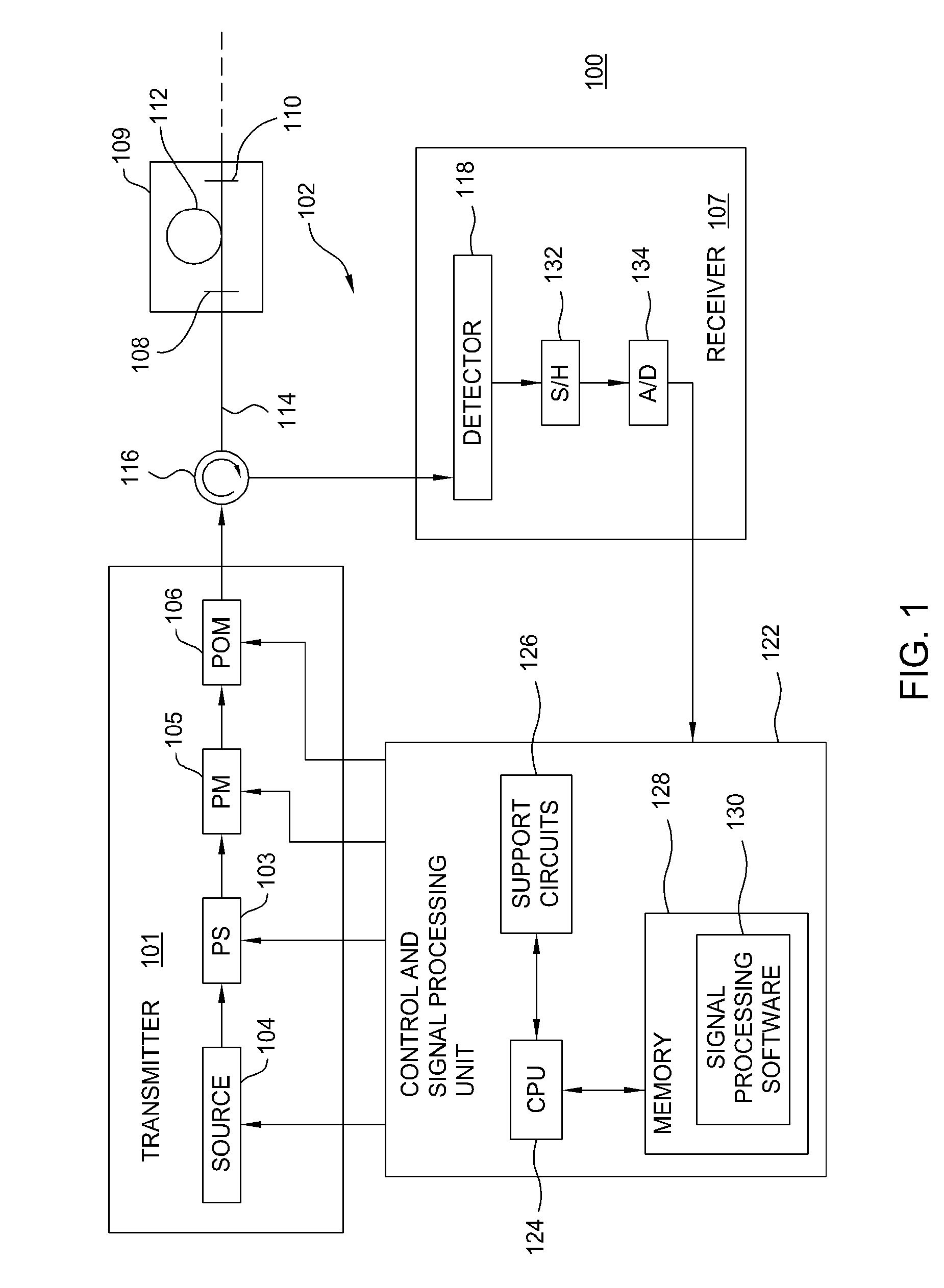
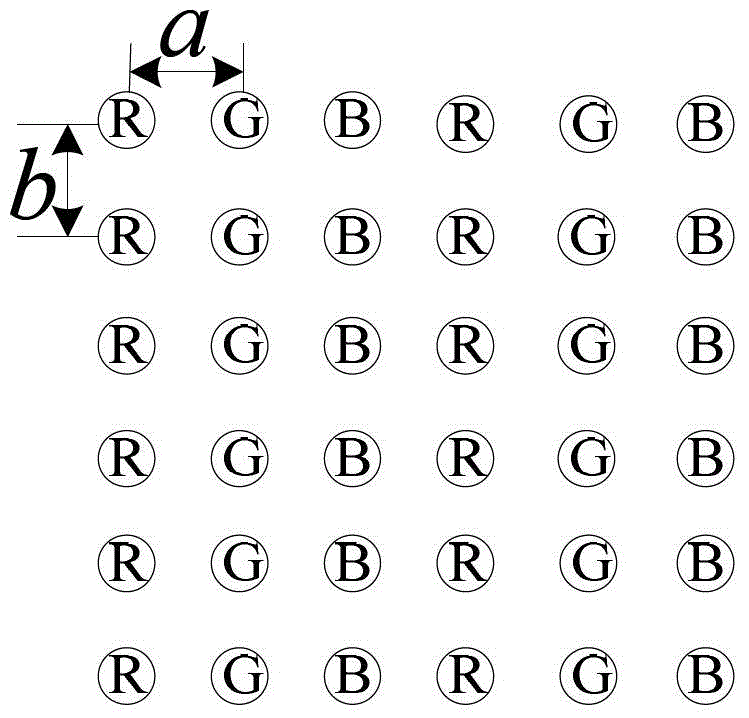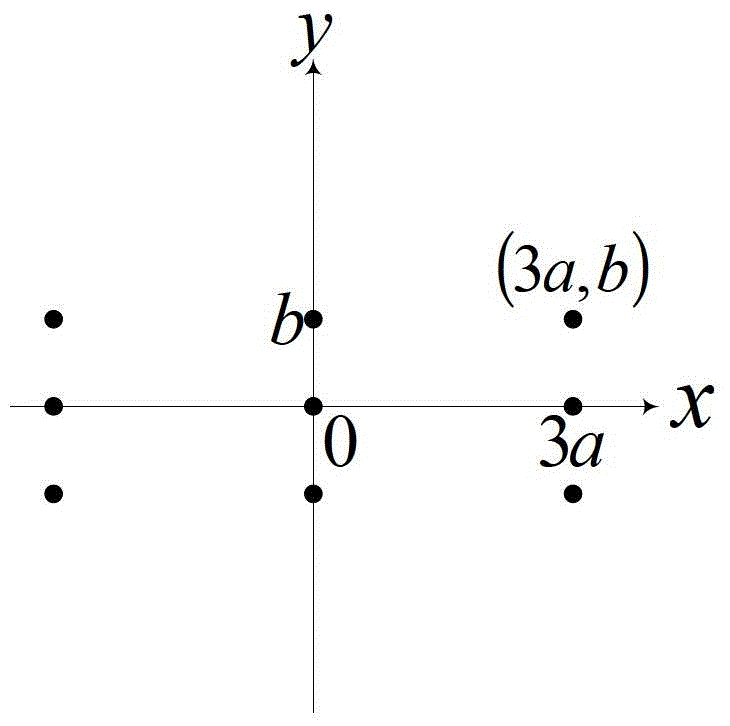Patents
Literature
210 results about "Nyquist frequency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
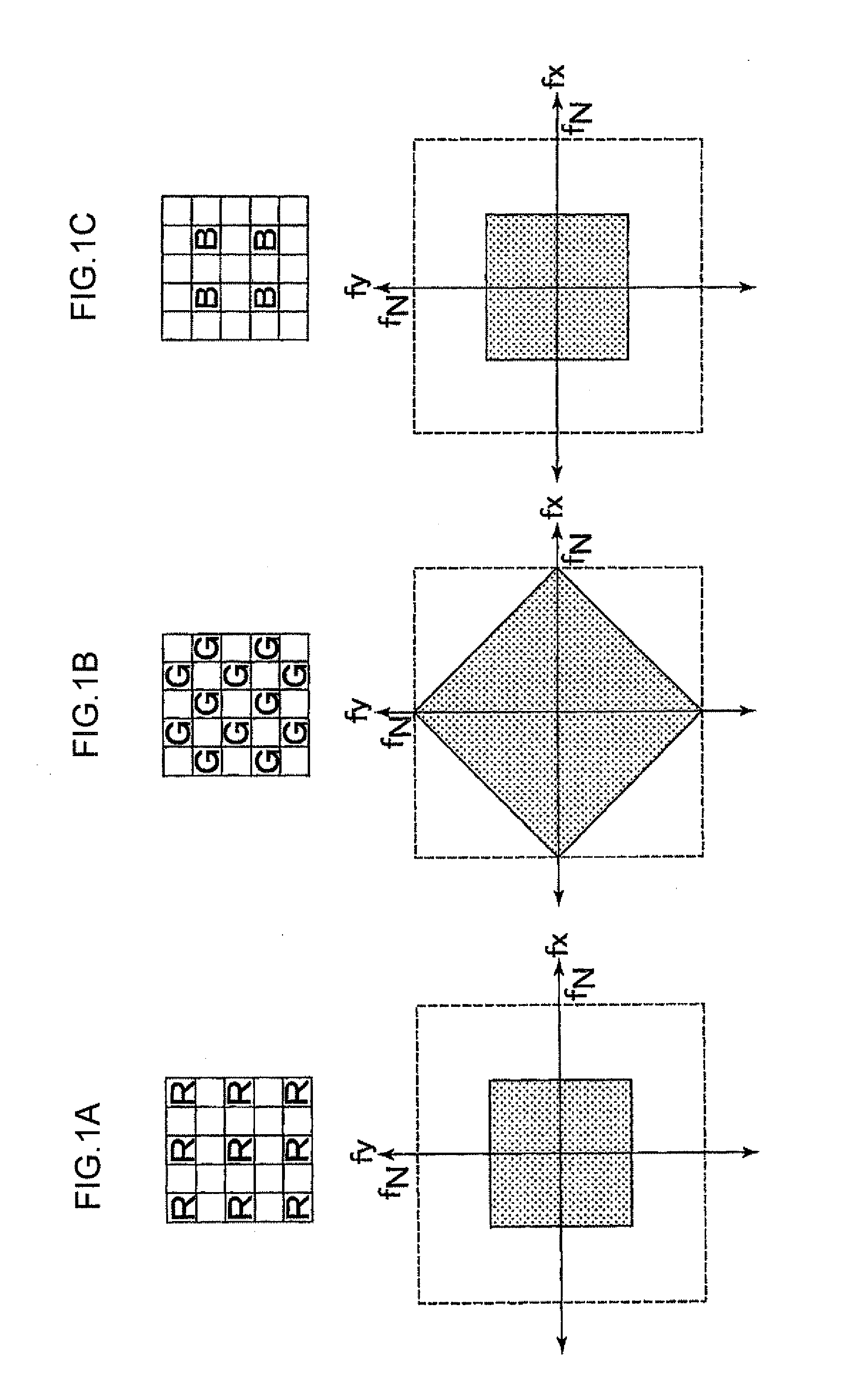
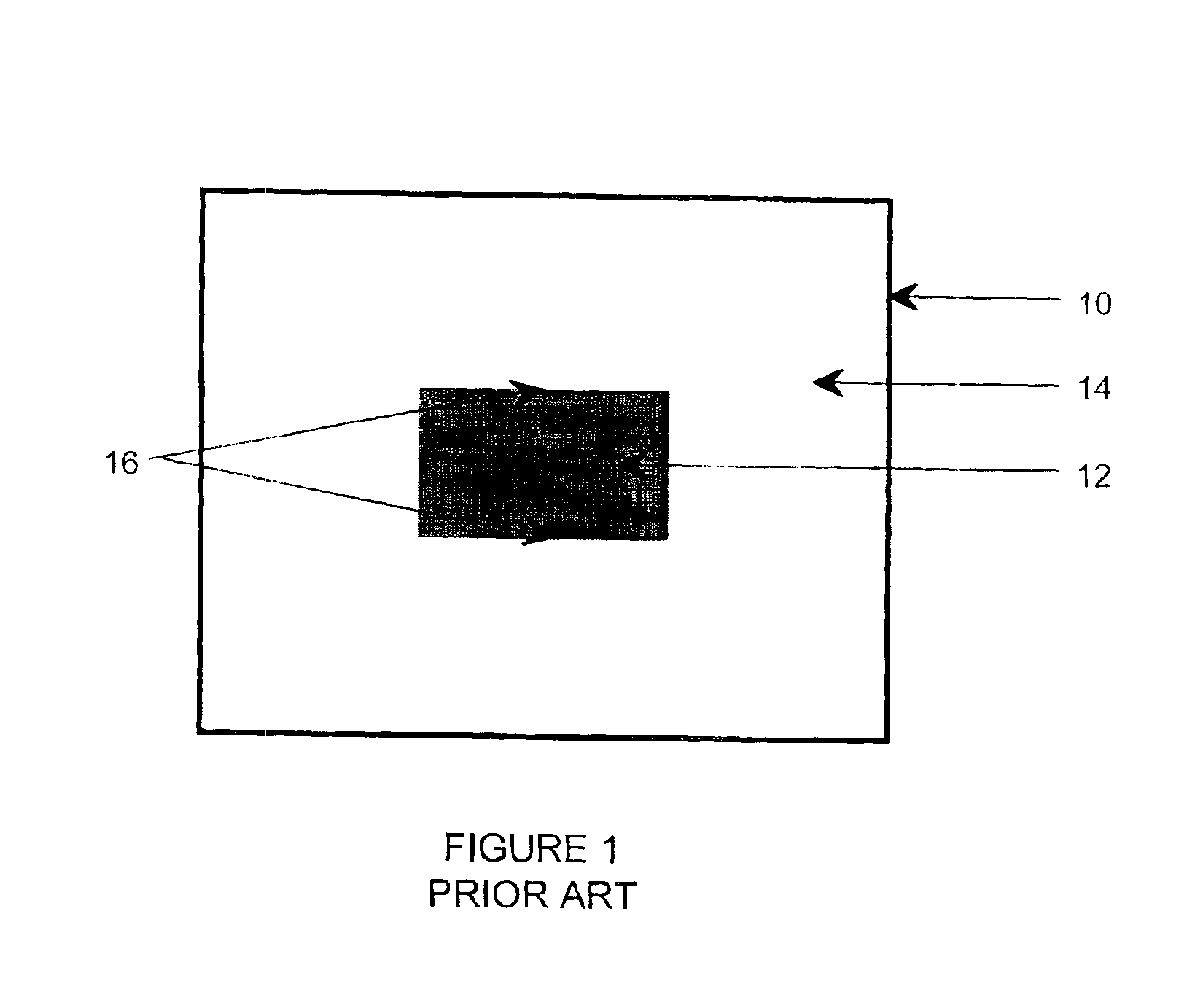
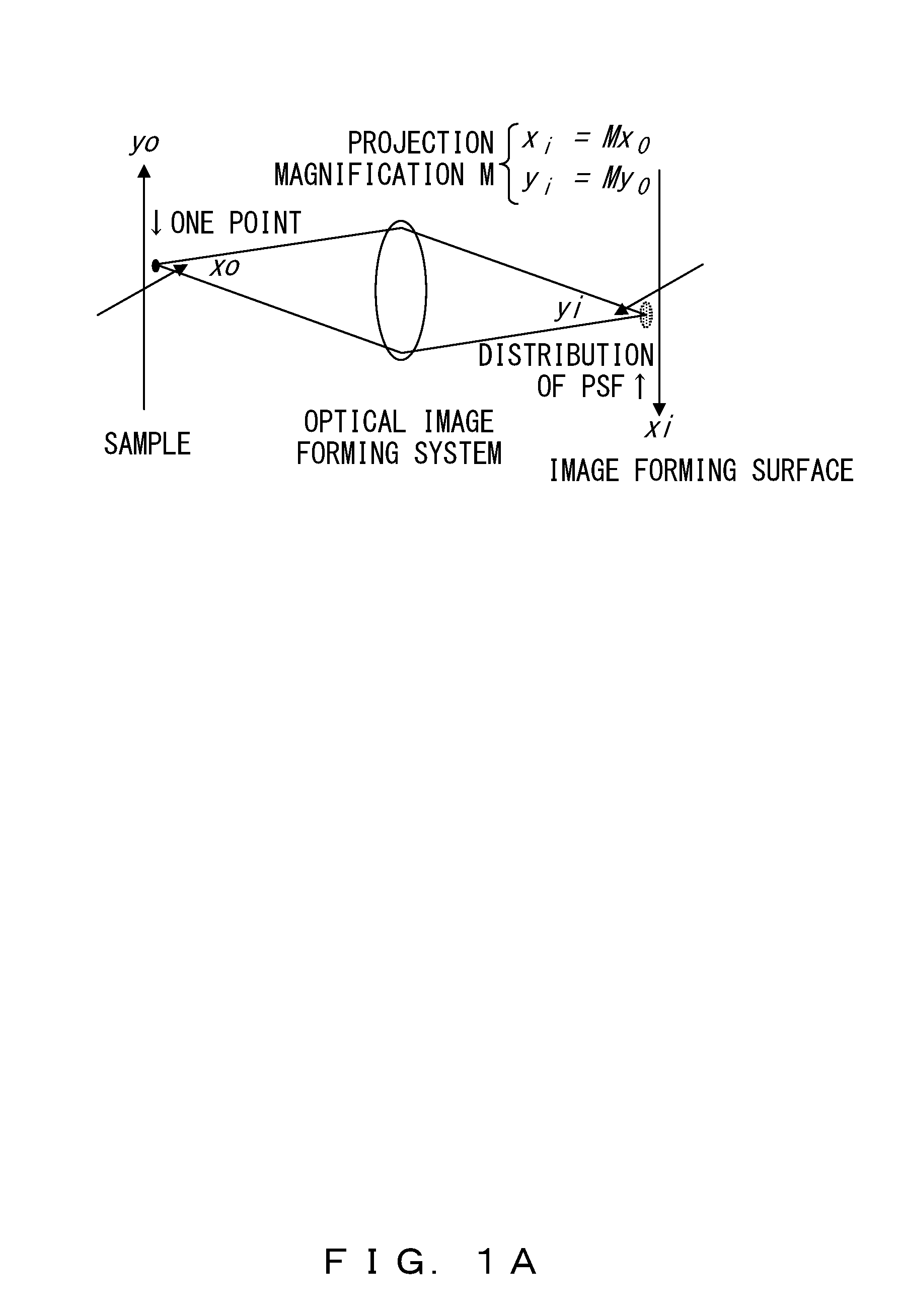
The Nyquist frequency, named after electronic engineer Harry Nyquist, is half of the sampling rate of a discrete signal processing system. It is sometimes known as the folding frequency of a sampling system. An example of folding is depicted in Figure 1, where fₛ is the sampling rate and 0.5 fₛ is the corresponding Nyquist frequency. The black dot plotted at 0.6 fₛ represents the amplitude and frequency of a sinusoidal function whose frequency is 60% of the sample-rate (fₛ). The other three dots indicate the frequencies and amplitudes of three other sinusoids that would produce the same set of samples as the actual sinusoid that was sampled. The symmetry about 0.5 fₛ is referred to as folding.
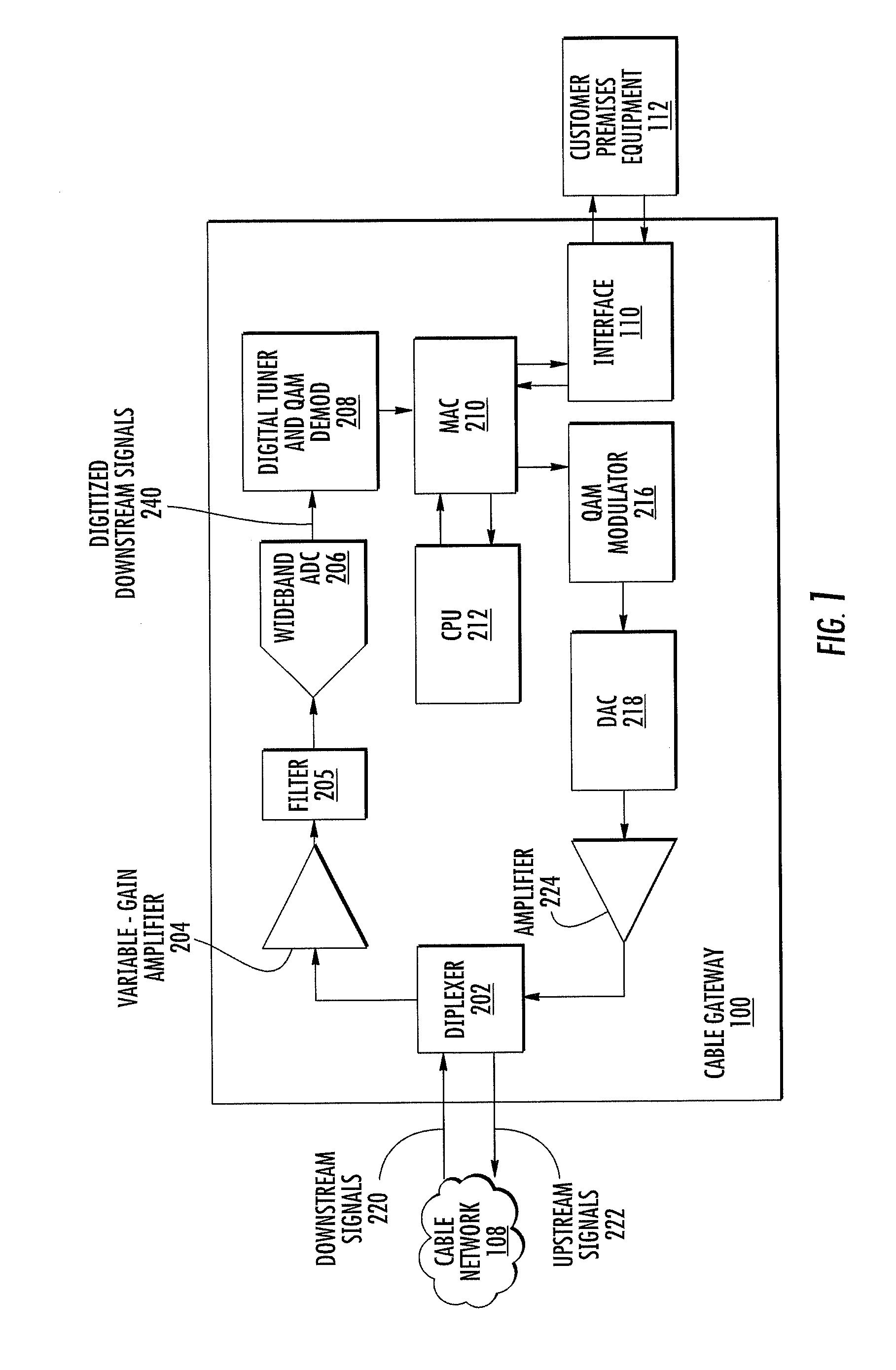
Optical arrangements for use with an array camera
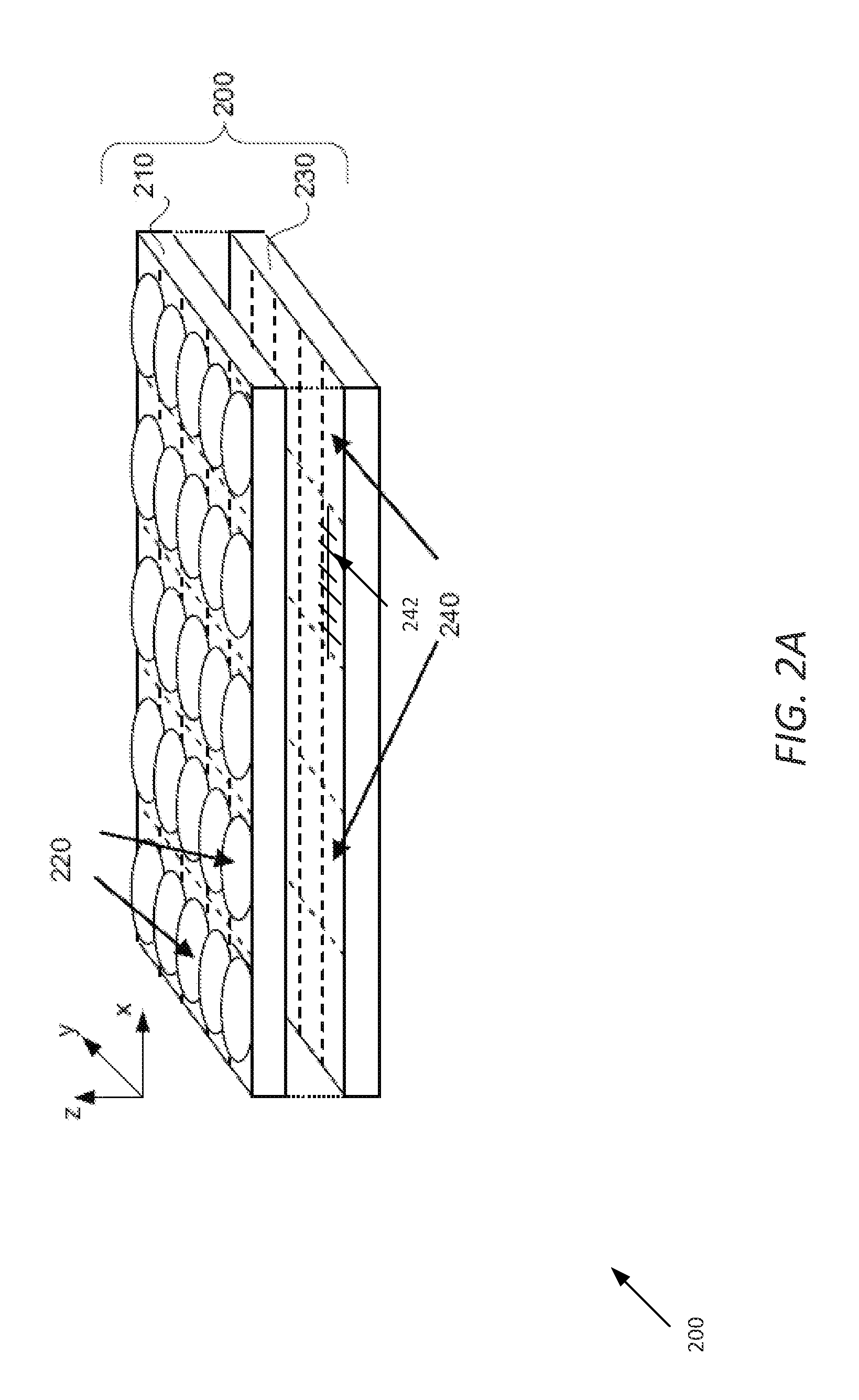
A variety of optical arrangements and methods of modifying or enhancing the optical characteristics and functionality of these optical arrangements are provided. The optical arrangements being specifically designed to operate with camera arrays that incorporate an imaging device that is formed of a plurality of imagers that each include a plurality of pixels. The plurality of imagers include a first imager having a first imaging characteristics and a second imager having a second imaging characteristics. The images generated by the plurality of imagers are processed to obtain an enhanced image compared to images captured by the imagers. In many optical arrangements the MTF characteristics of the optics allow for contrast at spatial frequencies that are at least as great as the desired resolution of the high resolution images synthesized by the array camera, and significantly greater than the Nyquist frequency of the pixel pitch of the pixels on the focal plane, which in some cases may be 1.5, 2 or 3 times the Nyquist frequency.
