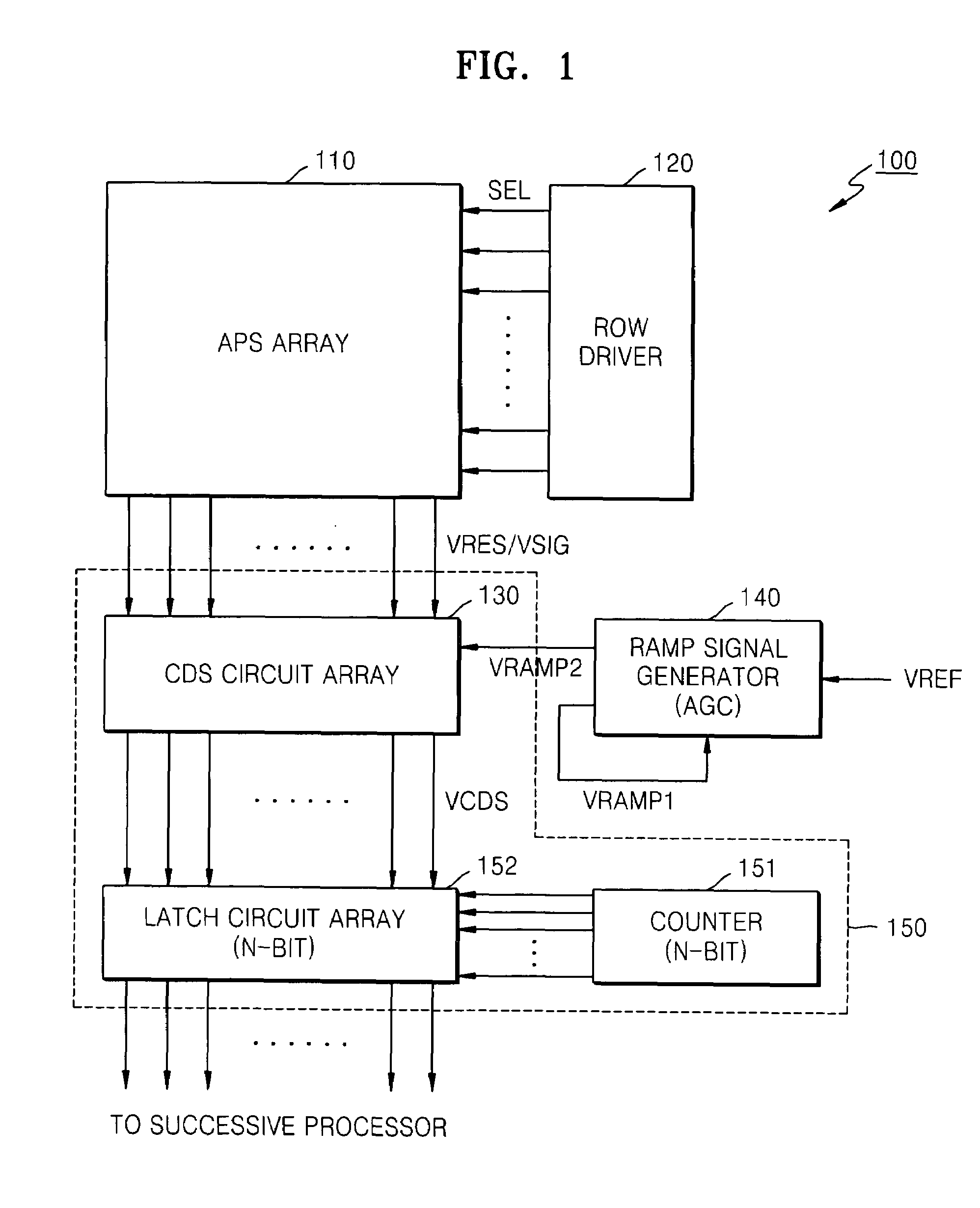
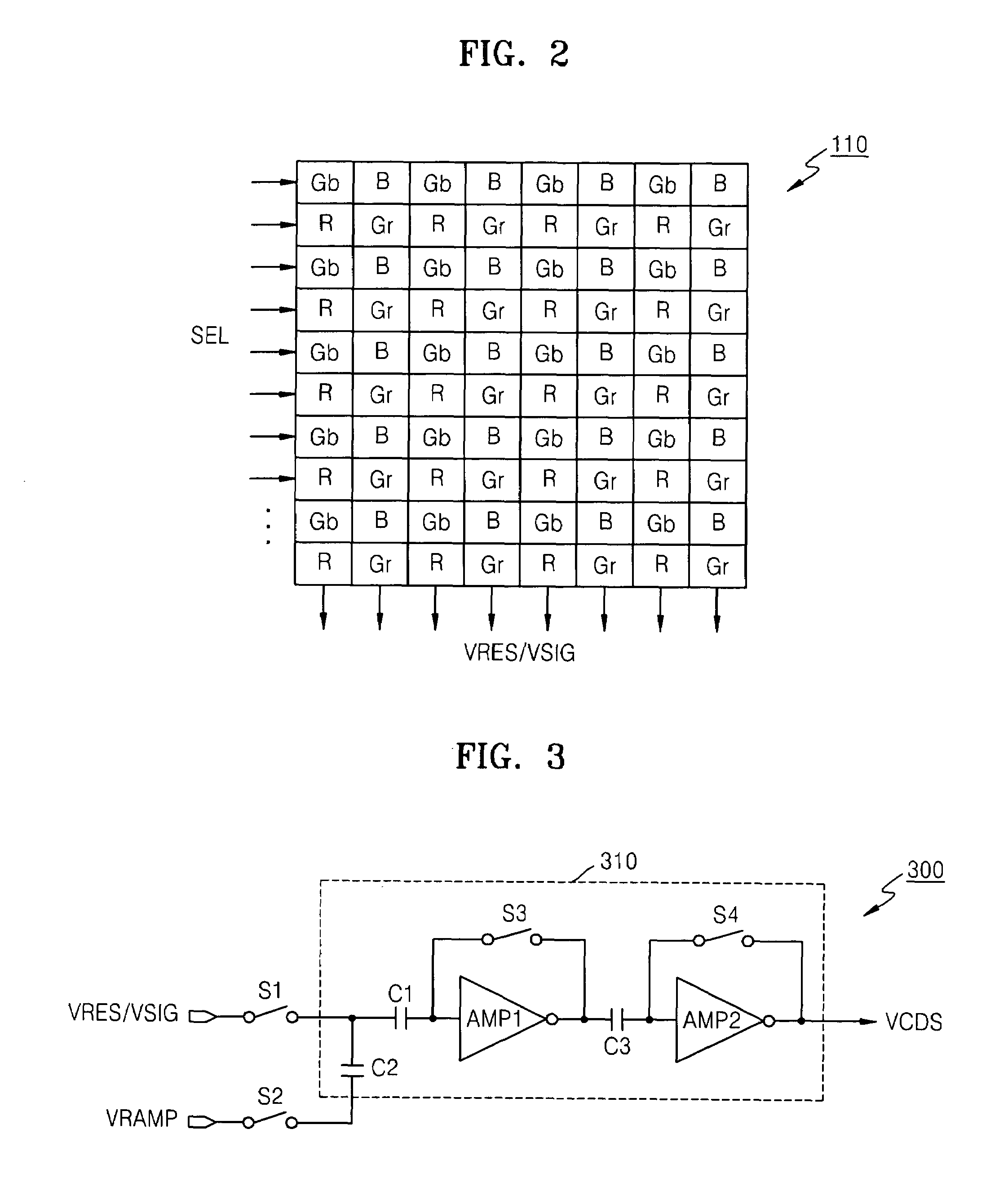
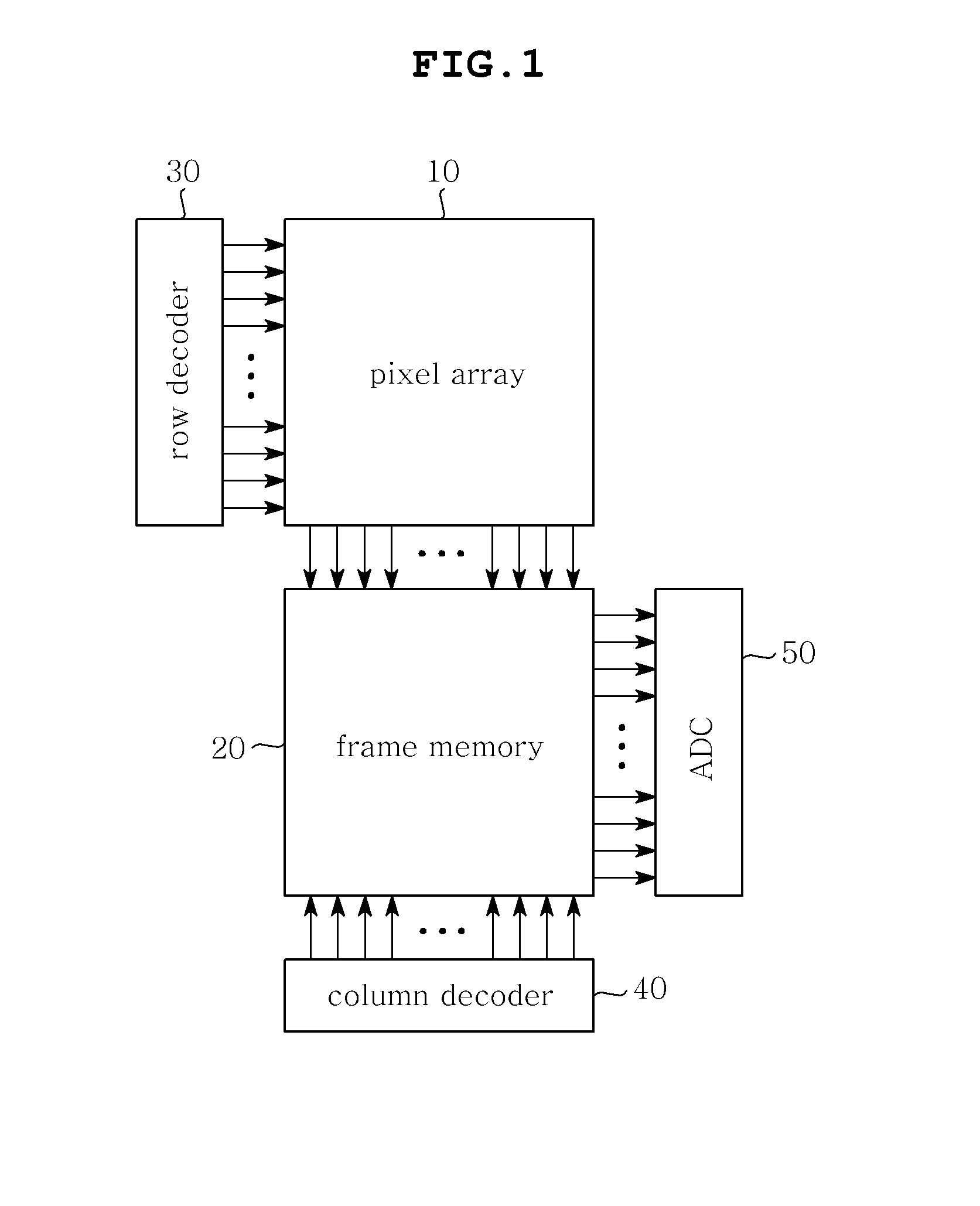Patents
Literature
447 results about "Correlated double sampling" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
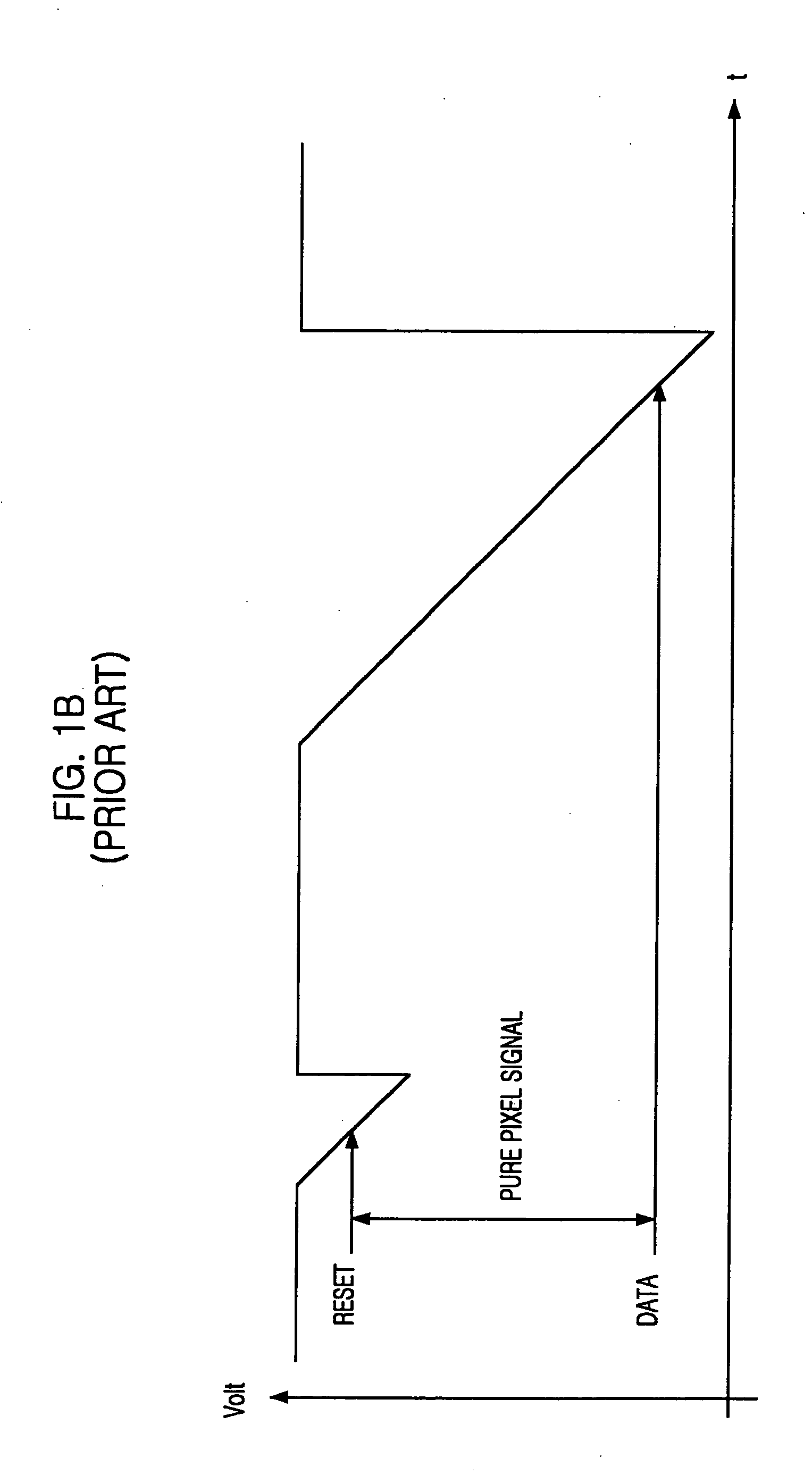
Correlated double sampling (CDS) is a method to measure electrical values such as voltages or currents that allows removing an undesired offset. It is used often when measuring sensor outputs. The output of the sensor is measured twice: once in a known condition and once in an unknown condition. The value measured from the known condition is then subtracted from the unknown condition to generate a value with a known relation to the physical quantity being measured.
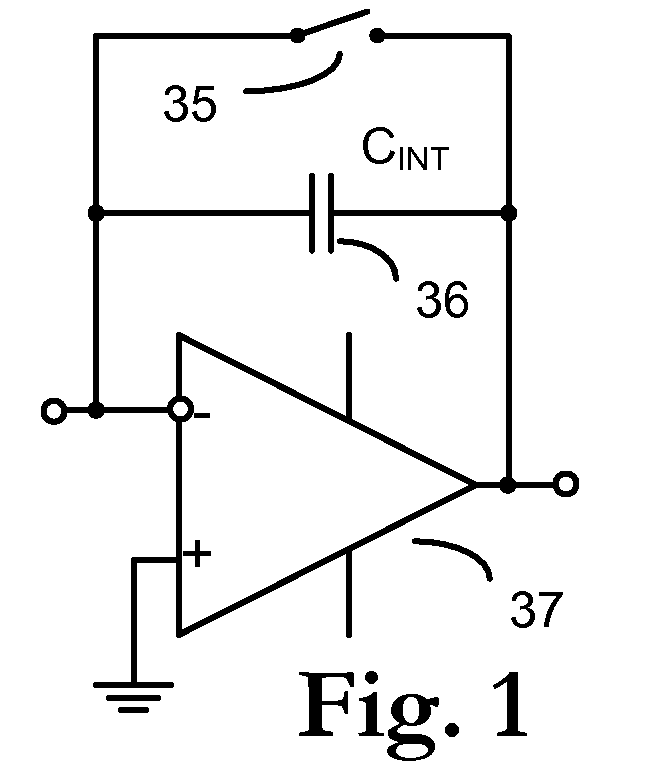
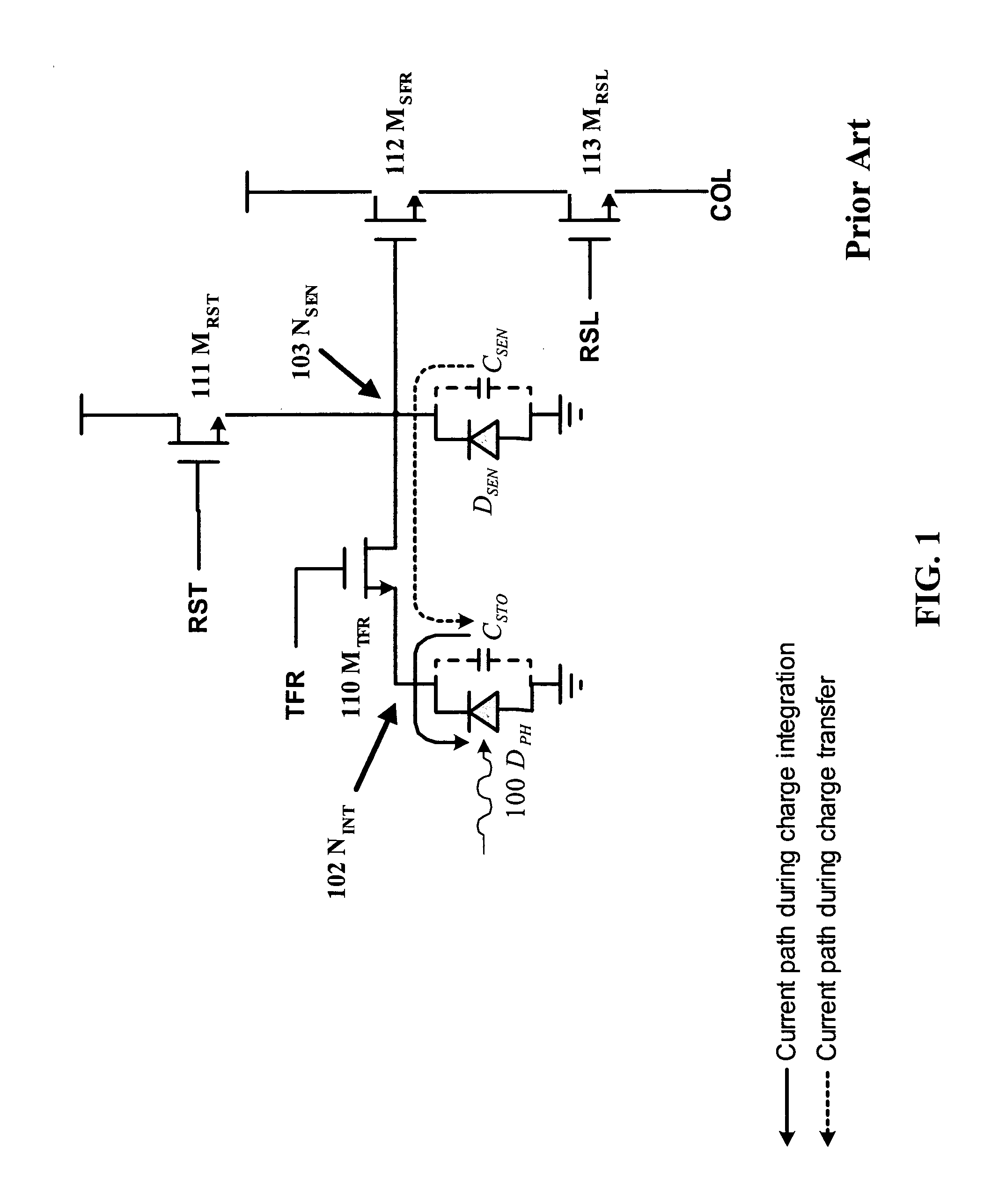
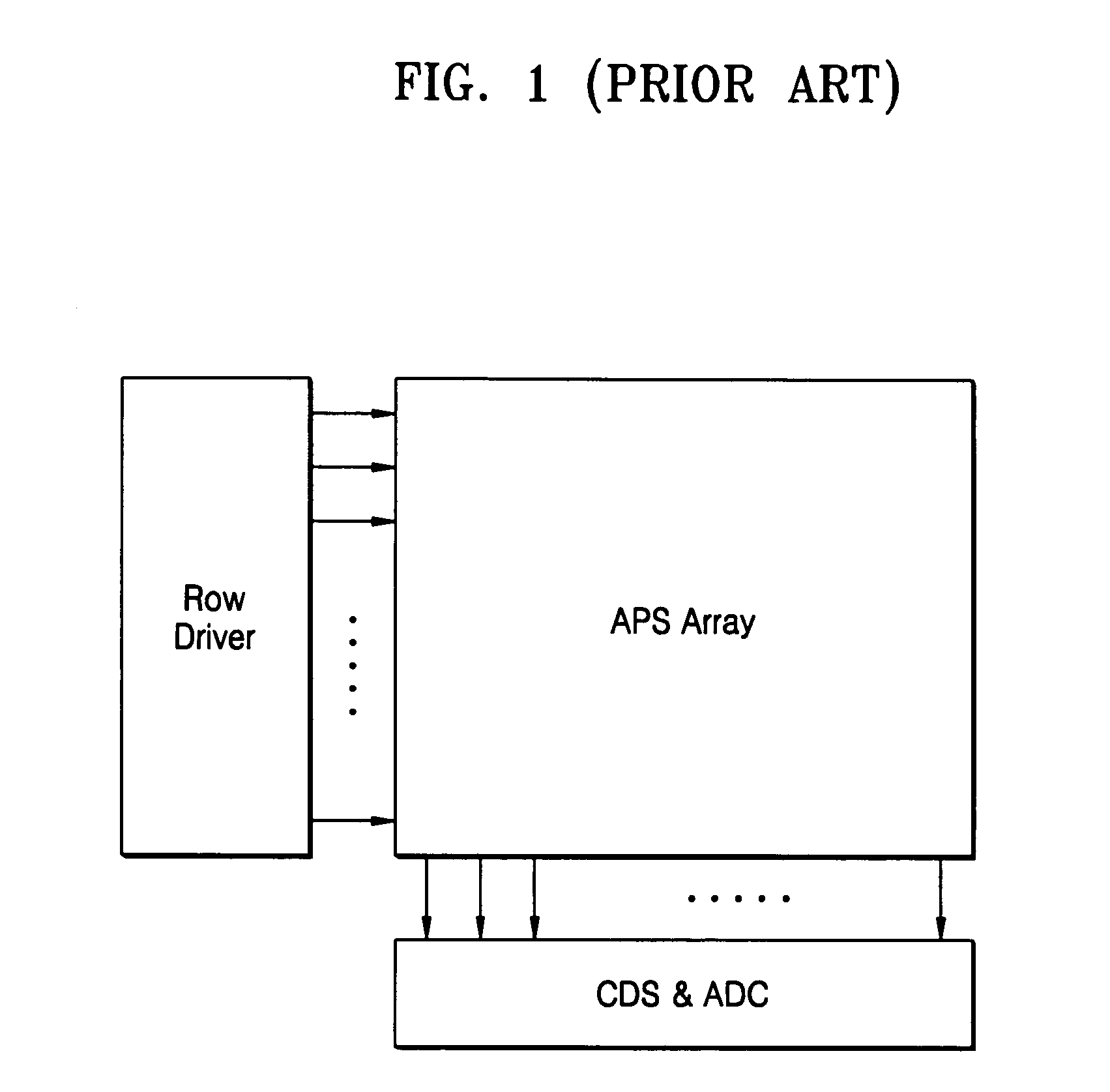
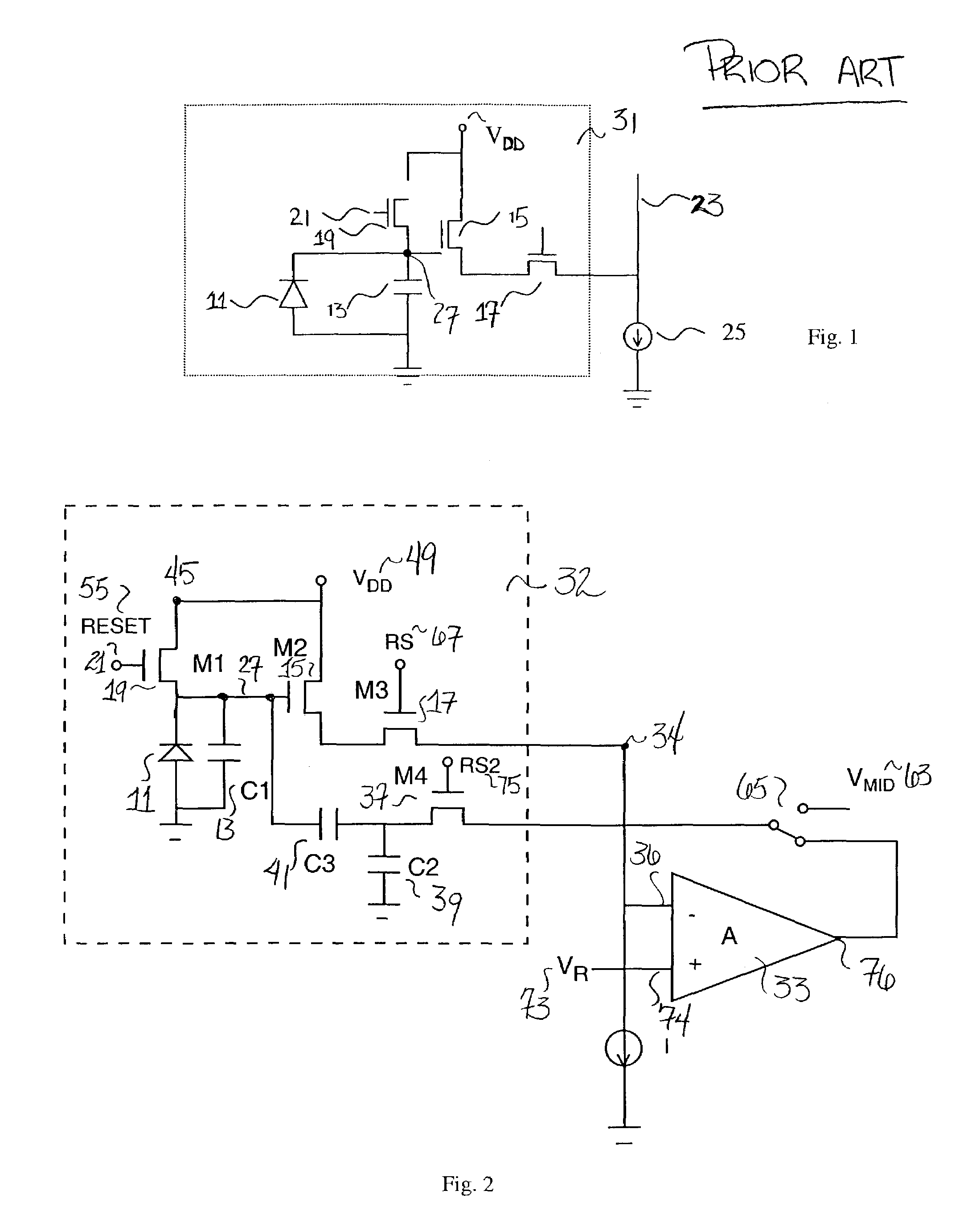
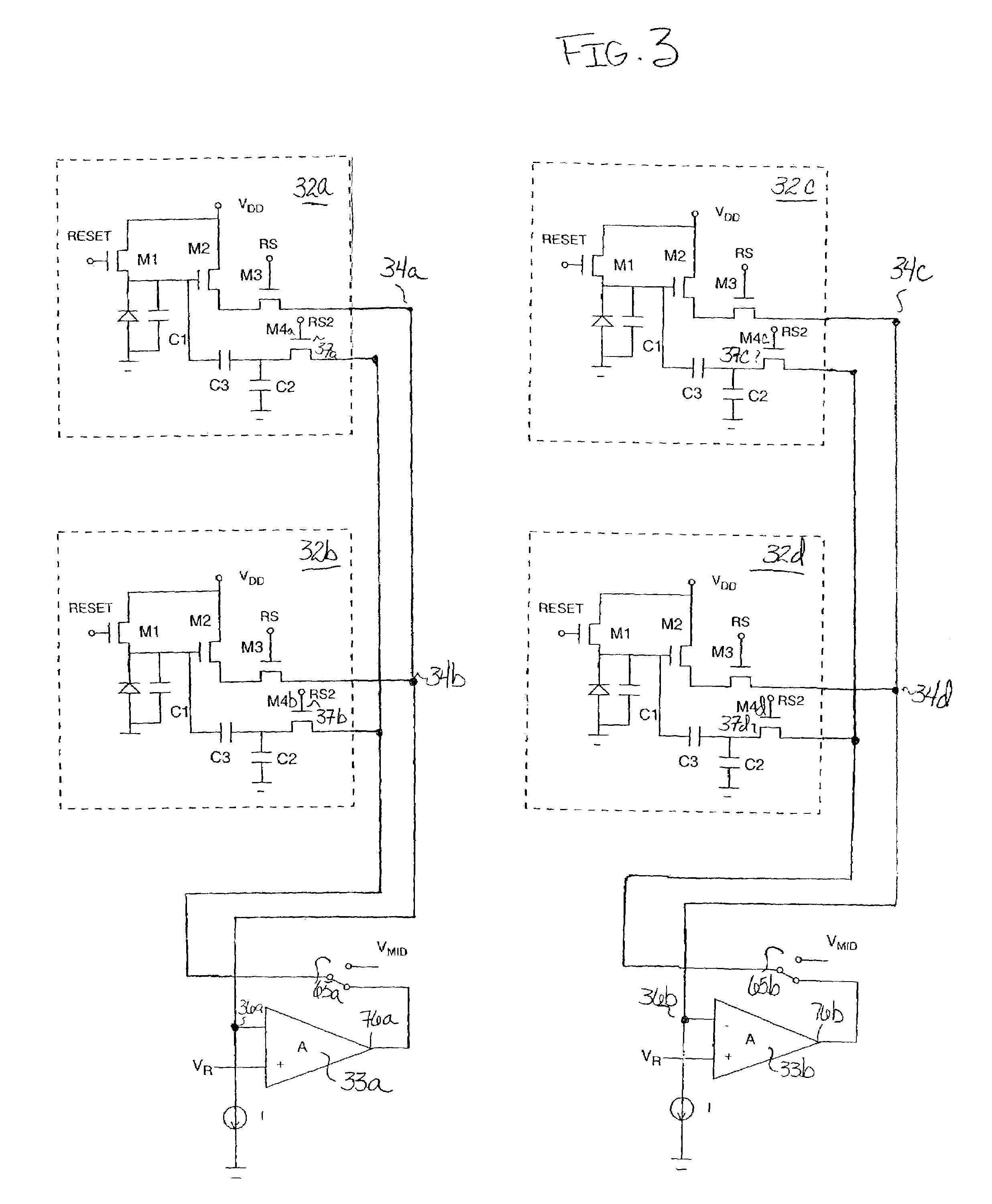
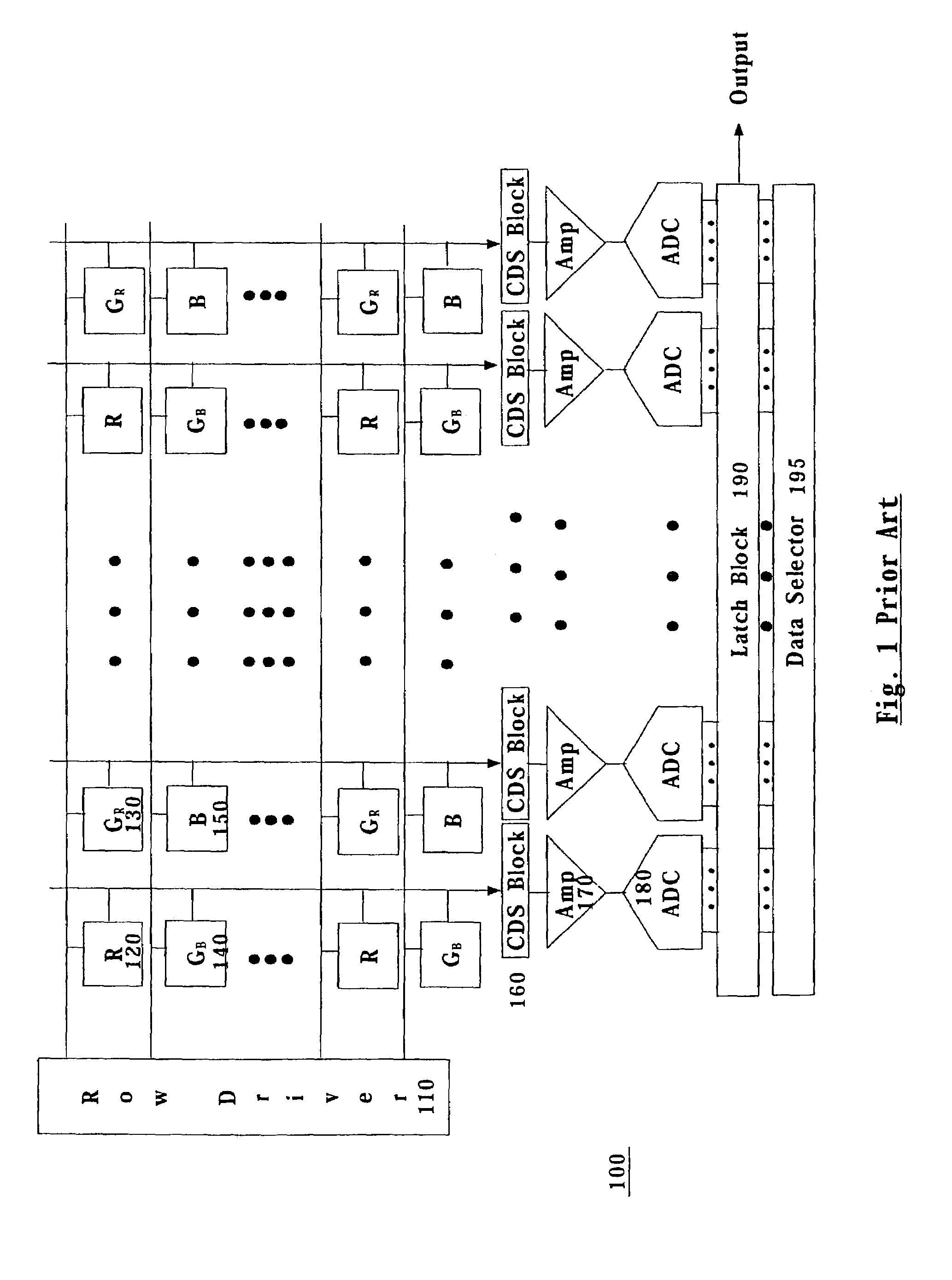
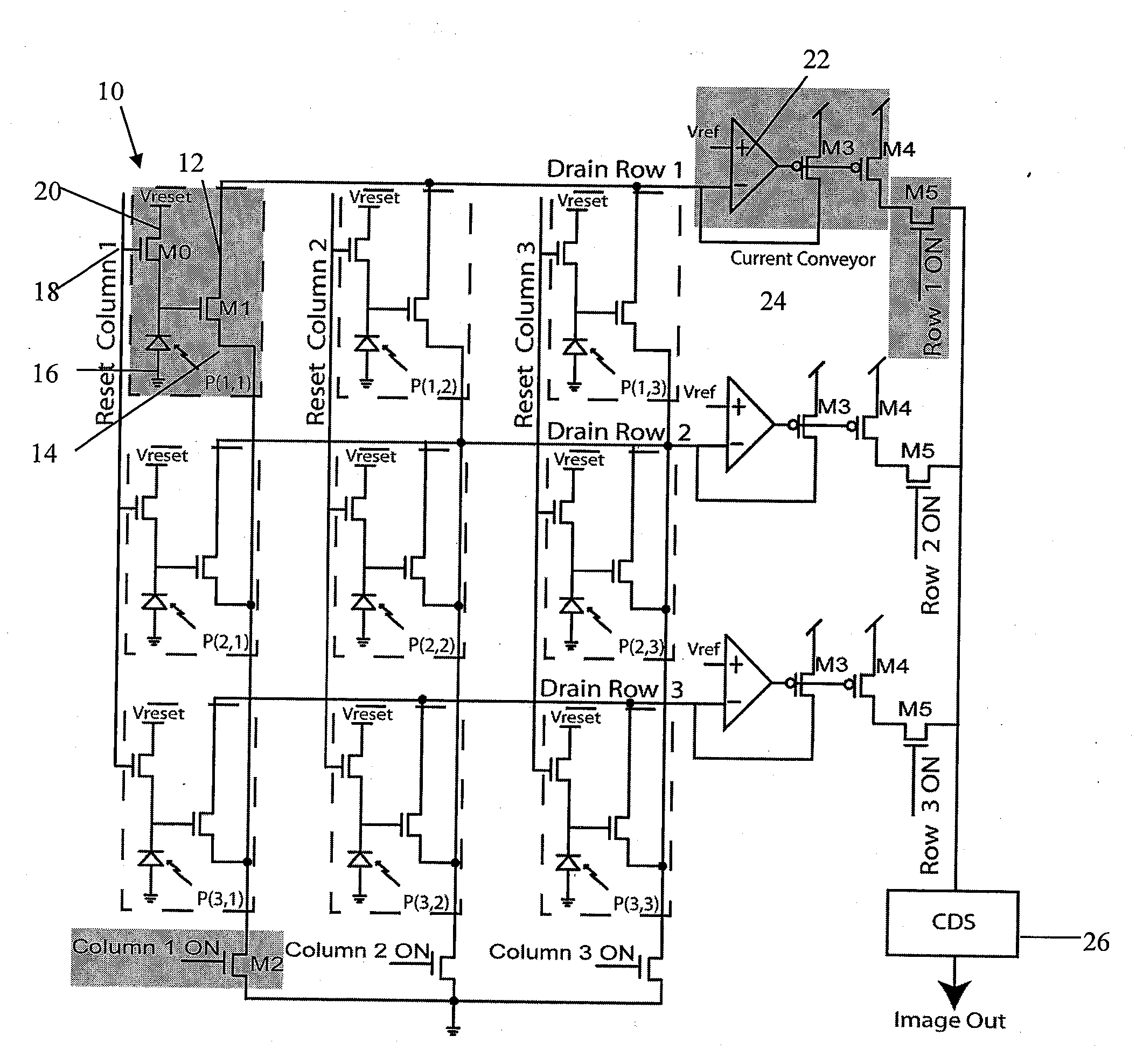
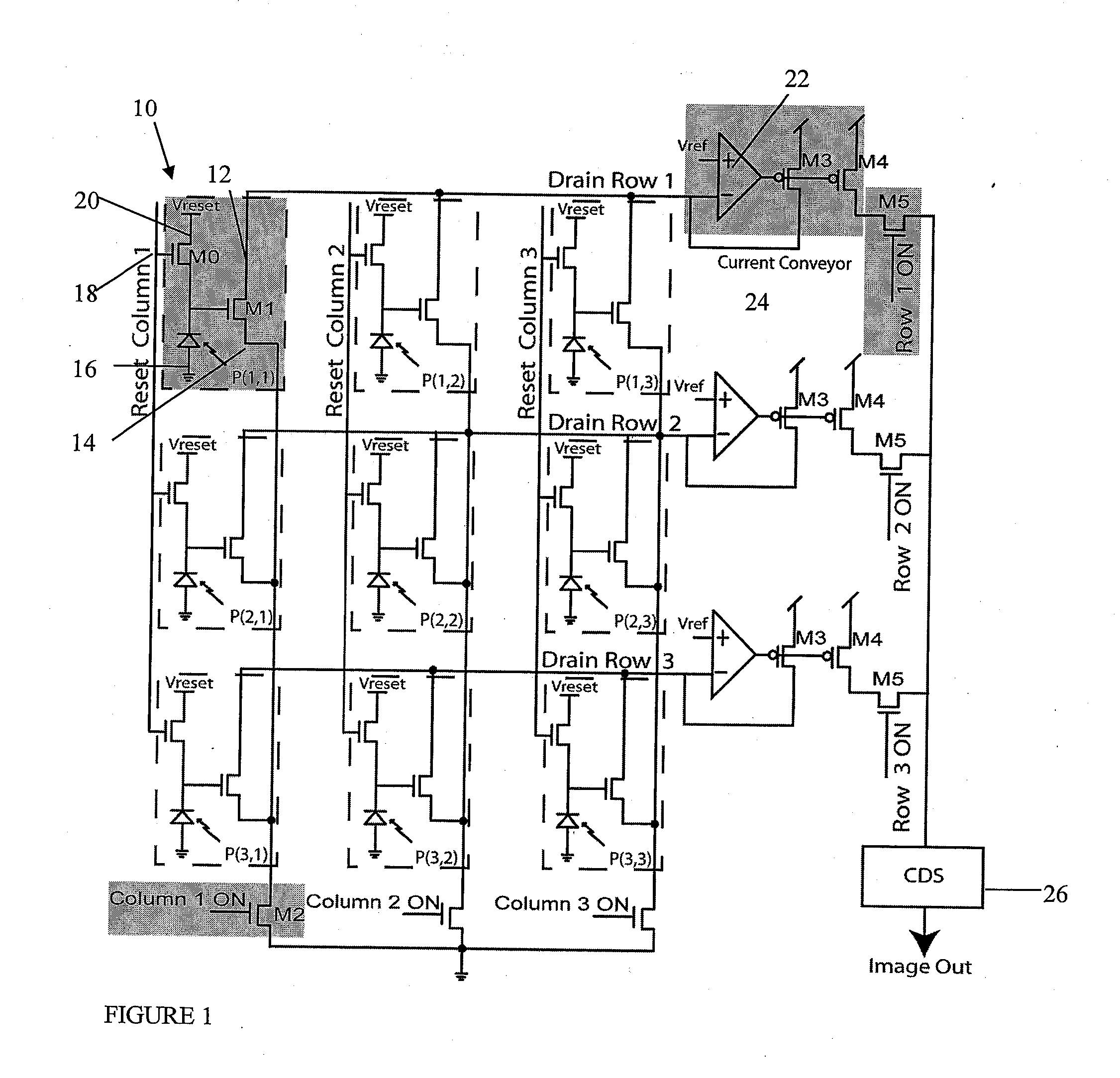
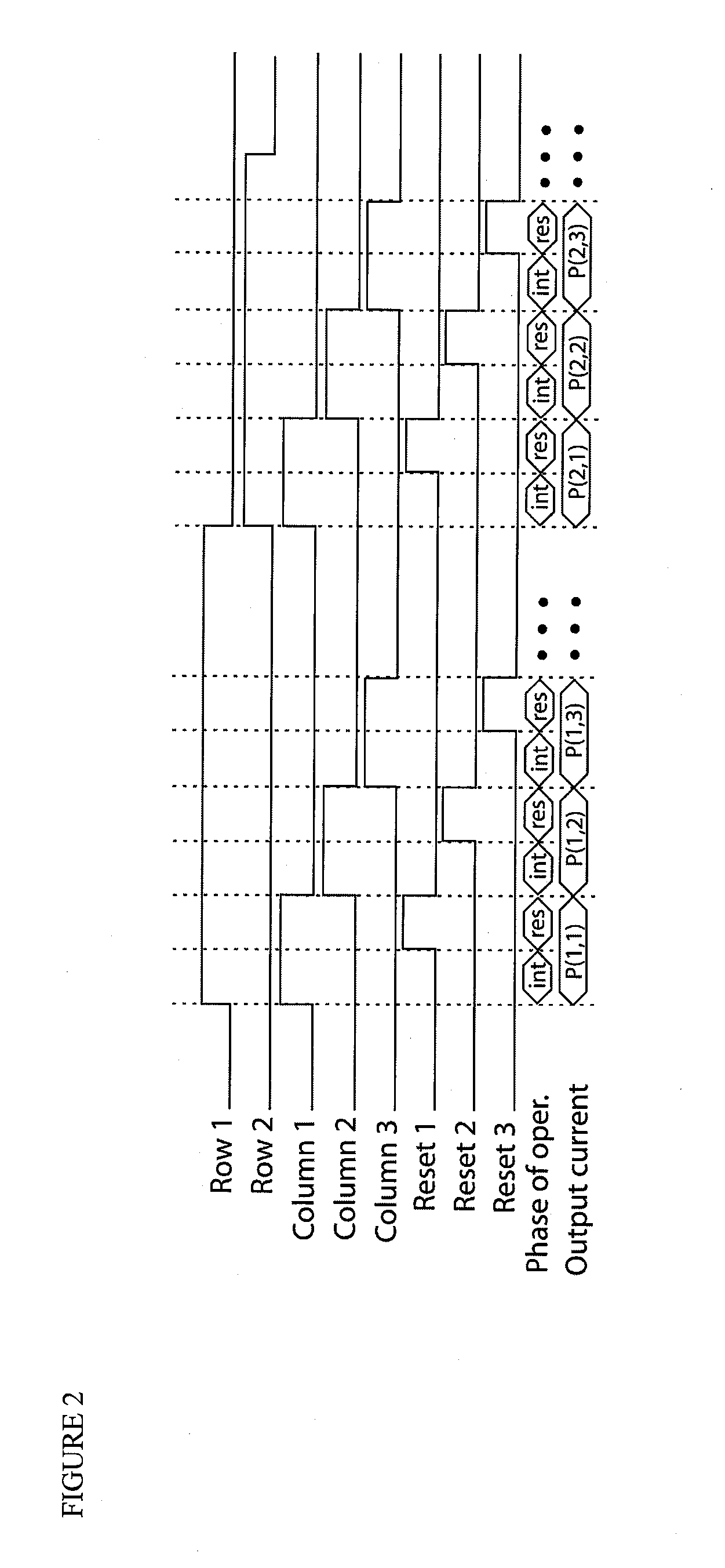
Circuit and method for cancellation of column pattern noise in CMOS imagers
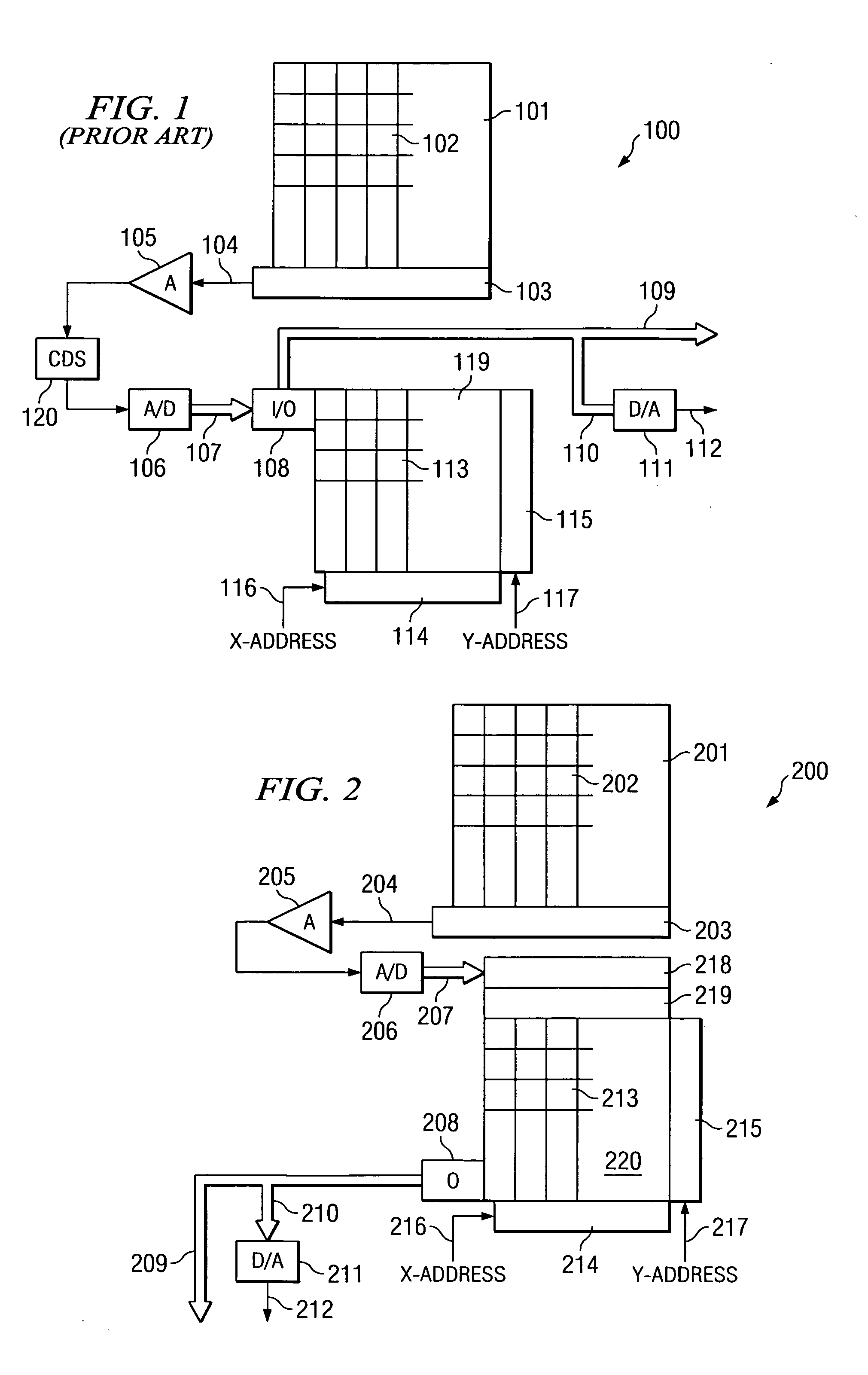
