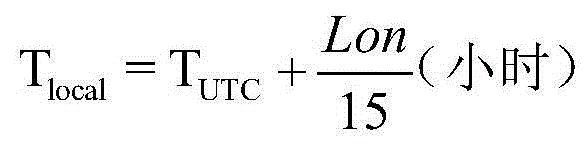Patents
Literature
64 results about "Solar time" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solar time is a calculation of the passage of time based on the position of the Sun in the sky. The fundamental unit of solar time is the day. Two types of solar time are apparent solar time (sundial time) and mean solar time (clock time).
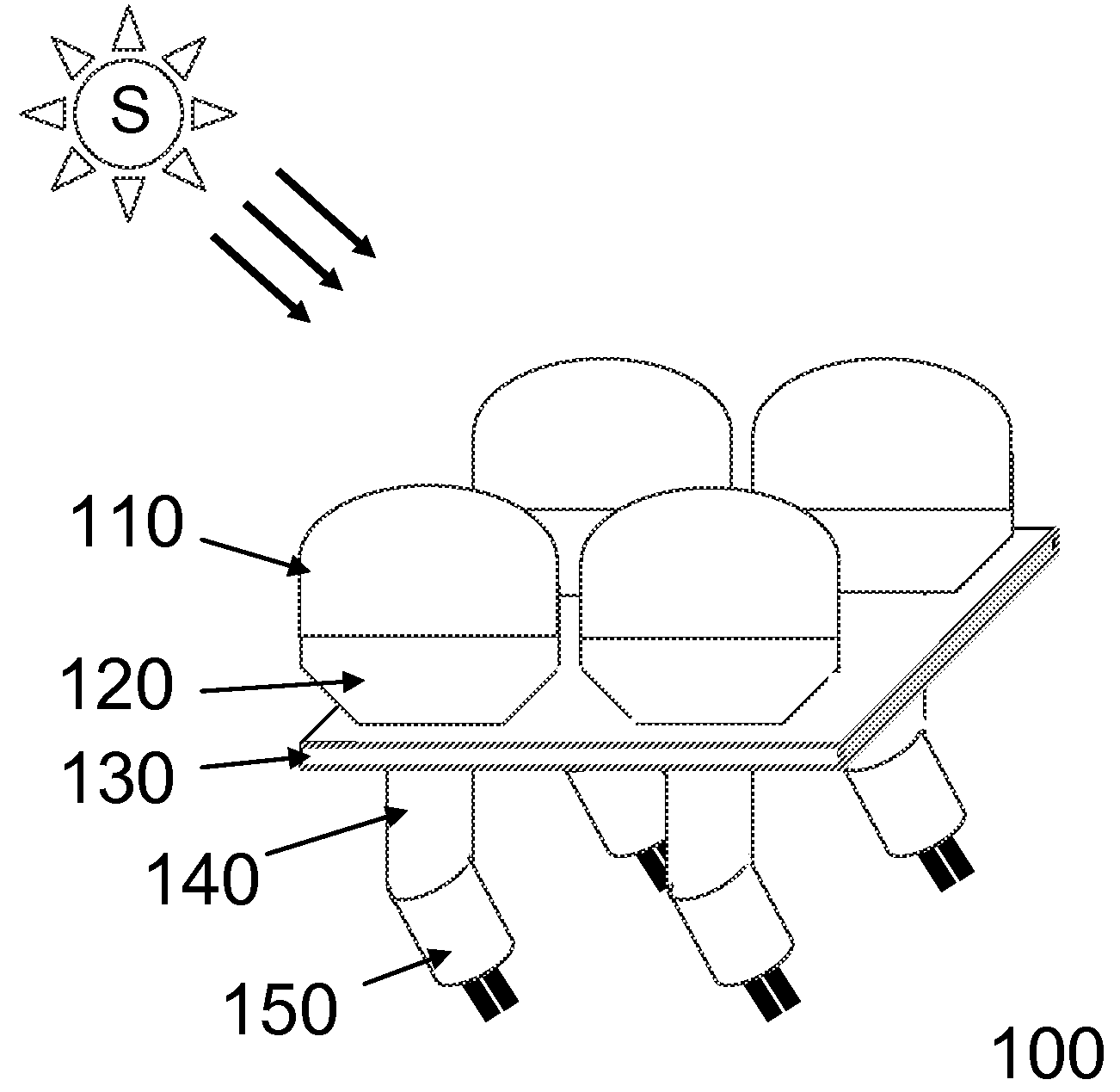
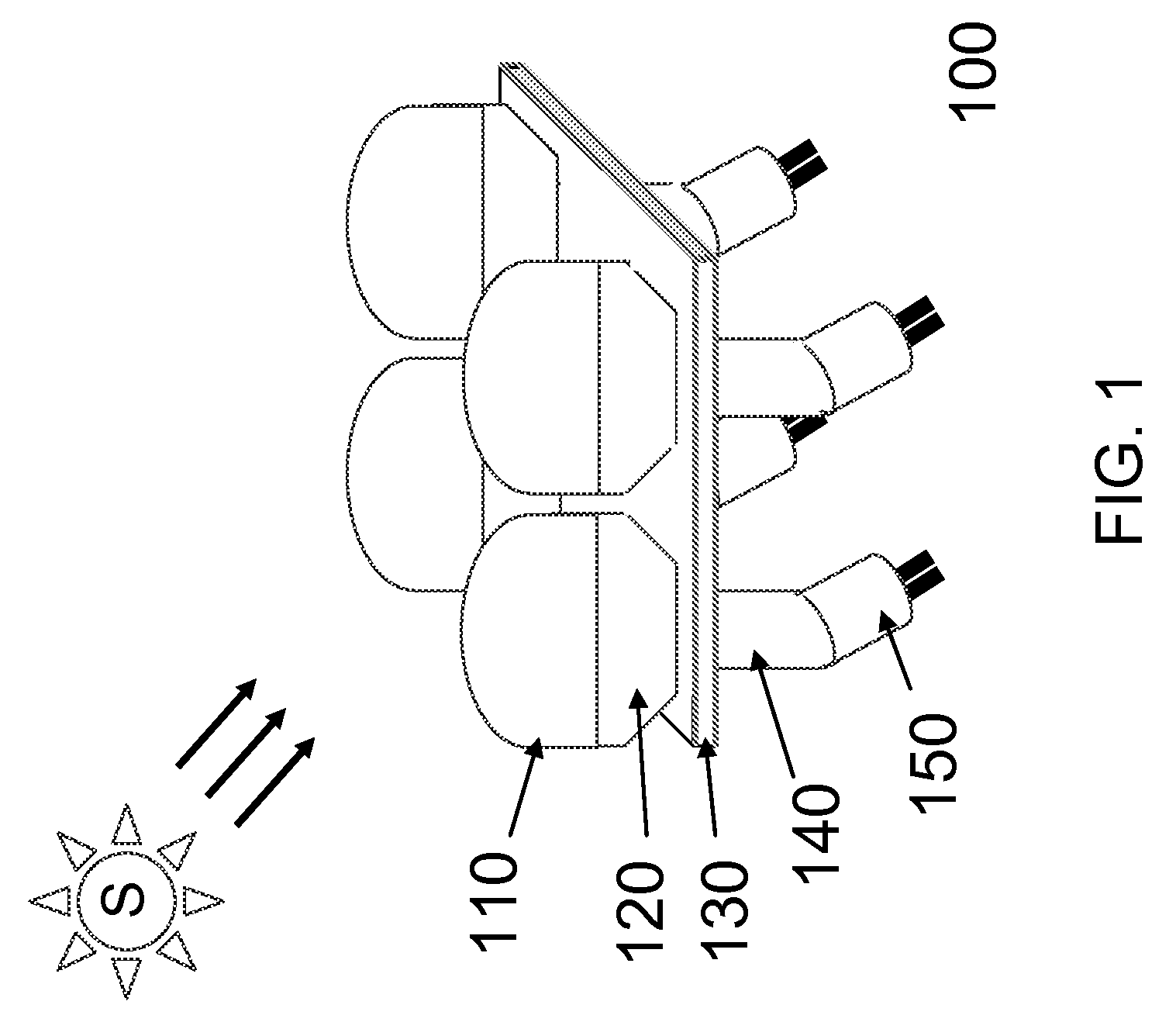
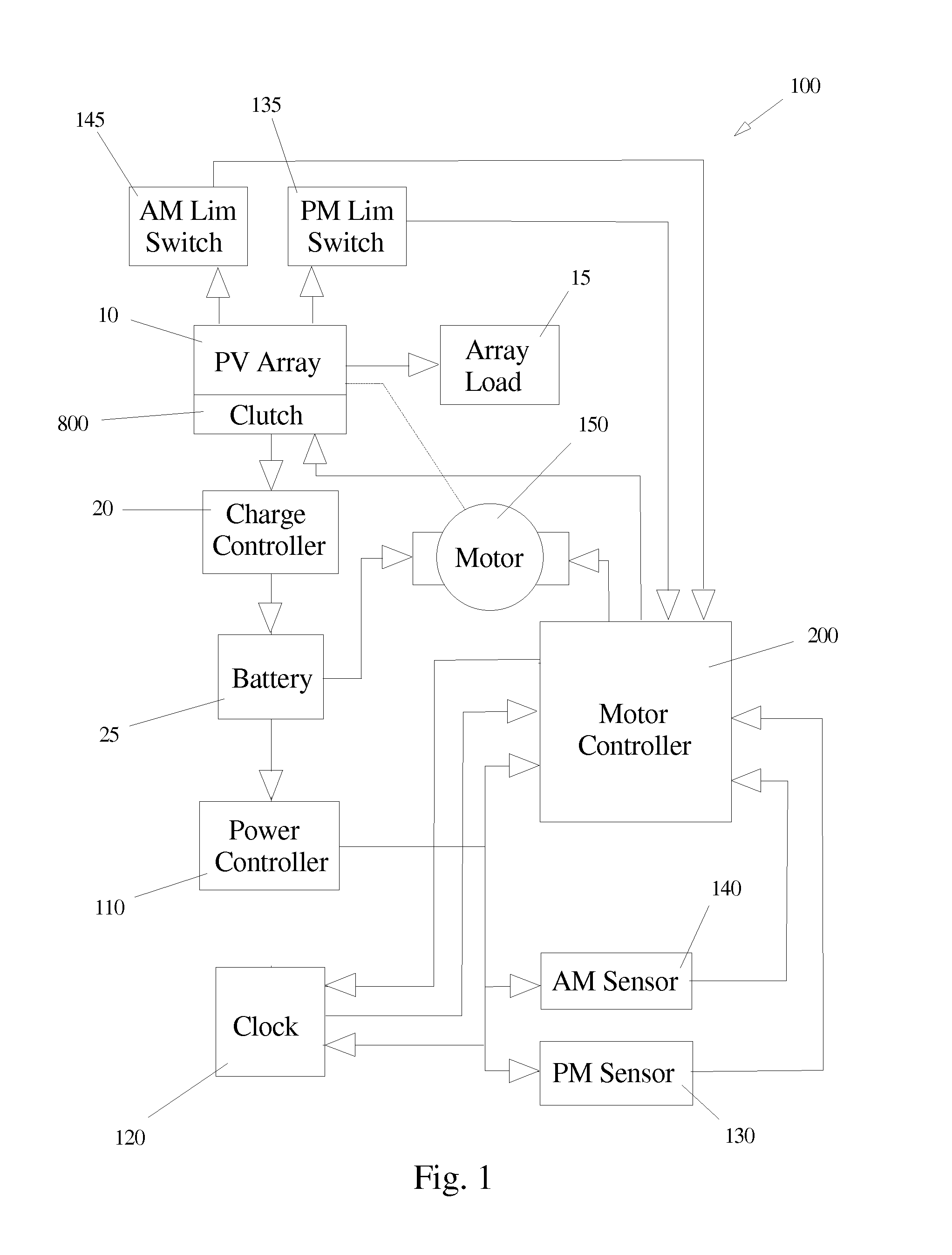
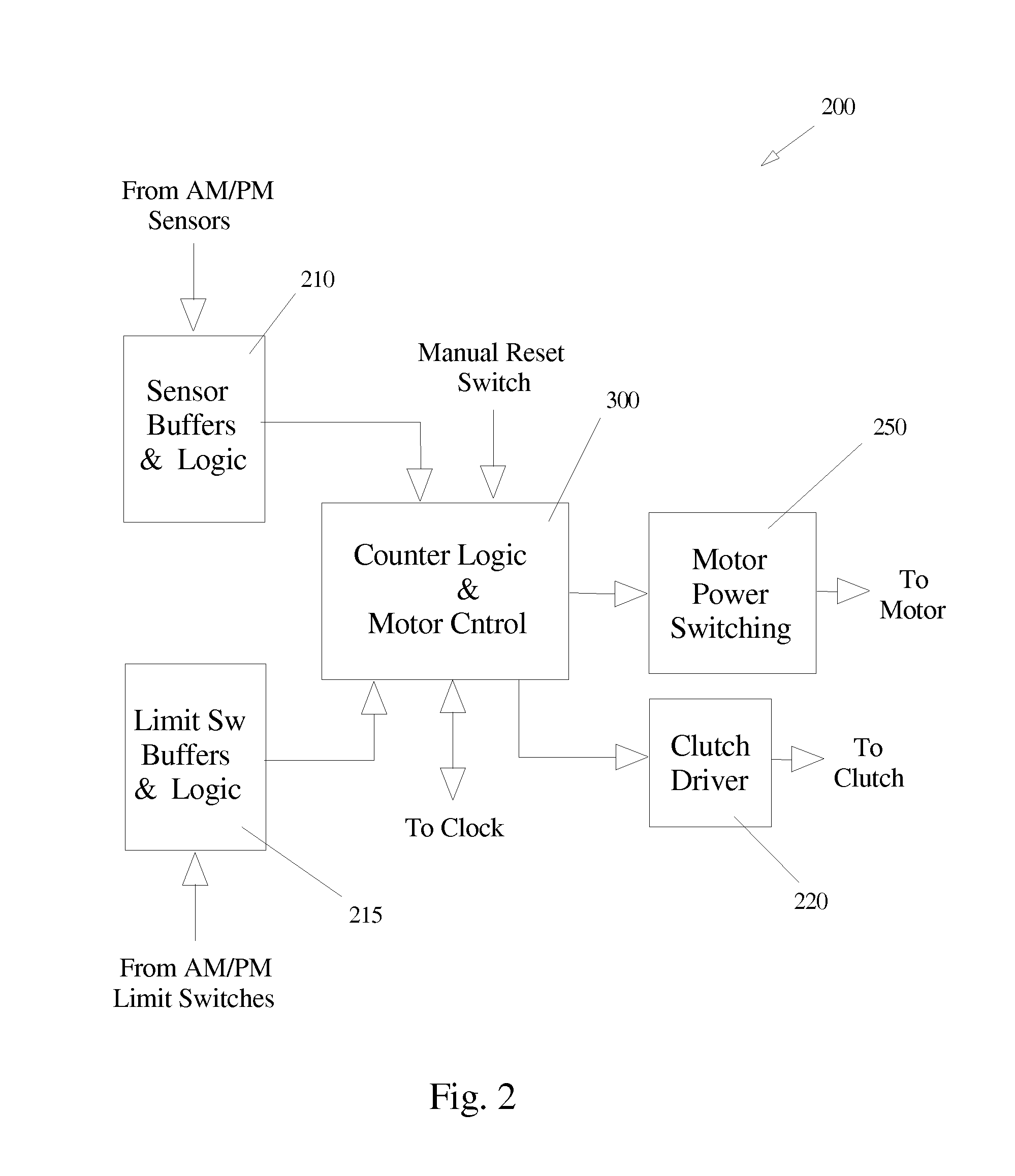
Apparatus and method of energy efficient illumination
ActiveUS20100295455A1Improve energy efficiencyReduce energy consumptionElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsIlluminanceEffect light
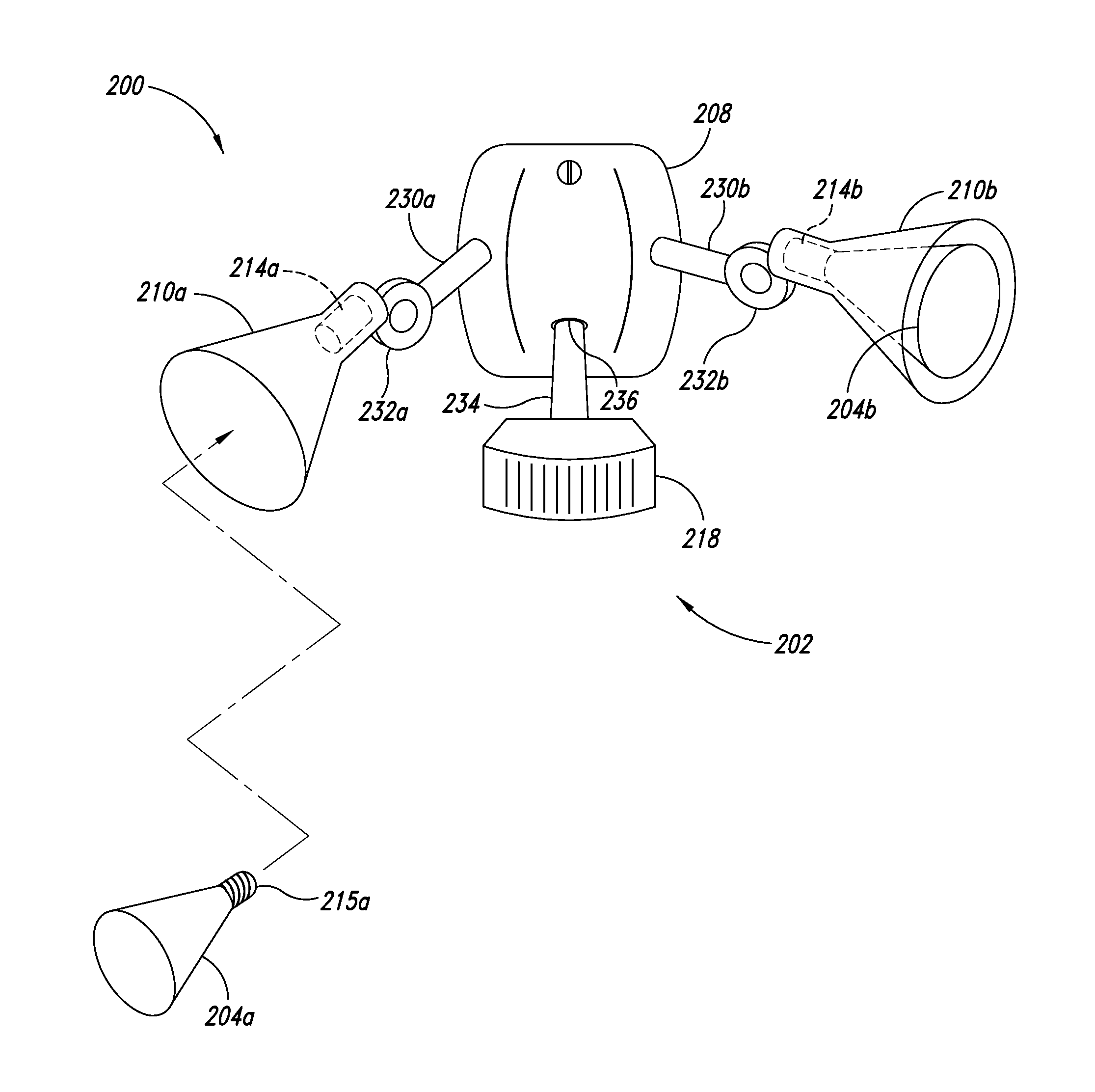
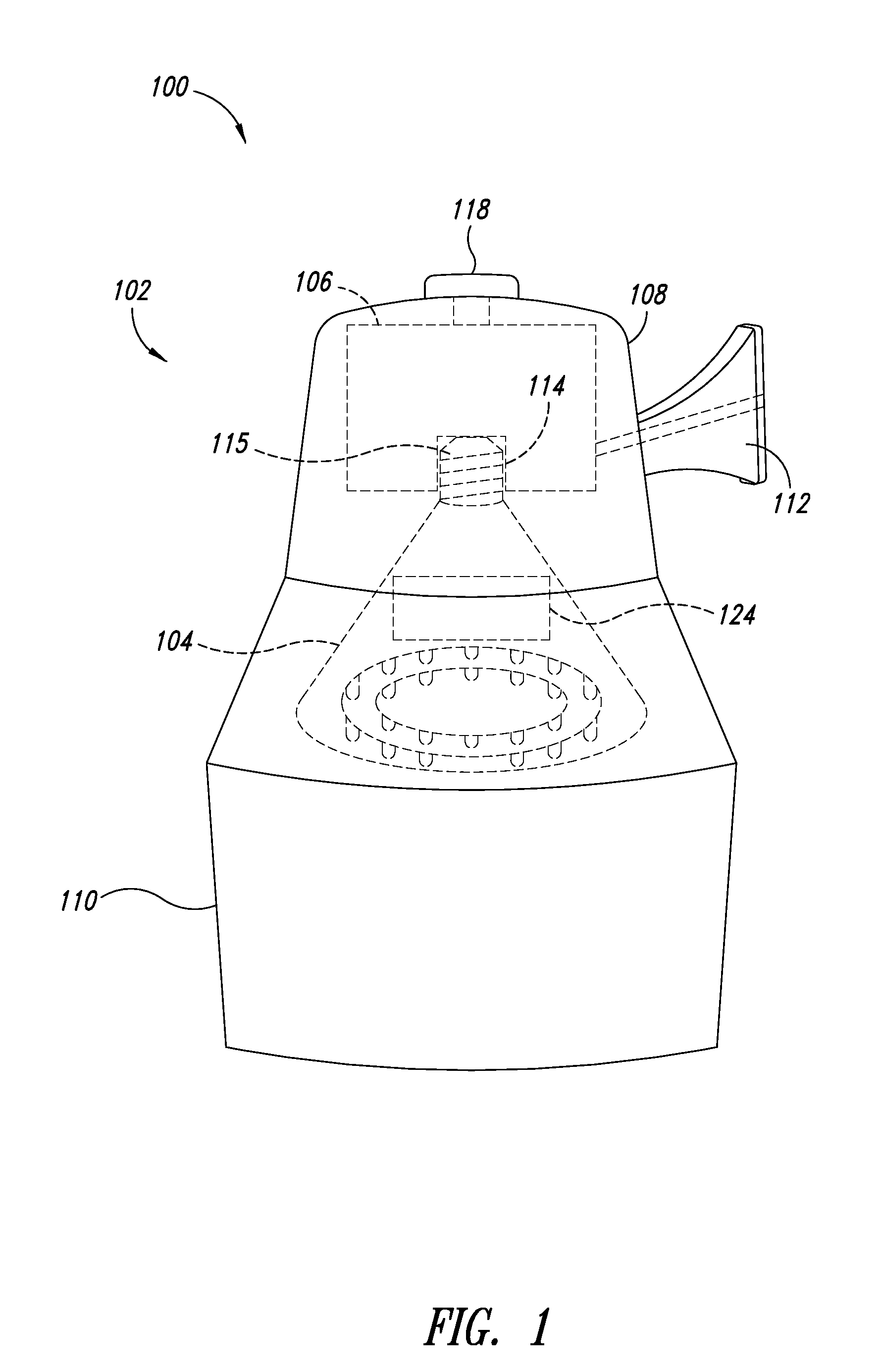
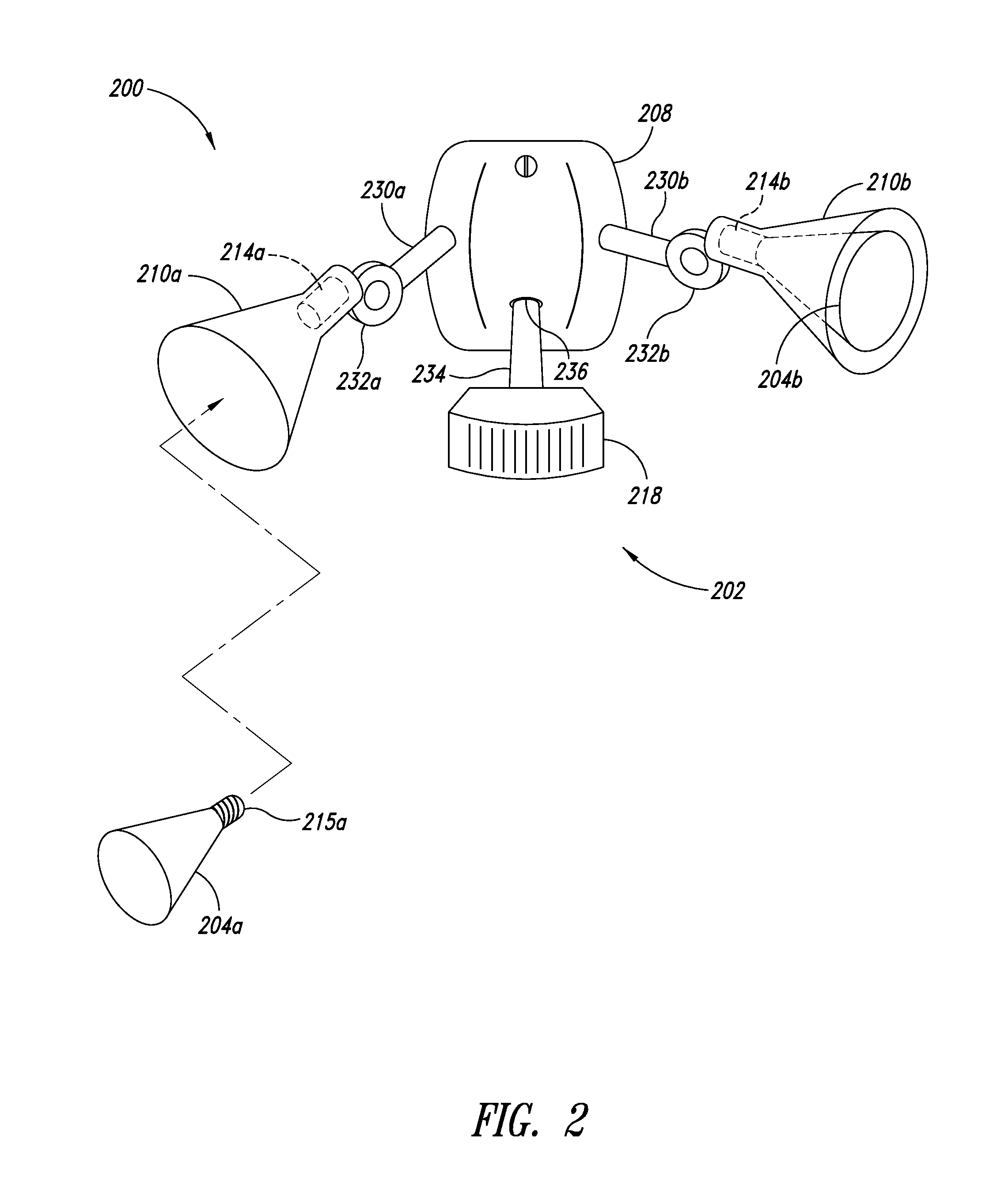
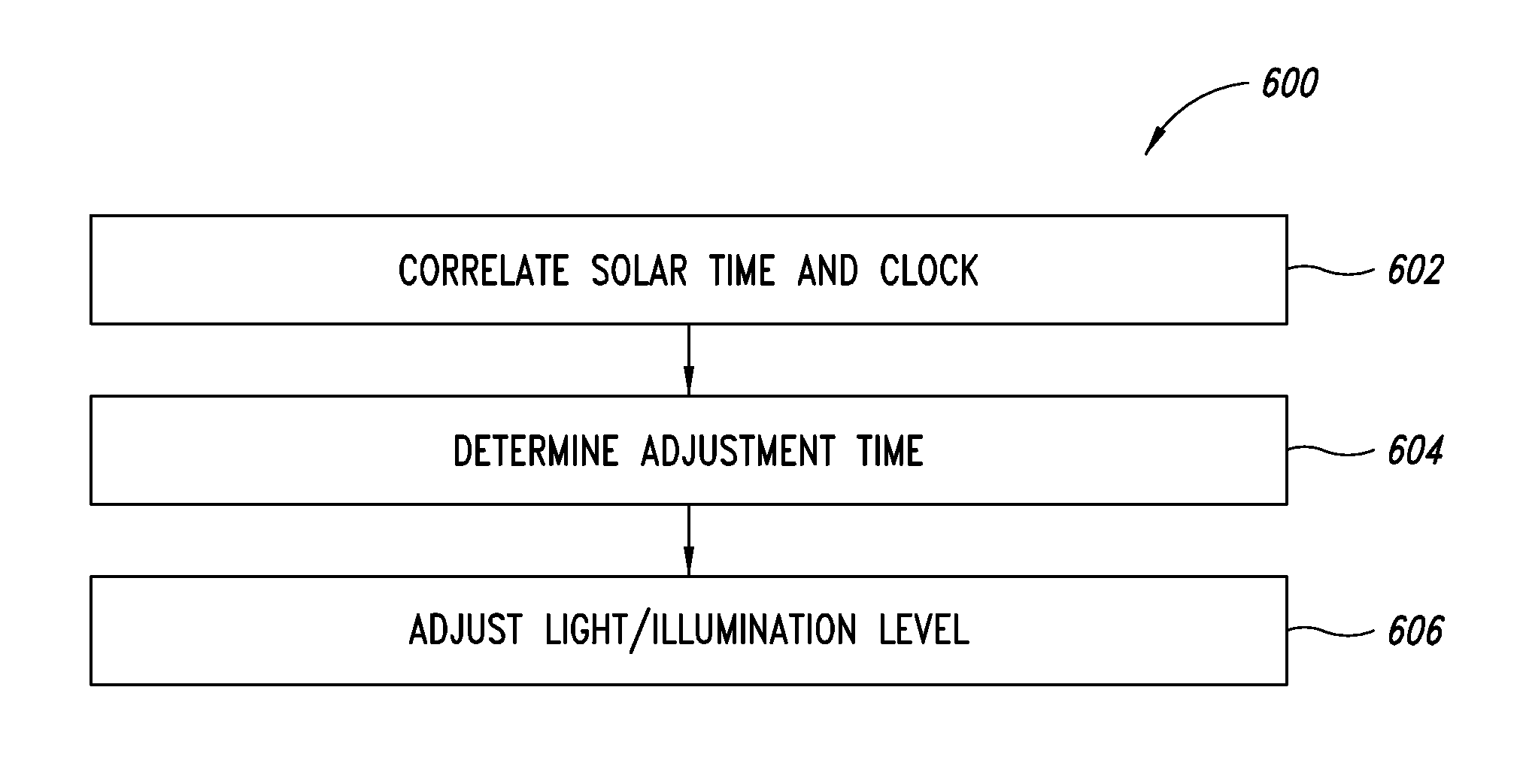
An illumination system correlates solar time to a clock and controls lighting or illumination based on time. The illumination system may turn ON light source(s) at a first level at a turn ON time, correlated to be around or at dusk, and turn OFF light source(s) at a turn OFF time, correlated to be around or at dawn. The illumination system may reduce a level of light output, and hence power consumption, at a time after turning ON a light source, and increases the level of light output at a time prior to turning OFF the light source. Turn ON, turn OFF, decrease and increase times may be determined based on recent levels of light or illumination in the environment, for example via average or median levels over a number of previous daily cycles. Filtering may eliminate aberrant events.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
Apparatus and method of energy efficient illumination
ActiveUS8508137B2Reduce energy consumptionReduce and eliminate affectElectrical apparatusElectric circuit arrangementsIlluminanceEffect light
An illumination system correlates solar time to a clock and controls lighting or illumination based on time. The illumination system may turn ON light source(s) at a first level at a turn ON time, correlated to be around or at dusk, and turn OFF light source(s) at a turn OFF time, correlated to be around or at dawn. The illumination system may reduce a level of light output, and hence power consumption, at a time after turning ON a light source, and increases the level of light output at a time prior to turning OFF the light source. Turn ON, turn OFF, decrease and increase times may be determined based on recent levels of light or illumination in the environment, for example via average or median levels over a number of previous daily cycles. Filtering may eliminate aberrant events.
