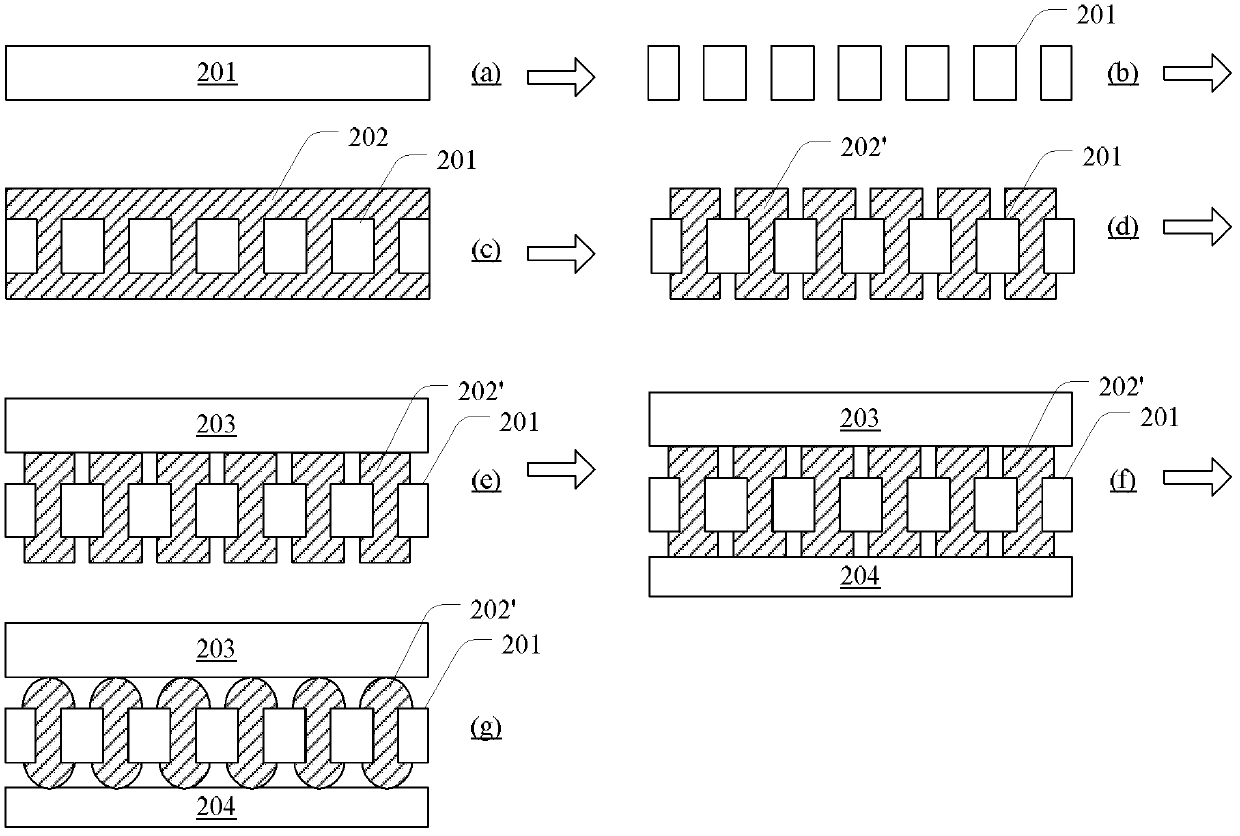
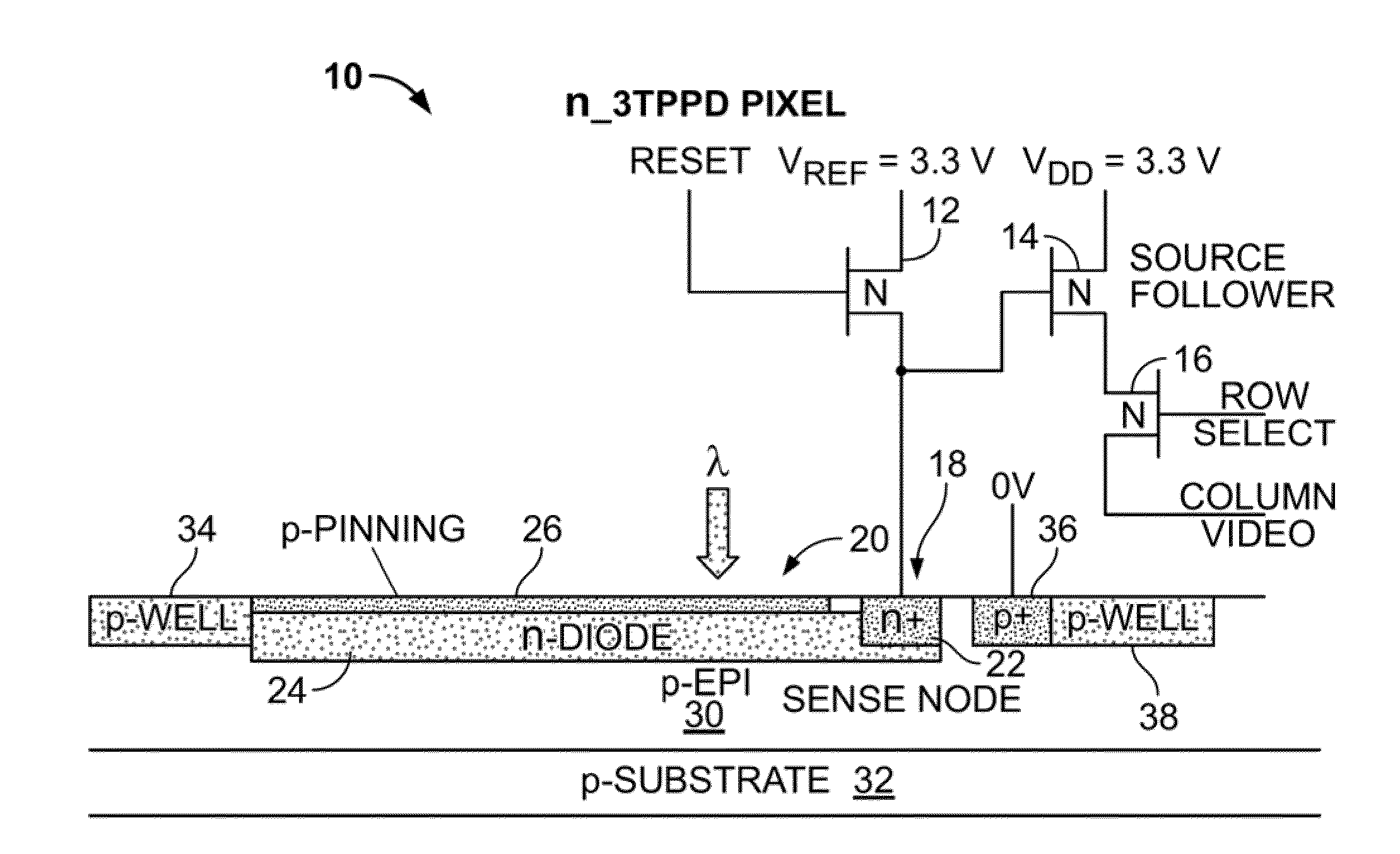
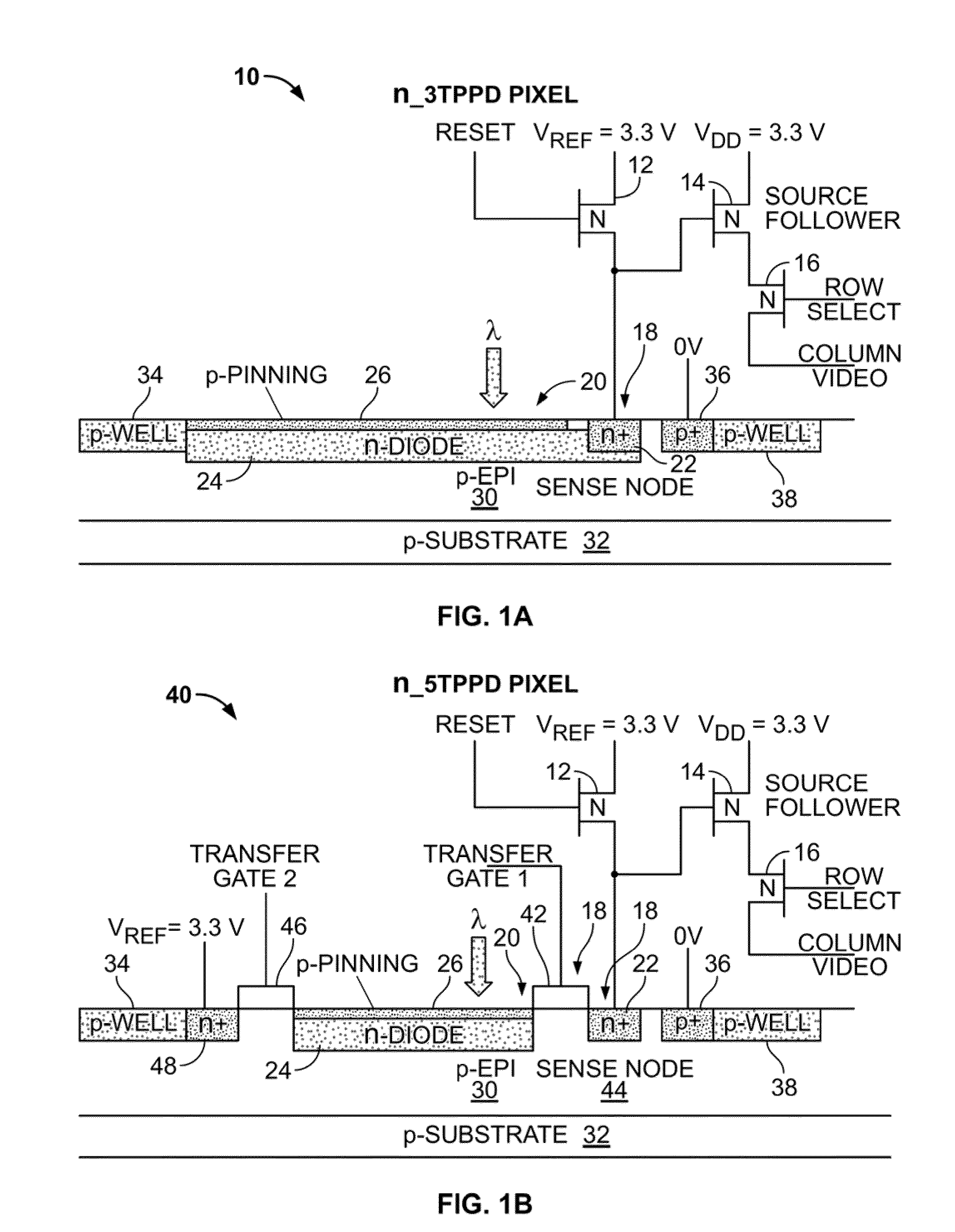
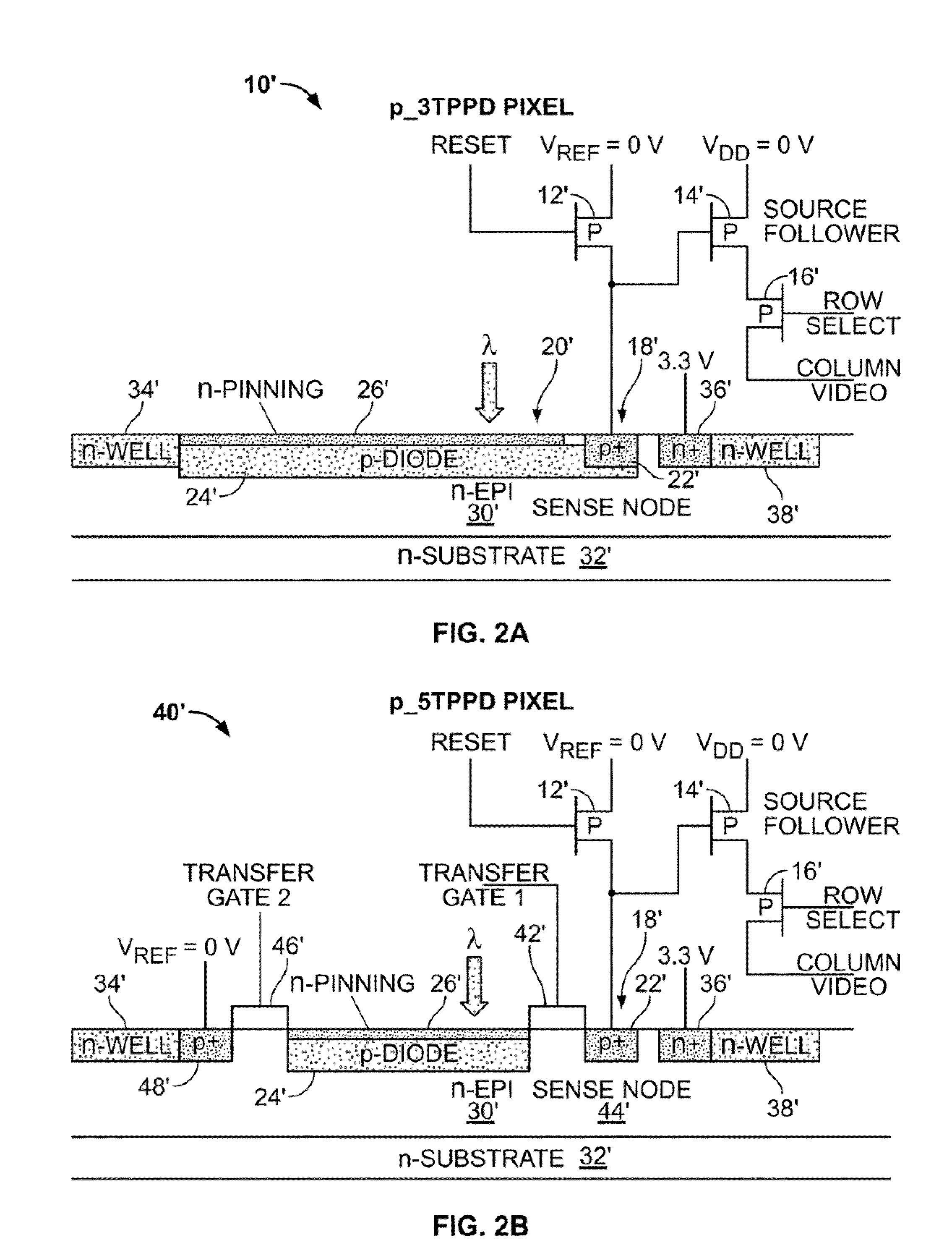
Patents
Literature
88 results about "Cmos pixels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
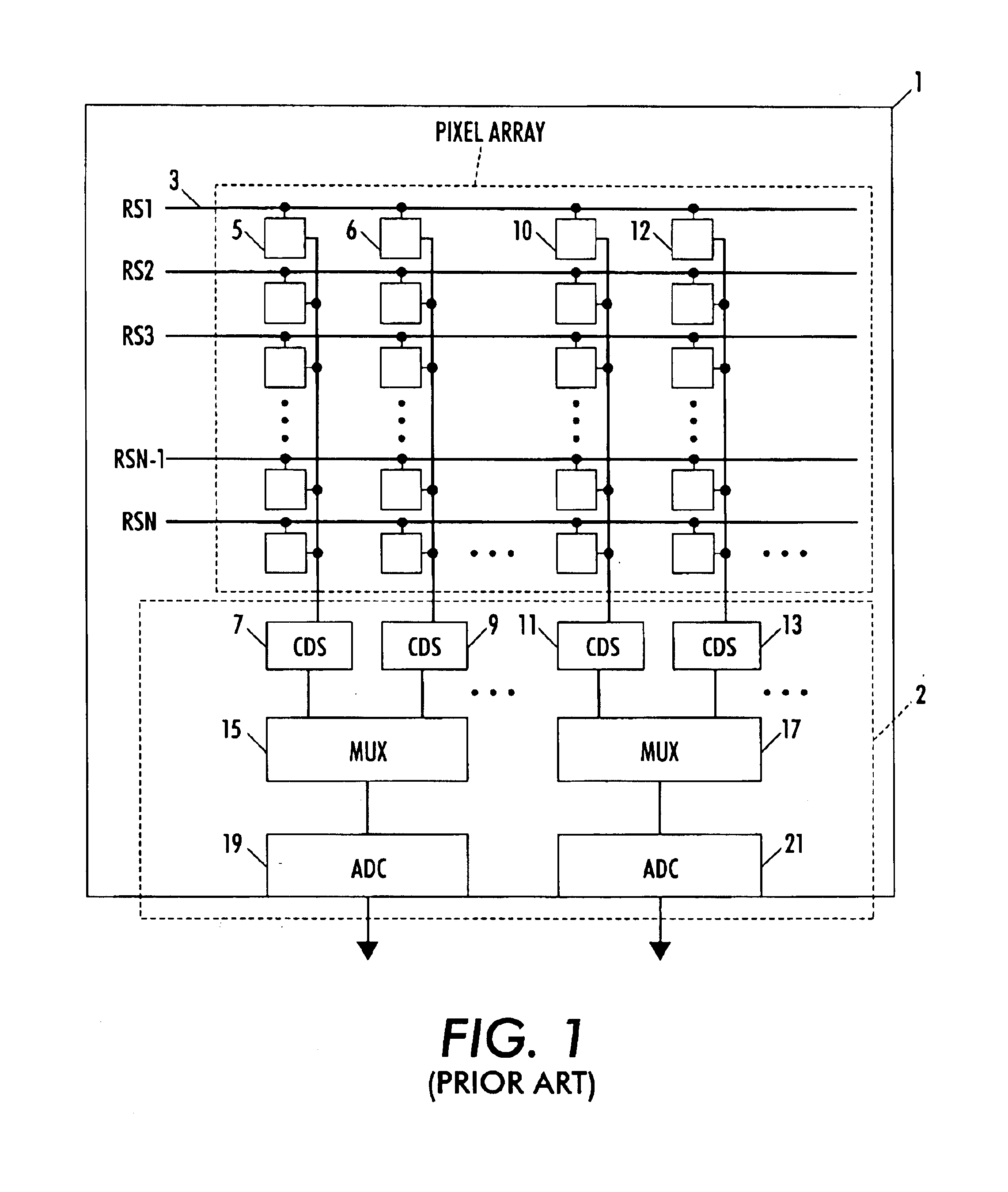
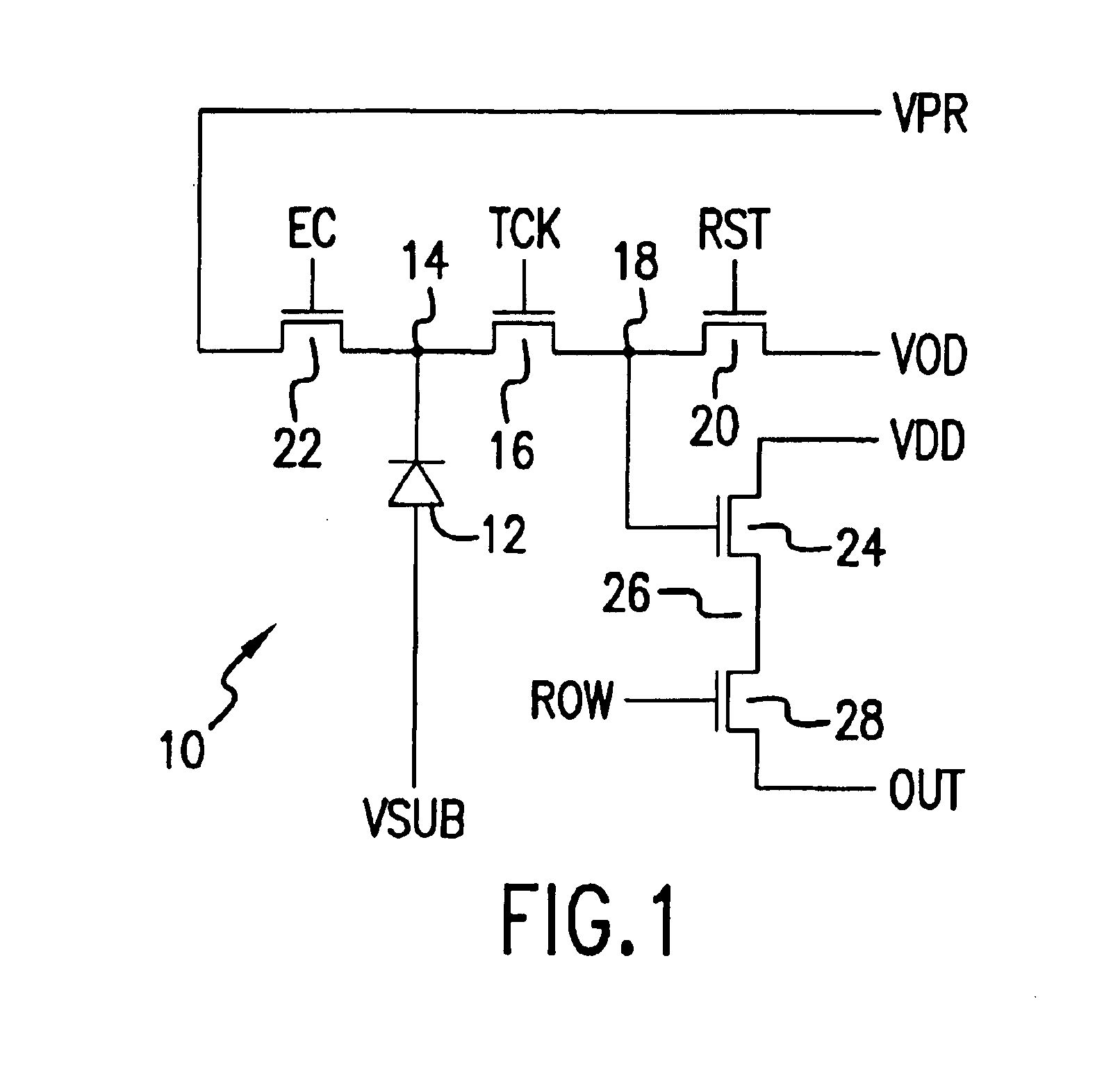
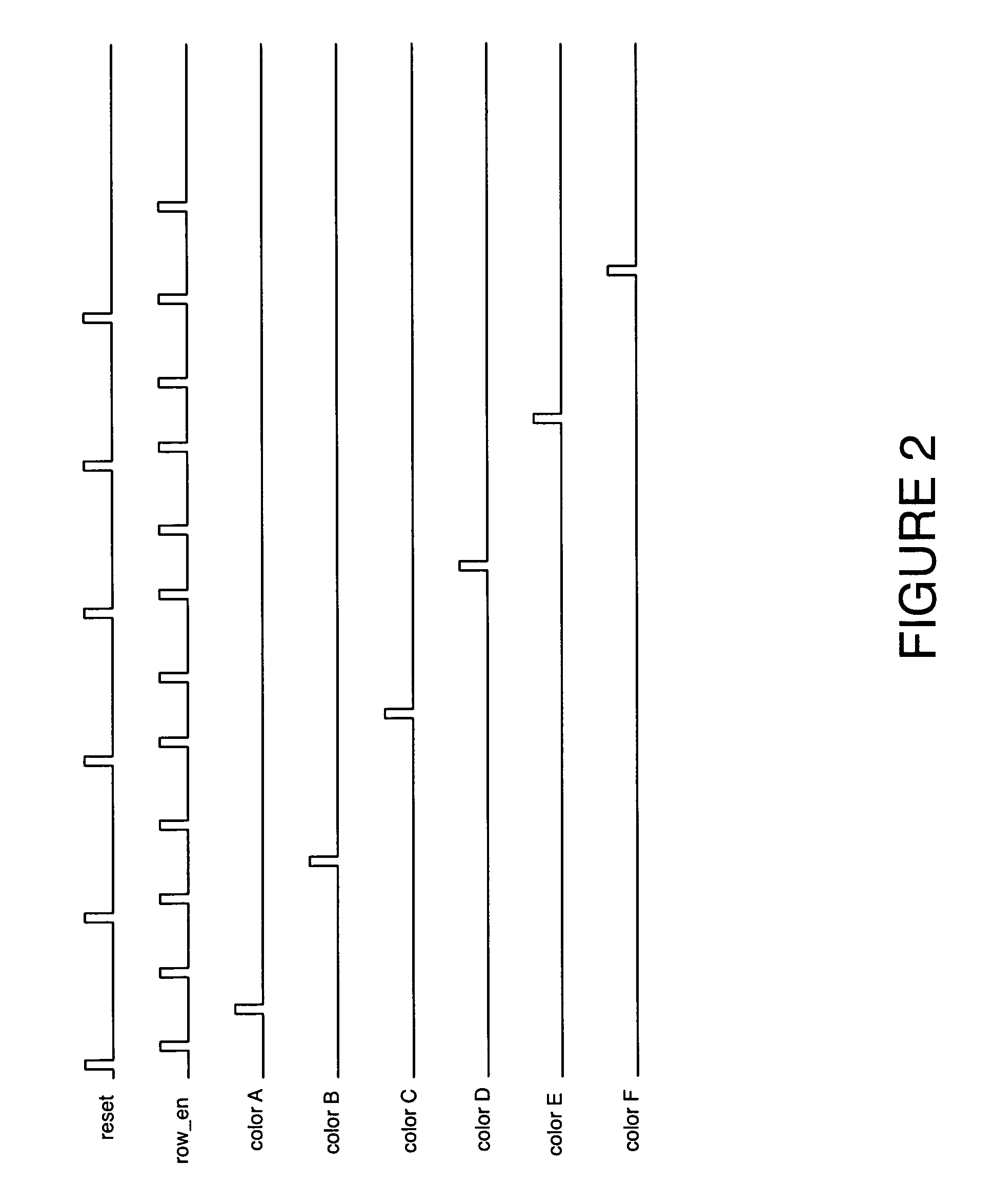
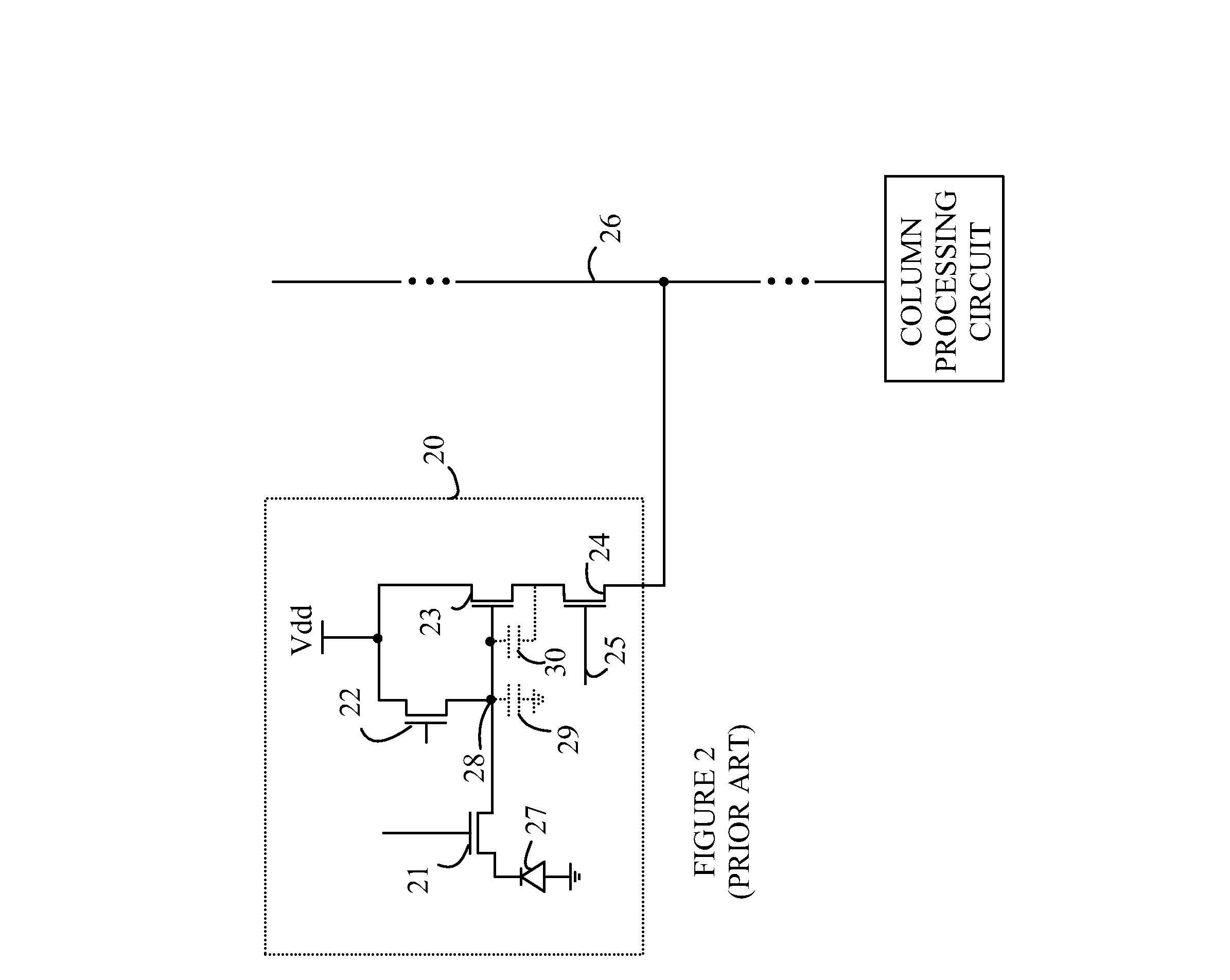
Circuit and method for cancellation of column pattern noise in CMOS imagers
ActiveUS6903670B1Corrects non-linearityCompensating for such errorTelevision system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsSignal processing circuitsAudio power amplifier
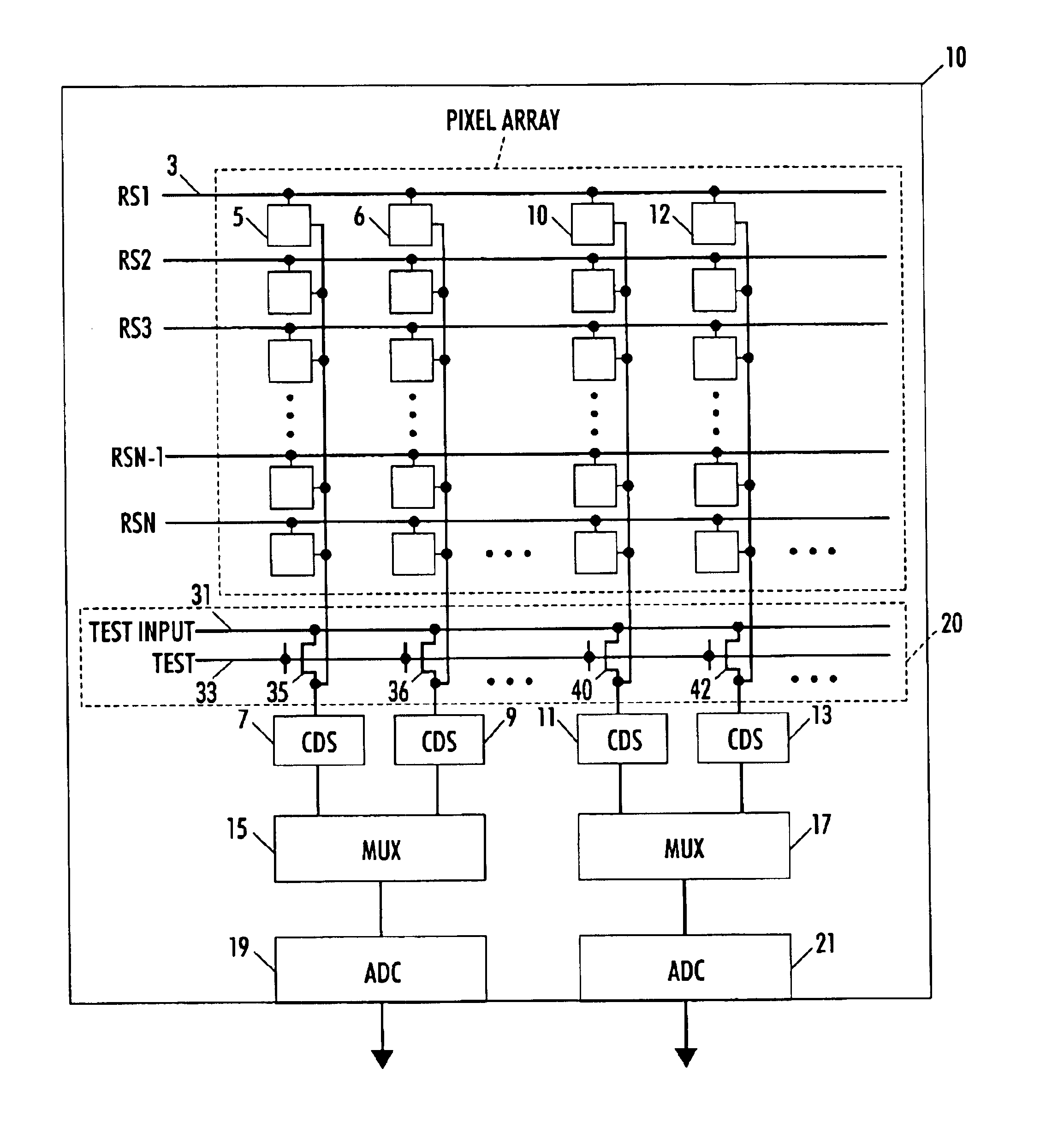
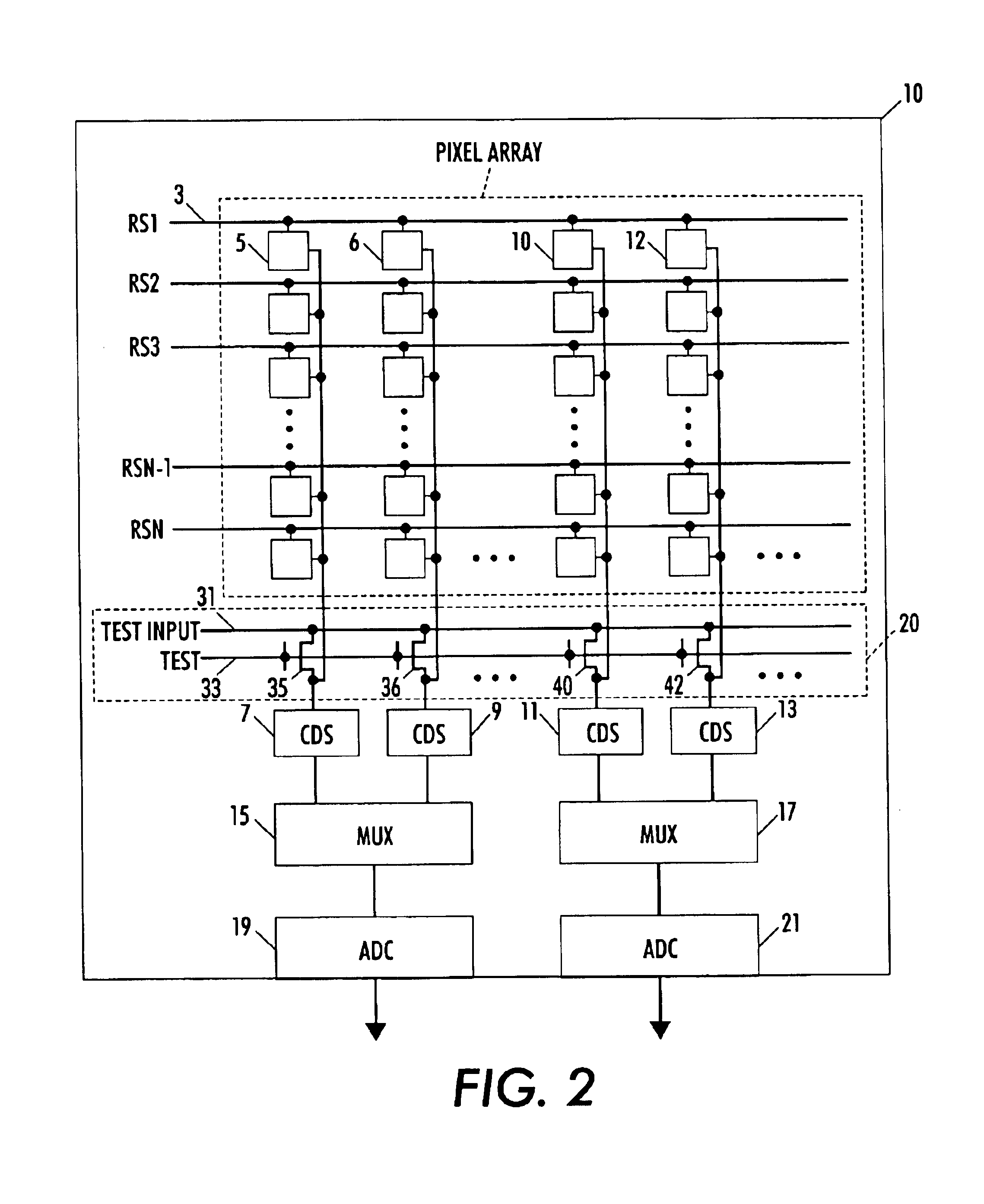
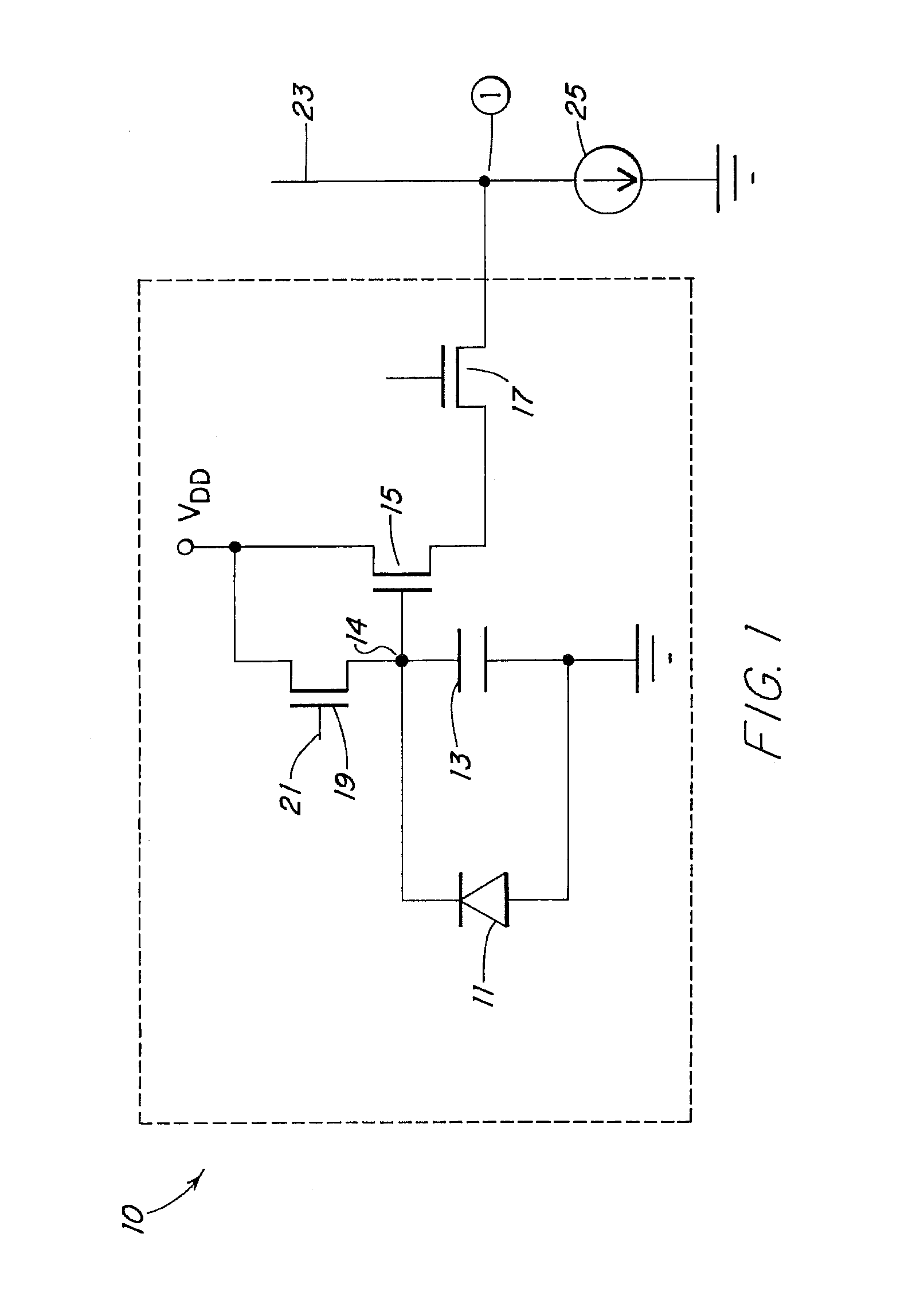
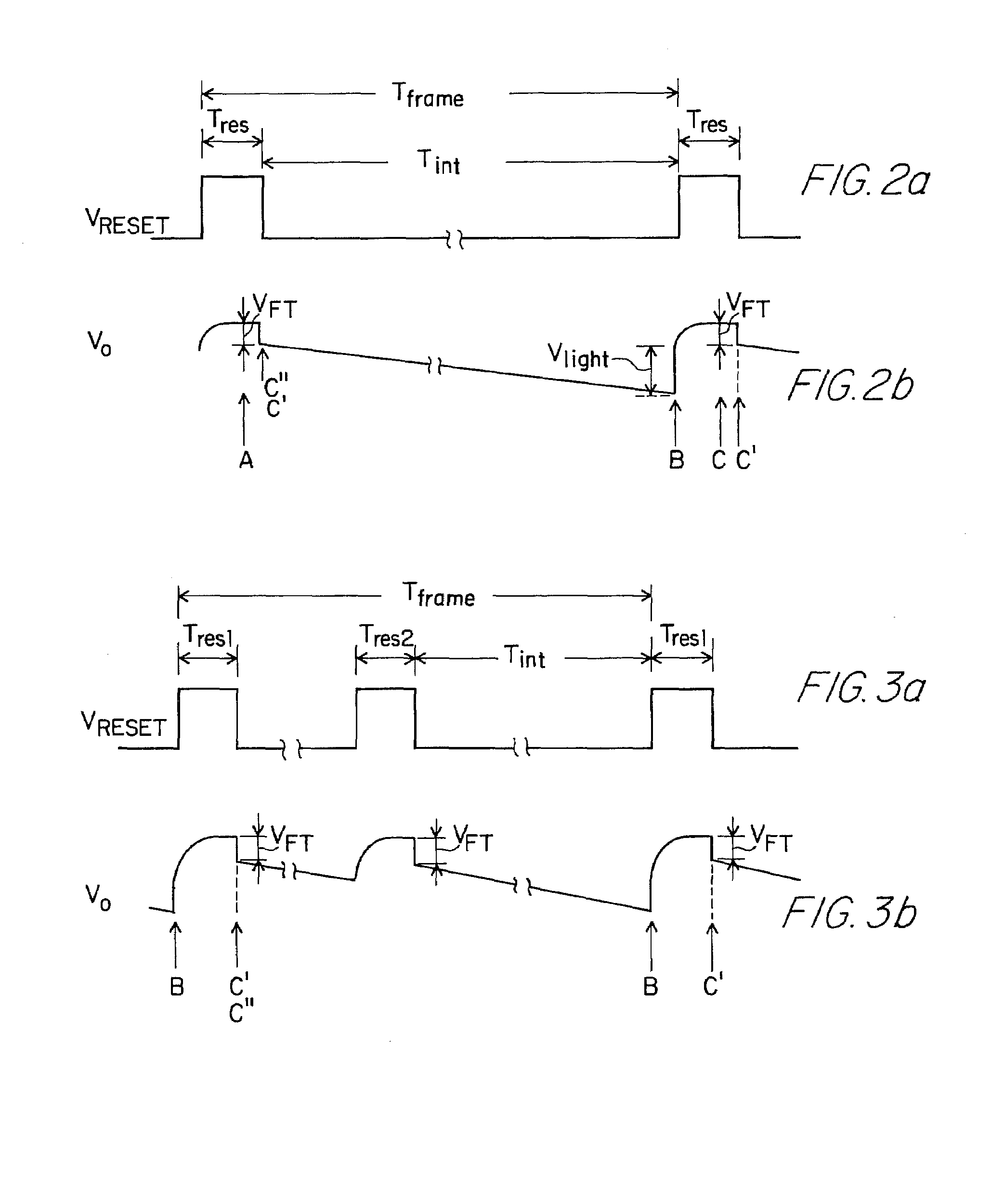
A circuit and method measure the output voltage of a CMOS pixel in a manner that substantially reduces all columnar pattern noise due to mismatches in the signal processing circuits including the correlated double sampling amplifiers and A / D converters. The circuit includes a test switch, operatively connected between a reference voltage source and a correlated double sampling amplifier, for applying a test voltage from the reference voltage source when the state of the test switch is ON to the correlated double sampling amplifier. The reference voltage source produces a voltage corresponding to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of a gain error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; a voltage