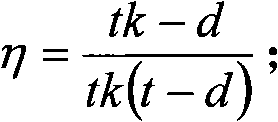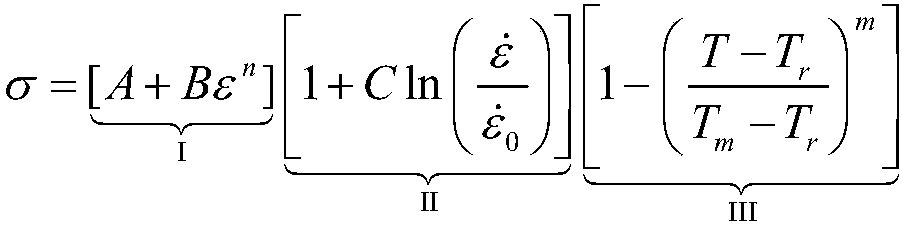Patents
Literature
133 results about "Flow stress" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
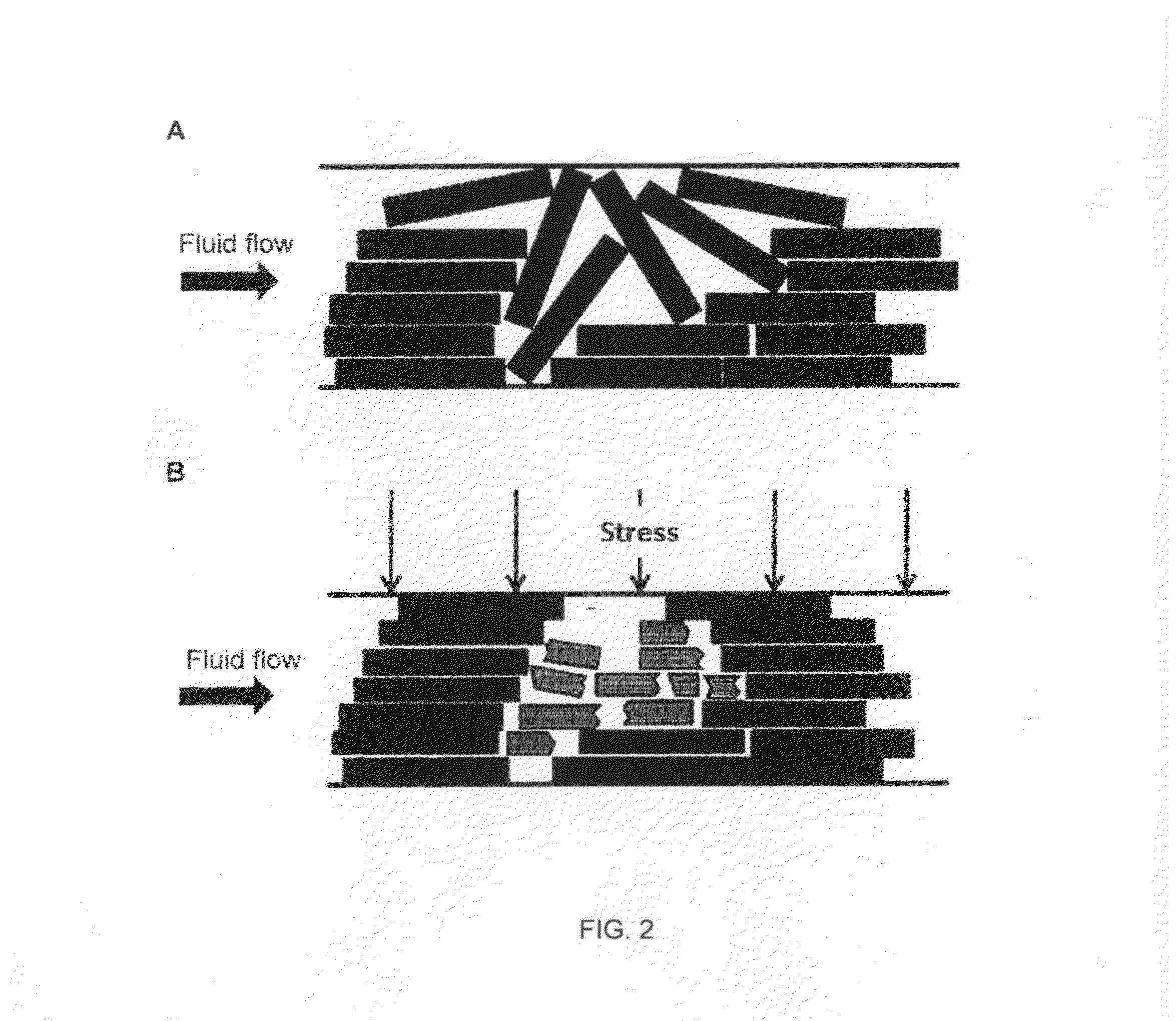
Flow stress is defined as the instantaneous value of stress required to continue plastically deforming the material - to keep the metal flowing. Hence, Flow stress can also be defined as the stress required to sustain plastic deformation at a particular strain.
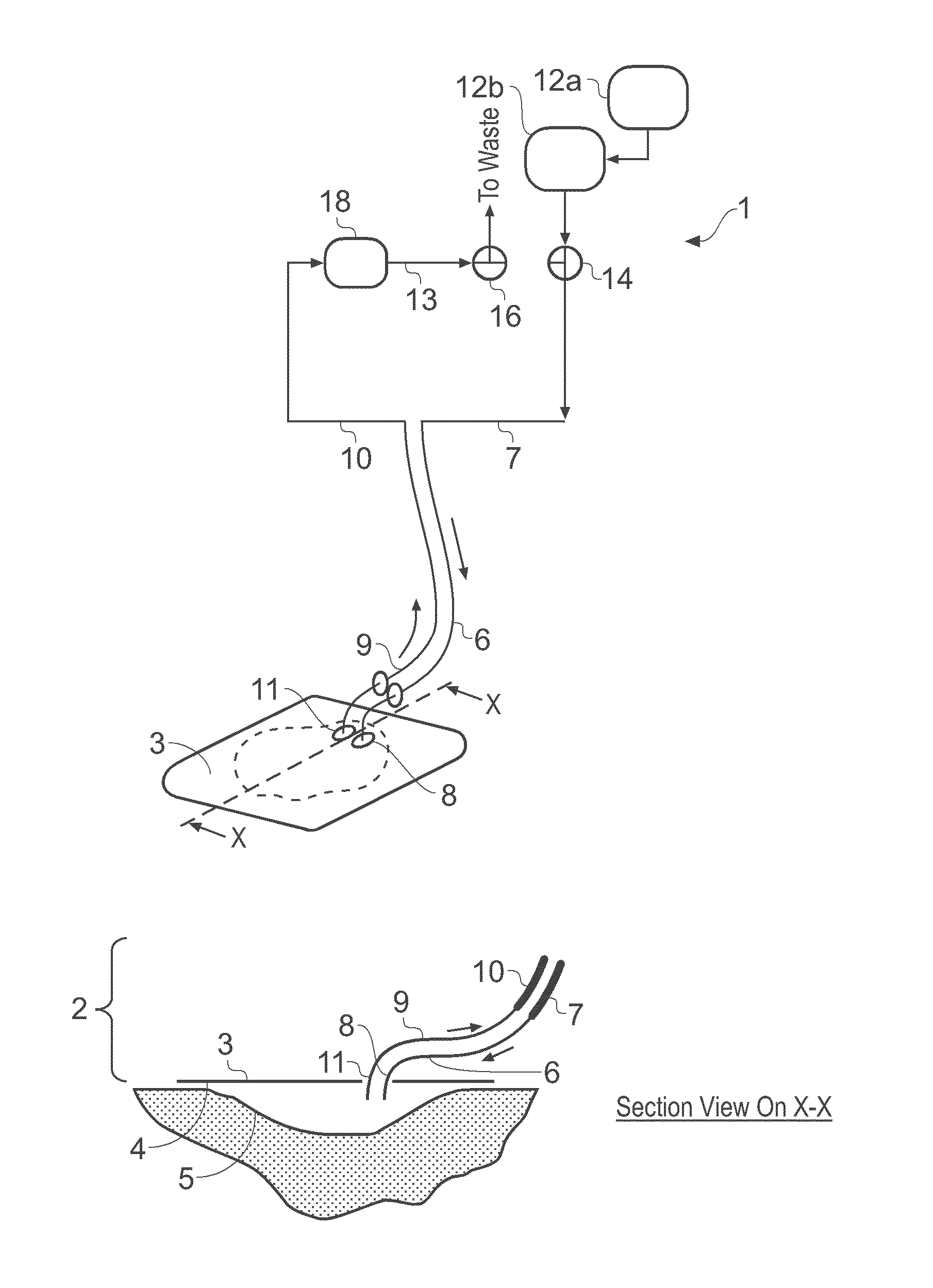
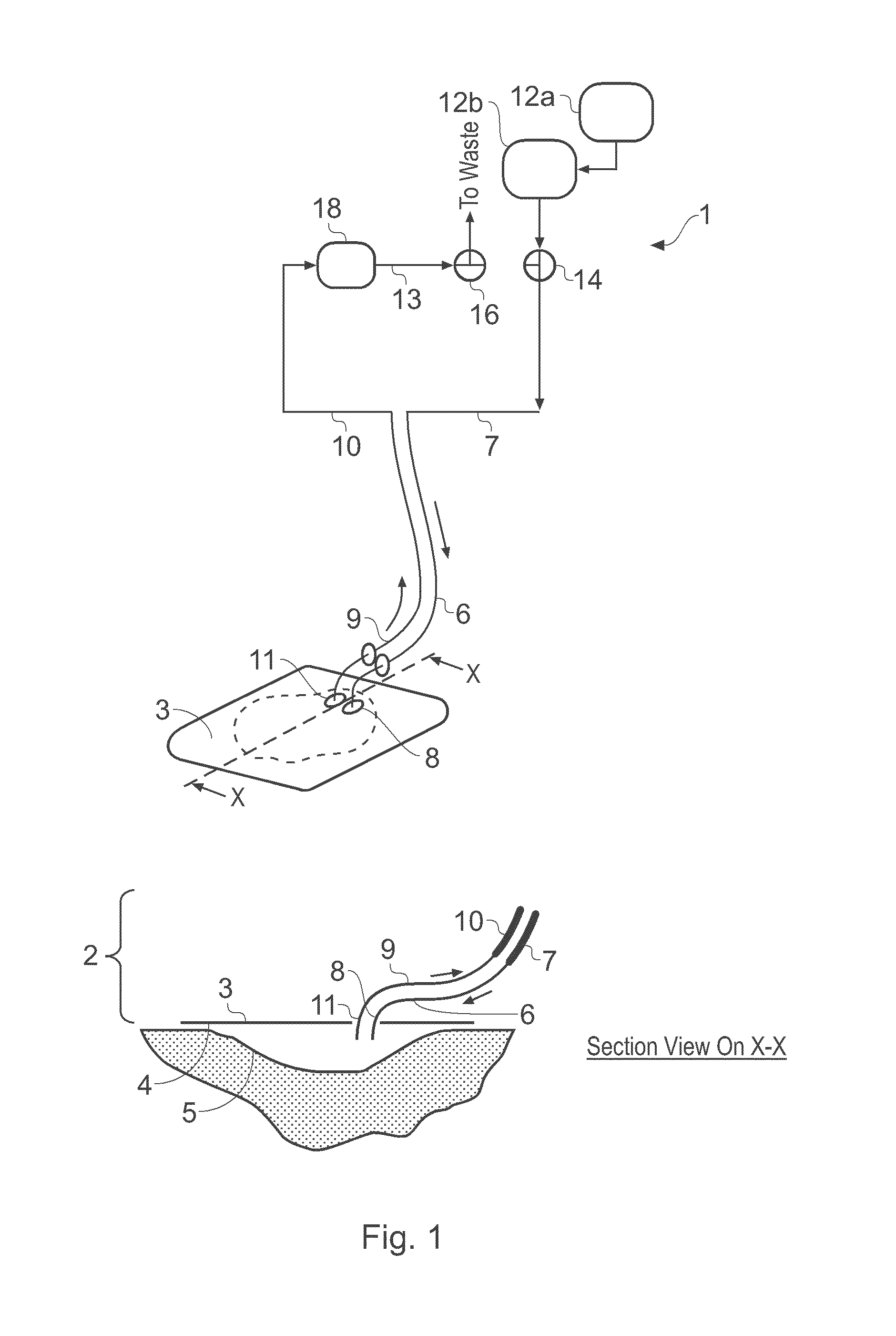
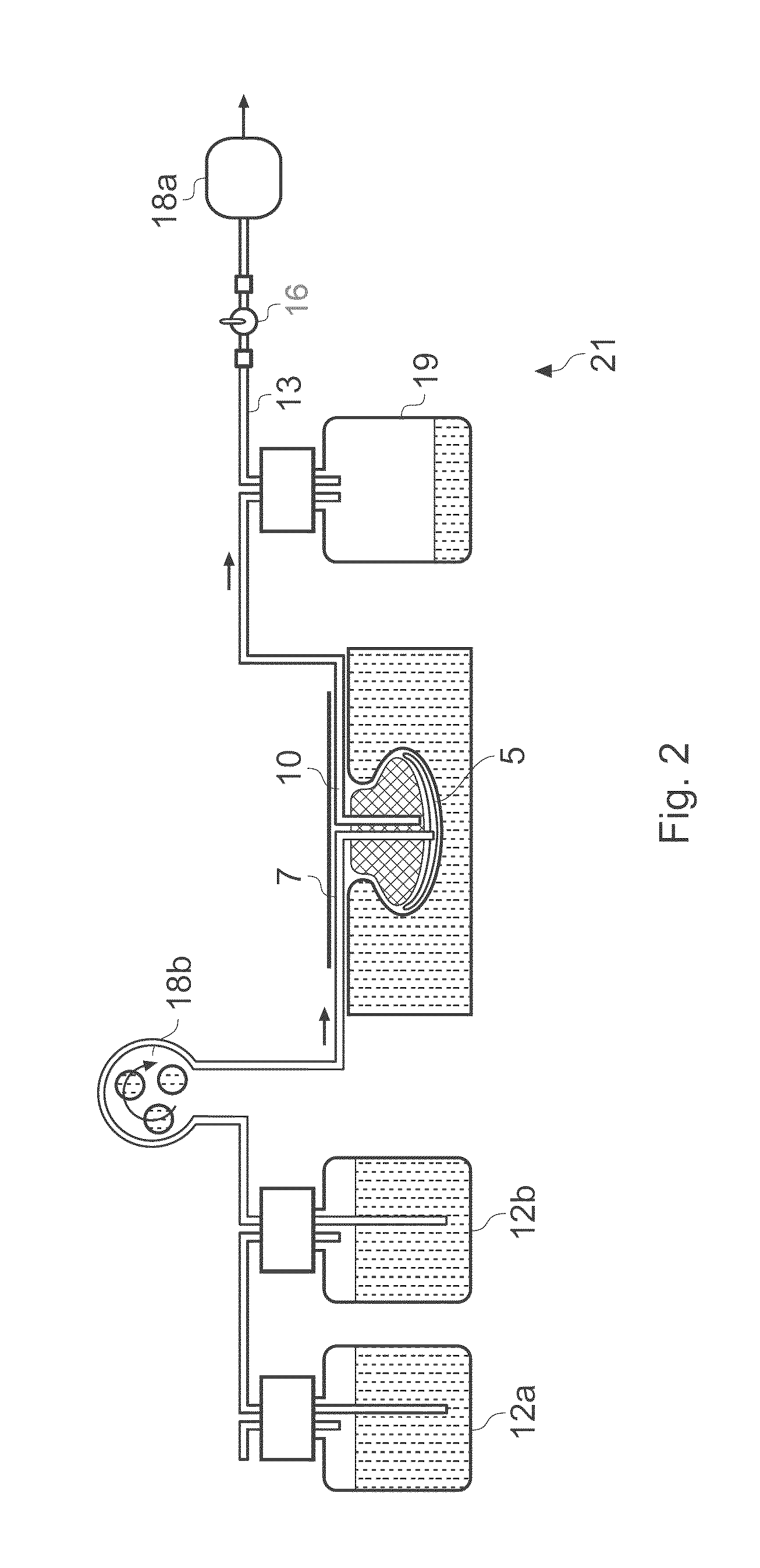
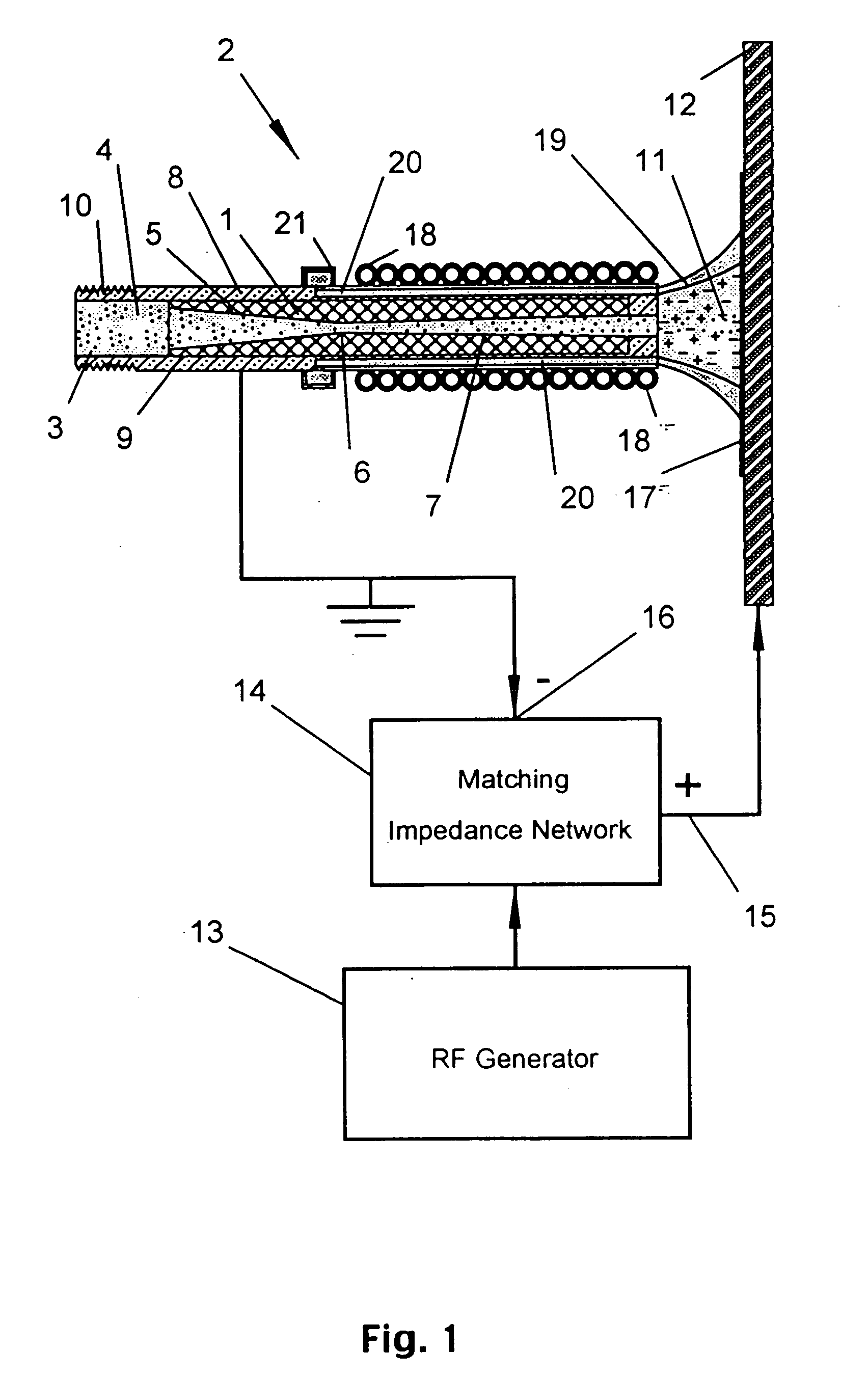
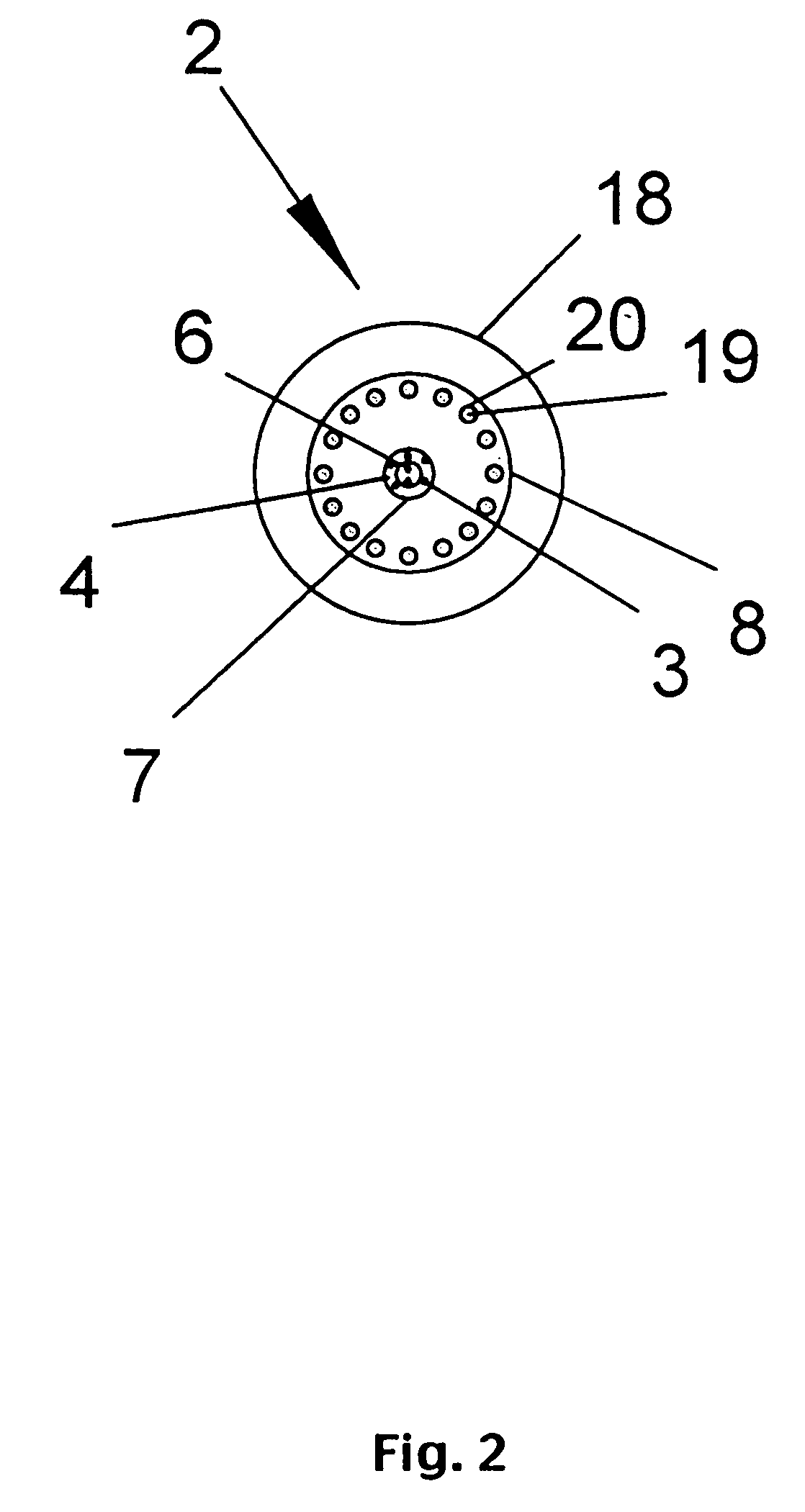
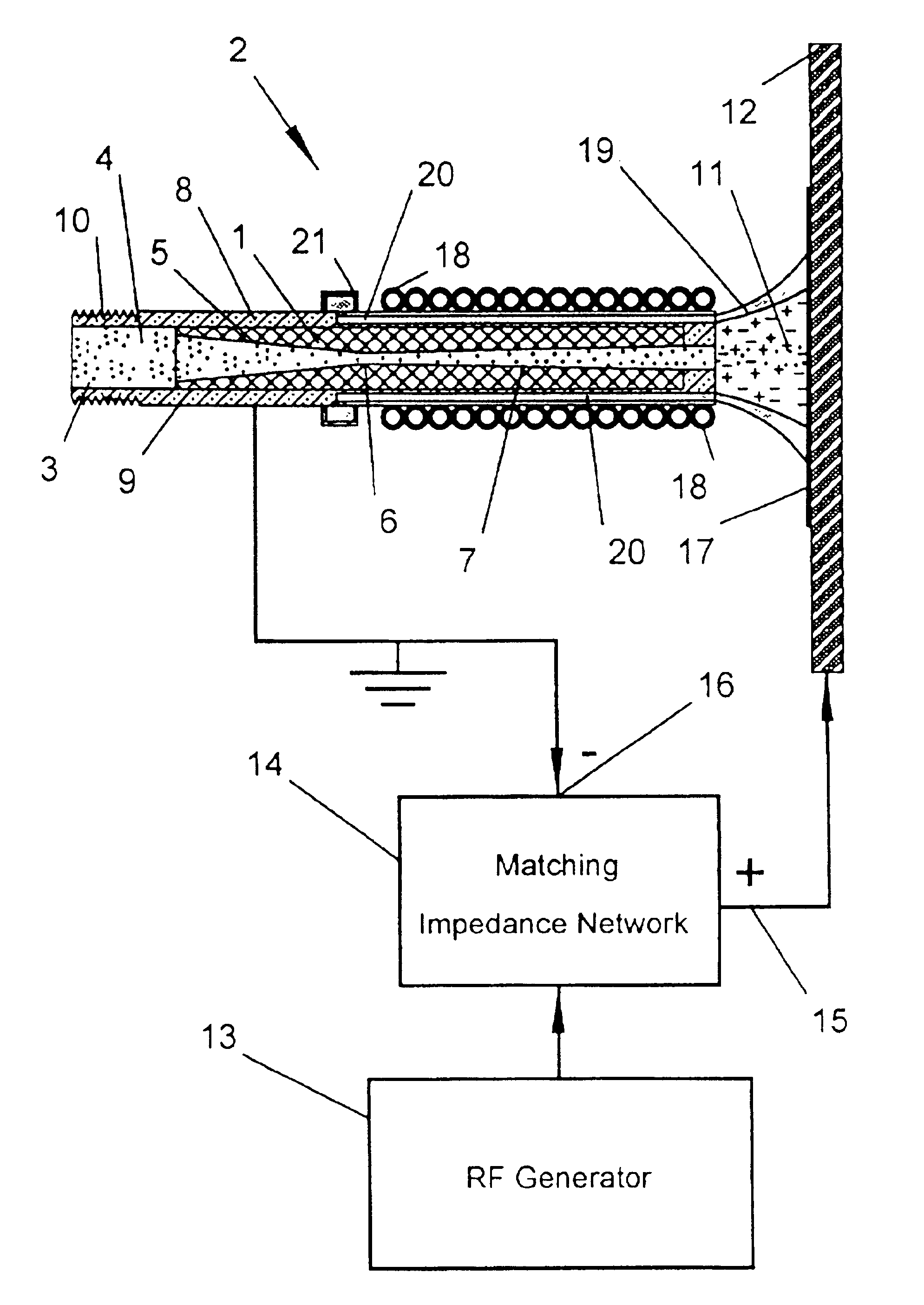
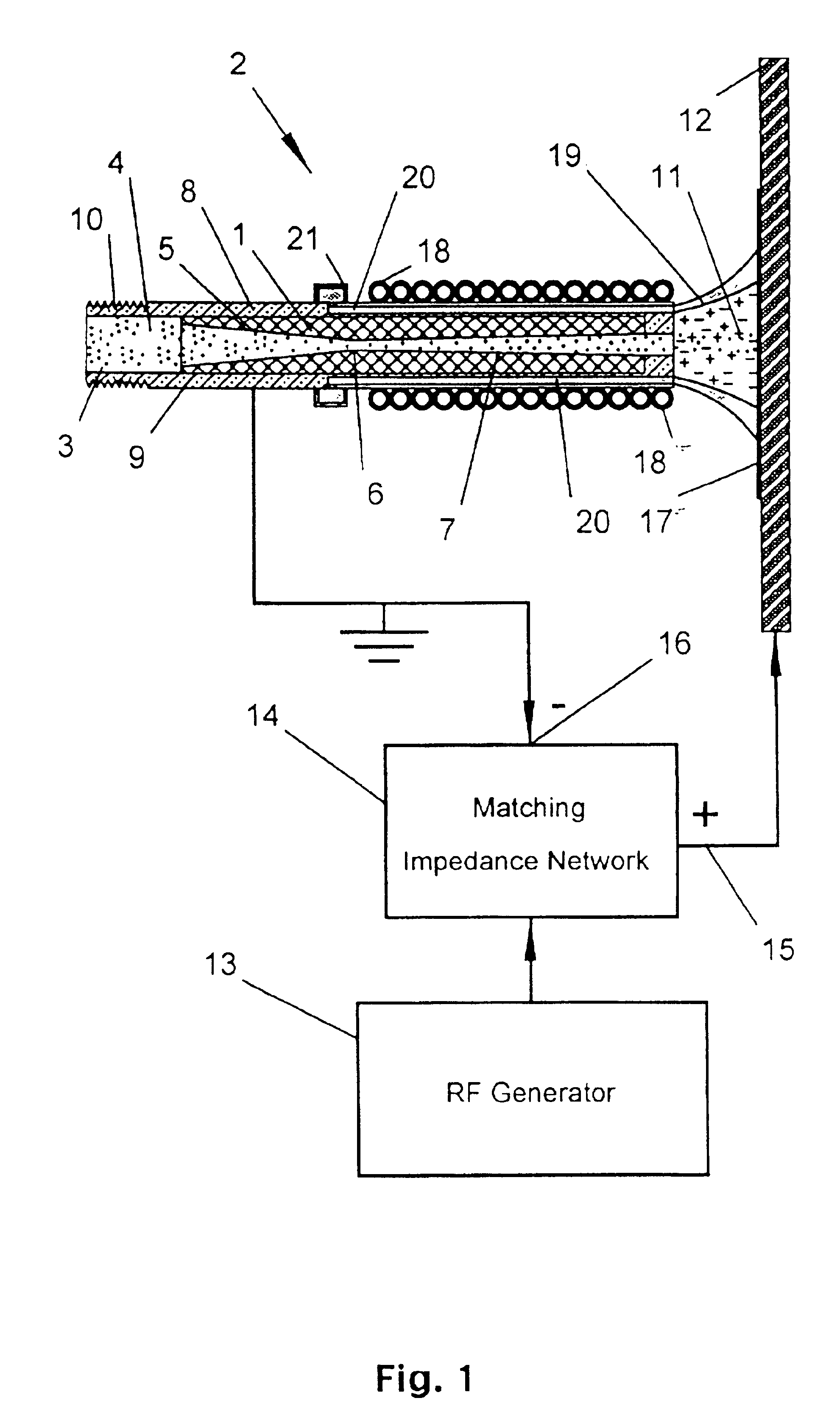
Wound treatment apparatus and method
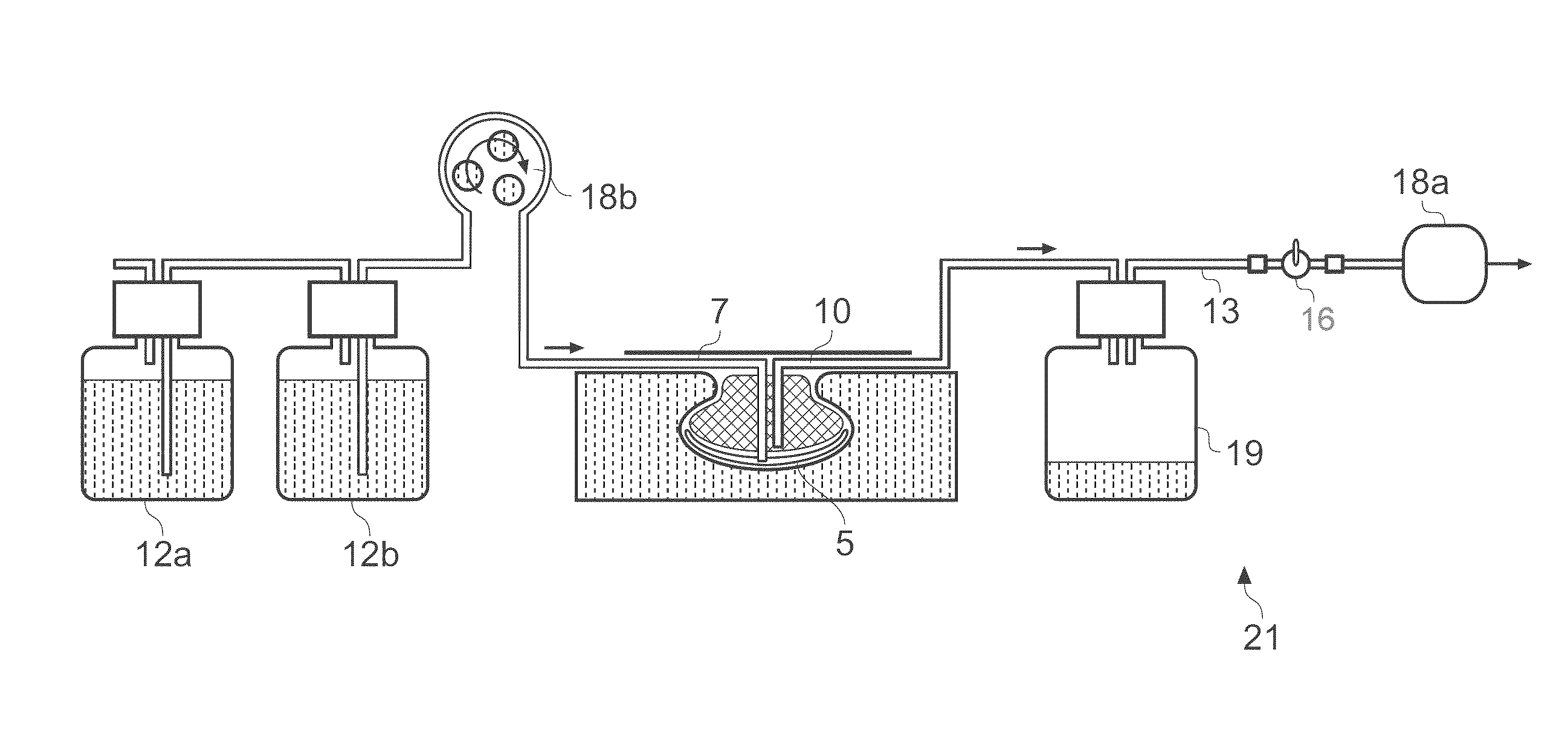
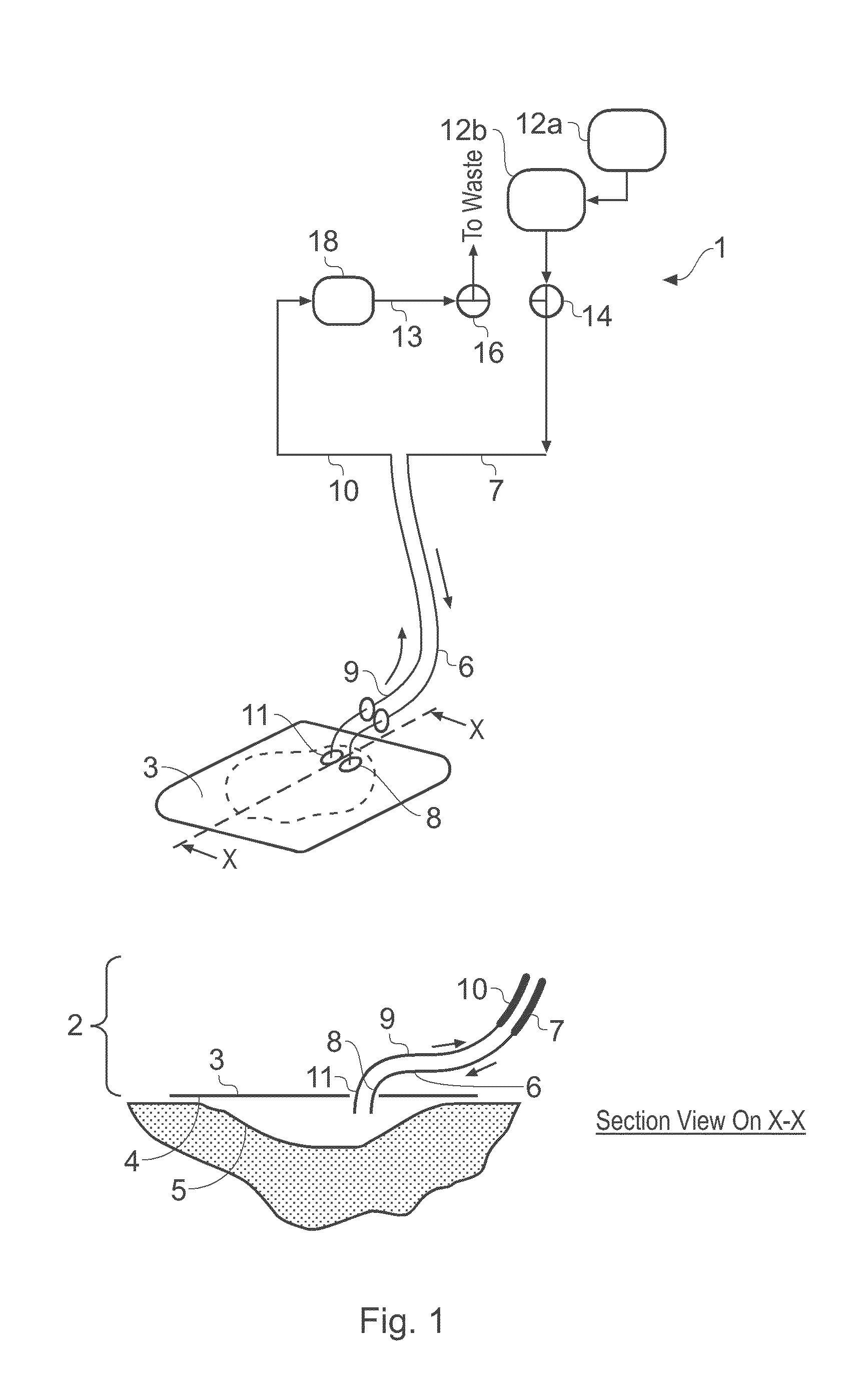
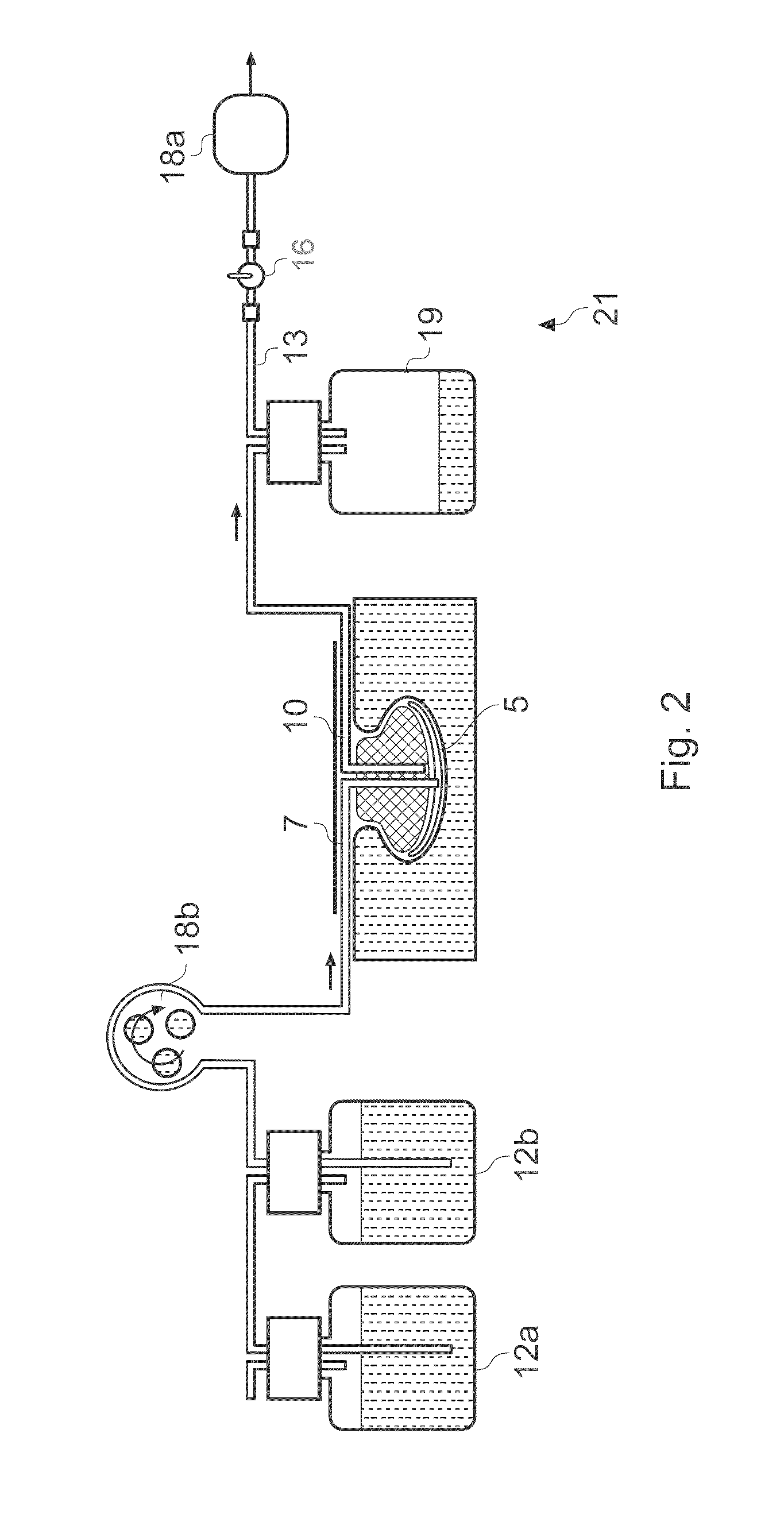
ActiveUS8529548B2Promote wound healingReduce bacterial loadCannulasInfusion devicesFlow stressThermal energy
An apparatus and method for aspirating, irrigating and / or cleansing wounds is provided. The apparatus and method include one or more of the following: simultaneous aspiration and irrigation of the wound, supplying of thermal energy to fluid circulated through the wound; supplying physiologically active agents to the wound; a biodegradable scaffold in contact with the wound bed; and application of stress or flow stress to the wound bed.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
System and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of high velocity powder particles using thermal plastic deformation
InactiveUS20050153069A1Reduced strengthEnhanced dynamic recovery of dislocation densityLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingFlow stressAcoustic wave
The invention relates to an apparatus and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of powder particles entrained in a subsonic or sonic gas jet onto the surface of an object. Under high velocity impact and thermal plastic deformation, the powder particles adhesively bond to the substrate and cohesively bond together to form consolidated materials with metallurgical bonds. The powder particles and optionally the surface of the object are heated to a temperature that reduces yield strength and permits plastic deformation at low flow stress levels during high velocity impact, but which is not so high as to melt the powder particles.
