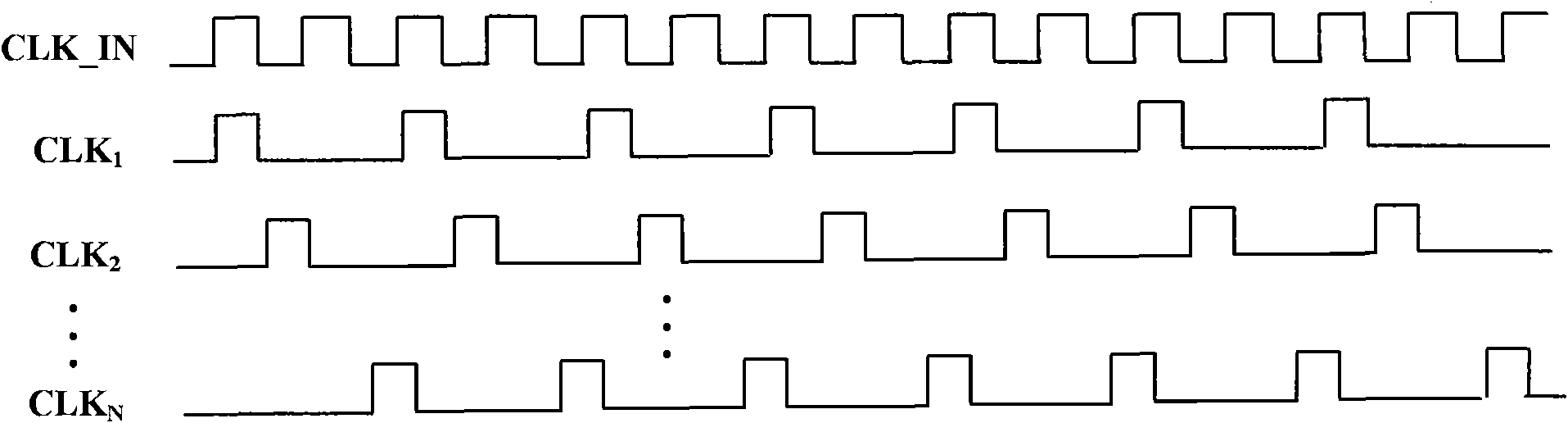
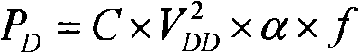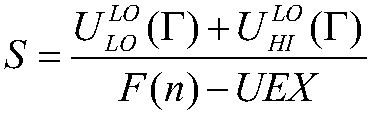Patents
Literature
252 results about "Dynamic power dissipation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
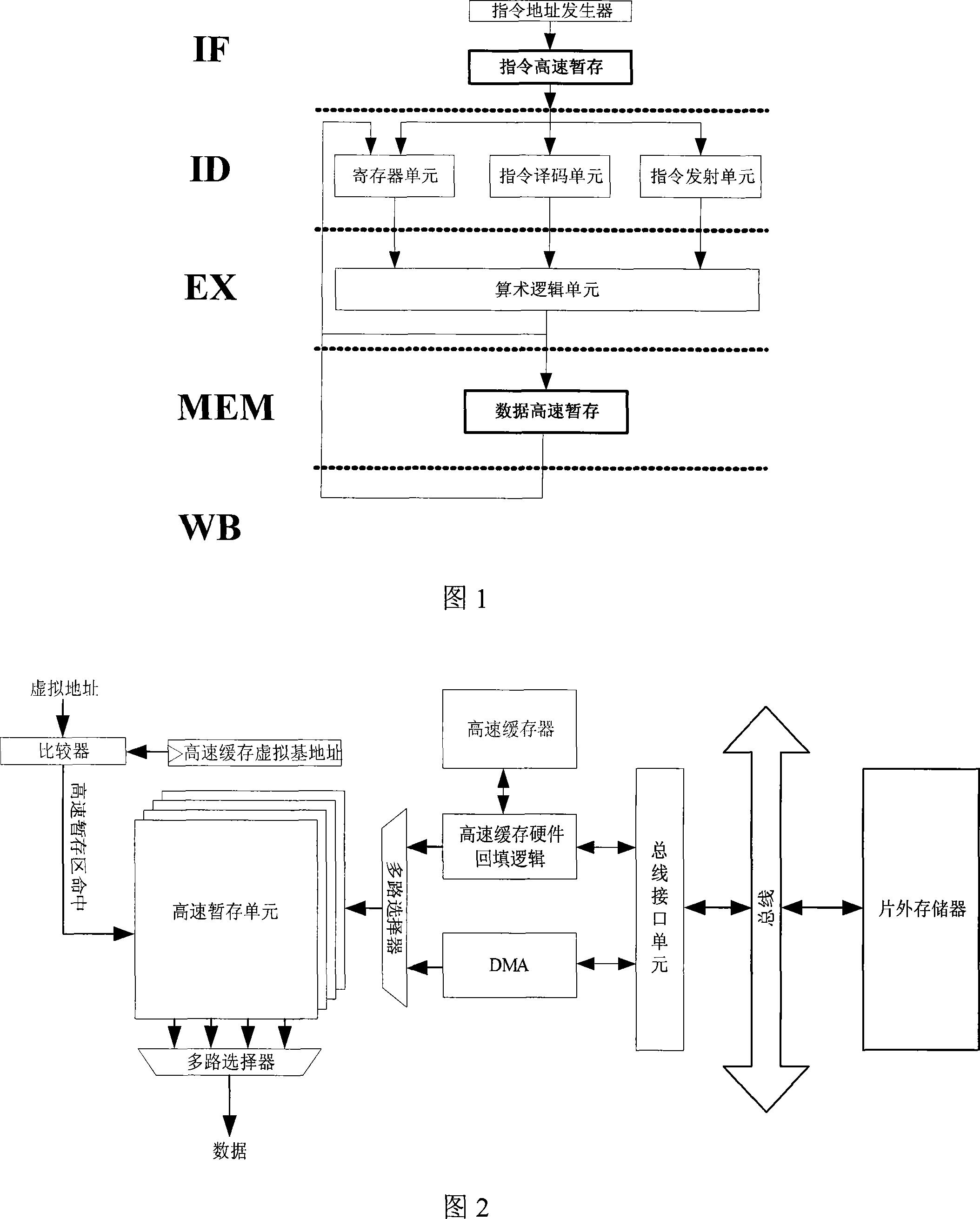
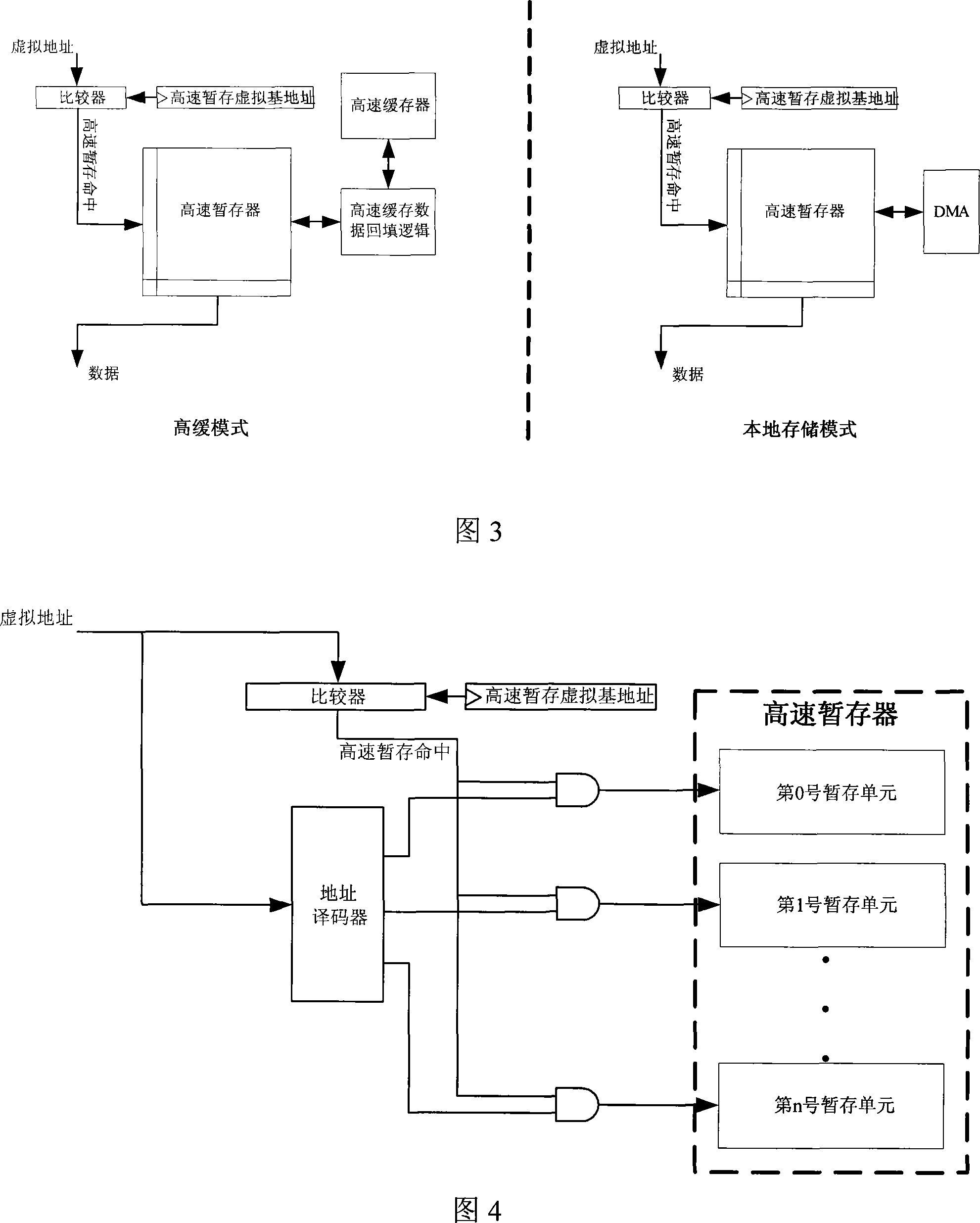
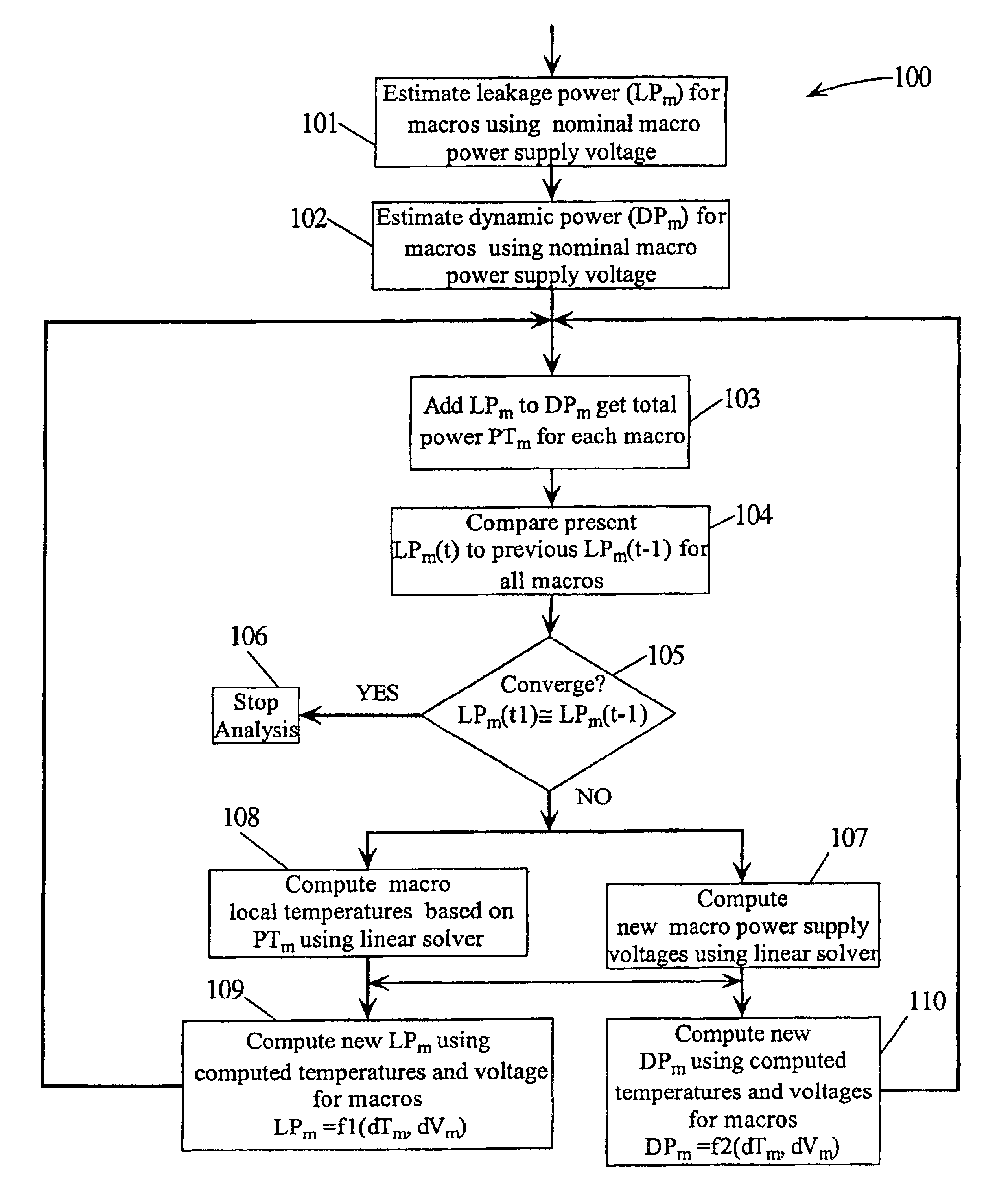
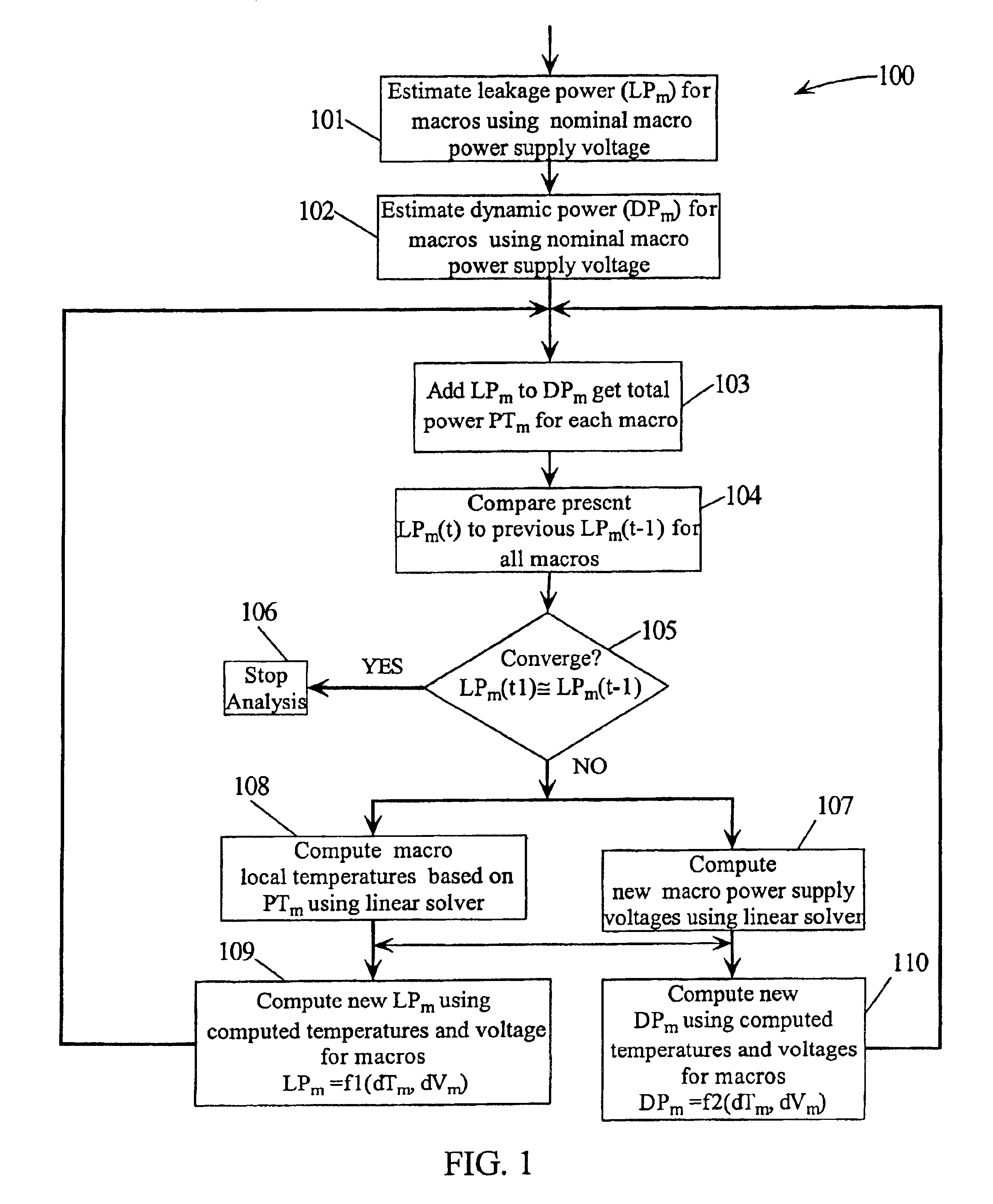
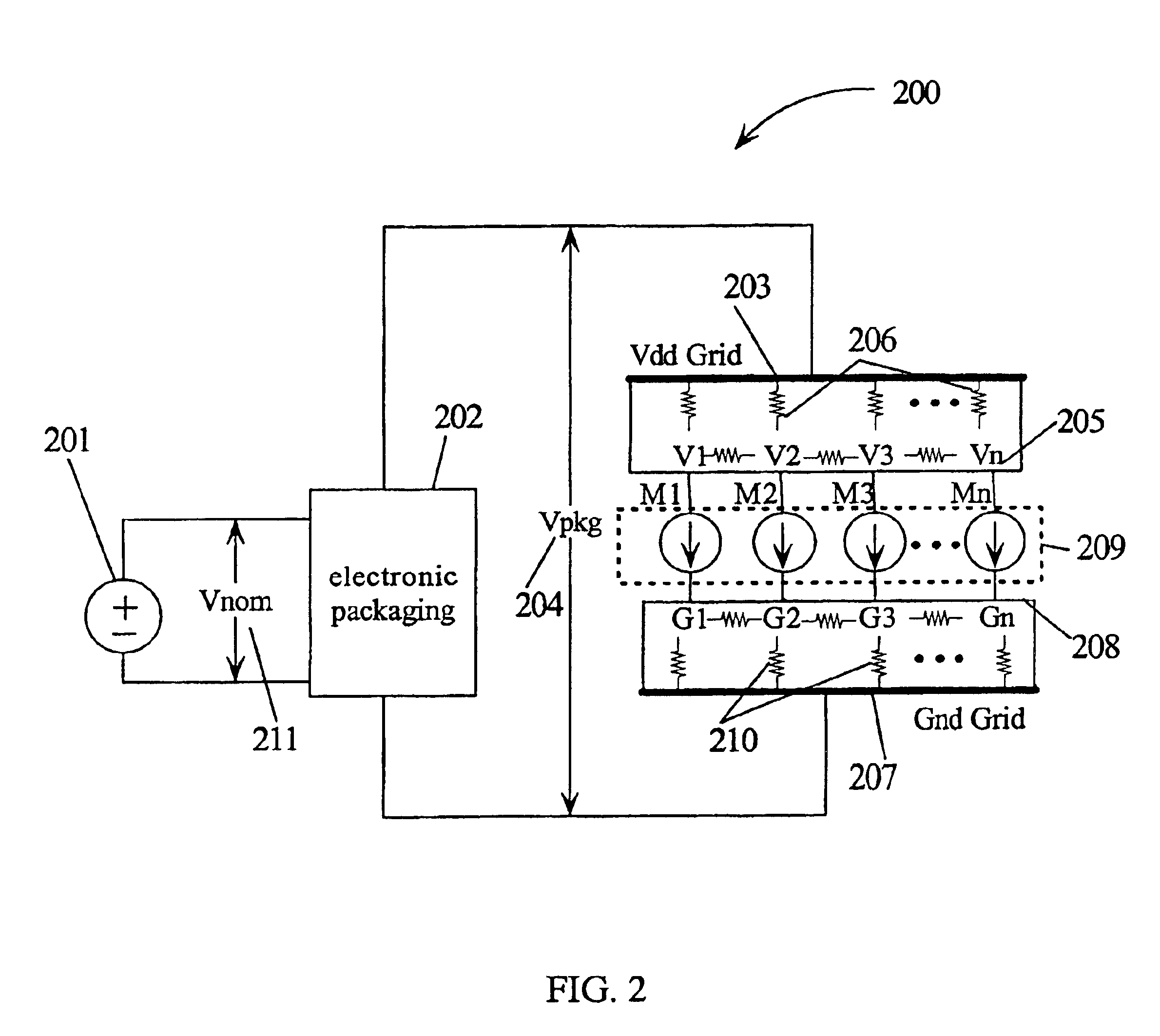
Method for determining the leakage power for an integrated circuit
InactiveUS6842714B1Electric devicesCurrent/voltage measurementElectrical resistance and conductanceElectric distribution network
A method for determining full chip leakage power first estimates leakage power and dynamic power for each circuit macro. The power supply voltage to each macro is first assumed to be nominal. The power dissipation for each macro is modeled as a current source whose value is the estimated power divided by the nominal power supply voltage. The power distribution network is modeled as a resistive grids. The thermal environment of the IC and its electronic package are modeled as multi dimensional grids of thermal elements. Algebraic multi-grid (AMG) methods are used to calculate updated circuit macro voltages and temperatures. The macro voltages and temperatures are updated and updated leakage and dynamic power dissipation are calculated. Iterations are continued until leakage power converges to a final value.
Owner:IBM CORP
Driving circuit unit, gate driving circuit and display device
The invention relates to a gate driving circuit and a display device. The gate driving circuit comprises multiple levels of driving circuit units connected in series. Each level of units comprises an inputting module for providing threshold voltage of a driving module, a driving module for responding to the threshold voltage and for sending a first clock signal to a signal outputting interface, a discharging module for responding to an output signal or a clock signal of an adjacent level and for coupling a control terminal of the driving module to a first voltage source, a clock feedthrough inhibiting module for stablizing the potential of the control terminal of the driving module under the control of the clock signal and the output signal of the adjacent level, and a low level maintaining module for stablizing the output signal at the potential of the first voltage source under the control of the clock signal. The driving circuit unit, gate driving circuit and display device provided by the invention employ single driving tube to realize the fast pull-up and pull-down of the output signal with sequential coordination, reducing the delay time of the rise and fall of the output signal at a low temperature, and employs the clock feedthrough inhibiting module to stablize the gate potential of the driving tube, reducing the corresponding dynamic power consumption.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL +1
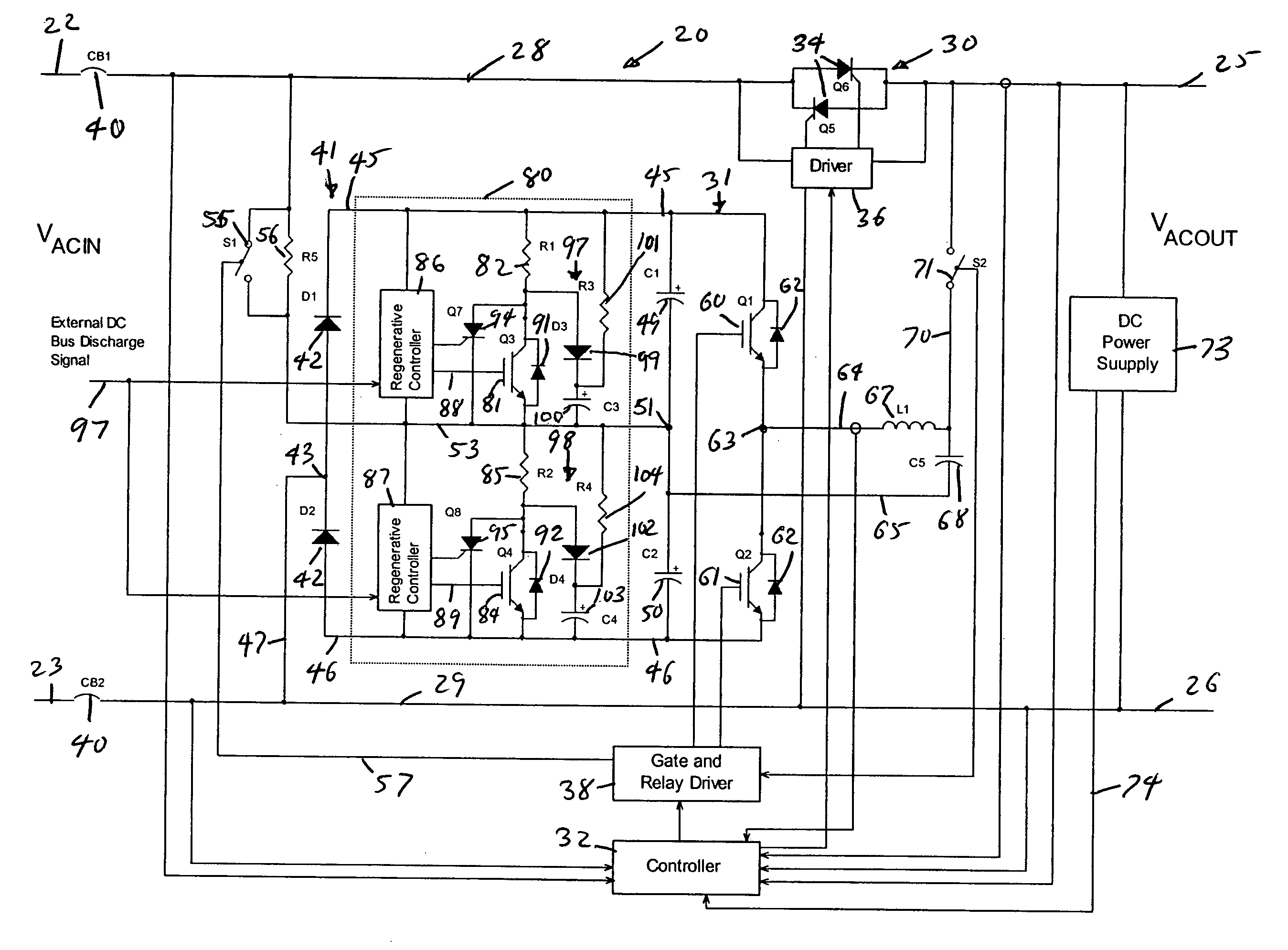
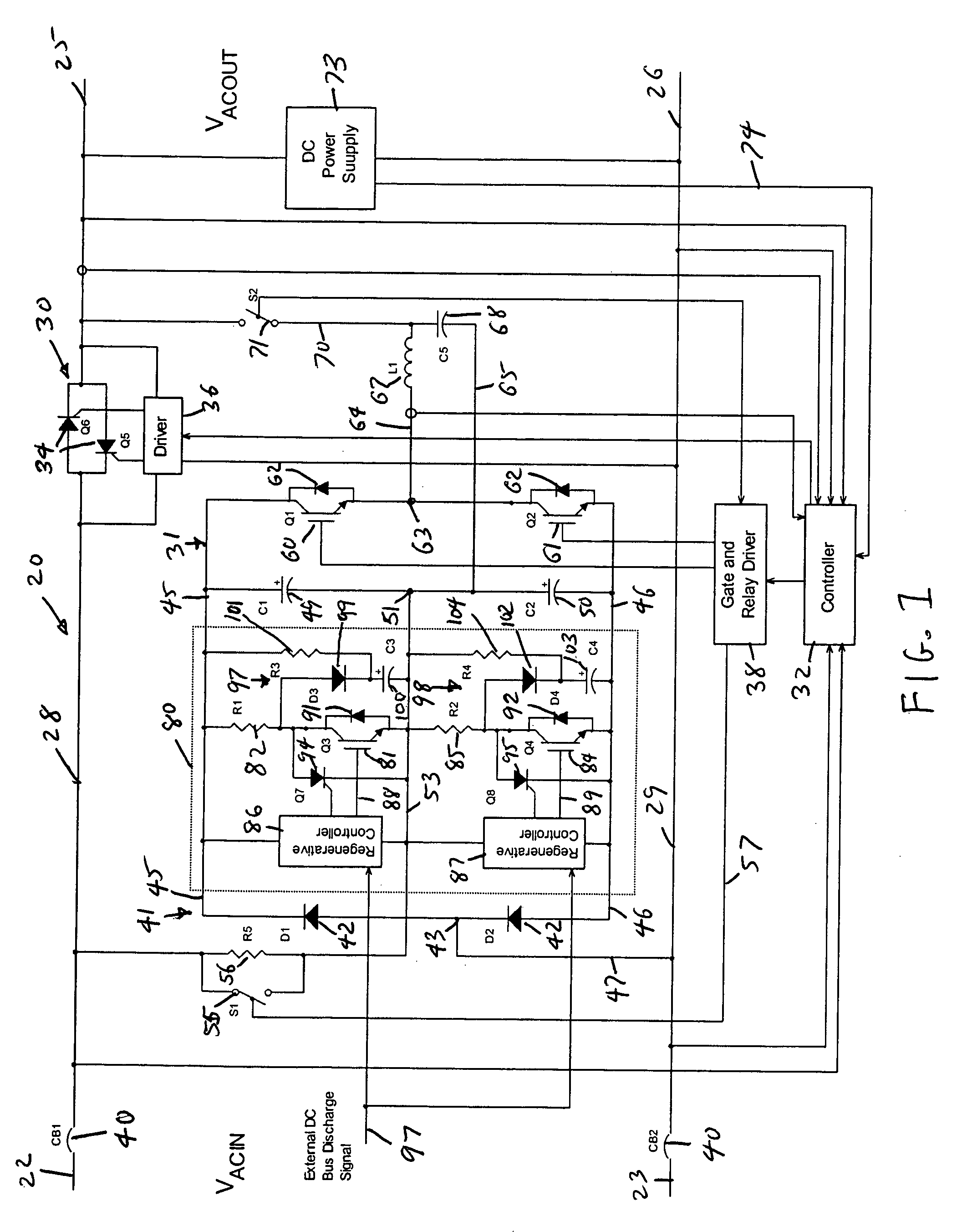
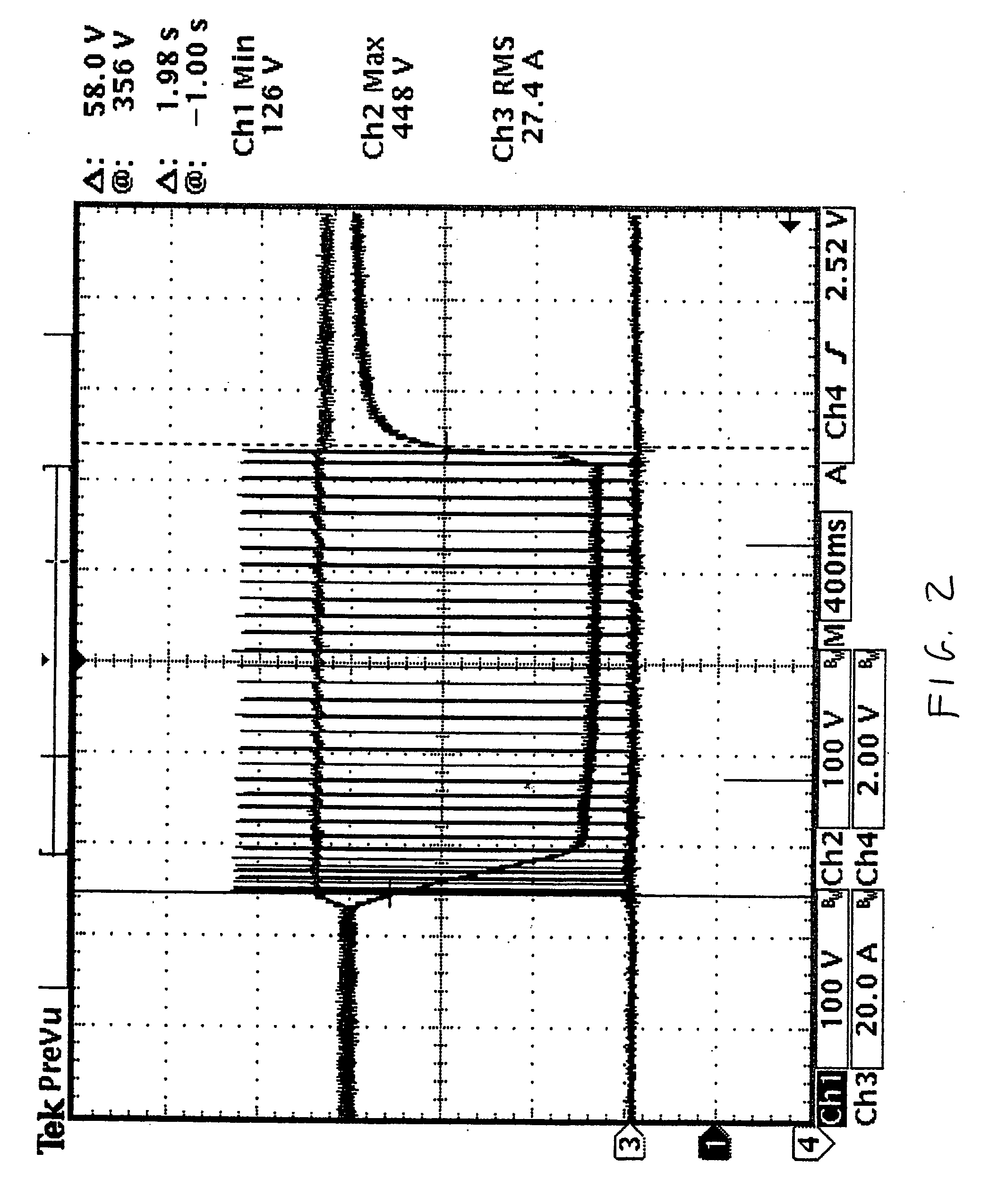
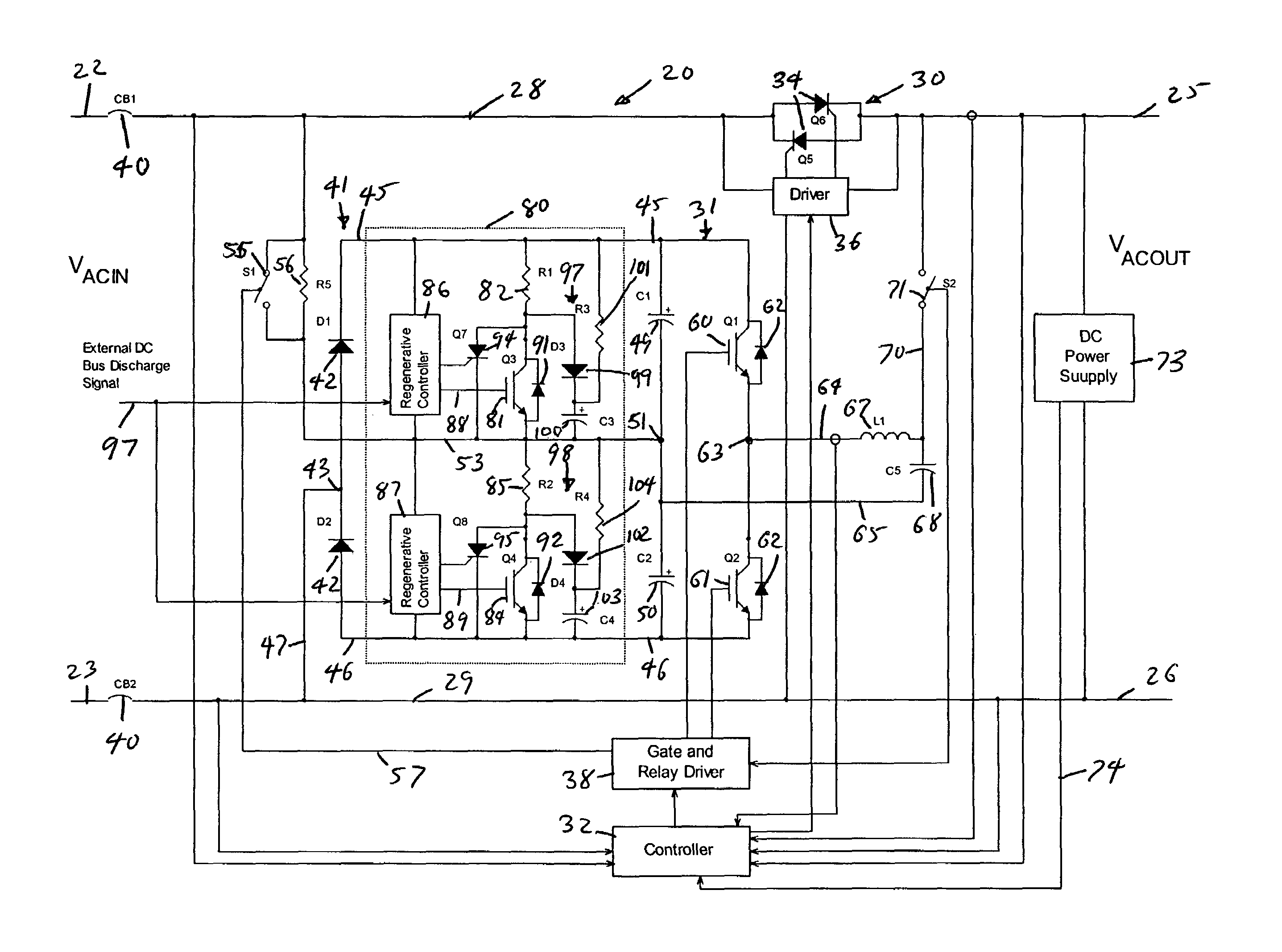
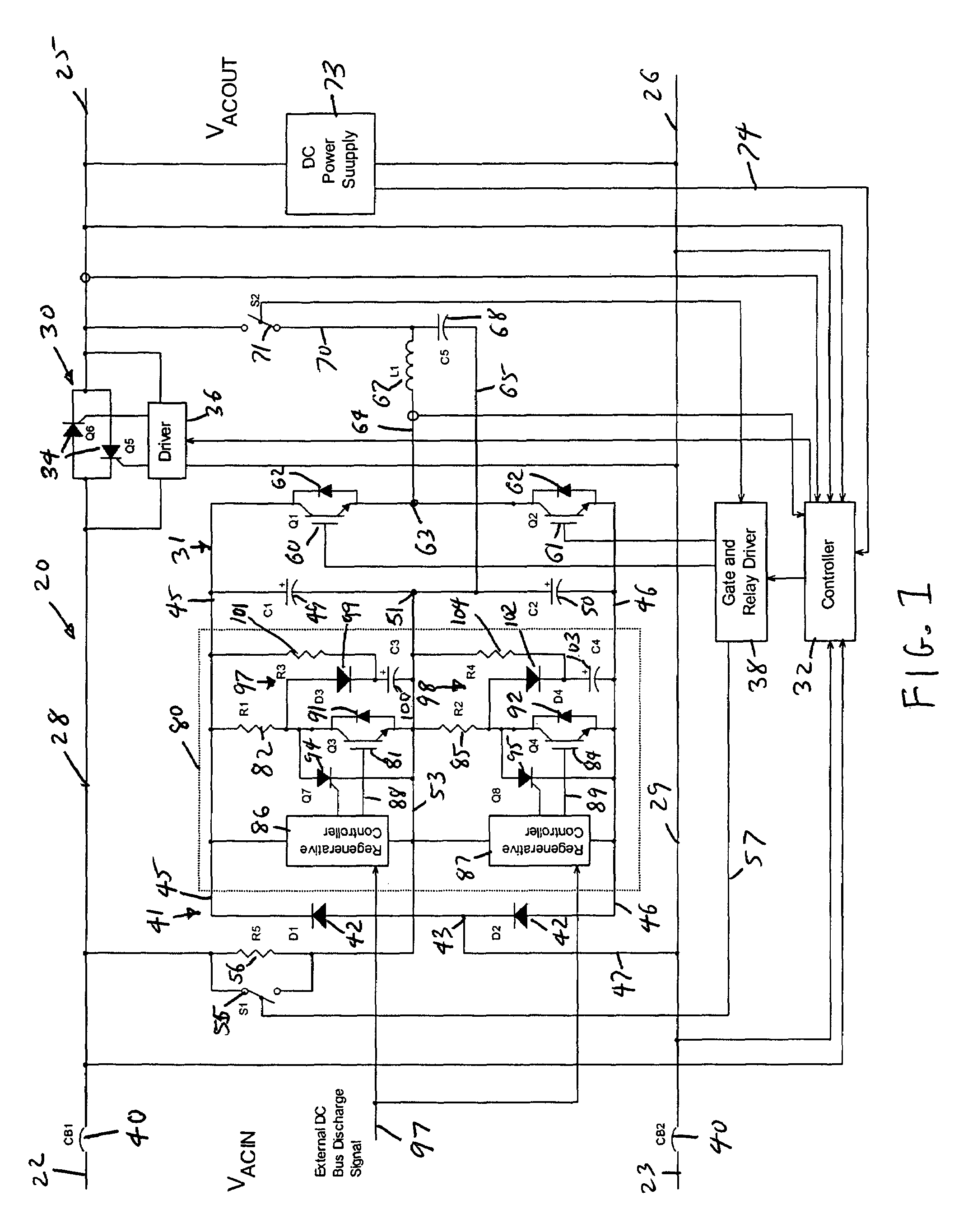
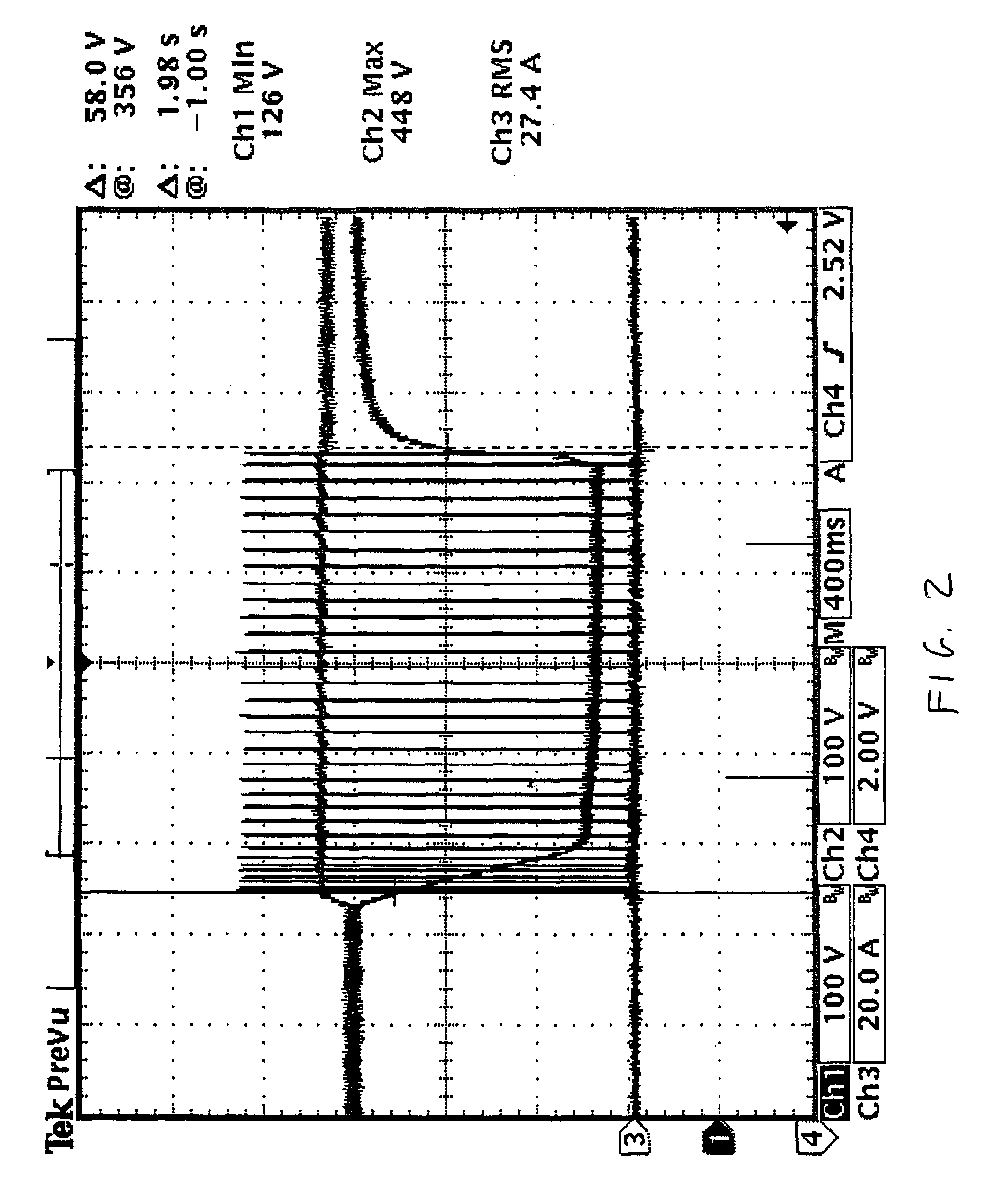
Power conversion and voltage sag correction with regenerative loads
ActiveUS20060202636A1Improve efficiencyLow costActive power filteringConversion with intermediate conversion to dcCapacitanceElectric force
