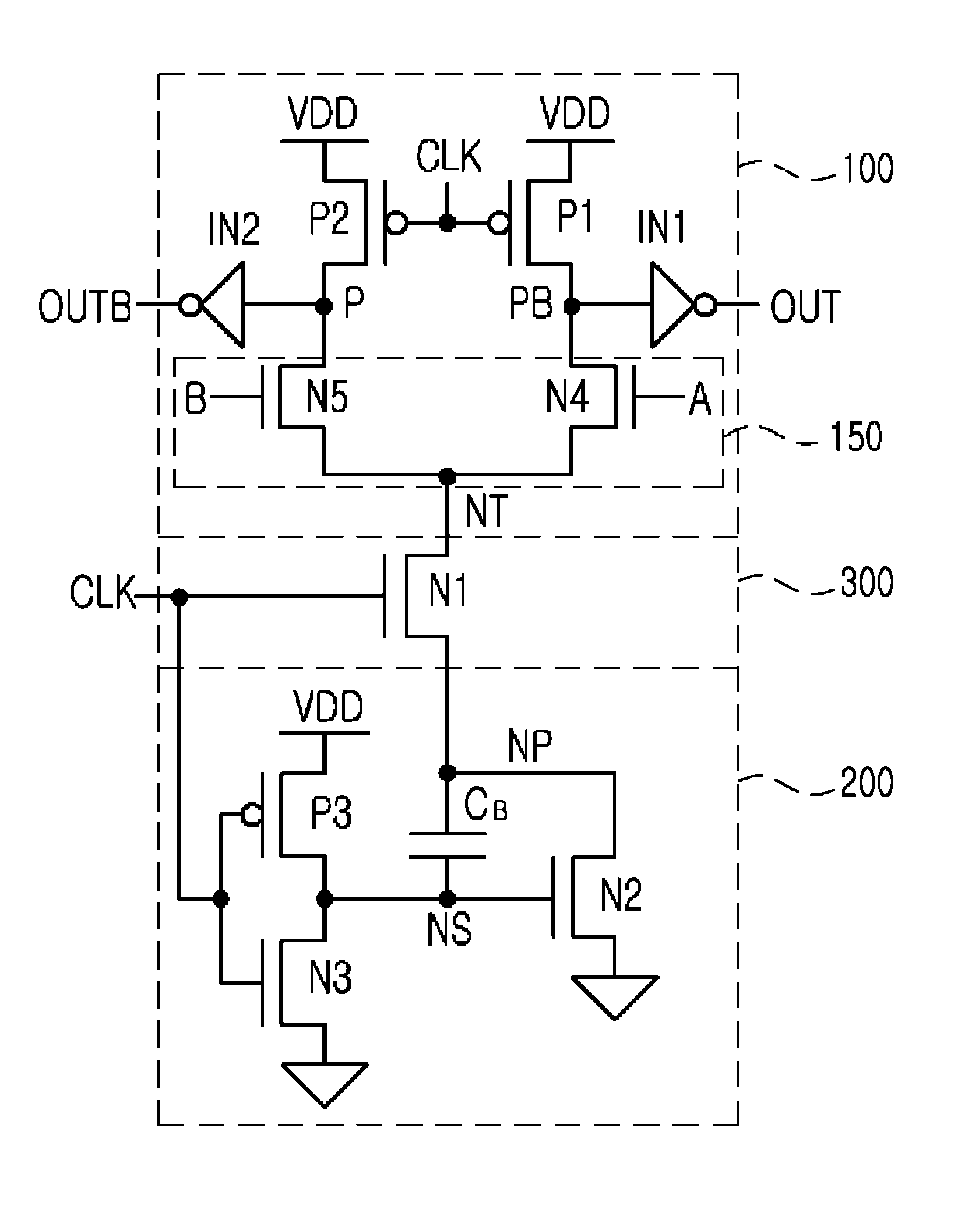
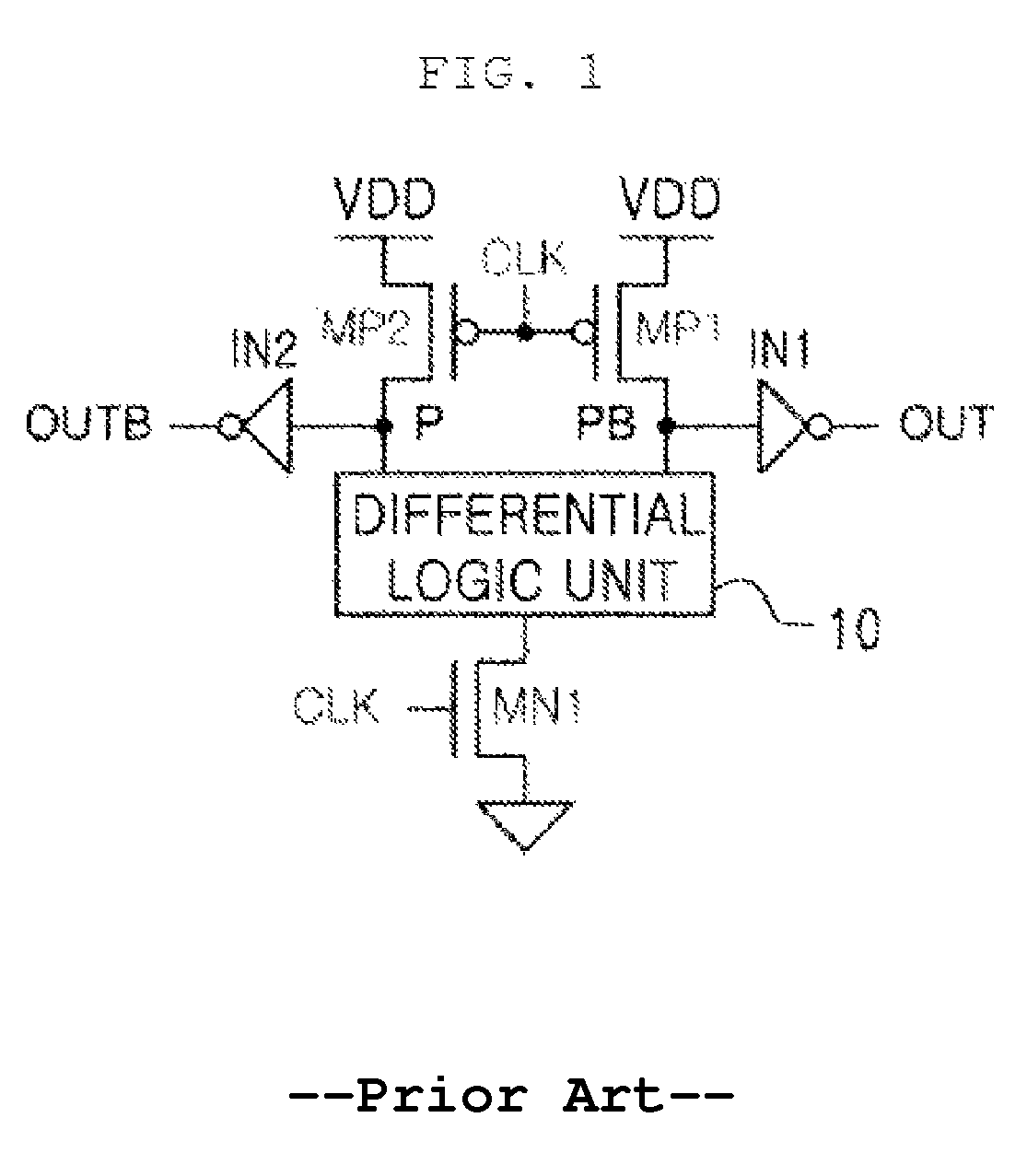
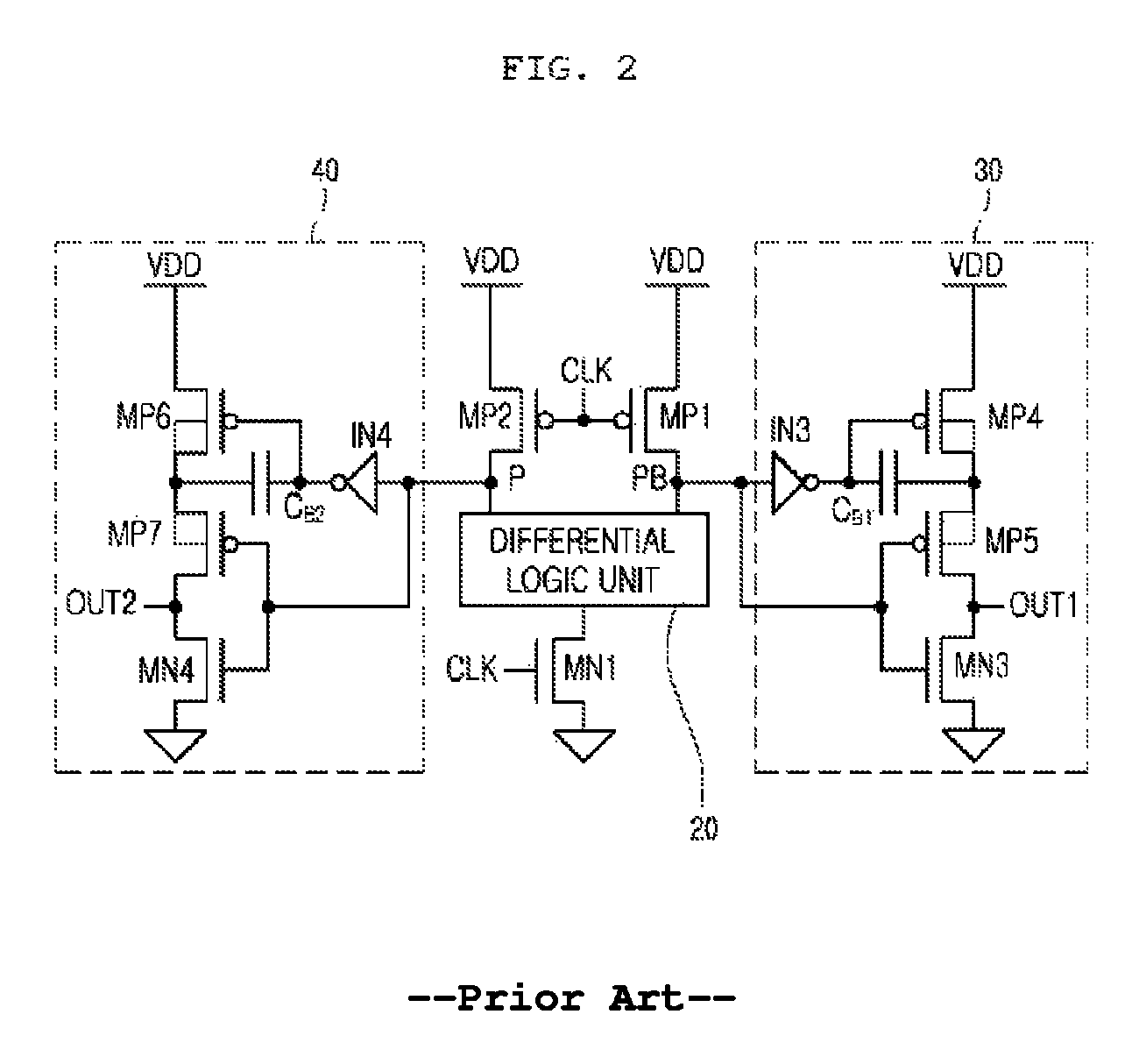
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Differential logic" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
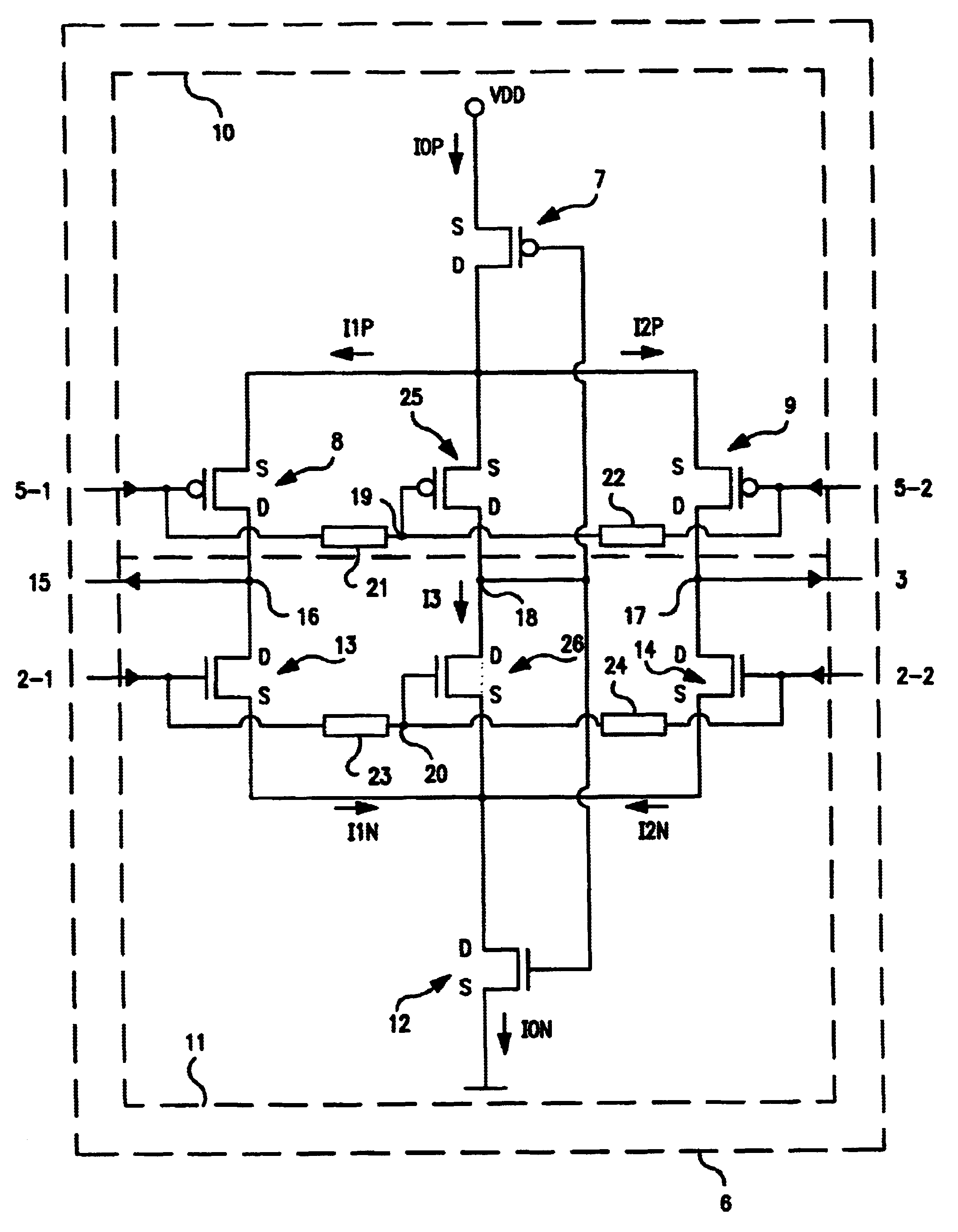
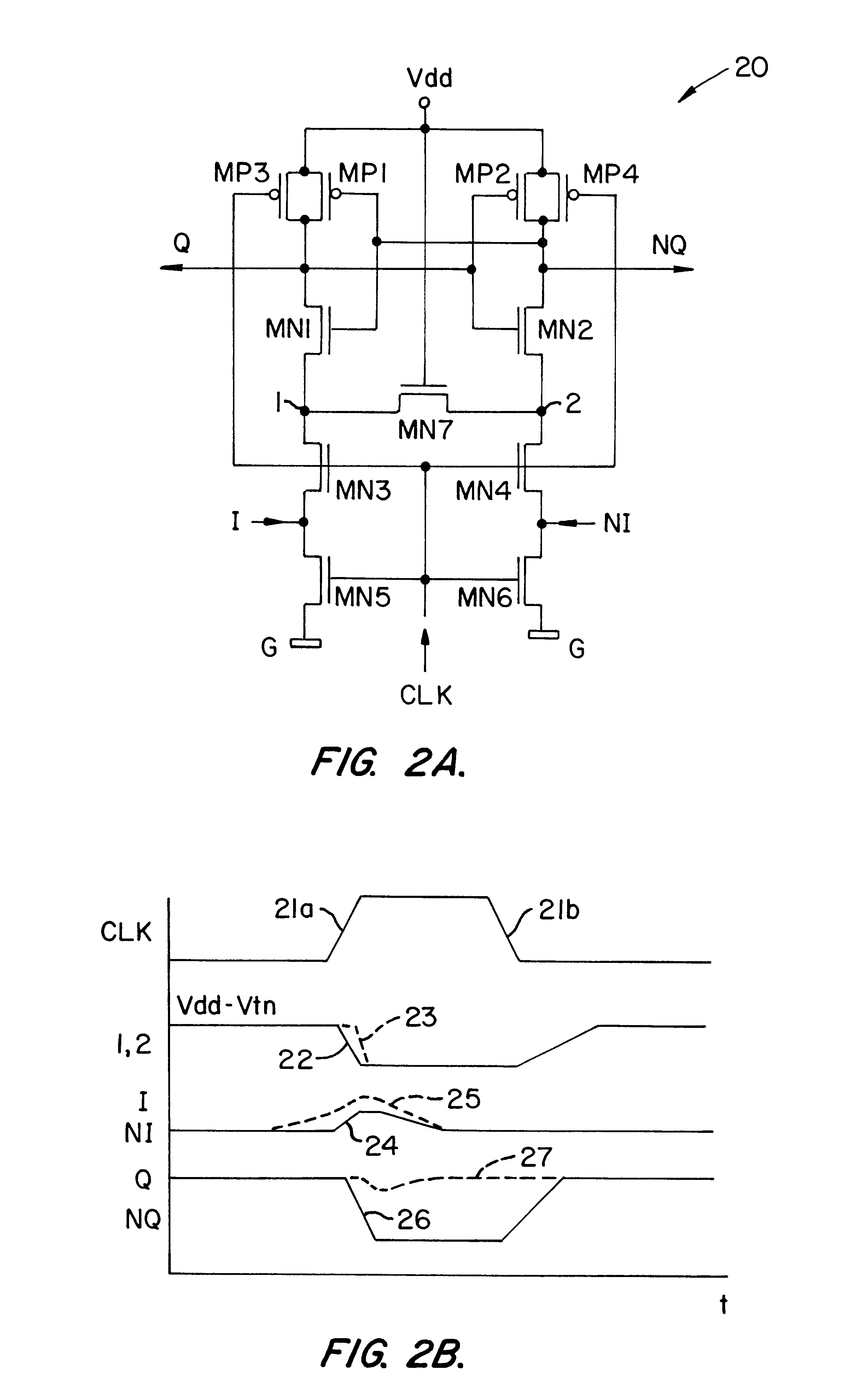
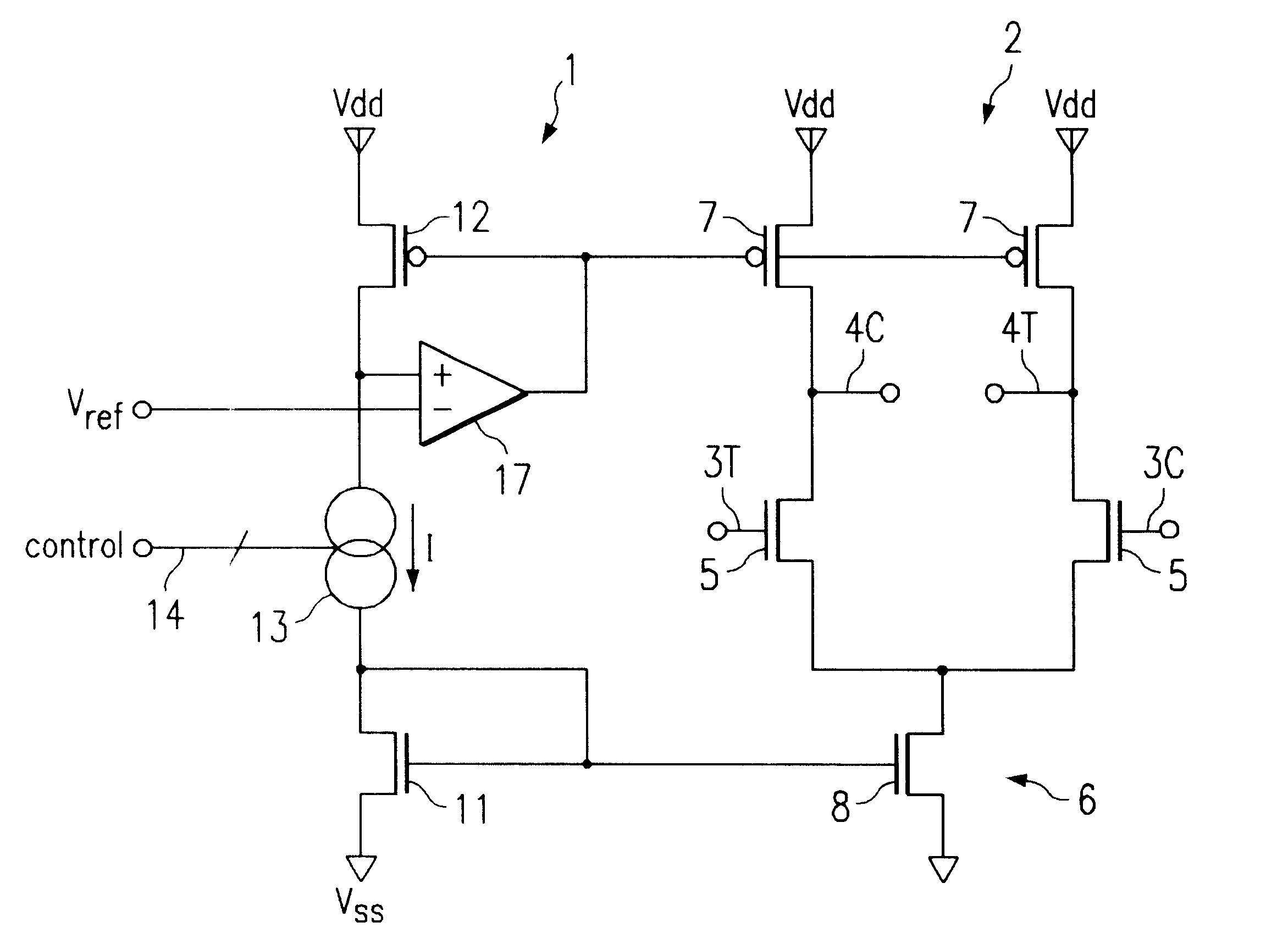
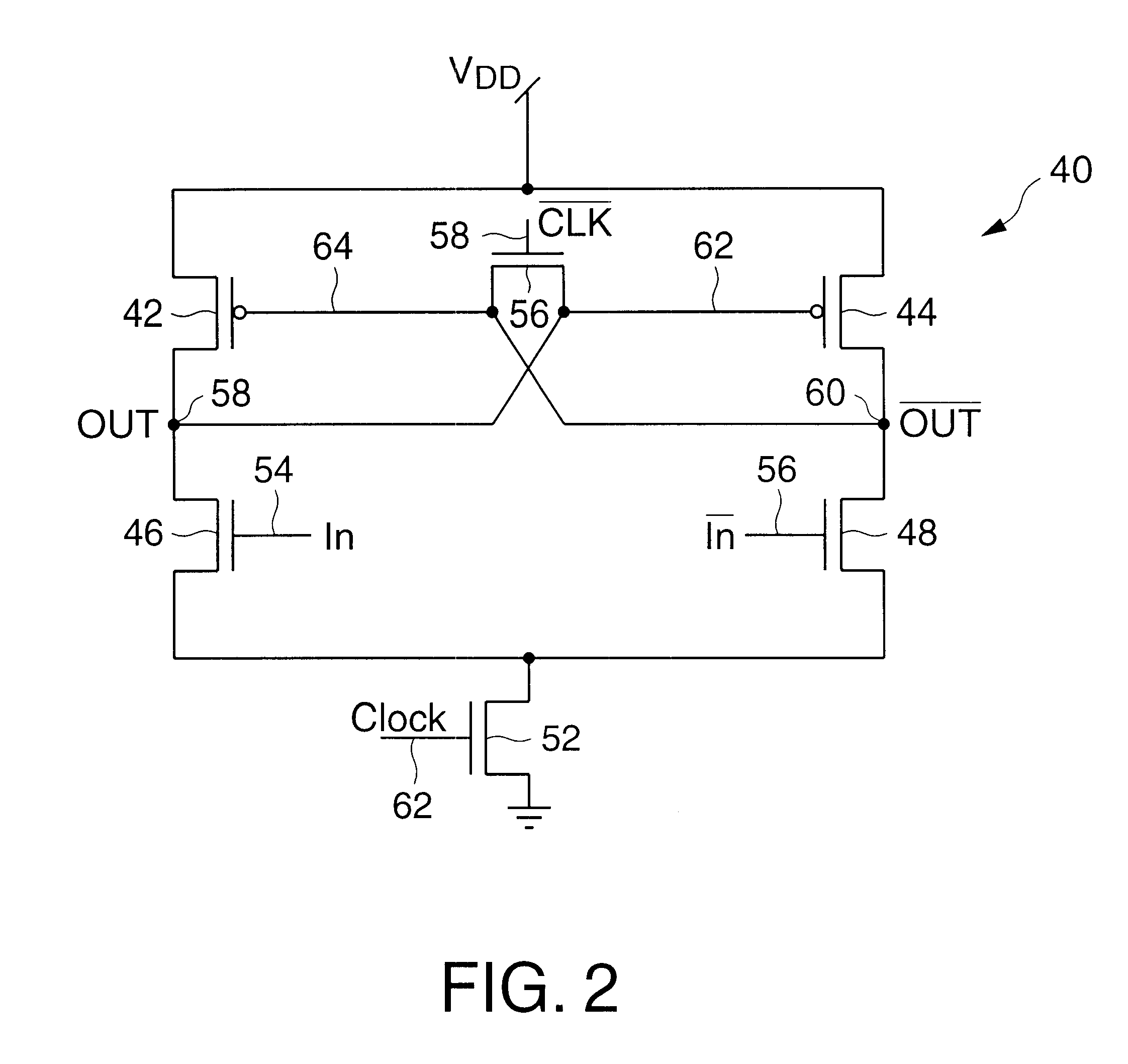
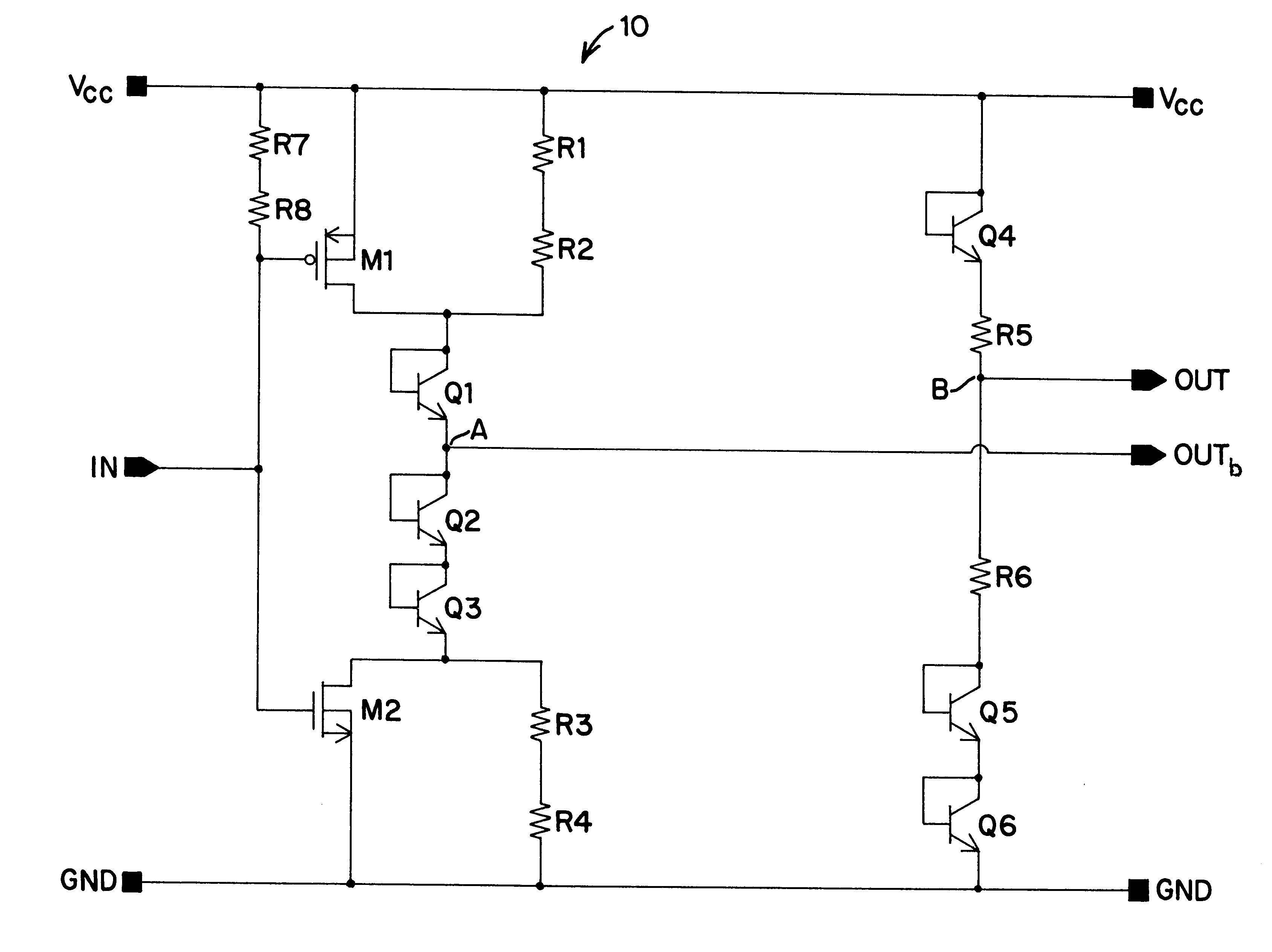
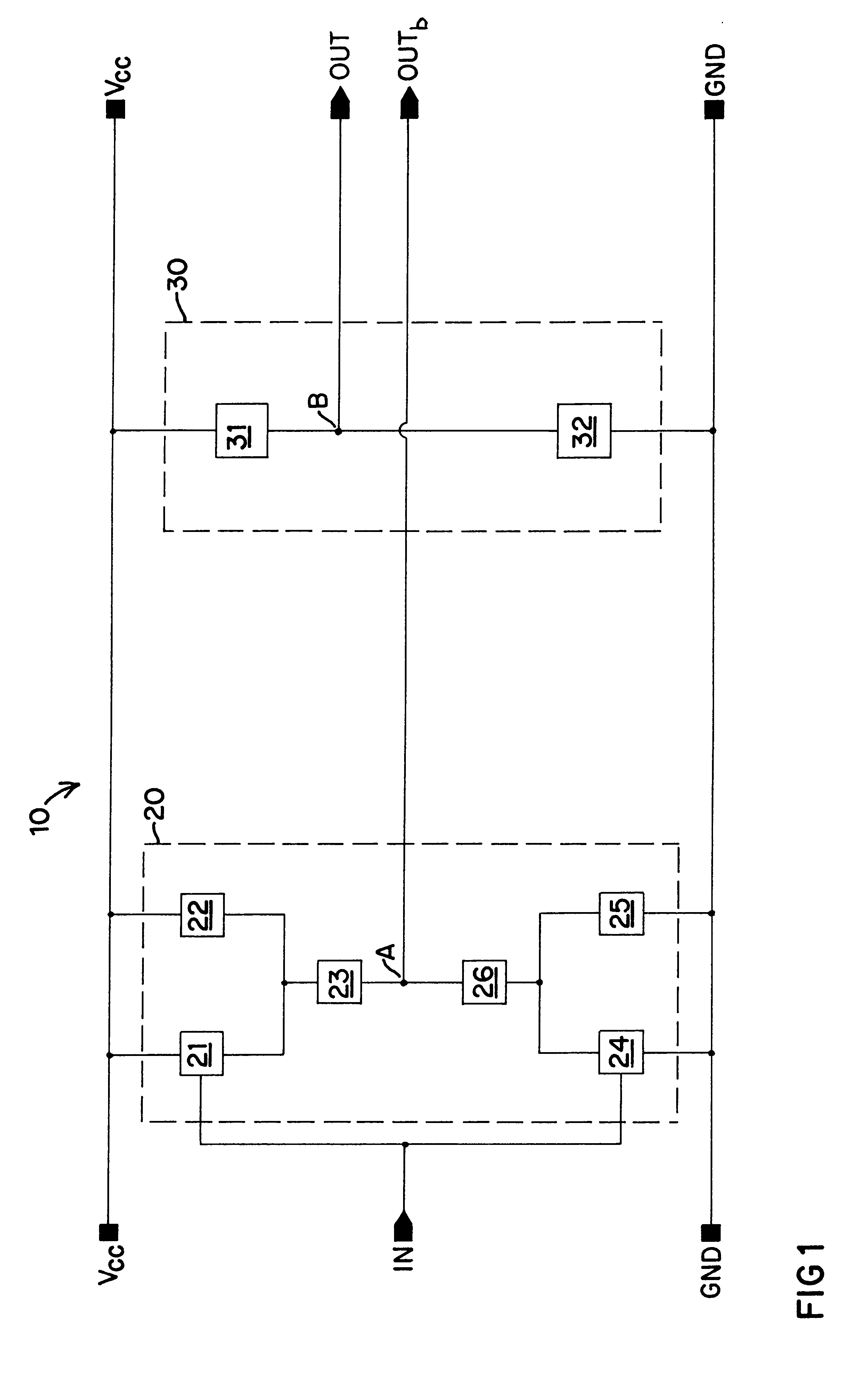
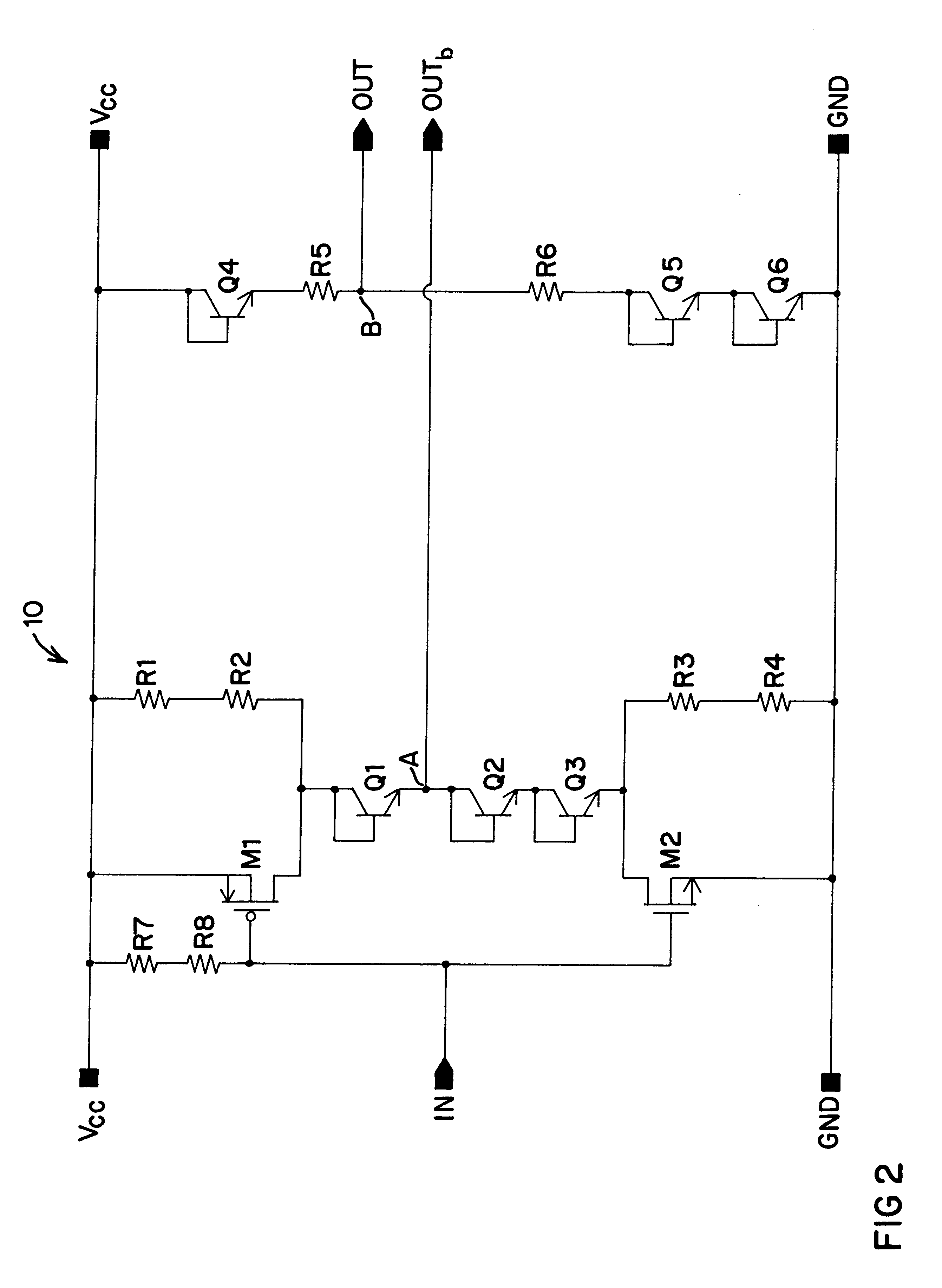
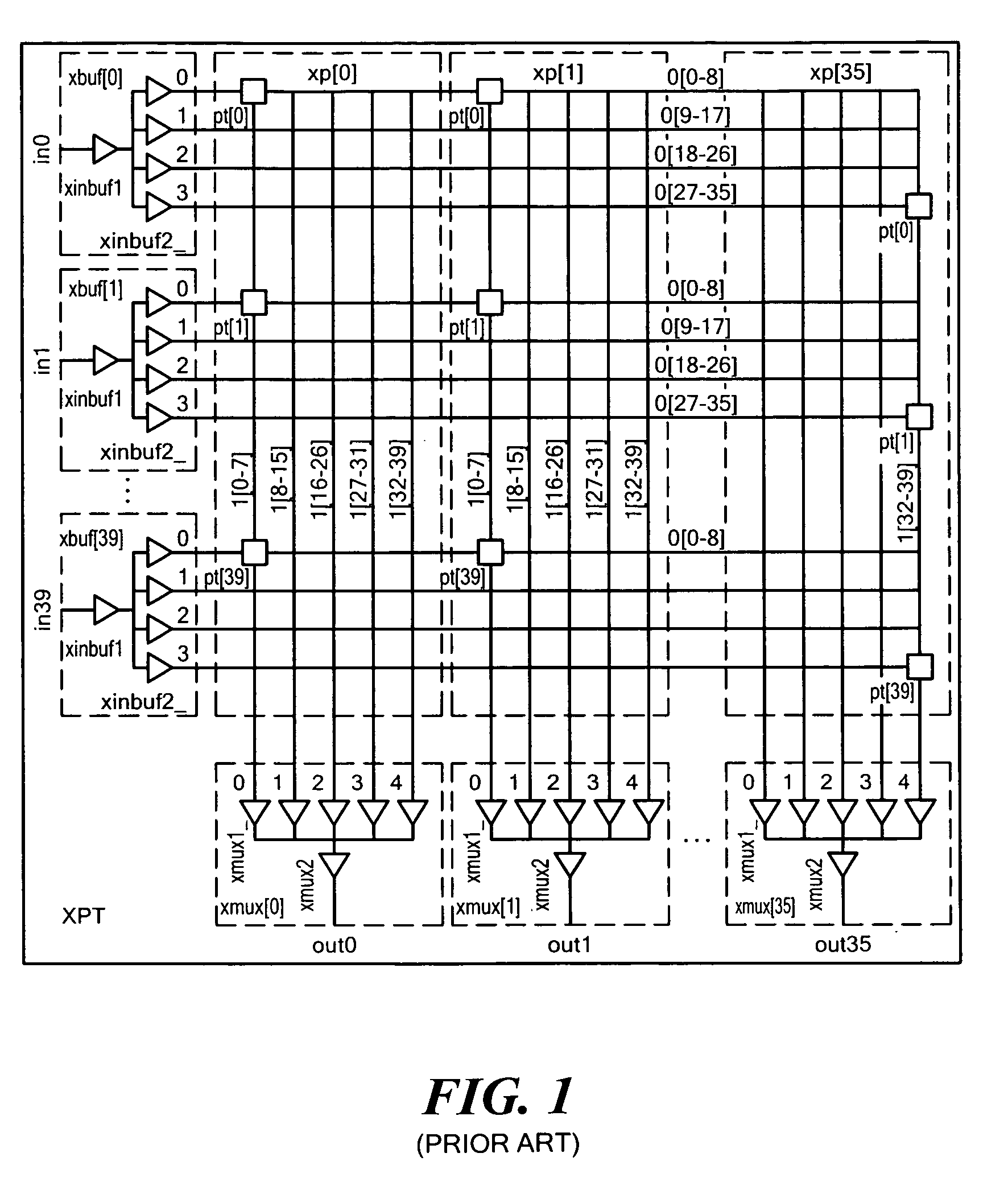
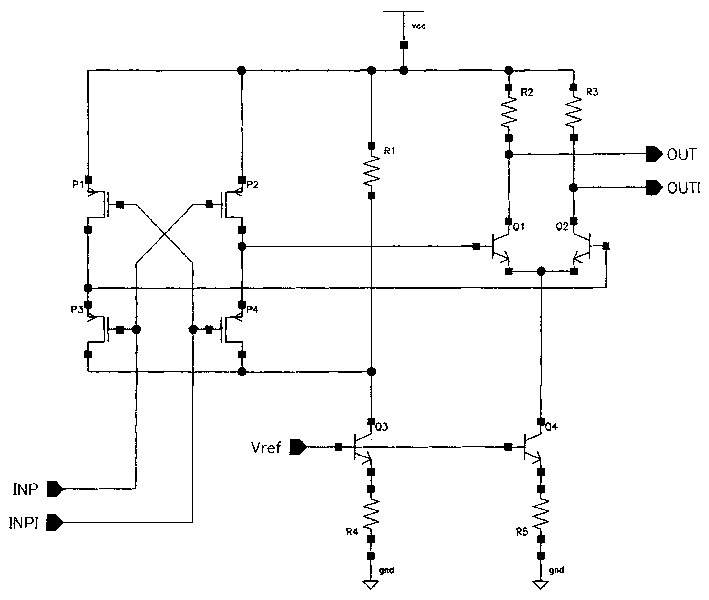
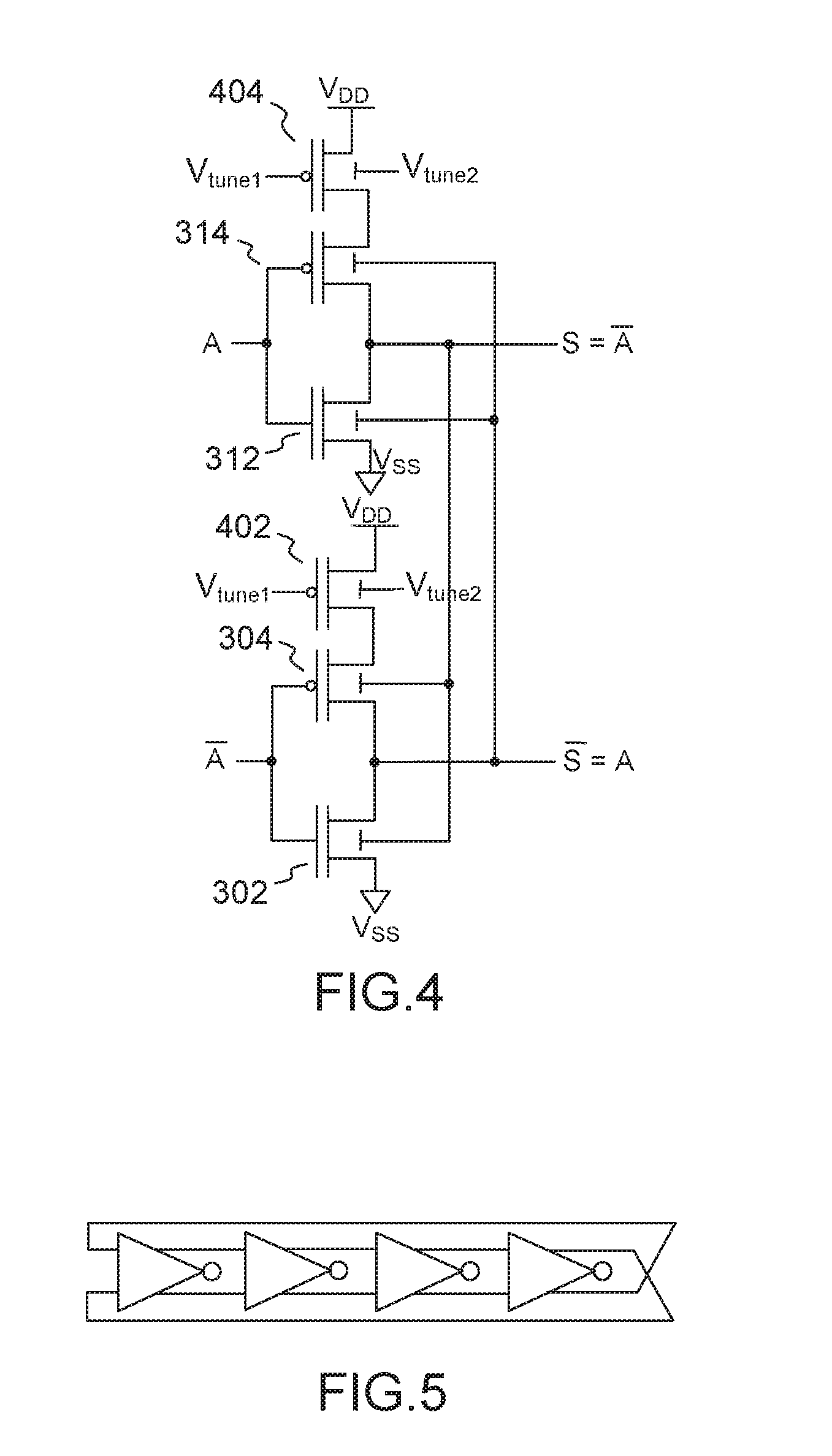
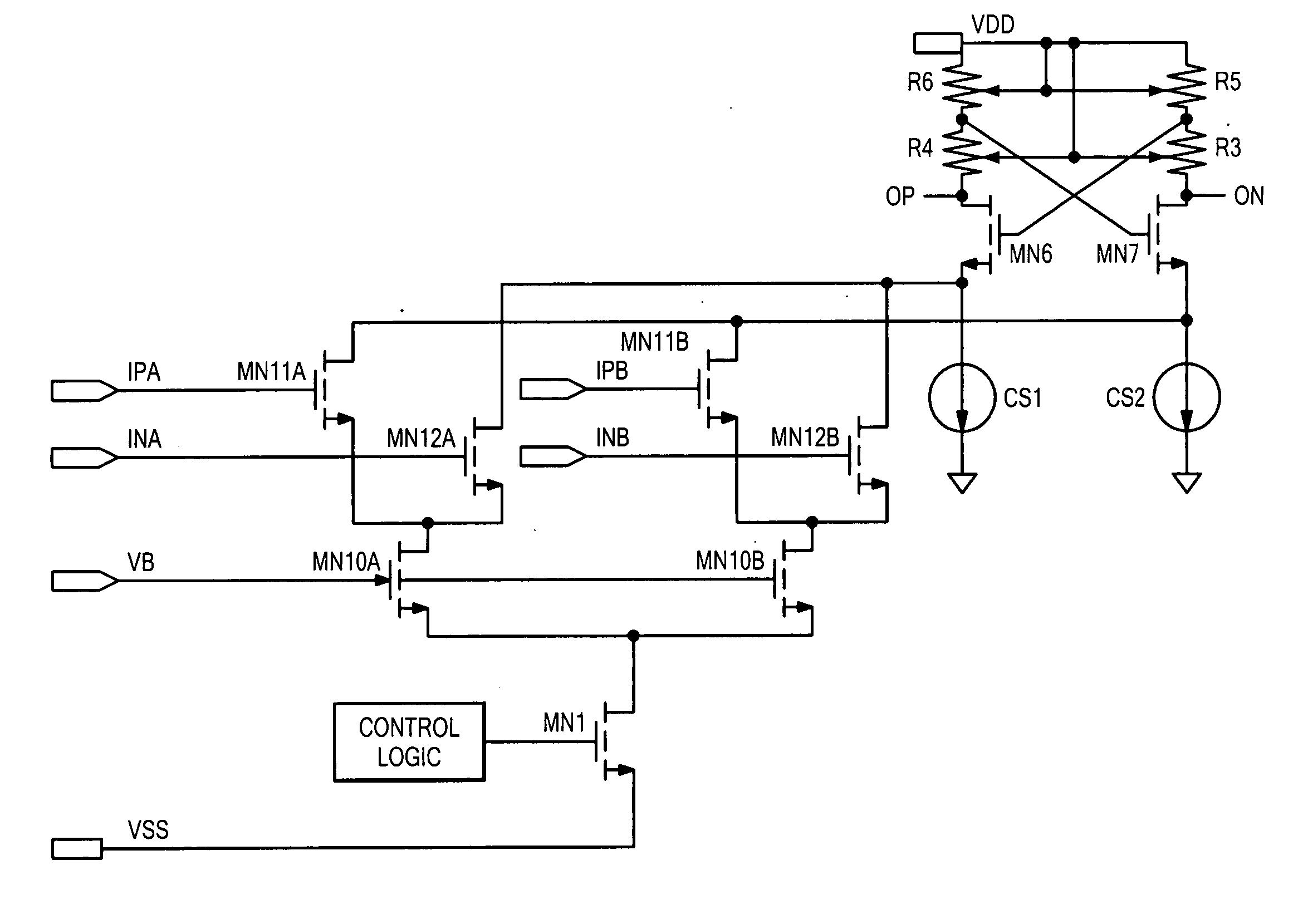
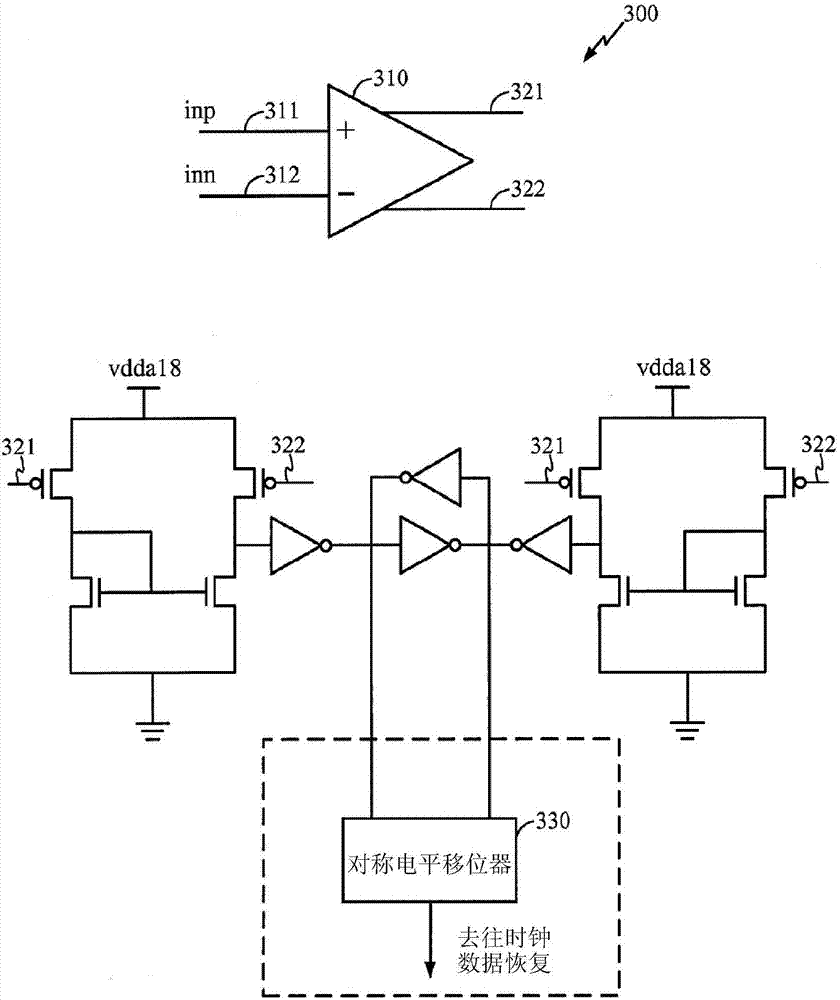
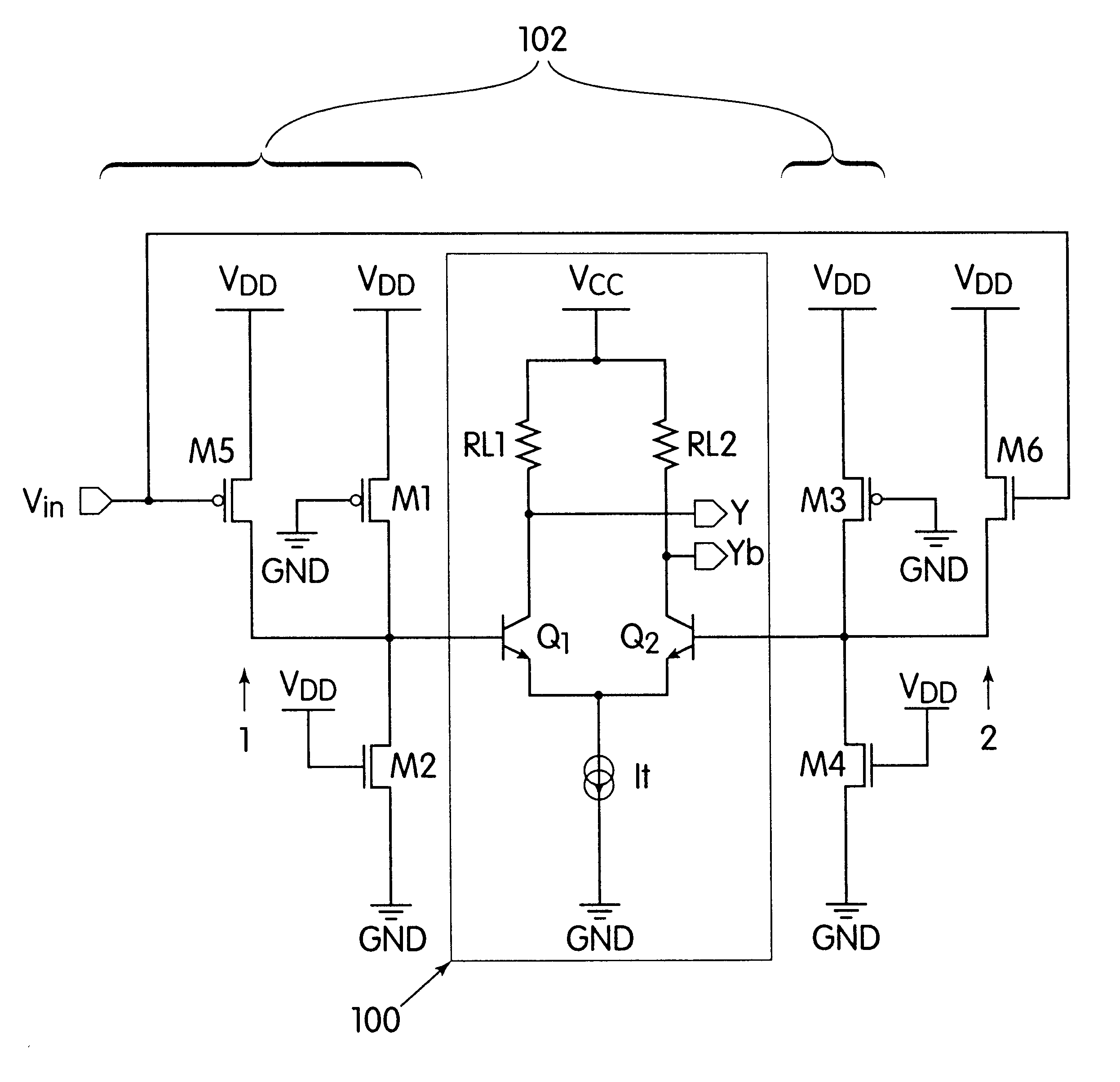
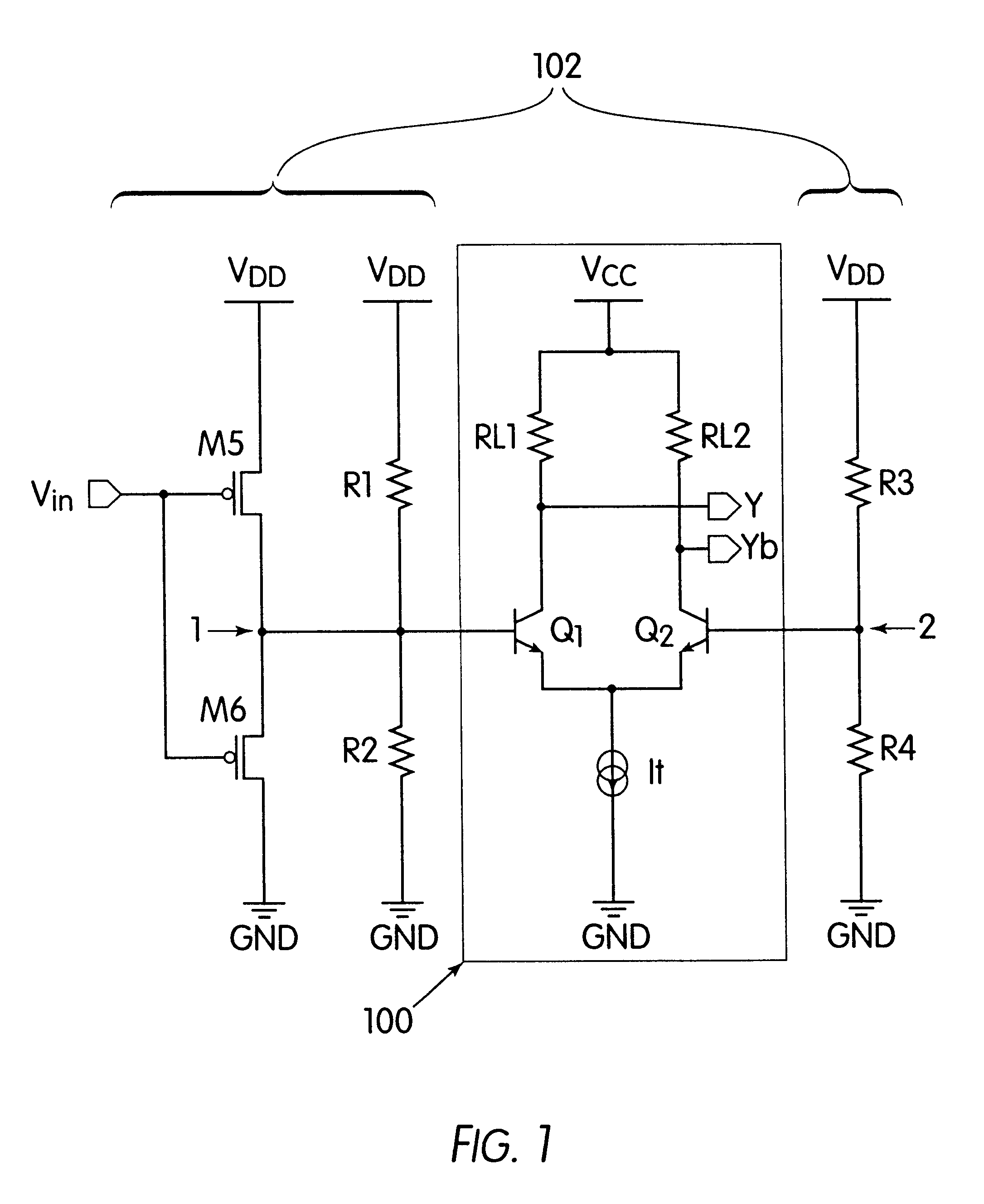
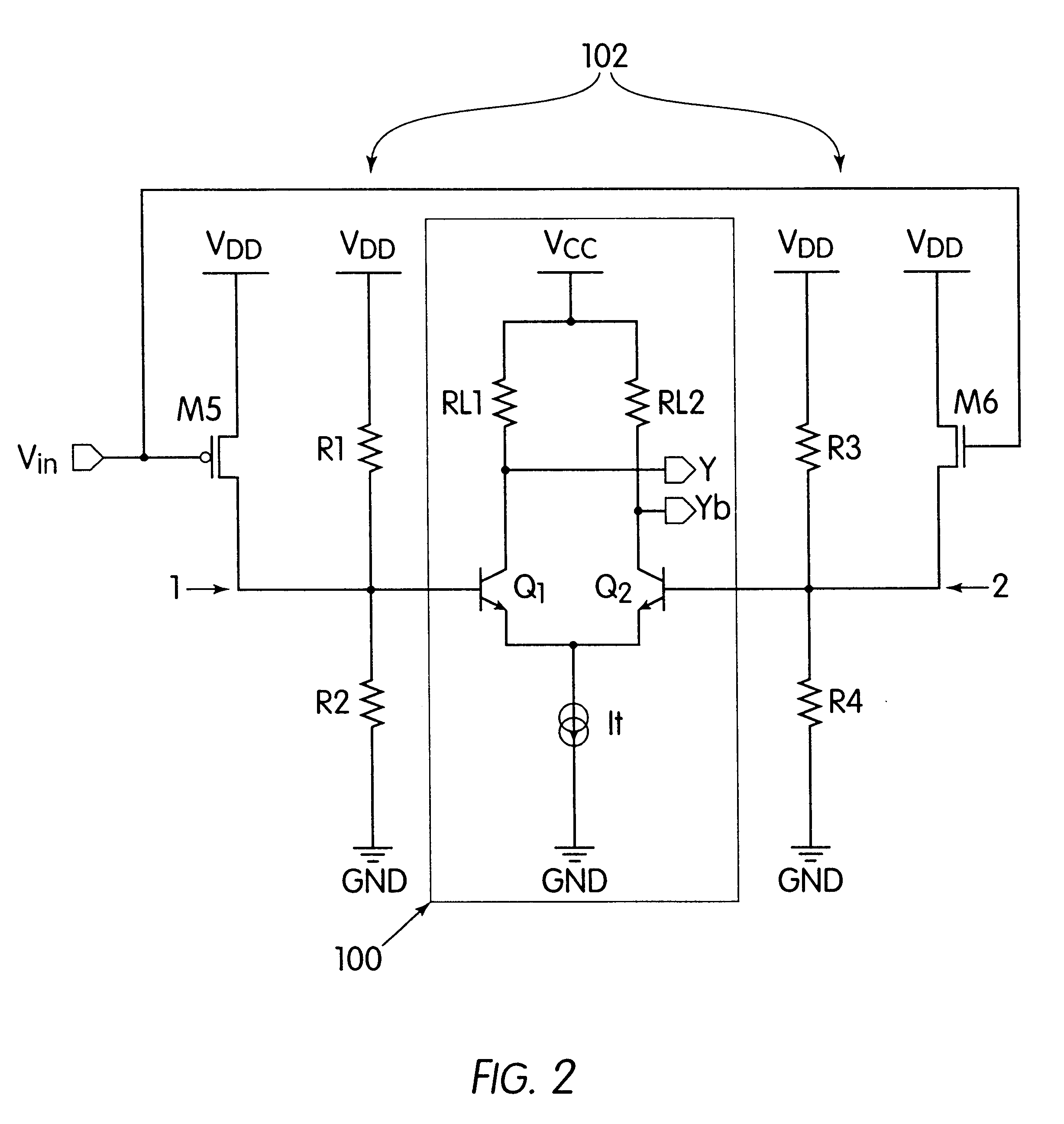
Differential to single-ended logic converter
InactiveUS6924668B2Easy to implementMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEngineeringSignal transition
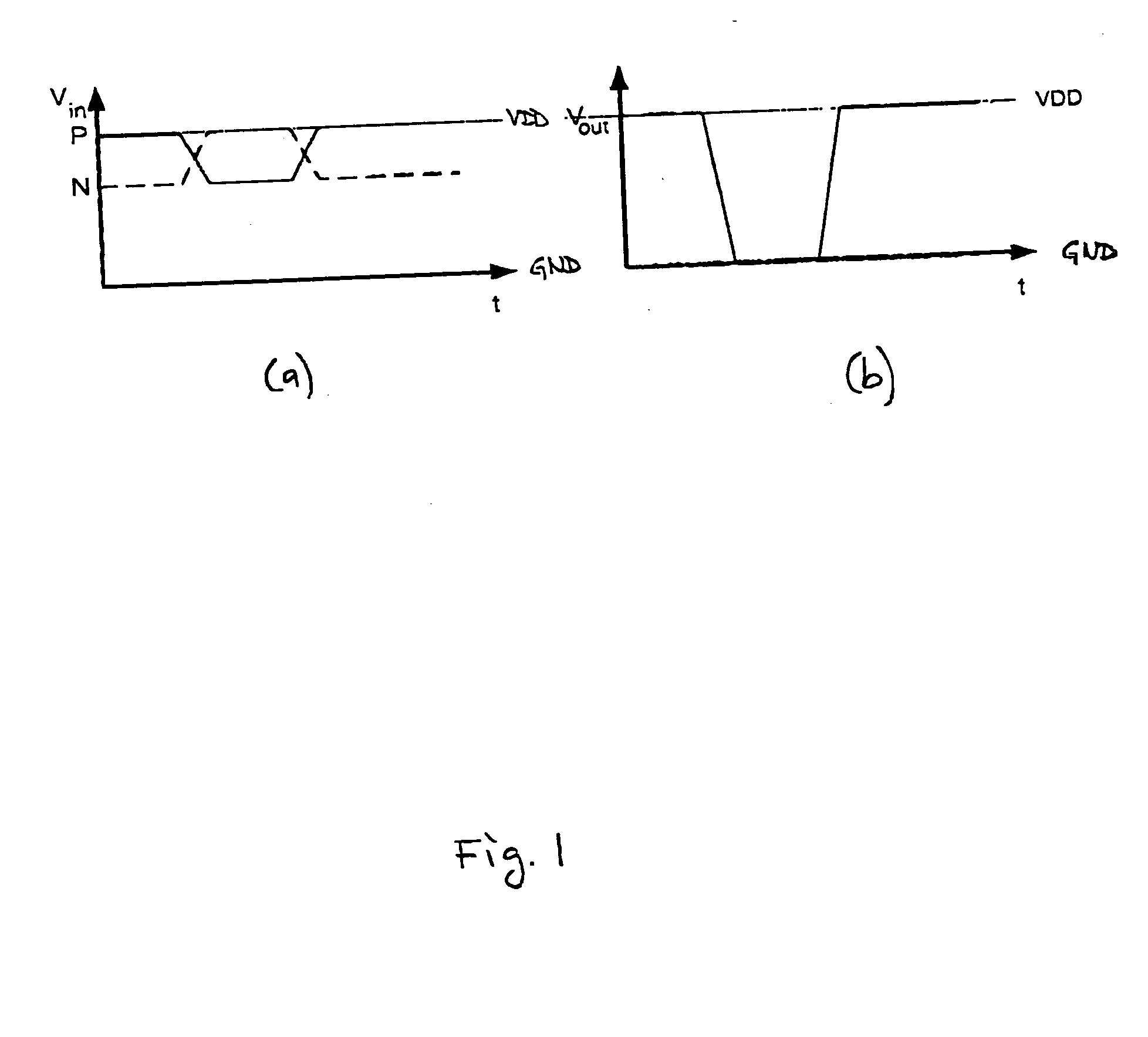
The present invention is a converter stage for converting a differential logic input signal and a corresponding common mode differential logic signal each having a first single-ended logic signal and a complementary second single-ended logic signal into a single-ended logic output signal. The converter stage comprises a first and a second differential stage each having a first and a second MOS transistor and a first and second current source for the differential stages. According to the invention the current sources are controlled by the voltage level which is centered between the mid-potentials of the common mode level differential logic signal and the mid-potential of the differential logic input signal.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