Owner:INNOVATION TECH INC
System and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of high velocity powder particles using thermal plastic deformation
InactiveUS6915964B2Modulus is reducedLower yield strengthMolten spray coatingSurface layering apparatusFlow stressAcoustic wave
The invention relates to an apparatus and process for solid-state deposition and consolidation of powder particles entrained in a subsonic or sonic gas jet onto the surface of an object. Under high velocity impact and thermal plastic deformation, the powder particles adhesively bond to the substrate and cohesively bond together to form consolidated materials with metallurgical bonds. The powder particles and optionally the surface of the object are heated to a temperature that reduces yield strength and permits plastic deformation at low flow stress levels during high velocity impact, but which is not so high as to melt the powder particles.
Owner:INNOVATION TECH INC
Alpha-beta type titanium alloy
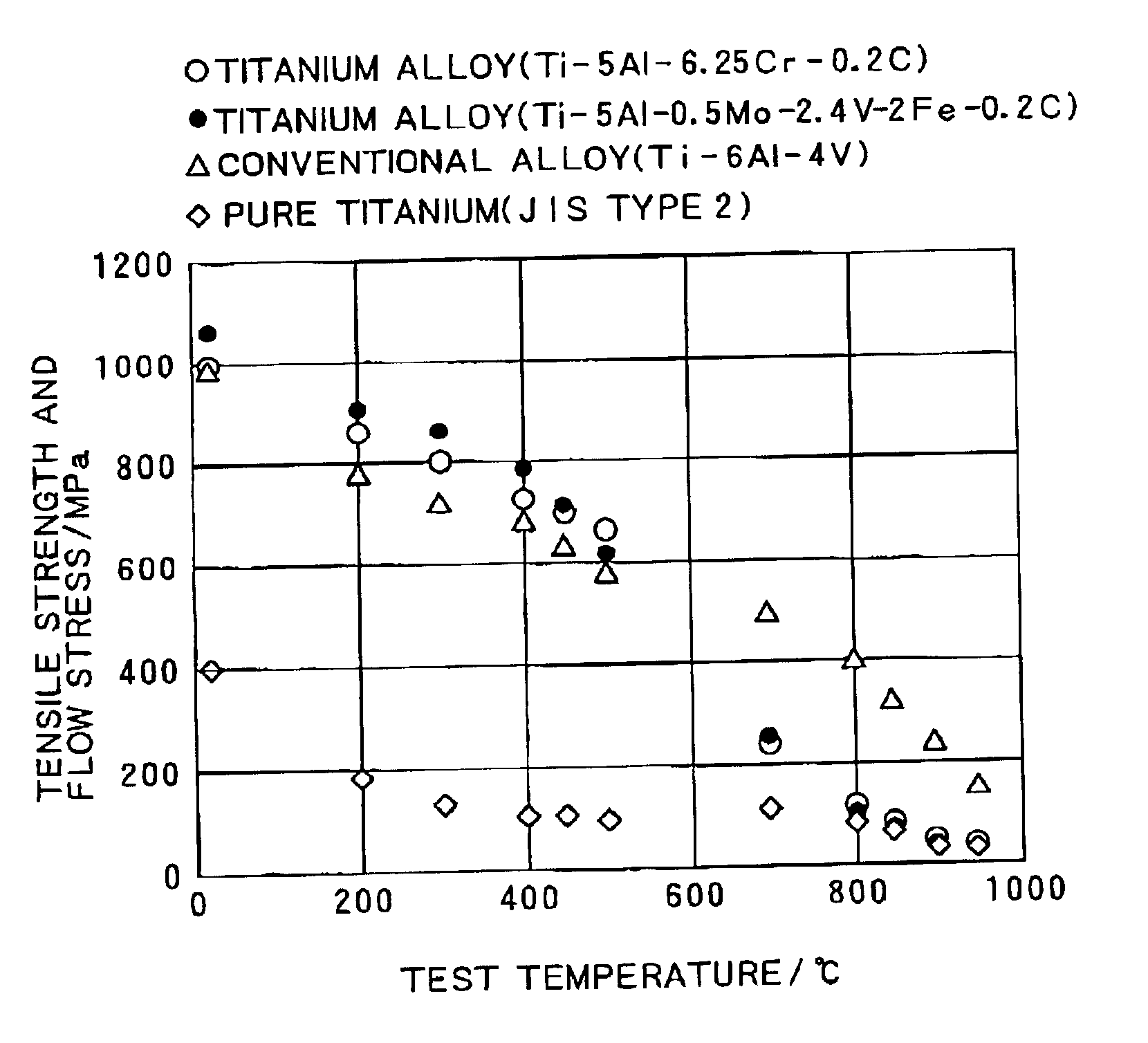
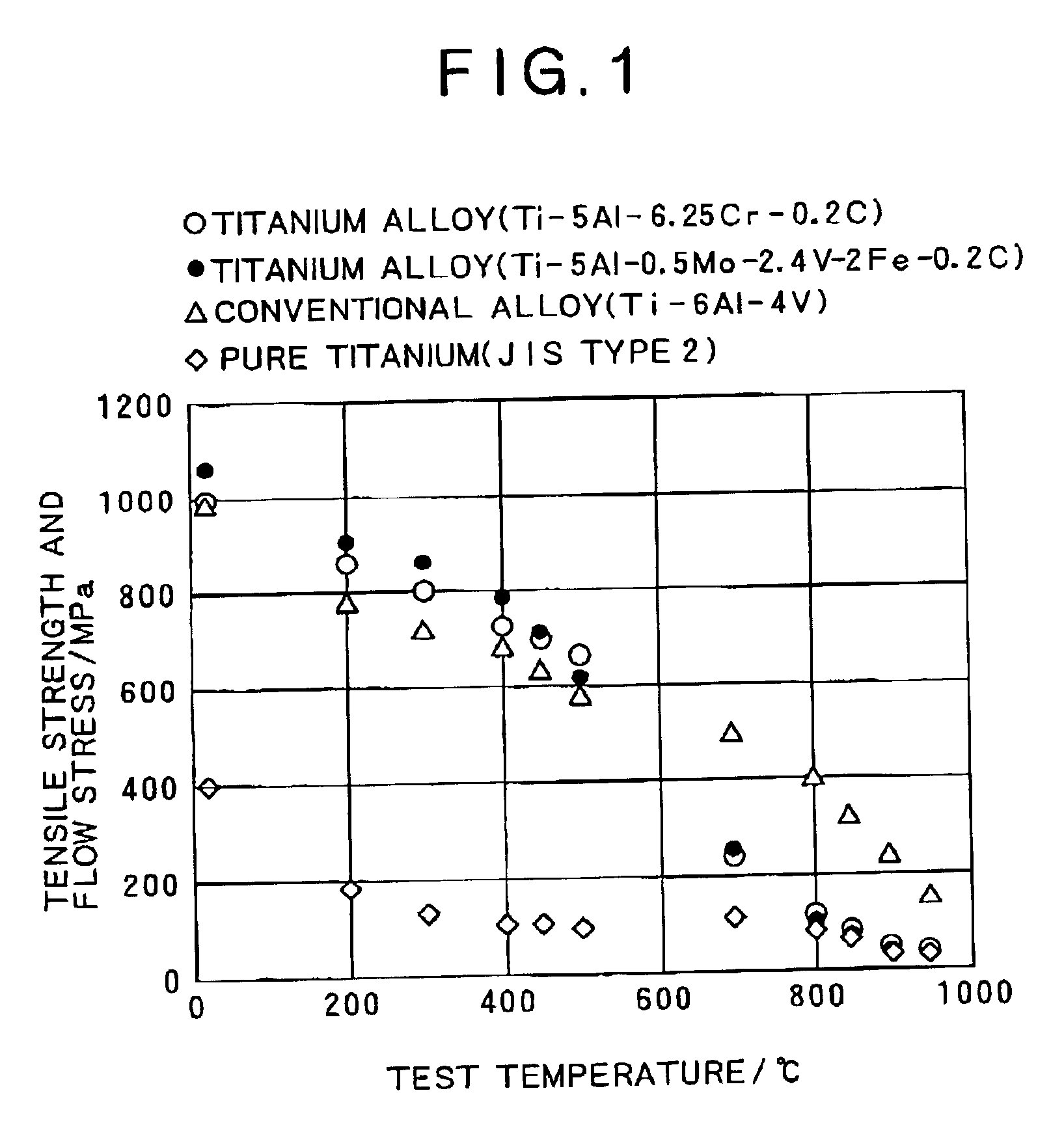
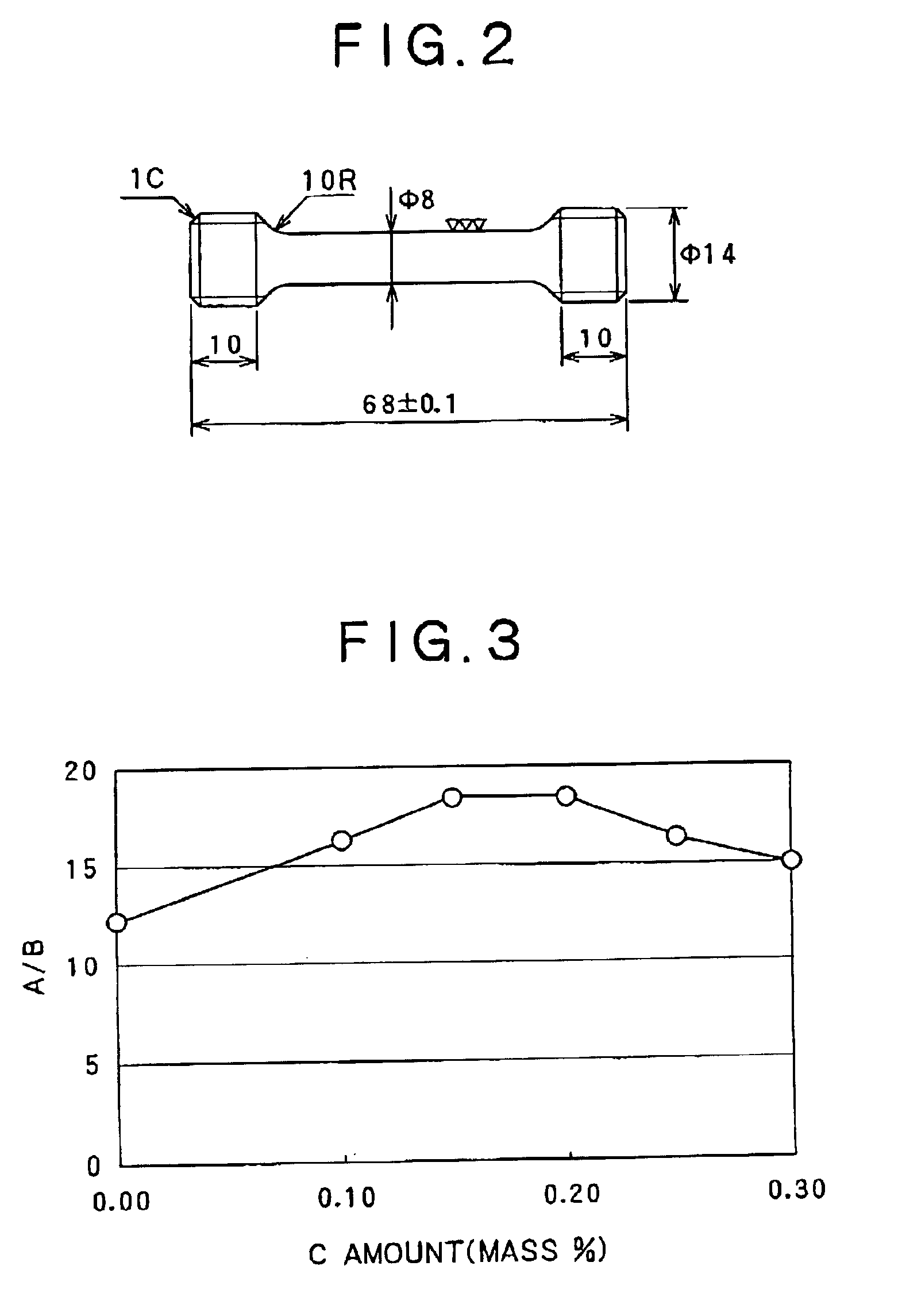
There is provided an α-β type titanium alloy having a normal-temperature strength equivalent to, or exceeding that of a Ti-6Al-4V alloy generally used as a high-strength titanium alloy, and excellent in hot workability including hot forgeability and subsequent secondary workability, and capable of being hot-worked into a desired shape at a low cost efficiently. There is disclosed an α-β type titanium alloy having high strength and excellent hot workability wherein 0.08-0.25% C is contained, the tensile strength at room temperature (25° C.) after annealing at 700° C. is 895 MPa or more, the flow stress upon greeble test at 850° C. is 200 MPa or less, and the tensile strength / flow stress ratio is 9 or more. A particularly preferred α-β type titanium alloy comprises 3-7% Al and 0.08-025% C as α-stabilizers, and 2.0-6.0% Cr and 0.3-1.0% Fe as β-stabilizers.
