Patents
Literature
455 results about "Power gating" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
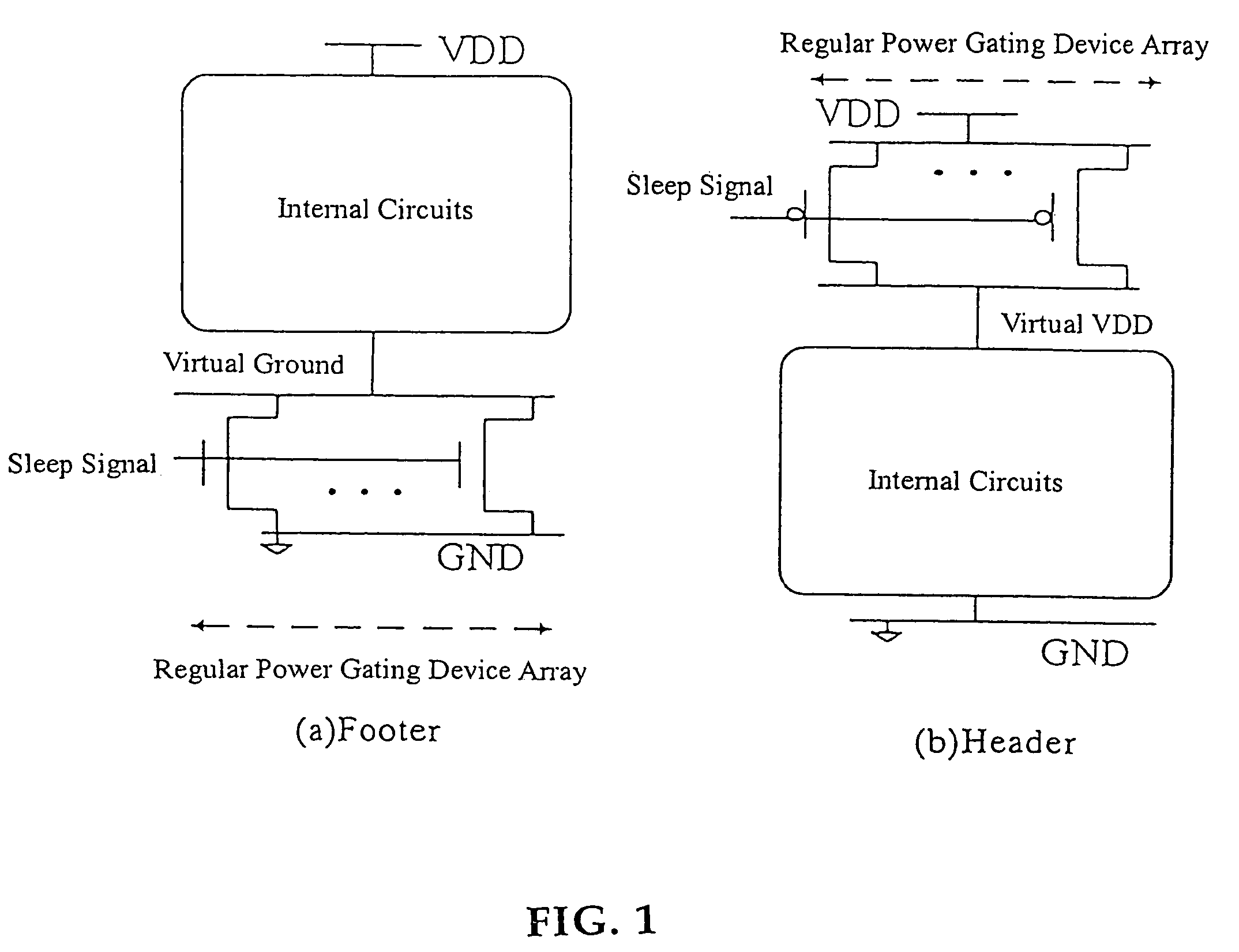
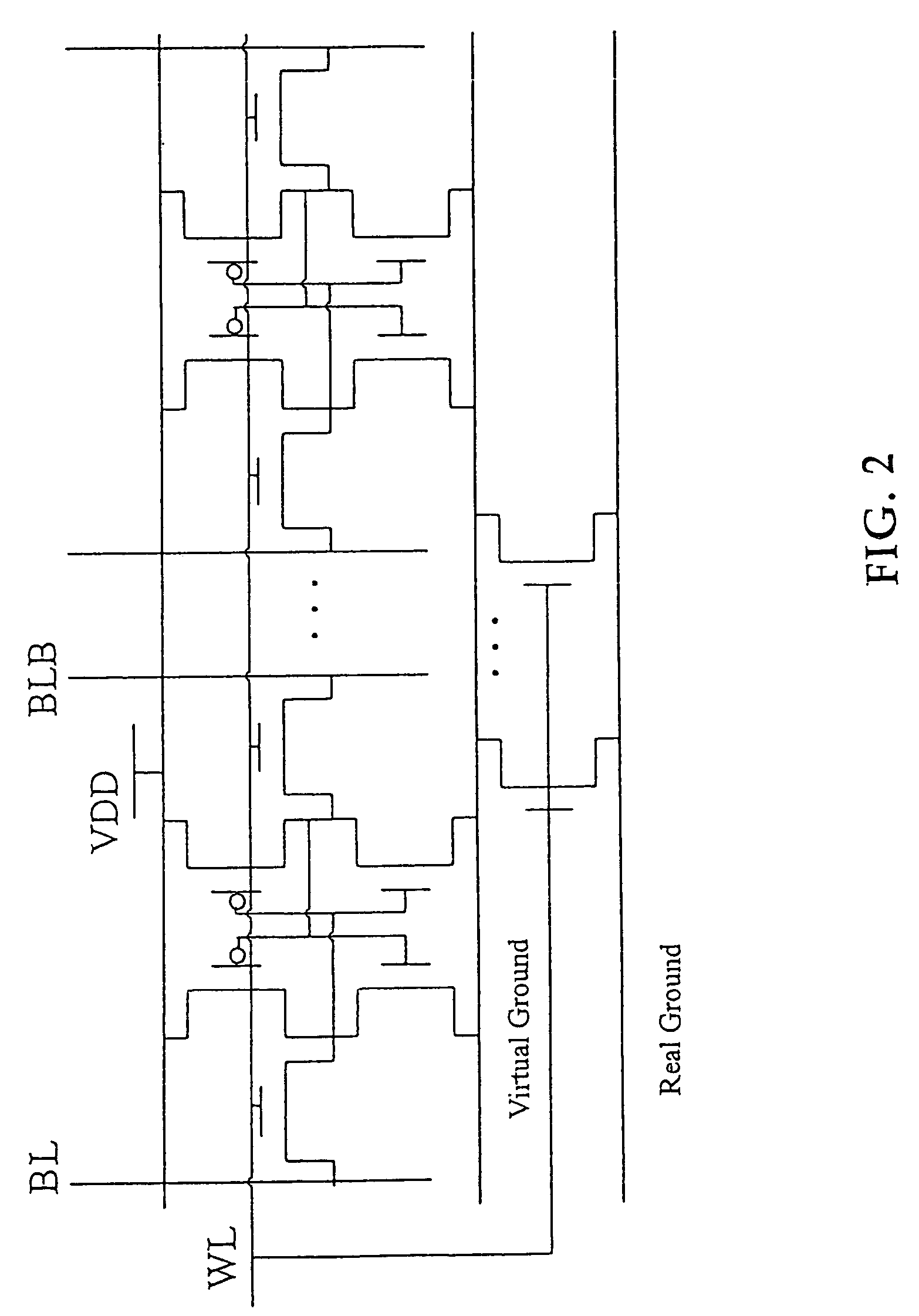
Power gating is a technique used in integrated circuit design to reduce power consumption, by shutting off the current to blocks of the circuit that are not in use. In addition to reducing stand-by or leakage power, power gating has the benefit of enabling Iddq testing.
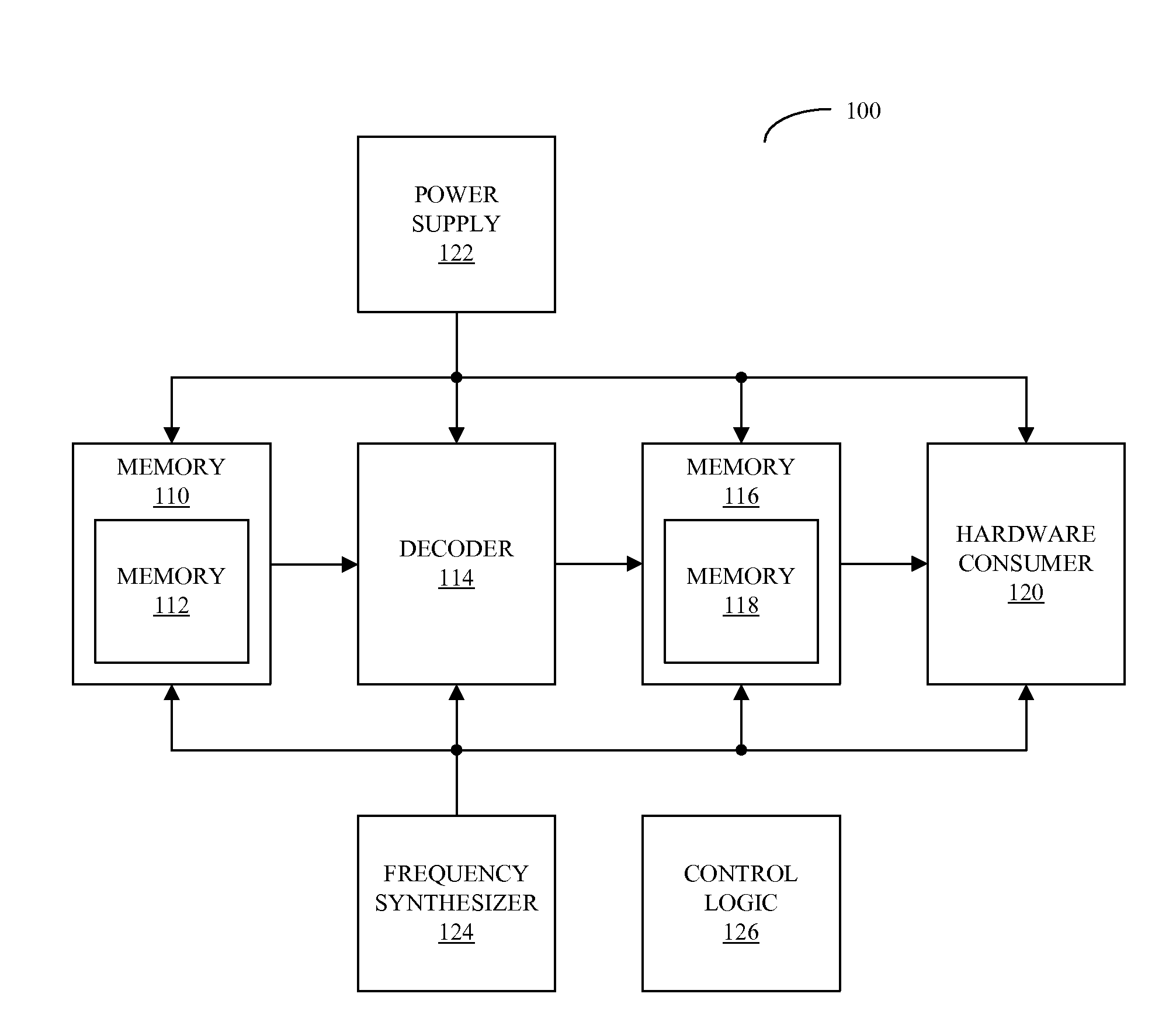
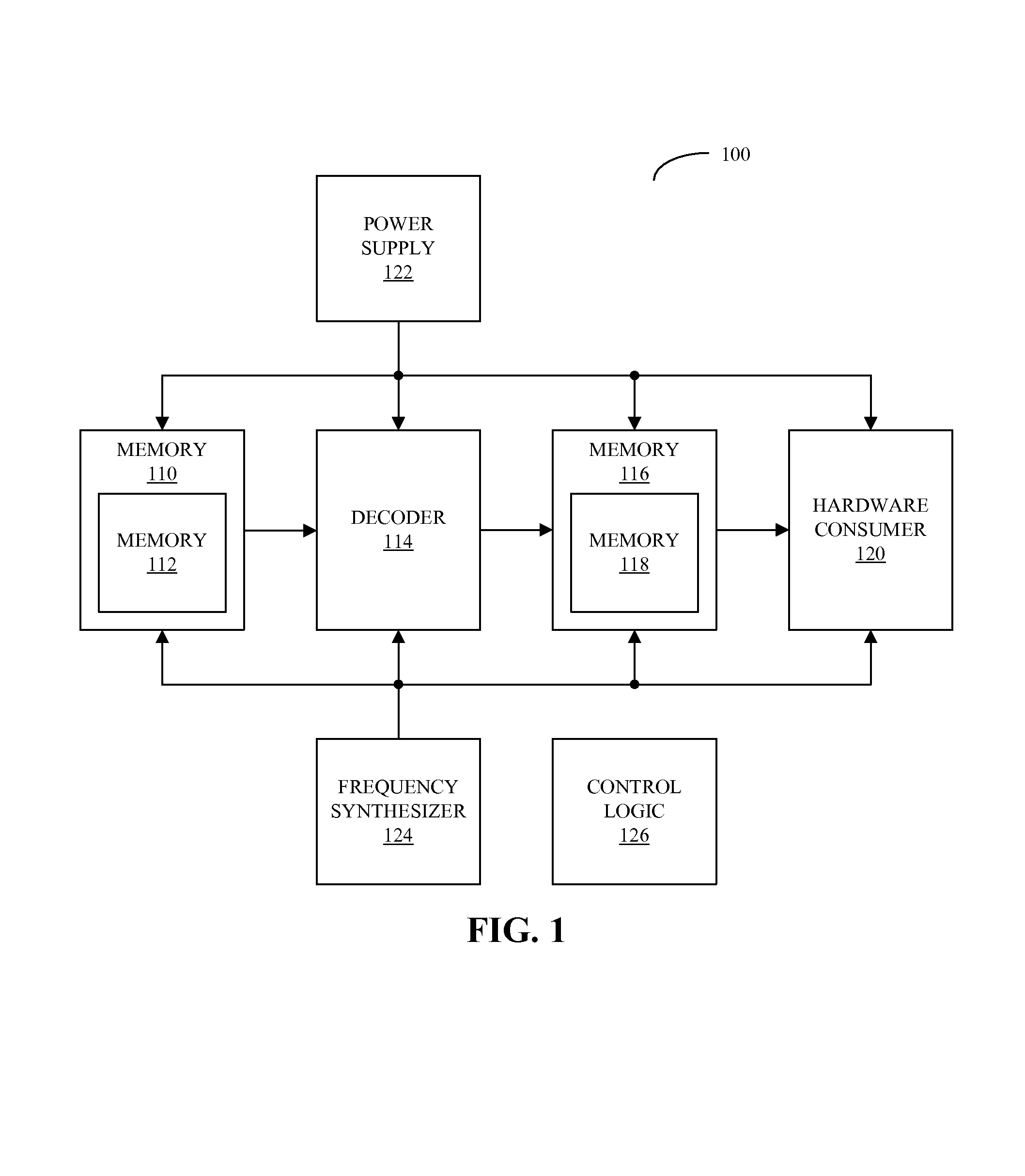
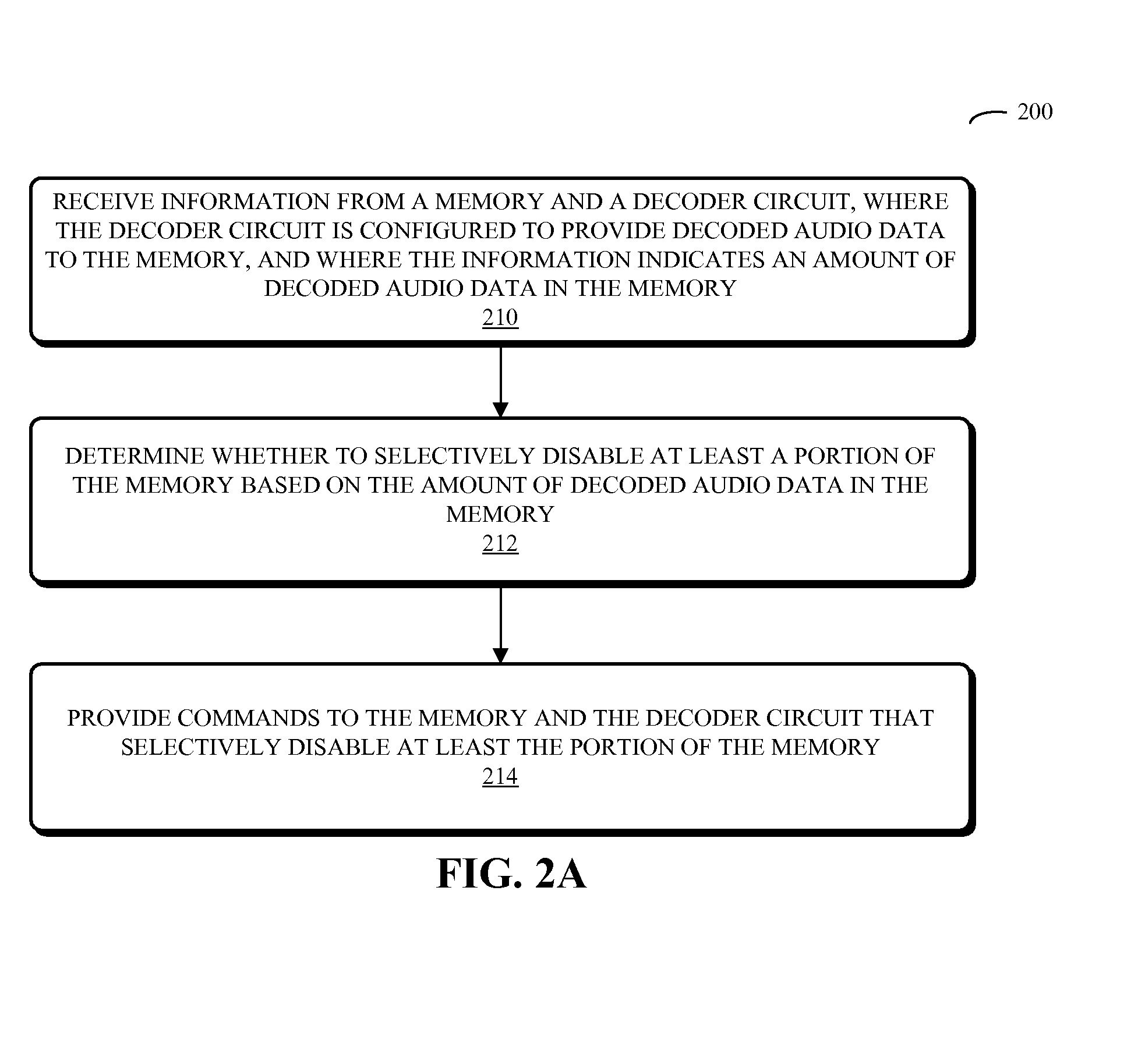
Power-gating media decoders to reduce power consumption
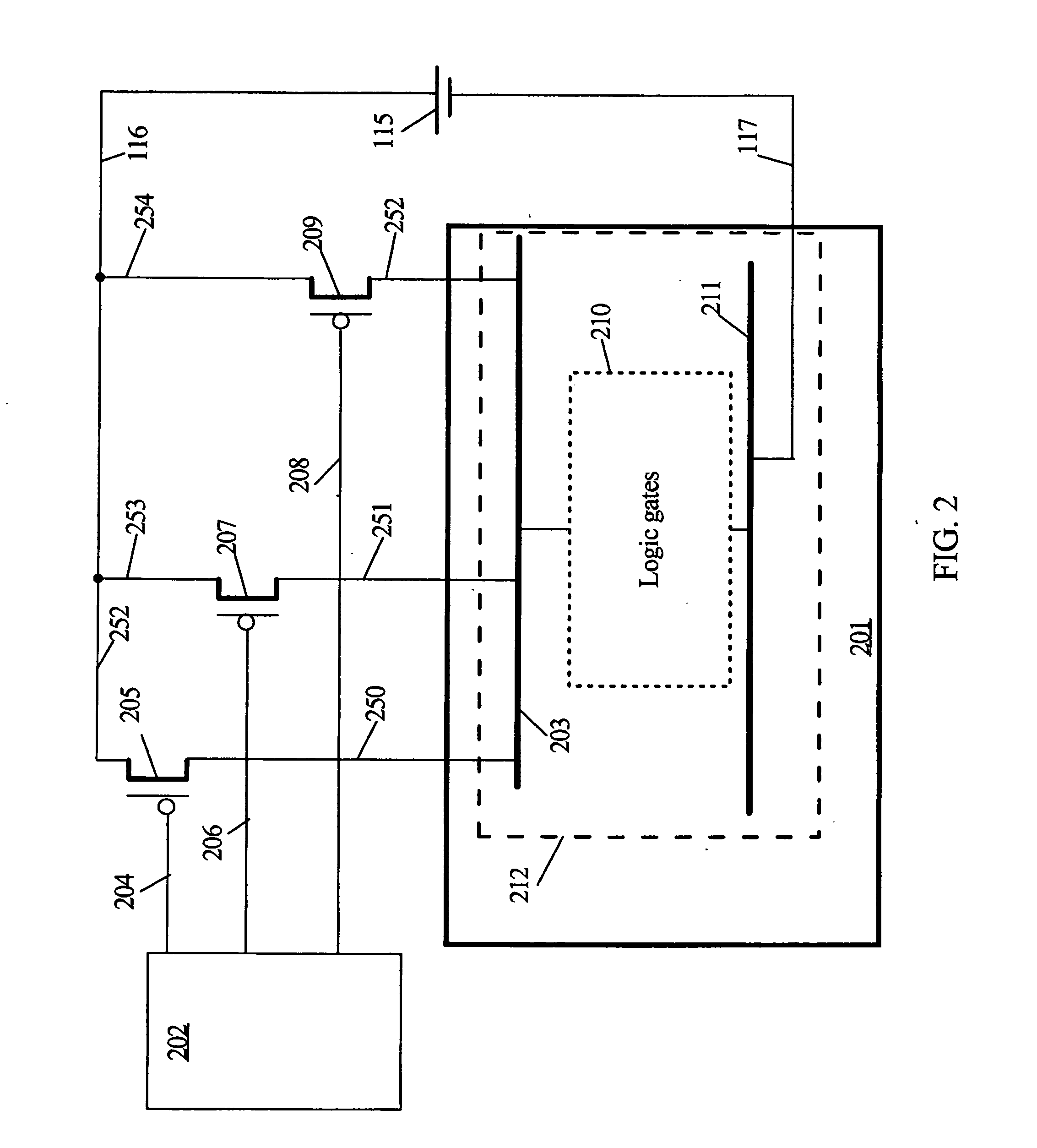
ActiveUS20090003115A1Reduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsElectricityHemt circuits
Embodiments of a system that reduces power consumption by power-gating media decoders are described. During operation of the system, a decoder circuit receives encoded audio data and outputs corresponding decoded audio data to a memory, which is electrically coupled to the decoder circuit. Moreover, control logic, which is electrically coupled to the memory and the decoder circuit, provides commands to the memory and the decoder circuit that selectively disable at least a portion of the memory based on an amount of decoded audio data in the memory.
Owner:APPLE INC
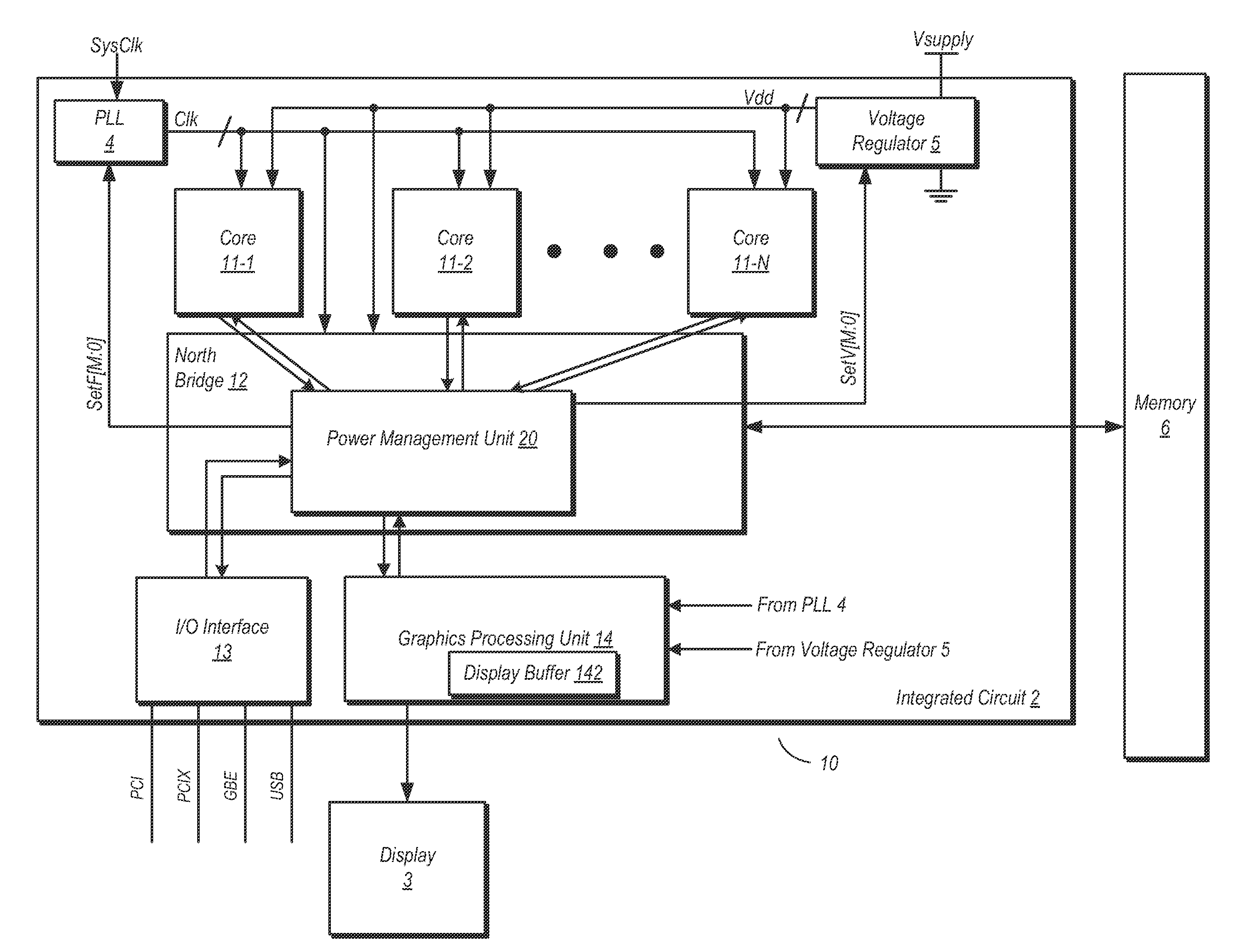
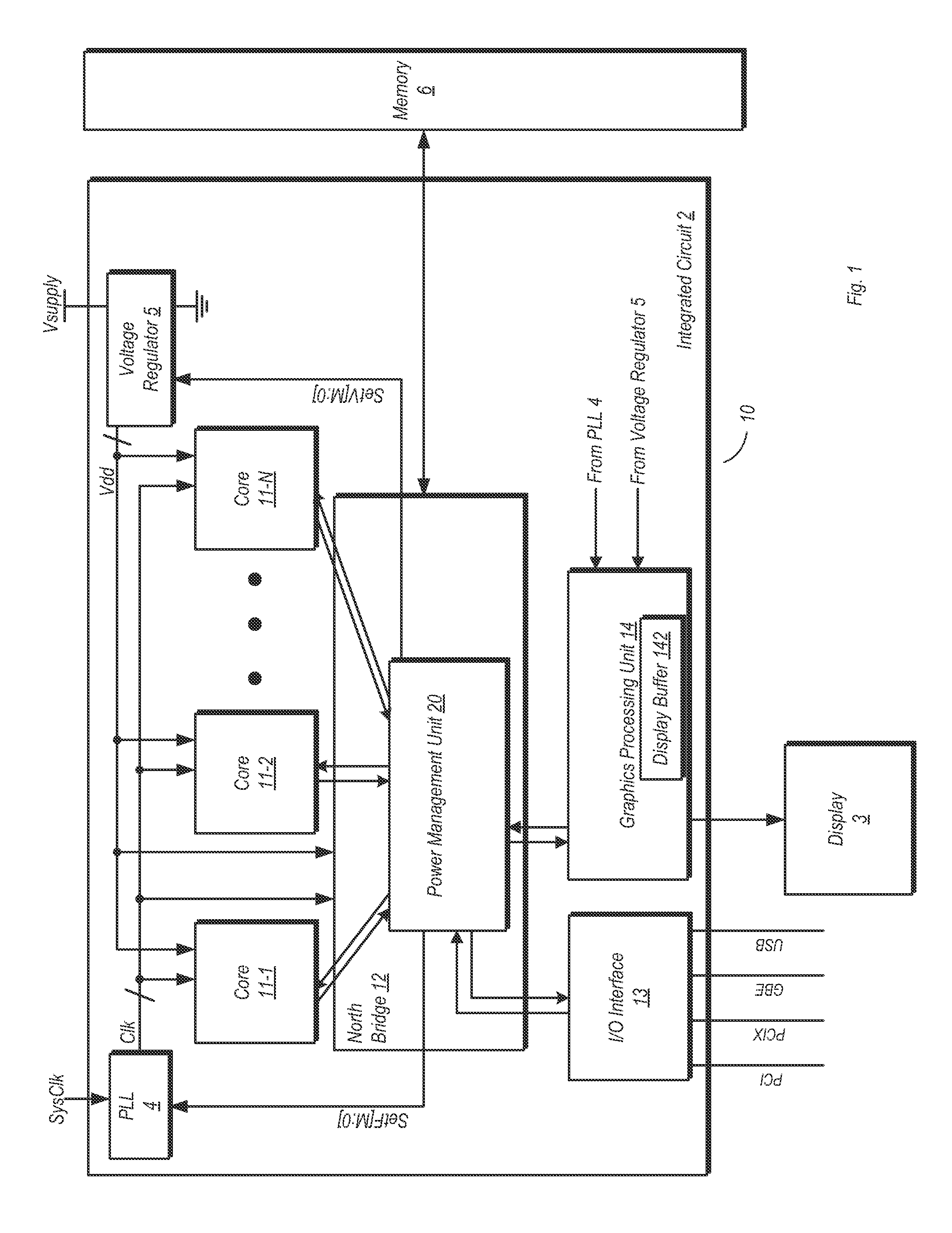
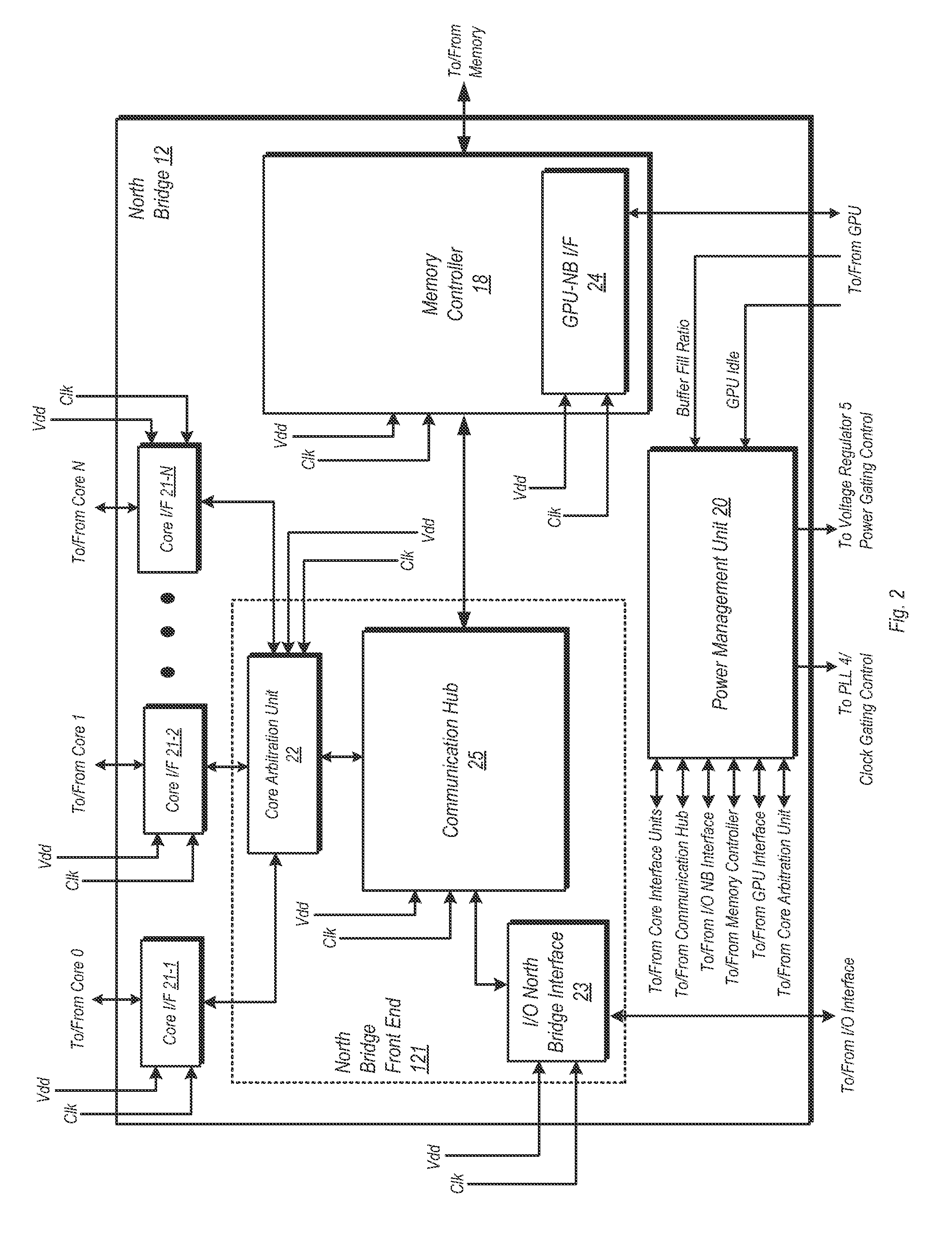
Function based dynamic power control
ActiveUS20120102344A1Energy efficient ICTGenerating/distributing signalsPower Management UnitMemory controller
A system and method for dynamic function based power control is disclosed. In one embodiment, a system includes a bridge unit having a memory controller and a communication hub coupled to the memory controller. The system further includes a power management unit, wherein the power management unit is configured to clock-gate the communication hub responsive to determining that each of a plurality of processor cores are in an idle state and that an I / O interface unit has been idle for an amount of time exceeding a first threshold. The power management unit is further configured to clock-gate the memory controller responsive to clock-gating the communication hub and determining that a memory coupled to the memory controller is in a first low power state. The power management unit may also perform power-gating of functional units subsequent to clock-gating the same.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
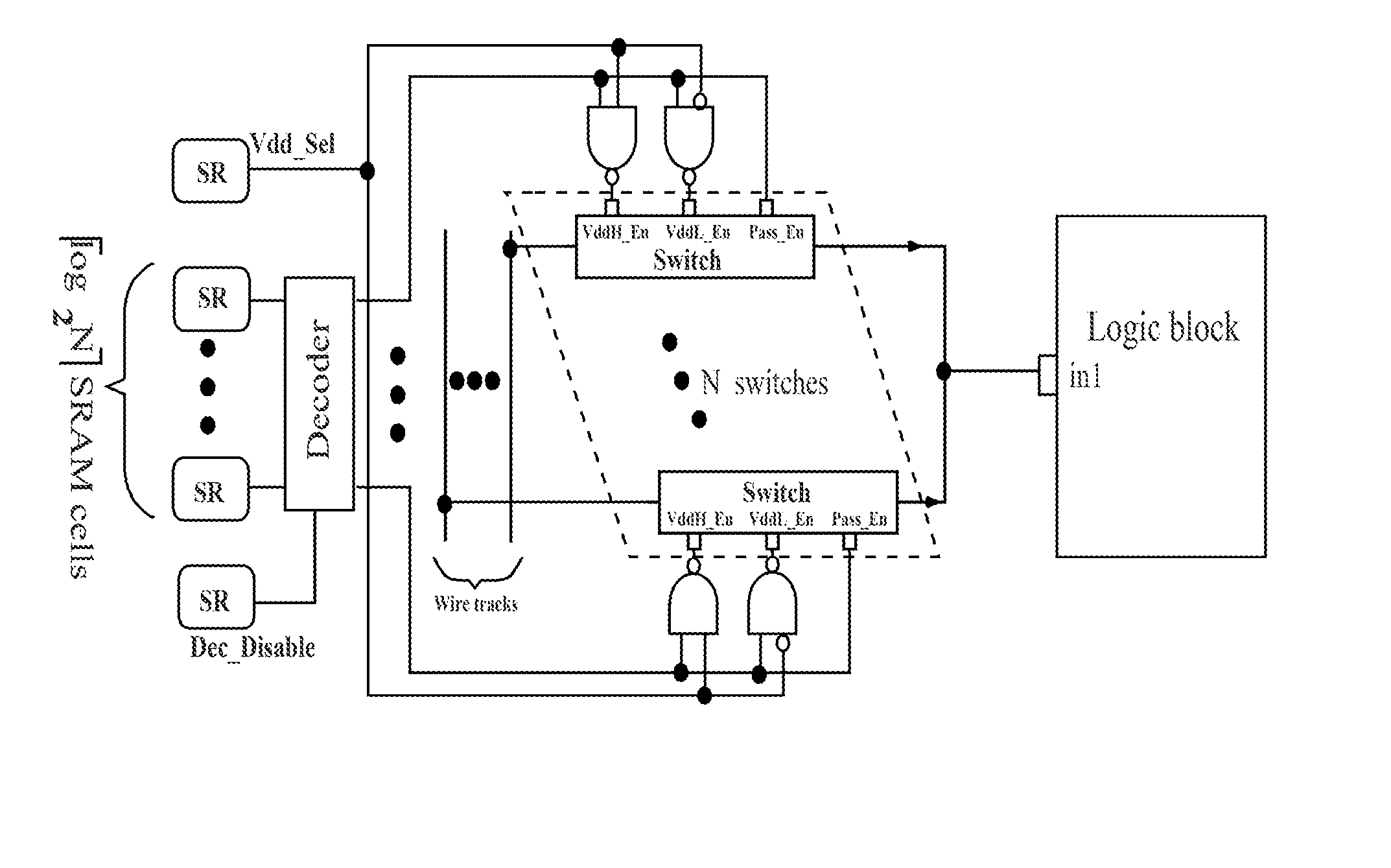
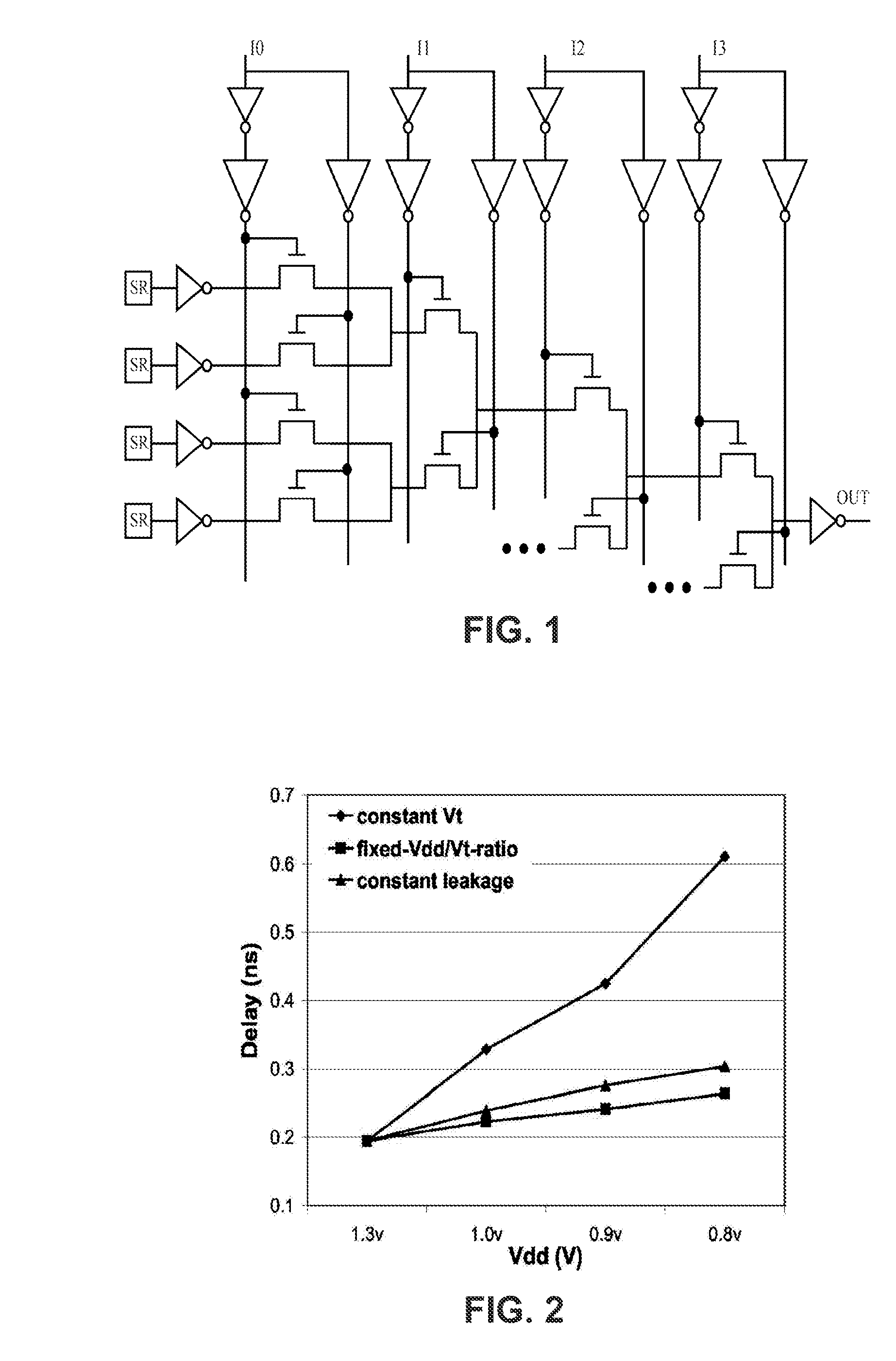
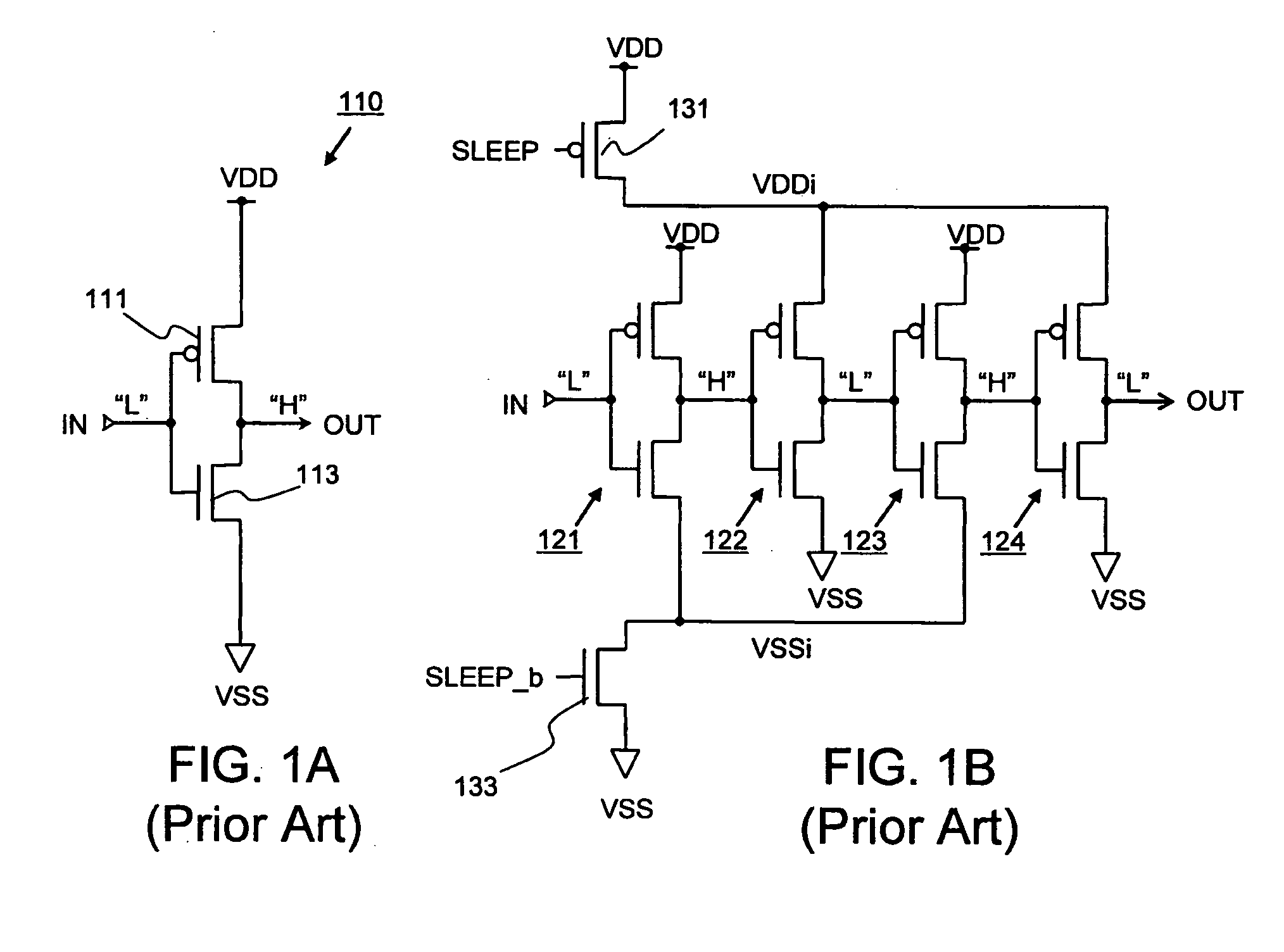
Low-power FPGA circuits and methods
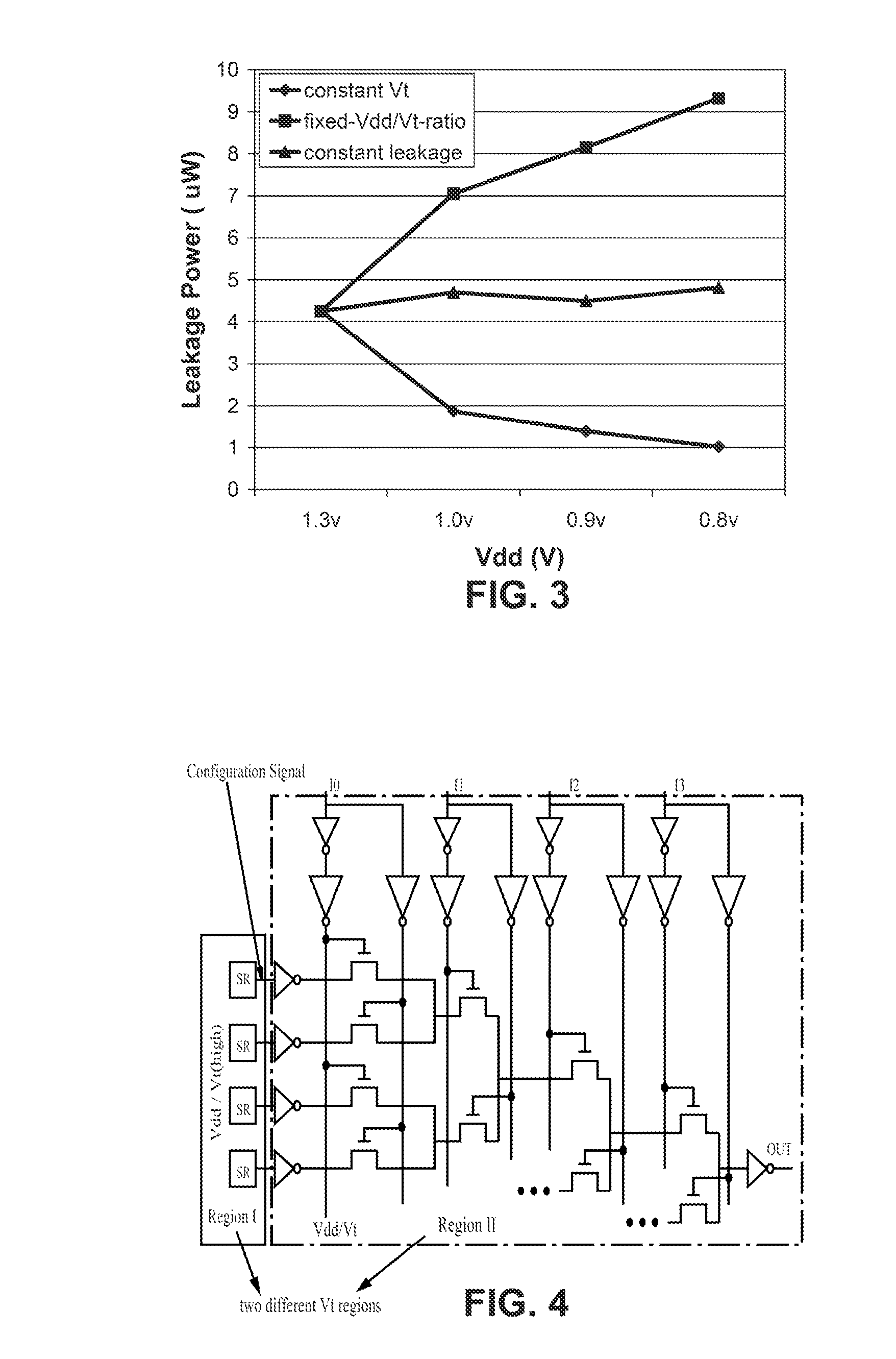
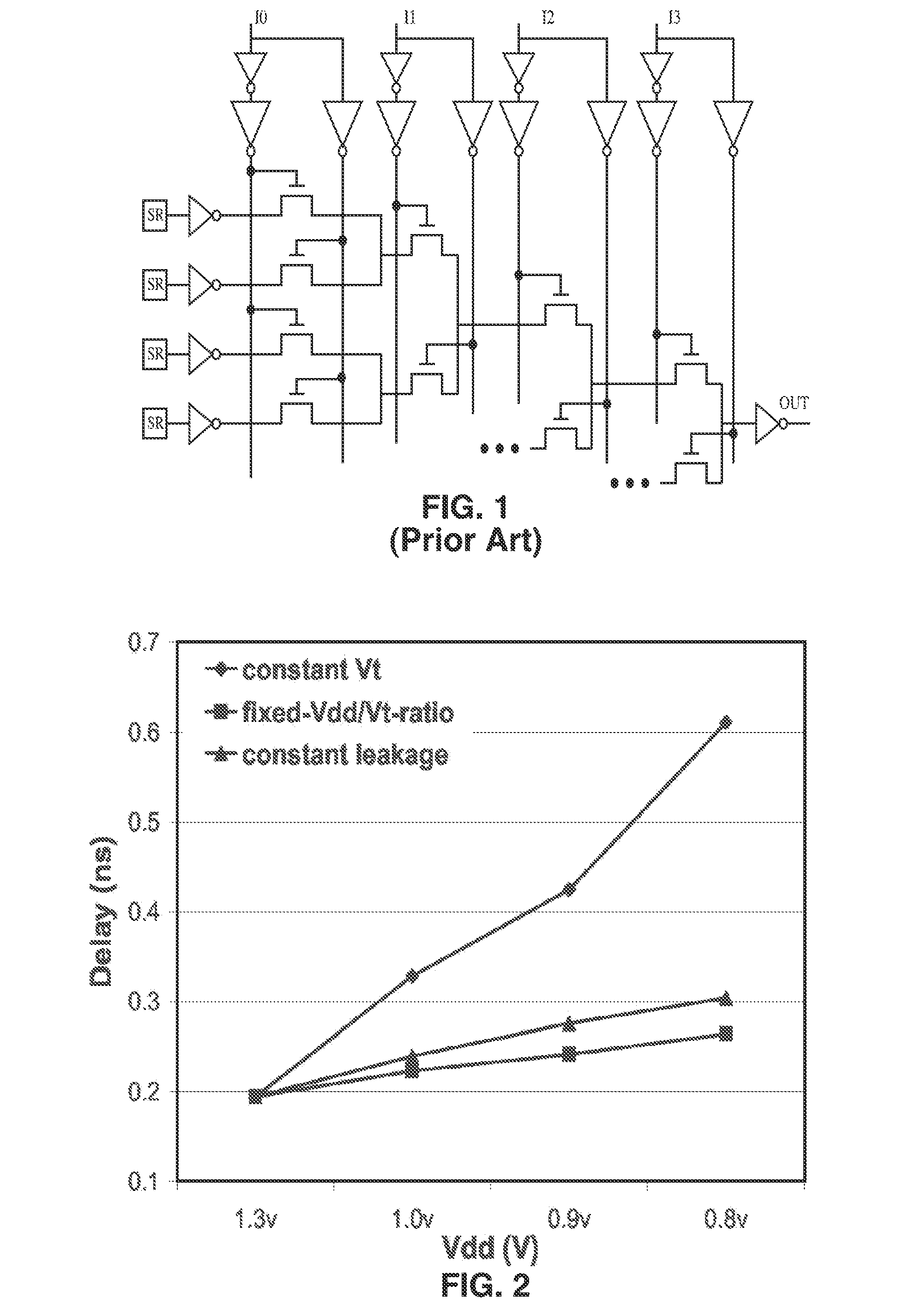
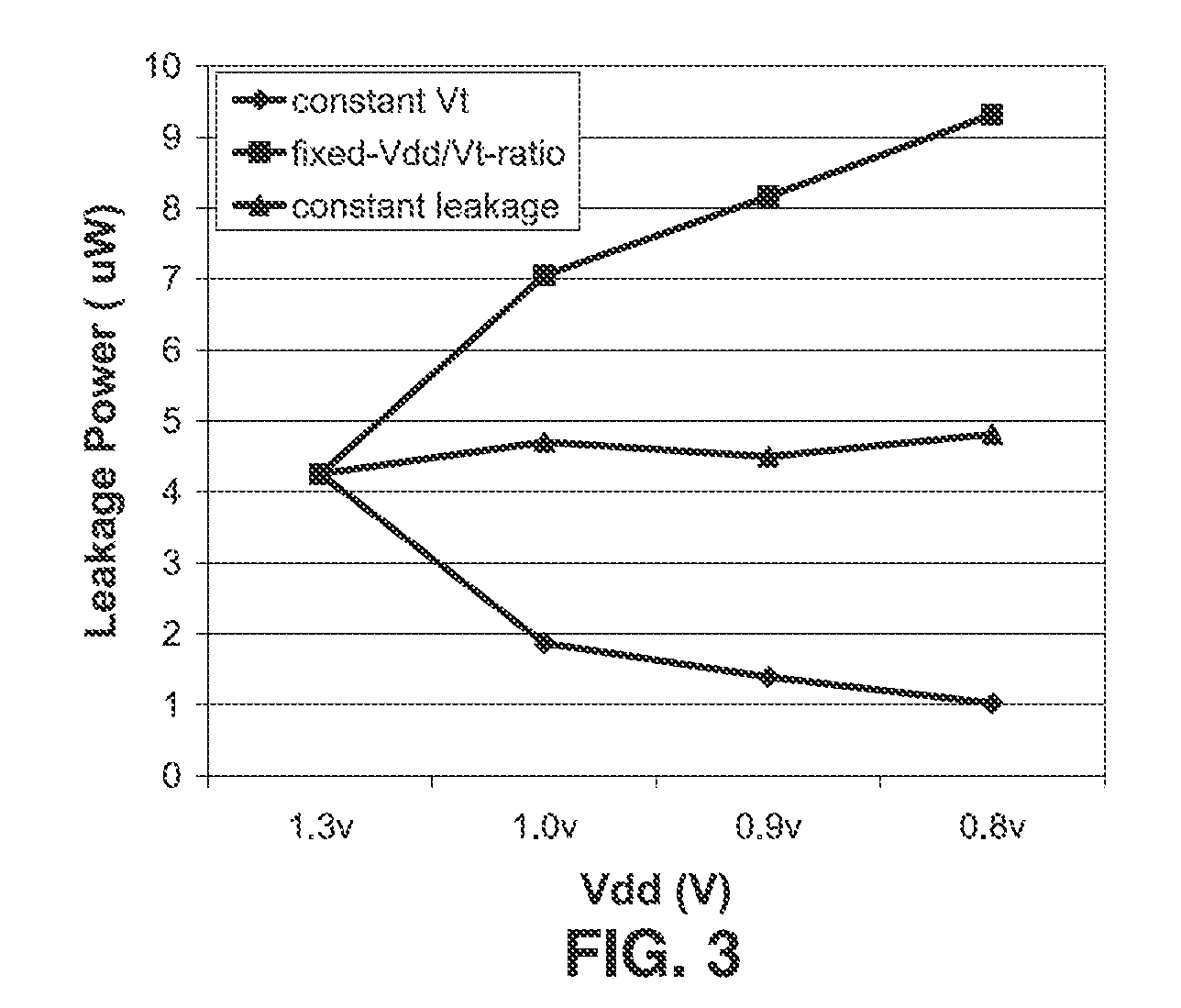
InactiveUS20070164785A1Increase profitReduce needSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringLeakage power
Field Programmable Logic Arrays (FPGAs) are described which utilize multiple power supply voltages to reduce both dynamic power and leakage power without sacrificing speed or substantially increasing device area. Power reduction mechanisms are described for numerous portions of the FPGA, including logic blocks, routing circuits, connection blocks, switch blocks, configuration memory cells, and so forth. Embodiments describe circuits and methods for implementing multiple supplies as sources of Vdd, multiple voltage thresholding Vt, signal level translators, and power gating of circuitry to deactivate portions of the circuit which are inactive. The supply voltage levels can be fixed, or programmable. Methods are described for performing circuit CAD in the routing and assignment process on FPGAs, in particular for optimizing FPGA use having the power reduction circuits taught. Routing methods describe utilizing slack timing, power sensitivity, trace-based simulations, and other techniques to optimize circuit utilization on a multi Vdd FPGA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Low-power FPGA circuits and methods
