Patents
Literature
180 results about "Transistor count" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The transistor count is the number of transistors on an integrated circuit (IC). It typically refers to the number of MOSFETs (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistors, or MOS transistors) on an IC chip, as all modern ICs use MOSFETs. It is the most common measure of IC complexity (although the majority of transistors in modern microprocessors are contained in the cache memories, which consist mostly of the same memory cell circuits replicated many times). The rate at which MOS transistor counts have increased generally follows Moore's law, which observed that the transistor count doubles approximately every two years.
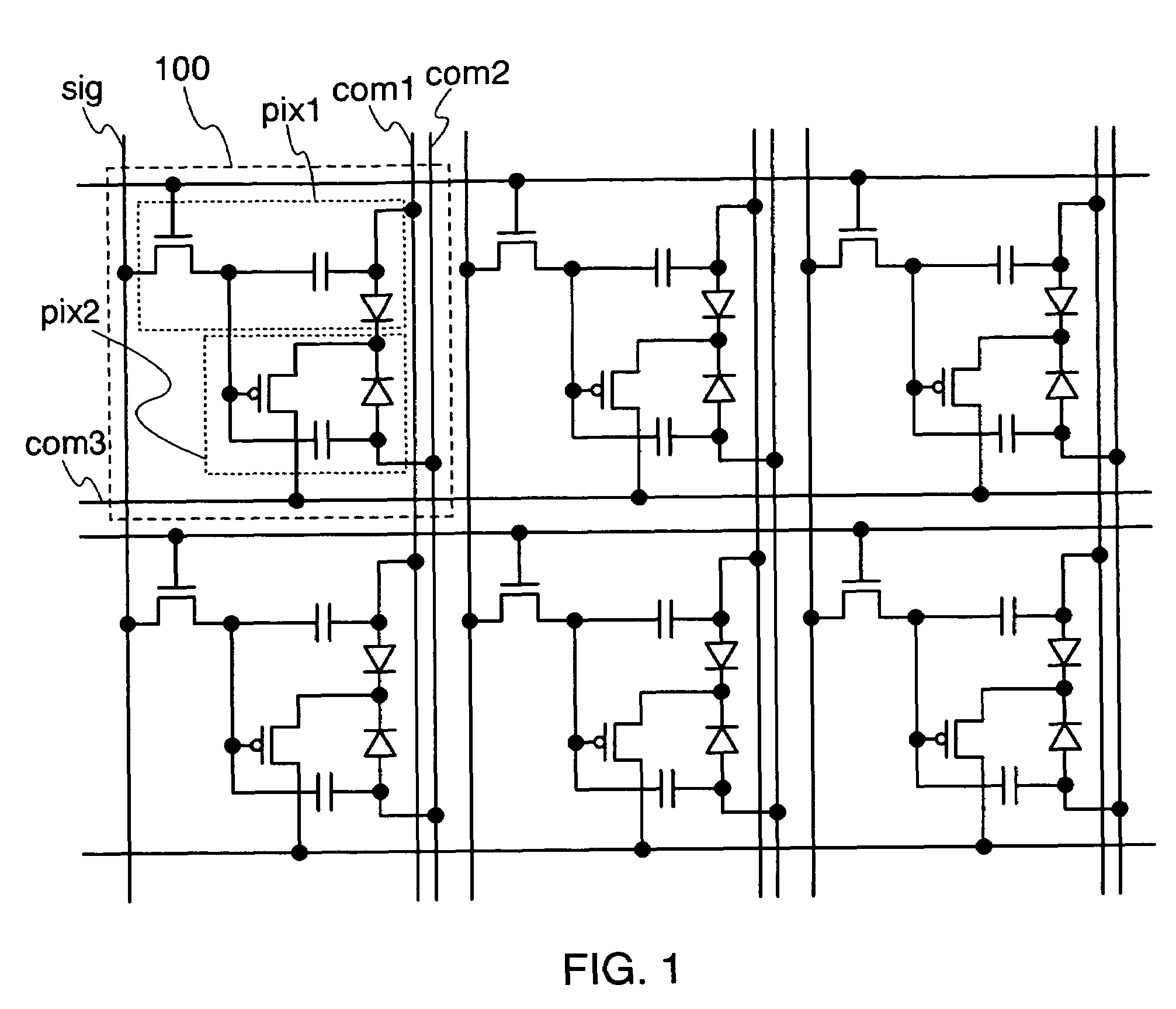
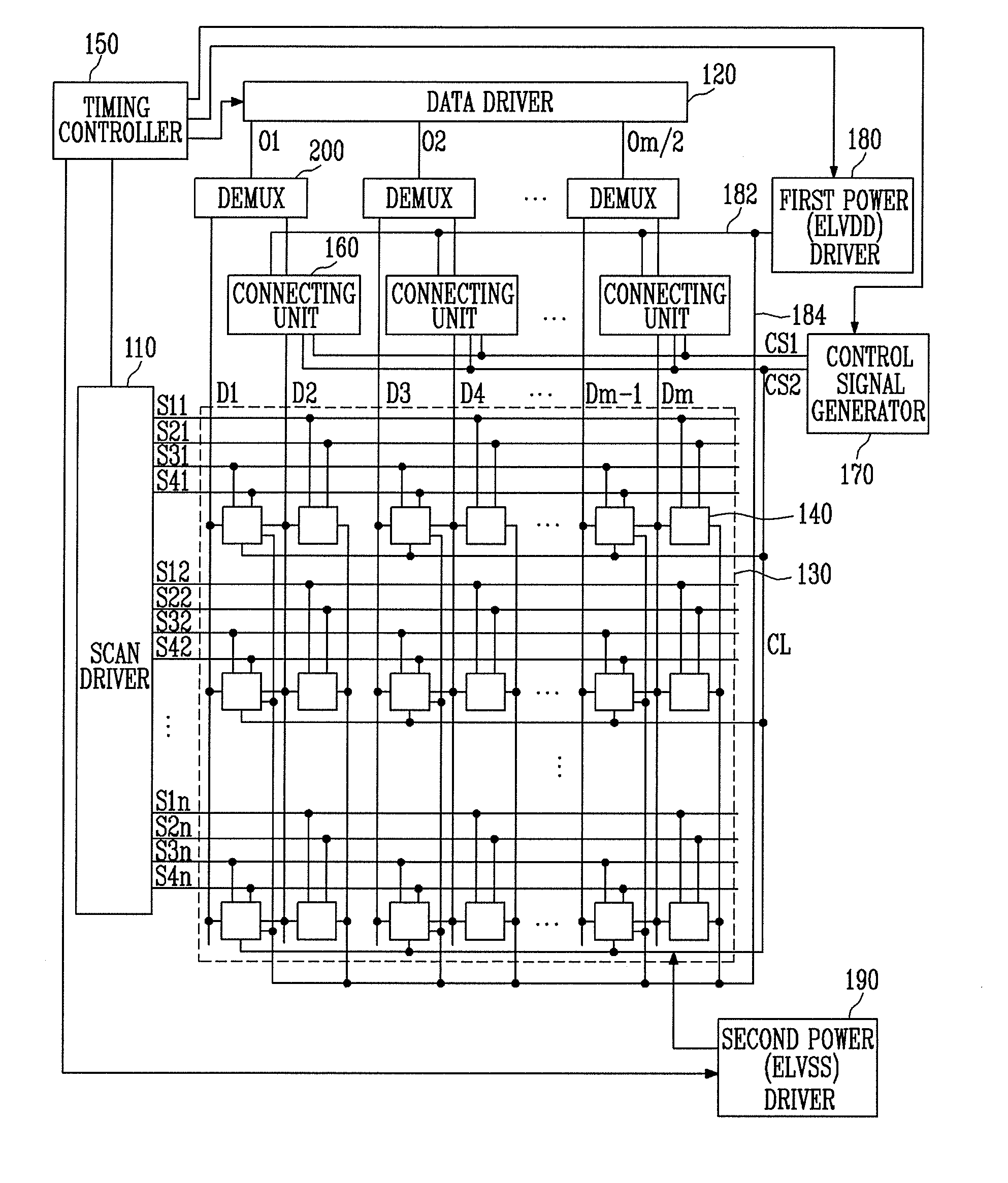
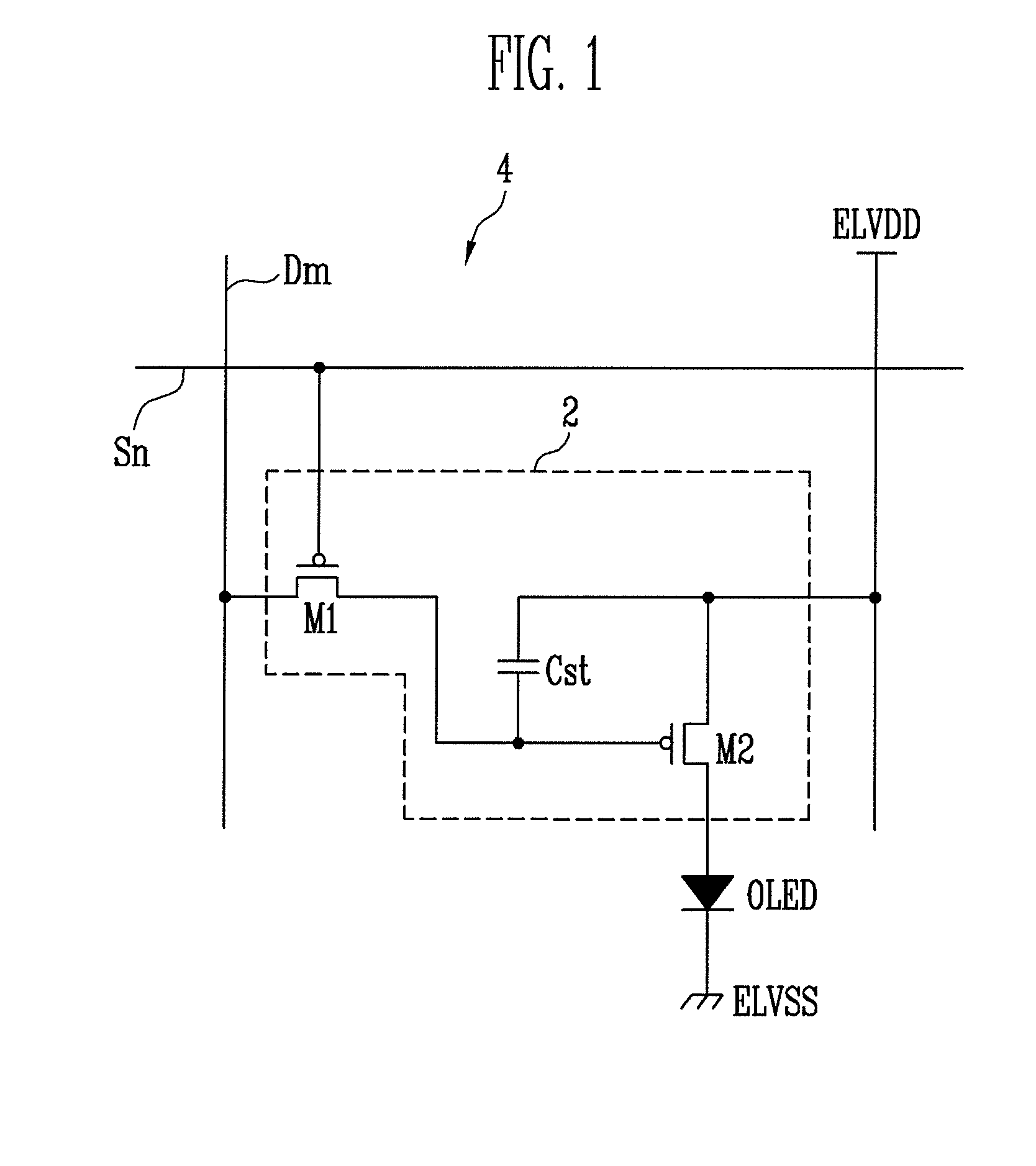
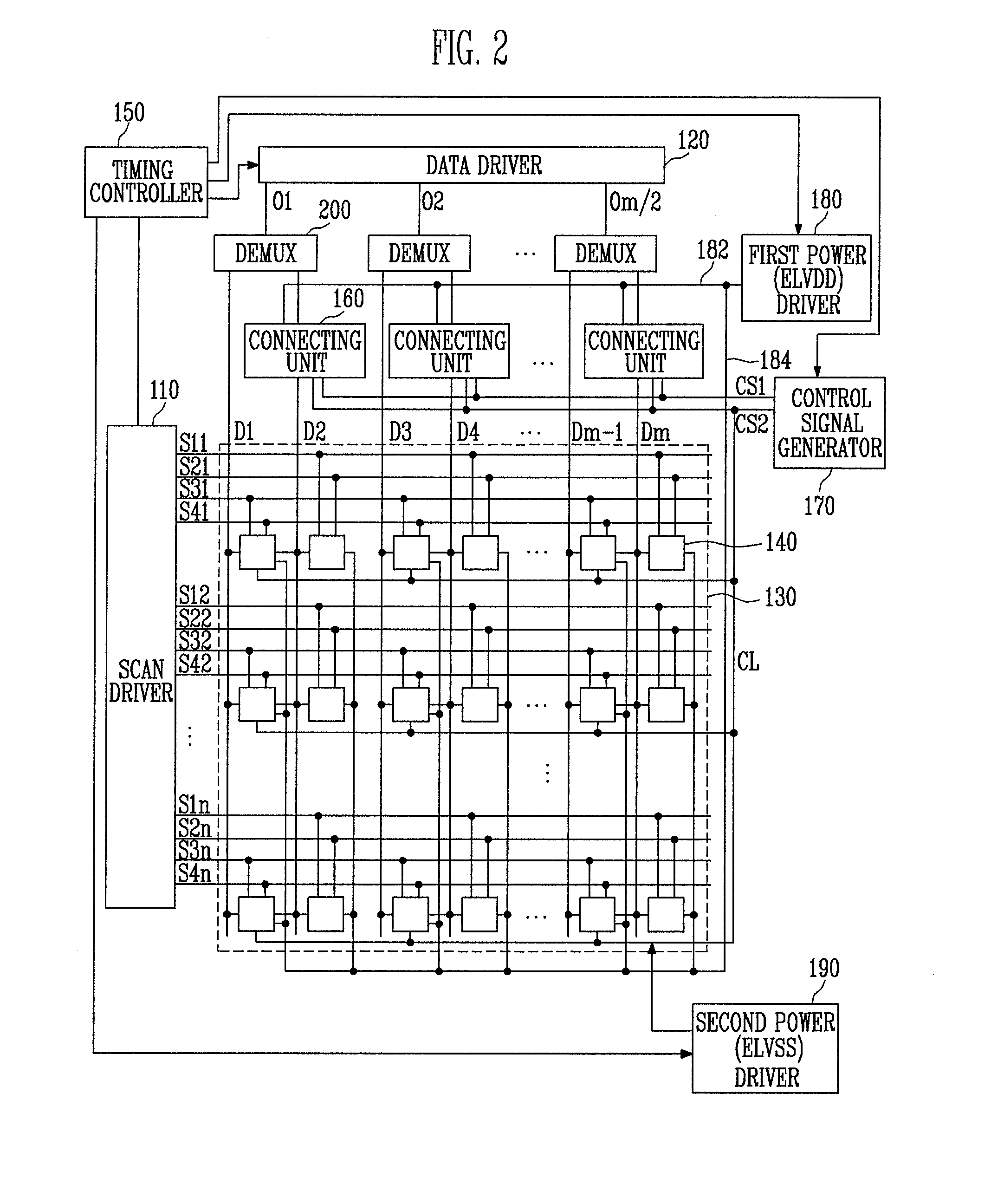
Active matrix organic light emitting diode display panel circuit
InactiveUS6970149B2Increase in sizeLower threshold voltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixDisplay device
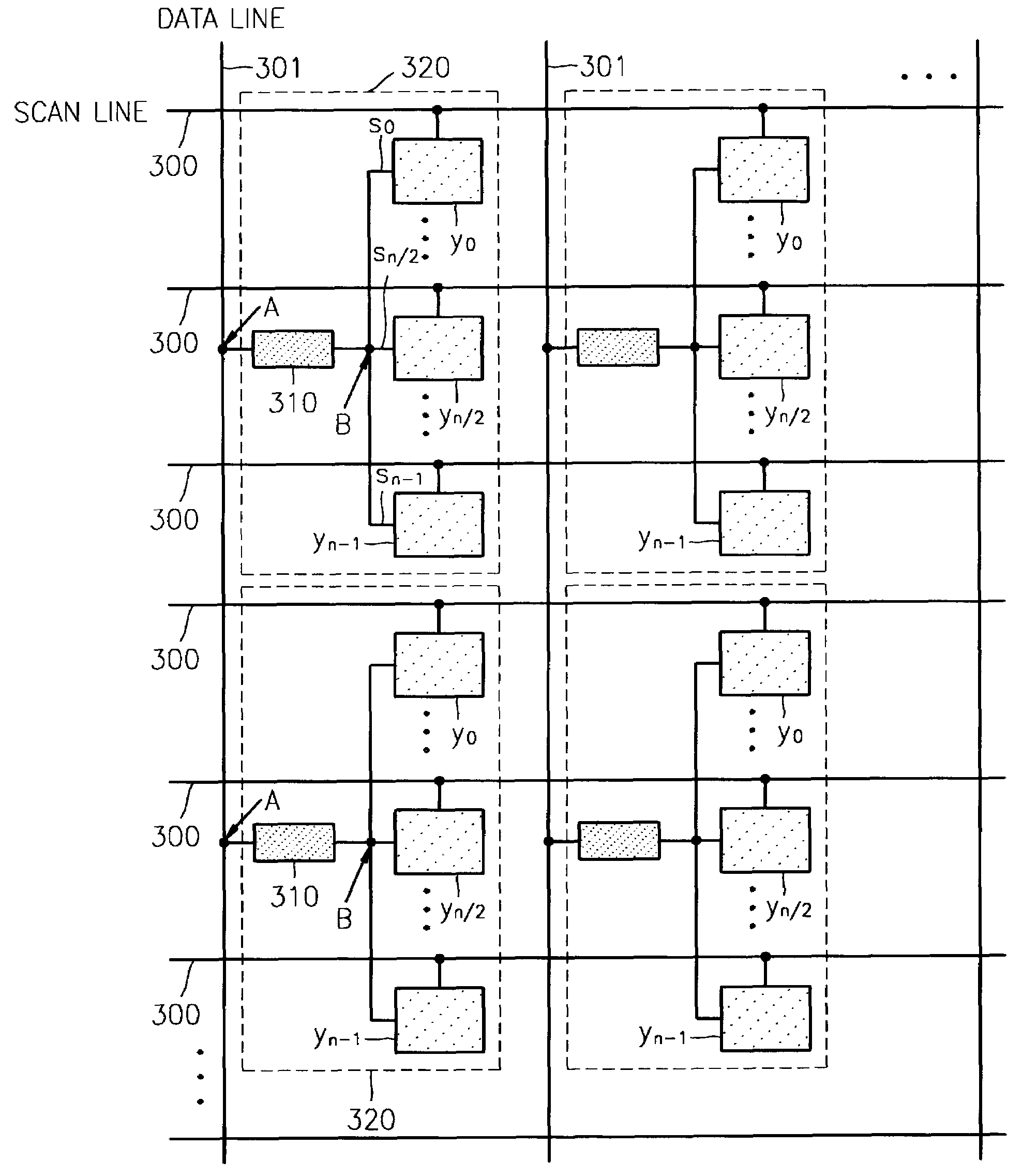
An active matrix organic light emitting diode display panel circuit capable of reducing current and brightness nonuniformities between pixels by including a threshold voltage compensation circuit block between a data line and the pixels is provided. The threshold voltage of a video signal loaded in a data line is compensated for while the video signal passes through the threshold voltage compensation circuit block and then provided to a driving transistor of the pixels. One threshold voltage compensation circuit block is connected commonly to a plurality of pixels, rather than be connected to every pixel, so that threshold voltage compensation can be achieved for high-quality, large-sized displays, without increasing the number of transistors for the pixels.
Owner:UNILOC 2017 LLC
Semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20070076467A1Reduce consumptionSmall sizeDigital storageSubthreshold leakage currentHemt circuits
An object of the present invention is to provide a technique of reducing the power consumption of an entire low power consumption SRAM LSI circuit employing scaled-down transistors and of increasing the stability of read and write operations on the memory cells by reducing the subthreshold leakage current and the leakage current flowing from the drain electrode to the substrate electrode. Another object of the present invention is to provide a technique of preventing an increase in the number of transistors in a memory cell and thereby preventing an increase in the cell area. Still another object of the present invention is to provide a technique of ensuring stable operation of an SRAM memory cell made up of SOI or FD-SOI transistors having a BOX layer by controlling the potentials of the wells under the BOX layers of the drive transistors.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
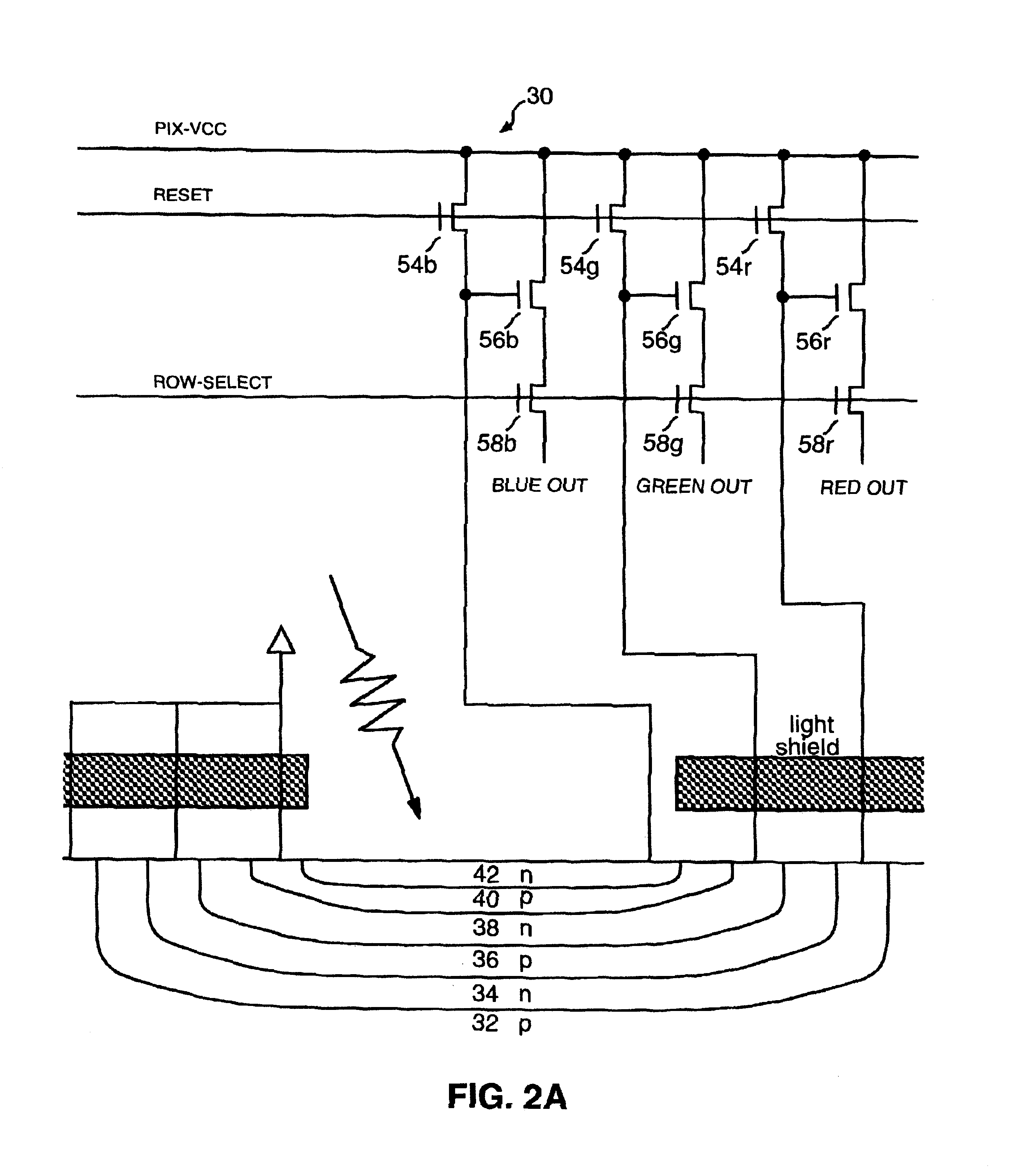
Simplified wiring schemes for vertical color filter pixel sensors
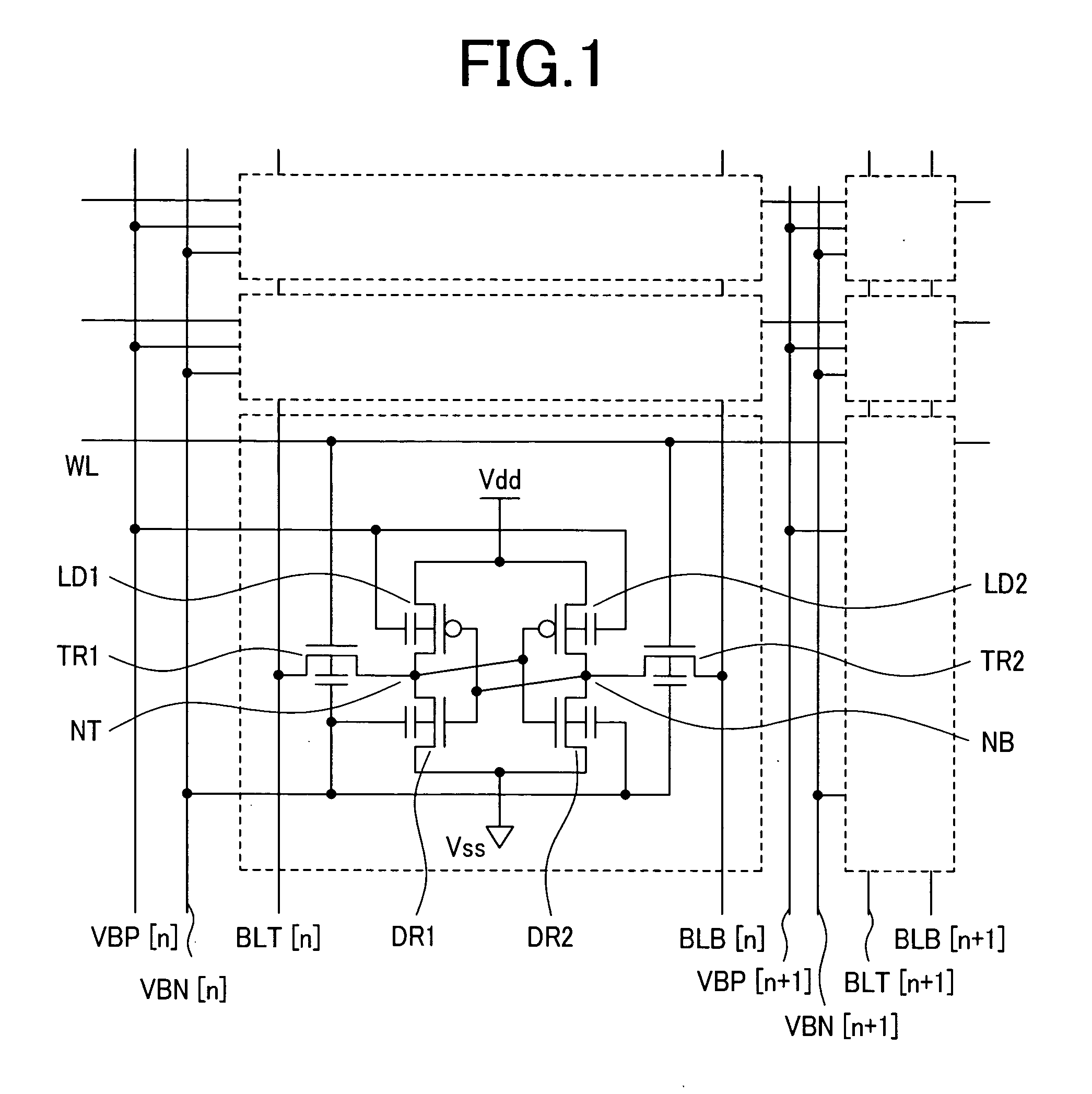
Vertical-color-filter pixel sensors having simplified wiring and reduced transistor counts are disclosed. In an embodiment, a single line is used for reference voltage, pixel reset voltage, and column-output signals in a VCF pixel sensor. In another embodiment, row-reset signals and row-enable signals are sent across a line that is shared between adjacent rows in an array of VCF pixel sensors. The present invention also provides an optimized layout for a VCF pixel sensor with shared row-reset, row-enable, reference voltage and column-output lines as well as a VCF pixel sensor in which source-follower voltage, source-follower amplifier voltage and row-enable signals all share a common line. These combined line embodiments can be used with a single column-output line as well as two row-enable lines. The embodiments can also be implemented in a VCF pixel sensor without a row-enable transistor.
