Patents
Literature
851 results about "Turn off time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
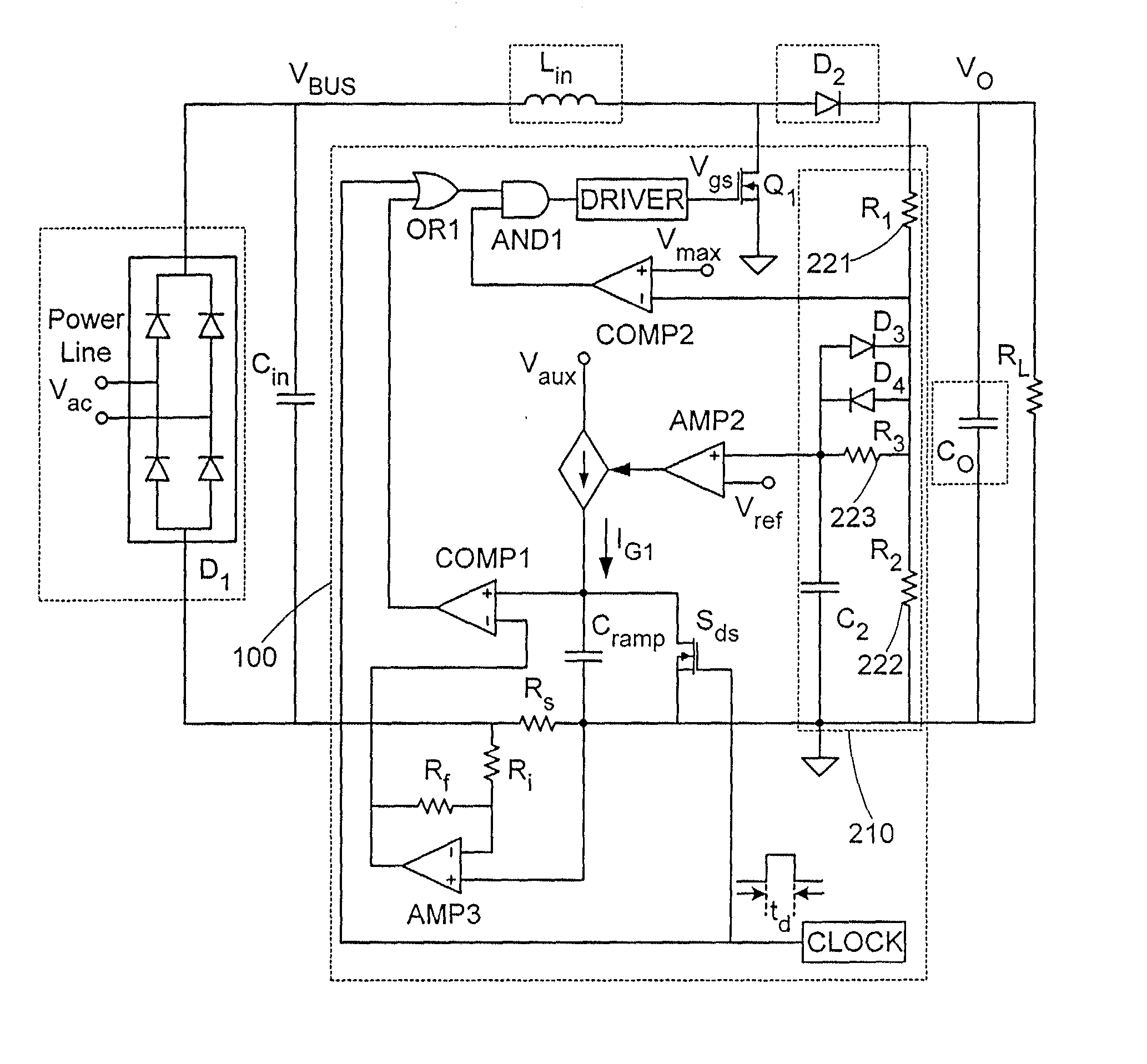
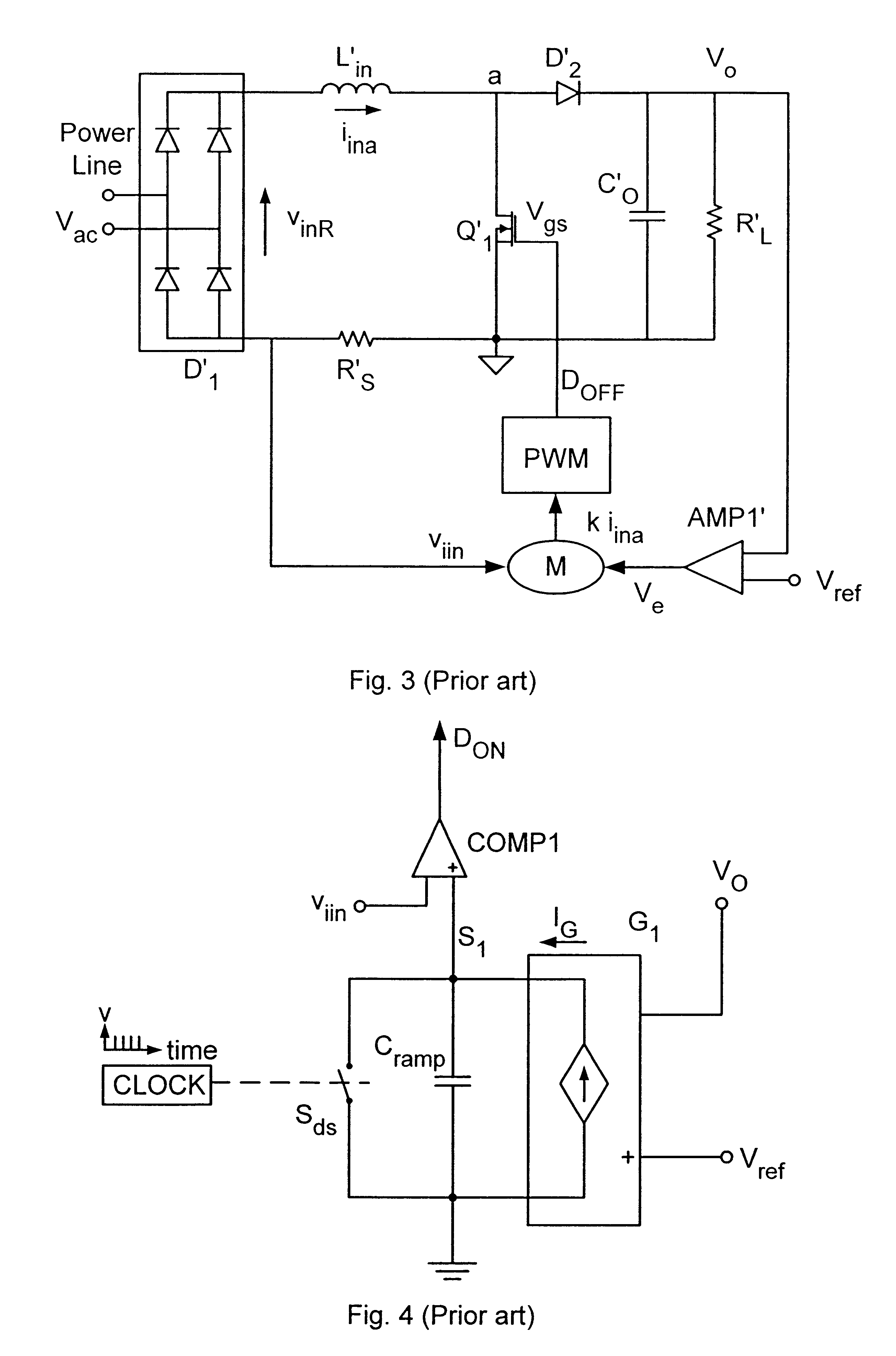
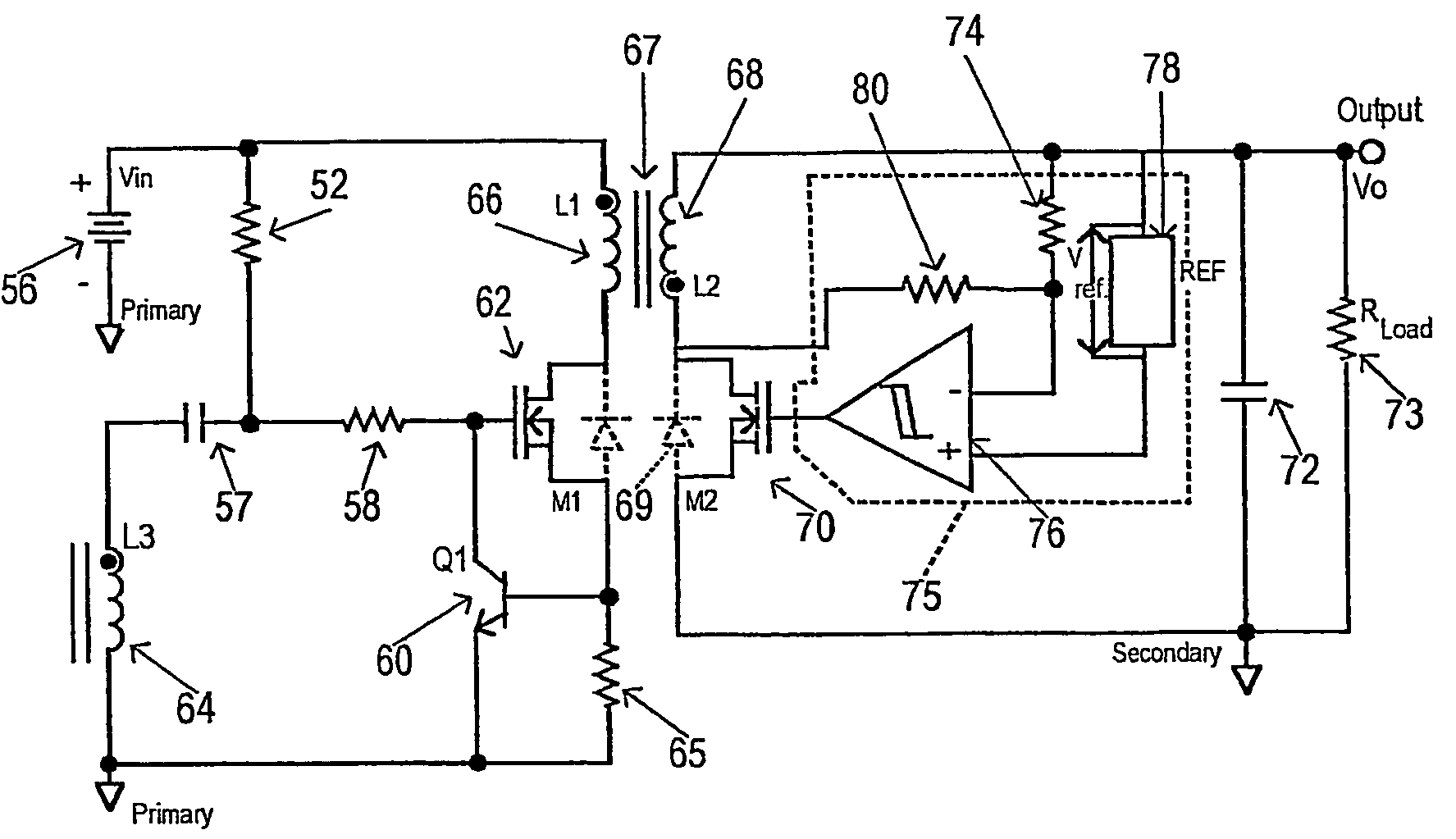
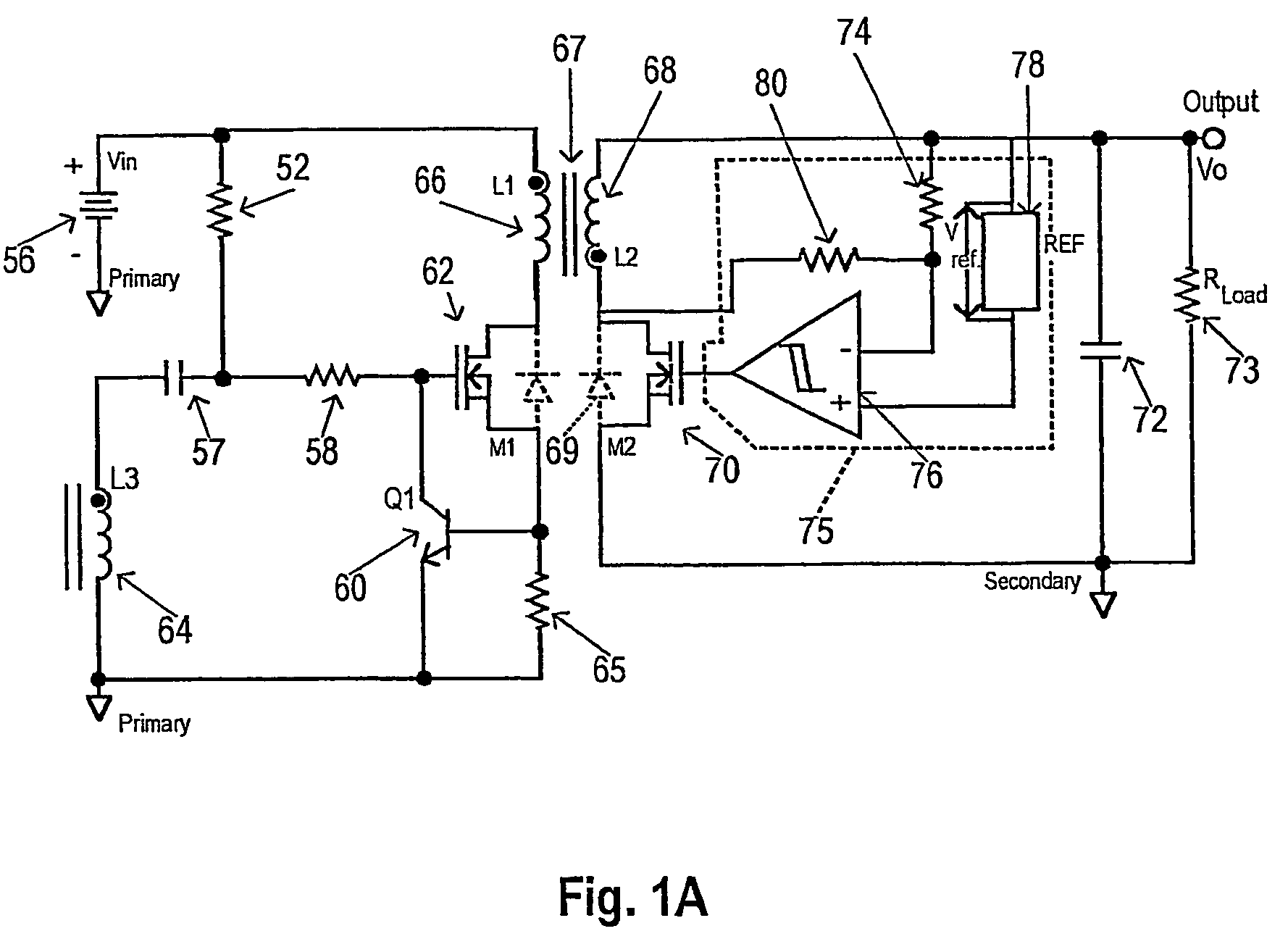
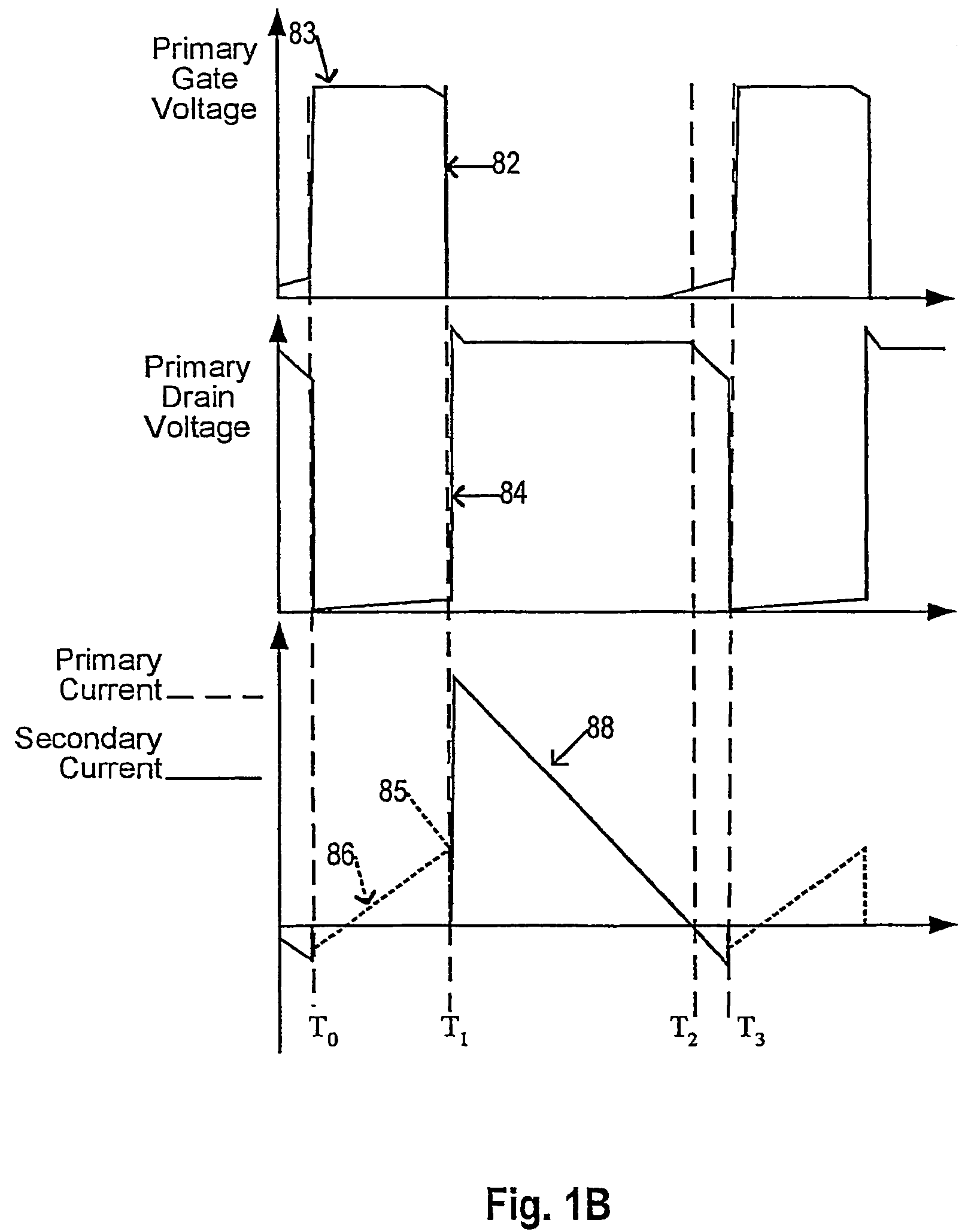
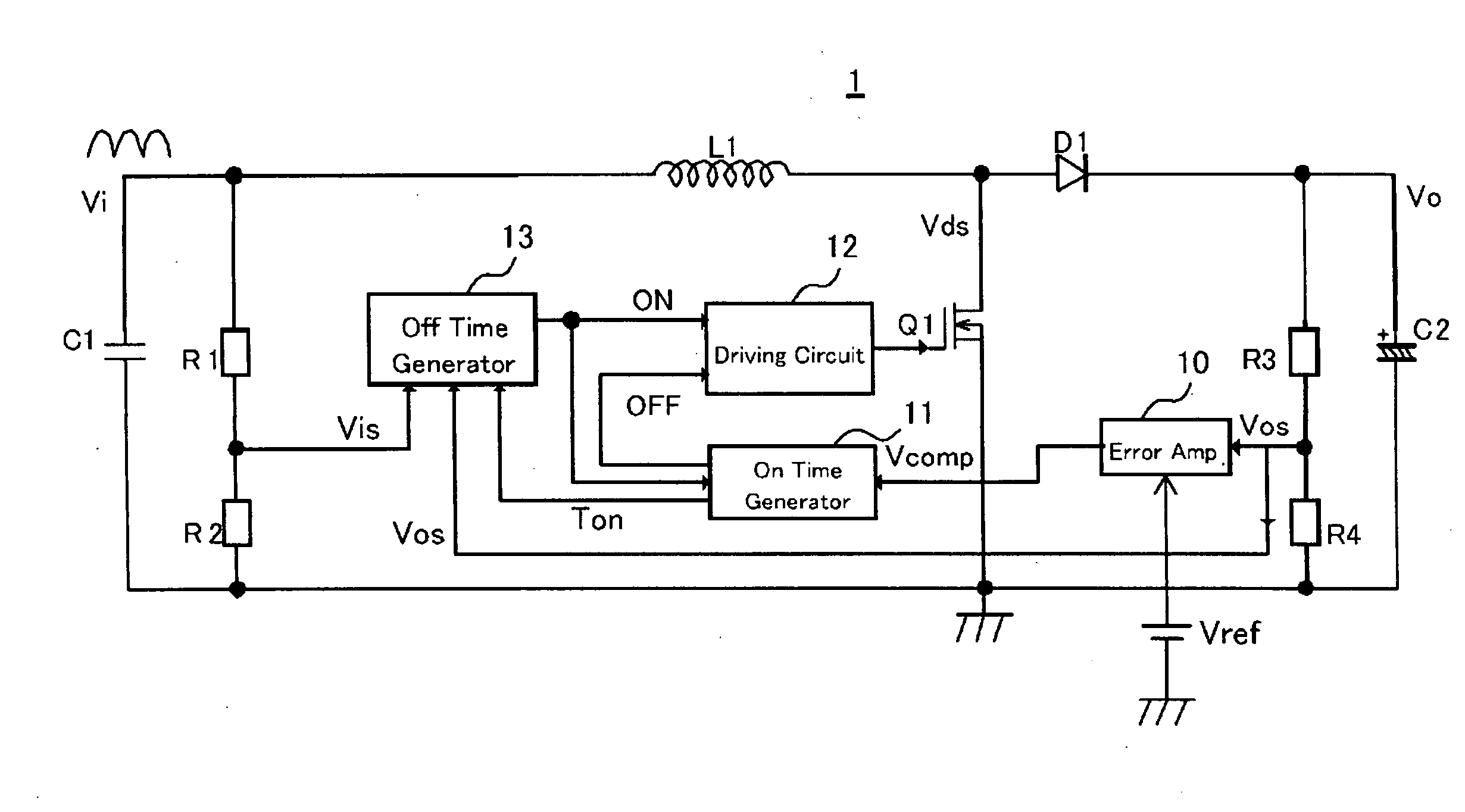
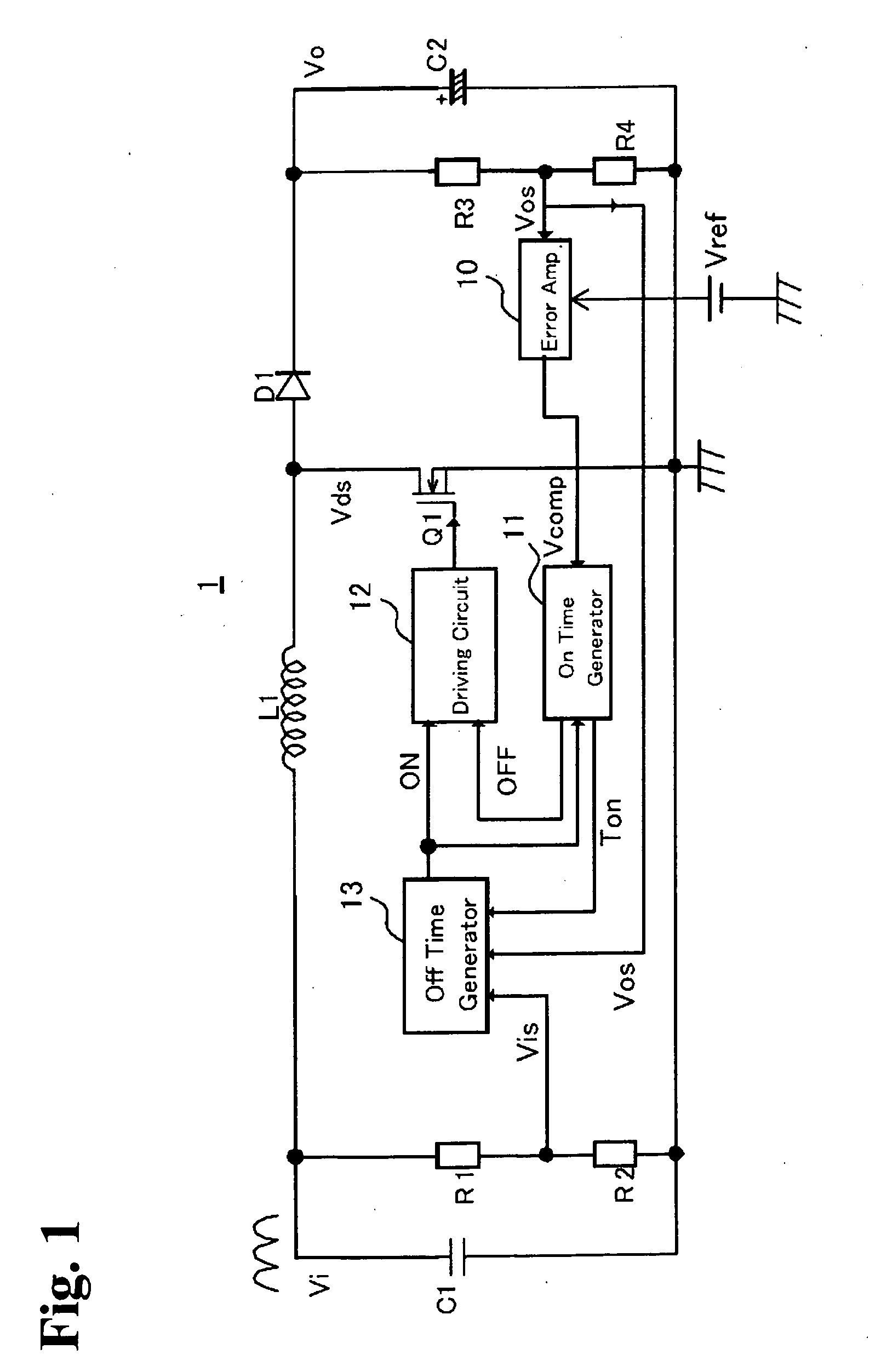
Method and apparatus for active power factor correction with minimum input current distortion
InactiveUS20030223255A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionActive power factor correctionHarmonics
A method for reducing the harmonics contents of an input current drawn from a power line into an electrical system without sensing an input voltage, the method comprising providing an active power factor correction controller with a switch module having a main switch and a timing device, wherein the main switch has an on-time correlated with an on-duty cycle duration, and an off-time correlated with an off-duty cycle duration, and maintaining a linear relationship between the off-duty cycle duration and the input current by using the timing device; and an apparatus for active power factor correction with minimum input current distortion, comprising an active power factor correction assembly that includes a main switch and a timing device, wherein the main switch has associated therewith an on-time correlated with an on-duty cycle duration, and an off-time correlated with an off-duty cycle duration, and wherein the timing device generates the mentioned on-time and off-time, and linearization means for maintaining a linear relation between the off-duty cycle duration and the input current.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
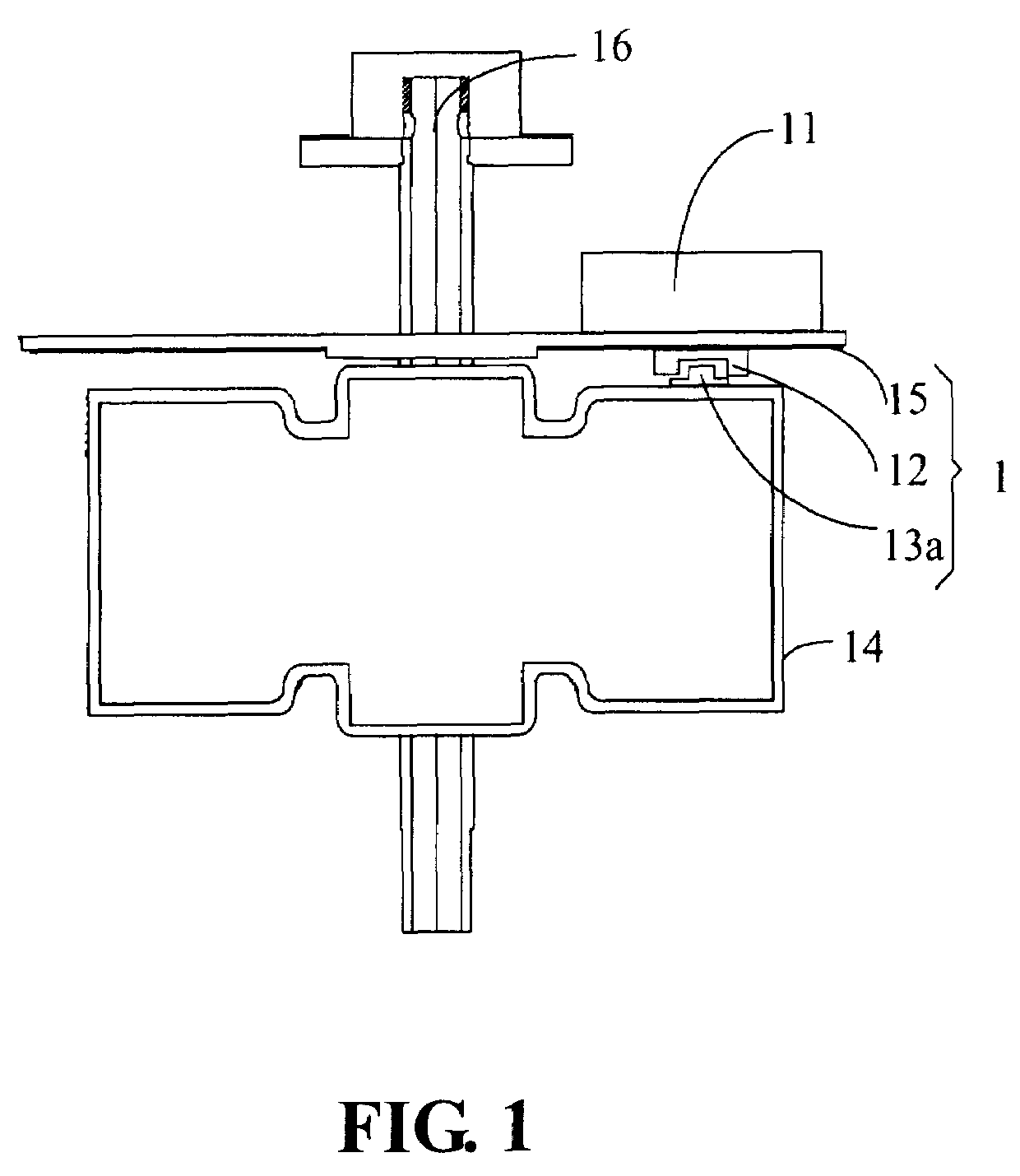
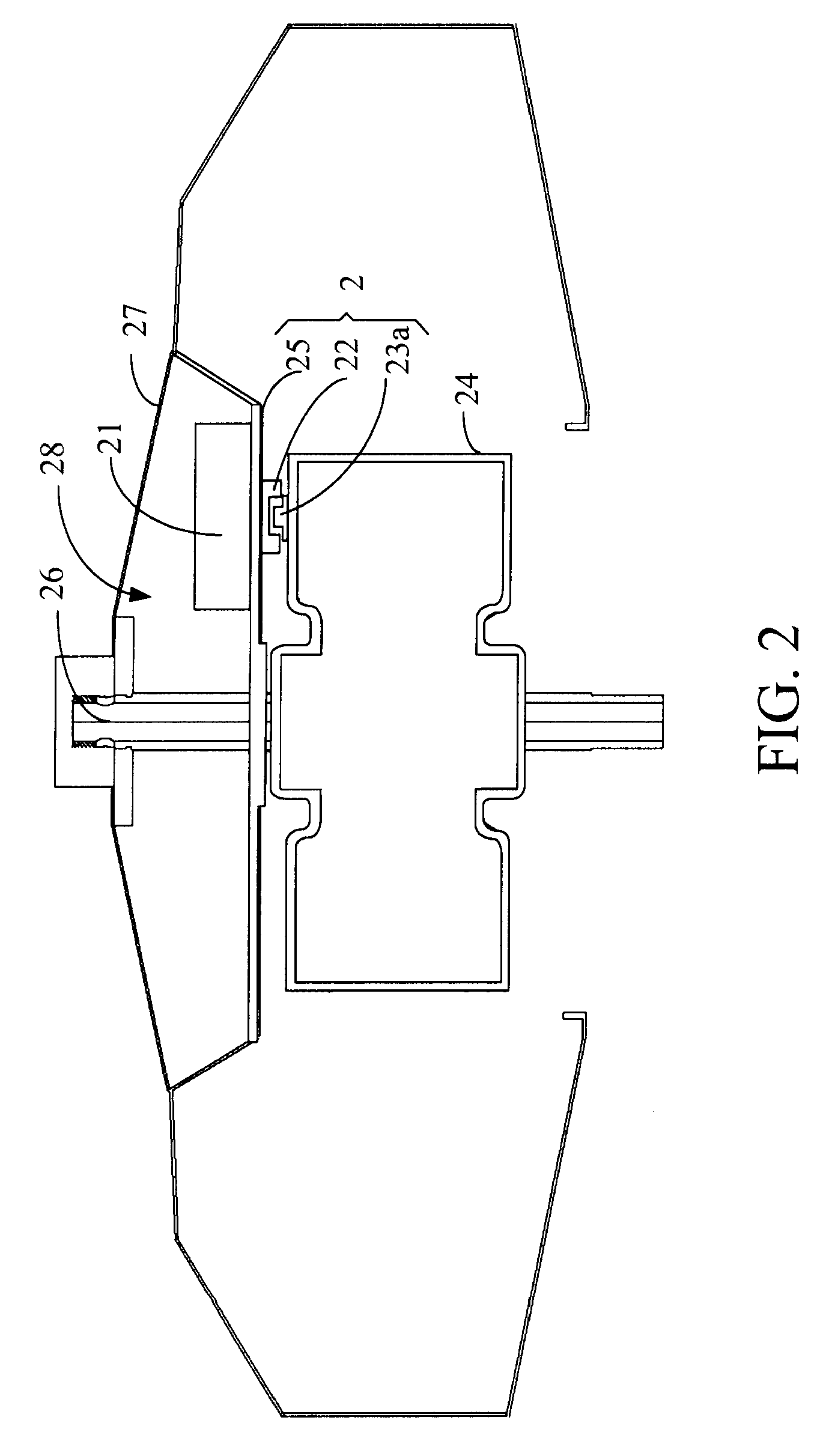
Driving apparatus for a ceiling fan
InactiveUS7664377B2Reduce the amount presentReduce in quantityPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesElectric testing/monitoringBrushless motorsCeiling fan
A driving apparatus for a DC brushless motor of a ceiling fan is provided. By setting at least one coder and one sensor outside the DC brushless motor, the driving apparatus can sense the position of magnetic poles of the motor for driving the motor. Meanwhile, a controller set with the motor stores the rotation speed of the motor before being turned off by detecting the turn-off time of a turn-on / off signal.
