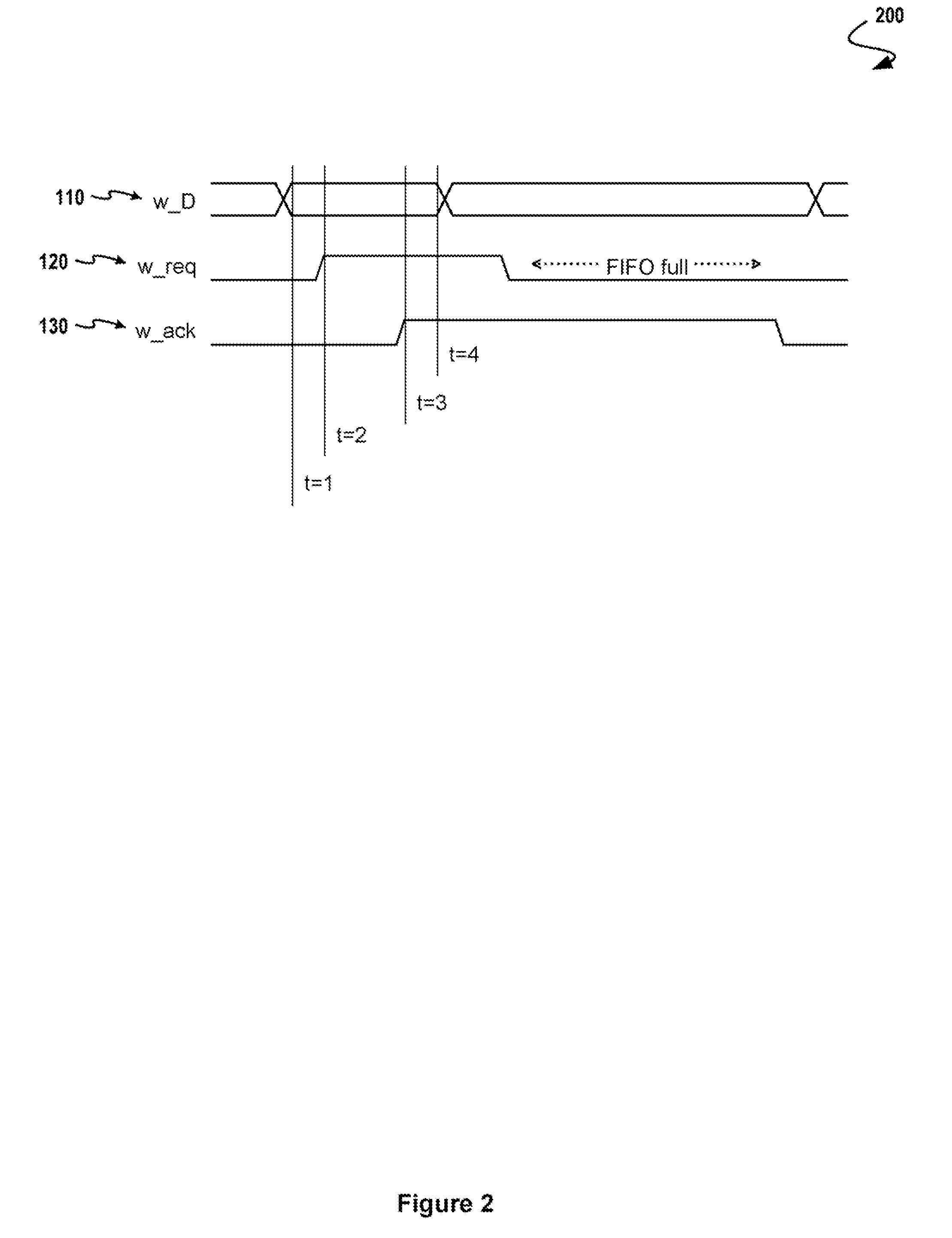Patents
Literature
297 results about "Metastability" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
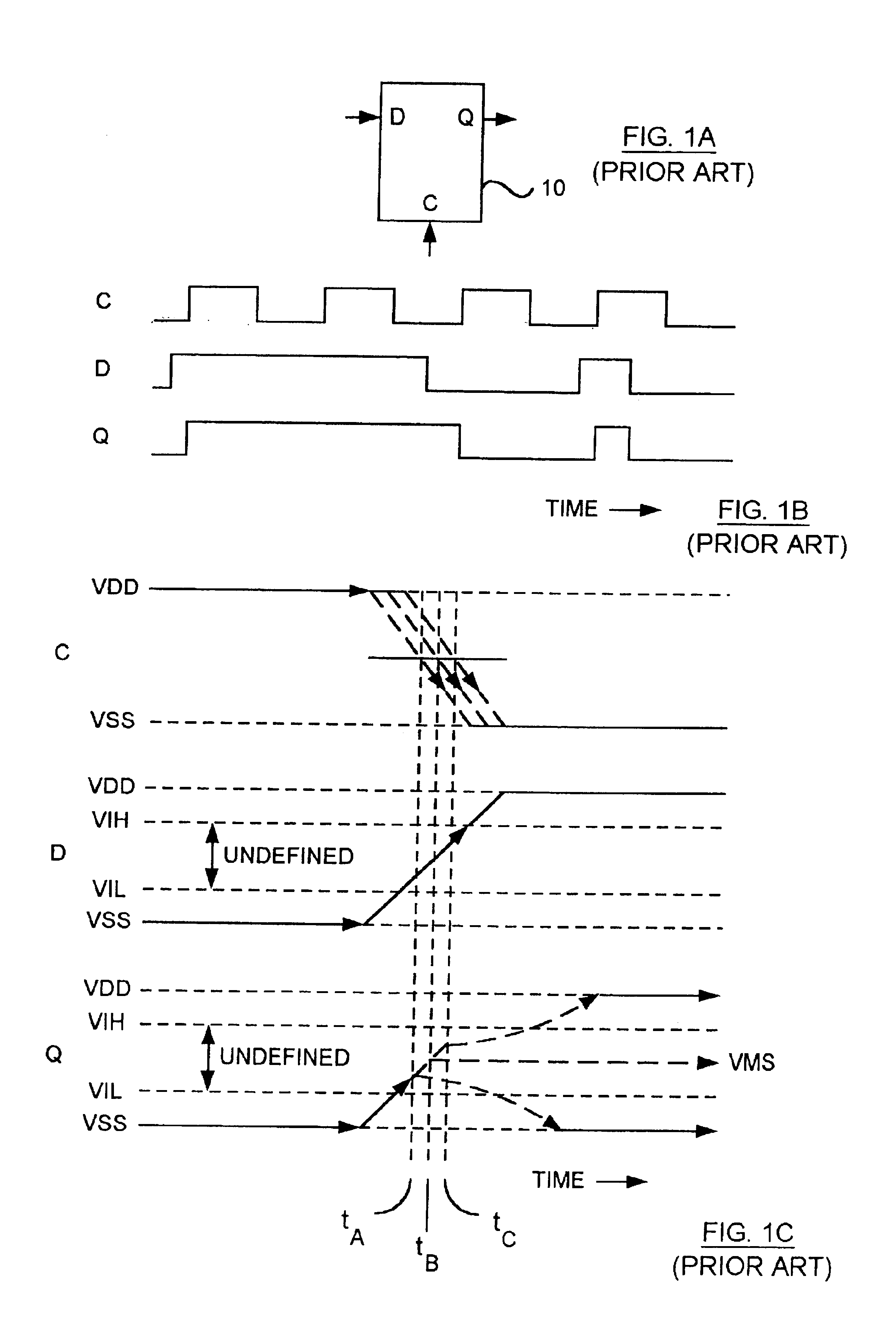
In physics, metastability is a stable state of a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy. A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball is only slightly pushed, it will settle back into its hollow, but a stronger push may start the ball rolling down the slope. Bowling pins show similar metastability by either merely wobbling for a moment or tipping over completely. A common example of metastability in science is isomerisation. Higher energy isomers are long lived as they are prevented from rearranging to their preferred ground state by (possibly large) barriers in the potential energy.
Articles having low wettability and methods for making
InactiveUS20070031639A1Low liquid wettabilityAnodisationMolten spray coatingEngineeringContact angle
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of high velocity powder particles using thermal plastic deformation
InactiveUS20050153069A1Reduced strengthEnhanced dynamic recovery of dislocation densityLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingFlow stressAcoustic wave
The invention relates to an apparatus and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of powder particles entrained in a subsonic or sonic gas jet onto the surface of an object. Under high velocity impact and thermal plastic deformation, the powder particles adhesively bond to the substrate and cohesively bond together to form consolidated materials with metallurgical bonds. The powder particles and optionally the surface of the object are heated to a temperature that reduces yield strength and permits plastic deformation at low flow stress levels during high velocity impact, but which is not so high as to melt the powder particles.
Owner:INNOVATION TECH INC
System and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of high velocity powder particles using thermal plastic deformation
InactiveUS6915964B2Modulus is reducedLower yield strengthMolten spray coatingSurface layering apparatusFlow stressAcoustic wave
The invention relates to an apparatus and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of powder particles entrained in a subsonic or sonic gas jet onto the surface of an object. Under high velocity impact and thermal plastic deformation, the powder particles adhesively bond to the substrate and cohesively bond together to form consolidated materials with metallurgical bonds. The powder particles and optionally the surface of the object are heated to a temperature that reduces yield strength and permits plastic deformation at low flow stress levels during high velocity impact, but which is not so high as to melt the powder particles.
Owner:INNOVATION TECH INC
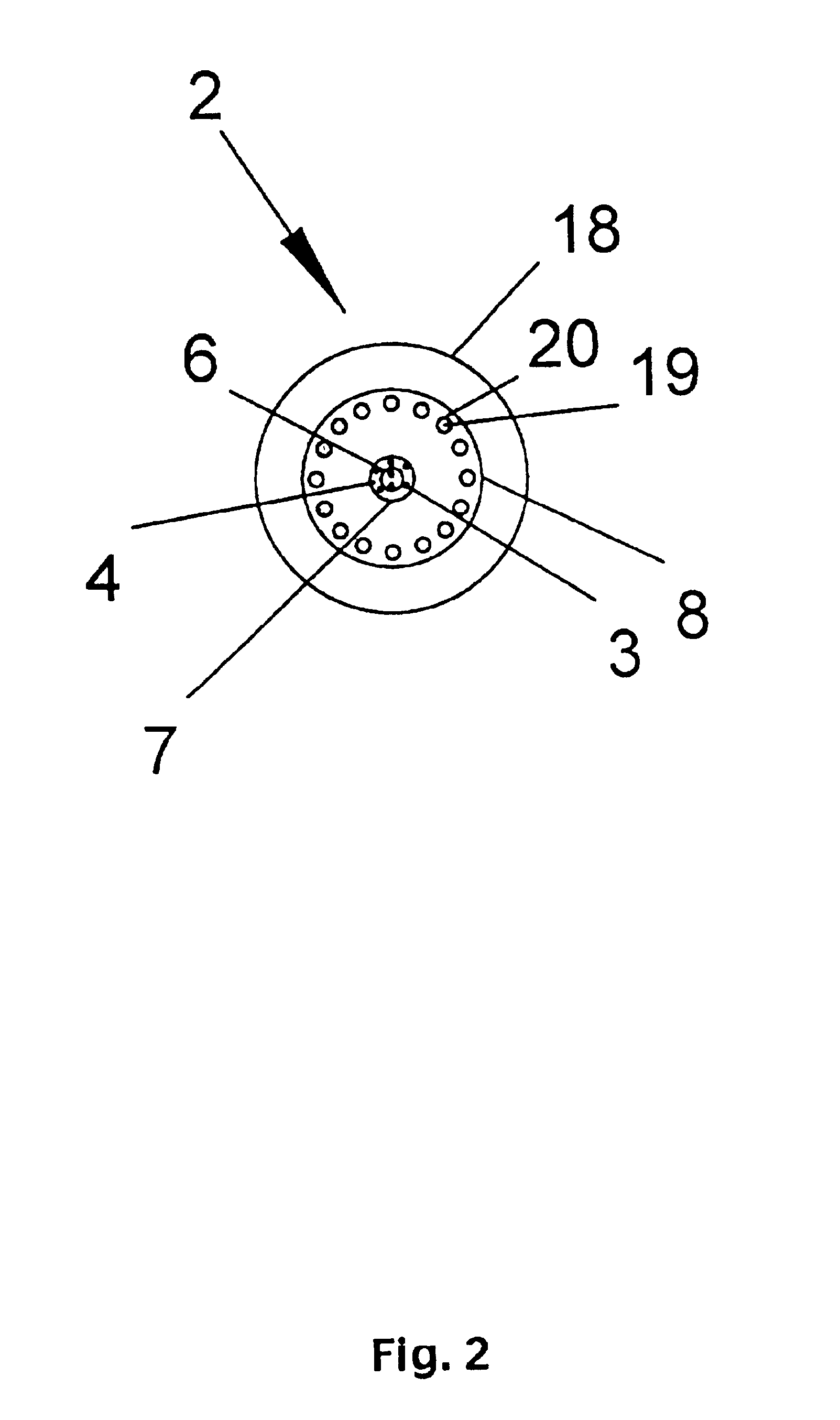
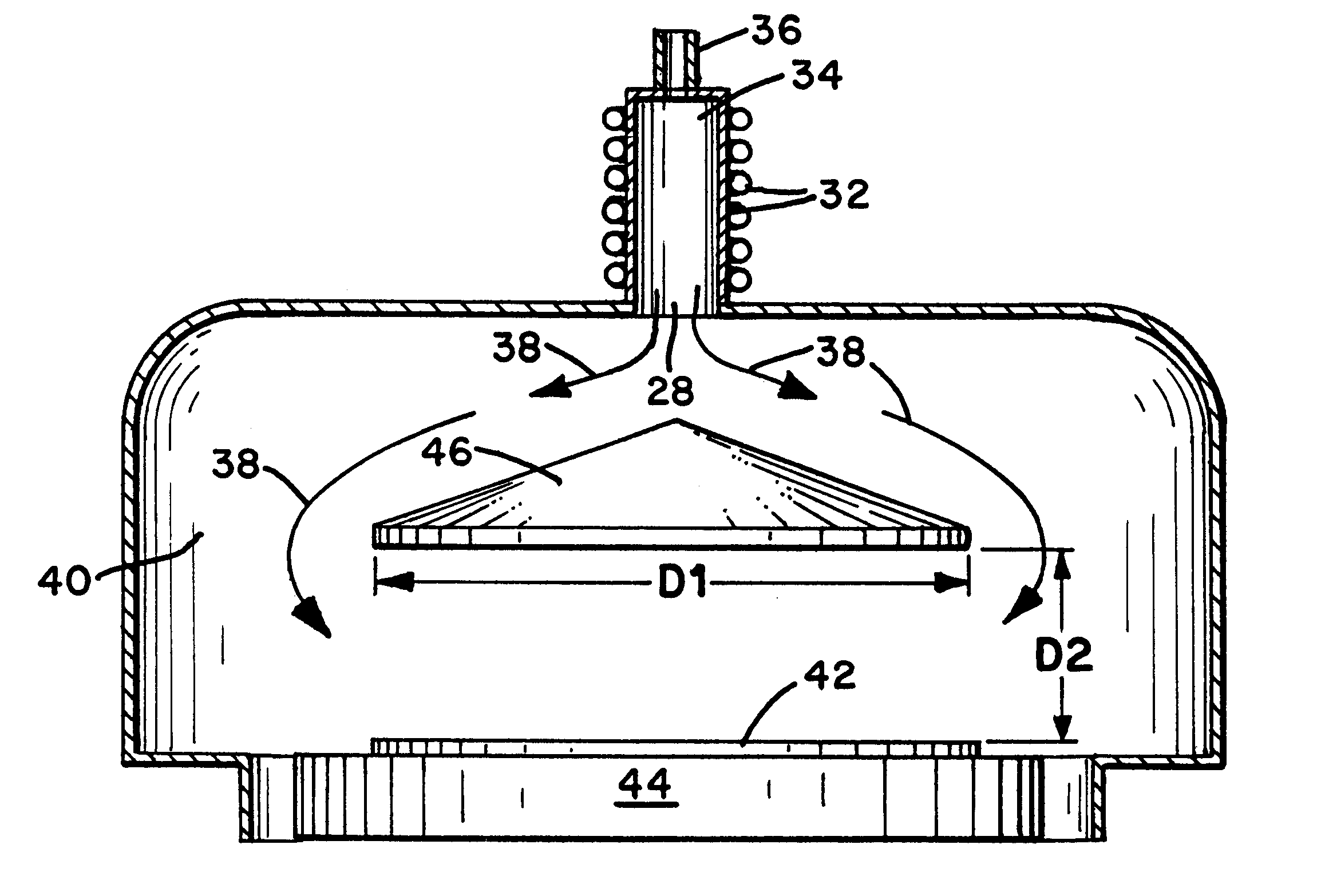
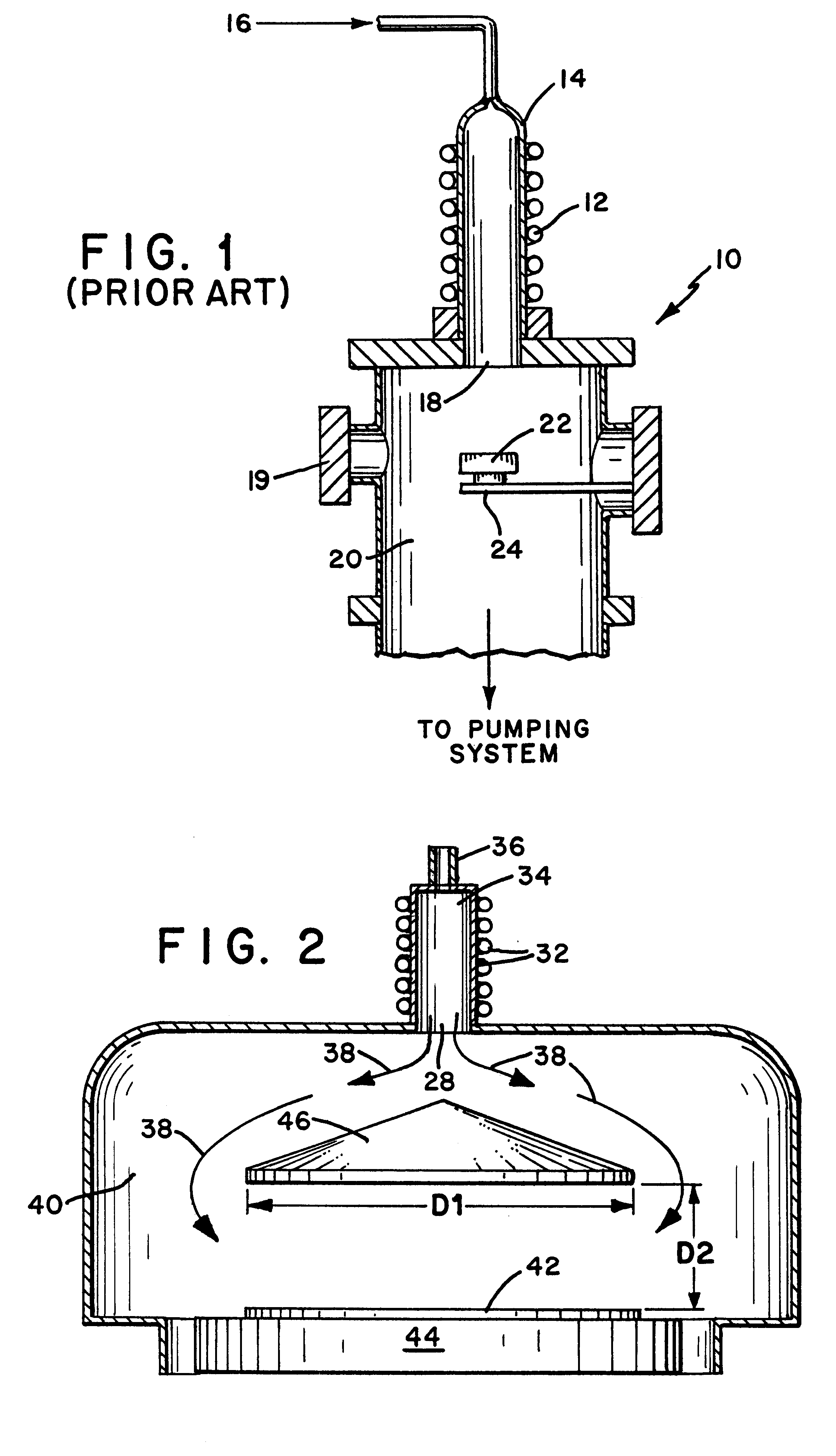
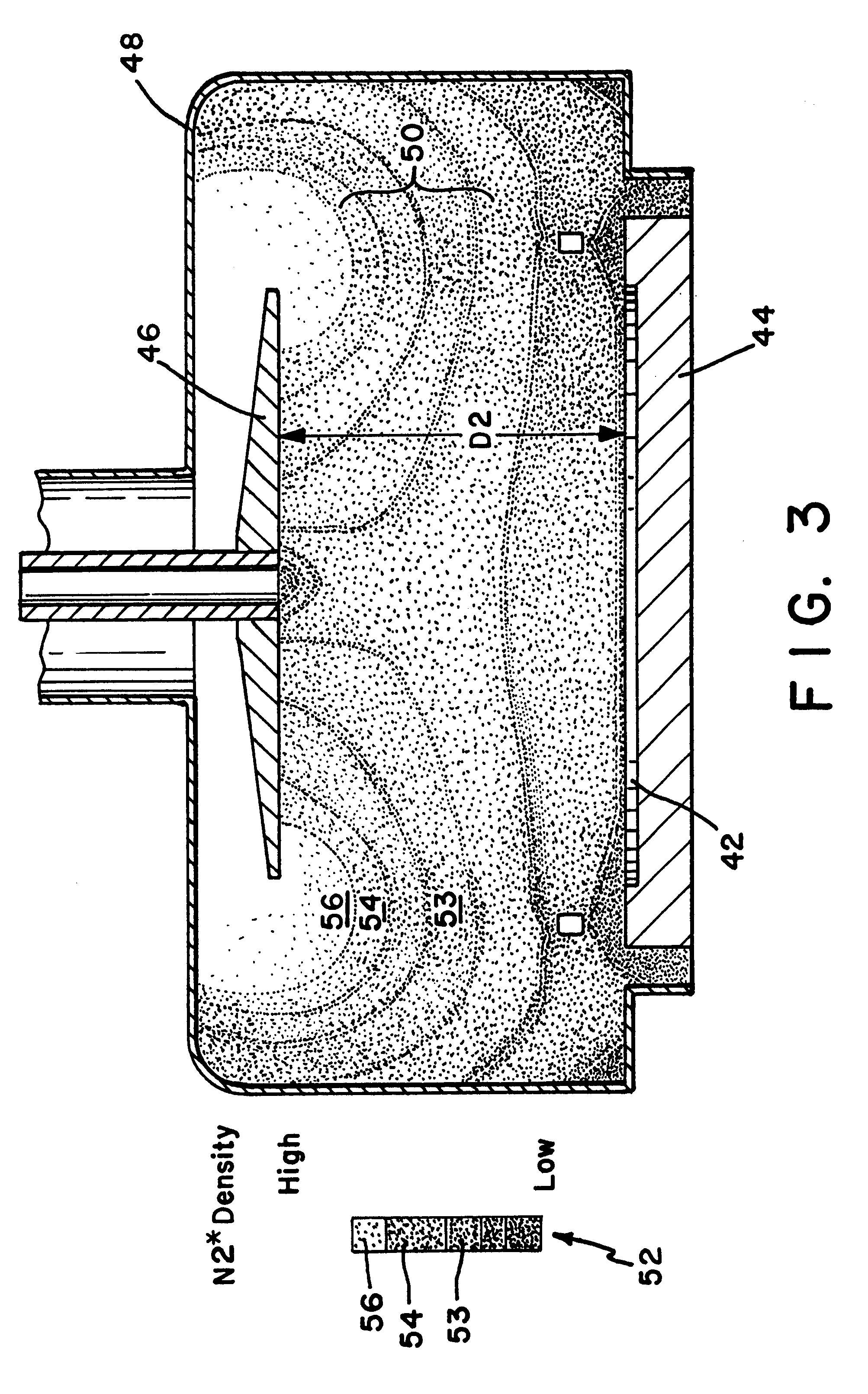
Apparatus and method for injecting and modifying gas concentration of a meta-stable or atomic species in a downstream plasma reactor
InactiveUS6287643B1Reduce lossesElectric discharge tubesPretreated surfacesRemote plasmaHigh density
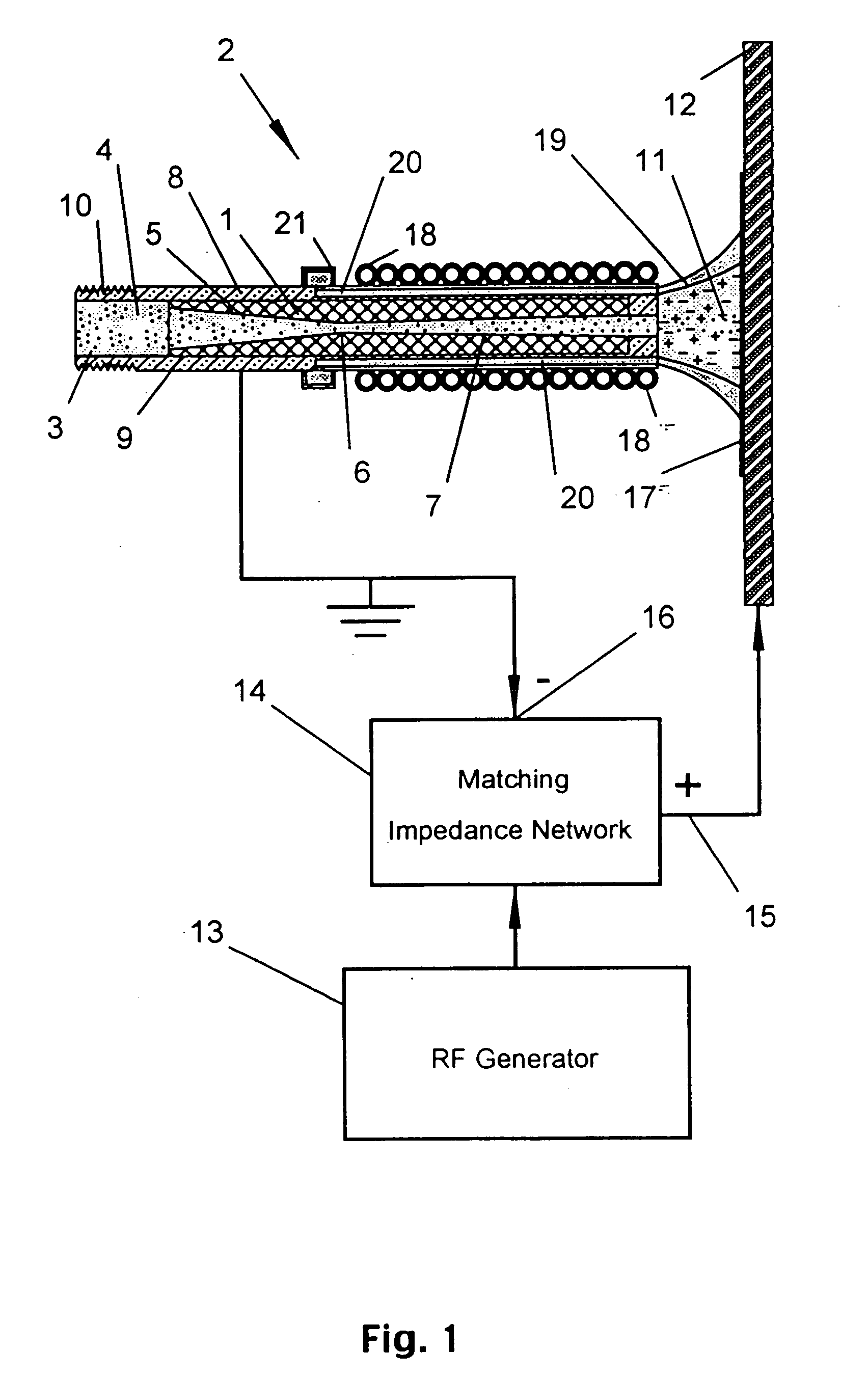
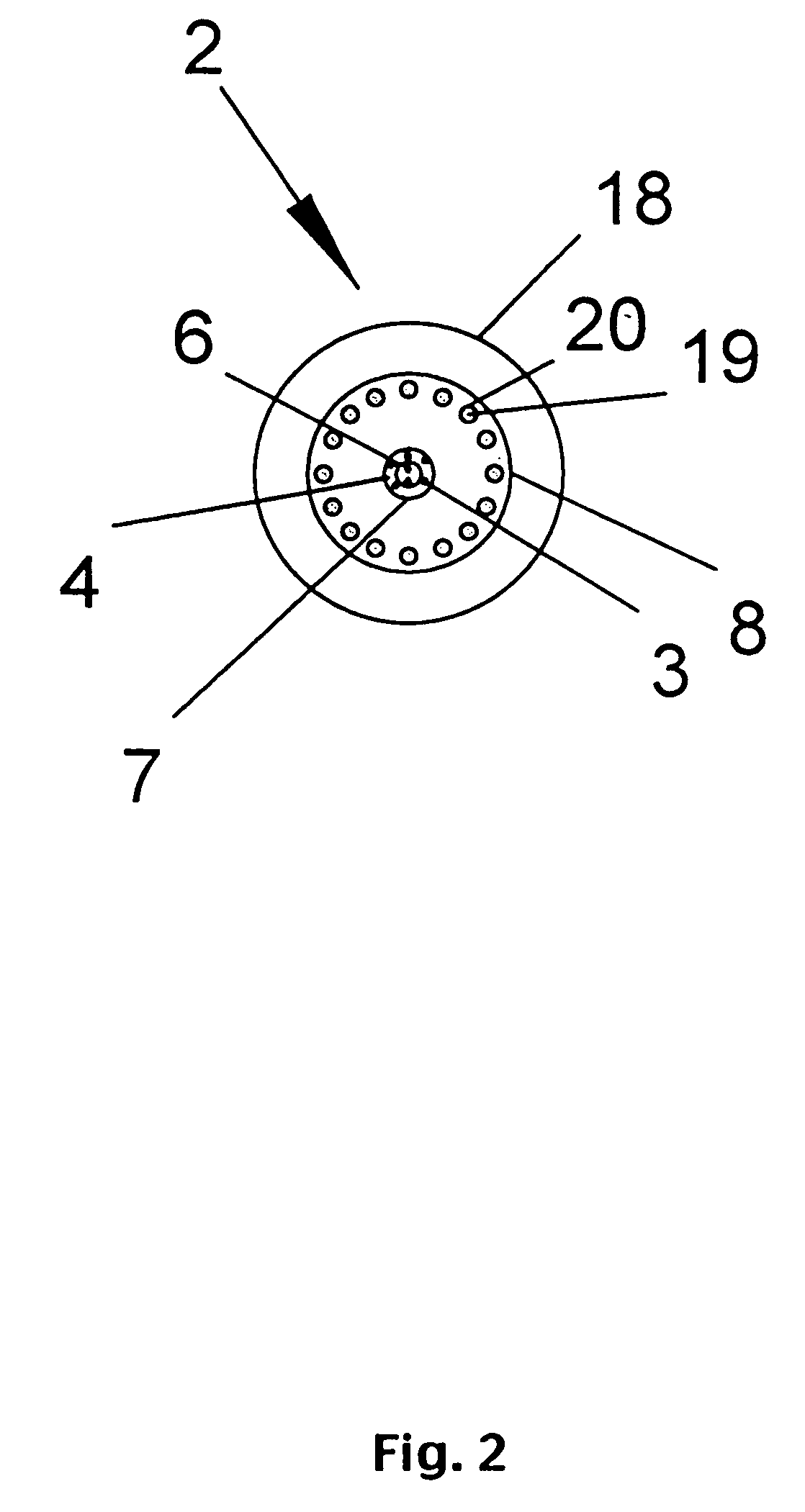
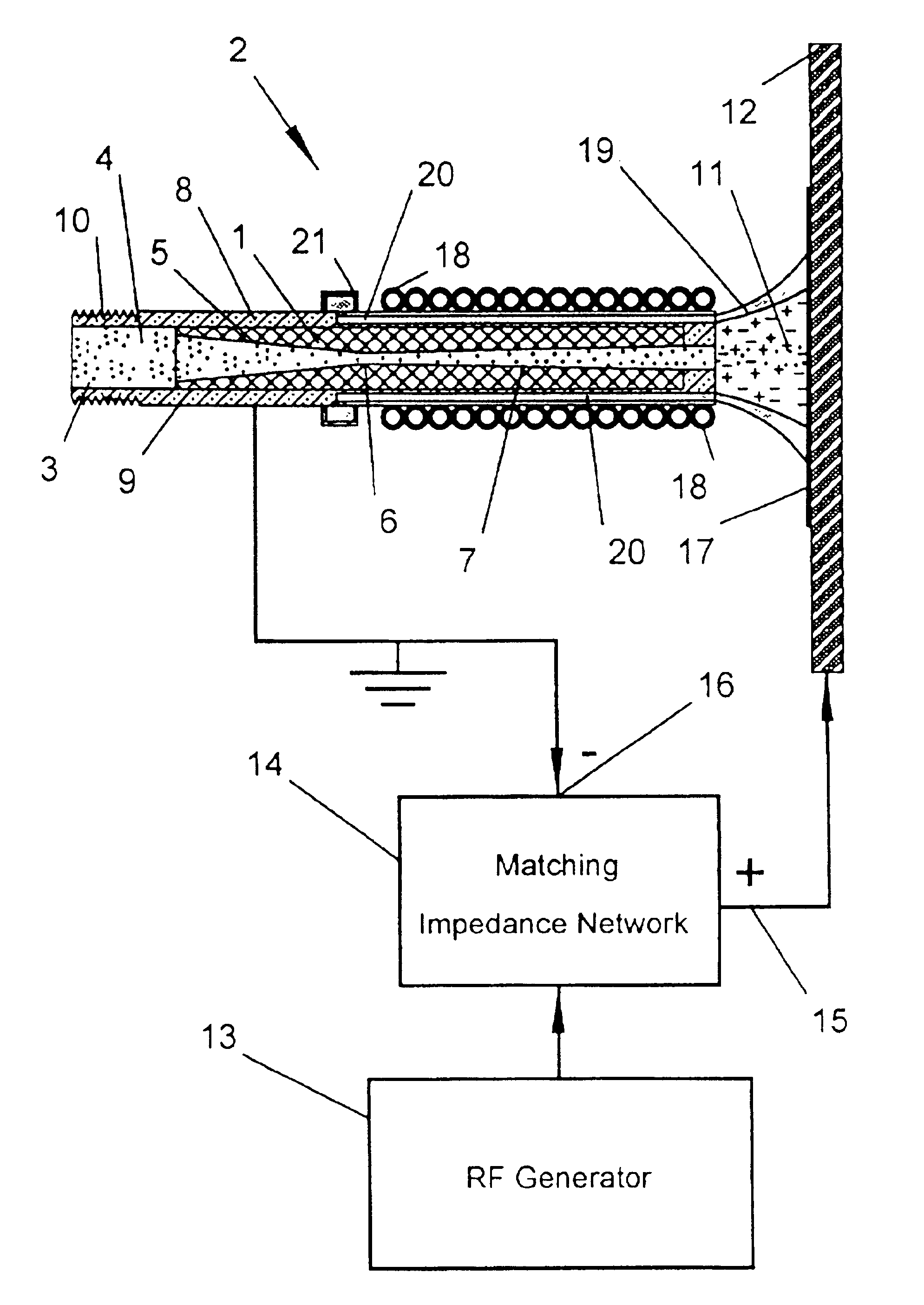
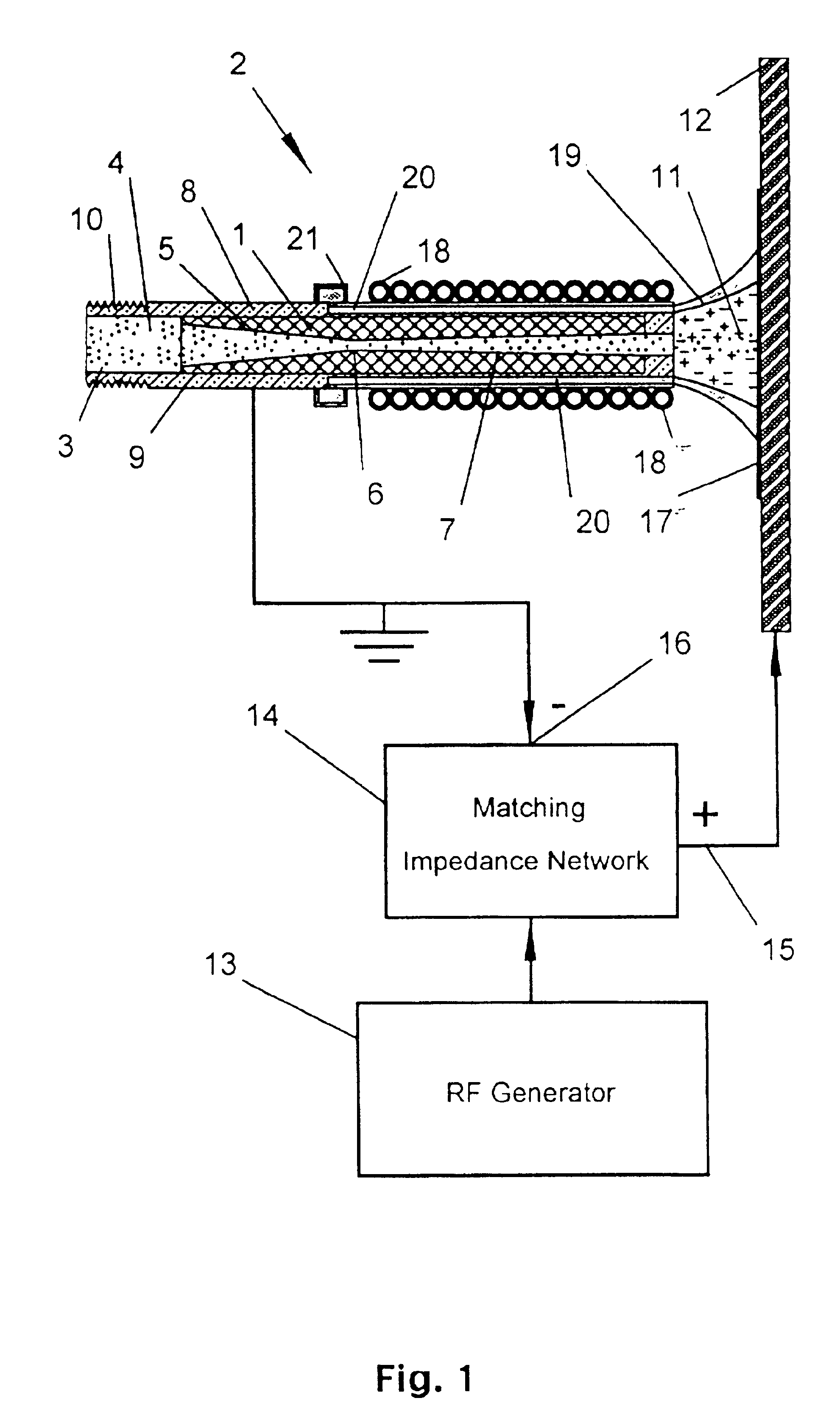
An apparatus and method for injecting gas within a plasma reactor and tailoring the distribution of an active species generated by the remote plasma source over the substrate or wafer. The distribution may be uniform, wafer-edge concentrated, or wafer-center concentrated. A contoured plate or profiler modifies the distribution. The profiler is an axially symmetric plate, having a narrow top end and a wider bottom end, shaped to redistribute the gas flow incident upon it. The method for tailoring the distribution of the active species over the substrate includes predetermining the profiler diameter and adjusting the profiler height over the substrate. A coaxial injector tube, for the concurrent injection of activated and non-activated gas species, allows gases to be delivered in an axially symmetric manner whereby one gas can be excited in a high density RF plasma, while the other gas can be prevented from excitation and / or dissociation caused by exposure to the plasma or heated surfaces in the source apparatus. The profiler is used in conjunction with the coaxial injector tube for redistributing the excited gases emerging from the injector tube, while allowing the non-excited gases to pass through its center.