Owner:FOTONATION CAYMAN LTD
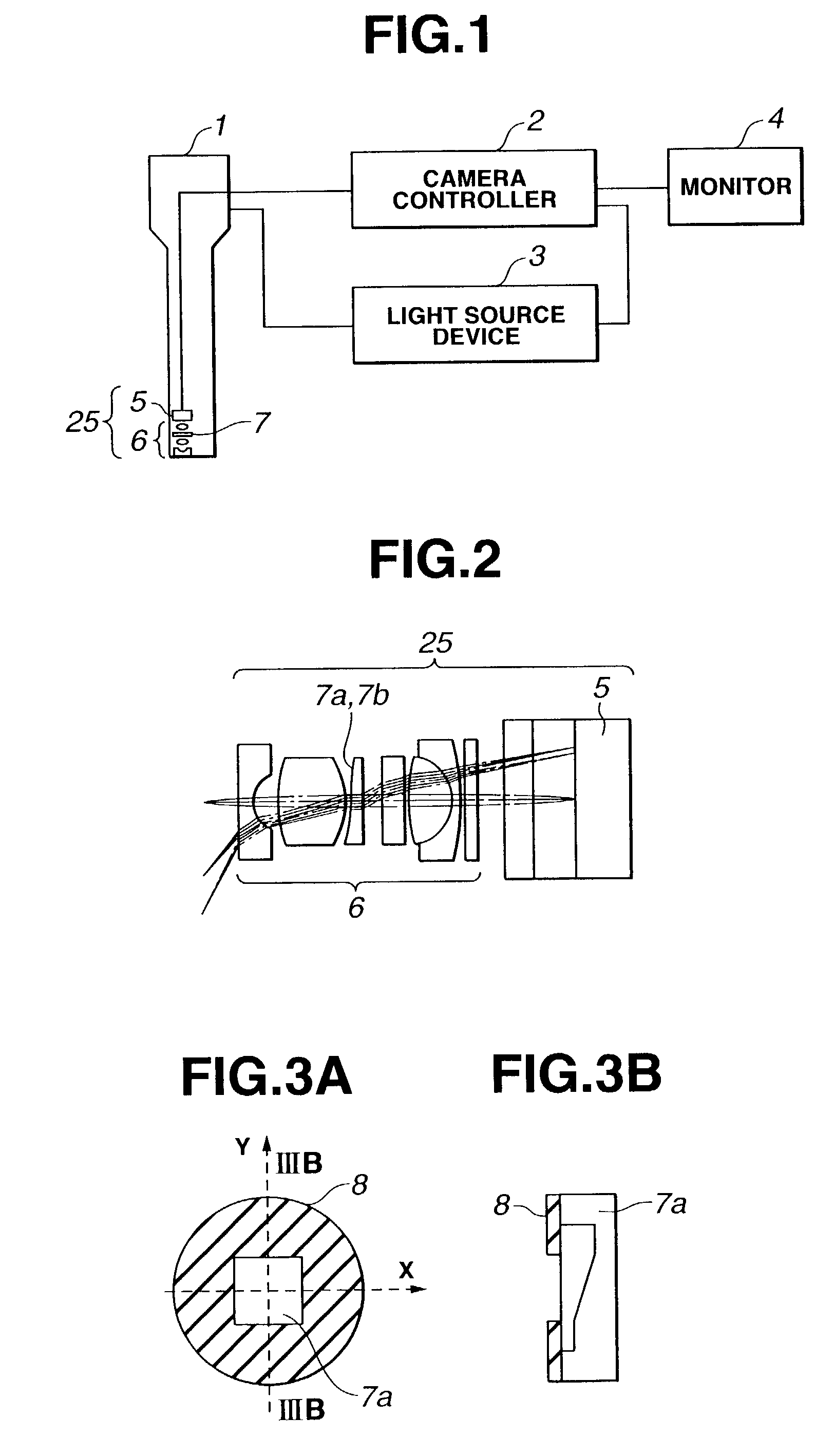
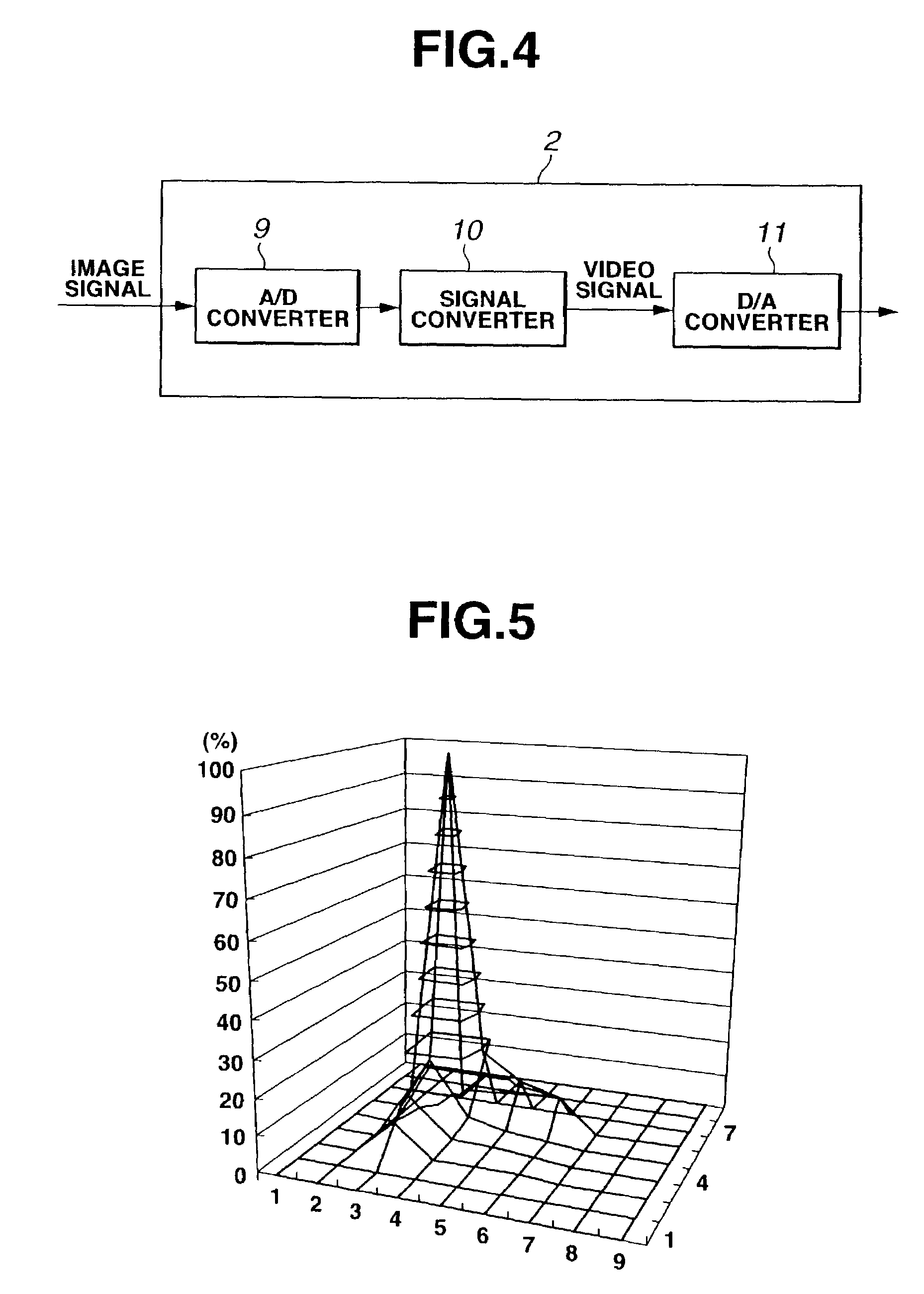
Endoscope and endoscope system with optical phase modulation member
InactiveUS6984206B2Add depthHigh-resolution imageTelevision system detailsSurgeryDepth of fieldImage signal
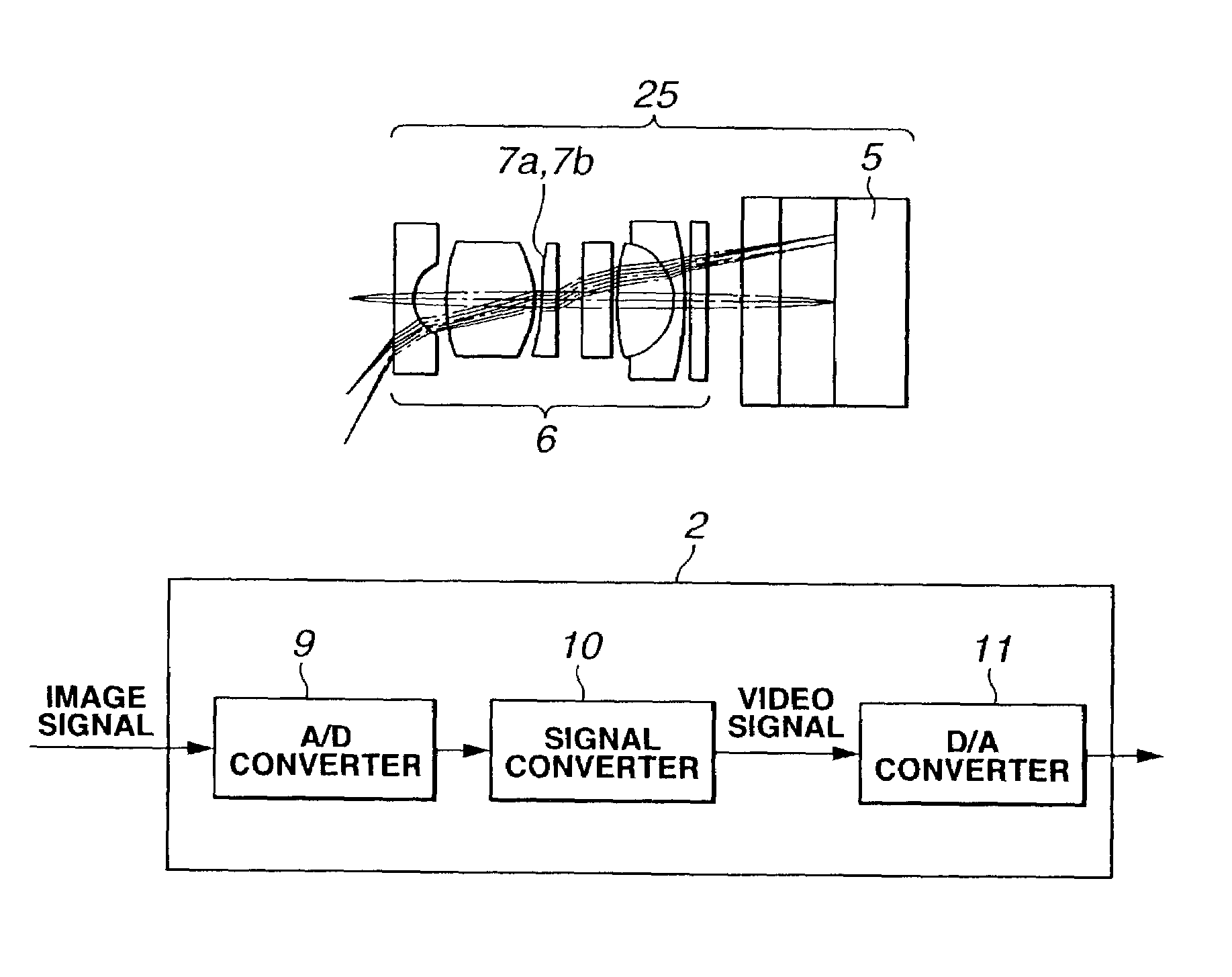
An endoscope system consists mainly of: an endoscope having a solid-state imaging device and an objective optical system that converges an object image on said solid-state imaging device; and a signal processing unit that processes an image signal produced by the endoscope so as to produce a video signal. The objective optical system includes an optical phase modulation member. The optical phase modulation member exhibits a response of 0.2 or more derived from an optical transfer function relative to a spatial frequency on the solid-state imaging device determined based on the Nyquist theorem, that is, a Nyquist frequency, over a wider range of distances than a depth of field offered by an objective optical system not having the optical phase modulation member.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
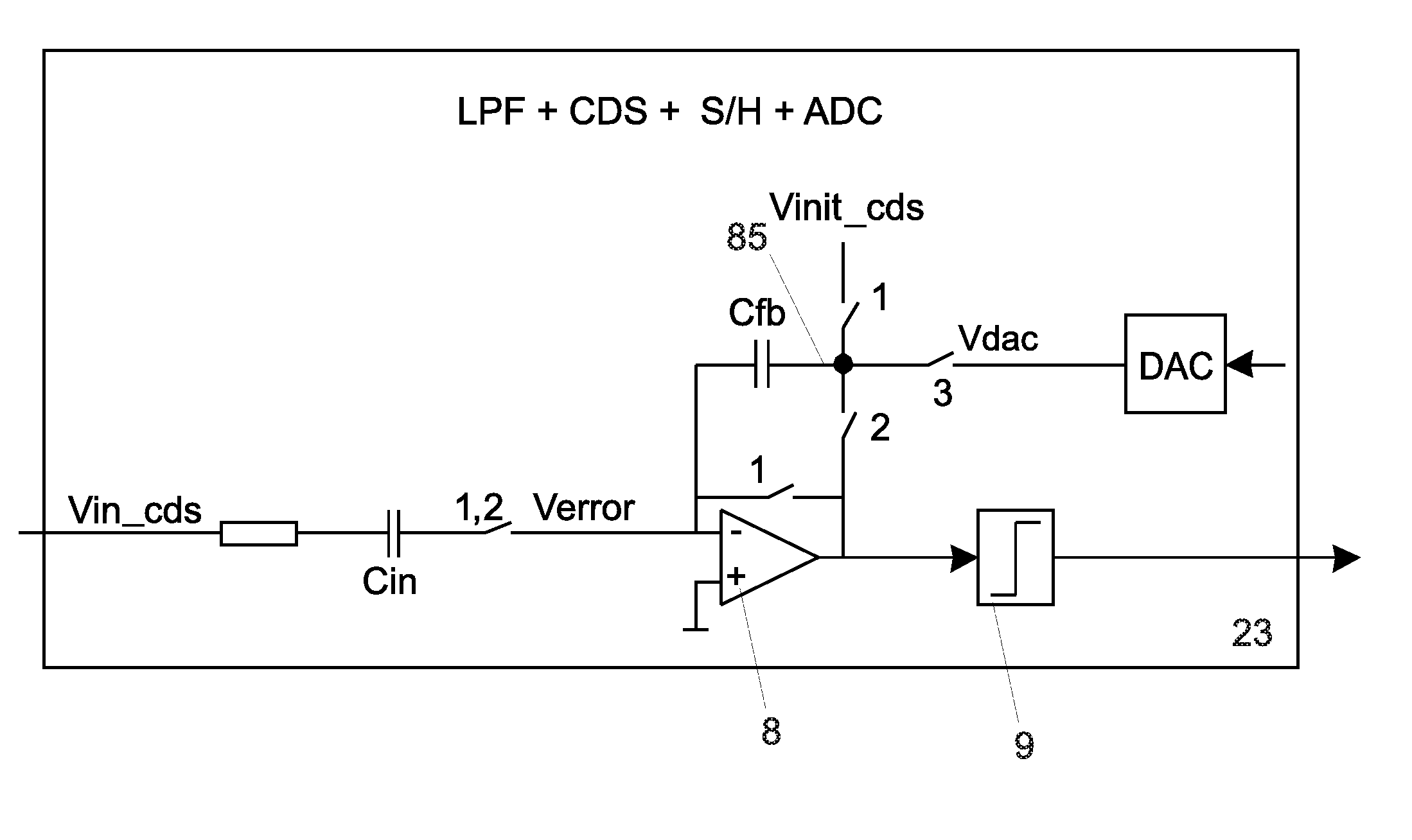
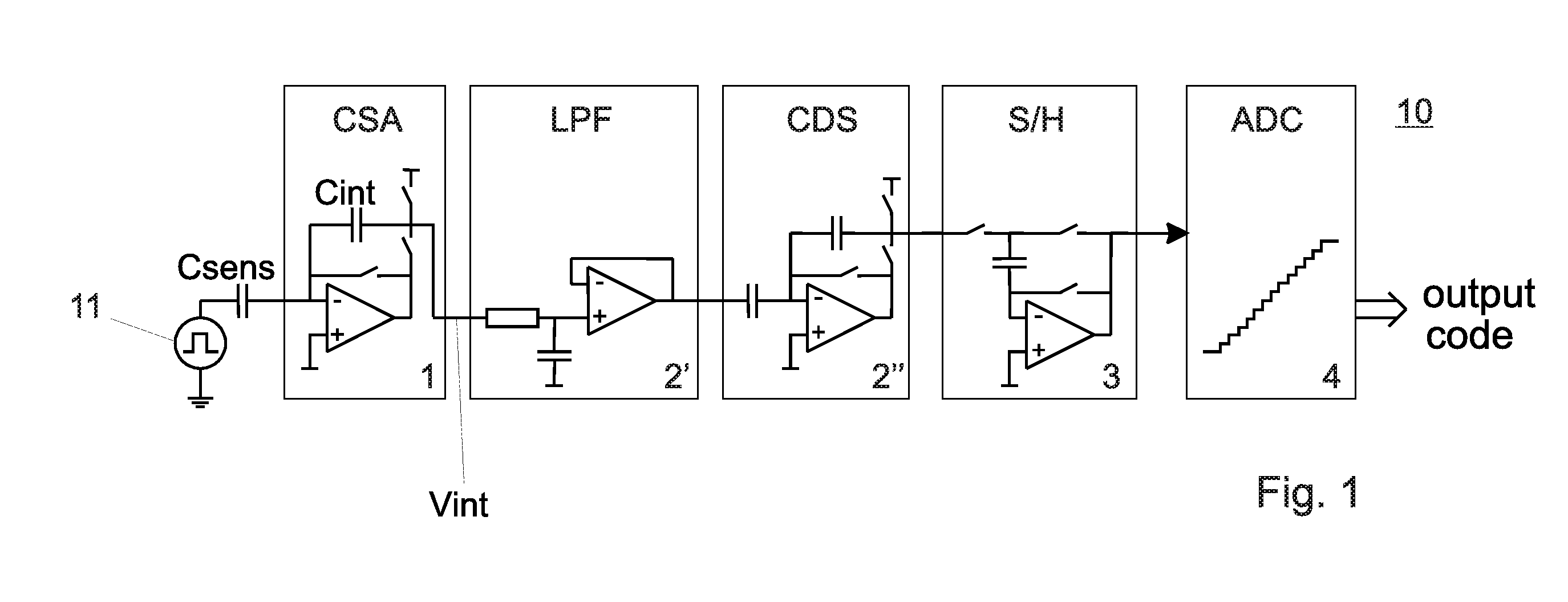
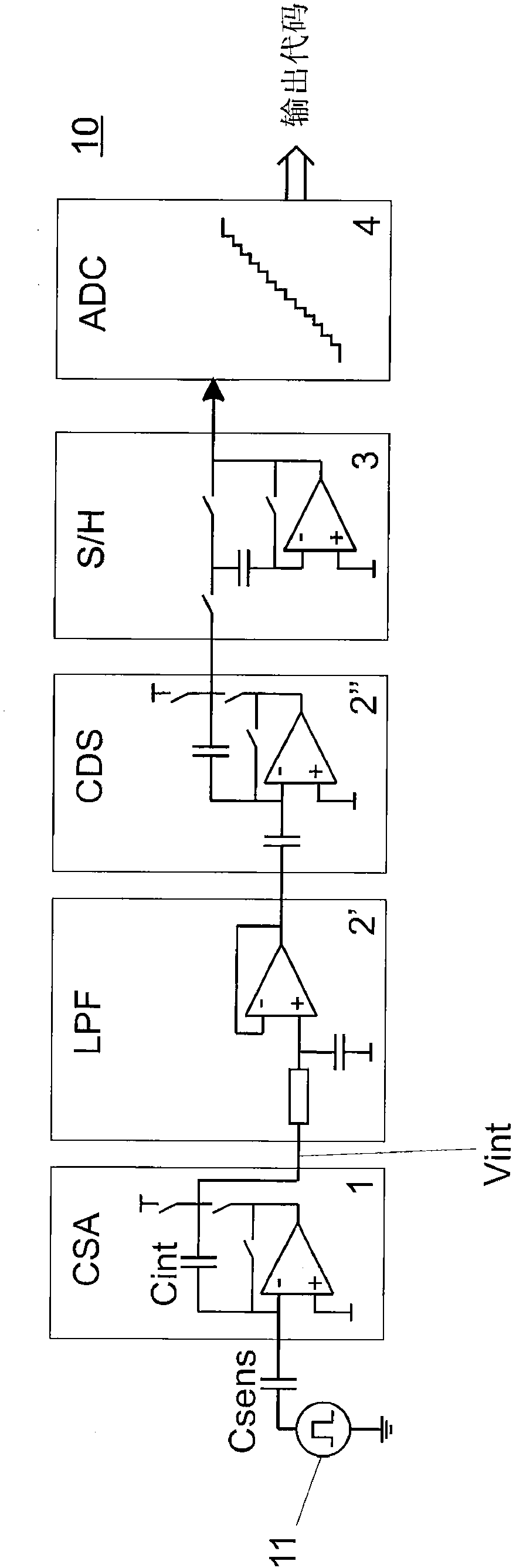
Circuit for capacitive touch applications
ActiveUS20110001492A1Reduce in quantityReduce consumptionAnalogue/digital conversionResistance/reactance/impedenceIntegratorLow-pass filter
A circuit for capacitive touch applications comprisinga charge integratora low pass-filtera correlated double sampler comprising an input capacitora sampler and holderan analog to digital convertersaid low pass-filter having a cut-off frequency lower than the Nyquist frequency of the sampler and holdersaid low pass filter comprising said input capacitor and a serial resistor.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON
Class of fixed partial response targets in a PRML sampled data detection channel
InactiveUS6249398B1Modification of read/write signalsRecord information storageFrequency spectrumMagnetic media
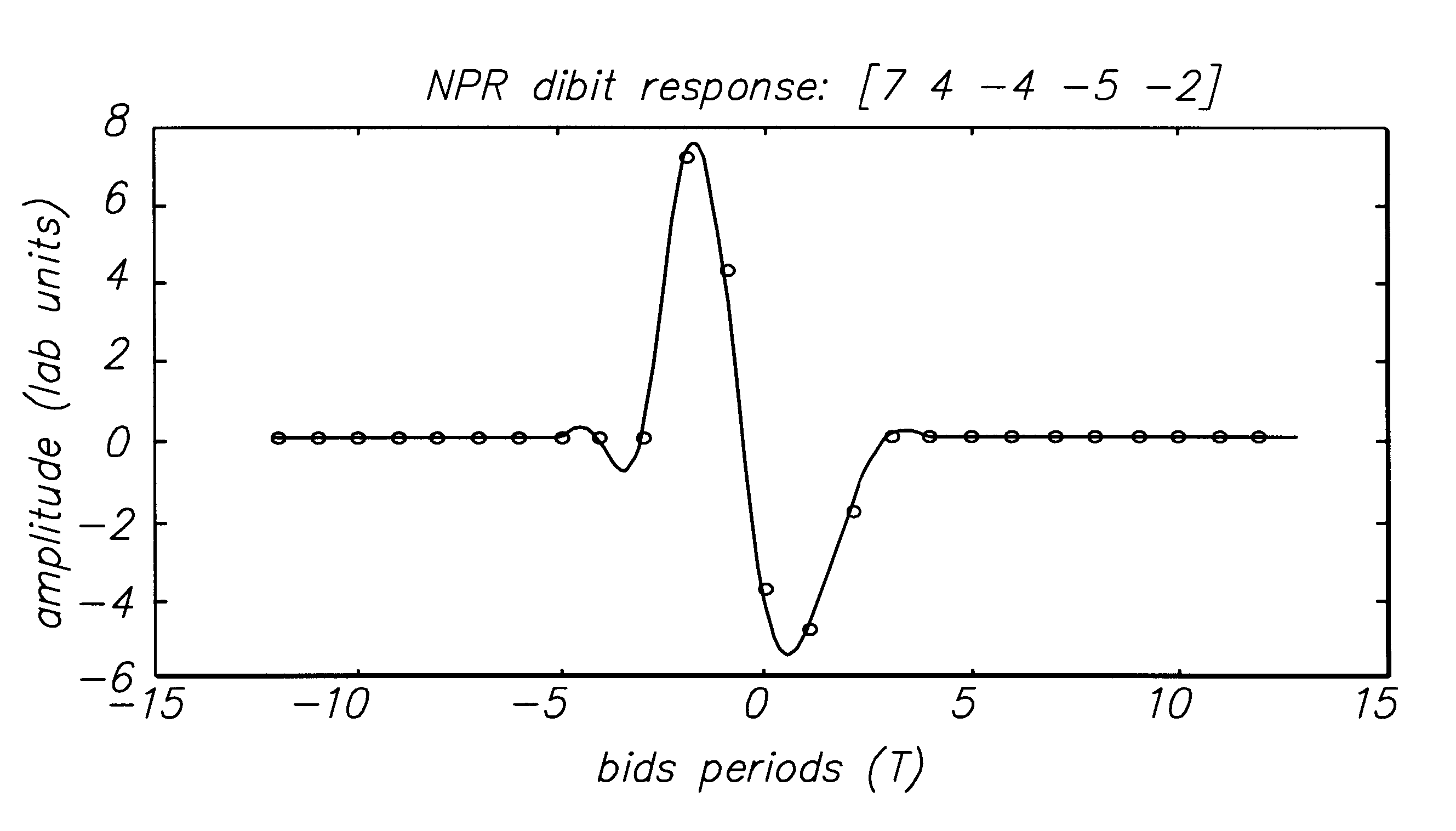
A new class of fixed partial response targets are disclosed for use in a PRML magnetic medium read channel. The preferred embodiment exhibits an equalization response characterized by the polynomial 7+4*D-4*D2-5*D3-2*D4, where D represents the unit delay operator. This read channel target provides improved matching to the inherent magnetic channel over the known canonical class of targets (1-D)(1+D){circumflex over ( )}N, and thereby reduces equalization losses. The improved spectral matching reduces amplification of noise in the channel, thereby reducing bit-error-rates. The new class of targets also exhibits a spectral null at DC, reducing problems for offset cancellation circuitry and making the disk drive less sensitive to thermal asperities. It also exhibits a spectral depression rather than a spectral null at the Nyquist frequency, making quasi-catastrophic error sequences virtually impossible. The new class of target simplifies coding and allows RLL code ratios that approach unity, improving effective recording densities, while significantly reducing BER.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC +1
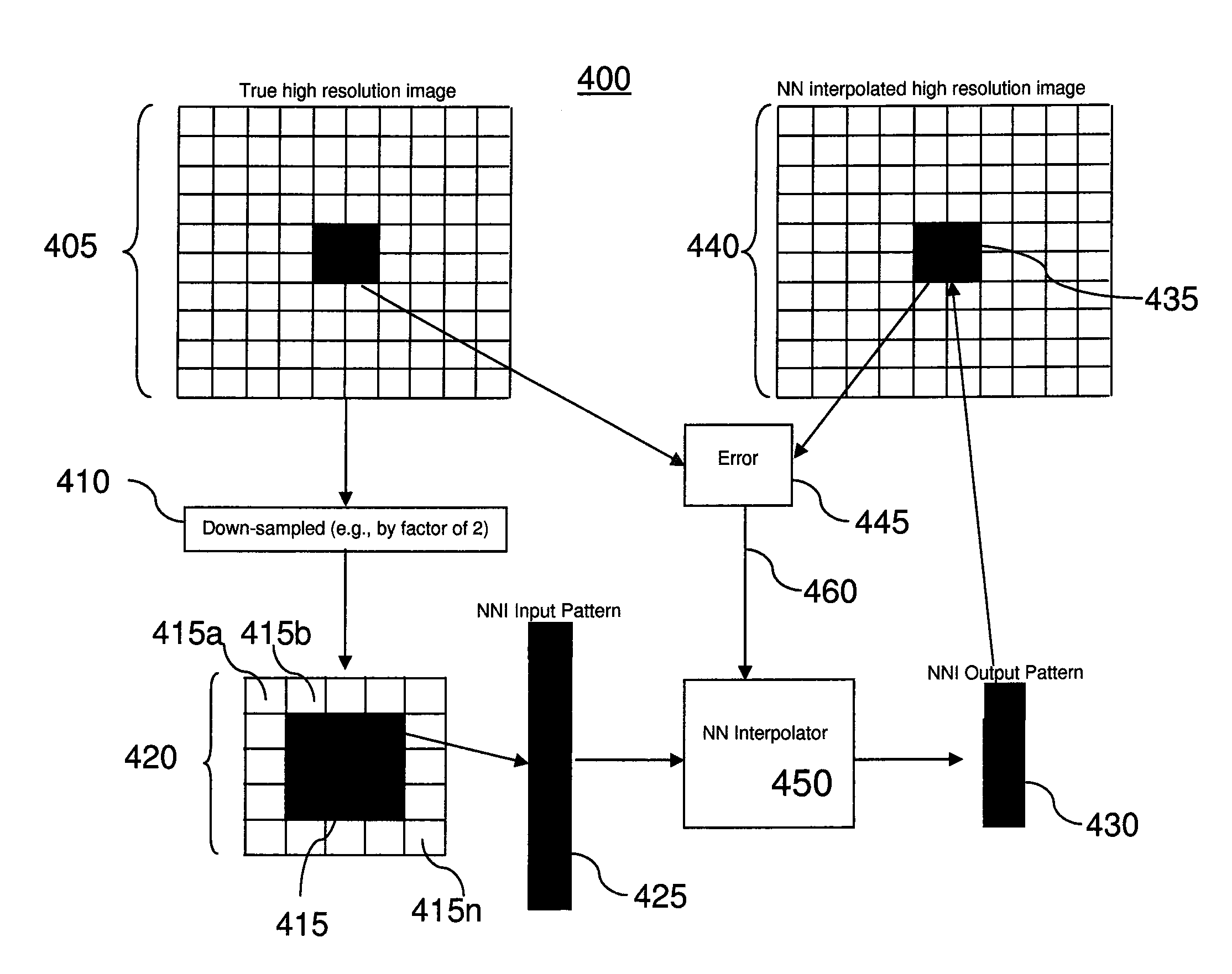
Methods and apparatus for super resolution scanning for cbct system and cone-beam image reconstruction
InactiveUS20130051519A1High resolutionQuality improvementReconstruction from projectionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationProjection imageImage resolution
Embodiments of methods and / or apparatus for 3-D volume image reconstruction of a subject, executed at least in part on a computer for use with a digital radiographic apparatus can obtain image data for 2-D projection images over a range of scan angles. For each of the plurality of projection images, an enhanced projection image can be generated. In one embodiment, through the application of a resolution increasing interpolator, a prescribed CBCT routine scanning mode with preset binning can increase a spatial resolution, Nyquist frequency or MTF.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Non-uniform sampling to extend dynamic range of interferometric sensors
ActiveUS20090122319A1Subsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementAcceleration measurementInterferometric sensorEngineering
Methods and apparatus for interrogating optical sensors with high slew rates using non-uniform sampling are provided. The transmission of optical signals in a non-uniform pattern is employed to allow for demodulation of fringe rates exceeding the commonly understood Nyquist frequency limit given as one half of the mean sampling frequency. By monitoring the time dependent fringe frequency and assuming that the fringe frequency has a limited bandwidth, only a limited bandwidth smaller than the Nyquist bandwidth around the instantaneous fringe frequency needs to be reconstructed at any time.