corresponding to ground to enable the determination of an offset error in the correlated double sampling amplifier and / or A / D converter; and a plurality of analog voltages ranging from analog ground to a full-scale voltage level to enable the determination of non-linearity errors in the A / D converter.
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
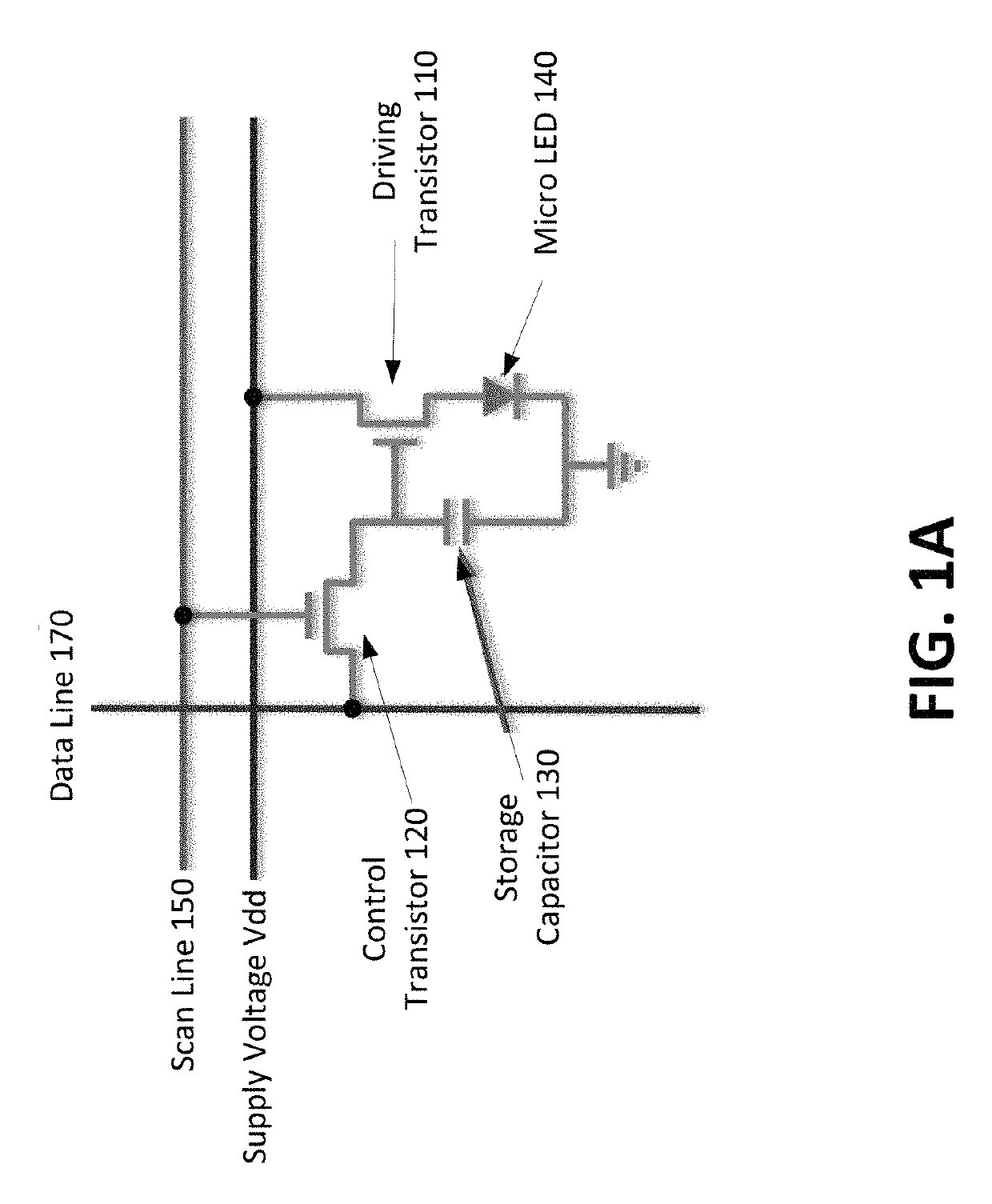
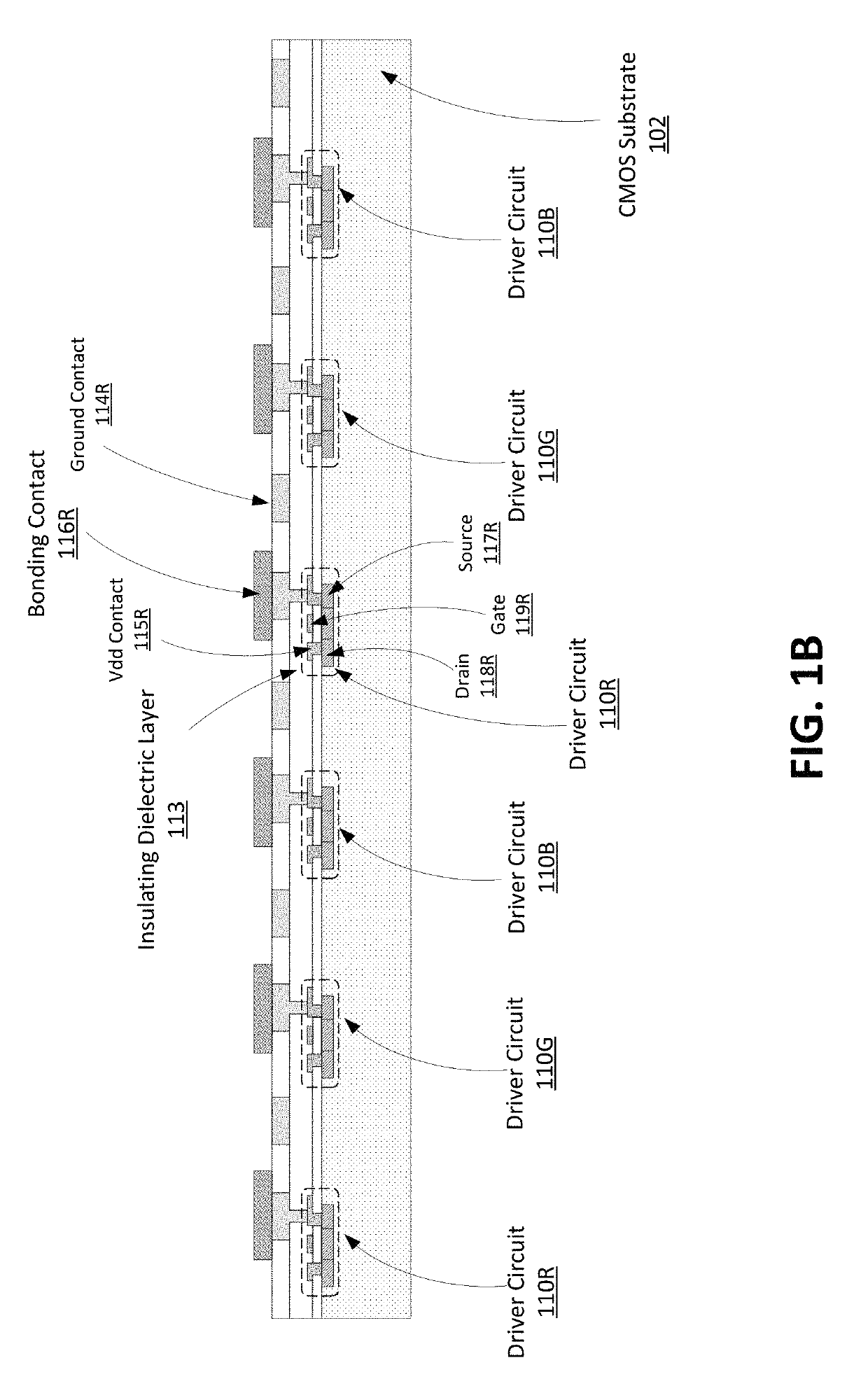
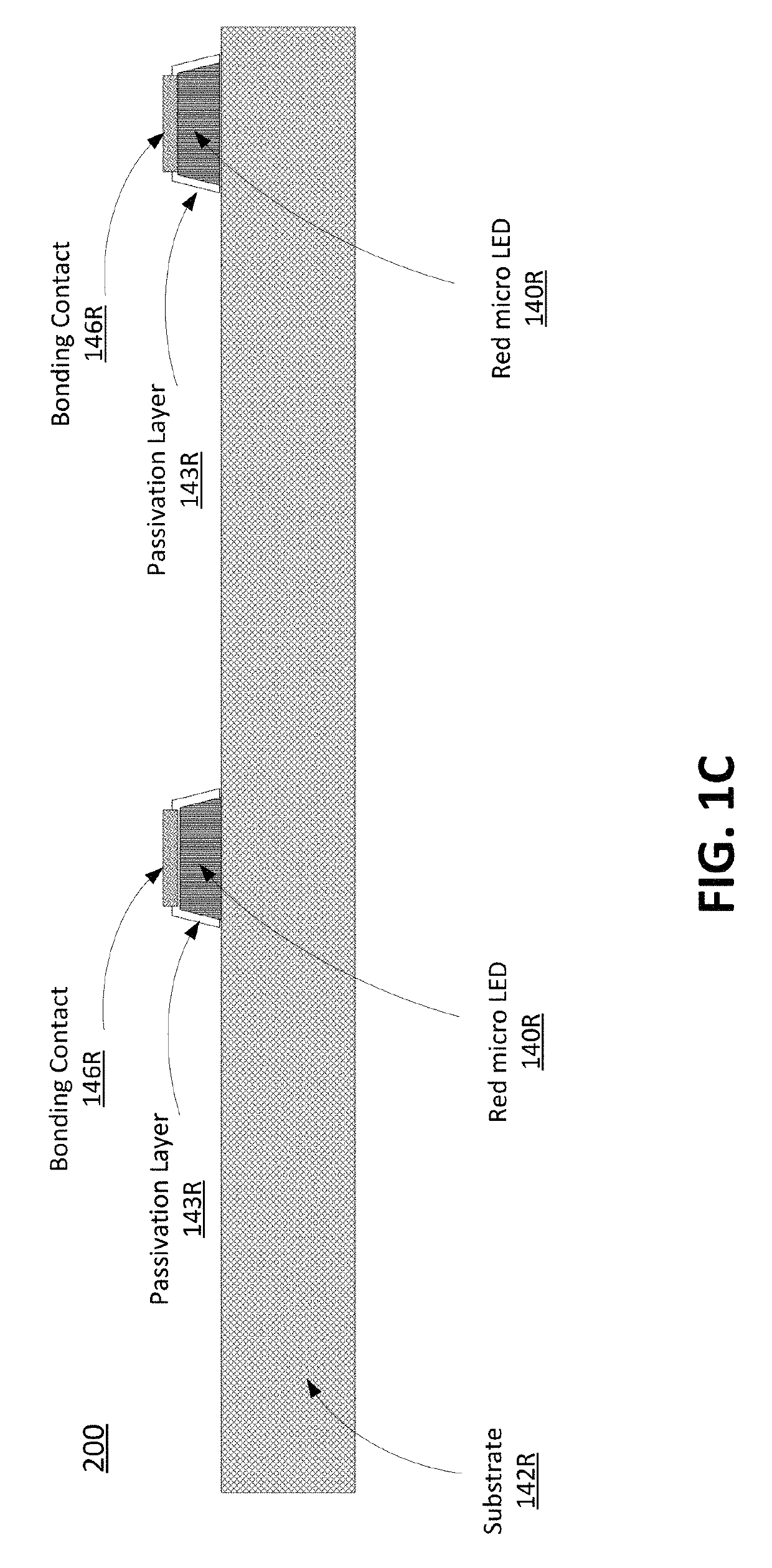
Mass Transfer Of Micro Structures Using Adhesives
ActiveUS20180166429A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicro structureLED display
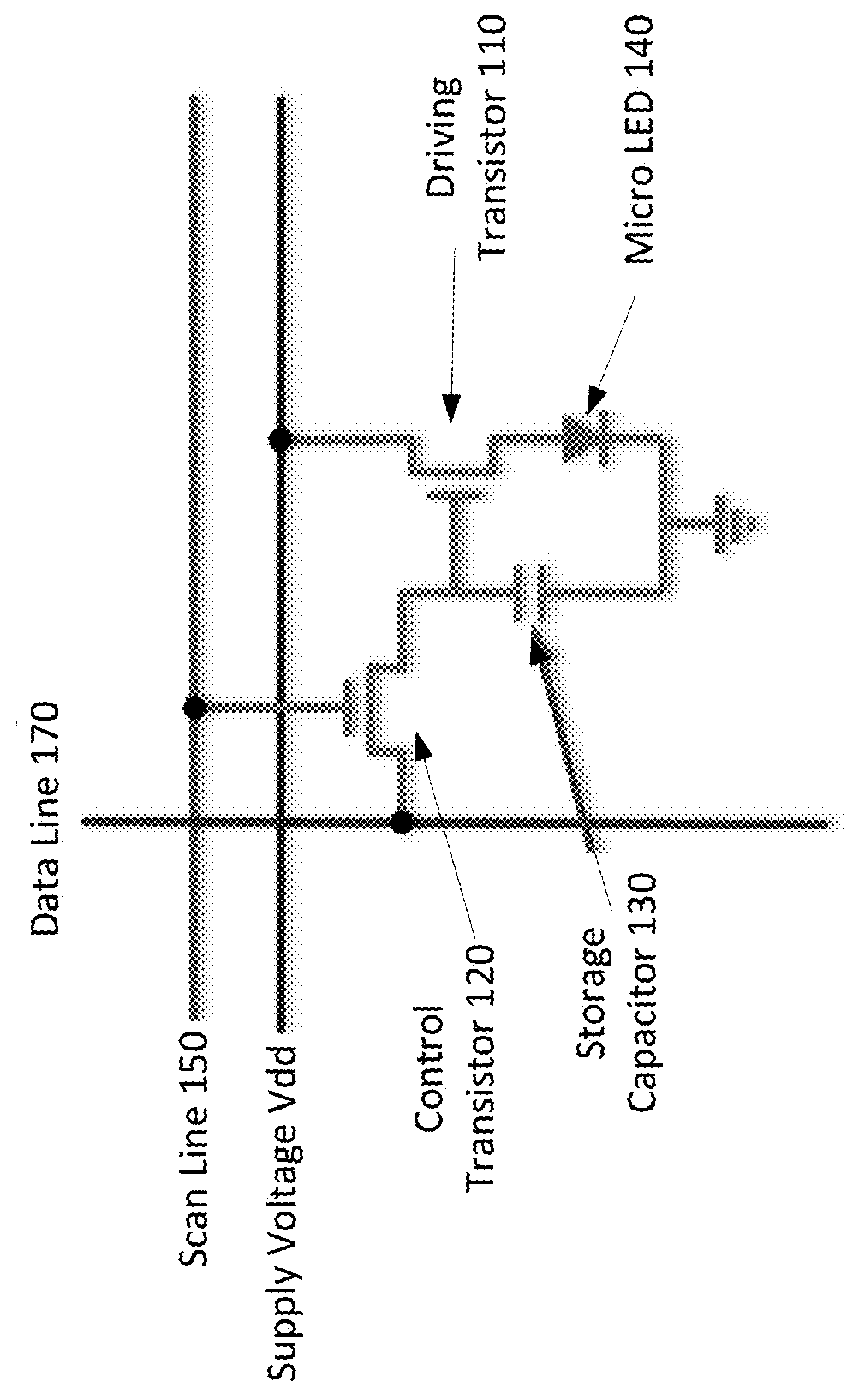
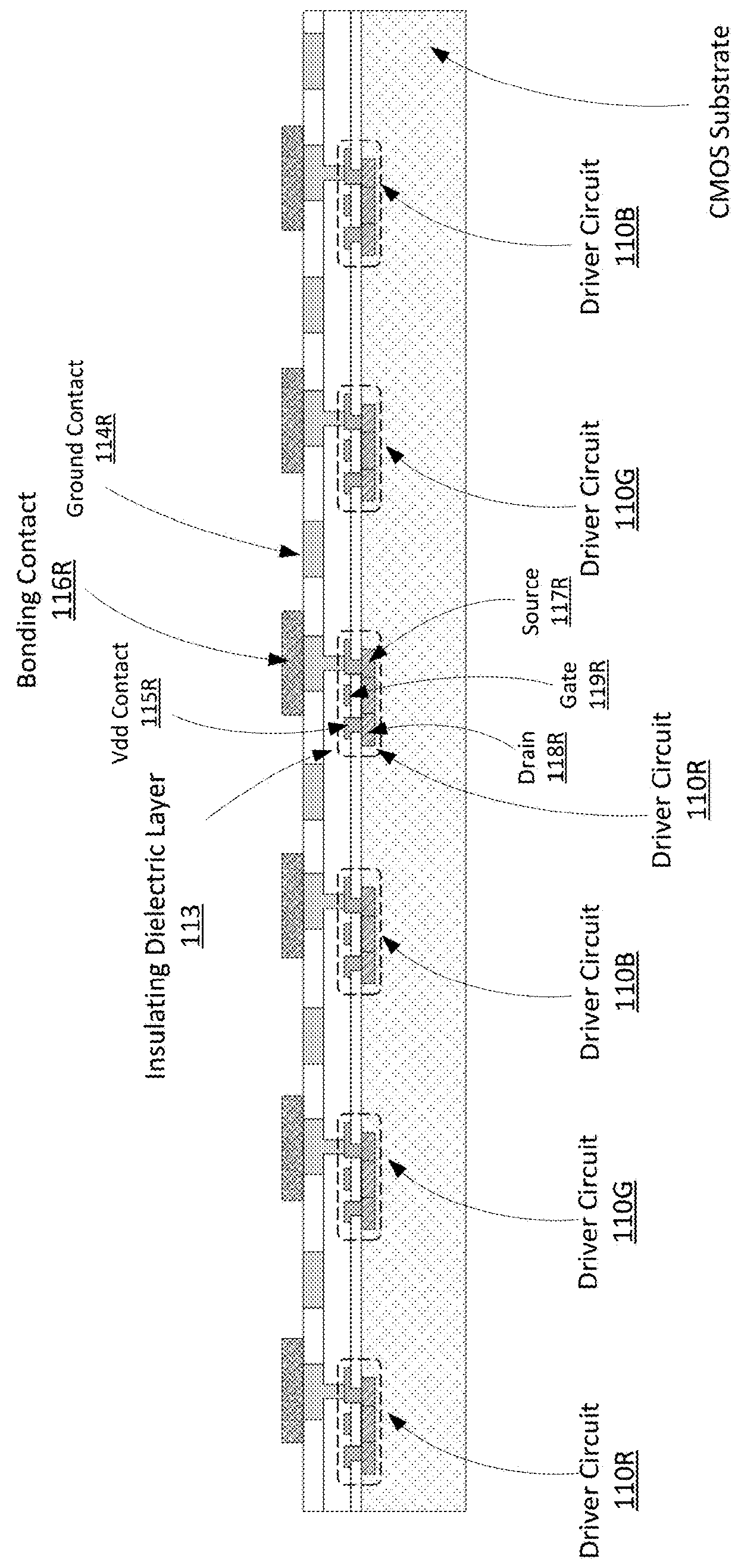
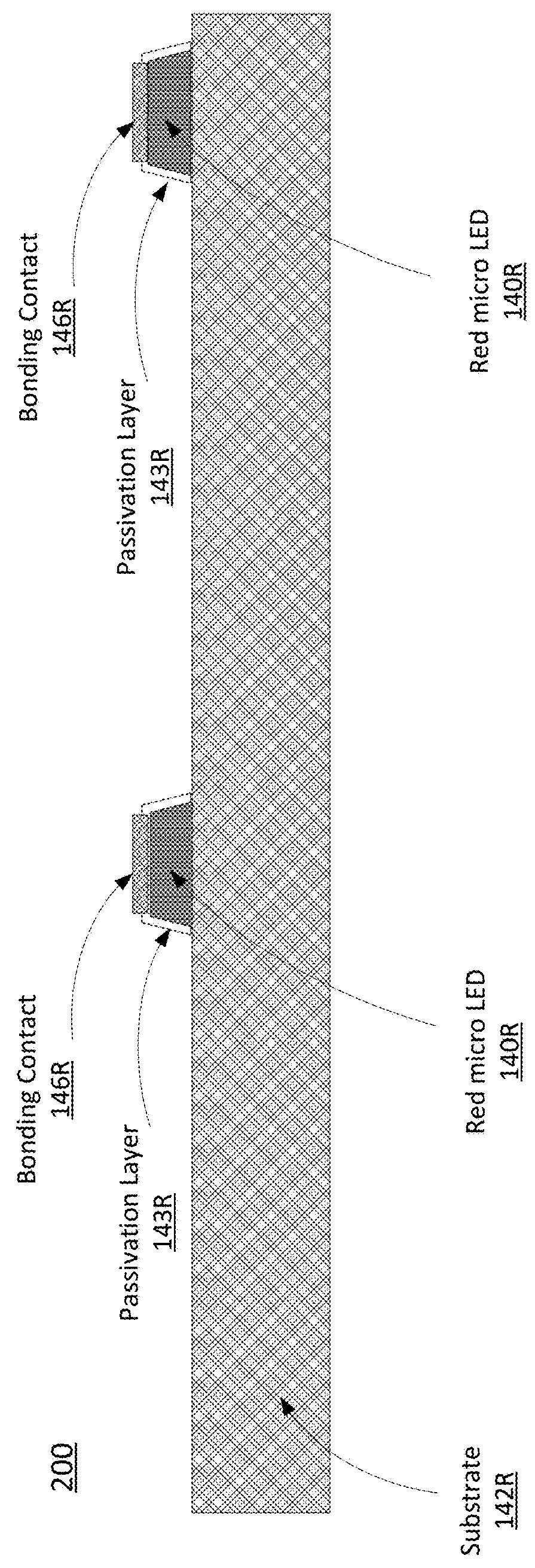
Mass transfer of micro structures are effected from one substrate to another using adhesives. In the context of an integrated micro LED display, a micro LED array is fabricated on a native substrate and corresponding CMOS pixel drivers are fabricated on a separate substrate. The micro LED substrate (e.g., sapphire) and the CMOS substrate (e.g., silicon) may be incompatible. For example, they may have different thermal coefficients of expansion which make it difficult to bond the micro LEDs to the pixel driver circuitry. The micro LED array is transferred to an intermediate substrate (e.g., silicon) by use of an adhesive. This intermediate substrate may be used in a process of bonding the micro LED array to the array of pixel drivers. The intermediate substrate is separated from the micro LED array by releasing the adhesive.