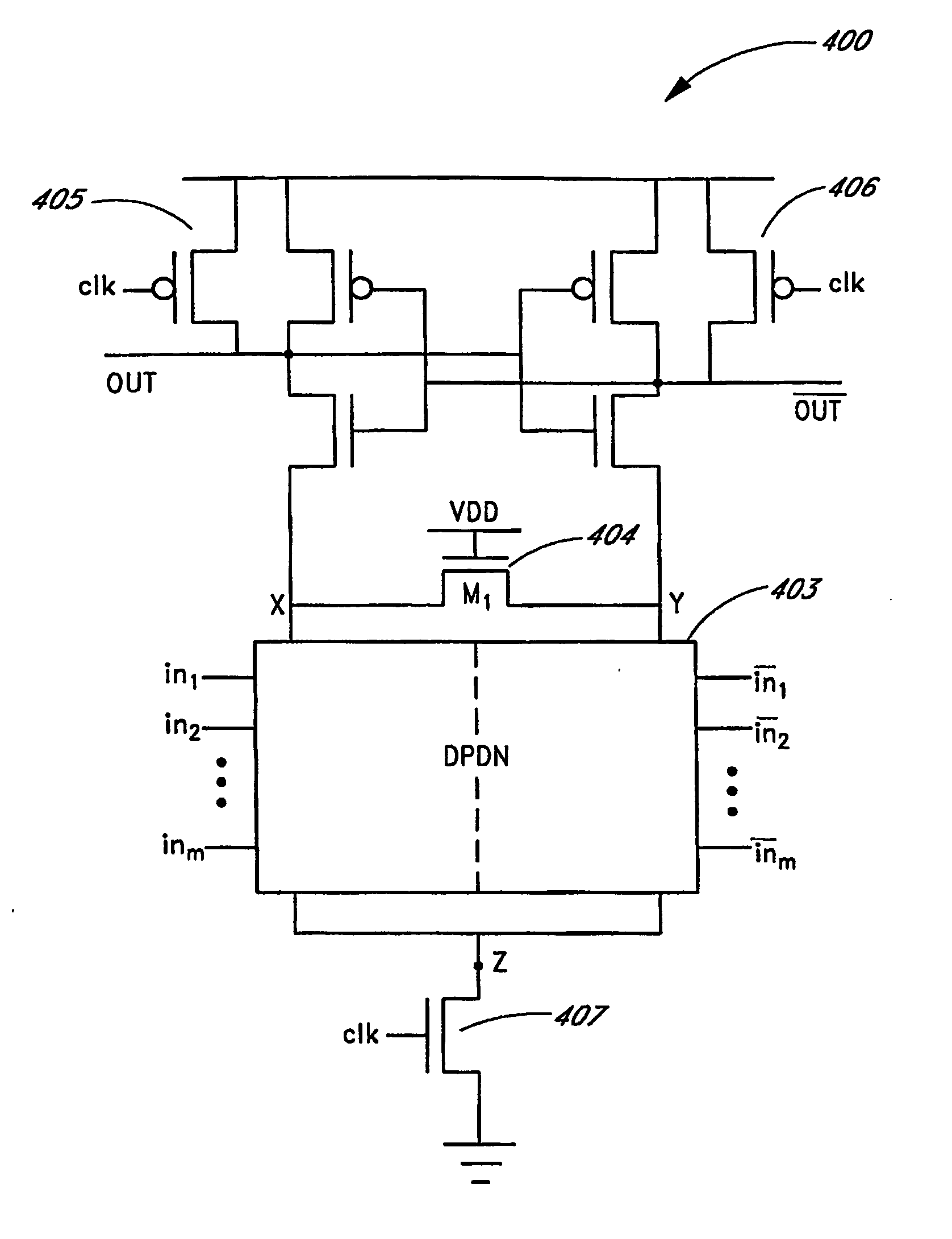
Dynamic and differential CMOS logic with signal-independent power consumption to withstand differential power analysis
InactiveUS7417468B2Logic circuits characterised by logic functionCurrent/voltage measurementPower analysisCapacitance
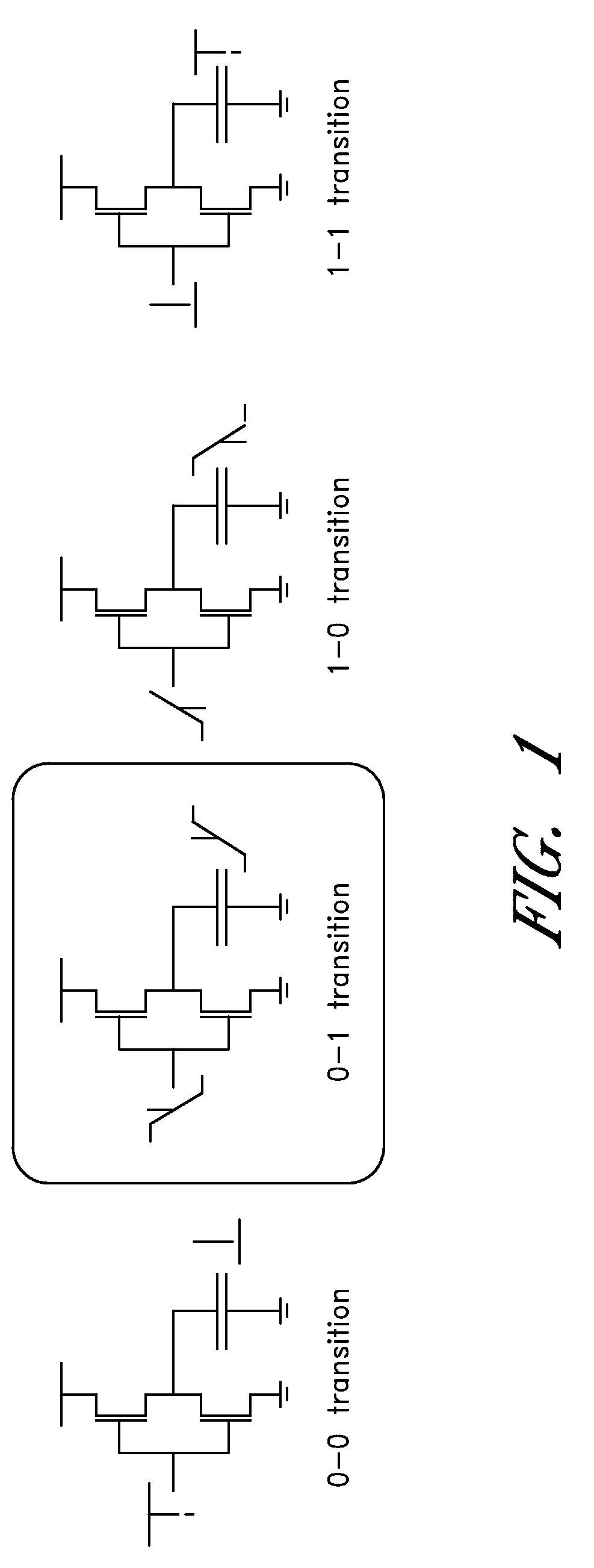
A dynamic and differential CMOS logic style is disclosed in which a gate uses a fixed amount of energy per evaluation event. The gate switches its output at every event and loads a constant capacitance. The logic style is a Dynamic and Differential Logic (DDL) style. The DDL style logic typically has one charging event per clock cycle and the charging event does not depend on the input signals. The differential feature masks the in-put value because a precharged output nodes is discharged during the evaluation phase. The dynamic feature breaks the input sequence: the discharged node is charged during the subsequent precharge phase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
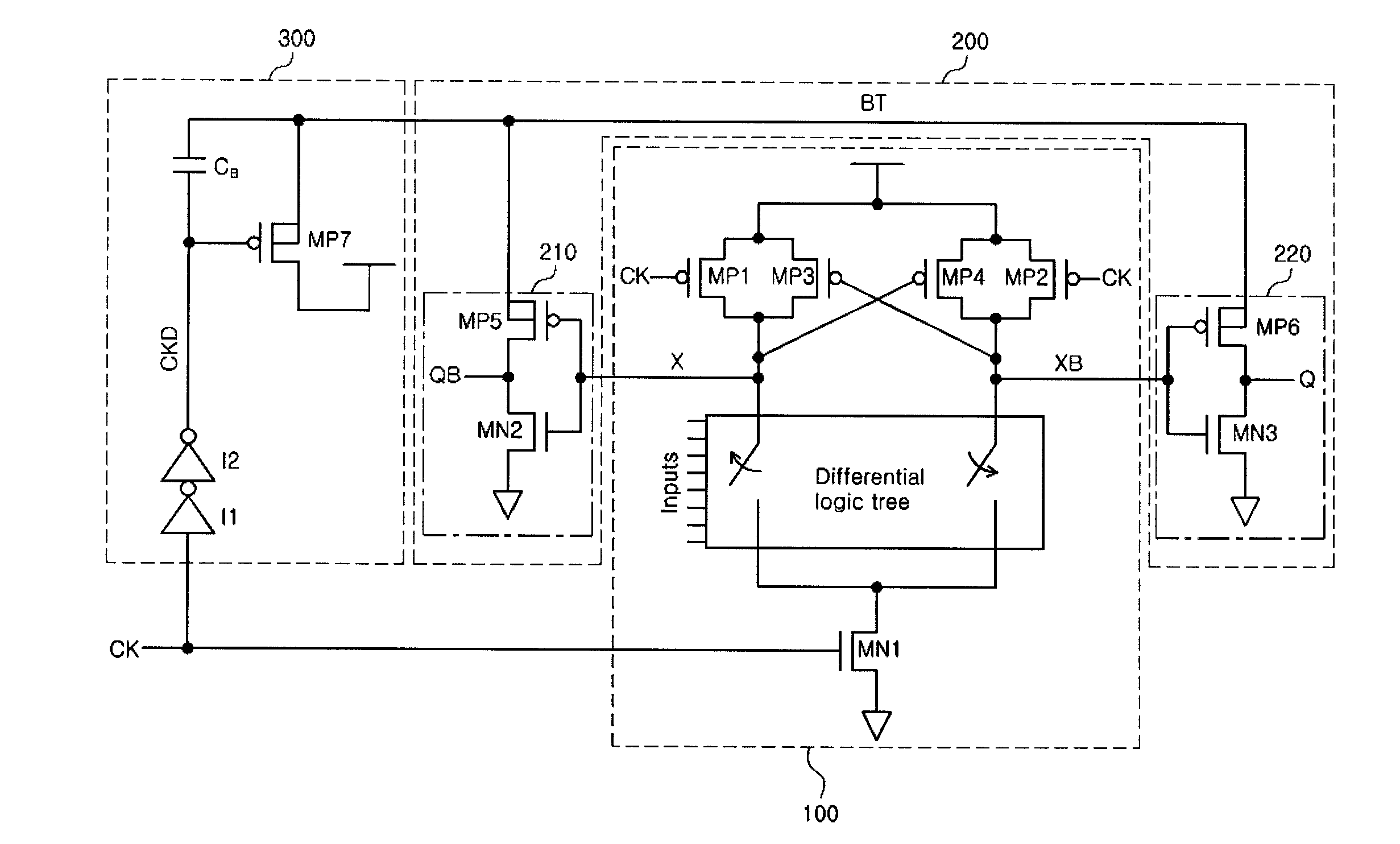
High-speed low-power sense amplifying half-latch and apparatus thereof for small-swing differential logic (SSDL)
A high-speed sense amplifier includes a pair of cross-coupled inverters coupled to intermediate nodes and then to differential inputs nodes by a control circuit. The intermediate nodes are coupled together by a accelerator transistor that forms a current path when the sense amplifier is placed in a sensing state to provide parallel discharge paths for one or the other of output nodes. During precharge, the accelerator transistor operates to equalize the intermediate nodes to ready them for the next sense phase.
