Patents
Literature
2247 results about "Power factor corrector" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
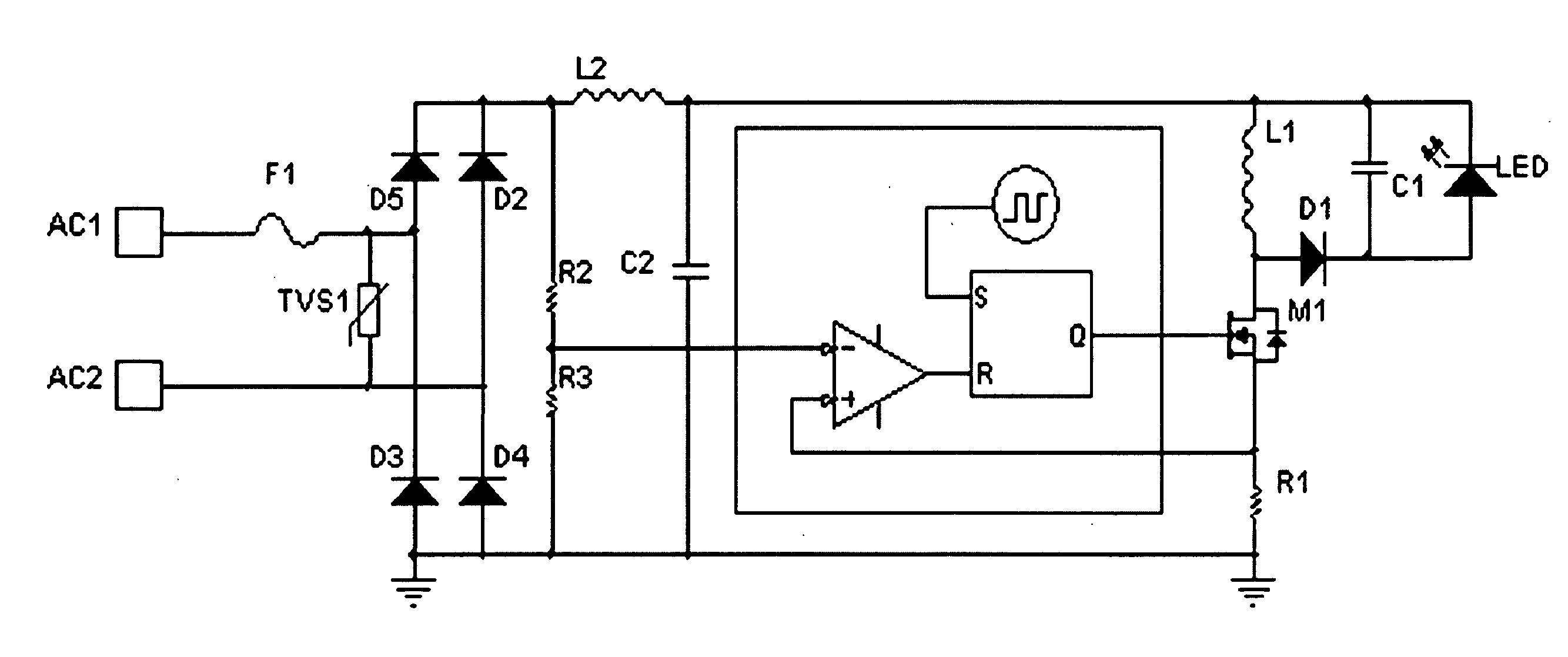
LED power supply with options for dimming
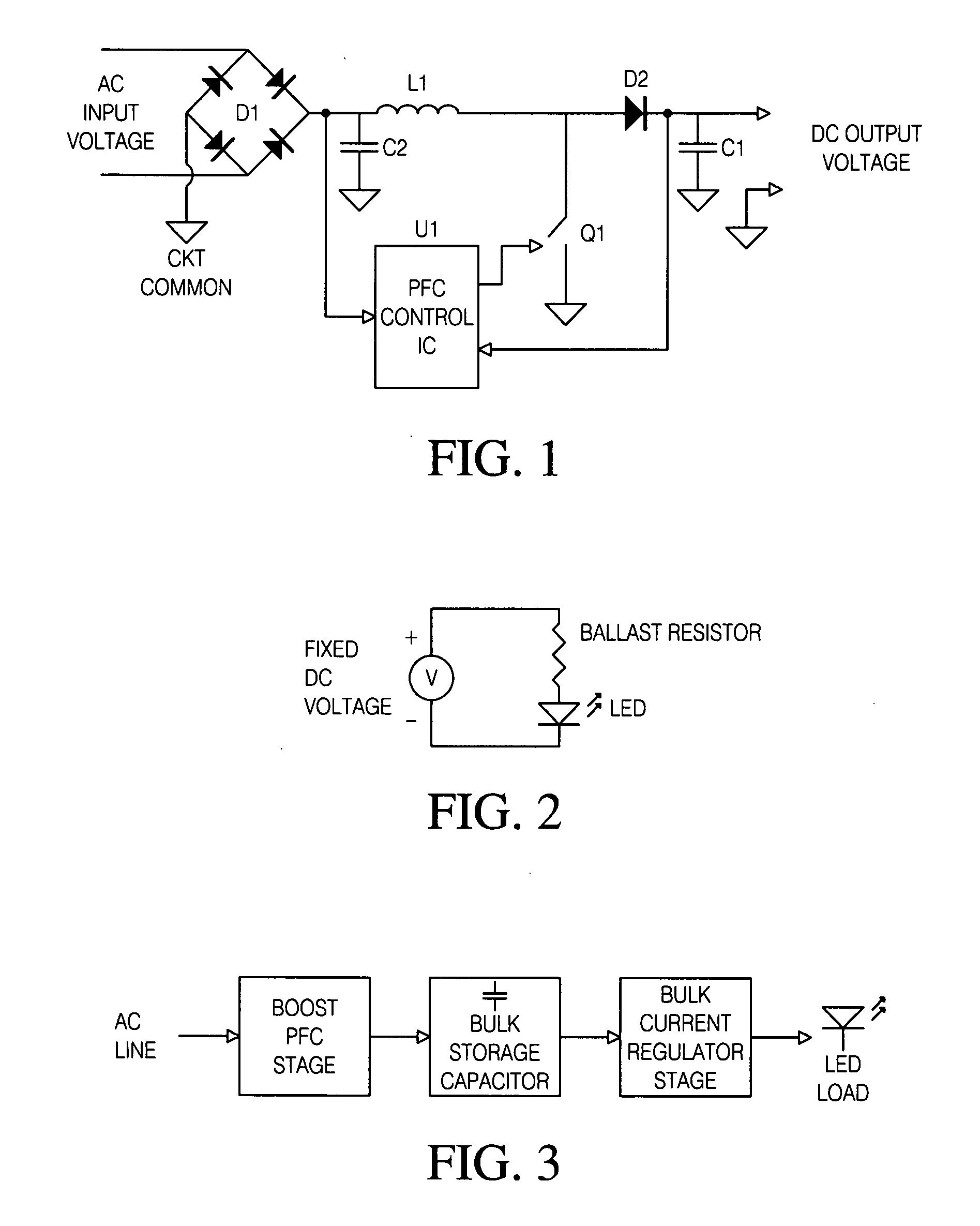
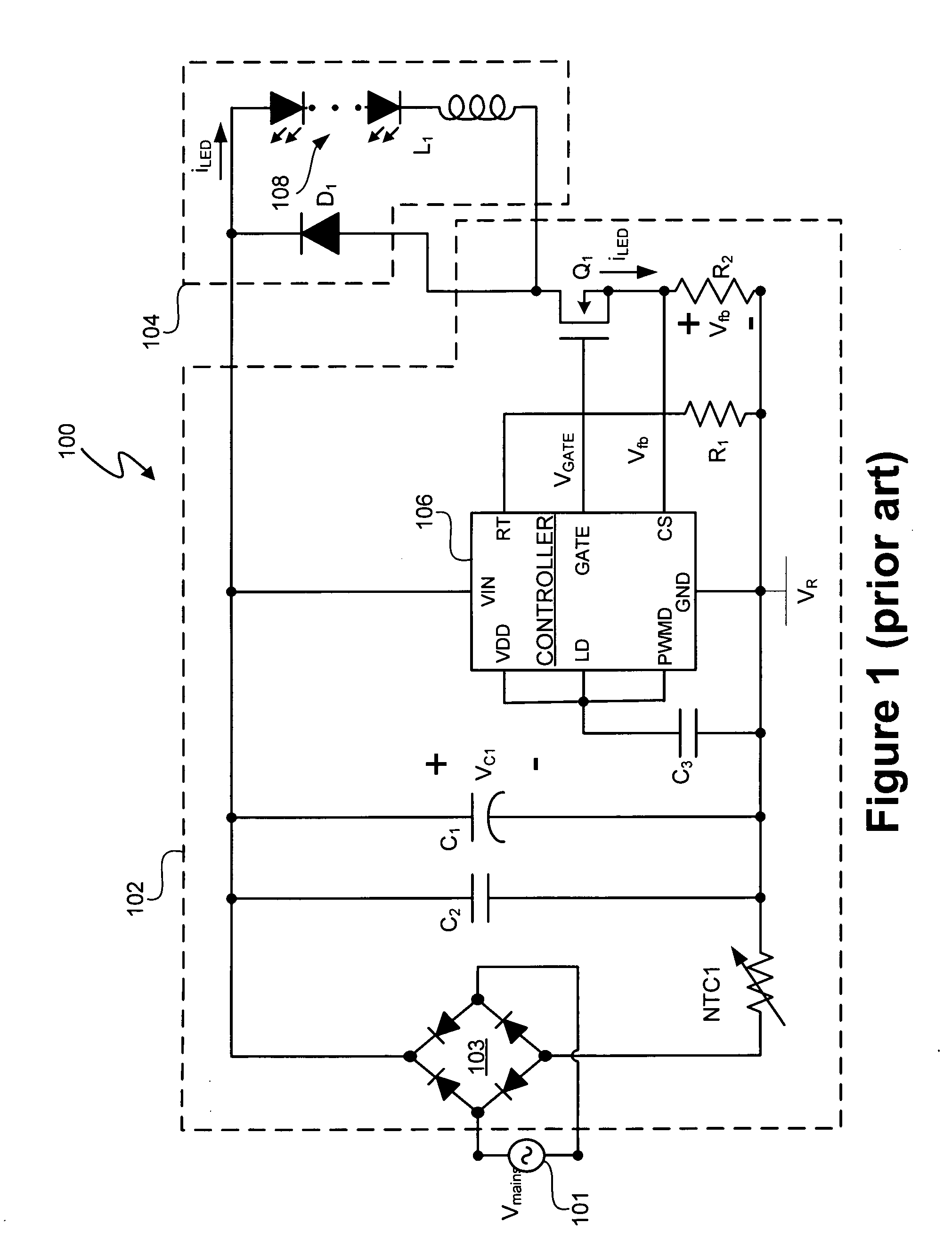
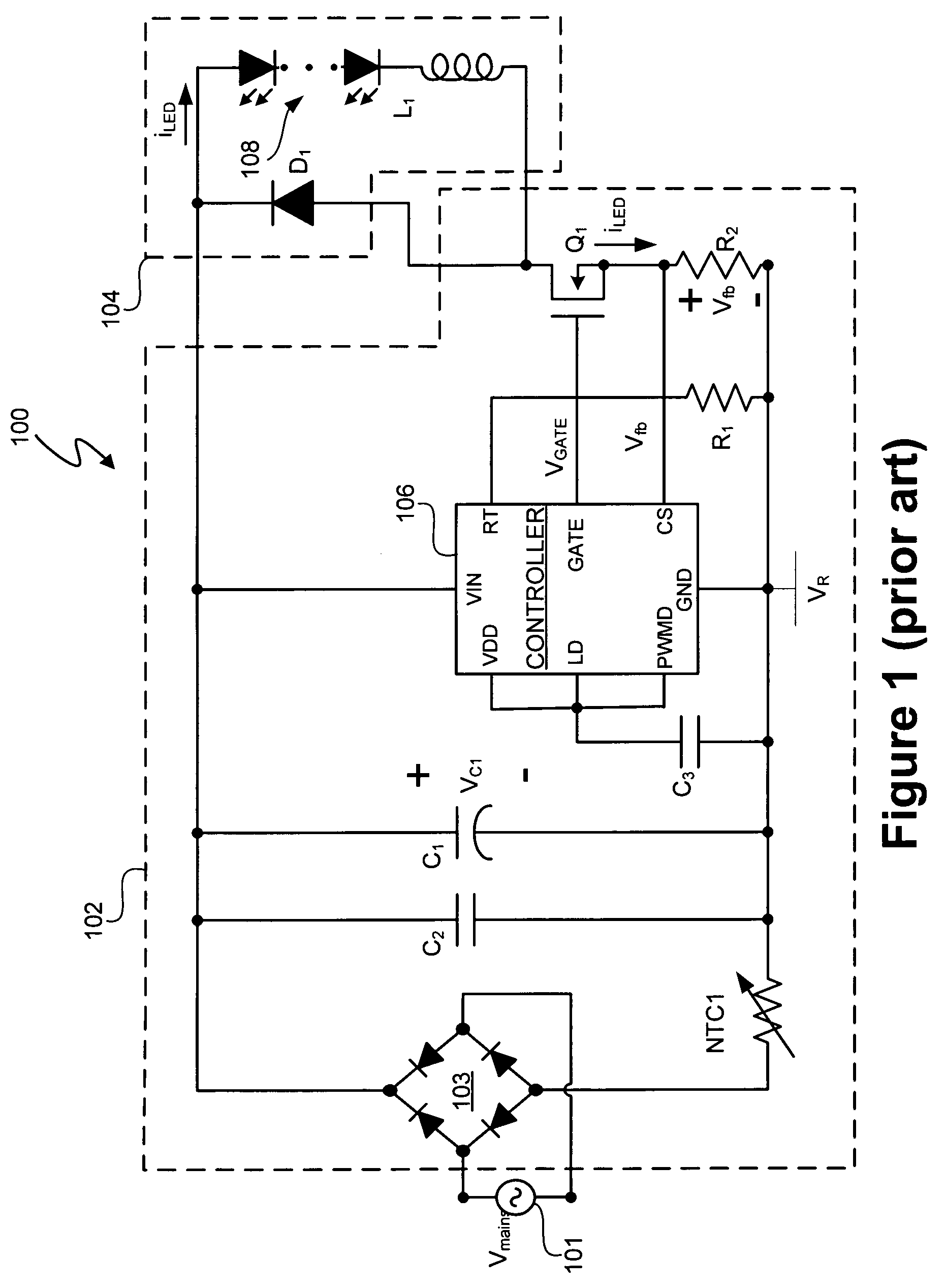
A LED driver circuit is disclosed that has the ability to drive a single series string of power LEDs. The LED driver circuit uses a single stage power converter to convert from a universal AC input to a regulated DC current. This single stage power converter current is controlled by a power factor correction unit. Furthermore, the LED driver circuit contains a galvanic isolation barrier that isolates an input, or primary, section from an output, or secondary, section. The LED driver circuit can also include a dimming function, a red, green, blue output function, and a control signal that indicates the LED current and is sent from the secondary to the primary side of the galvanic barrier.
Owner:KASTNER MARK ALLEN
Power control system for current regulated light sources
ActiveUS20080224636A1Electroluminescent light sourcesDc-dc conversionPower control systemEffect light
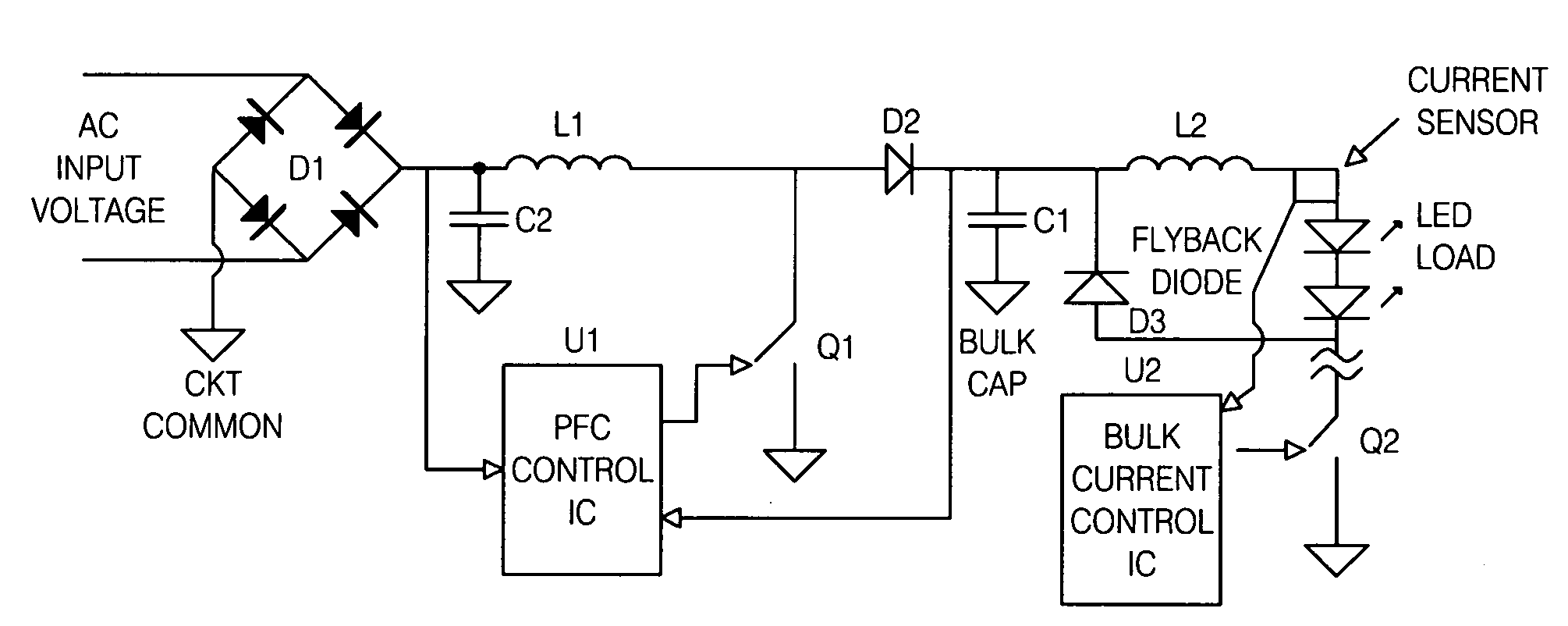
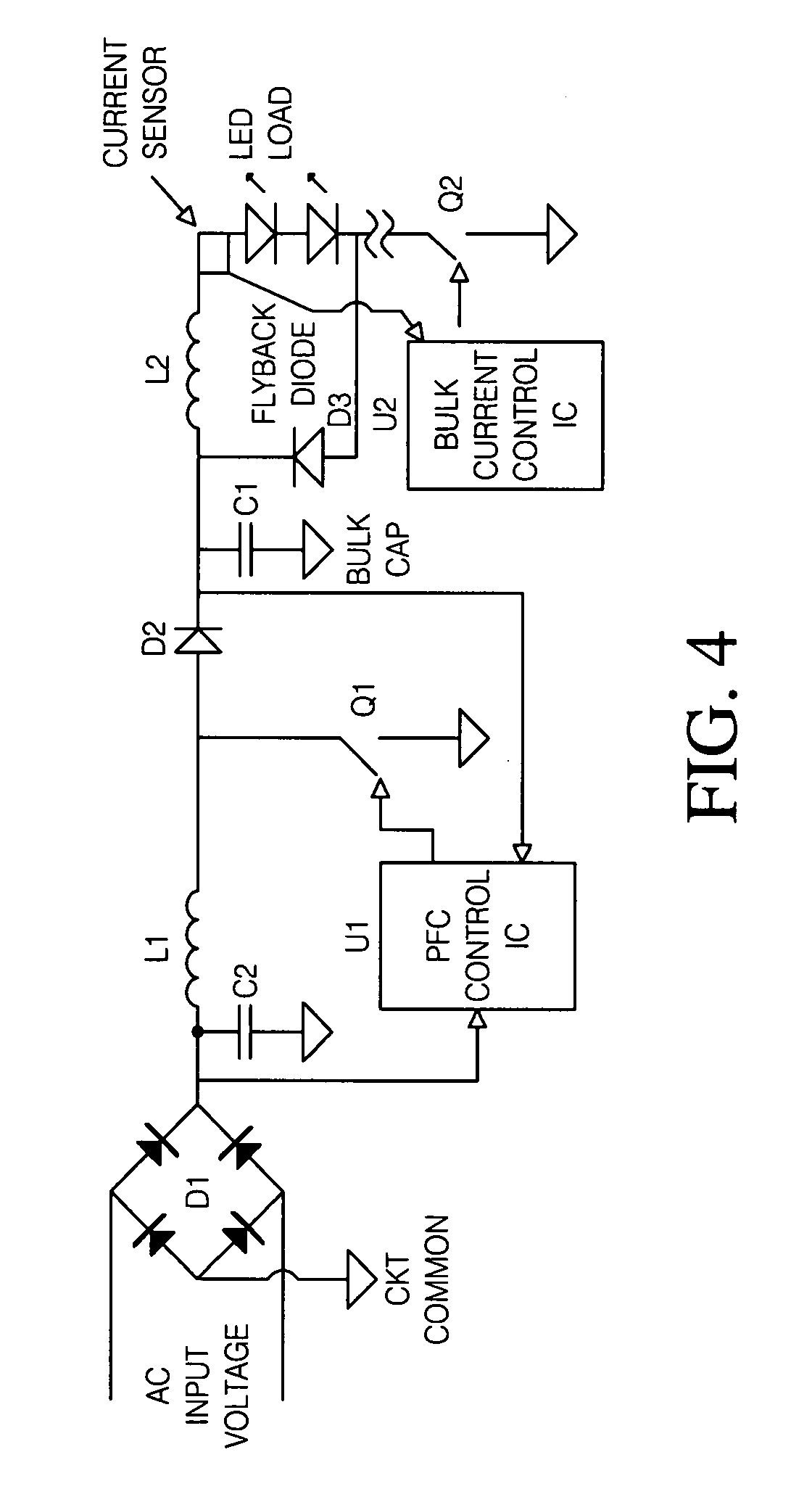
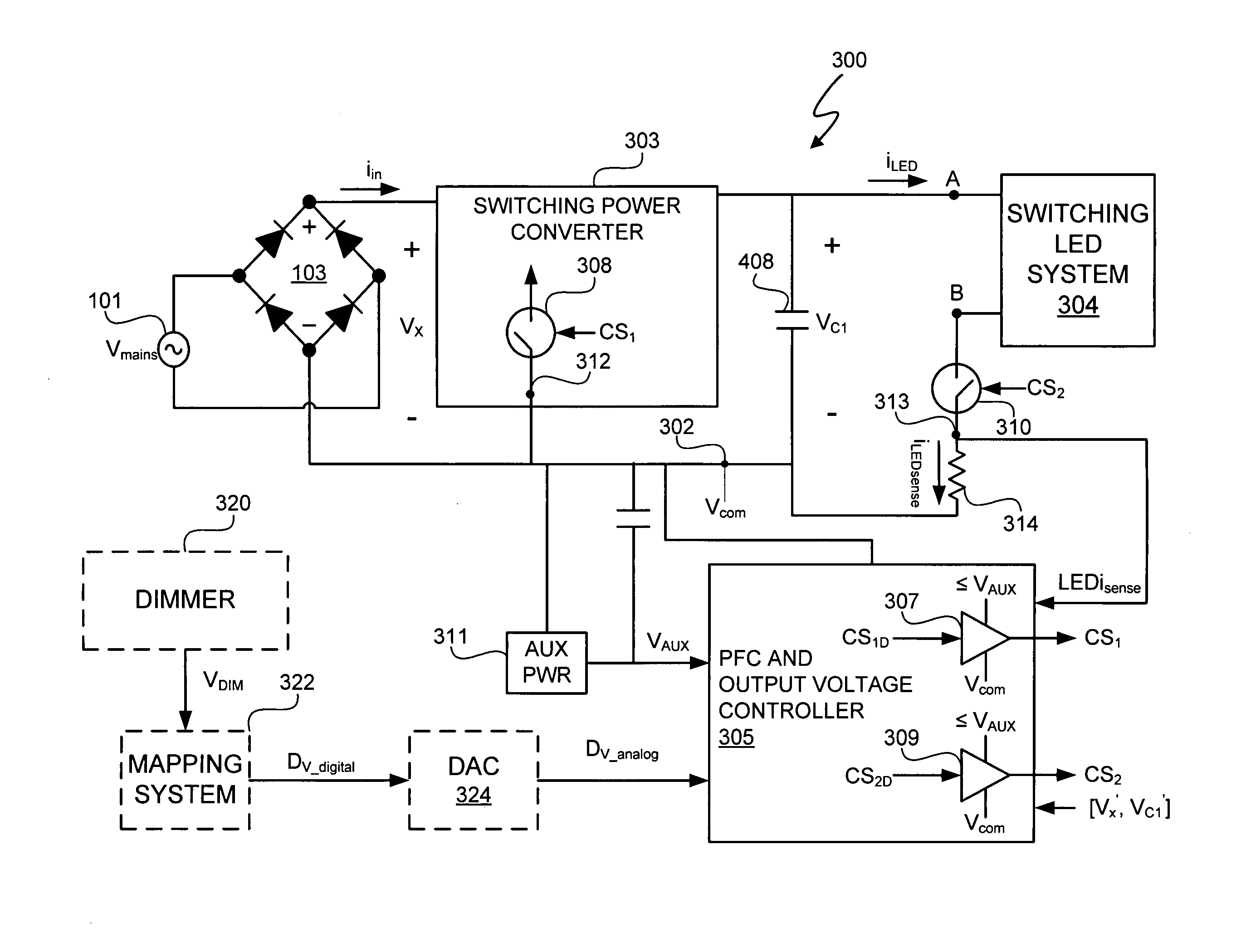
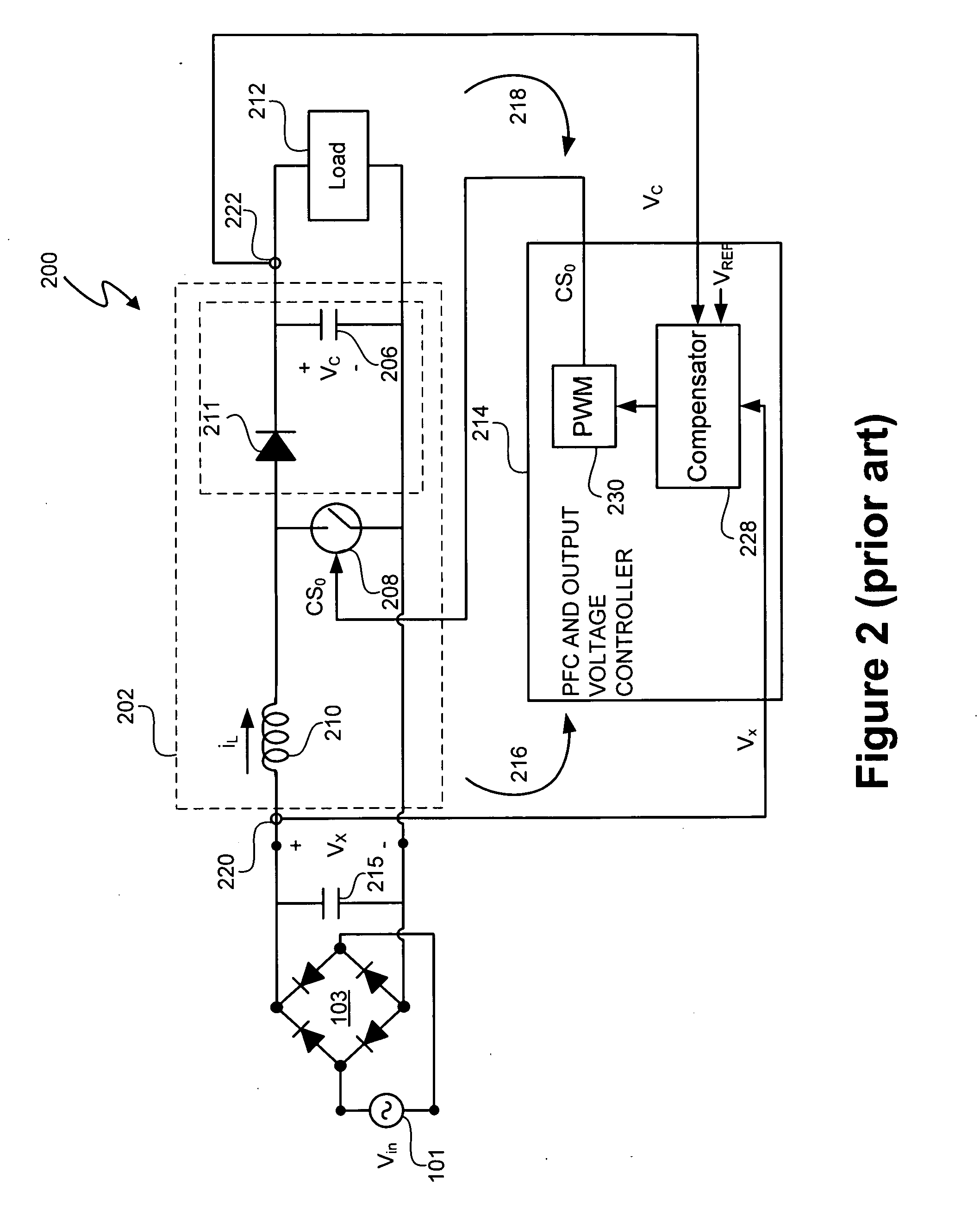
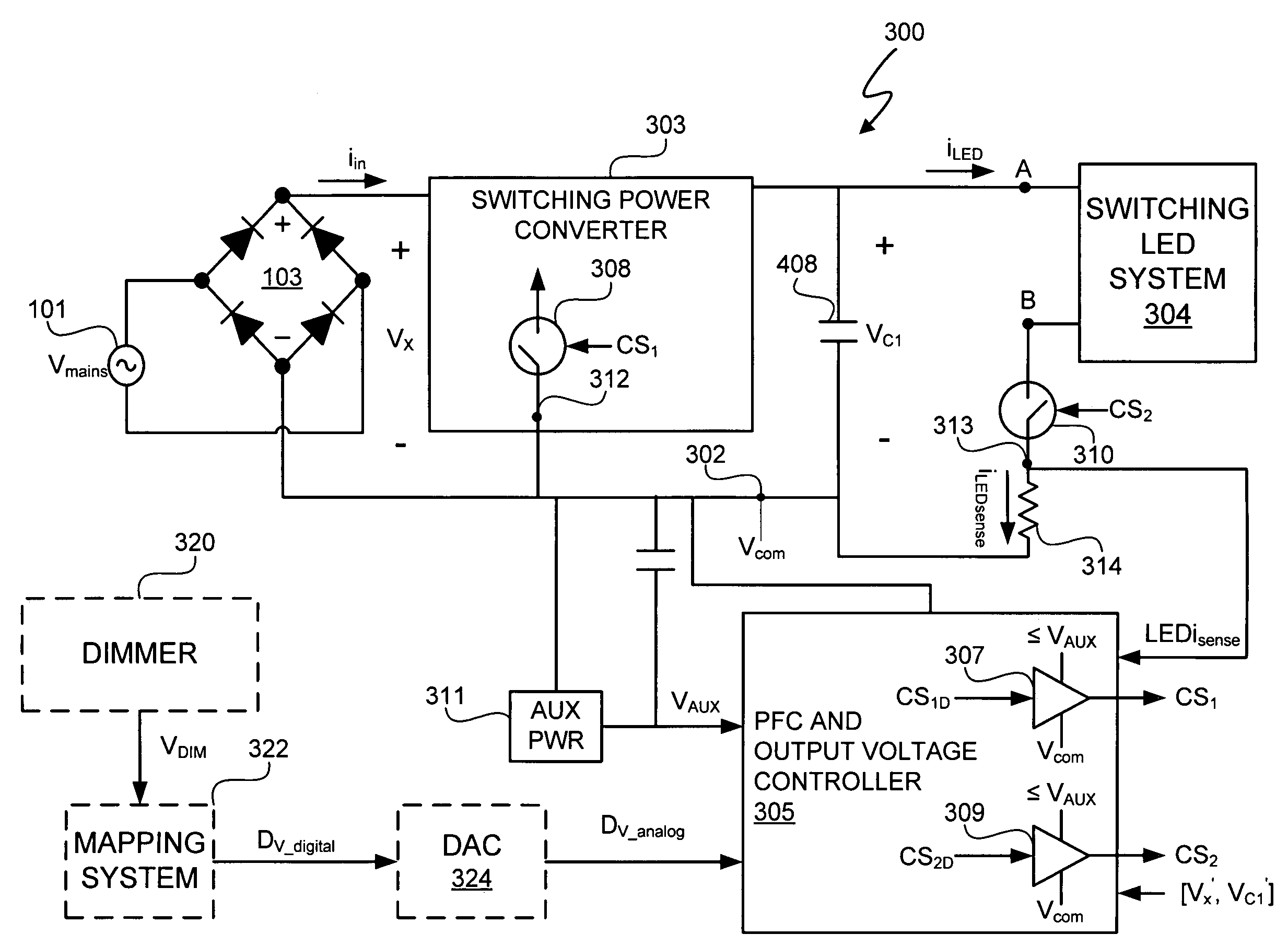
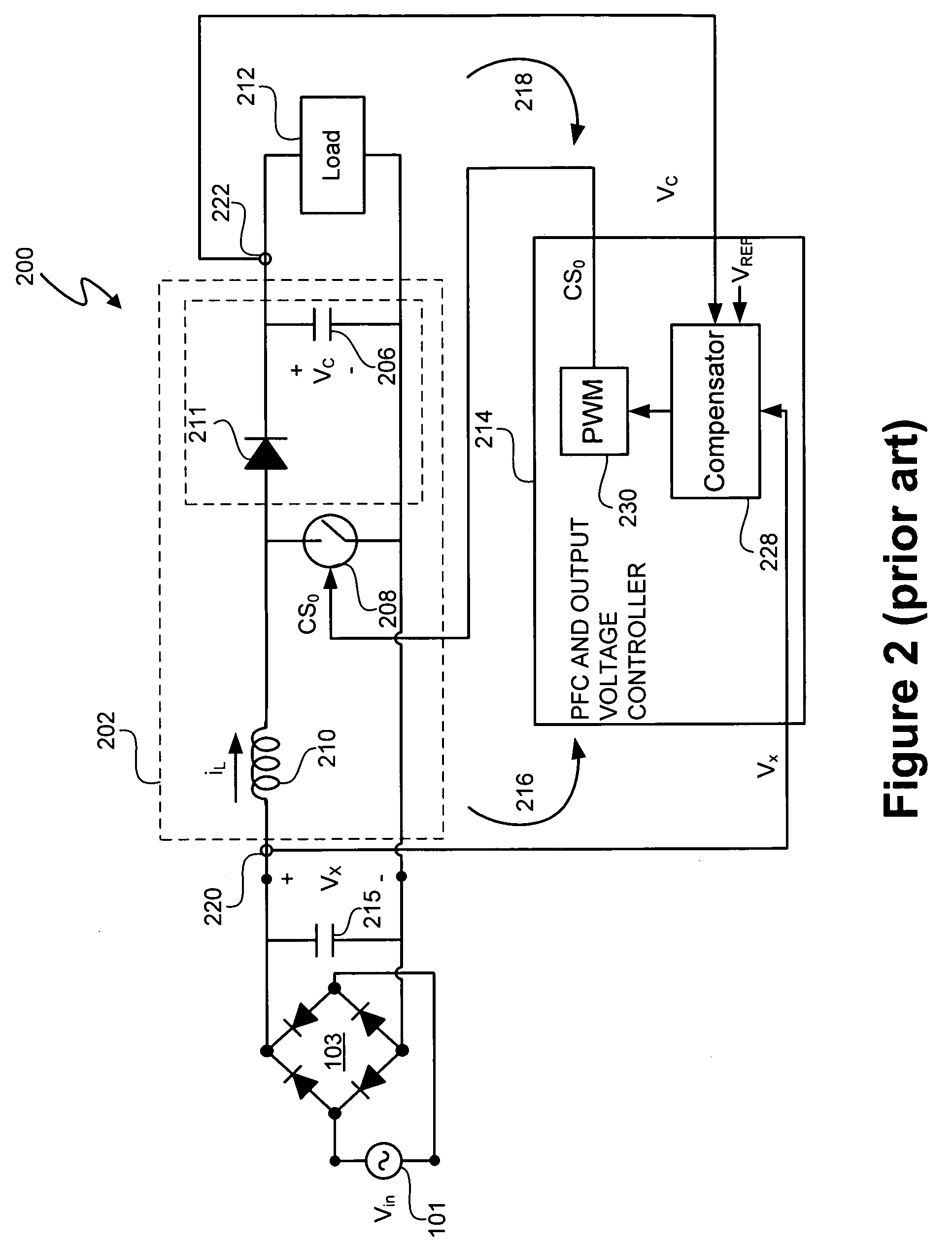
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system includes a PFC and output voltage controller and a LED lighting power system. The controller advantageously operates from an auxiliary voltage less than a link voltage generated by the LED lighting power system. The common reference voltage allows all the components of lighting system to work together. A power factor correction switch and an LED drive current switch are coupled