Owner:JADE BIRD DISPLAY SHANG HAI LTD
Camera with MOS or CMOS sensor array
InactiveUS6730900B2Low costMass productionTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOS sensorSensor array
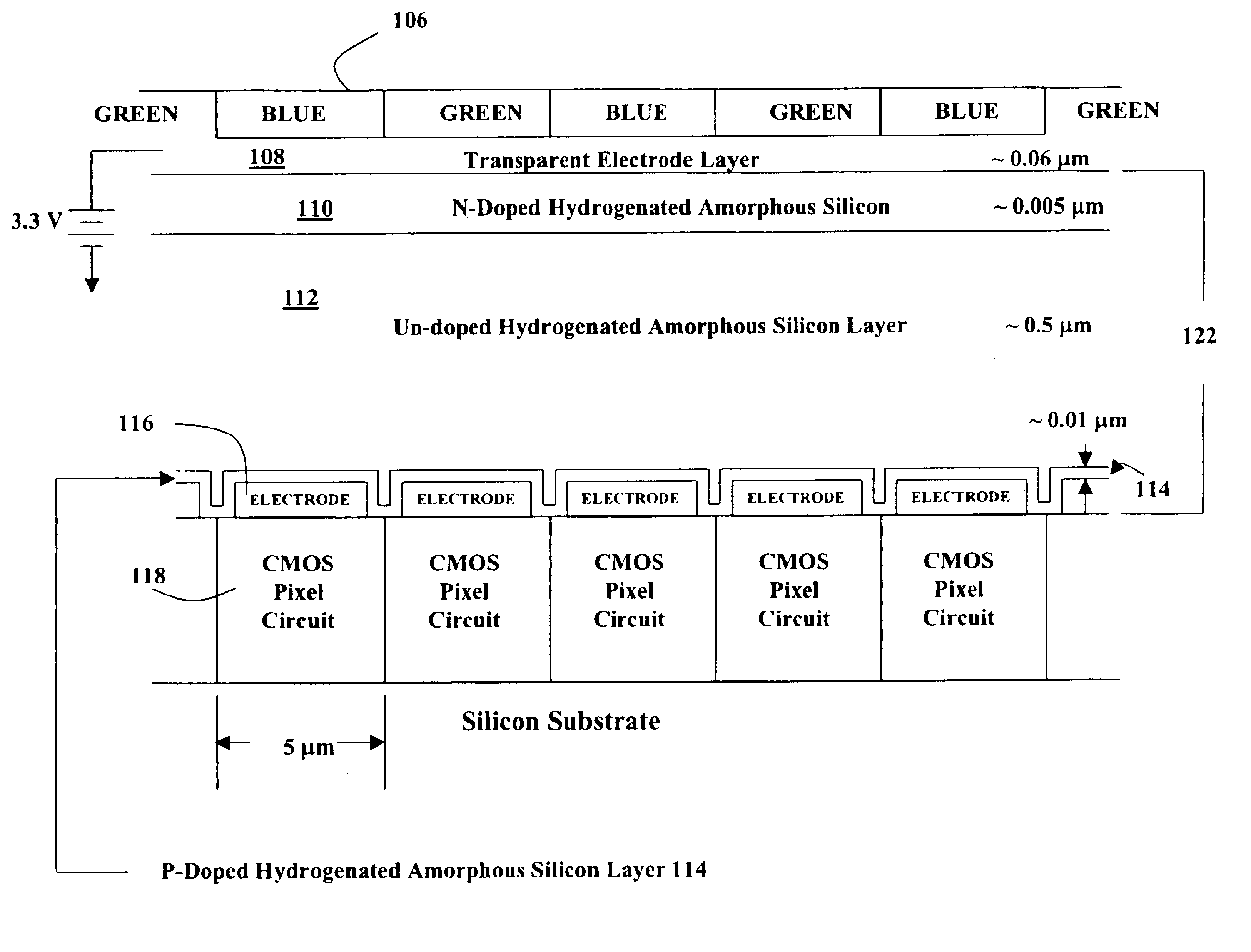
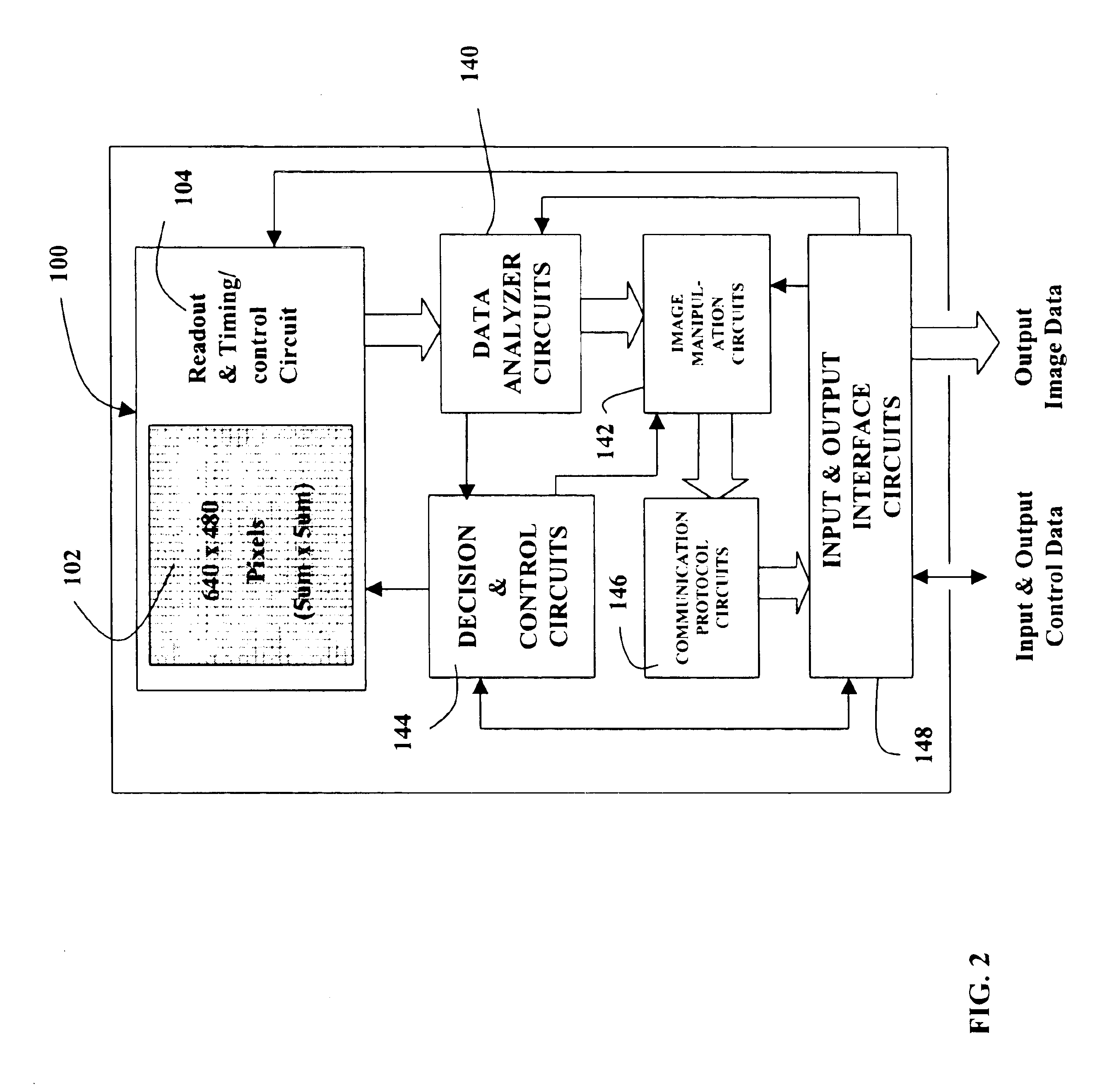
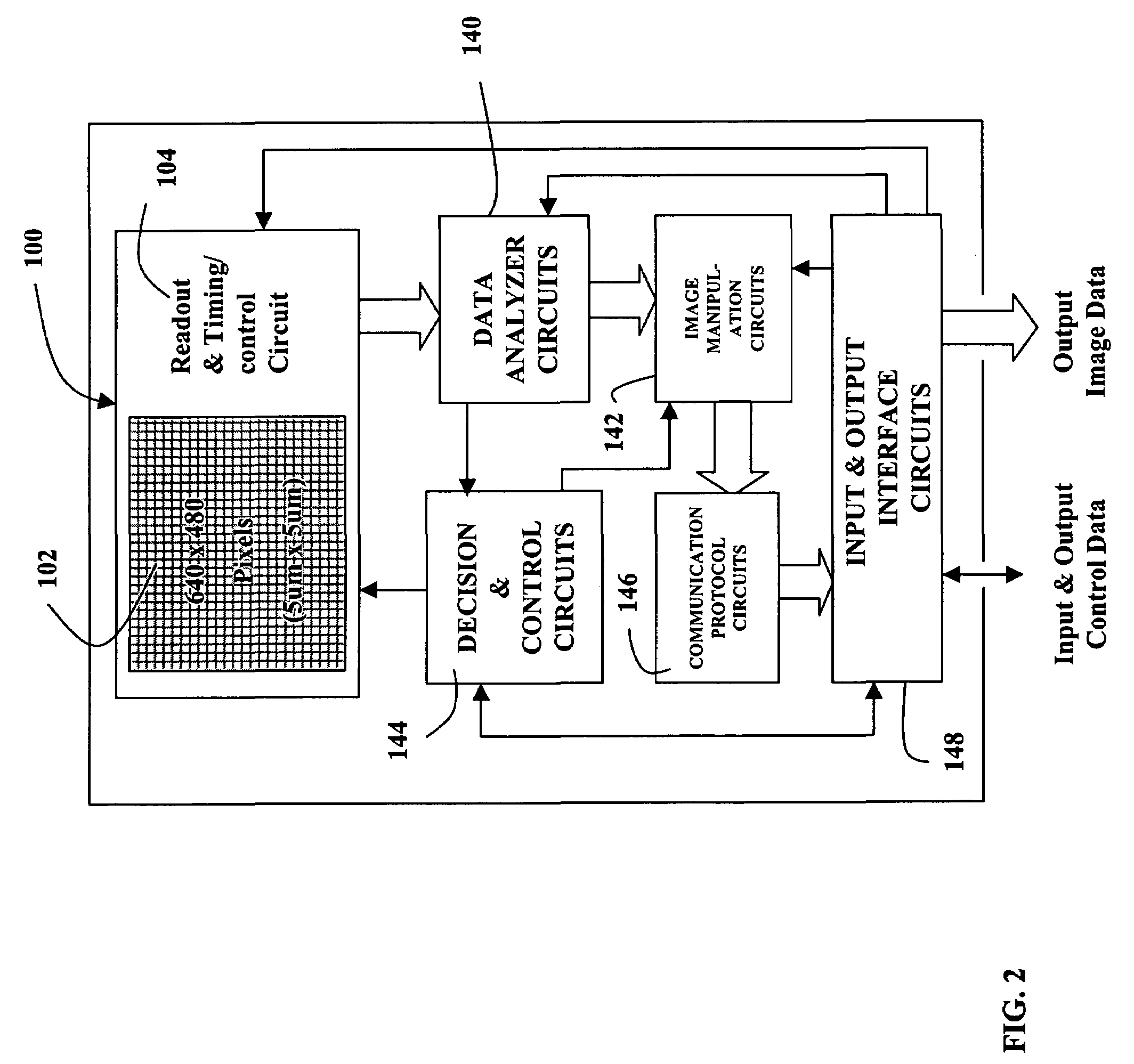
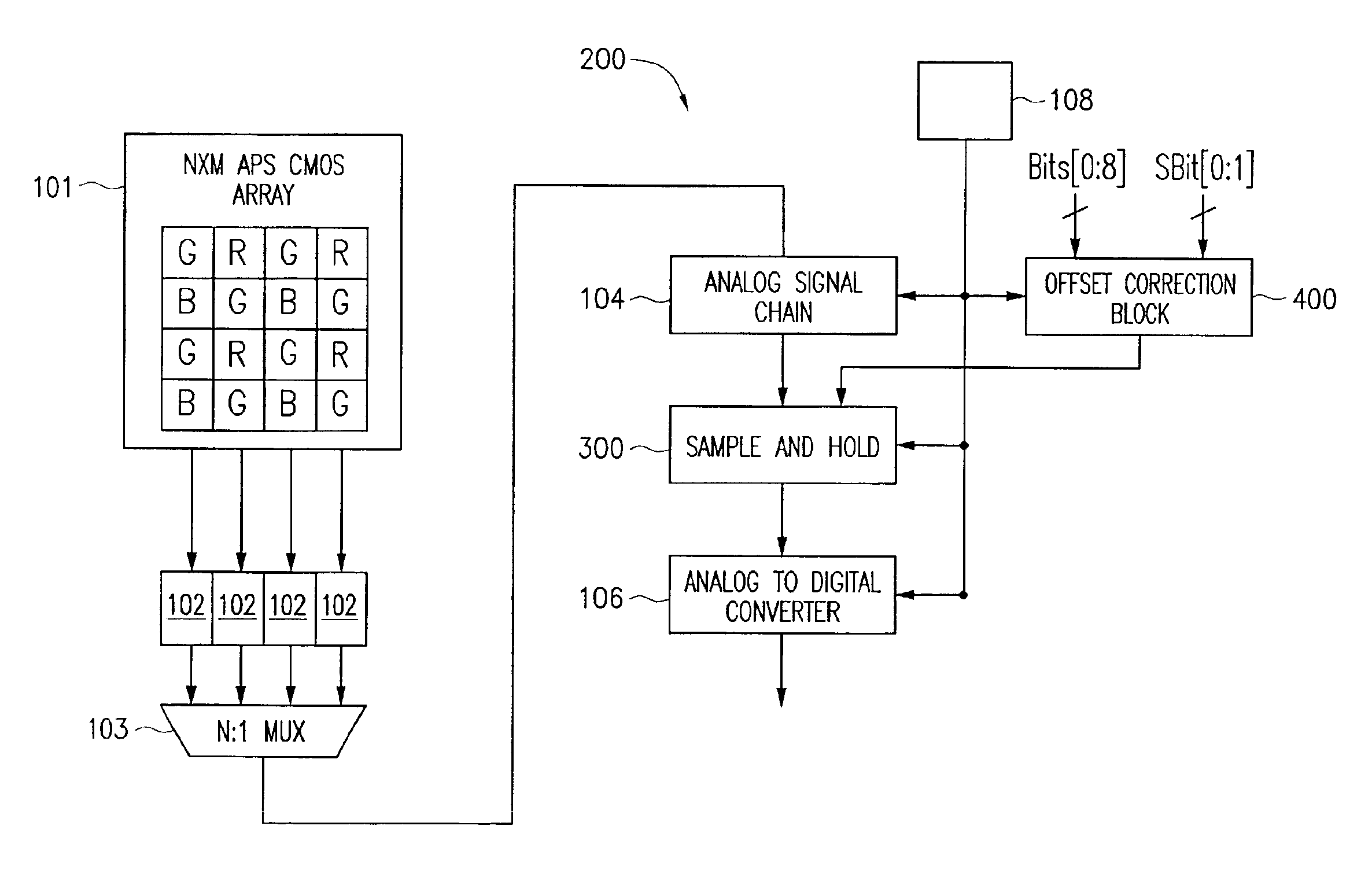
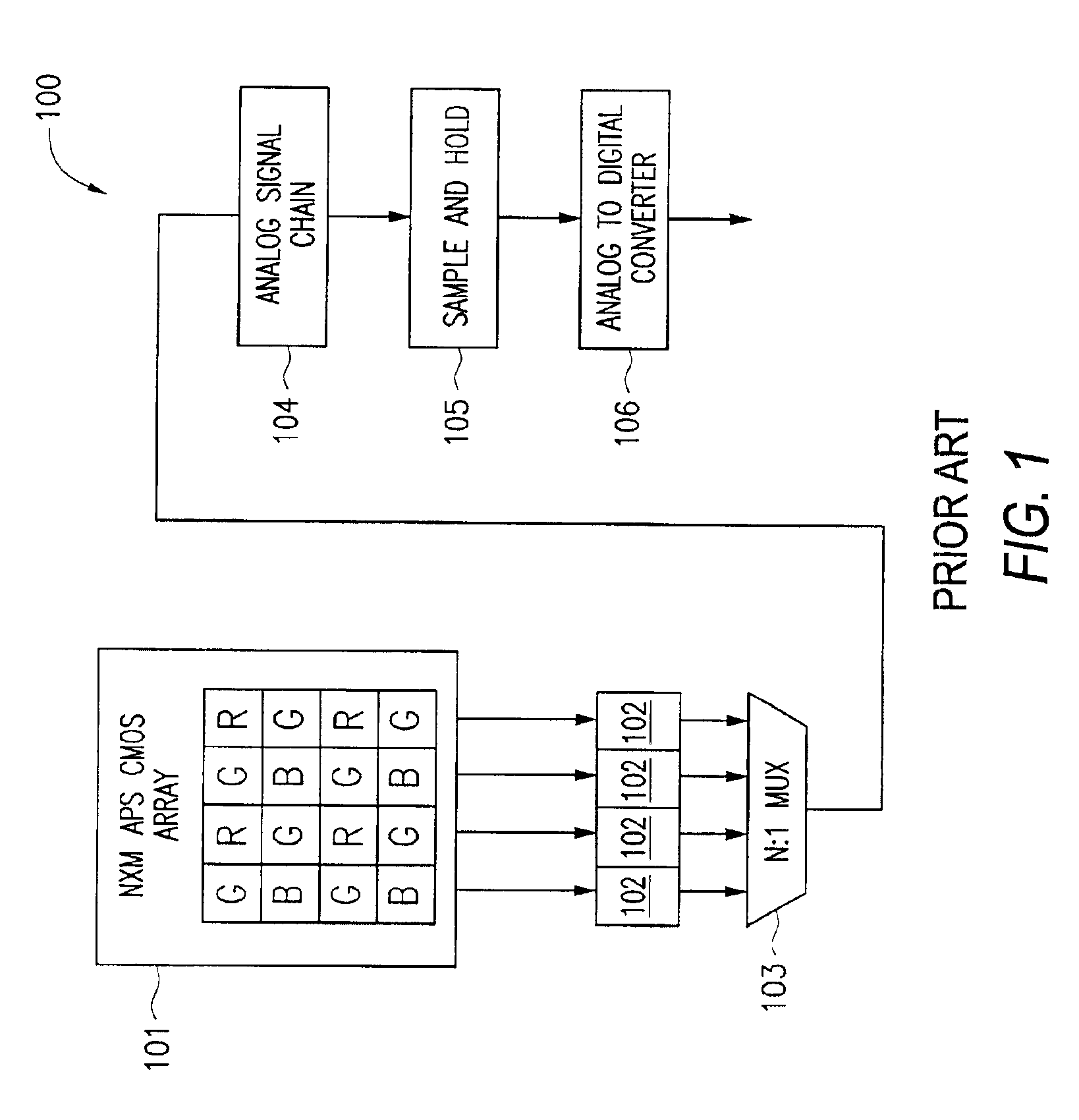
A novel MOS or CMOS based active sensor array for producing electronic images from electron-hole producing light. Each pixel of the array includes a layered photodiode for converting the electron-hole producing light into electrical charges and MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits located under the layered photodiodes for collecting the charges. The present invention also provides additional MOS or CMOS circuits in and / or on the same crystalline substrate for converting the collected charges into images and manipulating image data. The layered photodiode of each pixel is fabricated as continuous layers of charge generating material on top of the MOS and / or CMOS pixel circuits so that extremely small pixels are possible with almost 100 percent packing factors. In a preferred embodiment the sensor is a 0.3 mega pixel (3.2 mmx2.4 mm, 640x480) array of 5 micron square pixels which is compatible with a lens of {fraction (1 / 4.5 inch optical format. In a preferred embodiment the sensor along with focusing optics is incorporated into a cellular phone camera or a camera attachment the cellular phone to permit transmission of visual images along with the voice communication.
Owner:E PHOCUS
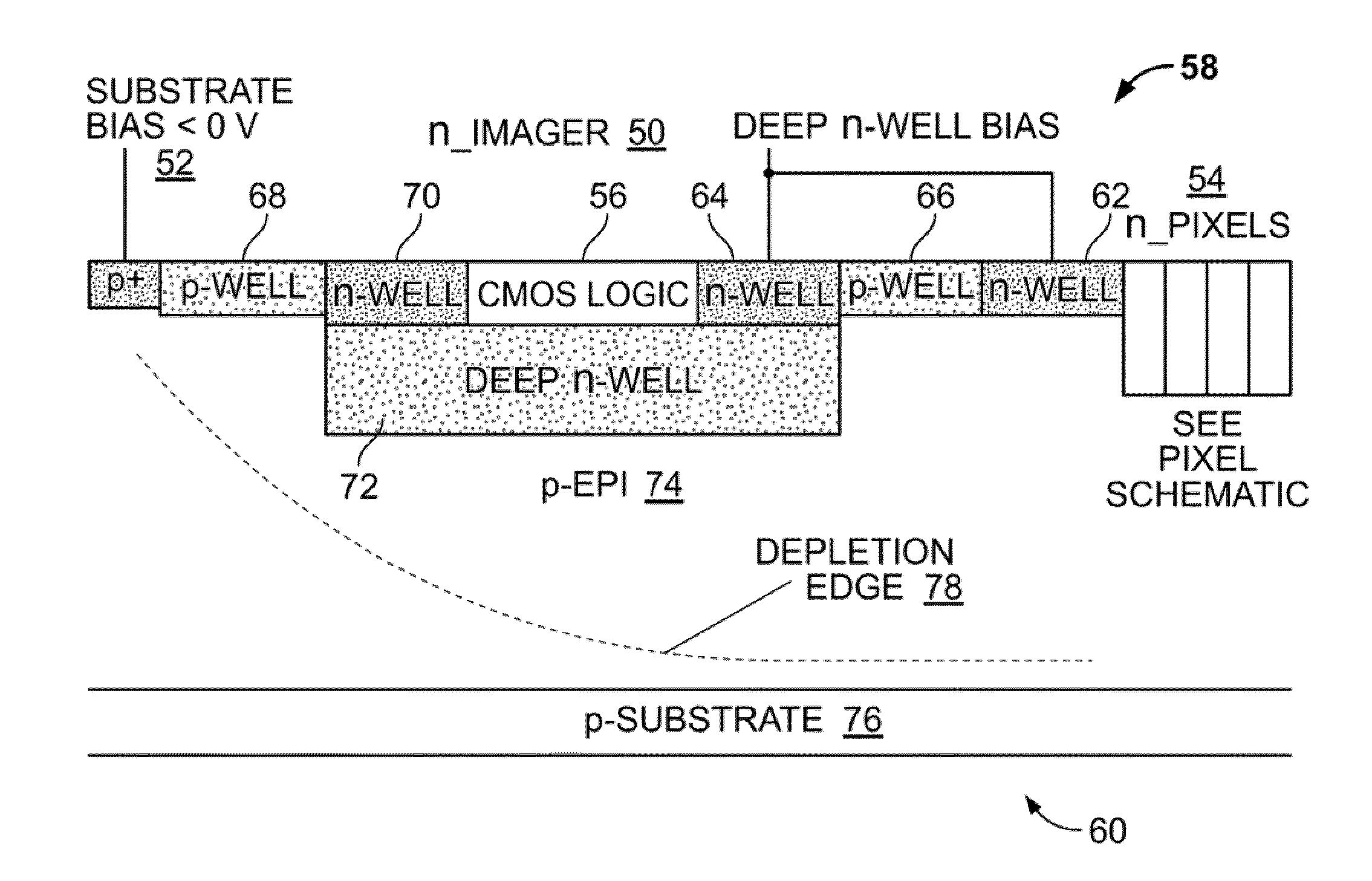
Substrate bias for CMOS imagers
ActiveUS20110024808A1Prevent floweringSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCmos pixelsEngineering
A CMOS image sensor is disclosed. The CMOS imager includes a lightly doped semiconductor substrate of a first conductivity type. At least one CMOS pixel of a second conductivity type is formed in the semiconductor substrate. The semiconductor substrate is configured to receive a bias voltage applied for substantially depleting the semiconductor substrate and for forming a depletion edge within the semiconductor substrate. A well of the second conductivity type substantially surrounds the at least one CMOS pixel to form a depletion region about the at least one CMOS pixel operable to form a minimum predetermined barrier to the depletion edge within the semiconductor substrate to pinch off substrate bias in proximity to the return contact.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
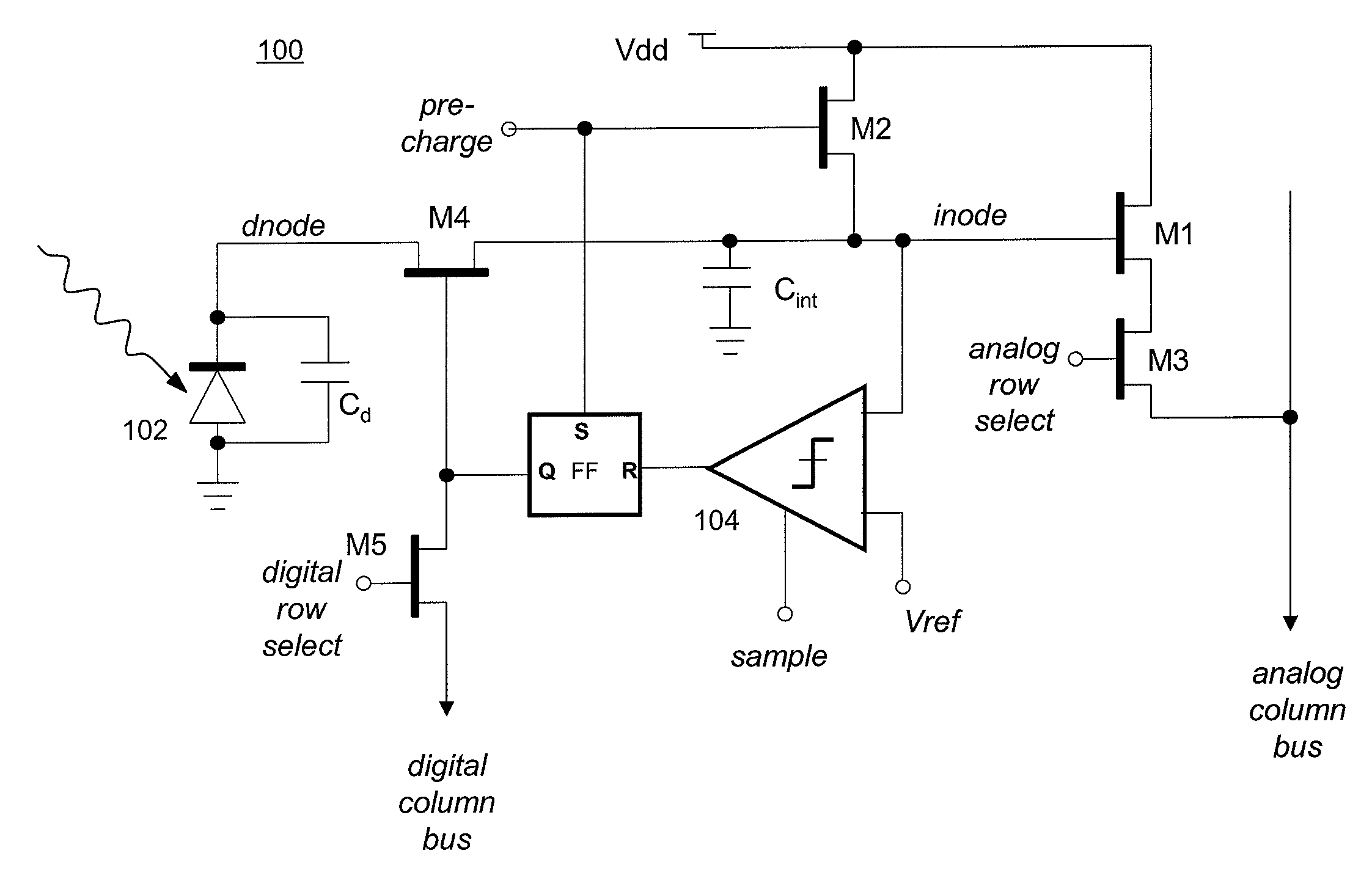
Mixed analog and digital pixel for high dynamic range readout
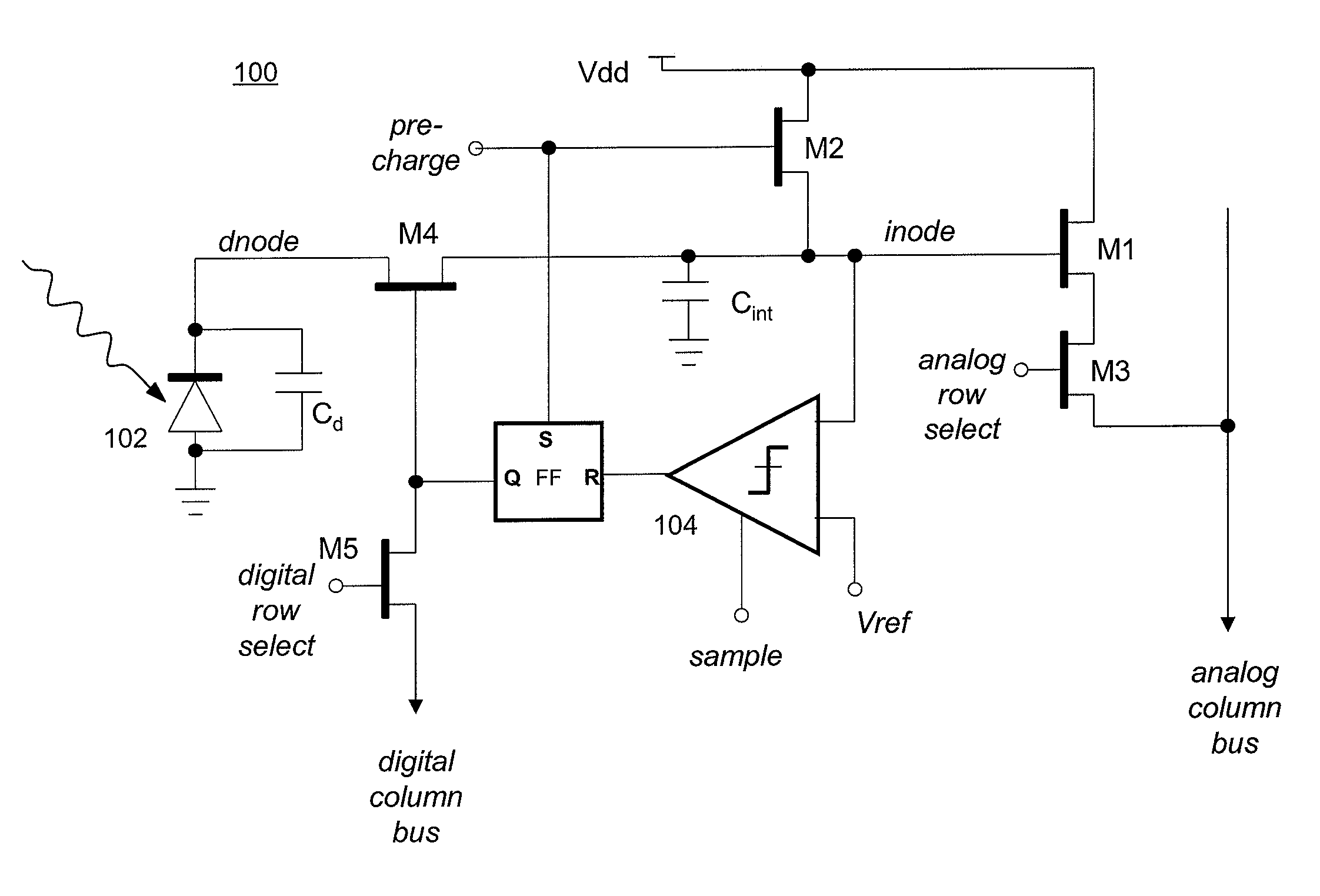
ActiveUS20080001065A1Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCmos pixelsExposure period
An improved CMOS pixel with a combination of analog and digital readouts to provide a large pixel dynamic range without compromising low-light performance using a comparator to test the value of an accumulated charge at a series of exponentially increasing exposure times. The test is used to stop the integration of photocurrent once the accumulated analog voltage has reached a predetermined threshold. A one-bit output value of the test is read out of the pixel (digitally) at each of the exponentially increasing exposure periods. At the end of the integration period, the analog value stored on the integration capacitor is read out using conventional CMOS active pixel readout circuits.
