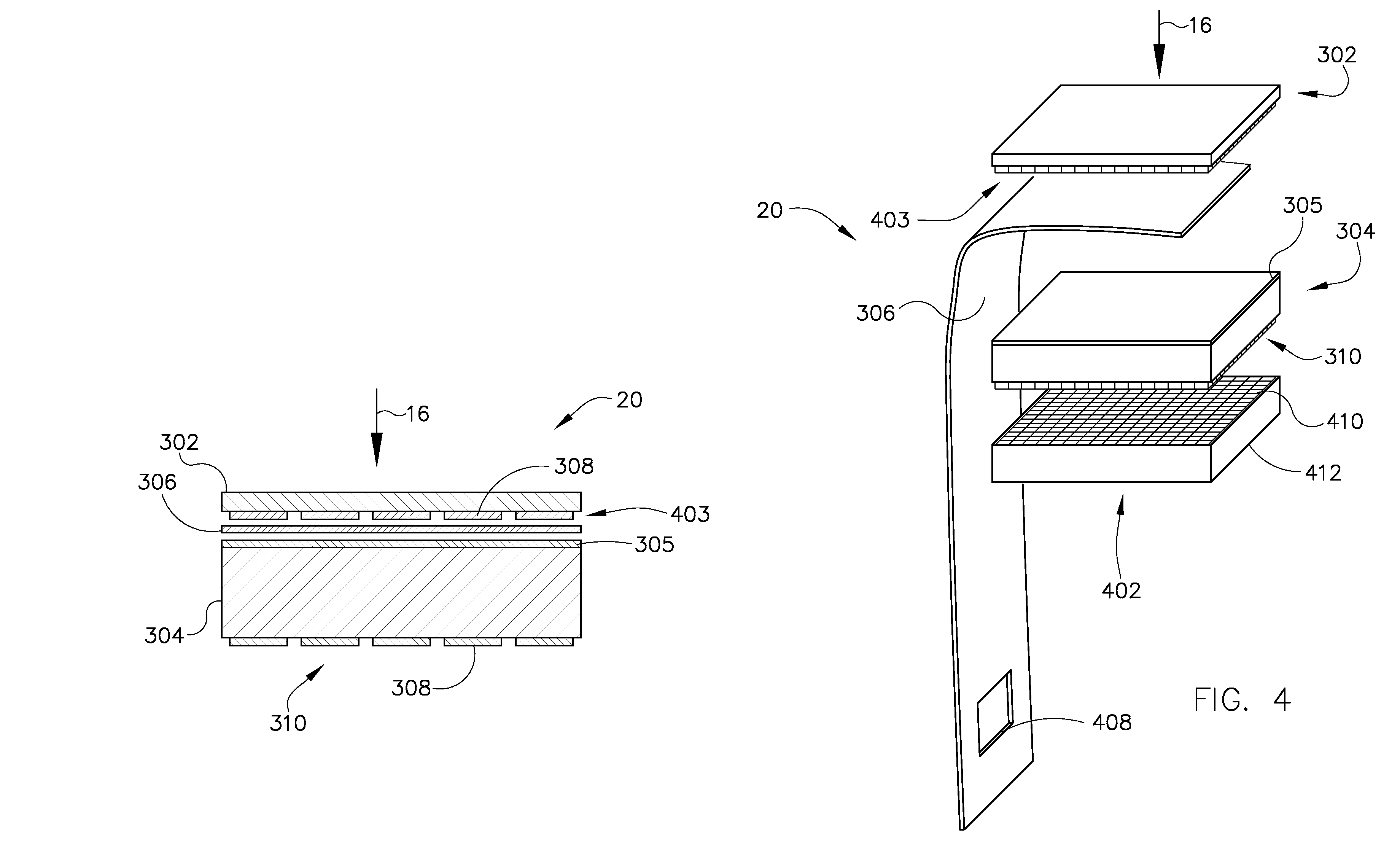
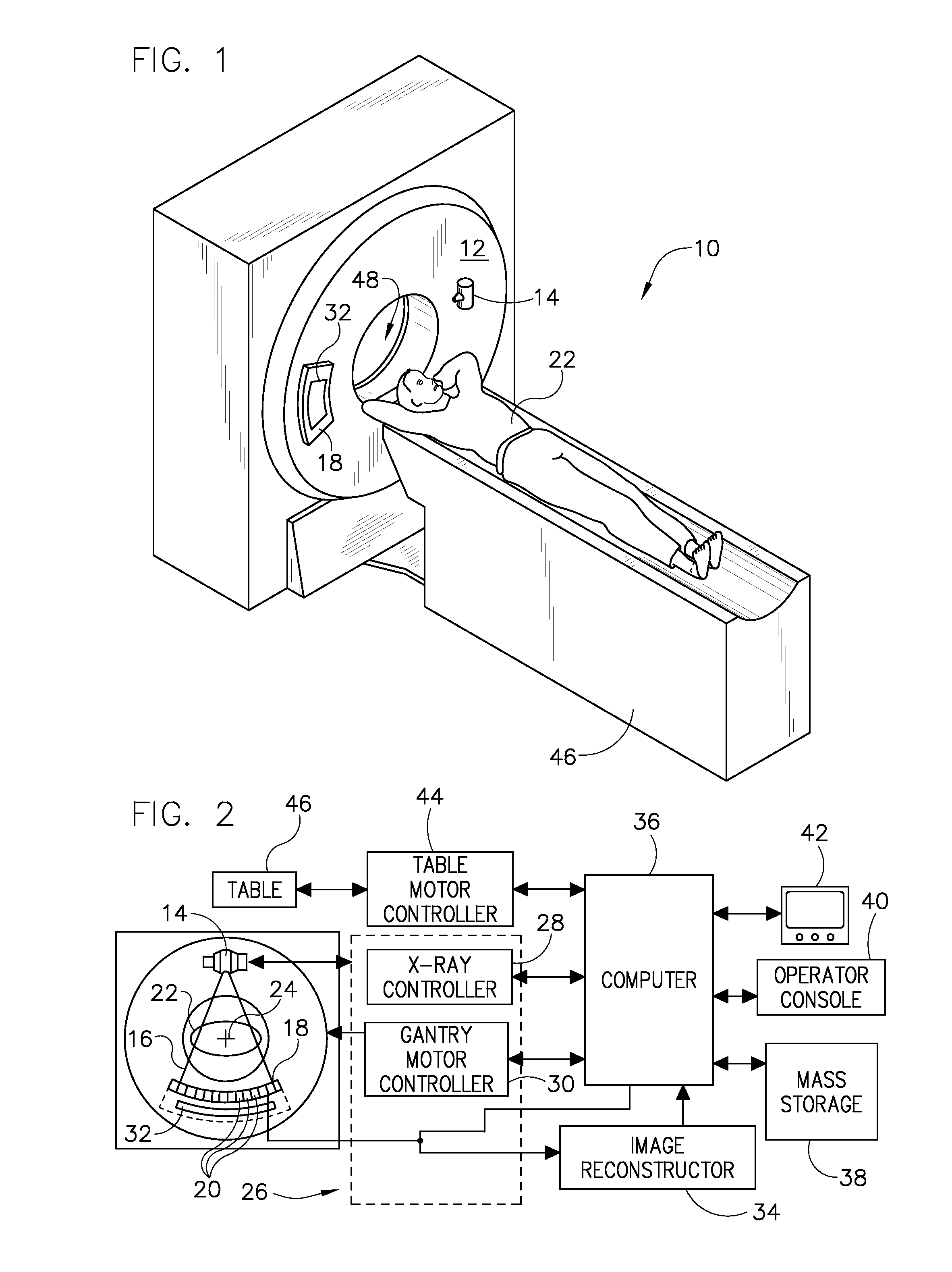
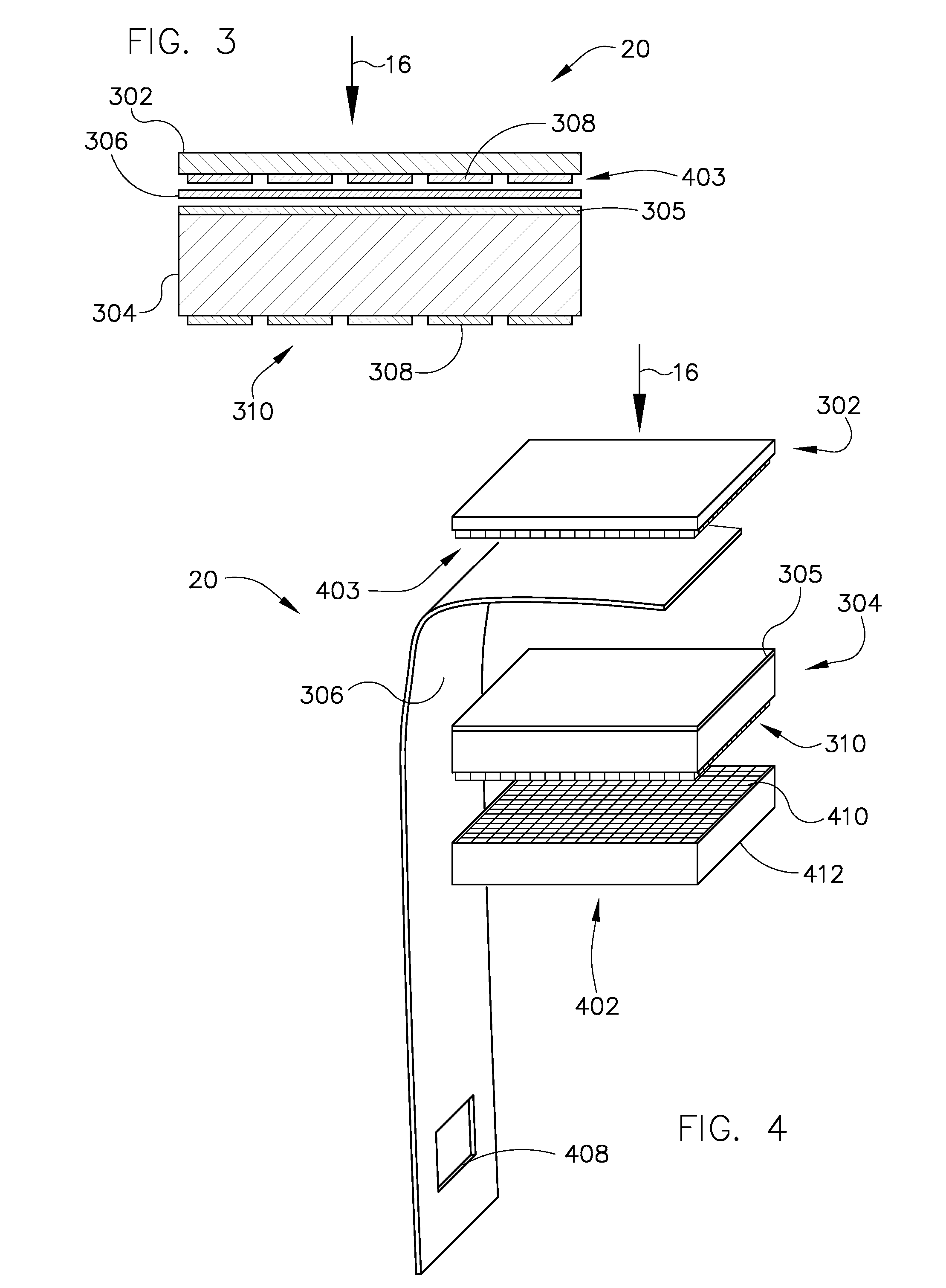
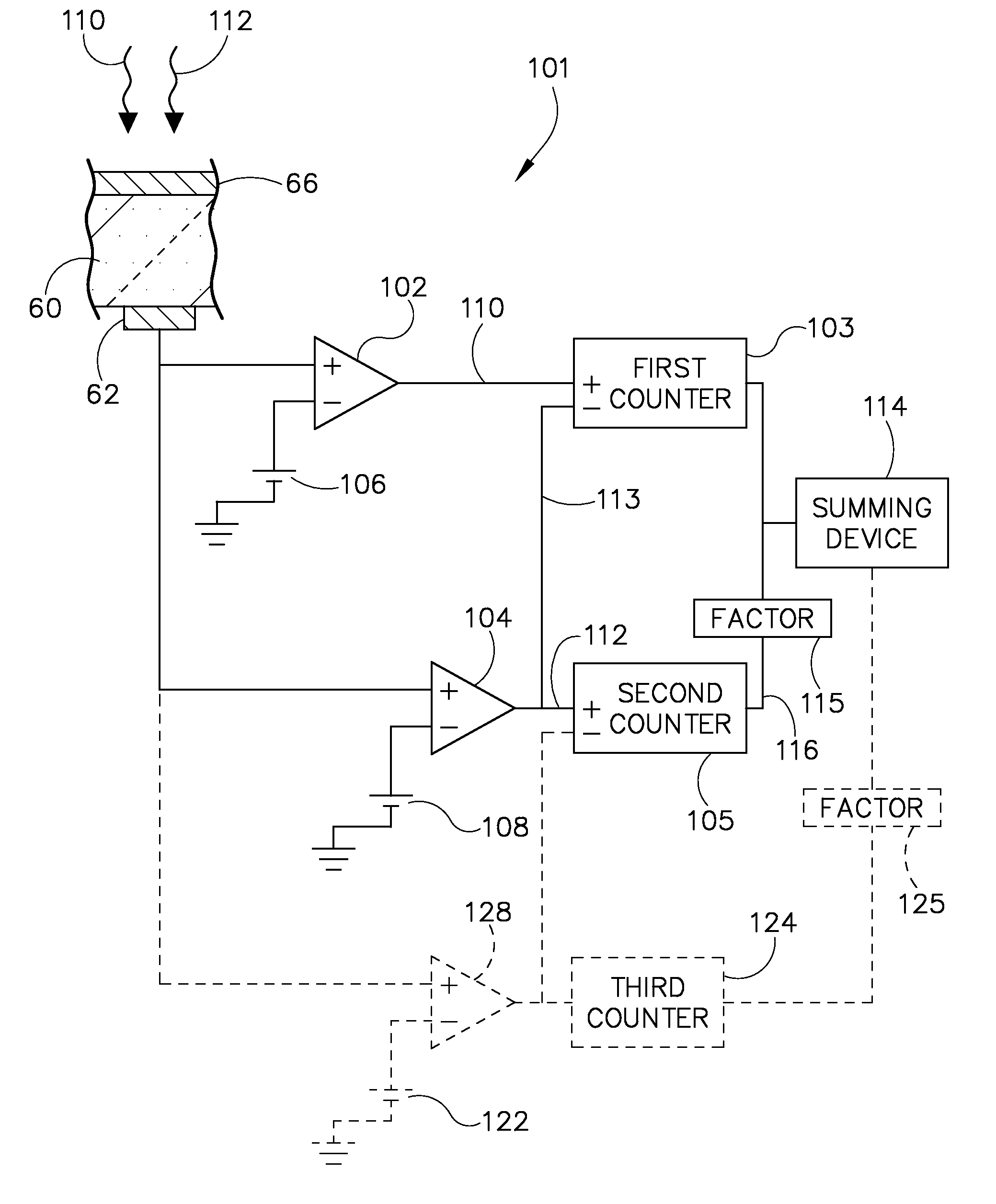
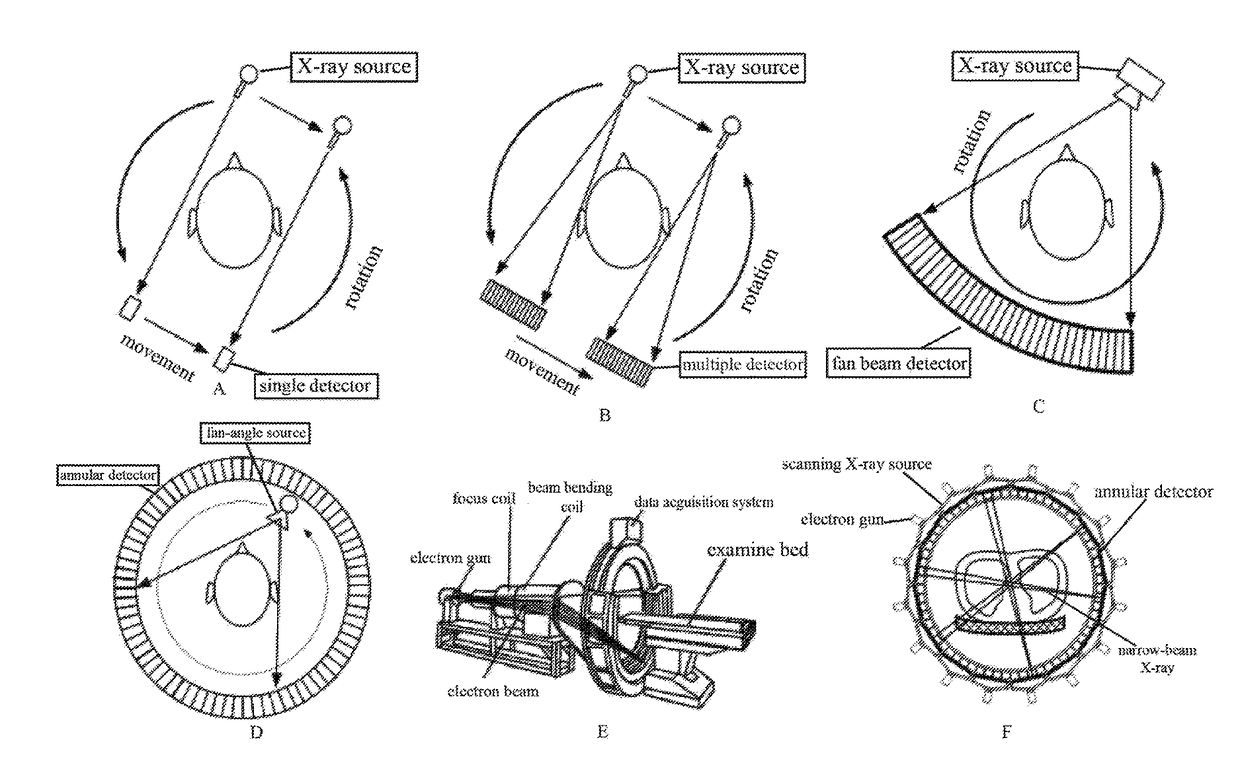
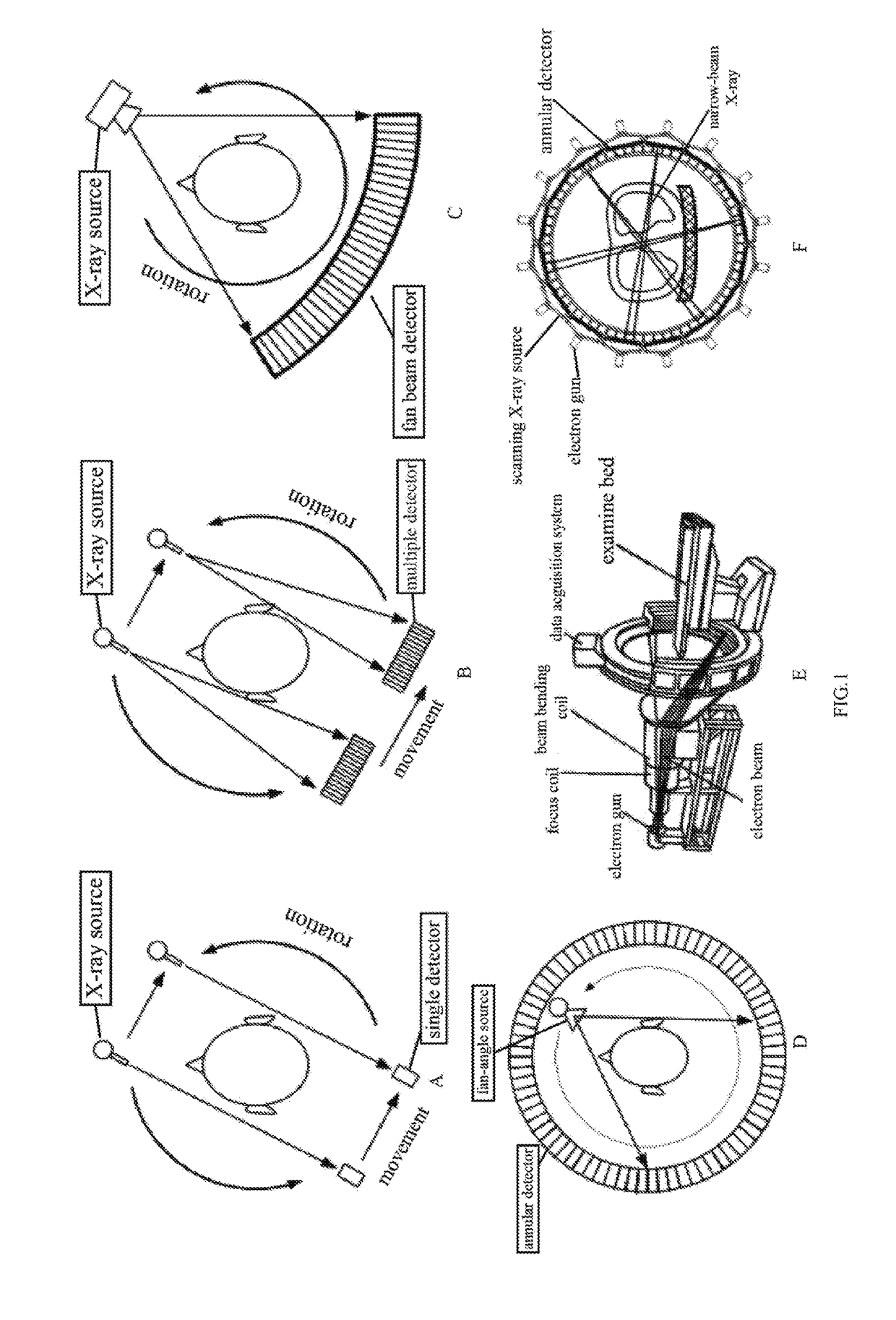
Patents
Literature
182 results about "Photon counting detector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Temporally- And Spatially-Resolved Single Photon Counting Using Compressive Sensing For Debug Of Integrated Circuits, Lidar And Other Applications
InactiveUS20110260036A1Improve instrument performanceFast acquisition timeTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesPhoton counting detectorSpatially resolved
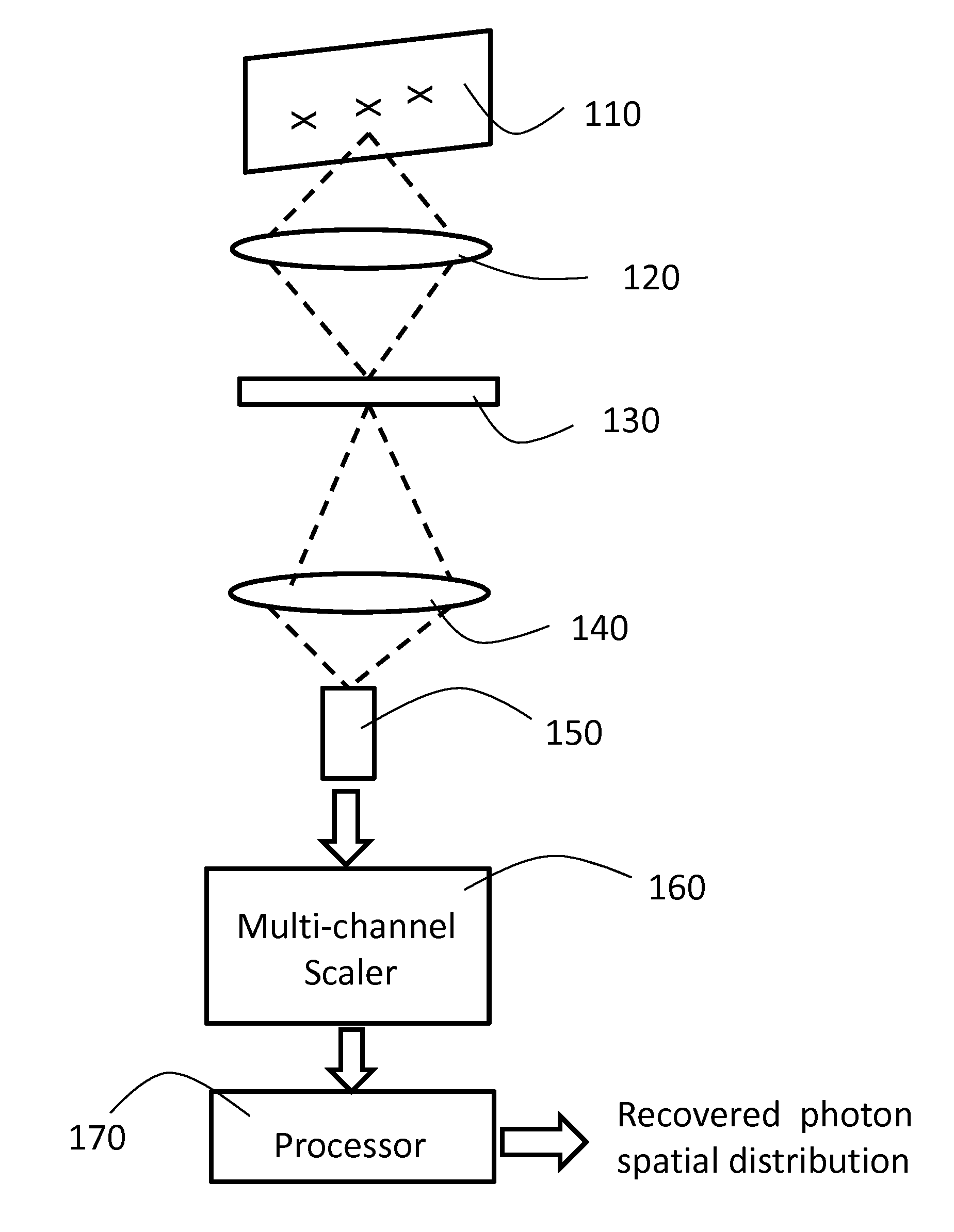
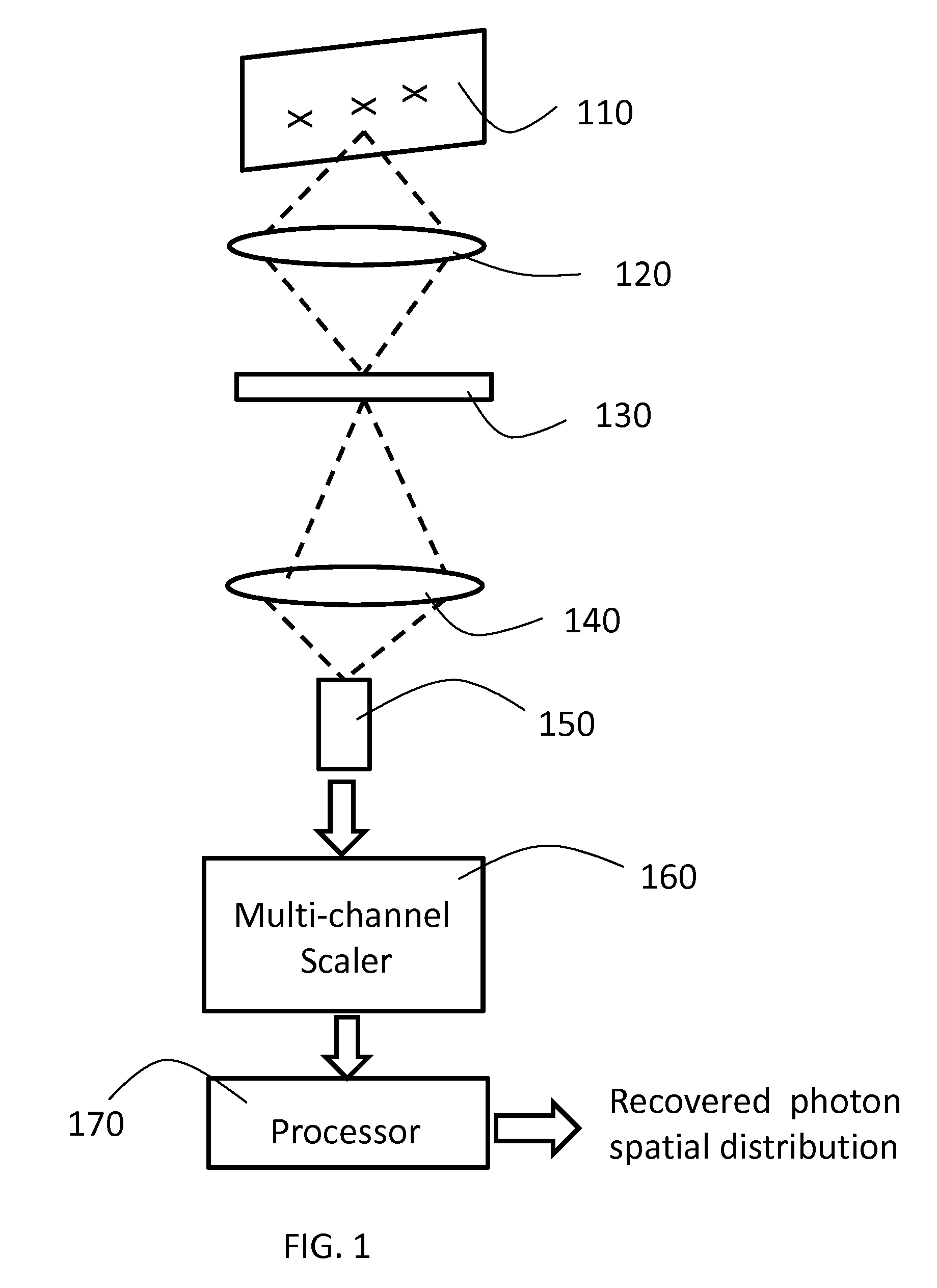
A method for photon counting including the steps of collecting light emitted or reflected / scattered from an object; imaging the object onto a spatial light modulator, applying a series of pseudo-random modulation patterns to the SLM according to standard compressive-sensing theory, collecting the modulated light onto a photon-counting detector, recording the number of photons received for each pattern (by photon counting) and optionally the time of arrival of the received photons, and recovering the spatial distribution of the received photons by the algorithms of compressive sensing (CS).
Owner:BARANIUK RICHARD G +2
High dqe photon counting detector using statistical recovery of pile-up events
InactiveUS20090039273A1Improving statistical recoveryReduce impactMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhoton counting detectorElectricity
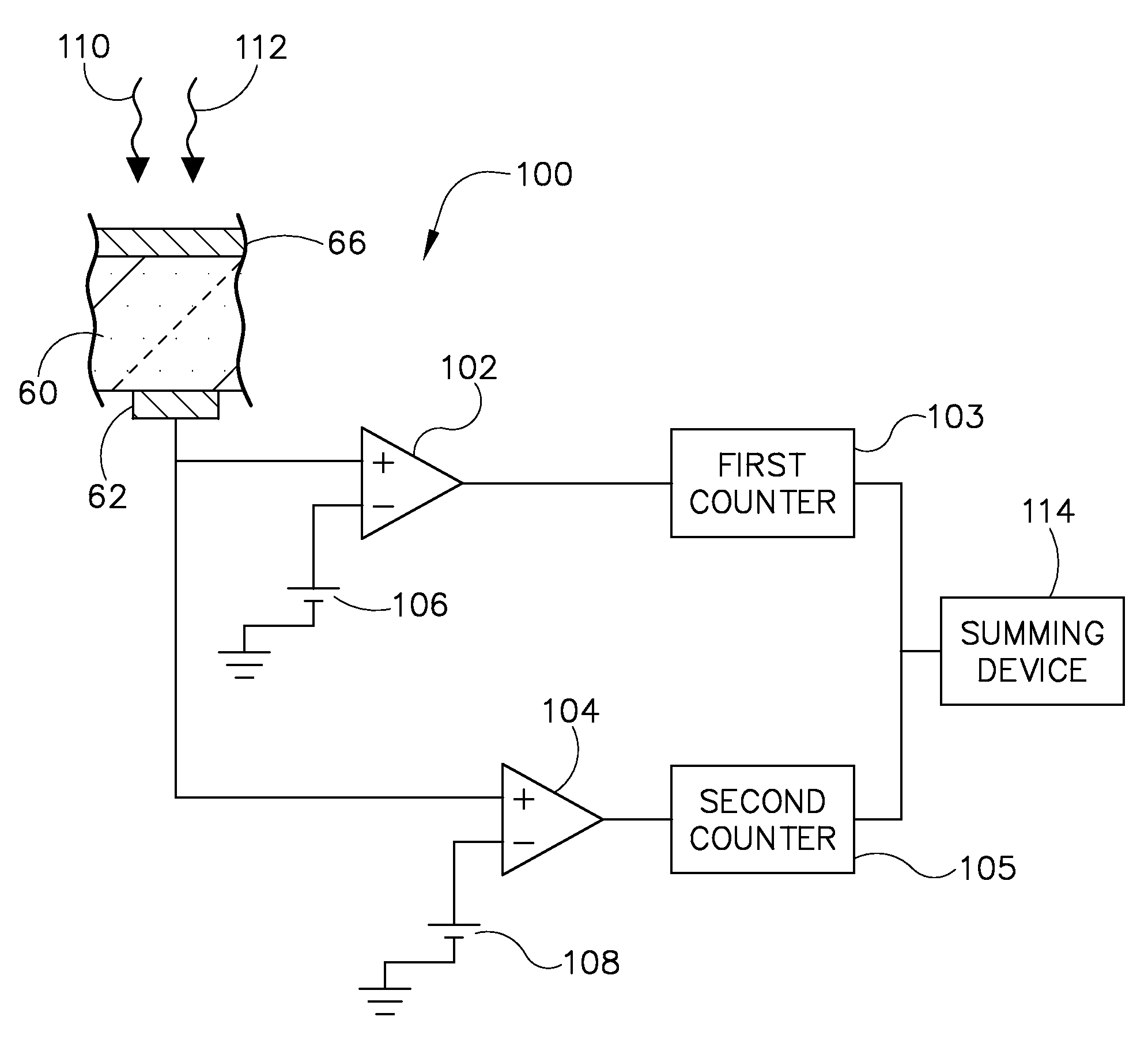
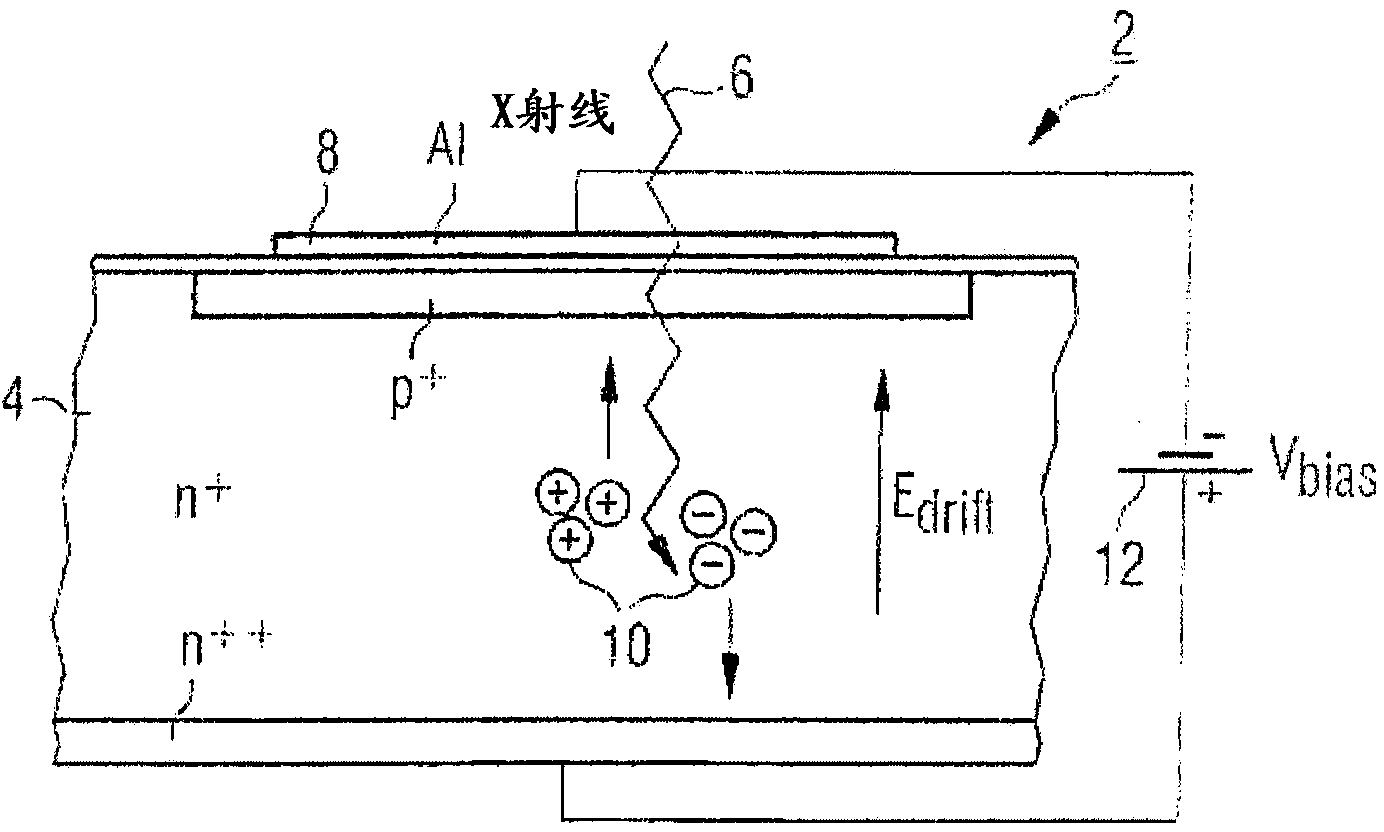
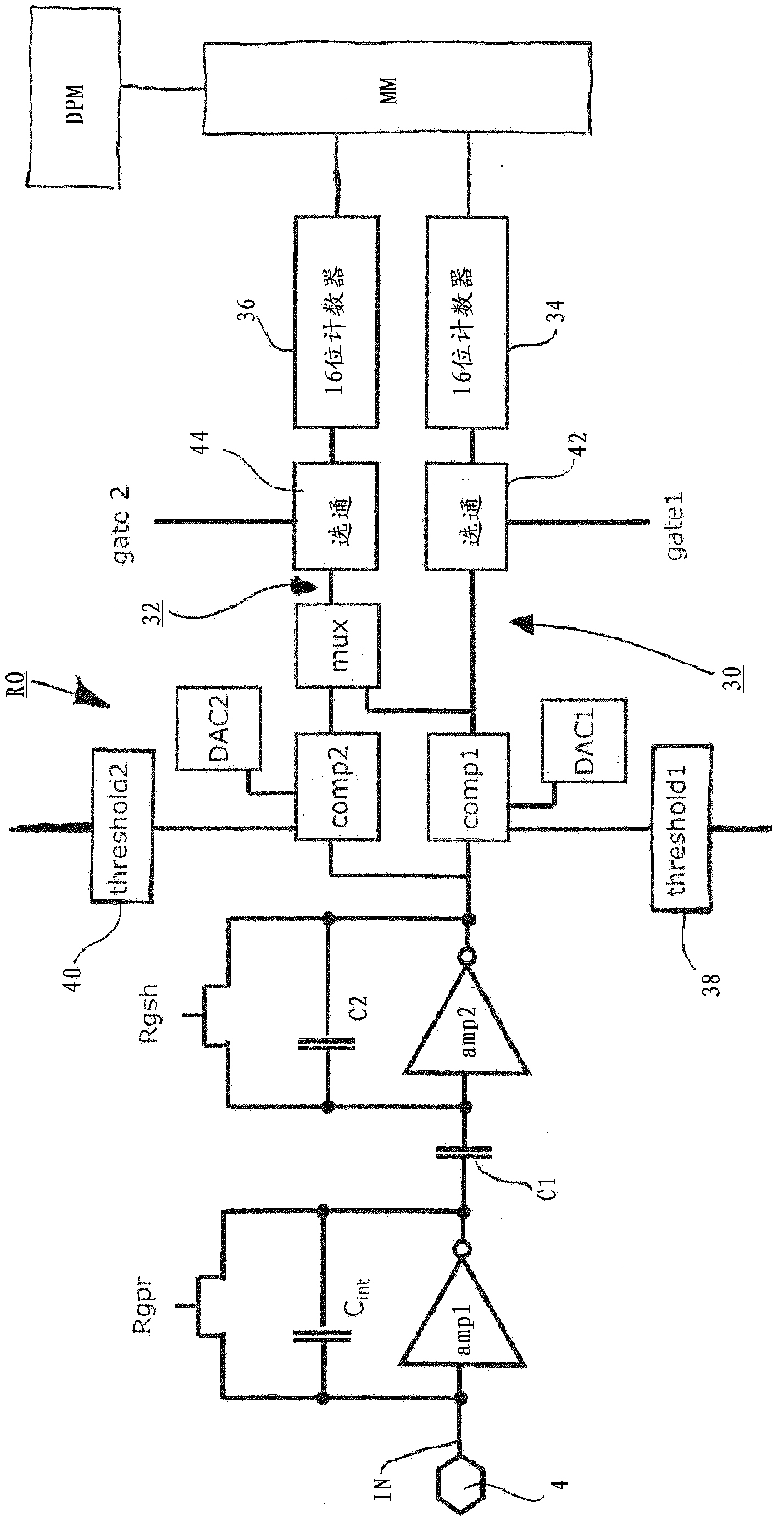
A photon-counting detector includes a direct conversion material constructed to directly convert an energy of at least one incident photon to an electrical signal indicative of the energy level of the at least one individual photon and a data acquisition system (DAS). The DAS includes a first comparator having a first signal level threshold that is less than an electrical