Owner:RHINE ELECTRONICS
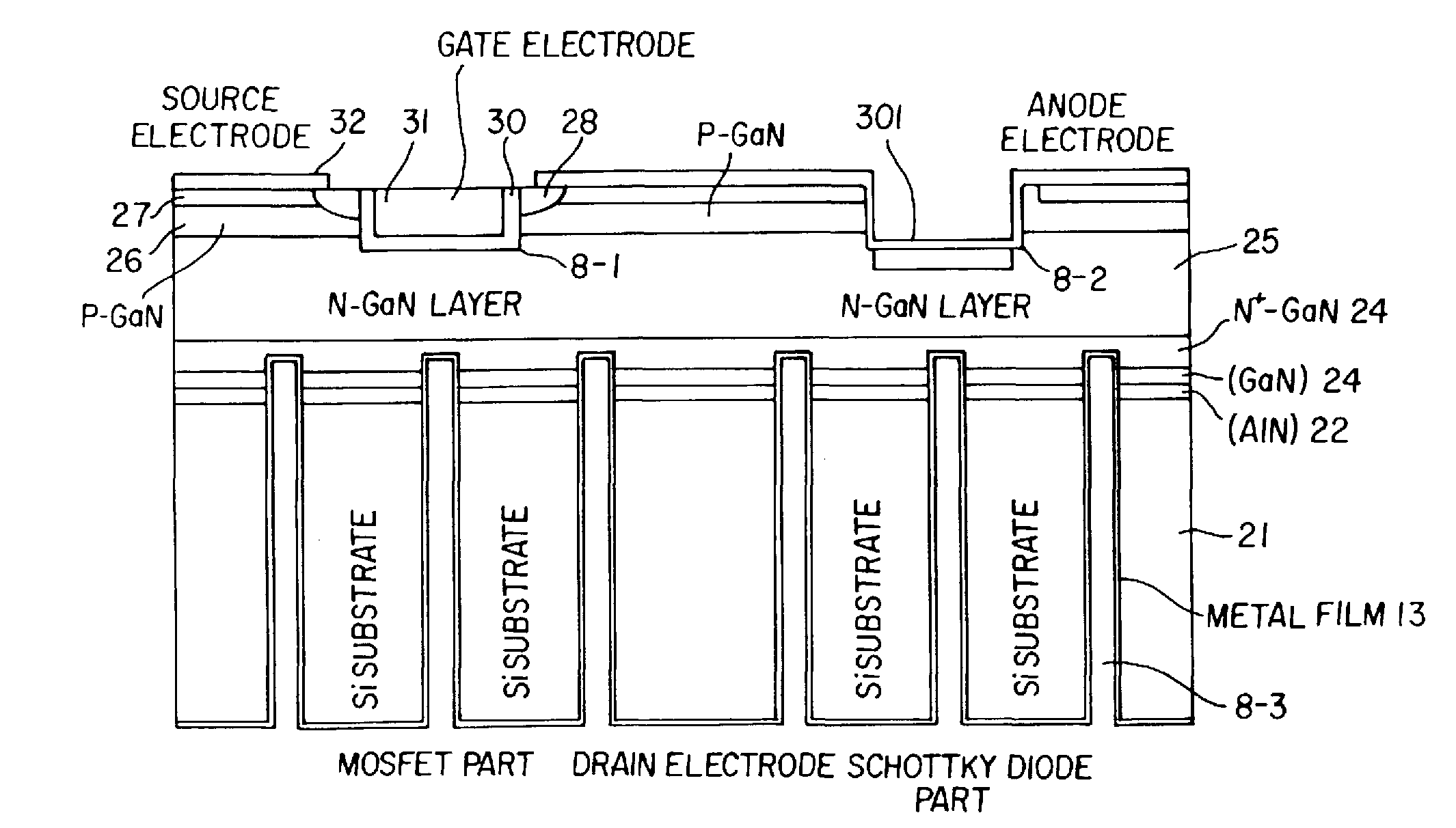
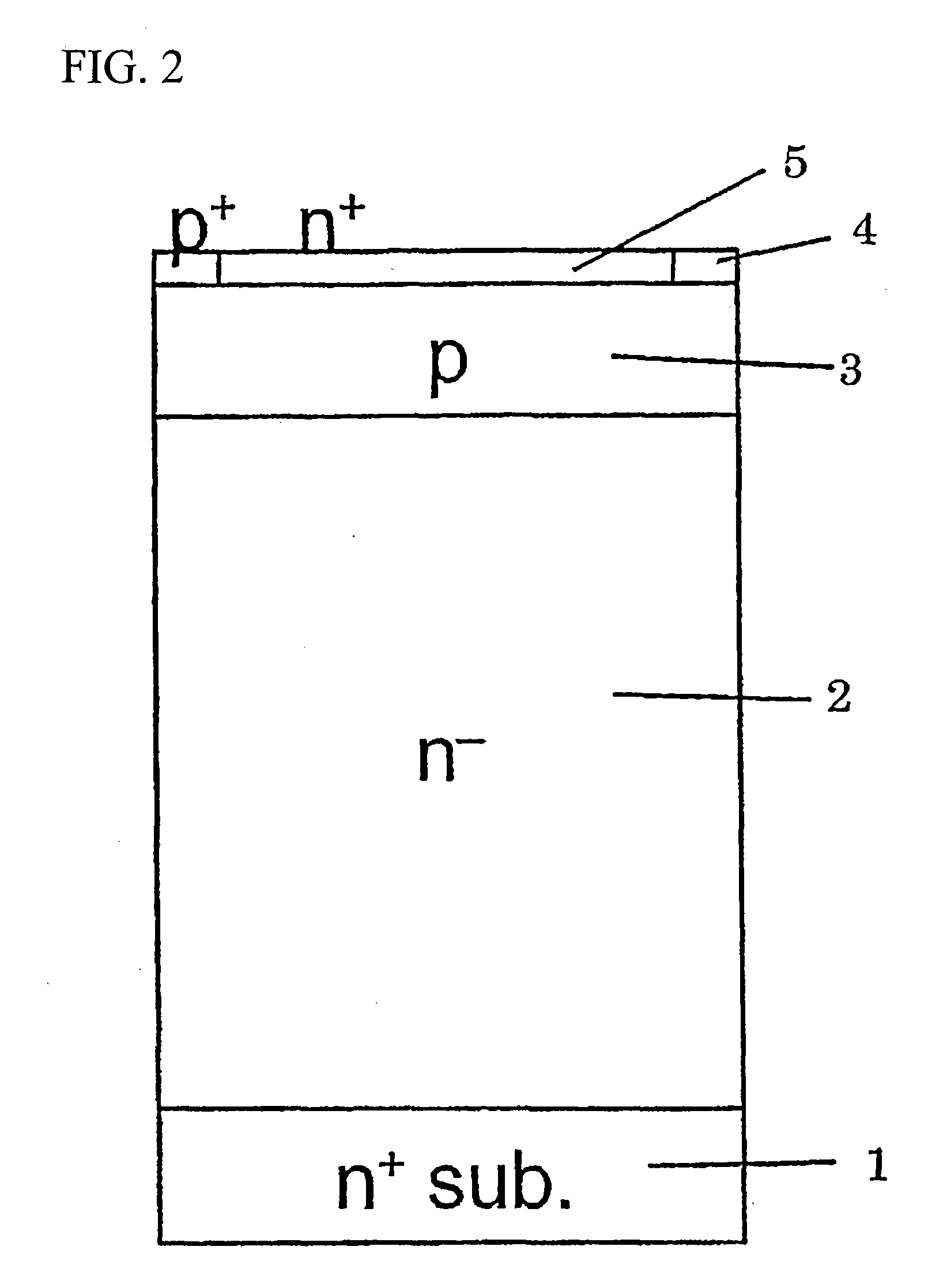
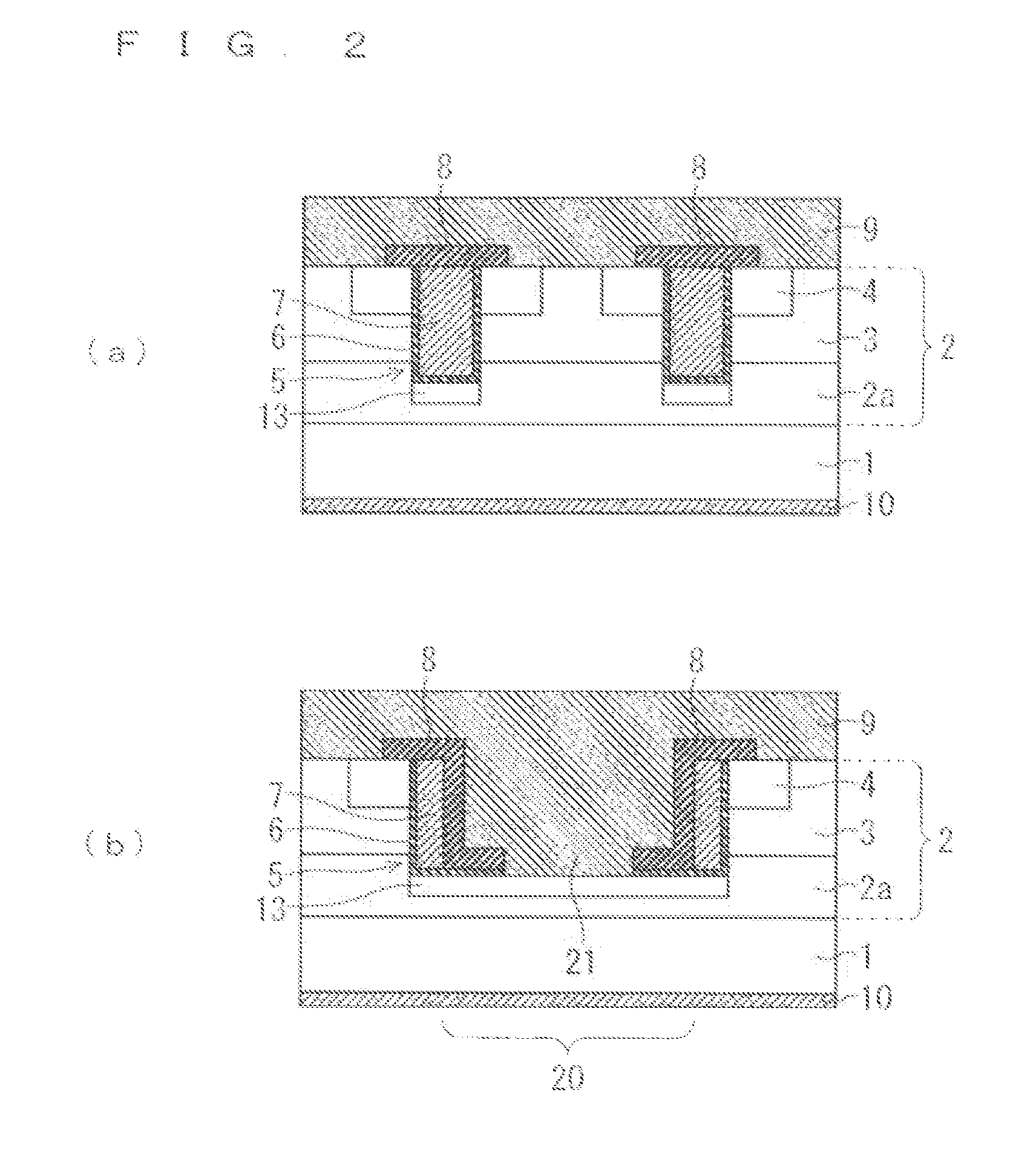
Wide band gap semiconductor device and method for producing the same
ActiveUS20090283776A1Lower on-resistanceShort reverse recovery timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiodeBroadbandWide band
A wide band gap semiconductor device is disclosed. A first trench in a gate electrode part and a second trench in a source electrode part (Schottky diode part) are disposed so that the first and second trenches are close to each other while and the second trench is deeper than the first trench. A metal electrode is formed in the second trench to form a Schottky junction on a surface of an n-type drift layer in the bottom of the second trench. Further, a p+-type region is provided in part of the built-in Schottky diode part being in contact with the surface of the n-type drift layer, preferably in the bottom of the second trench. The result is a wide band gap semiconductor device which is small in size and low in on-resistance and loss, and in which electric field concentration applied on a gate insulating film is relaxed to suppress lowering of withstand voltage to thereby increase avalanche breakdown tolerance at turning-off time.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
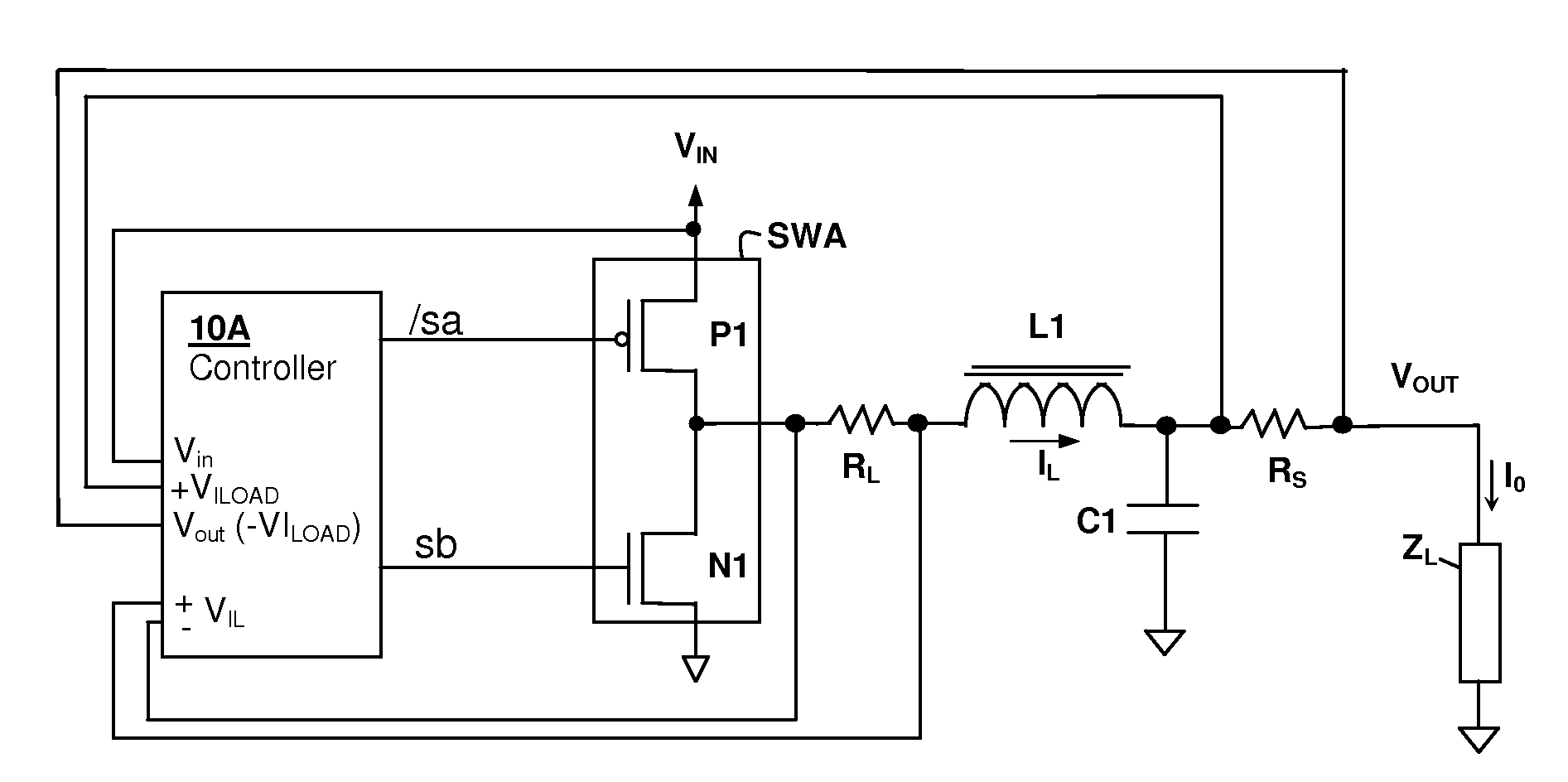
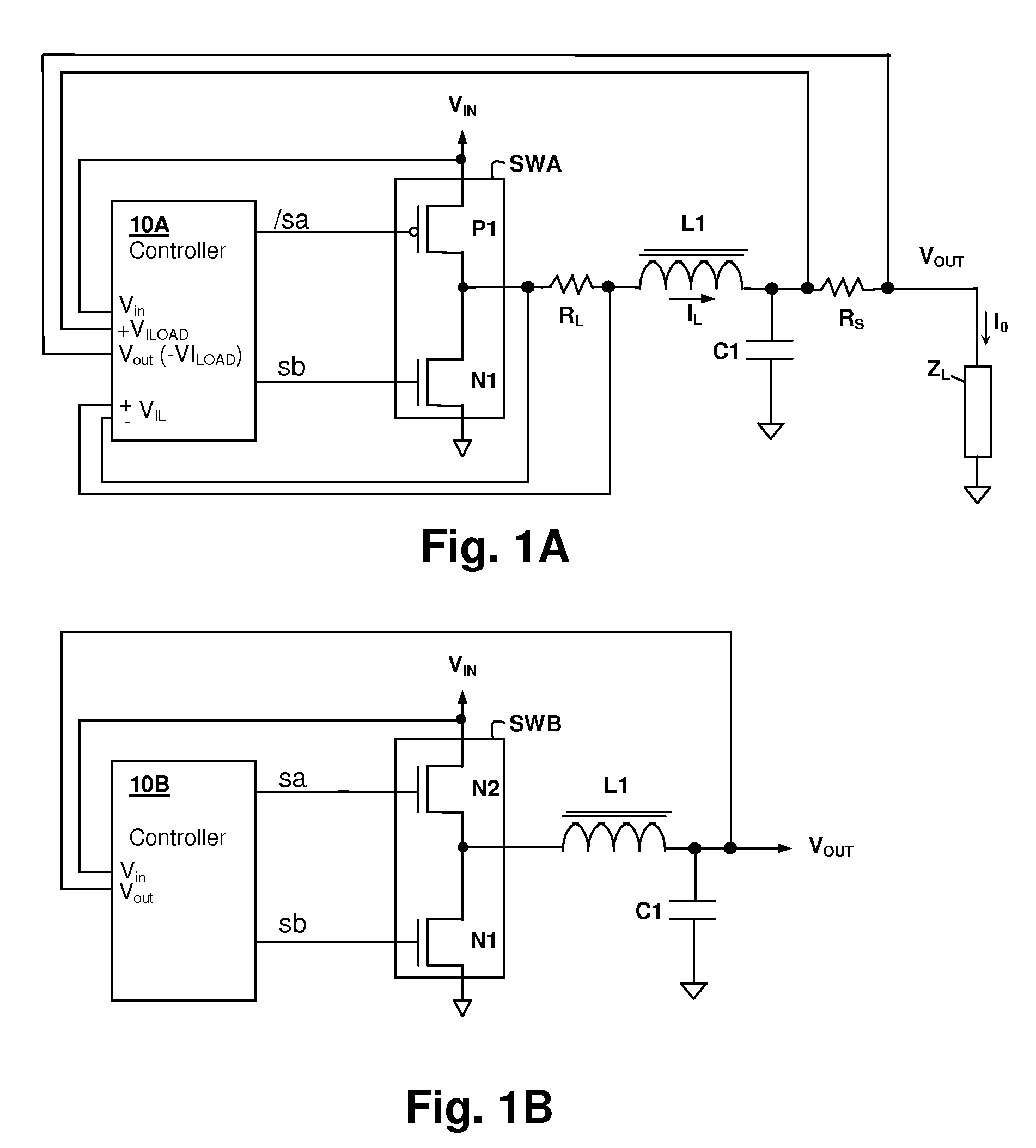
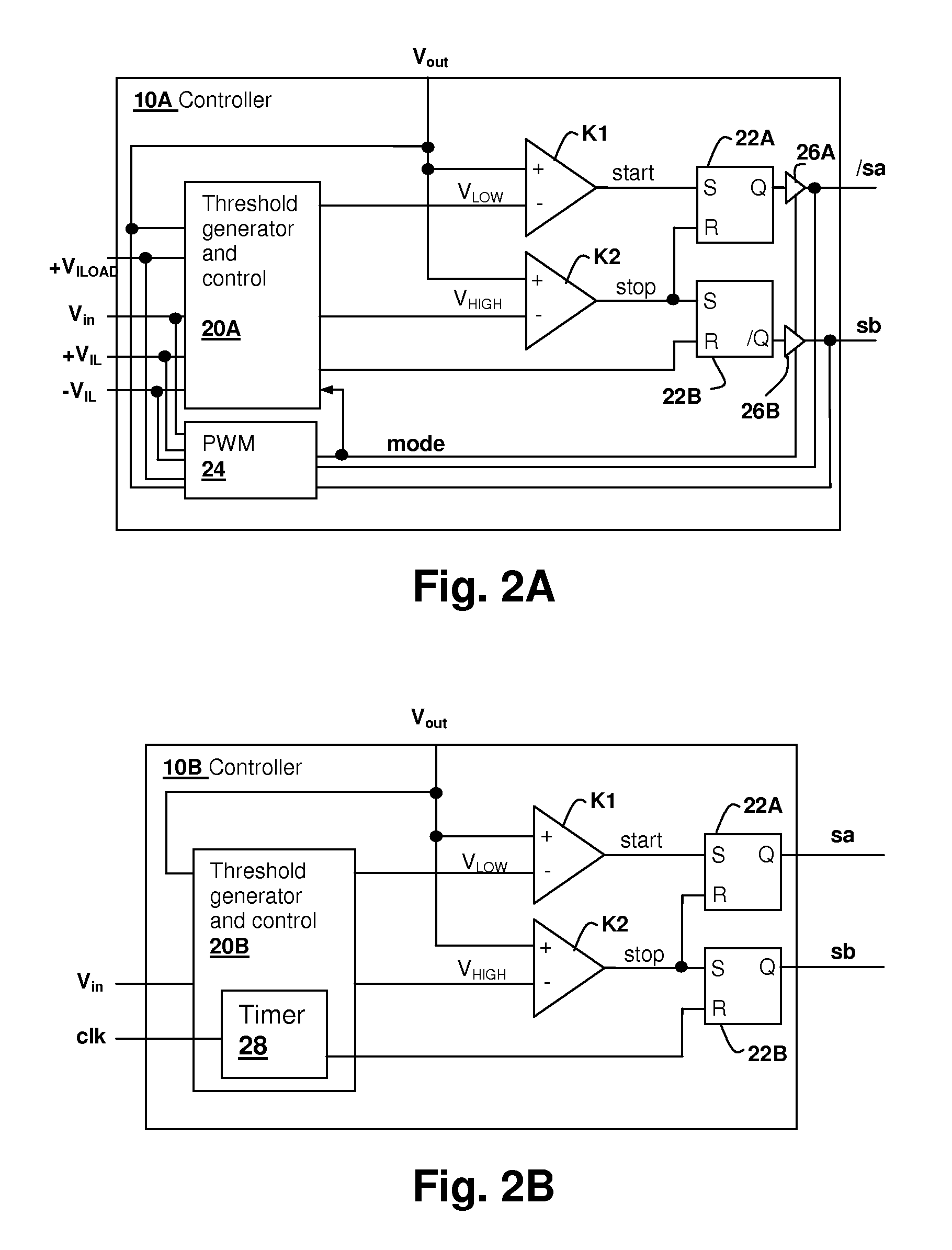
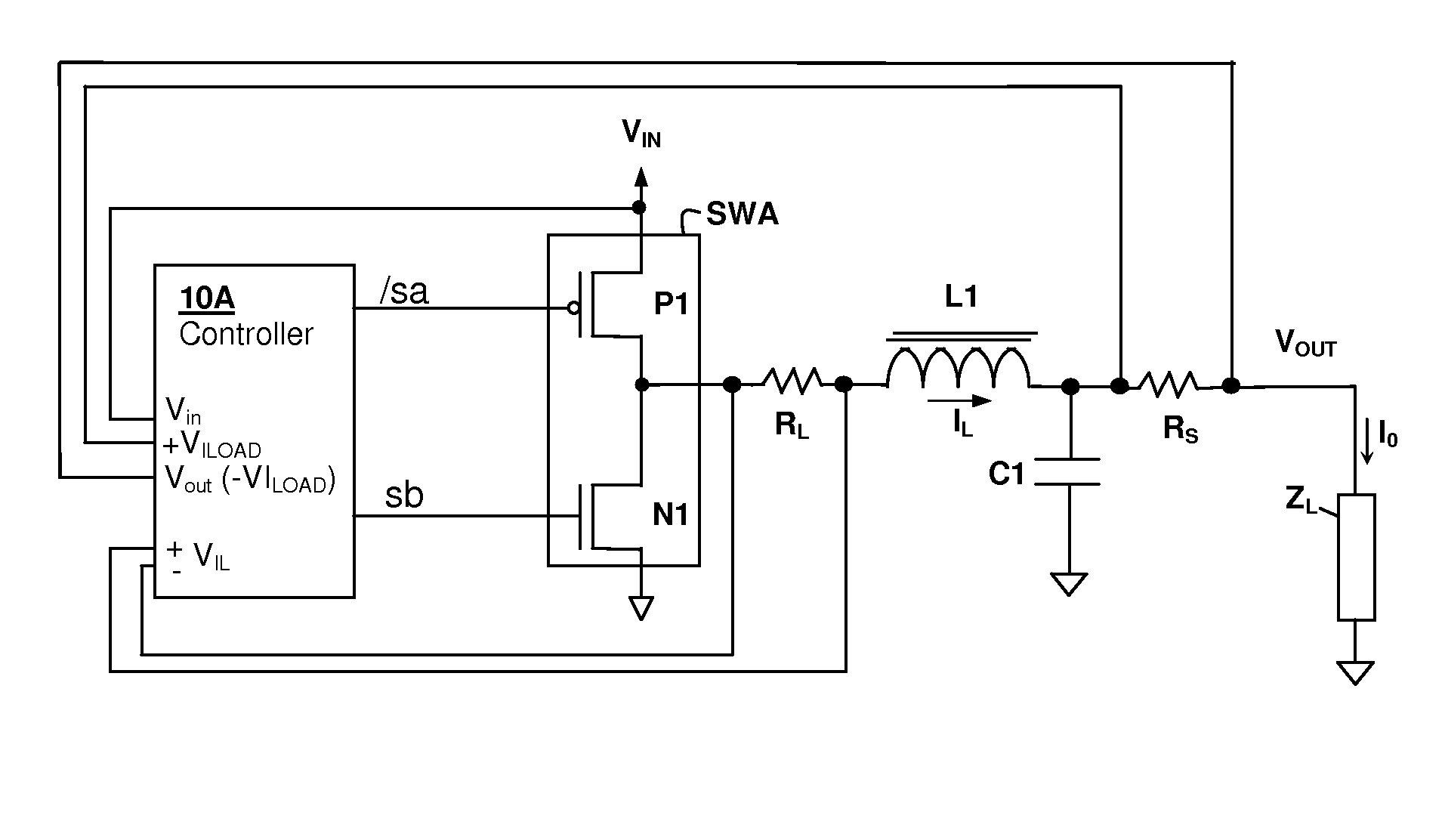
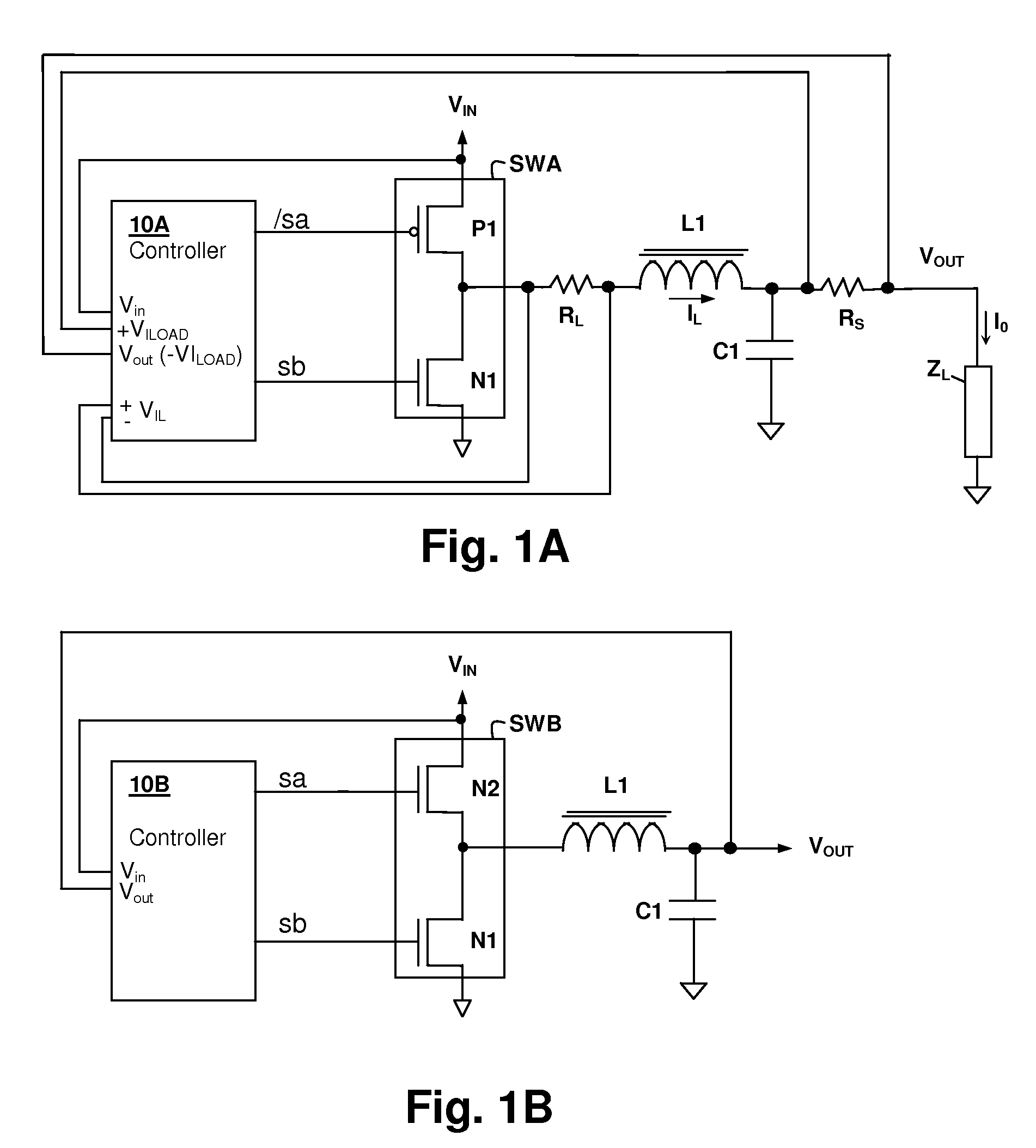
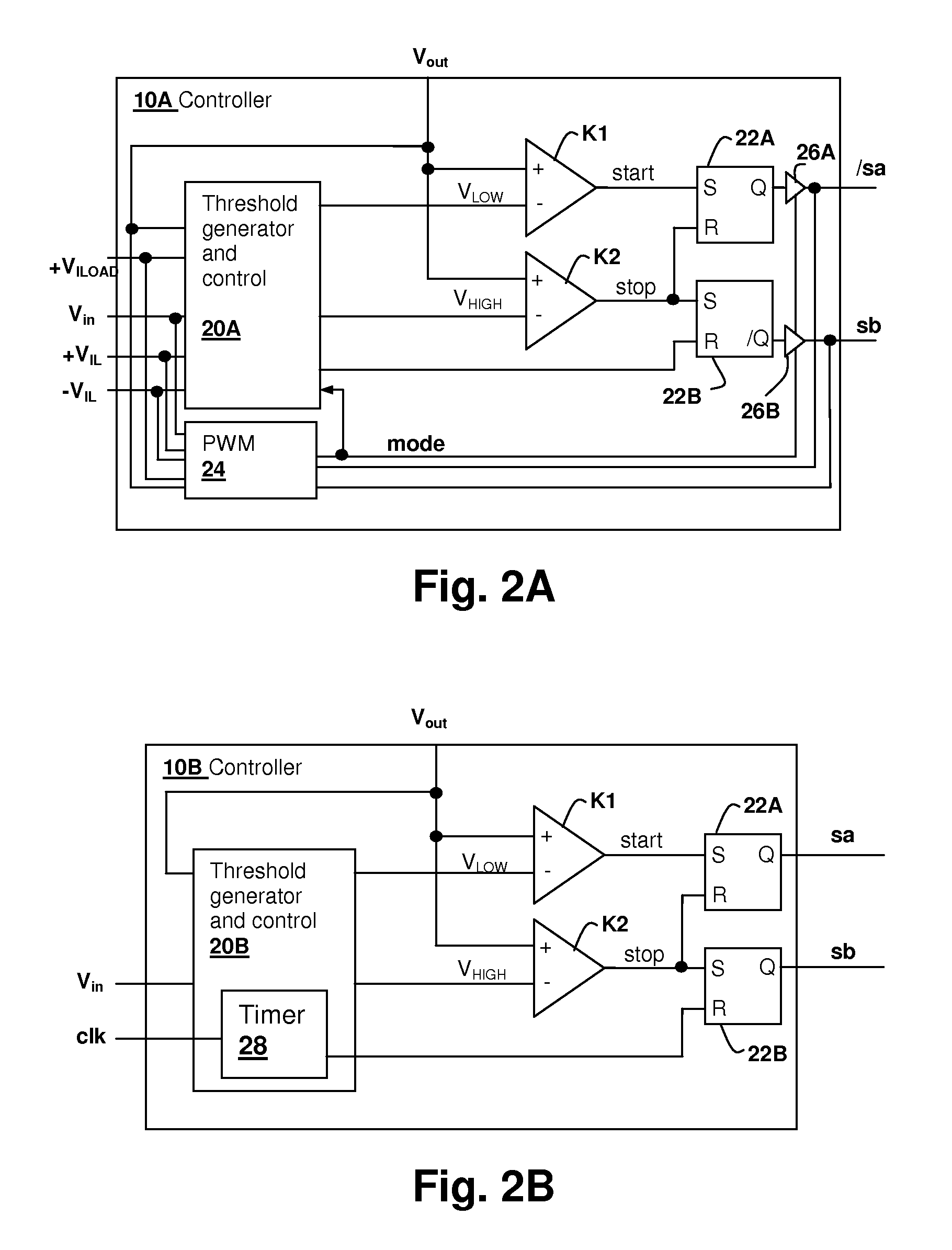
Hysteretic buck converter having dynamic thresholds
ActiveUS20090322300A1Improved ripple controlEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsBuck converterĆuk converter
A hysteretic buck converter provides improved regulation control, in particular for buck converter standby operation. A comparison circuit compares the output voltage of the buck converter to a waveform that is generated from an indication of the output current of the converter, so that the turn-on time of the converter is advanced as the output current demand increases. The resulting action anticipates a reduction in output voltage due to the increased current, preventing an excursion of the output voltage below the ripple voltage minimum. The turn-off time of the converter is controlled by an upper threshold that limits the ripple voltage maximum. The output current indication may be a measurement of output current, or may be a dynamic value calculated from the input voltage and the output voltage waveform.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
PFM and current controlled switching regulator
ActiveUS20070210772A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLinear controlControl signal
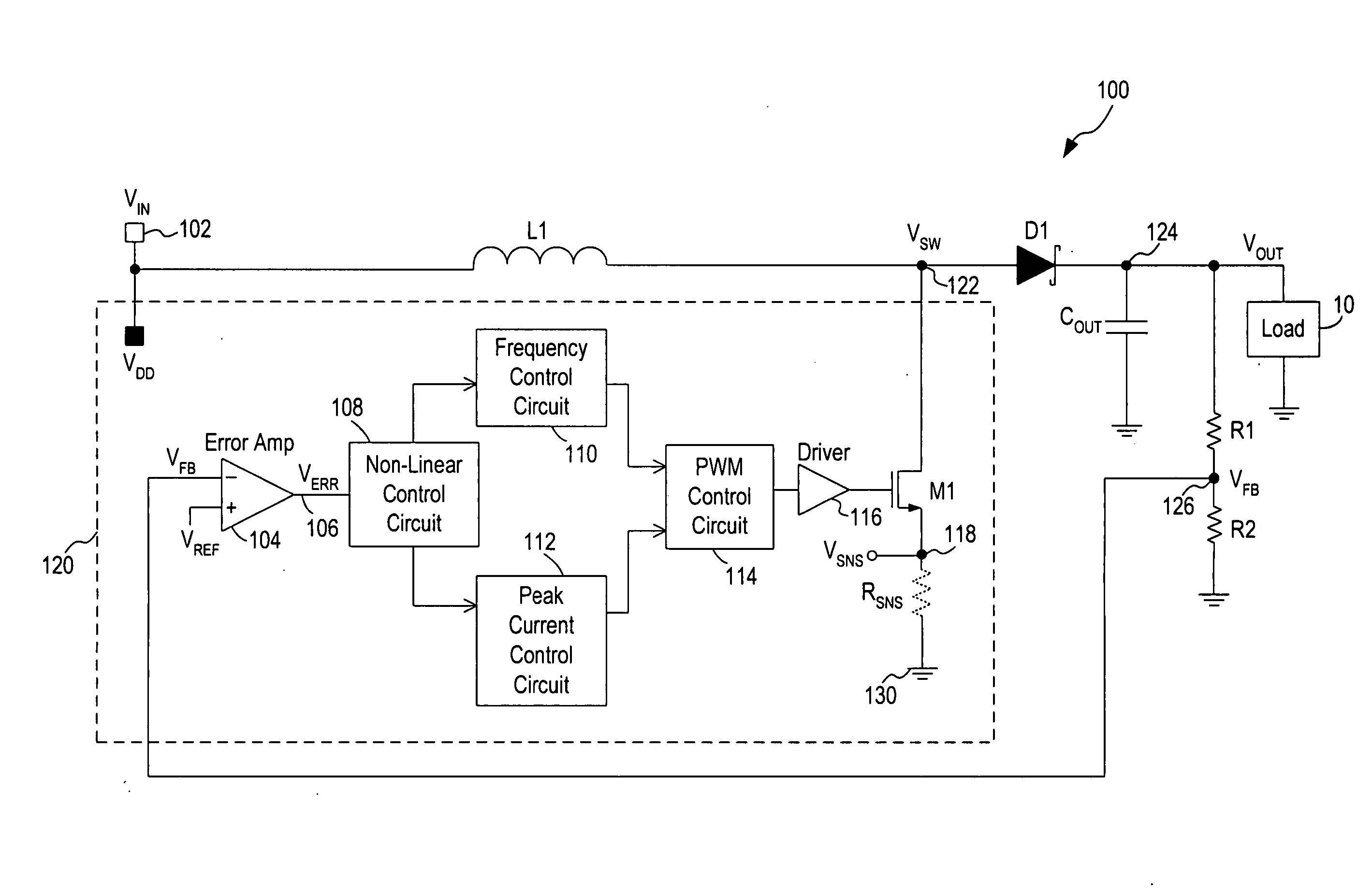
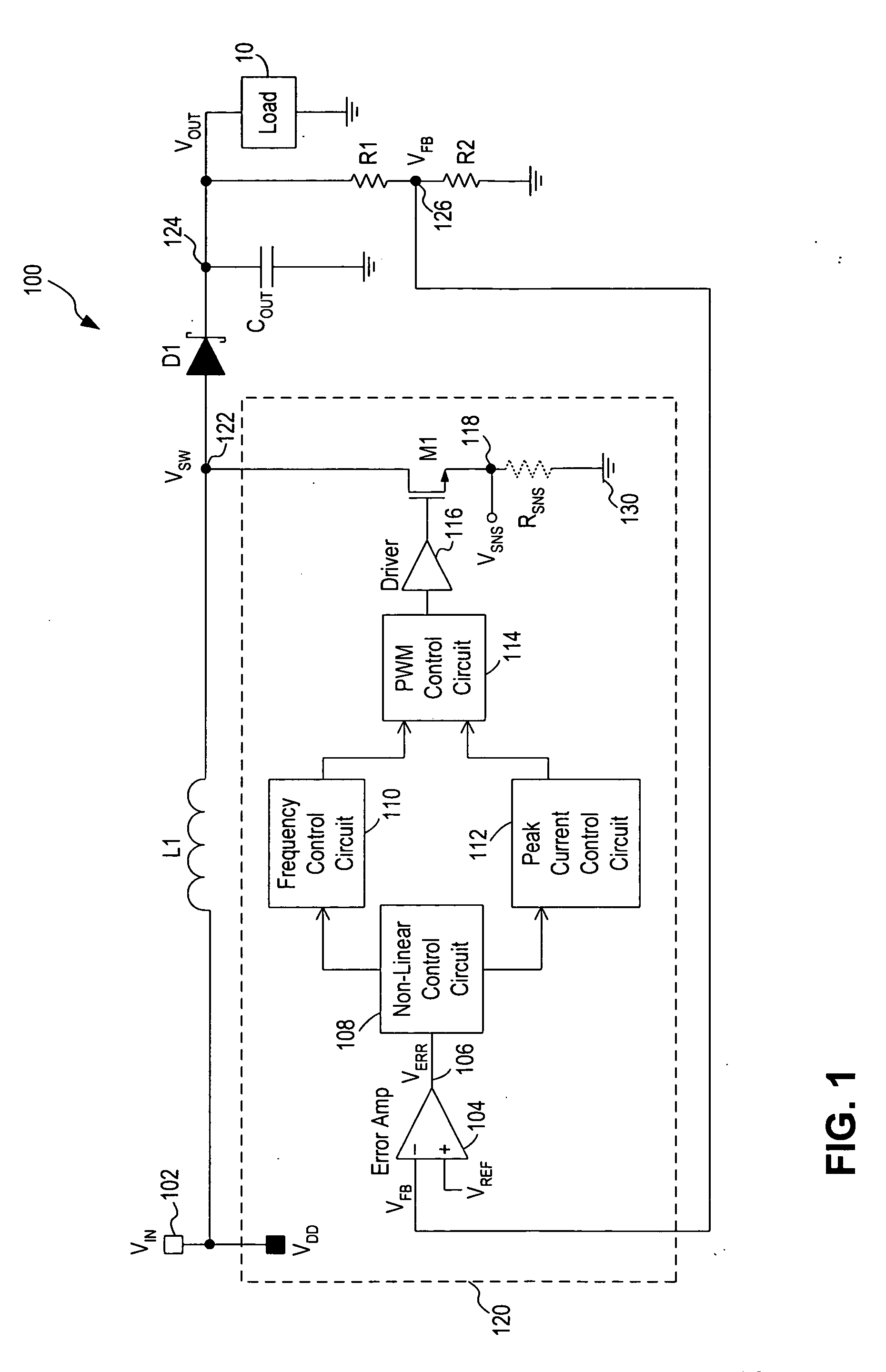
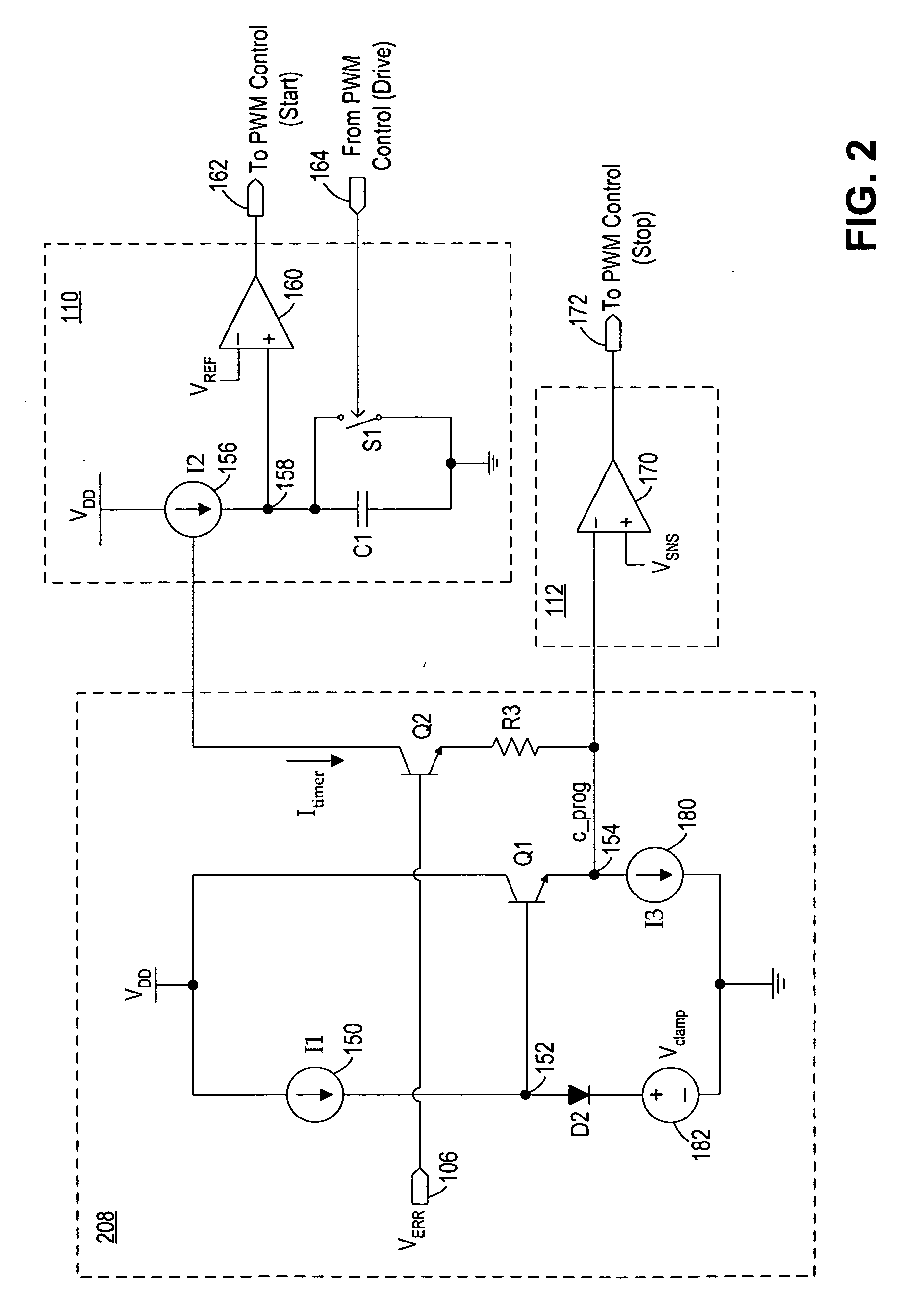
A circuit and method for controlling a switching regulator utilize a combination of variable off-time control (or frequency control) and variable peak current control to achieve high efficiency at a wide range of load conditions. A non-linear control circuit receives an error voltage and generates a first control signal for controlling a frequency control circuit and a second control signal for controlling a peak current control circuit. The frequency control circuit and the peak current control circuit operate in conjunction over the entire range of load conditions with the frequency control dominates at light load (or low power) conditions and the variable peak current control dominates at moderate to heavy load (or high power) conditions. The switching regulator transitions smoothly between frequency control and peak current control with continous loop gain throughout the transition region.