Owner:FOVEON
Three-dimensional transistor with double channel configuration
ActiveUS20090321835A1Function increaseFurther scalabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringControllability
A three-dimensional double channel transistor configuration is provided in which a second channel region may be embedded into the body region of the transistor, thereby providing a three-state behavior, which may therefore increase functionality of conventional three-dimensional transistor architectures. The double channel three-dimensional transistors may be used for forming a static RAM cell with a reduced number of transistors, while also providing scalability by taking advantage of the enhanced controllability of FinFETS and nano pipe transistor architectures.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Two transistor nor device
A NOR gate includes is constructed with two asymmetric FinFET type transistors instead of the conventional four-transistor NOR gate. The reduction in the number of transistors from four down to two allows for significant improvements in integrated semiconductor circuits.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Light emitting device and electronic device
InactiveUS7462897B2Improve reliabilityPrevent degradationStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesReverse biasLight emitting device
The invention is made in view of solving problems in reduction in yield and an aperture ratio in accordance with an increase in the number of transistors which form a pixel, increase in power consumption for holding predetermined luminance to provide a light emitting device having a noble pixel configuration. A light emitting device of the invention includes a unit for applying a forward bias voltage to a first light emitting element so that a first pixel emits light and applying a reverse bias voltage to a second light emitting element, and a unit for applying a reverse bias voltage to the first light emitting element so that the first pixel emits no light and applying a forward bias voltage to the second light emitting element.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
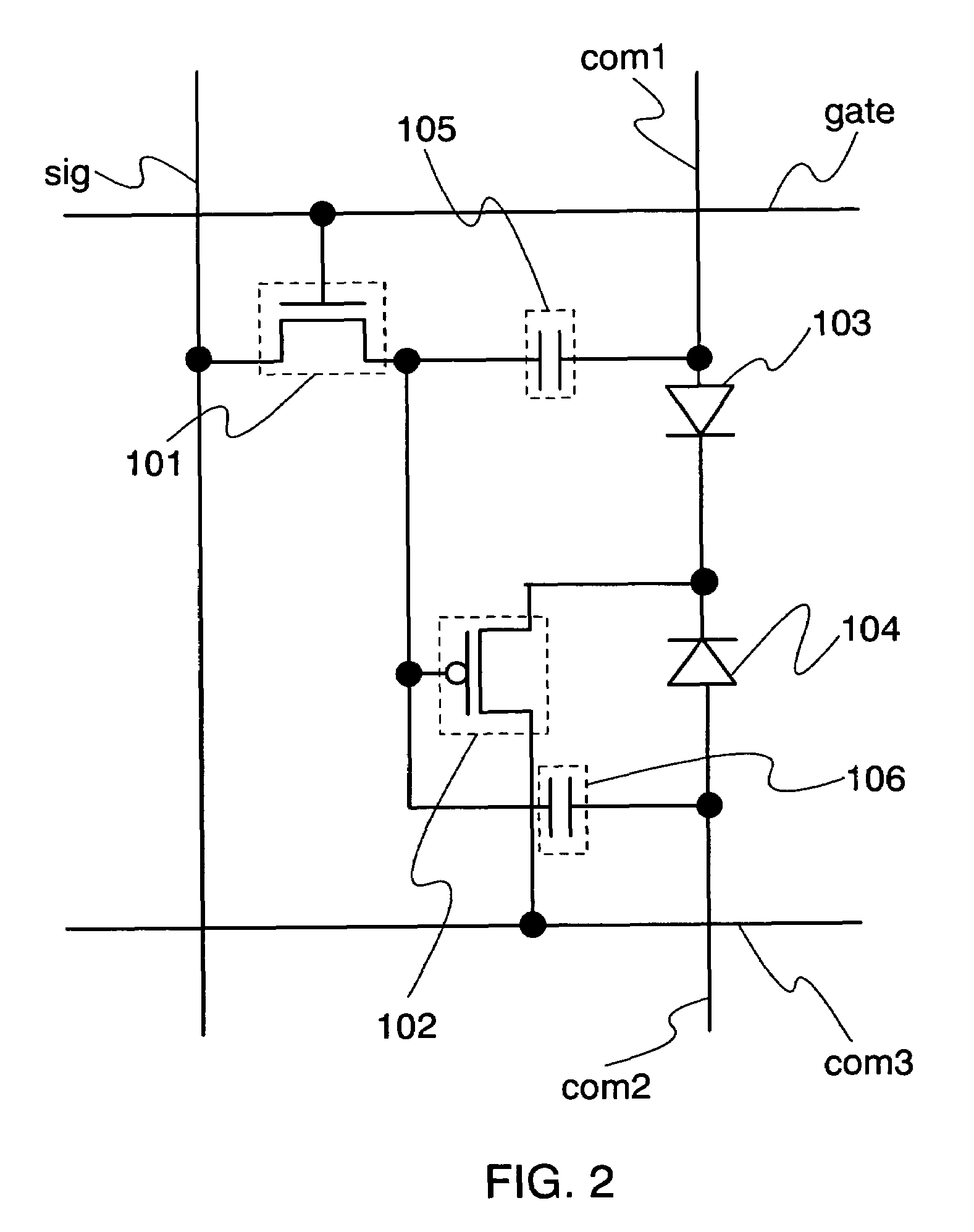
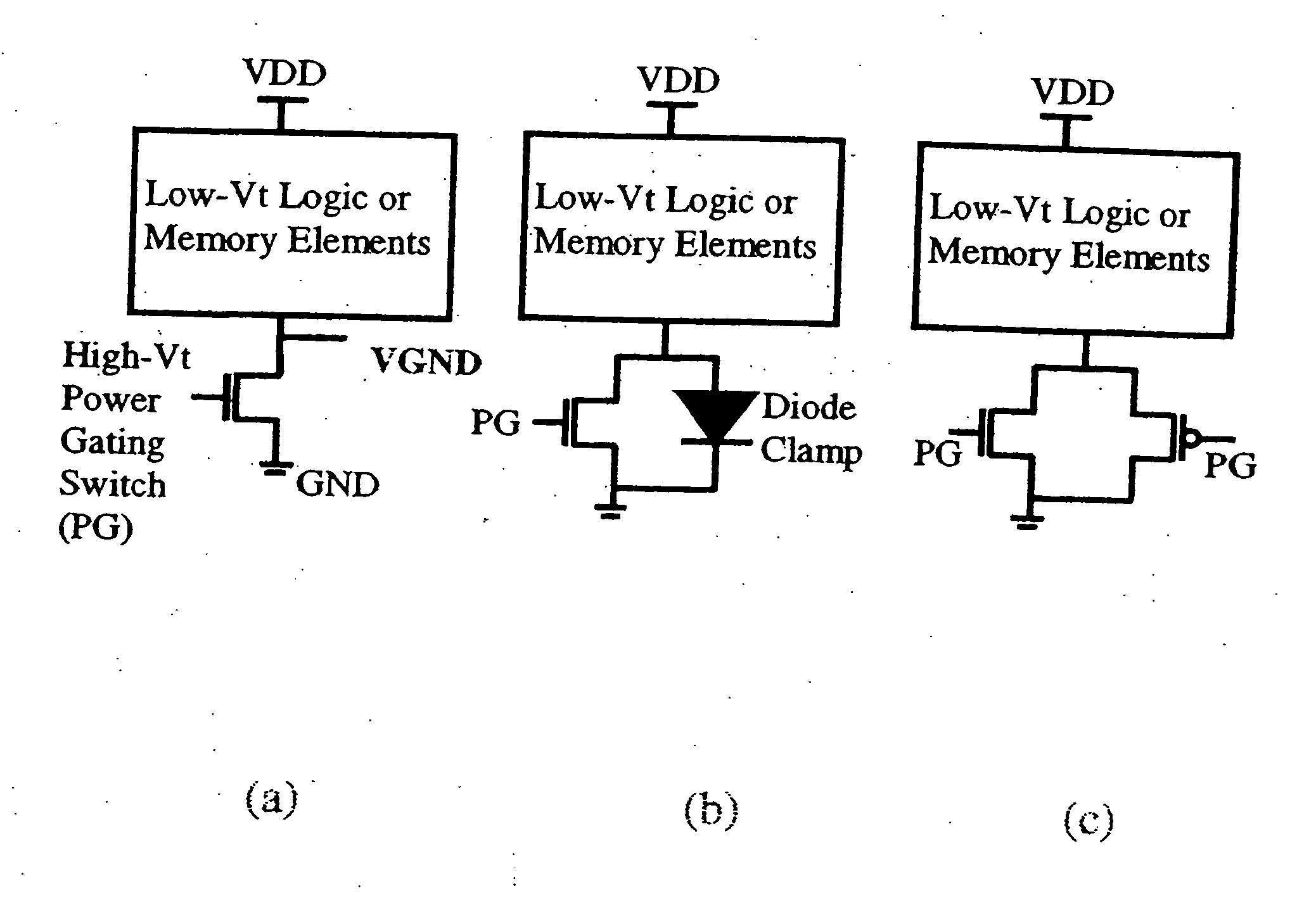
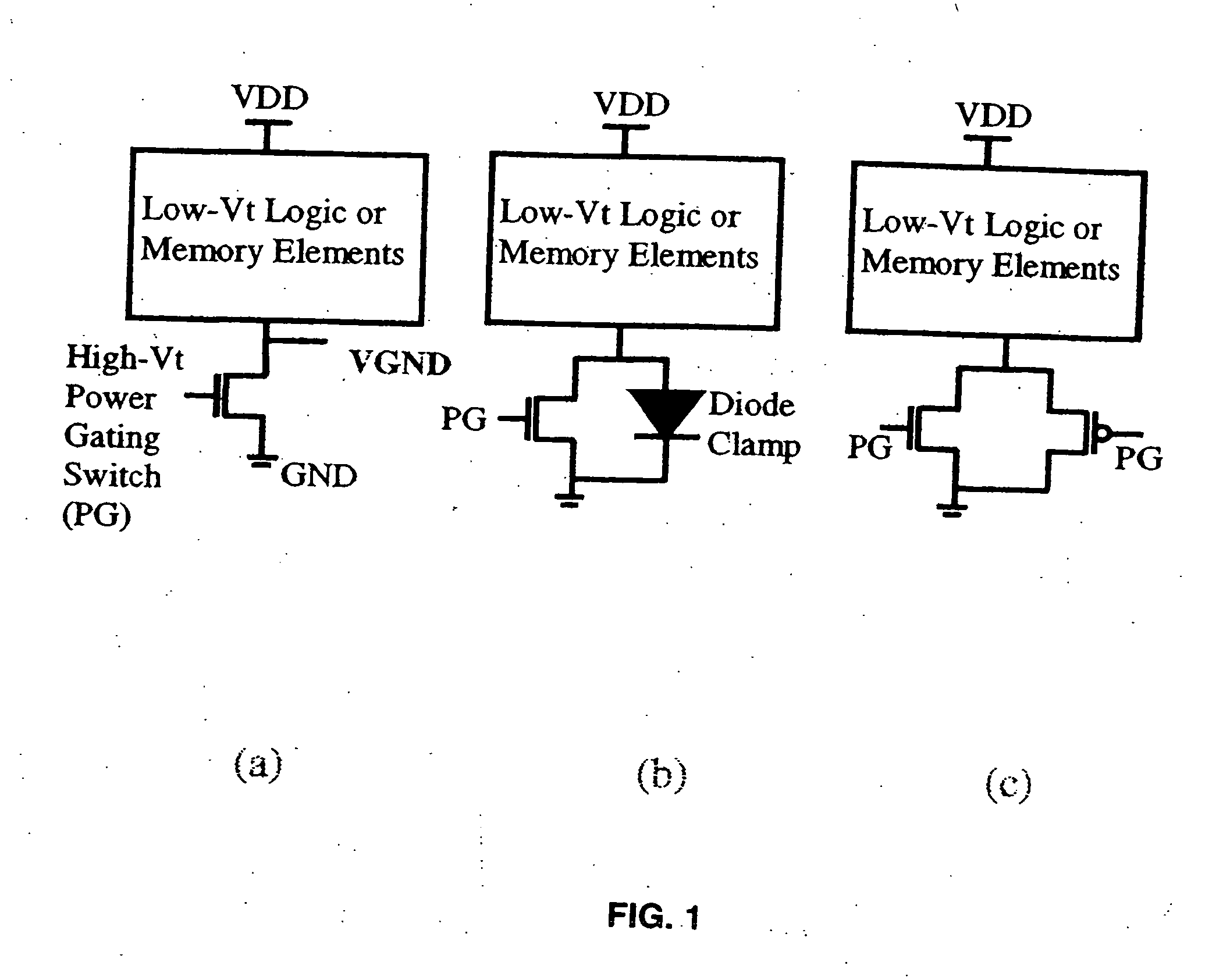
High-density low-power data retention power gating with double-gate devices
A new power gating structure with robust data retention capability using only one single double-gate device to provide both power gating switch and virtual supply / ground diode clamp functions. The scheme reduces the transistor count, area, and capacitance of the power gating structure, thus improving circuit performance, power, and leakage. The scheme is compared with the conventional power gating structure via mixed-mode physics-based two-dimensional numerical simulations. Analysis of virtual supply / ground bounce for the proposed scheme is also presented.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Methods and systems for network address lookup engines
InactiveUS20140219279A1Low power and die area efficiencyHigh speed packet dataratesTransmission path divisionCriteria allocationLongest prefix matchNetwork addressing
Internet routers are a key component in today's Internet. Each router forwards received packets toward their final destinations based upon a Longest Prefix Matching (LPM) algorithm select an entry from a routing table that determines the closest location to the final packet destination among several candidates. Prior art solutions to LPM lookup offer different tradeoffs and that it would be beneficial for a design methodology that provides for low power large scale IP lookup engines addressing the limitations within the prior art. According to embodiments of the invention a low-power large-scale IP lookup engine may be implemented exploiting clustered neural networks (CNNs). In addition to reduced power consumption embodiments of the invention provide reduced transistor count providing for reduced semiconductor die footprints and hence reduced die cost.
Owner:MCGILL UNIV
Amplification type solid-state image pickup device and driving method therefor
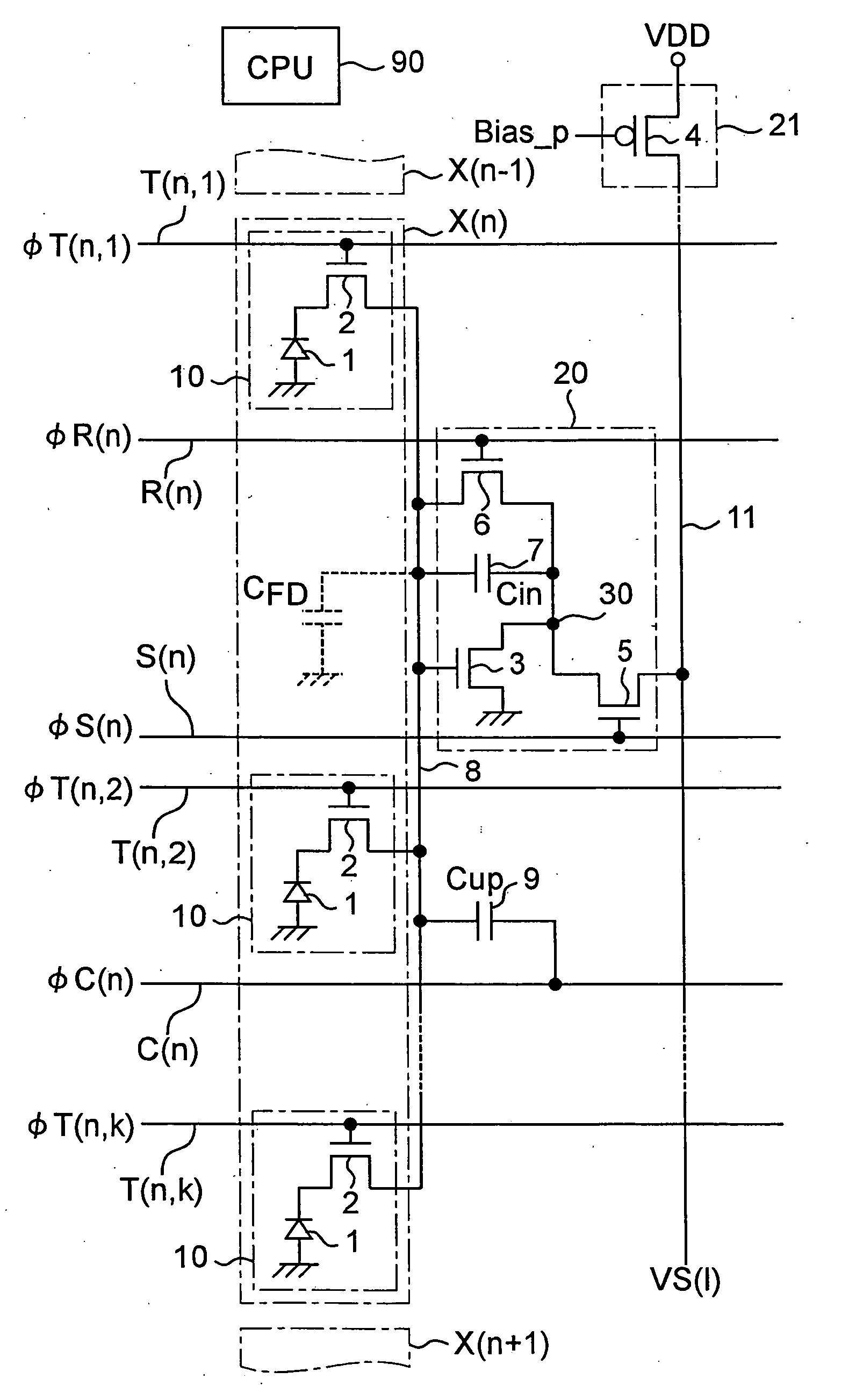
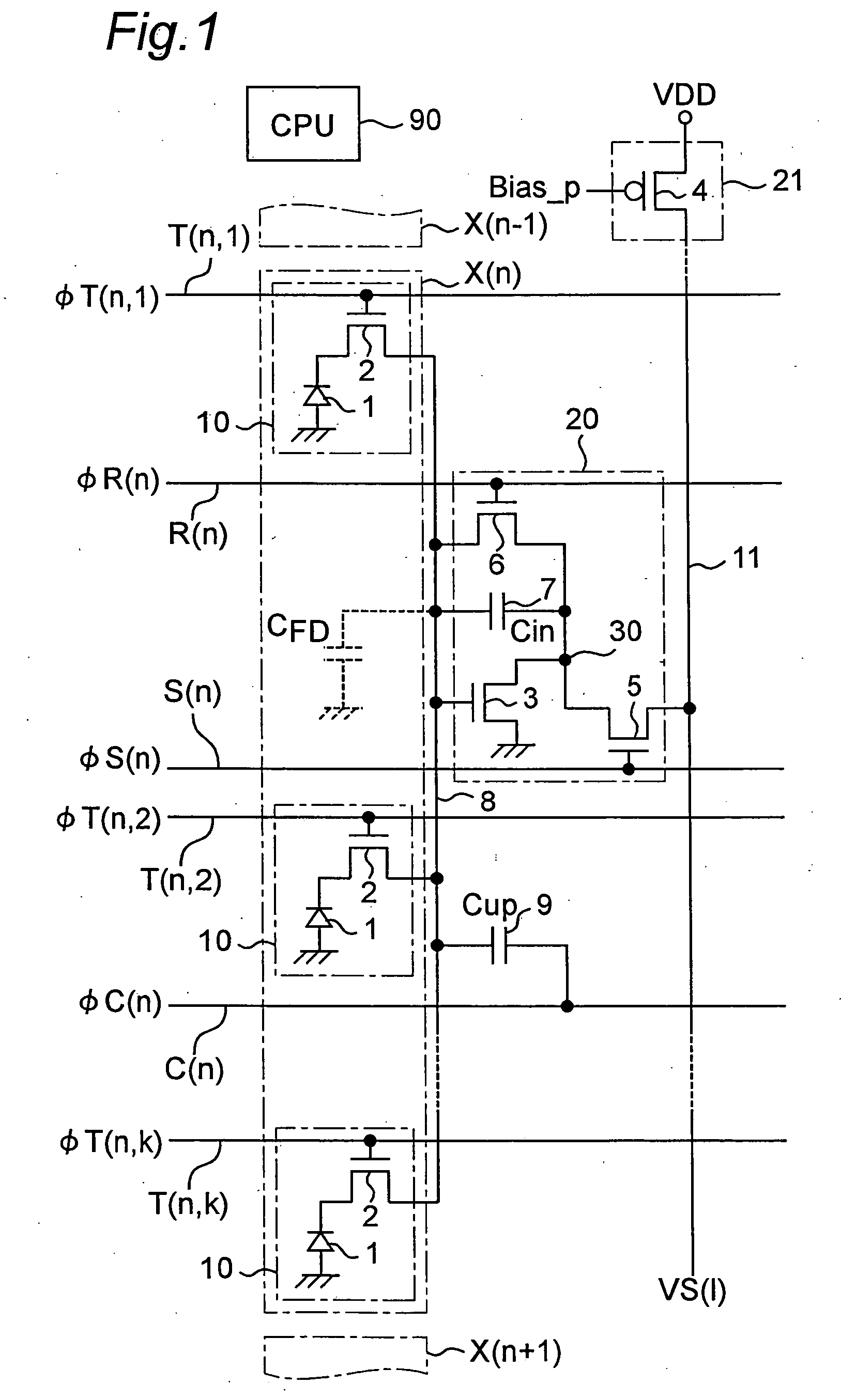
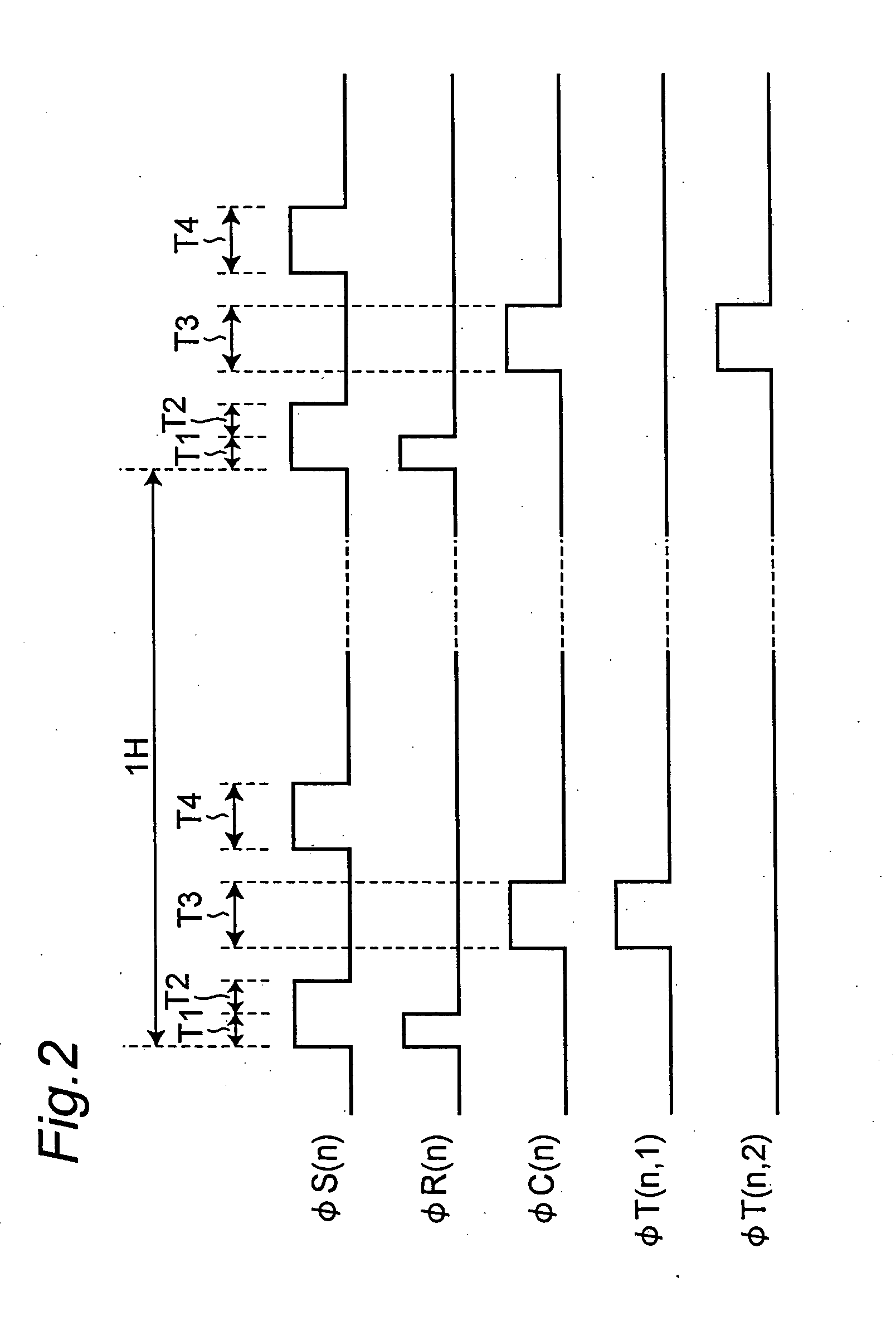
InactiveUS20050161712A1Noise-reduced high-quality imageShorten the counting processTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCapacitanceCharge detection
A plurality of pixel groups X(n) each comprising a plurality of pixels are set, and switched capacitor amplification parts are provided in correspondence to the pixel groups, respectively. Each of the switched capacitor amplification parts has a charge detection node to which output terminals of the transfer transistors of a corresponding pixel group X(n) are connected in common, an amplification part, a reset transistor, a first capacitance element, and a select transistor. A load part common to the switched capacitor amplification parts is provided. The load part is combined with the amplification parts of the switched capacitor amplification parts to constitute inverting amplifiers, respectively. By means of the above constitution, it is capable of obtaining a noise-reduced, high-quality image and which allows transistor count per pixel to be cut, thus allowing the pixel size to be reduced.