signal level that is indicative of a maximum energy of a spectrum of photons, the first comparator configured to output a count when the electrical signal level exceeds the first signal level threshold, and a second comparator having a second signal level threshold that is greater than or equal to the electrical signal level indicative of the maximum energy of the spectrum of photons, the second comparator configured to output a count when the electrical signal exceeds the second signal level threshold. The DAS further includes a device configured to determine a photon count based on the counts from the first and second comparators and to output the photon count for image reconstruction.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
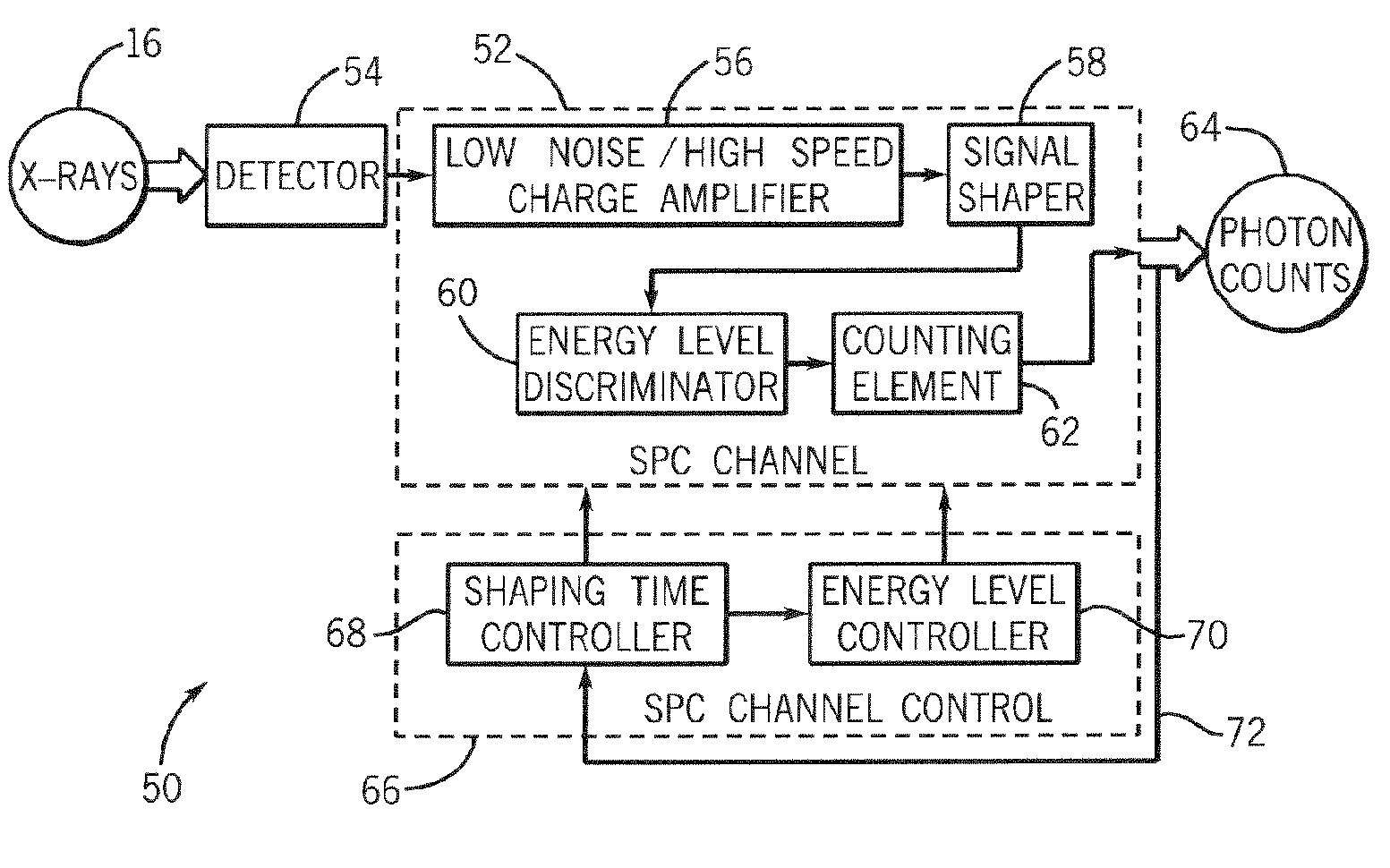
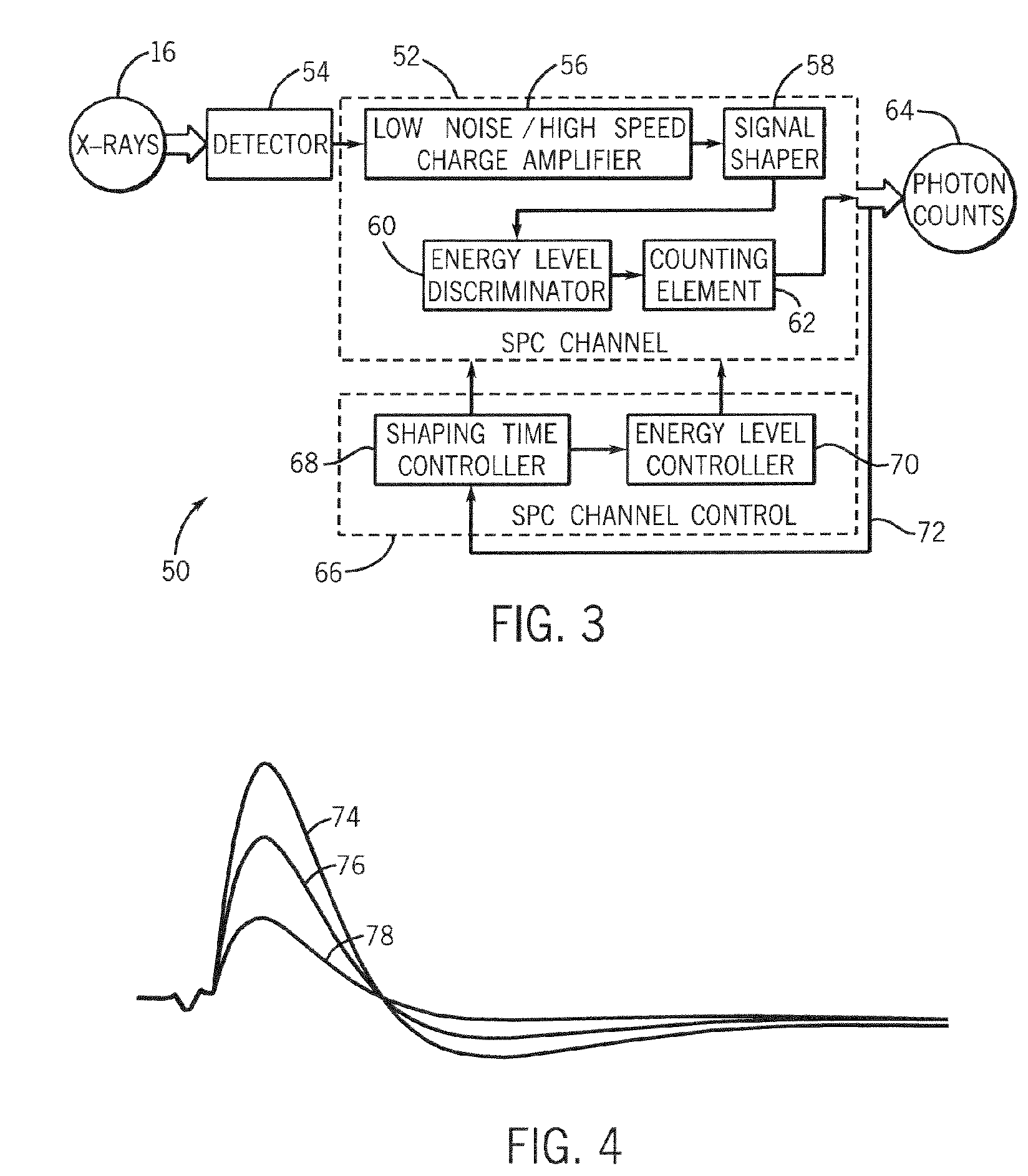
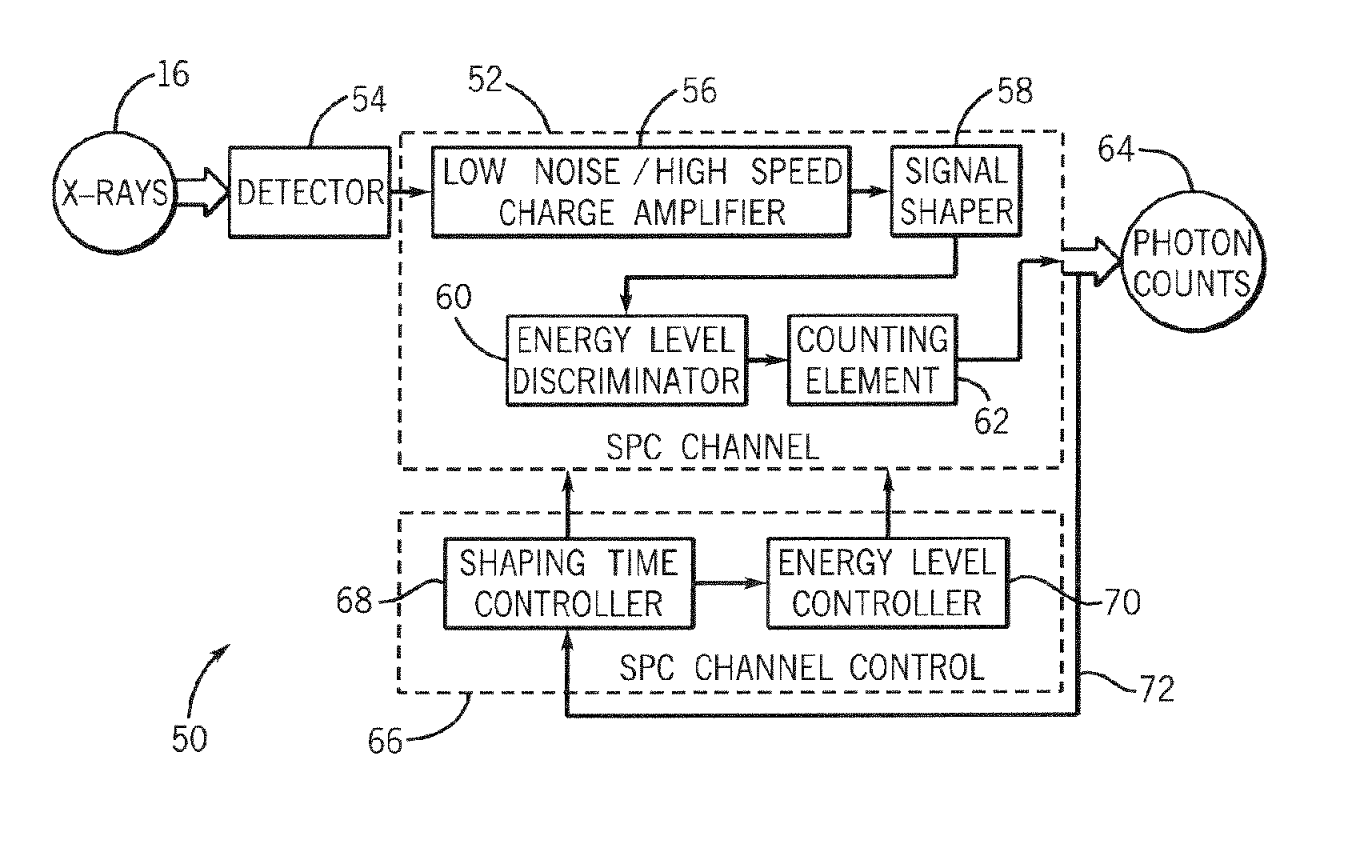
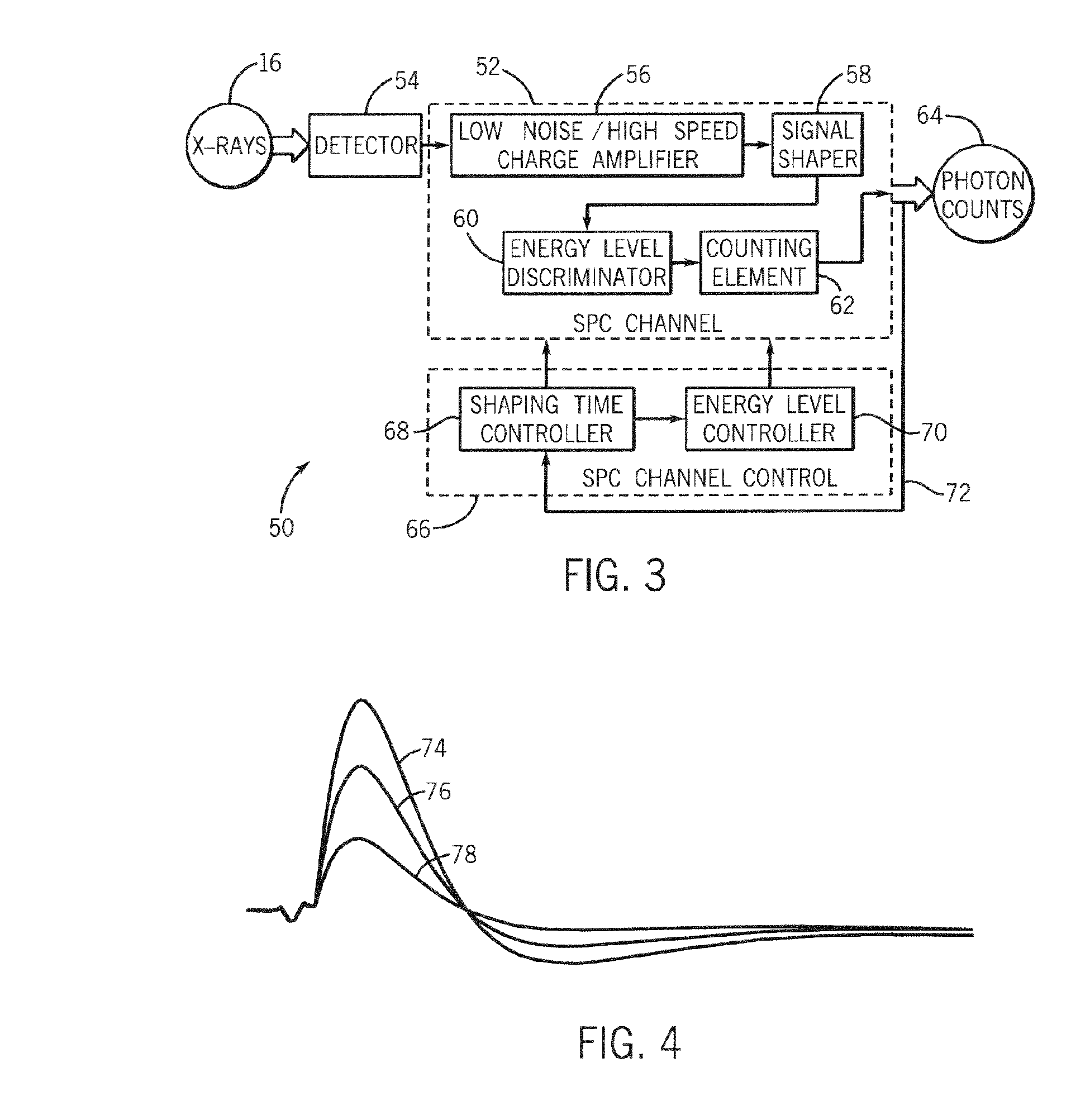
Method and system of dynamically controlling shaping time of a photon counting energy-sensitive radiation detector to accommodate variations in incident radiation flux levels
ActiveUS7149278B2Avoid saturationDetection sacrificedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorHigh flux
A method and system of counting and tagging radiation energy received by a radiation detector is presented. The method and system are designed to dynamically control the sampling window or shaping time characteristics of a photon counting detector to accommodate variations of flux experienced by the detector so as to preserve optimum detector performance and prevent saturation during high flux conditions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
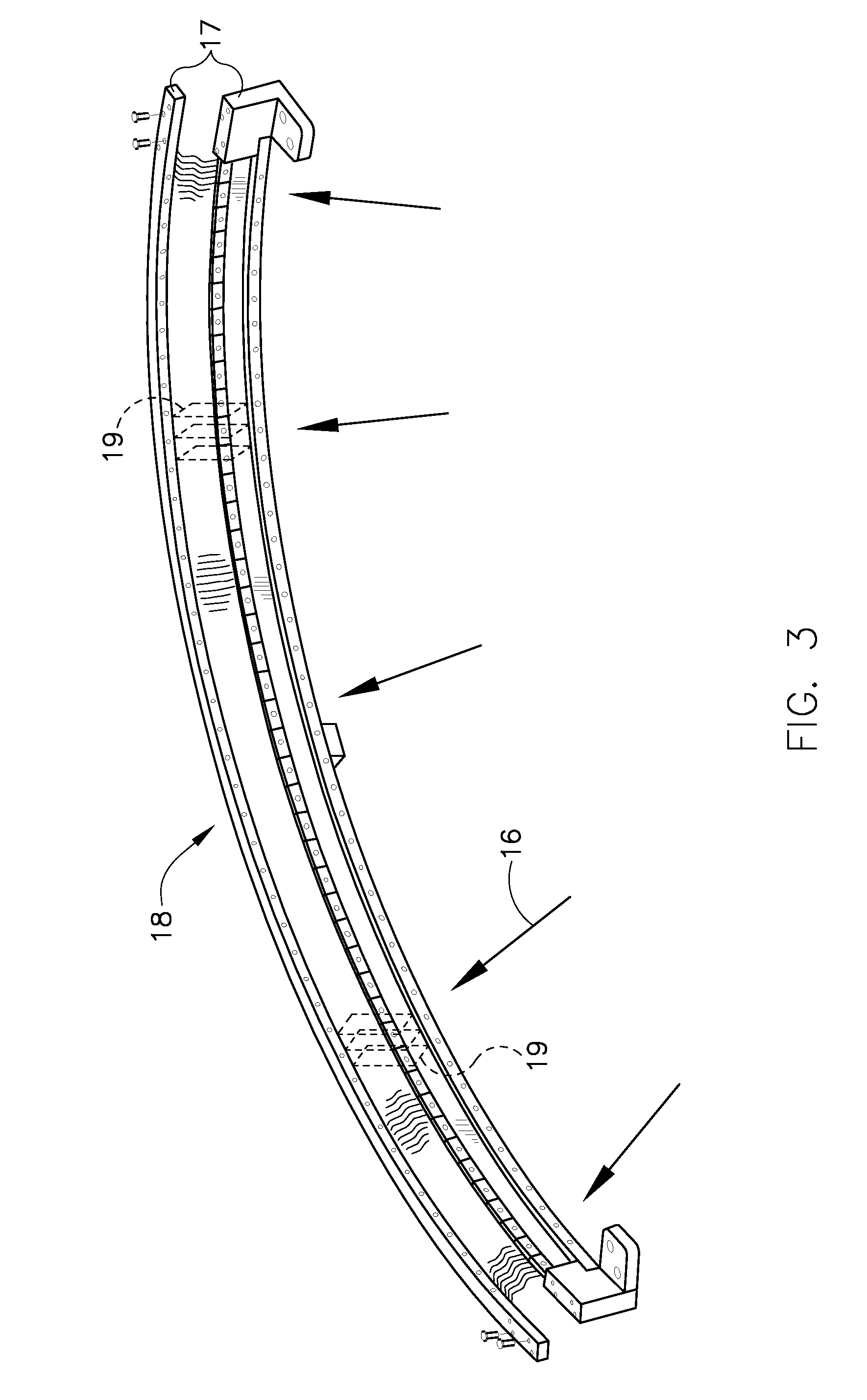
Directional radiation detector
InactiveUS20080277591A1Shorten the timeQuality improvementMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyPhoton counting detectorTomographic image