Owner:MICREL
Control circuit for current and voltage control in a switching power supply
ActiveUS20070115696A1Reduce load dependenceReduce noiseDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationConductor CoilVoltage control
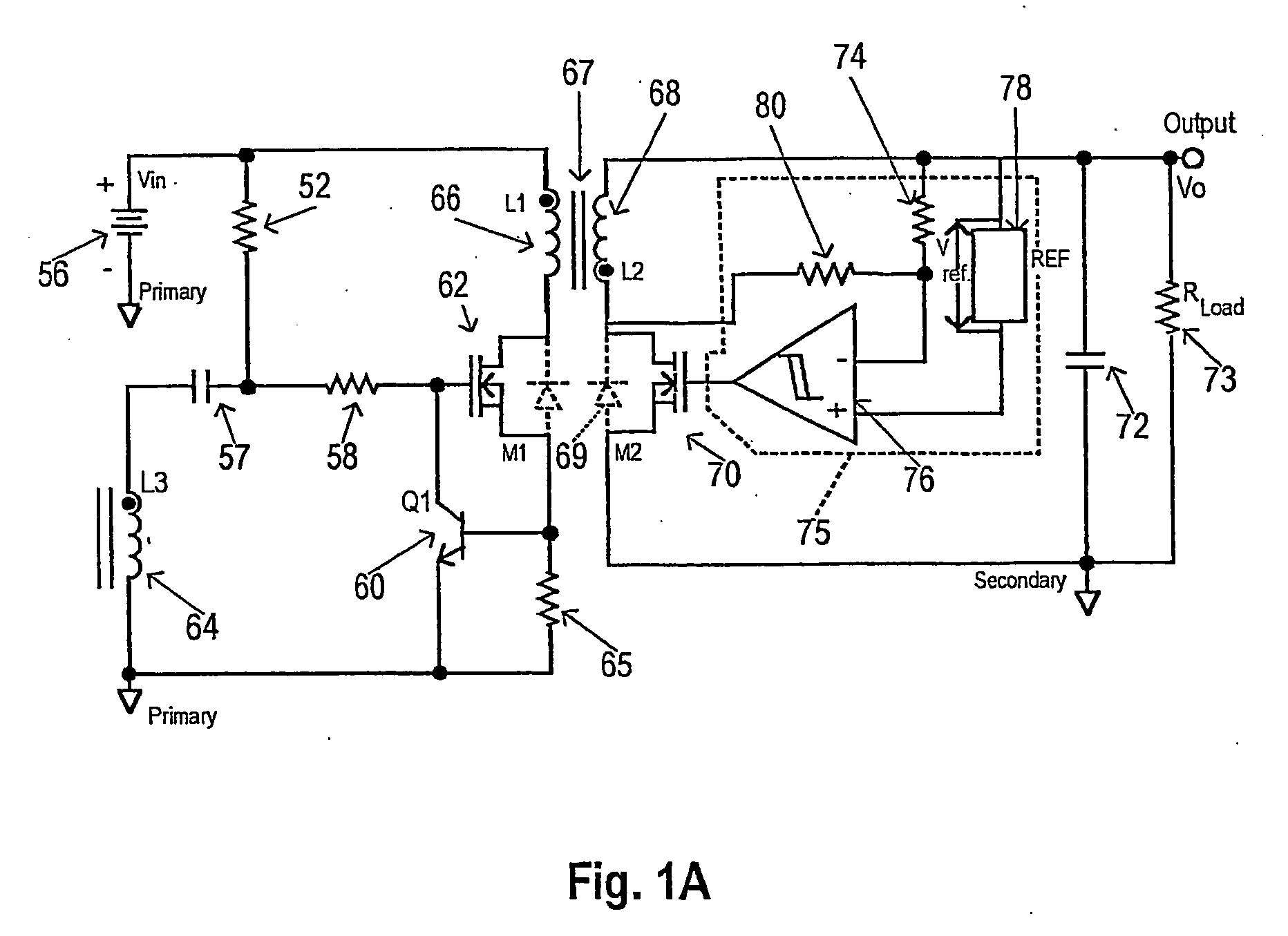
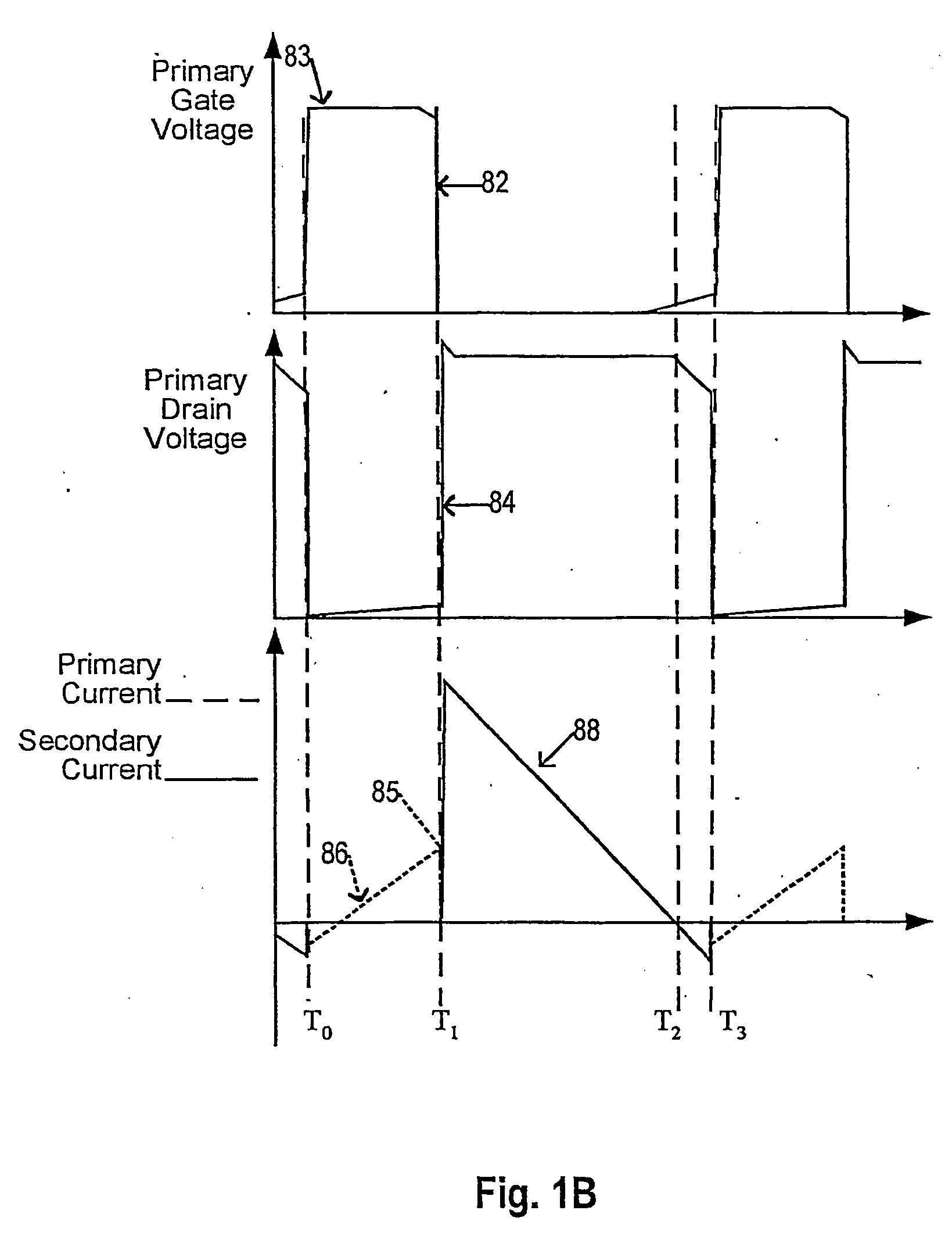
The present invention refers to a circuit for current and voltage control in a switching power supply controlled on the primary side, comprising a transformer with a primary-sided and a secondary-sided main winding, wherein energy pulses are transmitted from the primary side to the secondary side. Furthermore, a primary-sided switch switches on an off a primary current through the primary-sided main winding. A primary current comparator determines a switch-off time of the switch depending on the primary current. In order to reduce the load dependency of the output voltage, the control variable is variably amplified by a feedback network and additionally the control variable is reduced depending on the output load through a correction network. To reduce noise generated by the energy-rich pulse transmissions at low frequencies and the waviness of the output voltage, the control variable is fed back to the primary current comparator so that the duration during which the primary current flows through the primary-sided main winding is reduced differently. To reduce the susceptance to failure when determining the switch-on time, a comparator voltage depending on the control variable is generated as reference.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
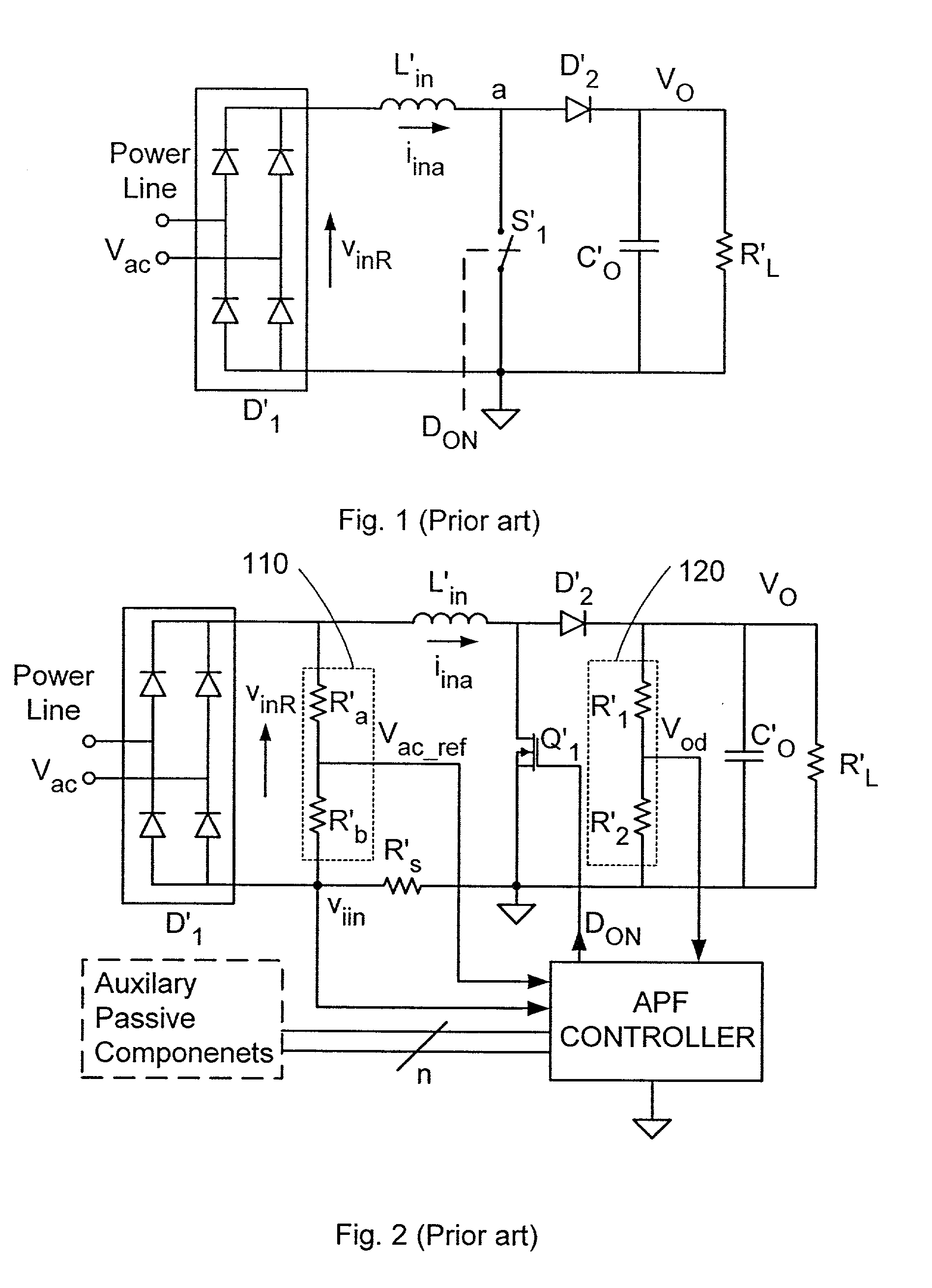
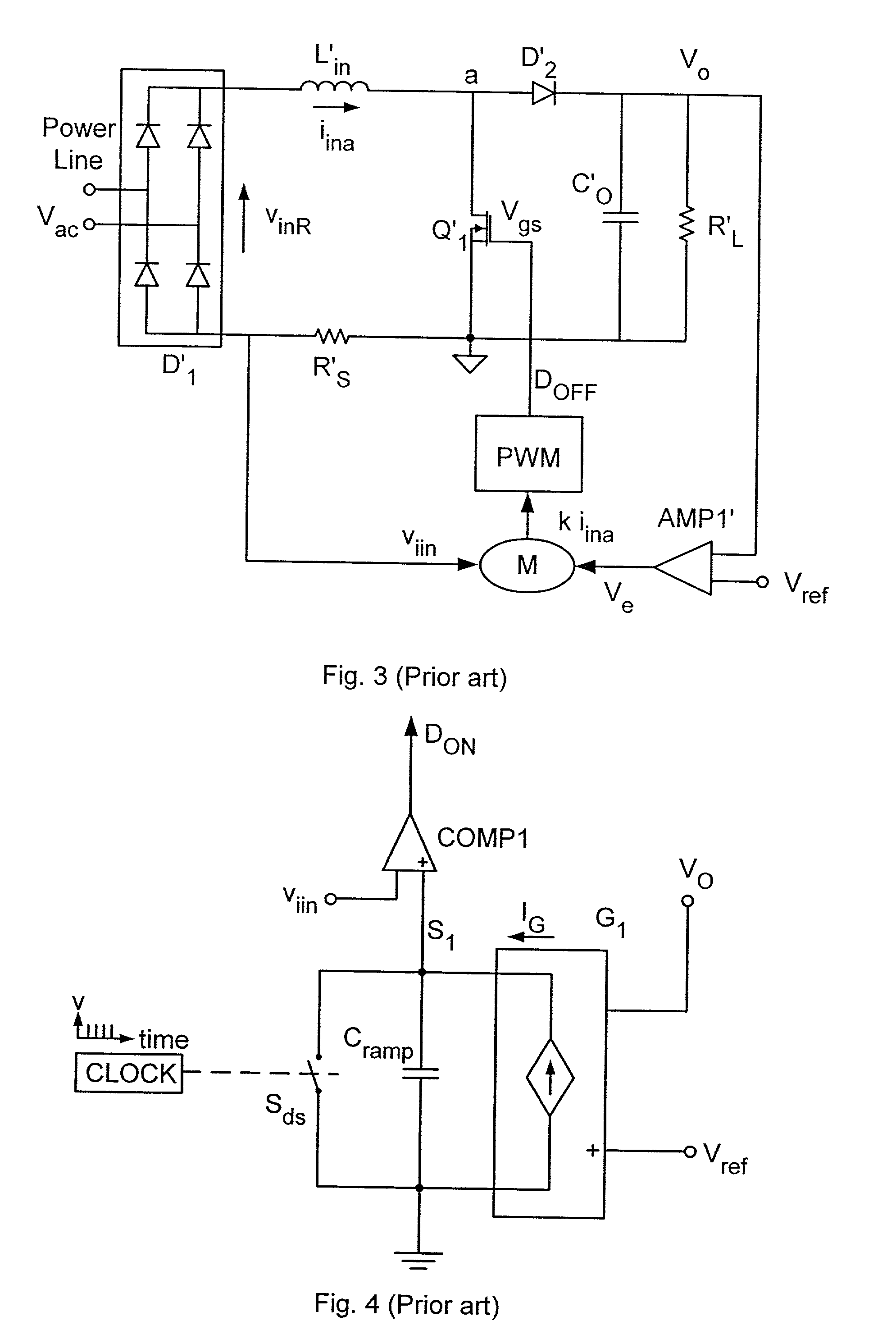
Method and apparatus for active power factor correction with minimum input current distortion
InactiveUS6728121B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHarmonicActive power factor correction
A method for reducing the harmonics contents of an input current drawn from a power line into an electrical system without sensing an input voltage, the method comprising providing an active power factor correction controller with a switch module having a main switch and a timing device, wherein the main switch has an on-time correlated with an on-duty cycle duration, and an off-time correlated with an off-duty cycle duration, and maintaining a linear relationship between the off-duty cycle duration and the input current by using the timing device; and an apparatus for active power factor correction with minimum input current distortion, comprising an active power factor correction assembly that includes a main switch and a timing device, wherein the main switch has associated therewith an on-time correlated with an on-duty cycle duration, and an off-time correlated with an off-duty cycle duration, and wherein the timing device generates the mentioned on-time and off-time, and linearization means for maintaining a linear relation between the off-duty cycle duration and the input current.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
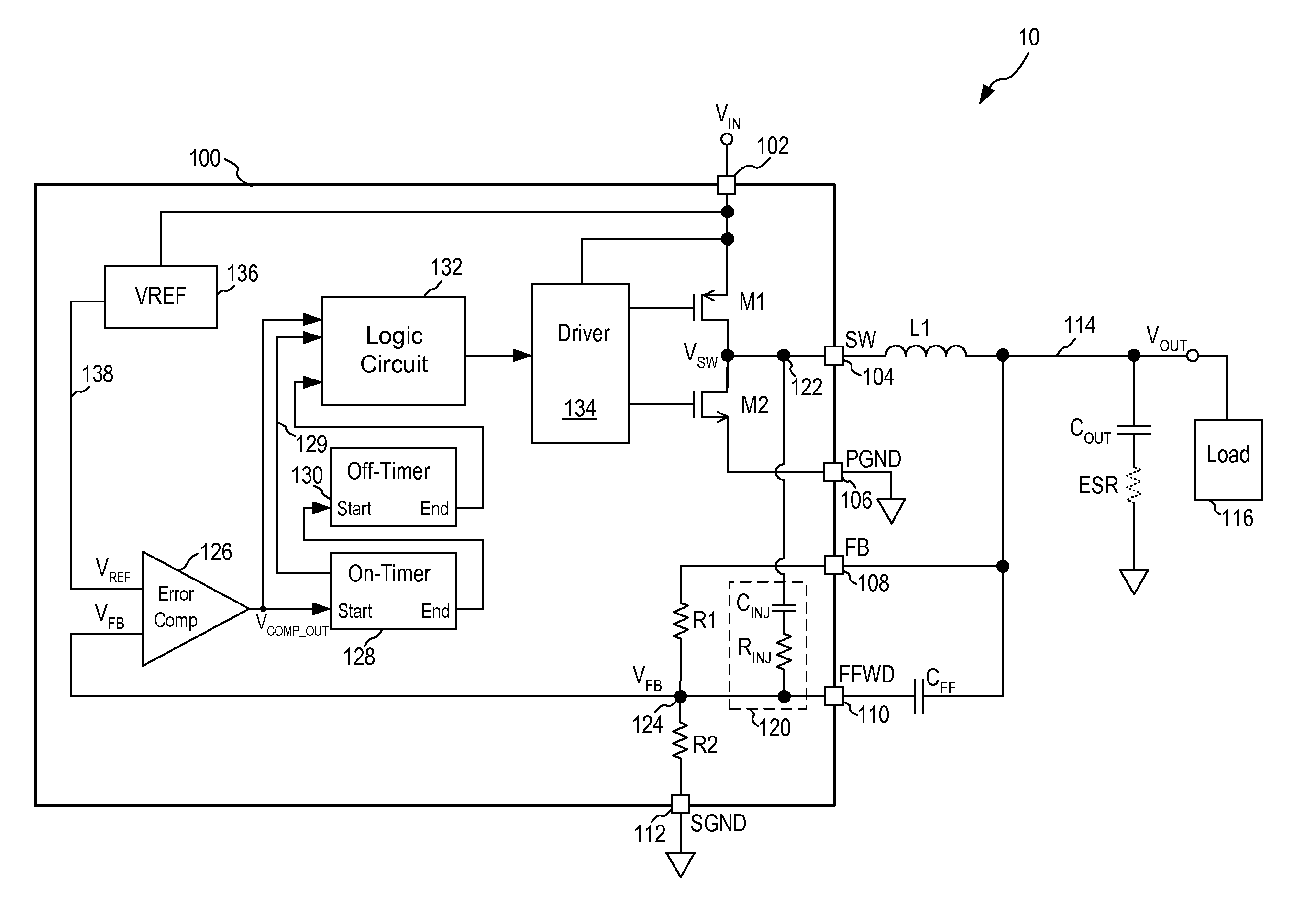
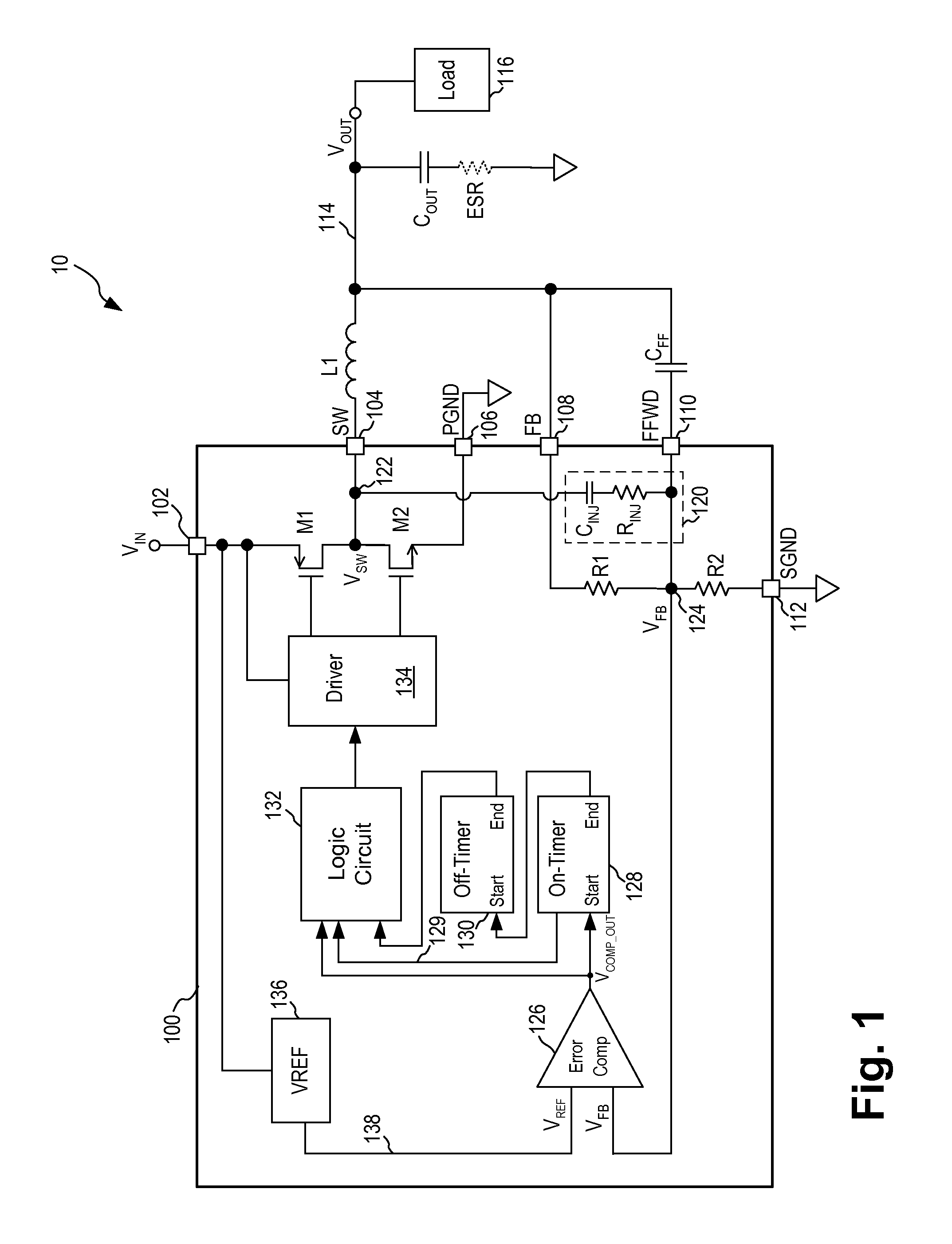
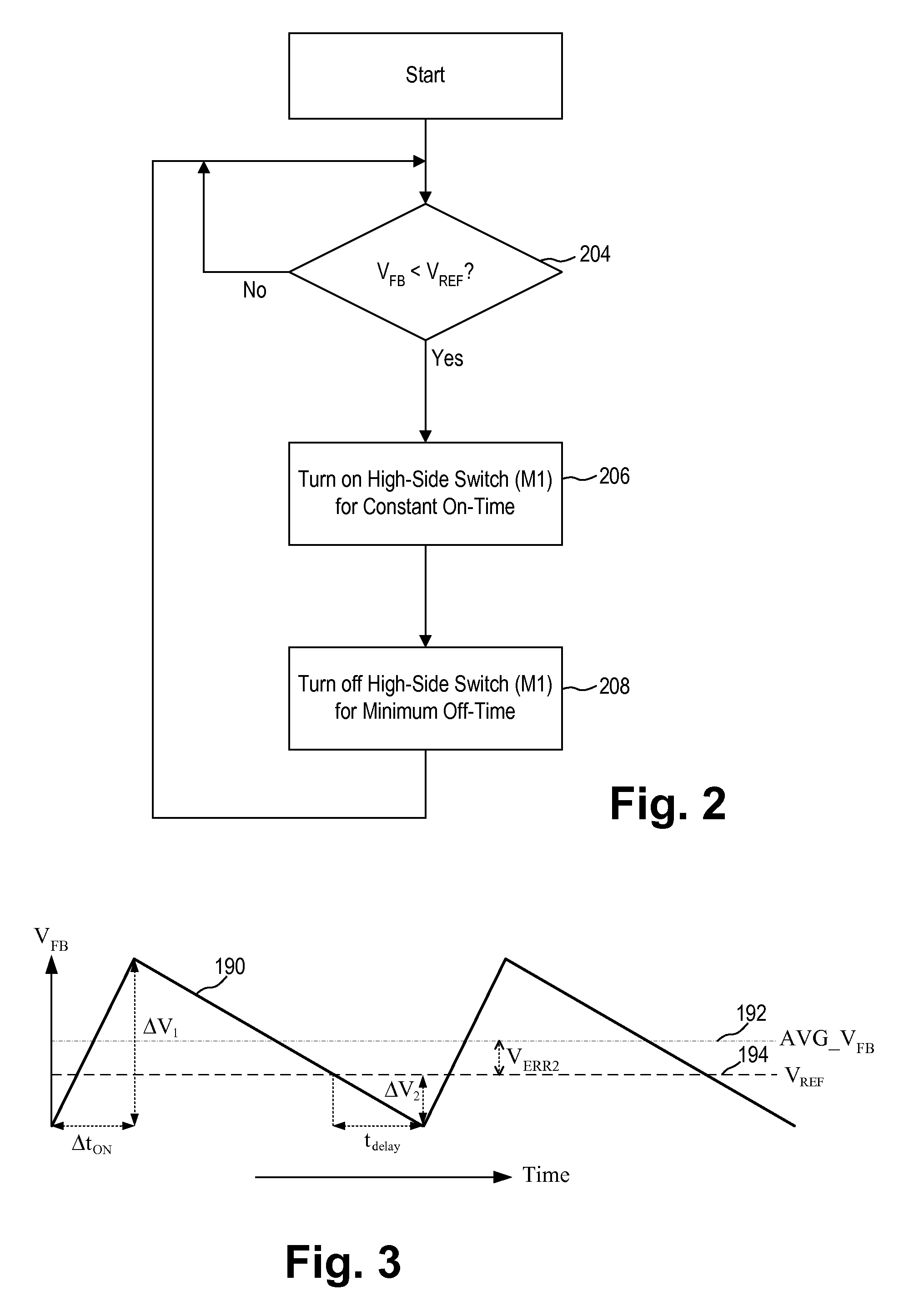
Constant On-Time Regulator With Increased Maximum Duty Cycle