to the common reference node and have control node-to-common node, absolute voltage that allows the controller to control the conductivity of the switches. The LED lighting system can utilize feed forward control to concurrently modify power demand by the LED lighting power system and power demand of one or more LEDs. The LED lighting system can utilize a common current sense device to provide a common feedback signal to the controller representing current in at least two of the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
Lighting system with power factor correction control data determined from a phase modulated signal
ActiveUS20080224629A1Lower effective resistanceElectroluminescent light sourcesSemiconductor lamp usageControl powerControl data
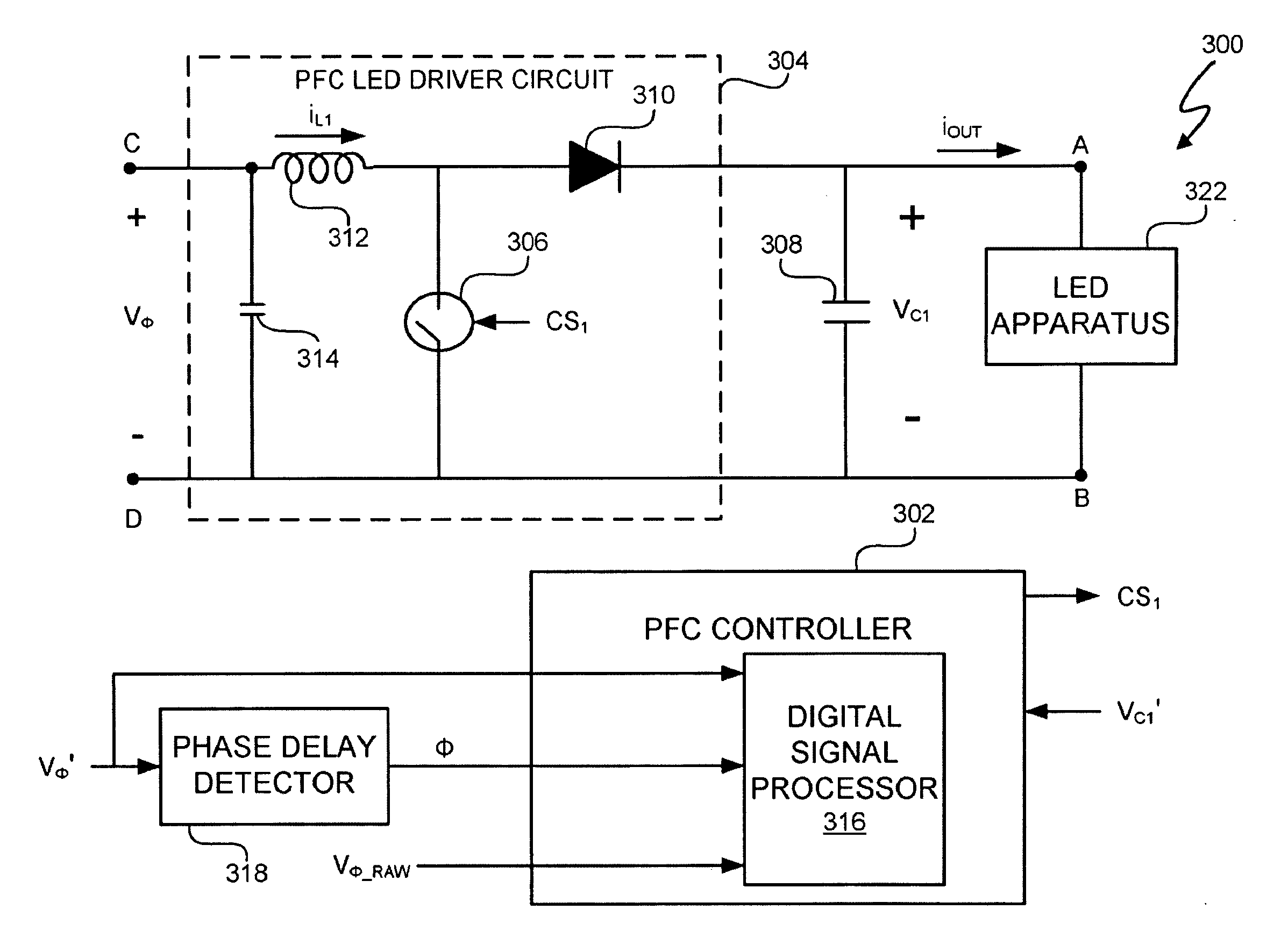
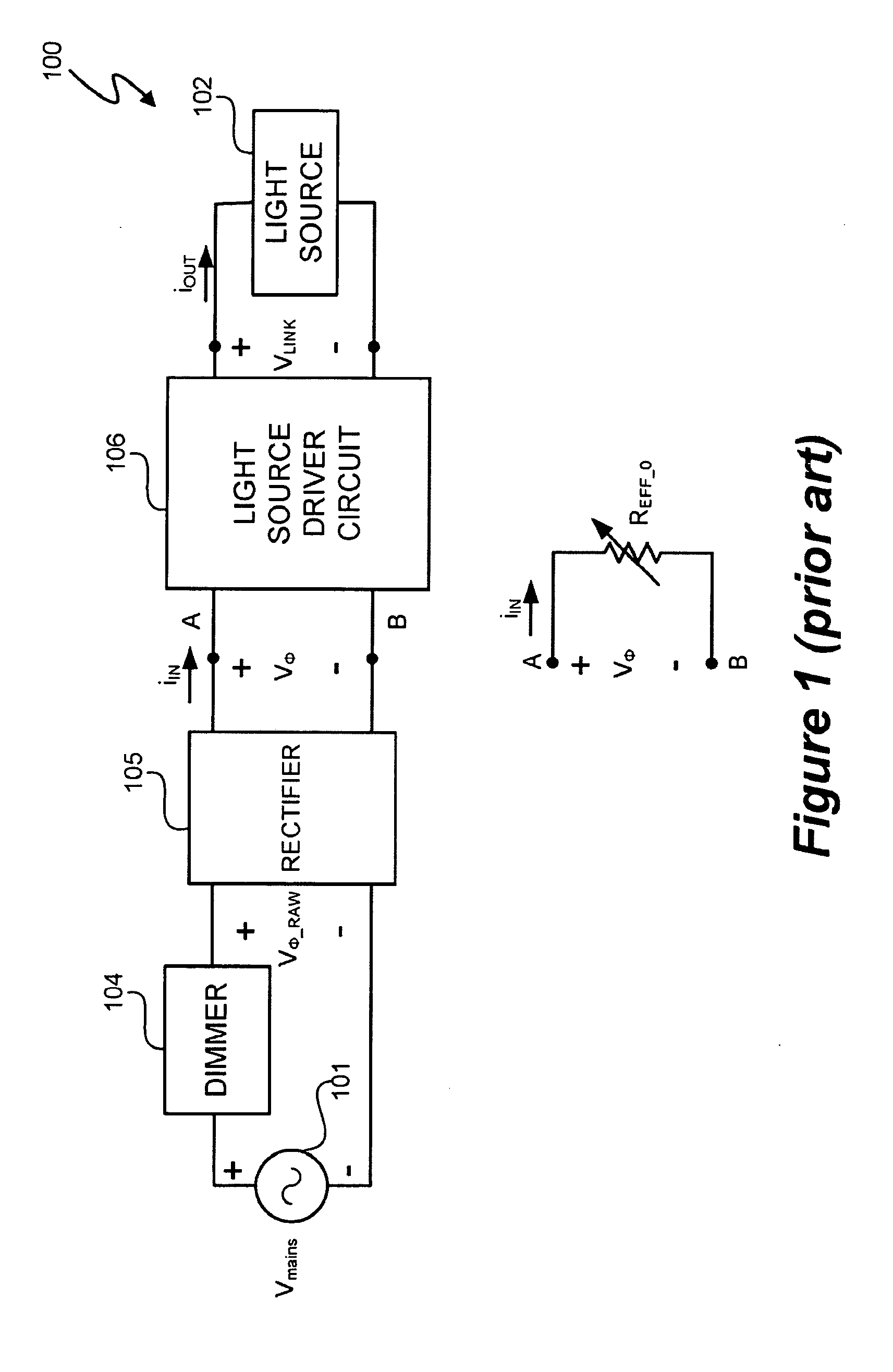
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system includes a power factor correction (PFC) controller that determines at least one power factor correction control parameter from phase delays of a phase modulated signal. In at least one embodiment, a peak voltage of the phase modulated signal is a PFC control parameter used bit the PFC controller to control power factor correction and generation of a link voltage by a PFC LED driver circuit. The phase delays are related to a peak voltage of the phase modulated signal. Thus, in at least one embodiment, detecting the phase delay in one or more cycles of the phase modulated signal allows the PFC controller to determine the peak voltage of the phase modulated signal.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
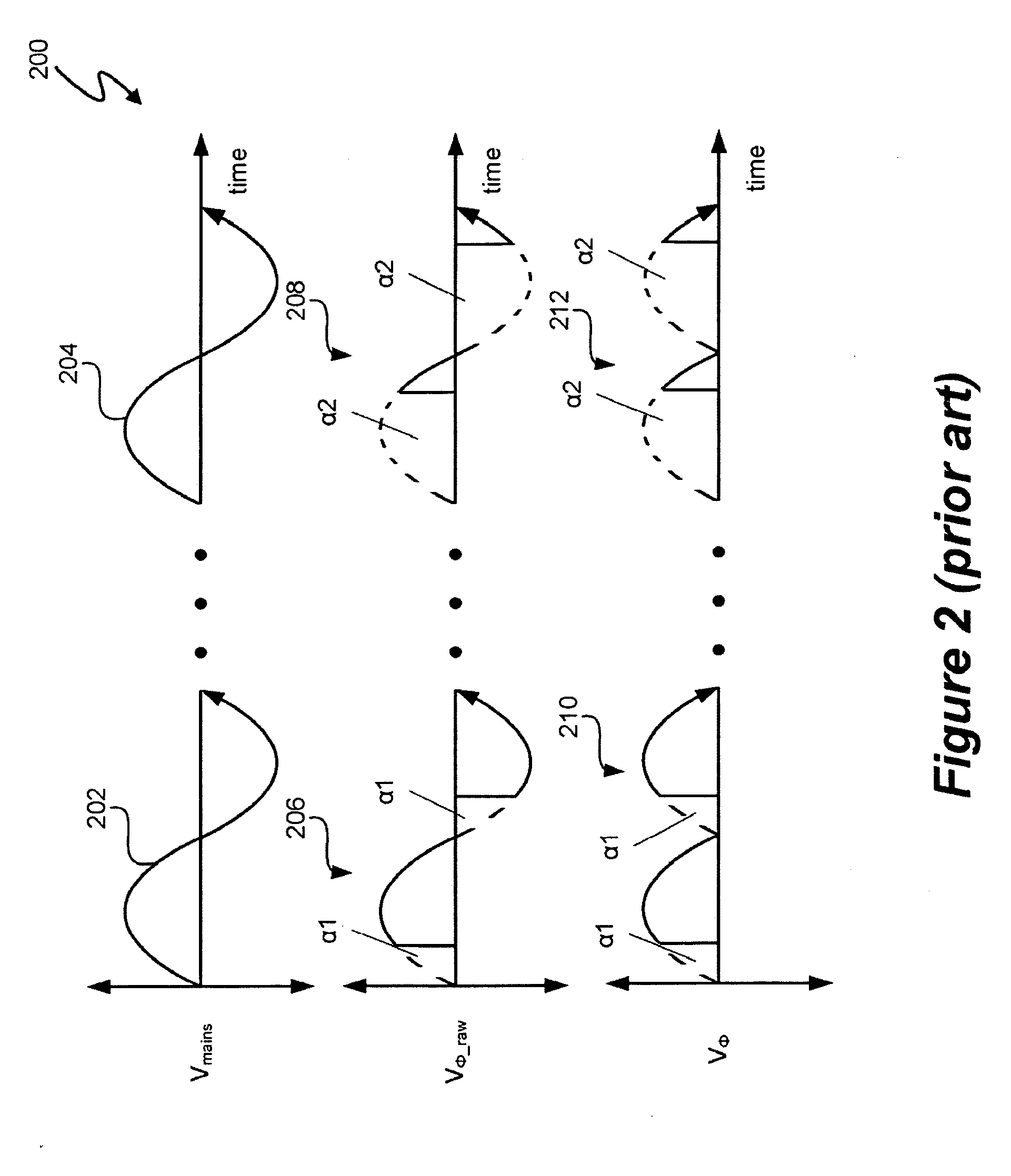
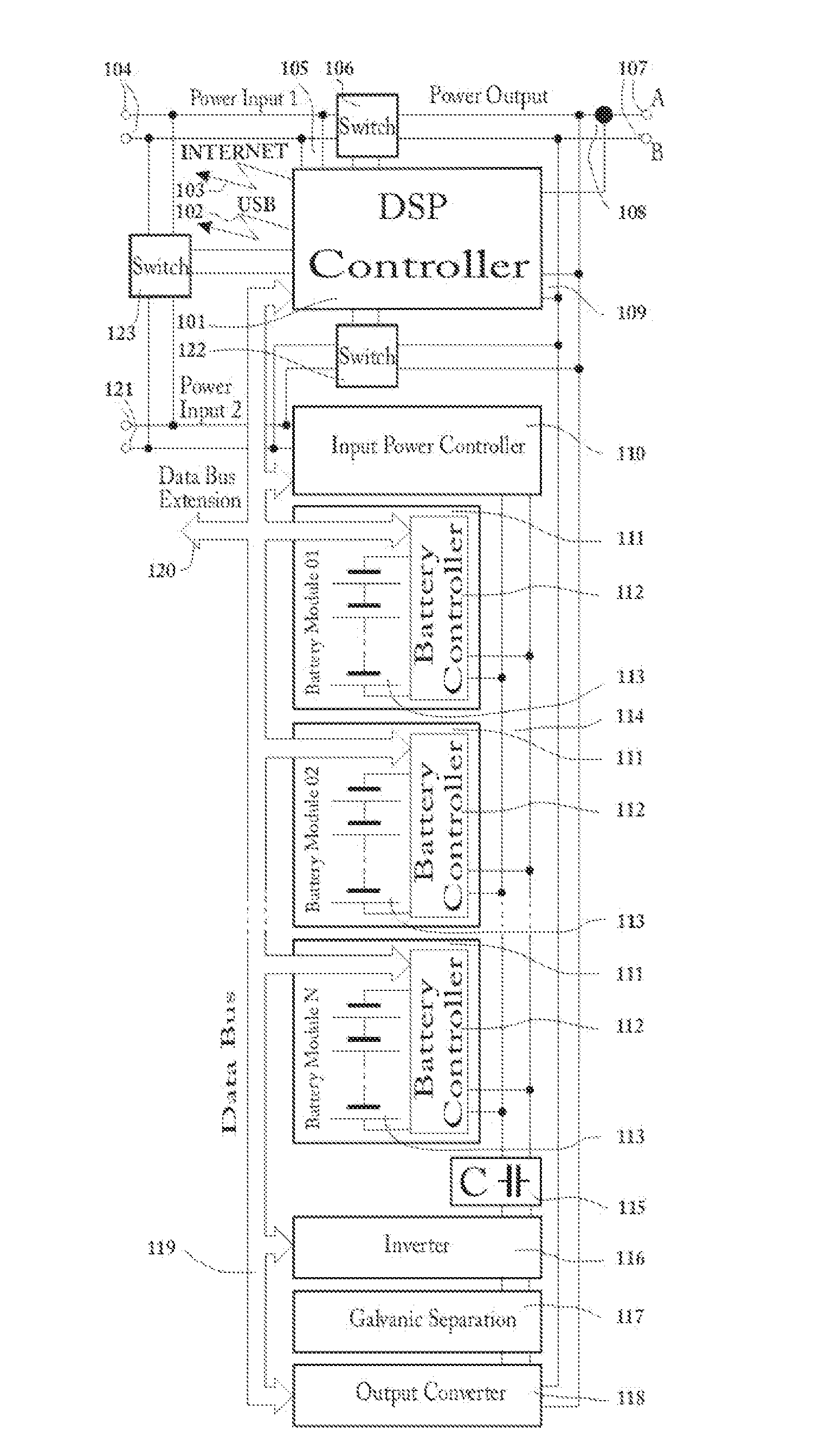
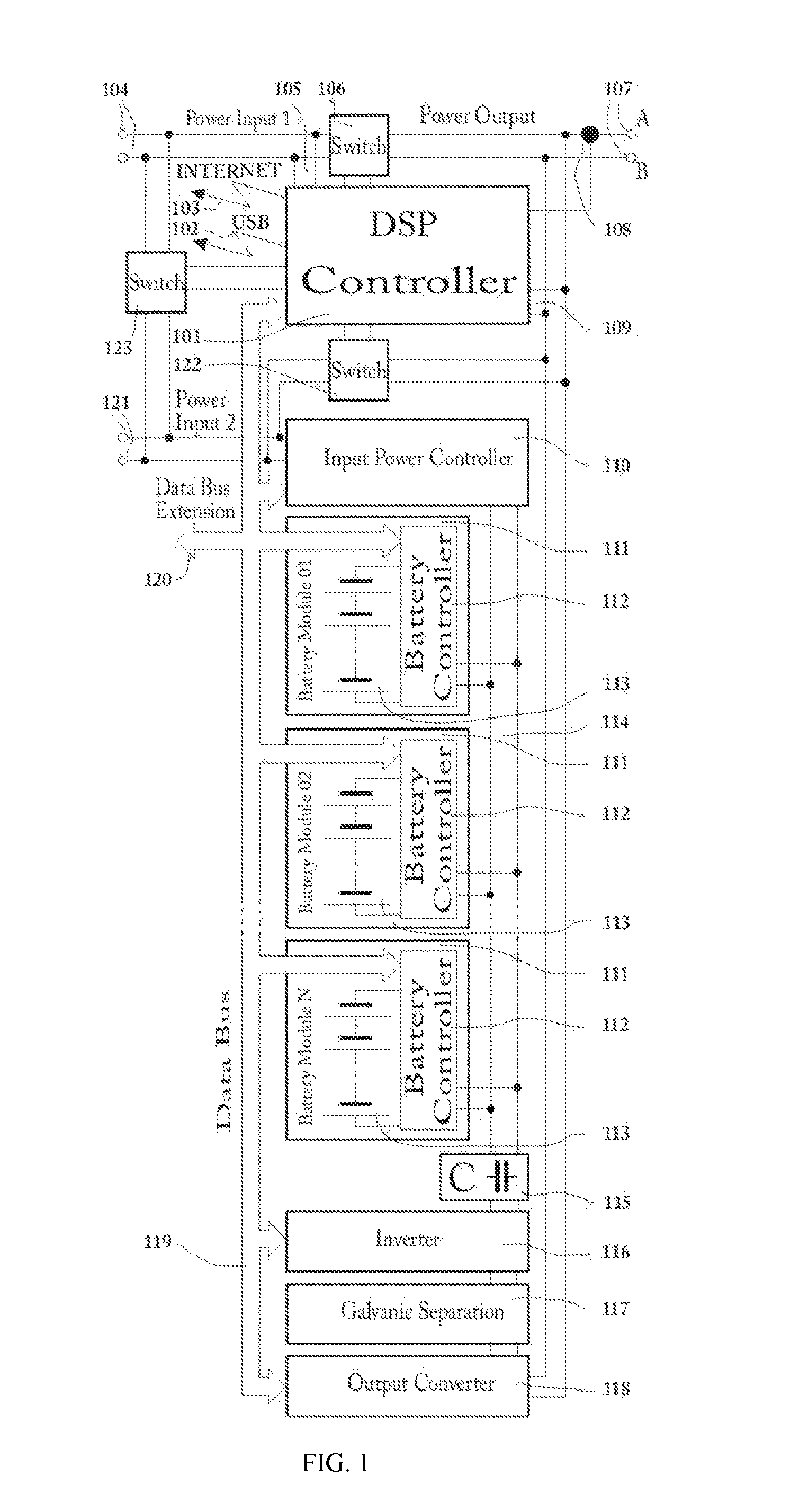
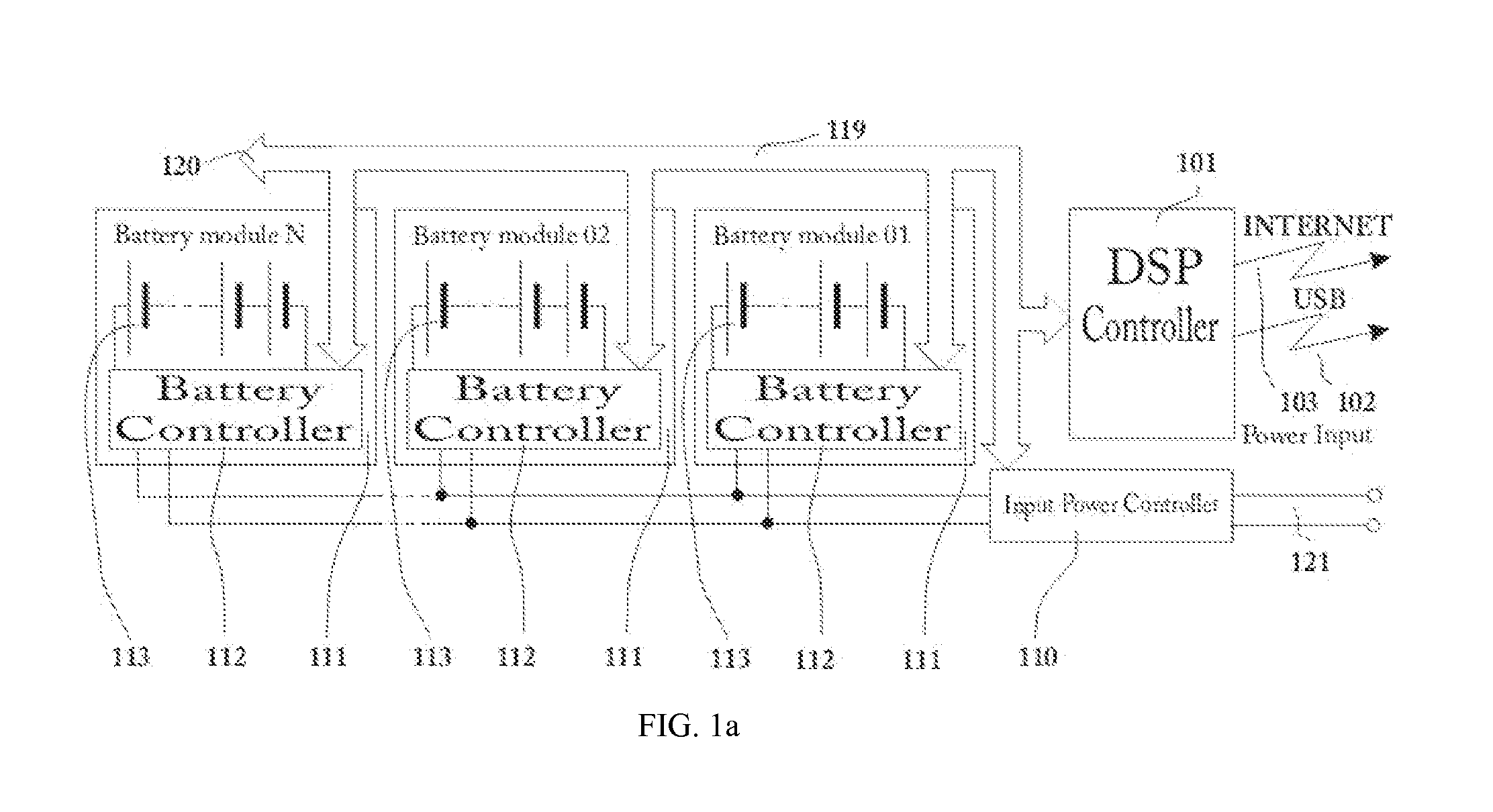
Multipurpose, universal Converter with battery control and real-time Power Factor Correction.