ActiveUS6903670B1Corrects non-linearityCompensating for such errorTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSignal processing circuitsAudio power amplifier
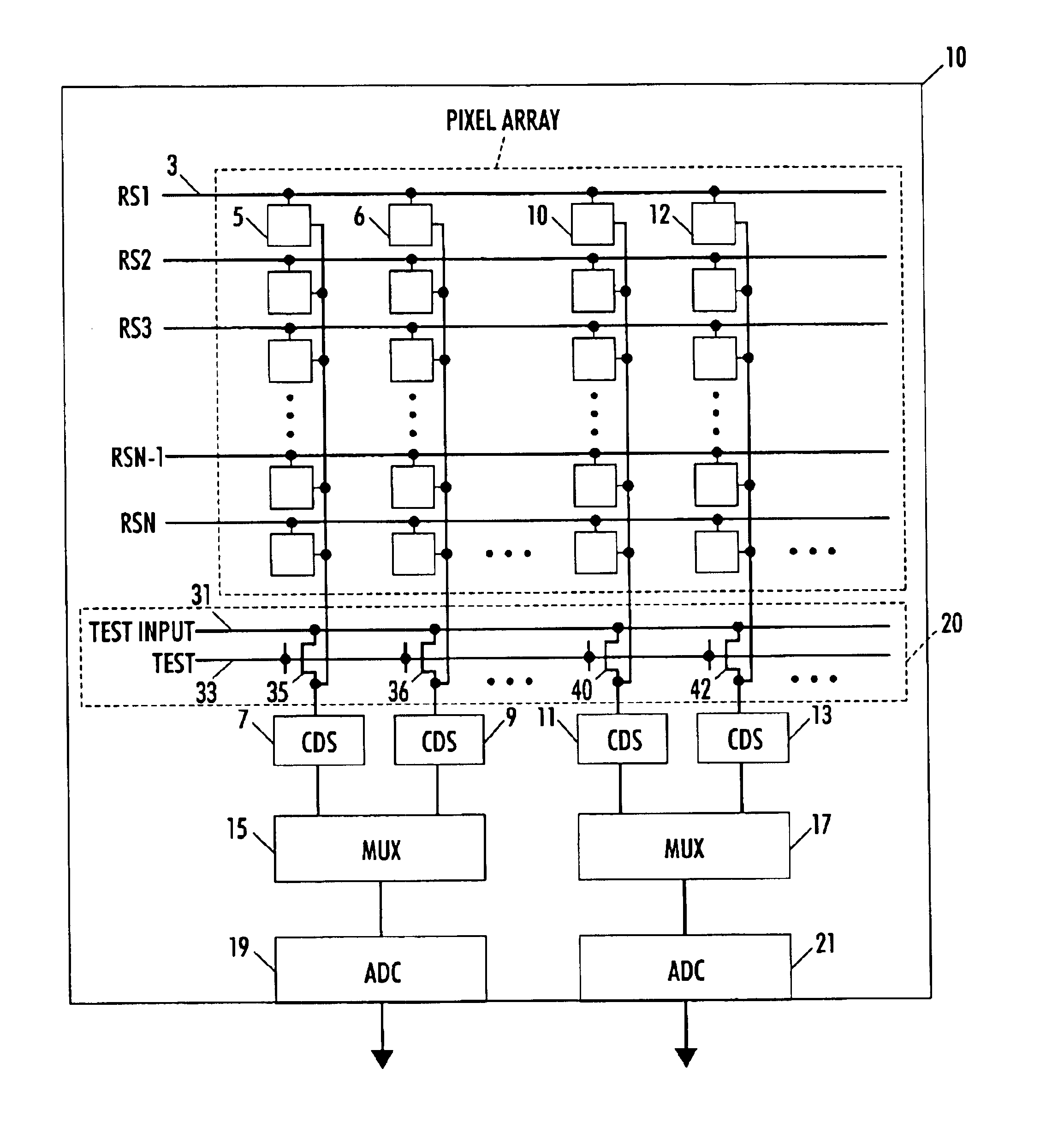
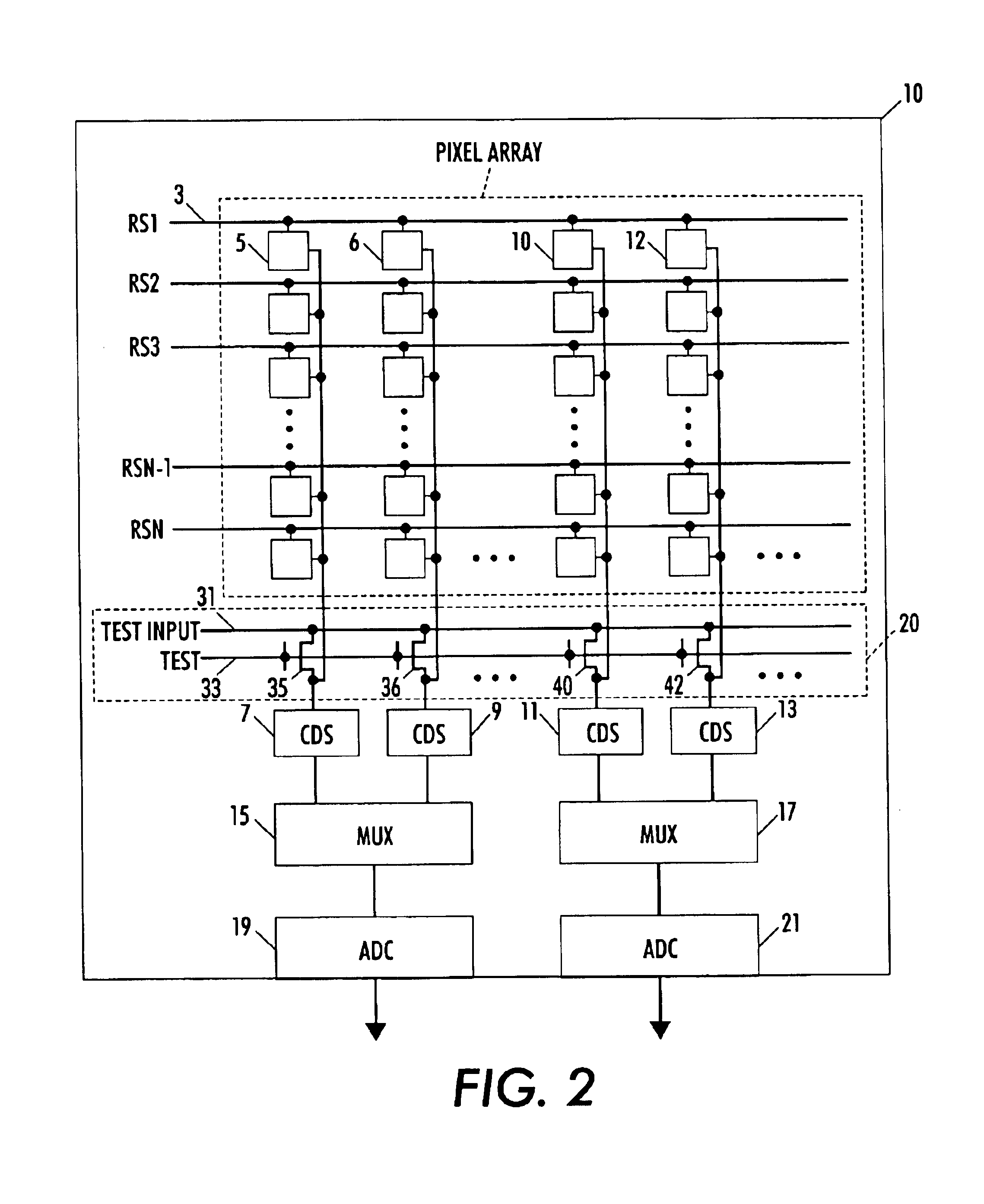
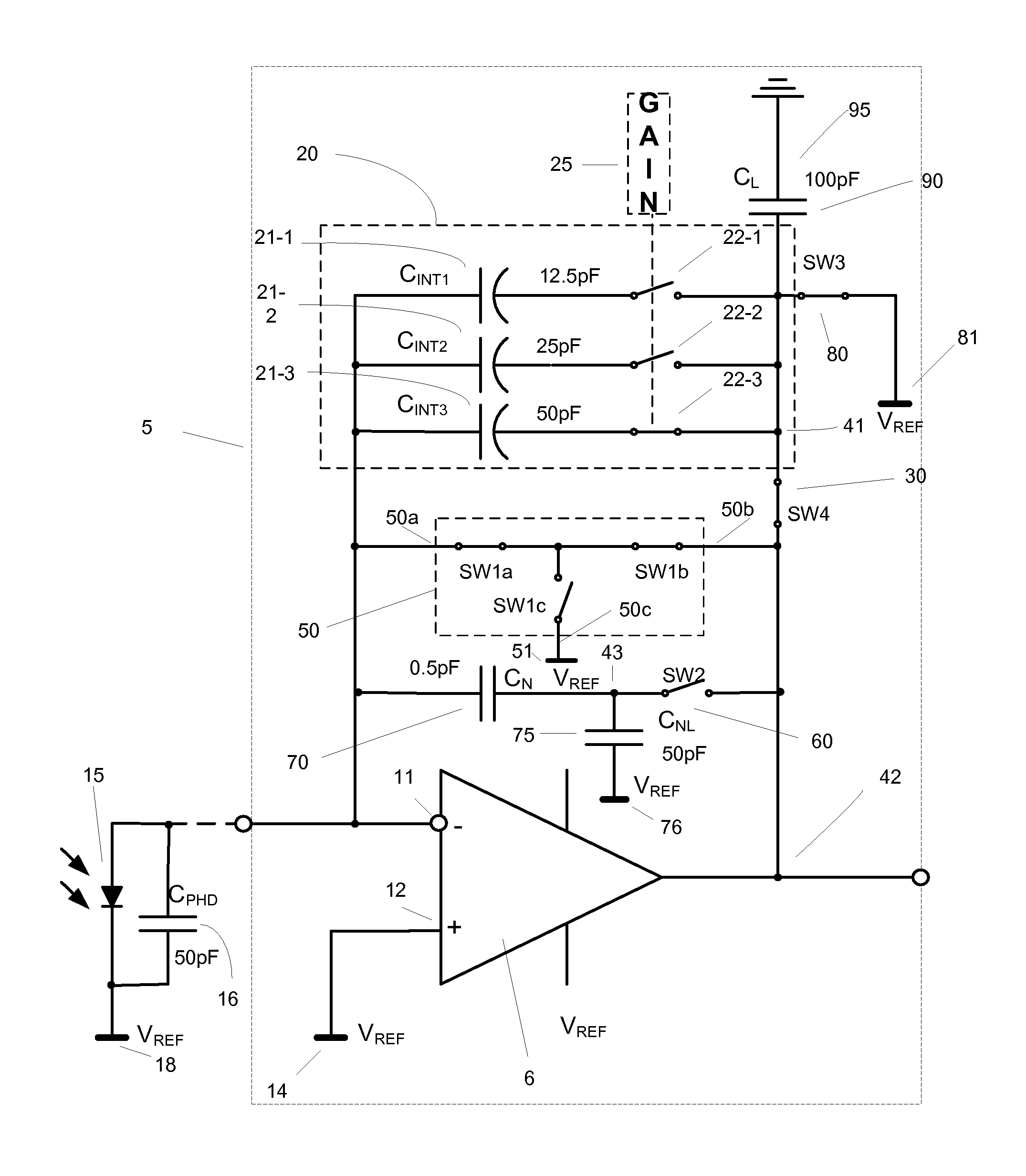
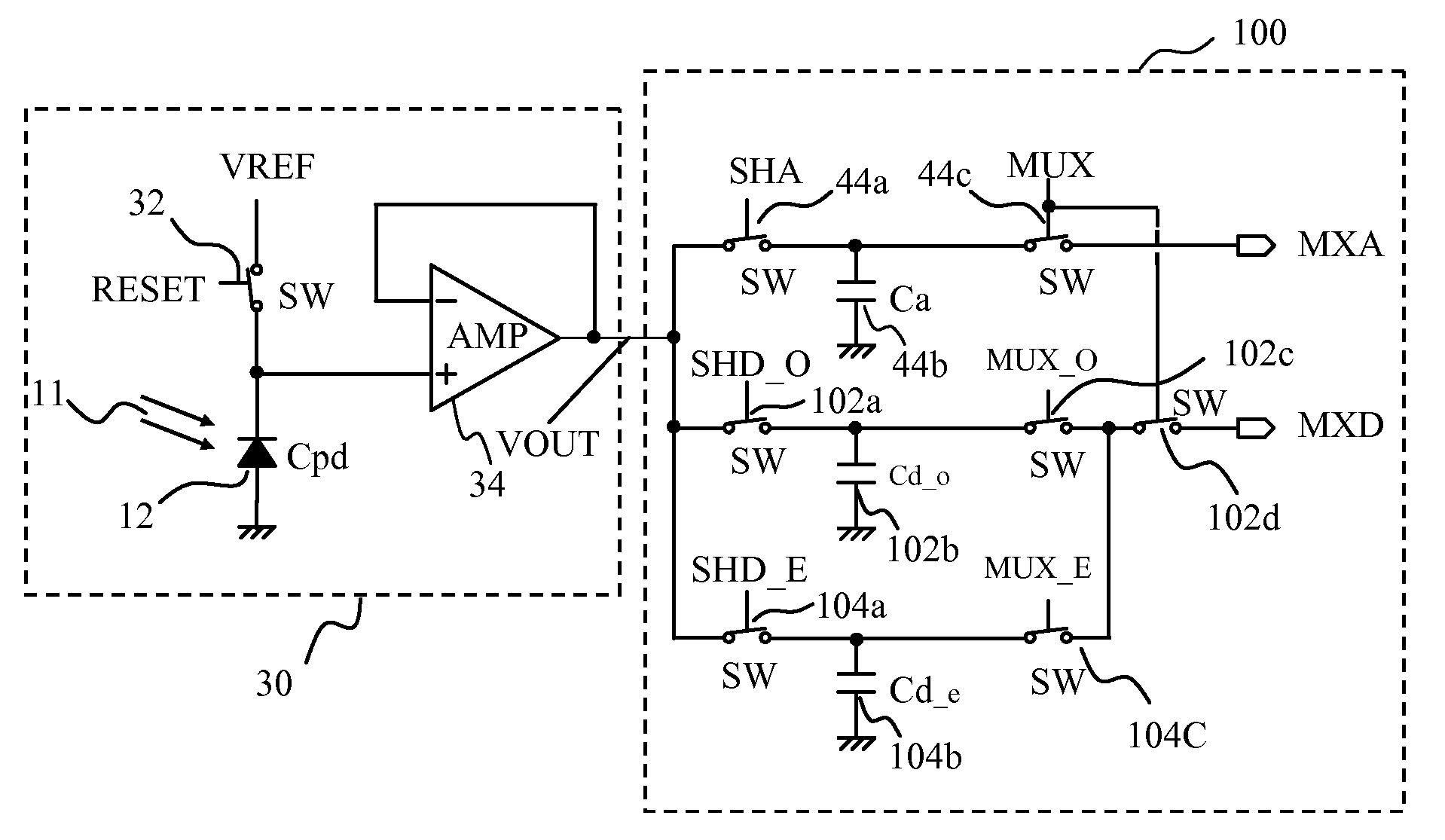
A circuit and method measure the output voltage of a CMOS pixel in a manner that substantially reduces all columnar pattern noise due to mismatches in the signal processing circuits including the correlated double sampling amplifiers and A / D converters. The circuit includes a test switch, operatively connected between a reference voltage source and a correlated double sampling amplifier, for applying a test voltage from the reference voltage source when the state of the test switch is ON to the correlated double sampling amplifier. The reference voltage source produces a voltage corresponding to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of a gain error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; a voltage corresponding to ground to enable the determination of an offset error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; and a plurality of analog voltages ranging from analog ground to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of non-linearity errors in the A / D converter.