Owner:SHARP KK
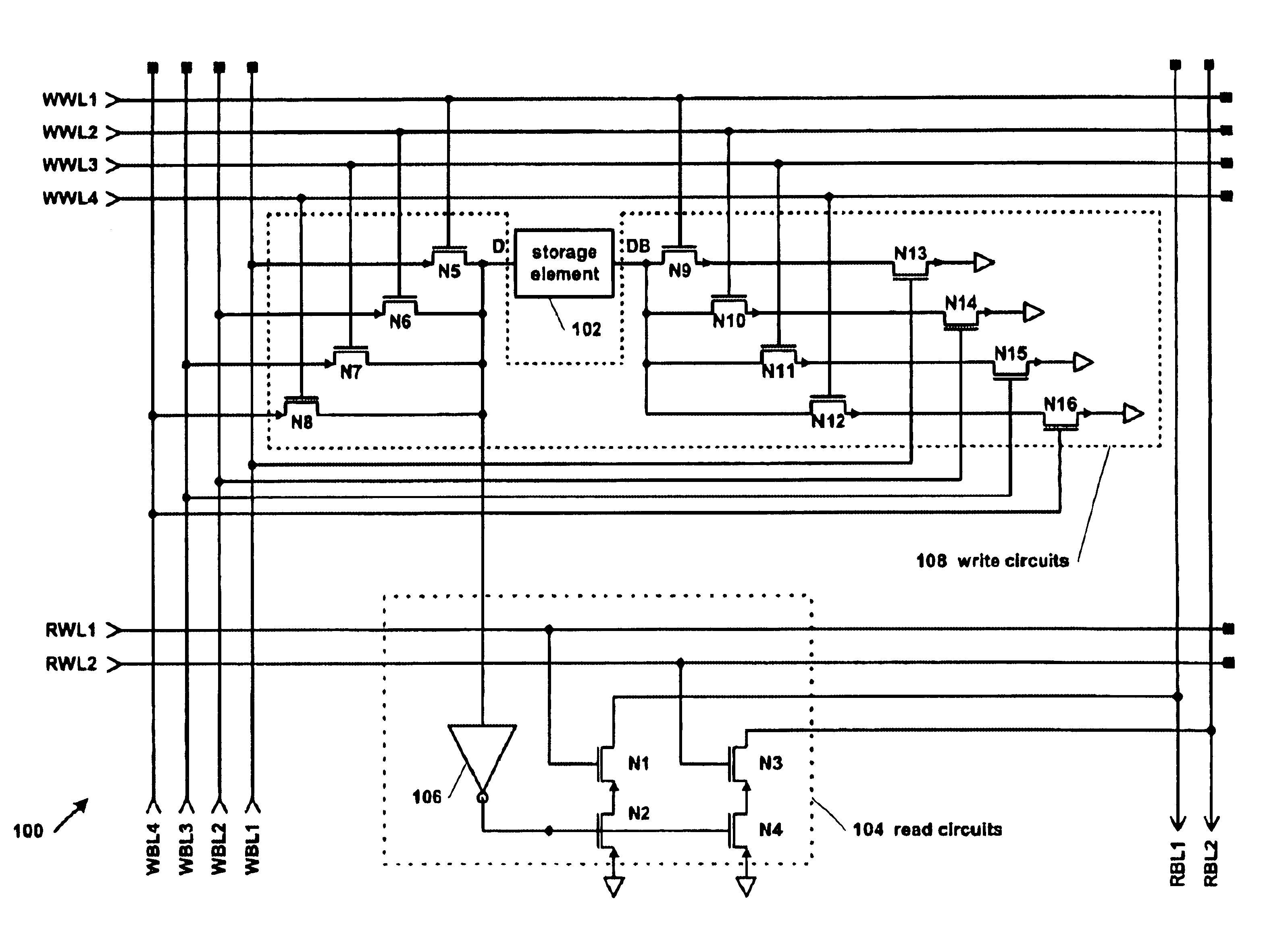
Reduced size multi-port register cell
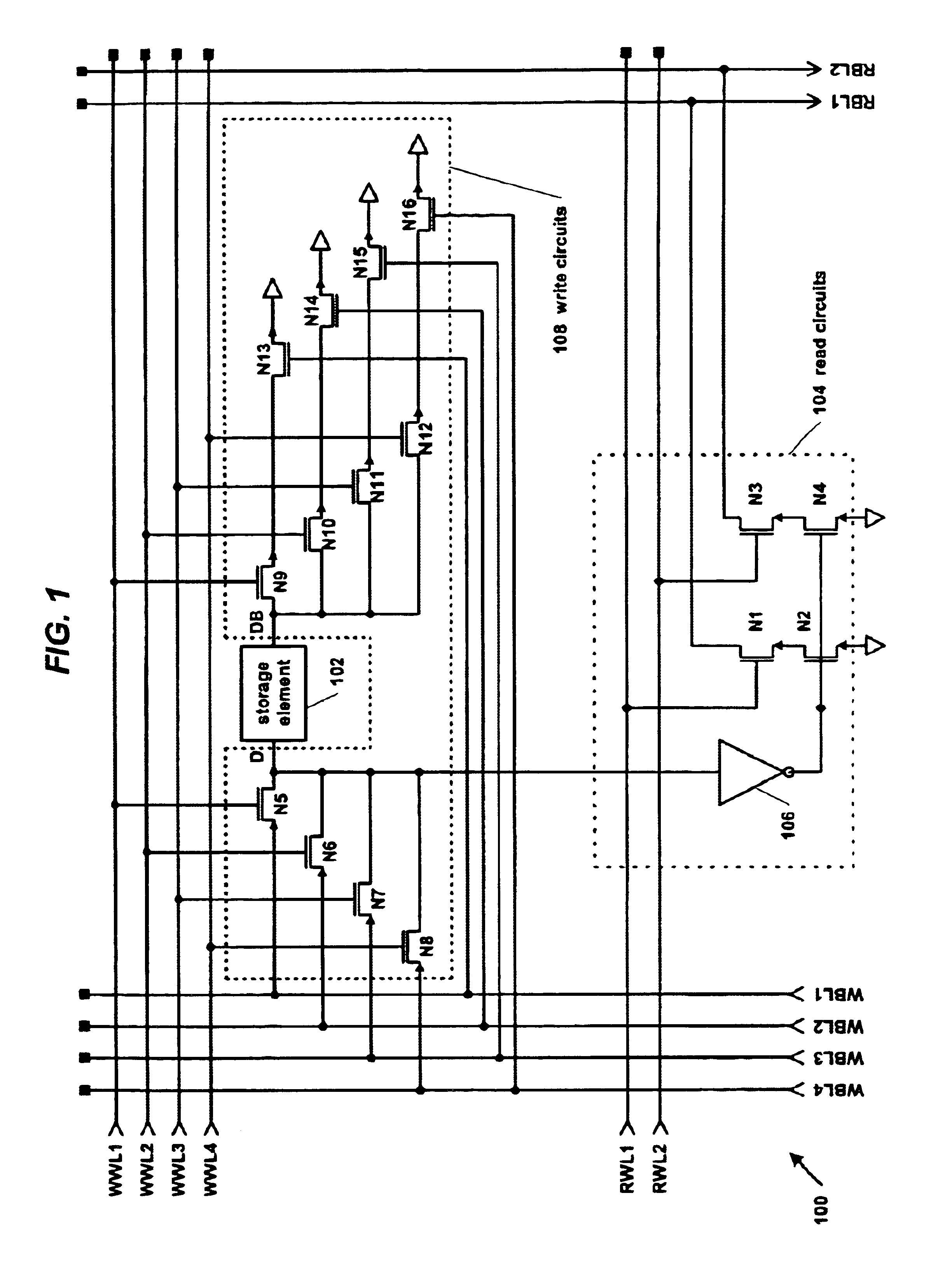
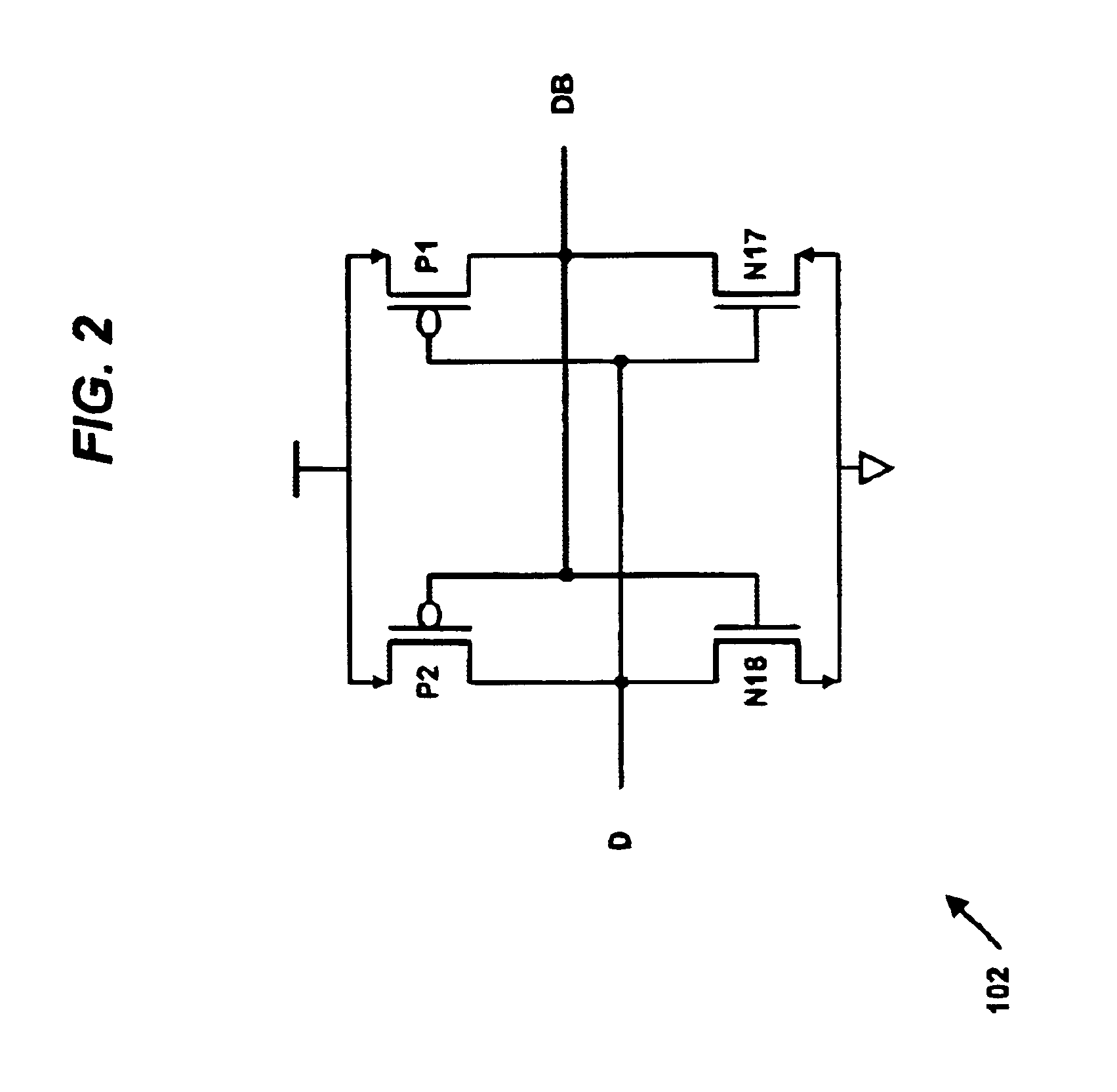
A multi-ported register cell that reduces the number of metal wires and / or transistors per write port. The cell includes a storage element that stores a bit. Each write port includes three transistors and two wires. The first transistor is coupled to a true input of the storage element. The second transistor is coupled to a complement input of the storage element. The first wire selectively turns on the first and second transistors of one of the ports. The second wire provides the update value. The third transistor selectively couples the second transistor to ground depending upon whether the second wire turns on the third transistor, thereby providing a complement of the update value to the second transistor. The cell also includes one or more read ports for reading the storage element bit. A multi-ported register file may be created from the cells.