Owner:OPTOPLAN
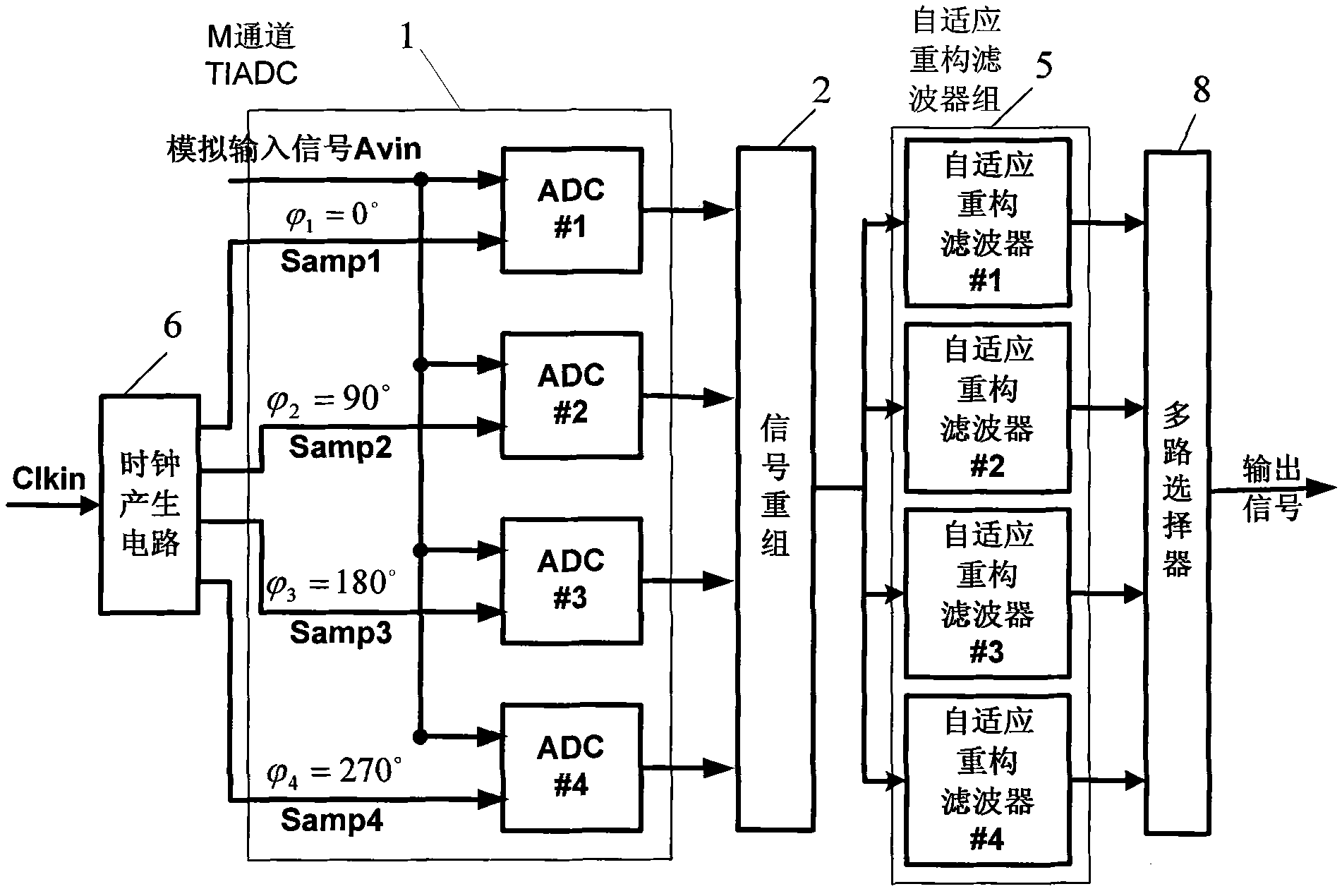
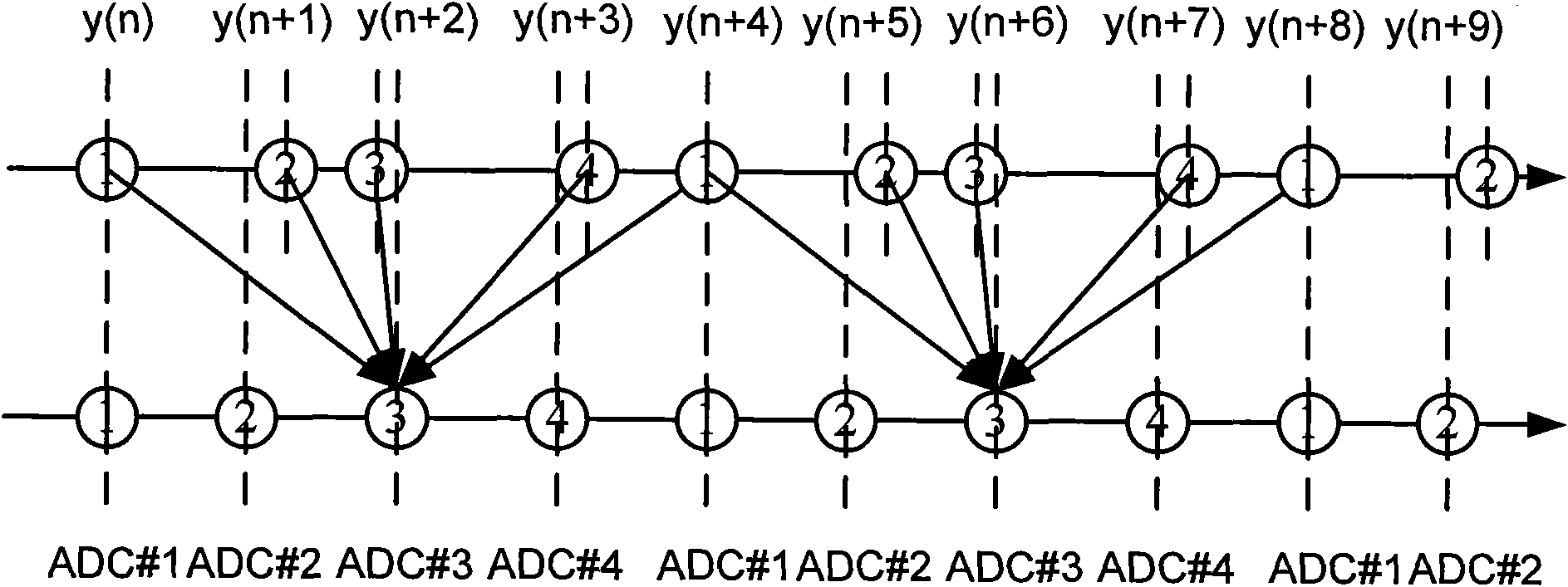
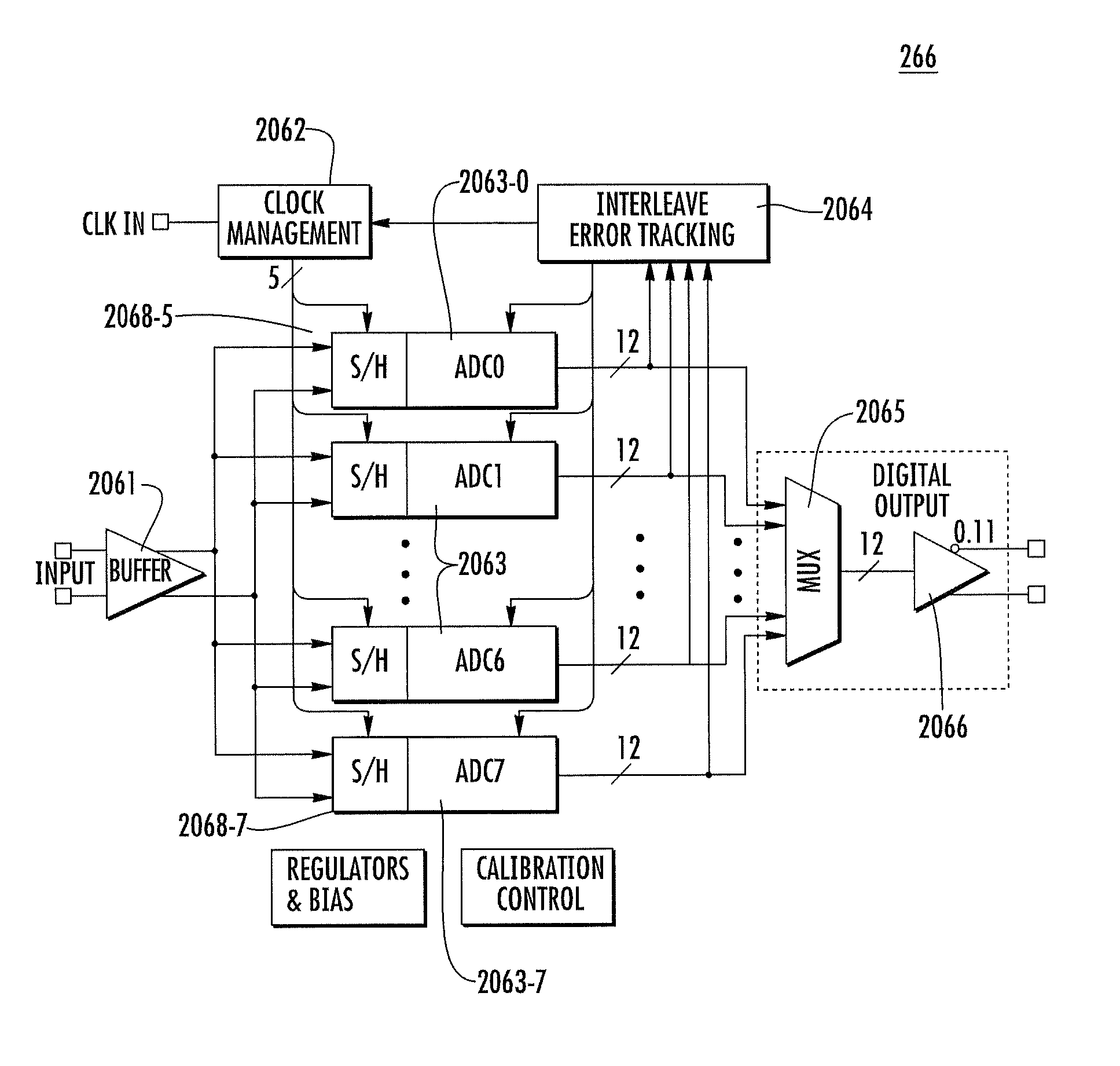
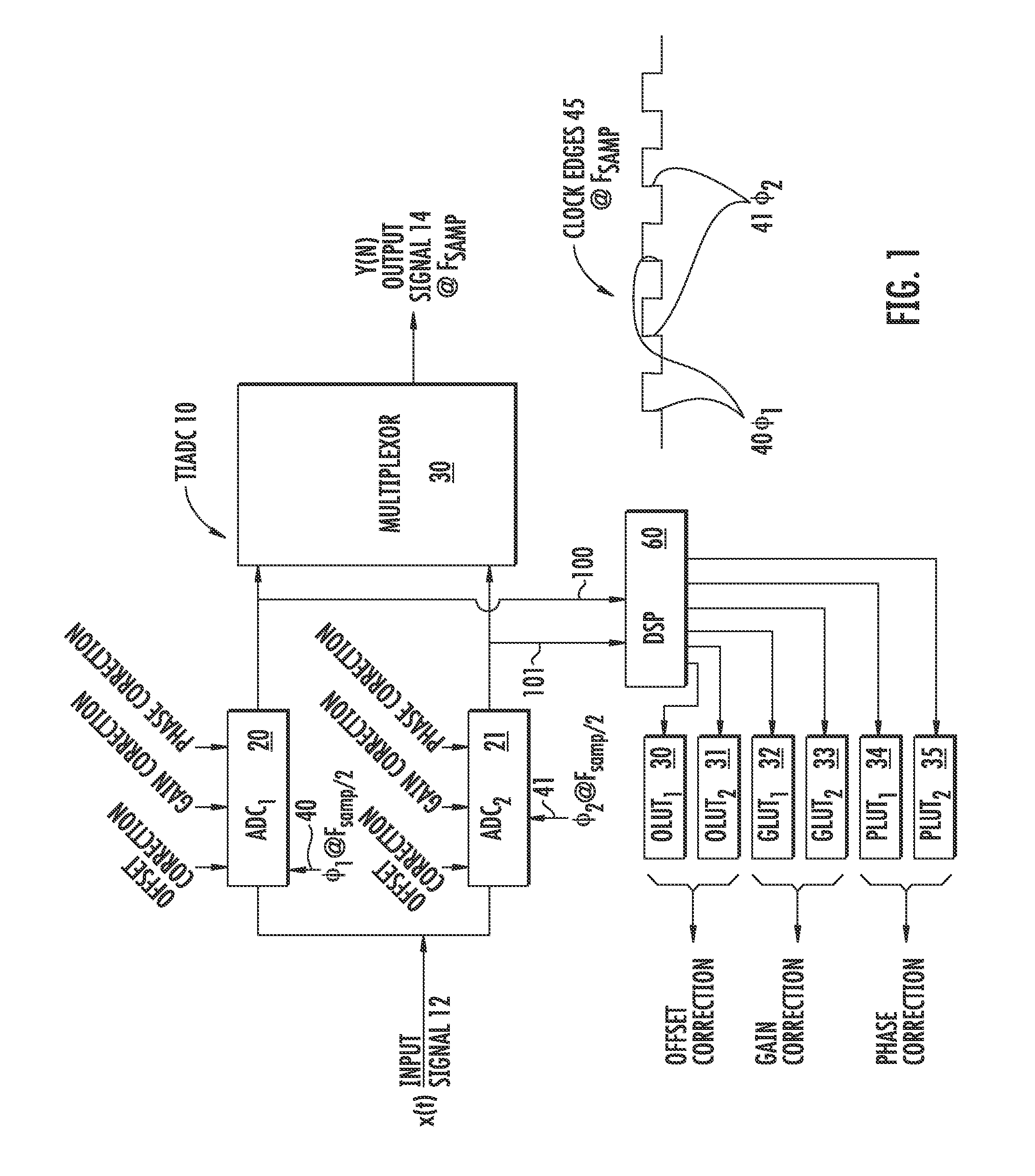
Self-adoptive correcting device of mismatch error of time-interleaved analog-digital converter
InactiveCN101888247AAvoid problems that are difficult to convert to hardware circuitsThere is no problem of implementation deviationAnalogue-digital convertersAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingTime errorDigital down converter
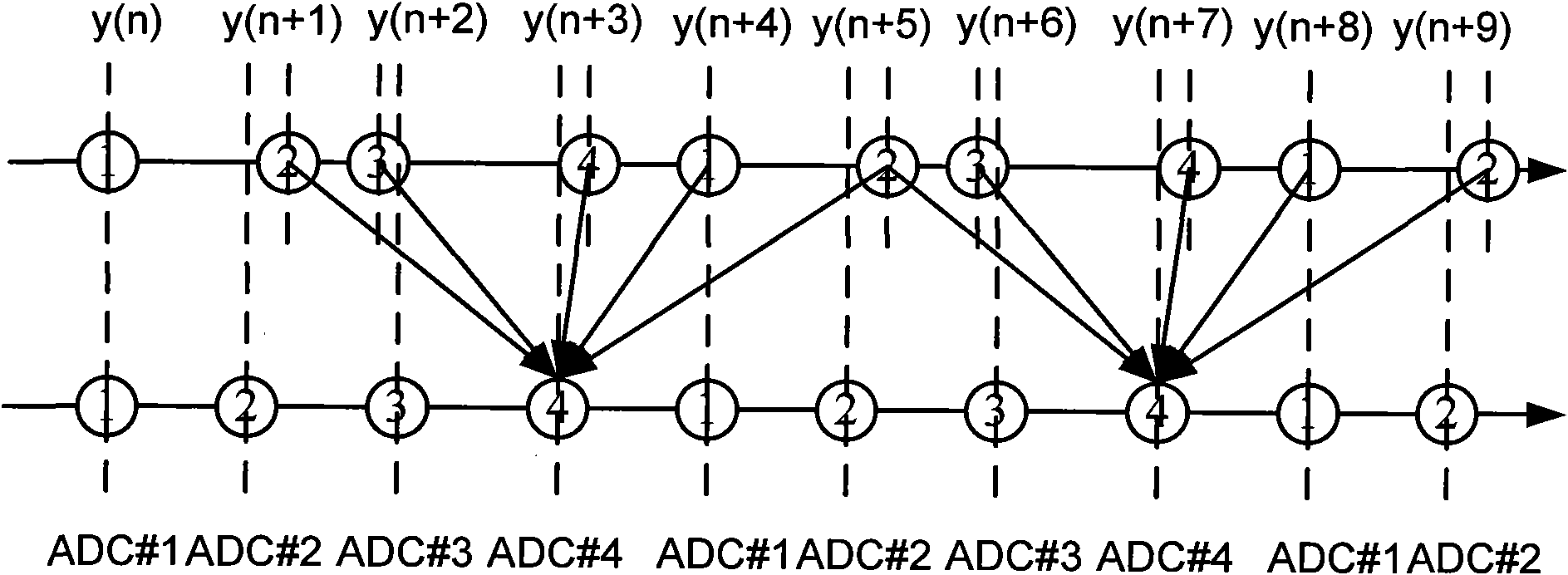
The invention discloses a self-adoptive correcting device of mismatch error of time-interleaved analog-digital converter, comprising an M channel TIADC, a signal recombination, a digital reference signal memorizer, a simulated reference signal generator, a self-adaptive reconstruction filter bank, a clock generation circuit and a subtraction device. Signals after passages are reconstructed are used to correct each passage instead of single correction on each passage, thereby solving the problem that when an input signal bandwidth is larger than the Nyquist frequency of each passage ADC, the time error can not be corrected due to aliasing. Each self-adoptive reconstruction filter is divided into a plurality of sub-filters for concurrent working, thereby not improving the requirement of thetreatment speed for a self-adoptive correcting filter while realizing the effect of signal recombination and ensuring the practicability of the hardware of the structure of the invention. A digital reference signal is internally installed in the device and is taken as a target to carry out the self-adoptive correction, pre-measuring or calculating a passage mismatch error is not needed, and the source of the error is not needed to be discriminated so that various mismatch errors can be corrected.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Beamformed ultrasonic imager with delta-sigma feedback control
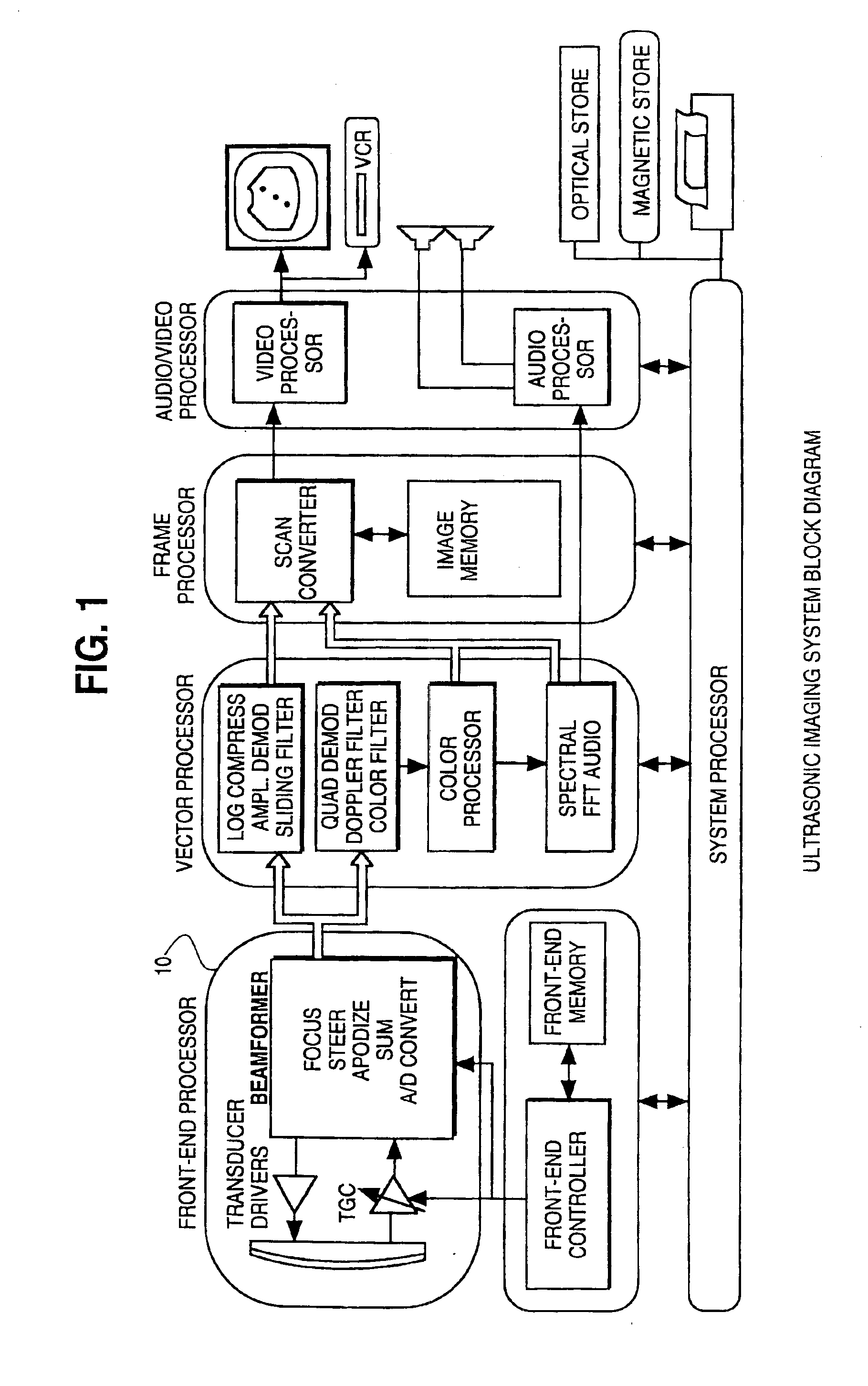
InactiveUS6208189B1Easy to operateRelatively small errorAnalogue/digital conversionUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingAnalog signal
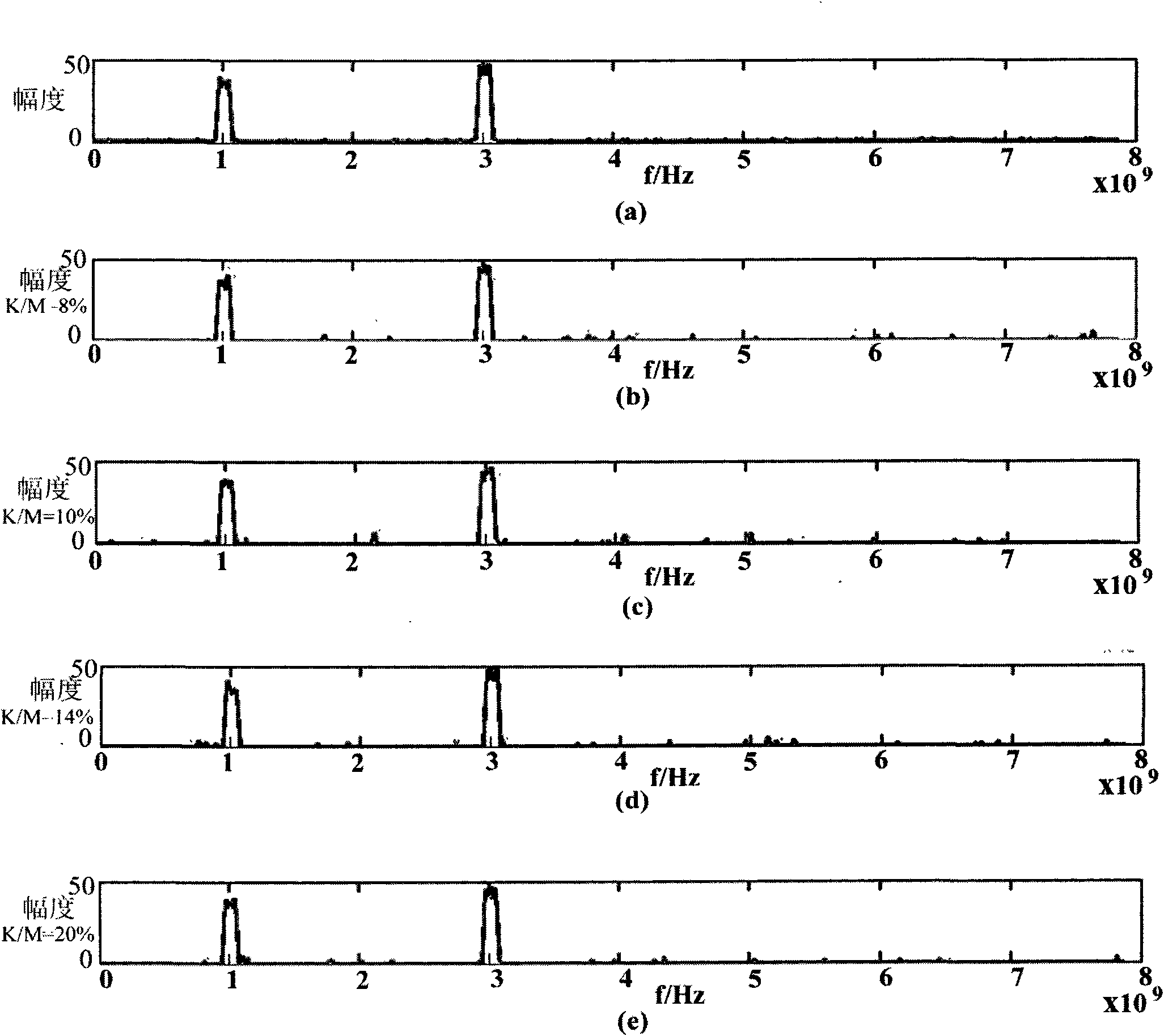
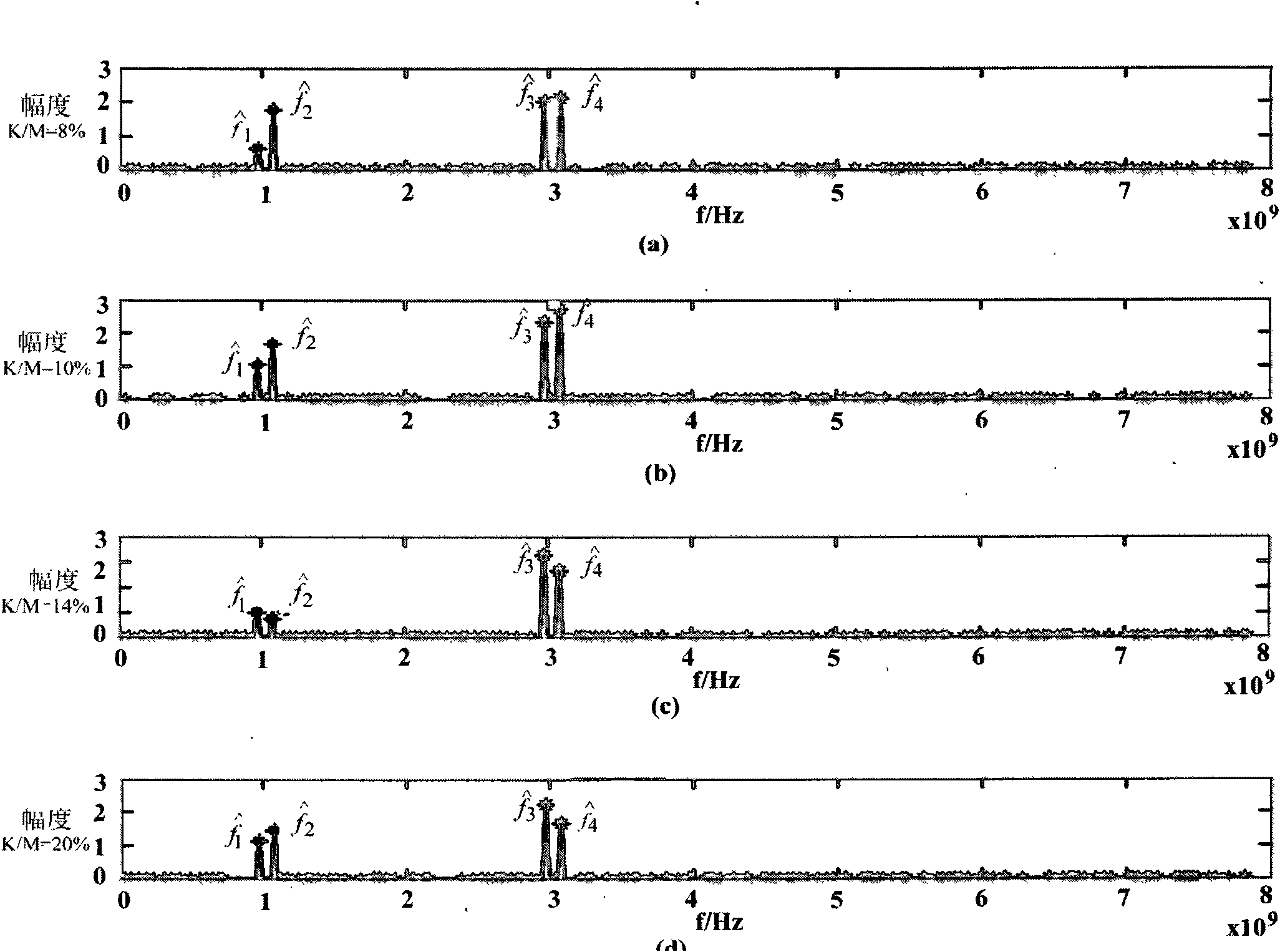
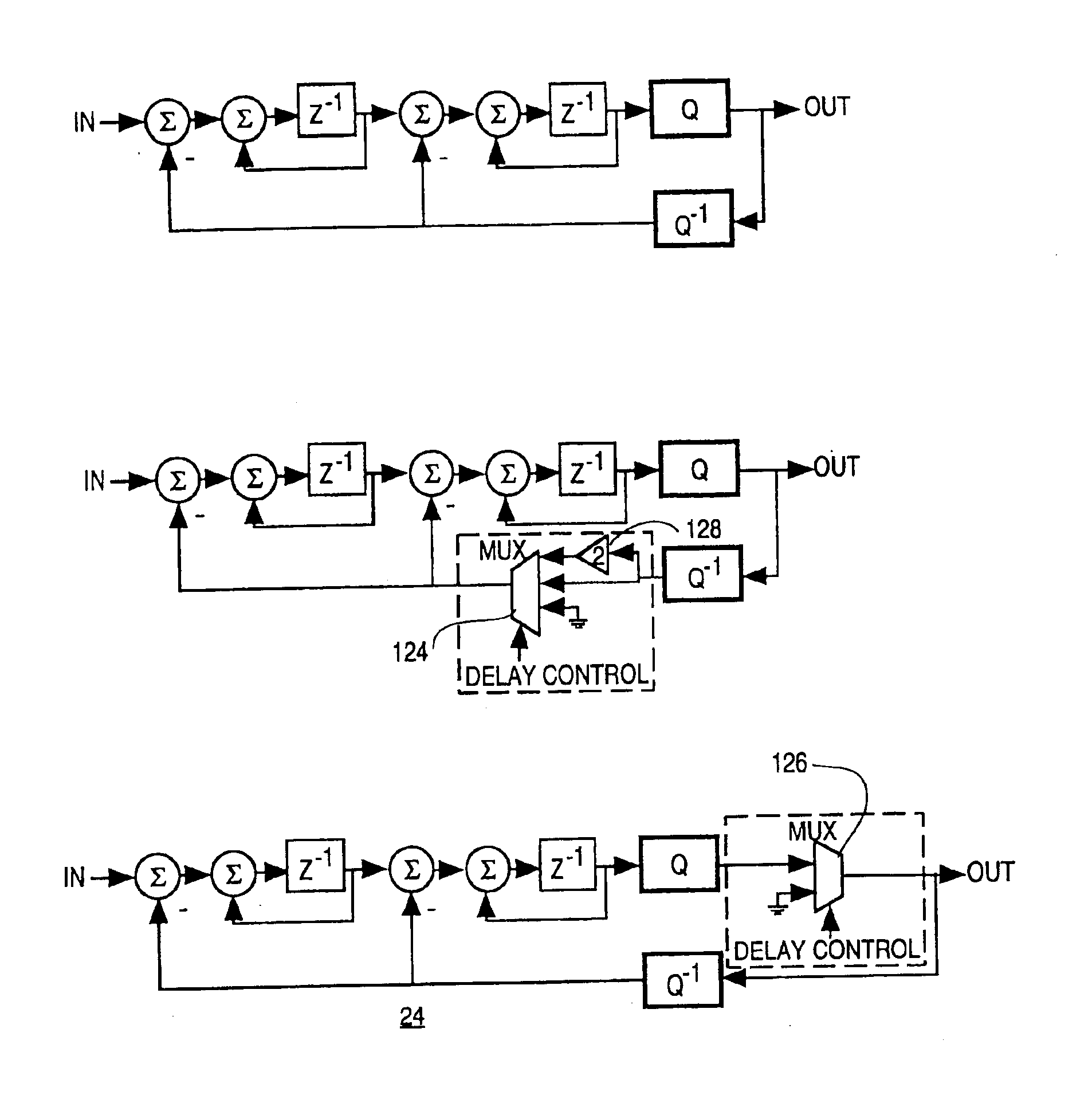
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing distortion in a dynamically delayed digital sample stream of an imaging system. The method includes the steps of delta-sigma modulating an input analog signal of the imaging system at a frequency above the Nyquist frequency of the input analog signal to generate a digital sample stream and changing a length of the sample stream to delay a portion of the sample stream while maintaining synchronism between a delta-sigma modulator and a demodulator of the system.
Owner:HITTITE MICROWAVE LLC
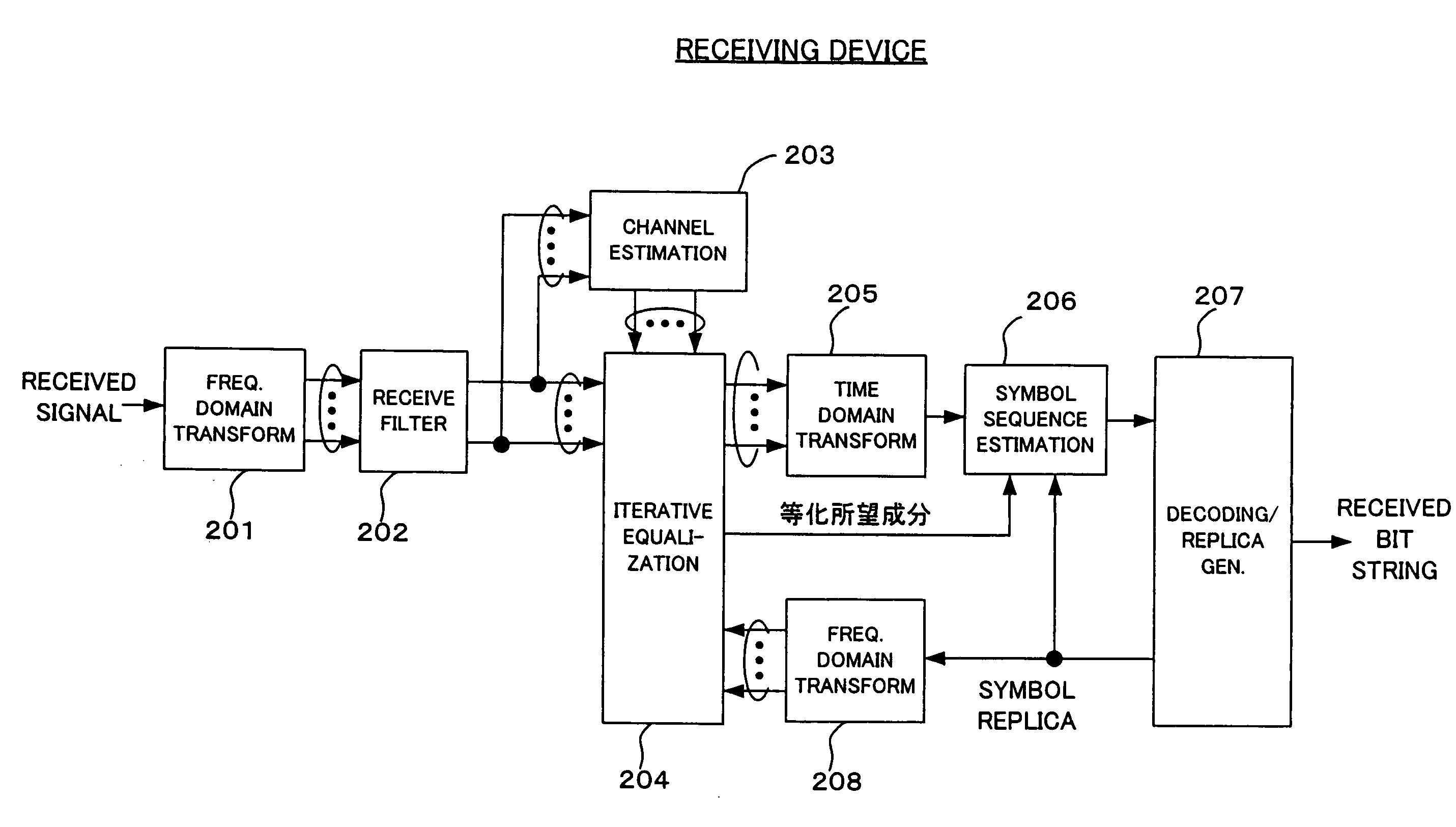
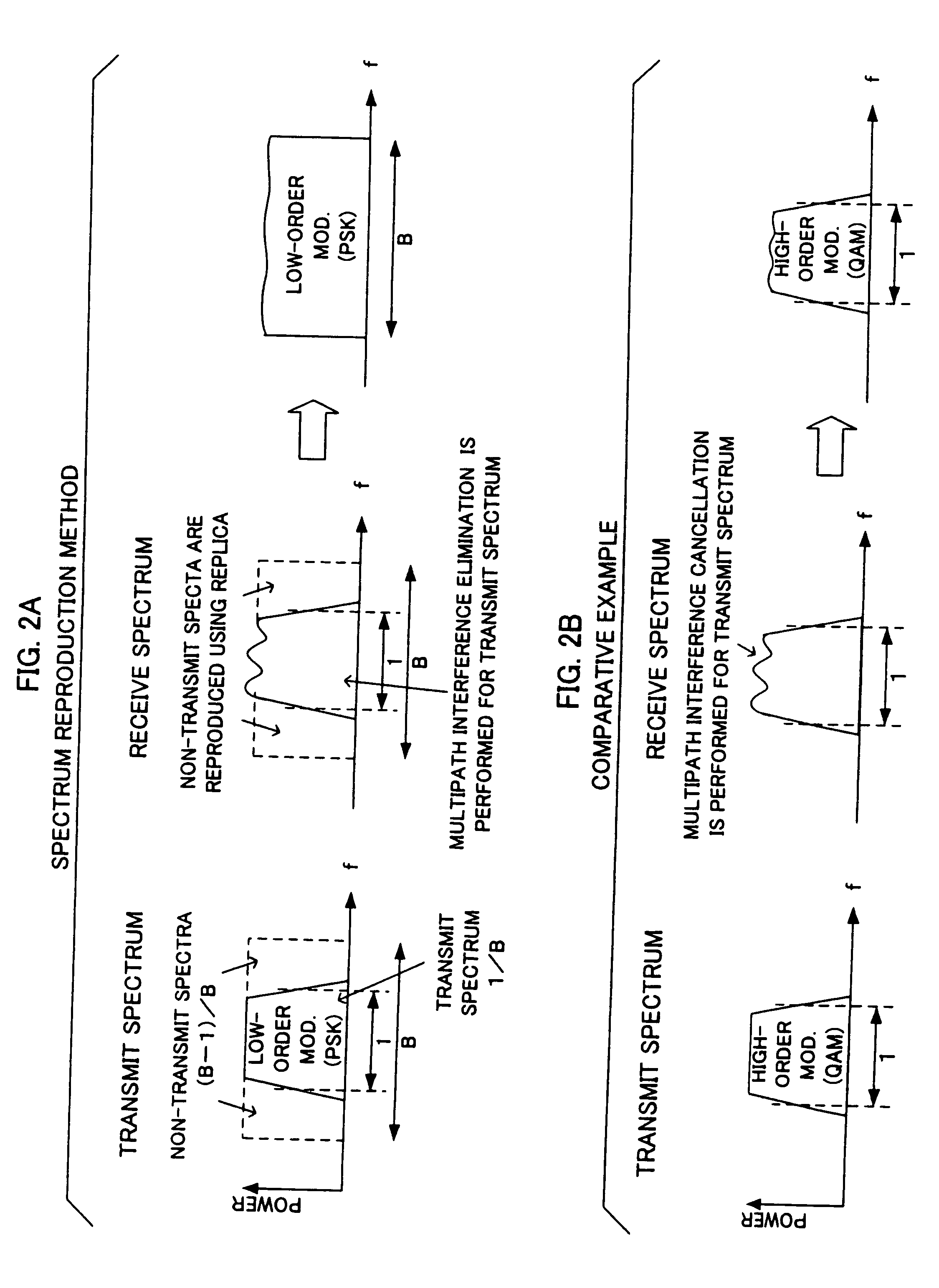
Radio communication method and device in single-carrier transmission system
ActiveUS20090323796A1Eliminate distractionsHigh speed transmissionMultiple-port networksError preventionFrequency spectrumInterference canceller