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
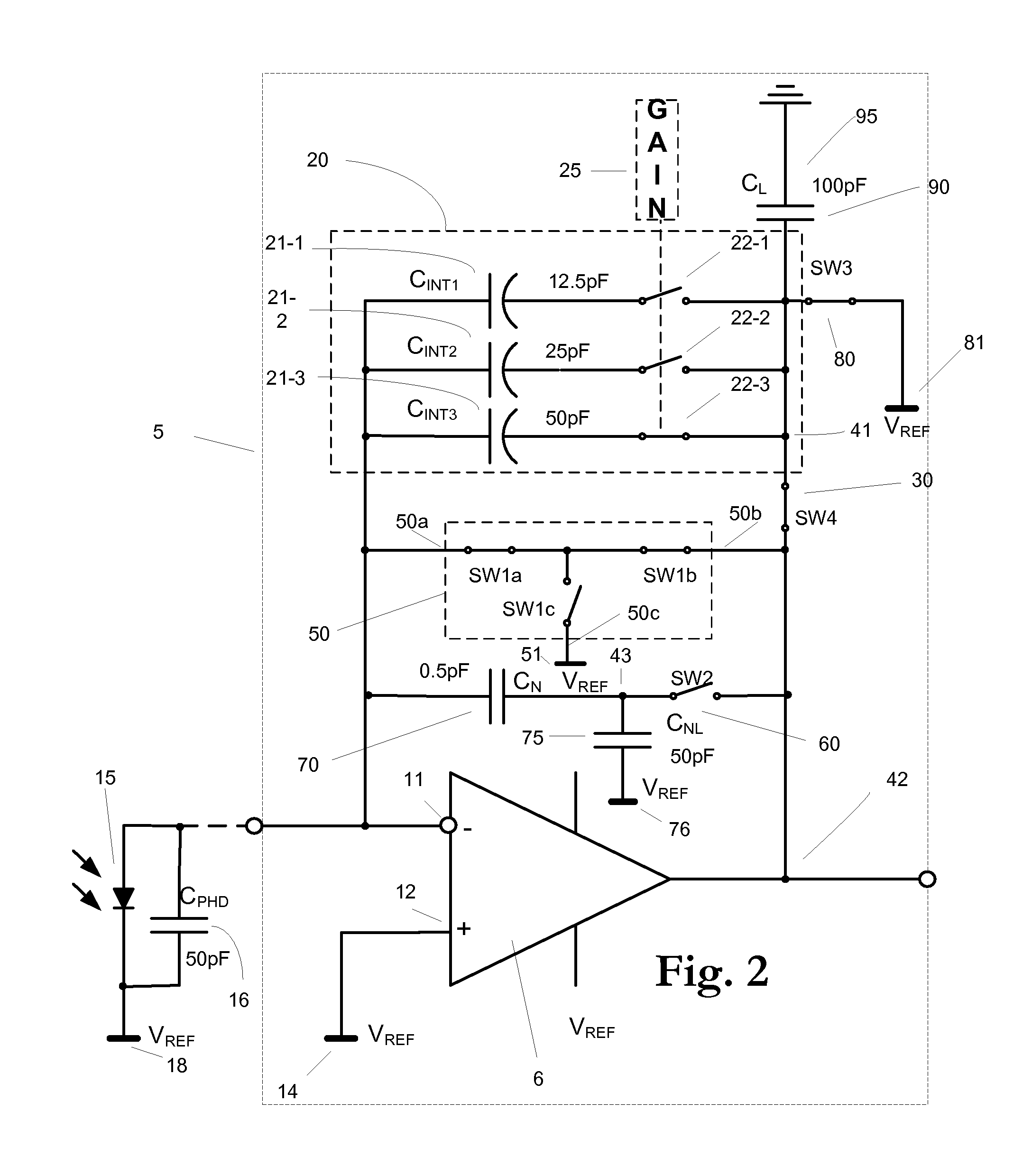
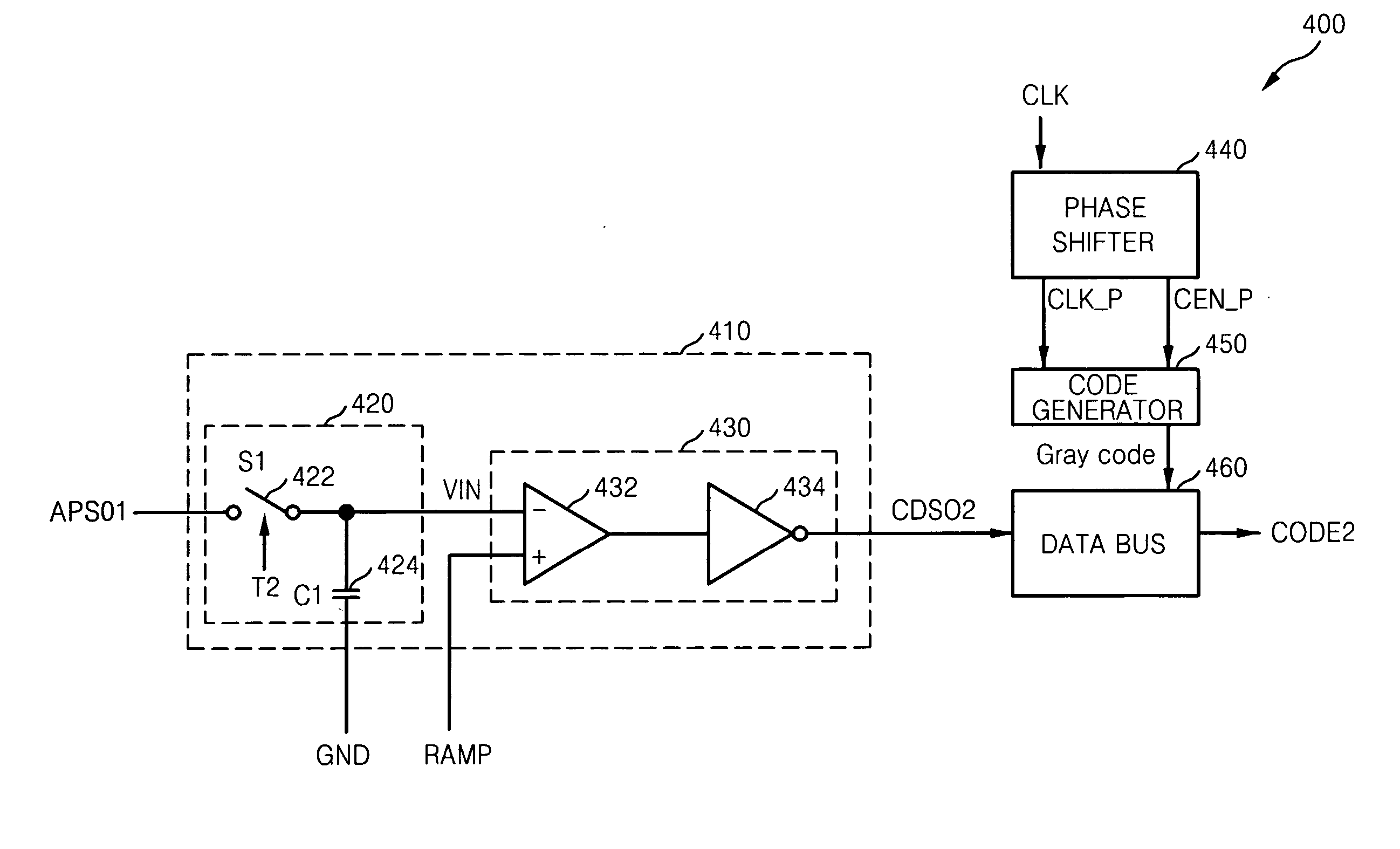
Apparatus for current-to-voltage integration for current-to-digital converter
InactiveUS20090273386A1Reduce charge injectionReduce demandComputing operations for integral formationComputing operations for integration/differentiationDigital down converterIntegrator
Owner:CUSTOM ONE DESIGN
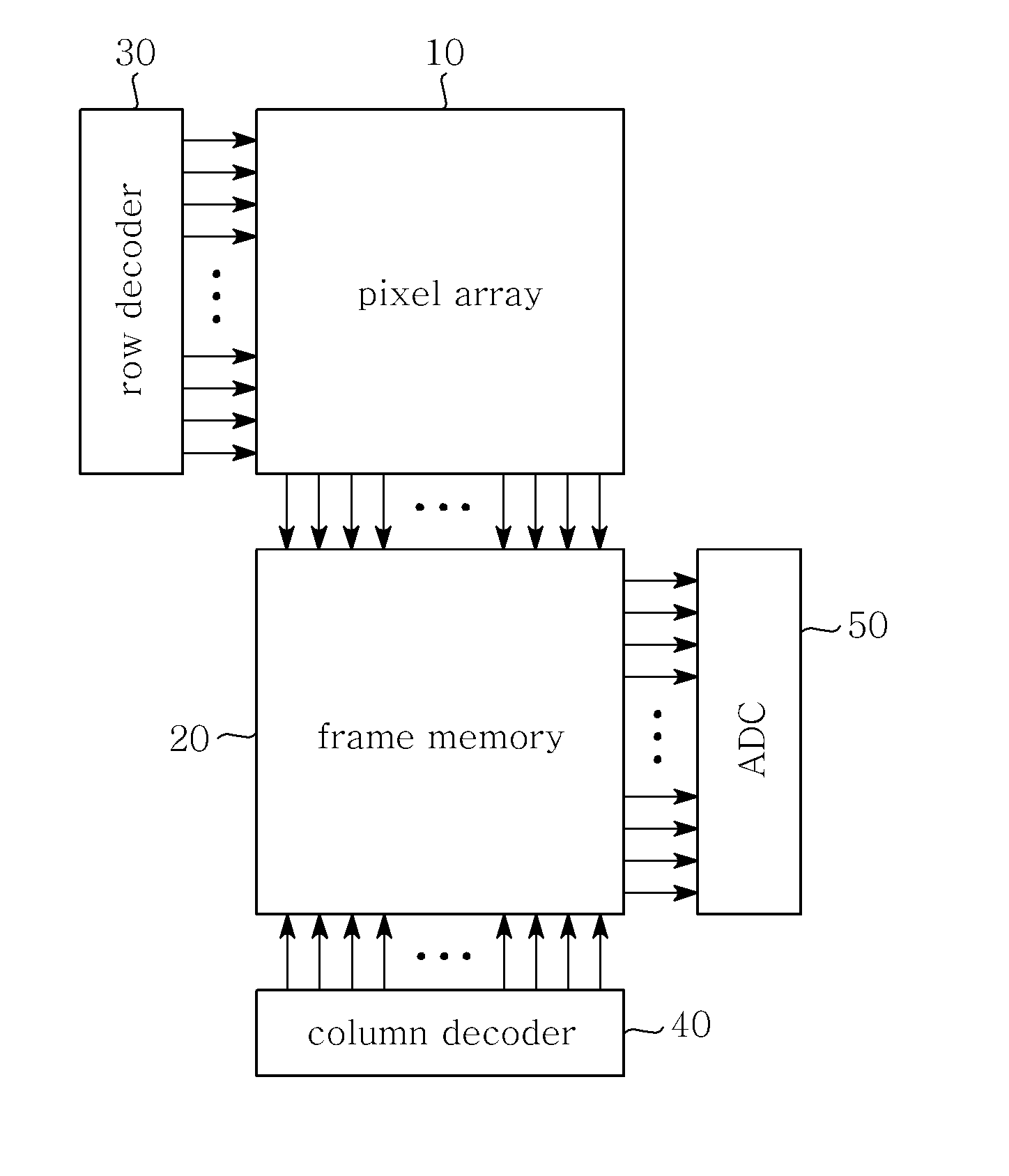
CMOS image sensor
InactiveUS20110194007A1Avoid chargingAvoid noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsEngineeringAnalog signal
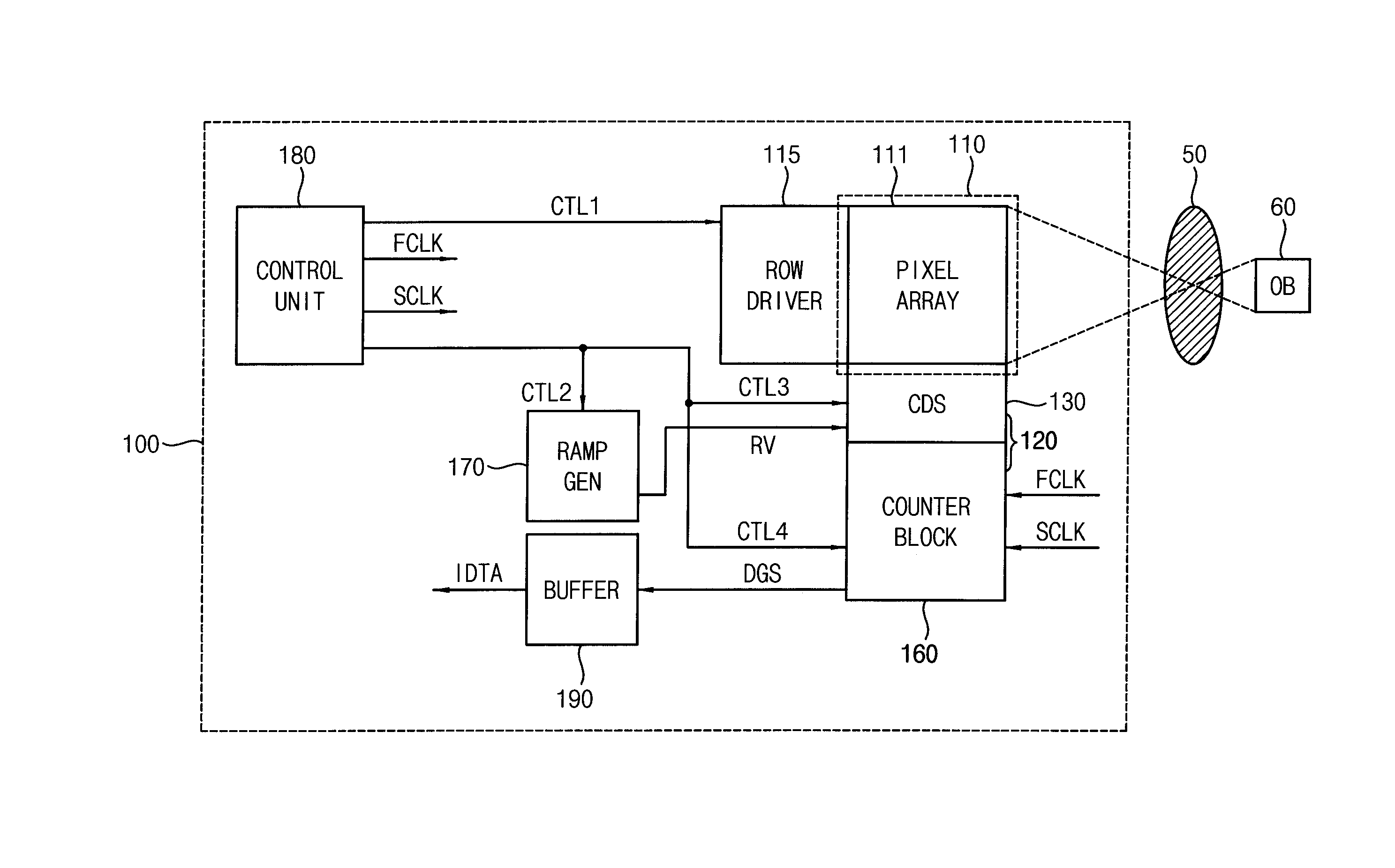
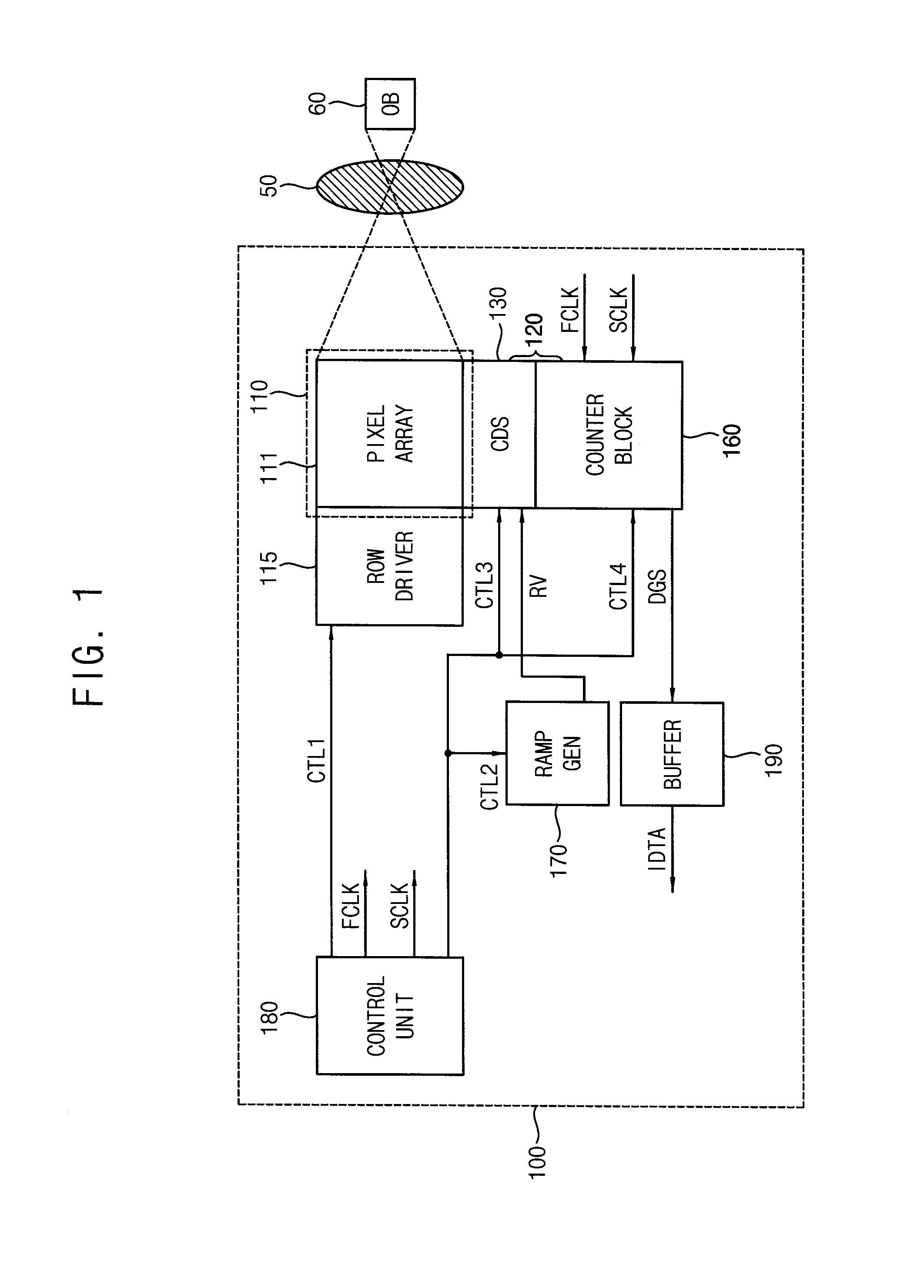
Disclosed herein is a Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) image sensor. The CMOS image sensor includes a pixel array, a frame memory, and an analog-to-digital converter. The pixel array includes N unit pixels for converting optical signals, caused by light, into electric signals. The frame memory eliminates offset voltage included in reset voltage and signal voltage transmitted from the pixel array and internal offset voltage, and performs Correlated Double Sampling (CDS) on the reset voltage and the signal voltage. The analog-to-digital converter converts an analog signal, transmitted from the frame memory, into a digital signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
In-pixel correlated double sampling pixel
InactiveUS20100271517A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPhotodetector
An in-pixel correlated double sampling (CDS) pixel and methods of operating the same are provided. The CDS pixel includes a photodetector to accumulate radiation induced charges, a floating diffusion element electrically coupled to an output of the photodetector through a transfer switch, and. a capacitor-element having an input node electrically coupled to an amplifier and through the amplifier to the floating diffusion element and an output node electrically coupled to an output of the pixel. The capacitor-element is configured to sample a reset value of the floating diffusion element during a reset sampling and to sample a signal value of the floating diffusion element during a signal sampling.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
Multi-resolution Image Sensor Array with High Image Quality Pixel Readout Circuitry
InactiveUS20090091648A1Improve performanceImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayCMOS sensor
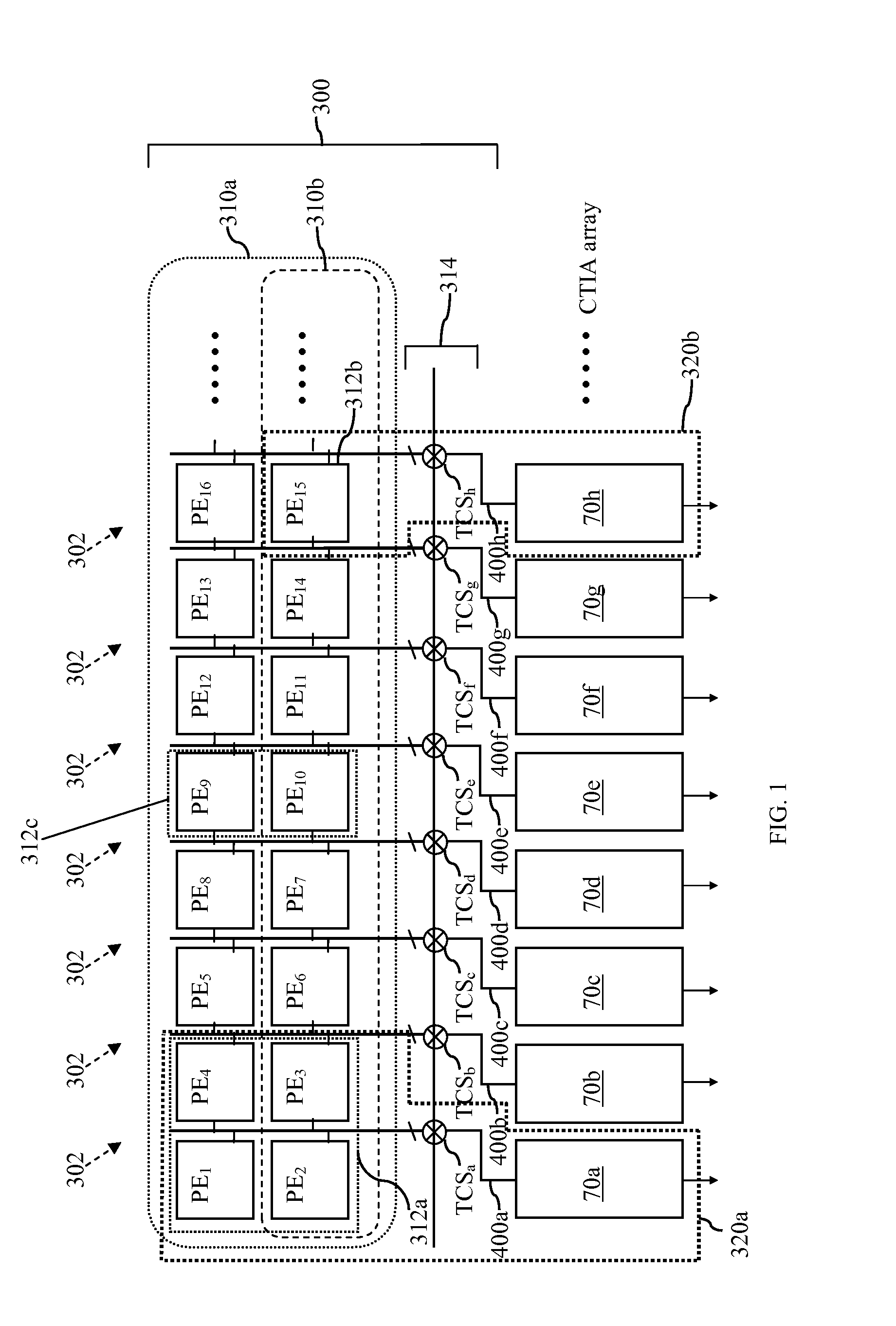
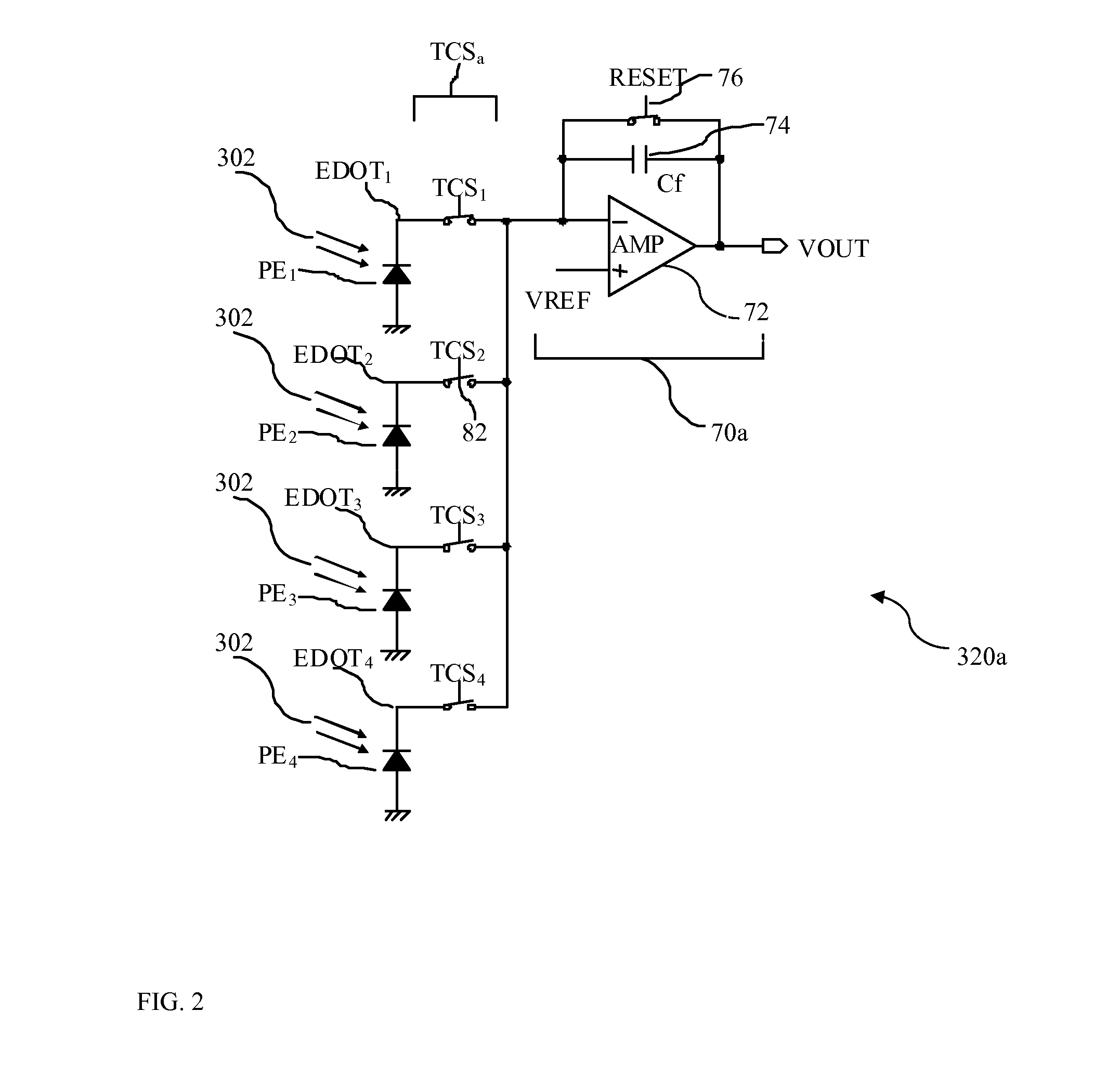
A configurable, compact multi-resolution linear image sensor array is disclosed. The multi-resolution image sensor array employs a spatial array of photoelectric sites with each site having an image output terminal and a cluster of switched photo-detector elements. To effect a high quality snapshot operation mode for a high pixel count array, a transfer control switch is added bridging each photo-detector element and its correspondingly connected negative input terminal of an operational amplifier to form an active pixel sensor circuit. To minimize a reset kTC noise associated with numerous traditional active pixel sensor circuits, an in-pixel KTC noise-correlated correlated multiple sampling (CMS) circuitry is also proposed to replace an otherwise traditional correlated double sampling (CDS) circuitry.