Owner:ELBRUS INT
Dynamic and differential cmos logic with signal-independent power consumption to withstand differential power analysis
InactiveUS20070057698A1Logic circuits characterised by logic functionCurrent/voltage measurementCapacitancePower analysis
A dynamic and differential CMOS logic style is disclosed in which a gate uses a fixed amount of energy per evaluation event. The gate switches its output at every event and loads a constant capacitance. The logic style is a Dynamic and Differential Logic (DDL) style. The DDL style logic typically has one charging event per clock cycle and the charging event does not depend on the input signals. The differential feature masks the in-put value because a precharged output nodes is discharged during the evaluation phase. The dynamic feature breaks the input sequence: the discharged node is charged during the subsequent precharge phase.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Circuit for controlling current levels in differential logic circuitry
InactiveUS6411159B1Arbitary function generatorsElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceVoltage range
A method and circuit are disclosed for controlling the current level of a differential logic circuit having a current source, input transistors which perform current steering based upon the input to the differential logic circuit, and load transistors. The circuit includes a first transistor that forms a current mirror with the current source, a second transistor coupled to the load transistors so that the operating characteristics of the load transistors substantially match the operating characteristics of the second transistor, and current source circuitry coupled between the first and second transistors. The current level selected in the current source circuitry sets the current level in the differential logic circuit and the resistance of the load transistors so that the output voltage swing of the differential logic circuit stays within an acceptable range of voltages, regardless of the selected current level.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
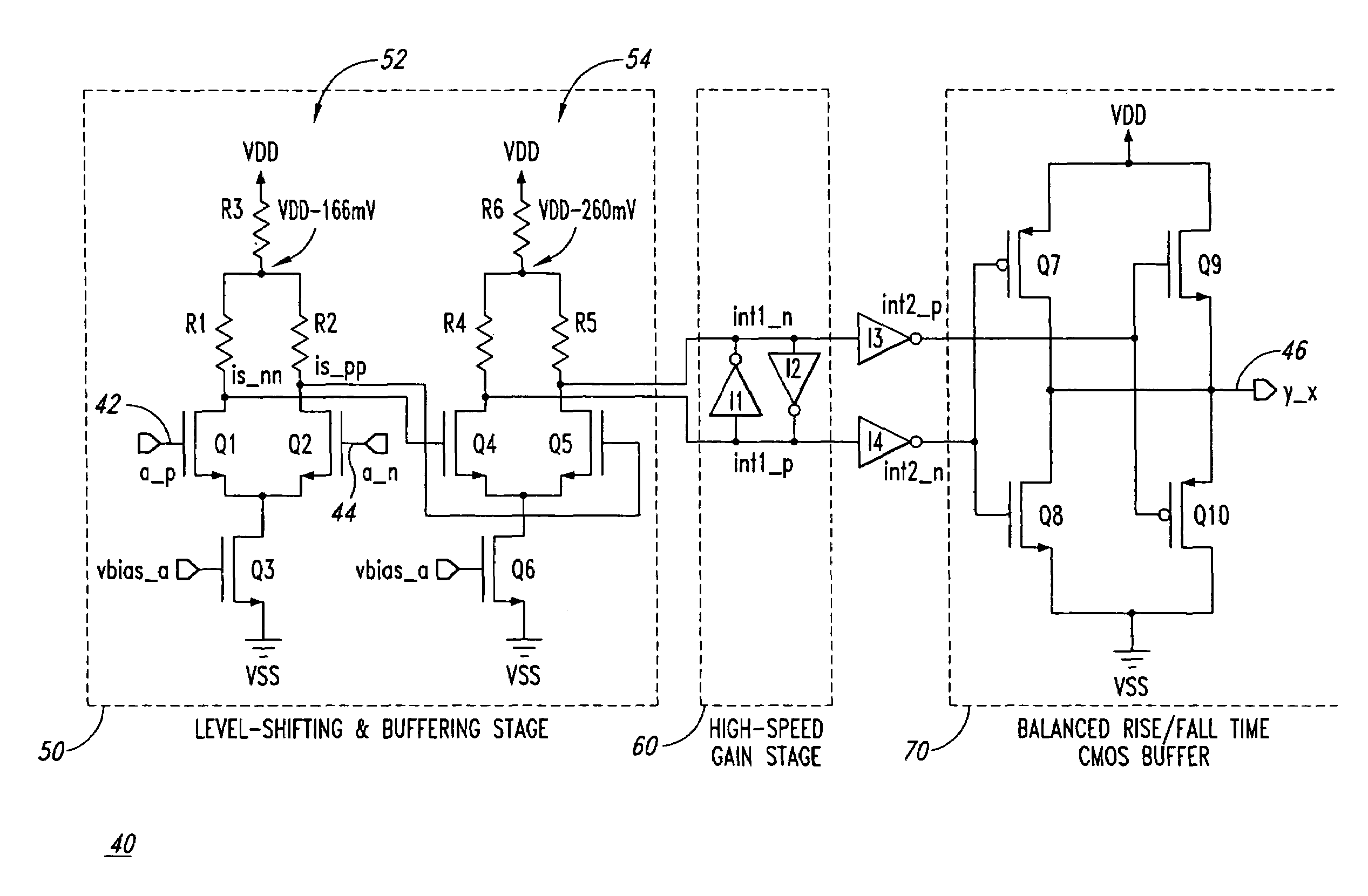
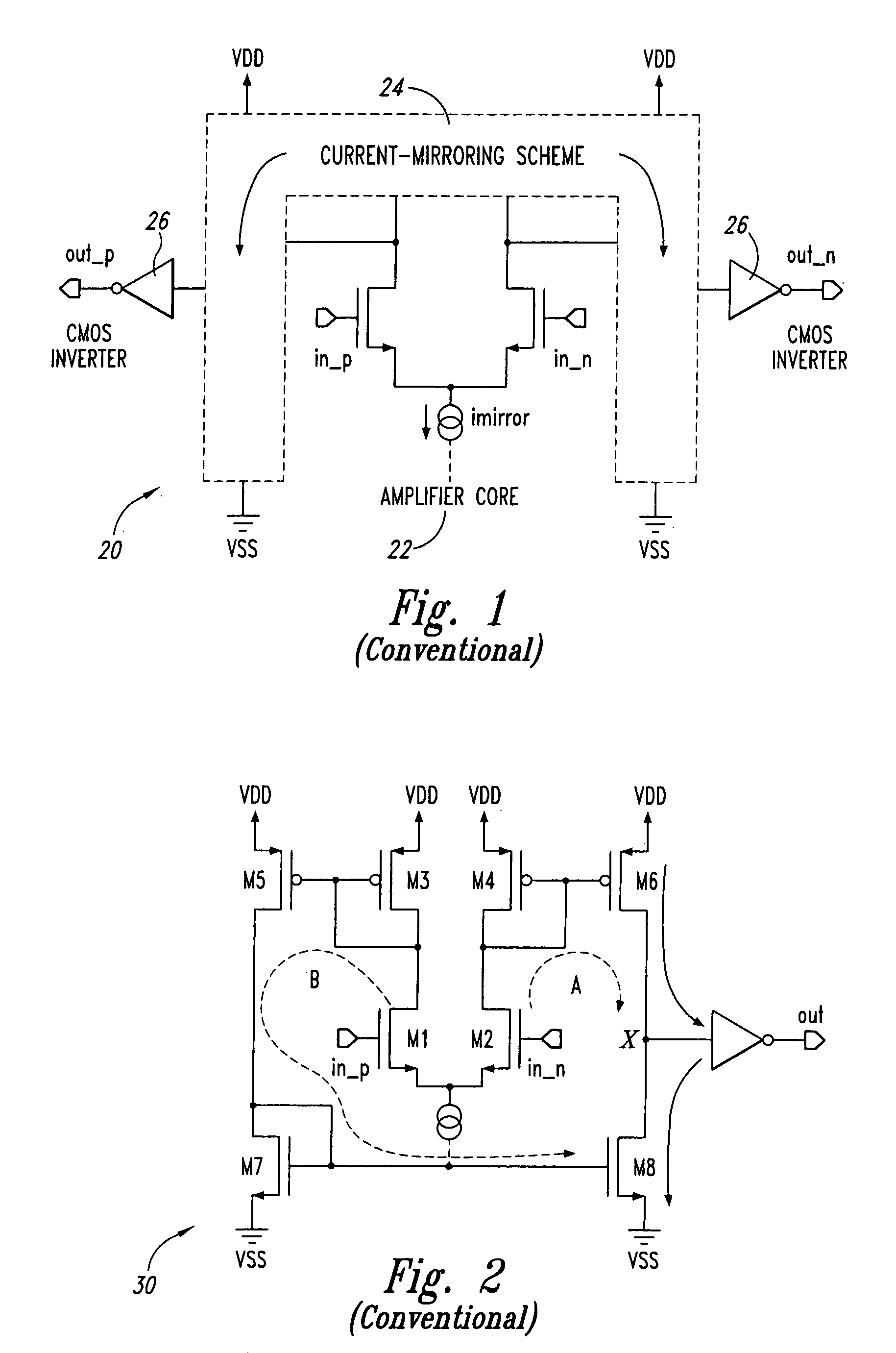
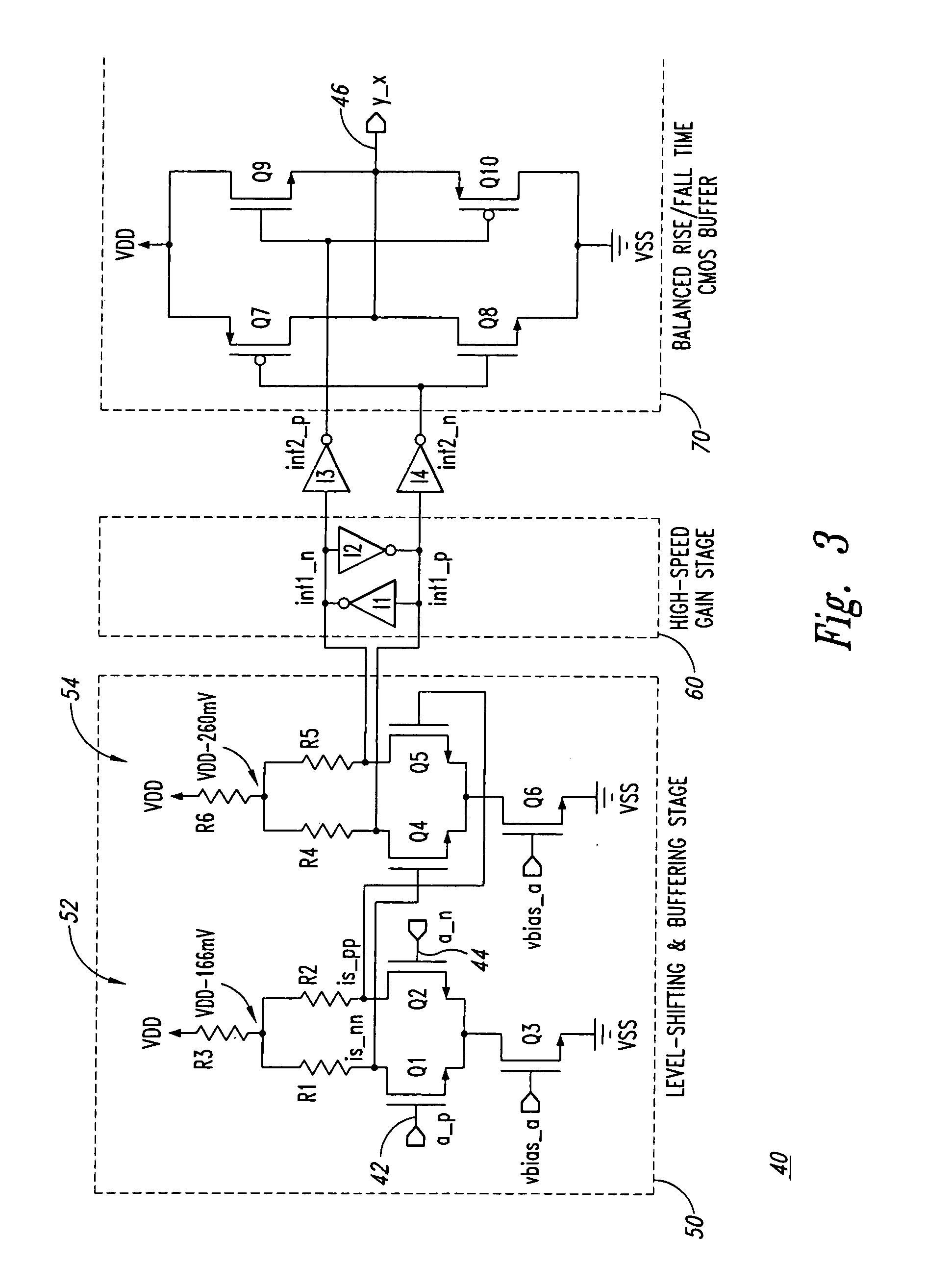
High-speed differential logic to CMOS translator architecture with low data-dependent jitter and duty cycle distortion
ActiveUS7301370B1Reduce skewReduces signal skewPulse automatic controlLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsLevel shiftingDuty cycle distortion
Disclosed are various embodiments of a differential logic to CMOS logic translator including a level-shifting and buffering stage configured to receive differential inputs and to provide resulting signals with lower common mode voltage. Further, a gain stage is included to receive the resulting signals and to provide increased swing signals. A CMOS buffer is also included and is configured to receive the increased swing signals and to provide a CMOS logic output. Also disclosed is a method of translating a differential logic signal to a CMOS logic signal including level-shifting and buffering differential input signals to provide resulting signals with lower common mode voltage. The method also includes using a gain stage to provide increased swing signals from the resulting lower common mode signals and using a CMOS buffer to provide a CMOS output from the increased swing signals.