Owner:INFRARED NEWCO
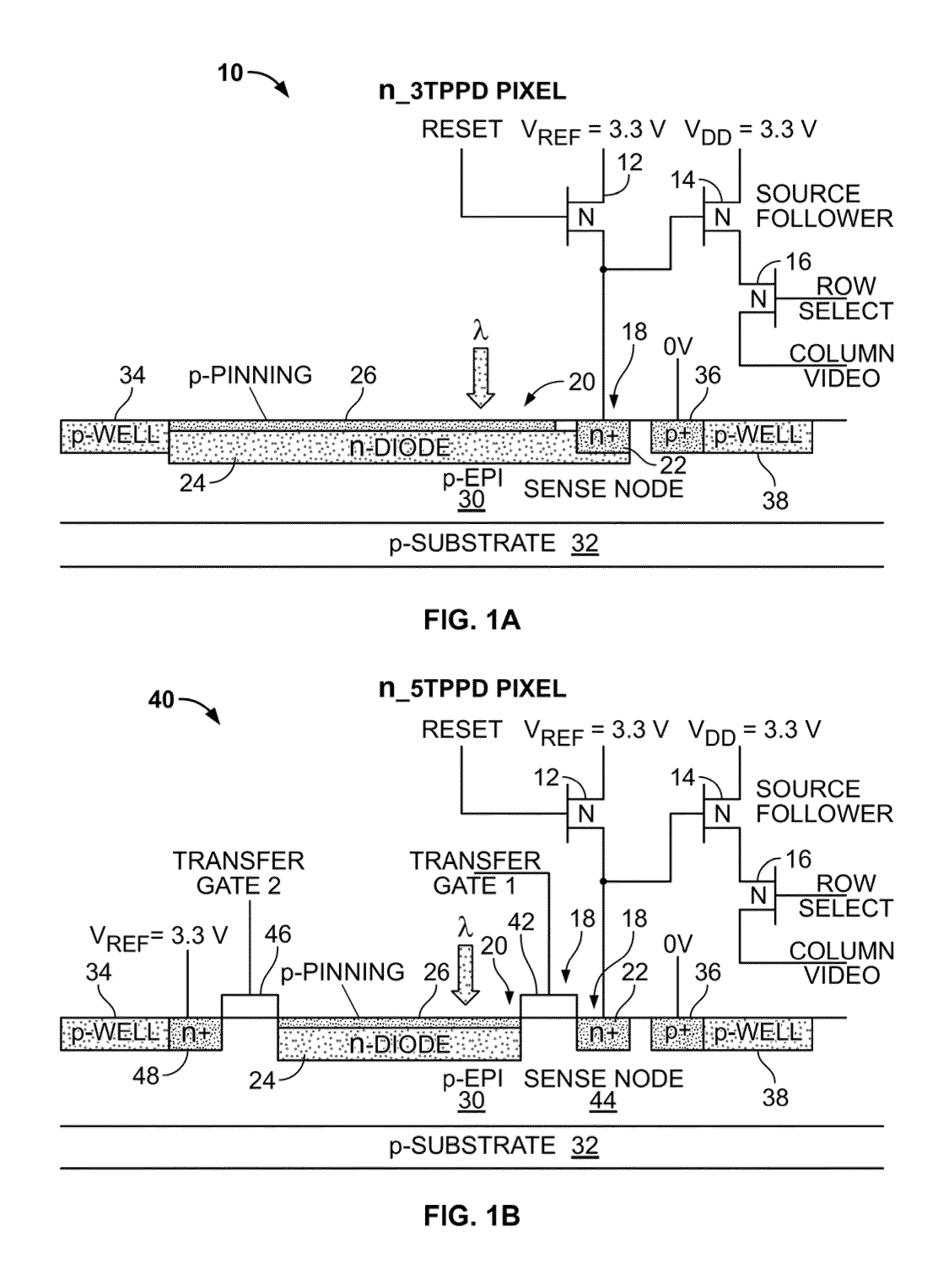
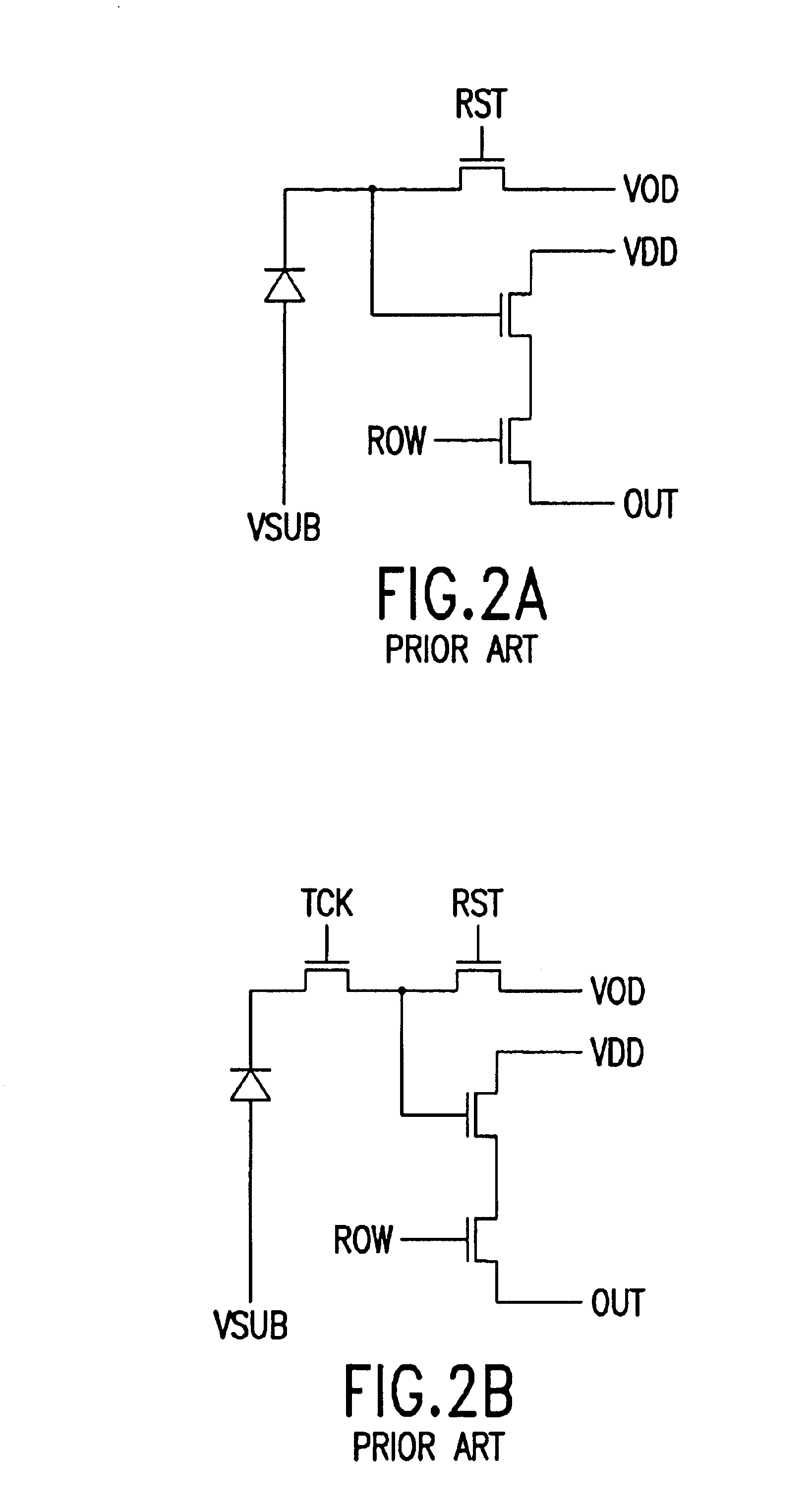
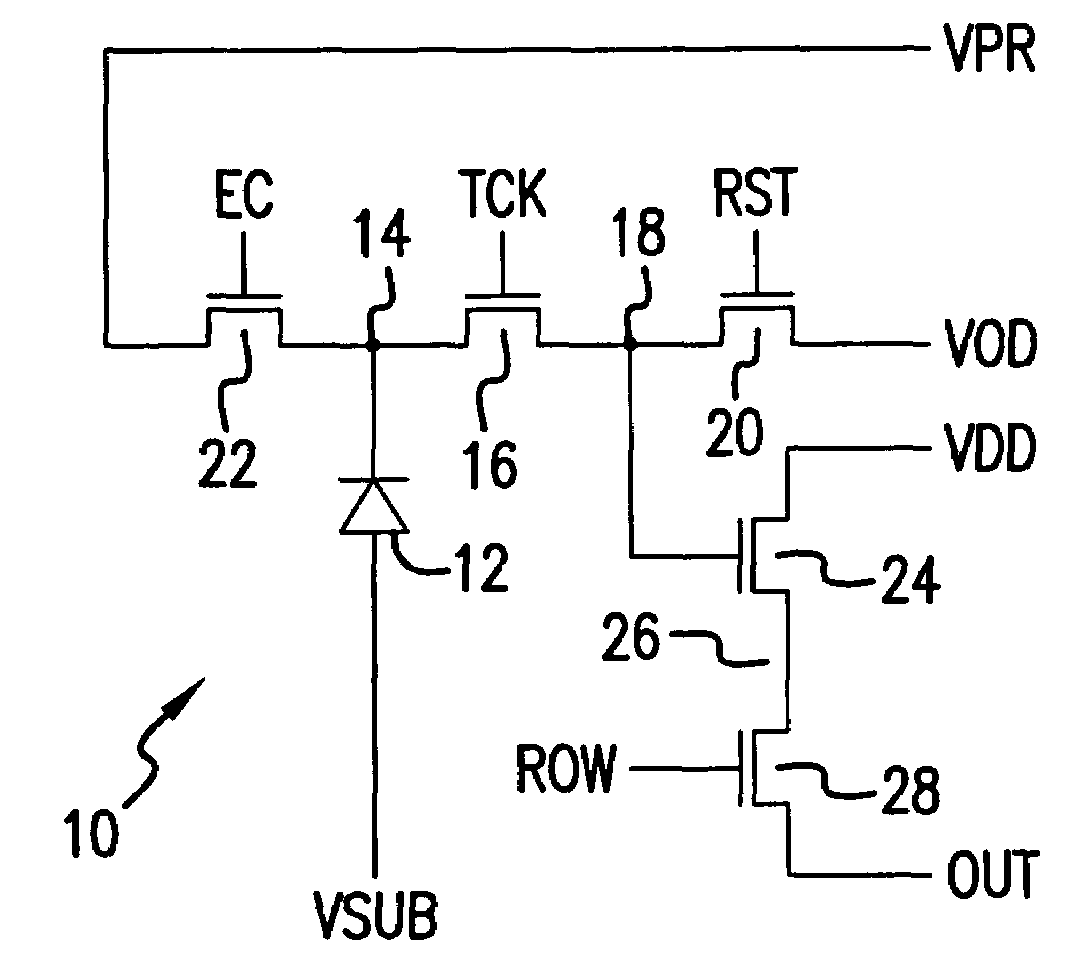
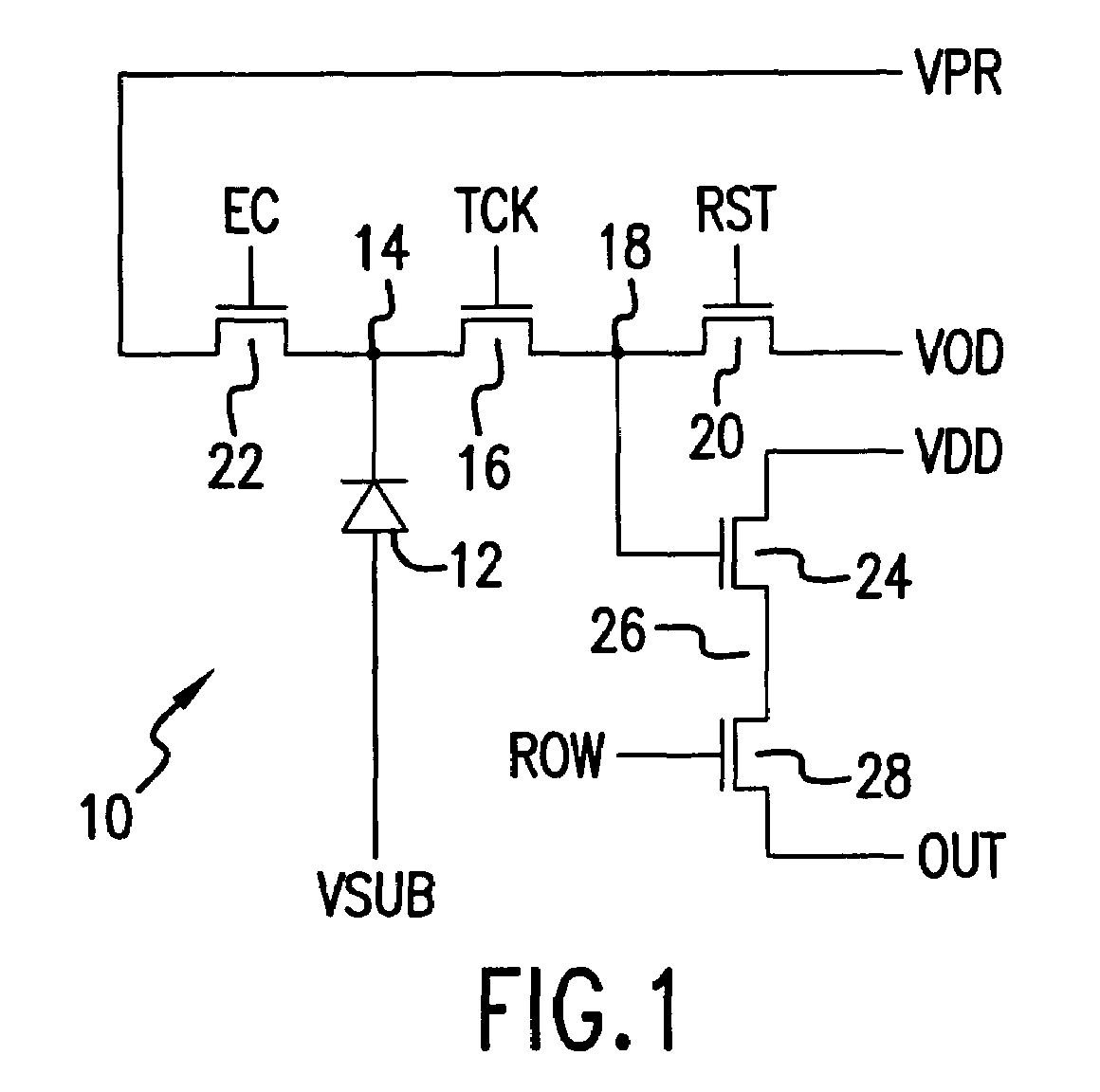
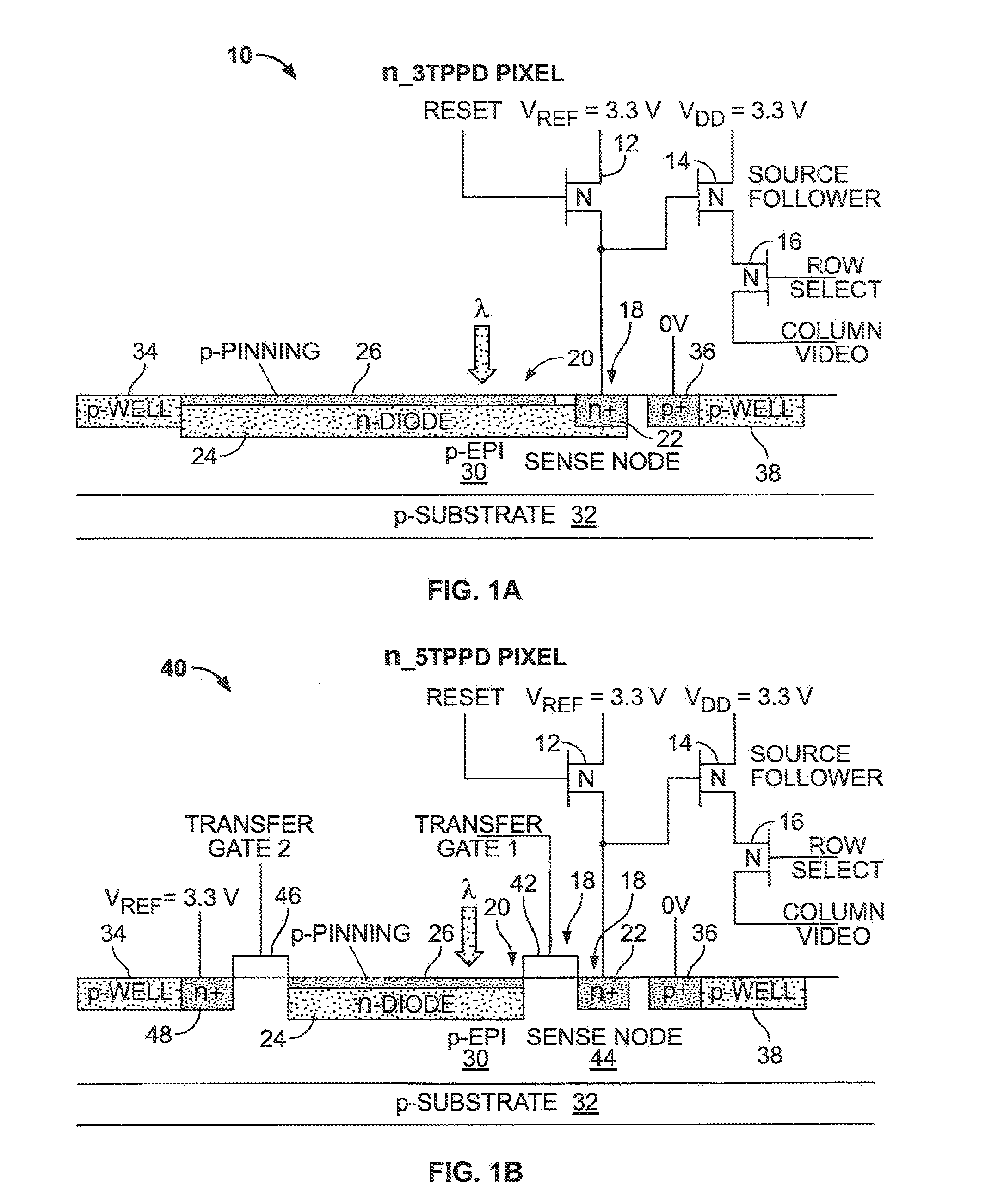
Five transistor CMOS pixel
InactiveUS6847070B2Eliminate rolling shutter artifactReduce Fixed Pattern NoiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCmos pixelsEngineering
A method of sensing radiation in a pixel includes applying a transfer clock signal, applying a pixel reset clock signal, and applying a pixel reset voltage. The applying a transfer clock signal applies the transfer clock signal to a gate electrode of a transfer gate transistor. The applying a pixel reset clock signal applies the pixel reset clock signal to a gate electrode of the pixel reset transistor. The applying a pixel reset voltage applies the pixel reset voltage to a drain of the pixel reset transistor. The method further includes switching the transfer clock signal to a high state, switching the pixel reset clock signal to a high state, switching the pixel reset voltage to a low state, switching the pixel reset voltage to a high state, and switching the pixel reset clock signal to a low state at a beginning of an integration cycle.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING INC
MOS or CMOS sensor with micro-lens array
InactiveUS7196391B2Increase the number of pixelsSmall sizeSolid-state devicesRadiation controlled devicesHigh-definition televisionCMOS sensor
Owner:E PHOCUS
Method and apparatus for proximate CMOS pixels
InactiveUS20060146158A1Reduce noiseLow costTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorProximate
An improved CMOS sensor integrated circuit is disclosed, along with methods of making the circuit and computer readable descriptions of the circuit.
Owner:RE SECURED NETWORKS LLC
Mixed analog and digital pixel for high dynamic range readout
ActiveUS7326903B2Television system detailsElectric signal transmission systemsCmos pixelsEngineering
An improved CMOS pixel with a combination of analog and digital readouts to provide a large pixel dynamic range without compromising low-light performance using a comparator to test the value of an accumulated charge at a series of exponentially increasing exposure times. The test is used to stop the integration of photocurrent once the accumulated analog voltage has reached a predetermined threshold. A one-bit output value of the test is read out of the pixel (digitally) at each of the exponentially increasing exposure periods. At the end of the integration period, the analog value stored on the integration capacitor is read out using conventional CMOS active pixel readout circuits.
Owner:INFRARED NEWCO +1
Method for cancellation of the effect of charge feedthrough on CMOS pixel output
ActiveUS7242429B1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCmos pixelsElectric charge
Owner:SMAL CAMERA TECH
CMOS active pixel sensor with a sample and hold circuit having multiple injection capacitors and a fully differential charge mode linear synthesizer with skew control
InactiveUS6861634B2Television system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMultiple injectionCapacitance
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
High-dynamic range image sensors
The dynamic range of existing CMOS image sensors is limited. The present invention introduces an extended dynamic range CMOS pixel sensor circuit. The extended dynamic range CMOS pixel sensor circuit is relatively similar to existing CMOS pixel sensors except that a charge pump has been added to recharge the pixel sensor when the pixel sensor is nearing charge depletion. Every firing of the charge pump is counted. To create a final output for the extended dynamic range CMOS pixel sensor circuit, the number of charge pump firings is combined with a final analog voltage reading of the pixel sensor circuit.
Owner:PETING MARK
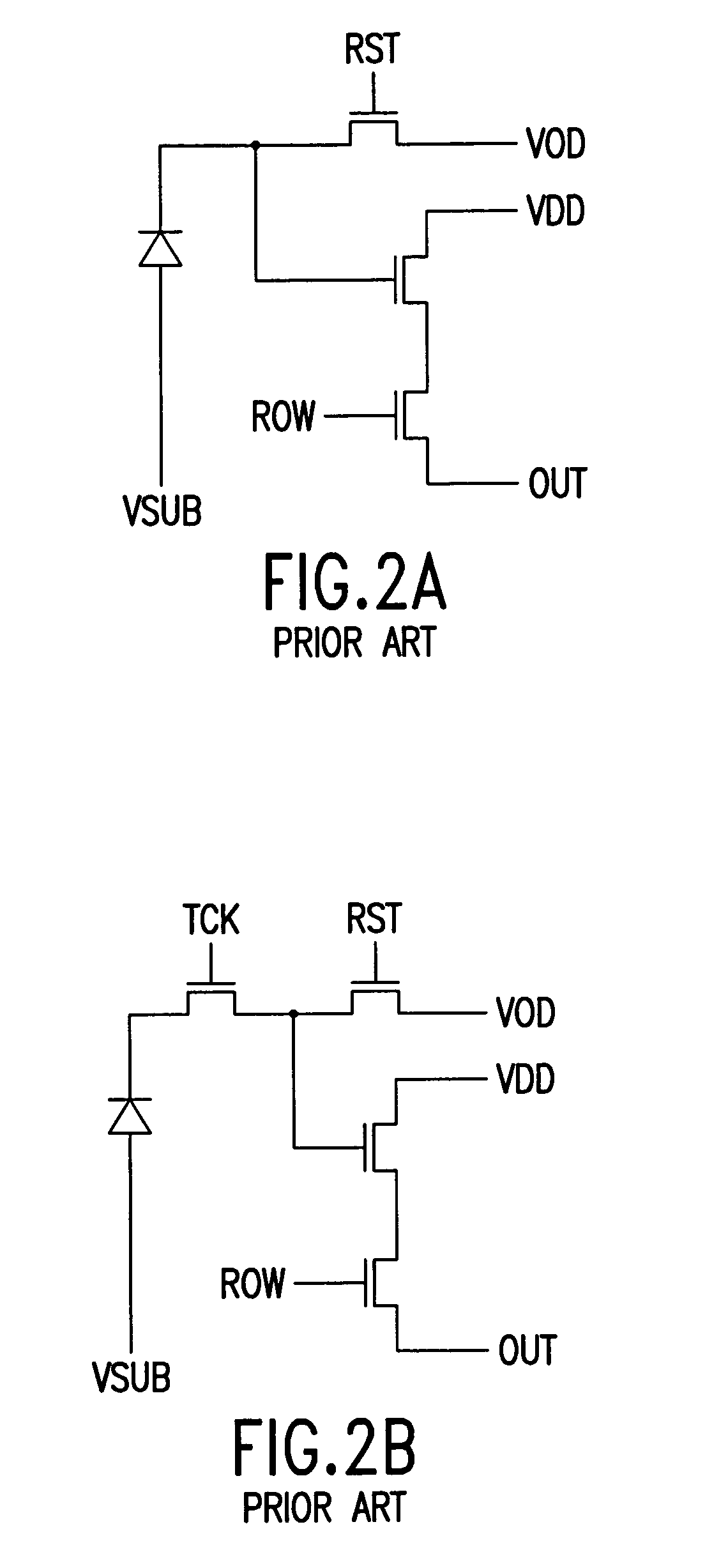
Five transistor CMOS pixel
InactiveUS7045753B1Eliminate rolling shutter artifactReduce Fixed Pattern NoiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsPhotovoltaic detectorsPhotodetector
A pixel includes five transistors, a photodetector and a storage node. A first transistor is coupled between the photodetector and the storage node. A second transistor includes a second transistor source and a second transistor drain. The second transistor source is coupled to the storage node. The second transistor drain is coupled to an output drain voltage. A third transistor includes a third transistor drain. The third transistor is coupled between the photodetector and a pixel reset voltage. The third transistor drain is coupled to the pixel reset voltage. The pixel reset voltage is different than the output drain voltage.
Owner:TELEDYNE DIGITAL IMAGING INC
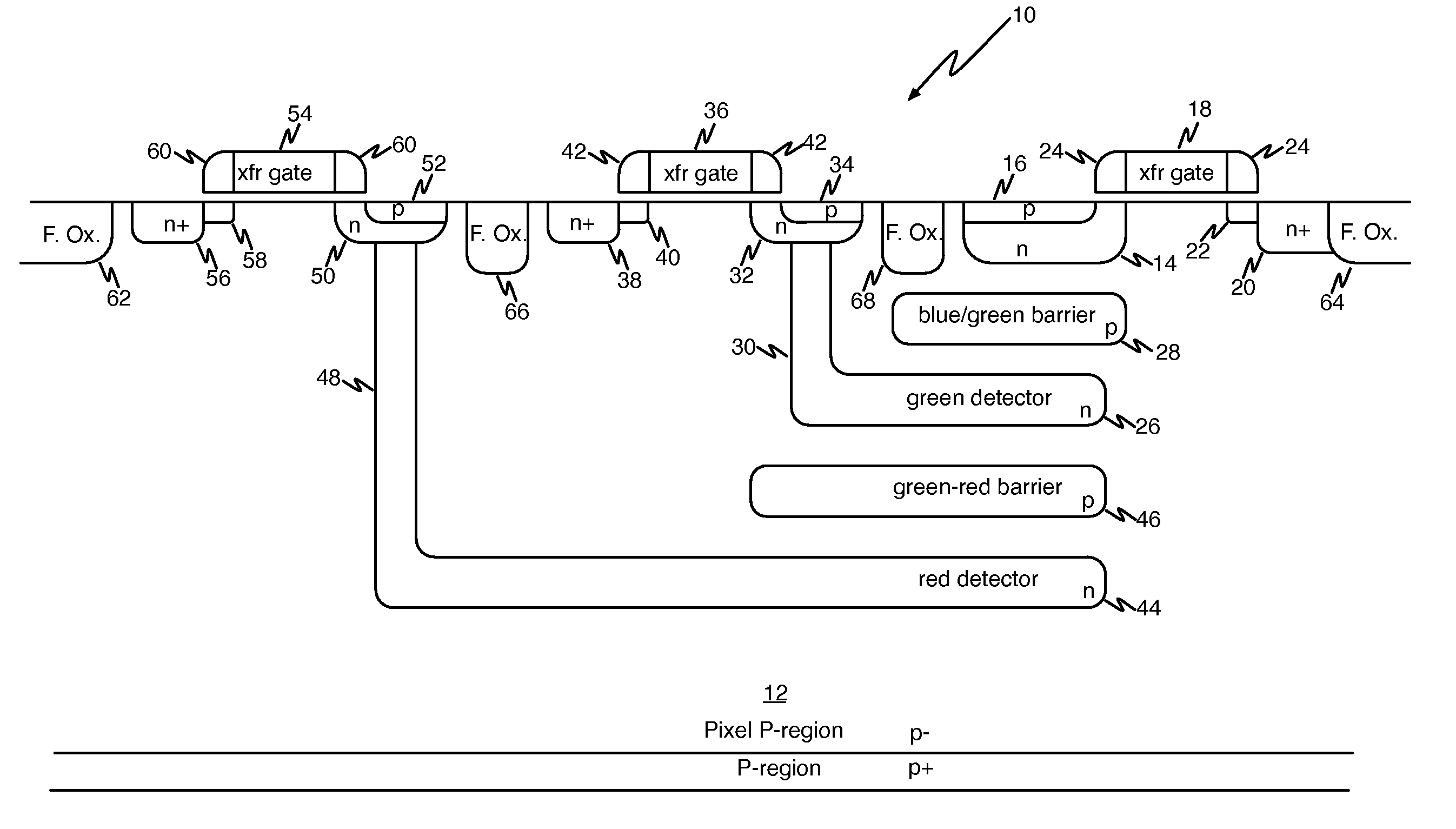
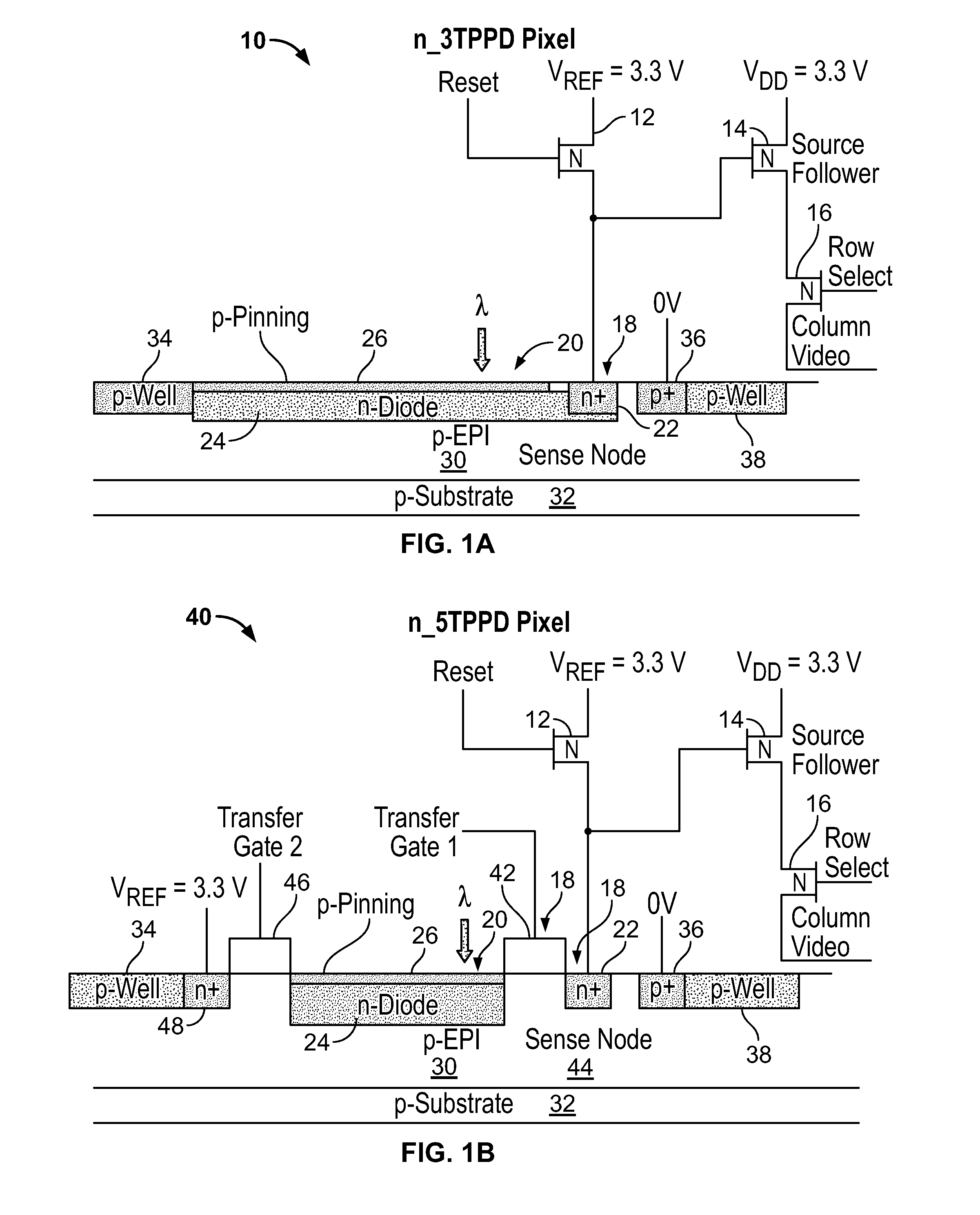
Pinned photodiode CMOS pixel sensor
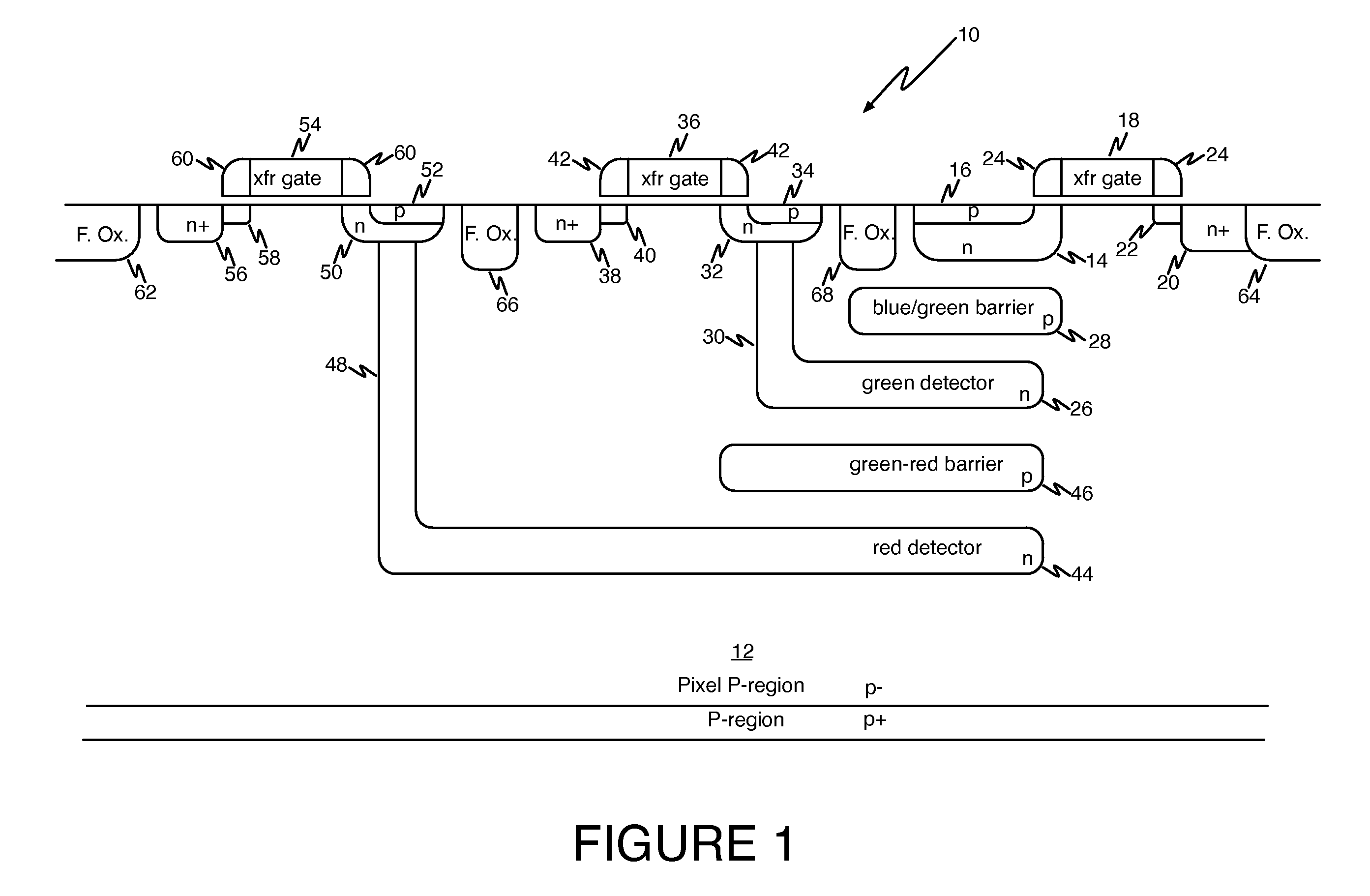
A multicolor CMOS pixel sensor formed in a p-type semiconductor region includes a first detector formed from an n-type region of semiconductor material located near the surface of the p-type region. A first pinned p-type region is formed at the surface of the p-type region over the first detector, and has a surface portion extending past an edge of the pinned p-type region. A second detector is formed from an n-type region located in the p-type semiconductor region below the first detector. A second-detector n-type deep contact plug is in contact with the second detector and extends to the surface of the p-type semiconductor region. A second pinned p-type region is formed at the surface of the p-type semiconductor region over the top of the second-detector n-type deep contact plug. A surface portion of the second-detector deep contact plug extends past an edge of the second pinned p-type region.