A method for imaging a body, including scanning the body so as to generate a tomographic image thereof, and analyzing the tomographic image to determine a location of a region of interest (ROI) within the body. The method includes providing single photon counting detector modules, each of the modules being configured to receive photons from a respective direction and to generate a signal in response thereto. The method further includes coupling each of the modules to a respective adjustable mount, adjusting each of the adjustable mounts so that the direction of the module coupled thereto is aligned with respect to the location so as to receive radiation from the ROI, operating each of the modules to receive the photons from the ROI, and, in response to the signal generated by each of the modules, generating a single photon counting image of the ROI.
Owner:ORBOTECH LTD
Apparatus and method for dynamic diagnostic testing of integrated circuits
InactiveUS6859031B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMagnetic property measurementsPhoton counting detectorElectricity
Owner:CREDENCE SYSTEMS
Full Beam Metrology For X-Ray Scatterometry Systems
ActiveUS20180106735A1Improve throughputImprove accuracyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImage analysisAngle of incidenceMetrology
Methods and systems for characterizing dimensions and material properties of semiconductor devices by full beam x-ray scatterometry are described herein. A full beam x-ray scatterometry measurement involves illuminating a sample with an X-ray beam and detecting the intensities of the resulting zero diffraction order and higher diffraction orders simultaneously for one or more angles of incidence relative to the sample. The simultaneous measurement of the direct beam and the scattered orders enables high throughput measurements with improved accuracy. The full beam x-ray scatterometry system includes one or more photon counting detectors with high dynamic range and thick, highly absorptive crystal substrates that absorb the direct beam with minimal parasitic backscattering. In other aspects, model based measurements are performed based on the zero diffraction order beam, and measurement performance of the full beam x-ray scatterometry system is estimated and controlled based on properties of the measured zero order beam.
