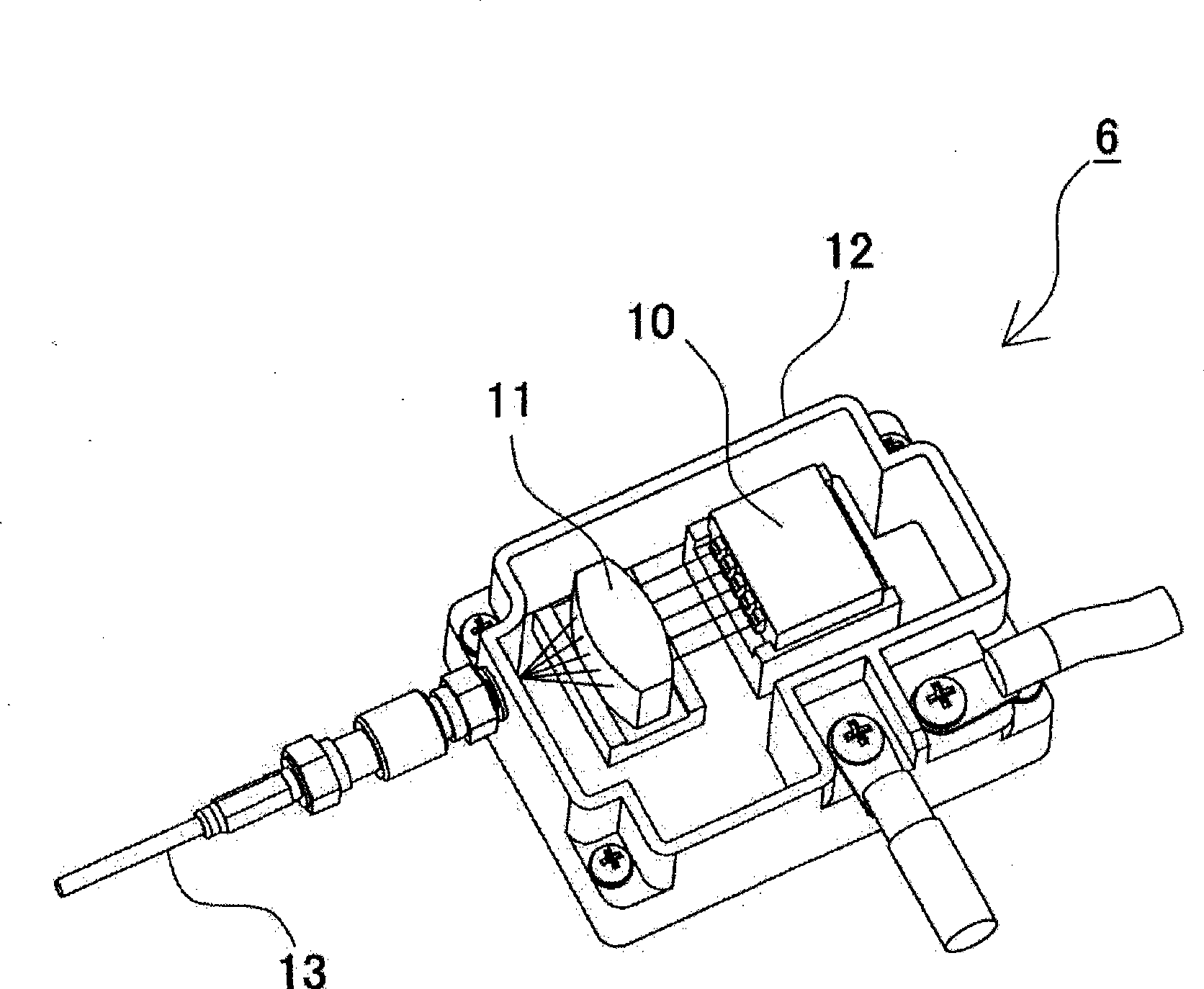
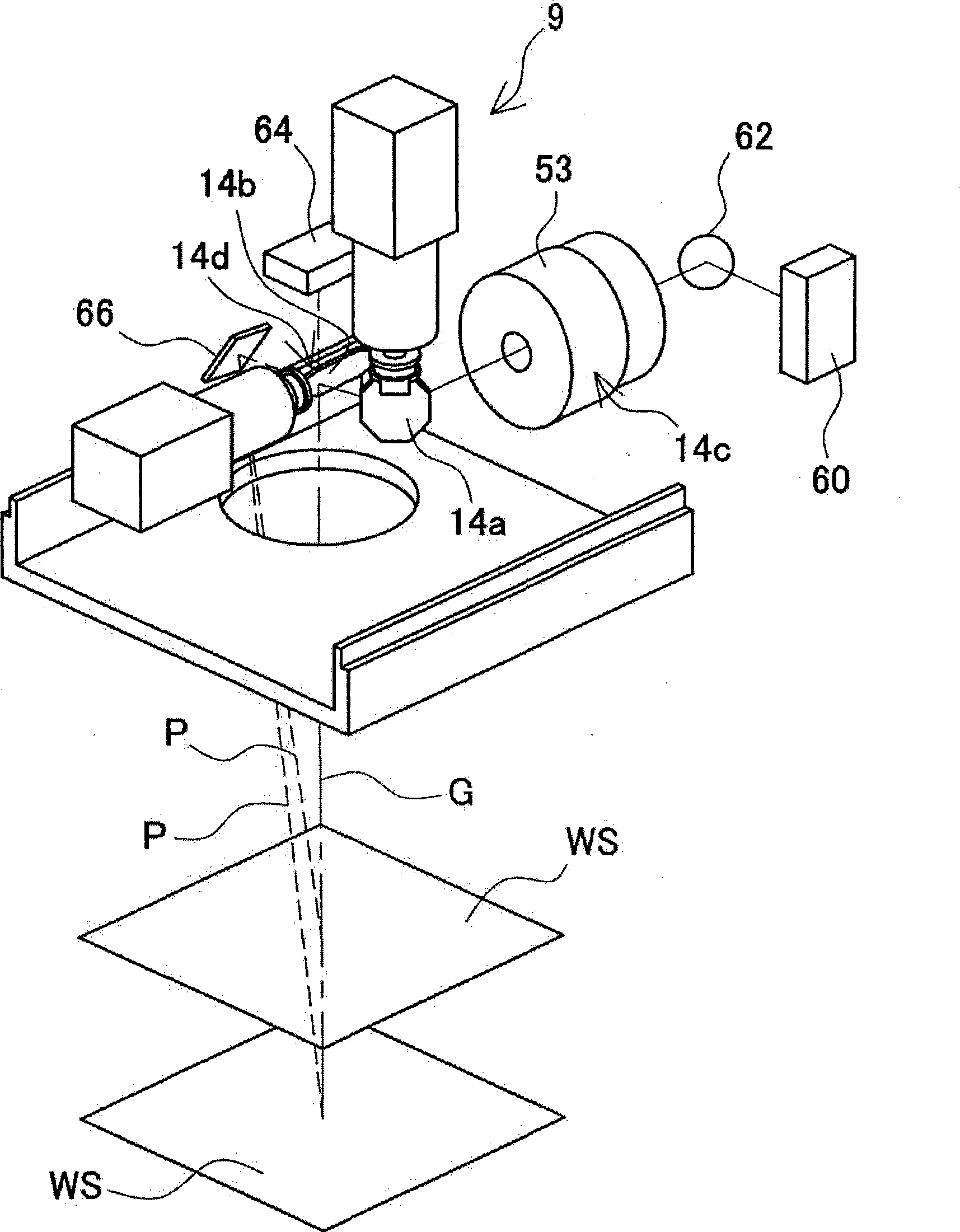
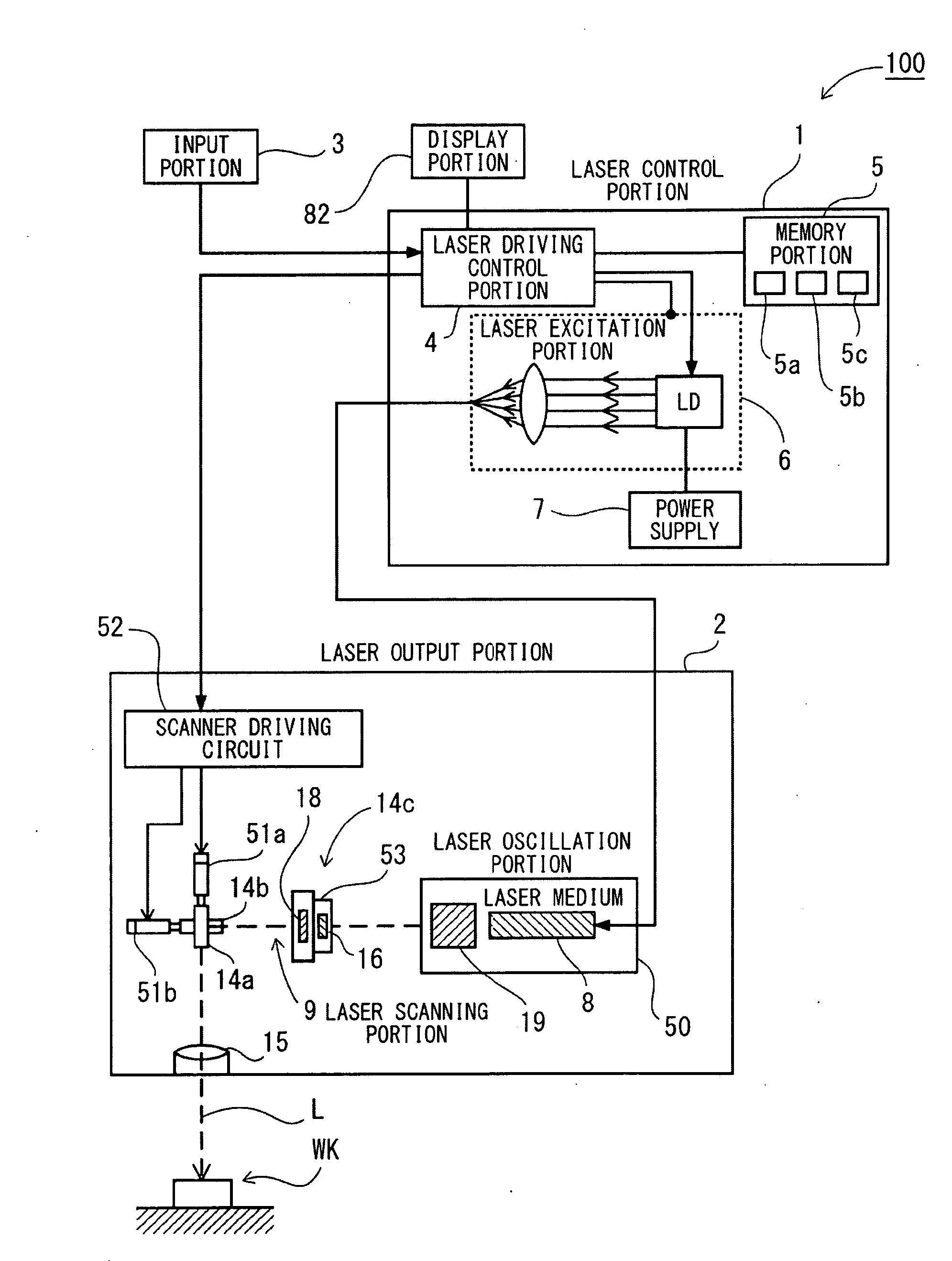
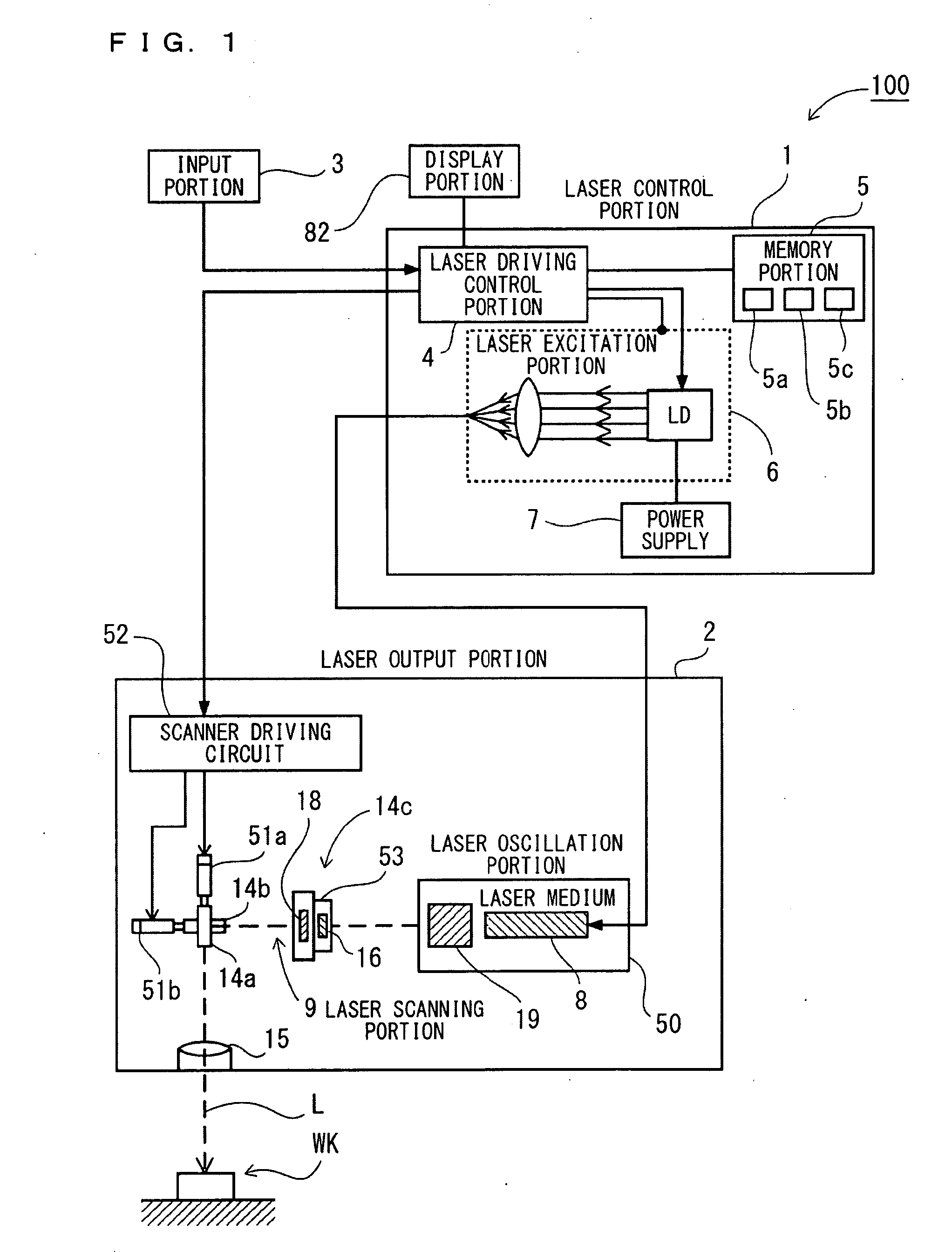
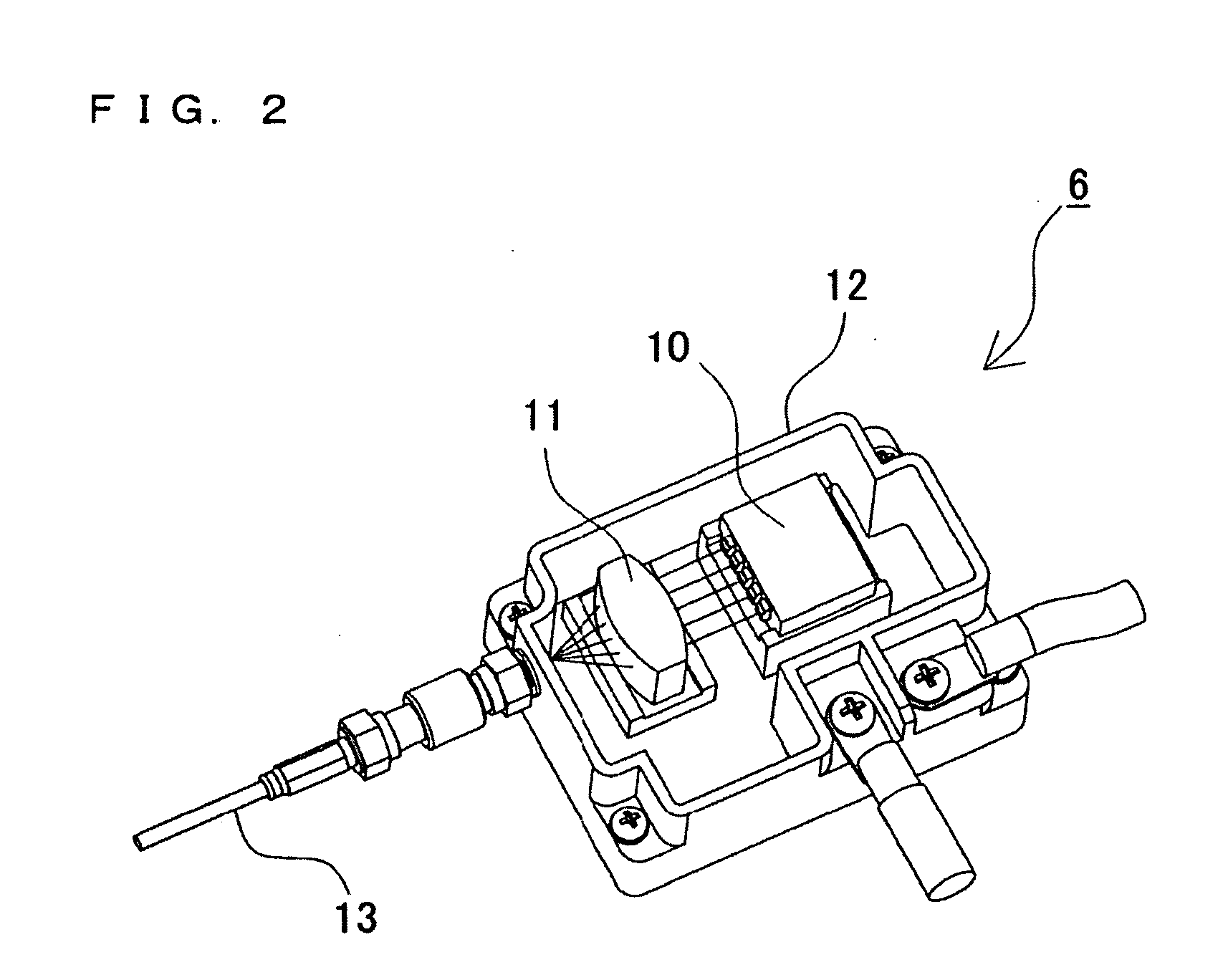
Laser processing apparatus, laser processing method, and method for making settings for laser processing apparatus
Owner:KEYENCE
Stereoscopic-image display apparatus
Mediums that are arranged opposite to an elemental-image display unit, that form two lens arrays having different principal planes together with substrates, and that switches a polarization direction of incident light corresponding to applied voltage, thereby making lens effect of either one of the lens arrays effective are included. By controlling the polarization direction synchronizing with a display timing of images to be displayed on the elemental-image display unit, the lens array to be effective is switched at each display timing, and images having different near or far direction are alternately displayed on the elemental-image display unit.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Lens array device and image display
InactiveCN101762896AEasy to controlEasy to switchSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsRefractive indexDisplay device
The lens array device includes: first and second substrates; a first electrode group formed on the first substrate to include transparent electrodes extending in a first direction; a second electrode group formed on the second substrate to include transparent electrodes extending in a second direction; and a liquid crystal layer with refractive index anisotropy arranged between the first and second substrates to produce a lens effect by changing the liquid crystal molecule alignment. The liquid crystal layer electrically changes into one of three states according to voltages applied to the first and second electrode groups. The three states include a state with no lens effect, a first lens state where a lens effect of a first cylindrical lens extending in the first direction is produced, and a second lens state where a lens effect of a second cylindrical lens extending in the second direction is produced.