A radio communication device for receiving a single-carrier signal transmitted in a partial spectrum of Nyquist frequency band, includes: an interference eliminator for eliminating interference from a received signal by spectrum reproduction of non-transmitted spectra using a symbol replica, to output an interference eliminated signal, wherein the interference includes intersymbol interference which is caused by symbols which are more than a predetermined distance away from a decision symbol point; a symbol sequence estimator for estimating a transmission symbol sequence by separating nearby intersymbol interference within the predetermined distance of the decision symbol point based on the interference eliminated signal, to output a decision signal; and a replica generator for generating the symbol replica from decoding result of the decision signal, wherein the symbol replica is fed back to the frequency-domain interference eliminator.
Owner:NEC CORP
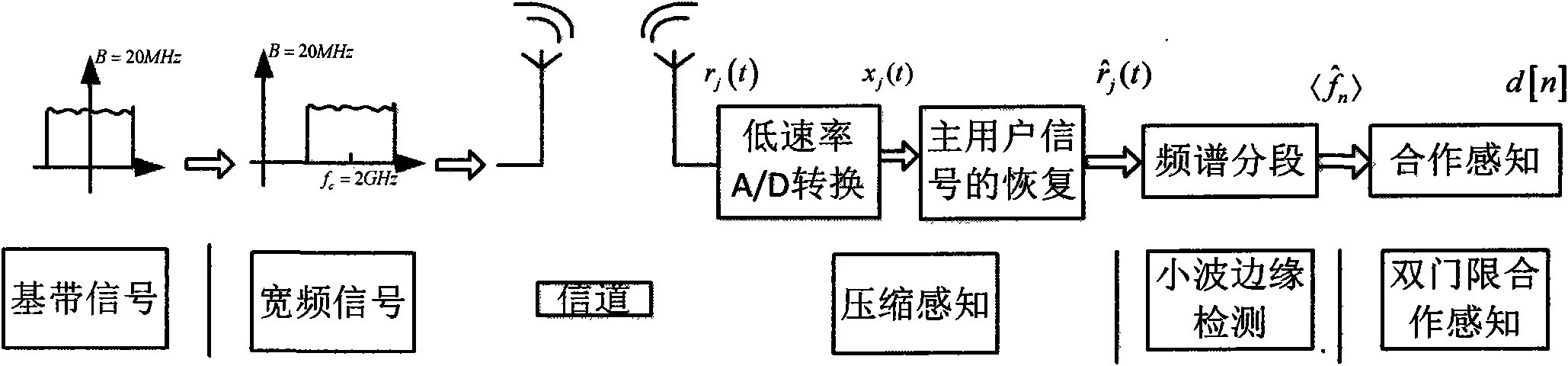
Double threshold cooperative sensing method in cognitive wireless network
The invention discloses a double threshold cooperative sensing method in a cognitive wireless network, comprising the following steps: 1. recovering a signal through local compressed sensing, and recovering the whole broadband frequency spectrum in the invention through the compressed sensing, thus a low-speed A / D commutator can be used, so as to lower the hardware requirement; 2. determining a sub frequency band, being capable of obtaining a frequency spectrum edge point of the recovered broadband frequency spectrum signal through the compressed sensing through a wavelet edge detection, and forming a plurality of sub frequency bands by segmenting the frequency spectrum; and 3. cooperative sensing: carrying out double threshold energy detection on all sub frequency bands by each cognitiveuser, transmitting the detection result to a fusion center for judgment to obtain the existing condition of the main user of the whole frequency spectrum, and self-adaptively determining the positionof the spectrum hole in the frequency band. Through the steps, the cognitive network can carry out sampling sensing on the main user signals under the condition of low nyquist frequency, and can self-adaptively determine the position of the spectrum hole in the frequency band.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Beamformed ultrasonic imager with delta-sigma feedback control
InactiveUS6867720B1Reduce distortion problemsElectric signal transmission systemsDelta modulationUltrasound imagingEngineering
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing distortion in a dynamically delayed digital sample stream of an imaging system. The method includes the steps of delta-sigma modulating an input analog signal of the imaging system at a frequency above the Nyquist frequency of the input analog signal to generate a digital sample stream and changing a length of the sample stream to delay a portion of the sample stream while maintaining synchronism between a delta-sigma modulator and a demodulator of the system.