InactiveUS20100281448A1Improve utilizationEasy to controlCAD circuit designMulti-objective optimisationComputer architectureMemory cell
Field Programmable Logic Arrays (FPGAs) are described which utilize multiple power supply voltages to reduce both dynamic power and leakage power without sacrificing speed or substantially increasing device area. Power reduction mechanisms are described for numerous portions of the FPGA, including logic blocks, routing circuits, connection blocks, switch blocks, configuration memory cells, and so forth. Embodiments describe circuits and methods for implementing multiple supplies as sources of Vdd, multiple voltage thresholding Vt, signal level translators, and power gating of circuitry to deactivate portions of the circuit which are inactive. The supply voltage levels can be fixed, or programmable. Methods are described for performing circuit CAD in the routing and assignment process on FPGAs, in particular for optimizing FPGA use having the power reduction circuits taught. Routing methods describe utilizing slack timing, power sensitivity, trace-based simulations, and other techniques to optimize circuit utilization on a multi Vdd FPGA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
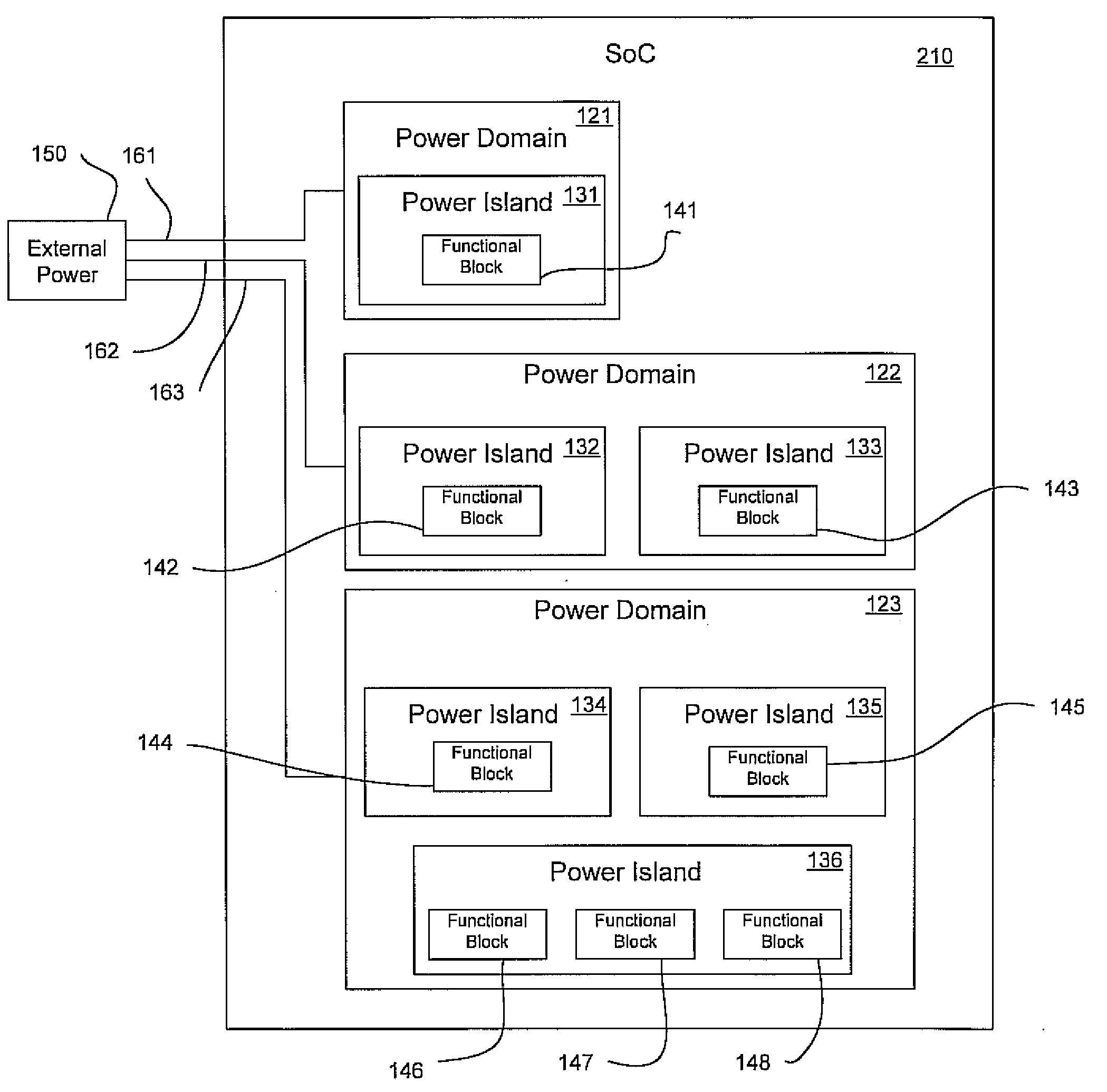
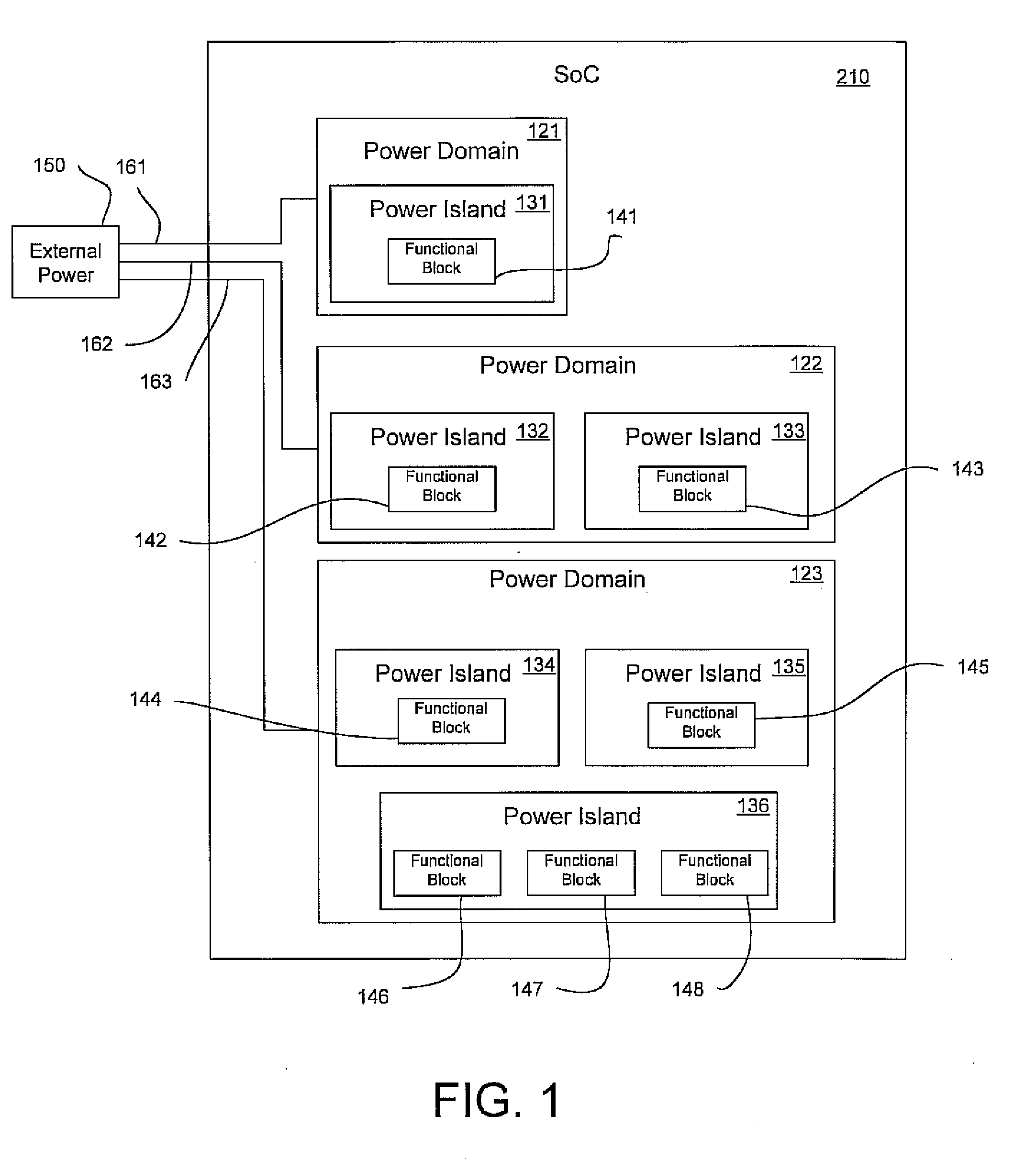
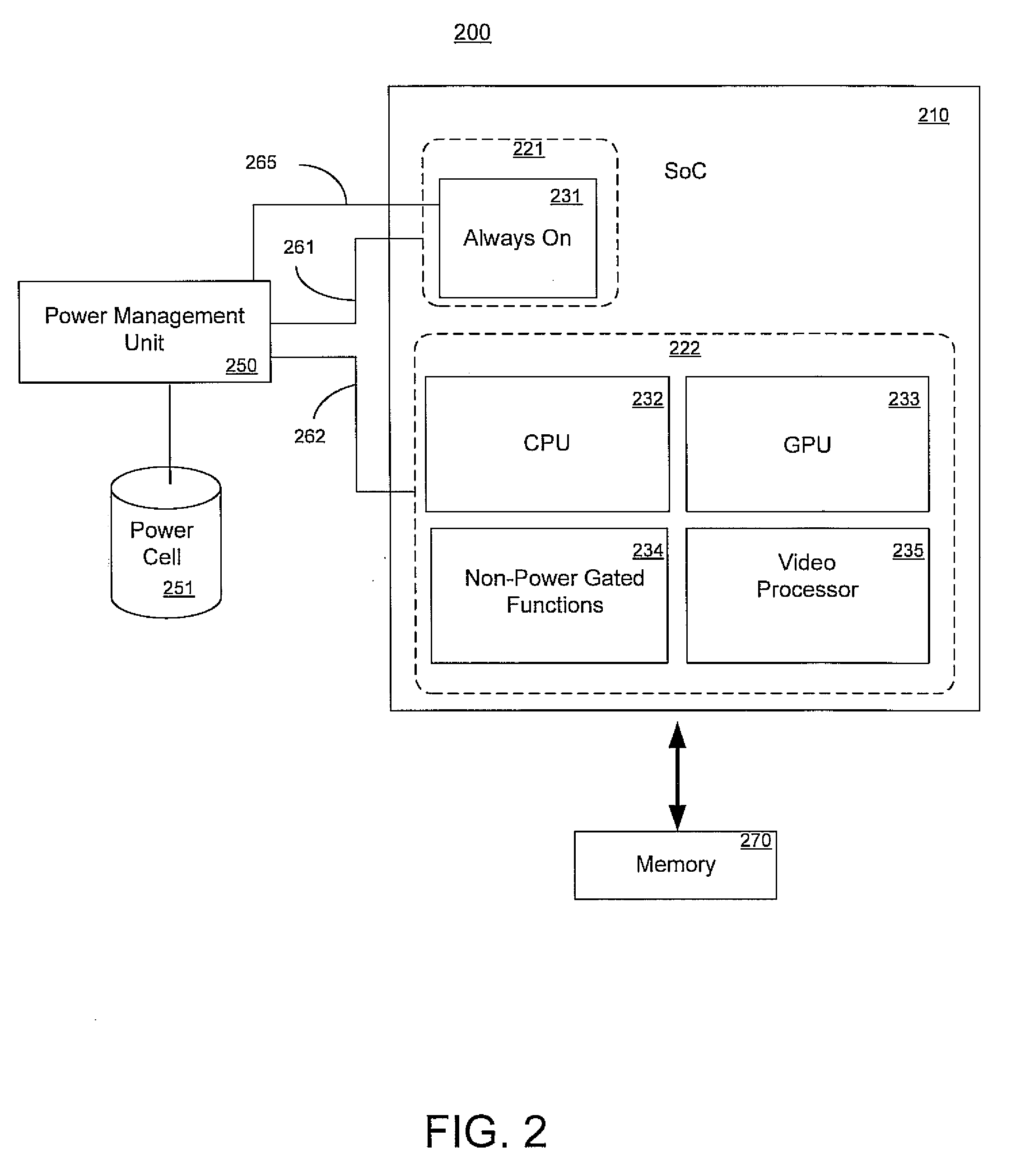
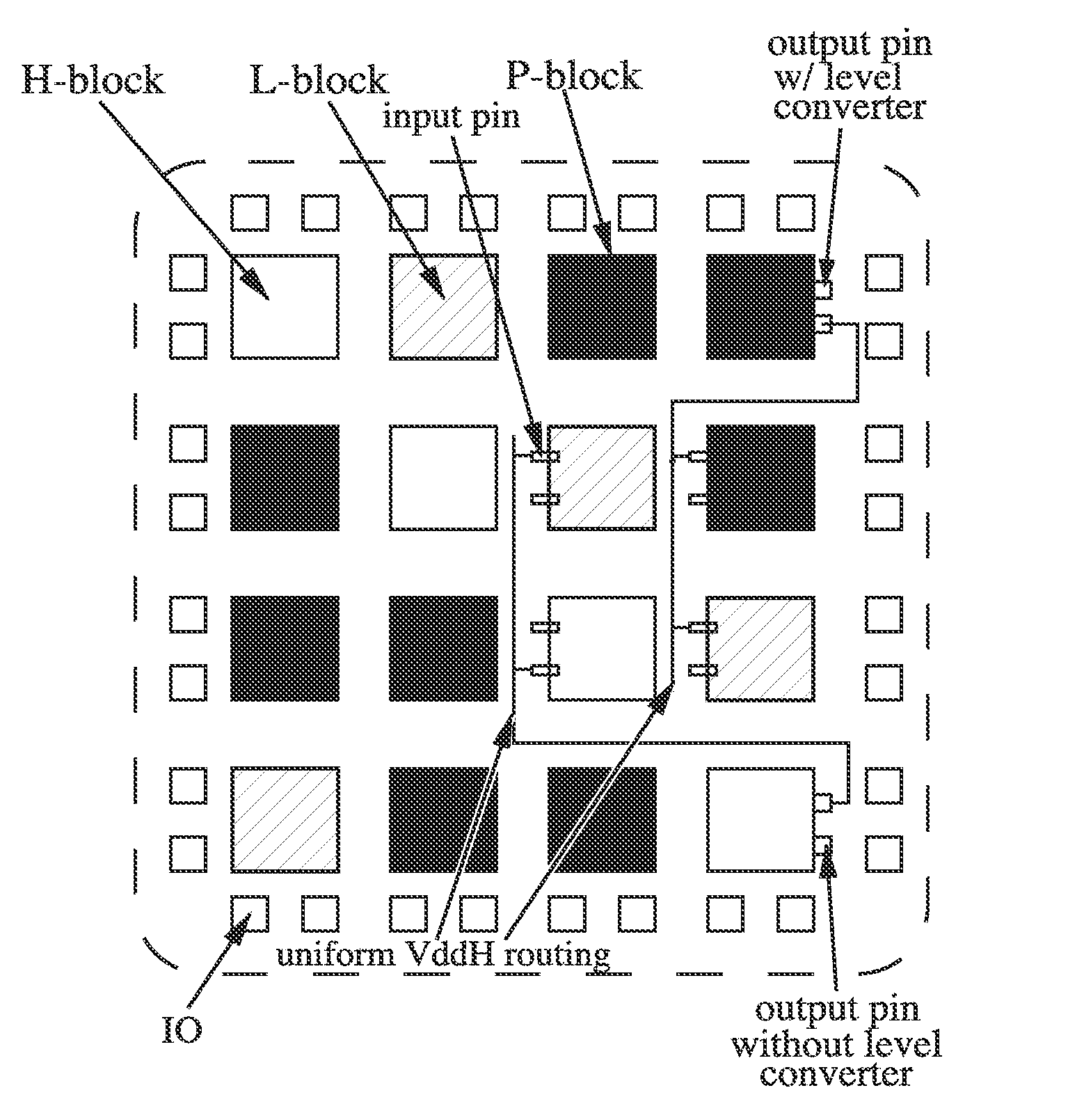
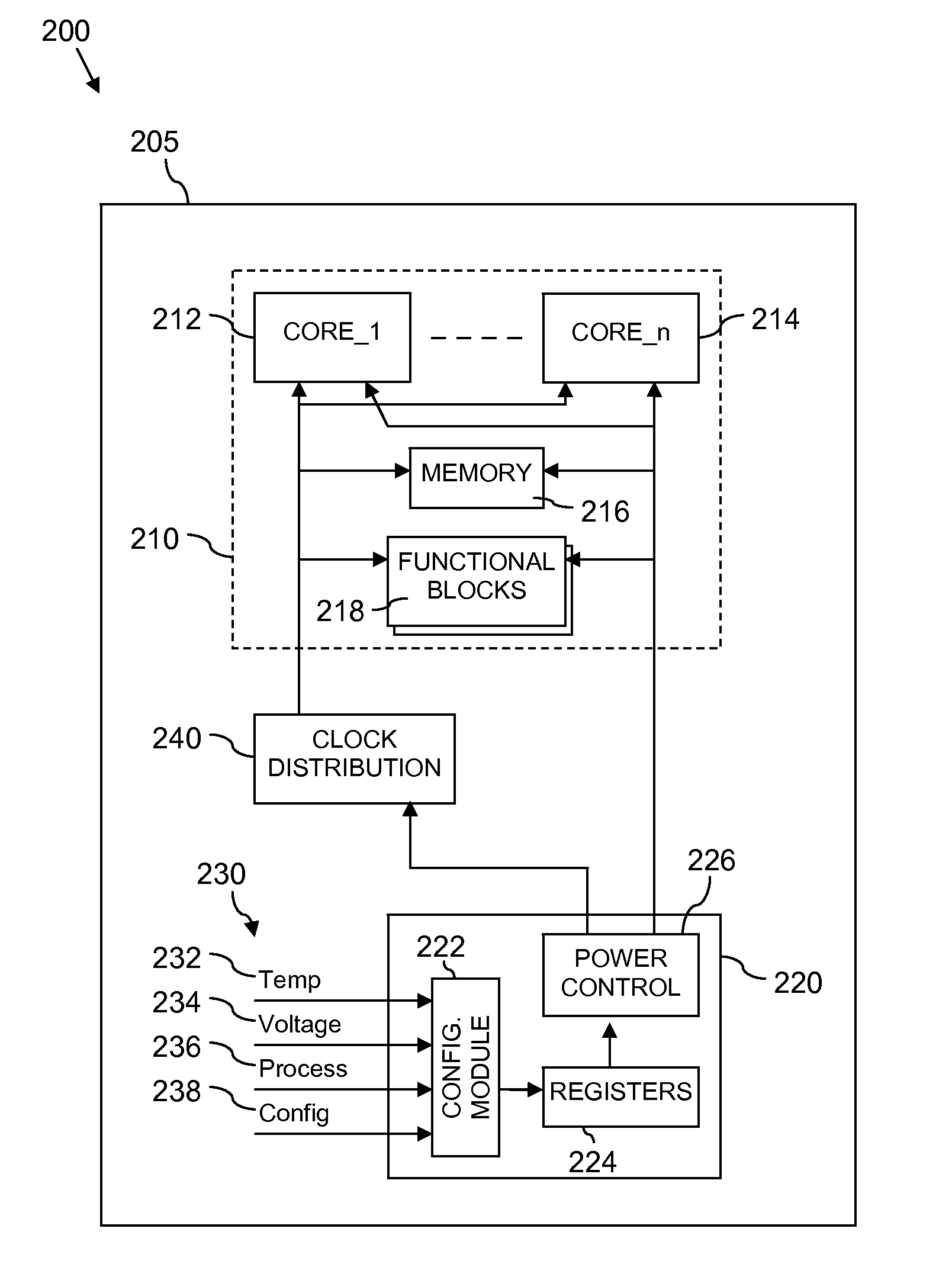
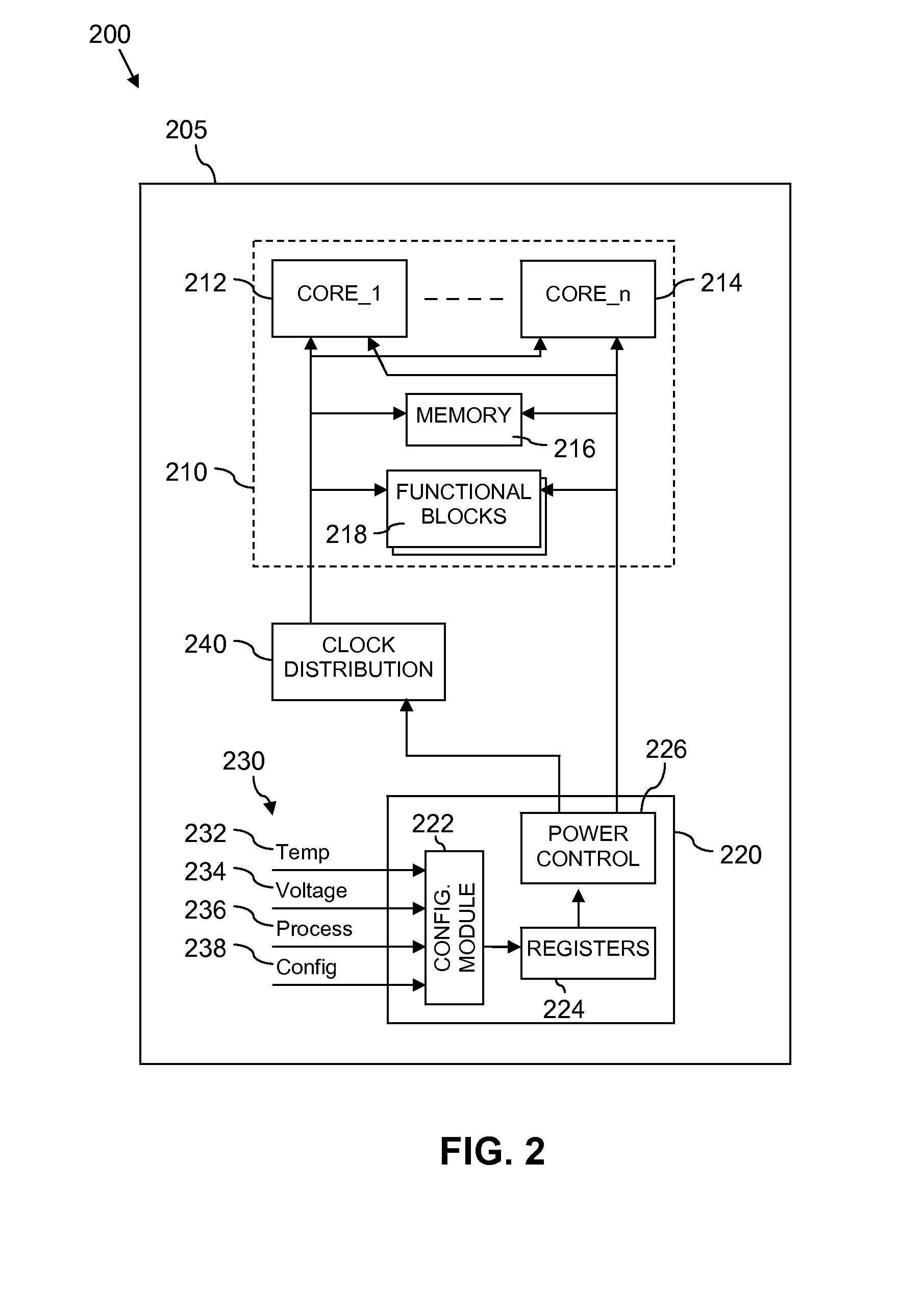
Integrated circuit device having power domains and partitions based on use case power optimization
ActiveUS20090201082A1Minimize leakage currentSolve the large leakage currentEnergy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsEngineeringPower domains
A programmable SoC (system on a chip) having optimized power domains and power islands. The SoC is an integrated circuit device including a plurality of power domains, each of the power domains having a respective voltage rail to supply power to the power domain. A plurality of power islands are included within the integrated circuit device, wherein each power domain includes at least one power island. A plurality of functional blocks are included within the integrated circuit device, wherein each power island includes at least one functional block. Each functional block is configured to provide a specific device functionality. The integrated circuit device adjusts power consumption in relation to a requested device functionality by individually turning on or turning off power to a selected one or more power domains, and for each turned on power domain, individually power gating one or more power islands.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
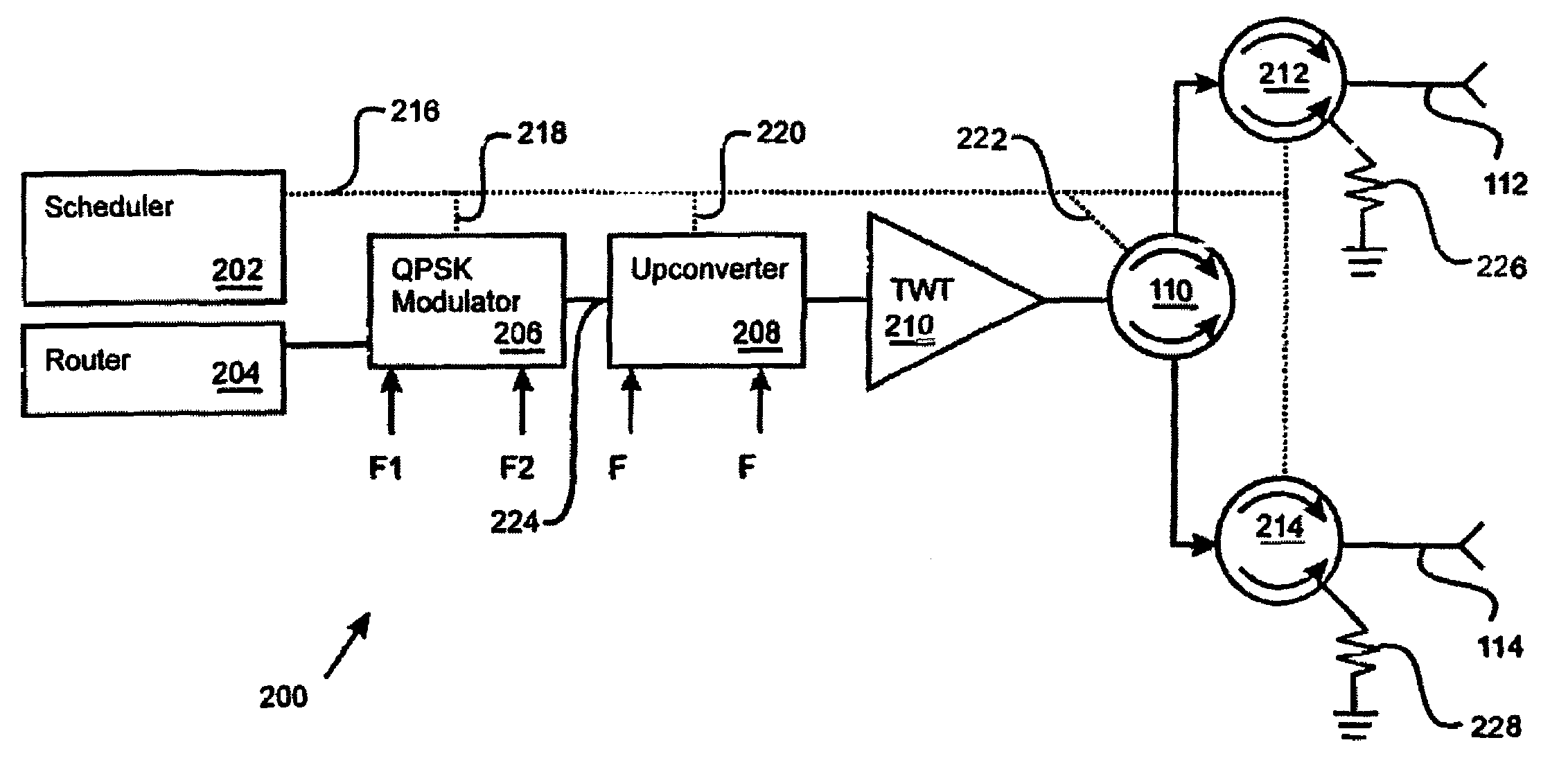
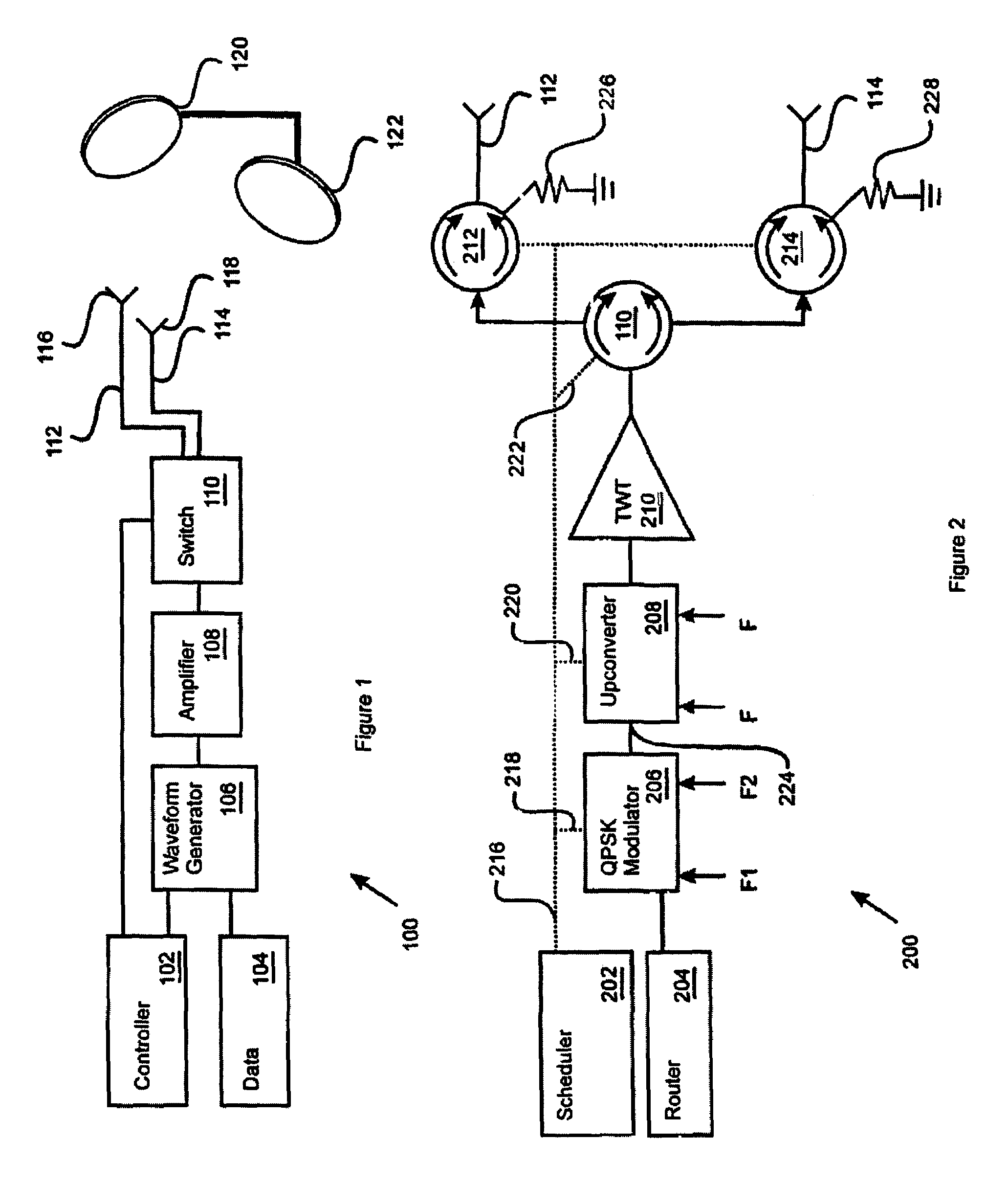
Beam hopping self addressed packet switched communication system with power gating
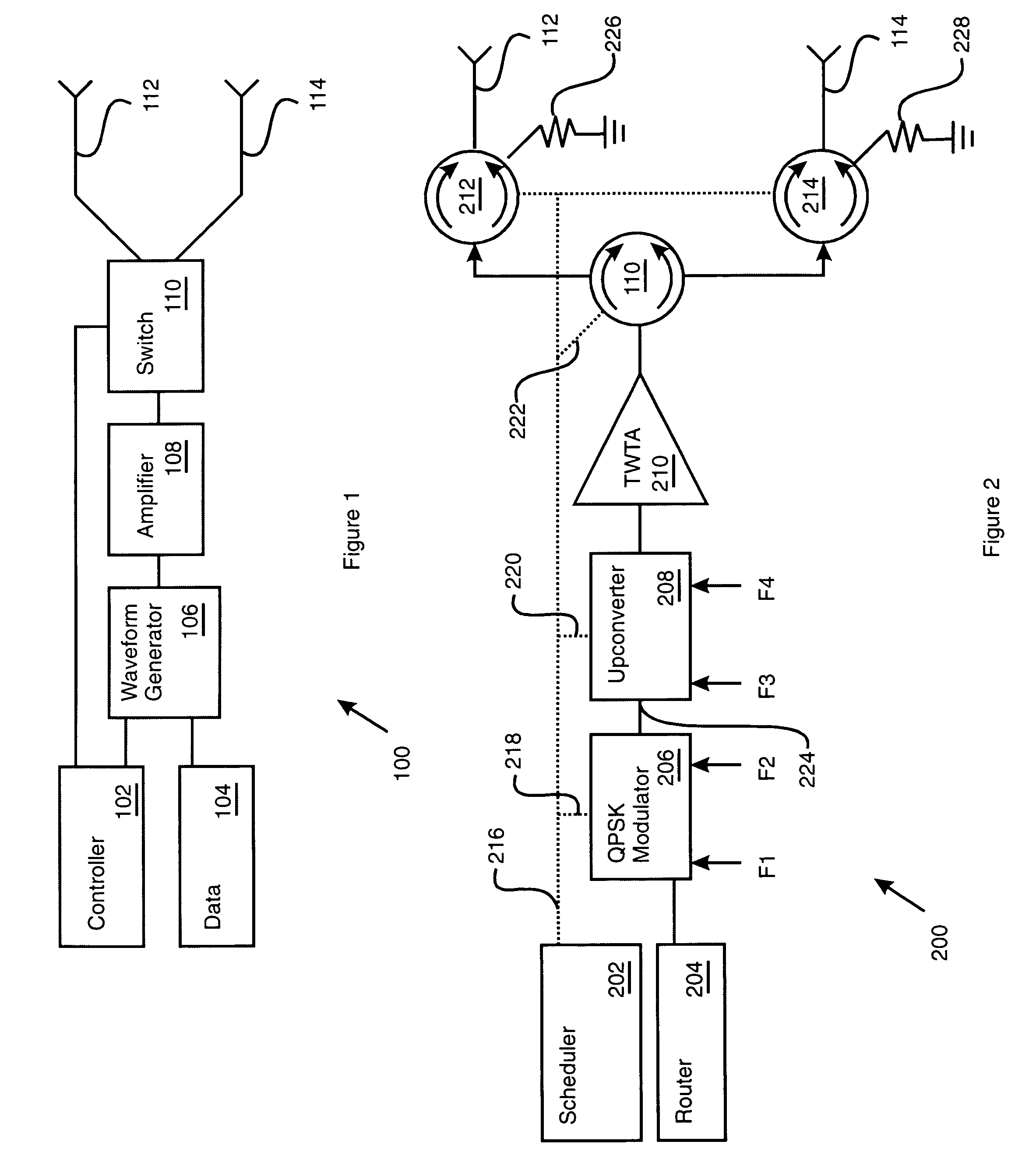
InactiveUS7068974B1Resonant long antennasRadio transmissionAudio power amplifierCommunications system
A downlink beam frame signal processing system (100) for a communication satellite includes a packet switch (608) that routes self addressed uplink data to a memory (804). The memory (804) stores queues for at least a first and a second downlink beam hop locations (302, 304). The processing system (100) also includes a power amplifier (108) that amplifies a waveform formed using the uplink data. A power gating circuit (1200) coupled to the power amplifier (108) includes a power gate input (1216) responsive to a power gating signal to remove RF power from at least a portion of the waveform before transmission.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
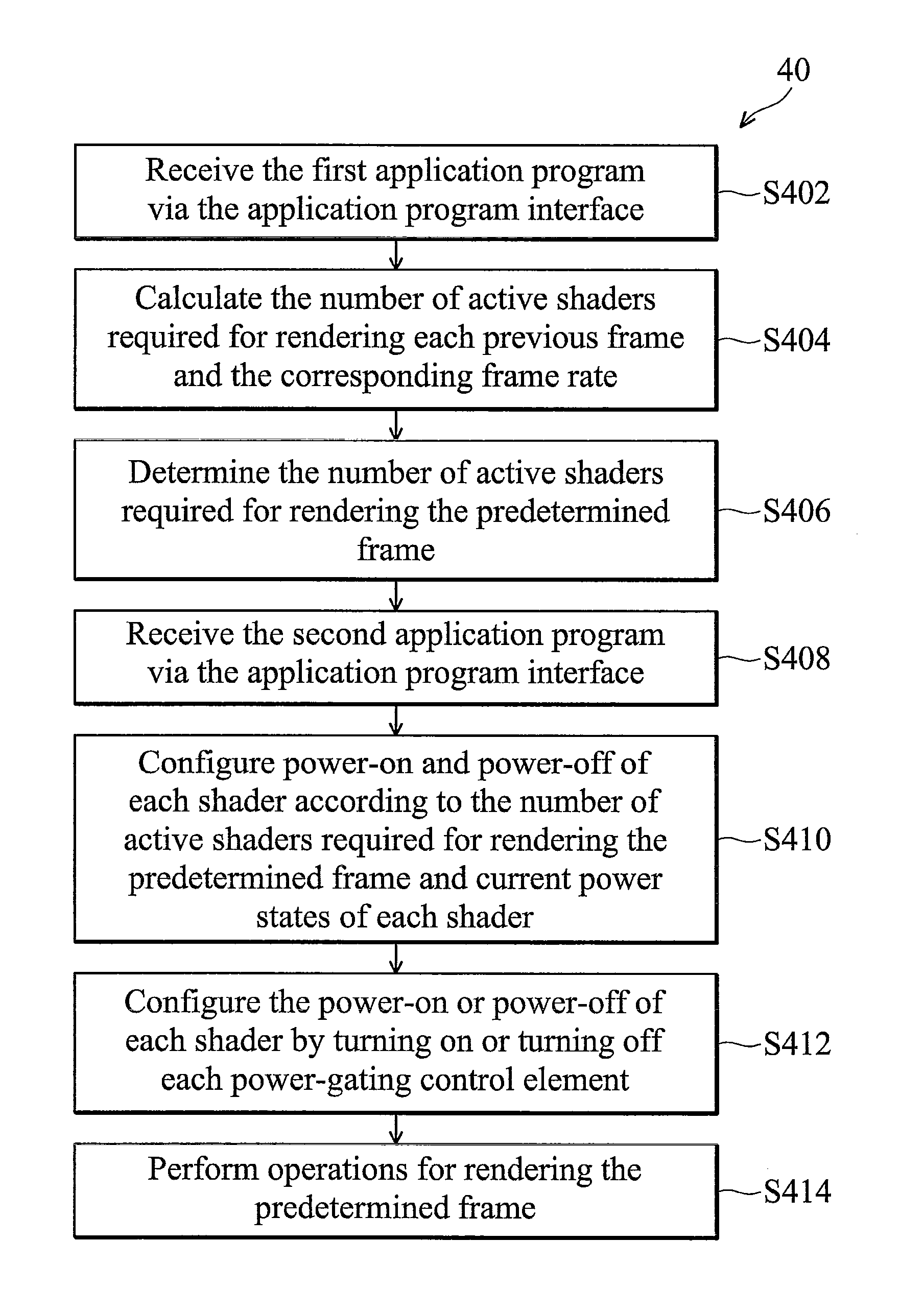
Graphics processing system with power-gating control function, power-gating control method, and computer program products thereof
InactiveUS20100295852A1Energy efficient ICTDigital data processing detailsComputational sciencePower gating