InactiveUS20130049471A1Fast feedbackAvoid distortionEnergy industryAc-dc network circuit arrangementsTotal harmonic distortionSmart grid
The Electric Power Converter has the qualifications for an uninterruptable power supply, battery management, energy conversion, micro-grid formation, Power Factor Correction including Total Harmonic Distortion correction in real time. Uninterruptable power supply's use is for always-on, real-time, all-time, reduced distortion with functions of load reduction and management during peak load events. The Electric Power Converter as well has the ability to provide maintenance for most types of batteries including charging and discharge regiments to increase the overall lifetime of a battery, the maintenance, incorporating restorative functions that can refurbish dead batteries or can further increase the overall efficiency and useful function of weaker / aged / defective batteries. Energy conversion capabilities allow for the conversion of AC or DC to AC or DC with high efficiency and ability to actively vary the frequency in accordance to the required parameters. The Electric Power Converter is able to establish and sustain a micro-grid with multiple and varying sources of power generation and load conditions. The Electric Power Converter is achieving dynamic, real-time, interactive Power Factor Correction (PFC) function with advanced voltage harmonic distortion correction with a high efficiency ratio. The Electric Power converter is designed to function with the emerging Smart Grid technologies and provide an overall higher level of operating efficiency and higher quality of electrical power.
Owner:3DFS L L C
High efficiency light source with integrated ballast
InactiveUS20100207536A1Improve circuit efficiencyImproving driver efficiencyElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesFrequency spectrumCharge current
The present invention relates to regulated power supplies or ballasts integrated with an LED light source. The invention provides a power factor correction scheme producing a greater circuit power factor and improved frequency spectrum characteristics, in which a voltage corresponding to the instantaneous inductor current is sampled and compared to a scaled sample of the rectified input AC line voltage. The line voltage sample modulates the inductor peak charge current in the envelope of the rectified AC voltage waveform. This drives the LED output voltage at a frequency of twice the input line voltage frequency, such that no flicker is perceived in the light output because the persistence in LED phosphor assists in averaging the flux output.
Owner:LIGHTING SCI GROUP
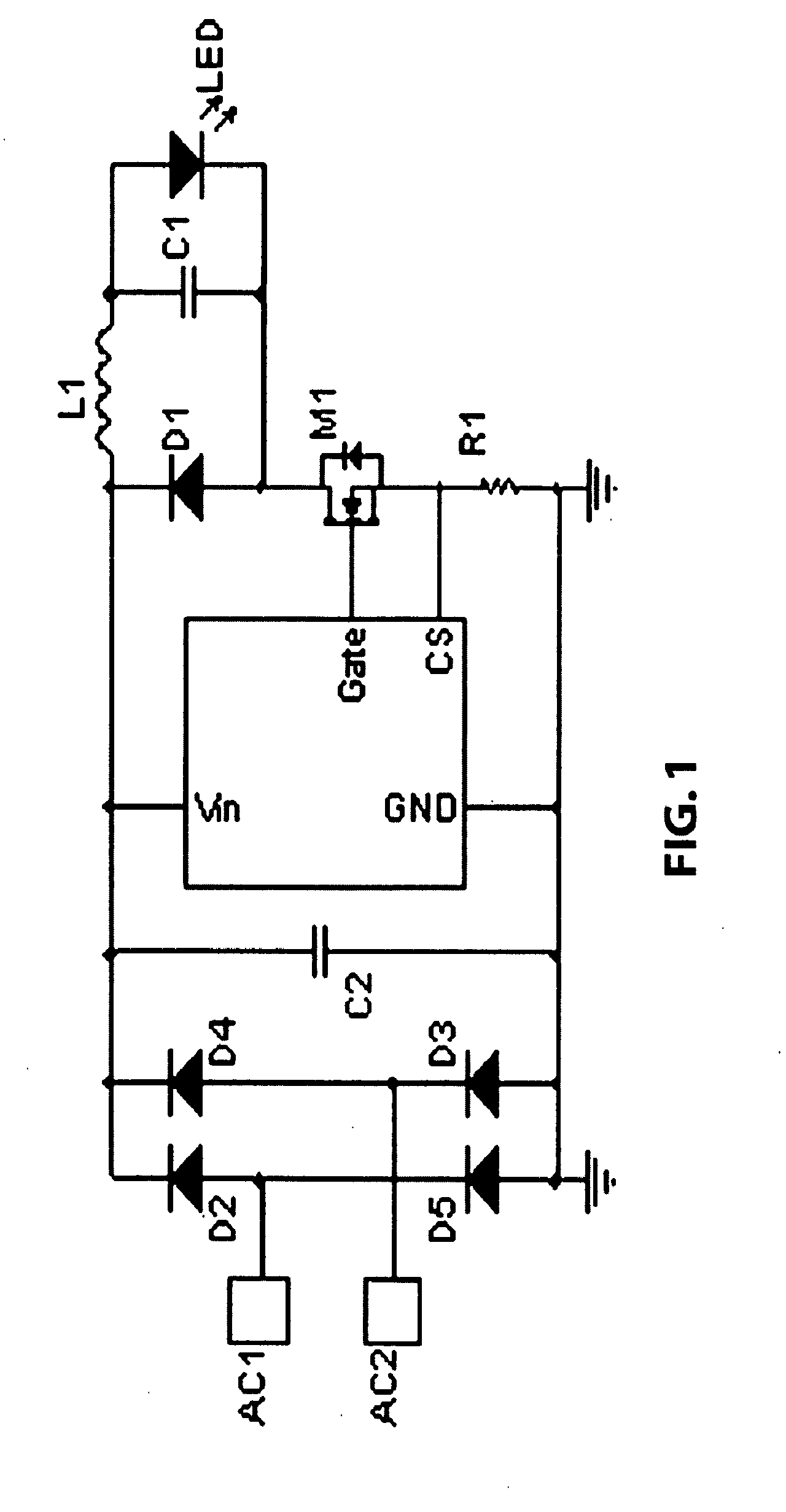
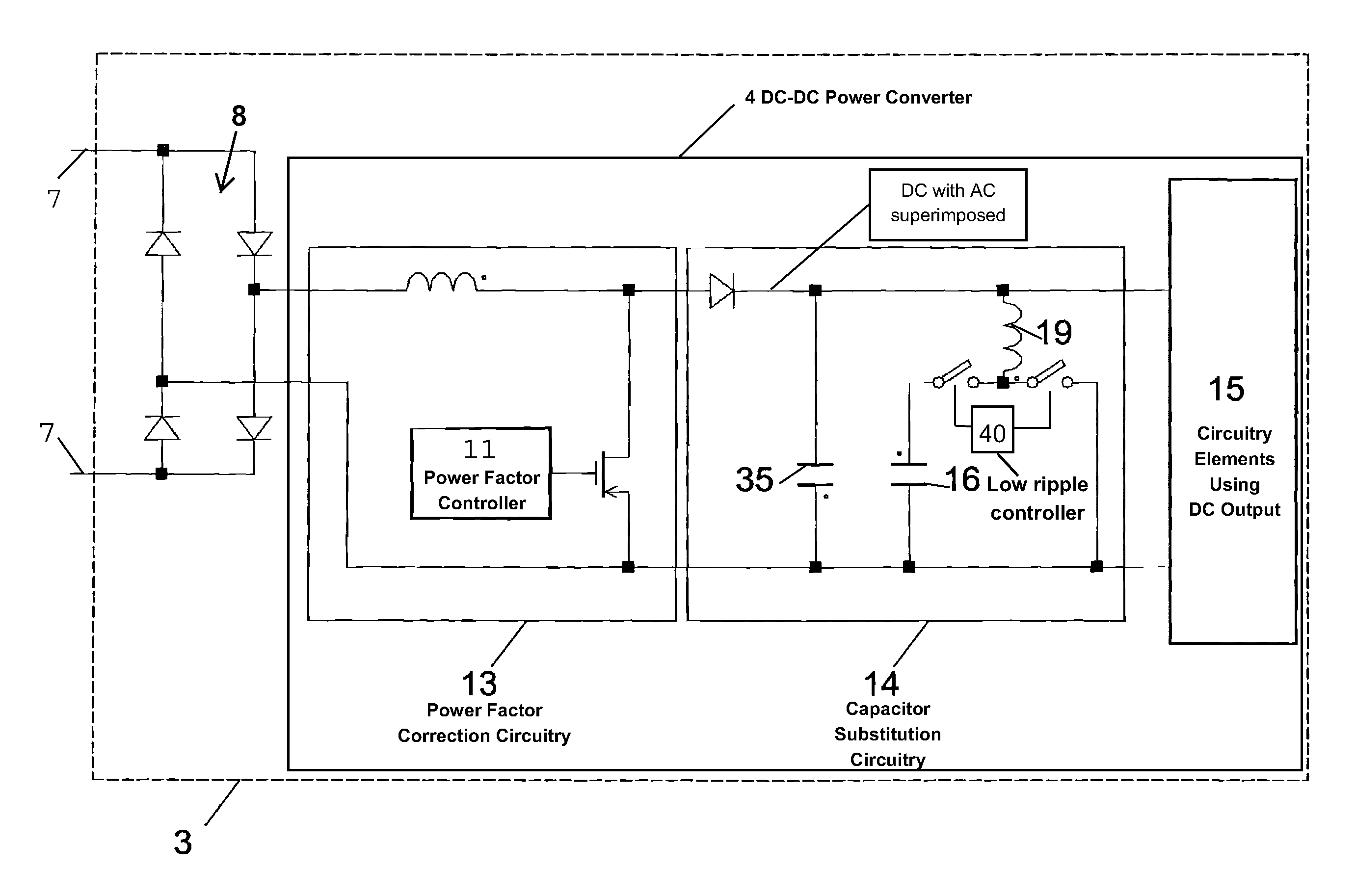
Solar power capacitor alternative switch circuitry system for enhanced capacitor life
InactiveUS7919953B2Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBoost controllerEngineering
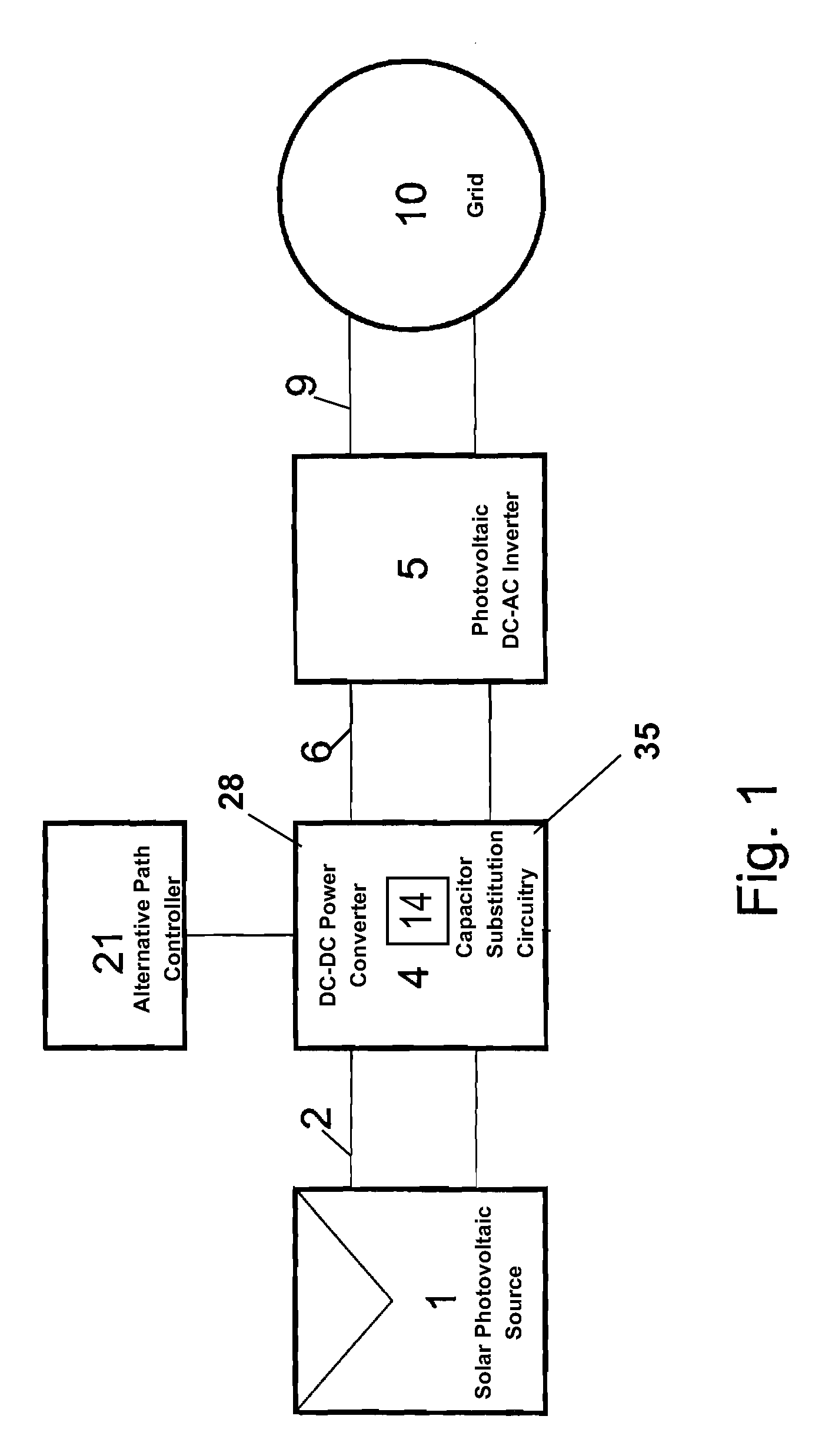
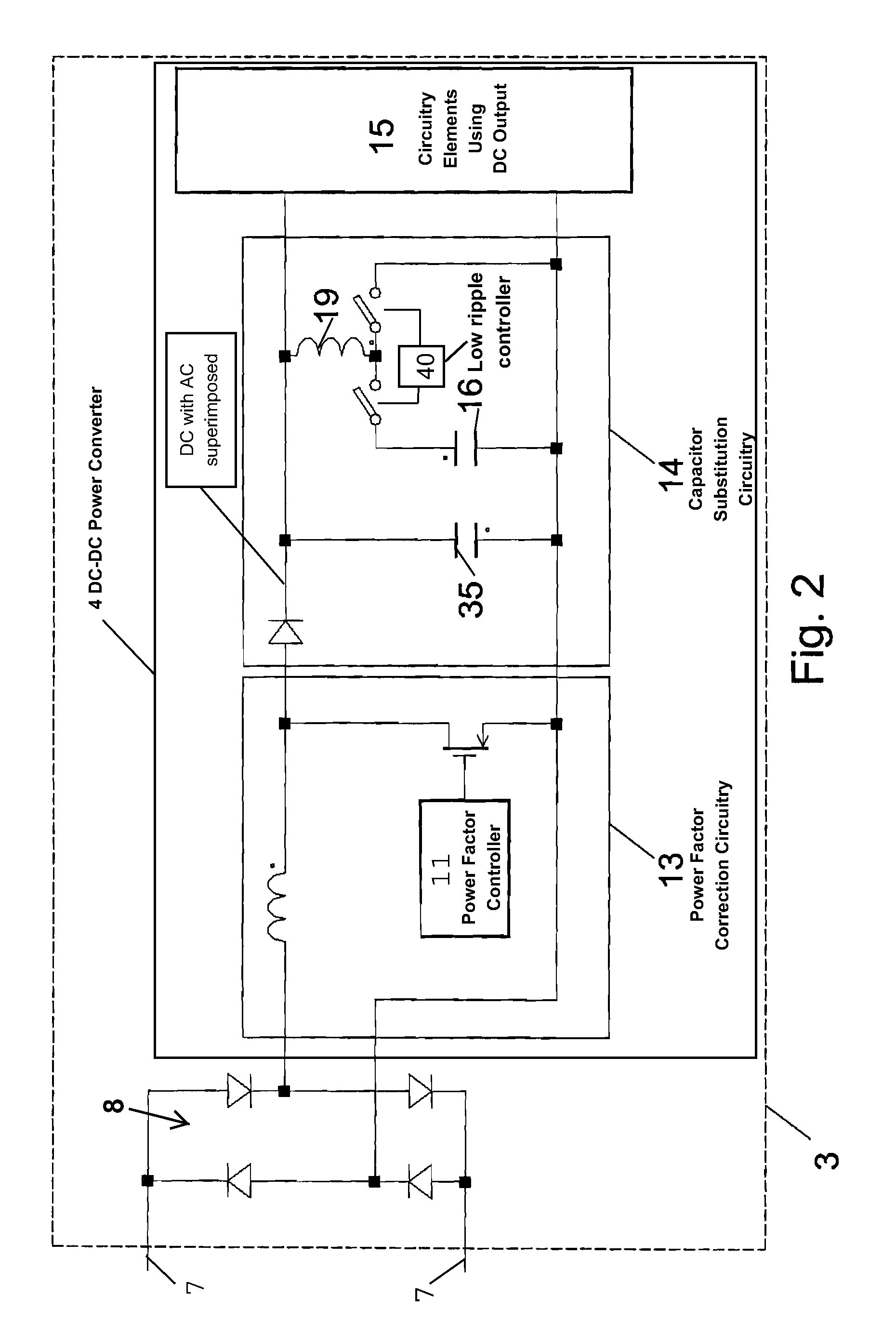
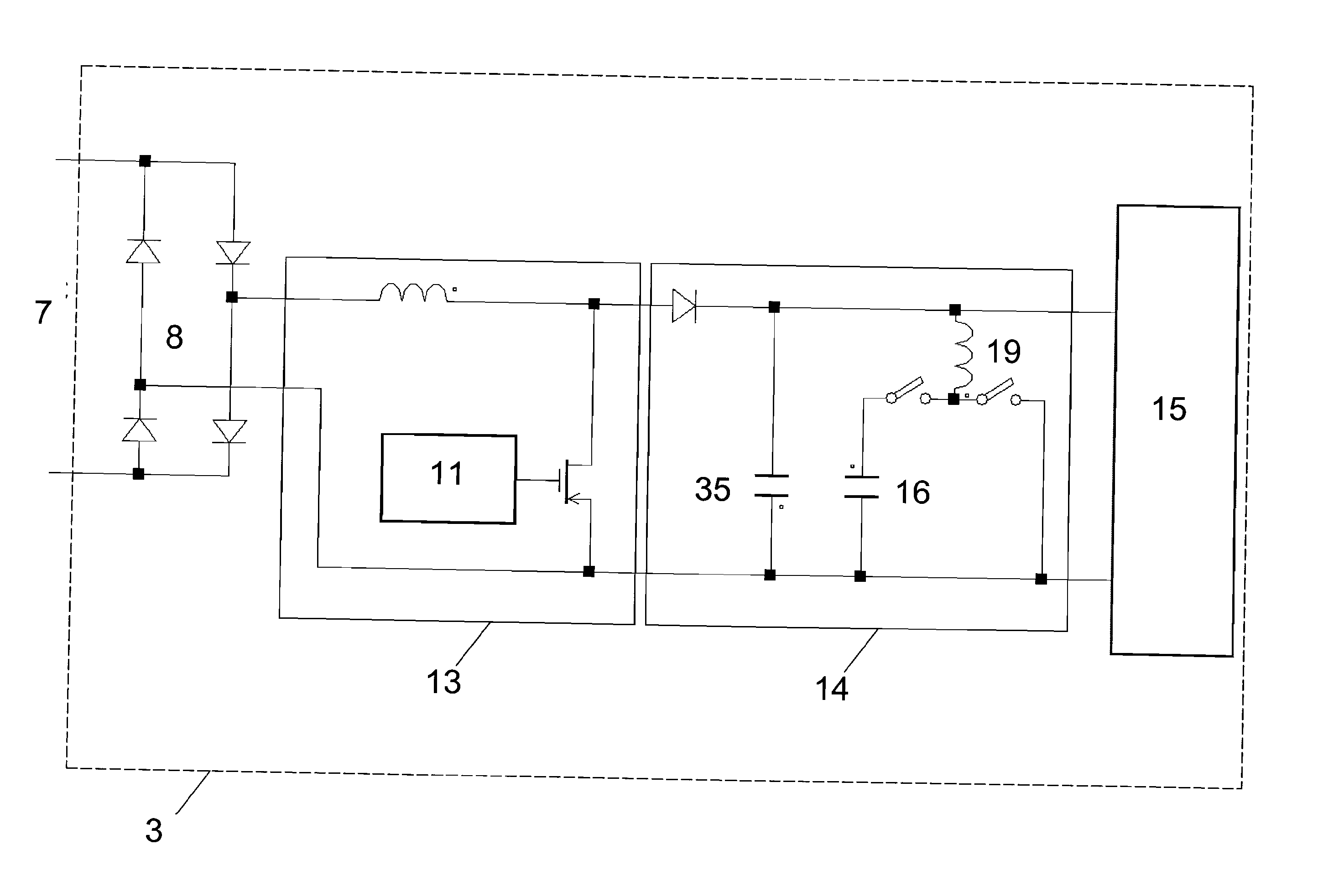
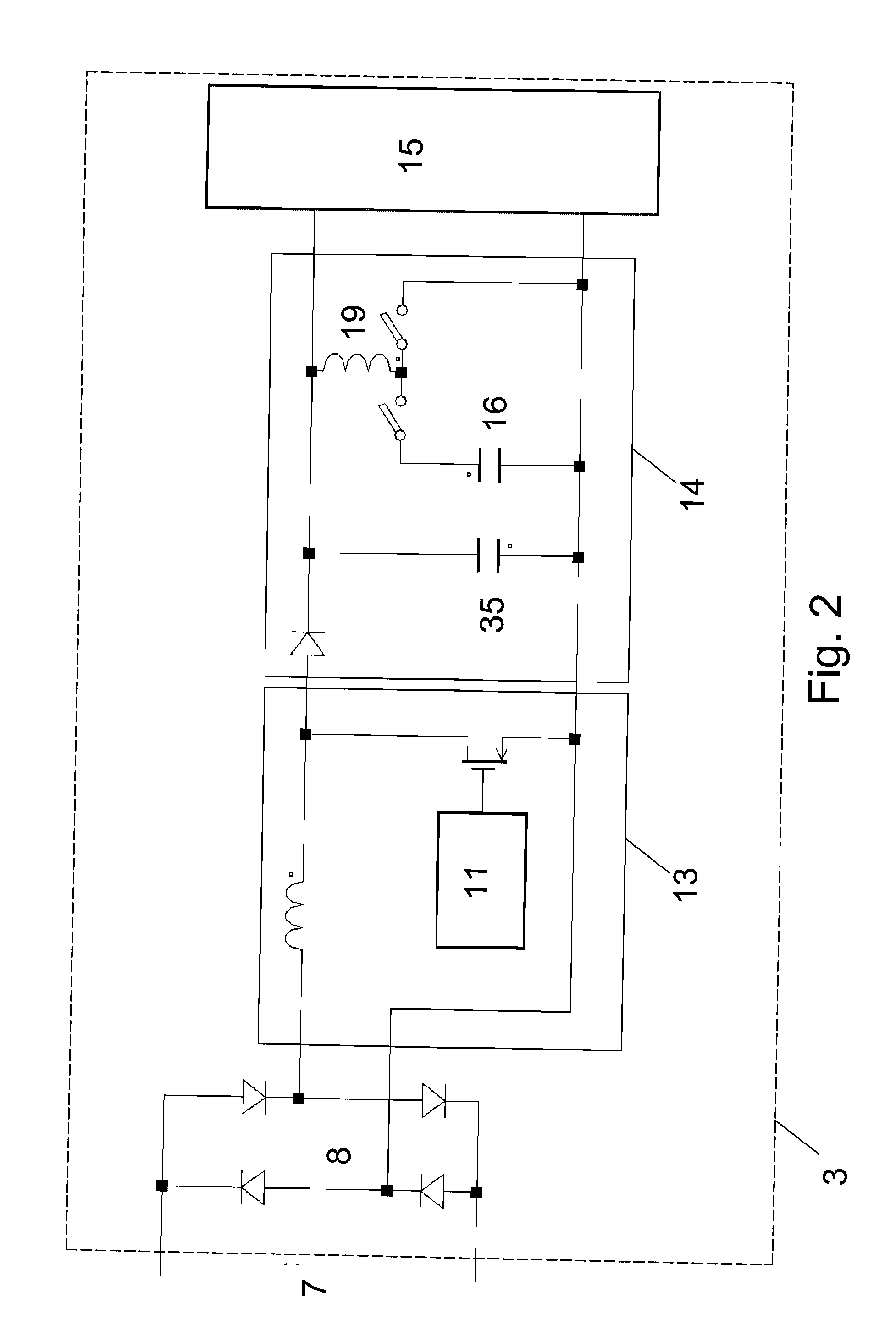
Reliability enhanced systems are shown where an short-lived electrolytic capacitor can be replaced by a much smaller, perhaps film type, longer-lived capacitor to be implemented in circuits for power factor correction, solar power conversion, or otherwise to achieve DC voltage smoothing with circuitry that has solar photovoltaic source (1) a DC photovoltaic input (2) internal to a device (3) and uses an enhanced DC-DC power converter (4) to provide a smoothed DC output (6) with capacitor substitution circuitry (14) that may include interim signal circuitry (28) that creates a large voltage variation for a replaced capacitor (16). Switchmode designs may include first and second switch elements (17) and (18) and an alternative path controller (21) that operates a boost controller (22) and a buck controller (23) perhaps with a switch duty cycle controller (32).