Owner:KLA CORP
Photon counting CT detector using solid-state photomultiplier and scintillator
ActiveUS7403589B1Improved saturation characteristicHigh gainMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorX-ray
A detector module for a CT imaging system includes a scintillator to convert x-rays to optical photons. The scintillator is optically coupled to a solid-state photomultiplier with internal gain to receive the optical photons and convert them into a corresponding electrical signal output.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system of energy integrating and photon counting using layered photon counting detector
InactiveUS7613274B2Improve dosing efficiencyReduce saturationRadiation/particle handlingTomographyPhoton counting detectorData acquisition
A diagnostic imaging system includes an x-ray source that emits a beam of x-ray energy toward an object to be imaged and an energy discriminating (ED) detector that receives the x-ray energy emitted by the x-ray energy source. The ED detector includes a first layer having a first thickness, wherein the first layer comprises a semiconductor configurable to operate in at least an integrating mode and a second layer having a second thickness greater than the first thickness, and configured to receive x-rays that pass through the first layer. The system further includes a data acquisition system (DAS) operably connected to the ED detector and a computer that is operably connected to the DAS. The computer is programmed to identify saturated data in the second layer and substitute the saturated data with non-saturated data from a corresponding pixel in the first layer.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
High DQE photon counting detector using statistical recovery of pile-up events
InactiveUS7696483B2Improving statistical recoveryReduce impactMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation intensity measurementPhoton counting detectorNoise level
A photon-counting detector includes a direct conversion material and a data acquisition system with a first comparator having a first signal level threshold indicative of a noise level of a spectrum of photons, the first comparator configured to output a count when the electrical signal level exceeds the first signal level threshold, and a second comparator having a second signal level threshold indicative of the maximum energy of the spectrum of photons, the second comparator configured to output a count when the electrical signal exceeds the second signal level threshold where a photon count is determined based on the counts from the first and second comparators.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
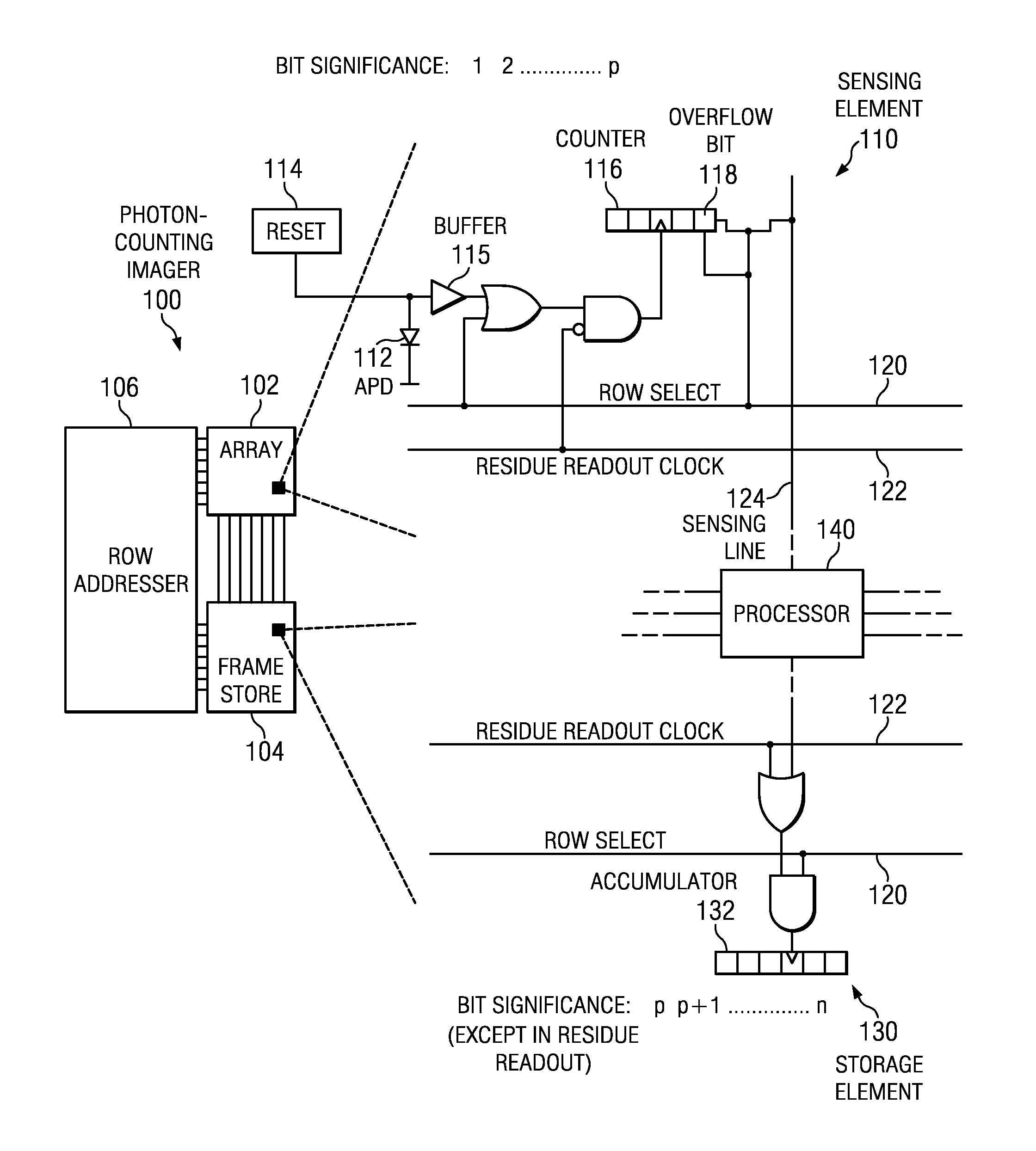
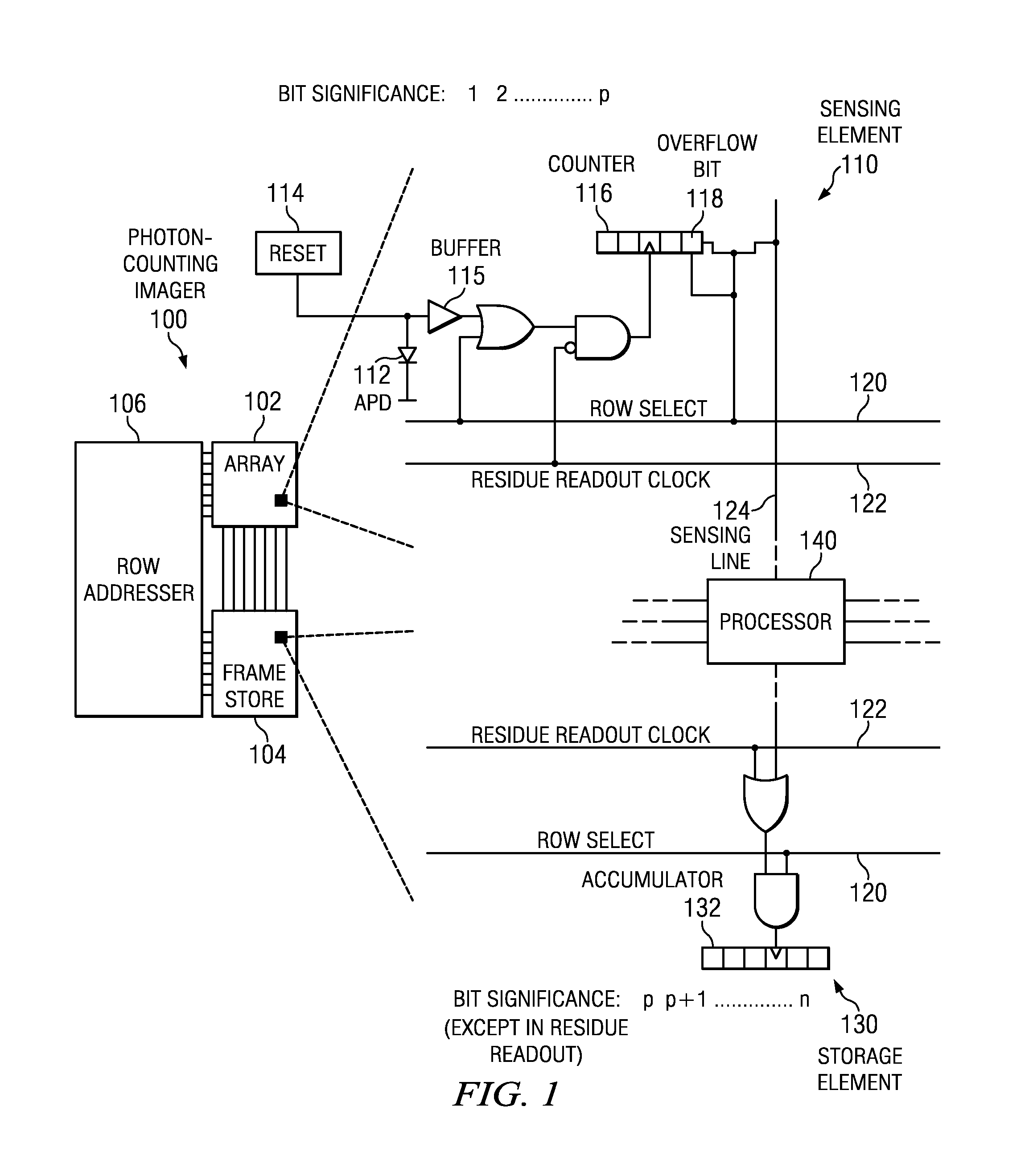
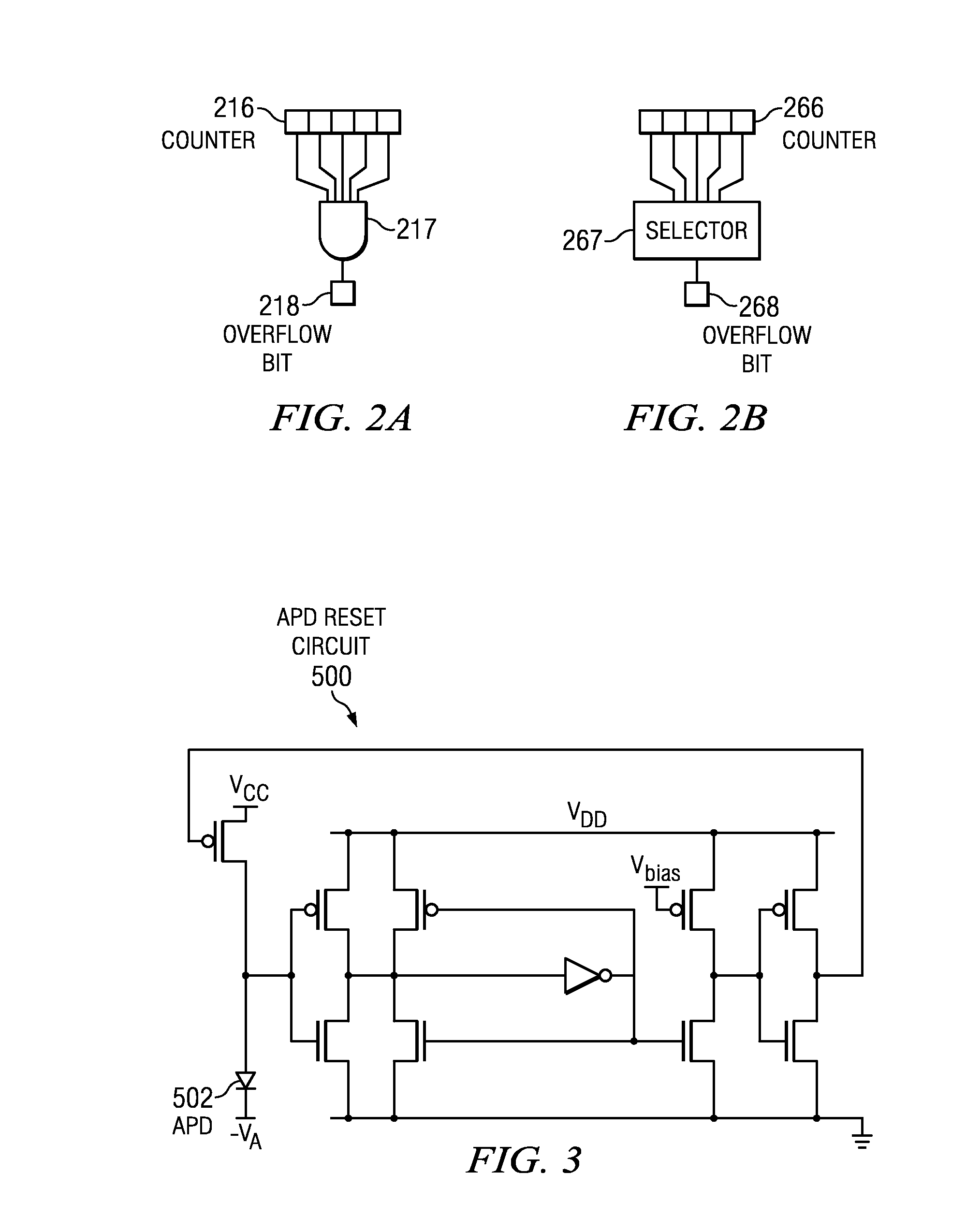
CMOS readout architecture and method for photon-counting arrays
ActiveUS20110235771A1Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton counting detectorCMOS
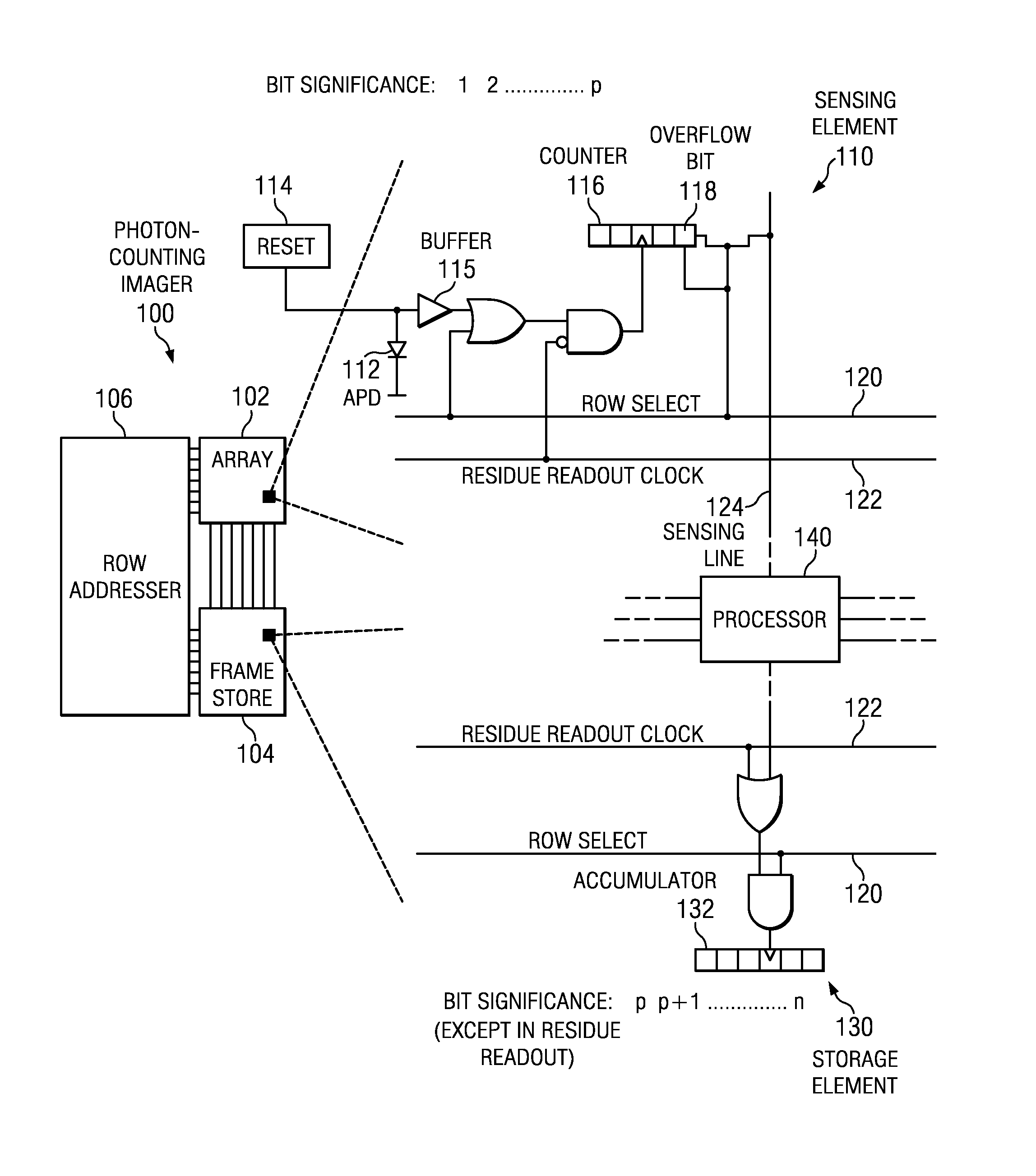
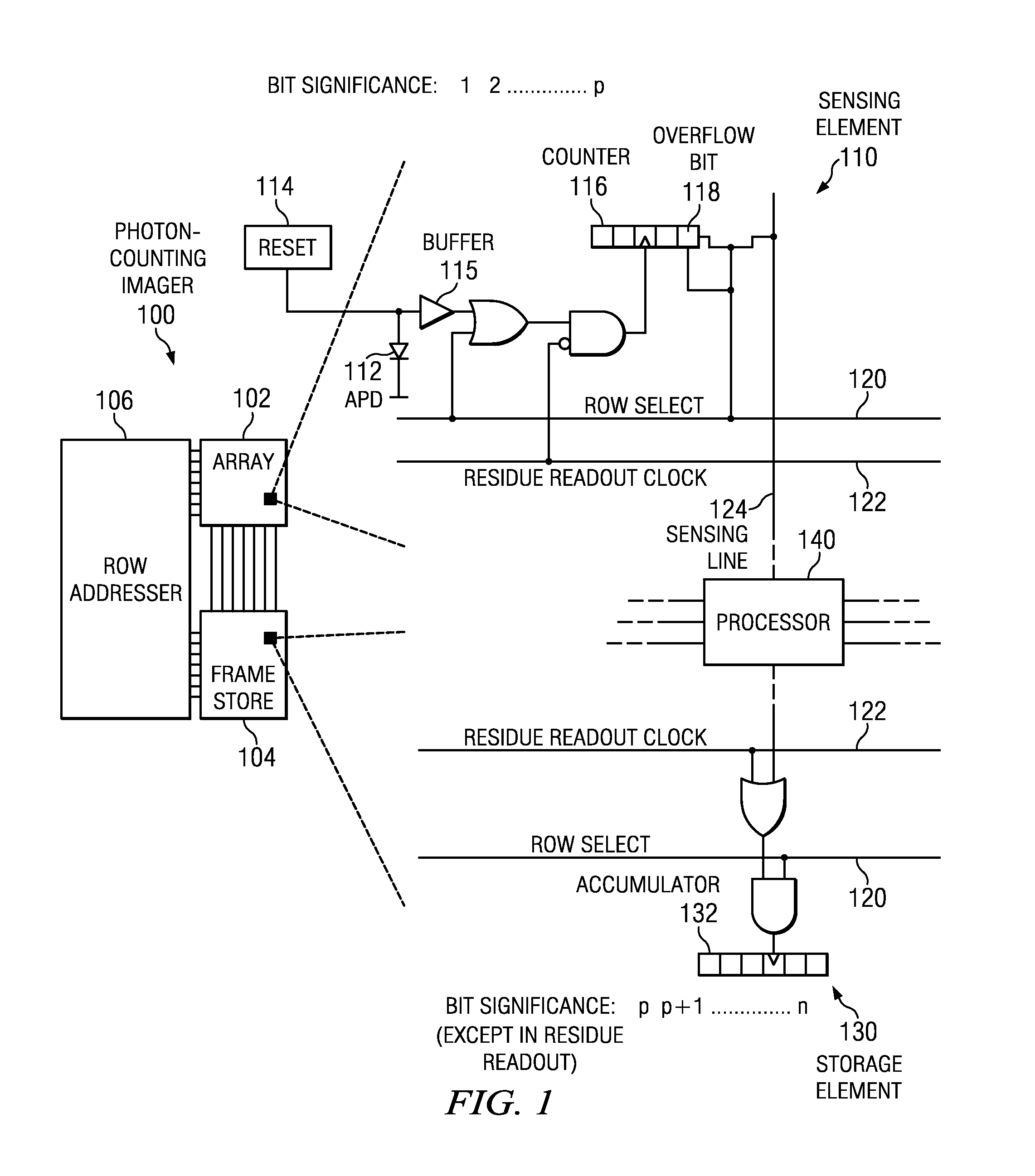
Embodiments of the present invention include complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) readout architectures for photon-counting arrays with a photon-counting detector, a digital counter, and an overflow bit in each of the sensing elements in the array. Typically, the photon-counting detector is a Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode (APD) that emits brief pulses every time it detects a photon. The pulse increments the digital counters, which, in turn, sets the overflow bit once it reaches a given count. A rolling readout system operably coupled to each sensing element polls the overflow bit, and, if the overflow bit is high, initiates a data transfer from the overflow bit to a frame store. Compared to other photo-counting imagers, photon-counting imagers with counters and overflow bits operate with decreased transfer bandwidth, high dynamic range, and fine spatial resolution.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and system of dynamically controlling shaping time of a photon counting energy-sensitive radiation detector to accommodate variations in incident radiation flux levels
ActiveUS20060056576A1Avoid saturationDetection efficiency sacrificedMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorHigh flux
A method and system of counting and tagging radiation energy received by a radiation detector is presented. The method and system are designed to dynamically control the sampling window or shaping time characteristics of a photon counting detector to accommodate variations of flux experienced by the detector so as to preserve optimum detector performance and prevent saturation during high flux conditions.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
CMOS readout architecture and method for photon-counting arrays
ActiveUS8426797B2Television system detailsMaterial analysis by optical meansCMOSPhoton counting detector