Owner:NOVELLUS SYSTEMS
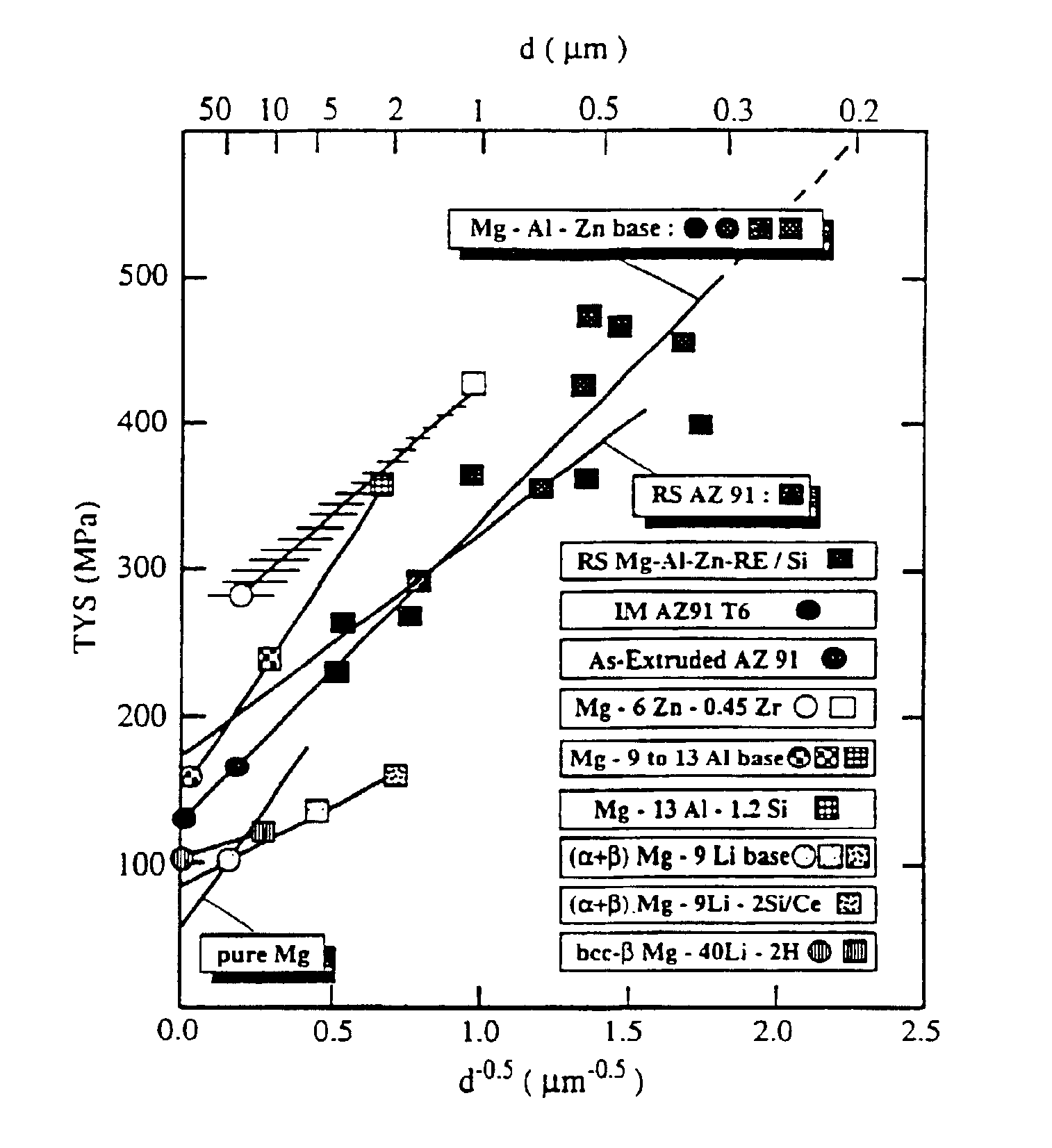
Selected processing for non-equilibrium light alloys and products
InactiveUS6908516B2Reduce resistanceMultiplies numberVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingGas phaseMaterials science
A new class of light or reactive elements and monophase α′-matrix magnesium- and aluminum-based alloys with superior engineering properties, for the latter being based on a homogeneous solute distribution or a corrosion-resistant and metallic shiny surface withstanding aqueous and saline environments and resulting from the control during synthesis of atomic structure over microstructure to net shape of the final product, said α′-matrix being retained upon conversion into a cast or wrought form. The manufacture of the materials relies on the control of deposition temperature and in-vacuum consolidation during vapor deposition, on maximized heat transfer or casting pressure during all-liquid processing and on controlled friction and shock power during solid state alloying using a mechanical milling technique. The alloy synthesis is followed by extrusion, rolling, forging, drawing and superplastic forming for which the conditions of mechanical working, thermal exposure and time to transfer corresponding metastable α′-matrix phases and microstructure into product form depend on thermal stability and transformation behavior at higher temperatures of said light alloy as well as on the defects inherent to a specific alloy synthesis employed. Alloying additions to the resulting α′-monophase matrix include 0.1 to 40 wt. % metalloids or light rare earth or early transition or simple or heavy rare earth metals or a combination thereof. The eventually more complex light alloys are designed to retain the low density and to improve damage tolerance of corresponding base metals and may include an artificial aging upon thermomechanical processing with or without solid solution heat and quench and annealing treatment for a controlled volume fraction and size of solid state precipitates to reinforce alloy film, layer or bulk and resulting surface qualities. Novel processes are employed to spur production and productivity for the new materials.
Owner:HEHMANN FRANZ
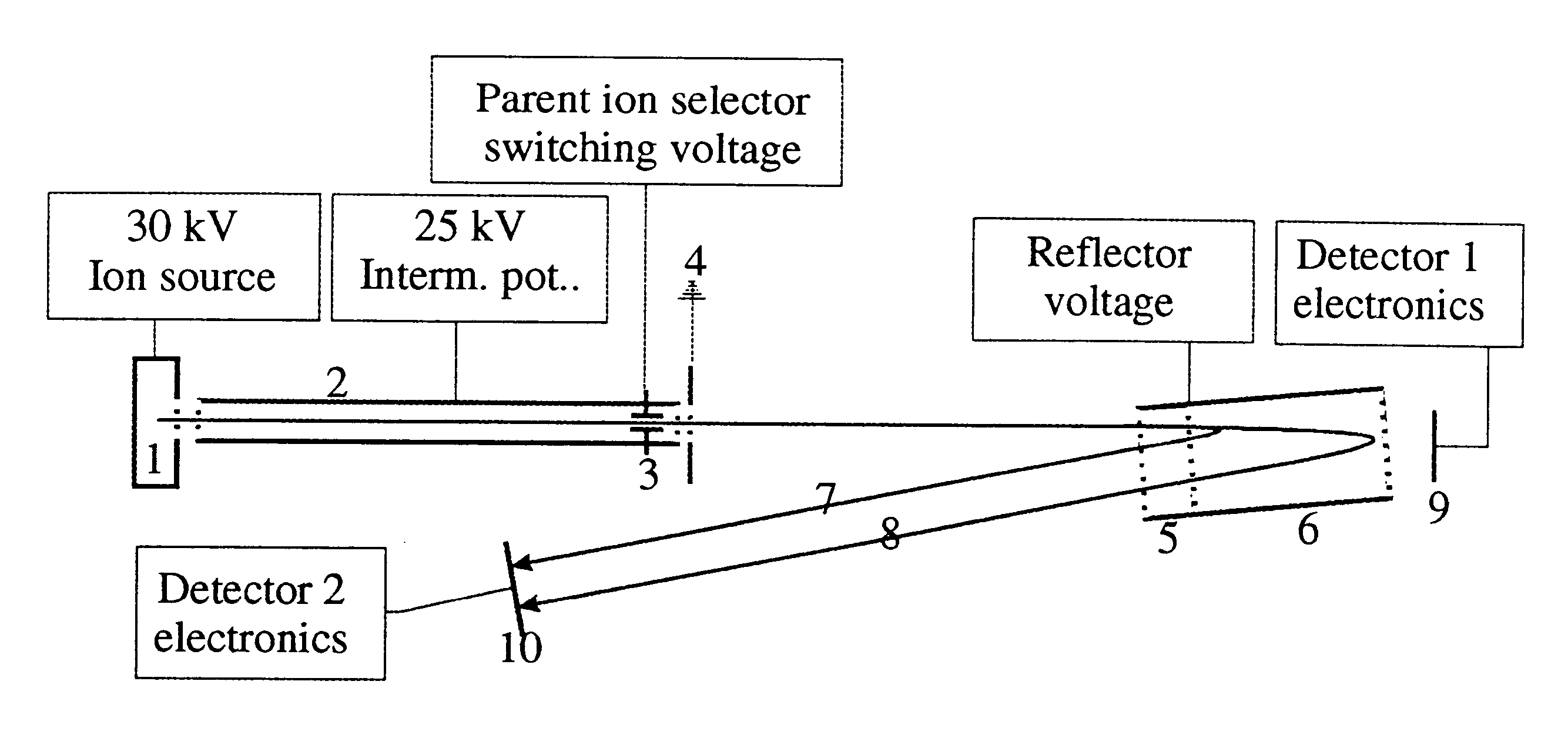
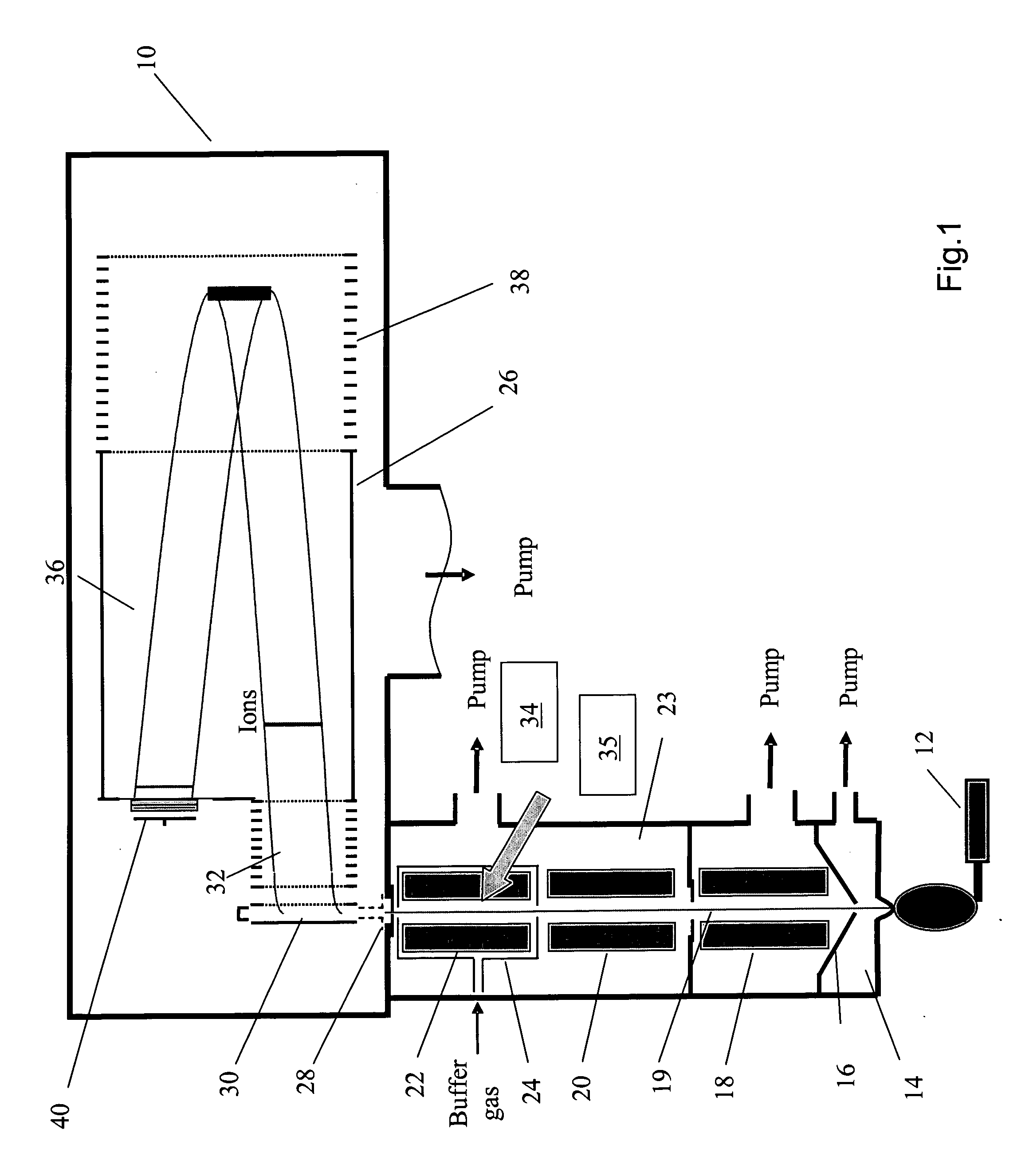
Daughter ion spectra with time-of-flight mass spectrometers
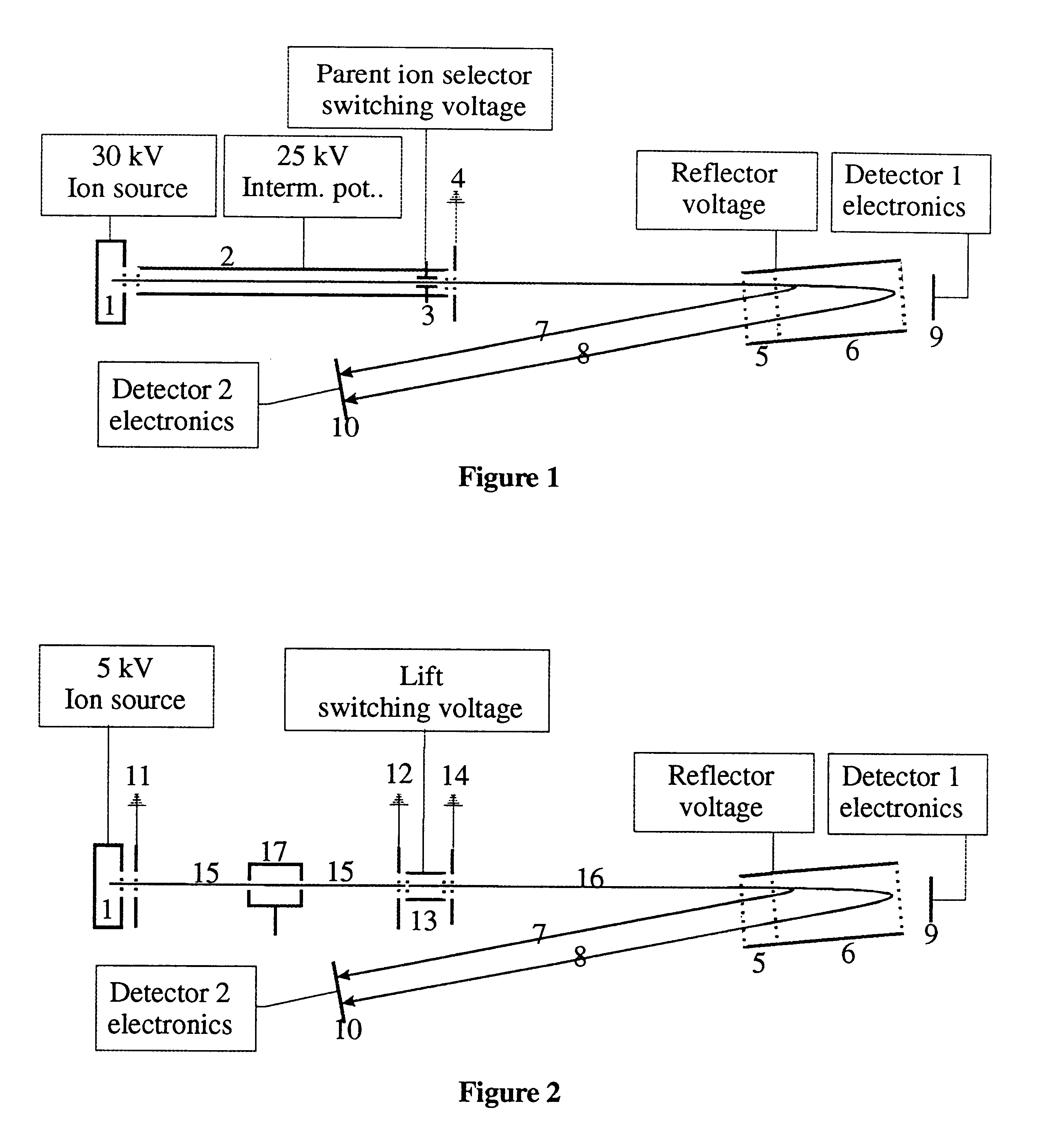
InactiveUS6300627B1Reduce delaysIncrease delayTime-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationHigh energyDecomposition
The invention relates to time-of-flight mass spectrometers for the measurement of daughter ion spectra (also called fragment ion spectra or MS / MS spectra) and corresponding measurement methods.According to the invention, the ions of an ion source are initially accelerated only to an intermediate level of energy, allowing them to decompose at that energy level by metastable decomposition or by collisionally induced fragmentation (CID). The ions are then accelerated in a second step to a high energy level. Light fragment ions gain a higher velocity than heavier fragment ions or non-decomposed parent ions. The spectrum of fragment ions can be detected separated by mass in either linear or reflector mode. An ion selector at the low energy level selects a single type of parent ion in order to avoid superpositions with fragment ions of other parent ions. A particularly preferred embodiment raises the potential of ions, for there second acceleration, during their flight through a small electrically isolated flight path chamber.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH
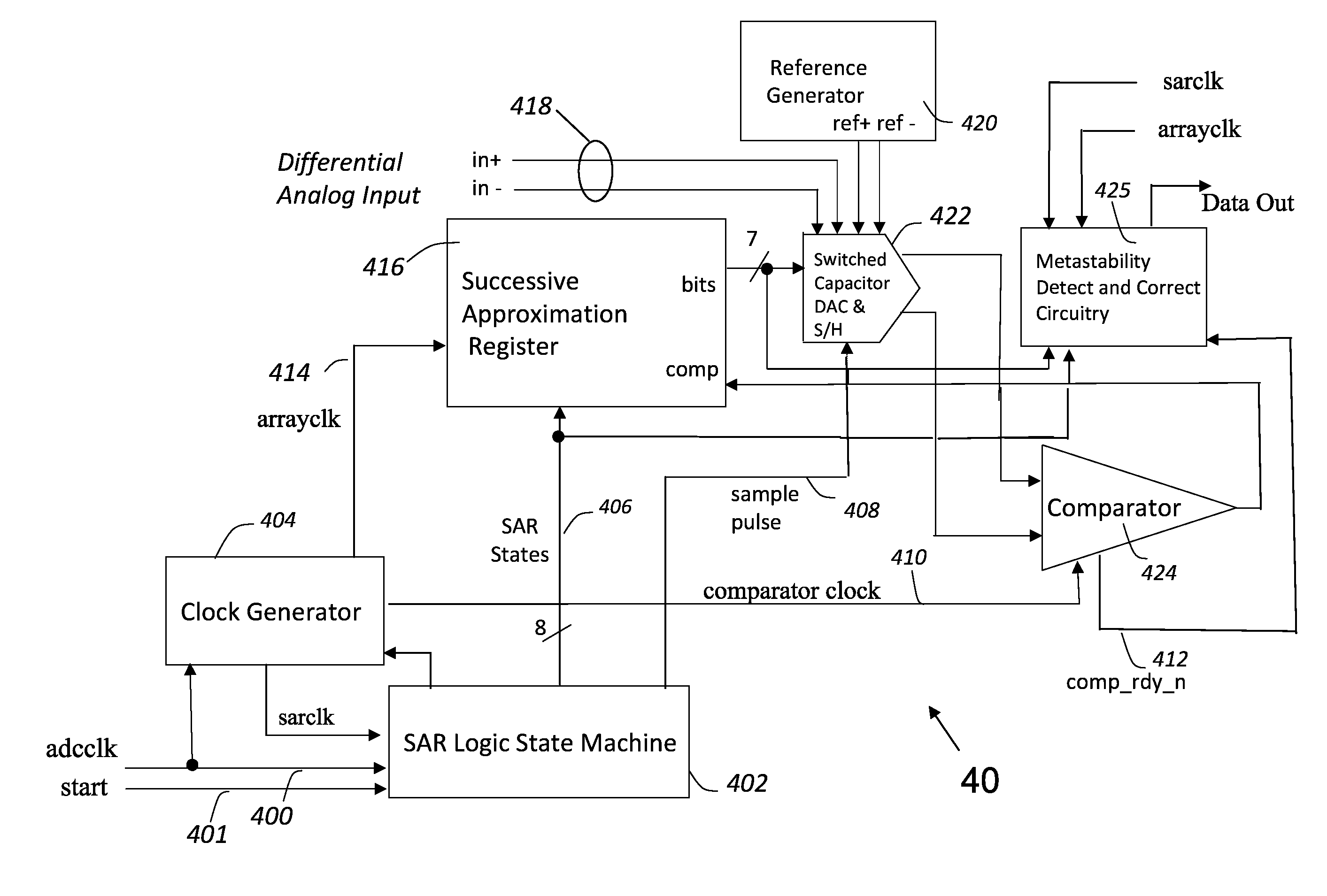
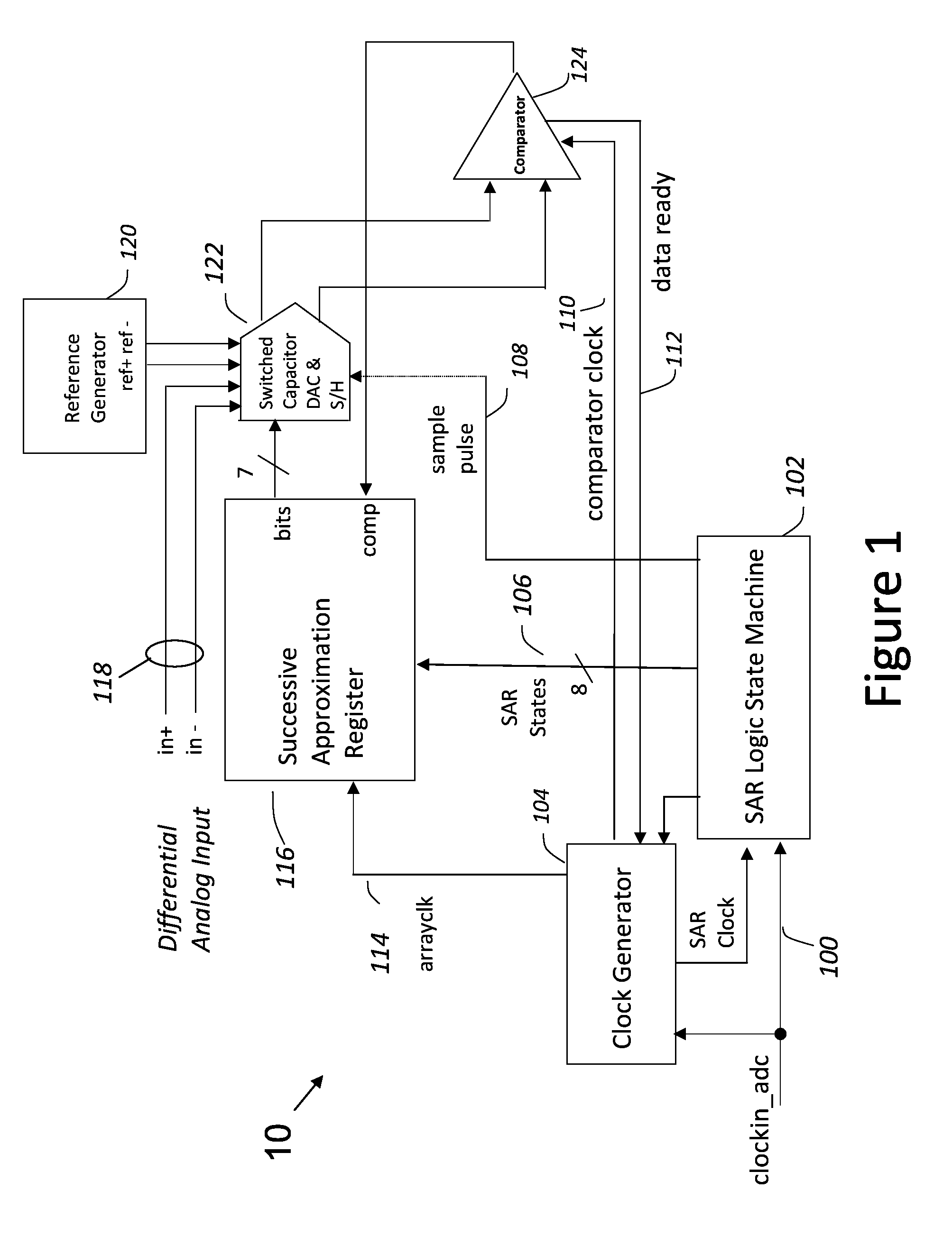
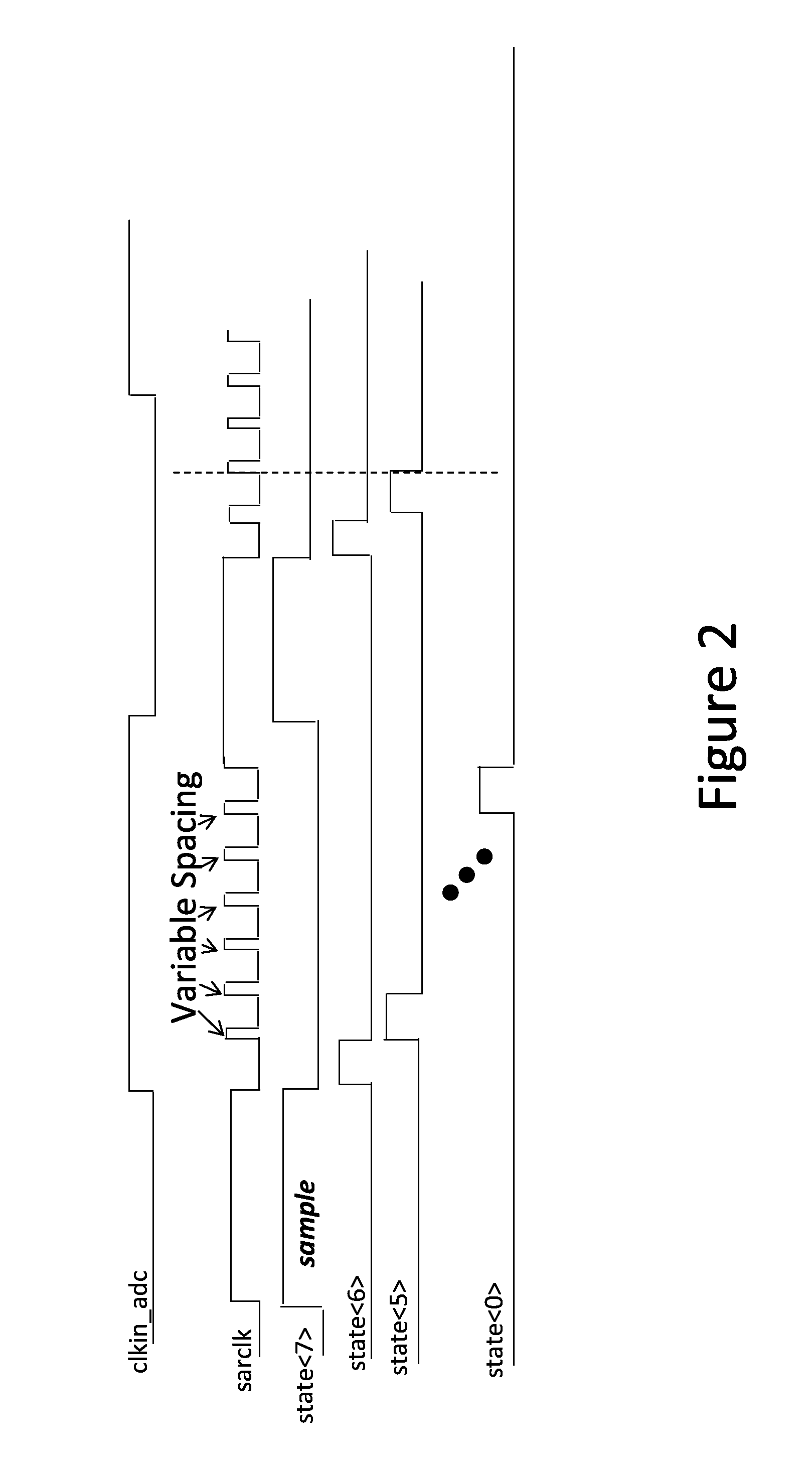
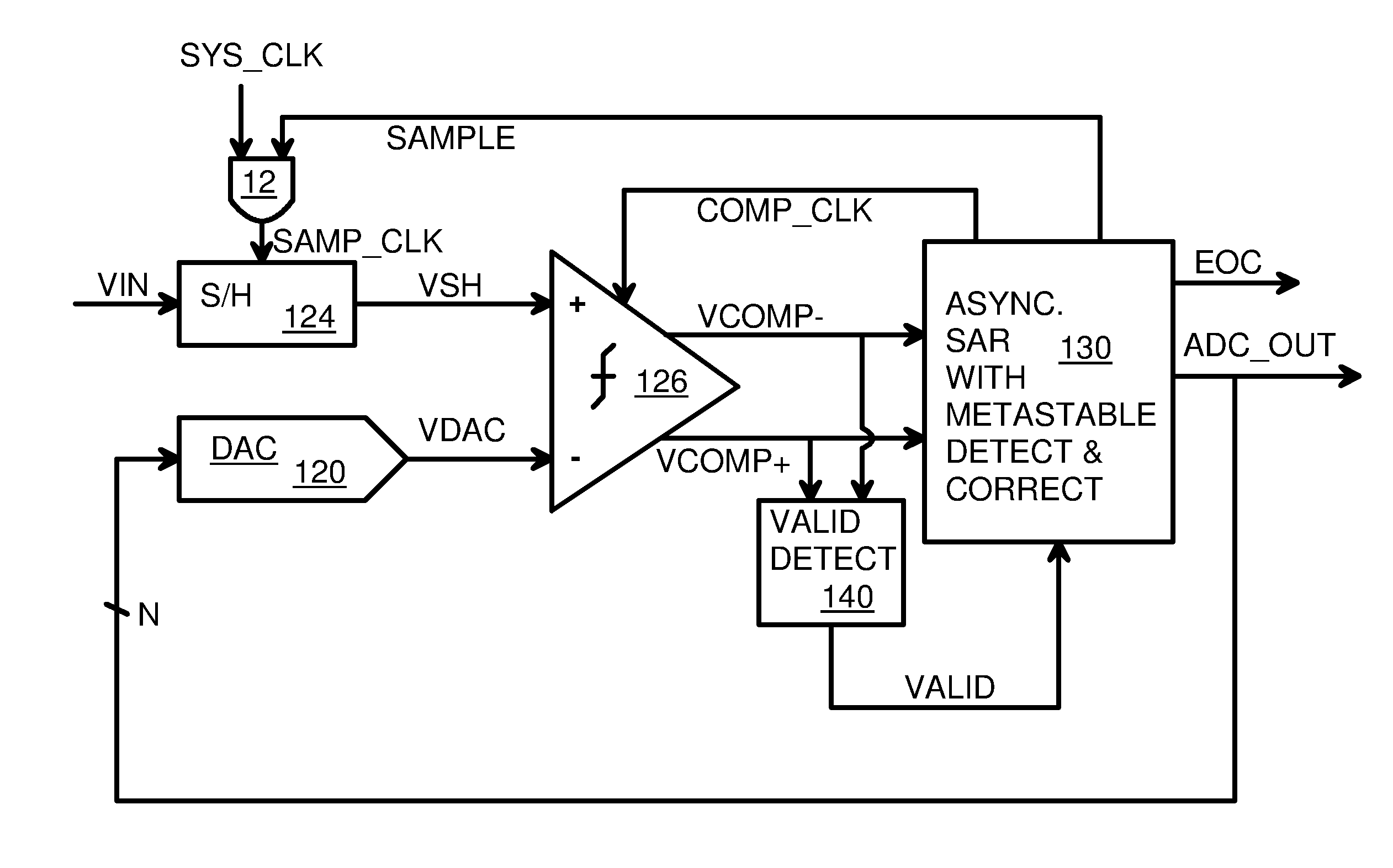
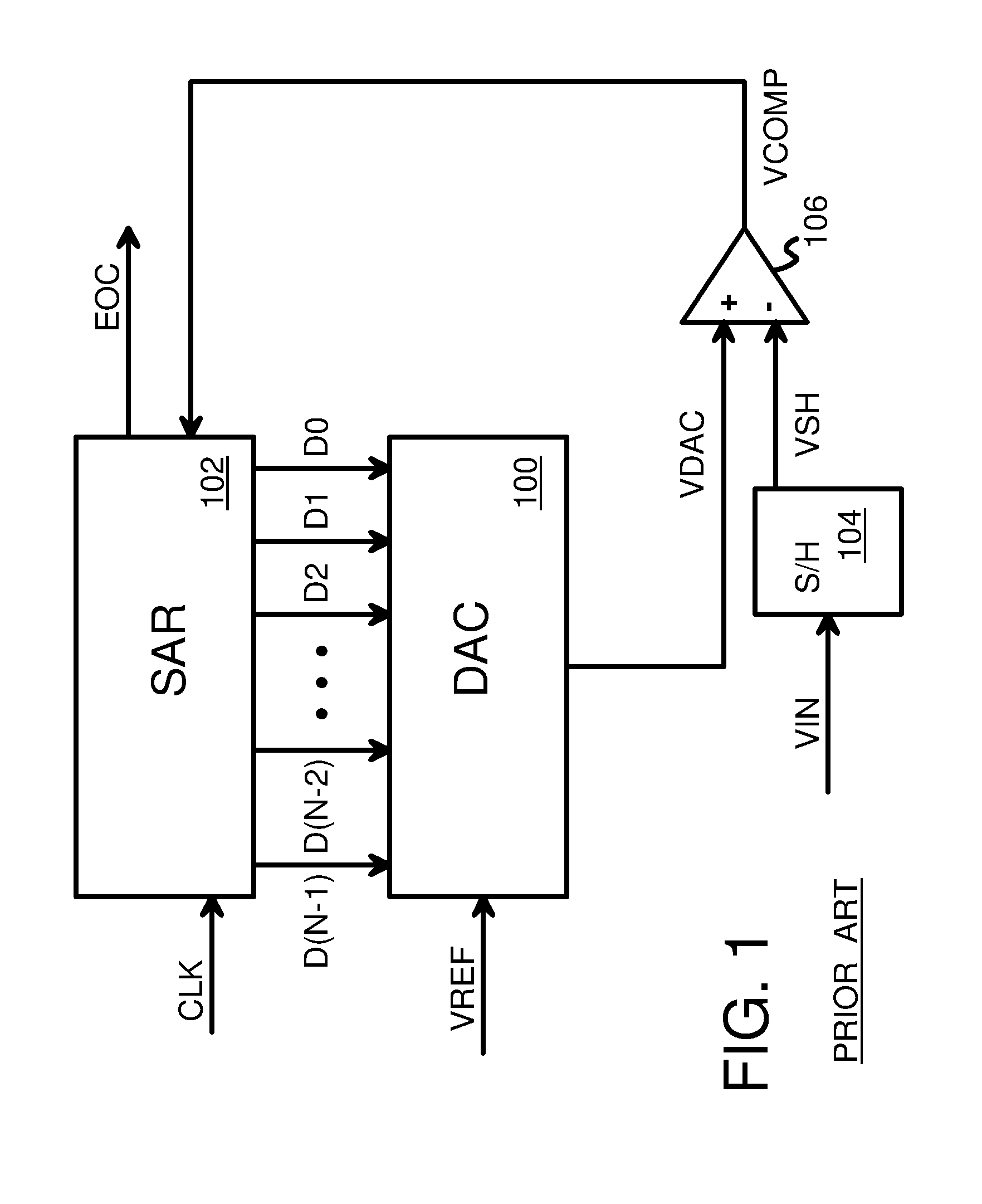
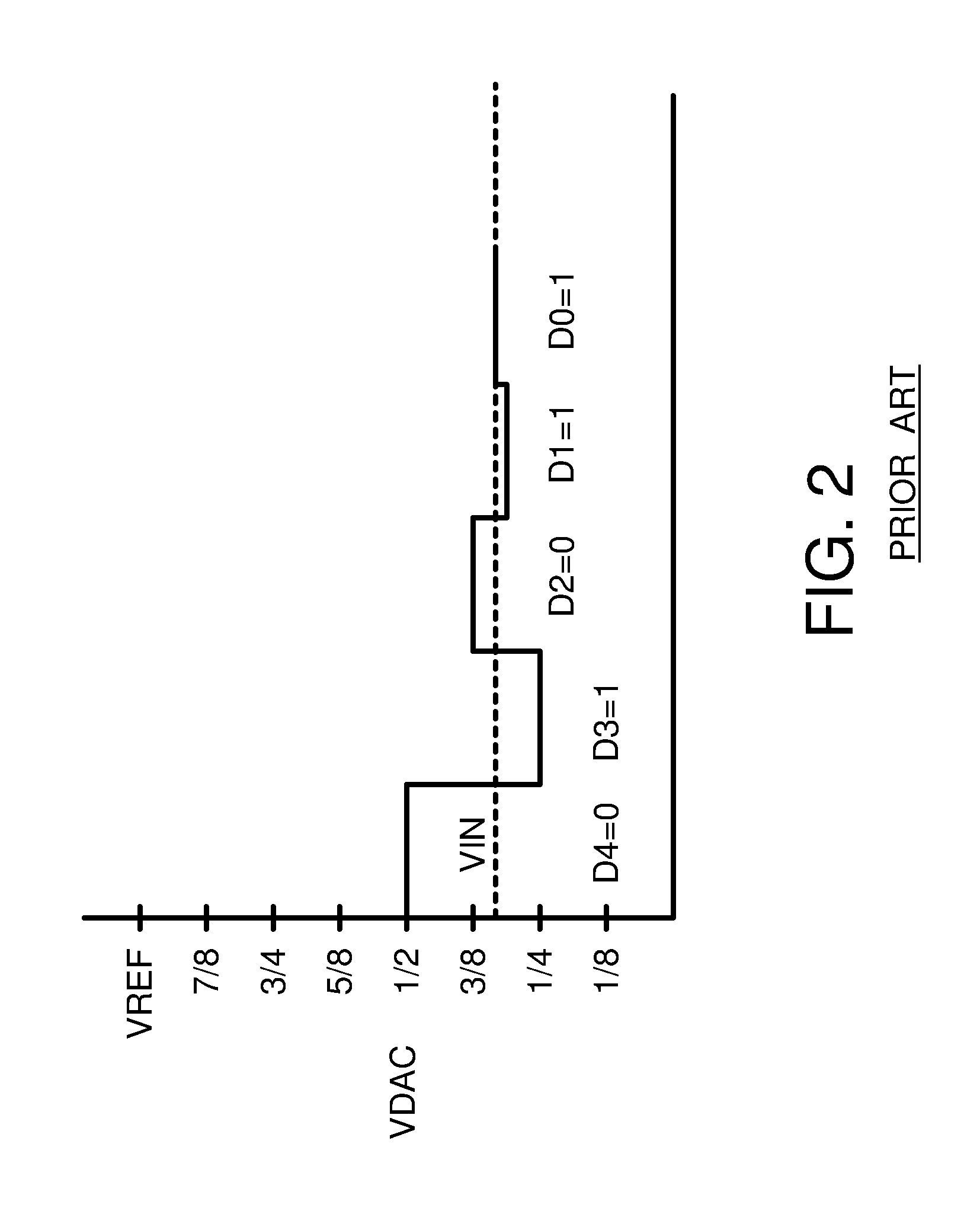
Metastability error detection and correction system and method for successive approximation analog-to-digital converters
ActiveUS8957802B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterNAND gate
A system and method are provided for the detection and correction of metastability errors in a successive approximation analog to digital converter (ADC). The successive approximation ADC (40) includes a comparator unit (424) that includes a NAND gate circuit (550) that outputs a comp_rdy_n signal when the comparator (500) has latched a result. ADC (40) includes a metastability detection and correction circuit (425) that includes a first logic circuit (700) that monitors the comp_rdy_n signal and detects a metastable event if that signal is not received within a portion of a conversion time period of the ADC. Responsive to detection of a metastable event, a second logic circuit (750) generates a correct conversion code at the output of the ADC. If no metastable event is detected during a conversion cycle of the ADC, the second logic circuit (750) outputs the conversion codes determined by the comparator (500).
Owner:CADENCE DESIGN SYST INC
Metastability effects simulation for a circuit description
ActiveUS7356789B2Detecting faulty computer hardwareElectrical testingProcessor registerComputer science
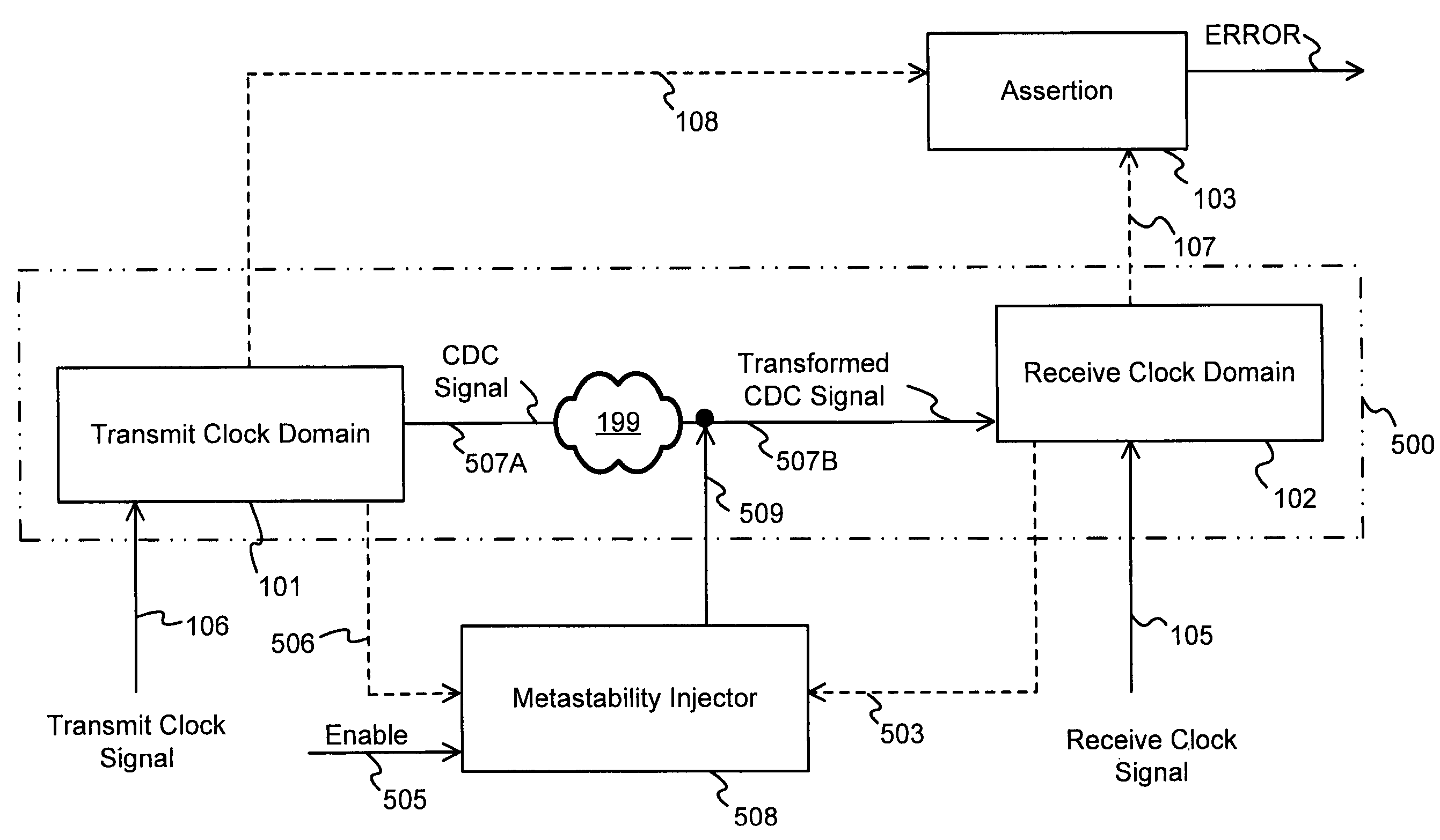
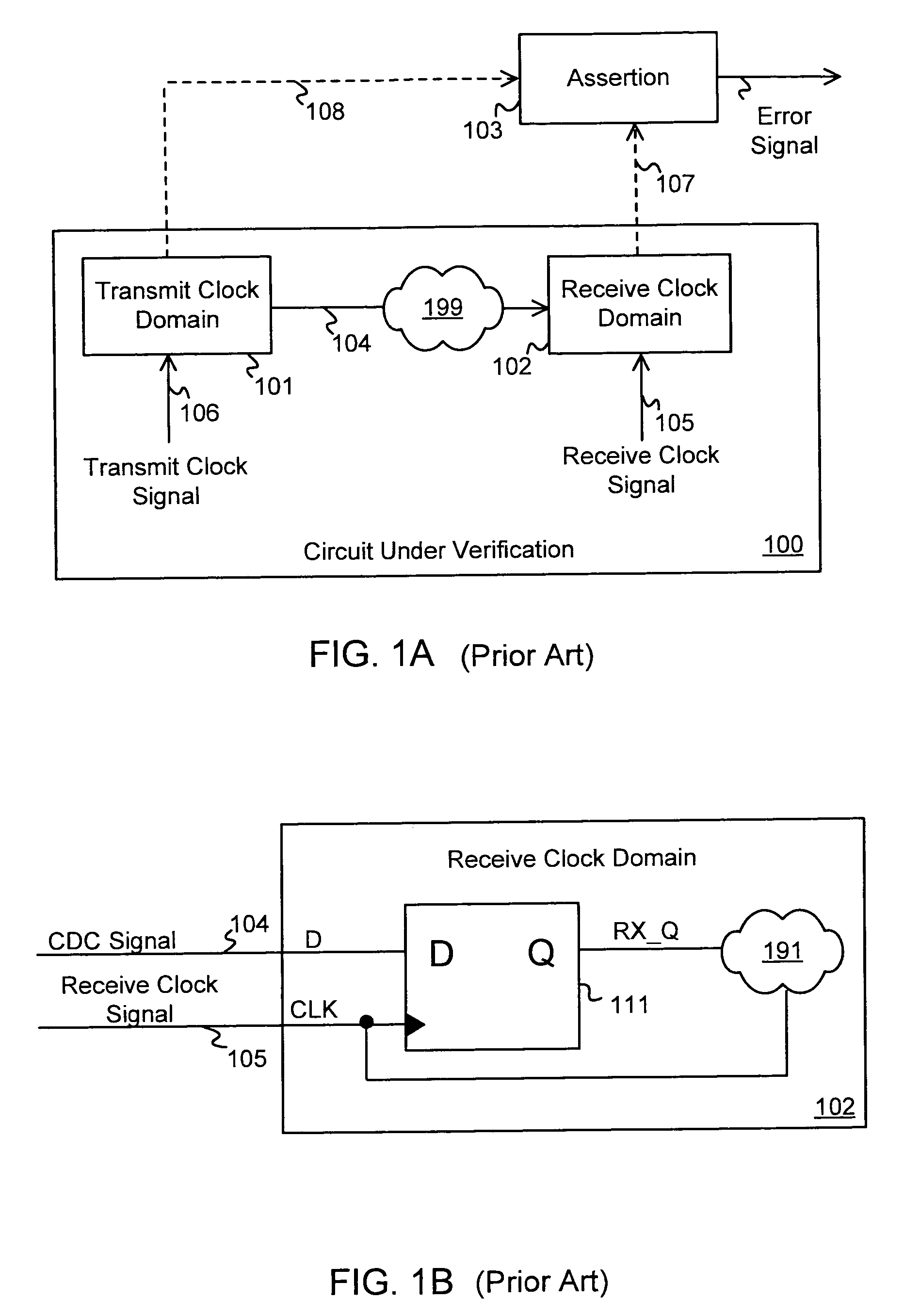
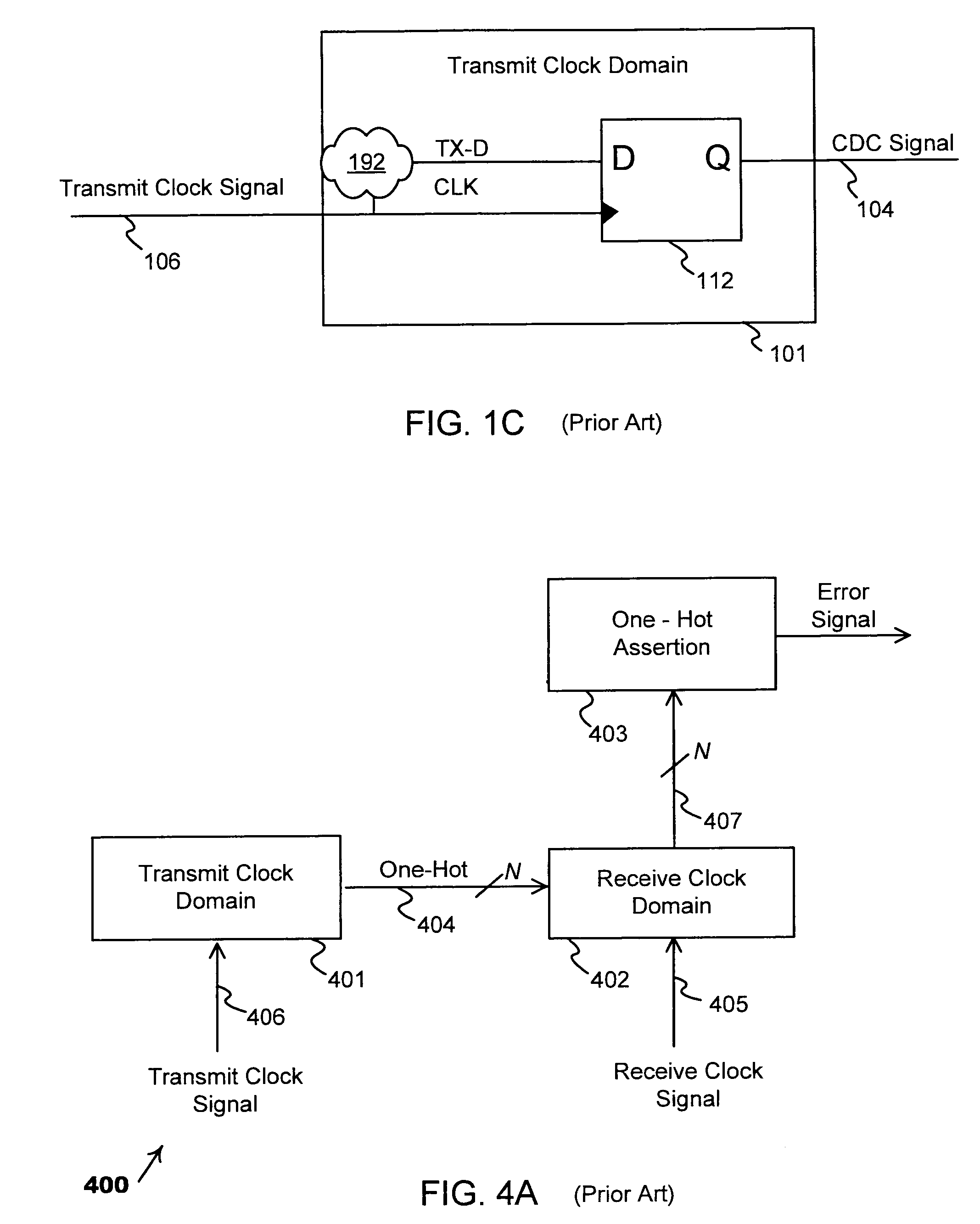
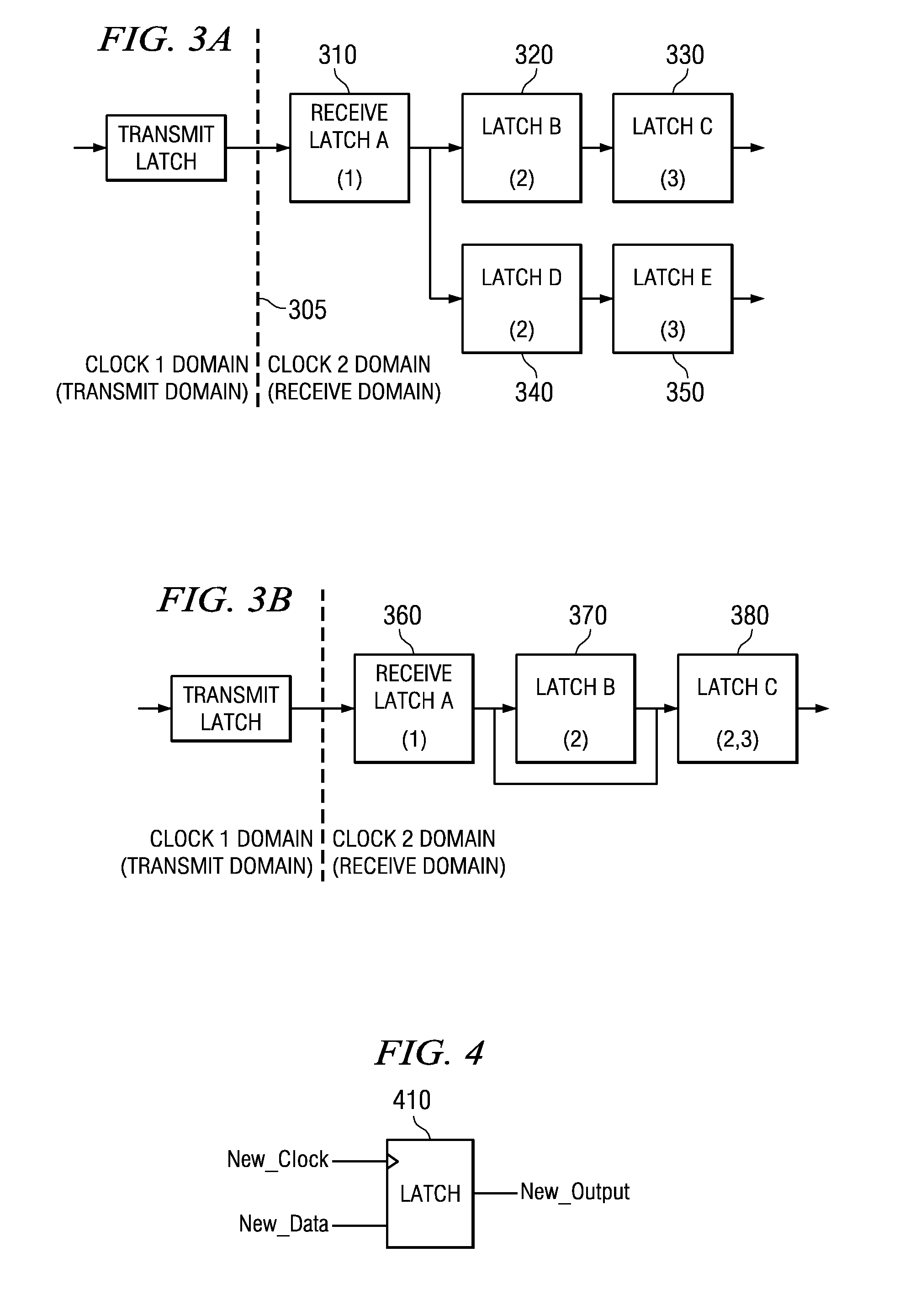
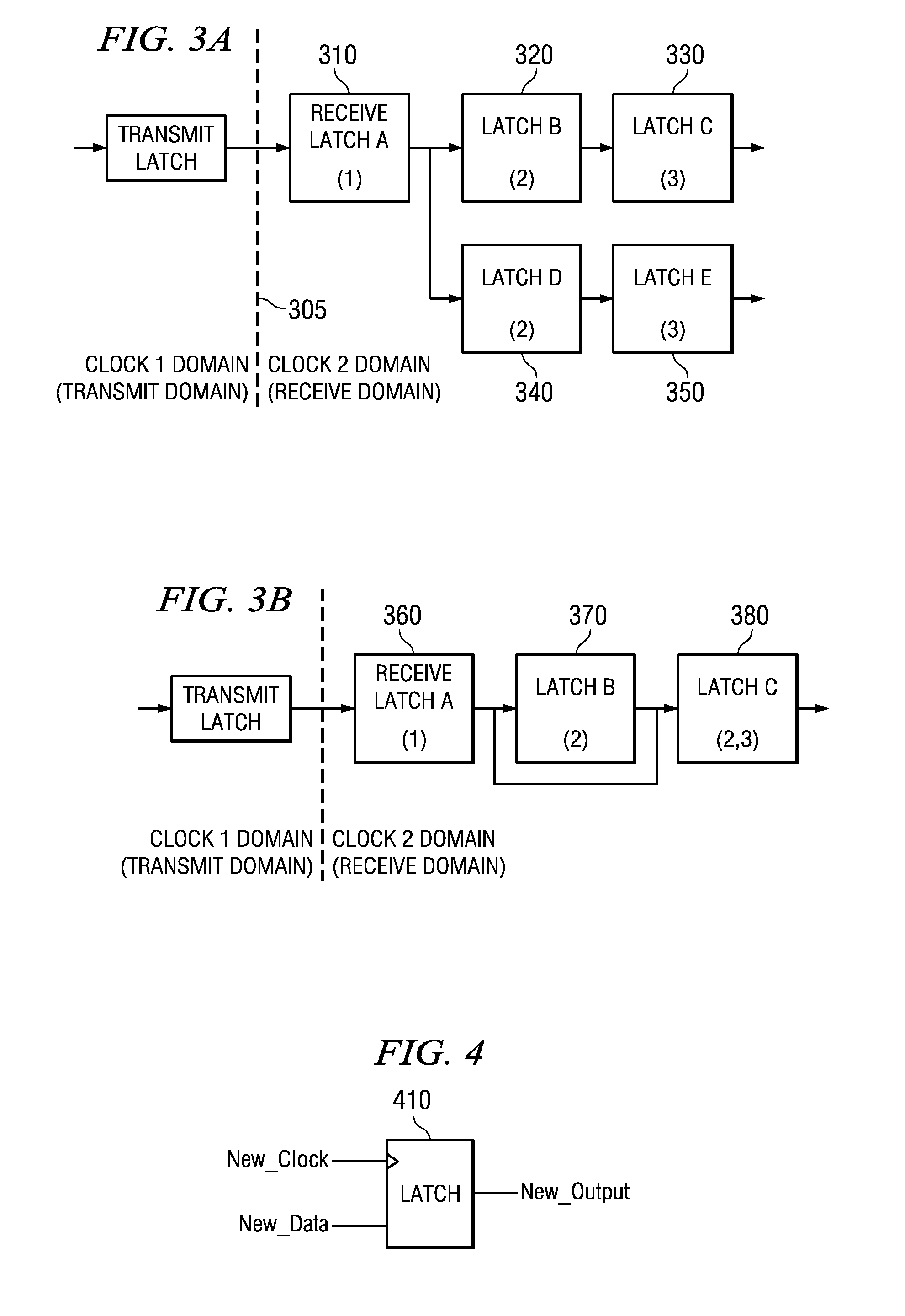
A circuit design that contains at least two clock domains is simulated using a novel system and method for injecting the effects of metastability. The system includes detectors for detecting, during simulation, when a clock in a transmit clock domain and a clock in a receive clock domain are aligned and when the input of a register receiving a clock-domain-crossing signal is changing. The system includes coverage monitors for measuring, during simulation, statistics related to metastability injection. The system accurately models the effects of metastability by, at appropriate times during simulation, pseudo-randomly inverting outputs of registers receiving clock-domain-crossing signals. By accurately modeling the effects of metastability, errors in the circuit design can be detected while simulating a pre-existing simulation test. The simulation with metastability effects injection is repeatable and requires no modification of pre-existing RTL design files or simulation test files.