Owner:SONY CORP
Light Emission Device and Light Emitter Using the Same
InactiveUS20090168419A1Reduce power consumptionReduce the temperaturePoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesLight emissionHigh luminance
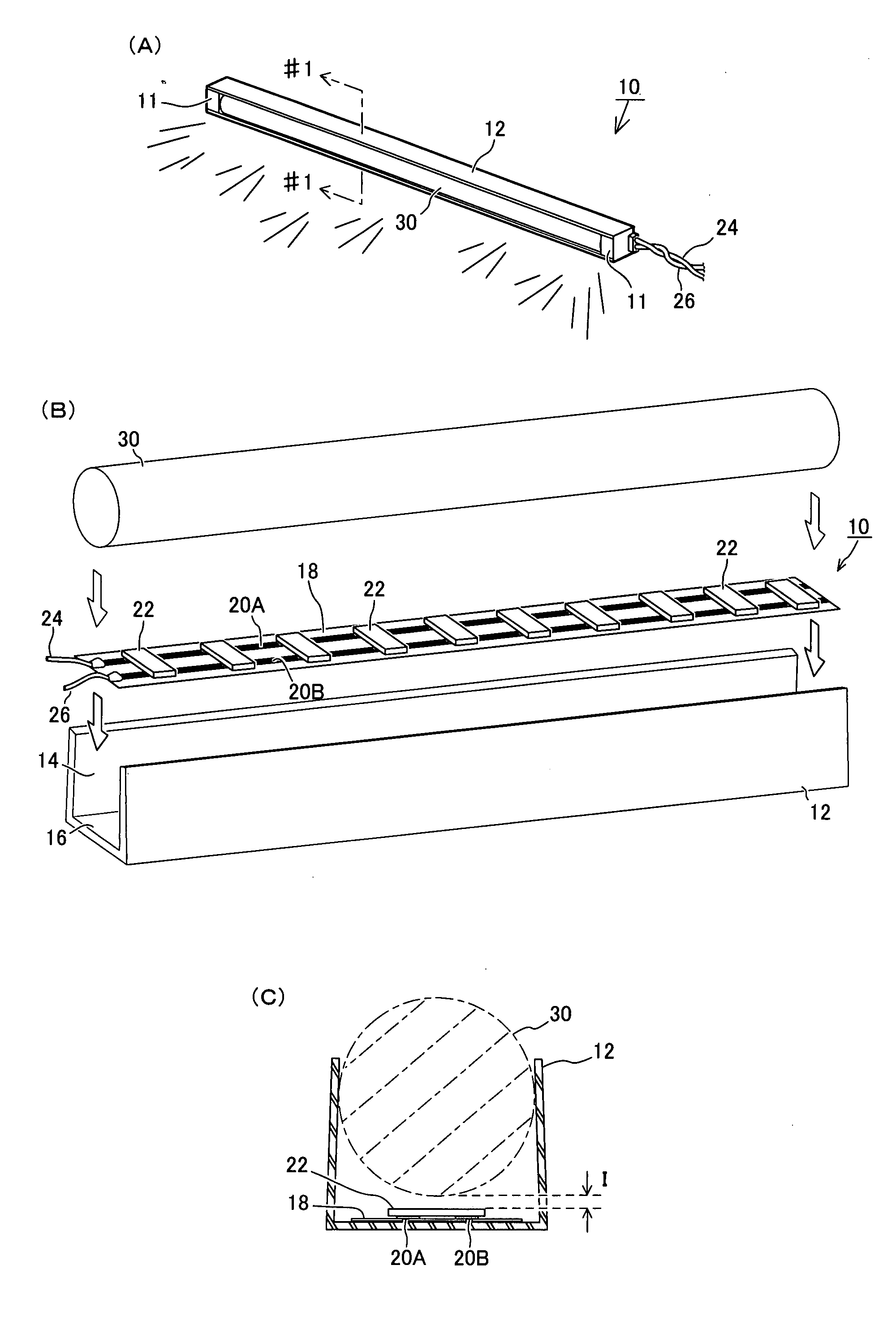
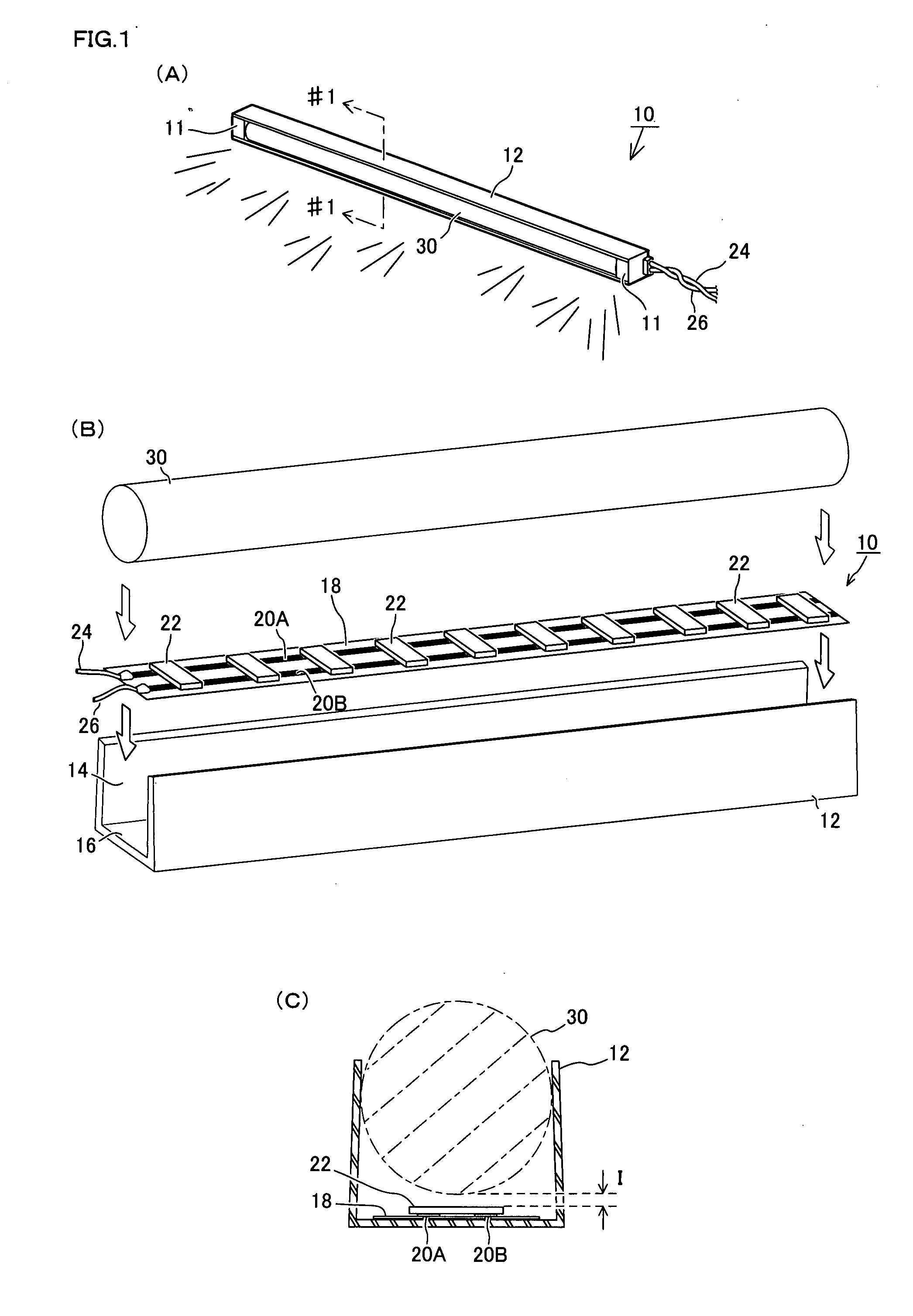
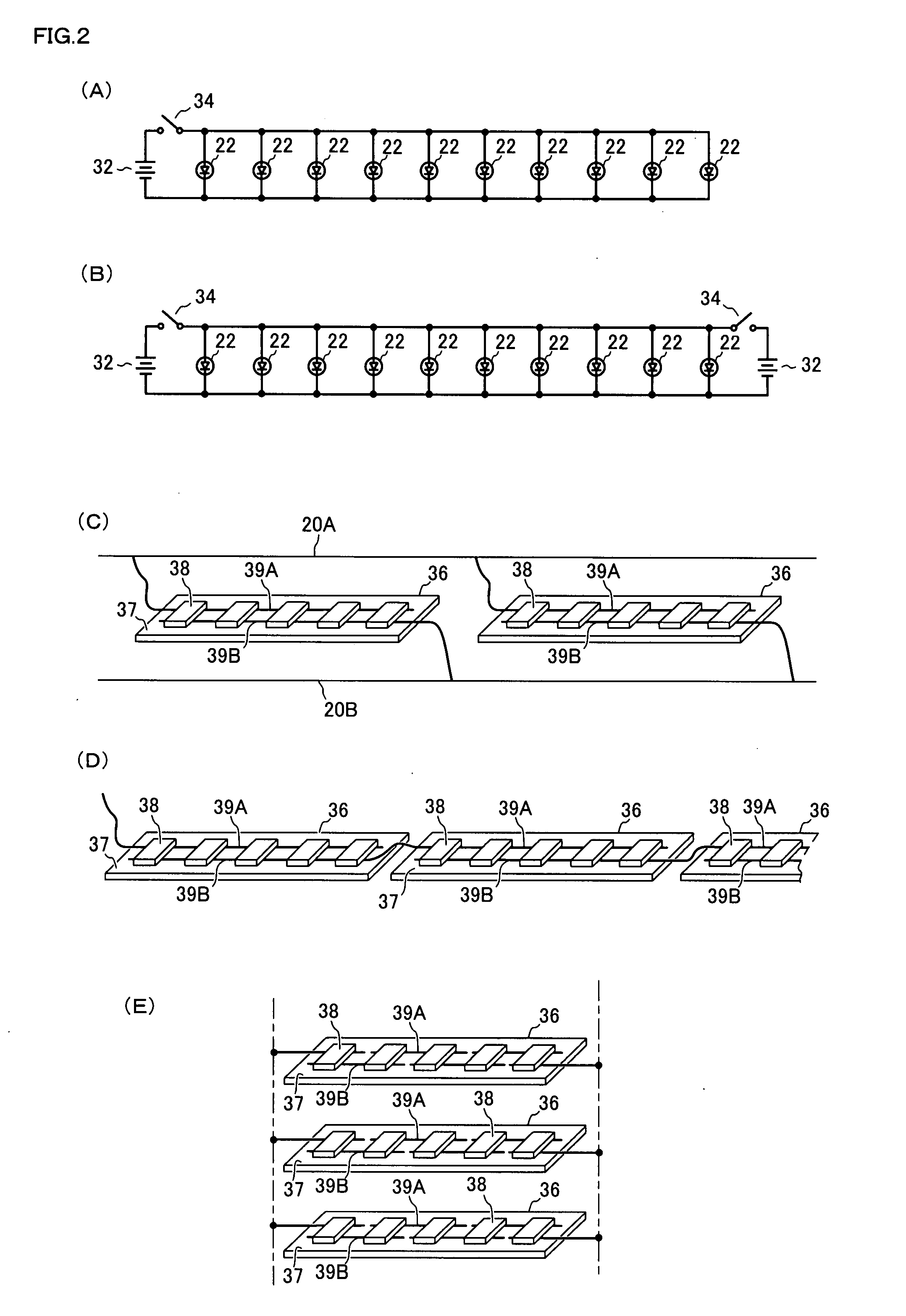
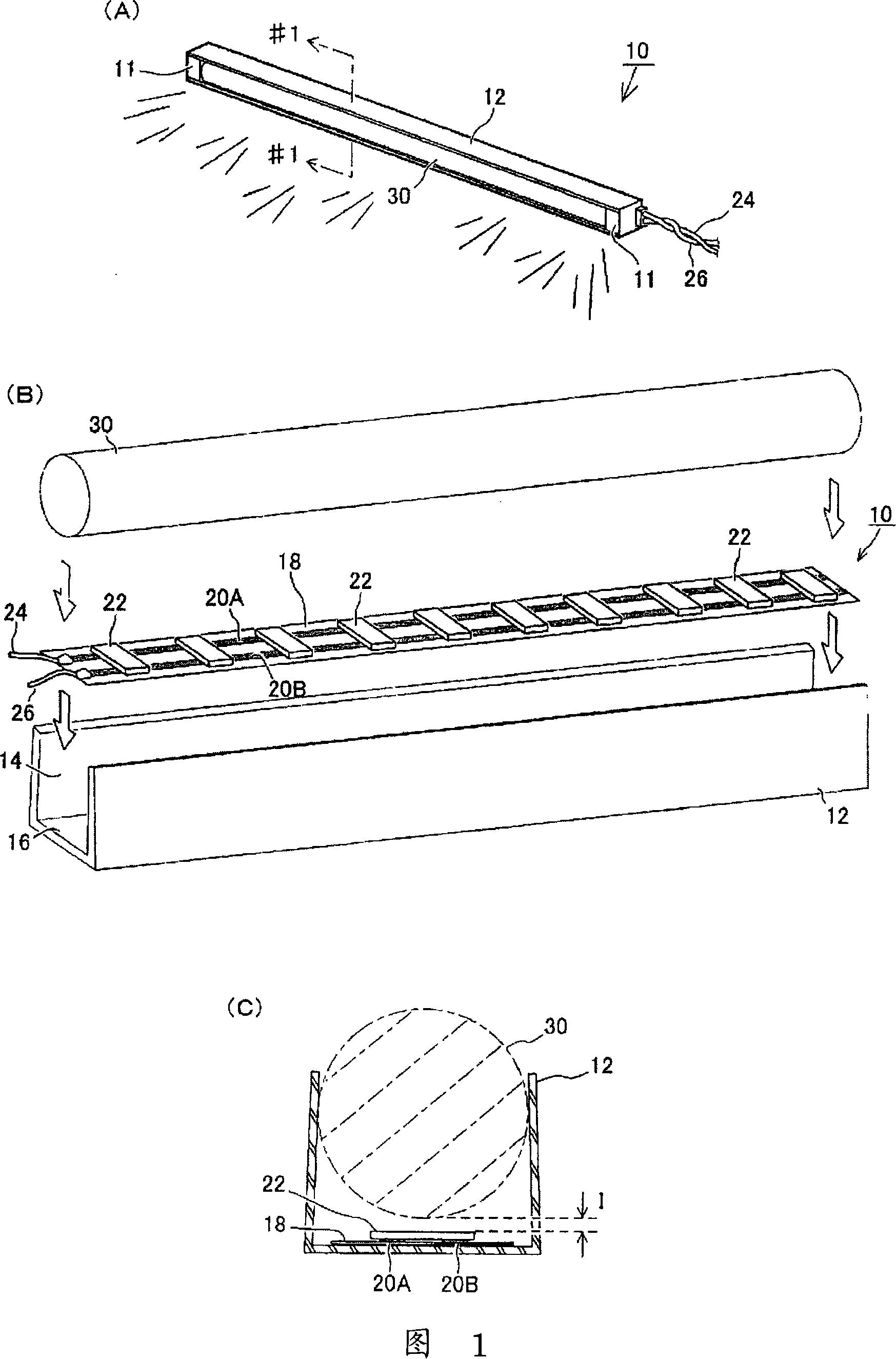
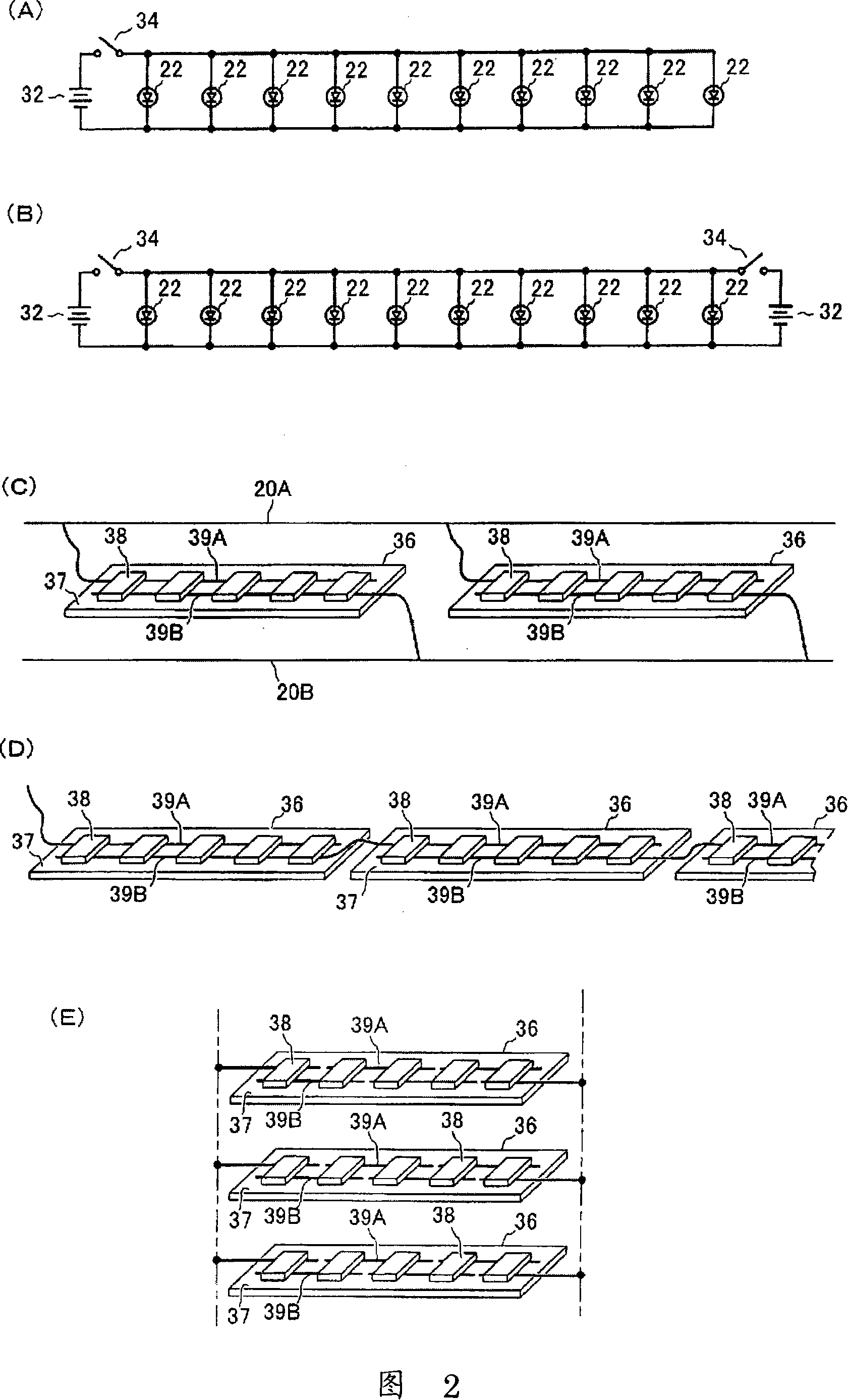
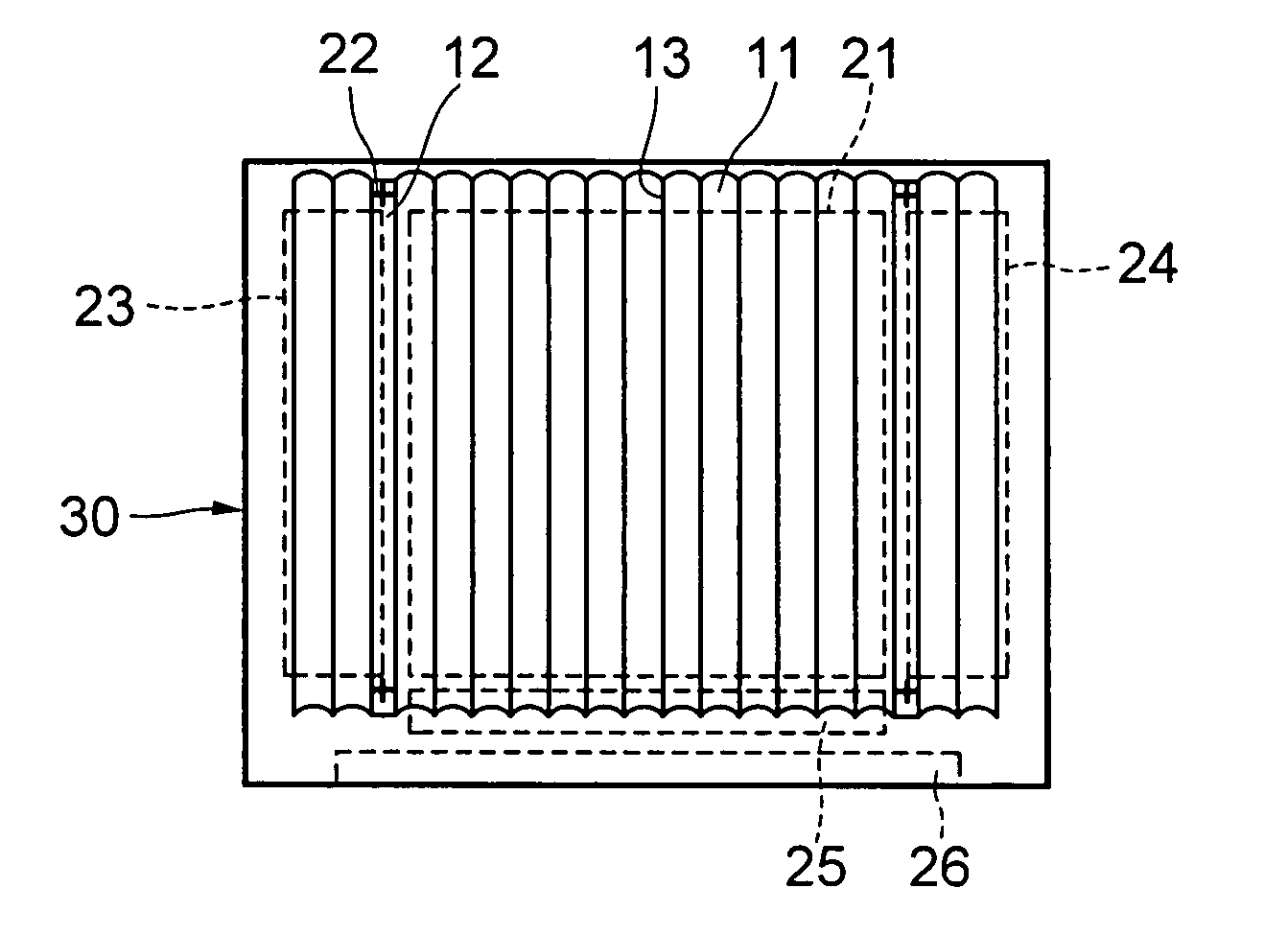
The present invention aims at: emitting a uniform light on the whole with a high luminance to provide a required bright illumination; suppressing increase of temperature and reducing power consumption; and permitting easy alteration of entire shape and size thereof.A light emission device 10 is provided, which comprises: a transparent element 30 of columnar shape having a substantially circular shape in section; a light cover 12 attached on outer surface of the transparent element 30 so as to securely sandwich and retain that particular outer surface of transparent element; and a plurality of LEDs 22 for applying lights to the transparent element 30, the plurality of LEDs 22 being provided in the light cover 12. Such LEDs 22 are disposed relative to said transparent element 30, such that a predetermined space I is essentially given between the LEDs 22 and the surface of the transparent element 30. Upon lights being emitted from the LEDs 22, the lights expands freely in an air zone between the LEDs 22 and the transparent element 30 and are therefore applied to that particular transparent element 30 from many angles. Then, the lights are refracted and diffused due to a lens effect of the transparent element 30, and emitted from an opening area 14 of the light cover 12 to the outside. When such light emission is viewed from the outside, it is observed that a whole of the transparent element 30 is illuminated uniformly with a high luminance.
Owner:LITEHOUSE TECH CORP
Wide-stripe single-mode diode-laser
InactiveUS20050041709A1Laser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsQuantum wellBroadband