A buck switching regulator receives an input voltage and provides a switching output voltage on a switch output node using a minimum on-time, variable off-time feedback control loop. The buck switching regulator includes an on-time control circuit for generating a first signal for turning off the high-side switch at the expiration of a first on-time duration or at the expiration of a maximum on-time. The first on-time duration is at least a minimum on-time and is allowed to expand to a maximum on-time when the feedback voltage remains less than a reference voltage. The maximum on-time includes a first maximum on-time and a second, extended maximum on-time. The second maximum on-time is applied when a minimum off-time was used for the high-side switch during the previous switching cycle. In another embodiment, the second maximum on-time is applied only when the switching regulator is not being current limited.
Owner:MICREL
Bipolar transistor drivers
InactiveUS20090040796A1Reduce impactEffectively allows the sensed voltage to be scaledTransistorEfficient power electronics conversionControl signalControl system
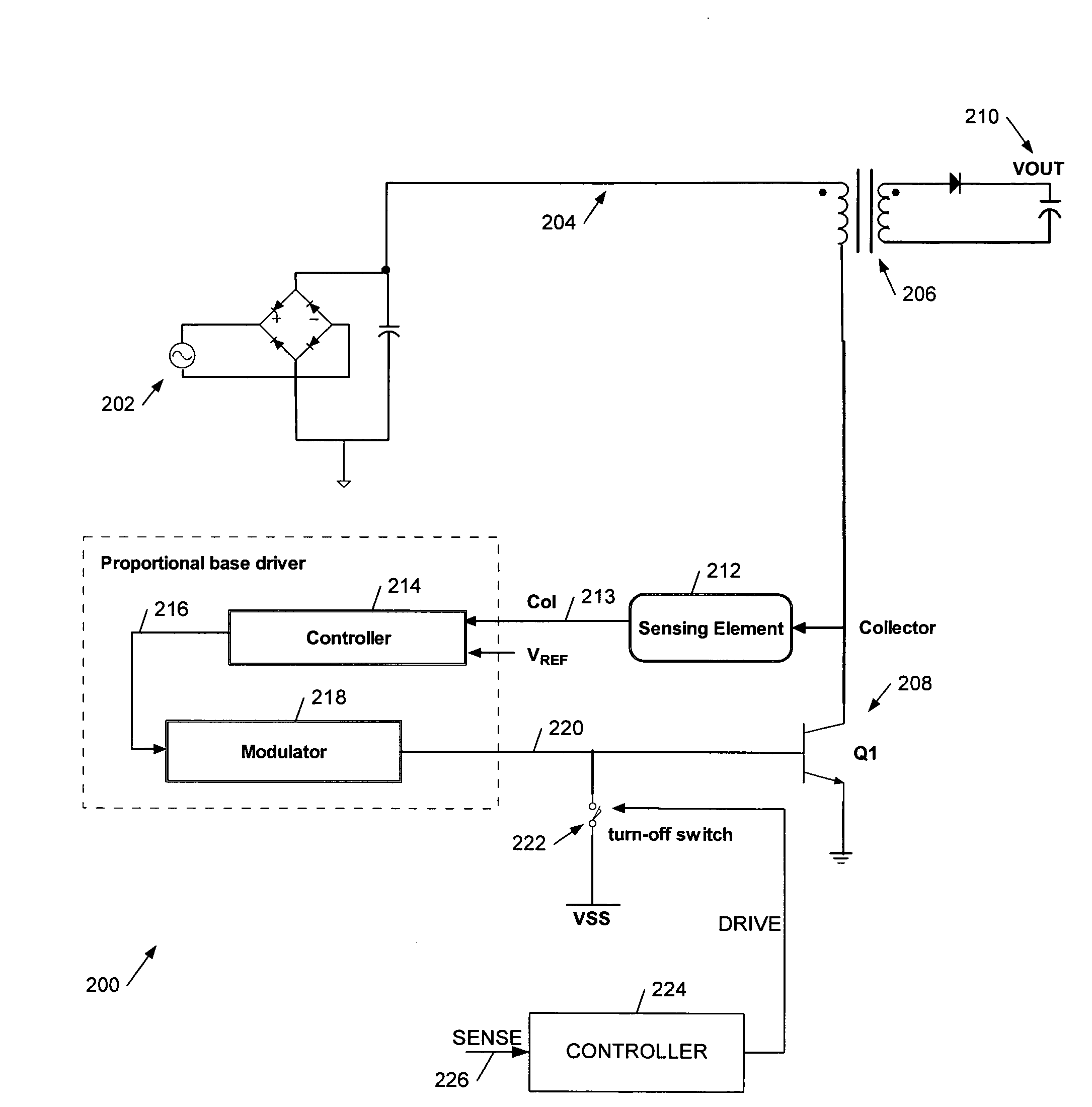
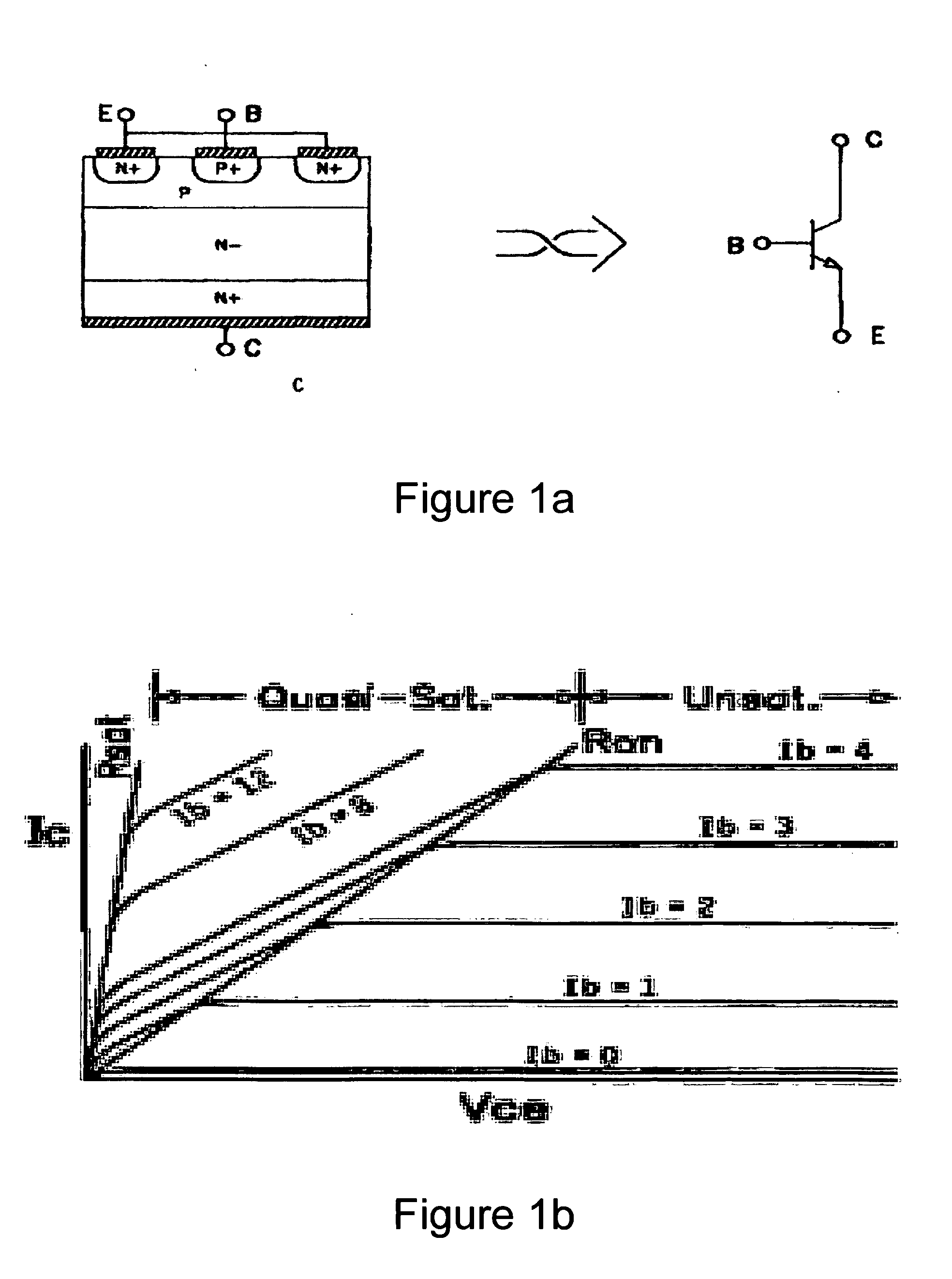
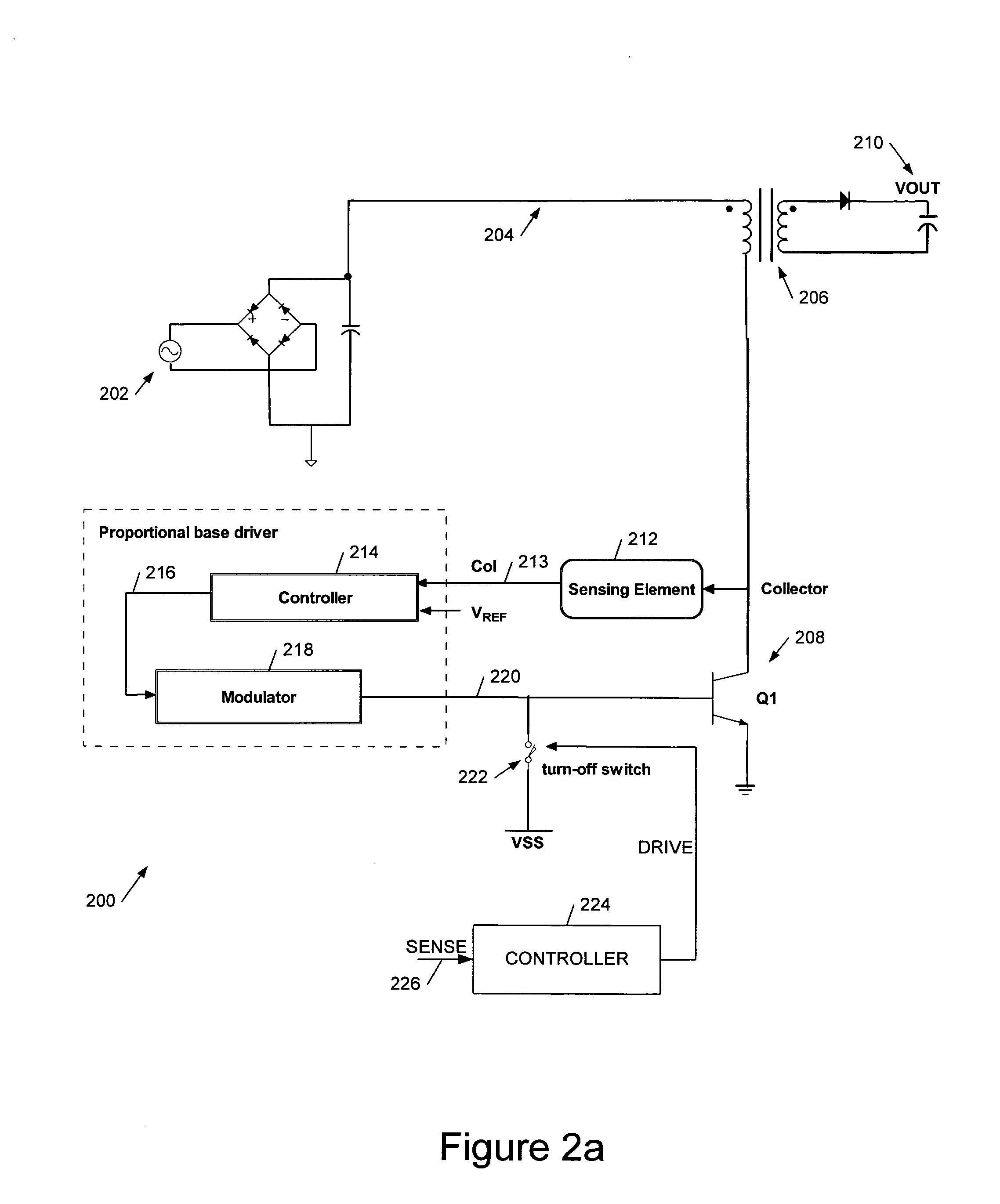
We describe a switching power converter comprising a bipolar switching device (BJT or IGBT) switching an inductive load, and including a closed-loop control system. The control system comprises a voltage sensing system to sense a voltage on a collector terminal of the switching device and provide a voltage sense signal; a controller; and a drive modulation system coupled to an output of the controller for modulating a drive to the control terminal of said bipolar switching device responsive to a controller control signal; wherein said controller is configured to monitor changes in the sensed voltage during a period when said switching device is switched on and to control said drive modulation system to control the degree of saturation of said bipolar switching device when the device is switched on and hence improve turn-off times.
Owner:POWER INTEGRATIONS INC
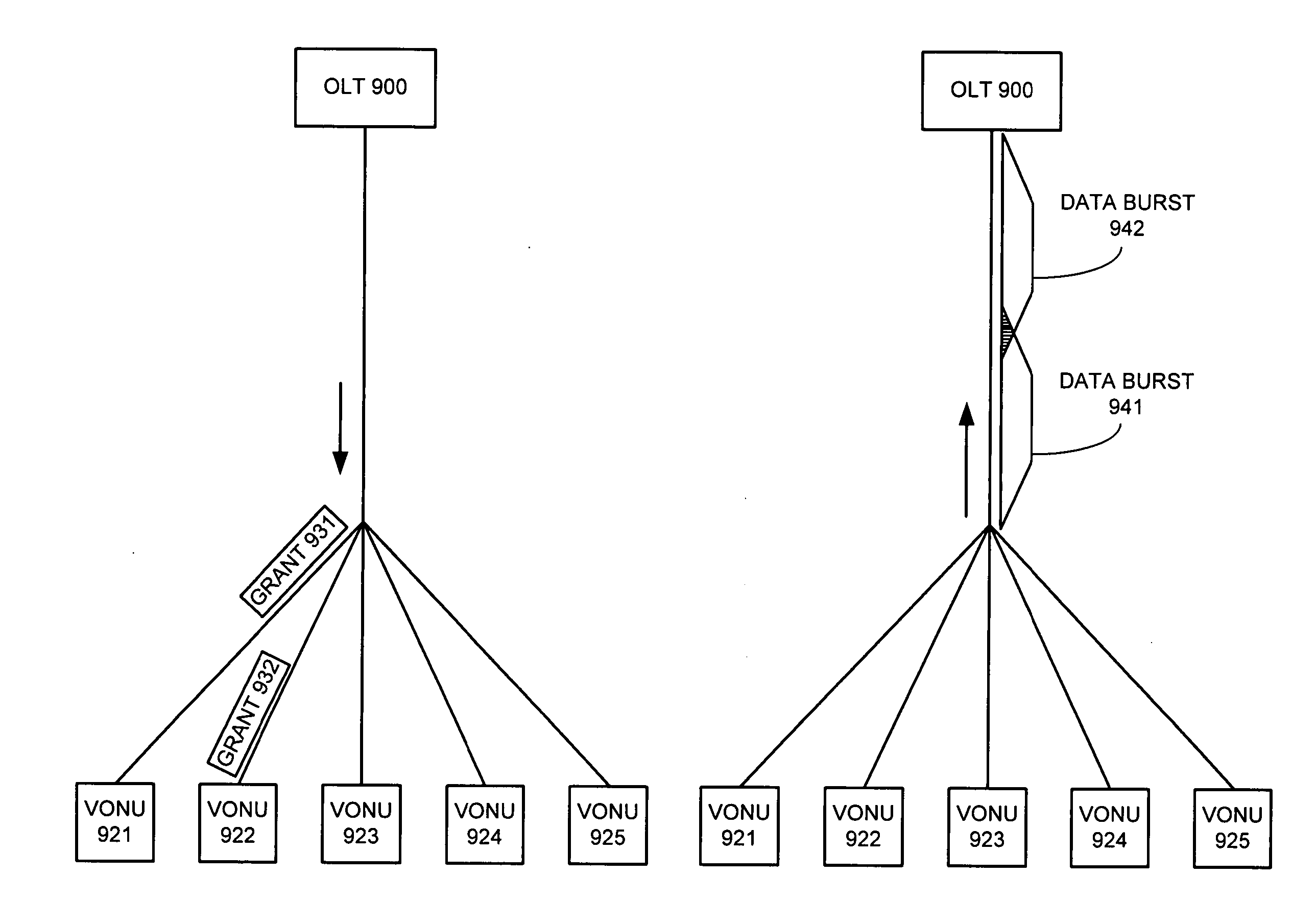
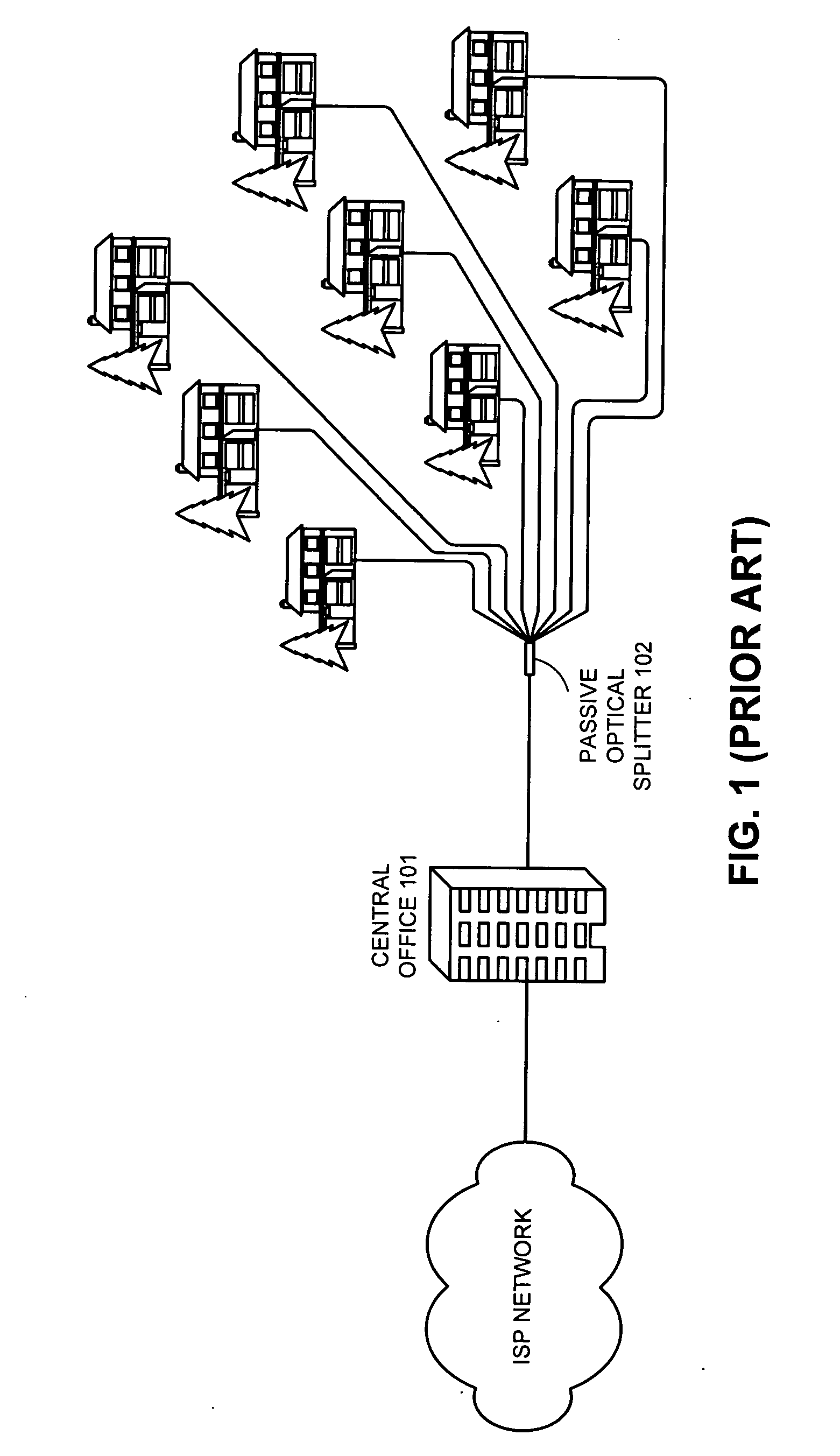
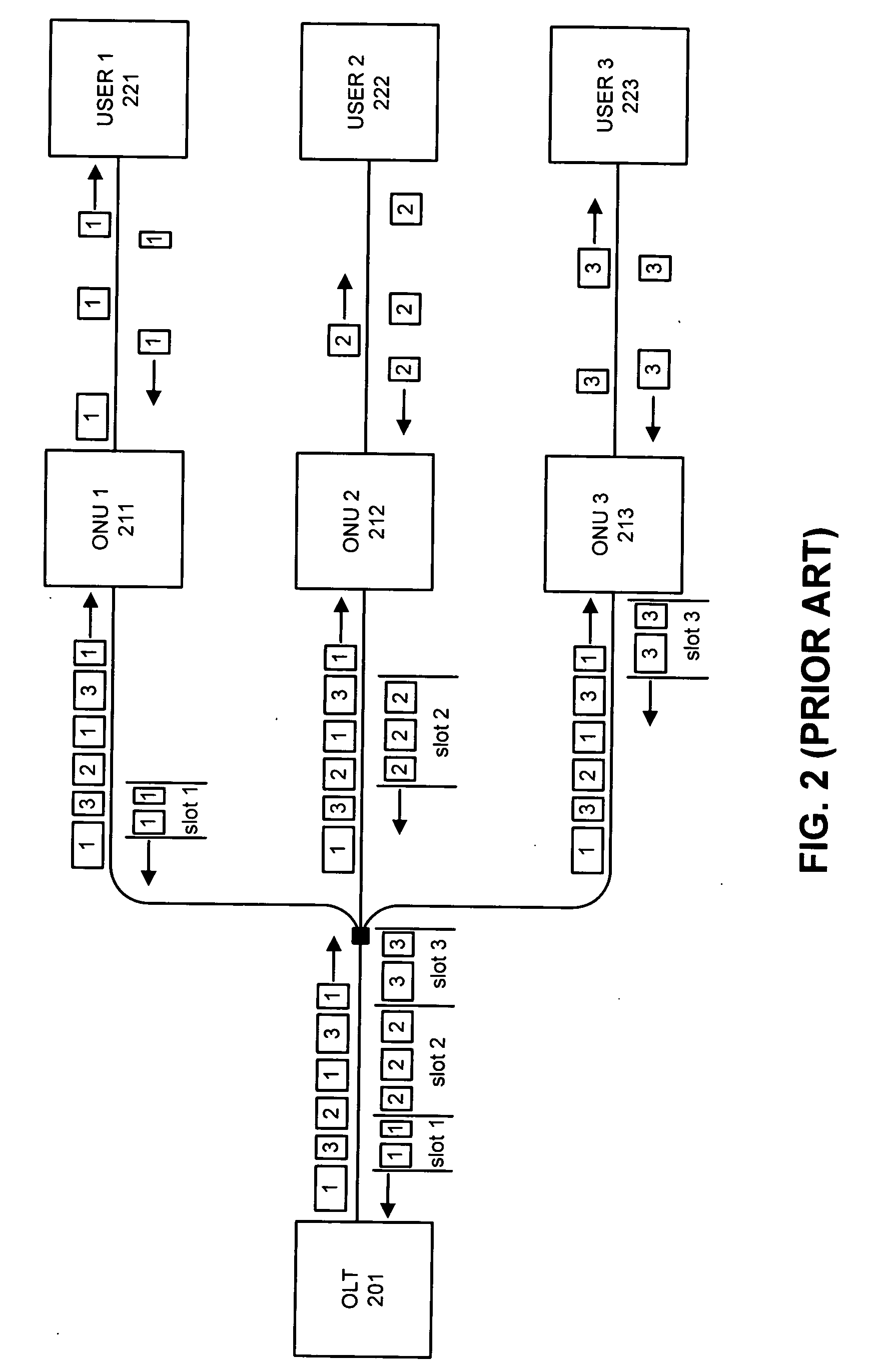
Method and apparatus for reducing data burst overhead in an ethernet passive optical network
InactiveUS20050041682A1Reduces data burst overheadMultiplex system selection arrangementsTime-division multiplexStart timeEthernet
One embodiment of the present invention provides a system that reduces data burst overhead in an Ethernet passive optical network which includes a central node and at least one remote node, wherein downstream data from the central node is broadcast to the remote nodes, and wherein upstream data from a remote node is transmitted to the central node in a unicast manner. During operation, the central node transmits grant messages to a number of remote nodes, wherein a grant message for a specified remote node assigns a start time and a duration of a transmission timeslot in which the specified remote node may transmit an upstream data burst. In response to the grant messages, the central node then receives a number of upstream data bursts, wherein the time gap between two consecutive upstream data bursts is less than the summation of a default laser turn-on time, a default laser turn-off time, an AGC period, and a CDR period.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
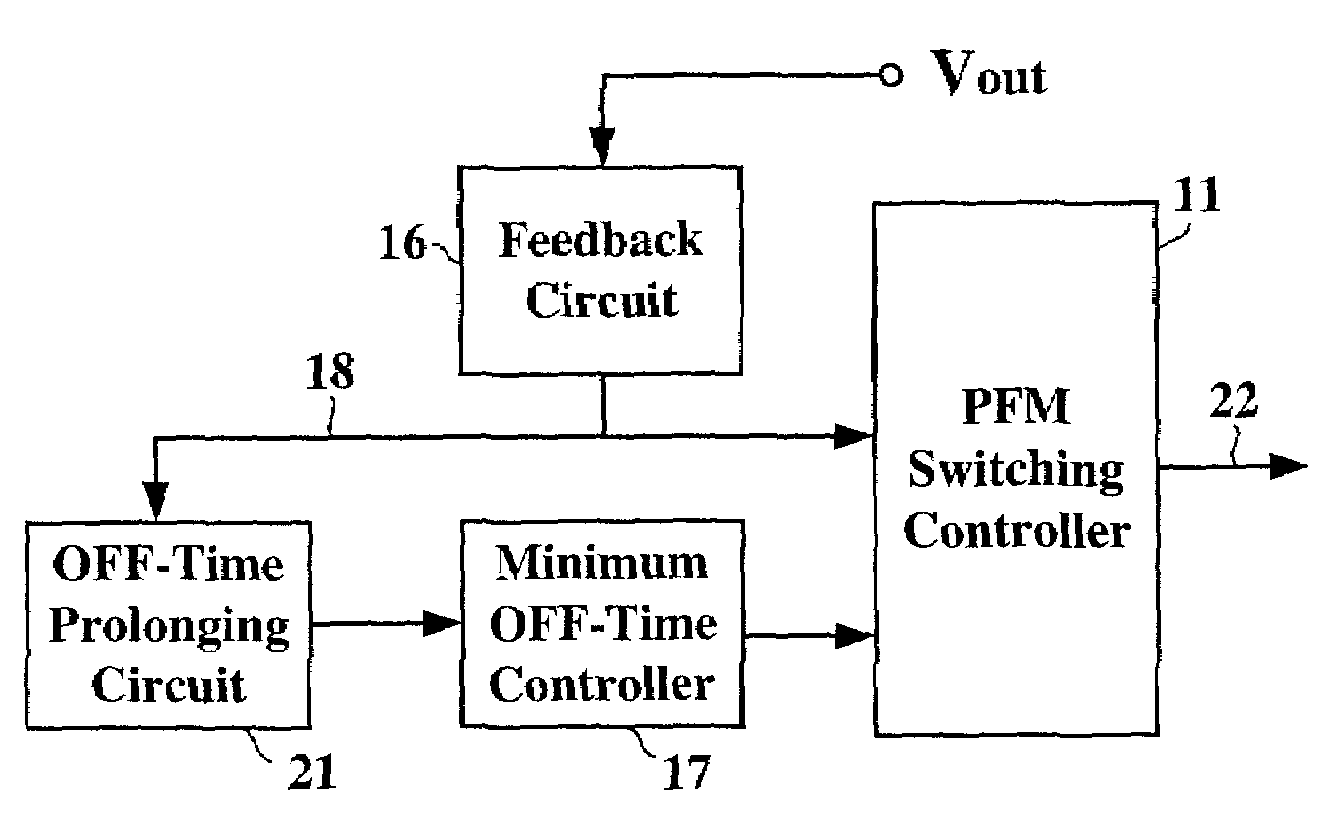
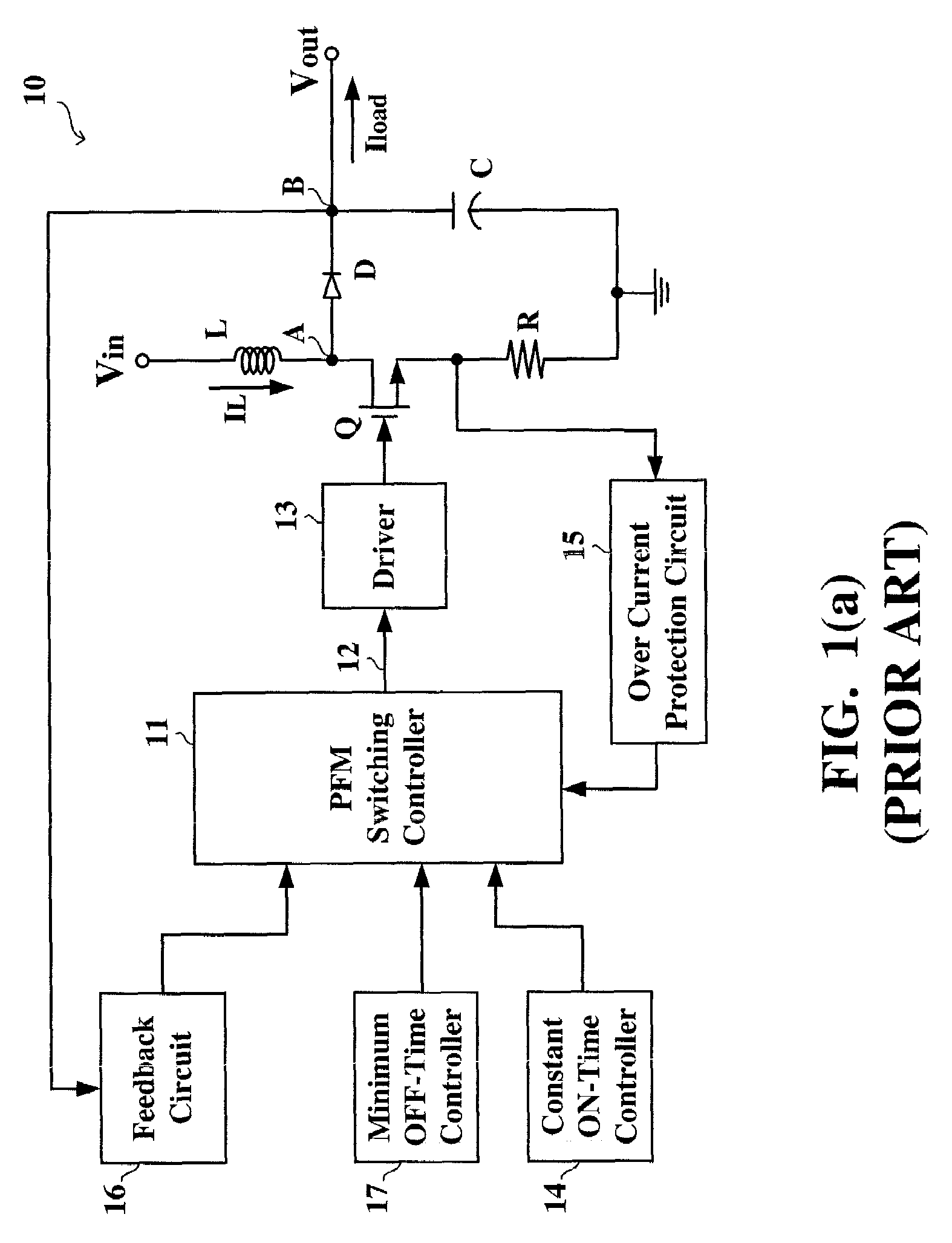
Pulse frequency modulated voltage regulator capable of prolonging a minimum off-time
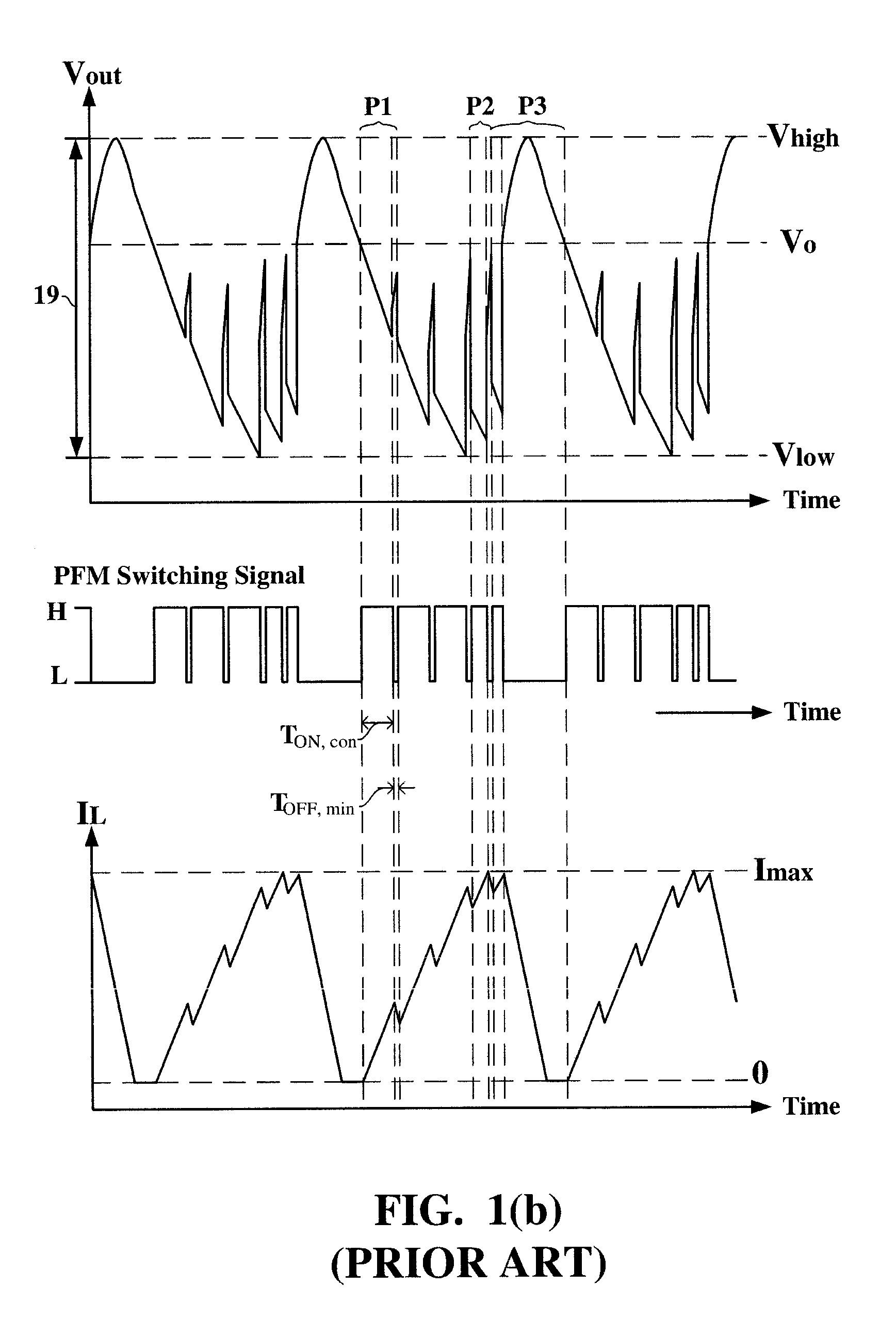
ActiveUS6972548B2Reduce rippleProlonging a minimum OFF-timeElectric variable regulationPower conversion systemsTime extensionEngineering