Owner:SIEMENS PROD LIFECYCLE MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE INC
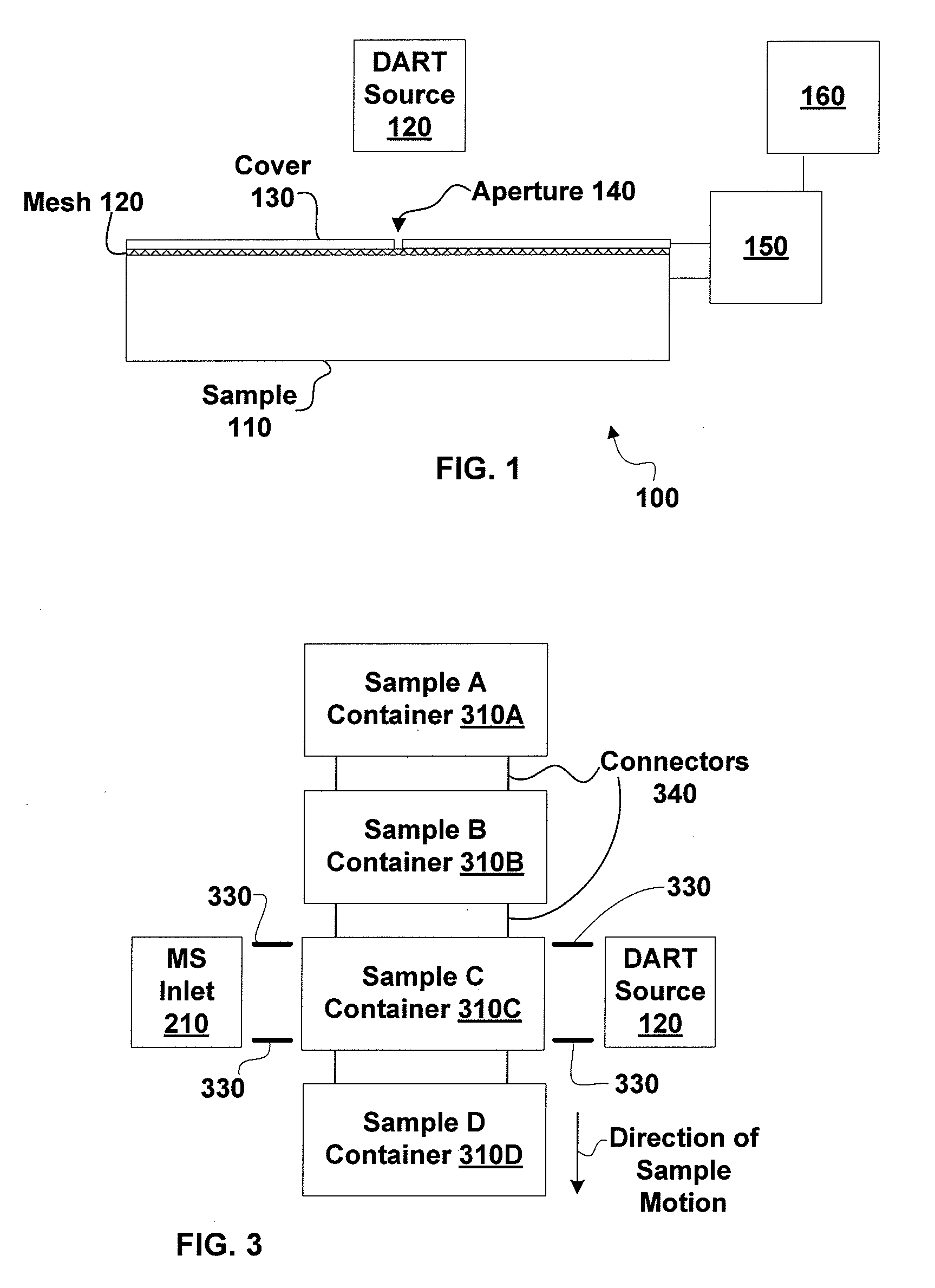
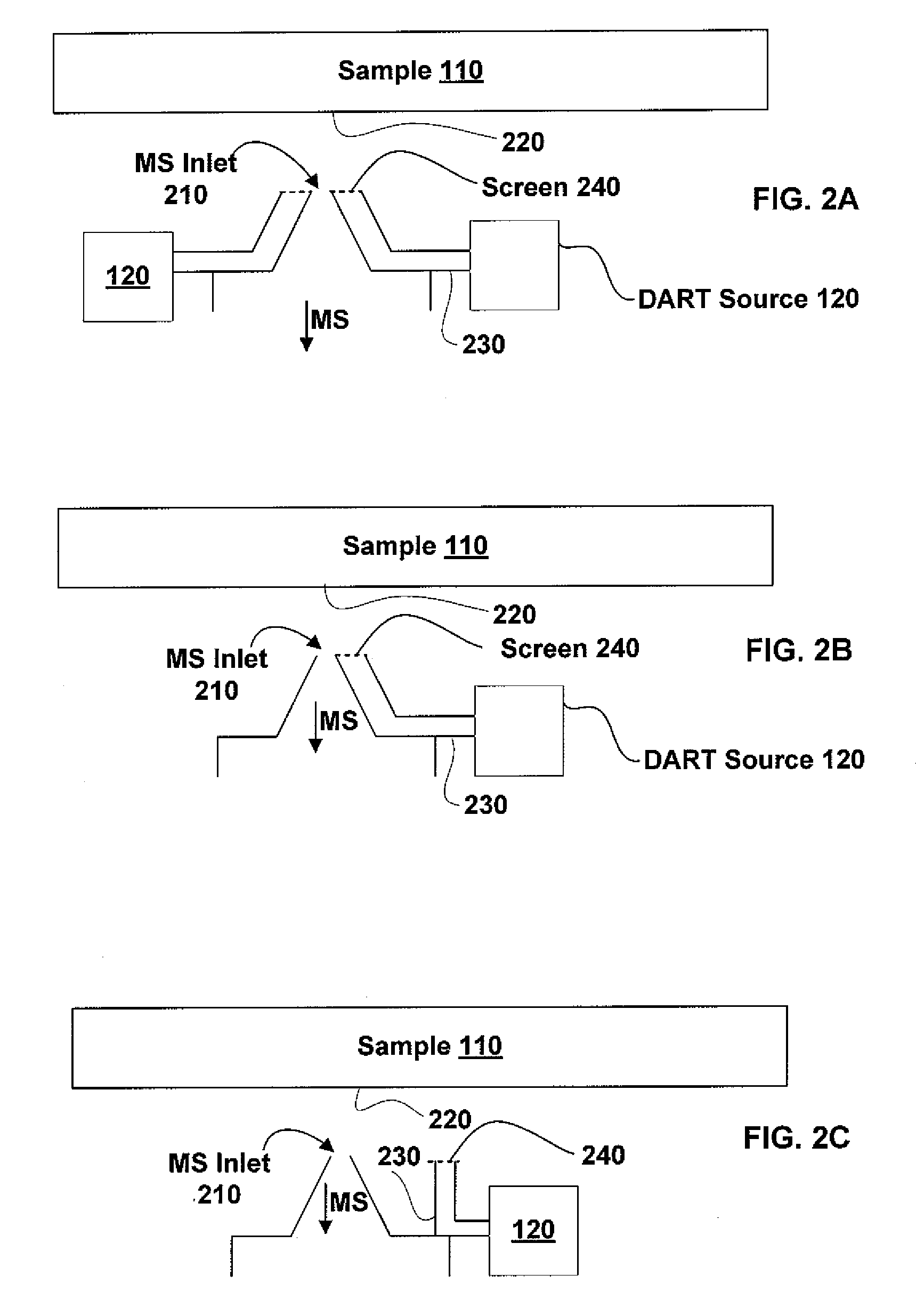
Sample imaging
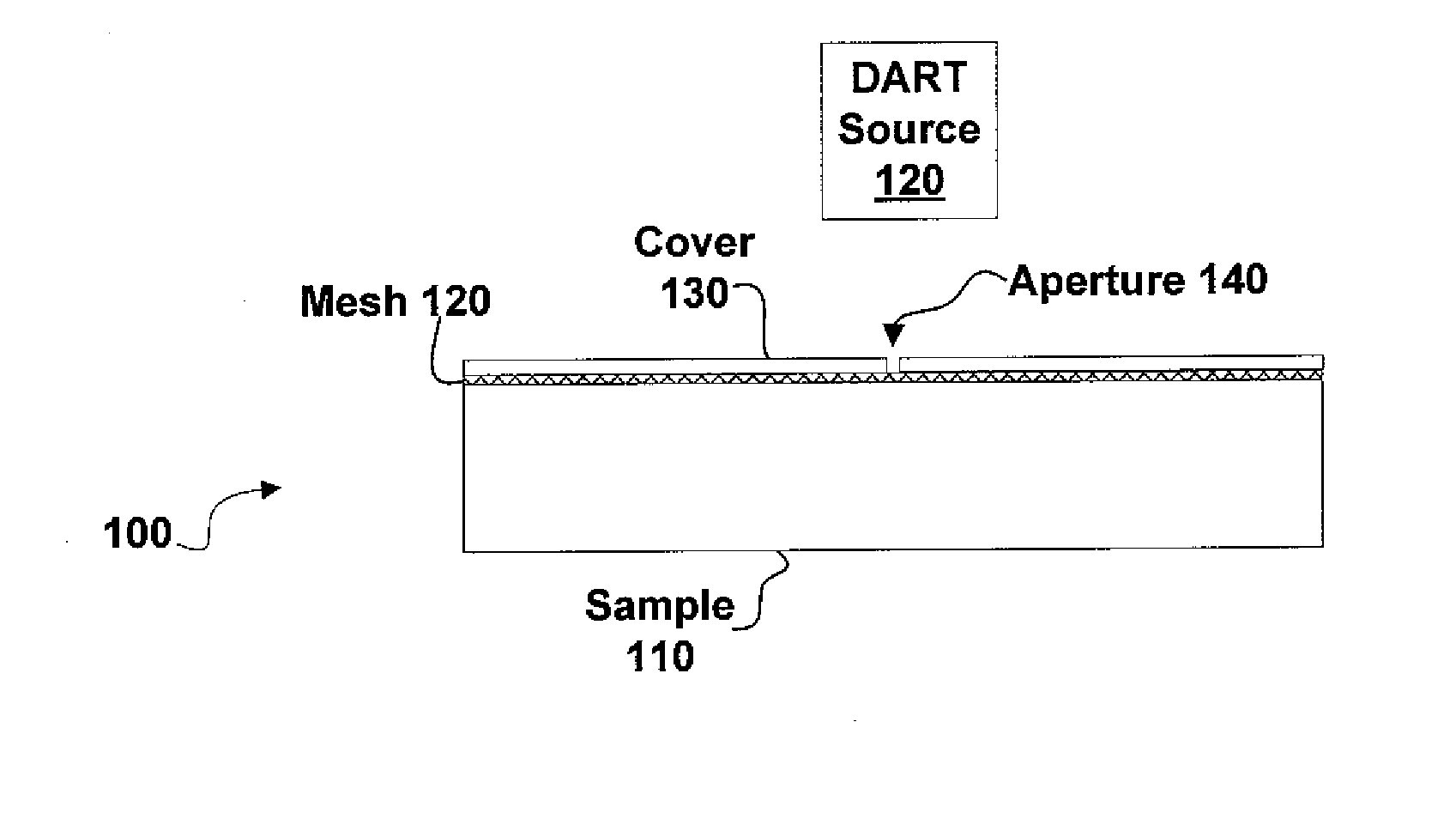
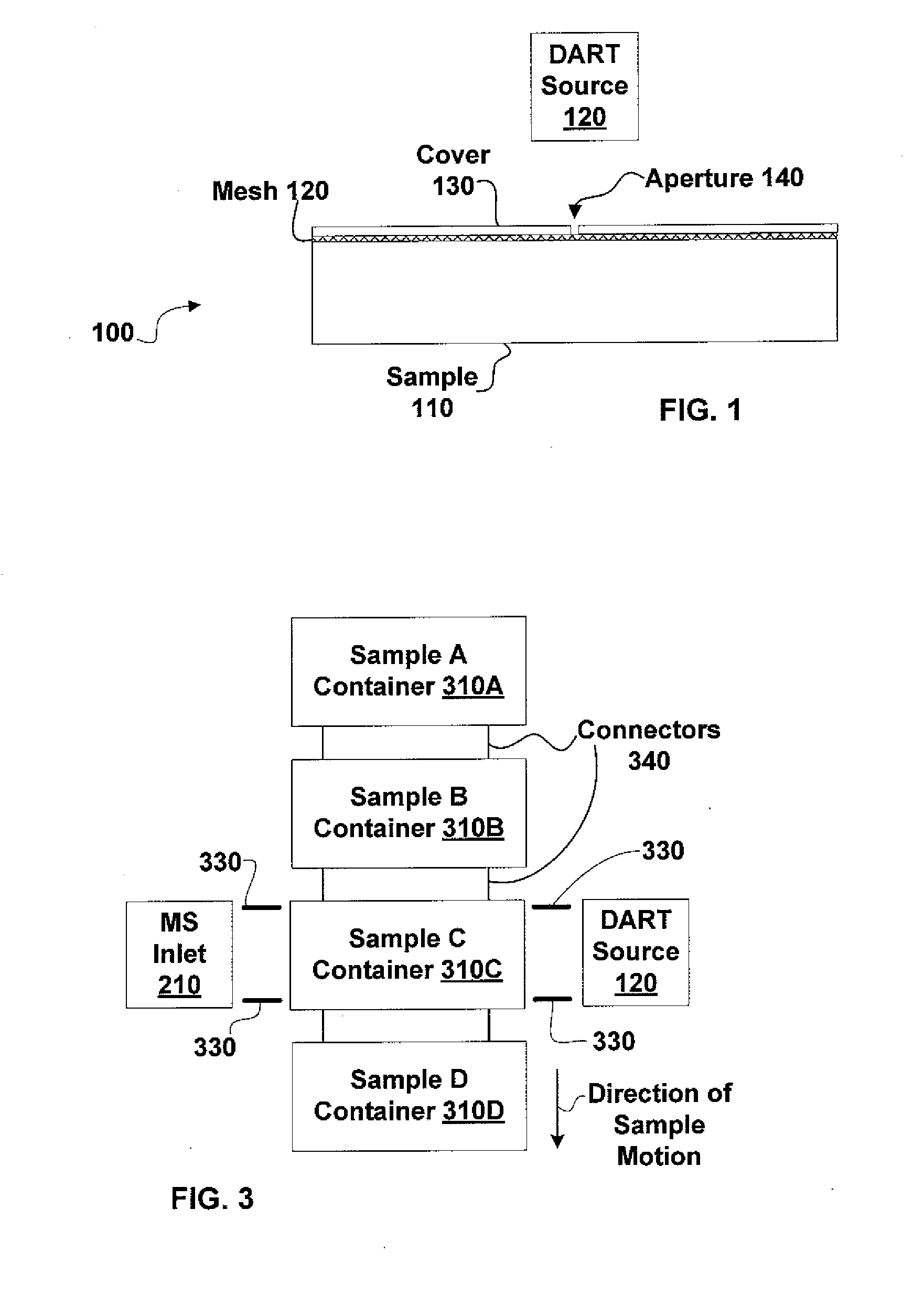
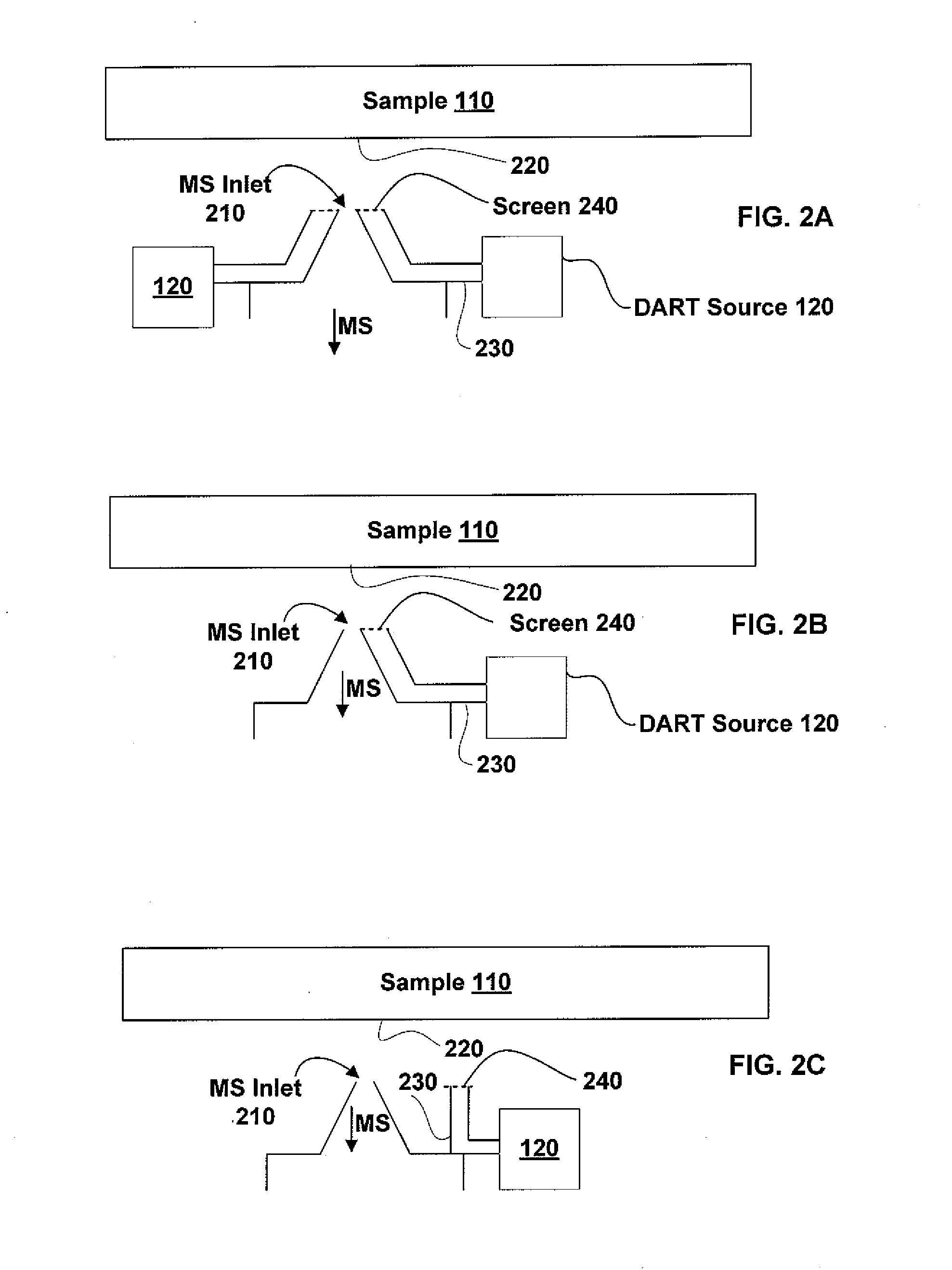
InactiveUS7196525B2Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansImaging particle spectrometryAtmospheric pressureIonization
Systems and methods of generating ions at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include spatially dependent analysis of a sample using an effusive ionization source. Systems and methods of isolating samples at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include using a barrier to prevent metastables or electrons from an effusive ion source from reaching a sample unless the sample is in an analysis position. Systems and methods of using metastables in collisionally induced dissociation are presented.