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Low voltage differential logic
InactiveUS6373292B1Multiple input and output pulse circuitsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLow voltageLogical Function
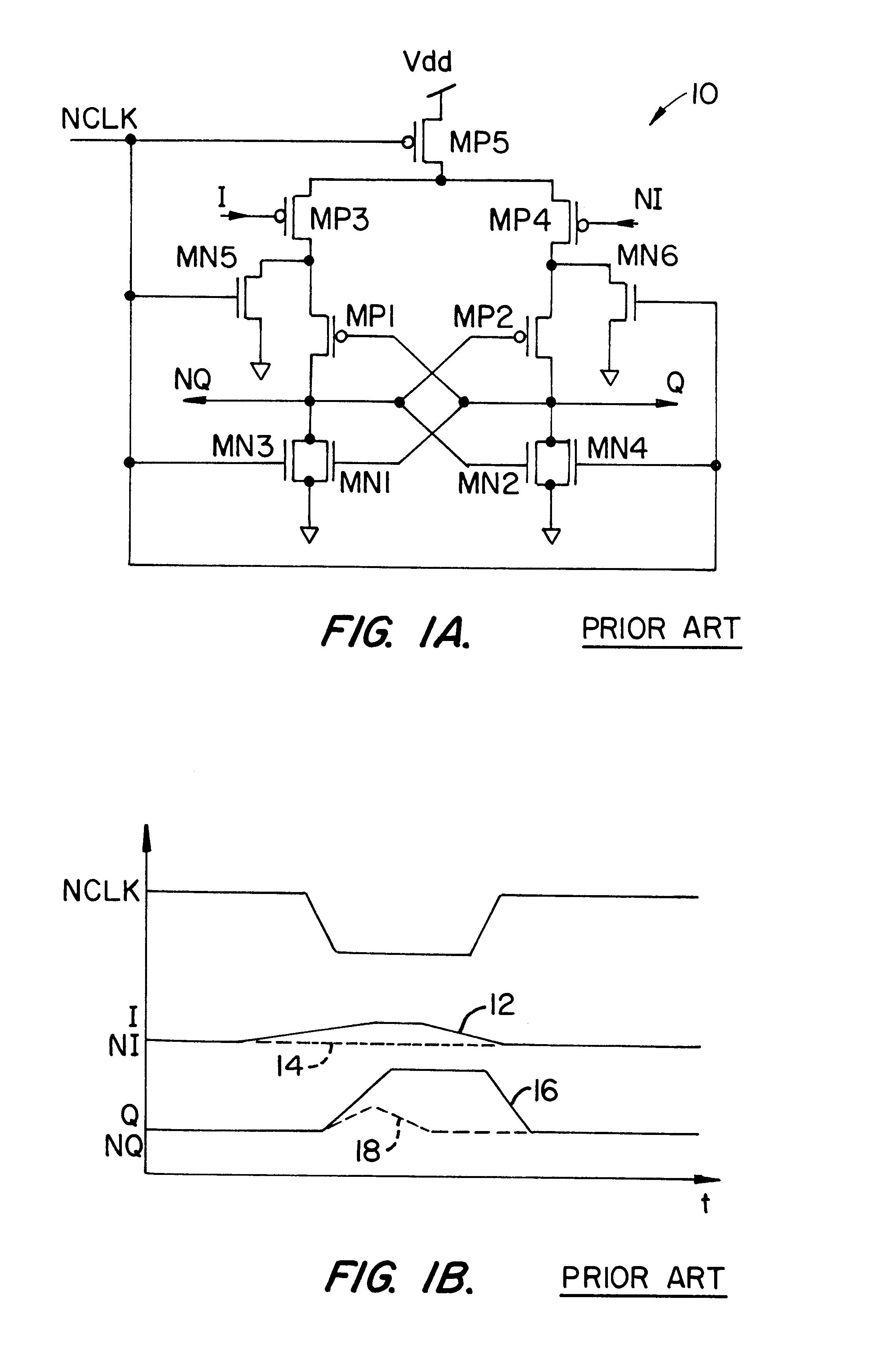
A low voltage differential circuit is described herein including a complementary logic tree having first, second and third inputs and two outputs, the logic tree for performing a desired logical function on signals received the the first input, thereby opening a pathway for current flow between at least one of the following: the second input and the first output, the second input and the second output, the third input and the first output, the third input and the second output. The circuit further includes a first transistor having a first gate, a first source, and a first drain, the first drain connected to the first output, the first source being connected to a supply voltage, a second transistor having a second gate, a second source, and a second drain, the second source connected to the first gate, the second drain connected to the first drain; and a third transistor having a third gate, a third source, and a third drain, the third source being connected to a supply voltage, the third gate being connected to the second drain, the third drain connected to the second source and the second output.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
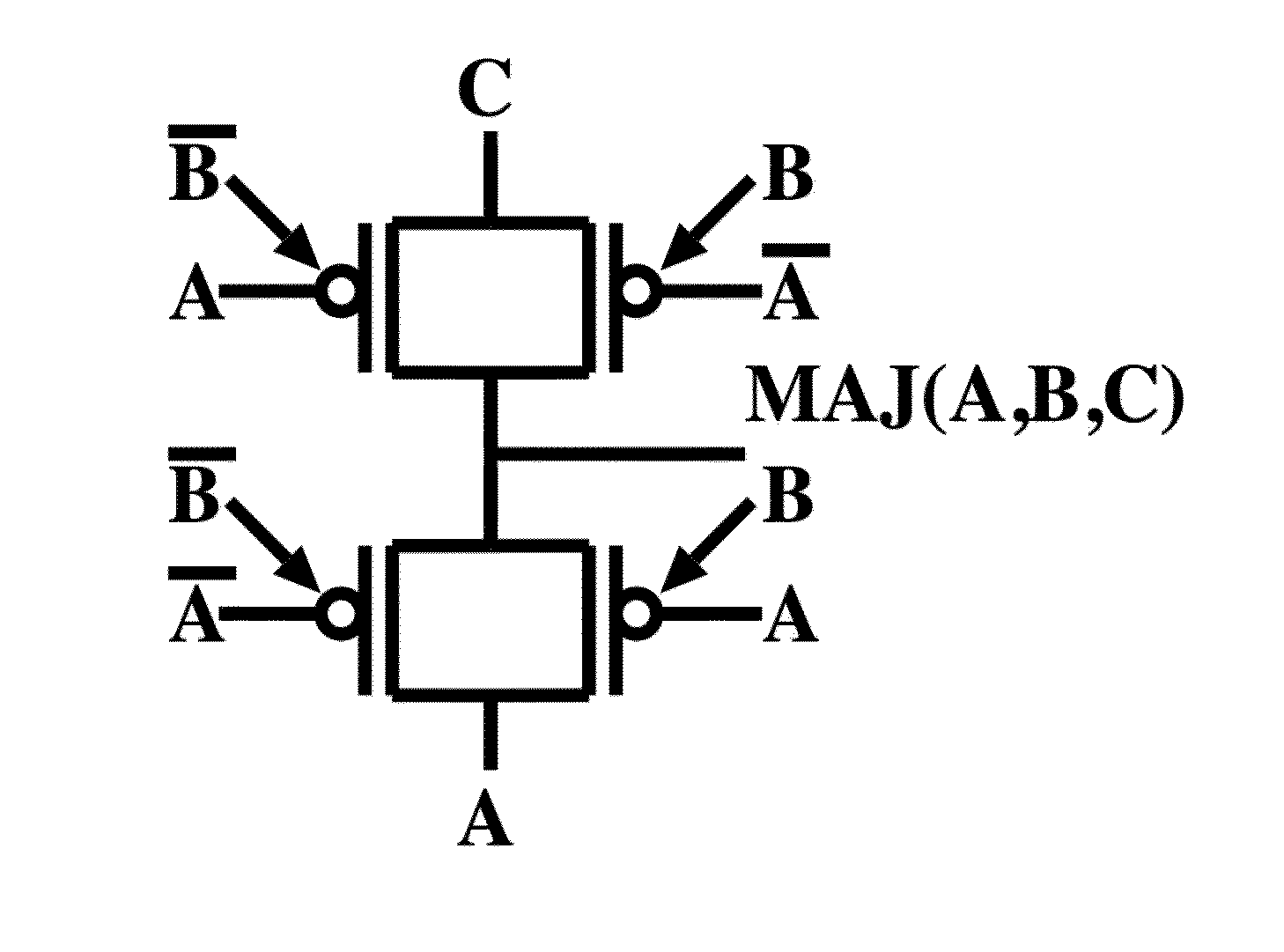
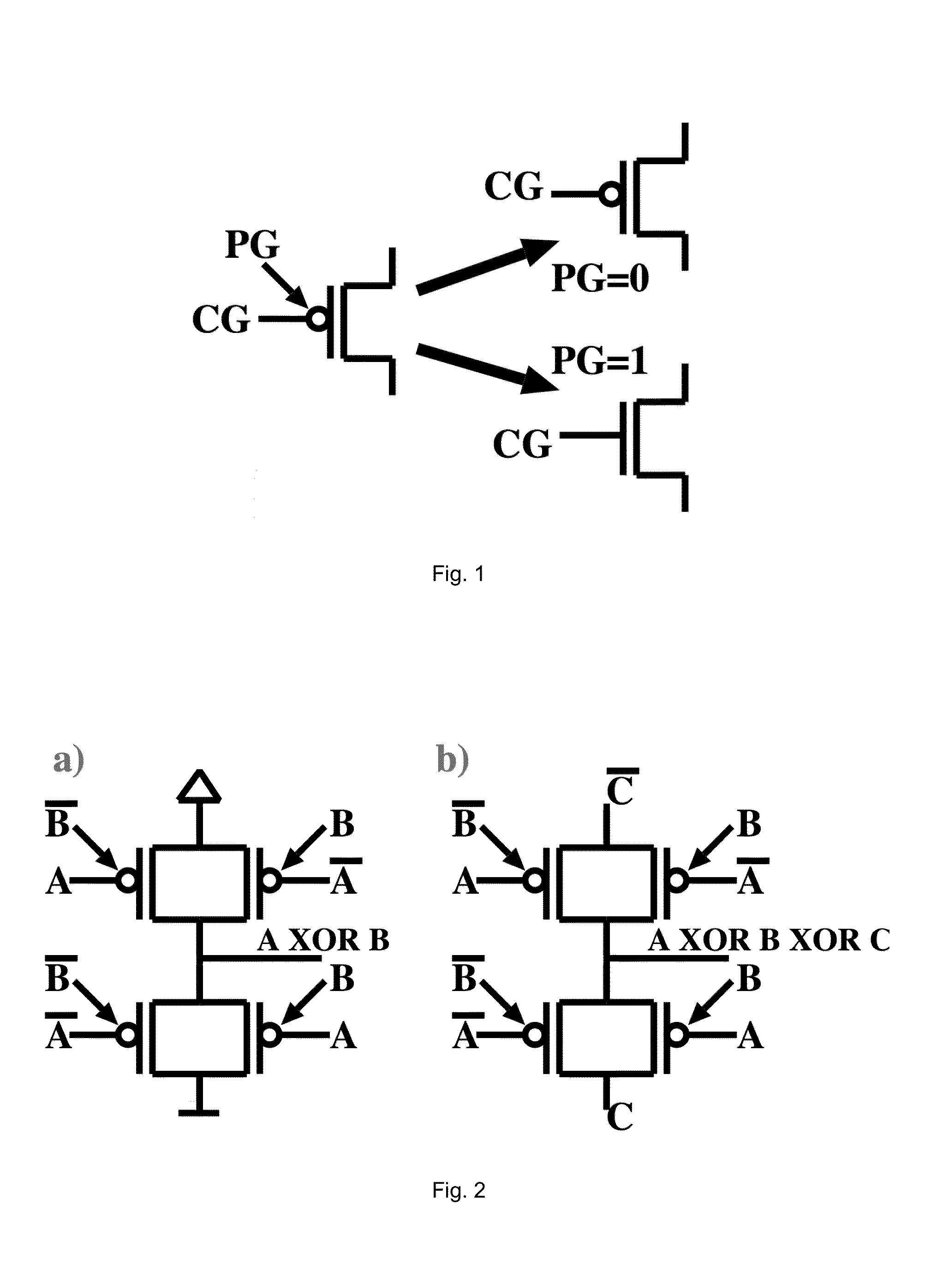
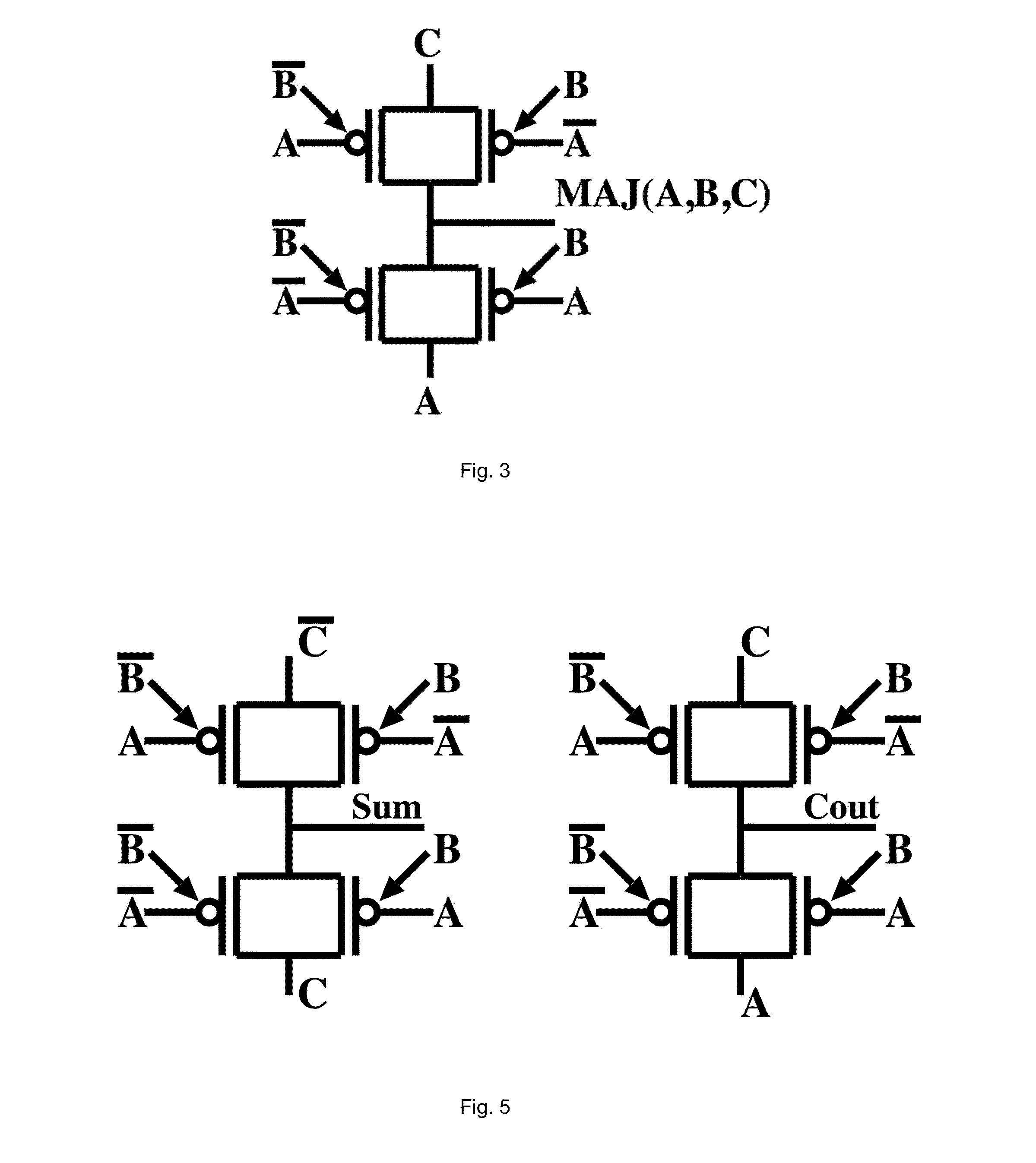
Controllable polarity FET based arithmetic and differential logic
ActiveUS20140043060A1Exclusive-OR circuitsMajority/minority circuitsTransmission gateElectrical polarity
A logic gate with three inputs A, B, and C, and one output implementing a function MAJ(A,B,C)=A*B+B*C+A*C comprising two mutually exclusive transmission gates (TGs) connected in series, based on two parallel double-gate controllable polarity devices, a polarity of each being controlled by input A and a conduction being controlled by input B, or vice-versa, in opposite polarities, and that route either an input A or C from one side of the transmission gates to the output.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
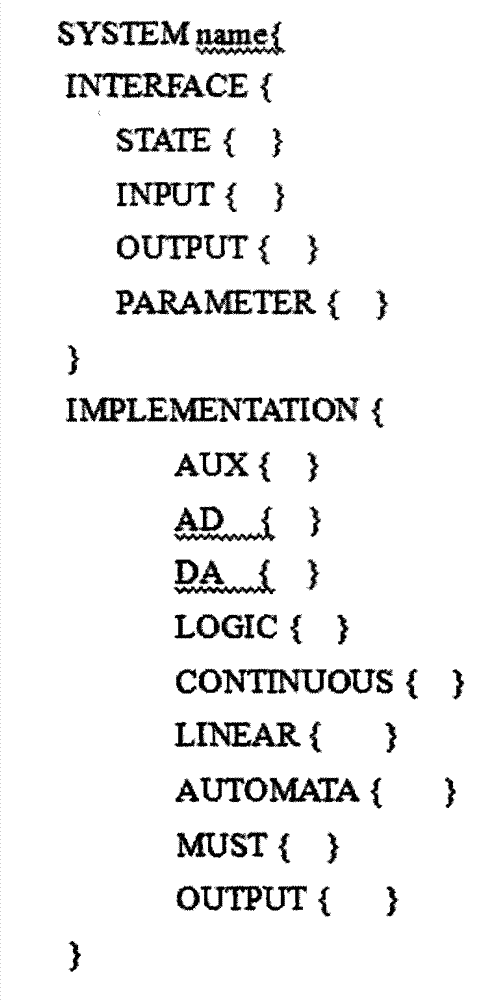
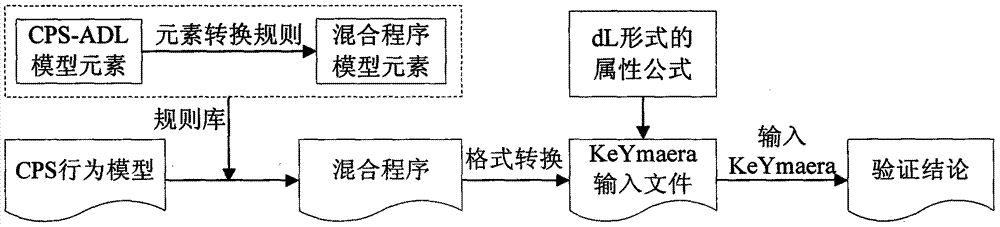
CPS (cyber physical system) modeling and verifying method based on conversion from CPS-ADL (architecture description language) model into hybrid program
InactiveCN103699743AImplement the rules for conversionSpecial data processing applicationsArchitecture description languageValidation methods
The invention discloses a CPS (cyber physical system) modeling and verifying method based on conversion from a CPS-ADL (architecture description language) model into a hybrid program. The method is mainly used for modeling a CPS and verifying attributes. The method is characterized in that a CPS is modeled on a CPS-ADL platform by the aid of an E-HYSDEL (expanded-hybrid system description language); a formalized definition HPM (hybrid program model) of an HP (hybrid program) model is given, and conversion rules among the CPS-ADL model elements and HP model elements are established when model conversion consistency is met; model description codes of a specific CPS are automatically converted into the hybrid program based on the conversion rules; input files of a KeYmaera are generated by the aid of the hybrid program and a dynamic differential logic description system attribute formula according to an input format of the KeYmaera of a theorem prover; the input files are opened in the KeYmaera to perform reasoning and verifying. The method and the mechanism based on conversion from the CPS-ADL model into the HP are elaborated, and the rules of conversion from the CPS-ADL model elements into the HP model elements are realized.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
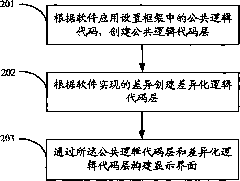
Method and device for realizing software reusability
ActiveCN102193793AImprove work efficiencyReduce development costsSpecific program execution arrangementsReusabilitySoftware
The invention discloses a method and a device for realizing software reusability. The method comprises the following steps of: setting a public logic code in a framework according to software application and establishing a public logic code layer; establishing a differential logic code layer according to a difference of software realization; and constructing a display interface according to the public logic code layer and the differential logic code layer. In the invention, the public logic code layer and the differential logic code layer are constructed respectively by setting the public logic code and the differential logic code in the framework according to software application, and the display interface is constructed according to the public logic code layer and the differential logic code layer, so that the aim of reusing a similar software product having the public logic code is fulfilled, the working efficiency is improved and the development cost is reduced.