Owner:KOBE STEEL LTD
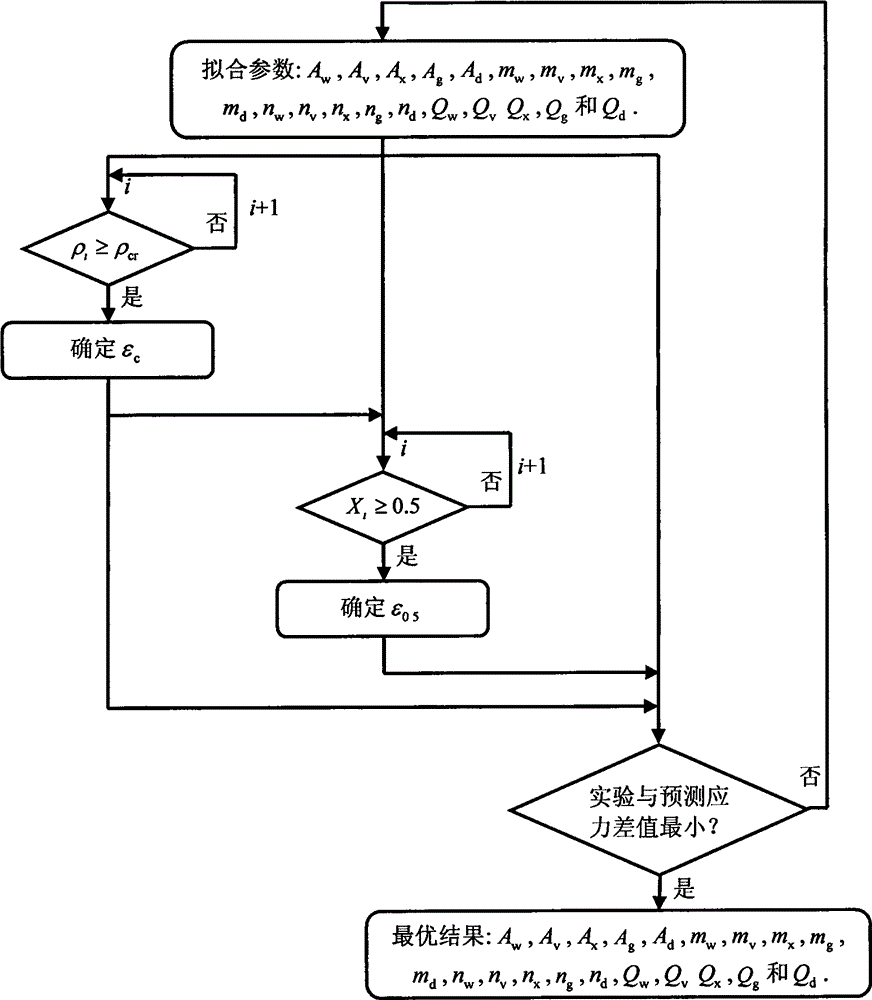
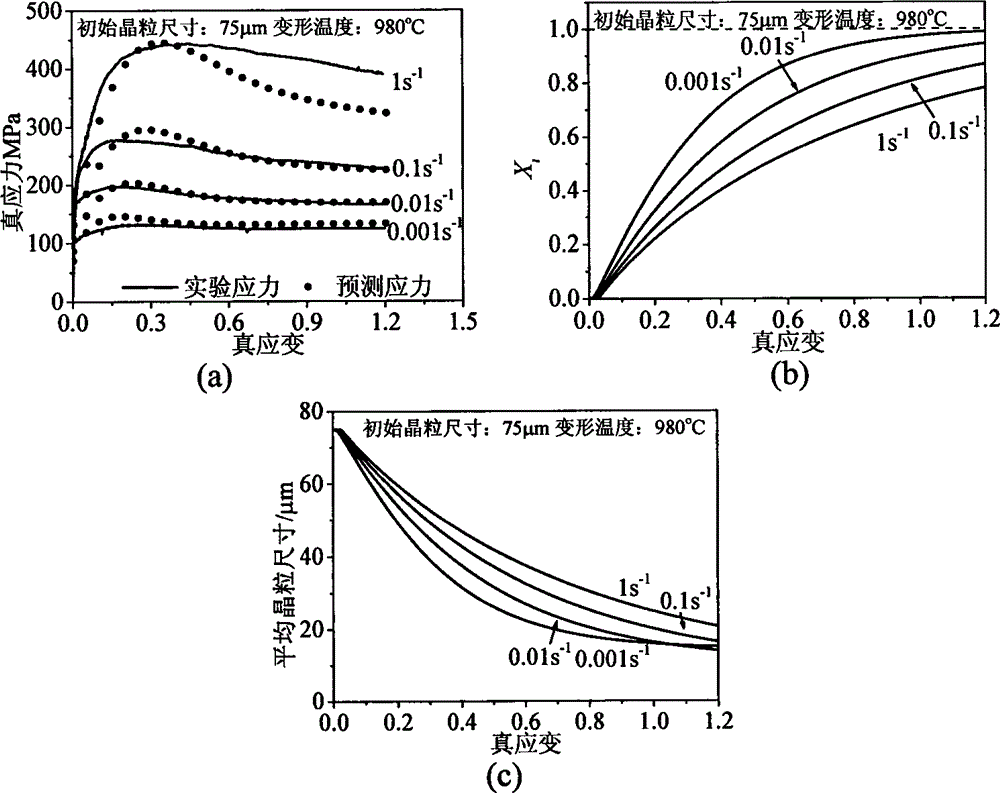
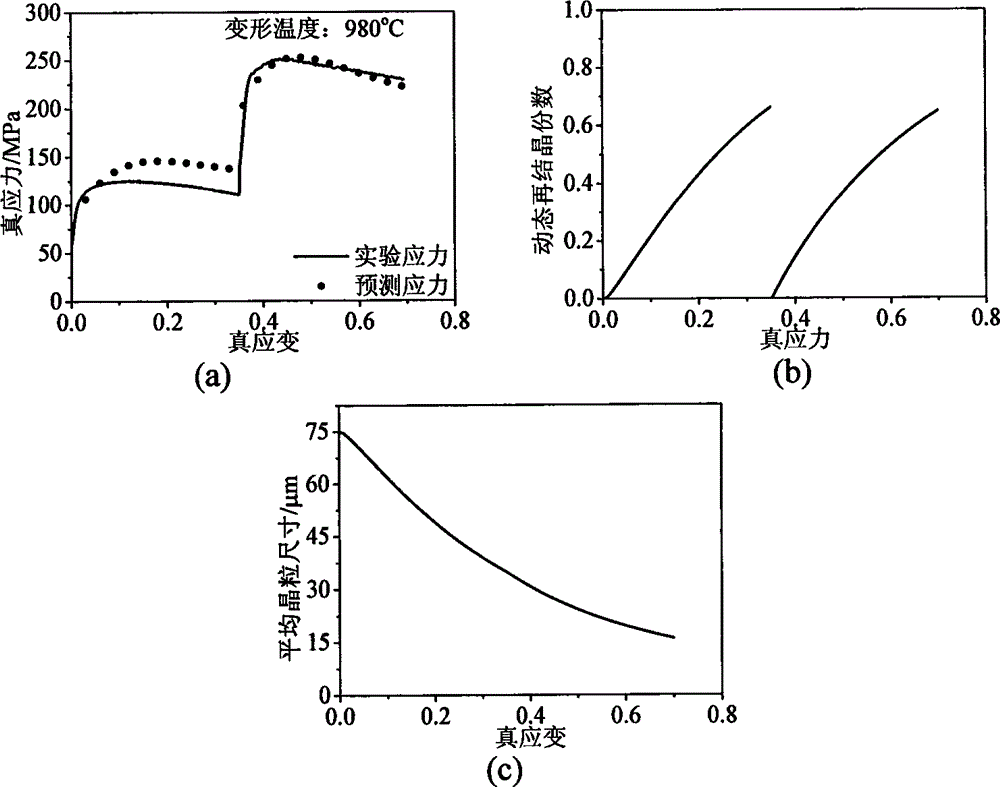
Method for predicting nickel base alloy high temperature flow stress and dynamic recrystallization behavior
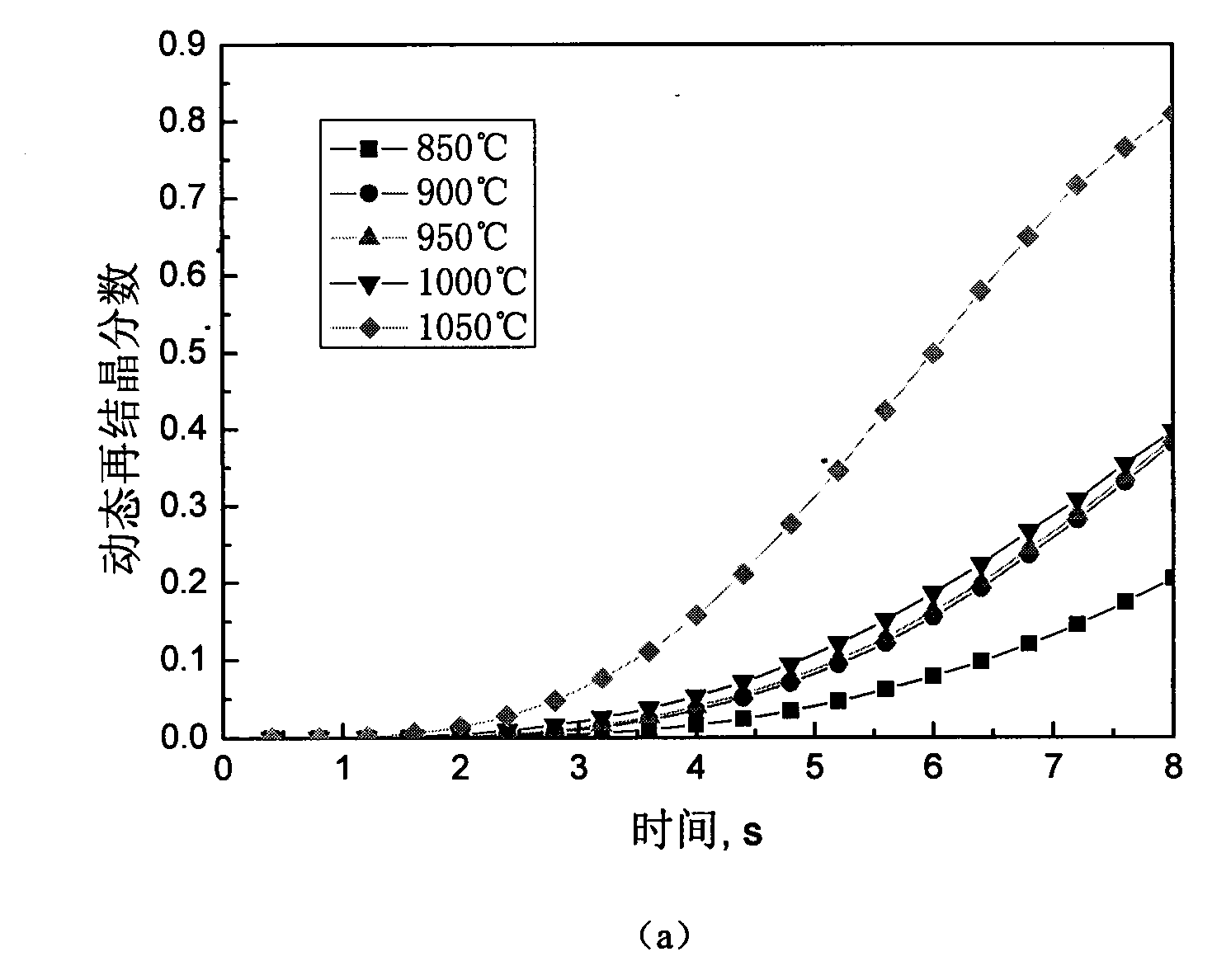
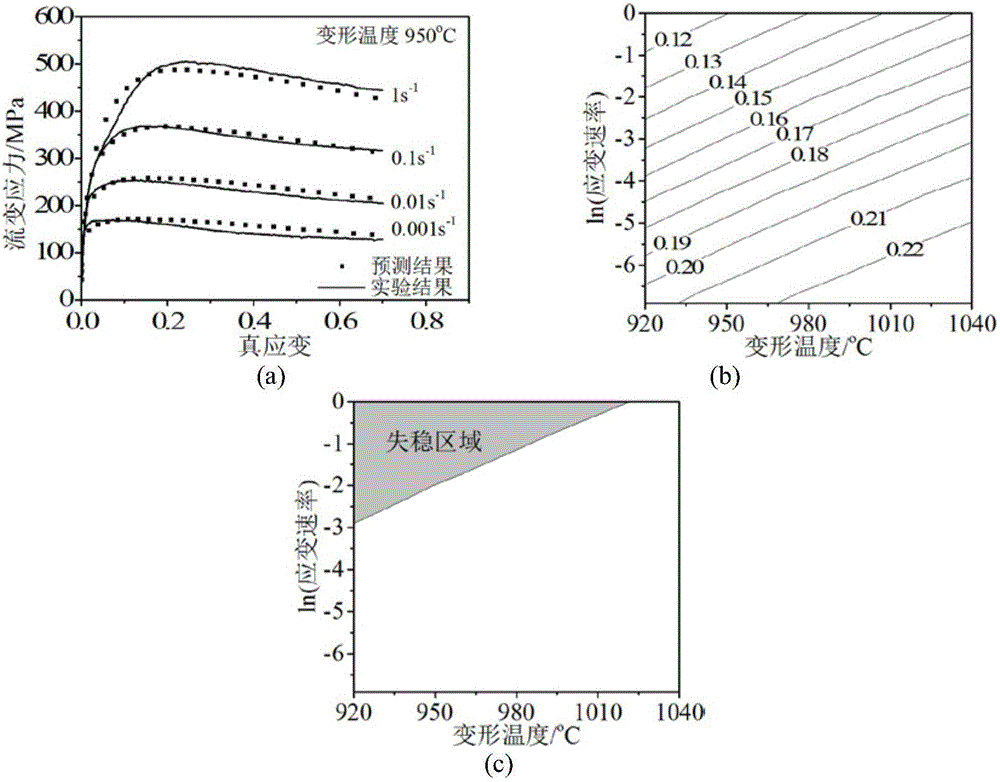
The invention discloses a method for predicting nickel base alloy high temperature flow stress and a dynamic recrystallization behavior. The method comprises the following steps: 1 obtaining true stress-true strain data of nickel base alloy by means of high temperature compression tests; 2 establishing a unified constructive model for predicting the nickel base alloy high temperature flow stress and the dynamic recrystallization behavior; 3 utilizing the numerical value difference principle, writing an iterative accumulation algorithm program, inserting numerical value simulation software, and by combining the true stress-true strain data of the nickel base alloy, determining material parameters of the unified constructive model for predicting the nickel base alloy high temperature flow stress and the dynamic recrystallization behavior; 4 predicting the nickel base alloy high temperature flow stress and the dynamic recrystallization behavior under the constant temperature and constant strain rate condition as well as under the variable temperature and variable strain rate condition. By means of the method, the nickel base alloy high temperature flow stress and the dynamic recrystallization behavior under the constant temperature and constant strain rate condition as well as under the variable temperature and variable strain rate condition can be predicted rapidly and accurately, and important technical guidance significance for formulating the nickel base alloy hot working process reasonably is achieved.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
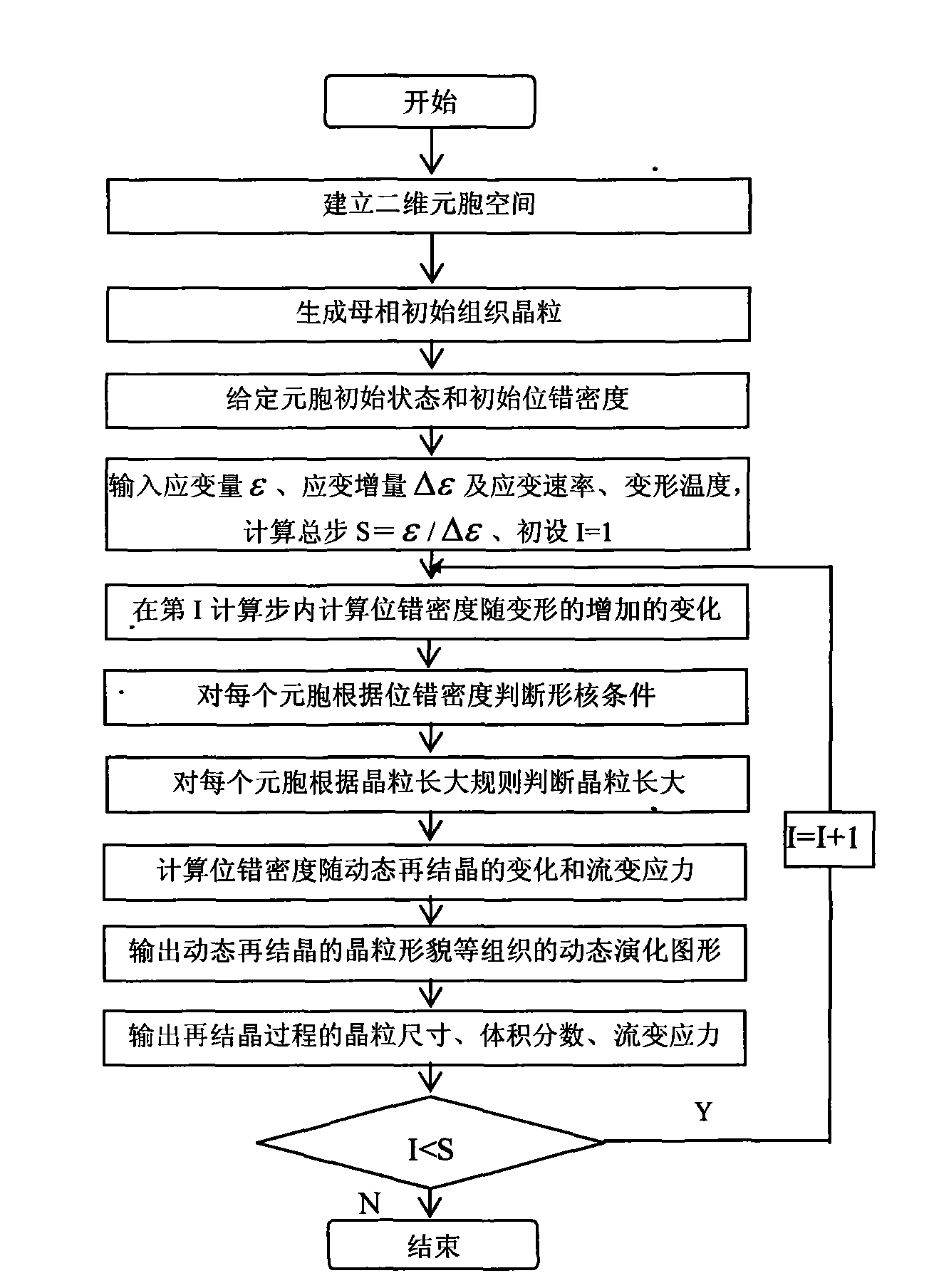
Method for predicting structure evolution of austenite dynamic recrystallization in thermal deformation of plate-strip steel
InactiveCN101591729AAccelerate development cycleQuantitativeHeat treatment process controlFlow stressCellular automation
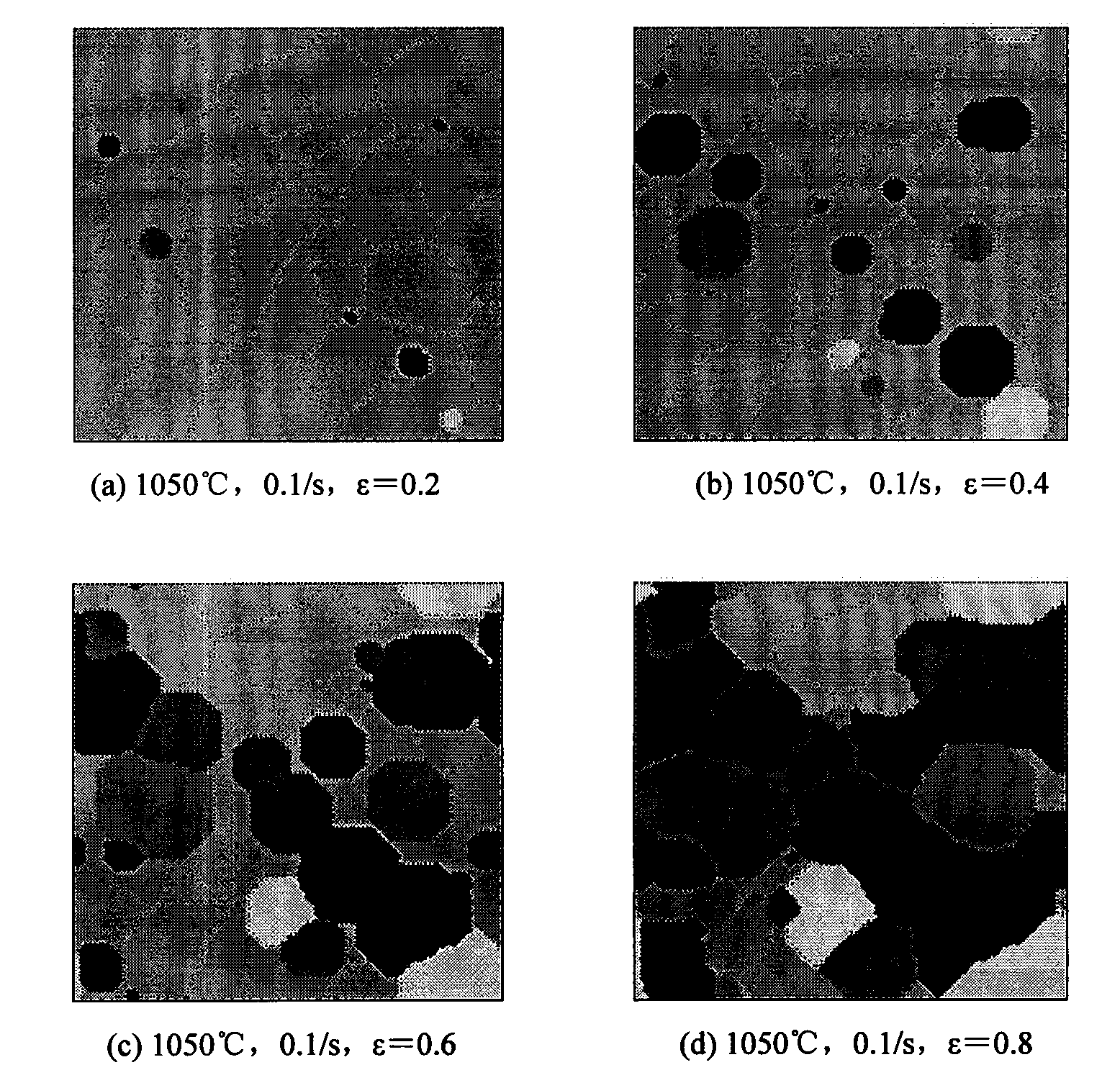
The invention relates to a method for predicting structure evolution of austenite dynamic recrystallization in thermal deformation of plate-strip steel, which belongs to the technical field of steel rolling. The method achieves the predictions of the transformed fraction, the grain size, the grain morphology and the flow stress of dynamic recrystallization by establishing a dynamic recrystallization physical metallurgical model and a dynamic recrystallization cellular automation model. The method achieves the reproduction of the structure evolution of a metal forming process by a computer, not only can save the experimental cost, but also can accelerate the development cycle of a new type of steel. The developed method for predicting the structure evolution of the austenite dynamic recrystallization in the thermal deformation of the plate-strip steel achieves the quantitative, precise and visual descriptions of the grain morphology, the volume fraction and the grain size of the recrystallization process, and can obtain important parameters of the flow stress and the like, thus the method is significant in further analyzing the evolution law of microstructures.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Method for vacuum scattering intermetallic compound for coupling TiAL
InactiveCN101176946AImprove diffusion abilityGood removal effectNon-electric welding apparatusBeta phaseThermal deformation
The invention relates to a TiAl-intermetallic-compound vacuum diffusing connection method, belonging to the TiAl-intermetallic-compound welding field, which overcomes the technical drawbacks of high temperature of diffusing connection and high pressure of diffusing connection in the prior TiAl-intermetallic-compound diffusing connection technology. The invention adopts hydrogenated titanium or titanium alloy chaff as the interface layer of diffusing connection. Ti3Al+TiAl dual phase (Alpha2+Gamma) organ can be formed under the temperature of diffusing connection titanium, which facilitates the formation of high-intensity connector lug of TiAl-intermetallic-compound diffusing connection. And hydrogen makes the flow stress of thermal deformation of titanium or titanium alloy decrease and the thermal plasticity increase, so that hydrogenated titanium or titanium alloy is prone to deform under high temperature. Meanwhile,, the self-diffusing capacity of hydrogen in titanium or titanium alloy and the diffusing capacity of solute are enhanced, more particularly, in Beta phase the capacities are more enhanced, so that hydrogen can accelerate the diffusing of the alloy elements, reduce the atomic combination energy and the diffusing activation energy, promote the diffusing coordinated deformation capacity, and the reliable diffusing connection of connector lug of TiAl-intermetallic-compound can be realized under comparatively low temperature.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Quick isothermal forging method and device for preparing less-deformable alloy cake blank
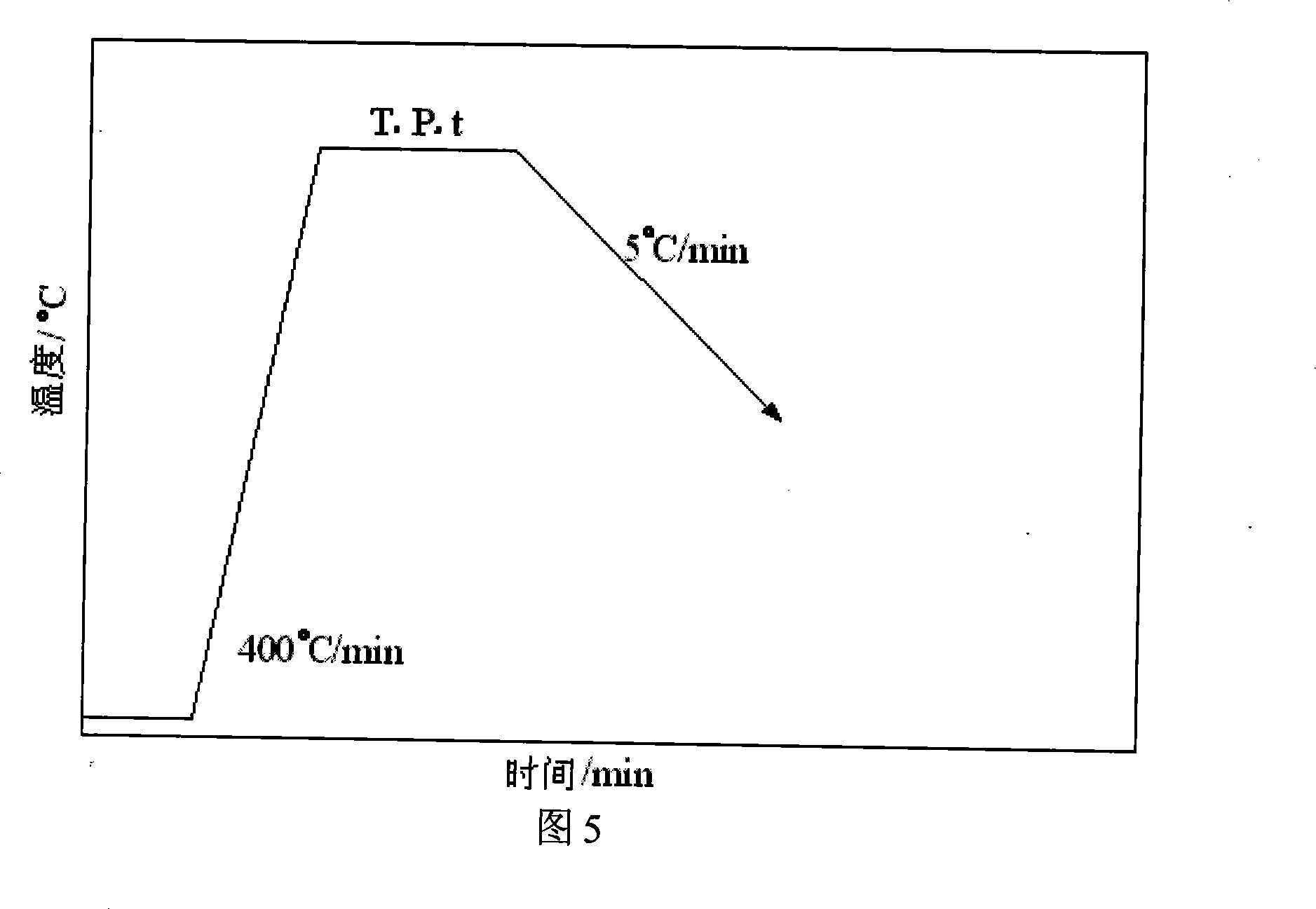
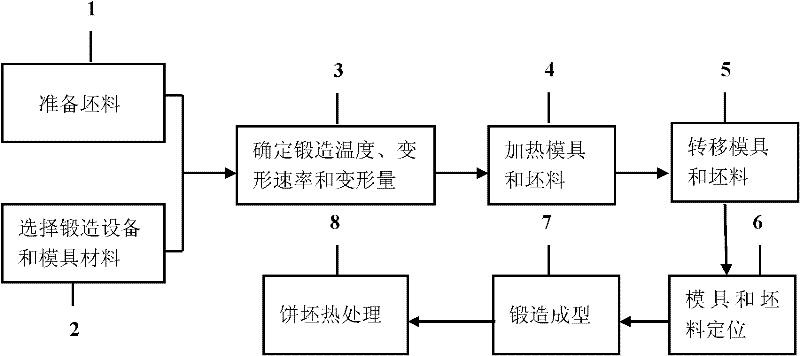
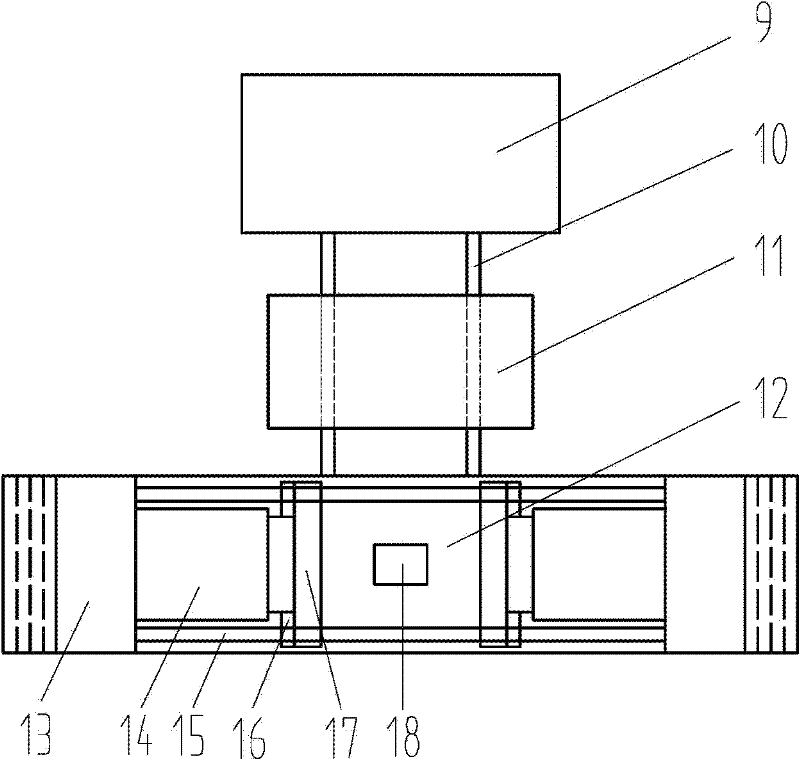
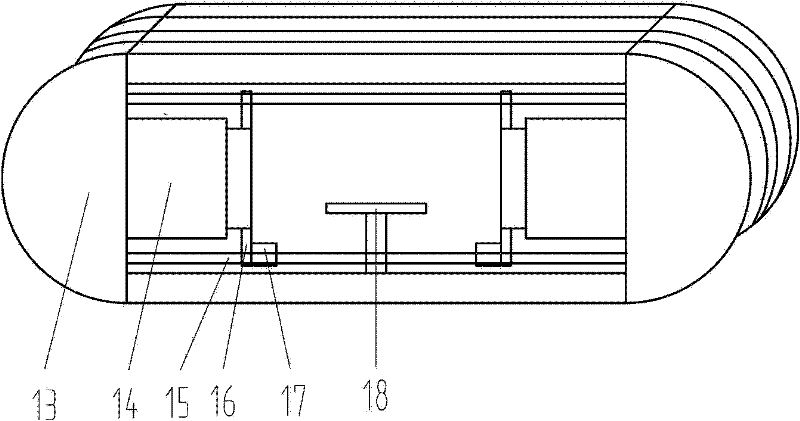
ActiveCN102303083AReduce manufacturing costReduce the cost of forging processForging press detailsFlow stressHigh volume manufacturing