Owner:EXPRESS IMAGING SYST
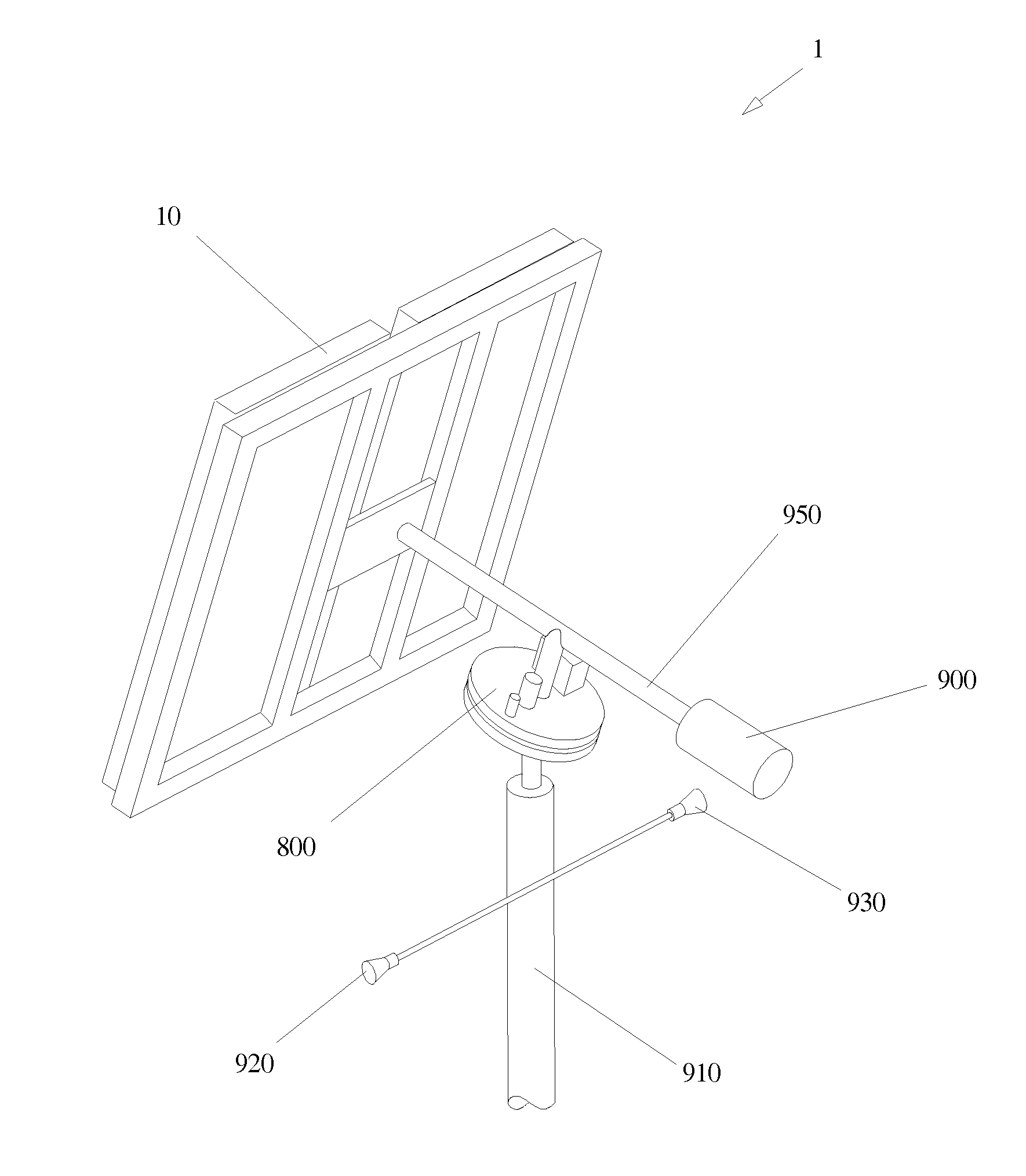
Control Method and Device for Quasi-Uniaxial Sun Chase of Solar Panels
InactiveUS20090301467A1High incident solar energySimple processPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyPresent methodLongitude
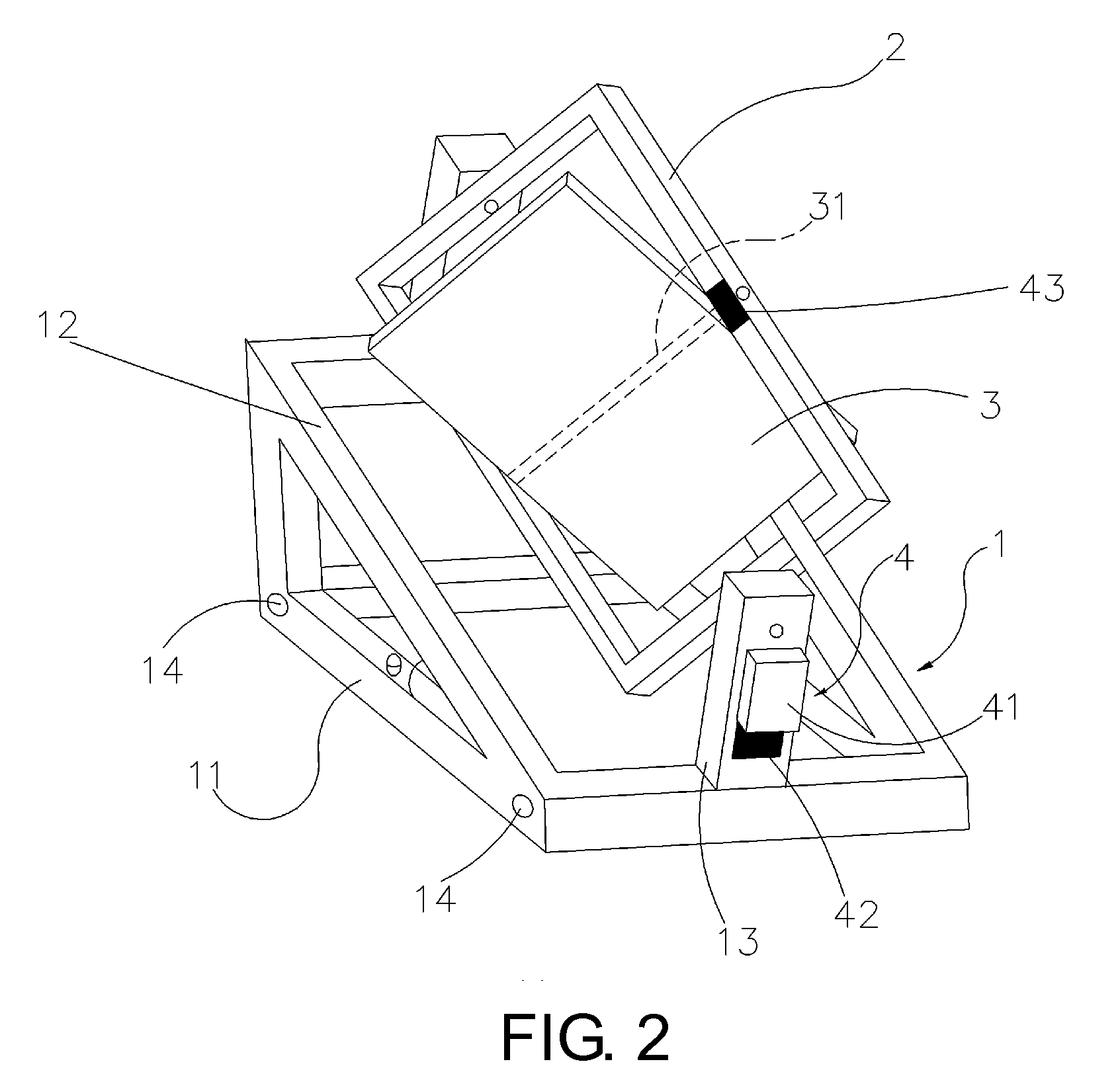
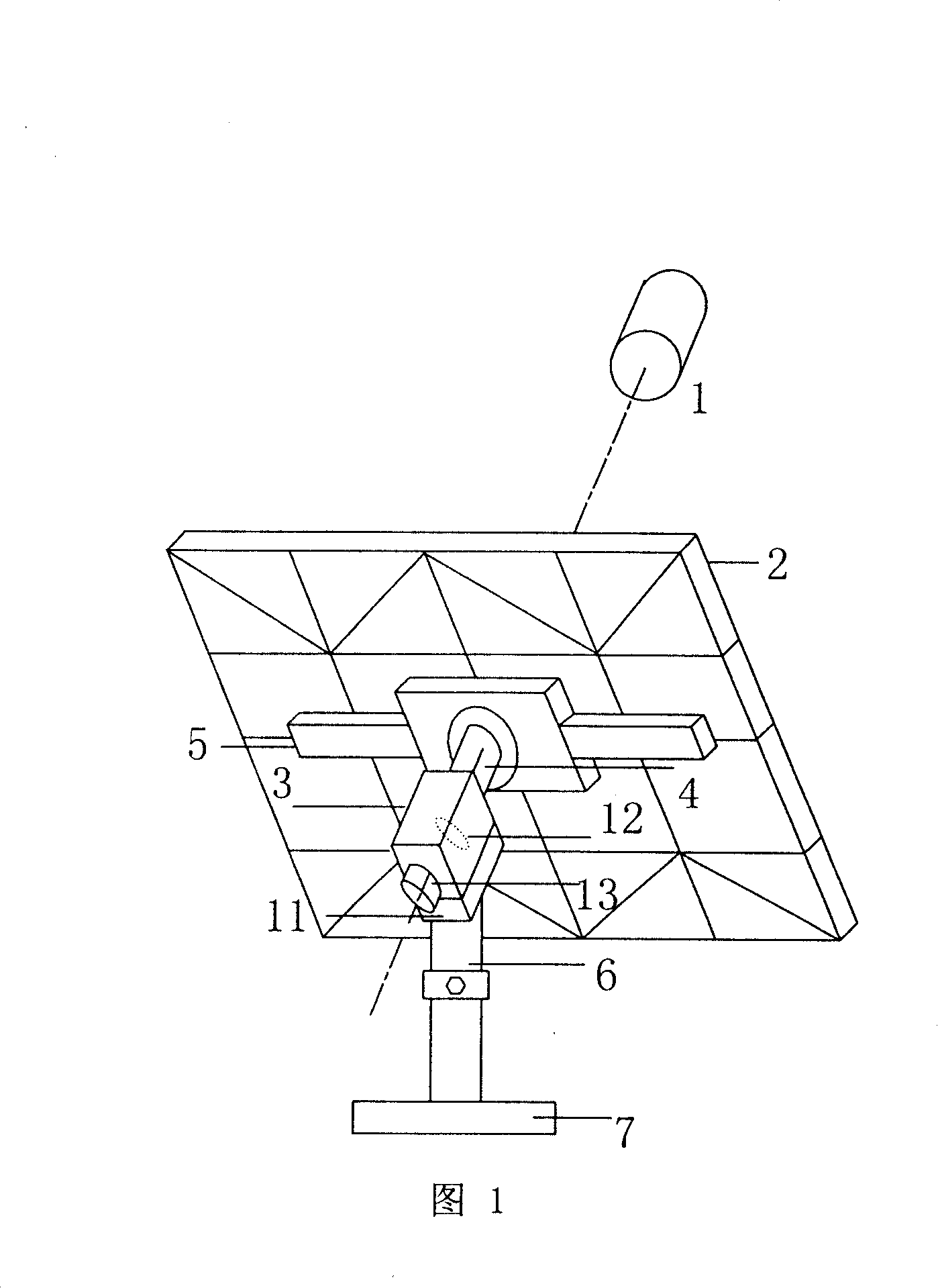
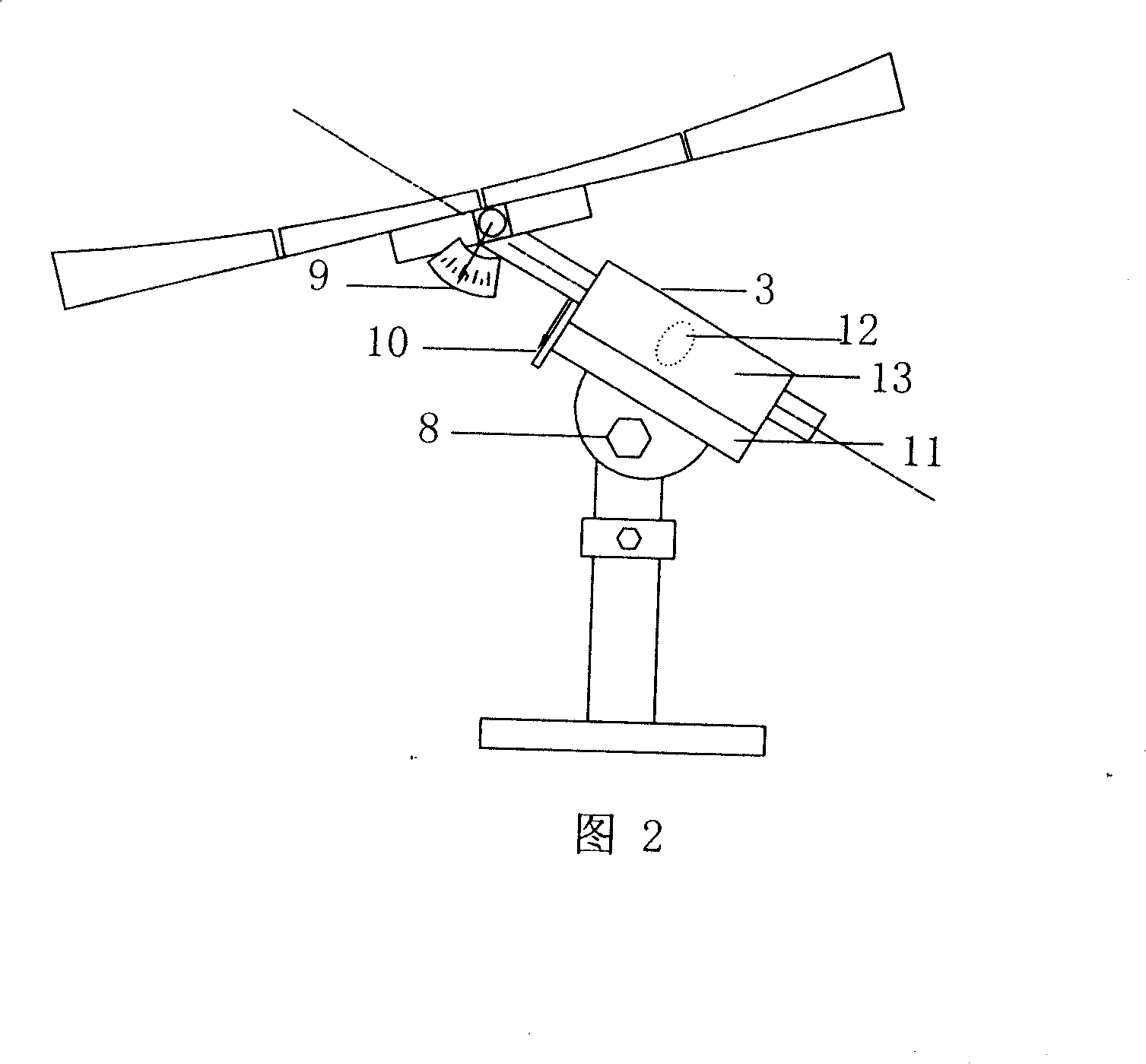
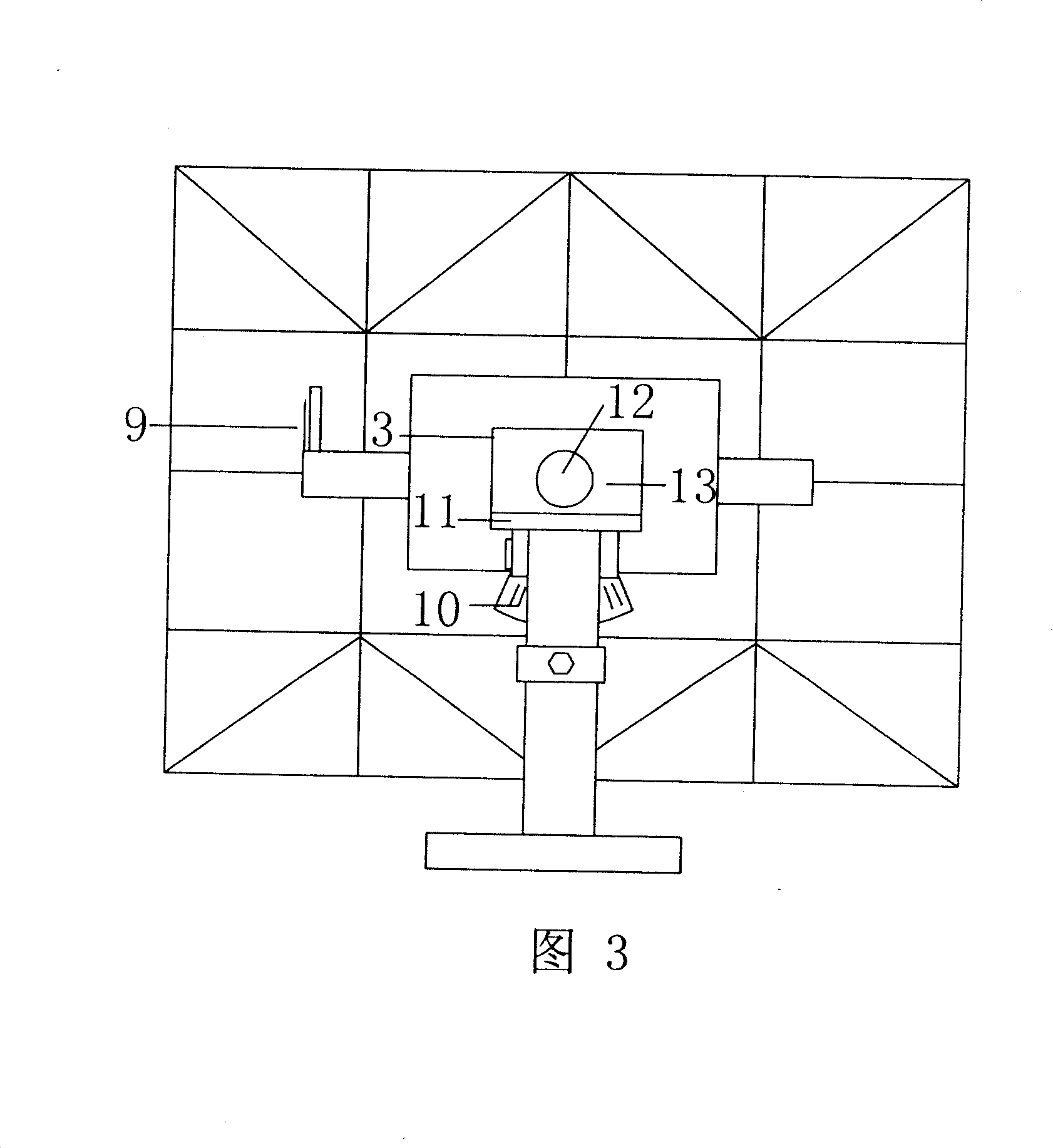
The present invention relates to a control method and device for quasi-uniaxial sun chase of solar panels. The present method uses uniaxial driving to perform real-time tracking of the zodiacal longitude position of solar “daily periodic change”, then abiding by seasonal “annual periodic change” to perform tracking fine tuning of less 0.25 degrees per day on celestial sphere declination. The present device includes a supporting unit with two corresponding holders on the end face, a frame body for solar panel installation configured between the said two holders, and a control mechanism including a setting unit as well as an enable unit connected to the frame body. Thereby, in addition to real-time correction to the corresponding position of the solar panel to Sun by setting the control mechanism to allow the solar panel to acquire higher incident solar energy. The present invention provides a simple device structure with lower operation power consumption.
Owner:CHENG HONG WEN
Greenhouse used as a solar panel support structure
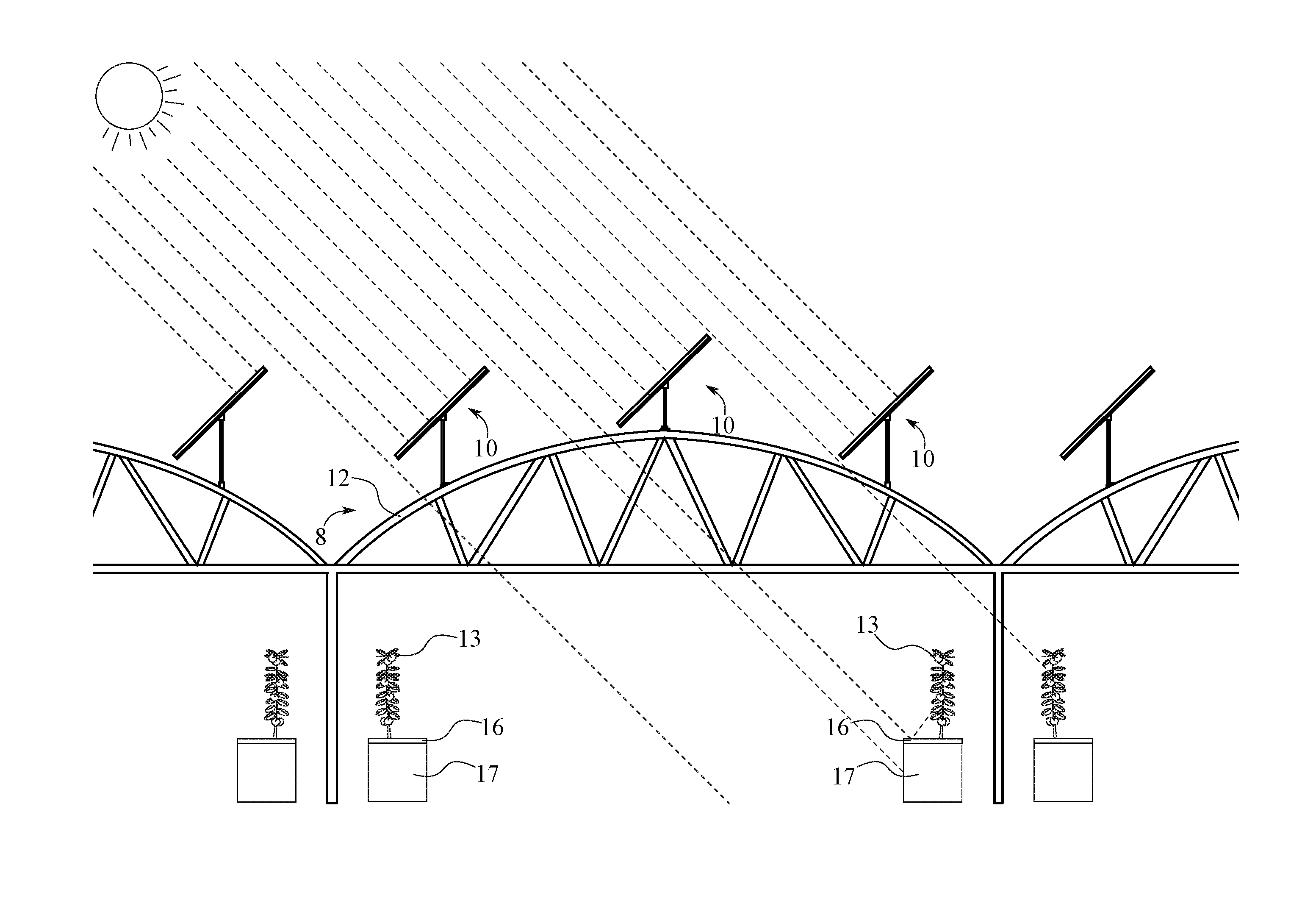
A greenhouse used as a solar panel support structure maintains the usability of the greenhouse through at least one solar panel assembly in order to produce electricity, as well as, optimize light exposure for enclosed plants. The at least one solar panel assembly includes an array and a solar tracker. The array is a photo-voltaic module to convert solar energy into electrical energy to power the greenhouse, other onsite devices, or to export excess energy to a local electrical grid. The array is positioned to receive sunlight to produce electrical energy or provide sunlight exposure to a plurality of plants positioned within the greenhouse. The solar tracker controls the position of the array to move in accordance to sun exposure during a solar day, to maximize electrical power generation, and to allow shade created by the array to move evenly within the greenhouse.
