Patents
Literature
95 results about "Flash ADC" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
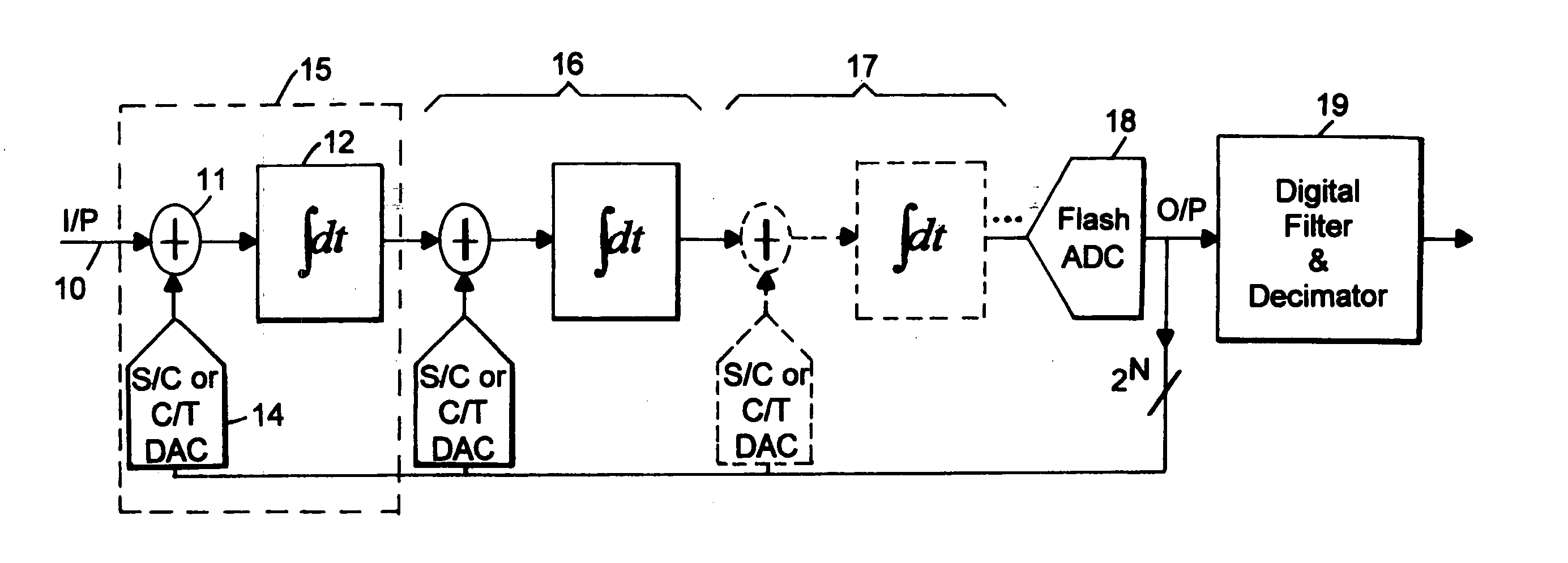
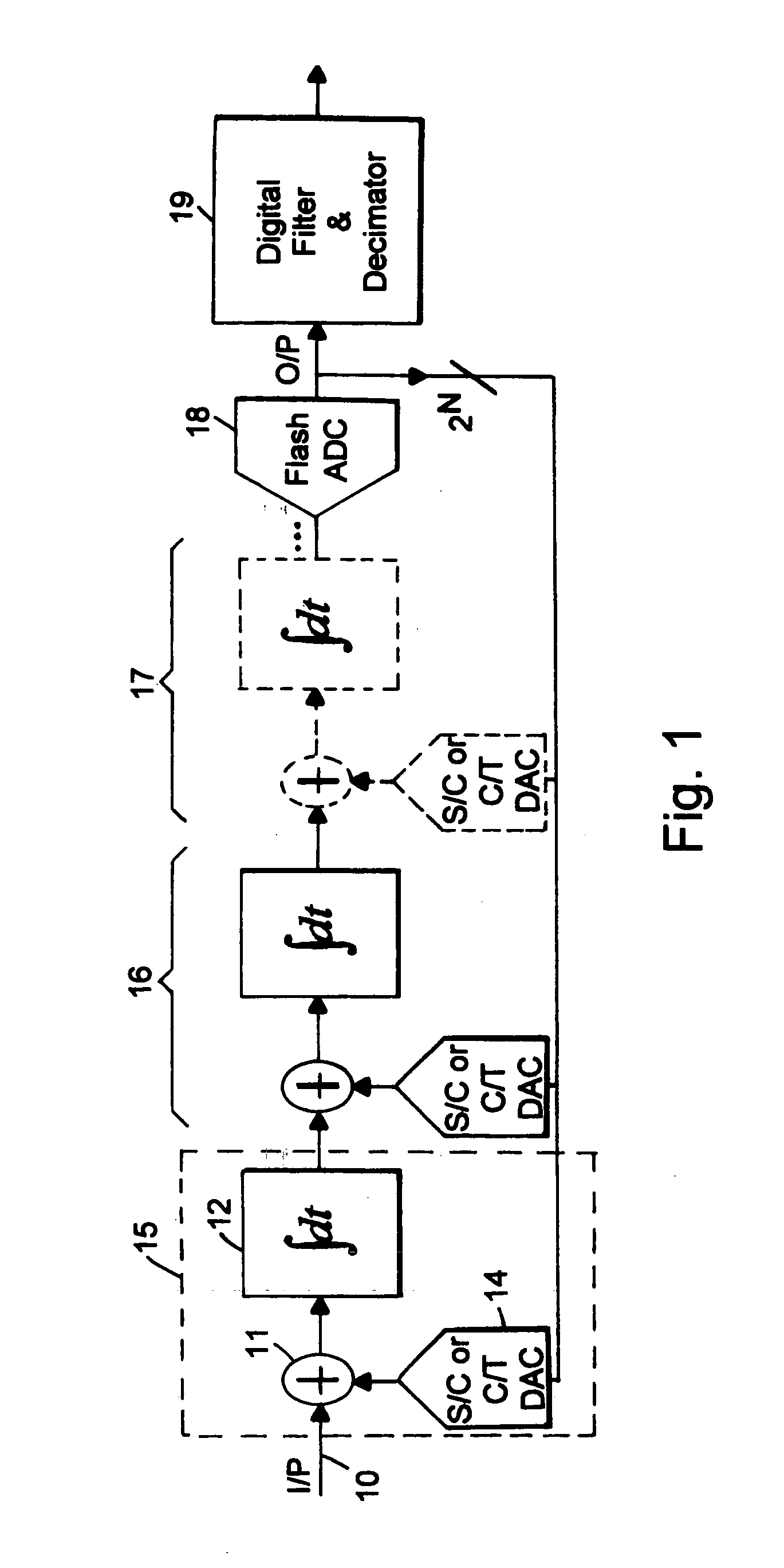
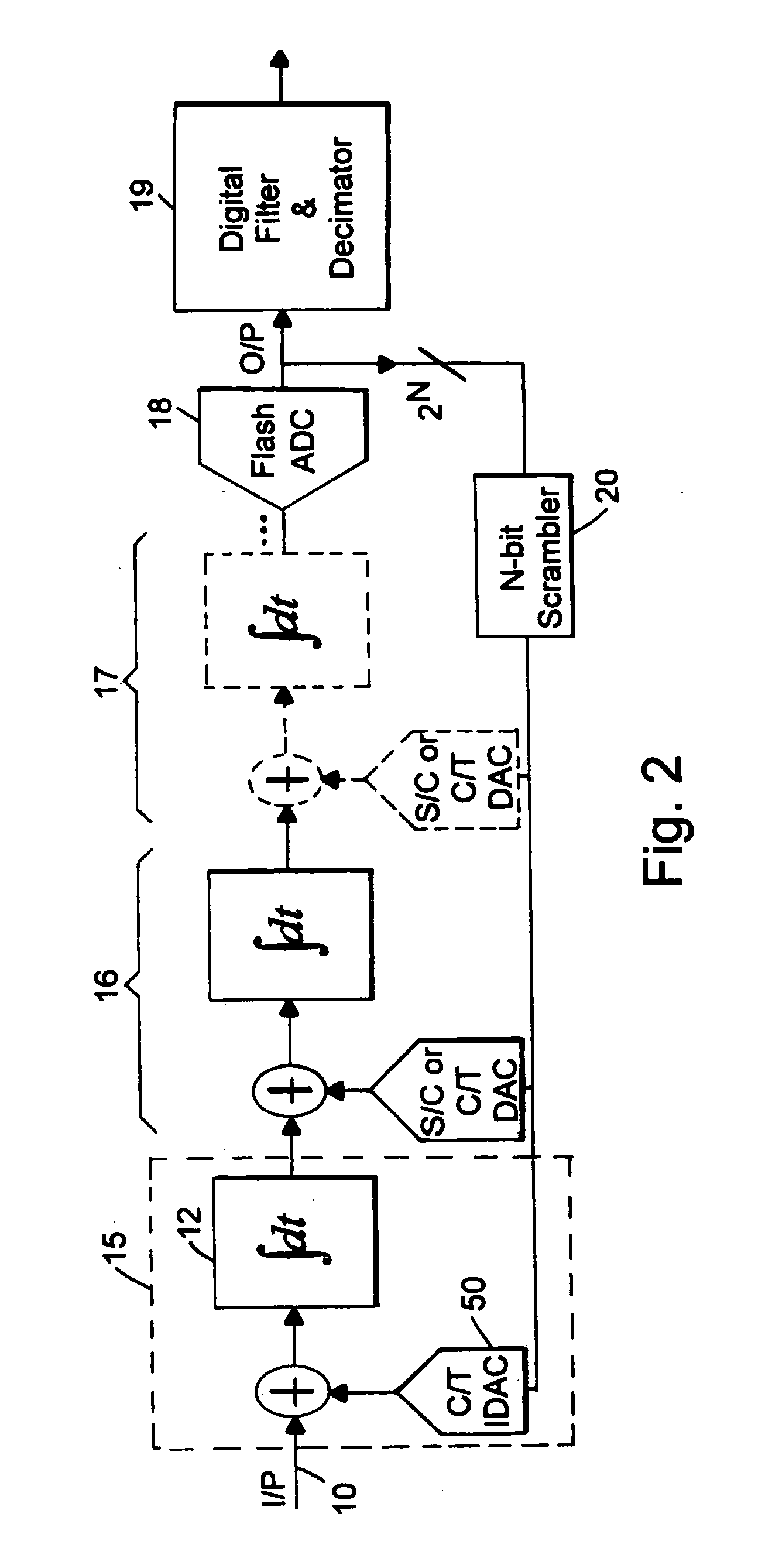
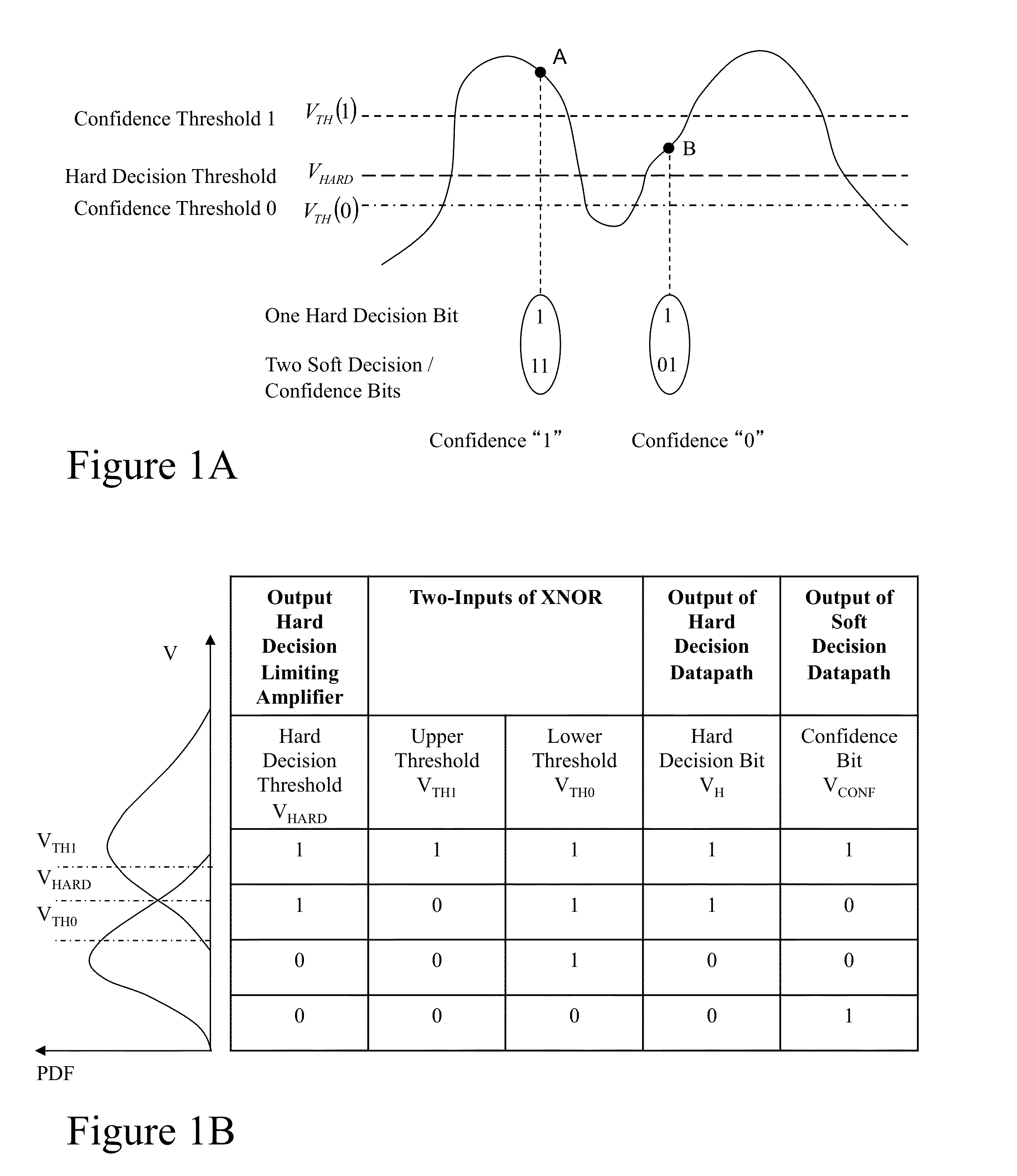
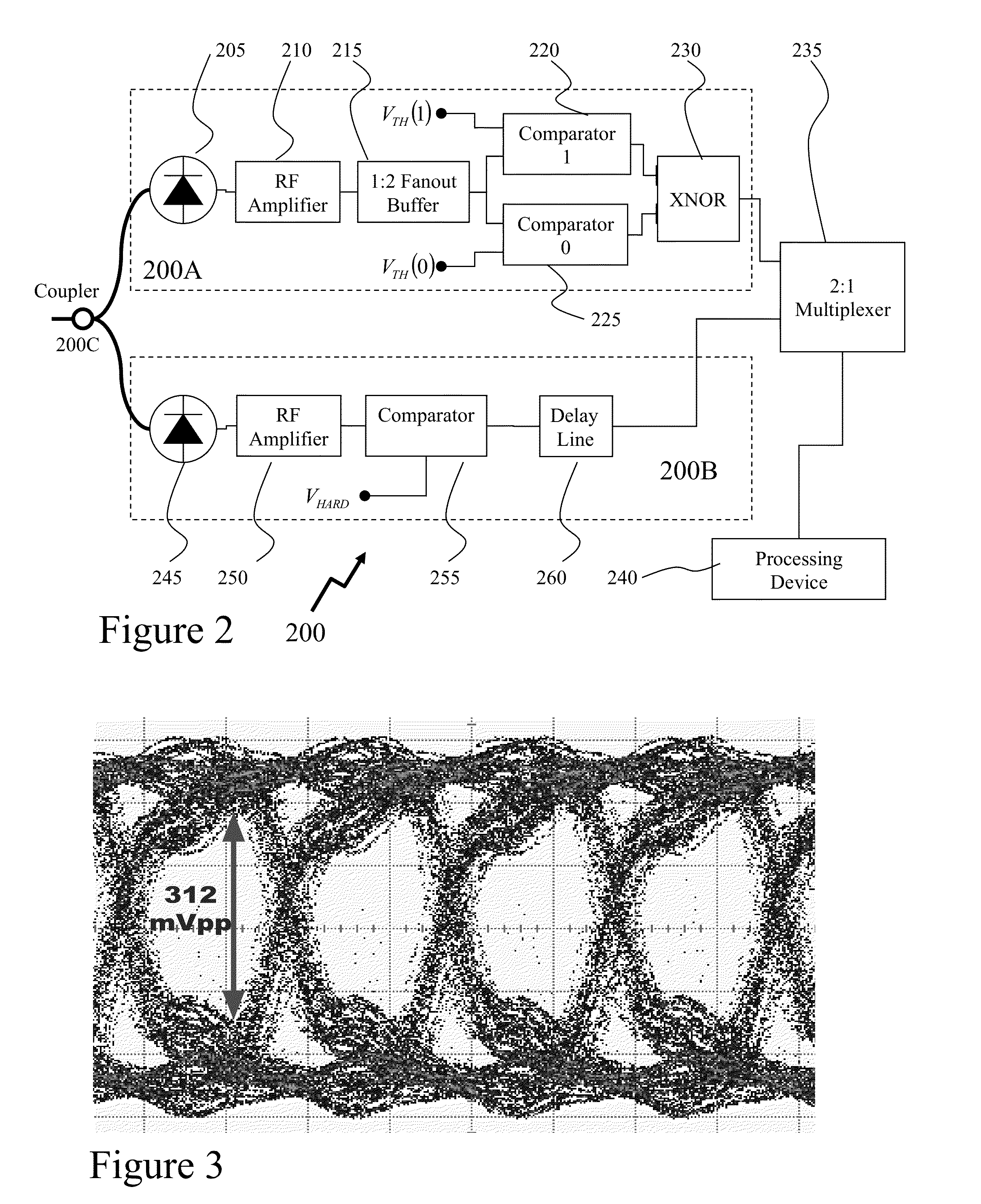
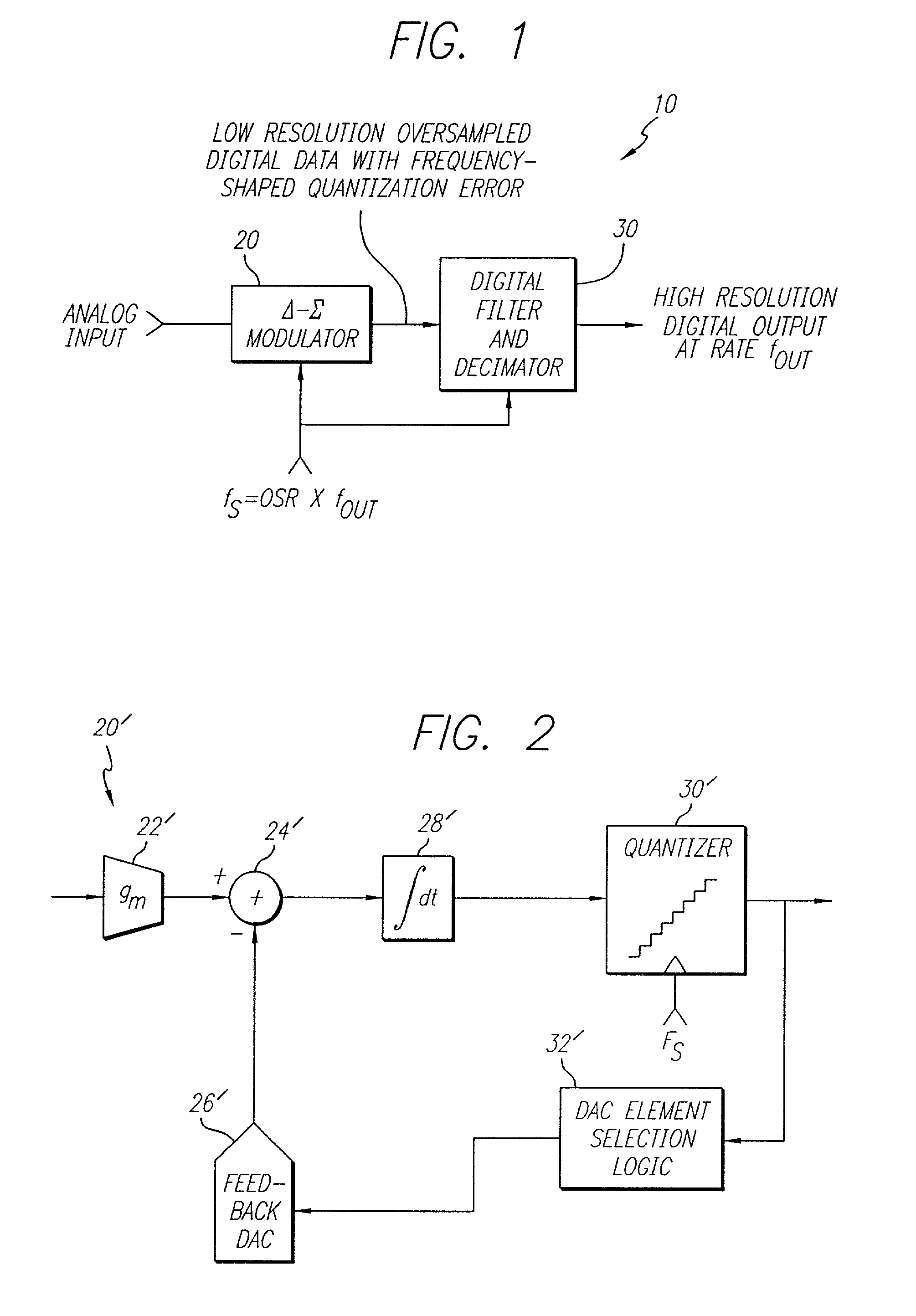
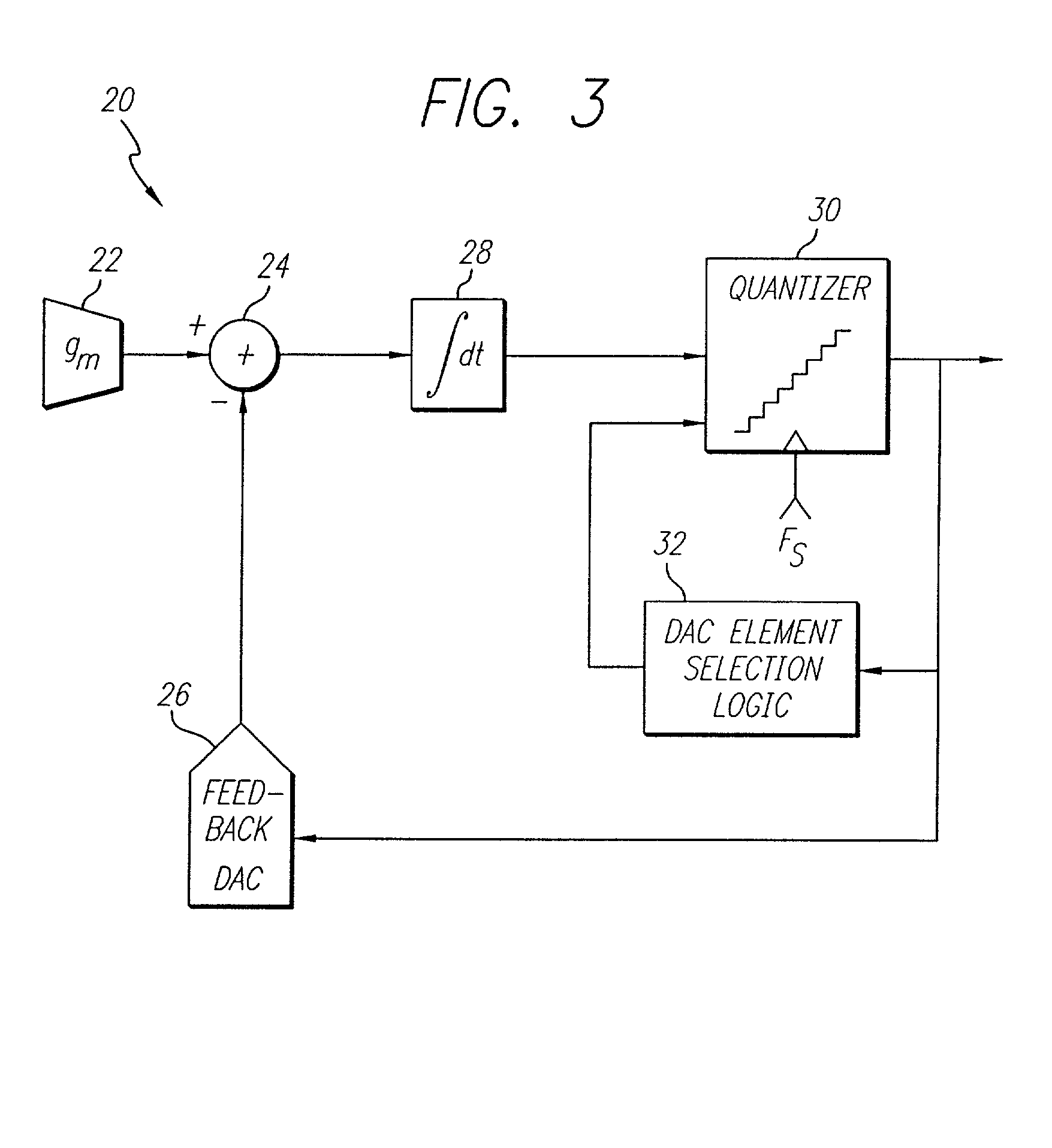
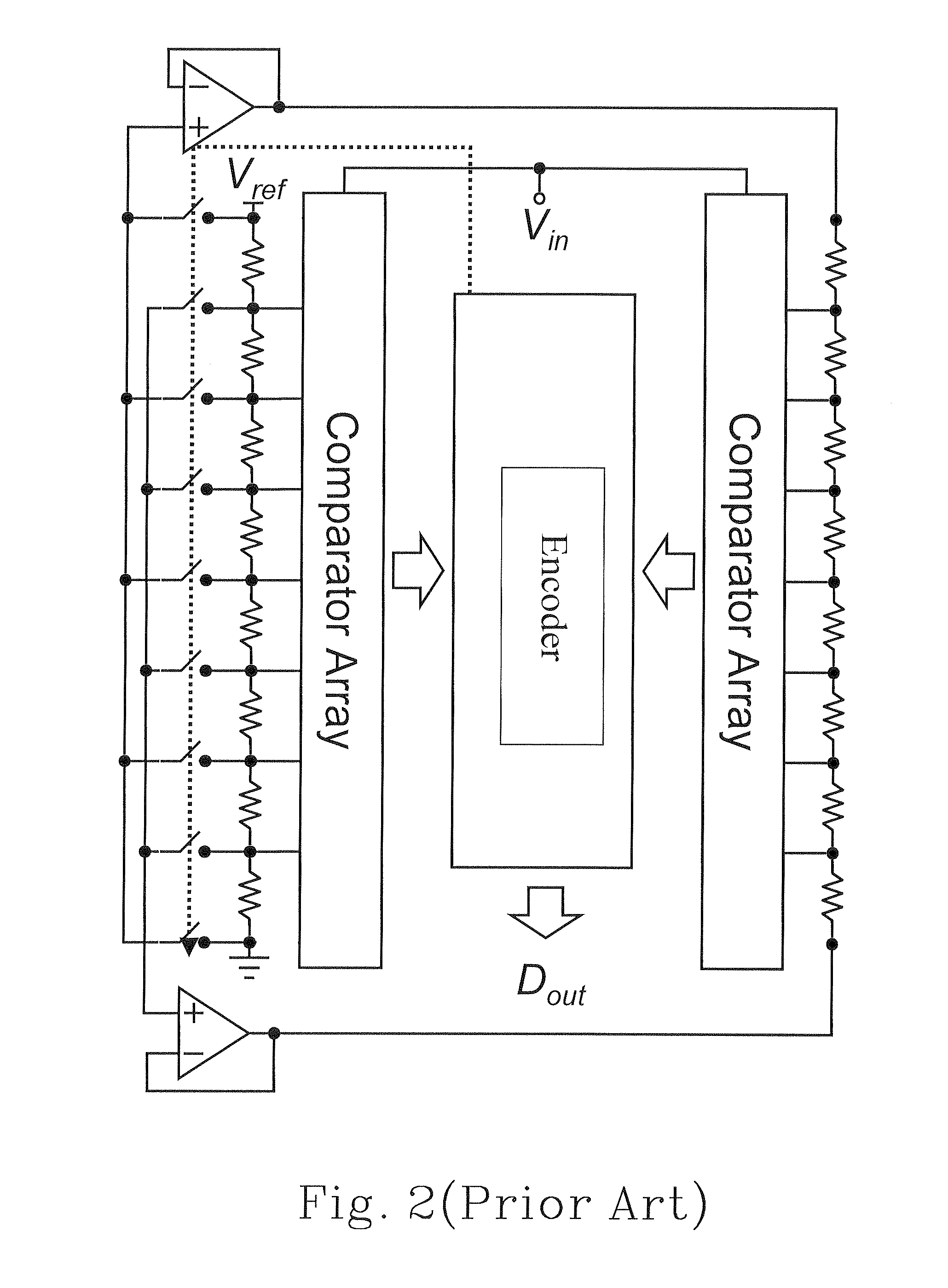
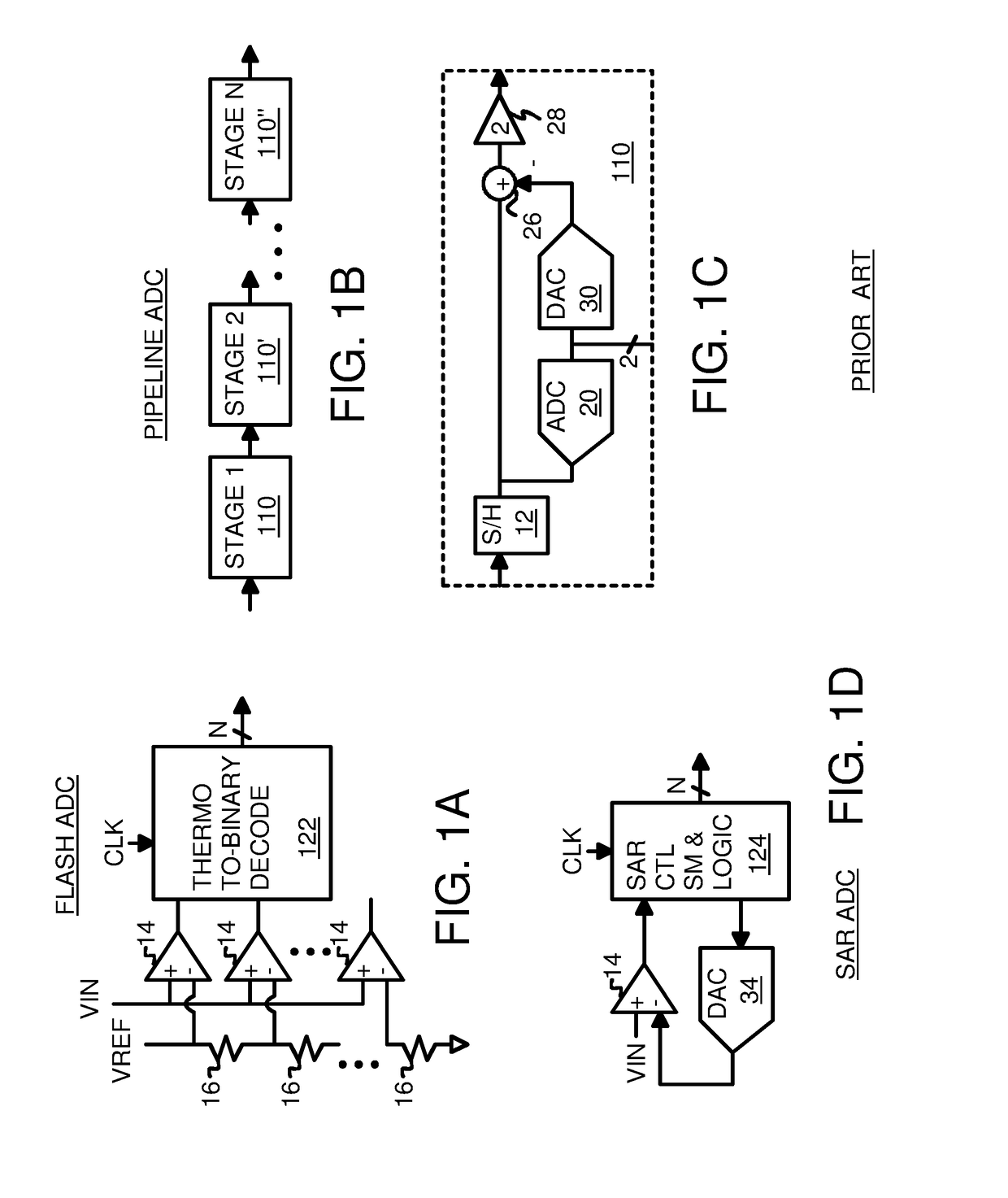
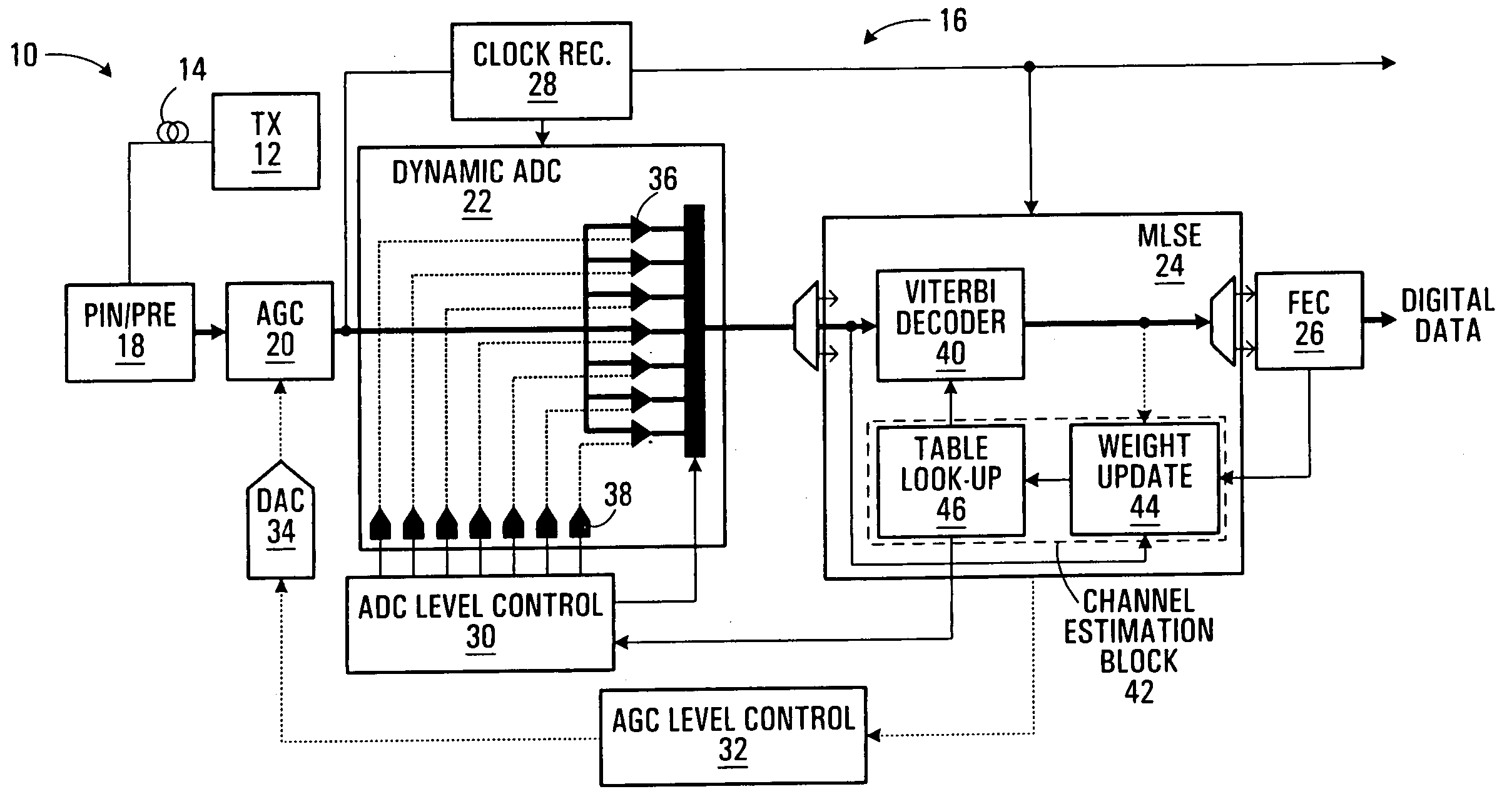
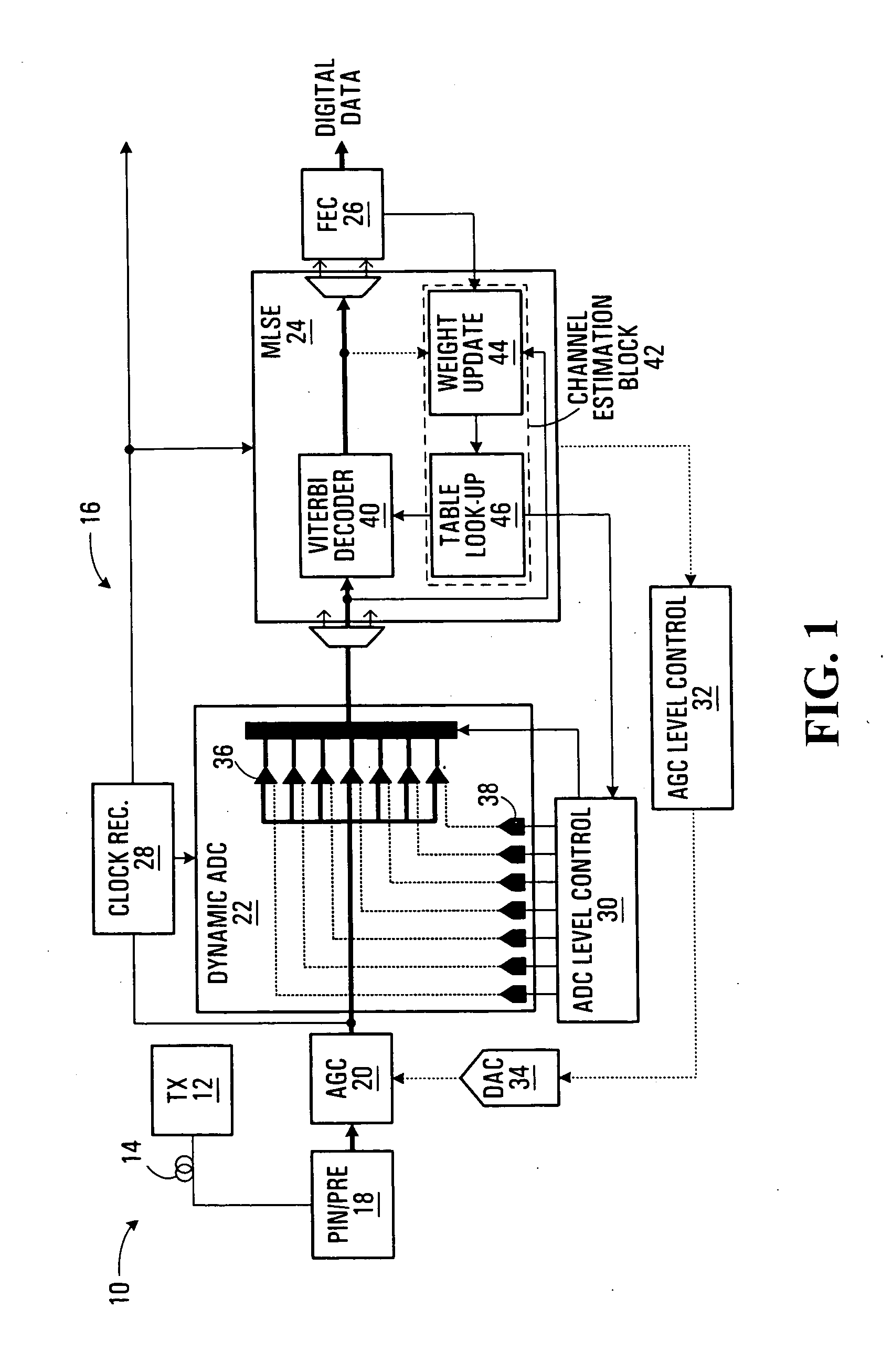
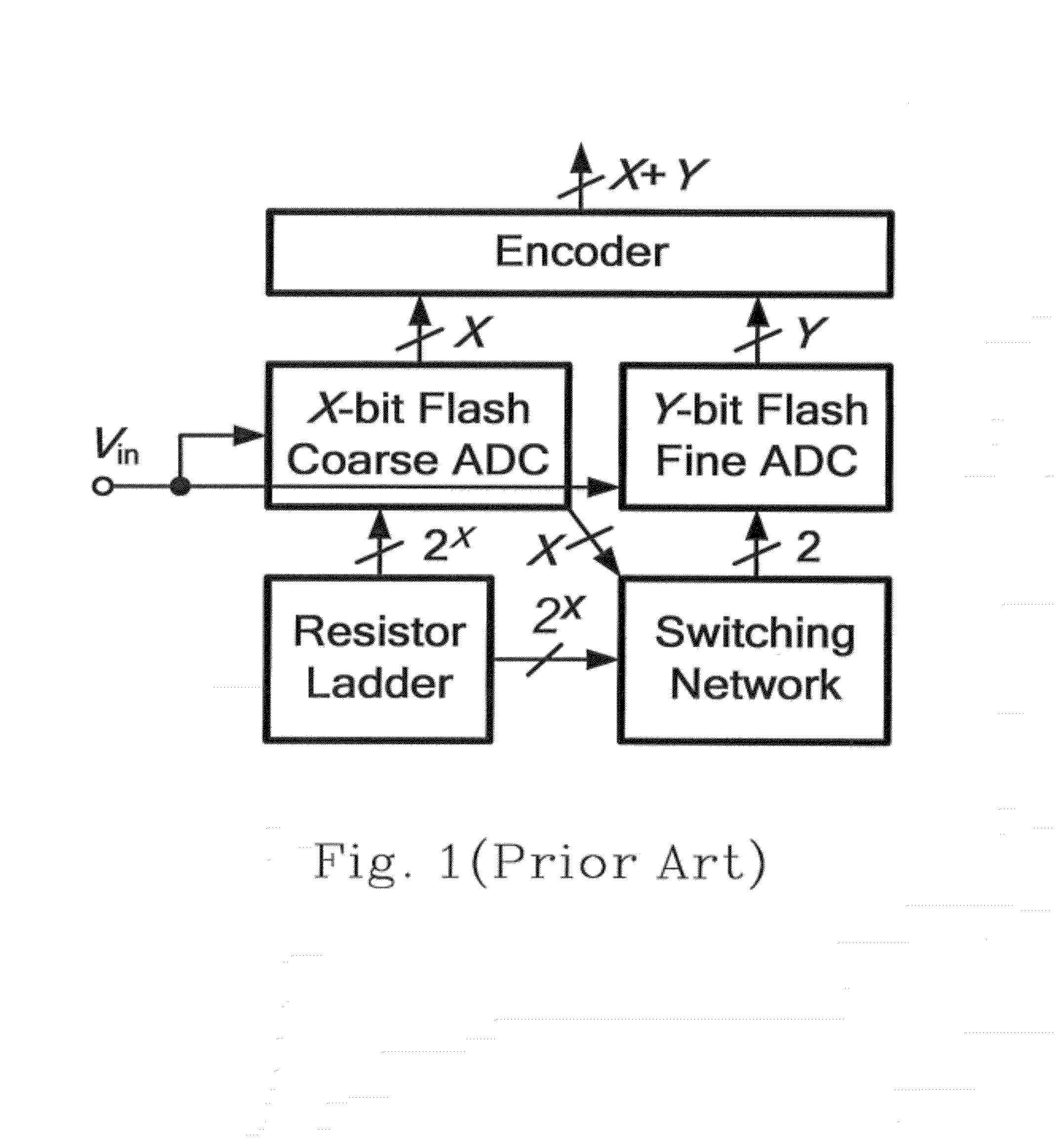
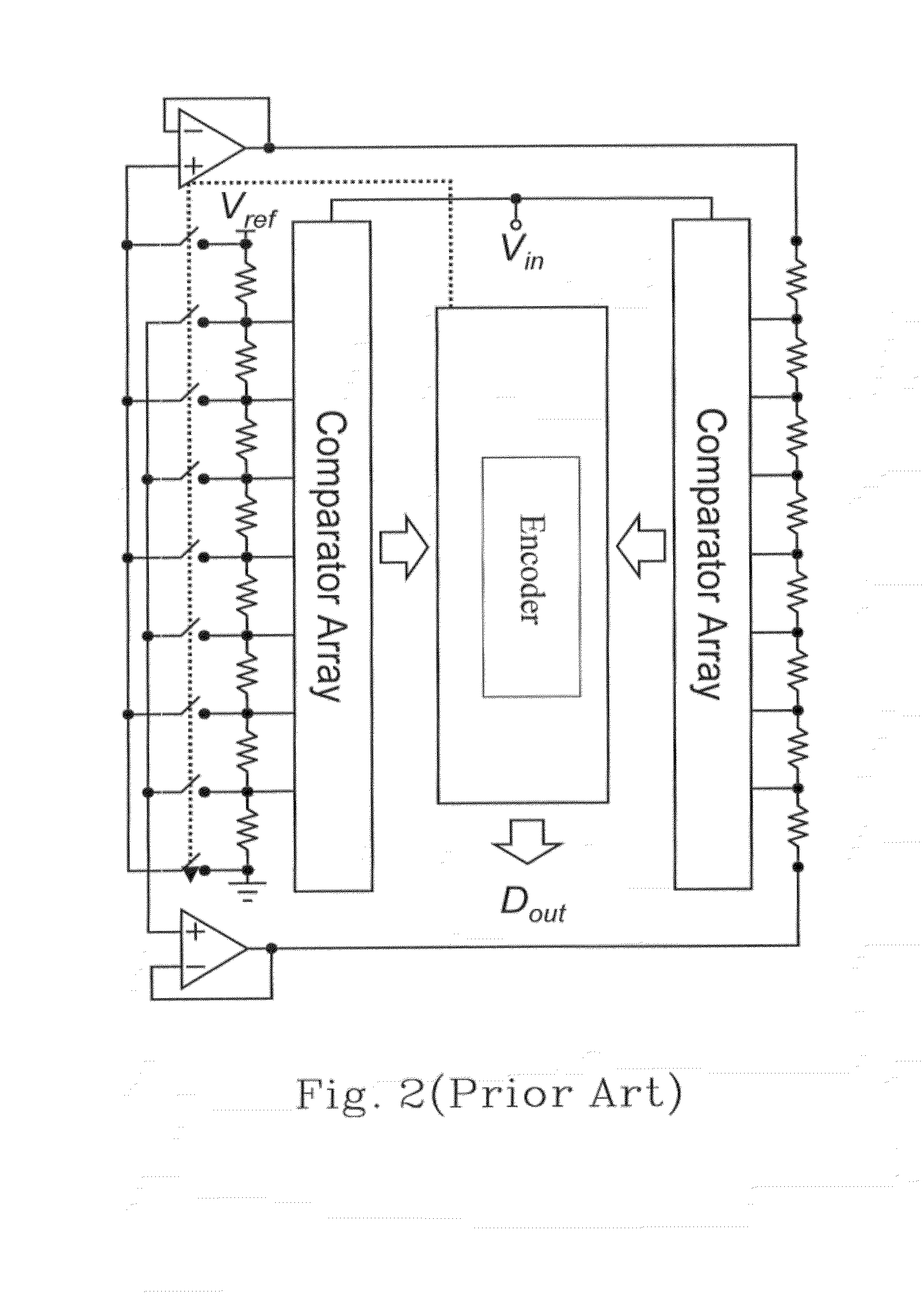
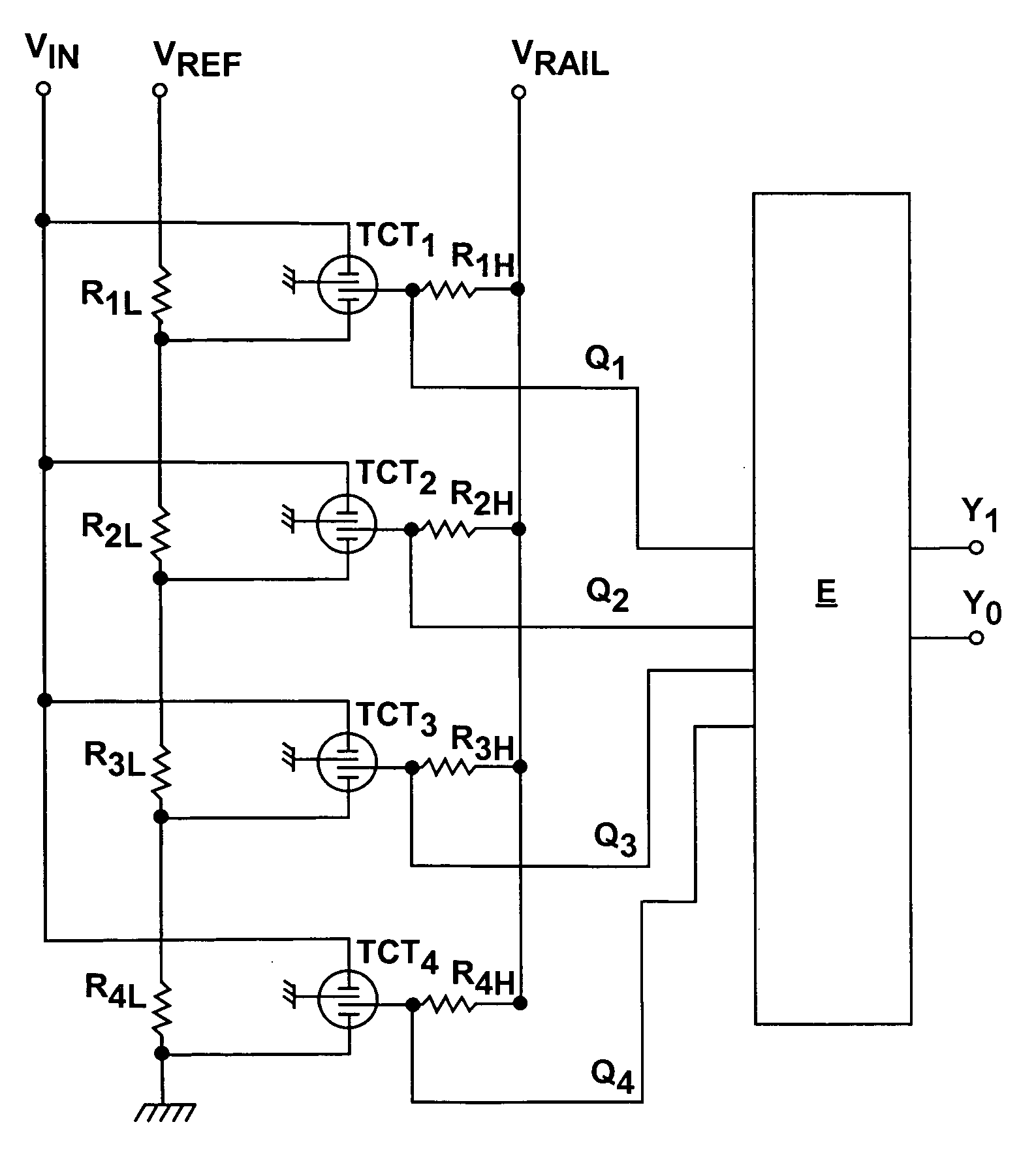
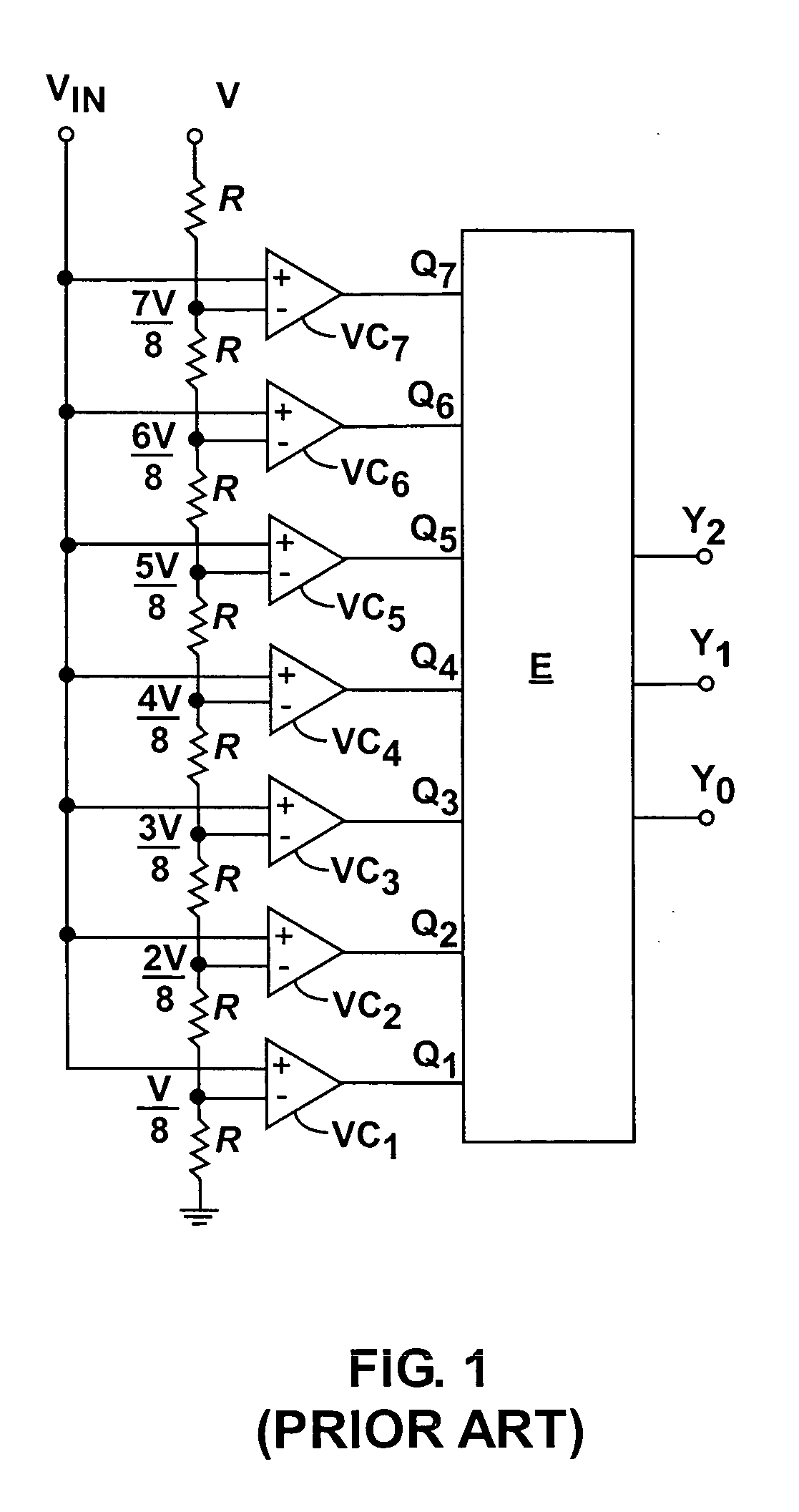
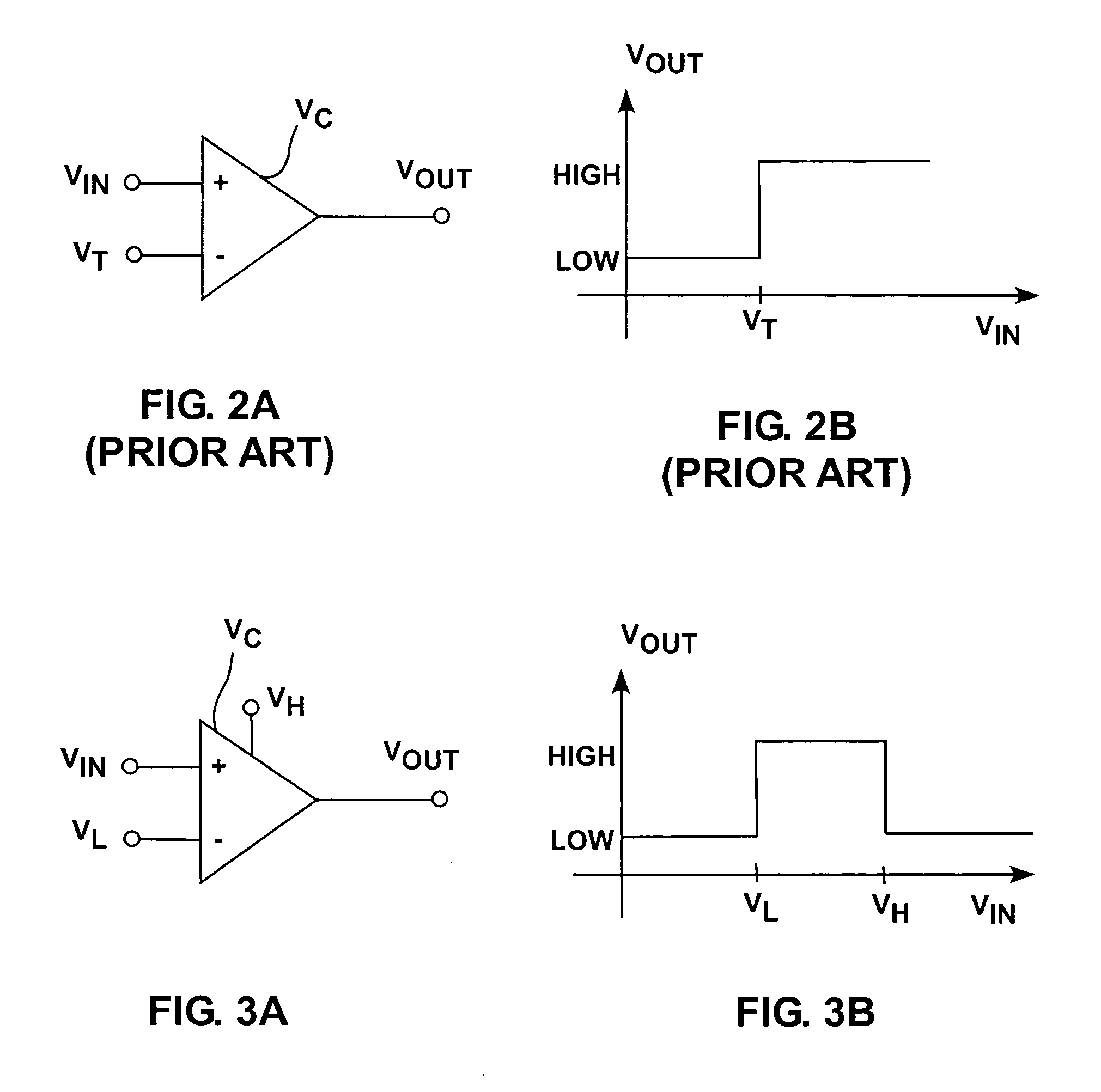
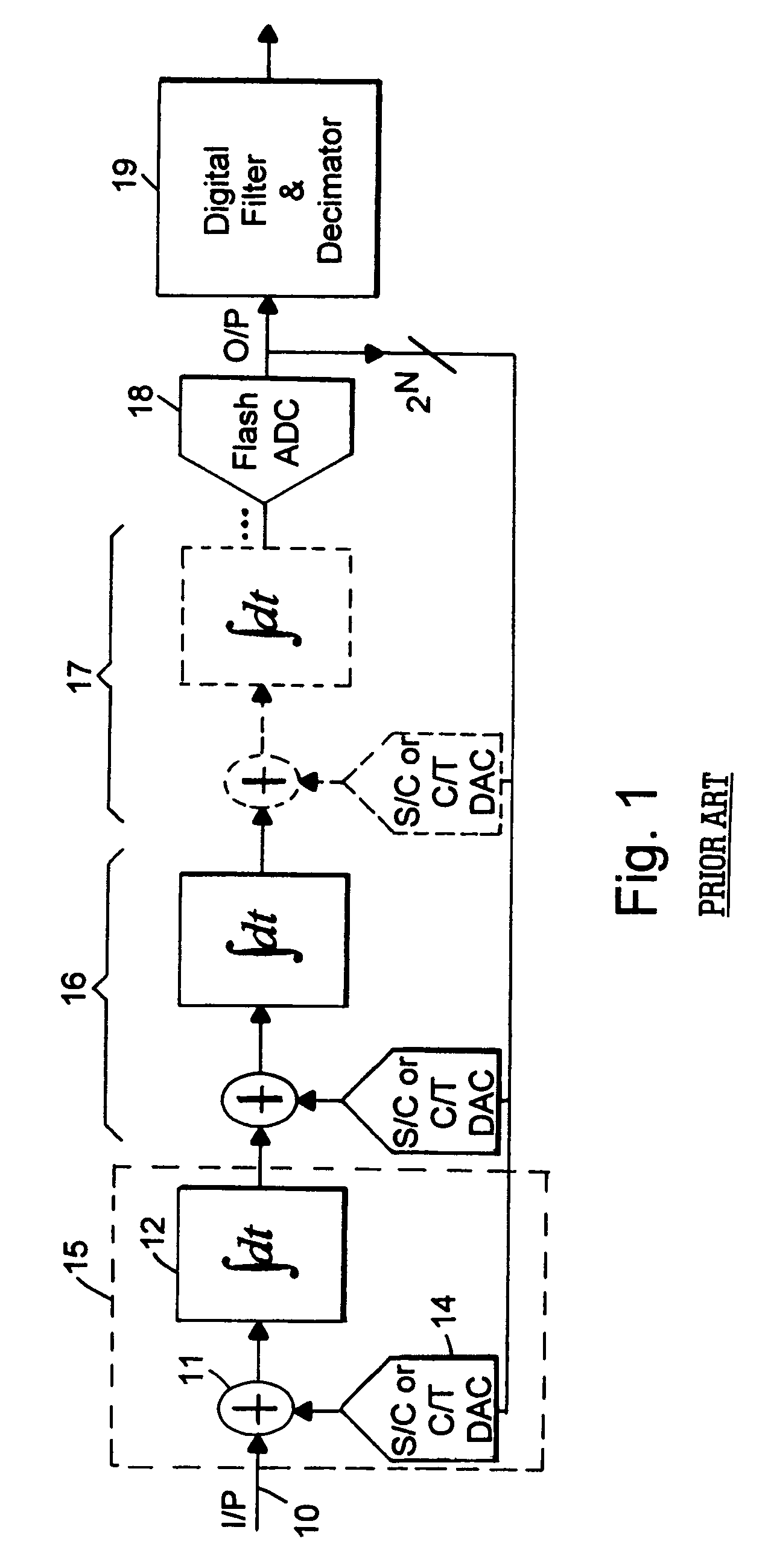
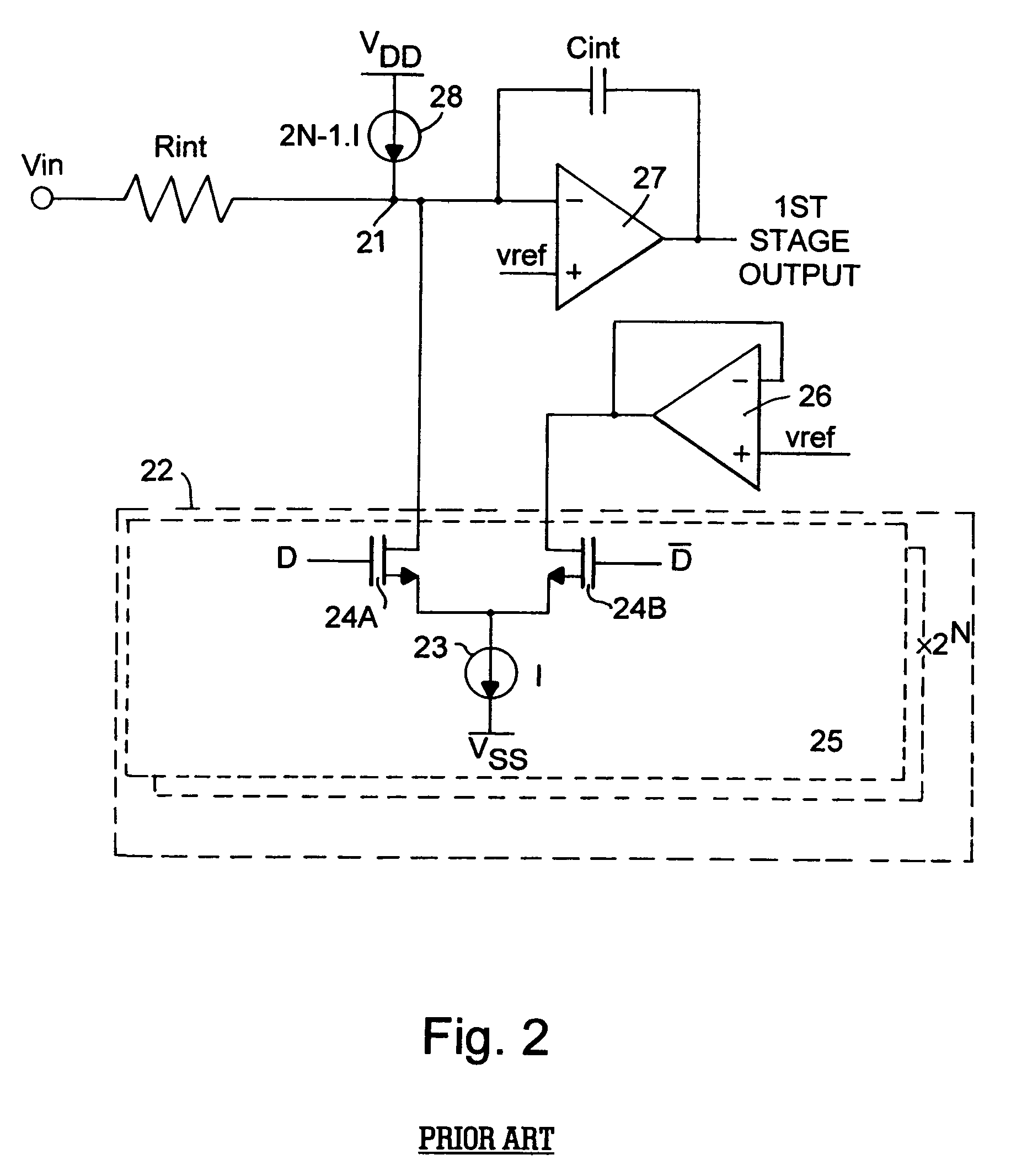
A flash ADC (also known as a direct-conversion ADC) is a type of analog-to-digital converter that uses a linear voltage ladder with a comparator at each "rung" of the ladder to compare the input voltage to successive reference voltages. Often these reference ladders are constructed of many resistors; however, modern implementations show that capacitive voltage division is also possible. The output of these comparators is generally fed into a digital encoder, which converts the inputs into a binary value (the collected outputs from the comparators can be thought of as a unary value).