Embodiments of the present invention include complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (CMOS) readout architectures for photon-counting arrays with a photon-counting detector, a digital counter, and an overflow bit in each of the sensing elements in the array. Typically, the photon-counting detector is a Geiger-mode avalanche photodiode (APD) that emits brief pulses every time it detects a photon. The pulse increments the digital counters, which, in turn, sets the overflow bit once it reaches a given count. A rolling readout system operably coupled to each sensing element polls the overflow bit, and, if the overflow bit is high, initiates a data transfer from the overflow bit to a frame store. Compared to other photo-counting imagers, photon-counting imagers with counters and overflow bits operate with decreased transfer bandwidth, high dynamic range, and fine spatial resolution.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
CT imaging system and method
ActiveCN103913472AImprove numerical stabilityImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionNumerical stabilityPhoton counting detector
The invention discloses a CT imaging system and a method. The method includes: conducting common CT scanning on an object to obtain a common CT image, then determining an area-of-interest in the image, making use of a photon counting detector to perform CT scanning on the area-of-interest from multiple energy windows, and then re-establishing a high resolution image of the area-of-interest. The photon counting detector is employed to collect the photon counting projection data of multiple energy windows, so that decomposition of multiple basis functions can be carried out, the energy spectrum can have high discrimination, and the numerical stability can be good.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
Dental imaging with photon-counting detector
ActiveUS20150004558A1Reduce exposureRadiation diagnostic device controlTomosynthesisPhoton counting detectorDigital imaging
An extra-oral dental imaging apparatus for obtaining an image from a patient has a radiation source; a first digital imaging sensor that provides, for each of a plurality of image pixels, at least a first digital value according to a count of received photons that exceed at least a first energy threshold; a mount that supports the radiation source and the first digital imaging sensor on opposite sides of the patient's head; a computer in signal communication with the digital imaging sensor for acquiring a first two-dimensional image from the first digital imaging sensor; and a second digital imaging sensor that is alternately switched into place by the mount and that provides image data according to received radiation.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Single photon counting detector system having improved counter architecture
ActiveCN103430533ABuildup problems are reduced or completely eliminatedIncrease the number of countsTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMultiplexingPhoton counting detector
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
Method and system for spectral computed tomography (CT) with inner ring geometry
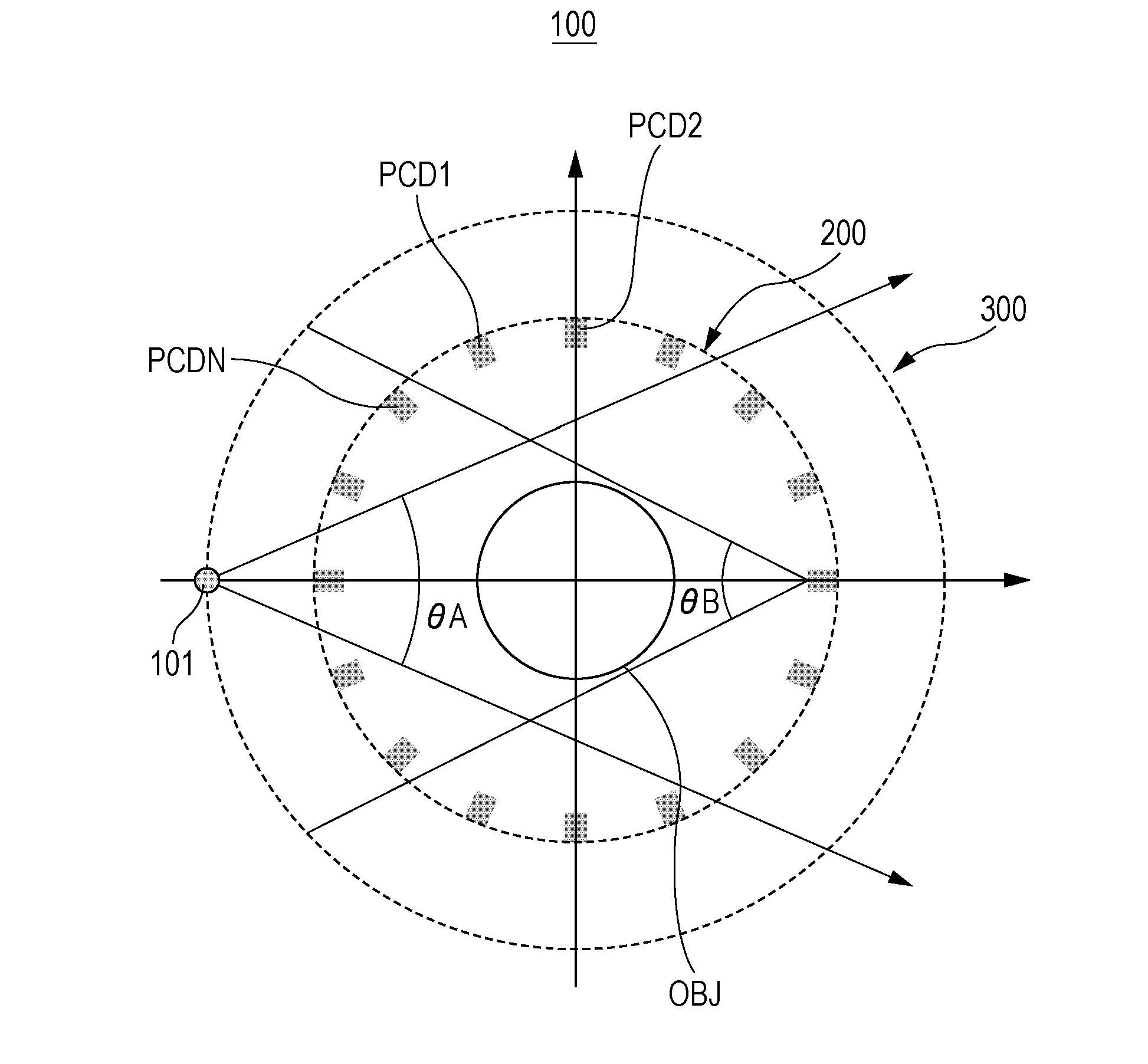
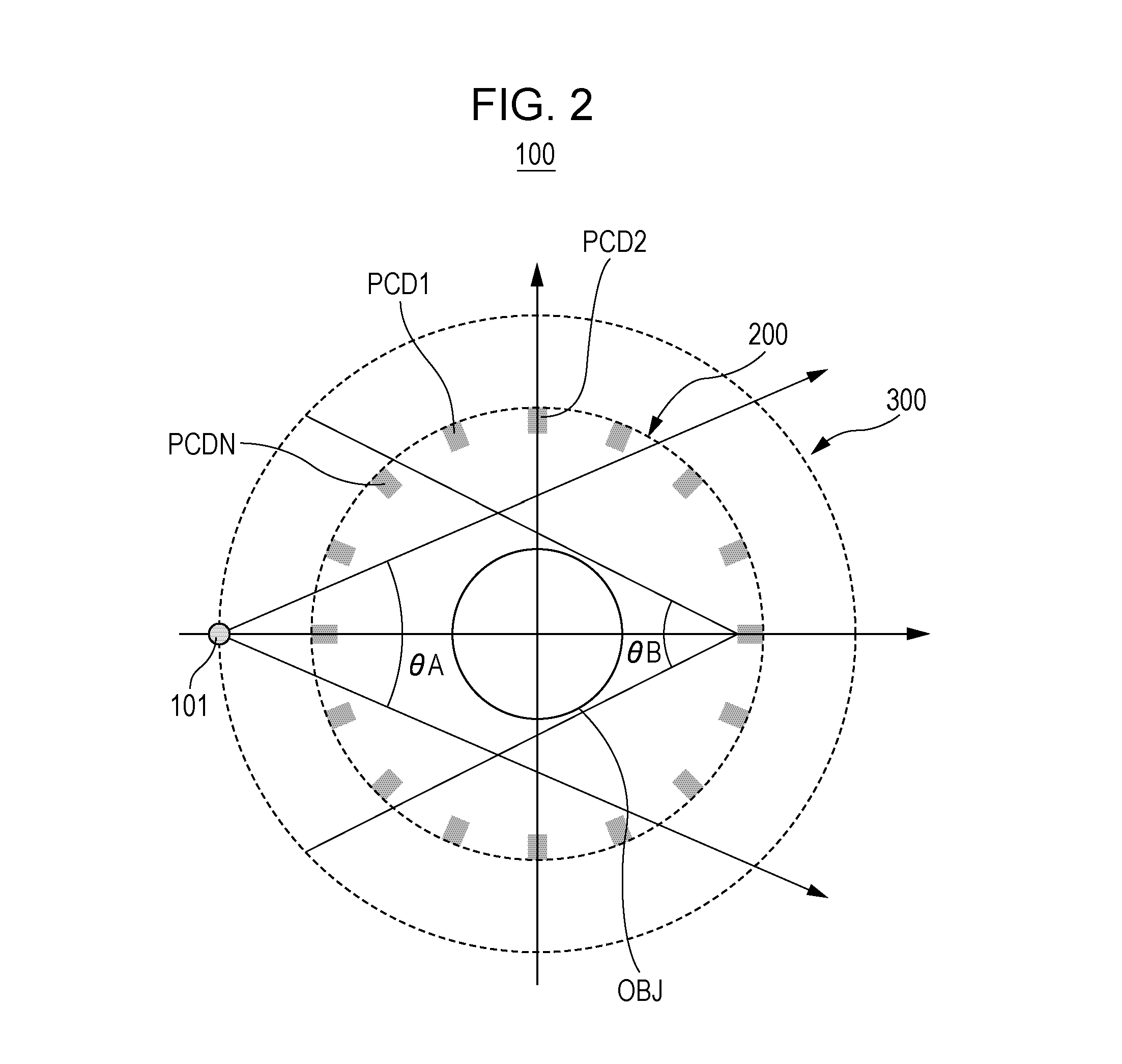
InactiveUS20150146844A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorComputed tomography
Photon counting detectors are sparsely placed at predetermined positions in the fourth-generation geometry around an object to be scanned in spectral Computer Tomography (CT). An X-ray emitting source rotates radially outside the sparsely placed photon counting detectors. Furthermore, the integrating detectors are placed in the third-generation in combination to the sparsely placed photon counting detectors at predetermined positions in the fourth-generation geometry.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
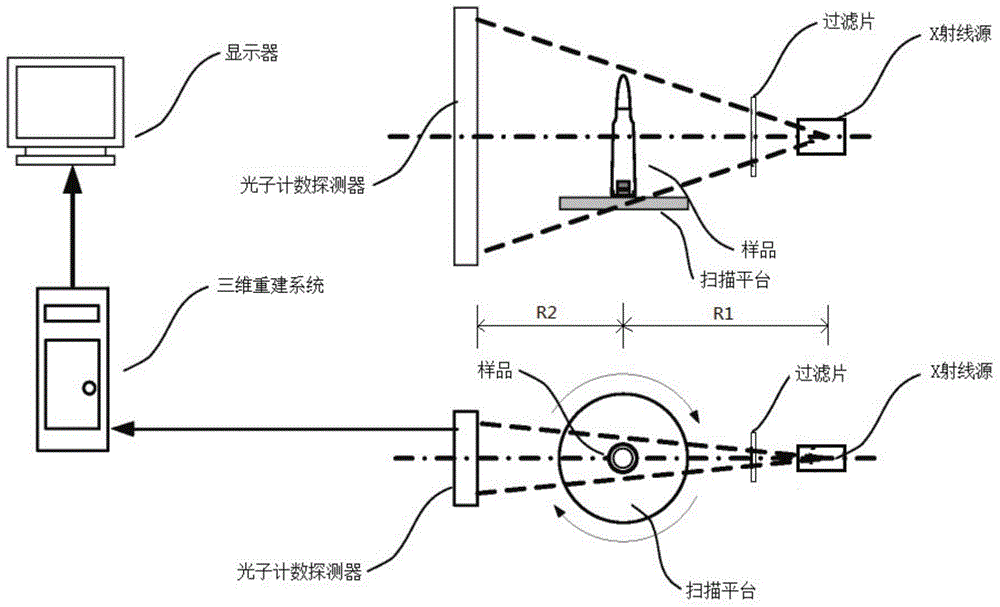
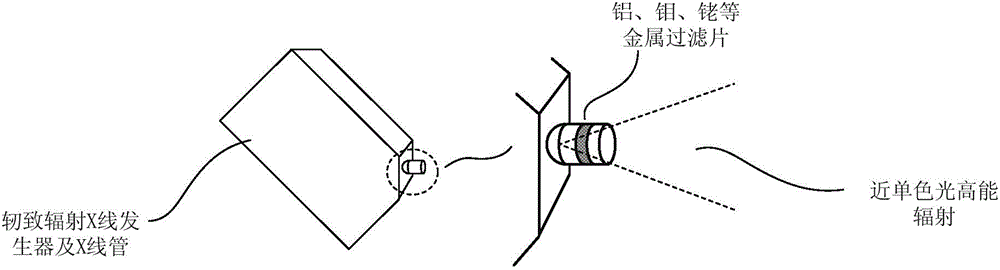
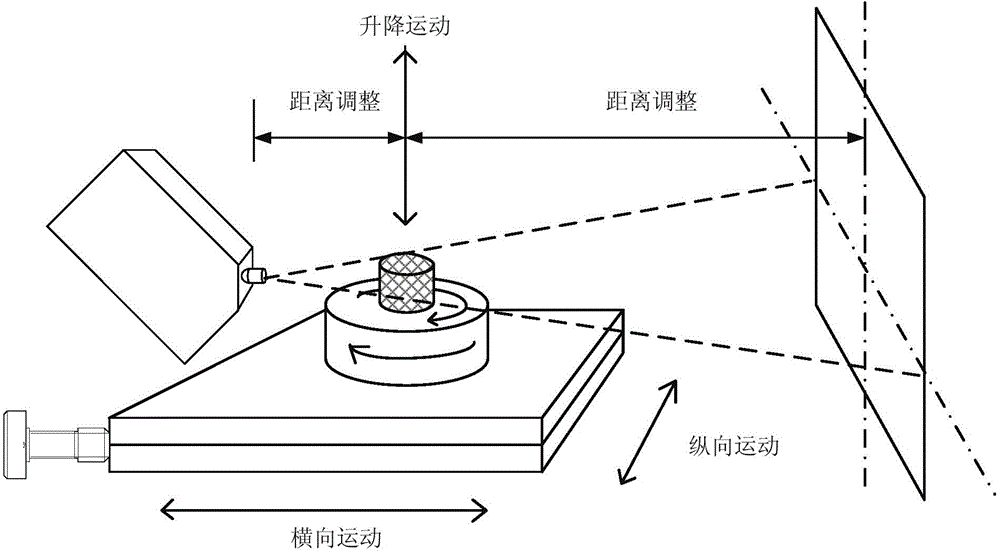
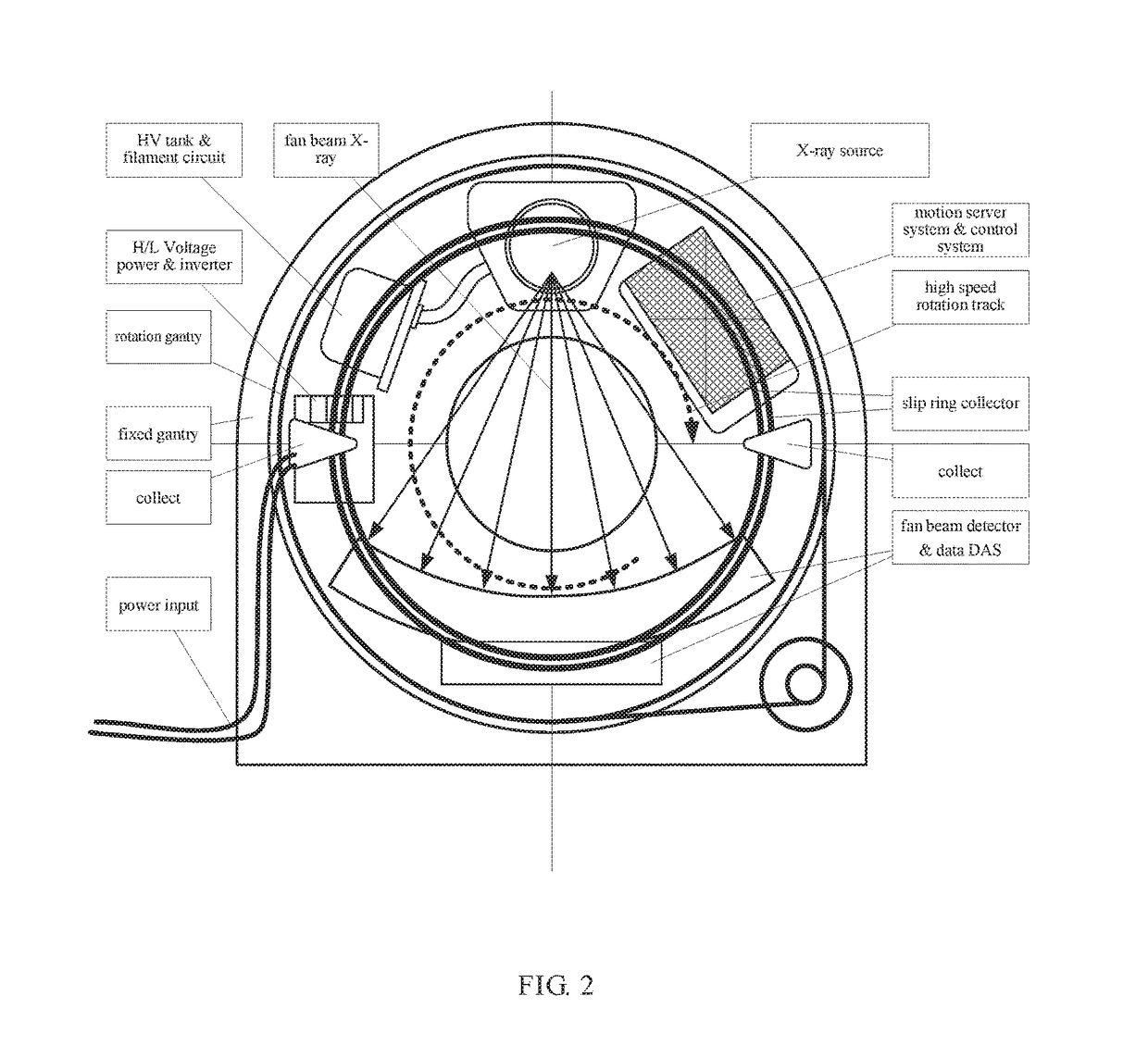
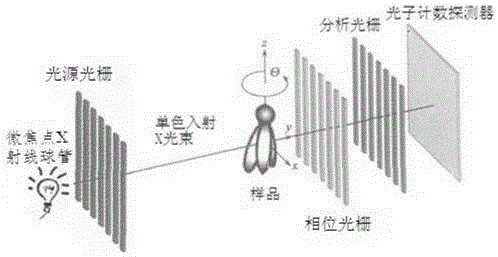
X-ray phase contrast imaging system based on photon counting, X-ray phase contrast imaging method realized by the system, and key equipment of X-ray phase contrast imaging method
ActiveCN104569002AEasy to observe subtle differencesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationX-Ray Phase-Contrast ImagingX-ray
The invention discloses an X-ray phase contrast imaging system based on photon counting and also discloses an X-ray phase contrast imaging method realized by the system and key equipment of the X-ray phase contrast imaging method. In the system, an X-ray source is used for emitting X rays to a sample on a scanning platform; when the X rays penetrate through the sample, photons carrying material characteristic information in a space position are generated and the photons of an imaging plane are counted by a photon counting detector to obtain projection data and energy data of the emitted photons; then data are transmitted to a three-dimensional reconstruction system; and the three-dimensional reconstruction system is used for reconstructing a three-dimensional structure and substance component types in the sample according to the projection data and the energy data, and carrying out digital dyeing on components of the sample, so that the substance components of the sample are identified. According to the X-ray phase contrast imaging system, weak absorption substances are subjected to nondestructive testing by adopting a photon counting technology, a phase contrast imaging technology and a three-dimensional reconstruction technology, and digital wax blocks with the energy resolution capability and the micro-grade or nano-grade space resolution capability can be obtained.