Owner:TENCENT TECH (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
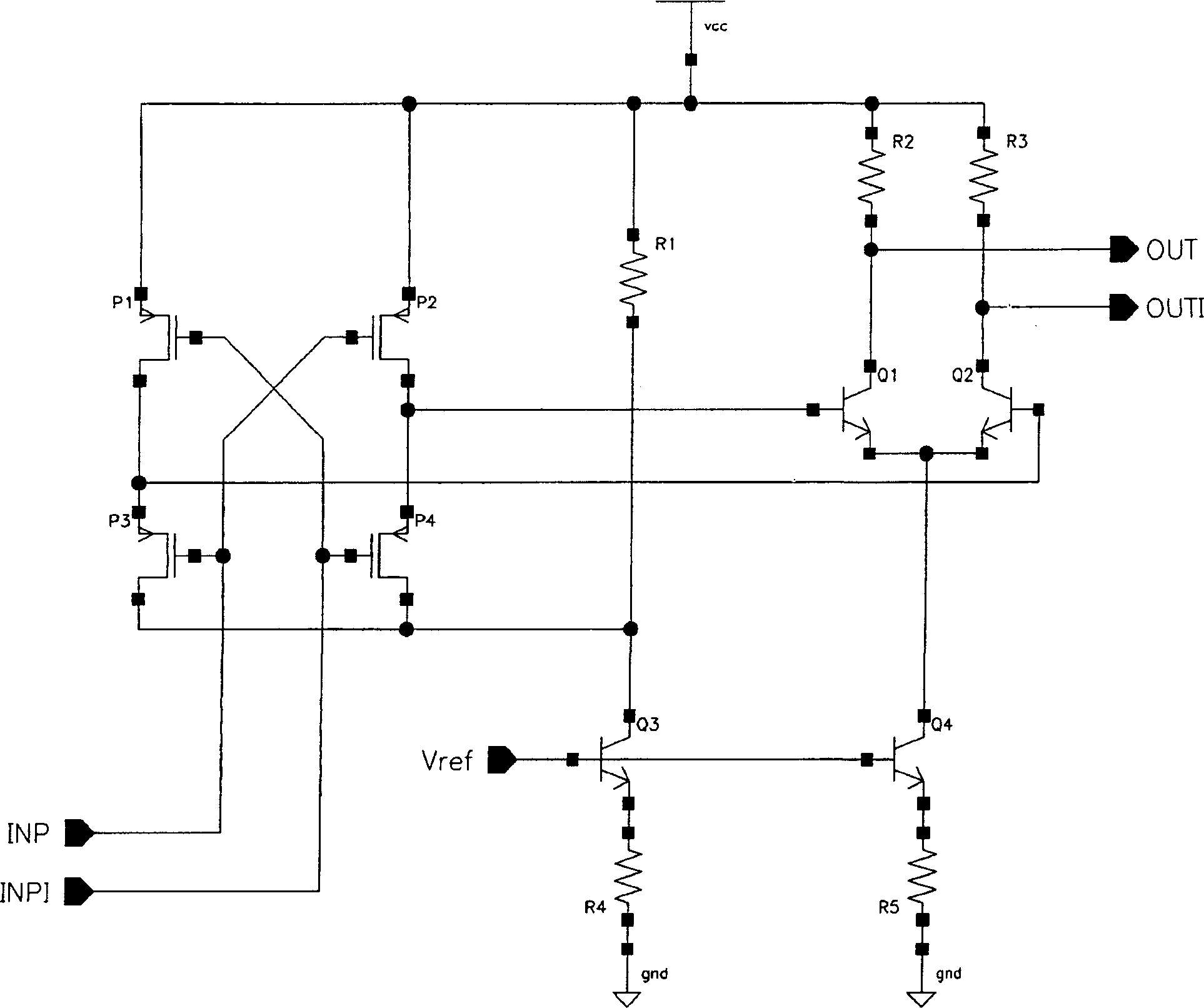
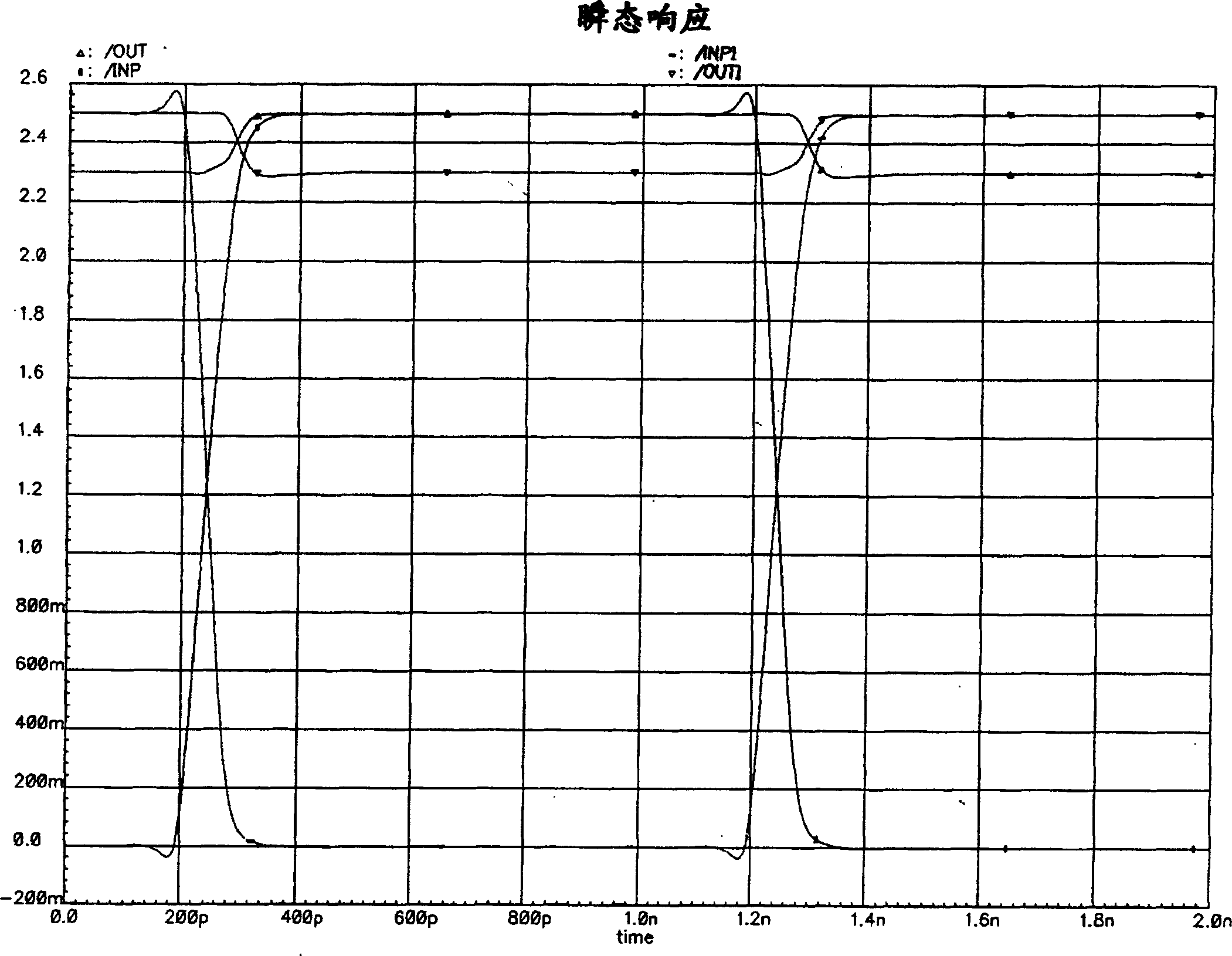
Comparator with output offset correction and mos logical circuit
ActiveCN1758540AMultiple input and output pulse circuitsAnalogue/digital conversion calibration/testingSignal onEngineering
Provided are comparators outputting offset calibration. A MOS current mode logic (MCML) circuit receives input signals and generates differential logic signals on output terminals thereof, and comprises a calibration unit coupled to the output terminals, calibrating output offsets at the output terminals according to digital calibration codes. An output stage is coupled to the differential logic signals at the output terminals of the MCML circuit to amplify the differential logic signal and generate a comparison resulting signal.
Owner:VIA TECH INC
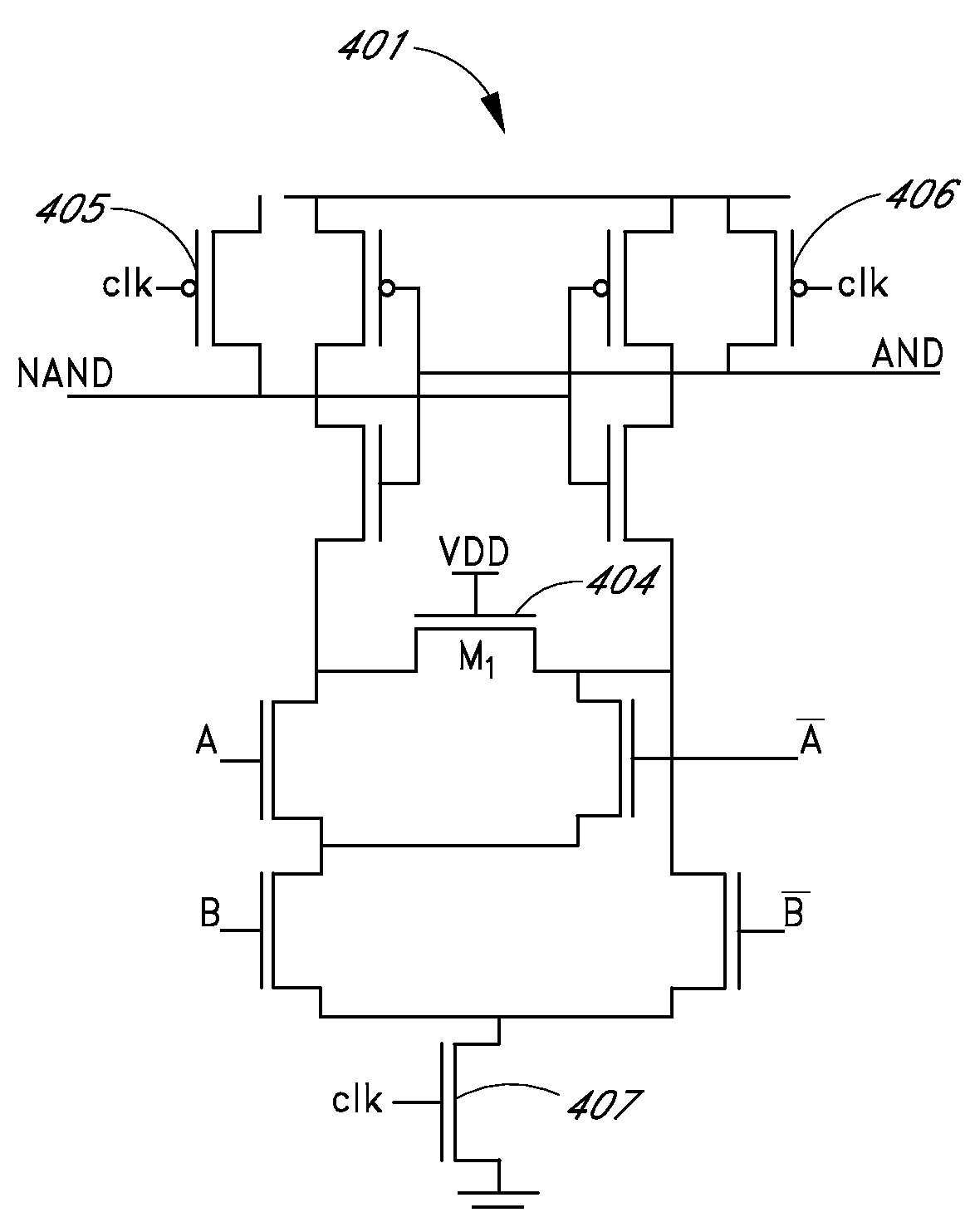
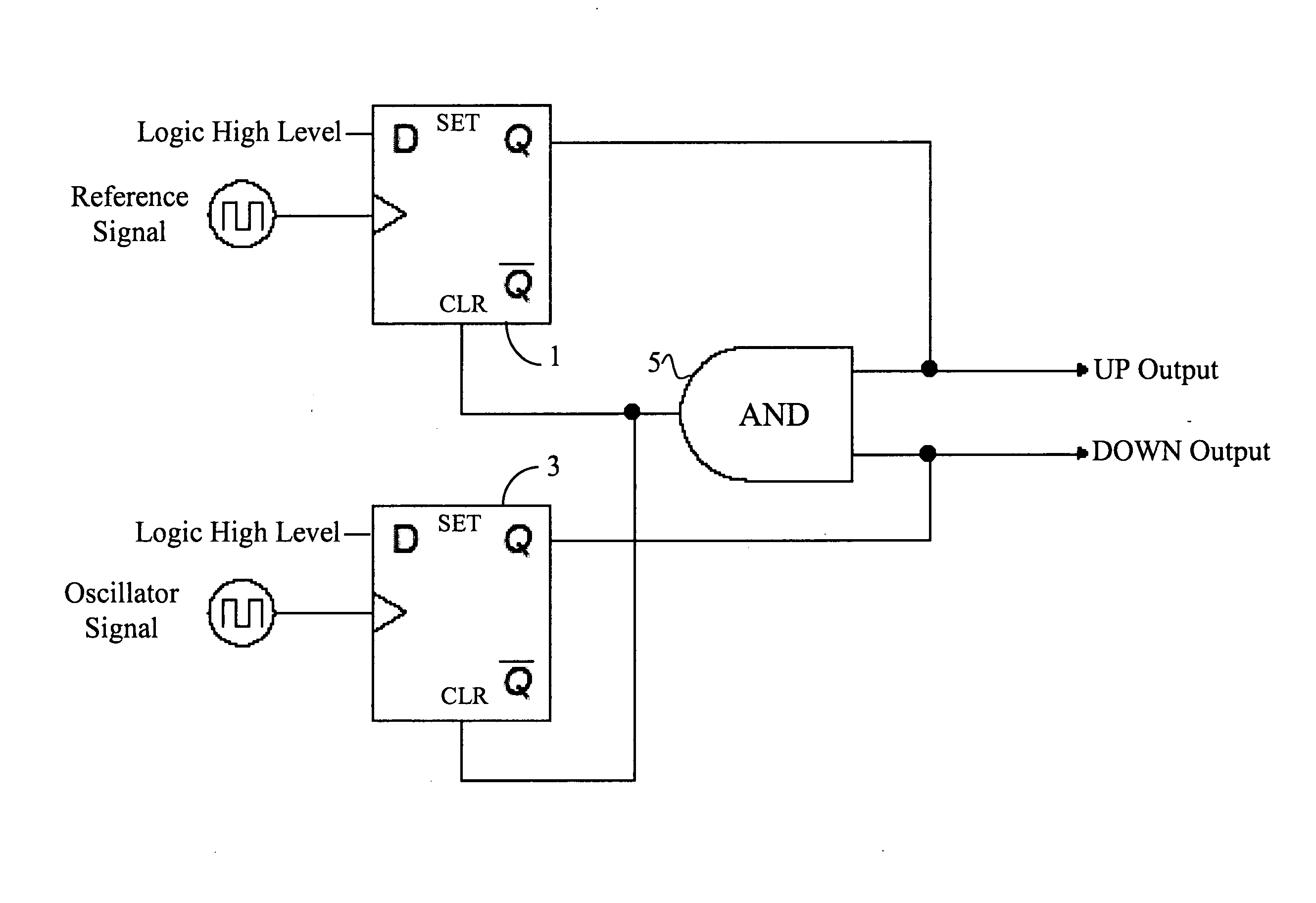
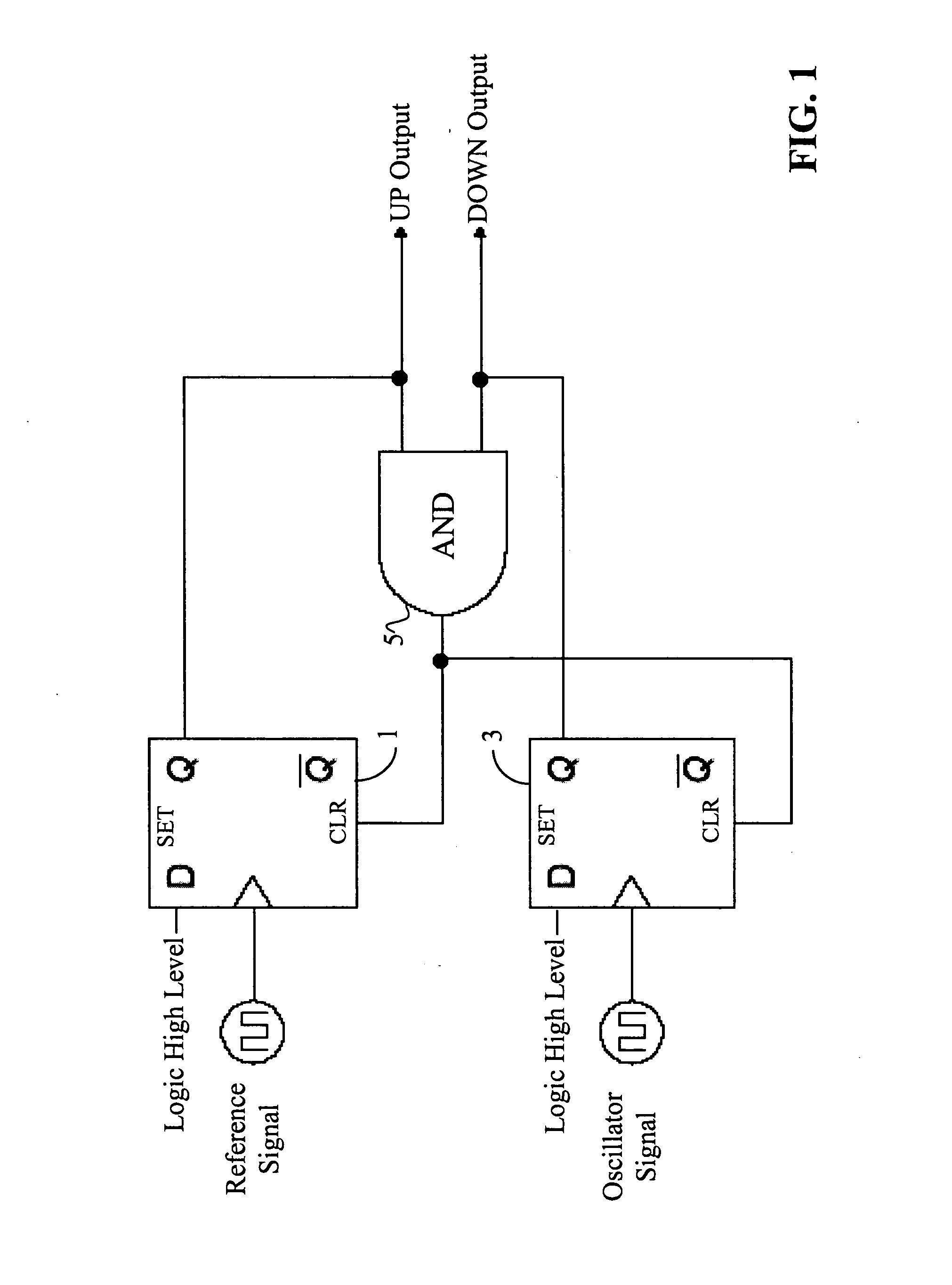
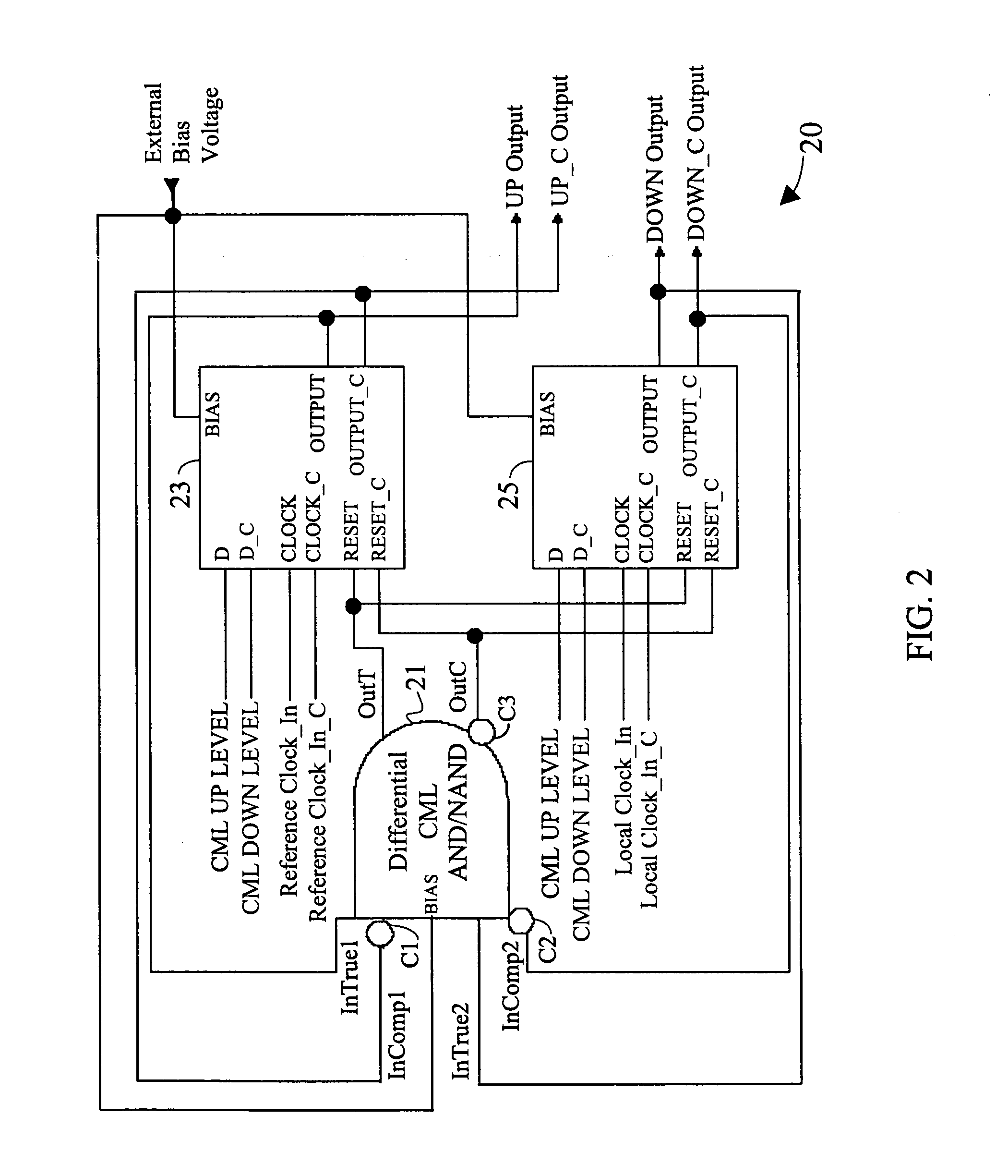
Differential current mode phase/frequency detector circuit
InactiveUS7038497B2High frequencyReduce noiseMultiple input and output pulse circuitsPulse automatic controlNAND logicDetector circuits
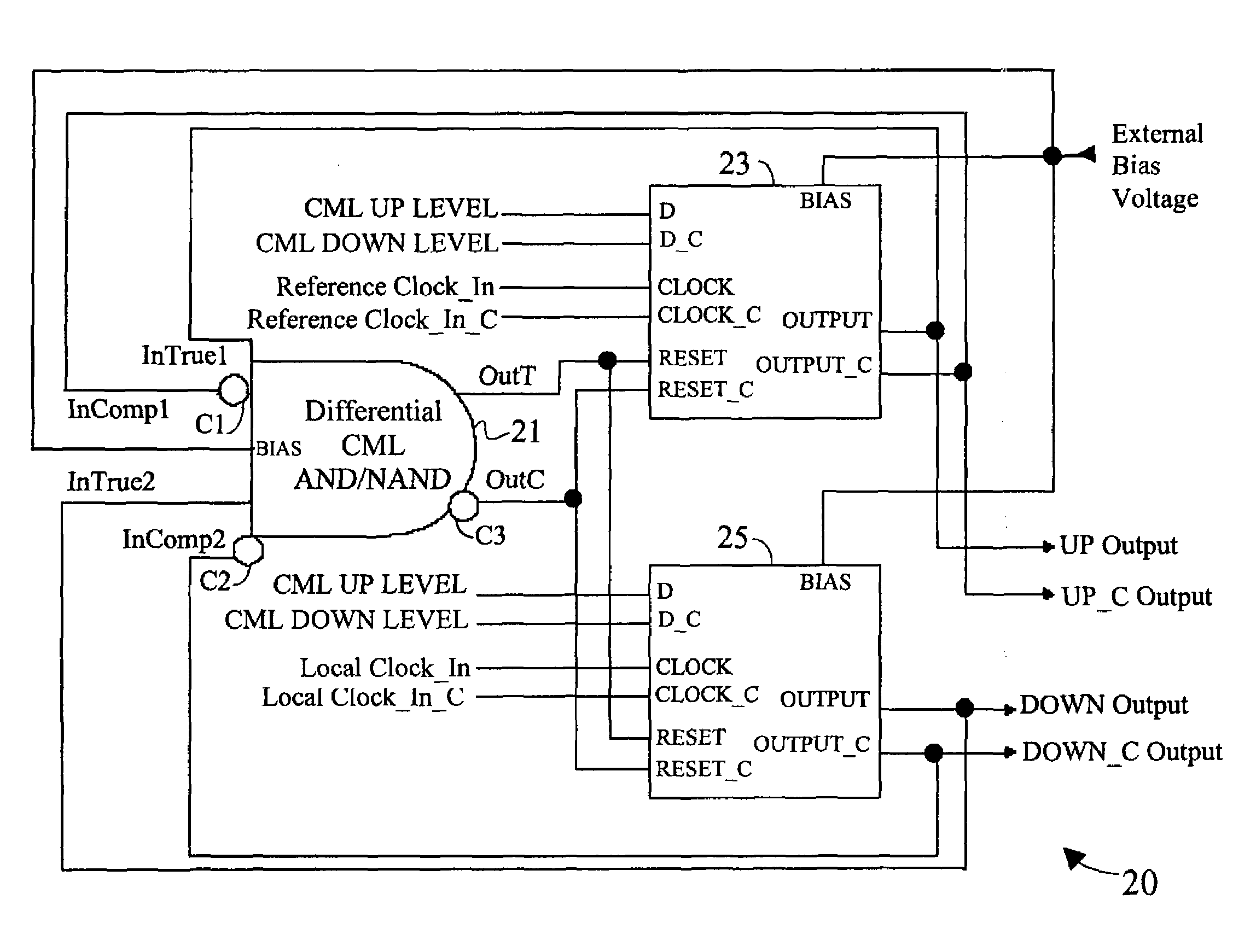
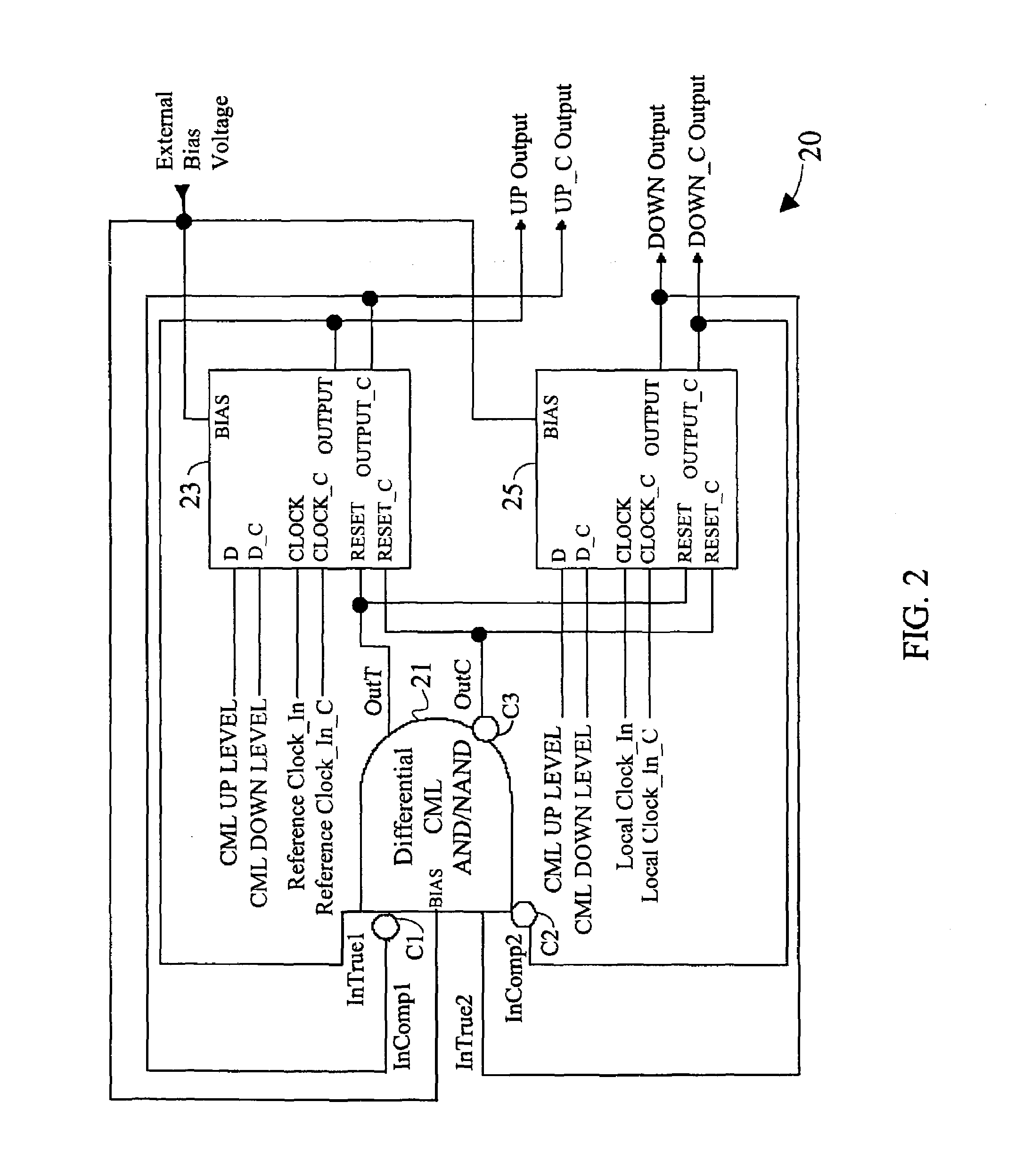
A fully differential phase and frequency detector utilizes a multi-function differential logic gate to implement a differential AND gate operation and provides a fully differential D-flip-flop. The multi-function differential logic gate has four inputs, which can be grouped into two pairs of true and complement signals. By selectively re-assigning the inputs to different signal pairs, the differential logic gate can be made to provide one of either simultaneous AND / NAND logic operations or simultaneous OR / NOR logic operations. The differential D-flip-flop is implemented following a master / slave configuration and is response to the true and complement forms of an input clock signal, an input reset input, and input data signal, and also provides true and complement forms of an output signal. All components within the phase and frequency detector are exemplified in CML circuit configuration.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Dual-edge synchronized data sampler
A dual-edge synchronized sampler having an efficient implementation for high speed and high performance operation is described. The sampler receives a data input signal and a clock input signal and uses an asynchronous level mode state machine to sample the data input signal responsive to level changes in the clock input signal. In some embodiments, the sampler includes at least one differential logic block for implementing the asynchronous level mode state machine. The sampler has symmetric clock-to-Q propagation delays for both rising and falling edges of the clock input signal. The sampler may include toggle functionality, and may include edge control logic for configuring the sampler as one of a rising edge and falling edge sampler.