Owner:TSO GREENHOUSES LLC
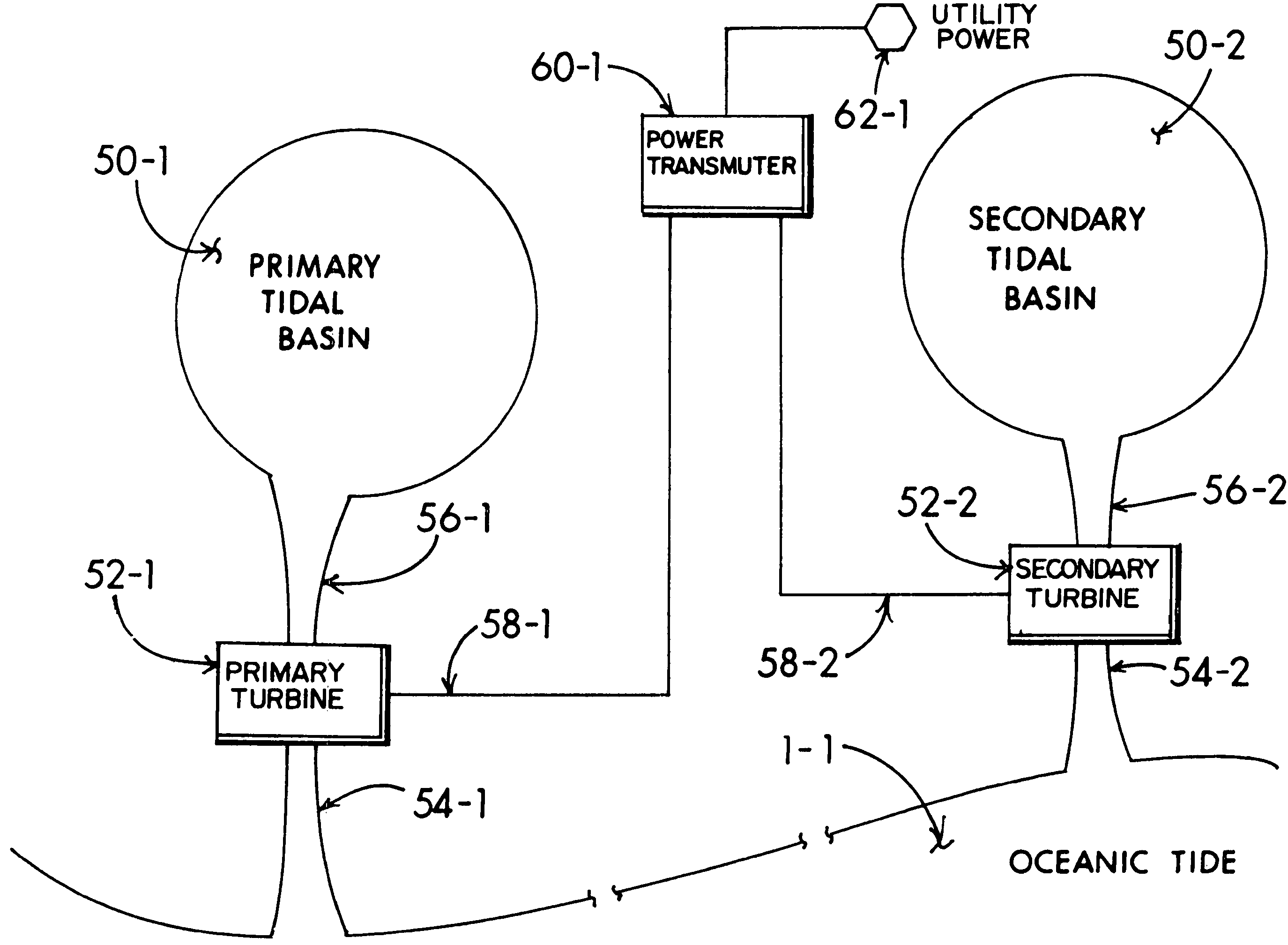
Staging of tidal power reserves to deliver constant electrical generation
InactiveUS7564143B1Power balanceConstant level of hydrodynamic energy conversionFluid couplingsMachines/enginesEngineeringElectric power
Oceanic tidal energy sources hydroelectric generating system coupled to a primary tidal basin through a bi-directional tideway exciting a turbine as a diurnal cycle tide waxes and wanes. A secondary tidal basin includes a tideway and turbine with flow modulated by a regulator gate to proportionately blend reserve tidewater capacity of the secondary tidal basin as a delayed resource compensating a slacking of the primary tidal flow with a graduated secondary tidal basin influx or outflow providing an aggregate summation of tidal energy acting upon the turbines to continuously drive generators and deliver a constant flow of electric power throughout the diurnal tidal cycle. Shunting excess tidal energy around the turbines during periods of reduced electric power demand furthers a full capacity of tidal resources in subsequent phases of the diurnal tidal day when solar day related power demand may increase.
Owner:WEBER HAROLD J
Synclecron time keeping apparatus
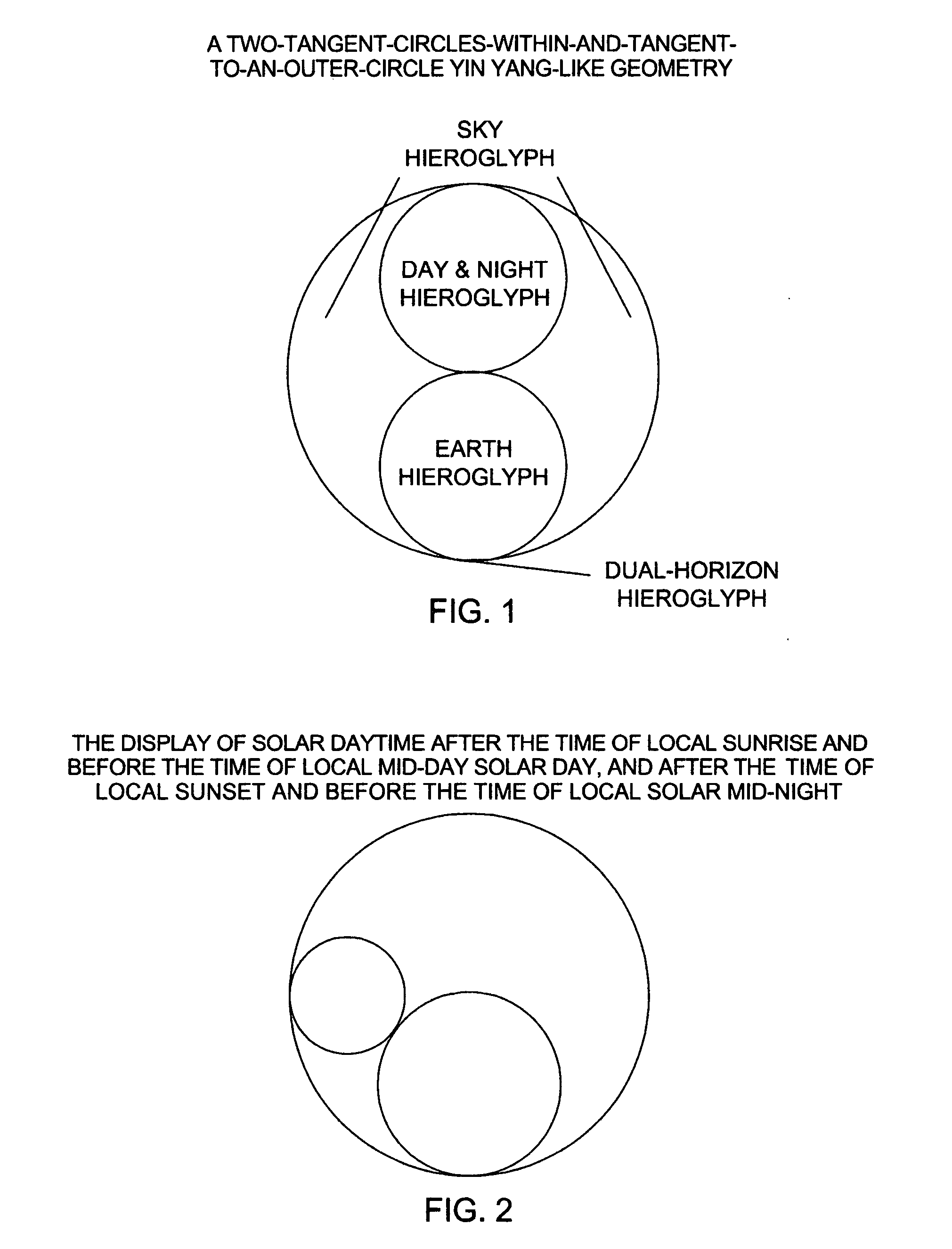
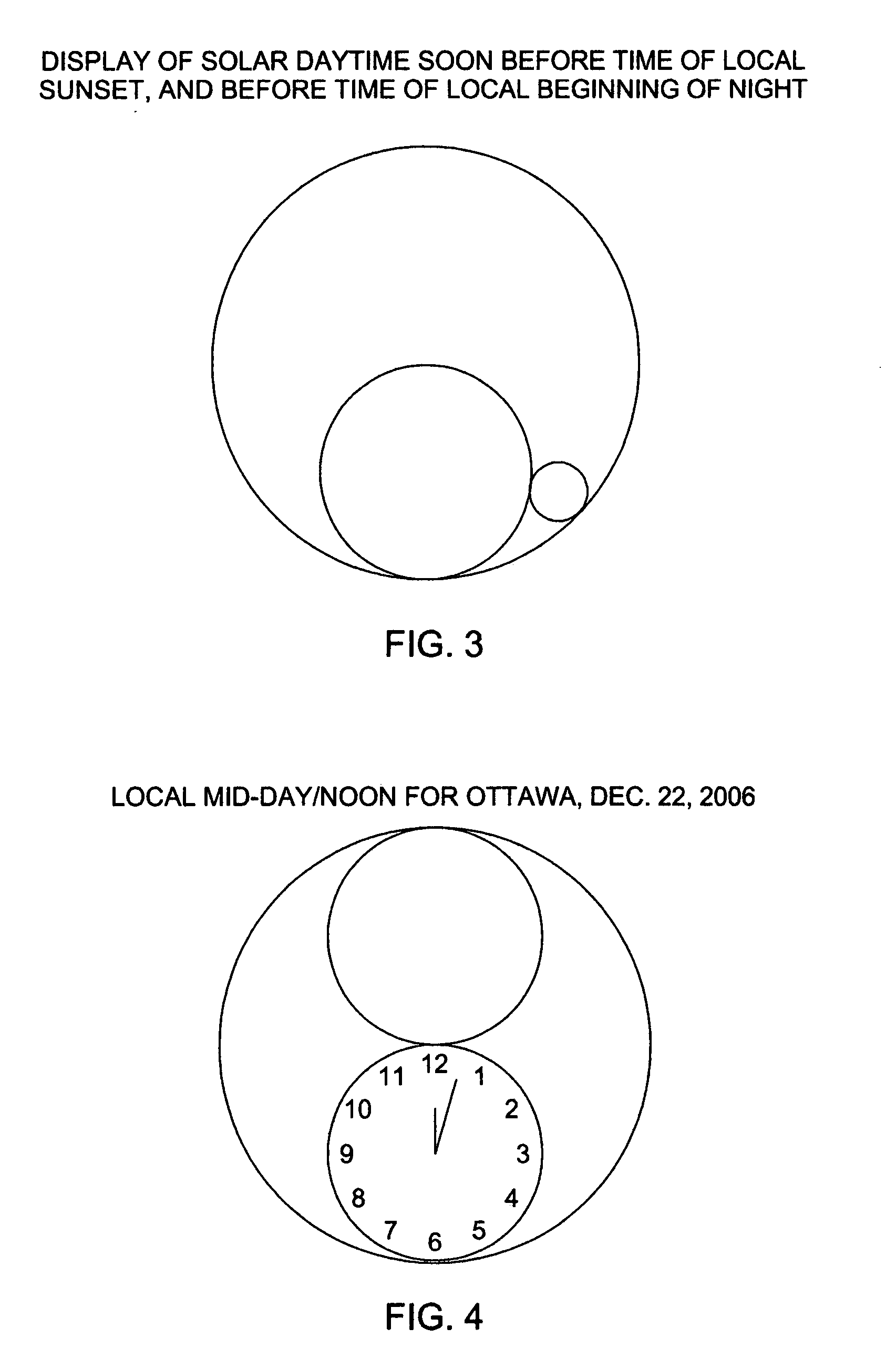
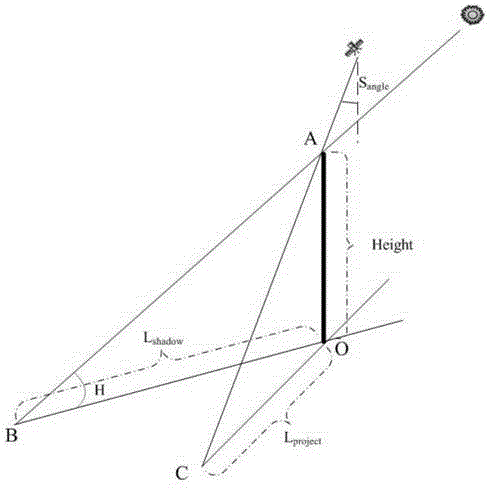
By enabling its users to see and thus more vividly experience local solar day and local solar night, etc., the Synclecron invention seeks to somewhat alleviate the modern-day problem of human separation from the flows and ebbs of natural time. It does so via providing a way of mapping and displaying the experiential passage of solar and other day and night to conventional displays of conventional time. The Synclecron invention achieves this by two means. First by utilizing waxing & waning, journeying pairs of hieroglyph circles that alternately travel twice a day through a hieroglyph sky around a hieroglyph earth. And, last, by using a rotating “minute-hour” indicator, which displays where the Synclecron invention's user is in local natural time during each “natural” one-twelfth hour of his or her local natural day and natural night. The invention thus provides a view of passage of local solar day and night, and other solar days and nights, not only personalized to one's latitude and longitude, but also tied to one's time of local sunrise and sunset. As a consequence, the Synclecron invention more wholly informs the minds and bodies of users about the daily and nightly passages of natural time which we each experience every moment of each day and night, and which are not typically derived from most conventional timepieces.
Owner:LANDSBERG YALE S
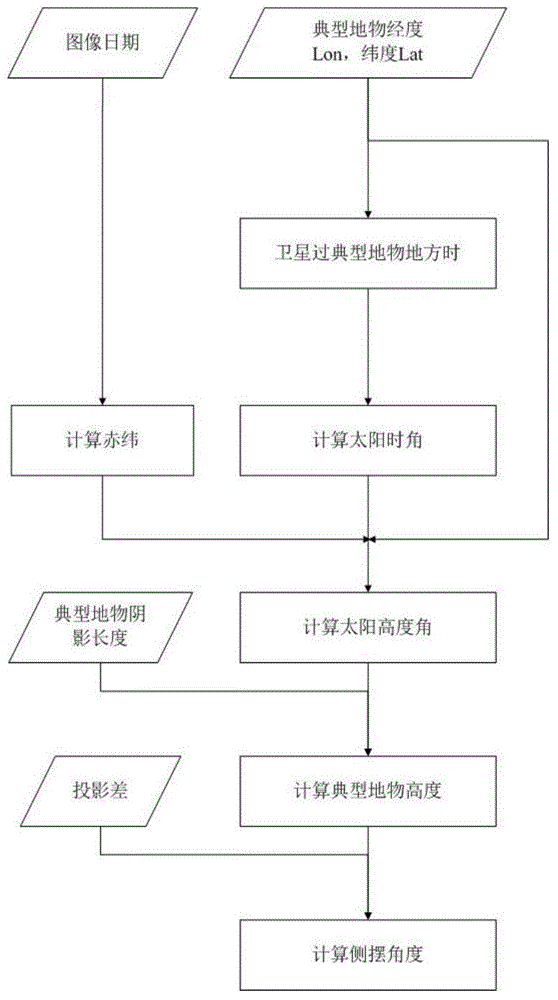
Satellite side-sway angle obtaining method based on image characteristics
A satellite side-sway angle obtaining method based on the image characteristics comprises the following steps: (1) obtaining the imaging date of a remote sensing image; (2) choosing a proper landmark on the remote sensing image, and obtaining latitude information of the landmark; (3) according to the parameters of the satellite orbit, obtaining the imaging local time (Tlocal) of the latitude of the landmark; (4) according to Tlocal, calculating the solar time angle (Tangle); (5) calculating the solar declination [delta] of the imaging date; (6) calculating the solar altitude according to [delta], Tangle, and the latitude (Lat) of the landmark; (7) measuring the shadow length (Lshadow) of the landmark on the remote sensing image, and calculating the height of the landmark (Height) by combining the solar altitude; (8) measuring the projection difference (Lproject) of the landmark on the remote sensing image, and finally calculating the side-sway angle (Sangle) when satellite imaging is carrying out according to the Height. The provided method can obtain the side-sway angle of a satellite through a remote sensing image by using the remote sensing satellite imaging mechanism and sunshine geometrical relationships, when the ephemeris data cannot be obtained.
Owner:CHINA CENT FOR RESOURCES SATELLITE DATA & APPL
Earth axis type solar furnace optical collector
InactiveCN101109581AEasy to controlLow costSolar heating energySolar heat collector controllersSynchronous motorSolar light
The invention provides an earth-axis type solar light condenser, which pertains to the heat utilization of solar energy. The solar light condenser traces by an earth-axis single axis, guarantees that the sun light is converged on a fixed point on the extended line of the earth axis during the tracing of sun light, and overcomes the shortcomings of prior light condenser such as complex tracing way and the variable condensed target. The rotary shaft of the light condenser is controlled by a synchronous motor, and traces the solar time angle; when the condensing lens is 45 degree to the rotary shaft, the condensing lens is at its zero; the tilt angle of the condensing lens is adjusted periodically so that the angle change of the condensing lens is half of the change in the declination angle. The shape of the condensing lens is a non-rotary symmetric curve allowing the calibration of astigmatism, for example, a tyre surface, which has light-condensing performance higher than spherical surface and parabolic surface, and the manufacturing way is similar to that for a parabolic surface. The light condenser can meet demands from the people in living, for example, boiled water, radiator and air conditioner, etc. By using a secondary light condenser, a high temperature for industrial production can be achieved, for example hydrogen manufacturing by solar energy, etc.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solar-To-Electricity Conversion System Using Cascaded Architecture of Photovoltaic and Thermoelectric Devices
InactiveUS20090250099A1Improve conversion efficiencyCost per output powerCircuit optical detailsThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectElectrical batteryEngineering physics
The invention addresses the area utilization and capital efficiency of systems for converting solar energy into electricity. A solid-state solar system includes photovoltaic and thermoelectric or thermionic cells. The system can be implemented in various configurations and by a solar insolation flux collection and concentration method to improve the area utilization and solar-to-electricity conversion efficiency. A thermal expansion matched multilayer board is also used to withstand ultra high concentration of solar insolation flux.
Owner:PAN ERIC TING SHAN
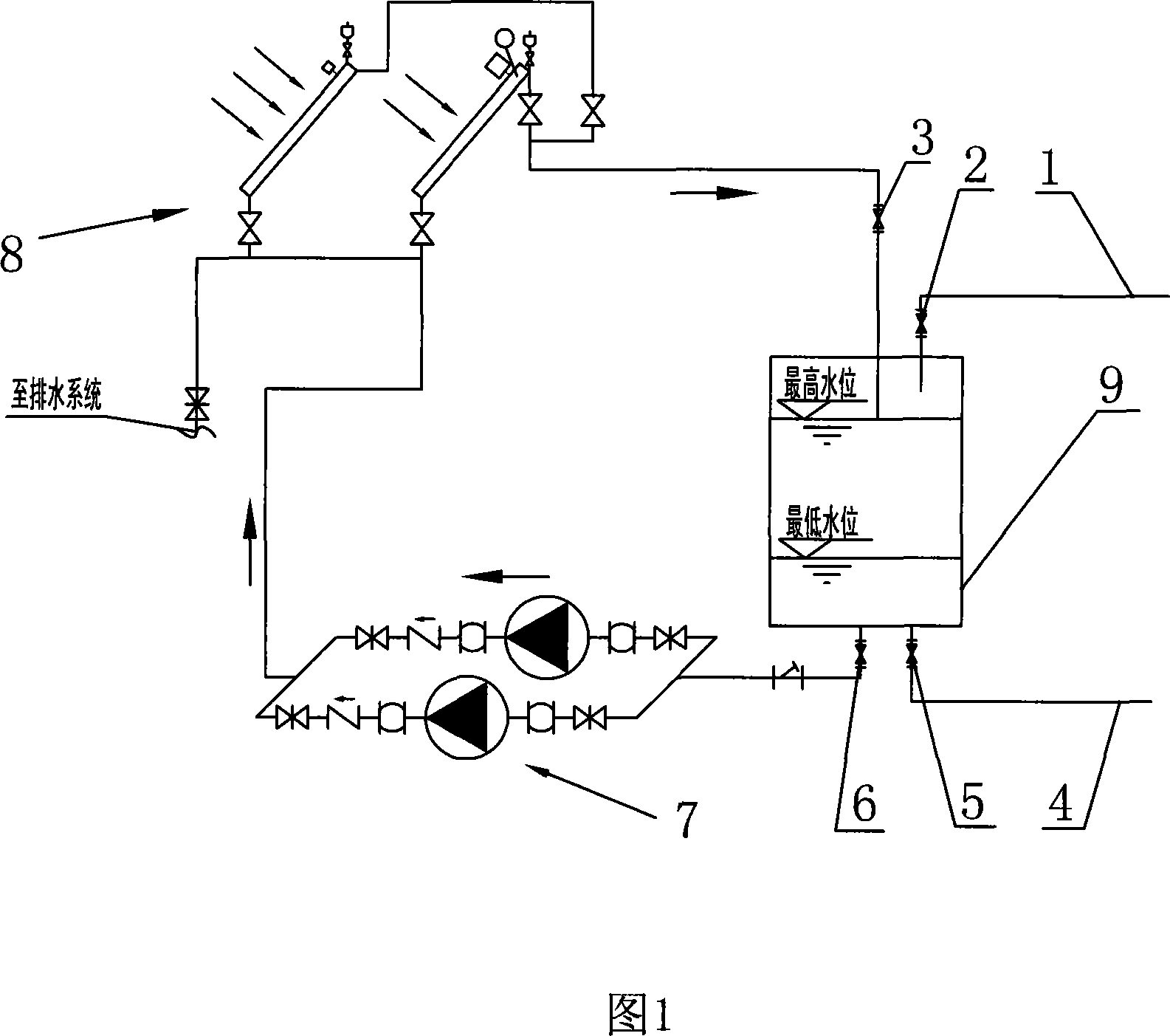
Solar hot water supply system and heating means thereof
ActiveCN101182940AIncrease effective volumeAuxiliary heat source savingSolar heat devicesDomestic hot-water supply systemWater savingSolar water
The invention discloses a solar hot water supply system and a heating method thereof, which solves the problem that the existing solar water heaters use many auxiliary heat sources. The solar hot water supply system includes a solar heat collector and a water pump, and also includes at least two water tanks, the circulating water outlet of each water tank is connected to the inlet of the water pump, and the outlet of the water pump is connected to the inlet of the solar heat collector, The outlet of the solar heat collector is connected to the water circulation return port of each water tank. The heating method is as follows: each water tank is poured into cold water; the water in each water tank is sequentially heated to the target temperature through the solar collector. Because a plurality of water tanks are arranged, when solar energy is not sufficient, solar energy can be used to heat the water in part of the water tanks to the target temperature, so as to provide water with a suitable temperature, and the auxiliary heat source is saved. The invention can be used in centralized hot water supply systems of various public buildings, and can also be used in households to provide domestic water.