A wide-stripe diode-laser includes a lower cladding region, a lower waveguide region, an active region, an upper waveguide region, and an upper cladding region all comprising semiconductor layers epitaxially grown on a semiconductor substrate. An elongated rectangular electrode on the upper cladding layer defines a stripe or pumped section. Adjacent the electrode is an unpumped section in which at least the quantum-well layer has been treated to cause the active region to be disordered. In this unpumped section, at least one area of the area is etched to a depth equal to or less than the thickness of the cladding region. The etched area provides a diverging lens effect in the waveguide region. The diverging lens effect expands the fundamental mode of the laser in the stripe to a width sufficient to improve single mode performance.
Owner:COHERENT INC
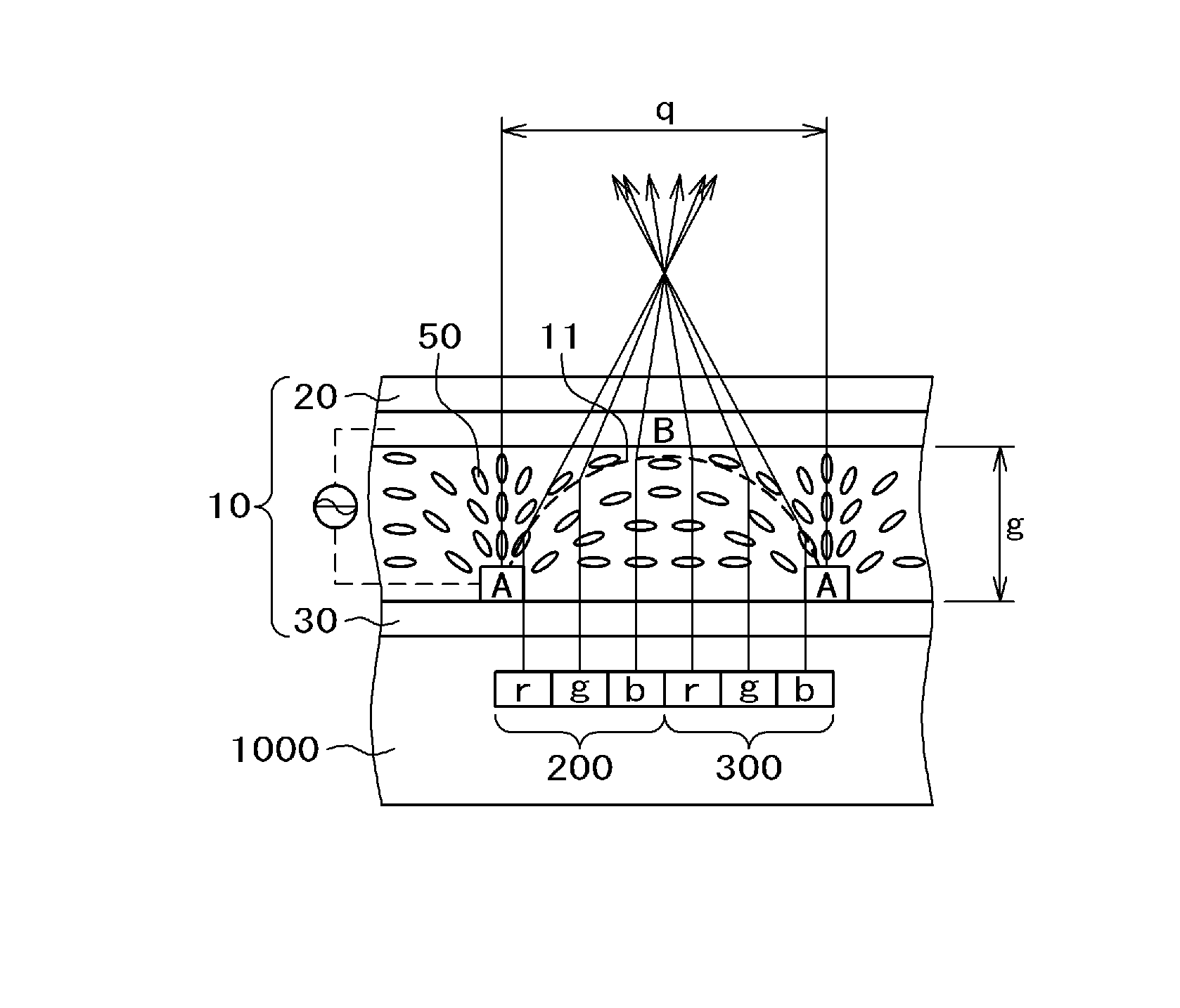
Liquid crystal display apparatus
InactiveUS20070229737A1Effective lightingSimple processNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayPhase shifted
A phase shift element formed on the outer surface of a glass substrate is formed of an organic PAS film, with a refractive index of approximately 1.5. There is atmospheric air (with a refractive index of 1.0) between the phase shift elements. A thickness of the phase shift element is set at 550 nm, a value obtained by substituting 550 nm for a center wavelength and 0.5 for Δn in D1Δn=center wavelength / 2. A phase shift element formed on the inner surface of the glass substrate is an SiN layer (with a refractive index of approximately 2.0). A substance between the phase shift elements is a flattened film which has a heatproof temperature of 600 degrees centigrade or above, a low refractive index, and flattened effect. A thickness of the flattened film may be equal to or larger than a thickness of the phase shift element and thus is set at 550 nm. Through installation of the phase shift elements having a lens effect, light of a back light is efficiently condensed on an aperture part of a pixel, thereby improving the condensation efficiency at the aperture part and increasing an amount of light transmitted through a liquid crystal display panel.