Owner:IP FIRST
Semiconductor device
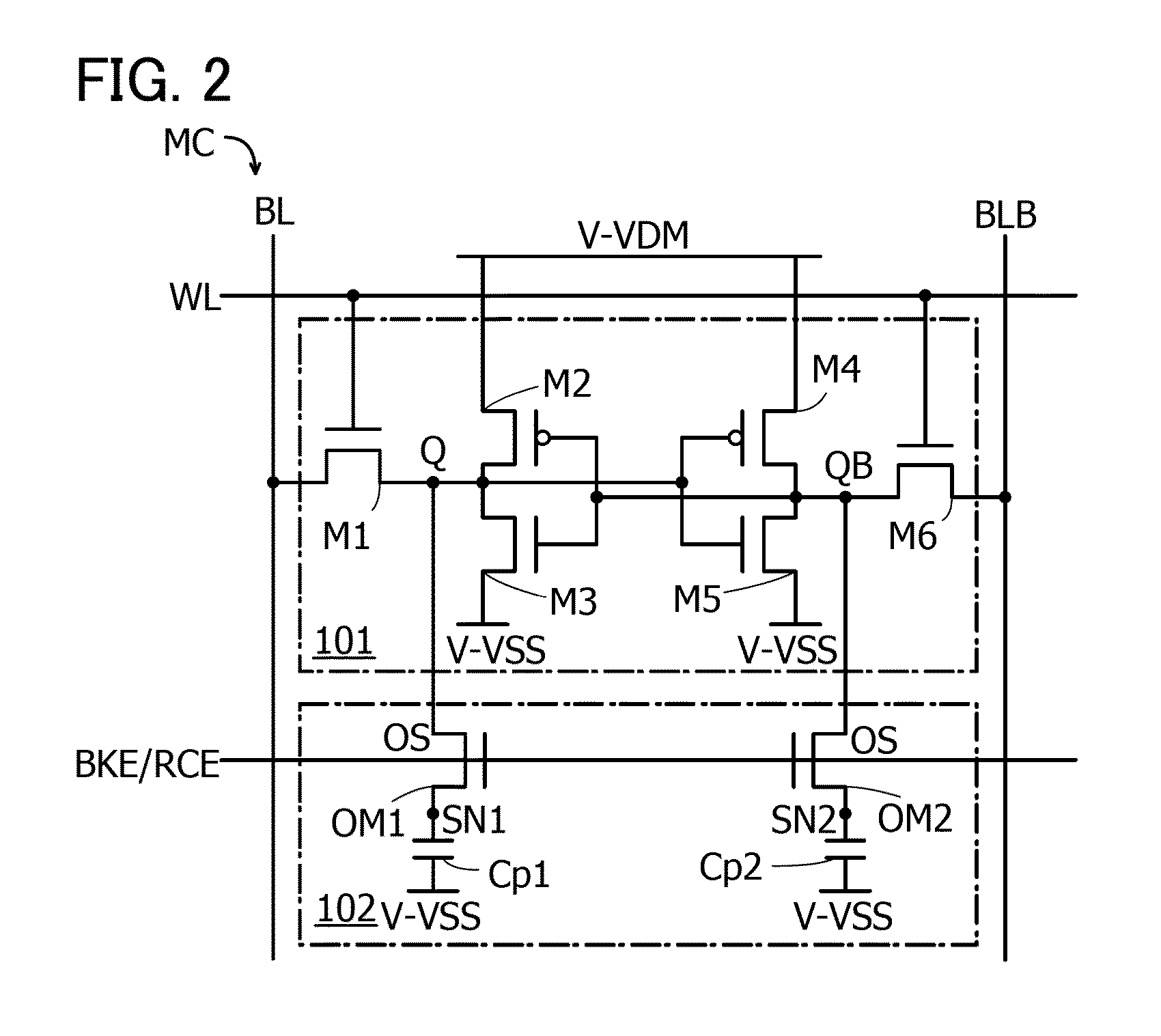
ActiveUS20130082760A1Reduce power consumptionCurrent flowStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesPower semiconductor deviceTransistor count
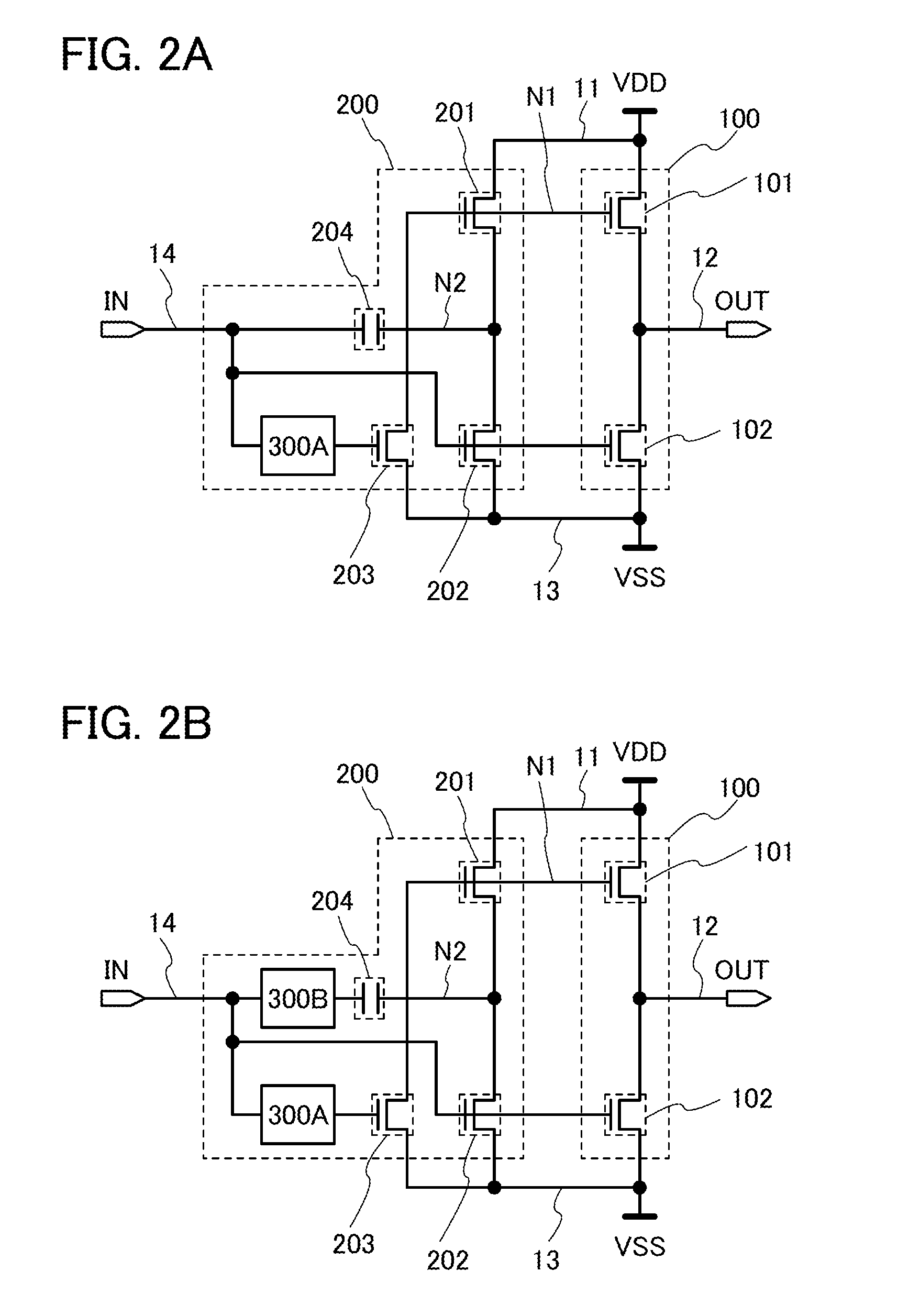
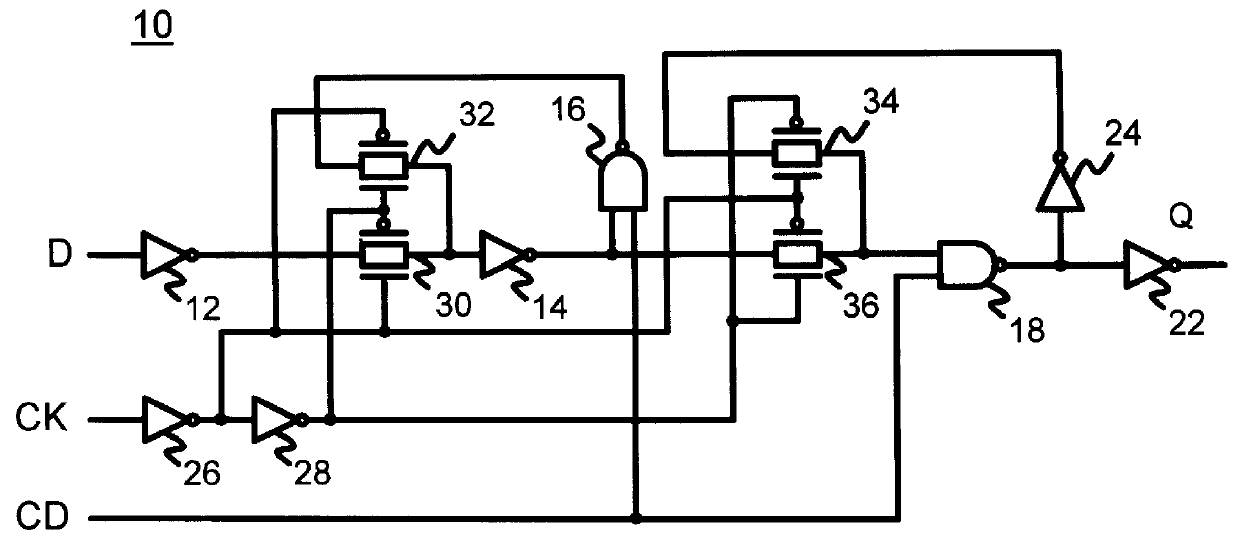
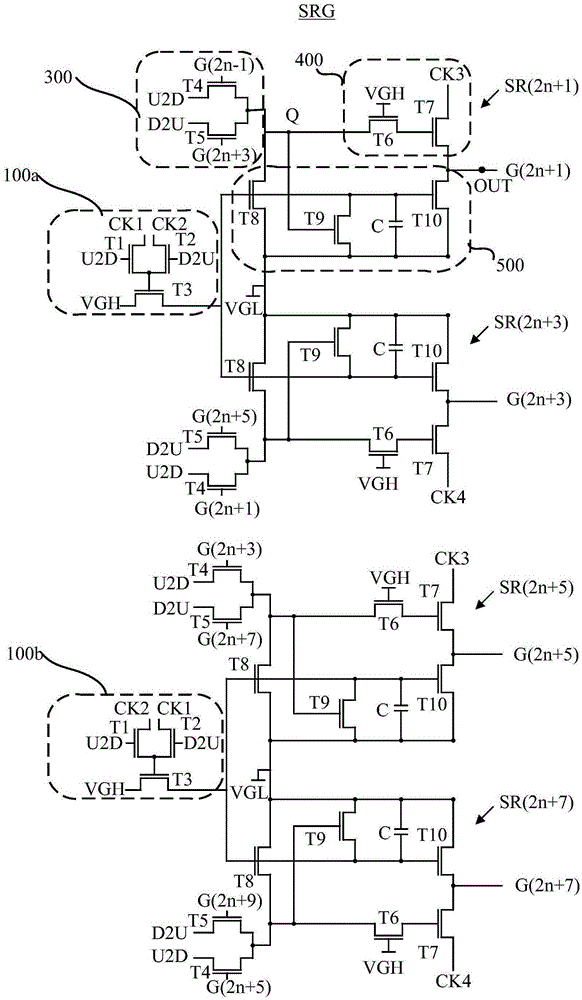
Provided is a semiconductor device exemplified by an inverter circuit and a shift register circuit, which is characterized by a reduced number of transistors. The semiconductor device includes a first transistor, a second transistor, and a capacitor.One of a source and a drain of the first transistor is electrically connected to a first wiring, and the other thereof is electrically connected to a second wiring. One of a source and a drain of the second transistor is electrically connected to the first wiring, a gate of the second transistor is electrically connected to a gate of the first transistor, and the other of the source and the drain of the second transistor is electrically connected to one electrode of the capacitor, while the other electrode of the capacitor is electrically connected to a third wiring. The first and second transistors have the same conductivity type.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Subunit, MAC array and bit width reconfigurable analog-digital hybrid in-memory calculation module
ActiveCN111431536AAvoid mismatchAvoid precision lossAnalogue/digital conversionElectric signal transmission systemsComputer hardwareComputer architecture
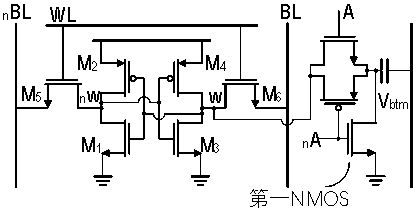
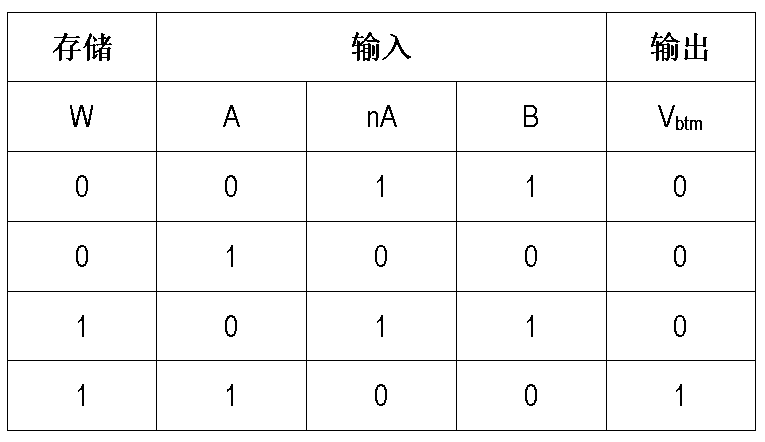
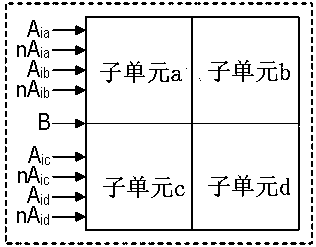
The invention relates to a subunit for analog-digital hybrid in-memory calculation for 1-bit multiplication, where only nine transistors are required. On this basis, it is provided that a plurality ofsubunits share a calculation capacitor and the transistors to form one calculation unit, so that the number of the transistors averaged from the subunits is close to eight. Then an MAC array is provided for multiply-add calculation, and comprises a plurality of calculation units, and the subunits in each unit are activated in a time division multiplexing mode. Furthermore, a differential system of the MAC array is provided, and the fault-tolerant capability of calculation is improved. Furthermore, the invention provides an analog-digital hybrid operation module used in the memory, which digitalizes the parallel analog output of the MAC array and performs the operation in other digital domains. The analog-to-digital conversion module in the operation module makes full use of the capacitorof the MAC array, so that the area of the operation module can be reduced, and the operation error can also be reduced. Furthermore, the invention provides a method for saving the energy consumption of the analog-to-digital conversion module by fully utilizing the data sparsity.
Owner:REEXEN TECH CO LTD
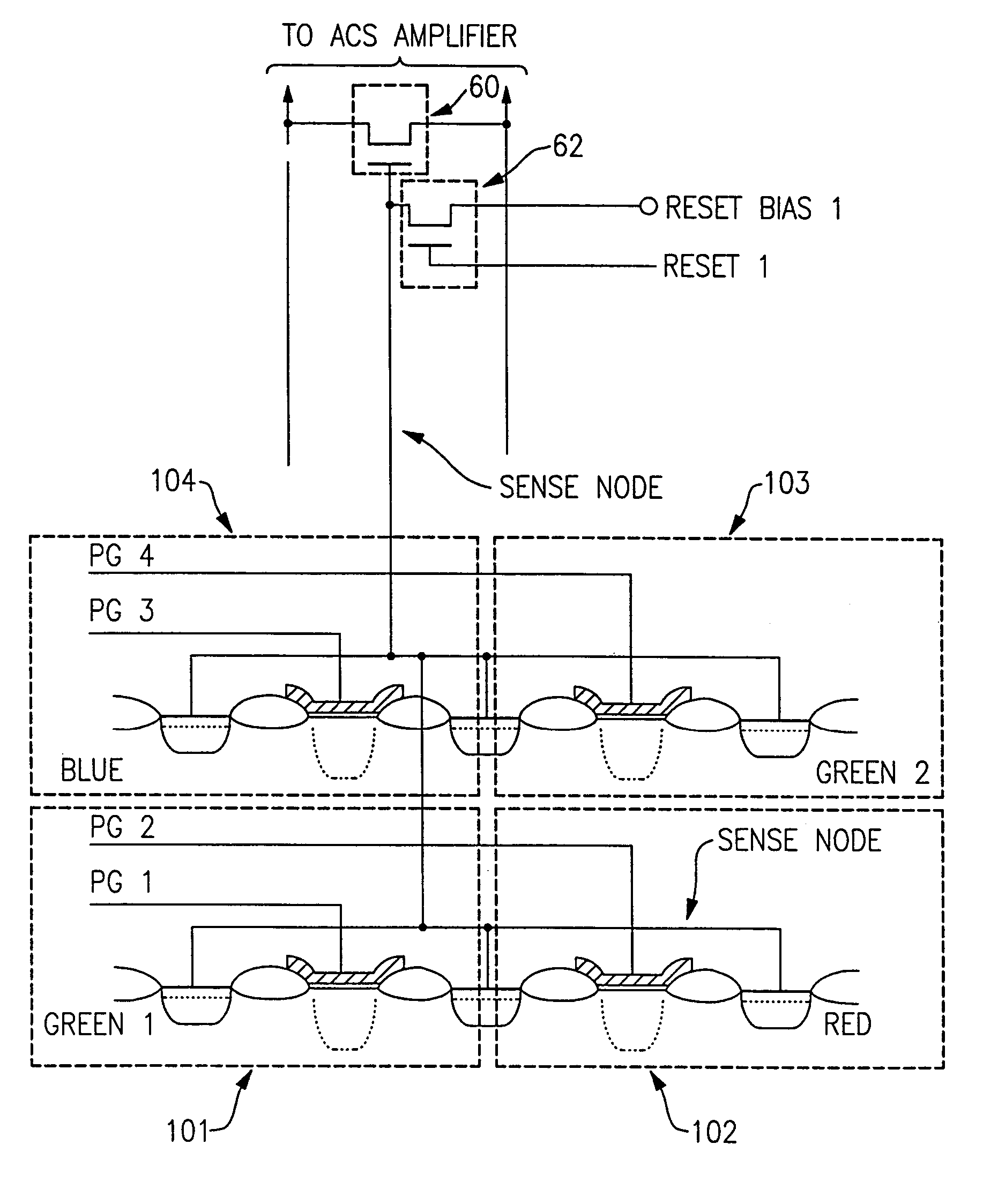
Solid state imager with reduced number of transistors per pixel
InactiveUS7057150B2Increases the amount of each pixelSimple structureTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A solid state imager with pixels arranged in columns and rows has the pixels are configured into groups of at least a first pixel and a second pixel, each said group sharing a pixel output transistor having a sense electrode and an output electrode and a reset transistor having a gate coupled to receive a reset signal and an output coupled to the sense electrode of the associated shared pixel output transistor. Each of the pixels has a photosensitive element whose output electrode is coupled to the sense electrode of the shared pixel output transistor and a gate electrode coupled to receive respective first and second pixel gating signals. This configuration reduces the number of FETs to two transistors for each pair of pixels, and also can achieve true correlated double sampling correction of FPN.
Owner:DYNAMAX IMAGING
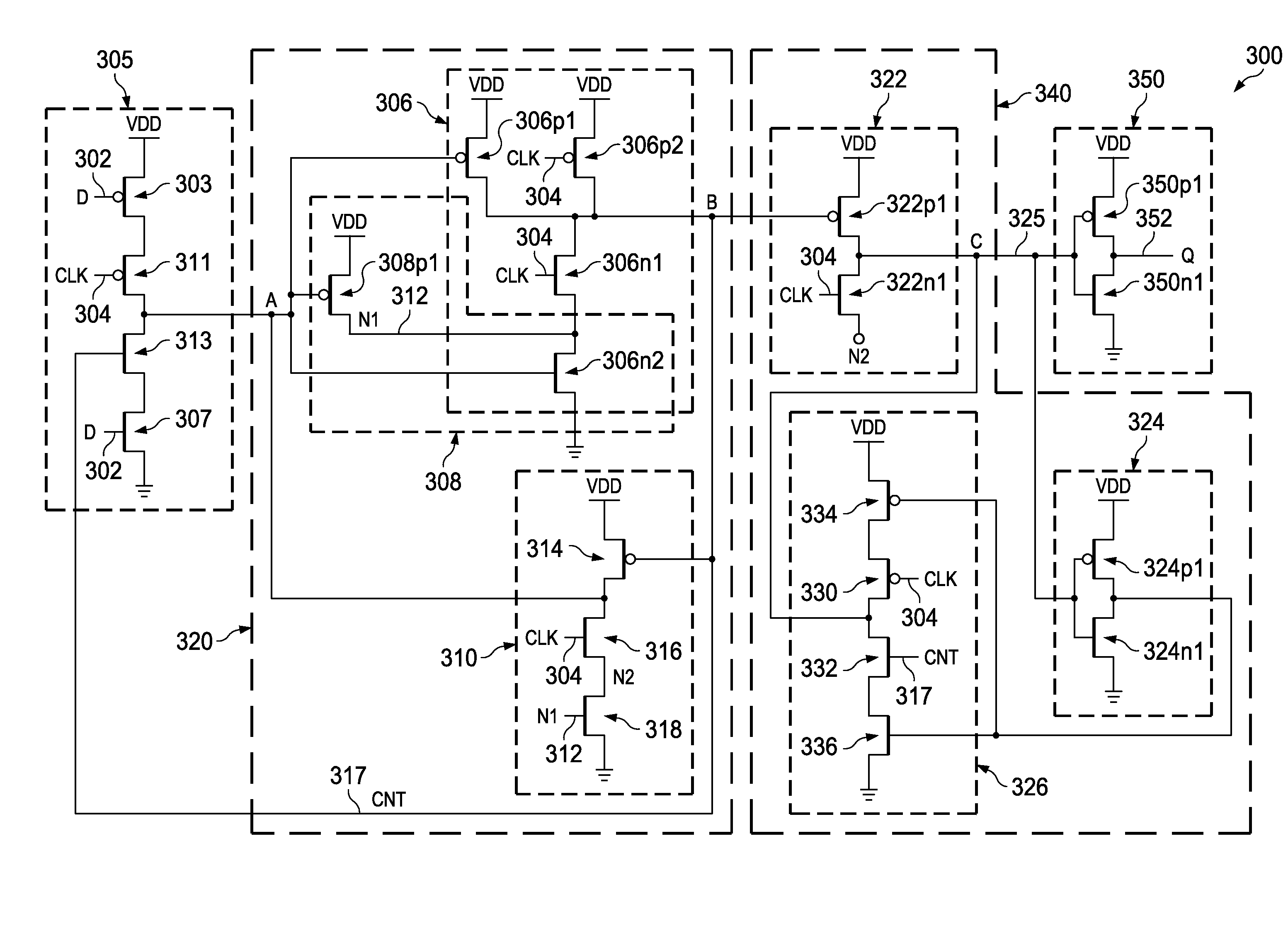
Versatile gate-array cell with interstitial transistors for compact flip-flops with set or clear
InactiveUS6144241AEasy to eliminateReduce in quantitySolid-state devicesElectric pulse generatorTransmission gateDirect feedback
A gate-array cell uses smaller and larger transistors. Four larger transistors are provided: two n-channel and two p-channel. A small p-channel transistor is placed between the contact tabs of the polysilicon lines of the two larger p-channel transistors, and between the p-channel transistors and a N-well tap. A small n-channel transistor is similarly placed between the contact tabs of polysilicon lines of the two larger n-channel transistors, and between the n-channel transistors and a P-well tap. The cell is slightly expanded in height to accommodate the two smaller transistors. The smaller transistors enable a reduction in the number of transistors required for latches and flip-flops. The smaller transistors allow a feedback inverter to directly connect to an input, since the input can easily over-power the feedback current. This is not possible for standard gate array cells having only one transistor size. Transmission gates are eliminated when direct feedback is feasible. Thus, the smaller transistors enable a reduction in transistor count as well as being smaller in size. Clear and set are provided by larger pull-down or pull-up transistors rather than NAND gates, since the larger pull-down and pull-up transistors can easily over-power the feedback inverters.
Owner:DIODES INC
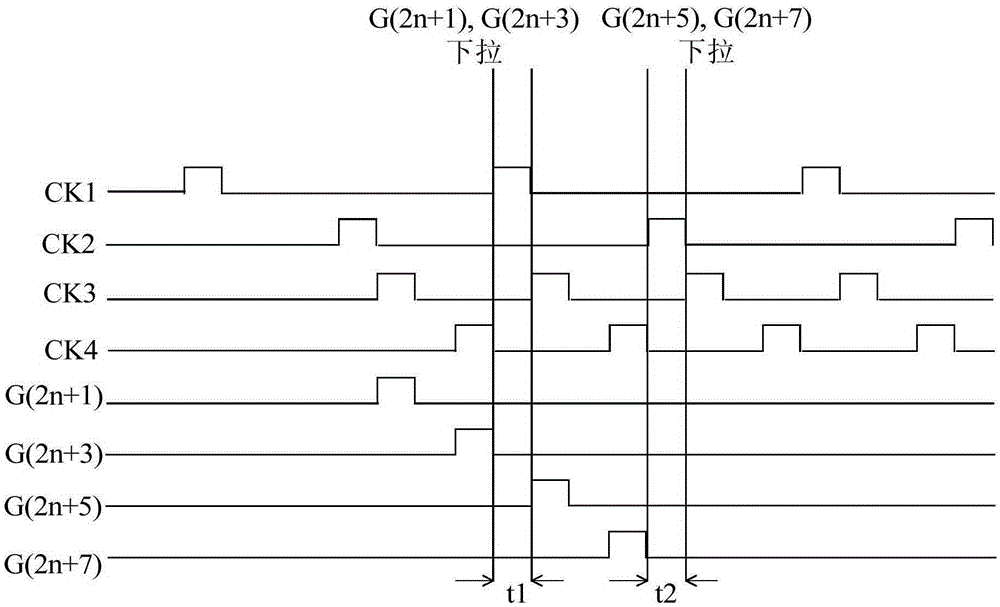
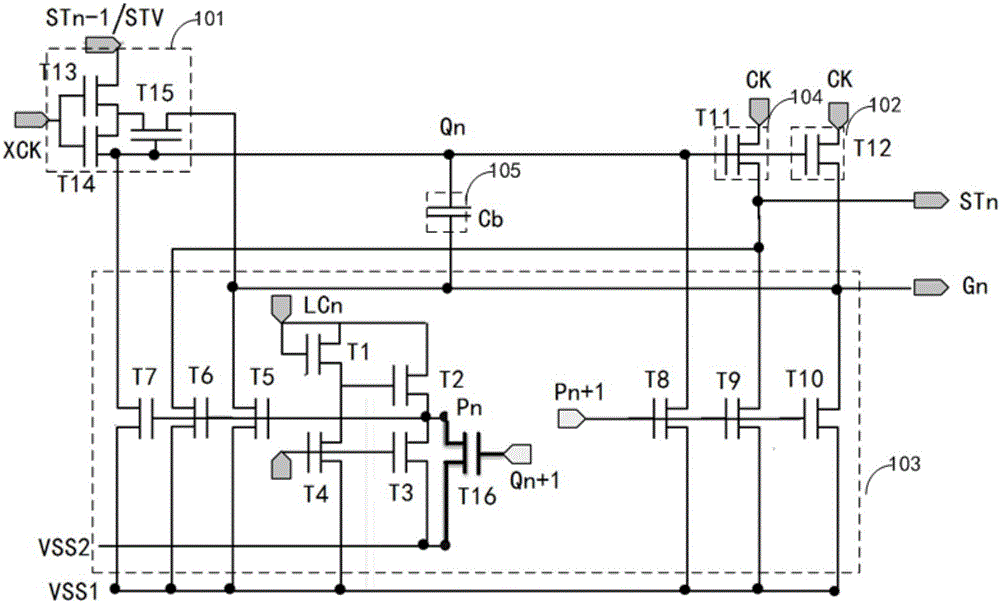
Gate drive circuit and display using same
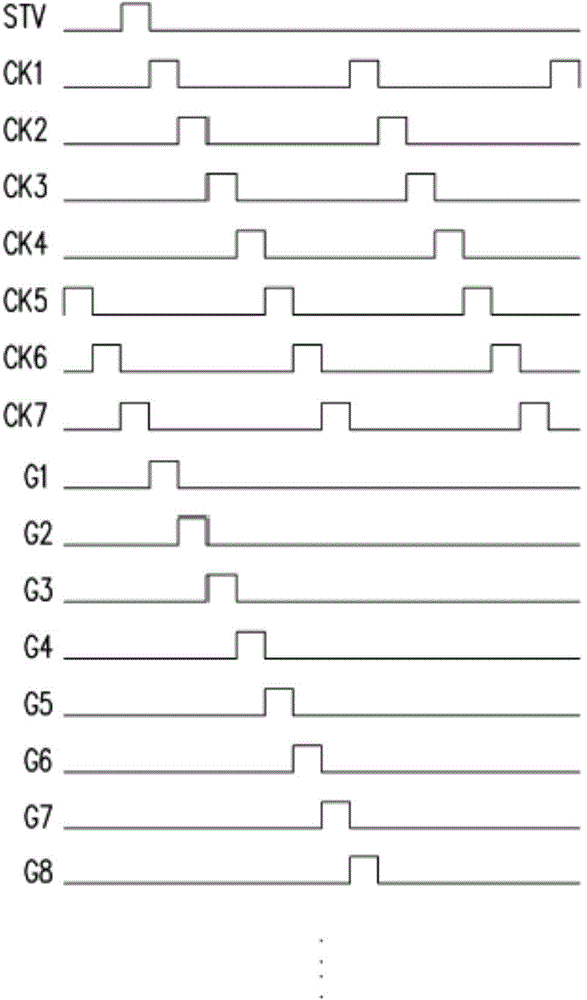
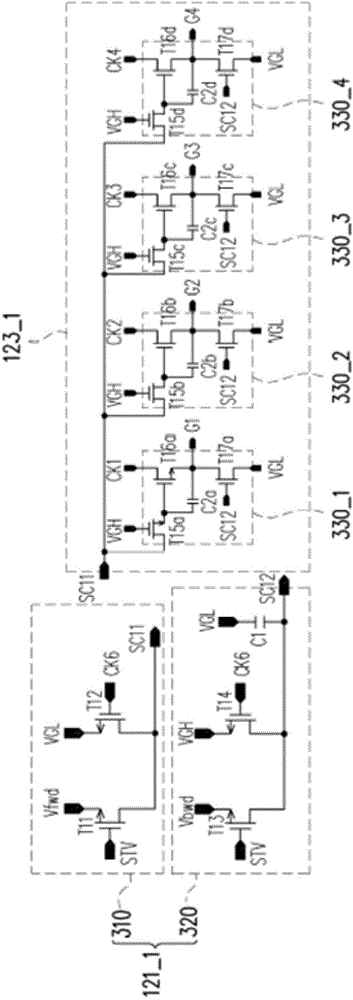
ActiveCN105405406AReduce power consumptionReduce in quantityStatic indicating devicesDigital storageDisplay deviceHemt circuits
A gate drive circuit comprises a plurality of GOA circuit units. Every two GOA circuit units share one drop-down circuit. Each drop-down circuit comprises a first transistor, a second transistor and a third transistor, wherein the gate of the first transistor is electrically connected with a first start signal, the drain of the first transistor is electrically connected with a first clock signal or a second clock signal, the gate of the second transistor is electrically connected with a second start signal, the drain of the second transistor is electrically connected with a second clock signal or a first clock signal, the gate of the third transistor is electrically connected with the source of the first transistor and the source of the second transistor, and the drain of the third transistor is electrically connected with a first fixed voltage. Every two GOA circuit units of the gate drive circuit share one drop-down circuit, and therefore the number of the transistors used by the gate drive circuit can be decreased, and the frequencies of the first clock signal and the second clock signal can be decreased. Due to the fact that the frequencies of the first clock signal and the second clock signal are decreased, the charging and discharging frequency of a stray capacitor is decreased, and the overall power consumption of the gate drive circuit is lowered.