The invention relates to a power-gating control method for a graphics processing unit having a unified shader unit, which includes a plurality of shaders. The method includes the steps of: rendering a plurality of previous frames; calculating a first number of active shaders for rendering each previous frame, and a corresponding frame rate of each previous frame; determining a second number of active shaders for rendering a next frame immediately following the previous frame according to the first number of active shaders and the corresponding frame rate of each previous frame; and activating corresponding shaders through one or more power-gating control elements according to the second number of active shaders.
Owner:INSTITUTE FOR INFORMATION INDUSTRY
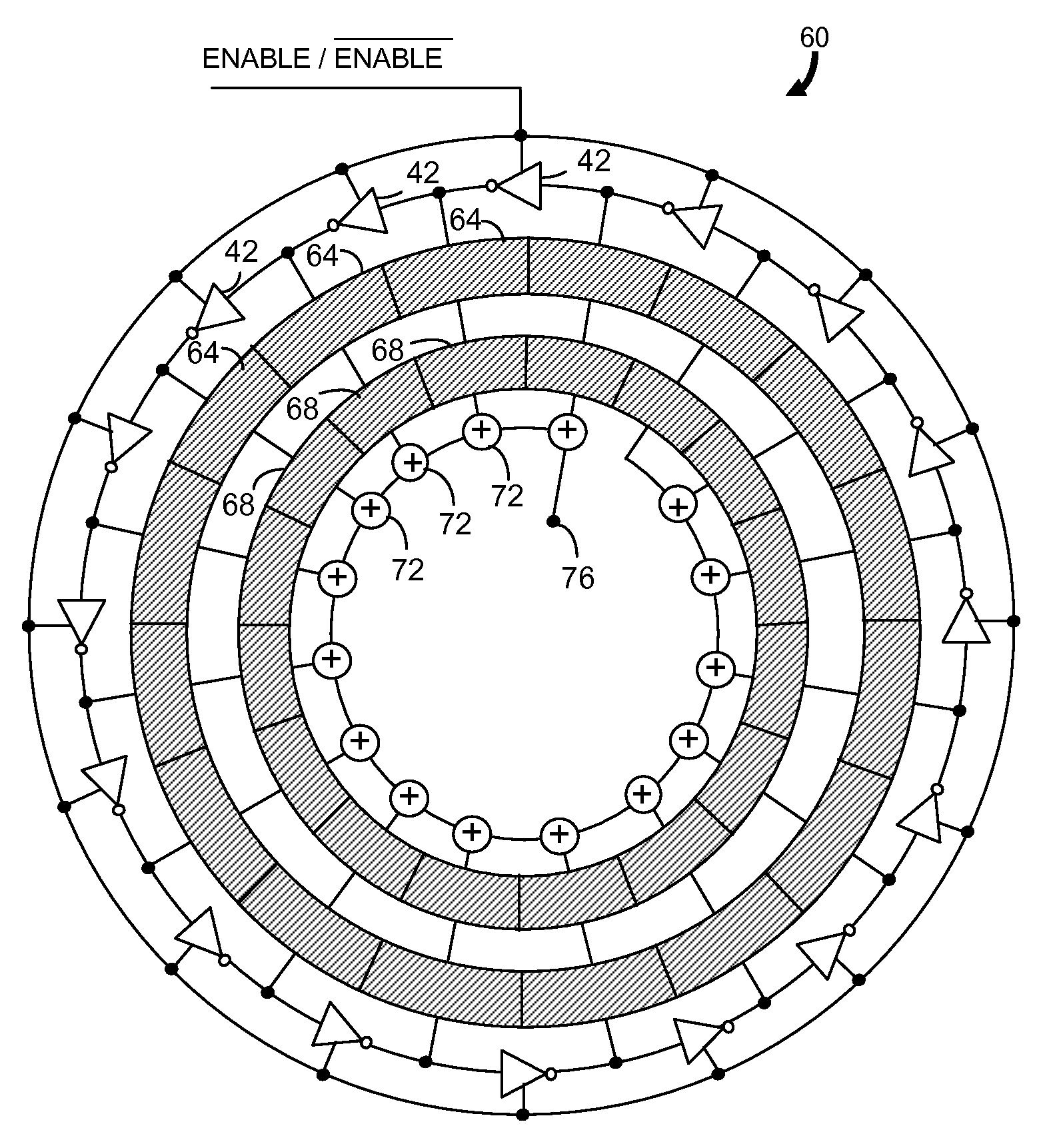
Gated ring oscillator for a time-to-digital converter with shaped quantization noise
ActiveUS20080069292A1Resolution timeContinuously circulated pulse countersCounting chain synchronous pulse countersImage resolutionNoise shaping
Described is a compact, lower power gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter that achieves first order noise shaping of quantization noise using a digital implementation. The gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter includes a plurality of delay stages configured to enable propagation of a transitioning signal through the delay stages during an enabled state and configured to inhibit propagation of the transitioning signal through the delay stages during a disabled state. Delay stages are interconnected to allow sustained transitions to propagate through the delay stages during the enabled state and to preserve a state of the gated ring oscillator time-to-digital converter during the disabled state. The state represents a time resolution that is finer than the delay of at least one of the delay stages. A measurement module determines the number of transitions of the delay stages.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
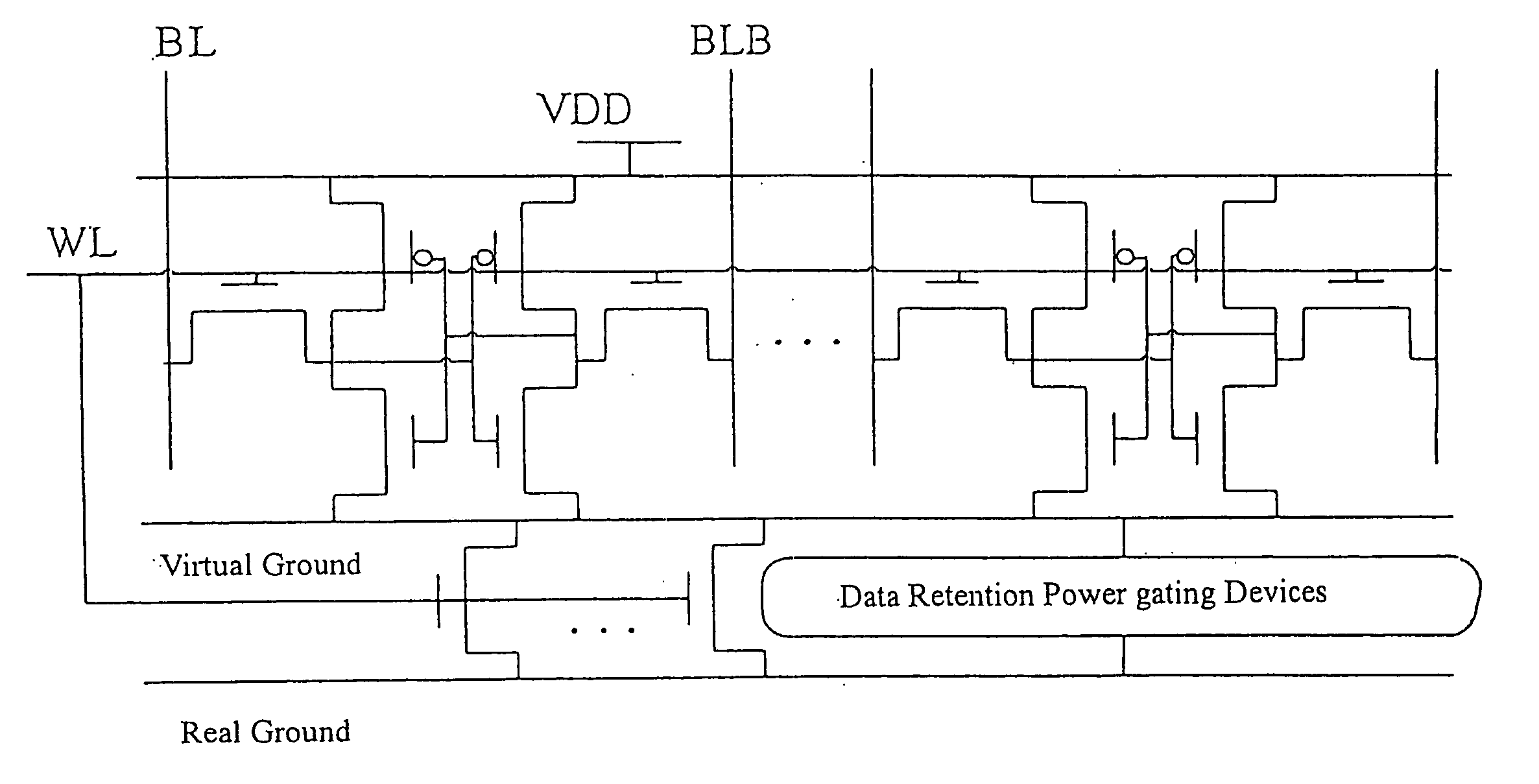
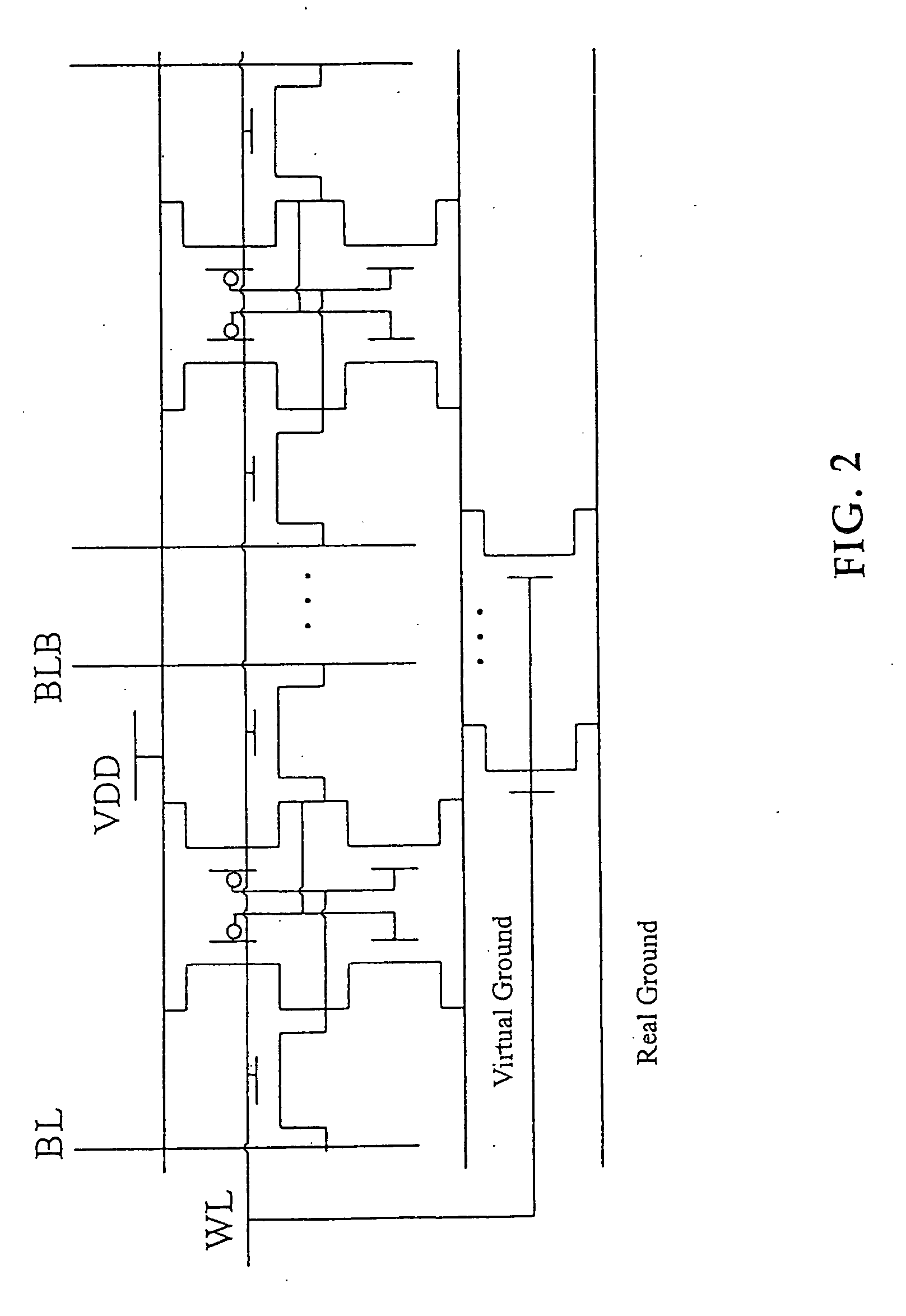
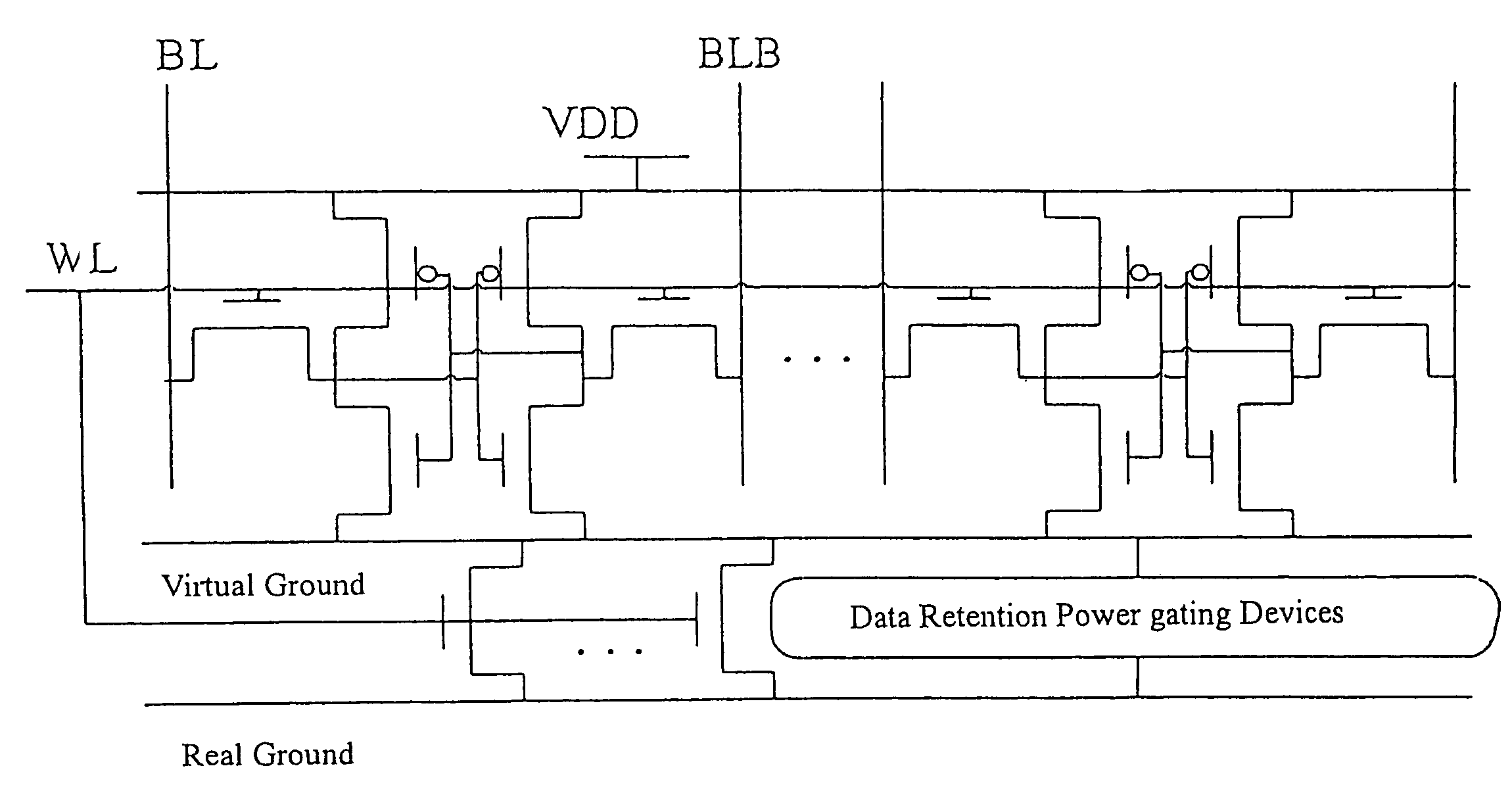
Power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes
InactiveUS20060119393A1Reduce leakage currentExtend lifetime of battery packReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalStatic noise marginOperation mode
The present invention provides a power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes and able to operate under multiple modes. A conventional power gating structure has only turn-on and turn-off functions, and is used to suppress a leakage current problem which has become more and more serious in advance manufacture processes, under a turn-off mode. However, in a memory circuit, such as latch, register and SRAM, when the power gate is turned off, a new power gating structure is required for data retention. The power gating structure of the present invention can be set into one of 4 different operational modes: a data retention mode for maintaining the static noise margin of the memory, an intermediate mode for reducing the interference on ground and power levels, an active mode used when the circuit operates in normal condition, and a standby mode used when the circuit does not operate.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Low-power FPGA circuits and methods
InactiveUS7714610B2Increase profitEasy to controlSolid-state devicesCAD circuit designEngineeringLevel converter
Field Programmable Logic Arrays (FPGAs) are described which utilize multiple power supply voltages to reduce both dynamic power and leakage power without sacrificing speed or substantially increasing device area. Power reduction mechanisms are described for numerous portions of the FPGA, including logic blocks, routing circuits, connection blocks, switch blocks, configuration memory cells, and so forth. Embodiments describe circuits and methods for implementing multiple supplies as sources of Vdd, multiple voltage thresholding Vt, signal level translators, and power gating of circuitry to deactivate portions of the circuit which are inactive. The supply voltage levels can be fixed, or programmable. Methods are described for performing circuit CAD in the routing and assignment process on FPGAs, in particular for optimizing FPGA use having the power reduction circuits taught. Routing methods describe utilizing slack timing, power sensitivity, trace-based simulations, and other techniques to optimize circuit utilization on a multi Vdd FPGA.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