Owner:HITTITE MICROWAVE LLC
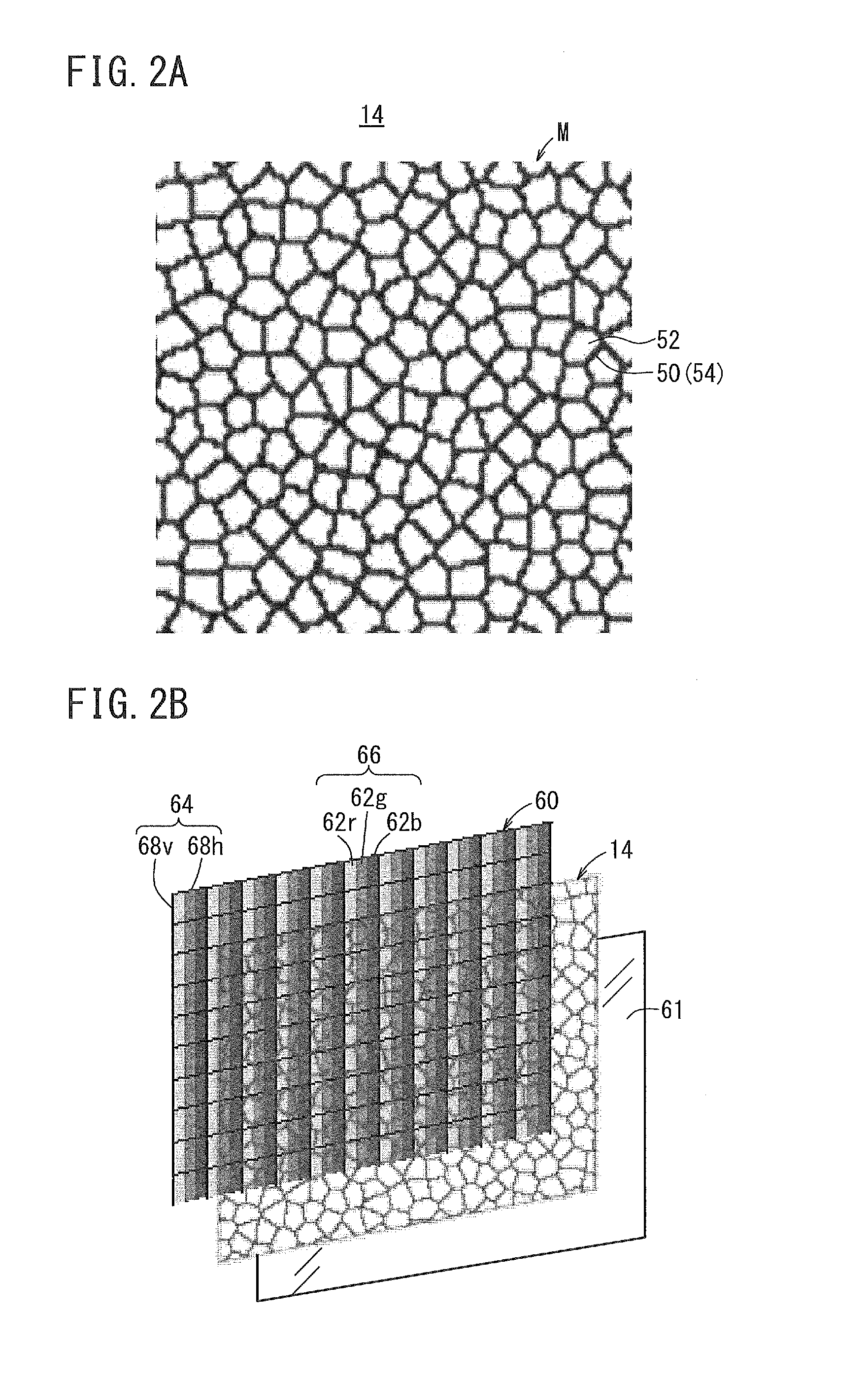
Digital camera and digital camera system
ActiveUS20100201853A1Improve image qualityMinimum of spurious resolution•colorTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCamera lensExtinction
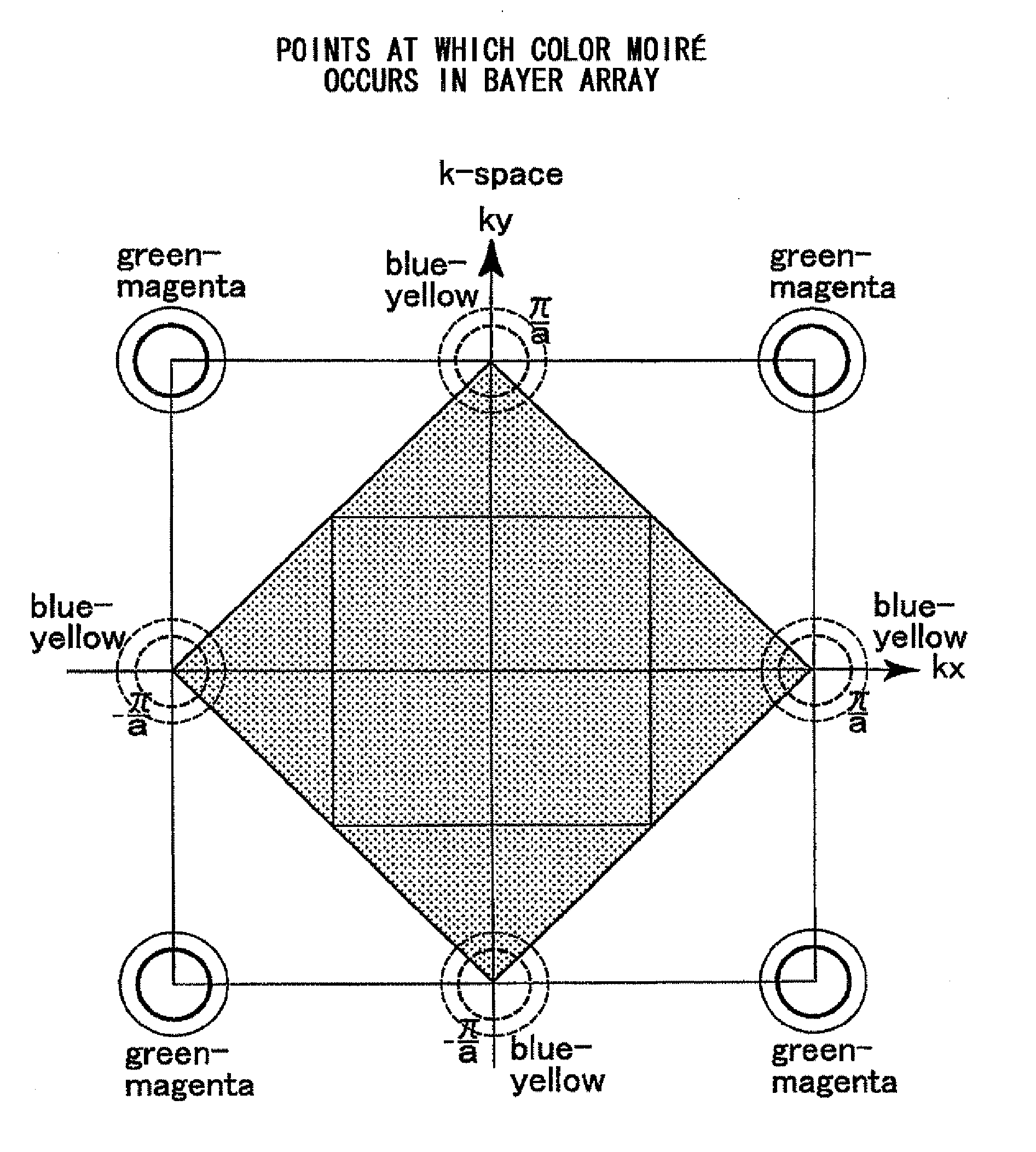
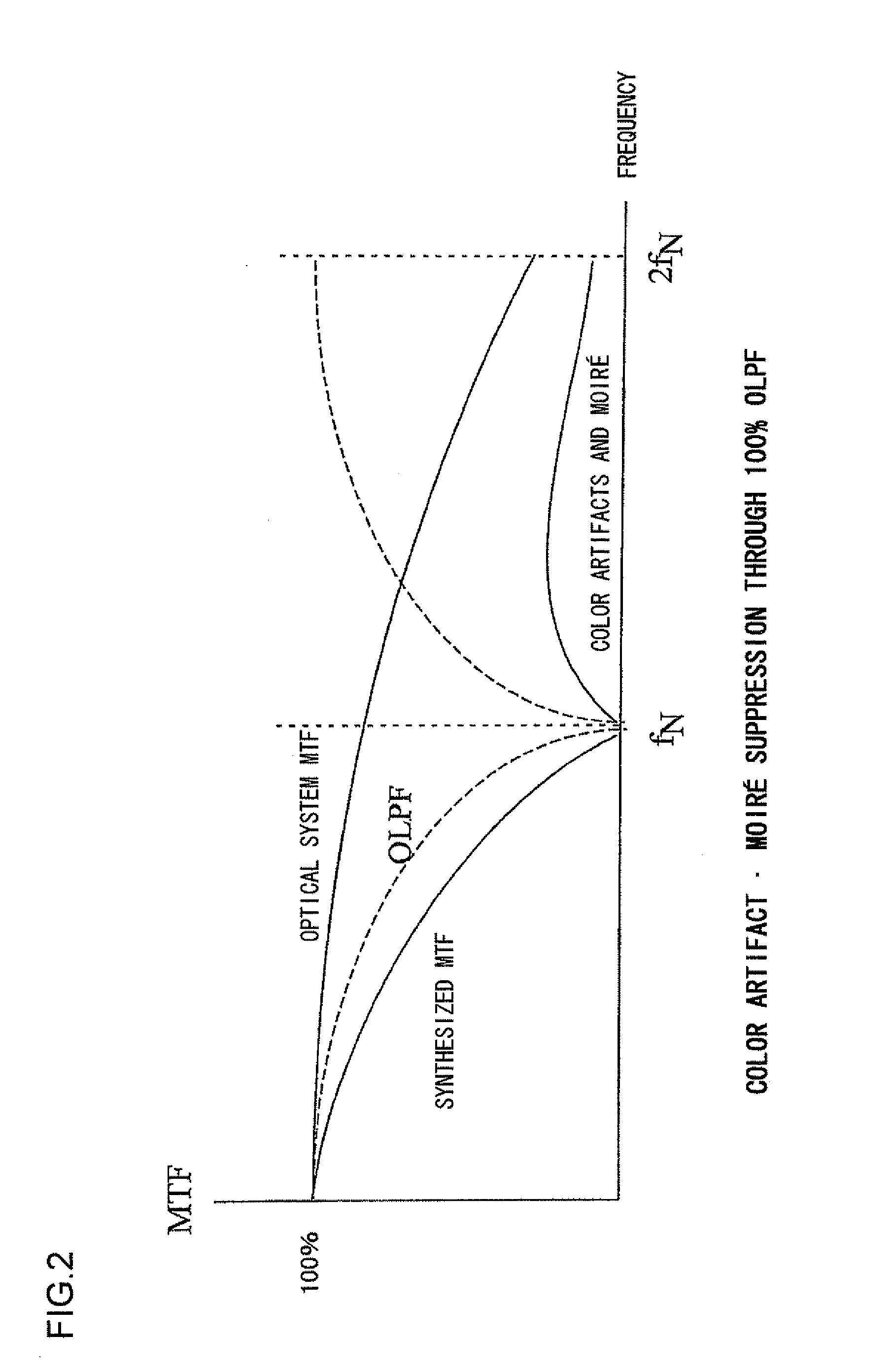
A digital camera includes: a lens unit that forms a subject image on an imaging plane; an image sensor that includes color filters each disposed at one of pixels disposed in a lattice-like pattern over pixel intervals (a, b) along two directions, an x direction and a y direction, extending perpendicular to each other, with color filters corresponding to a first color component among first through nth (n≧2) color components, disposed in a checkered pattern at pixels amounting to at least half an entire color filter density and color filters corresponding to remaining color components disposed at other pixels, and outputs image signals expressing the subject image; and an optical low pass filter unit at which light having passed through the lens unit and yet to enter the image sensor undergoes light beam separation along two diagonal directions ((1 / 2)a, (1 / 2)b)×(√2 / α) and ((1 / 2)a, −(1 / 2)b)×(√2 / α) relative to (x, y) coordinate axes, so as to achieve frequency modulation for the subject image to become extinct at a band formed by connecting spatial frequencies (α / (2a), 0) and (0, α / (2b)) at positions calculated by multiplying, by a multiplier α, a Nyquist frequency 1 / (2a) and a Nyquist frequency 1 / (2b) at the image sensor assumed respectively along the x direction and the y direction. When the pixel intervals (a, b) assumed along the two directions at the image sensor are both within a 2.5˜5 μm / pixel range, a position of an extinction frequency band is set for the optical low pass filter by setting the multiplier α for the Nyquist frequencies at the image sensor within a range of 1.5≦α≦3.5.
Owner:NIKON CORP
MTFC remote sensing image restoration method
ActiveCN101441764AEnhance texture detailsImprove clarityImage enhancementElectromagnetic wave reradiationFast algorithmPoint spread function
The invention discloses a method for restoring an MTFC remote sensing image, in particular an improved MTFC algorithm, and provides a rapid MTFC algorithm which combines a restoration algorithm based on a point spread function PSF. In a mode of constructing an MTF curve through the method, the downtrend of the MTF curve is adjusted through index; an MTF value in nyquist frequency is raised to about 0.5 so as to ensure that no large noise is brought; the rapid MTFC algorithm combines the advantages of the MTFC algorithm and the PSF restoration algorithm based on the point spread function PSF; the MTF curve is constructed through the MTFC algorithm; the point spread function PSF is estimated; the PSF algorithm is used to realize restoration; and the difference between the rapid algorithm and the restoration algorithm based on the point spread function PSF lies in the establishment of the PSF. The aim of the method is to improve definition of the image, strengthen the texture detail of the image, improve the quality of the image and increase no noise at the same time; and the processing speed and the processing effect can meet the requirement of batch production.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Device for measuring modulation transfer function of optical system and method thereof
InactiveCN101813558AAvoid Calibration WorkIncrease sampling rateTesting optical propertiesManufactured apparatusEngineering
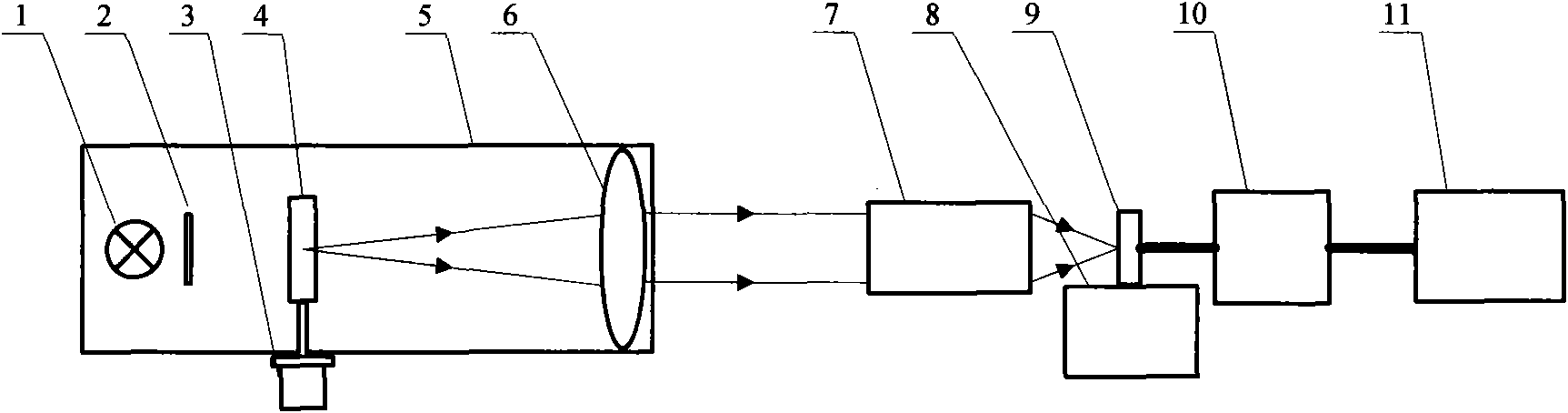
The invention discloses a device for measuring a modulation transfer function of an optical system and a method thereof. A target generator of the device comprises a knife edge target (4), a light source (1) and an electrical machine (3), wherein the electrical machine drives the knife edge target (4), so that an inclined angle beta is formed between the arrangement direction of a knife edge pixel (12) of the knife edge target (4) and that of a pixel (13) of an area array detector, and the inclined angle meets the following condition: ds=d sin beta, wherein the ds is a sampling distance, and the d is the size of the edge length of the pixel of the area array detector. When measuring, the modulation transfer function, the electrical machine drives the knife edge target (4) to rotate at the angle of beta to perform image data collecting and data processing so as to obtain modulation transfer function of the optical system to be measured. The invention adopts the knife edge target to realize an oversampling technology and improve the sampling rate, thereby being capable of measuring the modulation transfer function of the optical system to be measured without a relay amplifying system, being capable of measuring the maximum frequency which is higher than the Nyquist frequency of the area array detector, simplifying a measuring system, and avoiding complex assembling and correcting work when manufacturing apparatuses.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Interlace motion artifact detection using vertical frequency detection and analysis
InactiveUS6909469B2Reduce artifactsPreserves maximum amount of vertical detailTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsMaximum levelInterlaced video
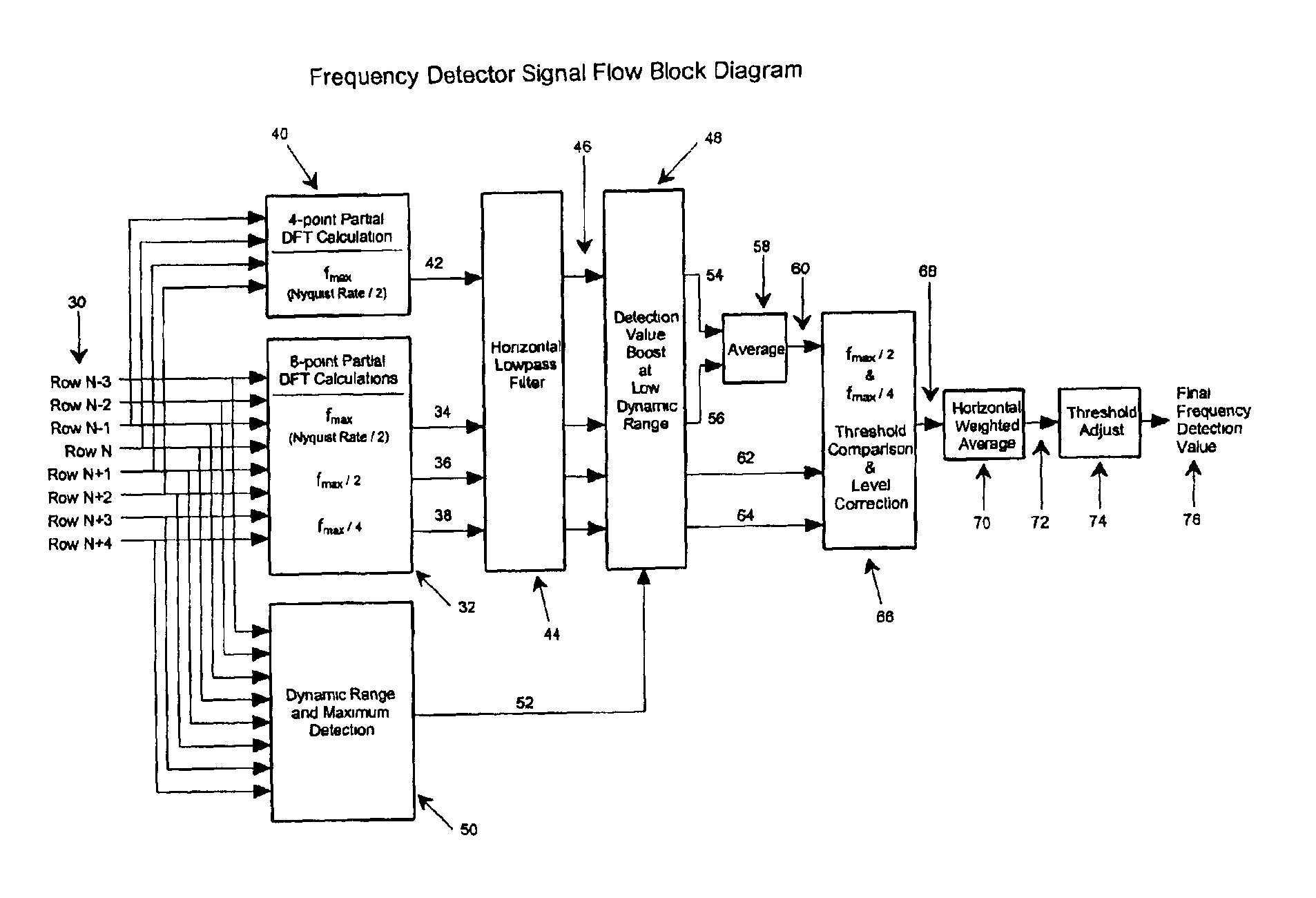
An interlace motion artifact detector which identifies video image spatial frequencies characteristic of motion artifacts. The detected frequency is the maximum which can be represented by the vertical sampling rate of the video format (i.e., the Nyquist frequency). This frequency is detected by a pair of partial Discrete Fourier Transforms (DFT) which each calculate only the frequency component of interest. Additional vertical frequency components at one half and one quarter the interlace motion artifact frequency are also detected via a partial DFT. The presence of these lower frequencies acts as an indication of an erroneous motion artifact detection. Additionally, the dynamic range and maximum level of the video data is used as an indication of when to boost the frequency detection levels in areas of low brightness and / or contrast.
Owner:LATTICE SEMICON CORP
Beamformed ultrasonic imager with delta-sigma feedback control
InactiveUS20030231125A1Reduce distortion problemsPreserving sample series monotonicityUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectric signal transmission systemsUltrasound imagingAnalog signal
A method and apparatus are provided for reducing distortion in a dynamically delayed digital sample stream of an imaging system. The method includes the steps of delta-sigma modulating an input analog signal of the imaging system at a frequency above the Nyquist frequency of the input analog signal to generate a digital sample stream and changing a length of the sample stream to delay a portion of the sample stream while maintaining synchronism between a delta-sigma modulator and a demodulator of the system.
Owner:HITTITE MICROWAVE LLC
Sample observation device for generating super resolution image
A sample observation device includes: an excitation light generation unit; an intermediate image forming unit projecting excitation light to a sample and forming an intermediate image of the sample at an intermediate image position with observing light; a confocal modulation unit modulating spatial intensity distributions of the excitation light and the intermediate image at the position; a modulation drive unit moving a pattern of the modulation unit; an image relay unit relaying on a image forming surface the intermediate image; an image pickup unit converting the distribution of relayed intermediate image into digital image data; and an image processing unit processing on the digital image data. Cutoff frequency of the relay unit and Nyquist frequency of the pickup unit exceed cutoff frequency of the forming unit, and the processing unit performs a high frequency enhancing process for enhancing the high frequency component exceeding the cutoff frequency of the forming unit.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Method of manufacturing conductive sheet, conductive sheet, and recording medium
InactiveUS20130255998A1Strong power capabilityDecreasing granular noiseConductive layers on insulating-supportsMagnetic/electric field screeningWire rodVisual perception
The method of manufacturing a conductive sheet of the present invention is provided with: a creation step for creating image data that indicates a meshed pattern; and an outputting step for outputting and forming wire materials on a base body on the basis of the created image data, and manufacturing a conductive sheet having the meshed pattern. The image data has, in convolution integration of a power spectrum of the image data and standard vision responsiveness of human beings, a characteristic of having each of the integration values at a spatial frequency band that is not less than 1 / 4 and not more than 1 / 2 of a Nyquist frequency corresponding to the image data to be greater than integration values at a null-space frequency.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Circuit for capacitive touch applications
A circuit for capacitive touch applications comprising: a charge integrator; a low pass-filter; a correlated double sampler comprising an input capacitor; a sampler and holder; an analog to digital converter. Said low pass-filter having cut-off frequency lower than the Nyquist frequency of the sampler and holder. Said low pass filter comprising said input capacitor and a serial resistor.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON
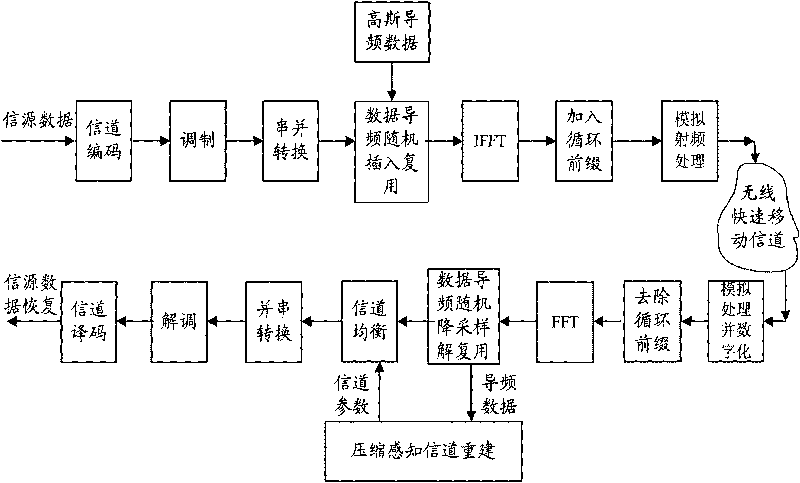
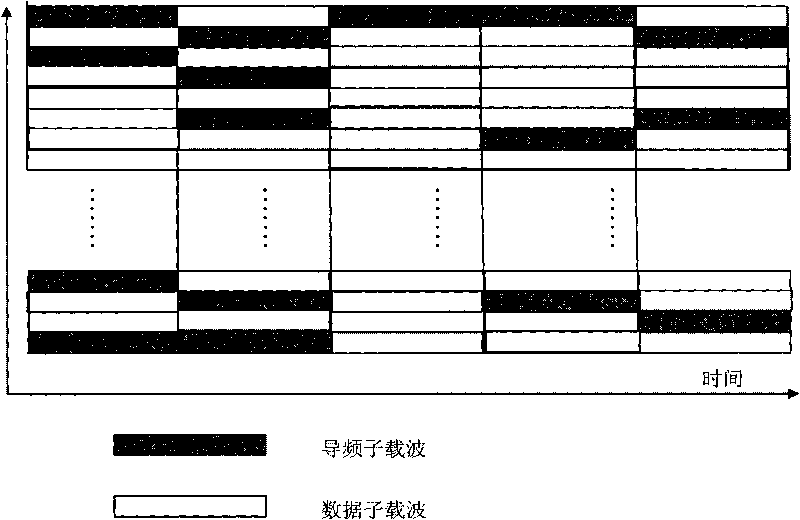
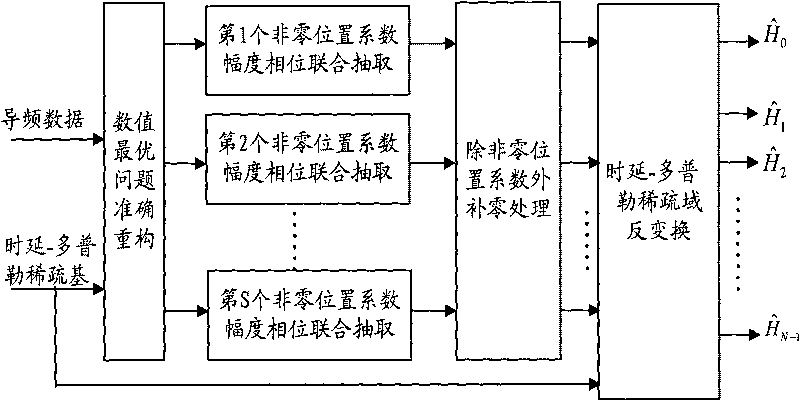
Method for estimating OFDM rapid-varying channels in low-density pilot-frequency distribution
InactiveCN101699807AImprove estimation accuracyAchieve estimatesMulti-frequency code systemsTransmitter/receiver shaping networksComputation complexityChannel parameter
The invention discloses a method for estimating OFDM rapid-varying channels in low-density pilot distribution. The method comprises: multiplexing Gaussian-distribution pilot-frequency data and to-be-transmitted data at a transmitting end according to a time-frequency random insertion mode; performing random down-sampling and multiplexing at a receiving end on a frequency far below Nyquist frequency; transmitting received pilot-frequency data which is obtained through multiplexing and corresponds to a pilot-frequency position to perform compressed sensing channel reconstruction; obtaining S nonzero channel values in a channel delay-Doppler sparse domain; and obtaining the channel parameters of all sub-carriers in a frequency domain through channel coefficient zero padding excepting S nonzero positions, as well as delay-Doppler sparse domain inverse transformation processing. The method has the advantages of performing random down-sampling on the frequency far below Nyquist frequency, utilizing the compressed sensing channel reconstruction to filter noise so as to improve the parameter estimation precision of OFDM rapid-varying channels under pilot-frequency distribution conditions low in signal-to-noise ratio and density and realizing high-precision channel parameter estimation and tracking, along with low estimation-calculation complexity and low bit error rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Sampling Method For Time-Interleaved Data Converters In Frequency-Multiplexed Communications Systems
ActiveUS20110128175A1Improve fidelityReduce power inputElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersFrequency reuseCommunications system
A wide band analog-to-digital converter used in a frequency multiplexed communication system. The converter includes a plurality, M, of time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter subunits (ADC subunits). The sampling rate, FS1, of the M ADC subunits is selected to locate one or more integer multiples of a Nyquist frequency of a respective subunit ADC in one or more guard bands, and / or such that one or more integer multiples of FS1 are also located in the guard bands.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
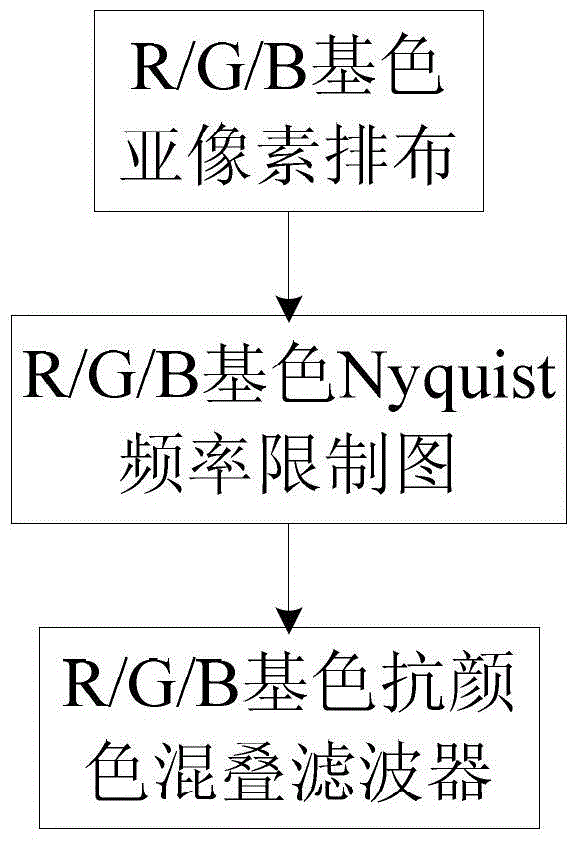
Two-dimensional sub-pixel sampling-based super-resolution display method and device
ActiveCN103338378AAchieving super-resolution displaysPreserve image detailImage enhancementColor signal processing circuitsAnti-aliasingImage resolution
The invention discloses a two-dimensional sub-pixel sampling-based super-resolution display method and a two-dimensional sub-pixel sampling-based super-resolution display device. Based on the characteristic of diversity of R, G and B primary color sub-pixel arrangement of flat panel display equipment, a Nyquist frequency limiting region of each primary color sub-pixel arrangement is calculated, and a group of R, G and B primary color anti-aliasing filters is designed on the basis of the calculated Nyquist frequency limiting region of each primary color sub-pixel arrangement, so that the aim of weakening and even eliminating the aliasing introduced by sub-pixel sampling is fulfilled while a high image sensing resolution is kept. According to the method and the device, corresponding anti-aliasing filtering is applied to R, G and B primary color components of an original image respectively, and then sub-pixel sampling is performed on the filtered image according to the spatial position structure of the two-dimensional sub-pixel arrangement of the display equipment. The visual perception resolution of the flat panel display equipment is improved at a lower cost on the premise of not changing any physical attribute, super-resolution display of the display equipment is realized, and meanwhile, the method is simple and easy to implement.
