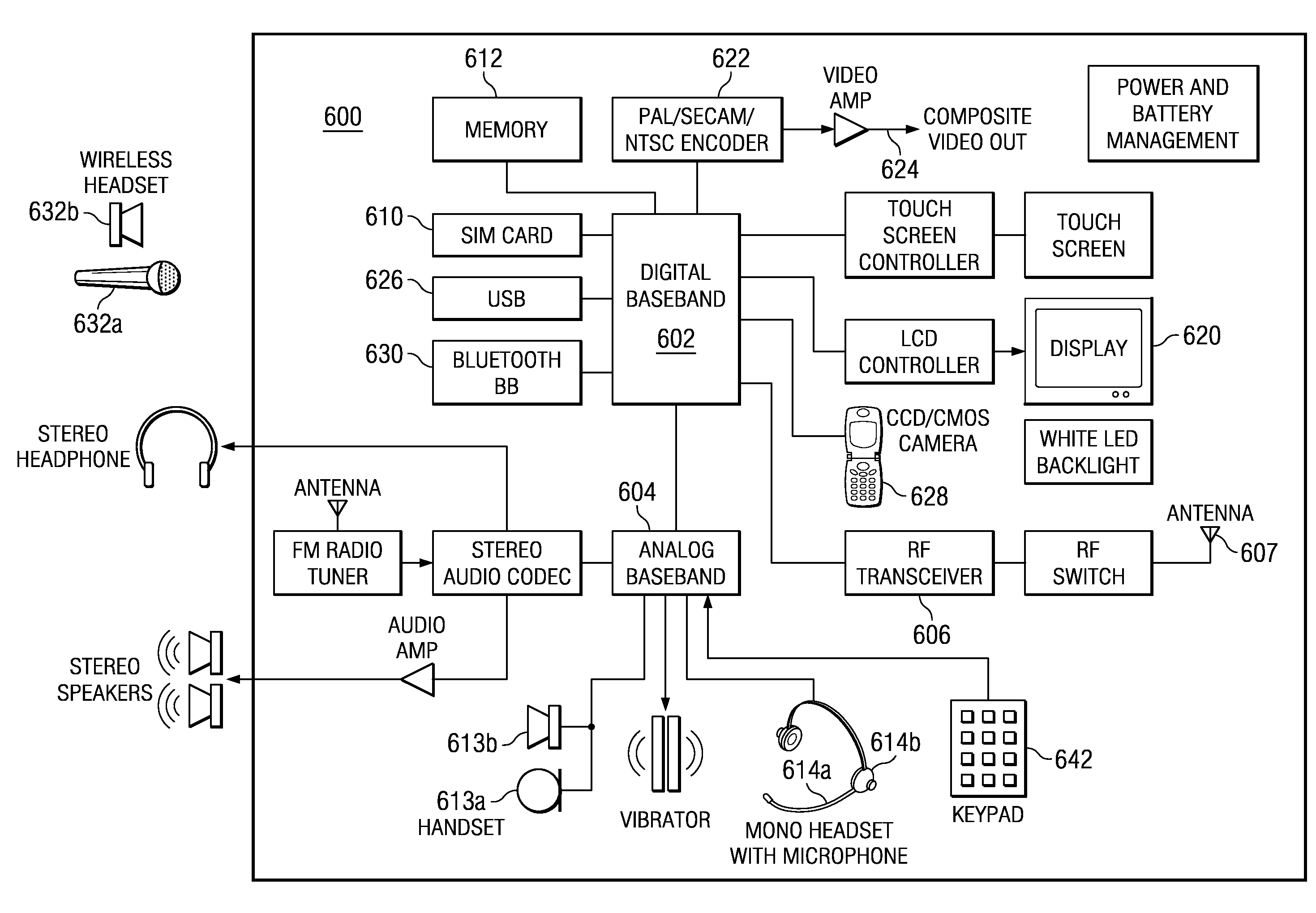
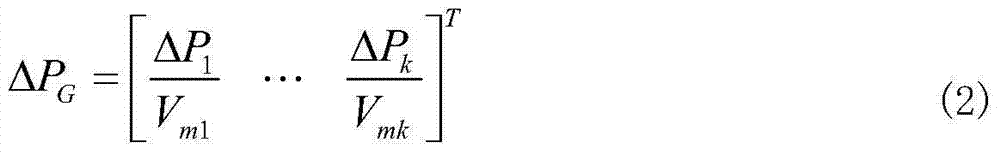
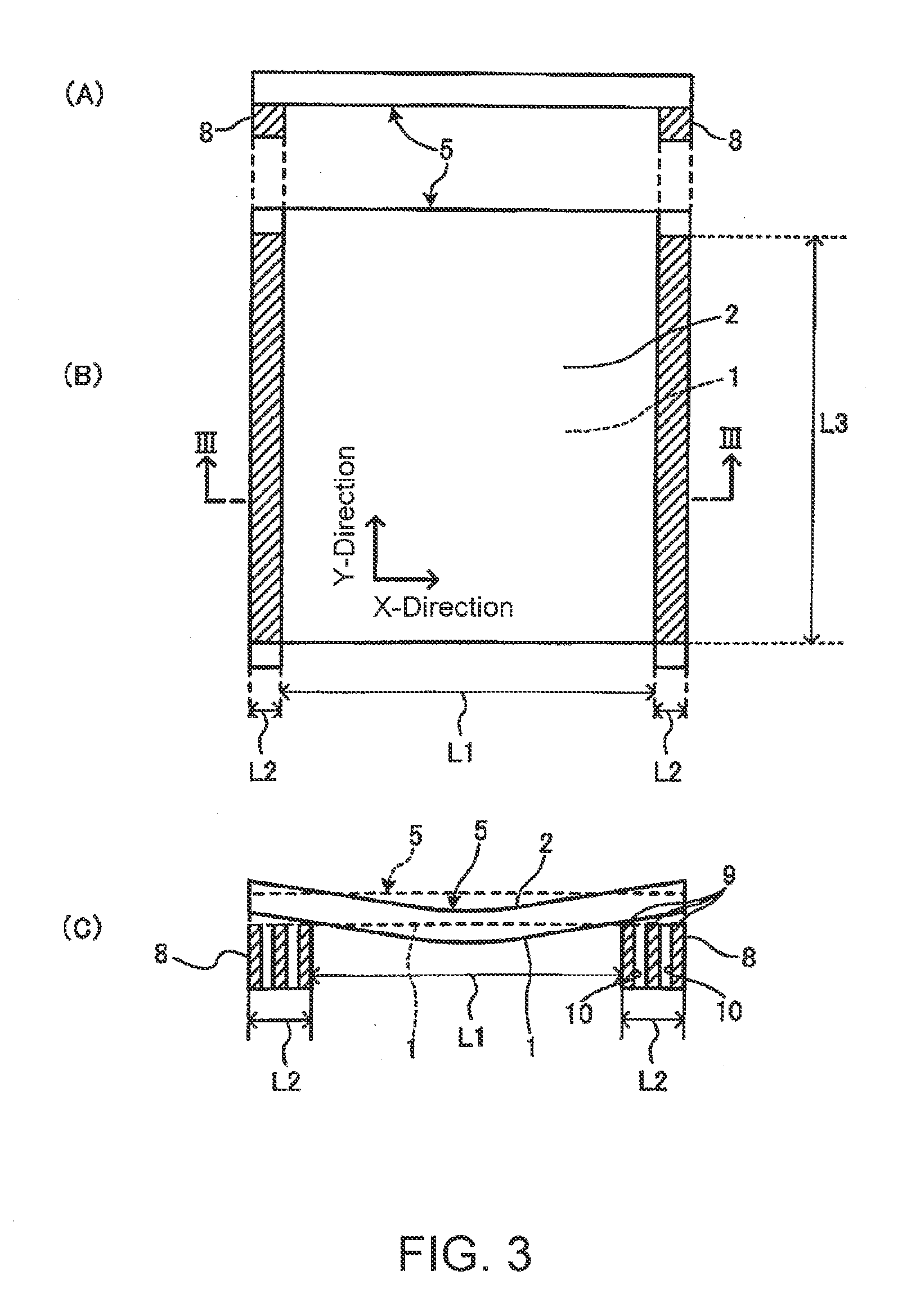
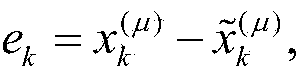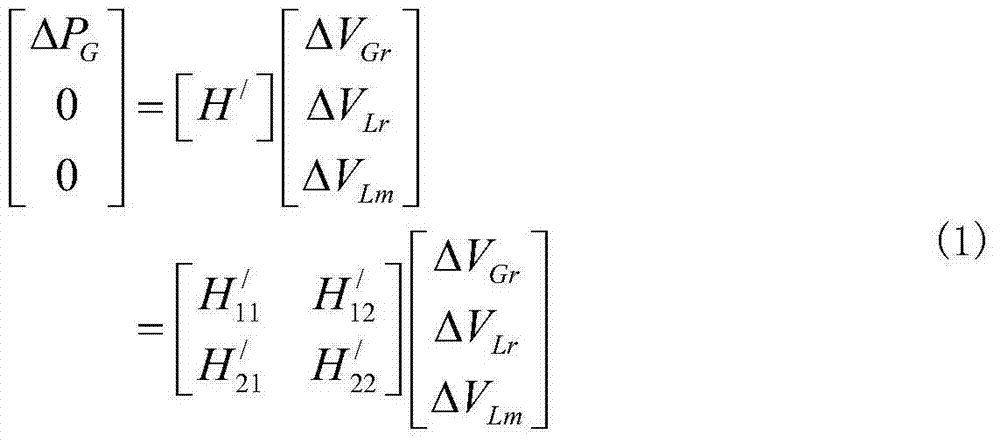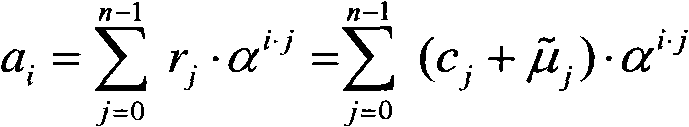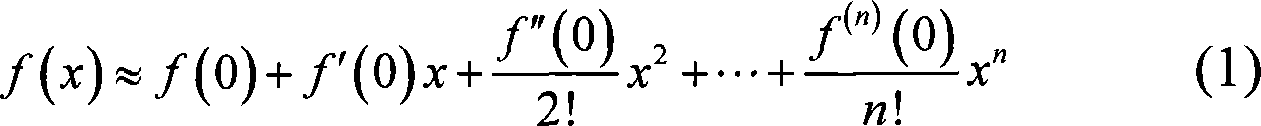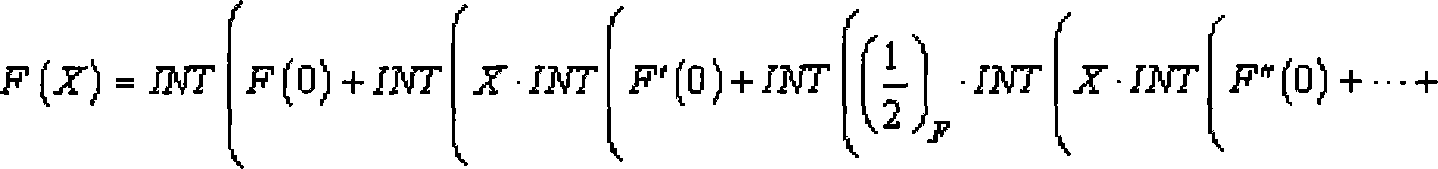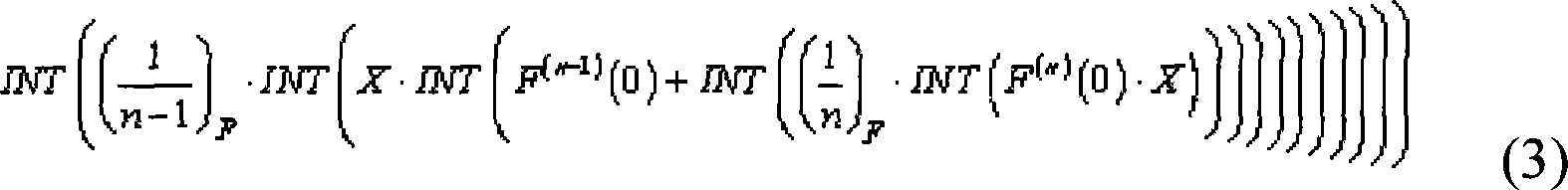Patents
Literature
52 results about "Polynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checks" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
These are polynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checks CRCs.
Method of isomorphic singular manifold projection still/video imagery compression
InactiveUS20020176624A1Reduction procedureReduce redundancyCharacter and pattern recognitionImage codingPattern recognitionImage compression
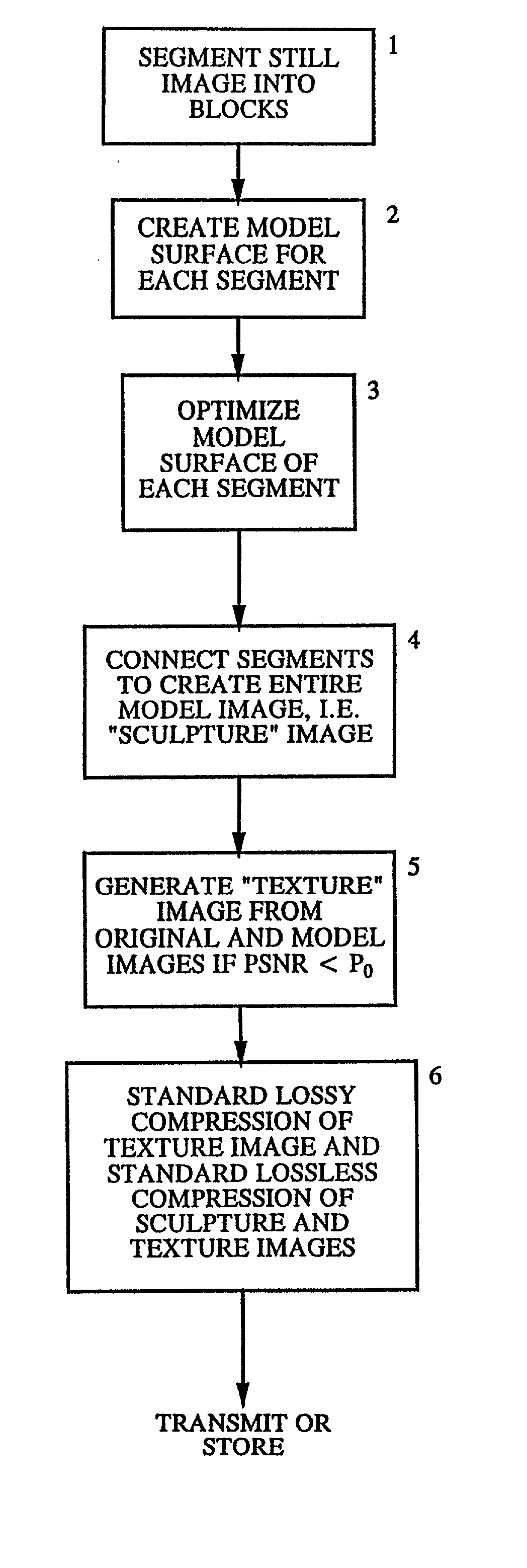
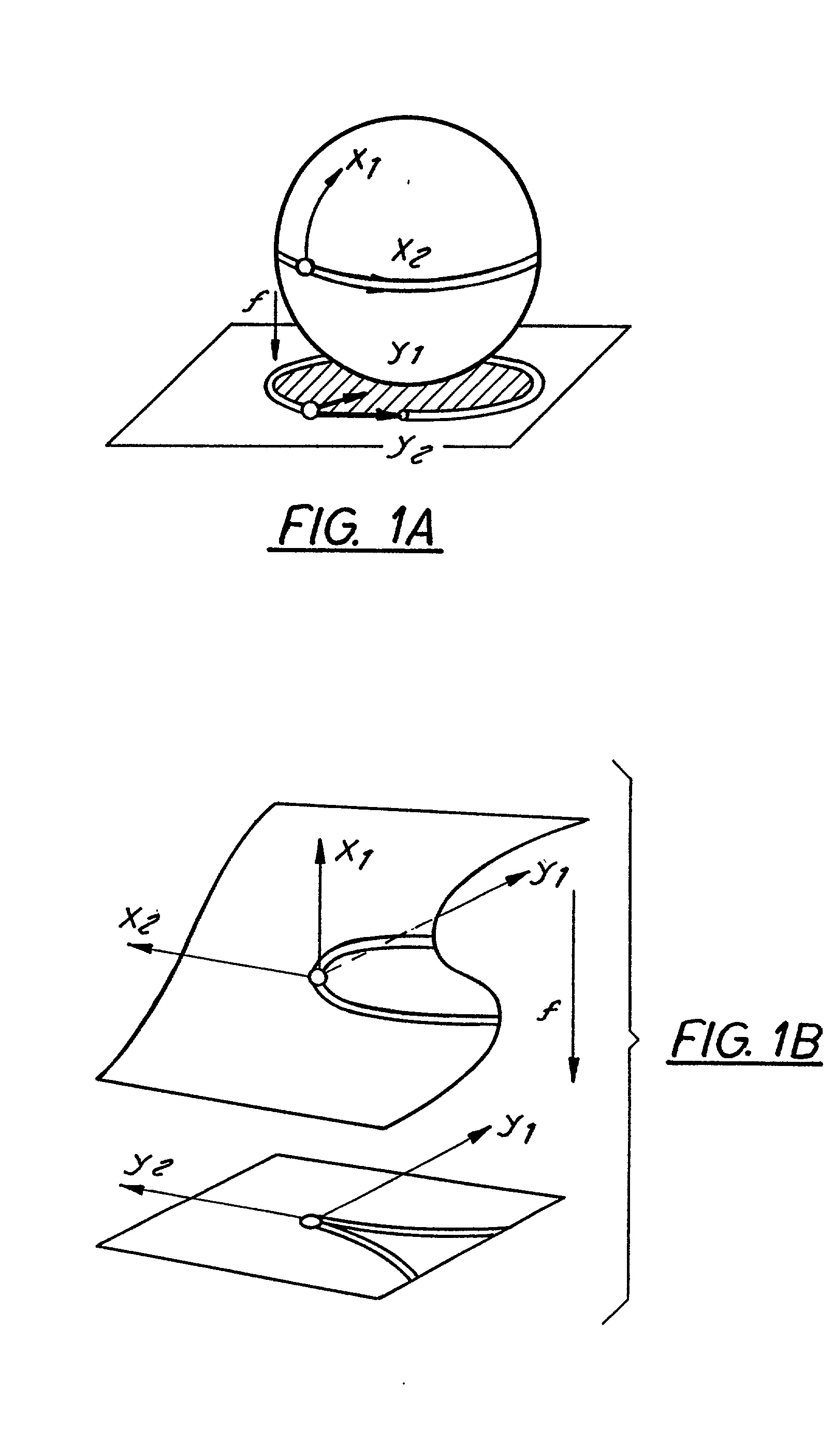
Methods and apparatuses for still image compression, video compression and automatic target recognition are disclosed. The method of still image compression uses isomorphic singular manifold projection whereby surfaces of objects having singular manifold representations are represented by best match canonical polynomials to arrive at a model representation. The model representation is compared with the original representation to arrive at a difference. If the difference exceeds a predetermined threshold, the difference data are saved and compressed using standard lossy compression. The coefficients from the best match polynomial together with the difference data, if any, are then compressed using lossless compression. The method of motion estimation for enhanced video compression sends I frames on an "as-needed" basis, based on comparing the error between segments of a current frame and a predicted frame. If the error exceeds a predetermined threshold, which can be based on program content, the next frame sent will be an I frame. The method of automatic target recognition (ATR) including tracking, zooming, and image enhancement, uses isomorphic singular manifold projection to separate texture and sculpture portions of an image. Soft ATR is then used on the sculptured portion and hard ATR is used on the texture portion.