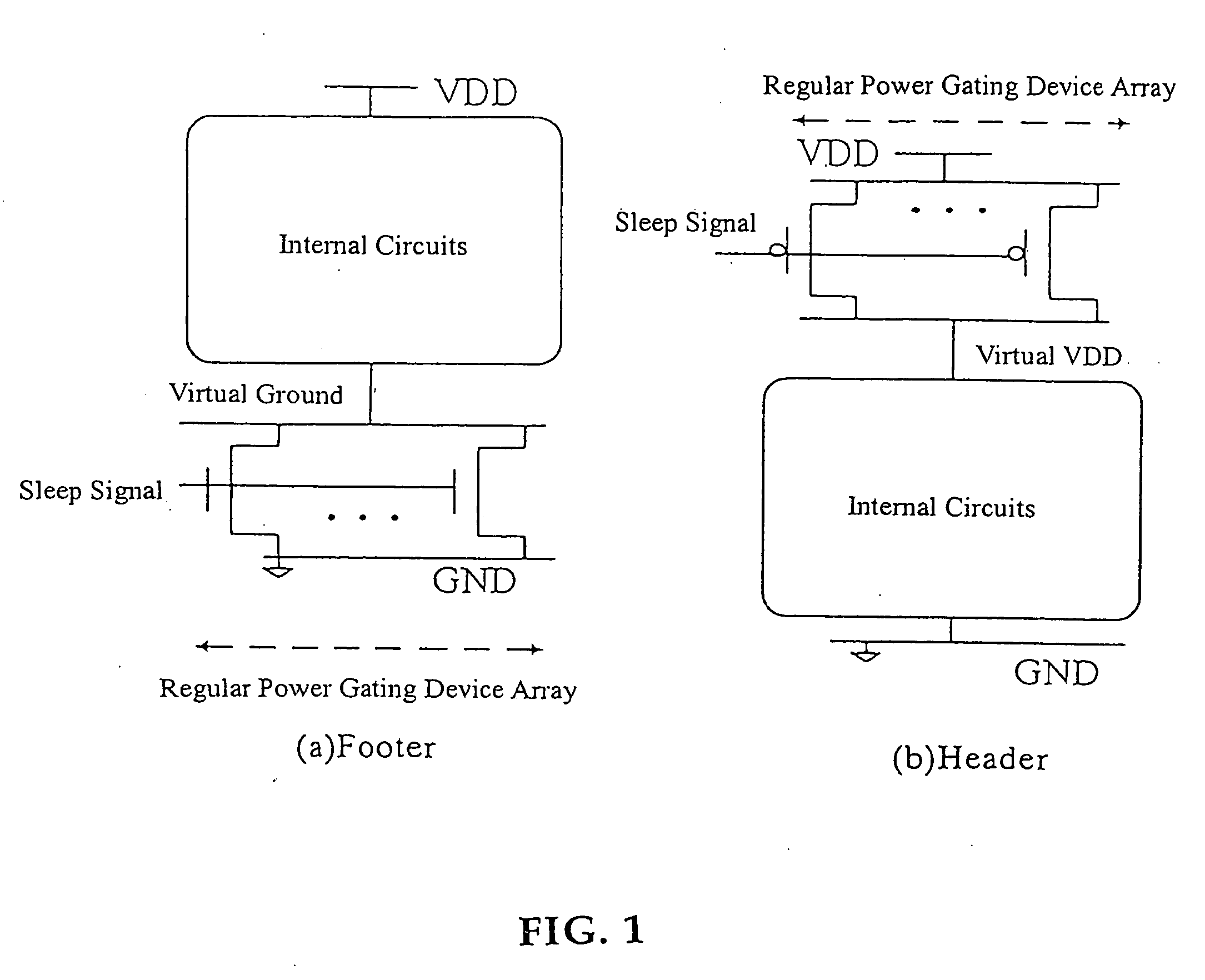
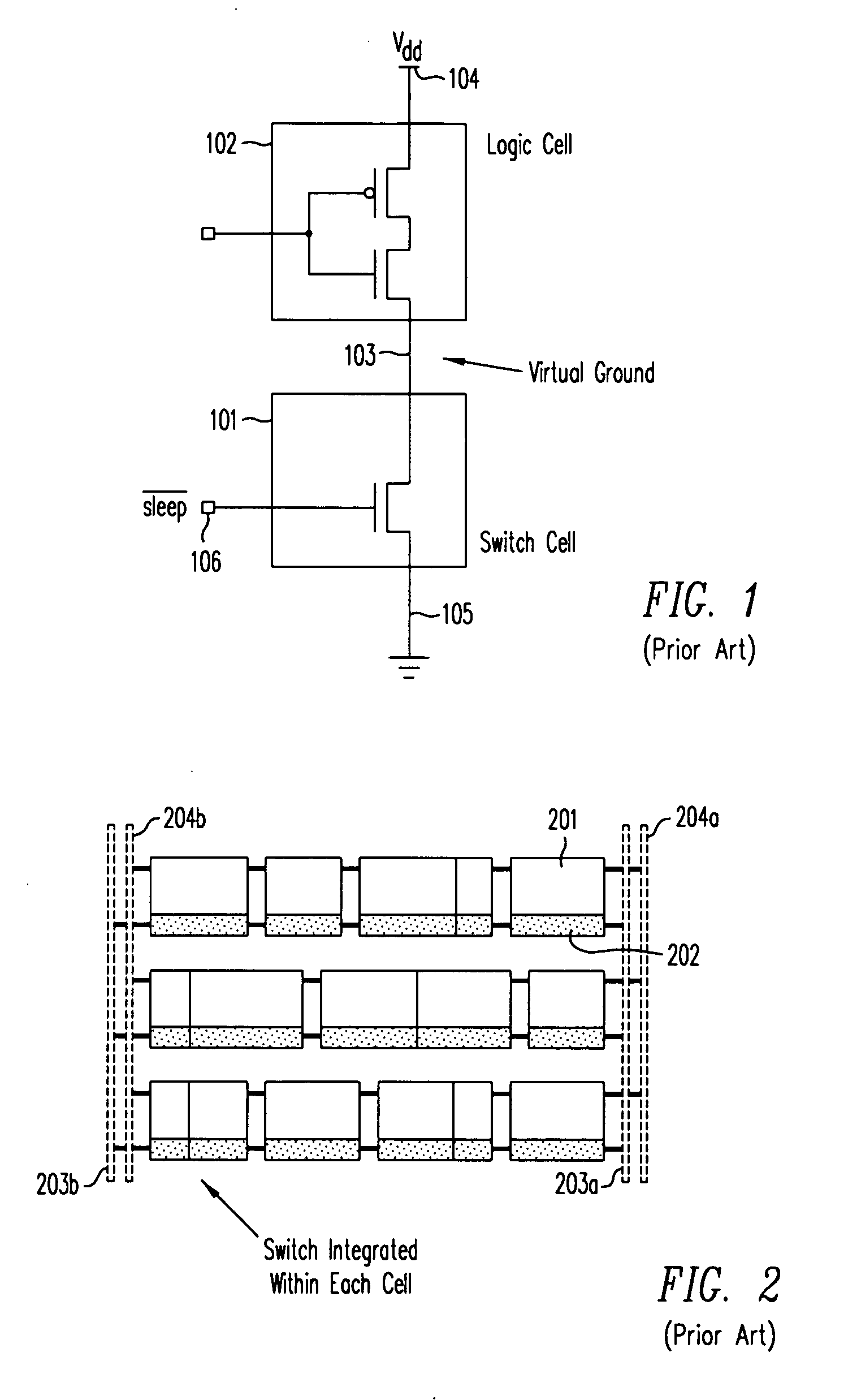
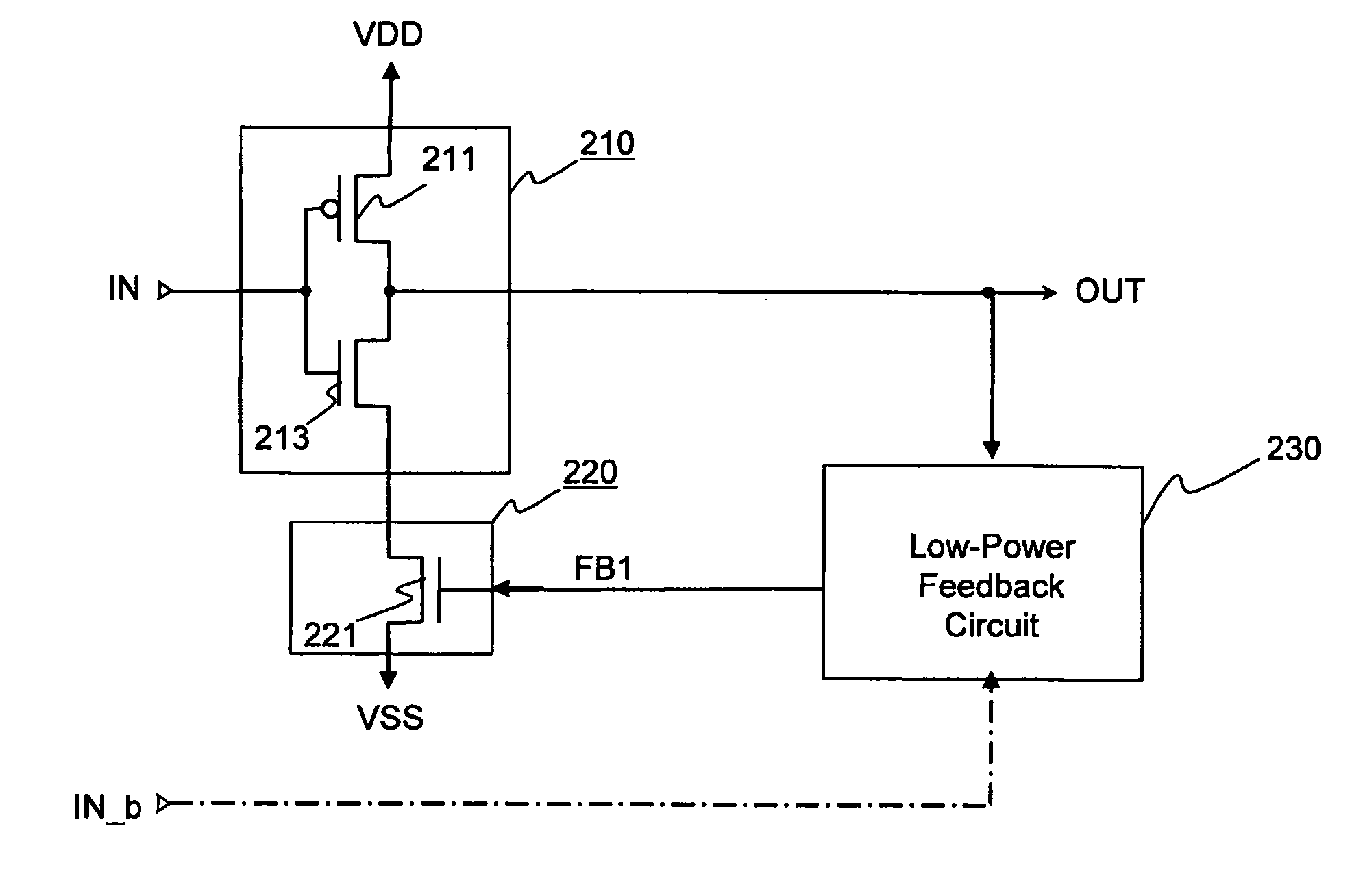
Power gating techniques able to have data retention and variability immunity properties
ActiveUS7126370B2Reduce power consumptionReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalManufacturing variabilityEngineering
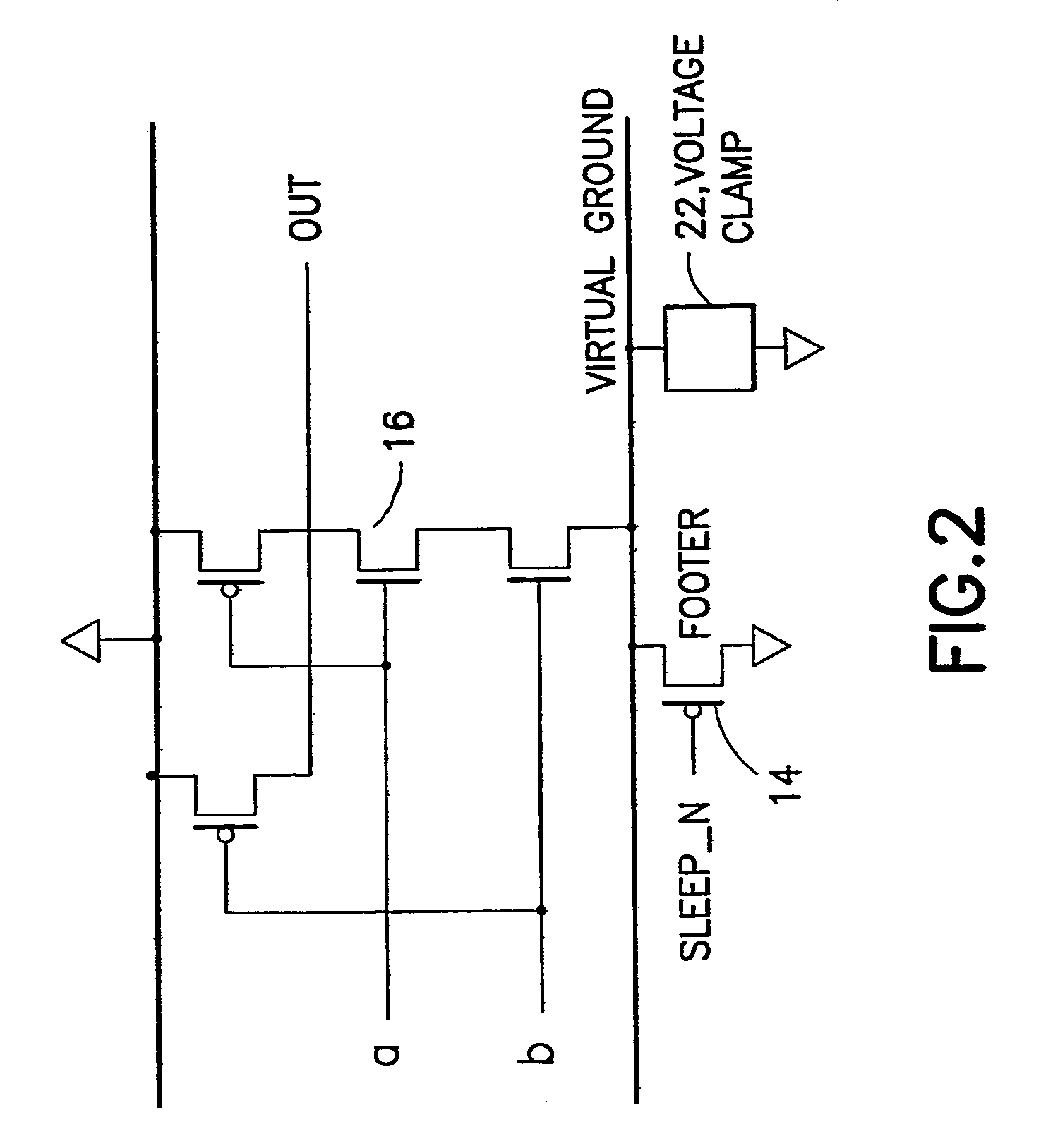
A power gated semiconductor integrated circuit comprises: (1) logic circuit to be power gated, said logic circuit having a virtual ground rail; (2) footer device disposed between said virtual ground rail and a ground rail for reducing power consumption of said logic circuit; and (3) virtual rail voltage clamp disposed electrically in parallel with said footer device for limiting the voltage at the virtual ground rail, the virtual rail voltage clamp comprising at least one NFET. A total of Nf NFETs are connected to the virtual ground rail of the integrated circuit for use as both virtual rail voltage clamps and footer devices. A quantity of Nmax-VC NFETs are scanned and perform the function of voltage clamps and the remaining (Nf−Nmax-VC) NFETs perform power gating. Manufacturing variability immunity and tuning of the variability immunity is achieved by adjusting the quantity Nmax-VC based upon testing of the manufactured integrated circuit.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
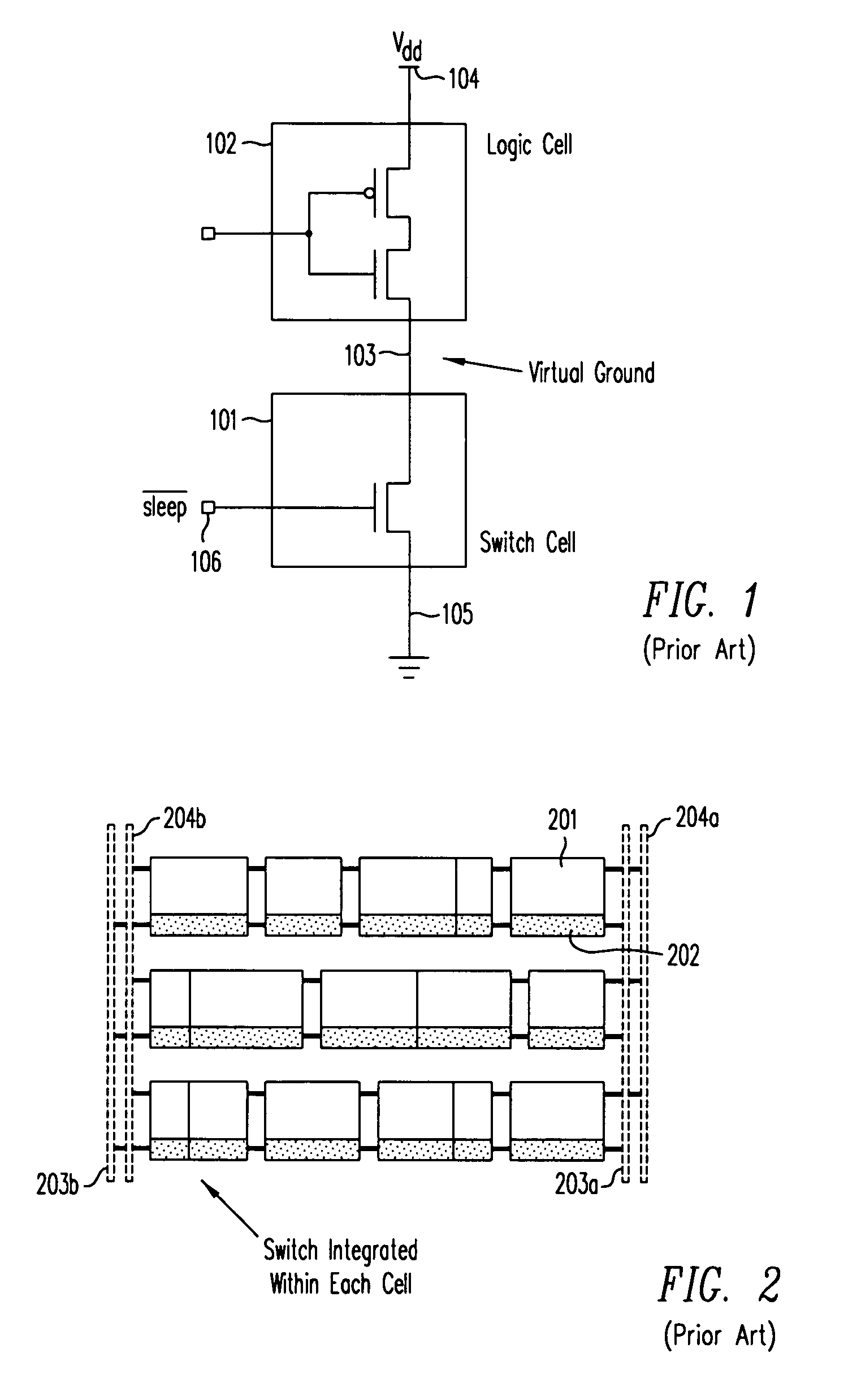
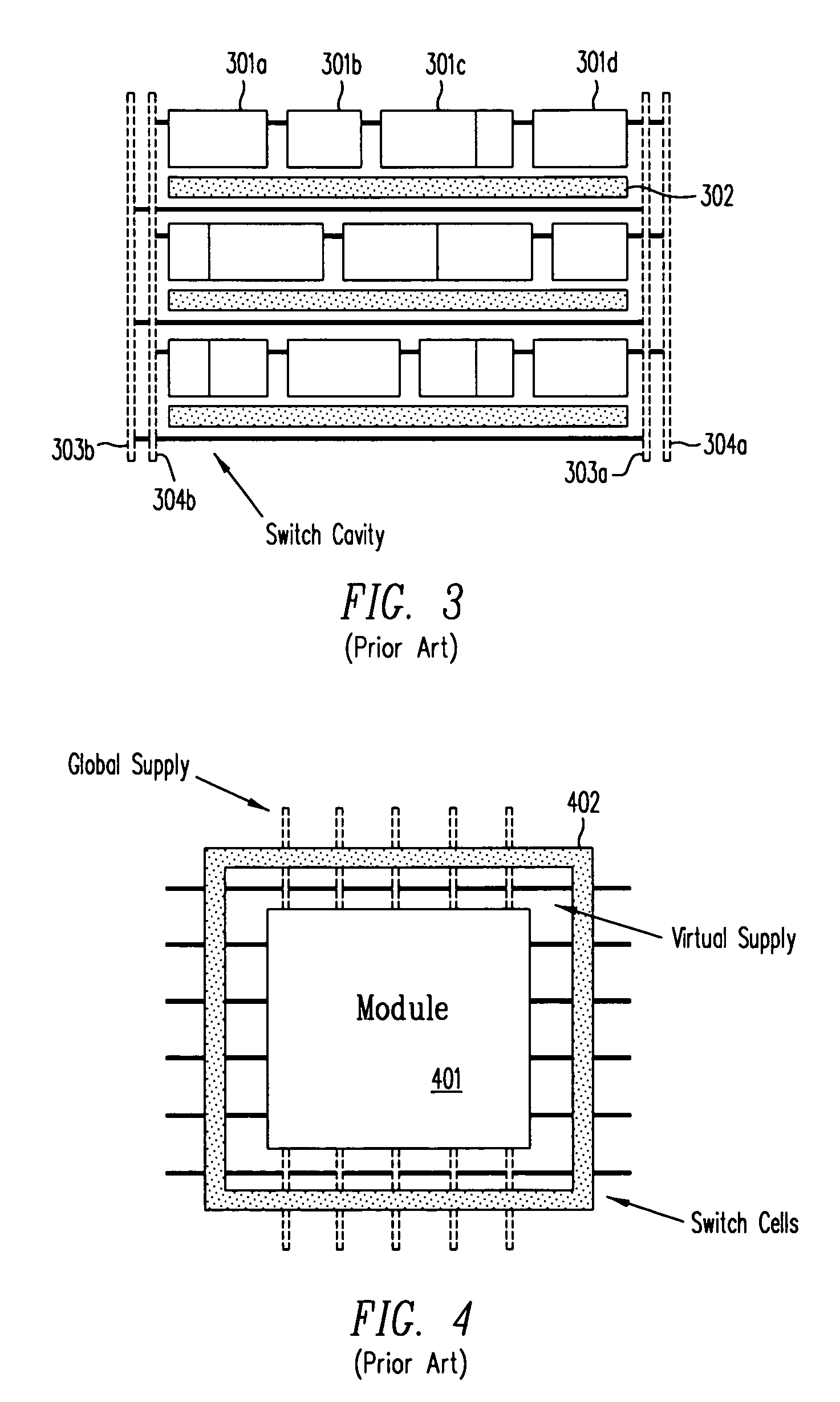
Power-gating cell for virtual power rail control
ActiveUS7276932B2Eliminate delaysReliability increasing modificationsMajority/minority circuitsControl signalPower grid
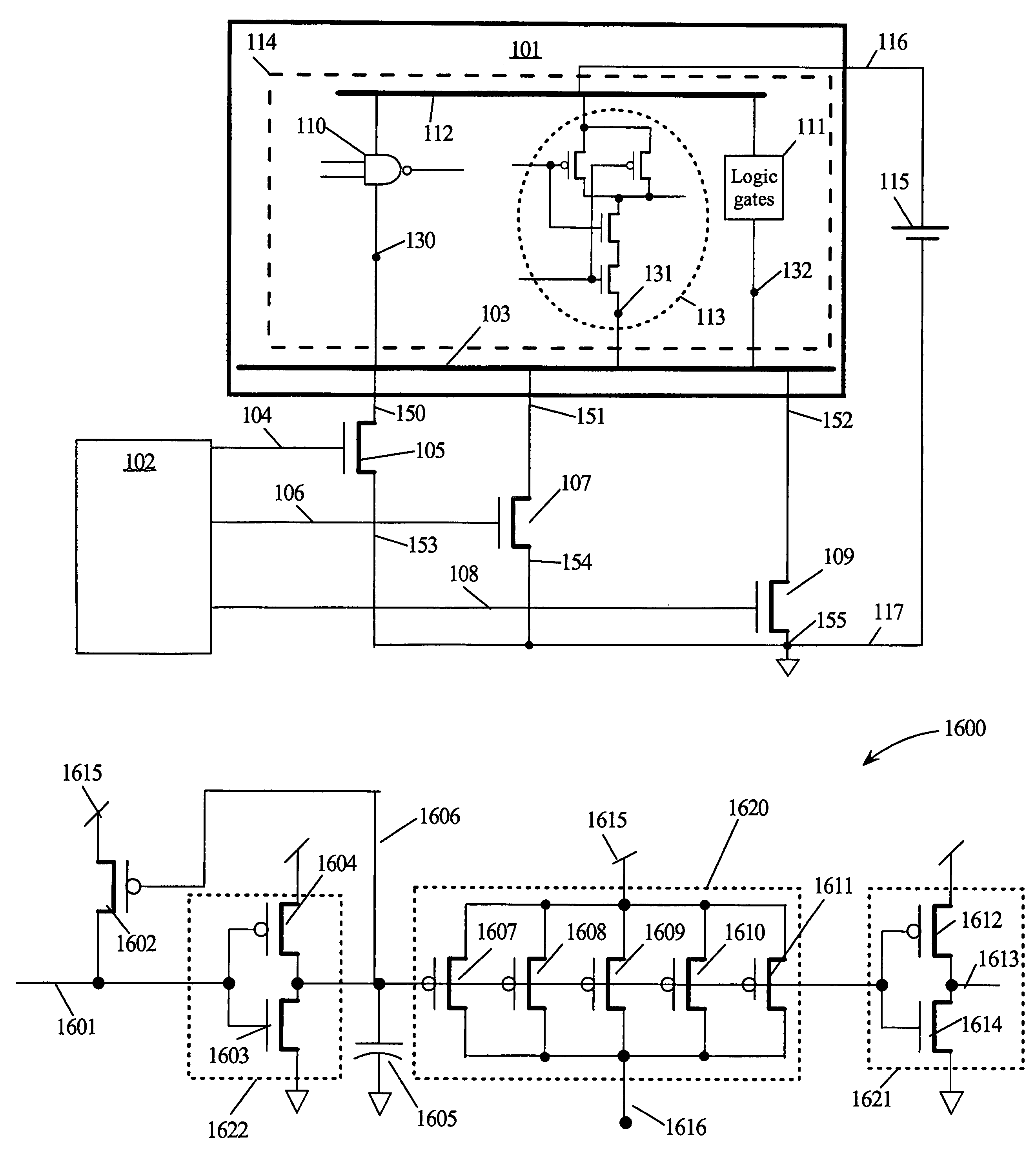
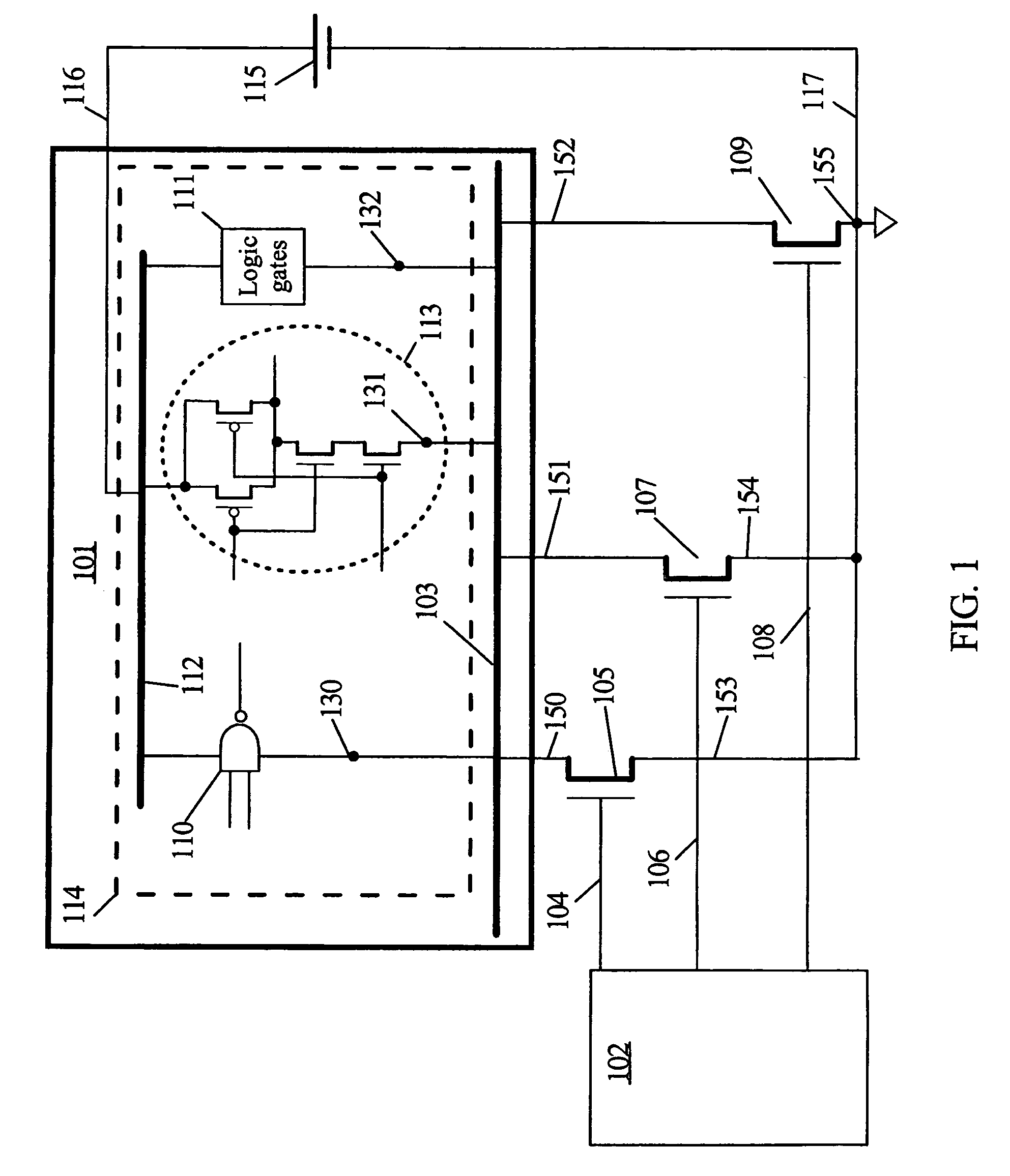
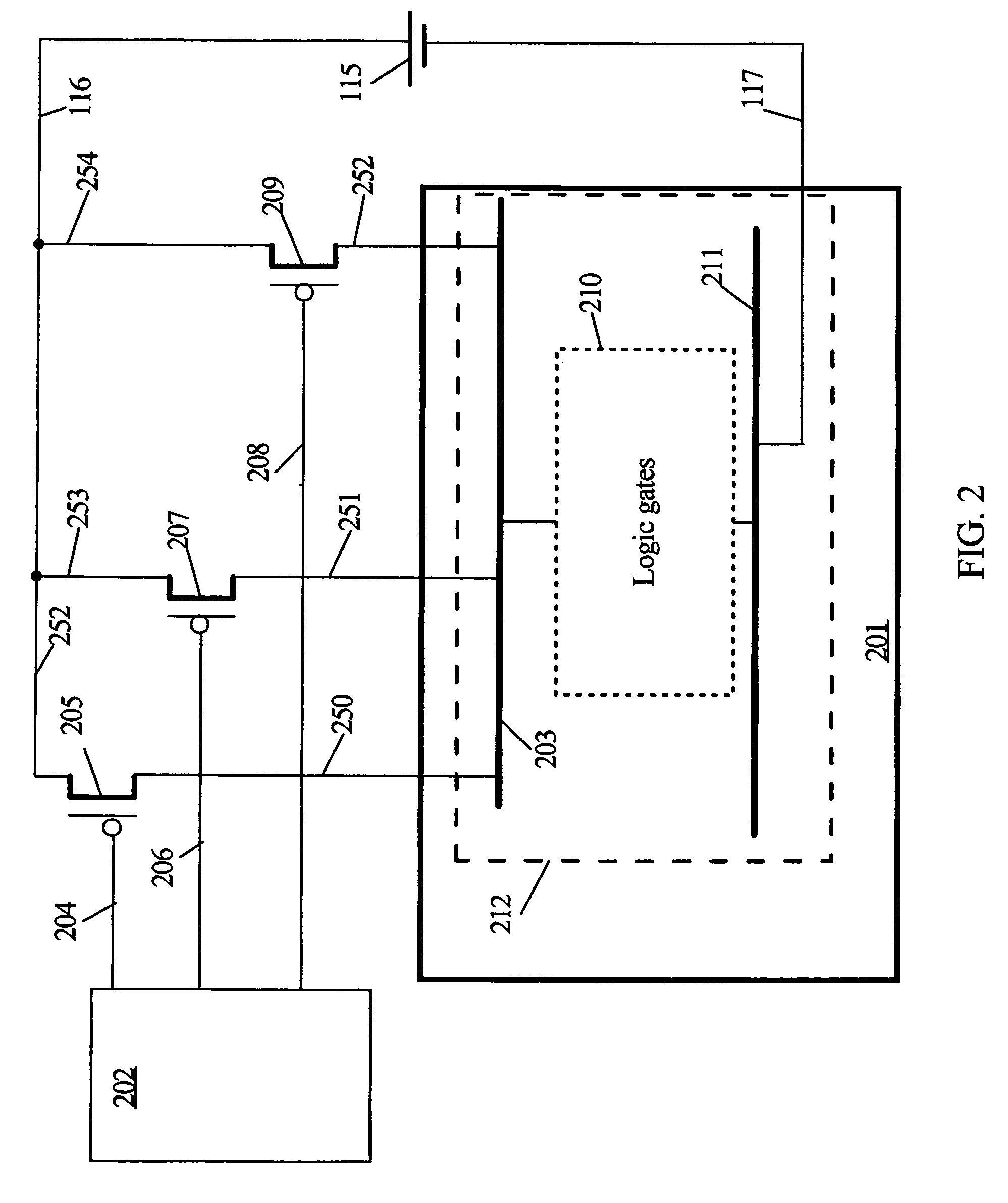
Virtual power-gated cells (VPC) are configured with control circuitry for buffering control signals and a power-gated block (PGB) comprising two or more NFETs for virtual ground rail nodes and PFETs for virtual positive rail nodes. Each VPC has a control voltage input, a control voltage output, a node coupled to a power supply voltage potential, and a virtual power-gated node that is coupled and decoupled from the power supply potential in response to logic states on the control input. The control signals are buffered by non-power-gated inverters before being applied to the input of a PGB. VPCs may propagate a control signal that is in phase with or inverted from a corresponding control signal at the control input. VPCs may be cascaded to create virtual power rails in chains and power grids. The control signals are latched at the cell boundaries or latched in response to a clock signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
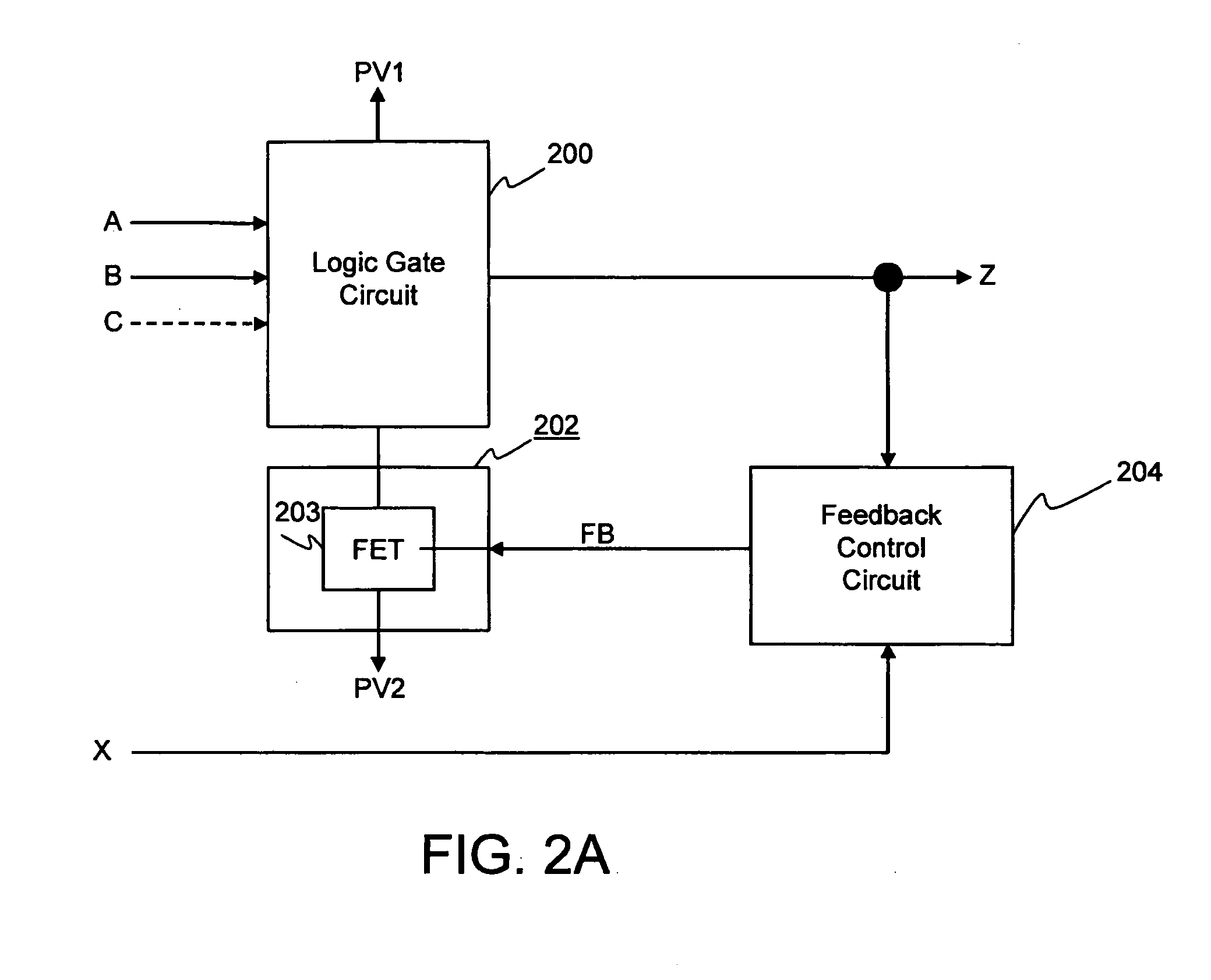
Power gating control module, integrated circuit device, signal processing system, electronic device, and method therefor
InactiveUS20130015904A1Energy efficient ICTPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringPower gating
An integrated circuit device comprising at least one signal processing module and a power gating control module arranged to control gating of at least one power supply to at least a part of the at least one signal processing module. The power gating control module is arranged to receive at least one operating parameter; configure at least one power gating setting of the power gating control module based at least partly on the at least one received operating parameter; and apply power gating for at least part of the at least one signal processing module in accordance with the at least one configured power gating setting.