Owner:CMOS SENSOR
Circuit for capacitive touch applications
ActiveUS20110001492A1Reduce in quantityReduce consumptionAnalogue/digital conversionResistance/reactance/impedenceIntegratorLow-pass filter
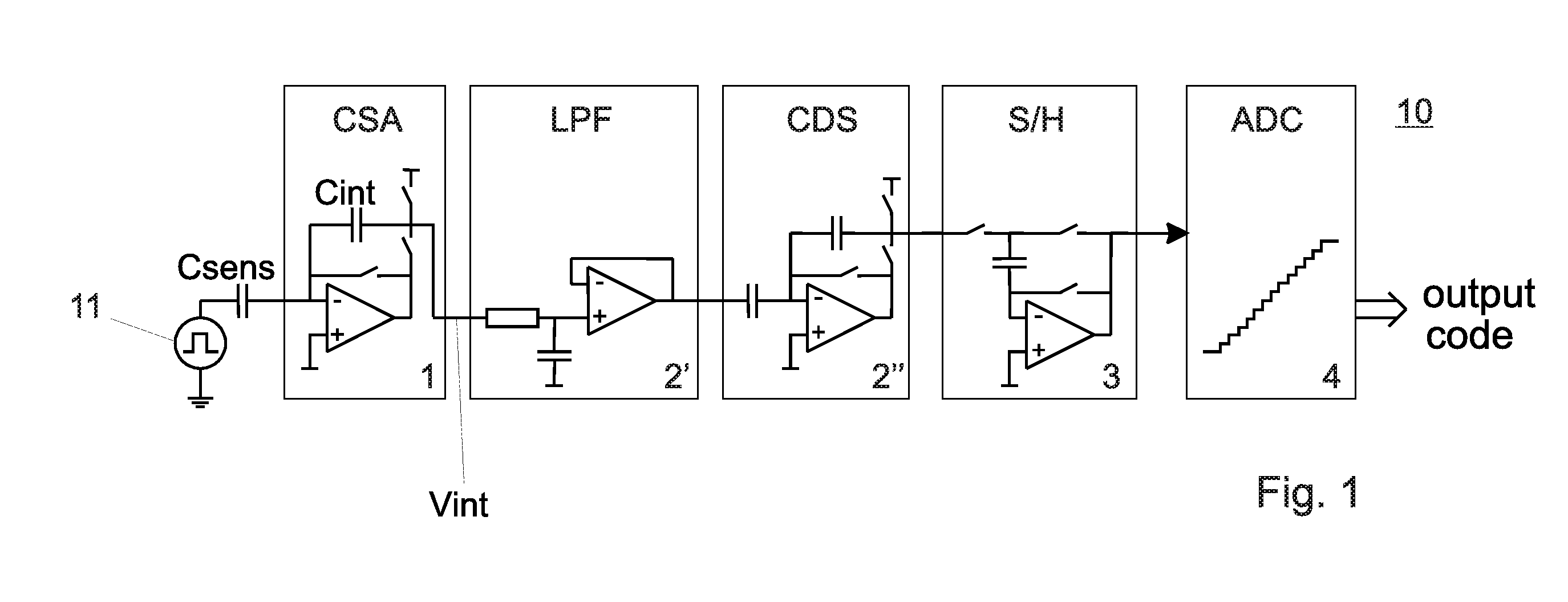
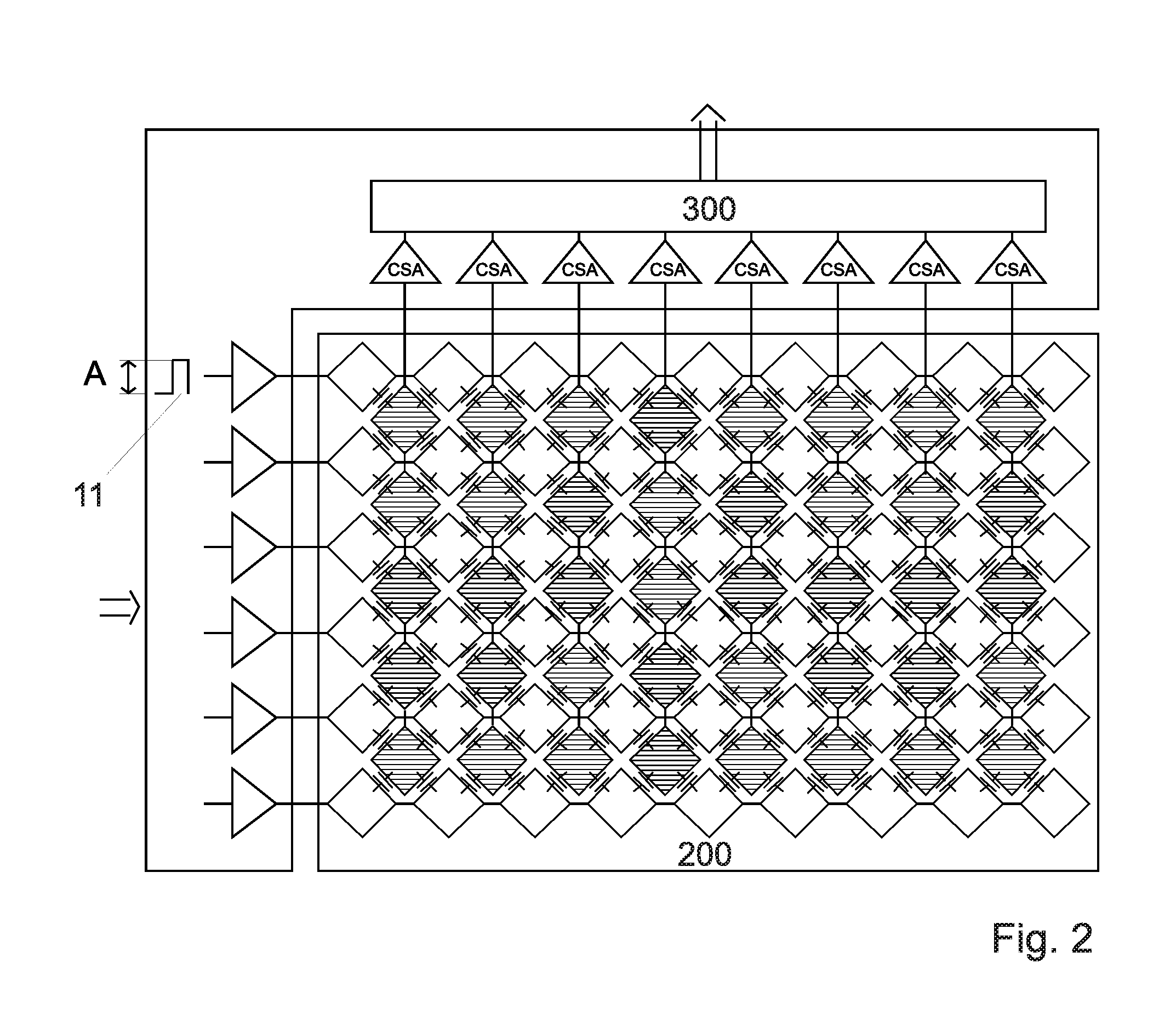
A circuit for capacitive touch applications comprisinga charge integratora low pass-filtera correlated double sampler comprising an input capacitora sampler and holderan analog to digital convertersaid low pass-filter having a cut-off frequency lower than the Nyquist frequency of the sampler and holdersaid low pass filter comprising said input capacitor and a serial resistor.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON
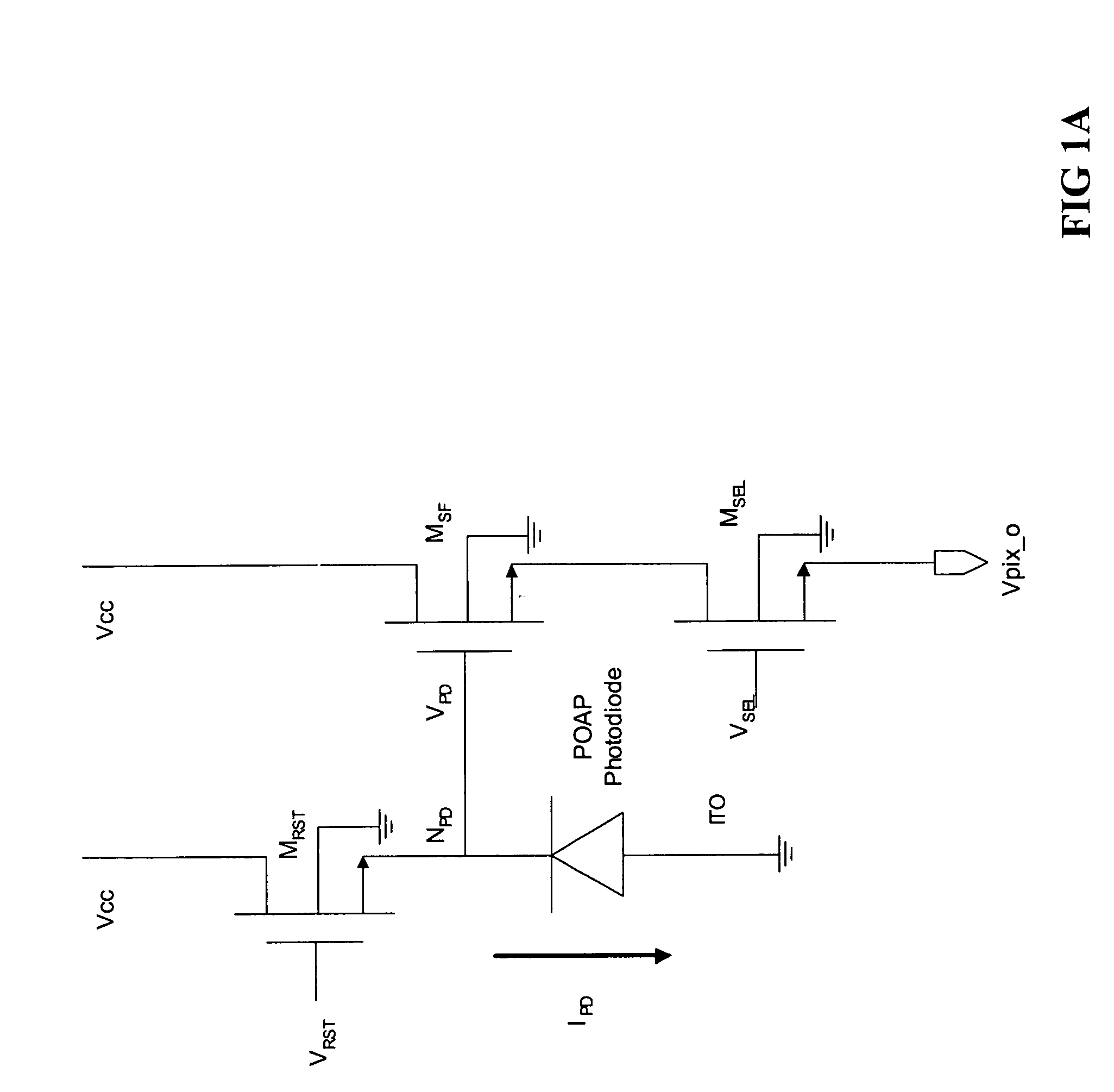
CMOS sensor with approximately equal potential photodiodes
InactiveUS20090224351A1Minimize and eliminate dark currentReduce and eliminate clock noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorCharge detection
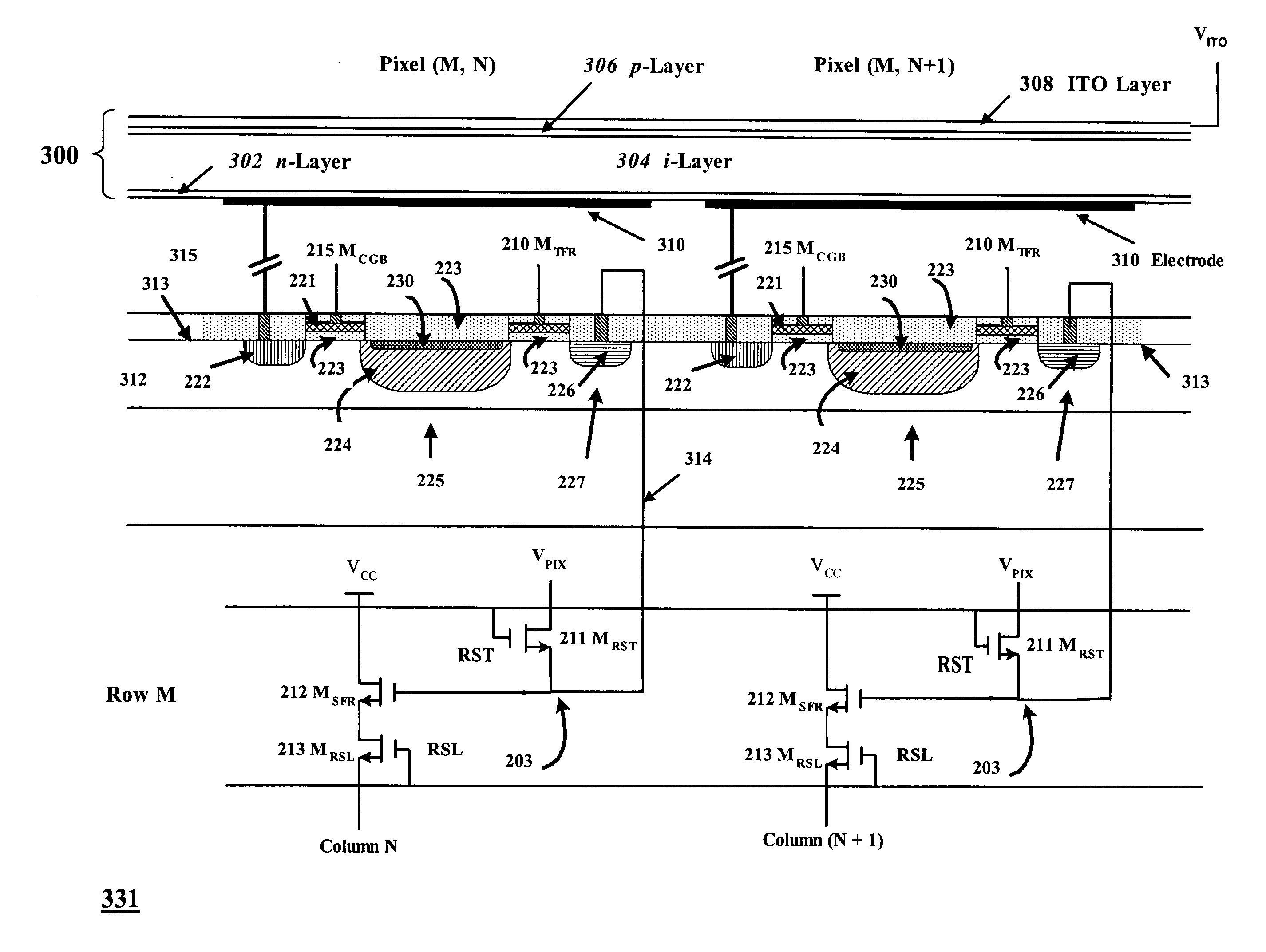
A MOS or CMOS based active pixel sensor designed for operation with zero or close to zero potential across the pixel photodiodes to minimize or eliminate dark current. In this preferred embodiment, the voltage potential across the pixel photodiode structures is maintained constant and close to zero, preferably less than 1.0 volts. This preferred embodiment enables the photodiode to be operated at a constant bias condition during the charge detection cycle. In preferred embodiments the pixel photodiodes are produced with a continuous pin or nip photodiode layer laid down over pixel electrodes of the sensor. In other preferred embodiments the pixel photodiode structures are produced beside and physically isolated from the regions where CMOS circuits are formed. In some of these preferred embodiments the isolated pixel photodiode structures are comprised of crystalline germanium deposited in cavities in a silicon substrate. This embodiment can be adapted especially for imaging at short wave infrared frequencies. Preferred embodiments are adapted for correlated double sampling.
Owner:E PHOCUS
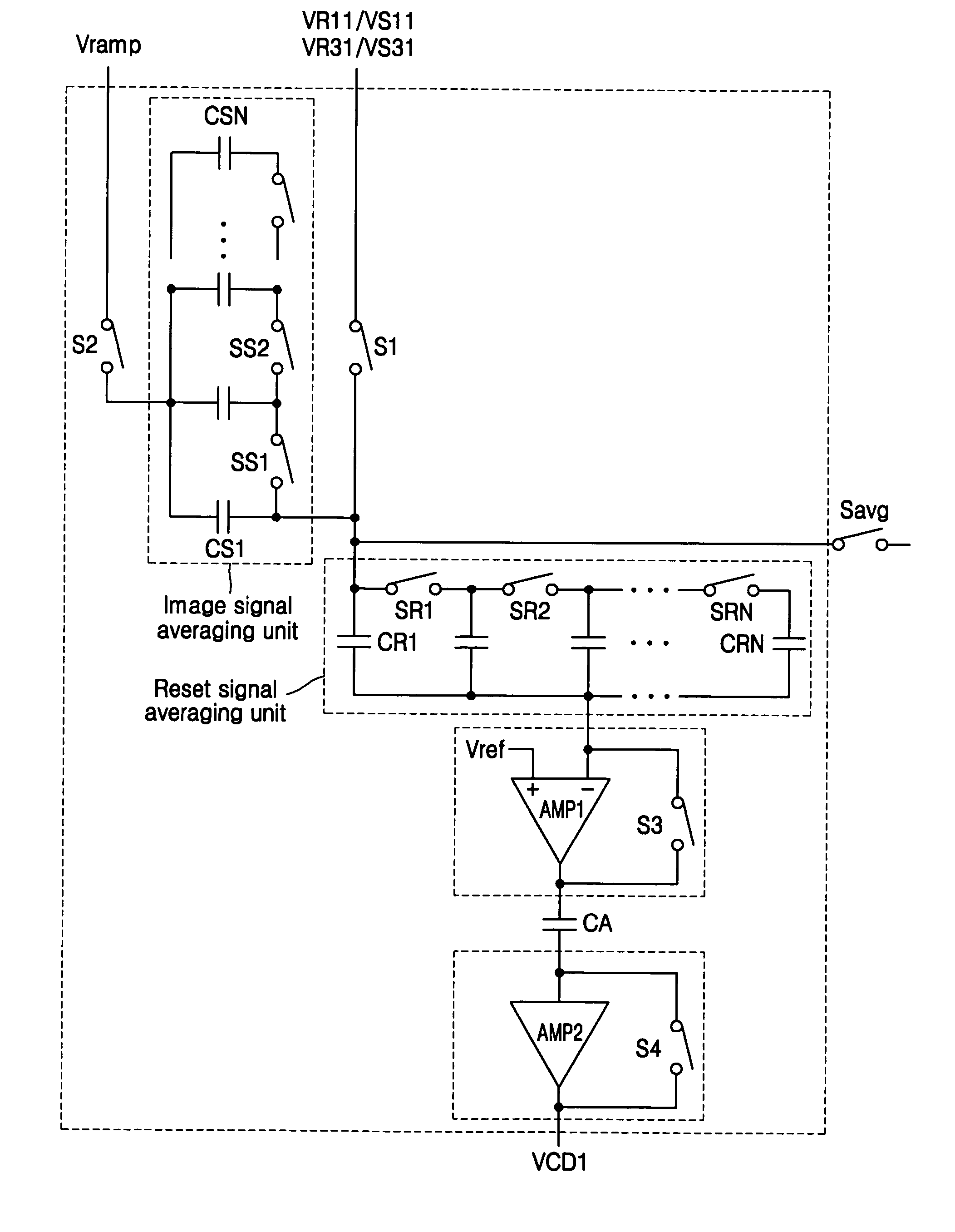
Method and circuit for performing correlated double sub-sampling (CDSS) of pixels in an active pixel sensor (APS) array
ActiveUS20050206752A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorSensor array
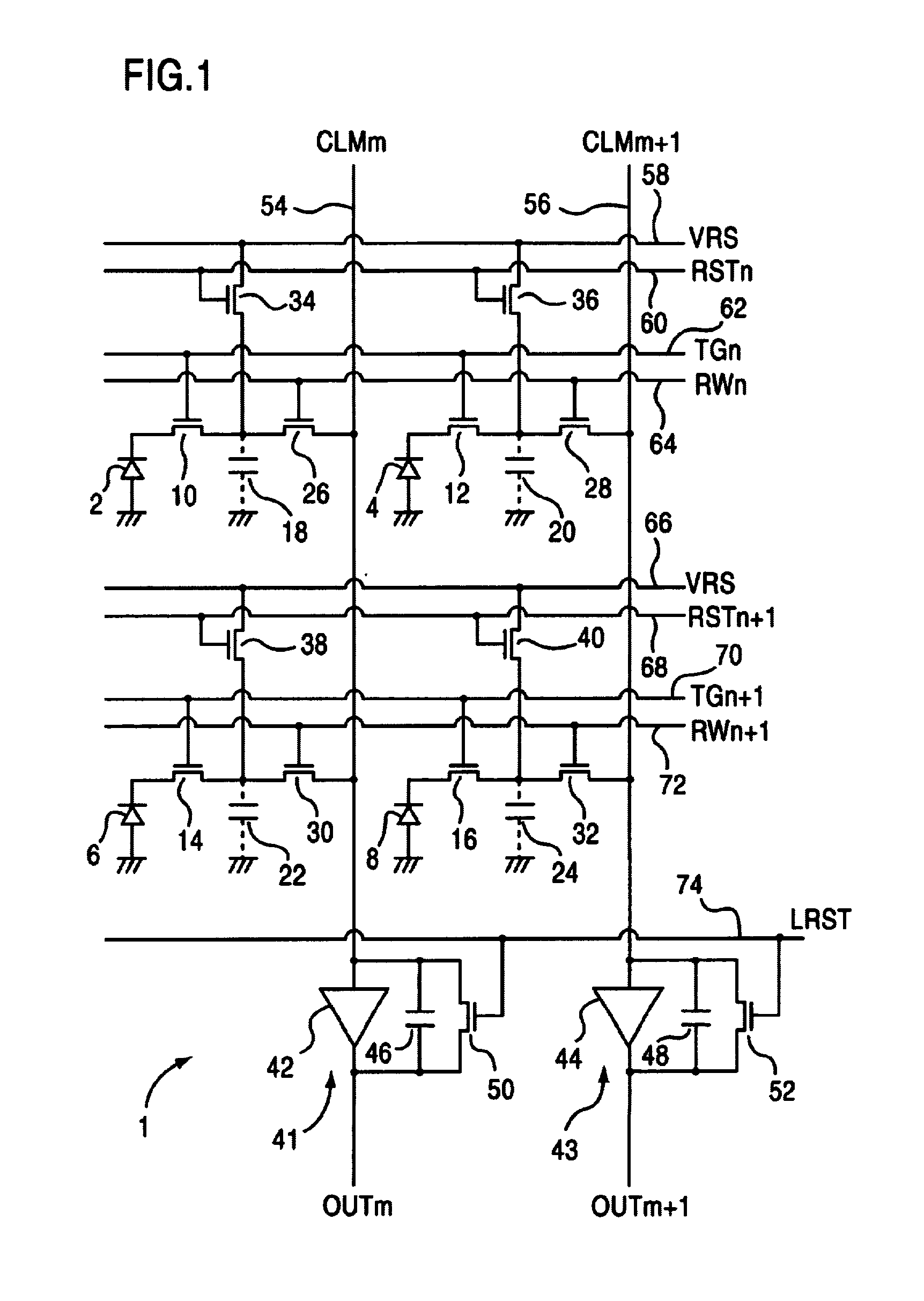
A method and circuit for performing Correlated Double Sub-Sampling (CDSS) of pixels in an active pixel sensor (APS) array. Each pixel outputs a reset voltage and then an image signal voltage. The method and the apparatus subsamples a plurality (L2 ) of pixels by: storing L2 analog reset charges output from the L2 pixels into a first set of (N2) storage capacitors, and combining the (L2) reset charges; storing L2 analog image signal charges output from the L2 pixels into a second set of (N2) storage capacitors, and combining the (L2) image charges; and then obtaining a differential voltage (VS−VR) by subtracting (in the analog-domain) the voltage (VR) represented by the combined (L2) reset charges from the voltage (VS) represented by the combined (L2) image signal charges. When L equals one, the circuit performs conventional Correlated Double Sampling CDS upon the one pixel. When L is greater than one, the circuit performs Correlated Double Sub-Sampling (CDSS) of the L2 pixels. Dynamic selection of a subsampling ratio B (where B equals 1:L2 and L ranges from 1 up to N) is supported. Averaging units used to combine the reset and image signal charges, and analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) for converting the differential voltage to a digital pixel data, may be commonly biased by the same variable bias voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Solid-state imaging device with the elimination of thermal noise
InactiveUS6975356B1Reduce the impactReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierCapacitor
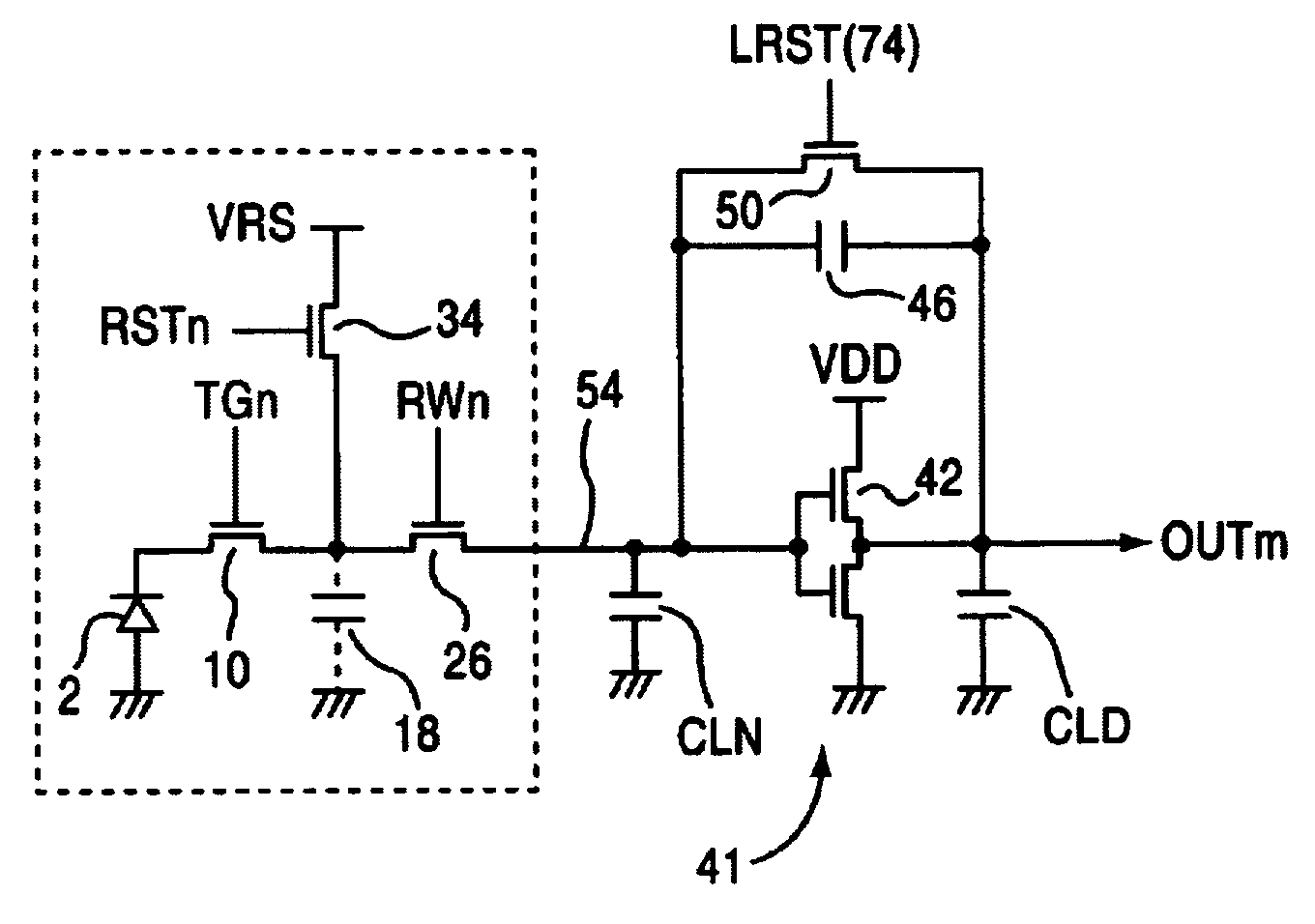
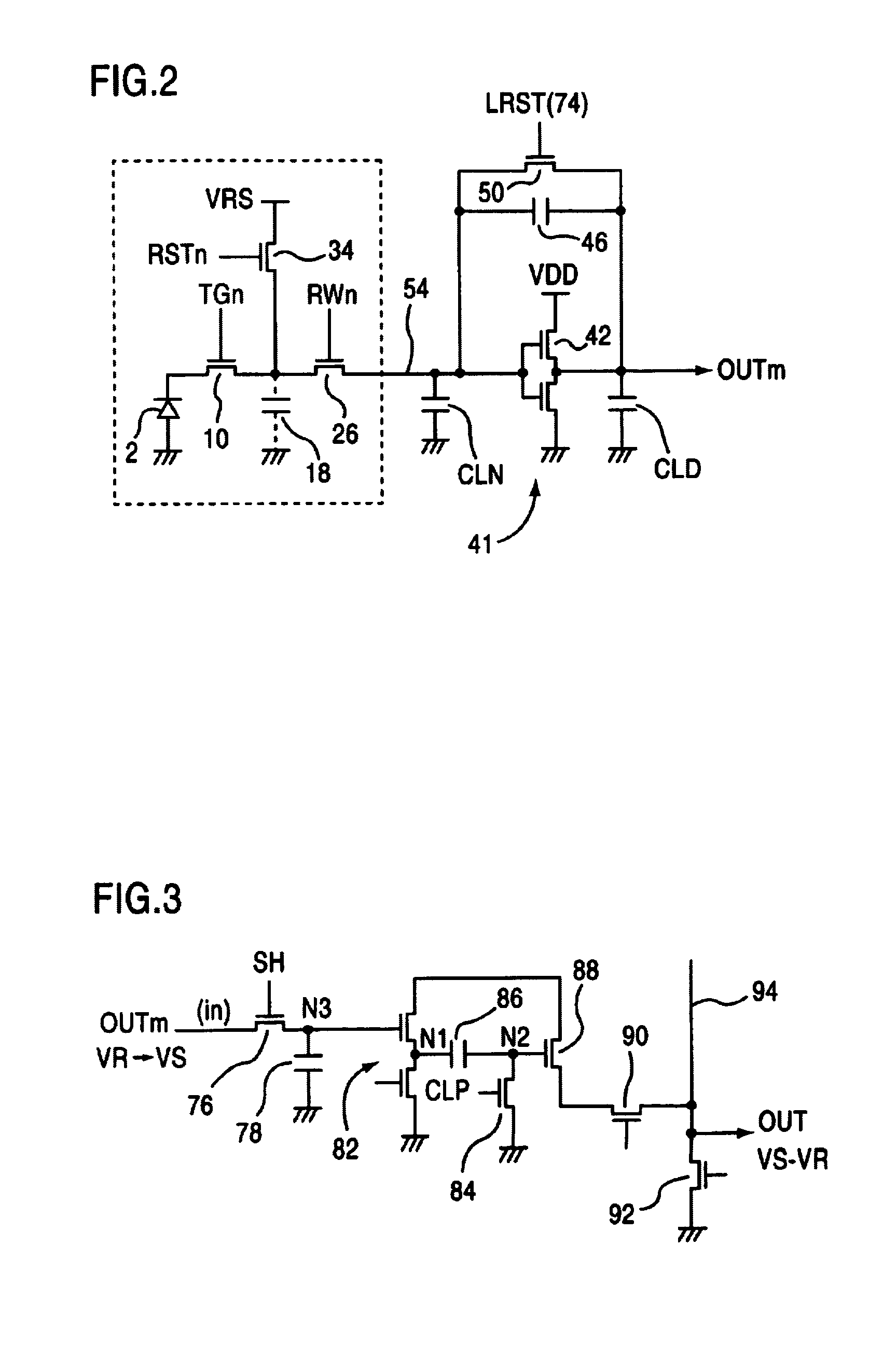
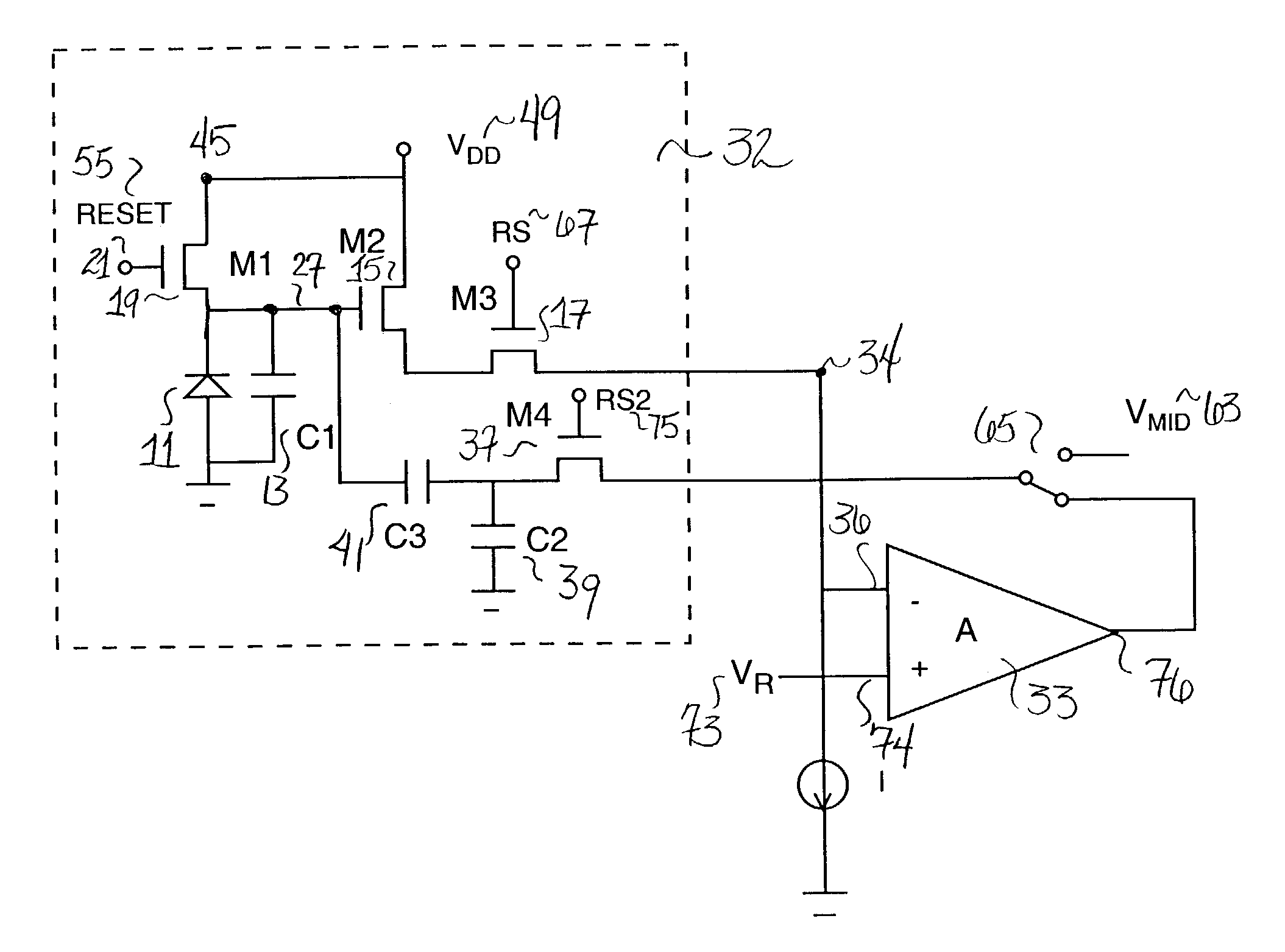
A solid-state imaging device comprises: a plurality of pixels including a light-sensitive portion (2) for photoelectrically converting incident light, a transfer gate (10) for transferring a charge stored in the light-sensitive portion, a resettable detection capacitor (18) for storing the charge transferred from the transfer gate, and a selection switch (26) for outputting a charge of the detection capacitor according to a selection signal RWn; a charge amplifier (41) for converting the detection capacitor charge, which is outputted from the pixels, to a voltage; and a correlated double sampling circuit (86) for obtaining a voltage difference between a reset level and a detected level converted by the charge amplifier. According to the above device, a thermal noise is eliminated due to the correlated double sampling circuit. Further, a fixed pattern noise is not generated due to the pixel circuit structure.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Pixel design including in-pixel correlated double sampling circuit
InactiveUS7277129B1Minimize chip areaLow costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierVoltage reference
An image sensor having a plurality of pixels, each including a sense node; an output node; a first device, connected to the sense node, producing a signal at the sense node that is proportional to incident light intensity at the pixel; at least one select node to receive a first select signal for selecting the pixel output node from the plurality of pixels; a reset device for resetting the pixel; and a sample and hold circuit including a sample node coupled to the sense node. At least one amplifier is provided, including a first input node to receive an output signal from the output node of a selected pixel and a second input node connected to a reference voltage source provided as a reference to reset a selected pixel. An amplifier output node is connected to couple an amplifier output signal to a selected pixel's sample and hold circuit.