Ultra-high-speed photonic-enabled ADC based on multi-phase interferometry
InactiveUS20120213531A1Overcome disadvantagesAnalogue/digital conversionAnalogue conversionUltra high speedPhotonics
A ultra high speed photonic Analog to Digital Converted (ADC) for sampling and quantizing an electrical voltage signal, internally enabled by photonics uses coherent optical detection architectures for photonic quantization. Coherent light is phase modulated by the test signal. Using an interferometer, or an array of interferometers the phase of modulated light is compared with a reference light. Flash ADC, successive approximation ADC and delta-sigma ADC configurations are presented.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
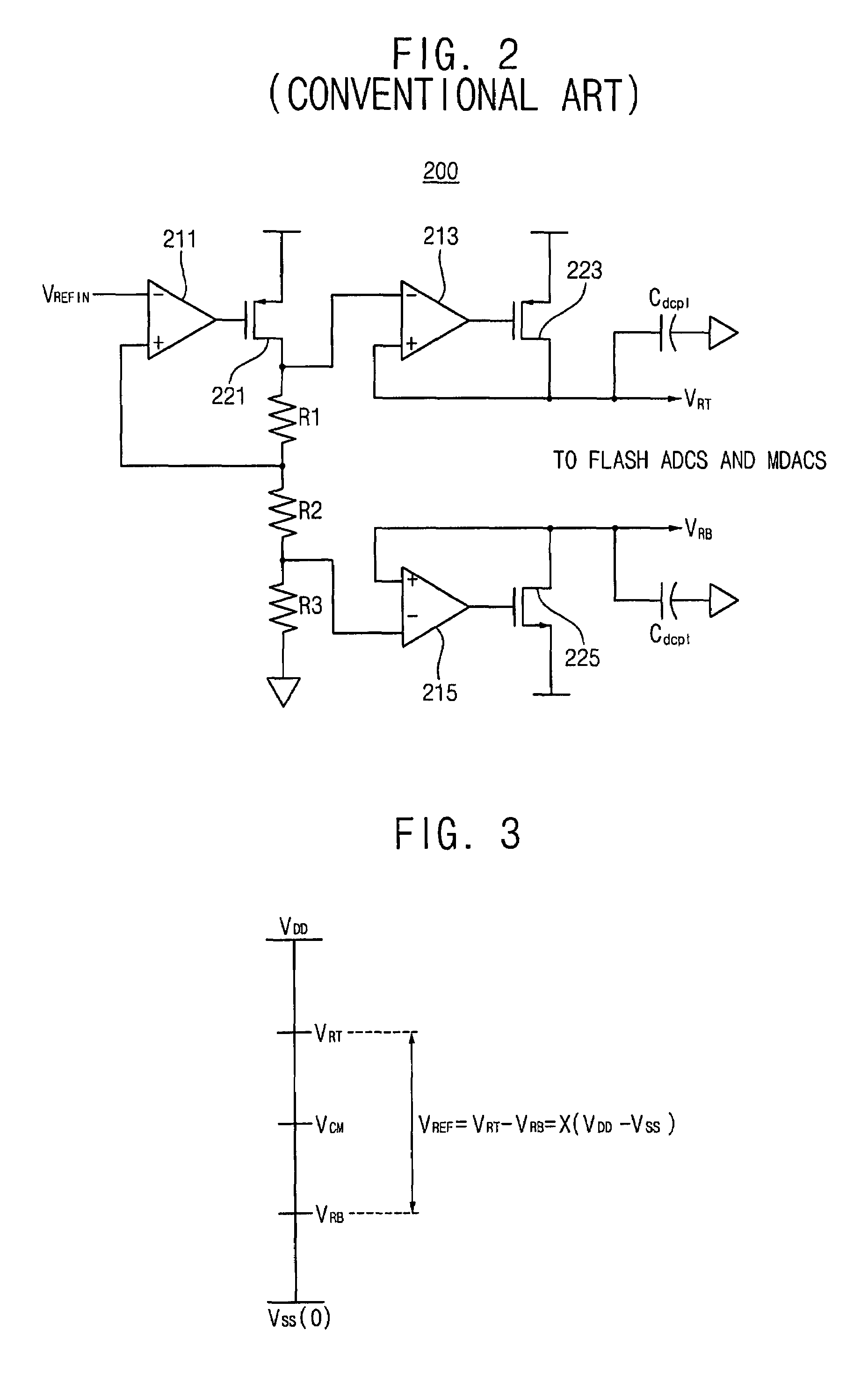
Flash ADC receiver with reduced errors
ActiveUS6980140B1Improve link qualityData representation error detection/correctionElectric signal transmission systemsSymbol decodingVoltage reference
Symbol decoding errors at a receiver utilising a flash analog to digital converter (ADC) can be reduced by adjusting a reference voltage level of the ADC where a decoding error rate at the reference voltage level exceeds a threshold.