Owner:NXP USA INC
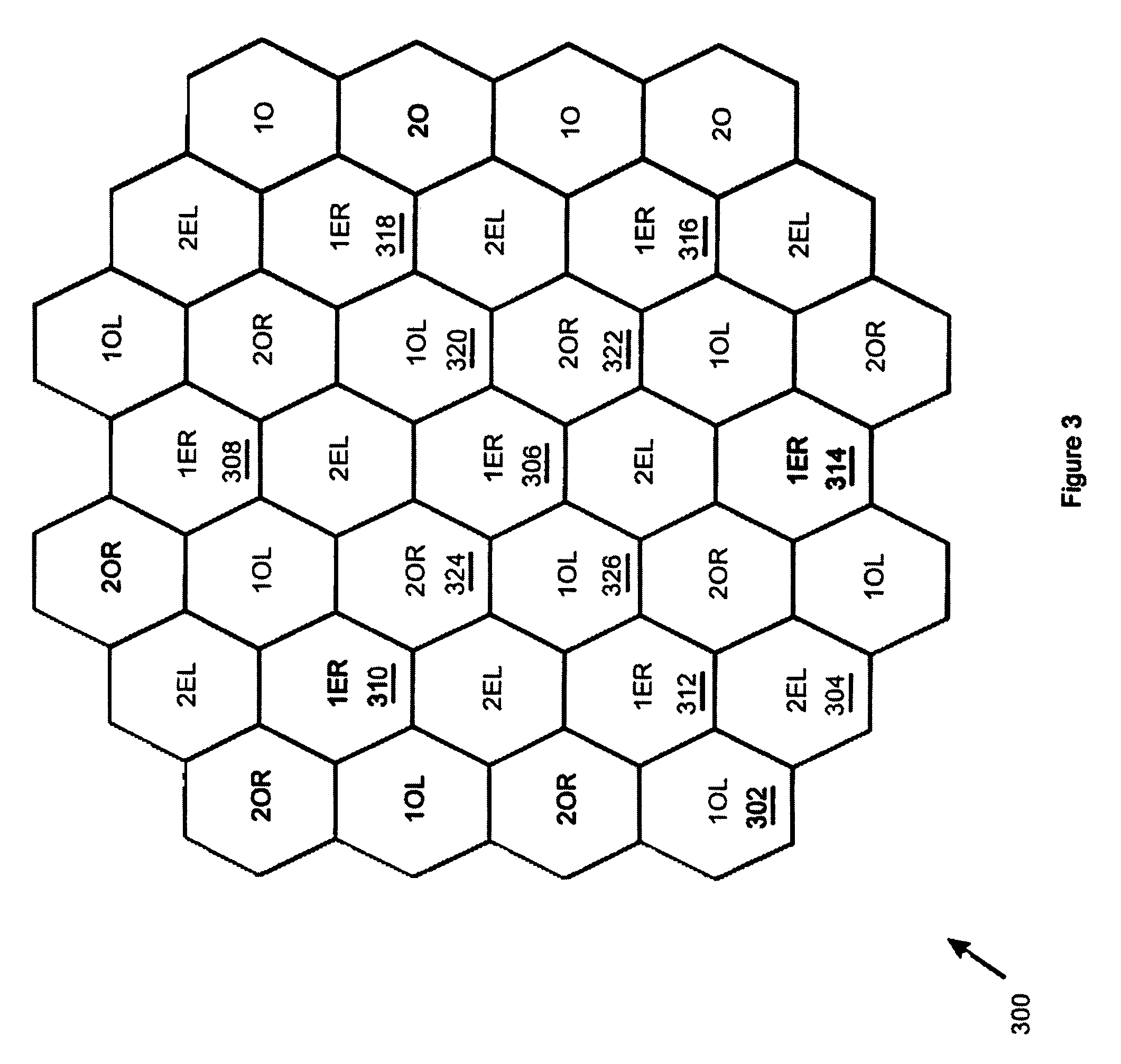
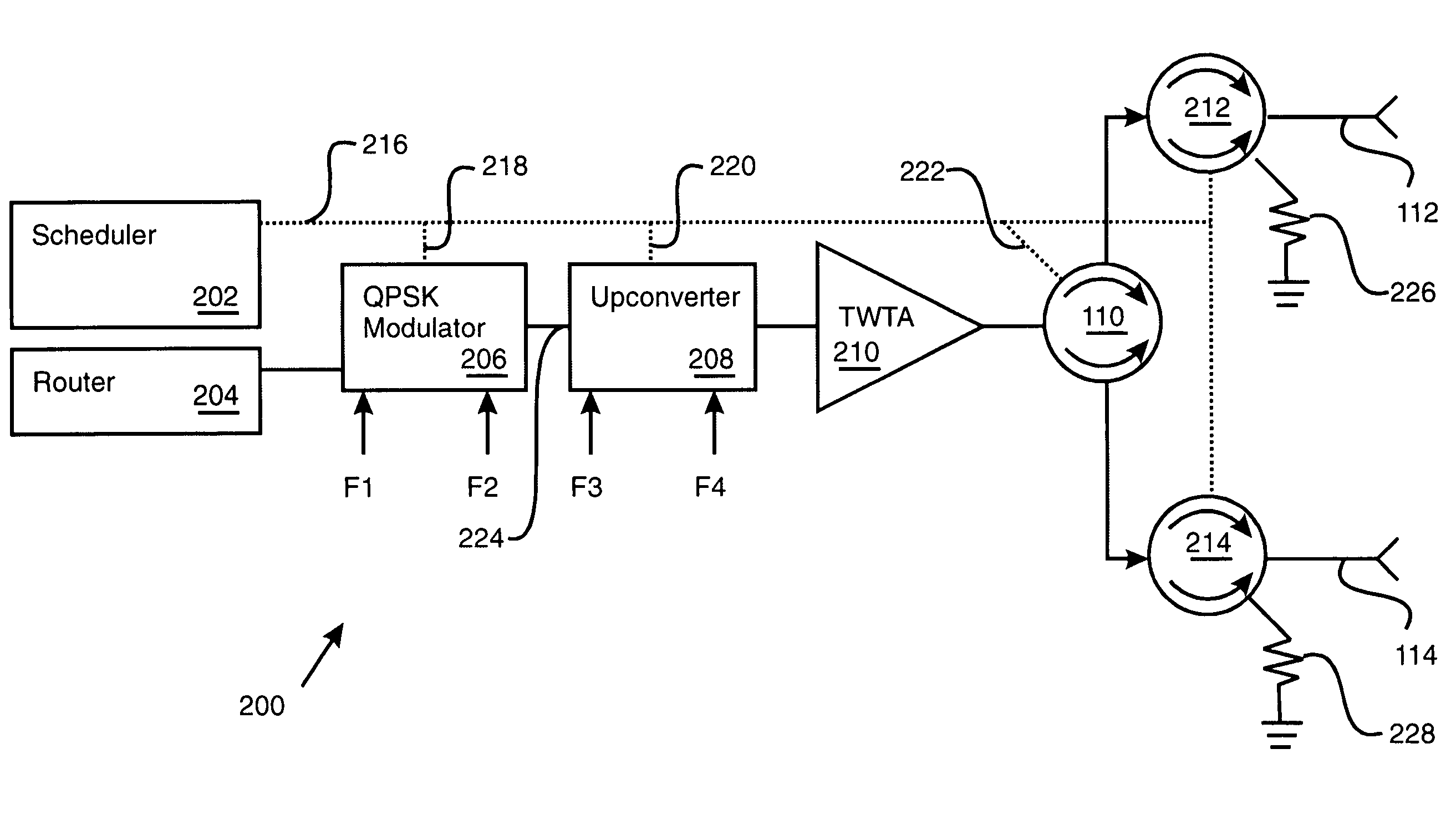
Beam laydown for hopped satellite downlink with adaptable duty cycle
InactiveUS7426386B1Reduce distractionsCosmonautic vehiclesCosmonautic partsControl theoryPower gating
A power gated variable hop cycle beam laydown (700) manifests itself as first cells (C, D) supported by a first hop cycle, second cells (G, H) supported by a second hop cycle, and transition cells (E, F) supported by a transition hop cycle. The transition hop cycle uses power gating to transition the laydown (700) from cells (C, D) operating at the first hop cycle to cells (G, H) operating at the second hop cycle. To this end, the transition hop cycle power gates its downlink beam for a portion of time needed to reduce interference between nearby (e.g., adjacent) cells.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
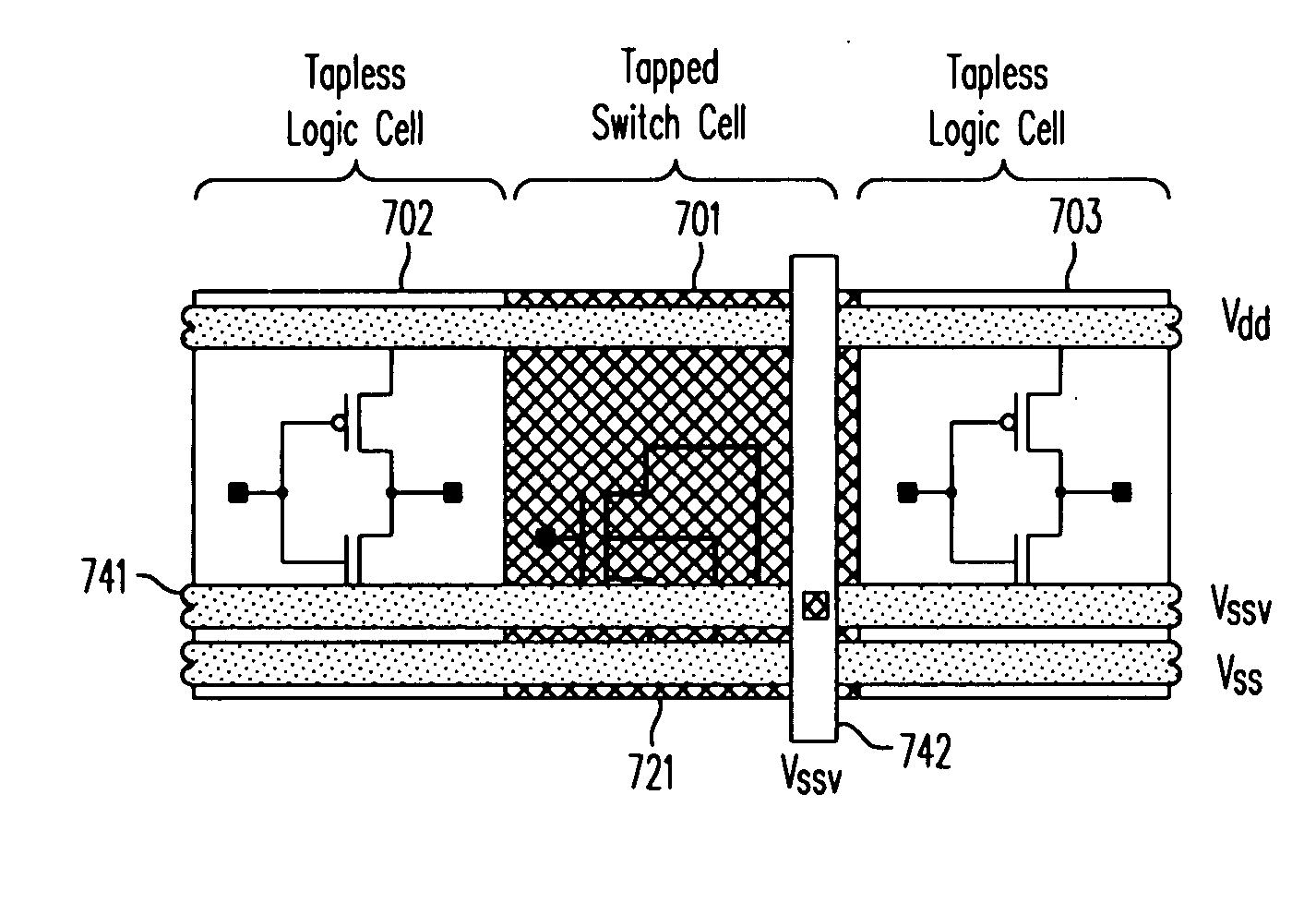
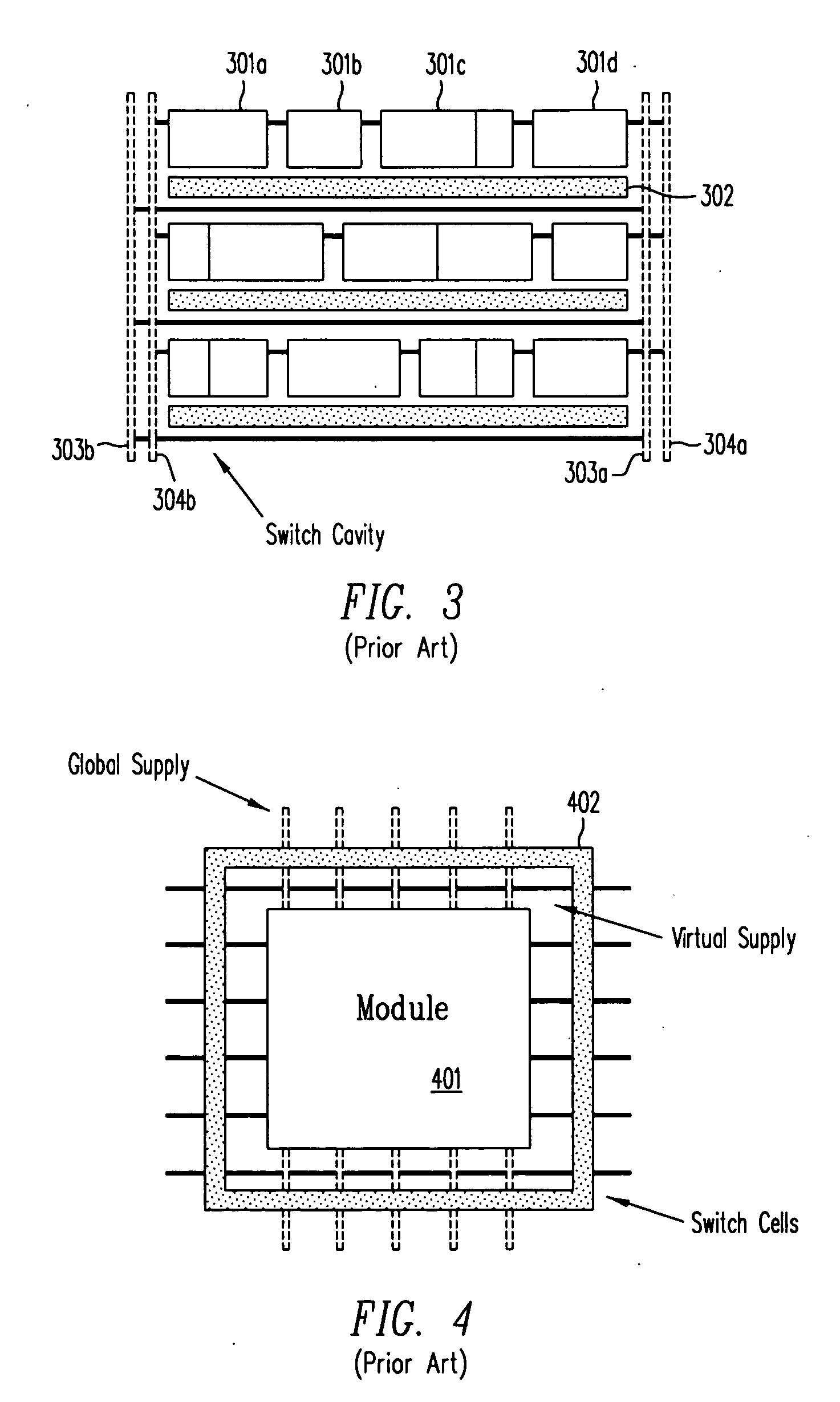
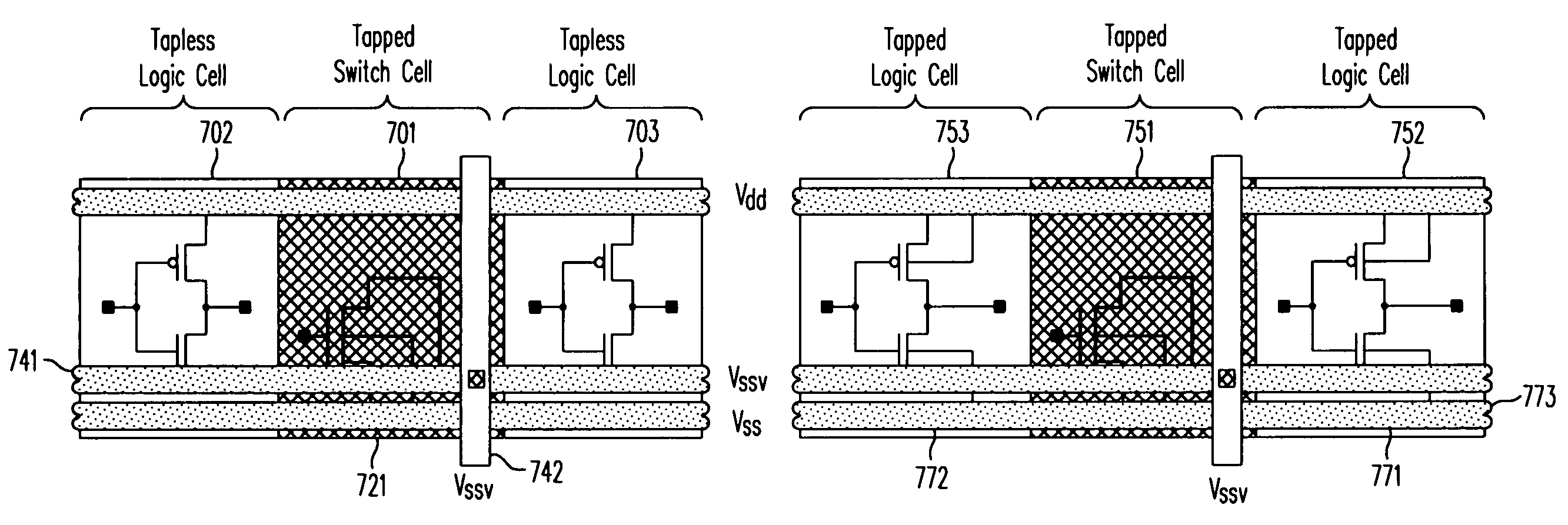
Design method and architecture for power gate switch placement and interconnection using tapless libraries
ActiveUS20070168899A1Less routing resourceHigh circuit densityLogic circuits characterised by logic functionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionContext sensitivity
A method and a structure provide a space efficient integrated circuit using standard cells and power gating by switch cells. The standard cells may be tapless, i.e., not provided a substrate connection to a power supply or ground rail by a tap within the cell. The substrate connection for these standard cells may be provided by the switch cells or by specialized tap cells. The tapless standard cells may include only a context-sensitive rail, which may be configured to be a virtual ground rail by a power gating connection to a switch cell or by a direct connection to a power supply or ground rail.
Owner:ANSYS
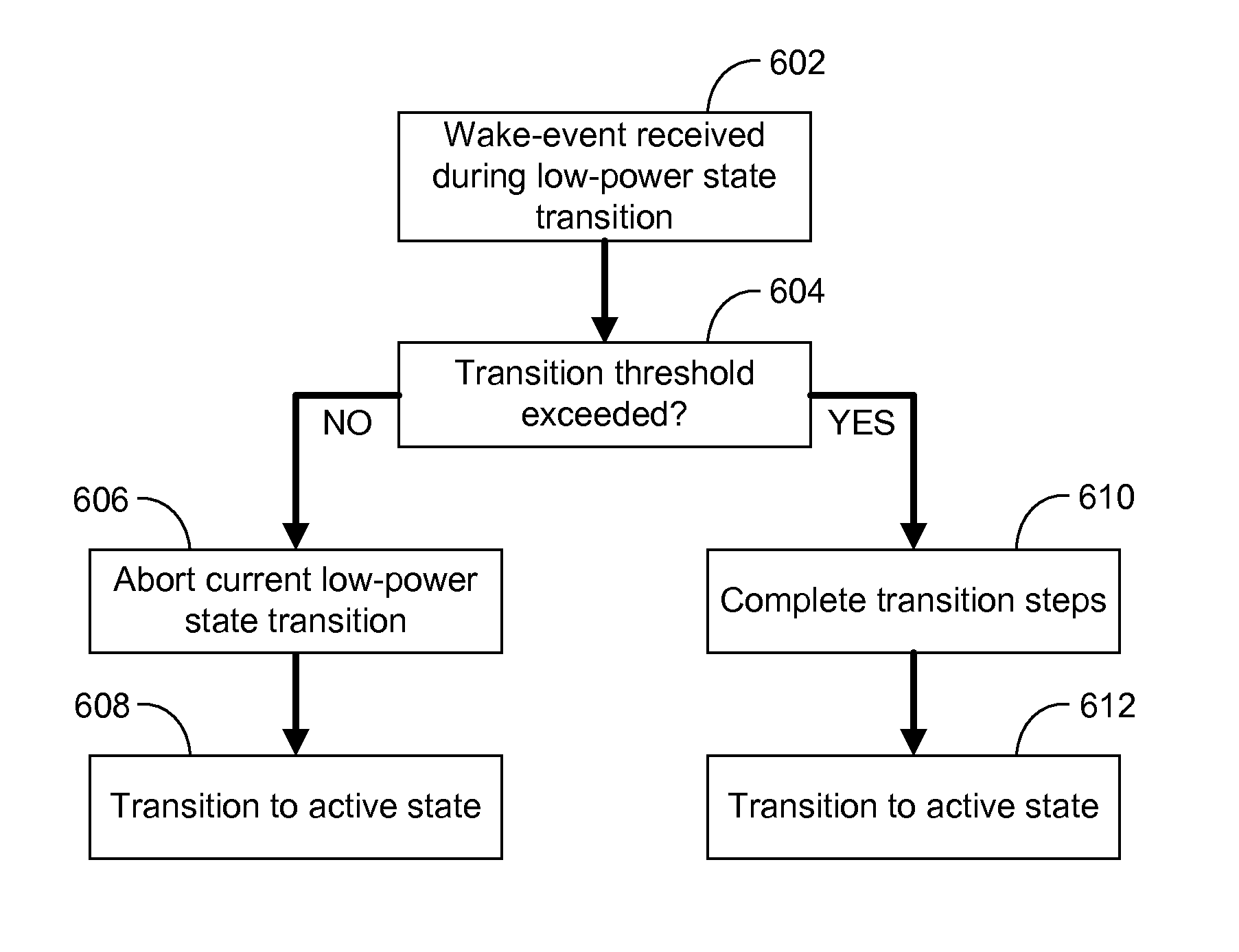
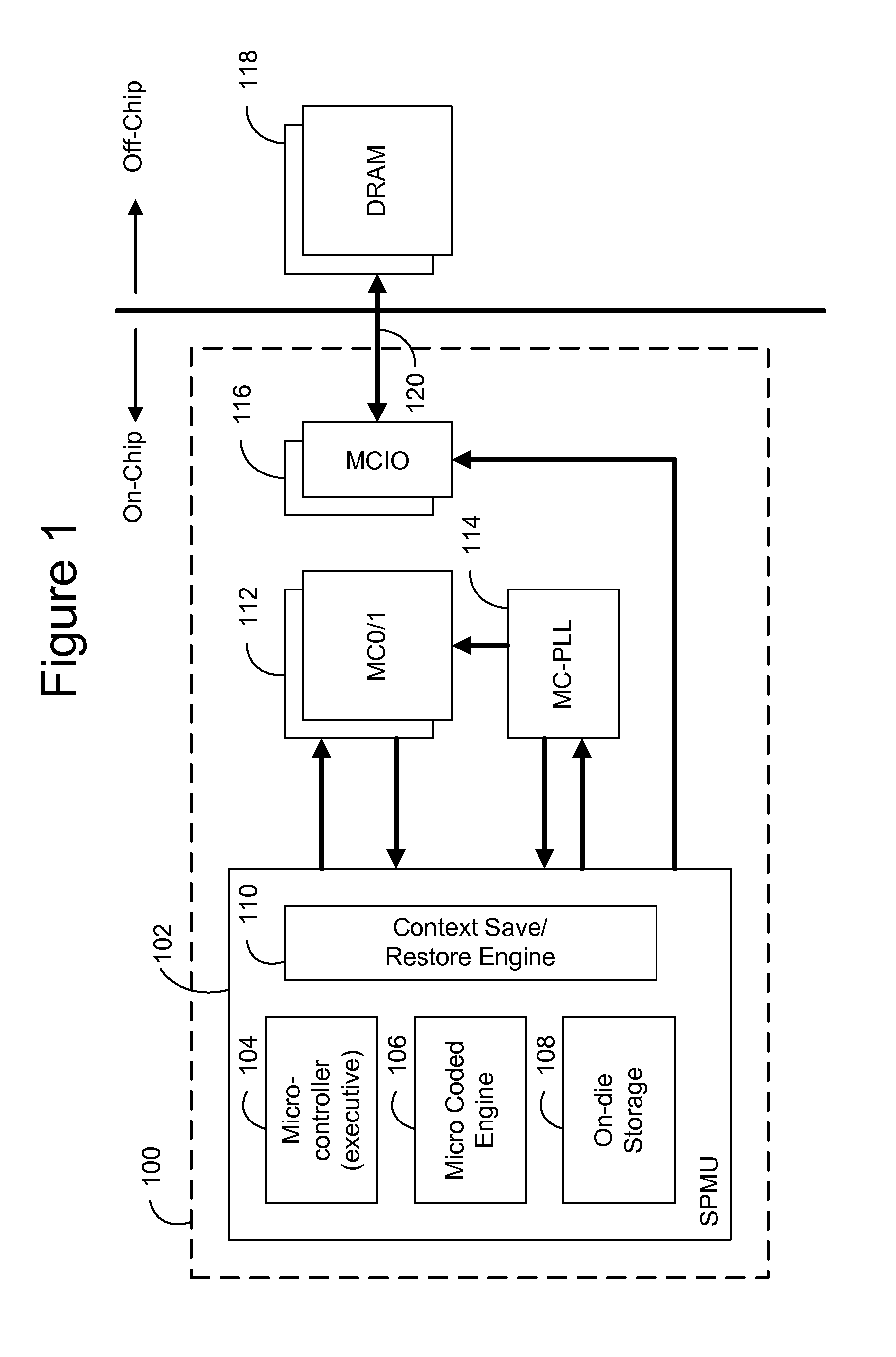
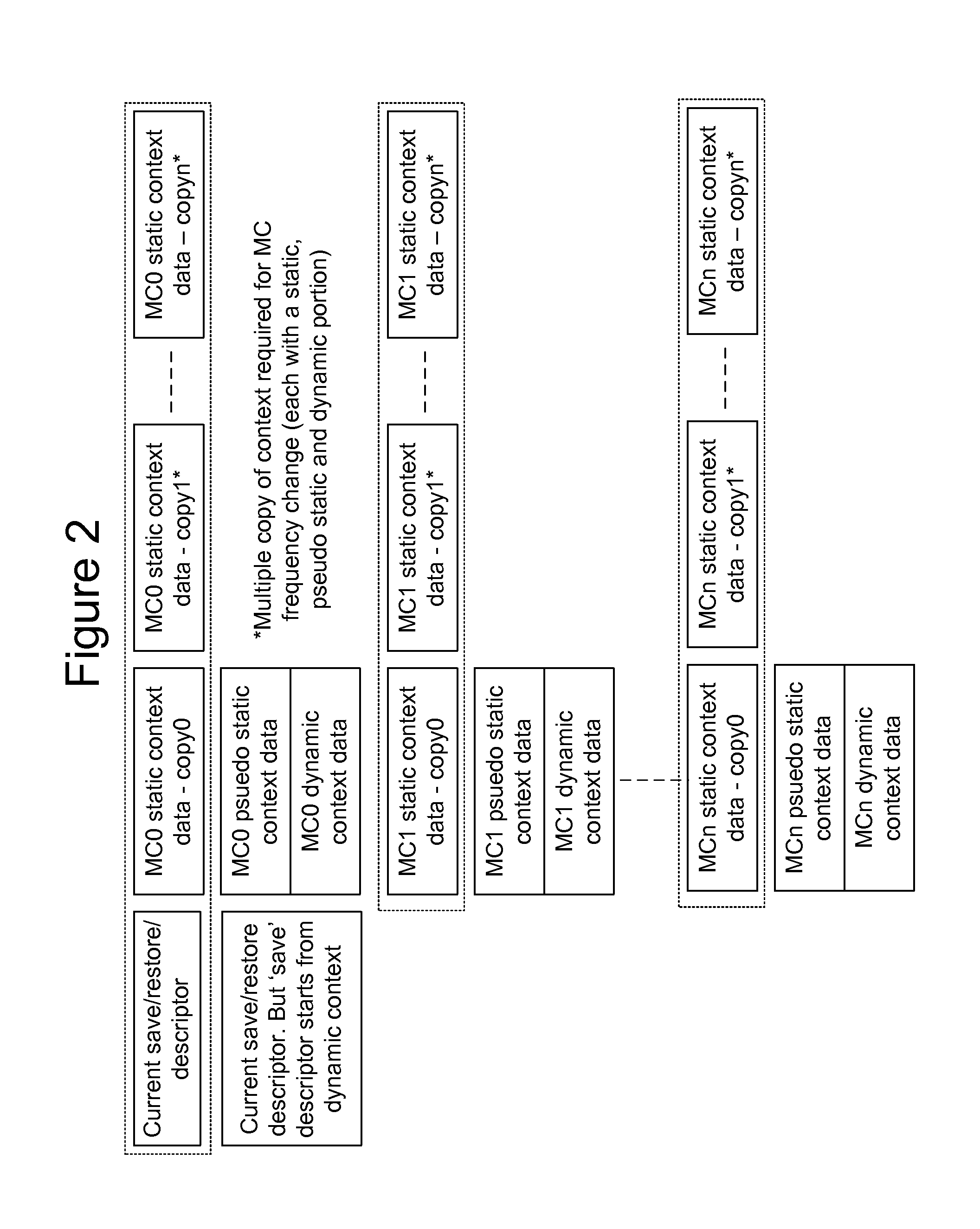
Training, power-gating, and dynamic frequency changing of a memory controller
ActiveUS20140032947A1Efficient state transitionVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingContext dataMemory controller
A method for managing a memory controller comprising selecting a low-power state from a plurality of low-power states. The method further comprises transitioning to the low-power and entering the low-power state when the transition is complete, provided a wake-event has not been received. An apparatus comprises a controller configured to select a power state for transition, a state-machine configured to execute steps for transitions between power states of a memory controller connected by a bus to a memory, a storage configured to store at least one context, and a context engine configured to stream, at the direction of the state-machine engine, the at least one context to the memory controller. Streaming comprises communicating N portions of context data as a stream to N registers in the memory controller. A context comprises a plurality of calibrations corresponding to a state selected for transition.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Semiconductor integrated circuit having current leakage reduction scheme
InactiveUS20070075743A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease speedTransistorReliability increasing modificationsCMOSNOR gate
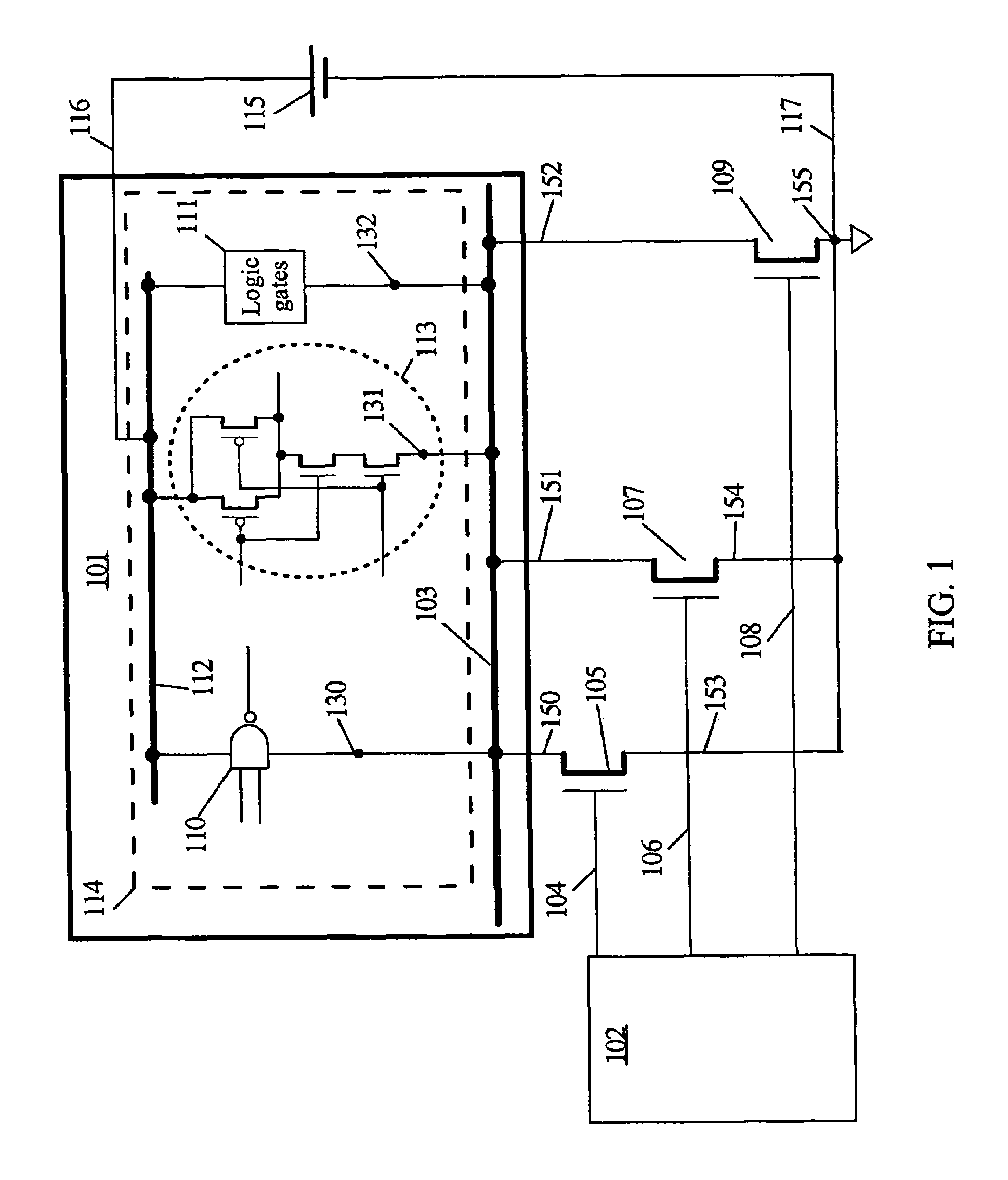
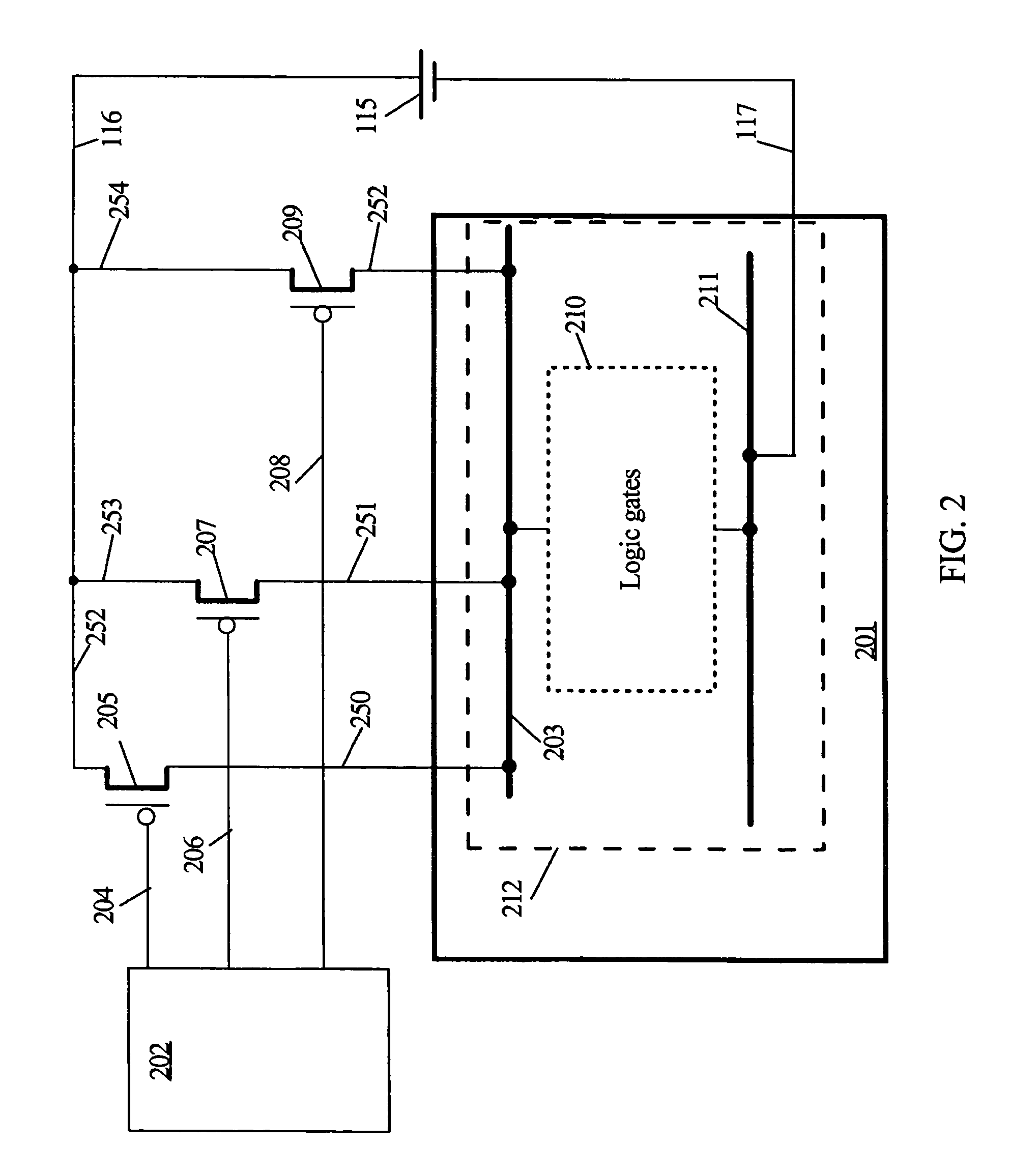
A semiconductor integrated circuit includes a CMOS controlled inverter consisting of series-connected PMOS and NMOS transistors. The source of the NMOS transistor is coupled to a ground line through an additional NMOS transistor for power gating of voltage VSS. The source of the PMOS transistor can be coupled to a power supply line through an additional PMOS transistor for power gating of voltage VDD. The inverter receives an input signal IN and its complementary version that has transitioned earlier than the input signal. In response to the input signal, the inverter produces an output signal. A NAND gate that receives the output signal and the complementary input signal controls the power gating NMOS transistor. A NOR gate that receives the output signal and the complementary input signal controls the power gating PMOS transistor. The power gating to the CMOS inverter is performed by feedback of the output signal and the complementary input signal, with the result that current leakage reduction through the CMOS controlled inverter is achieved. A self leakage reduction with power gating transistors is applicable to another type of logic gates such as NAND, NOR and Exclusive-OR, AND, OR.