Owner:PHYSICAL OPTICS CORP
Semiconductor device analyzer, method for analyzing/manufacturing semiconductor device, and storage medium storing program for analyzing semiconductor device
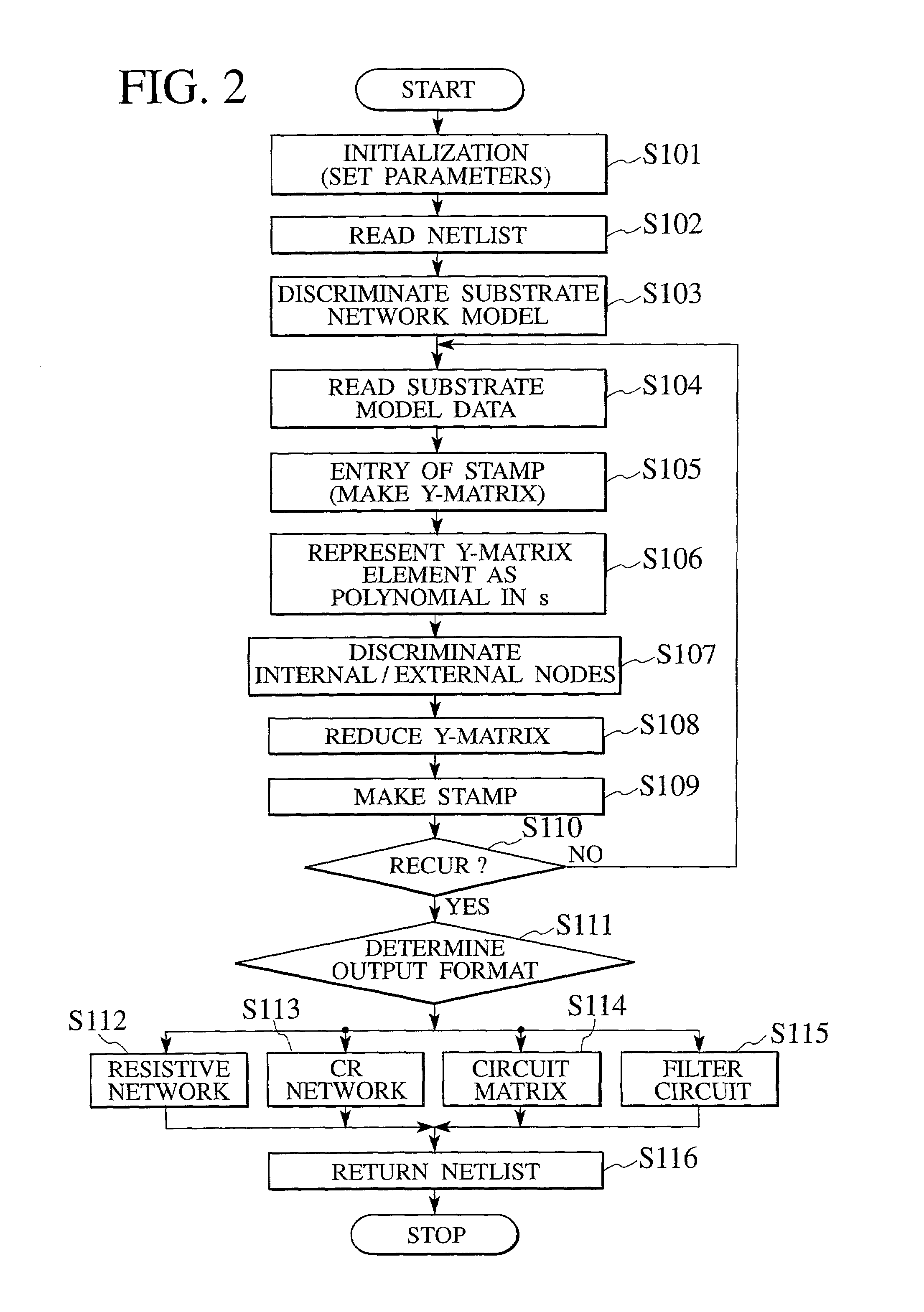
InactiveUS20010029601A1Efficiently and correctly analyzingEfficiently influence of parasiticAnalog circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareCapacitanceSubstrate network
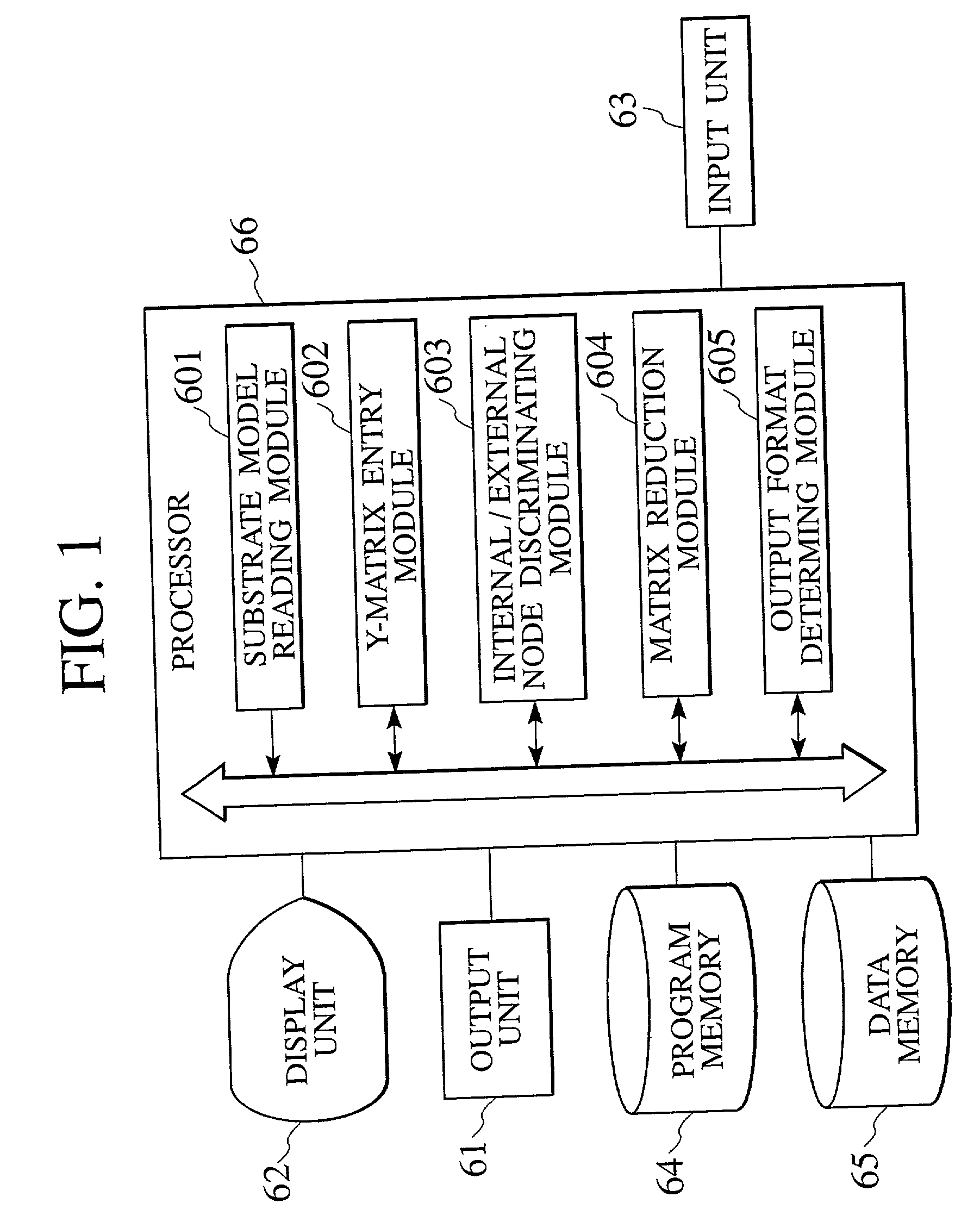
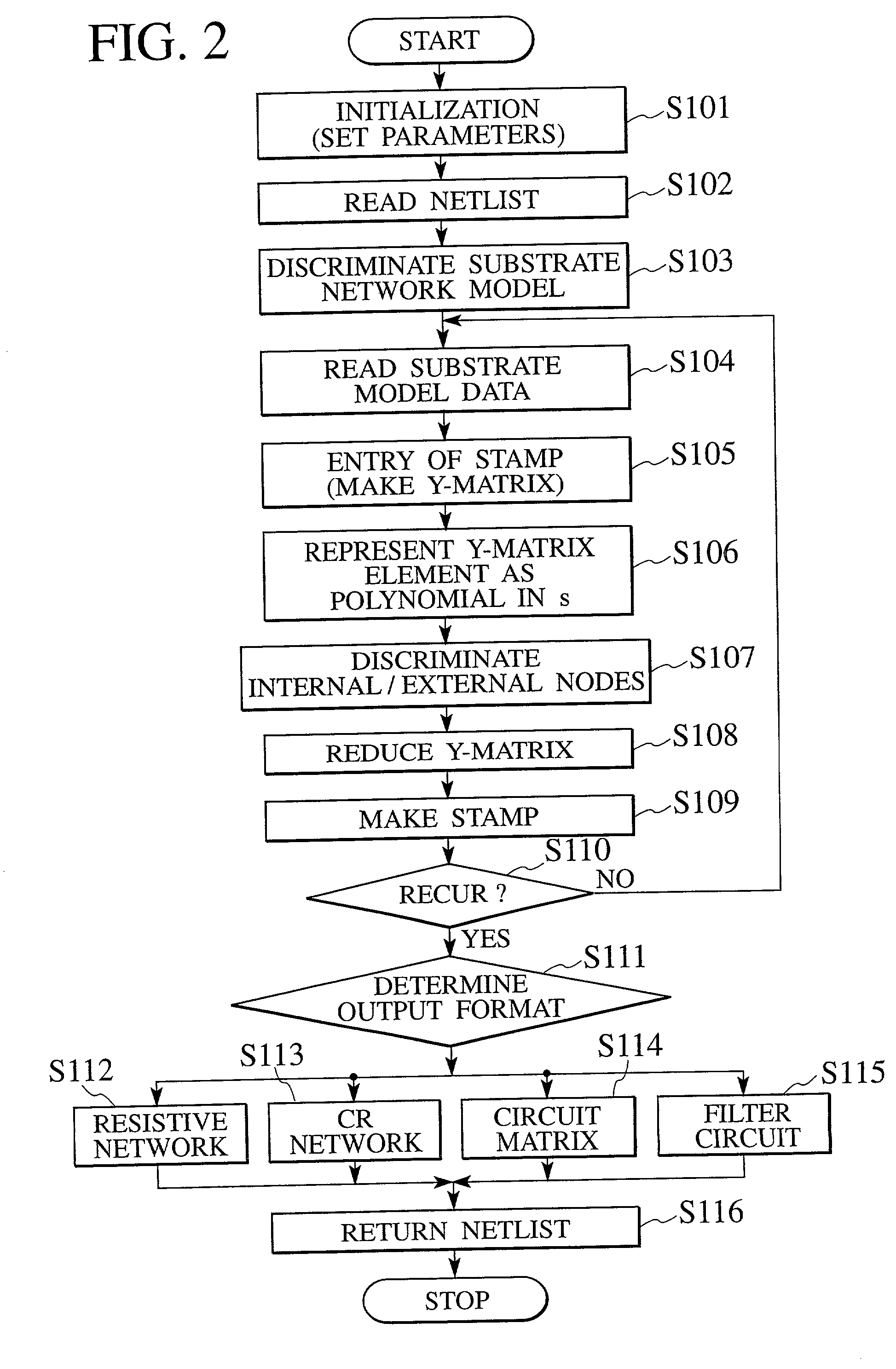
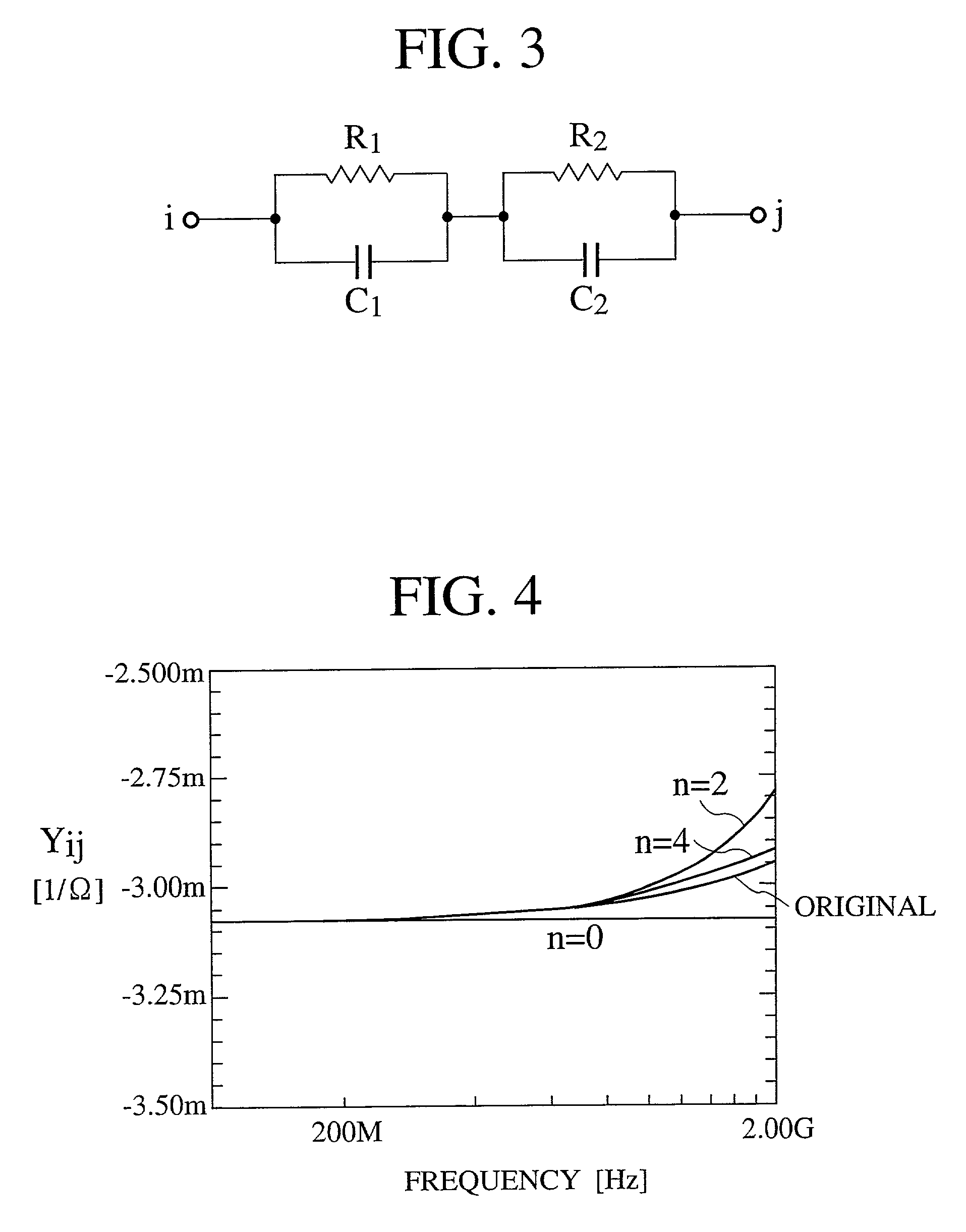
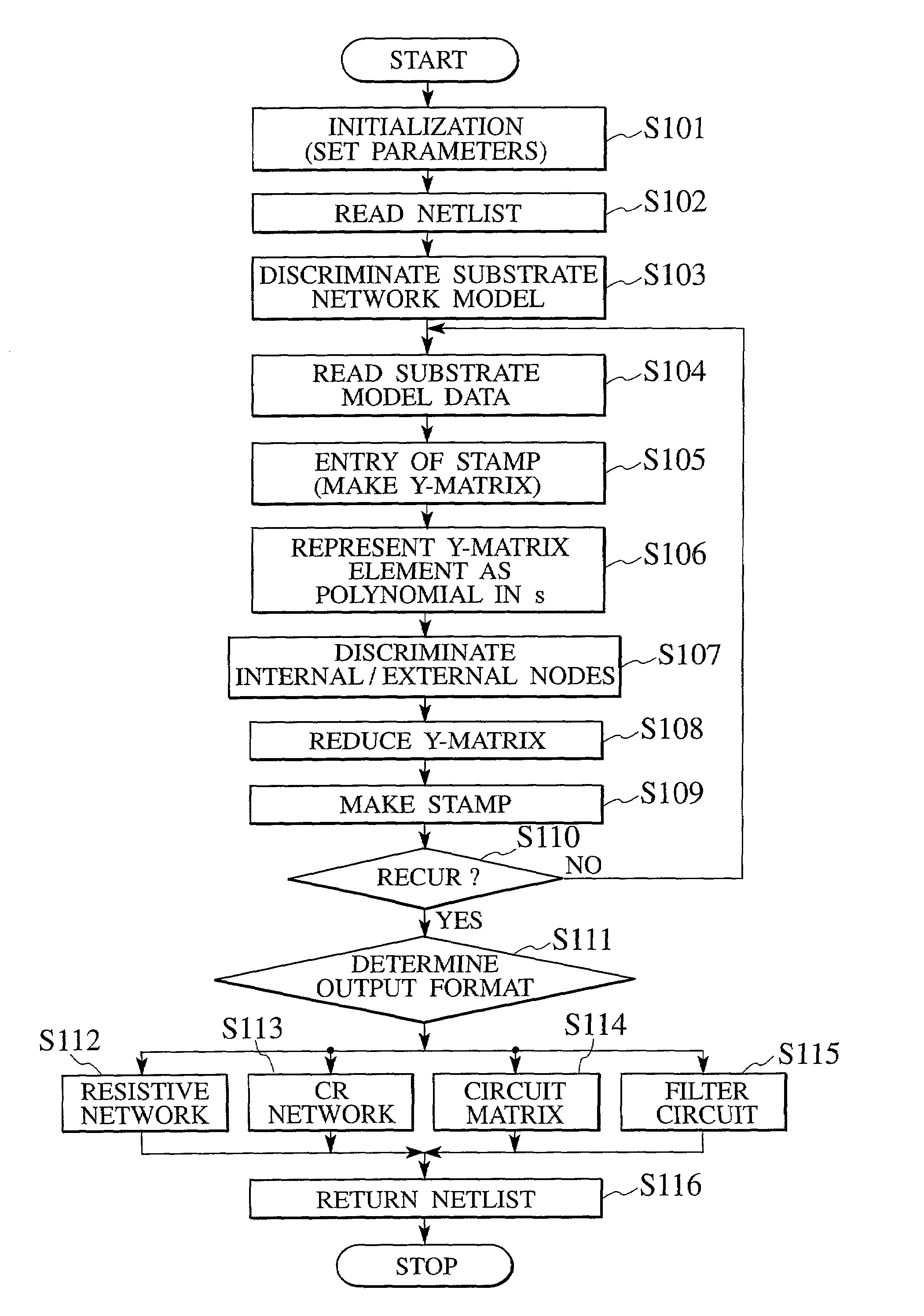
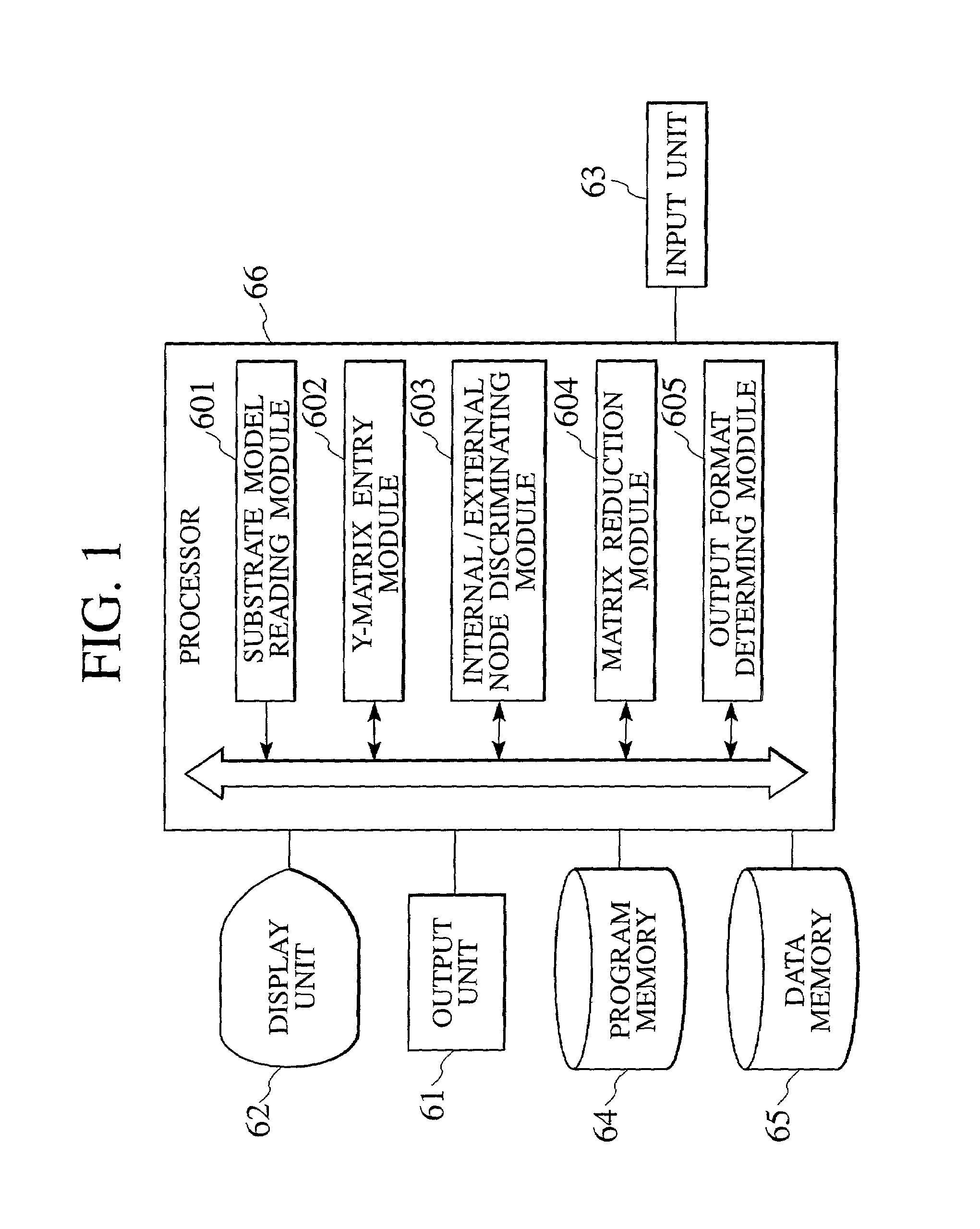
A semiconductor device analyzer has a substrate model reading module, a Y-matrix entry module, a discriminating module, a matrix reduction module, and an output format discriminating module. The substrate model reading module reads a substrate network model of three-dimensional meshes representing the substrate of a semiconductor device. The substrate network model is a network of resistive and capacitive elements and is used for the simulation and analysis of the semiconductor substrate. The Y-matrix entry module prepares a Y-matrix from the substrate network model, each element of the Y-matrix being expressed with a polynomial of differential operator "s". The discriminating module discriminates internal nodes to be eliminated from external nodes to be left among the nodes of the substrate network model. The matrix reduction module eliminates the internal nodes, thereby reducing the Y-matrix. The output format determining module determines an output format for an operation result.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor device analyzer, method for analyzing/manufacturing semiconductor device, and storage medium storing program for analyzing semiconductor device
InactiveUS7016820B2Efficient analysisExpand the scale of operationAnalog circuit testingDetecting faulty computer hardwareCapacitanceSubstrate network