Owner:WUHAN CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Photoelectric conversion film-stacked type solid-state imaging device
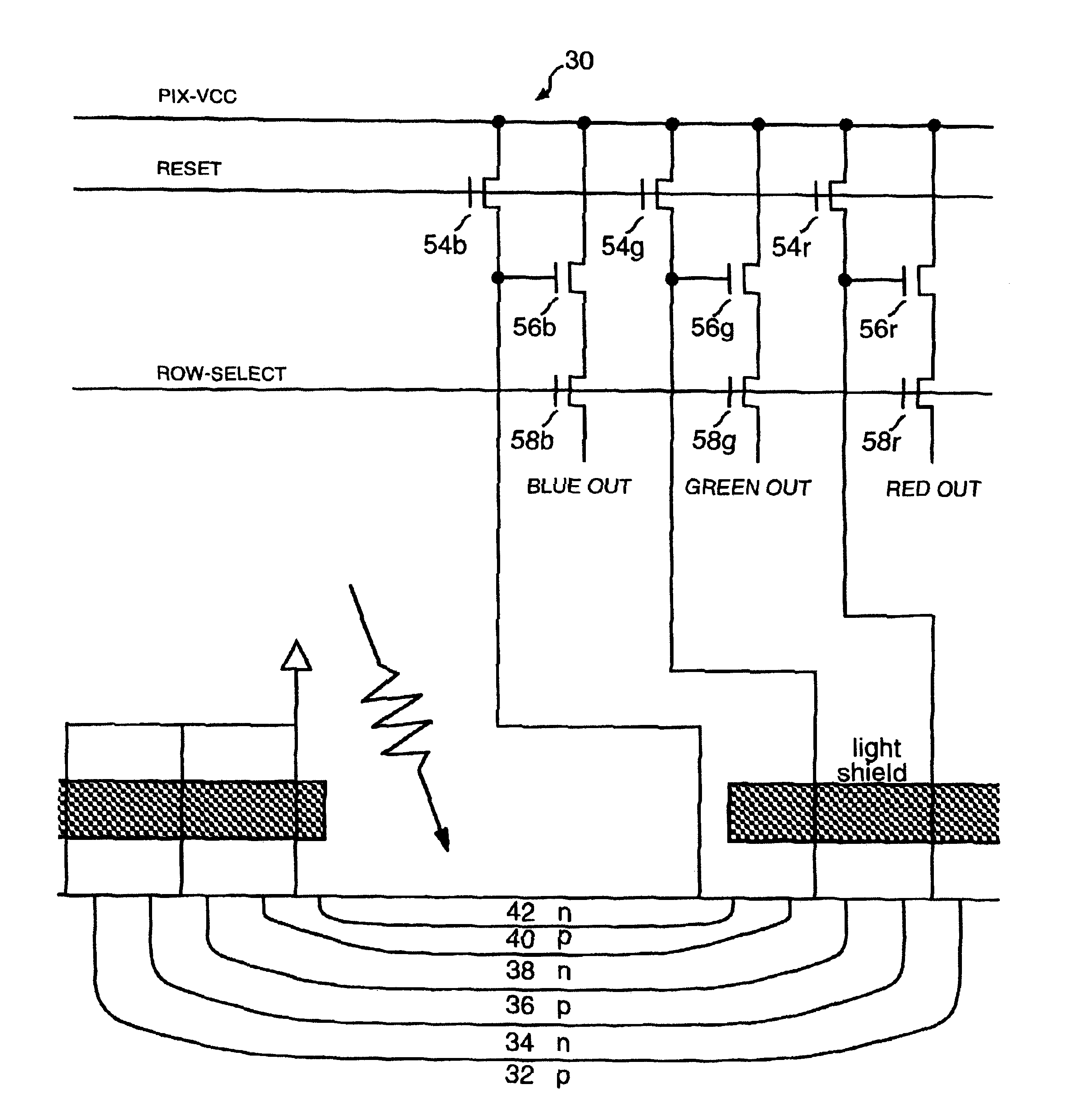
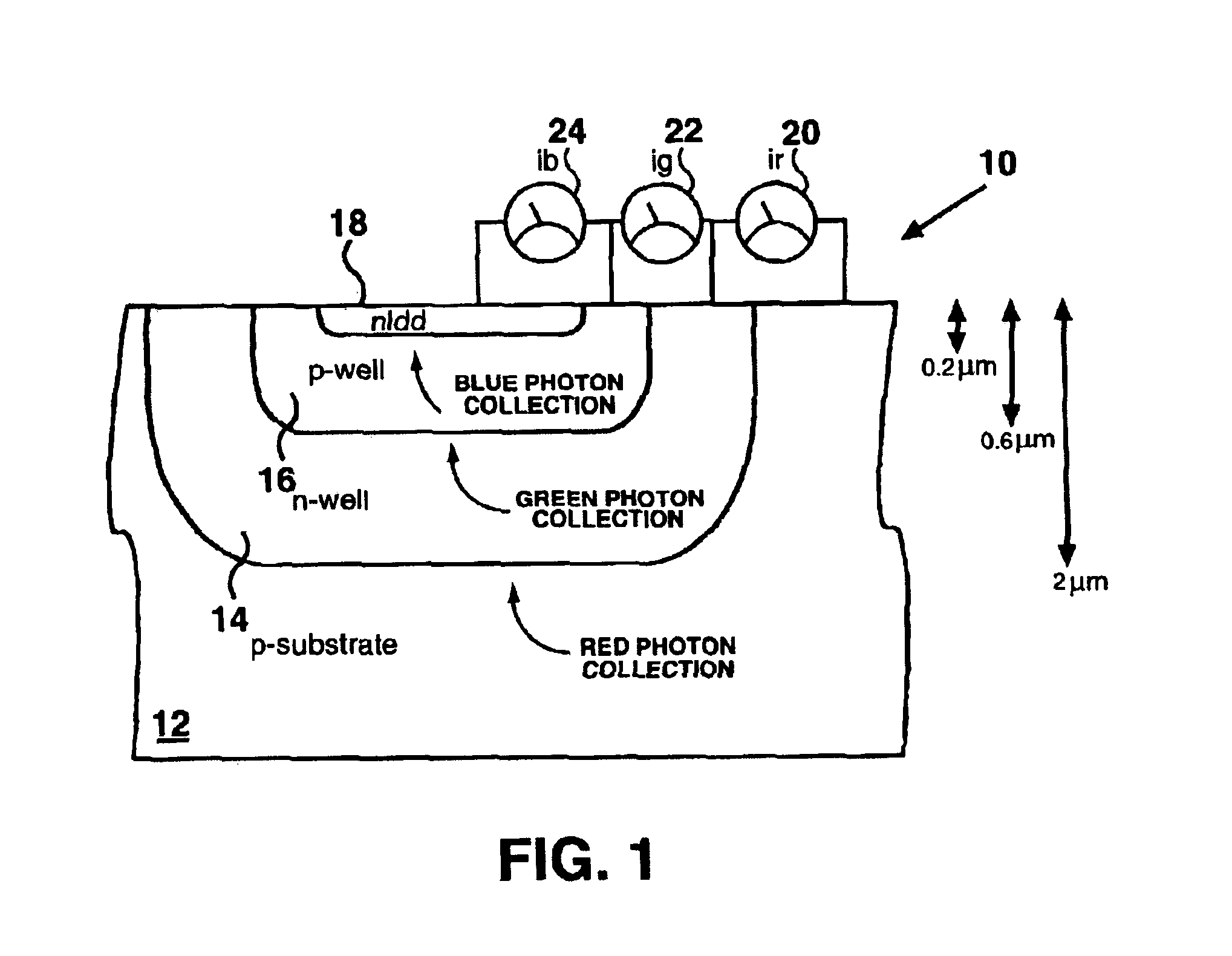
InactiveUS7217983B2Reduce manufacturing costSolid-state devicesSignal generator with single pick-up deviceCharge detectionEngineering
To provide a solid-state imaging device in which the number of transistors for each signal readout circuit provided in a semiconductor substrate side is reduced and the number of image signal readout lines is reduced, solid-state imaging device a semiconductor substrate; a stacked photoelectric conversion films detecting different colors contained in an incident light; and pixel electrode films partitioned in accordance with pixels, wherein the semiconductor substrate includes: a plurality of color selection transistors corresponding to one of the pixels, wherein the color selection transistors each corresponds to one of the photoelectric conversion films and connects to one of the pixel electrode films on the one of the photoelectric conversion films so as to be capable of selecting the one of the photoelectric conversion films; and a charge detection cell corresponding to one of the pixels, the charge detection cell being common to the photoelectric conversion films.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Tunnel transistor
InactiveUS10236364B1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringContact resistance
A tunnel field-effect transistor having source and drain contacts made from different electrically conductive materials enables independent optimization of contact resistance on the source and drain sides of the transistor. Dielectric caps on the gate electrode, source contact and drain contact made from different materials allow the selective removal of portions of the caps during gate, source and drain wiring. A wiring strap can be formed across the gate and drain to electrically connect two source contacts together. Multiple drain contacts or multiple gate electrodes may alternatively be electrically connected by wiring straps. Strap wiring facilitates placing transistors in closer proximity to increase the number of transistors for a given chip area.
Owner:ELPIS TECH INC
Display panel
InactiveCN105989812ANarrow frameReduce in quantityCathode-ray tube indicatorsShift registerDriver circuit
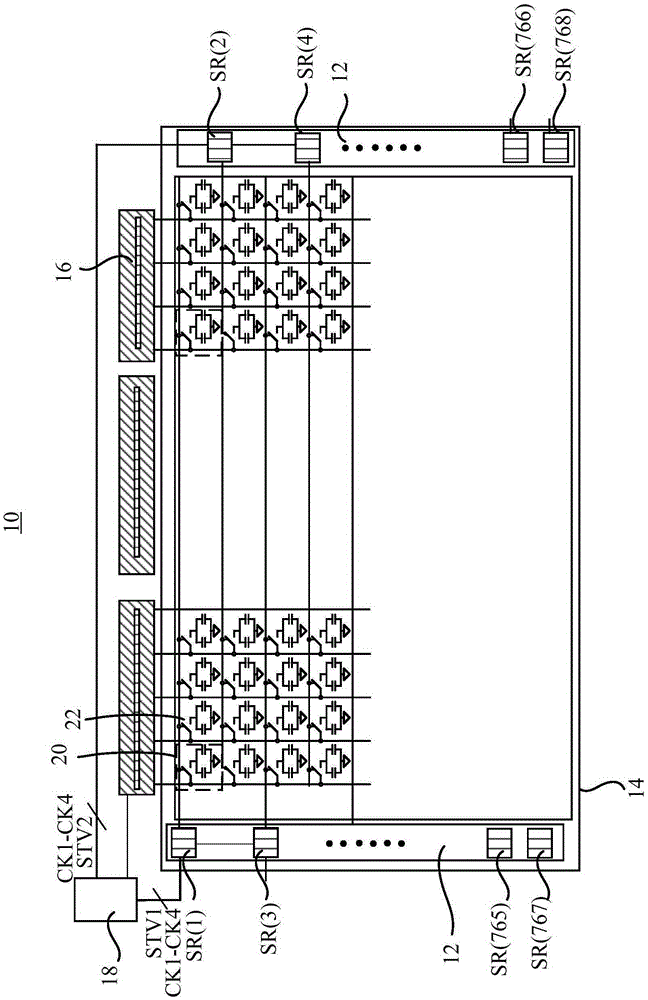
A display panel including a pixel array and a gate driver circuit is provided. The pixel array has a plurality of pixels. The gate driver circuit is used for providing a plurality of gate signals to the pixels and includes a plurality of shift registers and a plurality of demultiplexers. The shift registers respectively receive a first gate signal of the gate signals and a first clock signal of a plurality of clock signals to respectively provide a first control signal and a second control signal. The demultiplexers respectively receive a plurality of second clock signals of the clock signals, respectively turn-on according to the corresponding the first control signal, and respectively cut-off according to the corresponding second control signal. The display panel may reduce the number of transistors disposed on the gate driver circuit of the display panel to narrow the border of the display panel.
Owner:CHUNGHWA PICTURE TUBES LTD
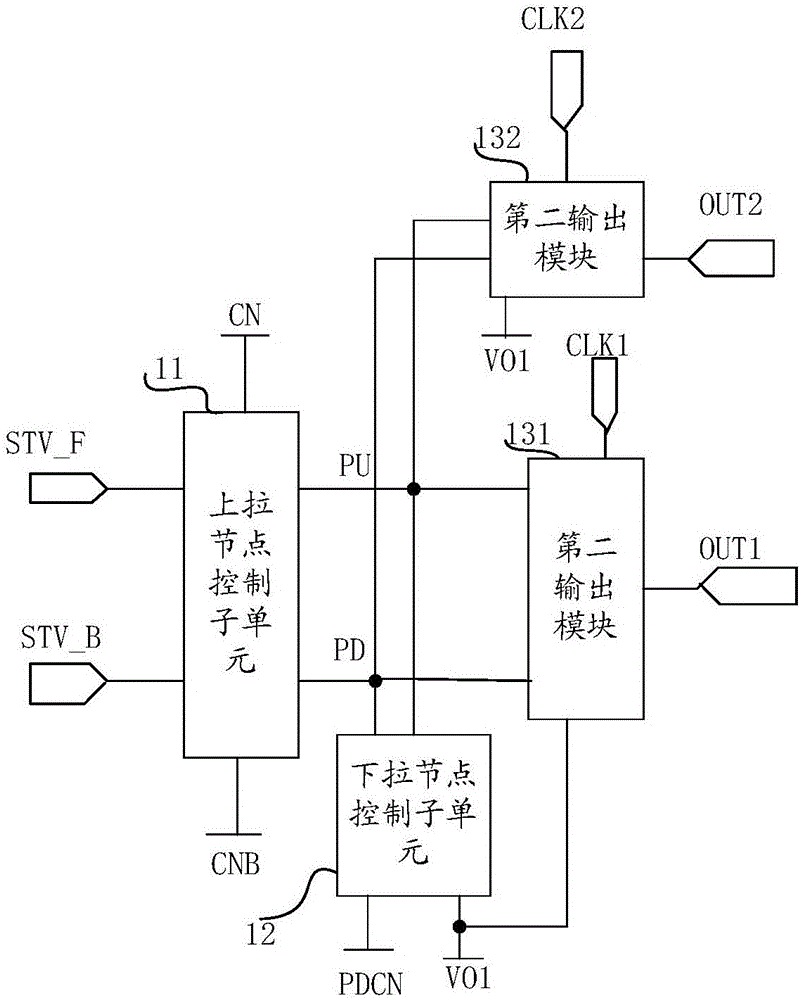
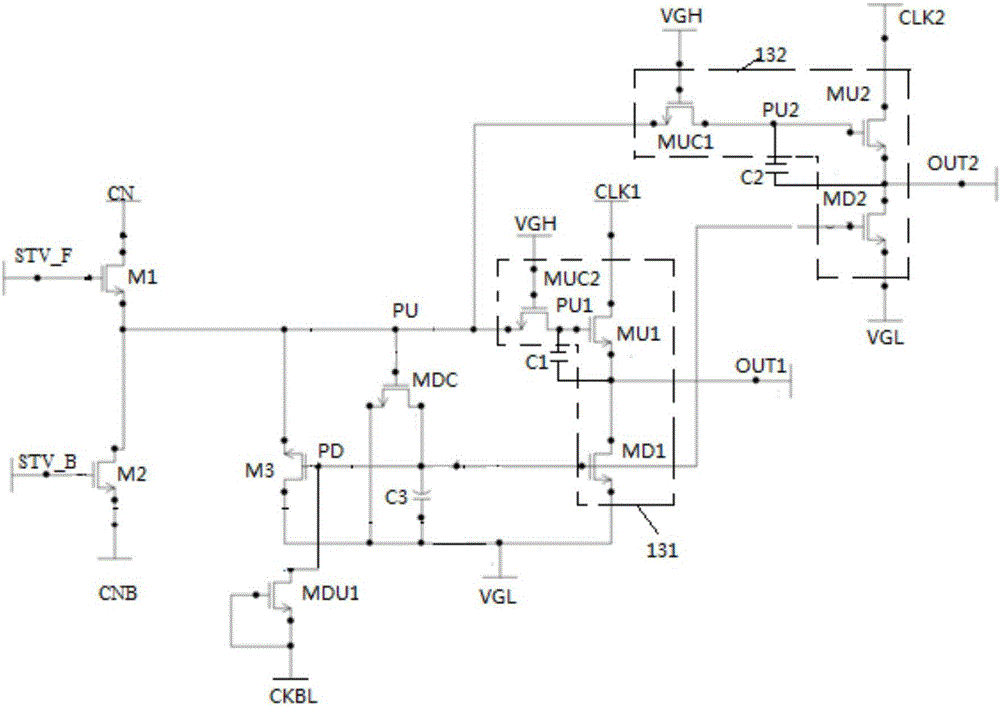
Shifting register unit, driving method, grid drive circuit and display device
InactiveCN106601175AImproved anti-static propertiesReduce in quantityStatic indicating devicesDigital storageShift registerTime segment
The invention provides a shifting register unit, a driving method, a grid drive circuit and a display device. The shifting register unit comprises a pull-up node control subunit, a pull-down node control subunit and an output subunit, wherein the output subunit comprises N output modules, an nth output module controls an nth grid drive signal output end to be connected with an nth clock signal output end under control of a pull-up node in an output phase, the nth grid drive signal output end is controlled to output a second electric level in an nth output time segment of the output phase, and n is a positive integer which is less than or equal to N. The shifting register unit can help solve a problem that a conventional grid drive circuit is large in transistor quantity, and a narrow frame cannot be easily realized.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