Owner:HITACHI DISPLAYS
Stereoscopic display device
InactiveUS20100238277A1Improve visibilityGood effectColor television detailsStereoscopic photographyRefractive indexDisplay device
A stereoscopic display device includes: a display panel having a display screen on which two-dimensional image is displayed, and configured to polarize image light of the image-displaying into a particular polarization direction; and a lens array element disposed to oppose the display screen of the display panel, and having a liquid crystal layer which includes liquid crystal molecules having a refractive index anisotropy and aligned in a predetermined orientation direction under no application of voltage. The lens array element is configured to electrically change the alignment of the liquid crystal molecules to generate a lens effect, and configured to selectively change a state of passing therethrough of the image light exiting from the display panel. The predetermined orientation direction of the liquid crystal molecules of the lens array element and the polarization direction of the image light are parallel to each other.
Owner:SONY CORP
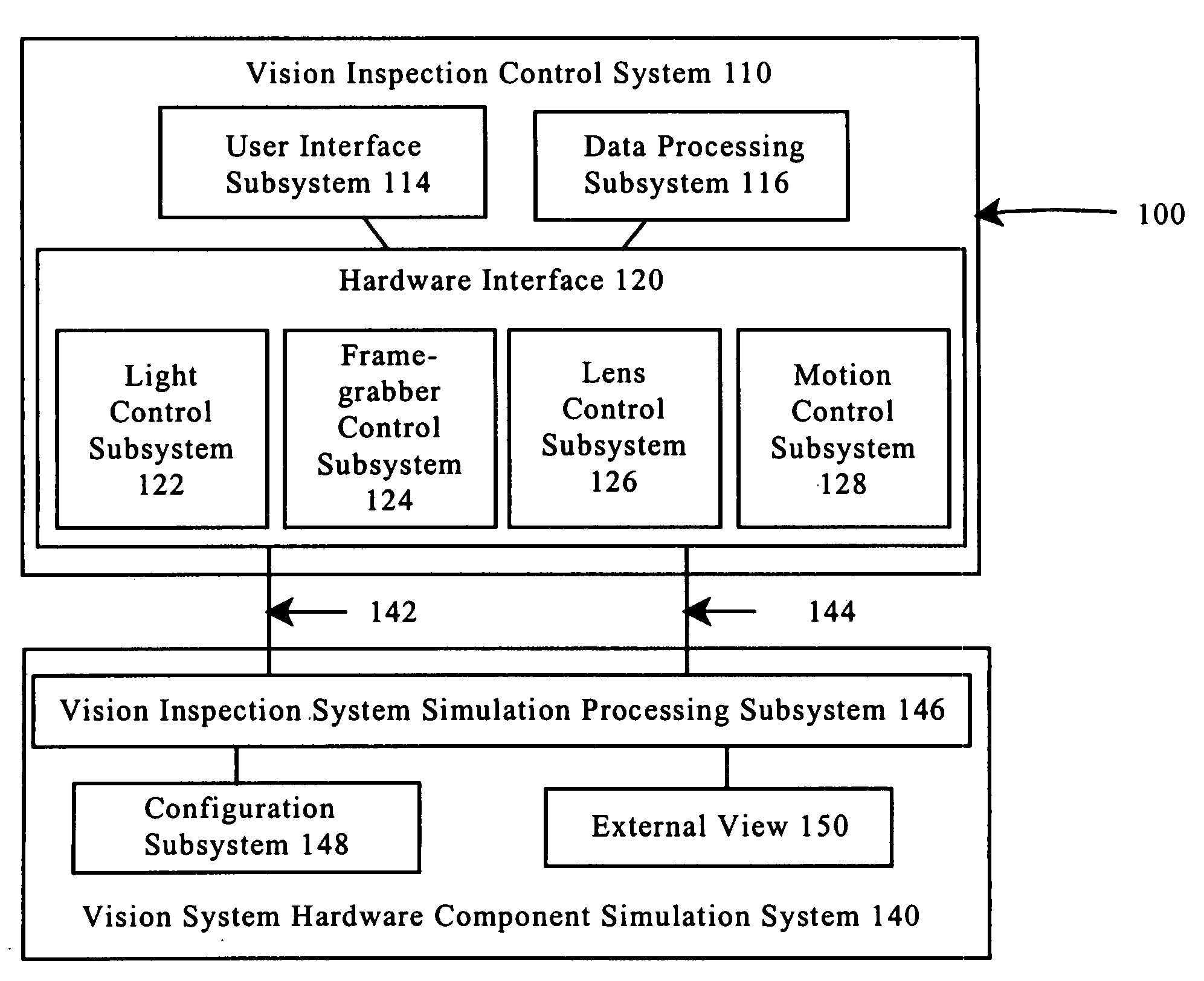
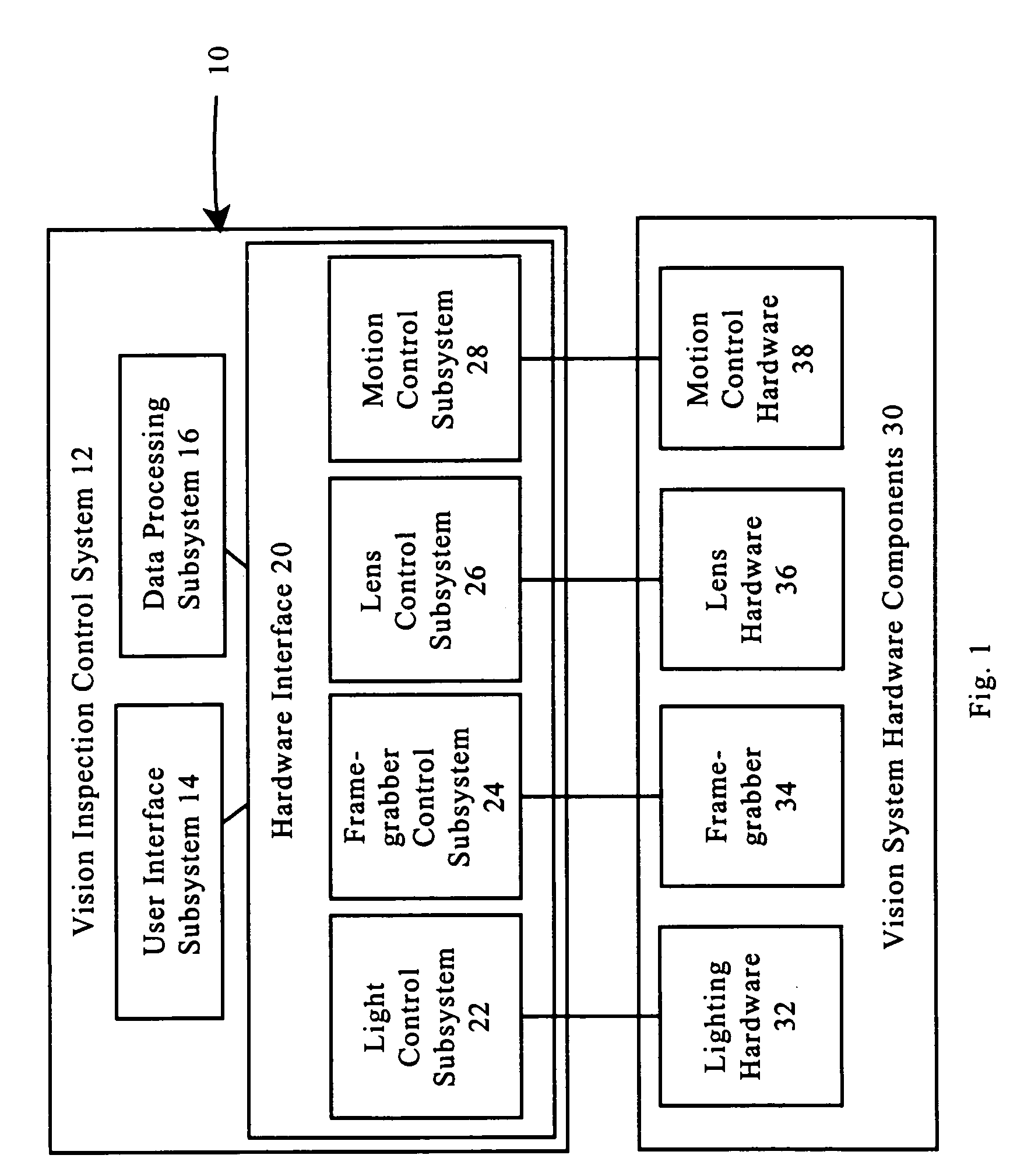
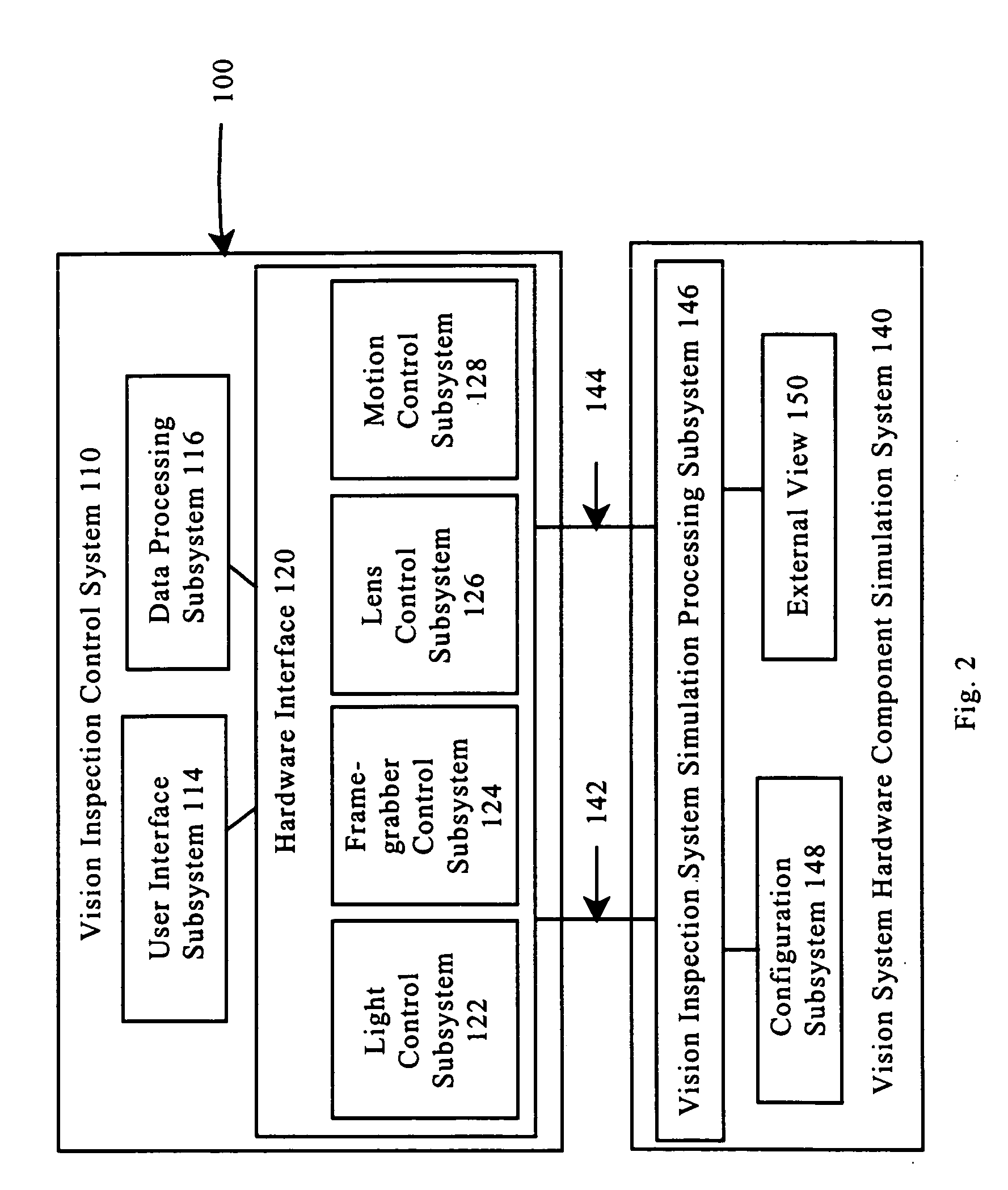
Hardware simulation systems and methods for vision inspection systems
InactiveUS7092860B1Reduce system downtimeAccelerated trainingCosmonautic condition simulationsComputer controlGraphicsCamera lens
The systems and methods of this invention provide simulated images to vision inspection systems. The simulated images emulate the vision of a vision inspection system. Graphical models of objects in a virtual world and lens effects models are used to provide the simulated images.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
System for correcting optical center linked with lens shift
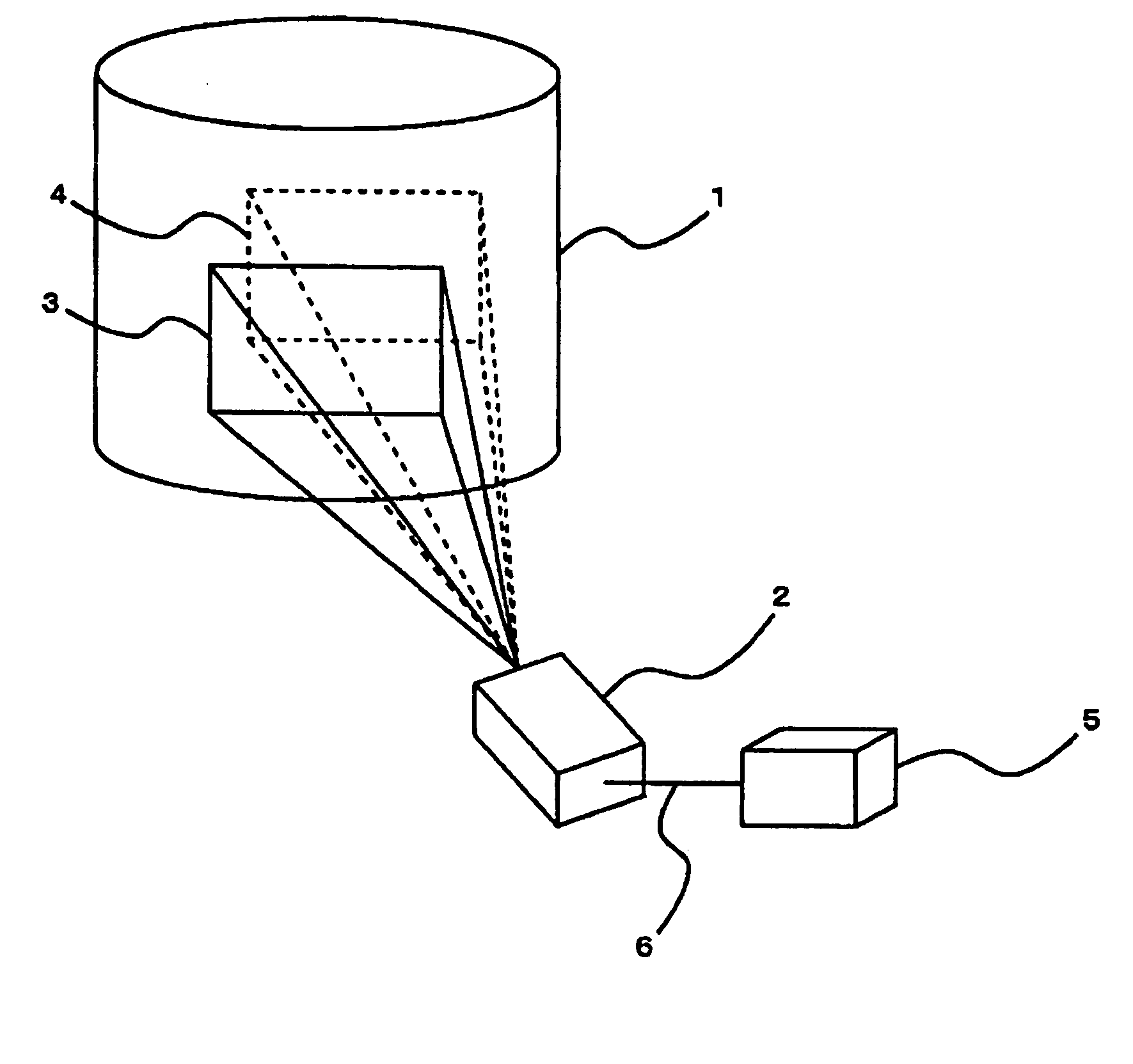
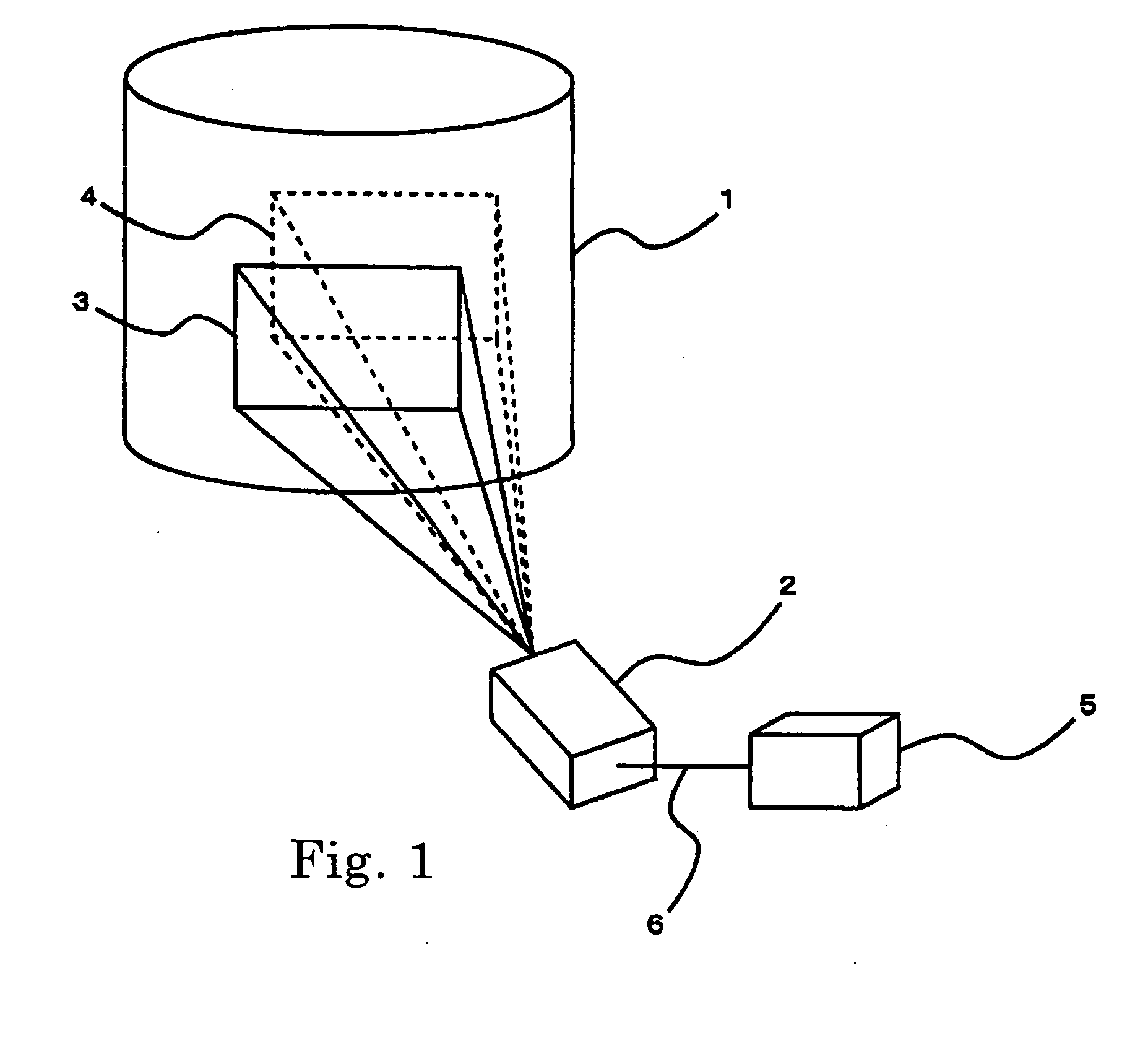
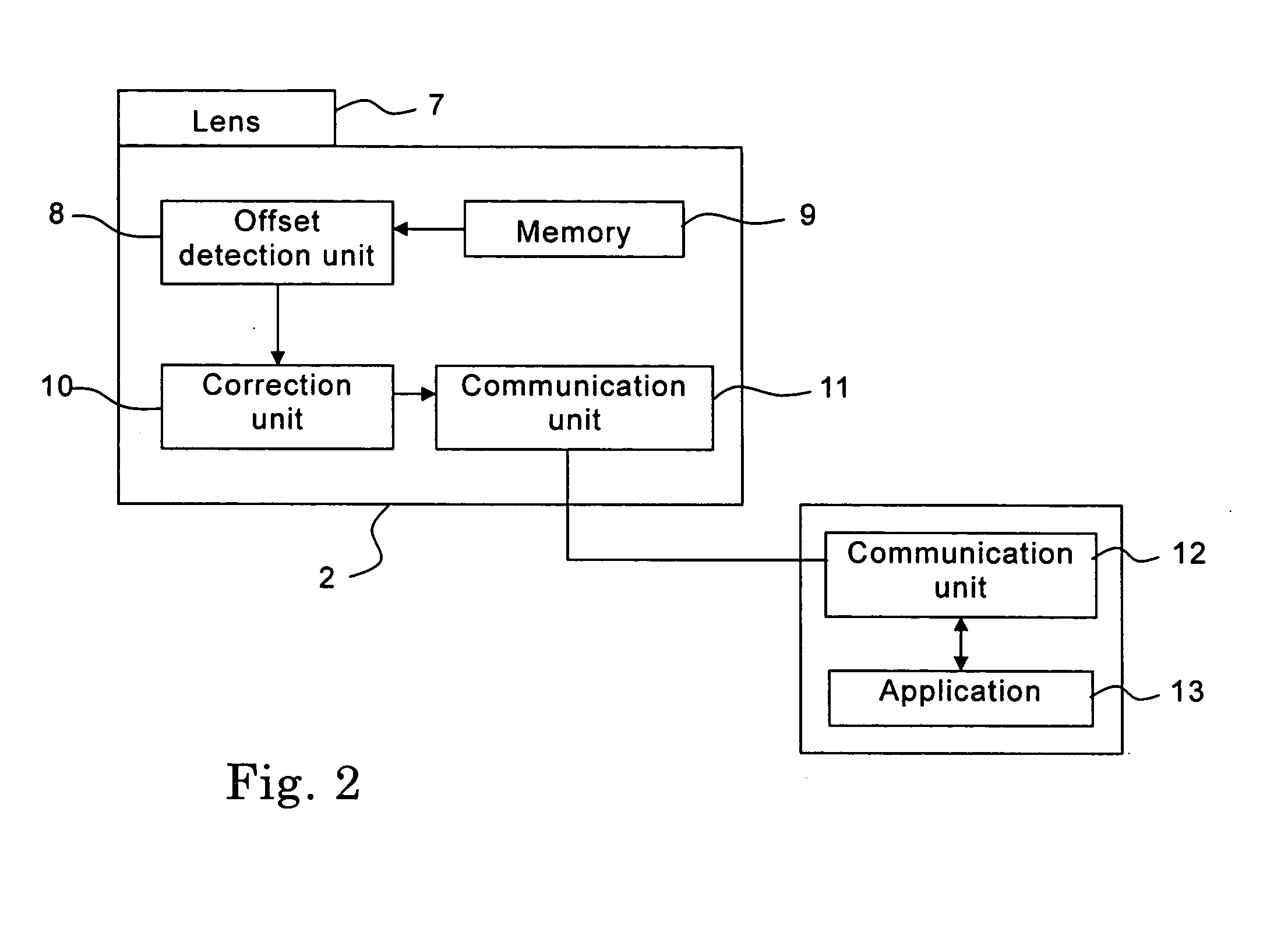
InactiveUS20050068506A1Television system detailsProjector focusing arrangementLens effectCenter effect
A system for correcting an optical center is provided with: a lens control unit for shifting a lens in vertical and horizontal directions; an offset detection unit for detecting a displacement of the optical center with respect to a screen on a basis of a magnitude of a shift of the lens effected by the lens control unit; a memory unit for storing in advance data on the centrally aligned location of the lens and also data on the positions of the optical center effected by lens shifts; and a correction unit for linking the displacement of the optical center detected by the offset detection unit with the data on the centrally aligned location of the lens and the data on the position of the optical center effected by the lens shift stored in the memory unit to correct the displacement of the optical center.
Owner:NEC VIEWTECH
Method capable of switching between different display modes and display device