Owner:FOVEON
X-ray detector and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103296036AImprove yieldLittle cross effectRadiation controlled devicesRadiation intensity measurementCmos pixelsInterconnection
The invention discloses an X-ray detector and a manufacturing method thereof. The X-ray detector comprises an interconnection substrate, bonding interconnection, a photovoltaic conversion device chip and a CMOS pixel reading chip, wherein the bonding interconnection penetrates through the interconnection substrate and is exposed out of the two main surfaces of the interconnection substrate, the photovoltaic conversion device chip is bonded with one main surface of the interconnection substrate, the CMOS pixel reading chip is bonded with the other main surface of the interconnection substrate, and a bonding pad of the photovoltaic conversion device chip is electrically connected with a bonding pad of the CMOS pixel reading chip through the bonding interconnection. According to the X-ray detector, working processes can be simplified, and reliability and yield can be improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ring pixel for CMOS imagers
ActiveUS20110024809A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCmos pixelsPhotodiode
A CMOS pixel is disclosed. The CMOS pixel includes a semiconductor substrate; a sense node formed in the semiconductor substrate and positioned substantially in the center of the CMOS pixel; a transfer gate formed about the sense node; and at least one photodiode formed about the transfer gate. A reset transistor, a source follower transistor, and a row select transistor are located substantially to one side of the CMOS pixel substantially adjacent to the photodiode. The sense node is operable to be floating. An implant may be formed about the photodiode configured to step potential in a direction toward the sense node.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
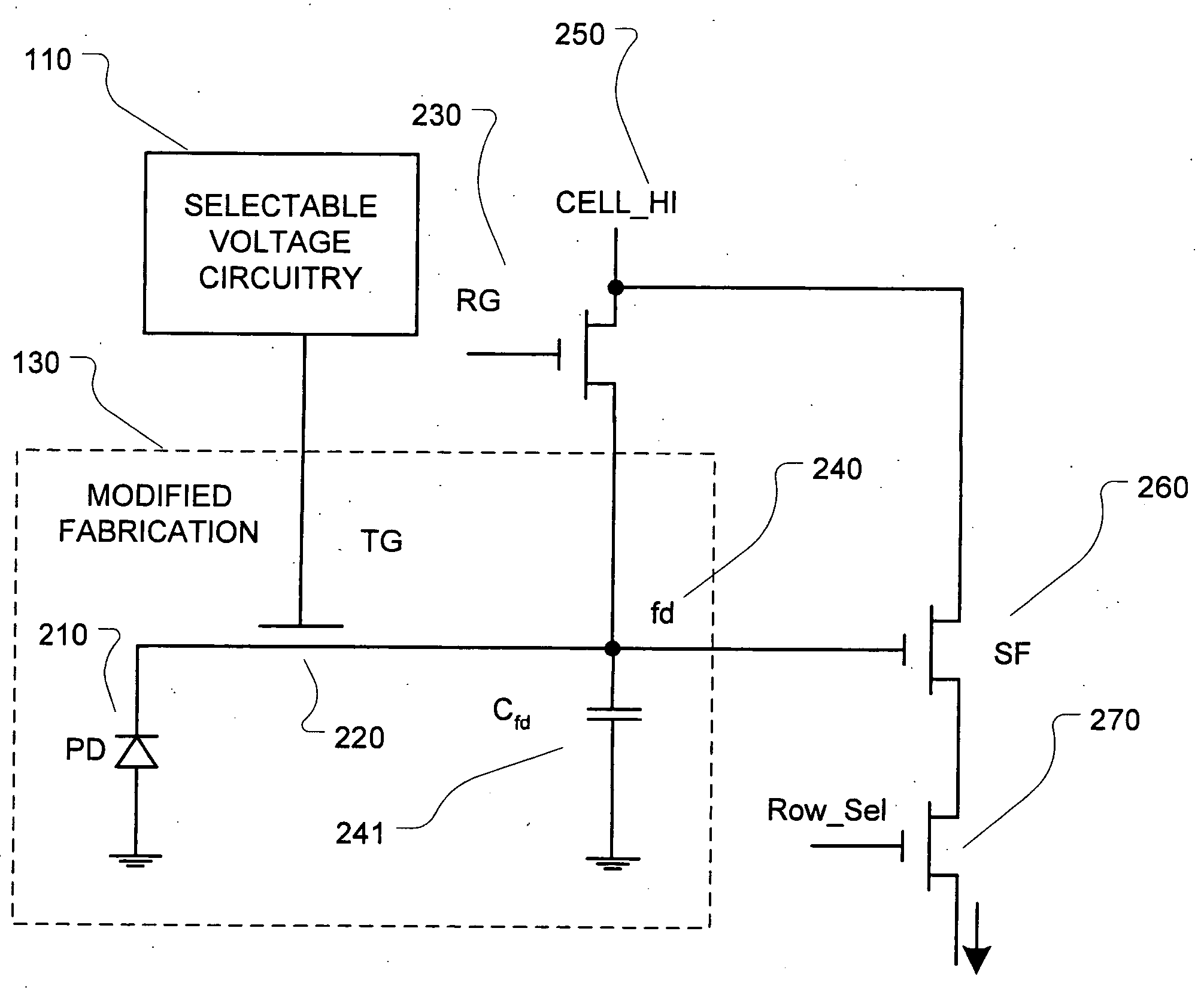
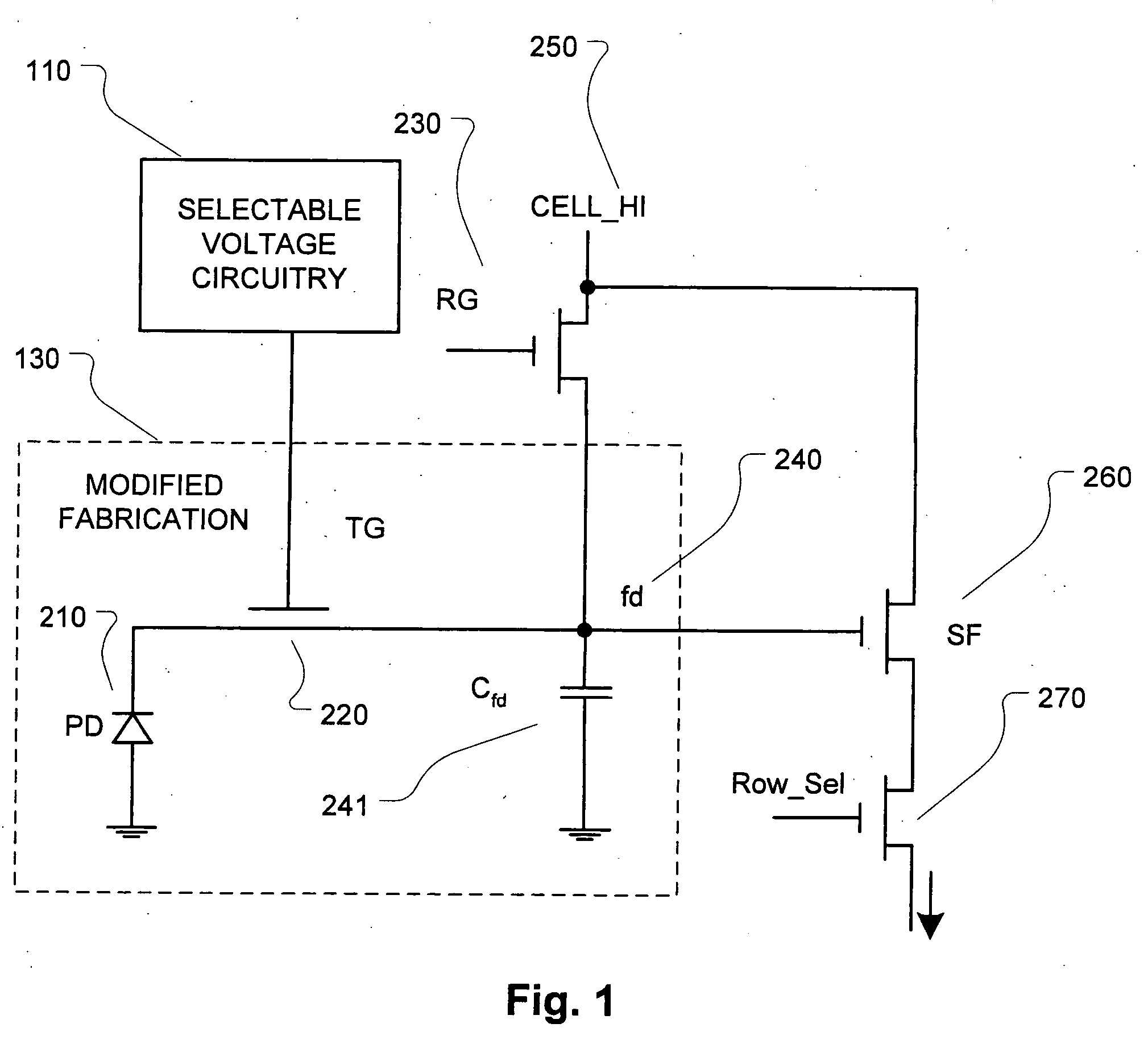
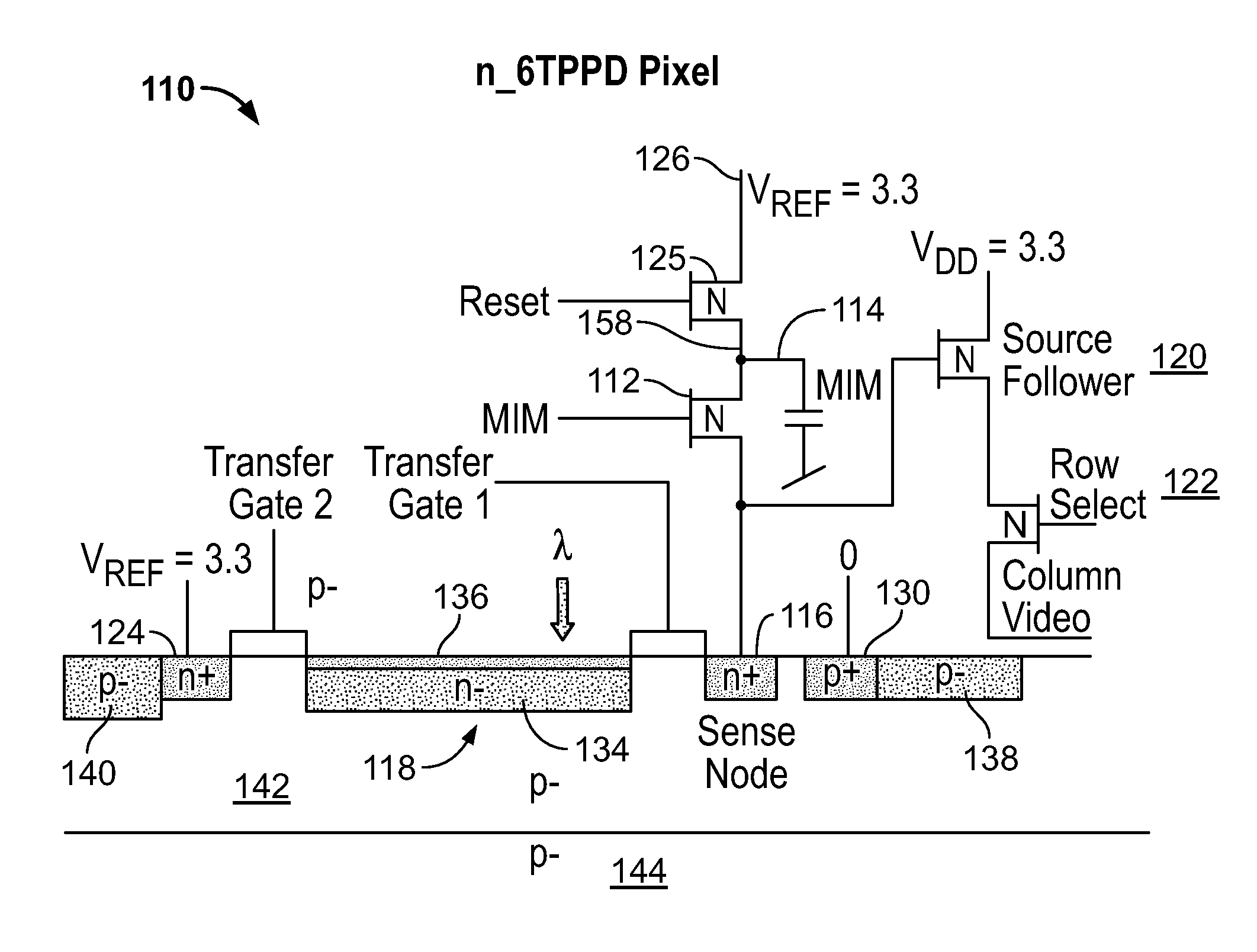
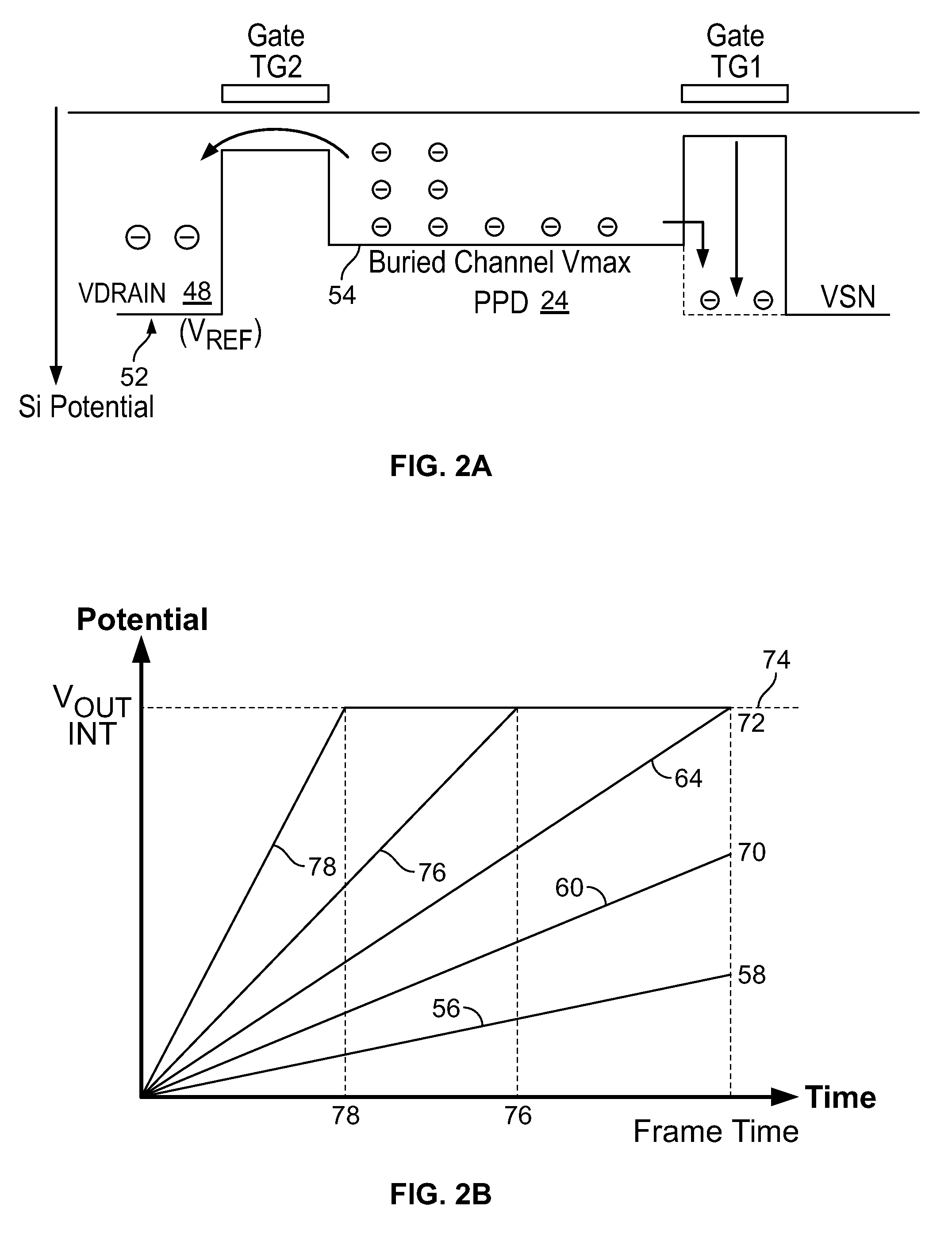
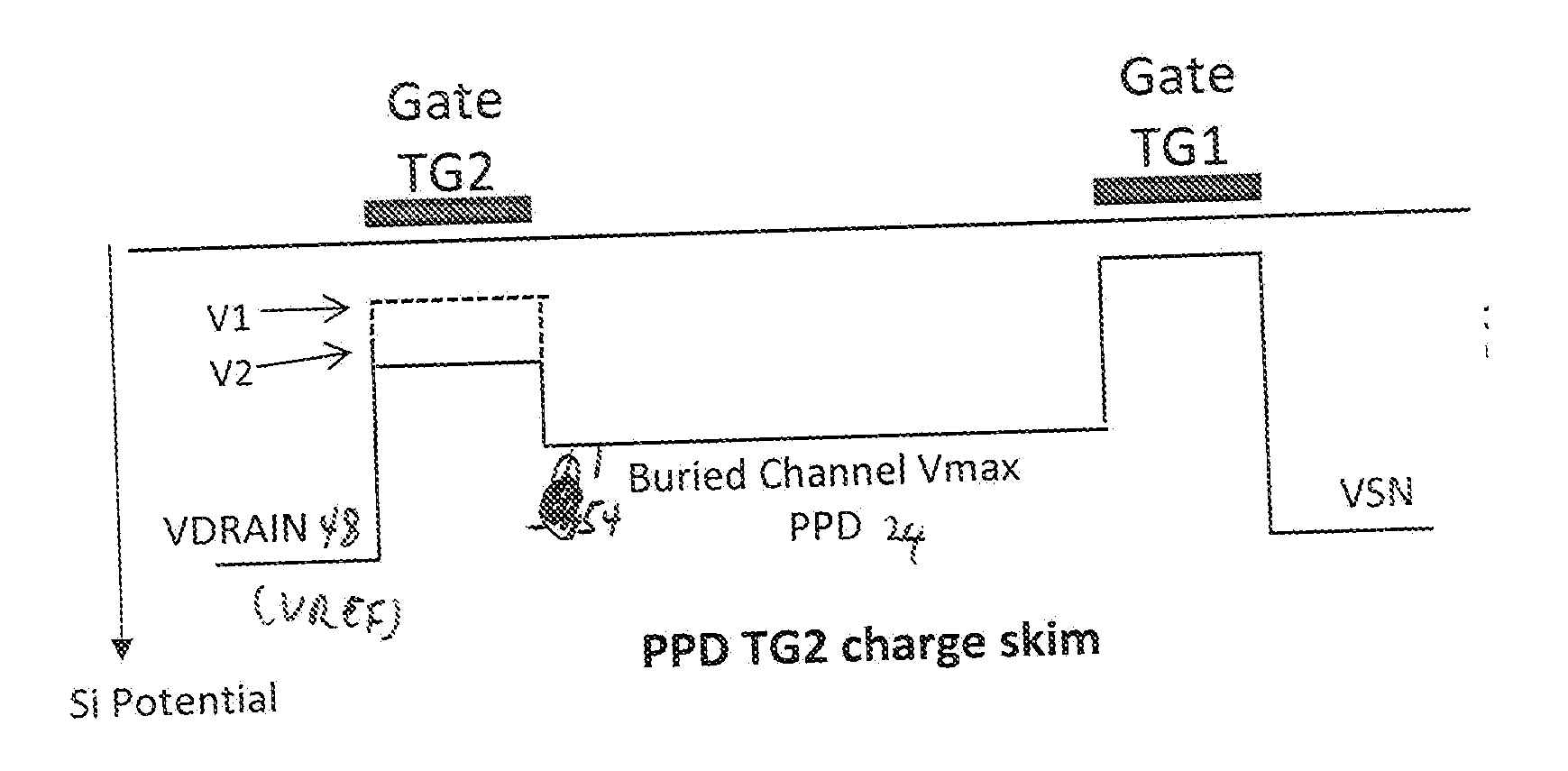
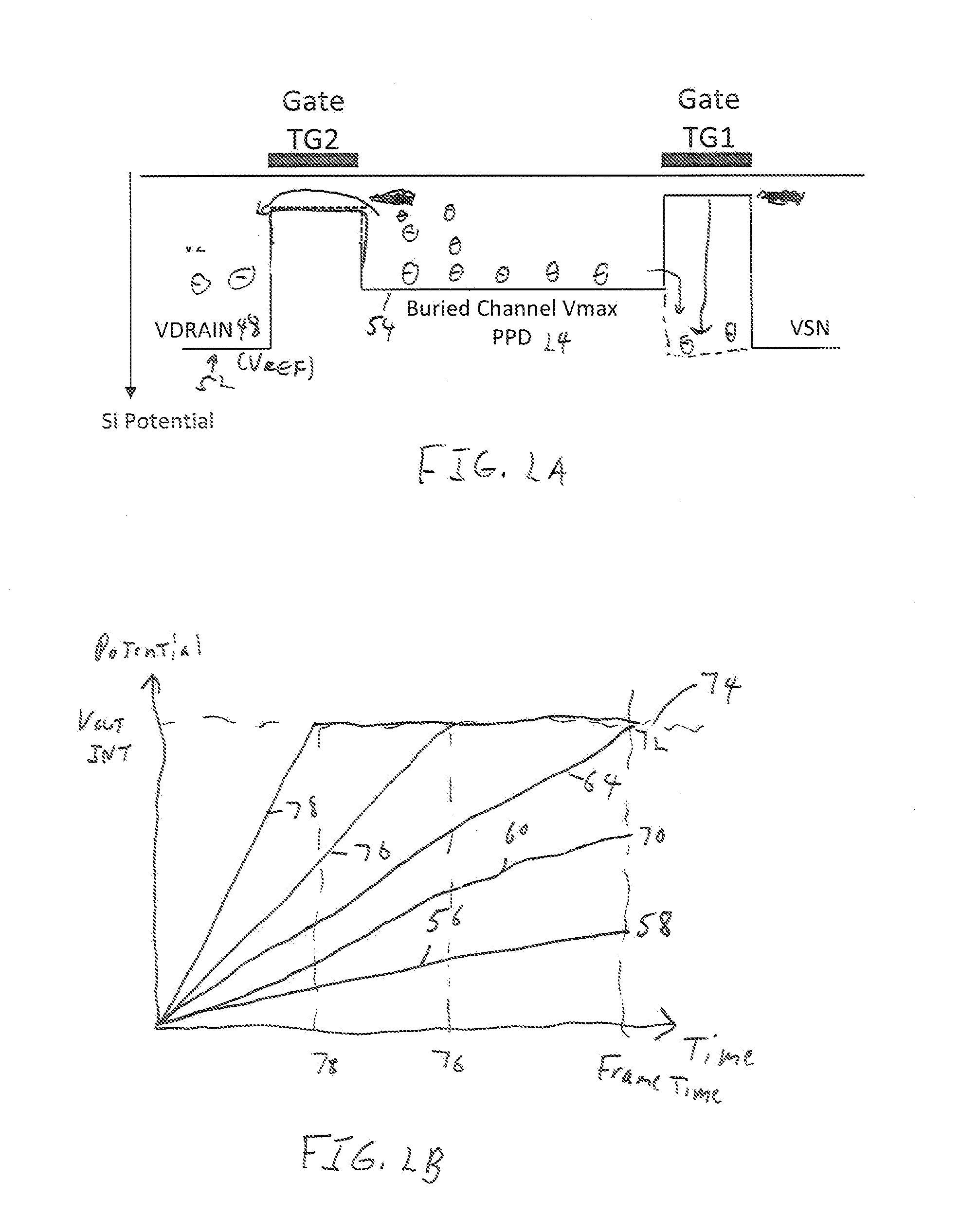
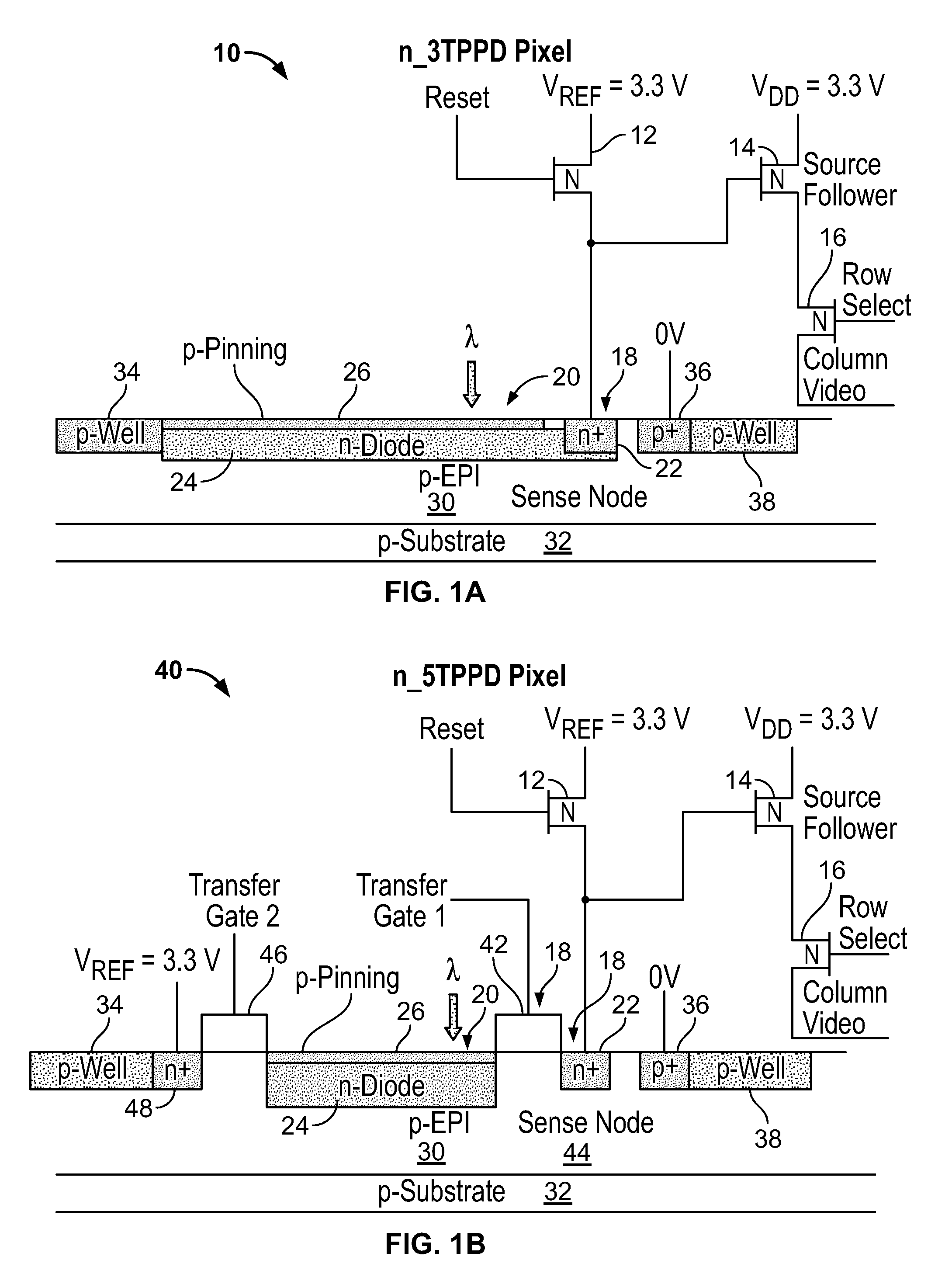
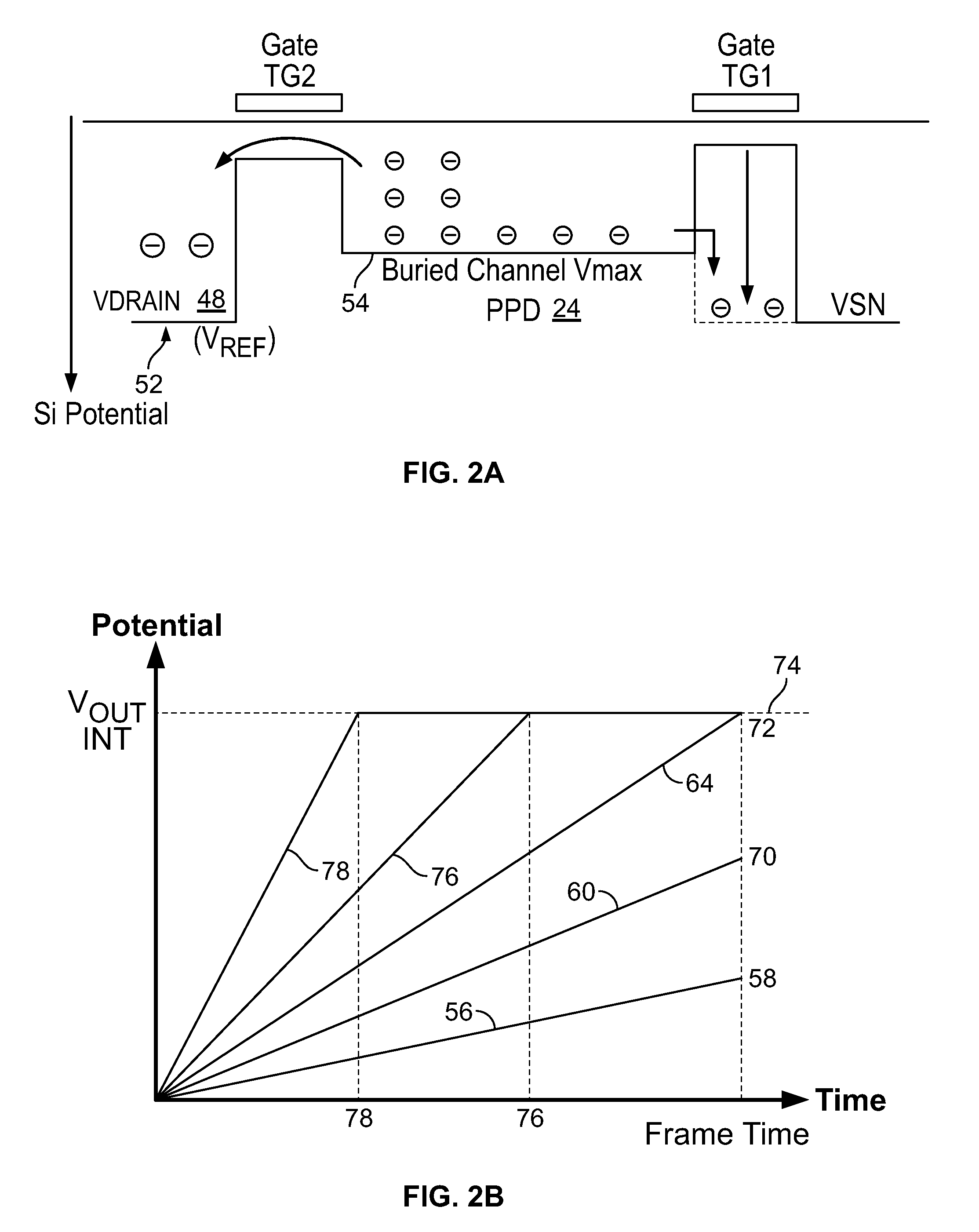
High Dynamic Range CMOS Pixel and Method of Operating Same
InactiveUS20120056080A1Increase in sizeIncreases magnitudeTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPotential wellCmos pixels
A method of operating a CMOS pixel is disclosed. The CMOS pixel includes a photodiode (PPD), a transfer gate coupled to the PPD, and an anti-blooming drain coupled to the transfer gate. A potential barrier is formed between a potential well underlying the PPD and the transfer gate. Charge is accumulated in the potential well in response to electromagnetic radiation during a first integration time. Excess charge is removed from the potential well to the anti-blooming drain that exceeds the first potential barrier. A size of the potential barrier is increased. Charge is accumulated in the potential well during a second integration time.