Drive circuit of active matrix type organic EL panel and organic EL display device using the same drive circuit
ActiveUS7109953B2Reduce brightness unevennessSuitableCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingActive matrixControl line
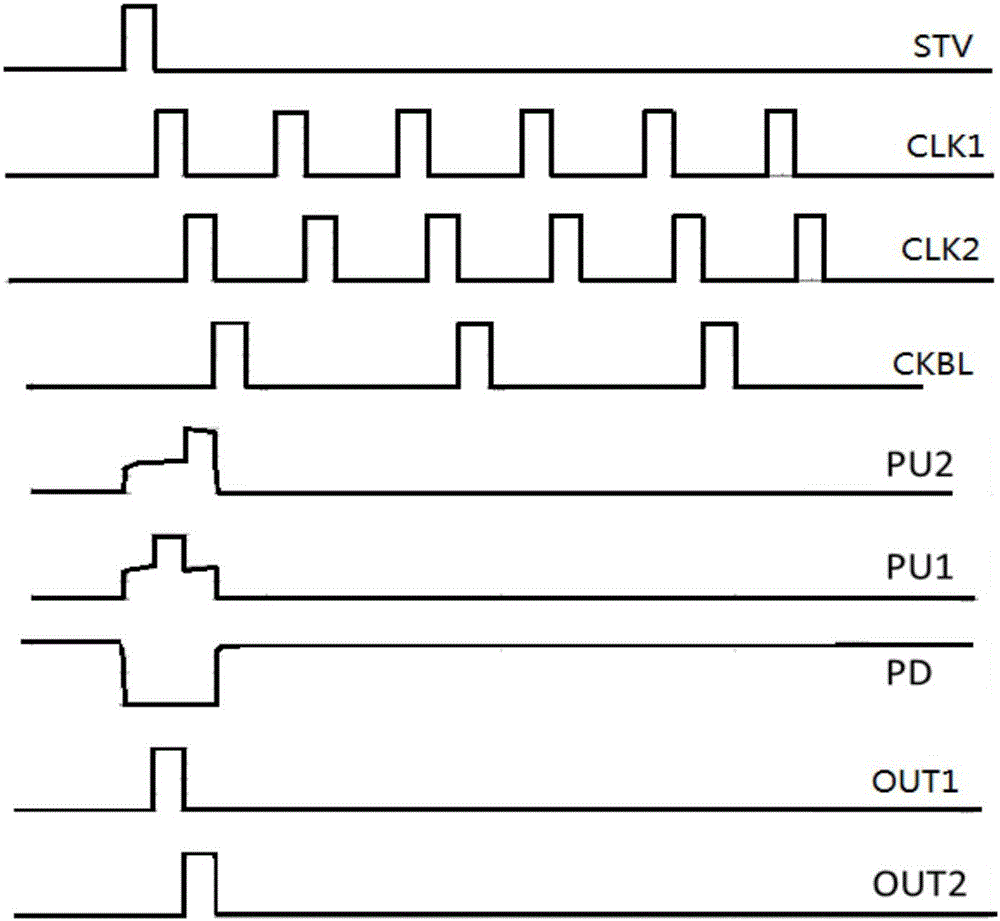
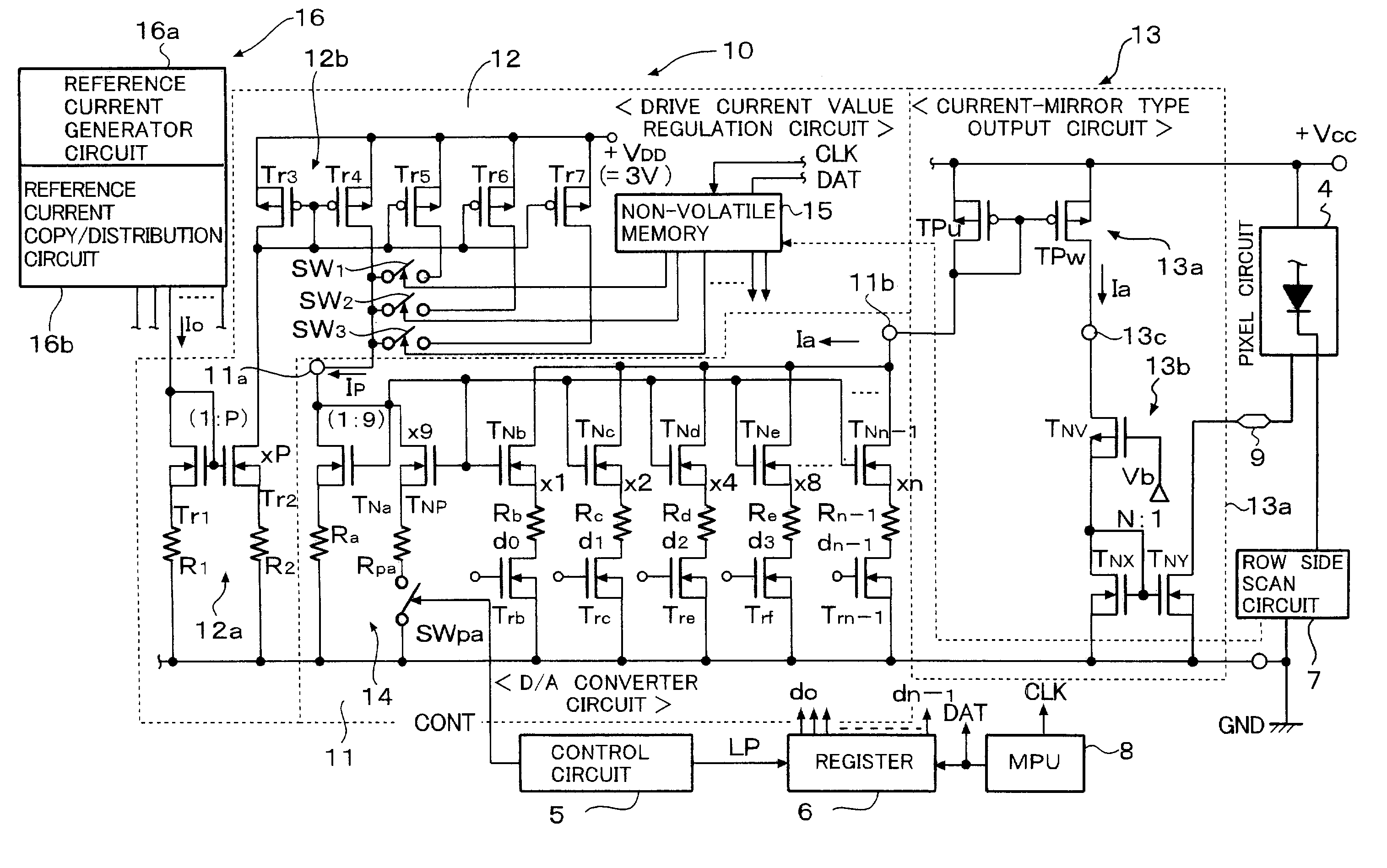
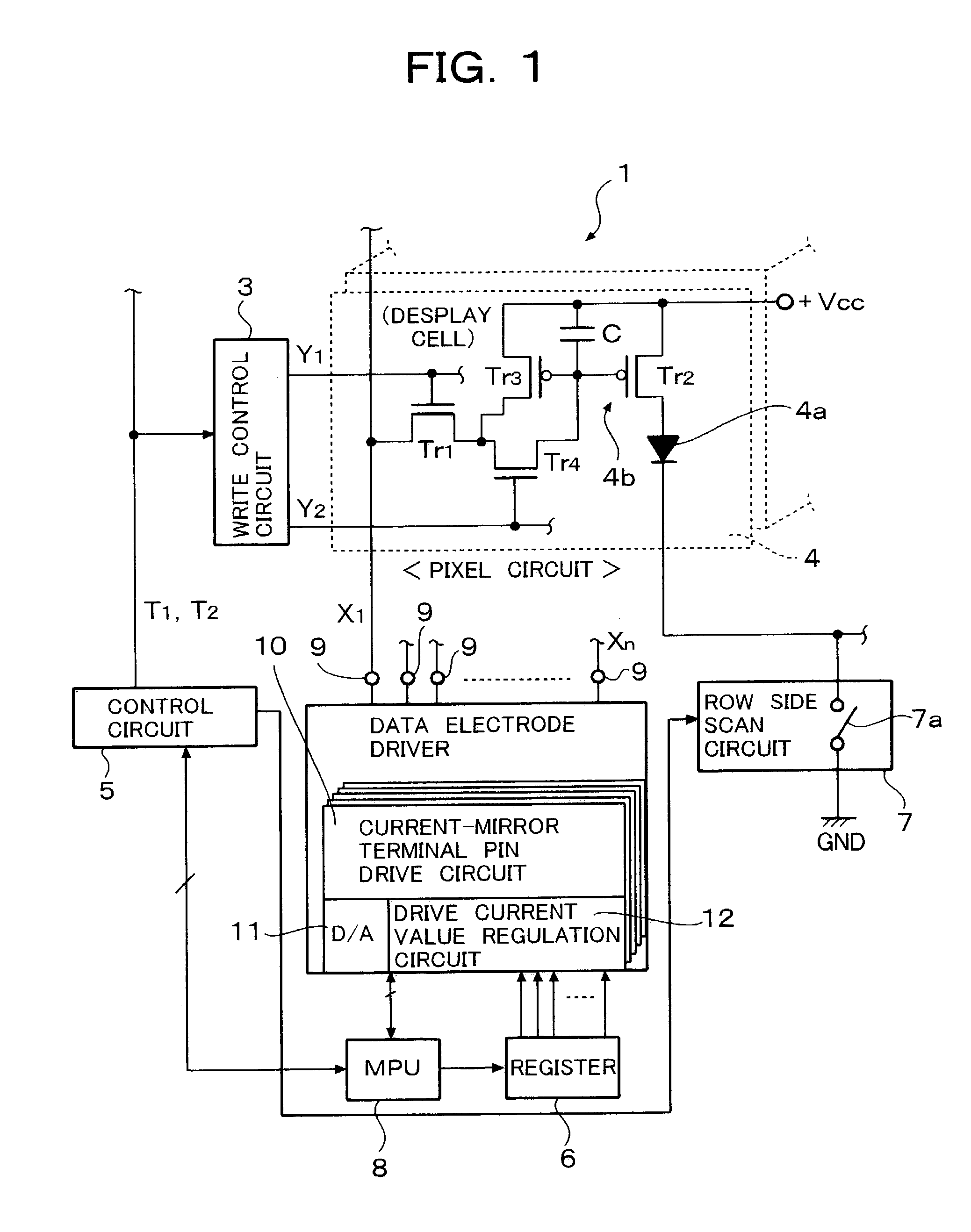
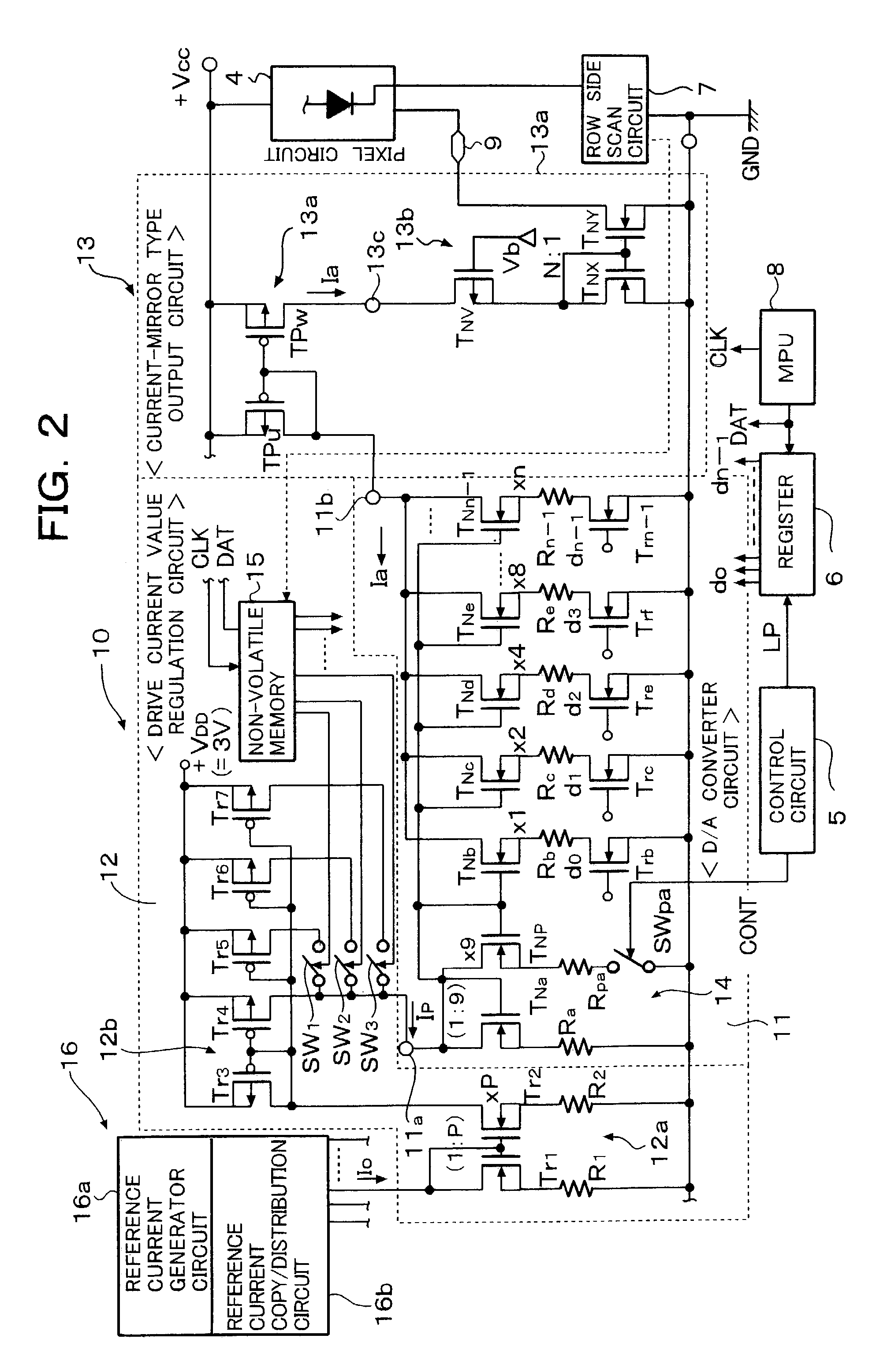
A drive current value is regulated by a current value regulator circuit of a current drive circuit provided externally of each pixel circuit, so that control lines for a program control provided in order to unify operating threshold values of drive transistors becomes unnecessary. Therefore, the number of transistors of each pixel circuit can be reduced and the circuit size of each pixel circuit can be reduced thereby.
Owner:ROHM CO LTD
Low-power-consumption xor/xnor gate circuit
InactiveCN102857217AReduce power consumptionReduce in quantityLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSemiconductor devicesComputer moduleLogic module
The invention discloses a low-power-consumption xor / xnor gate circuit which is characterized by comprising an input inverter module, a complementary transmission tube logic module and a differential series voltage switch logic module. The input inverter module is connected with the complementary transmission tube logic module which is further connected with the differential series voltage switch logic module. The low-power-consumption xor / xnor gate circuit has the advantages that transistors of the circuit are reduced without affecting circuit performances, so that power consumption of the circuit is effectively reduced. Further, the low-power-consumption xor / xnor gate circuit not only has xor logic functions but also has xnor logic functions.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
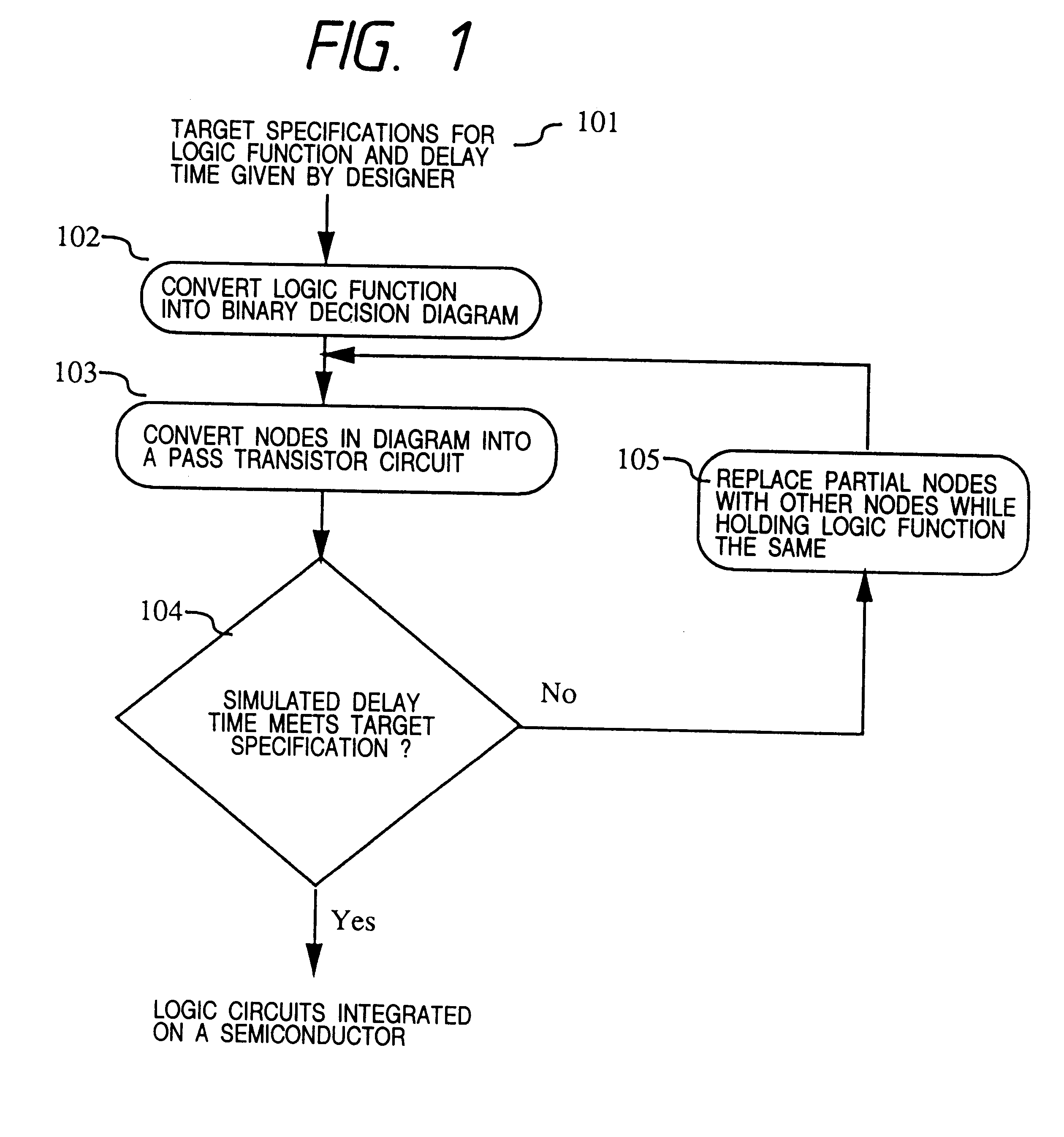
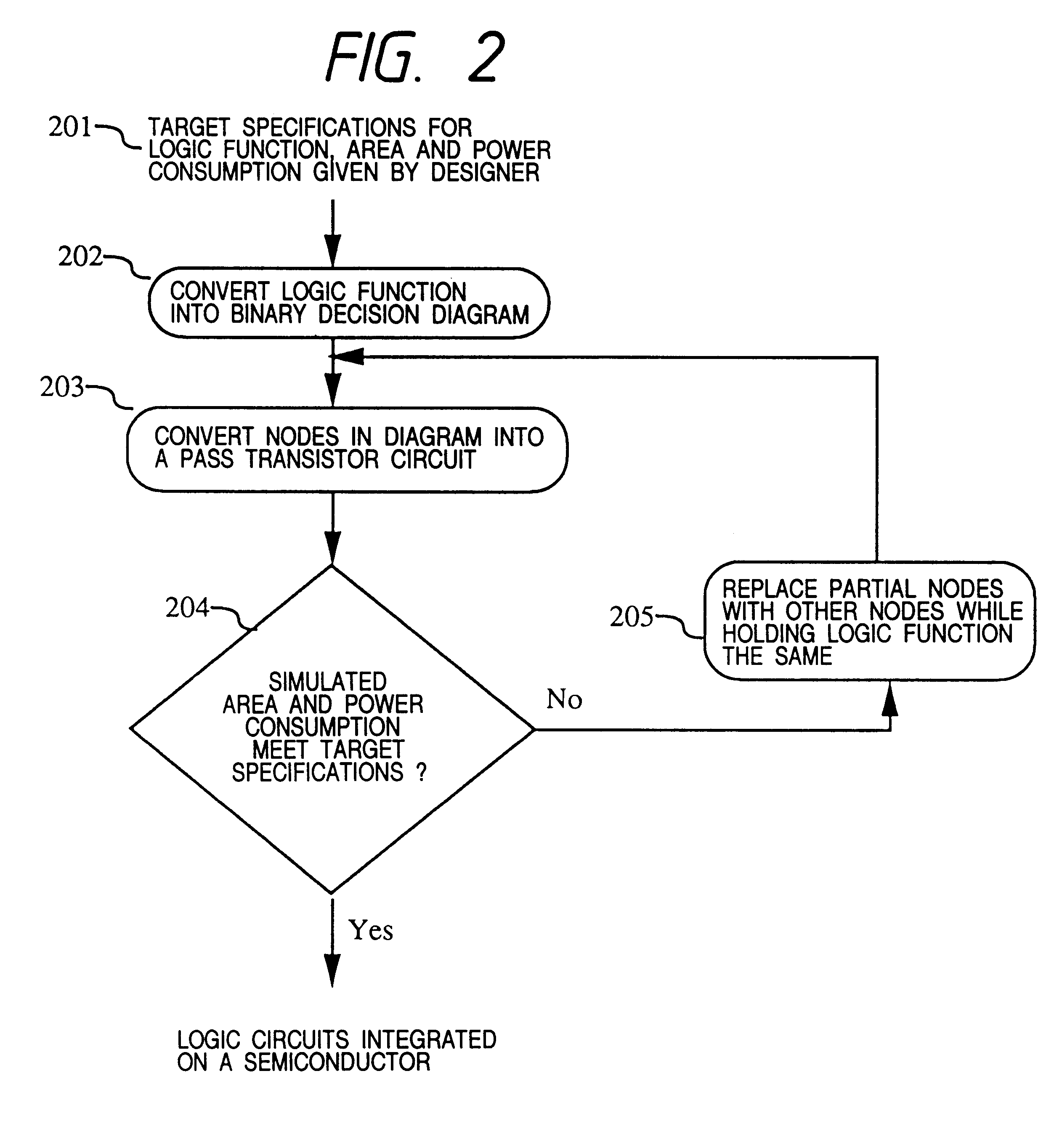
Method for designing semiconductor integrated circuit and automatic designing device
InactiveUS6260185B1Increase the areaIncrease consumptionAnalogue computers for heat flowComputer aided designIntegrated circuitLogic circuitry
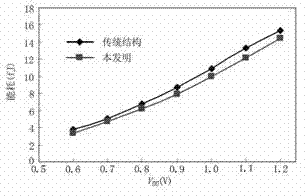
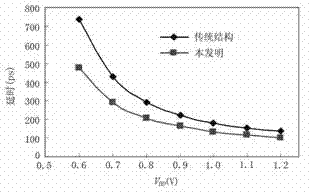
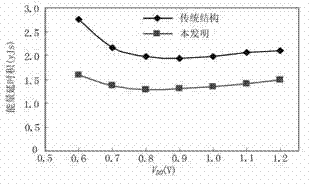
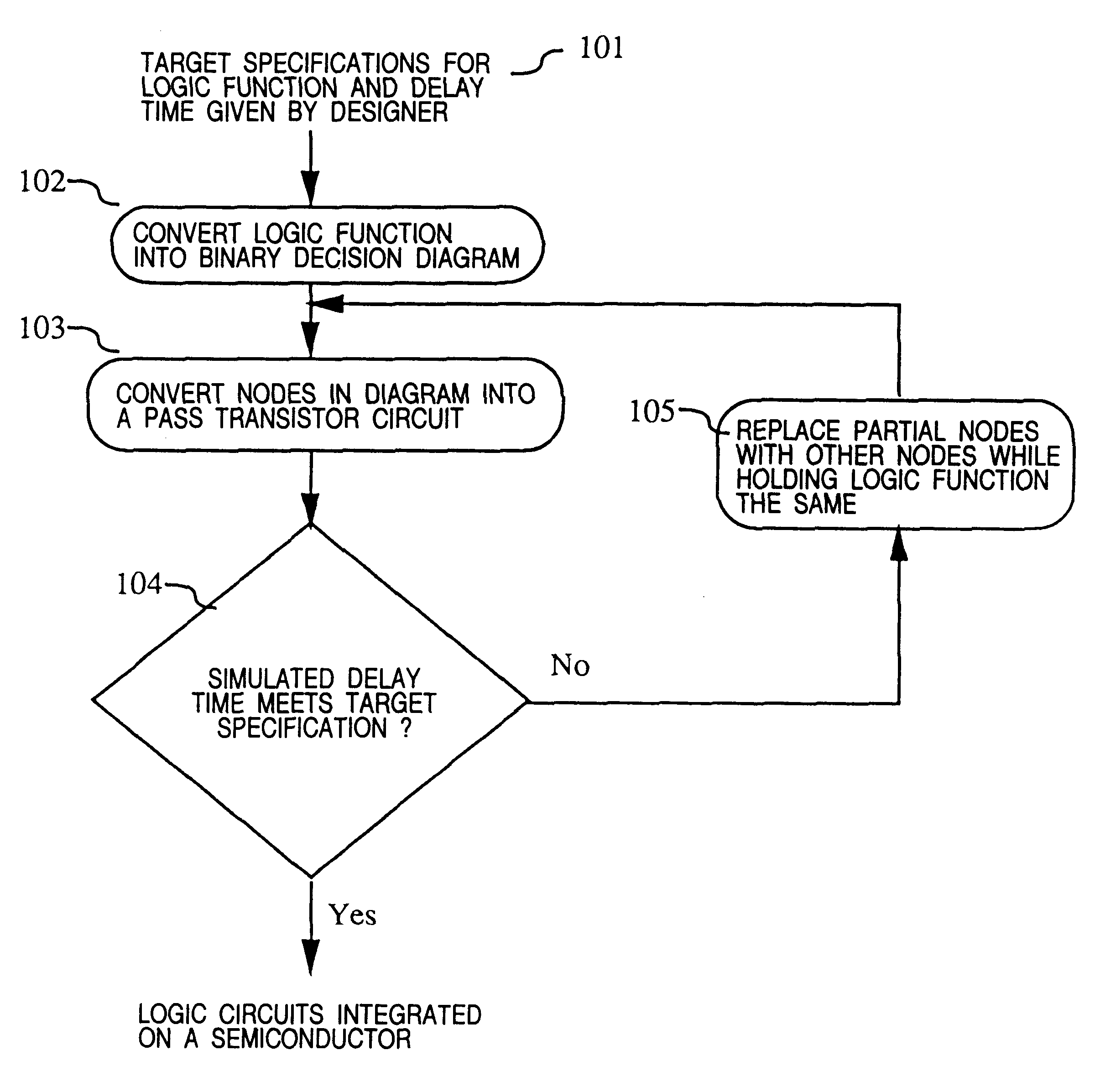
A program for automatically designing a logic circuit used for a method of designing a pass transistor circuit, by which the number of required transistors, delay time, power consumption and chip area of the pass transistor circuit is reduced. The program executes the following steps: a) receiving inputted logic functions which define the logical relationship between the inputs and the outputs, and an inputted target specification, b) generating a binary decision diagram from part of the logic functions received at (a), c) replacing the diagram nodes formed at (b) with pass transistor circuit, d) judging whether or not the simulation characteristics of the pass transistor circuit described in (c) meets the target specification described in (a), and executing the following steps when the judgment is "no", e) replacing part of the diagram generated by the procedure described in (b) with another diagram, f) allocating a new binary decision diagram to the control inputs of the nodes of the replaced diagram prepared at (e), and g) repeating the steps (c) and (d) for the diagram prepared at (f).
Owner:HITACHI LTD
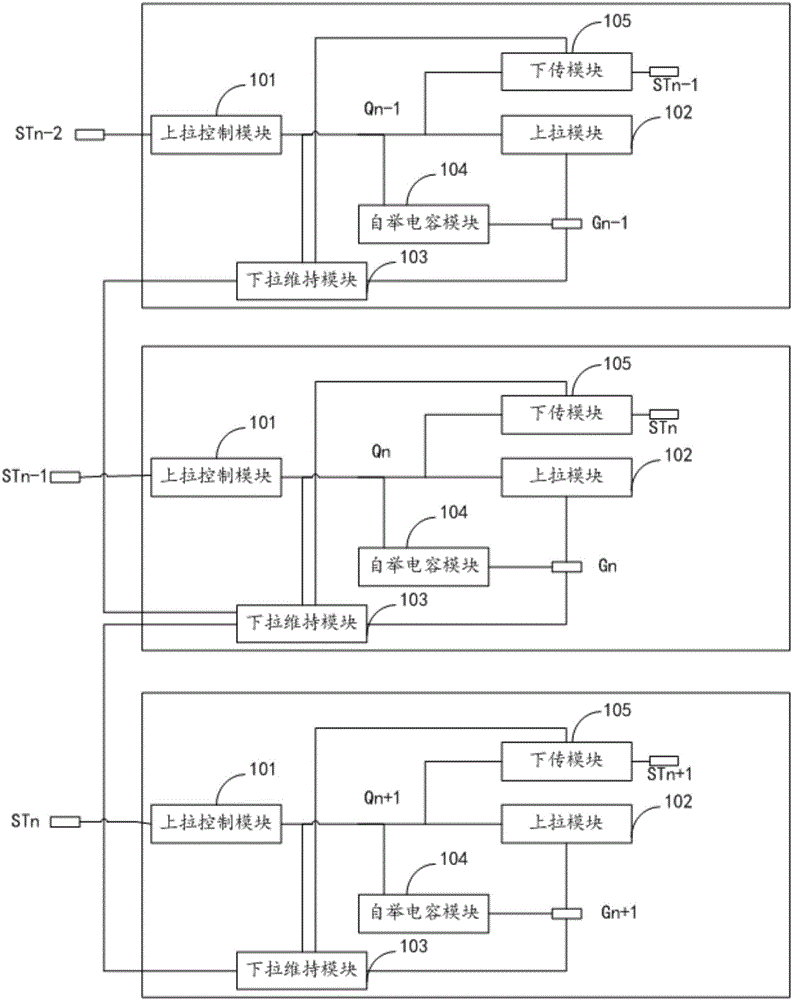
GOA drive circuit and liquid crystal display device
ActiveCN106448592AAvoid failureReduce in quantityStatic indicating devicesDigital storageCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
The invention provides a GOA drive circuit and a liquid crystal display device. The GOA drive circuit comprises multiple cascaded GOA units. A gate drive signal is outputted to the Nth horizontal scanning line Gn of a display area according to the Nth GOA unit. The Nth GOA unit comprises a pull-up module, a pull-up control module, a pull-down maintenance module, a download module and a bootstrap capacitance module. The pull-up module, the pull-down maintenance module and the bootstrap capacitance module are electrically connected with the Nth gate signal point Qn and the Nth horizontal scanning line Gn. The pull-up control module and the download module are connected with the Nth gate signal point Qn. The GOA drive circuit and the liquid crystal display device have the beneficial effects of reducing the number of thin-film transistors.