Owner:XIAN NOVASTAR TECH
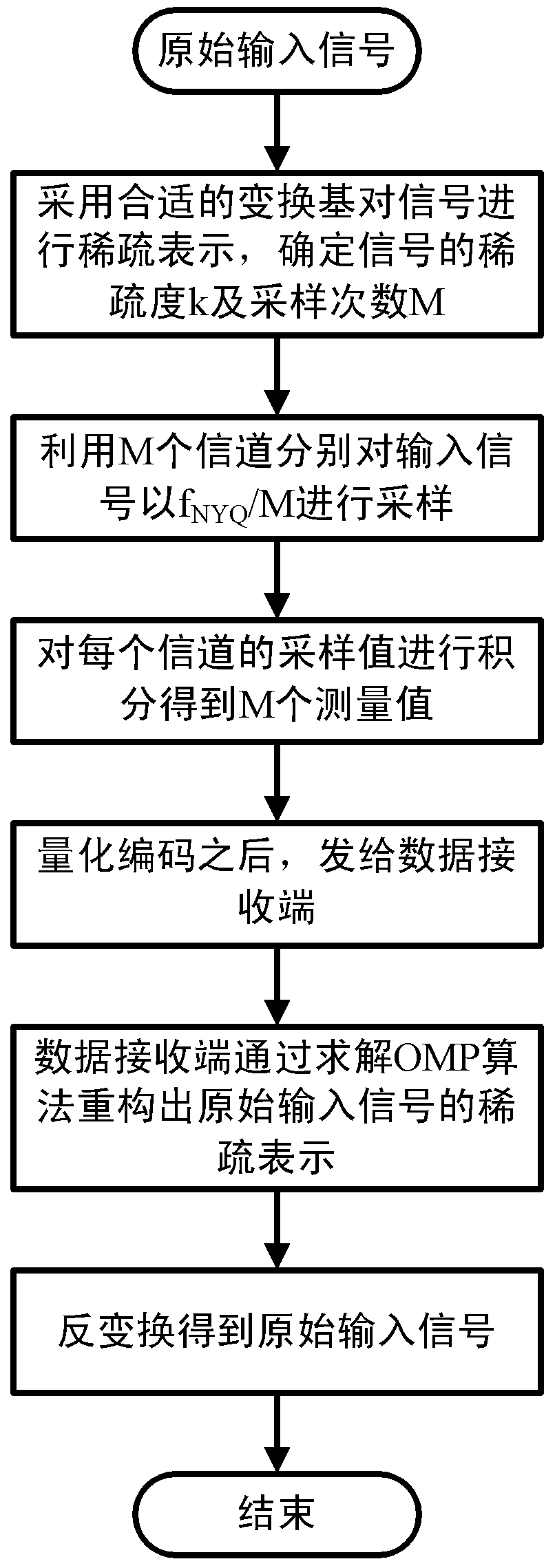
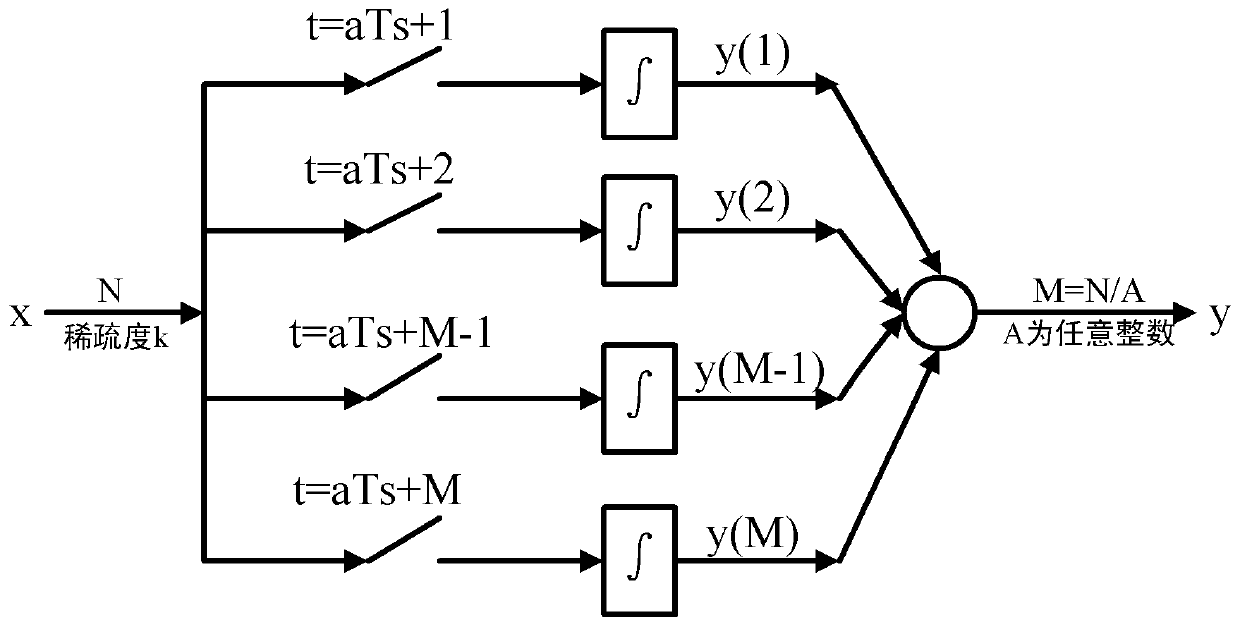
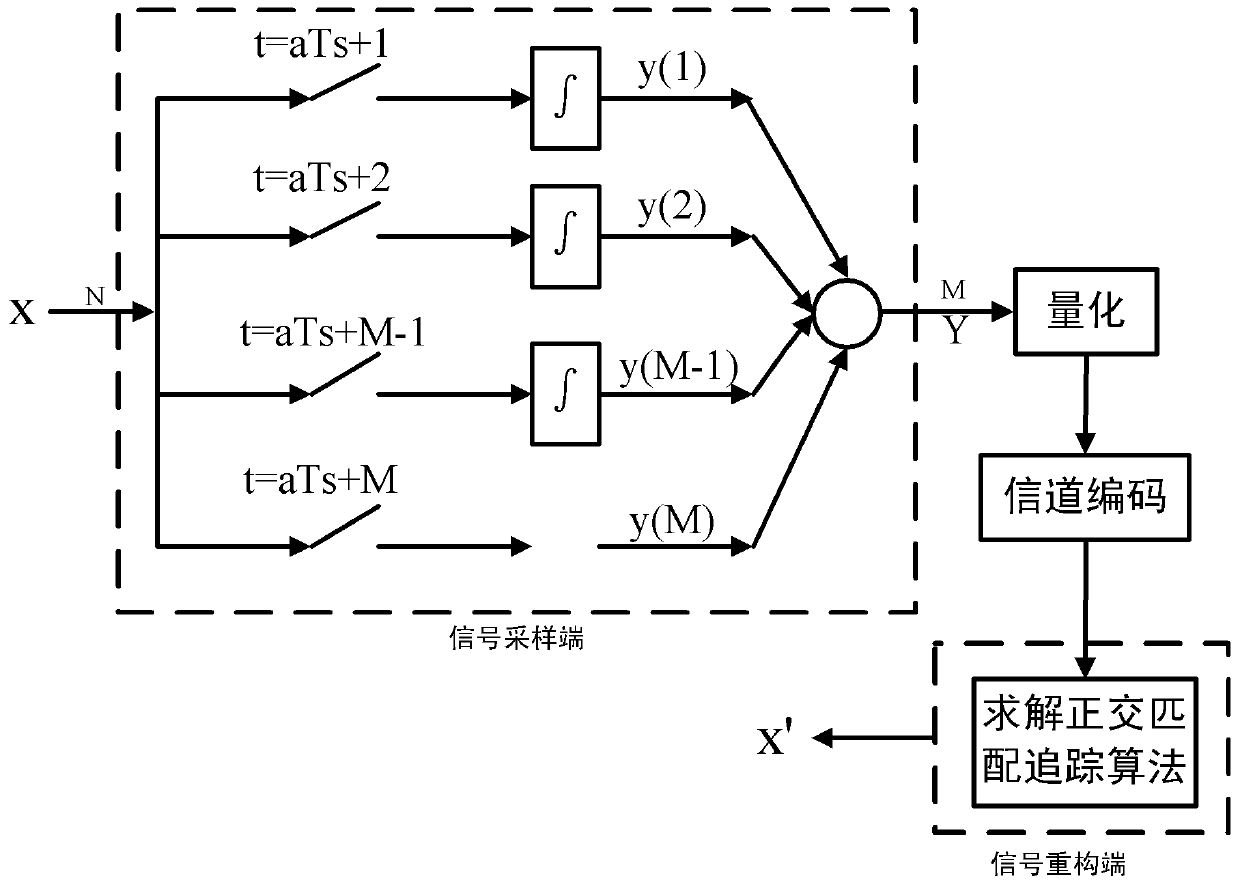
Signal collecting method with sampling frequency lower than Nyquist frequency
ActiveCN103346798AEasy to implementRelieve pressureCode conversionData acquisitionCompressed sensing
The invention discloses a signal collecting method with a sampling frequency lower than the Nyquist frequency. Firstly, an appropriate conversion basis matrix is selected for an input signal, sparsity expression is performed on the signal with the conversion basis matrix so as to determine the sparsity k of the signal, the sampling times M of compressive sampling are calculated with the sparsity, M channels are divided for respectively performing sampling on the signal in a fNTQ / M mode, integration is performed on the sampling value of each channel so as to obtain M measured values, and a reconstruction end reconstructs an original signal by solving the optimization problem. According to the signal collecting method with the sampling frequency lower than the Nyquist frequency, the compressed sensing principle serves as a basis so as to perform compressive sampling on sparse signals or signals capable of being expressed in a sparse mode with the frequency far lower than the Nyquist frequency, and limitation on the sampling frequency by the classic Nyquist sampling theorem is broken. Meanwhile, the signal collecting method with the sampling frequency lower than the Nyquist frequency is easy to carry out and reduces pressure in collecting, storing, transmitting and processing data.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Array Cameras Incorporating Optics with Modulation Transfer Functions Greater than Sensor Nyquist Frequency for Capture of Images used in Super-Resolution Processing
A variety of optical arrangements and methods of modifying or enhancing the optical characteristics and functionality of these optical arrangements are provided. The optical arrangements being specifically designed to operate with camera arrays that incorporate an imaging device that is formed of a plurality of imagers that each include a plurality of pixels. The plurality of imagers include a first imager having a first imaging characteristics and a second imager having a second imaging characteristics. The images generated by the plurality of imagers are processed to obtain an enhanced image compared to images captured by the imagers. In many optical arrangements the MTF characteristics of the optics allow for contrast at spatial frequencies that are at least as great as the desired resolution of the high resolution images synthesized by the array camera, and significantly greater than the Nyquist frequency of the pixel pitch of the pixels on the focal plane, which in some cases may be 1.5, 2 or 3 times the Nyquist frequency.
Owner:FOTONATION LTD
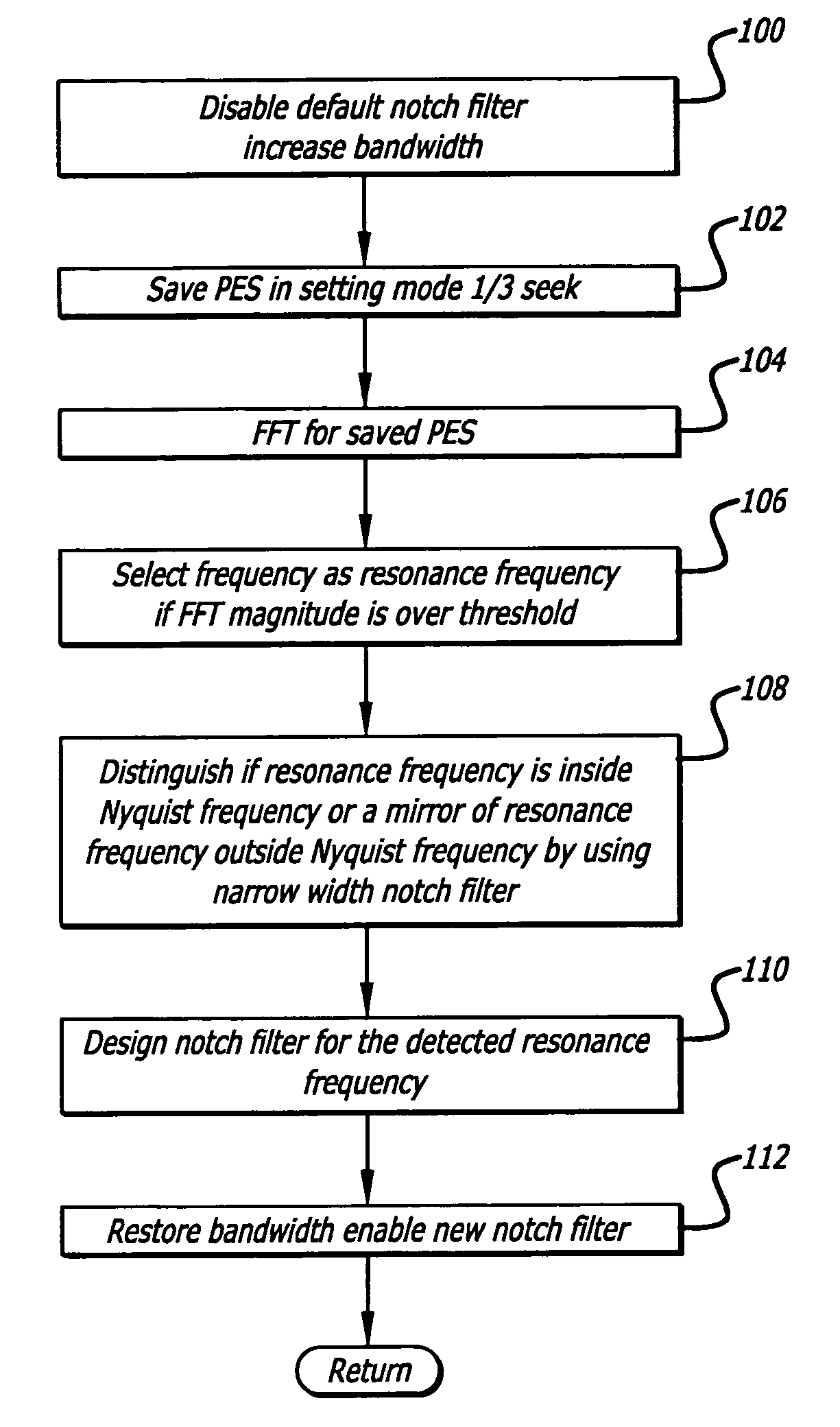
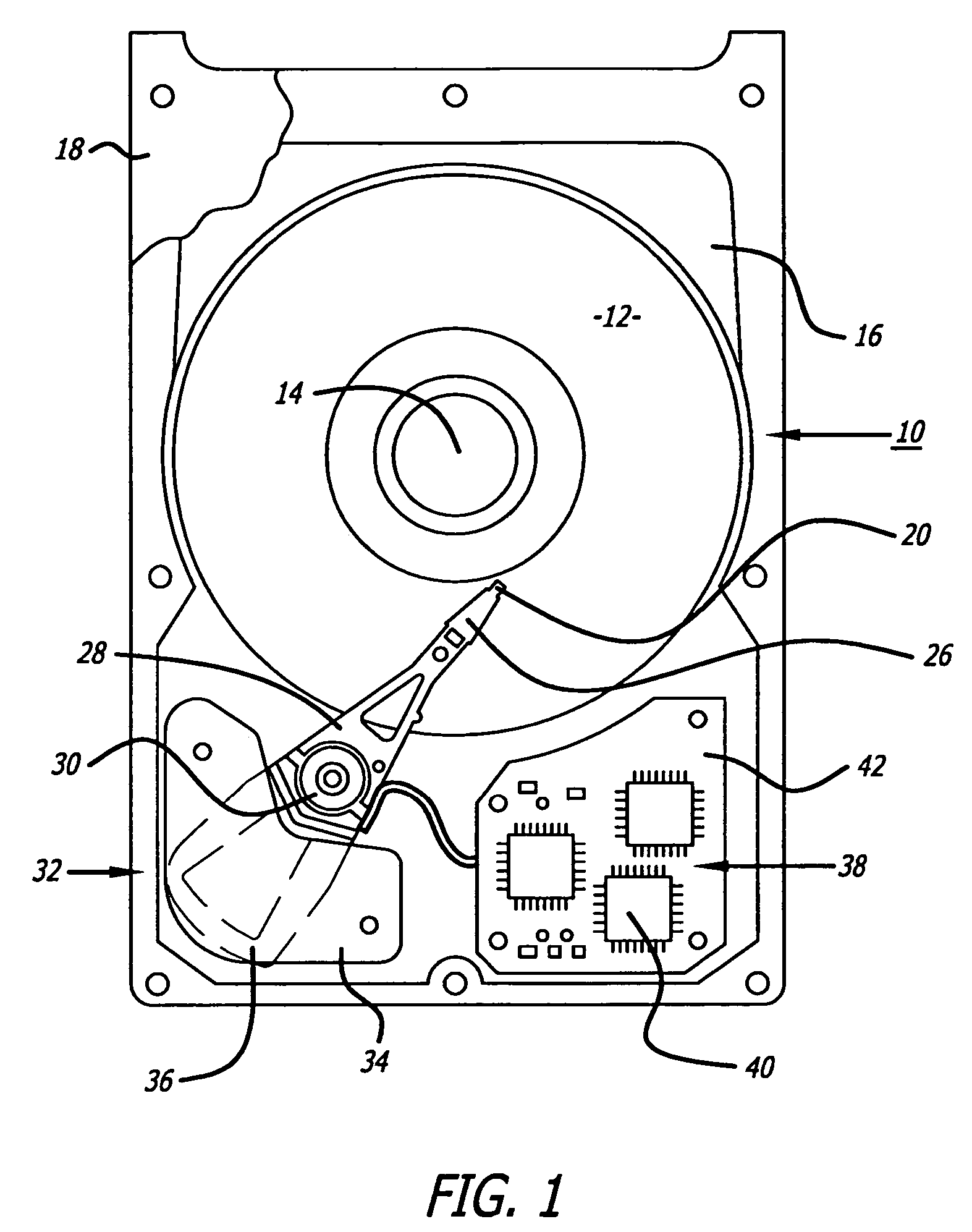
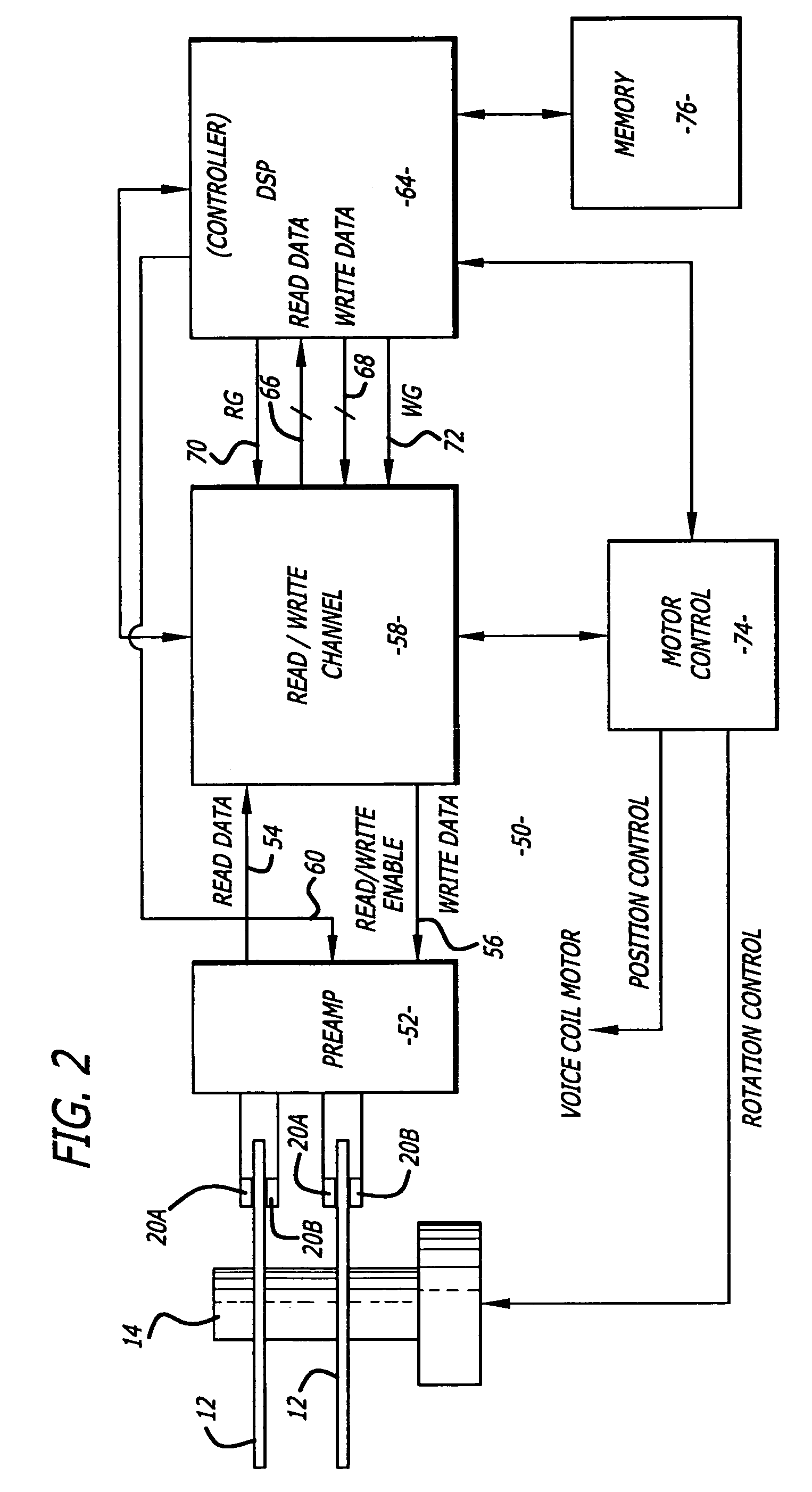
Method for resonance identification in hard disk drives
InactiveUS7158335B2Record information storageAlignment for track following on disksHard disc driveResonance