Owner:LEVINE PETER ALAN +1
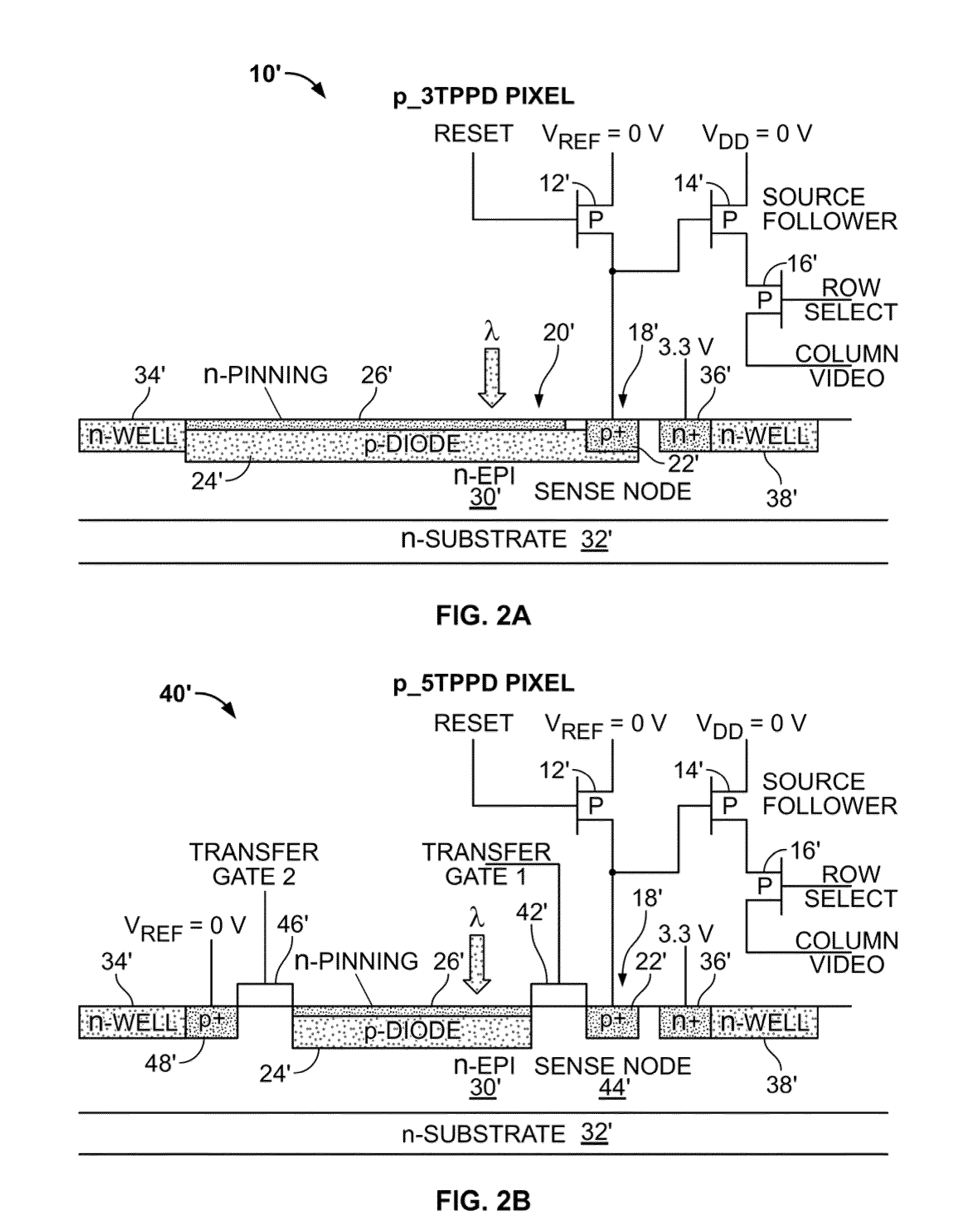
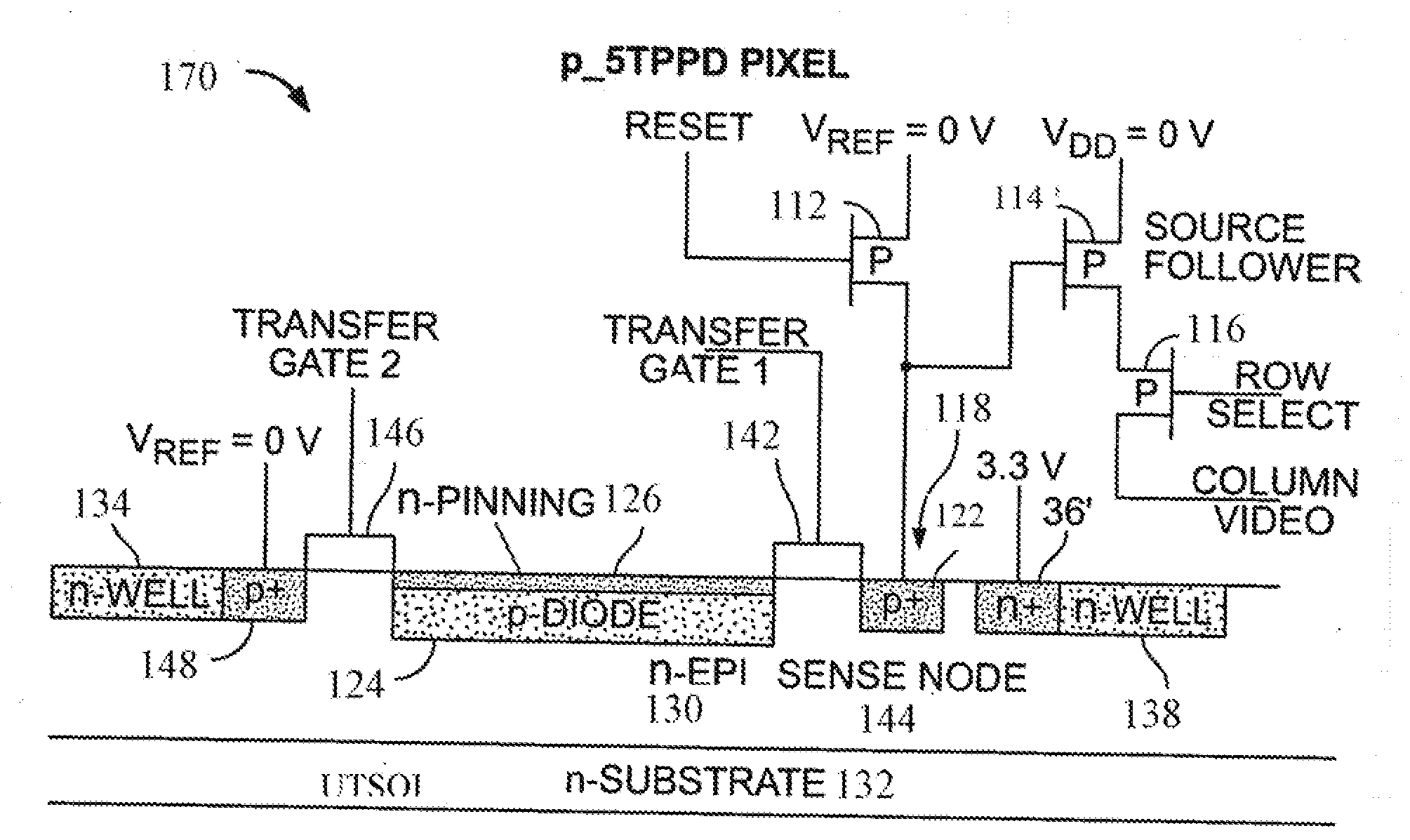
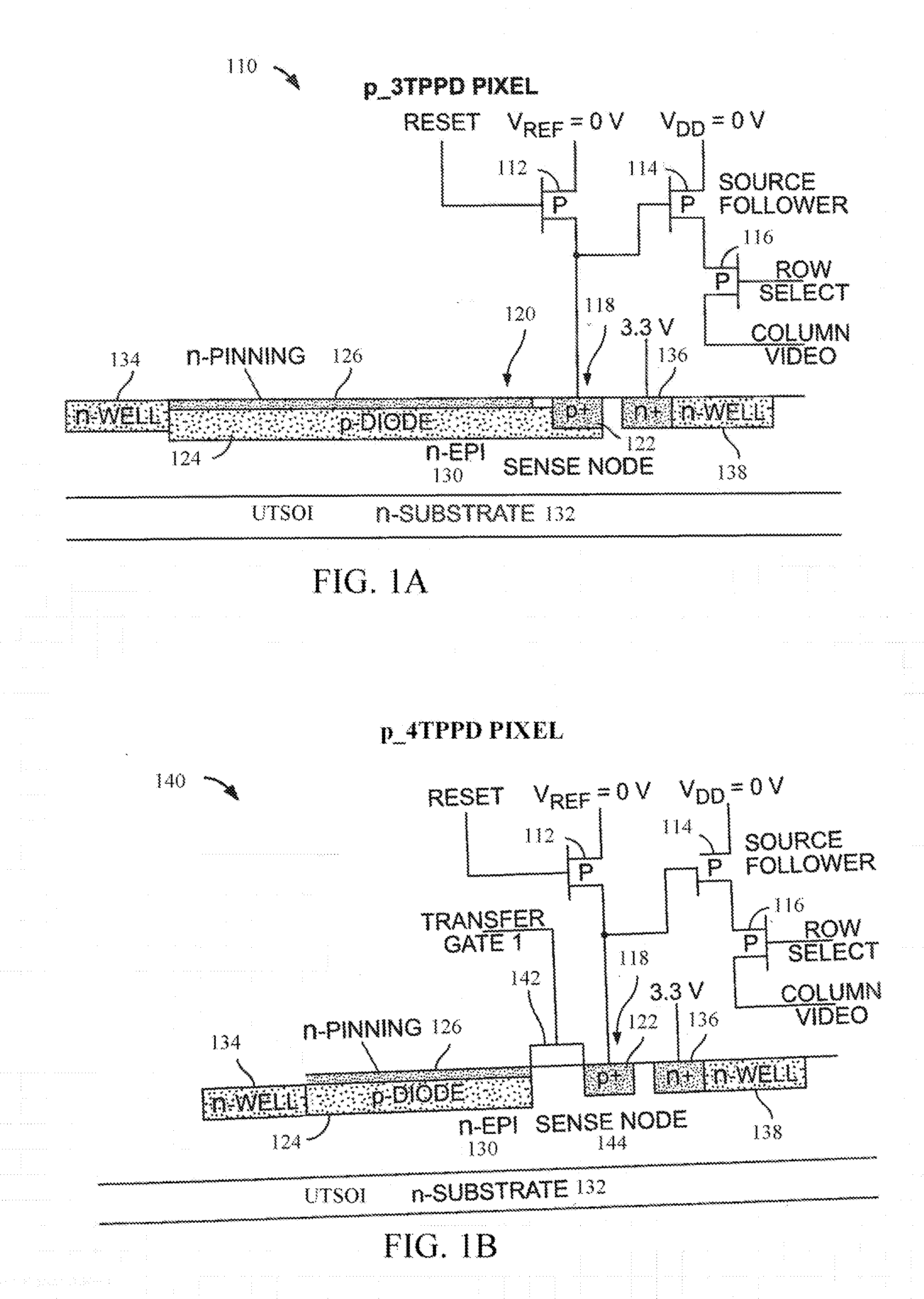
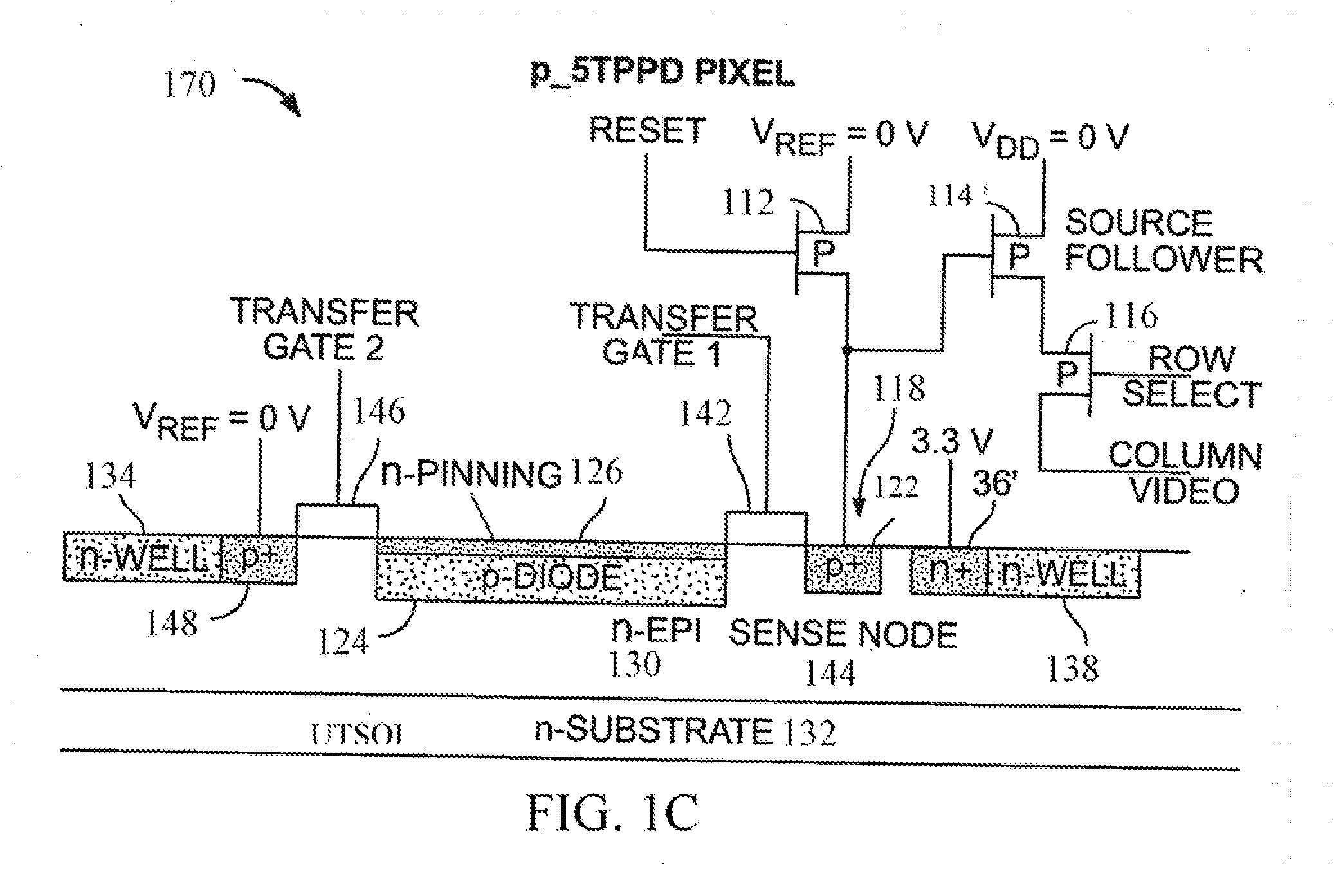
P-pixel CMOS imagers using ultra-thin silicon on insulator substrates (UTSOI)
InactiveUS20120104464A1Reduce concentrationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantCmos pixels
A CMOS image sensor is disclosed. The CMOS image sensor includes a semiconductor substrate having a surface. An epitaxial layer is grown on the surface. A p-type CMOS pixel formed substantially in the epitaxial layer. In one version of the CMOS image sensor, there exists a net n-type dopant concentration profile in the semiconductor substrate and the epitaxial layer which has a maximum value at a predetermined distance from the surface and which decreases monotonically on both sides of the profile from the maximum value within the semiconductor substrate and the epitaxial layer. In another version of the CMOS image sensor, there exists a net n-type dopant concentration profile in the semiconductor substrate and the epitaxial layer which has a maximum value at the surface and which decreases monotonically with increasing distance from the surface within the semiconductor substrate and the epitaxial layer.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
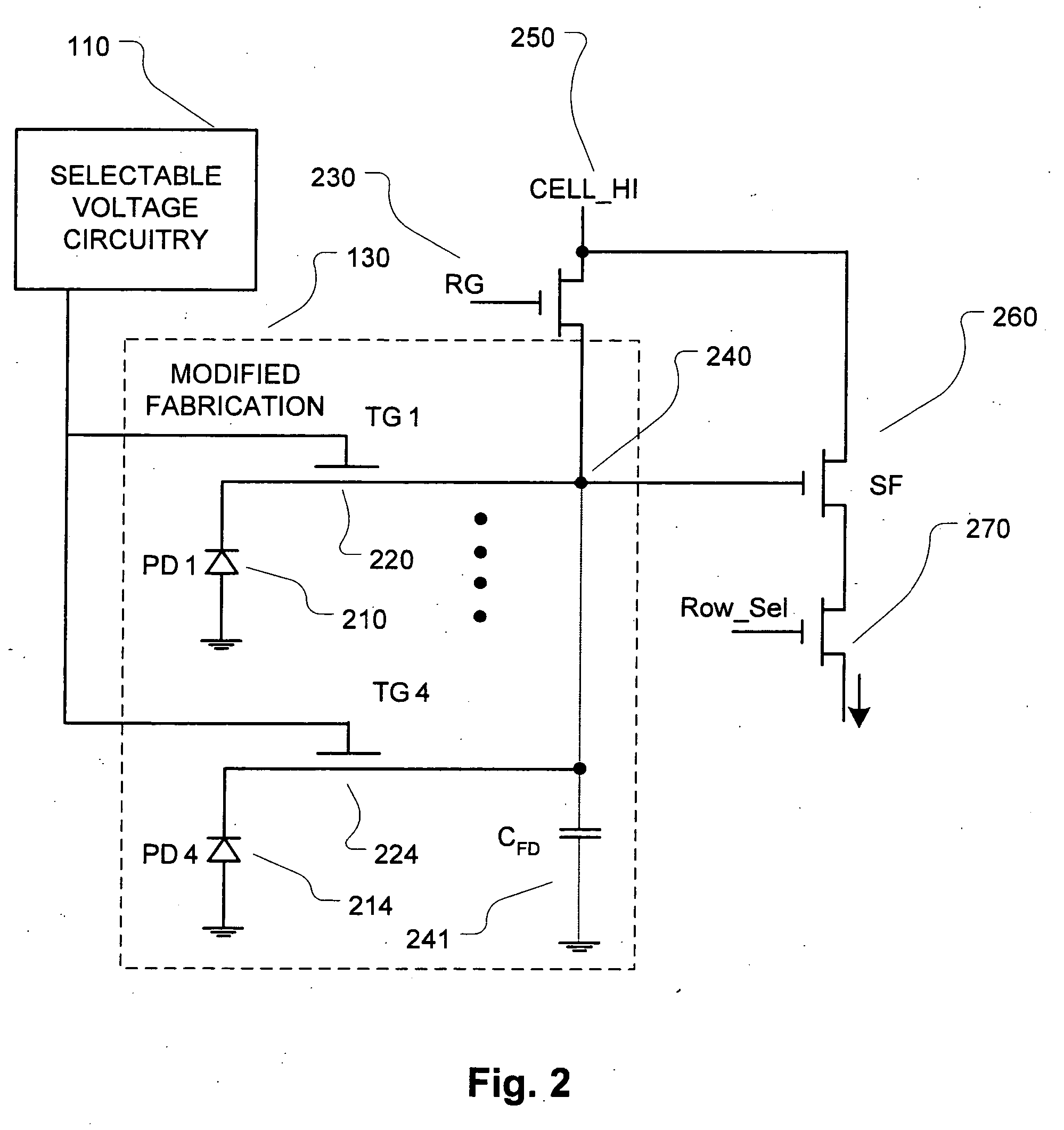
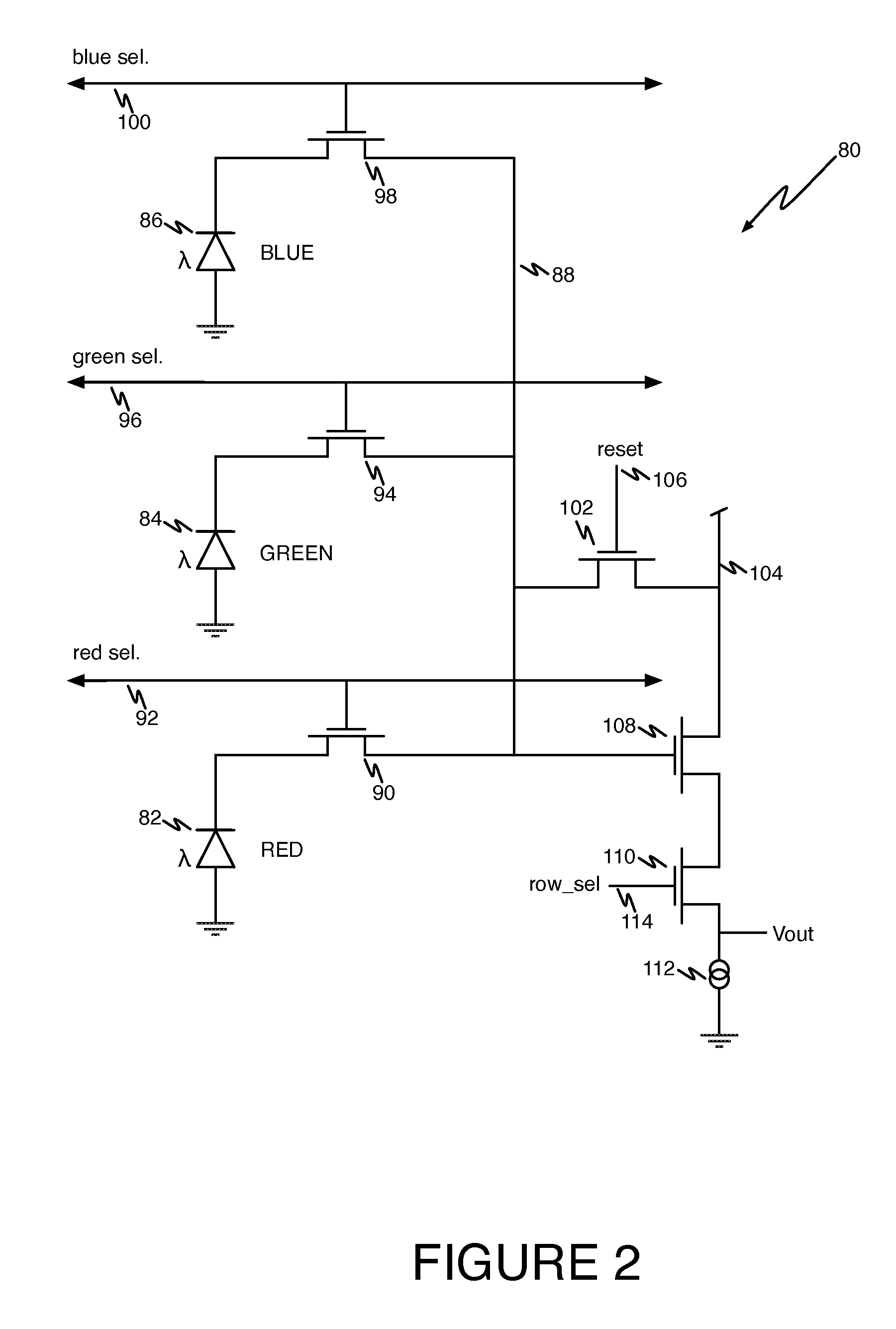
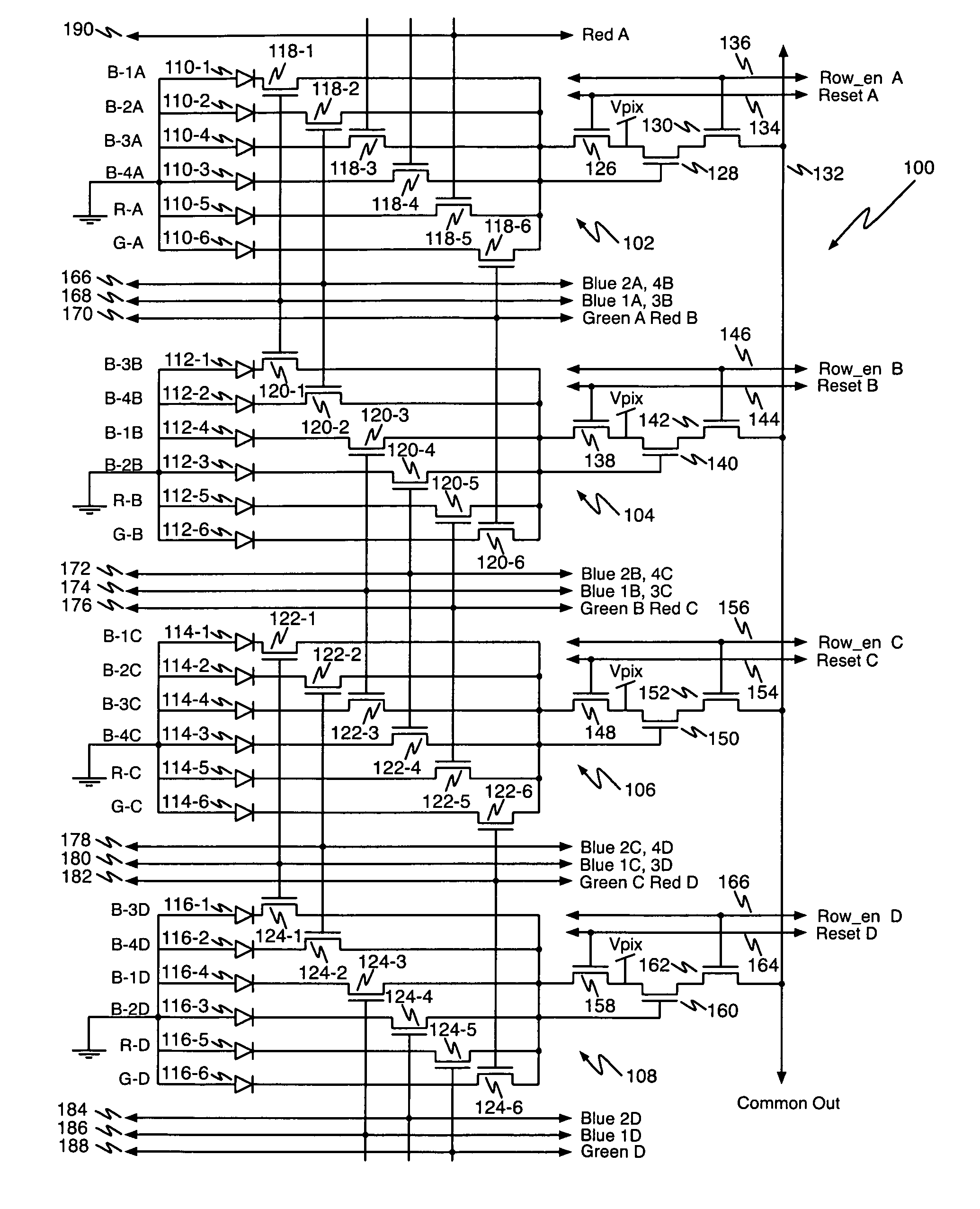
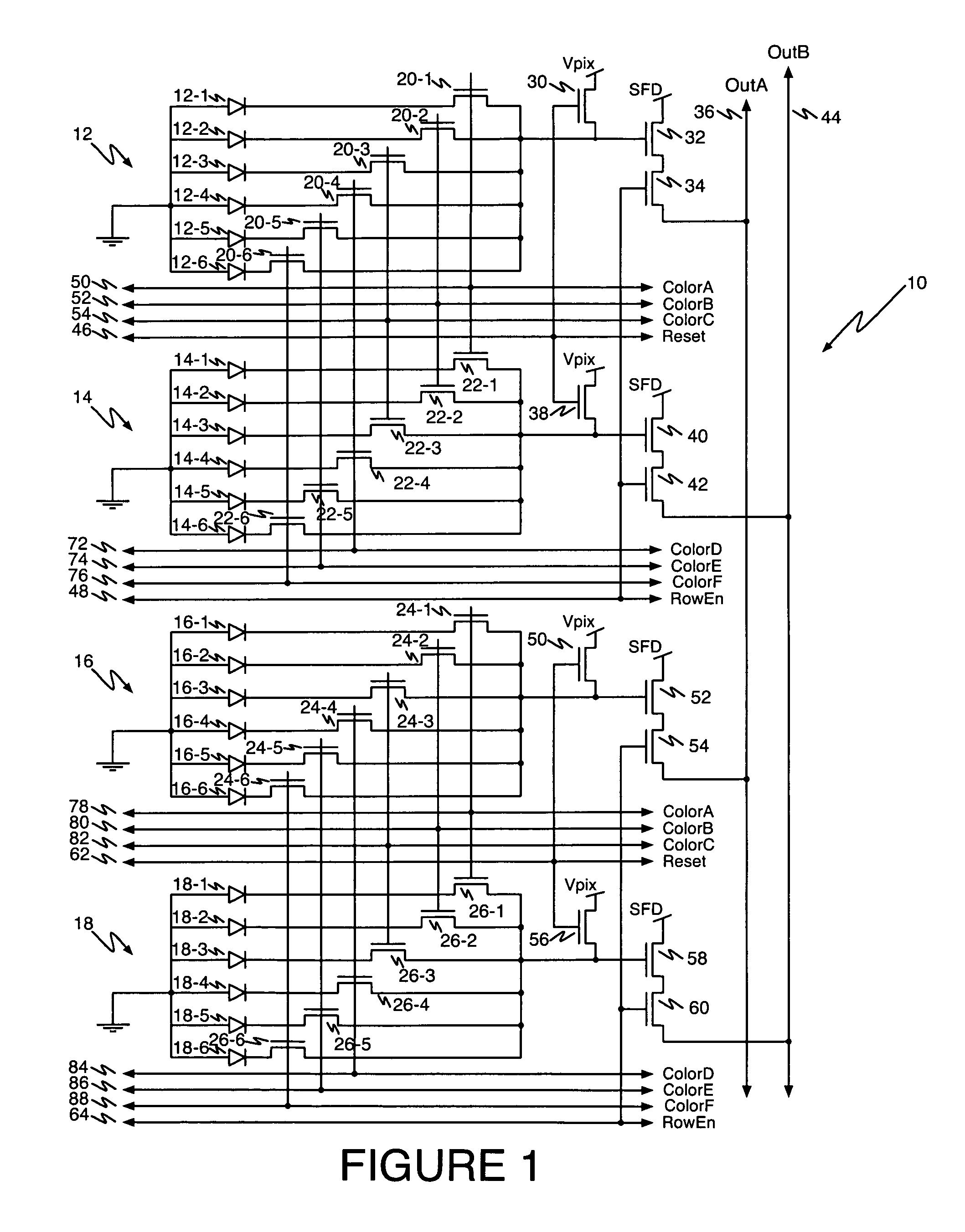
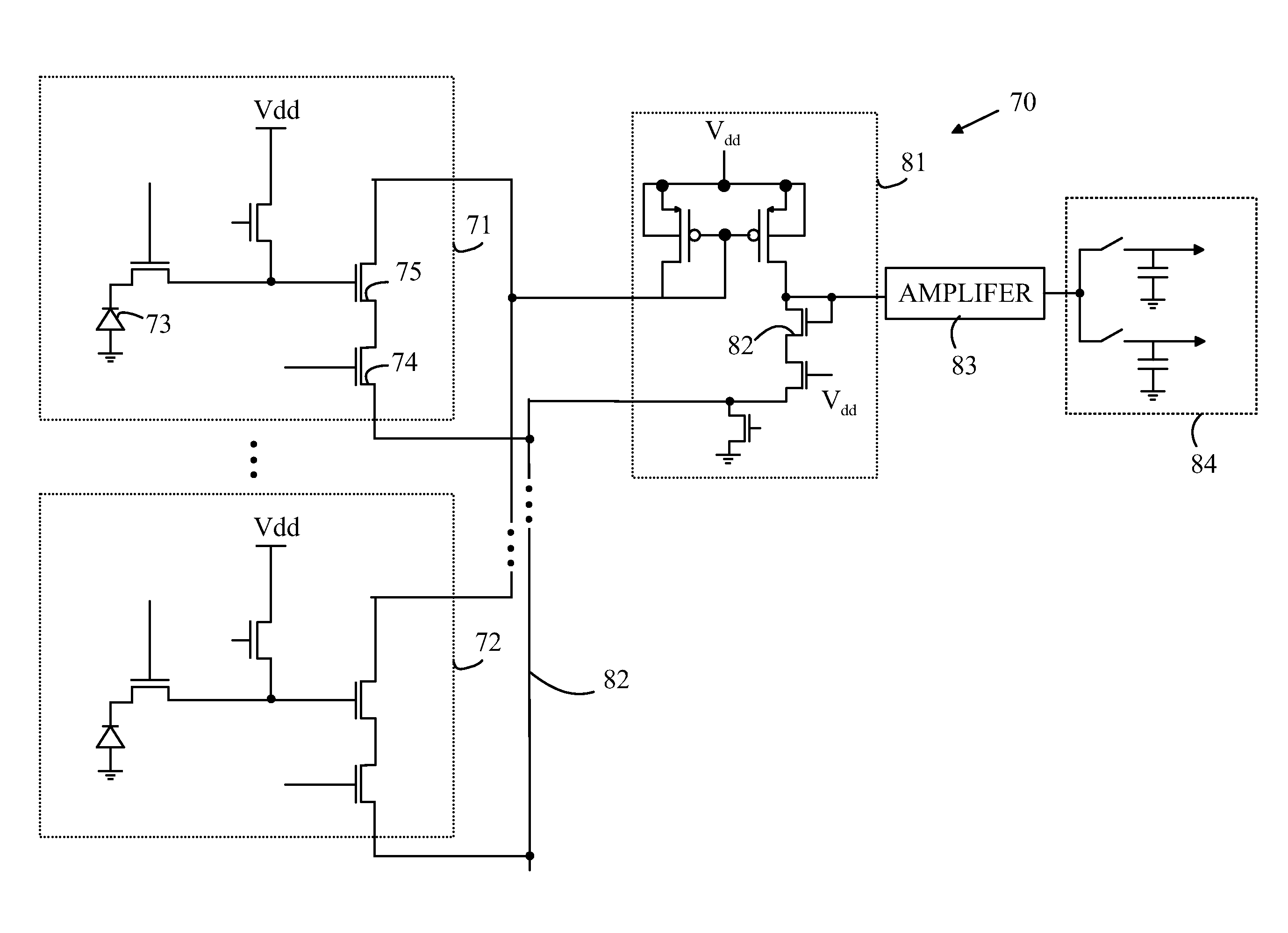
Multi-color CMOS pixel sensor with shared row wiring and dual output lines
ActiveUS7745773B1Reduce in quantityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesAudio power amplifierCmos pixels
An array of multicolor CMOS pixel sensors has a plurality of photosensors per pixel, each photosensor coupled to a single sense node through a select transistor having a select input, each pixel sensor including a reset transistor coupled to the sense node and having a reset input, an amplifier coupled to the sense node and a row-select transistor coupled to the amplifier. The select inputs and the reset inputs for pixel sensors in a pair of adjacent rows are coupled to select signal lines and reset signal lines associated with the pair of rows. The amplifier transistors in individual columns of each row are coupled to a column output line through a row-select transistor having a row-select input. The row-select inputs for pixel sensors in each row of the array are coupled to a row-select line associated with the row.