Owner:AMPT
Power control system for current regulated light sources
A light emitting diode (LED) lighting system includes a PFC and output voltage controller and a LED lighting power system. The controller advantageously operates from an auxiliary voltage less than a link voltage generated by the LED lighting power system. The common reference voltage allows all the components of lighting system to work together. A power factor correction switch and an LED drive current switch are coupled to the common reference node and have control node-to-common node, absolute voltage that allows the controller to control the conductivity of the switches. The LED lighting system can utilize feed forward control to concurrently modify power demand by the LED lighting power system and power demand of one or more LEDs. The LED lighting system can utilize a common current sense device to provide a common feedback signal to the controller representing current in at least two of the LEDs.
Owner:SIGNIFY HLDG BV
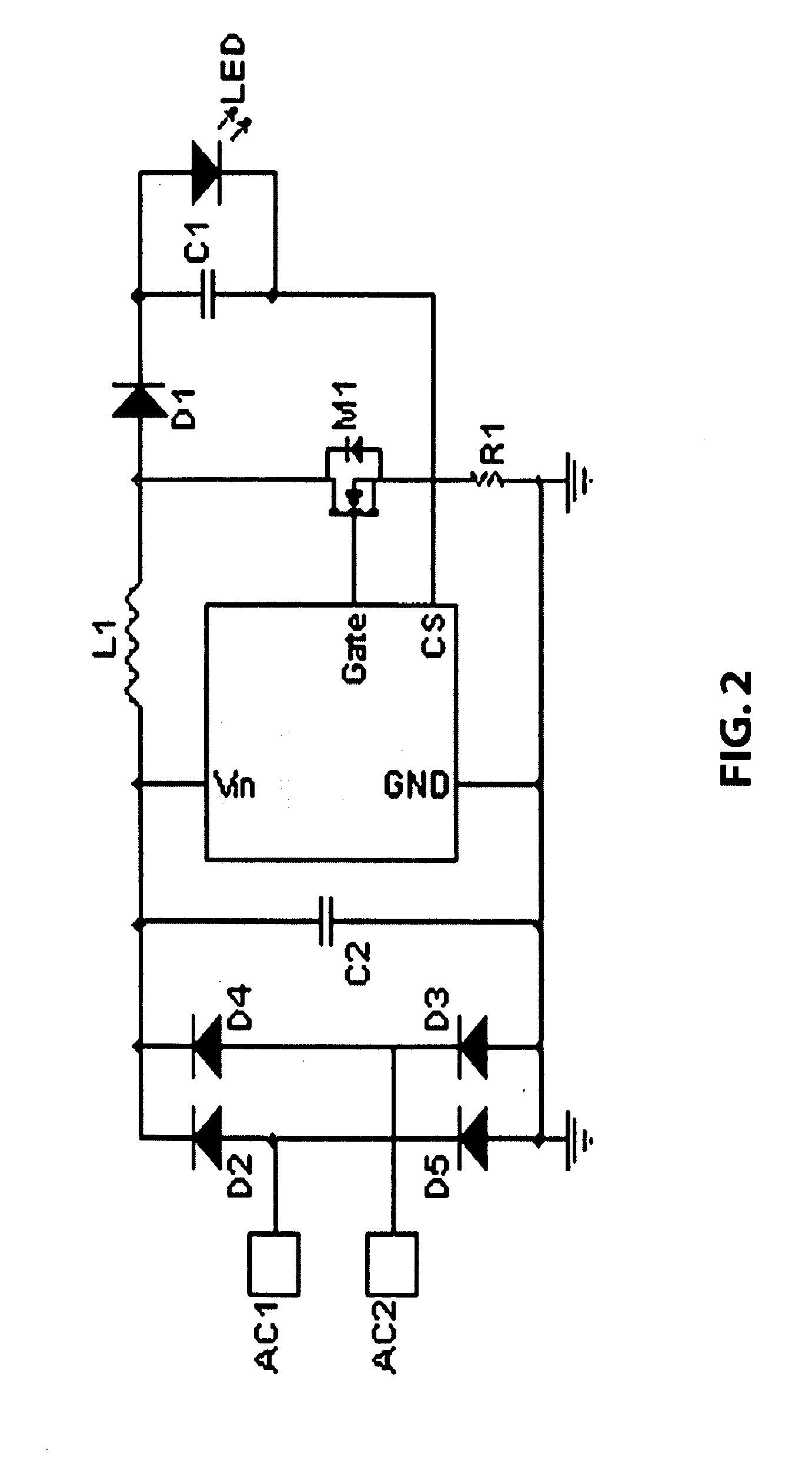
Alternative Switch Power Circuitry Systems
InactiveUS20110181251A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalConversion with intermediate conversion to dcBoost controllerEngineering
Reliability enhanced systems are shown where an short-lived electrolytic capacitor can be replaced by a much smaller, perhaps film type, longer-lived capacitor to be implemented in circuits for power factor correction, solar power conversion, or otherwise to achieve DC voltage smoothing with circuitry that has solar photovoltaic source (1) a DC photovoltaic input (2) internal to a device (3) and uses an enhanced DC-DC power converter (4) to provide a smoothed DC output (6) with capacitor substitution circuitry (14) that may include interim signal circuitry (28) that creates a large voltage variation for a replaced capacitor (16). Switchmode designs may include first and second switch elements (17) and (18) and an alternative path controller (21) that operates a boost controller (22) and a buck controller (23) perhaps with a switch duty cycle controller (32).
Owner:AMPT
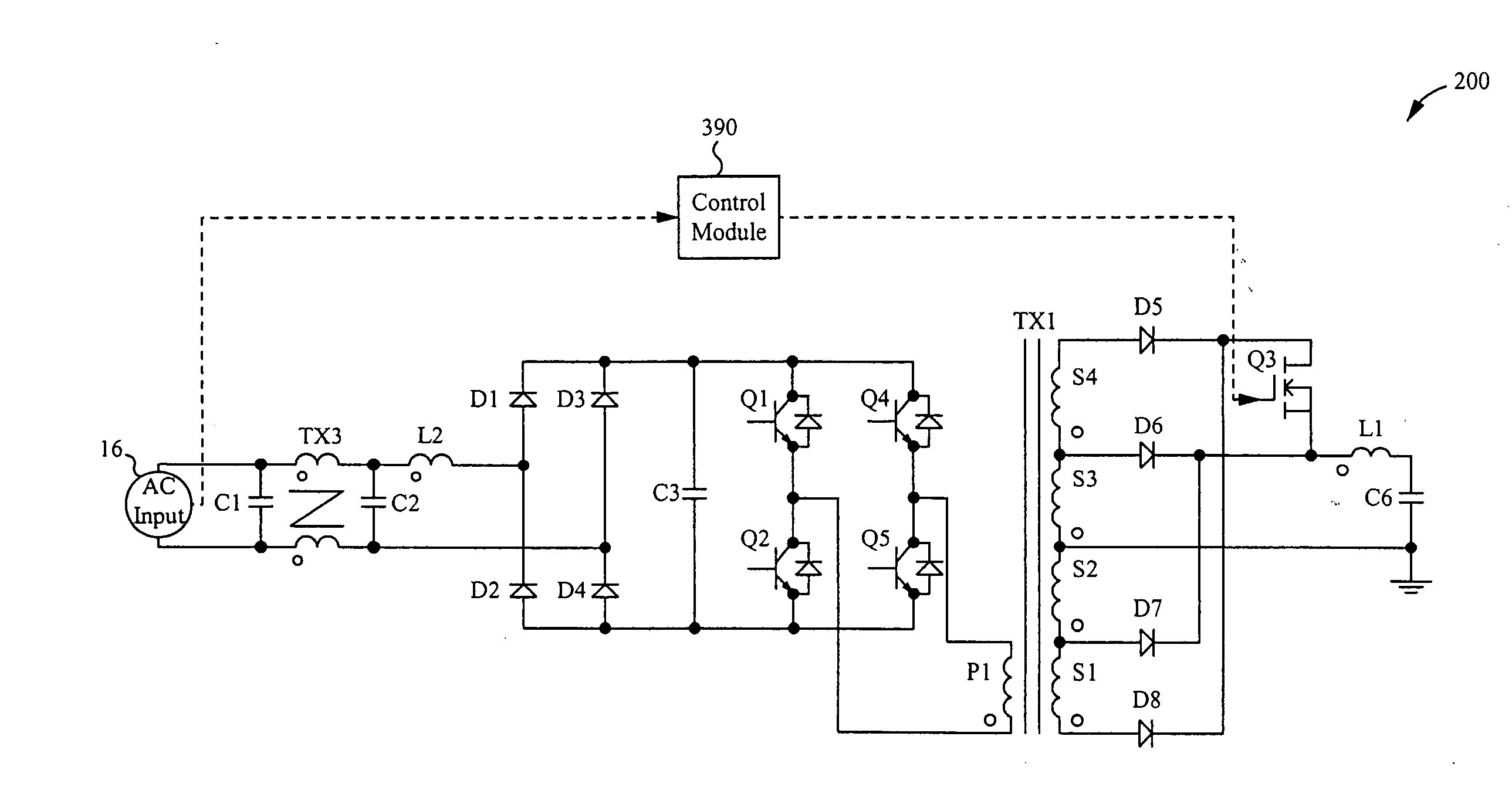
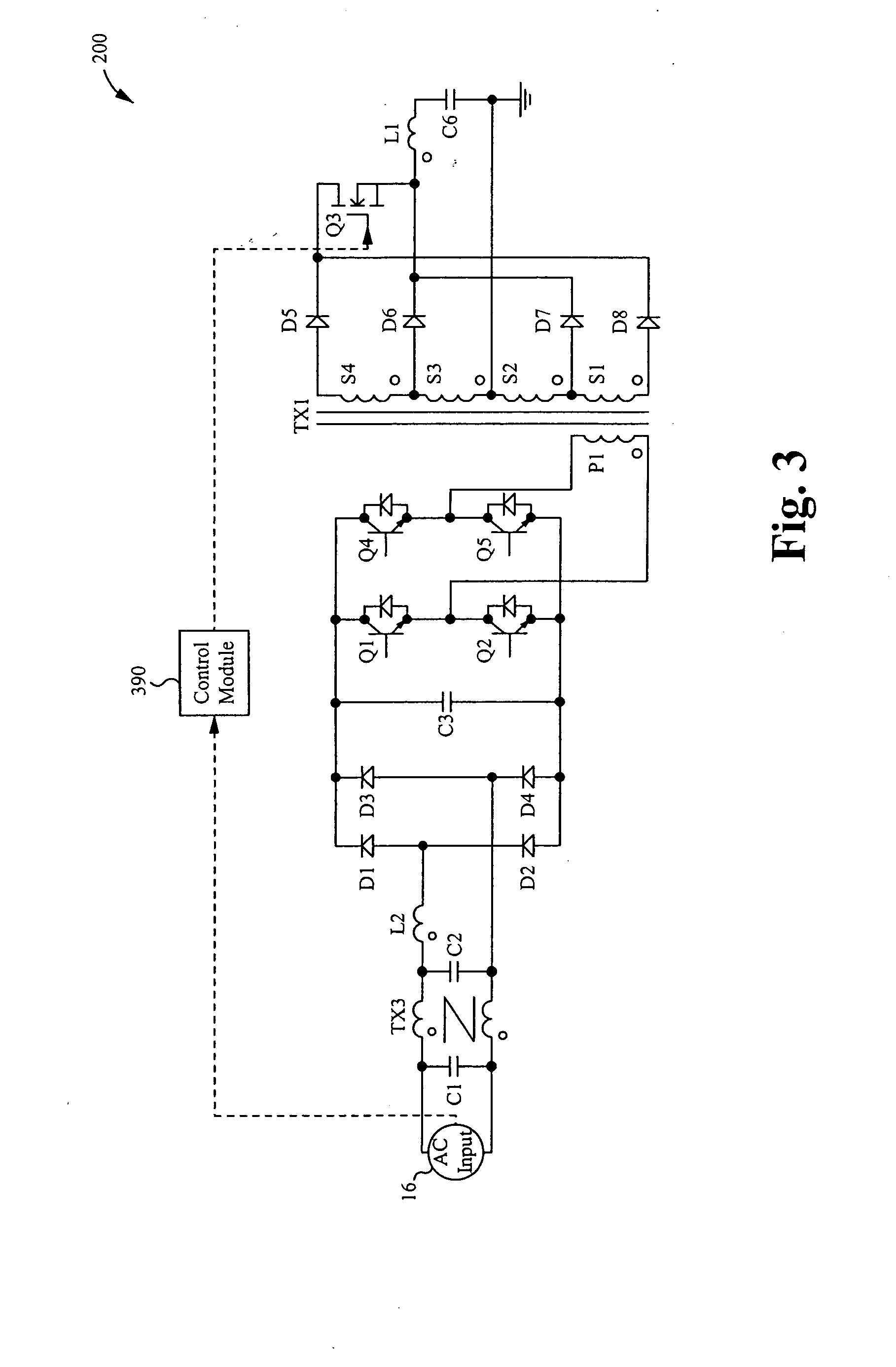
Highly efficient isolated AC/DC power conversion technique
ActiveUS20070081364A1Reduce circuit sizeReduce complexityAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransformerEngineering
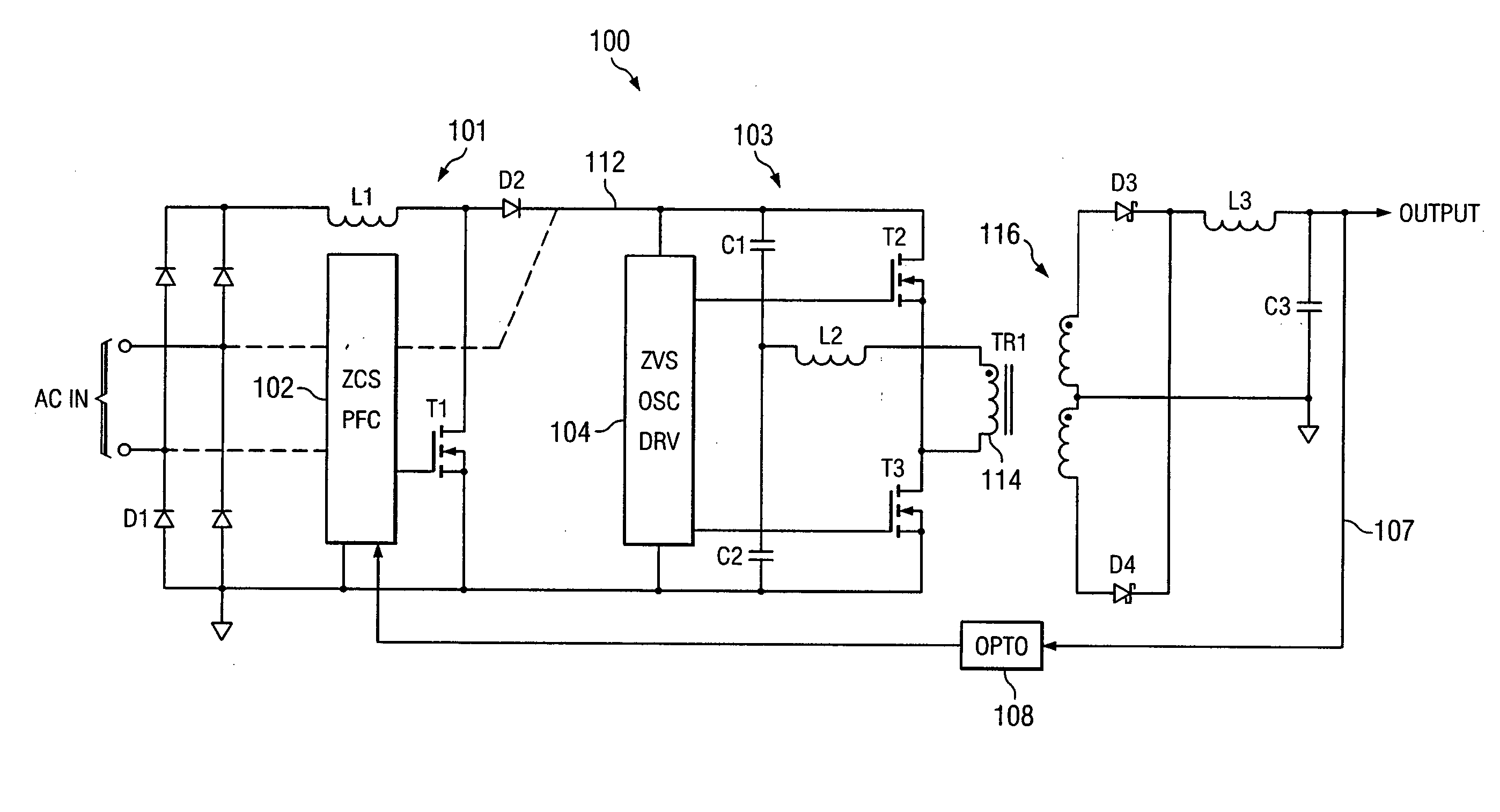
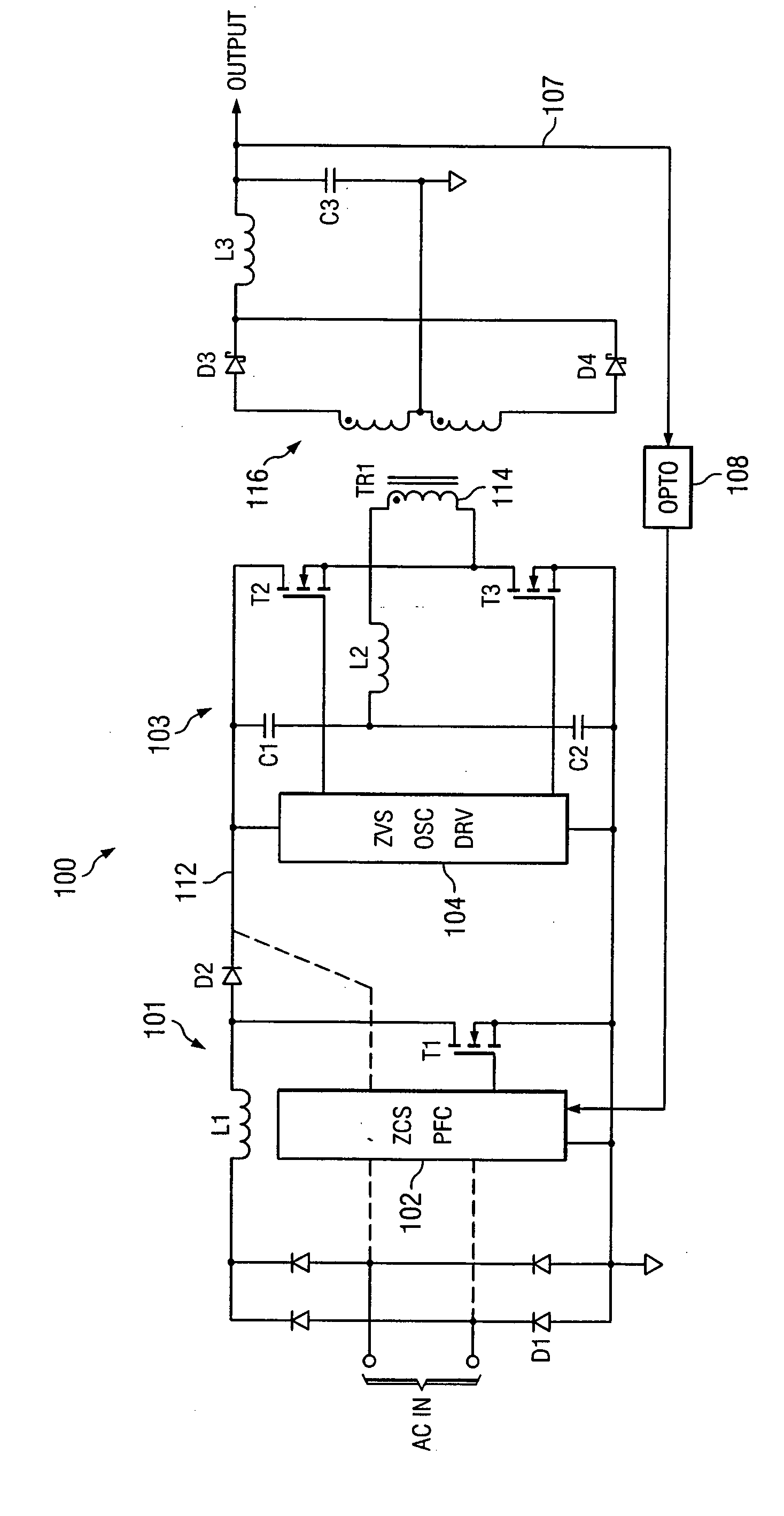
An AC-to-DC power converter that is capable of generating a regulated, isolated DC voltage output from a power factor corrected AC voltage input with improved efficiency. The AC-to-DC power converter is a two-stage power converter including a PFC stage connected in series to a power conversion stage. The PFC stage performs power factor correction using a zero current switching technique, and the power conversion stage includes a zero voltage switched half-bridge converter. The power conversion stage includes a transformer for providing the isolated DC voltage output. The AC-to-DC power converter includes a single feedback control loop for transferring error information from the DC voltage output to the PFC stage, thereby obtaining regulation of the DC voltage output.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
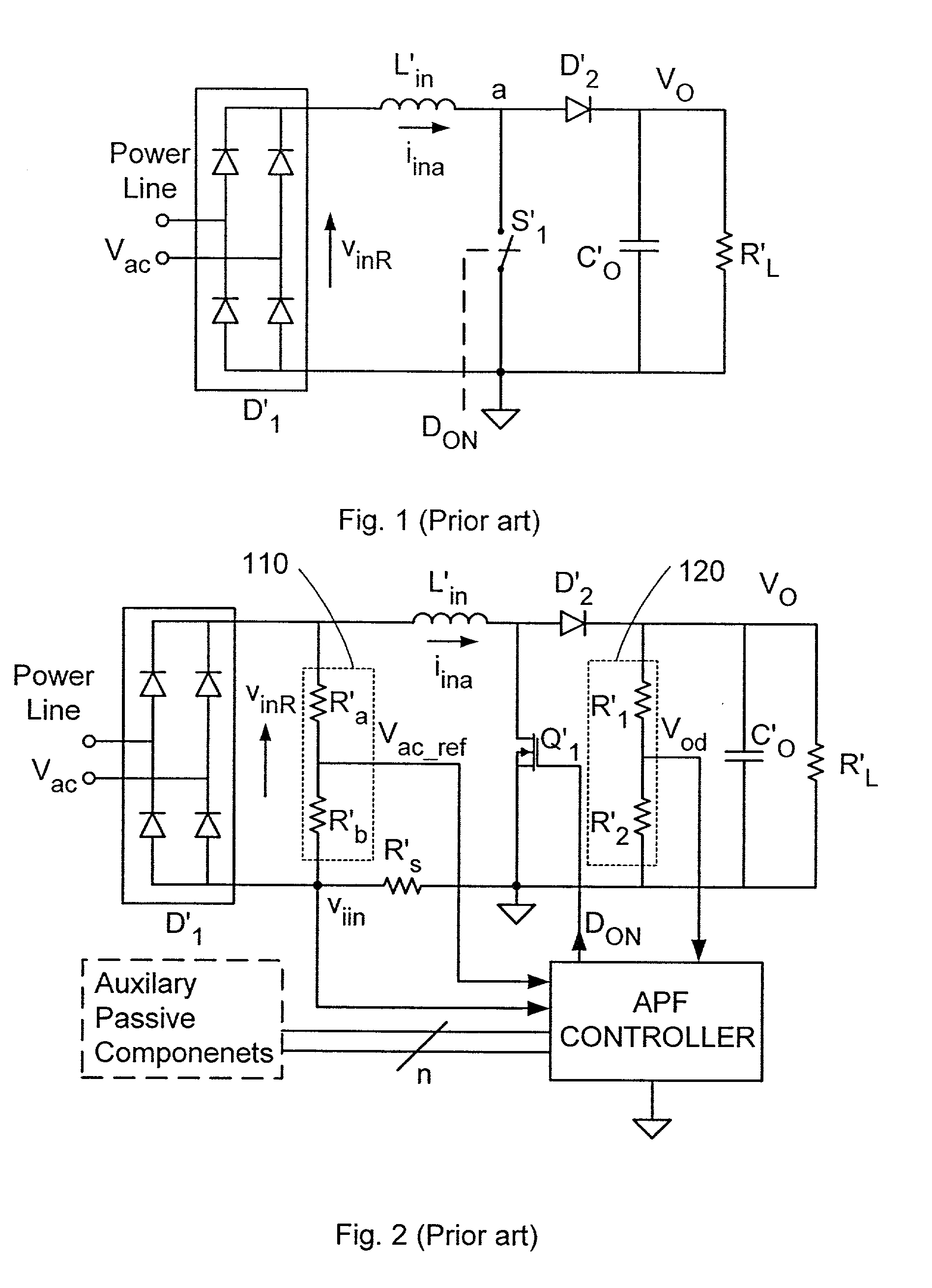
Topology and control method for power factor correction
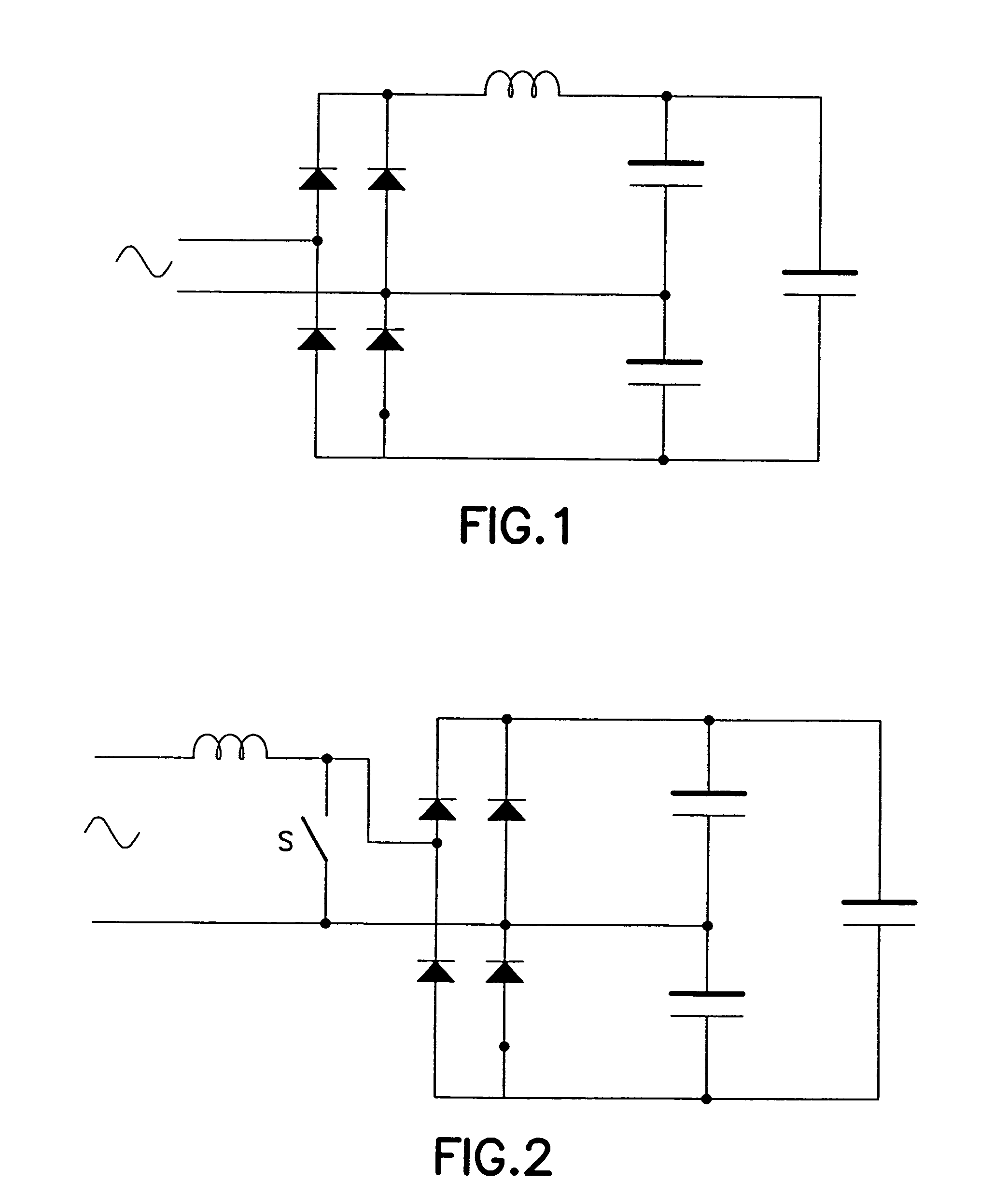
InactiveUS6344986B1Reduce electromagnetic interferenceReduce output voltageAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransverterInductor
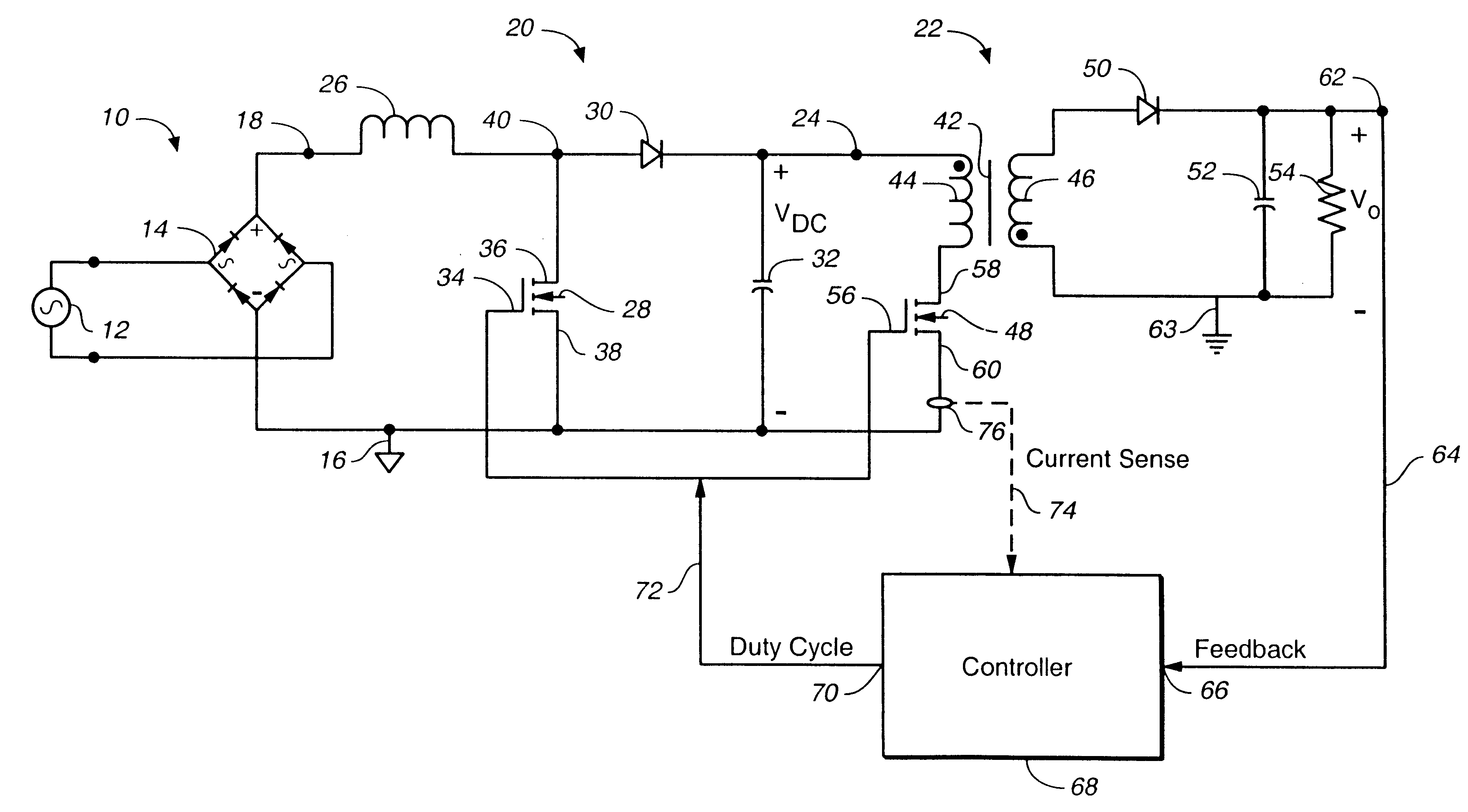
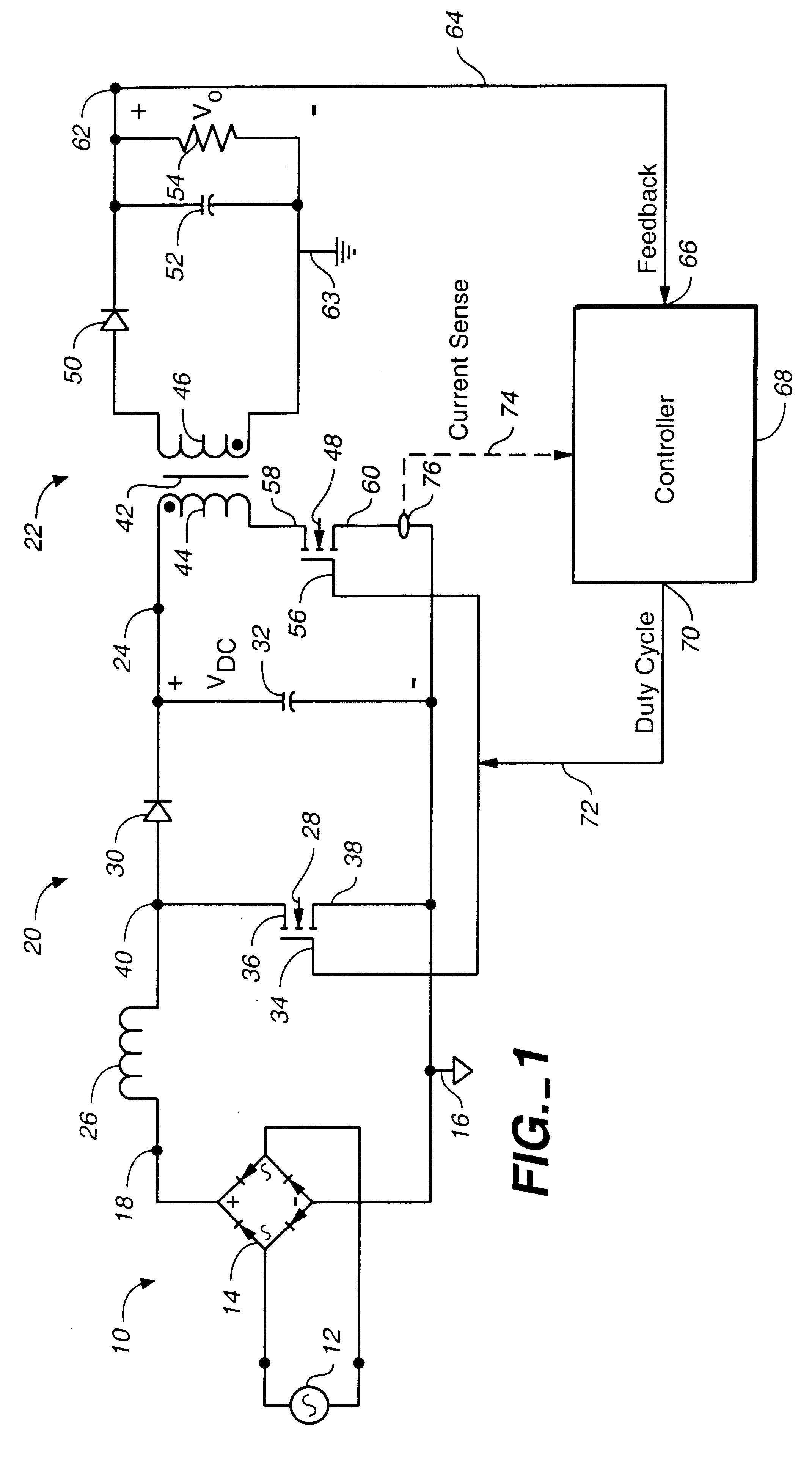