Owner:CIENA
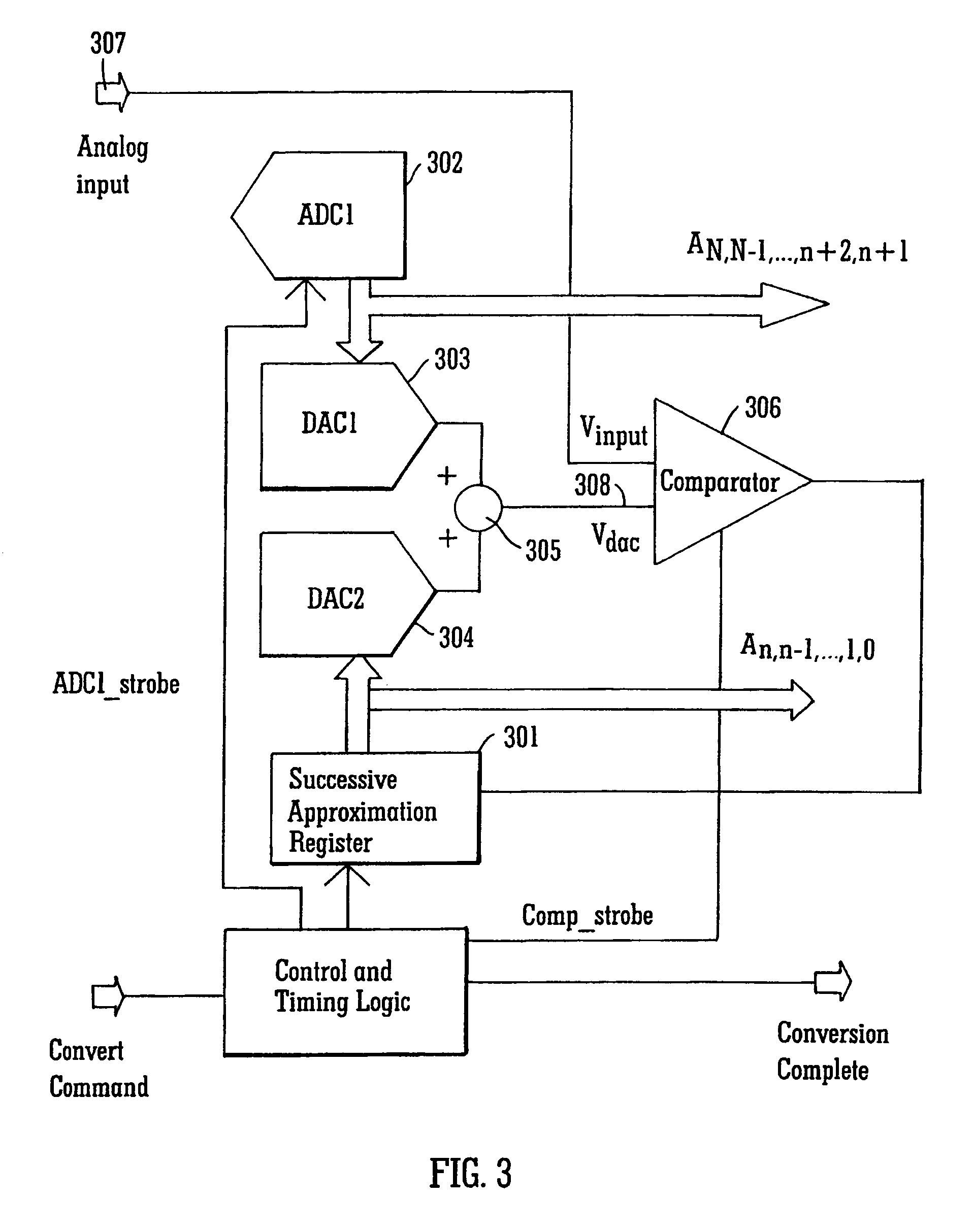
Successive approximation analog-to-digital converter with pre-loaded SAR registers
InactiveUS7038609B1Efficiently transitionEliminate effectiveElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterFlash ADC
A SAR converter having enhanced performance by virtue of effectively pre-loading the SAR's most significant bits with a value that makes the associated DAC output almost equal to the signal to be converted. A normal SAR conversion is then completed with the SAR bits that have not been pre-loaded. The value used to pre-load the most significant bits of the SAR is preferably obtained from a low-resolution, high-speed converter, such as a flash. The range of DAC bits used in the normal SAR part of the conversion may be increased such that errors up to a certain magnitude in the high-speed converter can be corrected. Reducing power consumption of a SAR system can be readily accomplished by reducing comparator supply voltage. For a SAR converter architecture using a CAPDAC array or CAPDAC (capacitor array DAC), fairly large variations in comparator input voltage can be expected under these circumstances. If the input voltage variation becomes too large, damage to the comparator input devices can occur, or inaccuracies may develop. In one embodiment of the invention, the most significant bits are provided by sampling the input signal through a flash ADC that does not suffer from the input voltage restriction described above.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
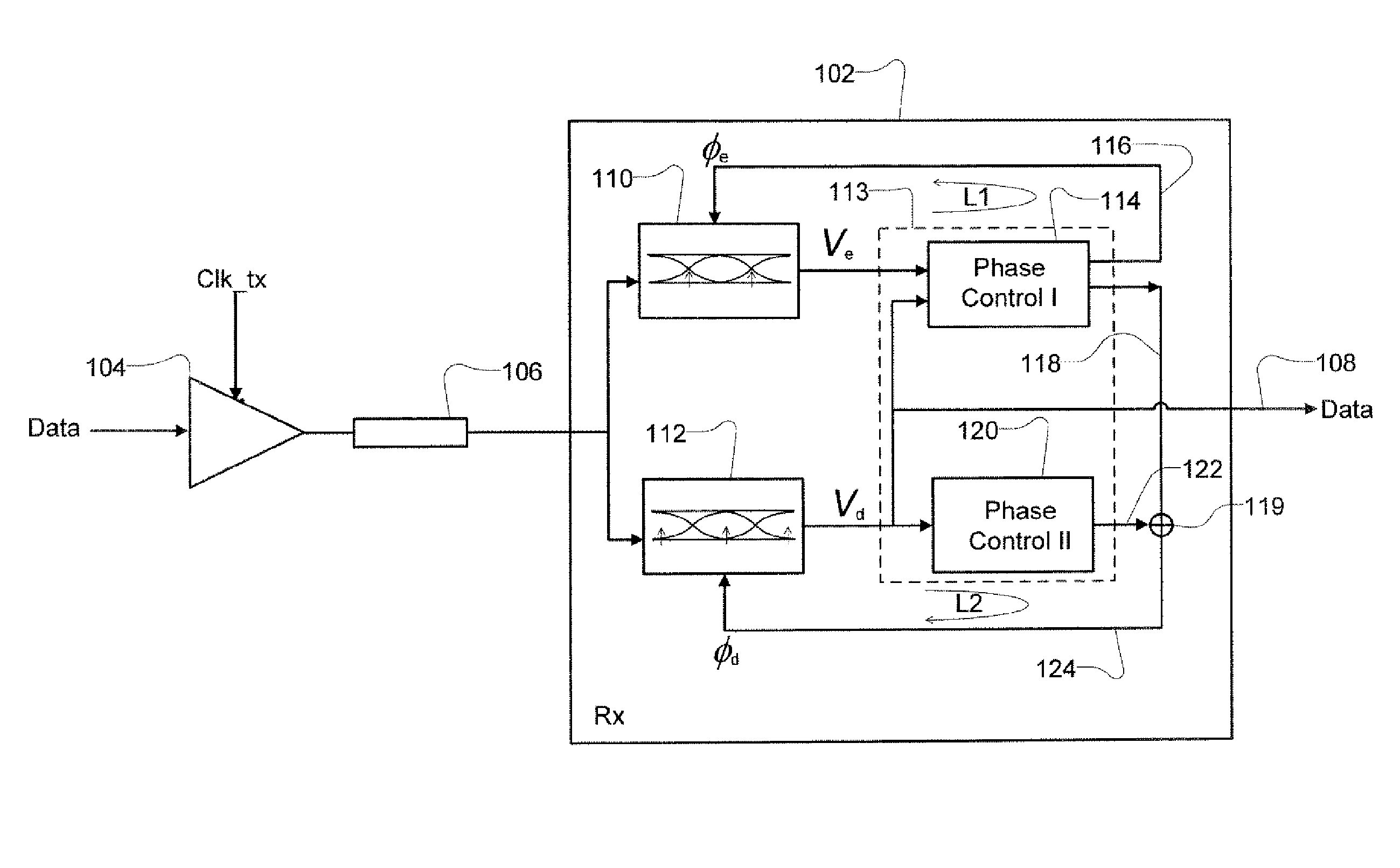
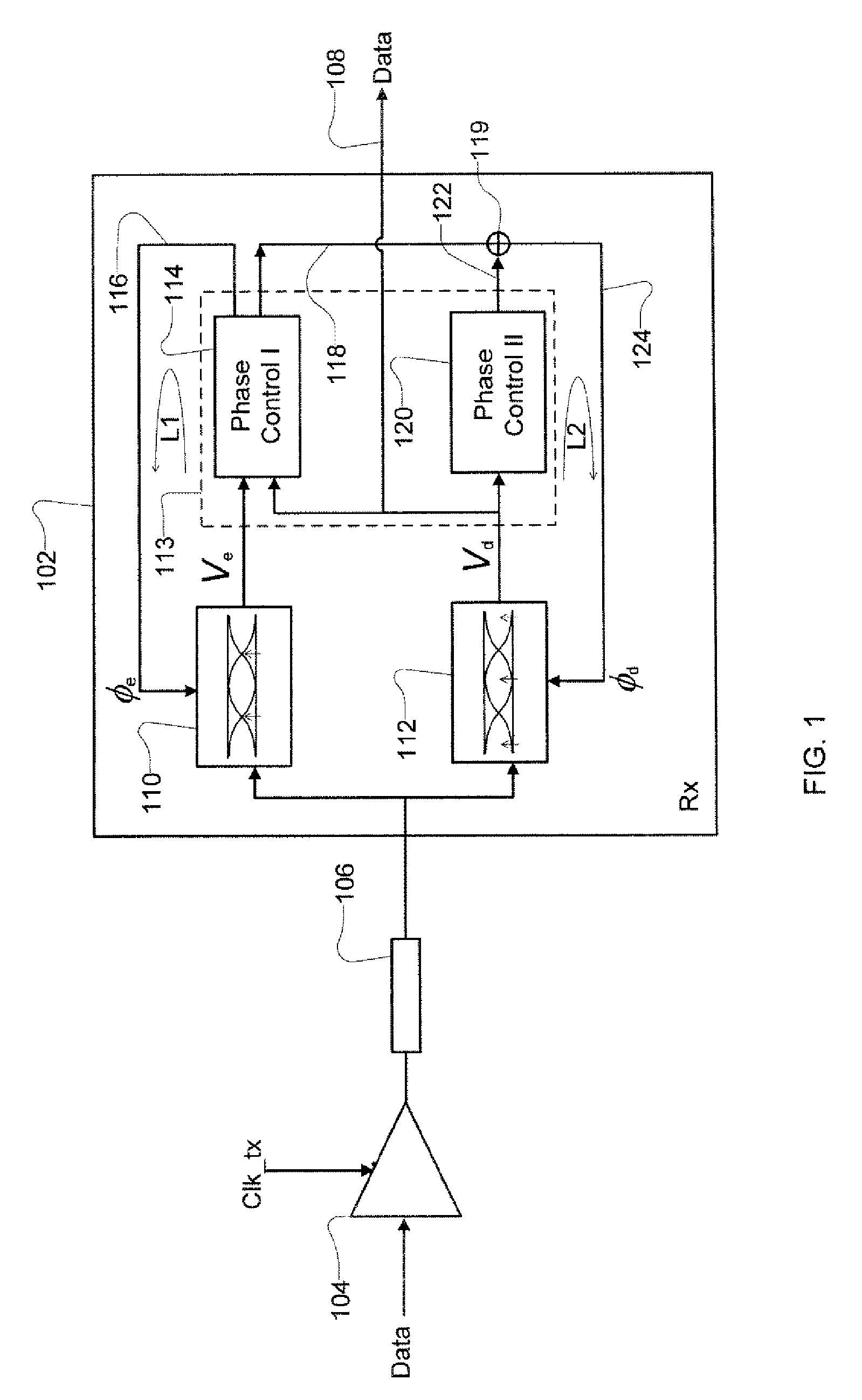
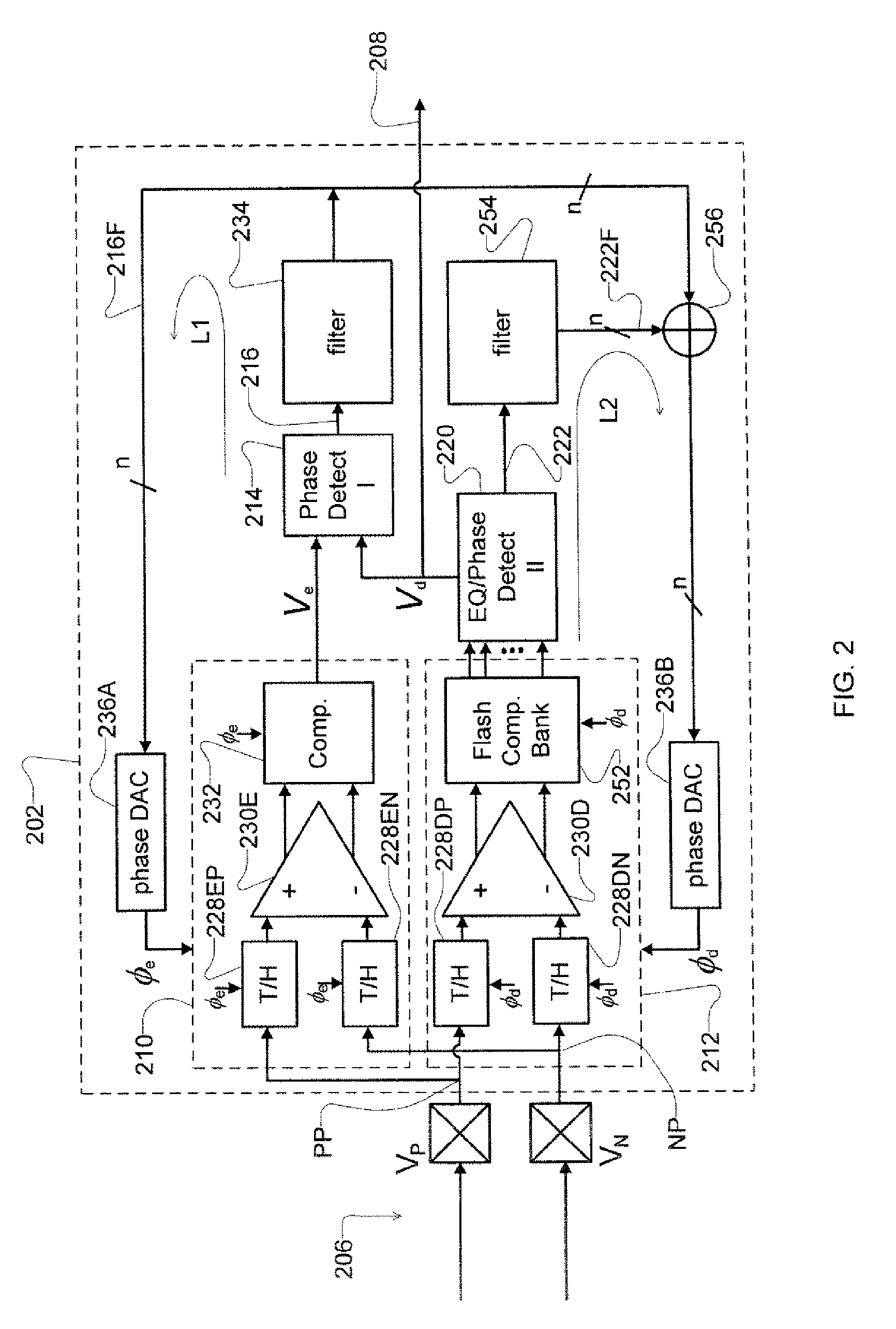
Receiver with enhanced clock and data recovery
ActiveUS8929496B2Receiver initialisationSynchronisation error correctionData transformationBang bang phase detector
A receiver device implements enhanced data reception with edge-based clock and data recovery such as with a flash analog-to-digital converter architecture. In an example embodiment, the device implements a first phase adjustment control loop, with for example, a bang-bang phase detector, that detects data transitions for adjusting sampling at an optimal edge time with an edge sampler by adjusting a phase of an edge clock of the sampler. This loop may further adjust sampling in received data intervals for optimal data reception by adjusting the phase of a data clock of a data sampler such a flash ADC. The device may also implement a second phase adjustment control loop with, for example, a baud-rate phase detector, that detects data intervals for further adjusting sampling at an optimal data time with the data sampler.
Owner:RAMBUS INC
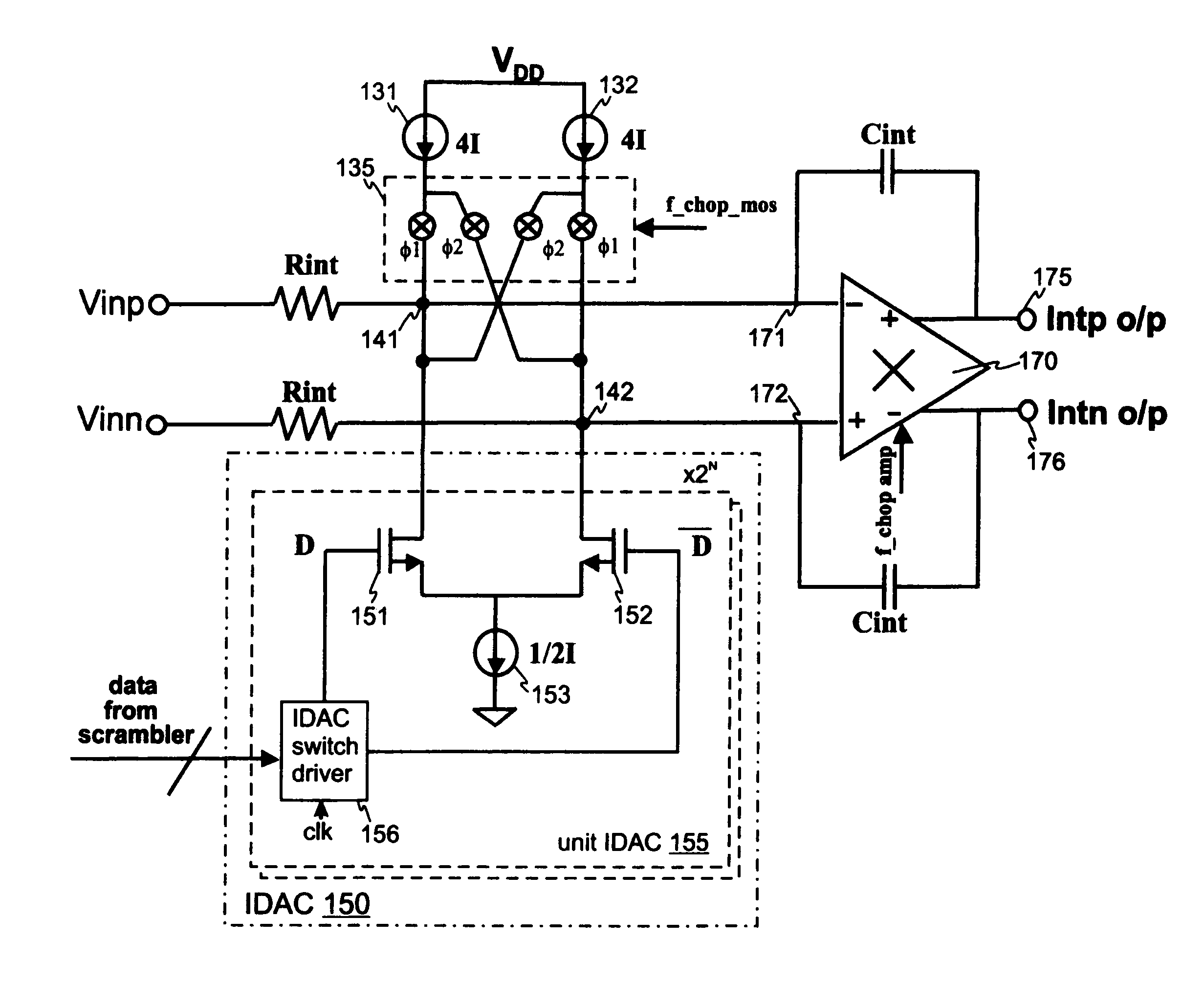
Differential front-end continuous-time sigma-delta ADC using chopper stabilisation
ActiveUS20060139192A1Less sensitive to substrate noiseReduce thermal noiseAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsIntegratorDigital feedback
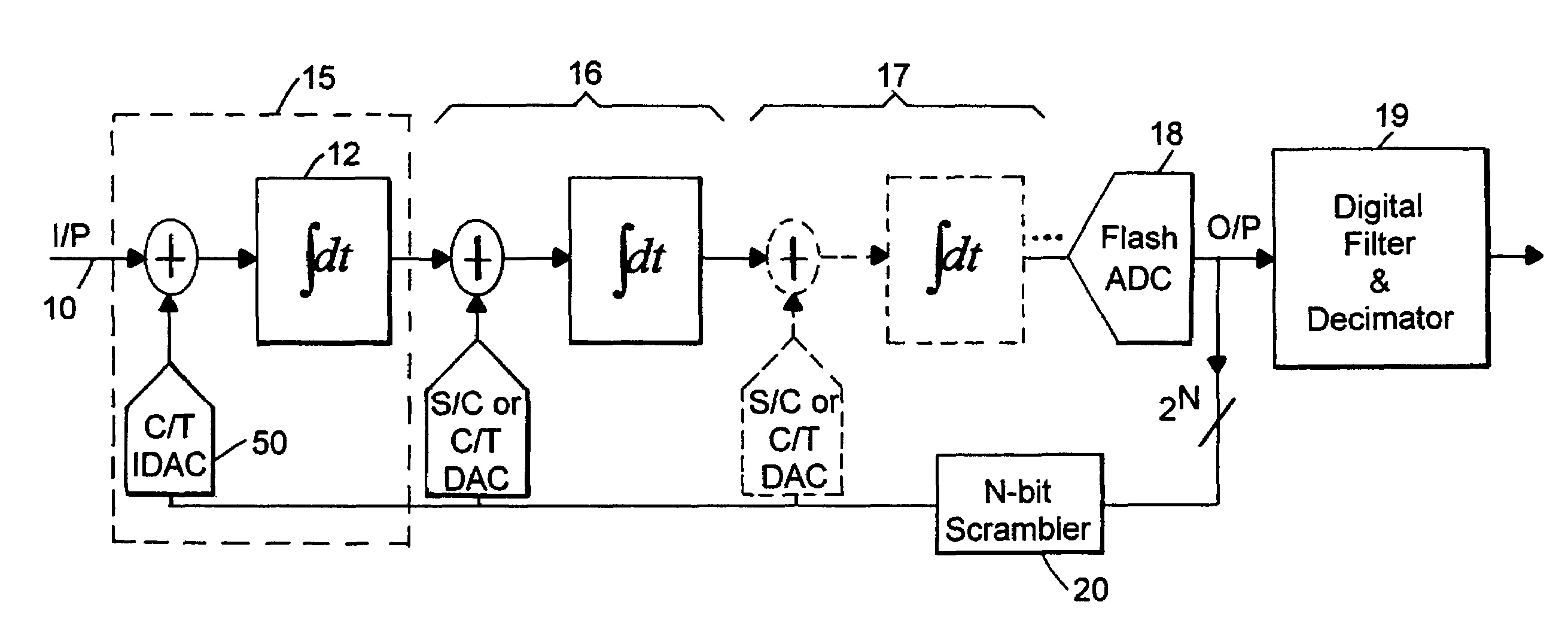
A multi-bit continuous-time sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter (ADC) has a differential input stage which receives an analog input signal current. A multi-bit feedback current digital-to-analog converter (IDAC) generates a multi-level feedback current depending on a digital feedback signal from a flash ADC. An integrator has a differential input that integrates the difference of the generated current by the multi-bit IDAC and the input signal current on a continuous-time basis. The input stage further comprises a first biasing current source and a second biasing current source which bias the input stage in a mid-scale condition. A first summing node connects to the first differential input line, a first differential input of the integrator and the first output branch. A second summing node connects to the second differential input line, a second differential input of the integrator and the second output branch. A set of chopping switches alternately connect the biasing current sources to the summing nodes in a first configuration and a second, reversed, configuration. The converter receives a modulator clock signal at a frequency FS and the chopping switches can operate at FS or a binary subdivision thereof. The integrator amplifier can also be chopper-stabilized.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Methods and Systems for Optical Receivers
ActiveUS20130294782A1Reduce complexityOther decoding techniquesCode conversionQuality of serviceFiber
Broadband access networks are driving the upgrade of DWDM networks from 10 Gb / s per channel to more spectrally-efficient 40 Gb / s or 100 Gb / s. Signal quality degradation due to linear and non-linear impairments are significant and error control coding and signal processing solutions play increasingly key roles in meeting increasing demand, providing improved quality of service, and reduced cost. It would be beneficial to reduce the power consumption of optical receivers for optical links exploiting for example LPDC encoding. Accordingly, the inventors have established a low complexity soft-decision front-end compatible with deployable LDPC codes in next-generation optical transmission systems. Beneficially the optical receiver design can be retro-fitted into deployed hard-decision based optical systems and replaces the 3-to-2 encoder of the prior art in the electrical portion of the receiver with a single gate design. Further, the design may act as a 2-bit Flash ADC in multimode fiber based optical receivers.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
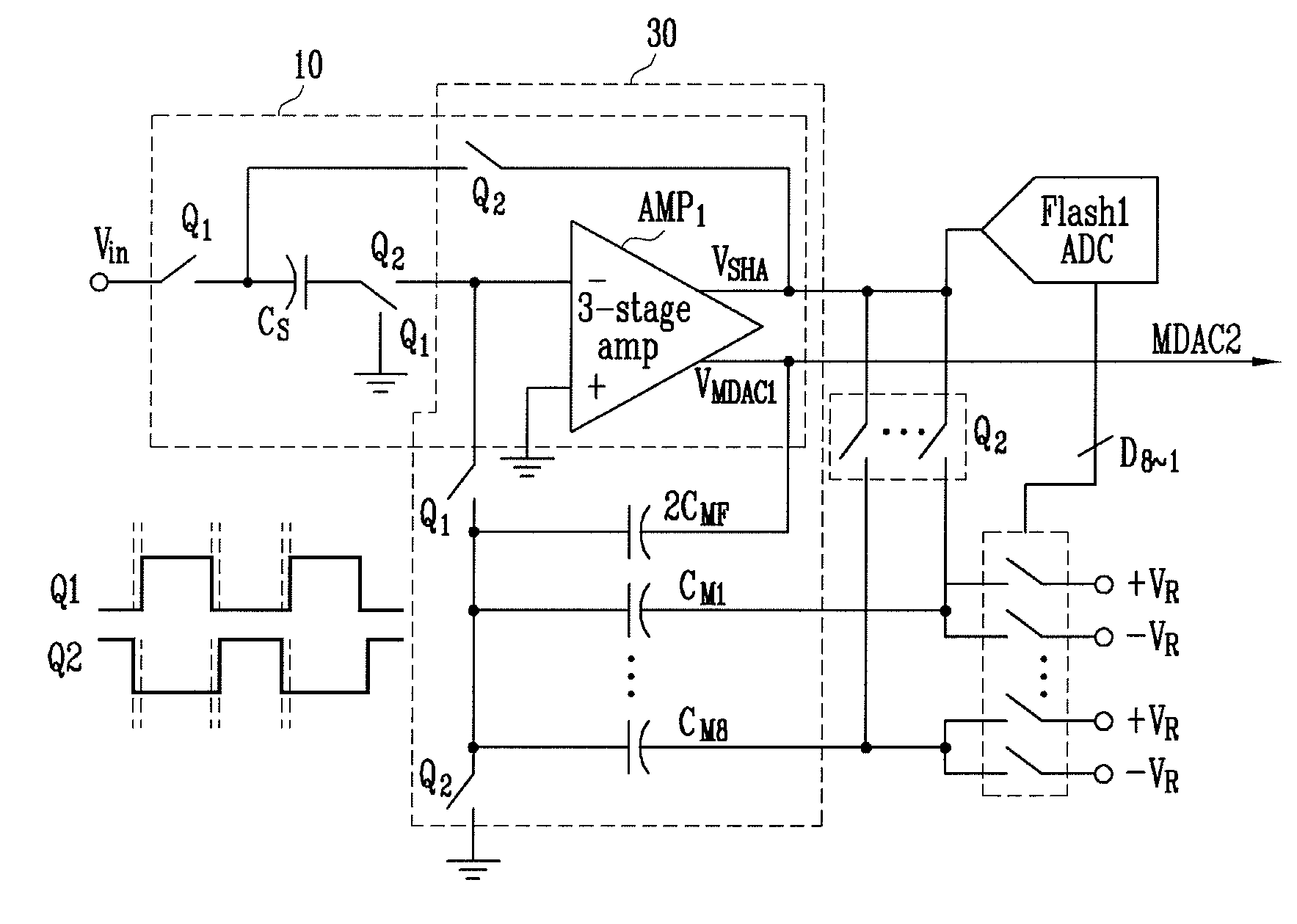
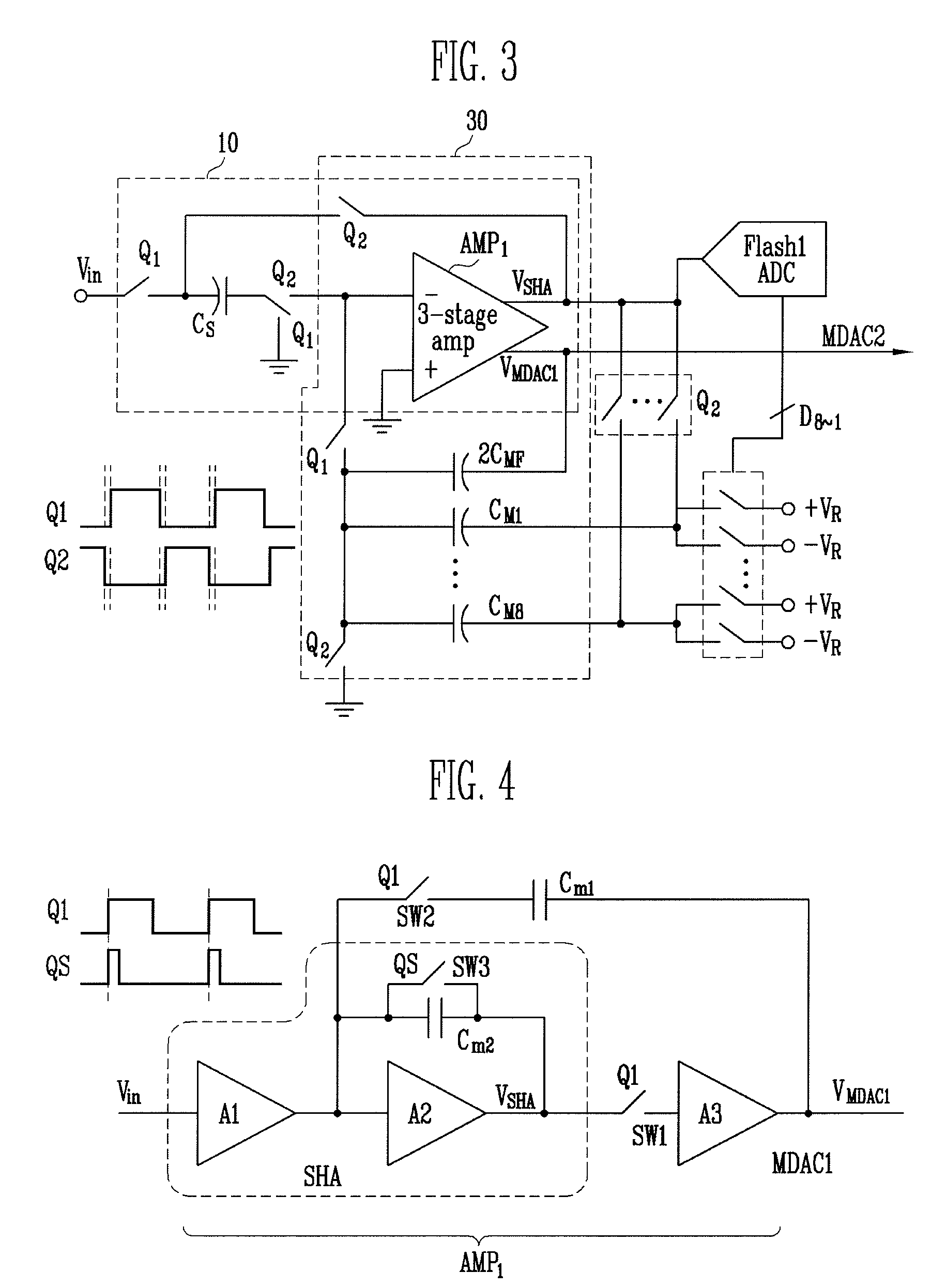
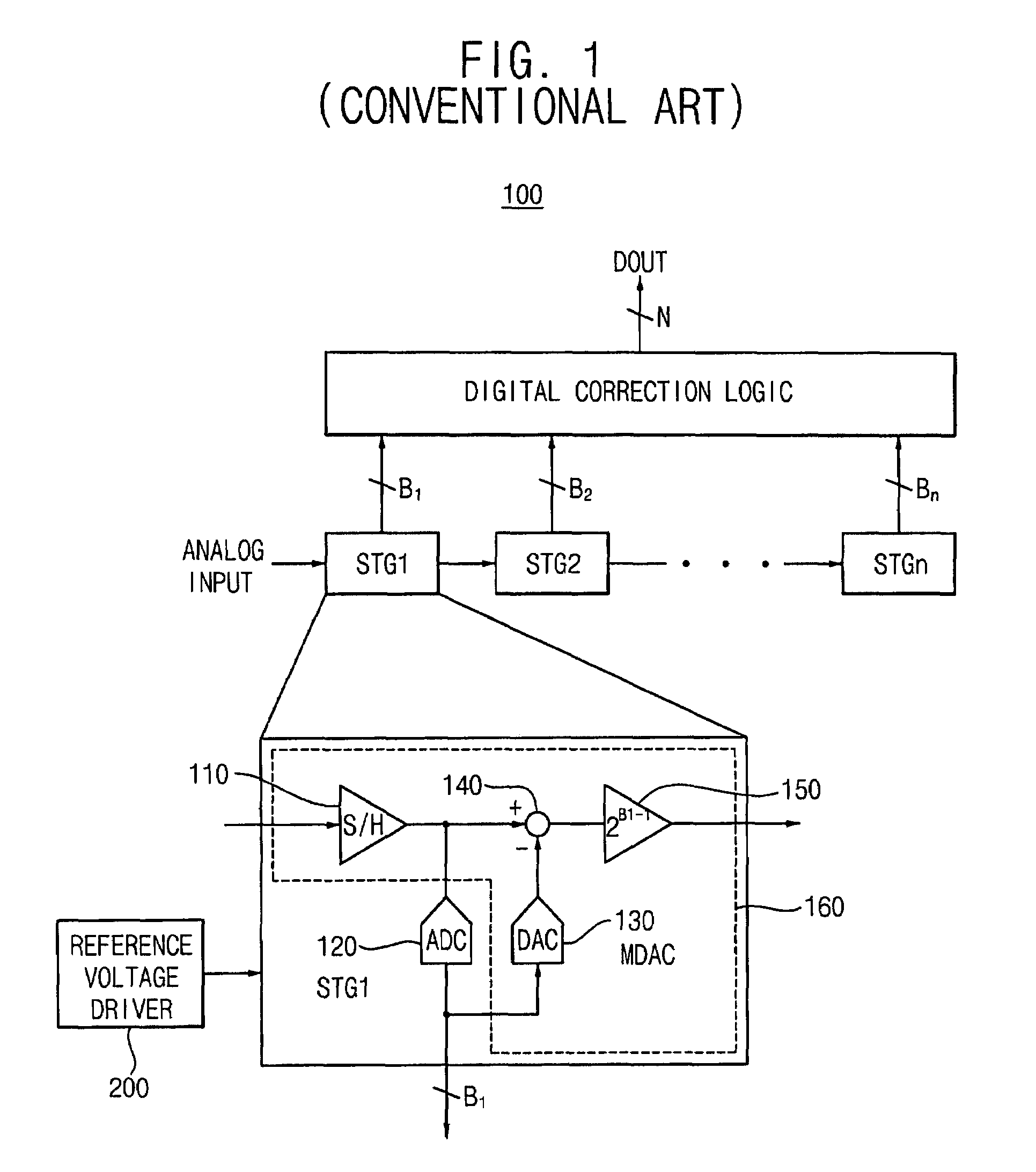
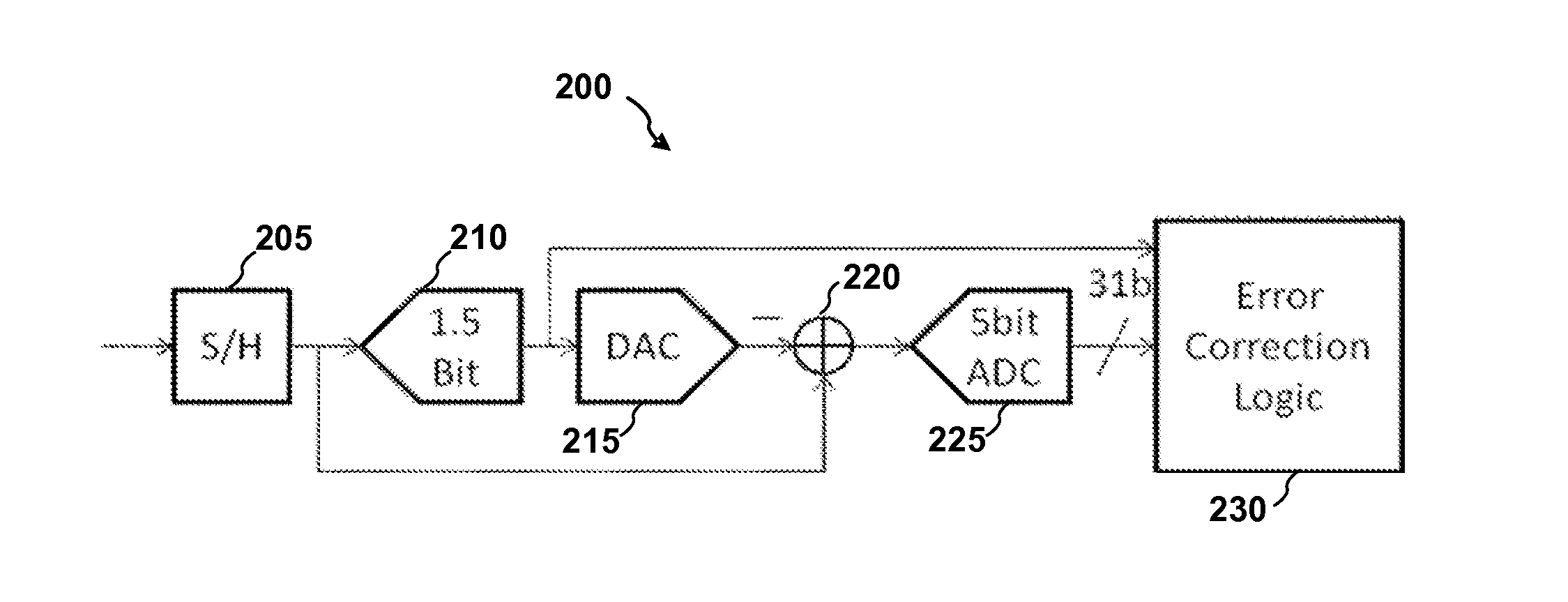
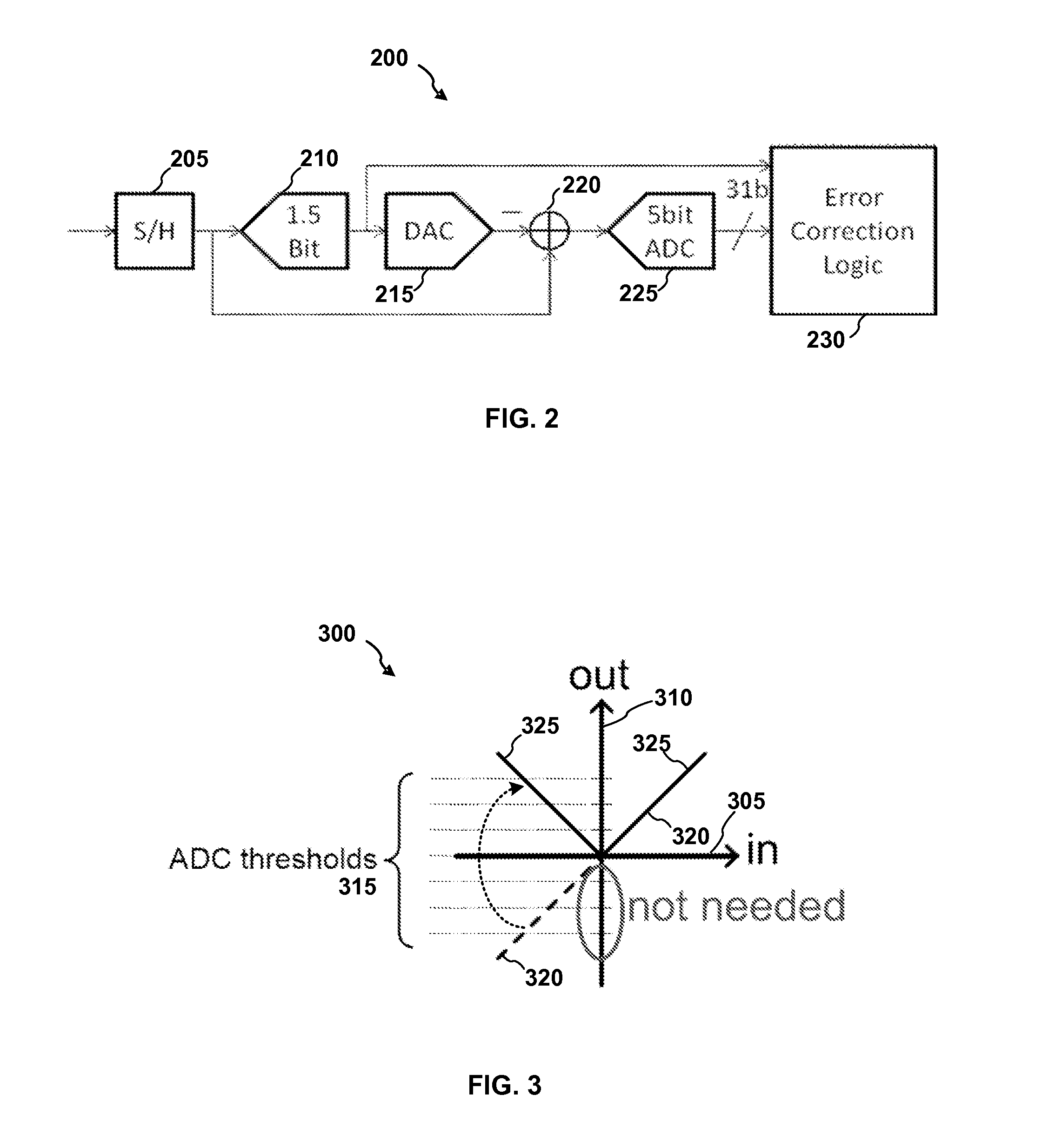
ADC first stage combining both sample-hold and ADC first stage analog-to-digital conversion functions
ActiveUS8604962B1Analogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsCapacitanceEngineering
A first stage circuit for a pipeline ADC first stage combines the functions of an input sample-and-hold-plus-amplifier (SHA) stage, and the functions of the first analog-to-digital conversion stage of an ADC, including a multiplying DAC (MDAC), stage-flash ADC (SFADC) comparators, and residue opamp (RAMP). The ADC first stage is duplicated, inputs and outputs are connected, and an autozero circuit using a switched-capacitor filter feedback loop controls the RAMP bias circuitry to reduce 1 / f noise and DC offsets. The sampling capacitors may be connected to the ADC input for one full sample clock time period and are disconnected from the analog input period before connecting the sampling capacitors to an amplifier voltage output or voltage reference, thereby sampling the input and allowing sufficient time for the SFADC comparators to resolve and control the MDAC capacitor settings with a low metastability error rate.
Owner:LEWYN CONSULTING
Ultra-high-speed photonic-enabled ADC based on multi-phase interferometry
InactiveUS8953950B2Overcome disadvantagesElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionUltra high speedPhotonics
A ultra high speed photonic Analog to Digital Converted (ADC) for sampling and quantizing an electrical voltage signal, internally enabled by photonics uses coherent optical detection architectures for photonic quantization. Coherent light is phase modulated by the test signal. Using an interferometer, or an array of interferometers the phase of modulated light is compared with a reference light. Flash ADC, successive approximation ADC and delta-sigma ADC configurations are presented.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Receiver Circuit
InactiveUS20080219390A1Increase clock frequencyGood tracking effectElectric digital data processingSynchronising arrangementComputer hardwareSign bit
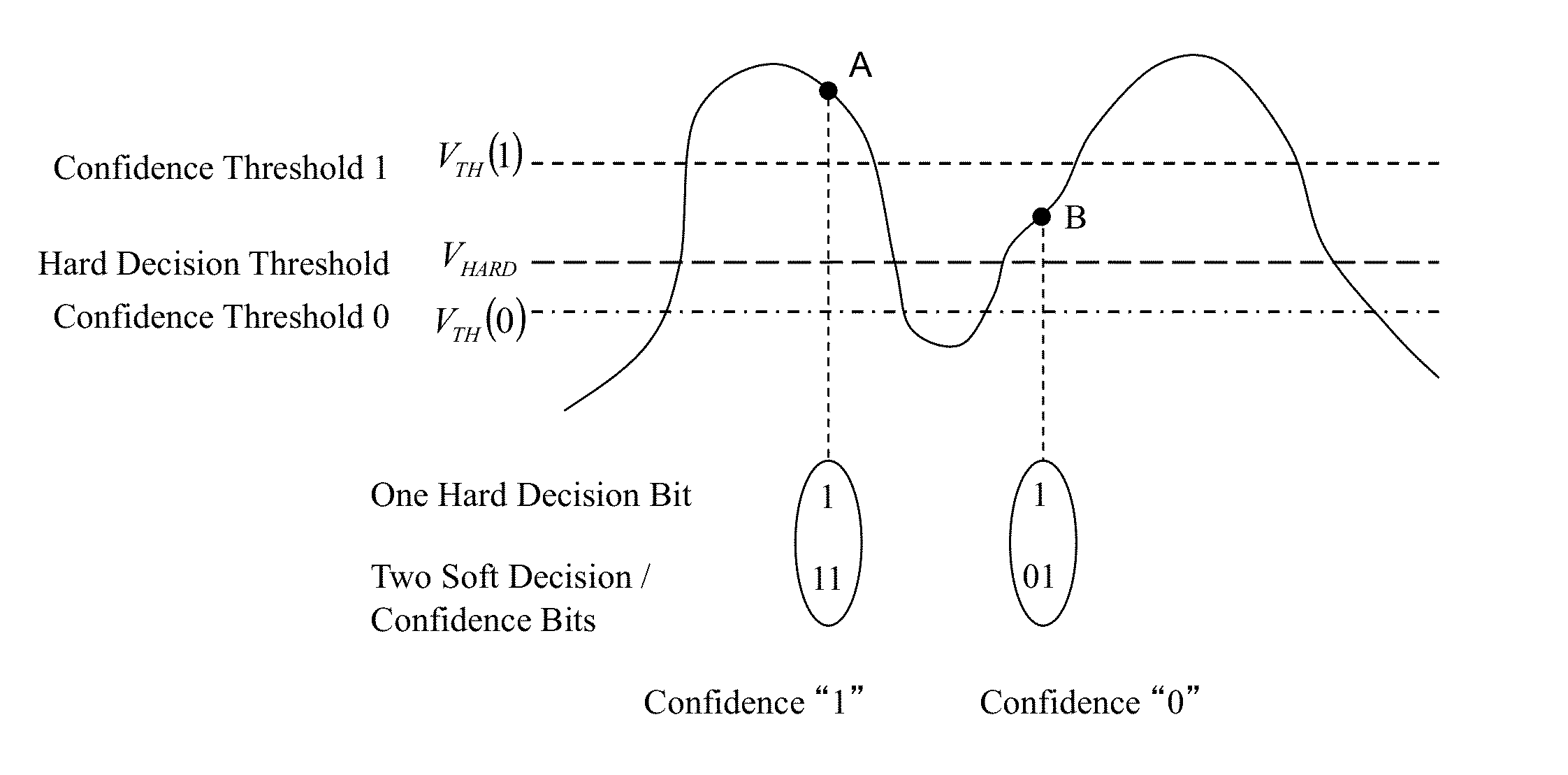
A thermometer code to sign and magnitude converter that is particularly useful in a flash ADC is provided. This comprises two conversion units. The first is a thermometer code to Gray code converter and the second a Gray code to sign and magnitude converter. Preferably, the Gray code is of a kind that has a sign bit and has the other bits symmetrically disposed about zero. This form is easily converted to a sign and magnitude code, which is advantageous as it reduces the latency of the converter, which is particularly useful at high data rates.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
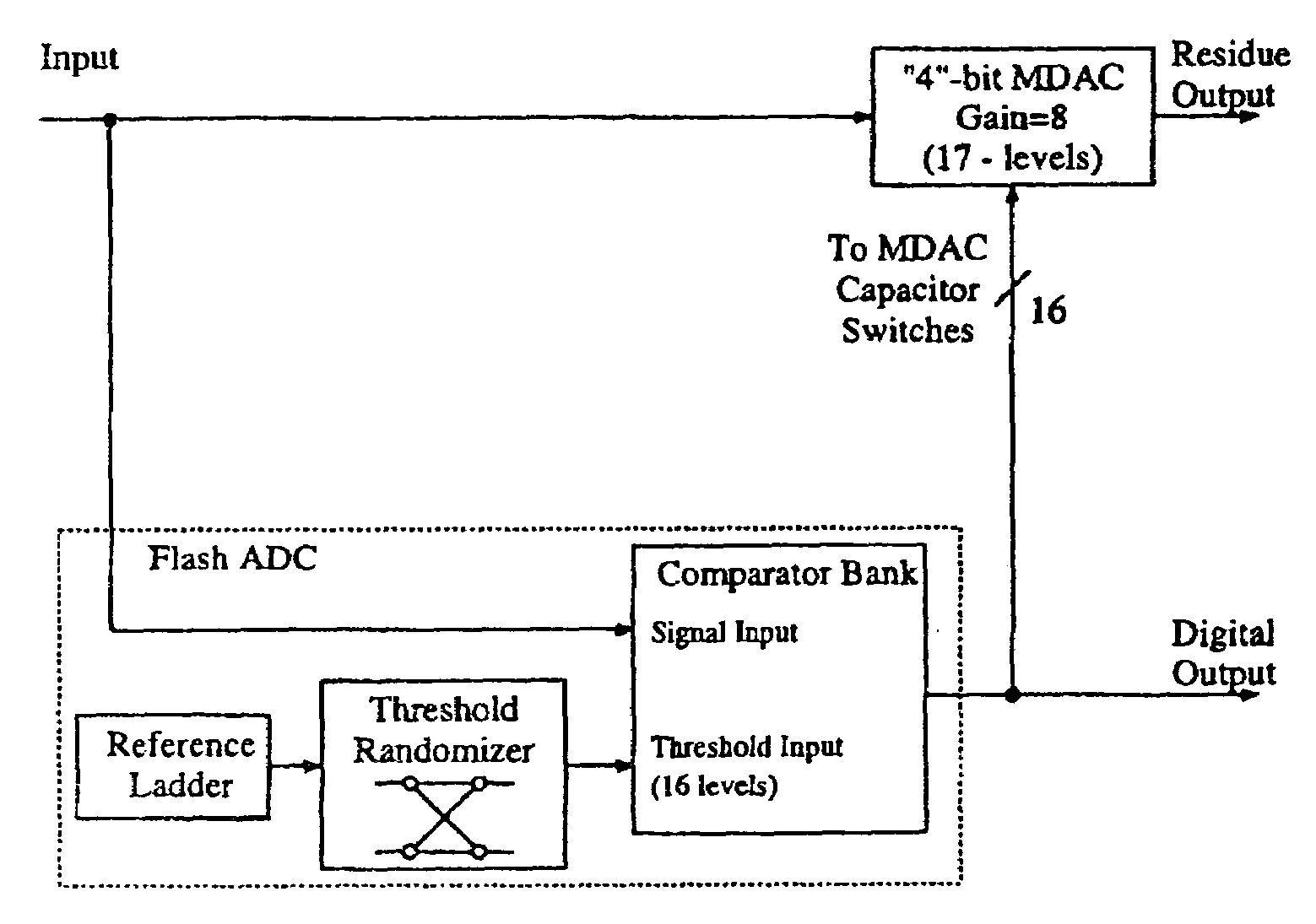
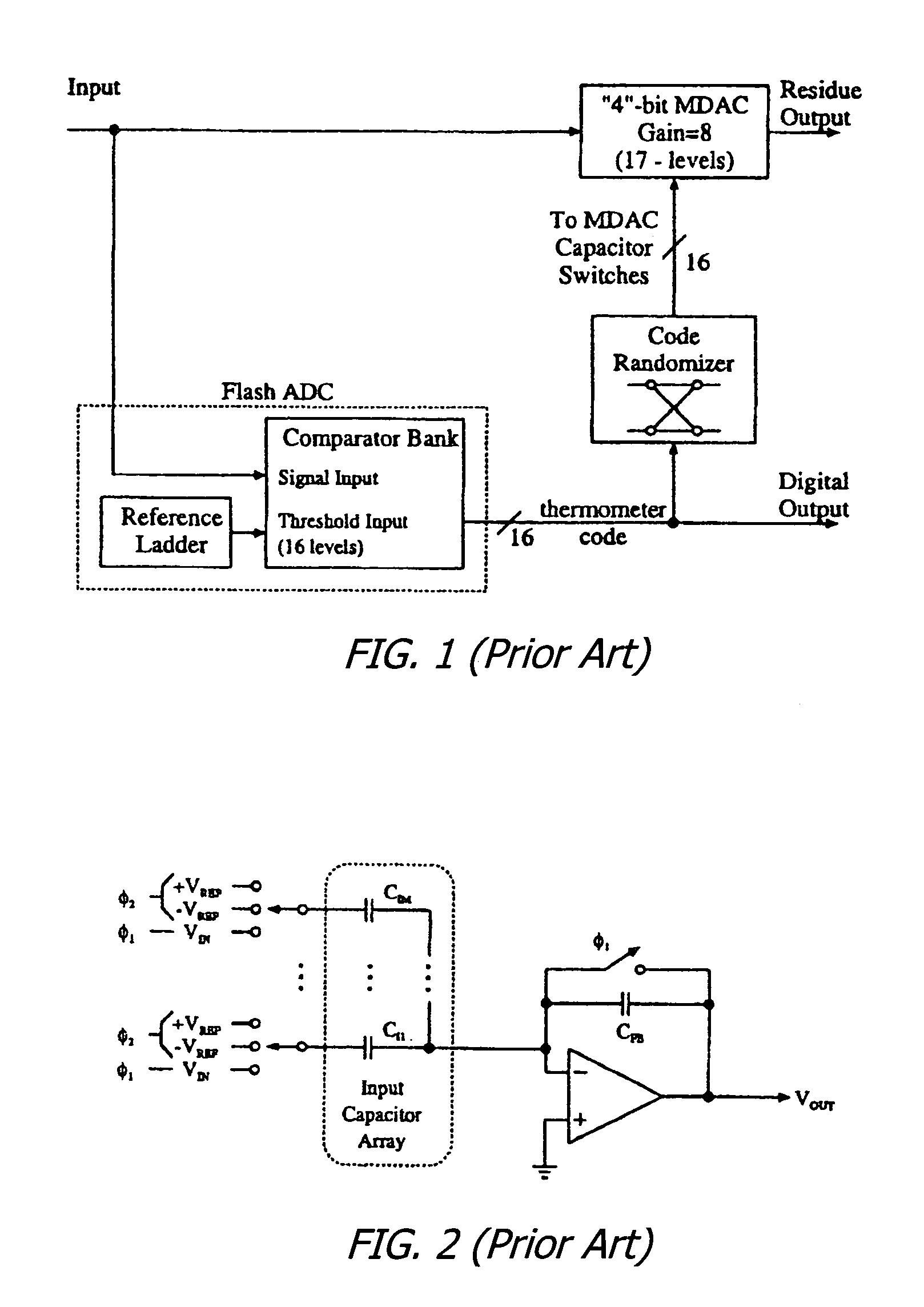
Dynamic element matching in high speed data converters
InactiveUS7002504B2Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersEngineeringFlash ADC
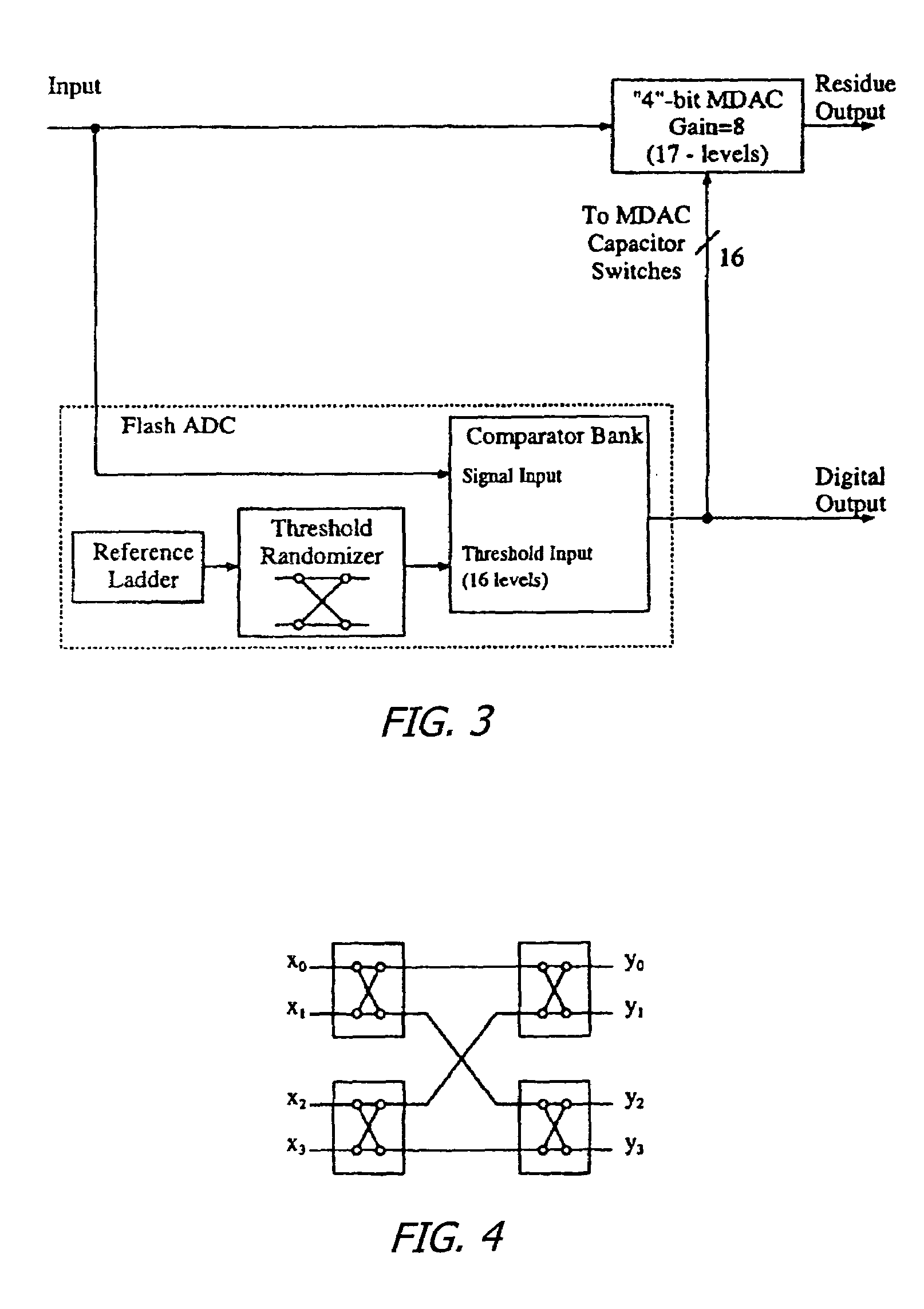
A method for providing dynamic element matching of capacitors in a pipelined analog to digital converter (ADC). Instead of randomizing the output of a flash ADC before providing the output of the ADC to the capacitor array, the threshold voltages from a reference ladder are randomized. This eliminates multiple, series connected switches of a randomizer between the output of a comparator bank and the capacitor array, and may be done during the time the output of the comparator bank of the flash ADC is latched, thereby not negatively impacting the speed of operation of the pipelined ADC.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
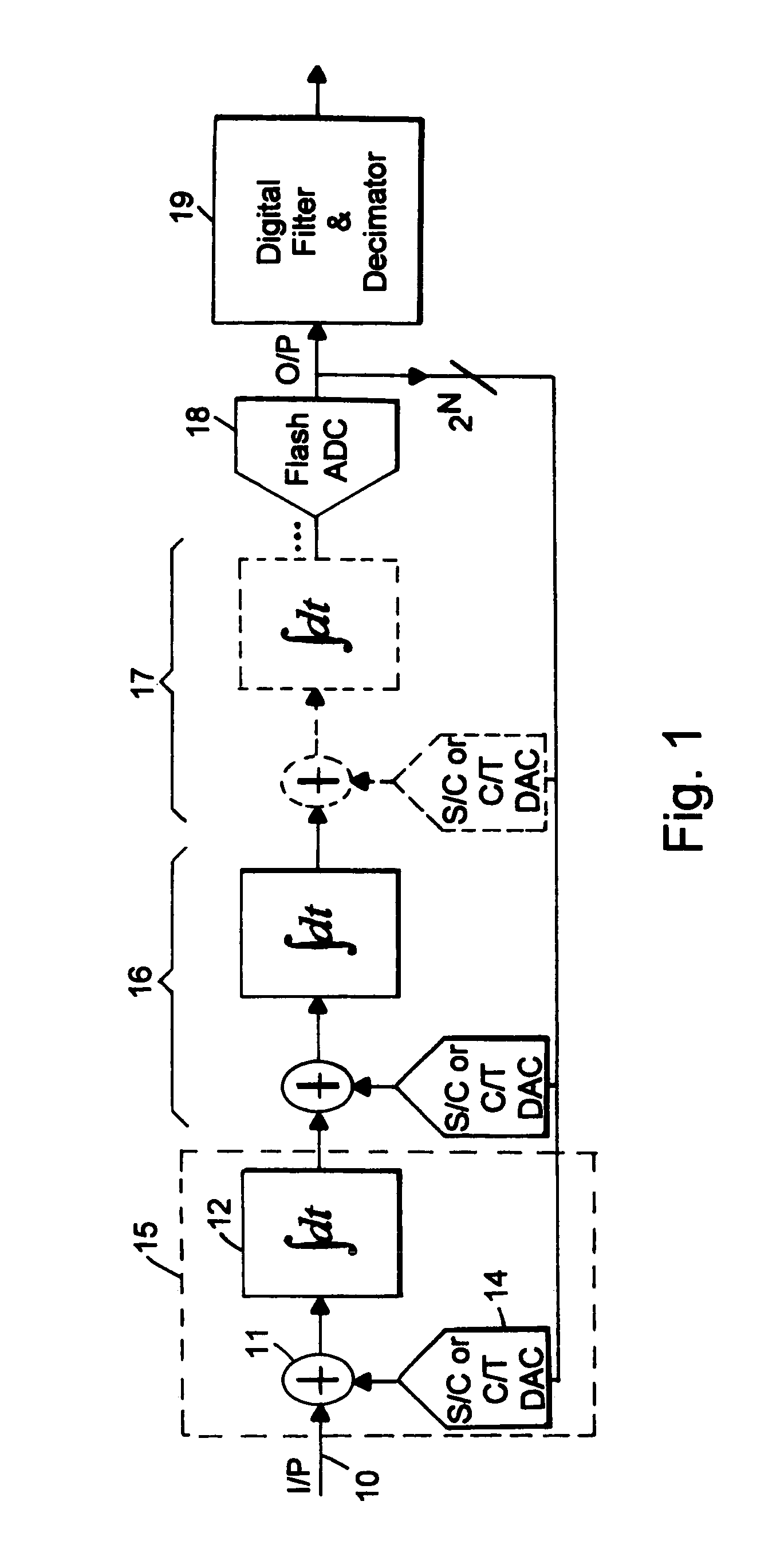
Multi-bit delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter with error shaping
InactiveUS6975682B2Increase delayDifferential modulationDigital video signal modificationCapacitanceDigital down converter
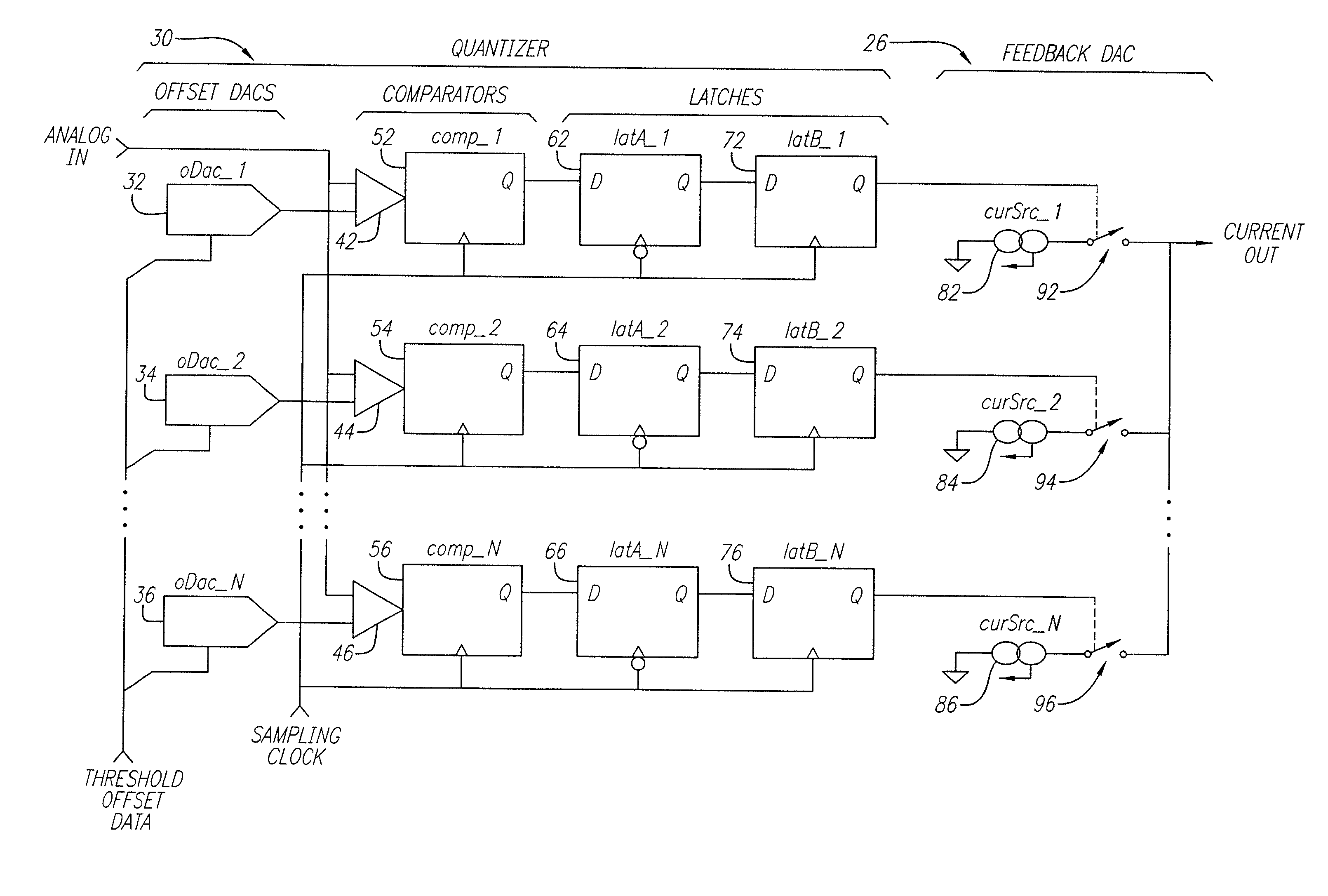
A quantizer adapted for use with a delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter. The quantizer includes first and second comparators adapted to compare an input analog signal to a threshold and provide a digital output in response thereto. First and second thresholds are provided to the first and second comparators respectively. In accordance with the present teachings, a mechanism is provided for changing the thresholds to minimize conversion errors. While the mechanism for changing the thresholds may be implemented with resistive and / or capacitive ladders, in the illustrative embodiment, digital-to-analog converters are utilized. The DACs are driven by error shaping logic. The inventive quantizer allows for an improved delta-sigma analog-to-digital converter design which combines an ADC and a DAC. The DAC reconstructs the analog equivalent of the digital output of the ADC. The ADC is a flash converter consisting of one comparator per threshold. The DAC operates by summing the outputs of a set of nominally identical unit elements. The DAC has the same number of elements as there are comparators in the flash ADC and each comparator drives one element of the DAC. A novel feature is that the thresholds of the comparators in the ADC can individually be dynamically adjusted, so that the correspondence between an element of the DAC and a particular threshold of the ADC can be varied from sample to sample under the control of logic circuitry. This arrangement allows the correspondence between DAC elements and ADC thresholds to be remapped without introducing any additional delay into the signal path between the ADC and the DAC. In a high speed continuous-time delta sigma modulator, this allows randomization or shaping of the mismatch errors of the DAC elements to be achieved without incurring any penalty in sample rate, nor adding any excess delay into the loop that might destabilize or otherwise degrade the operation of the modulator.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Flash ADC with variable LSB
InactiveUS7061421B1Electric signal transmission systemsEfficient power electronics conversionDriving currentDigital data
A differential analog-to-digital data converter (ADC) is disclosed for receiving a positive input signal and a negative input signal. A distributed resistive device is provided having taps associated therewith. A plurality of comparators each having a signal input and a reference input are provided, the signal input connected to one of the positive and negative input signals and the reference input connected to a tap on said distributed resistive device. A driver drives current through the distributed resistive device with one of the taps of the distributed resistive device disposed at substantially the other of the positive and negative input signals. A current varying device varys the current through the distributed resistive device to vary the voltage between taps.