Owner:NANOVISION TECHNOLOGY (BEIJING) CO LTD
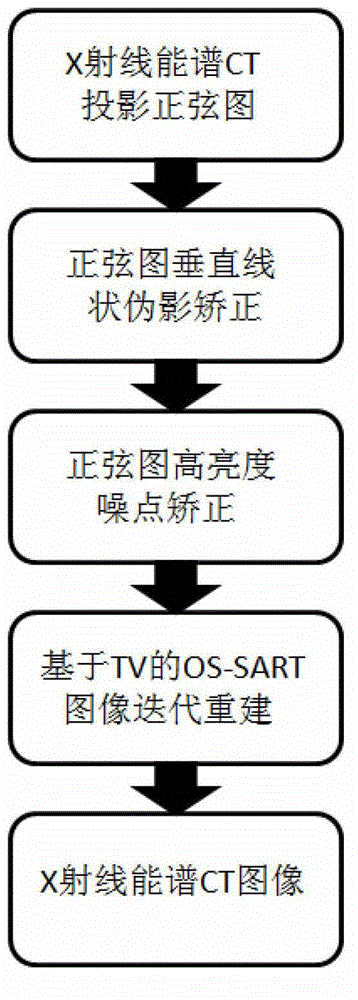
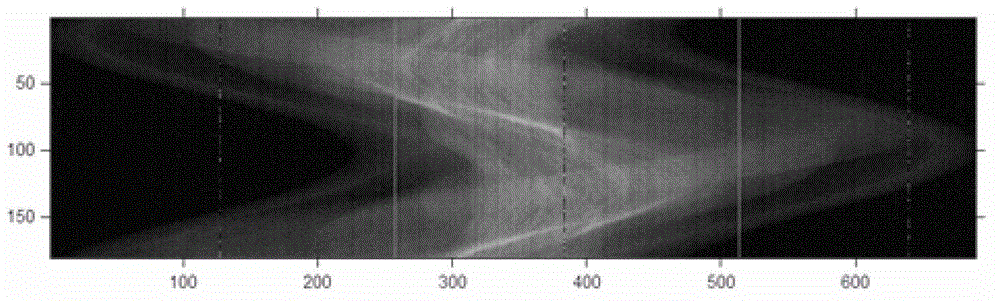
X-ray multi-energy spectrum computed tomography (CT) projection data processing and image reconstruction method
InactiveCN103150744ASuppresses vertical line artifactsEfficient removal2D-image generationReconstruction methodX-ray
The invention discloses an X-ray multi-energy spectrum computed tomography (CT) projection data processing and image reconstruction method, which mainly comprises an X-ray energy spectrum CT projection sinogram processing method and a compressed sensing-based accelerated iterative convergent reconstruction algorithm. The X-ray energy spectrum CT projection sinogram processing method mainly comprises the following steps of: (1) restraining vertical streaking artifacts in a projection sinogram; (2) removing high-brightness noisy points in the projection sinogram. The compressed sensing-based accelerated iterative convergent reconstruction algorithm refers to that image total variation (TV) minimization-based optimal constraint conditions and the ordered-subset simultaneous algebraic reconstruction techniques (OS-SART) are combined. As a number of defects still exist in a traditional X-ray energy spectrum CT detection system (X-ray energy resolution photon counting detector), more noise and artifacts exist in acquired projection data. According to the X-ray multi-energy spectrum CT projection data processing and image reconstruction method, X-ray multi-energy spectrum CT projection data are effectively preprocessed by utilizing a preprocessing means, and meanwhile, a TV-based OS-SART algorithm is introduced into X-ray multi-energy spectrum CT image reconstruction, and therefore, image iterative convergence is accelerated, and the noise and the artifacts in a reconstructed image is well restrained.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Multi-channel single photon counting measuring system based on digital lock phase de-multiplex
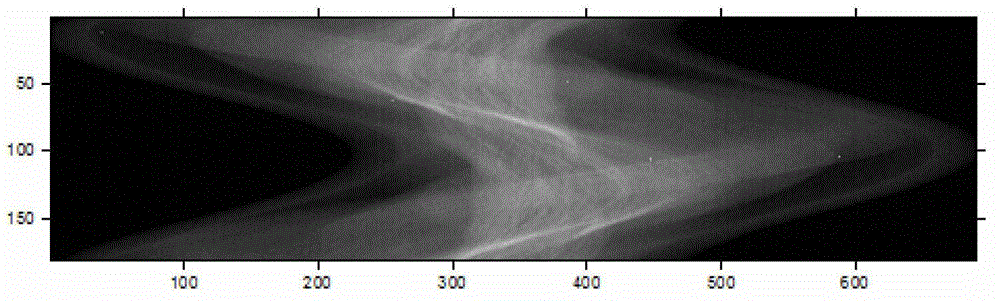
InactiveCN101832815AIncrease flexibilityHigh sensitivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectrical impulseOptical measurements
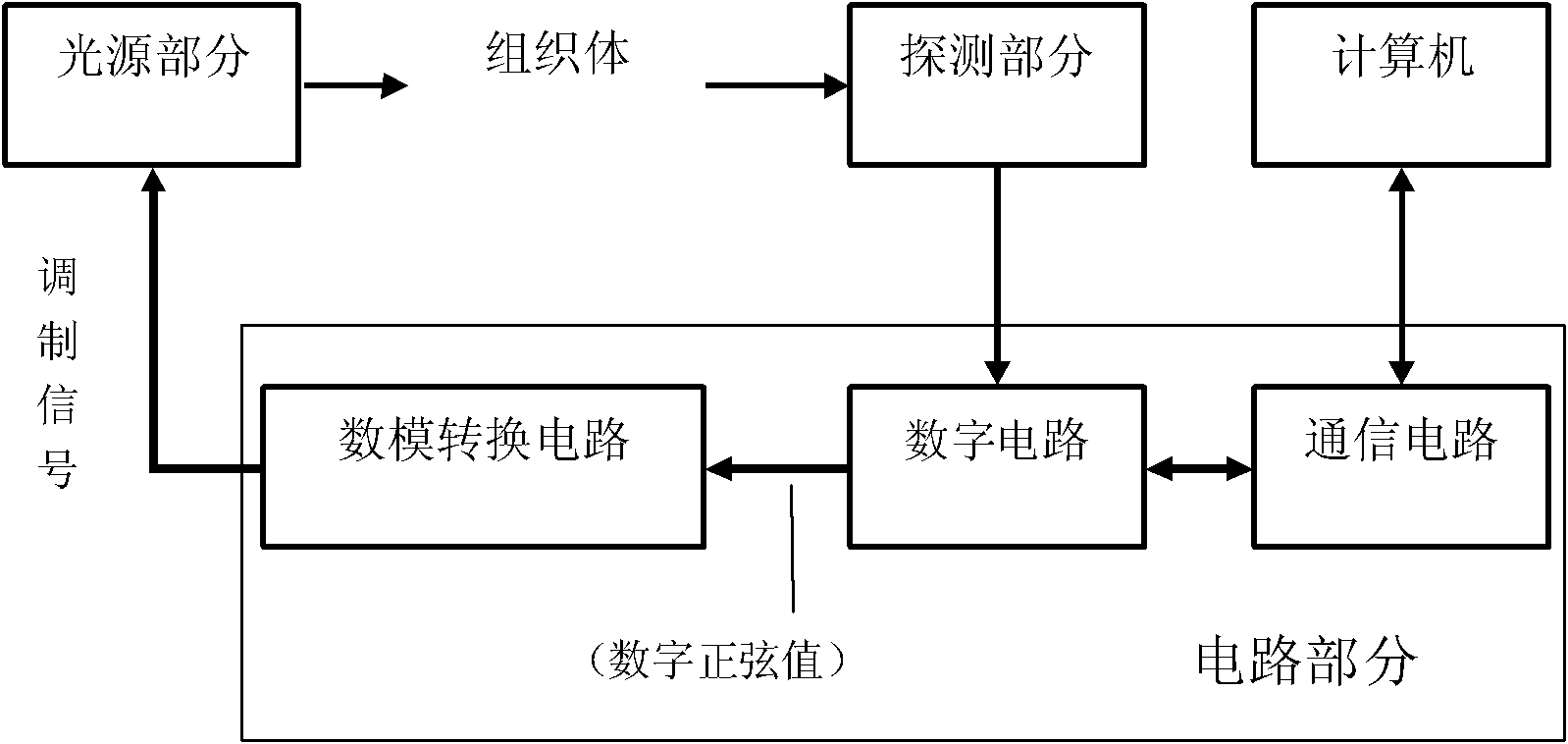
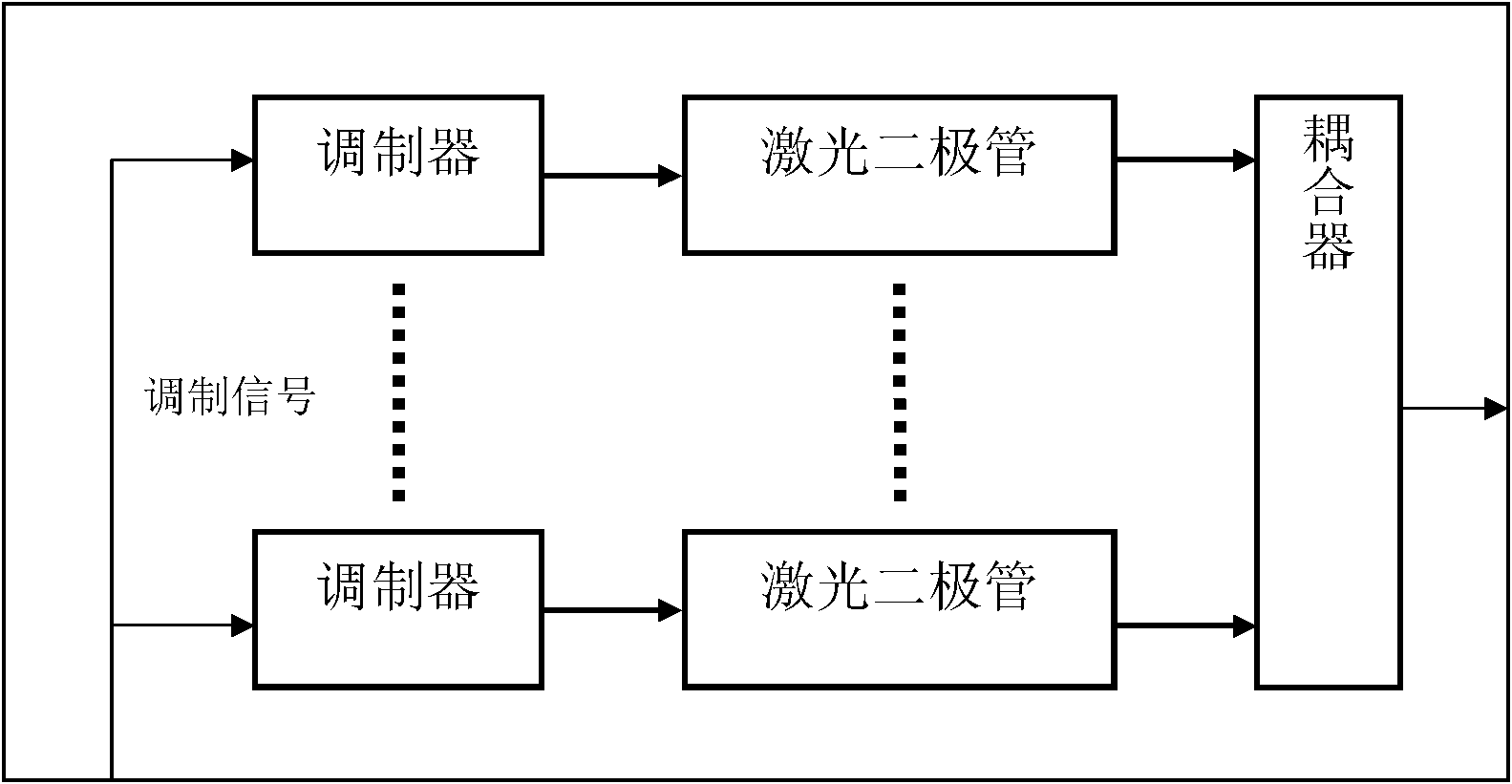
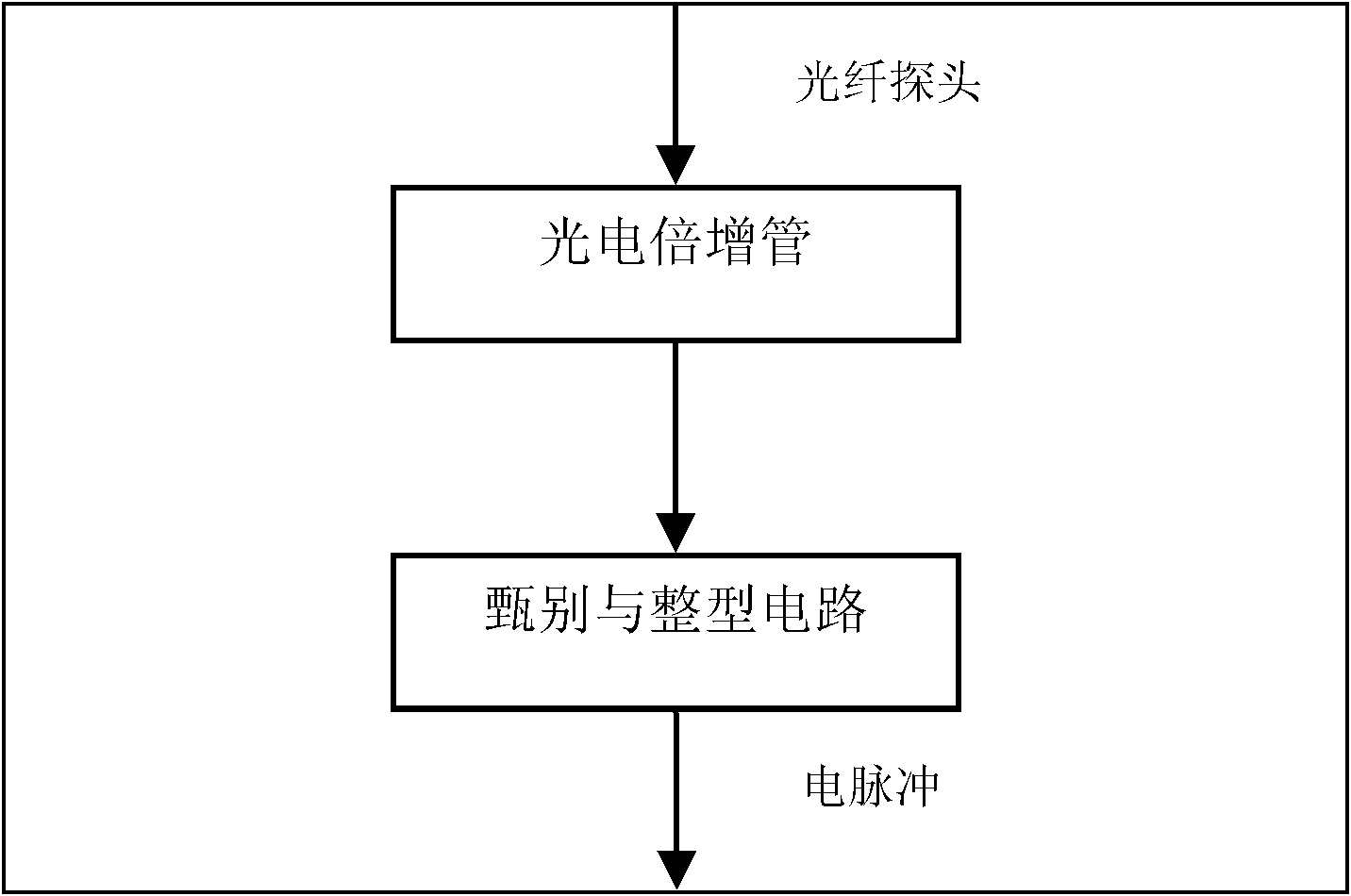
The invention belongs to the field of optical measurement, relating to a multi-channel single photon counting measuring system based on digital lock phase de-multiplex. The system comprises a light source part, a measuring part, a digital-to-analogue conversion circuit, a digital circuit, a communication circuit and a computer, wherein the digital circuit outputs a digital sine to obtain a simulative sine wave through the digital-to-analogue conversion circuit, a laser modulator modulates the amplitude of a laser and couples a plurality of beams of modulated lasers with different frequencies into one beam to form into a light source of frequency division multiplexing, the light source irradiates an object to be measured, an emitted weak diffused light is captured by a single photon counting measurer, and an electric pulse is outputted through a circuit; and the digital lock phase arithmetic which is tightly combined with the single photon counting is realized by the digital circuit, and a mixed signal from different light resources is extracted in a separating way in a passageway of the measurer according to a preset parameter when receiving the electric pulse to obtain the intensity information of an emergent light which corresponds to each light source. The system shortens the measuring time, reduces the complexity thereof, improves the flexibility of the circuit, and reduces the measuring error.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
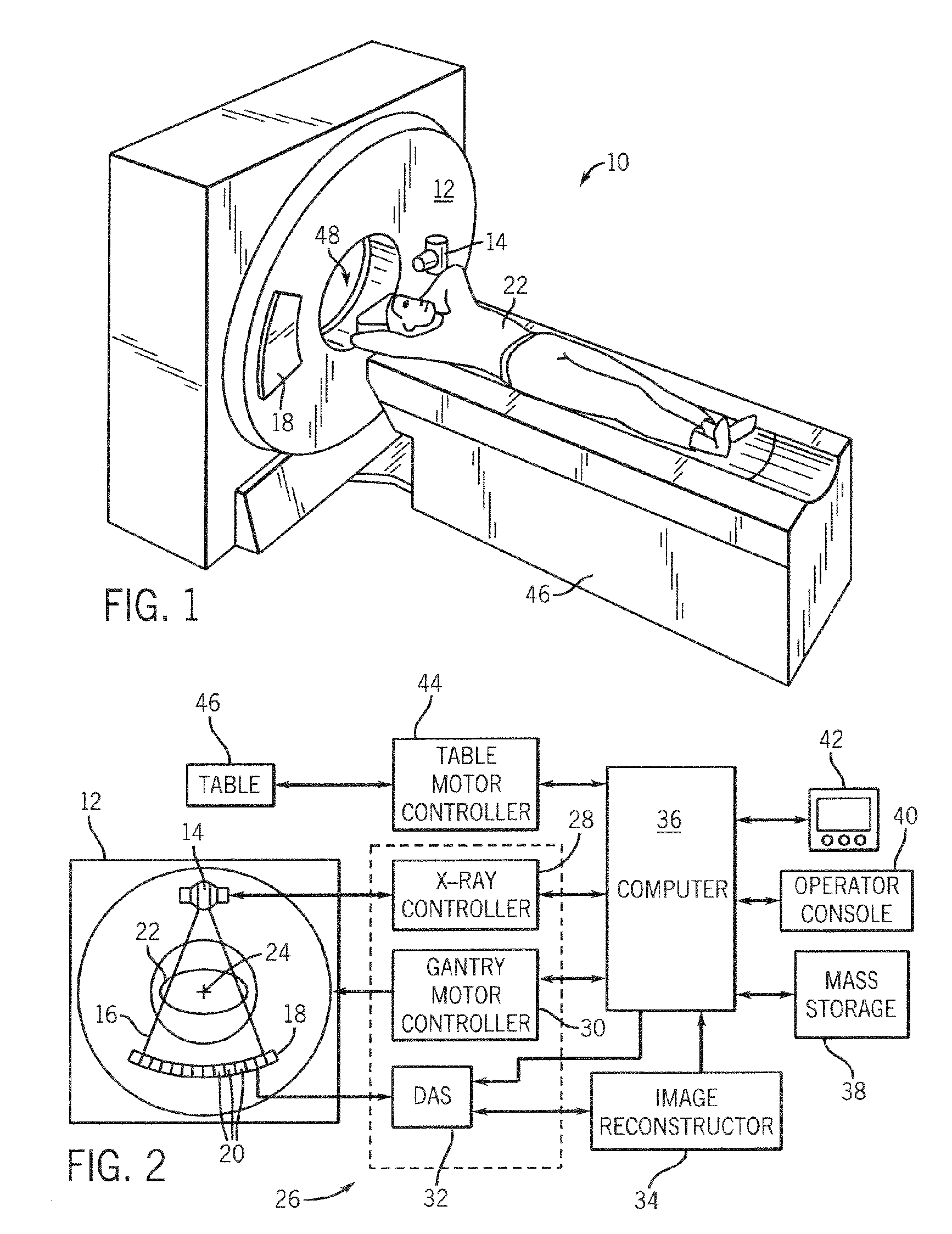
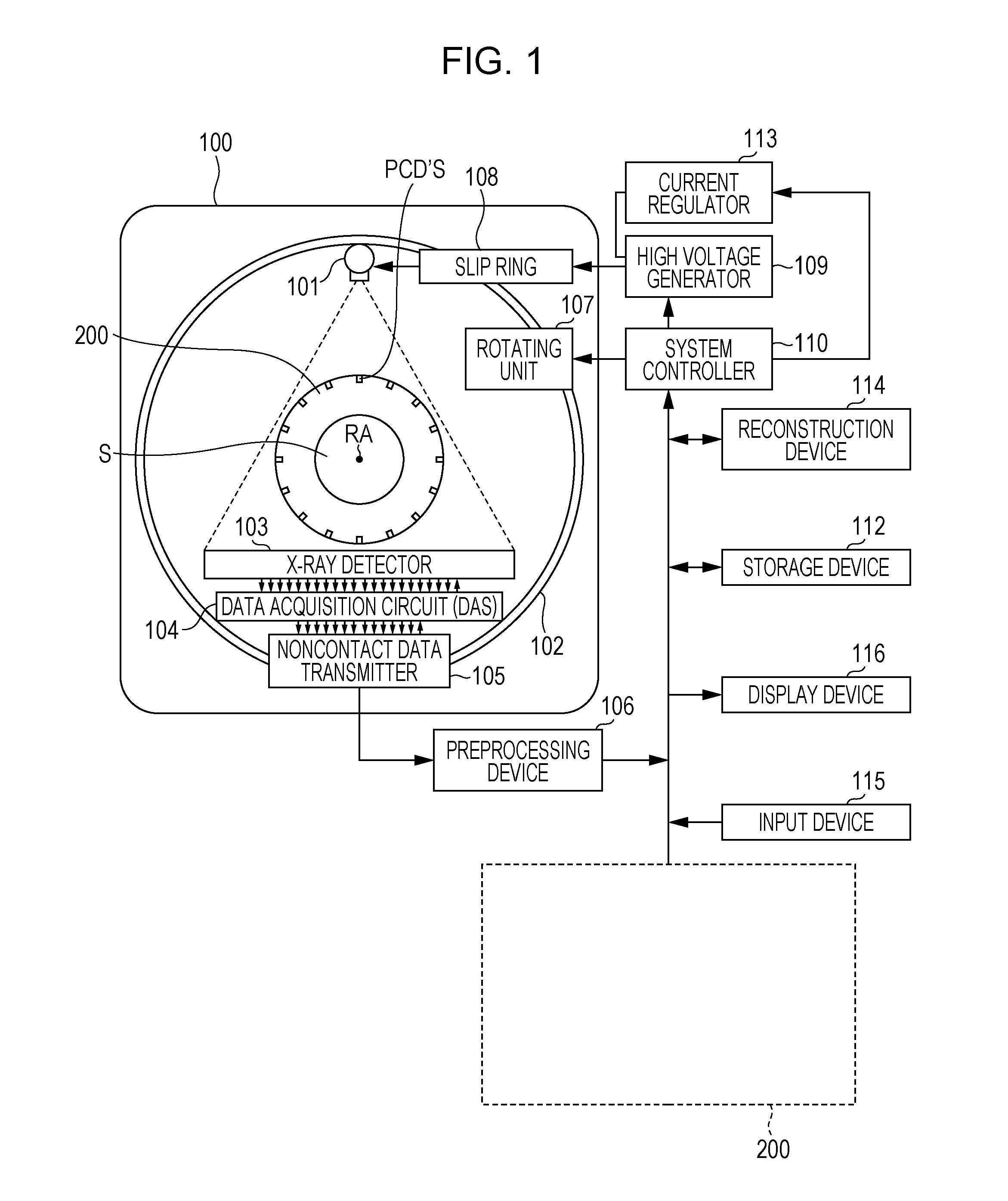
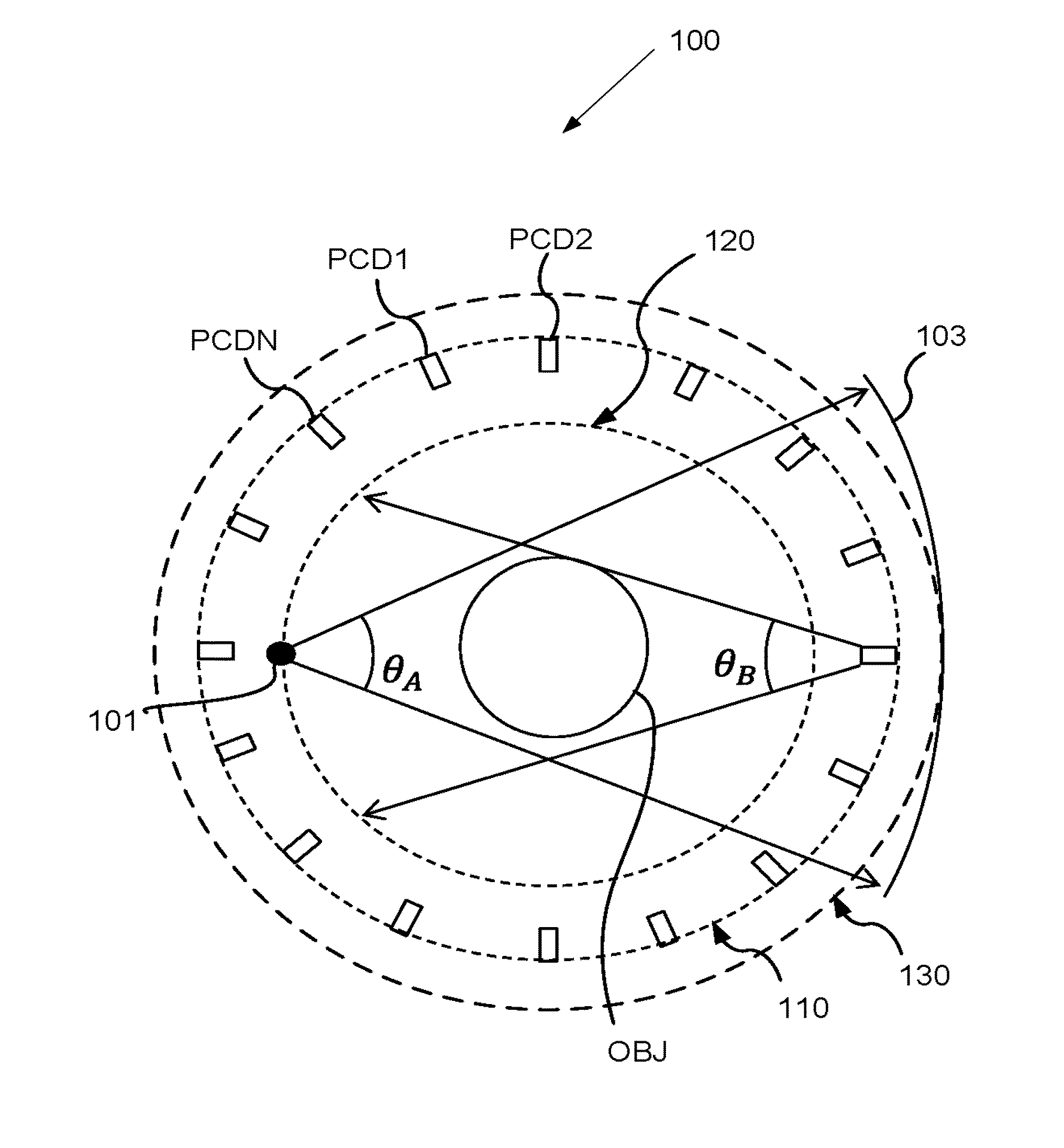
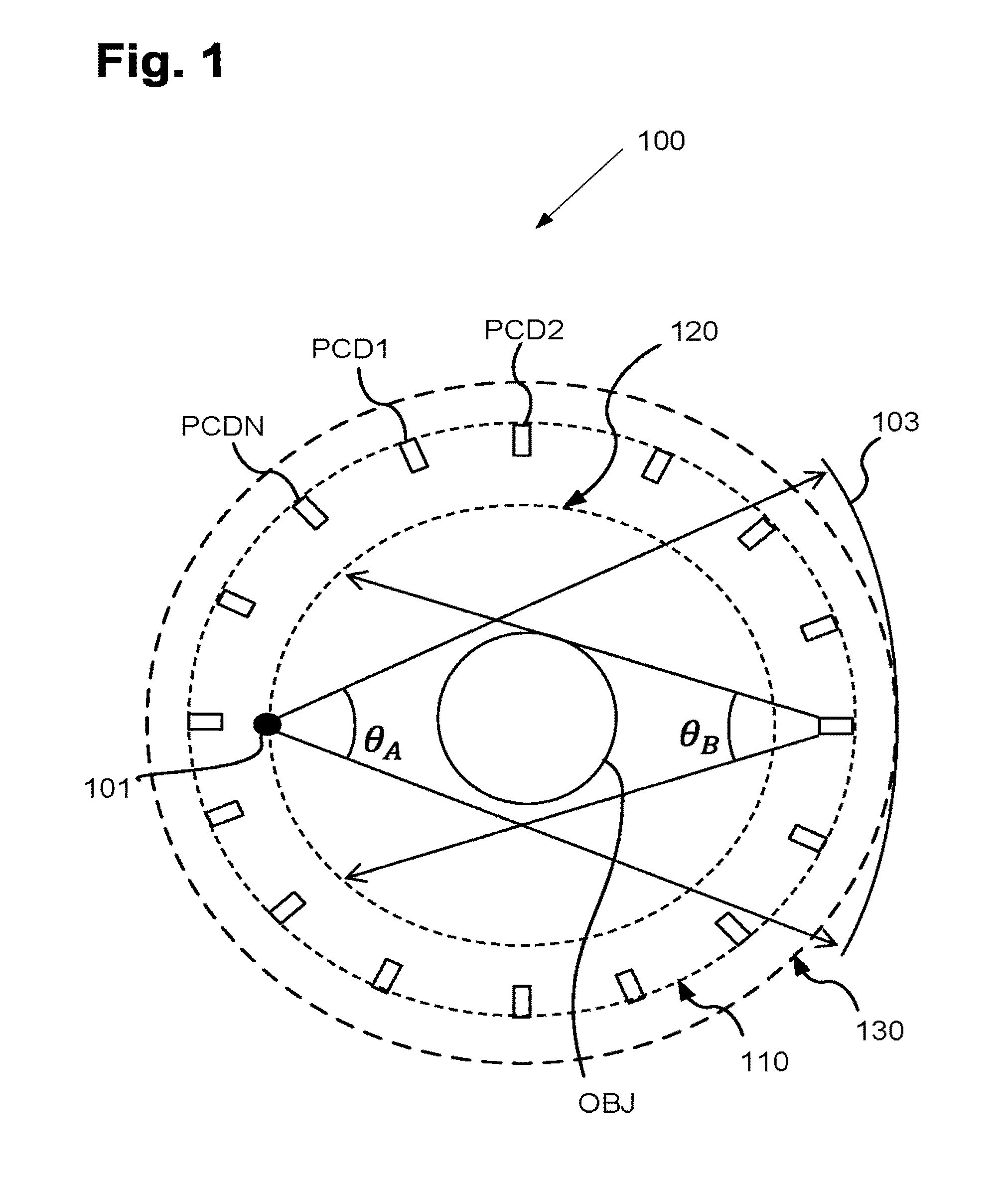
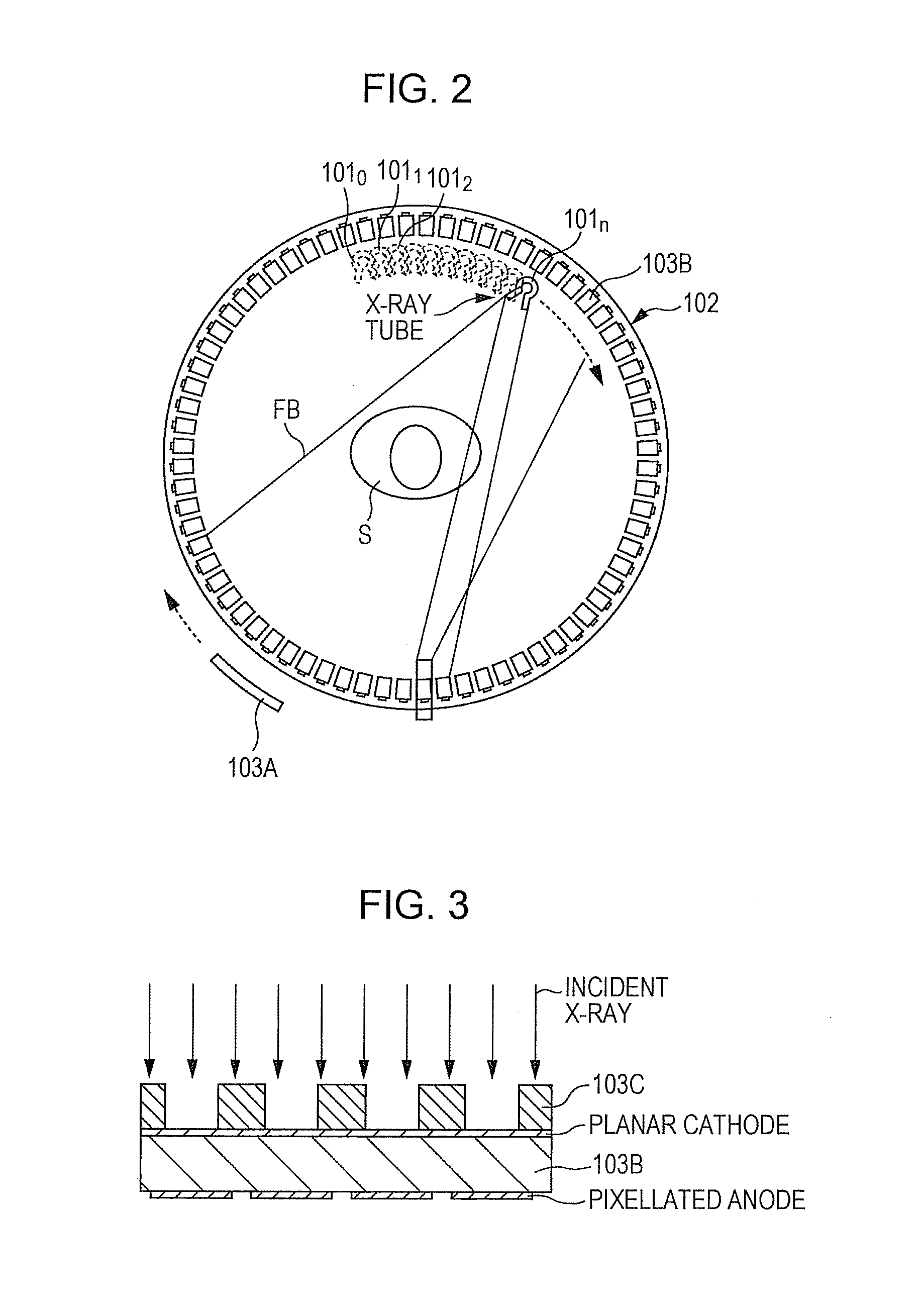
Stationary real time ct imaging system and method thereof
ActiveUS20170164910A1Solve the slow scanning speedReduce manufacturing difficultyPatient positioning for diagnosticsComputerised tomographsPhoton counting detectorHuman–machine interface
The present invention discloses a stationary real-time CT imaging system, comprising an annular photon counting detector, an annular scanning x-ray source, and a scanning sequence controller. Under the control of the scanning sequence controller, the annular scanning x-ray source emits x-ray, and the x-ray penetrates the object being tested and projects onto the corresponding annular photon counting detector. The annular photon counting detector delivers the corresponding exposure information through the main scanning machine and the main controlling unit to a CT main machine and a human-machine interface unit. The image reconstruction is completed in the CT main machine and the human-machine interface unit. By electronically controlling and switching x-ray projection positions in order, the scanning speed is enhanced by tens of times, thereby obtaining dynamic 3D images. The use of the photon counting detector enables the access to absorption data and energy data, thereby allows for real-time data reconstruction.