In a power factor corrected AC-to-DC power supply system, a DC-to-DC power converter is coupled to the output of an AC-to-DC power converter in order to produce a regulated DC output signal from a rectified AC input signal. The AC-to-DC power converter and the DC-to-DC power converter each includes a switch for controlling the operation of their respective power converter. The AC-to-DC converter includes an inductor. The system provides power factor correction for minimizing harmonic distortion by including a controller that receives the regulated DC output voltage as a feedback signal, and in response, produces a series of drive pulses having predetermined constant duty cycle. These pulses are simultaneously fed to each switch, to operate the respective converters alternately between ON and OFF states. When the AC-to-DC converter is driven by a fixed duty cycle of the series of pulses, power factor correction is improved since the current flowing through the inductor is substantially proportional to the waveform of the rectified AC input signal. By preselecting the value of the inductor, the AC-to-DC converter is operable in a discontinuous mode when the instantaneous rectified AC input signal is low and in a continuous mode when the instantaneous rectified AC input signal is high.
Owner:ASTEC INT LTD
PFC apparatus for a converter operating in the borderline conduction mode
InactiveUS6469917B1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHemt circuitsEngineering
Power factor correction apparatus, for a switching power supply fed by an array of rectifying diodes and consisting of at least an input inductor, a contact of which is connected in series with a contact of the array, and of a power switch connected between the other contact of the array and the other contact of the input inductor that comprises circuitry for identifying, in each cycle determined by the switching frequency of the power supply, whenever the instantaneous value of the current through the inductor reaches a minimal value; circuitry for switching the power switch to its conducting state in response to the minimal current through the inductor; circuitry for reflecting the current flowing through the inductor by a measurable or simulated parameter; and circuitry for providing indication, in each cycle, by using the parameter, the indication being related to the timing until the peak value of the current, that corresponds to a specific load, has been essentially reached, or to the time from the moment that the current reaches the minimal value until the timing, and for switching the power switch to its non-conducting state in response to the indication.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
Method and apparatus for controlling power factor correction
ActiveUS7266001B1Small sizeReduce Harmonic DistortionEfficient power electronics conversionAc-dc conversionAverage currentEngineering
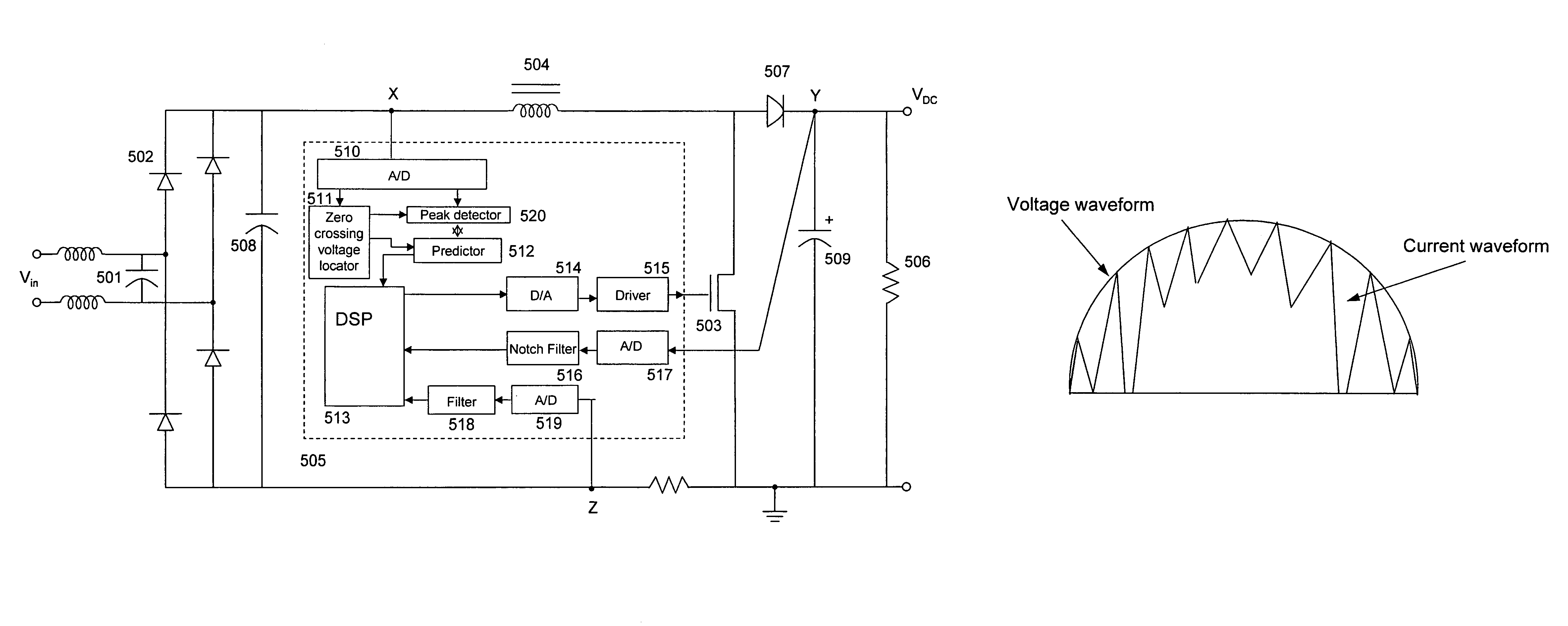
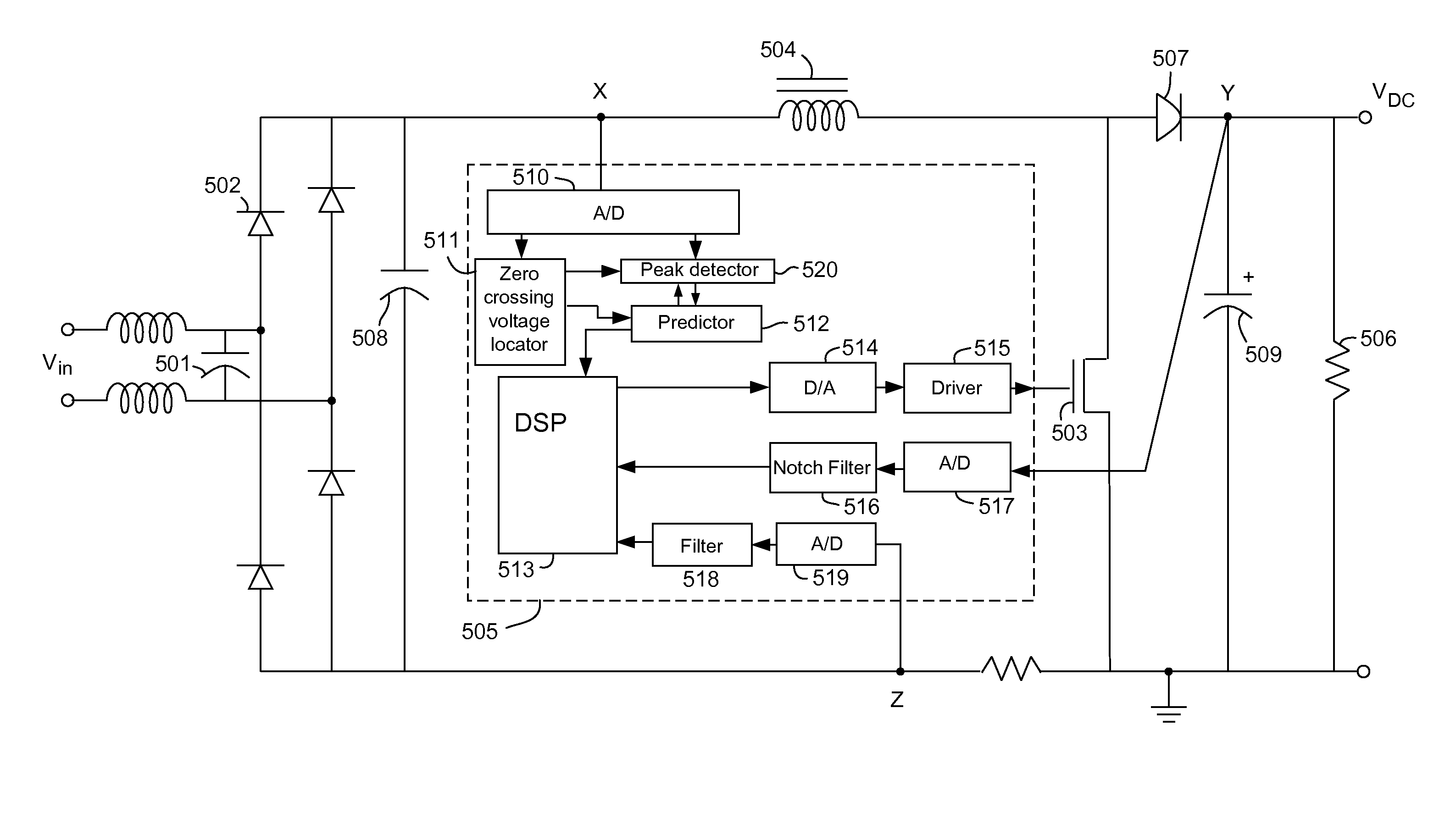
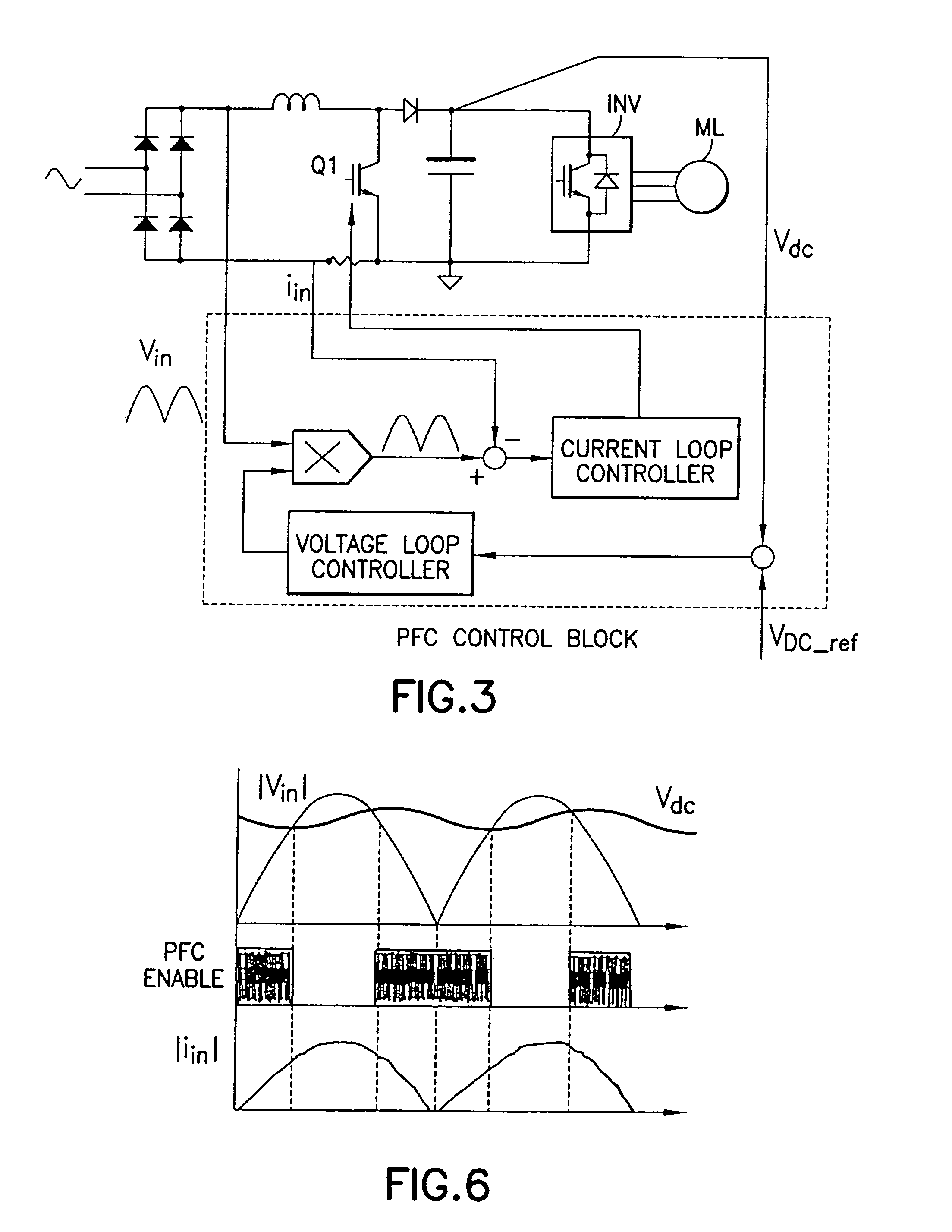
In a method and apparatus for controlling power factor correction in mixed operation modes, a frequency of the input voltage is obtained by detecting the zero crossing points of the input voltage. A peak of the input voltage is obtained by detecting input voltage with 90 degree phase. Thus, the present invention predicts the input voltage by its frequency and peak and the characteristic of the sine wave. A digital signal processor computes the duty and frequency of a boost switch, switching the operation mode of the boost converter among continuous mode, critical mode and discontinuous mode according to input voltage or the load. According to another aspect, the operation is switched to critical mode from the average current mode when a zero current is detected before the charging and recharging cycle of the boost switch is finished.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