An embodiment of the invention provides a method capable of switching between different display modes and a display device, and particularly provides a method capable of switching between 2D (two-dimensional) display, 3D (three-dimensional) display and double-vision display and a display device. The display device comprises a display panel, a slit grating device positioned on a light-emitting side of the display panel and a liquid crystal lens on a light-emitting side of the slit grating device. The slit grating device is capable of enabling the display device to form a 3D effect. The liquid crystal lens equivalently forms a concave lens effect when double-vision display is performed by the display device so as to diffuse a first image and a second image sent by the display panel to a first visual area and a second visual area respectively, and the liquid crystal lens equivalently forms a plane light-transmitting effect when 3D display is performed by the display device so as to transmit a left eye image and a right eye image sent by the display panel.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
Light emitting device and light emitting object using the same
InactiveCN101128695AAvoid temperature riseLight evenlyPoint-like light sourceElongate light sourcesLight emitting deviceLens effect
The present invention relates to a light emitting device and a light emitting object using the light emitting device. The entire part of the light emitting device can emit light uniformly with sufficient brightness according to the purpose of use, in which a rise in temperature is suppressed and electric power consumption is reduced, and that can easily cope with a change in the entire shape and size. The light emitting device (10) is constructed from a bar-like transparent body (30) having a substantially circular cross-section, a light cover (12) installed on the outer periphery of the transparent body (30) and holding the outer periphery of the transparent body (30), and LEDs (22) arranged in the light cover (12) and introducing light into the transparent body (30). The LEDs (22) are disposed so as to keep a predetermined distance (I) from the surface of the transparent body (30). When the LEDs (22) emit light, the light enters into the transparent body (30) from many directions because of an airspace between the LEDs (22) and the transparent body (30), refracted and diffused by a lens effect of the transparent body (30), and emitted to the outside from an opening (14) of the light cover (12). When seen from the outside, the entire transparent body (30) emits light uniformly and brightly.
Owner:LITEHOUSE TECH CORP
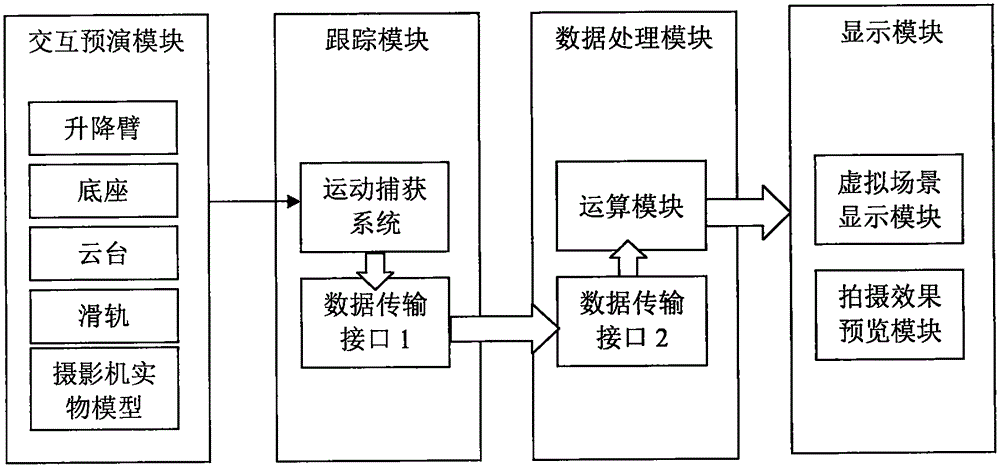
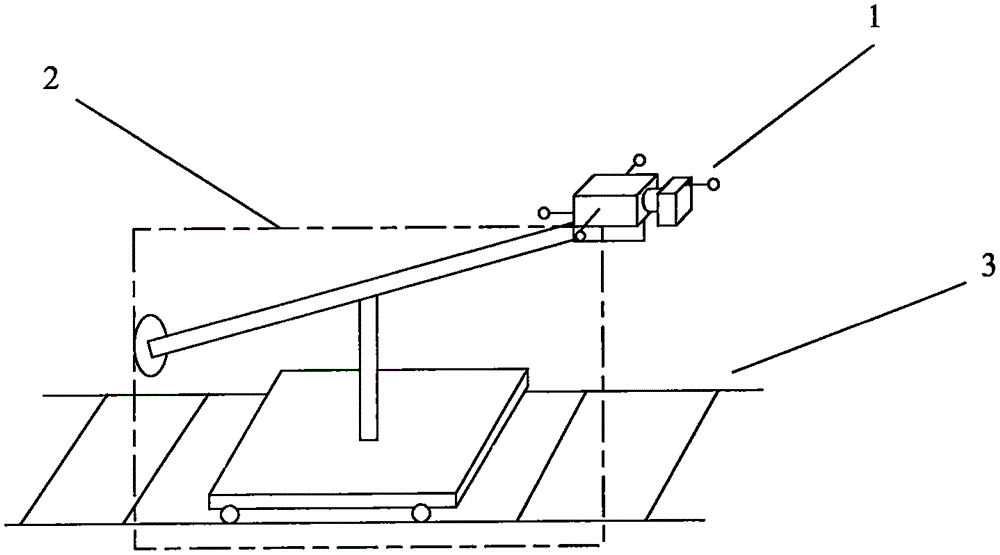
Virtual simulation method and system of camera motion control system in film shooting
InactiveCN105488457AImprove interactivityReduce shooting costsTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionCamera controlCamera lens
The invention discloses a virtual simulation method and system of a camera motion control system in film shooting, and belongs to the technical field of camera control. The method and the system cause a film creator to more visually regulate the motion track and the picture sequence of the camera according to own operation habits and visual angles, picture planning and the like in the early stage of film shooting, utilizes three-dimensional virtual simulation to design a satisfactory lens effect for the creator, automatically calculates the parameters of the camera motion control system which plans to be adopted, and precisely controls the space coordinates of the camera lens so as to improve the interaction of the camera motion control system, save the shooting cost of the lens which uses the camera motion control system and greatly improve the digital manufacture quality and efficiency of the film.