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
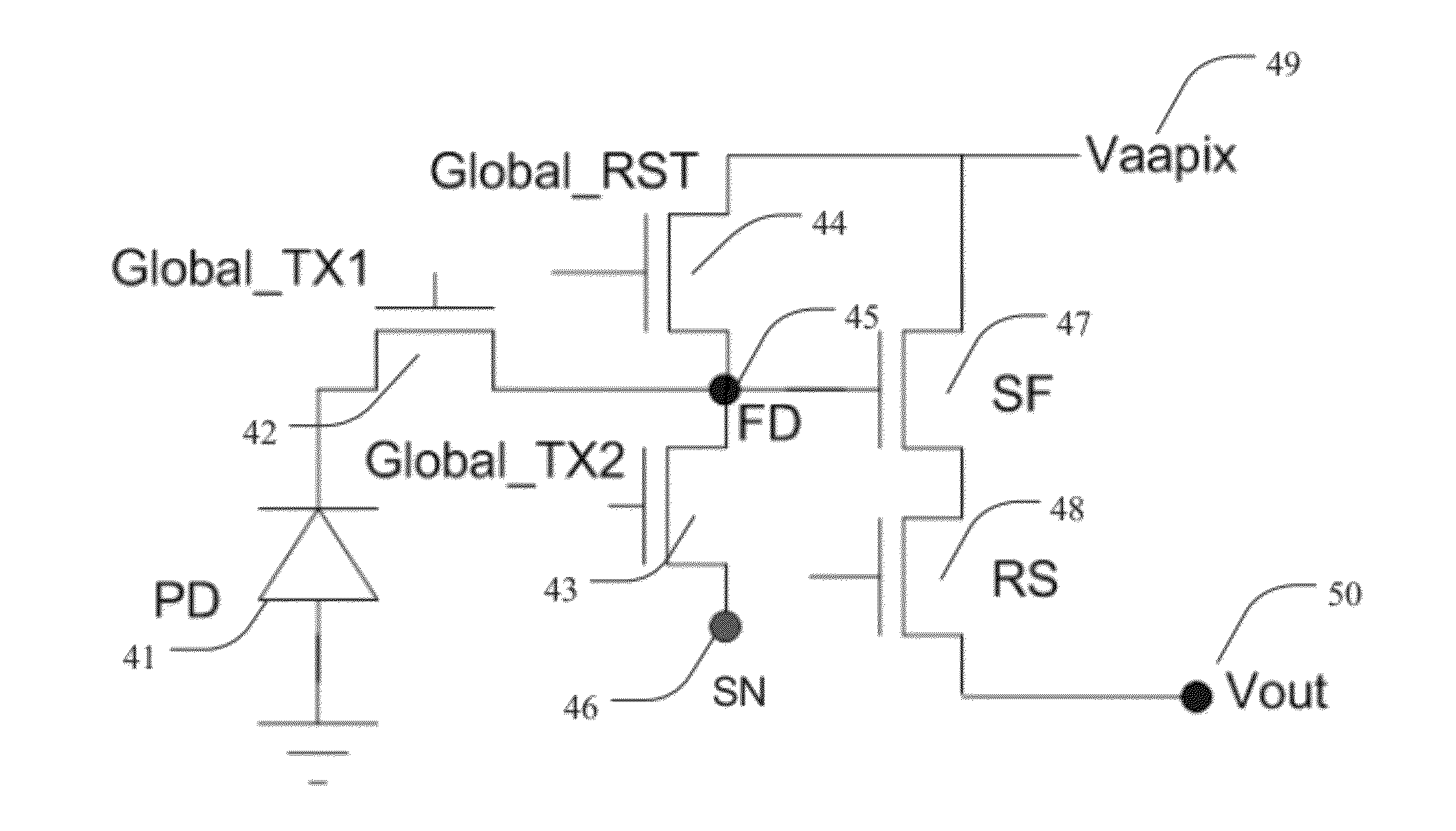
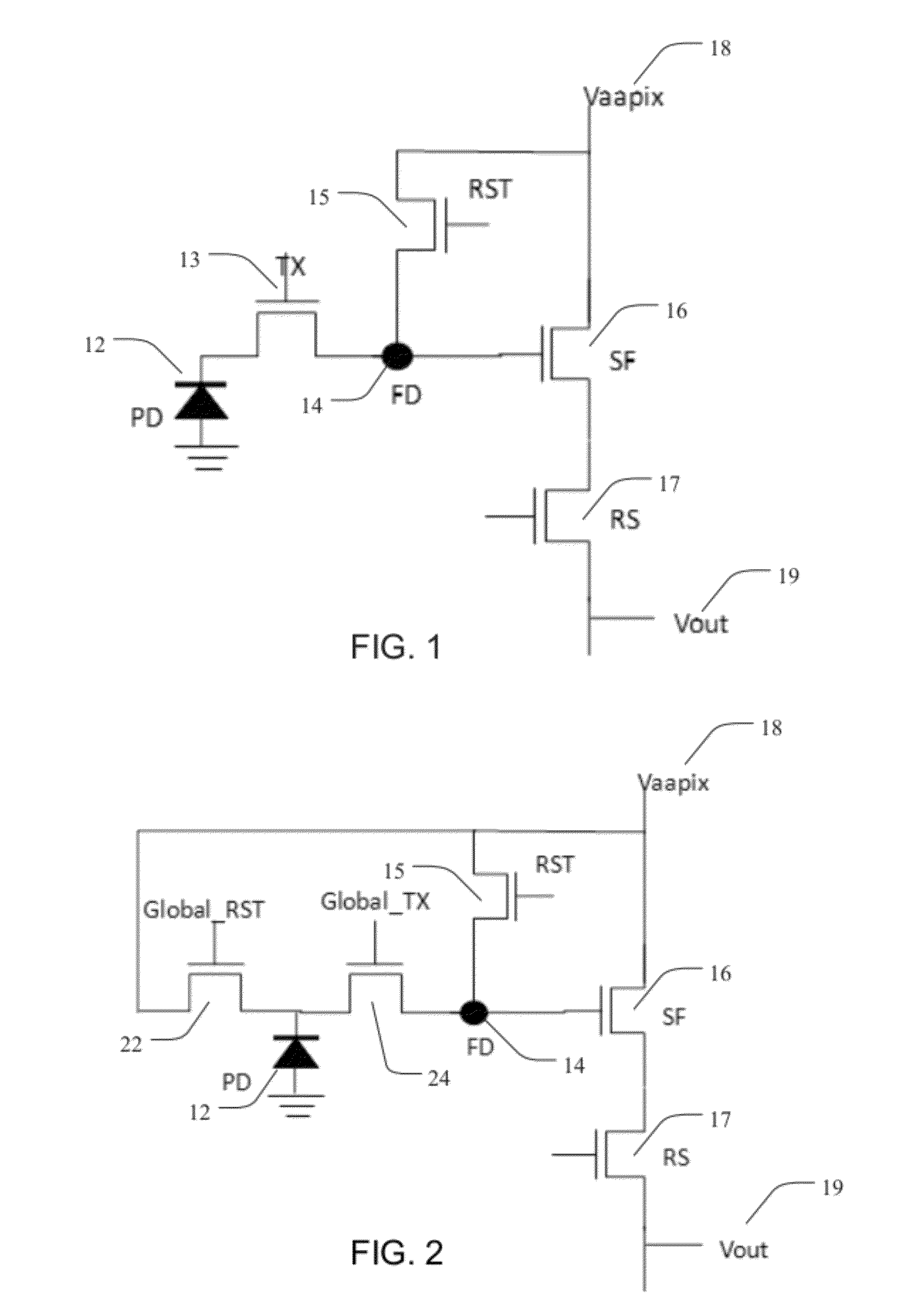
Photodetecting imager devices having correlated double sampling and associated methods
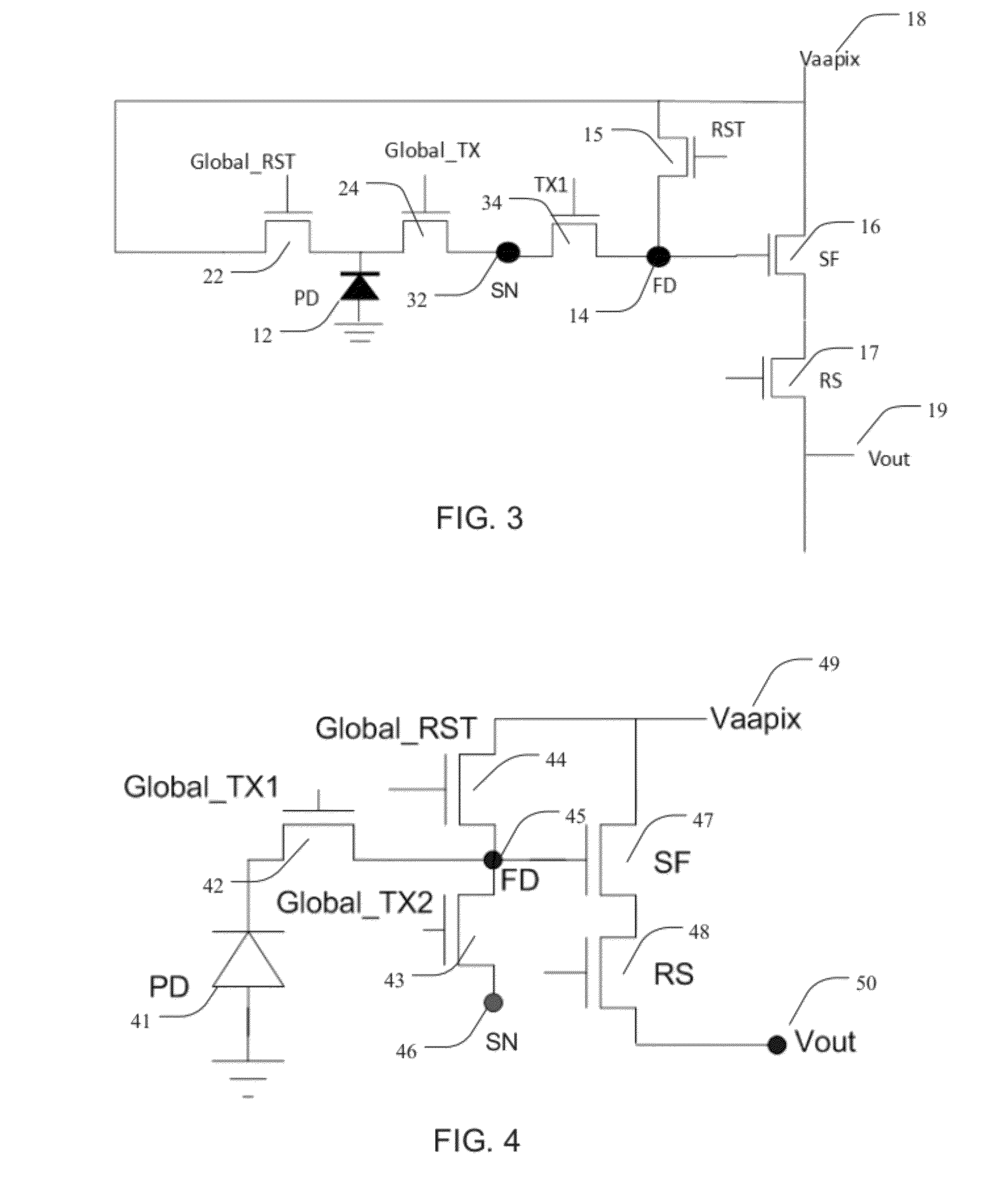
ActiveUS20120326008A1Provide protectionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringFloating diffusion
Transistor pixel devices, imagers, and associated methods are provided. In one aspect, a transistor pixel device includes a photodiode coupled to a floating diffusion region (FD), a storage node (SN), and a power supply, wherein the FD is coupled between the photodiode and the power supply. The device also includes a first global transfer transistor coupled between the photodiode and the FD for gating between the photodiode and the FD and a second global transfer transistor coupled between the FD and the SN for gating between the FD and the SN. A global reset select transistor is coupled between the FD and the power supply, wherein an open state of the global reset select transistor prevents accumulation of electrical charge at the photodiodes. A source follower transistor is coupled to the FD and to the power supply, where the source follower is operable to receive electrical signal from the FD.
Owner:SIONYX
Touch analog front end and touch sensor controller having the same
ActiveUS20160124544A1Eliminate low frequency noiseDoubling sensitivity of a touch inputDetails for portable computersInput/output processes for data processingCapacitanceIntegrator
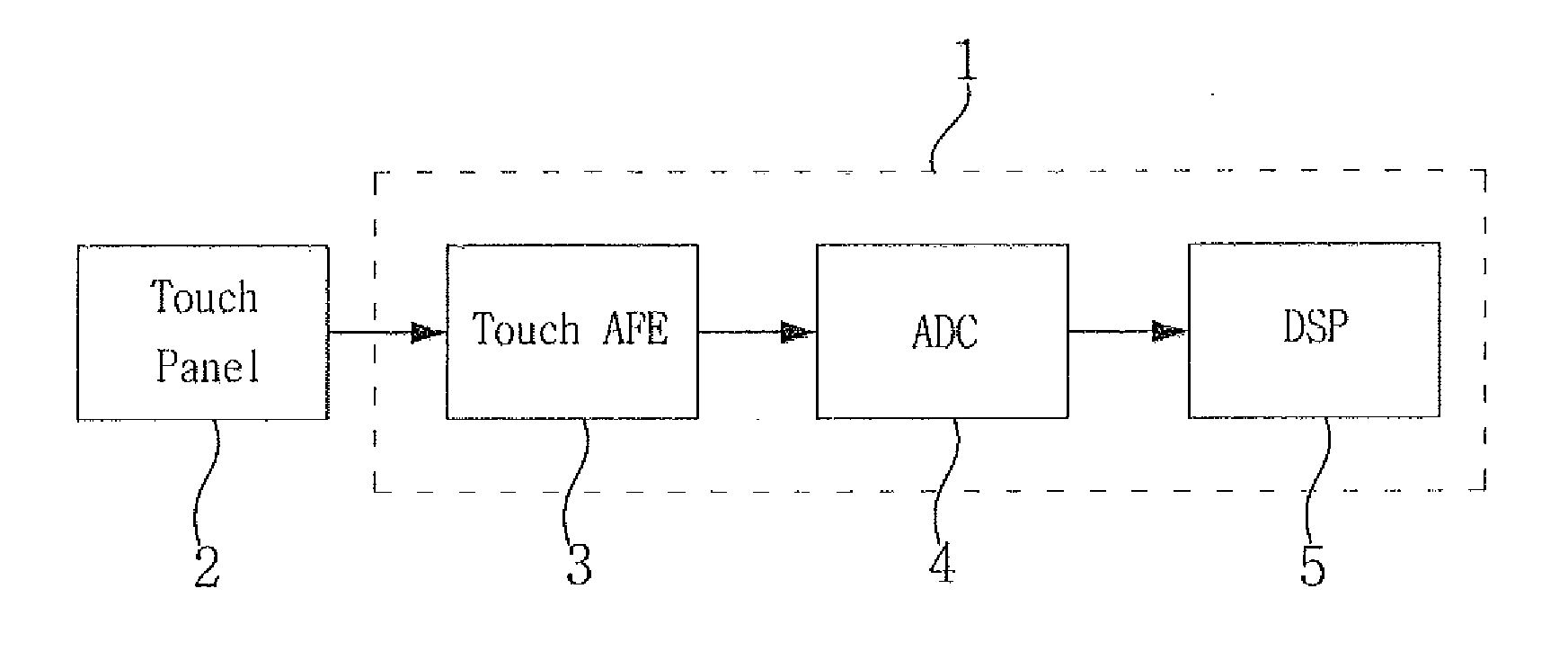
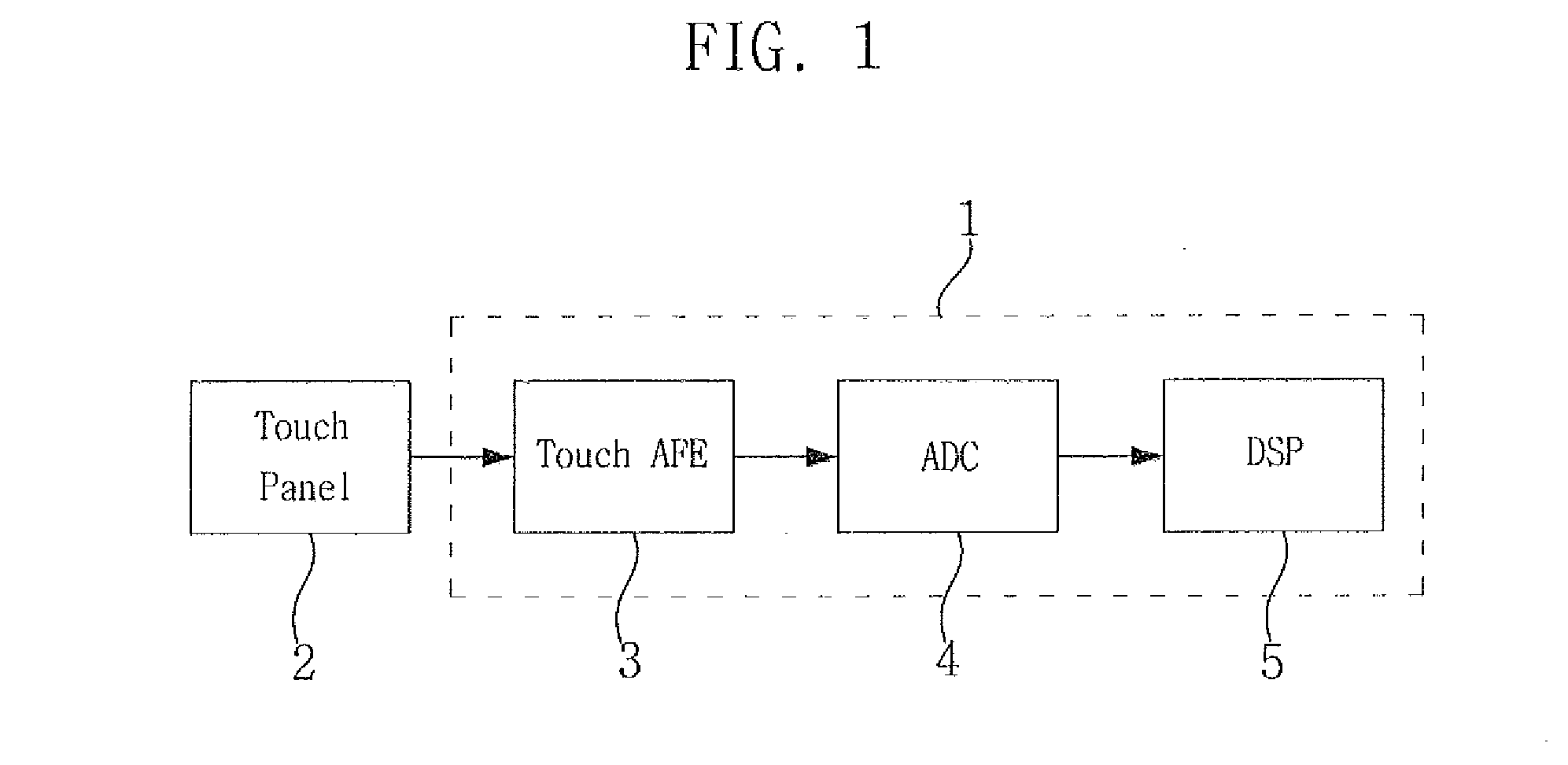
A touch analog front-end (AFE) for a touch sensitive screen may include a transmitter configured to charge a touch panel and a receiver configured to sense the touch panel. The receiver may include a charge-to-voltage (C2V) converter configured to convert a change of capacitance received from the touch panel into a voltage signal, a correlated double sampling (CDS) block configured to convert the voltage signal into a differential signal and to sample each of the positive and the negative signals of the differential signal, and an integrator configured to accumulate a difference between the sampled positive and negative signals.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
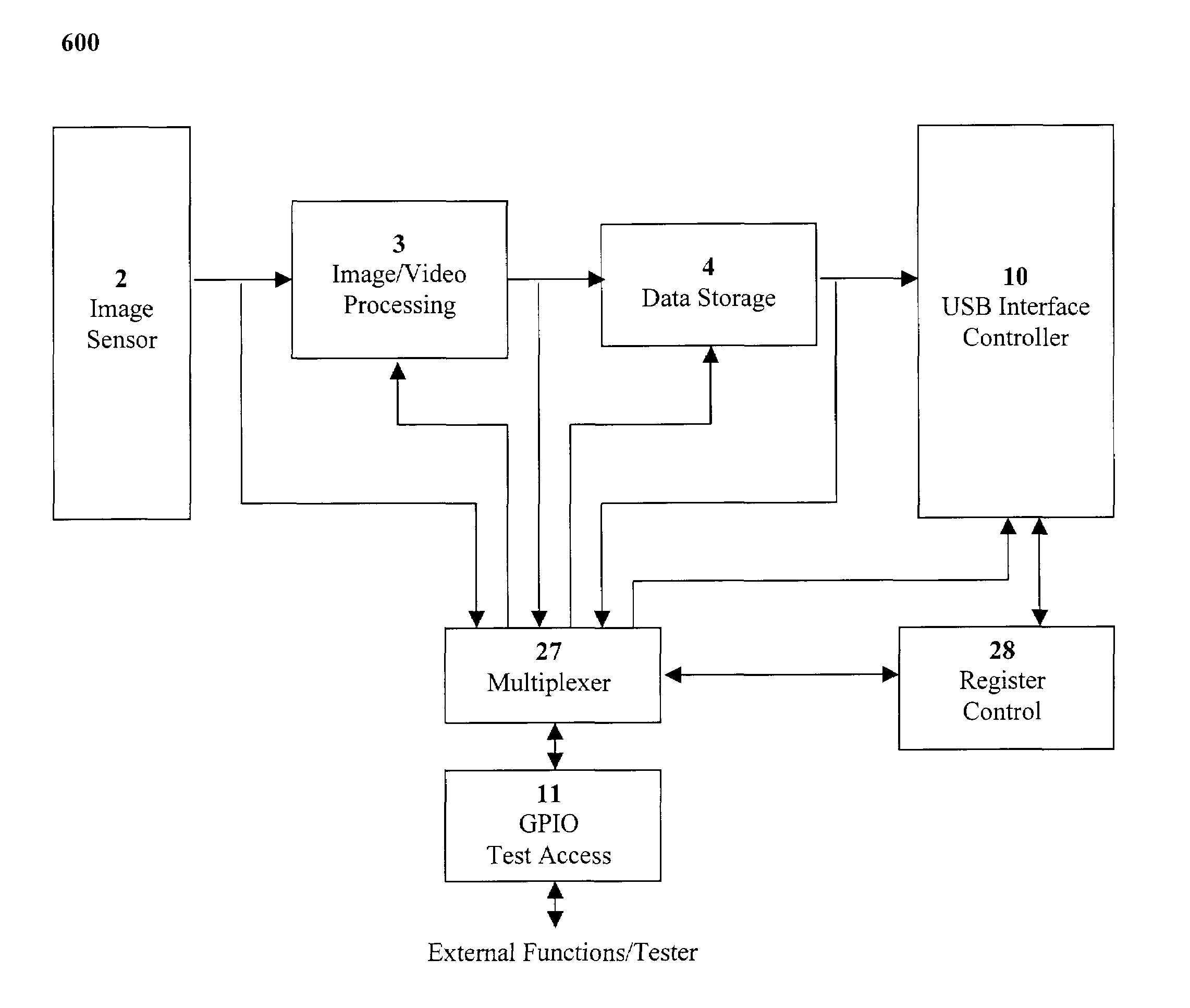
Method and system for single-chip camera
InactiveUS7113203B1Small sizeReduce power consumptionTelevision system detailsPicture signal generatorsDigital dataSensor array
Method and system for a single-chip camera where an image sensor is a single-chip digital color imaging device that incorporates a sensor array that captures still or full-motion video and converts the images to digital data. Moreover, the image sensor employs a built-in correlated double sampler, an internal analog-to-digital converter, and a timing circuitry. Output from the sensor is an 8-bit or more raw data, horizontal sync signals, and vertical sync signals. The output raw data may then be fed into a compression circuit that generates packets of compressed output data. The compressed data is transmitted with a USB transceiver using isochronous packets. The packets are then received, decompressed, and color processed by a host PC.