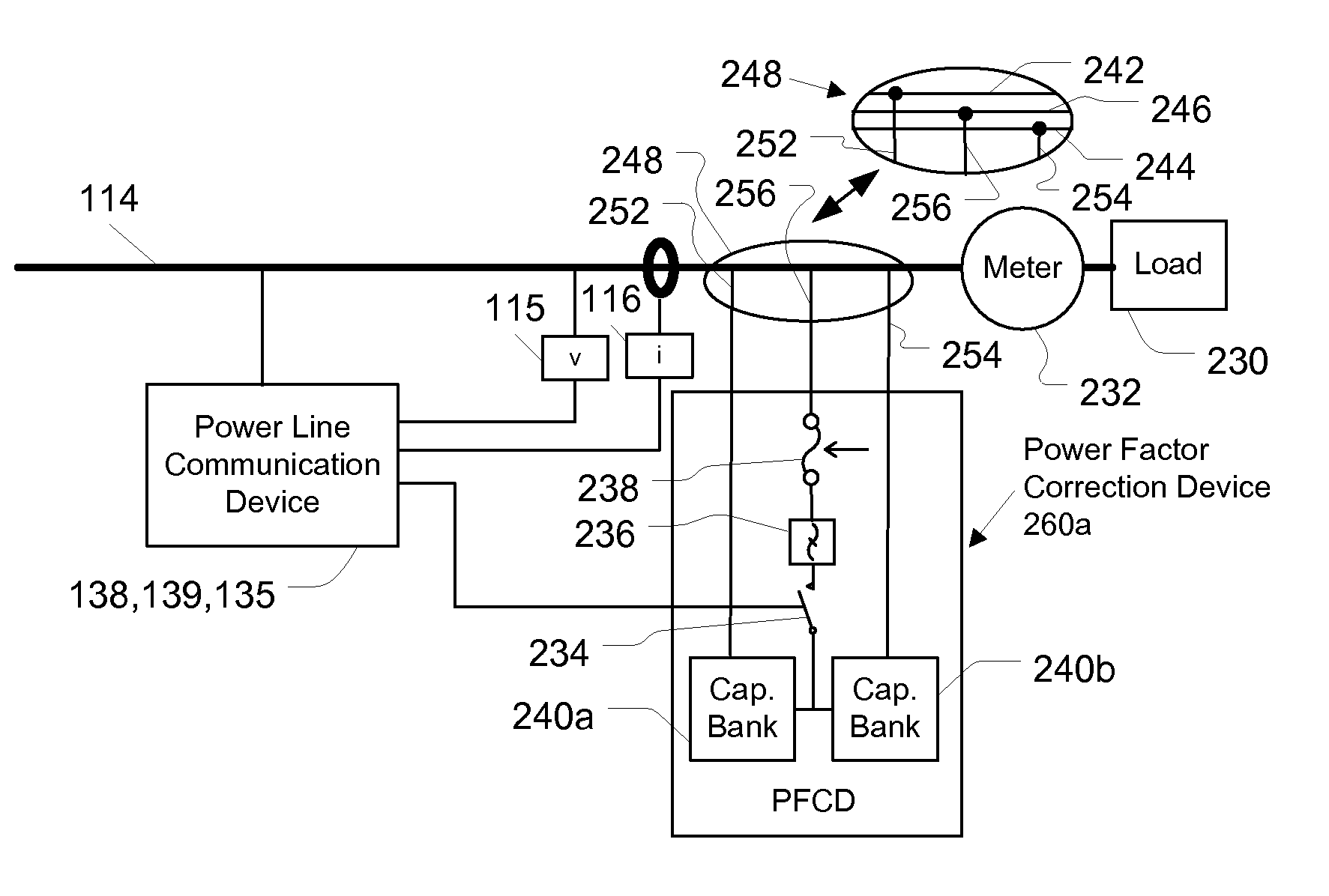
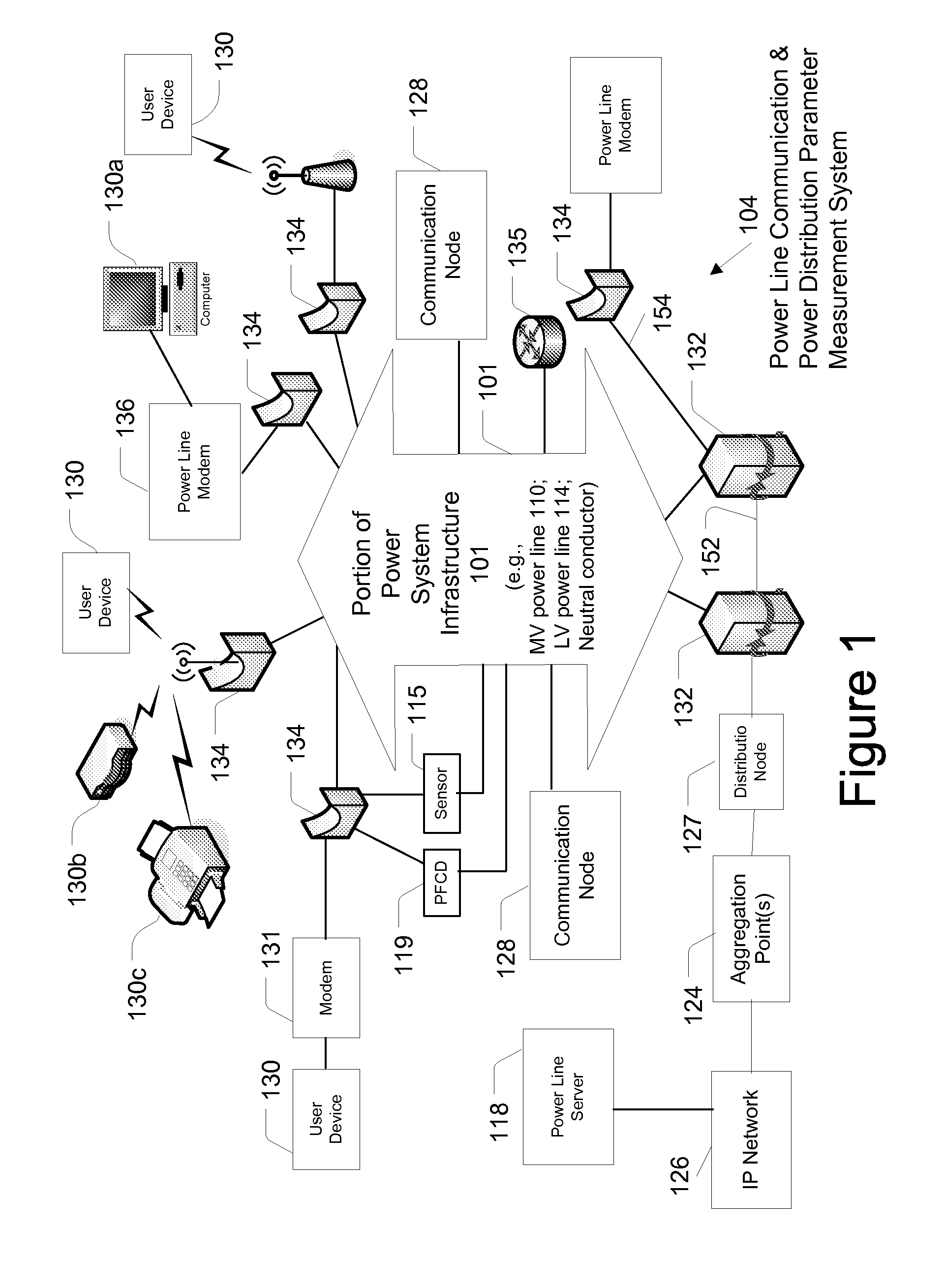
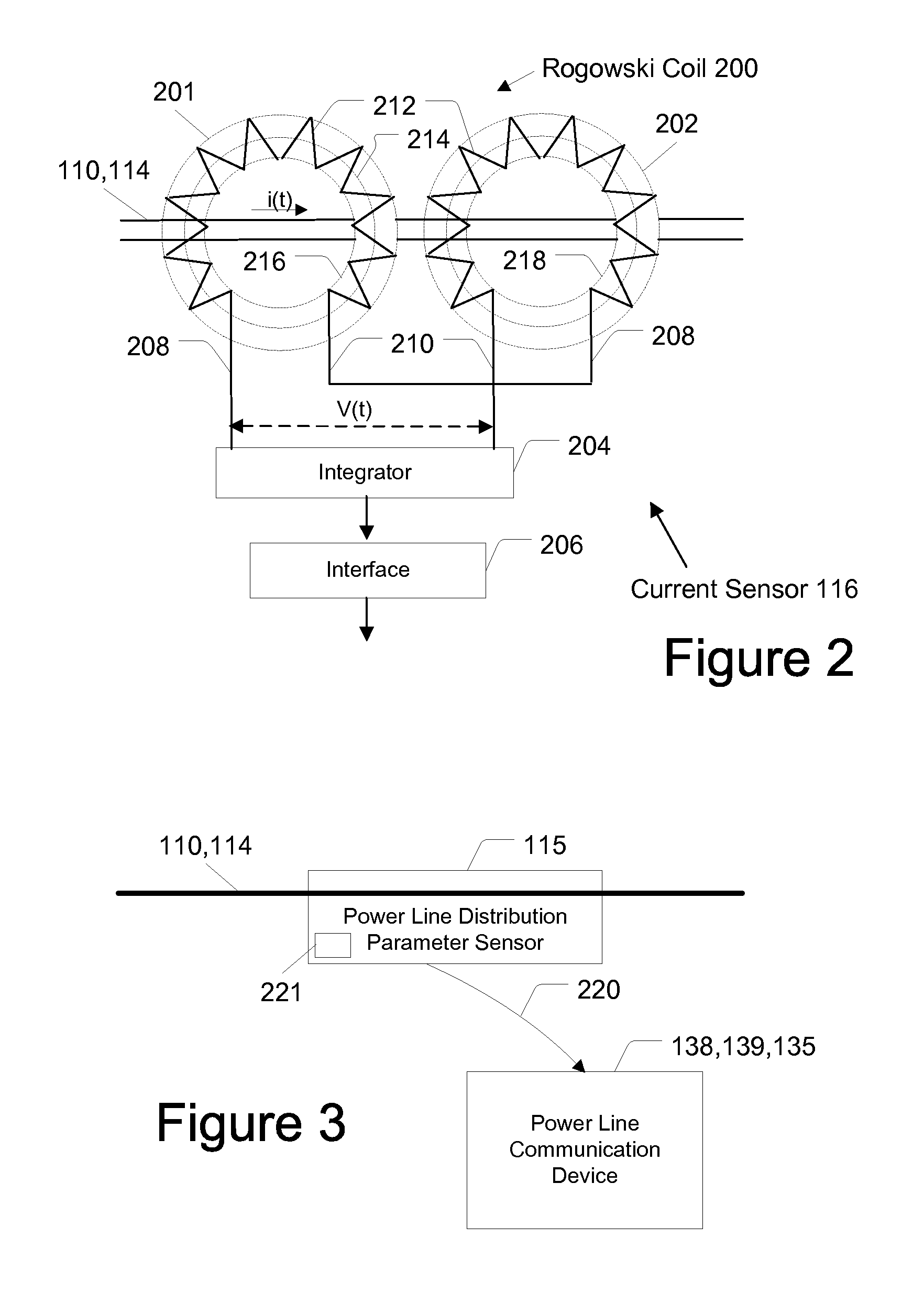
Method and System for Providing Power Factor Correction in a Power Distribution System
ActiveUS20080106241A1AlarmsElectric variable regulationPower-line communicationPower factor corrector
A device for providing power factor correction of a low voltage subnet that includes a low voltage feeder line that is connected to one or more low voltage power supply lines that supply power to one or more customer premises is provided. In one embodiment, the device includes a power factor measurement module configured to measure power parameters for determining a power factor of the power traversing the low voltage subnet; a power factor correction assembly configured to vary a capacitance connected to the low voltage feeder of the low voltage subnet; a controller in communication with the power factor measurement assembly and the power factor correction assembly. The controller may be configured to cause the power factor correction assembly to change the capacitance based on the determined power factor. The controller may form part of a power line communication device configured to provide communications to the one or more customer premises.
Owner:S&C ELECTRIC
Method and apparatus for active power factor correction with minimum input current distortion
InactiveUS20030223255A1Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionActive power factor correctionHarmonics
A method for reducing the harmonics contents of an input current drawn from a power line into an electrical system without sensing an input voltage, the method comprising providing an active power factor correction controller with a switch module having a main switch and a timing device, wherein the main switch has an on-time correlated with an on-duty cycle duration, and an off-time correlated with an off-duty cycle duration, and maintaining a linear relationship between the off-duty cycle duration and the input current by using the timing device; and an apparatus for active power factor correction with minimum input current distortion, comprising an active power factor correction assembly that includes a main switch and a timing device, wherein the main switch has associated therewith an on-time correlated with an on-duty cycle duration, and an off-time correlated with an off-duty cycle duration, and wherein the timing device generates the mentioned on-time and off-time, and linearization means for maintaining a linear relation between the off-duty cycle duration and the input current.
Owner:GREEN POWER TECH LTD
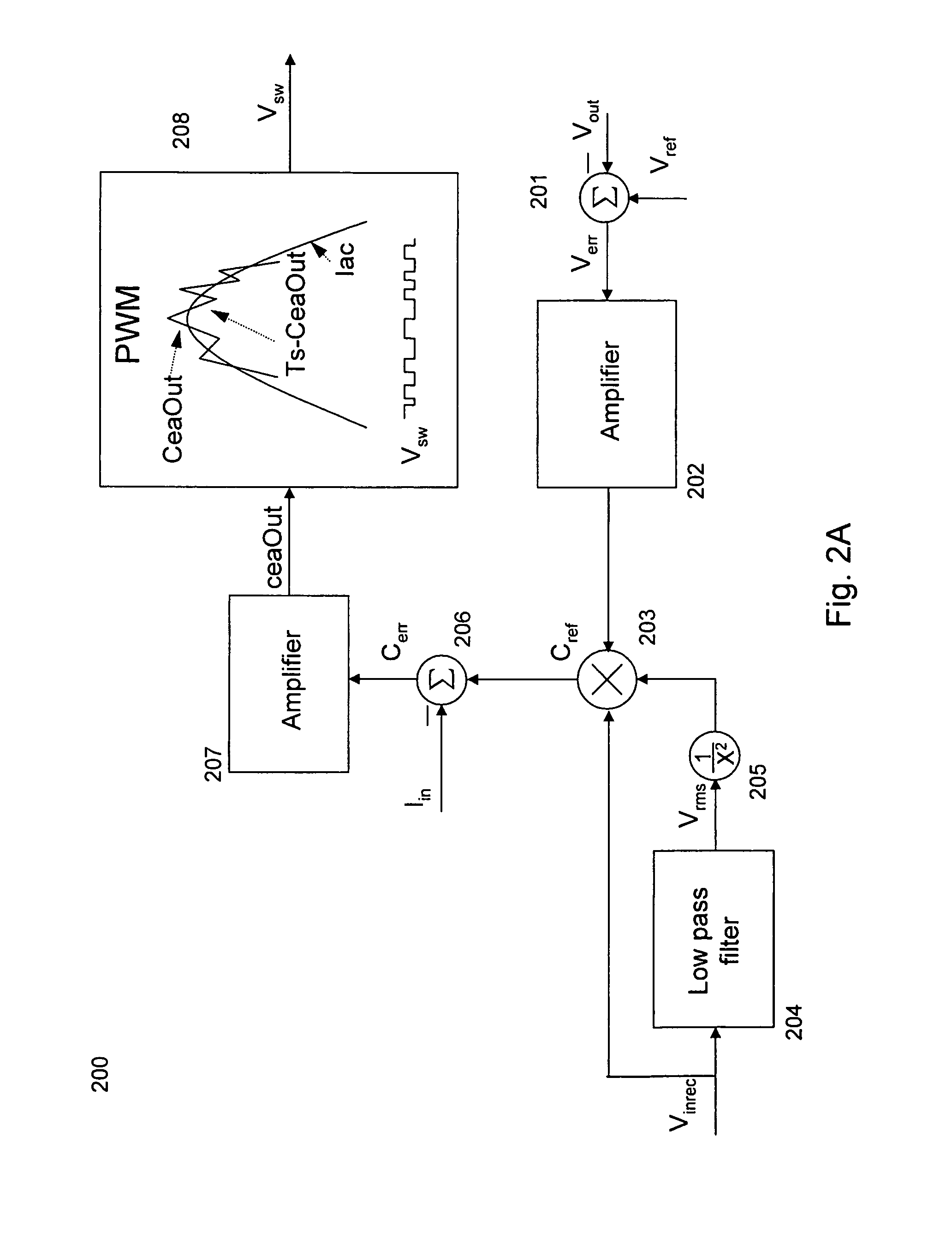
Parallel current mode control
InactiveUS20050270813A1Unity power factor for AC-DC converterLow costAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionCurrent mode controlMode control
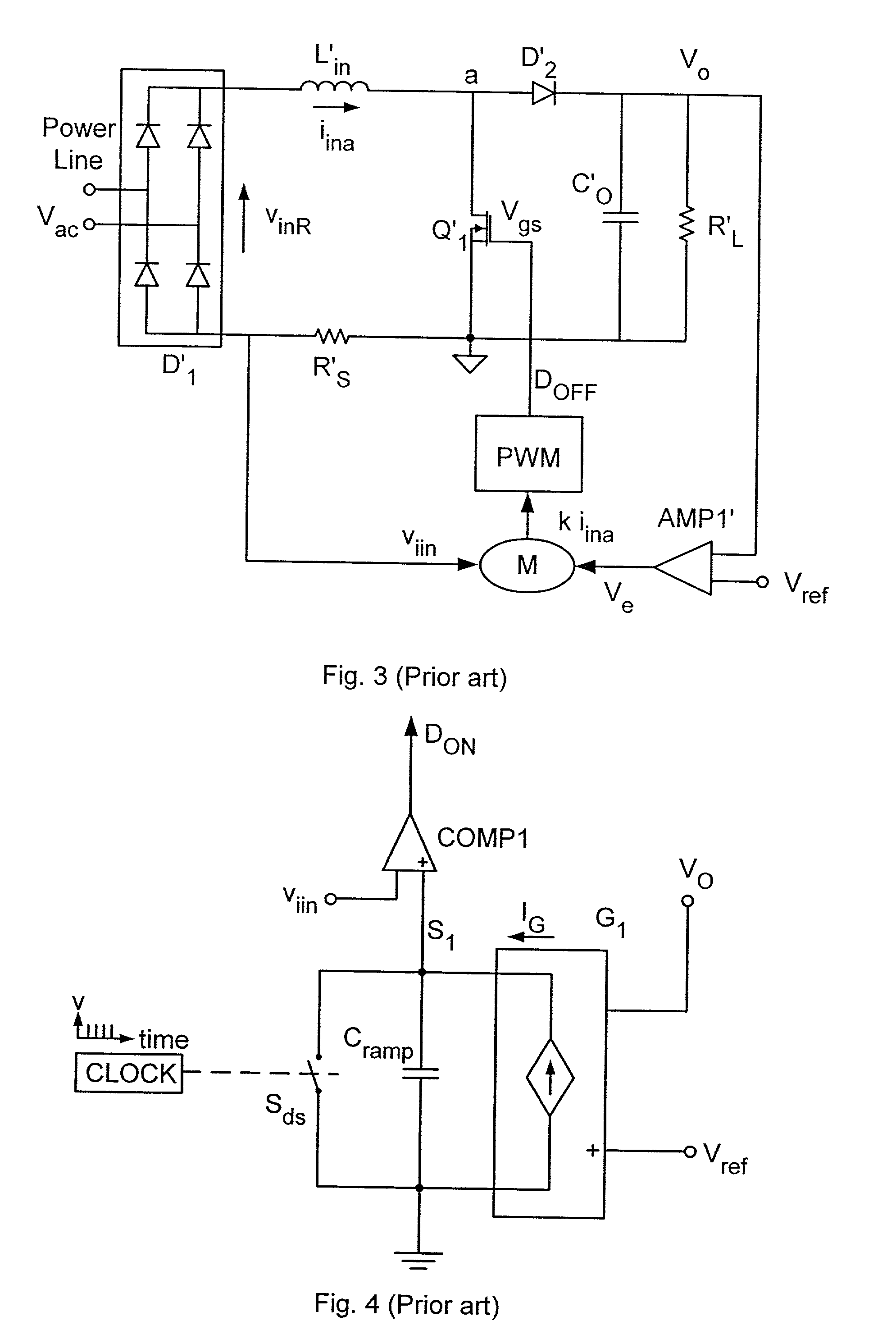
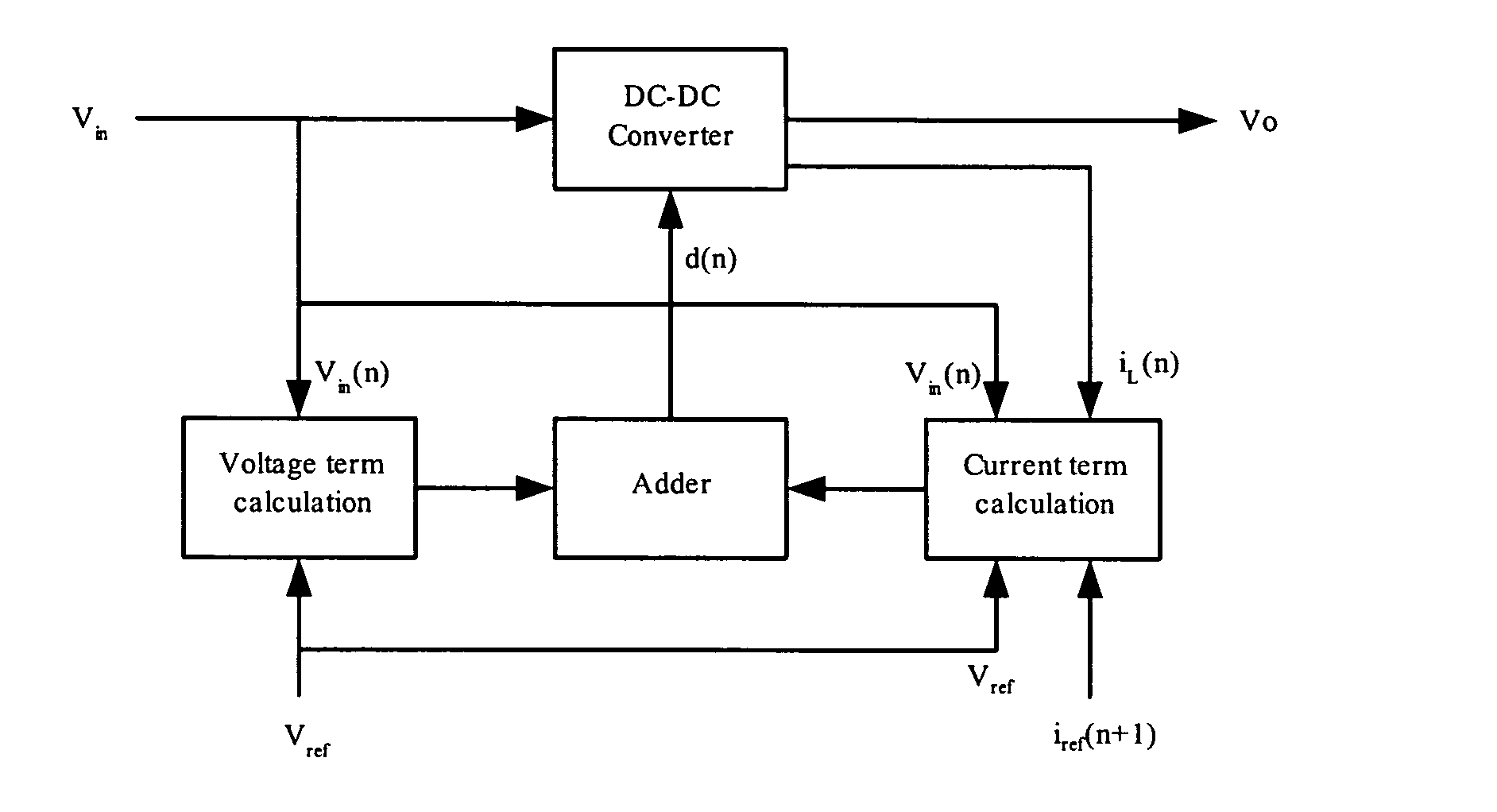
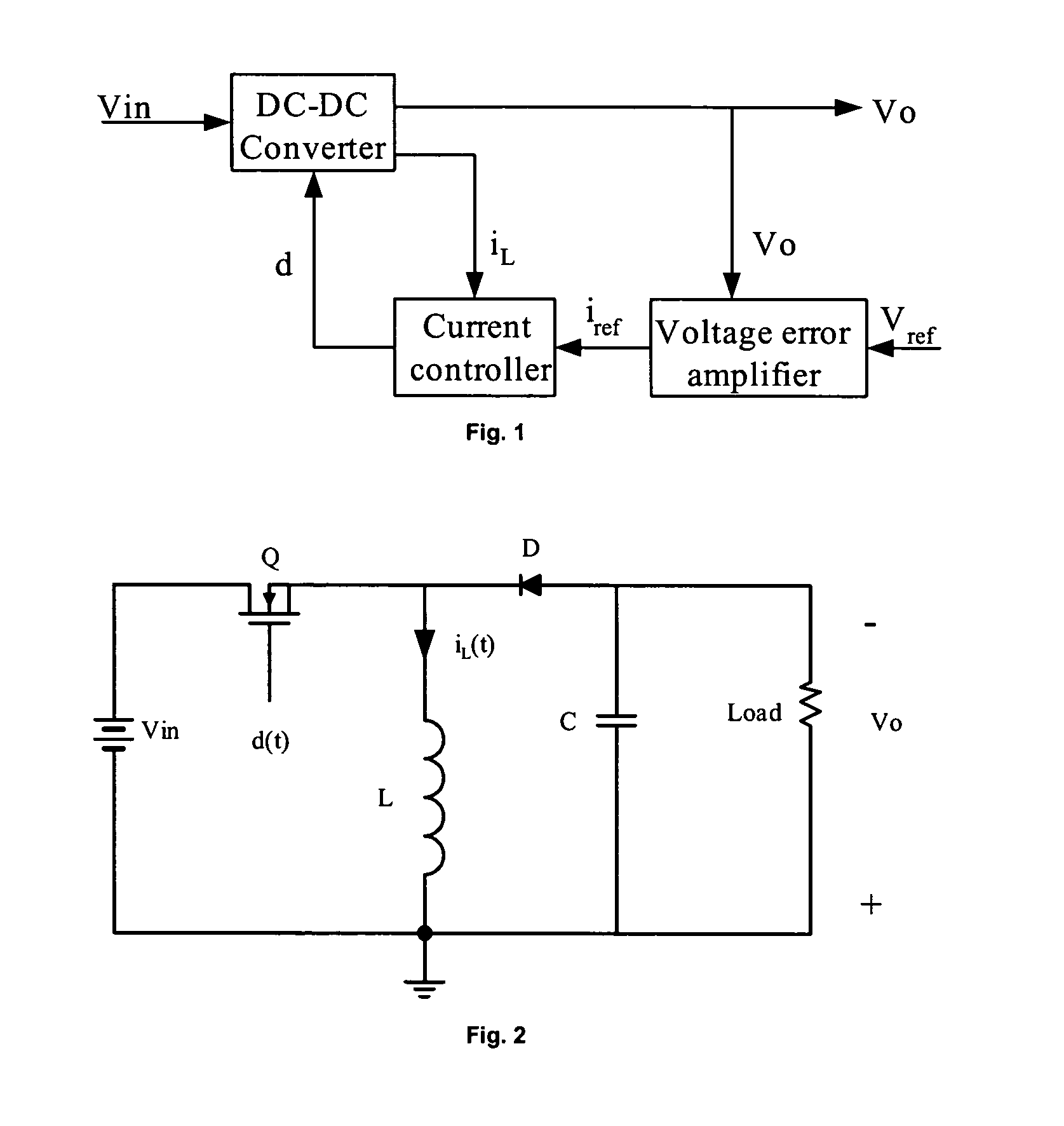
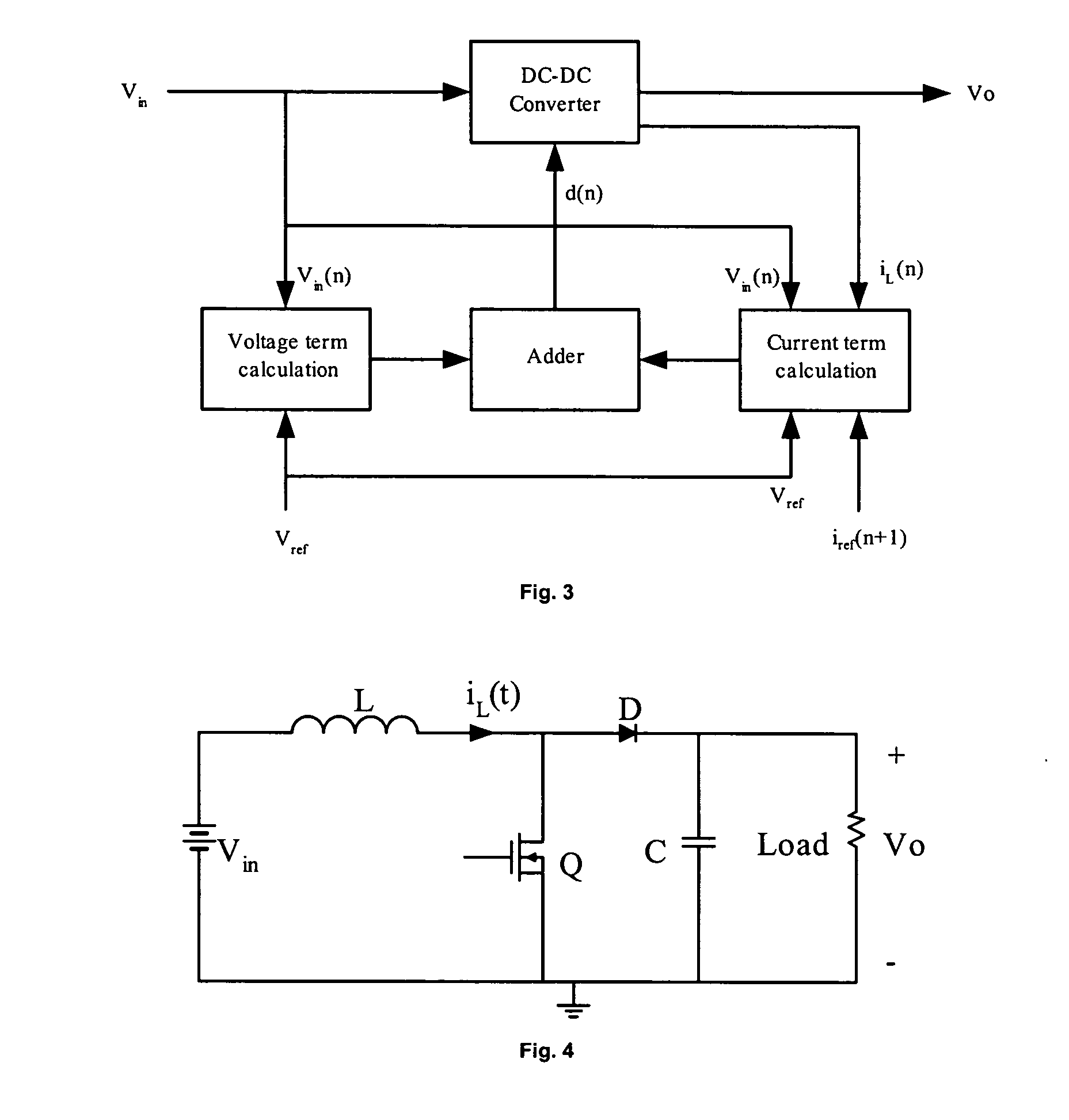
A method and apparatus to implement parallel current mode control that is suitable for digital and analog implementation. A duty cycle algorithm is composed of a voltage term and a parallel current term which depends on the inductor current change between the inductor current value at the beginning of a switching cycle and the reference inductor current value at the end of that switching cycle. Parallel current mode control can be applied to all DC-DC converters, including both non-isolated and isolated topologies. It can also be applied to AC-DC converters with power factor correction.