Owner:FOVEON
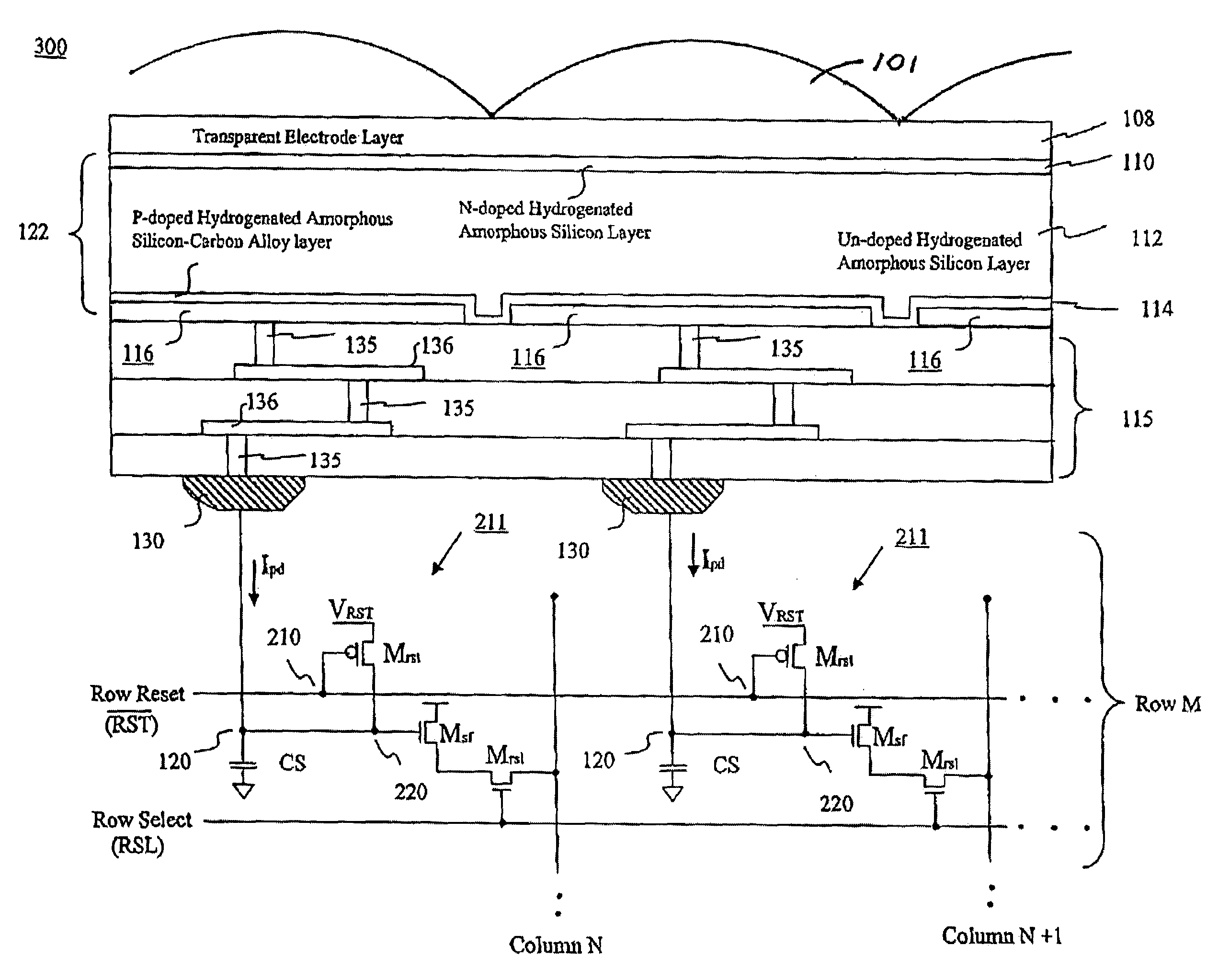
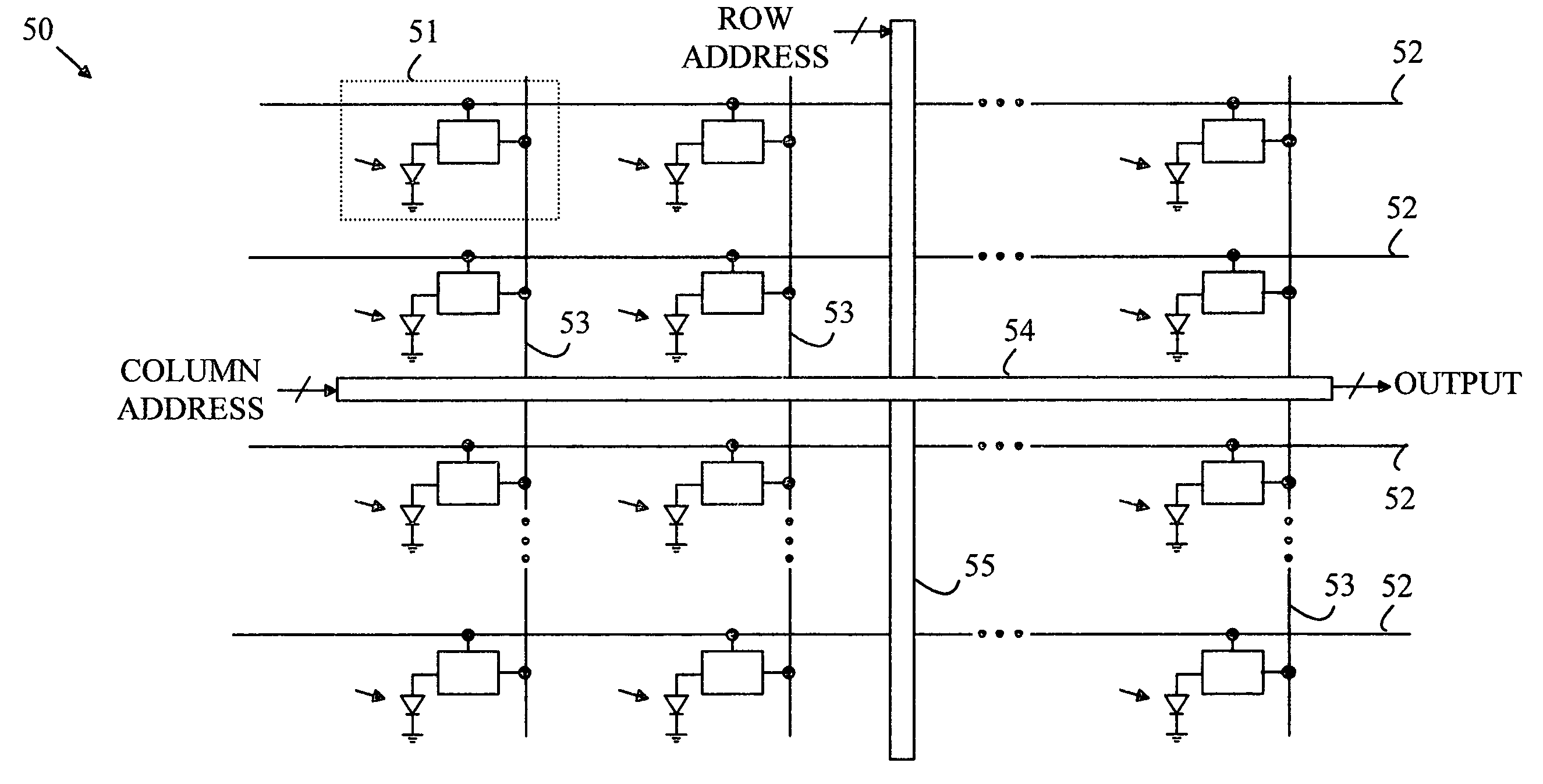
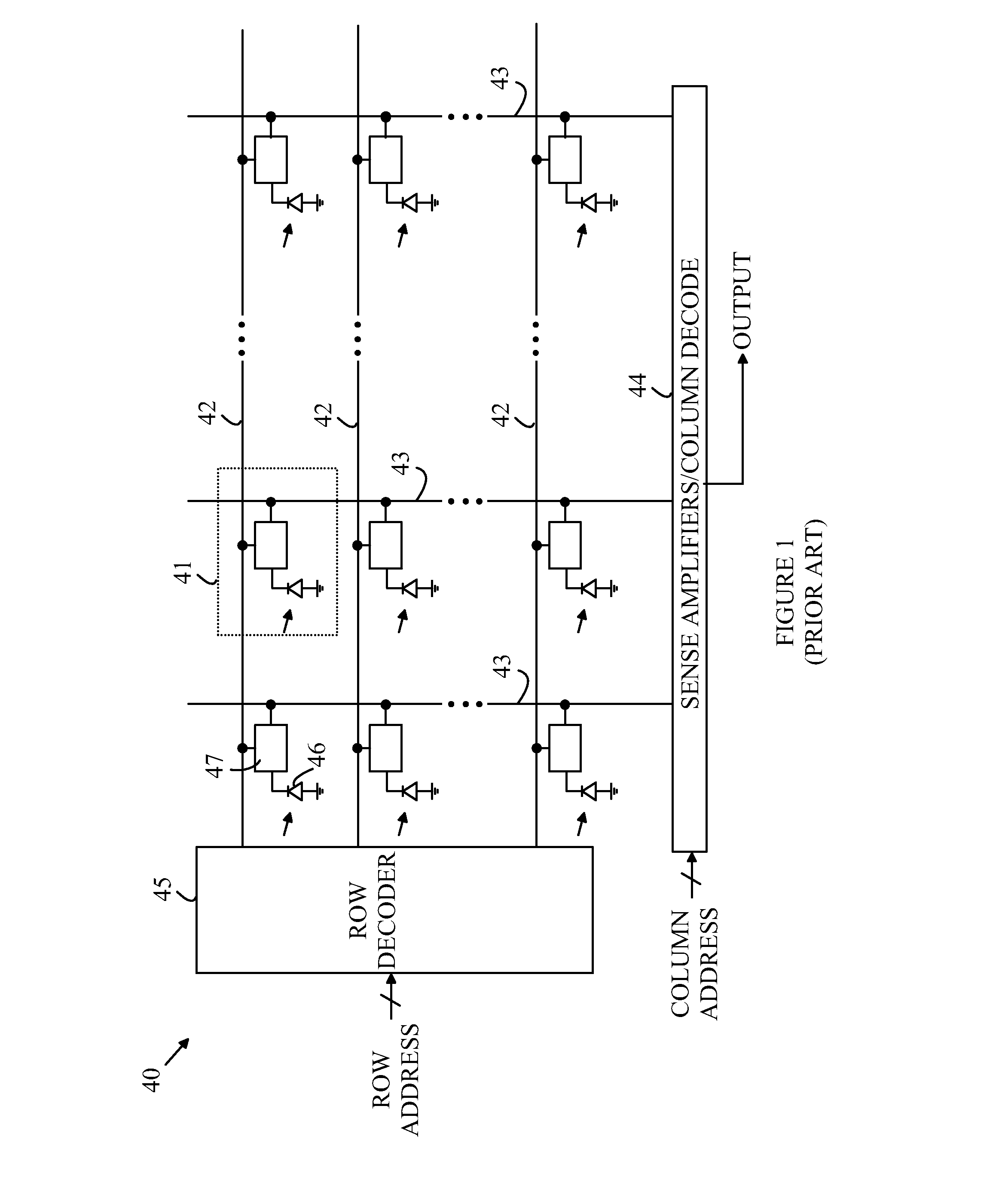
CMOS image sensors adapted for dental applications
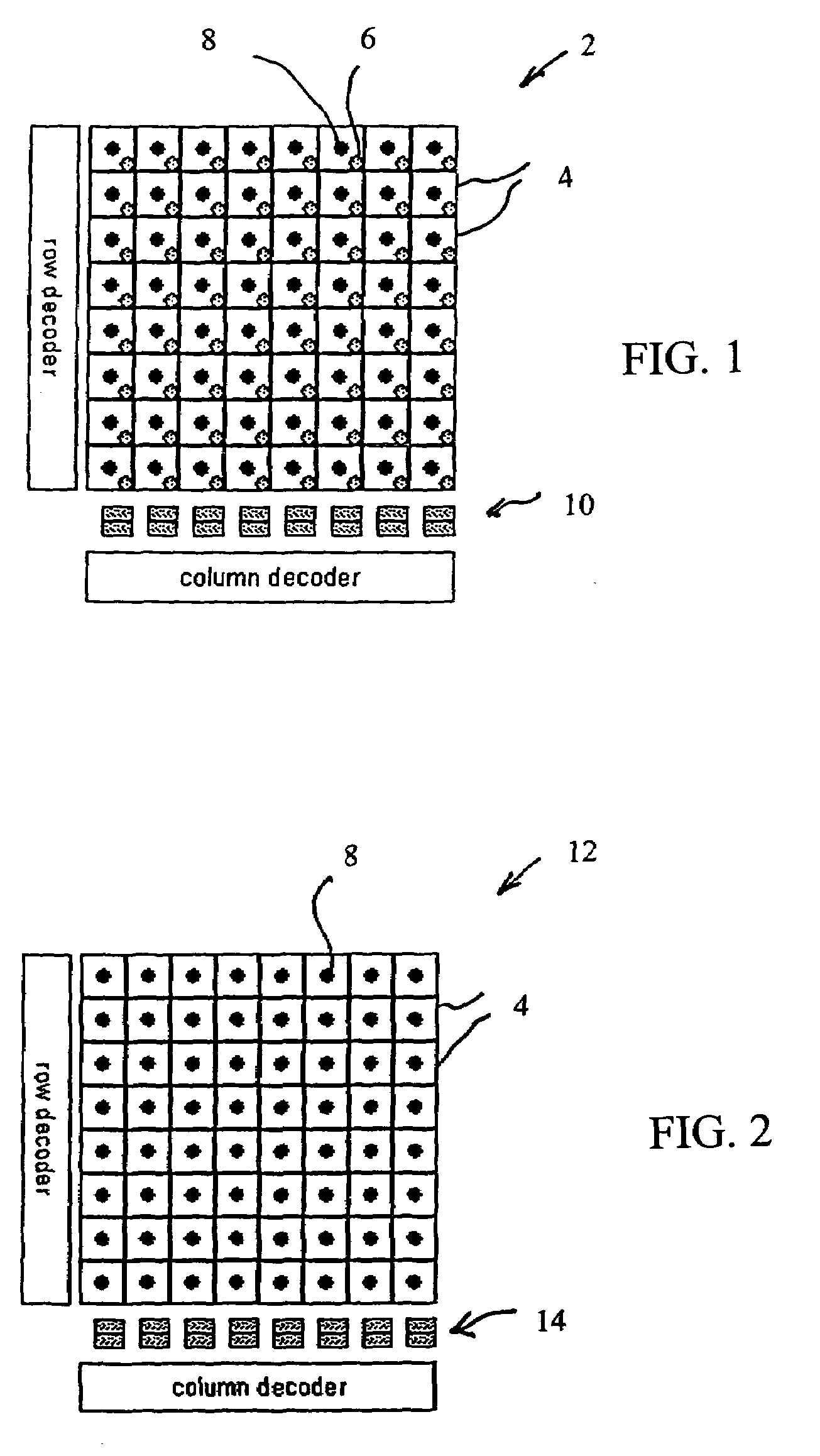
An image sensor having a two-dimensional array of CMOS pixel sensors, a row decoder and a column decoder is disclosed. The two-dimensional array of CMOS pixel sensors is organized as a plurality of rows and columns that are addressed with the aid of row and column decoders. At least one of the column decoder or the row decoder is located between two of the rows or two of the columns, respectively. X-rays are converted to light that is detected by the image sensor by a layer of scintillation material that overlies the two-dimensional array. The internally located decoder or decoders facilitate sensors in which the two-dimensional array includes a rectangular array having a chamfered corner such that rows or columns that extend into the chamfered corner have lengths that are less than rows or columns, respectively, that do not extend into the corners.
Owner:BAE SYST IMAGING SOLUTIONS
High dynamic range CMOS pixel and method of operating same
InactiveUS20120056079A1Increase in sizeIncreases magnitudeTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPotential wellCmos pixels
A method of operating a CMOS pixel is disclosed. The CMOS pixel includes a photodiode (PPD), a transfer gate coupled to the PPD, and an anti-blooming drain coupled to the transfer gate. A potential barrier is formed between a potential well underlying the PPD and the transfer gate. Charge is accumulated in the potential well in response to electromagnetic radiation during a first integration time. Excess charge is removed from the potential well to the anti-blooming drain that exceeds the first potential barrier. A size of the potential barrier is increased. Charge is accumulated in the potential well during a second integration time.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
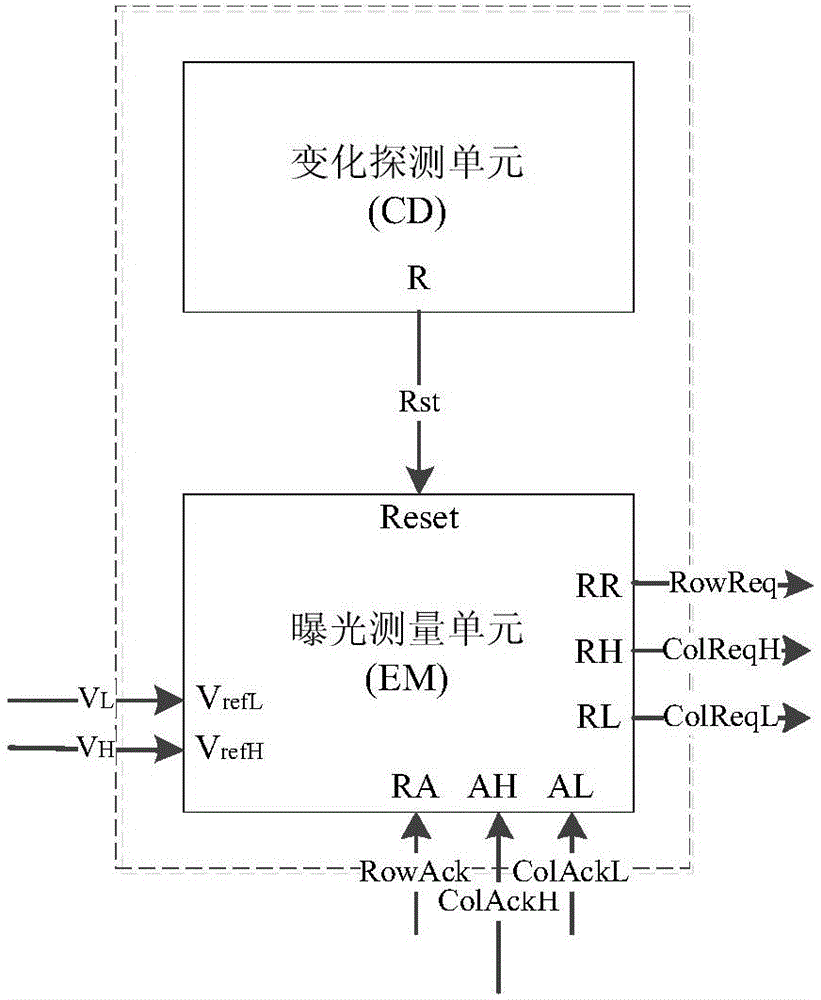
Asynchronous CMOS pixel circuit with light adaptive threshold voltage adjustment mechanism
InactiveCN103607546AHigh measurement accuracyShort response timeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsControl signalSmall range
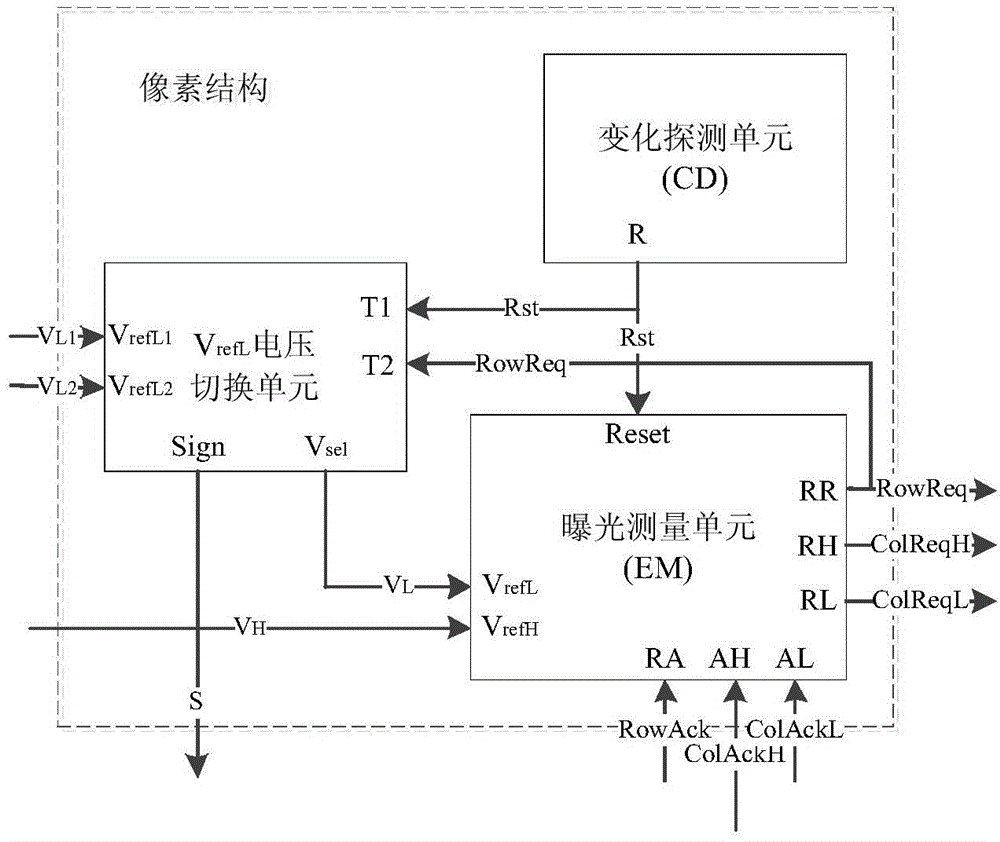
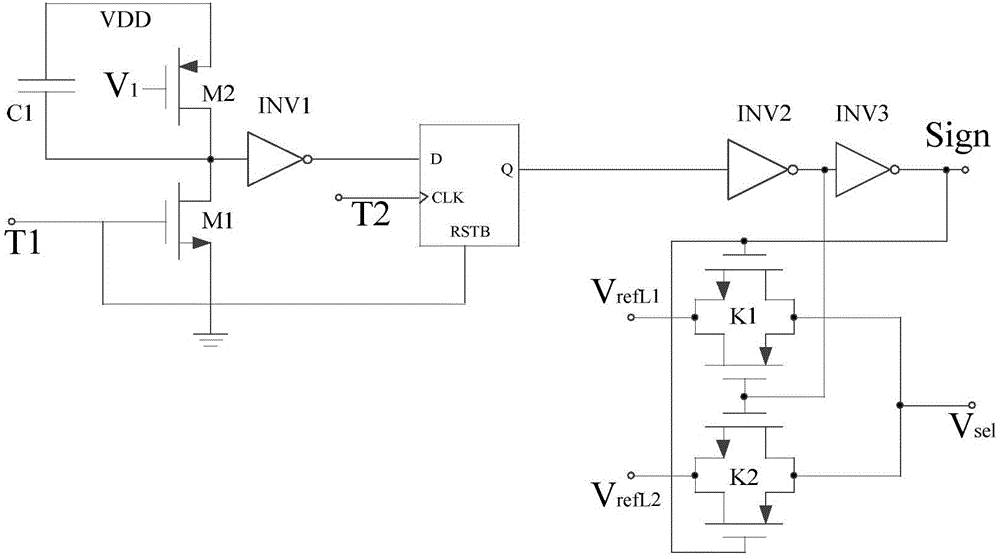
The invention relates to a digital-analog hybrid integrated circuit design field and provides an asynchronous CMOS pixel circuit with a light adaptive threshold voltage adjustment mechanism. The objectives of the invention are to maintain the advantages of high dynamic range and low fixed-model noise of a circuit, and compress time for measuring light intensity in a relatively small range, and improve the response speed of the circuit. In order to achieve the above objectives, the following technical schemes are adopted: the asynchronous CMOS pixel circuit with the light adaptive threshold voltage adjustment mechanism is composed of a light intensity change detection unit (CD), an exposure measurement unit (EM) using a PWM mode and a VrefL reference voltage switching unit; and output signals Rst of the output end R of the change detection unit are connected with the input end Reset of the exposure measurement unit and the input end T1 of the VrefL reference voltage switching unit and are respectively used for controlling signals of measurement initiating of the exposure measurement unit and controlling the evaluation of light intensity. The asynchronous CMOS pixel circuit with the light adaptive threshold voltage adjustment mechanism of the invention is mainly applied to the digital-analog hybrid integrated circuit design.
Owner:天津市晶奇国际贸易有限公司
Active pixel structure with improved charge transfer
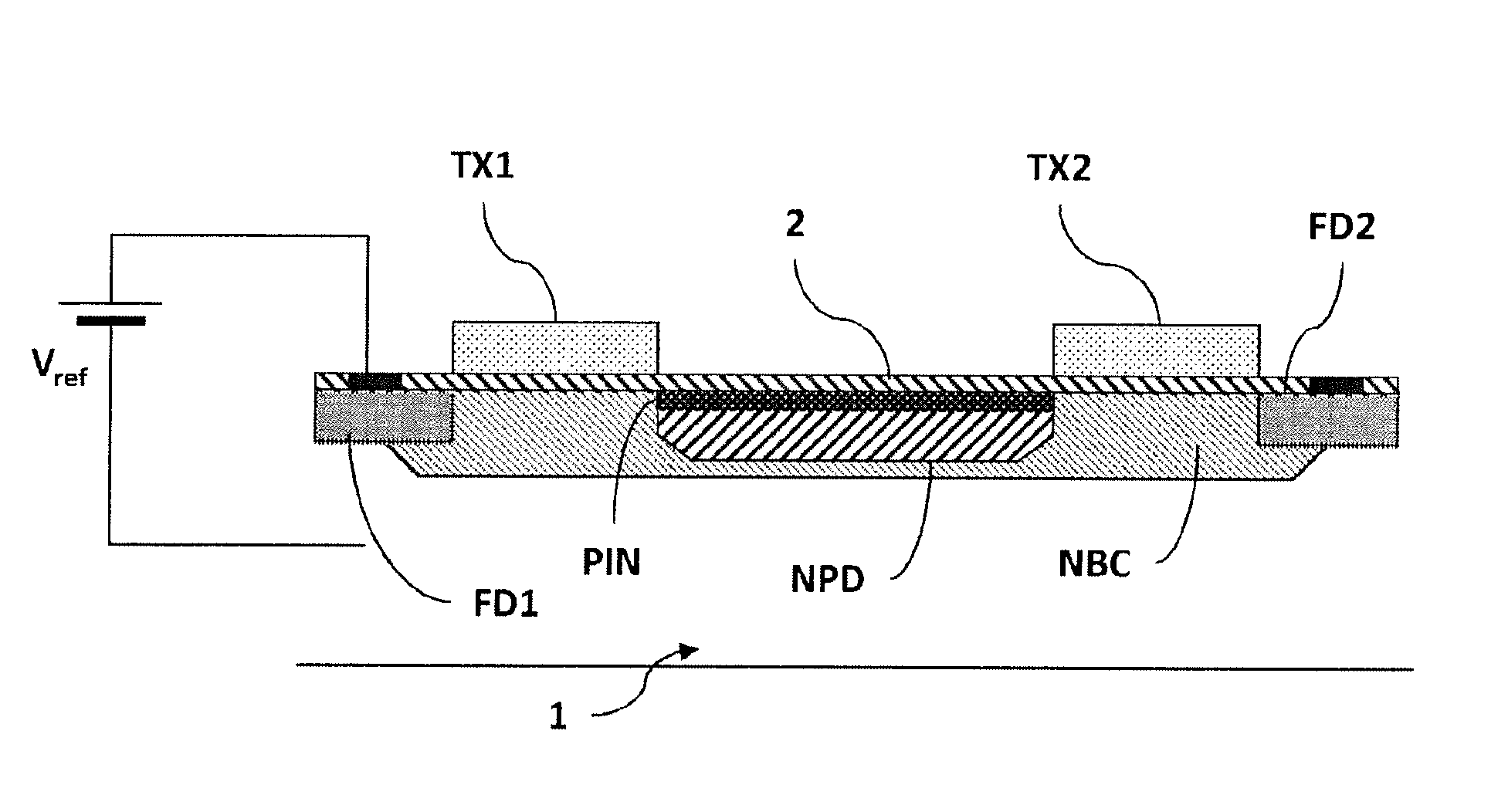
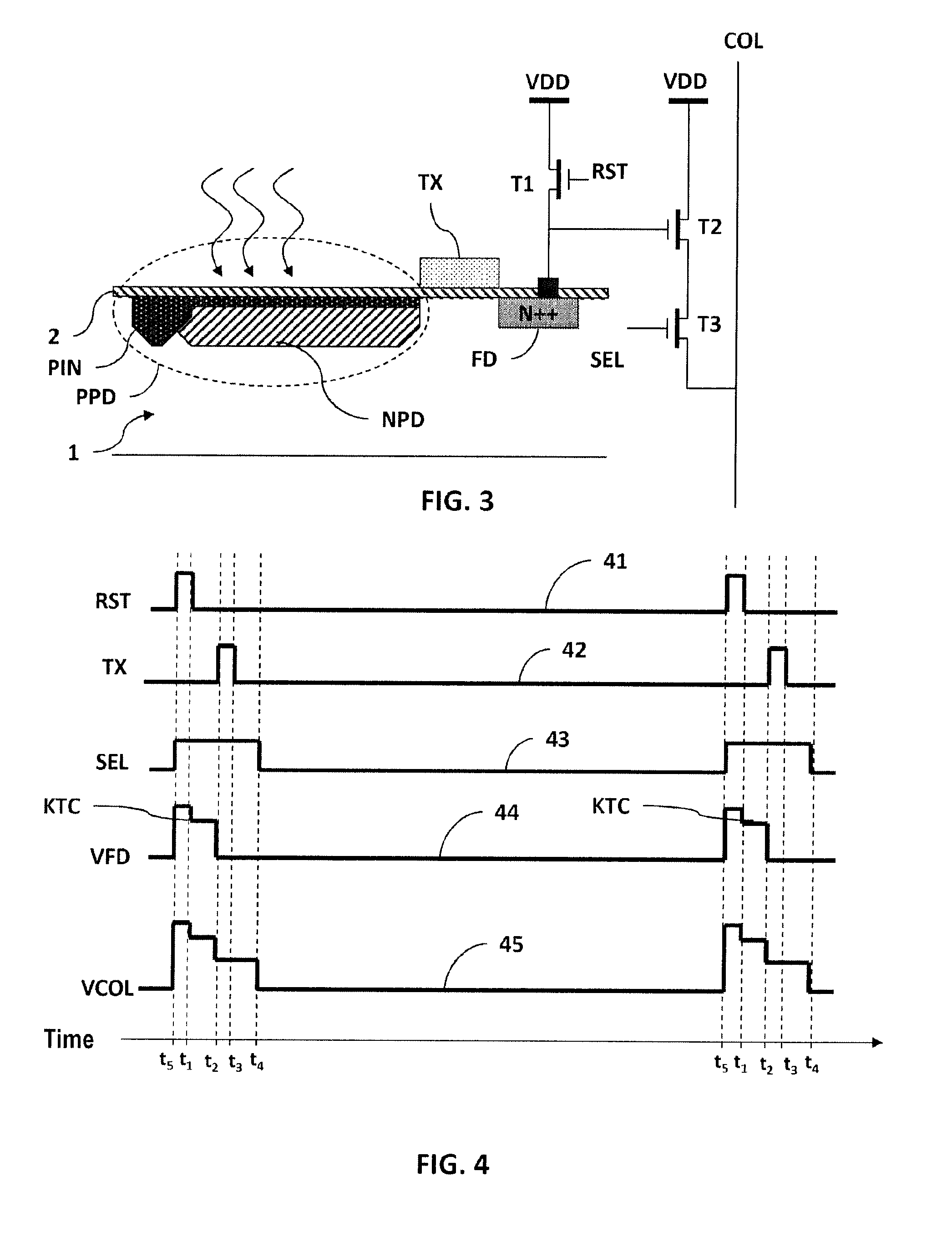
ActiveUS20150008493A1Without deteriorationTransistorSolid-state devicesCmos pixelsPhotoelectric conversion
The invention relates to an active CMOS pixel structure comprising: at least one photoelectric conversion zone (NPD) defined by n-doping of the substrate, said zone accumulating an amount of charge during an exposure to light and comprising a p-doped surface zone (PIN); and at least one MOS transfer transistor (TX), the gate of said transfer transistor (TX) being electrically insulated from the substrate and being used to control transfer of said charge from said photoelectric conversion zone (NPD) to said floating diffusion node (FD), in which the gate of said transfer transistor (TX) partially covers said p-doped surface zone (PIN), and said photoelectric conversion zone (NPD) extends under said gate of said transfer transistor (TX) at least as far as the end of the p-doped surface zone (PIN).