In dynamic voltage sag correctors and other power conversion equipment having a DC bus that is subject to over-voltage conditions due to power being fed back by a regenerative load, a bus discharge switching device and a discharge resistor are connected in series across the DC bus lines. The discharge switching devices are switched on to discharge the energy storage device connected to the bus, or to separately discharge the two capacitors of a split capacitor DC bus, to eliminate the over-voltage conditions. The discharge switching devices may be switched on and off periodically with a selected duty cycle to discharge energy from the energy storage capacitor or other energy storage device through the discharge resistor at a rate which does not exceed the power rating of the discharge resistor. The discharge switching device may be switched with a fixed duty cycle or with a variable duty cycle that is based on the dynamic power dissipation characteristics of the discharge resistor.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
Automatic control method for system power consumption
ActiveCN101477403AReduce complexityPower supply for data processingComputer resourcesAutomatic control
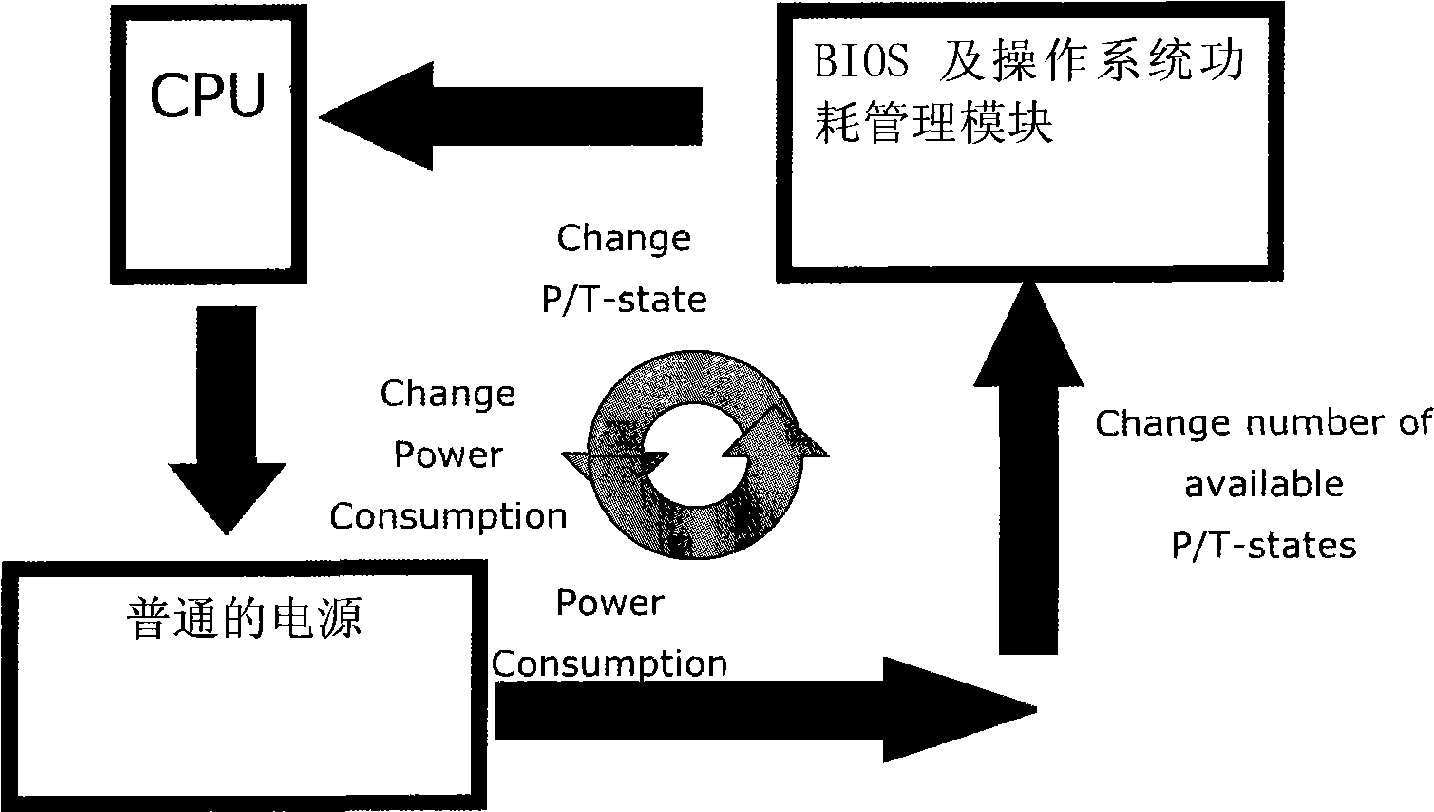
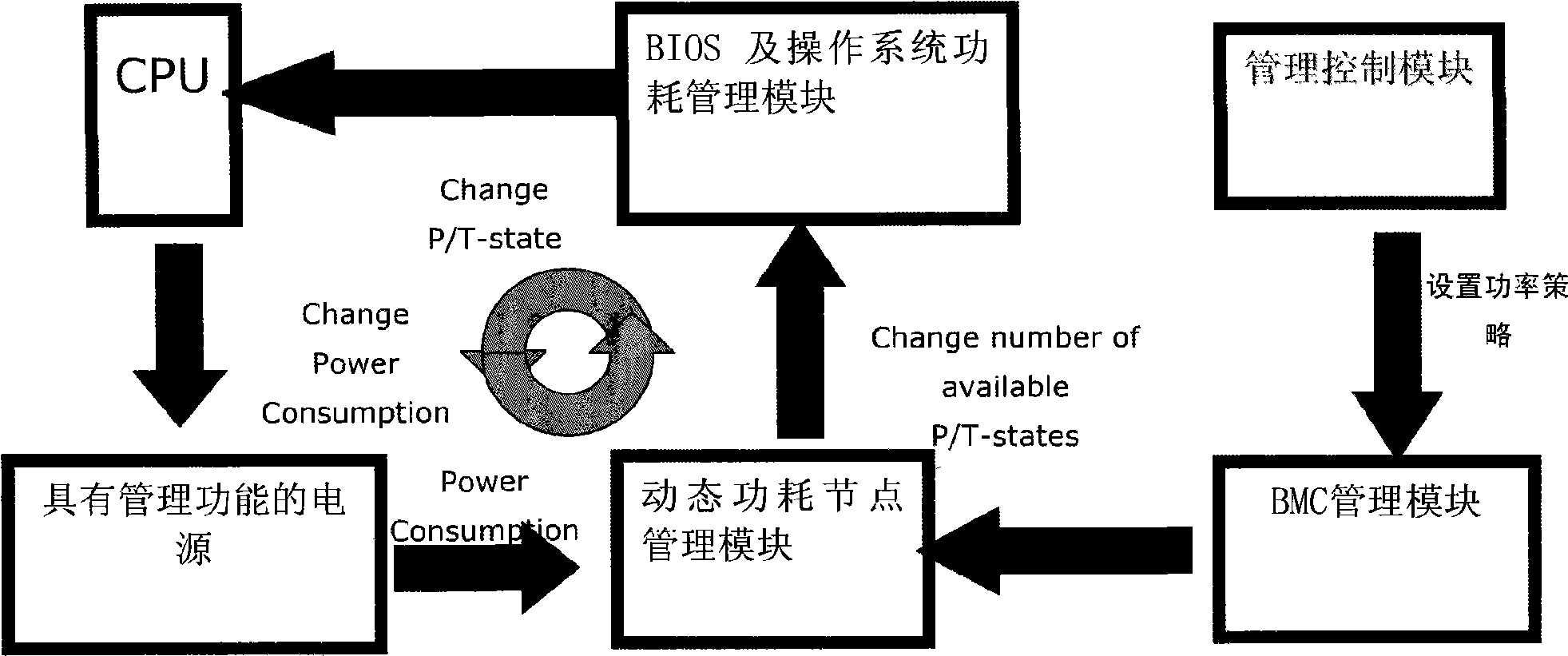
The invention provides a system power consumption automatic control method, which aims at a server or a group of computers to define a target power consumption value, timely adjusts a frequency control system of a CPU (computer processing unit) to run under the target power consumption value through a power consumption control management module, and achieves the purpose of controlling the power consumption. The power consumption control management module comprises an IPMI management control module, a power management module provided with a PMBUS communication bus, a dynamic power consumption node management module, a power management module, a management control platform, a BMC management module and a power consumption management module for BIOS and an operating system. The method of the invention is based on the flexible extension properties of the modular components, and each module as a modular component in the system can carry out flexible configuration, thereby reducing the complexity of the system management; moreover, the method covers the shortage that a traditional network server which takes computer resources as the core can't automatically adjust a power value set in advance, and enables the servers to be more applicable to the complex high performance commercial application fields which save more energy at present, thereby having broad development prospect.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
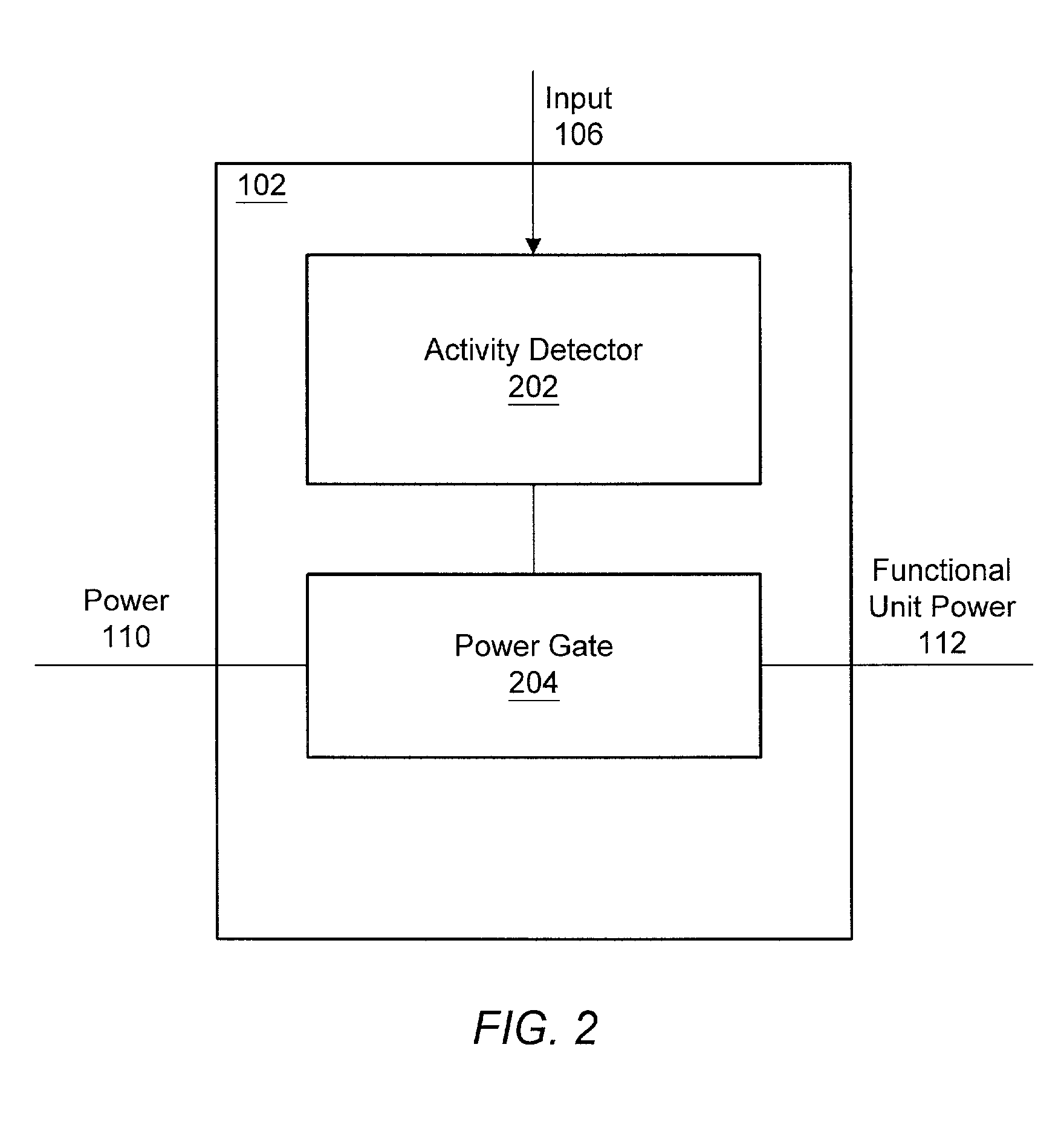
Apparatus and method for decreasing power consumption in an integrated circuit
ActiveUS6976182B1Reduce overall static and dynamic power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingEngineeringEmbedded system
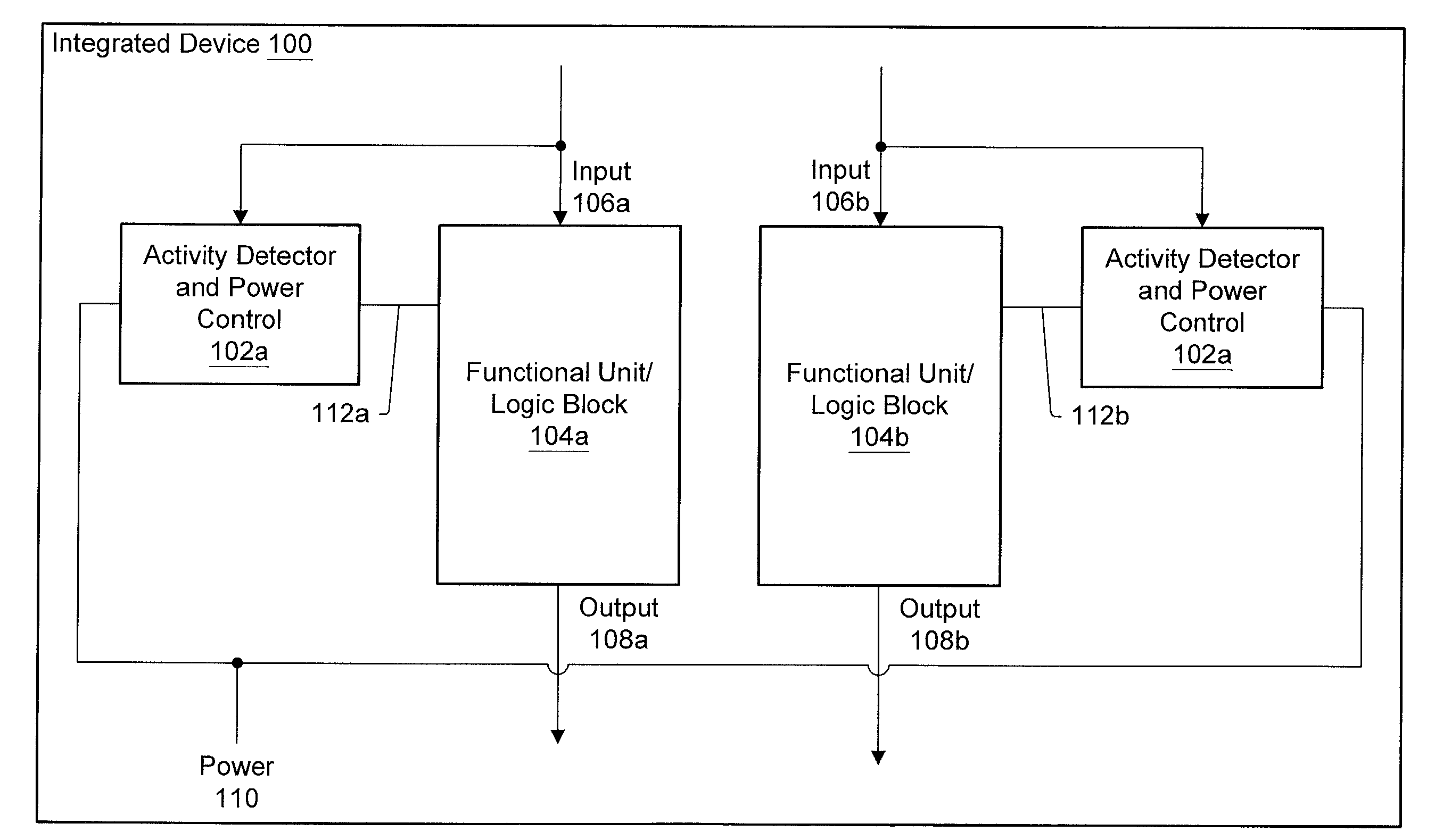
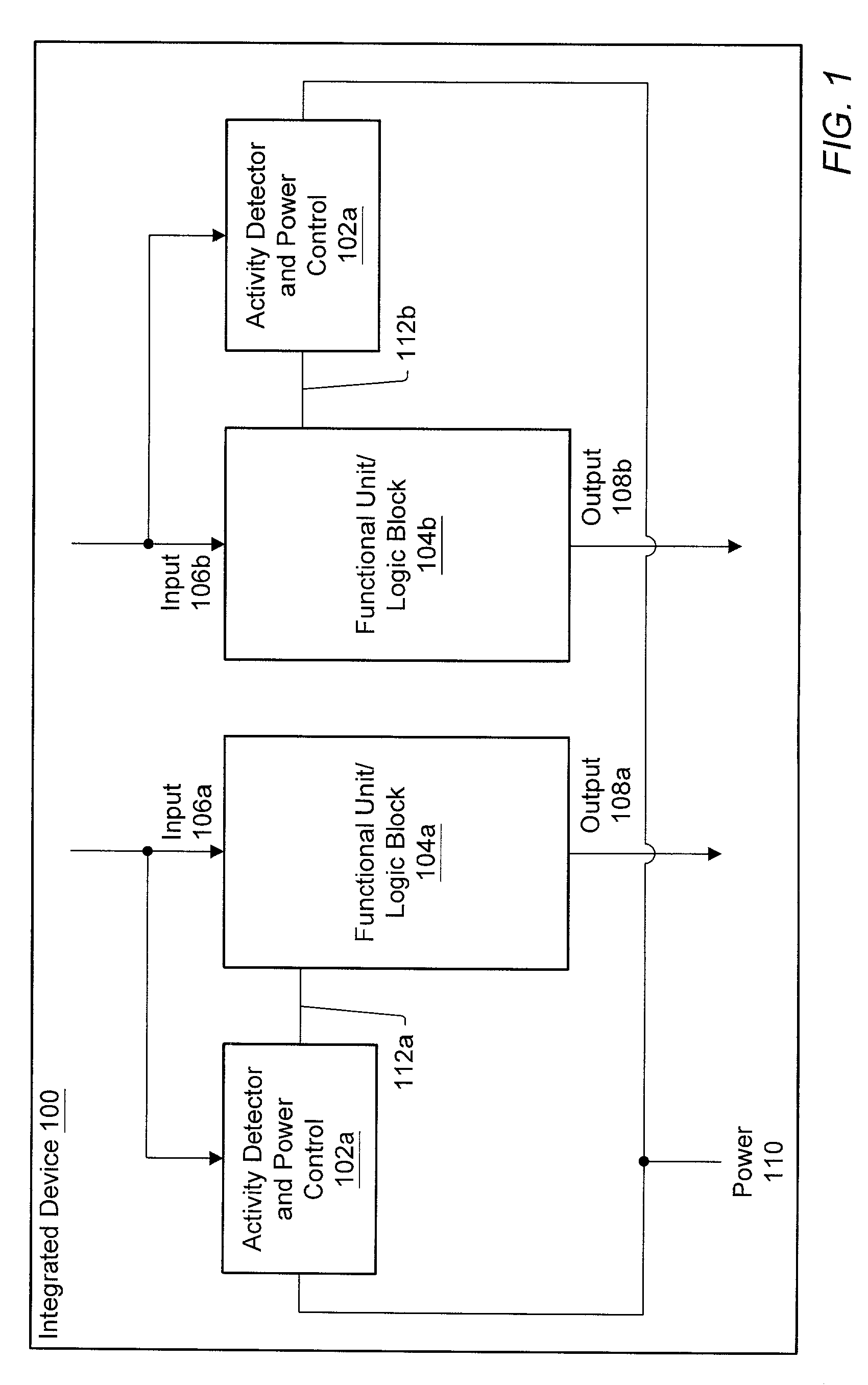
An integrated circuit may have separate power control for a number of different functional units. Ancillary to some of the functional units may be an activity detector and power control unit which monitors input to its functional unit to determine when the functional unit will be inactive. When an activity detector and power control unit determines that a particular functional unit is or will be inactive, it may disable power to its functional unit while the functional unit is inactive. When activity detector and power control unit determines that activity will resume for its functional unit, it enables power to its functional unit. Thus, the activity detector and power control unit for each such functional unit functions to control power to its respective functional unit so that during periods of inactivity, inactive functional units are powered down to reduce the overall static and / or dynamic power consumption for the integrated device.