Owner:DIALOG SEMICONDUCTOR INC
Reduced flicker AC LED lamp with separately shortable sections of an LED string
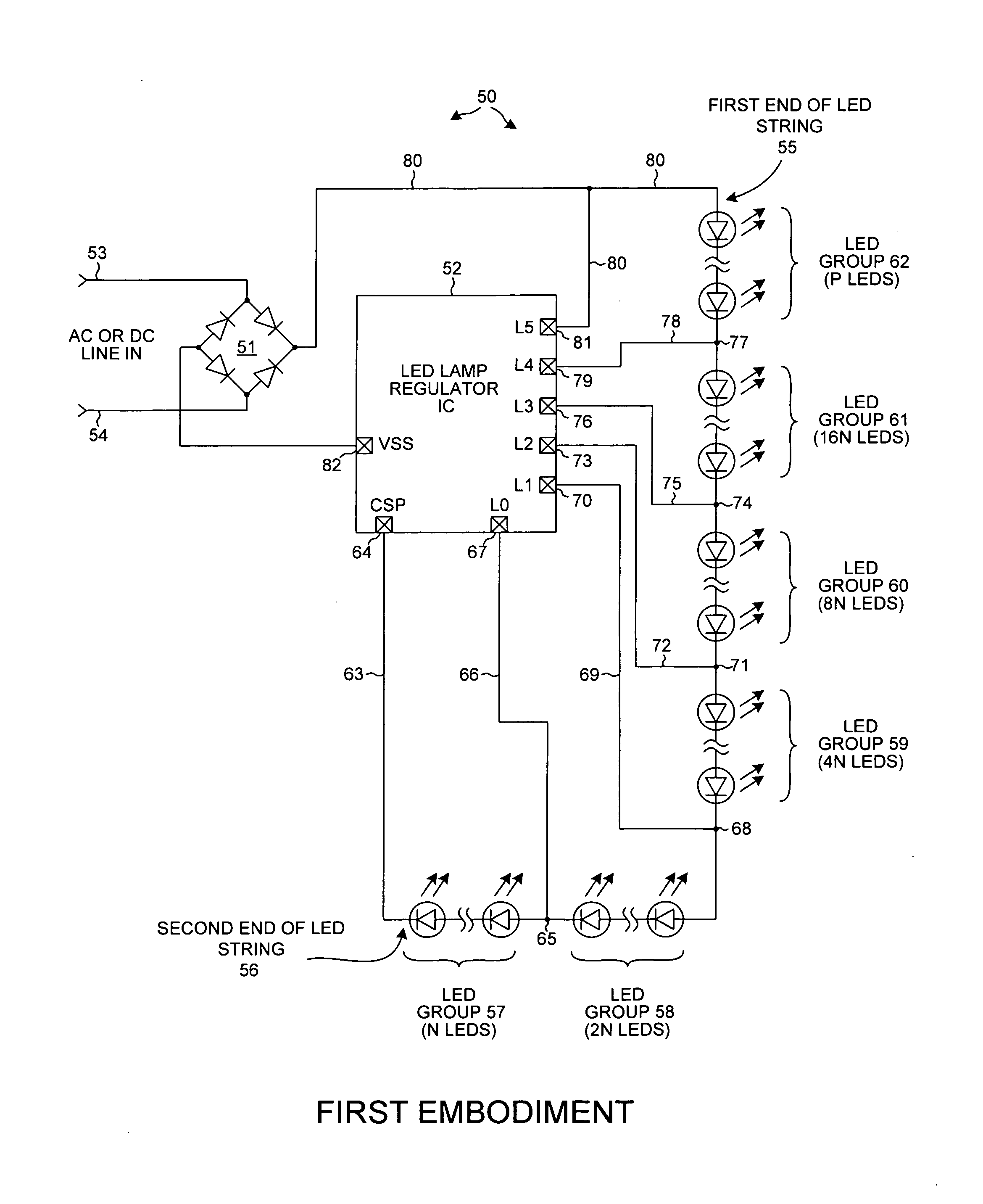
ActiveUS20110227489A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower switchingPeak value
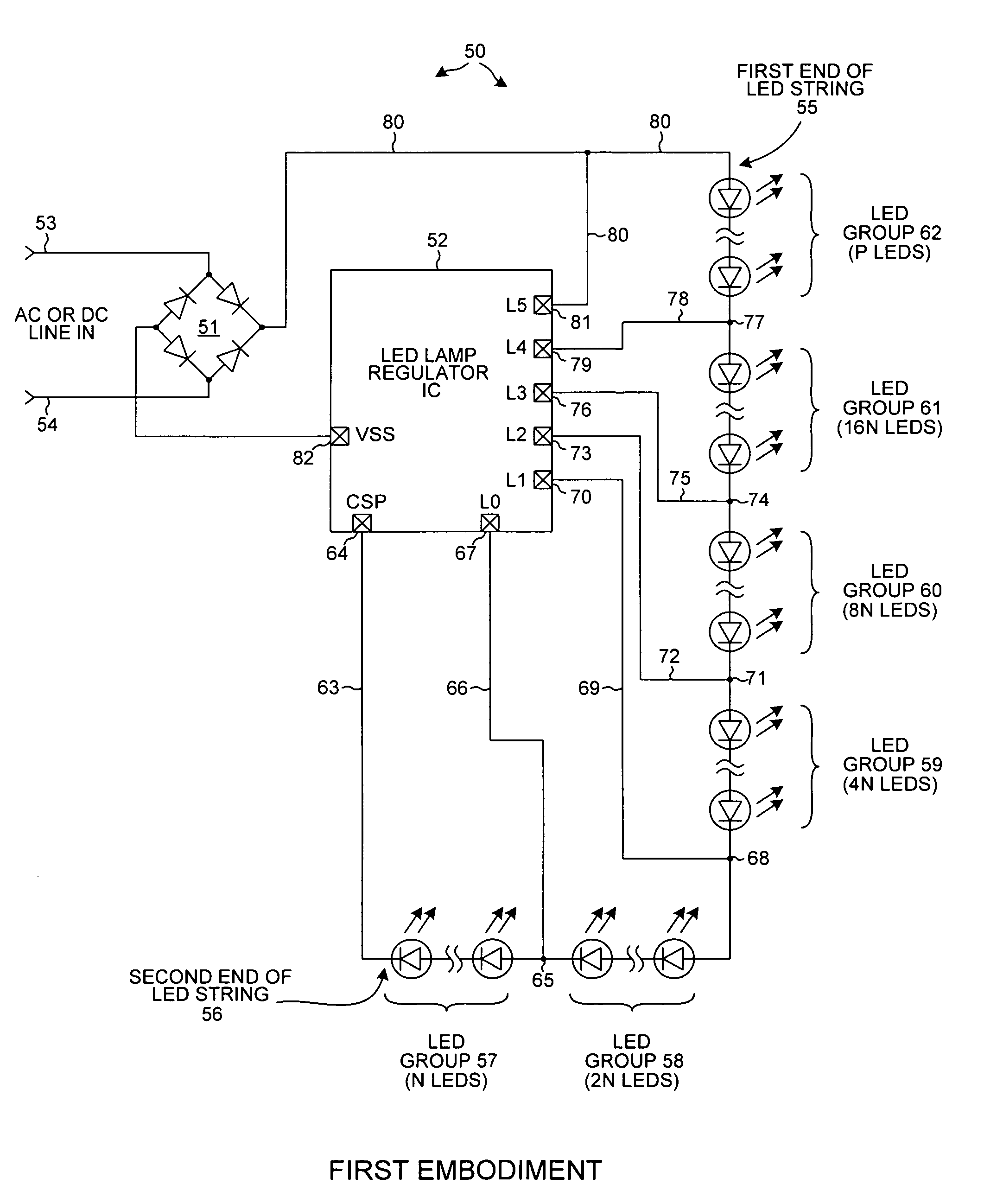
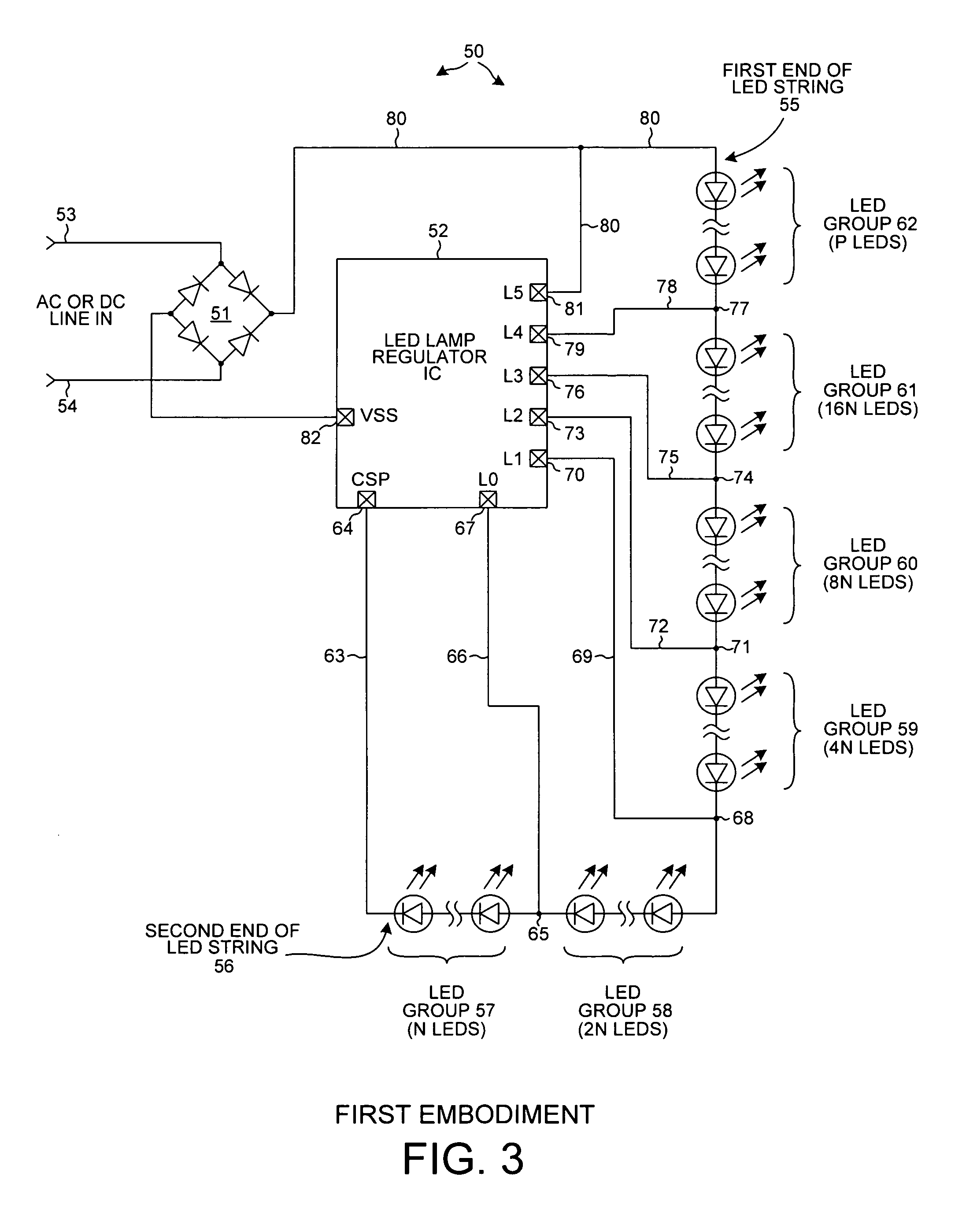
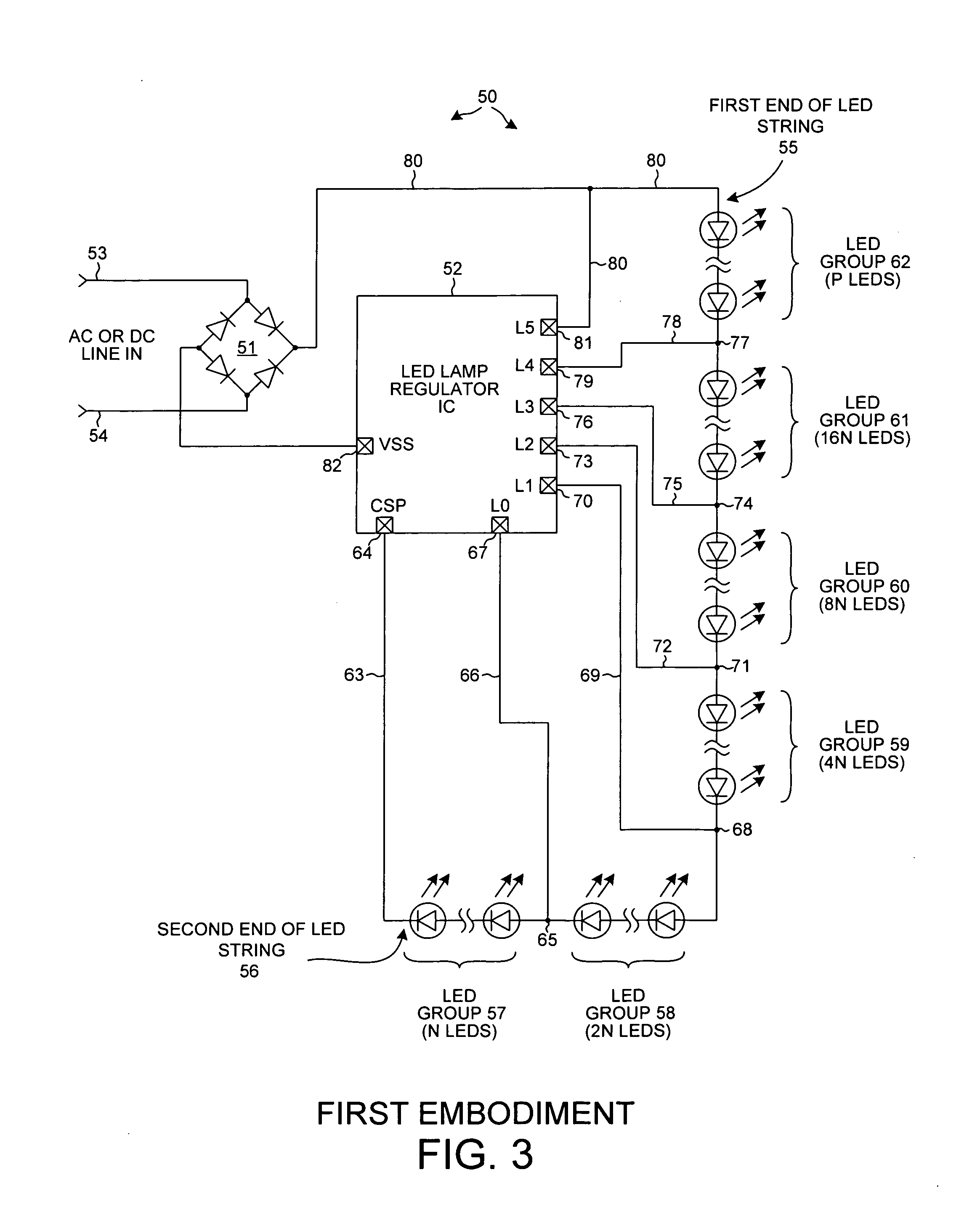
An LED lamp with an integrated circuit, a rectifier, and a string of series-connected LEDs rectifies an incoming AC signal. The integrated circuit includes power switches that can separately and selectably short out a corresponding one of several groups of LEDs in an LED string across which the rectified AC signal is present. As the voltage across the string increases, the integrated circuit controls the power switches to increase the number of LEDs through which current flows, whereas as the voltage across the string decreases the integrated circuit controls the power switches to decrease the number of LEDs through which current flows. The flow of LED string current is broken to reduce flicker. Alternatively, a valley fill capacitor peaks LED current during the valleys of the incoming AC signal to reduce flicker. LED current is regulated to provide superior efficiency, reliability, power-factor correction, and lamp over-voltage, -current, and -temperature protection.
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
Resonant power factor correction converter
ActiveUS20090290385A1Increase pressureBurdenAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionMass storageSingle stage
An AC-to-DC power converter configured to provide power factor correction and a single isolated low-voltage output. The power converter includes a single-stage resonant power converter including an isolation transformer, a resonant tank, a rectifier, and a bulk storage capacitor coupled to an output of the isolation transformer. In typical applications, at least one non-isolated power converter is coupled to the output of the single-stage isolated power factor correction converter.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Circuits, systems, methods, and software for power factor correction and/or control
ActiveUS7292013B1Minimize periodMinimize powerAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionImage resolutionPower factor control
Circuits, systems, methods and software for controlling a power conversion and / or correcting and / or controlling a power factor in such conversion(s). The present invention generally takes a computational approach to reducing or minimizing zero current periods in the critical mode of power converter operation, and advantageously reduces zero current periods in the critical mode of power converter operation, thereby maximizing the power factor of the power converter in the critical mode and reducing noise that may be injected back into AC power lines. The present power factor controller allows for greater design flexibility, reduced design complexity, and reduced resolution and greater tolerance for error in certain parameter measurements useful in power factor correction and / or control.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Fast charger for high capacity batteries
InactiveUS20050046387A1Reduce heatMinimise currentCircuit monitoring/indicationDifferent batteries chargingFast chargingHertz
A highly efficient fast charger for high capacity batteries and methods for fast charging high capacity batteries. The fast charger preferably comprises a rectified AC input of single or preferably three phases, with an optional power factor corrected input, minimally filtered with high frequency, high ripple current capacitors, which is switched with a power switching circuit in the “buck” configuration into an inductor / capacitor output filter. Metallized film capacitors are employed, to minimize the rectified 360 Hertz AC component filtering while providing transient switch protection and ripple current requirements for the buck regulator, to provide a high current fast charger with substantially improved power factor. High power, high frequency switching with minimized output filter size provides a highly filtered DC output. The fast charger is adapted to be constructed in a modular design for simple maintenance.
Owner:AKER WADE POWER TECH
Two-stage converter using low permeability magnetics
InactiveUS6952355B2Improve power factorProvide protectionEfficient power electronics conversionDc-dc conversionDesign strategyPower density
The use of low permeability magnetic material (NSME) with the disclosed design strategies form a two-stage isolated output converter system with the distinct advantages of superior density, efficiency, thermal operating bandwidth, service life, transient survival, and form factor flexibility over the prior art. These improvements are realized by, optimized application of NSME, efficient rectifying flyback management techniques, inclusion of switching buffers that substantially reduce switching losses. The instant invention provides power factor correction, output regulation, inrush limiting, over voltage, over current, over temperature, and transient protection, multi-converter load sharing, hot swapability, and fault signals.The disclosed system is designed, specified, and certified to function from −40 deg. C. to +65 deg. C. from a 180 vac to 264 vac 50 / 60 Hz input line and supports 1000 watts of output or 600 watts from 90 vac to 120 vac 50 / 60 Hz line input at greater then 0.95 power factor and features a packaged power density of 14 watts per cu. in. at high line.