Owner:CCDI BEIJING INT ARCHITECTURAL DESIGNCONSULTANTS +1
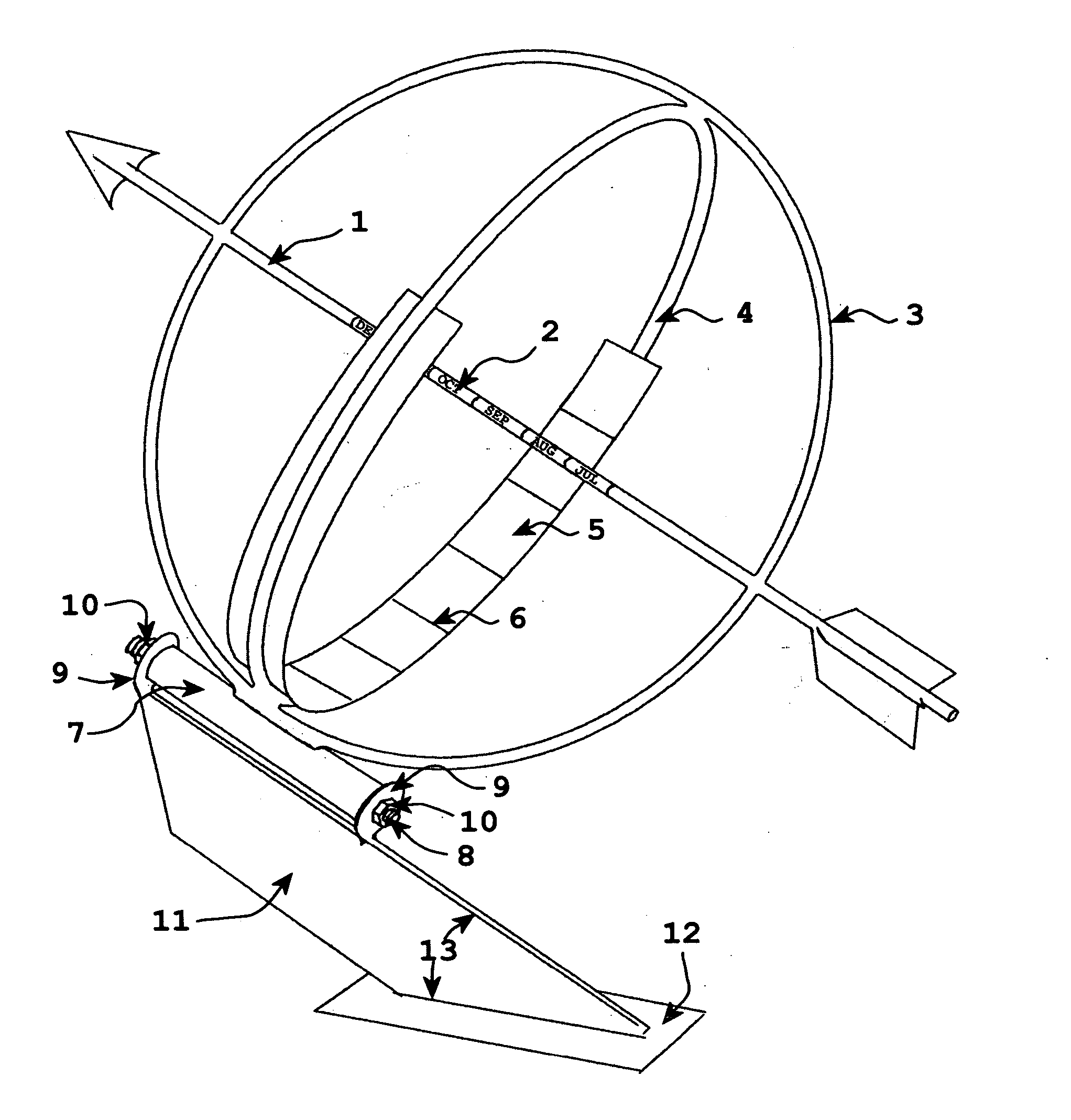
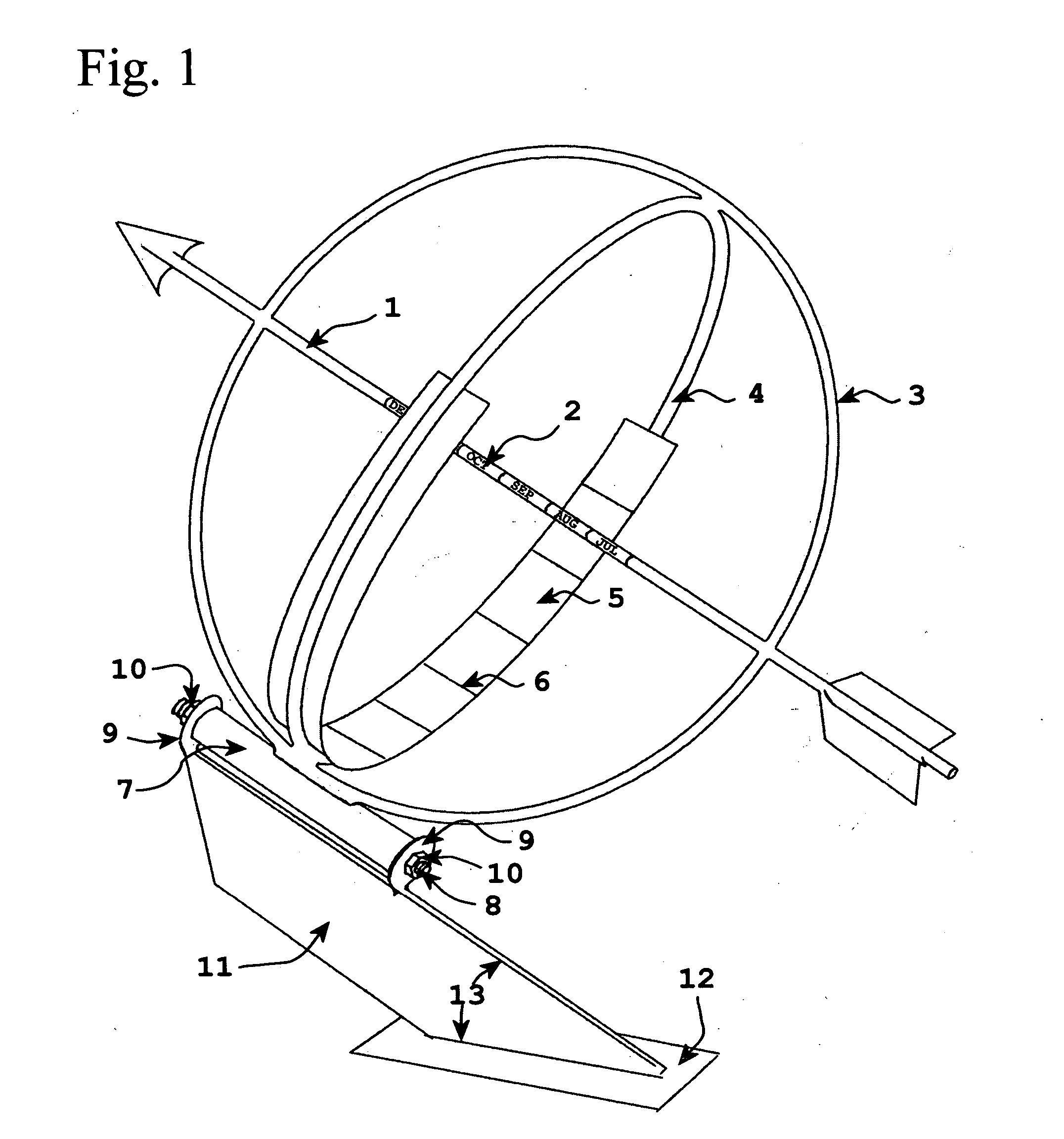
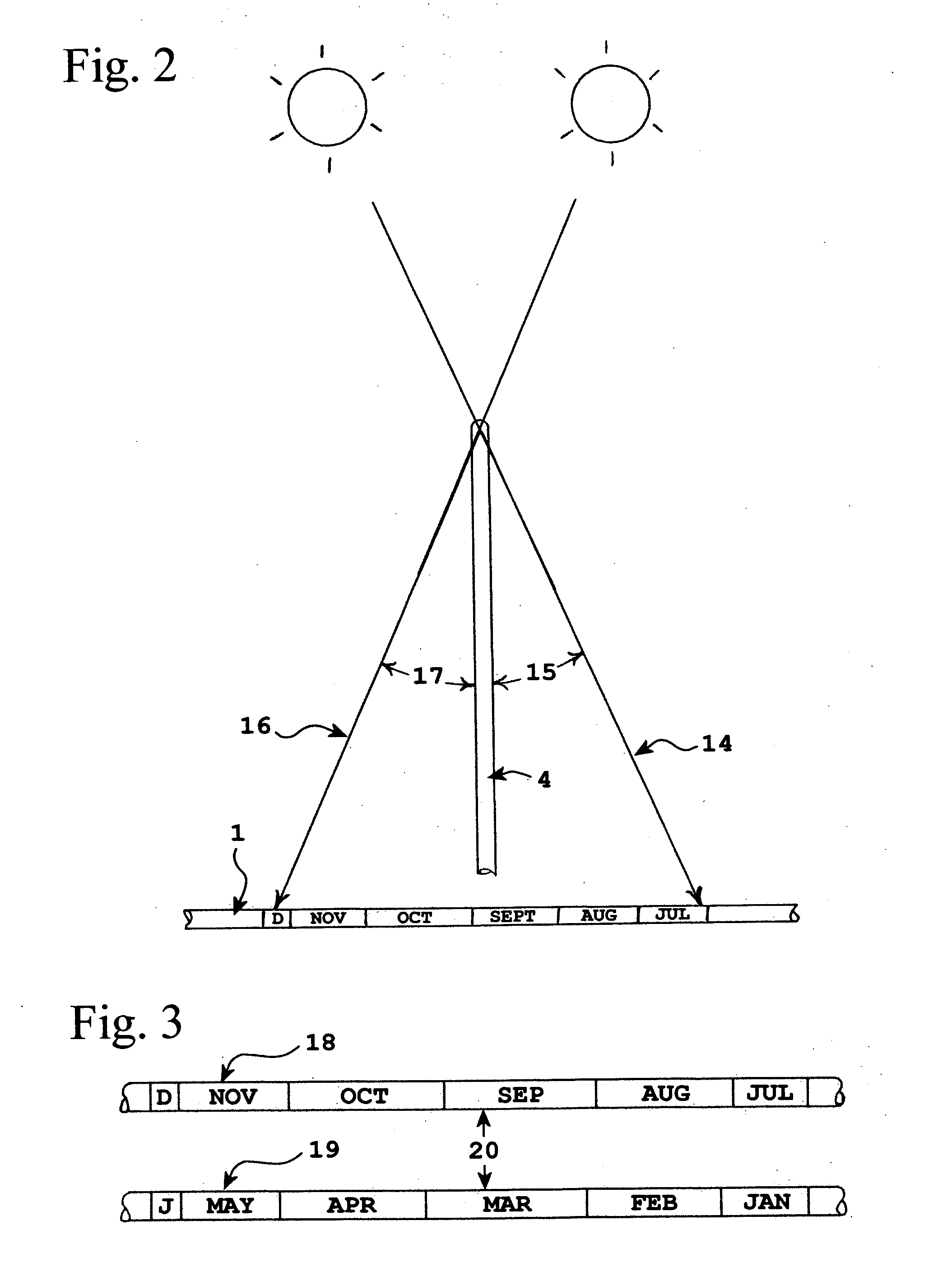
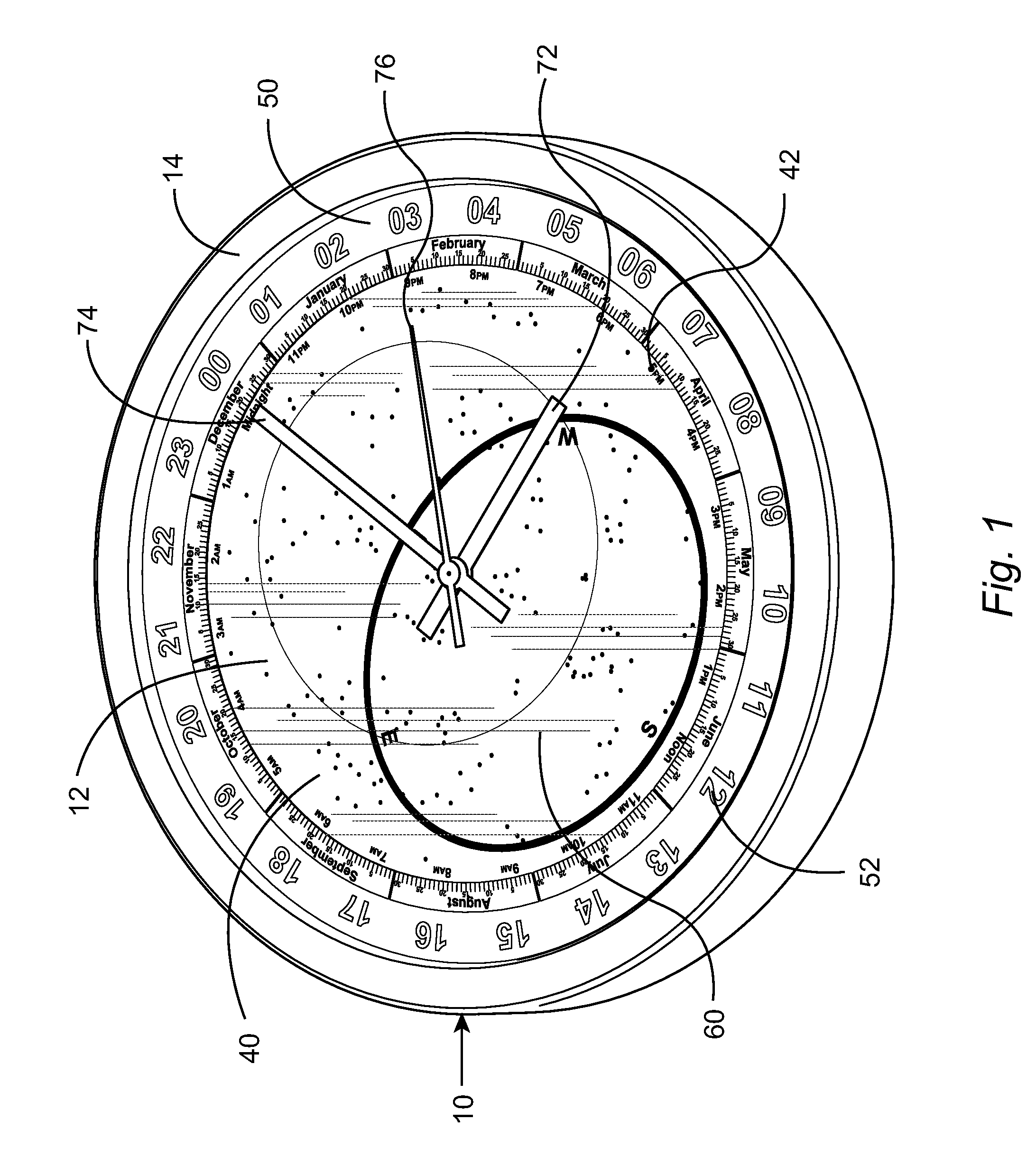
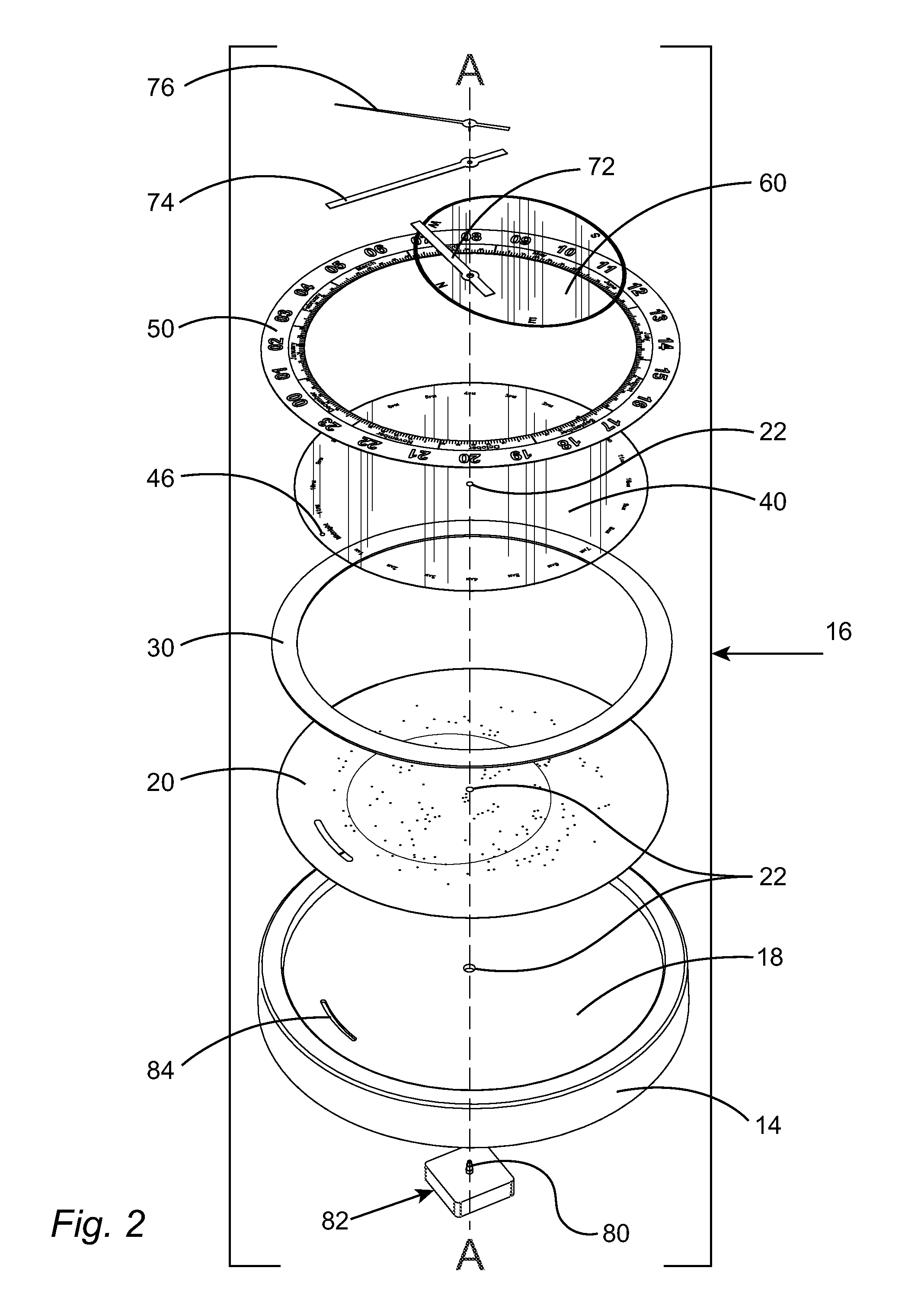
Equatorial sundial with simple time and date interpretation
InactiveUS6871407B1Intuitive interpretationVisual indicationElectric indicationSundialEquatorial ring
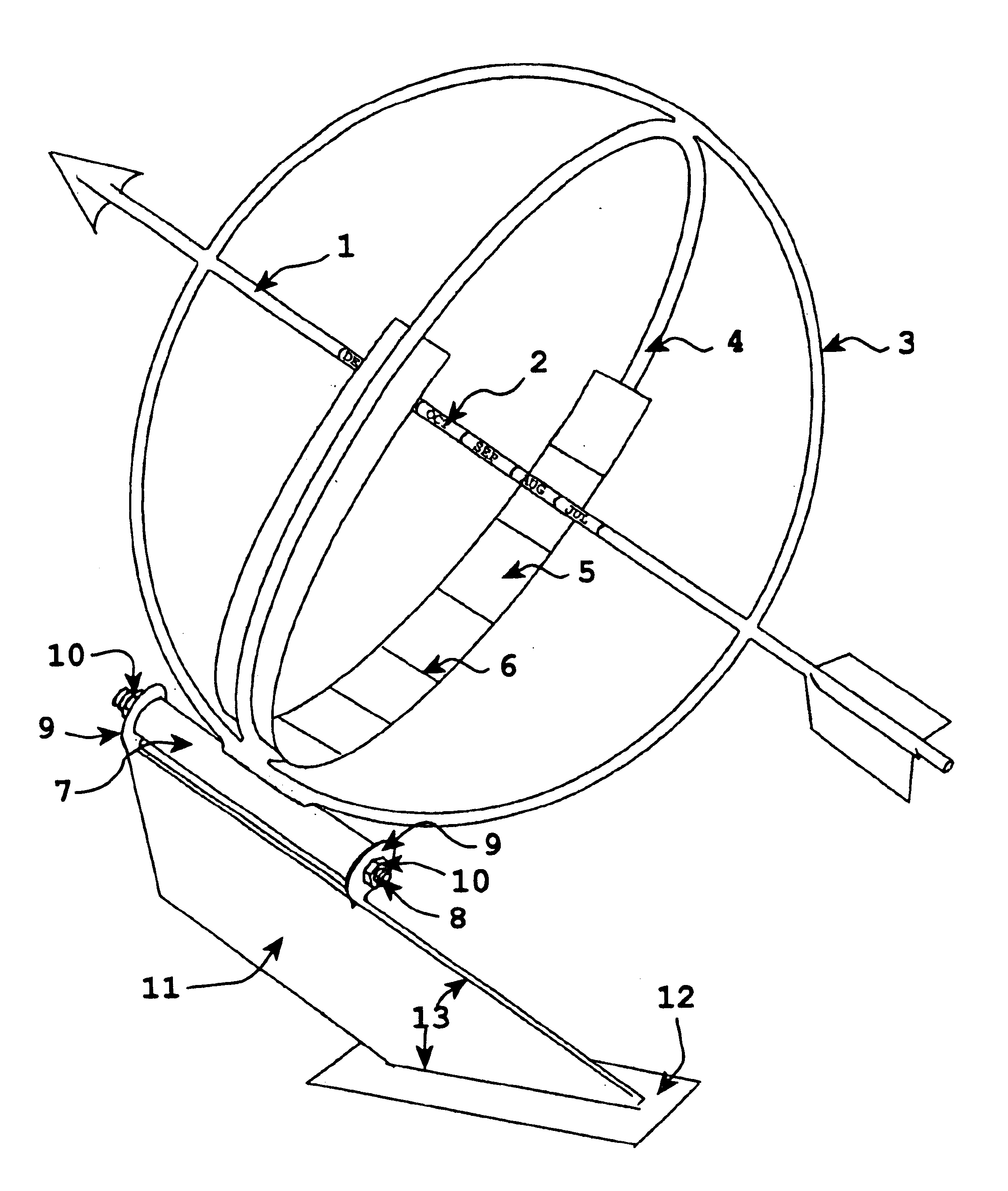
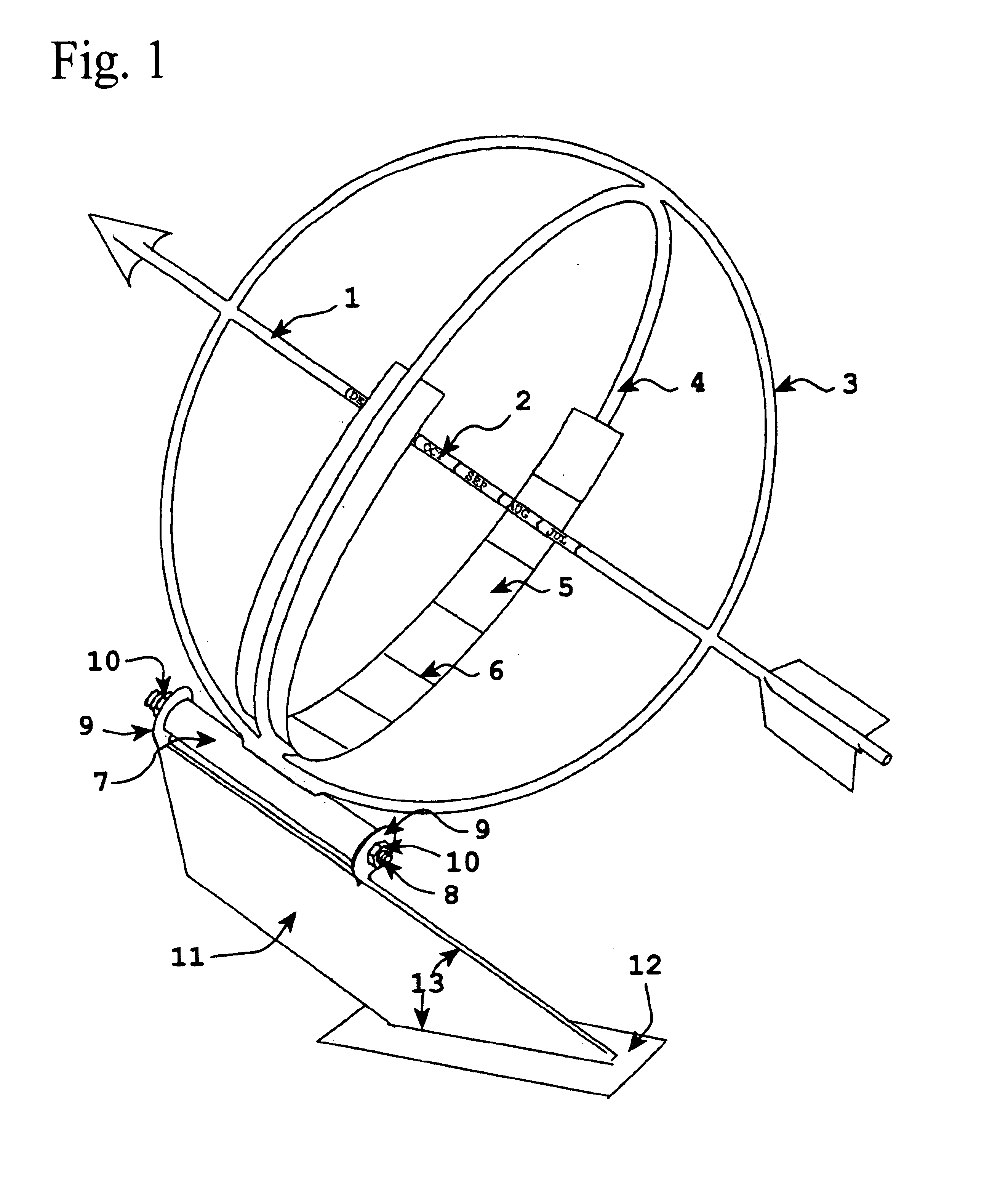
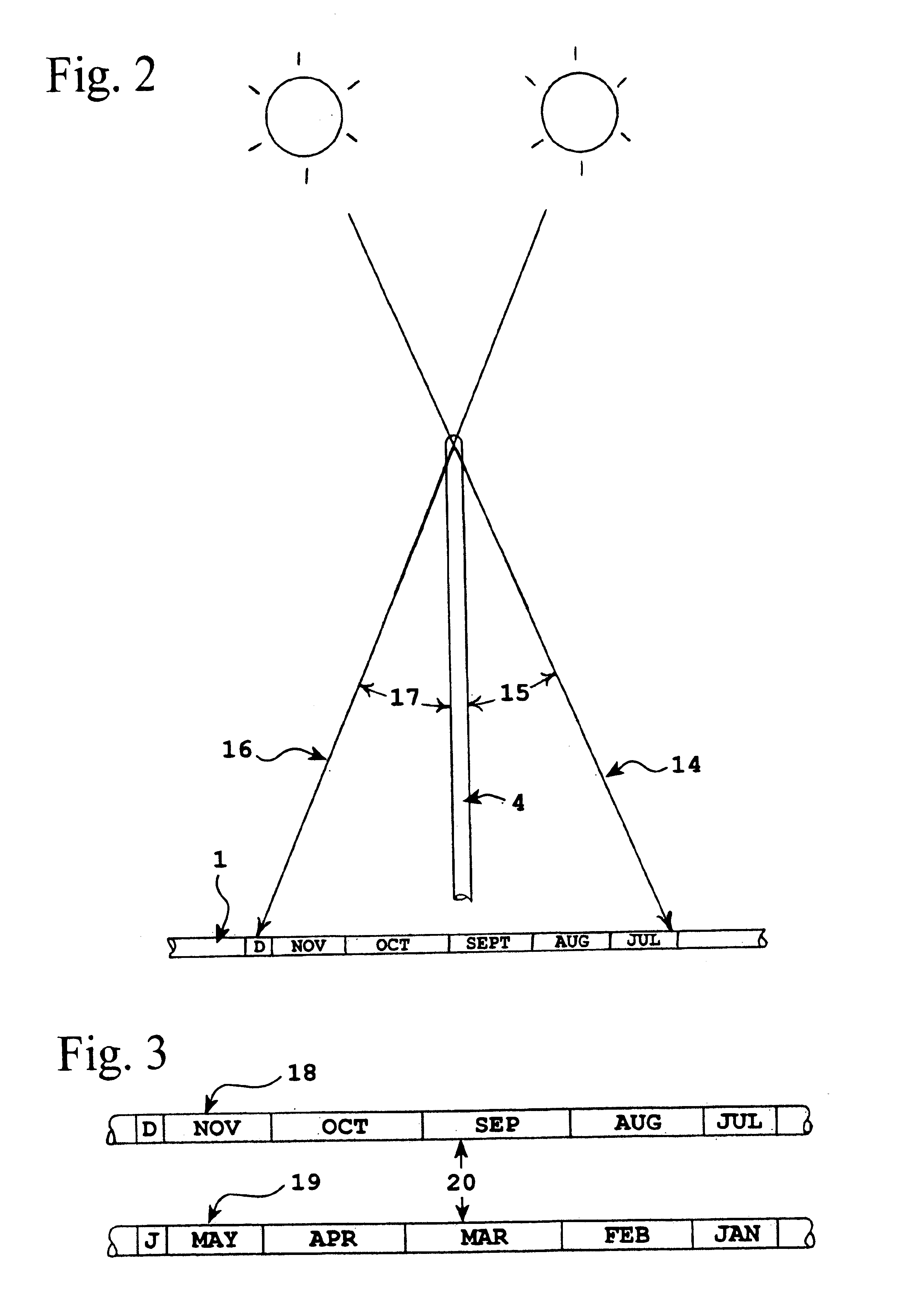
This invention represents an improvement to an equatorial sundial comprising an independent simultaneous single scale indication of both time and date as represented from a primary and secondary gnomon. This allows one unfamiliar with the physics of an equatorial sundial to with simple observation quickly assess both time and date as a singular measurement. The sundial displays conventional time measurement on a single scale transcribed on the equatorial ring from a primary gnomon aligned with the polar axis. The improvement includes a date scale transcribed on the primary gnomon that is cast a shadow from the secondary gnomon comprised of the upper equatorial ring. Since the sun maintains an essentially equivalent angle of declination throughout the day, the shadow cast by the upper equatorial ring (secondary gnomon) on the primary gnomon (containing the date scale) remains consistent in position and date can be observed at any time of the solar day.