The invention discloses a quick isothermal forging method and device for preparing a less-deformable alloy cake blank. The device comprises a heating device, an automatic feeding device, a horizontal hydraulic forging device, a blank positioning device and a flame heating device. A mould material used by the device is a nickel-based alloy with creep strength which is higher than the flow stress of a forged high-temperature alloy under corresponding forging temperature and deformation rate. In the method, a homogenized electroslag remelting continuous directional solidification technology or other processes with maneuverability can be selected for preparing a high-alloyed less-deformable alloy directional solidification billet, as well as a fine grain billet prepared by adopting the processes, such as powder metallurgy and the like. The method and the device have the advantages of short production period, convenience for control and low cost, and are suitable for mass production of large-size high-clean and uniform tissue high-alloying less-deformable alloy cake blanks.
Owner:CENT IRON & STEEL RES INST
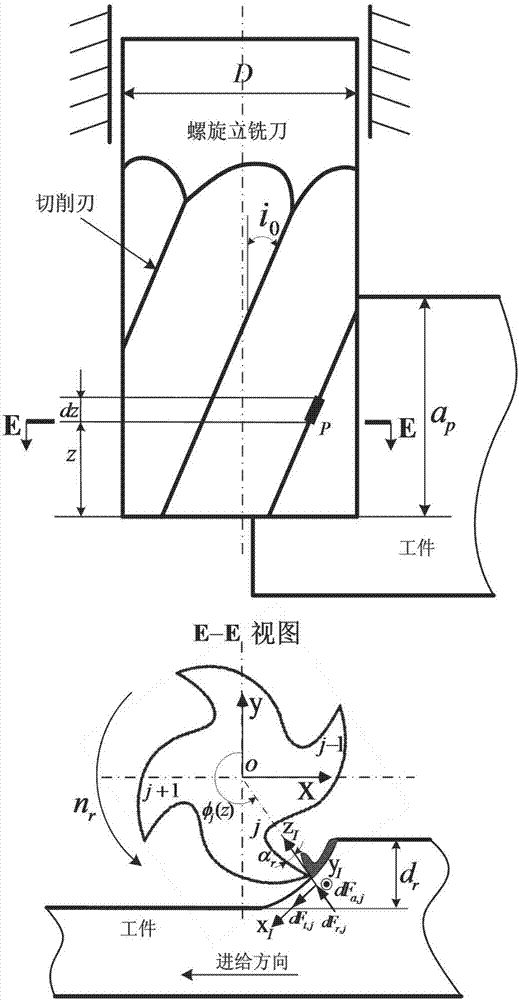
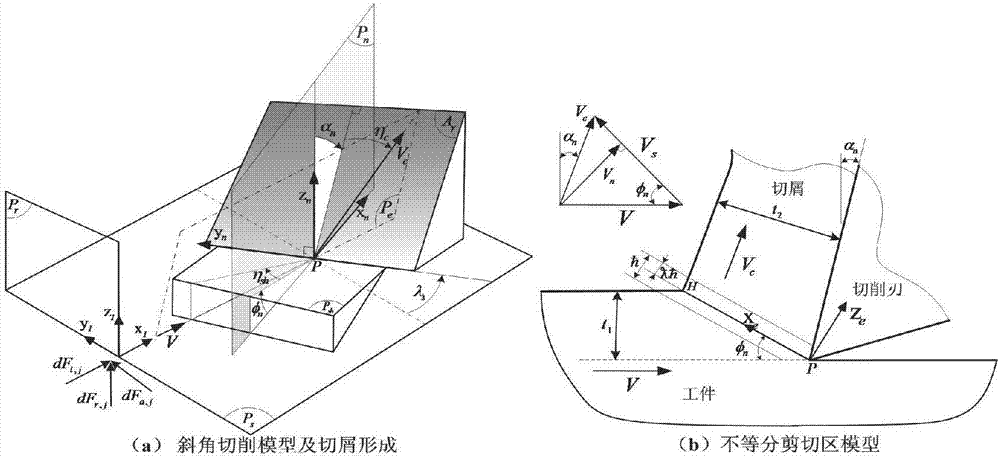
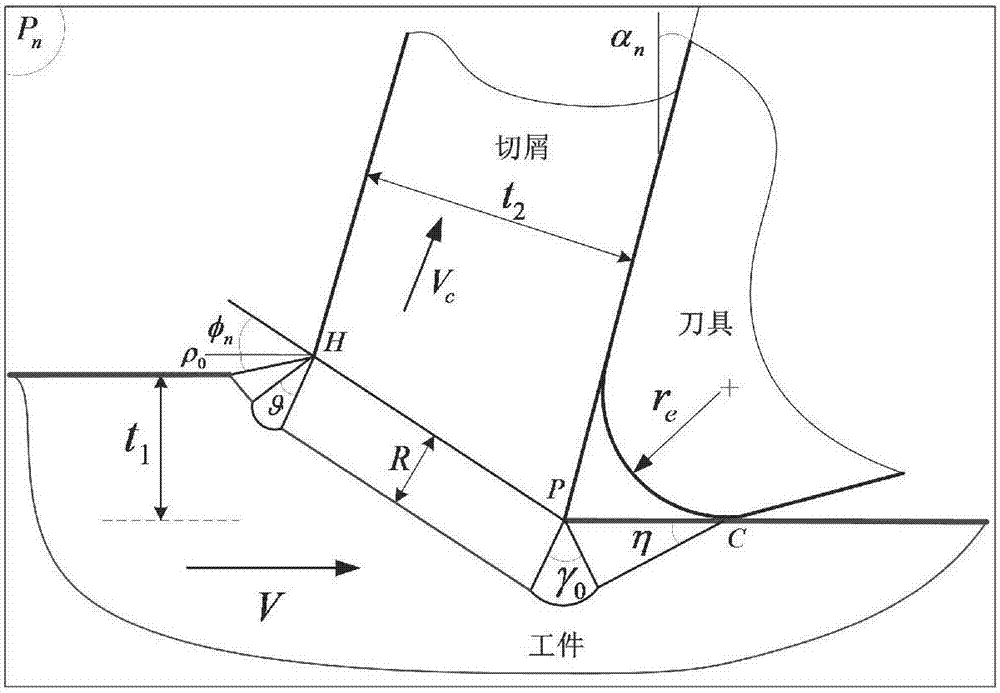
Analyzing and modelling method of milling force of flat spiral end milling cutter
InactiveCN107330138ACutting Force PredictionImprove accuracyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFlow stressModel method
The invention relates to an analyzing and modelling method of milling force of a flat spiral end milling cutter. According to the method, workpiece material characteristics, cutter geometry, cutting conditions and milling modes serve as model input parameters, consideration is given to the influence on the cutting force by a cutter cutting edge radius, a variable sliding friction coefficient and cutter bounce, shear flow stress is calculated through a Johnson-Cook constitutive model in a model, each cutting edge of the milling cutter is scattered into multiple microelements in the cutter axis direction, the cutting characteristic of each microelement is equivalent to an inclined cutting process, cutting force exerted on each cutting microelement is obtained through an analytical model of inclined cutting force, then cutting force of all the cutting microelement is superposed, and a milling force value of the milling cutter is obtained. According to the analyzing and modelling method of the milling force of the flat spiral end milling cutter, cutting mechanism, relevant stress, strain and a strain rate in the cutting process and the distribution situation of the temperature can be reflected truly, the milling force can be quickly predicted only by inputting the cutting conditions and workpiece characteristic parameters, and the method is high in accuracy and rapidity.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
Refracturing well and layer selecting method based on four-dimensional crustal stress dynamic change
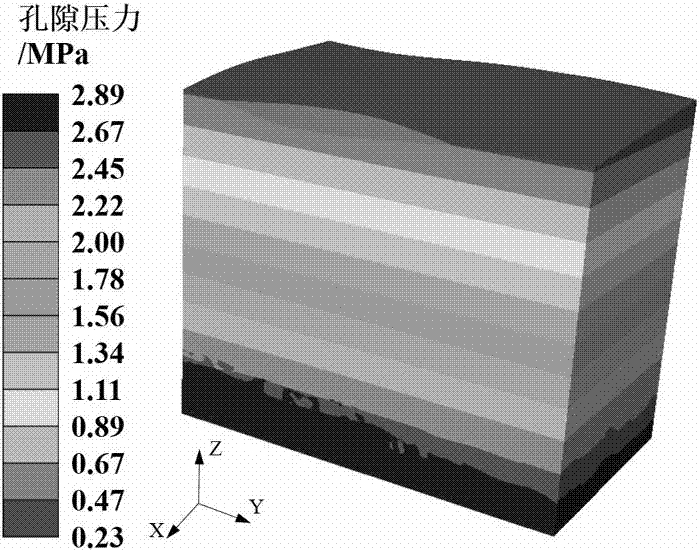
ActiveCN106991236ATo overcome the problem of inability to accurately reflect the change of ground stress in the process of oil and gas developmentOvercoming the problem of changing ground stressGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationFlow stressCoupling
The invention discloses a refracturing well and layer selecting method based on four-dimensional crustal stress dynamic change. The method includes the steps that S1, a three-dimensional geologic model is set up; S2, a three-dimensional oil deposit model is set up, and producton / injection dynamic parameters are used for predicting a three-dimensional pore pressure field and a temperature field of different periods; S3, a three-dimensional crustal stress model is set up; S4, an initial three-dimensional crustal stress field is formed; S5, a four-dimensional dynamic crustal stress model is set up; S6, interstifial flow-stress coupling solution is carried out, and dynamic crustal stress and pore elastic parameters are analyzed and calculated; S7, a refractured well and layer position are selected preliminarily; S8, interstifial flow-stress-fracture damage coupling model of refracturing is set up; S9, the final fracturing layer segment is determined. The refracturing well and layer selecting method has the advantages of being capable of accurately reflecting the change condition of dynamic crustal stress and pore elastic parameters in the oil and gas development process, optimizing the refractured well and layer position by combining the interstifial flow-stress-fracture damage coupling model, effectively improving oil and gas recovery degree and avoiding aquifer communicating.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
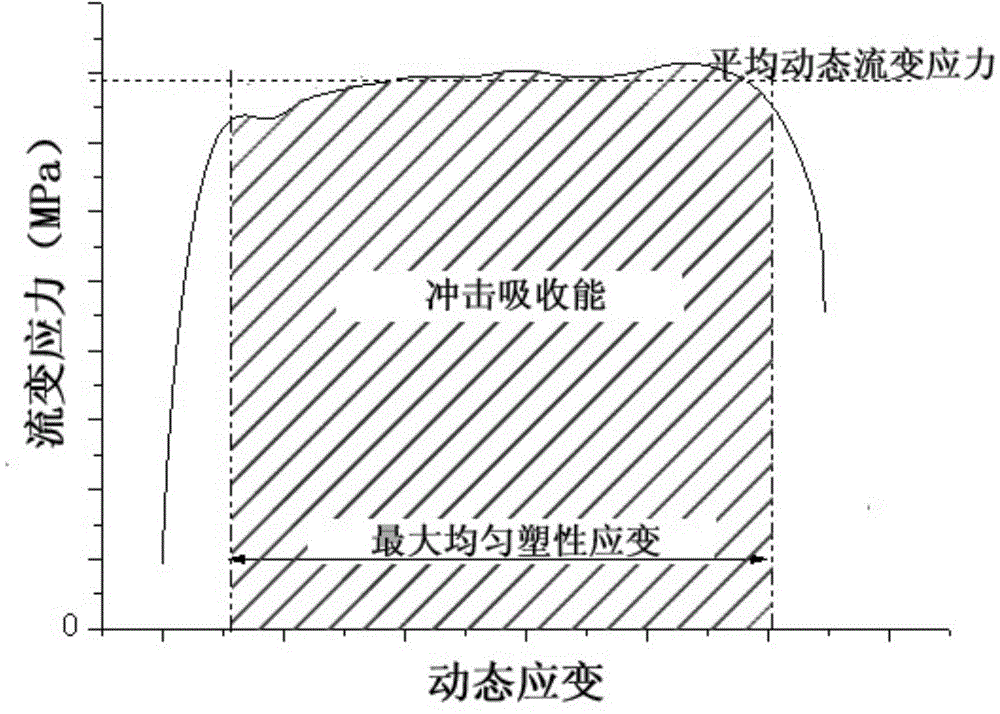
Preparation method for titanium alloy with high dynamic bearing performance and low cost
The invention relates to a preparation method for a titanium alloy with a high dynamic bearing performance and a low cost. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) setting the ranges of the target ingredients of the alloy, wherein from composition, the alloy comprises the following elements in percentage by weight: 2.5-7.0% of aluminium, 2.0-5.5% of vanadium, not greater than 2.5% of iron, 0.1-0.3% of oxygen and the balance of titanium; (2) proportioning according to the target ingredients of the alloy; (3) smelting, and deforming and processing; (4) carrying out heat treatment and surface cleaning on the finished product. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the high dynamic bearing capacity of the titanium alloy is guaranteed through reasonable processing and heat treatment regimes; the impact absorption energy is not less than 300J / cm<3>; when the average dynamic flow stress is not less than 1500MPa, the maximum uniform plastic strain is not less than 0.17; when the average dynamic flow stress is not less than 1400MPa, the maximum uniform plastic strain is not less than 0.20; when the average dynamic flow stress is not less than 1300MPa, the maximum uniform plastic strain is not less than 0.22.