A semiconductor device analyzer has a substrate model reading module, a Y-matrix entry module, a discriminating module, a matrix reduction module, and an output format discriminating module. The substrate model reading module reads a substrate network model of three-dimensional meshes representing the substrate of a semiconductor device. The substrate network model is a network of resistive and capacitive elements and is used for the simulation and analysis of the semiconductor substrate. The Y-matrix entry module prepares a Y-matrix from the substrate network model, each element of the Y-matrix being expressed with a polynomial of differential operator “s”. The discriminating module discriminates internal nodes to be eliminated from external nodes to be left among the nodes of the substrate network model. The matrix reduction module eliminates the internal nodes, thereby reducing the Y-matrix. The output format determining module determines an output format for an operation result.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
System and method for representing a general two dimensional spatial transformation
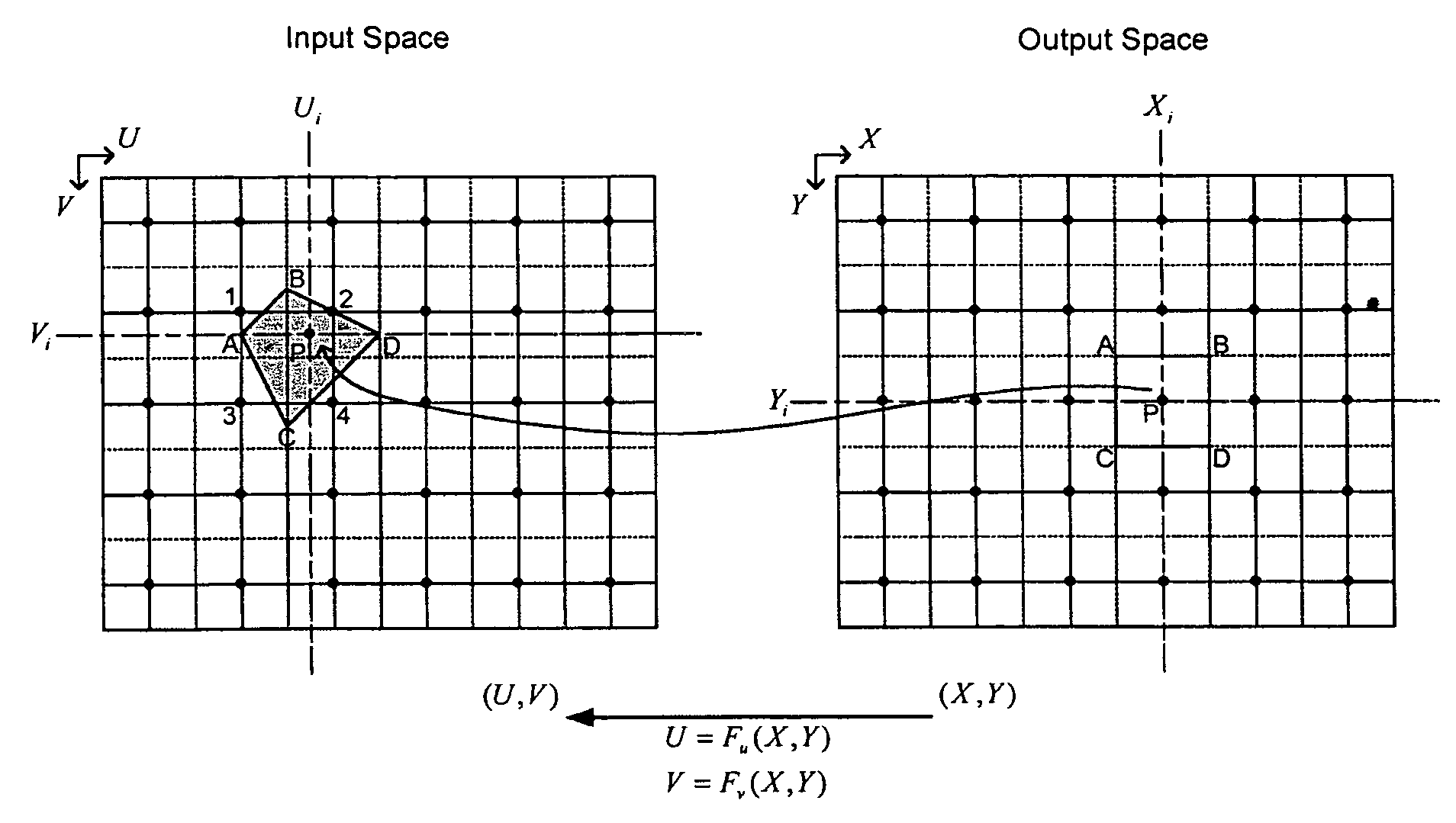
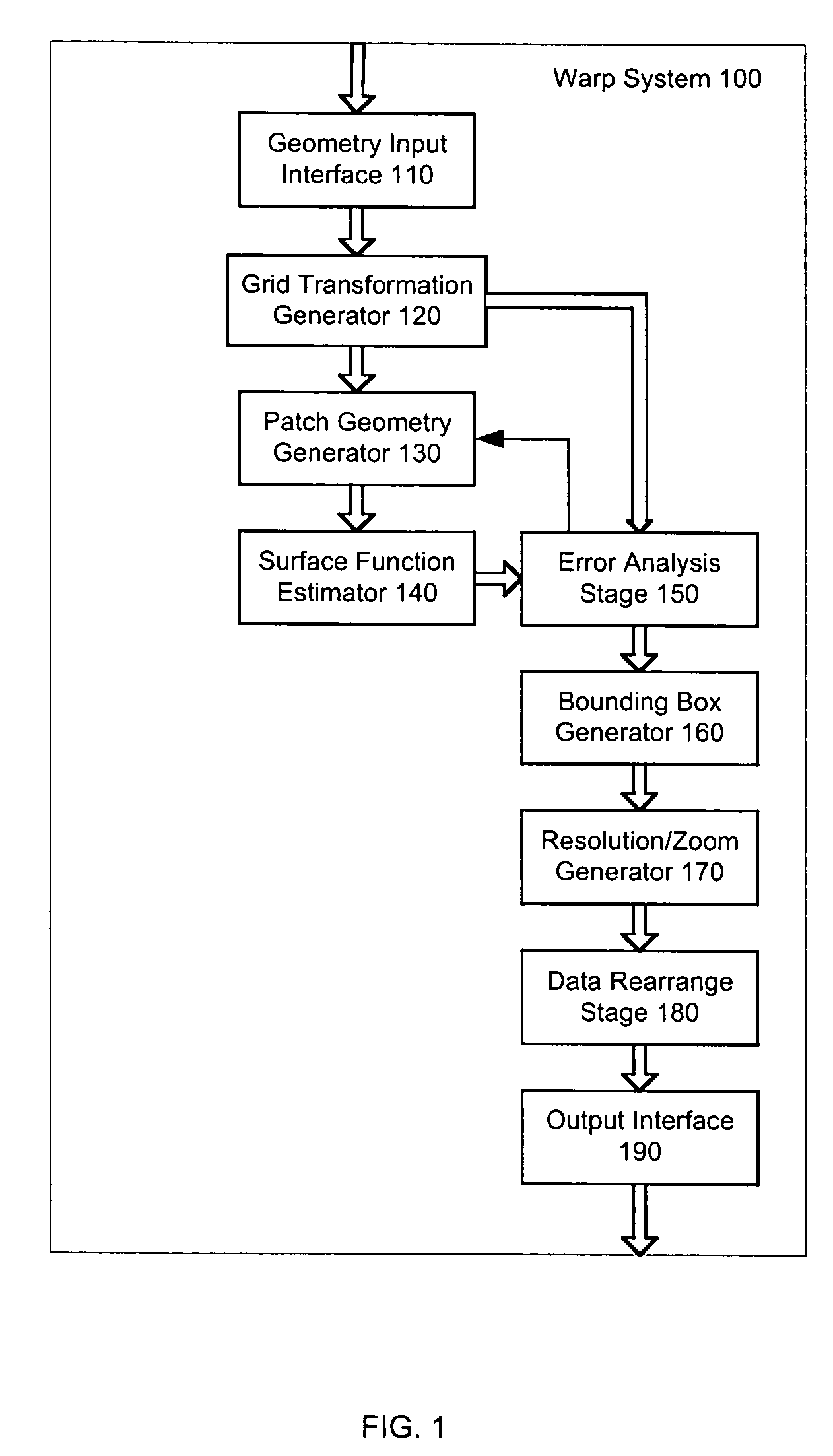
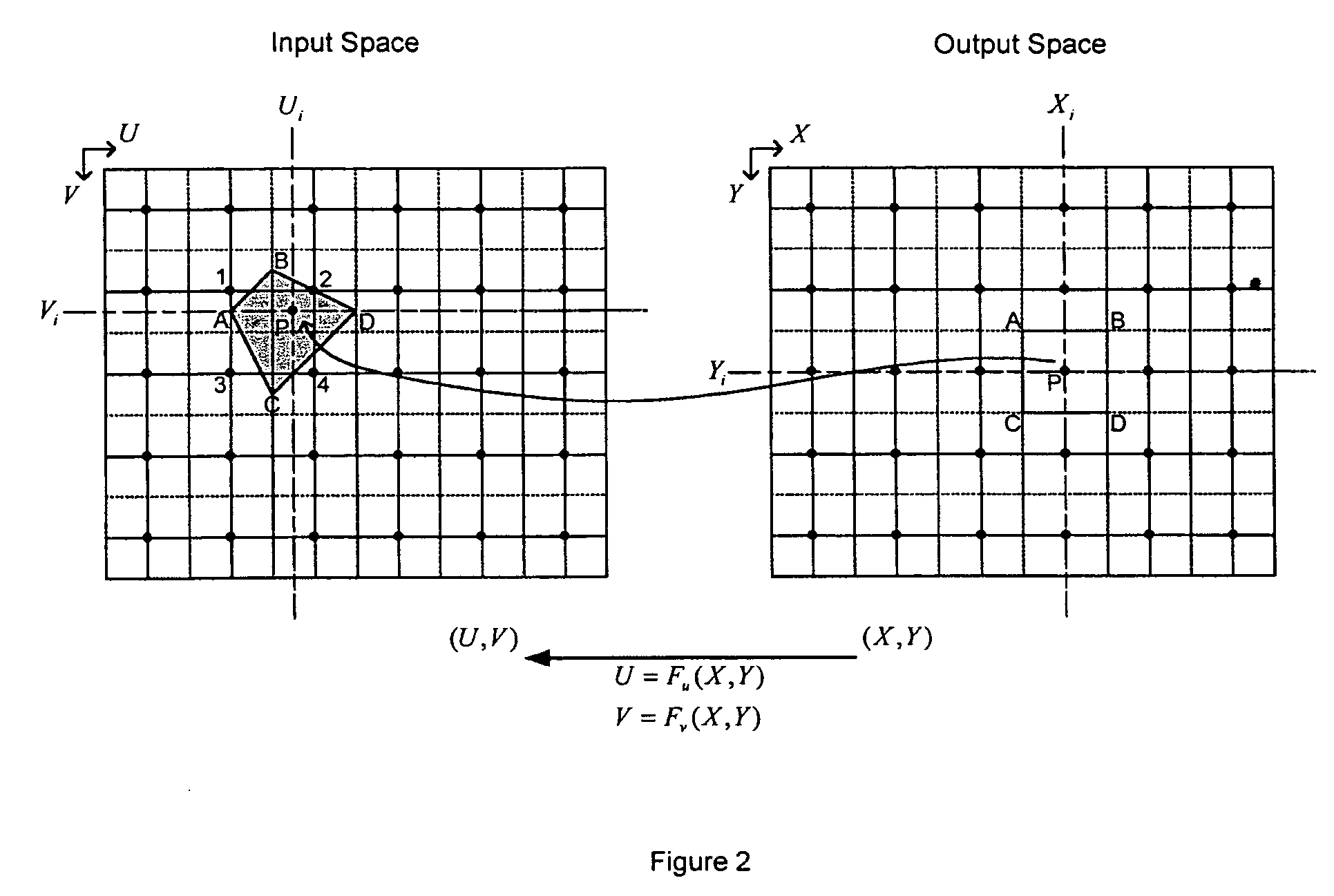
ActiveUS7324706B2Geometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionData setSpatial transformation
A system and method for representing a two-dimensional spatial transformation that describes the transformation by an inverse mapped grid data set. The grid data for each coordinate is surface fitted on an array of rectangular patches defined in the output space using numerical techniques. Error analysis determines whether a finer mesh resolution is required for surface fitting. The spatial transformation is then defined by the array of rectangular surface patches and the set of surface coefficients such that the spatial transformation can be executed through evaluation of the surface polynomials. The two-dimensional surface polynomial representation allows the transformation to be easily adjusted for scale changes and zooming and panning effects.