Owner:NANOVISION TECHNOLOGY (BEIJING) CO LTD
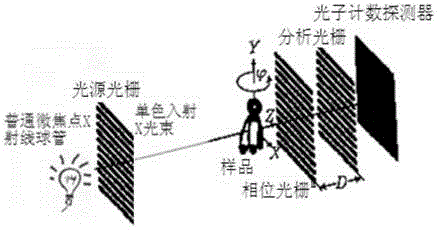
X-ray imaging system and method based on grating phase contrast and photon counting
The invention discloses an X-ray imaging system and method based on grating phase contrast and photon counting. X-rays become coherent X-rays after being shaped through a light source grating; the coherent X-rays containing phase changes after penetrating through samples form beam-split X-rays through a phase grating; the phase changes of the X-rays are converted into light intensity changes after the X-rays pass an analyzing grating; a photon counting detector is used for recording phase contrast information of the X-rays with different intensities; sectional images based on phase contrast are obtained through a three-dimensional reconstruction system; finally, components and interior fine structure information of the soft tissue samples are obtained. The system and method can be used for detecting soft tissue samples in the pathology department, the radiology department and the scientific research department of a hospital, early lesion information such as small lesions in the tissue samples can be found easily, and the detection rate is greatly increased.
Owner:NANOVISION TECHNOLOGY (BEIJING) CO LTD
Hybrid passive/active multi-layer energy discriminating photon-counting detector
InactiveUS20160206255A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingPhoton counting detectorX-ray
A photon-counting detector apparatus is configured to receive X-rays transmitted from an X-ray source. The photon-counting detector apparatus includes a first photon-counting detector having a first detecting material configured to detect photons using a first set of energy bins. The photon-counting detector apparatus also includes a second photon-counting detector arranged above the first photon-counting detector relative to an incidence direction of the X-rays transmitted from the X-ray source. The second photon-counting detector has a second detecting material configured to detect photons using a second set of energy bins. The first set of energy bins differs from the second set of energy bins.
Owner:CANON MEDICAL SYST COPRPORATION
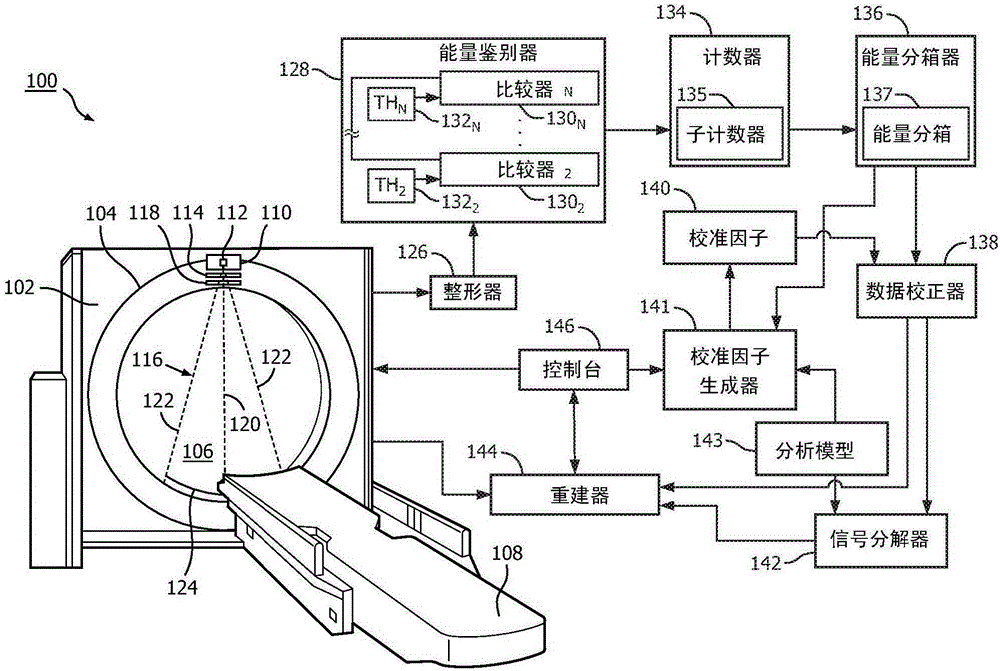
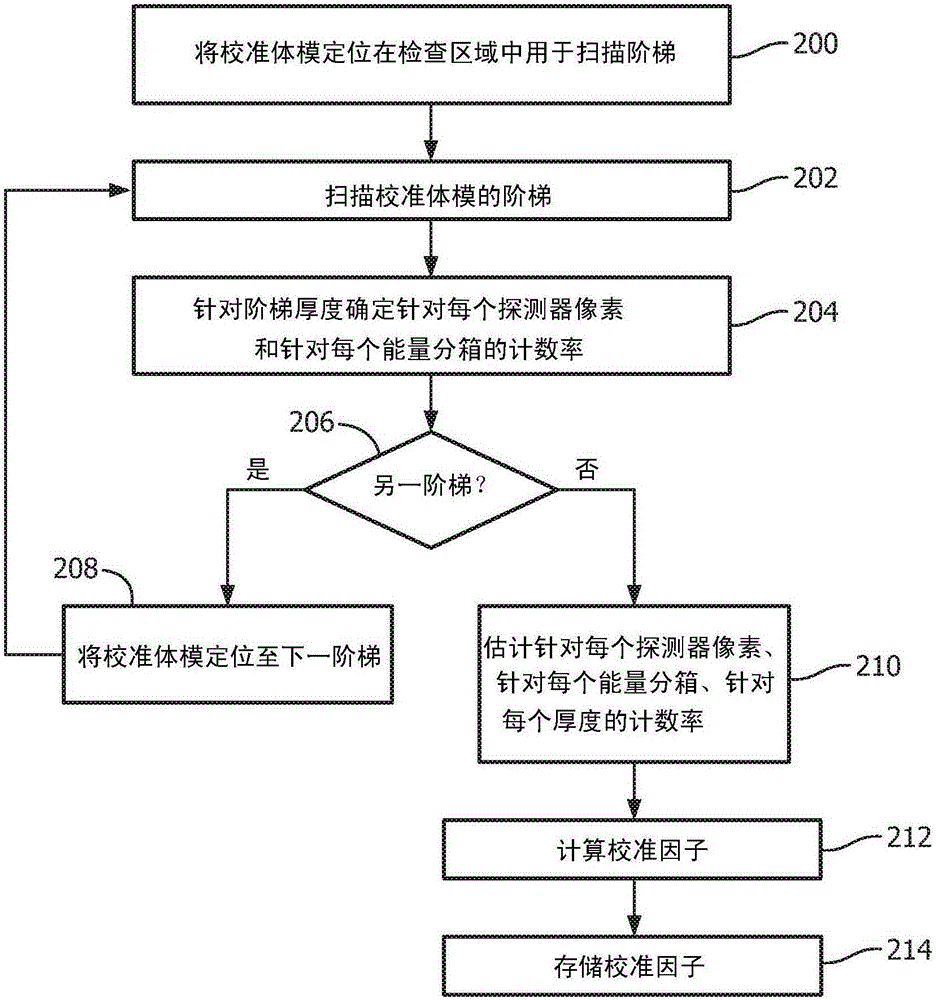
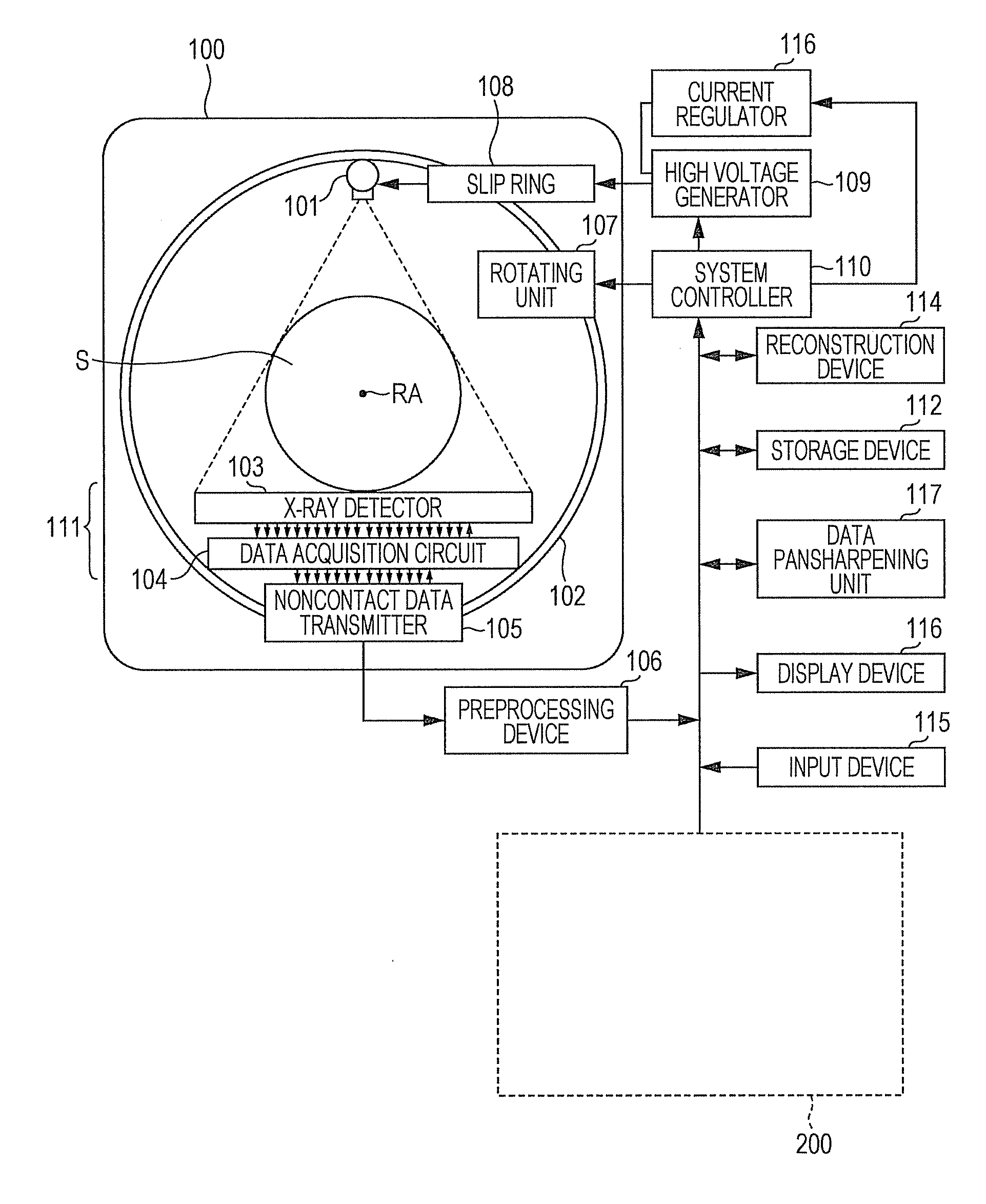
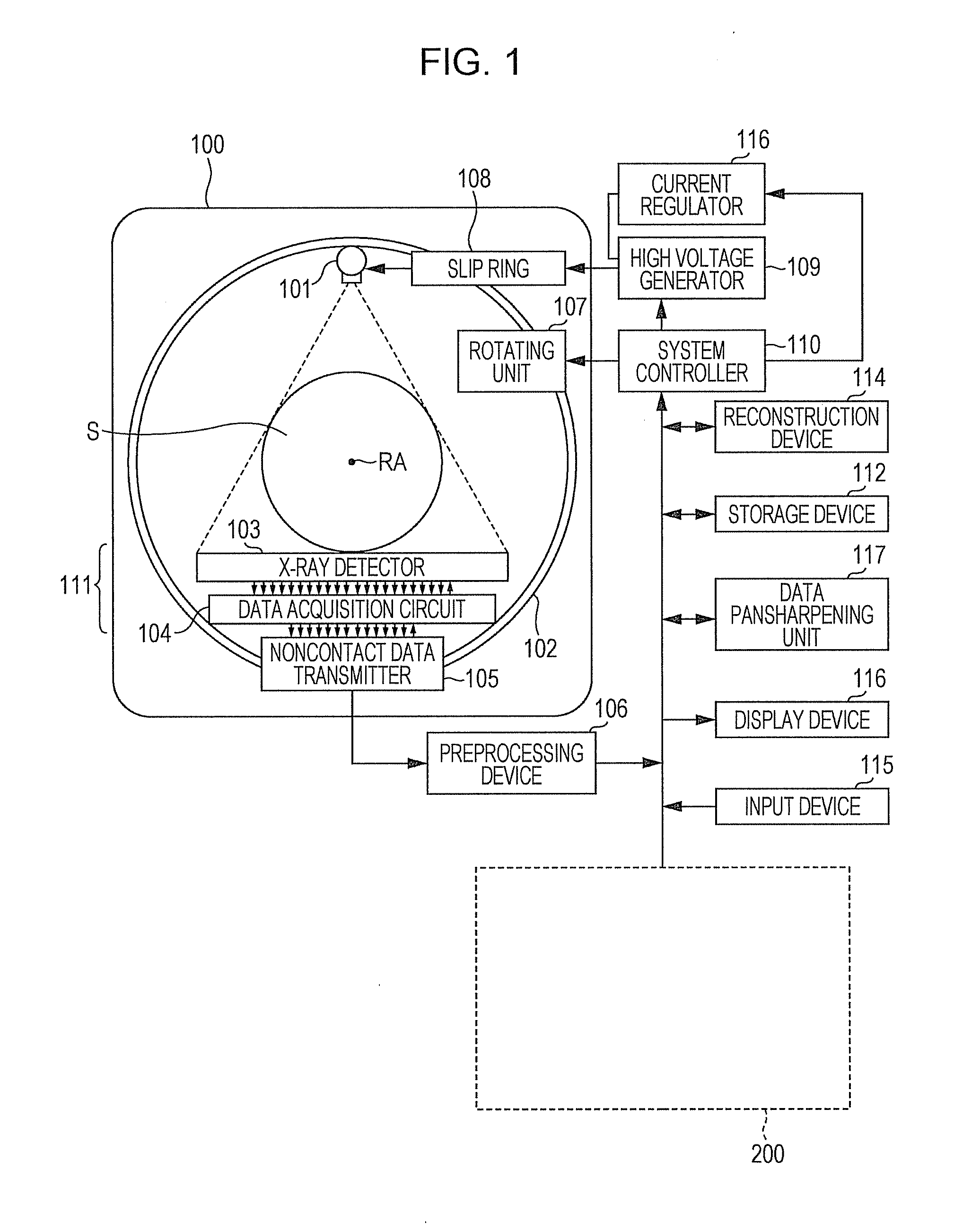
Photon-counting detector calibration
A method includes determining calibration factors for calibrating photon-counting detectors of a spectral imaging system by combining a heuristic calibration of the photon-counting detectors and an analytical calibration of the photon-counting detectors and generating a set of photon-counting calibration factors based on the combining of the a heuristic calibration and the analytical calibration. The photon-counting calibration factors, when applied to measured energy-resolved data from the photon-counting detectors of a spectral CT scan of a subject or object, mitigate spectral distortion caused by a radiation intensity profile shaper that filters a radiation beam of the spectral CT scan.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
X-ray apparatus, data processing apparatus and data processing method
ActiveUS20180214113A1Accurate countSlow changeTesting starch susbtancesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationPhoton counting detectorSoftware engineering
Based on counts detected by a photon counting detector, a characteristic of X-ray attenuation amounts μt is acquired for each X-ray energy bin. This characteristic is defined by a plurality of mutually different known thicknesses t and linear attenuation coefficients in the X-ray transmission direction. This substance is composed of a material which is included in an object and which is the same in type as the object or which can be regarded as being similar to the object in terms of the effective atomic number. Correcting data for replacing the characteristic of the X-ray attenuation amounts μt by a linear target characteristic are calculated. The linear target characteristic is set to pass through the origin of a two-dimensional coordinate having a lateral axis assigned to thicknesses t and a longitudinal axis assigned to the X-ray attenuation amounts μt. The correcting data are calculated for each X-ray energy bin.