Owner:SPARKMAN O DAVID +1
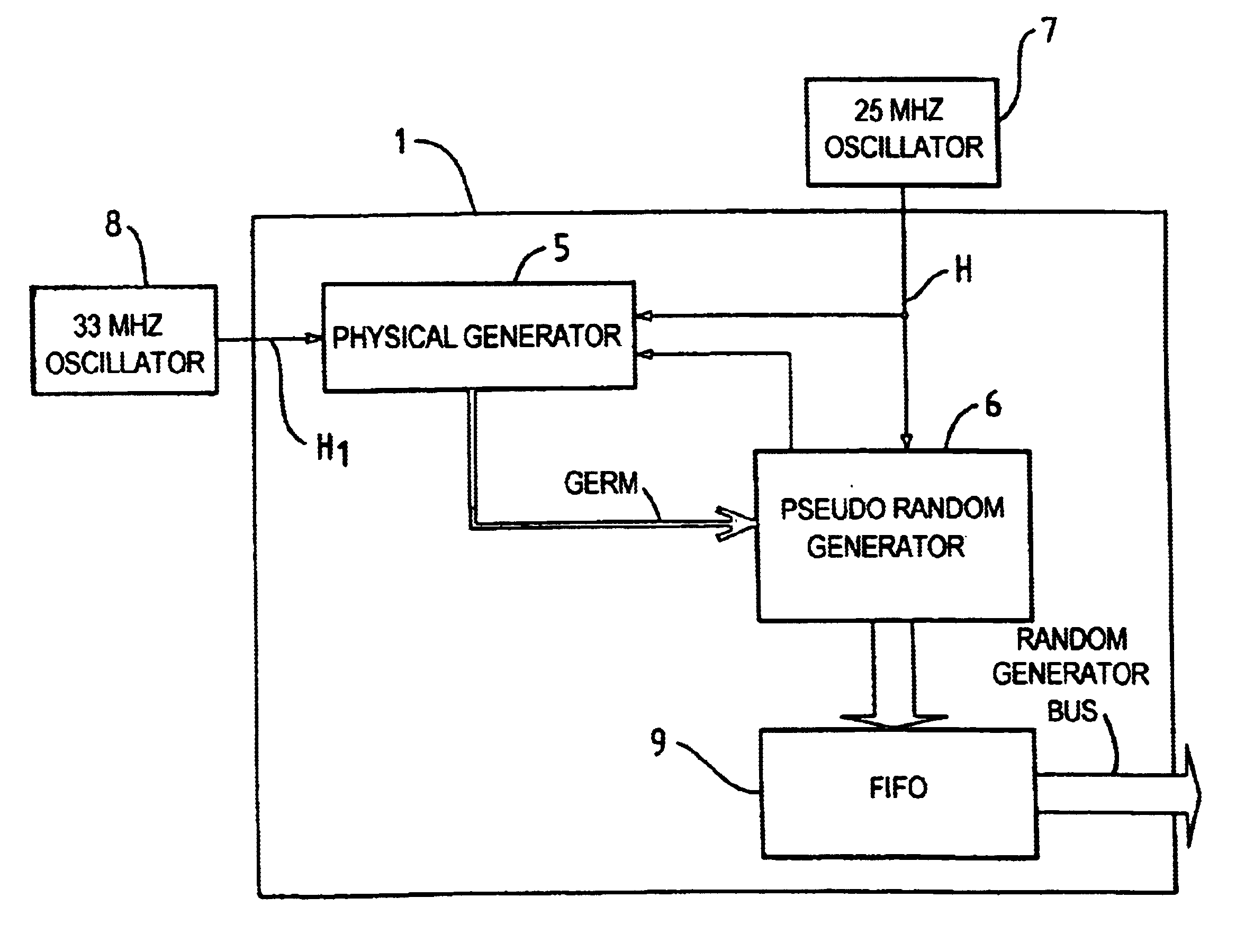
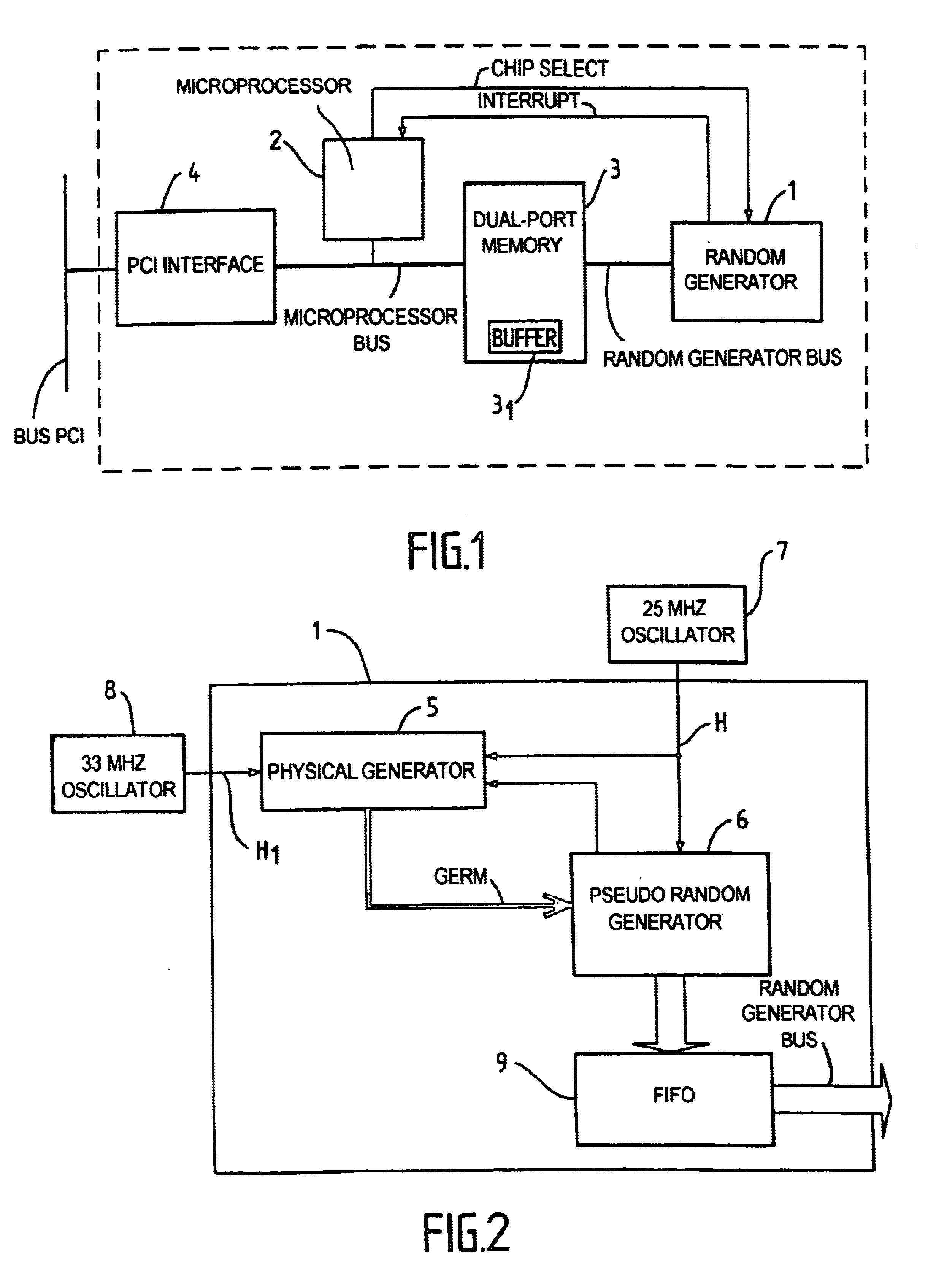
High speed random number generation
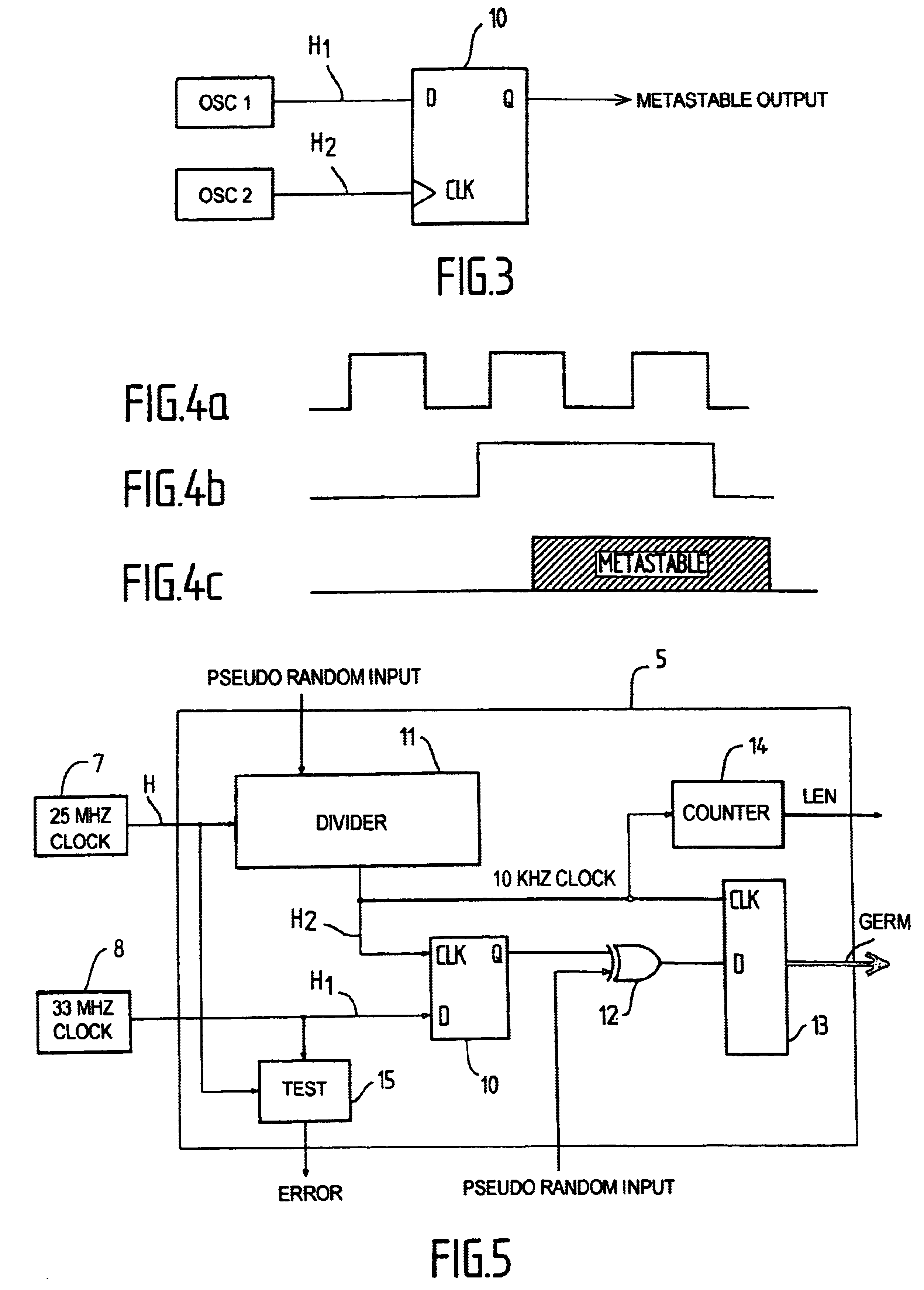
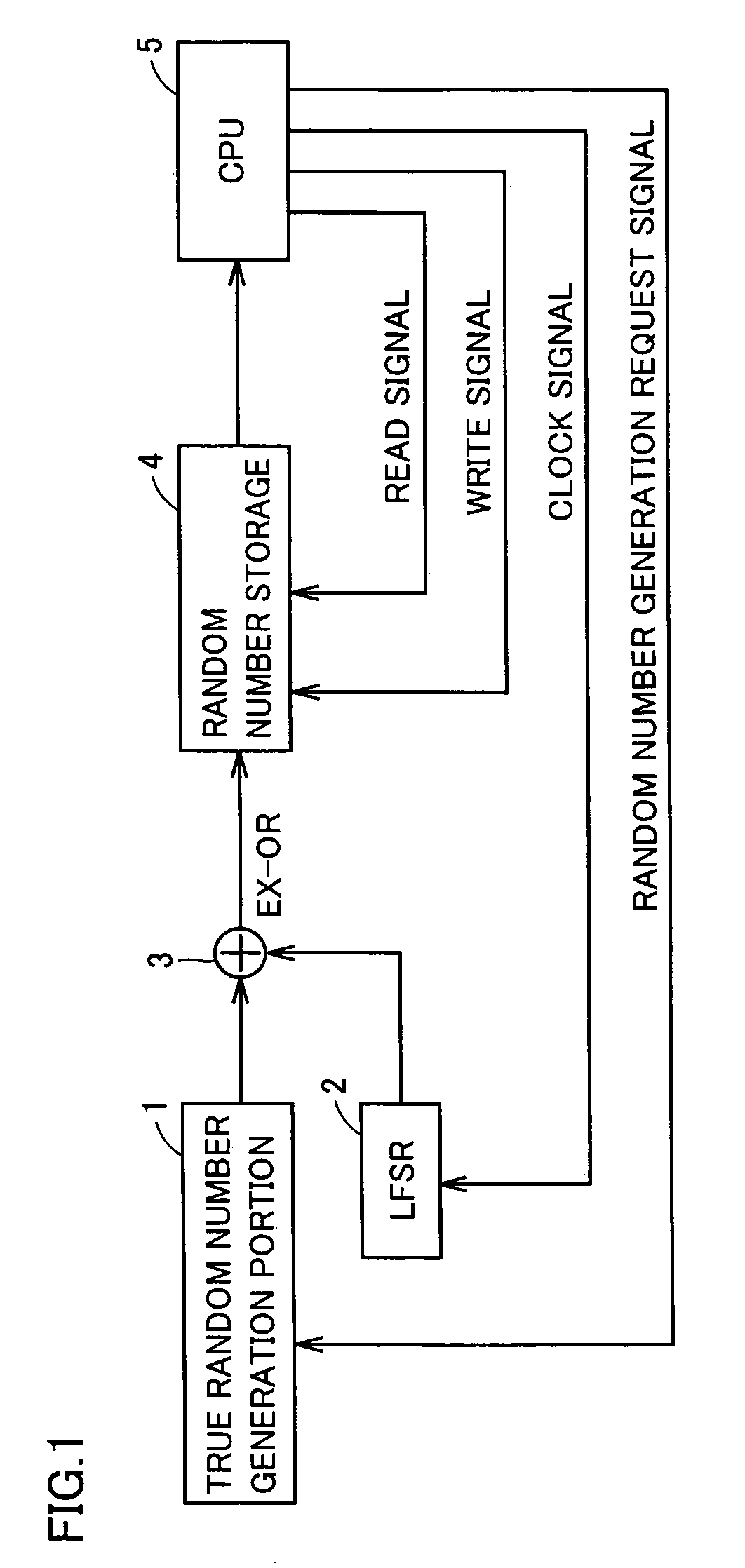
InactiveUS6714955B2Quality improvementReduce complexityRandom number generatorsDigital function generatorsInternal memoryPhase noise
A high-speed random number generator (1) comprising a physical random number generator, having a data input, an output and a pseudo-random generator coupled to the output of the physical random generator. The pseudo-random generator has an input adapted to receive a germ delivered by the physical generator and deliver at an output a pseudo-random output signal. The physical generator comprises a logic circuit that includes at least a data input (D) and a clock input (CLK), the data input (D) receiving a first "high frequency" clock signal H1 and the clock input (CLK) receiving a second "low frequency" clock signal H2, with the "high frequency" signal H1 being sampled by the "low frequency" signal H2. The two clock signals H1 and H2 are of different frequencies respectively and issue from two different first (OSC1 and OSC2) operating asynchronously from one another and not adhering to the setup time of the logic circuit (10). The logic circuit is arranged to deliver at an output a signal in an intermediate state qualified as metastable between "0" and "1" and being constituted by a random number sequence. The metastability of the signal obtained as an output from the logic circuit (10) is accentuated by phase noise of the first oscillator (OSC1) generating the "high frequency" signal H1. The pseudo-random generator is arranged to re-inject part of the pseudo-random output signal into the physical generator. An internal memory stores the random numbers obtained as output signals from the pseudo-random generator. The two generators run on the same second "high frequency" clock H generated by the external oscillator (7).
Owner:BULL SA
Metastable CID
InactiveUS20060250138A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansImaging particle spectrometryAtmospheric pressureIonization
Systems and methods of generating ions at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include spatially dependent analysis of a sample using an effusive ionization source. Systems and methods of isolating samples at atmospheric pressure are presented. These systems and methods include using a barrier to prevent metastables or electrons from an effusive ion source from reaching a sample unless the sample is in an analysis position. Systems and methods of using metastables in collisionally induced dissociation are presented.
Owner:SPARKMAN O DAVID +1
Asynchronous successive-approximation-register analog-to-digital converter (SAR ADC) in synchronized system
ActiveUS9484945B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersComputer hardwareAnalog signal
A correcting asynchronous Successive-Approximation Register (SAR) analog-to-digital converter (ADC) detects and corrects metastability errors. An analog signal is synchronously sampled by a system clock, but data bits are converted asynchronously. A valid detector compares true and complement outputs of a comparator that compares the sampled voltage to a DAC voltage generated from digital test value from the SAR. Once the true and complement outputs diverge past logic thresholds, the valid detector activates a VALID signal indicating that comparison is completed. The compare result is then latched in as a data bit and the SAR advances to the next test value. Once all bits have been converted, an End-of-Conversion (EOC) is signaled. If the EOC does not occur by the end of the system clock, a metastability error is detected. The current bit that never finished comparison is forced high and all other unconverted bits are forced low.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
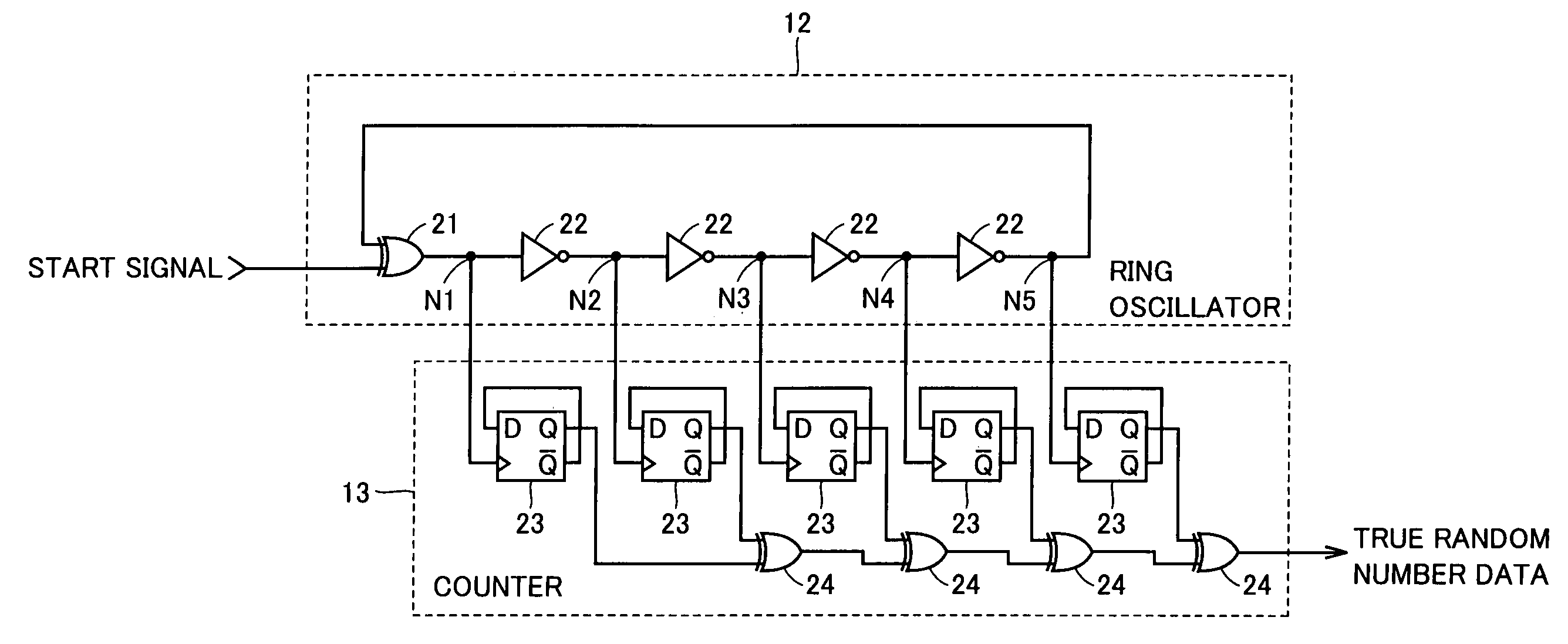
Random number generator with ring oscillation circuit
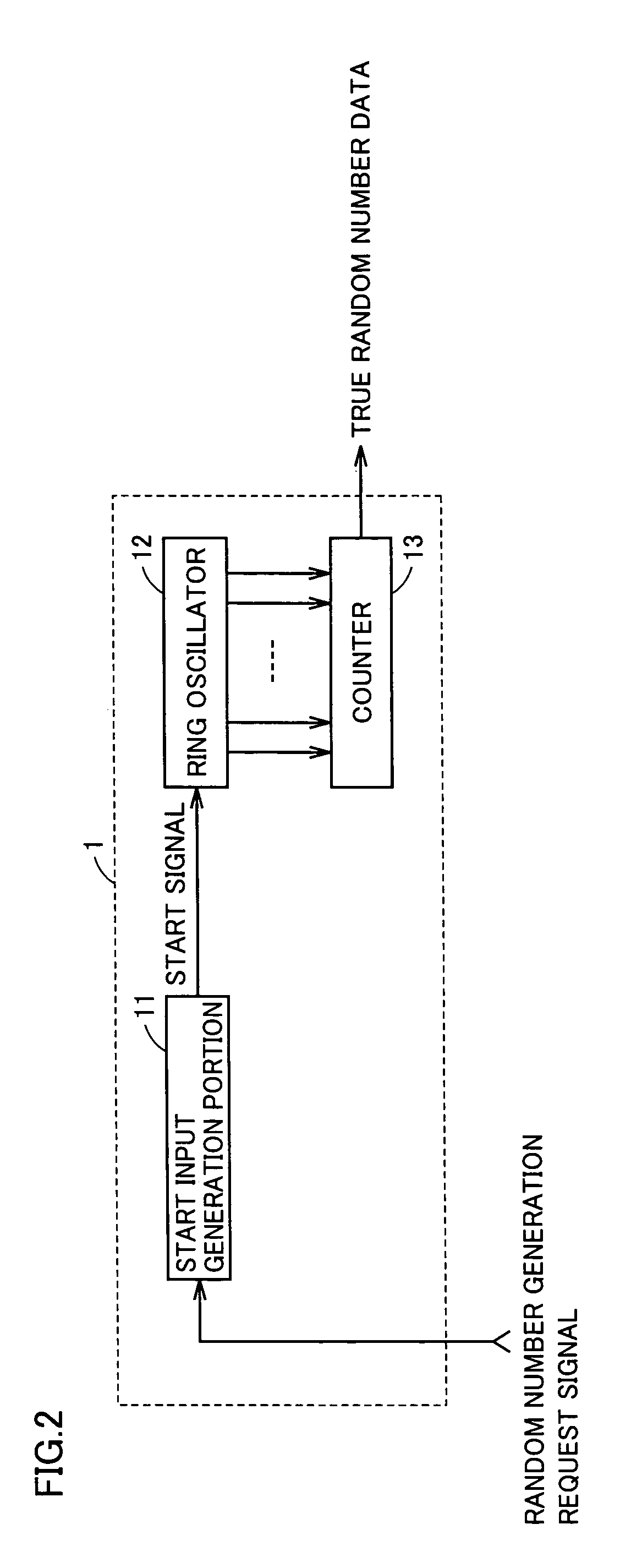
ActiveUS7424500B2Reduce power consumptionImprove performanceRandom number generatorsElectrical apparatusStable stateDelayed time
A random number generator includes a ring oscillator having an EX-OR gate and four inverters together forming a loop. This loop enters stable state for a start signal having the low level and oscillates for the start signal having the high level. When the start signal has a pulse of a width shorter than the loop's delay time, output nodes responsively, sequentially enter metastable state hovering between the high and low levels. The metastable waveform becomes smaller with time and finally disappears. As metastable state cannot be controlled in longevity, it disappears at any random number node. A counter thus outputs a signal serving as true random number data depending on the longevity of the metastable state. A random number generator miniaturized and having reduced power consumption, and of high performance can thus be implemented.
Owner:RENESAS LSI DESIGN CORP +1
Clock switch circuit
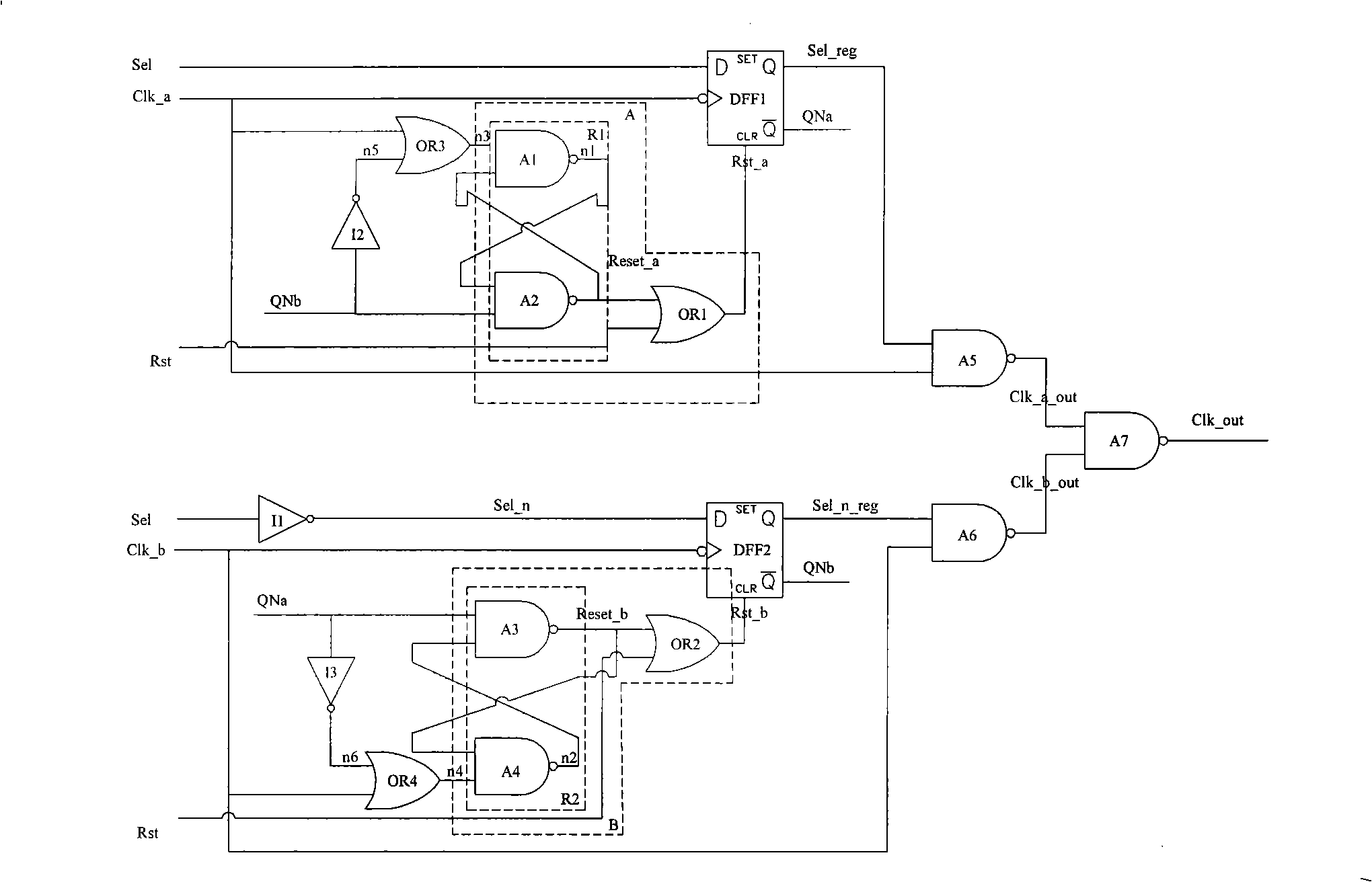
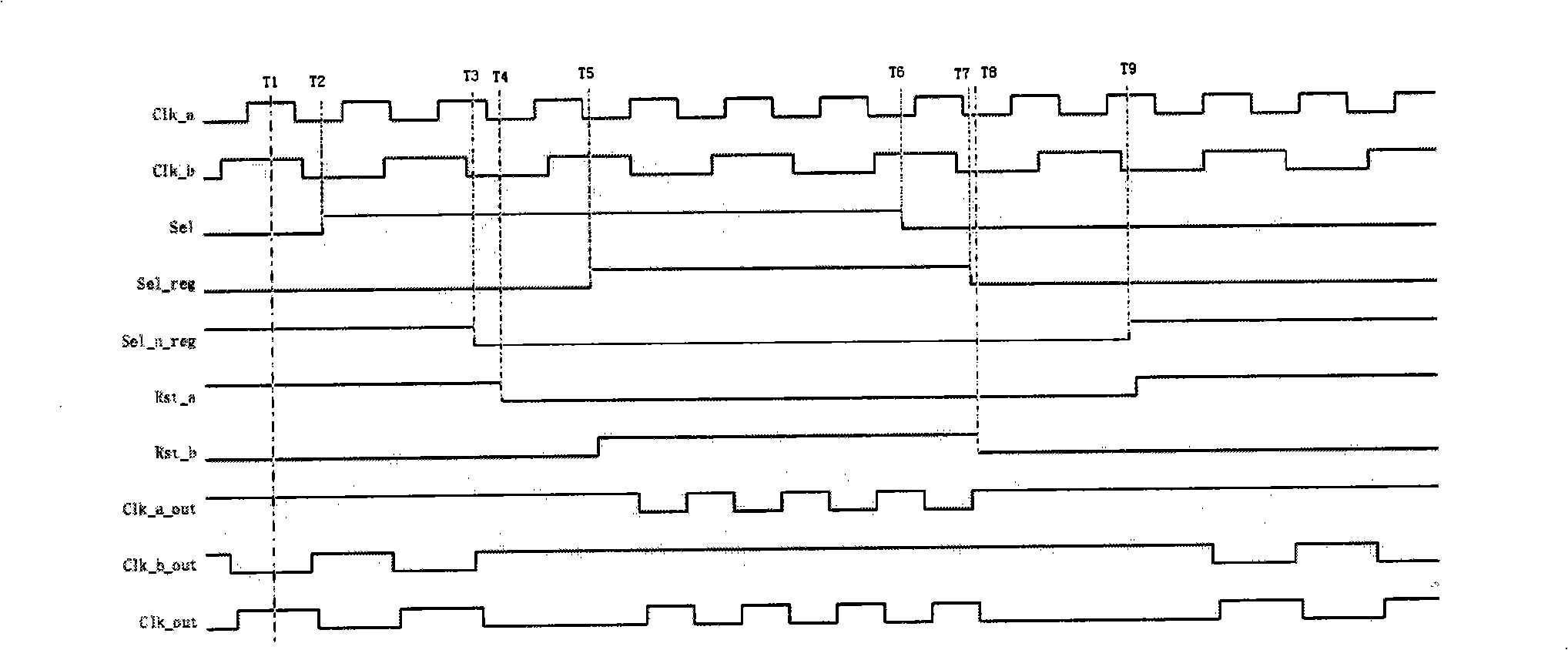
InactiveCN101299159AAvoid metastabilityGenerating/distributing signalsPulse manipulationMetastabilityElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention discloses a clock commutation circuit, which resolves technical problem of producing bur and metastable state. The clock commutation circuit of the invention is composed of two reset producing circuits, two OR gates, three NOT gates, two D-flip-flops and a clock output circuit, the reset producing circuits and the NOT gates constitutes a RS latch. Compared with the prior technology, when the first clock is switched to the second clock, the gating signal of the first clock is switched off when the first clock is at a low level, meanwhile the reset outputting signal of the second RS latch is released, the gating signal of the second clock is switched-on when the second clock is at a low level, thereby avoiding the bur during the clock switch. The reset producing circuit ensures that the asynchronous reset terminal of the D-flip-flop executes the synchronization operation to the reset signal through the RS latch circuit when the clock is at a low level, thereby avoiding the production of metastable state.
Owner:INVENGO INFORMATION TECH
Modeling metastability in circuit design
ActiveUS7139988B2CAD circuit designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationComputer scienceCircuit design
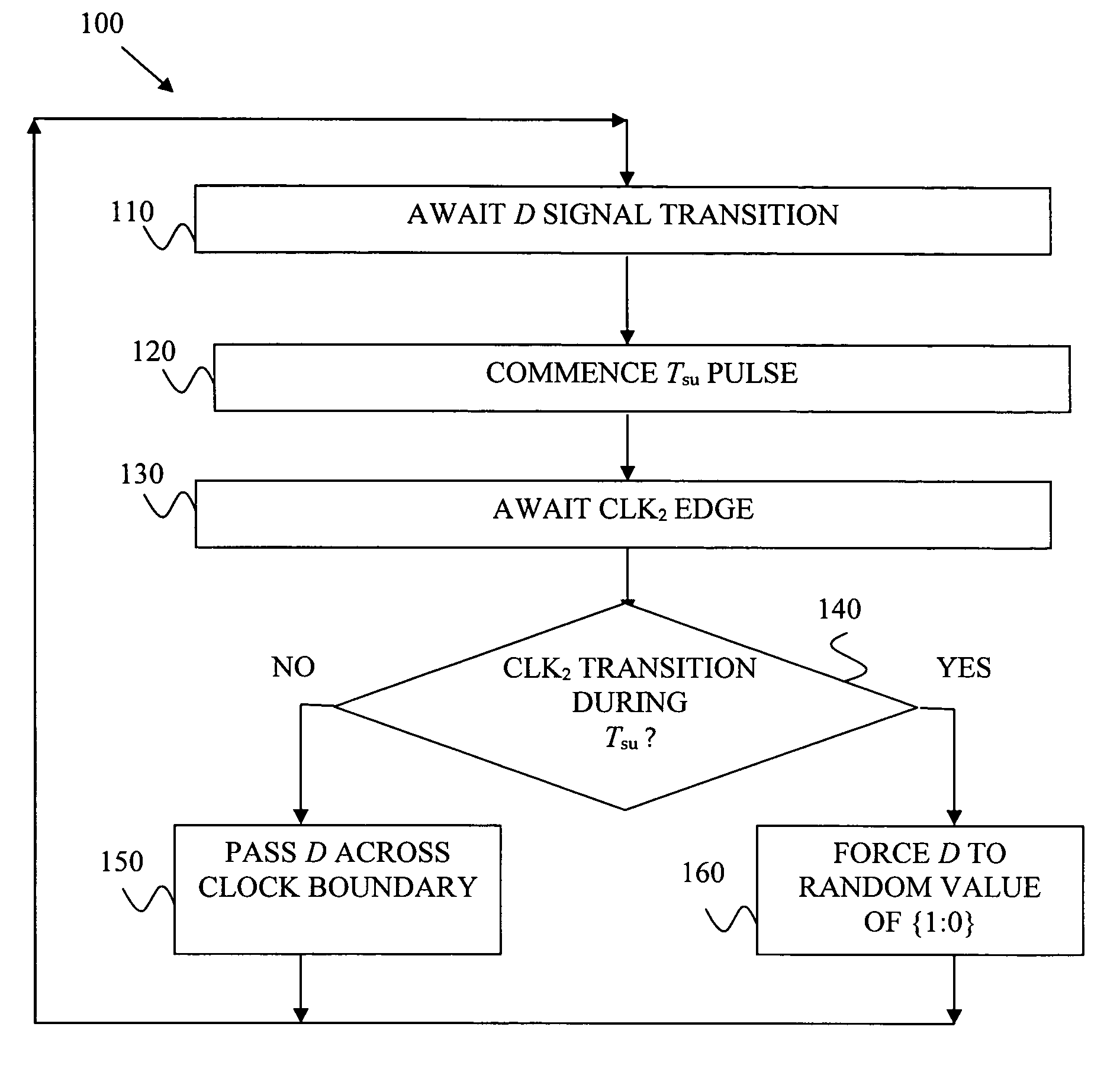
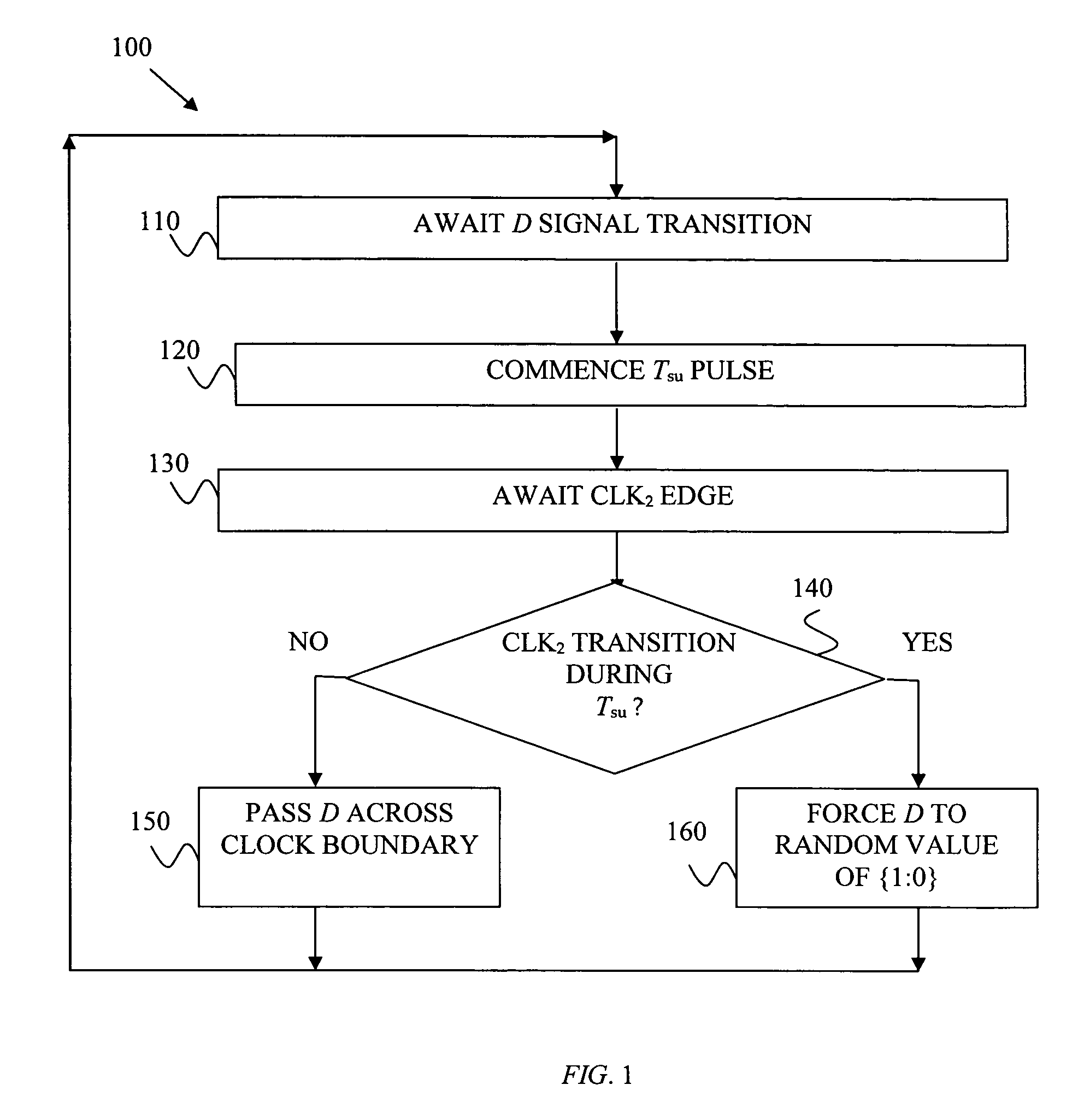
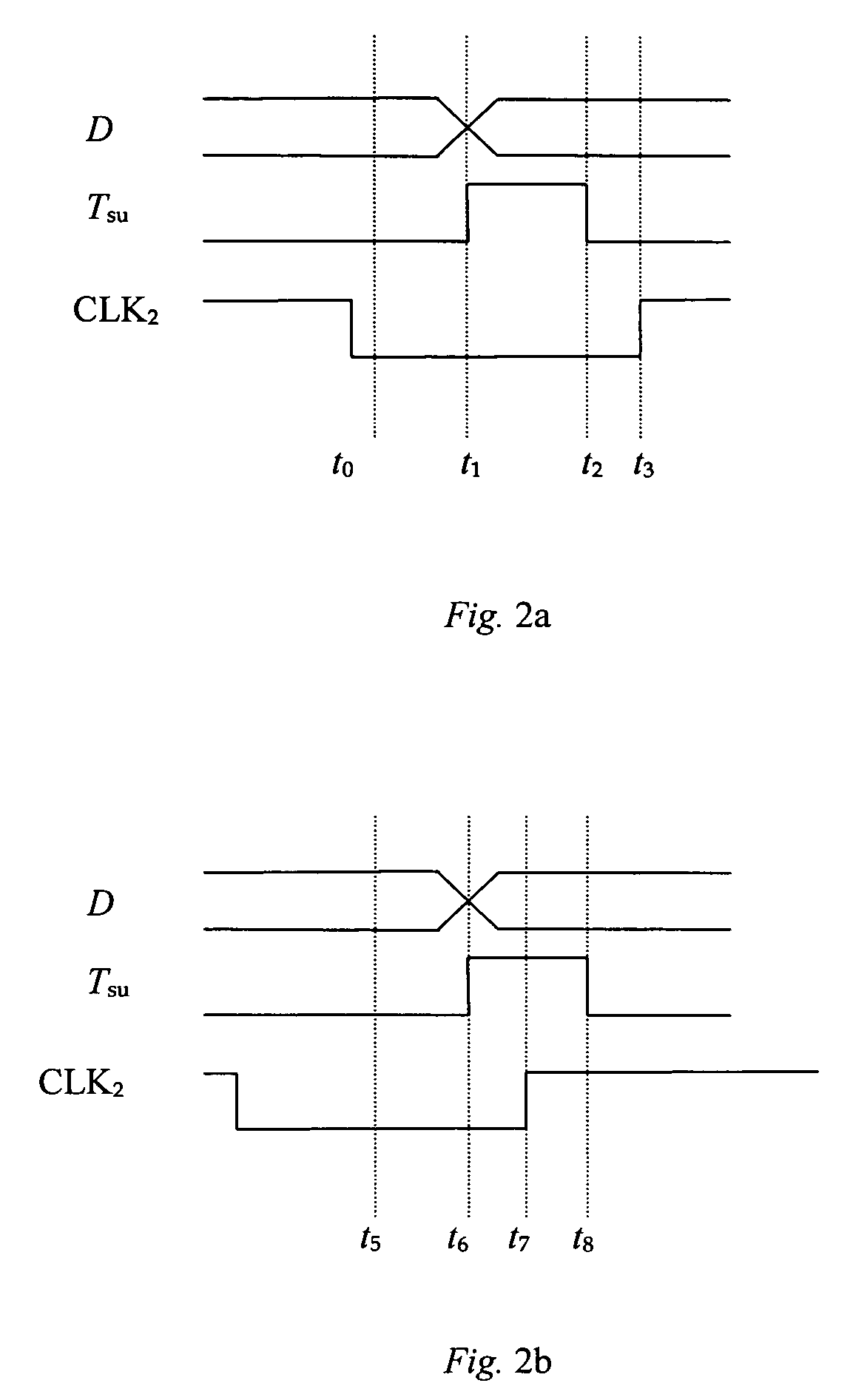
A computer program (100, 200) encoded in a computer-programmable medium, and for causing a computer to perform circuit design. The code causes the computer to perform a set of steps. The steps comprise describing a first set of circuitry and describing a second set of circuitry. The steps also comprise describing a digital signal for passing from the first set of circuitry to the second set of circuitry and detecting (230) transitions of the digital signal with respect to a timing constraint (240) of at least a portion of the second set of circuitry. Lastly, the steps comprise, responsive to detecting metastability with respect to timing of a transition of the digital signal relative to the timing constraint of at least a portion of the second set of circuitry, forcing (160) the digital signal to a random value and passing the random value to the second set of circuitry.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
ADC first stage combining both sample-hold and ADC first stage analog-to-digital conversion functions
ActiveUS8604962B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceEngineering
A first stage circuit for a pipeline ADC first stage combines the functions of an input sample-and-hold-plus-amplifier (SHA) stage, and the functions of the first analog-to-digital conversion stage of an ADC, including a multiplying DAC (MDAC), stage-flash ADC (SFADC) comparators, and residue opamp (RAMP). The ADC first stage is duplicated, inputs and outputs are connected, and an autozero circuit using a switched-capacitor filter feedback loop controls the RAMP bias circuitry to reduce 1 / f noise and DC offsets. The sampling capacitors may be connected to the ADC input for one full sample clock time period and are disconnected from the analog input period before connecting the sampling capacitors to an amplifier voltage output or voltage reference, thereby sampling the input and allowing sufficient time for the SFADC comparators to resolve and control the MDAC capacitor settings with a low metastability error rate.