Owner:ADVANCED SILICON TECH
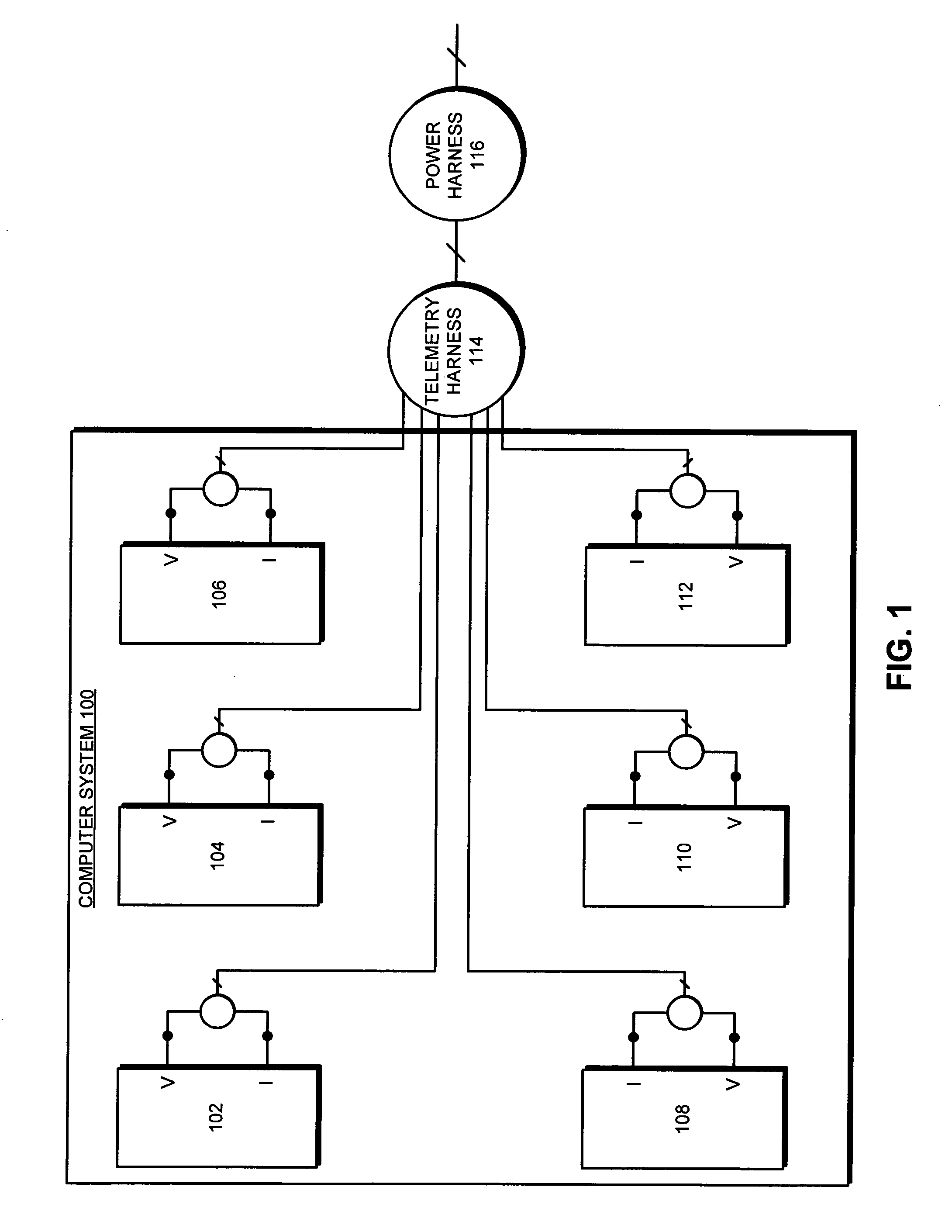
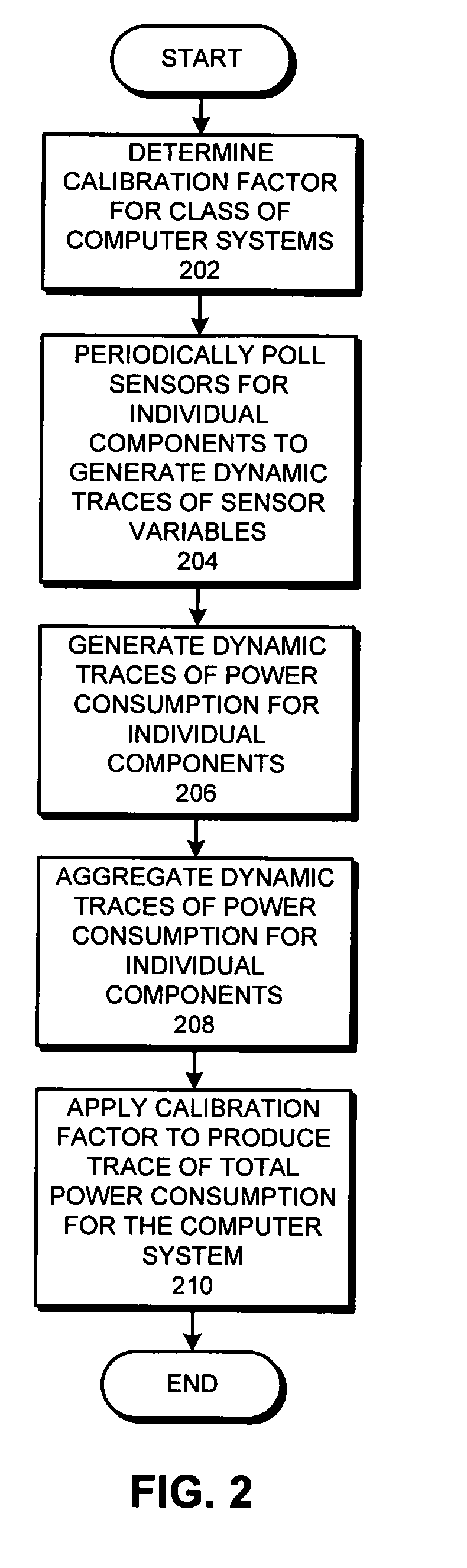
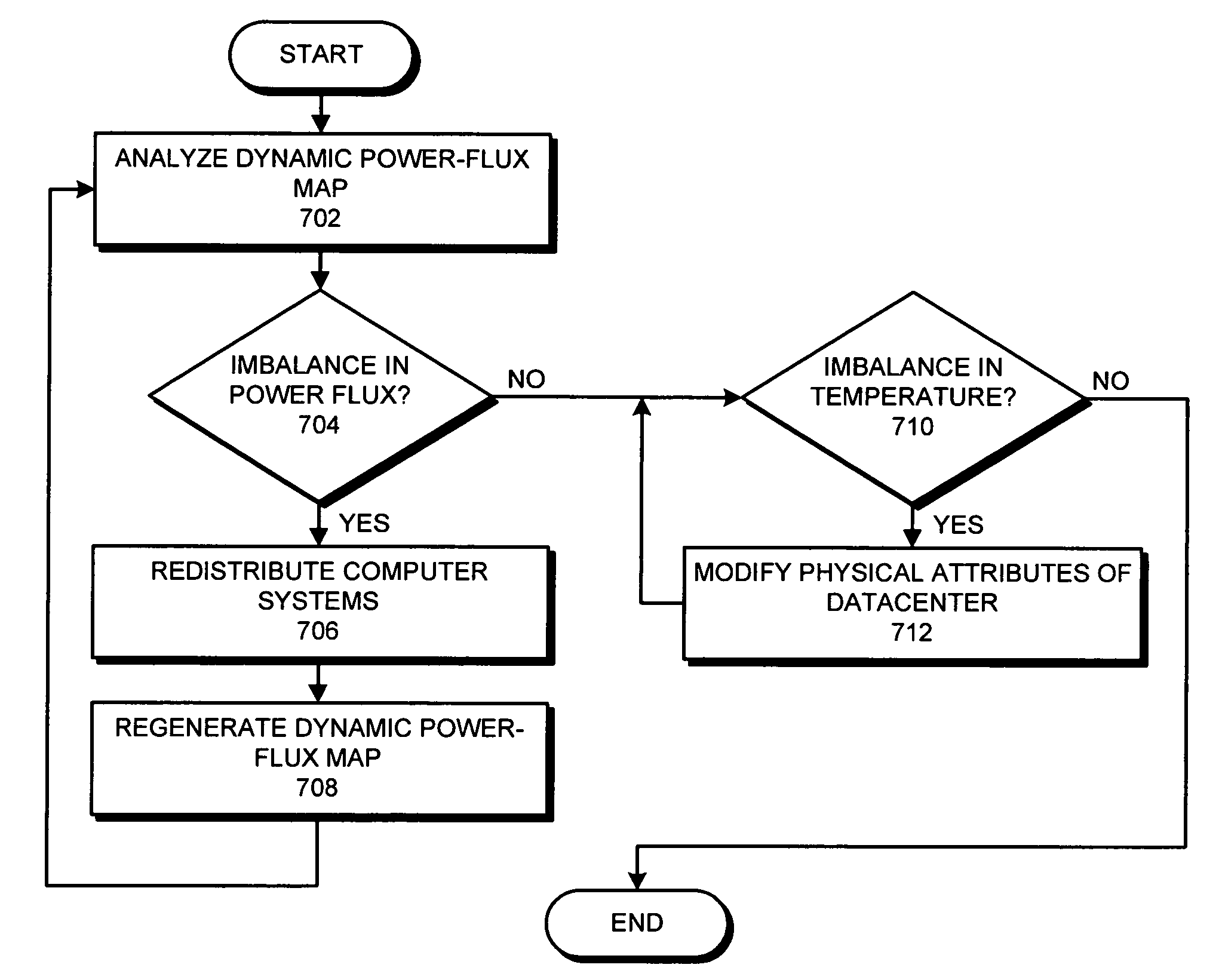
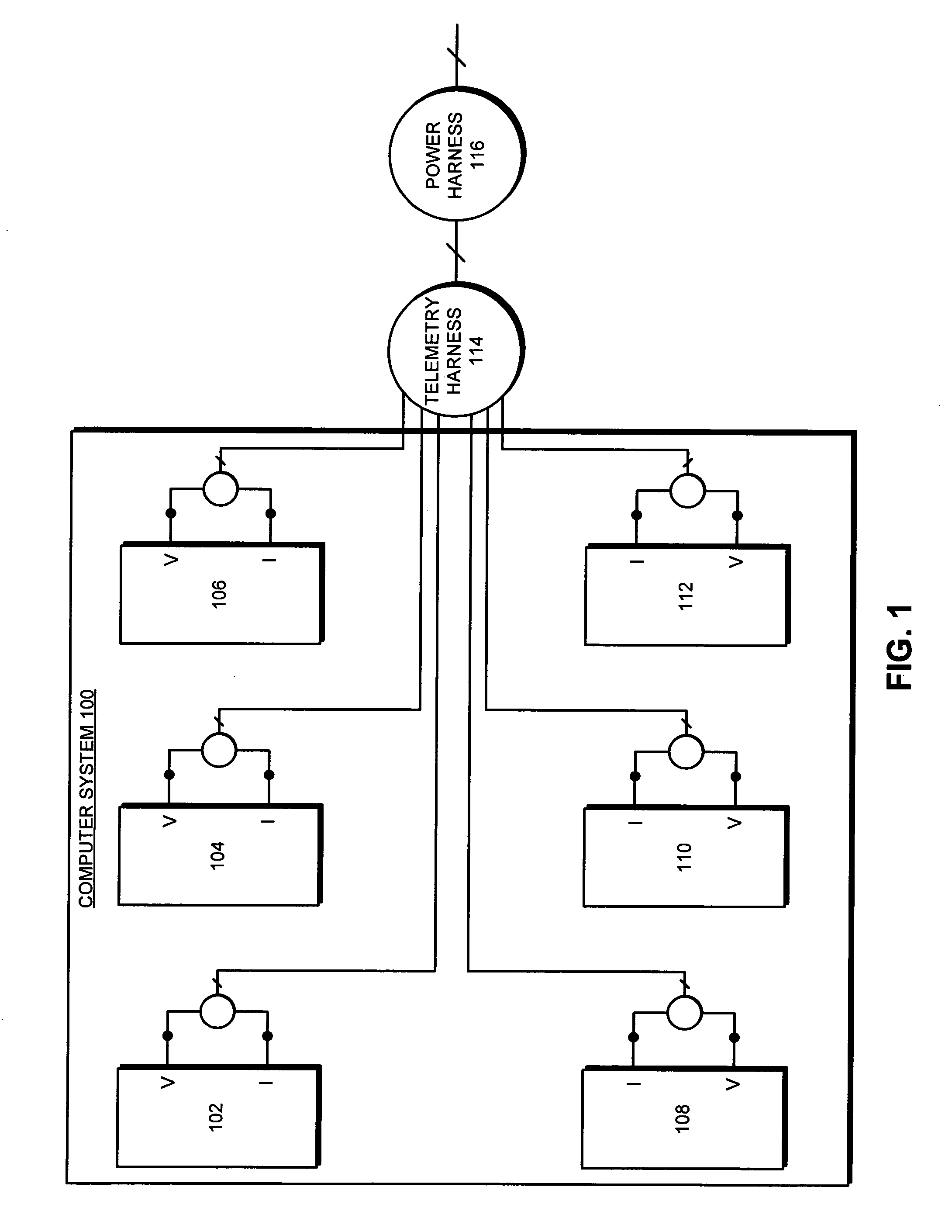
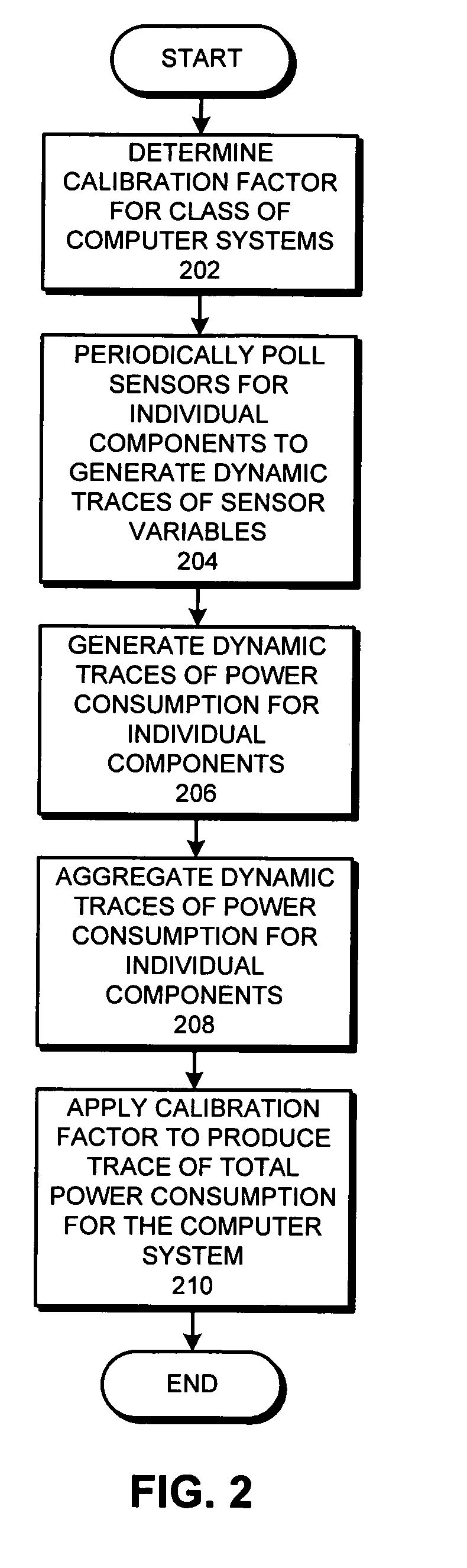
Method and apparatus for generating a dynamic power-flux map for a set of computer systems
A system that generates a dynamic power-flux map for a set of computer systems. During operation the system determines the locations of the computer systems. Next, the system receives dynamic traces of power consumption for the computer systems, wherein a dynamic trace of power consumption for a given computer system is generated based on dynamic traces of monitored inferential variables for the given computer system. The system then correlates the locations of the computer systems with the dynamic traces of power consumption for the computer systems, and generates the dynamic power-flux map for the set of computer systems based on the correlated locations and the dynamic traces for the computer systems.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
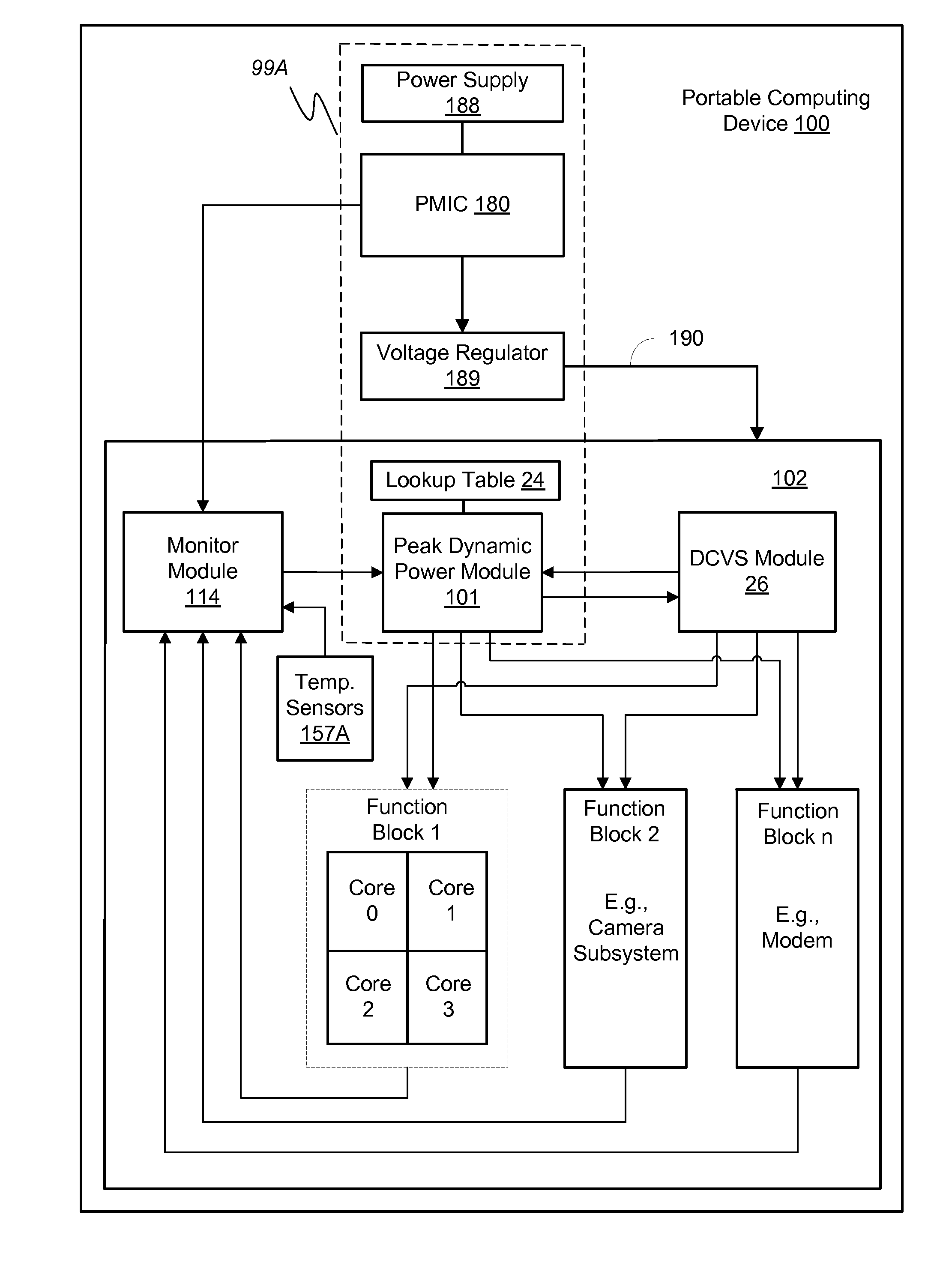
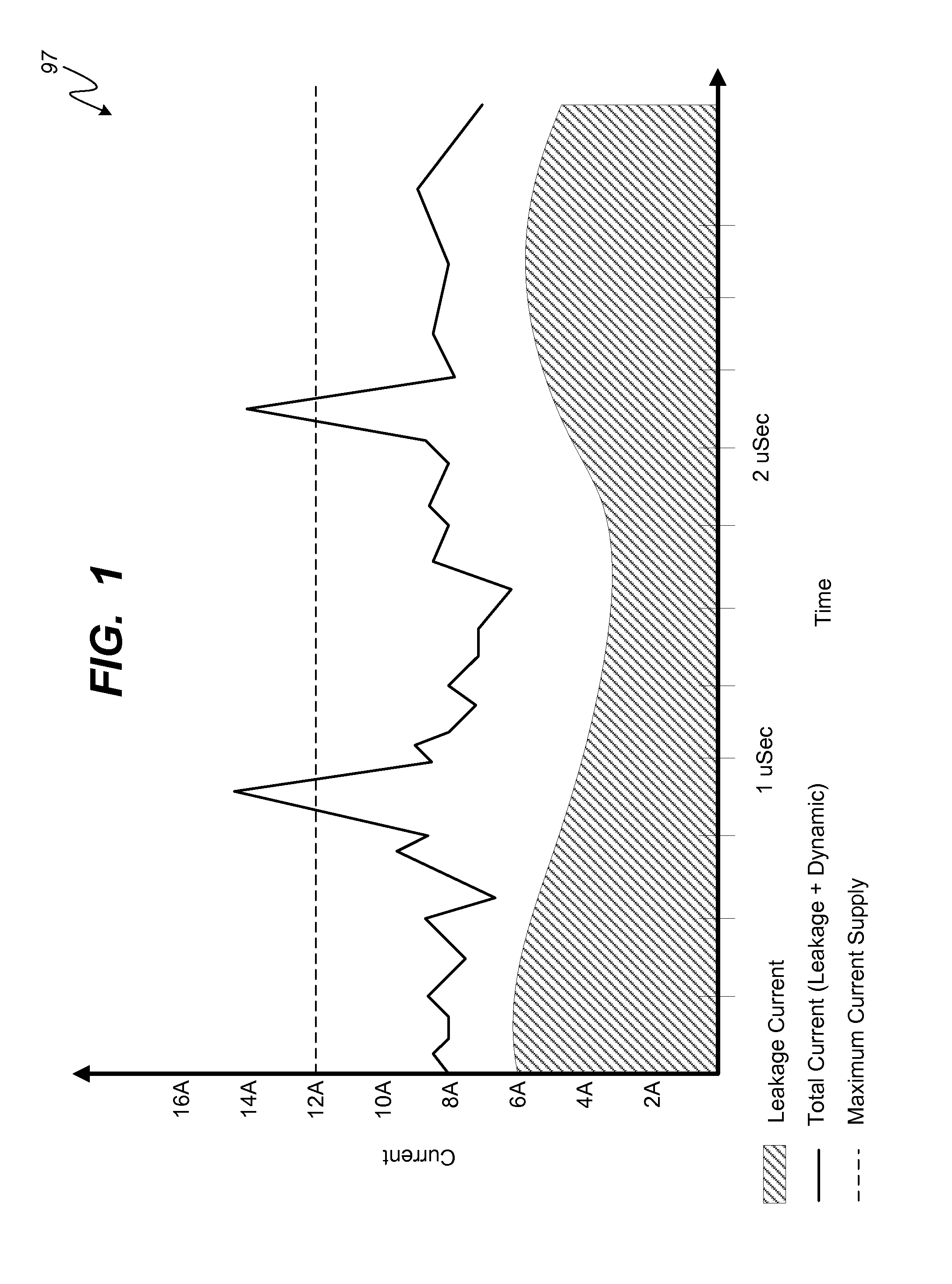
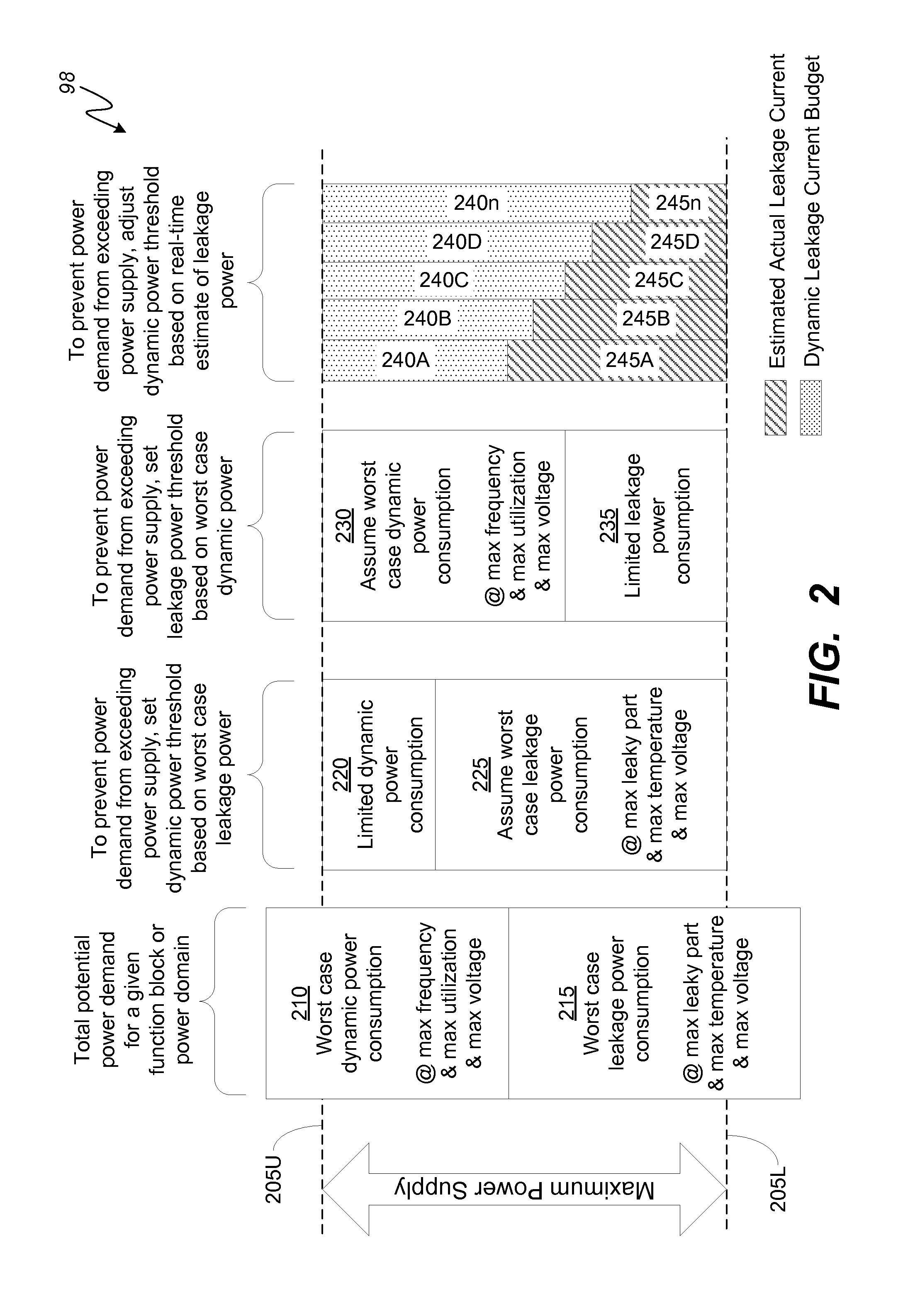
System and method for peak dynamic power management in a portable computing device
ActiveUS20160179164A1A large amountHardware monitoringPower supply for data processingQuality of serviceElectricity
Various embodiments of methods and systems for dynamically adjusting a peak dynamic power threshold are disclosed. Advantageously, embodiments of the solution for peak dynamic power management optimize a peak dynamic power threshold based on estimations of real-time leakage current levels and / or actual power supply levels to a power domain of a system on a chip (“SoC”). In this way, embodiments of the solution ensure that a maximum amount of available power supply is allocated to dynamic power consumption for processing workloads at an optimum performance or quality of service (“QoS”) level without risking that the total power consumption (leakage power consumption+dynamic power consumption) for the power domain exceeds the power supply capacity.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
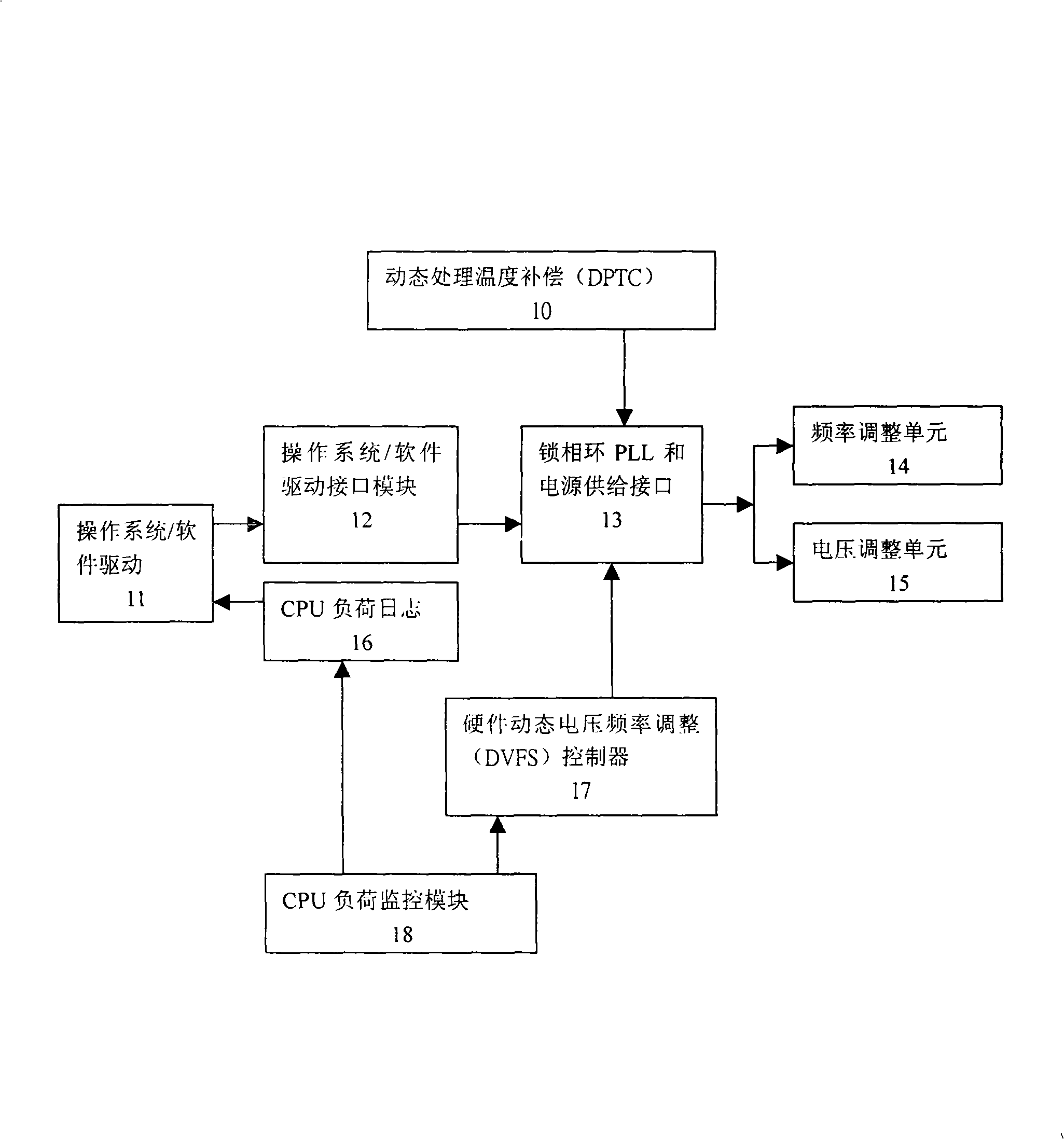
Method for regulating dynamic voltage frequency in power supply management technique
InactiveCN101281415AImprove the shortcomings of short use time, system stability, and poor reliabilityExtended use timeVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingOperational systemTime of use
The invention relates to a dynamic voltage frequency adjustment method in the power management technology, which comprises steps: collecting different hardware signals; writing a hardware dynamic voltage frequency adjustment controller and a corresponding register of a CPU loading log; reading CPU loading log information via an operating system / software drive, and inputting the information into an interface module of the operating system / software drive after analyzing; and reading dynamic processing temperature compensation, the hardware dynamic voltage frequency adjustment controller, the information processed by the interface module of the operating system / software drive; outputting to a corresponding frequency adjustment and voltage adjustment unit via related algorithm analysis, so as to complete adjusting system real time dynamic voltage frequency. The invention adjusts working frequency according to system performance demands, and correspondingly reduces system working voltage and reduces dynamic power dissipation. The invention greatly improves shortcomings of short service life of the battery, bad system stability and reliability brought in by the traditional simple power management technology. The invention can use various embedded system devices such as the portable multimedia recording and playing device, and smart phone.