Owner:GEO SEMICONDUCTOR INC
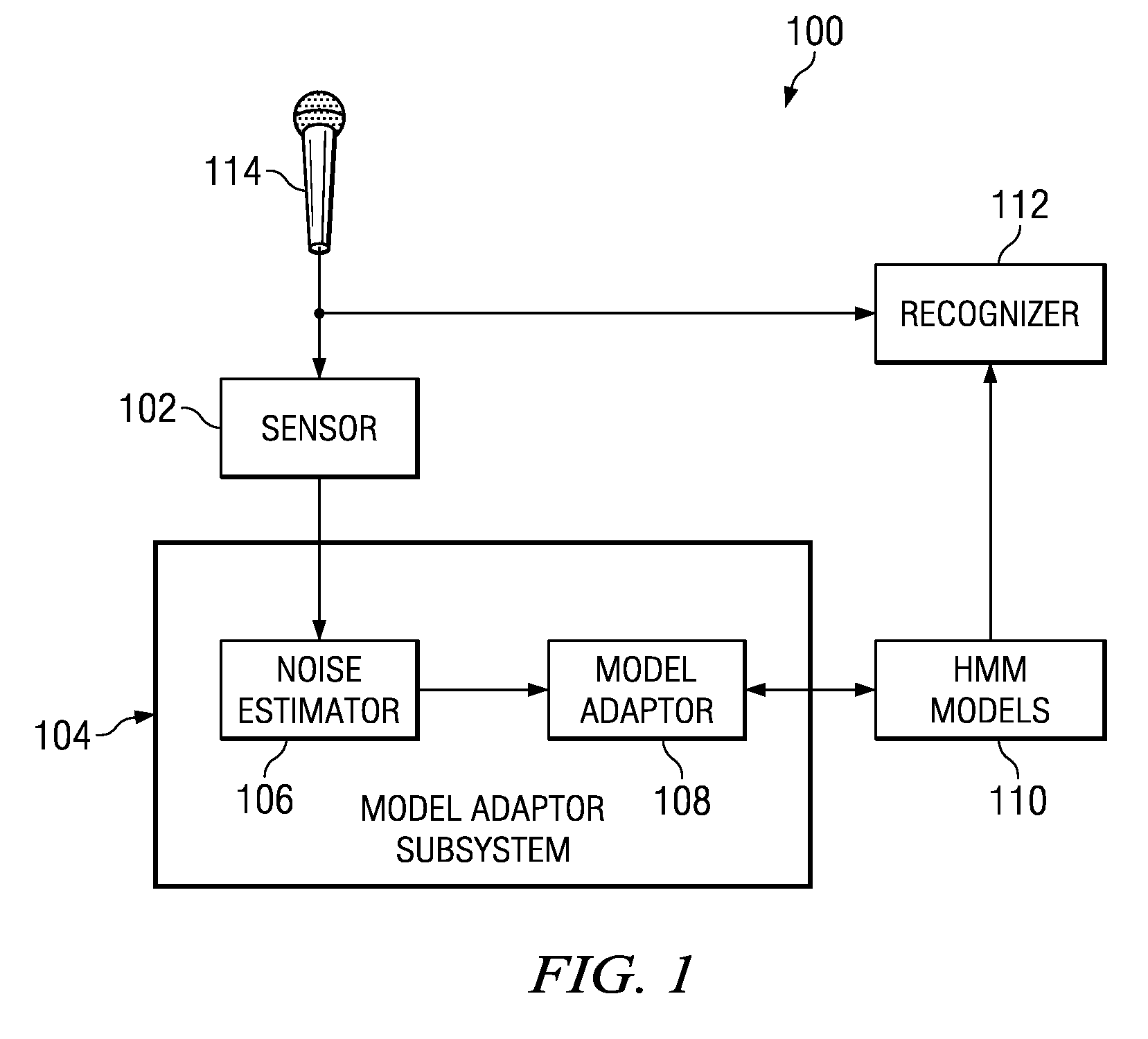
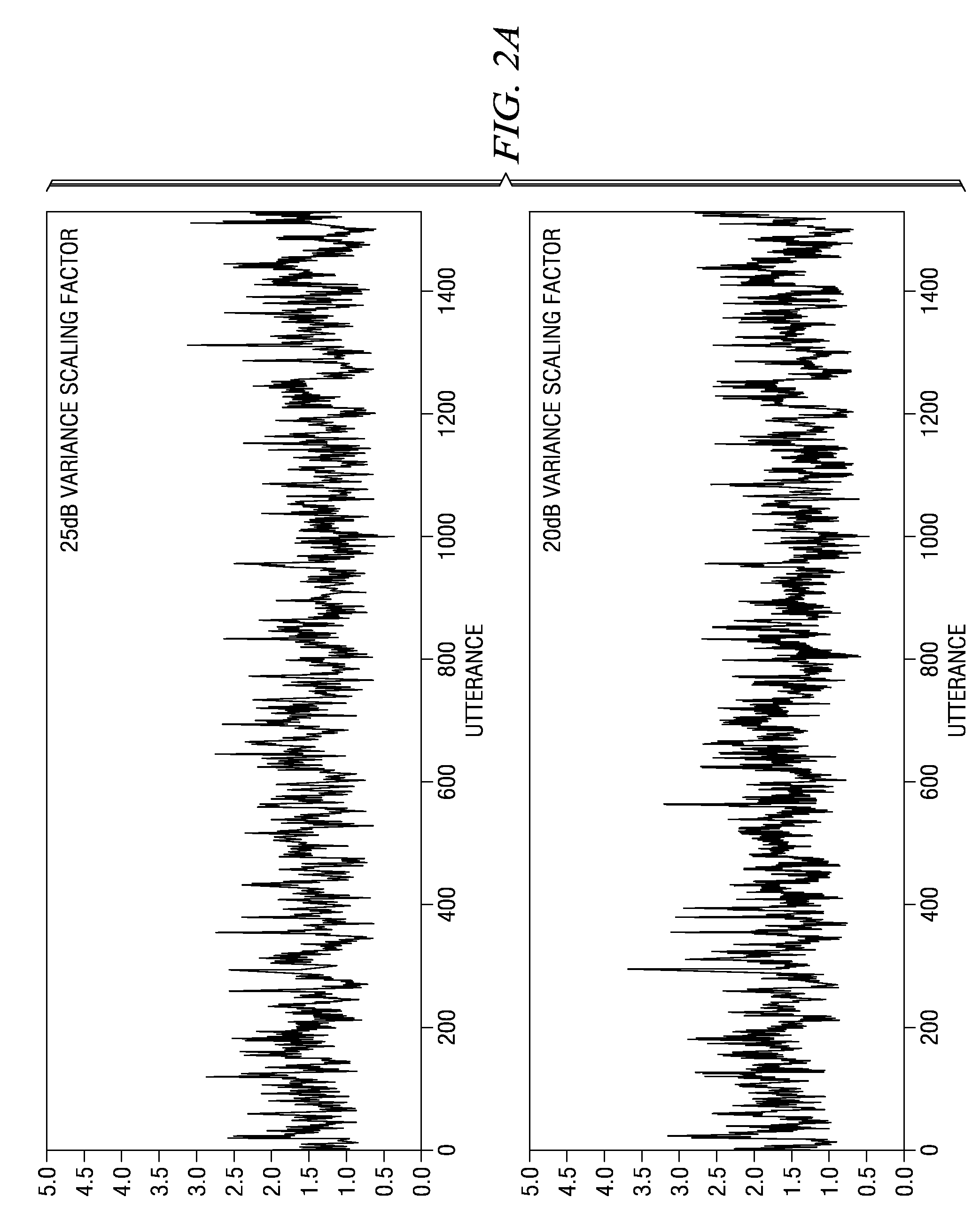
Weighted sequential variance adaptation with prior knowledge for noise robust speech recognition
A method for adapting acoustic models used for automatic speech recognition is provided. The method includes estimating noise in a portion of a speech signal, determining a first estimated variance scaling vector using an estimated 2-order polynomial and the noise estimation, wherein the estimated 2-order polynomial represents a priori knowledge of a dependency of a variance scaling vector on noise, determining a second estimated variance scaling vector using statistics from prior portions of the speech signal, determining a variance scaling factor using the first estimated variance scaling vector and the second estimated variance scaling vector, and using the variance scaling factor to adapt an acoustic model.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
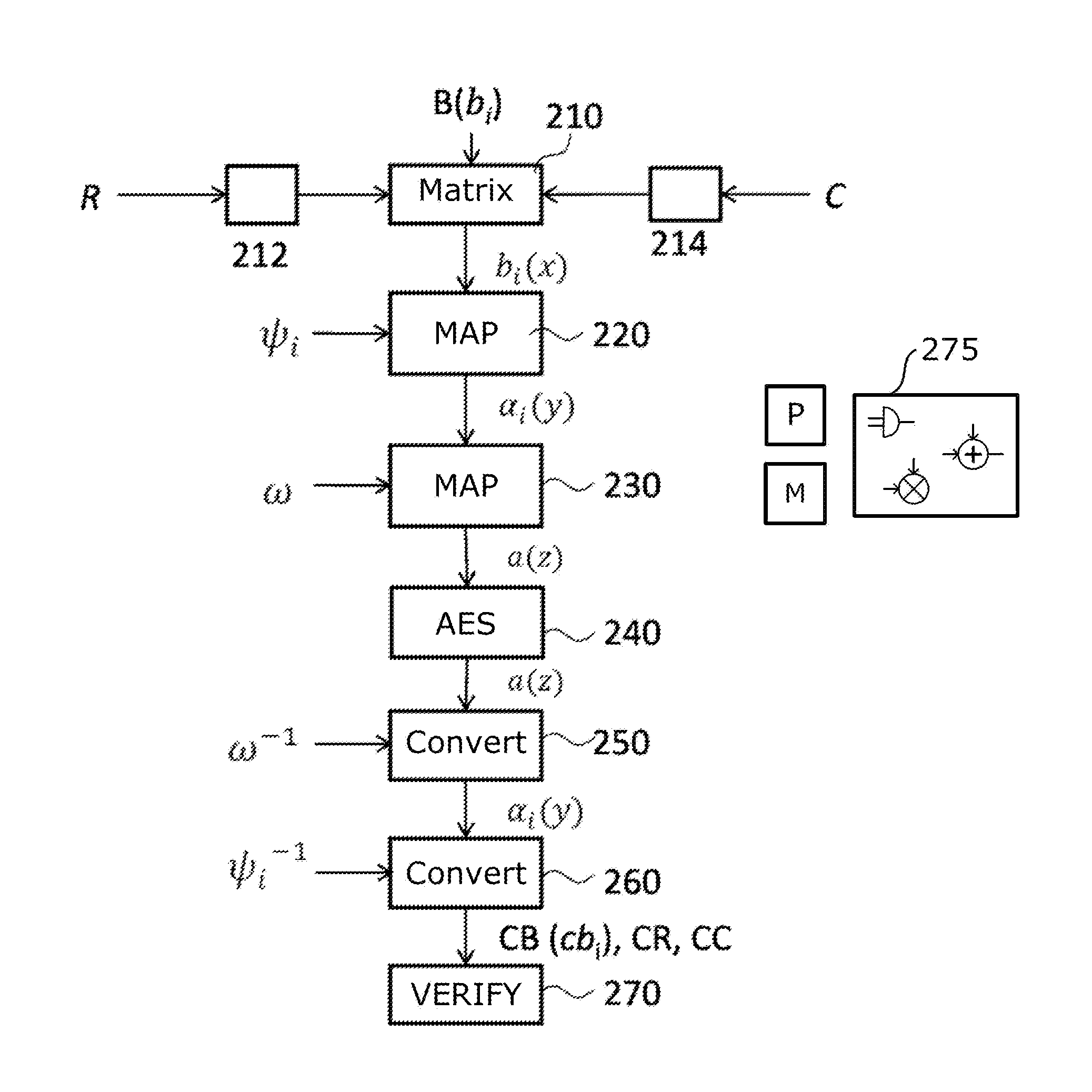
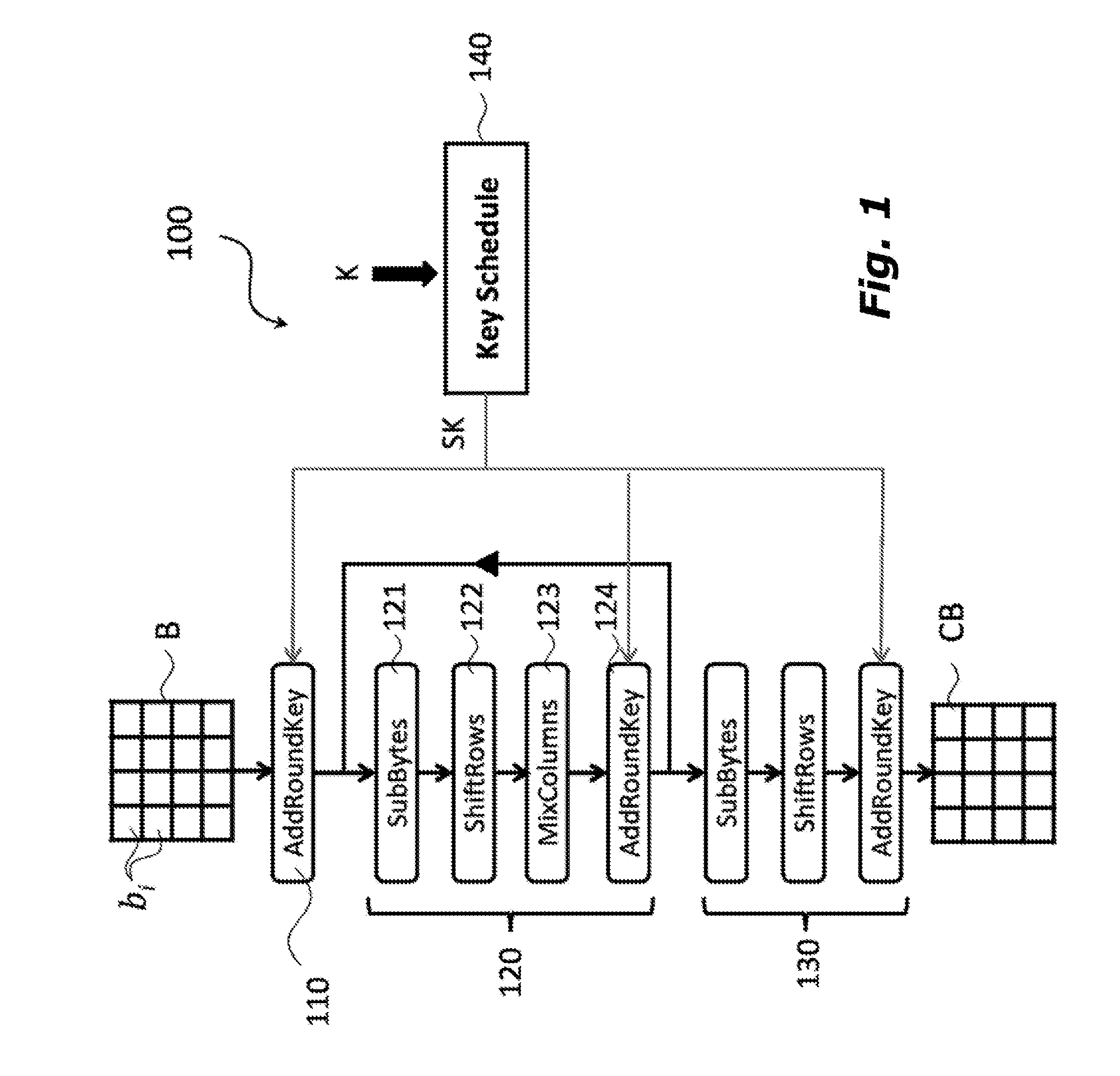
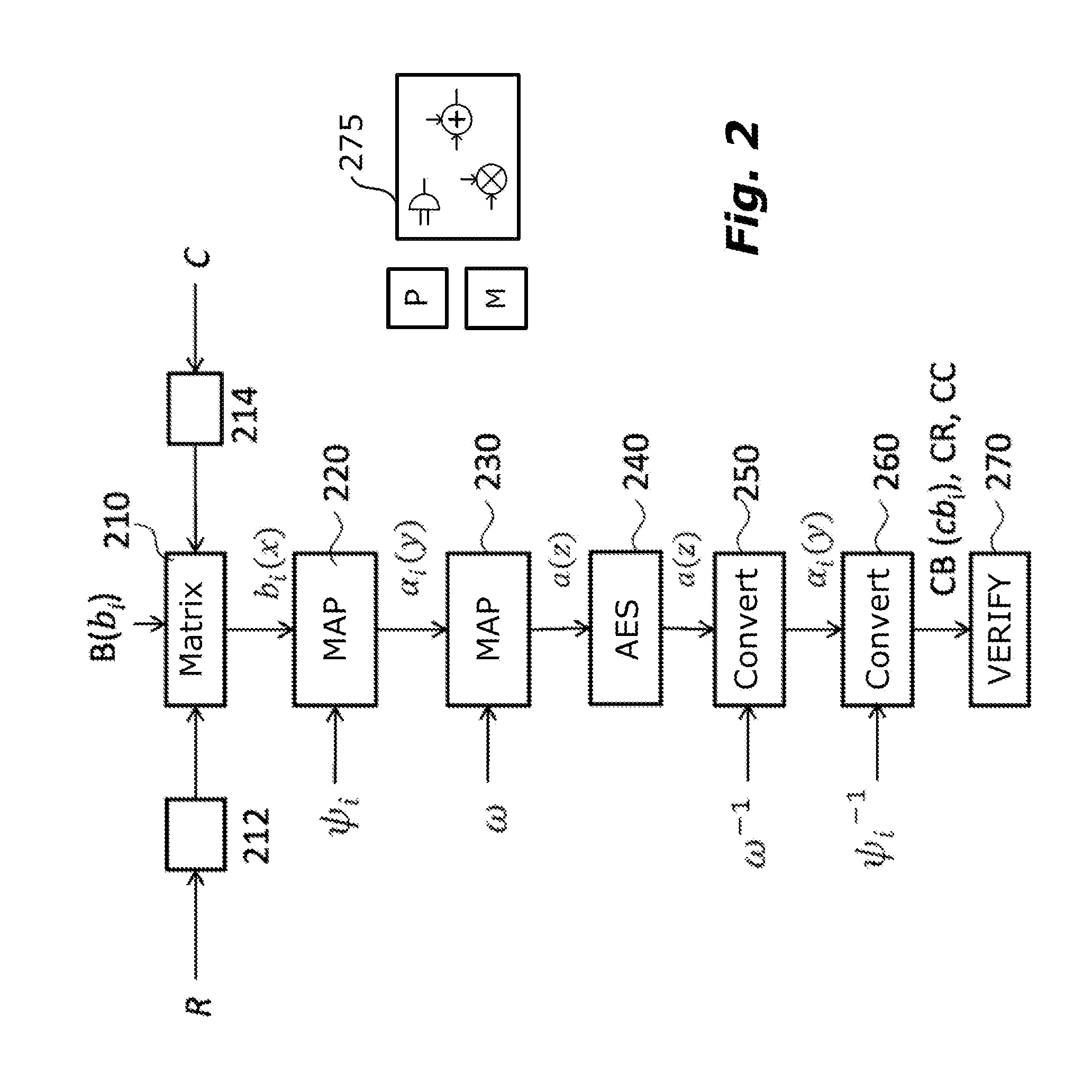
Method for performing an encryption of an aes type, and corresponding system and computer program product
ActiveUS20150270967A1Improve securityMultiple keys/algorithms usagePublic key for secure communicationChinese remainder theoremTheoretical computer science
A polynomial representation (bi(x)) in an AES finite field(Z2[x](r(x)))of input bytes (bi) of a state matrix (B) is obtained. A plurality (1) of irreducible polynomials (fi(y)) and a moving map (ψi) are used to map each polynomial (bi(x)) of the polynomial representation into a respective field of polynomials(Z2[y](fi(y)))computed with respect to one of the irreducible polynomials (fi(y)), to obtain respective moved polynomials (αi(y)). The moved polynomials (αi(y)) are mapped into a polynomial (a(z)) of a polynomial ring(Z2[z](p(z))),obtained by applying an isomorphism (ω) between the fields of polynomials(Z2[y](fi(y)))and the polynomial ring(Z2[z](p(z)))based upon the Chinese remainder theorem (CRT). AES encryption is applied to the polynomial (a(z)). The polynomial (a(z)) is reconverted into the AES finite field(Z2[x](r(x)))to obtain an encrypted state matrix (CB).
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
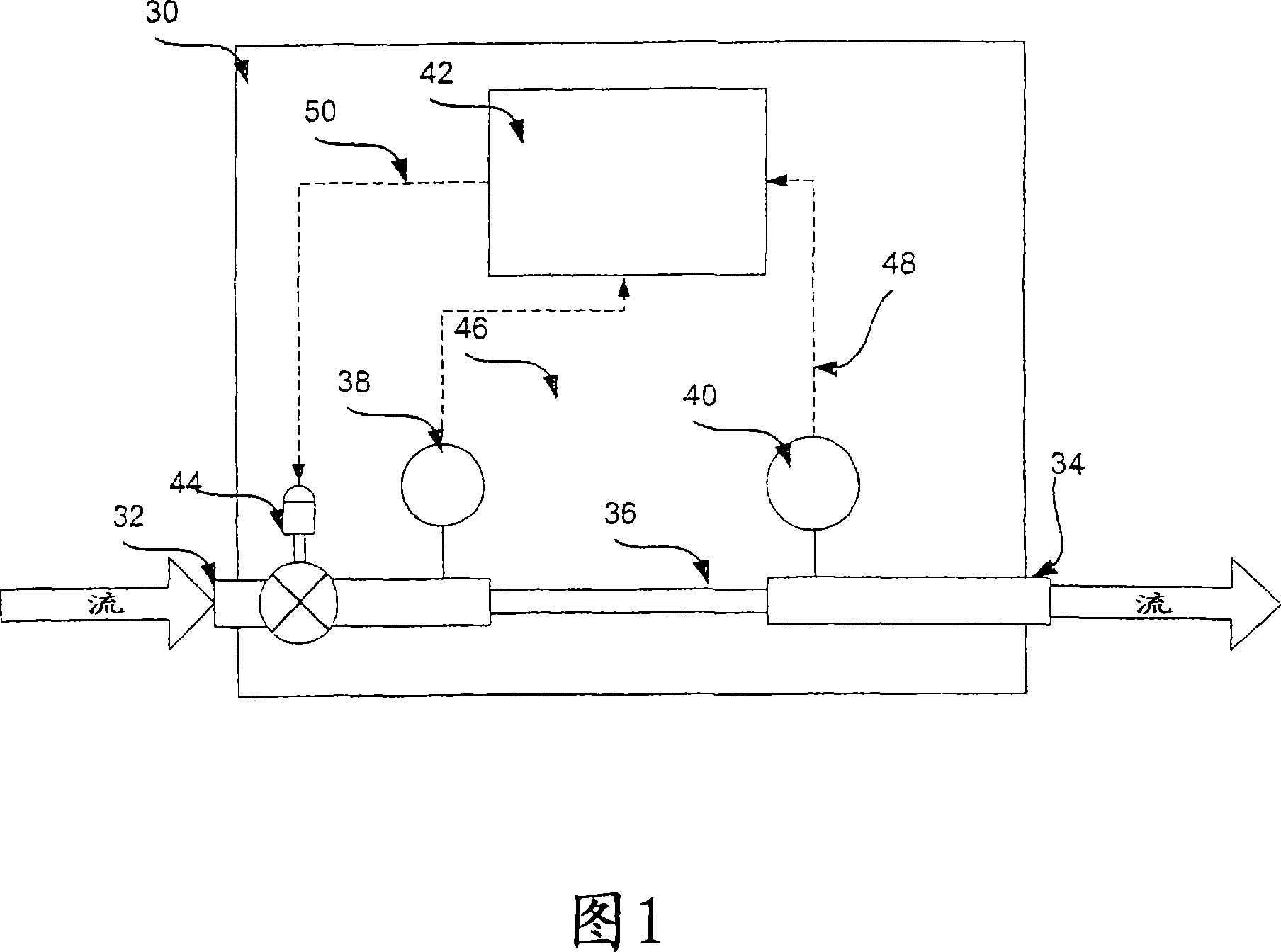
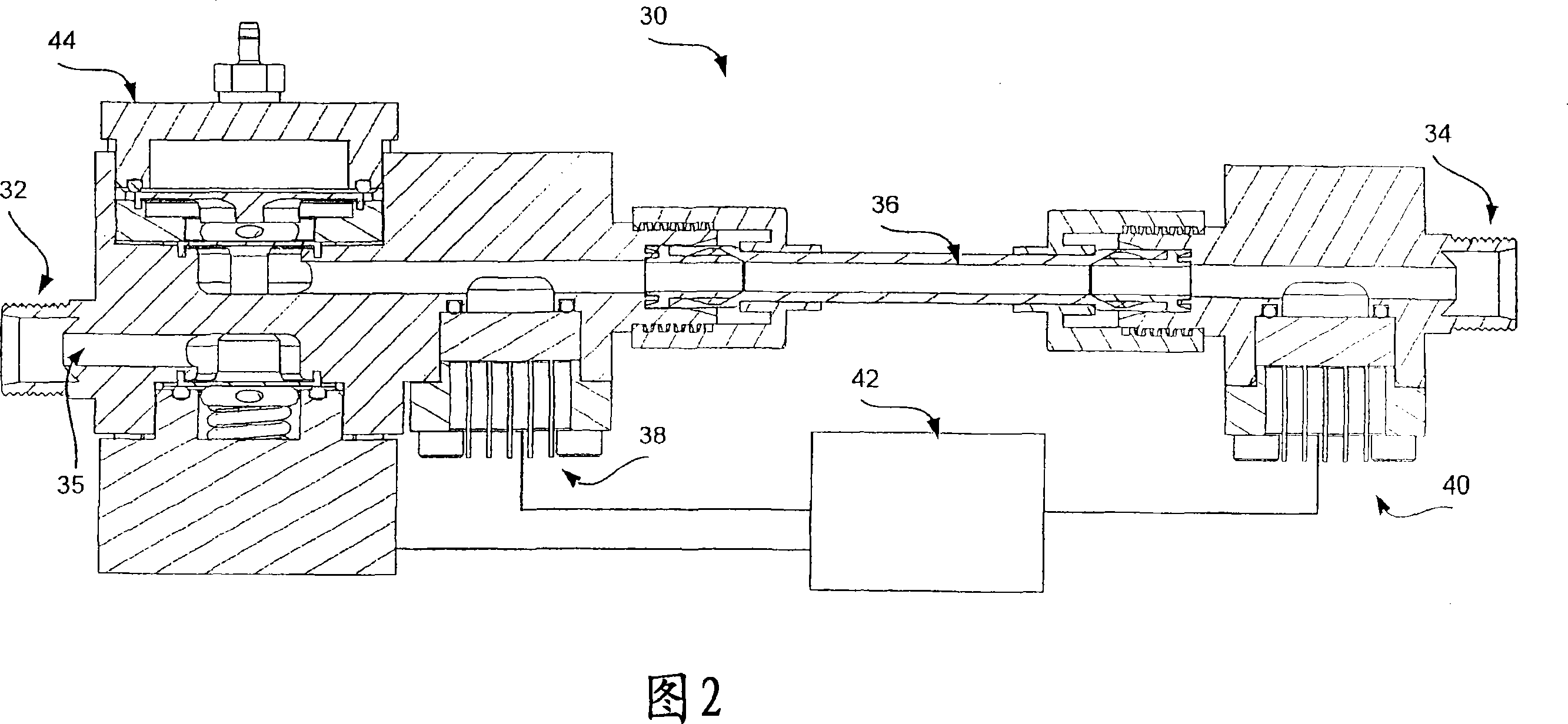
System and method for calibration of a flow device
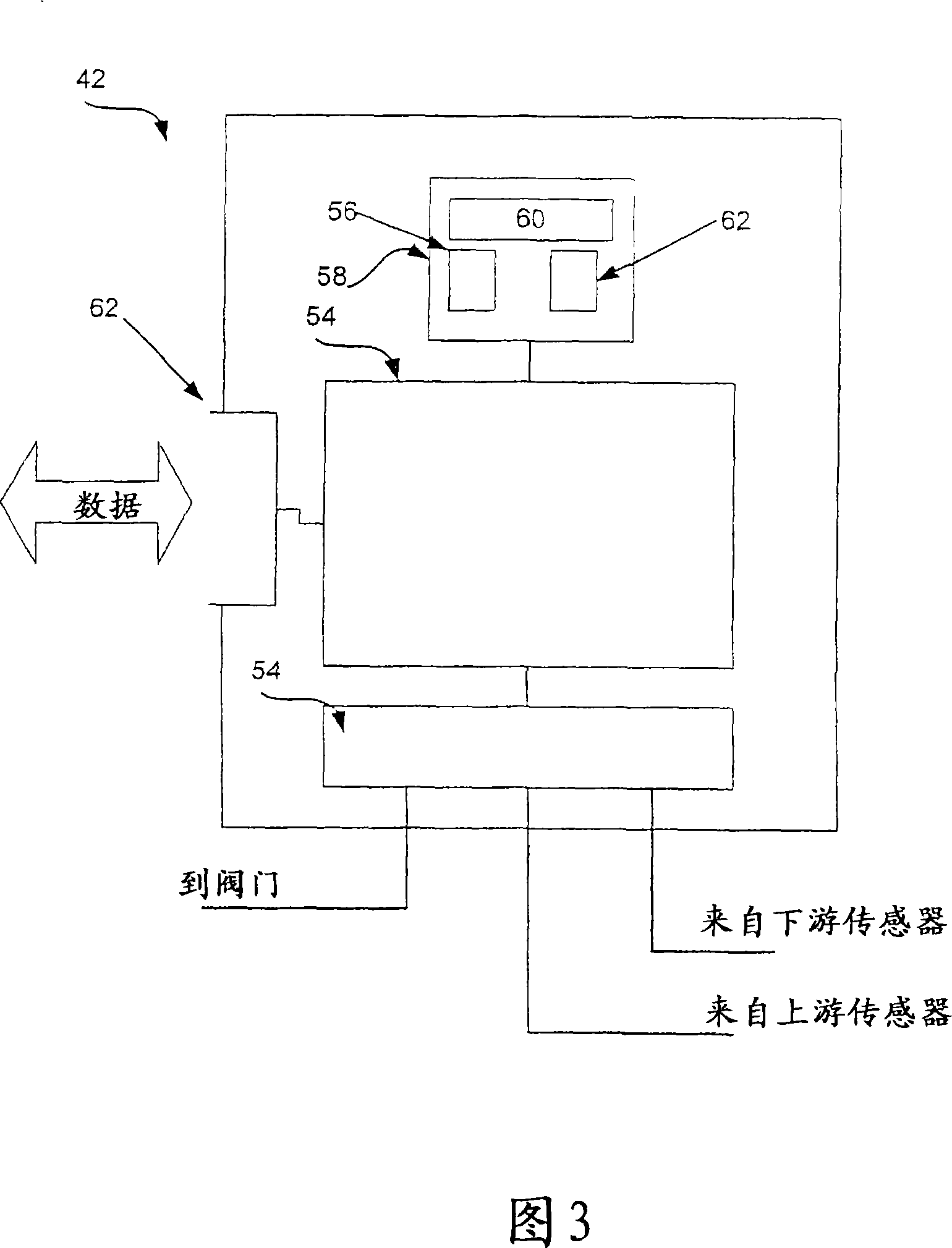