In a pulse frequency modulated (PFM) voltage regulator, a PFM switching controller is provided to generate a PFM switching signal for converting a DC voltage source to an output voltage. A minimum OFF-time controller provides the PFM switching signal with a minimum OFF-time. In response to the output voltage, a feedback circuit generates a feedback signal. When the output voltage is lower than a predetermined target voltage, an OFF-time prolonging circuit prolongs the minimum OFF-time in response to the feedback signal. In other words, a time of delivering energy to a capacitor from an inductor may be prolonged by the OFF-time prolonging circuit. Therefore, a ripple of the output voltage is effectively reduced when the PFM voltage regulator is operated in a heavy loading condition.
Owner:GLOBAL MIXED MODE TECH
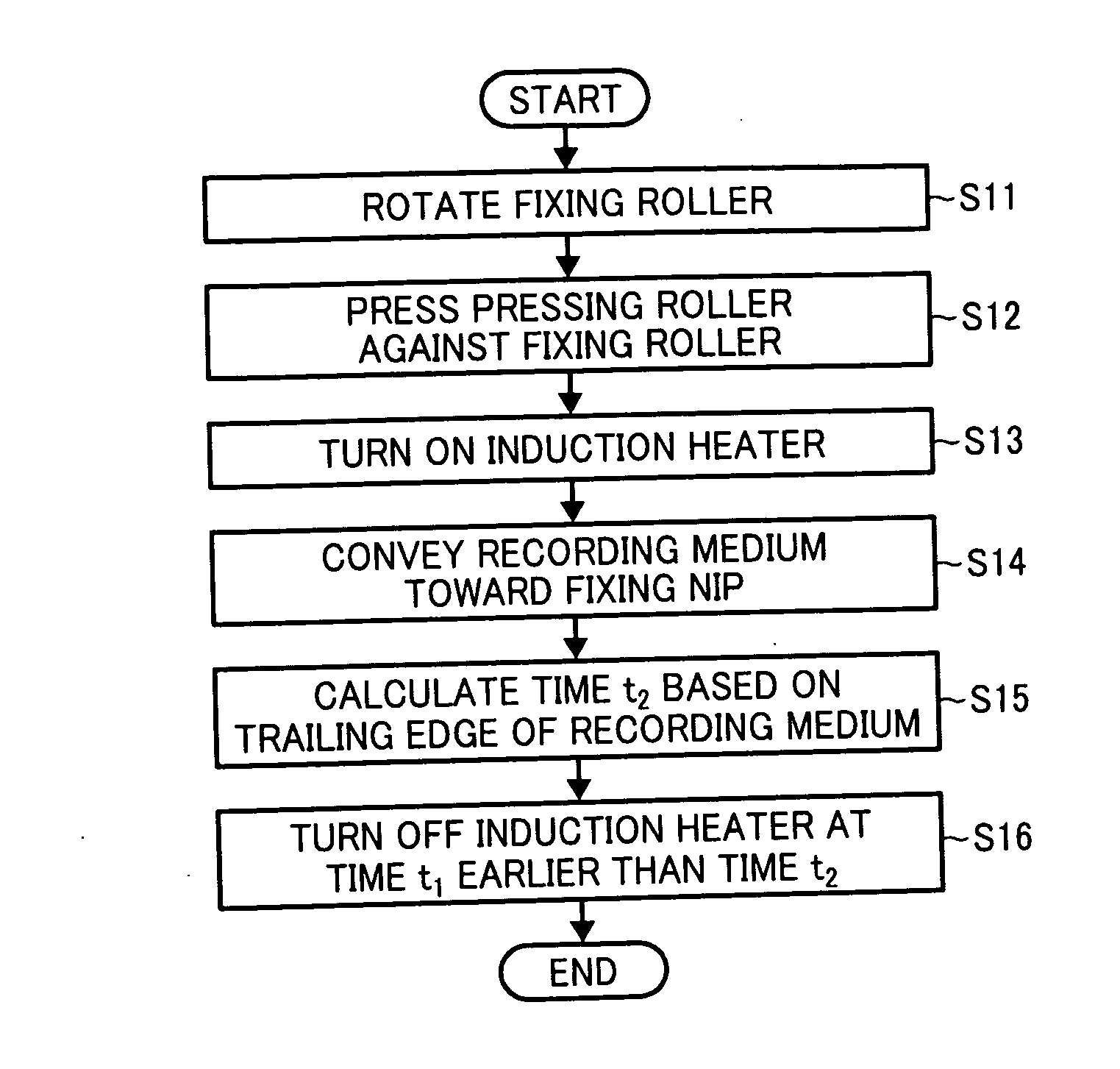
Fixing Device, Image Forming Apparatus Incorporating Same, And Method For Fixing Toner Image On Recording Medium
A fixing device includes a pressing rotary body pressed against a fixing rotary body to form a fixing nip therebetween through which a recording medium bearing a toner image is conveyed; a heater to heat the fixing rotary body, disposed opposite a circumferential surface of the fixing rotary body and upstream from the fixing nip a predetermined circumferential distance along the circumferential surface of the fixing rotary body in a direction of rotation of the fixing rotary body; a heater driver to turn on and off the heater; a timing calculator to calculate a reference time at which a trailing end portion of the recording medium in a conveyance direction of the recording medium reaches the fixing nip; and a heater driver controller to cause the heater driver to turn off the heater at a turn-off time earlier than the reference time.
Owner:RICOH KK
Frequency jittering control circuit and method for a pfm power supply
ActiveUS20130051089A1Apparatus with intermediate ac conversionPulse duration/width modulationControl signalSwitching frequency
A frequency jittering control circuit for a PFM power supply includes a pulse frequency modulator to generate a frequency jittering control signal to switch a power switch to generate an output voltage. The frequency jittering control circuit jitters an input signal or an on-time or off-time of the pulse frequency modulator to jitter the switching frequency of the power switch to thereby improve EMI issue.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
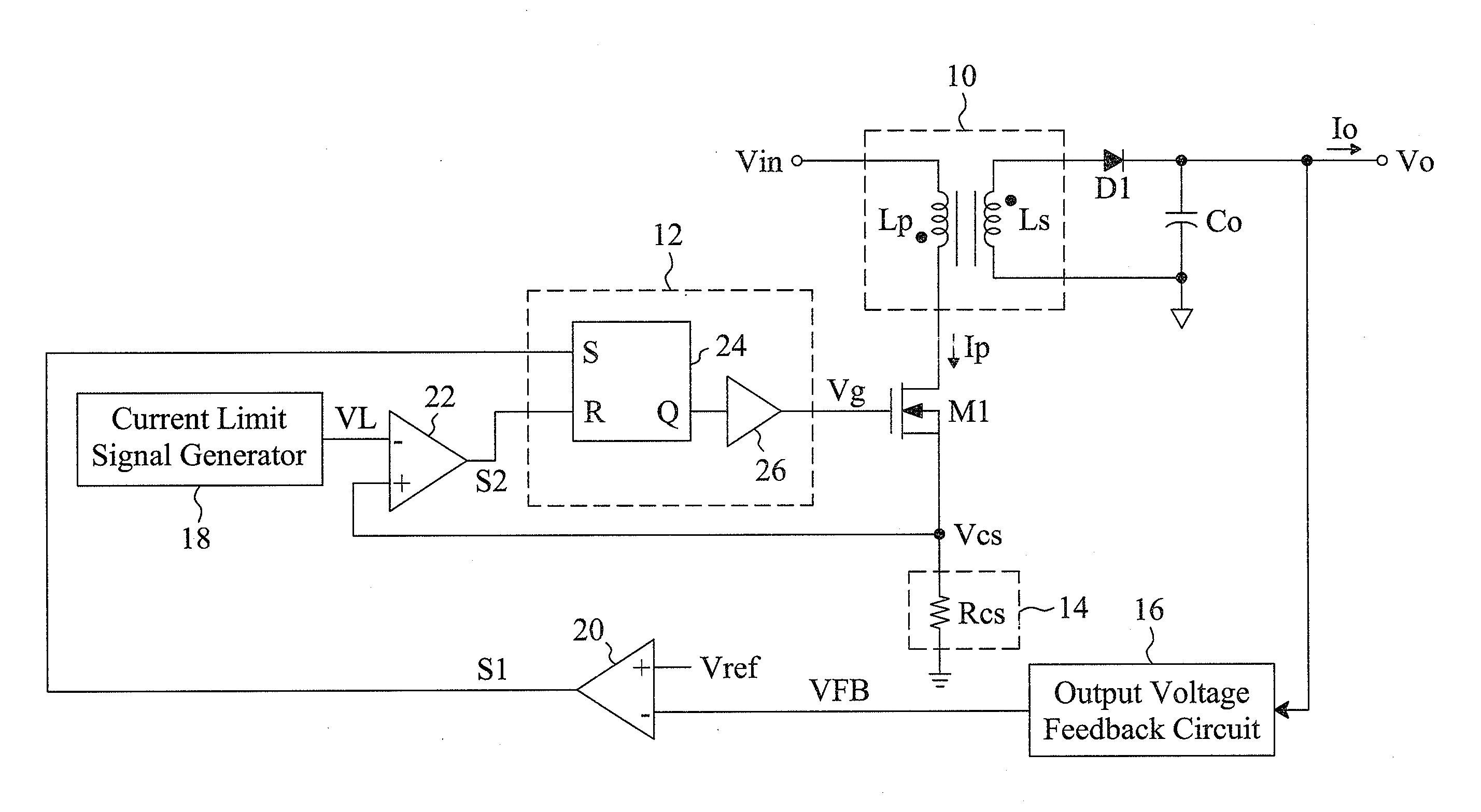
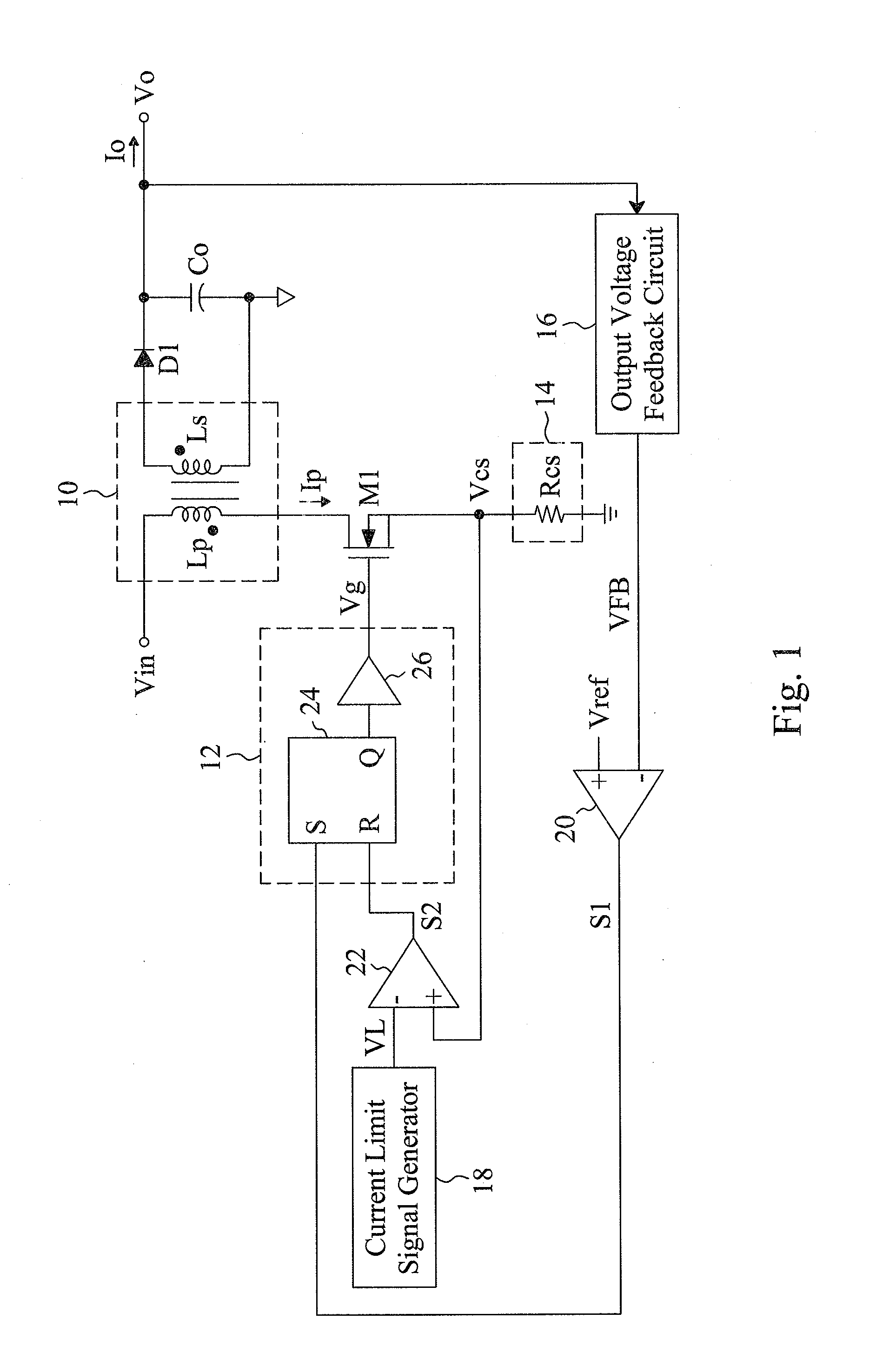
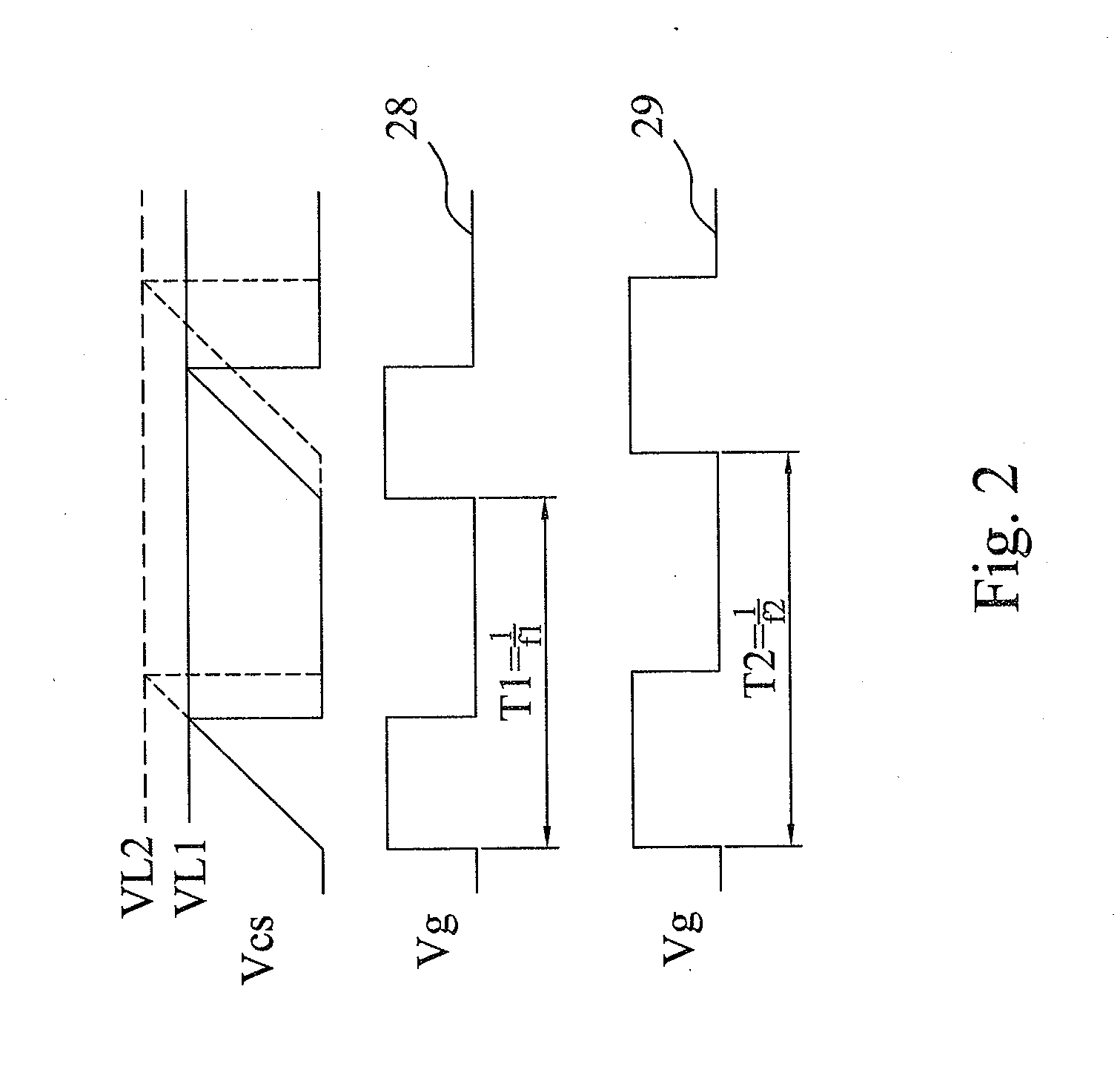
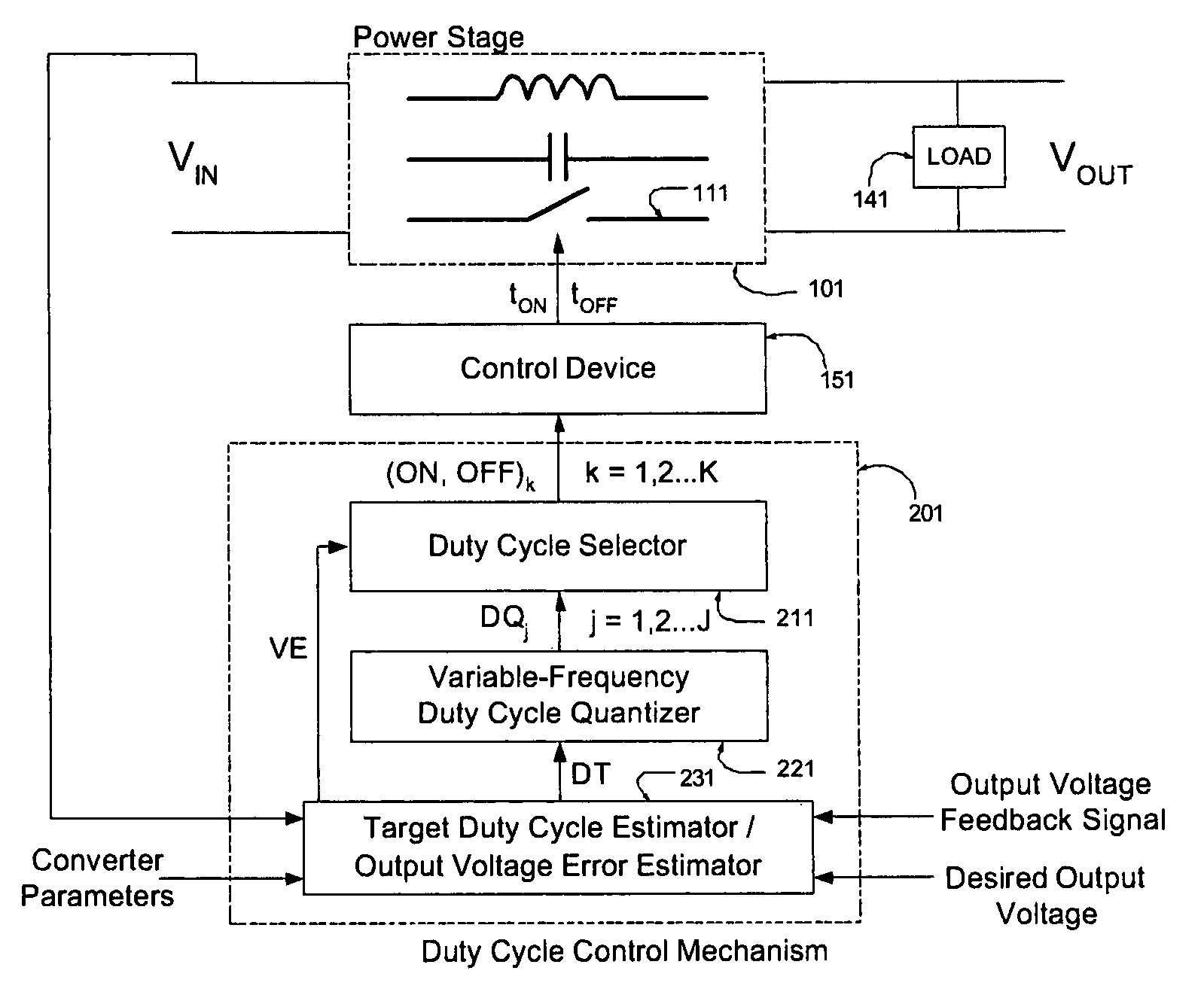
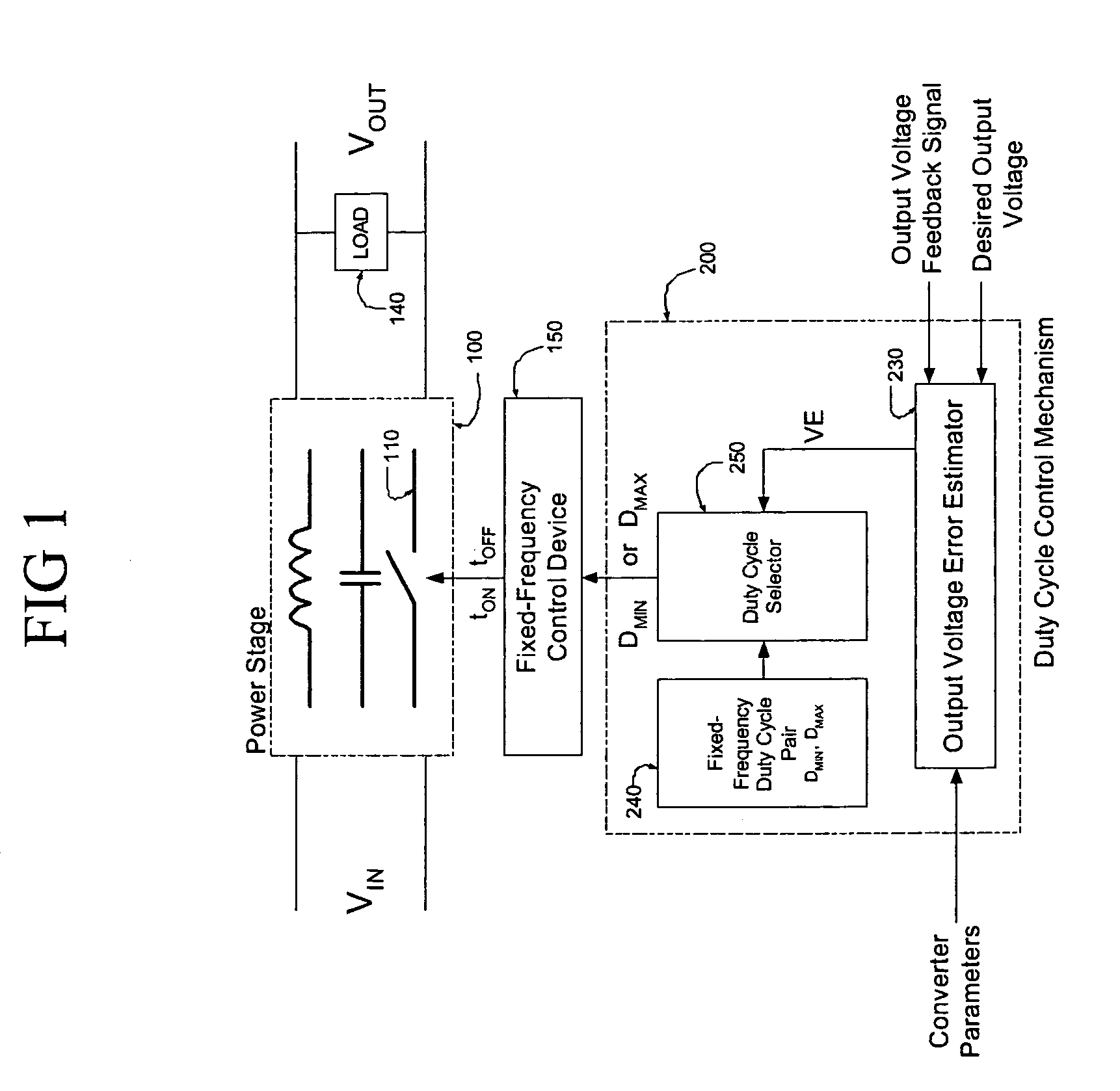
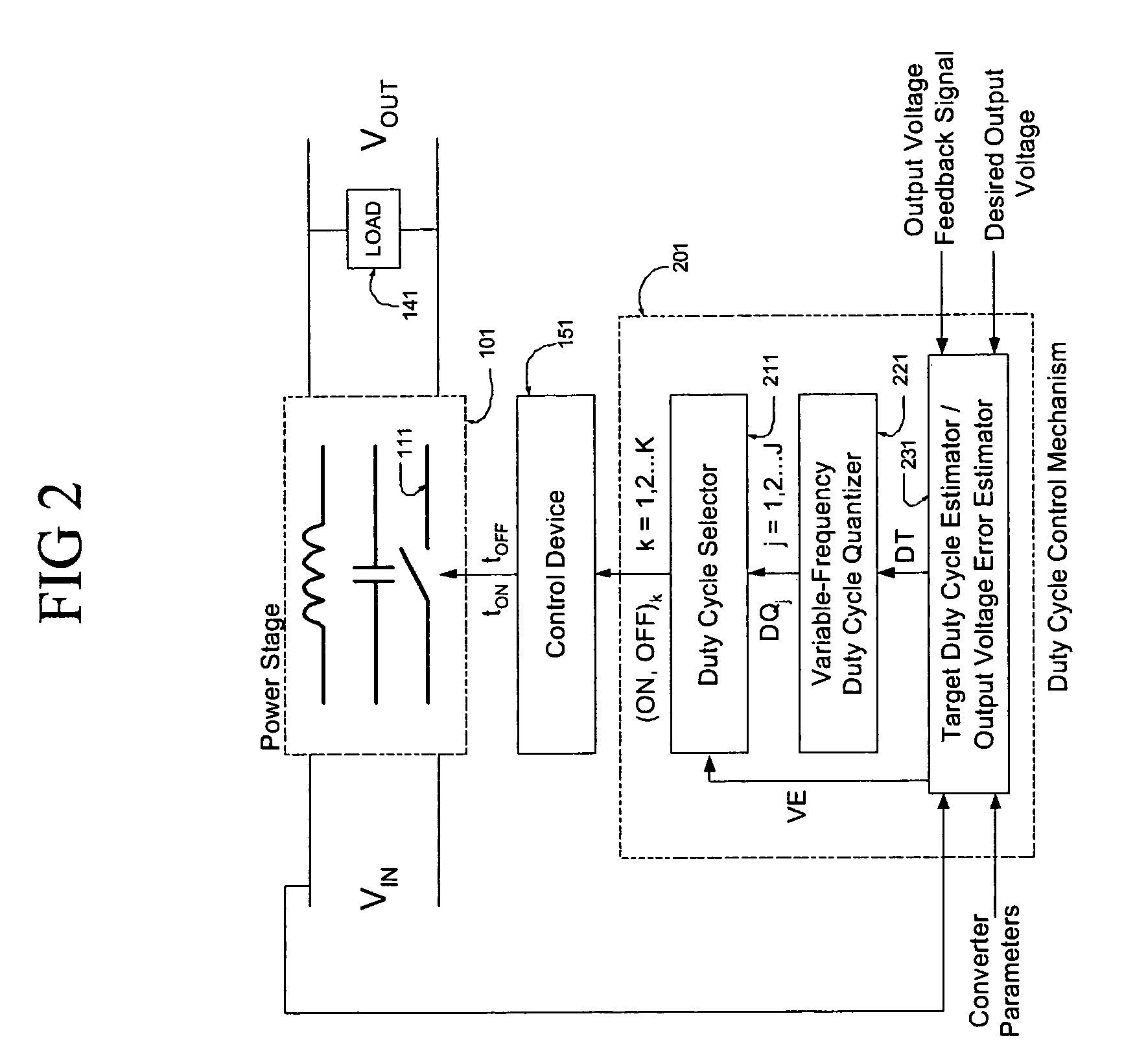
Digital voltage regulator for DC/DC converters
InactiveUS6992469B1Reduce delaysDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationTemporal resolutionImage resolution
A digitally-controlled, DC / DC converter includes at least one switched-mode power stage for the purpose of converting an input voltage (Vin) into an output voltage (Vout); the power stage including at least one controllable switching device, which is turned ON and OFF by a control device with temporal resolution Δt. The converter further includes a duty cycle control mechanism for controlling the duty cycle of the controllable switching device, the duty cycle control mechanism including a mechanism for estimating the output voltage error; a mechanism for estimating the target duty cycle; a duty cycle quantization mechanism for determining, for a target duty cycle estimate, a first set of quantized ON time / OFF time pairs suitable for controlling the switching device; and a selector mechanism for determining the turn ON and turn OFF times of said controllable switching device by choosing, cycle by cycle, an ON time / OFF time pair from a second set of quantized ON time / OFF time pairs, derived from said first set, choosing in such a manner that the amplitude of the output voltage error is continually minimized.