Owner:MAEGLI JACK WILLIAM
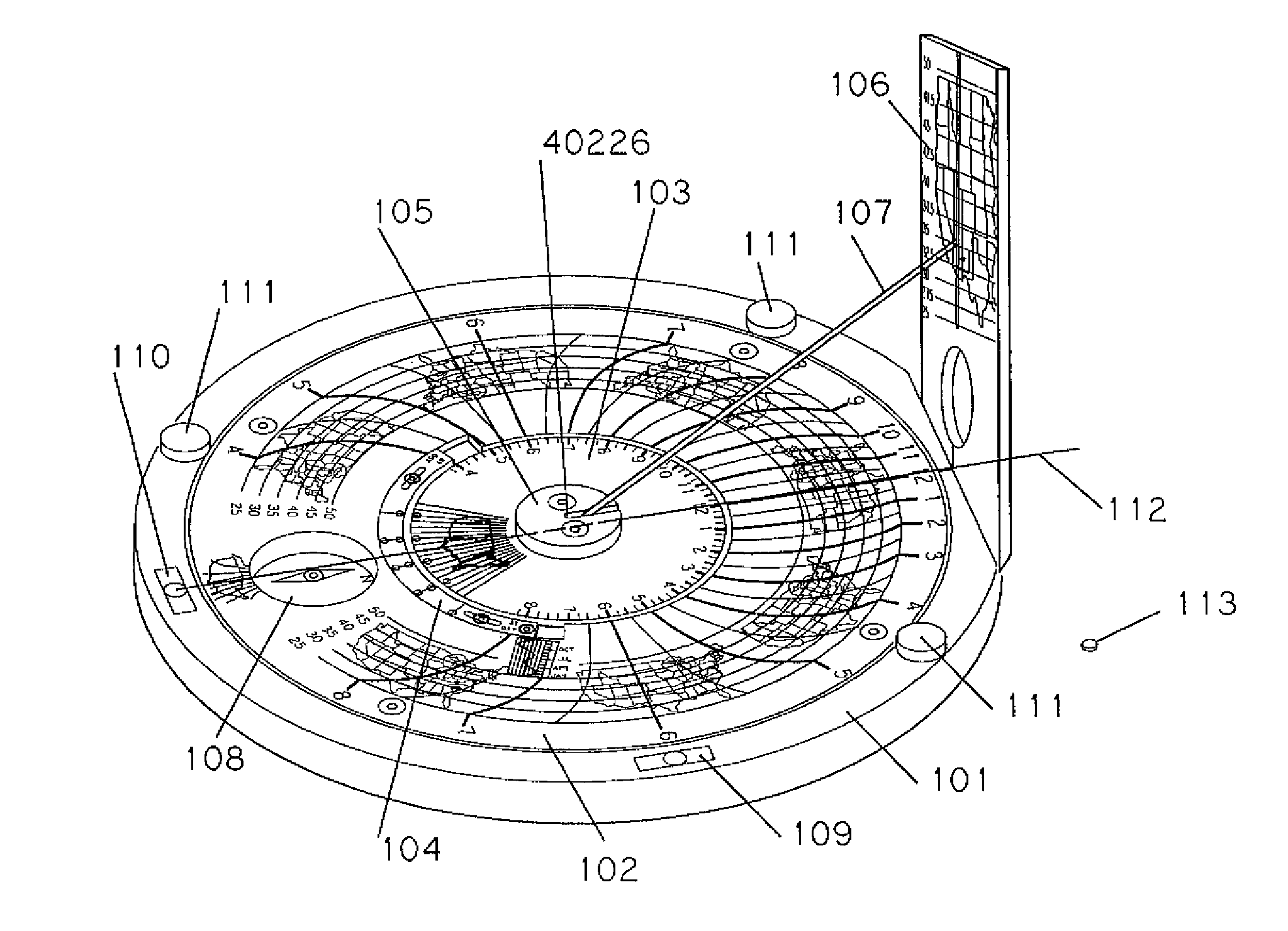
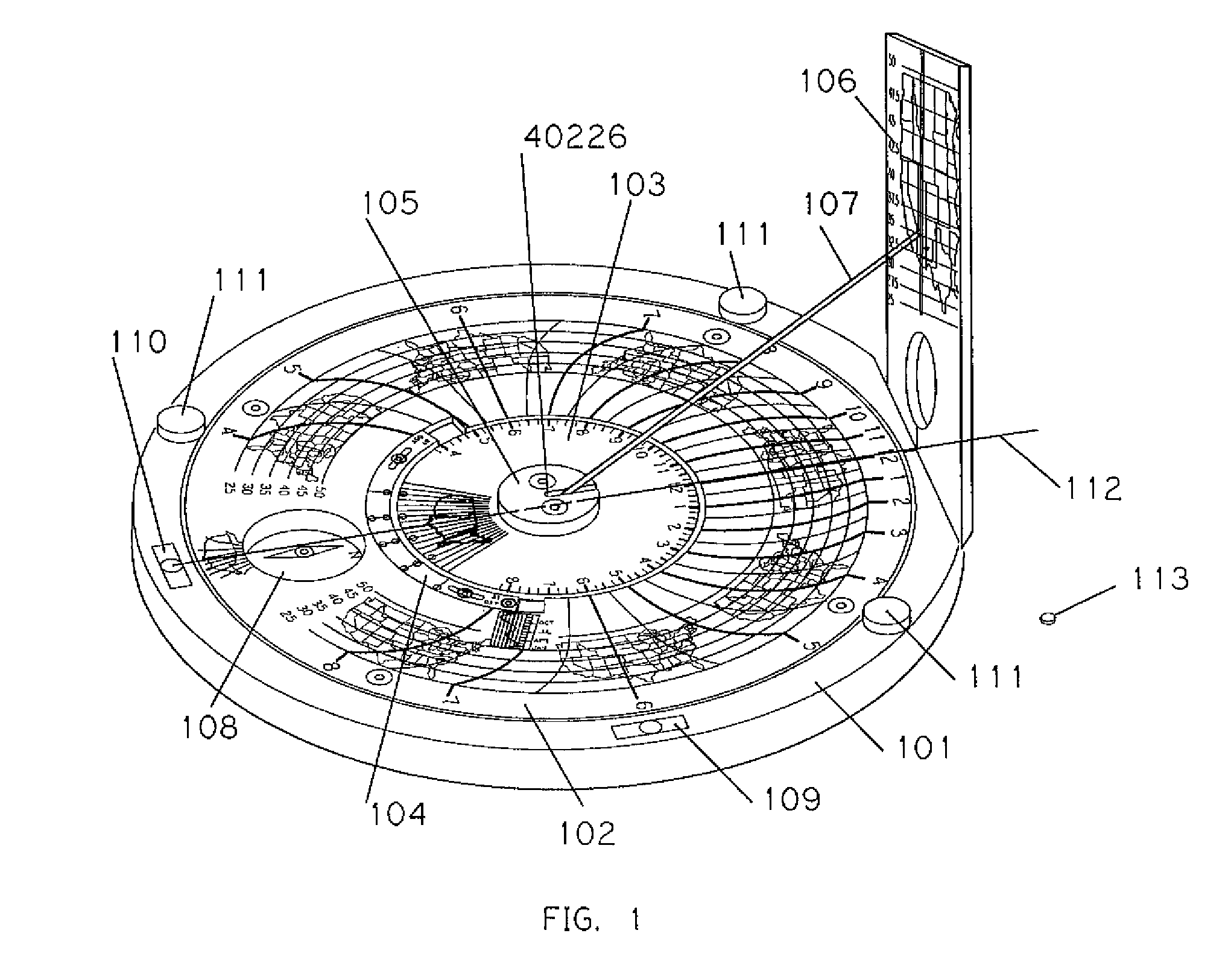
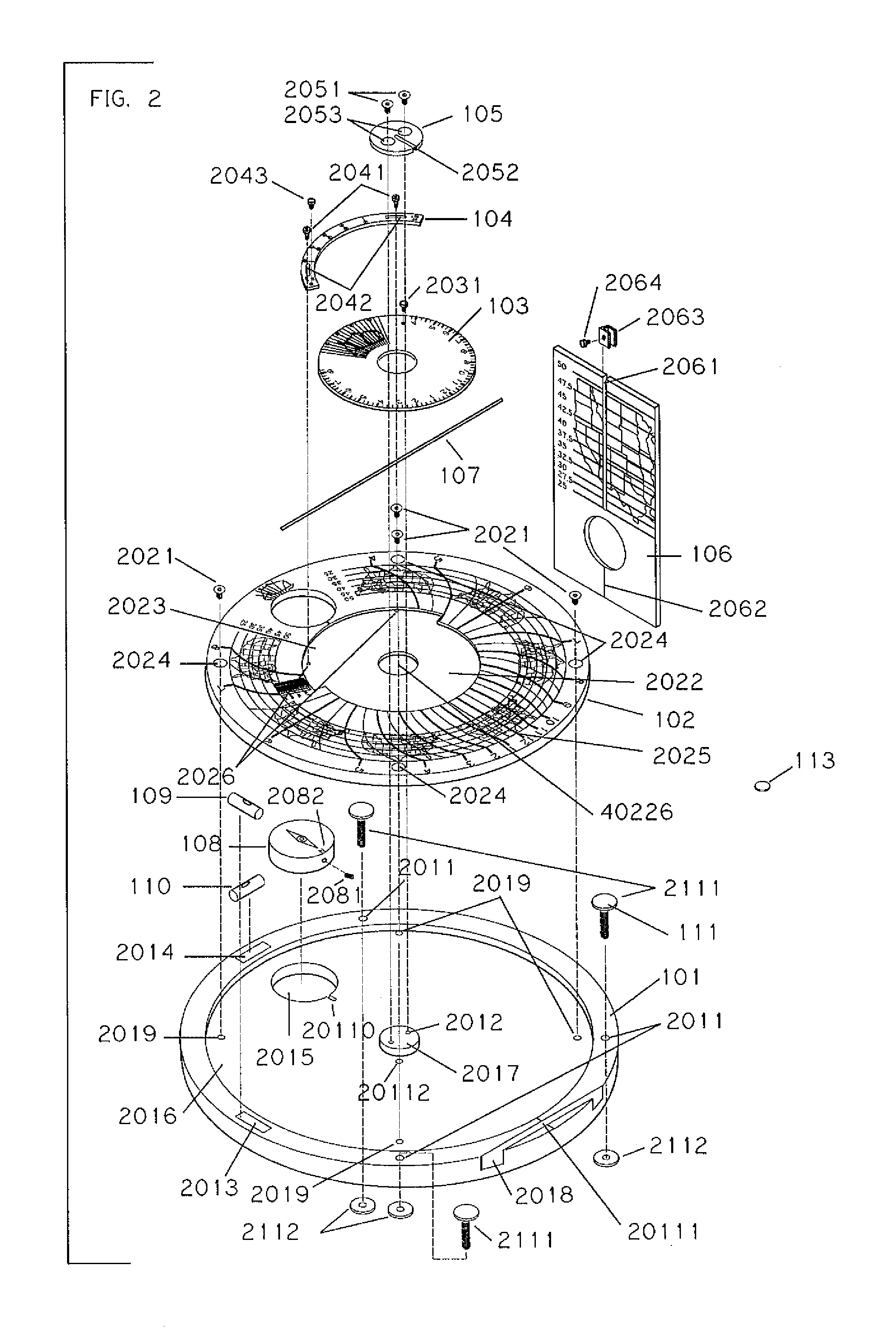
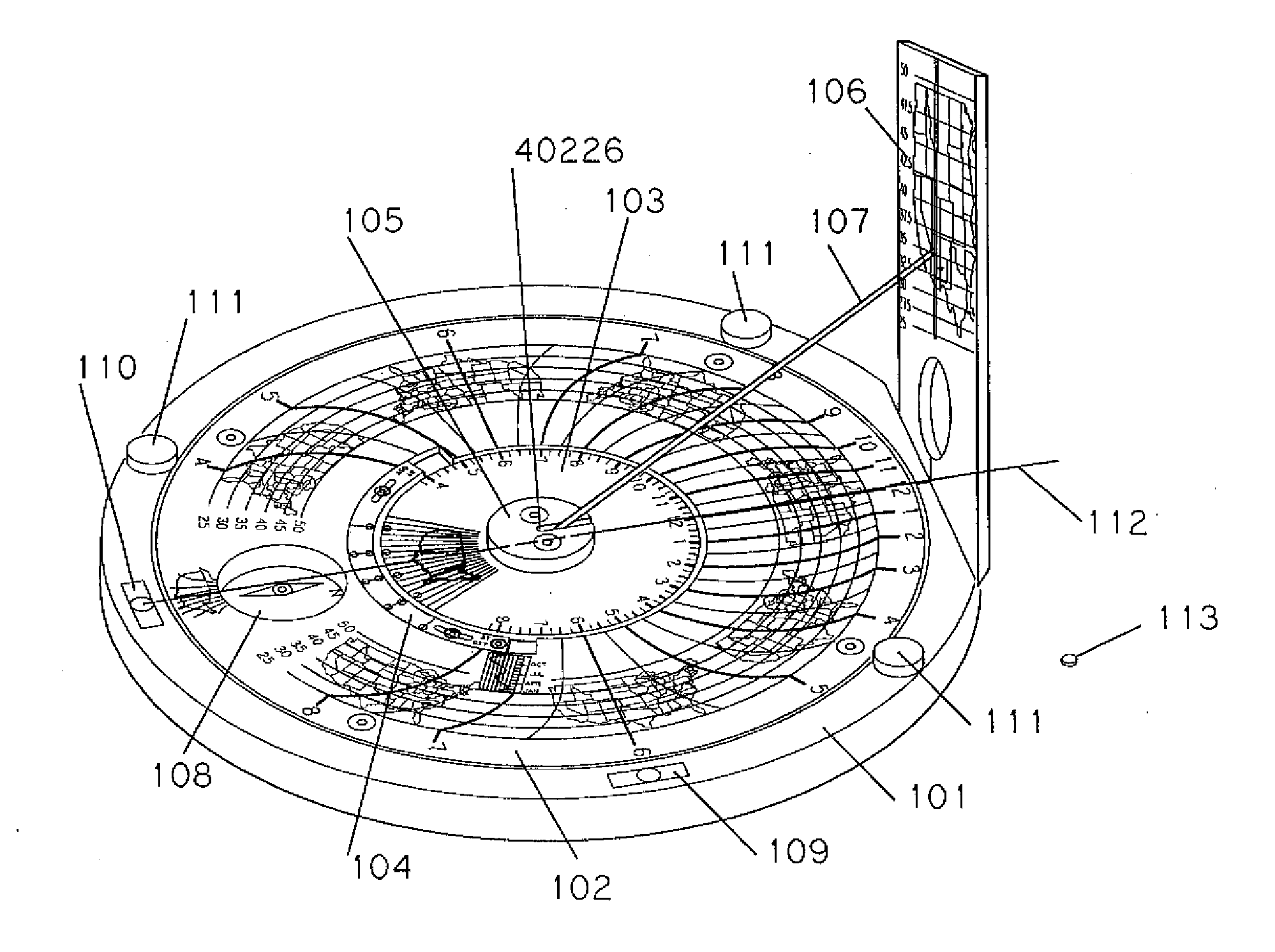
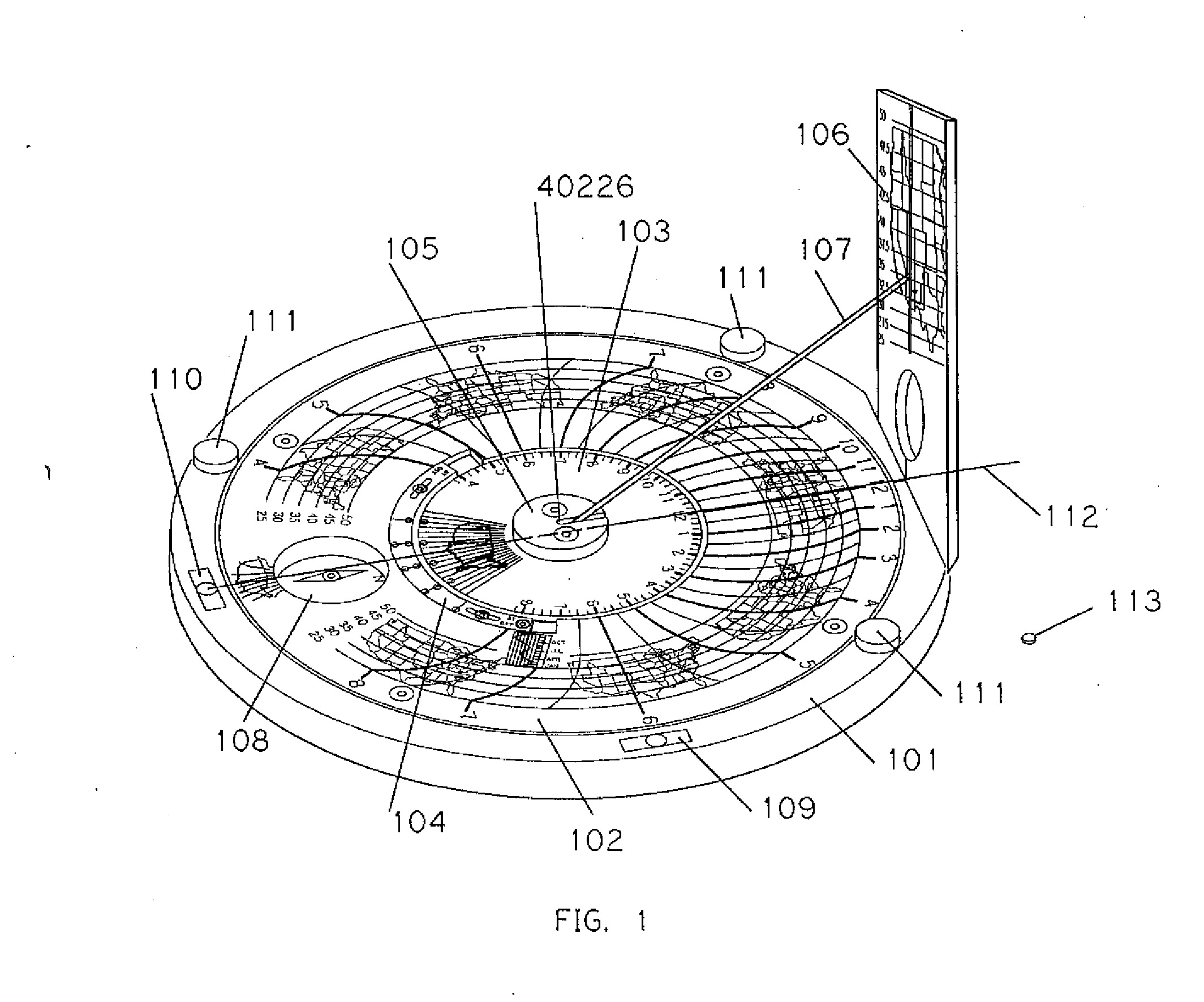
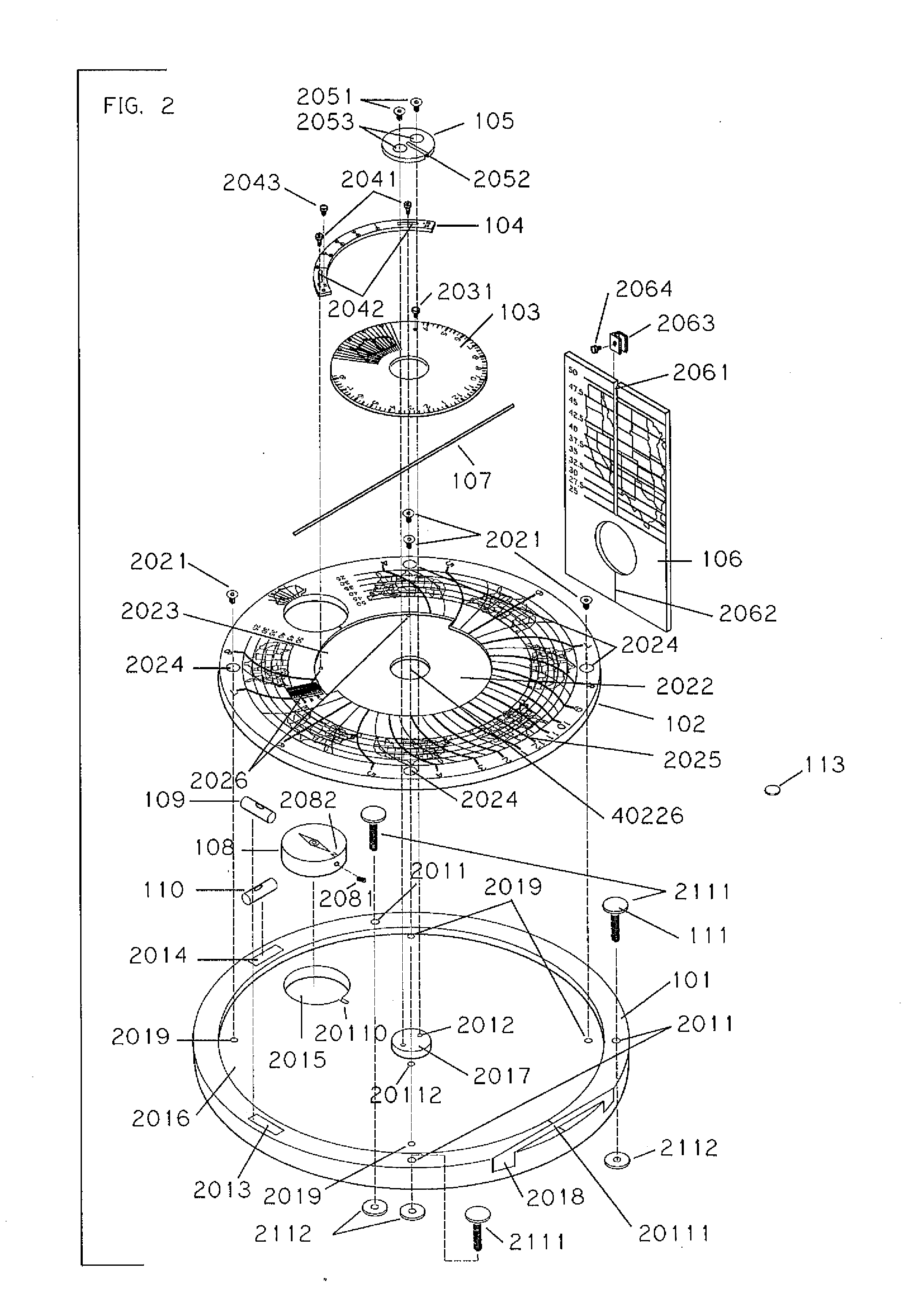
Sundial for telling solar time and clock time across a range of latitudes and longitudes
A sundial for telling apparent solar time and clock time across a range of latitudes and longitudes. A solar dial is formed with an index point and a noon hour point. A plurality of concentric latitude indicia are centered at the index point and at least one map indicium is overlaid by the concentric latitude indicia where the map indicium has geographic latitudes corresponding with the concentric latitude indicia on the solar dial. The solar dial also includes a plurality of solar time indicia radiating generally outward from the index point drawn with respect to the noon hour point according to the hour line equation at each concentric latitude indicia intercept. An elongated gnomon projects from the index point, whereby the sun's shadow cast by the gnomon intersects the solar time indicia in relation to the concentric latitude indicia to provide a reading of apparent solar time for the user's location on the map indicium.
Owner:KEELE RICHARD
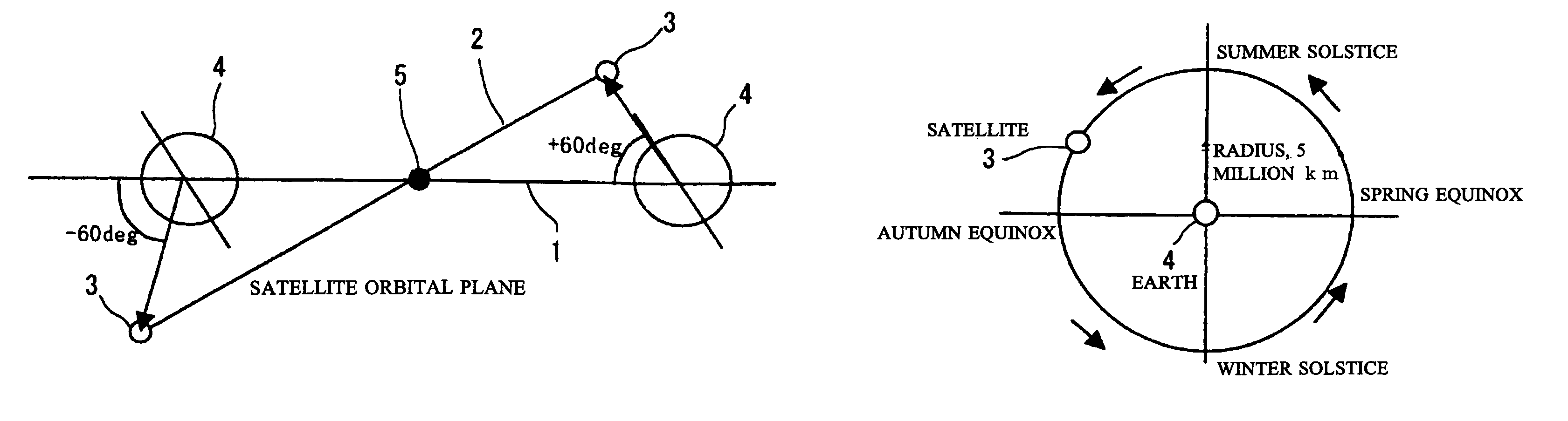
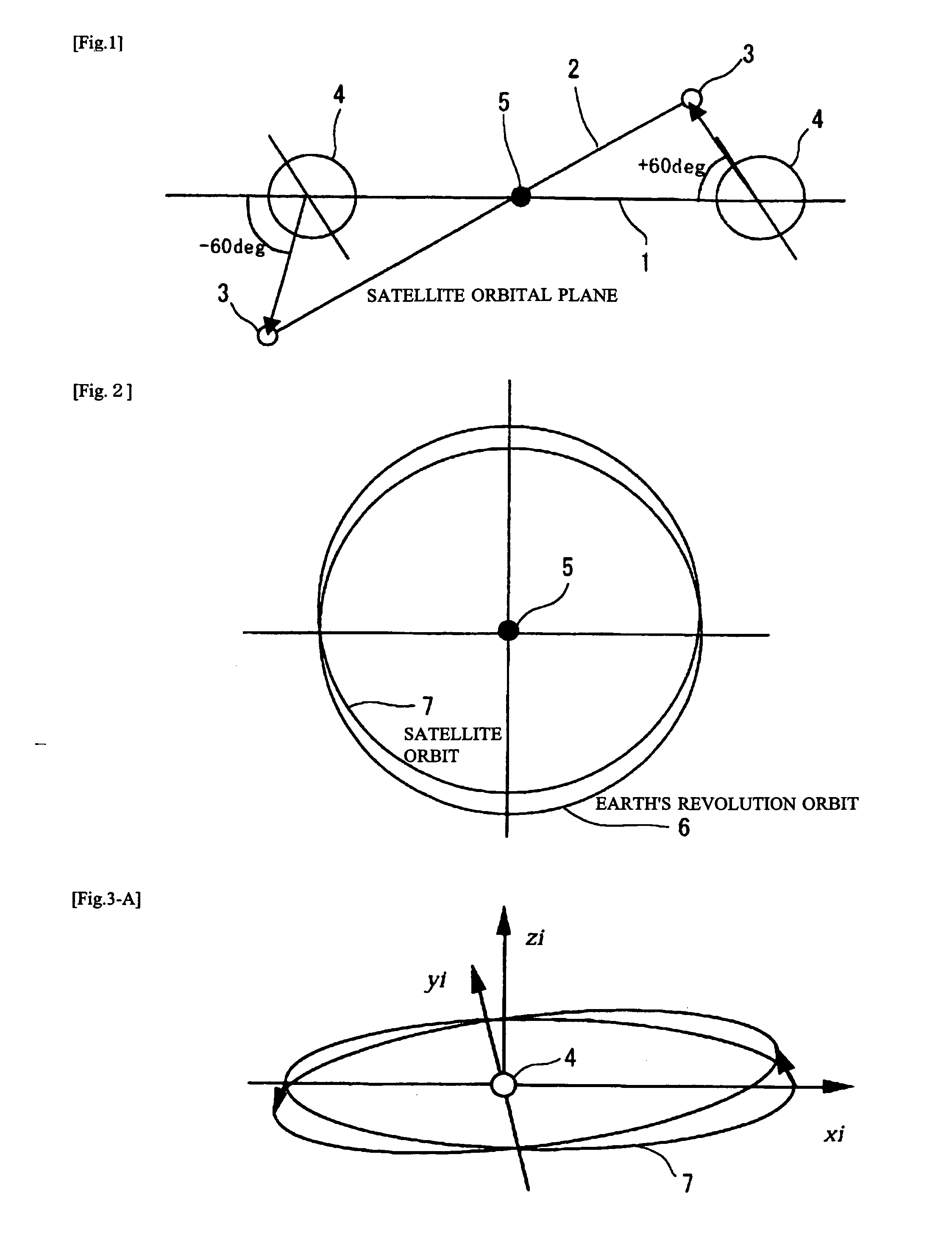
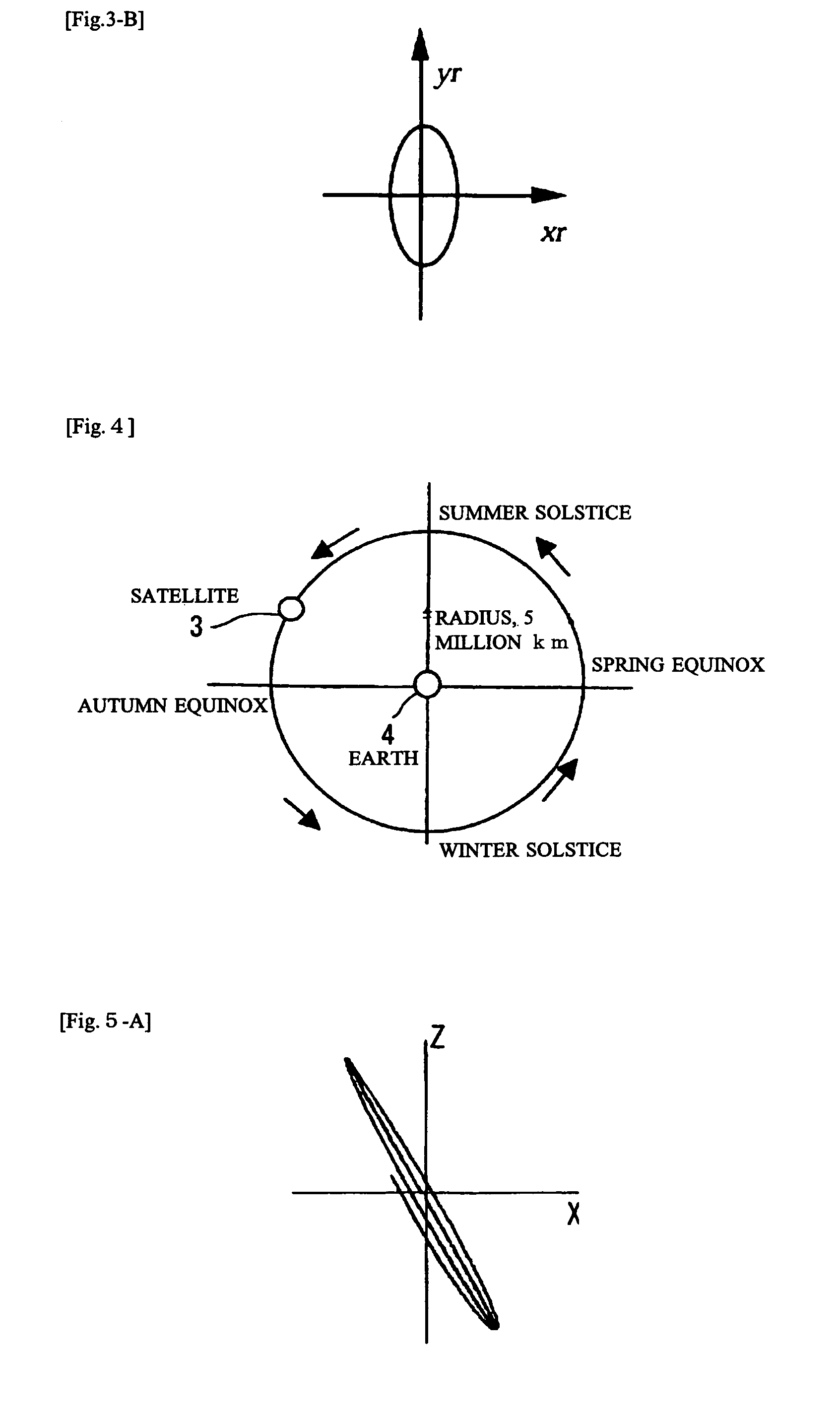
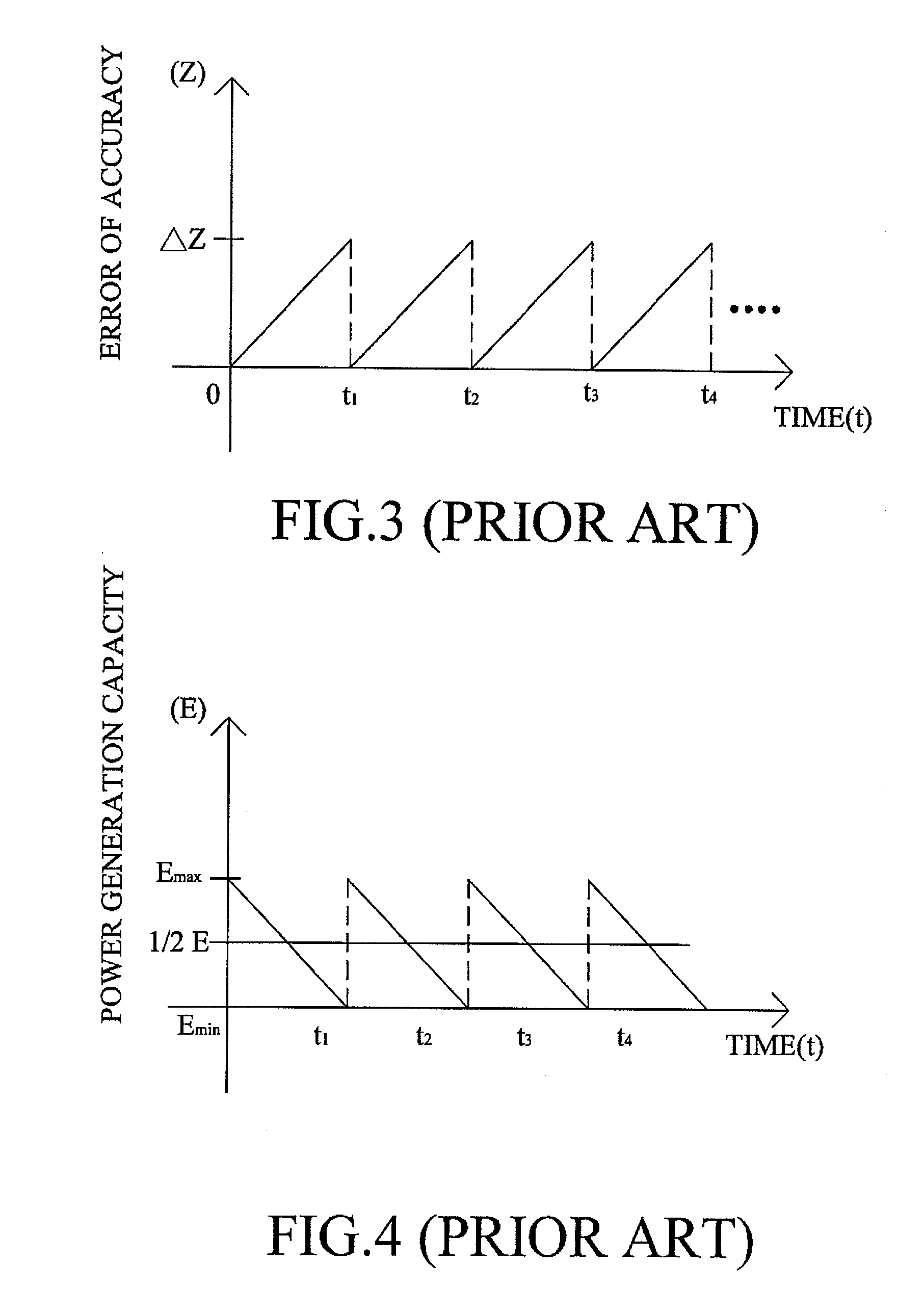
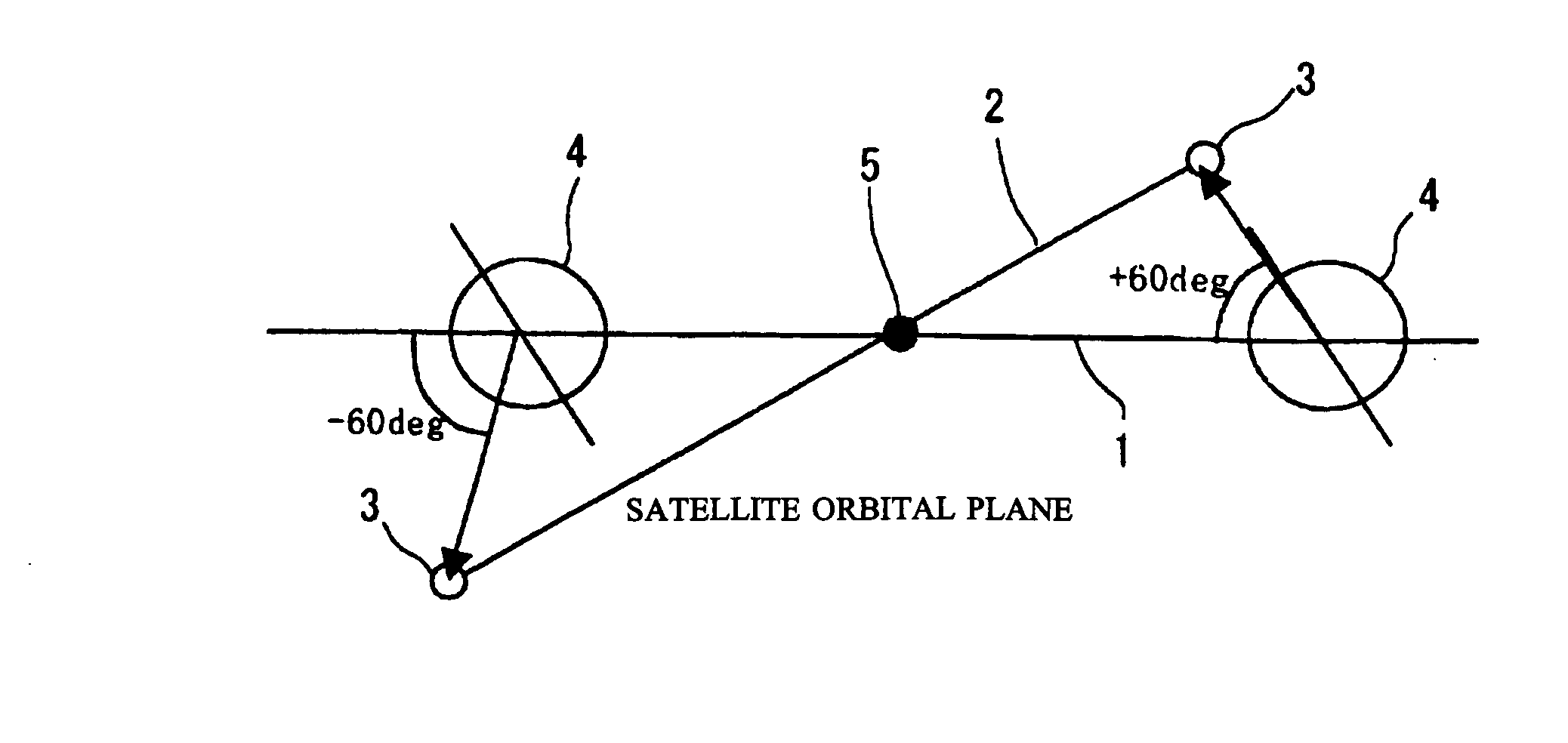
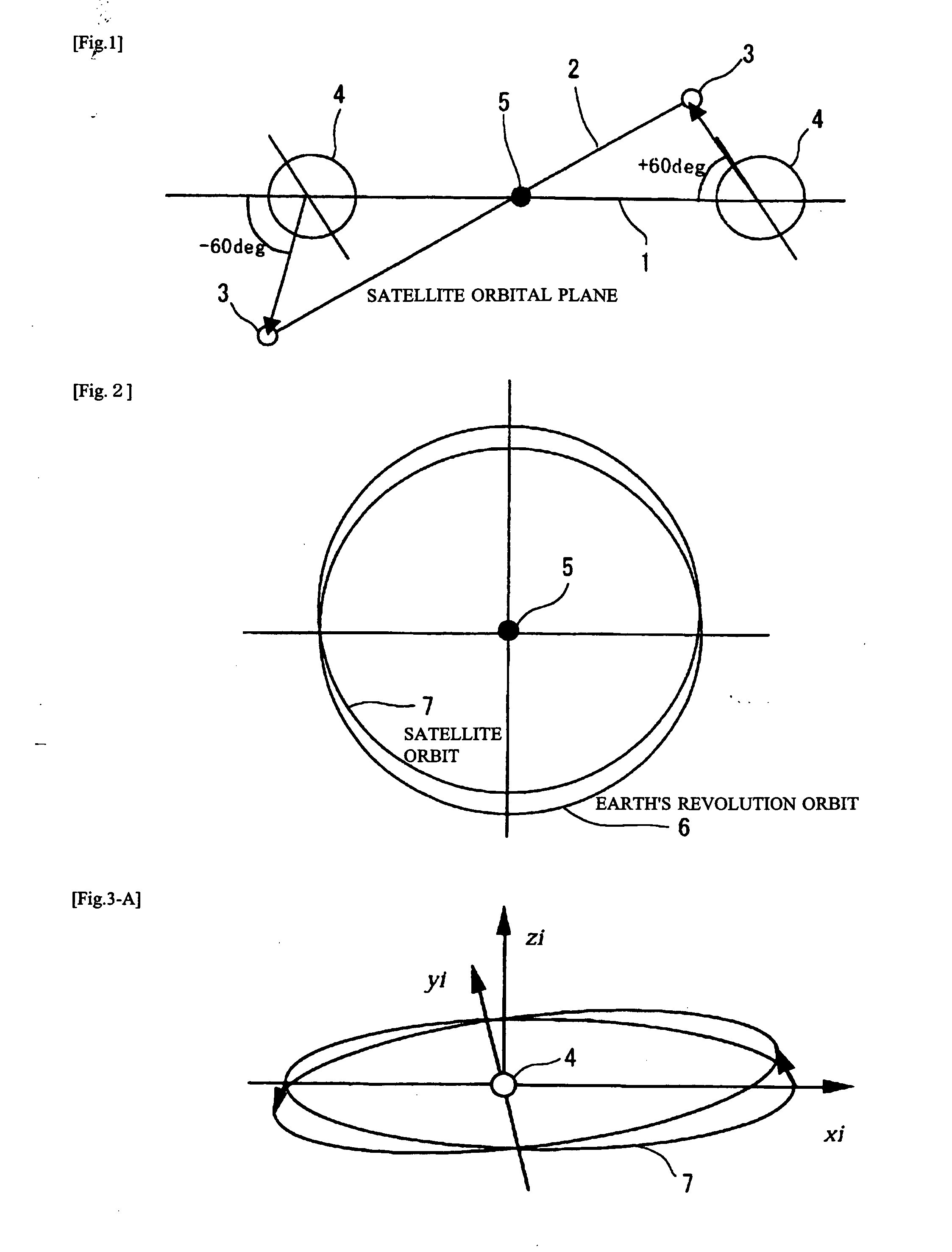
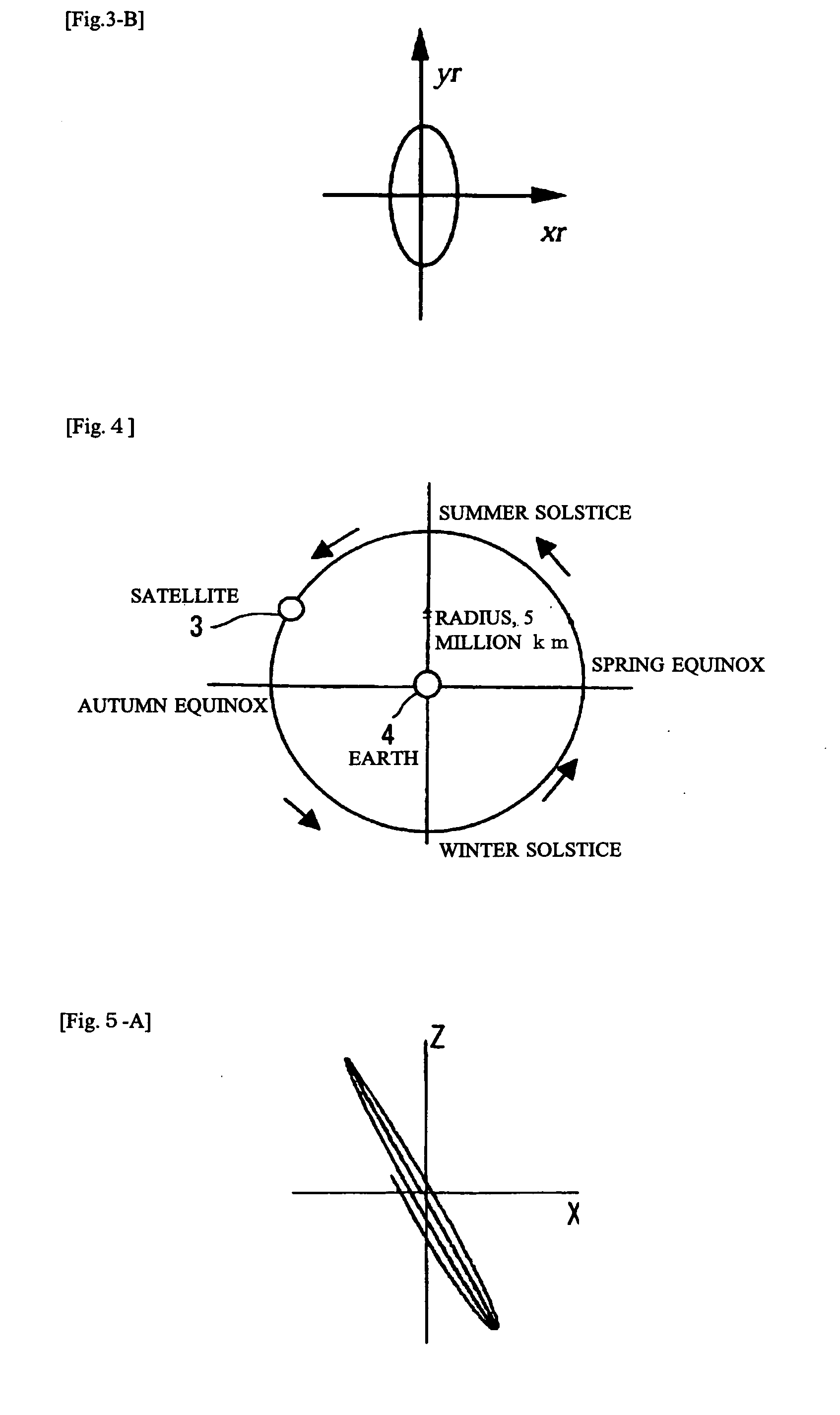
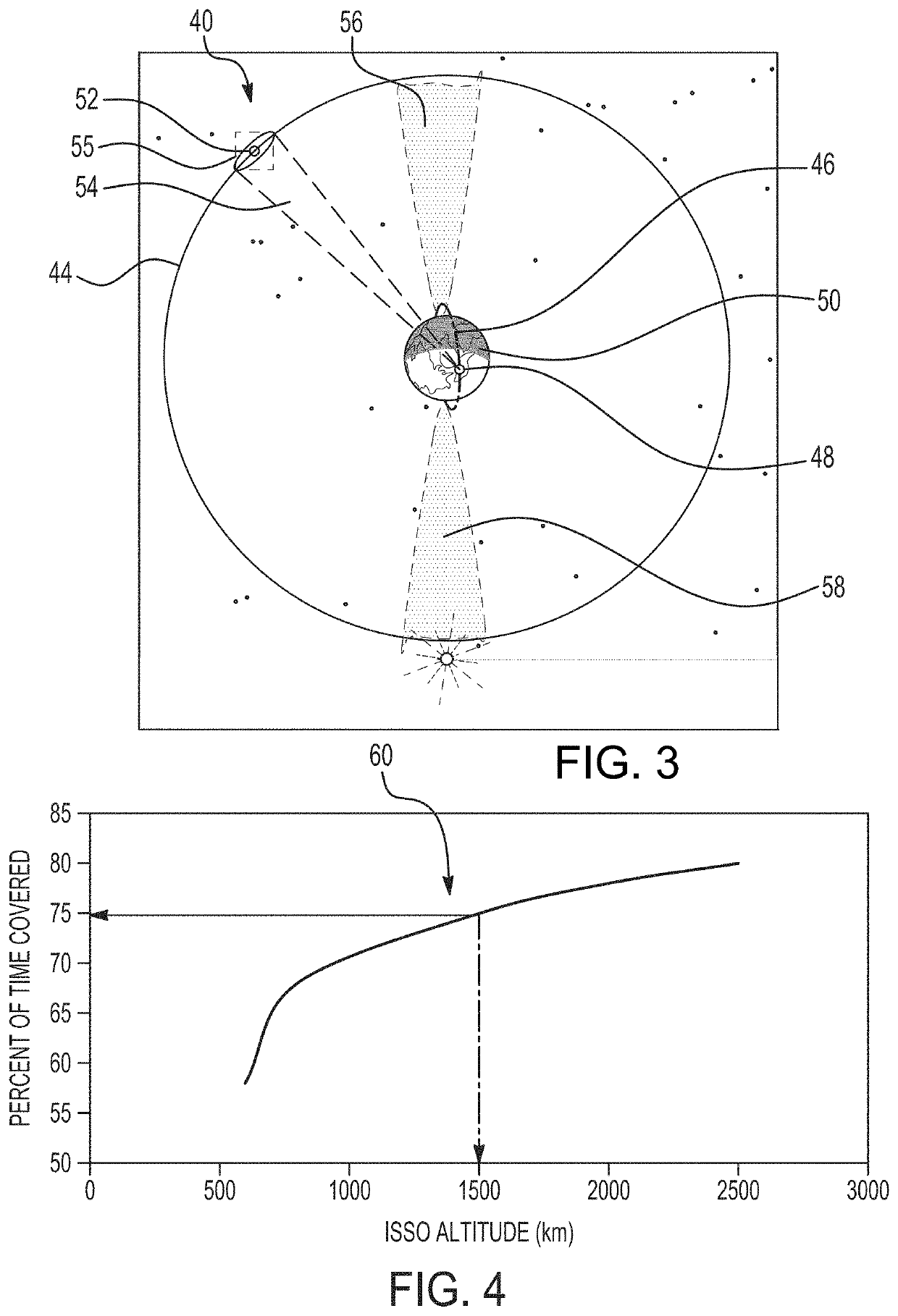
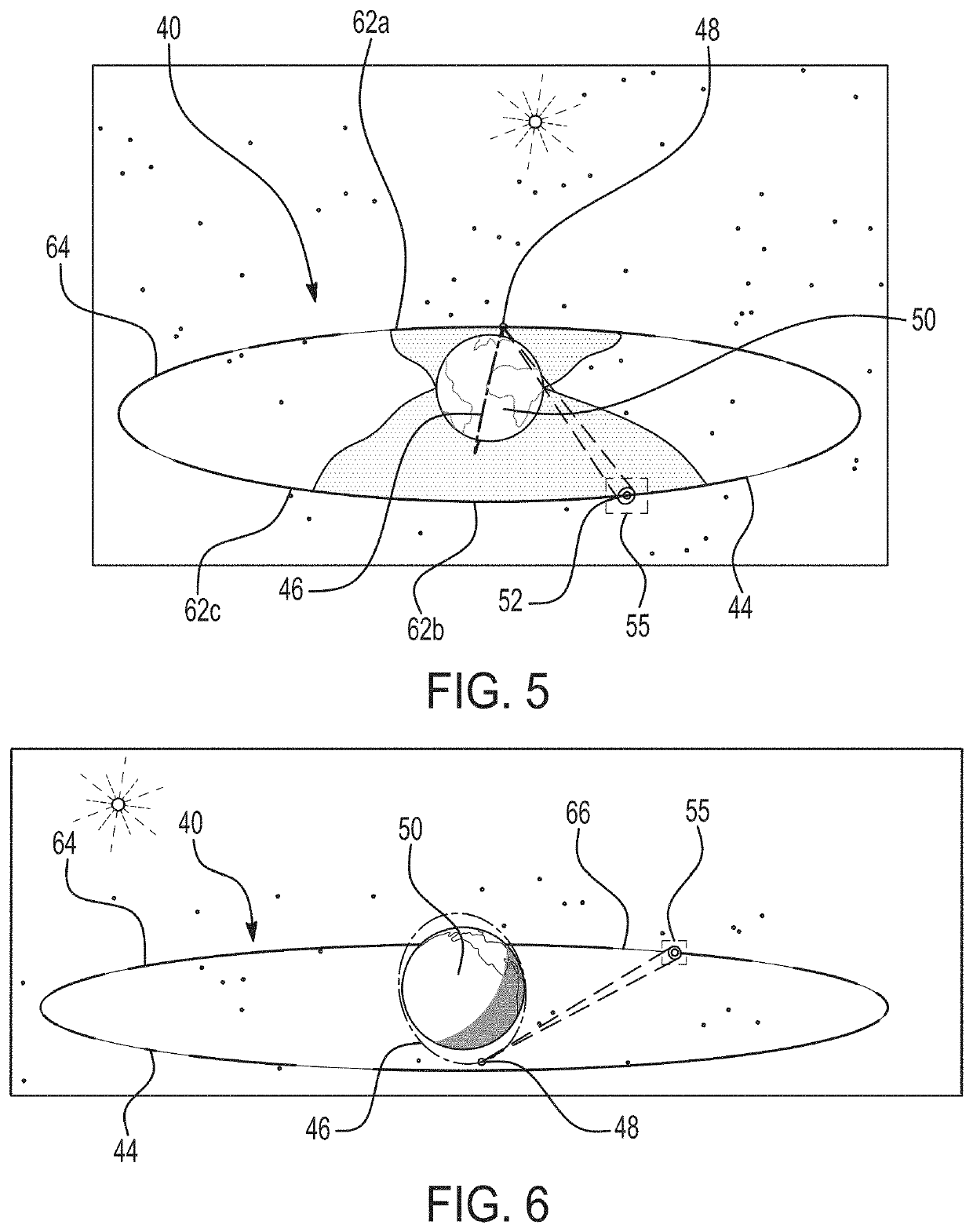
Ultrahigh altitude sun-synchronous orbit satellite system
InactiveUS7806369B2Increase distanceImprove accuracyArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusNatural satelliteElliptic motion
An ultrahigh altitude sun-synchronous orbit satellite system having one or plural satellites orbiting the sun such that the satellites revolve around the earth in a substantially circular or elliptic motion at an altitude of several million kilometers from the earth, beyond the sphere of earth gravity influence. The satellites are placed on an orbital plane relative to both the sun and the earth and keep a distance and geometry between the satellites, sun and earth substantially constant. The satellite system performs any one of the services of space observation, global observation, and satellite communication. The satellites orbit the sun with both inclination and eccentricity distinct from those of the revolution of the earth and revolve around the earth with a sun synchronous property in which the local solar time is kept constant at a point on the surface of the earth directly beneath the satellite.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
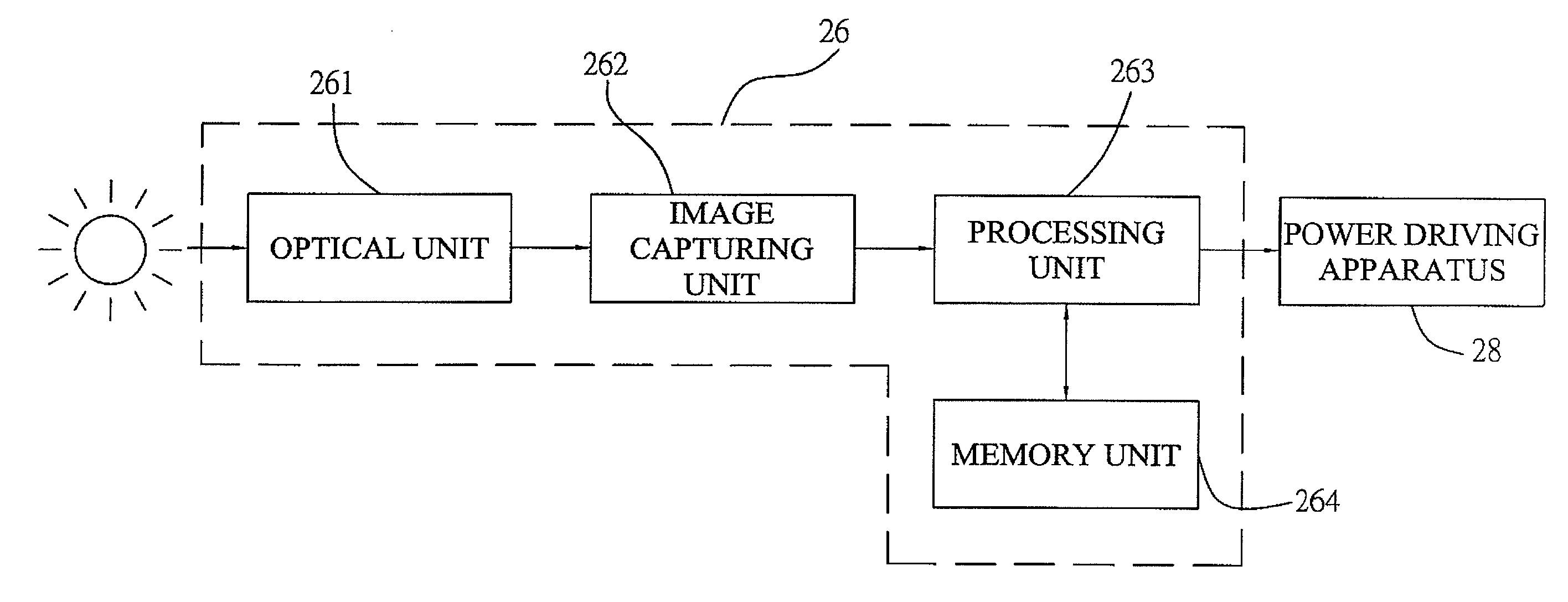