Owner:上海摩飞电子科技有限公司
Power conversion and voltage sag correction with regenerative loads
ActiveUS7158393B2Improve efficiencyLow costActive power filteringConversion with intermediate conversion to dcVoltage sagDC-BUS
In dynamic voltage sag correctors and other power conversion equipment having a DC bus that is subject to over-voltage conditions due to power being fed back by a regenerative load, a bus discharge switching device and a discharge resistor are connected in series across the DC bus lines. The discharge switching devices are switched on to discharge the energy storage device connected to the bus, or to separately discharge the two capacitors of a split capacitor DC bus, to eliminate the over-voltage conditions. The discharge switching devices may be switched on and off periodically with a selected duty cycle to discharge energy from the energy storage capacitor or other energy storage device through the discharge resistor at a rate which does not exceed the power rating of the discharge resistor. The discharge switching device may be switched with a fixed duty cycle or with a variable duty cycle that is based on the dynamic power dissipation characteristics of the discharge resistor.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION
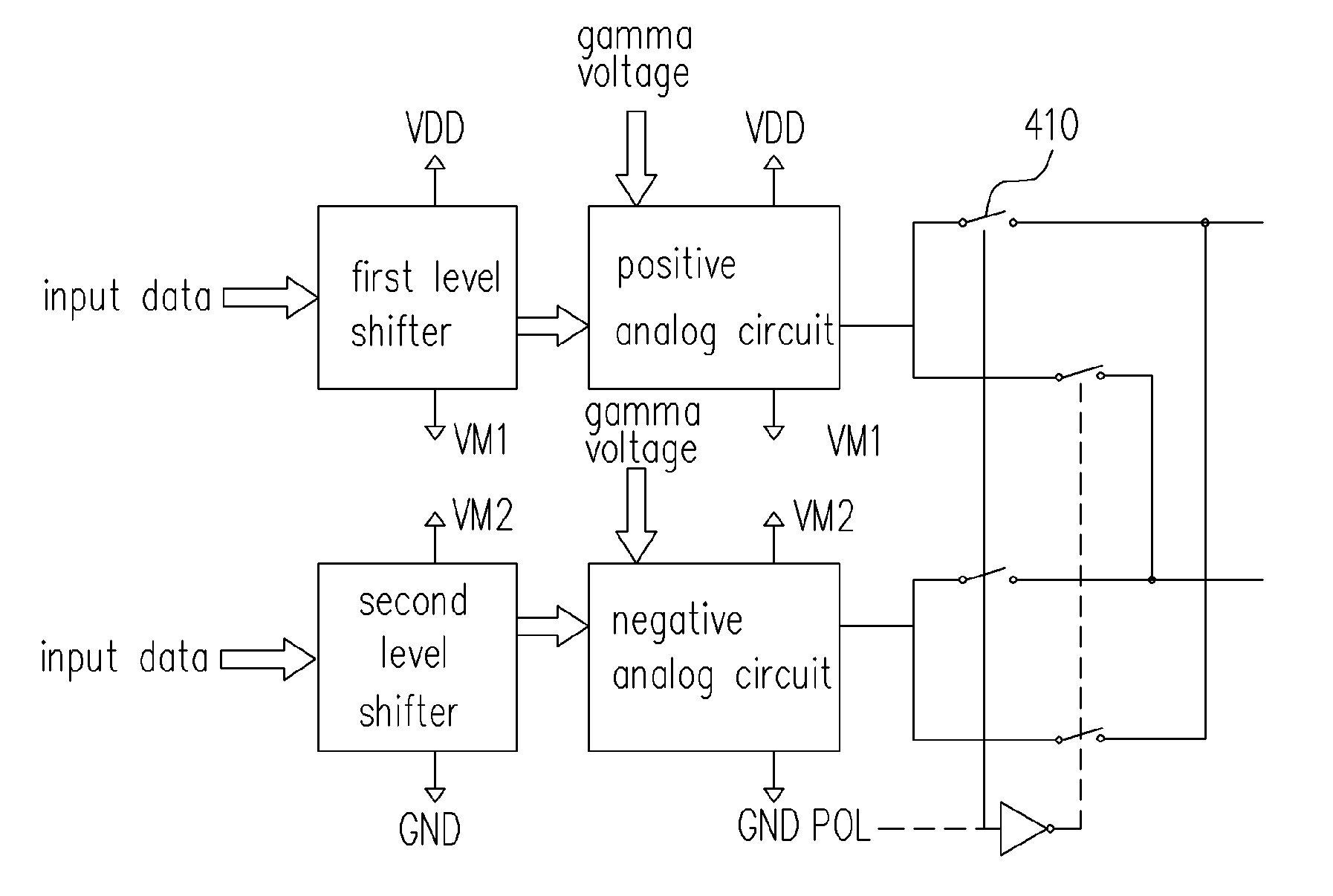
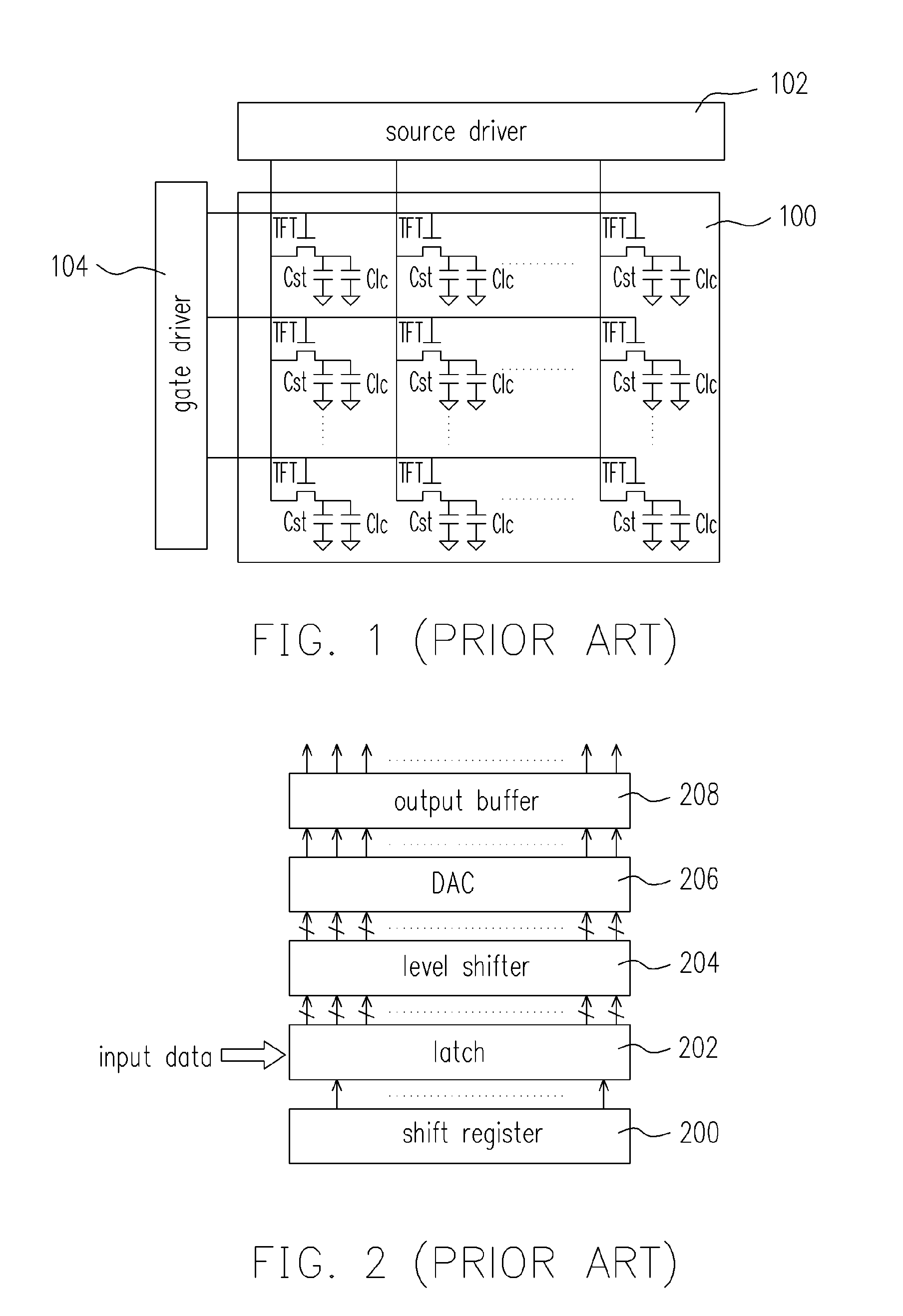
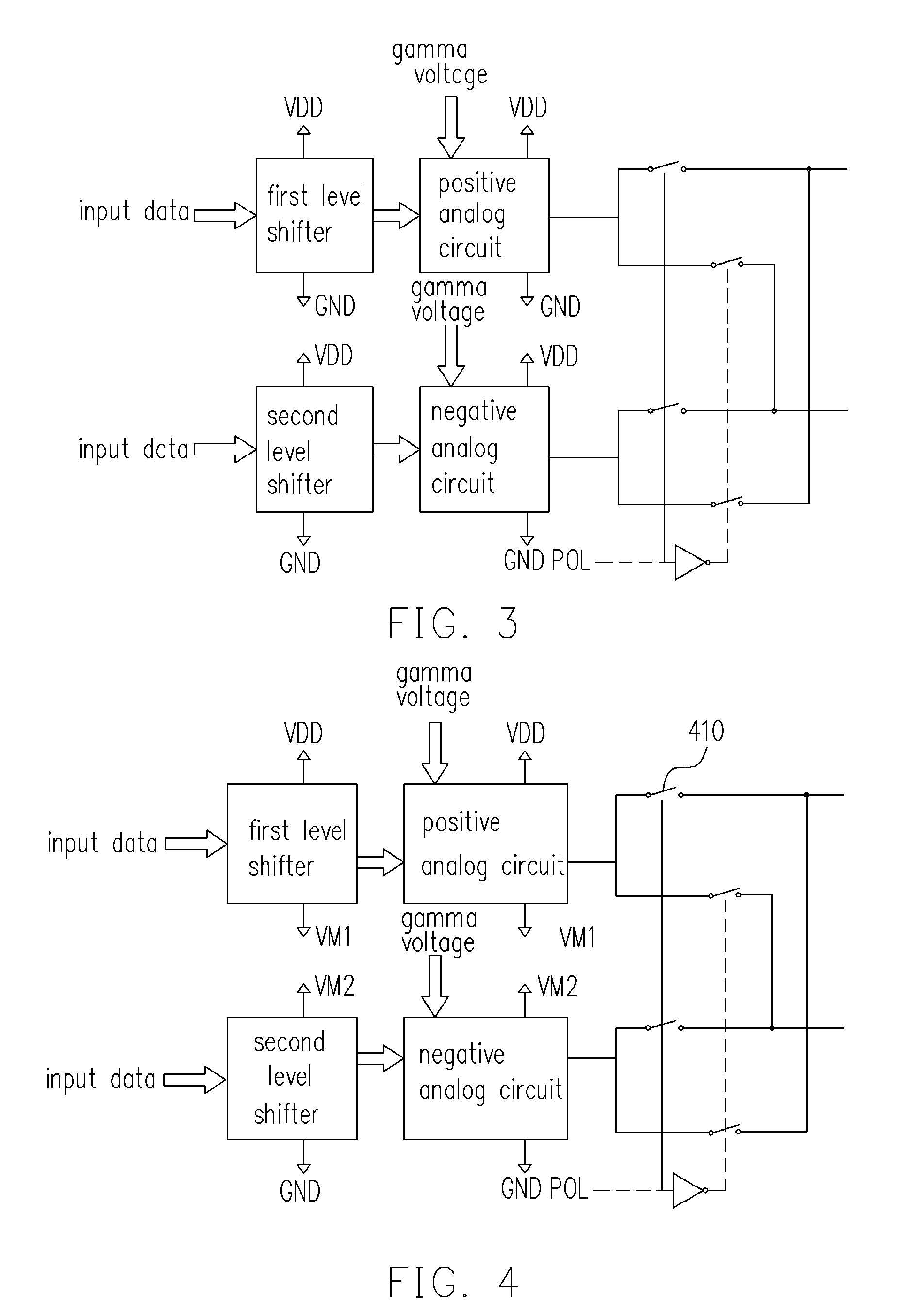
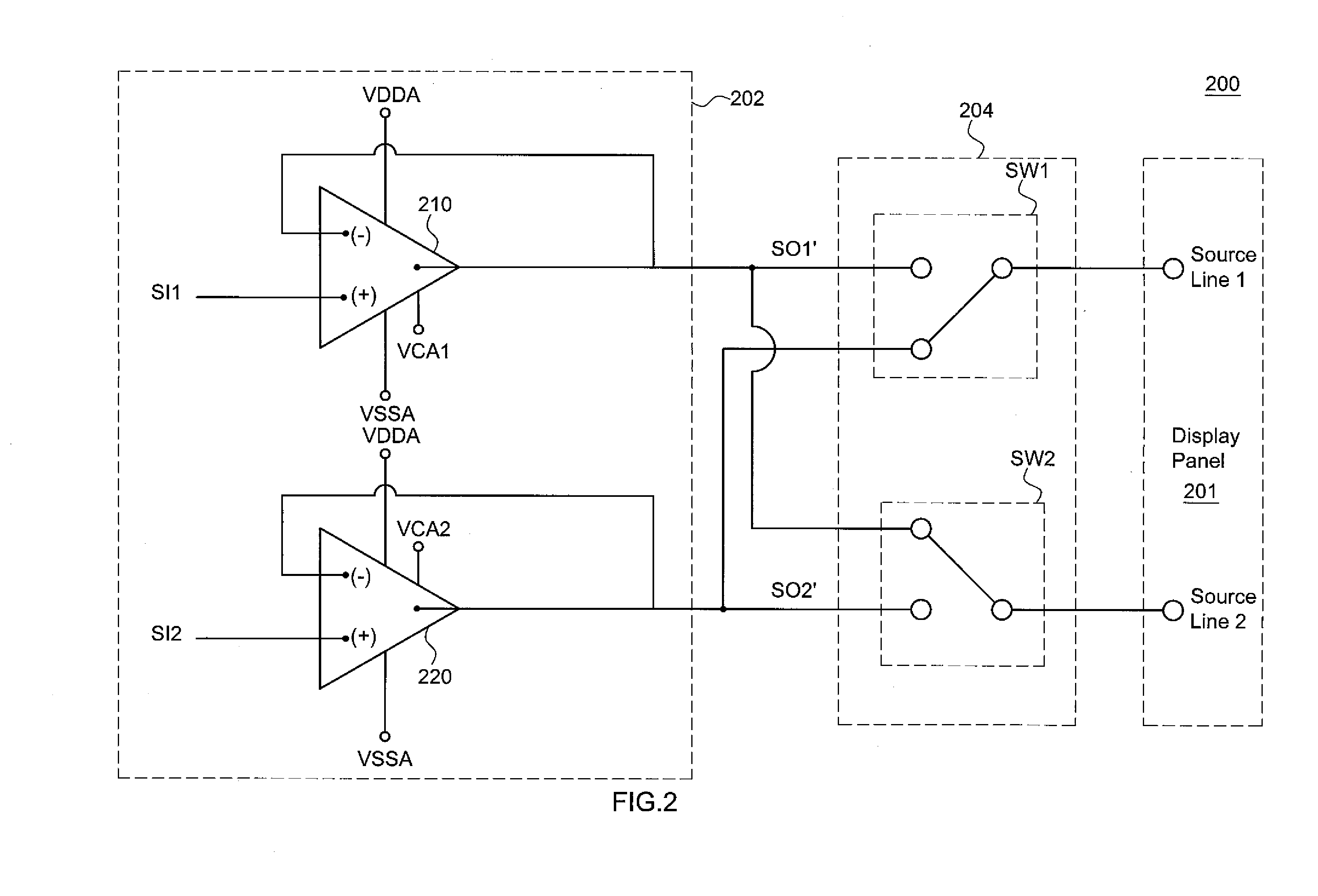
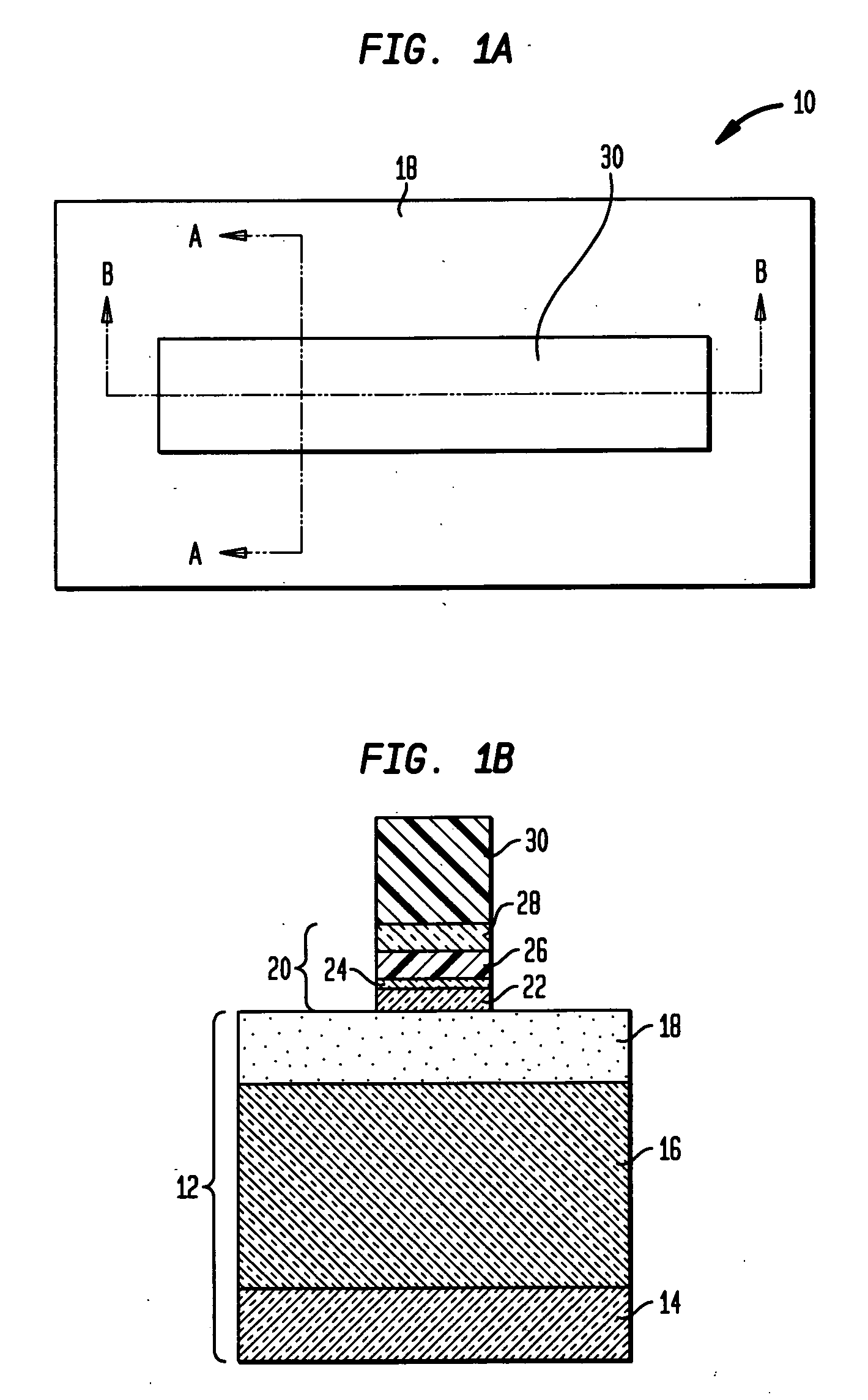
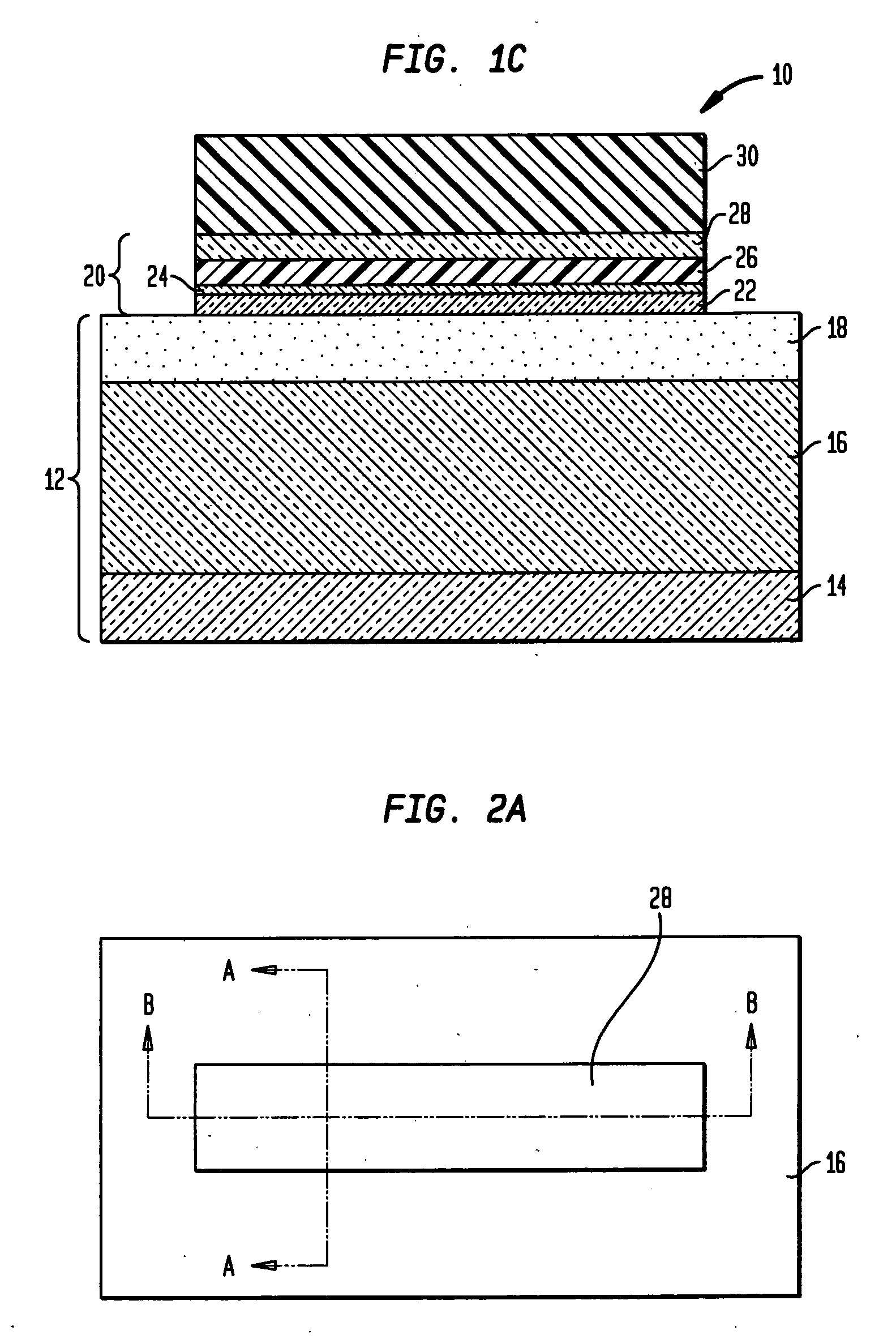
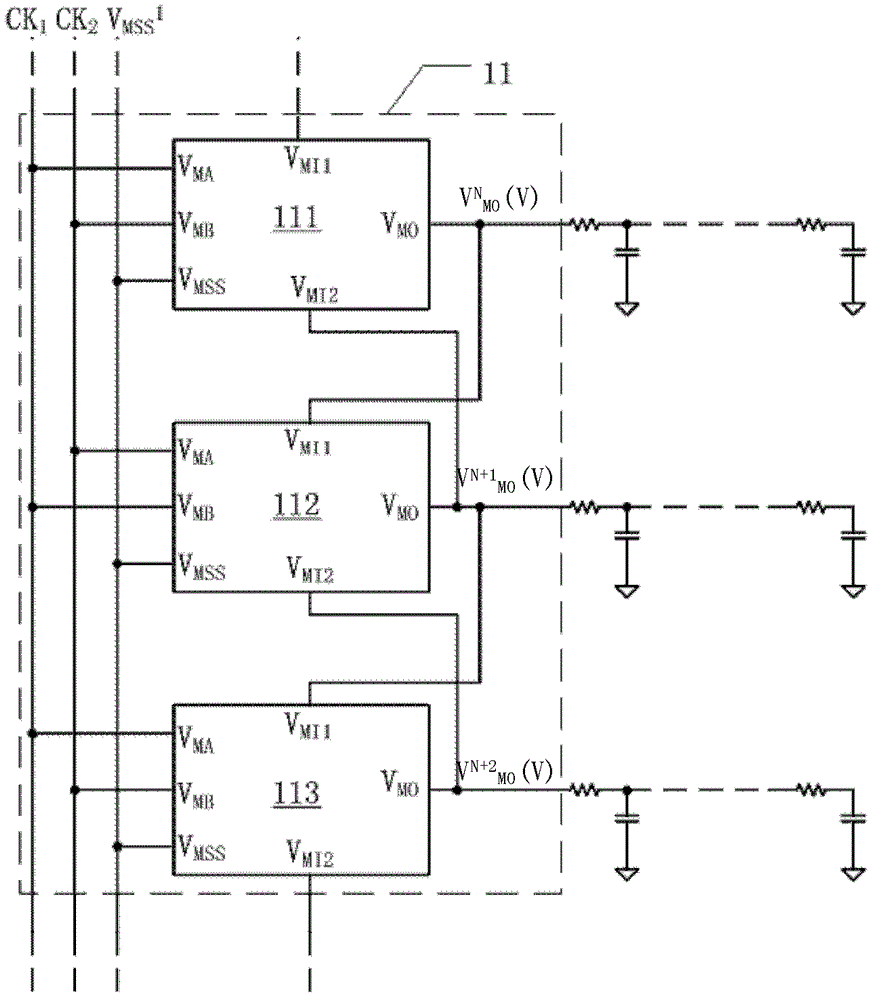
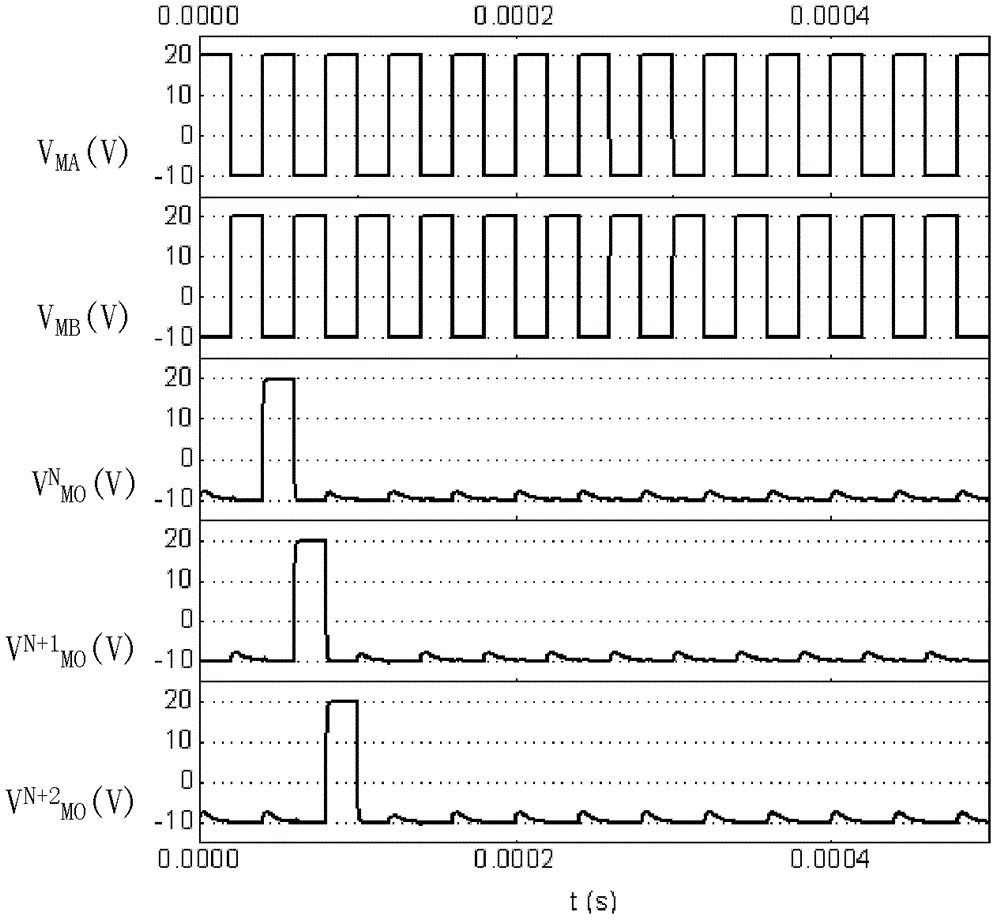
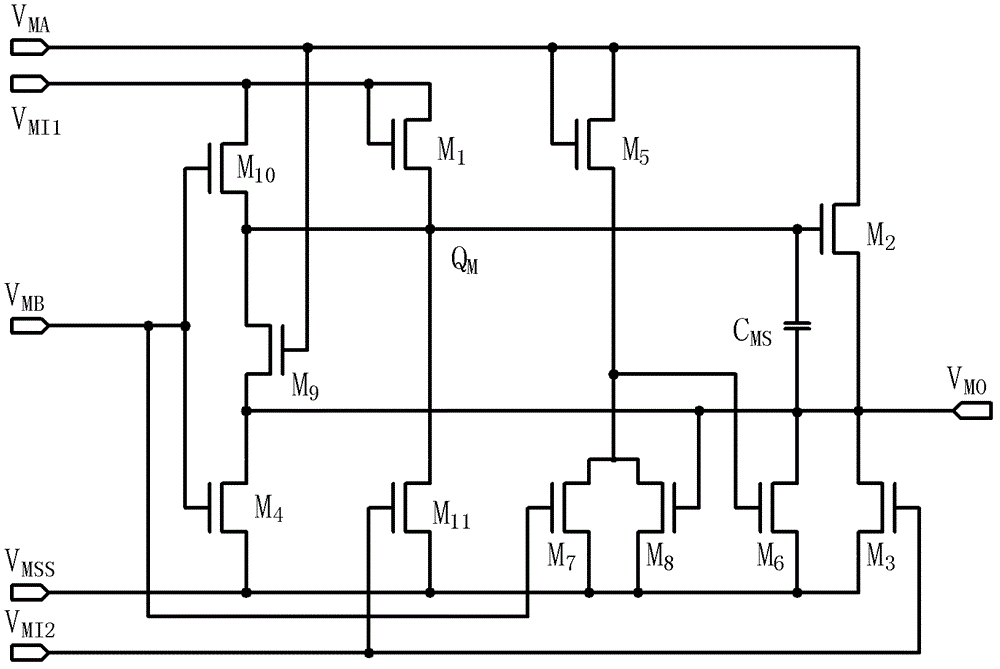
[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]
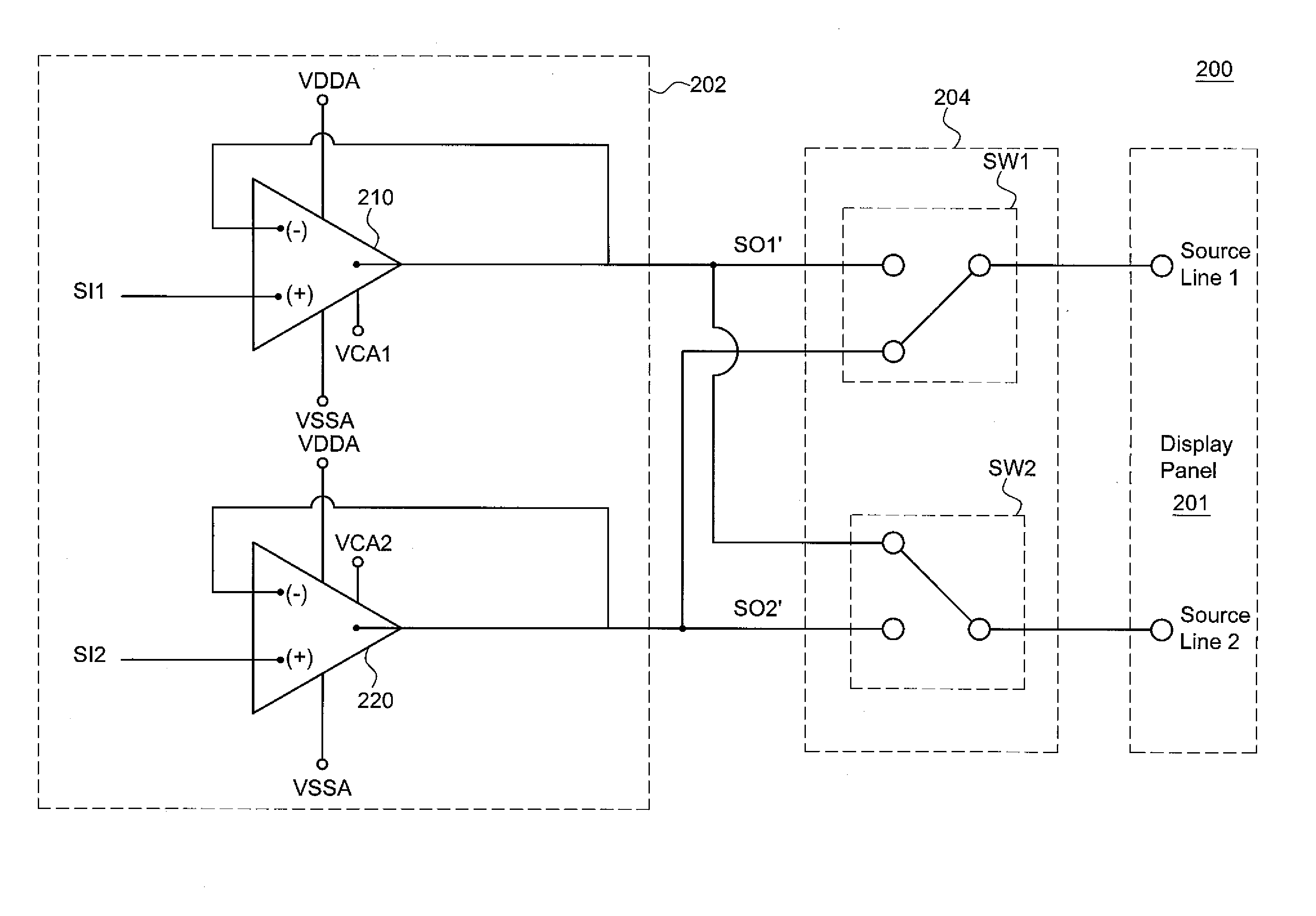
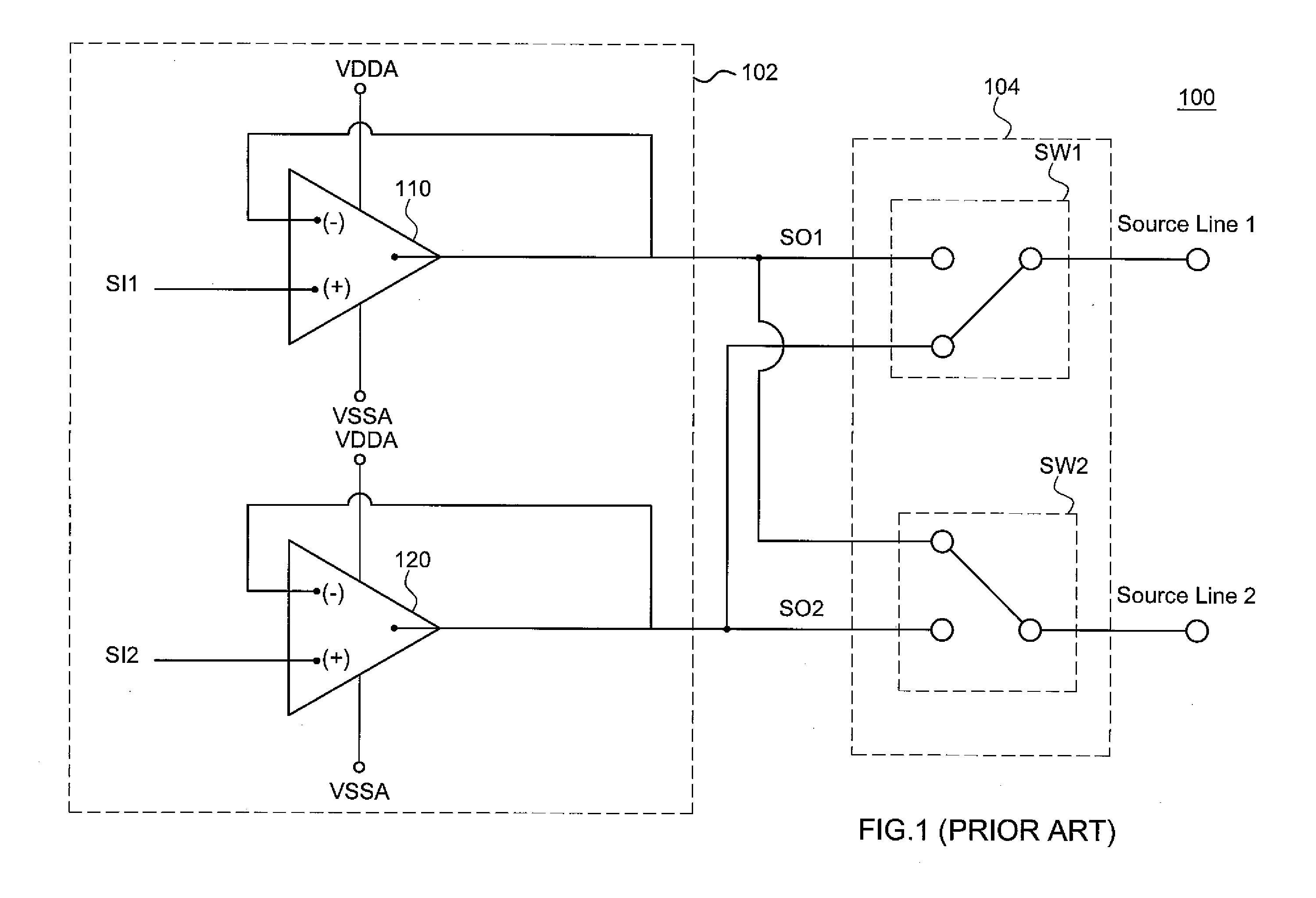
InactiveUS20050206629A1Reduce the amplitudeReduce dynamic power consumptionPulse automatic controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoltage amplitudeLiquid-crystal display
A low-power-consumption source driver for a liquid crystal display is provided. Morethan one middle voltage level for the level shifter and the output buffer is provided, in addition to the power supply voltage level VDD and the ground level GND, to provide different voltage levels for image data of different polarities. Hence, amplitude of the operational voltage of the level shifters and the analog circuits with different polarities can be reduced. It also can reduce the amplitude of the operational voltage of the level shifter and can reduce significantly the dynamic power consumption of the level shifter and the DAC. Because the voltage amplitude of the circuit is reduced and a low-voltage tolerated device can be used, so that the present invention can further reduce the cost of the circuit.