Owner:PHOTONIC IMAGING SOLUTIONS INC
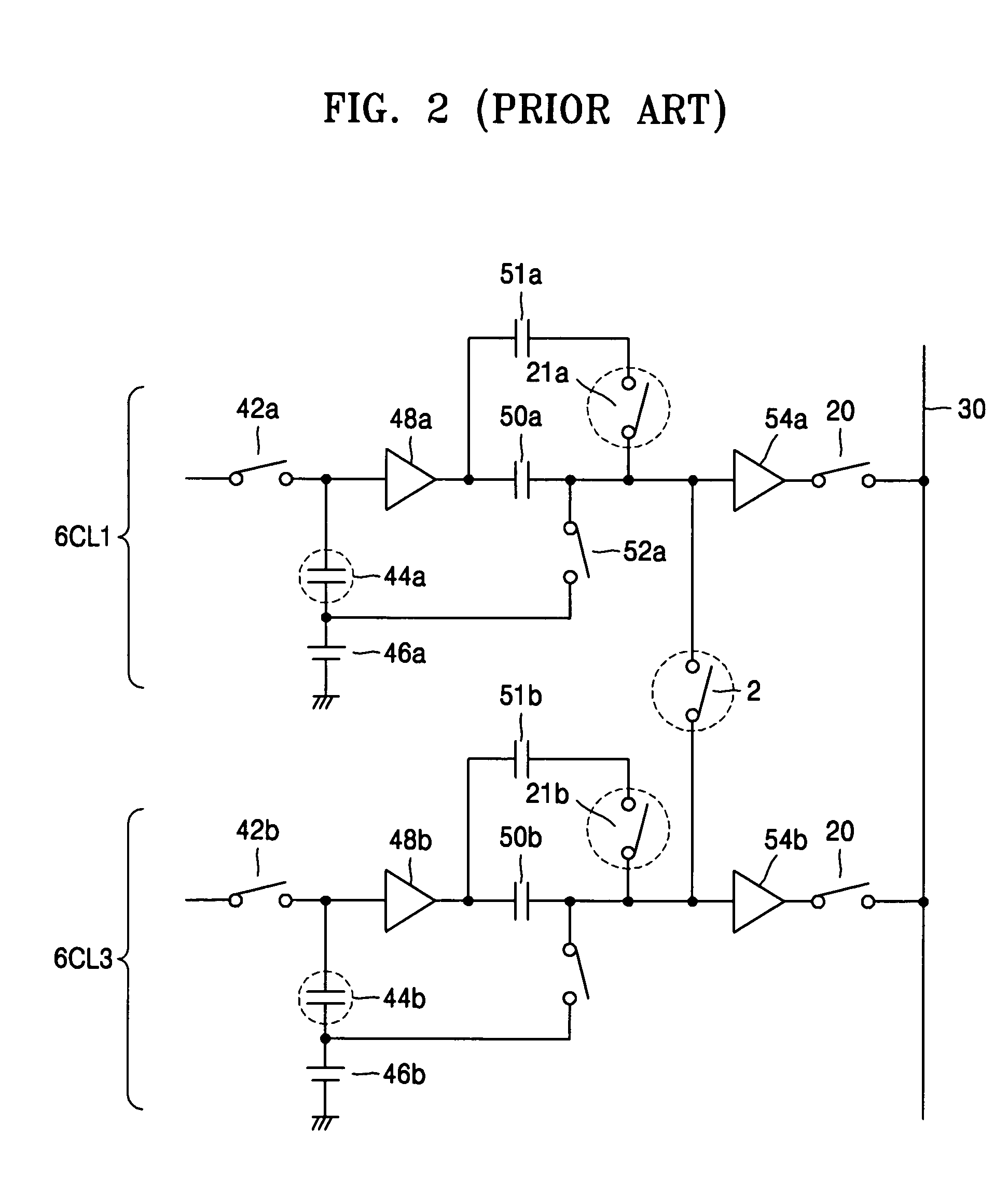
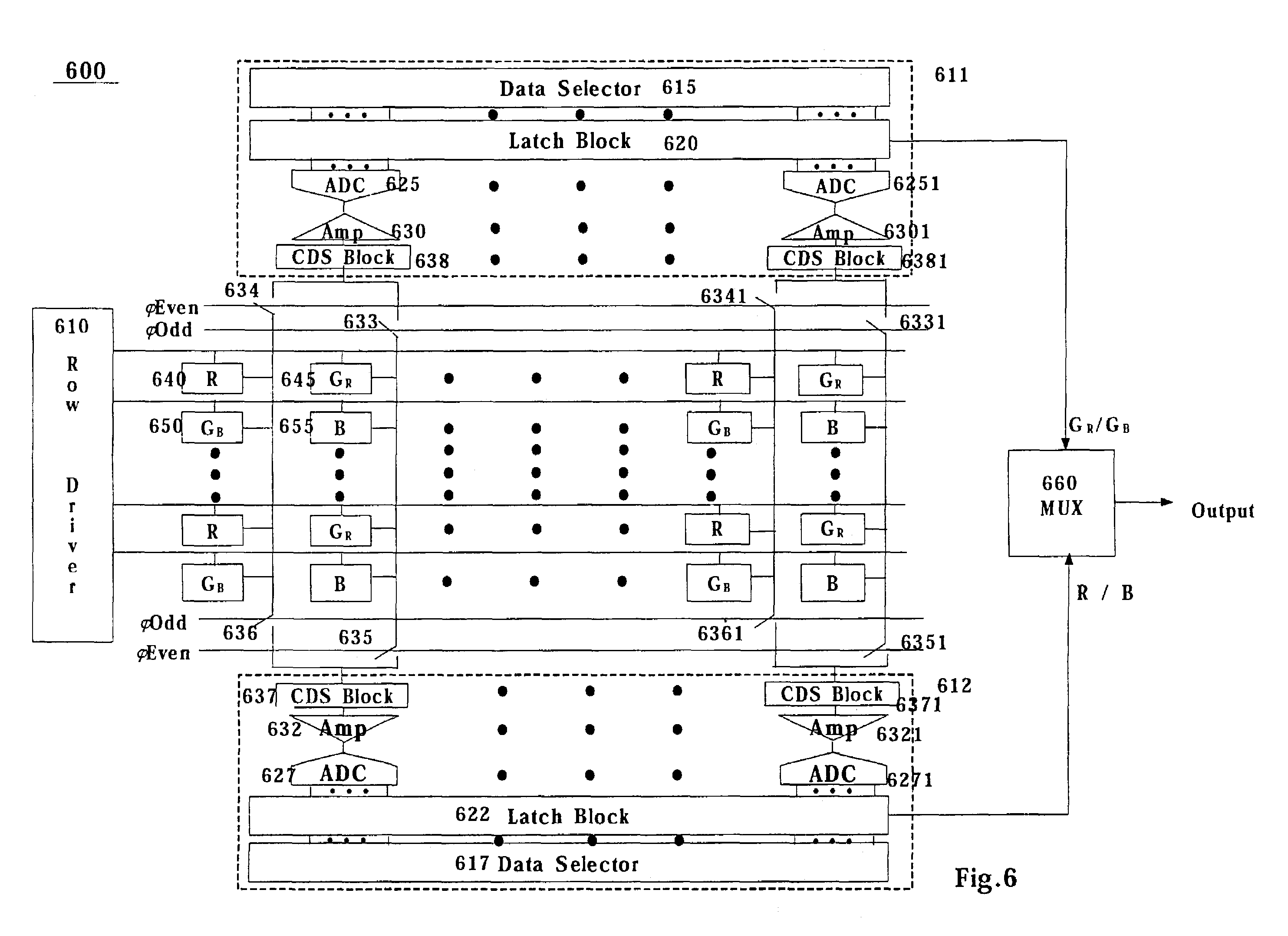
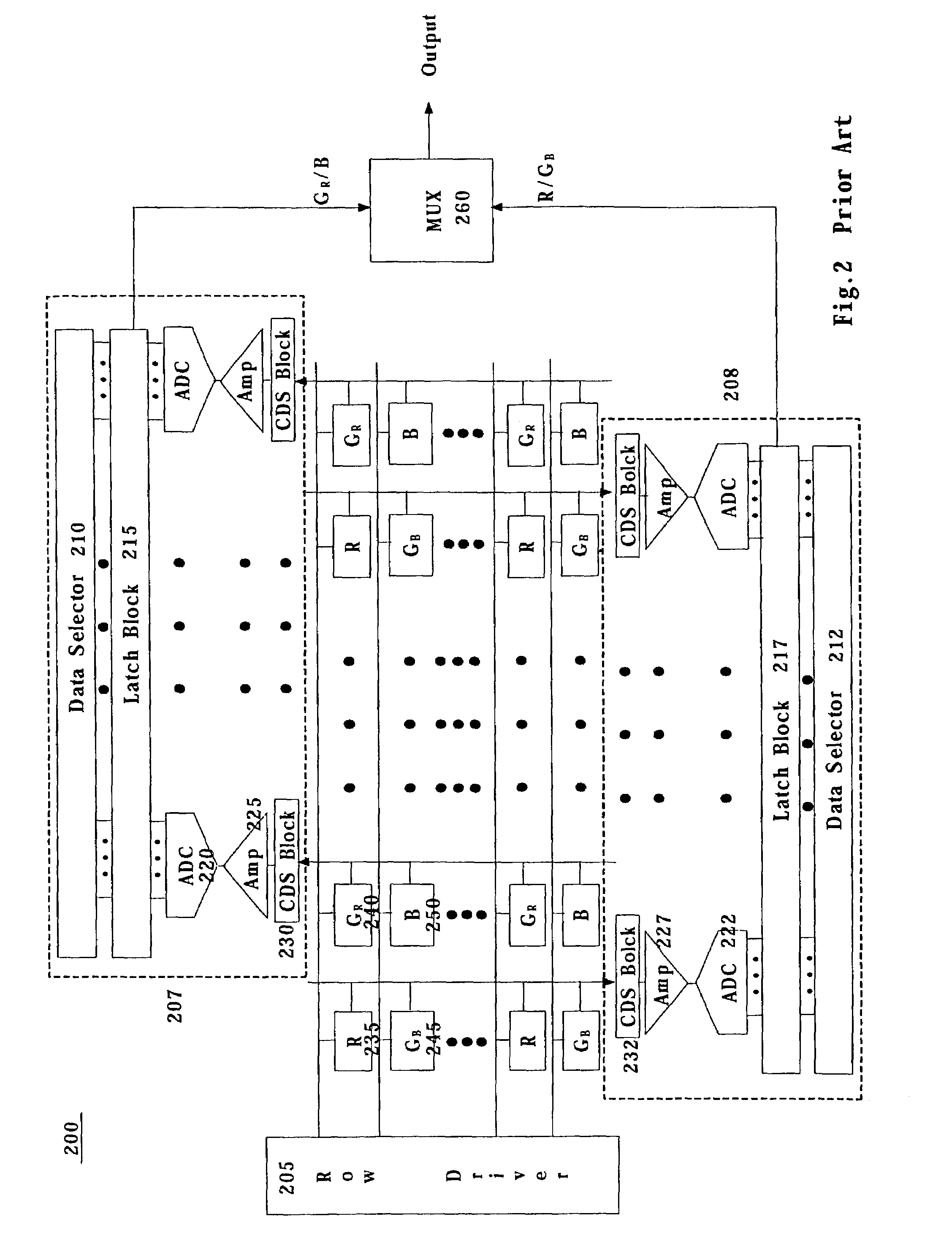
Circuit and method for reducing fixed pattern noise
ActiveUS7408443B2Reduce pattern noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorSensor array
An image sensor and method, which includes a switching device for establishing a connection between at least one column line and one of at least two analog-to-digital converter blocks, where at least one of the at least two analog-to-digital converter blocks is connectable to at least two rows of a plurality of unit pixels. An image sensor and method, where, if a row line is odd, column outputs from odd column lines of an active pixel sensor array are connected to a first correlated double sampling block and column outputs from even column lines of the active pixel sensor array are connected to a second correlated double sampling block and if the row line is even, column outputs from odd column lines of the active pixel sensor array are connected to the second correlated double sampling block and column outputs from even column lines of the active pixel sensor array are connected to the first correlated double sampling block. An image sensor and method where a first subset of a plurality of unit pixels are connected to a first correlated double sampling block and a second subset of the plurality of unit pixels are connected to a second correlated double sampling block, where the first subset of the plurality of unit pixels are blue and red pixels and the second subset of the plurality of unit pixels are green pixels. A circuit and method for reducing fixed pattern noise.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
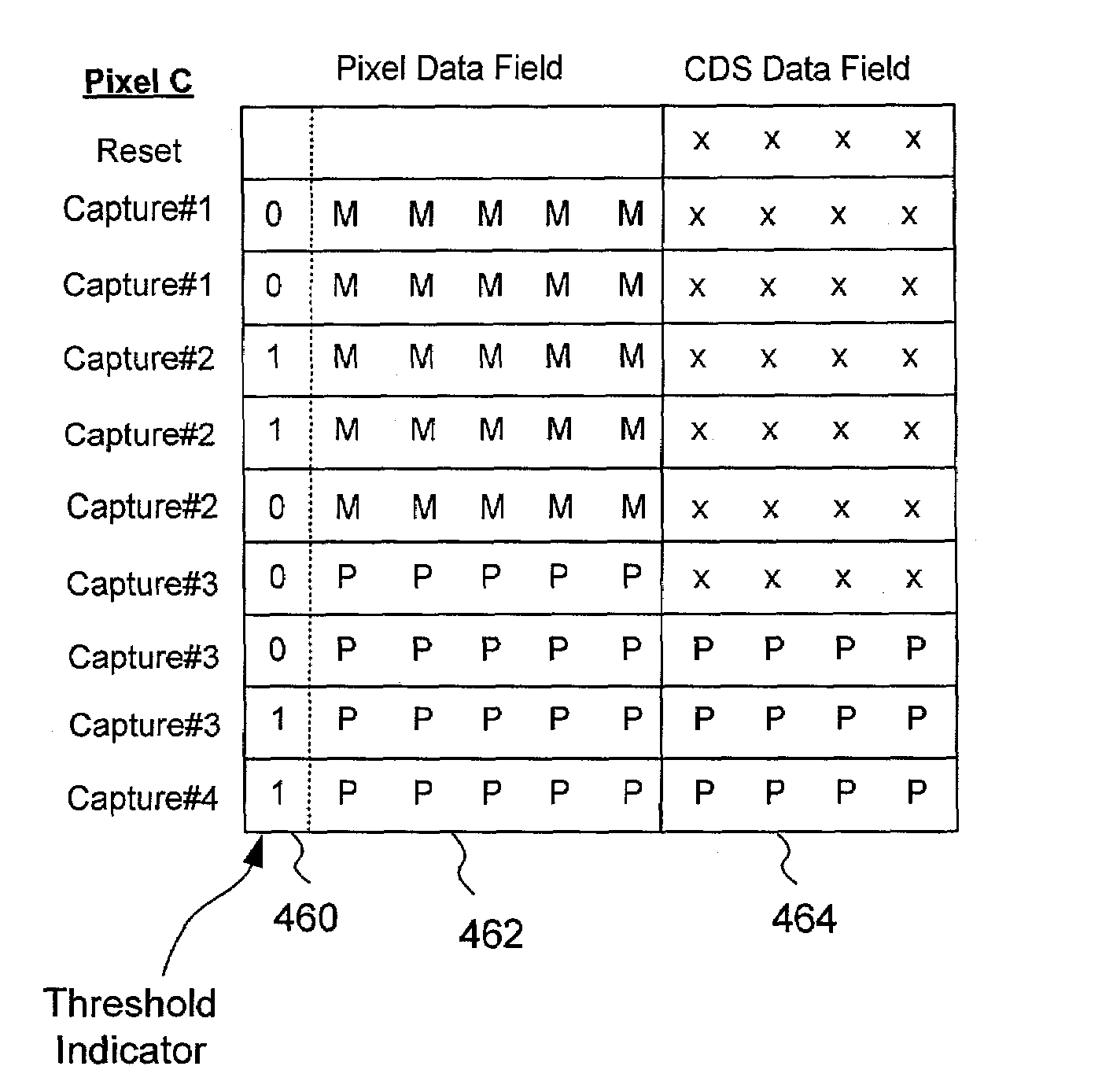
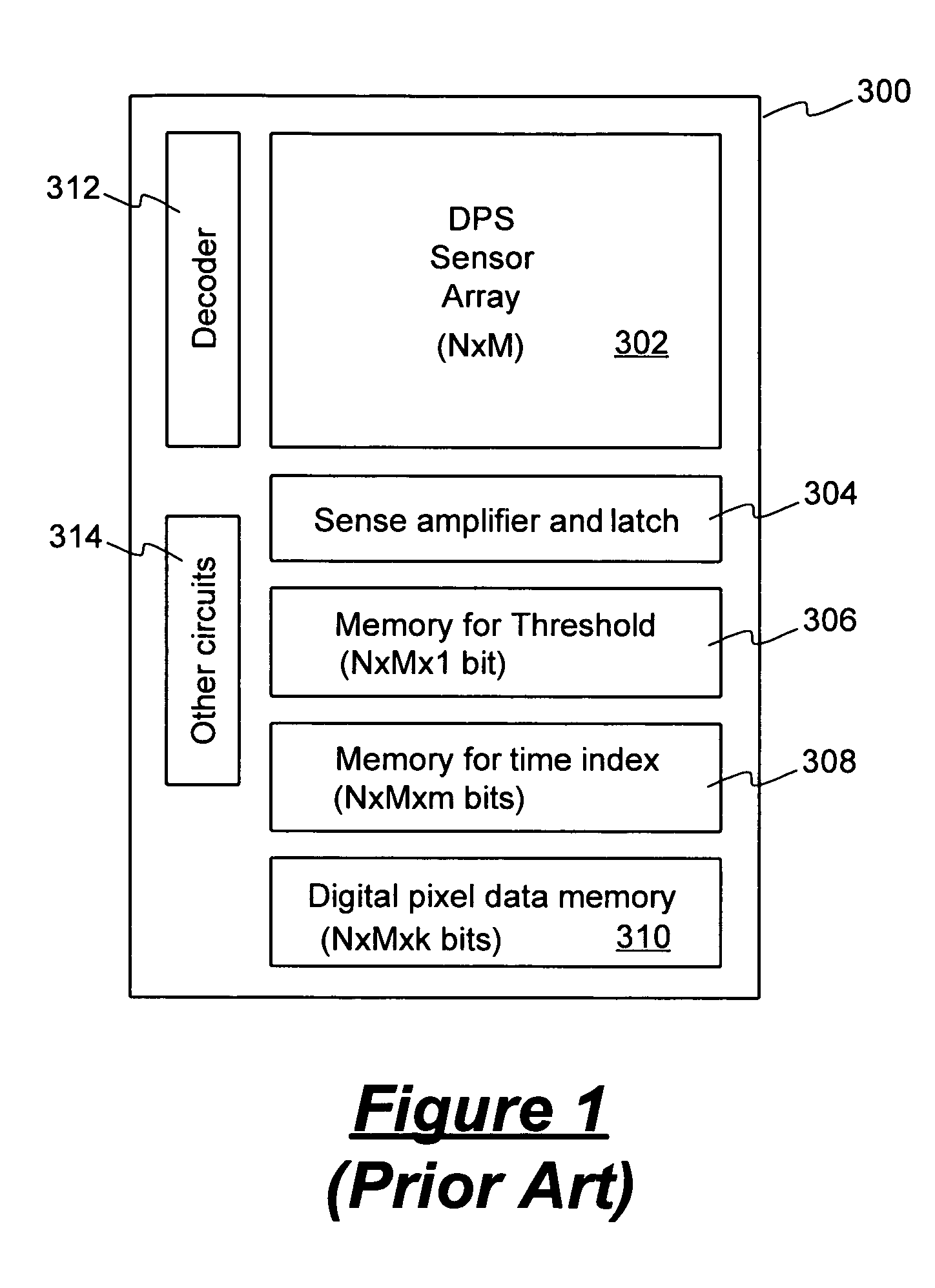
Method for capturing and storing image information for multiple sampling operations in a digital pixel sensor
ActiveUS6963369B1Easy to useSmall sizeTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsSensor arrayData field
A method for storing image information in a digital pixel sensor is disclosed for reducing the size of the memory needed to facilitate multiple sampling and correlated double sampling. In one embodiment, an image sensor includes a sensor array of pixel elements generating digital pixel data and a data memory for storing pixel data of each pixel element. The data memory allocates for each pixel element an m-bit pixel data field for storing pixel data and an n-bit CDS data field for storing reset value associated with each pixel element. The data memory stores m+n bits of pixel data in the pixel data field and the CDS data field for pixel data exceeding the predetermined threshold level. The data memory stores m bits of pixel data in the pixel data field for pixel data not exceeding the predetermined threshold level.
Owner:PIXIM
Image sensor circuits including sampling circuits used therein for performing correlated double sampling
InactiveUS7133074B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsAudio power amplifierPre-charge
A CMOS image sensor circuit includes an array of sensing elements which integrate electrical charge according to the light intensity thereon. In order to measure the accumulated charge voltage at the individual sensing elements, and thus obtain the image data from the array, a sampling circuit is provided. The sampling circuit operates using a high-gain amplification stage and an auto-zero amplifier to perform correlated double sampling, which enables non-linear influences which may arise in the array to be reduced in the measuring process. The sampling circuit can also include a sample and hold circuit arranged to account for a feed-through effect arising from pre-charge circuitry in the sensing elements. The sample and hold circuit can be included within the feed-back loop of the high-gain amplification stage for further increases in linear performance.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
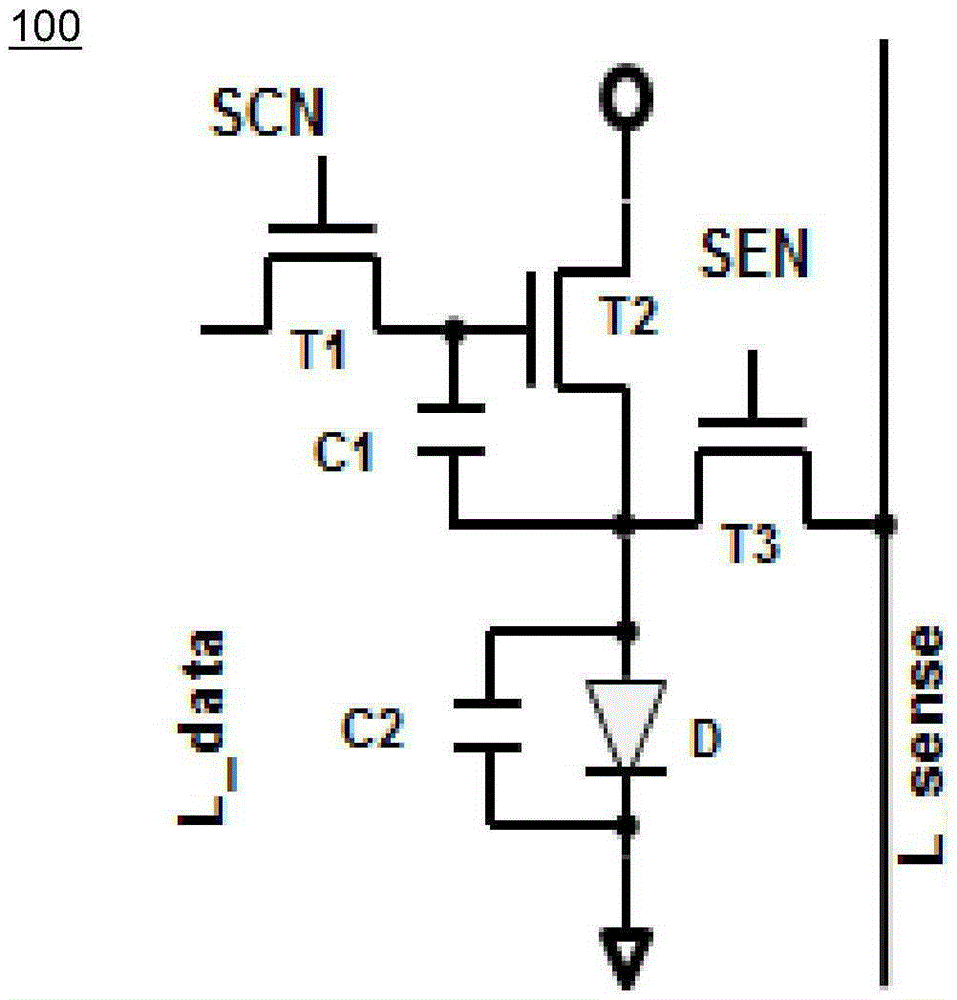
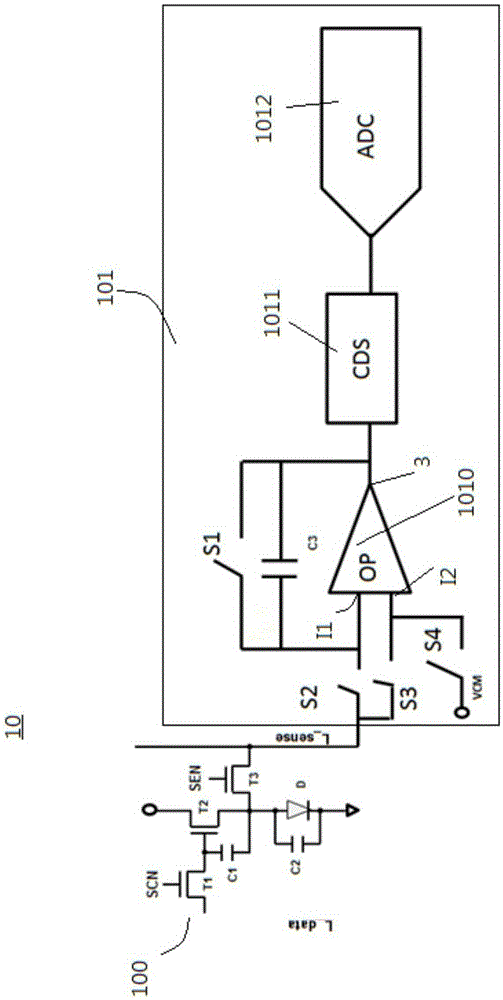
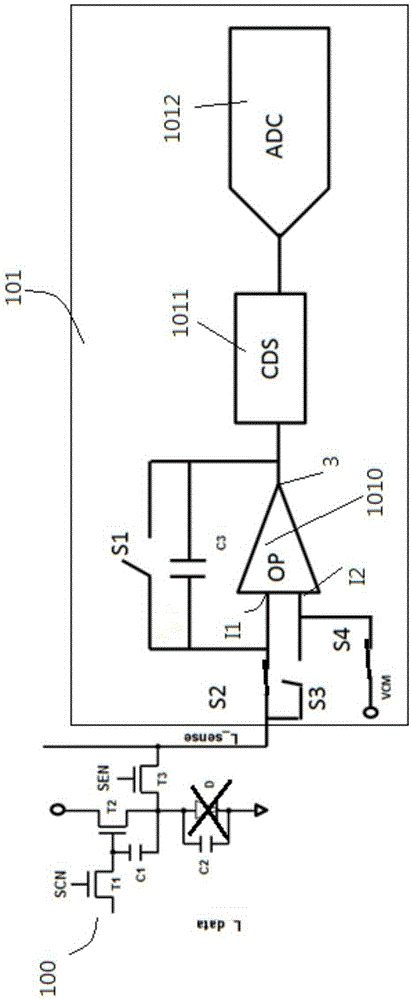
Sensing circuit and corresponding OLED display equipment
Owner:TCL CHINA STAR OPTOELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
Lossless nonlinear analog gain controller in image sensor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveUS7379011B2Delayed slopeIncrease the slopeTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCMOS sensorEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
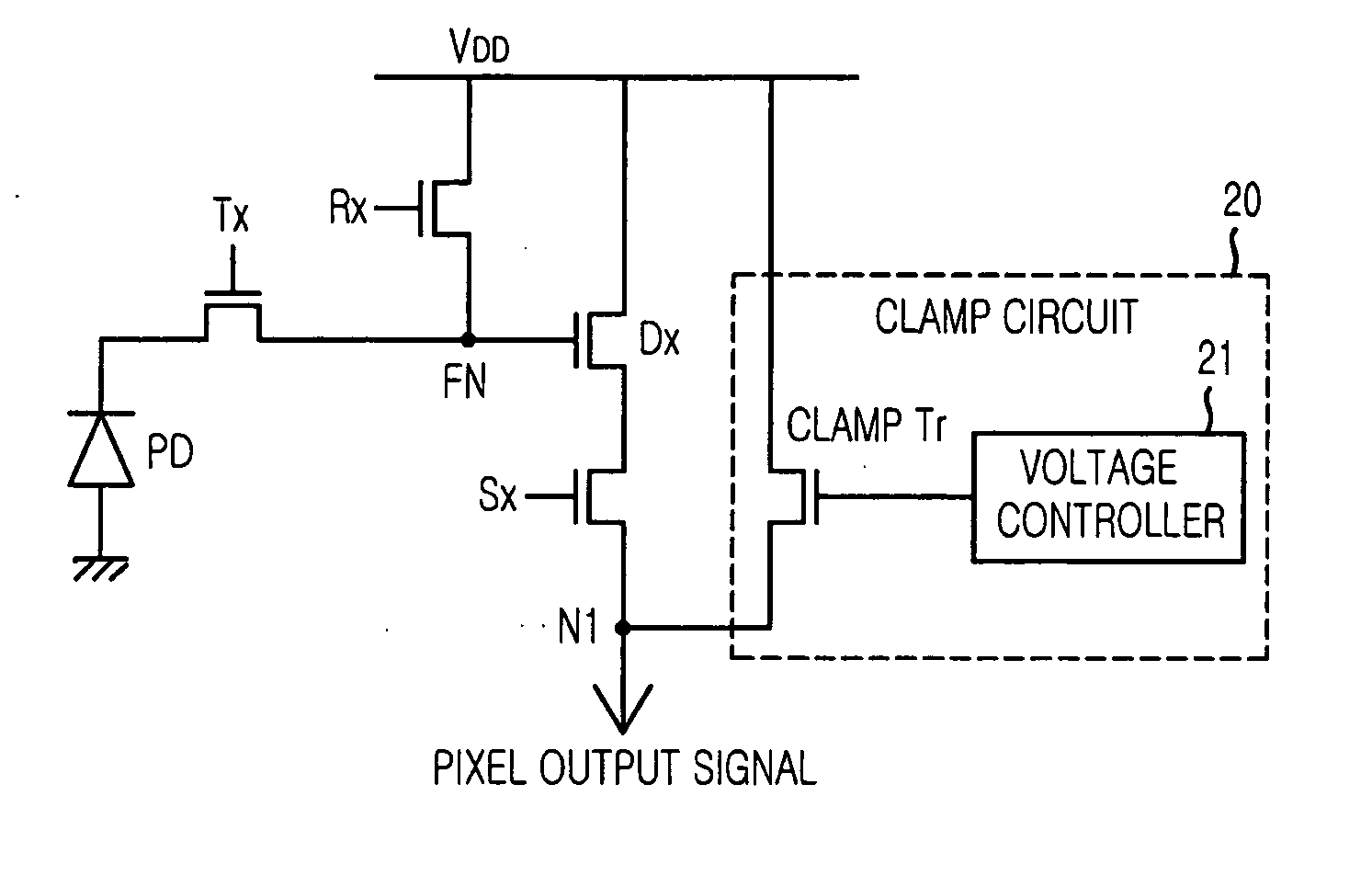
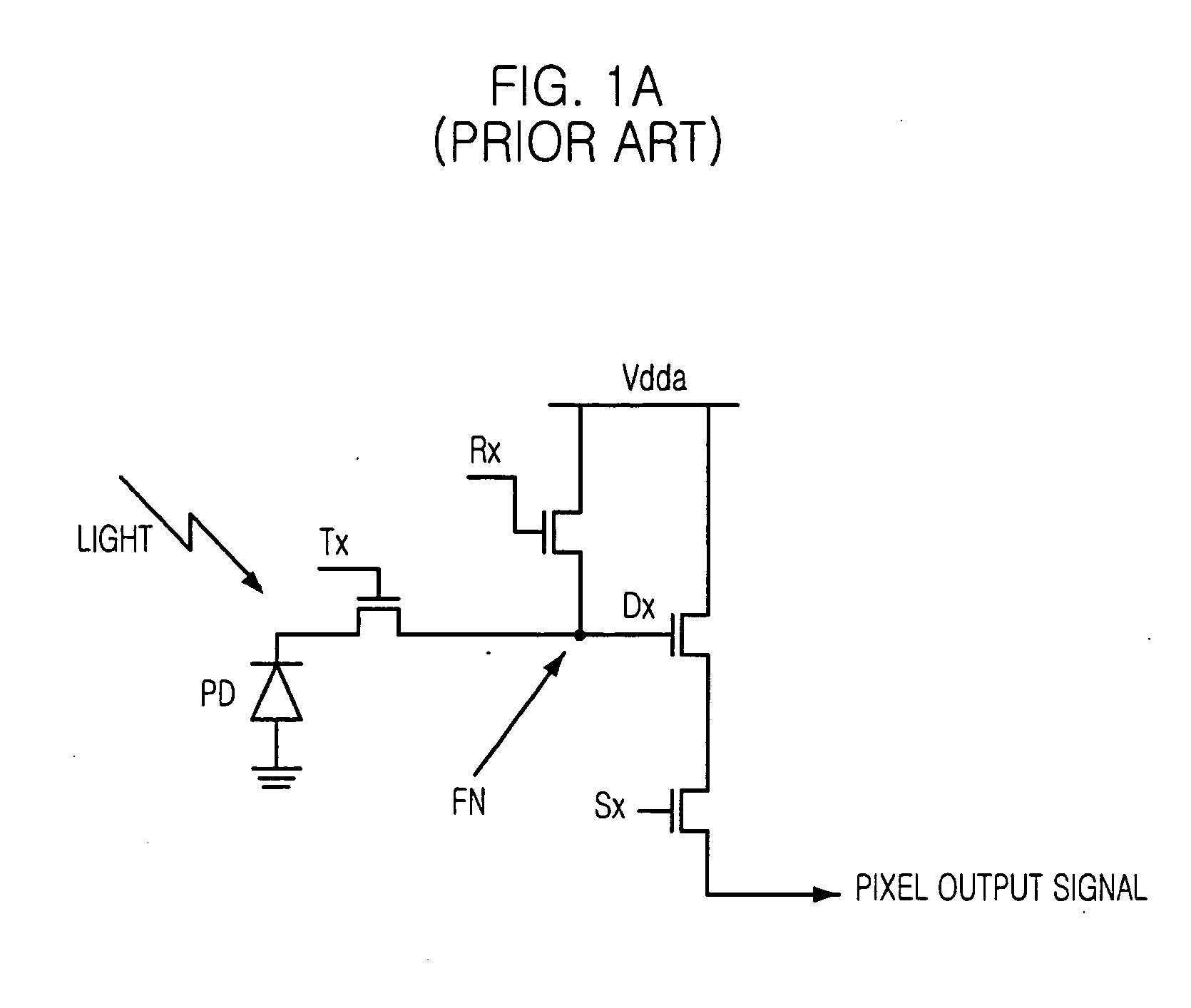
Image sensor having clamp circuit
ActiveUS20040155973A1Quality improvementEffectively reducing a dark phenomenonTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImaging qualityComputer science
An image sensor of the present invention prevents the phenomenon that surrounding background of a bright object reflecting or emitting strong light like the sun is presented at dark and improves image quality of the image sensor by controlling the brightness of the bright object. The image sensor using correlated double sampling technology which outputs data of an object by using difference between a reset voltage signal and a data voltage signal of a unit pixel includes a plurality of unit pixels arranged in a matrix, each outputting the reset voltage signal and the data voltage signal; a plurality of clamping means, each coupled to each unit pixels for clamping up the reset signal to a predetermined voltage level; and a voltage controlling block for adjusting voltage level supplied to a gate of each of clamping means.