Owner:SILICON LAB INC
Multi-bit pipeline analog-to-digital converter capable of altering operating mode
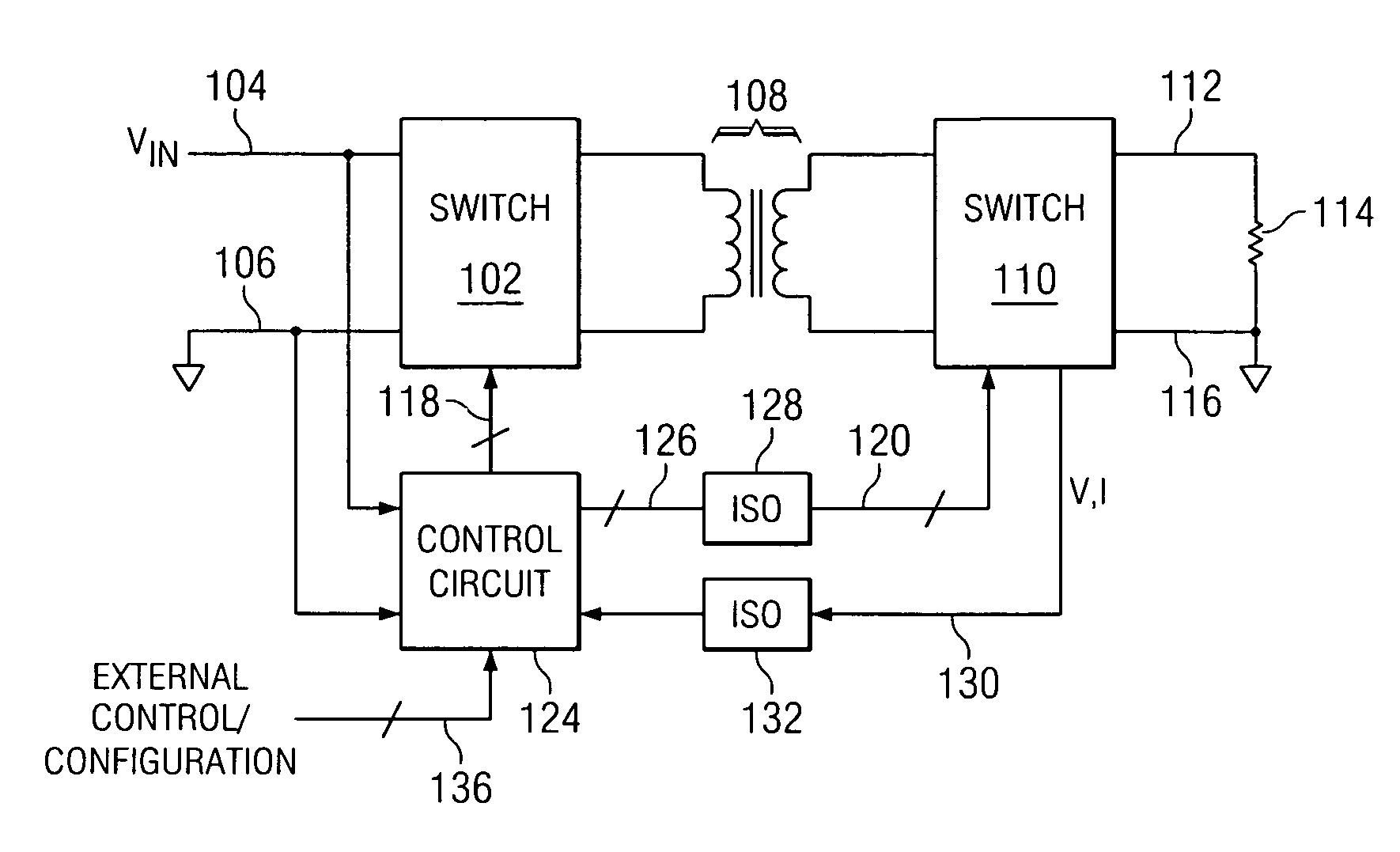
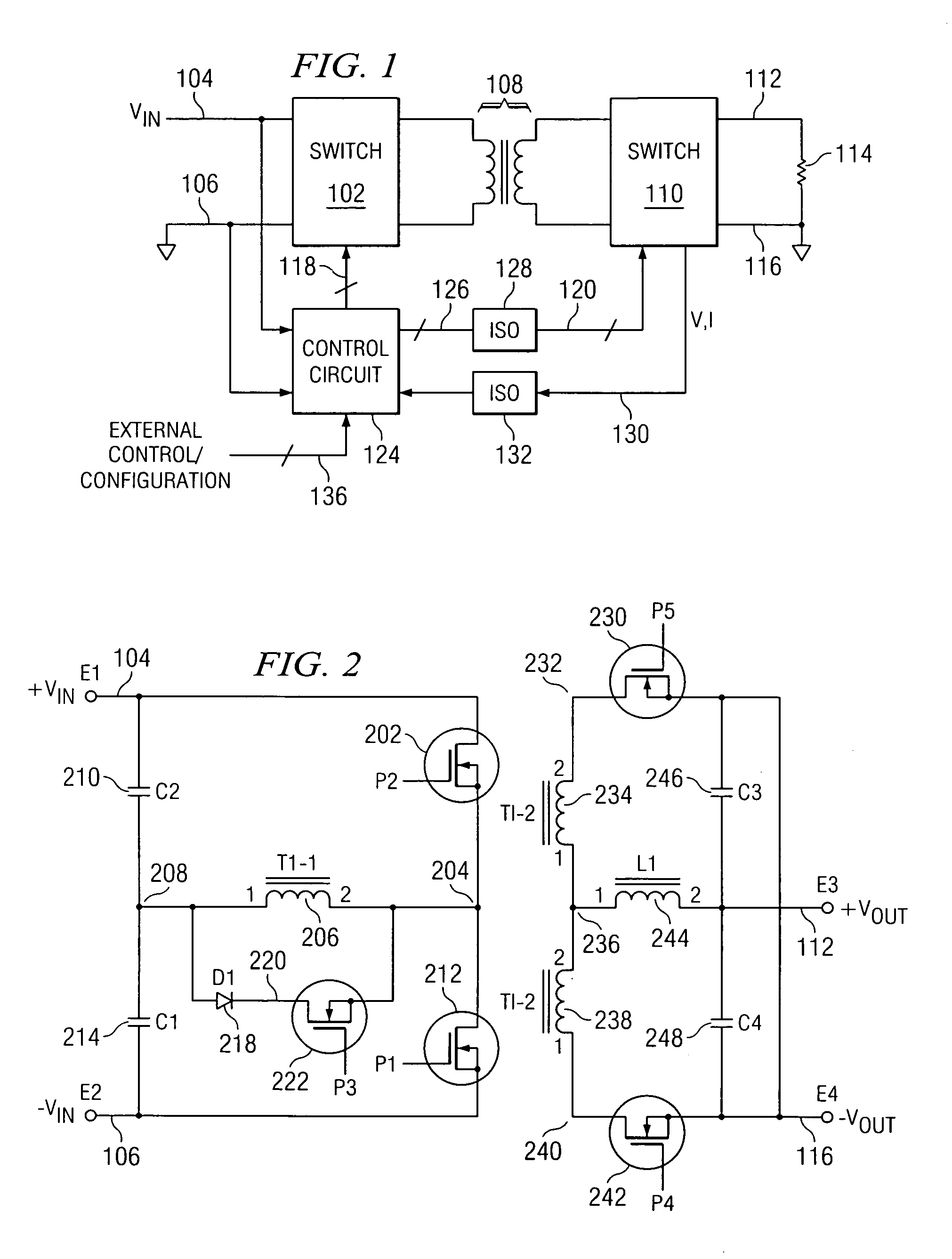
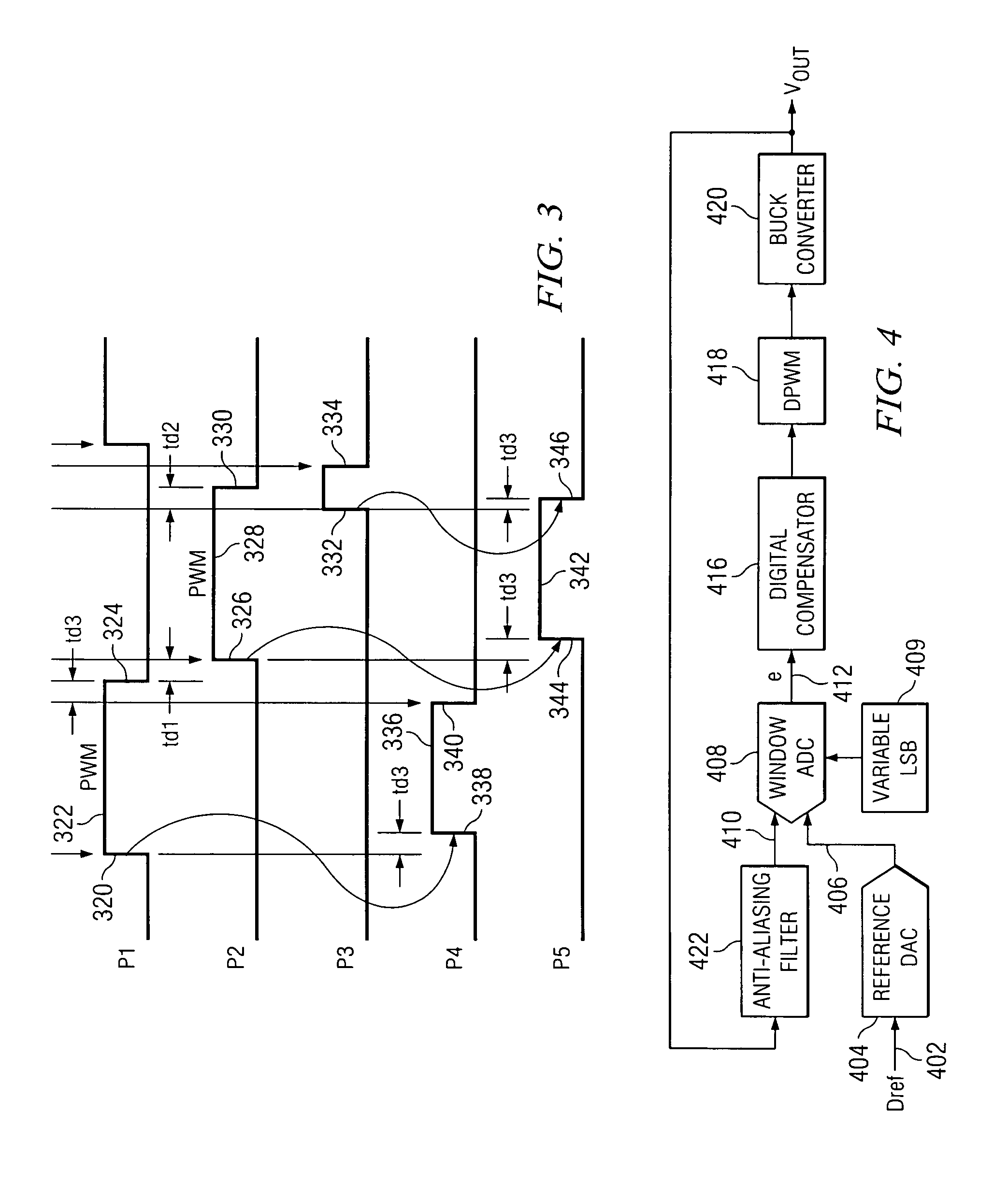
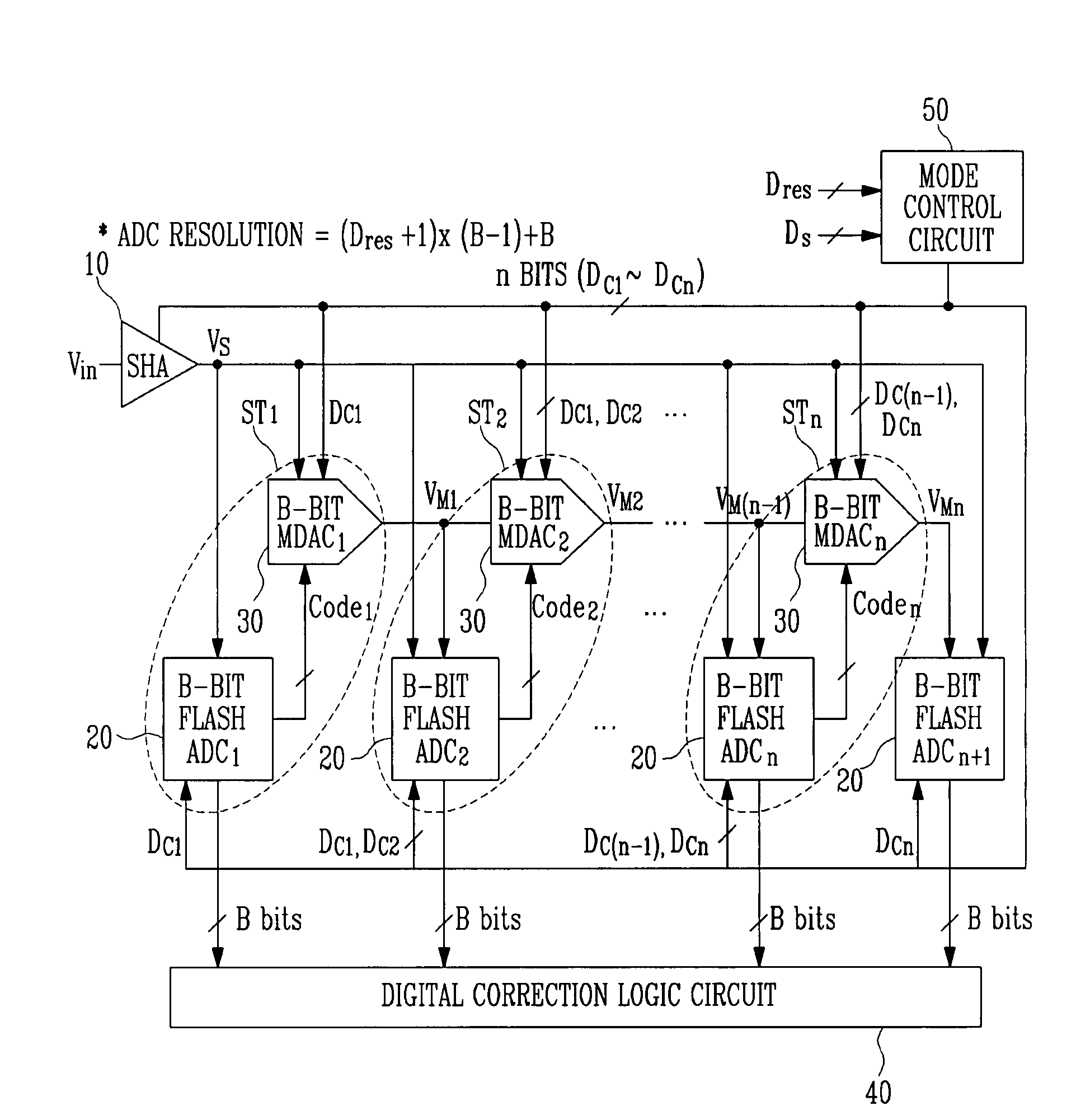
InactiveUS20080129567A1Minimize power consumptionPower saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsControl signalMode control
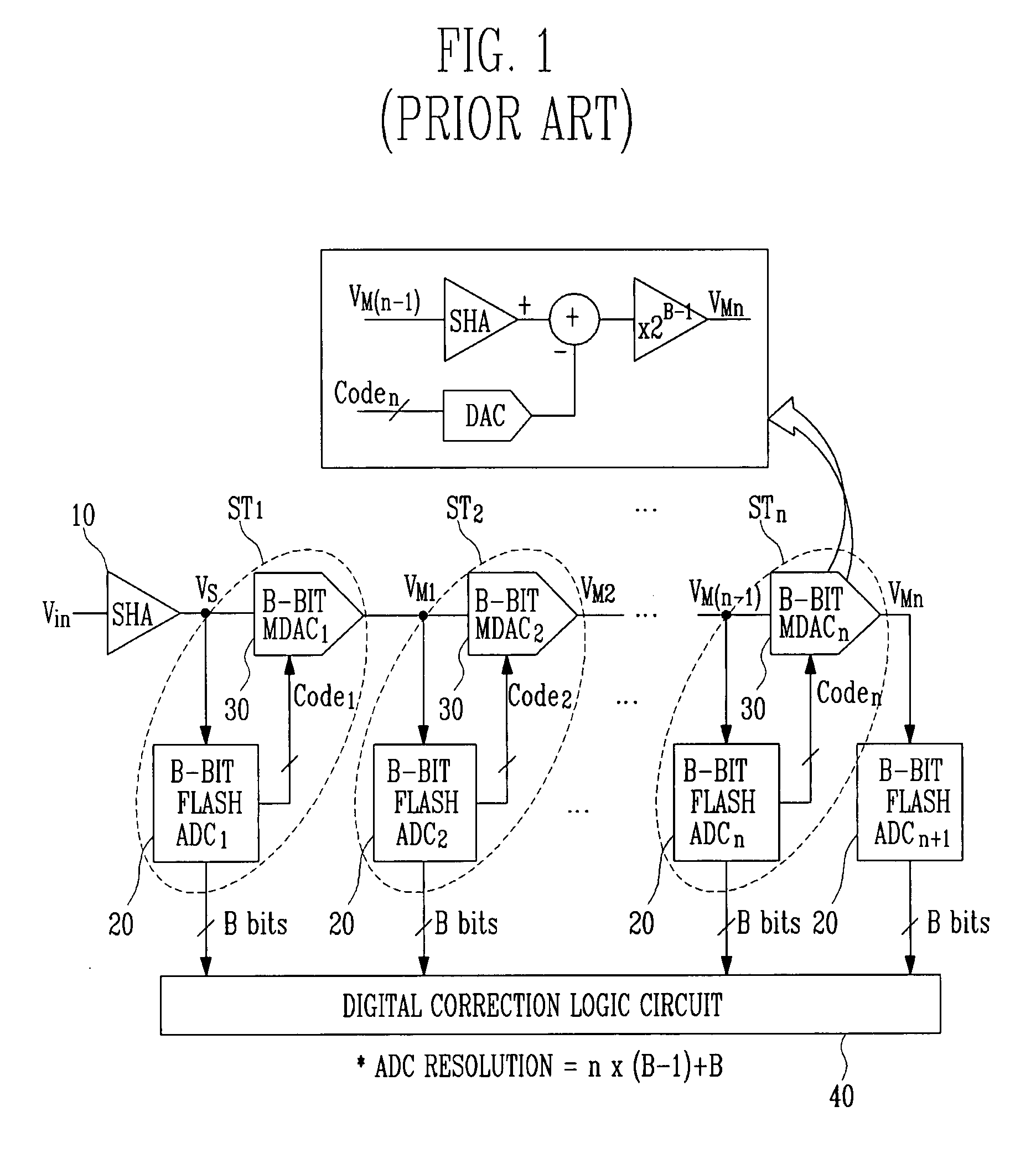
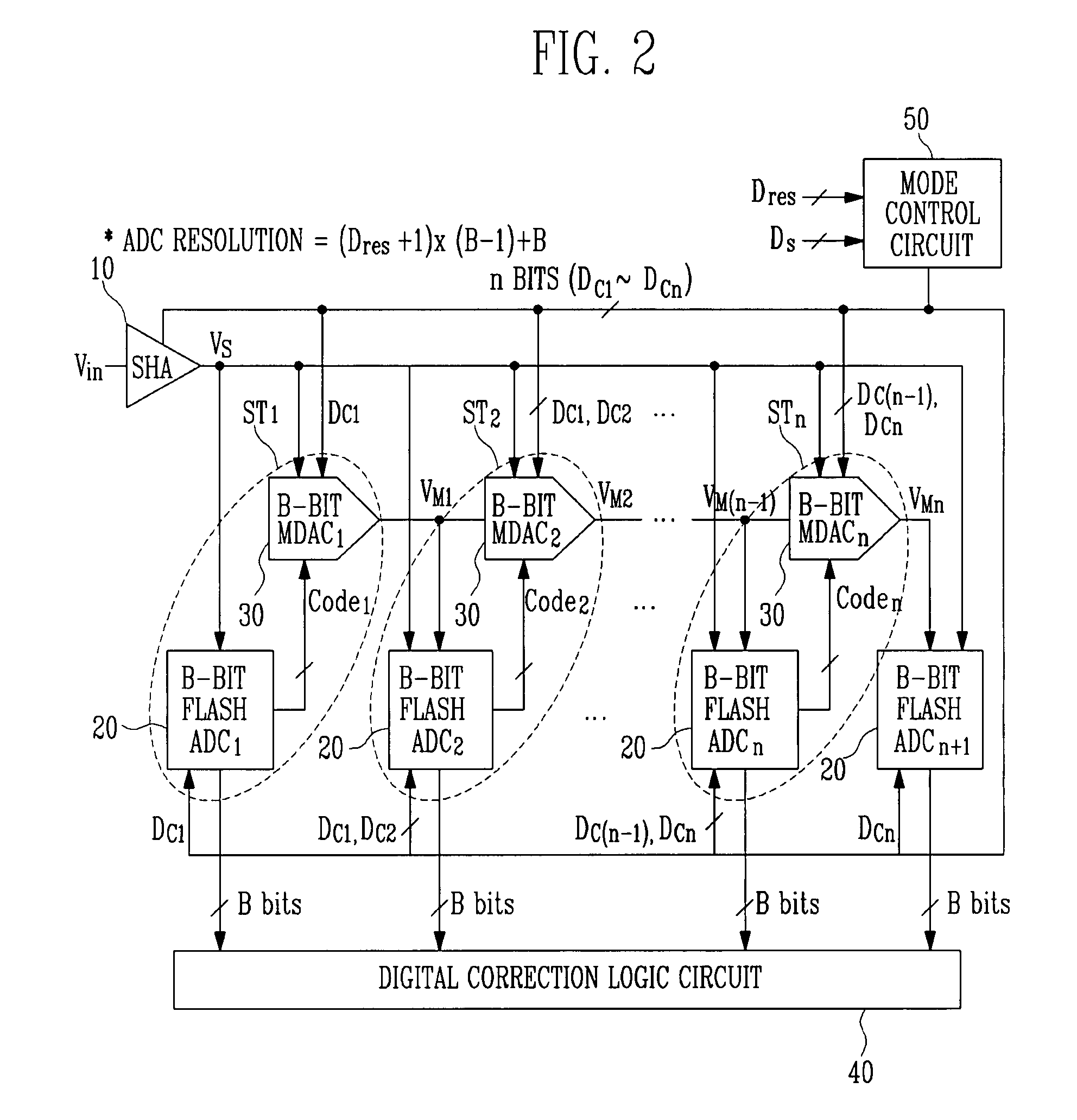
Provided is a multi-bit pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) capable of altering an operating mode. The ADC includes: a sample-and-hold amplifier (SHA) for sampling and holding an input analog voltage; an n+1 number of B-bit flash ADCs for receiving an analog signal and converting the analog signal into a digital signal to output the digital signal; an n number of B-bit multiplying digital-to-analog converters (MDACs) for converting a difference between the digital signal output from the B-bit flash ADC and the front-stage output signal into an analog signal to output the analog signal to the next stage; and a mode control circuit for generating n-bit control signals to control the B-bit flash ADC and the B-bit MDAC according to required resolution and operating frequency. In the multi-bit pipeline ADC, an operating mode is altered by controlling the number of stages in a pipeline and a signal path according to required resolution and operating frequency, so that power consumption can be minimized under the corresponding operating condition and signals can be processed in a variety of ways.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
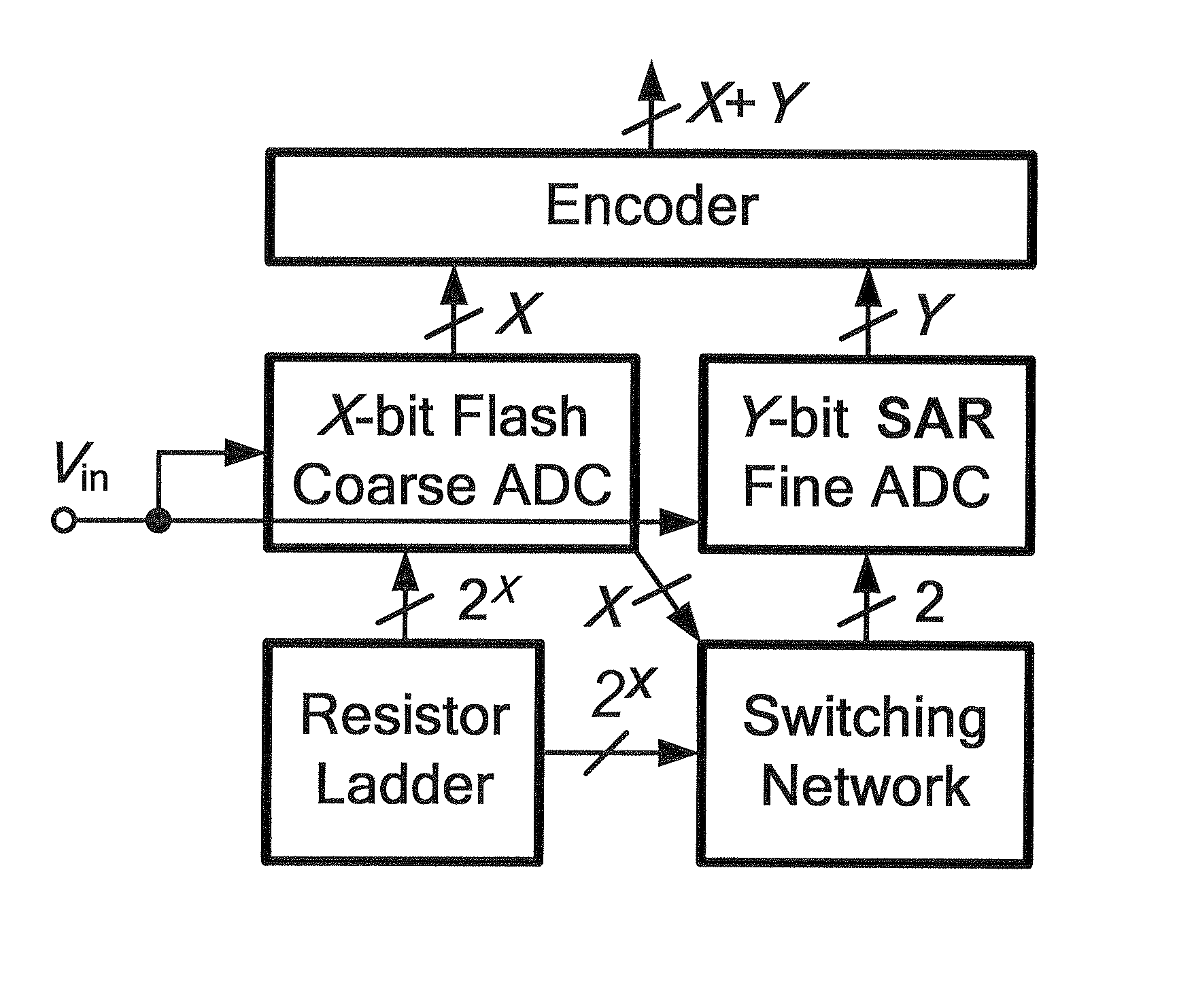
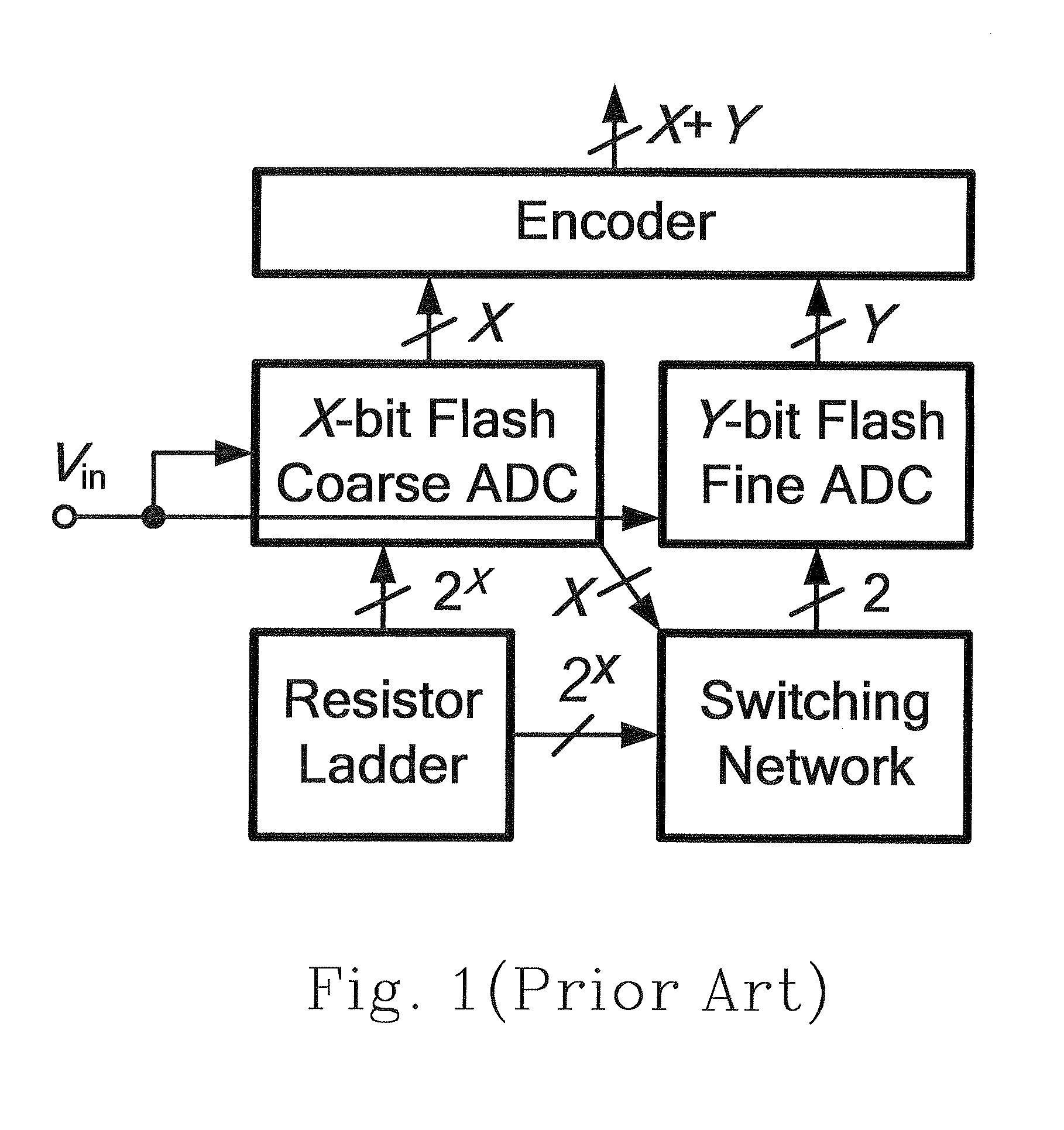
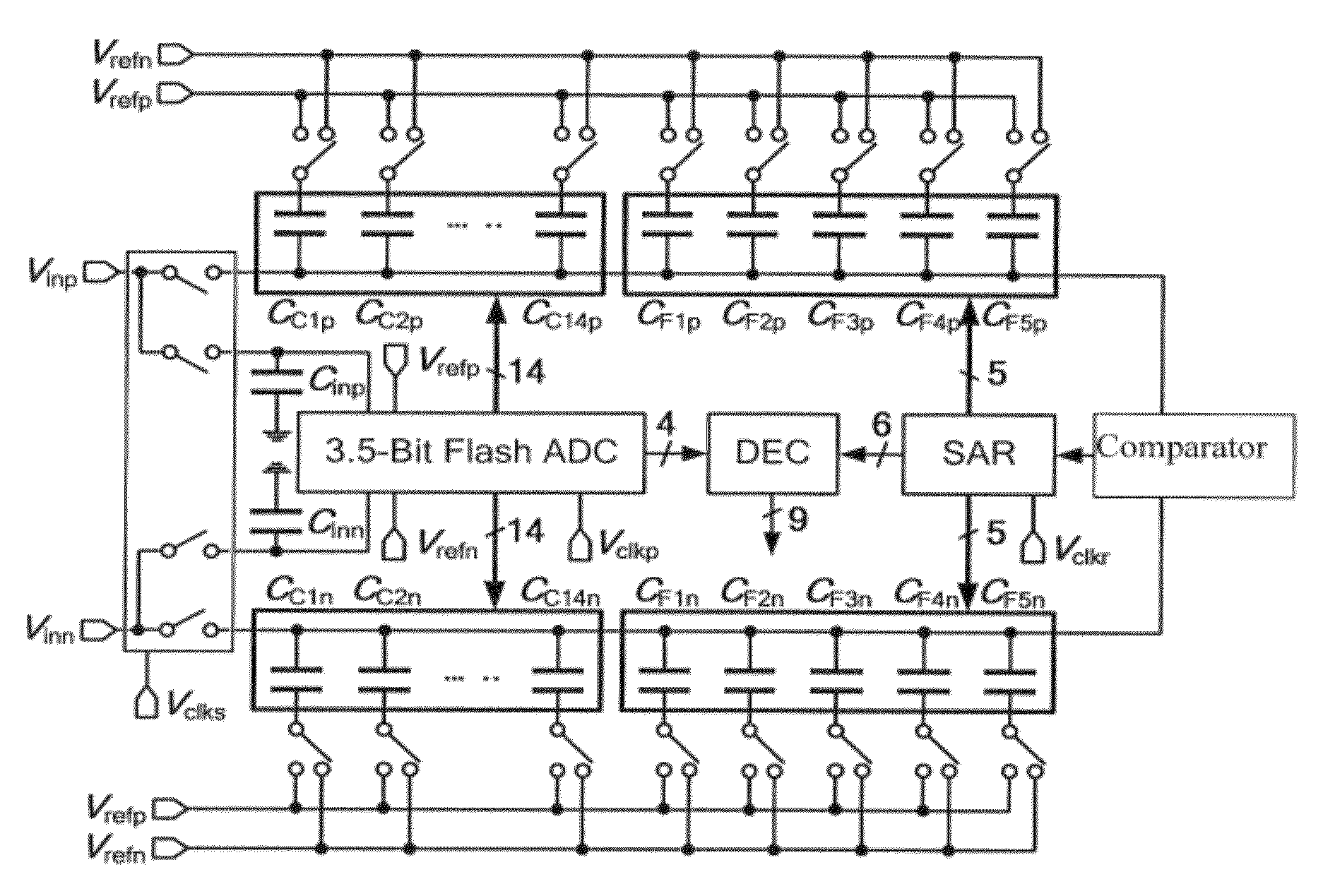
Subrange analog-to-digital converter and method thereof
InactiveUS20120154193A1Improves differential non-linearity (DNL)Fast sampling speedComputing operations for integral formationElectric signal transmission systemsDigital down converterEngineering
The configurations and adjusting method of a subrange analog-to-digital converter (ADC) are provided. The provided subrange ADC includes a X.5-bit flash ADC, a Y-bit SAR ADC and a (X+Y)-bit segmented capacitive digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
Multi-stage hybrid analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS10103742B1Electric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierLeast significant bit
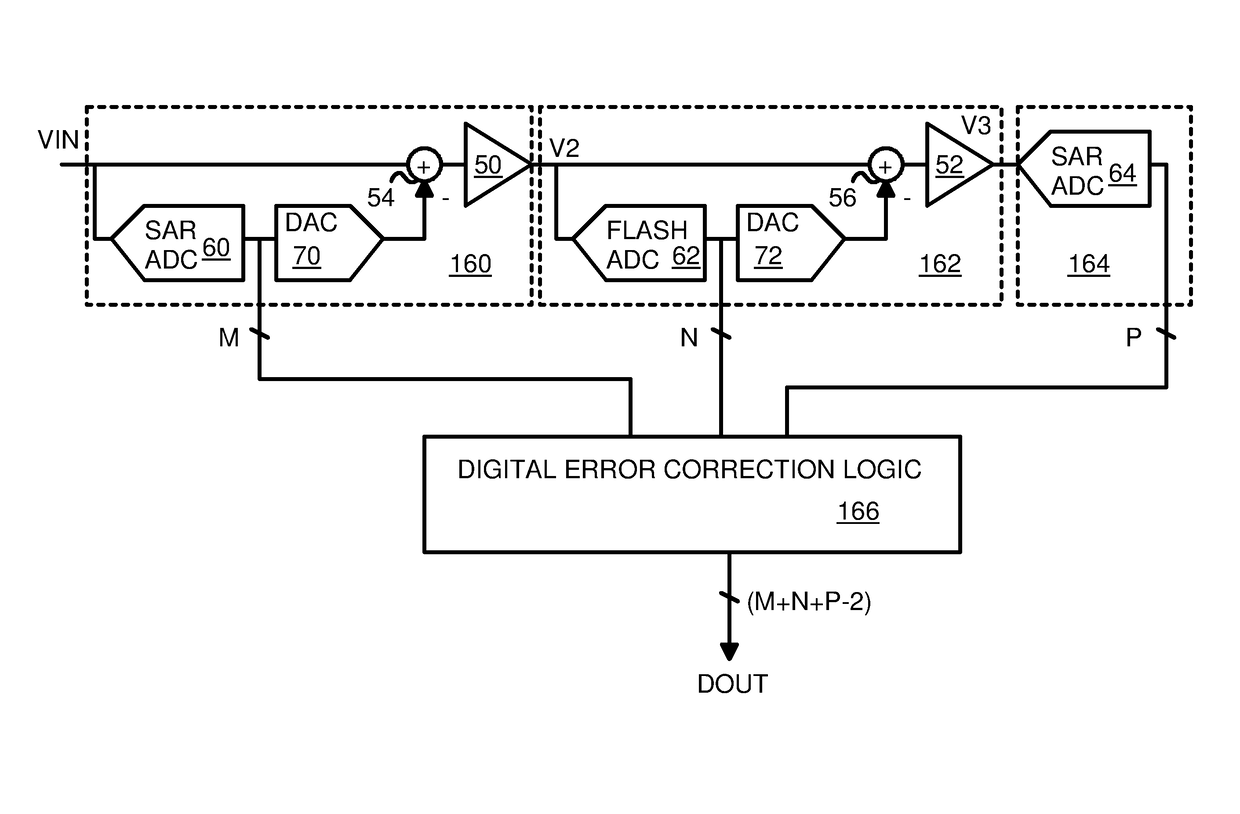
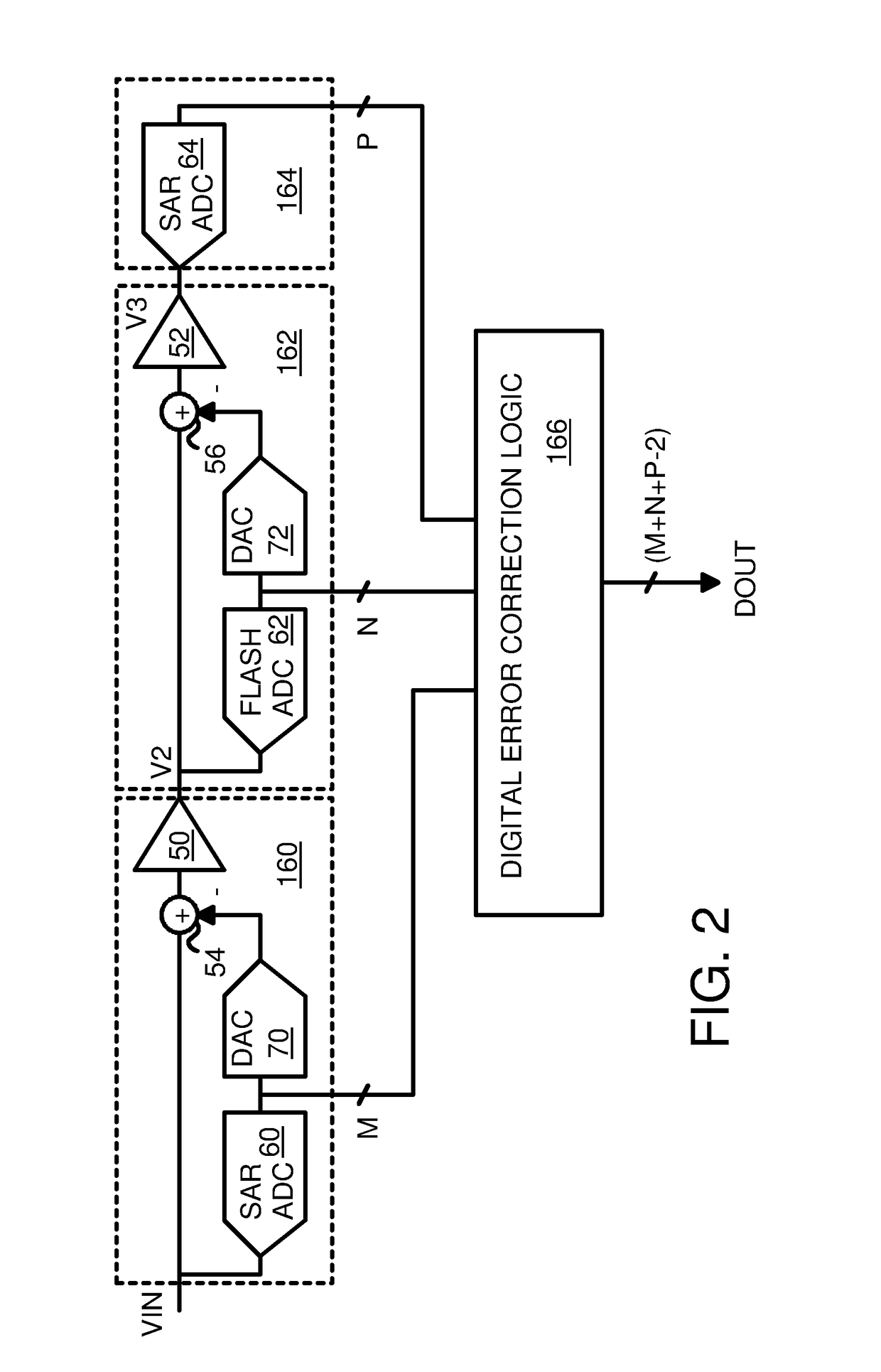