Solar tracking apparatus and solar electric power generation system thereof
InactiveUS20090260618A1Precise alignmentFollow fastPhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringSolar power
The present invention provides a solar tracking apparatus for use with a power driving apparatus. The solar tracking apparatus includes: a memory unit for recording a first solar image; an image capturing unit for capturing a second solar image; and an processing unit for obtaining difference between the first solar image and the second solar image; wherein the processing unit activates the power driving apparatus in response to the difference. Furthermore, the present invention also provides a solar power generation system using the solar tracking apparatus. Besides the solar tracking apparatus, the solar power generation system also includes a solar panel; the power driving apparatus for adjusting the position of the solar panel, wherein the processing unit of the solar tracking apparatus activates the power driving apparatus based on the difference so that the solar panel is aligned with the sun to gather the solar energy of the sun.
Owner:SOLAPOINT CORP
Ultrahigh Altitude Sun-Synchronous Orbit Satellite System
InactiveUS20080029650A1Increase distanceImprove accuracyArtificial satellitesSpacecraft guiding apparatusSynchronous orbitCelestial sphere
A system which comprises a sun-synchronous orbit satellite (3) revolving around the sun (5) and apparently revolving around the earth at a period of approximately one year while keeping the direction and the geometry to the sun and the earth (4) constant at an ultrahigh altitude of several millions km keeping clear of the influence zone of the earth, and which provides any of astronomical or global observation service and communication service. An observation satellite, which meets such conditions that a vector normal to a virtual orbital plane centering around the earth is substantially fixed regardless of revolution, can sweep the substantially entire celestial sphere during a single revolution while avoiding the effect of light and heat from the earth, and can keep a local solar time at a sub-satellite point on the surface of the earth constant, can be attained. A communication satellite, where the substantially hemisphere of the earth can be covered at a time simultaneously with one satellite and the substantially entire region of the earth can be covered with a small number or three satellites, is attained. Geometrical relations with the sun and the earth can be frozen approximately by the adjustment of the i / e ratio or by the use of perturbation by the attraction of the earth gravity. Operation from launch to insertion into an intended orbit can be achieved with significantly low fuel consumption by utilizing the perturbation owing to the attraction of the earth gravity.