Owner:LEWYN CONSULTING
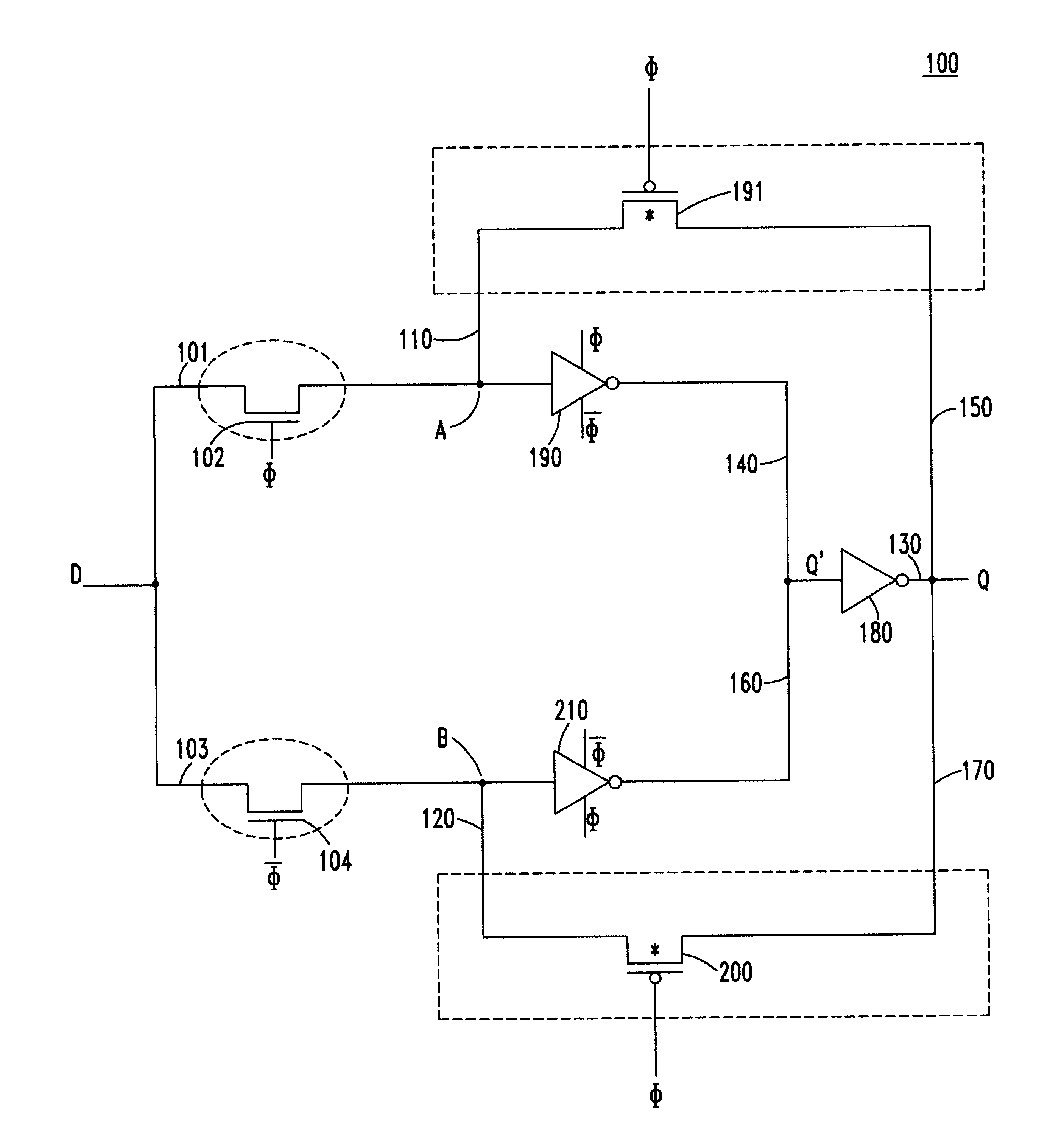
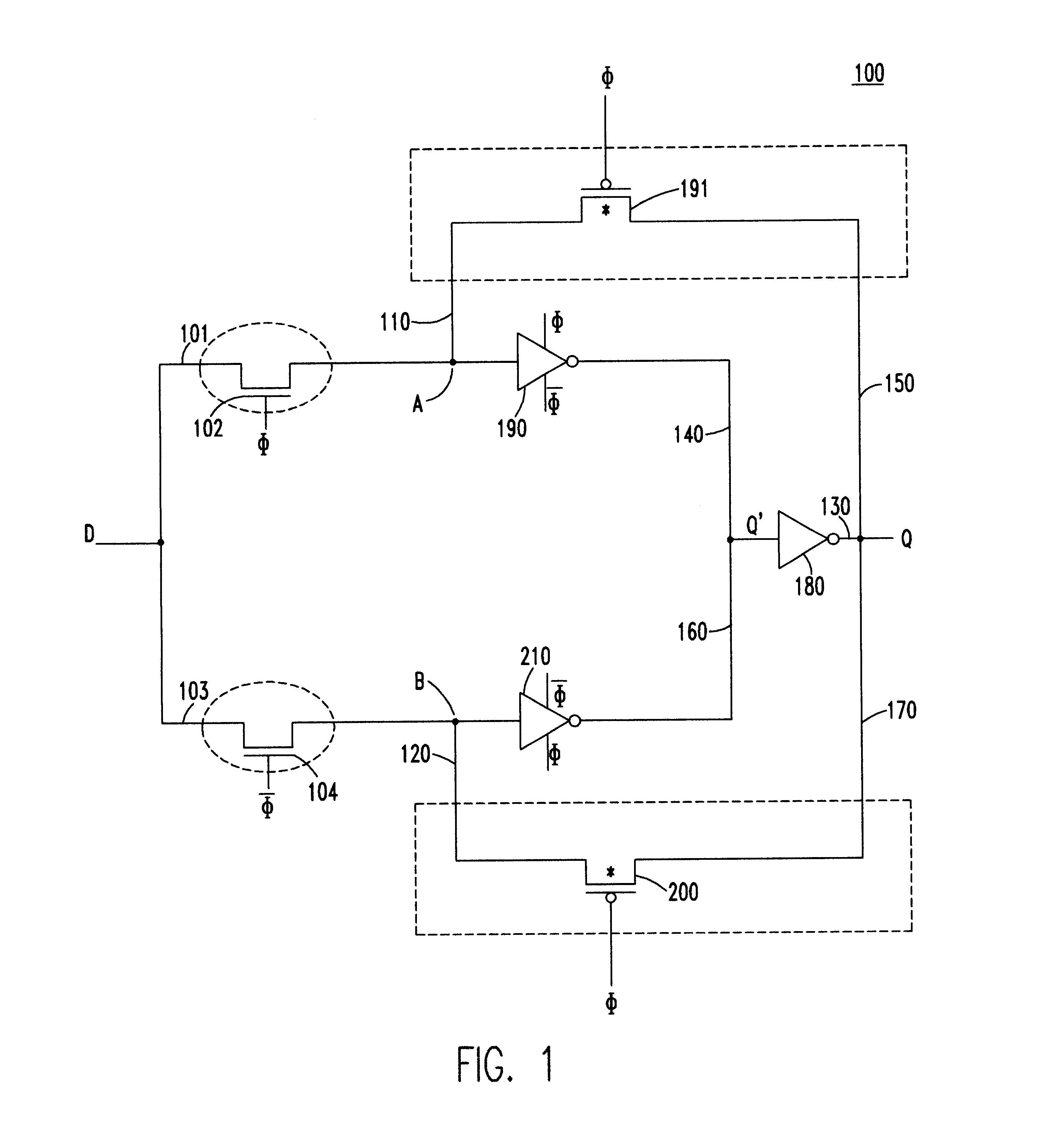
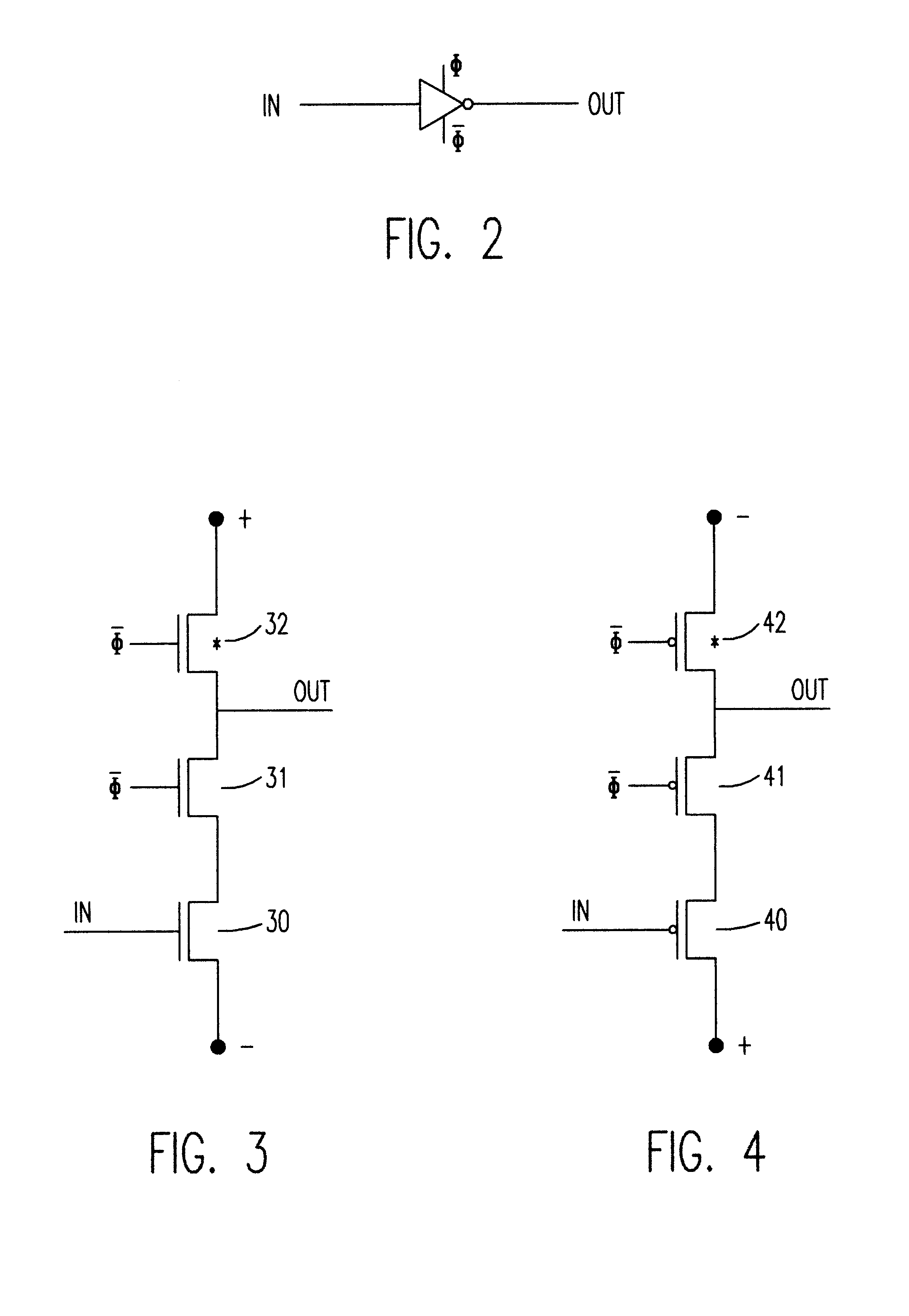
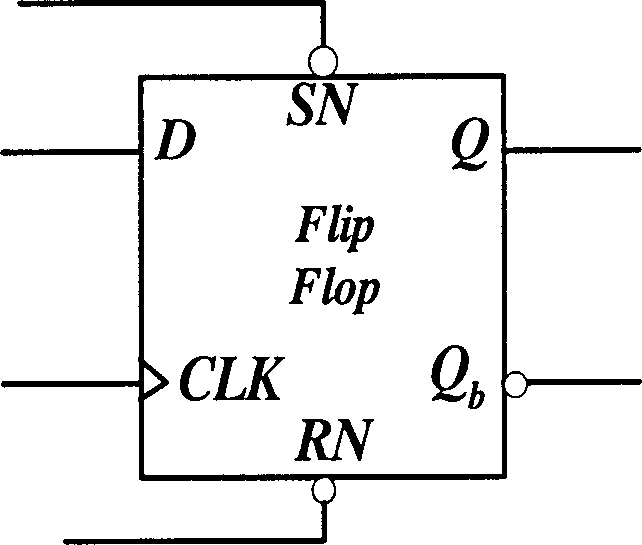
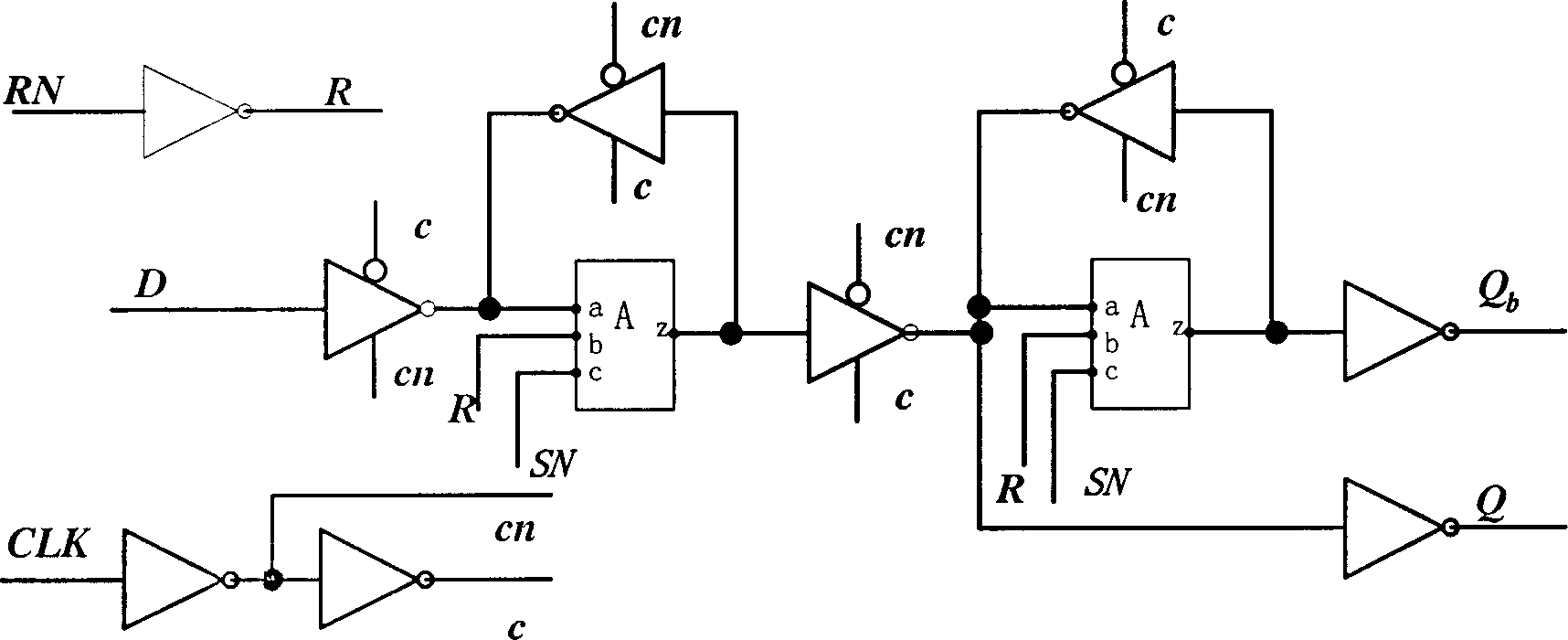
Reduced-transistor, double-edged-triggered, static flip flop
A static, double-edge-triggered flip-flop has an upper data path and a lower data path connected between a data input node and an output terminal. The upper path includes a switch connected to a first data loop, and the lower path includes a switch connected to a second data loop. The first and second data loops share a forward path having a data-inverting circuit. In addition, each loop has a feedback path which contains only one element in the form of a switch. However, no data-inverting circuit is included in either of the feedback paths. Advantageously, all the elements of the flip-flop may be constructed using MOSFET transistors implemented according to any one of a variety of semiconductor technologies. In more than one particularly advantageous embodiments, the flip-flop is constructed using a total of twelve transistors. Through this simplified two-loop design, operational efficiency is improved, low metastability is achieved and costs of manufacture are lowered, all while maintaining low power requirements.
Owner:IBM CORP
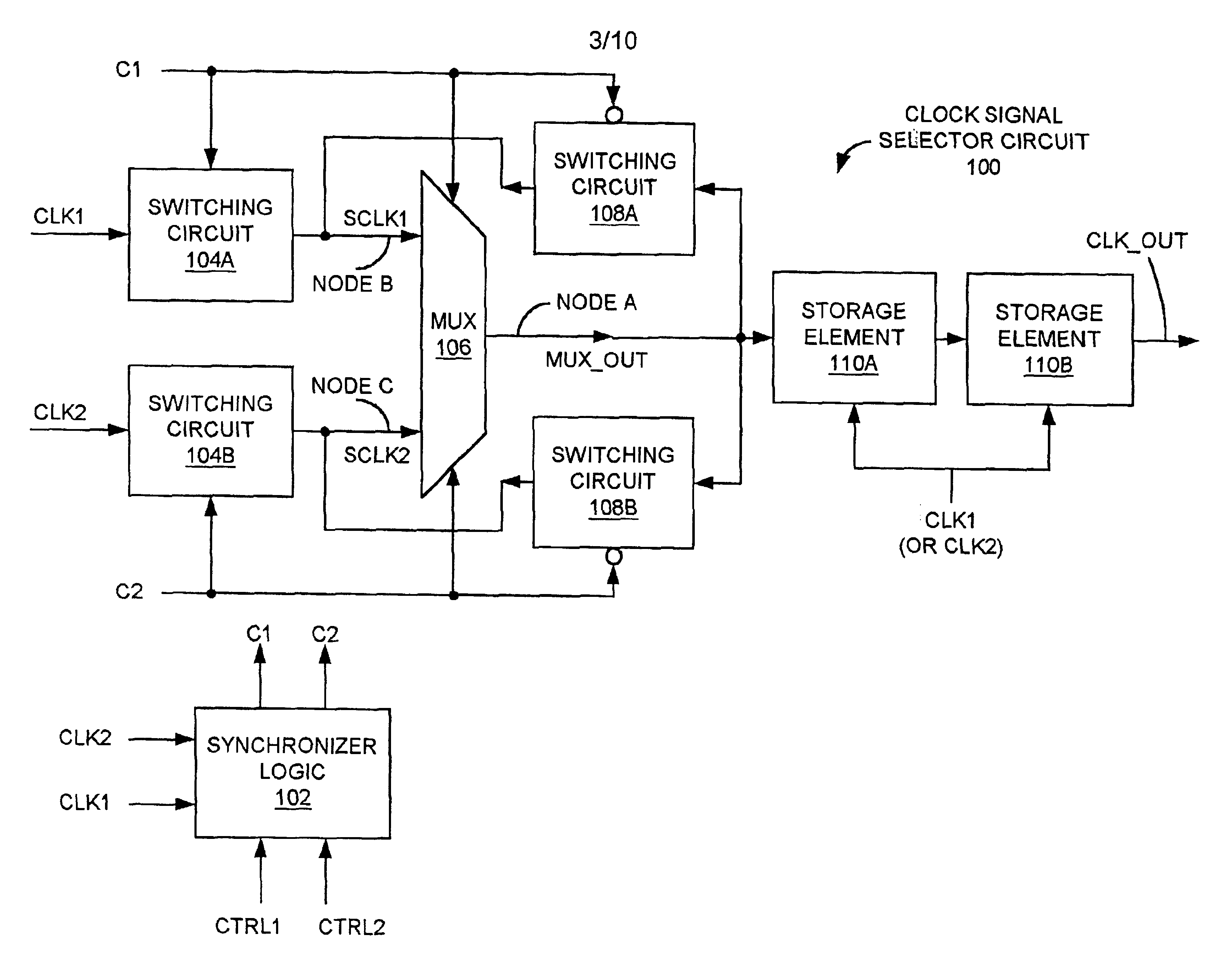
Clock signal selector circuit with reduced probability of erroneous output due to metastability
InactiveUS6927604B2Reduce error rateElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorMultiplexerControl signal
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
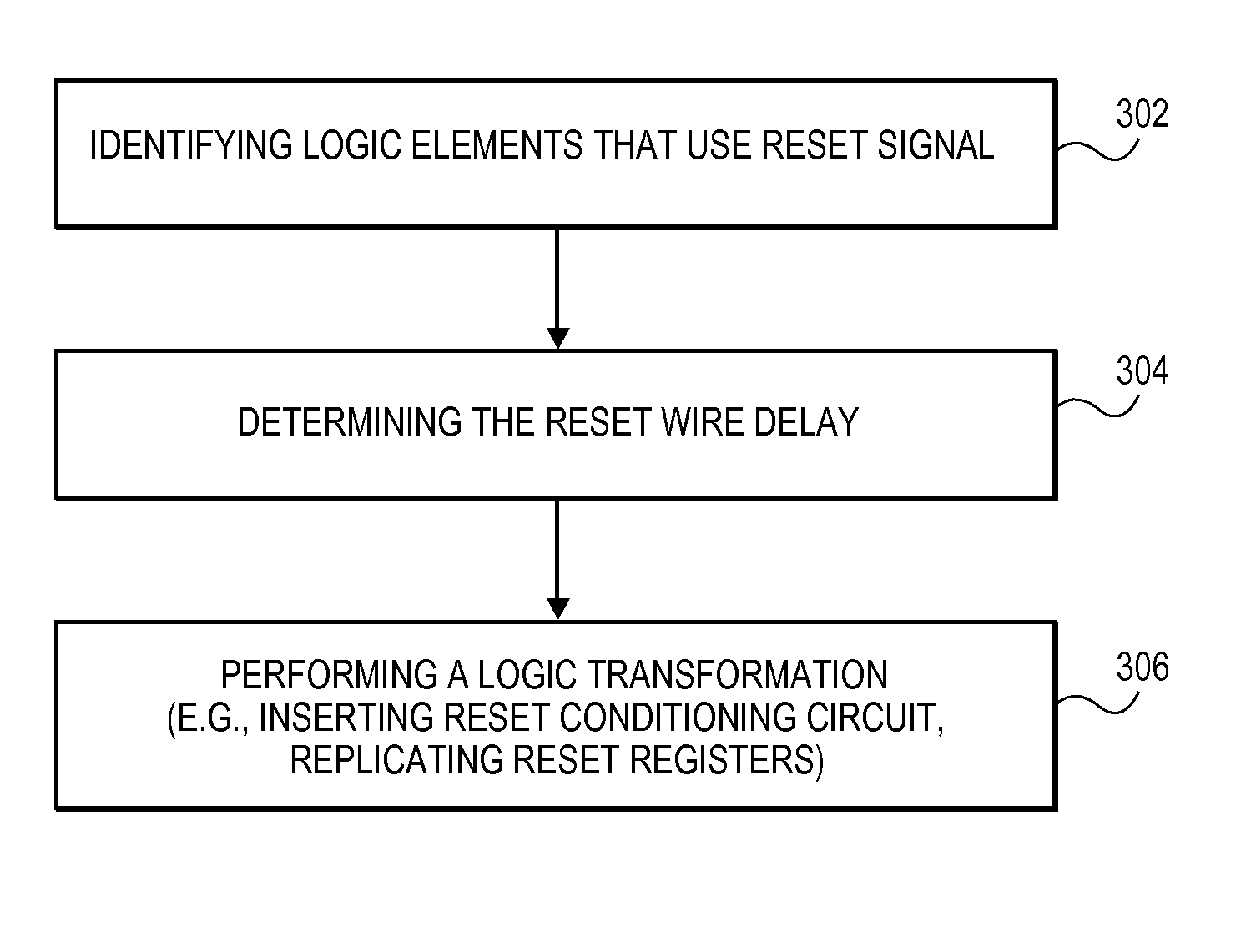
Methods and apparatuses for reset conditioning in integrated circuits
ActiveUS7594211B1Reduce metastability problemReliable signalData resettingComputer aided designPropagation delayProcessor register
Embodiments of the present invention disclose methods and apparatuses to reduce metastability problem related to propagation delay of reset signals in integrated circuits, with preferred applications in automatic physical synthesis for RTL (register transfer level) netlist. In an embodiment, a reset conditioning circuit is inserted into the original integrated circuit to make the reset behavior more reliable to avoid unpredictable states, especially for the de-assertion state of the reset signal. The reset conditioning circuit can provide an asynchronous reset signal output with extended duration so that all the load registers employing asynchronous reset signal will get the reset properly. Further, the reset conditioning circuit can modify the timing of the reset signal so that its de-assertion edge is synchronized with a rising clock edge. In another embodiment, the reset conditioning circuit replicates a synchronous reset signal to provide a reset signal closer to loads or registers at a plurality of circuit modules or partitions. The generation of the reset conditioning circuit is well suitable for physical synthesis of RTL netlists, especially for automatic physical synthesis.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
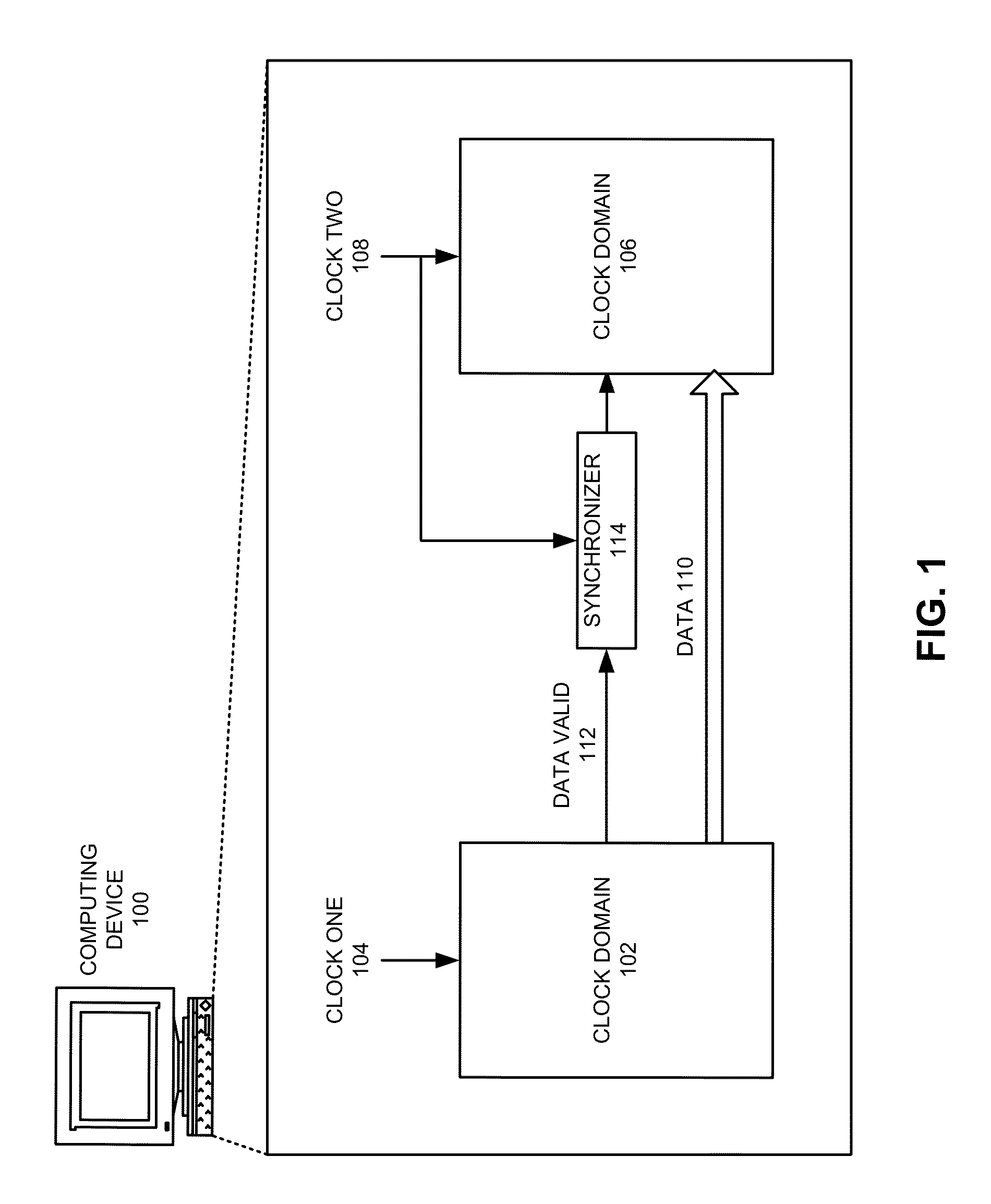
Asynchronous Scheme for Clock Domain Crossing
ActiveUS20110204932A1Pulse automatic controlDigital data processing detailsComputer scienceControl logic
Apparatus and methods for clock domain crossing between a first clock domain and a second clock domain. The apparatus comprises a first control logic element for processing a handshake signal and producing a first arbiter input signal. Concurrently a second control logic element processes a second handshake signal and produces a second arbiter input signal. Exemplary embodiments include exactly one arbiter element inputting the first arbiter input signal, inputting the second arbiter input signal, outputting a first clocking signal to the first sequential element and outputting a second clocking signal to the second sequential element. For managing metastability by controlling the timing of the clocking inputs of the sequential devices, the apparatus includes a first controllable lock delay element selected to satisfy the setup constraint of the second sequential element, and a second controllable lock delay element selected to satisfy the hold constraint of the second sequential element.