A hybrid Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC) has multiple stages. A first stage and a final stage each use a Successive-Approximation Register (SAR) ADC to generate the Most-Significant-Bits (MSBs) and the Least-Significant-Bits (LSBs) over successive internal cycles. Middle stage(s) use a faster flash ADC with multiple comparators in parallel to generate the middle binary bits, which are then re-converted by a Digital-to-Analog Converter (DAC) and subtracted from the stage's input analog voltage to generate a difference that is amplified by a residual amplifier that outputs an amplified voltage to the next stage. The first stage also has this multiplying DAC structure to convert the MSBs to an amplified voltage to the first of the middle stages. Finally, digital error correction logic removes redundant binary bits between stages. Initial and final SAR stages of 4 and 8 bits with a 4-bit middle stage provide a hybrid ADC of 14-bit precision.
Owner:HONG KONG APPLIED SCI & TECH RES INST
Flash ADC receiver with reduced errors
ActiveUS20050280568A1Reduce errorsImprove link qualityData representation error detection/correctionElectric signal transmission systemsSymbol decodingVoltage reference
Symbol decoding errors at a receiver utilising a flash analog to digital converter (ADC) can be reduced by adjusting a reference voltage level of the ADC where a decoding error rate at the reference voltage level exceeds a threshold.
Owner:CIENA
High-speed analog-to-digital conversion system with flash assisted parallel SAR architecture
ActiveUS8884801B1Power saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsImage resolutionEngineering
The present invention is directed to signal processing systems and methods thereof. In various embodiments, the present invention provides an analog-to-digital conversion (ADC) system that includes a flash ADC portion and a time-interleaved parallel SAR portion. For an n-bit ADC process, the flash ADC portion converts k MSBs of the n bits during a single cycle, and the SAR portion converts n−k LSBs in m number of cycles. The SAR portion includes a number of SAR channels that perform A / D conversion in parallel, and the k MSB from the course flash converter is verified for errors by the SAR portion and allows a net saving of the power consumption by reducing the number of fine resolution SARs. There are other embodiments as well.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
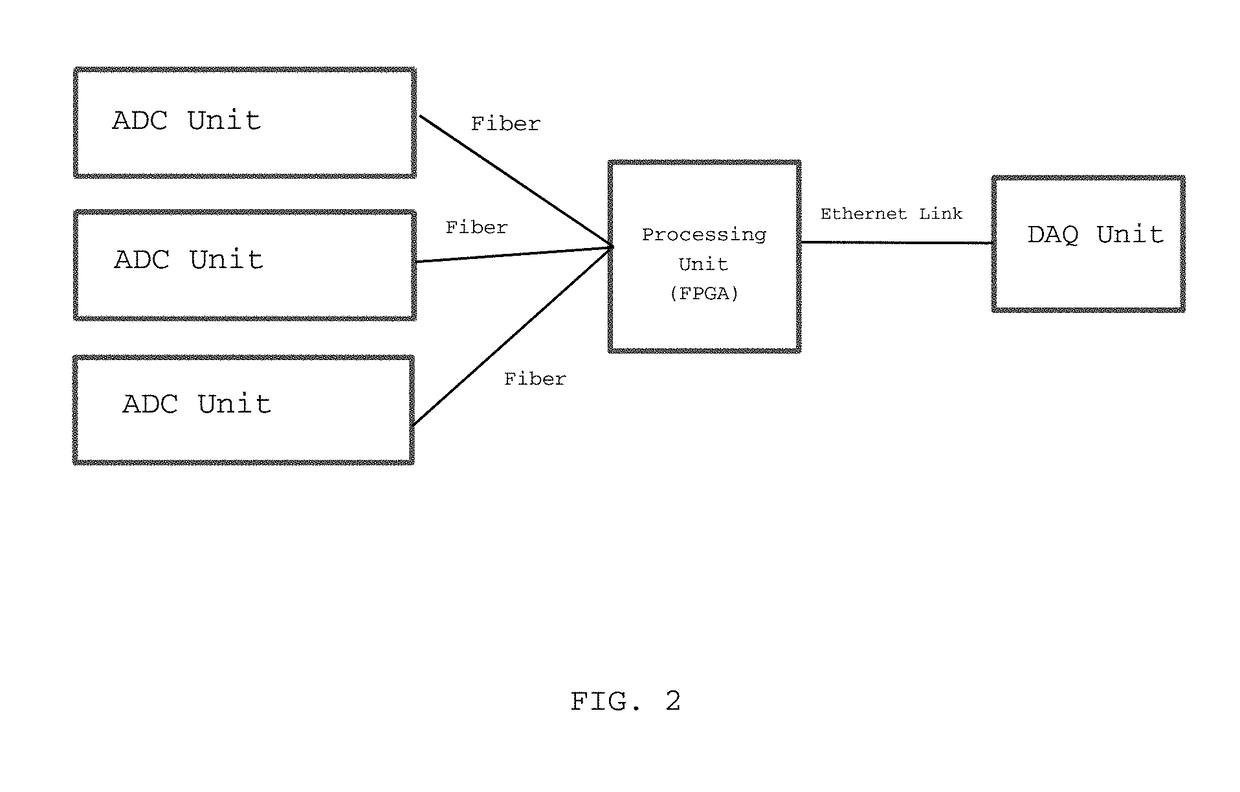
Method and apparatus to digitize pulse shapes from radiation detectors
ActiveUS10027340B1Improve scalabilityReduce data volumeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital/analogue conversionData acquisitionDetector array
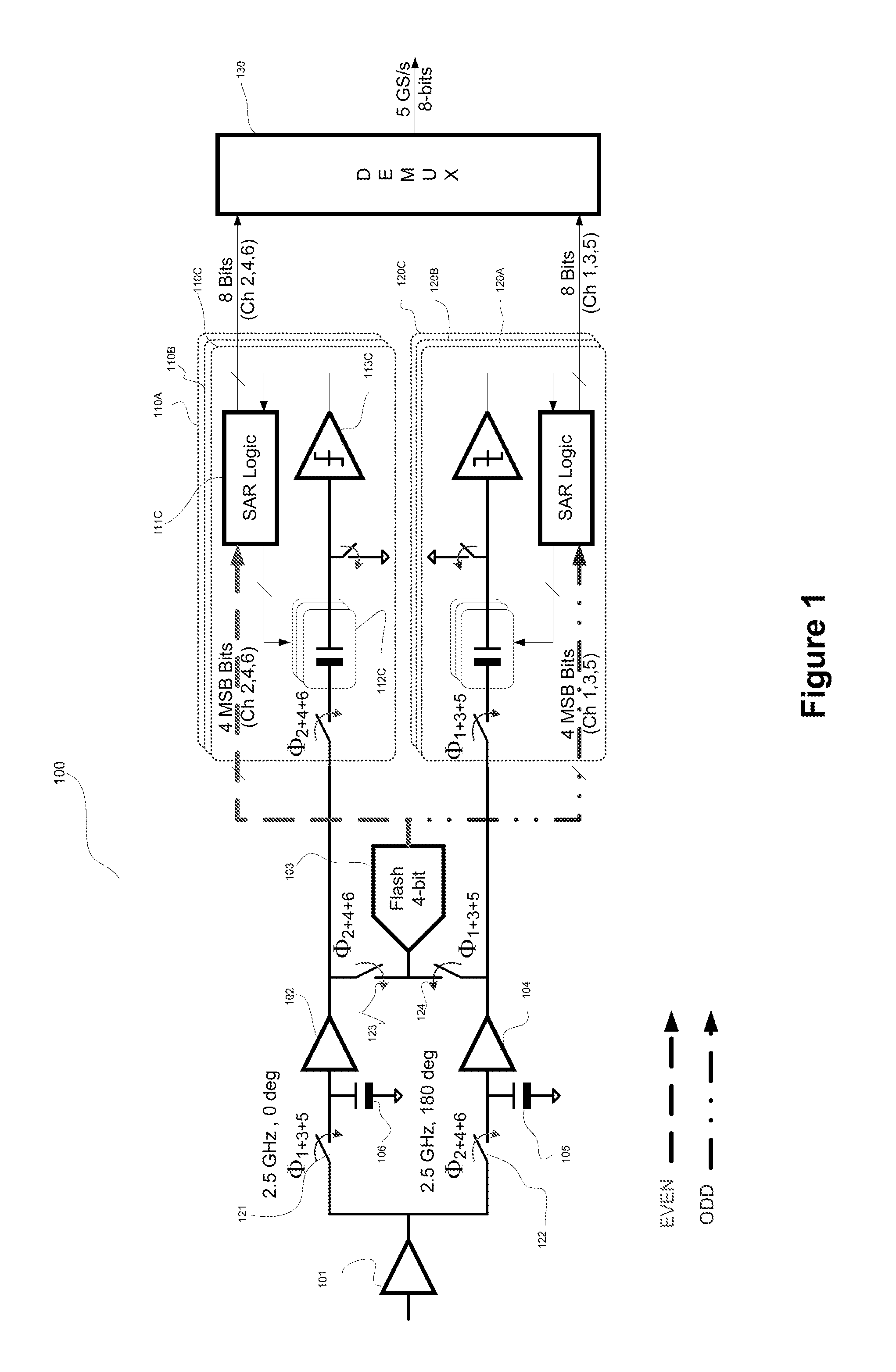
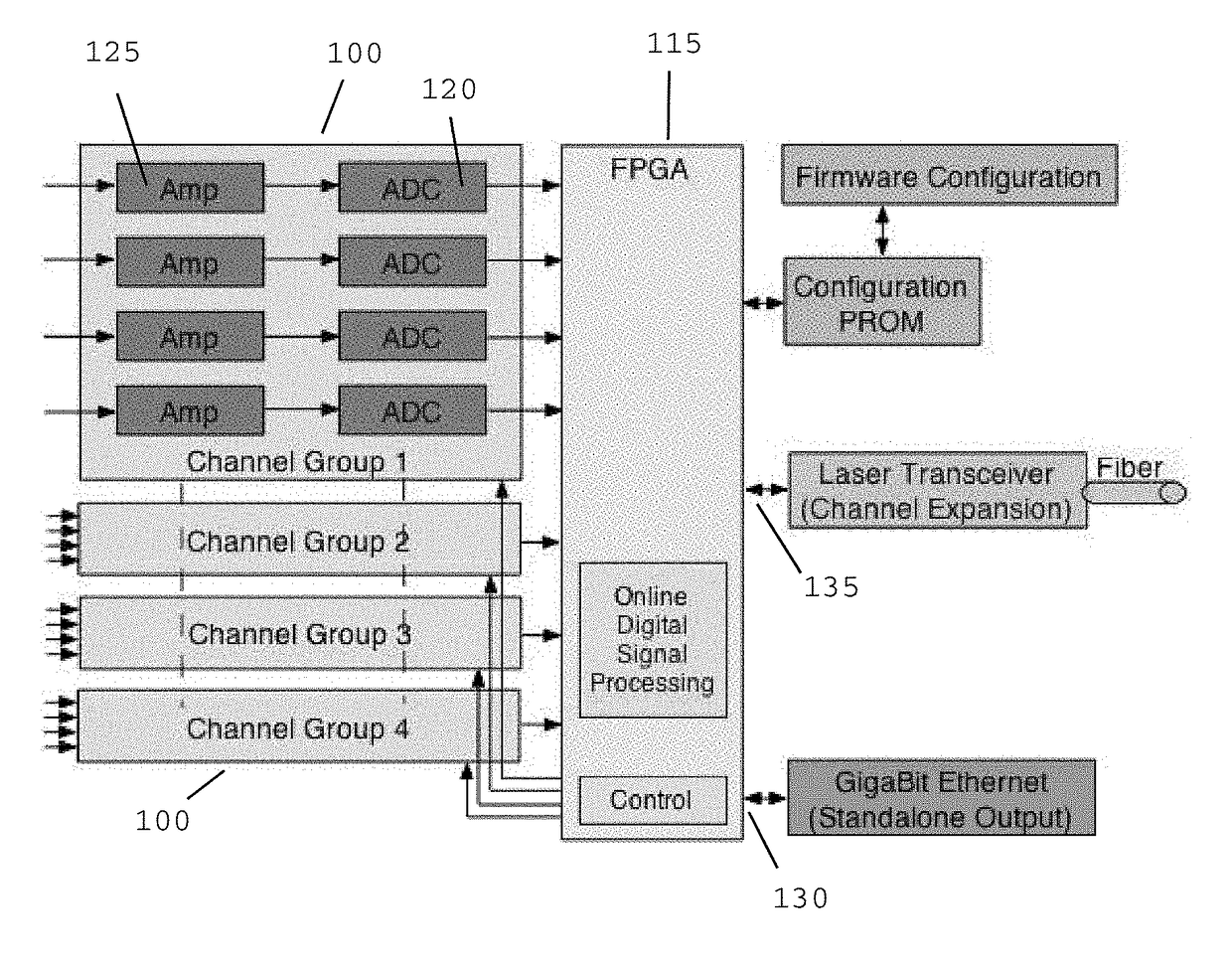
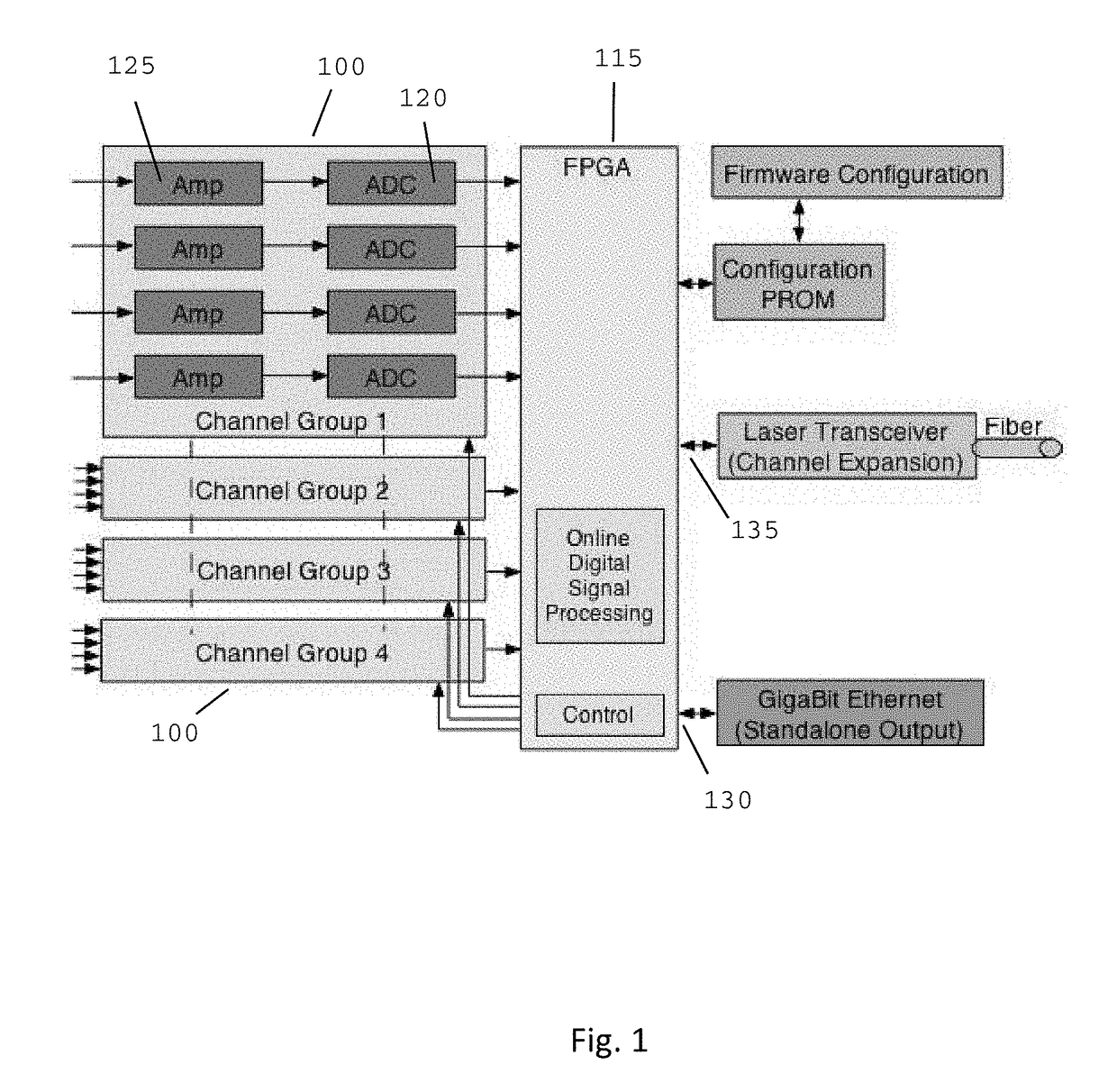
A field programmable gate array based multi-channel flash ADC unit combined with a high speed multi-lane data communications channel / Ethernet-like modular intercommunication providing a complete but easily expandable high-speed data acquisition system. This apparatus and method permits high-speed pulse-shape digitalization allowing position resolution imaging of particles having a range of energies and is scalable to achieve the efficient capture of coincident data from large electromagnetic detector arrays.