Owner:JAPAN AEROSPACE EXPLORATION AGENCY
Equatorial sundial with simple time and date interpretation
InactiveUS20050060900A1Intuitive interpretationVisual indicationElectric indicationSundialEquatorial ring
This invention represents an improvement to an equatorial sundial comprising an independent simultaneous single scale indication of both time and date as represented from a primary and secondary gnomon. This allows one unfamiliar with the physics of an equatorial sundial to with simple observation quickly assess both time and date as a singular measurement. The sundial displays conventional time measurement on a single scale transcribed on the equatorial ring from a primary gnomon aligned with the polar axis. The improvement includes a date scale transcribed on the primary gnomon that is cast a shadow from the secondary gnomon comprised of the upper equatorial ring. Since the sun maintains an essentially equivalent angle of declination throughout the day, the shadow cast by the upper equatorial ring (secondary gnomon) on the primary gnomon (containing the date scale) remains consistent in position and date can be observed at any time of the solar day.
Owner:MAEGLI JACK WILLIAM
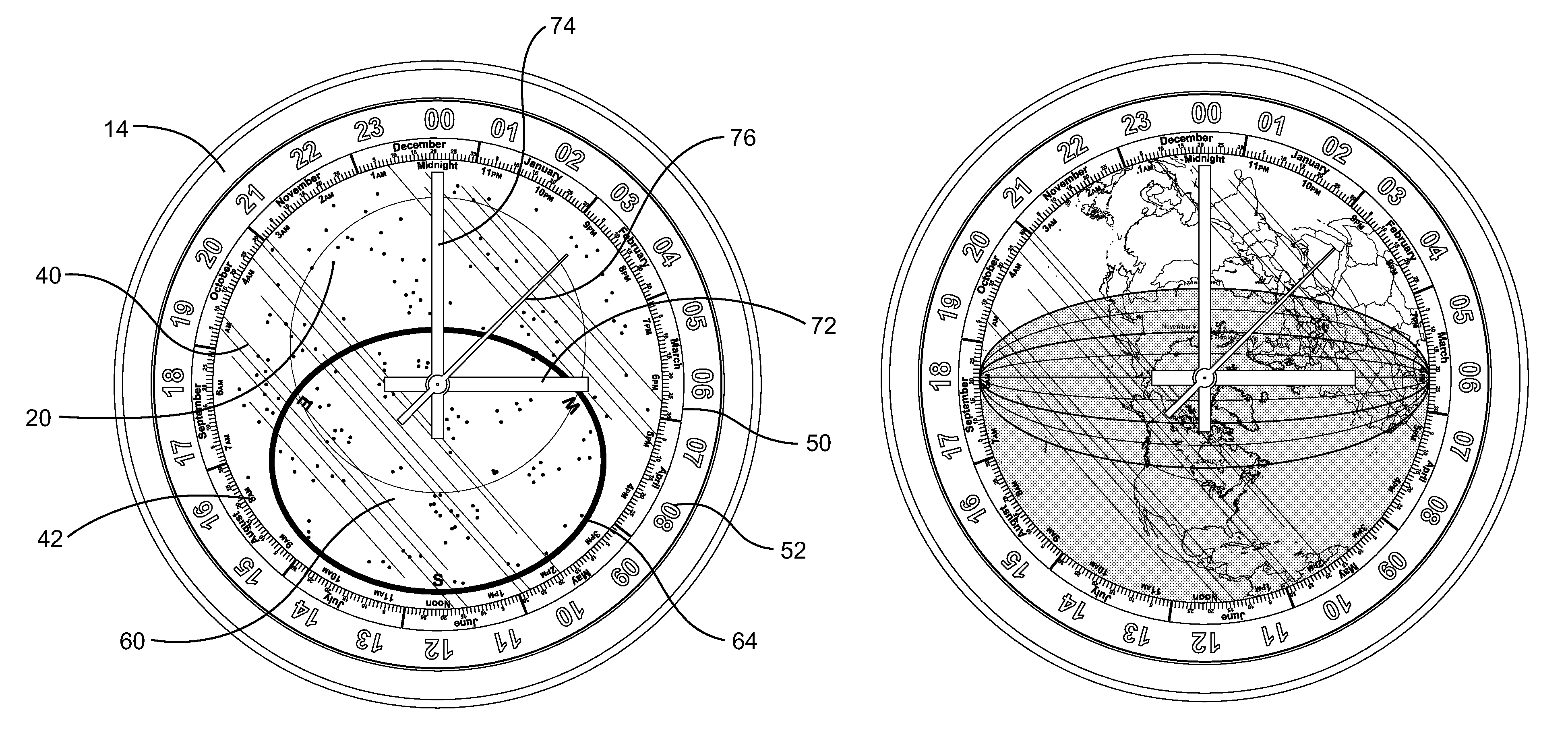
Planisphere clock
A timepiece for displaying a planisphere and indicating a portion of the planisphere. Another exemplary embodiment is a clock that displays both sidereal and solar time, while indicating a portion of the planisphere at a particular time. Another exemplary embodiment of the timepiece includes an adjustment feature that allows a user to adjust the portion of the planisphere indicated to a particular geographic location. An exemplary embodiment may contain a celestial or terrestrial planisphere. As a result, an exemplary embodiment of the timepiece may provide valuable information about the planisphere at any particular sidereal or solar time.
Owner:TRIDENT DESIGN
Solar-To-Electricity Conversion Sub-Module
InactiveUS20090250096A1Circuit optical detailsThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectHigh concentrationElectricity
The invention addresses the area utilization and capital efficiency of systems for converting solar energy into electricity. A solid-state solar submodule includes photovoltaic and thermoelectric or thermionic cells. The submodule can be implemented in various configurations and by a solar insolation flux collection and concentration method to improve the area utilization and solar-to-electricity conversion efficiency. A thermal expansion matched multilayer board is also used to withstand ultra high concentration of solar insolation flux.
Owner:PAN ERIC TING SHAN
High-sensitivity coronagraph stray light detection device
ActiveCN111060289AHigh sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityTesting optical propertiesPhoton counting detectorOptical radiation
The invention provides a high-sensitivity coronagraph stray light detection device, and relates to the field of astronomical target observation and detection. The device comprises a low-brightness solar simulation device, a band-pass filter and a single-photon counting imaging detector. The band-pass filter is arranged between the coronagraph to be measured and the single-photon counting detector,and the single-photon counting detector is arranged on the focal plane of the coronagraph to be measured; the low-brightness solar simulation device emits 32'full-view-field simulated sunlight to enter the coronagraph to be detected, the band-pass filter performs wavelength selection on a wave band to be detected, and the single-photon counting imaging detector detects stray light brightness andsolar sun surface brightness of the coronagraph to be detected. The stray light inhibition capability of the coronagraph can be detected by respectively measuring the solar sun surface radiation and the stray light radiation of the coronagraph, and the difficulty that the stray light inhibition capability of the coronagraph cannot be directly detected by utilizing the solar radiation due to the influence of atmospheric scattering in a low-altitude area is overcome.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clock Operated Step Function Solar Tracker
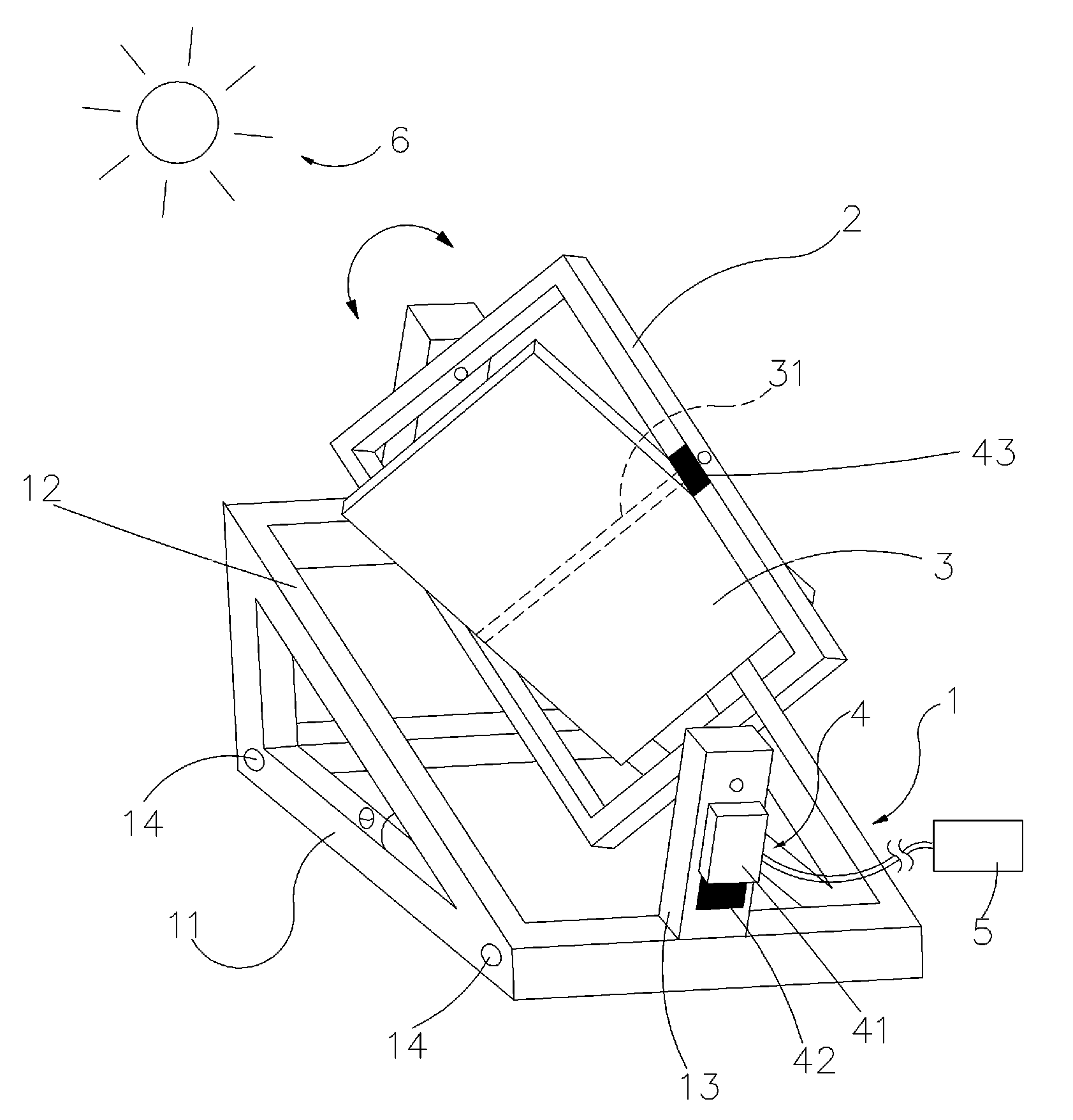
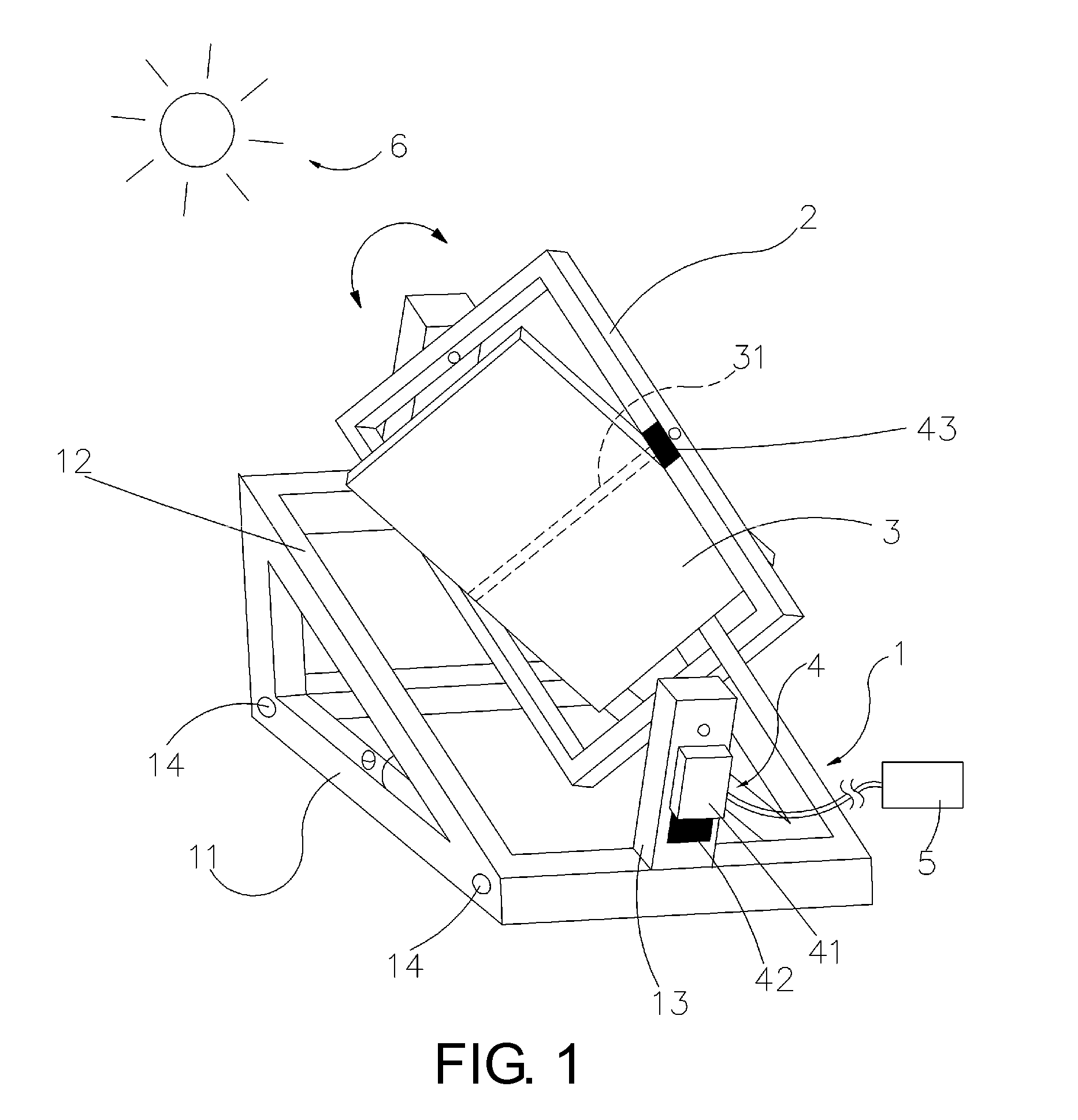
InactiveUS20120174963A1Low costGood energy capture performancePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyEngineeringSolar tracker
The present invention describes a solar panel system tracker that closely approximates the output levels of an actively tracked system but at significantly reduced levels of complexity and cost. The present invention utilizes a clock that generates a five degree step function which moves the solar panel system in five degree increments over the period of the solar day. This provides approximately thirty-five separate adjustments throughout the day, yielding an aggregate output performance of approximately 90 percent compared to a fully tracked system.
Owner:THOMPSON BRUCE A
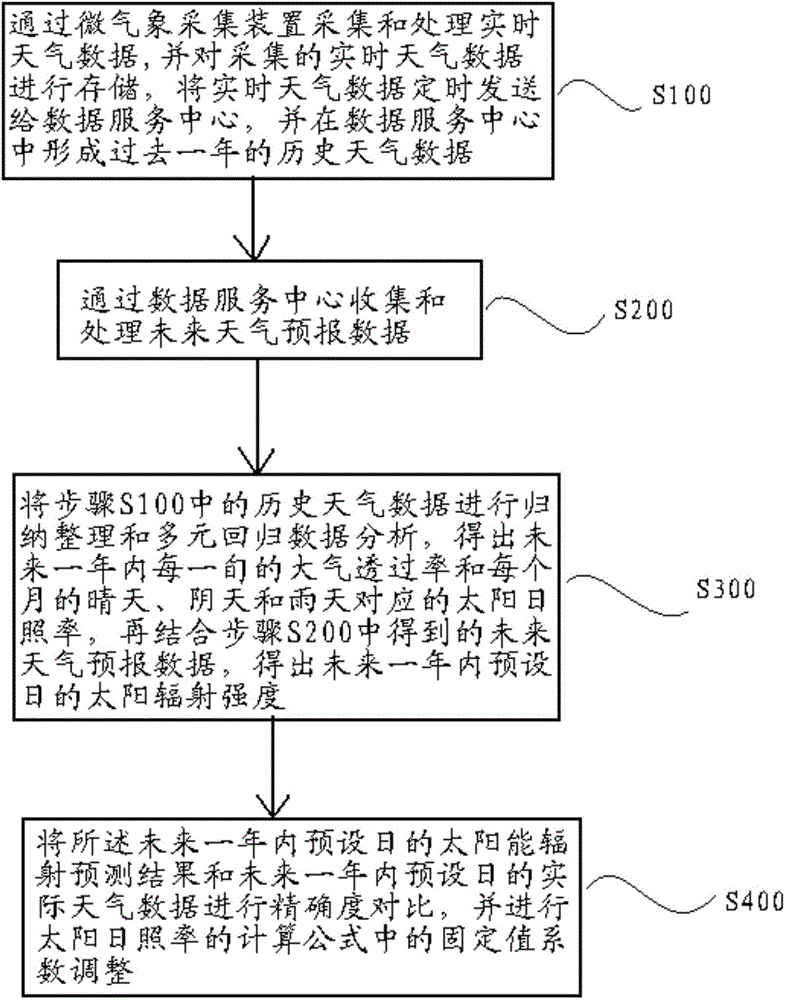
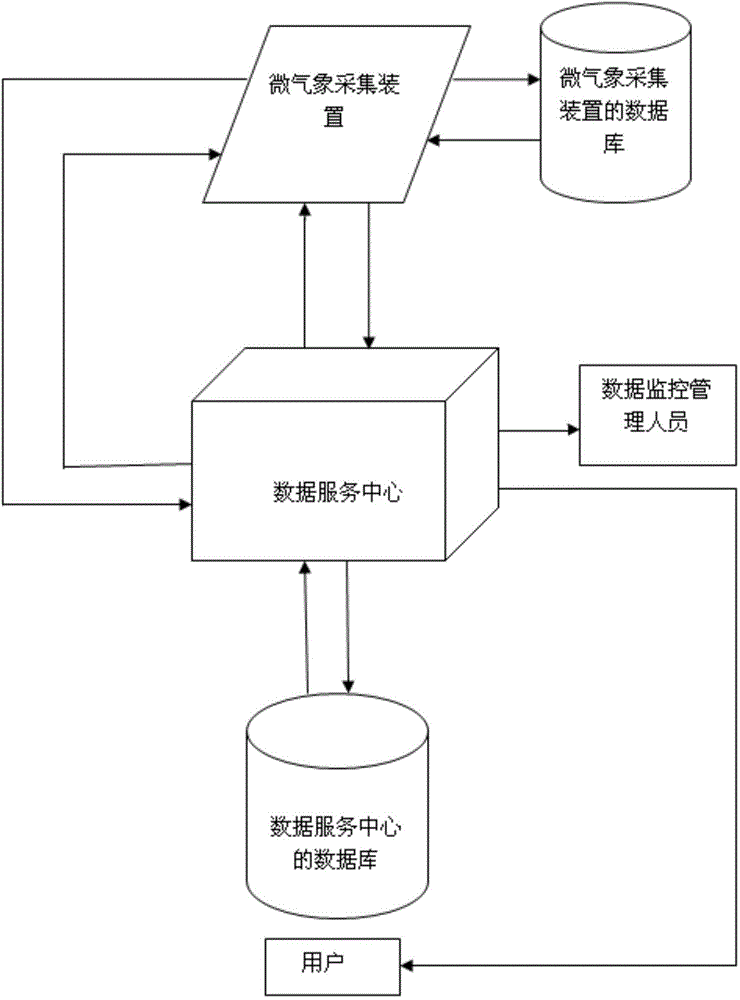
Distributed type solar radiation prediction method and system based on micro-meteorology data
ActiveCN103984991AImprove power qualityImprove schedulabilityForecastingComputer scienceWeather data
The invention relates to a distributed type solar radiation prediction method based on micro-meteorology data. The distributed type solar radiation prediction method comprises the following steps that S100, a micro-meteorology collection device collects, processes and stores real-time weather data and sends the real-time weather data to a data service center regularly, and historical weather data are formed in the data service center; S200, the data service center collects and processes future weather forecast data; S300, the historical weather data obtained in the S100 are summed up and sorted up, multiple regression data analysis is carried out on the historical weather data, the atmospheric transmissivity of each period of ten days within the next year and the sunshine durations corresponding to the sunny days, the cloudy days and the rainy days of every month are obtained and are combined with the future weather forecast data obtained in the S200, and the sun radiation intensity of the future days can be obtained. The distributed type solar radiation prediction method based on the micro-meteorology data can accurately predict the solar radiation intensity of the future days.
Owner:WUHAN DONGRI TECH
Sundial for telling solar time and clock time across a range of latitudes and longitudes
A sundial for telling apparent solar time and clock time across a range of latitudes and longitudes. A solar dial is formed with an index point and a noon hour point. A plurality of concentric latitude indicia are centered at the index point and at least one map indicium is overlaid by the concentric latitude indicia where the map indicium has geographic latitudes corresponding with the concentric latitude indicia on the solar dial. The solar dial also includes a plurality of solar time indicia radiating generally outward from the index point drawn with respect to the noon hour point according to the hour line equation at each concentric latitude indicia intercept. An elongated gnomon projects from the index point, whereby the sun's shadow cast by the gnomon intersects the solar time indicia in relation to the concentric latitude indicia to provide a reading of apparent solar time for the user's location on the map indicium.
Owner:KEELE RICHARD
Method for analyzing household photovoltaic shelter
InactiveCN109379042AImprove exception handling progressReduce operating expensesPhotovoltaic monitoringPhotovoltaic energy generationPhotovoltaic power stationDistributed power
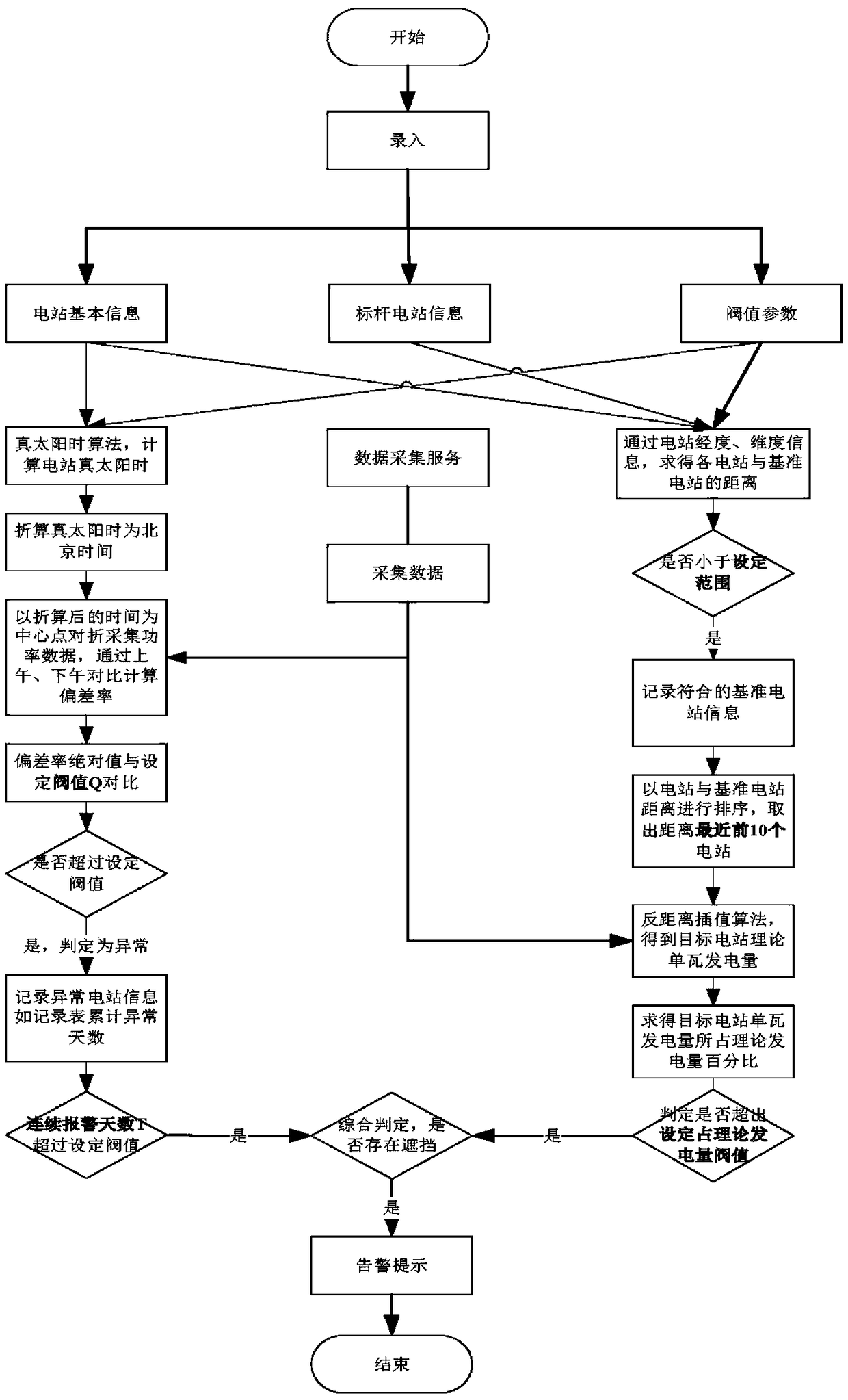
The invention relates to the field of distributed photovoltaic technology, in particular to a method for analyzing a household photovoltaic shelter, which comprises the steps of: establishing a distributed power station basic information data archive, and inputting information; determining a calculation result after the data is substituted into a true solar time algorithm calculation model and aninverse distance weighted algorithm calculation module for calculation; if the determining results of the true solar time algorithm calculation model and the inverse distance weighted algorithm calculation module are both abnormal, determining that a shelter exists; otherwise, only recording determination result details; giving a warning prompt to the abnormal power station. The method can quicklyand accurately diagnose the power generation anomaly of a distributed photovoltaic power station, and can timely notify a user and an operation and maintenance worker, improves the abnormal treatmentschedule of the power station, reduces the operating cost of the power station, ensures the power generation reliability of the power station, and increases the generated energy and the revenue of the power station.