Owner:INPHI +1
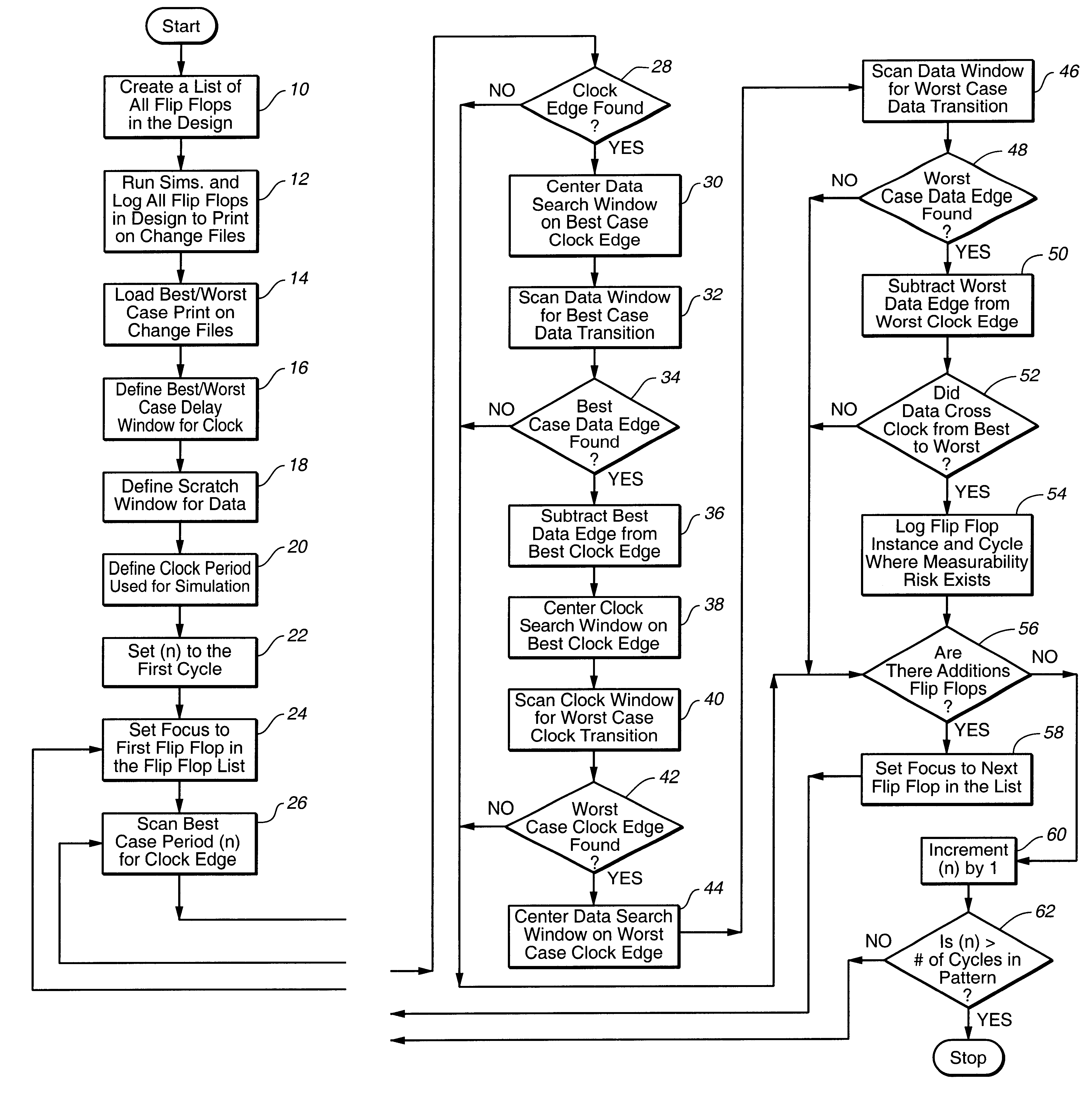
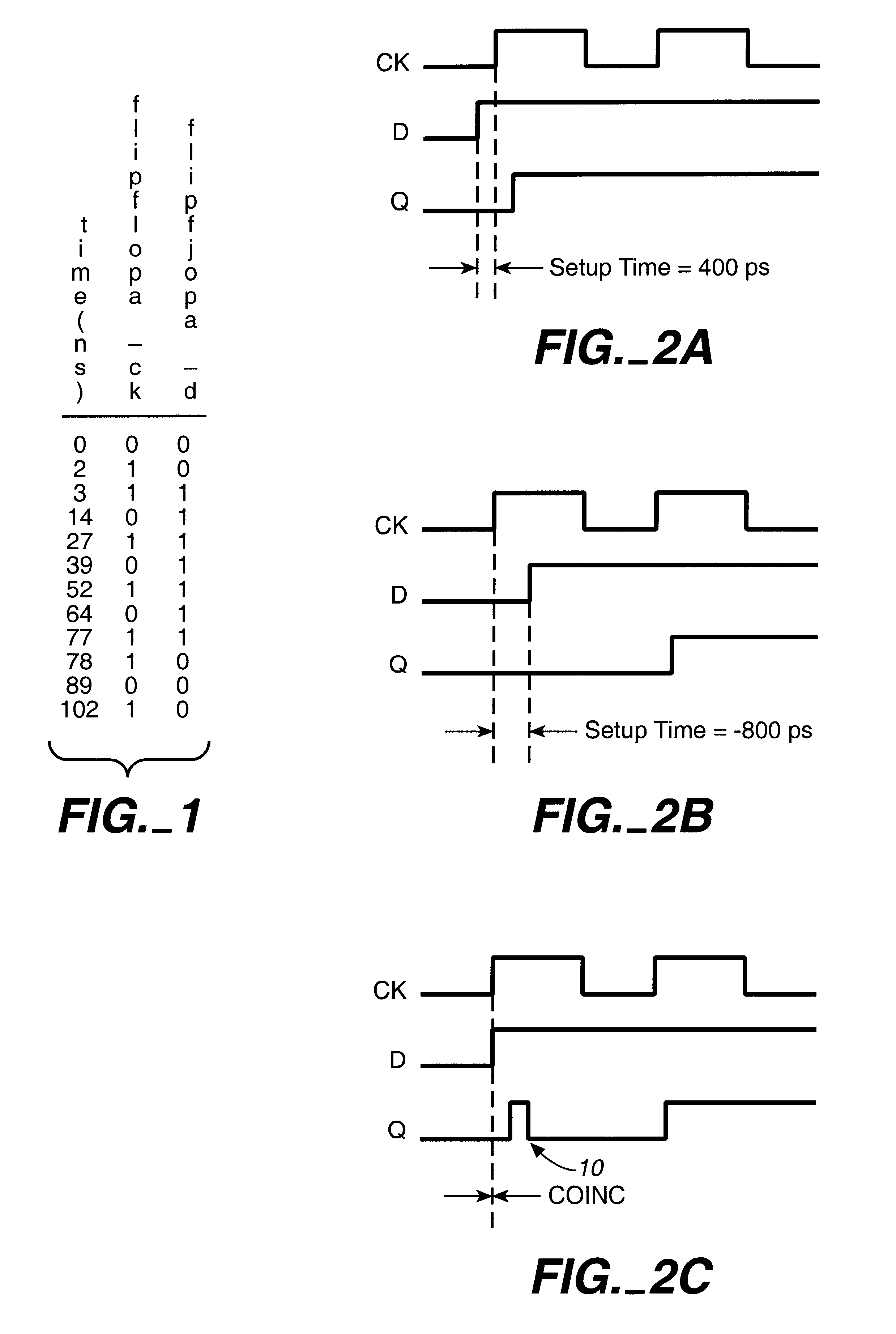
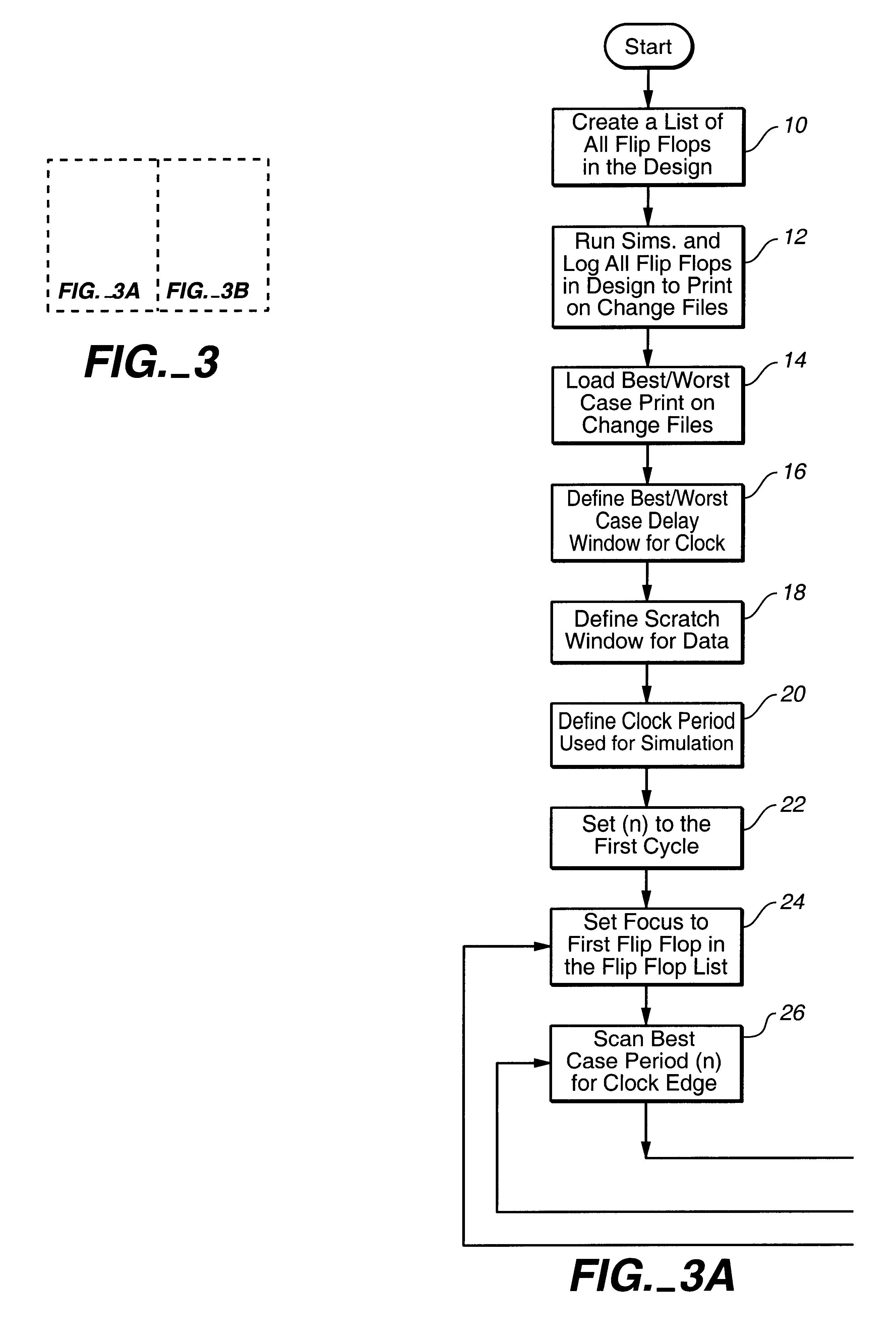
Metastability risk simulation analysis tool and method
A metastability risk simulation analysis device and method for identifying metastability risks of a design. The metastability risk simulation analysis device includes computer readable code which is configured to analyze simulation information relating to the design and determine whether the design presents a metastability risk. Desirably, the computer readable code is configured to determine whether two signals, such as a data signal and a clock signal of a synchronous element of the design, cross over each other thereby presenting a metastability risk, and is configured to generate a summary report identifying those synchronous elements of the design which present a metastability risk. Preferably, the computer readable code is configured to analyze simulation information relating to best case and worst case simulations of the design, and is configured to scan the simulation information to identify an edge of a clock signal and an edge of a data signal of the best case and worst case simulations and determine whether the signals cross each other.
Owner:BELL SEMICON LLC
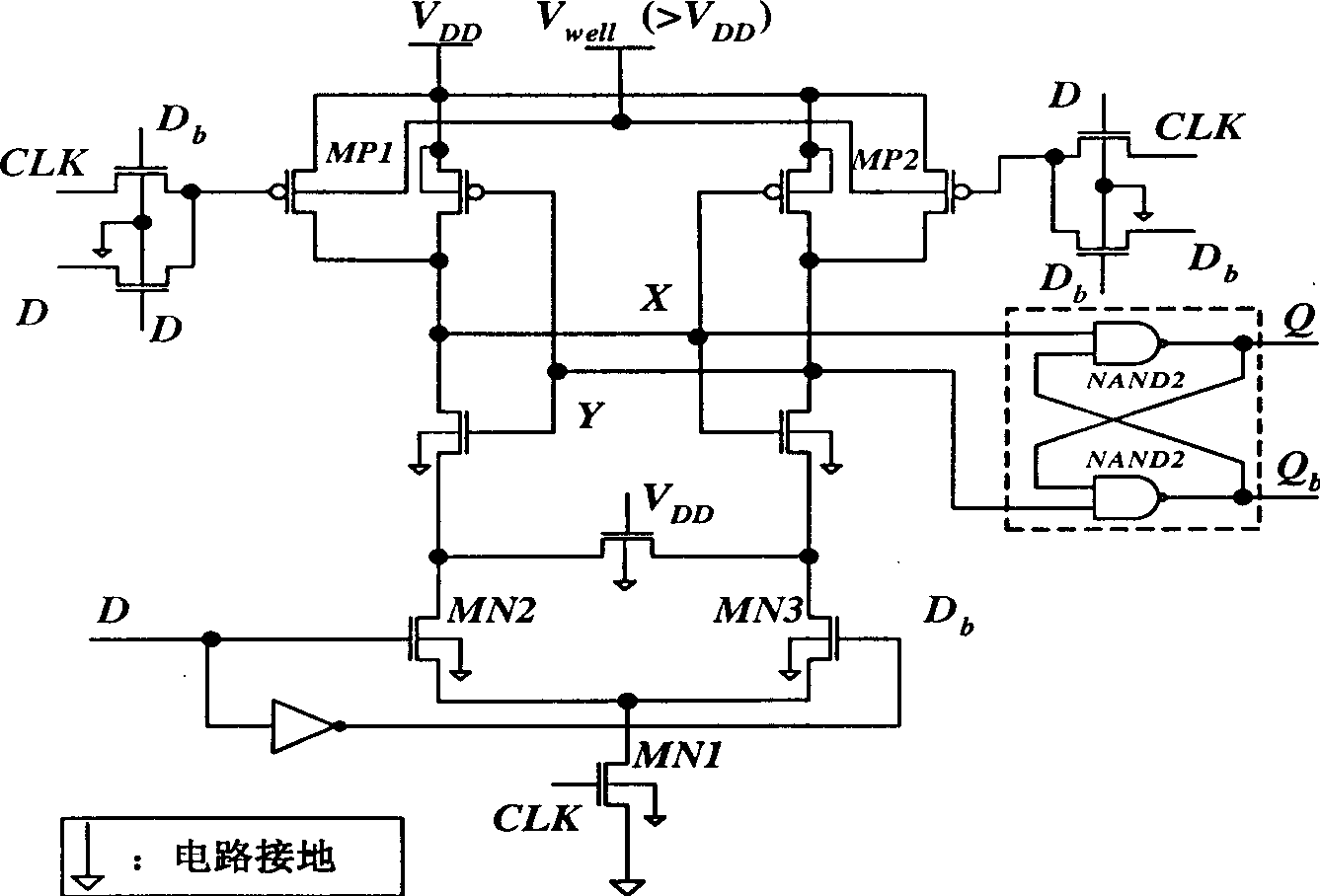
D trigger with resetting and/or setting functions, and based on conditional preliminary filling structure
InactiveCN1697319ASimple structureReduce areaElectric pulse generatorAudio power amplifierControl signal
Characters of the invention are as following: besides structure of sensitive amplifier is adopted in latch in first stage, pull-up and pull-down are carried out for two complemental output ends by using two pieces of P tubes and two pieces of N tubes at power source end and complemental output ends respectively. Control signals pulled-up and pulled-down are set and reset signals. Two pieces of phase latches in single clock with identical circuit parameter are adopted in latch in second stage. Potential retention unit structured from two inverters connected at headers is added between output ends of two pieces of phase latches. Comparing prior art, the invention saves energy 20% under same testing condition. Moreover, the invention possesses features of simple structure, small area of circuit, good characteristics of circuit time delay, setup time and metastable state time.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
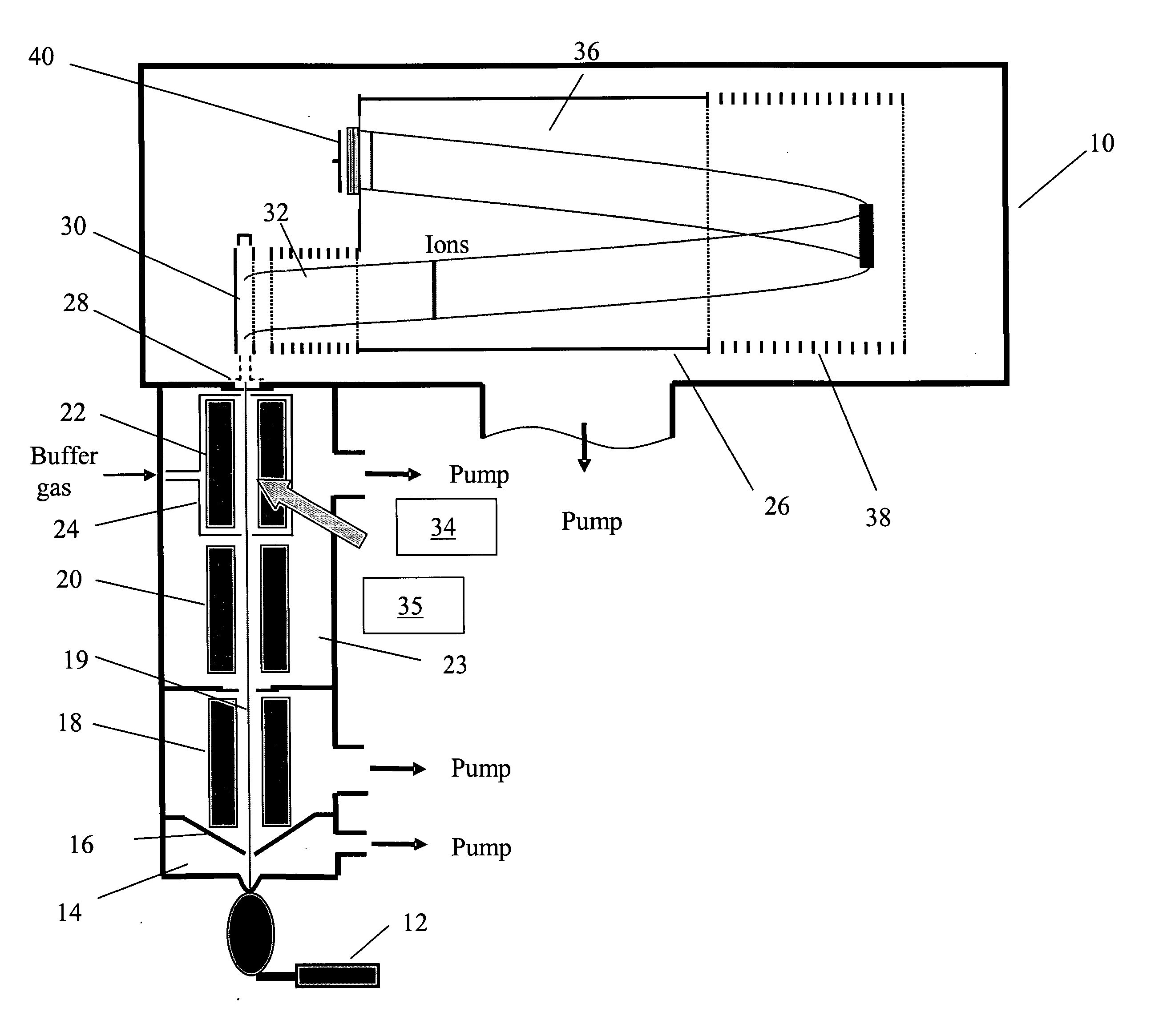
Method and apparatus for ion fragmentation in mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20050258353A1Stability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryMass-to-charge ratio
An apparatus for mass analyzing molecules includes a mass spectrometer configured to select precursor ions having a mass to charge ratio range, a metastable species generator configured to generate a metastable species for introduction into the mass spectrometer, and a mass detector configured to detect a mass of the product ions. The apparatus also includes interaction region in the mass spectrometer where the precursor ions fragment into product ions via interaction of the precursor ions with the metastable species.
Owner:SCI & ENG SERVICES
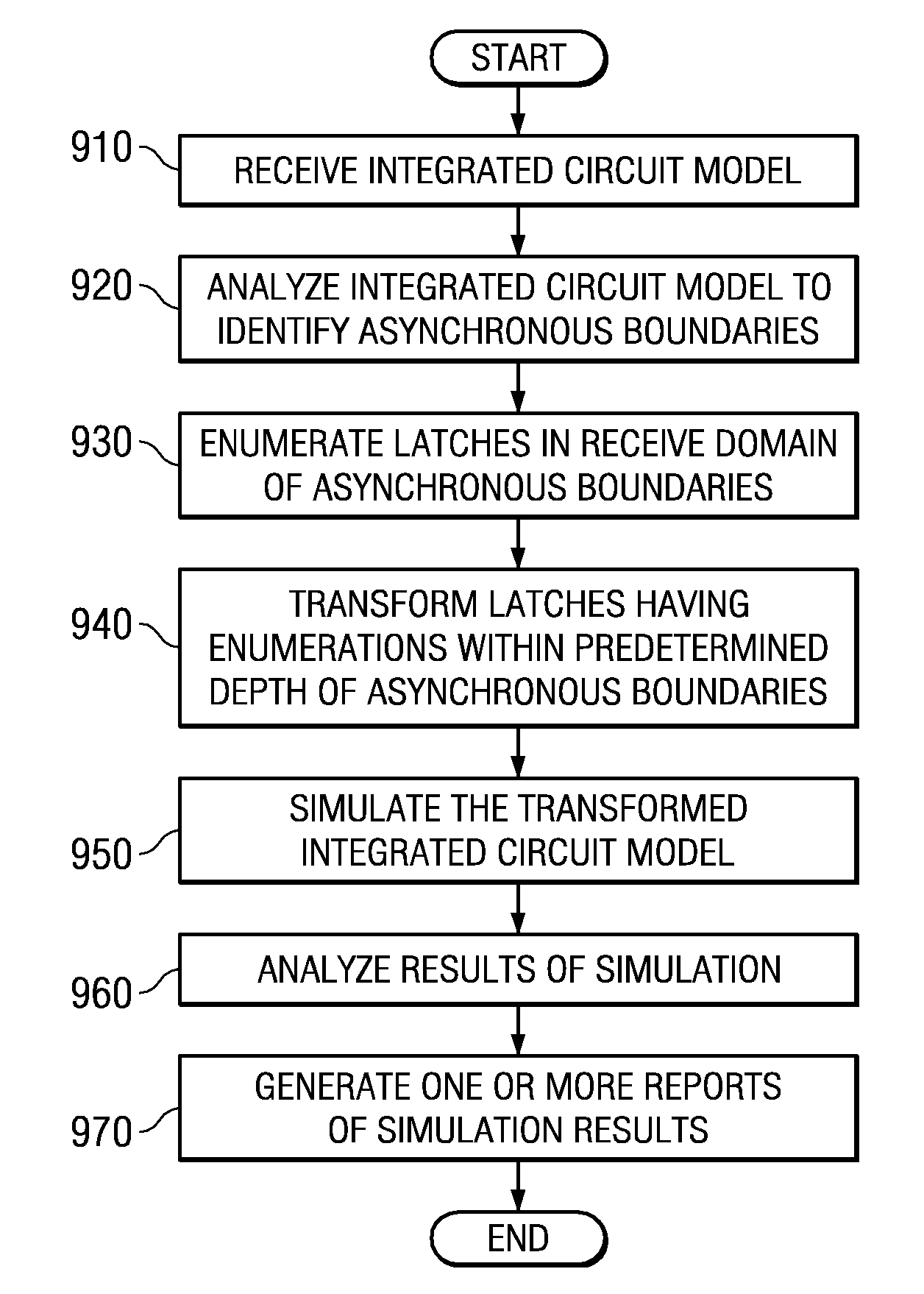
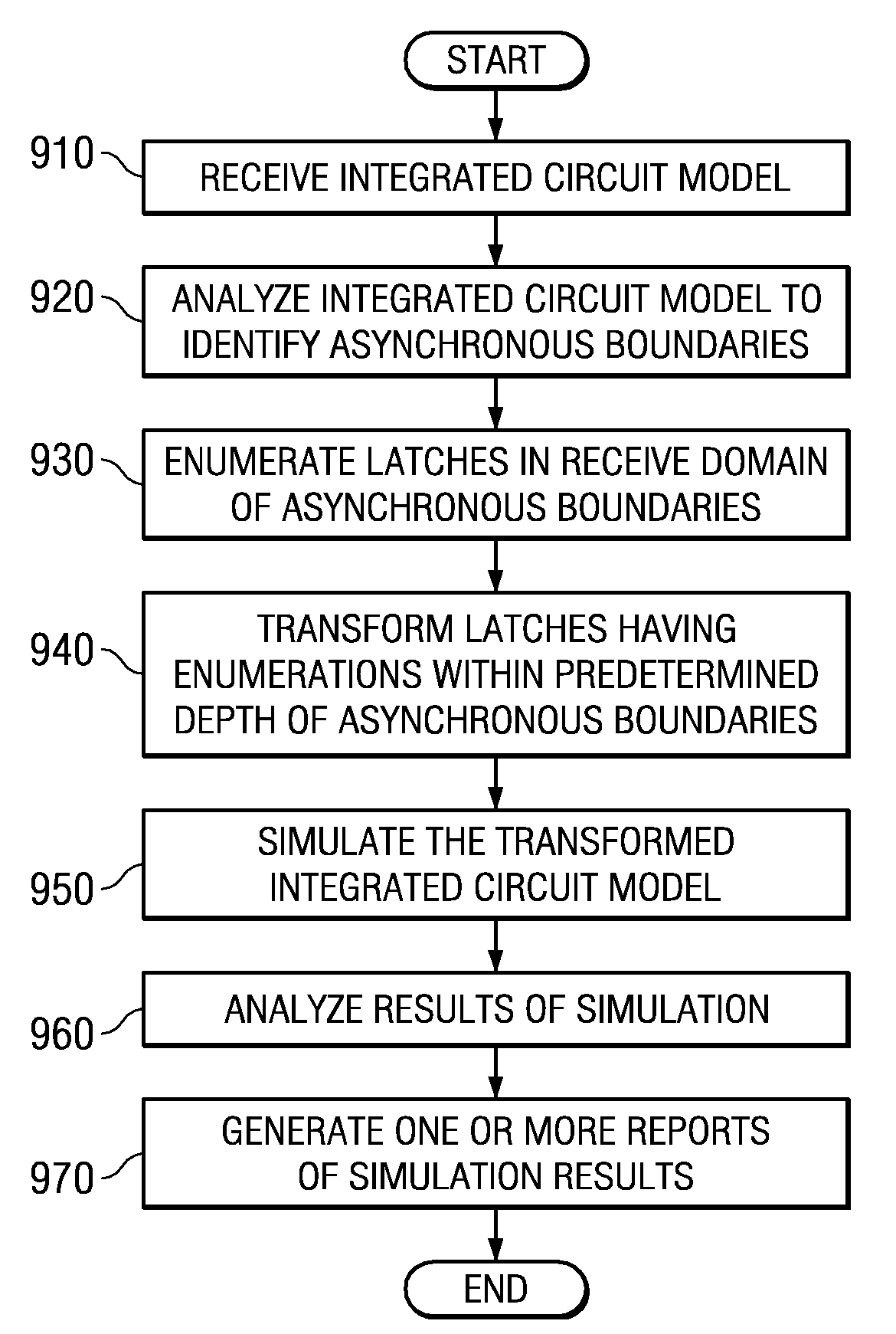
System and Method for Modeling Metastability Decay Through Latches in an Integrated Circuit Model
InactiveUS20080072188A1Improve approximationMade preciselyAnalogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designHardware implementationsComputer science
A system and method for modeling metastability decay through latches in an integrated circuit model are provided. With the system and method, asynchronous clock boundaries are identified in the integrated circuit model and latches in a receive clock domain are enumerated. Latches within a range of the asynchronous clock boundary are selected for transformation. These latches are transformed into metastability decay latches using new latch primitive logic that models the decay of an indeterminate value. The metastability decay latches maintains an indeterminate value during a metastability time period and achieve a randomly selected logic value at the end of the metastability time period. The transformed integrated circuit model may then be simulated and the results analyzed to generate reports of the integrated circuit model's operation. The transformed integrate circuit model more accurately represents the actual operation of the hardware implementation of the integrated circuit model.