Owner:CONVERSANT INTPROP MANAGEMENT INC
Power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes
InactiveUS7190187B2Maintain efficiencyActive powerReliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalEngineeringOperation mode
The present invention provides a power gating structure having data retention and intermediate modes and able to operate under multiple modes. A conventional power gating structure has only turn-on and turn-off functions, and is used to suppress a leakage current problem which has become more and more serious in advance manufacture processes, under a turn-off mode. However, in a memory circuit, such as latch, register and SRAM, when the power gate is turned off, a new power gating structure is required for data retention. The power gating structure of the present invention can be set into one of 4 different operational modes: a data retention mode for maintaining the static noise margin of the memory, an intermediate mode for reducing the interference on ground and power levels, an active mode used when the circuit operates in normal condition, and a standby mode used when the circuit does not operate.
Owner:NAT CHIAO TUNG UNIV
Power-gating cell for virtual power rail control
ActiveUS20060055391A1Eliminate delaysReliability increasing modificationsMajority/minority circuitsControl signalPower grid
Virtual power-gated cells (VPC) are configured with control circuitry for buffering control signals and a power-gated block (PGB) comprising two or more NFETs for virtual ground rail nodes and PFETs for virtual positive rail nodes. Each VPC has a control voltage input, a control voltage output, a node coupled to a power supply voltage potential, and a virtual power-gated node that is coupled and decoupled from the power supply potential in response to logic states on the control input. The control signals are buffered by non-power-gated inverters before being applied to the input of a PGB. VPCs may propagate a control signal that is in phase with or inverted from a corresponding control signal at the control input. VPCs may be cascaded to create virtual power rails in chains and power grids. The control signals are latched at the cell boundaries or latched in response to a clock signal.
Owner:IBM CORP
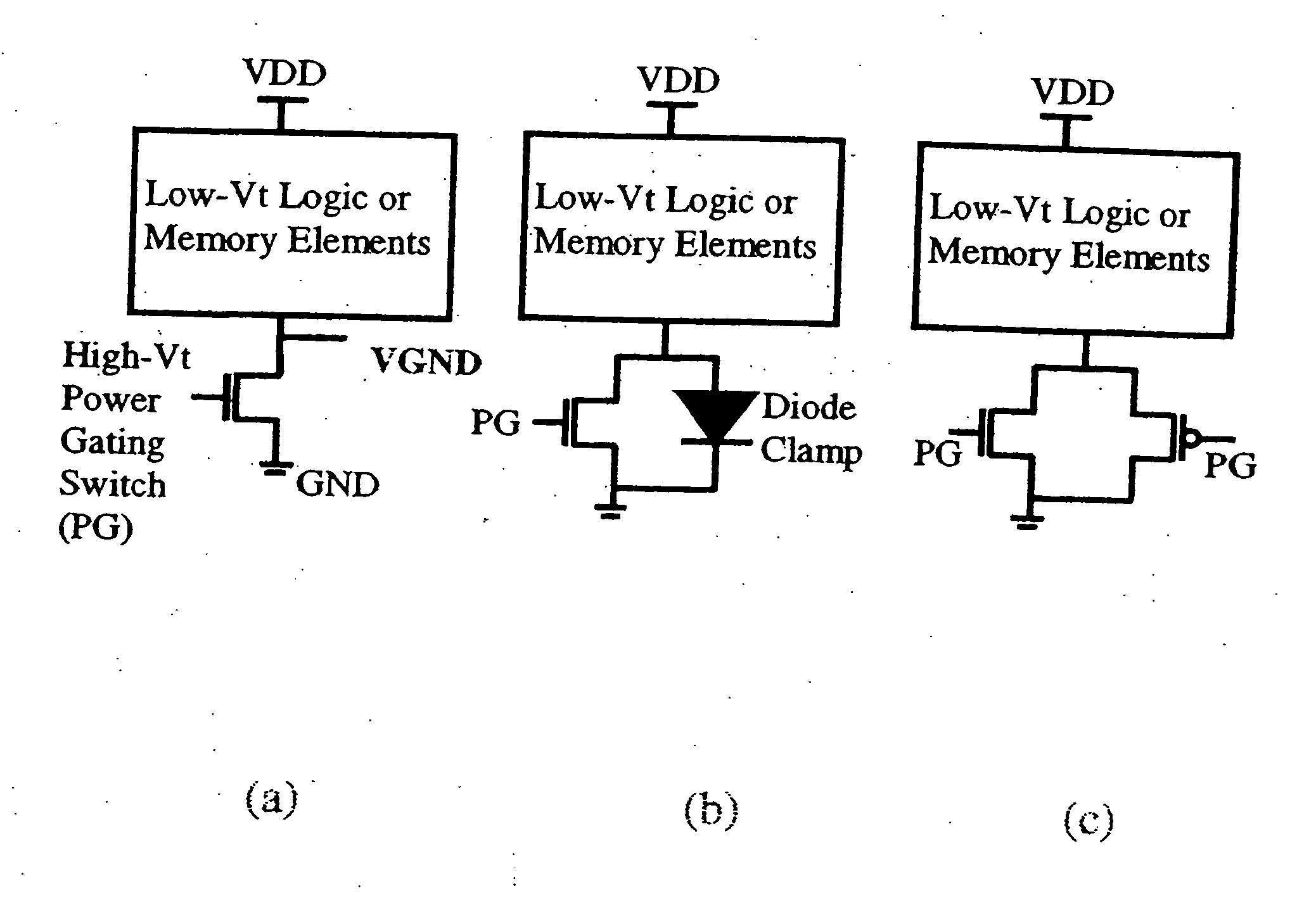
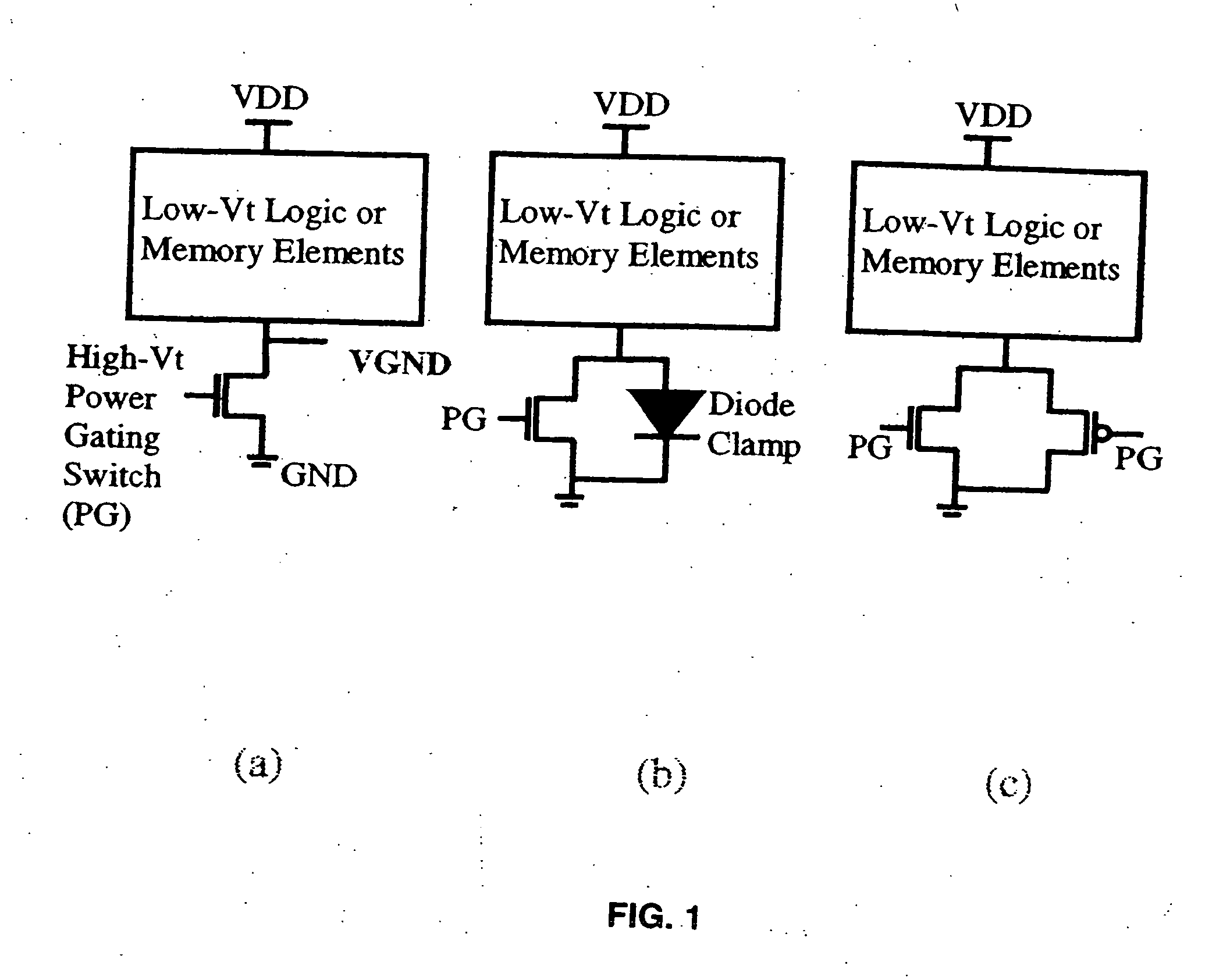
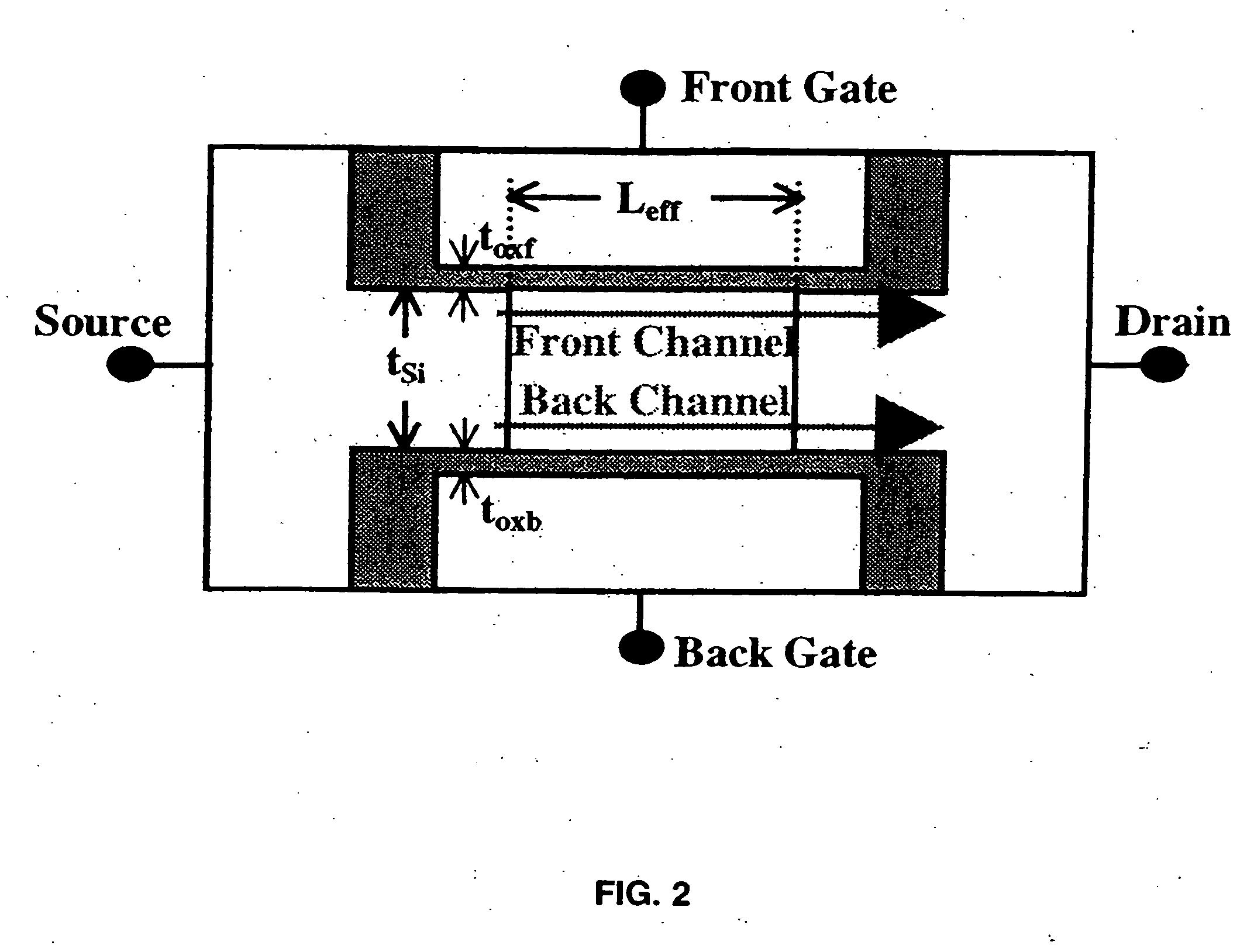
High-density low-power data retention power gating with double-gate devices
A new power gating structure with robust data retention capability using only one single double-gate device to provide both power gating switch and virtual supply / ground diode clamp functions. The scheme reduces the transistor count, area, and capacitance of the power gating structure, thus improving circuit performance, power, and leakage. The scheme is compared with the conventional power gating structure via mixed-mode physics-based two-dimensional numerical simulations. Analysis of virtual supply / ground bounce for the proposed scheme is also presented.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Dynamic leakage control circuit
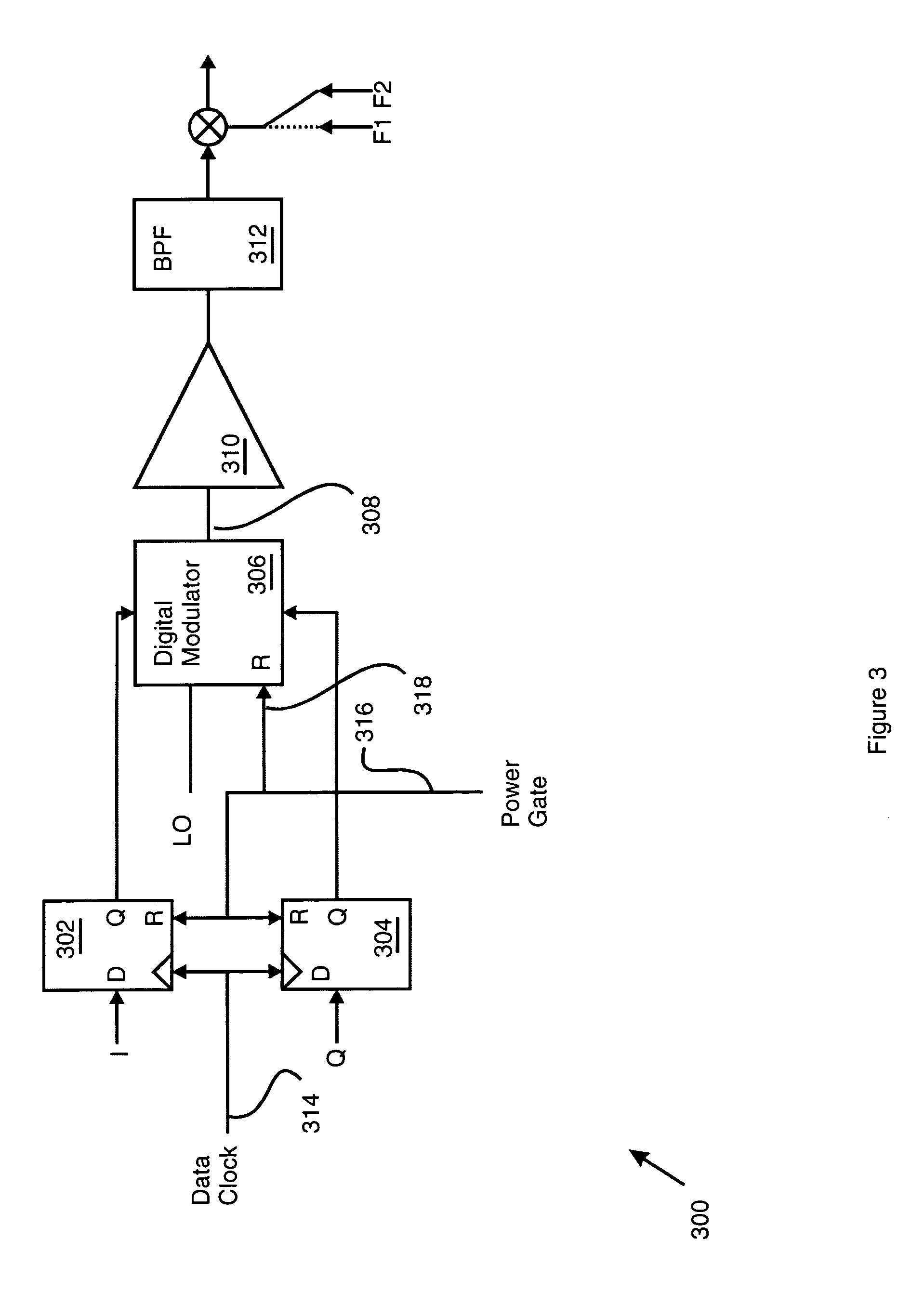
InactiveUS7266707B2Digital data processing detailsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsData signalEngineering
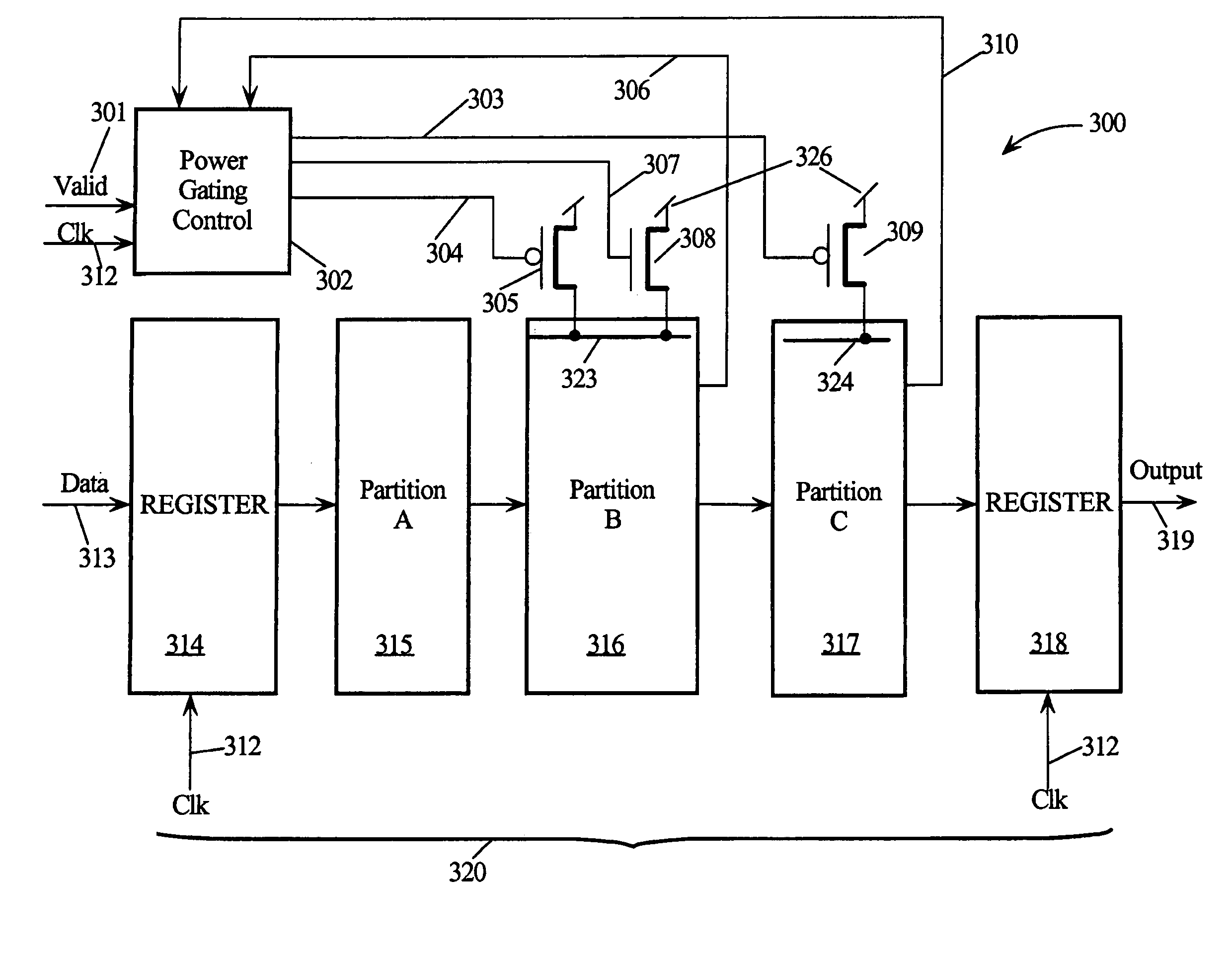
A low power consumption pipeline circuit architecture has power partitioned pipeline stages. The first pipeline stage is non-power-gated for fast response in processing input data after receipt of a valid data signal. A power-gated second pipeline stage has two power-gated modes. Normally the power rail in the power-gated second pipeline stage is charged to a first voltage potential of a pipeline power supply. In the first power gated mode, the power rail is charged to a threshold voltage below the first voltage potential to reduce leakage. In the second power gated mode, the power rail is decoupled from the first voltage potential. A power-gated third pipeline stage has its power rail either coupled to the first voltage potential or power-gated where its power rail is decoupled from the first voltage potential. The power rail of the second power-gated pipeline stage charges to the first voltage potential before the third power-gated pipeline stage.
Owner:IBM CORP
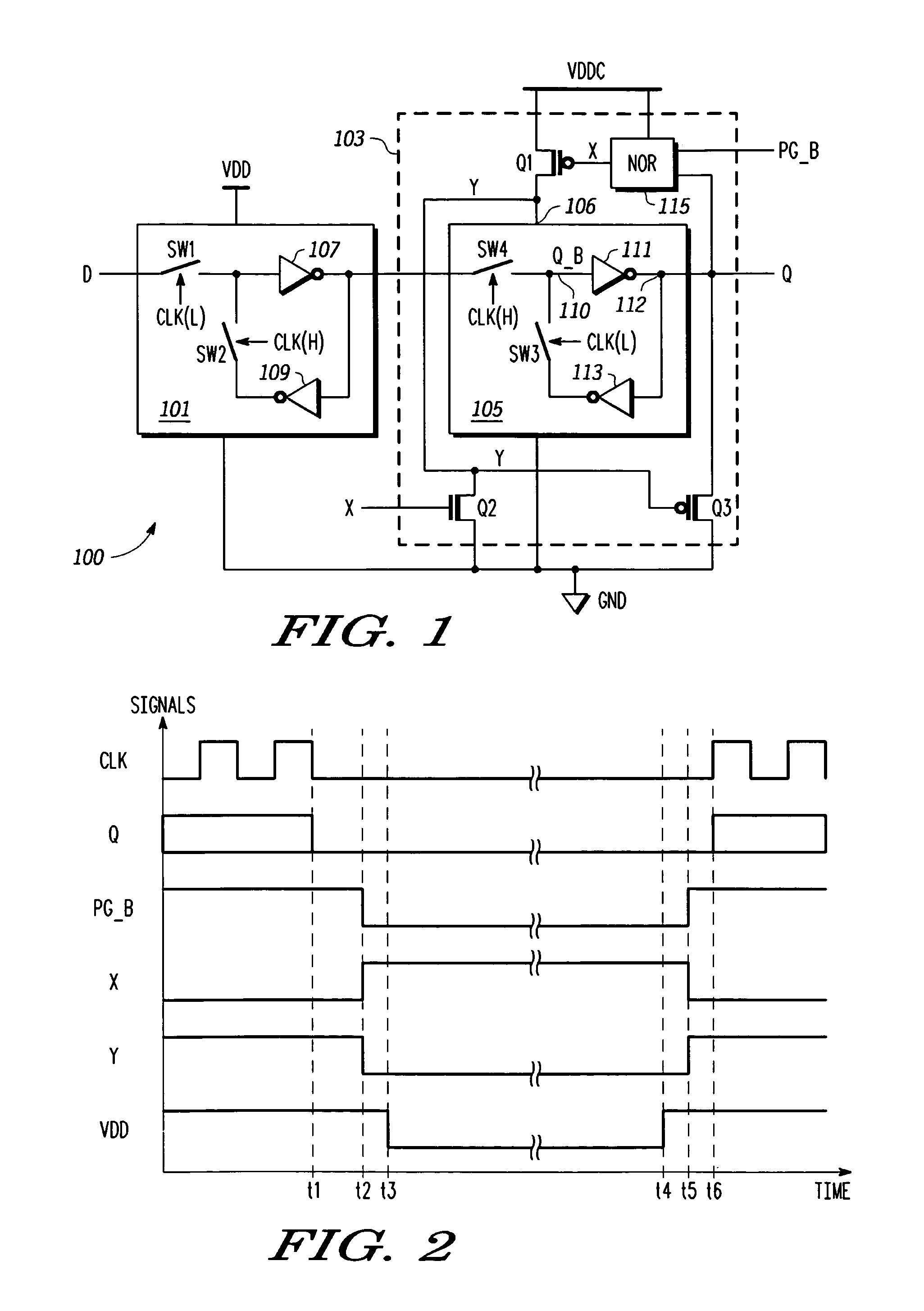
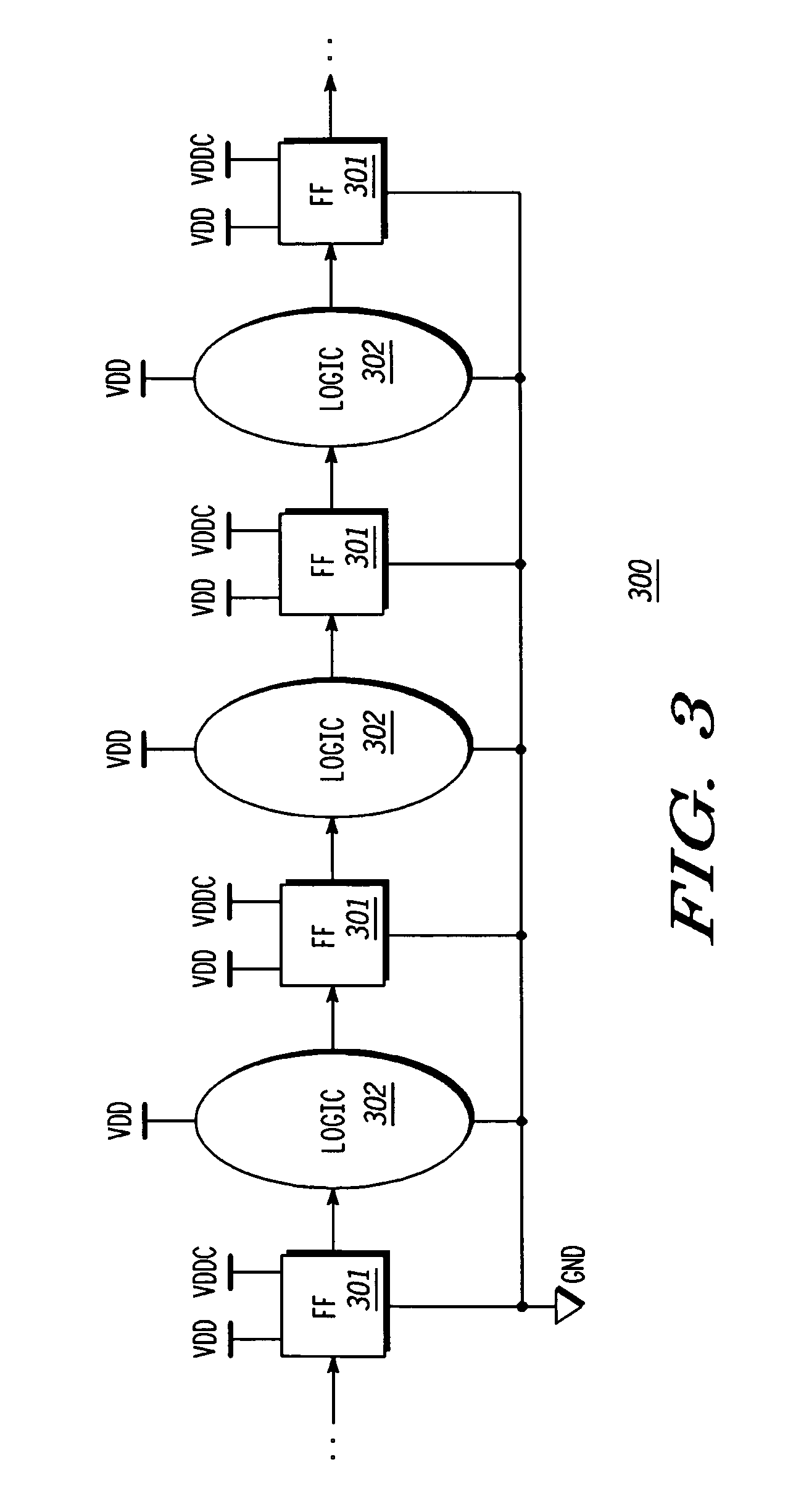
State retention power gating latch circuit
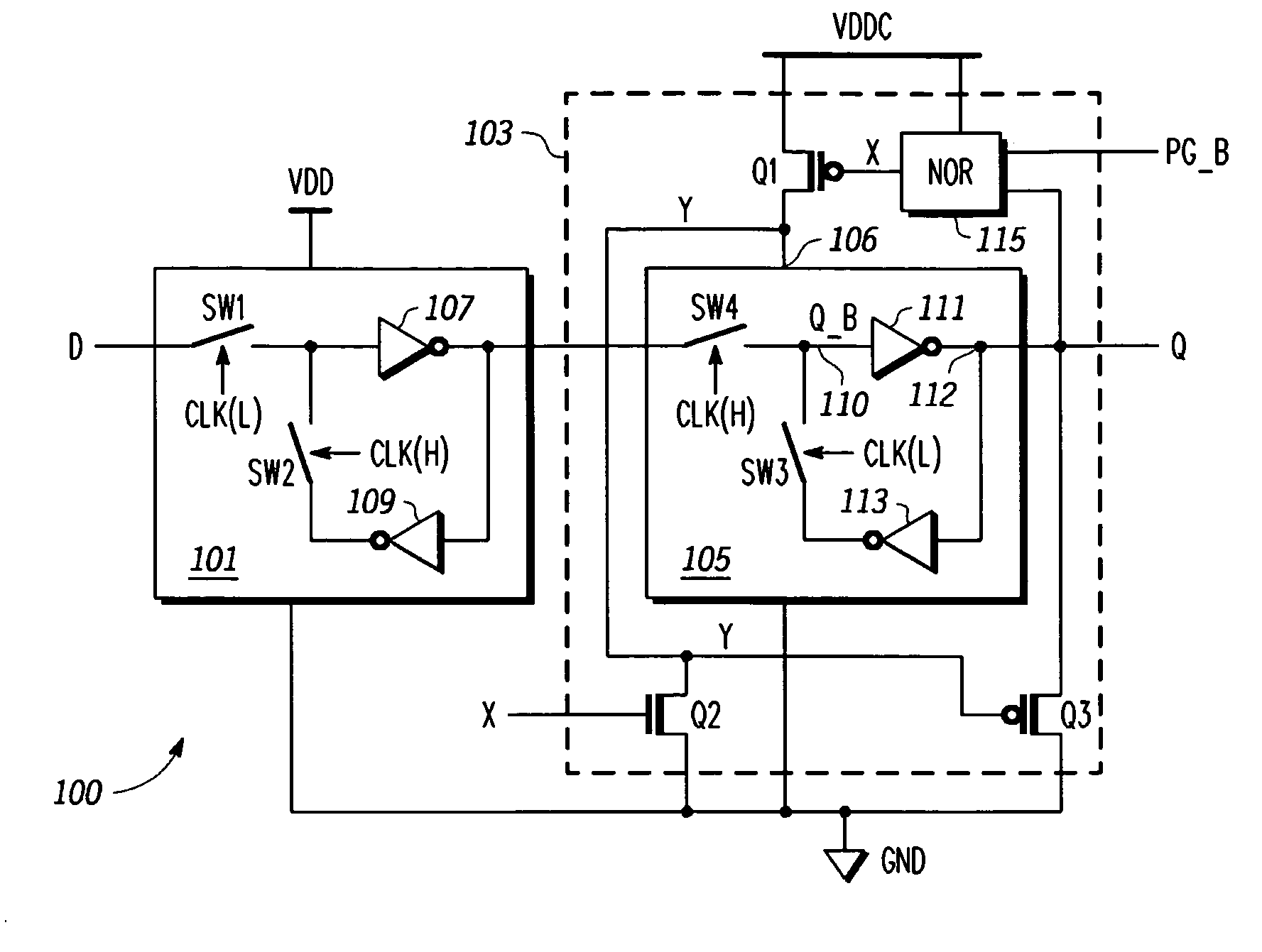
A method of power gating a latch including detecting a state of the latch, detecting a power gate signal, providing power to the latch while the power gate signal is negated, and removing power from the latch when the power gate signal is asserted and the latch is in a predetermined state. The method may include any one or more of pulling a node of the latch to a selected state while the power gate signal is asserted to ensure that the latch powers up in the predetermined state, providing a signal indicative of the latch state and the power gate signal to respective inputs of a logic gate having an output indicative thereof, switching a supply voltage to a power input of the latch based on a state of the output of the logic gate, and closing a switch to pull a node of the latch low.
Owner:NXP USA INC
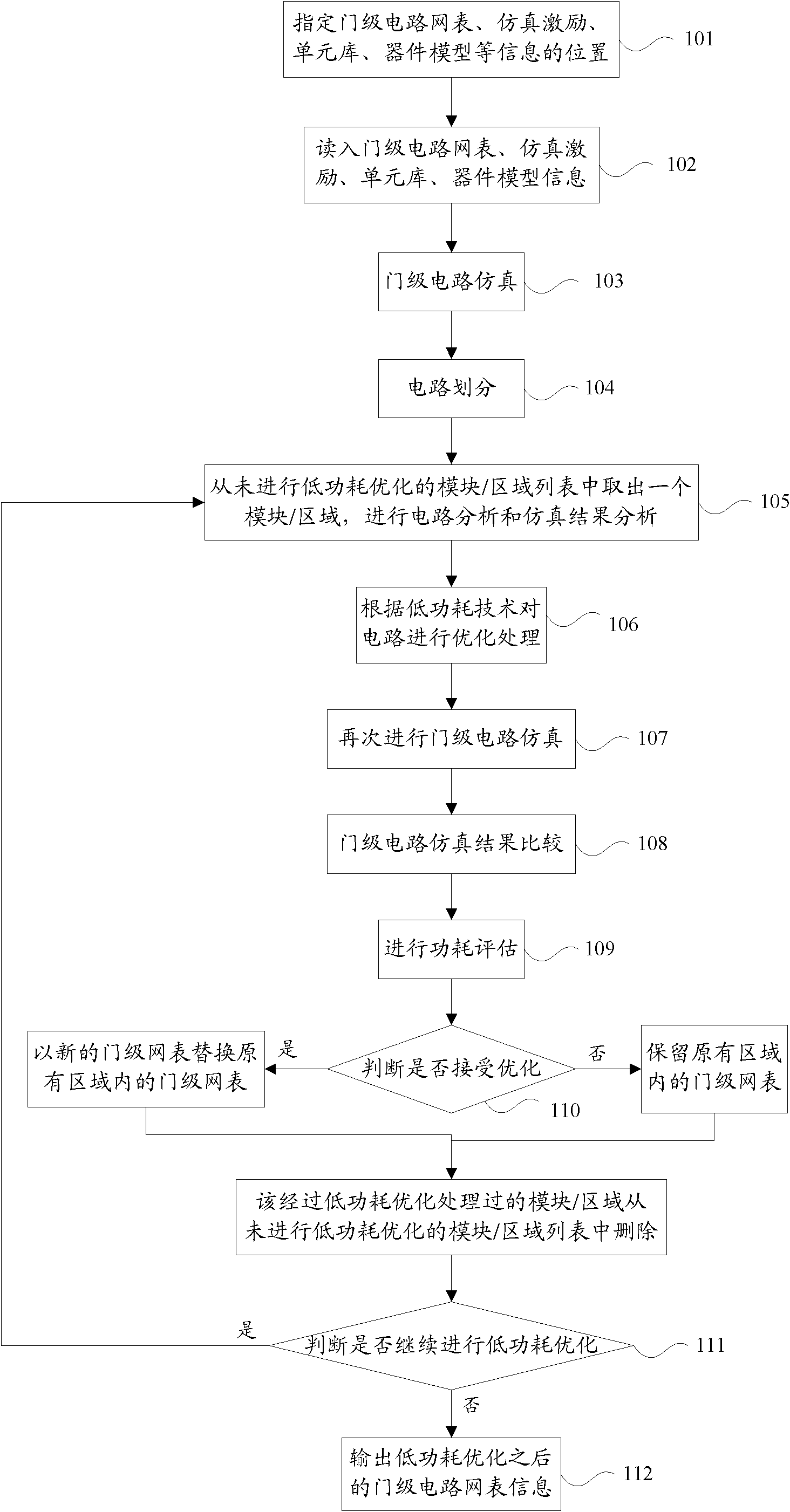
Optimization method of low-power-consumption circuit design
ActiveCN102314525AReduce power consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsLow power dissipationPower gating
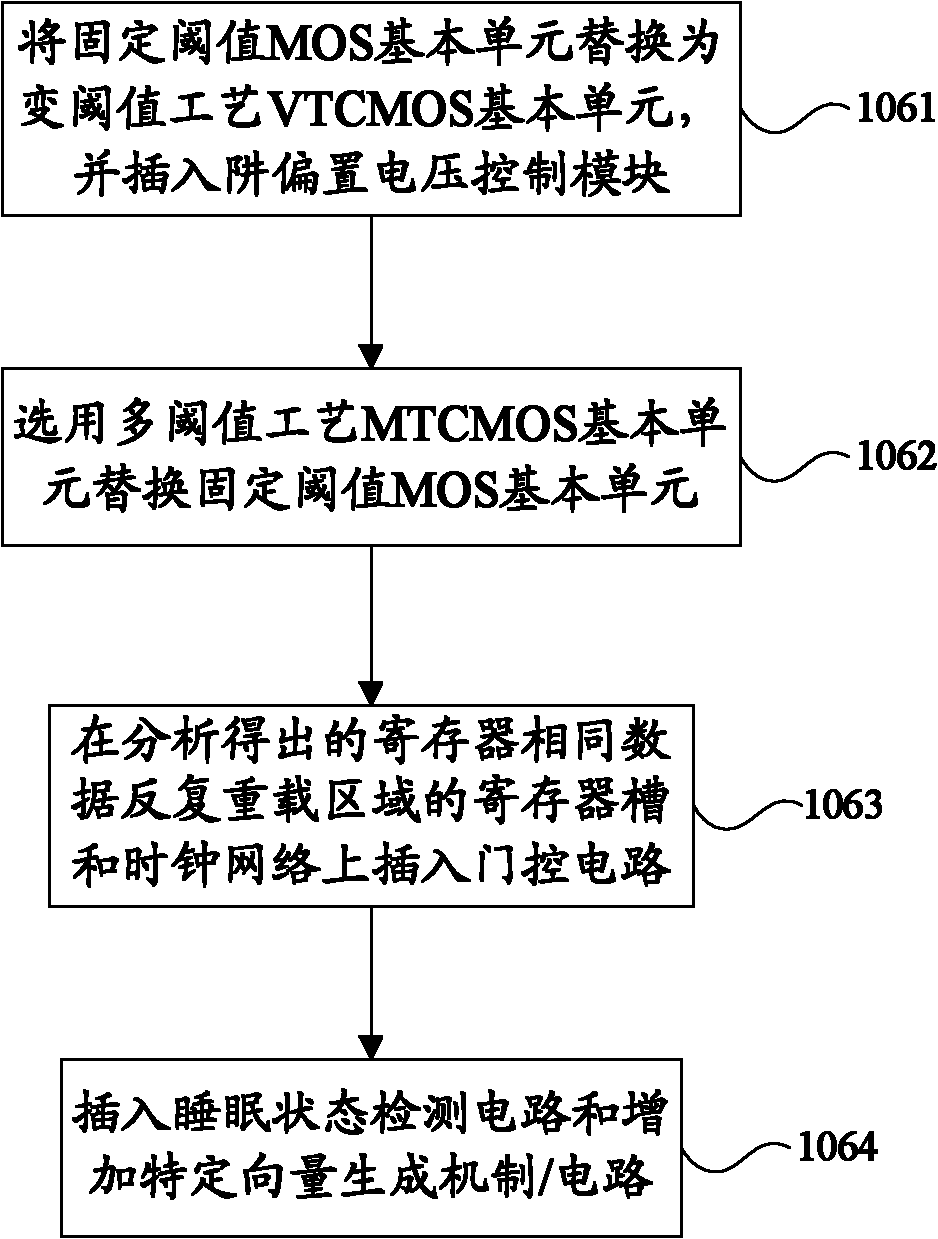
The invention discloses an optimization method of a low-power-consumption circuit design, belonging to the field of automation of integrated circuits. The optimization method comprises the following steps of: assigning positions of information of a gate-level circuit network table, simulation excitation, a unit library and a device model, reading the information in to execute the gate-level circuit simulation, partitioning gate-level circuits, executing circuit analysis and simulation result analysis, and executing optimization processing on the circuits according to the analysis results based on low-power-consumption technologies. According to the optimization method disclosed by the invention, the design of the gate-level circuit network table is optimized, and a part of units are inserted and / or replaced in the circuit network table to support the low-power-consumption technologies of an MTCMOS (Multi-threshold Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor), a VTCMOS (Variable Threshold Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor), power source gate control, multi-voltage and DVFS (Dynamic Voltage and Frequency Scaling), power gating d the like, thus the power consumption of a chip system is the minimum on the premise of ensuring circuit performances of the chip system.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Design method and architecture for power gate switch placement and interconnection using tapless libraries
ActiveUS7509613B2Logic circuits characterised by logic functionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInterconnectionEngineering
A method and a structure provide a space efficient integrated circuit using standard cells and power gating by switch cells. The standard cells may be tapless, i.e., not provided a substrate connection to a power supply or ground rail by a tap within the cell. The substrate connection for these standard cells may be provided by the switch cells or by specialized tap cells. The tapless standard cells may include only a context-sensitive rail, which may be configured to be a virtual ground rail by a power gating connection to a switch cell or by a direct connection to a power supply or ground rail.