Owner:INTELLECTUAL VENTURES II
CMOS imaging for ALC and CDS
ActiveUS20050001143A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsFloating diffusionPhoto conversion
Embodiments of the invention provide pixel cells that allow both automatic light control and correlated double sampling operations. The pixel cell includes first and second photo-conversion devices that can be separately read out. For example, the second photo-conversion device can be the pixel cells' floating diffusion region, with an area and doping profile suitable for photo-conversion. An image sensor may include an array of pixel cells, some or all of which have two photo-conversion devices, and peripheral circuitry for reading out signals from the pixel cells. The image sensor's readout circuitry may monitor charge generated by the second photo-conversion devices to determine when to read out signals from the first photo-conversion devices.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Image sensor and analog to digital converter and analog to digital converting method thereof
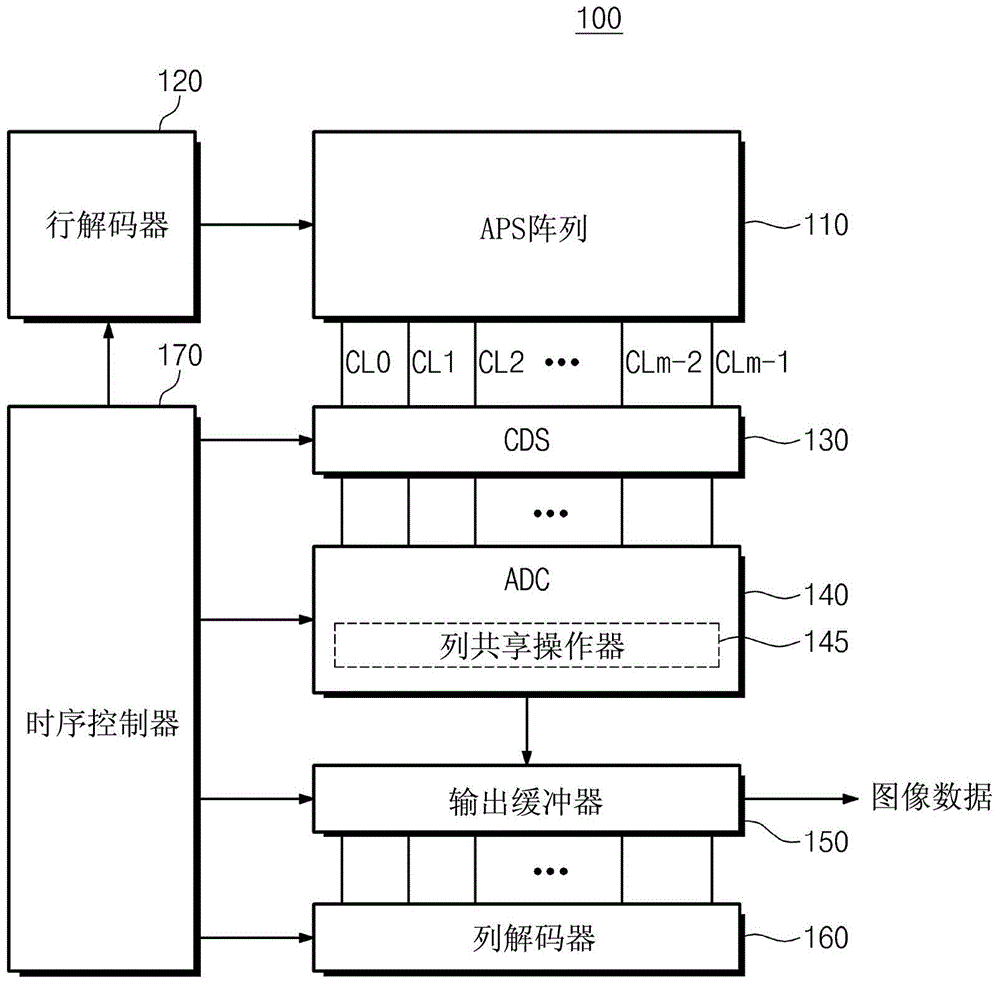
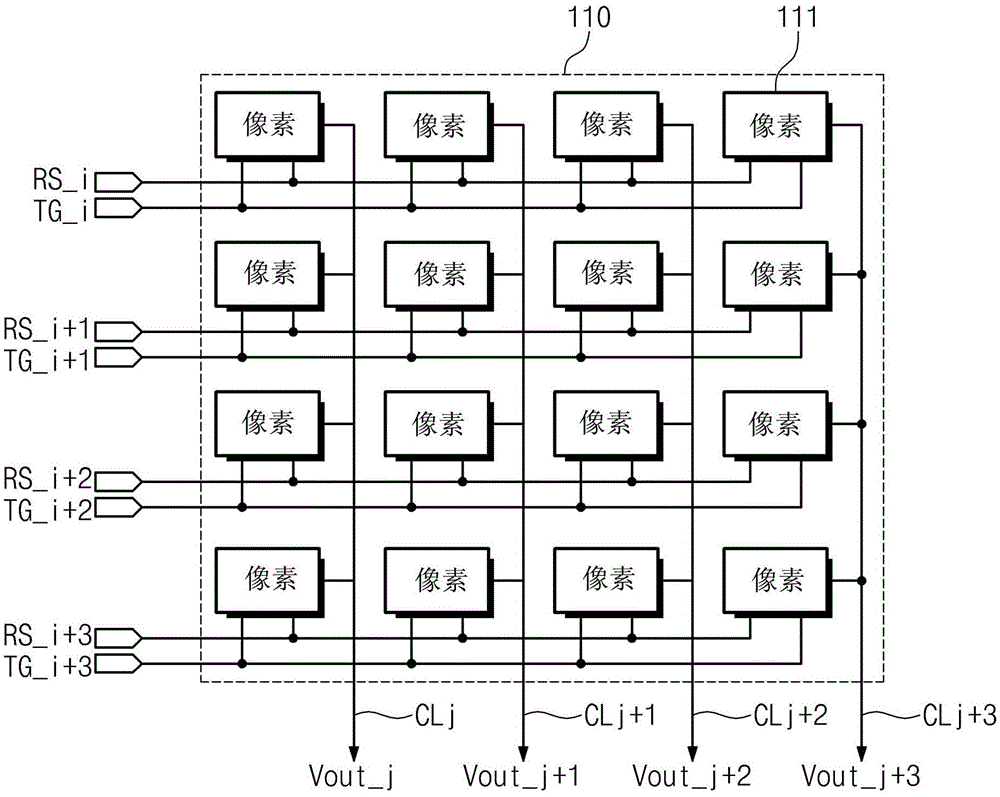
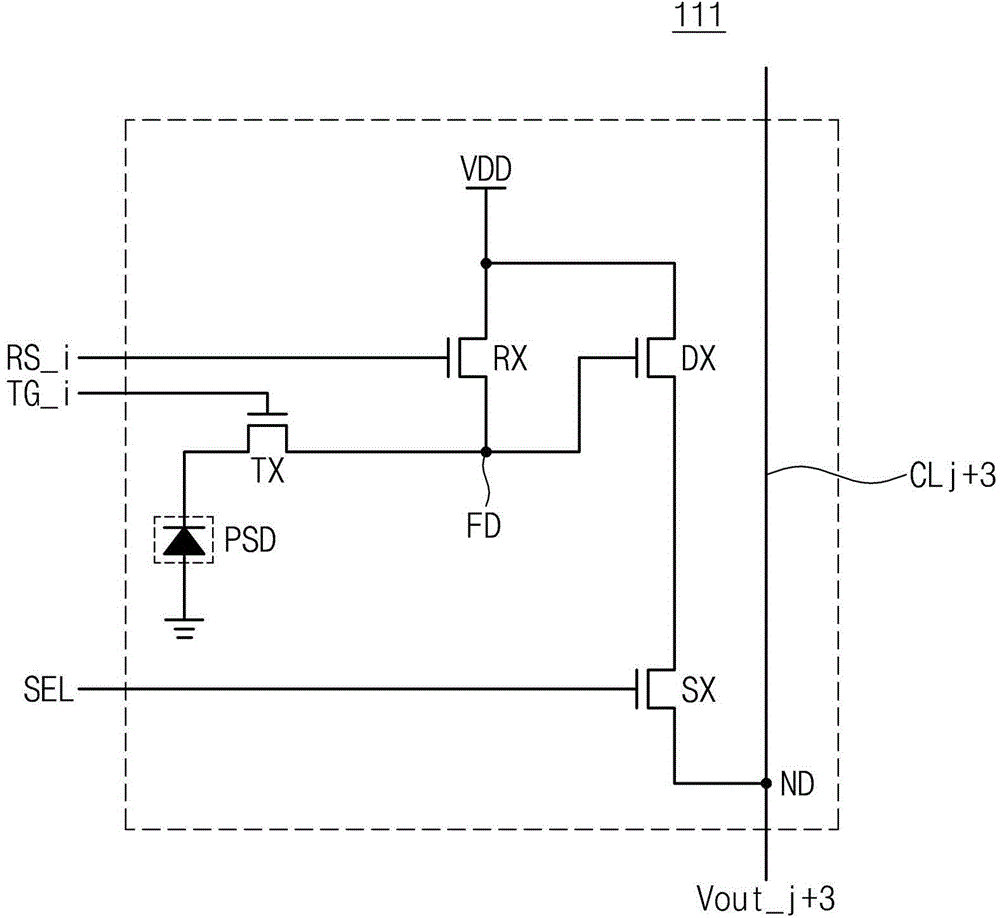
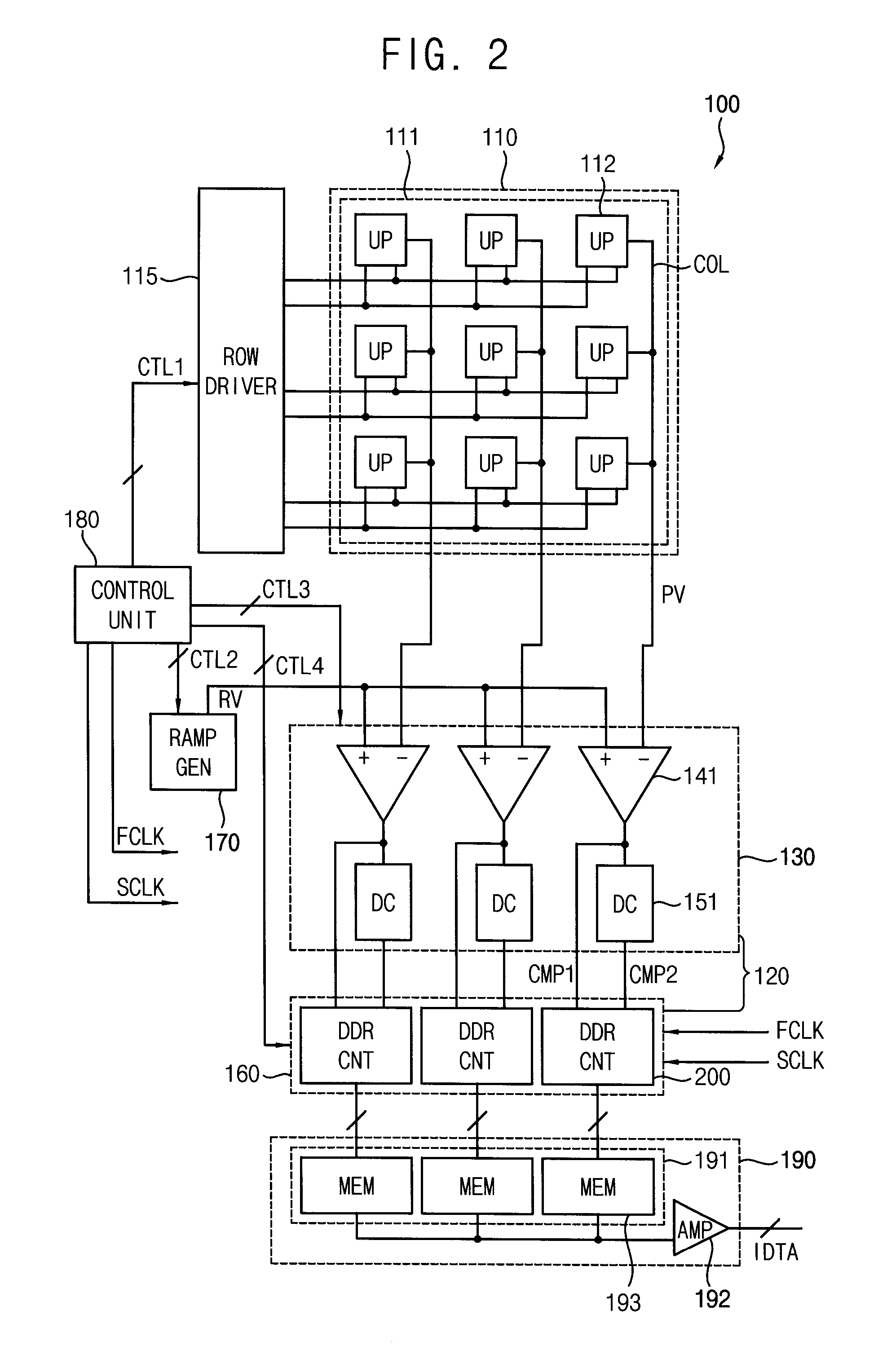
An image sensor is provided. The image sensor includes a pixel array having active pixel sensors arranged in rows and columns; a correlated double sampler that converts sensing signals transferred from pixels sensors selected from the active pixel sensors to correlated double sampling signals and outputs a conversion result by column; and an analog-to-digital converter that converts the correlated double sampling signals corresponding to plural columns to digital signals using a global code. The analog-to-digital converter includes a column shared operator that performs a digital conversion operation on correlated double sampling signals corresponding to two or more columns of the plural columns.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Low noise image sensing system and method for use with sensors with very small pixel size
ActiveUS20050078205A1Small pixel sizeLow photon noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsDigital dataLow noise
The image sensing system includes integrating charge in an image sensor array; transferring the charge out of the image sensor array; converting the charge to a digital signal; combining the digital signal with digital data stored in a memory device to form an integrated signal; storing the integrated signal in the memory device such that the integrated signal becomes the digital data; and repeating the above steps multiple times during a frame time cycle. This system allows for very small pixel sizes in the image sensor. The digital integration process eliminates the need for using correlated double sampling circuits to reduce kTC noise, and is also beneficial for reduction of analog-to-digital digitization noise.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
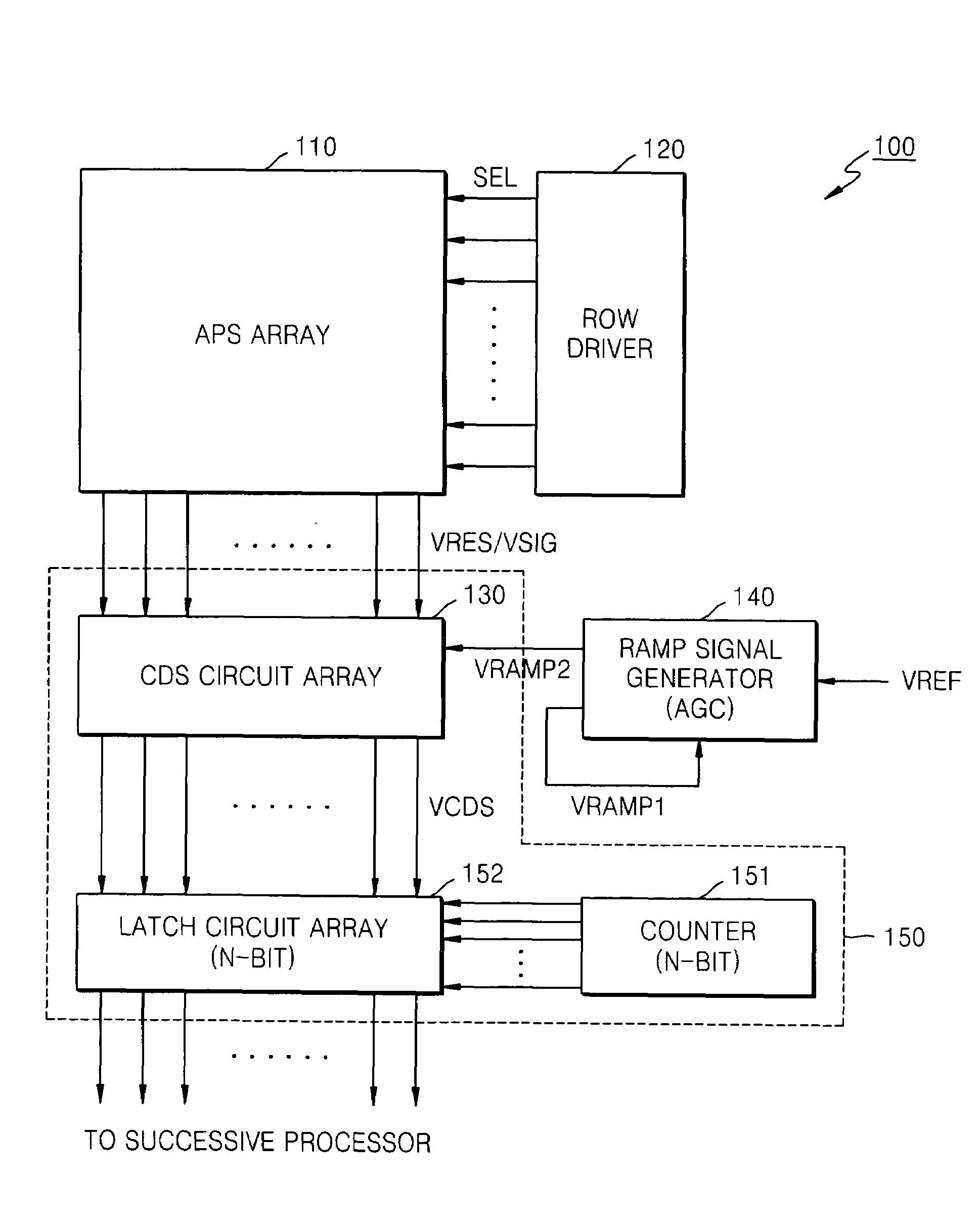
Counter circuit, analog-to-digital converter, and image sensor including the same and method of correlated double sampling
ActiveUS20150028190A1Reduce power consumptionReduce in quantityPower saving provisionsTelevision system detailsAnalog-to-digital converterComputer science
A counter circuit includes a first counter and a second counter. The first counter is configured to count a first counter clock signal which toggles with a first frequency to generate upper (N−M)-bit signals of N-bit counter output signals, in response to a first counting enable signal based on a first comparison signal during a coarse counting interval. N and M are natural numbers, N is greater than M, and M is greater than or equal to 3. The second counter is configured to count a second counter clock signal which toggles with a second frequency which is higher than the first frequency to generate lower M-bit signals of the N-bit counter output signals, in response to a second counting enable signal based on the first comparison signal and a second comparison signal during a fine counting interval which follows the coarse counting interval.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Current/voltage mode image sensor with switchless active pixels
ActiveUS20080291309A1Efficient implementationEffectively reducing size (pitch)Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorHigh resolution imaging
A voltage and current mode active pixel sensor for high resolution imaging is presented. The photo pixel is composed of a photodiode and two transistors: reset and transconductance amplifier transistor. The switch transistor is moved outside the pixel, allowing for lower pixel pitch and increased linearity of the output photocurrent. The reset and amplifier (readout) transistors may also be shared among adjacent pixels by the introduction of transfer switches between the photodiodes and the source of the reset transistor and the gate of the readout transistor. The switch transistor outside the pixels provides biasing voltages or currents to the readout transistors to selectively turn them on when readout of the corresponding photodiode is desired and turns the readout transistor off when the corresponding photodiode is not to be read out. The increased linearity of the image sensor has greatly reduced spatial variations across the image after correlated double sampling and the column fix pattern noise is greatly improved.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Apparatus and method for CDS and ADC with multiple samplings in image sensor
ActiveUS20080094494A1Reduce random noiseTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsTime segmentRandom noise
For analog to digital conversion with correlated double sampling in an image sensor, a pixel signal from a given pixel is sampled to generate a respective sampled signal N-times, with N>1 within a horizontal scan time period. A ramp signal is generated with a respective ramping portion for each respective sampled signal. Each respective sampled signal is compared with a respective ramping portion to generate a respective comparison signal that determines a respective digital code. The N respective digital codes are summed to generate a final digital code with reduced random noise.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
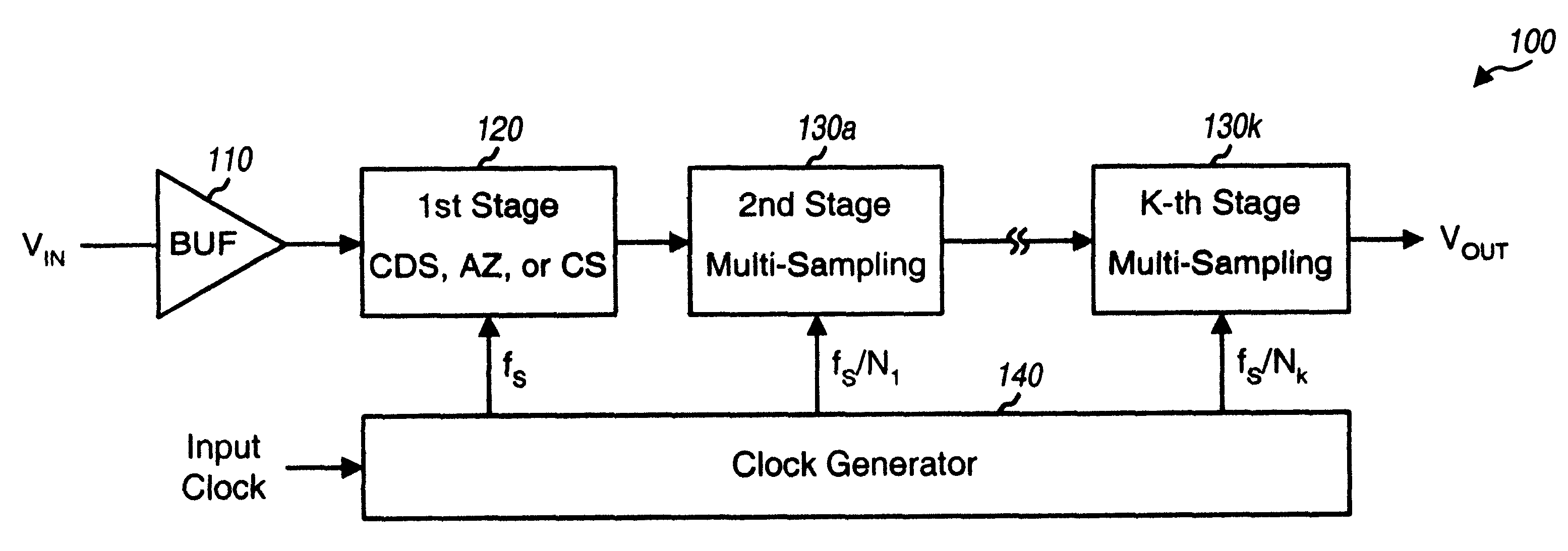
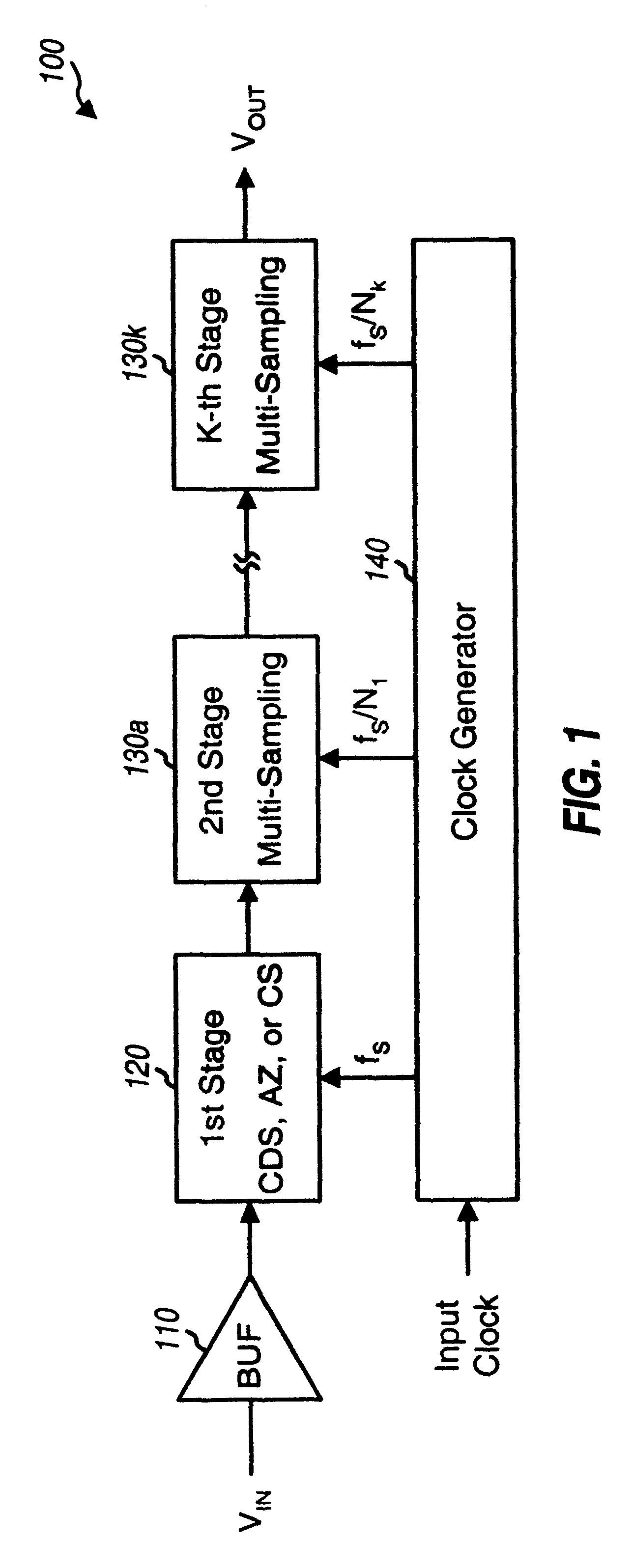