Owner:BEIJING FILM ACAD
Phase Plate For Phase-Contrast Electron Microscope, Method For Manufacturing the Same and Phase-Contrast Electron Microscope
InactiveUS20080202918A1Avoid it happening againElectric discharge heatingElectric discharge tubesElectron microscopeLens effect
A phase plate (10) for phase-contrast electron microscopes is characterized by comprising a conductive core phase plate (14) which has a phase plate body (11) and a phase plate support (12) supporting it and is arranged in the path of electrons having passed through the objective lens of an electron microscope and in which the phase plate body (11) is so supported on the phase plate support (12) having an opening (13) as to cover at least a part of the opening (13) and a conductive shield thin film (15) covering the periphery of the core phase plate (14) including the upper and lower sides thereof. Consequently, a phase plane for phase-contrast electron microscopes preventing the lens effect incident to charging completely and applicable to the field of material science, its manufacturing method and a phase-contrast electron microscope can be provided.
Owner:NAGAYAMA IP HLDG
Liquid crystal display device and liquid crystal lens
ActiveUS20130077013A1High mechanical strengthStable maintenanceNon-linear opticsLensLiquid-crystal displayLens effect
In a liquid crystal display device enabling three-dimensional display using a liquid crystal lens, both mechanical strength and a liquid crystal lens effect are satisfied. The liquid crystal lens is bonded onto an upper polarizing plate of a liquid crystal display panel with a bonding material. The liquid crystal lens includes an upper substrate, a lower substrate and a liquid crystal layer sandwiched therebetween. The upper substrate of liquid crystal lens has a thickness larger than a total of the thickness of the lower substrate of the liquid crystal lens and the thickness of the liquid crystal display panel. Thereby, it is possible to realize a liquid crystal display device satisfying both the mechanical strength and liquid crystal lens effect.
Owner:JAPAN DISPLAY INC
Optical element array, display device, and method of manufacturing display device, optical element array and optical element array molding die
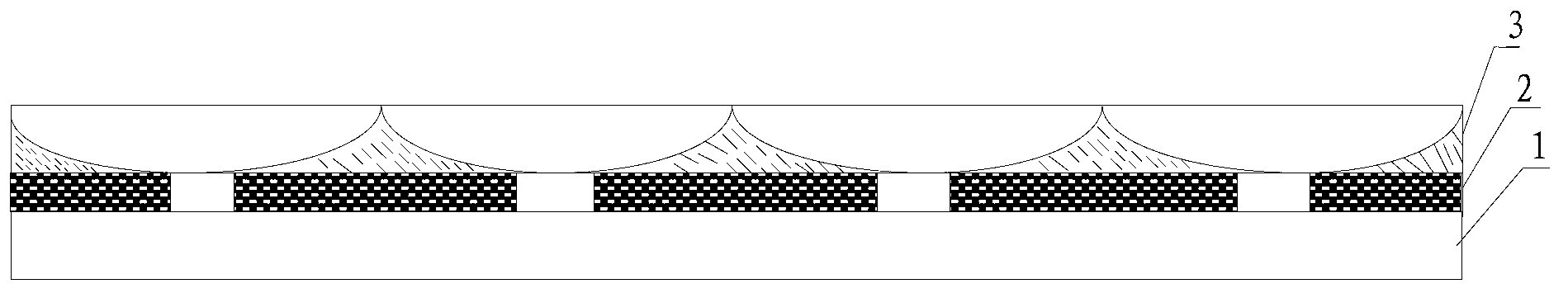
ActiveUS20080068720A1Low costImprove accuracyOptical articlesNon-linear opticsDisplay deviceEngineering
The present invention provides an optical element array that enables lens mounting at low cost and high precision, a display device enabling stereoscopic display using the optical element array, and a method of manufacturing the display device. A lens sheet of the present invention is configured by a plurality of unit lenses and a non-periodic flat part, the non-periodic flat part functioning as a lens reference mark for positioning. A display device is configured using the lens sheet such that the non-periodic flat part of the lens sheet overlaps a positioning mark of a display panel. Since the non-periodic flat part serving as the lens reference mark is arranged on the positioning mark, observation shift of the positioning mark due to lens effect in time of alignment does not occur, and high precision alignment is realized.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
Transmissive and reflective film absorption measurement method and device for thermal lens
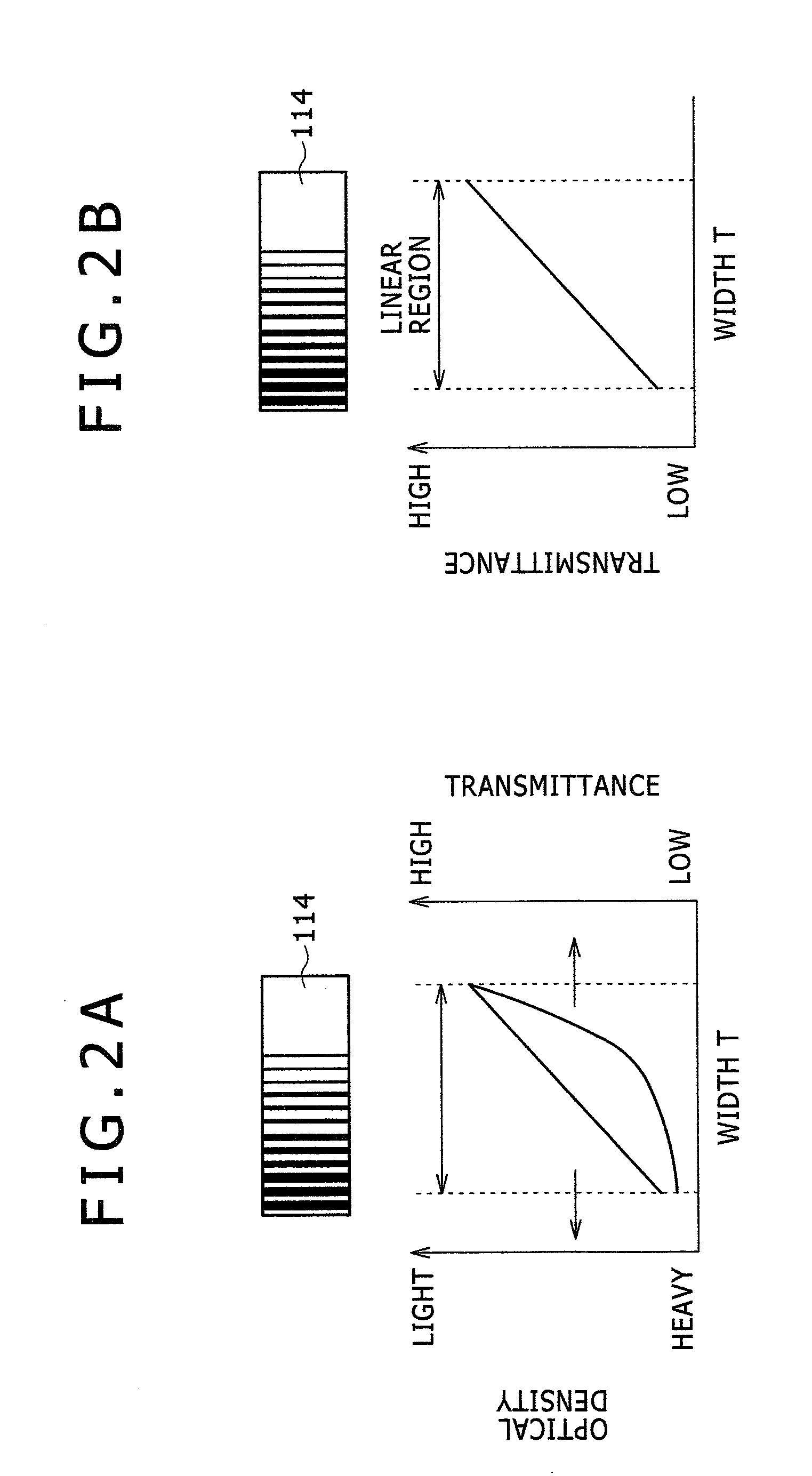
InactiveCN1632527ASolve the defect of poor linearityImprove linearityColor/spectral properties measurementsPhotovoltaic detectorsImage resolution
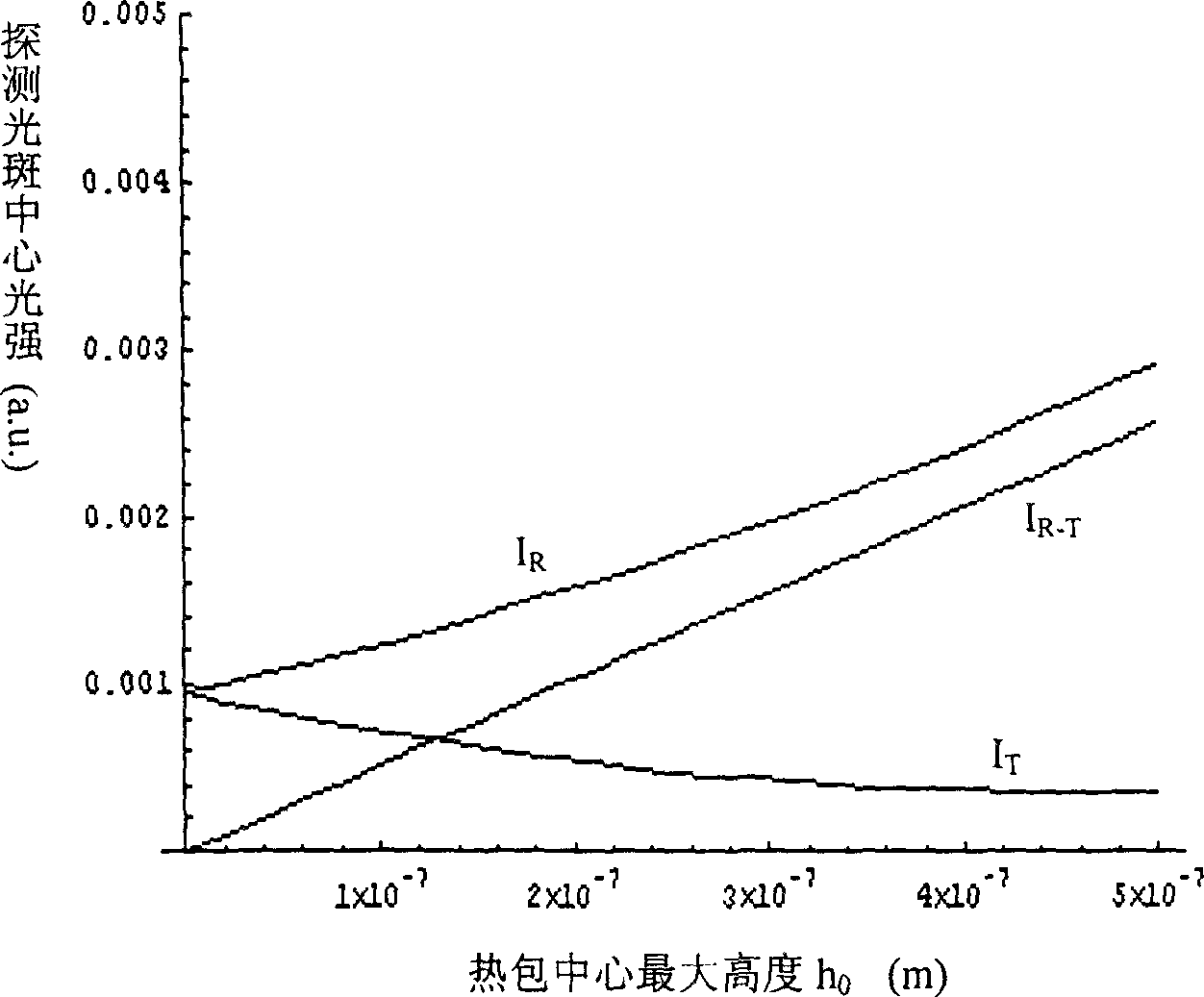
This invention relates to a thermal lens reflective film absorption measurement method and its device, which are based on thermal lens film absorption measurement method and surface thermal lens film absorption to simultaneously measure the detecting laser center light intensity signals I#-[R] and I#-[T] reflected and transmitted in the light thermal lens effect. It is to make the light intensity received by two photoelectricity detectors equal by adjusting the amplifying times of the photoelectricity detector or fixing attenuator in the reflection and transmission light paths. In this way it gets the thermal lens reflection and transmission signals S#-[RT]ú¢(I#-[R]-I#-[T]) / I#-[0] which is at a proportion with the film absorption rate in a large range.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Laser Processing Apparatus, Laser Processing Method, and Method For Making Settings For Laser Processing Apparatus
InactiveUS20090154504A1Eliminate operationIntuitive effectLaser detailsPrintingLaser processingOptical axis
It is an object to enable easily adjusting a focus position for coping with thermal lens effects. There is provided a laser-light scanning portion including a Z-axis scanner capable of adjusting the focus position of laser light in the direction of the optical axis, an X-axis scanner and a Y-axis scanner. Further, there are provided a laser driving control portion for controlling a laser oscillation portion and the laser-light scanning portion, a processing-condition setting portion for setting a laser-light outputting condition and a processing pattern as processing conditions for processing in a desired processing pattern, and an amount-of-correction identification section for identifying, as an amount of focus-position correction, the deviation of the focus position in the direction of the optical axis which is caused by thermal lens effects induced based on the laser-light outputting condition set by the processing-condition setting portion. During irradiation of the laser light, the laser driving control portion scans the laser light, in such a way as to add the amount of focus-position correction identified by the amount-of-correction identification section to the processing condition set by the processing-condition setting portion.