Owner:KIAWE FOREST
Vacuum pipeline docking technology and high-speed permanent maglev train system
InactiveCN101823488AGet off fastWill not affect high-speed passingRailway tunnelsRailway componentsEngineeringElectric power
The invention provides a vacuum pipeline docking technology and a high-speed permanent maglev train system. With the station-training docking technology, the door closing time of the maglev train inside the vacuum pipeline can be shortened for scores of seconds, so the rapid on-off can be realized. When a telescopic door and a separation cabin door are withdrawn to be close to the wall of the vacuum pipeline, the high-speed pass of the tray is free from being influenced. The telescopic door is locked by a permanent magnet suction disc, and the locking force is free from being controlled by the electric power, so the gas leakage and pressure relief caused by the invalid locking for sudden power down can be prevented. The energy can be remarkably saved, the energy can be saved by more than 97 percent compared with that of high-speed track train, and the energy can be saved by more than 99 percent compared with that of the airplane.
Owner:刘忠臣
Apparatus and method of energy efficient illumination
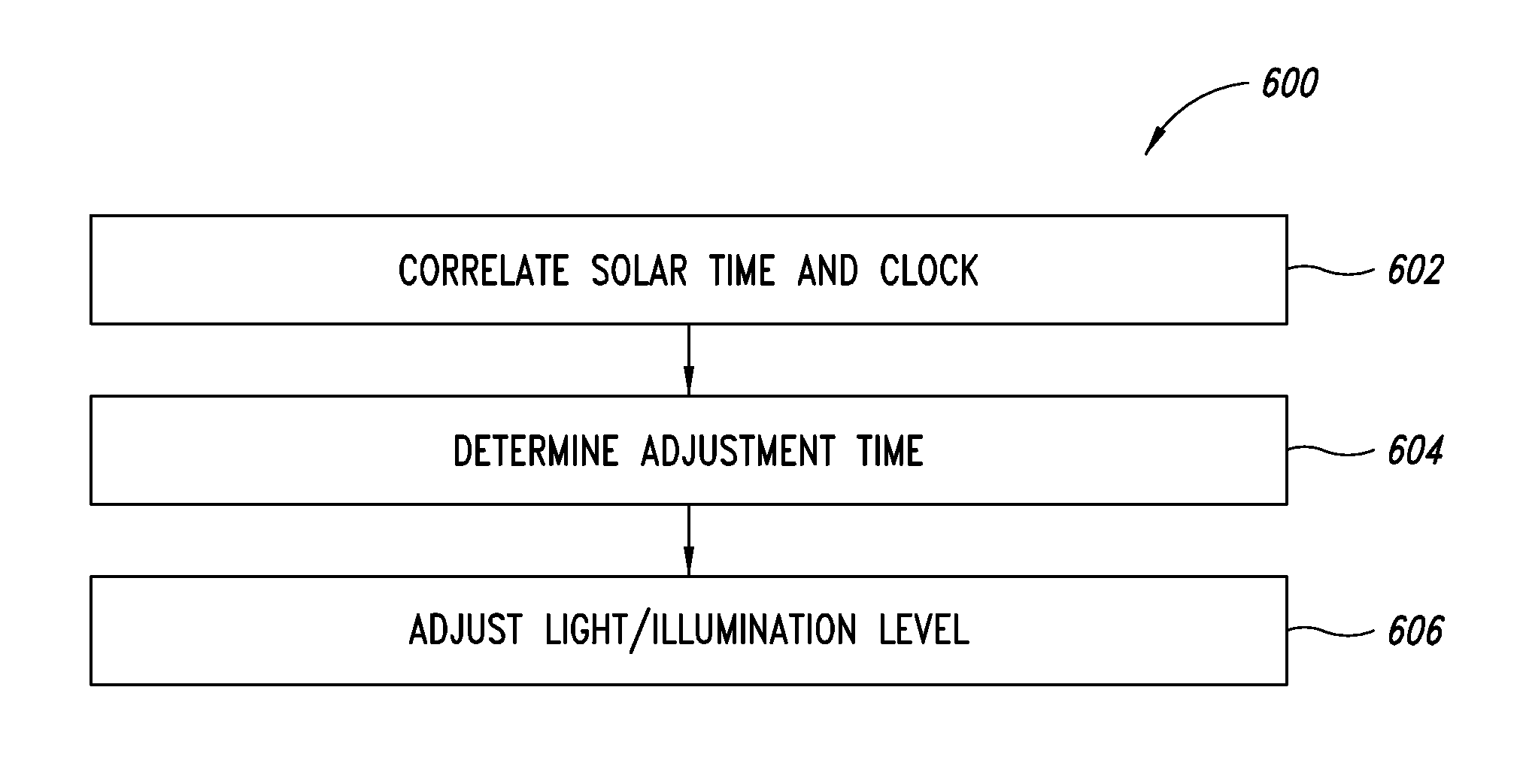
ActiveUS20100295455A1Improve energy efficiencyReduce energy consumptionElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsIlluminanceEffect light
An illumination system correlates solar time to a clock and controls lighting or illumination based on time. The illumination system may turn ON light source(s) at a first level at a turn ON time, correlated to be around or at dusk, and turn OFF light source(s) at a turn OFF time, correlated to be around or at dawn. The illumination system may reduce a level of light output, and hence power consumption, at a time after turning ON a light source, and increases the level of light output at a time prior to turning OFF the light source. Turn ON, turn OFF, decrease and increase times may be determined based on recent levels of light or illumination in the environment, for example via average or median levels over a number of previous daily cycles. Filtering may eliminate aberrant events.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
Hysteretic buck converter having dynamic thresholds
InactiveUS8008902B2Improved ripple controlEfficient power electronics conversionEmergency protective circuit arrangementsPower flowBuck converter
A hysteretic buck converter provides improved regulation control, in particular for buck converter standby operation. A comparison circuit compares the output voltage of the buck converter to a waveform that is generated from an indication of the output current of the converter, so that the turn-on time of the converter is advanced as the output current demand increases. The resulting action anticipates a reduction in output voltage due to the increased current, preventing an excursion of the output voltage below the ripple voltage minimum. The turn-off time of the converter is controlled by an upper threshold that limits the ripple voltage maximum. The output current indication may be a measurement of output current, or may be a dynamic value calculated from the input voltage and the output voltage waveform.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
Soft switching high efficiency flyback converter
InactiveUS20050270001A1Easy to useSmall sizeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSoft switchingConductor Coil
DC-DC converters such as flyback converters achieve self-regulation by communication information between primary and secondary circuits through the power transformer. Operating in accordance with a generalized concept or algorithm, the converter can be bi-directional and self-regulating. Control of the turn OFF times of semiconductor switches in first and second circuits coupled to first and second windings of the power transformer determines whether power flow is in one direction through the converter or the other direction. Turn ON timing of each semiconductor switch is when there is a reverse current through the switch and voltage across the switch is at or near zero. Turn OFF of a switch can be controlled from one or more operating parameters of the converter such as output voltage, in which case the converter's self-regulation is affected through duty cycle variation with variations in output voltage.
Owner:DET INT HLDG LTD
Apparatus and method of energy efficient illumination
ActiveUS8508137B2Reduce energy consumptionReduce and eliminate affectElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsIlluminanceEffect light
An illumination system correlates solar time to a clock and controls lighting or illumination based on time. The illumination system may turn ON light source(s) at a first level at a turn ON time, correlated to be around or at dusk, and turn OFF light source(s) at a turn OFF time, correlated to be around or at dawn. The illumination system may reduce a level of light output, and hence power consumption, at a time after turning ON a light source, and increases the level of light output at a time prior to turning OFF the light source. Turn ON, turn OFF, decrease and increase times may be determined based on recent levels of light or illumination in the environment, for example via average or median levels over a number of previous daily cycles. Filtering may eliminate aberrant events.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
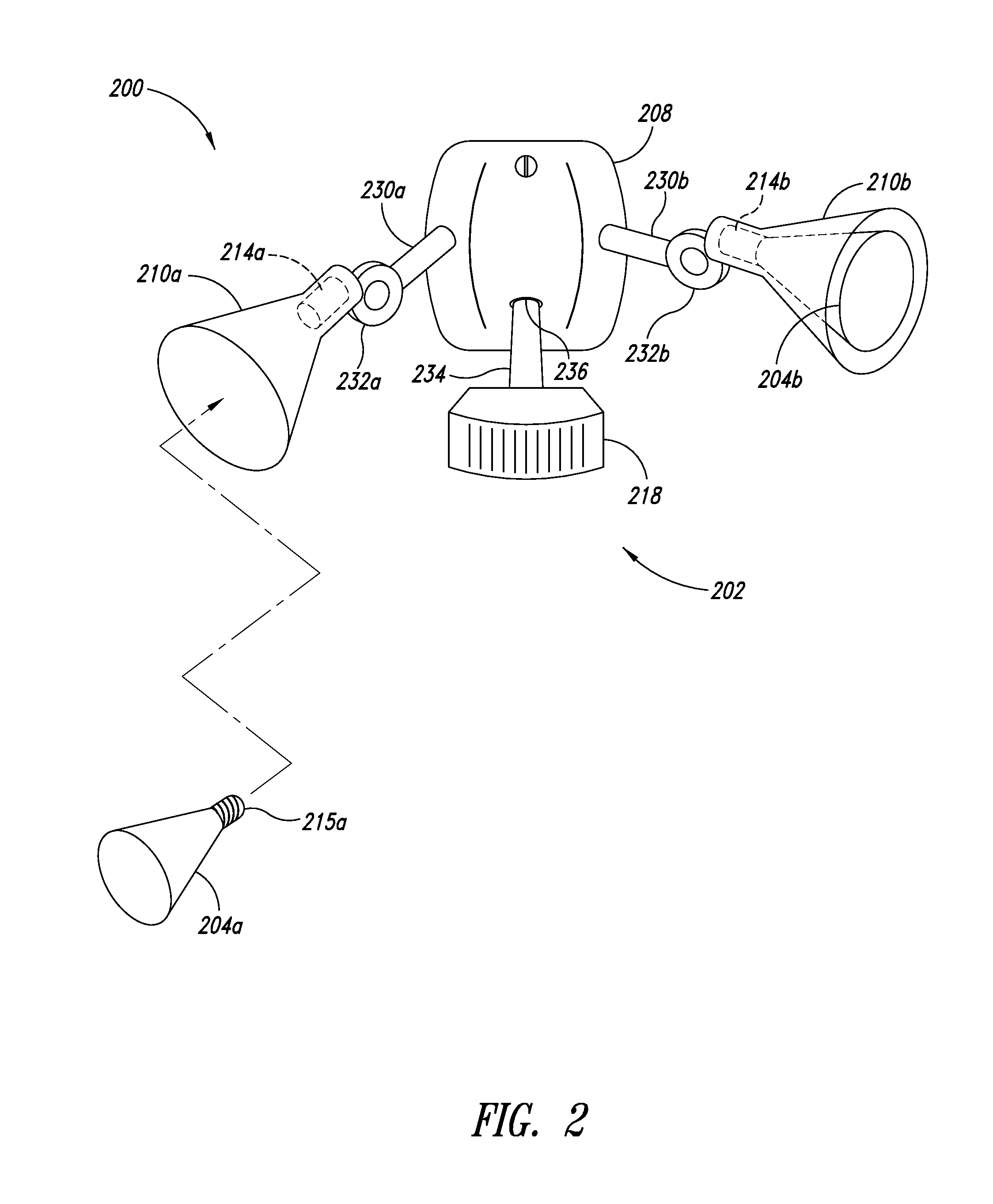
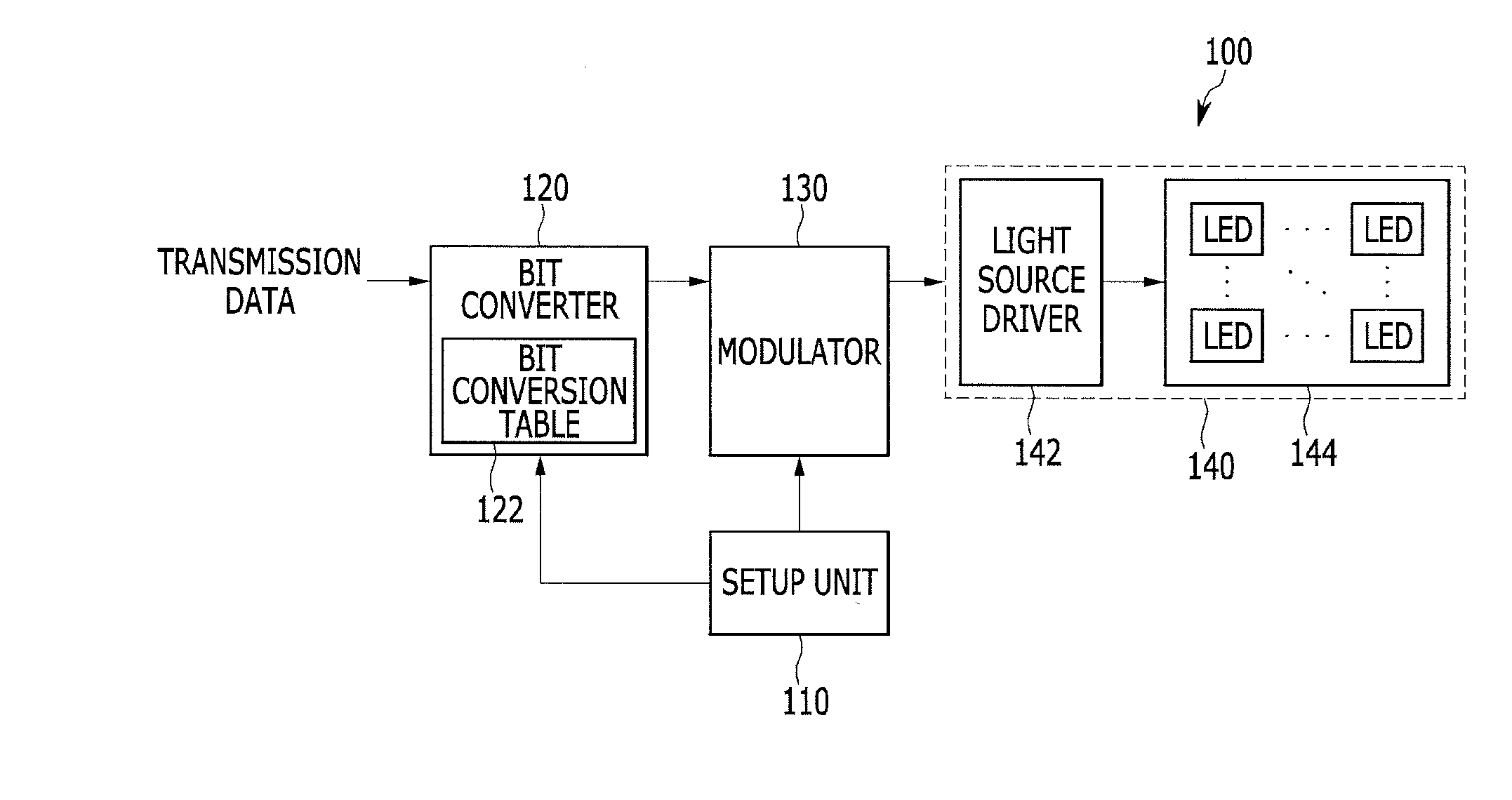
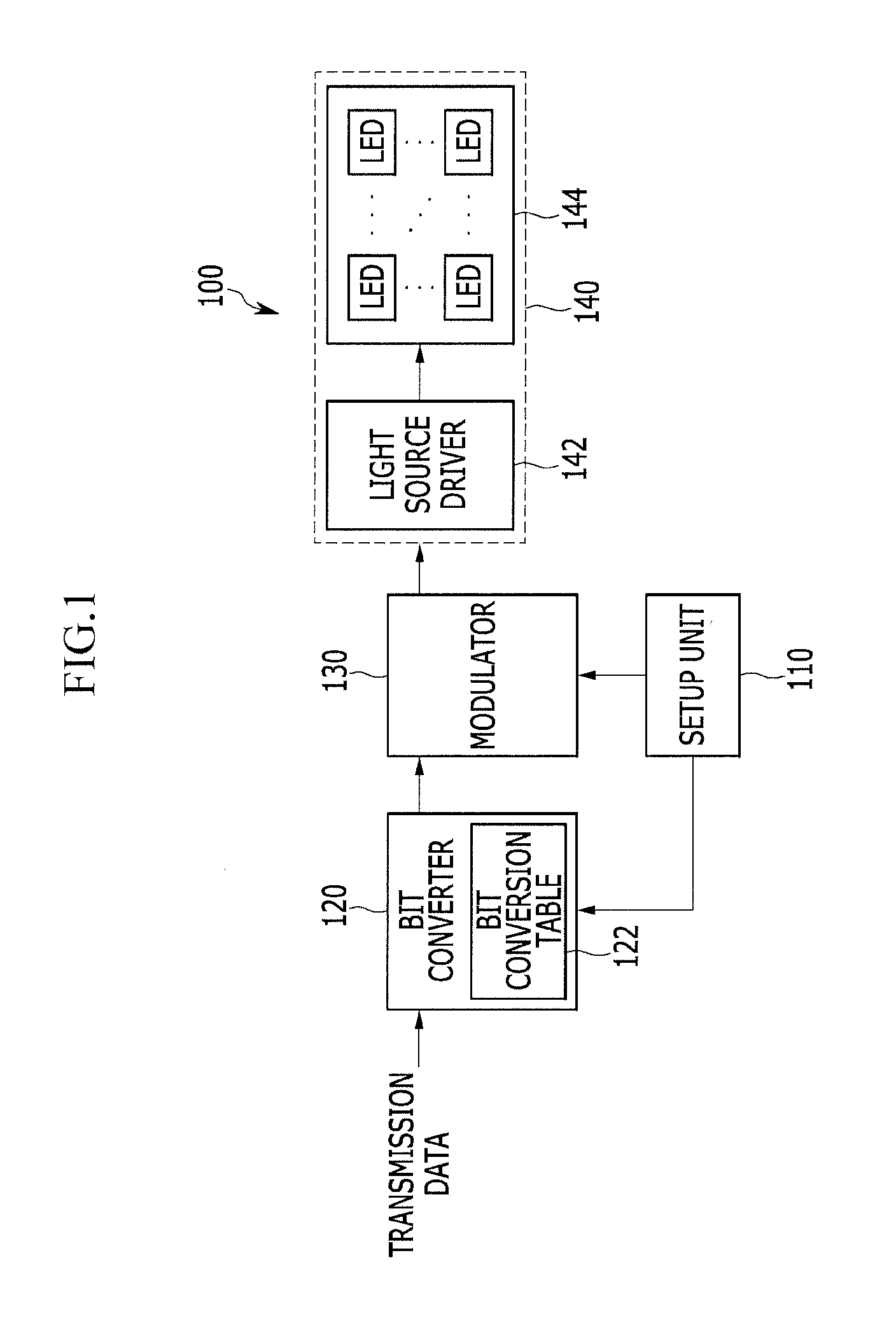
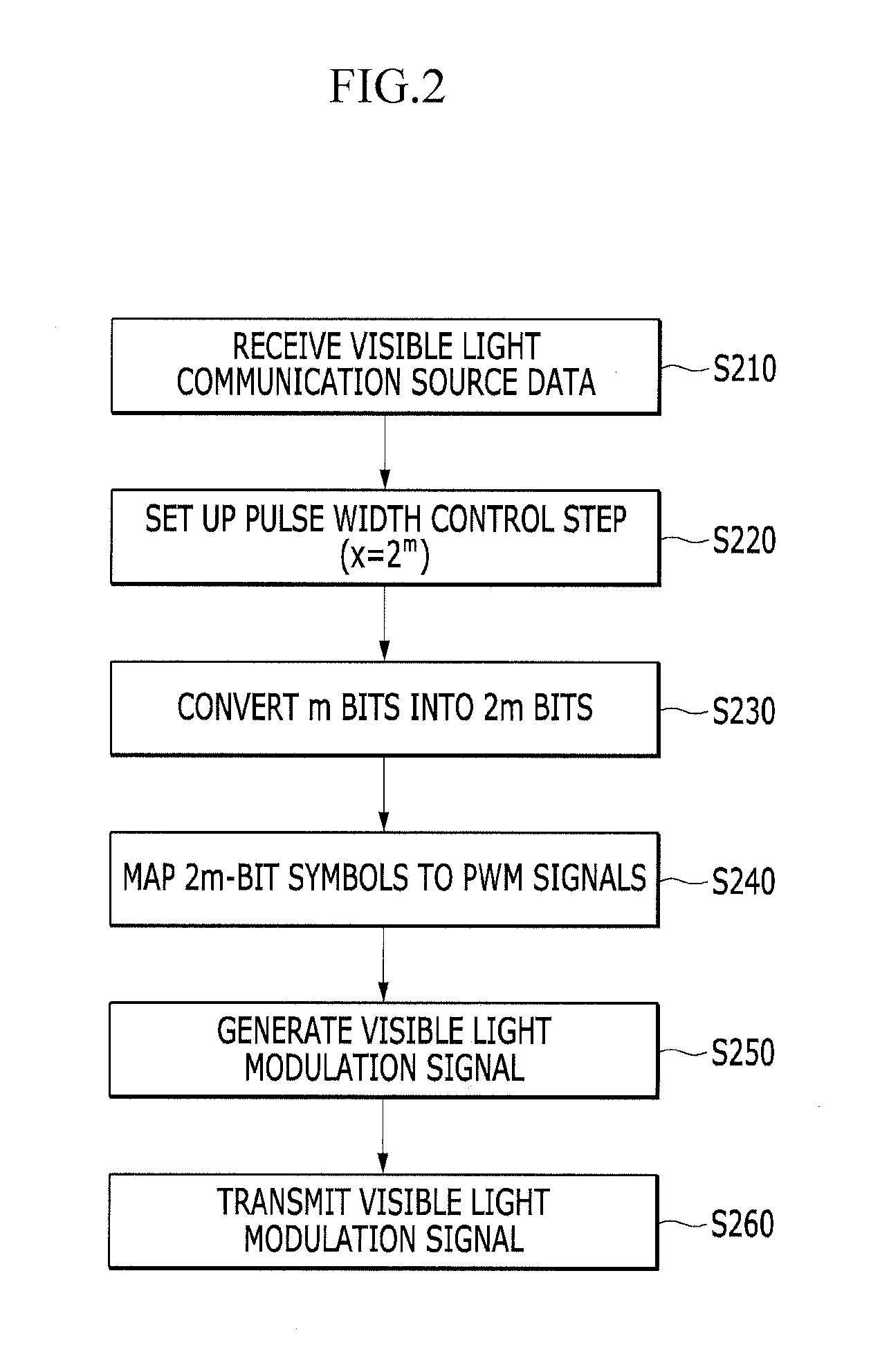
Data transmitting and receiving apparatus and method for visible light communication
InactiveUS20120087676A1Reduce brightnessReduce flickerClose-range type systemsElectromagnetic transmittersPwm signalsTurn on time
An apparatus for transmitting data for visible light communication sets up the pulse width control step of pulse width modulation (PWM) in a unit time interval, modulates each symbol of VLC source data input into a PWM signal in accordance with the pulse width control step, generates a visible light modulation signal by controlling the turn-on time or turn-off time of a plurality of light emitting diodes (LEDs) in response to the PWM signal, and transmits the visible light modulation signal.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Soft switching high efficiency flyback converter
InactiveUS7450402B2Easy to useSmall sizeDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationSoft switchingEngineering
DC-DC converters such as flyback converters achieve self-regulation by communication information between primary and secondary circuits through the power transformer. Operating in accordance with a generalized concept or algorithm, the converter can be bi-directional and self-regulating. Control of the turn OFF times of semiconductor switches in first and second circuits coupled to first and second windings of the power transformer determines whether power flow is in one direction through the converter or the other direction. Turn ON timing of each semiconductor switch is when there is a reverse current through the switch and voltage across the switch is at or near zero. Turn OFF of a switch can be controlled from one or more operating parameters of the converter such as output voltage, in which case the converter's self-regulation is affected through duty cycle variation with variations in output voltage.