Owner:BAOJI TITANIUM IND +1
Austenitic stainless steel sheet and method for producing same
ActiveCN105452505AHigh intensityImprove toughnessFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesFlow stressCarbide
Provided is an austenitic stainless steel sheet which has a product of the 10% flow stress at a strain rate of 1000 / s and the uniform elongation at a strain rate of 0.1 / s of 450 MPa or more and also has high strength at a high strain rate and improved ductility at a low strain rate. An austenitic stainless steel sheet containing, in % by mass, 0.02 to 0.30% of C, 10.0 to 25.0% of Cr, 3.5 to 10.0% of Ni, 0 to 3.0% of Si, 0.5% to 5.0% of Mn, 0.10 to 0.40% of N, 0 to 3.0% of Mo, 0 to 3.0% of Cu, 0 to 0.10% of Ti, 0 to 0.50% of Nb and 0 to 1.0% of V, wherein the value determined by the following formula: C + 3 * N is 0.4% or more, and the remainder is made up by Fe and impurities. In the austenitic stainless steel sheet, the Md30 value which is defined by formula (1) is 0 to 50 DEG C inclusive, the volume ratio of each of a Cr carbide and a Cr nitride is 1% or less, and the average crystal particle diameter of a parent phase is 10 [mu]m or less.
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Thermal hydro-mechanical drawing forming method for dot matrix self-impedance electrical heating plates
InactiveCN102139304ARealize controllable flexible heatingRaise the forming limitShaping toolsOhmic-resistance heating detailsDot matrixEngineering
The invention relates to a thermal hydro-mechanical drawing forming method for dot matrix self-impedance electrical heating plates, and belongs to the technical field of the thermal hydraulic forming of the plates. The method comprises the following steps of: fully filling liquid into a cavity of a female die serving as a liquid pond; when the plates are driven by a male die to enter the female die, forming the plates by reverse pressure generated when the liquid is compressed; embedding pin type electrodes inside pressure plates according to the distribution of dot matrixes, and performing self-impedance electrical heating on flanges of the plates by using contact resistors between the electrodes and the plates; adjusting the distribution of temperature fields of the flanges by changing the distribution law of the dot matrixes of the electrodes and adjusting the heating current of each heating electrode; adjusting the flow stress of heating points by changing the temperature of each mass point on the flanges so as to control the flow of metal by the asynchronous flow of the metal mass points on the flanges; and coordinating the deformation process of the metal by the asynchronousdeformation of each mass point on the flanges due to the temperature to fulfill the aim of improving the limit drawing ratio of the plates. The method has the advantages that: the heating speed is high, the effect is good, the plates can be heated controllably and flexibly, and the forming limit of the plates is improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
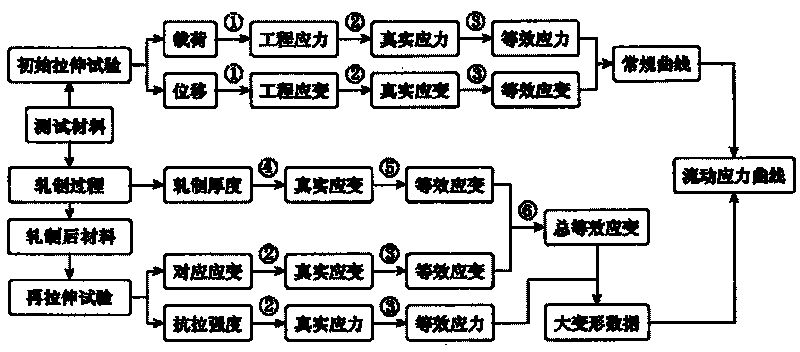
Method for measuring large deformation flow stress curve of metal plate
ActiveCN101692028AExpand the scope of testingMeet the needs of simulationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFlow stressStress–strain curve
The invention discloses a method for measuring a large deformation flow stress curve of a metal plate in the field of metal plate volume forming engineering, which comprises the following steps: taking the metal plate, and performing initial stretching test to acquire a real stress-strain curve; acquiring an equivalent strain interval of a subsequent rolling process; diving the equivalent strain interval into n equal parts to acquire the thickness of the plate after each theoretical rolling; taking n blocks of the metal plate, and cold-rolling and machining each block of the metal plate according to the thickness of the plate after theoretical rolling to acquire n actual thickness and then acquire each actual rolling equivalent strain; performing re-stretching test for the cold-rolled n metal plate blocks to acquire n subsequent flow stresses and n subsequent real strains; and further acquiring n data points to acquire the large deformation flow stress curve of the metal plate. The method of the invention can provide accurate material performance parameters for the numerical simulation in a plate volume forming process, and provide basis for engineering personnel to select an extrapolation model.
Owner:内蒙古中盛科技集团有限公司
Constant-temp. forging in the air for nickel-base super heat-resistant alloy
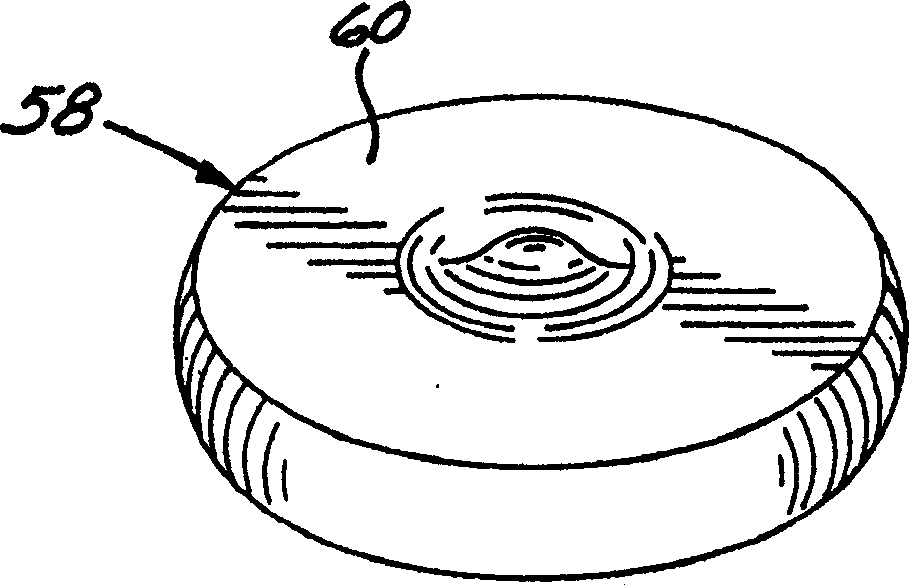
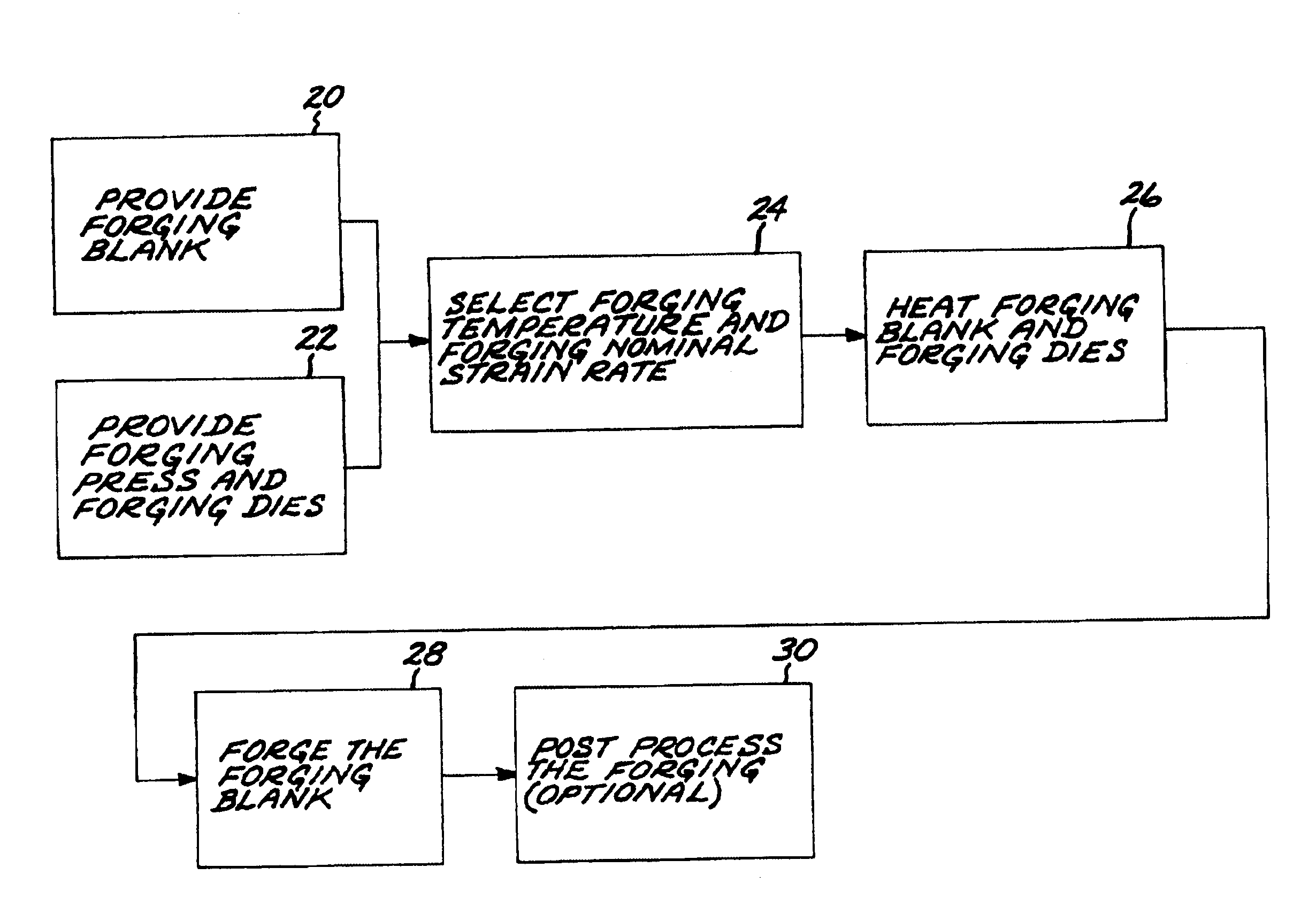
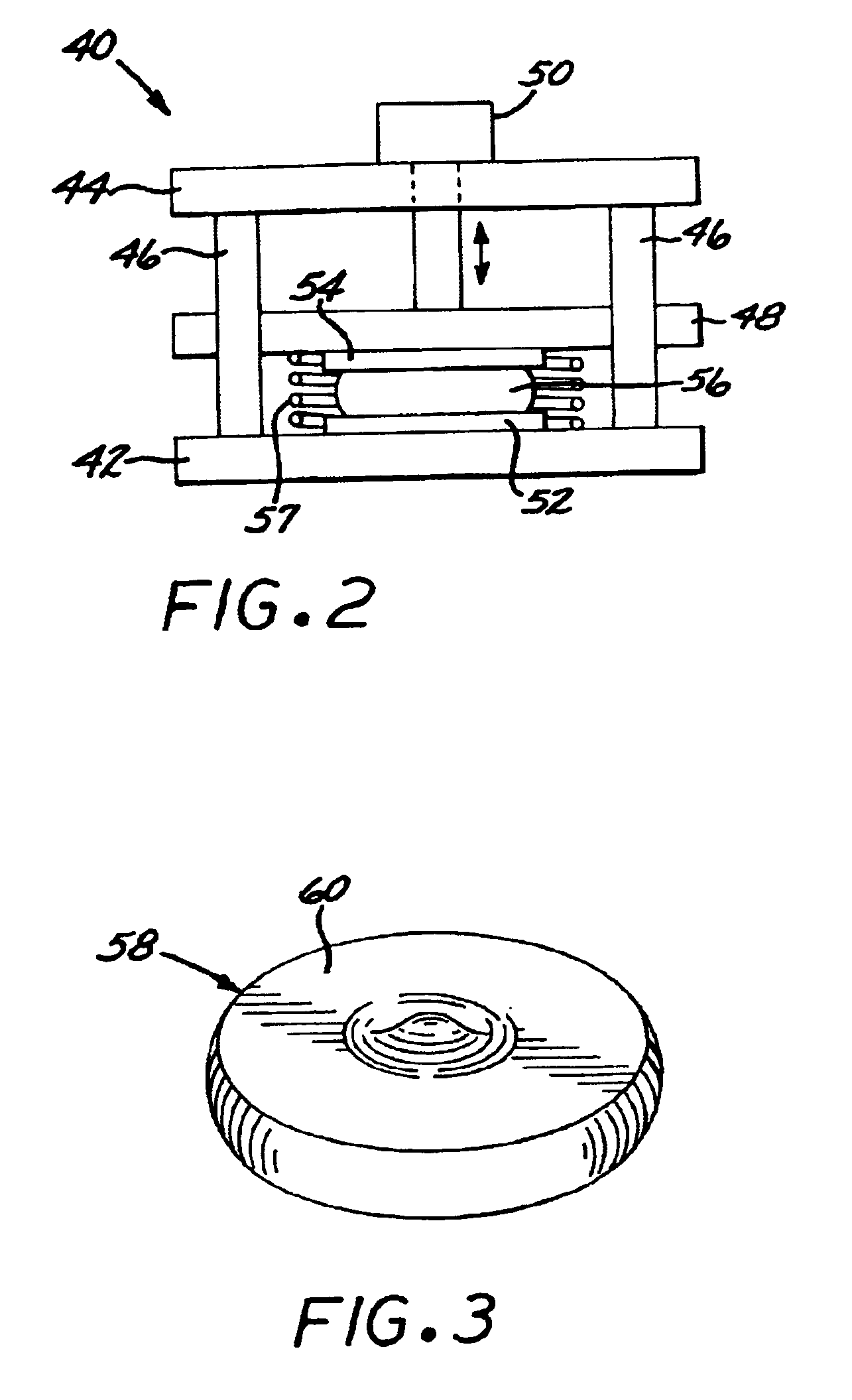
A superalloy made of a forging nickel-base superalloy such as Rene TM 88DT or ME3 is forged in a forging press (40) having forging dies (52, 54) made of a die nickel-base superalloy. The forging is accomplished by heating a superalloy workpiece to a forging temperature of from about 1700 DEG F to about 1850 DEG F, and forging at that forging temperature and at a nominal strain rate. The die nickel-base superalloy is selected to have a creep strength of not less than a flow stress of the forging nickel-base superalloy at the forging temperature and strain rate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Isothermal forging of nickel-base superalloys in air
A superalloy made of a forging nickel-base superalloy such as Rene™ 88DT or ME3 is forged in a forging press having forging dies made of a die nickel-base superalloy. The forging is accomplished by heating to a forging temperature of from about 1700° F. to about 1850° F., and forging at that forging temperature and at a nominal strain rate. The die nickel-base superalloy is selected to have a creep strength of not less than a flow stress of the forging nickel-base superalloy at the forging temperature and strain rate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Assembled type movable blast wall
InactiveCN103628583AStrong matchingQuick assemblyBuilding constructionsProtective buildings/sheltersFlow stressEnergy absorption
An assembled type movable blast wall is formed by a plurality of blast wall units in an assembled mode. Each blast wall unit comprises a base, front pull rods, rear compression bars, a supporting frame, energy absorption layers and connecting bolts. Each supporting frame is fixed on the upper surface of the corresponding base, and one or more energy absorption layers are arranged inside each supporting frame in a filling mode. The energy absorption layers are formed by a plurality of prefabricated bodies which are made of EPS flow state concrete in an arrayed mode. A plurality of slide-resistant piles are distributed on the lower surface of each base. When multiple energy absorption layers are arranged, a middle layer is arranged between every two adjacent energy absorption layers. The assembled type movable blast wall can be deformed easily when undergoing impulse loads of the outside, the deformation is large, however, the flow stress level is quite low, in the compression deformation process, a large amount of power is consumed, the power is converted into energy dissipated in all sorts of modes like deformation, collapsing, fracturing and cell wall friction of holes in the structure, and thus the outside impact energy can be effectively absorbed. The assembled type movable blast wall further has the advantages of being rapid in assembling, low in cost and strong in stability.
Owner:AIR FORCE UNIV PLA
Composite Preform Having a Controlled Fraction of Porosity in at Least One Layer and Methods for Manufacture and Use
InactiveUS20090269605A1Reduce failure rateReduce flow stressExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusFlow stressPorosity
The invention provides clad billet for hot working plastic deformation processes for the production of clad products, including, but not limited to, clad pipe and tubing by extrusion of a hollow, bicomponent composite billet having a fully dense structural component and a partially dense component of a specialty alloy at a fraction of porosity predetermined to provide a flow stress compatible with that of the structural component. The components are diffusion bonded to the predetermined fraction of porosity in the specialty component by application of heat and pressure over time, including by hot isostatically pressing the billet components. Computer modeling techniques can be used to determine processing conditions for obtaining flow stress compatibility.