Owner:NEW IMAGING TECH
Laminated complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor and image processing method
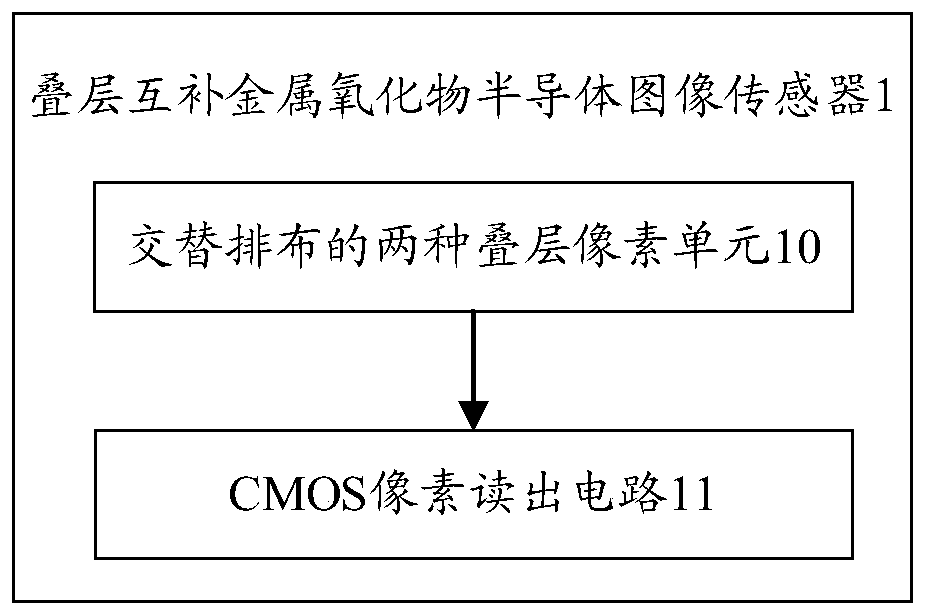
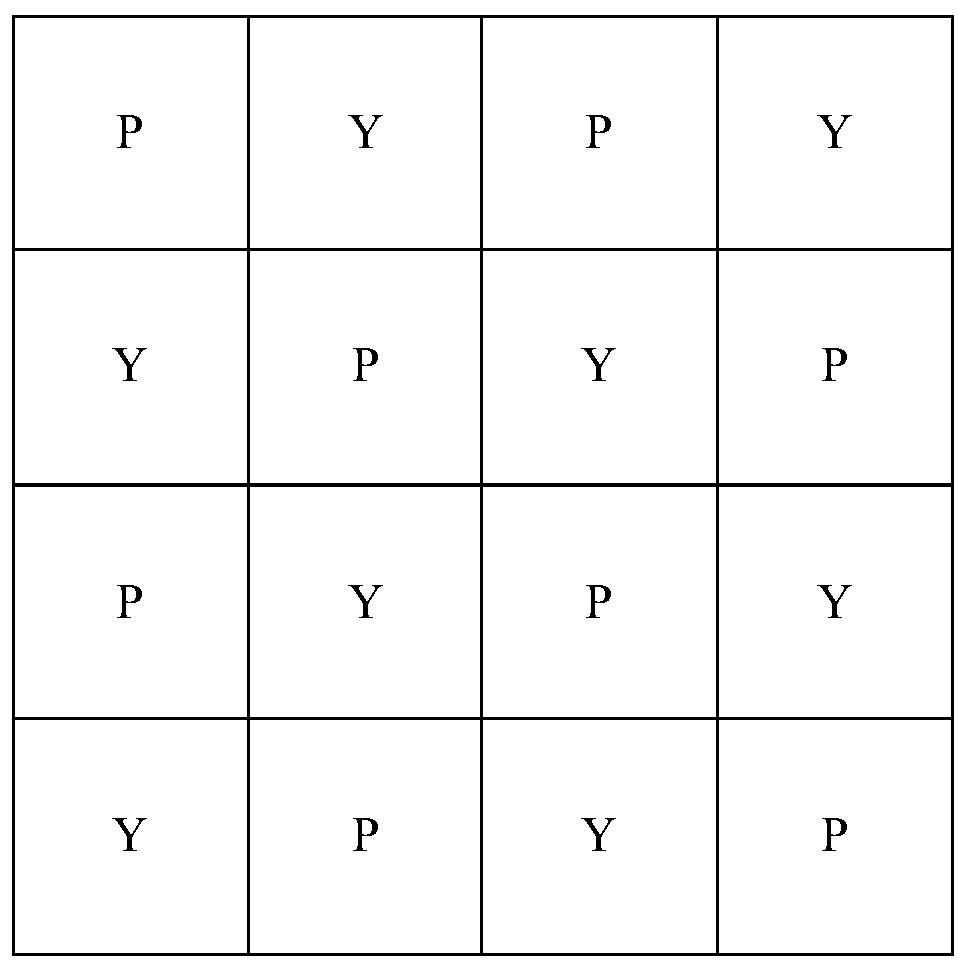
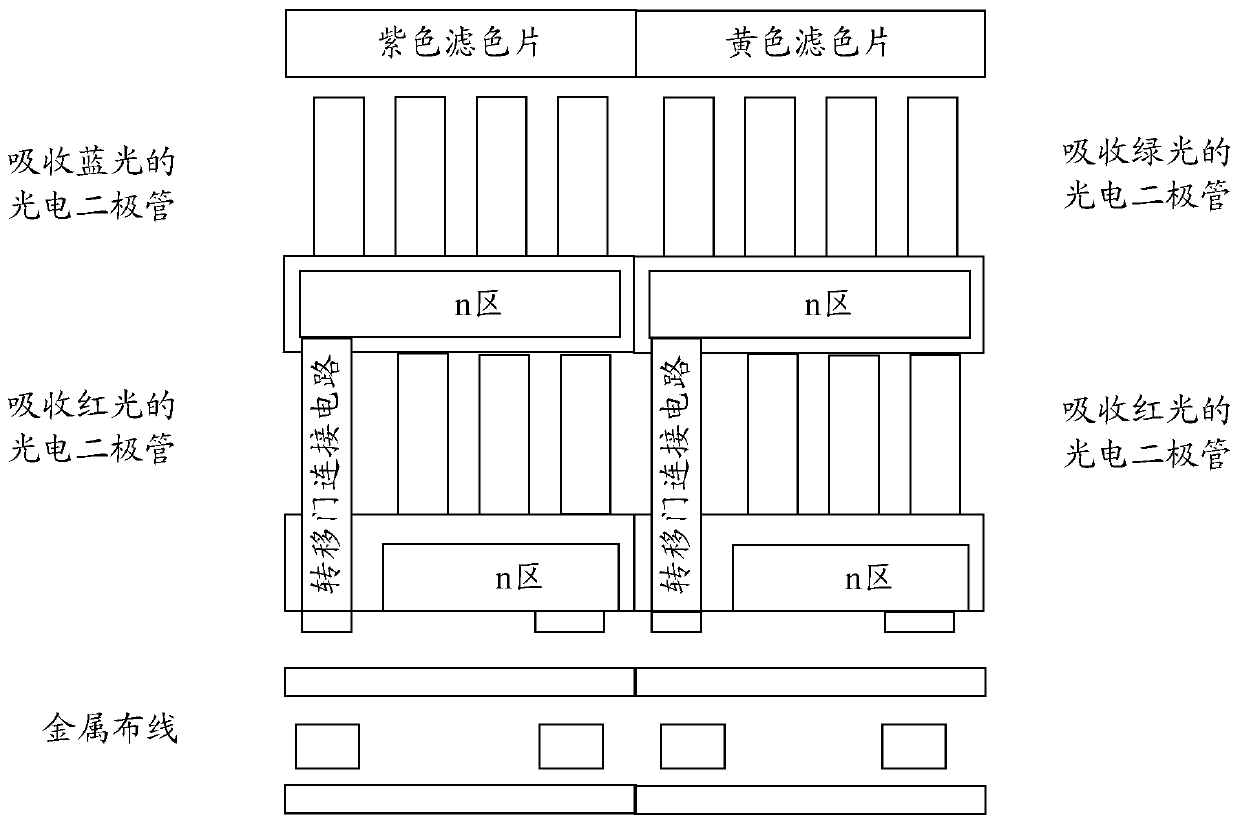
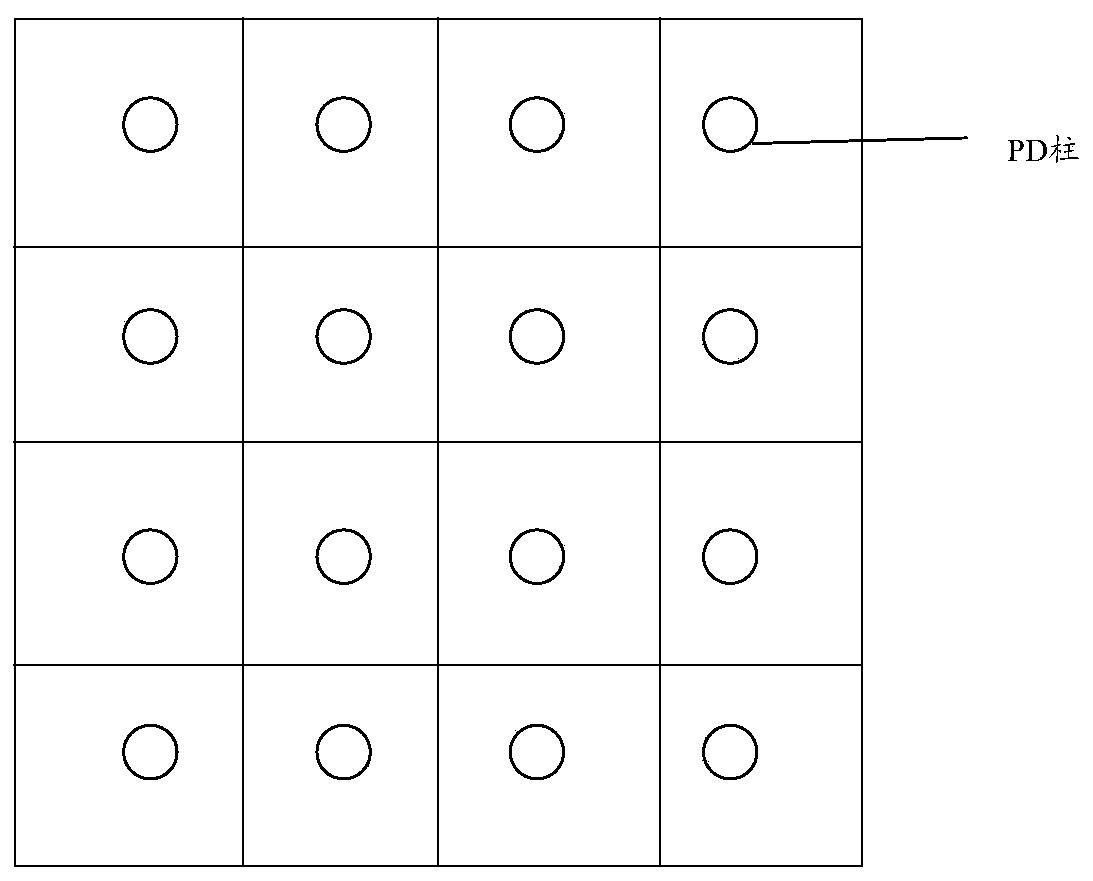
InactiveCN110536084AReduce power consumptionReduce the number of signalsTelevision system detailsColor television detailsImaging processingCmos pixels
The embodiment of the invention provides a laminated complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor and an image processing method. The laminated complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor includes: two laminated pixel units alternately arranged; the two laminated pixel units comprise photodiode PD columns of three sizes, wherein two layers of PD columns are respectively arranged on each laminated pixel unit in the two laminated pixel units; wherein the two layers of photodiode PD columns comprise PD columns of two sizes, the sizes of the PD columns of each layer in the two layers of PD columns are the same, and the two laminated pixel units utilize the PD columns of the three sizes to absorb RGB three-color light respectively and convert optical signals corresponding to the RGB three-color light into electric signals corresponding to the RGB three-color light; the CMOS pixel reading circuits are connected with the output ends of the two laminated pixel units, each layer of PD column is connected with one CMOS pixel reading circuit, and the CMOS pixel reading circuits are used for amplifying electric signals and reading the electric signals.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Mass transfer of micro structures using adhesives
ActiveUS10325893B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicro structureLED display
Mass transfer of micro structures are effected from one substrate to another using adhesives. In the context of an integrated micro LED display, a micro LED array is fabricated on a native substrate and corresponding CMOS pixel drivers are fabricated on a separate substrate. The micro LED substrate (e.g., sapphire) and the CMOS substrate (e.g., silicon) may be incompatible. For example, they may have different thermal coefficients of expansion which make it difficult to bond the micro LEDs to the pixel driver circuitry. The micro LED array is transferred to an intermediate substrate (e.g., silicon) by use of an adhesive. This intermediate substrate may be used in a process of bonding the micro LED array to the array of pixel drivers. The intermediate substrate is separated from the micro LED array by releasing the adhesive.
Owner:JADE BIRD DISPLAY SHANG HAI LTD
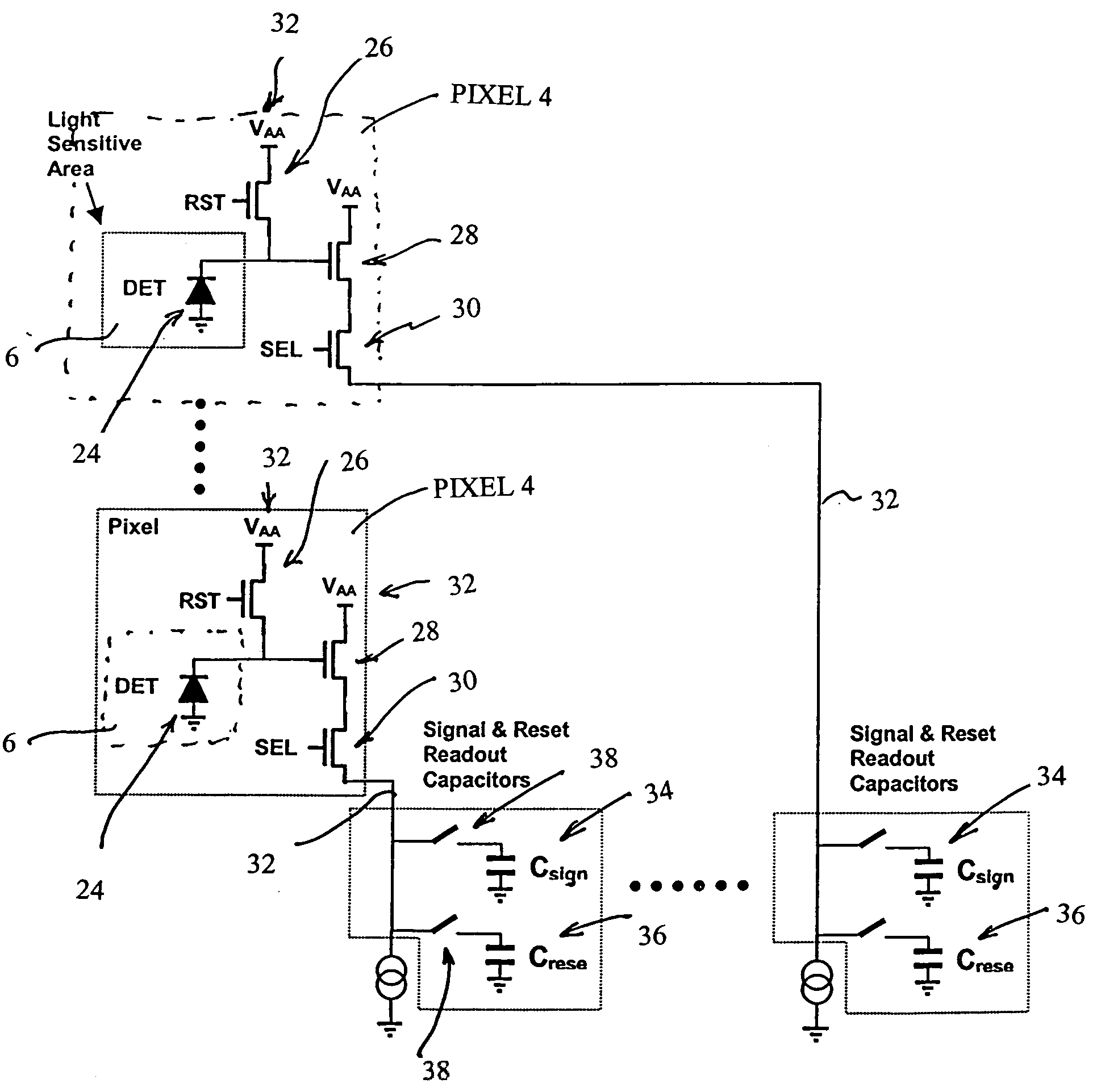
Frame-shuttered CMOS image sensor with simultaneous array readout
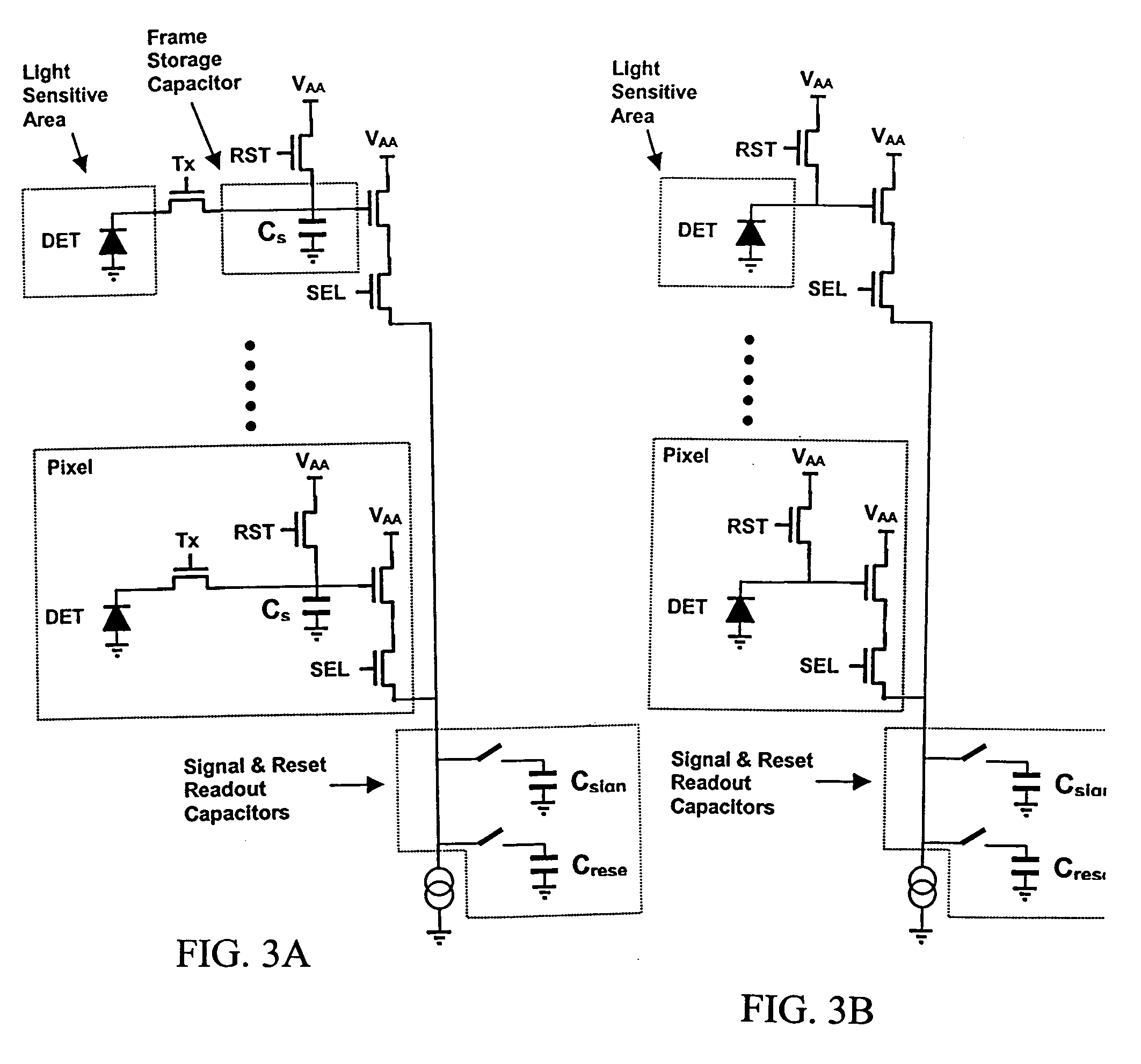
ActiveUS7274009B2Drawback can be obviatedReduce usageTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsElectrical conductorCmos pixels
A frame shuttered CMOS image sensor with simultaneous array readout. An array of CMOS pixels are printed on a silicon substrate. Within each pixel is a light sensitive region comprising a photo sensitive diode for converting photons into electrical charge and at least three transistors to permit reading of reset electrical charges and collected electrical charges and for re-setting the photosensitive diode. The sensor includes an array of signal and re-set readout capacitors located on the substrate but outside of the pixel array. Metal conductors printed in said substrate connect each pixel in said pixel array with a signal capacitor and a re-set capacitor in array of signal and re-set readout capacitors. Transistor switches printed in said substrate but outside of said pixel array are used to isolate the signal and re-set capacitors from each other and from the pixels. Control circuitry is provided for re-setting simultaneously each of the pixels in the pixel array, for collecting simultaneously re-set signals from each pixel on to one of the reset capacitors in the array of readout capacitors and for collecting simultaneously integrated pixel signals from each pixel on to one of the signal capacitors in the array of readout capacitors. Readout circuitry is provided for reading charges collected on the array of signal and re-set capacitors.
Owner:FORZA SILICON
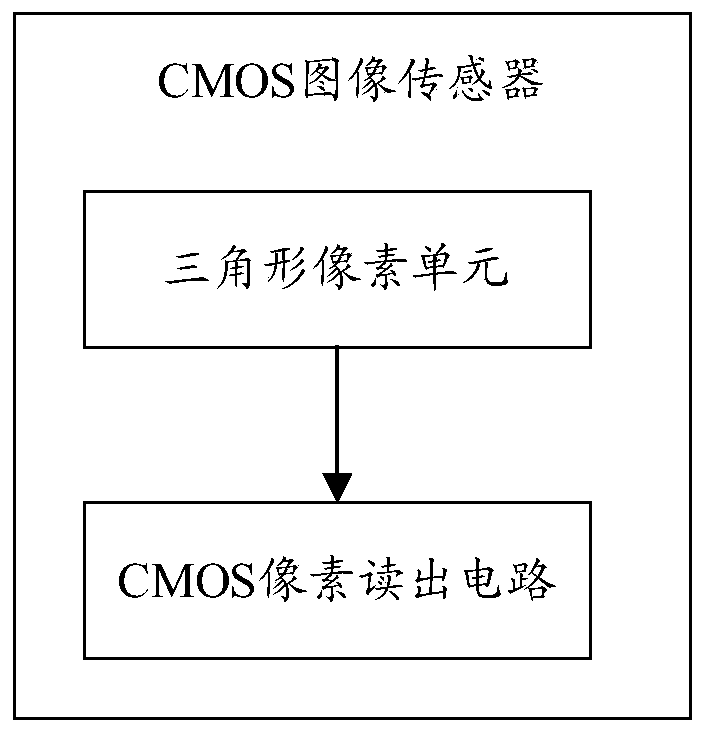
CMOS image sensor, image processing method and storage medium
PendingCN110379824AIncrease pixel densityImprove the layout densityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImaging processingCmos pixels
The embodiment of the application provides a CMOS image sensor, an image processing method and a storage medium. The CMOS image sensor comprises triangular pixel units arranged in a hexagonal array and a CMOS pixel readout circuit connected with the triangular pixel units, wherein each triangular pixel unit is internally provided with a photodiode PD column and uses the photodiode PD column to absorb RGB monochromatic light and convert a corresponding optical signal into an electric signal, and the CMOS pixel readout circuit is used for amplifying and reading out the electric signals.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
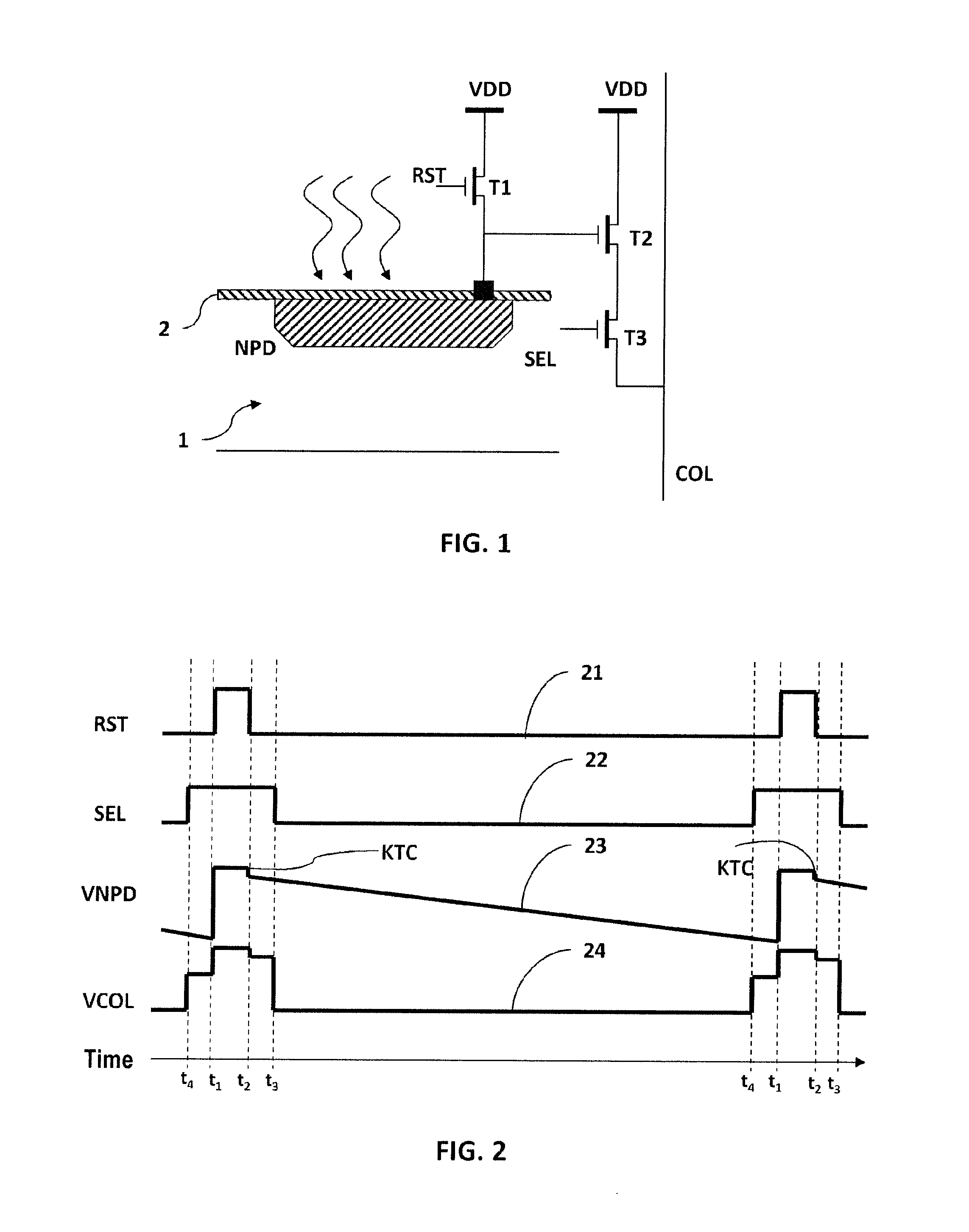
Low Noise CMOS Pixel Array
InactiveUS20130070134A1Television system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow noisePhotodetector
An imaging array having a plurality of pixels is disclosed. Each pixel includes a photodetector that converts light to charge, a floating diffusion node, a first amplification stage connected to the floating diffusion node, and a select gate that connects the pixel to a second amplification stage. The first and second amplification stages form a current mirror. The first amplification stage includes a buried channel device. In one aspect of the present invention, the current minor has an overall voltage gain of between 0.9 and 1.1. In another aspect of the invention, the second amplification stage is shared by a plurality of pixels.
Owner:BAE SYST IMAGING SOLUTIONS
High-dynamic CMOS pixel unit and a signal collection method thereof
ActiveCN106791507AIncrease the effective photosensitive rangeIncrease storage capacityTelevision system detailsColor television detailsCapacitanceCmos pixels
The invention provides a CMOS pixel unit and a signal collection method thereof. The CMOS pixel unit is characterized in that a positive electrode of a photosensitive diode is connected with a negative electrode of a power source, a strong light processing circuit is connected with a drain electrode of a first NMOS tube and a source electrode of a second NMOS tube and is used for adding a storage capacitance for an electric signal when the photosensitive diode is irradiated by strong light, the positive electrode of an array current source is connected with the drain electrode of a third NMOS tube and serves as a signal output end of the high-dynamic CMOS pixel unit, the negative electrode of the array current source is connected with the negative electrode of the power source, the source electrode of the first NMOS tube is connected with the negative electrode of the photosensitive diode and is used for conducting the photosensitive diode, the source electrode of the second NMOS tube is connected with the drain electrode of the first NMOS tube, the drain electrode of the second NMOS tube is connected with the positive electrode of the power source and is used for realizing restoration of an output signal, and the source electrode of the third NMOS tube is connected with a strong light processing circuit and is used for realizing selective connection of each pixel unit and an array output end.
Owner:SHANGHAI INTEGRATED CIRCUIT RES & DEV CENT +1
High dynamic range CMOS pixel and method of operating same
InactiveUS8766157B2Increase in sizeIncreases magnitudeTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPotential wellCmos pixels
A method of operating a CMOS pixel is disclosed. The CMOS pixel includes a photodiode (PPD), a transfer gate coupled to the PPD, and an anti-blooming drain coupled to the transfer gate. A potential barrier is formed between a potential well underlying the PPD and the transfer gate. Charge is accumulated in the potential well in response to electromagnetic radiation during a first integration time. Excess charge is removed from the potential well to the anti-blooming drain that exceeds the first potential barrier. A size of the potential barrier is increased. Charge is accumulated in the potential well during a second integration time.
Owner:SRI INTERNATIONAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com