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
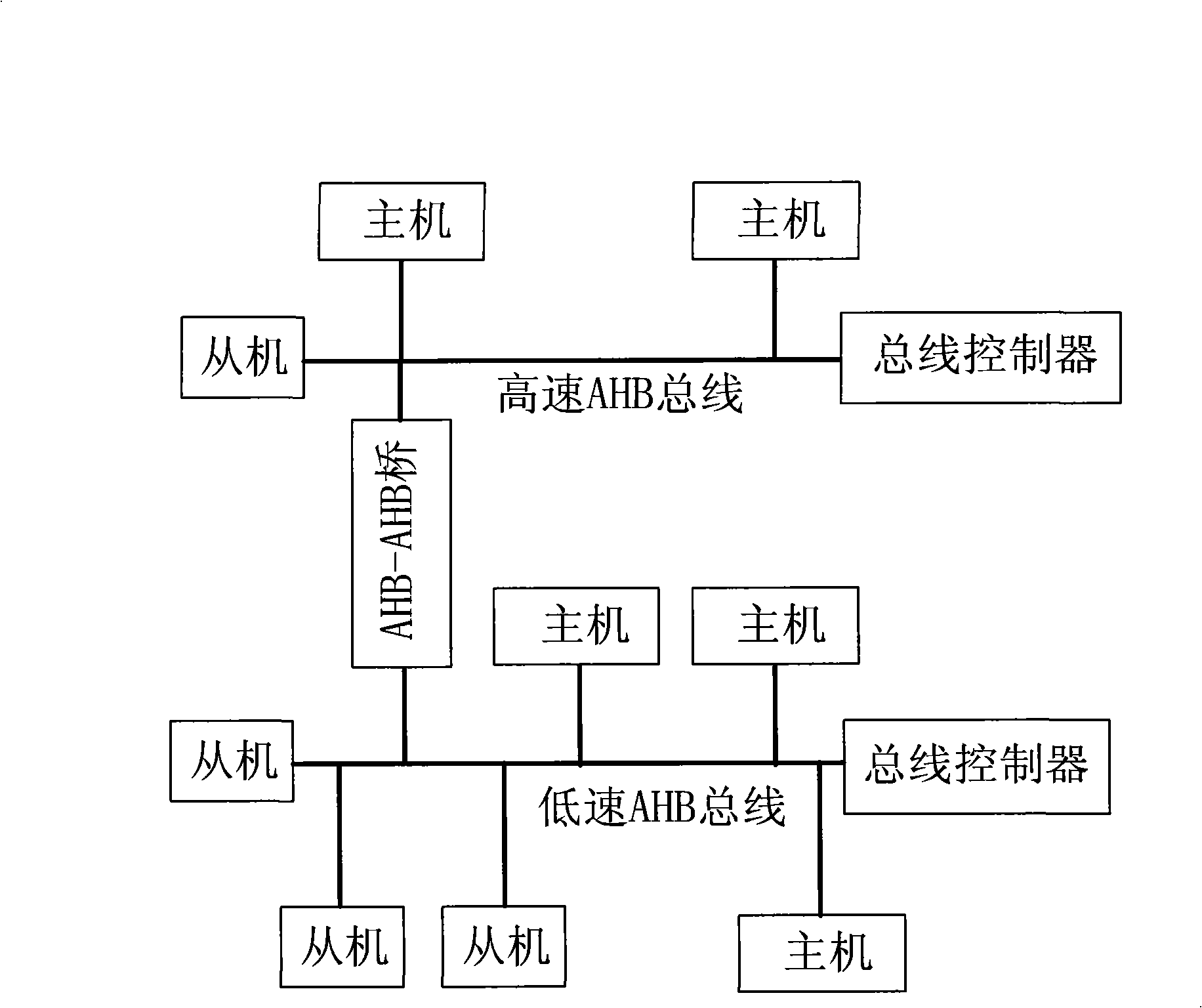
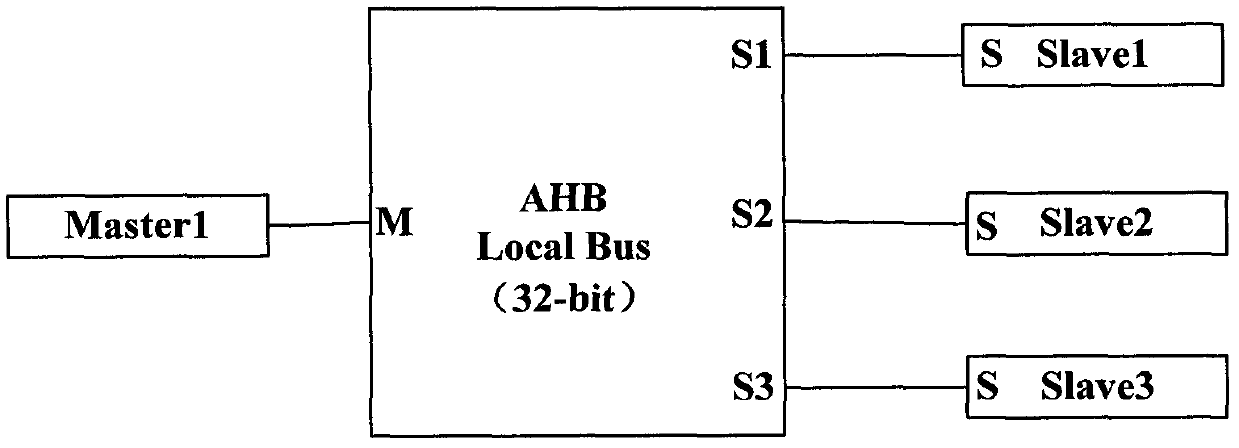
Dynamic multi-clock low power consumption AHB bus design method for SOC
ActiveCN101493717AReduce power consumptionEnergy efficient ICTPower supply for data processingLow speedGrating
The invention relates to a design method of a dynamic multi-clock AHB bus with low power consumption used for SOC. The method adopts a multi-clock gating register to realize the control of clock signals of each module; when a certain module is needed to work, a corresponding grating signal is opened so as to lead the module to work normally; otherwise, the grating signal is closed, the clock does not work and then the dynamic turning of a logic gate can be reduced so as to achieve the purpose of reducing the system dynamic power consumption; moreover, an AHB-AHB bridge is adopted and a plurality of AHB buses can be adopted and then the high-speed and low-speed devices all can be connected with the different AHB buses; the AHB buses are mutually connected through the AHB-AHB bridge; and the clock frequency of certain modules can be reduced so as to achieve the purpose of reducing the dynamic power consumption.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Source driver and liquid crystal display using the same
InactiveUS7292217B2Reduce the amplitudeReduce dynamic power consumptionPulse automatic controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsVoltage amplitudeLiquid-crystal display
Owner:NOVATEK MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Dynamic power consumption control method for multithread predication by stack depth
InactiveCN101216725AImprove the effective hit rateImprove effectivenessMultiprogramming arrangementsPower supply for data processingIdle timeFood consumption
A dynamic power consumption controlling method using the depth of stacking for multithreading prediction is suitable for supplying power to the battery. The method includes various idle mode components of low power consumption and uses the devices of multi-task imbedded system. The method includes the following steps: step one: using the cluster mode of operating request to describe the characteristics of the sequence Phi of operating request by a single thread to the components and devices; step 2: using two-stage hashtable to predict the probability distribution of the request interval under single thread mode; step 3, taking the thread as an independent request source and grouping the request source according to the task to which the thread belong and the entry address of the thread; step 4: calculating, according to the possibility distribution of the idle time of the components or devices, the optimum overtime threshold kopt and the optimum power consumption mode sopt under multiple power consumption modes and single thread. The method improves the effective hit rate for prediction and further reduces the power consumption for the idle consumption-manageable components.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
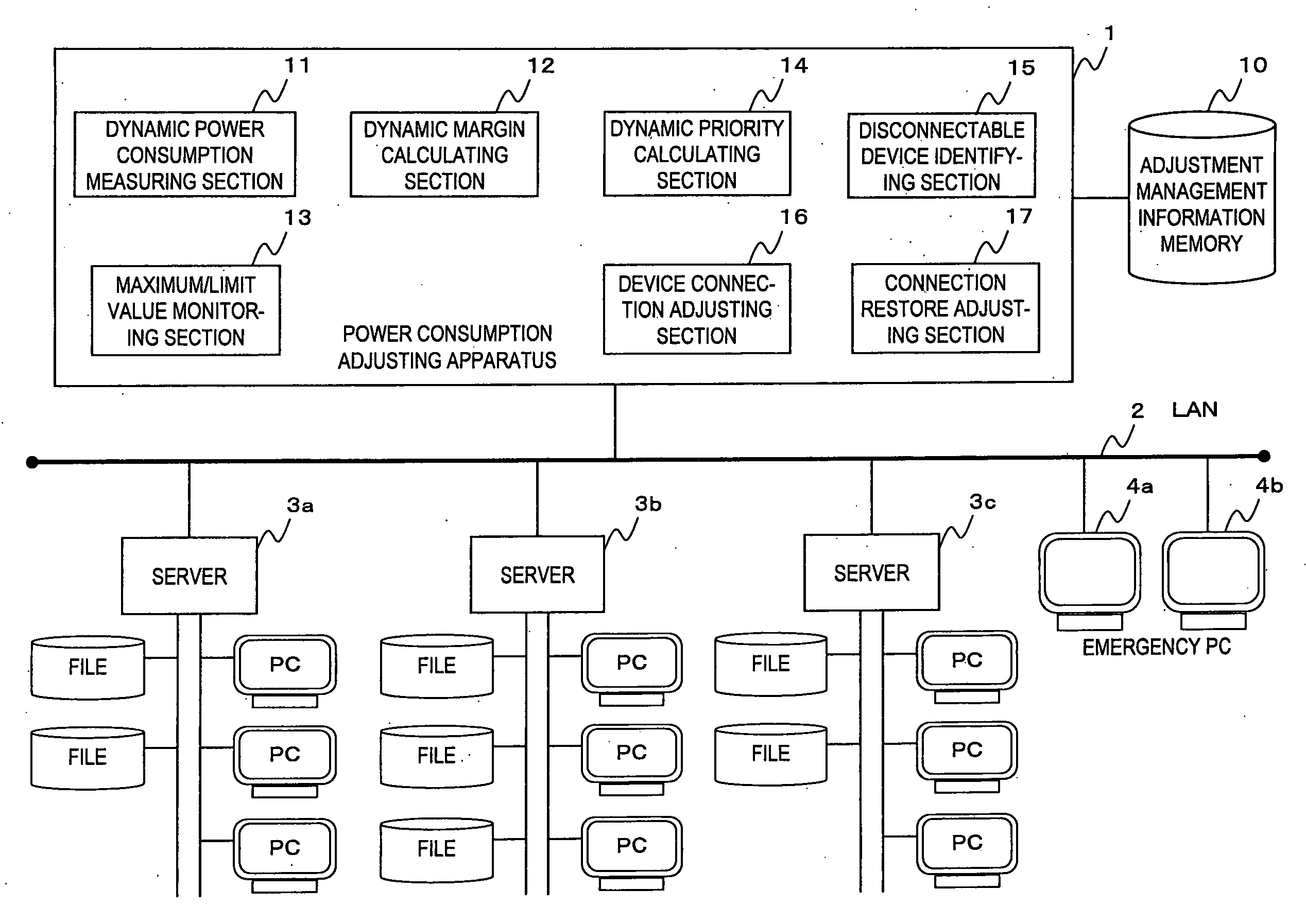
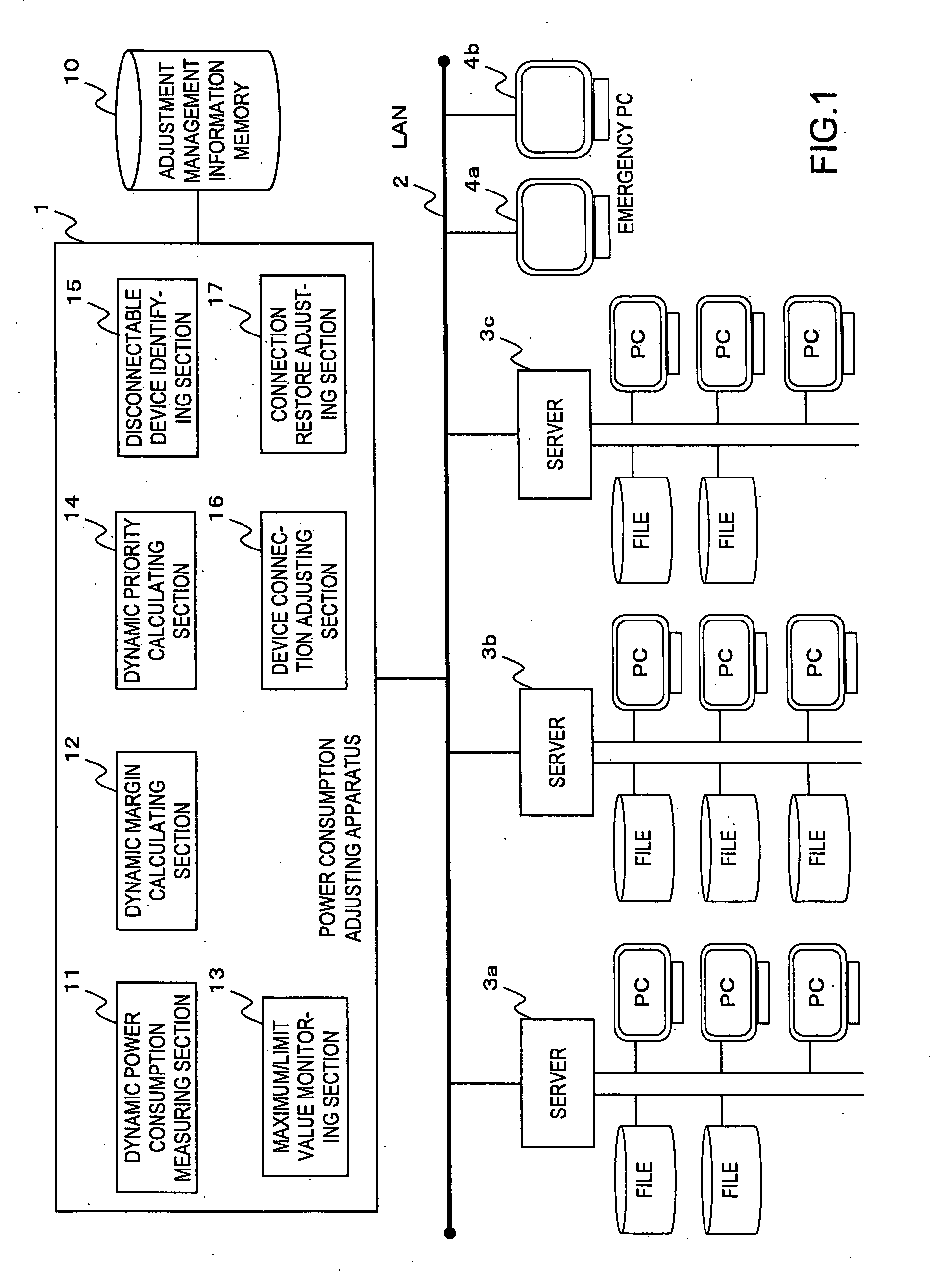
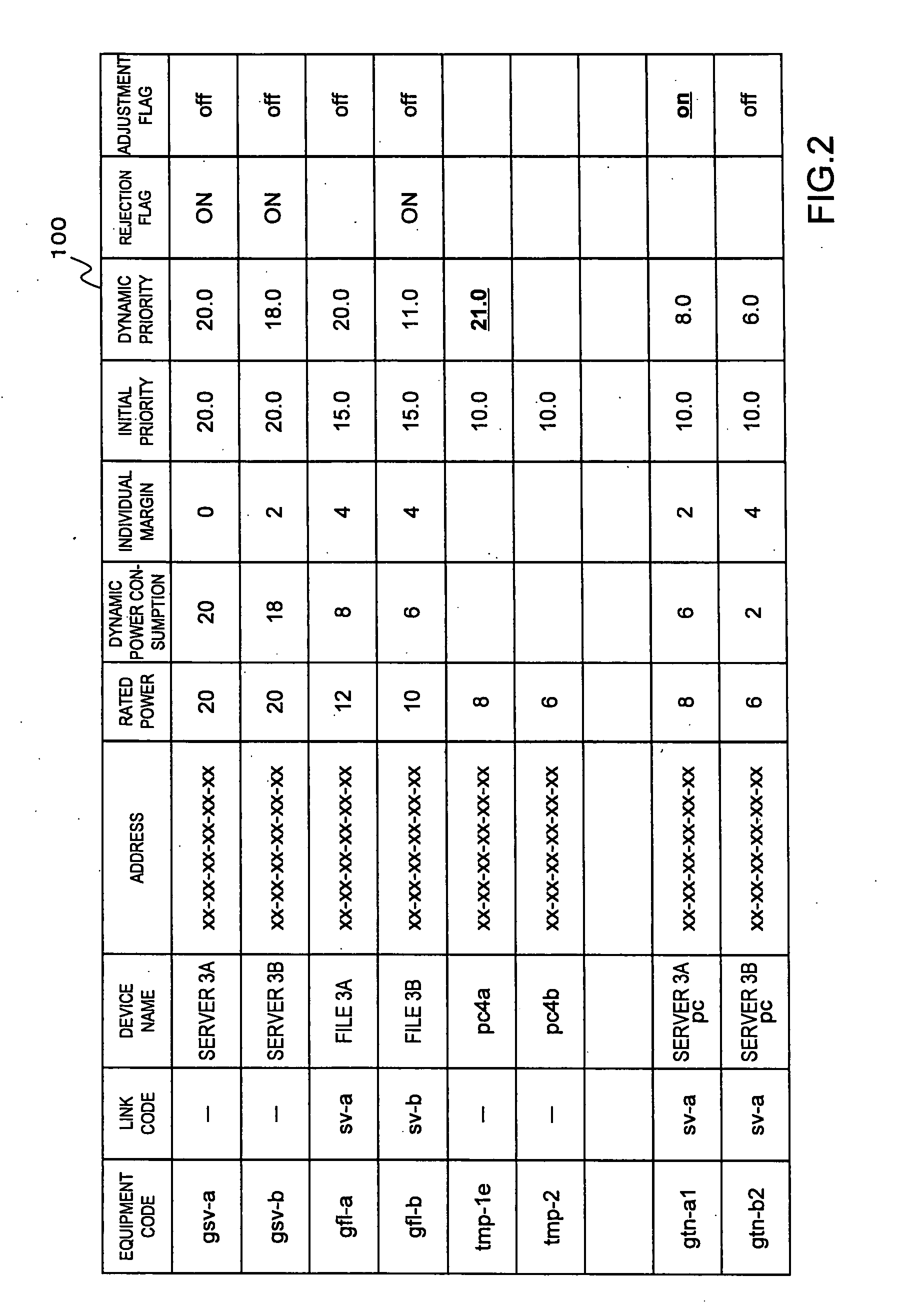
Power consumption adjusting apparatus and processing method
InactiveUS20080155284A1Adjust power consumptionLarger individual dynamic marginVolume/mass flow measurementPower supply for data processingEngineeringLower priority
An apparatus measures a dynamic power consumption in each of component devices at a time intervals and subtracts the sum of the dynamic power consumptions from a predetermined maximum value to obtain a dynamic margin. When a request for connecting an emergency device to a power supply is issued, the apparatus compares the rated power consumption in the emergency device with the dynamic margin. If the rated power consumption in the emergency device exceeds the dynamic margin, the apparatus selects, as a disconnectable device, a component device having an individual margin calculated by subtracting the dynamic power consumption from the rated power consumption is greater than an excess of power amount over the dynamic margin of the rated power consumption in the emergency device and the lowest priority. The apparatus issues an instruction to power the emergency device if the rated power consumption in the emergency device is less than or equal to the dynamic margin, issues an instruction to power off the disconnectable device if the rated power consumption in the emergency device exceeds the dynamic margin, and issues an instruction to power on the emergency device after the power-off of the disconnectable device is confirmed.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method for testing dynamic power consumption of servers
InactiveCN104572419AImprove accuracyImprove effectivenessHardware monitoringEnergy efficient computingDynamic power dissipationEngineering
The invention discloses a method for testing dynamic power consumption of servers, and belongs to the field of tests for power consumption of servers. The method includes particular steps of 1, constructing SPECpower test platforms and preparing test environments; 2, running SUT (system under test) ends and CCS (central control station) ends; 3, carrying out SPECpower tests on the SUT ends and the CCS ends and running scripts for reading data of power consumption of various components; 4, collecting test results after the tests are completed and processing and analyzing the test results. The method has the advantages that the shortcoming that data of dynamic power consumption of different components of integral machines under different load conditions cannot be acquired by PTU (parallel transmission unit), memtest, IOmeter test tools and the like can be overcome, the accuracy and the validity of the test data can be improved, and the conversion efficiency of power sources further can be evaluated when different types of power are outputted by the power sources; the method for testing the dynamic power consumption of the servers is simple in operation and high in automation degree and practicality, labor can be saved, the accuracy of the data of the dynamic power consumption of the various components of the servers can be effectively guaranteed, and the method is an extremely effective method for testing the dynamic power consumption of the various components of the servers.
Owner:LANGCHAO ELECTRONIC INFORMATION IND CO LTD
Method and apparatus for generating a dynamic power-flux map for a set of computer systems
A system that generates a dynamic power-flux map for a set of computer systems. During operation the system determines the locations of the computer systems. Next, the system receives dynamic traces of power consumption for the computer systems, wherein a dynamic trace of power consumption for a given computer system is generated based on dynamic traces of monitored inferential variables for the given computer system. The system then correlates the locations of the computer systems with the dynamic traces of power consumption for the computer systems, and generates the dynamic power-flux map for the set of computer systems based on the correlated locations and the dynamic traces for the computer systems.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and device for designing standard cell library and integrated circuit
InactiveCN101539958AIncrease profitReduce dynamic power consumptionSpecial data processing applicationsDesign standardStandard Template Library
The invention discloses a method and a device for designing a standard cell library. The method comprises a step of designing a common standard cell, and also comprises a step of designing a double-edge flip-flop cell, and the step of designing the double-edge flip-flop cell comprises: when determining the type of the standard cell, adding the double-edge flip-flop cell to the standard cell type; designing a schematic diagram of the double-edge flip-flop cell; and designing a diagram of the double-edge flip-flop cell. A mold of the double-edge flip-flop cell is established, and the method for establishing the mold comprises the following steps of: establishing a rising edge comprehensive library and a falling edge comprehensive library for the double-edge flip-flop; and establishing a double-edge flip-flop simulated library for the double-edge flip-flop. The invention also discloses a method and a device for designing an integrated circuit. Due to the method and the device, the rising edge and the falling edge for each jump of the clock signal can serve the logical function of a chip, so that the jumping frequency of the clock, needed to complete the same logical function, is reduced, and the dynamic energy consumption of the circuit is also lowered.