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Line driver circuit for a semiconductor memory device
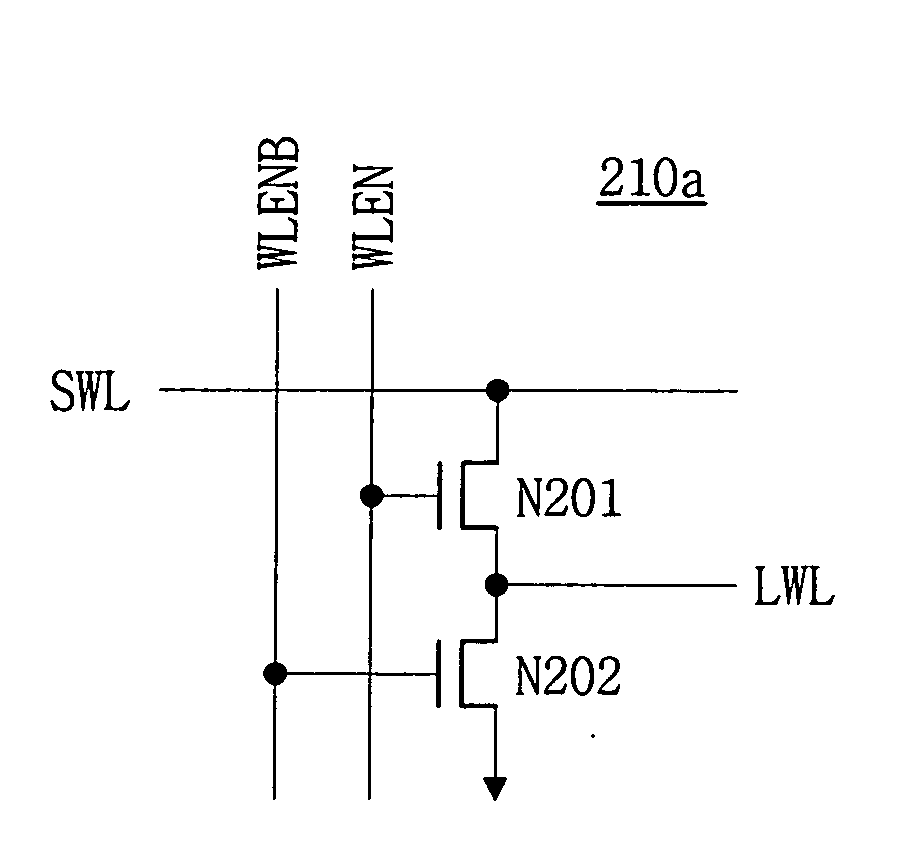
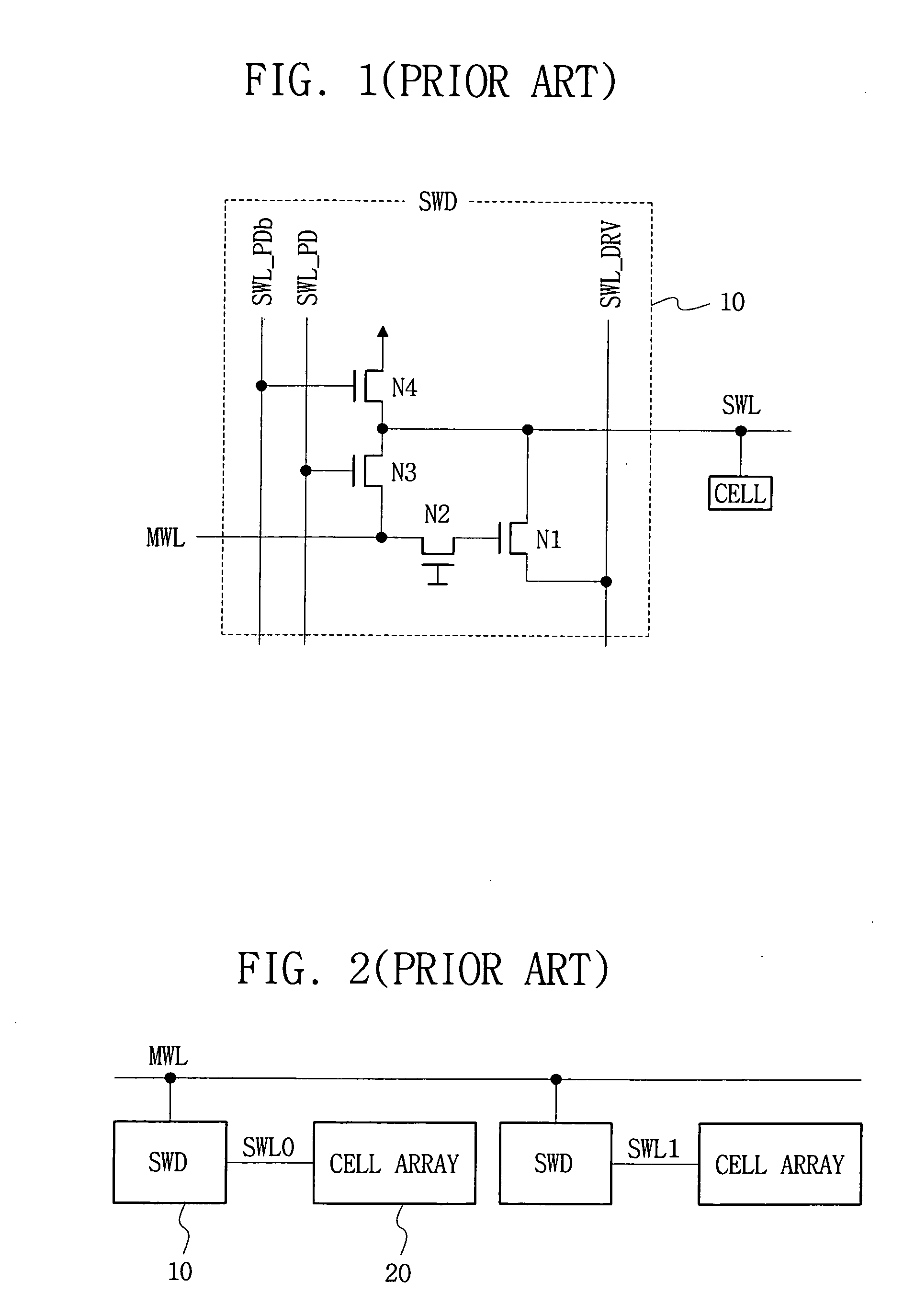
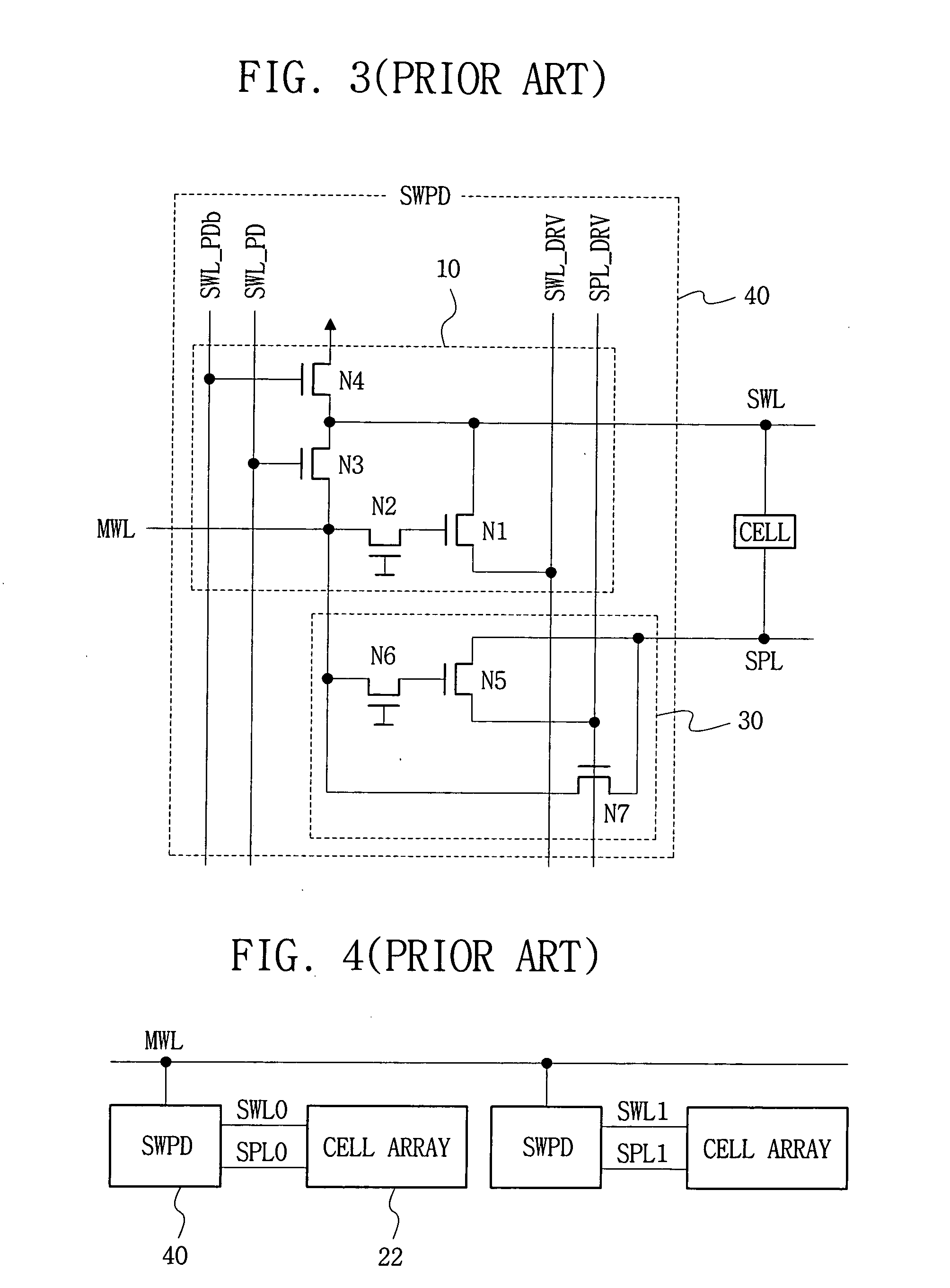
A semiconductor memory device having a word line driver circuit configured in stages. A plurality of sub word line driver circuits are connected, in parallel, to each main word line, and provide a sub word line enable signal to a selected sub word line in response to a main word line enable signal provided through a main word line. A plurality of (local) word line driver circuits are connected in parallel, to each sub word line and provide a local word line enable signal to a selected local word line in response to the (main / sub) word line enable signal so as to operate a plurality of memory cells connected to the selected local word line. The transistor count and layout area of a semiconductor memory device decreases and a reduced chip area can be achieved.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
High density test structure array to support addressable high accuracy 4-terminal measurements
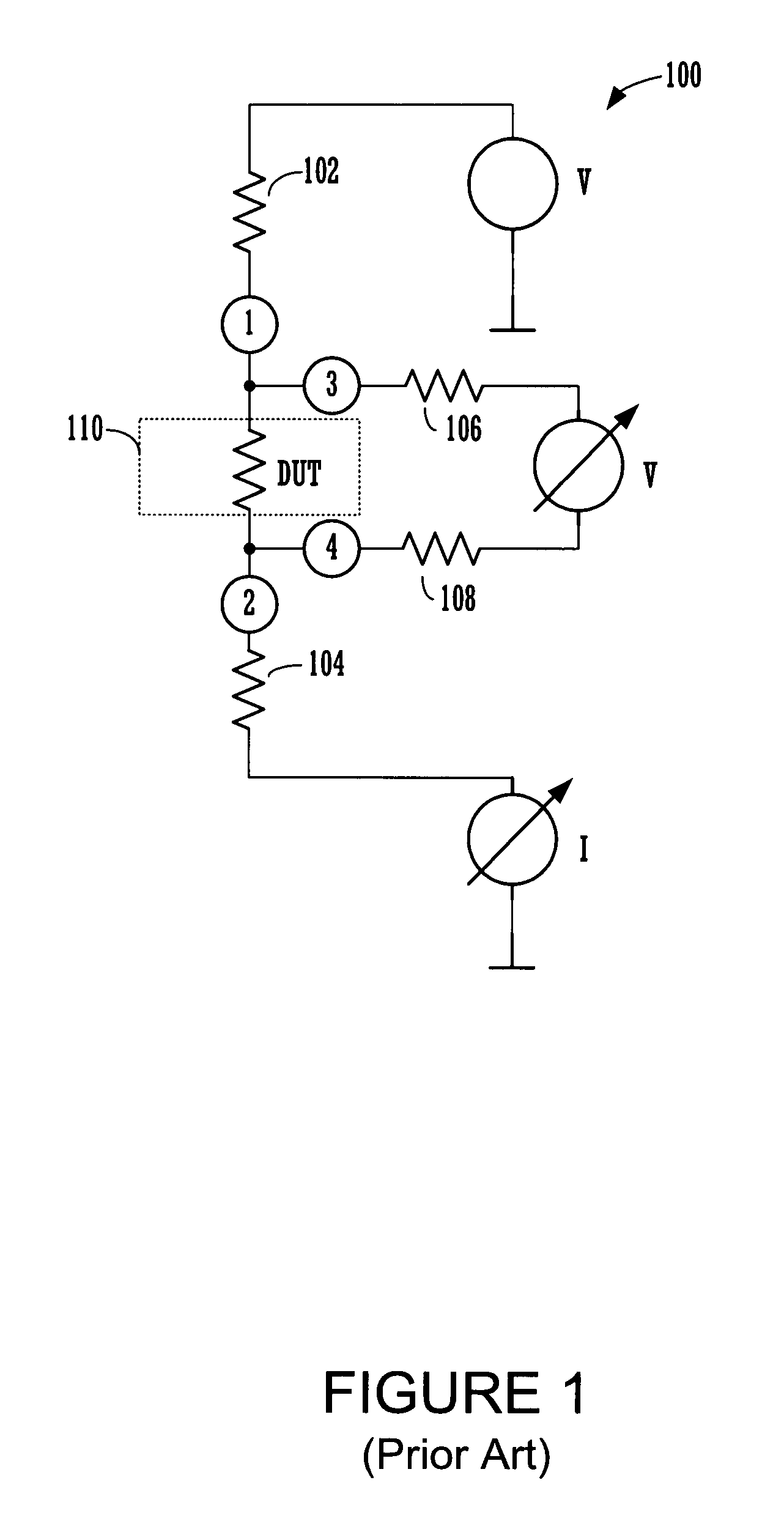
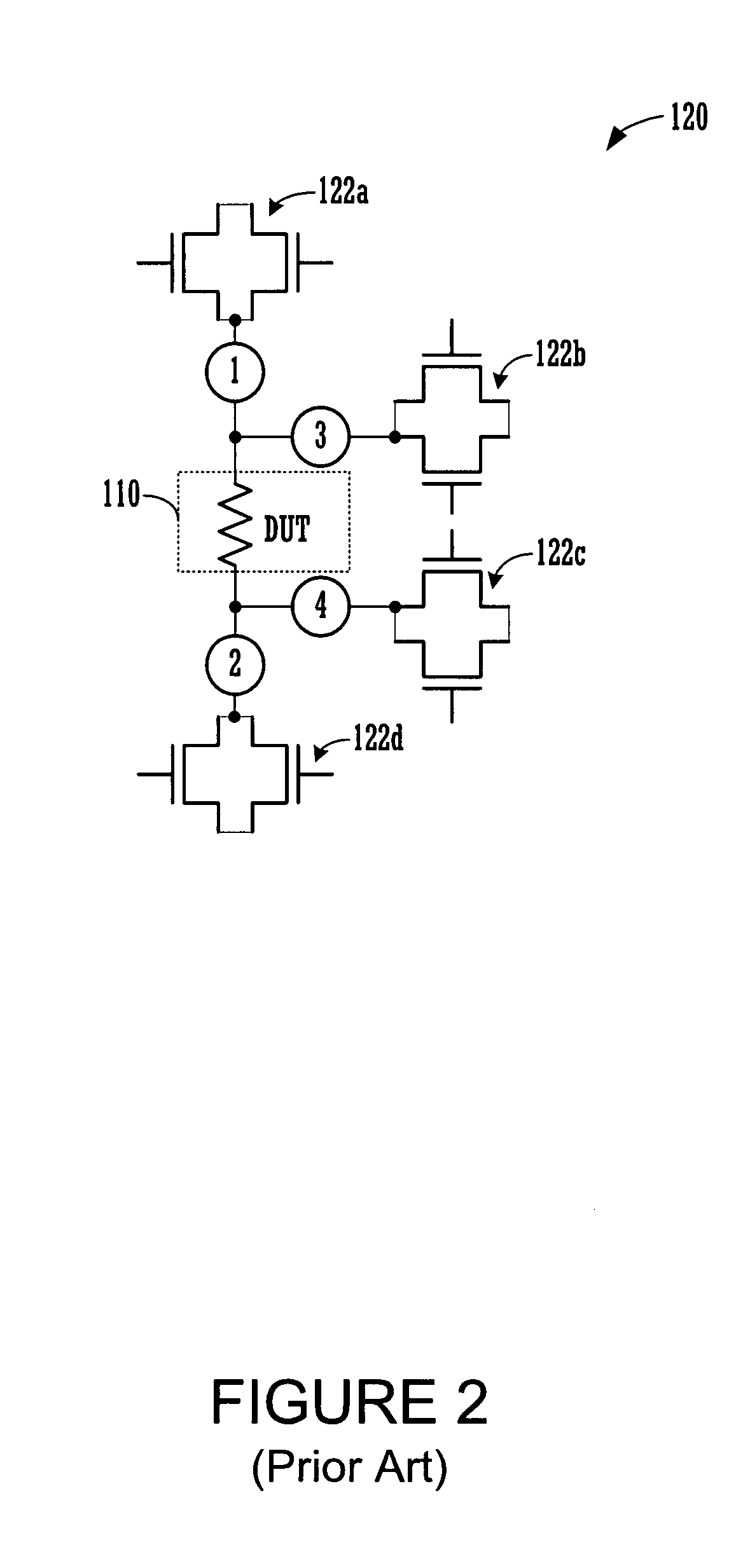
InactiveUS7902852B1Reduce the amount requiredDecrease necessary areaIndividual semiconductor device testingHigh densityMeasurement point
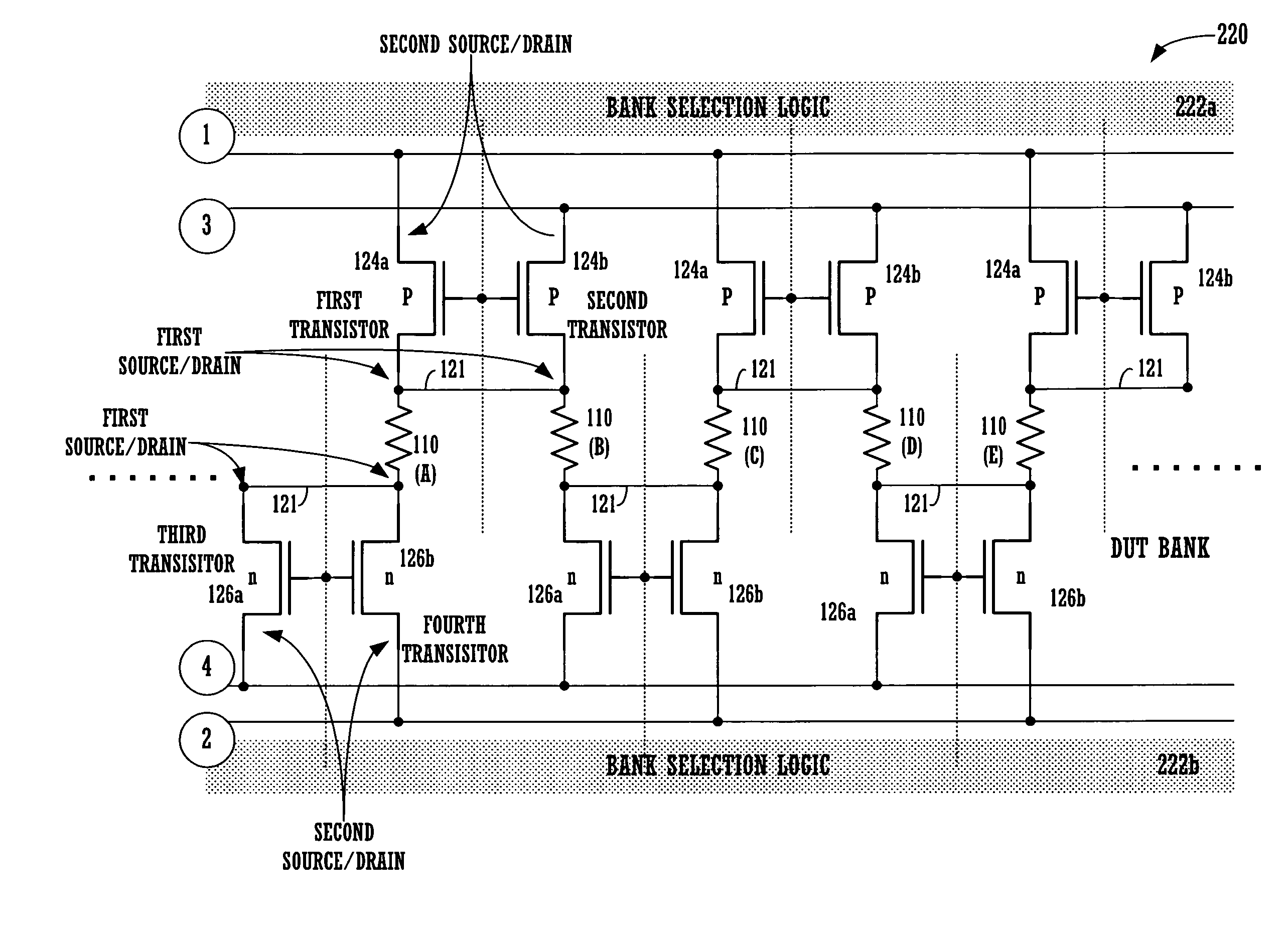
Circuits for performing four terminal measurement point (TMP) testing of devices under test (DUT) is provided. The DUT and the circuit is to be defined on a semiconductor chip. The circuit includes a DUT having a first terminal and a second terminal, where the first terminal of the DUT is connectable to a first terminal measurement point and a third terminal measurement point, and the second terminal of the DUT is connectable to a second terminal measurement point and a fourth terminal measurement point. A first transistor is provided to select access to the first terminal measurement point, a second transistor is provided to select access to the third terminal measurement point, a third transistor is provided to select access to the second terminal measurement point; and a fourth transistor is provided to select access to the fourth terminal measurement point. In one example, the DUT is linked to neighboring DUTs, and selected ones of the first through fourth transistors are shared, thus reducing the number of transistors per DUT in a DUT bank, and reducing the area needed to implement DUT bank testing for addressable 4-TMP testing. The compact circuitry further enables DUT bank stacking in rows, addressing of columns of DUTs for conditional testing, and three dimensional stacking of DUT banks on different levels.