Owner:BODYCOTE IMT INC
High-Nb-TiAl alloy diffusion bonding method
ActiveCN103785944AQuality improvementReduce processing costsFurnace typesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesFlow stressAxial pressure
The invention discloses a high-Nb-TiAl alloy diffusion bonding method. According to the method, firstly, vacuum diffusion bonding is carried out on a forged high-Nb-TiAl alloy at a low temperature, and then vacuum annealing treatment is carried out on diffusion bonding samples. By effectively combining high-Nb-TiAl alloy diffusion bonding with vacuum annealing treatment, the joint quality of high-Nb-TiAl alloy diffusion bonding is significantly improved, and the microscopic structure of a weldment can be controlled. Meanwhile, axial pressure stress smaller than alloy flow stress is applied in the diffusion bonding process, so that materials are prevented from being deformed in the diffusion bonding process. The microscopic structure of a diffusion bonding joint obtained through the method is free of unclosed holes, weld interfaces disappear completely, structural evolution is thorough, and the diffusion bonding joint is high in quality.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Press die for electrically assisted manufacturing
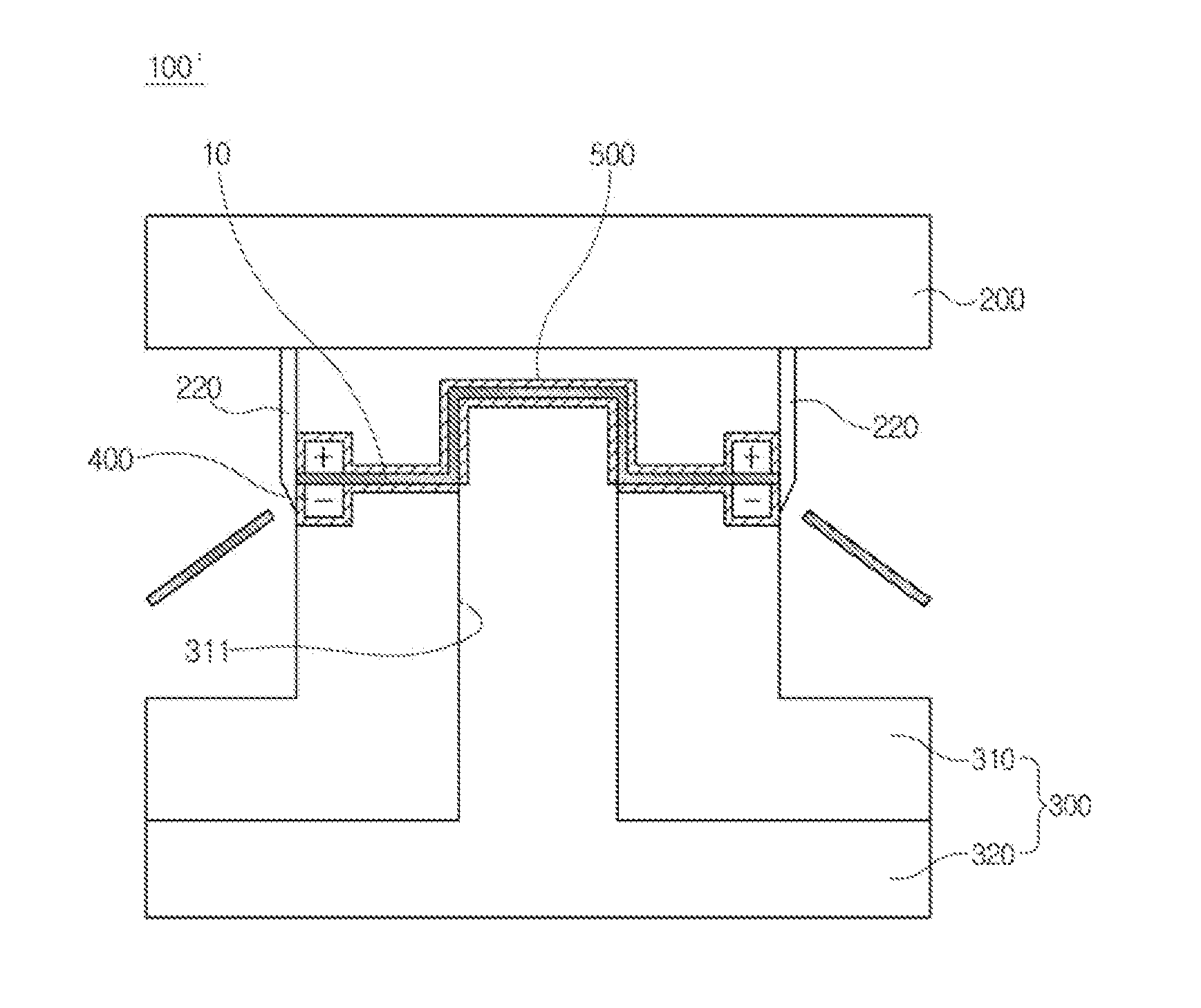
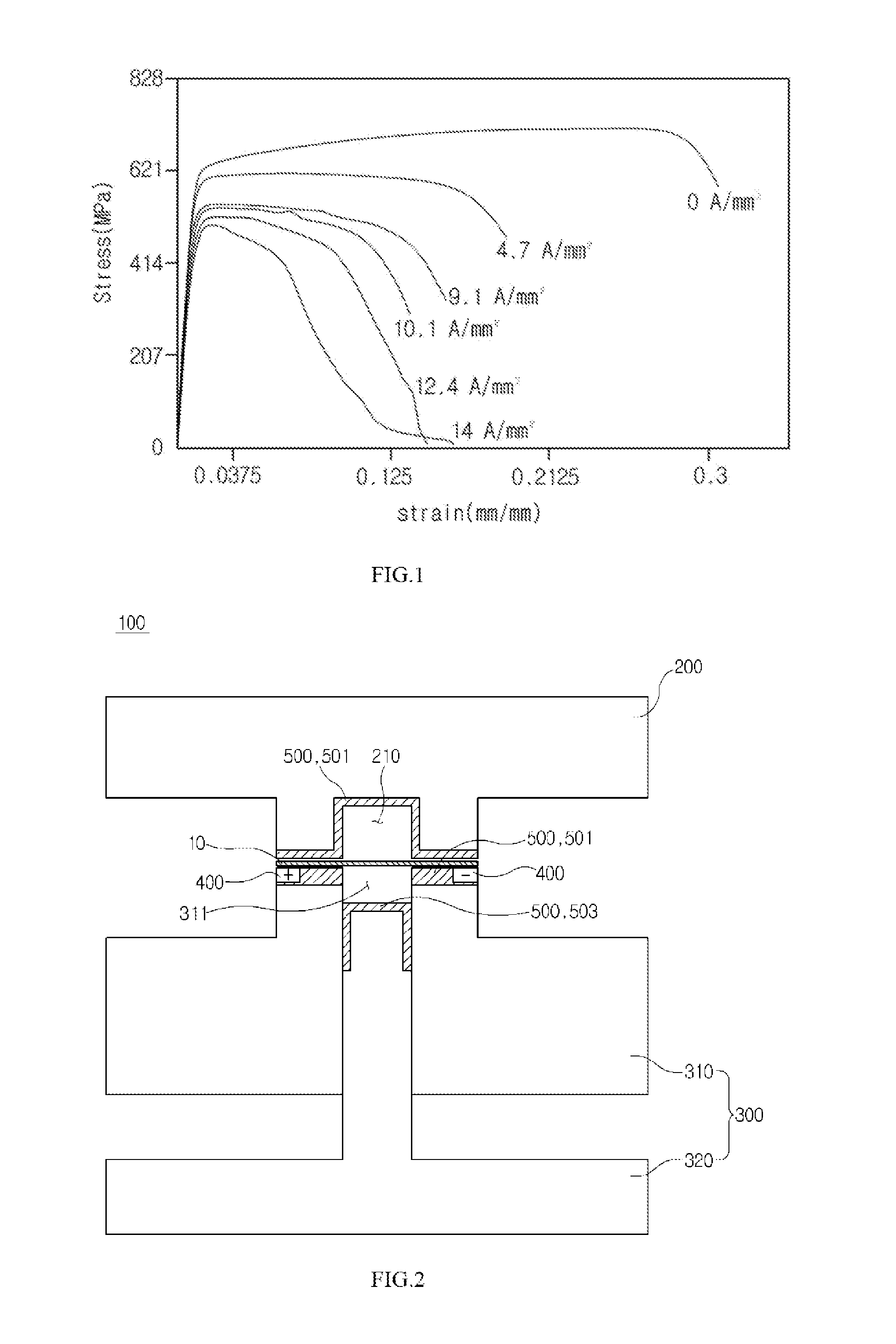
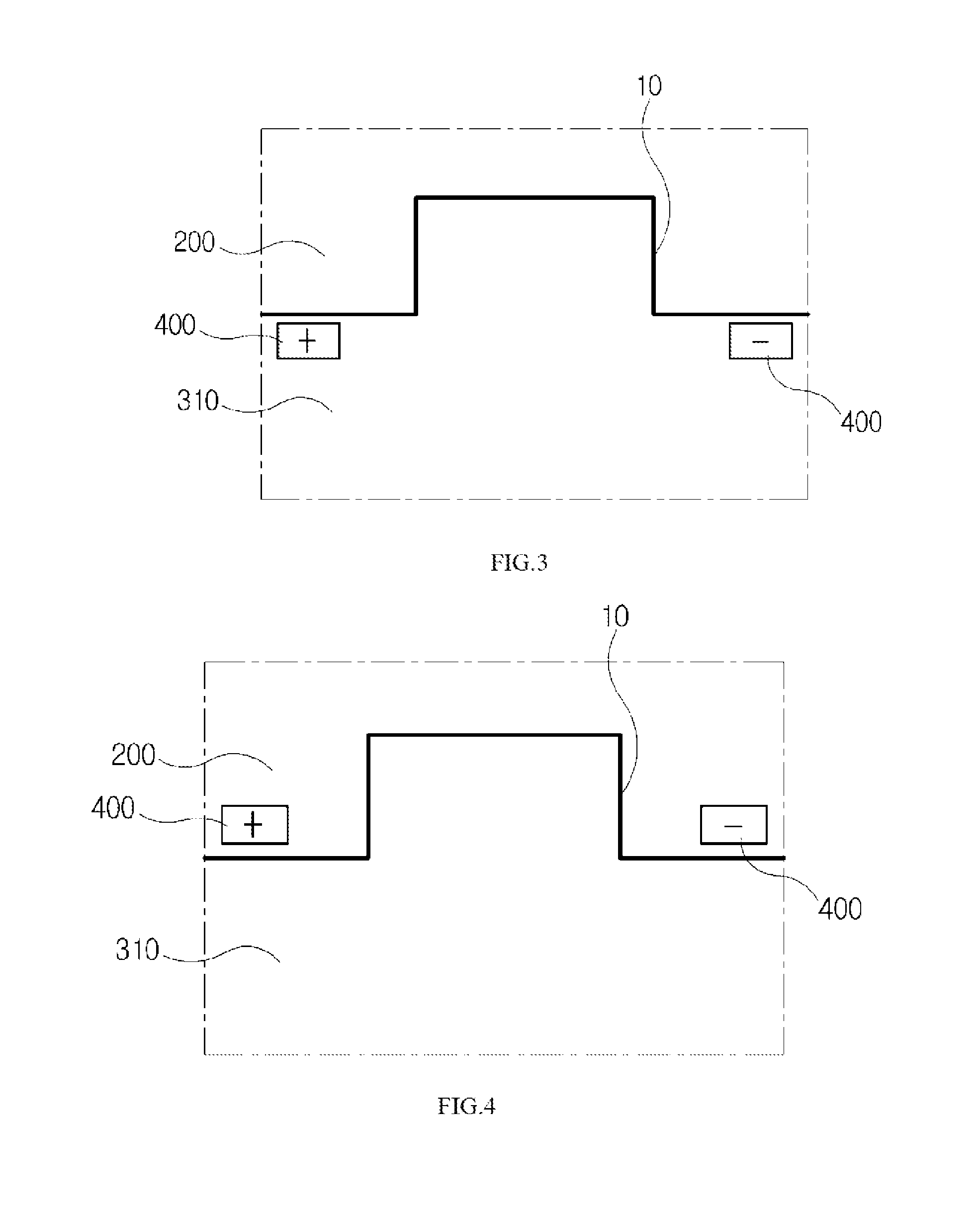
The invention discloses a press die for electrically assisted manufacturing performing plastic working at a relatively lower temperature than hot working by using an electroplasticity effect that a flow stress inside a material is reduced when a current is applied to the material, the press die for electrically assisted manufacturing comprising: an upper die and a lower die configured to be disposed at upper and lower portions, having the material disposed therebetween; and at least one electrode pair configured to be disposed in the upper die or the lower die, wherein the electrode pair is configured so that electrodes having different polarities in a width direction of the material face each other.
Owner:MYUNGSHIN IND CO LTD +3
Preparation method of iron-based amorphous alloy-copper multilayer composite plate
ActiveCN103895313AAchieve preparationFlexible and efficient preparation methodLaminationLamination apparatusComposite plateAmorphous metal
The invention discloses a preparation method of an iron-based amorphous alloy-copper multilayer composite plate. By combining a vacuum diffusion bonding technology and a hot rolling bonding technology, the multilayer composite plate is prepared; in processes of vacuum diffusion bonding and hot rolling bonding, processing temperatures are selected to be in an amorphous alloy super-cooled liquid region; by adopting the characteristics of low viscosity, small flow stress and element diffusion acceleration of the amorphous alloy in the super-cooled liquid region, the iron-based amorphous alloy and the copper can be effectively connected, thus the iron-based amorphous alloy-copper multilayer composite plate can be successfully prepared. In a hot rolling process, a thin-layer surface is stressed by shearing force, so that fresh metals in the thin-layer surface are exposed in a short time and contacted and bonded with each other in the presence of pressure, thus effective welding is formed at an interface; in a vacuum annealing process, the element diffusion distance in the interface can be further increased, so that the metallurgy bonding strength can be improved, and the rolling stress can be released.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Residual intensity evaluation method of corrosion defect contained steam injection pipeline compensator bent pipe
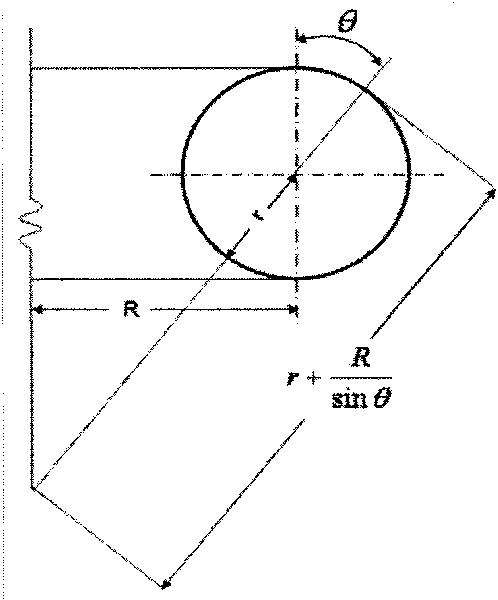
ActiveCN101726456AAvoid stress concentrationHigh engineering practical valueMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing mechanical meansMean diameterFlow stress
The invention relates to a residual intensity evaluation method of a corrosion defect contained steam injection pipeline compensator bent pipe, which comprises the following steps of: computing the bearing capacity of the bent pipe through a formula plimit=Sigma f / (r Eta+3r2 Alpha Eta 2), wherein plimit in the formula is the ultimate bearing capacity of the bent pipe, Sigma f is the flow stress of a pipe, r is the mean radius of the bent pipe, alpha is the ellipticity of the bent pipe, Eta is an intermediate variable, t in the formula is the wall thickness of a pipeline, d is a defect depth, k is an intermediate variable, L in the formula is a defect length and Dm is the mean diameter of the bent pipe; carrying out full-size hydrostatic bursting test verification by utilizing the compensator bent pipe with corrosion defects, and comparing a measured value with a theoretical value, wherein the theoretical value is smaller, and an error is 24.7 percent. A result indicates that the method has higher engineering utility value and reasonable safe reliability.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
Method for producing an article by superplastic shaping and diffusion welding
InactiveCN101166589AEliminate deformationReduce in quantityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusFlow stressAviation
The invention relates to metal forming, more specifically, to methods for producing titanium alloy articles by superplastic shaping and diffusion welding. The inventive method is particularly suitable for aviation engine building for producing a fan blade-type part. The inventive method for producing an article by superplastic shaping and diffusion welding from at least two titanium alloy blanks consists in designating connectable and not-connectable sections on the surface of at least one blank, in assembling the blanks into a packet, in heating said packet to a specified temperature (T), in exposing it to a specified pressure (p) in such a way that the blanks are connected to each other by diffusion welding and a semi-finished product is obtained, in heating and supplying a pressurised working medium into the semi-finished product internal cavity for superplastically shaping at least one blank in such a way that a desirably shaped article is produced. Said method differs from known methods in that the diffusion welding is carried out through titanium alloy plates whose flow stress is less than the blank flow stress, mainly, when the article is made from at least three blanks and a connection preventing material is applied to the non-connectable sections of at least one part of at least one blank surface.