Embodiments of the present invention provide a system (200) and method for rapid calibration of a flow device (30). A flow device can be provided with a calibration flow curve (e.g., represented by an n G01F 25 / 00 G05B 15 / 00 16 25 10 2005 / 8 / 12 101048645 2007 / 10 / 3 000000000 Entegris Inc. United Laverdiere Marc Mcloughlin Robert Niermeyer J. Karl dujuan 11038 The Patent Agency of the Chinese Council for the Promotion of International Trade (CCPIT) No.1 Waidajie, Fuxingmen, Beijing 100086 United 2004 / 8 / 13 60 / 601,424 2007 / 3 / 23 PCT / US2005 / 028741 2005 / 8 / 12 WO2006 / 020870 2006 / 2 / 23 English
Owner:ENTEGRIS INC
Method for scalarly multiplying points on an elliptic curve
InactiveUS20090136025A1Optimal reduction attributesReduce weightPublic key for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsEllipsePolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checks
A method performs scalar multiplication of points on an elliptic curve by a finite expandable field K of a first field Fp of a p>3 characteristic, wherein said characteristic p has low Hamming weight and the expandable field has a polynomF(X)+Xd−2 of order d in the polynomial representation thereof.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
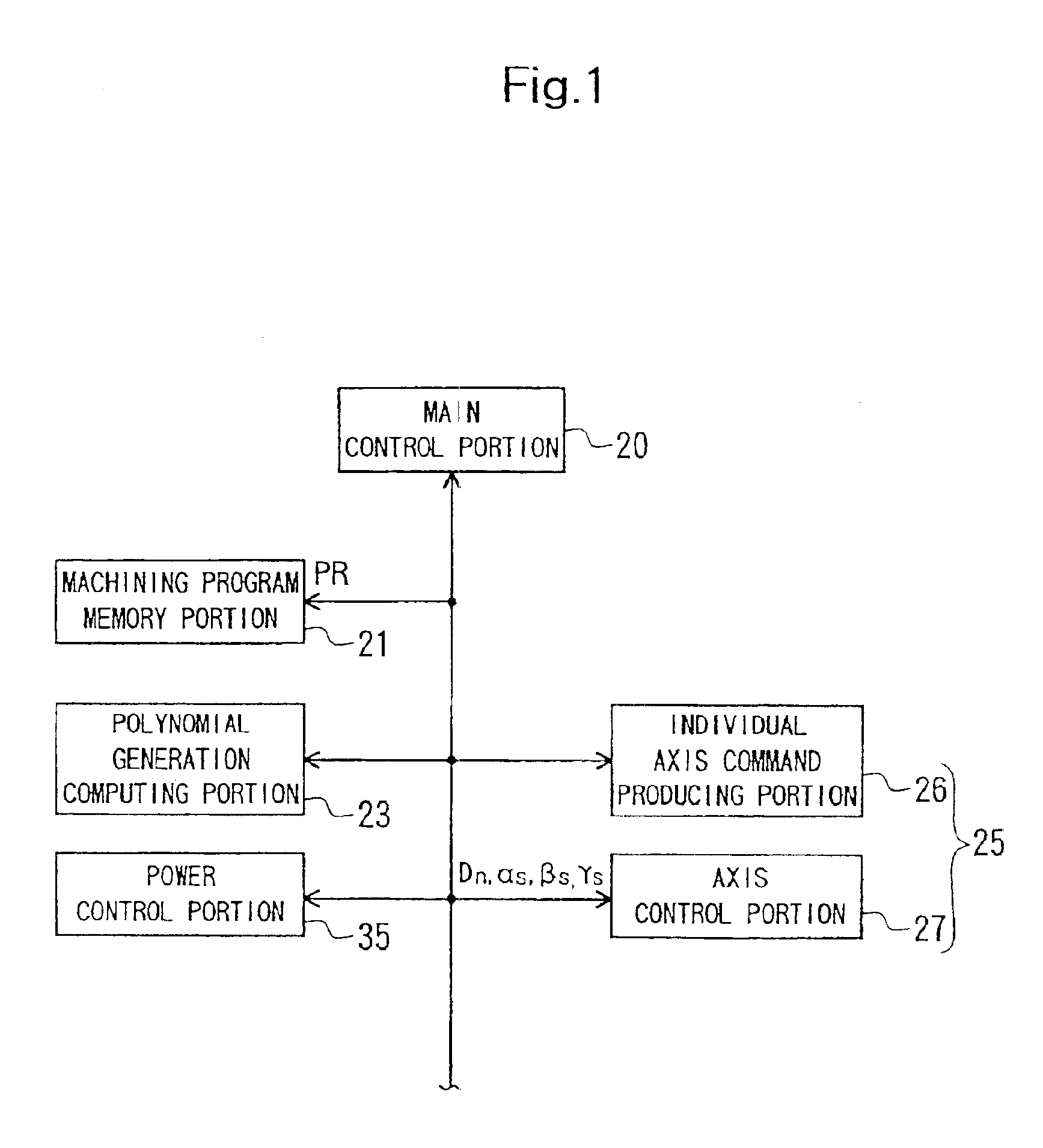
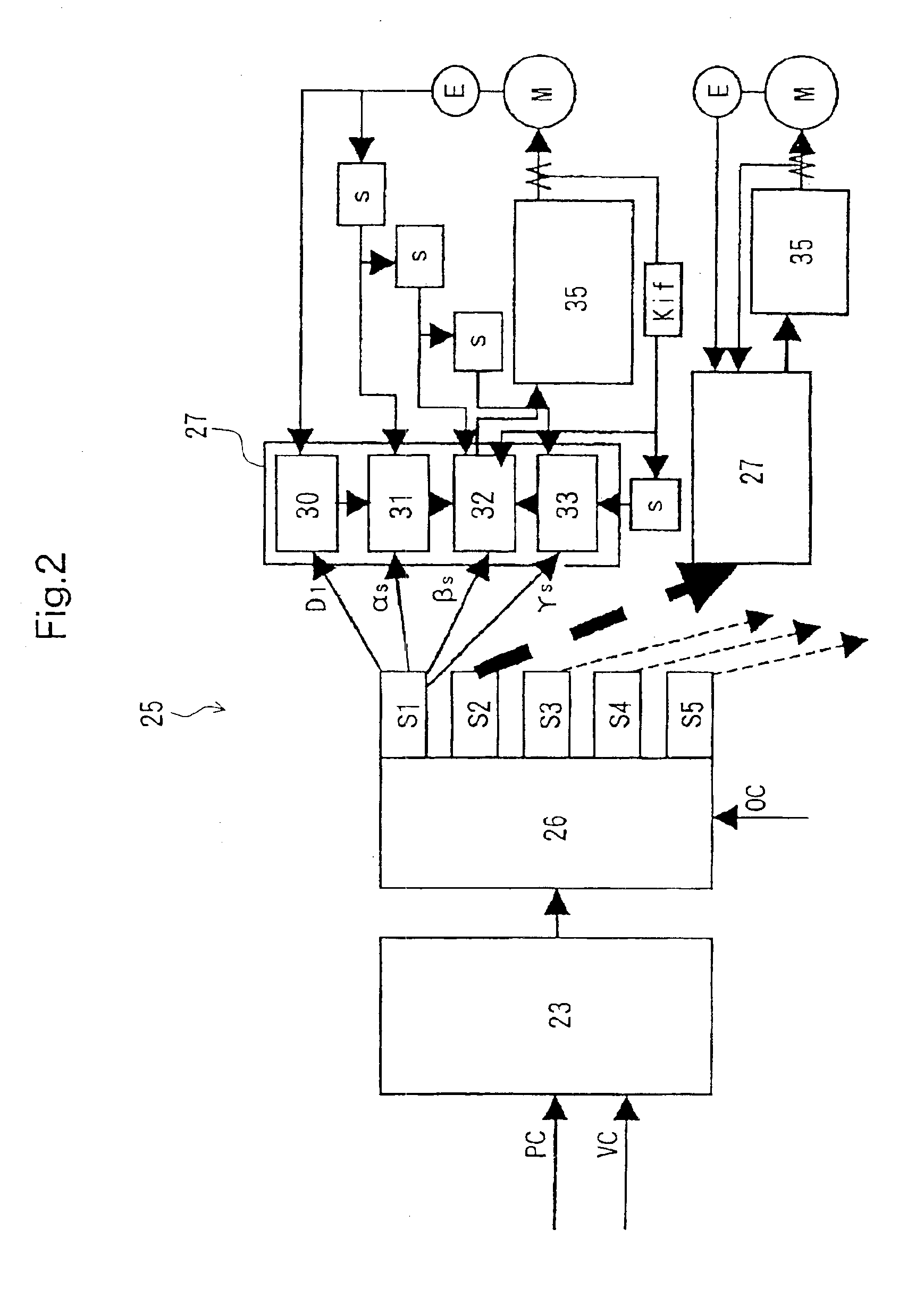
Numerically controlled method
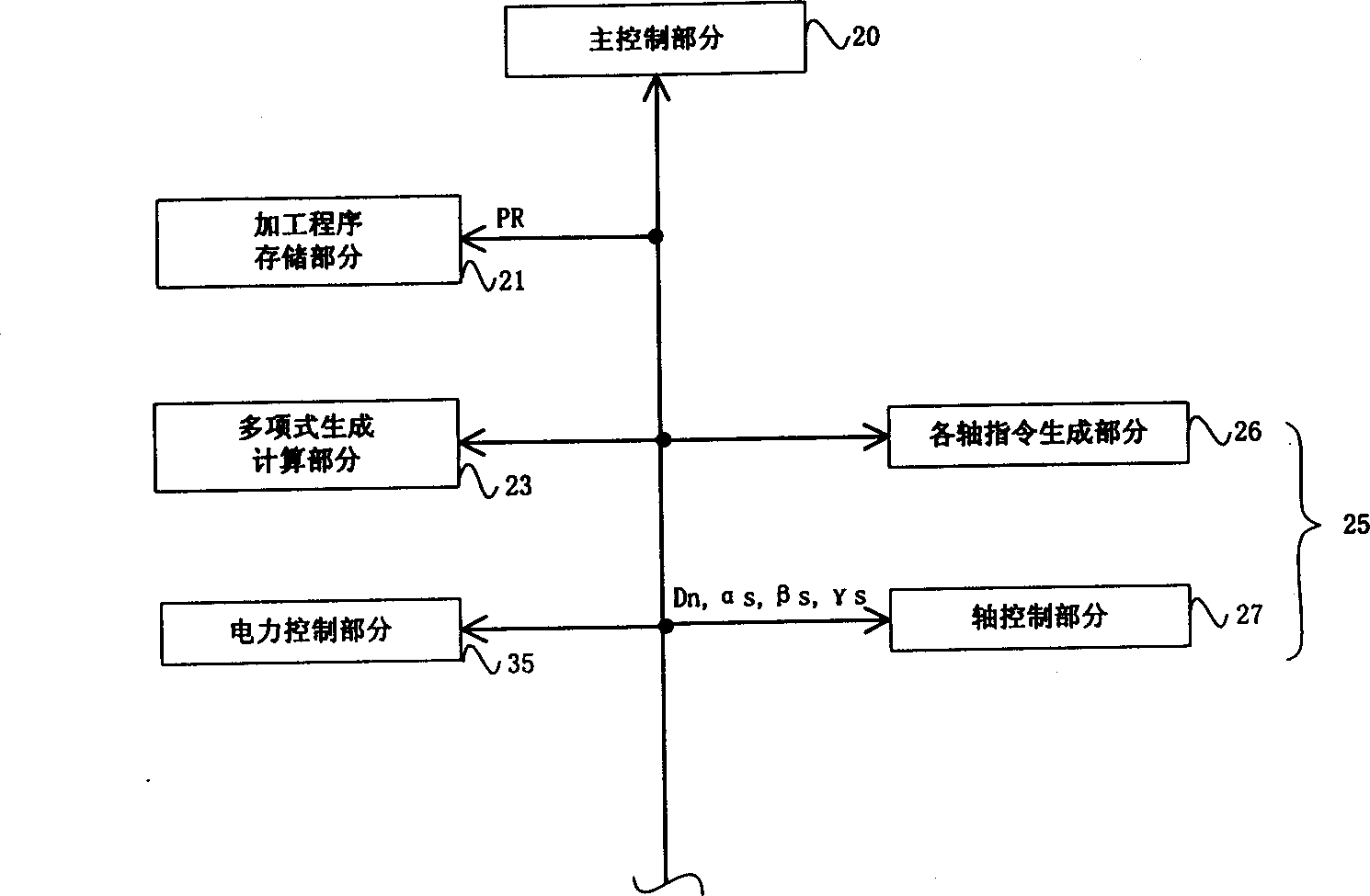
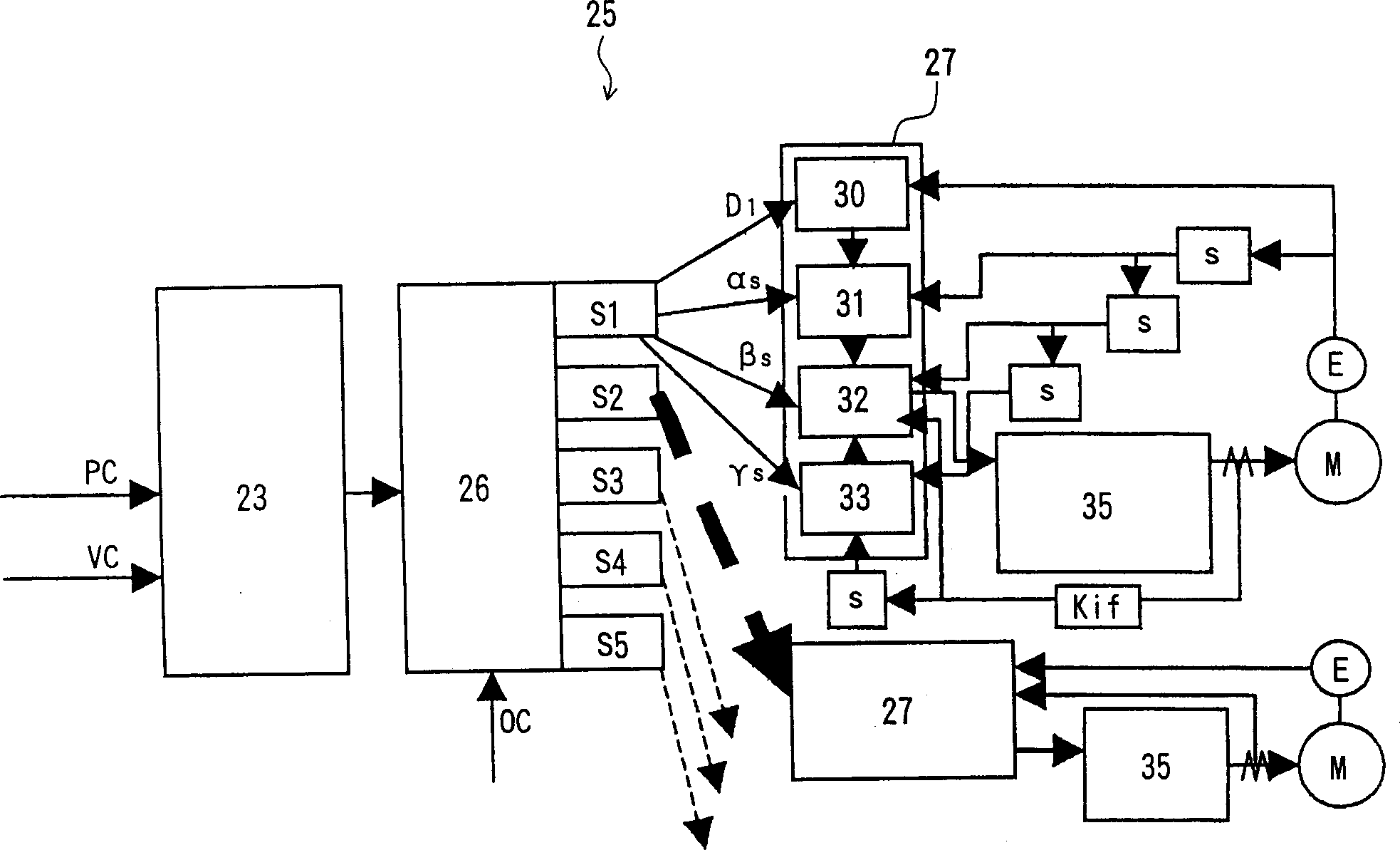
InactiveUS6922607B2Reduce irregularitiesReduce positioningComputer controlSimulator controlTime functionPolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checks
Owner:YAMAZAKI MAZAK KK
A method of geostationary satellite orbit uncertainty evolution based on differential algebra
ActiveCN109255096AReduce computing timeHigh precisionComplex mathematical operationsNatural satelliteDynamic models
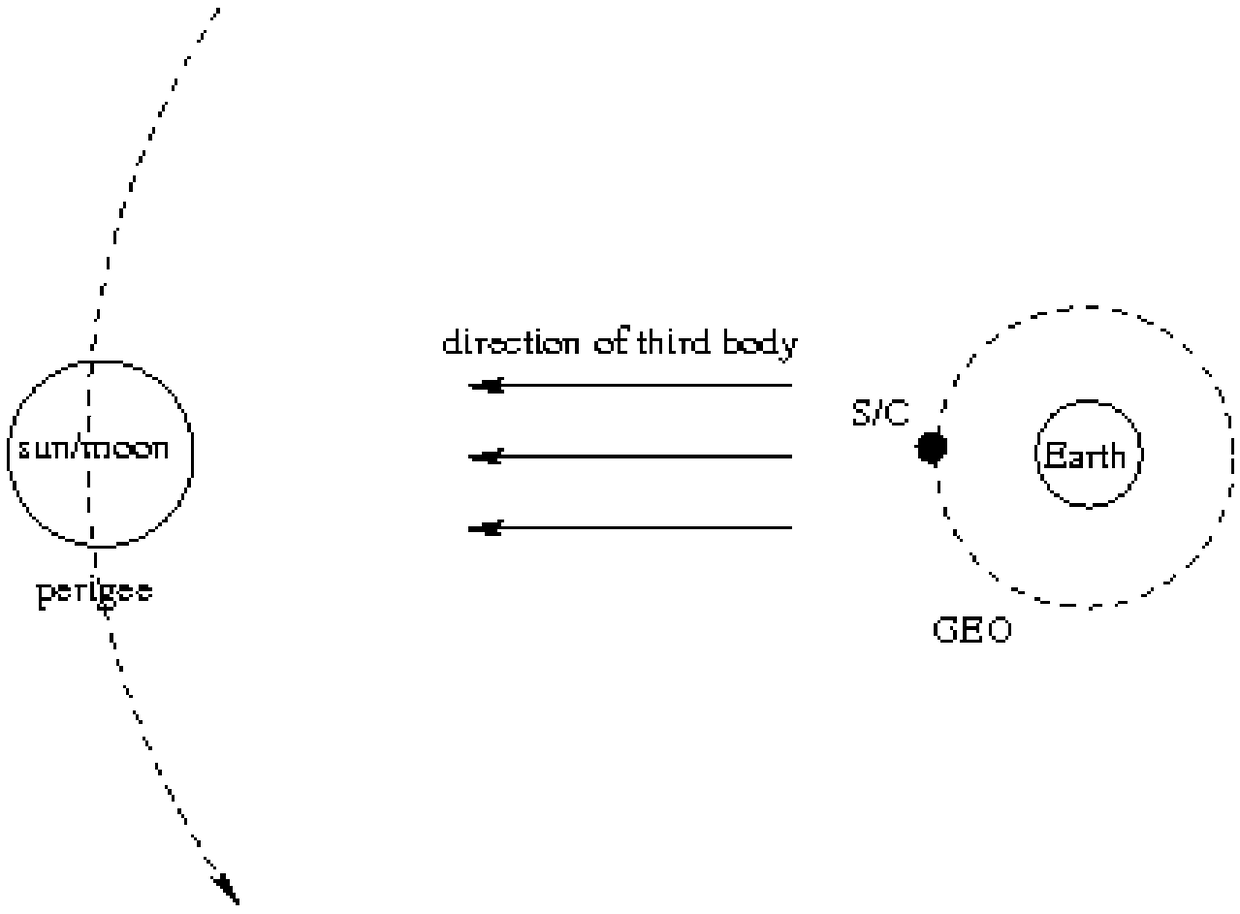
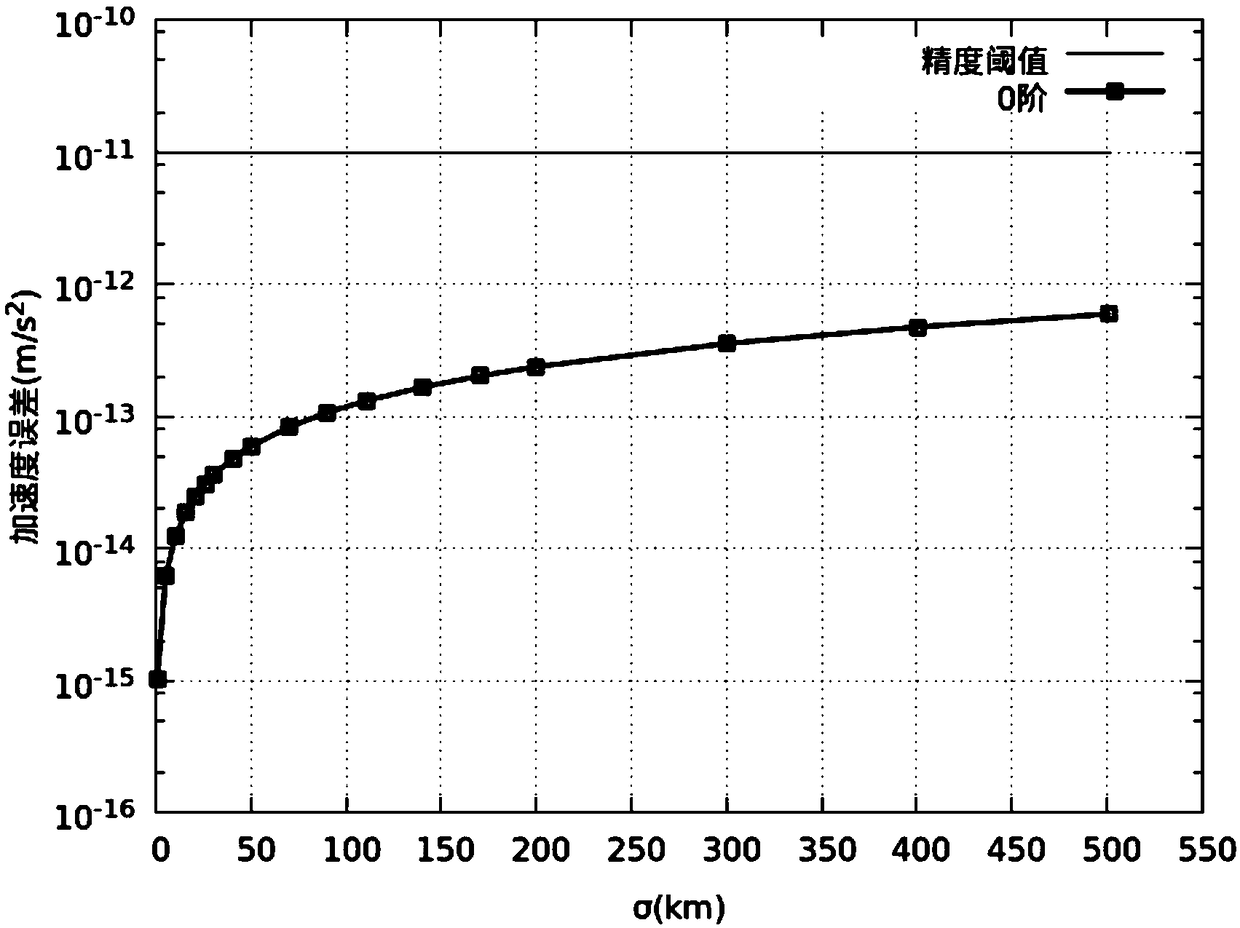
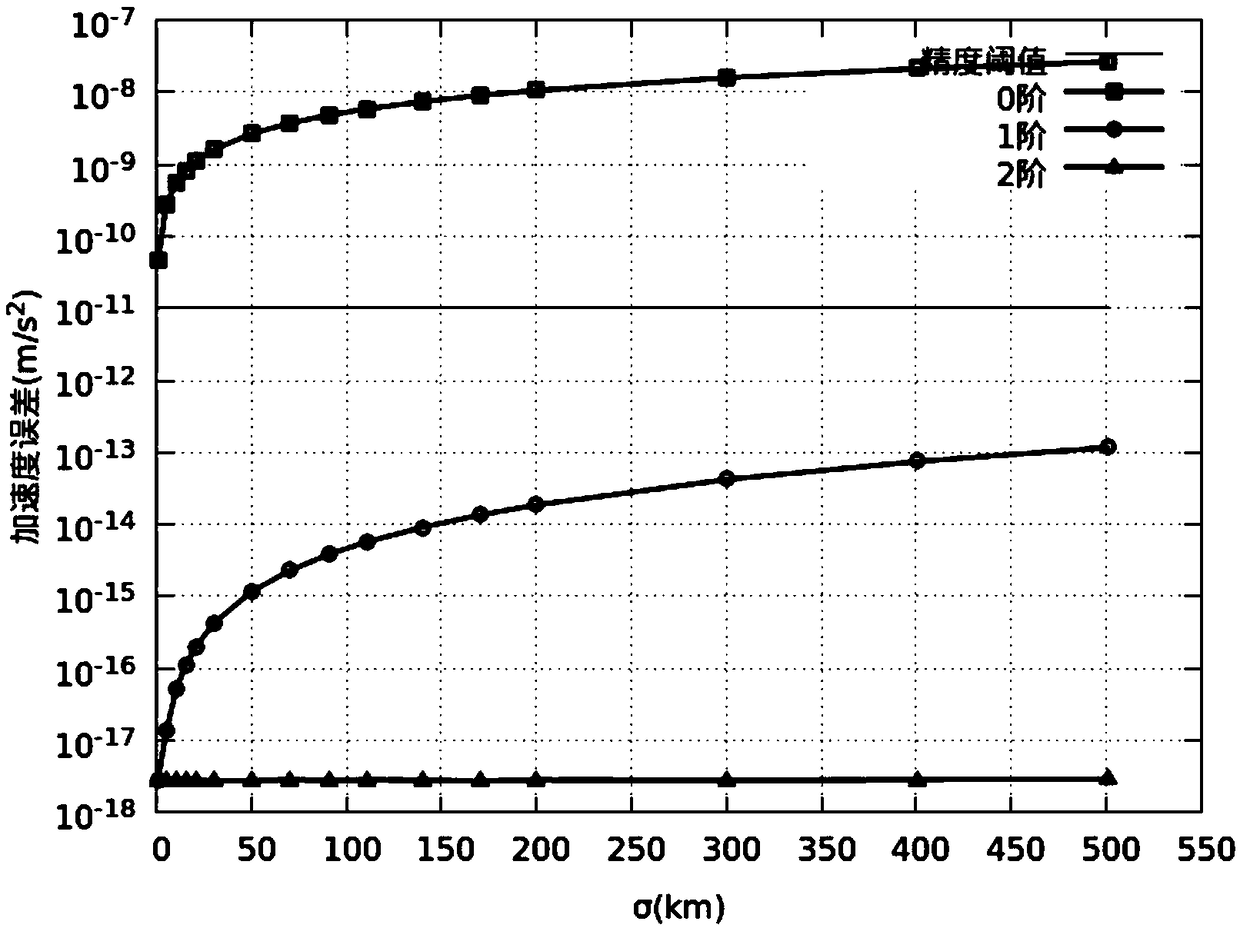
The invention discloses an orbital uncertainty analysis method based on differential algebra technology. Based on Taylor expansion of multivariate functions and polynomial operation framework, and based on the dynamic model of geosynchronous satellite orbit element description, solar pressure to the kinetic model, the third gravitational perturbation and the three perturbation terms of the Earth'soblateness are added in the dynamic model , the right term of the dynamic model is expanded along the nominal orbit by Taylor expansion, the expansion polynomial with initial deviation as variable isobtained, Under the frame of differential algebra, the orbital state expressed by the polynomial with the initial deviation as