A hard disk drive that redefines a notch filter of the drive. The update process may include initially disabling all notch filters and inducing a seek operation of the disk drive heads. A position error signal is read during a settling time of the seek operation and processed to determine the frequency of the signal. The frequency is selected as a resonant frequency if the error signal magnitude exceeds a threshold value. The notch filter is then redefined in accordance with the selected resonant frequency. The controller may also perform a routine to determine whether the resonant frequency is above or below a Nyquist frequency. Unlike prior art techniques, the method disclosed can obtain the resonant frequency without sweeping the excitation signal of the disk drive voice coil motor.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
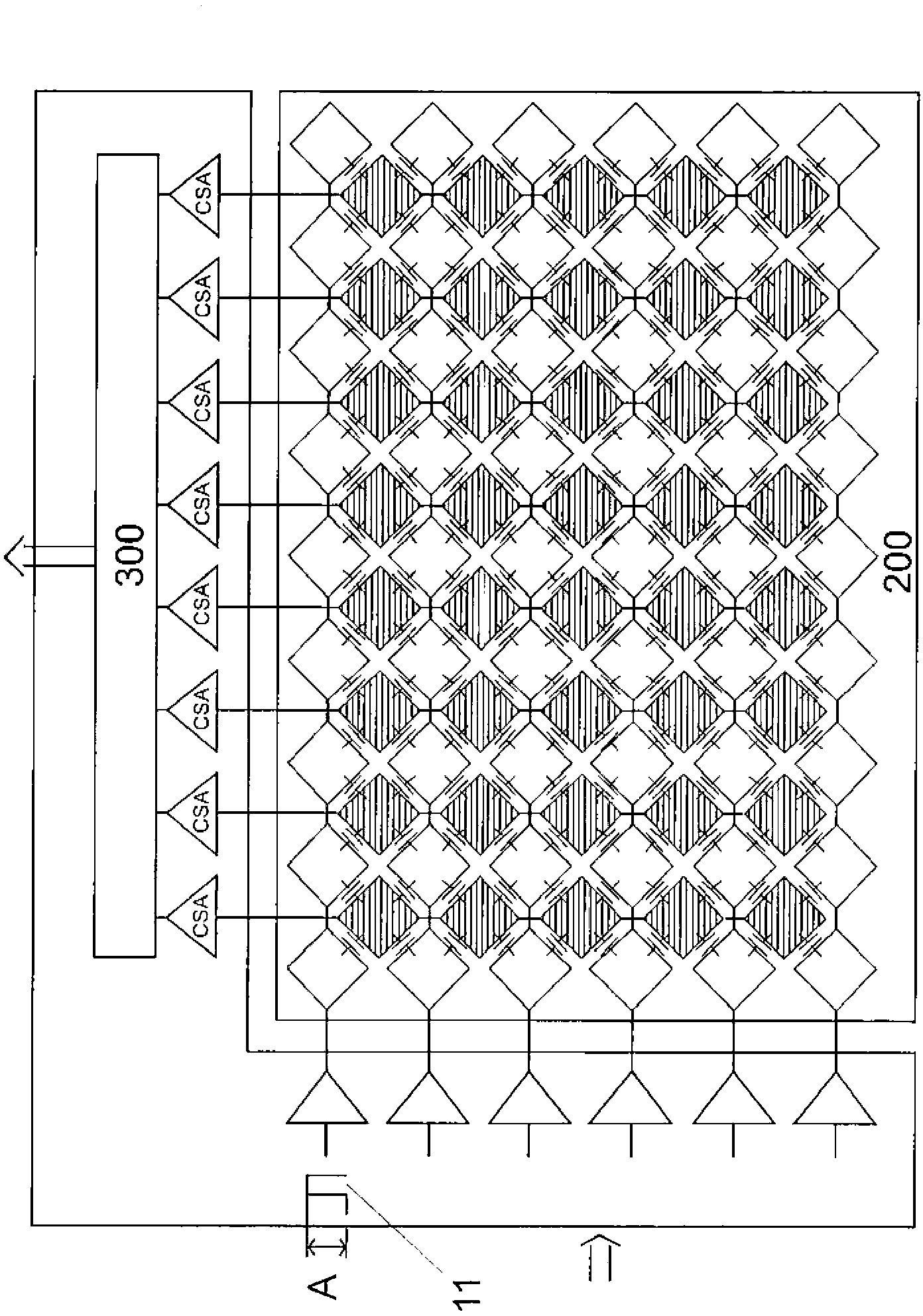
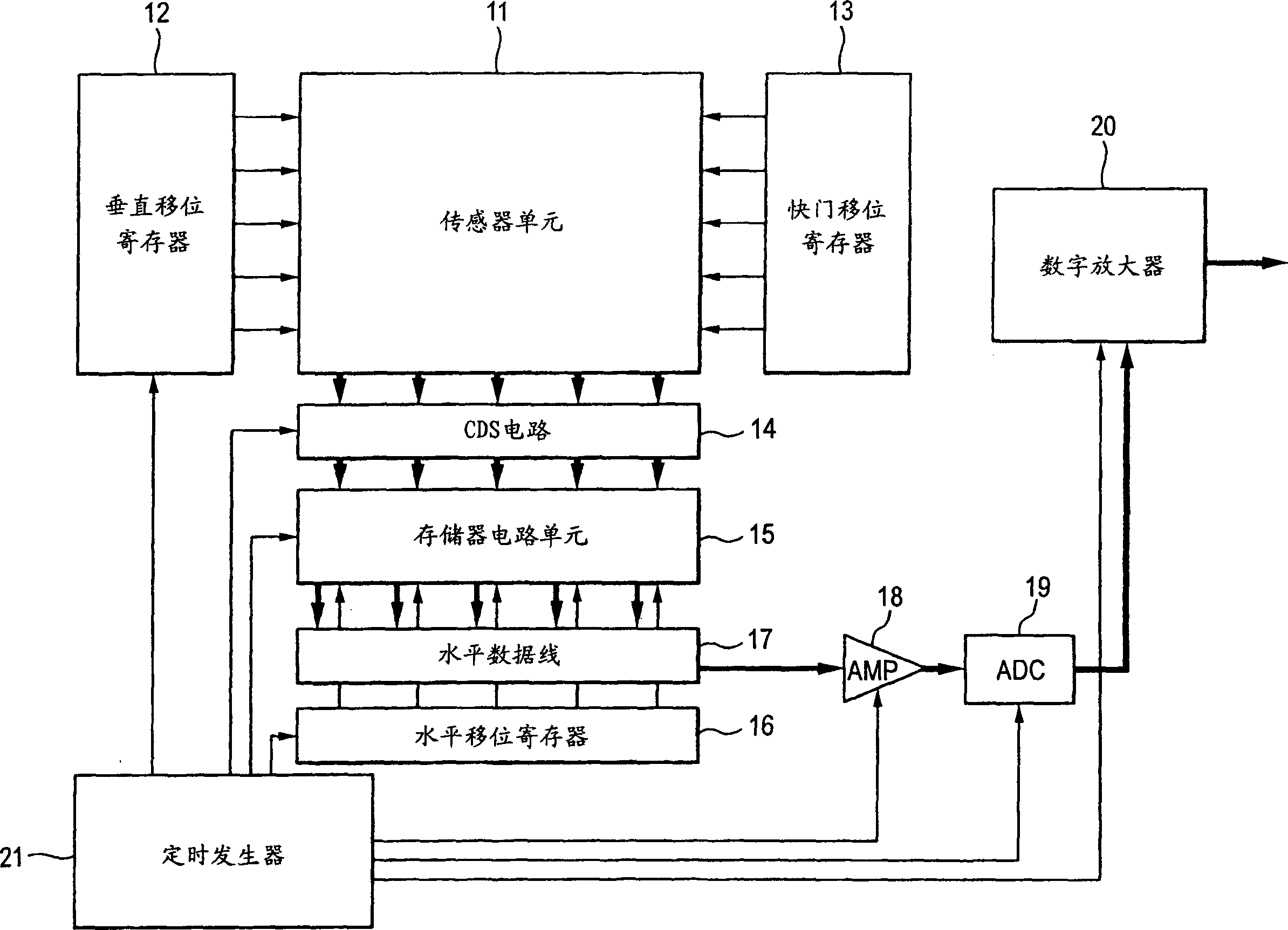
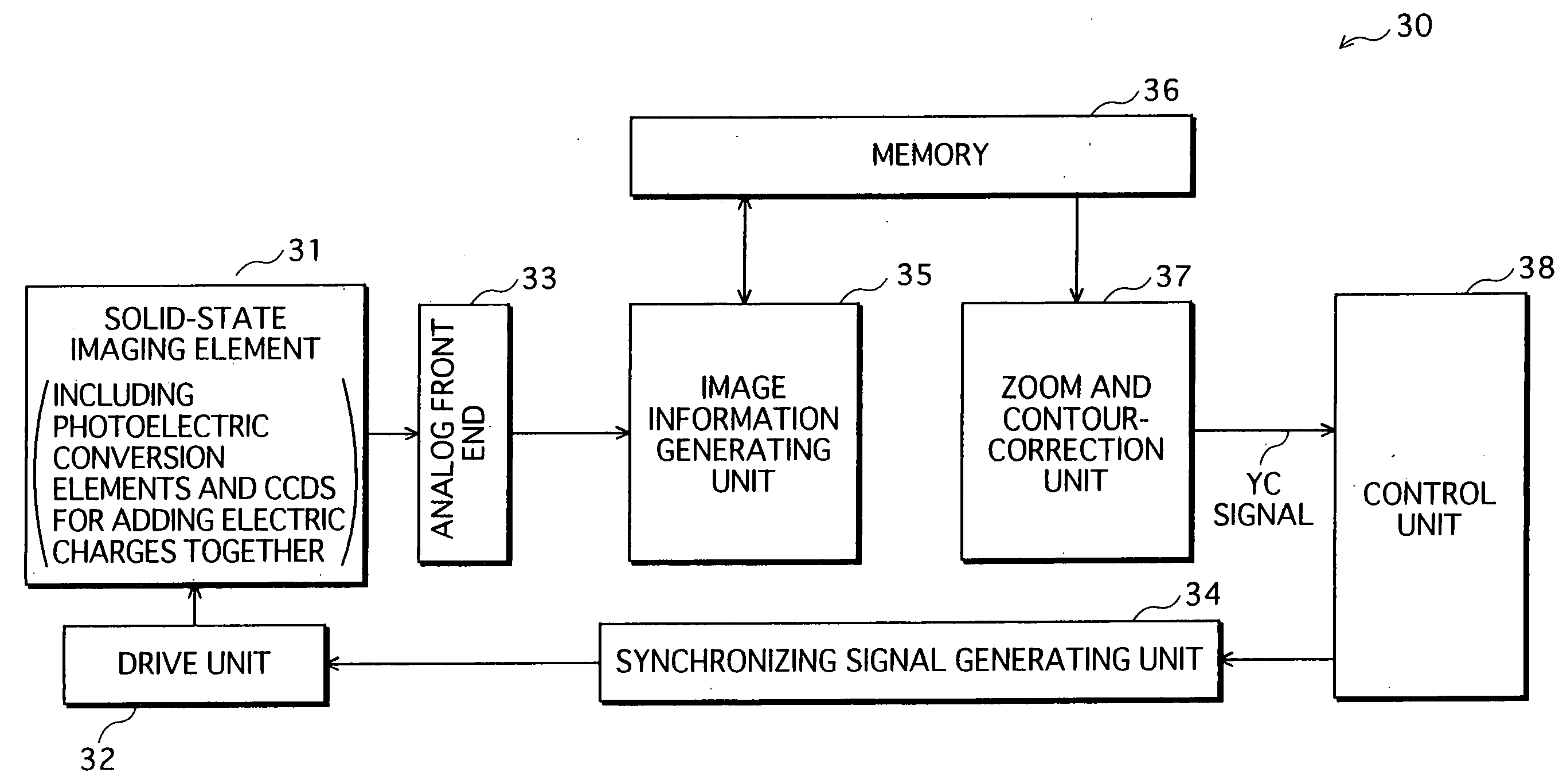
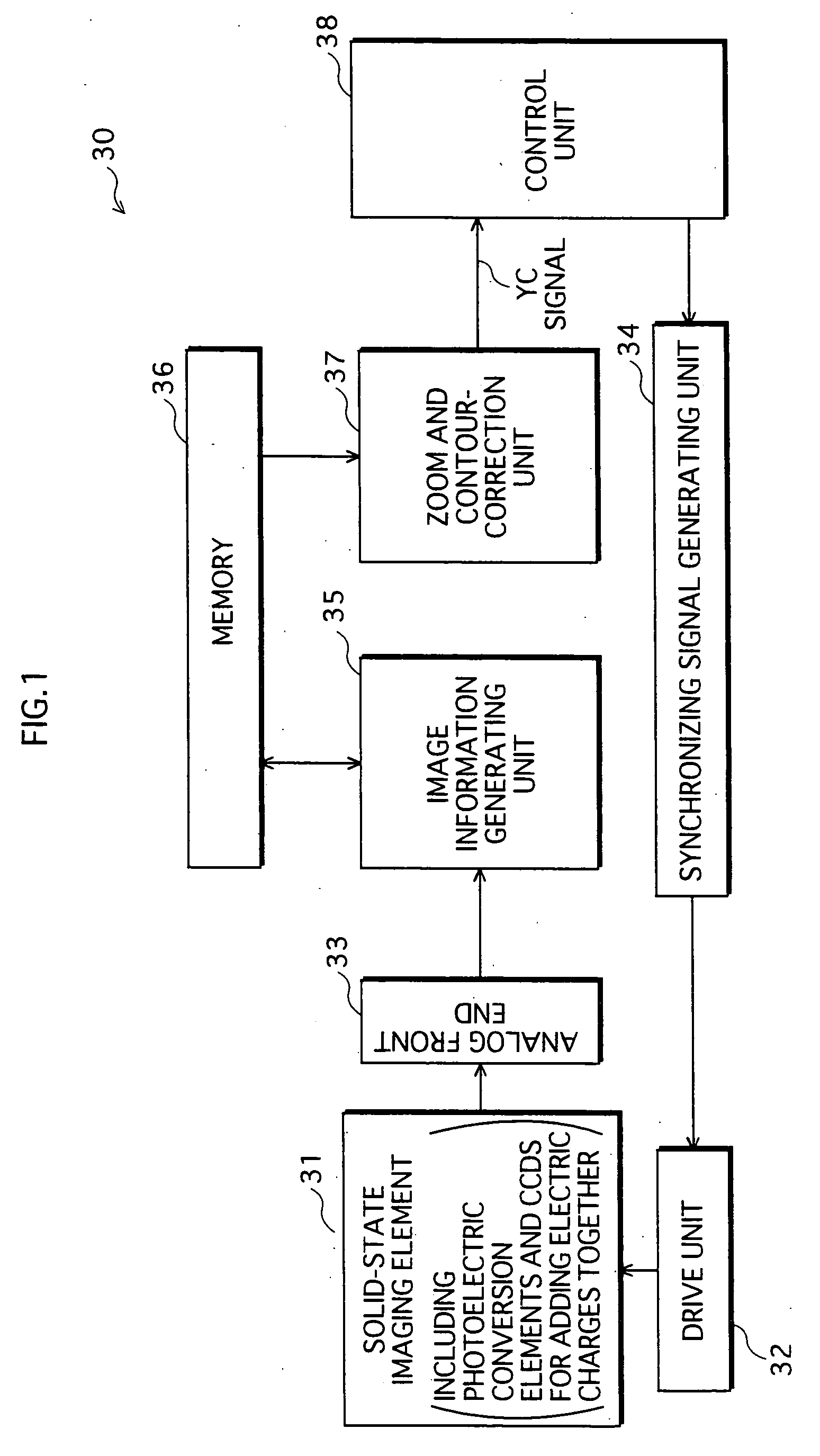
Solid-state image pickup device and drive method thereof
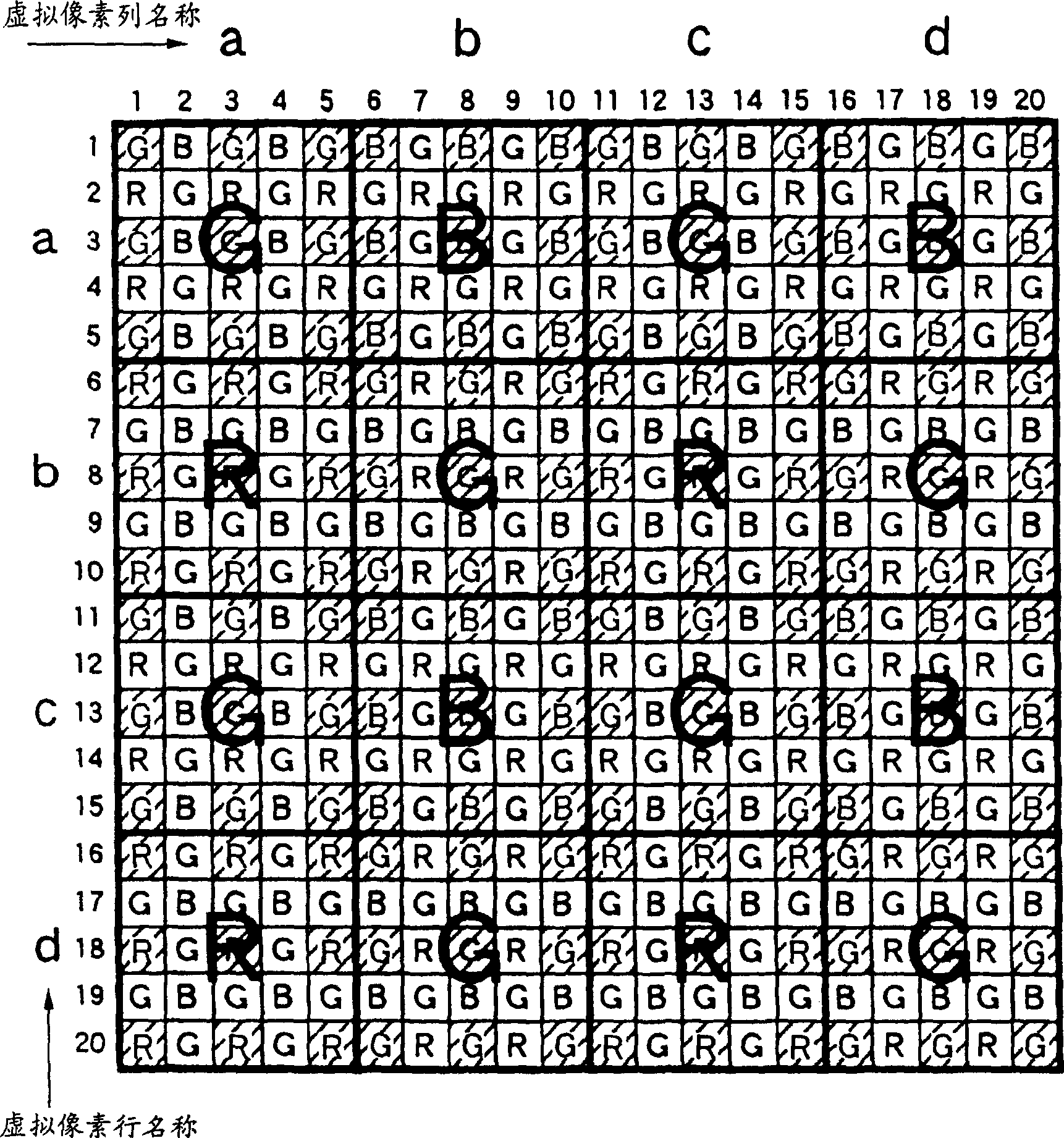
InactiveCN1774935AIncrease distanceIncrease pixel areaTelevision system detailsSignal generator with single pick-up deviceComputer scienceNyquist frequency
If pixel reading is simply skipped while keeping the pixel information order and spatial positional relationship the same as in the read-all-pixels mode, the distance between the read-out pixels increases. Thus reducing the Nyquist frequency and increasing the folding noise. A 5×5 pixel block is used as a unit pixel block. The pixel information in the first, third and fifth rows of the first, third and fifth columns of the pixel arrangement is added as an output of the ath row and ath column of the unit pixel block and output. The pixel information of the first, third and fifth rows of the sixth, eighth and tenth columns of the pixel arrangement is added as an output of the ath row and bth column of the unit pixel block and output. Addition and output are repeated in the same manner until the last row or a row close to the last row. Afterwards, the pixel information of the sixth, eighth and tenth rows of the first, third and fifth columns are added together as the output of the bth row and ath column of the unit pixel block and output. Similar operations are repeated so that sparse addition is repeated for readout of all arbitrary pixels.
Owner:SONY GRP CORP
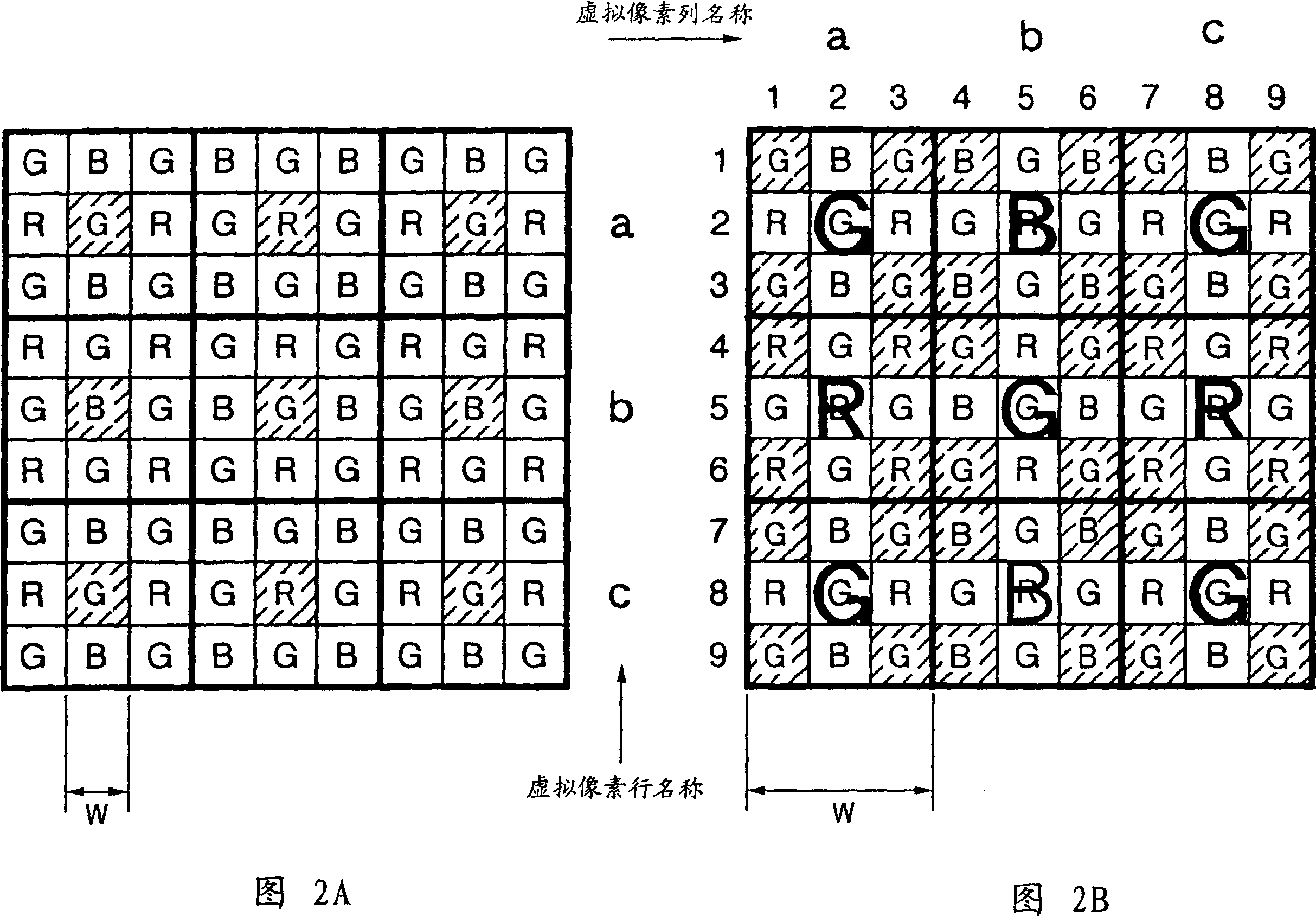
Imaging device
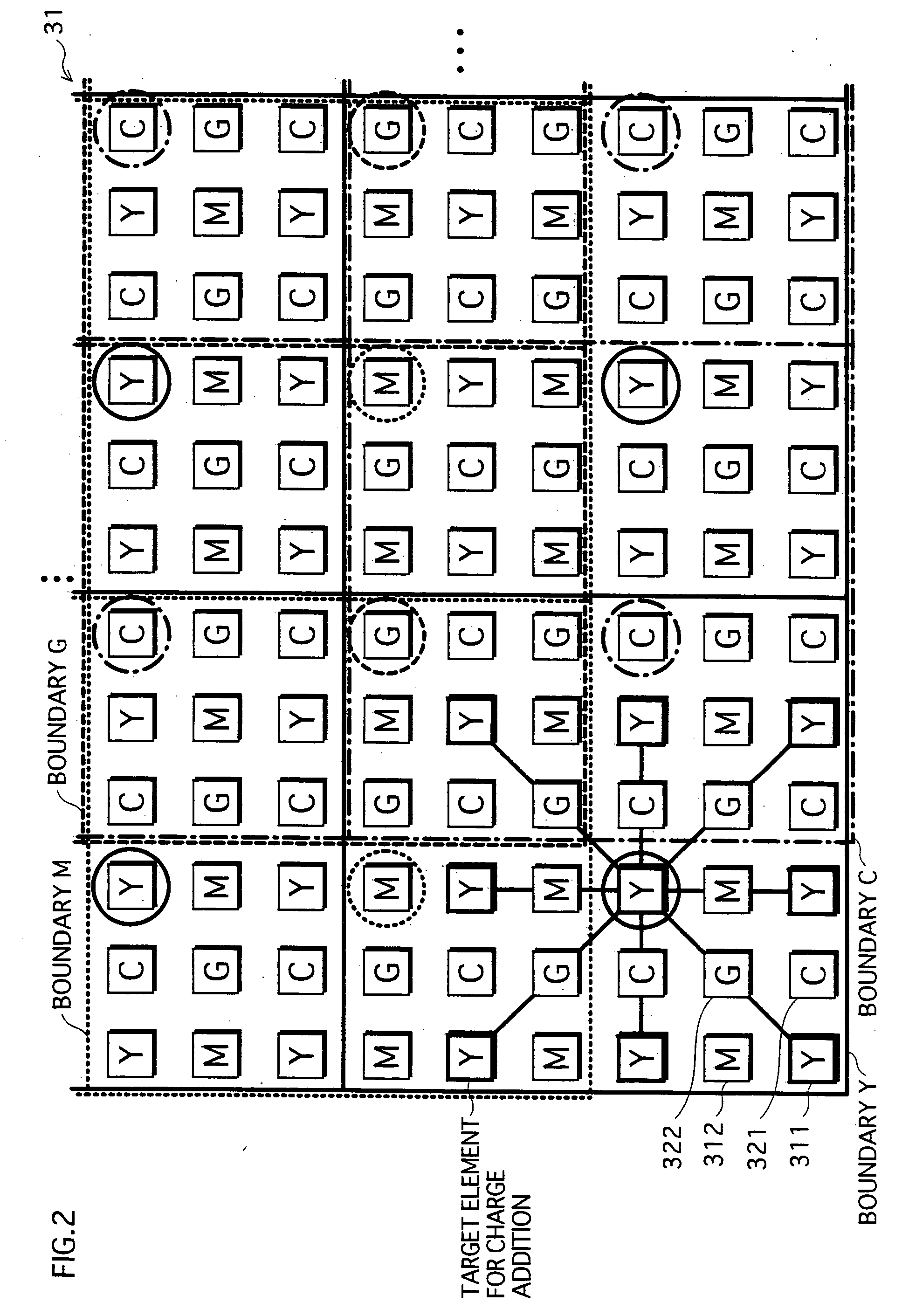
ActiveUS20050068426A1Improve image qualityReduce noiseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsImage resolutionImaging quality
A solid-state imaging element includes photoelectric conversion elements having a complementary or Bayer color filter array. The solid-state imaging element adds together electric charges stored in nine photoelectric conversion elements having color filters of one of multiple colors in each portion of six rows and six columns, to obtain a resulting electric charge, and outputs the resulting electric charge as one pixel. A portion for one of the colors deviates from a portion for each of the other colors by three rows and / or three columns. This pixel-addition operation produces an effect of a spatial low pass filter, thereby reducing signal components exceeding a Nyquist frequency corresponding to a target resolution. Consequently, aliasing noise in an image with the target resolution is reduced, and therefore higher image quality can be achieved, when compared with a conventional resolution reduction technique.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
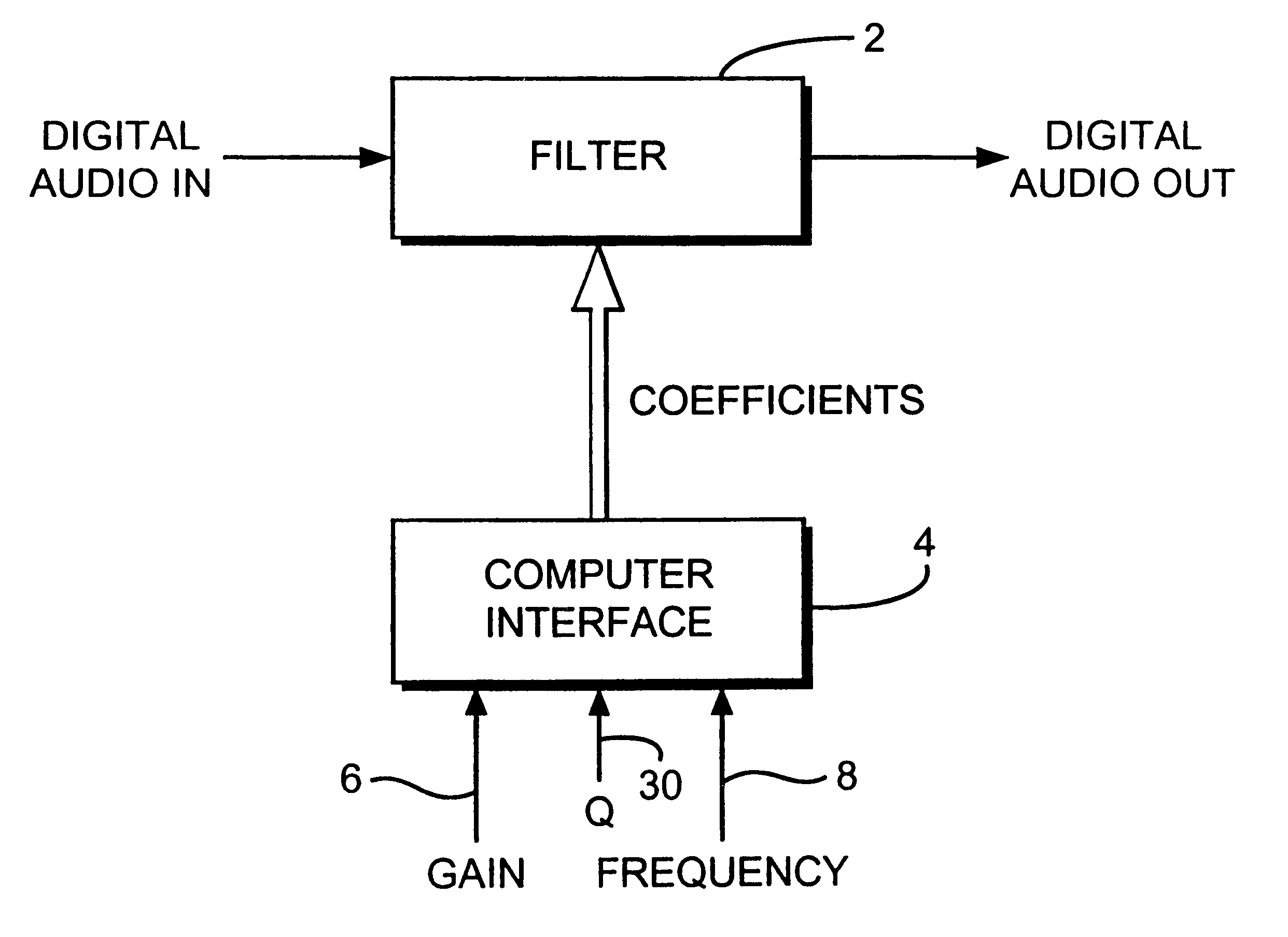