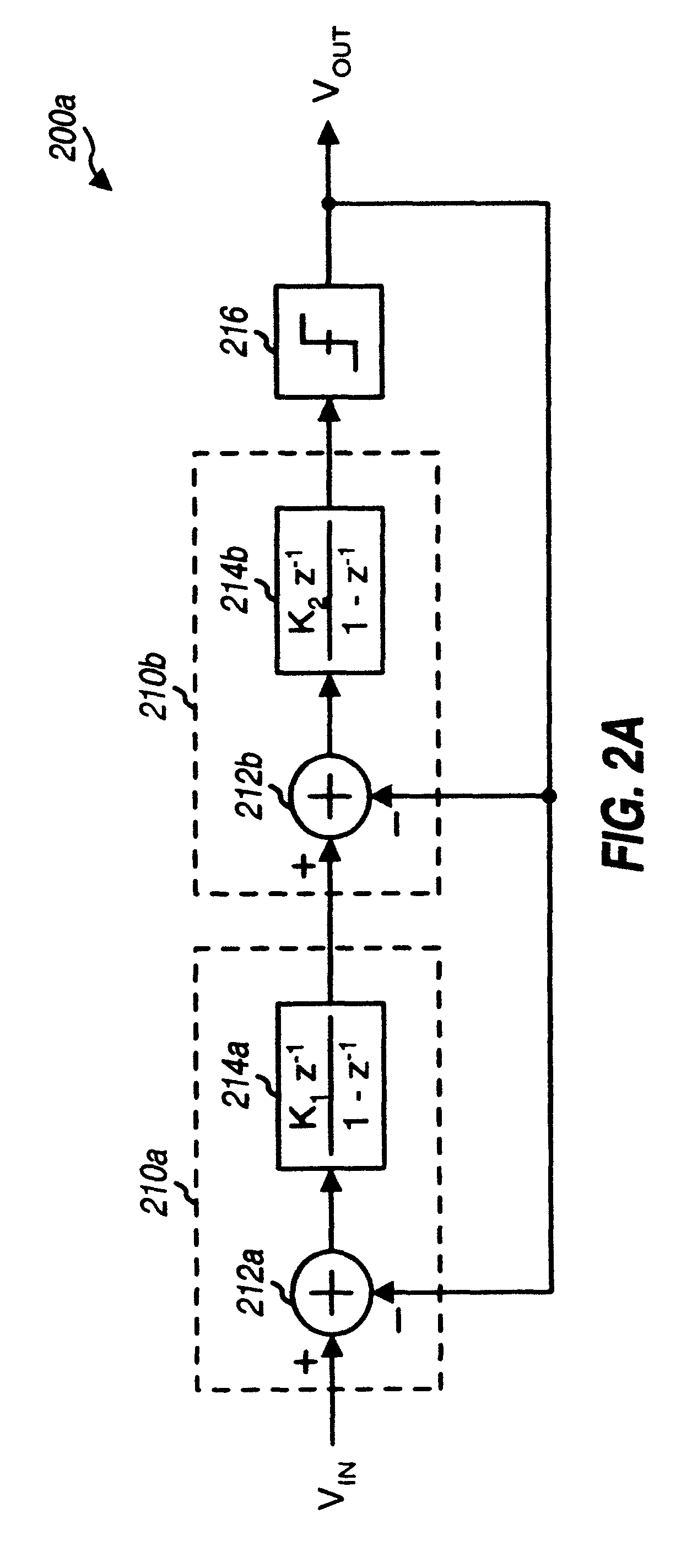
Hybrid multi-stage circuit
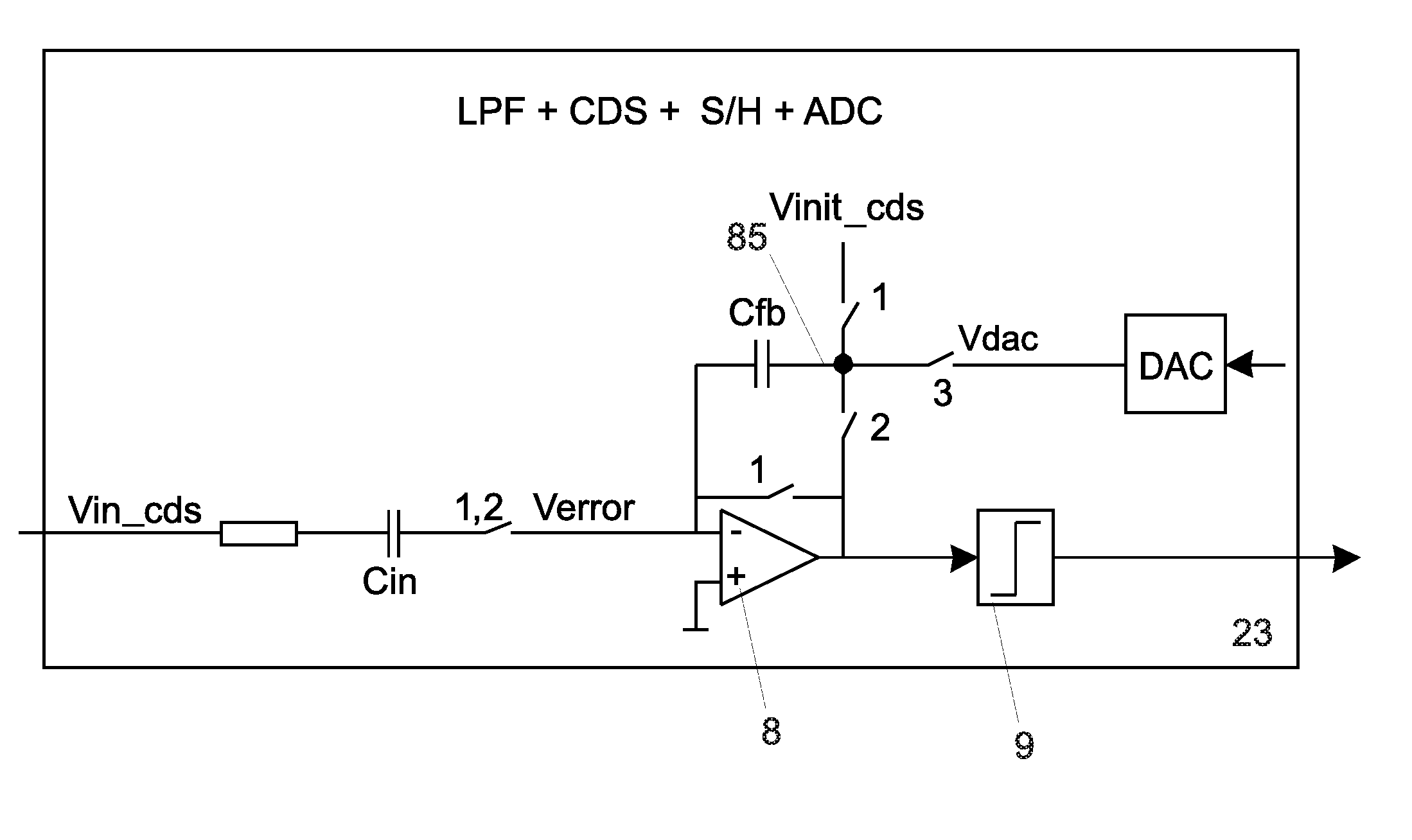
A multi-stage circuit that includes a number of stages, with at least one stage being of a first type and at least one stage being of a second type. Each stage receives either a circuit input signal or an output signal from a preceding stage, processes (e.g., filters) the received signal, and provides a respective output signal. Each first type (or second type) stage operates based on one or more clock signals having a frequency of fS (or fS / N), where fS is the sampling frequency and N is an integer greater than one. Each first type stage may be implemented with a correlated double-sampling circuit, an auto-zeroing circuit, or a chopper stabilization circuit. Each second type stage may be implemented with a multi-sampling (i.e., double-sampling or higher order sampling) circuit. The multi-stage circuit may be designed to implement a lowpass filter, a DELTASIGMA ADC, or some other circuit.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
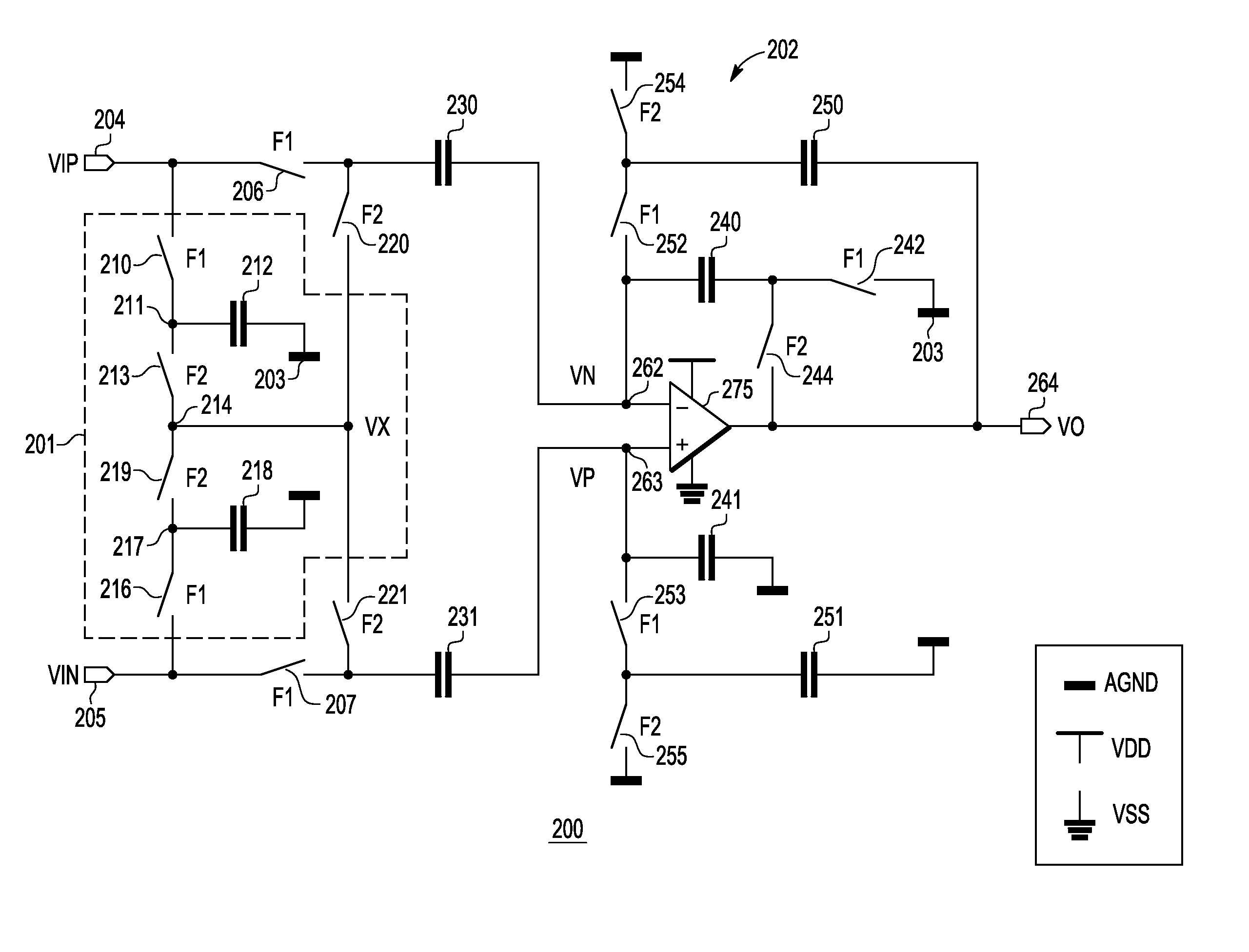
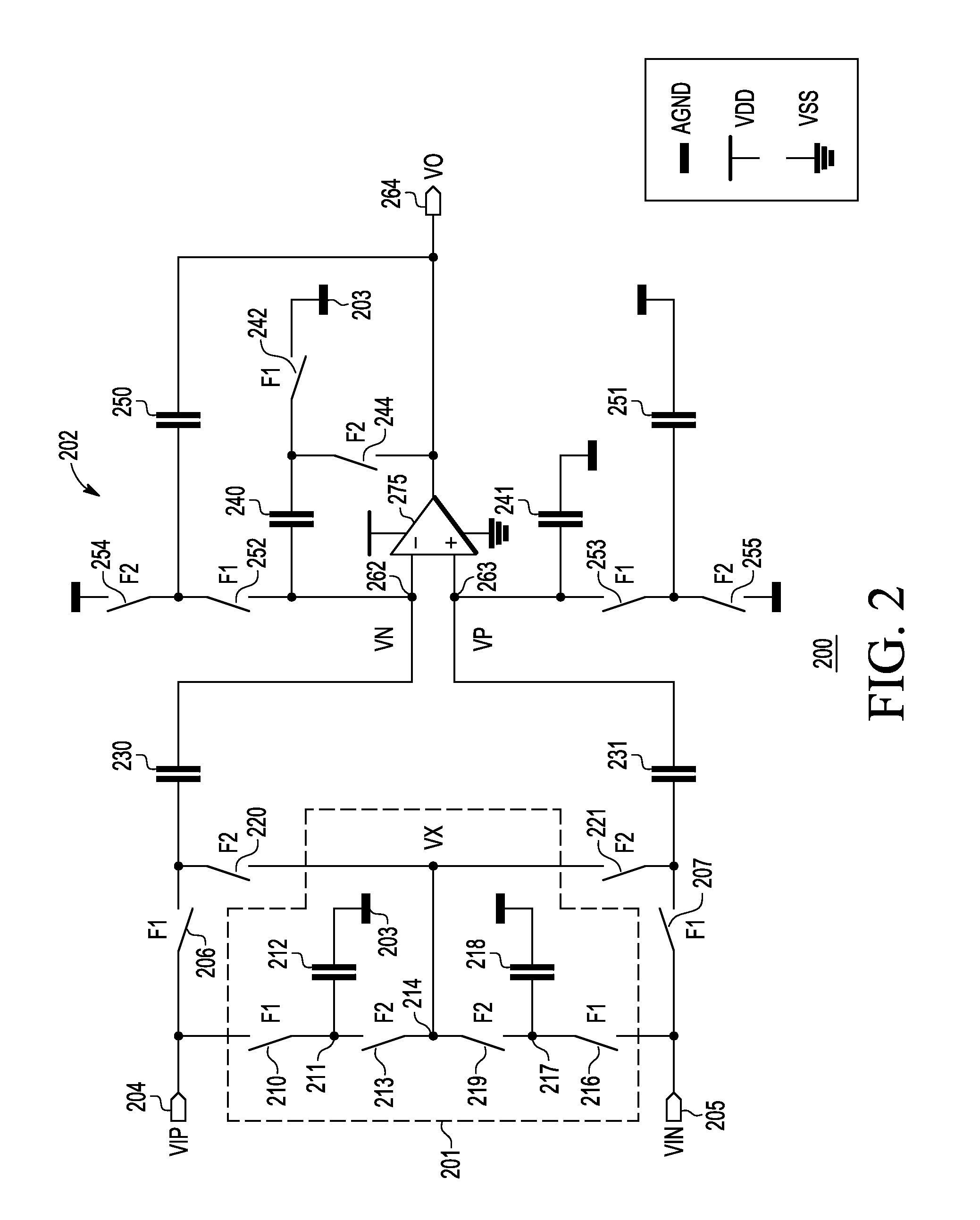
Switched-capacitor amplifier circuit
InactiveUS8198937B1Amplifier modifications to raise efficiencyDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceAudio power amplifier
A switched-capacitor amplifier circuit (200 and 300) with rail-to-rail capability without requiring a rail-to-rail operational amplifier includes a switched-capacitor amplifier (202 and 302) and an input network (201) coupled to the switched-capacitor amplifier. The switched-capacitor amplifier includes a non-rail-to-rail operational amplifier (275 and 375). The input network prevents the non-rail-to-rail operational amplifier from receiving an input differential signal that has a common-mode voltage at or near rails of the non-rail-to-rail operational amplifier. Voltages at input terminals of the operational amplifier remain near analog ground, which is an arbitrary voltage level between the rails, during both phases of switching in the switched-capacitor amplifier. In one embodiment, the switched-capacitor amplifier uses a correlated double sampling technique.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Column analog-to-digital conversion apparatus and method supporting a high frame rate in a sub-sampling mode
InactiveUS7230558B2Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSample ModeHigh frame rate
A column analog-to-digital conversion apparatus includes a first correlated double sampling (CDS) and comparison unit of a CDS and comparison circuit for generating a first comparison result signal in response to a first pixel output signal and a ramp signal, a second CDS and comparison unit of the CDS and comparison circuit for generating a second comparison result signal in response to the first pixel output signal and the ramp signal in a sub-sampling mode, and a data buffer for determining a code value of a most significant bit (MSB) based on the second comparison result signal, determining code values of remaining lower bits based on a counting value outputted from a counter, and generating a digital code including the MSB and the remaining lower bits.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Analog optical black clamping circuit for a charge coupled device having wide programmable gain range
ActiveUS6940548B2Overall design flexibilityHighly programmableTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsIntegratorAudio power amplifier
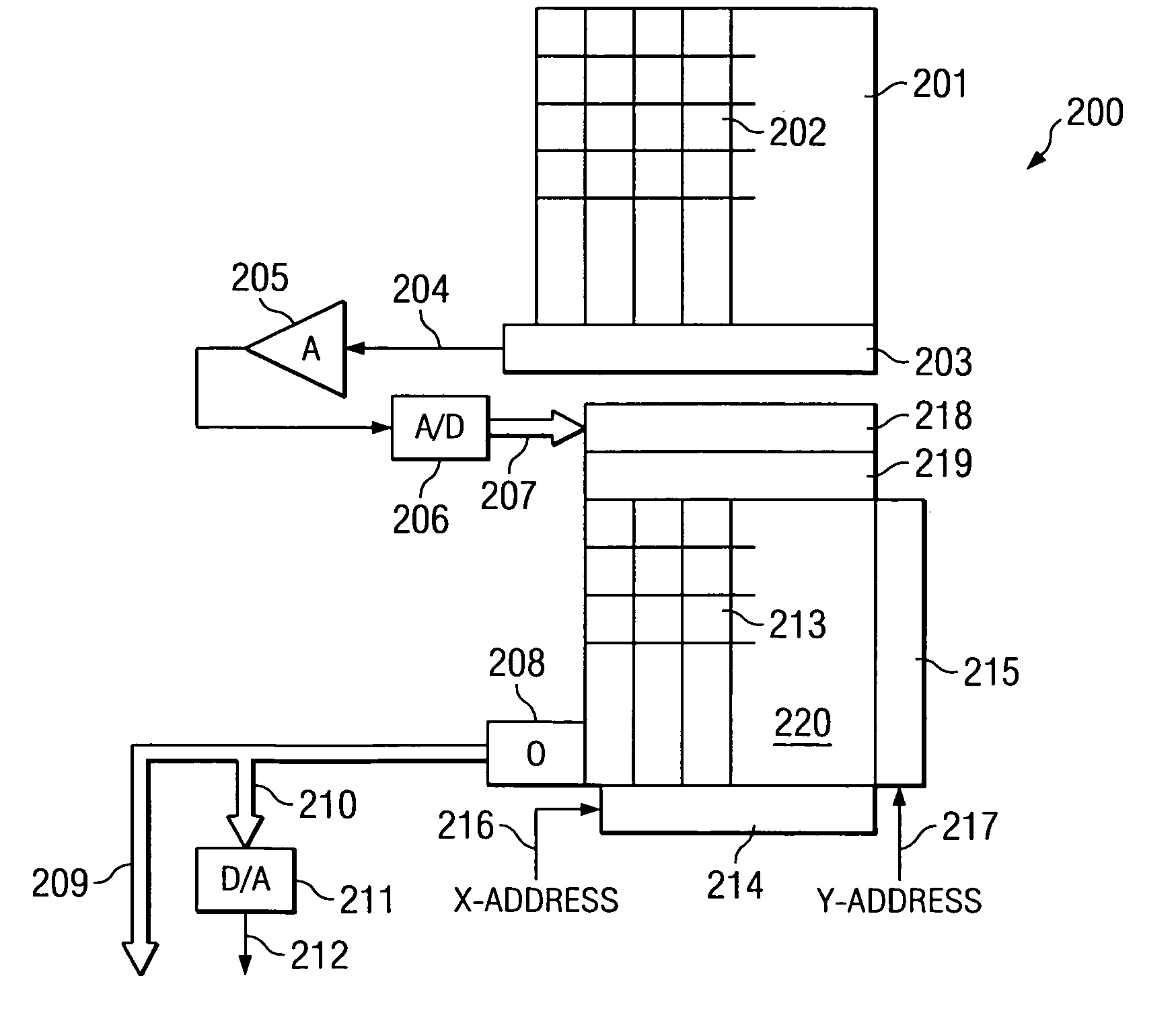
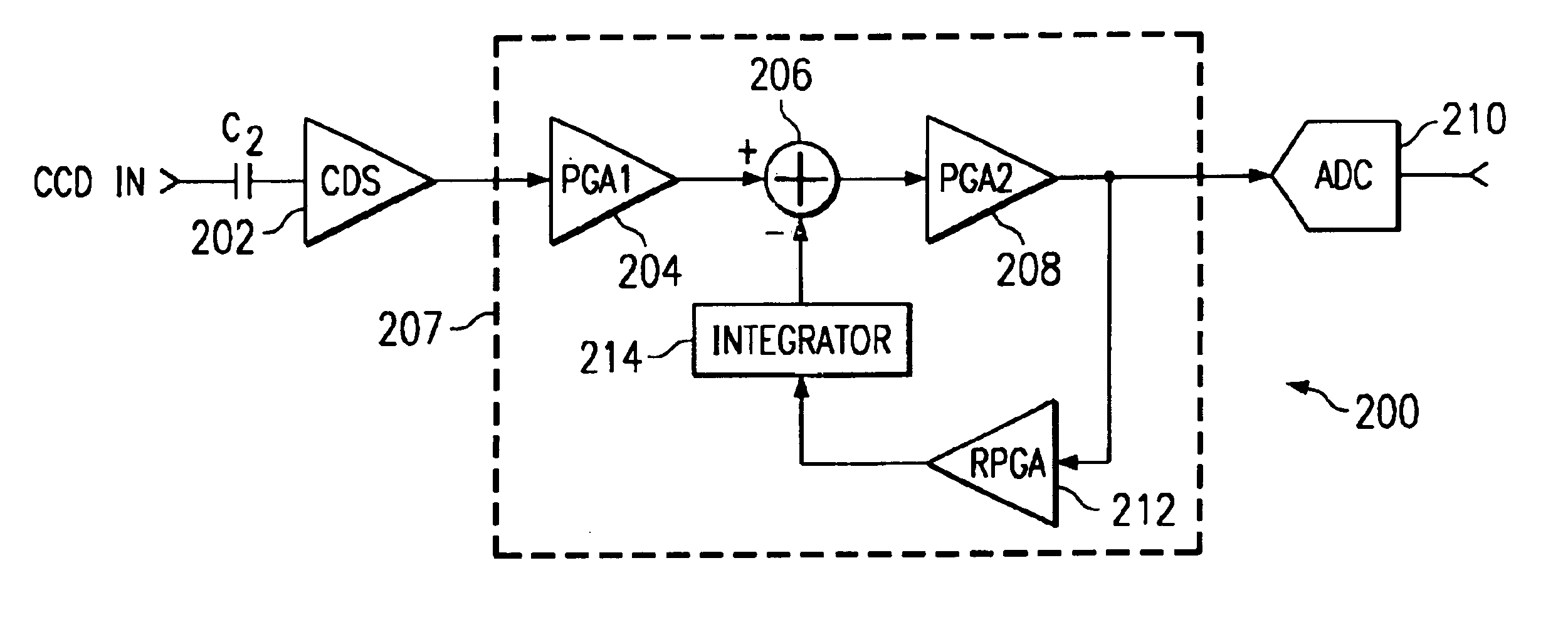
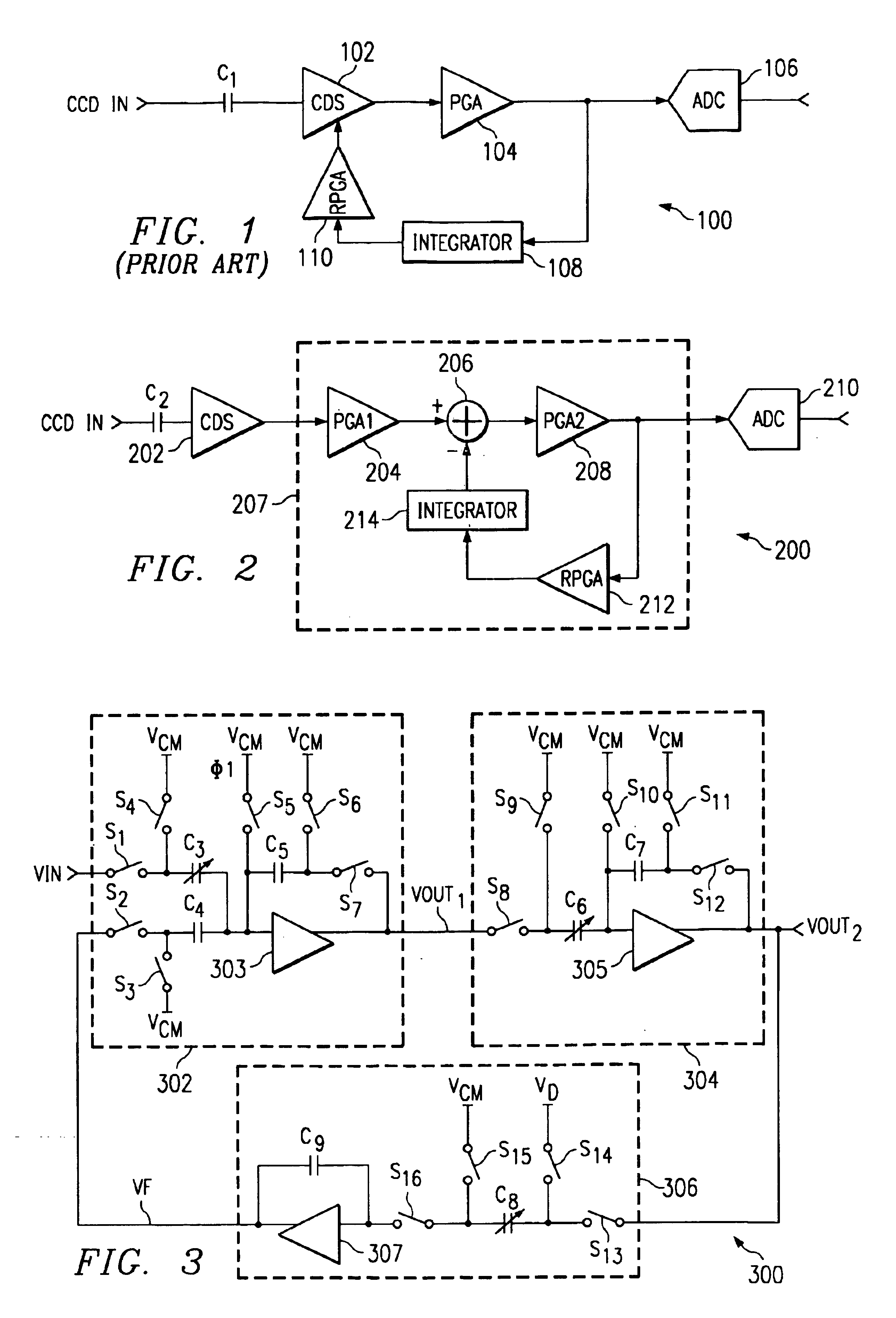
An image processing apparatus (200) for a charge coupled device including analog front end circuitry having optical black and offset correction, whereby the offset and optical black correction circuit is programmable. The present invention includes a first circuit (202, 204, 206, 208, 210) to sample the incoming optical black signal output from a CCD. This first circuit includes a correlated double sampler (202) coupled to a first programmable gain amplifier (204). An adder (206) connects between the first programmable gain amplifier (204) and a second gain amplifier (208) for adding in the optical black offset to the optical black signal input from the CCD. A second circuit (212, 214) includes a reverse programmable gain amplifier (212) connected to the output of the second programmable gain amplifier (208) to amplify the optical black level inversely proportional to the gain from the second programmable gain amplifier (208). The second circuit (212, 214) also includes an integrator (214) coupled to the reverse programmable gain amplifier (212) to integrate the difference between the incoming signal and the desired optical black value. The second circuit (212, 214) couples to the adder (206) to add the positive and negative difference to the optical black signal. An analog-to-digital converter (210) converts the sampled signal for further processing at the output of the image processing apparatus (200).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Photoelectric conversion element, image reading device, image forming apparatus, image reading method, and computer-readable recording medium
ActiveUS20170201700A1Television system detailsColor television detailsAudio power amplifierImage formation
A photoelectric conversion element includes: light receiving elements that convert an optical signal into an electrical signal per pixel; offset fixing units that fix an offset of an output level of each of the light receiving elements to a reference level; analog / digital conversion units that convert signals respectively corresponding to a signal level being converted from an optical signal and output by the light receiving elements and a reset level output independent of an optical signal, into digital signals, according to the reference level; amplifier units that amplify a signal; and correlated double sampling units that perform correlated double sampling per each of the light receiving elements by using a signal based on the reset level and a signal based on the signal level, wherein the amplifier units amplify the signal corresponding to the reset level and the signal corresponding to the signal level before implementing the correlated double sampling.
Owner:RICOH KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com