Owner:北京芯汇中秀电子技术有限公司
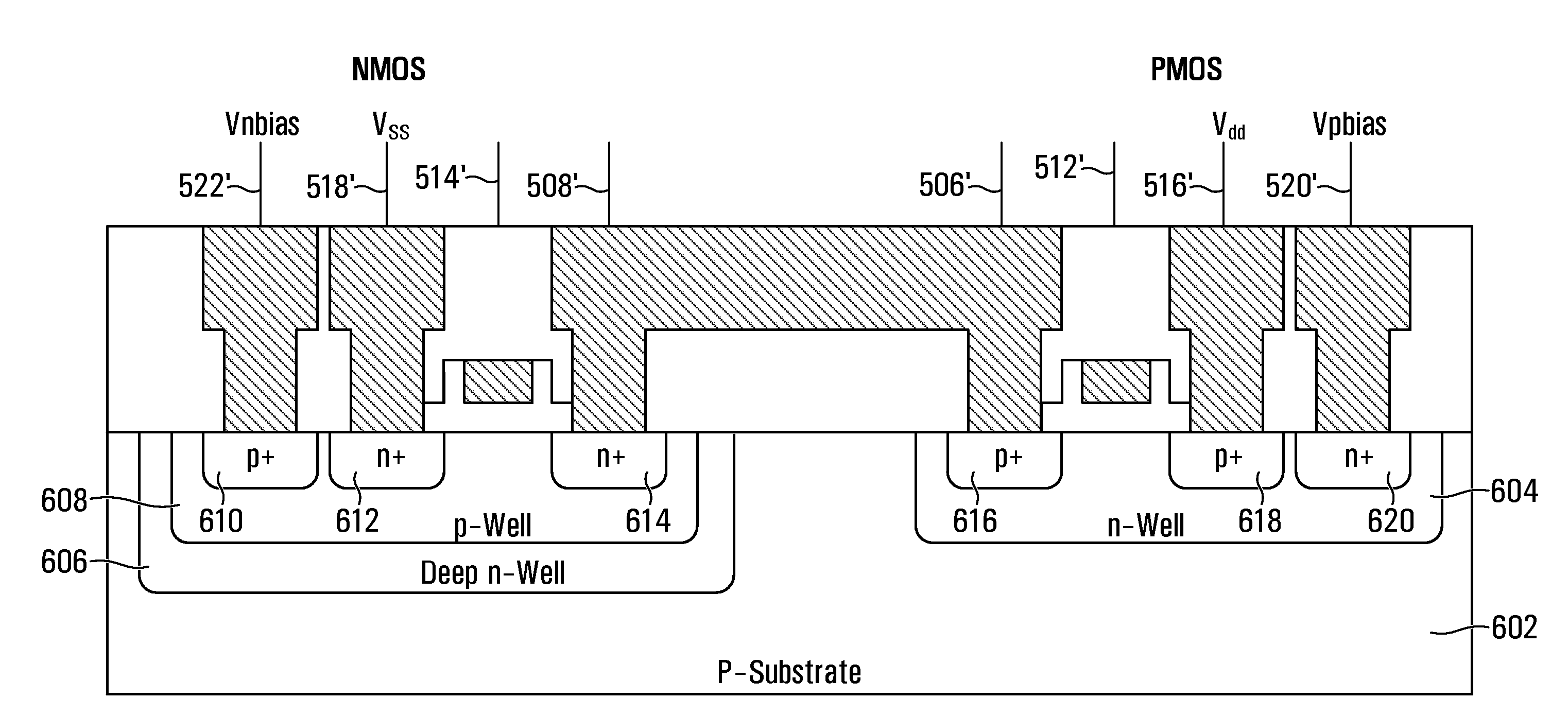
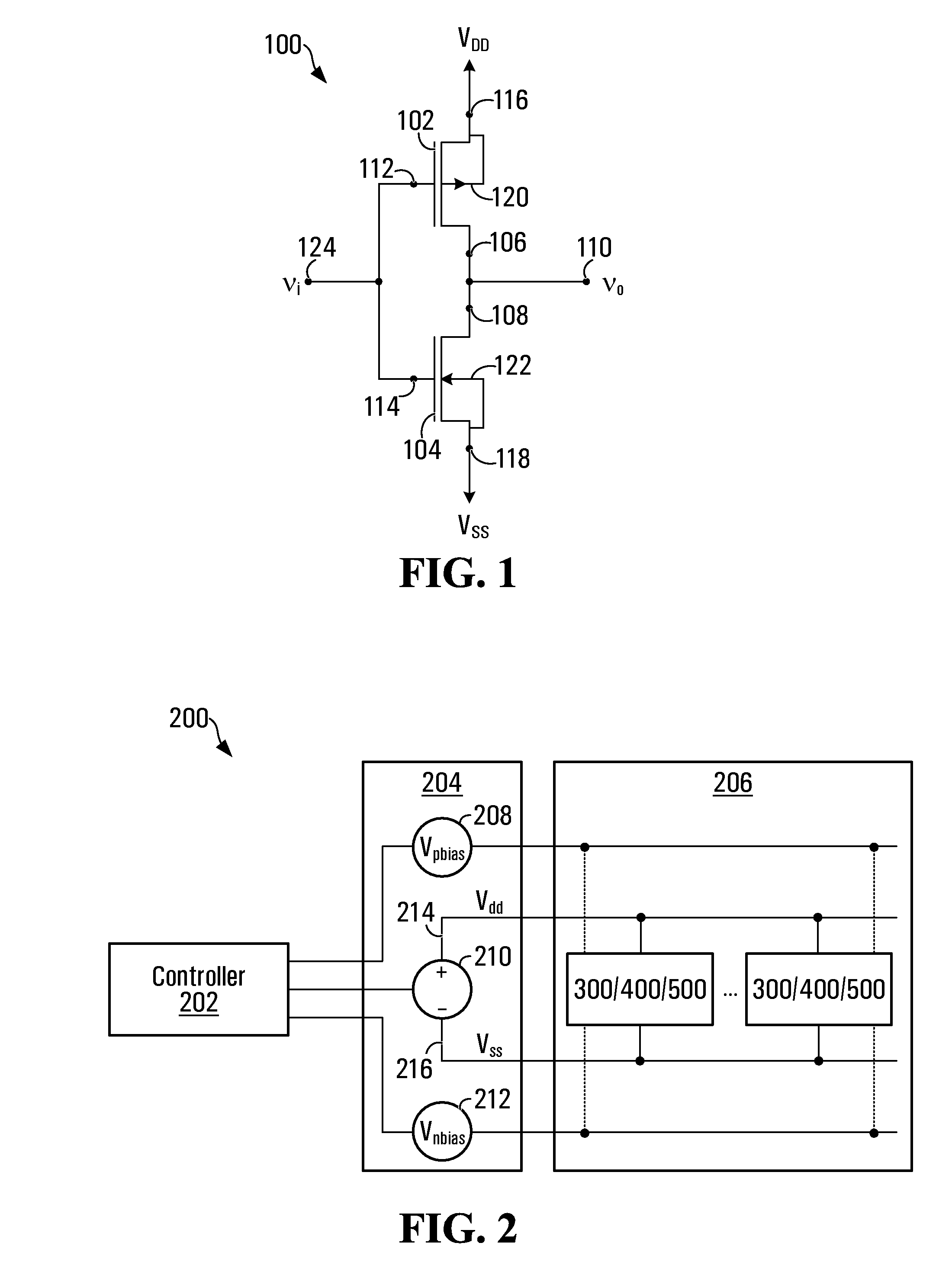
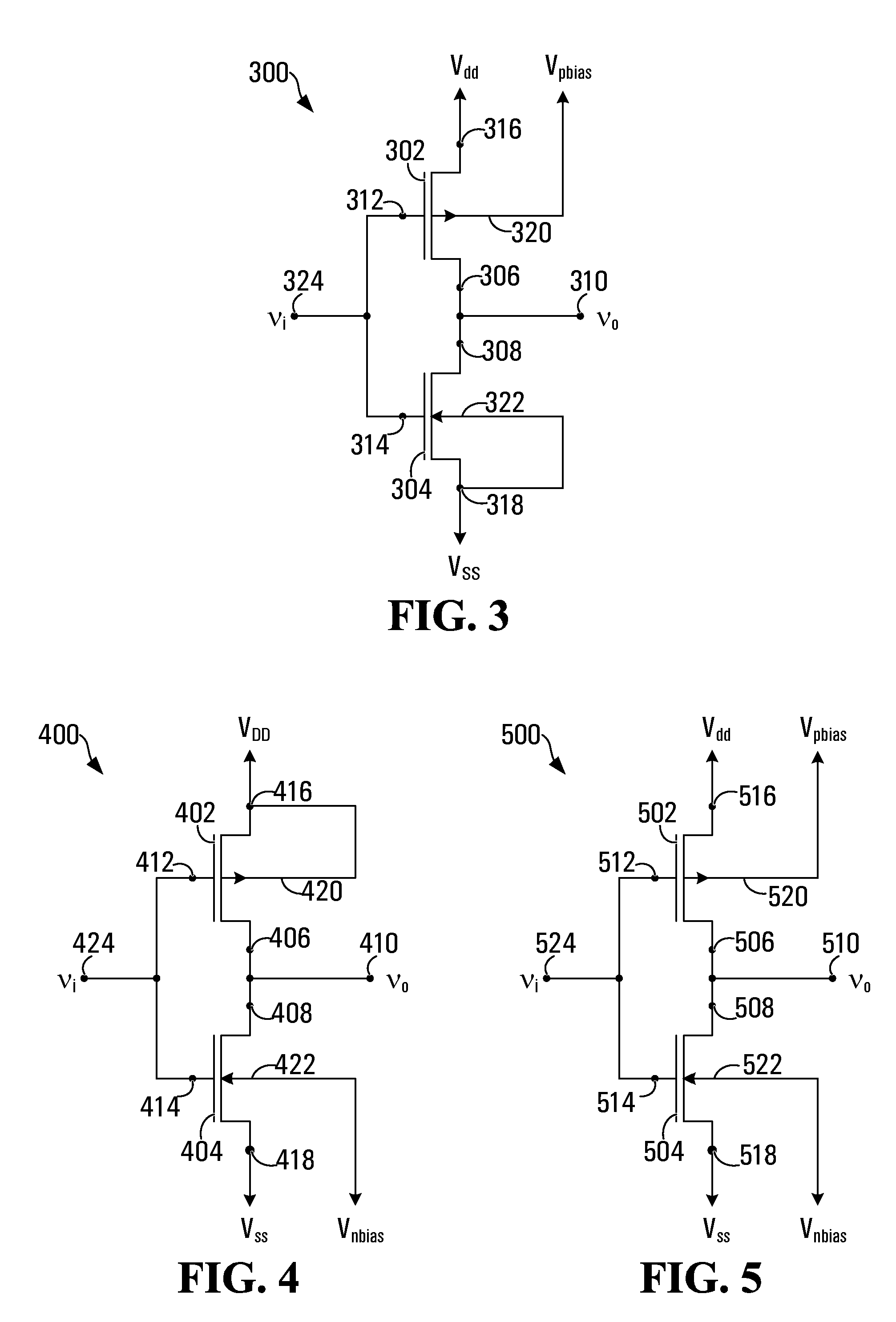
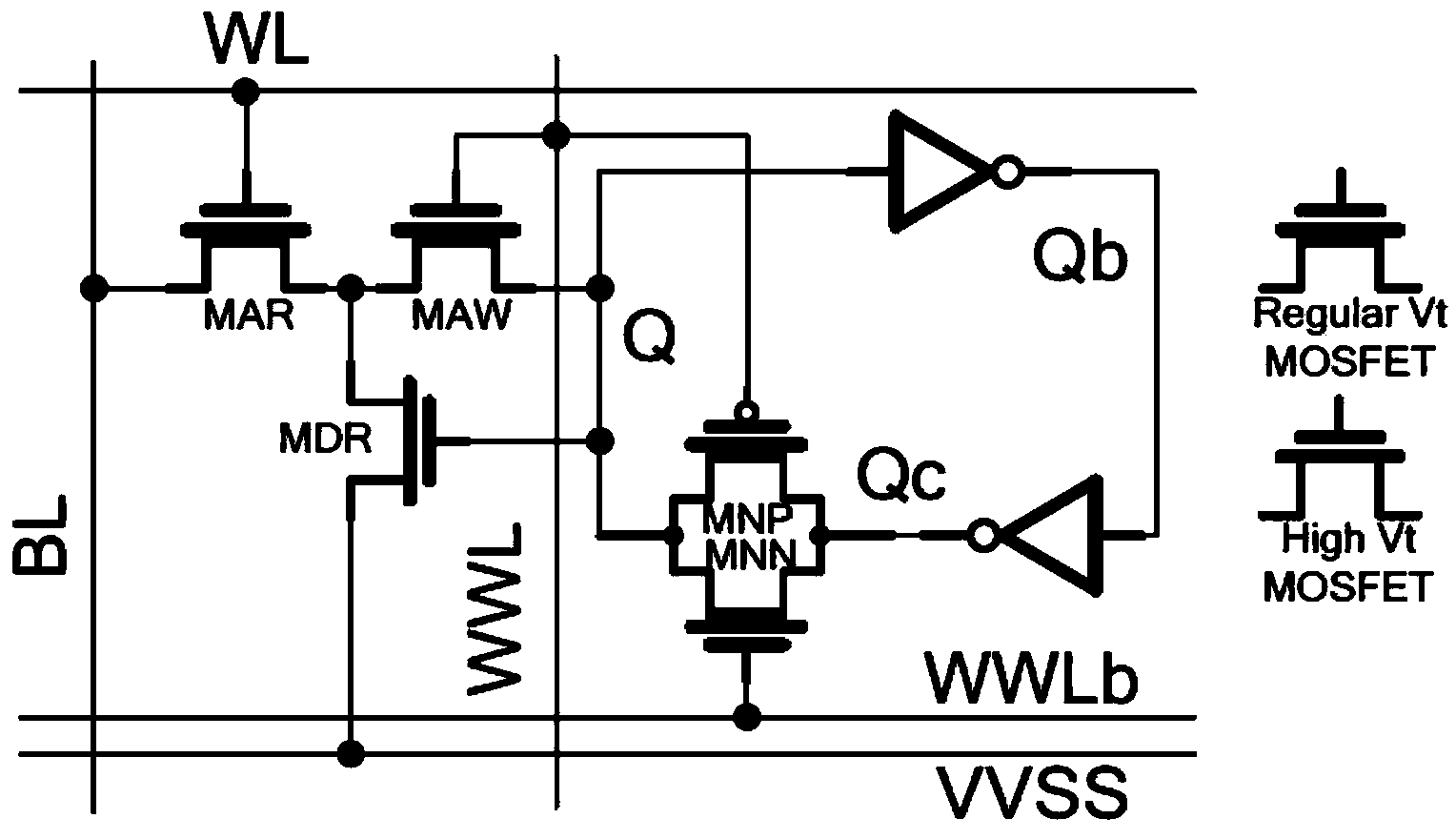
Multi-threshold voltage-biased circuits
InactiveUS20090160531A1Limit leakage currentPower reduction in field effect transistorsSolid-state devicesLow voltageField-effect transistor
A circuit and a method of operation to reduce dynamic and static power dissipation in the circuit are disclosed. The circuit is multi-threshold, voltage-biased and includes a p-channel field effect transistor (FET) and an n-channel FET. A source terminal of the p-channel FET interconnects to a higher-voltage rail of a power supply and a source terminal of the n-channel FET interconnects to a lower-voltage rail of the power supply. At least one of the FETs includes a back contact. The circuit may be operated by applying a fixed bias voltage to the back contact. The fixed bias voltage is independent of the power supply voltage which may be varied. In a normal state, the supply voltage is adjusted to decrease dynamic power consumption. In a low power state, the supply voltage is further adjusted to limit leakage current. The circuit may optionally include a second fixed biasing voltage source so that both FETs are biased.
Owner:ATI TECH INC
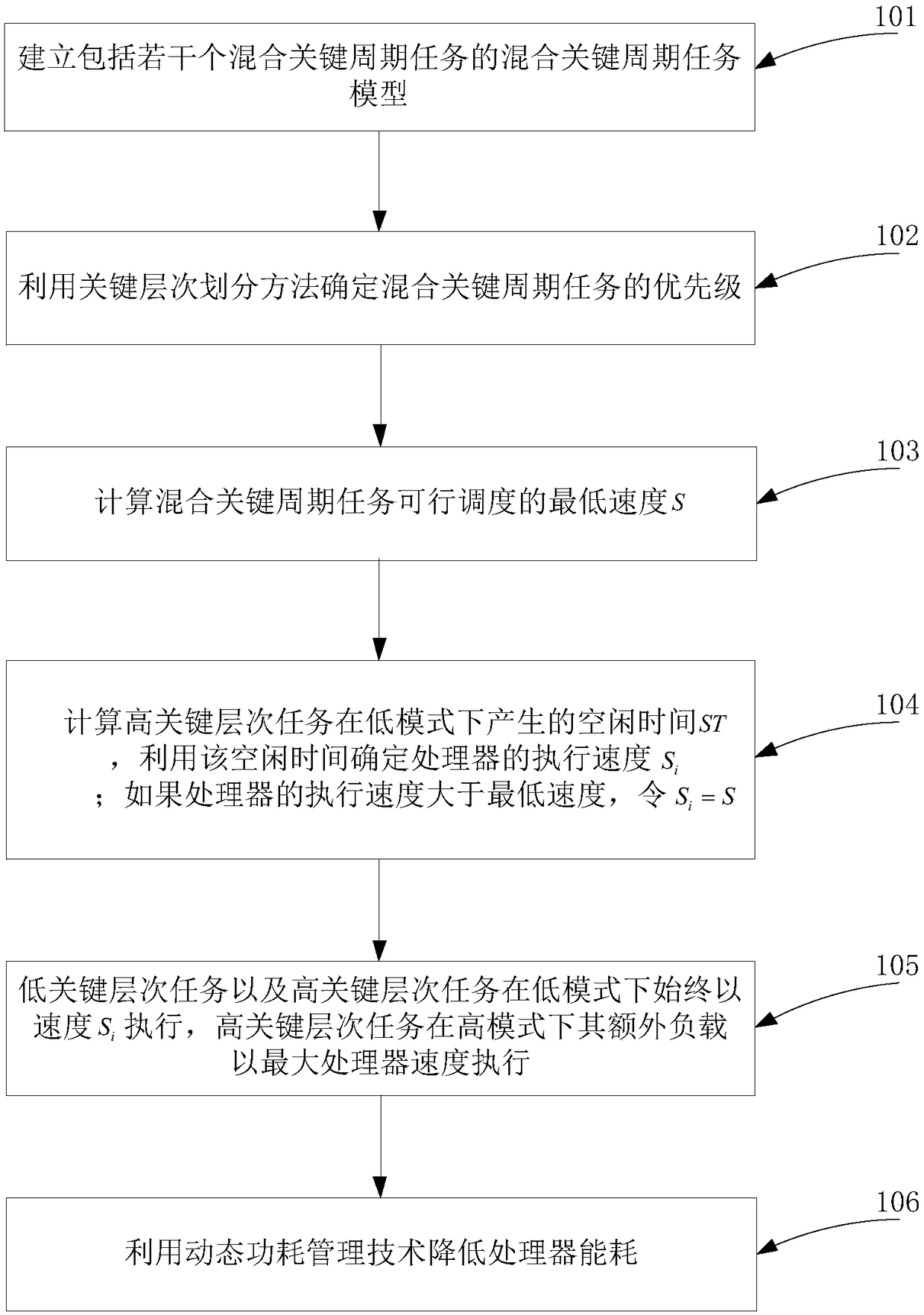
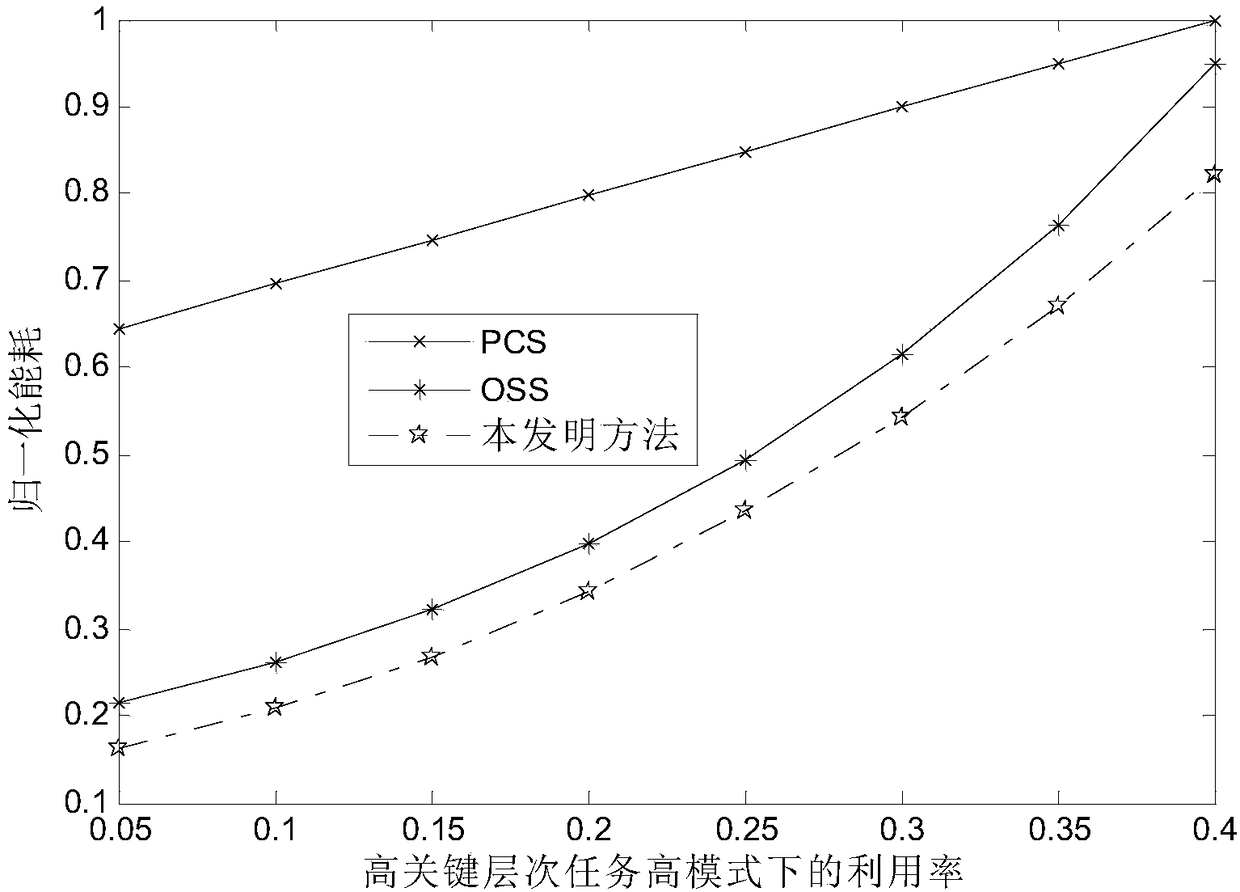
Energy consumption optimization method for fixed priority periodic task in hybrid critical system
ActiveCN108984292AReduce energy consumptionEnsure full implementationProgram initiation/switchingResource allocationCritical levelIdle time
The invention relates to an energy consumption optimization method for a fixed priority periodic task of a hybrid critical system, the method comprising the following steps: establishing a hybrid critical periodic task model comprising a plurality of hybrid critical periodic tasks; determining priority of hybrid critical periodic tasks by using the critical hierarchy partitioning method; calculating the lowest feasible speed S of hybrid critical period task scheduling; calculating an idle time ST generated by a task of a high critical level in a low mode, and determining an execution speed Siof the processor by using the idle time, wherein the low level critical tasks and high level critical tasks are always executed at speed Si in low mode, and the high critical level tasks are executedat maximum processor speed with extra load in high mode; using dynamic power management technology to reduce processor power consumption. The method of the invention effectively reduces the system energy consumption by utilizing the idle time generated by the high-critical-level tasks and the dynamic power consumption management technology.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
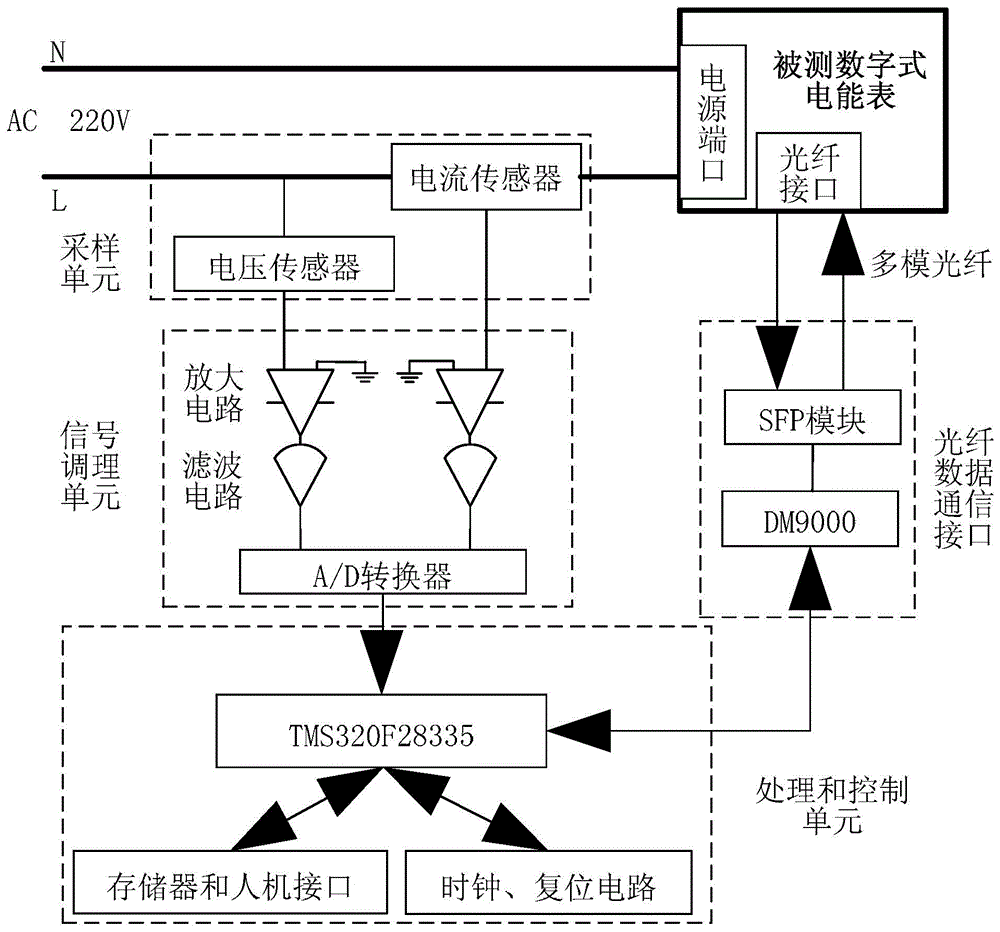
Digital type electric energy meter power consumption measuring device and method
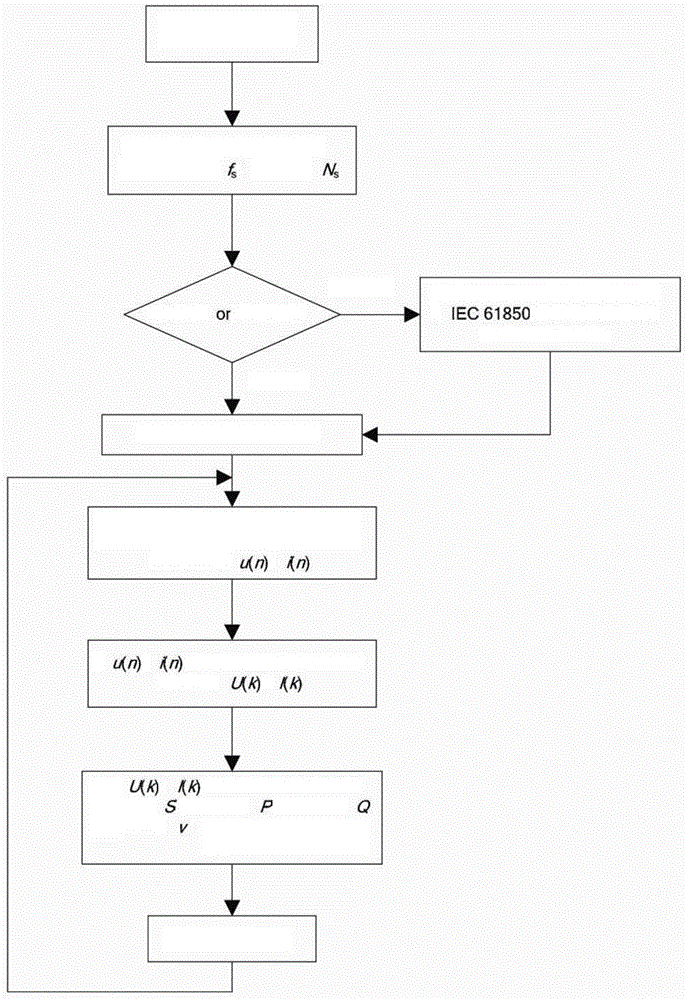
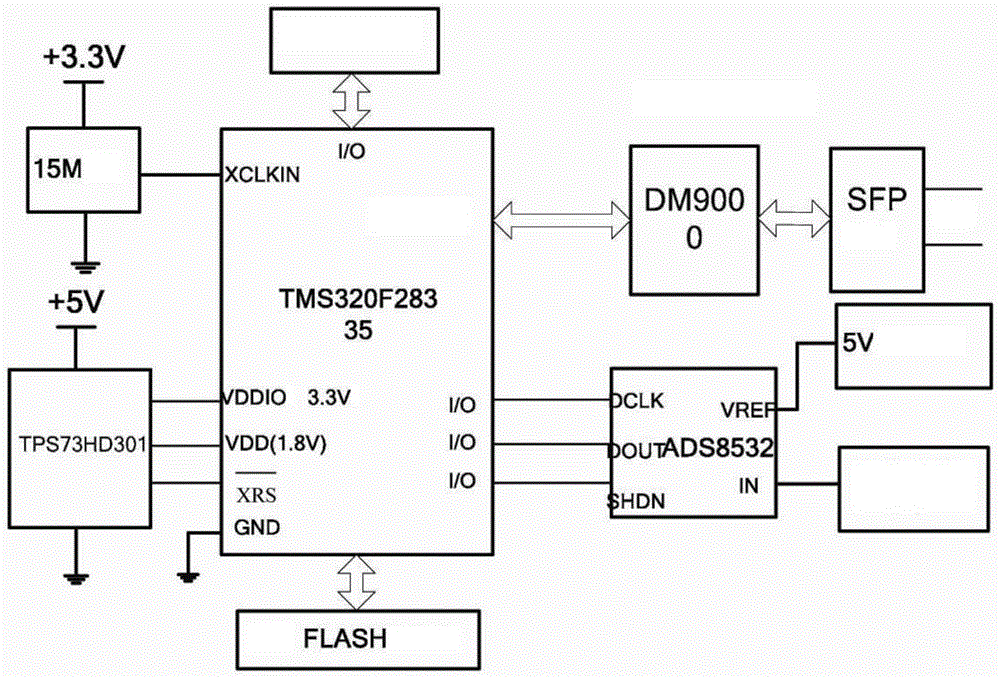
ActiveCN104569902AGuaranteed energy savingGuaranteed uptimeElectric devicesElectric power measurementPower qualityMeasurement device
The invention discloses a digital type electric energy meter power consumption measuring device and method. An optical fiber data communication interface is adopted to communicate with a measured digital type electric energy meter in real time, in a 'measuring mode' and a 'standby mode' of the digital type electric energy meter, voltage and current signals of a power supply loop of the measured digital type electric energy meter can be acquired in real time, the real-time power consumption value of the measured digital type electric energy meter in the 'measuring mode' and the 'standby mode' can be accurately analyzed by using a rapid Fourier frequency domain conversion technique, and whether the power consumption meets relevant technical requirements can be judged. Compared with a method that only the static power consumption of the electric energy meter is measured by using an ordinary multimeter, the method is relatively high in accuracy, complex wiring and electric shock hazard are avoided, the measuring process is full-automatic, the static power consumption and the dynamic power consumption can be measured in real time, the electric energy quality of an alternative-current power supply of the measured digital type electric energy meter is effectively evaluated, and the energy conservation and the reliable operation of intelligent substation equipment are ensured.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +2
Charge pump circuit with low power consumption
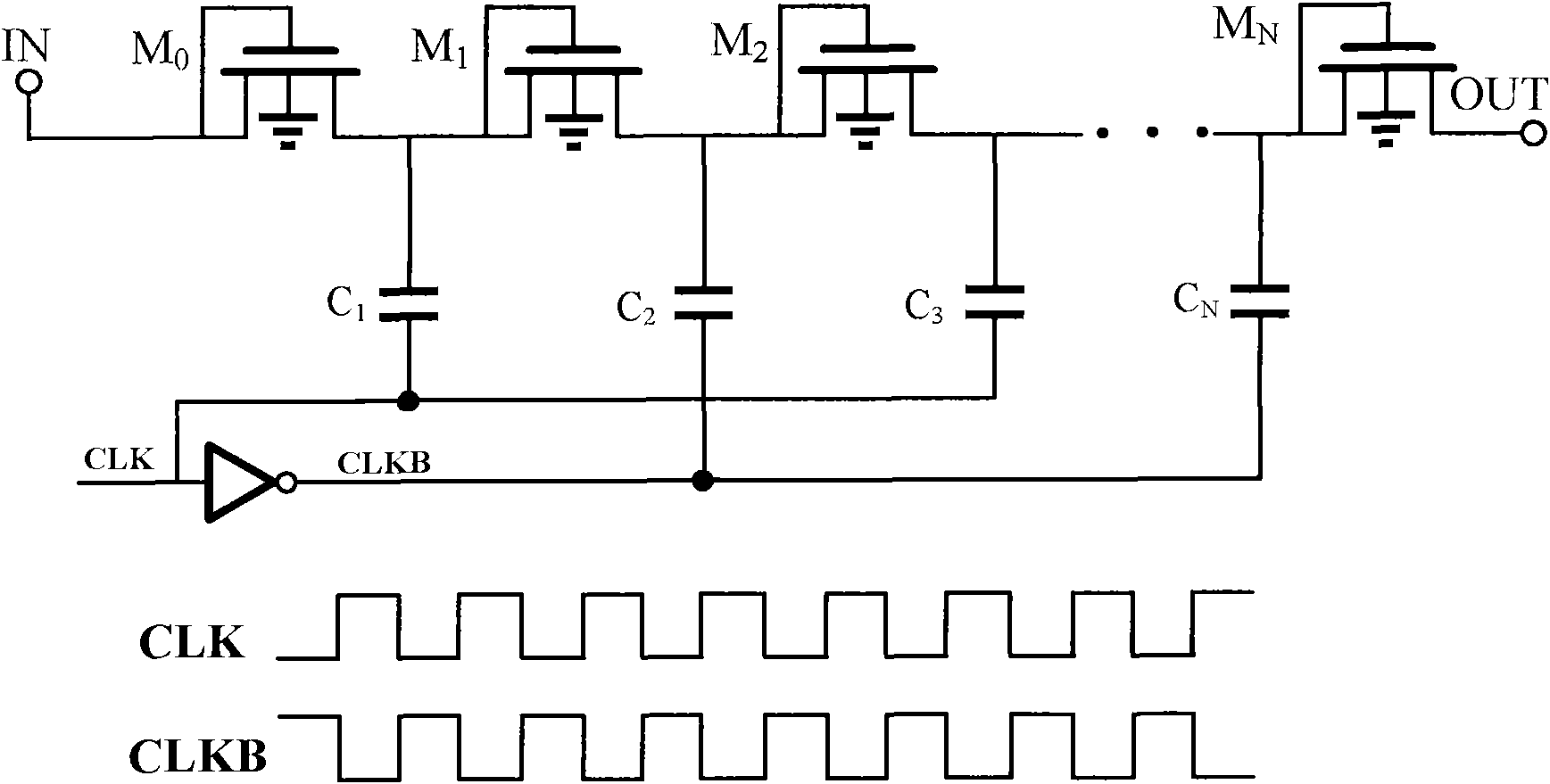
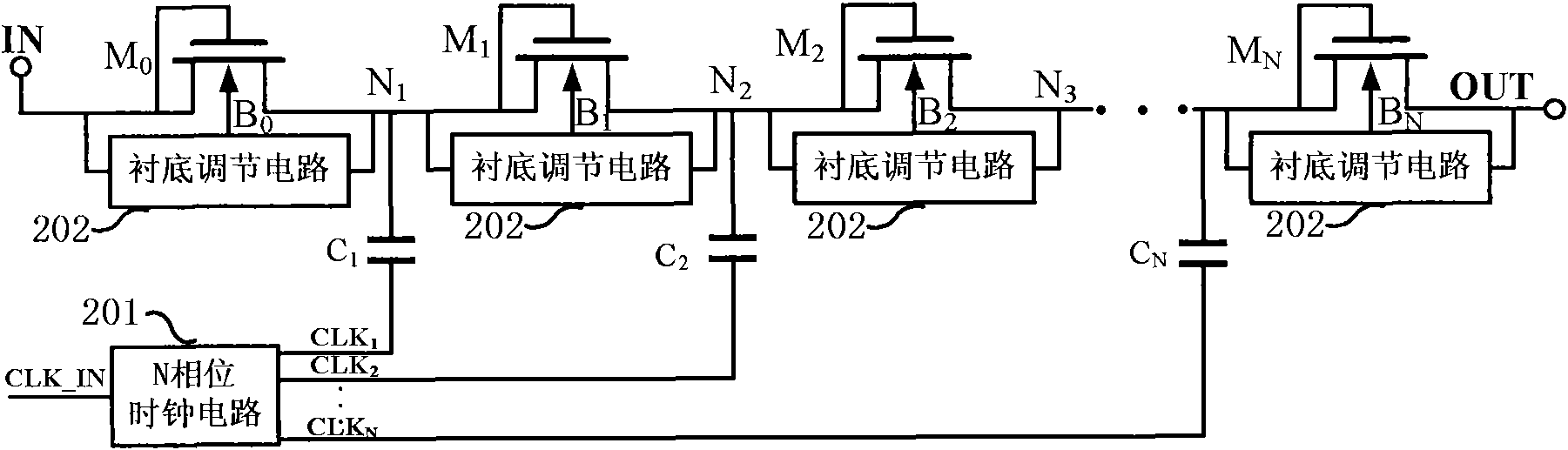
InactiveCN101867290AReduce peak currentApparatus without intermediate ac conversionCapacitancePeak value
The invention relates to a charge pump circuit with low power consumption. The charge pump circuit comprises a multiphase clock generation circuit, a charge transmission transistor, a substrate adjustment circuit of the charge transmission transistor and a capacitor element, wherein one end of the capacitor element is connected to a serial connection joint of the charge transmission transistor, and the other end is connected to clock signals generated by the multiphase clock circuit; the plurality of clock signals output by the multiphase clock generation circuit have different phases, and each clock signal is connected to the corresponding capacitor element so that the charge pump only charges one capacitor when working at different moments. The invention can effectively avoid larger transient current and transient power consumption caused by charging the plurality of capacitors in the traditional charge pump circuit at the same time, and thereby the dynamic power consumption and power peak current are reduced when the charge pump works.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Apparatus and method for high speed voltage regulation