Owner:JEFFERSON SCI ASSOCS LLC
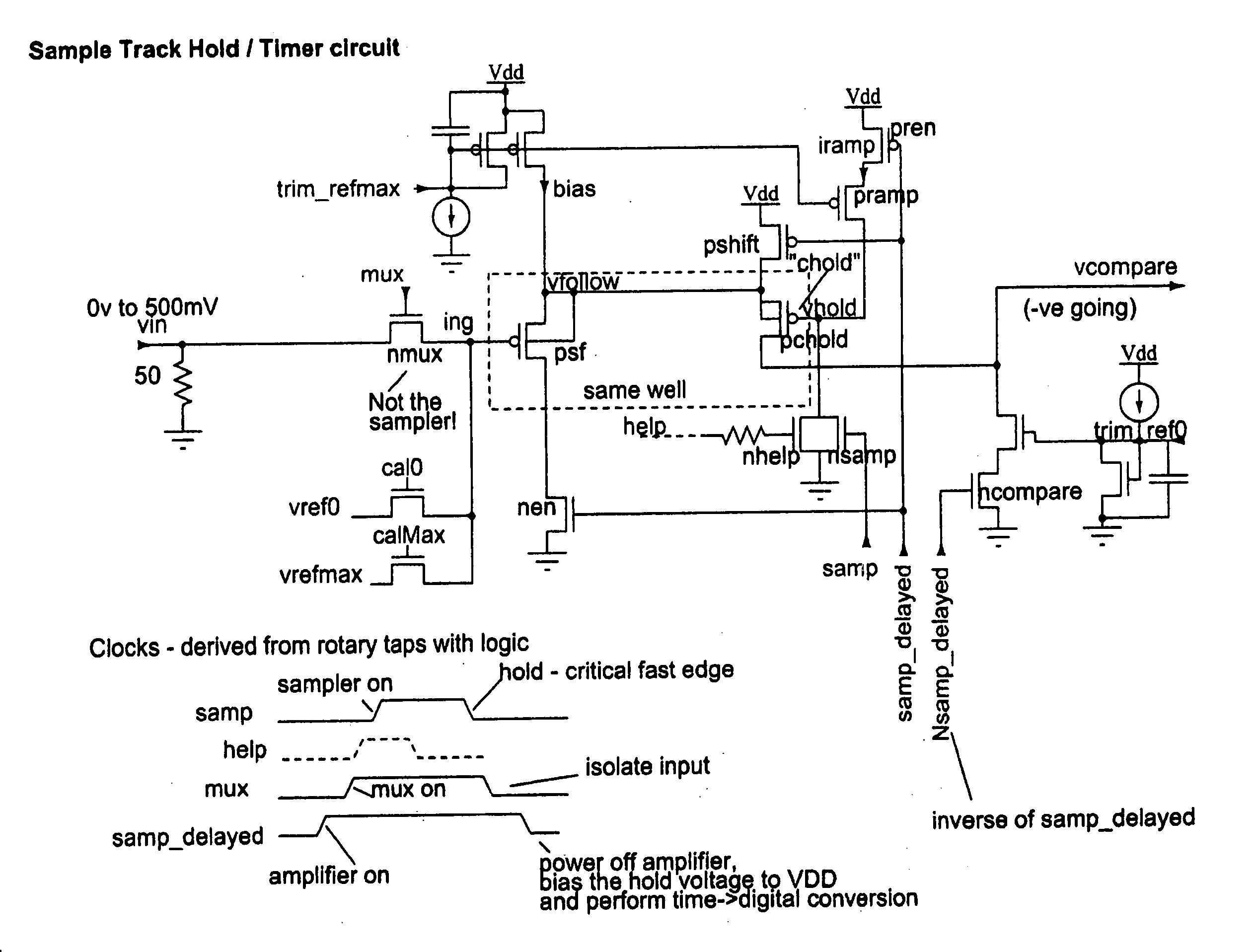
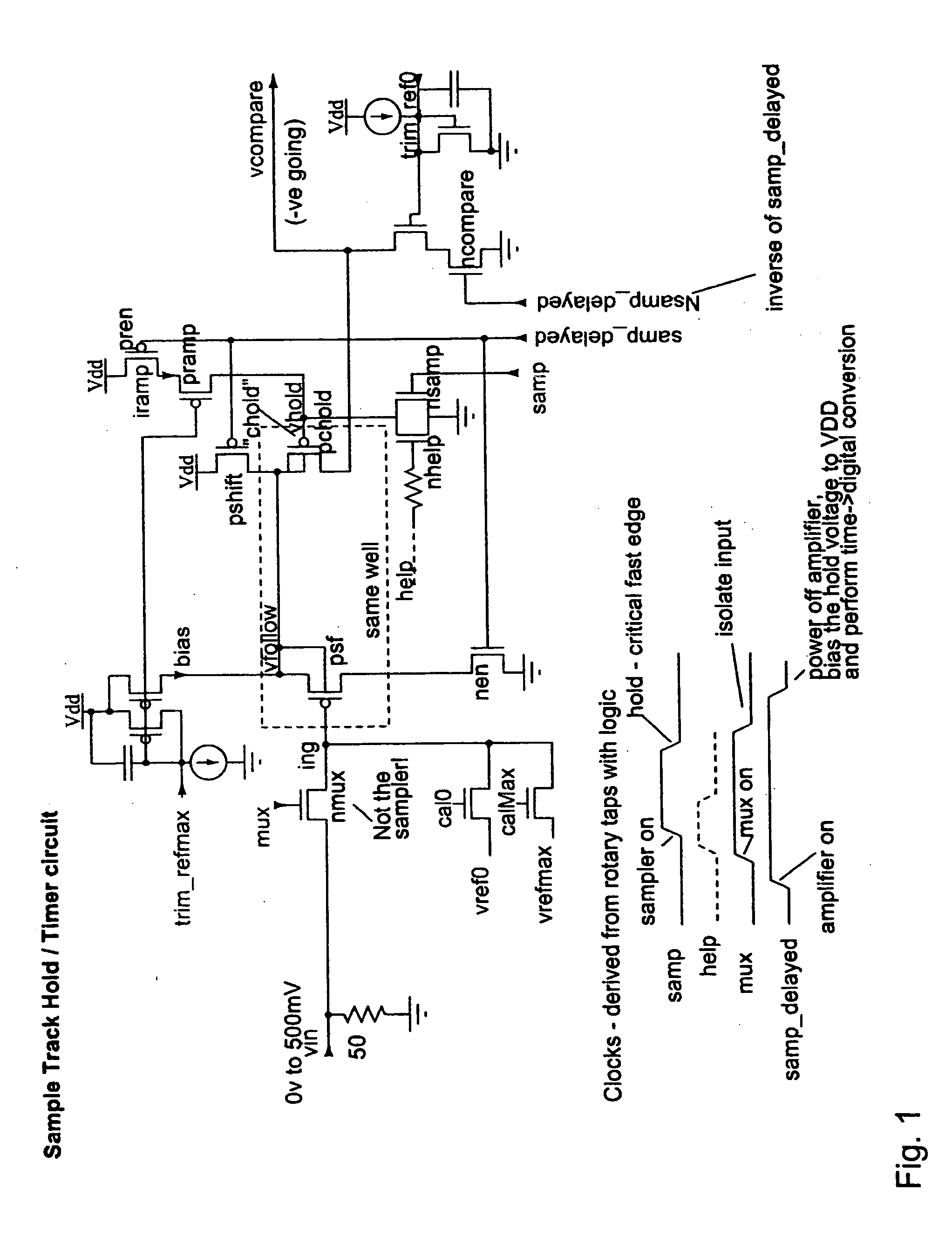
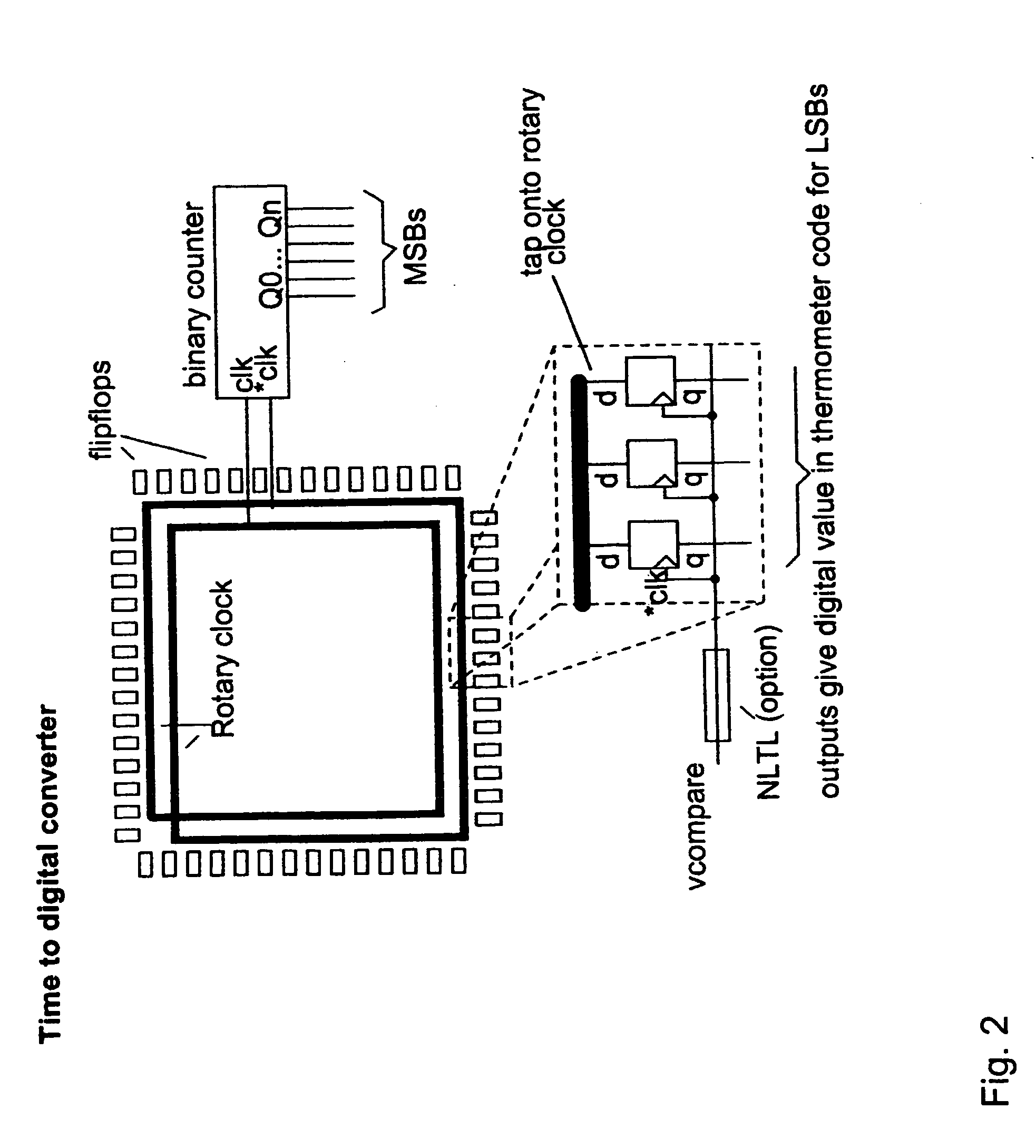
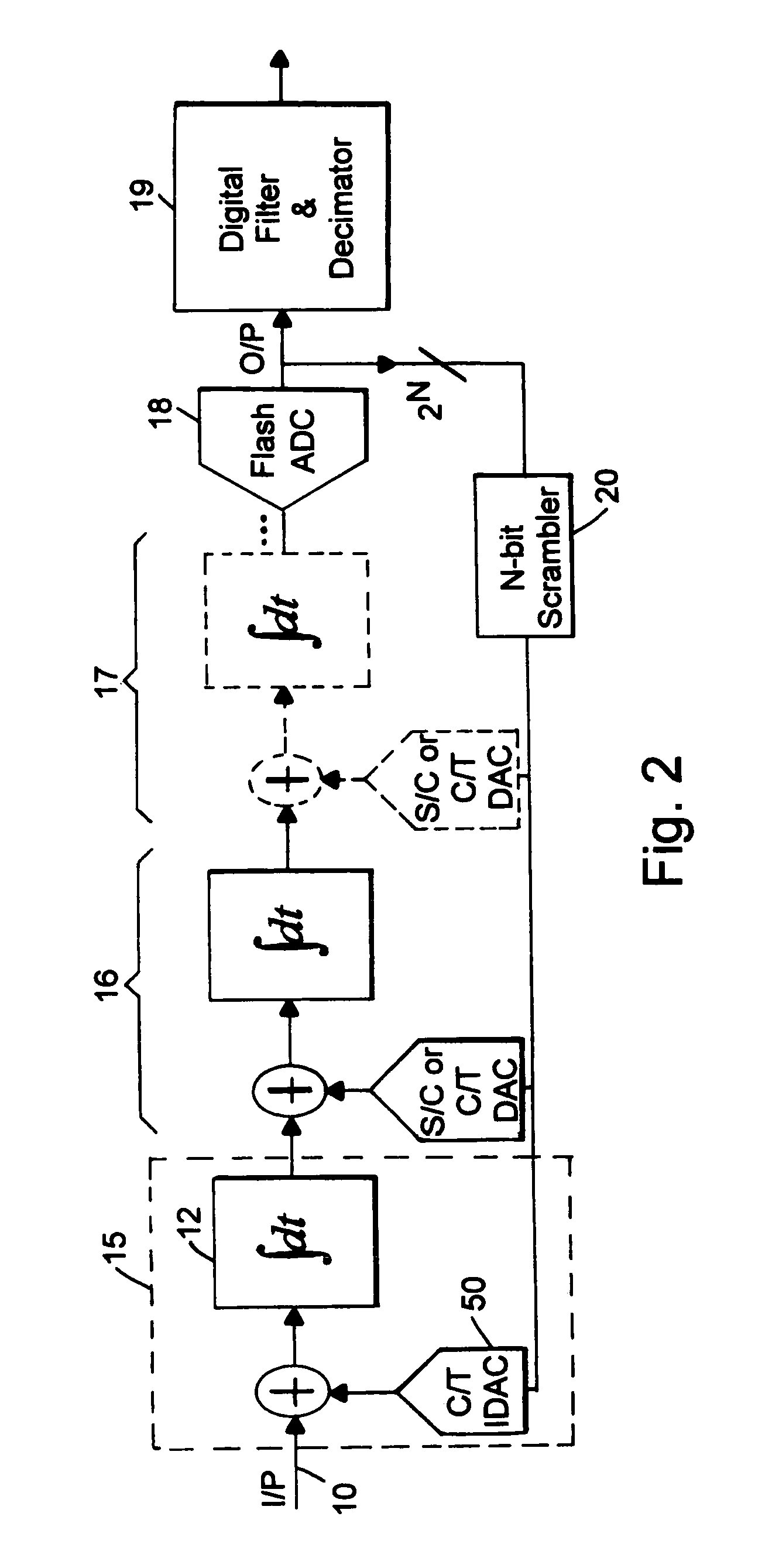
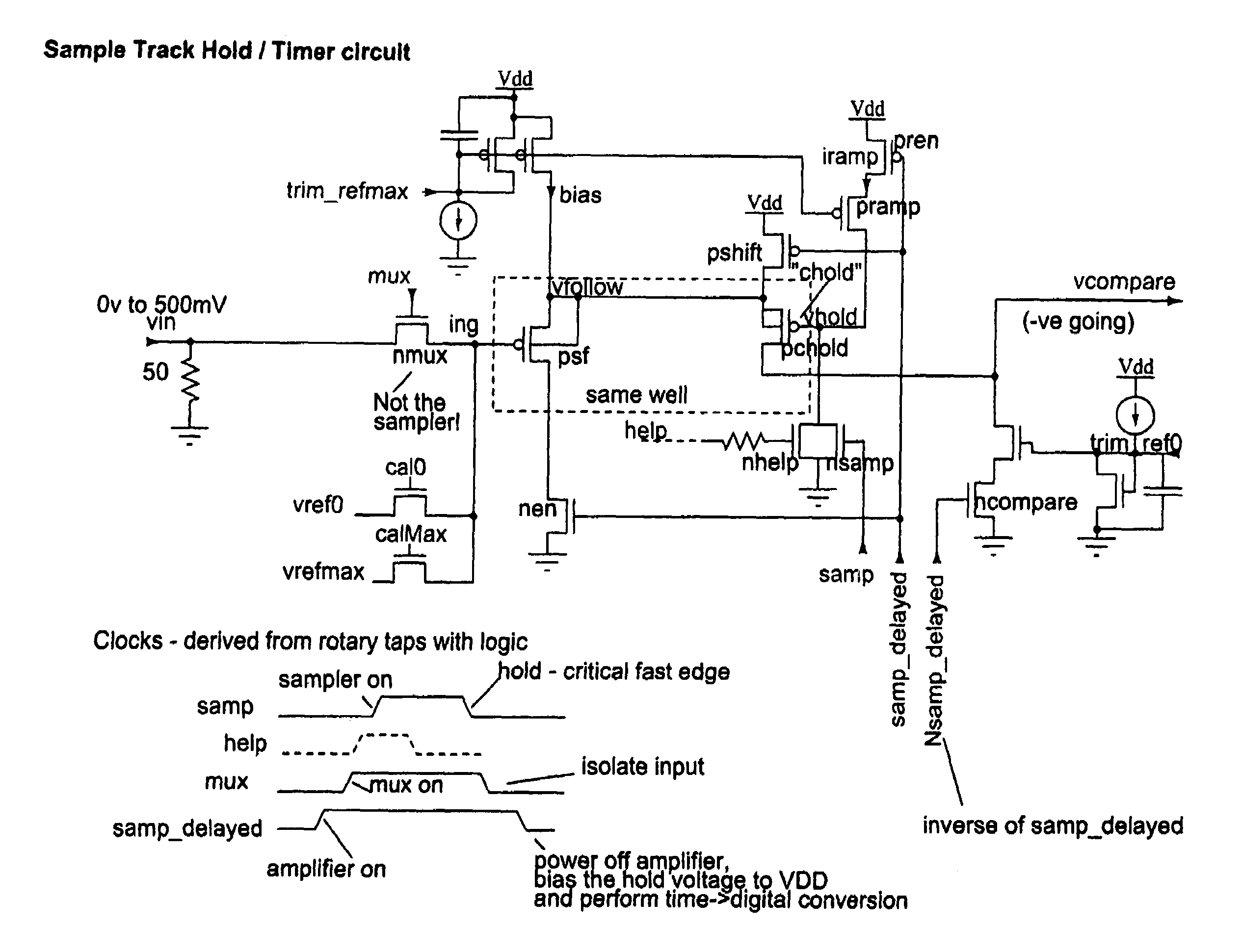
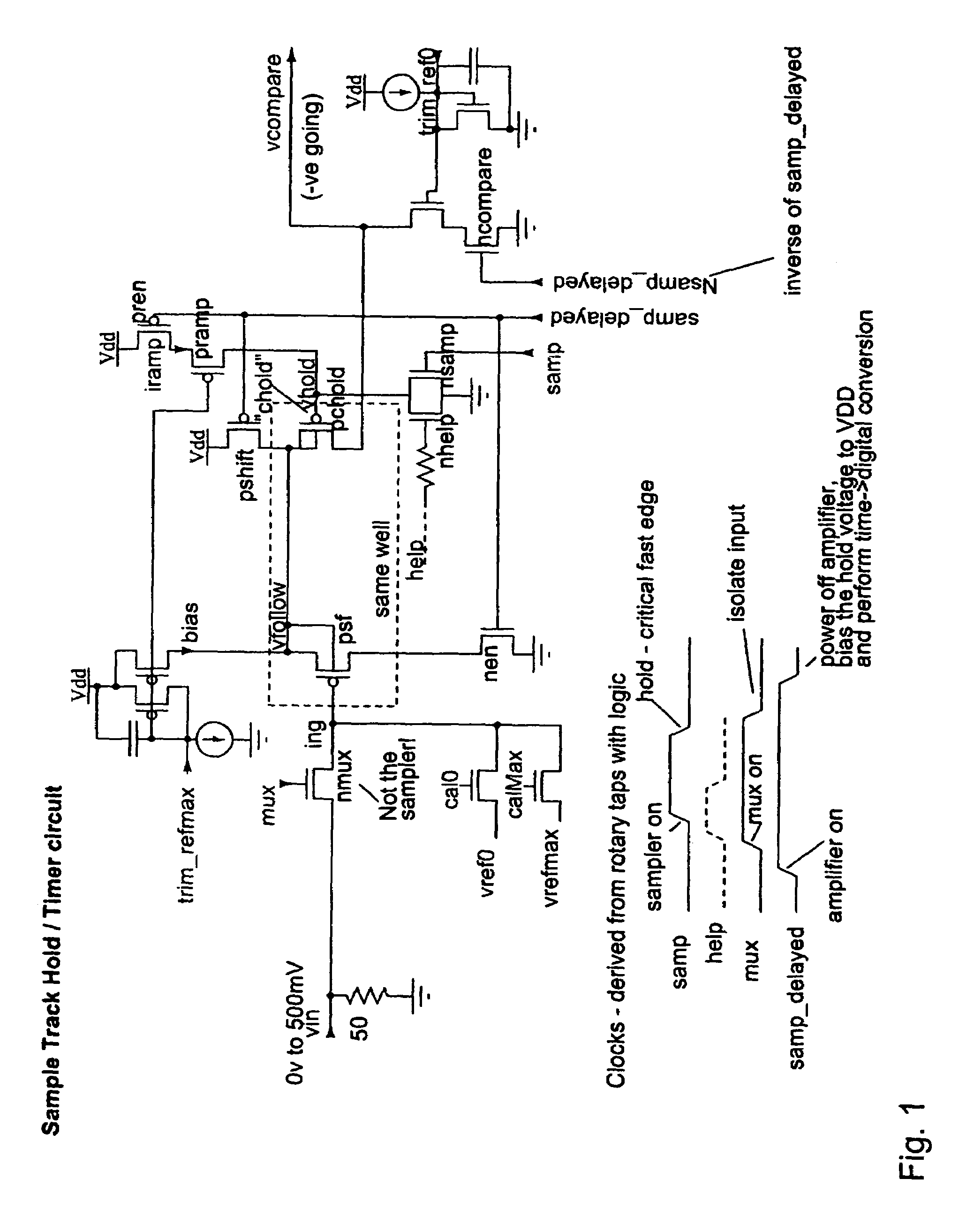
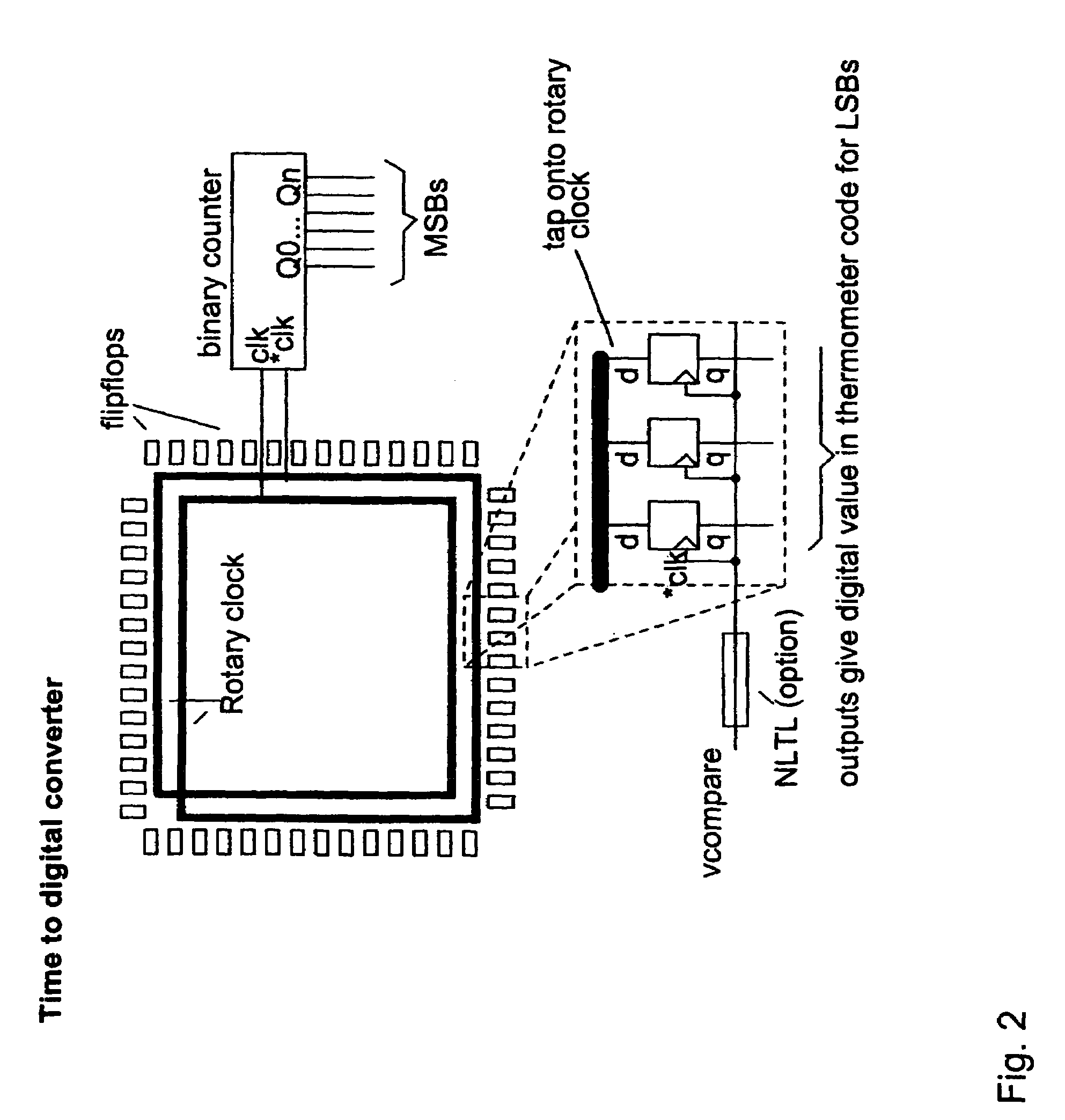
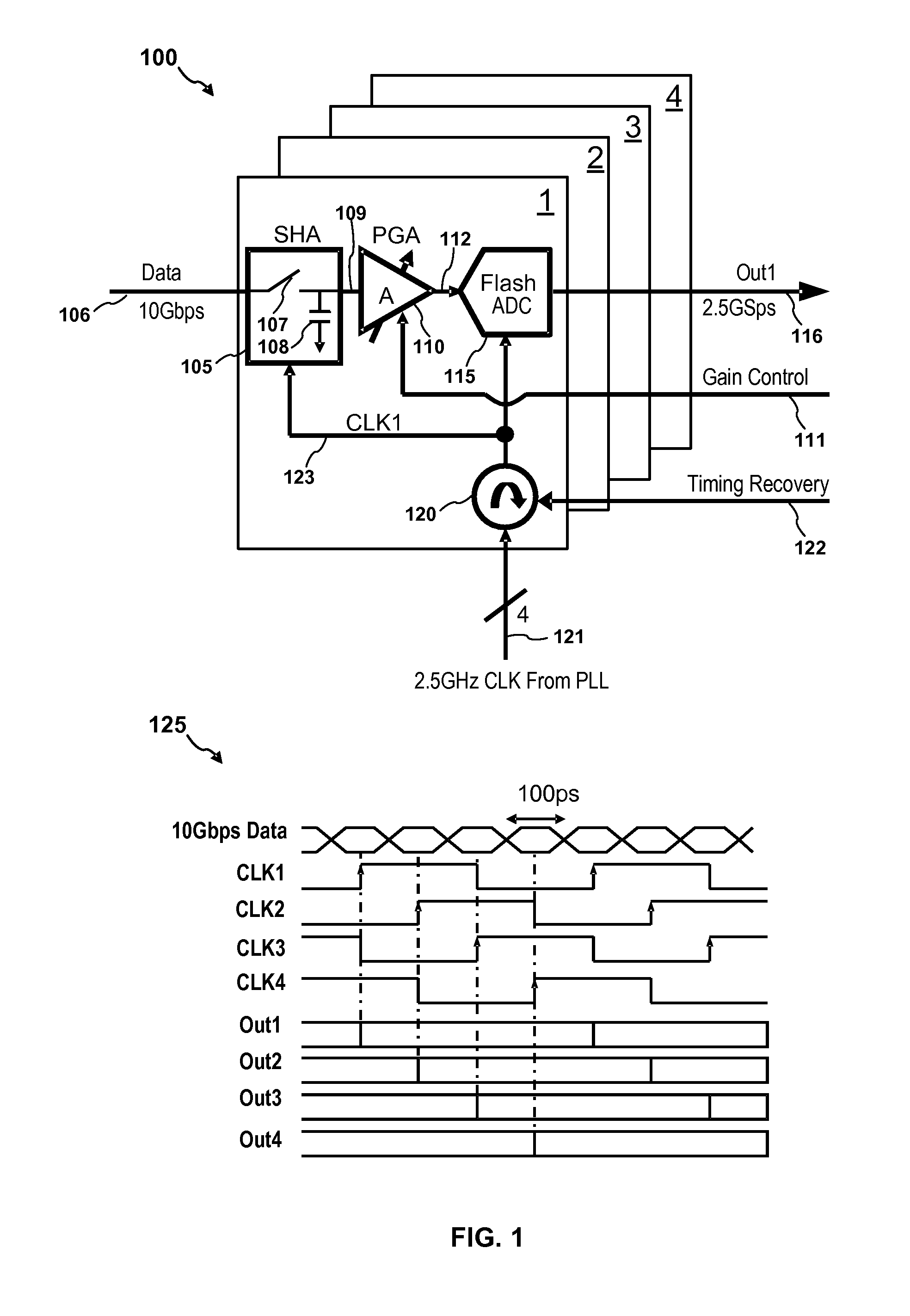
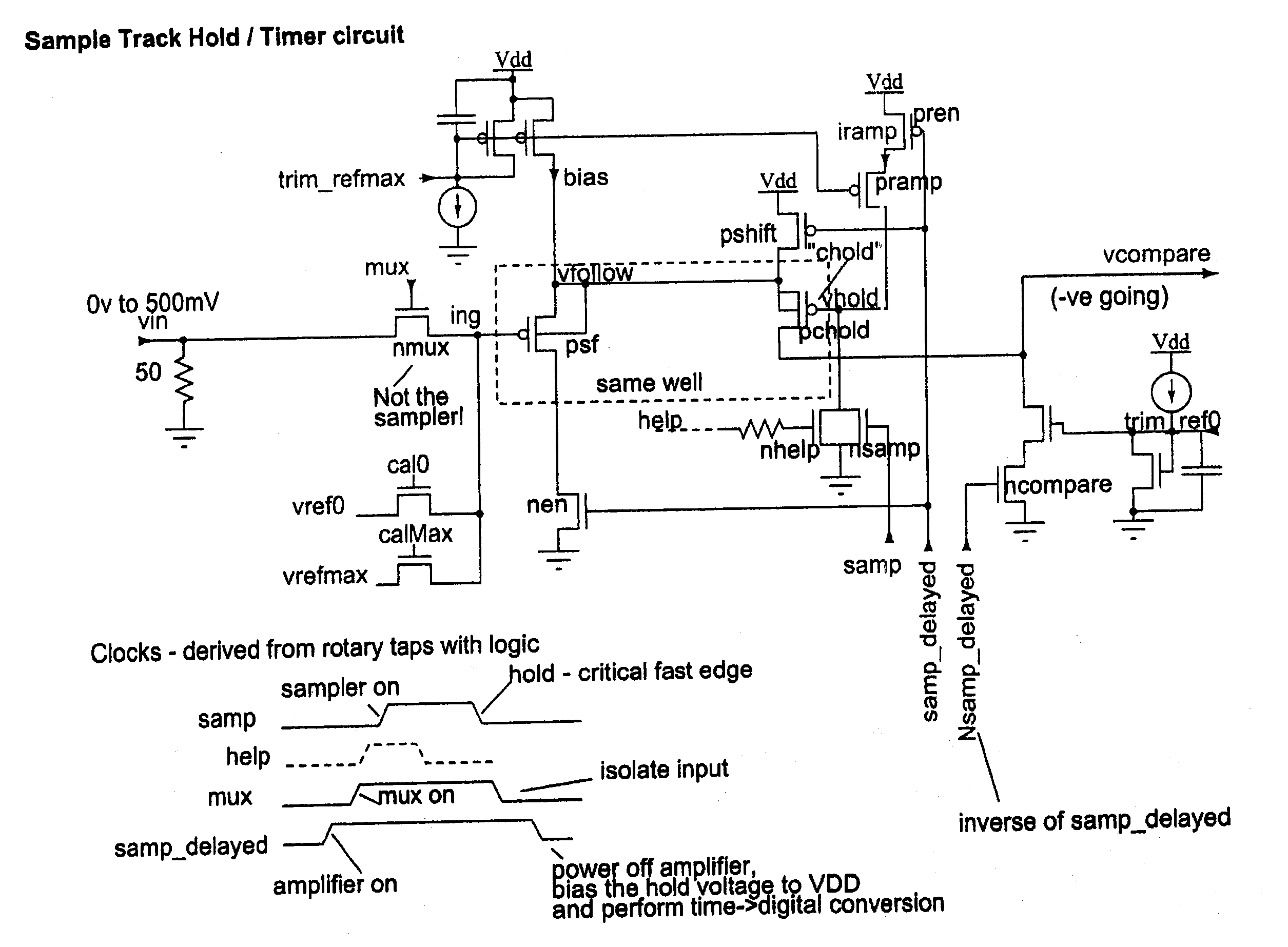
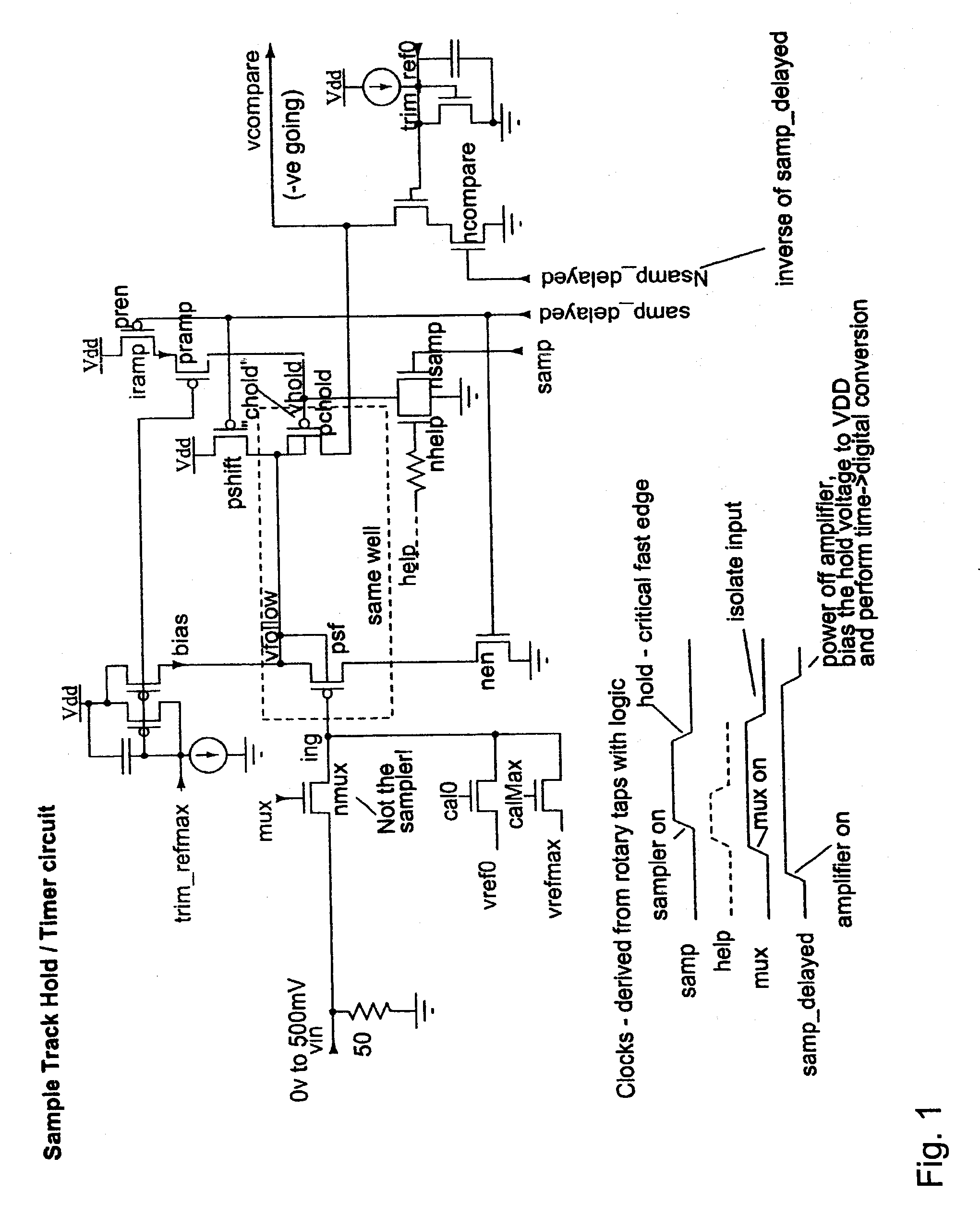
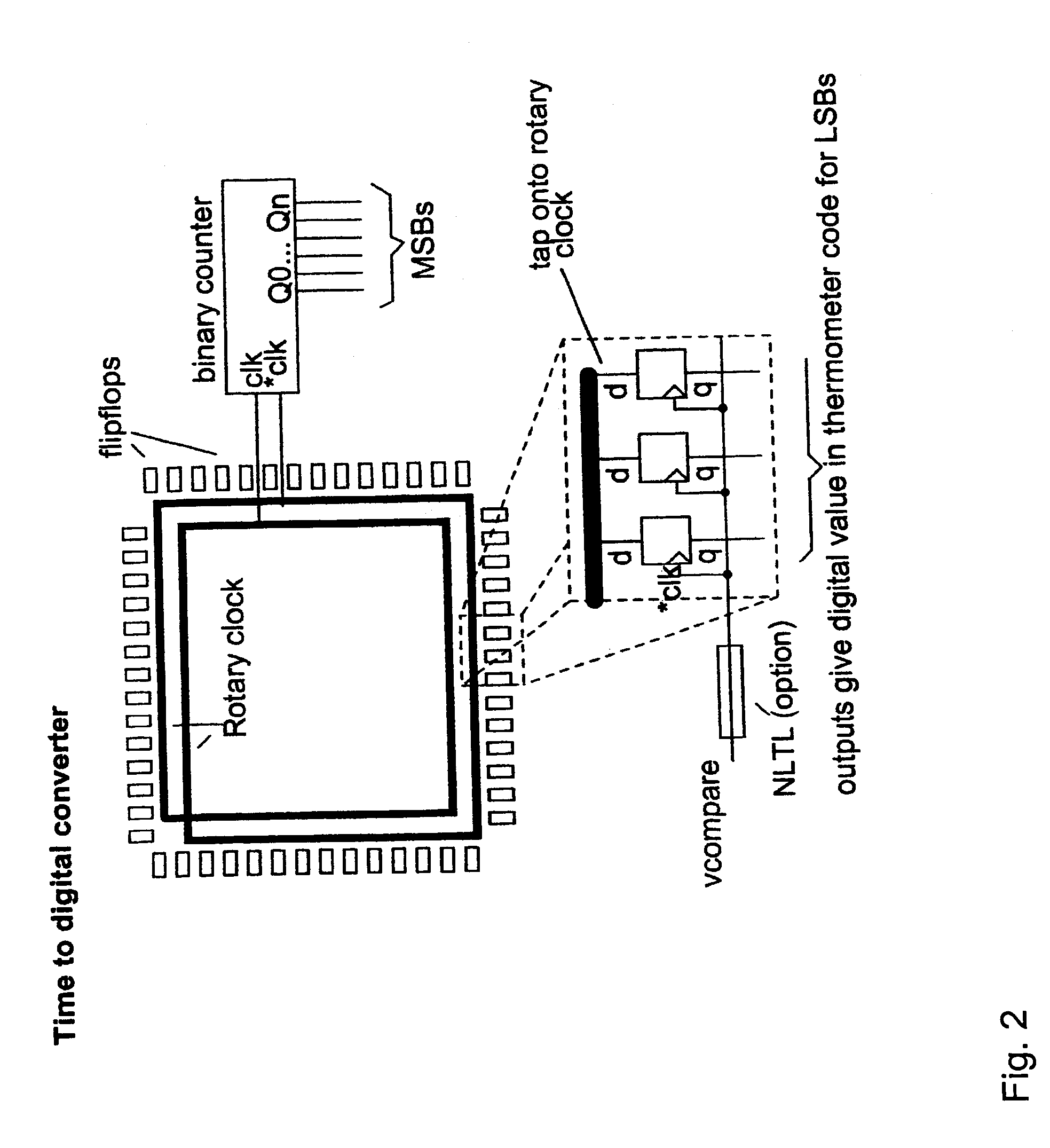
Rotary flash ADC
ActiveUS20060071844A1Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlIntegratorClosed loop
A system and method for converting an analog signal to a digital signal is disclosed. The system includes a multiphase oscillator preferable a rotary oscillator, a sample and hold circuit, an integrator and a time-to-digital converter. The multiphase oscillator has a plurality of phases that are used in the time-to-digital converter to measure the time of a pulse created by the integrator. The edges of the pulse may optionally be sharpened by passing the pulse through a non-linear transmission line to improve the accuracy of the measurement process. To cut down on noise a tuned power network provides power to the switching devices of the rotary oscillator. Calibration is performed by fragmenting the sample and hold circuit and integrator and performing a closed loop calibration cycle on one of the fragments while the other fragments are joined together for the normal operation of the sample and hold and integrator circuits.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
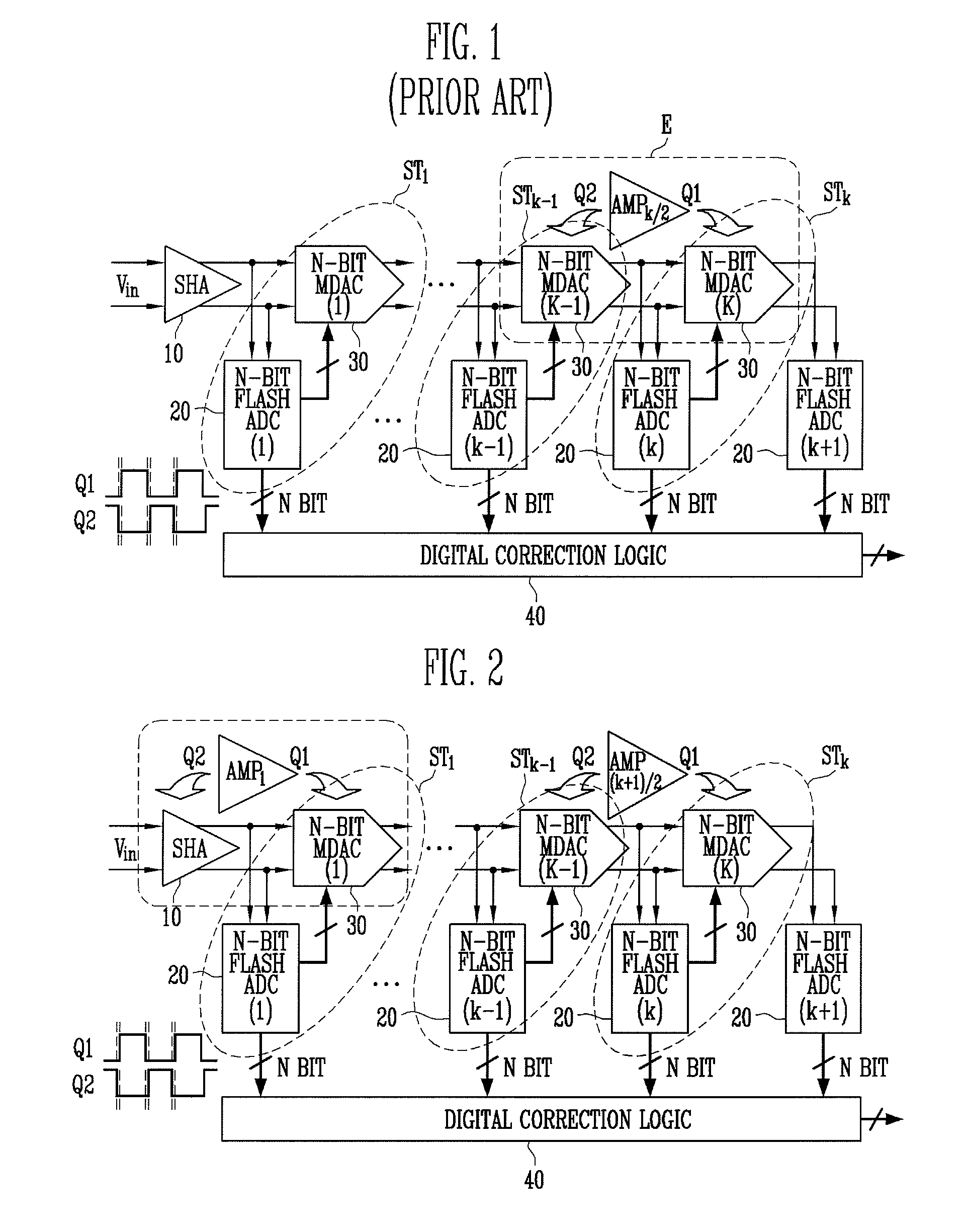
Multi-bit pipeline analog-to-digital converter having shared amplifier structure
ActiveUS7397409B2Reduce consumptionSmall sizeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterEngineering
A multi-bit pipeline analog-to-digital converter (ADC) having a shared amplifier structure includes: a sample-and-hold amplifier (SHA) for sampling and holding an input analog voltage and removing a sampling error of the input voltage; N-bit flash ADCs of first to K-th stages receiving analog signals, converting them into digital signals and outputting the digital signals; N-bit multiplying digital-to-analog converters (MDACs) of first to K-th stages converting differences between the digital signals output from the N-bit flash ADCs and output signals of preceding stages back into analog signals and outputting the analog signals; and a three-stage amplifier connected to an output of the N-bit MDAC of the first stage at a first clock and an output of the SHA at a second clock, wherein intergers N>= and K>=2. An amplifier can be shared between an SHA and an MDAC of a first stage, thereby reducing power consumption and chip size.In the multi-bit pipeline ADC, an amplifier can be shared between an SHA consuming much power and an MDAC of a first stage, so that power consumption and chip size can be reduced.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
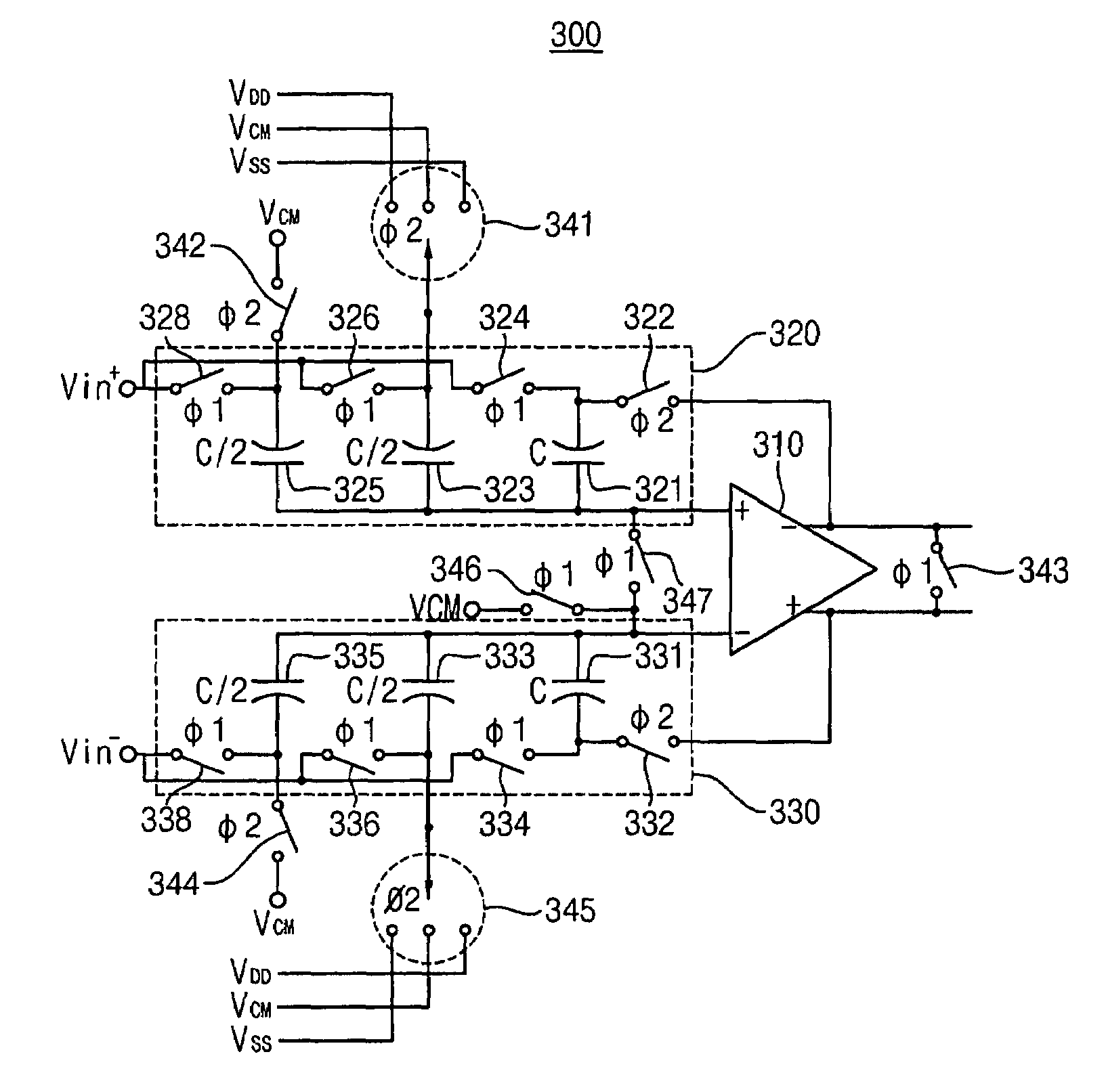
Pipelined analog-to-digital converter and method of analog-to-digital conversion
InactiveUS7515086B2Reduce power consumptionSmall sizeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersDigital down converterDigital analog converter
A pipelined analog-to-digital converter (ADC) has a multistage structure, and the pipelined ADC includes a plurality of stages that form the multistage structure. Each of the stages includes a sample-and-hold (S / H) circuit, a flash ADC, and a digital-to-analog converter (DAC). The S / H circuit converts an analog input signal to a digital signal. The flash ADC detects a digital bit corresponding to the analog input signal. The DAC converts the digital signal to an analog signal, and amplifies a residue signal, which is a difference between the input analog signal and the converted analog signal, that is provided as an analog input signal of the next stage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Differential front-end continuous-time sigma-delta ADC using chopper stabilization
ActiveUS7193545B2Improve Noise PerformanceSmall sizeAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsIntegratorDigital feedback
A multi-bit continuous-time sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter (ADC) has a differential input stage which receives an analog input signal current. A multi-bit feedback current digital-to-analog converter (IDAC) generates a multi-level feedback current depending on a digital feedback signal from a flash ADC. An integrator has a differential input that integrates the difference of the generated current by the multi-bit IDAC and the input signal current on a continuous-time basis. The input stage further comprises a first biasing current source and a second biasing current source which bias the input stage in a mid-scale condition. A first summing node connects to the first differential input line, a first differential input of the integrator and the first output branch. A second summing node connects to the second differential input line, a second differential input of the integrator and the second output branch. A set of chopping switches alternately connect the biasing current sources to the summing nodes in a first configuration and a second, reversed, configuration. The converter receives a modulator clock signal at a frequency FS and the chopping switches can operate at FS or a binary subdivision thereof. The integrator amplifier can also be chopper-stabilized.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Rotary flash ADC
ActiveUS7209065B2Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlDigital down converterIntegrator
A system and method for converting an analog signal to a digital signal is disclosed. The system includes a multiphase oscillator preferable a rotary oscillator, a sample and hold circuit, an integrator and a time-to-digital converter. The multiphase oscillator has a plurality of phases that are used in the time-to-digital converter to measure the time of a pulse created by the integrator. The edges of the pulse may optionally be sharpened by passing the pulse through a non-linear transmission line to improve the accuracy of the measurement process. To cut down on noise a tuned power network provides power to the switching devices of the rotary oscillator. Calibration is performed by fragmenting the sample and hold circuit and integrator and performing a closed loop calibration cycle on one of the fragments while the other fragments are joined together for the normal operation of the sample and hold and integrator circuits.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
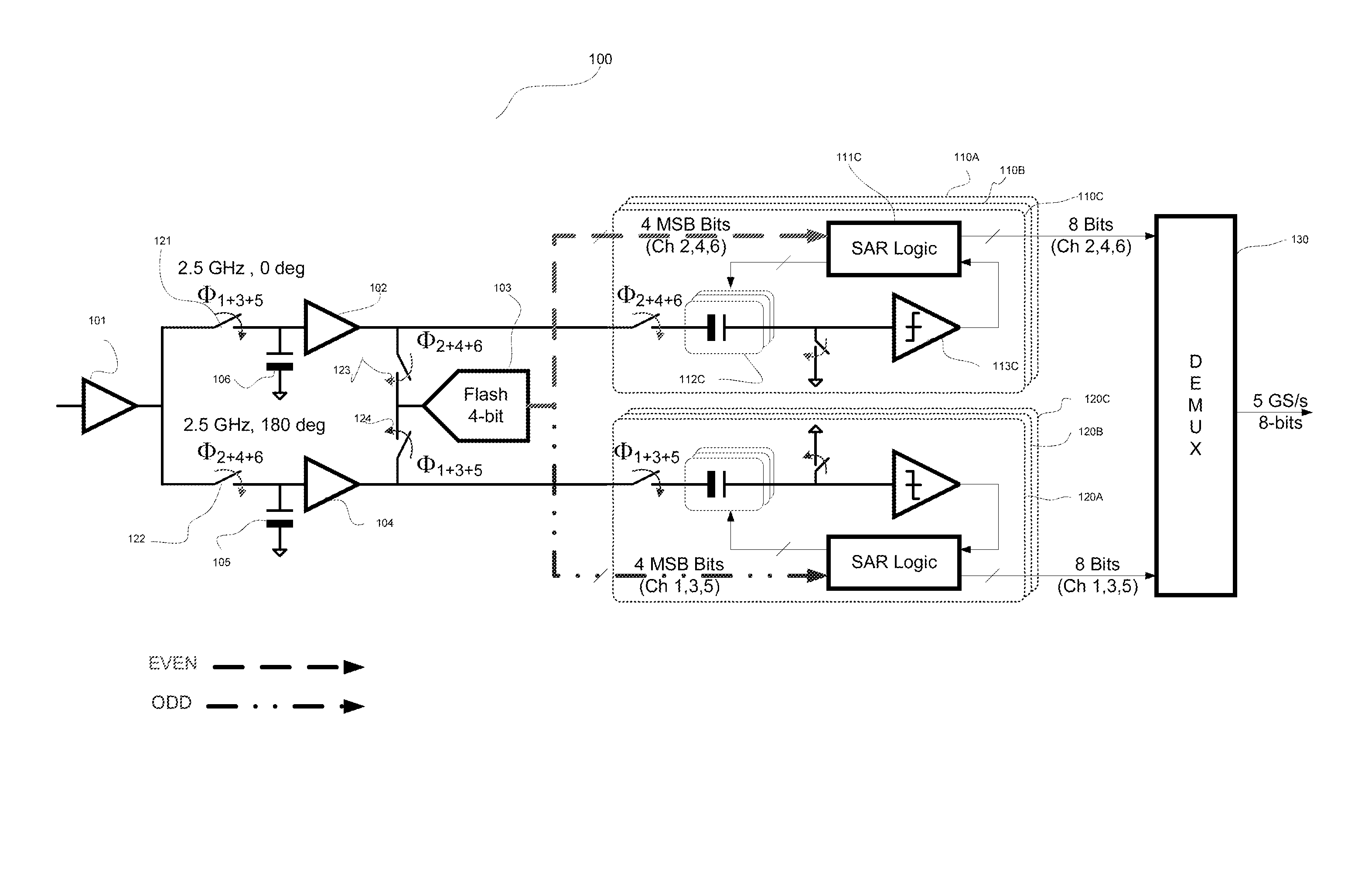
DSP receiver with high speed low ber ADC
ActiveUS20140104086A1Increase speedLow area requirementElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingEngineeringFlash ADC