Owner:KEYENCE
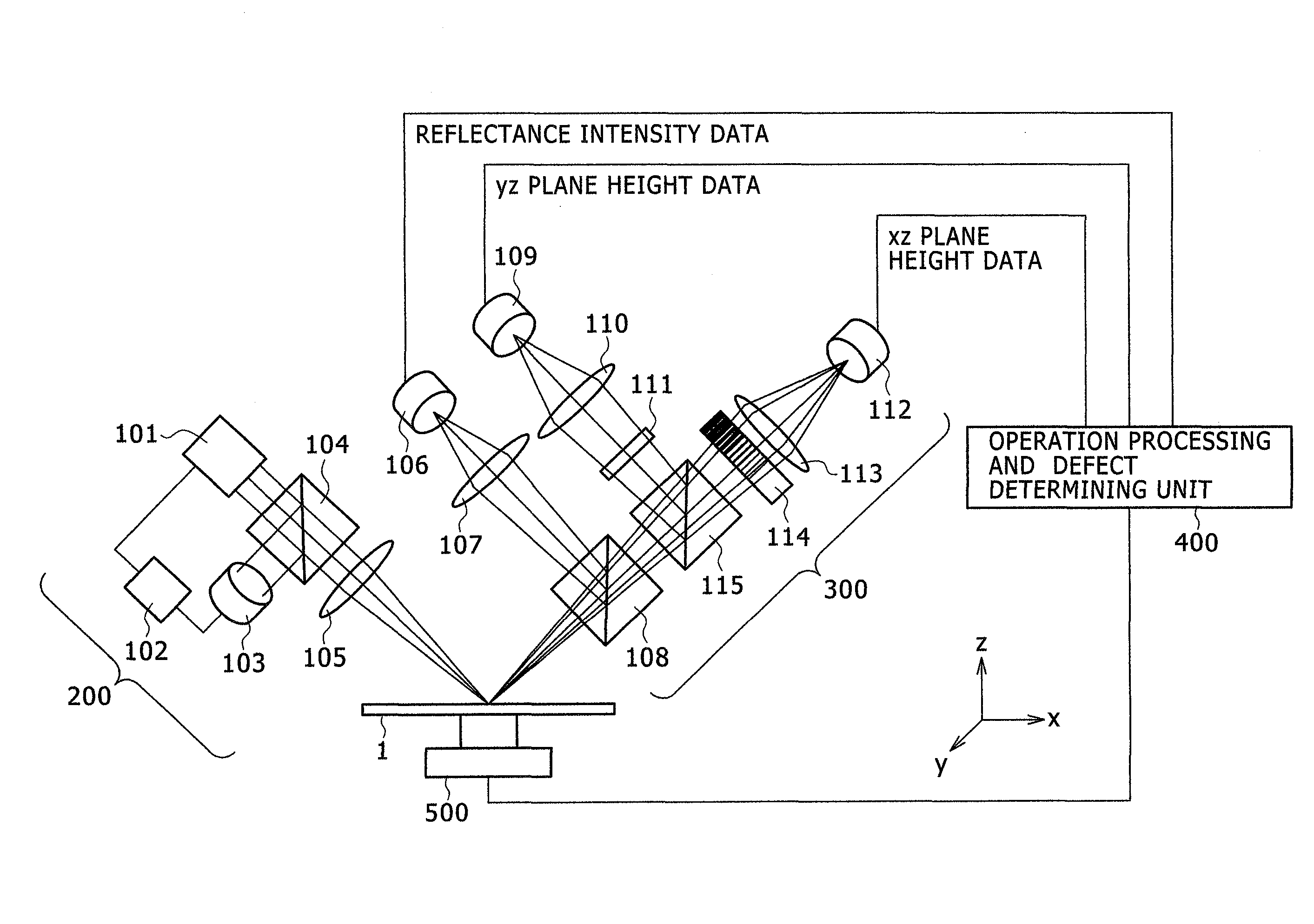
Surface defect inspecting apparatus with defect detection optical system and defect-detected image processing
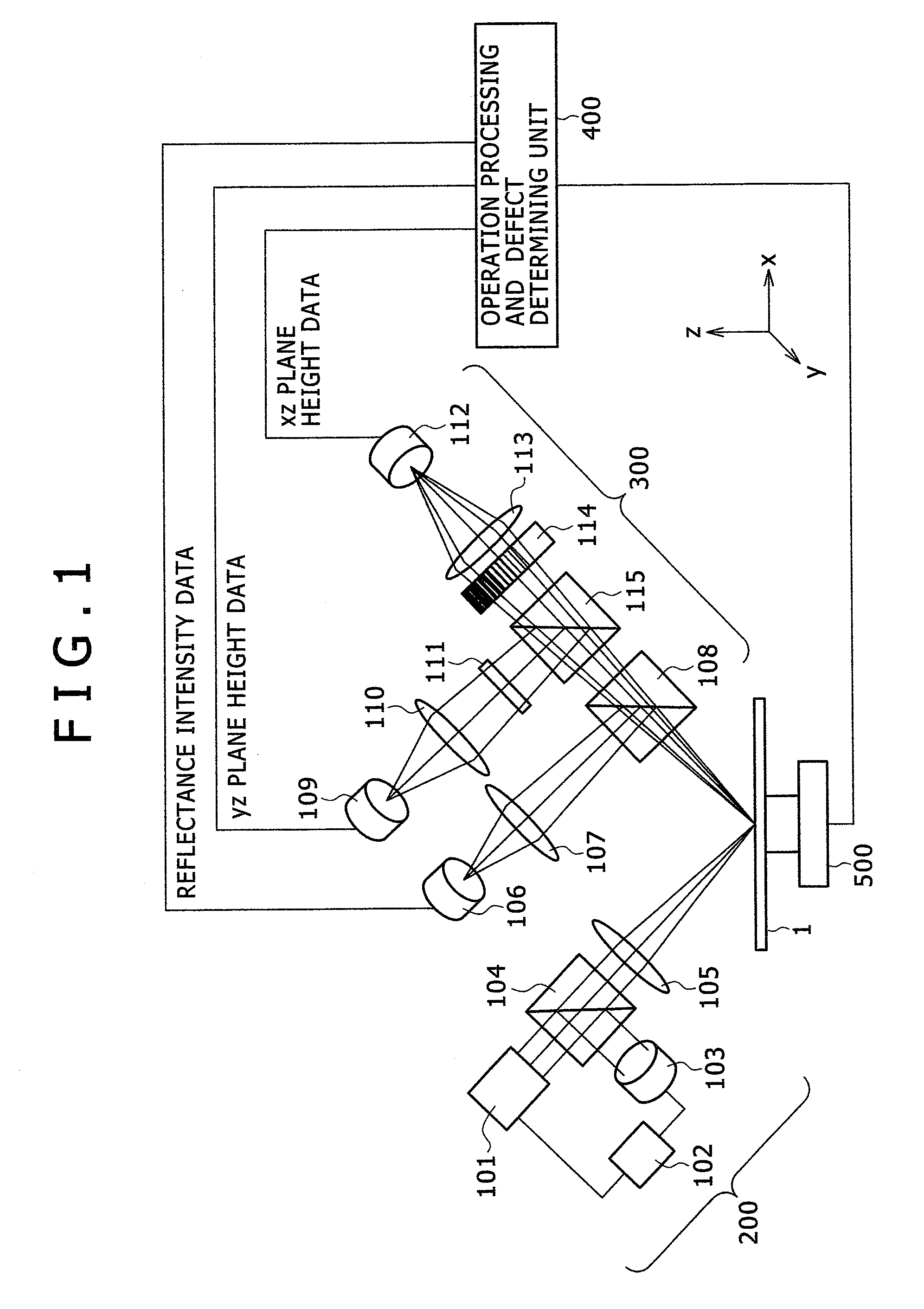
InactiveUS8018585B2Improve accuracyAccurate detectionScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationCompact discImaging processing
There is provided a defect inspecting apparatus, which includes an irradiating optical system of irradiating a light beam on a surface of a face plate of a disk mounted on a stage to scan the surface of the face plate, a light-receiving optical system of receiving specular reflection light that has transmitted a shading filter with a shading difference that changes an amount of the specular reflection light from the face plate resulting from the light beam irradiated on the disk, and a processing unit of identifying defects on the surface of the face plate from the change in amount of the specular reflection light that has transmitted a filter, so that a size and a height of the defect can be measured with high accuracy when irregular defects are determined, which is not easily achieved by a conventional lens effect.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Optical element array, display device, and method of manufacturing display device, optical element array and optical element array molding die
ActiveCN101144865ALow costHigh precisionOptical articlesSteroscopic systemsDisplay deviceEngineering
The present invention provides an optical element array capable of mounting lenses with low cost and high precision, a display device capable of stereoscopic display using the optical element array, and a method of manufacturing the display device. The lens sheet of the present invention is configured by a plurality of unit lenses and a non-periodic flat portion which functions as a reference mark for positioning. The display device is configured using a lenticular sheet such that the non-periodic planar portion of the lenticular sheet overlaps the alignment marks of the display screen. Since the non-periodic flat portion as the lens reference mark is arranged on the alignment mark, observation shift of the alignment mark due to the lens effect does not occur during the alignment time, and high-precision alignment is achieved.
Owner:NEC LCD TECH CORP
2D/3D (two-dimensional/three-dimensional) switching type stereoscopic display and control method thereof
ActiveCN102096229ACompensation for refractive index mismatchCompensate for distance mismatchStatic indicating devicesSteroscopic systemsRefractive indexDisplay device
The invention provides a 2D / 3D (two-dimensional / three-dimensional) switching type stereoscopic display and a control method thereof. The 2D / 3D switching type stereoscopic display comprises a display panel, a polarization rotator and a lens component, wherein the display panel is used for providing an image with polarization direction; the polarization rotator is used for rotating the polarization direction of the image so as to lead the 2D / 3D switching type stereoscopic display to be switched between a 2D display state and a 3D display state; the lens component is provided with a first direction and a second direction which are mutually vertical; and in theory, the lens component generates a non-lens effect for the images with the polarization directions positioned in the first direction, and generates a lens effect for the images with the polarization directions positioned in the second direction. The polarization rotator is configured to lead the polarization direction and the first direction or the second direction to form an included angle less than 45 degrees. By adopting the method, the mismatch of refractive index of the lens component in the 2D display state or the distance mismatch between the display panel and the lens component in the 3D display state can be effectively compensated, so that the display effect can be improved.
Owner:SUPERD CO LTD
System and method for image correction
ActiveUS20100265358A1Improve efficiencyEffective correctionTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsImage correctionHardware implementations
A system and method for correcting image data. Embodiments of the present invention provide calibration and image correction to overcome various lens effects including lens shading and lens imperfections. In one embodiment, the correction of image data is performed via utilization of a spline surface (e.g., Bezier surface). The use of spline surfaces facilitates efficient hardware implementation. The image correction may be performed on a per channel and illumination type basis. In another embodiment, the present invention provides a method for determine a spline surface to be used for calibrating an image signal processor to be used in correcting image data.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Method for regulating and controlling crystalline silicon surface corrugated structure based on plasmoid lens effect
ActiveCN108568594AImprove machining accuracyImprove controllabilityLaser beam welding apparatusMicro nanoNano structuring
The invention relates to a method for regulating and controlling a crystalline silicon surface corrugated structure based on a plasmoid lens effect and belongs to the technical field of femtosecond laser application. According to the method, a metal nano-ring structure is processed on based silicon plated with a noble metal film in advance by fundamental frequency femtosecond laser pulse after single frequency multiplication is adopted, a second beam of single traditional fundamental frequency gauss femtosecond laser pulse acts on the nano-ring structure, and processing of a base crystalline silicon surface ring-shaped concentric corrugated structure is realized under the action of the plasmoid lens effect of a noble metal nano-structure. When linear polarization femtosecond laser pulse isadopted, the processed corrugated structure is distributed in a semi-ring shape and a corrugated symmetrical shaft is perpendicular to the laser polarization direction; when circular polarization femtosecond laser pulse is adopted, the processed corrugated structure is in a ring distribution shape in a centrosymmetric way. According to the method, efficient and accurate control of the surface periodical micro-nano structure form is realized, and crucial application value in the aspects of surface wettability and image storage is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Corner pumping method for plate strip and its solid laser gain module
InactiveCN1398028AImprove power densityImprove uniformityExcitation process/apparatusActive medium shape and constructionEngineeringGain
An angle pump method and its solid laser gain module used in strips is to apply an angle pump structure in which the pump light source is put at the corners of the strip, so the pump light will emit into the strip from its corner plane. Center of the strip contains one or more doped areas and the surrounding linking are not doped. Most of the pump light is restricted in the strip absorbed many times due to the complete reflection, so as to get a rather long absorption length and high absorption efficiency. Strips are in the structure of doped at the center not doped around to ensure the pump light is absorbent at the strip center, reducing thermal lens effect and stress birefringence effect, avoiding strip distortion.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Stereo display device and liquid crystal lens thereof
ActiveCN102253562AImprove viewing effectReduce moiré formationSteroscopic systemsNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayImaging quality
The invention discloses a stereo display device and a liquid crystal lens thereof. The liquid crystal lens comprises a first substrate, a second substrate, a liquid crystal layer, a first electrode layer and a second electrode layer, wherein the first substrate and the second substrate are arranged at a certain interval; the liquid crystal layer is arranged between the first substrate and the second substrate; the first electrode layer is arranged between the first substrate and the liquid crystal layer; and the second electrode layer is arranged between the second substrate and the liquid crystal layer; the first electrode layer and the second electrode layer are used for producing electric fields, so that the liquid crystal layer can produce a lens effect; and the first electrode layer comprises a plurality of strip electrodes, the strip electrodes are arranged at a certain interval, and each strip electrode is provided with a structure with gradually-changed transmittance along a direction perpendicular to the extending direction of the strip electrode. Through the mode above, by using the stereo display device and liquid crystal lens disclosed by the invention, the imaging quality can be improved, and a good image display effect can be achieved.
Owner:SUPERD CO LTD
Position-measuring device
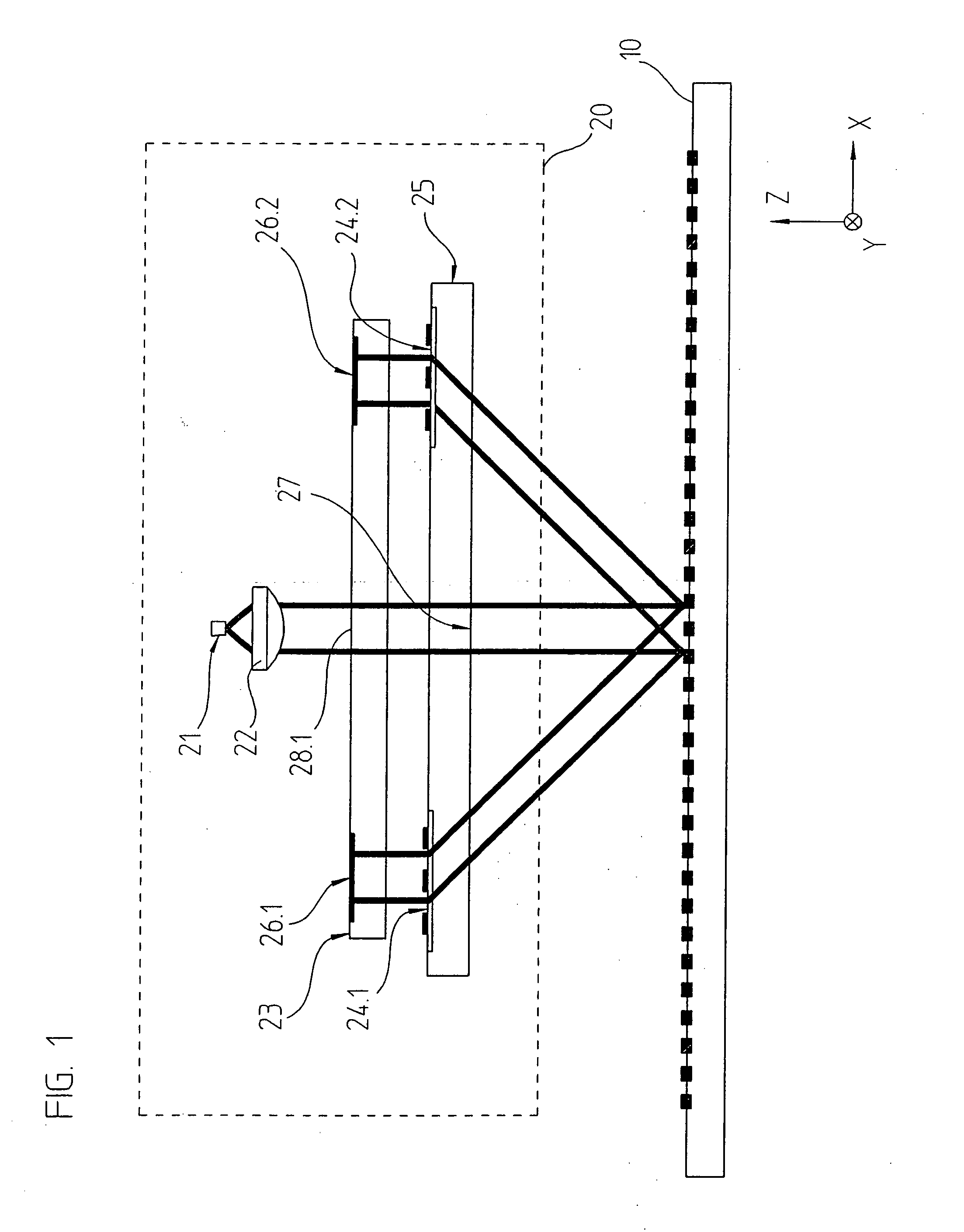
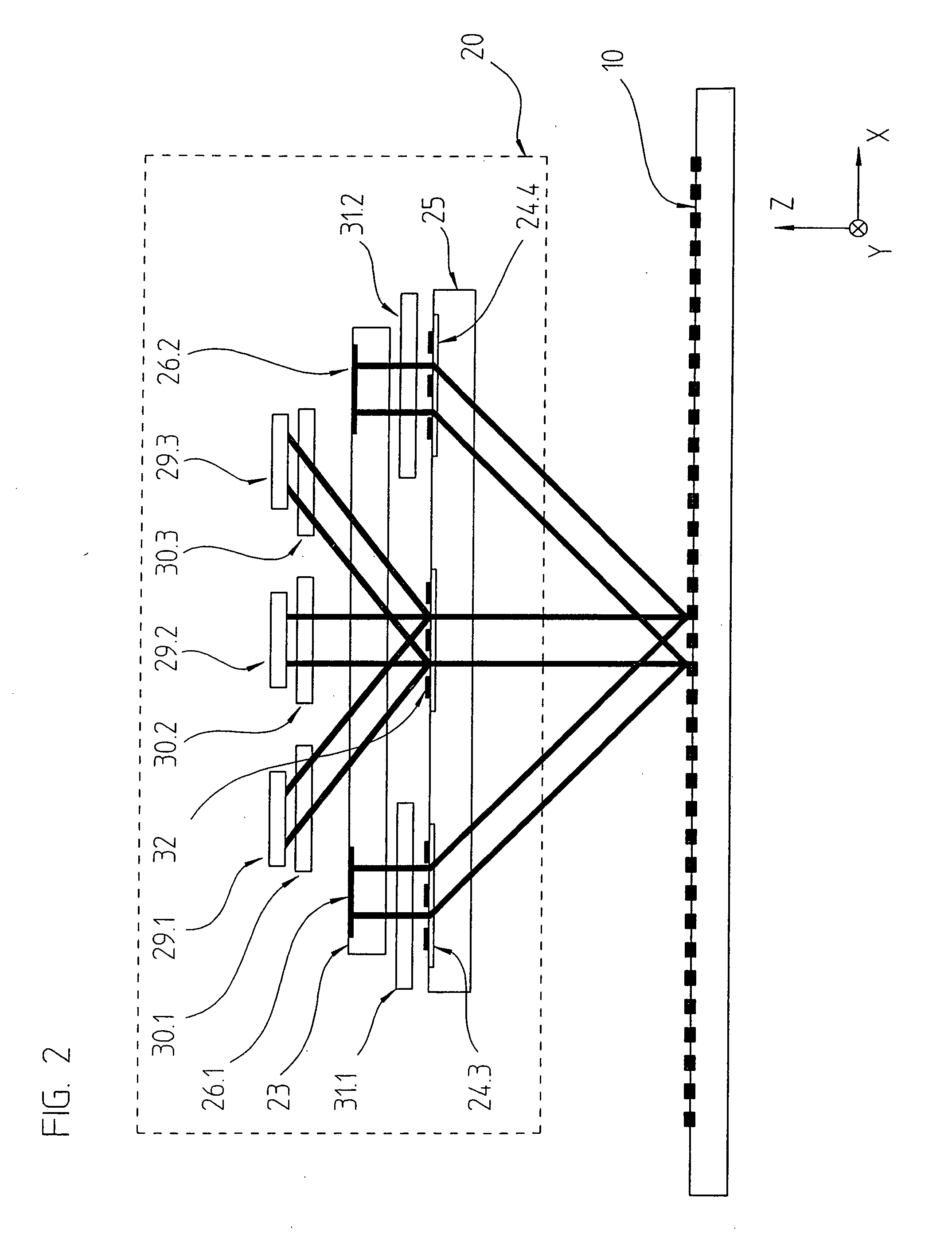
ActiveUS20070013920A1Compact structureSimple and cost-effective assemblyUsing optical meansConverting sensor output opticallyGratingLight beam
In a position-measuring device for recording the relative position of a scanning unit and a measuring graduation that is movable with respect to the latter in at least one measuring direction, the scanning unit includes a plurality of grating structures as well as at least one reflector element. The elements in the scanning unit are arranged such that the beams of rays diffracted by the measuring graduation pass through first grating structures in the scanning unit, subsequently impinge on the reflector element, from which there takes place a retroreflection in the direction of the measuring graduation, and the partial beams of rays then pass through second grating structures and then once again impinge upon the measuring graduation. The first and the second grating structures are arranged such that, upon the first and second passing through of the partial beams of rays, a defined lens effect on the partial beams of rays results.