variable at any time is obtained, and the concrete value of the initialdeviation is brought into the polynomial result to obtain the state of the final spacecraft. The invention analyzes the optimal expansion order, the balance calculation time and the calculation precision according to different perturbation forces. The method can be used to analyze the orbit evolution of geostationary satellites with initial state deviation and parameter uncertainty, and can also be used in other spacecraft orbit evolution and attitude evolution missions.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
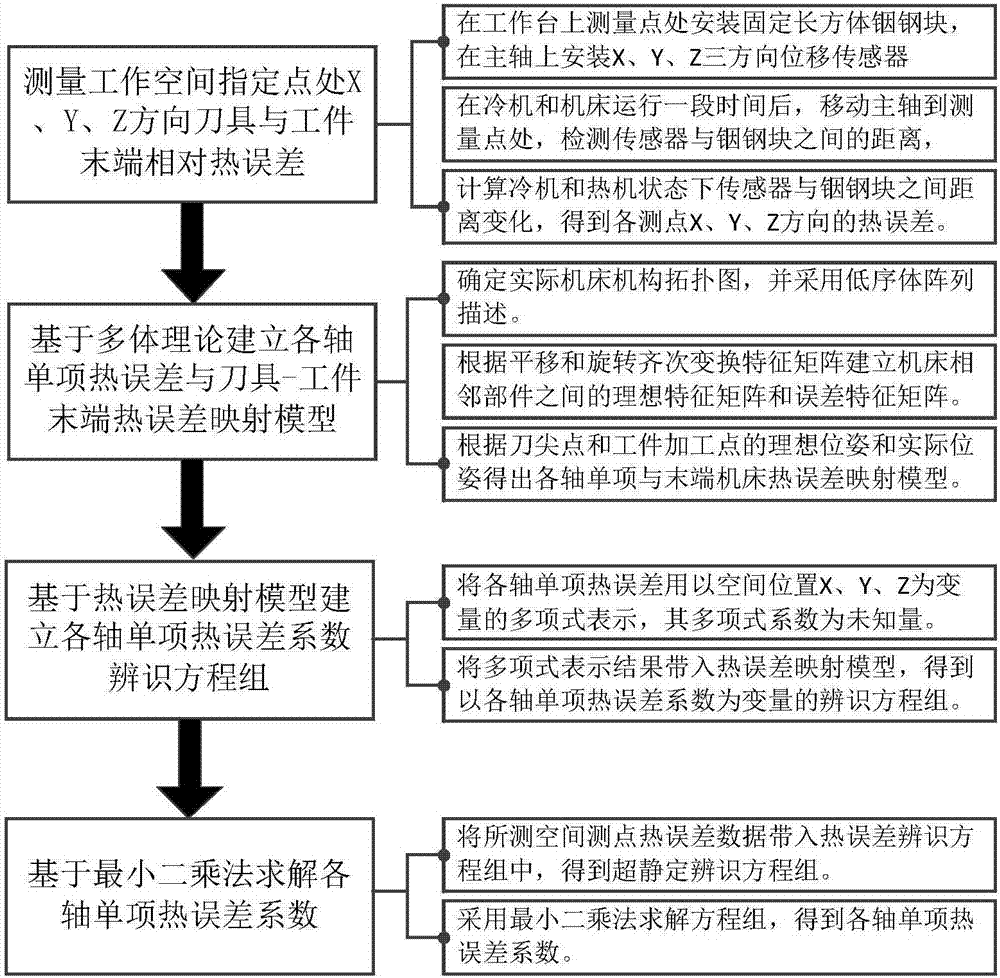
Establishing method for thermal error identification model of machine tool working space
InactiveCN107081638ARapid identificationEasy to measureAutomatic control devicesMeasurement/indication equipmentsEngineeringError coefficient
The invention discloses an establishing method for a thermal error identification model of machine tool working space. The establishing method comprises the following steps: step I: measuring relative thermal errors of tools in the X direction, the Y direction and the Z direction at a specified point of working space and the tail end of a workpiece; step II: establishing a mapping model between single thermal error of each axle and thermal errors of the tail end based on a many-body theory; step III: expressing single thermal error of each axle through a polynomial, and establishing a single thermal error coefficient identification equation set of each axle based on the thermal error mapping model; and step IV: dissolving a single thermal error coefficient of each axle based on a least square method, and identifying single thermal error, expressed through the polynomial, of each axle. The establishing method can realize quick identification for the single thermal error of each axle through thermal error measurement of the tool at each point of the machine tool working space and the tail end of the workpiece, is quick and convenient to measure and operate, and is high in identification precision.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Satellite image system error correction method based on bias matrix with time factor
InactiveCN101839713ASimple methodEliminate systematic errorsPicture interpretationAlgorithmSample image