Owner:JOB
Dental imaging with photon-counting detector
ActiveUS9743893B2Reduce exposureRadiation diagnostic device controlTomosynthesisPhoton counting detectorDigital imaging
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
Dental imaging with photon-counting detector
ActiveUS20170311910A1Reduce exposureTelevision system detailsRadiation diagnostic device controlPhoton counting detectorDigital imaging
An extra-oral dental imaging apparatus for obtaining an image from a patient has a radiation source; a first digital imaging sensor that provides, for each of a plurality of image pixels, at least a first digital value according to a count of received photons that exceed at least a first energy threshold; a mount that supports the radiation source and the first digital imaging sensor on opposite sides of the patient's head; a computer in signal communication with the digital imaging sensor for acquiring a first two-dimensional image from the first digital imaging sensor; and a second digital imaging sensor that is alternately switched into place by the mount and that provides image data according to received radiation.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL LLC
Sinogram (DATA) domain pansharpening method and system for spectral ct
ActiveUS20150043796A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionResolution PropertyPhoton counting detector
A hybrid CT dataset is obtained from a combination of an integrating detector and a photon-counting detector. The hybrid CT dataset contains sparse spectral energy data and dense energy integration data. The dense panchromatic data sets inherit the resolution properties of the integrating detector while the sparse spectral data sets inherit the spectral information of the photon-counting detector. Subsequently, the sparse spectral energy data sets are pansharpened based upon at least one dense panchromatic data set that lacks spectral information according to a pansharpening algorithm.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF CHICAGO +2
Direct conversion photon counting detector
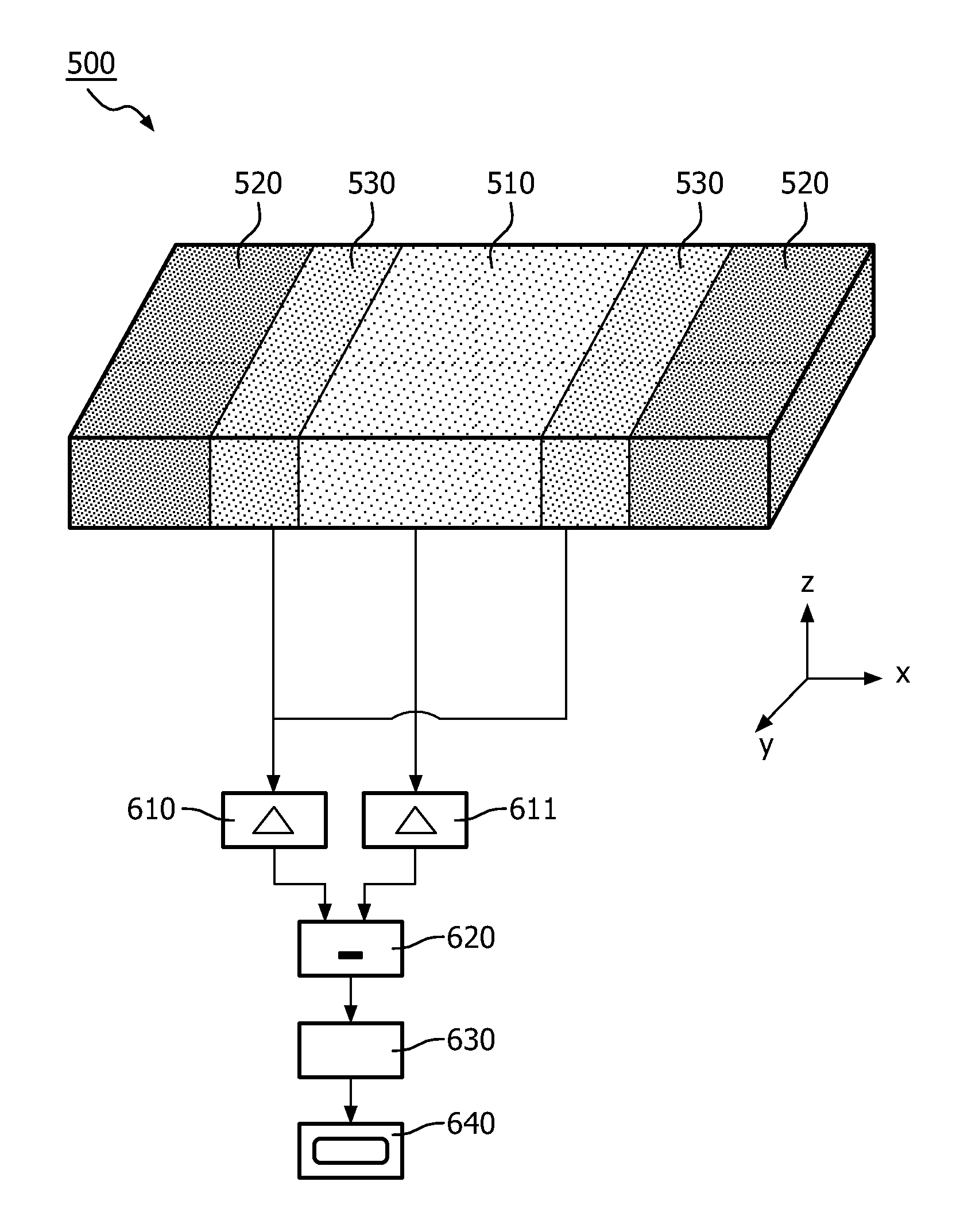
The present invention discloses a pixilated direct conversion photon counting detector with a direct conversion material layer and a pixilated electrode. Individual electrode pixels are segmented into three segments (510, 520, 530), wherein one of the segments (520) is operated at a more electrically repellant value than that of the other two (510, 530). Said other two segments are connected to electric circuitry (610, 611, 620, 630) that is arranged to generate signals which are indicative of a count of electrons or holes that approach each of the respective electrode pixel segments and to subtract the generated signals from each other.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Ultraviolet spherical micro-channel plate photo counting and imaging detector
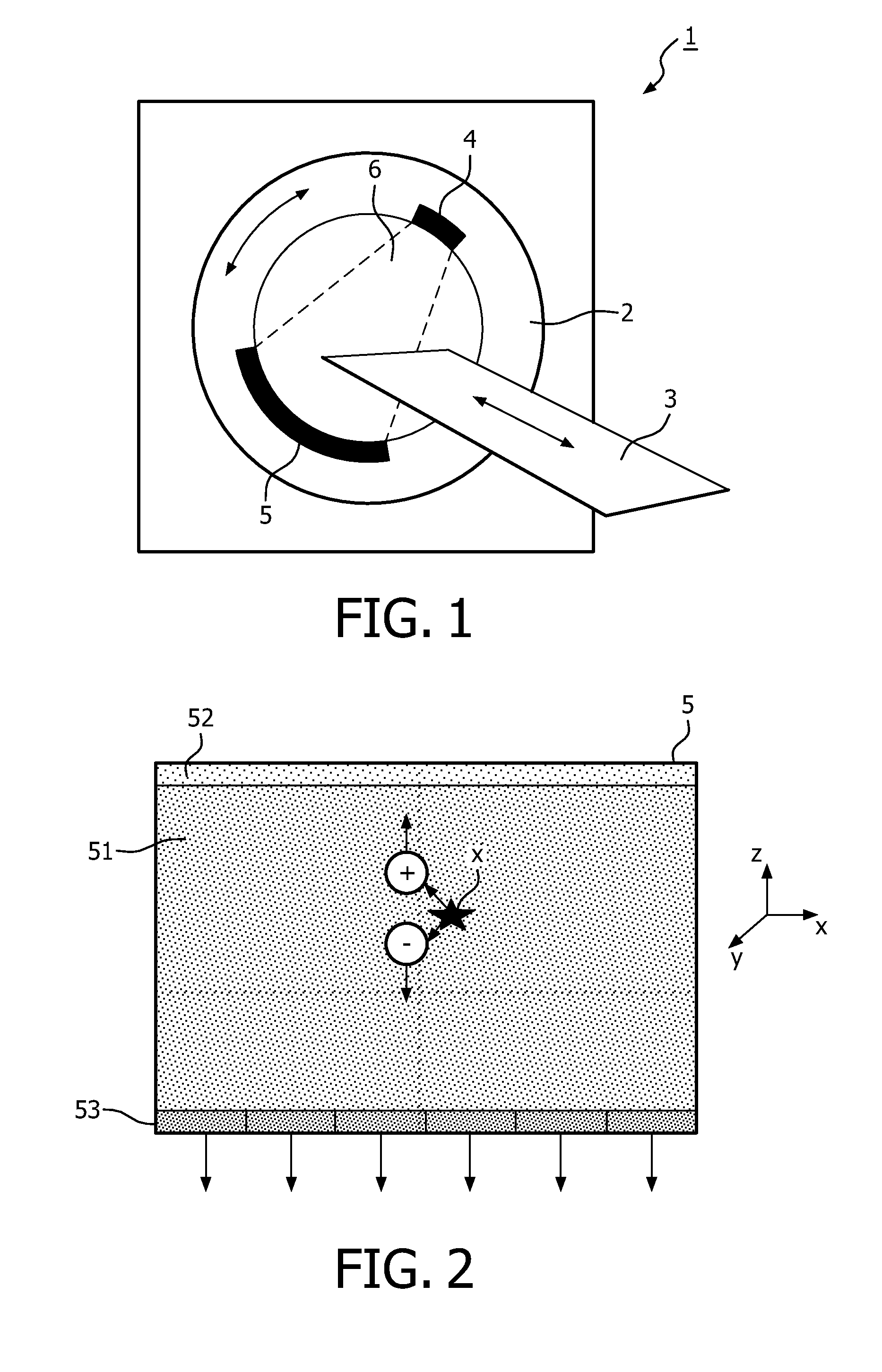
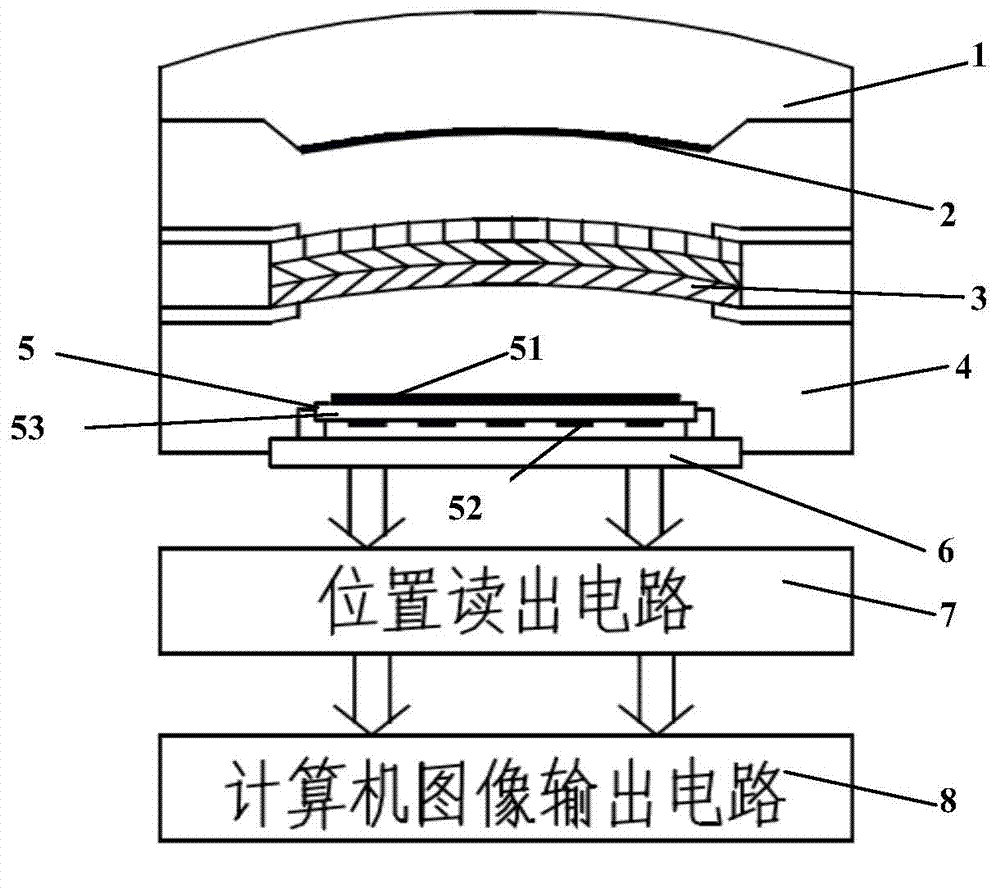
InactiveCN103792004AReduce spherical aberrationImprove image qualityPhotometry electrical circuitsLow noiseImaging quality
The invention relates to an ultraviolet spherical micro-channel plate photo counting and imaging detector. The ultraviolet spherical micro-channel plate photo counting and imaging detector comprises an photoelectric cathode, a micro-channel plate, a position sensitive anode, an input window, a metal output window, a position reading circuit and a computer image output circuit, wherein the photoelectric cathode, the micro-channel plate and the position sensitive anode are arranged in a vacuum shell from top to bottom; the input window is arranged at the front end of the vacuum shell; the metal output window is arranged at the rear end of the vacuum shell and provided with a metal output electrode; the position reading circuit and the computer image output circuit are placed on the outer portion of the vacuum shell. The input window is connected with the vacuum shell and the metal output window in a sealed mode to form a vacuum airtight structure which is integrally formed. A layer of conductive thin capable of allowing ultraviolet rays to transmit is plated on the inner surface of the input window and the photoelectric cathode is manufactured on the conductive film. The input window and the micro-channel plate are in the shape of convex spherical faces with the curvature radius being the same. The ultraviolet spherical micro-channel plate photo counting and imaging detector can reduce the spherical aberration of a large-view-field imaging system and improve the imaging quality of the system, and can be used as a single-photo counting detector. The ultraviolet spherical micro-channel plate photo counting and imaging detector has single-photo sensitivity and meanwhile, an ultraviolet cathode has very low noise.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
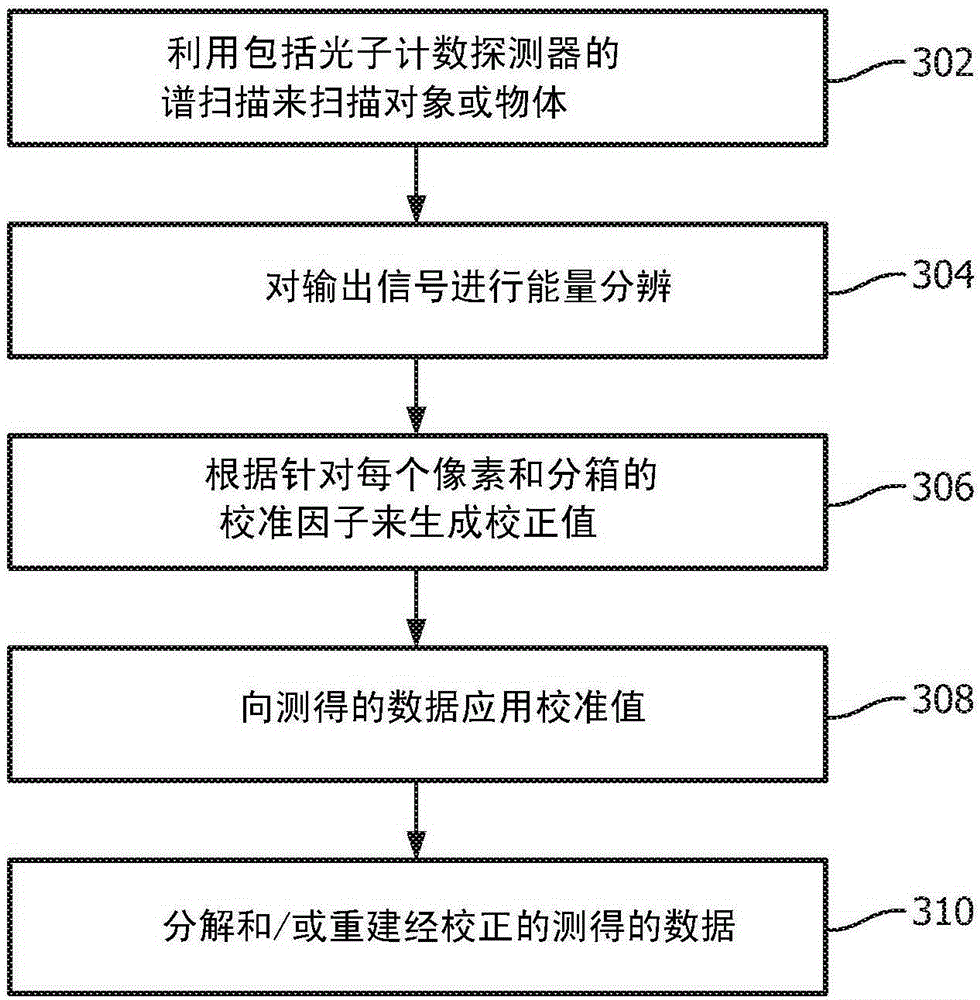
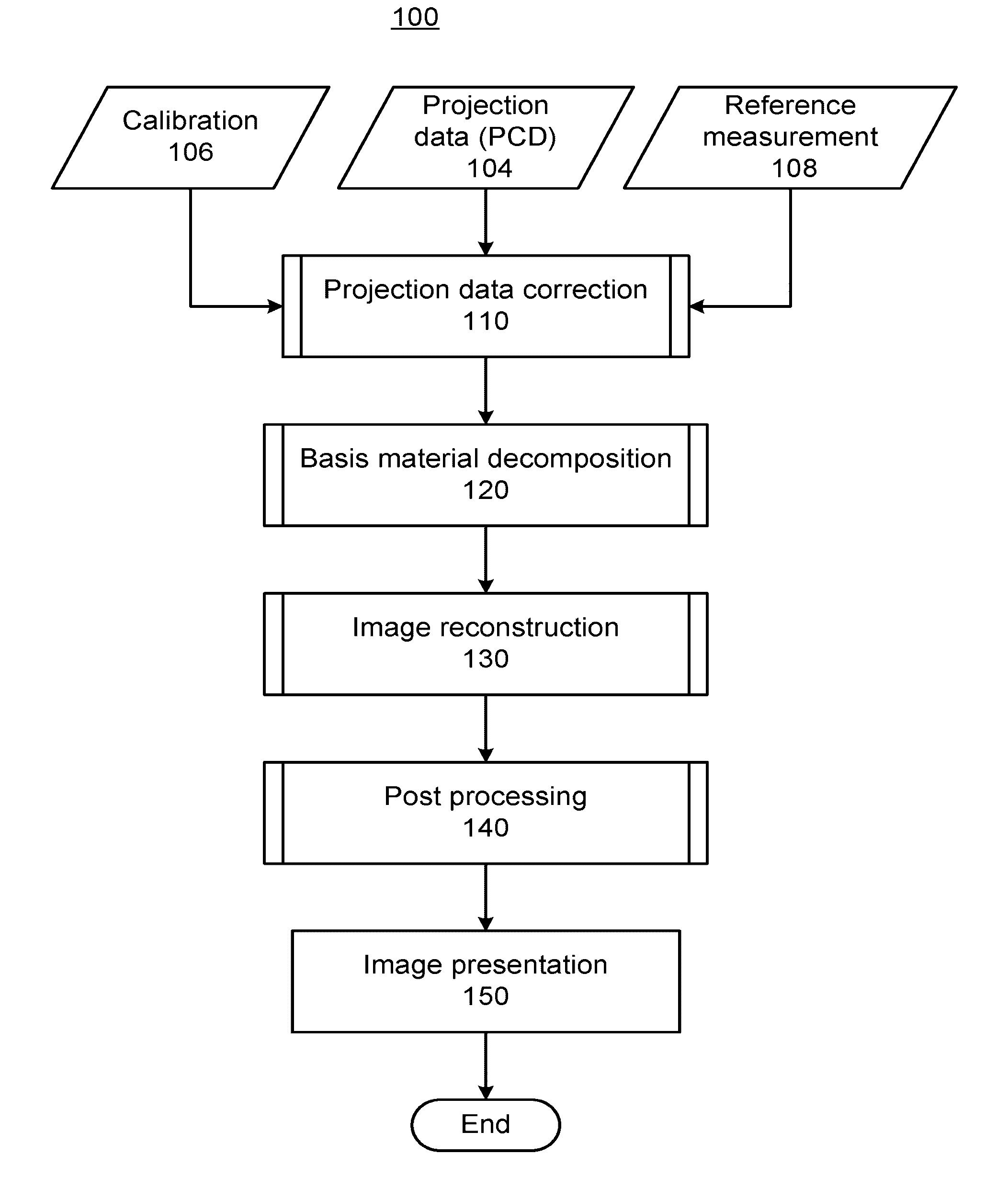
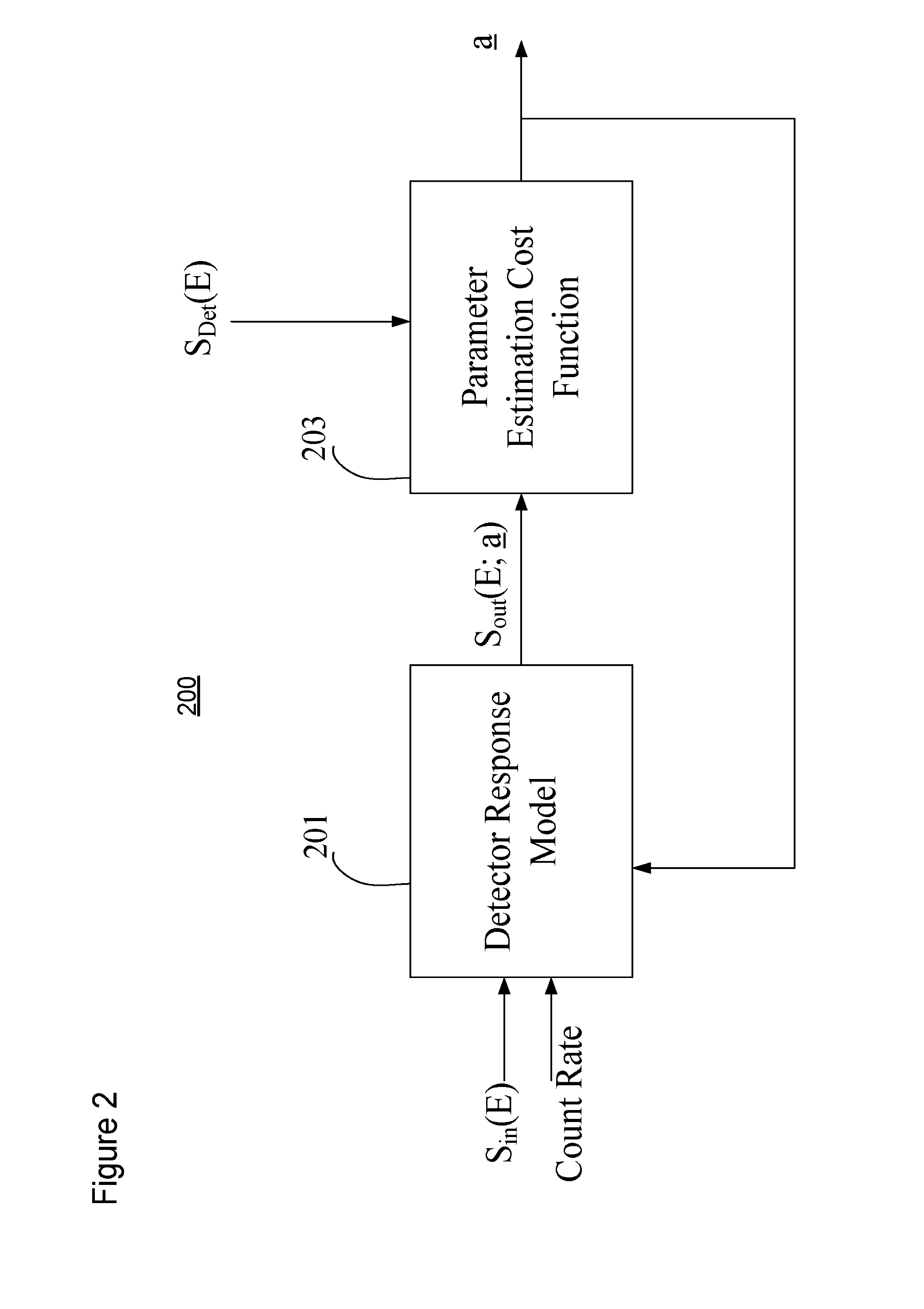
Pre-reconstruction calibration, data correction, and material decomposition method and apparatus for photon-counting spectrally-resolving x-ray detectors and x-ray imaging
ActiveUS20160287205A1Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionFrequency spectrumImage post processing
An apparatus and method of processing X-ray projection data obtained using photon-counting detectors and having multiple spectral components. The processing of the projection data includes correcting for nonlinear detector response, where the detector response model includes: pileup, ballistic deficit effects, polar effects, and characteristic X-ray escape. The processing of the projection data also includes a material decomposition mapping the projection data from spectral components into material components corresponding to high-Z and low-Z materials. The material decomposition includes a noise balancing process where the allocation of spectral components between a high-energy and a low-energy combination of spectral components is adjusted such that both high- and low-energy components have signal-to-noise ratios of similar magnitude. For computed tomography (CT) applications, material decomposition can be followed by image reconstruction and then image post-processing and presentation. For non-CT applications, material decomposition can be followed by image post-processing and presentation.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com