Owner:INST SVERKHPLASTICHNOSTI METAL
Wound treatment apparatus and method
ActiveUS20160354535A1Promote wound healingReduce bacterial loadCannulasEnemata/irrigatorsFlow stressThermal energy
An apparatus and method for aspirating, irrigating and / or cleansing wounds is provided. The apparatus and method include one or more of the following: simultaneous aspiration and irrigation of the wound, supplying of thermal energy to fluid circulated through the wound; supplying physiologically active agents to the wound; a biodegradable scaffold in contact with the wound bed; and application of stress or flow stress to the wound bed.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
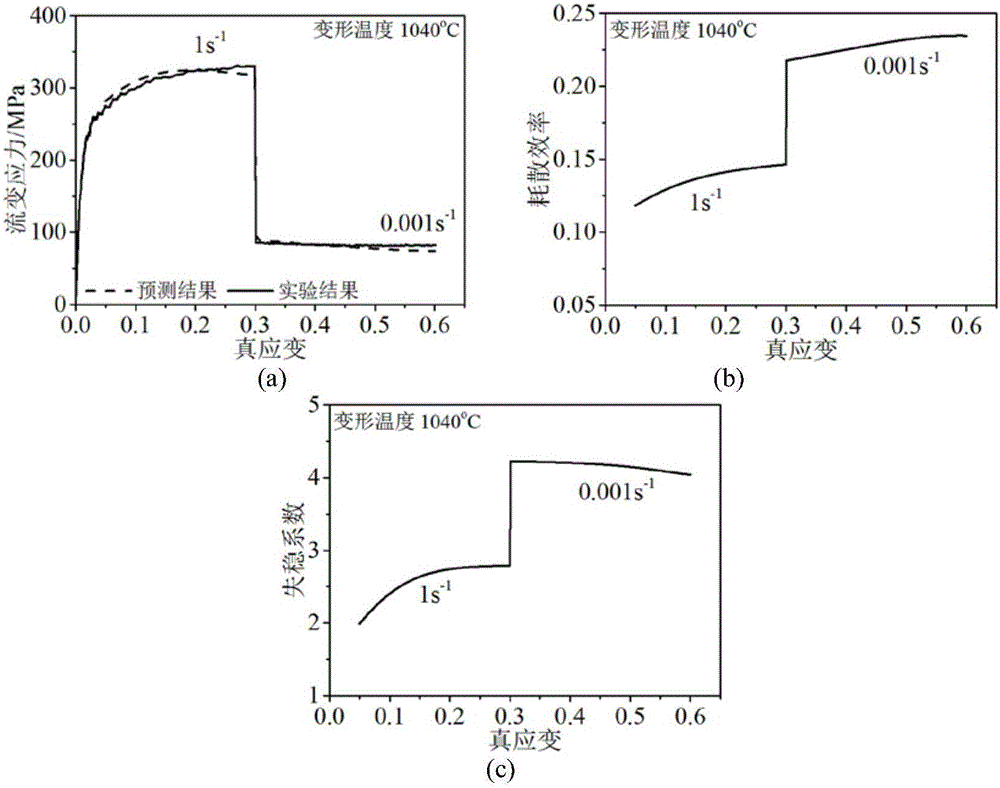
Method estimating hot-working performance of metal material
InactiveCN105651620AAccurate assessmentMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesFlow stressThermal deformation
The invention discloses a method estimating hot-working performance of a metal material. The method comprises the following steps: (1), subjecting the metal material to high-temperature compression testing under designed thermal deformation conditions so as to obtain tree-true strain data; (2), establishing a modified hyperbolic sine constitutive model for describing high-temperature flow stress of a metal material, through programming; (3), establishing a hot-working dissipation efficiency estimation model and an instability judging module of the metal material, through programming; (4), using a high temperature flow stress prediction model established in steps (2) and (3), hot-working dissipation efficiency estimation model and instability judging model to predict flow stress of the metal material, hot-working dissipation rate and instability coefficient under any condition so that hot-working performance of the metal material is comprehensively estimated under any deformation condition. The method enables the hot-working performance of the metal material to be accurately and quickly estimated, and significant technical guidance is provided for reasonable arrangement of the-working process of the metal material is reasonably formulated.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
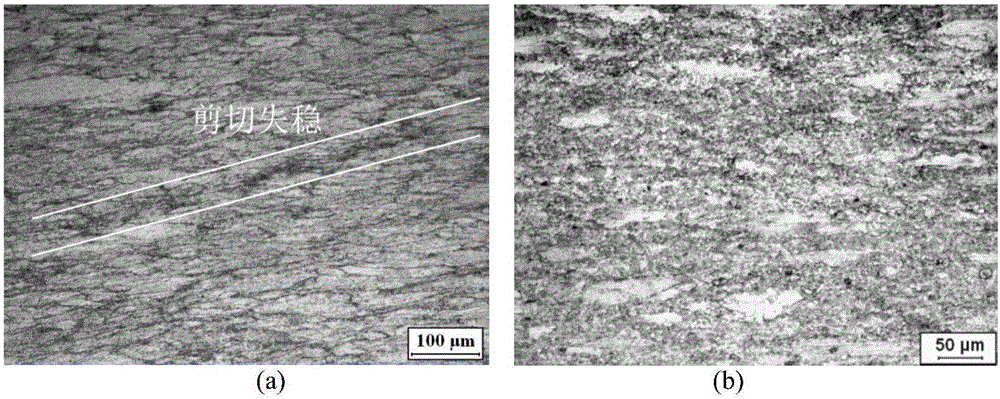
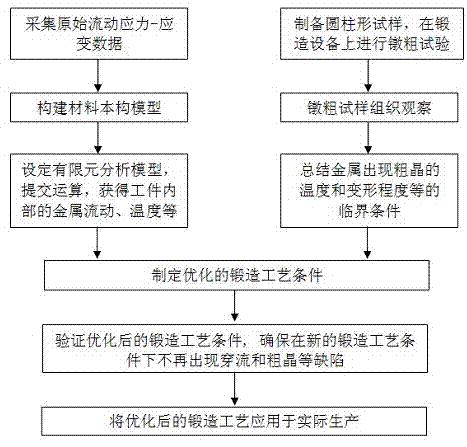
Method for analyzing and preventing forging through flow and coarse-grain defects
InactiveCN102831265AAvoid reoccurrenceOptimizing the forging processSpecial data processing applicationsFlow stressCritical condition
The invention relates to a method for analyzing and preventing the forging through flow and the coarse grain defect, which comprises the following steps of: firstly, acquiring the original flow stress-strain data of a metal through an isothermal constant-strain-rate compression test, and constructing a constitutive model of the material; then, importing the data into finite element numerical simulation software, establishing a numerical analysis model, and calculating the metal flow, the stress strain and the temperature field distribution conditions inside a forging piece after the completion of calculation; additionally, physically simulating the forging process of the metal through an upsetting test to obtain the critical conditions such as temperature, strain and the like of the metal coarse grain; and analyzing the causes to the through flow and the coarse grain by combining the test results of numerical simulation and physical simulation, optimizing the forging process, and simulating to verify the optimized forging process in the finite element software. In the invention, the finite element numerical simulation technology and the physical simulation technology are innovatively combined, the optimization of the forging process is realized, the optimized forging process conditions can be verified, so that the material and energy sources can be saved, and the efficiency is increased.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Ultrasonic-assisted fine blanking process and die
InactiveCN103611774AReduce flow stressImprove fine blanking performanceShaping toolsEjection devicesFlow stressUltrasonic assisted
The invention relates to an ultrasonic-assisted fine blanking process and device. According to the process, ultrasonic wave is input to a male die during the process of fine blanking to allow the male die to resonate, the bottom of the male die vibrates under high frequency, and accordingly the features of the traditional fine blanking formation are changed and the quality of blanks is improved. Compared to the traditional fine blanking, the ultrasonic-assisted fine blanking process has the advantages that forming property of fine blanking material is improved, flow stress of the material is reduced, and the quality of fine-blanked parts is improved; forming load is reduced, and the service life of the fine blanking die is prolonged. The invention further designs an ultrasonic-assisted fine blanking die device. The ultrasonic-assisted fine blanking process and device is significant to widening the range of fine blanking materials, improving the quality of fine blanks and prolonging the service life of the fine blanking die.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Hydraulic fracturing system
ActiveUS20130014946A1Increase injection rateFluid removalDrilling compositionFlow stressHydrostatic pressure
A method is given for fracturing a formation, in particular far-field in a tight formation, in which at least a portion of the proppant is crushable in situ at some point during pumping, during fracture closure, or at higher Fluid flow stresses experienced later during fracture closure. The closure stress or hydrostatic stress is estimated, then a proppant is selected that is at least partially crushable at that closure stress, and then the fracturing treatment is performed with at least a portion of the total proppant being the selected crushable proppant.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
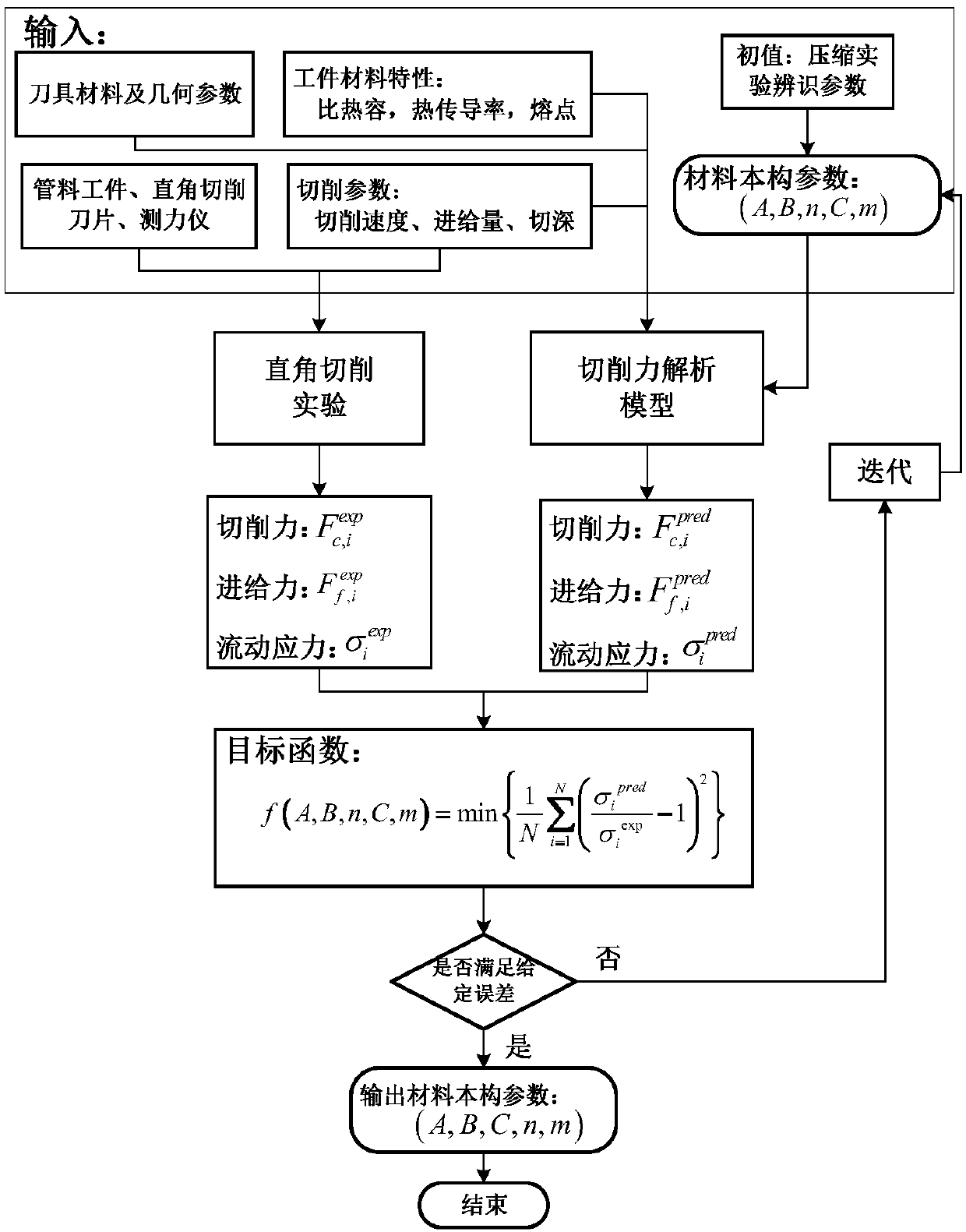
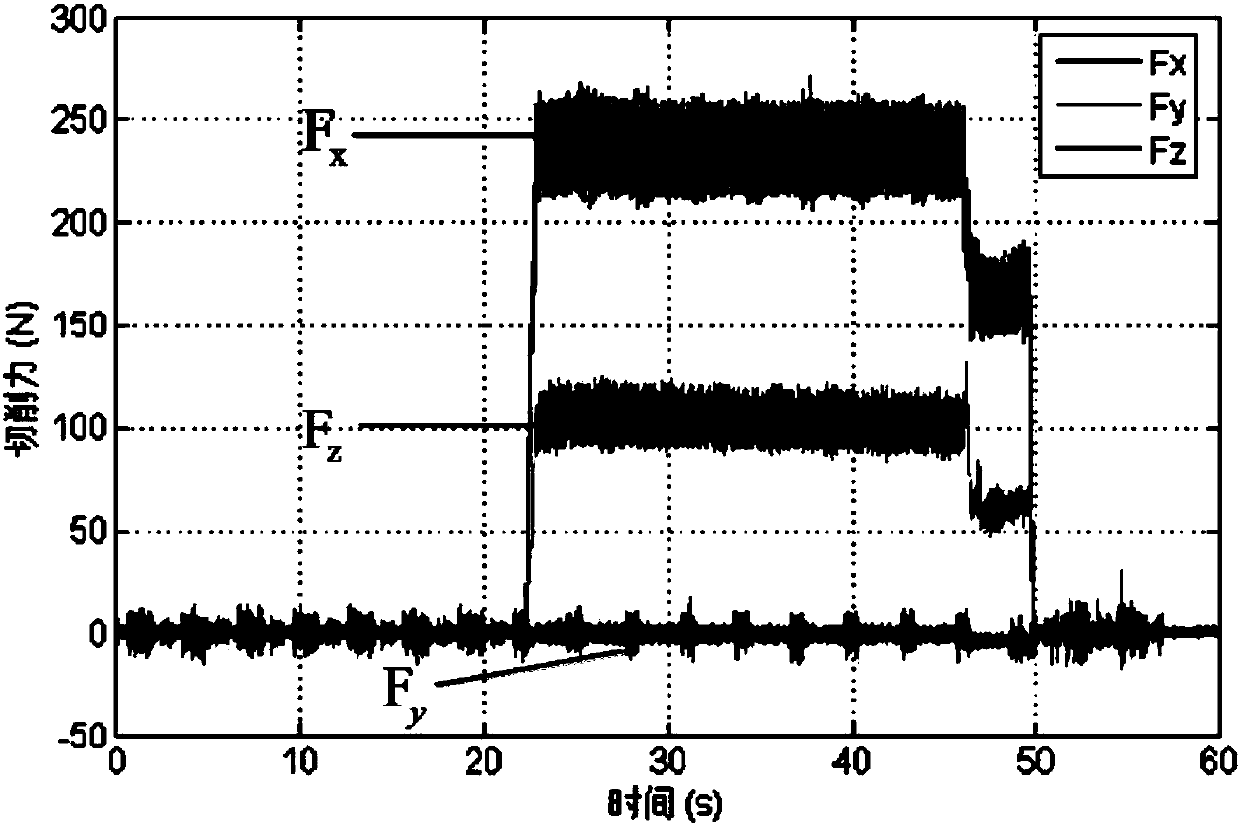
Recognition method of metal material cutting constitutive model parameters
InactiveCN107330137AImprove efficiencyLow costDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFlow stressMetallic materials
The invention relates to a recognition method of metal material cutting structure model parameters. The method comprises the following steps of 1, adopting a JC constitutive model to describe a cutting constitutive model of a material; 2, conducting compression experiment and fitting on a metal material specimen to solve JC constitutive model parameters of the metal material under a low strain rate; 3, using the constitutive model parameters obtained by recognition through the compression experiment in the step 2 as an initial value to establish an optimization target function; 4, setting a standard value of an error between an experiment value of a flow stress and a predicted value, and obtaining a structure parameter optimal solution of the metal material specimen based on a genetic optimization algorithm; 5, verifying the correctness of the parameters obtained by recognizing the JC structure model of the metal material. According to the recognition method of the metal material cutting structure model parameters, the flow stress value obtained through the JC structure model is very close to an actual flow stress value of the metal material, and the efficiency in the process of recognizing the constitutive model parameters is very high; meanwhile, a special apparatus is not needed to conduct a large quantity of compression experiments, and therefore the cost is lowered.
Owner:WUHAN INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
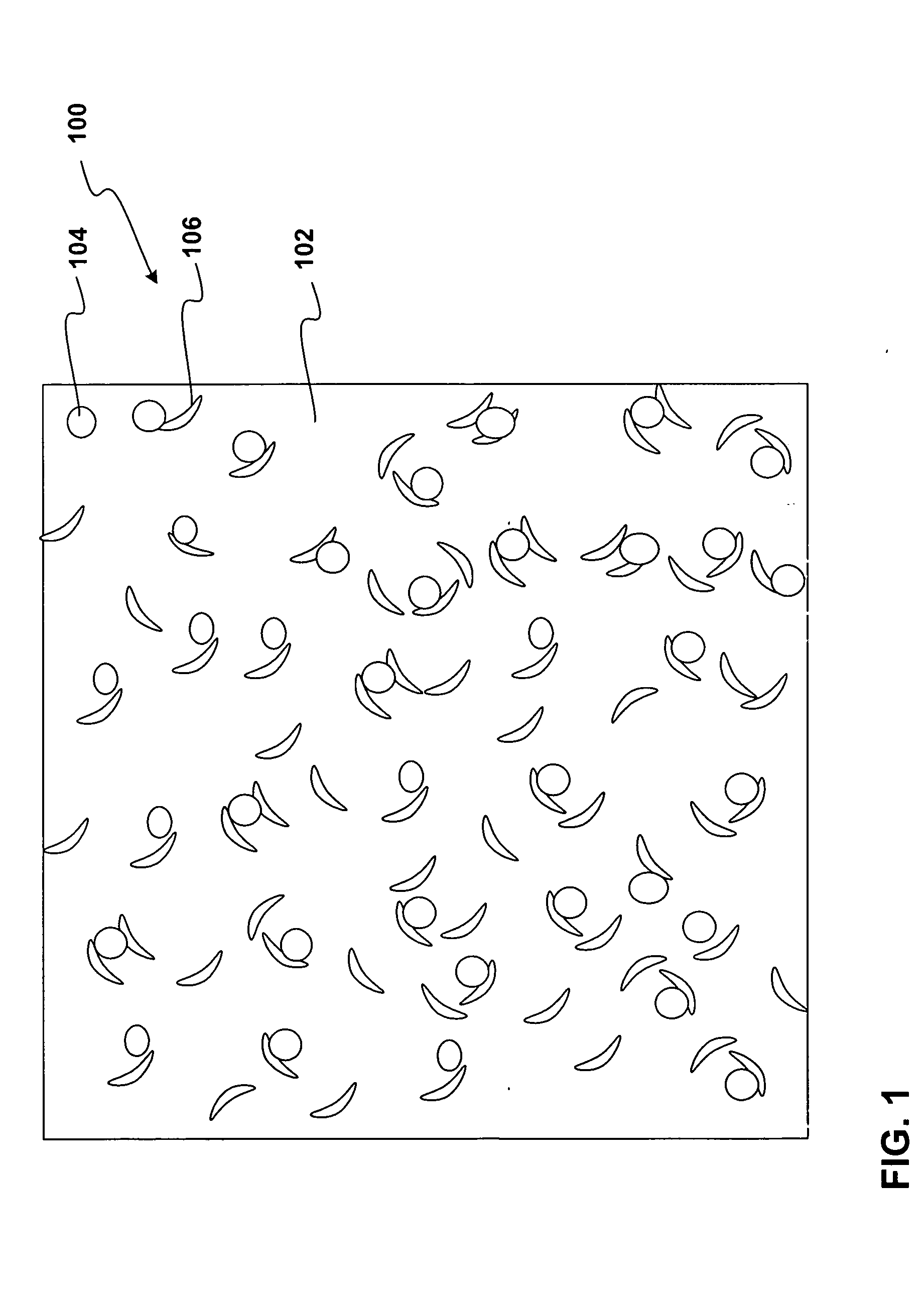
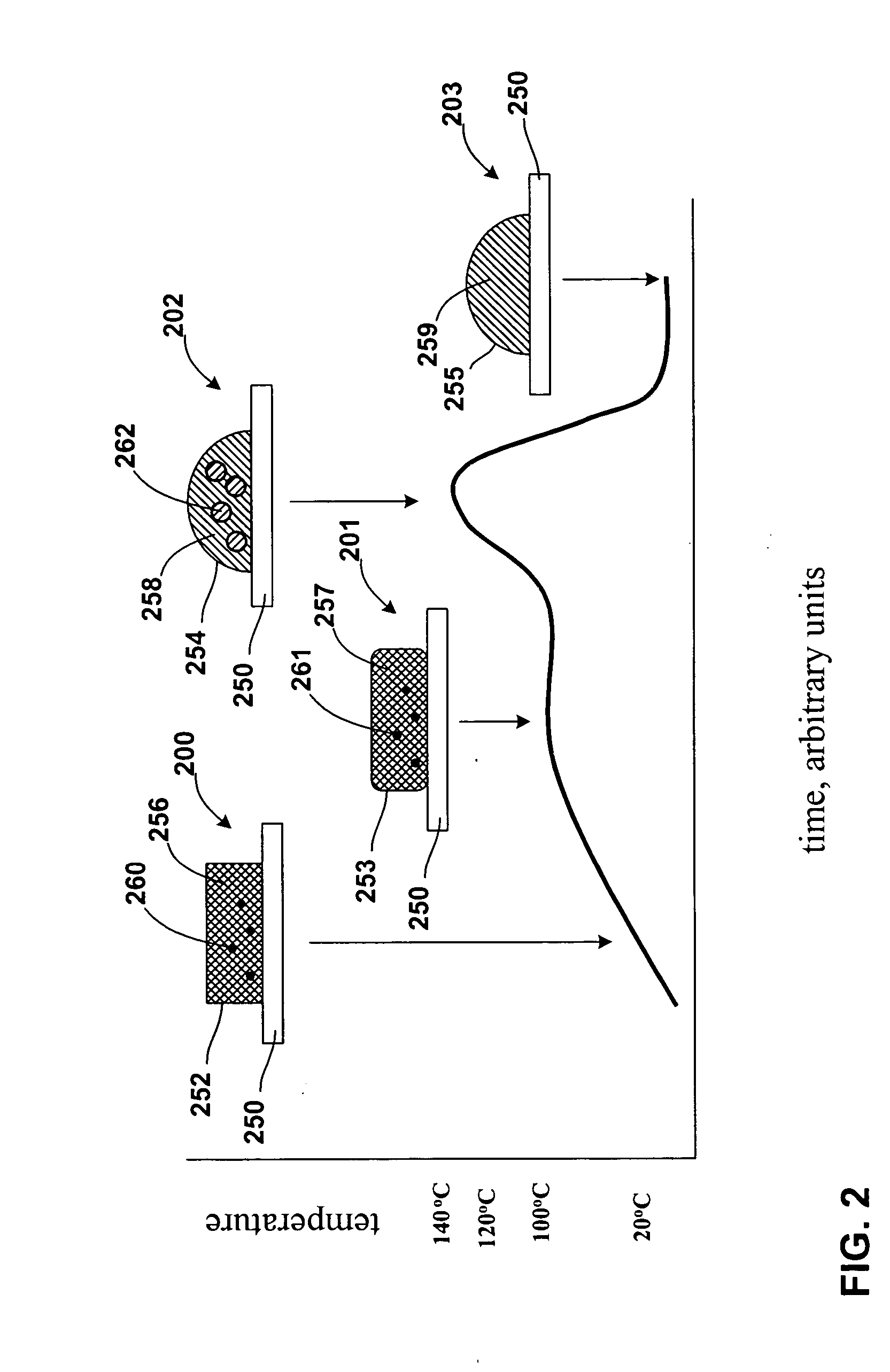
Stress-relief layers and stress-compensation collars with low-temperature solders for board-level joints, and processes of making same
InactiveUS20060068579A1Final product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsFlow stressManufacturing technology
A stress-relief layer is formed by dispensing a polymer upon a substrate lower surface under conditions to partially embed a low melting-point solder bump that is disposed upon the lower surface. The stress-relief layer flows against the low melting-point solder bump. A stress-compensation collar is formed on a board to which the substrate is mated, and the stress-compensation collar partially embeds the low melting-point solder bump. An article that exhibits a stress-relief layer and a stress-compensation collar is also included. A computing system that includes the low melting-point solder, the stress-relief layer, and the stress-compensation collar is also included.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com