Owner:SATURN ELECTRONICS & ENG
Power factor correction converter including input current detecting circuit
ActiveUS8395366B2Accurate detectionAppropriatelyAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionDigital signal processingInductor
A low-cost PFC converter capable of detecting an inductor current including a DC component and performing appropriate correction of a power factor with low loss includes a diode bridge that rectifies an AC voltage input from an AC input power supply Vac, a series circuit including an inductor and a switching element, a rectifying and smoothing circuit that is connected in parallel to the switching element and that includes a diode and a smoothing capacitor, and a digital signal processing circuit that performs on / off control on the switching element so that an input current input from the AC input power supply Vac has a similar waveform with respect to an AC voltage. A current flowing through the inductor during an off period of the switching element is detected using a current detecting resistor, and a decreased voltage of the current detecting resistor is sampled at the middle of the off period of the switching element, thereby detecting an average value of the input current.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Switching power converter and control system
ActiveUS8076920B1Efficient power electronics conversionElectroluminescent light sourcesEnergy transferControl signal
A switching power converter tracks a time-varying input voltage during each cycle of the input voltage to provide power factor correction. The switching power converter includes a switch with a frequency and duty cycle modulated control signal. The switch controls the transfer of energy between the input and output of the switching power converter. The frequency of the control signal is greater than a frequency of the input signal. The control signal frequency is modulated during each cycle of the input voltage so that energy transferred from the switching power tracks the energy supplied to the switching power converter.
Owner:CIRRUS LOGIC INC
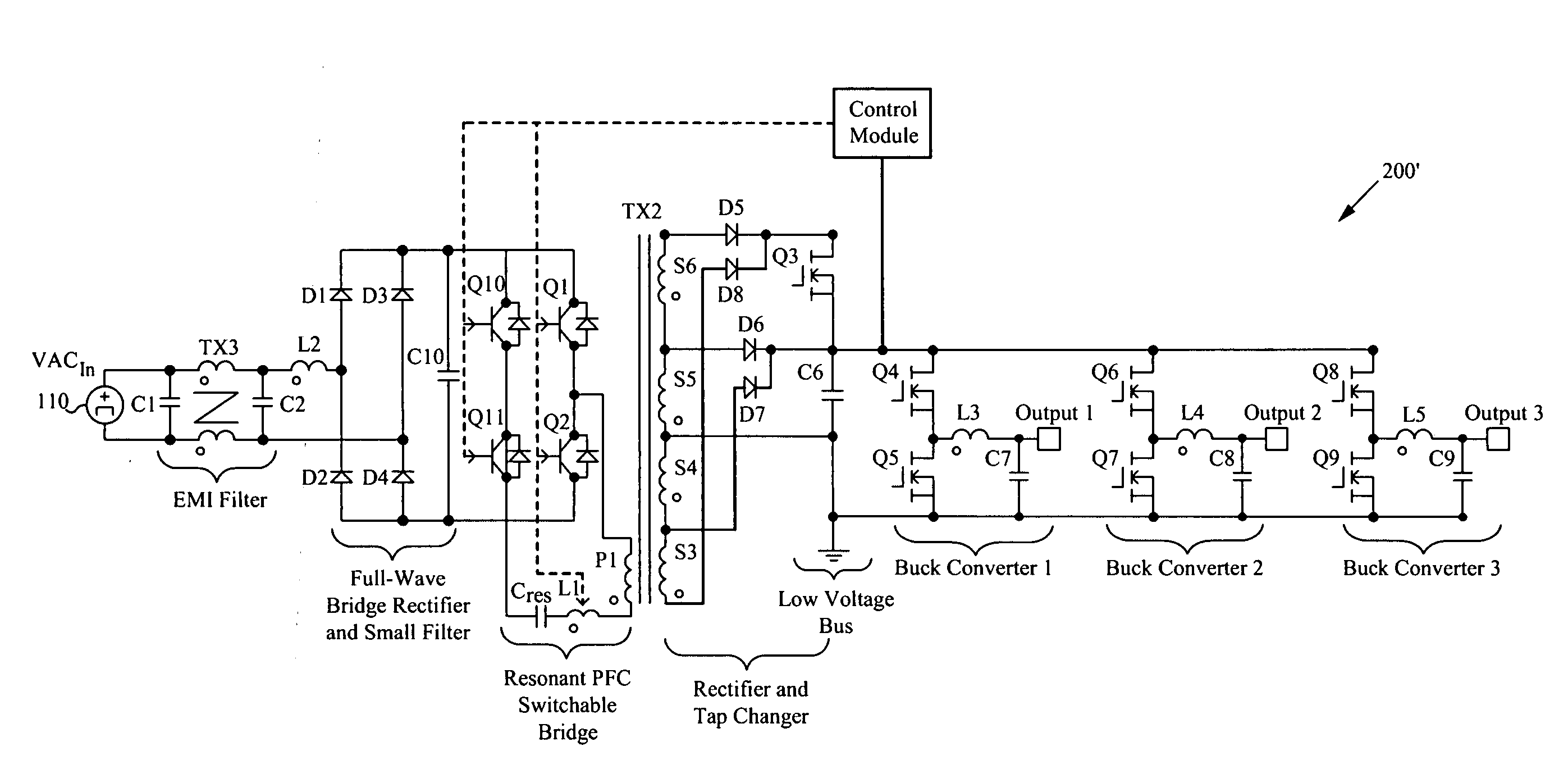
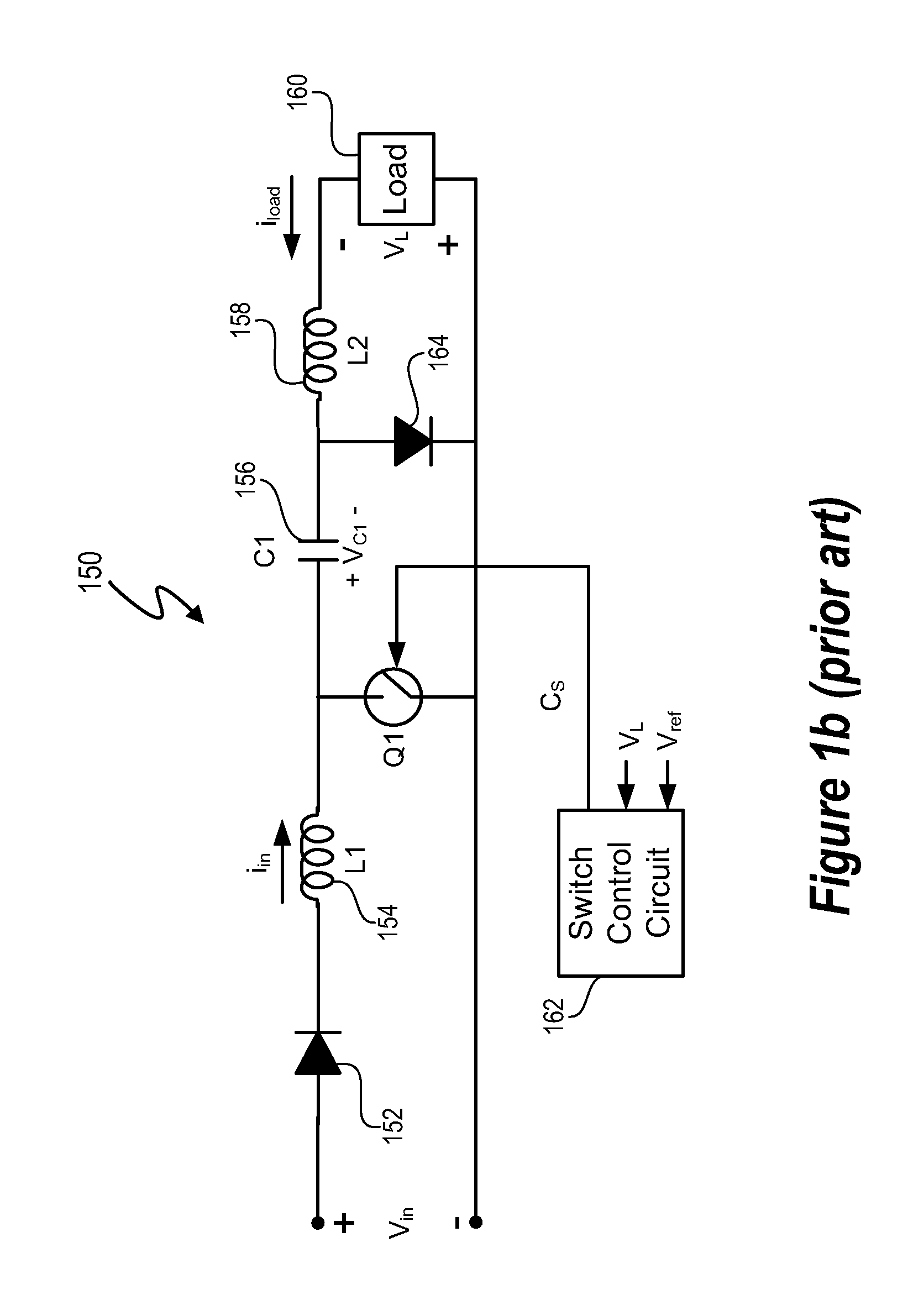
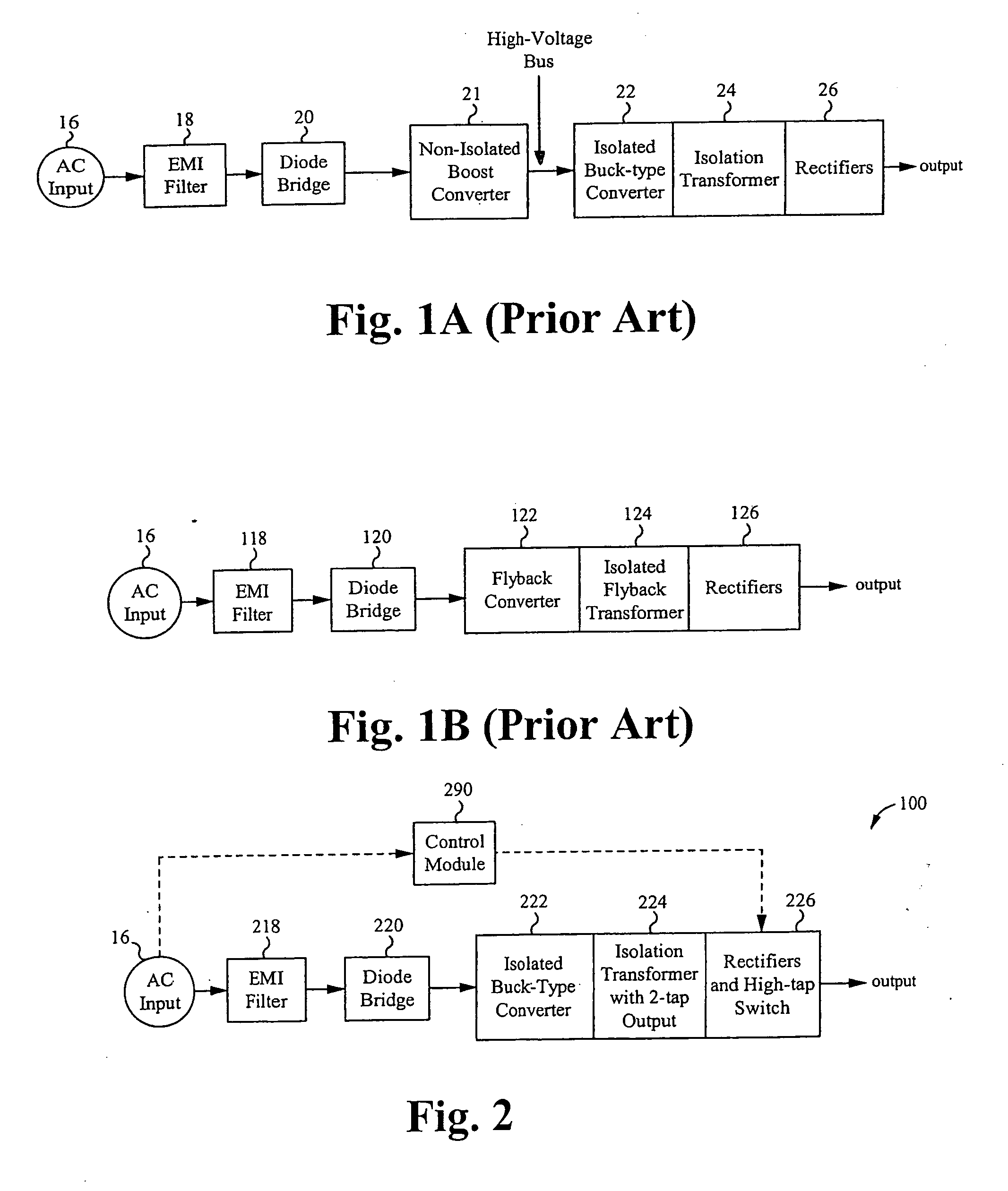
High power factor isolated buck-type power factor correction converter
ActiveUS20090290384A1Improve power factorMinimize component stressDc network circuit arrangementsEfficient power electronics conversionFull waveTap changer
A regulated power factor corrected power supply apparatus is provided. The apparatus includes an input rectifier circuit for receiving an input AC voltage and outputting a full-wave rectified DC voltage. A single-stage isolated buck-type converter is coupled with the input circuit. The converter circuit comprises an isolated buck-type converter circuit including an isolation transformer. An output rectifier and semiconductor tap switch are coupled to a secondary winding of the isolation transformer. The tap switch couples a larger portion of the secondary winding to an output bulk capacitor during the portions of the input sinewave half-cycle, which are low in amplitude. The tap switch enables the single-stage isolation buck-type converter to operate over a much larger portion of the input sinewave, but also allows the converter to operate at high-efficiency over the majority of the input sinewave.
Owner:MYPAQ HLDG LTD
Power factor correction boost converter with continuous, discontinuous, or critical mode selection
ActiveUS7733678B1Small sizeReduce Harmonic DistortionAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionConstant powerAverage current
In a method and apparatus for controlling power factor correction in mixed operation modes, a frequency of the input voltage is obtained by detecting the zero crossing points of the input voltage. A peak of the input voltage is obtained by detecting input voltage with 90 degree phase. Thus, the present invention predicts the input voltage by its frequency and peak and the characteristic of the sine wave. A digital signal processor computes the duty and frequency of a boost switch, switching the operation mode of the boost converter among continuous mode, critical mode and discontinuous mode according to input voltage or the load. According to another aspect, the operation is switched to critical mode from the average current mode when a zero current is detected before the charging and recharging cycle of the boost switch is finished. Overcurrent protection may be achieved by controlling current in response to detected voltage to provide a substantially constant power level. The overcurrent protection may be adaptive in nature.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
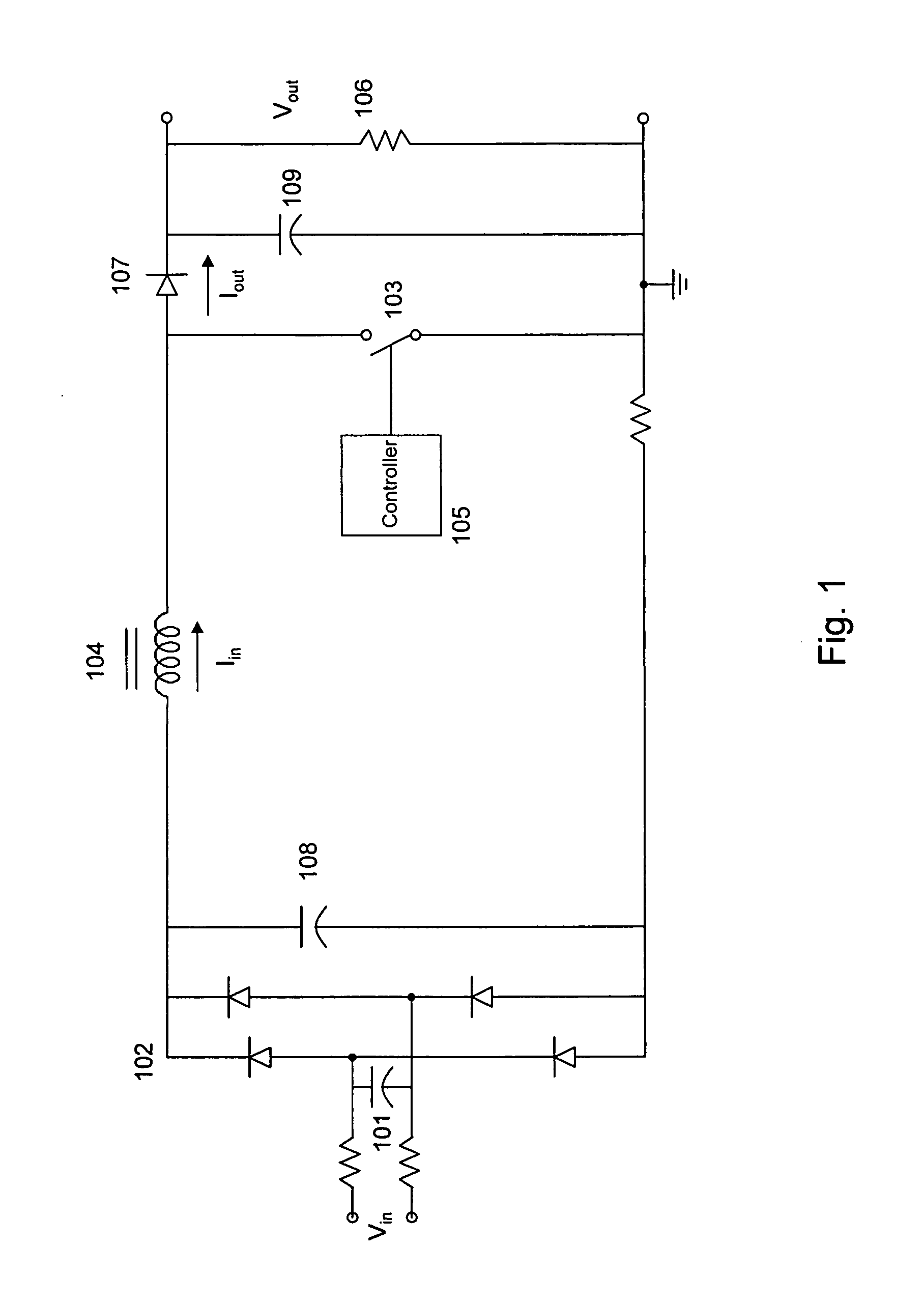
Power supply apparatus and methods with power-factor correcting bypass mode
InactiveUS6906933B2Corrected power factorLimited bandwidthEfficient power electronics conversionConversion with intermediate conversion to dcPower factor correctorAC power
A power supply apparatus, such as an uninterruptible power supply, includes an AC input configured to be coupled to an AC power source and an AC output. The apparatus also includes an AC / DC converter circuit, e.g., a boost rectifier circuit, with an input coupled to the AC input. The apparatus further includes a DC / AC converter circuit, e.g., an inverter circuit, configured to be coupled between an output of the AC / DC converter circuit and the AC output. A bypass circuit is operative to establish a coupling between the AC input to the AC output in a first (e.g., bypassed) state and to interrupt the coupling in a second (e.g., “on line”) state. The AC / DC converter circuit is operative to control current at the AC input when the bypass circuit is in the first state. For example, the AC / DC converter circuit may be operative to control current at the AC input to correct a power factor at the AC input port when bypassed, such that the AC / DC converter circuit may act as a line conditioner in the bypassed state.
Owner:EATON INTELLIGENT POWER LIMITED
Power factor corrected single-phase AC-DC power converter using natural modulation
InactiveUS7564706B1Reduce lossesMost efficientAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionLevel shiftingElectric power system
A power factor corrected (pfc) ac-dc converter has a modified boost input and a modified buck output. Unlike the prior art boost input, the boost switch returns to the output, not to ground. Unlike the prior art buck output stage, a third switch connects to the input. This allows much of the input current to pass through the converter to the output. There is no input current measurement, but nearly ideal power factor correction is achieved through “natural modulation.” A preferred pfc ac-dc converter uses a variable dc-dc transformer on its output, as a post regulator, to provide dielectric isolation and to provide voltage level shifting. The output of the pfc ac-dc converter has the control characteristics of a buck converter, so it is a natural mate for the variable dc-dc transformer. An ac-dc buck converter is most efficient at its maximum duty cycle. It cannot regulate for a lower input voltage, but it can reduce its duty-cycle to control for higher input voltages. A variable dc-dc transformer is most efficient at its maximum ratio. It cannot regulate for a higher input voltage, but it can reduce its effective turns ratio to control for a lower input voltage. With a small overlap in their control ranges, both parts of the power system can operate at maximum efficiency. The variable dc-dc transformer controls the output voltage for nominal and low input voltage. The ac-dc buck converter limits over-voltage transients.
Owner:HERBERT EDWARD
LED drive circuit with dimming function and lamp
ActiveCN101835314ASolve the problem that the LED cannot be dimmed directlyElectroluminescent light sourcesElectric light circuit arrangementDIACControl signal
The invention discloses an LED drive circuit with dimming function and a lamp. The LED drive circuit comprises a TRIAC dimmer; the TRIAC dimmer receives an alternating-current input voltage and generates a cut phase voltage signal; the cut phase voltage signal is rectified by a rectifying module and then coupled to a dimming signal generator; and a power factor correcting controller receives an output signal of the dimming signal generator, reflects a feedback signal of LED brightness, and outputs a switching control signal to control the on and off of a switching tube so as to drive an LED. The dimming of the LED is implemented by adjusting a conduction angle of the TRIAC dimmer.
Owner:CHENGDU MONOLITHIC POWER SYST
Power supply with integrated bridge and boost circuit
InactiveUS6738274B2Small sizeAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionAlternating currentSwitching power
An alternating current to direct current switching power supply, with power factor correction, and having an integrated rectifying bridge and boost circuit.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
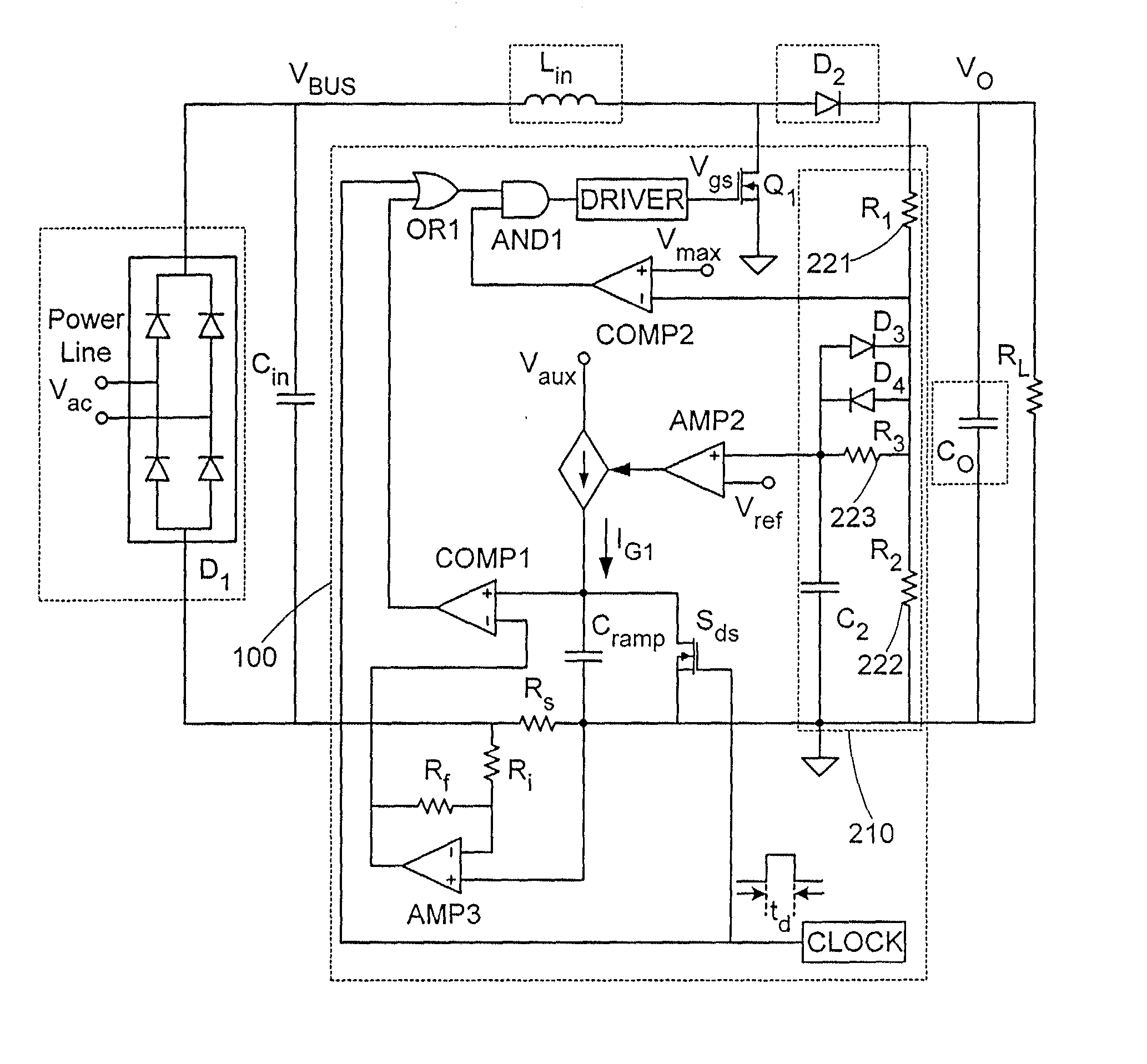
High frequency partial boost power factor correction control circuit and method
ActiveUS7148664B2Efficient power electronics conversionElectric variable regulationReference currentEngineering
A circuit for providing power factor correction includes a boost converter circuit with a boost inductance and a power factor correction switch and a control circuit. The control circuit provides a pulse width modulated signal to control the on time of a PFC switch, and also includes a power factor correction pulse width modulated device receiving as inputs a rectified AC input voltage, a DC bus voltage, a signal proportional to the current through the inductor and a reference current signal. The power factor correction pulse width modulated device also includes a pulse width modulated generator operable to provide the pulse width modulated signal to control the on time of the PFC circuit and a pulse width modulated blanking device operable to provide an enable / disable signal to disable the pulse width modulated generator when predetermined conditions are met.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AMERICAS CORP
AC LED lamp involving an LED string having separately shortable sections
ActiveUS20110227490A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesPower switchingEngineering
An LED lamp includes a rectifier, an integrated circuit and a string of series-connected LEDs. The lamp receives an incoming AC signal such that a rectified version of the signal is present across the LED string. The integrated circuit includes a plurality of power switches. Each power switch is coupled so that it can separately and selectably short out a corresponding one of several groups of LEDs in the string. As the voltage across the string increases the integrated circuit controls the power switches such that the number of LEDs through which current flows increases, whereas as the voltage across the string decreases the integrated circuit controls the power switches such that the number of LEDs through which current flows decreases. LED string current flow is controlled and regulated to provide superior efficiency, reliability, anti-flicker, regulation against line voltage variations, power factor correction, and lamp over-voltage, over-current, and over-temperature protection.
Owner:ACTIVE SEMI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com