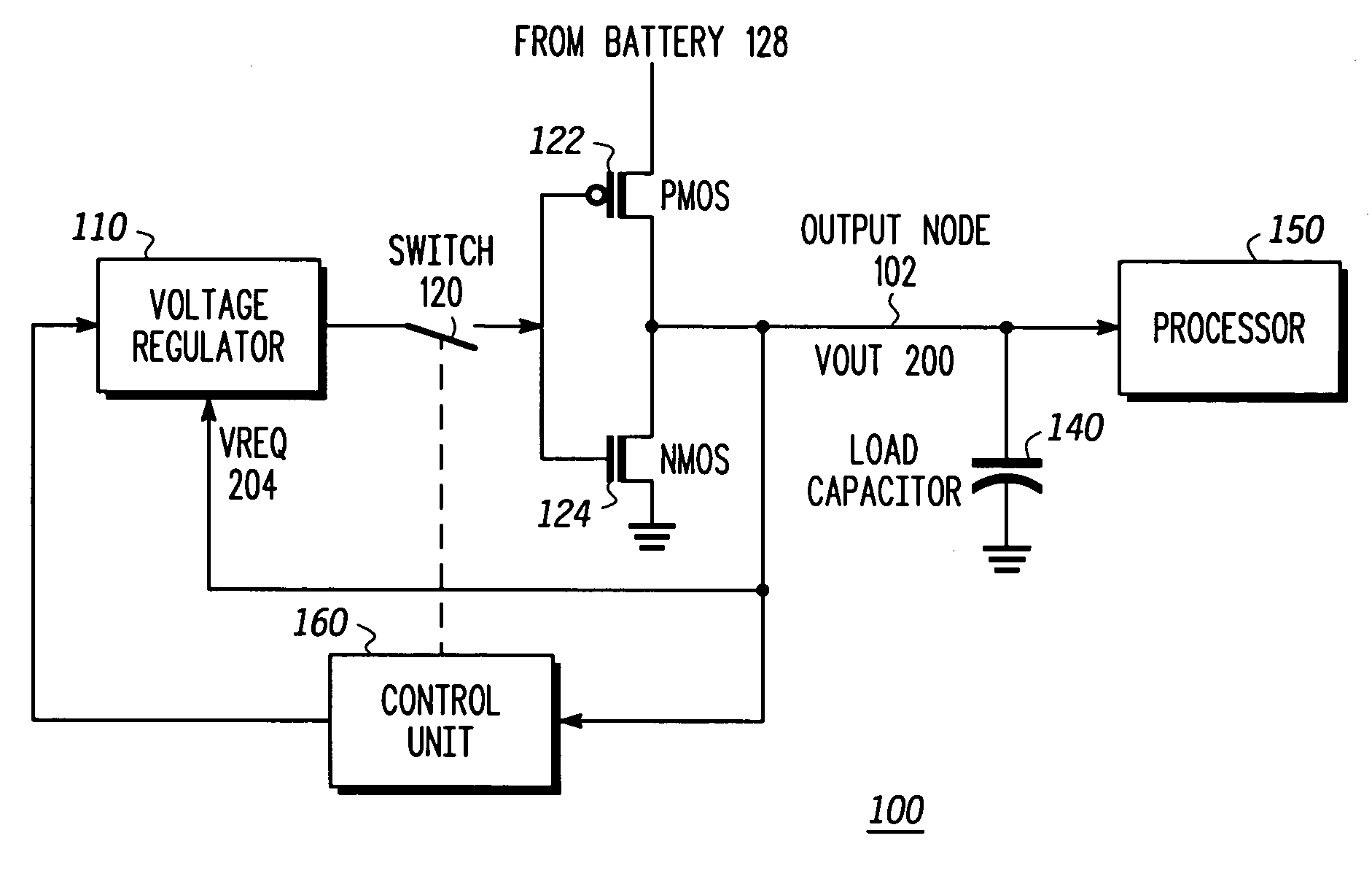
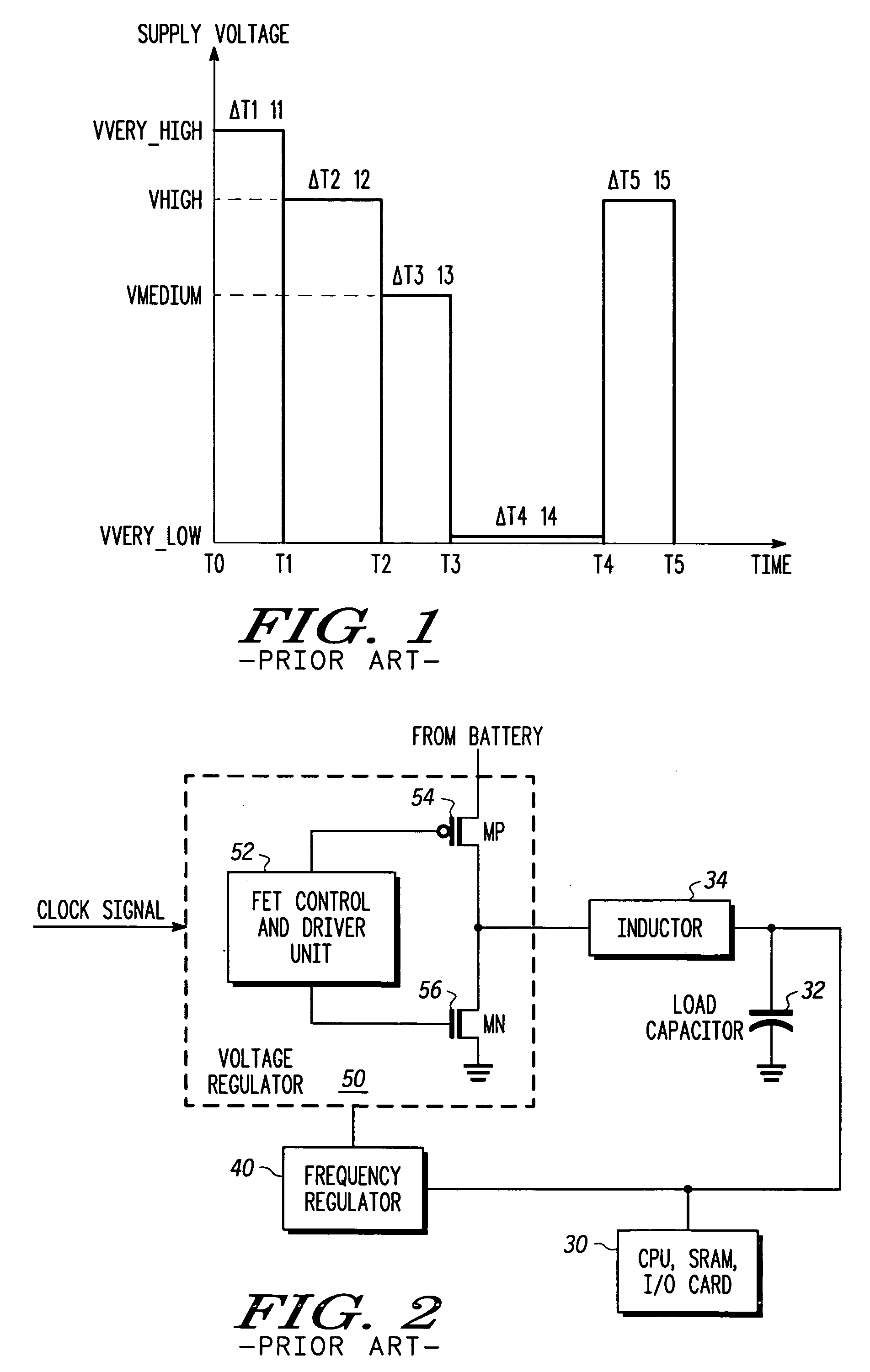
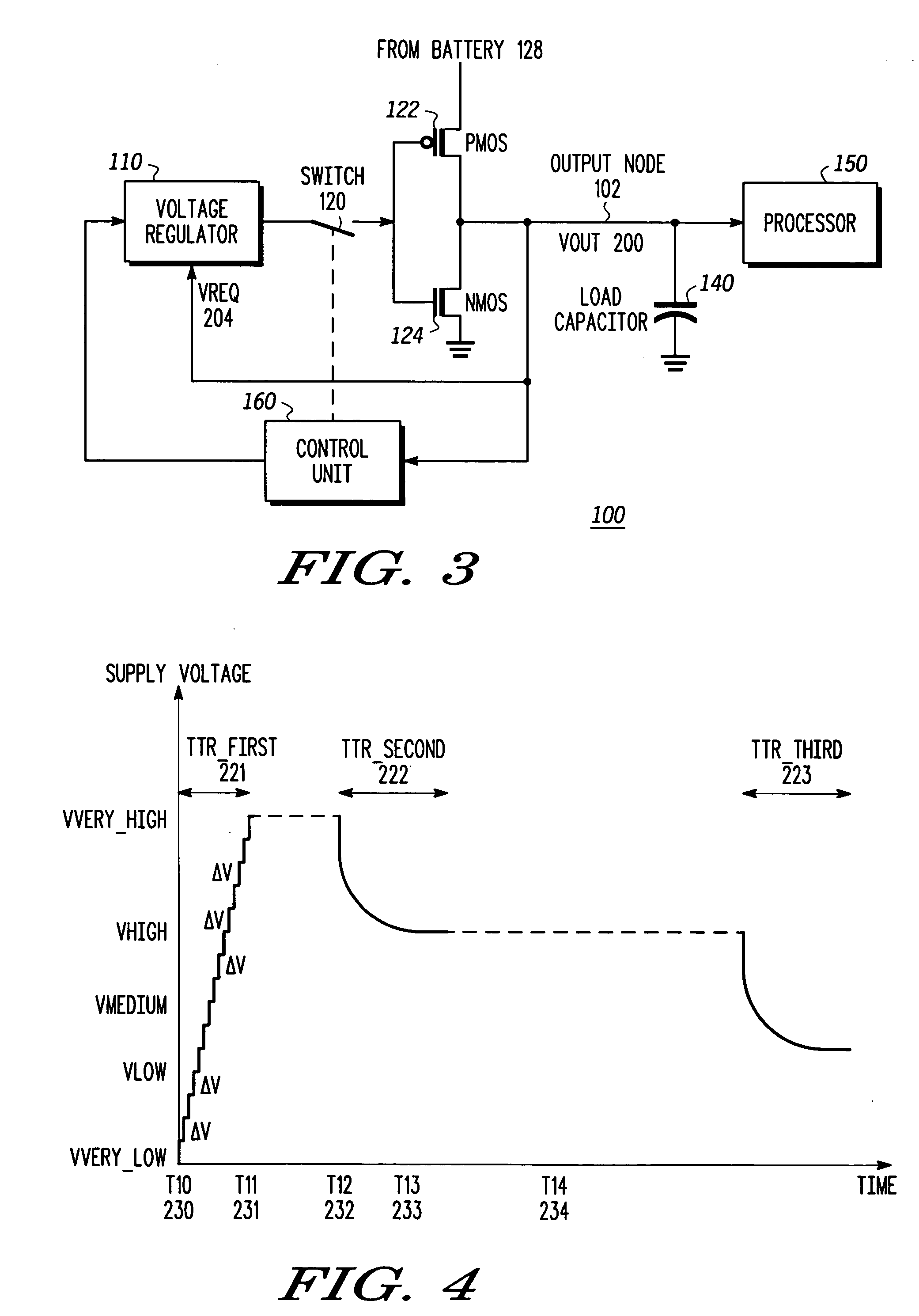
A high-speed voltage regulating apparatus and a method for high-speed voltage regulation. The apparatus includes: (A) a regulator, adapted to provide a regulated voltage; (B) switching circuitry, connected to the regulator, adapted to either (i) connect the regulator to an output node or (ii) disconnect the regulator from the output node; whereas the output node is connected to a dynamic power consuming device and to a load capacitor; (C) control logic, connected to the regulator, adapted to receive at least an indication reflecting a voltage of the output node and to control the switching circuitry such that the regulator is disconnected from the output node to facilitate a decrease in the voltage of the output node. The method includes: (A) determining whether to (i) decrease a voltage of an output node, (ii) to maintain the voltage of the output node or to (iii) increase the voltage of the output node; (B) allowing a voltage of an output node to decrease by disconnecting a regulator from the output node; whereas the output node is coupled to a dynamic power consuming device and to a load capacitor; and (C) providing a regulated voltage corresponding to a required voltage of the output node, if determining to maintain the voltage of the output node or to increase the voltage of the output node.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
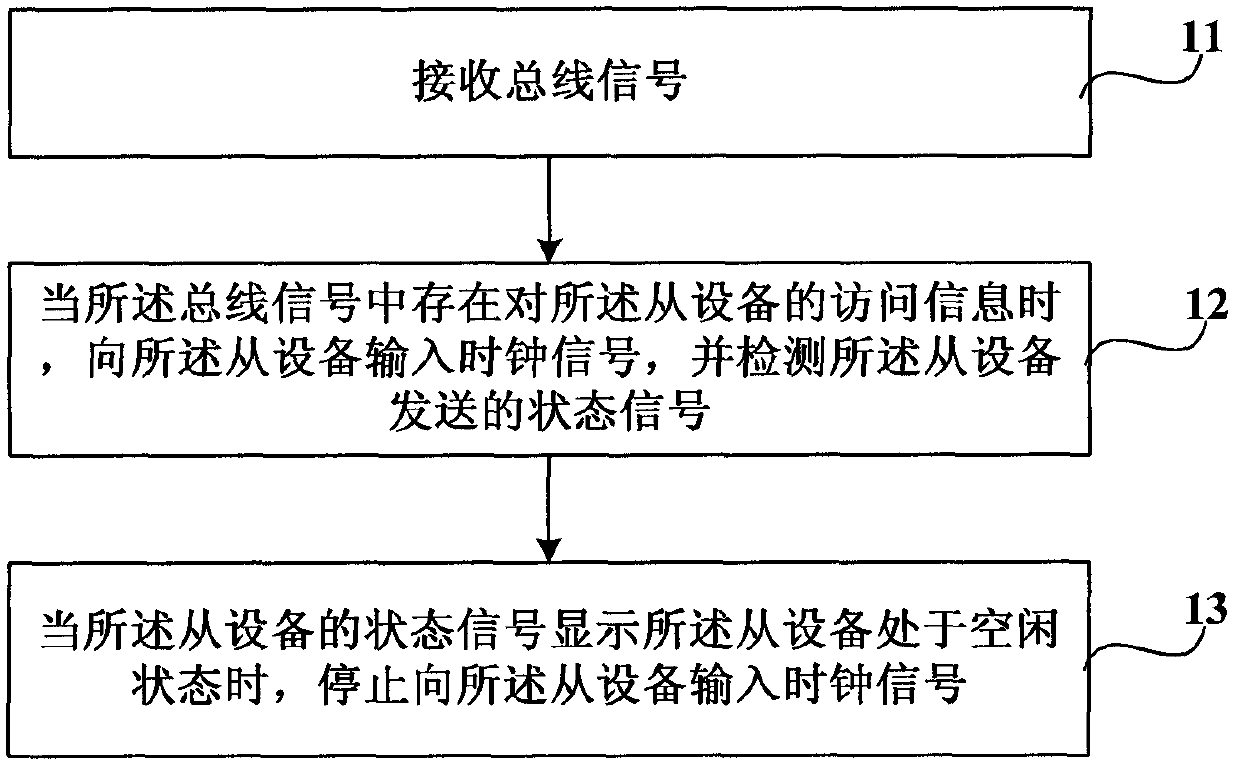
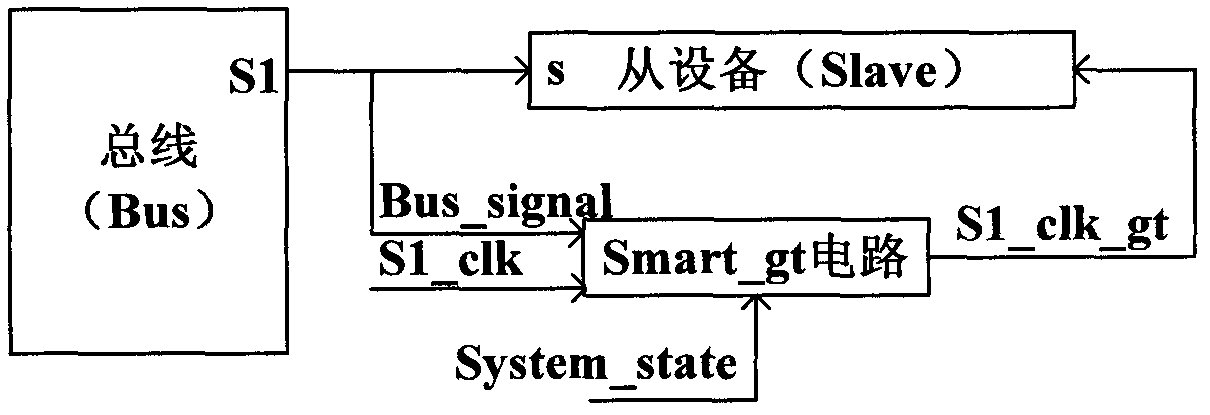
Method for reducing dynamic power dissipation and electronic device
InactiveCN102439535AReduce dynamic power consumptionAvoid flippingEnergy efficient ICTPulse automatic controlHemt circuitsEngineering
The present invention relates to a method for reducing a dynamic power dissipation and an electronic device. The method is used to reduce the dynamic power dissipation of a slave unit, and comprises the steps of receiving a bus signal when access information of the slave unit is existed in the bus signal; inputting a clock signal to the slave unit and detecting a state signal sent by the slave unit; when the state signal of the slave unit displays that the slave unit is located in a free state, stopping inputting the clock signal to the slave unit. In the invention, by controlling work clocks of chip inner device modules, such as the slave unit, etc. via the bus signal and the slave unit, the chip inner device module is avoided from generating an unnecessary circuit turnover under a non-work state, to thereby achieve the purpose of reducing the dynamic power dissipation of the chip inner device module.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
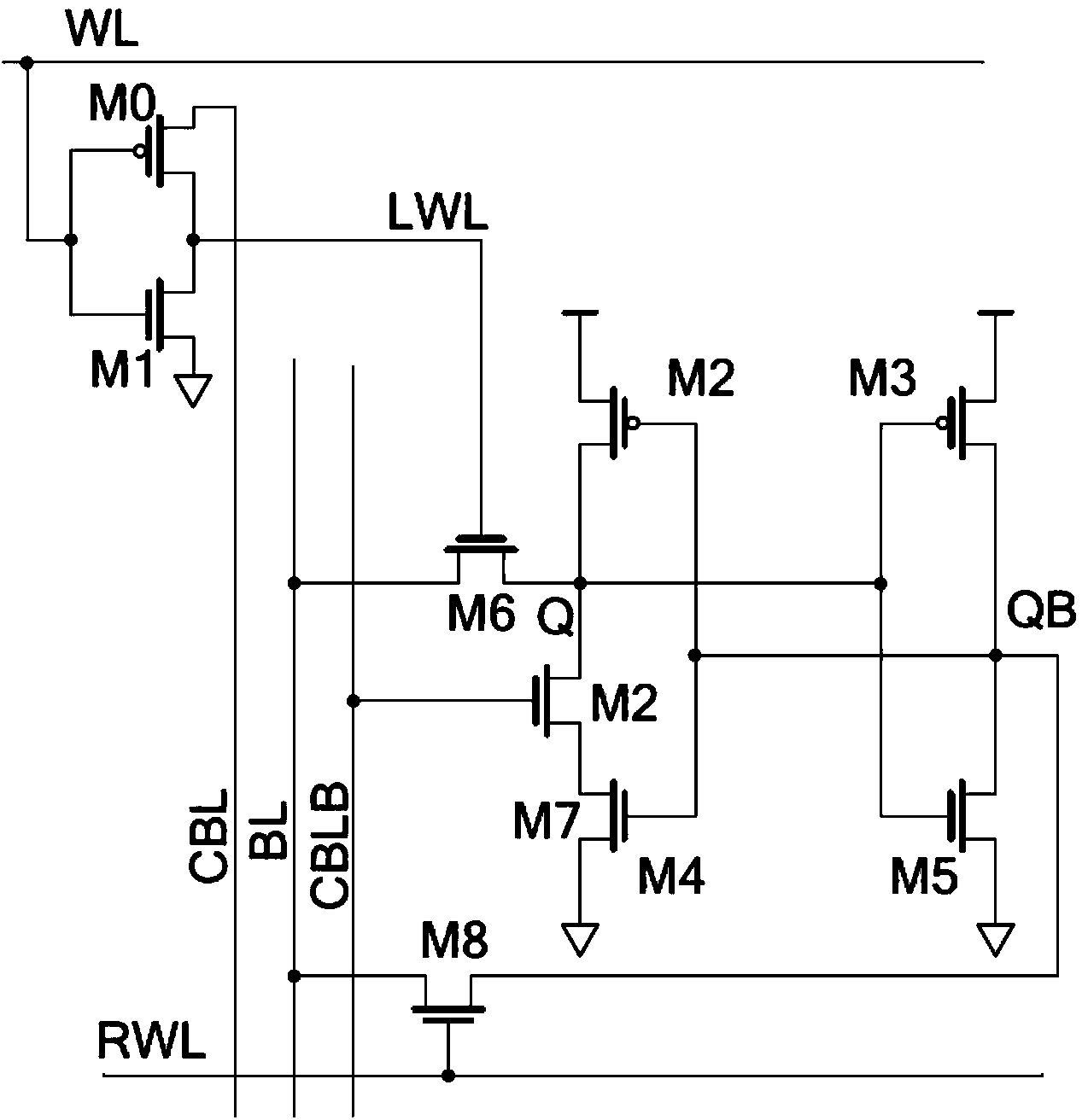
Storage unit circuit with adaptive leakage current cutoff mechanism
InactiveCN102176323AReduce dynamic power consumptionReduce leakage powerDigital storageBit lineSub threshold
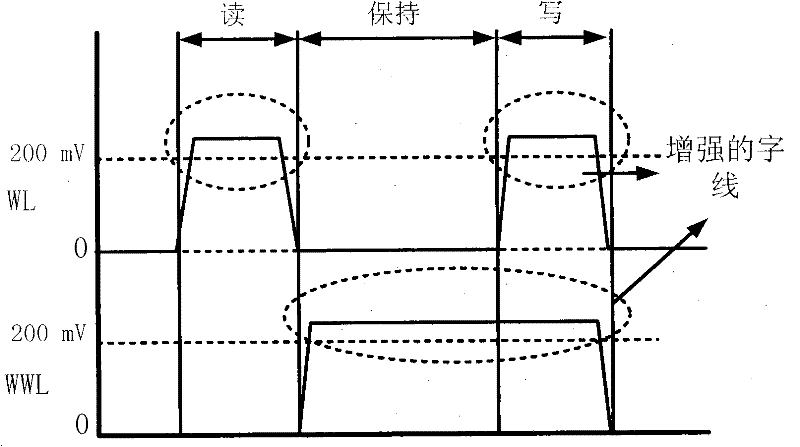
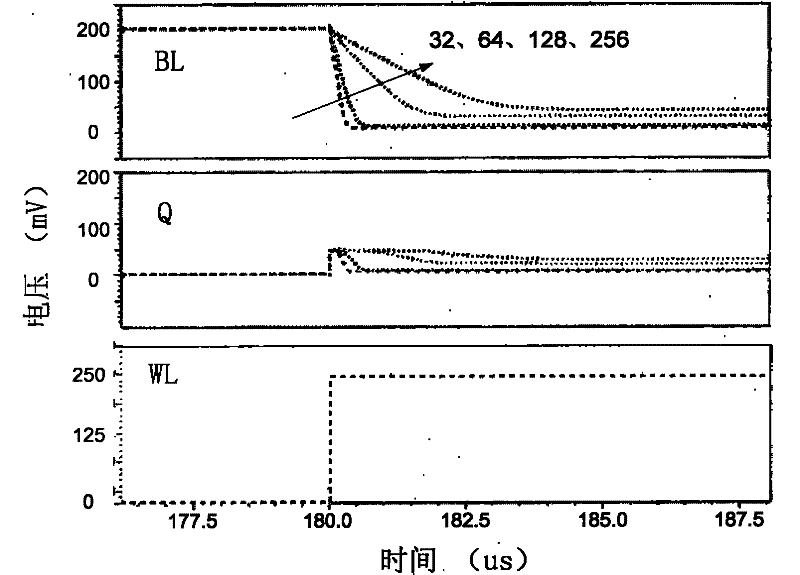
The invention provides a storage unit circuit with an adaptive leakage current cutoff mechanism, which is a dual-port read-writing sub-threshold storage unit circuit. The circuit comprises a first inverter and a second inverter which are connected in a cross coupling way; the two inverters are connected between complementary bit lines through an equalizer pipe; and the grid end of the equalizer pipe is connected with an enhanced word line. The invention overcomes the defects of the prior art and provides the sub-threshold storage unit circuit with low power consumption and high robustness; and the sub-threshold storage unit circuit can reduce leakage power consumptions in dynamic operation and static operation while the leakage power at the same time on the premise of not increasing dynamic power consumption or reducing performance, and can balance each index of a storage unit so as to optimize system performance.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Buffering circuit with reduced dynamic power consumption
ActiveUS20110032240A1Reduce dynamic power consumptionPulse automatic controlCathode-ray tube indicatorsAudio power amplifierCharge current
A buffering circuit with reduced power consumption is provided. The output buffering circuit includes first and second amplifier circuits. The first amplifier circuit includes a first input stage and a first output stage both coupled between a first power voltage and a second power voltage lower than the first power voltage, and an assistant discharging unit configured to provide a discharging current flowing from a first output node to a first intermediate power voltage during a discharging operation of the first amplifier circuit. The second amplifier circuit includes a second input stage and a second output stage both coupled between the first power voltage and the second power voltage, and an assistant charging unit configured to provide a charging current flowing from a second intermediate power voltage to a second output node during a charging operation of the second amplifier circuit. The first and second amplifier circuits can have reduced output voltage ranges and hence reduced total power consumption.