The invention relates to a satellite image system error correction method based on bias matrix with a time factor. The problem of system error correction comes down to the solution of two bias angles of a camera going around a satellite body, aiming at linear variation rules of the geometric positioning error of an image in a certain in-orbit testing period, a first order polynomial with the time factor is used for expressing the bias angles, the first order polynomial is solved based on the selected sample images and the error compensation of a plurality of automatically extracted control points, and thereby the bias matrix of any satellite images in the period is obtained and is substituted in a co-linearity condition equation to realize the effective compensation and the correction of the geometric positioning system error. According to the in-orbit testing results, the method is simple and feasible, the system errors changing with time can be effectively eliminated and the long-term stability of the precision of the system geometrically corrected product is kept.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for efficiently implementing the advanced encryption standard
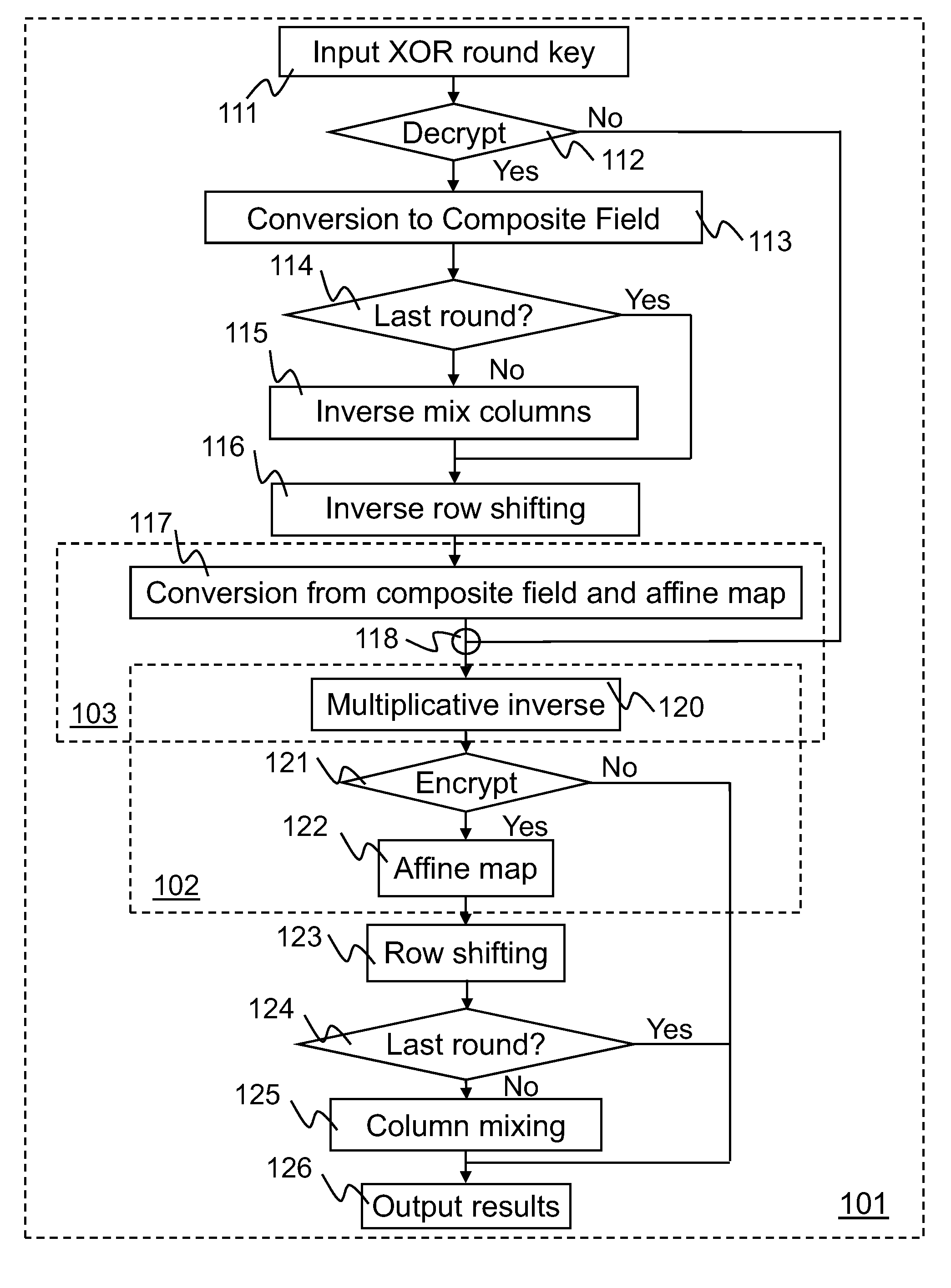
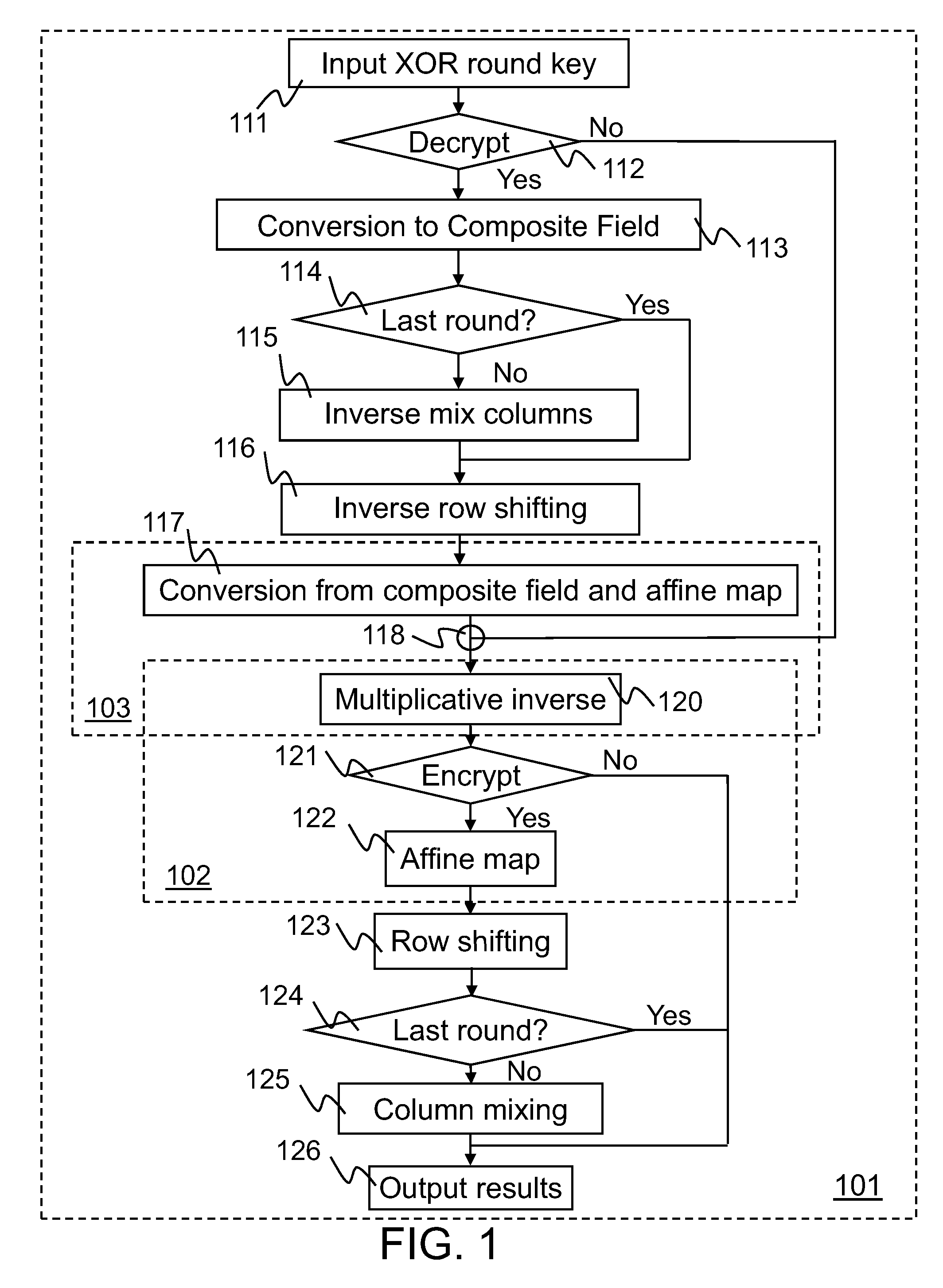
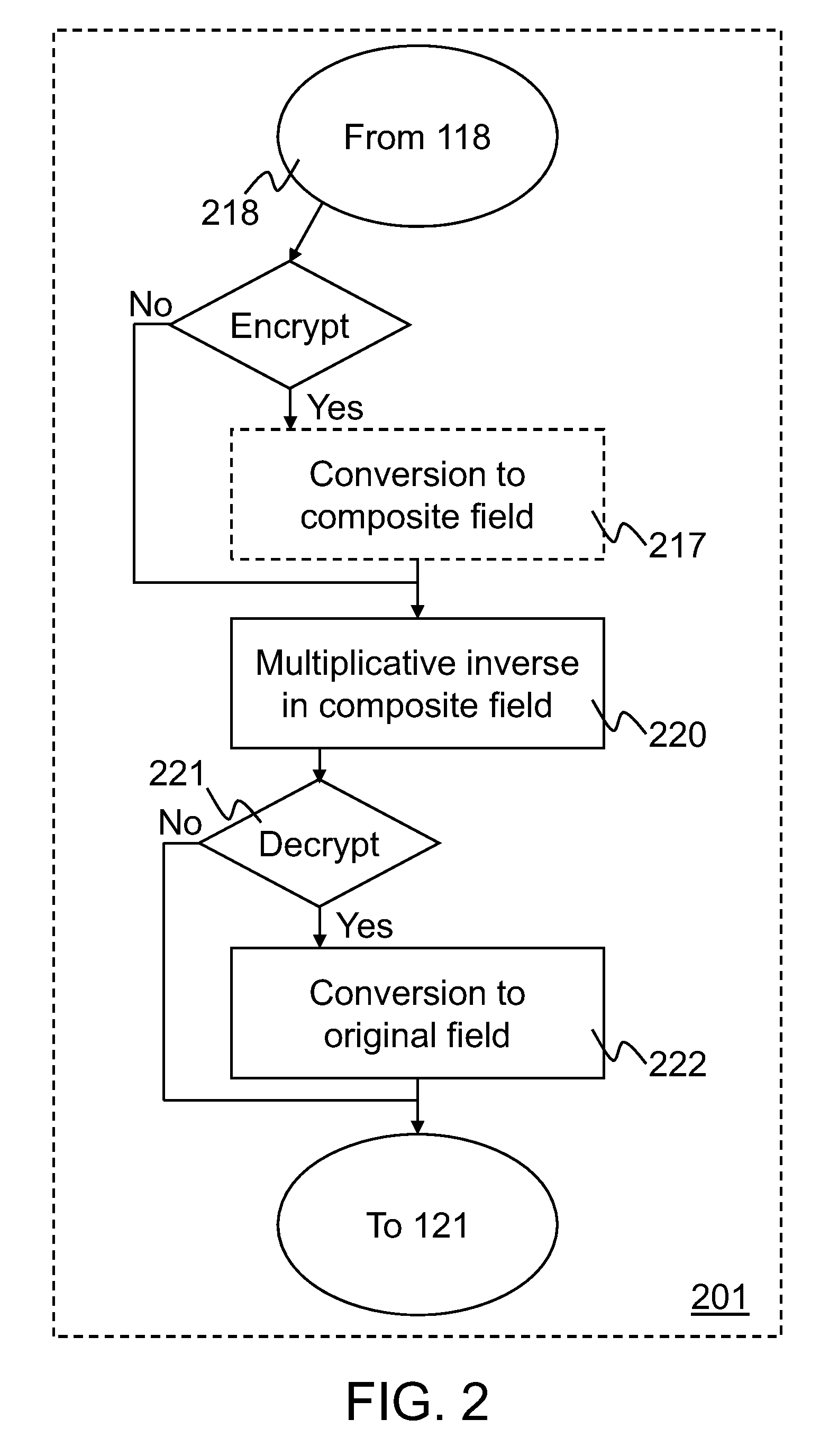
InactiveUS20090172068A1Instruction analysisComputer security arrangementsS-boxComputer graphics (images)
Implementations of Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) encryption and decryption processes are disclosed. In one embodiment of S-box processing, a block of 16 byte values is converted, each byte value being converted from a polynomial representation in GF(256) to a polynomial representation in GF((22)4). Multiplicative inverse polynomial representations in GF((22)4) are computed for each of the corresponding polynomial representations in GF((22)4). Finally corresponding multiplicative inverse polynomial representations in GF((22)4) are converted and an affine transformation is applied to generate corresponding polynomial representations in GF(256). In an alternative embodiment of S-box processing, powers of the polynomial representations are computed and multiplied together in GF(256) to generate multiplicative inverse polynomial representations in GF(256). In an embodiment of inverse-columns-mixing, the 16 byte values are converted from a polynomial representation in GF(256) to a polynomial representation in GF((24)2). A four-by-four matrix is applied to the transformed polynomial representation in GF((24)2) to implement the inverse-columns-mixing.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Polynomial filtering fault detecting method for nonlinear system