Owner:IBM CORP
Reference clock re-timing scheme in electronic circuits
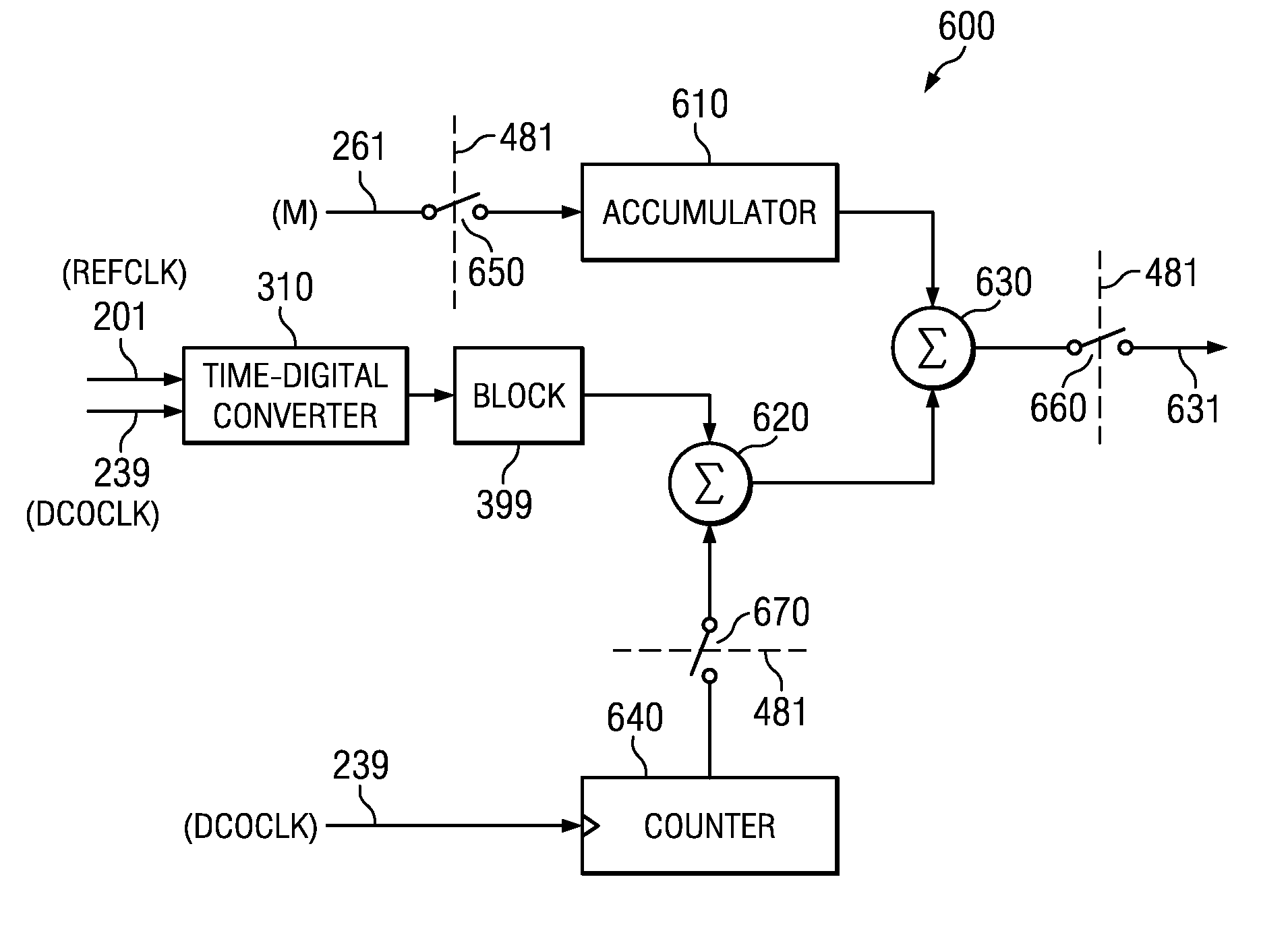
ActiveUS20130211758A1Pulse automatic controlDigital variable/waveform displayActive edgePhase detector
A phase detector includes a counter to generate the integer portion of a number of complete cycles of an output clock at each active edge of a reference clock. A time to digital converter in the phase detector generates the fractional portion of the number of complete cycles of the output clock at each active edge of the reference clock. The sum of the fractional portion and the integer portion is subtracted from an accumulated value obtained by accumulating a pre-determined number to generate an error signal as the output of the phase detector. The counter is read at an active edge of one of two re-timed clocks derived from the reference clock. Each of the two re-timed clocks is generated based on a comparison of the fractional portion with a pair of thresholds. Errors due to metastability in reading the counter are thereby avoided.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
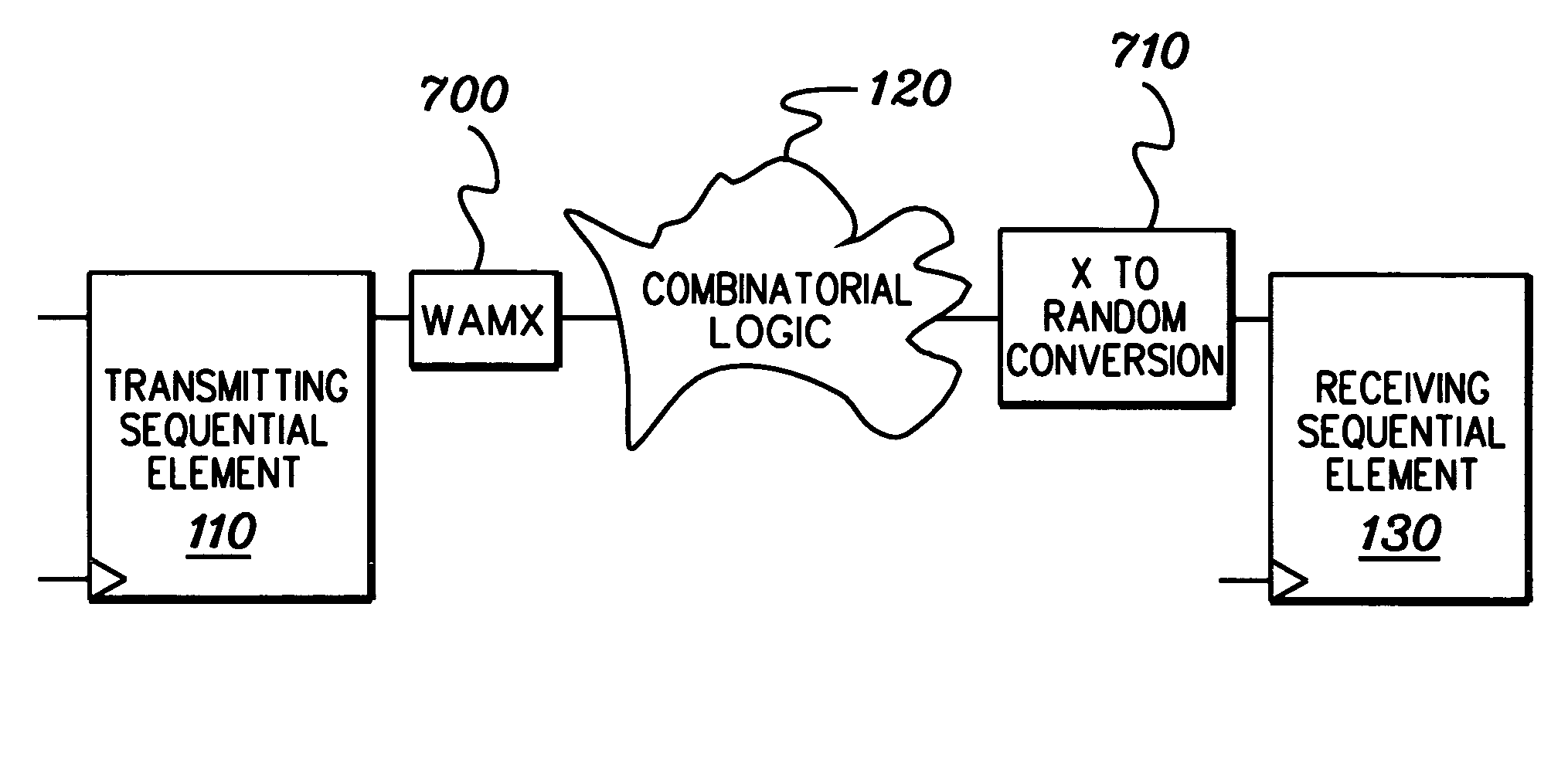
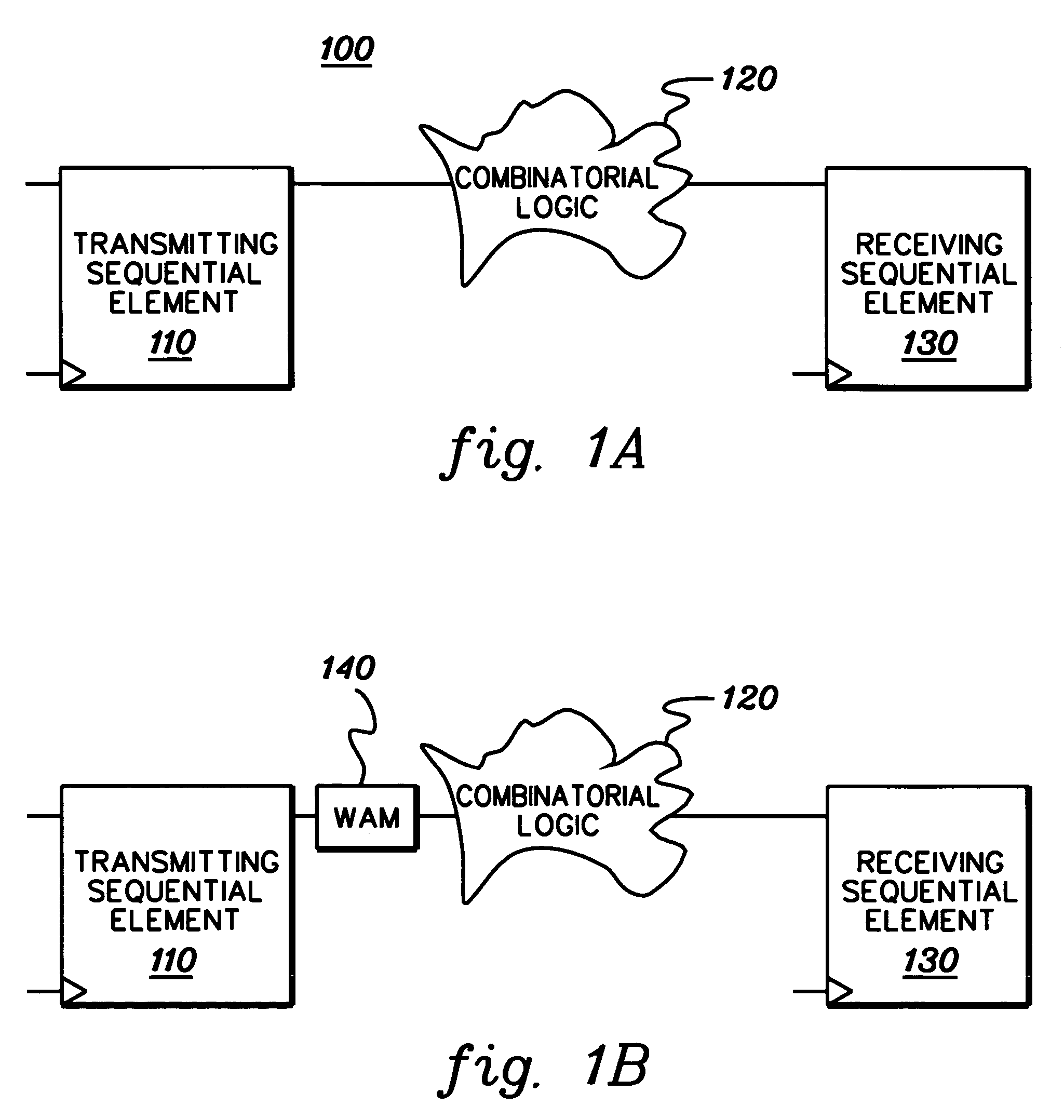
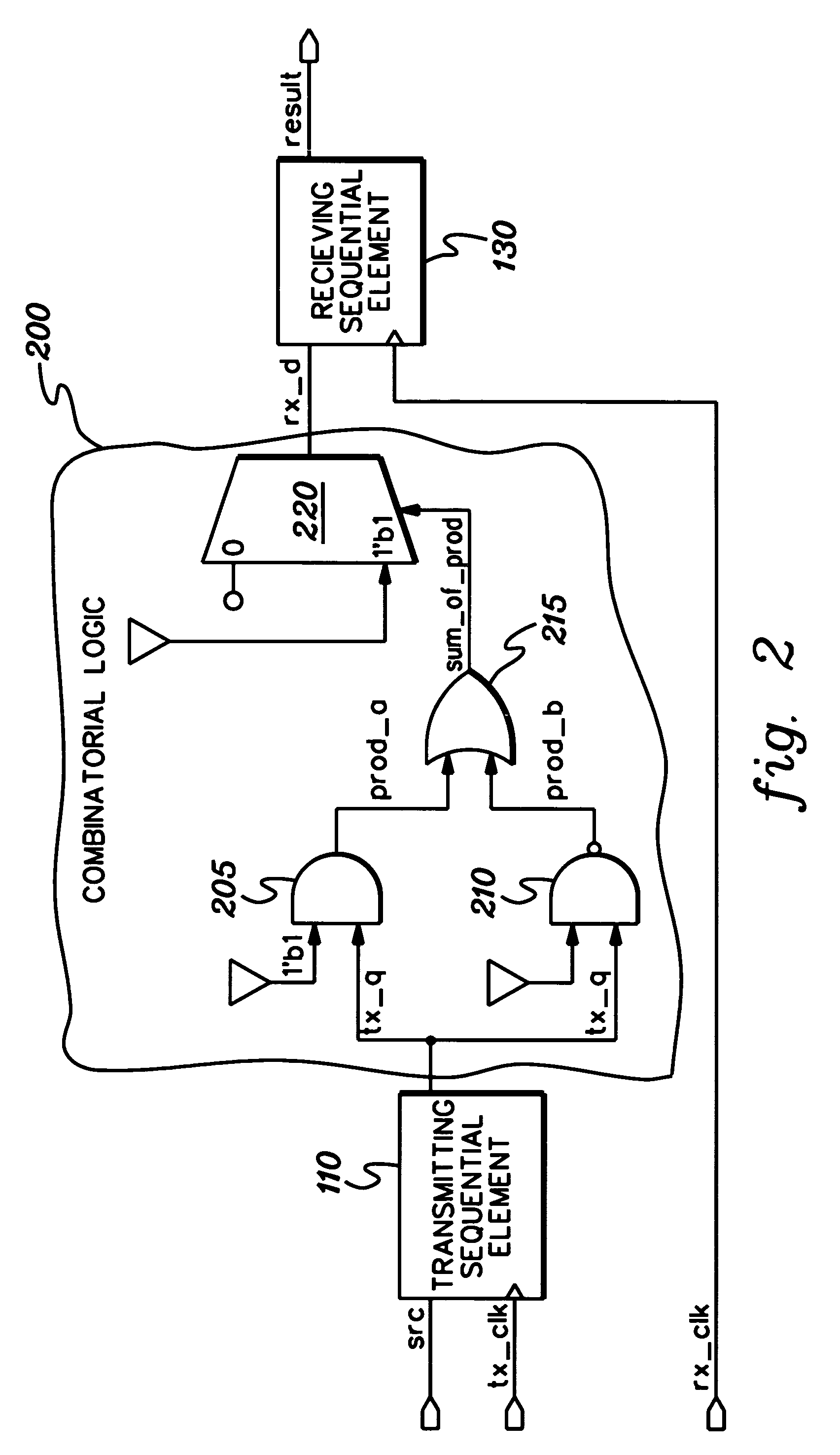
Method, apparatus, and computer program product for facilitating modeling of a combinatorial logic glitch at an asynchronous clock domain crossing
InactiveUS7333926B2Inserting of the simulation value of X into the combinatorial logic can be facilitatedFacilitate automatic propagation of the simulation value XDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputation using non-denominational number representationLogic modelingPath generation
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided for facilitating combinatorial logic modeling at an asynchronous clock domain crossing. The modeling technique employs a simulation value of X in combinatorial logic at the asynchronous clock domain crossing of a circuit being modeled to facilitate modeling of a potential combinatorial logic glitch at the crossing during metastability periods thereof. Employing the simulation value of X includes: generating one or more equivalent functional equations for one or more combinatorial paths through the combinatorial logic at the crossing; propagating the simulation value of X through the combinatorial logic using the at least one equivalent functional equation; and then converting the simulation value of X at an output of the combinatorial logic of the asynchronous clock domain crossing to a random logic value for further propagation within the circuit being modeled.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
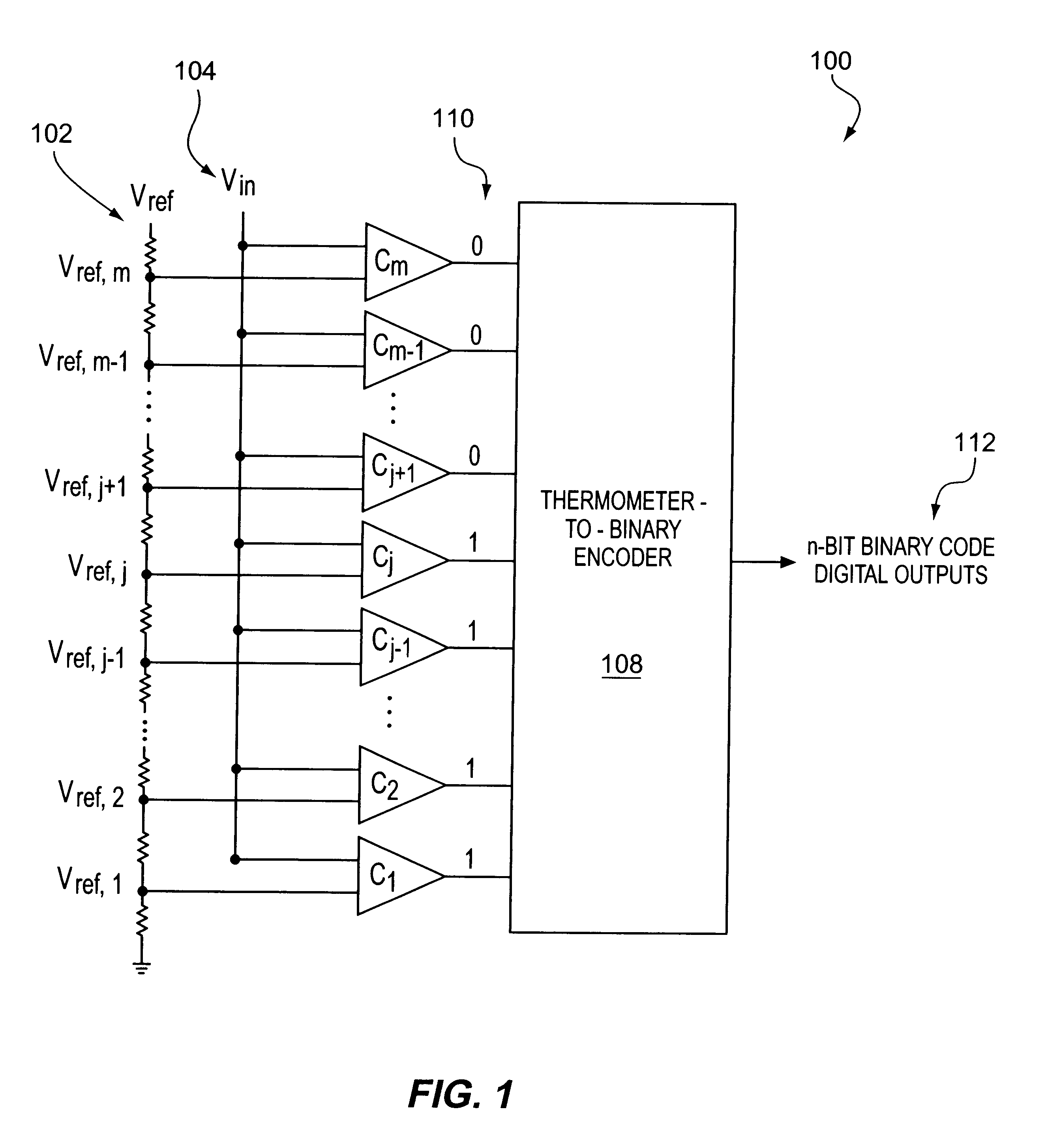
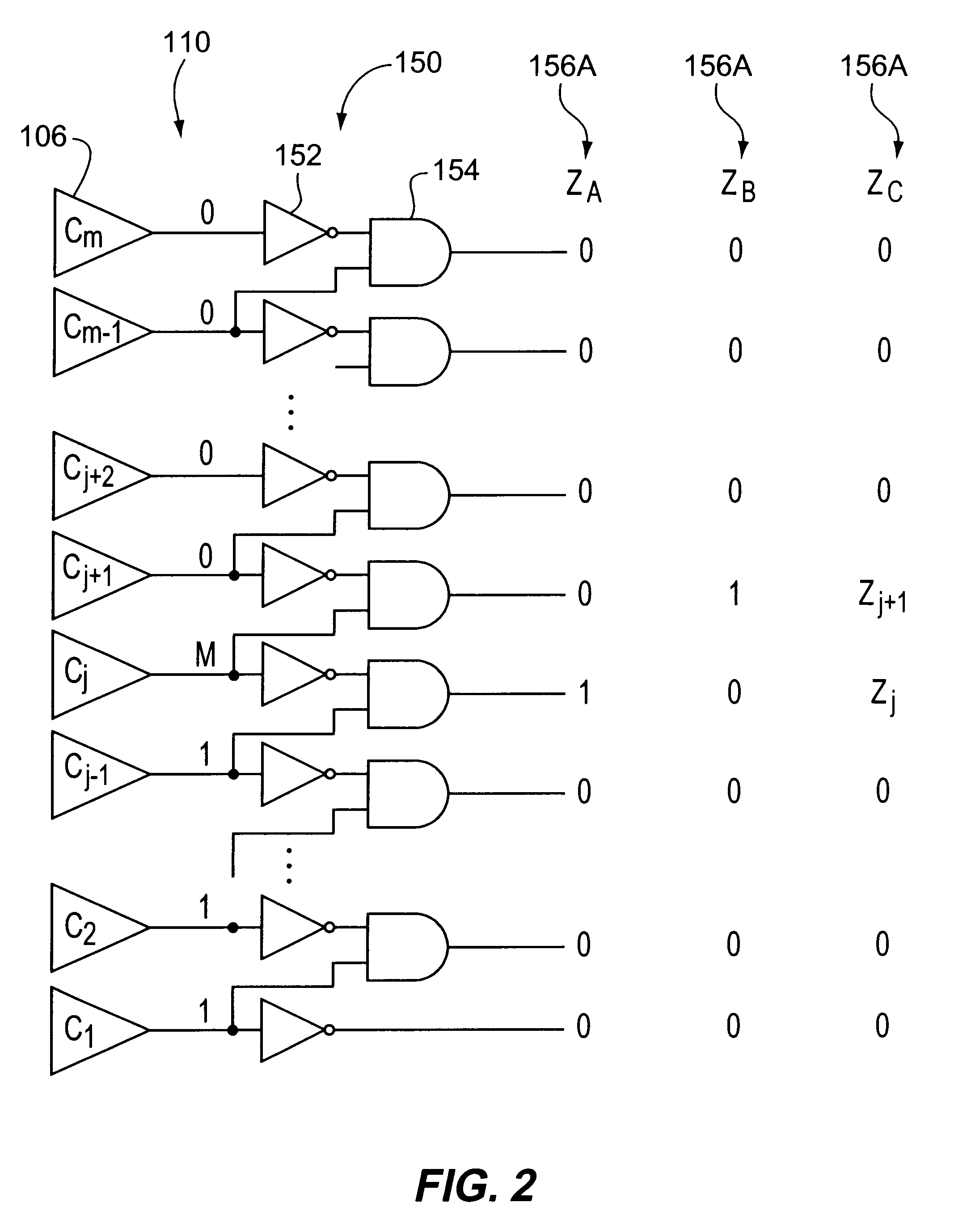
Architecture to reduce errors due to metastability in analog to digital converters
InactiveUS6222476B1Electric signal transmission systemsPhysical parameters compensation/preventionDigital down converterTransition point
A system and method for reduced metastability errors in an analog-to-digital converter ("ADC") are disclosed. The ADC comprises comparators configured to output a thermometer code and a thermometer-to-binary encoder for converting the thermometer code to a digital output. The thermometer-to-binary encoder includes a transition detection logic to generate a transition codeword having at least one transition bit corresponding to a transition point in the thermometer code, an intermediate encoding logic to encode the transition codeword into first intermediate signals, a converter logic to convert the first intermediate signals into converted intermediate signals such that same converted intermediate signals result from first intermediate signals corresponding to a transition codeword having more than one transition bit and first intermediate signals corresponding to another transition codeword having one of the more than one transition bit, and a converted signals mapper for mapping the converted signals to the digital output. The transition detection logic may include inverters and AND gates where a threshold voltage of each inverter is preferably greater than a threshold voltage of each corresponding AND gate to which the output of each inverter is input.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Method for modeling metastability decay through latches in an integrated circuit model
InactiveUS7484192B2Analogue computers for electric apparatusComputer aided designIntegrated circuit layoutHardware implementations
Mechanisms for modeling metastability decay through latches in an integrated circuit model are provided. Asynchronous clock boundaries are identified in the integrated circuit model and latches in a receive clock domain are enumerated. Latches within a range of the asynchronous clock boundary are selected for transformation. These latches are transformed into metastability decay latches using new latch primitive logic that models the decay of an indeterminate value. The metastability decay latches maintains an indeterminate value during a metastability time period and achieve a randomly selected logic value at the end of the metastability time period. The transformed integrated circuit model may then be simulated and the results analyzed to generate reports of the integrated circuit model's operation. The transformed integrate circuit model more accurately represents the actual operation of the hardware implementation of the integrated circuit model.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
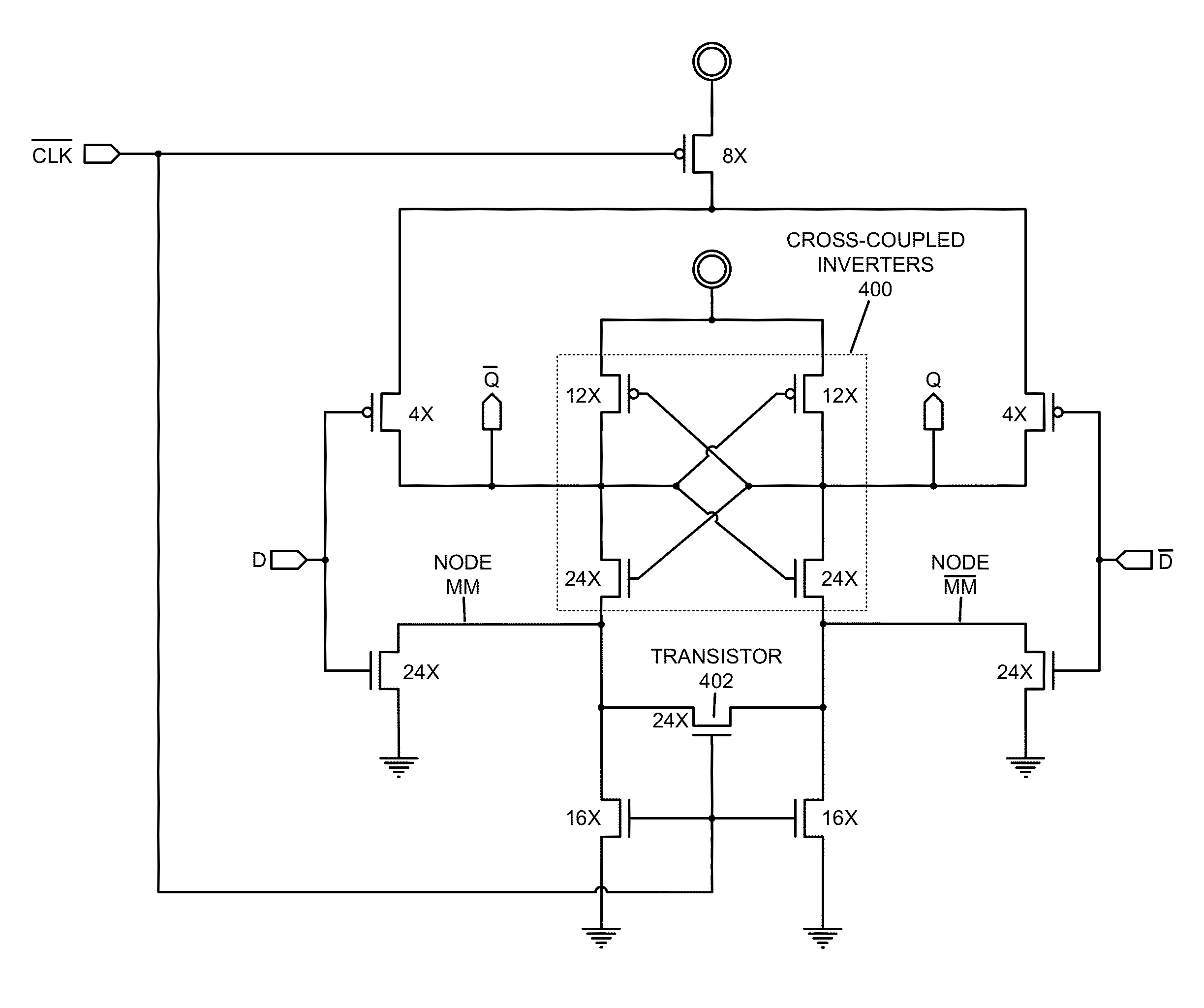
Synchronizer latch circuit that facilitates resolving metastability
ActiveUS20130135017A1Facilitates resolving metastability issueRapidly resolving metastabilityPulse automatic controlElectric pulse generatorNetwork connectionInput control
The disclosed embodiments provide a synchronizer latch circuit that facilitates resolving metastability issues. This synchronizer latch circuit includes a set of lightly loaded, cross-coupled transistors that form a metastable resolving and state-holding element that is coupled to two outputs. An incoming synchronization signal creates a voltage difference between the two outputs, but does not directly force a state change for the outputs. Instead, the data and clock inputs control transistors that allow neighboring power sources and / or ground network connections to weakly influence the outputs. The cross-coupled transistors then amplify the resulting voltage difference to generate valid output voltages, even when the data input and clock signal are received at roughly the same time. Thus, the synchronizer latch circuit facilitates rapidly resolving metastability and improving synchronizer performance.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com