Owner:HIMAX TECH LTD +1
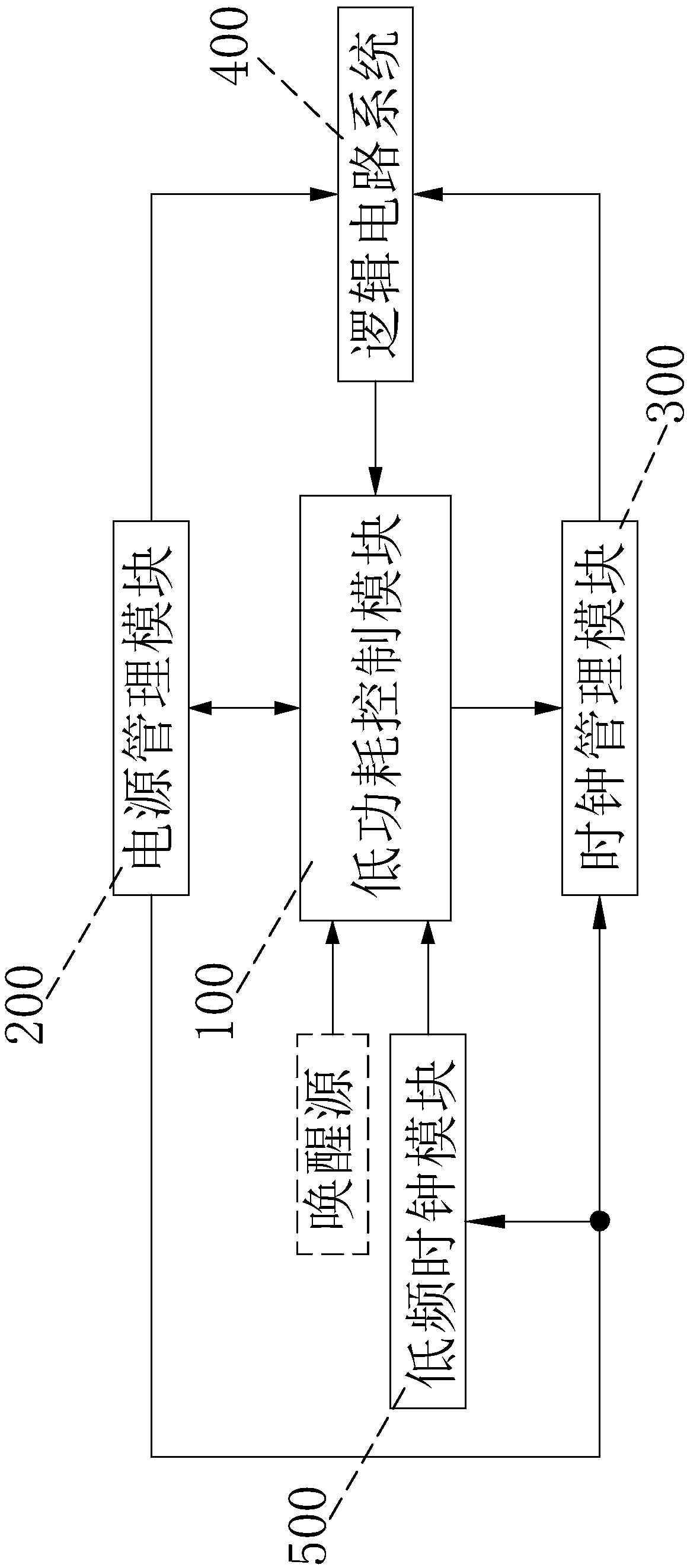
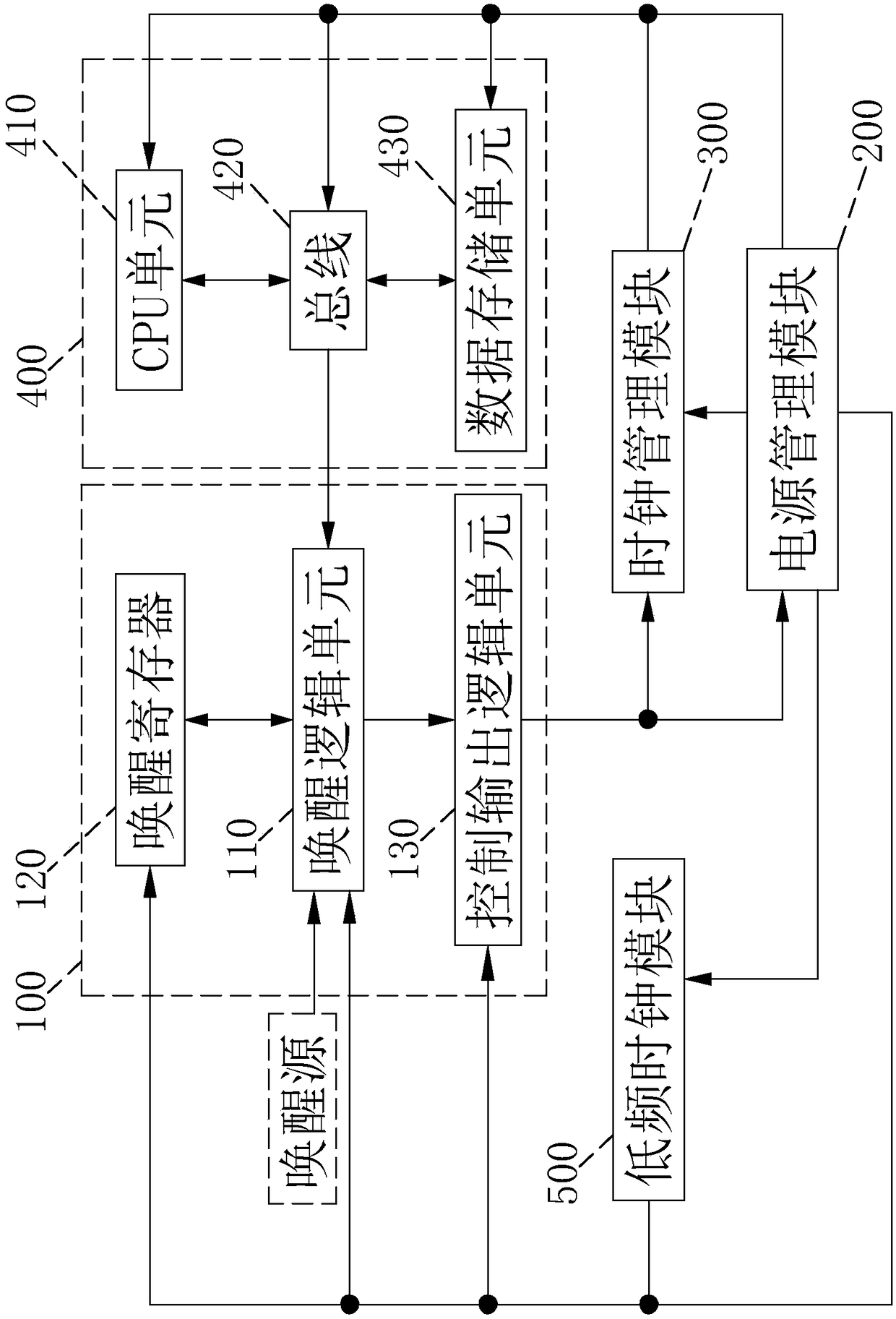
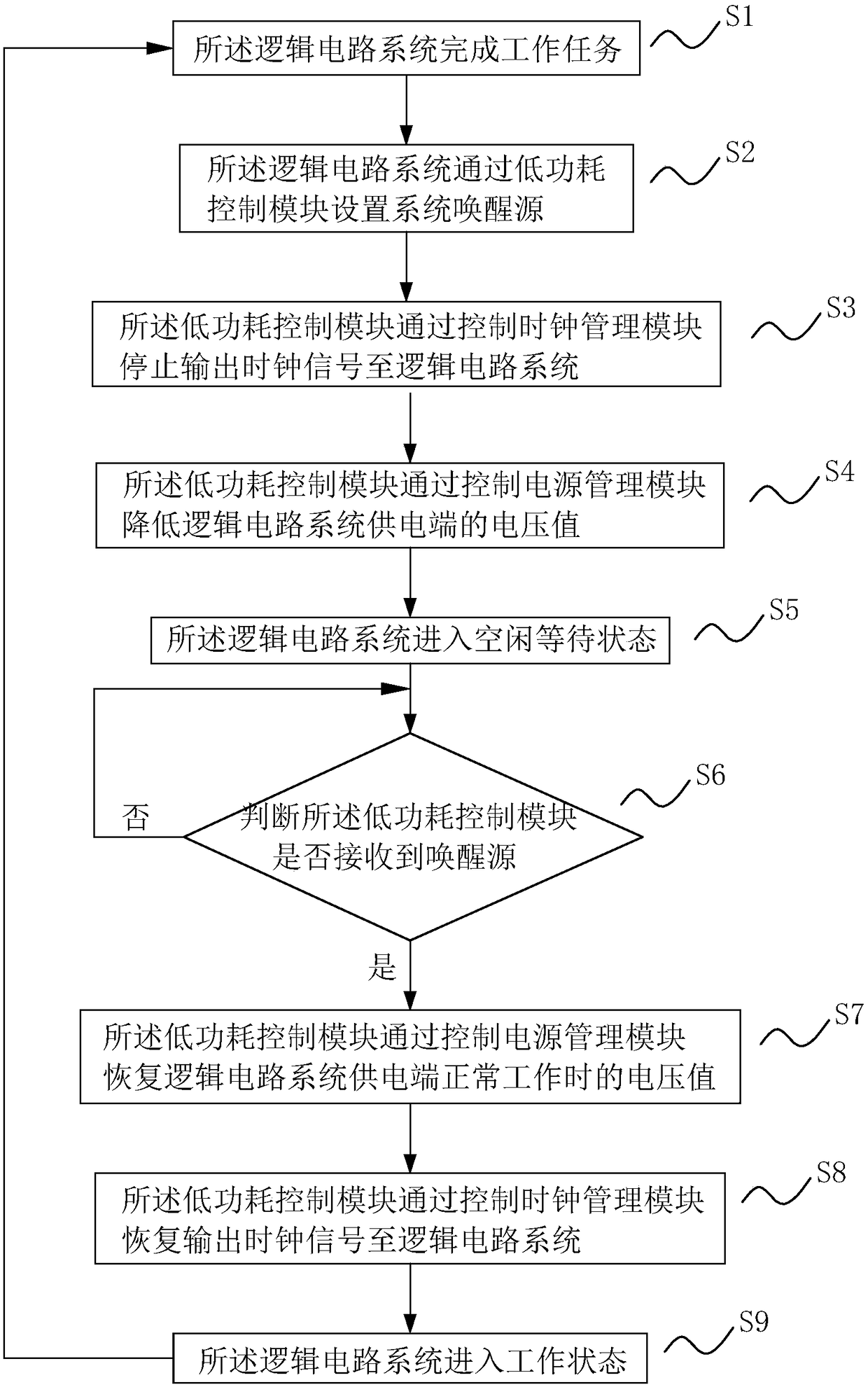
Small-size SoC ultra-low power consumption control circuit and method
InactiveCN108089689AEliminate logic dynamic powerReduce leakage power consumptionPower supply for data processingUltra low powerLogical circuit
The invention discloses a small-size SoC ultra-low power consumption control circuit and method. The circuit structurally comprises a logic circuit system, a low power consumption control module a power management module, a clock management module and a low-frequency clock module. When an idle state is required, a voltage value at a power supply end of the logic circuit system is reduced, by the low power consumption control module on hardware, to only keep a data state in the logic circuit system and not support a lowest value of signal reversal, and meanwhile, a clock source of the logic circuit system is closed to eliminate logic dynamic power consumption and reduce electric leakage power consumption to be the lowest; and moreover, software is not required for storing a system operationstate, and when awakening is carried out, the software is not required to restore the scene and the next instruction of the system can be directly operated, so that the awakening speed is improved and the user experience is strengthened.
Owner:珠海慧联科技有限公司
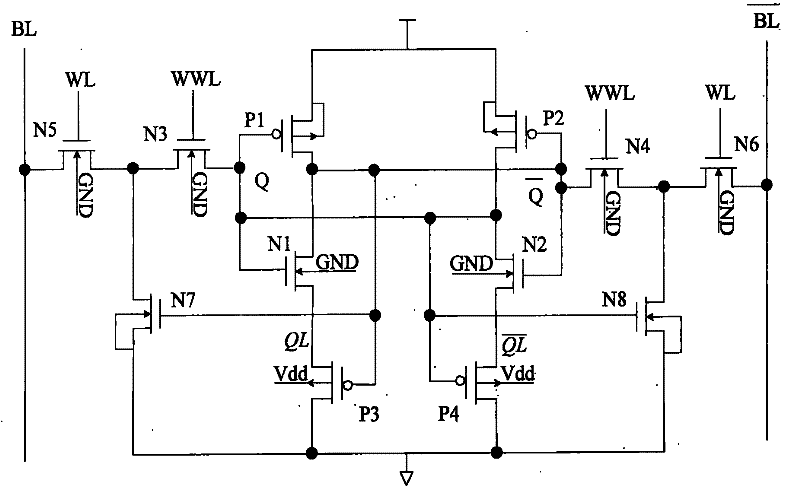
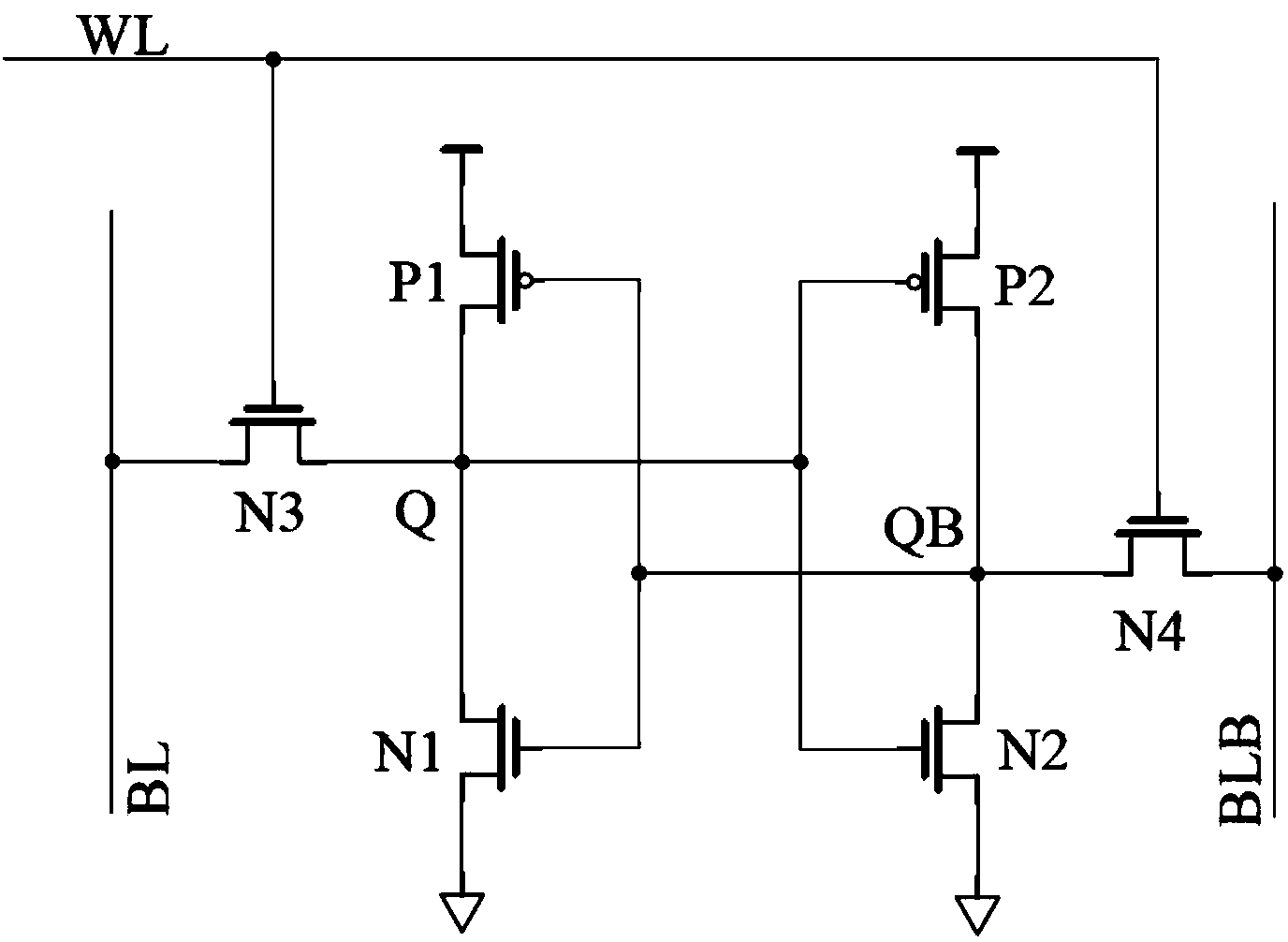
Novel 12-tube SRAM (Static Random Access memory) unit circuit capable of simultaneously increasing read noise tolerance and writing margin
ActiveCN104299644AEliminate the half-choice problemSolve the reading half-choice problemDigital storageStatic random-access memoryWrite margin
The invention discloses a novel 12-tube SRAM (Static Random Access memory) unit circuit capable of simultaneously increasing read noise tolerance and writing margin, and the novel 12-tube SRAM unit circuit can eliminate a partial-select problem and solve a read partial-select problem and a writing partial-select problem, a stability problem cannot be caused, and additionally, no additional power is consumed. Experiments measure that compared with a traditional 6T unit, the read dynamic power consumption and the writing dynamic power consumption of an array with the total number of 128 are respectively reduced by 81.3% and 88.2% when a column decoding unit (CMUX) is 4; additionally, according to the circuit, the read noise tolerance is greatly increased, so that the read noise tolerance is similar to the noise tolerance in a hold mode and reaches 2.3 times of that of the traditional 6T unit; in addition, according to the circuit, a feedback structure of a phase inverter is interrupted, so that the writing margin is increased and reaches 1.41 times of that of a traditional 6T SRAM unit.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
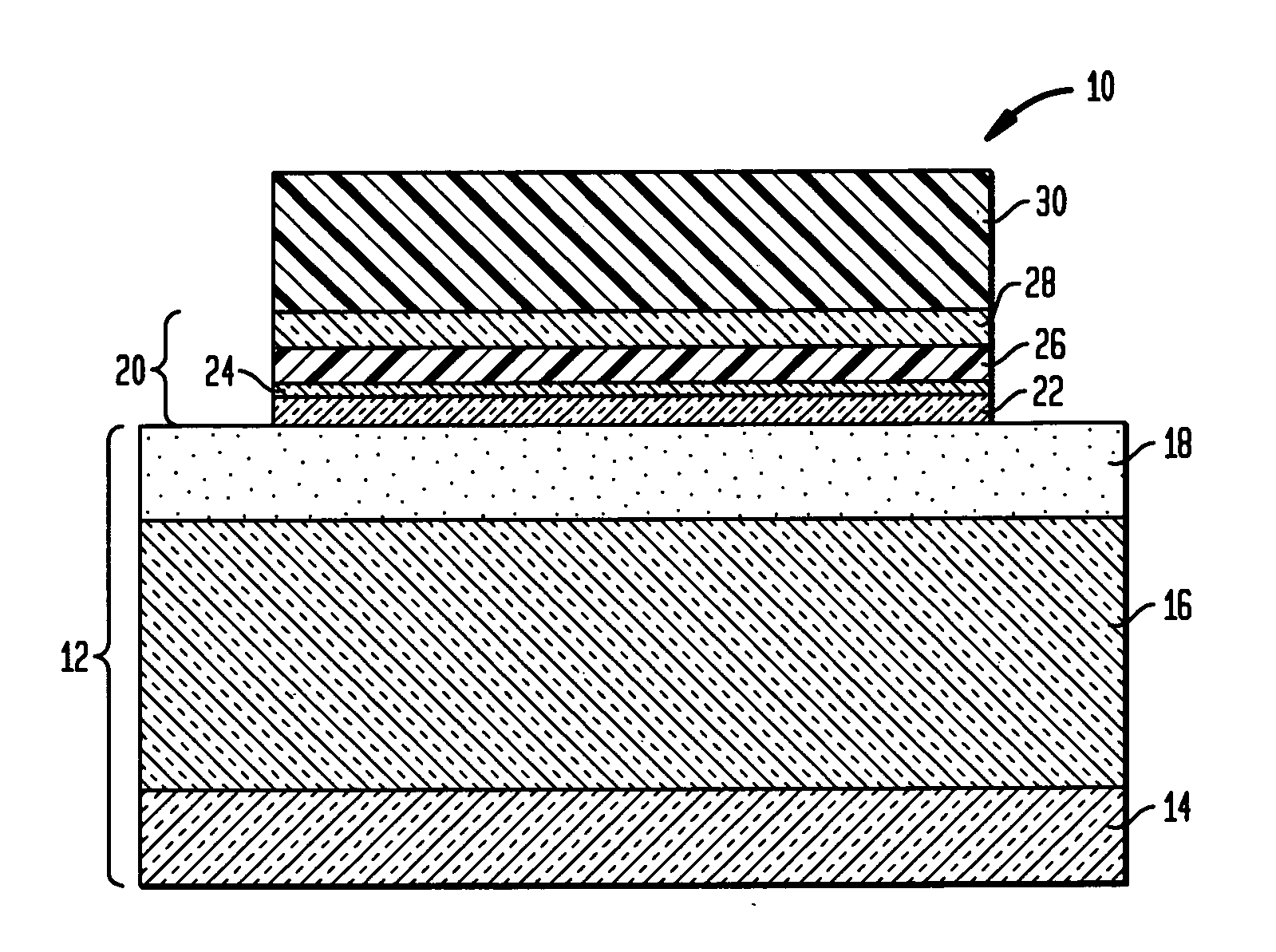
Body capacitor for SOI memory description
InactiveUS20060189110A1Minimize overlap capacitanceEffective holdingTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureChip size
A semiconductor structure having a body capacitance plate, which is formed with a process that assures that the body capacitance plate is self-aligned to both the source line (SL) diffusion and the bitline diffusion is provided. Thus the amount of overlap between the SL and the bitline diffusions and the body capacitance plate is precisely controlled. More specifically, the present invention forms the structure of a 1T-capacitorless SOI body charge storage cell having sidewall capacitor plates using a process that assures that there is 1) minimal overlap between plate and source / drain diffusions, and 2) that the minimal overlap obtained in the present invention is precisely controlled and is not subject to alignment tolerances. The inventive cell results in larger signal margin, improved performance, smaller chip size, and reduced dynamic power dissipation relative to the prior art.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
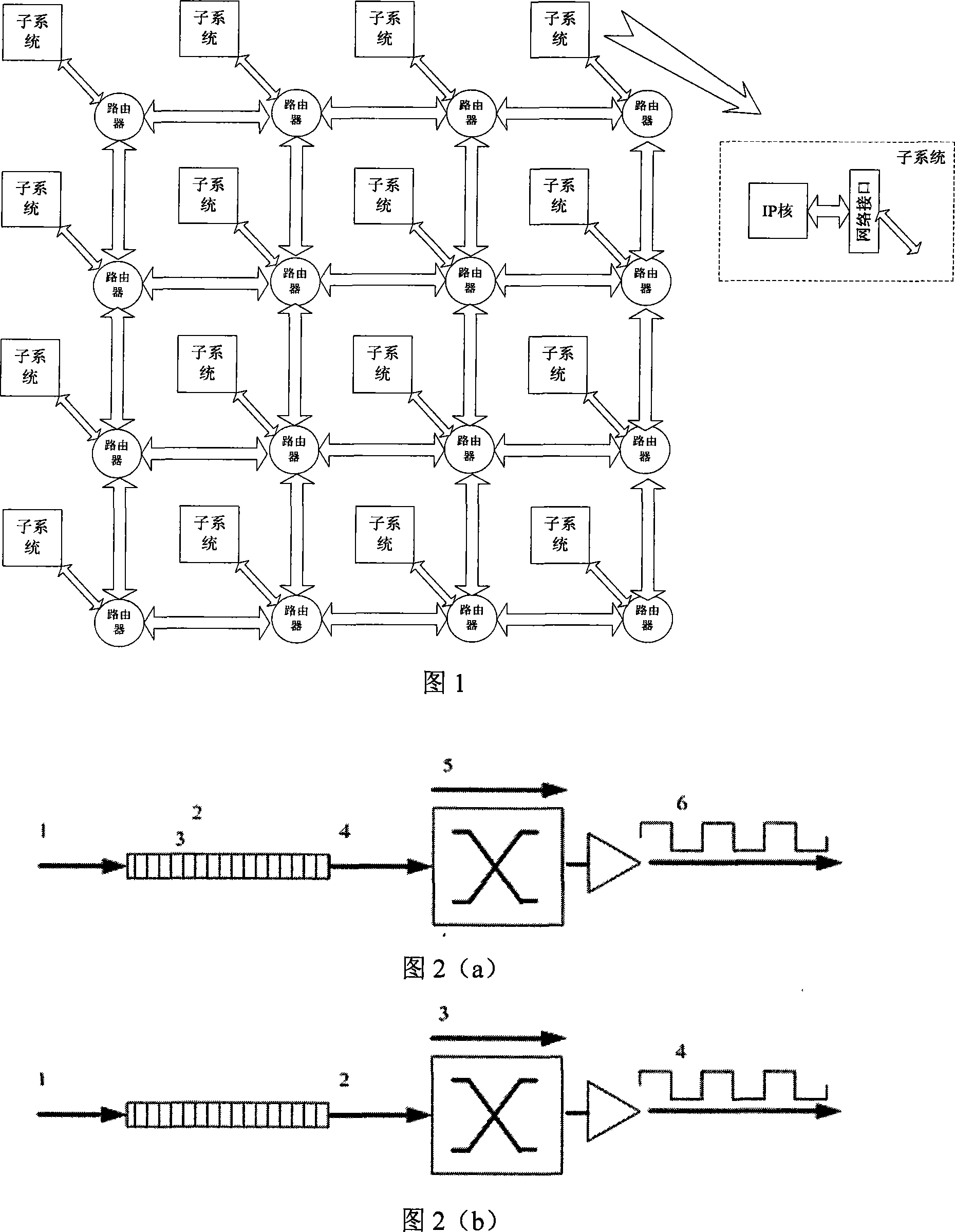
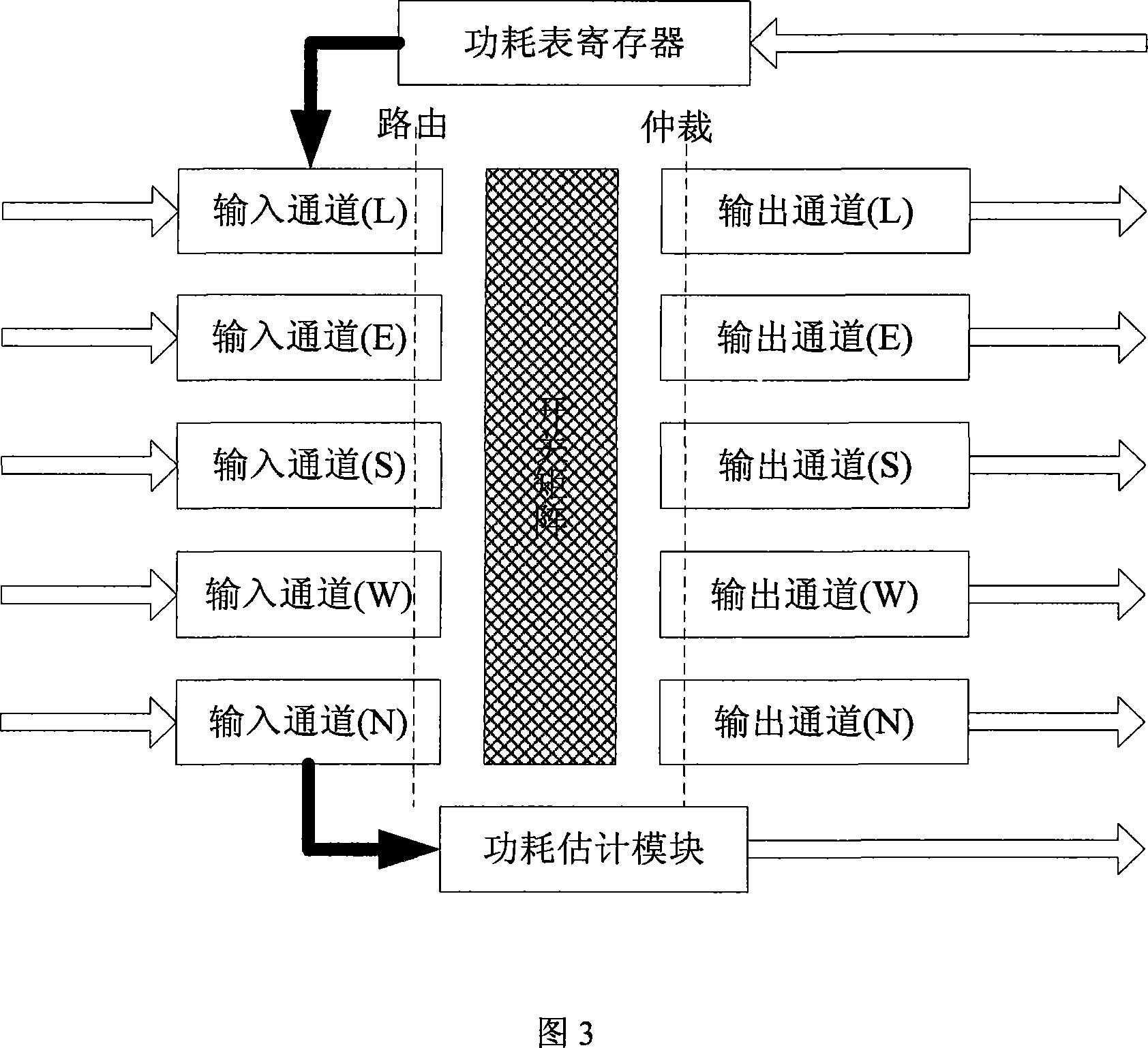
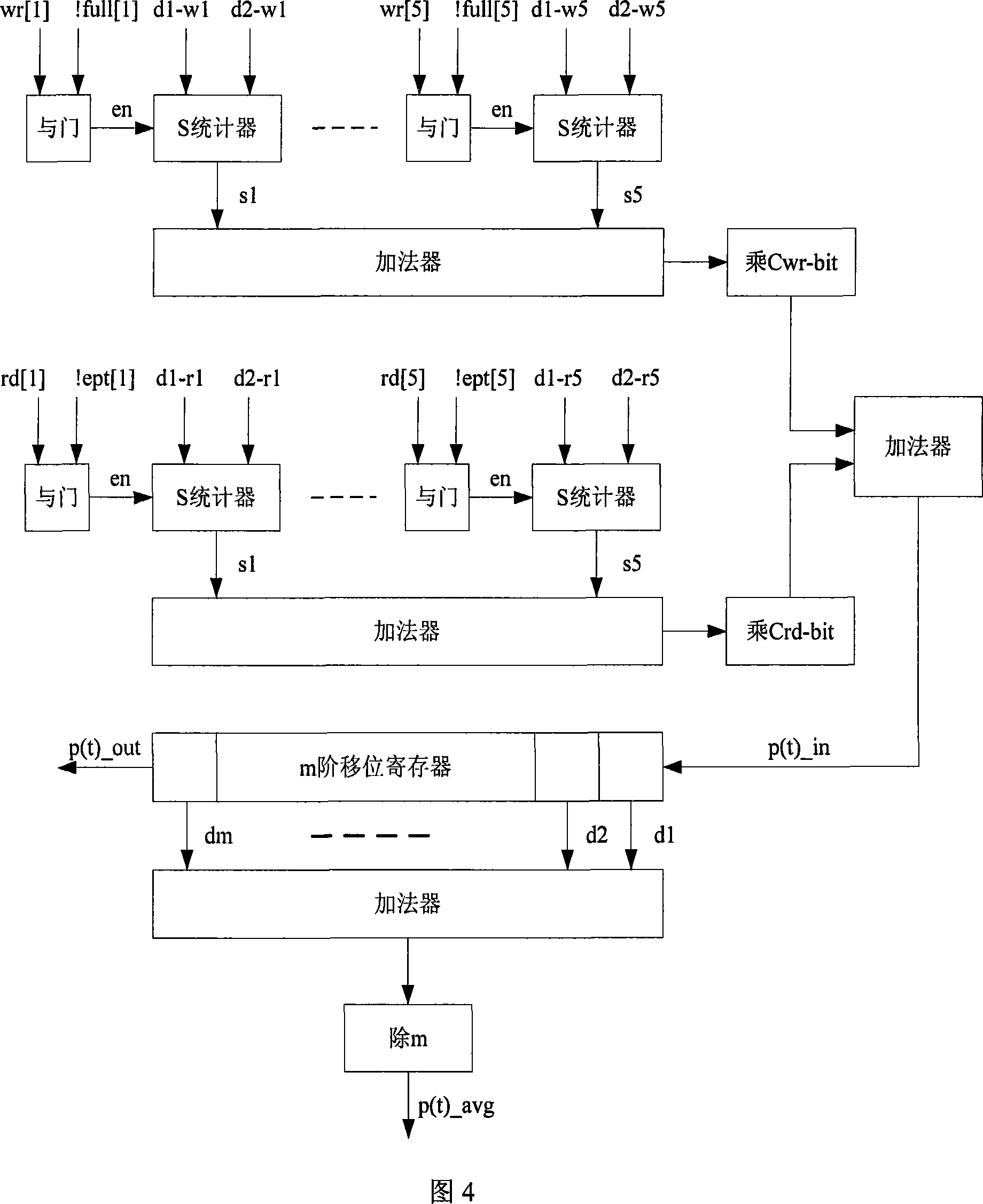
Router power consumption model based on network on chip
The invention discloses a router power model on the basis of a network-on-chip, which simplifies router operations into four power dissipation links namely write-cache, read-cache, a bestride switch and a bestride link according to the power dissipation specific weight and attributes dynamic power dissipation to bit flipping activities which are triggered when a present data film arrives, and numbers the power dissipation by the bit flipping activities to obtain the router power model. Considering that the implementation complexity which is required by the network-on-chip requirements to the power model is as low as possible, the invention can adopt the statistical average in stead of the instantaneous sampled value to obtain a power dissipation simplified model. Hardware implementation methods of two power dissipation models are given out aiming at a five-channel rooter structure, the simplified model is introduced to a self-adaptive routing algorithm, which realizes the power dissipation distribution optimization of the network-on-chip. The router power model which is proposed by the invention has low algorithm complexity and simple realization, is suitable for network-on-chip, and can be used in research and application in the aspects of power dissipation performance statistics, the power dissipation distribution optimization, thermal protection and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Design method of low-power consumption high performance high speed scratch memory
InactiveCN101178690AReduce overheadCutting costsEnergy efficient ICTMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressSwitching time
The invention discloses a design method of a high speed register with low power consumption and high capacity. On the one hand, the invention prevents the invalid visiting to the high speed register by beforehand obtaining the information whether the high speed register is hitting and reduce the dynamic power consumption; on the other hand, the invention divides the storing district in to a number of physical blocks and only visit 1 / n of the total size under the hitting status of the high speed working-storage section, the dynamic power consumption is 1 / n of the original situation. The invention saves the switching time of the dummy address to the physical address, reduces the extra hardware spending brought by the address switching and reduces the whole power consumption of the system byadopting the dummy address to search the high speed register. The invention can greatly reduce the power consumption of the high speed register and greatly elevate the whole capacity of the highly embedding type processor being utilized, which has the advantages of low hardware cost and simple design realization.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00000.png)
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00001.png)
![[source driver and liquid crystal display using the same] [source driver and liquid crystal display using the same]](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/e88e2294-b4cf-4ae2-a43e-a258af6a2325/US20050206629A1-20050922-D00002.png)