Owner:ANSYS
Control circuitry for power gating virtual power supply rails at differing voltage potentials
InactiveUS7219244B2Reliability increasing modificationsPower reduction by control/clock signalLevel shiftingSingle stage
A single-stage level shifting circuit is used to interface control signals across the boundary between voltage domains with differing positive or ground voltage potentials Asserted states are determined by the difference between the positive voltages potentials and the ground potentials. A lower positive power supply potential is not used to turn OFF PFET coupled to a higher positive power supply potential. Likewise a higher ground power supply potential is not used to turn OF NFETs coupled to a power domain where is significant ground shift. The single stage level shifting circuit has keeper devices that hold asserted states using voltages within the power gated domain.
Owner:IBM CORP
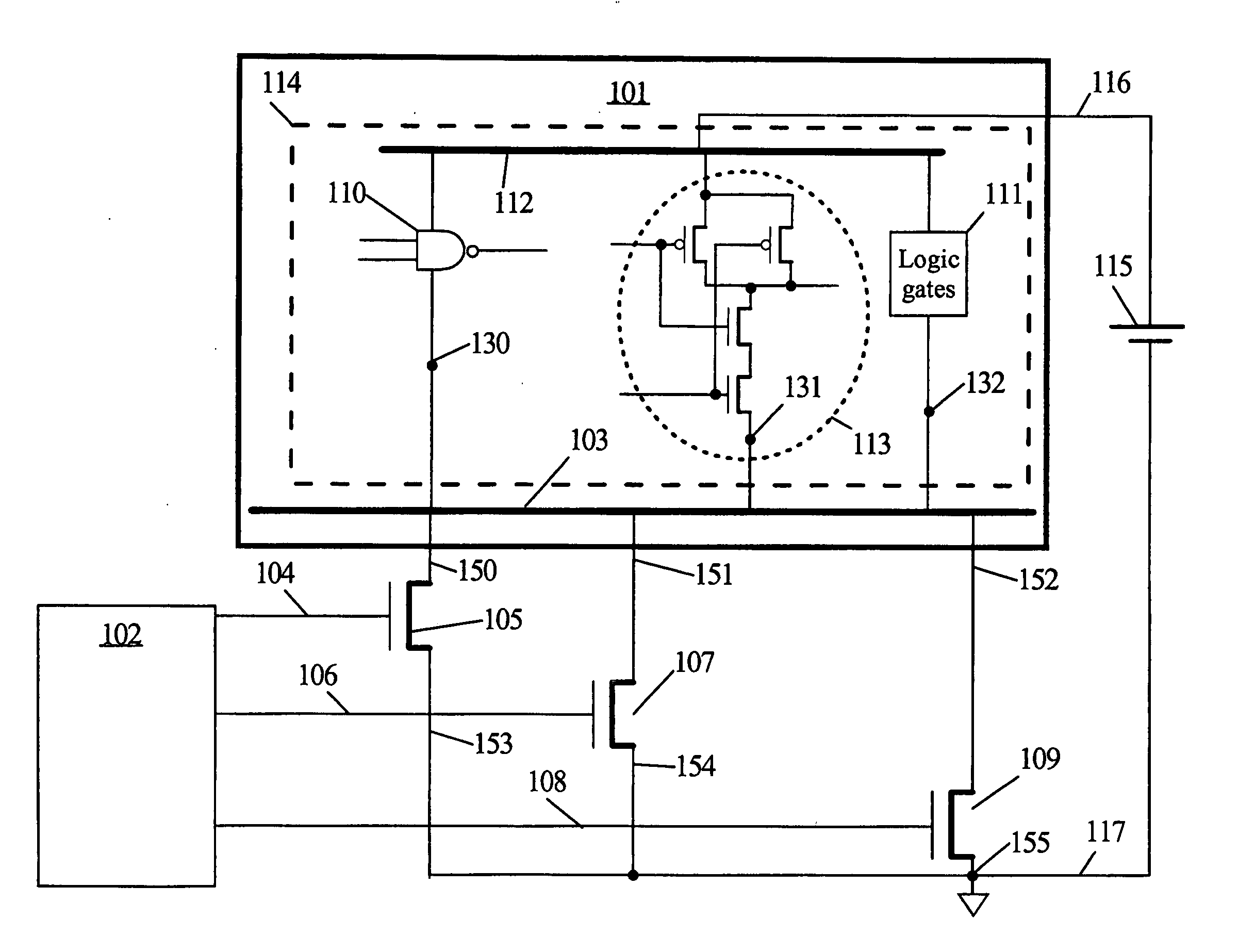
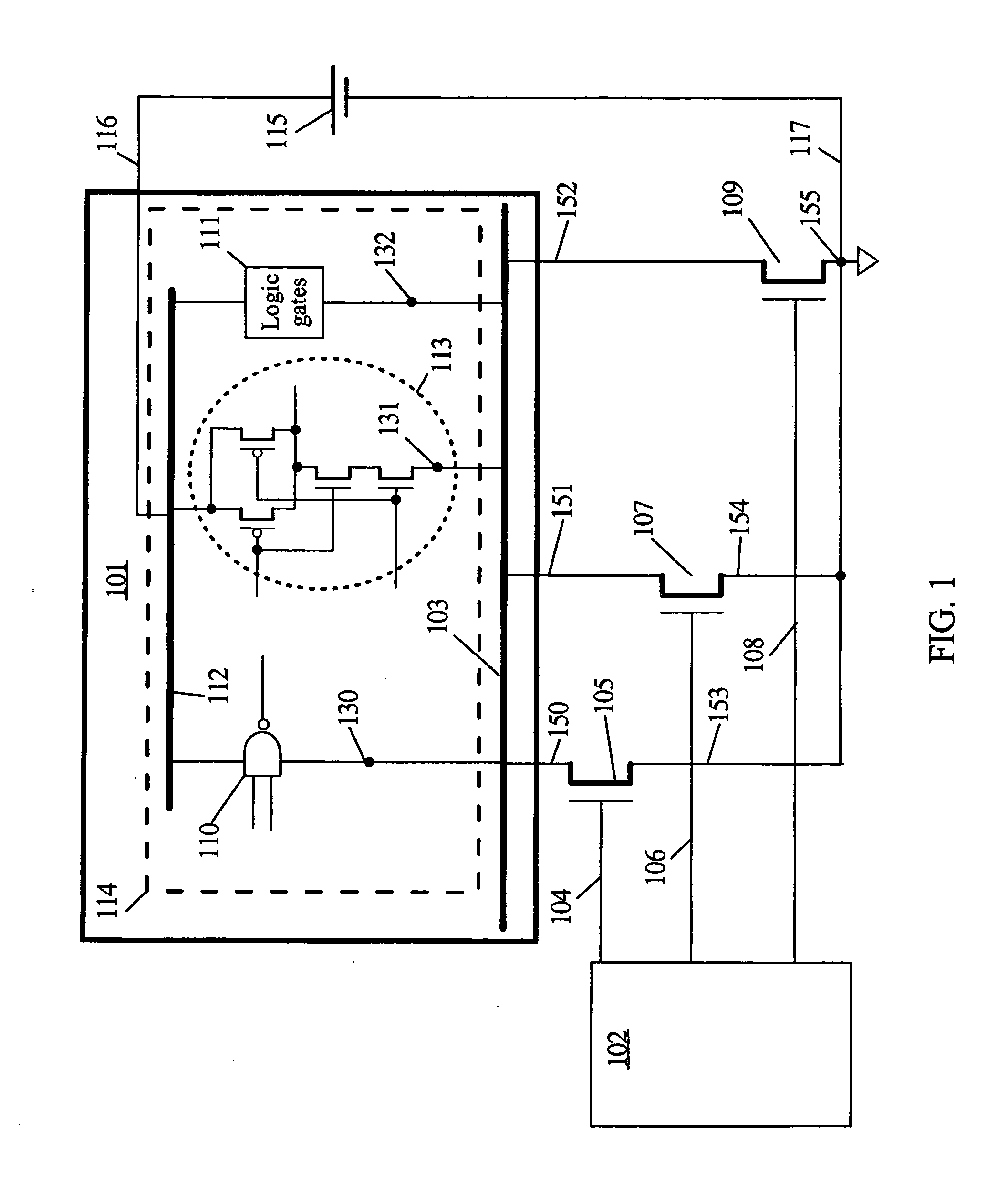
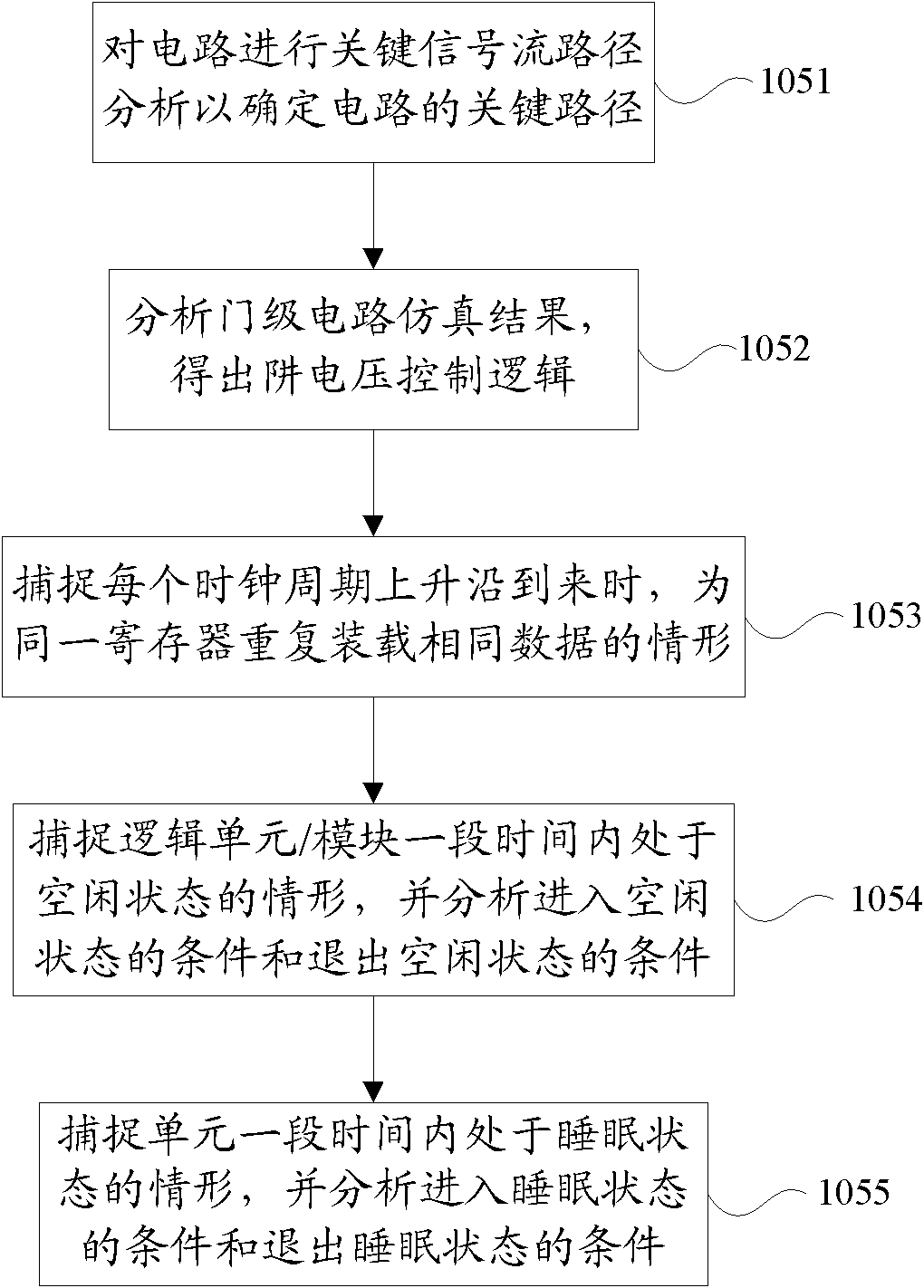
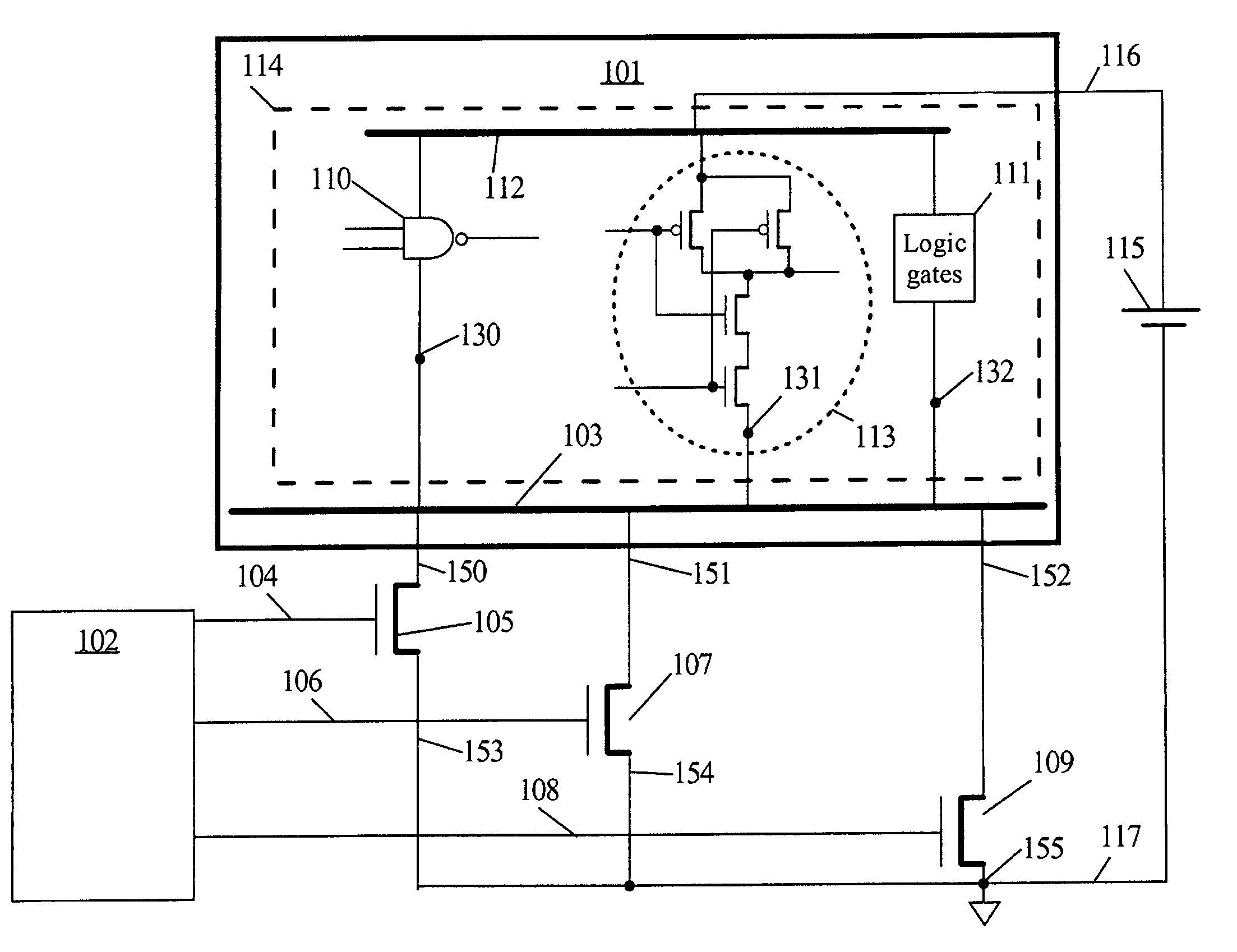
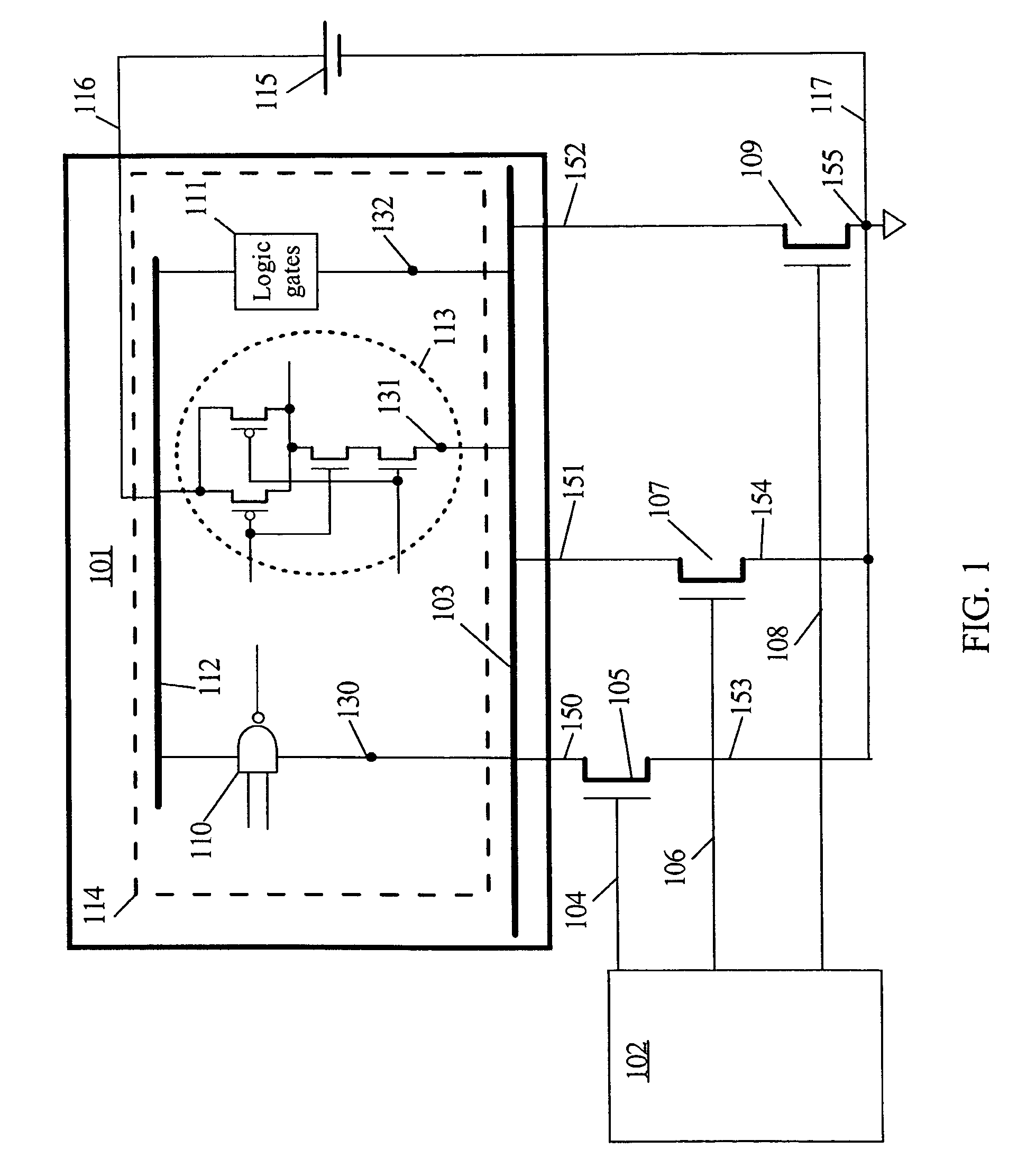
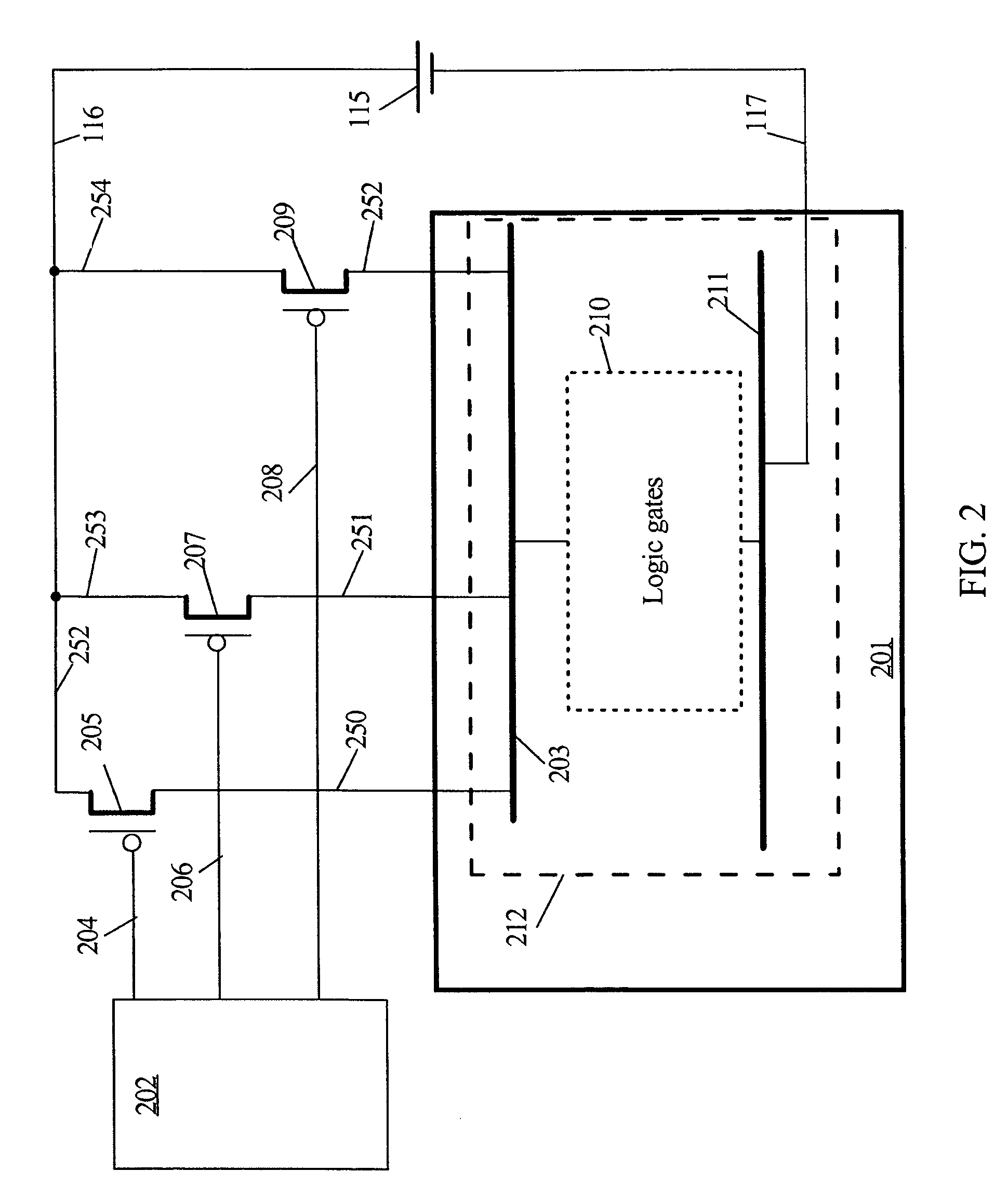
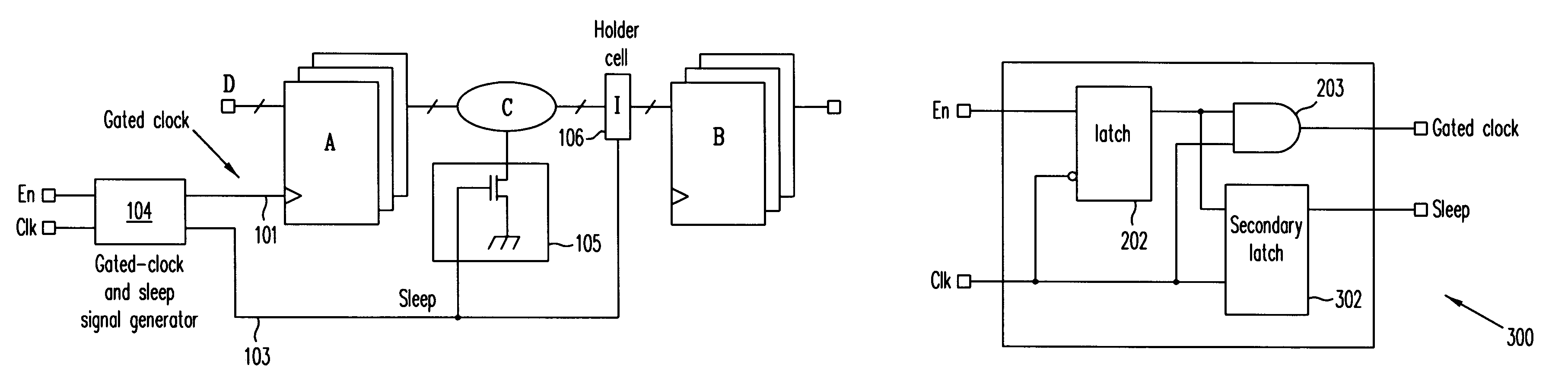
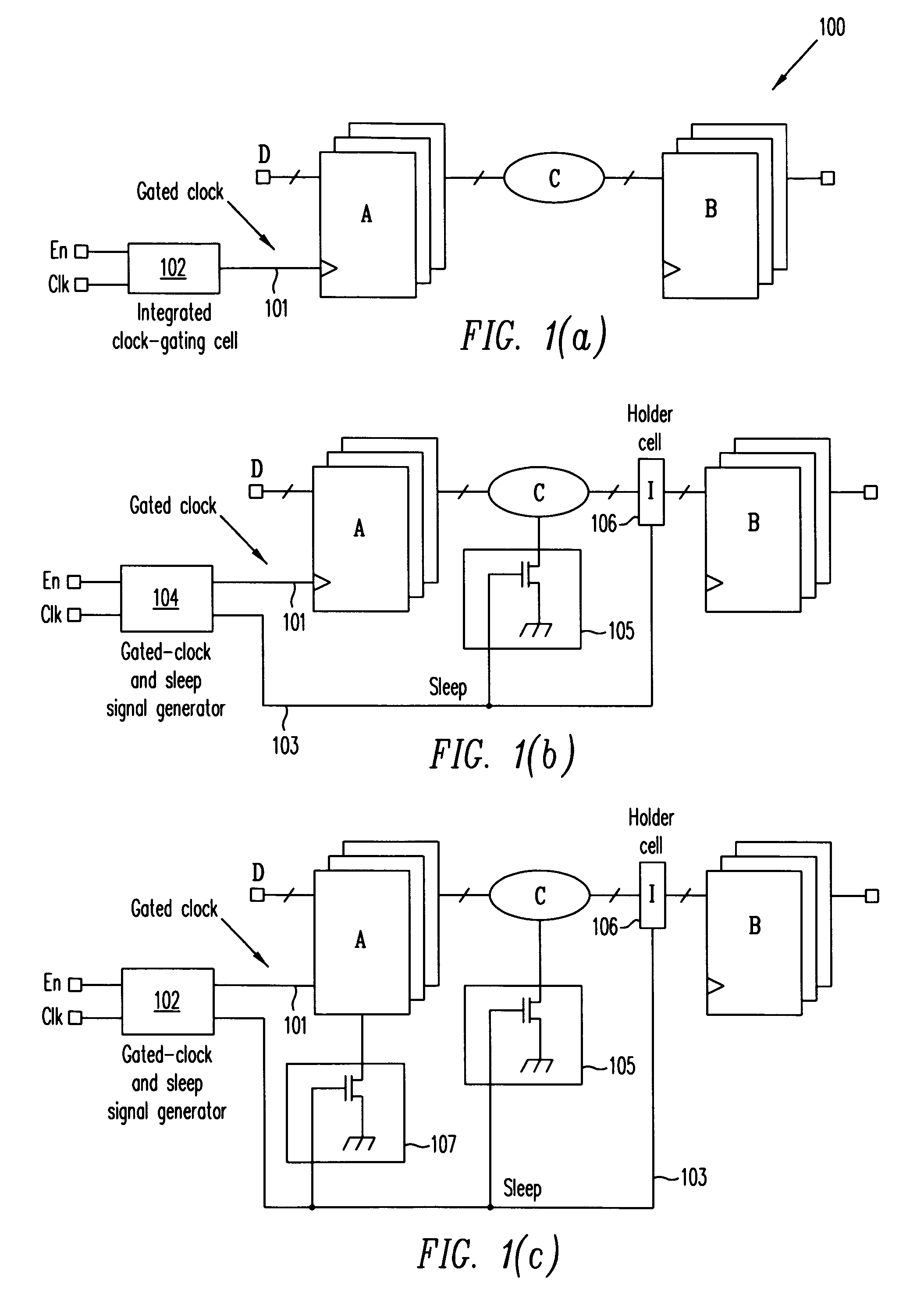
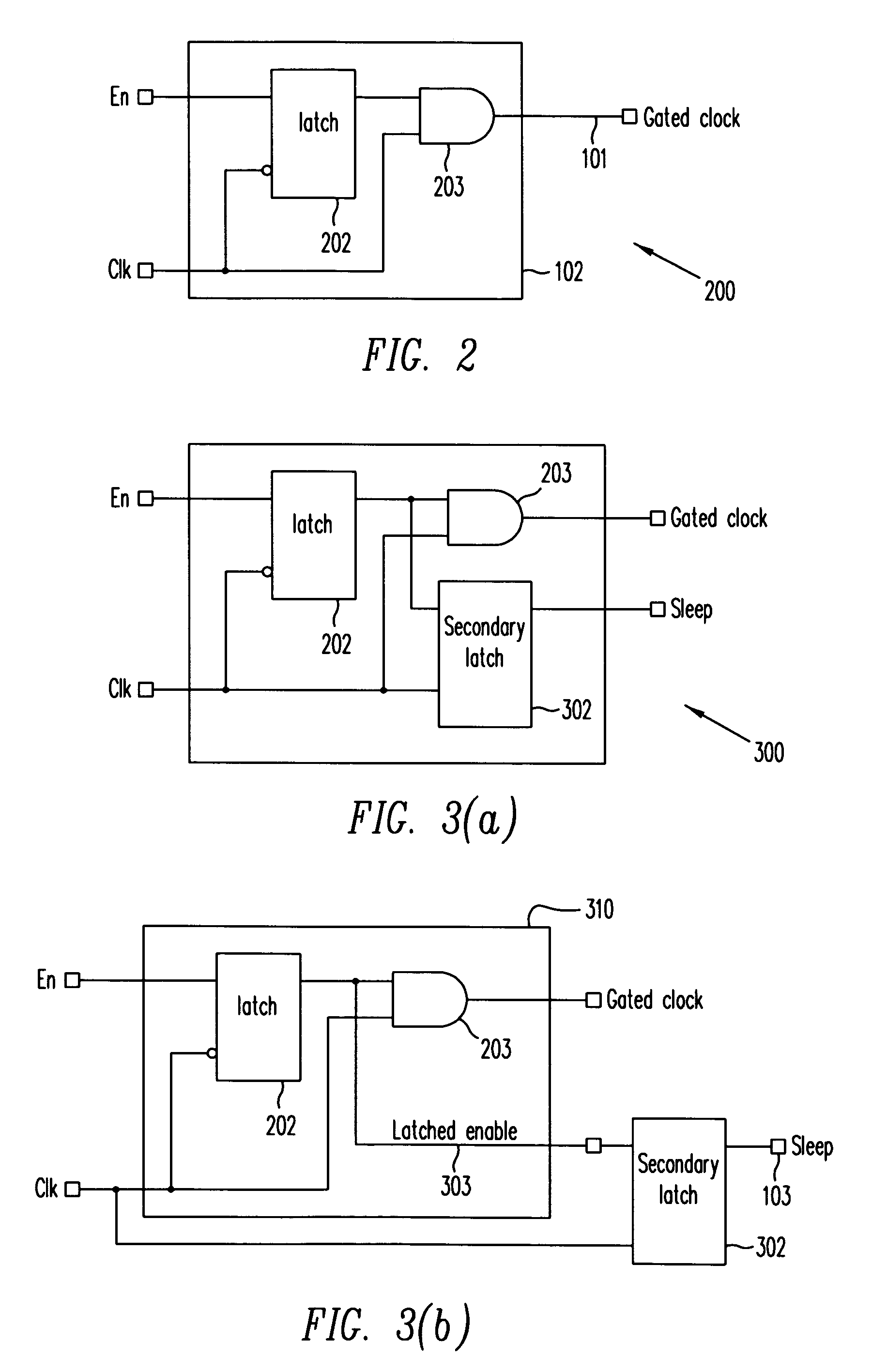
Automatic extension of clock gating technique to fine-grained power gating
A method extends a clock-gating technique to provide a sleep signal for controlling switch circuits that reduce active leakage power. Using this extension of the clock-gating technique, fine-grained power-gating is achieved. The method automatically identifies, at an RTL or a gate level, the logic circuits that can be power-gated. The method of the present invention derives a sleep signal for fine-grained power-gating that may be applicable to both time-critical and non-time-critical designs.