Owner:DR JOHANNES HEIDENHAIN GMBH
Laser light generating device and method of fabricating the same
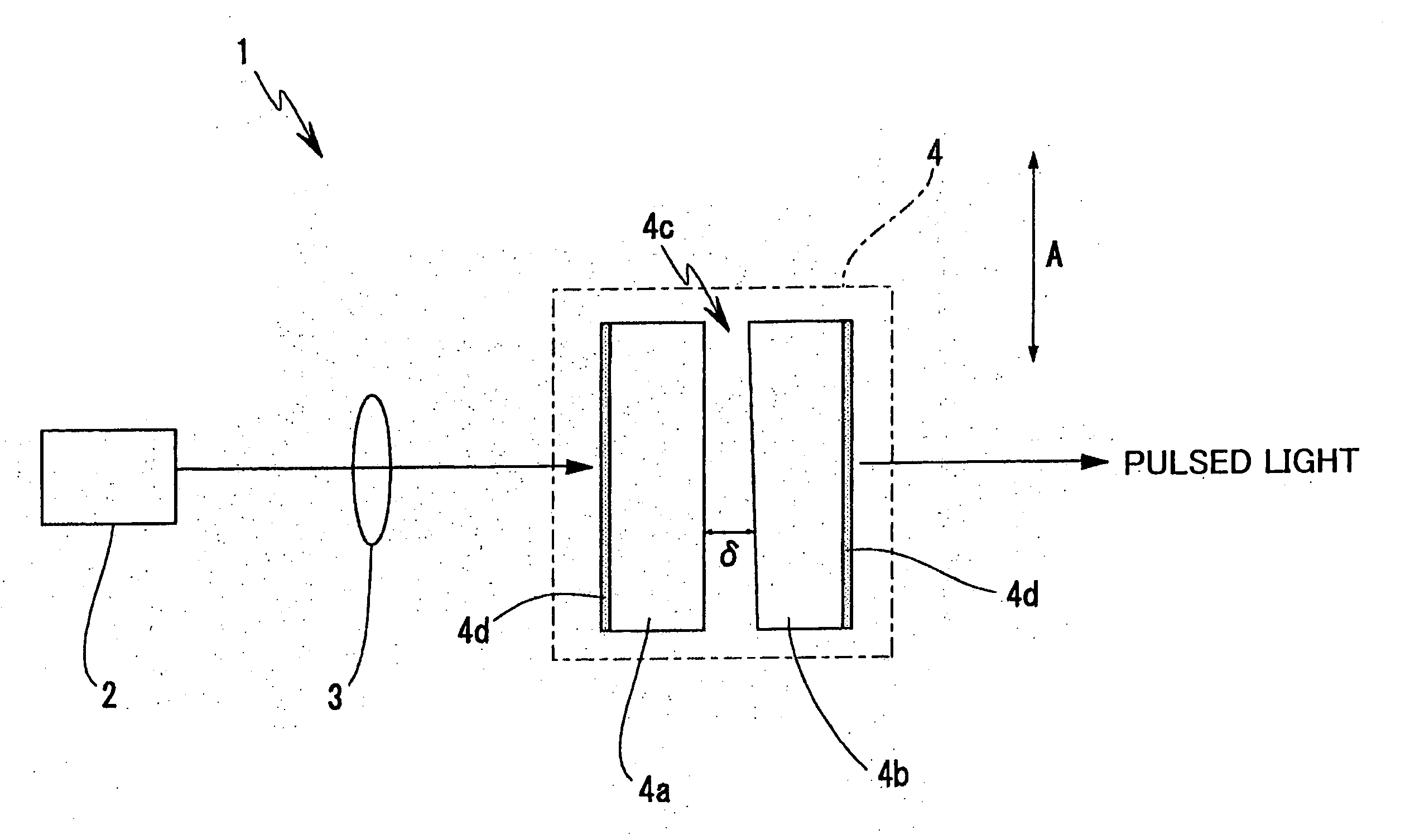
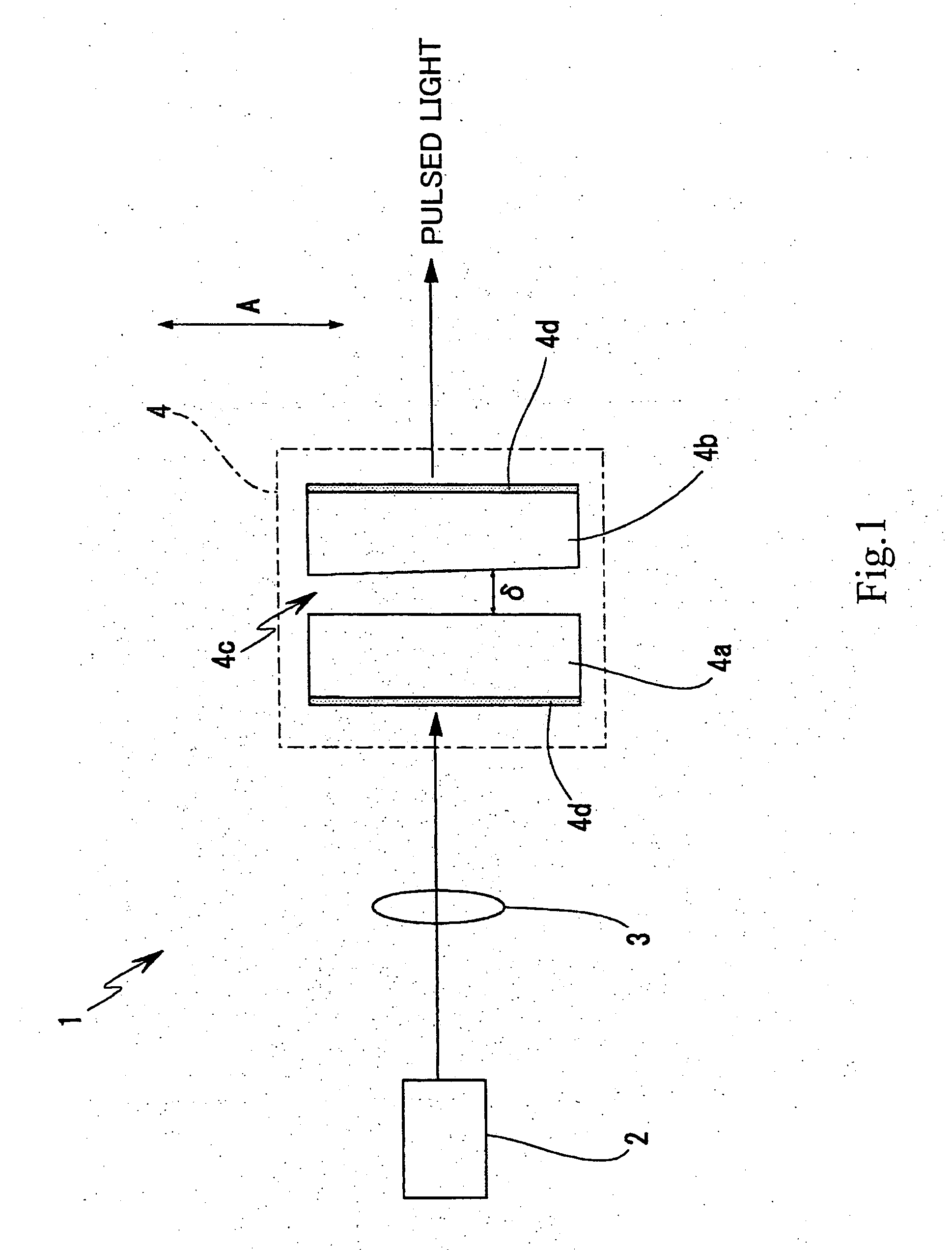
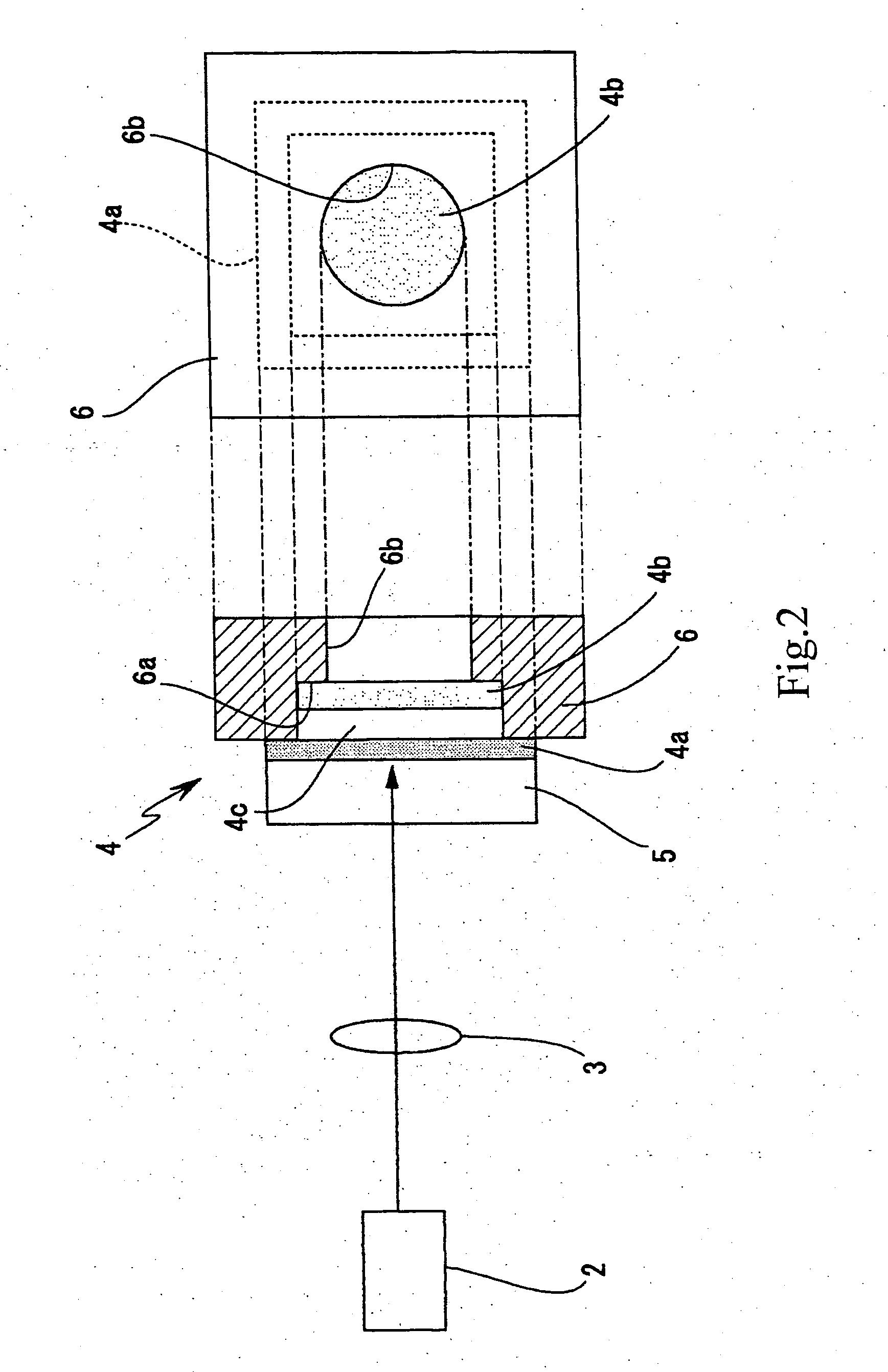
InactiveUS20050078719A1Susceptible to vibrationOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialPath lengthOperating point
In a laser light generating device, the stability against vibration and time-dependent changes will be improved, and influences of temperature changes exerted on the resonator will be reduced. In a laser light generating device (1) which includes an excitation light source (2) for generating a continuous-wave excitation light and a solid-state laser resonator (4) based on using thermal lens effect caused by heat generation at a position of excitation, the solid-state laser resonator further includes a laser medium (4a), a saturable absorber (4b), an intermediate medium (4c) and reflection means (4d) as the constituents. Influence of vibration is reduced by bonding a substrate of the laser medium (4a) and a substrate of the saturable absorber (4b) so as to integrate them. By adopting a configuration which does not need any method of selecting operating point based on temperature changes and is less susceptible to heat, and by relatively moving the excitation optical system and the resonator in the positional relation of the both to thereby adjust the light path length of the resonator, so as to make it possible to select a stable operating point.
Owner:SONY CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com