Methods and apparatuses are described for a DSP receiver with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) having high speed, low BER performance with low power and area requirements. Speed is increased for multi-path ADC configurations by resolving a conventional bottleneck. ADC performance is improved by integrating calibration and error detection and correction, such as distributed offset calibration and redundant comparators. Power and area requirements are dramatically reduced by using low BER rectification to nearly halve the number of comparators in a conventional high speed, low BER flash ADC.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Rotary flash ADC
ActiveUS20070176816A1Electric signal transmission systemsPulse automatic controlIntegratorClosed loop
A system and method for converting an analog signal to a digital signal is disclosed. The system includes a multiphase oscillator preferable a rotary oscillator, a sample and hold circuit, an integrator and a time-to-digital converter. The multiphase oscillator has a plurality of phases that are used in the time-to-digital converter to measure the time of a pulse created by the integrator. The edges of the pulse may optionally be sharpened by passing the pulse through a non-linear transmission line to improve the accuracy of the measurement process. To cut down on noise a tuned power network provides power to the switching devices of the rotary oscillator. Calibration is performed by fragmenting the sample and hold circuit and integrator and performing a closed loop calibration cycle on one of the fragments while the other fragments are joined together for the normal operation of the sample and hold and integrator circuits.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Subrange analog-to-digital converter and method thereof
InactiveUS8310388B2Improves differential non-linearity (DNL)Fast sampling speedComputing operations for integral formationElectric signal transmission systemsFlash ADCAnalog-to-digital converter
The configurations and adjusting method of a subrange analog-to-digital converter (ADC) are provided. The provided subrange ADC includes a X.5-bit flash ADC, a Y-bit SAR ADC and a (X+Y)-bit segmented capacitive digital-to-analog converter (DAC).
Owner:NAT CHENG KUNG UNIV
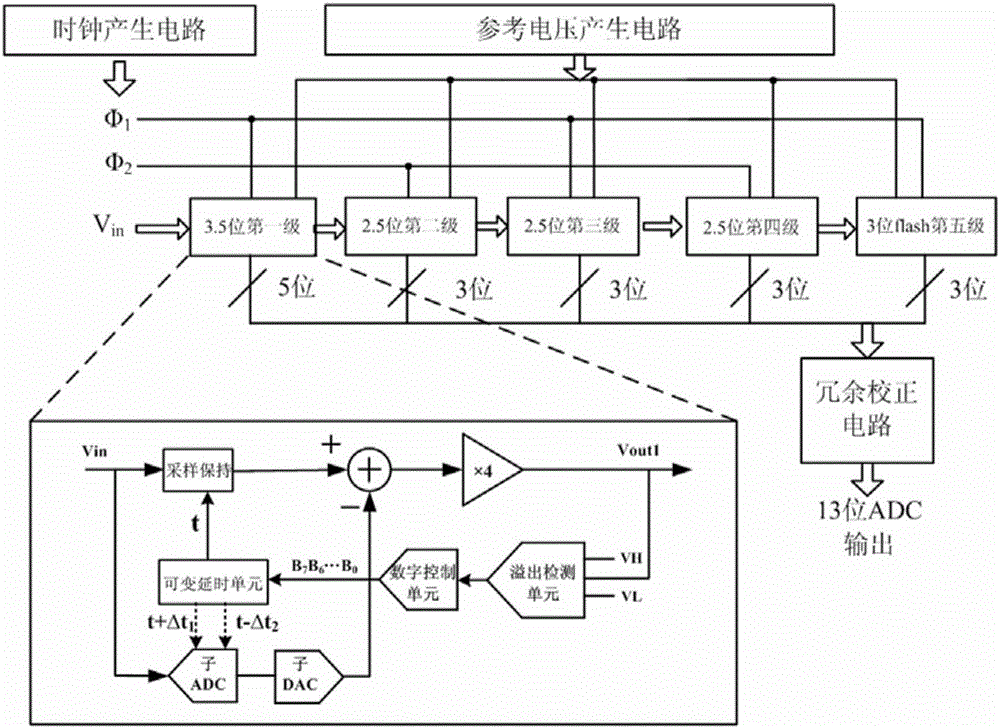
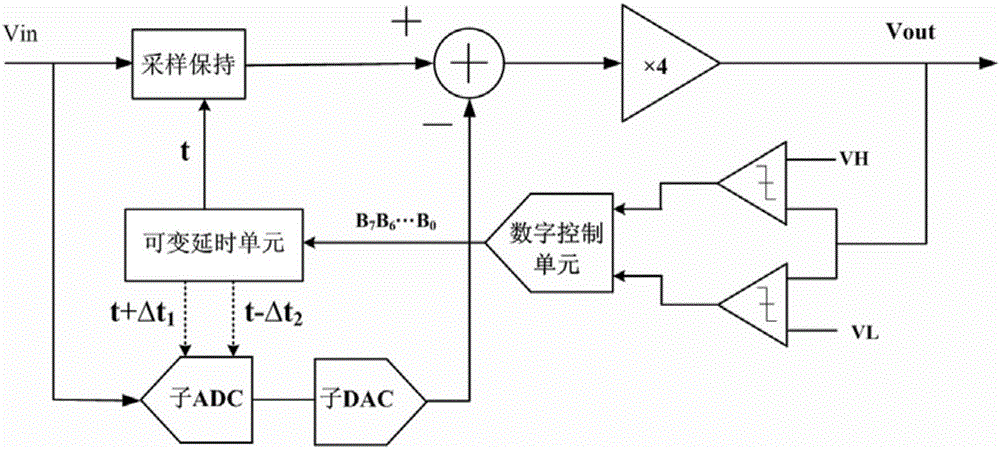
12-bit high speed streamline analog-to-digital converter with background calibration function
InactiveCN105024697AReduce power consumptionGood high frequency performanceAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingDigital down converterVoltage reference
The invention discloses a 12-bit high speed streamline analog-to-digital converter with a background calibration function. The 12-bit high speed streamline analog-to-digital converter with a background calibration function utilizes a sample hold circuit structure without a front end and the whole streamline has five levels, wherein the first streamline level is 3.5-bit; the second streamline level to the fourth streamline level are 2.5-bit; and the fifth streamline level is 3-bit flash ADC. The 12-bit high speed streamline analog-to-digital converter with a background calibration function is featured in that in the streamline, the first streamline level utilizes a 3.5-bit MDAC structure with overflow bit and is integrated with a sampling time deviation calibration module which is used for realizing correction of the sampling time deviation of two sampling networks including an MDAC and a sub ADC; besides, the analog-to-digital converter also includes a reference voltage generation circuit which is used for providing stable reference voltage for each streamline level, a clock generation circuit which is used for providing a accurate clock for each streamline level, and a redundancy correction circuit for misalignment addition of output coding. The 12-bit high speed streamline analog-to-digital converter with a background calibration function of the invention has the advantages of being low in power consumption, and being able to realize high speed application when the process size is small.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
1-Of-N A/D converter
InactiveUS6972702B1Power saving provisionsElectric signal transmission systemsBuck converterĆuk converter
A flash analog-to-digital converter (ADC). Each comparator of the flash ADC has an OFF-ON-OFF transfer function. For each analog value to be converted, only one comparator is in the ON condition, and the other comparators are in the OFF condition. In this way, the average power consumption of the flash ADC is much less than the average power consumption of prior similar devices.
Owner:HRL LAB
Feedback DAC chopper stabilization in a CT single-ended multi-bit sigma delta ADC
ActiveUS7227481B2Reduce flicker noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionDigital feedbackEngineering
A multi-bit sigma-delta analog-to-digital converter (ADC) has a single-ended input for receiving an analog input signal. A multi-bit feedback current digital-to-analog converter (IDAC) generates a multi-level feedback current depending on a multibit digital feedback signal from a Flash ADC. The feedback current is summed with the input signal with the feedback current. The summed signal is integrated on a continuous-time basis. The IDAC is selectively connectable to the summing node via a first path and a second path. The first path transmits current from the IDAC to the summing node with a first polarity and the second path transmits current from the IDAC to the summing node with an inverted polarity. This can reduce flicker noise and can allow the converter to operate without any mid-scale biasing current sources.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
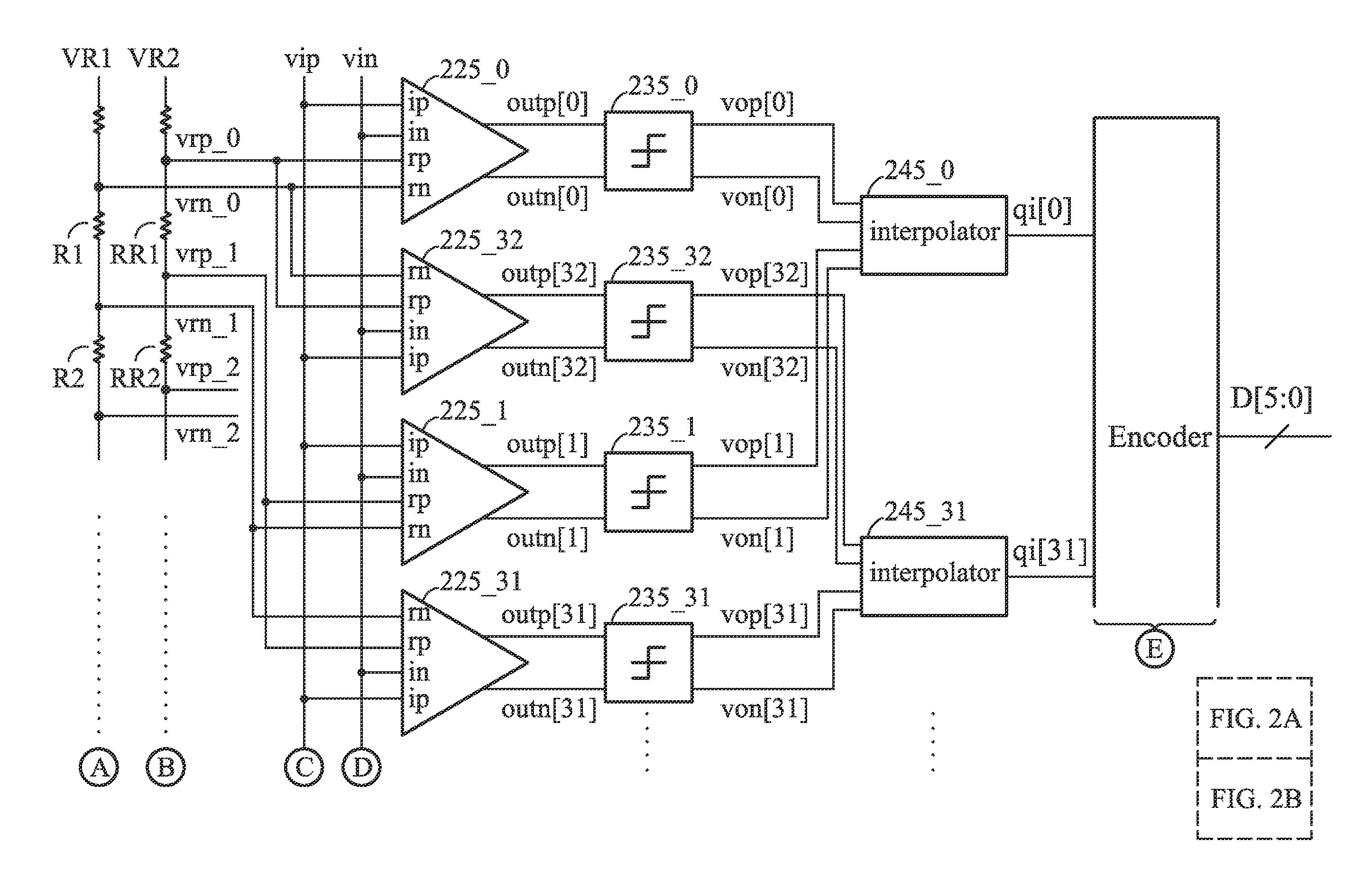
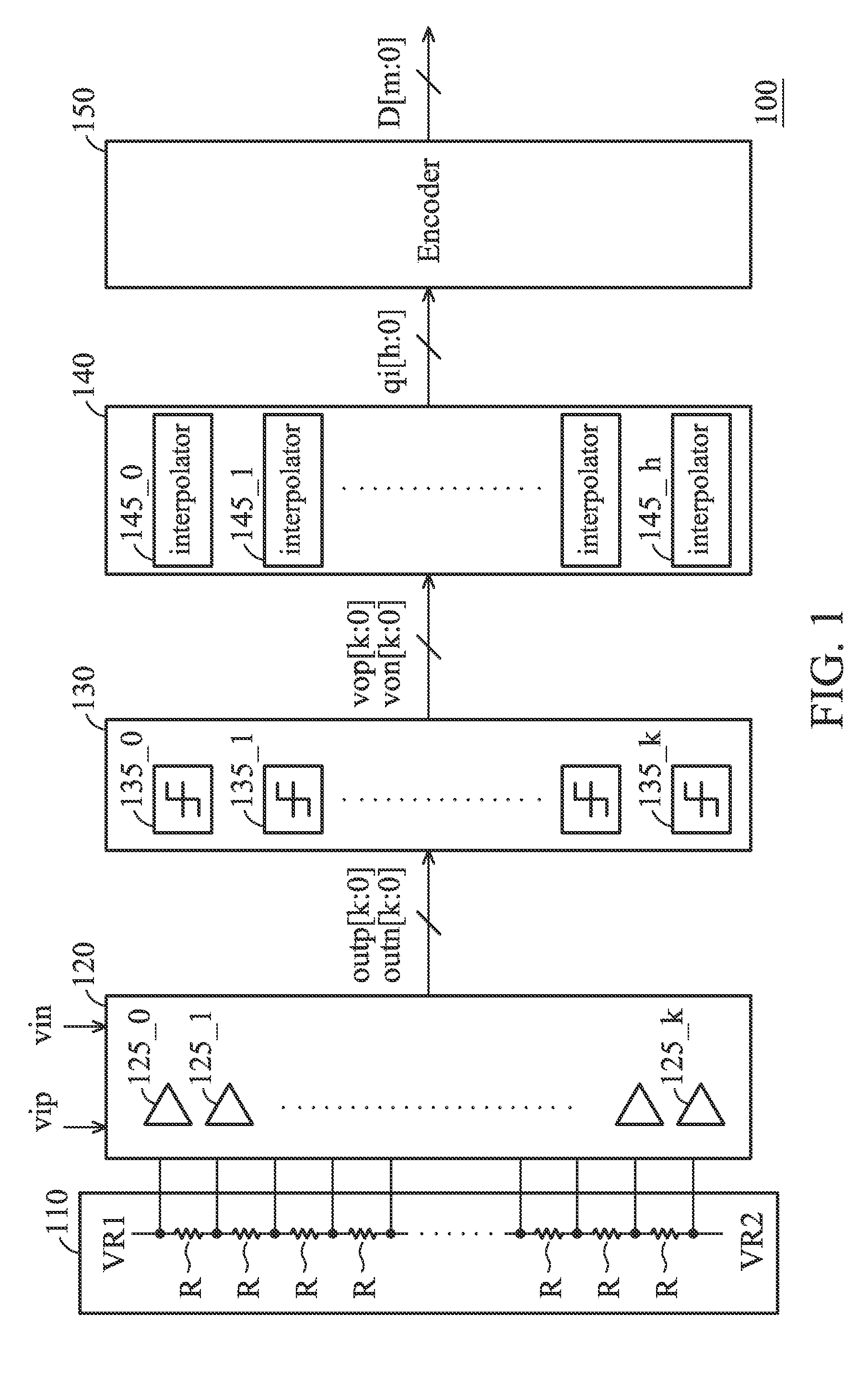
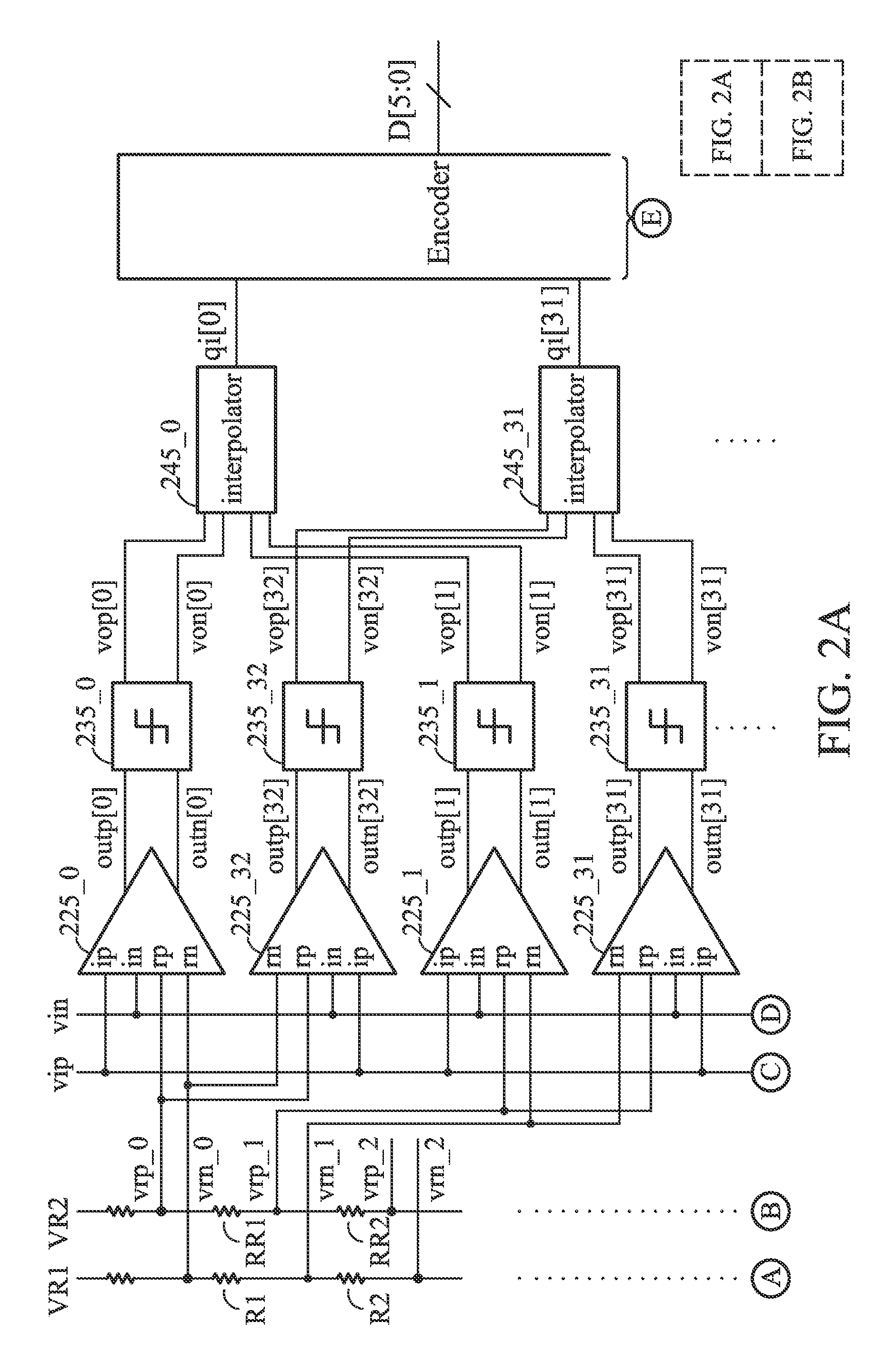
Flash ADC with interpolators
ActiveUS9467160B2Reduce in quantityElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAudio power amplifierVoltage reference
An ADC is provided. The ADC includes a plurality of pre-amplifiers, dynamic comparators coupled to the pre-amplifiers, interpolators and an encoder. Each pre-amplifier provides a pair of differential outputs according to a pair of differential analog signals and a first reference voltage and a second reference voltage different from the first reference voltage. Each dynamic comparator provides a first comparing signal and a second comparing signal according to the pair of differential outputs of the corresponding pre-amplifier. Each interpolator provides an interpolating signal according to the first and second comparing signals of two of the dynamic comparators. The encoder provides a digital output according to the interpolating signals. The first and second comparing signals are the same in a reset phase, and the first and second comparing signals are complementary according to the pair of differential outputs of the corresponding pre-amplifier in an evaluation phase.
Owner:MEDIATEK INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com