Owner:DET INT HLDG LTD
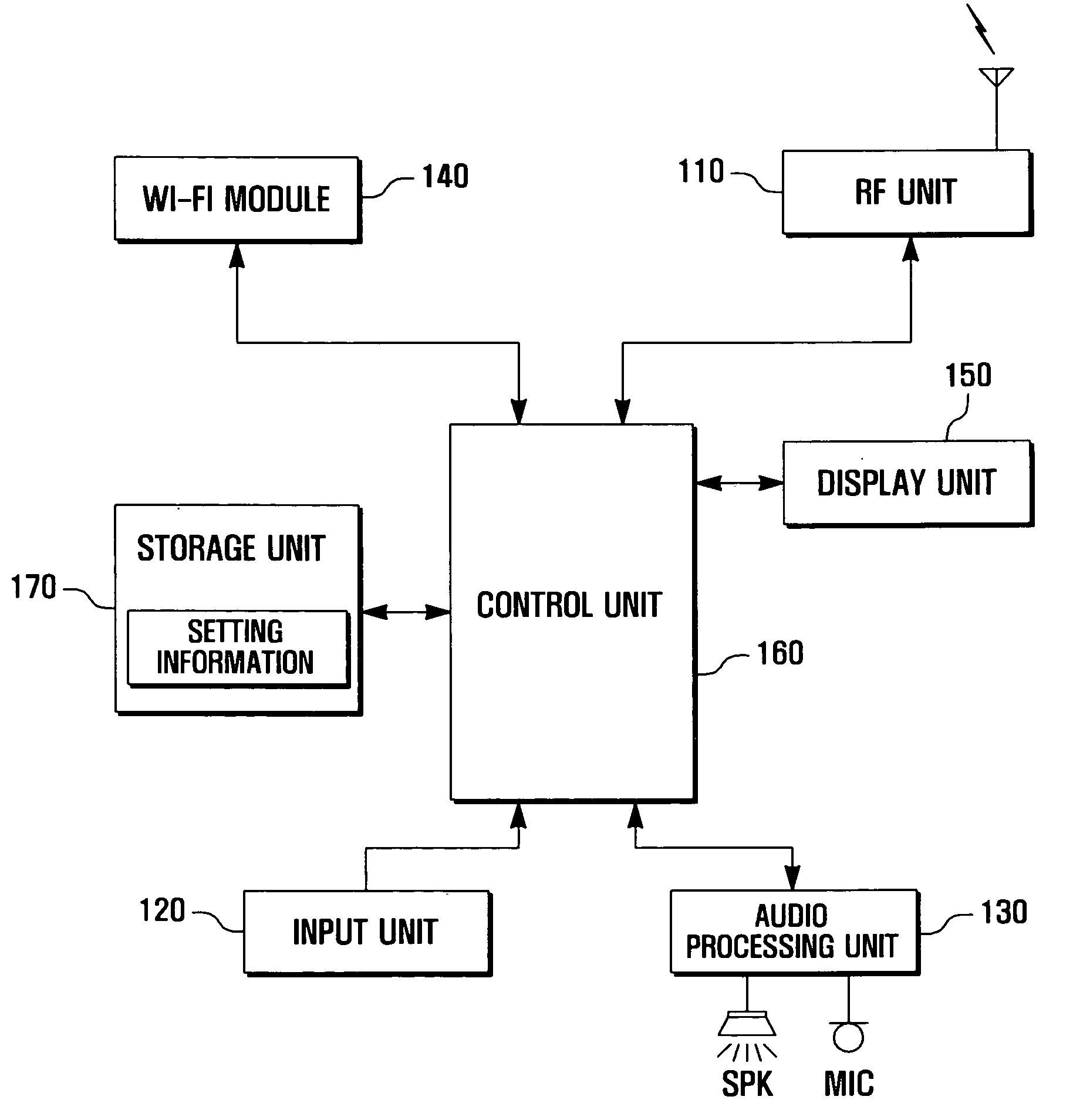
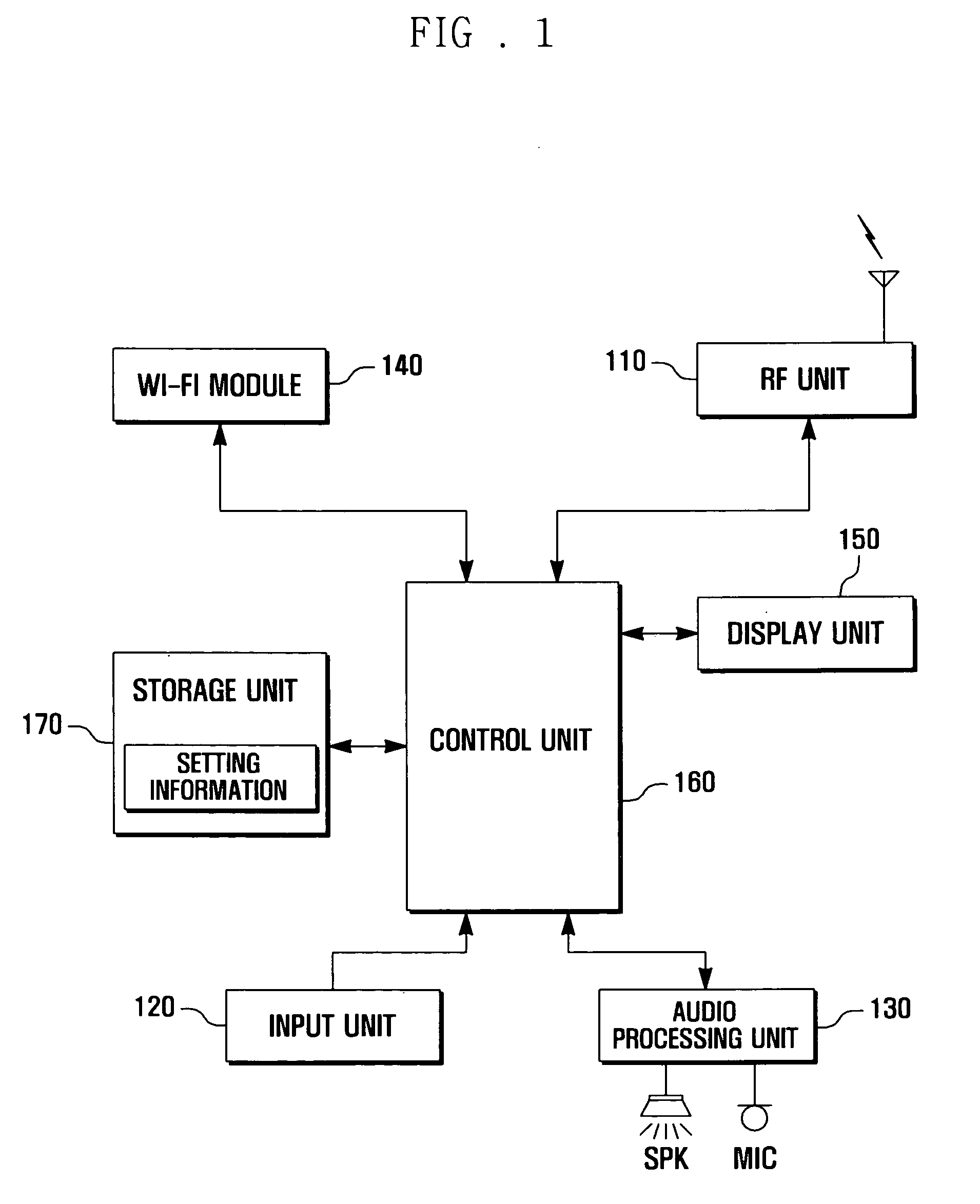
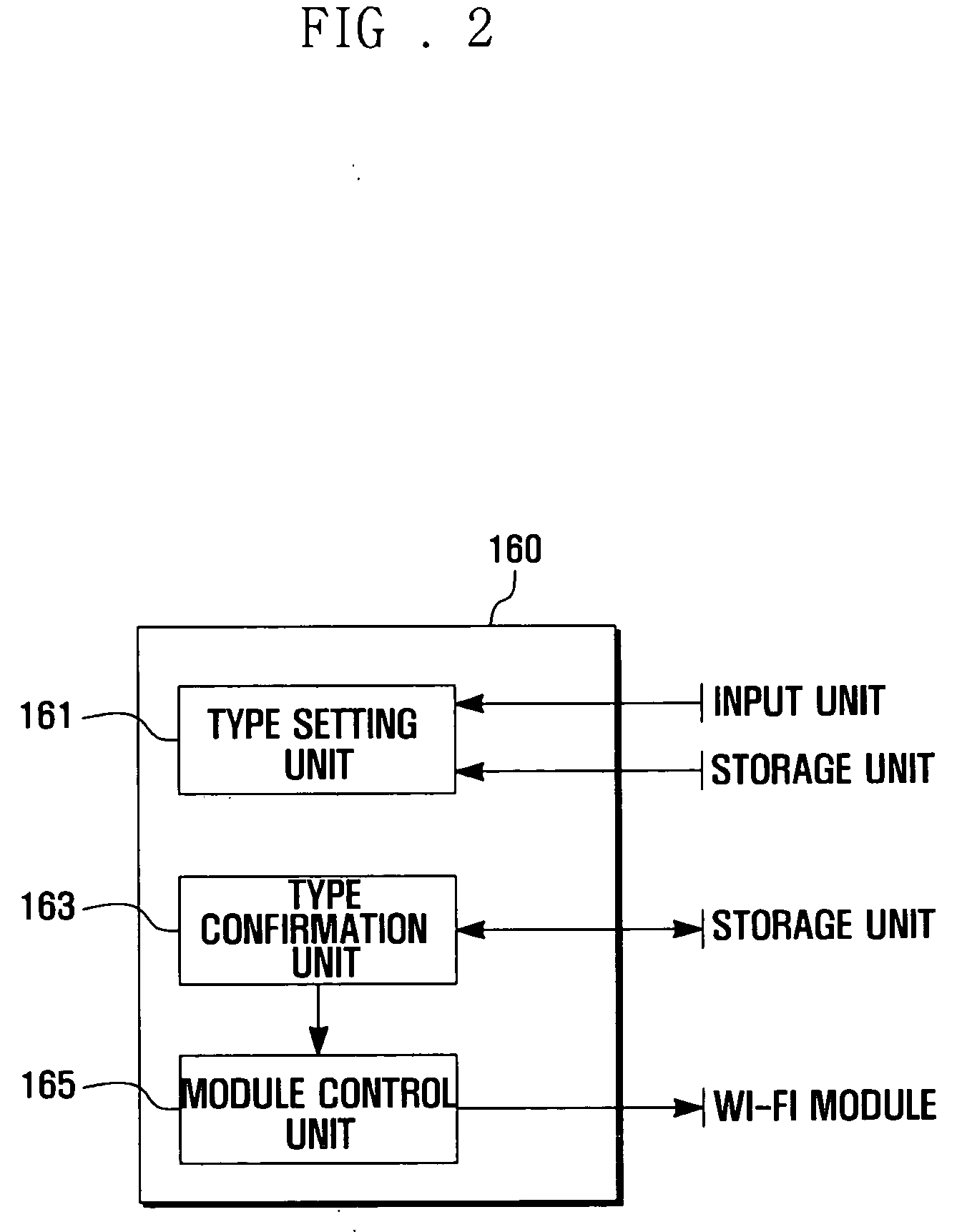
Power saving method of portable terminal and portable terminal supporting the same
A Wi-Fi module provided in the portable terminal is controlled in such a manner that it is turned on or turned off according to a type setting information item including a setup value defining at least one of: a turn-on time interval of the Wi-Fi module, a turn-off time interval of the Wi-Fi module, and a frequency scanning period of the Wi-Fi module in the turn-on status, and scanning is executed according to the set frequency scanning period in the turn-on status.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
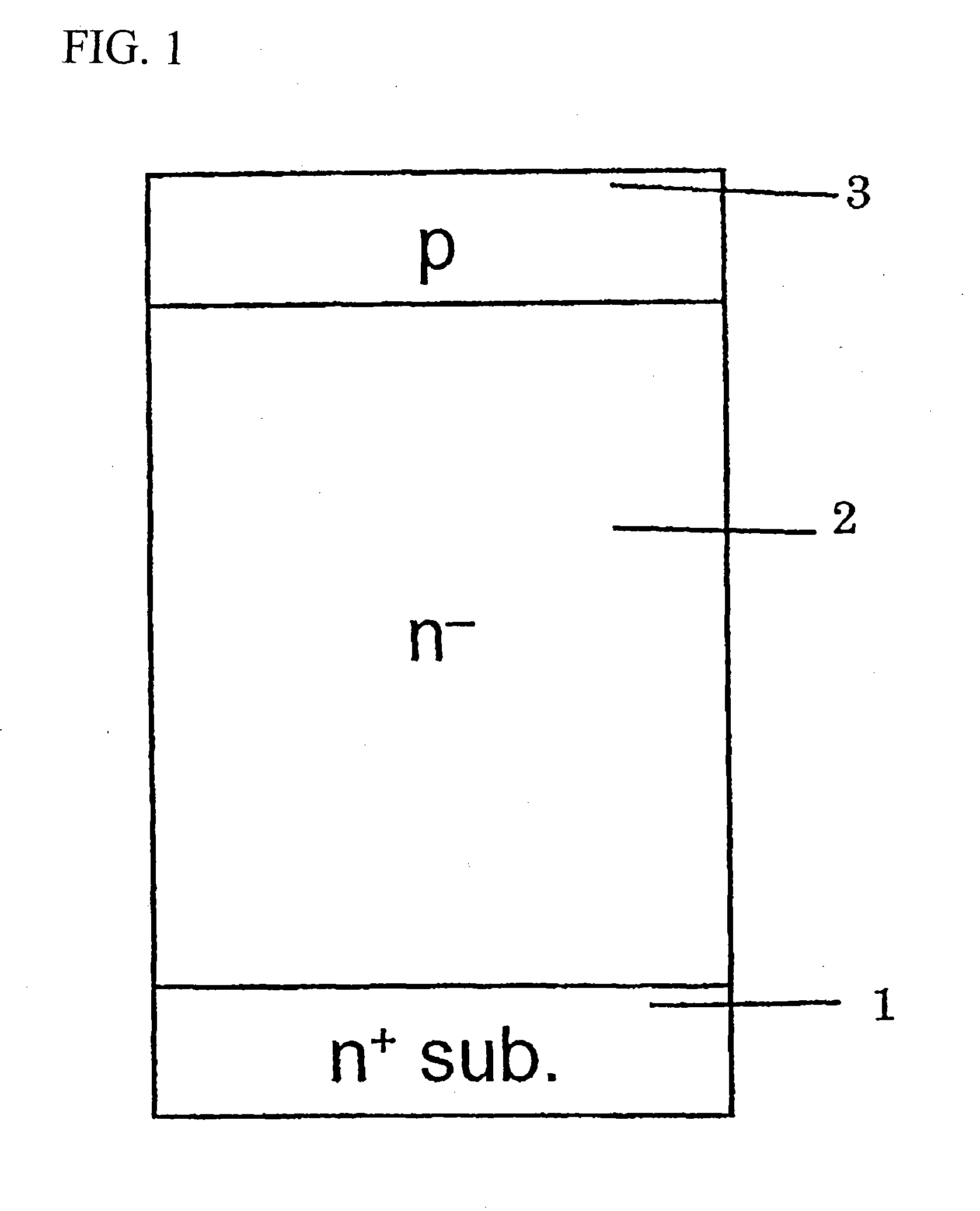
Semiconductor device and manufacturing method therefor
ActiveUS20130285140A1Avoid contactResistance valueTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPower semiconductor devicePower flow
A trench-gate type semiconductor device that can prevent breakdown of a gate insulating film caused by a displacement current flowing into a protective diffusion layer at a portion of a trench underlying a gate electrode at a turn-off time and simultaneously improves a current density by narrowing a cell pitch. The semiconductor device includes a gate electrode embedded into a trench penetrating a base region. The gate electrode is disposed into a lattice shape in a planar view, and a protective diffusion layer is formed in a drift layer at the portion underlying thereof. At least one of blocks divided by the gate electrode is a protective contact region on which the trench is entirely formed. A protective contact for connecting the protective diffusion layer at a bottom portion of the trench and a source electrode is disposed on the protective contact region.
Owner:MITSUBISHI ELECTRIC CORP
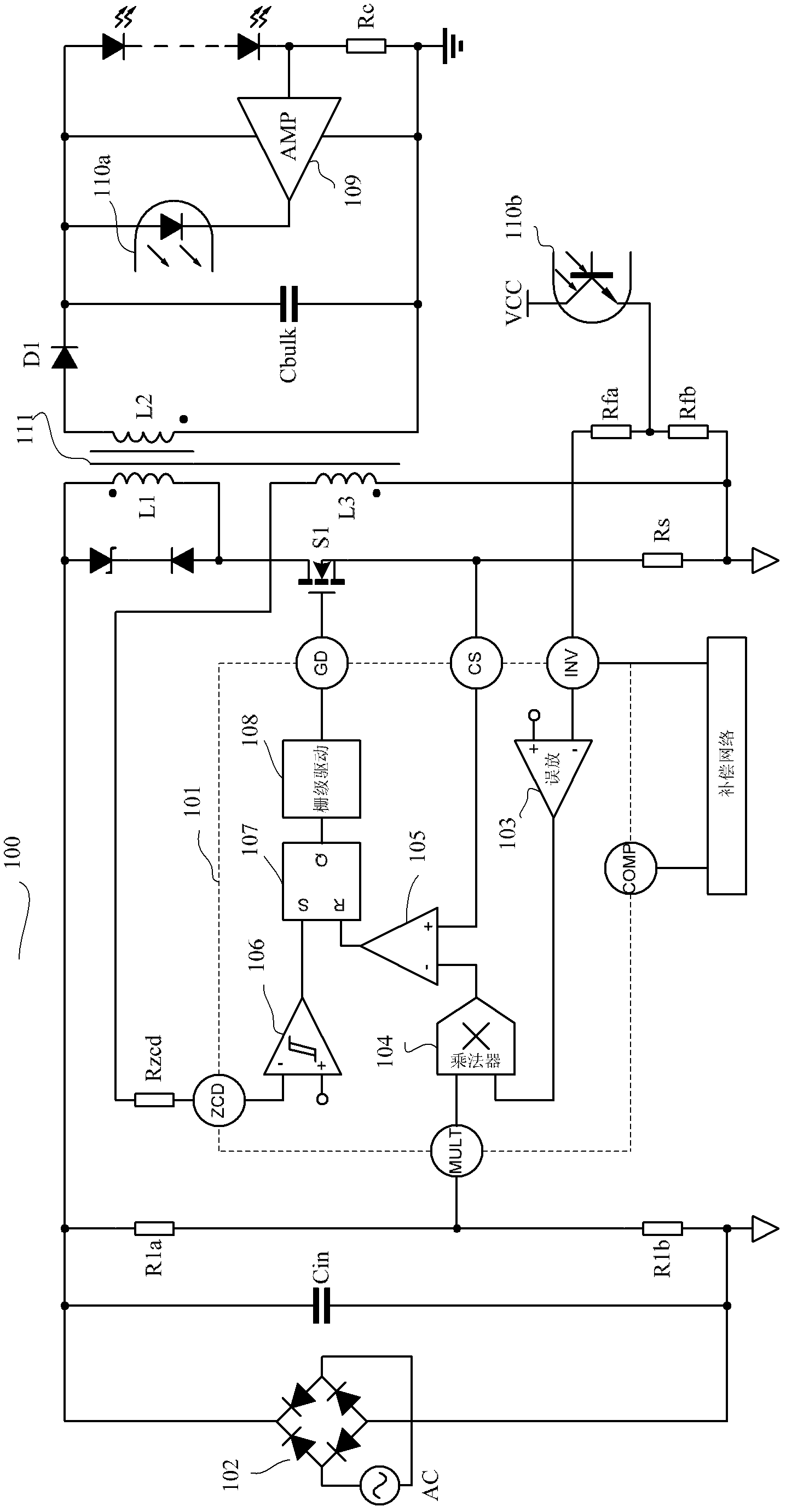
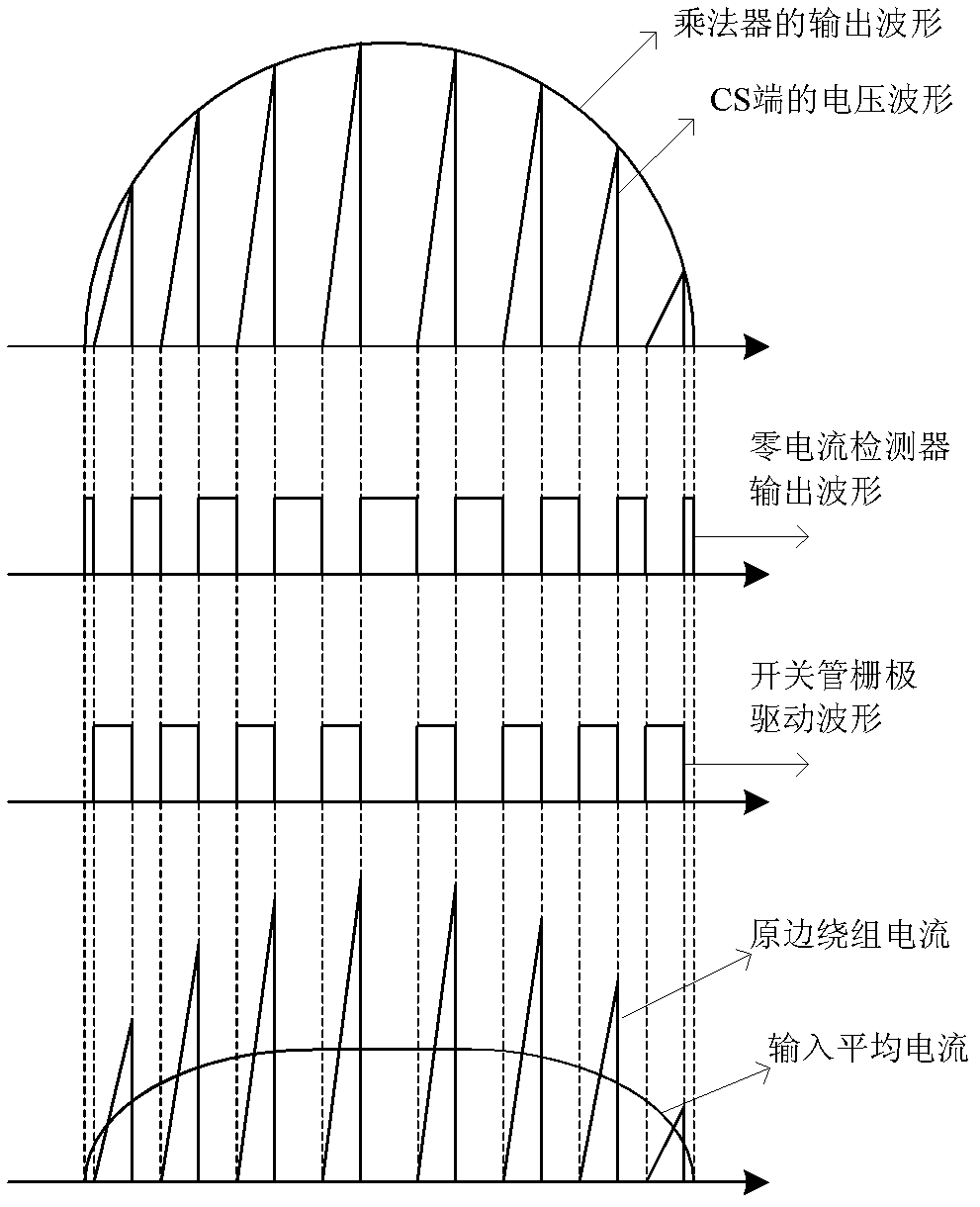
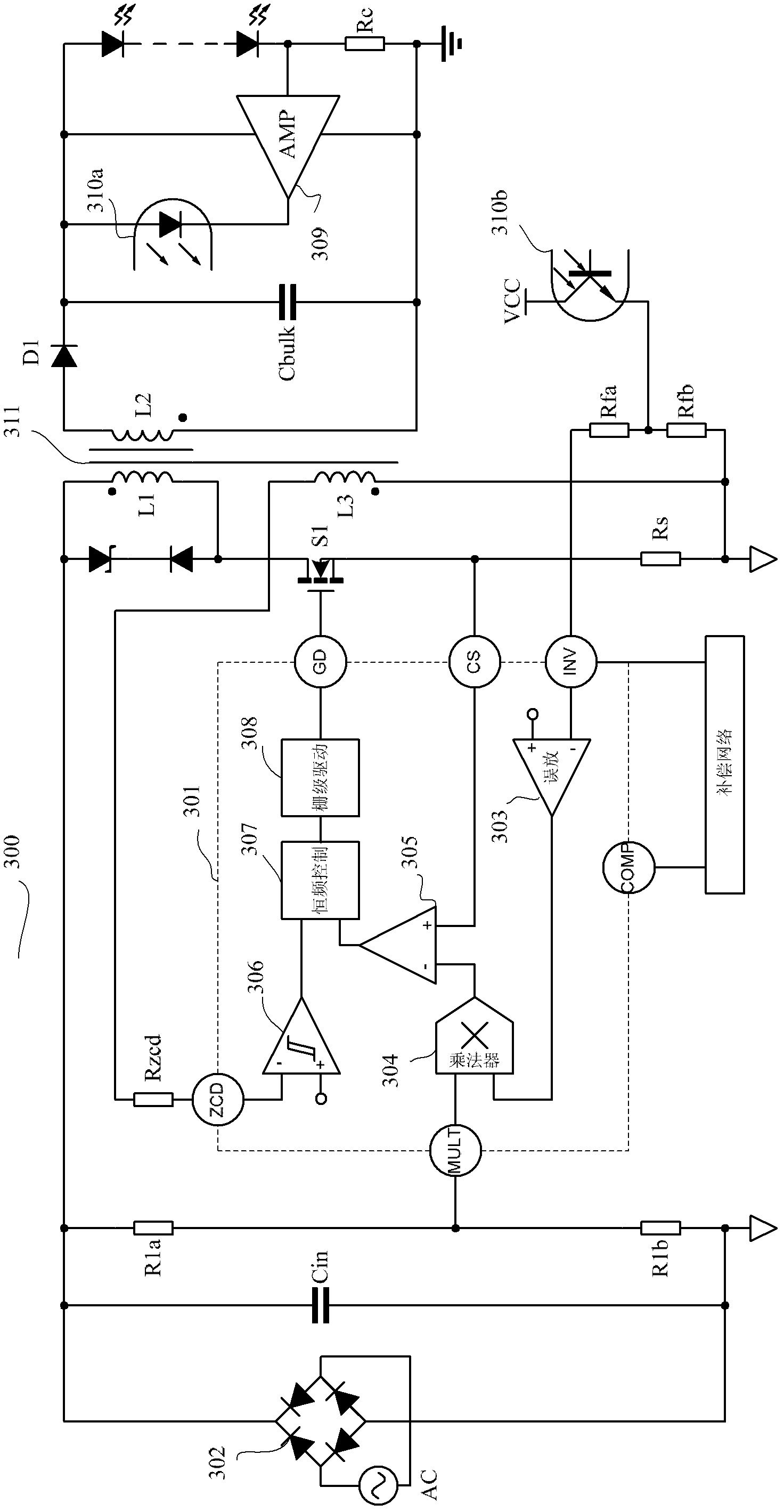
LED drive circuit and switch power supply containing drive circuit
ActiveCN102497711AImprove power factorAc-dc conversionDc-dc conversionConstant frequencySwitching frequency
The invention discloses an LED drive circuit which comprises an error amplifier, a multiplier, a current induction comparator, a zero current detector, a constant frequency control module and a drive circuit. The constant frequency control module is employed in the invention, and turn-off time of a switch tube is fixed and is determined by the constant frequency control module. So when a system is in a half period of input alternating current, switch frequency is not changed any more, the frequency is fixed, and input current and input voltage of a switch power supply are completely same.
Owner:HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS
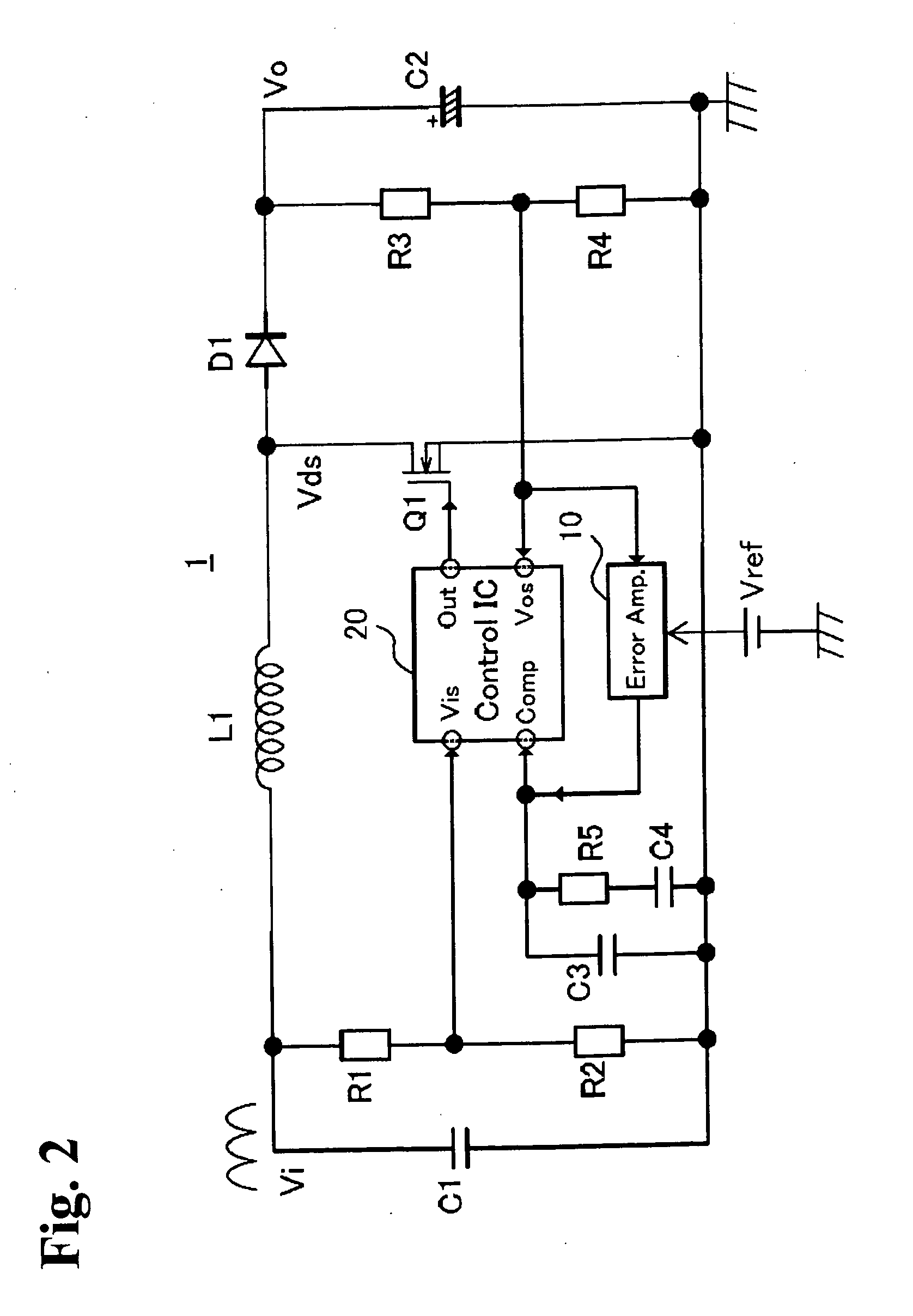
Power factor correction power supply unit, and control circuit and control method used in the same
ActiveUS20100109626A1Simple processAvoid running continuouslyEfficient power electronics conversionElectrical energyVoltage referenceEngineering
A power factor correction power supply unit for correcting a power factor includes a switching device, an input voltage detection circuit, an output voltage detection circuit, an error amplifier for outputting an error signal obtained by amplifying a difference between an output voltage detection signal and a reference voltage, an ON width generation circuit for generating an ON time width, an OFF width generation circuit for generating an OFF time width of the switching device, and a switching device driving circuit. The drive circuit conducts an ON / OFF control over the switching device upon receiving a turn-on timing signal for turning on the switching device as soon as the OFF time width is terminated and upon receiving a turn-off timing signal for turning off the switching device as soon as the ON time width is terminated.