Owner:XILINX INC
High-speed differential logic buffer
ActiveUS7236011B2Switching accelaration modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionRC time constantCascode
A circuit for a high speed digital buffer has an active load circuit connected to an output of the digital buffer. The active load circuit loads the buffer output with an active inductance to reduce the RC time constant at the buffer output. The active load circuit may be based on two active devices connected to the buffer output so as to form a differential cascode circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Constant delay zero standby differential logic receiver and method
InactiveUS6920187B2No standby powerConstant propagation delayMultiple input and output pulse circuitsContinuous to patterned pulse manipulationPropagation delayDifferential signaling
A differential receiver circuit on an integrated circuit consumes substantially no standby power, has constant propagation delay regardless of the input common mode bias, has acceptable common mode rejection and includes first and second pass circuits and buffers to receive differential input signals. The first pass circuit provides a true output signal based on a differential between the “true” buffered signal and the complimentary buffered signal. The second pass circuit provides a “complementary” output signal based on a differential between the complimentary buffered signal and the “true” buffered signal. The differential receiver circuit rejects common mode biases that may be present on the received differential signals without varying propagation delay times.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High speed low skew CMOS to ECL converter
InactiveUS6175249B1Minimum delayReduce offsetReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEm couplingĆuk converter
A logic level converter for translating CMOS logic signals to into differential logic signal pairs such as those associated with ECL levels. The converter includes a first converter branch coupled to the switchable CMOS level input and it provides a first switchable translated output. A second converter branch is not coupled to the input nor is it coupled to the first converter branch. The second converter branch provides a fixed reference signal output around which the output of the first converter branch switches. Changes in the input signal to the first converter branch cause its output potential to be more than or less than the potential of the fixed reference signal supplied by the second converter branch. The components of the respective branches may be tailored to position the fixed signal at a selectable level and to define the differential between the two output signals. The current associated with the converter is mirrored through both branches to minimize the effects of fabrication, temperature, and / or power supply vagaries.
Owner:SEMICON COMPONENTS IND LLC
High-speed differential logic multiplexer
A circuit for a high speed digital multiplexer has an active load circuit connected to an output of the digital multiplexer. The active load circuit loads the multiplexer output with a transimpedance stage with low input resistance to reduce the RC time constant at the multiplexer output. The active load circuit may be based on two active devices connected to the multiplexer output so as to form a differential cascode circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Differential high speed cmos to ecl logic converter
InactiveCN1467913ASmall propagation delaySmall Pulse Width DistortionElectric pulse generatorLogic circuit interface arrangementsEngineeringLevel converter
A logic level converter for translating differential CMOS logic signals to into differential logic signal pairs such as those associated with ECL levels. The converter includes two components. A first component consists of two branches coupled to the switchable CMOS level input and it provides a first switchable translated output. The second component is an ECL current switch. The current associated with the converter is mirrored through the branches to minimize the effects of fabrication, temperature, and / or power supply vagaries, as well as a very fast and tolerance independent signal level translation.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Differential current mode phase/frequency detector circuit
InactiveUS20050242843A1Reduce noiseHigh frequencyReliability increasing modificationsMultiple input and output pulse circuitsDetector circuitsNAND logic
A fully differential phase and frequency detector utilizes a multi-function differential logic gate to implement a differential AND gate operation and provides a fully differential D-flip-flop. The multi-function differential logic gate has four inputs, which can be grouped into two pairs of true and complement signals. By selectively re-assigning the inputs to different signal pairs, the differential logic gate can be made to provide one of either simultaneous AND / NAND logic operations or simultaneous OR / NOR logic operations. The differential D-flip-flop is implemented following a master / slave configuration and is response to the true and complement forms of an input clock signal, an input reset input, and input data signal, and also provides true and complement forms of an output signal. All components within the phase and frequency detector are exemplified in CML circuit configuration.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
CMOS differential logic circuit using voltage boosting technique
ActiveUS8907701B2Prevent slowdownImprove energy efficiencyReliability increasing modificationsLogic circuits coupling/interface using field-effect transistorsCapacitancePropagation delay
The present invention discloses a CMOS differential logic circuit. The CMOS differential logic circuit includes a precharge differential logic unit, which is precharged to a source voltage in response to a clock signal and is configured to output voltage having an increased load-driving ability using a boosting voltage; a voltage-boosting unit, which is pulled down by a ground voltage in response to the clock signal and is configured to boost the pulled-down voltage using capacitive coupling and output the boosting voltage; and a switching unit, which is configured to couple the precharge differential logic unit and the voltage-boosting unit in response to the clock signal. The propagation delay of a signal from the input terminal to the output terminal of a circuit in a low-source-voltage environment can be reduced, and the operating speed of the circuit and energy efficiency of the operation thereof can be improved.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
Method for preventing healthy phase bus-bar differential protection mal-operation during circuit reclosing period
ActiveCN103326331ASolve the problem of misoperation of non-fault phase bus differential protectionAvoid shockEmergency protective circuit arrangementsEngineeringDifferential protection
The invention relates to a method for preventing healthy phase bus-bar differential protection mal-operation during a circuit reclosing period. The method comprises one of the following measures: (1), optimizing secondary system indexes for changing TA for the bus into 5P20, and enabling a value TA which is 8 times of the rated current to be far from 10% of error curve edge; (2), arranging a high-low constant value action area for differential protection; (3), adding harmonic restraining criteria to take up anti-saturation measures in logic and adding the harmonic restraining criteria, wherein the harmonic restraining coefficient is less than 0.1; and (4), and replacing power frequency differential logic by power frequency variable differential logic when the added power frequency variable comprehensive criterion bus generates external faults.
Owner:STATE GRID CORP OF CHINA +1
Method and device for auto-calibration of multi-gate circuits
ActiveUS20160301365A1Power reduction in field effect transistorsSwitching accelaration modificationsLogic cellEngineering
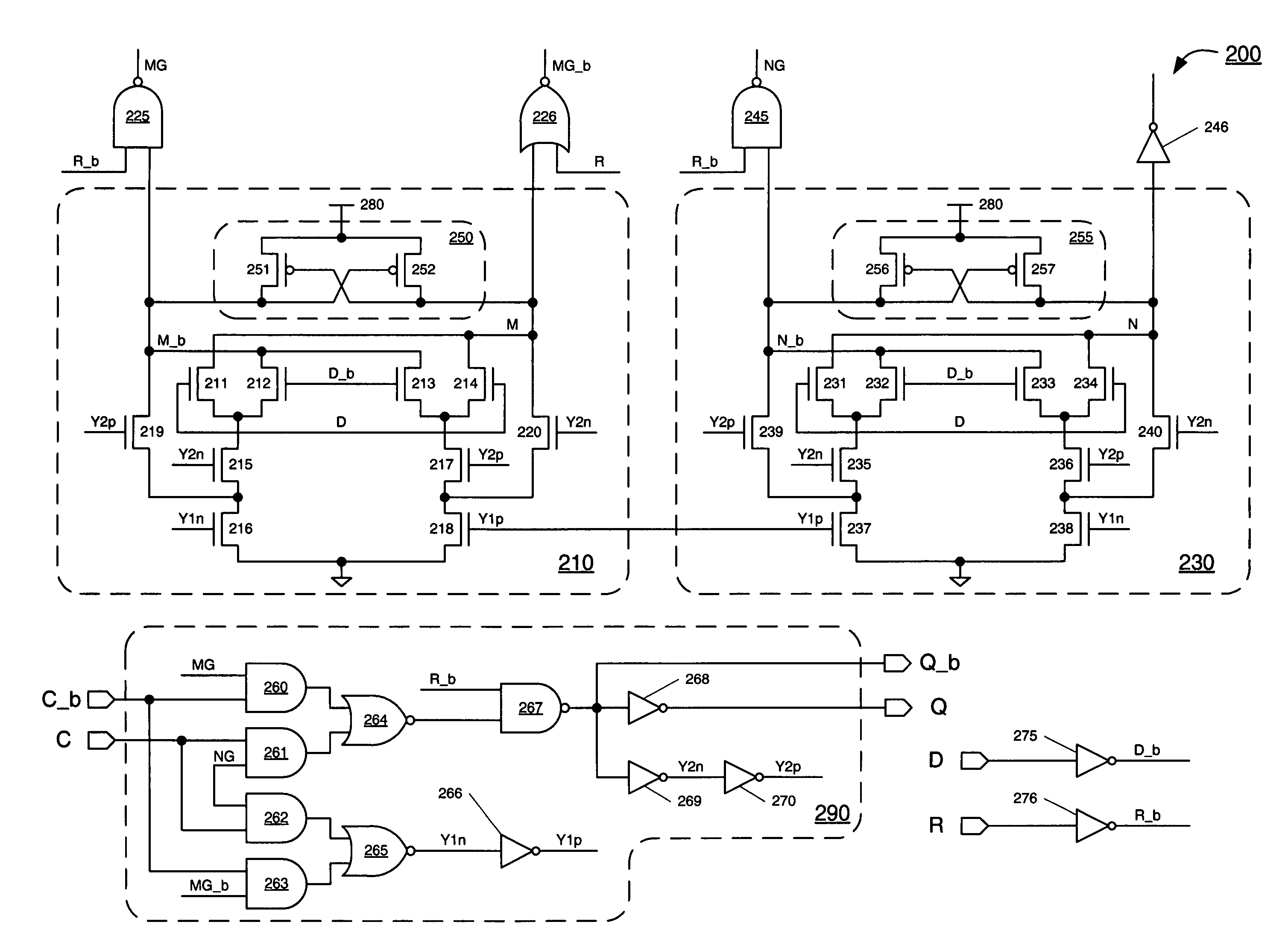
A differential-logic logic circuit chained with another differential-logic circuit comprises a first logic cell composed of back-gate transistors, the first cell having a first input for receiving a first input signal and having an output for delivering a first output signal, and a second logic cell complementary to the first cell, composed of back-gate transistors, the second cell having as many inputs as the first cell, each input able to receive an input signal complementary to the respective input signal of the first cell, the second cell having an output for delivering a second output signal complementary to the first output signal of the first cell. The first output signal of the first cell is applied to the back gate of each transistor of the second cell, and the second output signal of the second cell is applied to the back gate of each transistor of the first cell.
Owner:UNIV DE NICE +1
Apparatus for outputting complementary signals using bootstrapping technology
ActiveUS7928792B2Improve switching performanceSimple structurePulse automatic controlElectronic switchingDifferential signalingVIT signals
Disclosed herein is an apparatus for outputting complementary signals using bootstrapping technology. The apparatus for outputting complementary signals includes a precharaged logic block, one or more output nodes, and a bootstrapping circuit block. The precharged differential logic block generates a differential signal depending on an input signal. The one or more output nodes output the complementary signals depending on the differential signal. The bootstrapping circuit block is shared by the one or more output nodes, and amplifies the complementary signals.
Owner:RES & BUSINESS FOUND SUNGKYUNKWAN UNIV
High-speed differential logic multiplexer
ActiveUS20060061390A1Reduce RC time constantElectronic switchingDigital storageRC time constantMultiplexer
A circuit for a high speed digital multiplexer has an active load circuit connected to an output of the digital multiplexer. The active load circuit loads the multiplexer output with a transimpedance stage with low input resistance to reduce the RC time constant at the multiplexer output. The active load circuit may be based on two active devices connected to the multiplexer output so as to form a differential cascode circuit.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
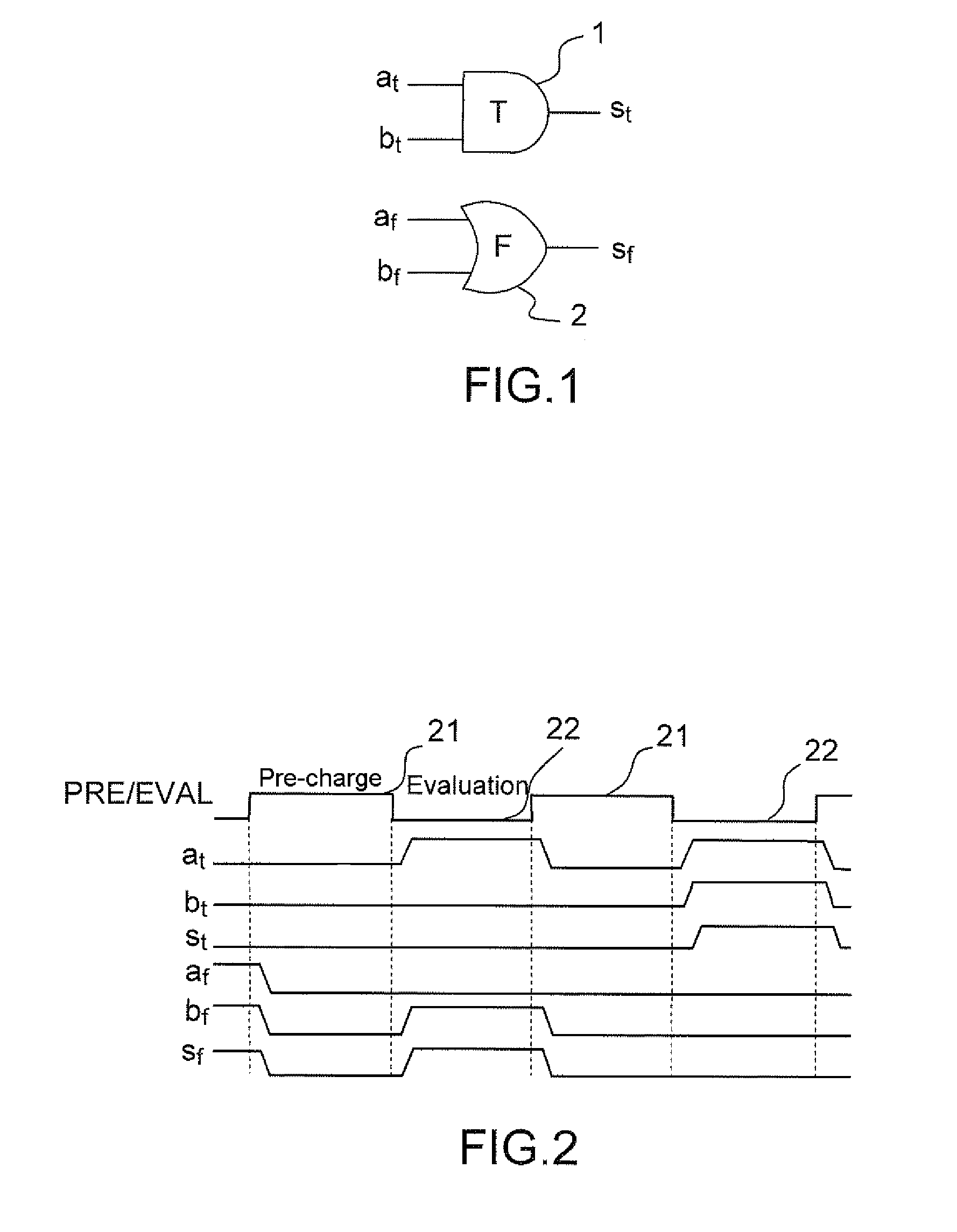
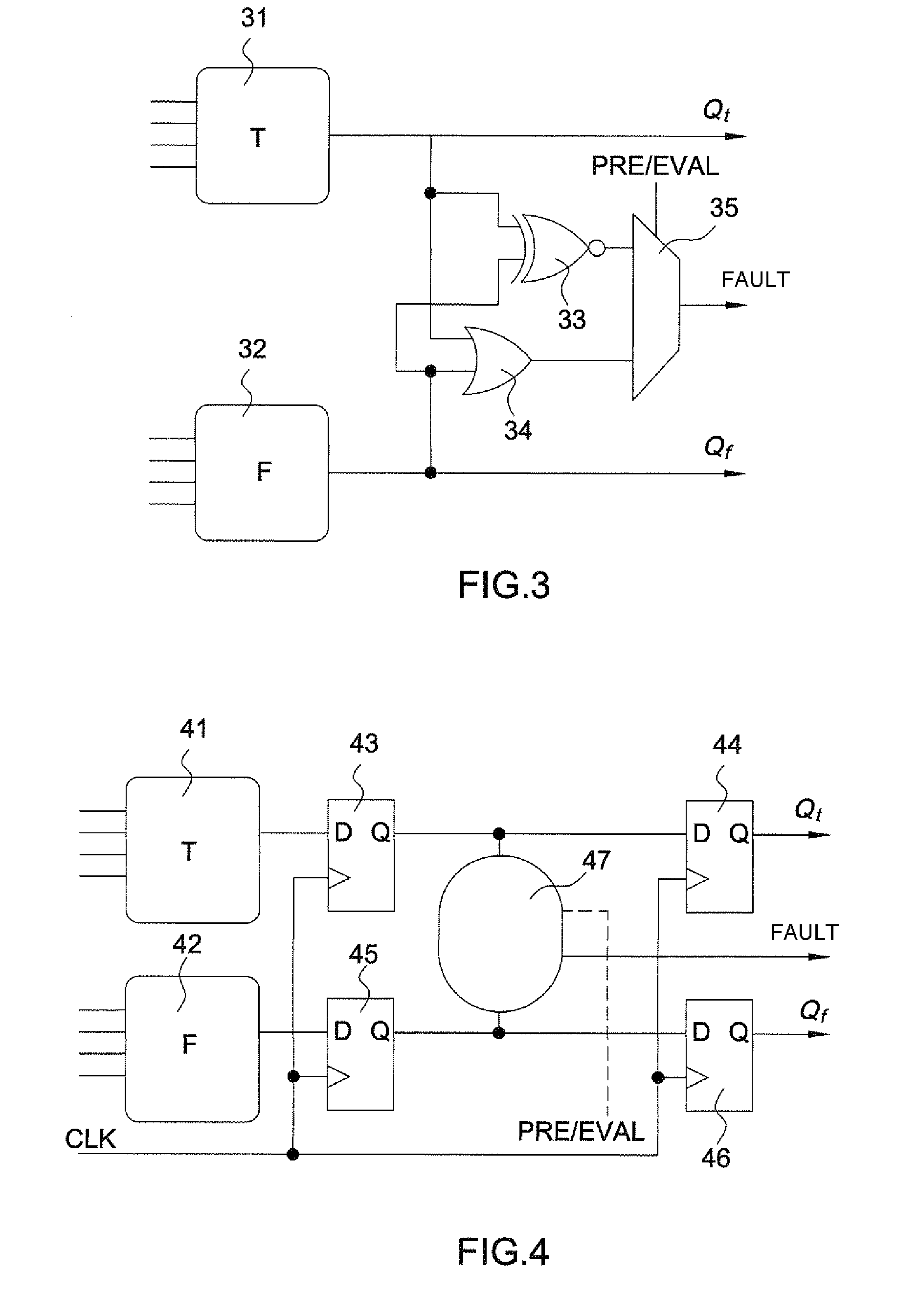
Method for detecting abnormalities in a cryptographic circuit protected by differential logic, and circuit for implementing said method
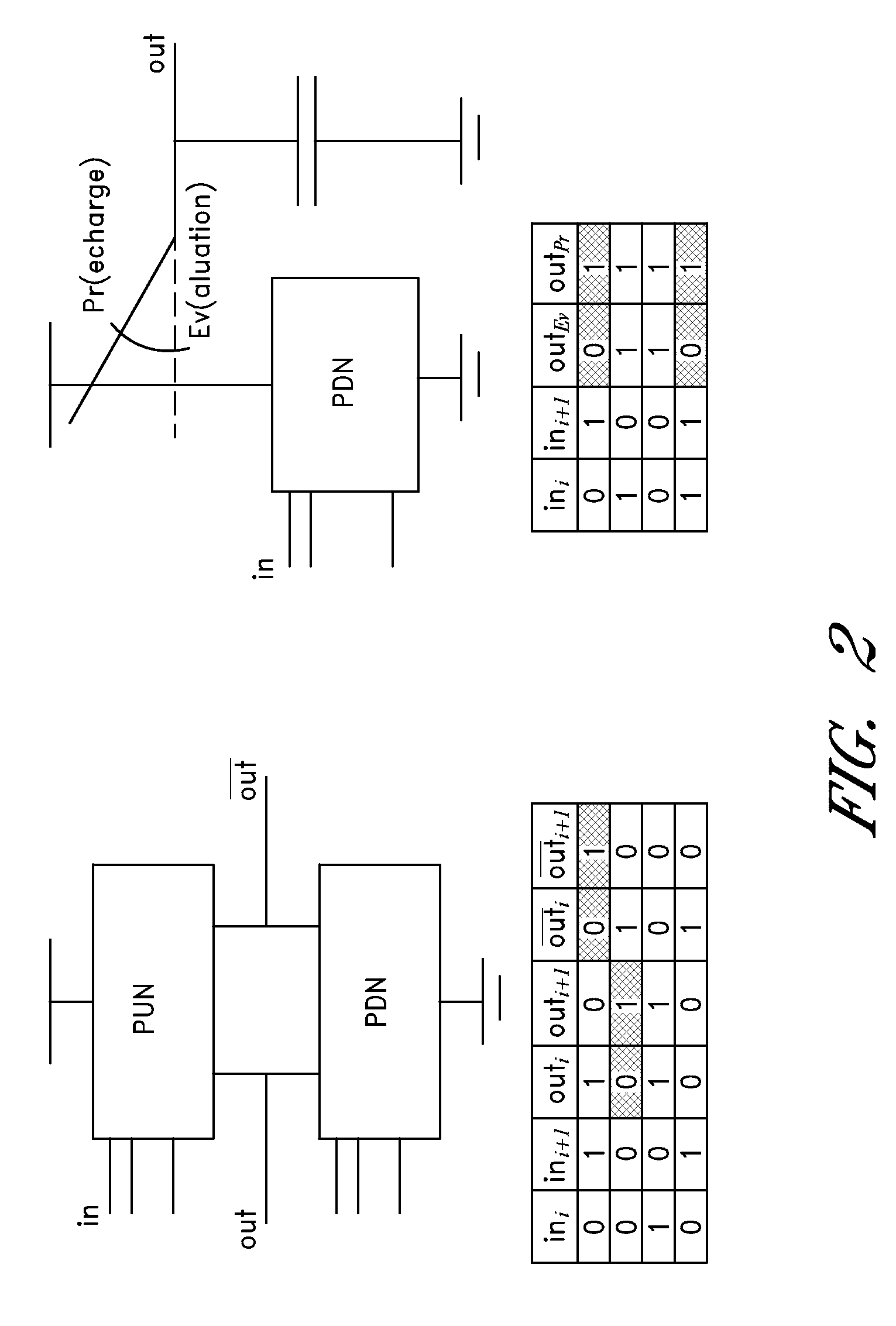
In a method for detecting anomalies in a circuit protected by differential logic and which processes logic variables represented by a pair of components, a first network of cells carrying out logic functions on the first component of said pairs, a second network of dual cells operating in complementary logic on the second component, the logic functions being carried out by each pair of cells in a pre-charge phase placing the variables in a known state on input to the cells and followed by an evaluation phase where a calculation is performed by the cells, the method includes detecting an anomaly by at least one non-consistent state.