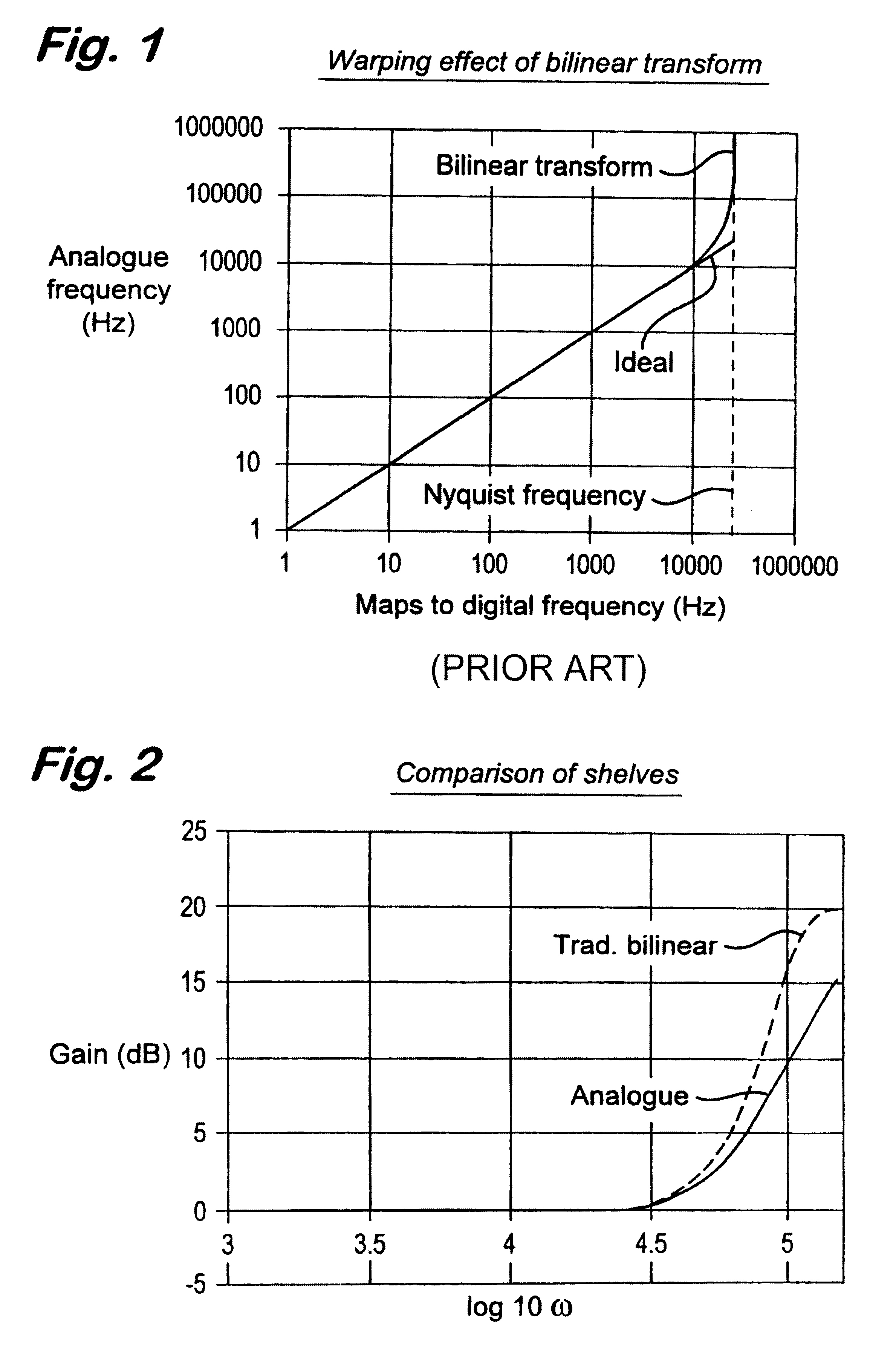
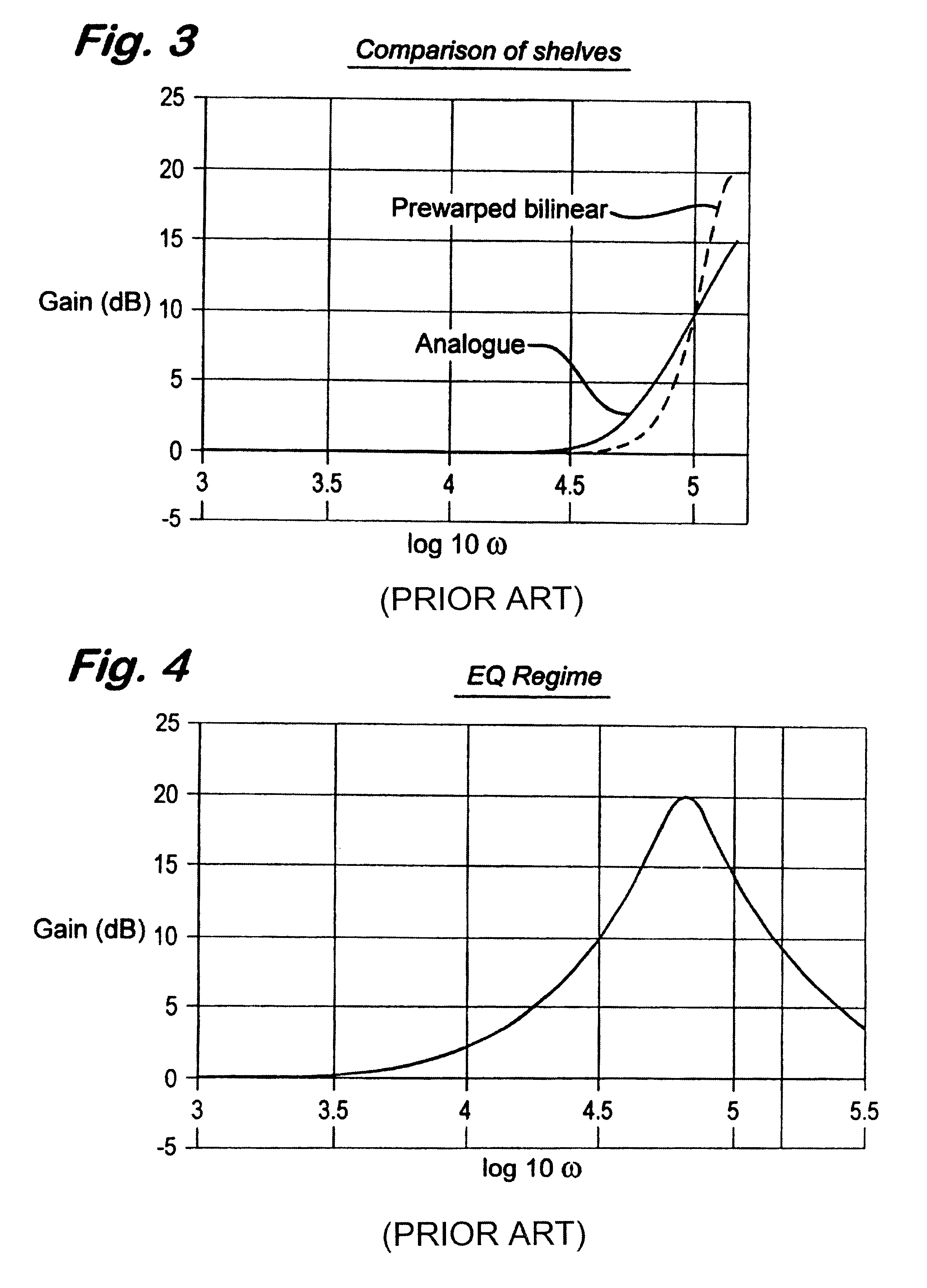
Digital filters
InactiveUS6581080B1Maintains algorithmic stabilityImprove matchDigital technique networkComplex mathematical operationsControl signalAnalogue filter
A technique for generating coefficients for a digital filter. A gain control signal with a value of reference gain and a frequency control signal with a value of reference frequency are provided. A plurality of gain and / or frequency points are calculated, according to a model of the frequency / gain characteristic of a prototype analog filter, at frequencies equal to and less than a Nyquist frequency (where the Nyquist frequency is half the sampling frequency of the digital frequency) and which match corresponds to gain and / or frequency points in the corresponding digital filter characteristic. Pre-warped parameters of a model of the analogue filter are calculated from the calculating points and a transform is applied to the resulting pre-warped analogue model, thus, converting the pre-warped analog model into the digital domain. Coefficients from the transformed model are generated and applied to the filter, thereby generating the coefficients of the digital filter.
Owner:SONNOX
Sampling method for time-interleaved data converters in frequency-multiplexed communications systems
ActiveUS8310387B2Improve fidelityReduce power inputElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersFrequency reuseCommunications system
A wide band analog-to-digital converter used in a frequency multiplexed communication system. The converter includes a plurality, M, of time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter subunits (ADC subunits). The sampling rate, FS1, of the M ADC subunits is selected to locate one or more integer multiples of a Nyquist frequency of a respective subunit ADC in one or more guard bands, and / or such that one or more integer multiples of FS1 are also located in the guard bands.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
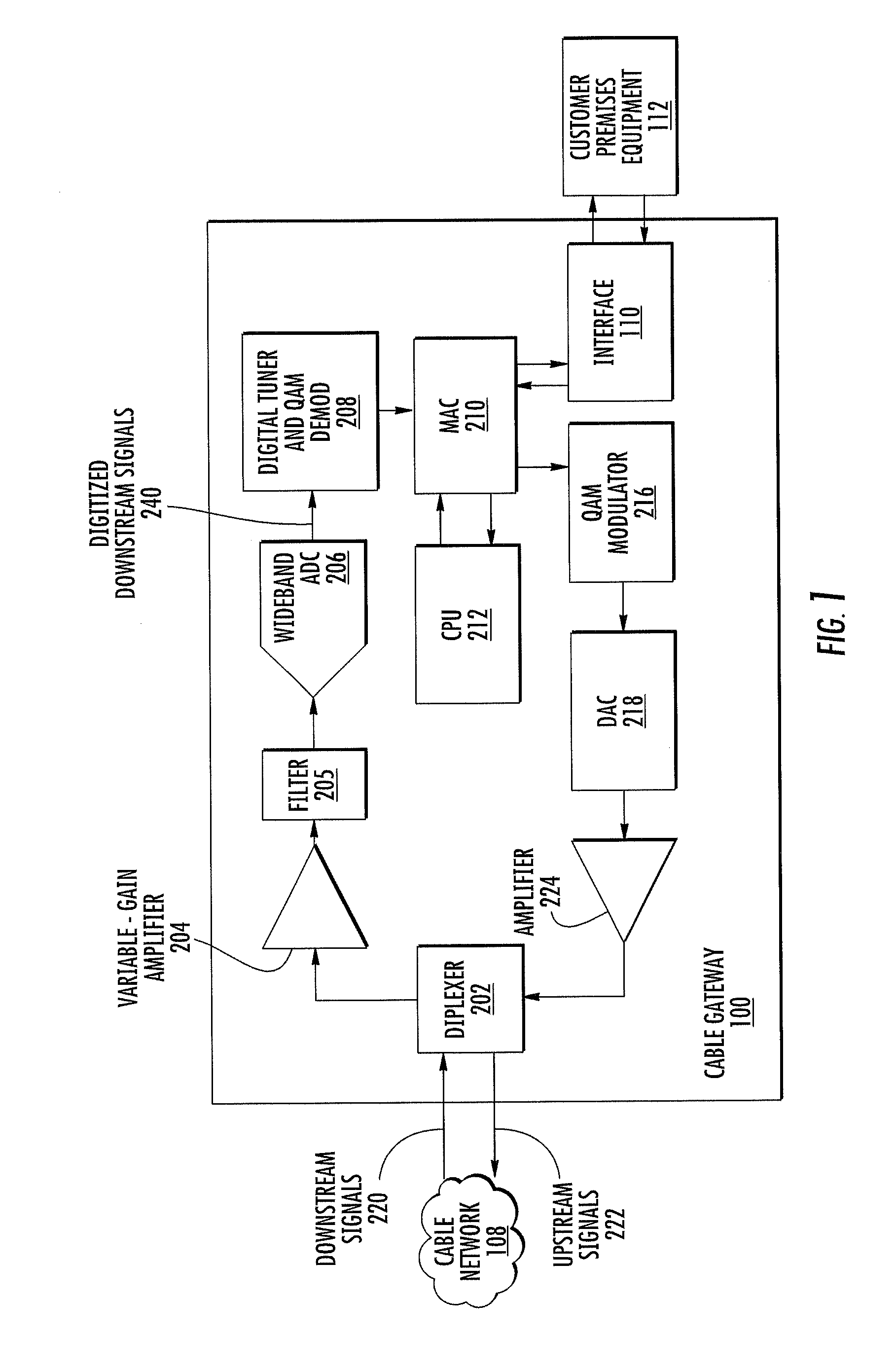
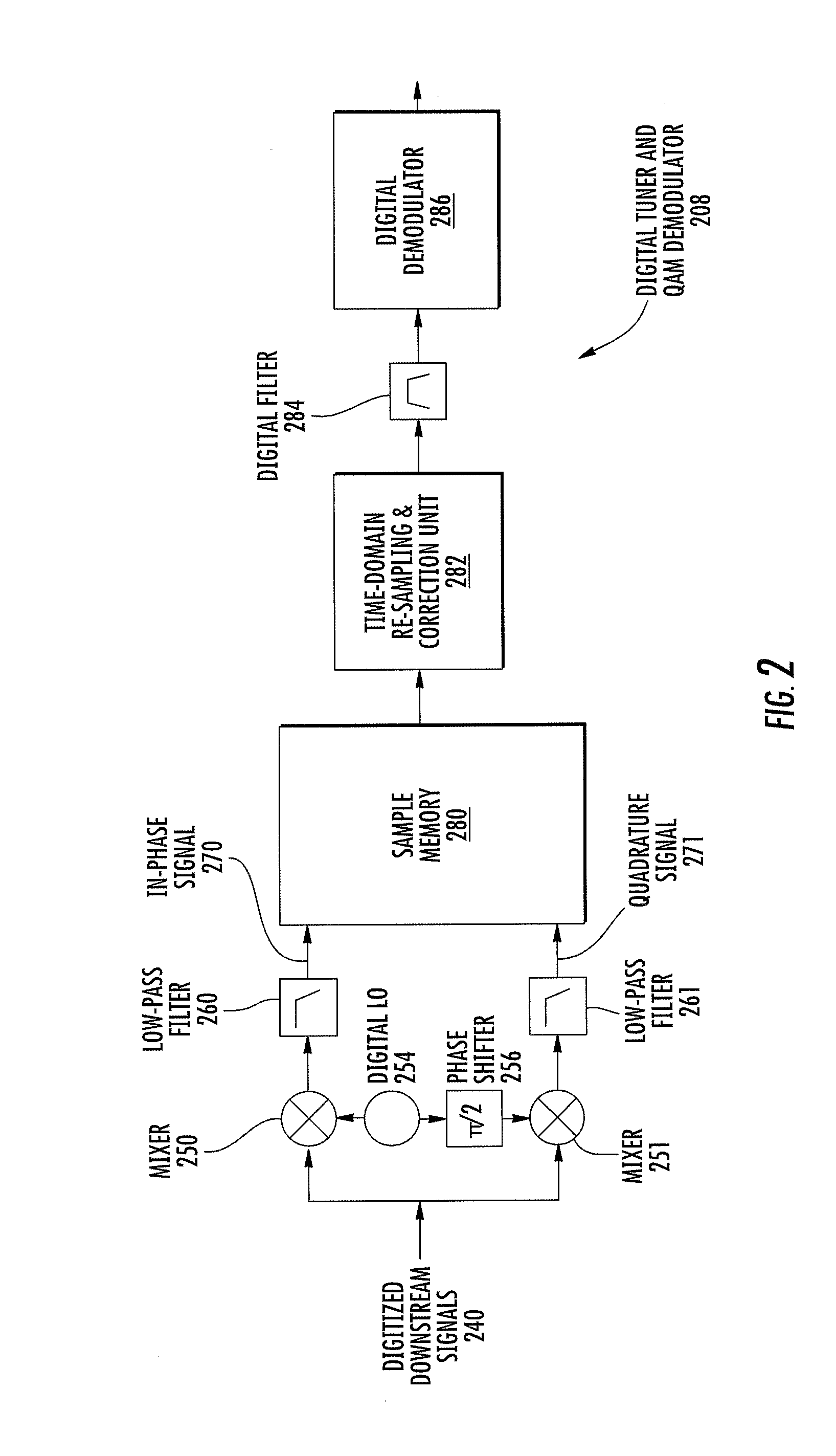
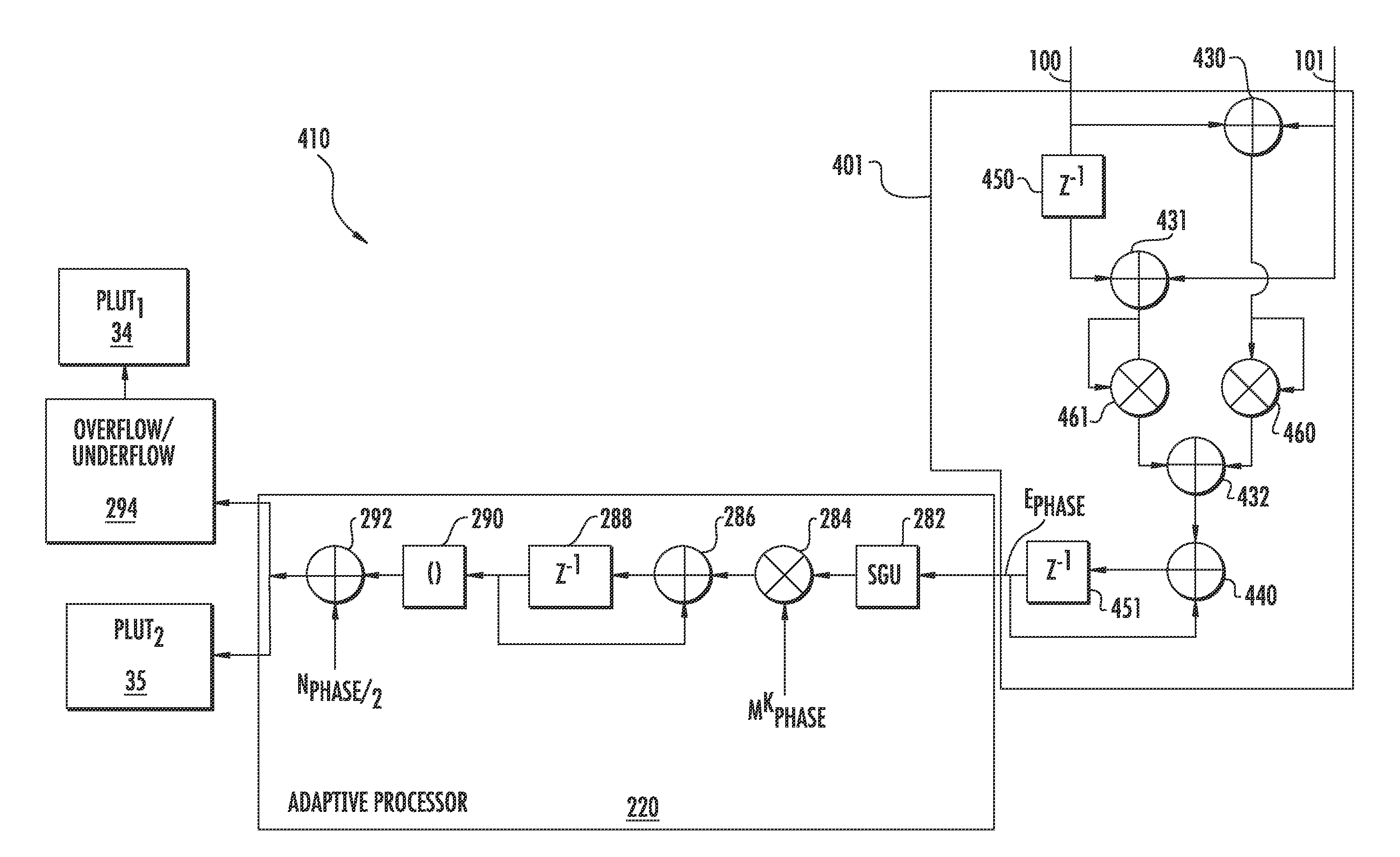
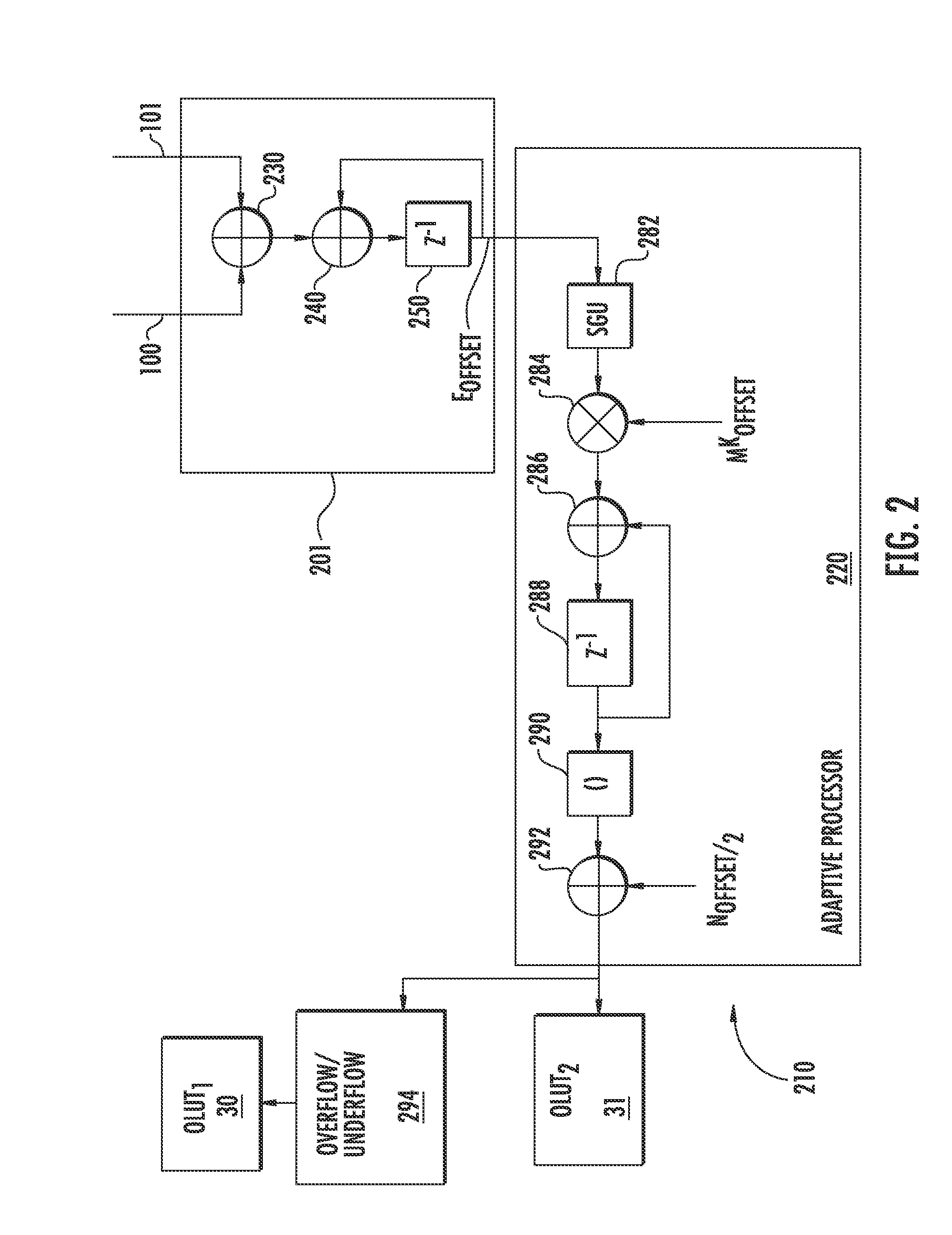
Error estimation and correction in a two-channel time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter
ActiveUS20100164763A1Minimize the differenceMultiple-port networksElectric signal transmission systemsTime errorDigital down converter
A two-channel time-interleaved analog-to-digital converter (TIADC) system that provides for estimation and correction of offset, gain, and sample-time errors. Error in the offsets of the two ADCs that form the TIADC produces a spurious signal at the Nyquist frequency that can be used to minimize the difference of offsets of the ADCs. The difference in gain between the two ADCs produces spurious signals reflected around the Nyquist frequency whose magnitudes can be reduced by minimizing the difference in signal power between the two ADCs. An Automatic Gain Control loop corrects the scaling of the input signal due to the average of the gains of the ADCs. Phase error produces spurious signals reflected around the Nyquist frequency that are π / 2 out of phase with those due to the gain error. Minimizing the difference between the correlation of consecutive signals from the ADCs reduces the magnitude of these image tones.
Owner:INTERSIL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com