Owner:FUJI ELECTRIC CO LTD
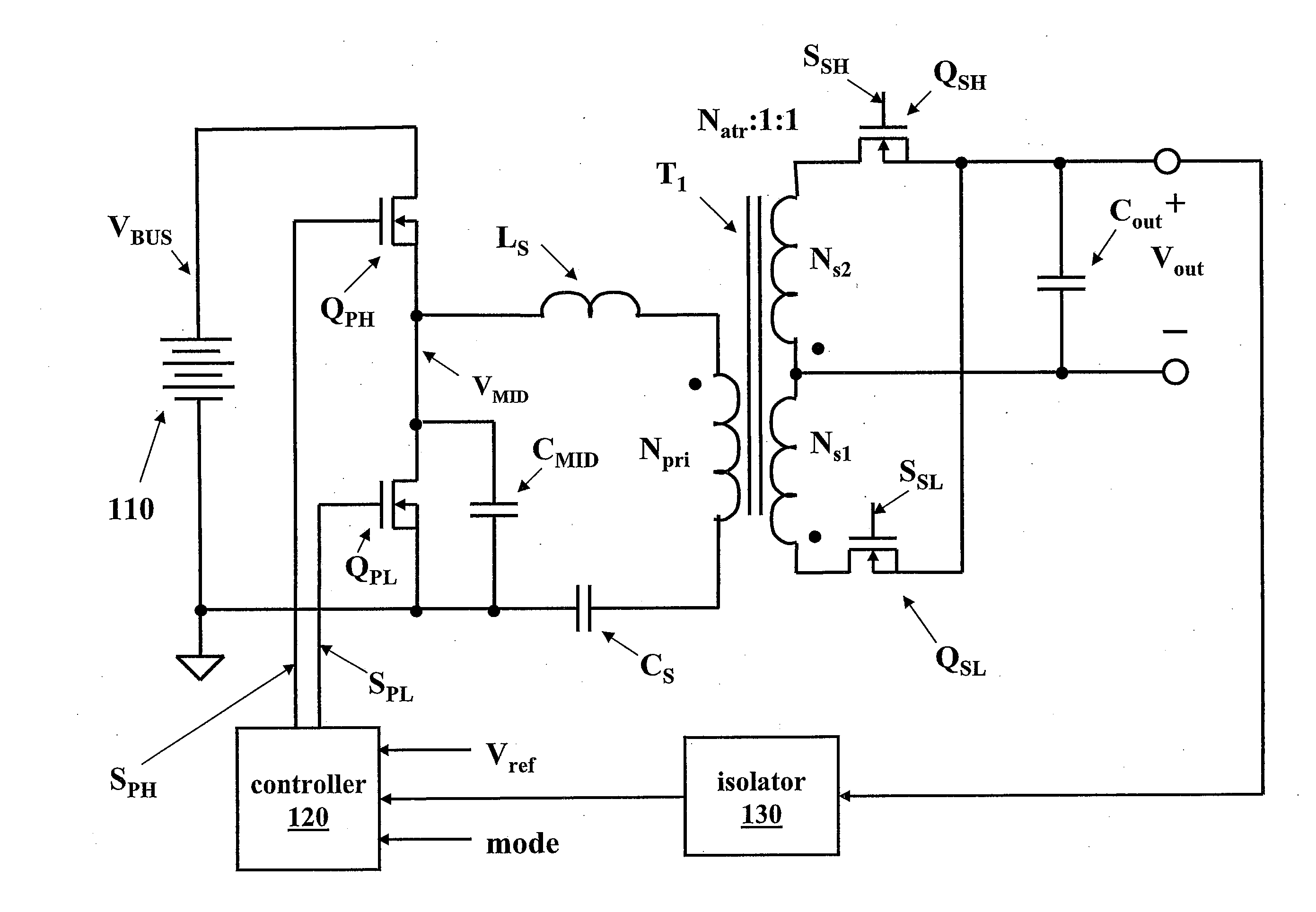
Controller for a Resonant Switched-Mode Power Converter
ActiveUS20110267844A1Efficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionPower switchingSwitching frequency
An embodiment of the invention relates to an LLC power converter including a controller configured to regulate an output characteristic of the power converter by controlling a power converter switching frequency. In a first mode of operation, the controller turns off a secondary-side power switch earlier than a turn-off time of a primary-side power switch by a time difference that is controlled by a resistor coupled to an external circuit node. In a second mode of operation, the controller turns on a secondary-side power switch at substantially the same time as the primary-side power switch, and turns off the secondary-side power switch after a maximum on time that is a nonlinear function of a load current of the power converter. The nonlinear function is a substantially constant function of the load current for a value of the load current higher than a threshold value.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Control circuit for DC-DC current transformer and method thereof
ActiveCN101728954AImprove light load efficiencyFast dynamic responsePulse generatorApparatus with intermediate ac conversionDc currentReverse current
The invention provides a control circuit for a DC-DC current transformer and a control method thereof; the control circuit comprises a self-adaption constant time breakover control circuit, a voltage feedback circuit, a minimum turn-off time control circuit, a logic circuit, a reverse current comparison circuit and a driving circuit; the control circuit has rapid dynamic response and self-adaption constant breakover time of a main circuit switching tube, and the circuit is simple without compensating network.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
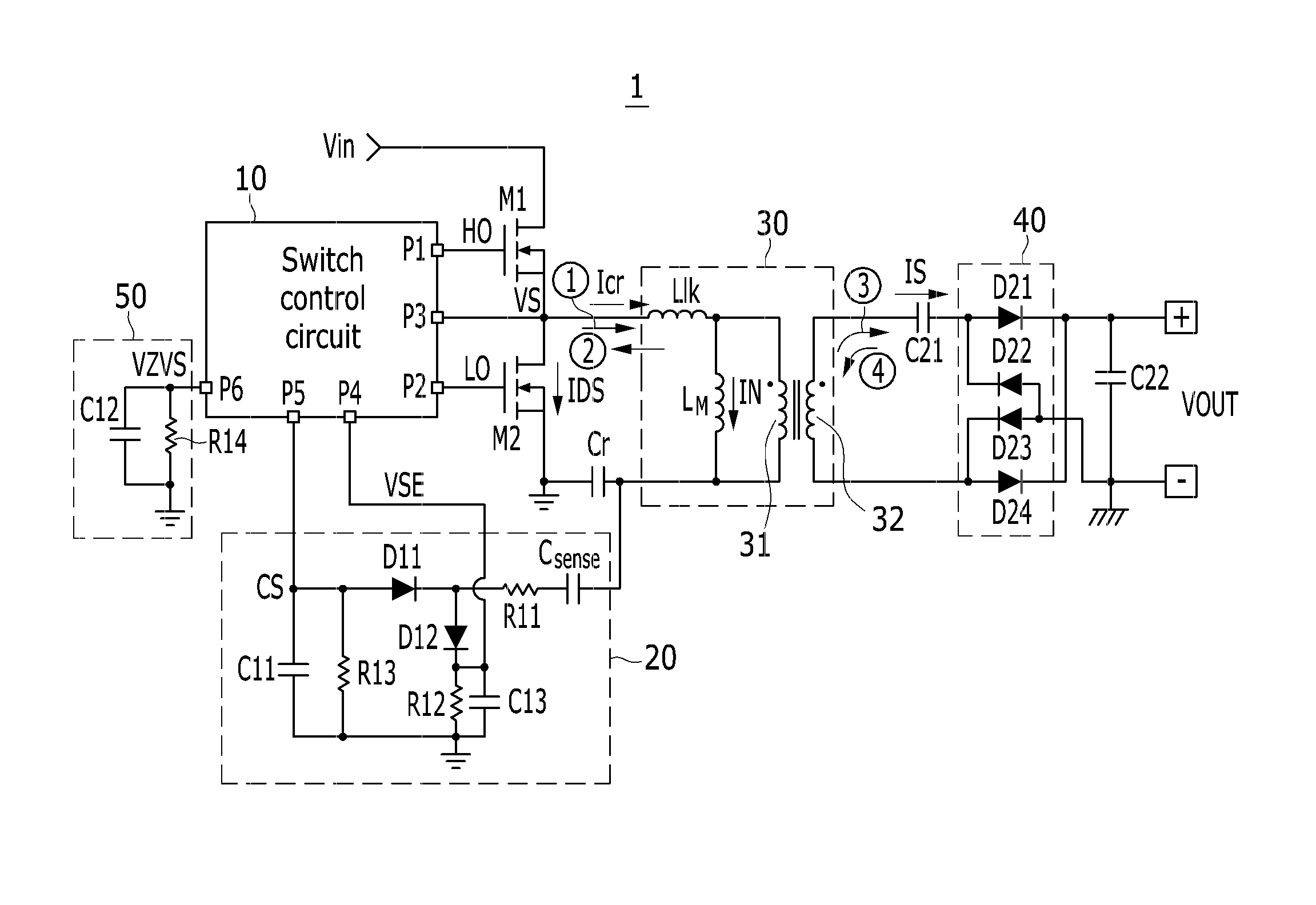
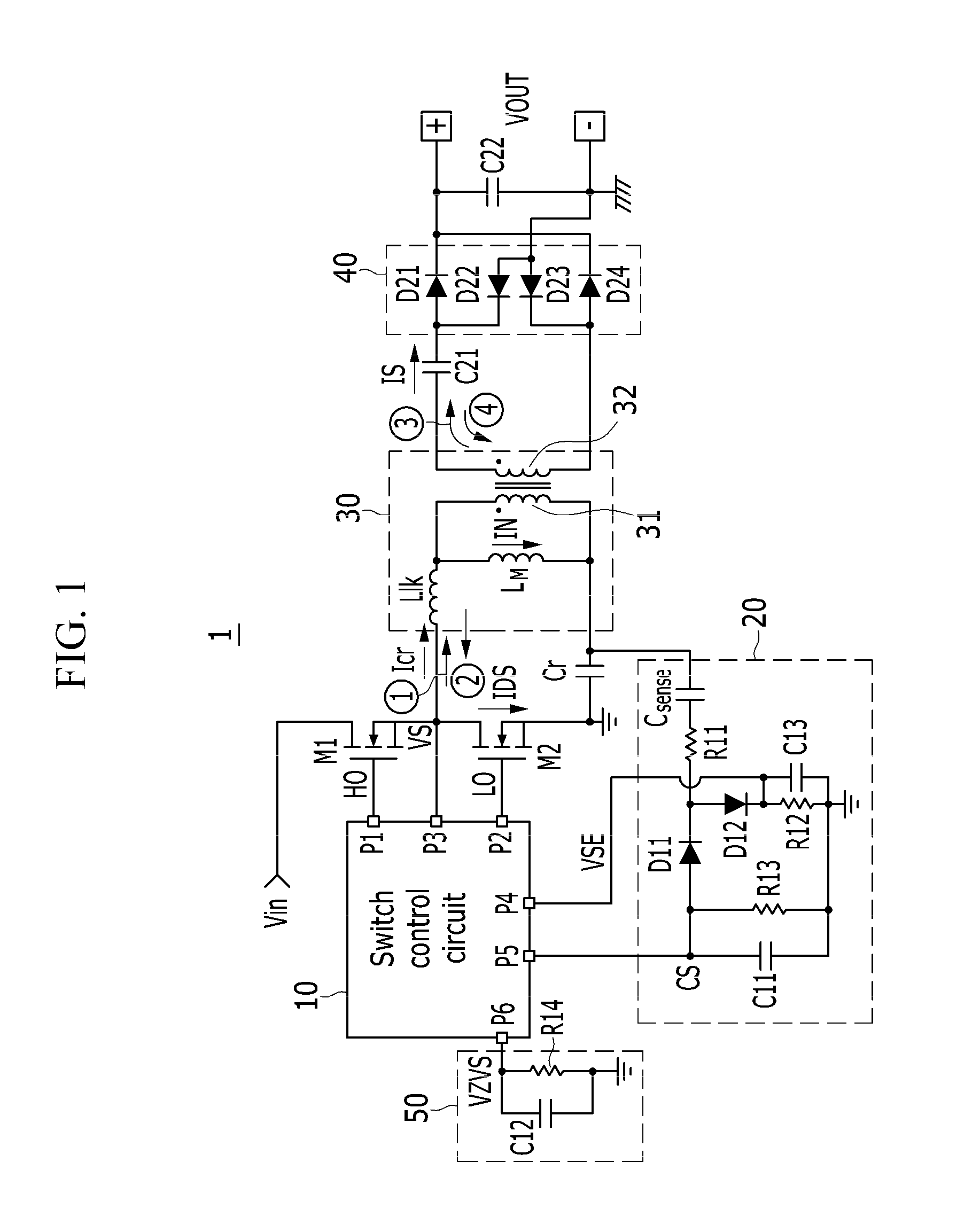
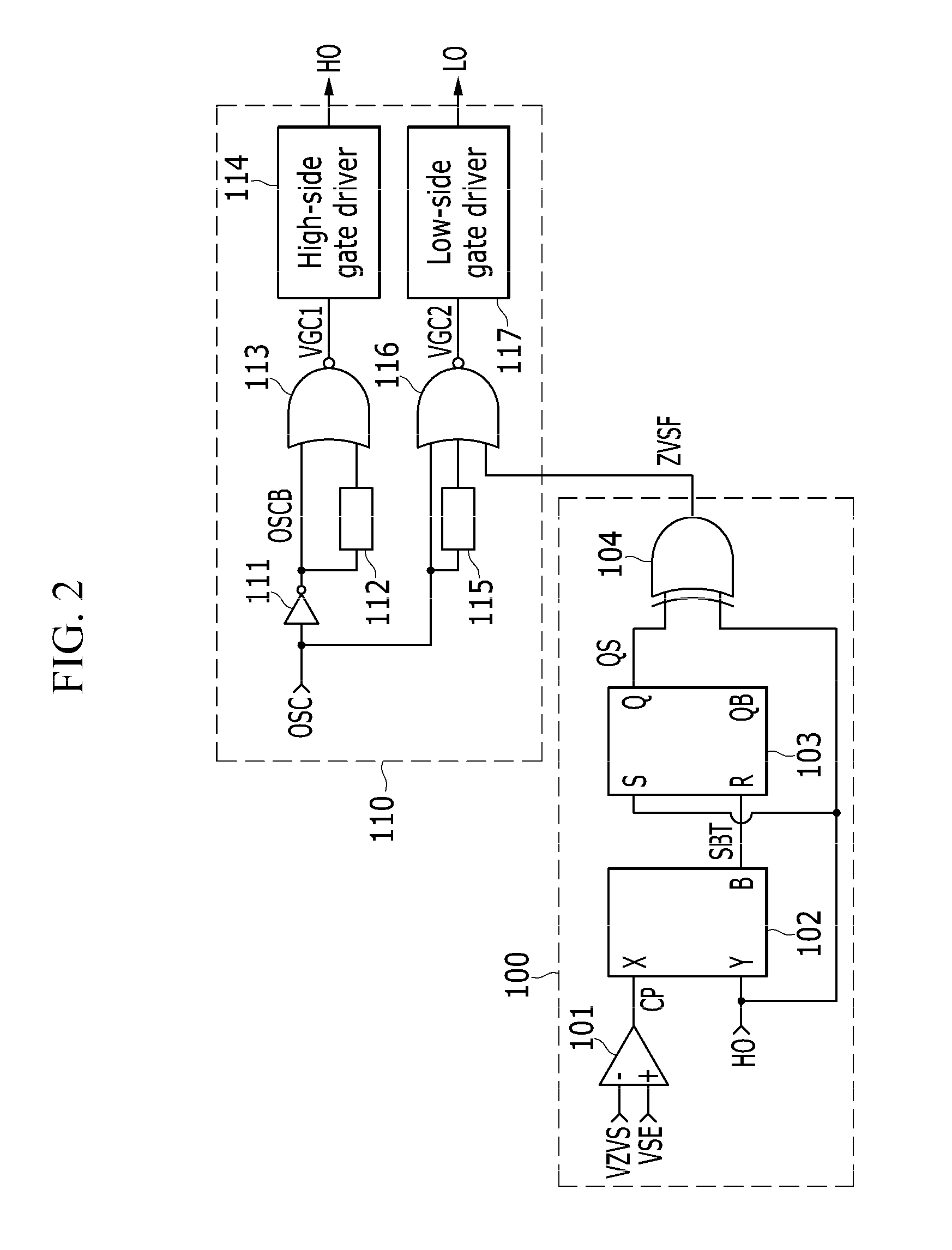
Switch control circuit, power supply device comprising the same and driving method of the power supply device
InactiveUS20140286056A1Limit its operationEfficient power electronics conversionApparatus with intermediate ac conversionPower flowSwitching cycle
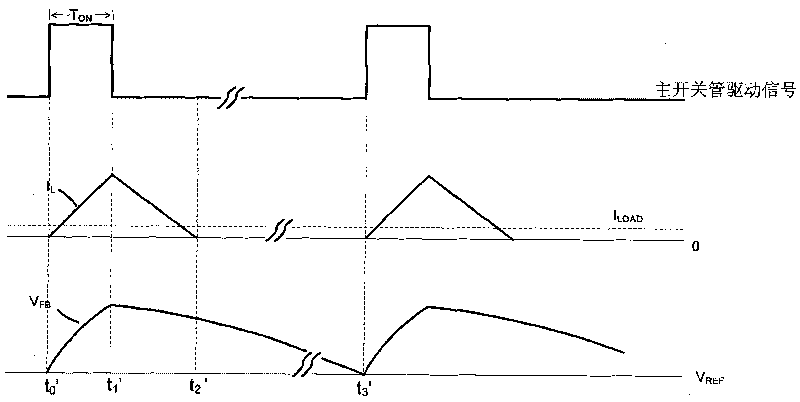
The invention relates to a switch control circuit, a power supply including the same, and a method for driving the power supply. The power supply includes: a first switch; a second switch coupled in series to the first switch; a transistor coupled to a node where the first switch and the second switch are coupled; a resonance capacitor coupled between the transformer and a primary side ground and to which a resonance current flows; a sense circuit generating a first sense voltage that depends on the resonance current when the resonance current is a positive current; and a switch control circuit detecting a zero voltage switching failure by sensing the resonance current using the first sense voltage at a turn-off time of the first switch for every switching cycle of the first and second switches.
Owner:FAIRCHILD KOREA SEMICON
Emission current subdivision control circuit based on magnetic source electromagnetic method
InactiveCN101807864AReduce current off timeReduce the current off time to reduce the impact of the primary field in shallow detectionDc-ac conversion without reversalPrimary fieldTurn off time
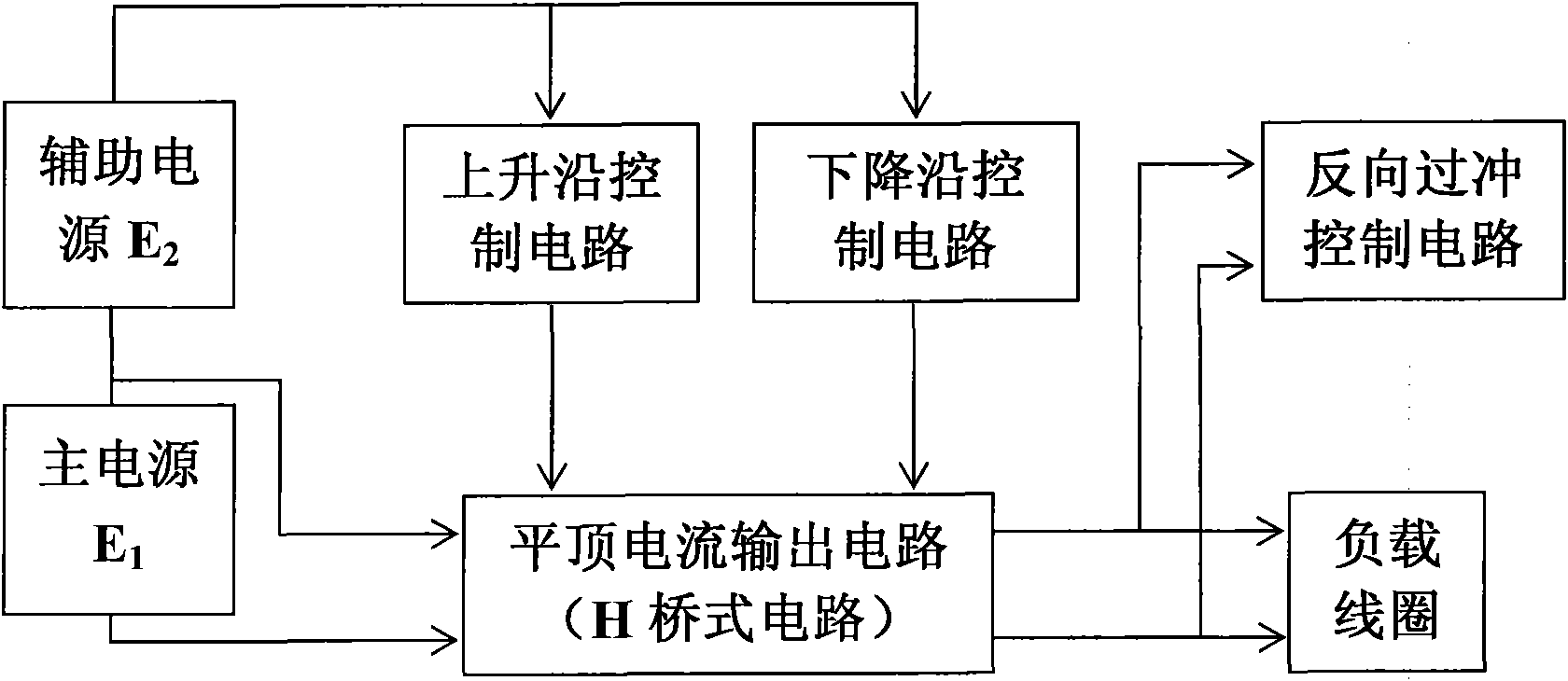
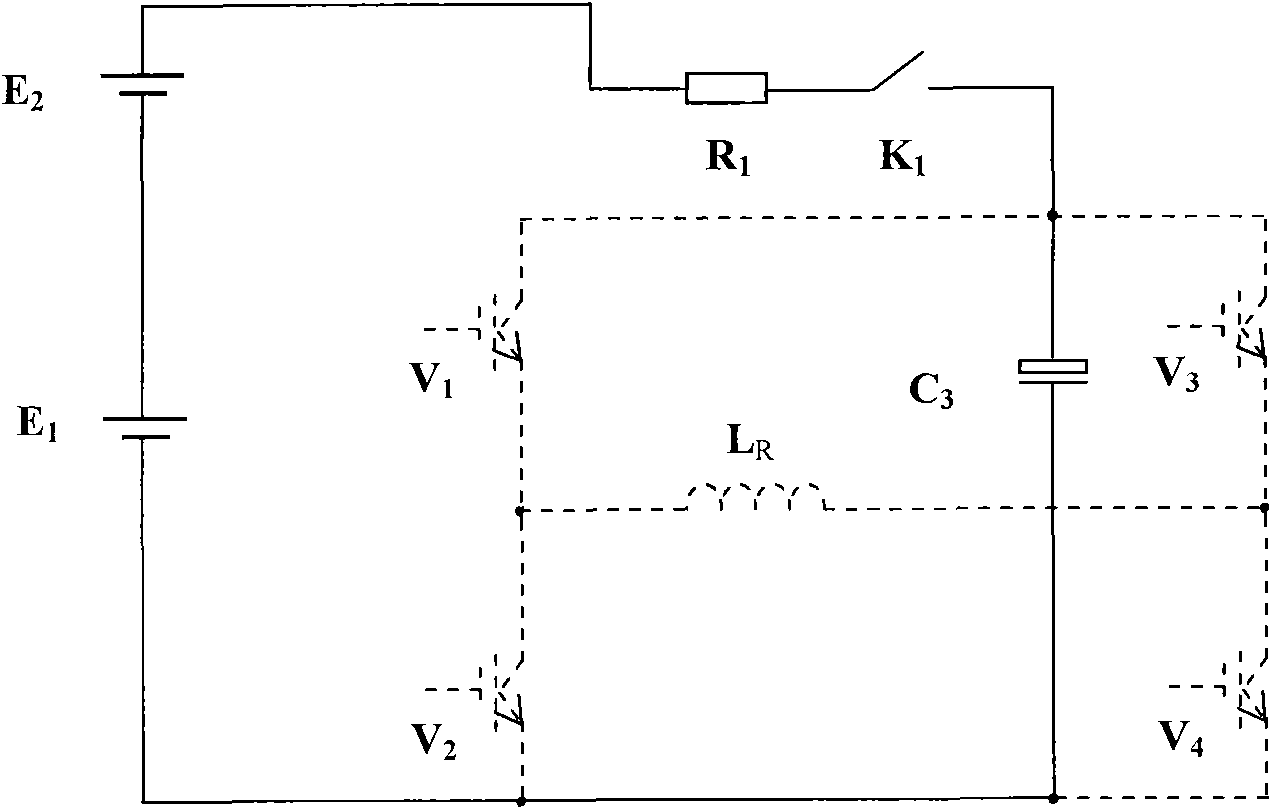
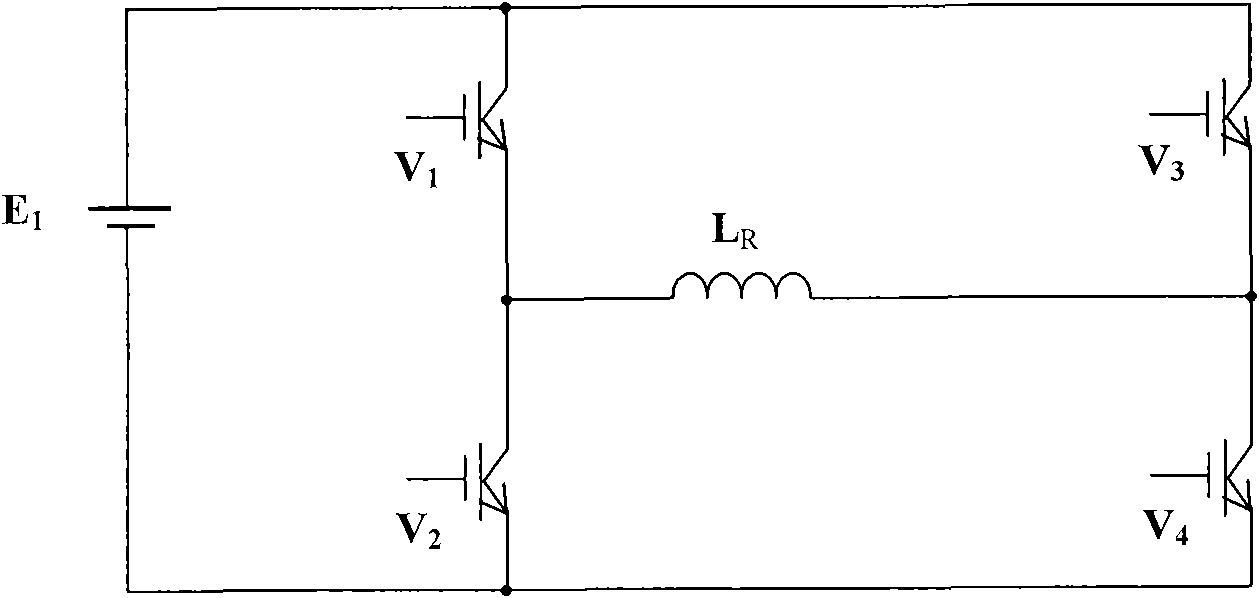
The invention relates to an emission current subdivision control circuit based on a magnetic source electromagnetic method. The emission current subdivision control circuit based on a magnetic source electromagnetic method adopts a four-division accurate control mode, and is formed in a way that a primary power supply is connected with loading coils and is connected in parallel with a reverse overshooting control circuit through an H bridge inversion main circuit for outputting flat-top current, and after passing through an auxiliary power supply, the positive end of the primary power supply is respectively connected in parallel with a rising edge control circuit and a falling edge control circuit on the H bridge inversion main circuit. Compared with the prior art, the invention adopts the output current subdivision control, solves the conflict of mutual restriction between the flat-top section control and the rising edge and falling edge control mode, reduces the ripples and the electromagnetic interference of the flat-top current, decreases the turn-off time of the output current, and reduces the effect of the primary field in the shallow detection result interpretation of a large-magnetic moment transient electromagnetic device. Simultaneously, the invention reduces the switching number of the power device, reduces the switching loss of the power device, simplifies the control circuit, saves the cost and improves the efficiency.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
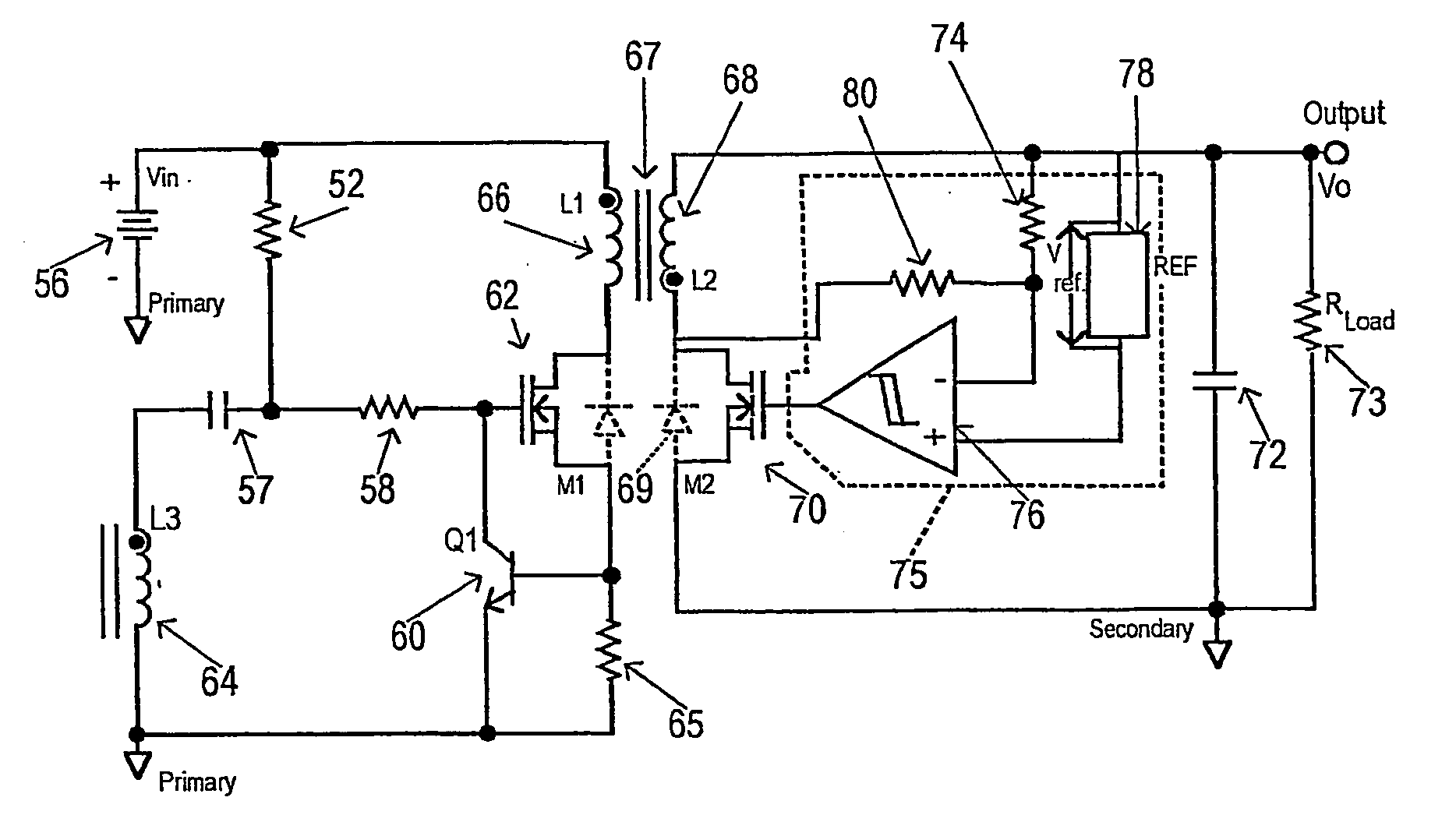
Method and arrangement for regulating low output voltages in multiple output flyback DC/DC converters
InactiveUS6459595B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcConductor CoilControl circuit
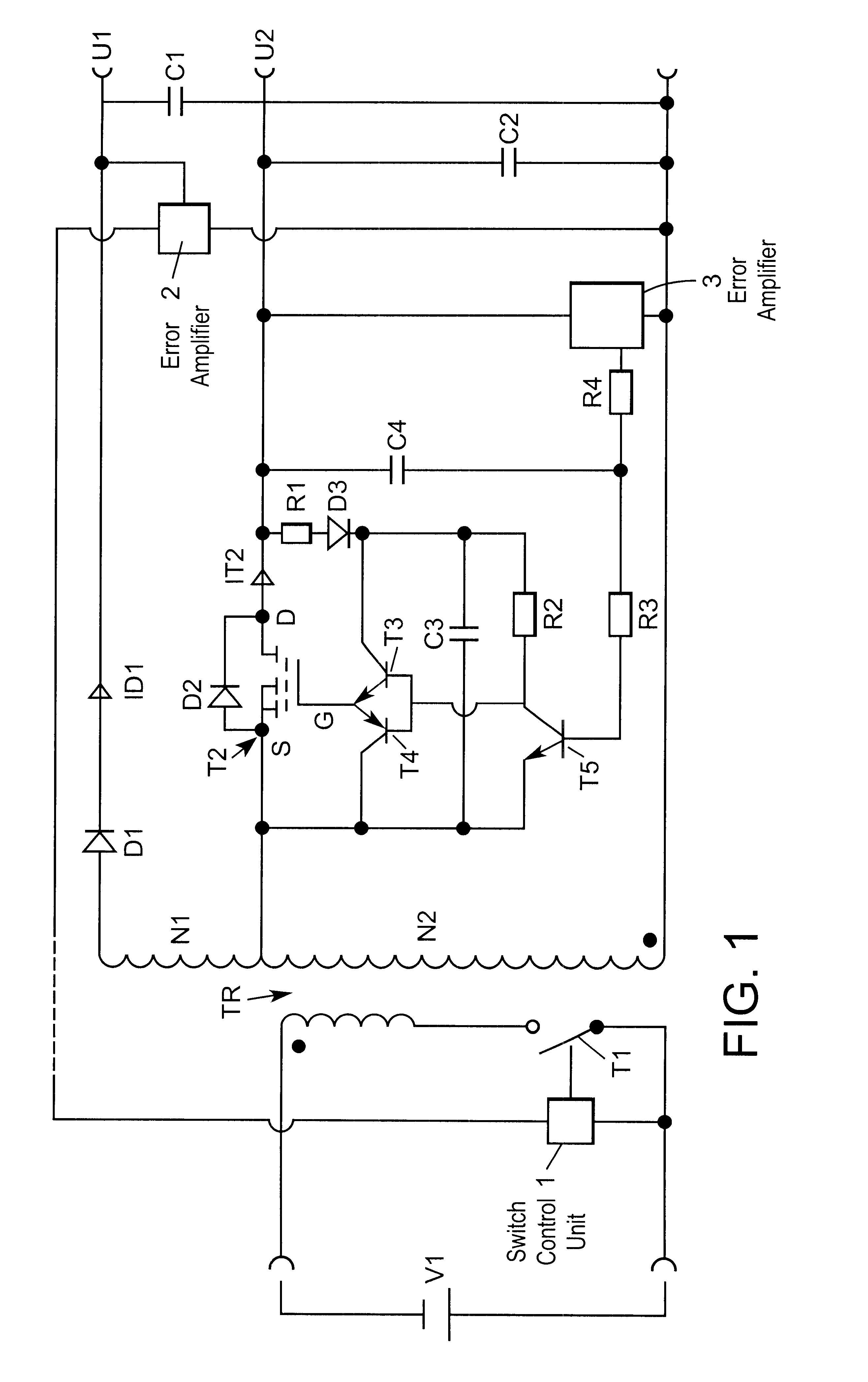
Methods and arrangements are provided for regulating low output voltages in multiple output flyback DC / DC converters that generate, in addition to a main output DC voltage, at least one additional output DC voltage. Converter arrangements include a transformer with a primary winding connected in series with a primary switch, a first secondary winding connected in series with a first rectifier to a first output capacitor for generating the main output DC voltage, and a secondary winding connected in series with a synchronous rectifier to a second output capacitor for generating the additional output DC voltage. An error amplifier is arranged to compare the actual value of the additional output DC voltage with a desired value, and a control circuit is interconnected between the error amplifier and the synchronous rectifier to adjust the turn-off time of the synchronous rectifier in response to the ratio between the actual value of the additional output DC voltage and the desired value to adjust the actual value to the desired value.
Owner:UNWIRED PLANET
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com