Owner:ANSYS
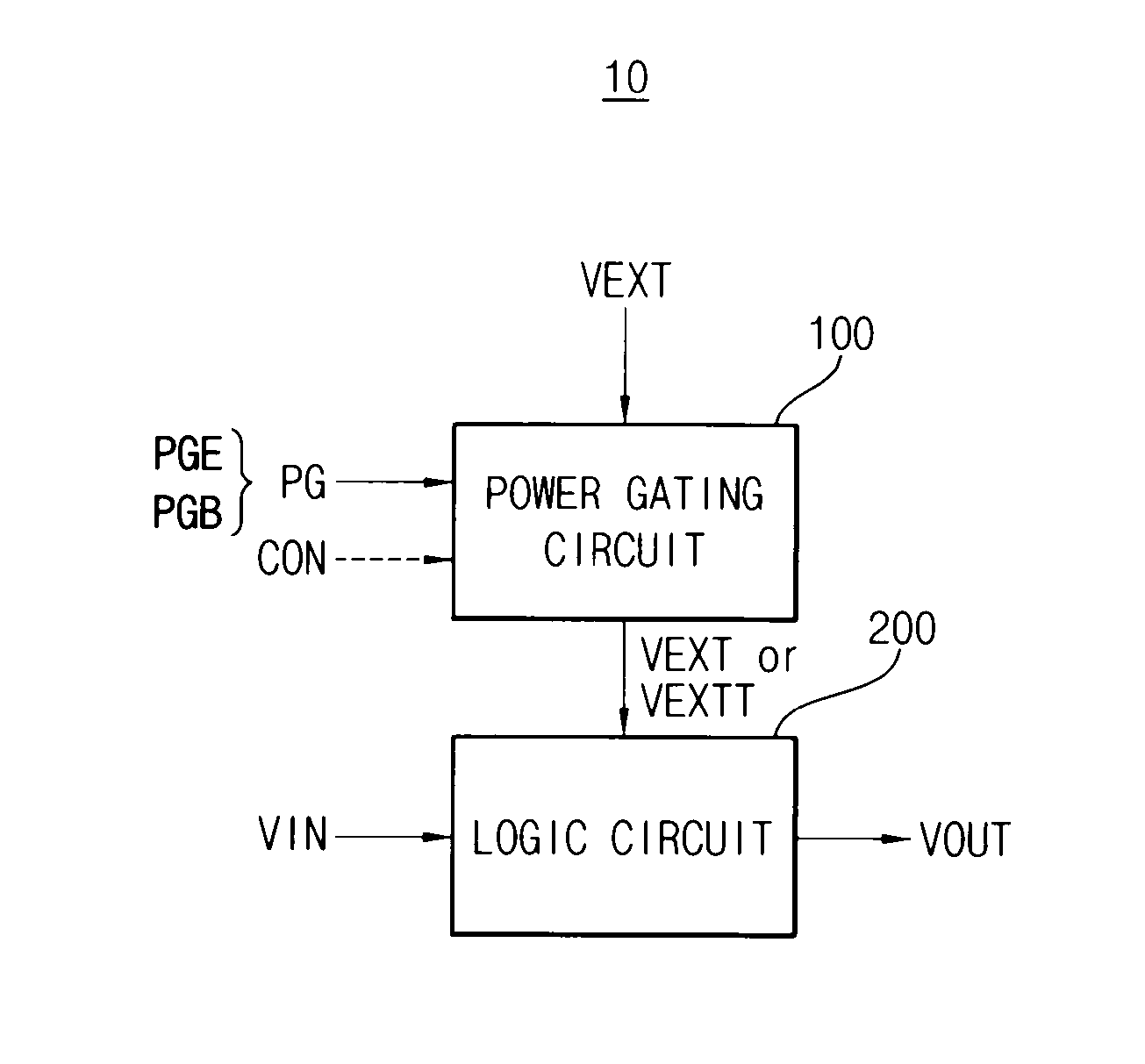
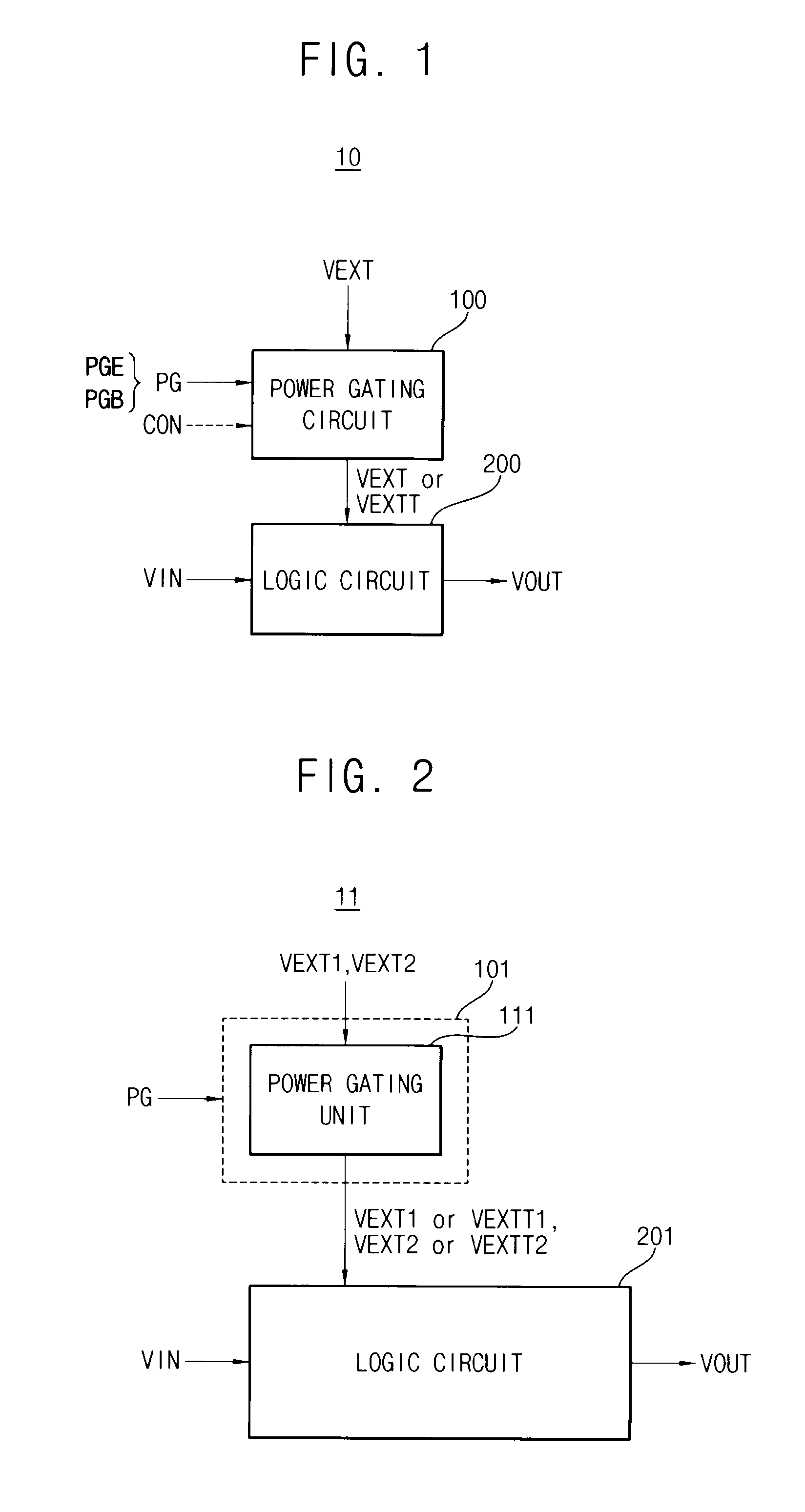
Integrated circuit having power gating function and semiconductor device including the same
InactiveUS20120200345A1Reduce power consumptionData retentionPower reduction by control/clock signalStatic storageDevice materialEngineering
An integrated circuit includes a logic circuit and a power gating circuit. The logic circuit generates an output signal based on an input signal and a first power supply voltage in a normal operation mode, and maintains a voltage level of the output signal as a stand-by logic level based on a second power supply voltage in a stand-by mode. A magnitude of the second power supply voltage is smaller than a magnitude of the first power supply voltage. The power gating circuit entirely applies the first power supply voltage to the logic circuit based on a power gating signal in the normal operation mode, and partially applies the second power supply voltage to the logic circuit based on the power gating signal in the stand-by mode.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Multi-core apparatus and method for restoring data arrays following a power gating event
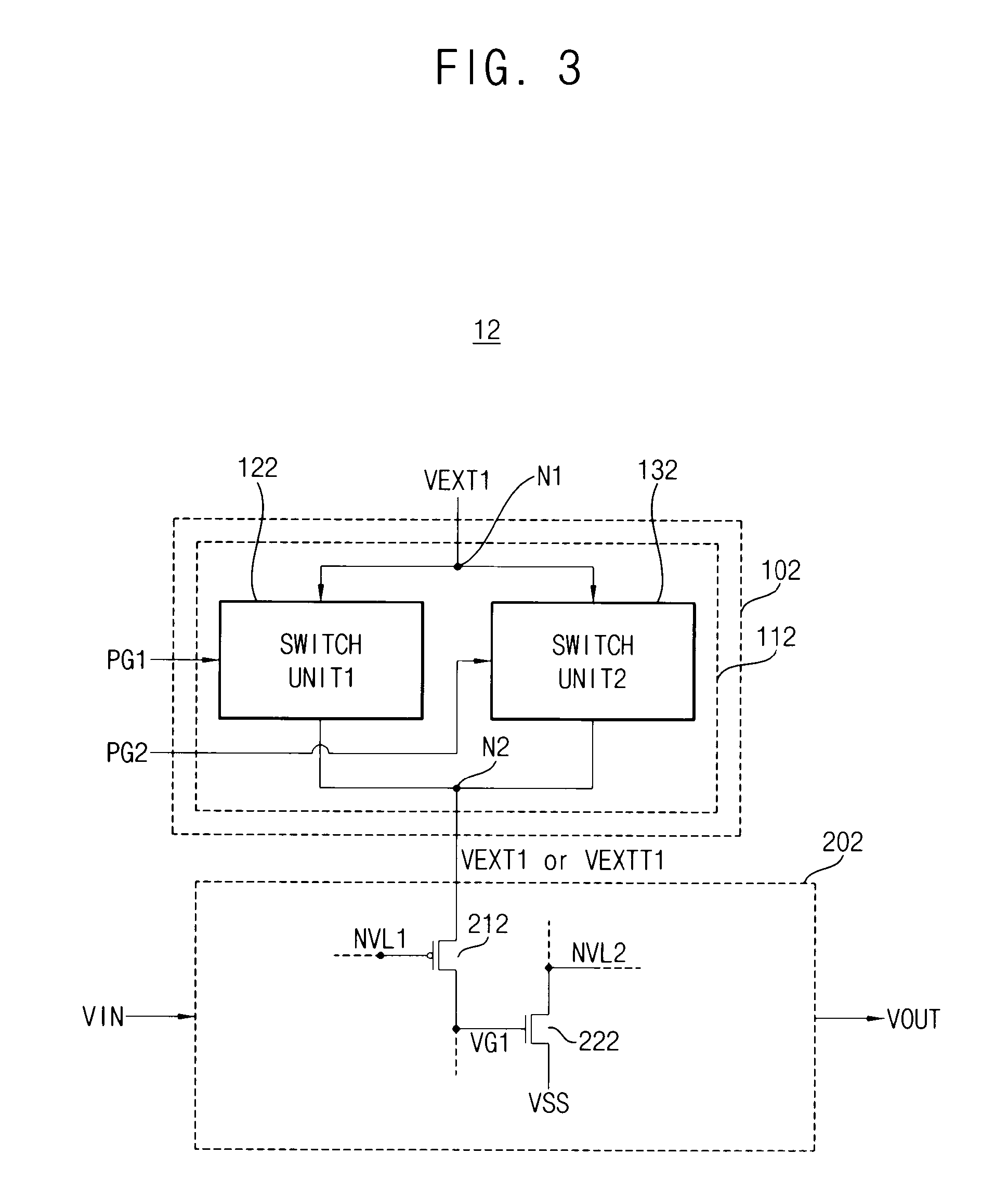
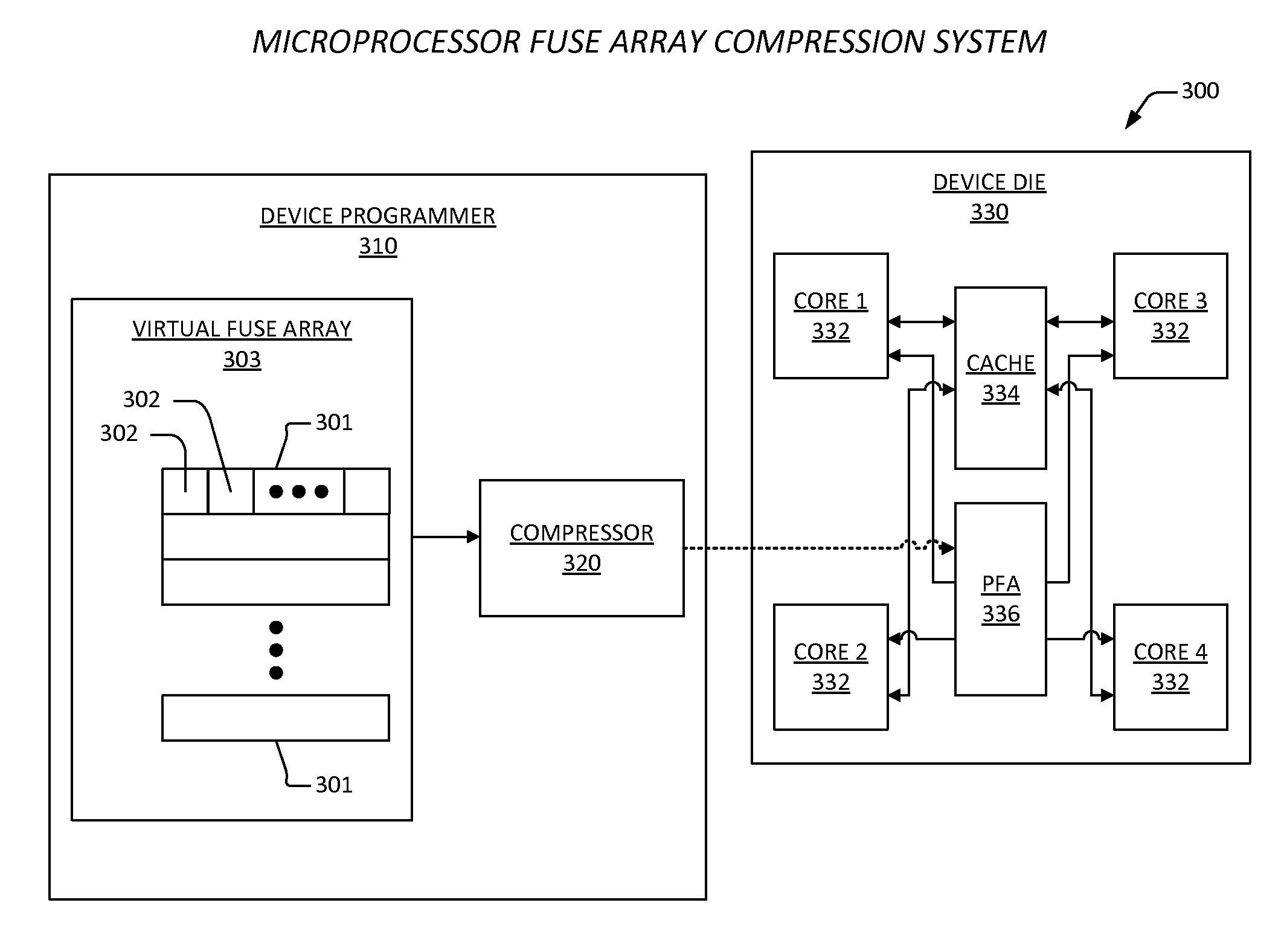
ActiveUS20150338904A1Good techniqueMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer hardwarePower-on reset
An apparatus includes a fuse array and a plurality of cores. The fuse array is programmed with compressed data. Each of the plurality of cores accesses the fuse array upon power-up / reset to read and decompress the compressed data, and to store decompressed data sets for one or more cache memories within the each of the plurality of cores in a stores that is coupled to the each of the plurality of cores. Each of the plurality of cores has reset logic and sleep logic. The reset logic employs the decompressed data sets to initialize the one or more cache memories upon power-up / reset. The sleep logic determines that power is restored following a power gating event, and subsequently accesses the stores to retrieve and employ the decompressed data sets to initialize the one or more caches following the power gating event.
Owner:VIA ALLIANCE SEMICON CO LTD
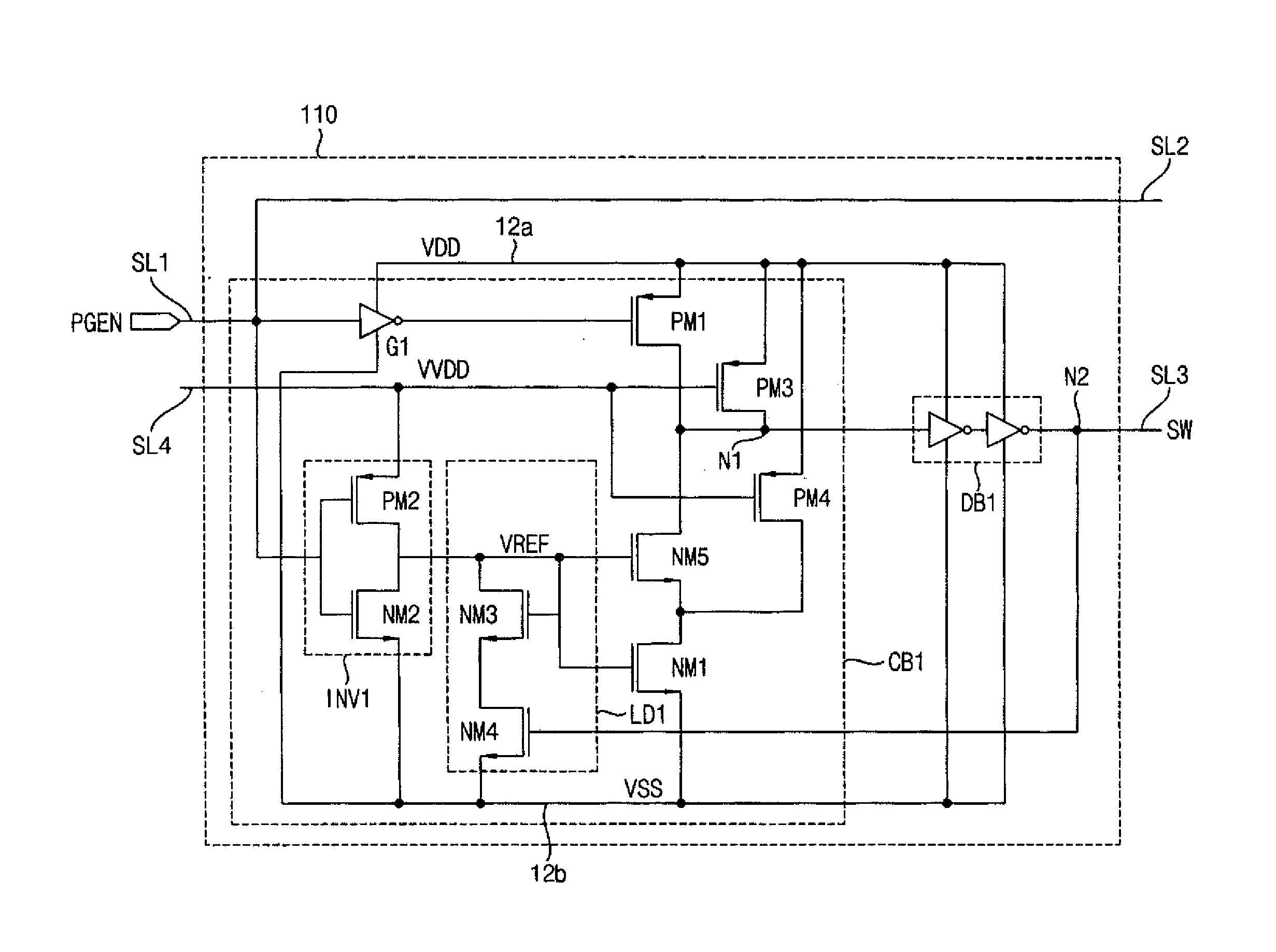
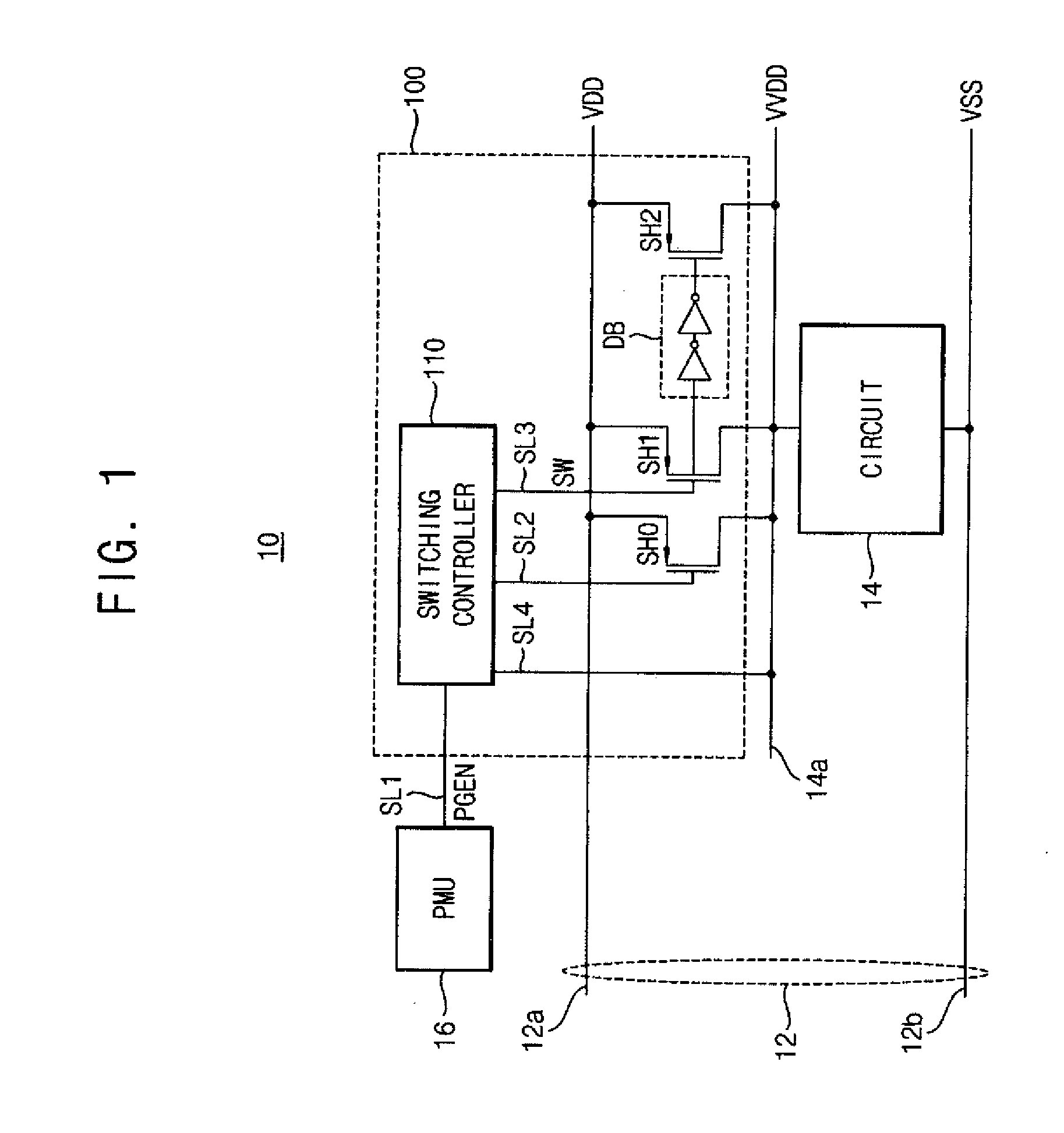
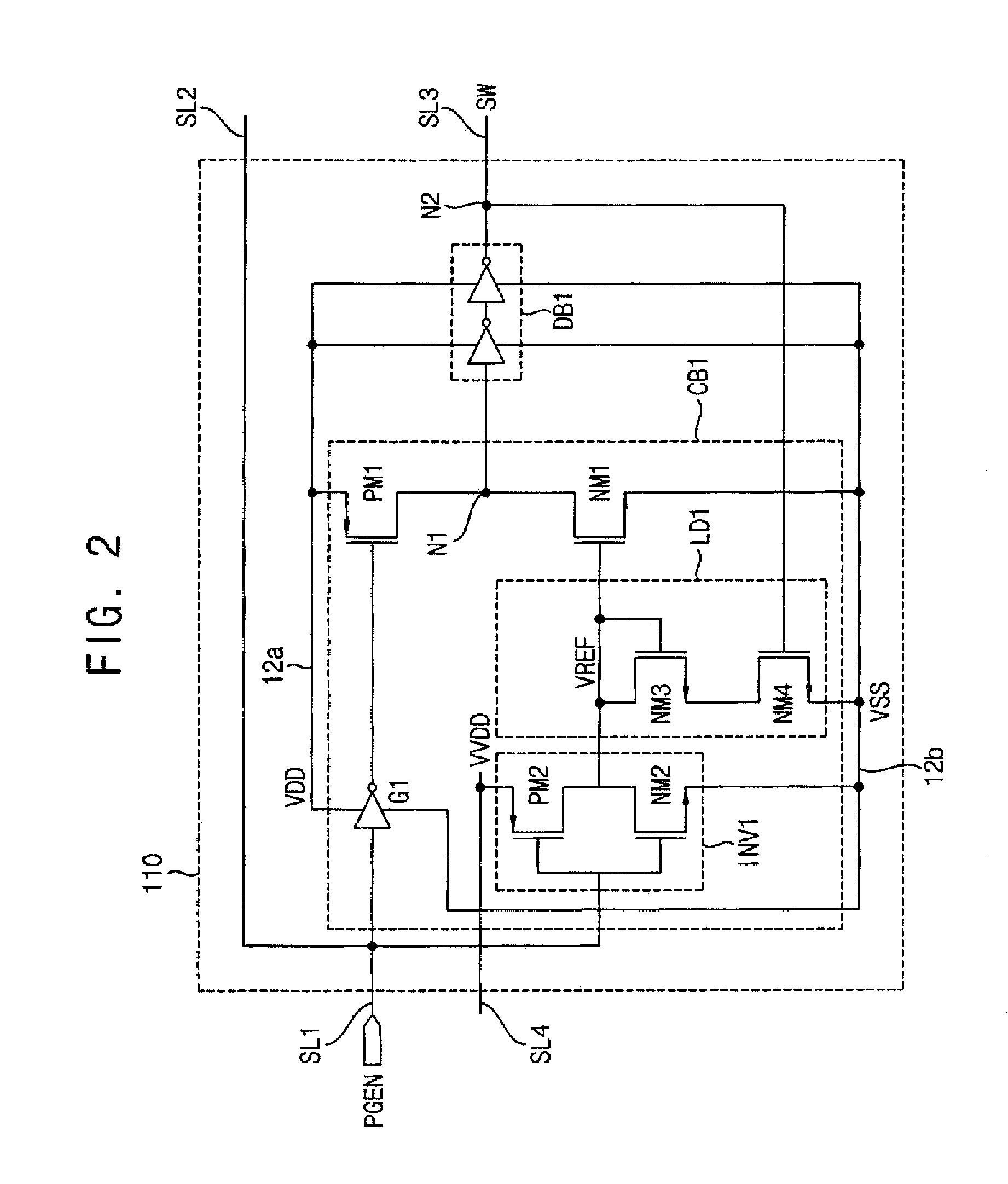
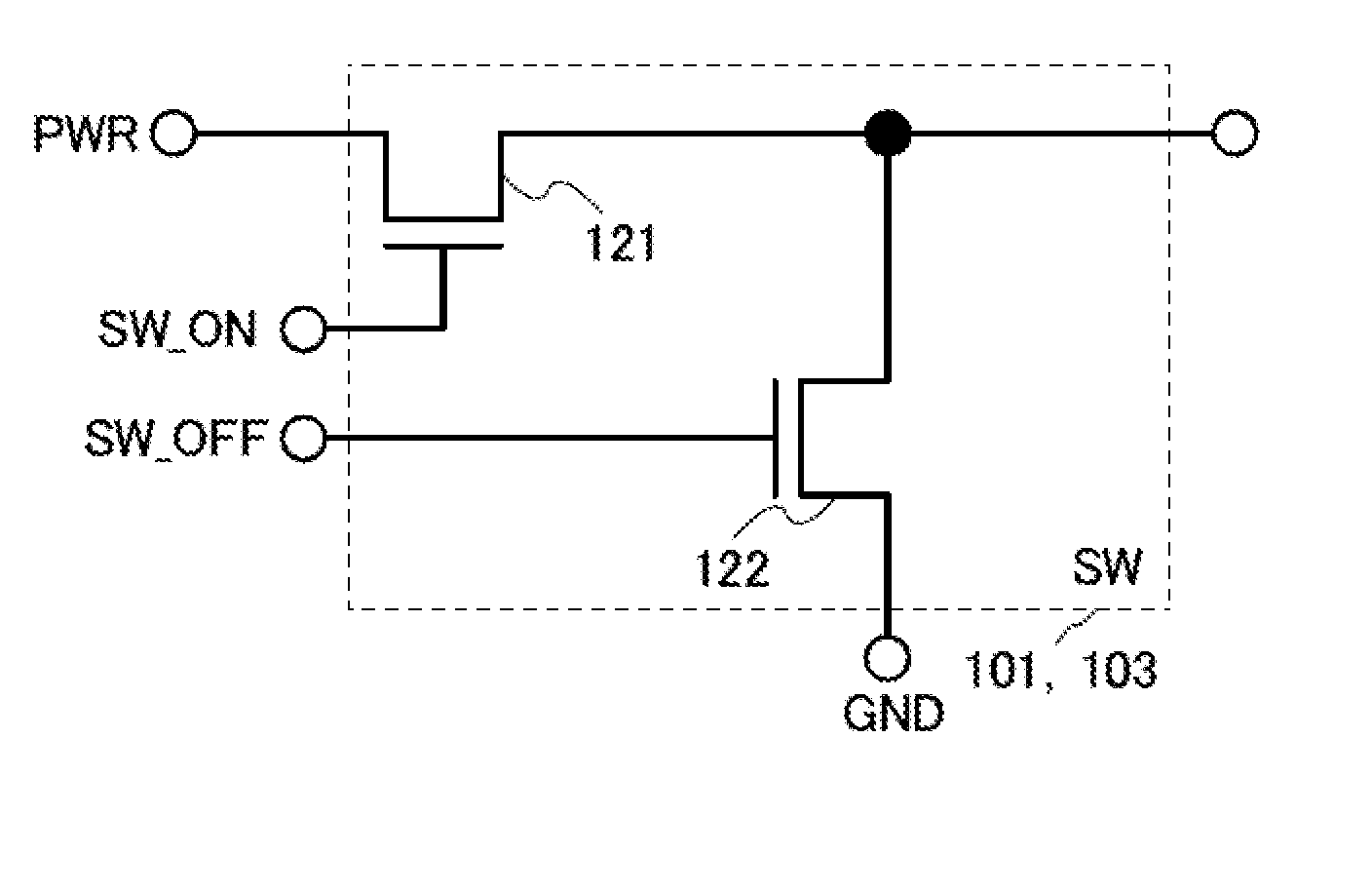
Power gating circuit
ActiveUS20140015590A1Great time delayReduce areaPower reduction by control/clock signalElectronic switchingElectricityVoltage reference
A power gating circuit includes a first current switch, a second current switch, and a switching controller. The first current switch is connected between a power rail and a circuit block operated by an operating supply voltage, and provides a first current when turned on. The second current switch is connected between the power rail and circuit block, and provides a second current larger than the first current when turned on. The switching controller turns on first current switch when transitioned from a sleep mode to an active mode to change the operating supply voltage using the first current, generates a reference voltage based on the operating supply voltage that changes more slowly than the operating supply voltage, and turns on the second current switch based on the reference voltage to provide the second current to the circuit block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device
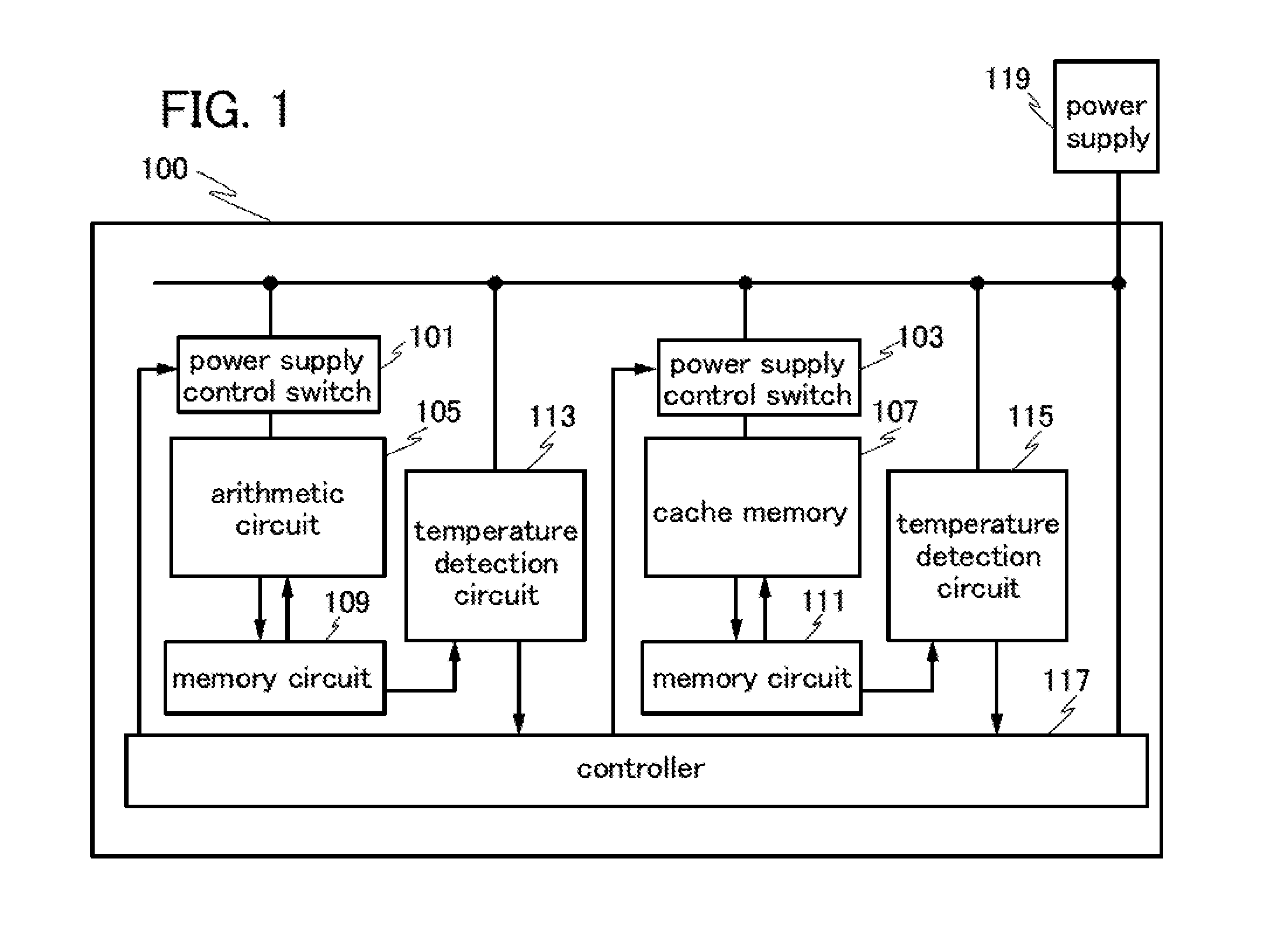
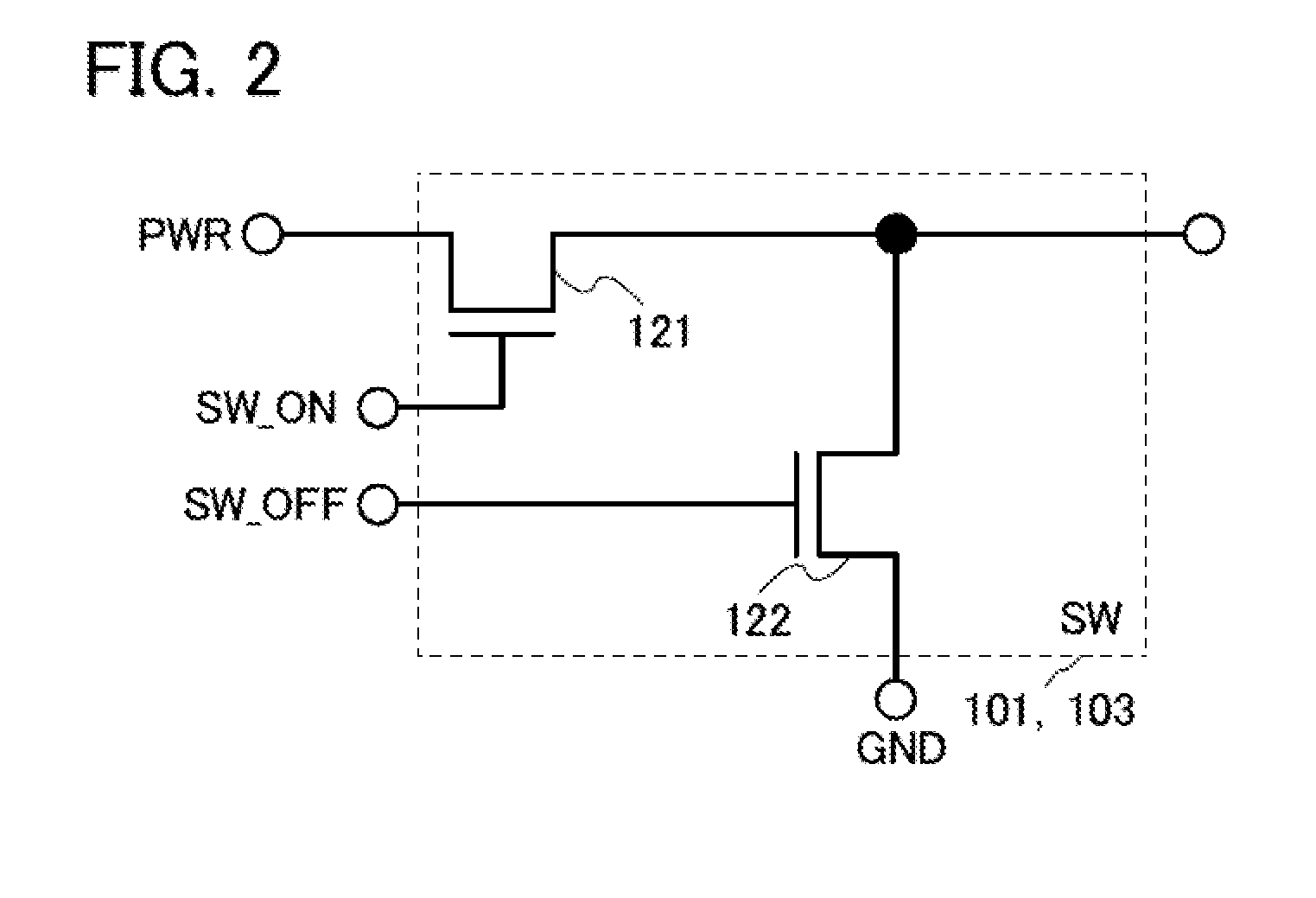
InactiveUS20130235689A1Reduce power consumptionIncrease speedTransistorDigital data processing detailsElectricityHemt circuits
To provide a semiconductor device including a plurality of circuit blocks each of which is capable of performing power gating by setting off periods appropriate to temperatures of the respective circuit blocks. Specifically, the semiconductor device includes an arithmetic circuit, a memory circuit configured to hold data obtained by the arithmetic circuit, a power supply control switch configured to control supply of the power supply voltage to the arithmetic circuit, a temperature detection circuit configured to detect the temperature of the memory circuit and to estimate overhead from the temperature, and a controller configured to set a period during which supply of the power supply voltage is stopped in the case where a power consumption of the arithmetic circuit during the period is larger than the overhead period and to control the power supply control switch.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com