Owner:河北隆基泰和云能源科技有限公司
Structure of armillary sphere system for ancient water-powered astronomical clock tower
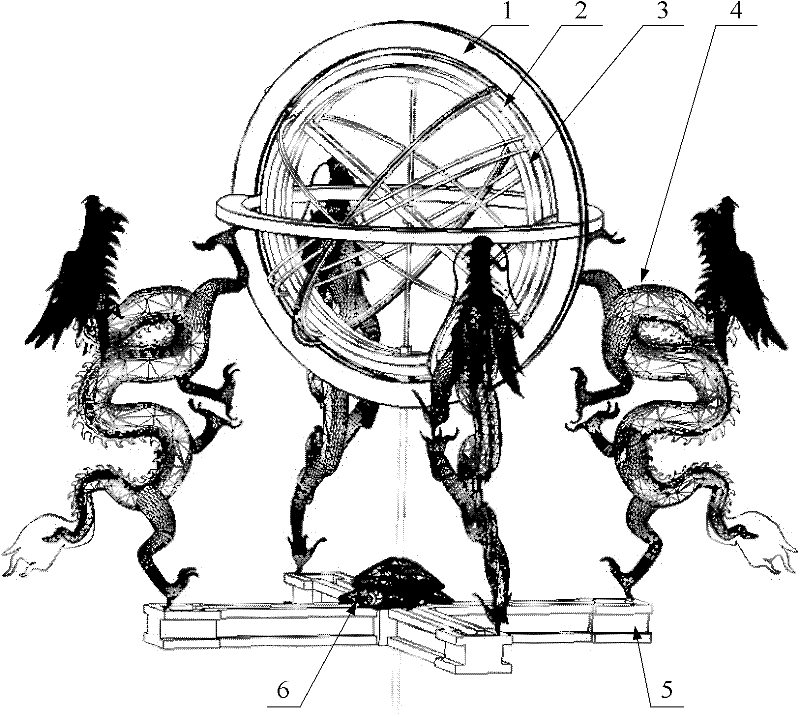
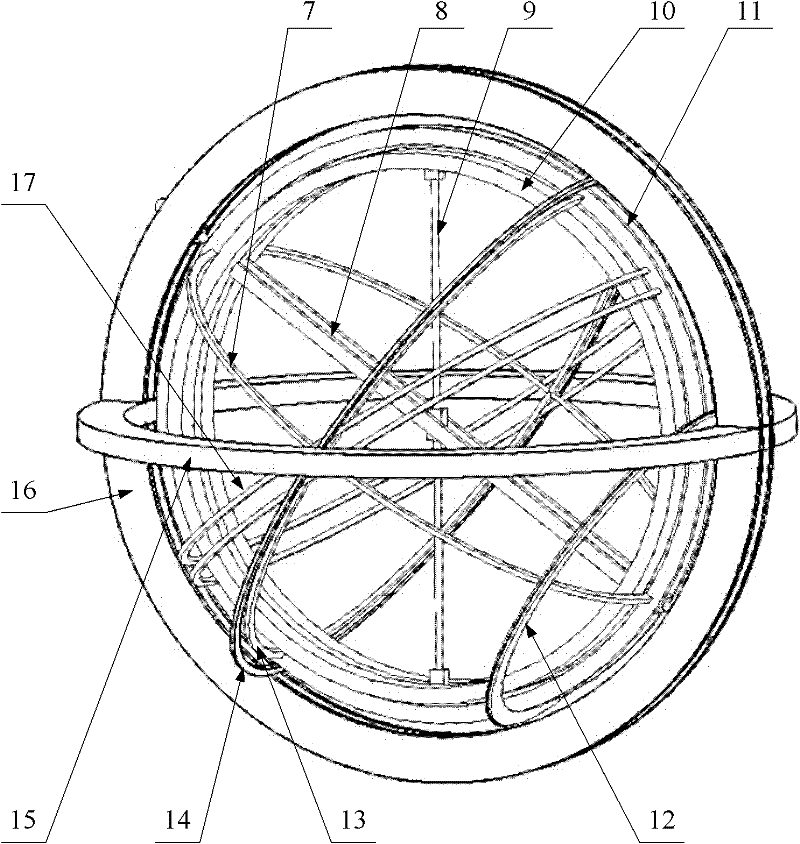
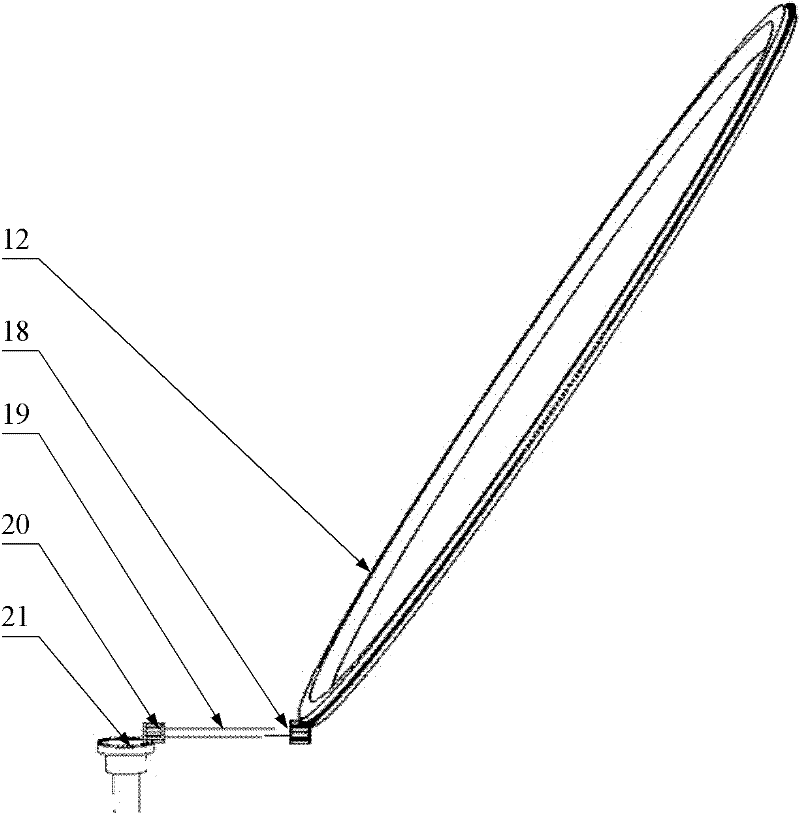
InactiveCN102394027AAccuracy adjustablePlanetaria/globesClock driving mechanismsArmillary sphereAstronomical clock
The invention discloses a structure of an armillary sphere system for an ancient water-powered astronomical clock tower. The structure comprises a six-cardinal-point component which is supported by four dragon pillars on a water instep, wherein an upward moon structure is arranged on the six-cardinal-point component; a three-luminary set is arranged in the six-cardinal-point component; a sighting-tube ring is arranged in the three-luminary set; the three-luminary set and the sighting-tube ring can respectively rotate around a same axis; a certain angle is formed between the axis and the horizontal plane; a turtle base is arranged on the water instep; a supporting pillar for a driving system is hidden in the turtle base; the three-luminary set can follow the motion of a star; on the basis of the adjustment for a weft angle of the sighting-tube ring and a meridian position of a sighting tube, the sighting tube can be used for tracking and observing the star; under the action of the driving system, the three-luminary set can be used for distinguishing a solar day from a sidereal day; and the upward moon structure and the water instep structure can be used for adjusting the precision of the structure of the armillary sphere system. The structure provided by the invention can be used for distinguishing the solar day from the sidereal day and conveniently adjusting the precision.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Automatic extraction method for sun outline
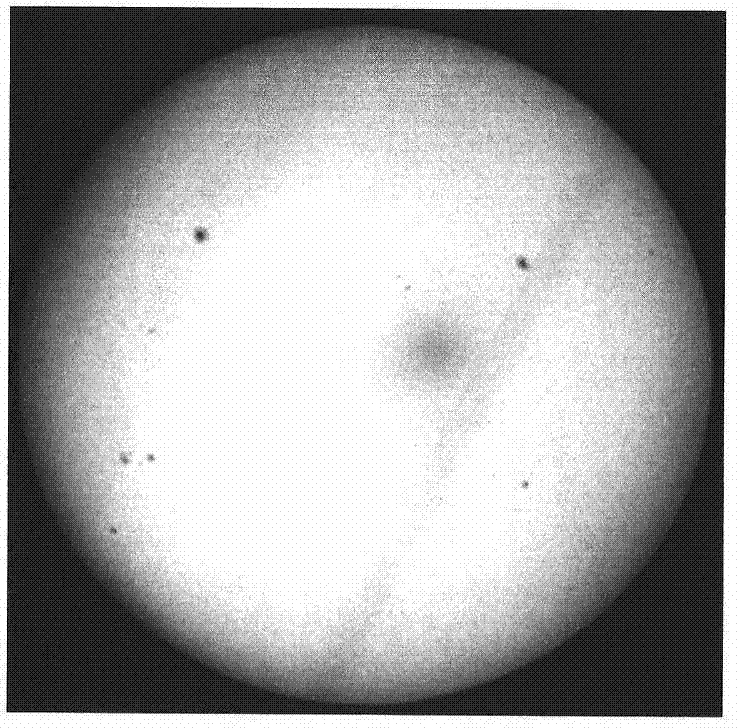
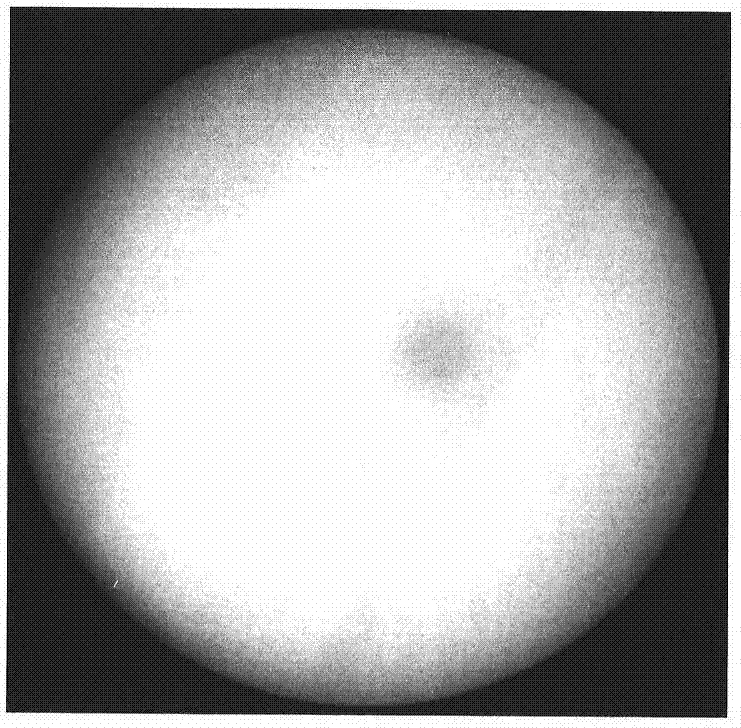
InactiveCN104778469AGuaranteed to be free from interferenceImprove processing efficiencyImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSolar physicsSolar observation
The invention belongs to the solar physics of the field of astronomy in China and provides an automatic extraction method for the sun outline. The method comprises the following steps: aiming at the full-disk monochromatic image of the Huairou Solar Observing Station of the National Astronomical Observatories of China, obtaining the gray scale information of the solar limb by using morphological close operation and erosion operation; then, extracting a limb coordinate by using a self-adaptive threshold method; finally, fitting the limb coordinate by combining a least square fitting method, and thus obtaining a connected solar limb binary image. Compared with other international algorithms, the method can process lower-quality solar observation data with instrument noise and fills the blank of domestic related fields. The method has important significance and practical value on determining the solar disk radius and the earth-sun distance, calculating the position of solar activity in the solar disk and researching the evolution law of the sun outline.
Owner:NAT ASTRONOMICAL OBSERVATORIES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
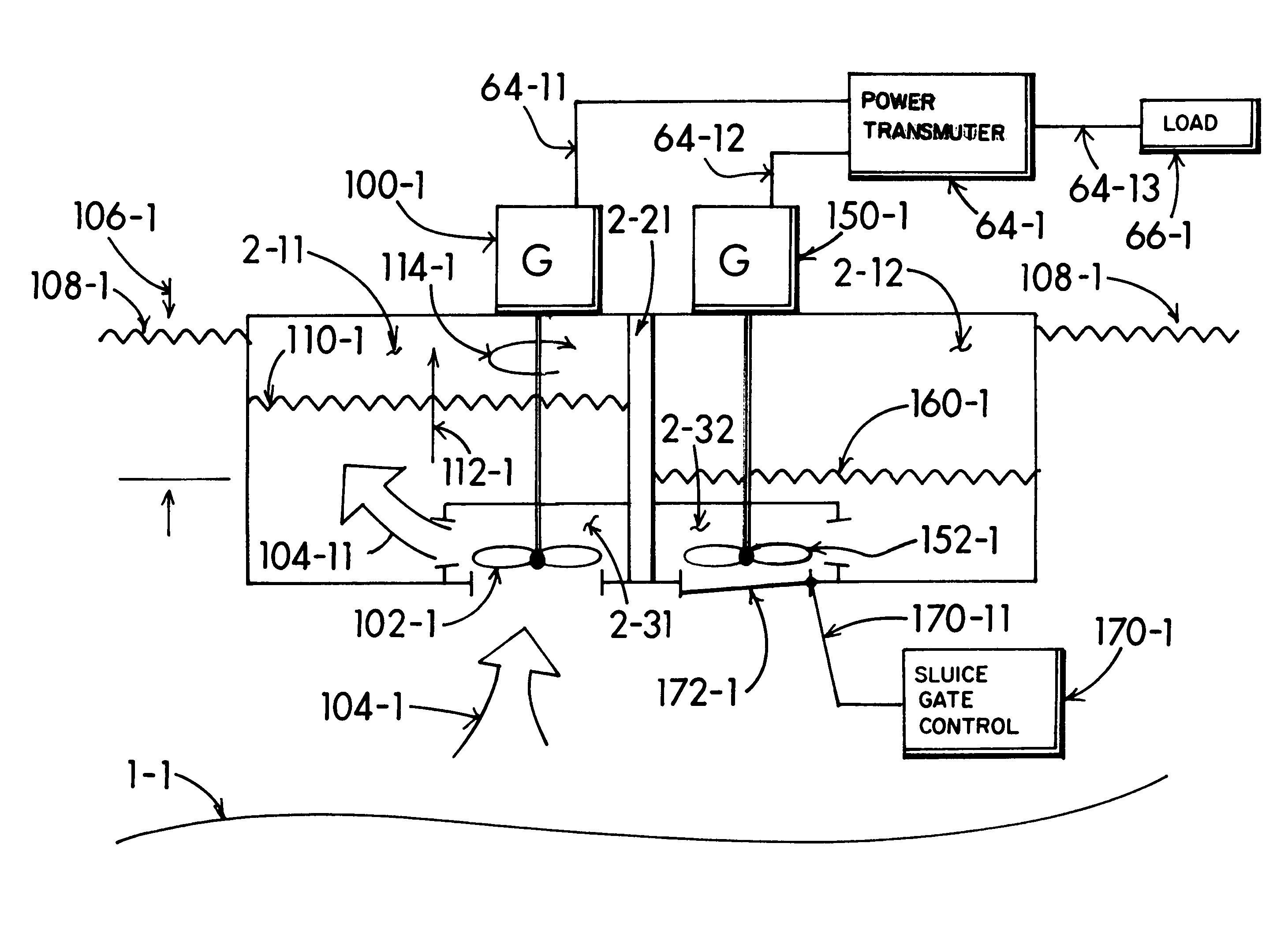
Graduating a flow of tidal reserves during periods of tidal flood produces uninterrupted electrical generation
InactiveUS7795749B1Power balanceConstant level of hydrodynamic energy conversionFluid couplingsMachines/enginesEngineeringElectric power
Oceanic tidal energy sources hydroelectric generating system coupled to a primary tidal reservoir through a bi-directional tideway exciting a primary turbine as a diurnal cycle tide waxes and wanes. A secondary tidal reservoir includes a tideway and secondary turbine with flow modulated by a gradated control of a sluice gate to proportionately blend reserve tidewater capacity of the secondary tidal reservoir as a delayed resource of virtual tidal influx and reflux. An aggregate summation of tidal energy acting upon the turbine driven generators delivers a constant flow of electric power throughout the diurnal tidal cycle. A tertiary tidal reservoir operating in alternation with the secondary tidal reservoir optimizes the secondary turbine drive during slack-tide. Shunting excess tidal energy around the turbines during periods of reduced power-demand supplements tidal resources in subsequent phases of the diurnal tidal day when solar-day related power-demand may increase.
Owner:SAVVYSTUFF PROPERTY TRUST
Solar timer using GPS technology
In a GPS-equipped device such as a smart phone or a tablet computer with a compatible operating system, a useful dynamic display of directional and timing information is provided based on GPS data obtained through conventional means processed according to computational modules or applications stored on the device. These displays include a solar timer, a compass dial and other date, time and location-based information. Underlying the displayable information is a database of information that is processed with input from an accurate compass employing a calculated reference line based on two time-separated GPS readings and a direction parameter.
Owner:LONESTAR INVENTIONS LP
Method for processing medical information
InactiveCN105787264AEasy to useMedical equipmentSpecial data processing applicationsGeolocationComputer science
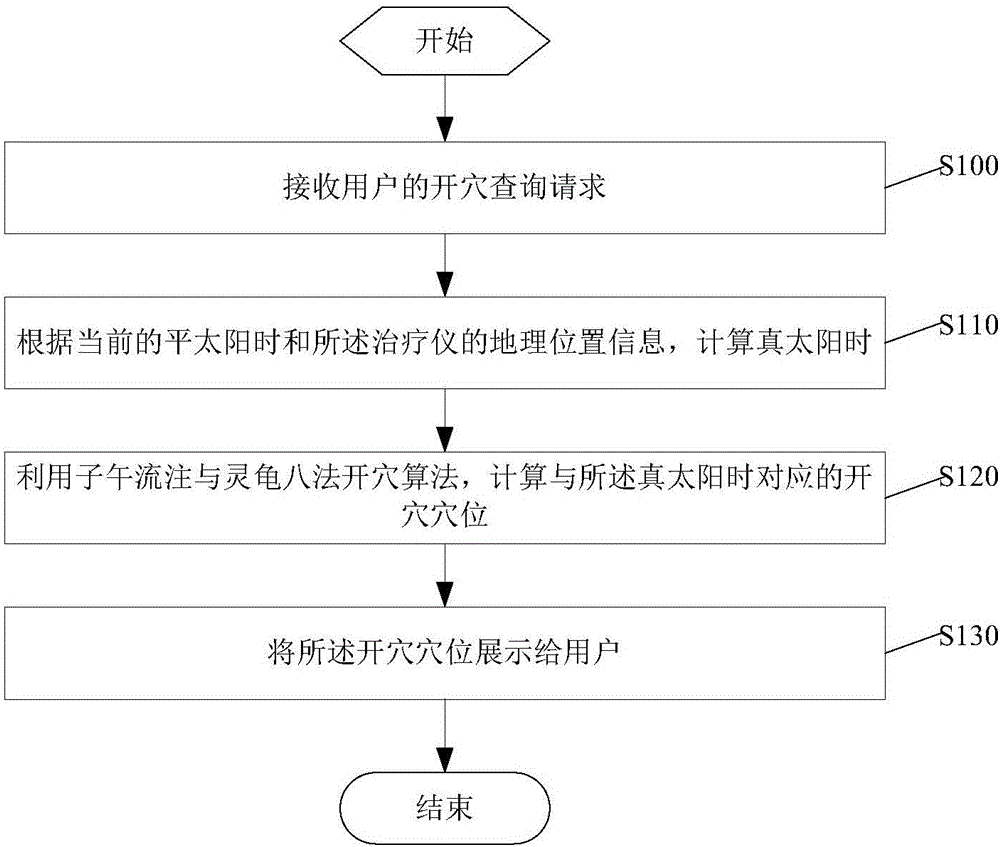
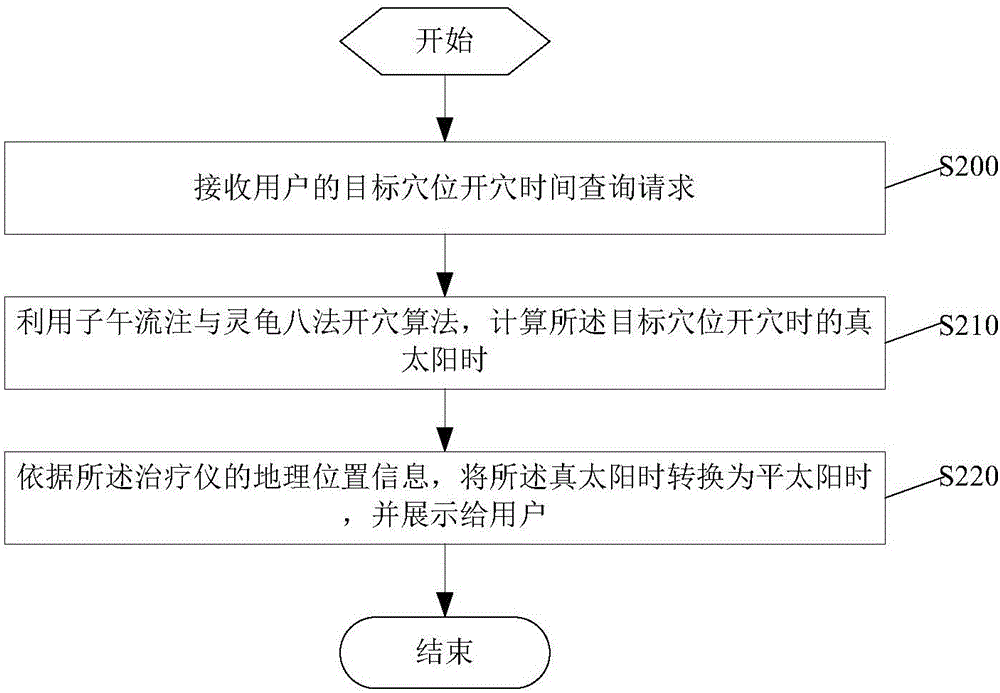
The invention discloses a method for processing medical information.The method includes the steps that a point opening query request of a user is received, then true solar time is calculated according to current mean solar time and geographical location information of therapeutic equipment, a point opening acupuncture point corresponding to the true solar time is calculated through a meridian stream and intelligent turtle eight-method point opening algorithm, and the point opening acupuncture point is displayed to the user.According to the acupuncture information query method, the point opening acupuncture point query function can be provided for the user, and great convenience is brought for the user to the use the method.
Owner:北京佳时正通科技有限责任公司
Space surveillance orbit
PendingUS20220135255A1Reduce in quantityImprove observation coverage timeLaunch systemsArtificial satellitesMidnightEclipse
A satellite system includes a satellite in an orbit that is configured to reduce a number of exclusion regions and improve the observation coverage of resident space objects (RSOs) positioned in near Earth orbits. The satellite system includes at least one satellite positioned in a sun synchronous orbit (SSO) with a noon / midnight nodal crossing. The altitude of the SSO is between 1000 and 2000 kilometers and the satellite includes at least one sensor arranged on the satellite that is configured for detection, tracking, and / or identification. Using the noon / midnight nodal crossing is advantageous in that three main exclusion regions, the sun, eclipse, and Earth exclusion regions, are combined into only two exclusion regions for improved performance of the satellite system in observing RSOs.
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
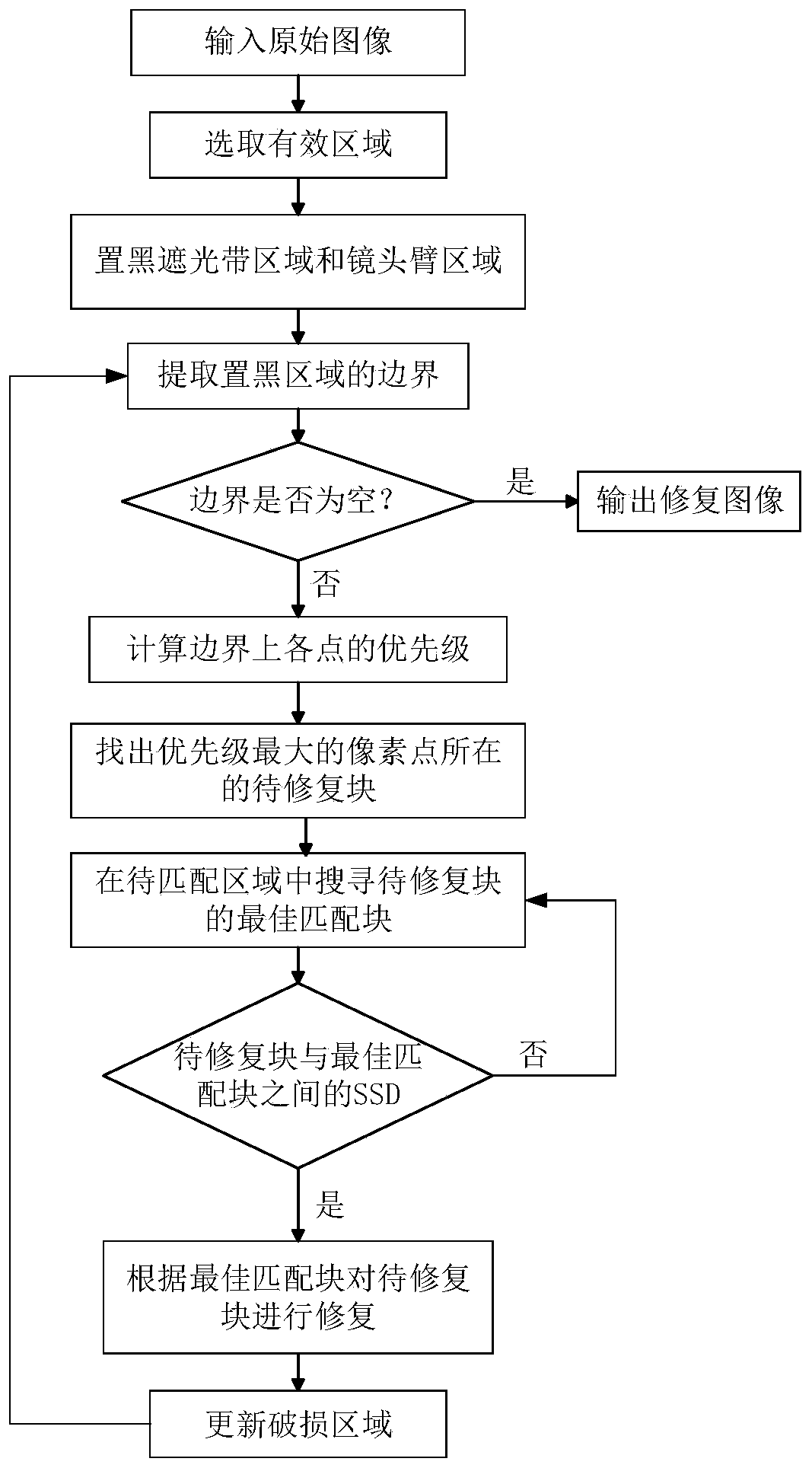
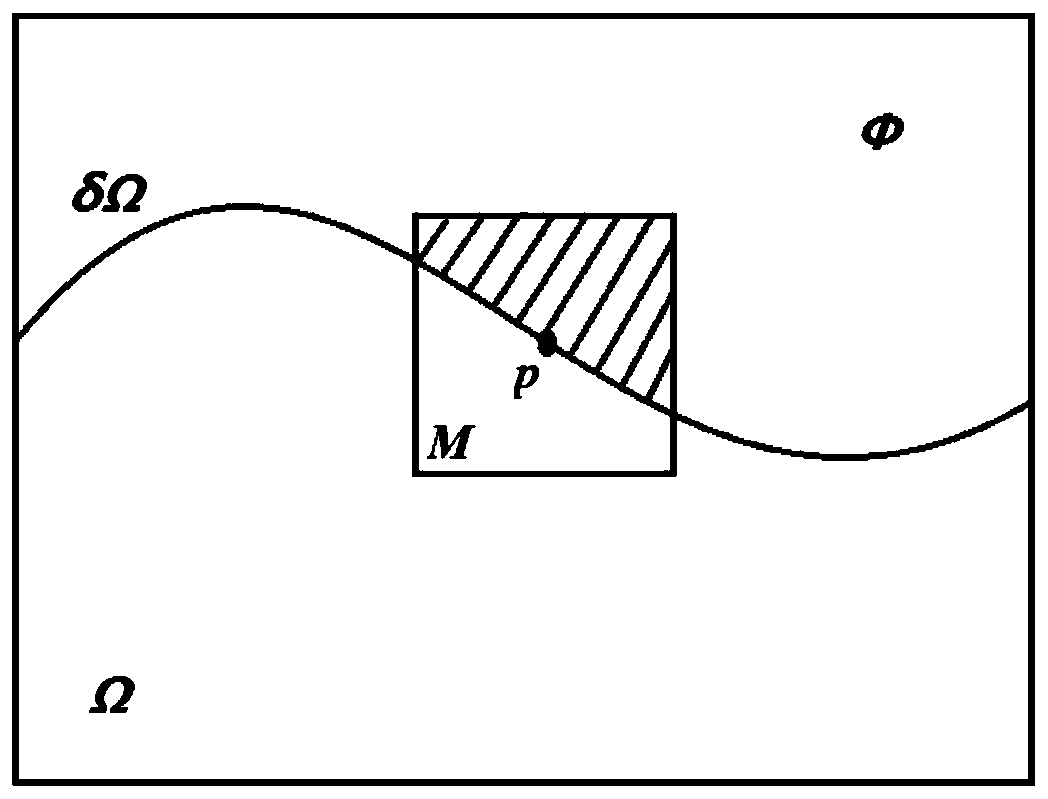
A foundation cloud picture restoration method based on an improved Criminisi algorithm
ActiveCN109727217AFix fast and stableSimple structureImage enhancementImage analysisRestoration methodLongitude
The invention relates to the technical field of digital image processing, and provides a new foundation cloud picture restoration method which can better restore an image of a foundation cloud picture, expand an effective area of the cloud picture and automatically mark the positions of a shading belt and a lens arm in the cloud picture, namely, determine a to-be-restored area and restore the foundation cloud picture. According to the technical scheme, the foundation cloud picture repairing method based on the improved Criminisi algorithm comprises the following steps that 1, the position of ato-be-repaired area is extracted; (1) determining the shooting time of a TSI cloud picture and the longitude and latitude of the position where equipment is located, (2) calculating the solar declination angle Delta, (3) calculating the solar time angle omega, (4) calculating the solar azimuth angle Gamma s and the zenith angle theta z, (5) determining the position of a shading band, (6) determining the position of a lens arm, and (2) repairing the cloud picture.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com