Owner:INST MINES TELECOM
Level shifter for differential signals with balanced transition times
ActiveCN102907000AManipulation where pulse delivered at different timesElectric pulse generatorCapacitanceDifferential signaling
A level shifter (400) and method are provided for balancing rise and fall times of a signal. An input circuit (420, 413) receives a differential logic signal (Inp, Inn) with two complimentary logic levels. A level transition balancing circuit (420) balances the rise and fall times of a level shifted version of each complimentary logic level during a transition from a first to a second of the logic levels and a level shift. A logic element (430) stores and provides outputs (outp, ounn) of the level shifted versions of the logic levels. The level transition balancing circuit (420) includes a capacitor (421) in parallel with a field-effect transistor (422) for each input. The capacitor destabilizes inputs to the logic element and balances the transition using the capacitance and a level (435, 436) previously stored in the logic element.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
Differential-input circuit
InactiveUS6429691B1Reduce consumptionLow efficiencyLogic circuits characterised by logic functionLogic circuit interface arrangementsVoltageDifferential logic
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Differential logic circuit, frequency divider, and frequency synthesizer
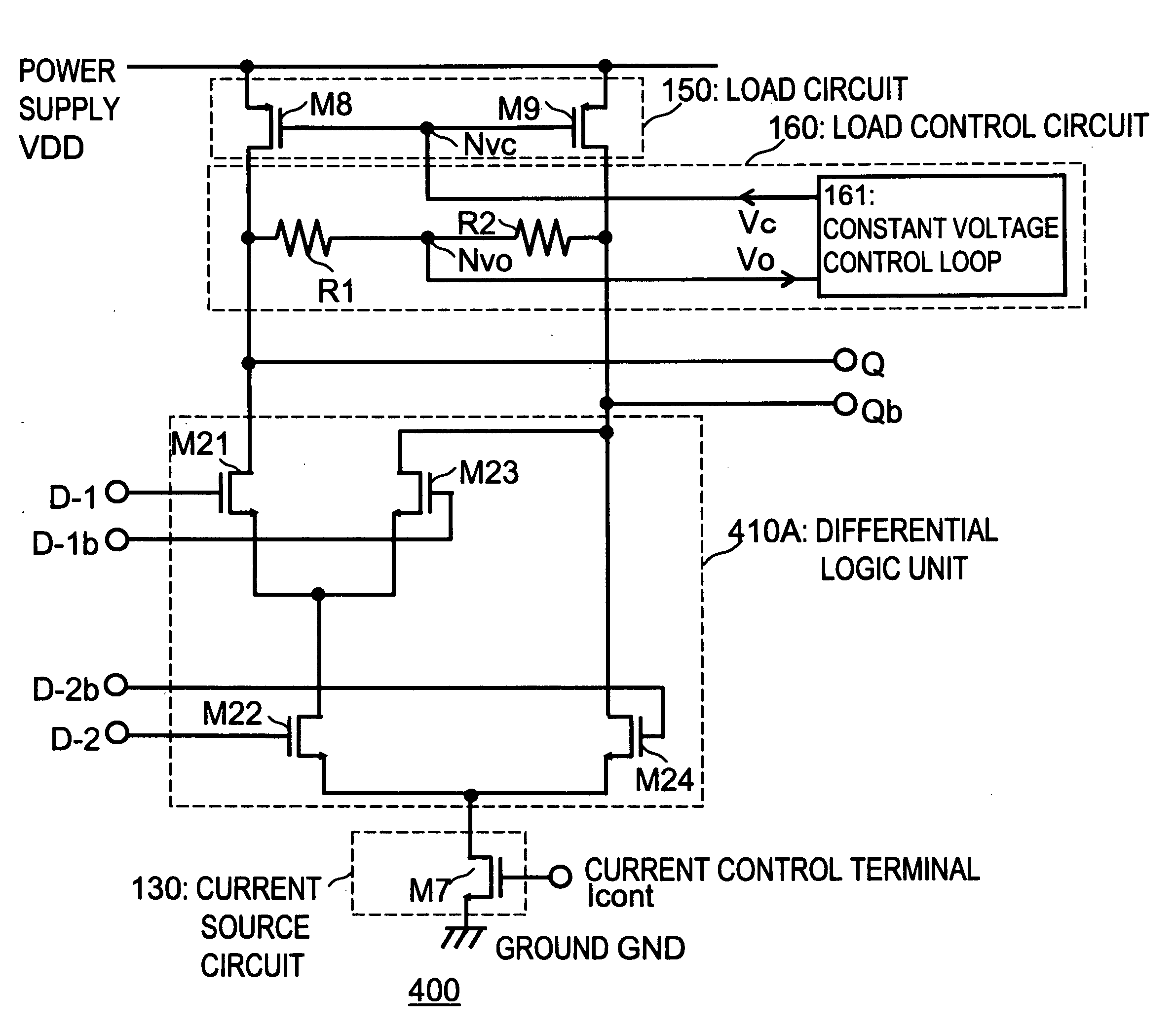
InactiveUS20110181320A1Run at high speedReduce power consumptionLogic circuits characterised by logic functionCounting chain pulse countersLoad circuitPower flow
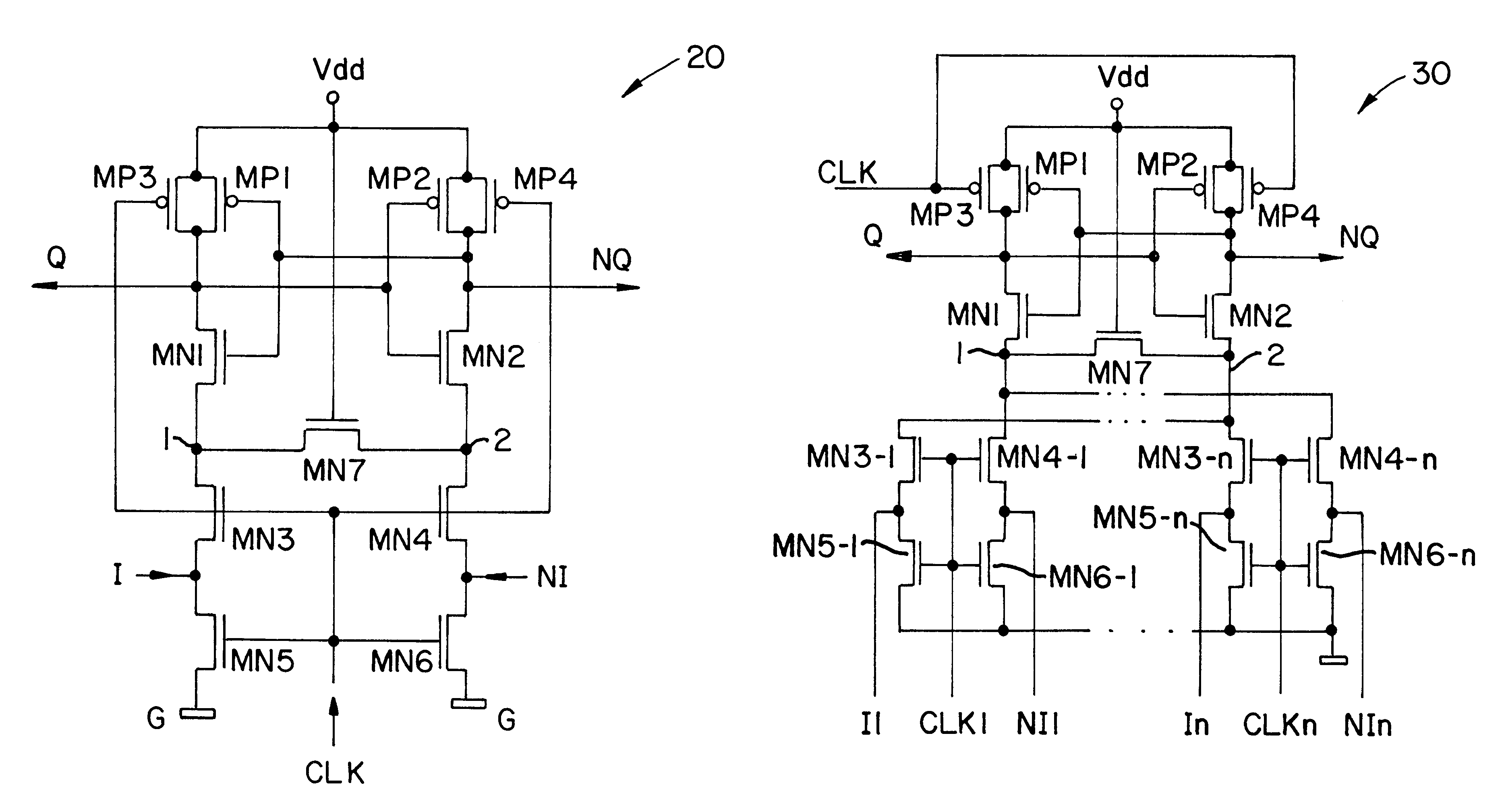
A differential logic circuit includes: a differential logic unit which receives a plurality of logic signals, performs a logic operation, and outputs a result of the logic operation from a pair of differential signal output terminals thereof; and a current source circuit which supplies current to the differential logic unit and which controls a magnitude of the current. The differential logic circuit further includes: a load circuit connected to the differential signal output terminals; and a load control circuit which is connected to the load circuit and controls a load of the load circuit such that a direct-current output voltage of the pair of differential signal output terminals is constant.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Differential to single-ended logic converter
InactiveUS20050068063A1Easy to implementMultiple input and output pulse circuitsLogic circuits characterised by logic functionEngineeringCurrent source
The present invention is a converter stage for converting a differential logic input signal and a corresponding common mode differential logic signal each having a first single-ended logic signal and a complementary second single-ended logic signal into a single-ended logic output signal. The converter stage comprises a first and a second differential stage each having a first and a second MOS transistor and a first and second current source for the differential stages. According to the invention the current sources are controlled by the voltage level which is centered between the mid-potentials of the common mode level differential logic signal and the mid-potential of the differential logic input signal.
Owner:LONGITUDE SEMICON S A R L
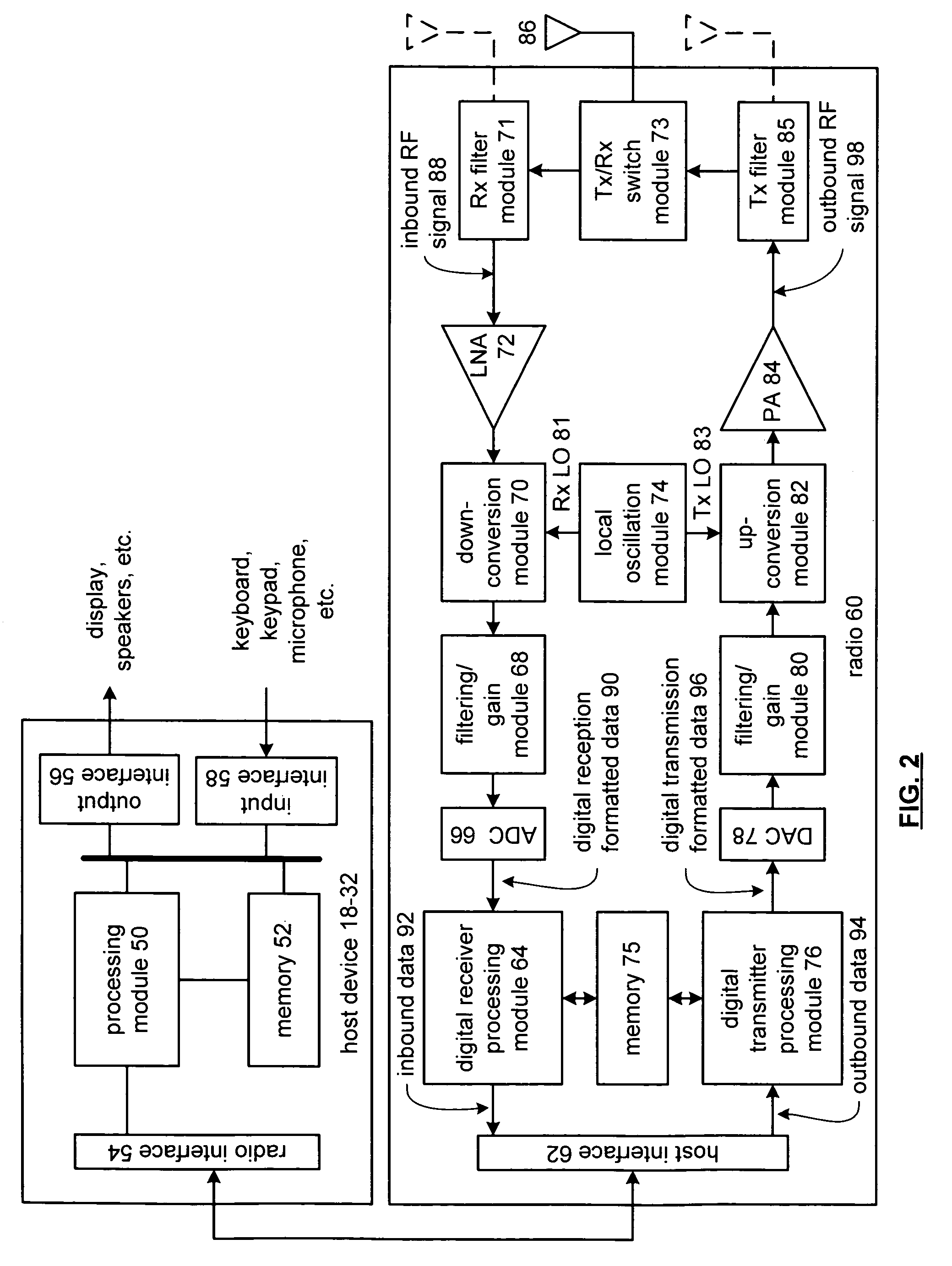
High speed differential signaling logic gate and applications thereof
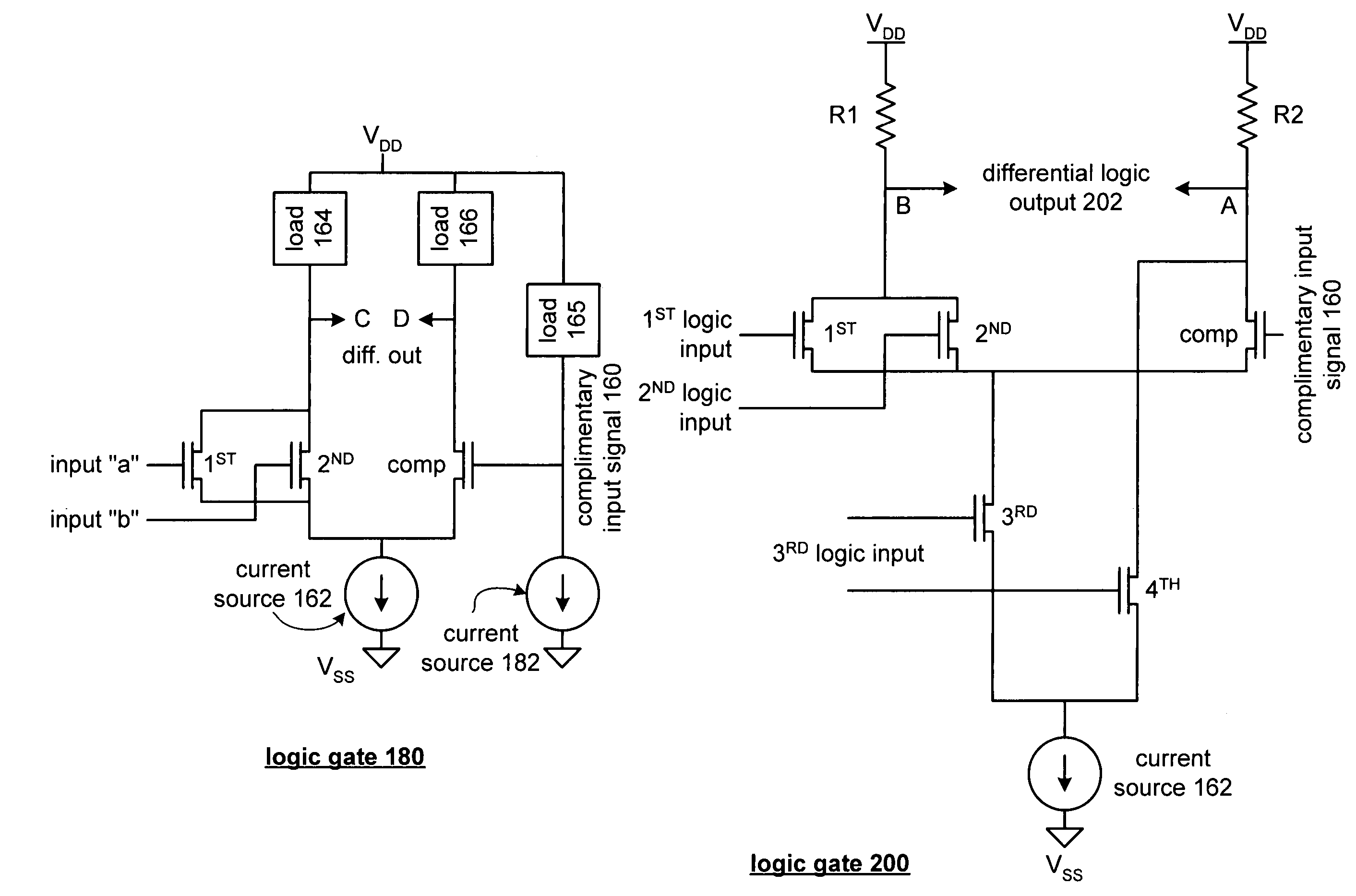
A high-speed differential signaling logic gate includes a 1st input transistor, 2nd input transistor, complimentary transistor, current source, a 1st load, and a 2nd load. The 1st input transistor is operably coupled to receive a 1st input logic signal, which may be one phase of a first differential input signal. The 2nd input transistor is coupled in parallel with the 1st input transistor and is further coupled to receive a 2nd input logic signal, which may be one phase of a 2nd differential input signal. The complimentary transistor is operably coupled to the sources of the 1st and 2nd input transistors and to receive a complimentary input signal, which mimics the other phase of the 1st differential logic signal and the 2nd differential logic signal. The current source sinks a fixed current from the 1st and 2nd input transistors and the complimentary transistor. The 1st load is operably coupled to the drains of the 1st and 2nd input transistors to provide a 1st phase of a differential logic output. The 2nd load is coupled to the drain of the complimentary transistor to provide a 2nd phase of the differential logic output.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com