Owner:PDF SOLUTIONS INC
Semiconductor device, electronic component, and electronic device
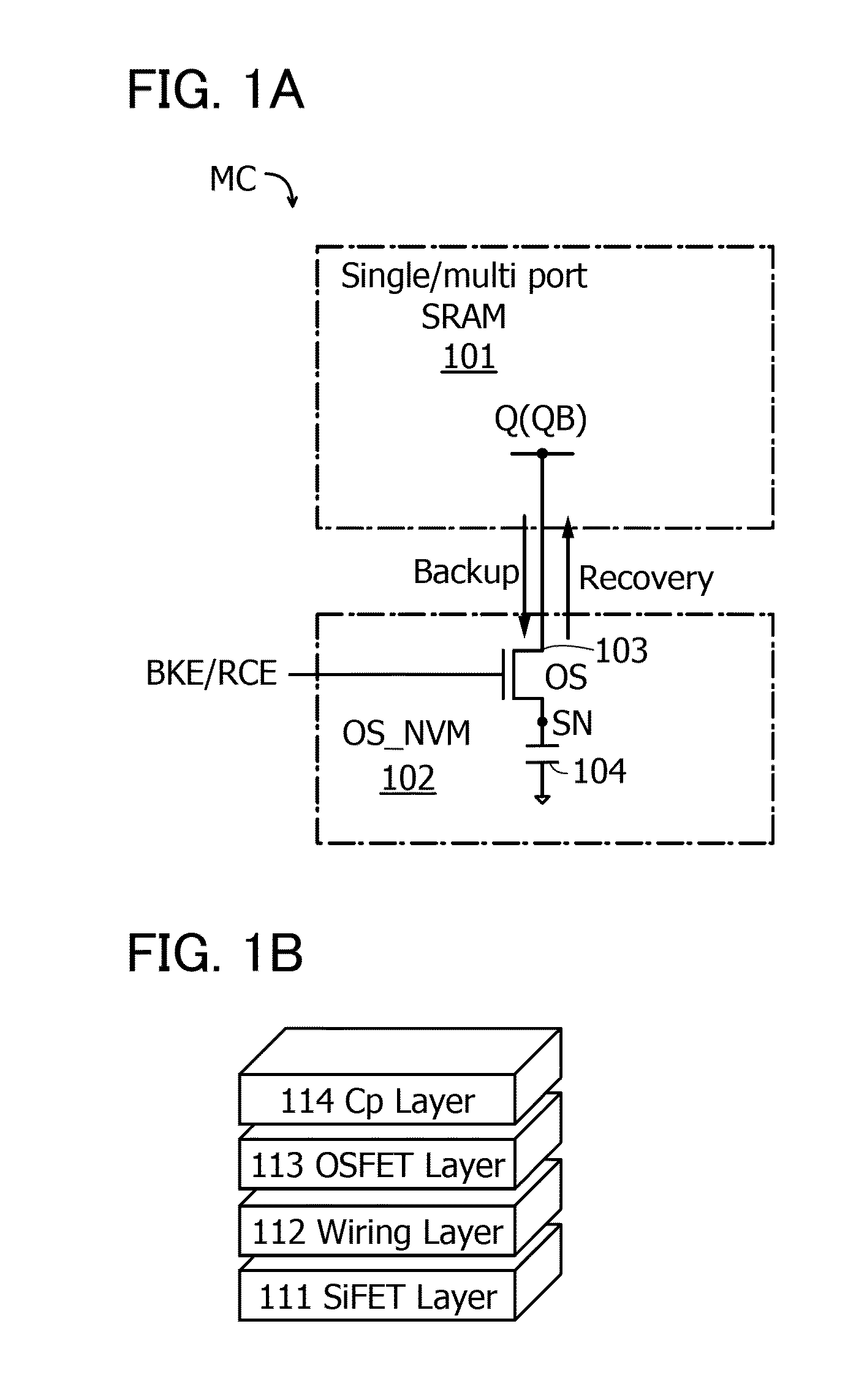
InactiveUS20150294991A1Increase the areaIncrease speedSolid-state devicesDigital storageEngineeringData memory
A semiconductor device having a novel structure. A multiport SRAM and a data memory portion including an OS transistor are stacked. Since the multiport SRAM includes more wirings and transistors, an area increase is not caused by an increase in the number of transistors in the data memory portion including an OS transistor. An increase in the number of transistors in the data memory portion enables static operation. Thus, the data memory portion can achieve stable recovery operation, higher speed operation, and simplification.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low-power-consumption short pulse generation circuit and low-power-consumption pulse type D trigger
The invention discloses a low-power-consumption short pulse generation circuit and a low-power-consumption pulse type D trigger. The low-power-consumption short pulse generation circuit is characterized by comprising a first P-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect transistor (PMOSFET), a first N-channel MOSFET (NMOSFET), a first NAND gate and a first phase inverter. The low-power-consumption pulse type D trigger is characterized by comprising the low-power-consumption short pulse generation circuit, an input phase inversion circuit, a clock control complementary MOS (CMOS) logic D latch unit and an output phase inversion circuit. The invention has the advantages that: under the condition of no influence of the performance of the circuit, the quantity of the transistors of the circuit is small; the structure is simpler; and the power consumption of the circuit is effectively reduced.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Organic light emitting display device
InactiveUS20120019500A1Reducing and minimizing numberCompensation Threshold VoltageCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingScan lineDisplay device
An embodiment relates to an organic light emitting display device that has a simple structure and compensate threshold voltage of a driving transistor.The organic light emitting display device that operates in an initializing period, a scan period, and an emission period divided from one frame, includes: first pixels positioned in odd-numbered vertical lines; second pixels positioned in even-numbered vertical lines; first scan lines and second scan lines formed horizontal lines and coupled with the second pixels; third scan lines and fourth scan lines formed in the horizontal lines and coupled with the first pixels; and a scan driver driving the first scan lines and the fourth scan lines, in which the number of transistors in the first pixels is different from the number of transistors in the second pixels.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
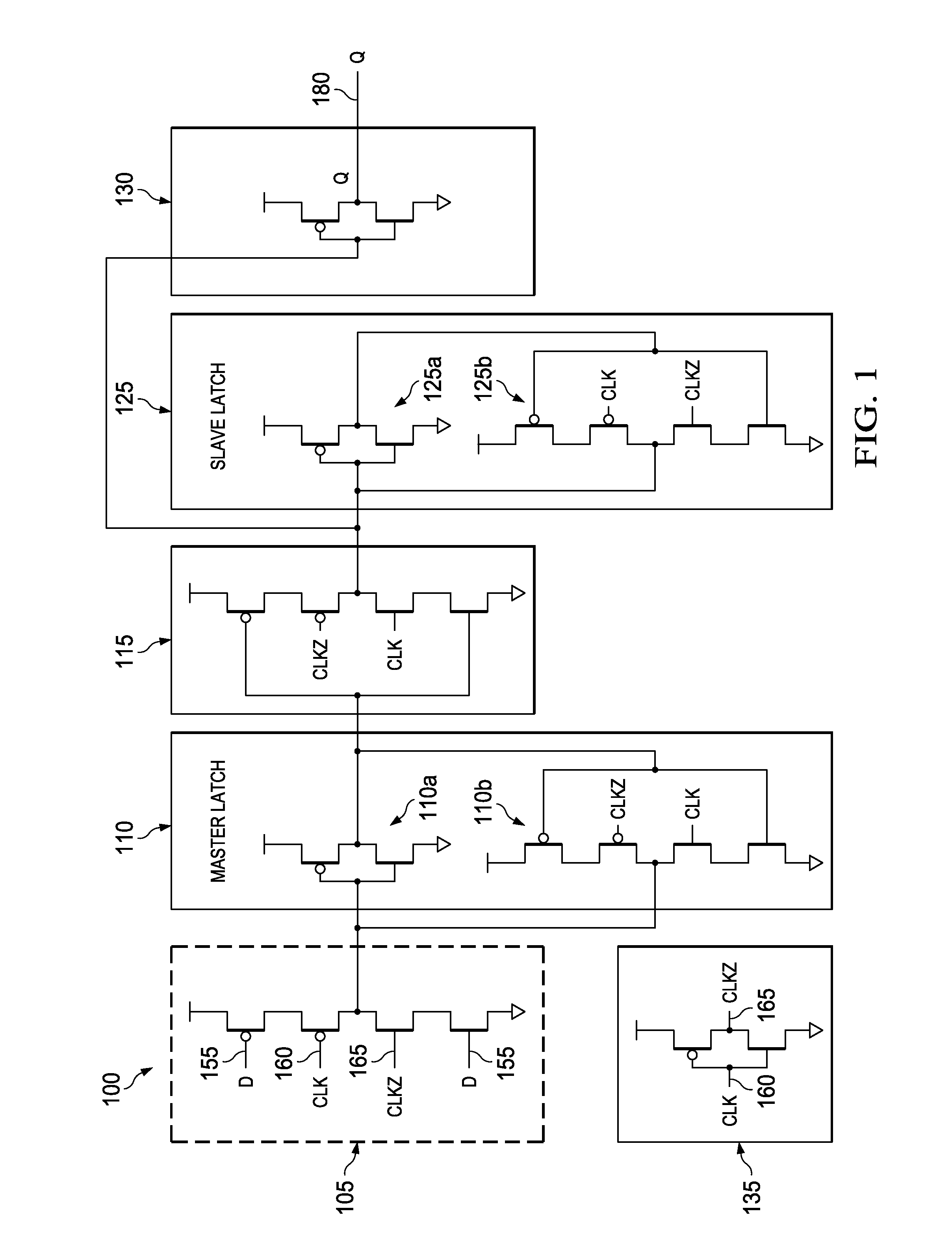
Flip-flops with low clock power
The disclosure provides a flip-flop that utilizes low power as a result of reduced transistor count. The flip-flop includes a tri-state inverter that receives a flip-flop input and a clock input. A master latch is coupled to an output of the tri-state inverter and provides a control signal to the tri-state inverter. The control signal activates the tri-state inverter. A slave latch receives an output of the master latch and the control signal. An output inverter is coupled to an output of the slave latch and generates a flip-flop output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
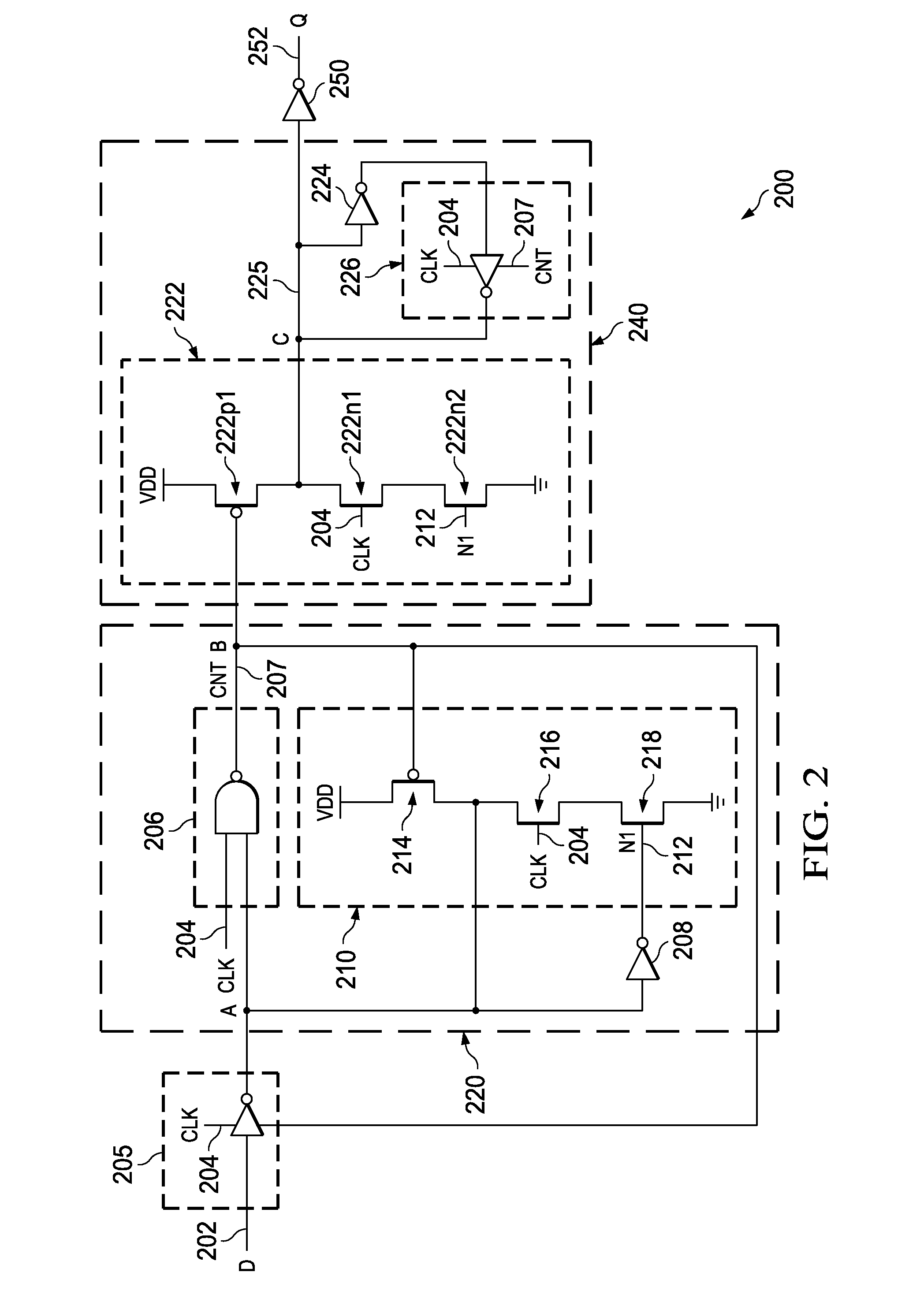
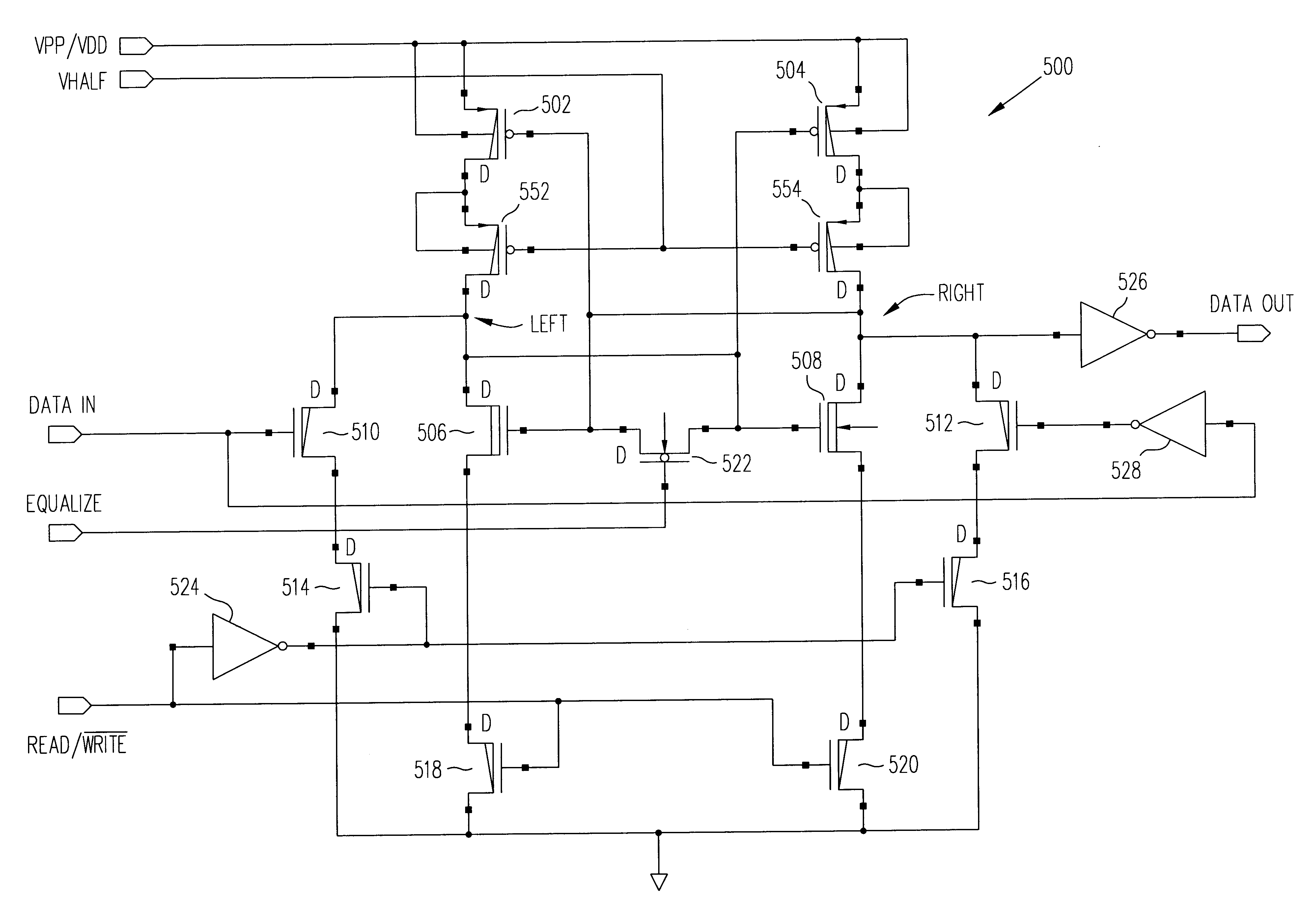
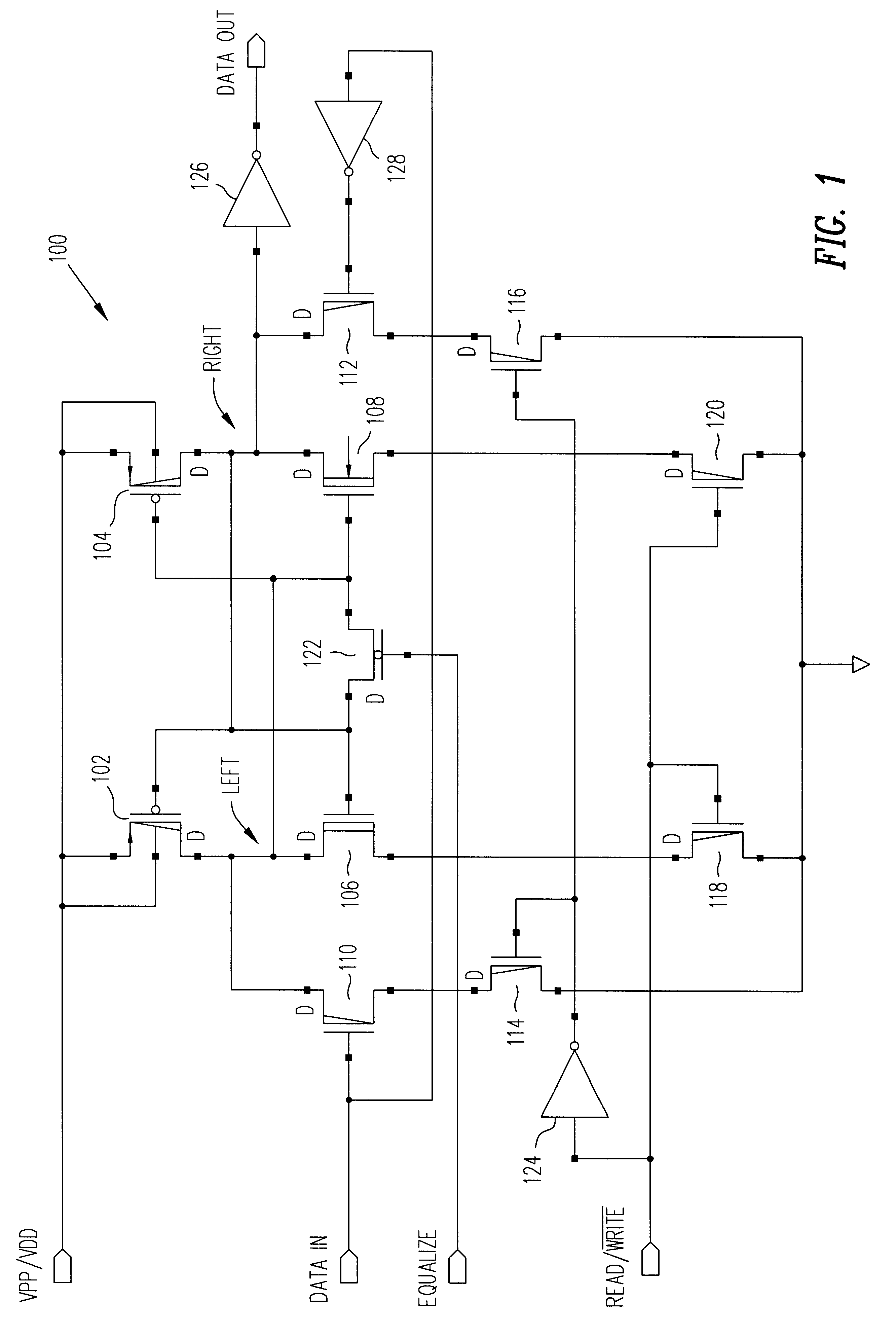
Non-volatile latch circuit that has minimal control circuitry
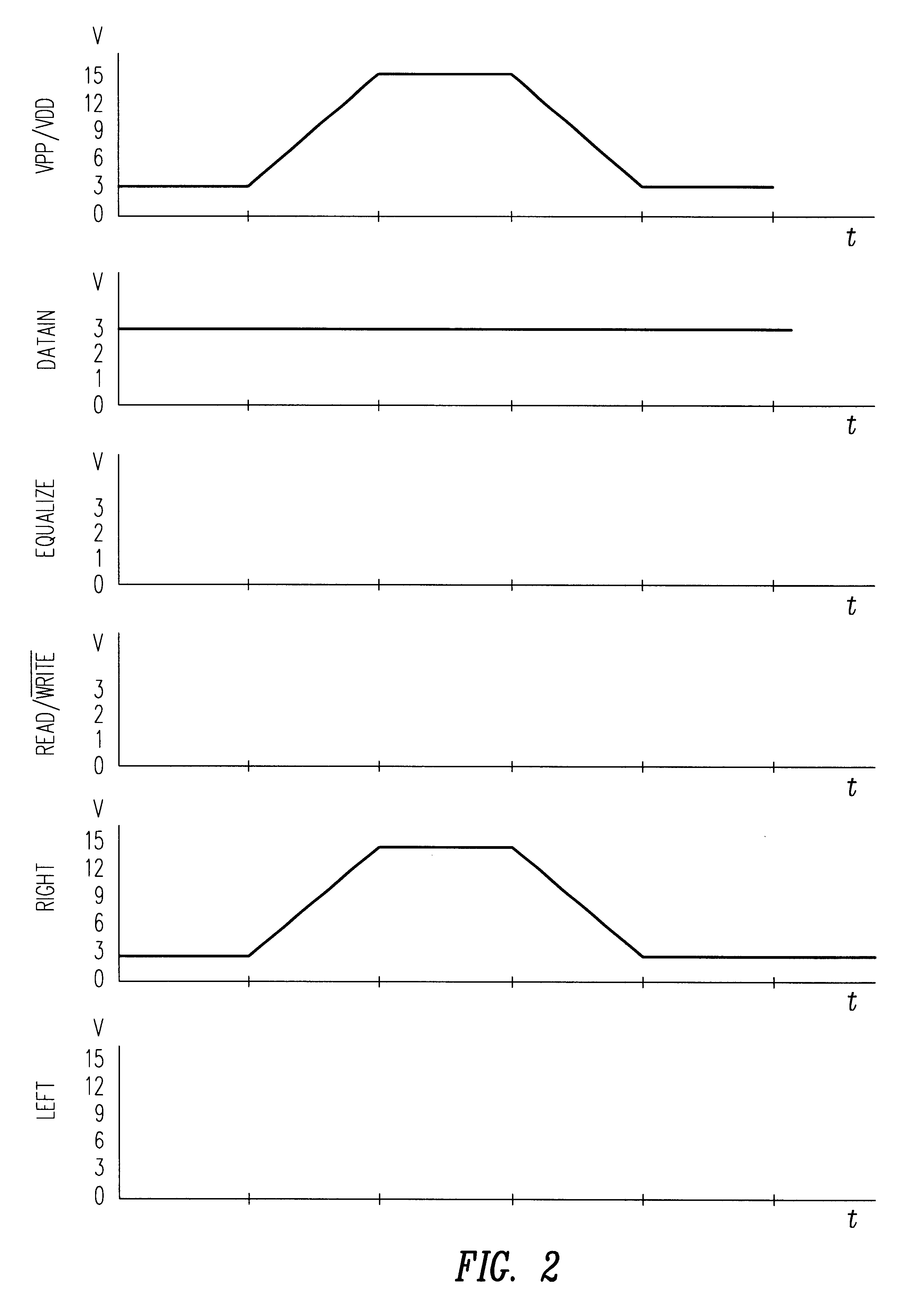
A non-volatile latch circuit that has minimal control circuitry is disclosed. The non-volatile latch circuit is typically used in applications where only several bits of data need to be stored in non-volatile memory. The non-volatile latch circuit can be programmed and read using three control signals: a programming voltage / supply voltage signal, a data in signal, and a read / {overscore (write signal. By using fewer control signals, the number of transistors used to implement the control circuitry within the non-volatile latch circuit is reduced and thus the non-volatile latch circuit consumes less chip area / volume on an integrated circuit device.
Owner:FAIRCHILD SEMICON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com