The invention discloses a polynomial filtering fault detecting method for a nonlinear system. The polynomial filtering fault detecting method comprises the steps of approximating by a polynomial, i.e., expressing m-order kronecker powers of a system state variable and a measurement output variable of the nonlinear system respectively by a polynomial to obtain a polynomial approximation model composed of a mu-order polynomial and a (mu+1)-order polynomial remainder term; expressing the (mu+1)-order polynomial remainder term in the polynomial approximation model as a low-order polynomial under the condition that no faults exist, wherein the coefficient of the low-order polynomial is equal to the product of a proportion matrix and an indefinite matrix; obtaining an augmented state evolution equation based on the proportion matrix and the indefinite matrix; designing a filter, i.e., establishing a filter function according to the augmented state evolution equation to obtain an estimated value of the system state variable at the (k+1)th moment; determining a filter gain coefficient to ensure that the upper bound of a square deviation of an augmented state evaluation error is minimum at the (k+1)th moment; detecting a fault, i.e., determining a detection threshold at the kth moment, and determining a fault detection policy according to the detection threshold.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
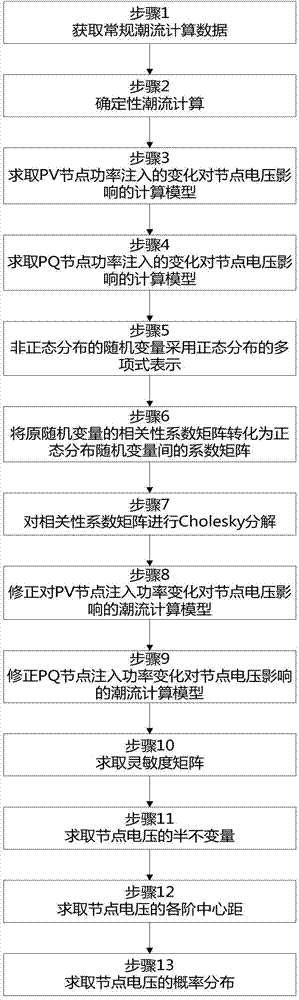
Probabilistic load flow calculation method for calculating variable correlation
ActiveCN104751006AGuaranteed calculation accuracyCalculation speedSpecial data processing applicationsNew energyProbabilistic CTL
The invention provides a probabilistic load flow calculation method for calculating variable correlation. The method includes the steps: (1) acquiring conventional load flow calculation data and performing certainty load flow calculation; (2) gaining a calculation model for the influence of PV (photovoltaic) node and PQ (performance qualification) node power injection change on node voltage; (3) representing abnormally distributed random variables by normally distributed polynomials; (4) switching the related random variables into unrelated random variables by Cholesky decomposition; (5) performing probabilistic load flow calculation for the variables. Calculation speed is increased while calculation precision is ensured, the method is applicable to analysis, safety assessment and the like for large-scale intermittent energy grid-connected complicated power grid system, and the new energy acceptance capacity of an electric power system can be improved.
Owner:CHINA ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
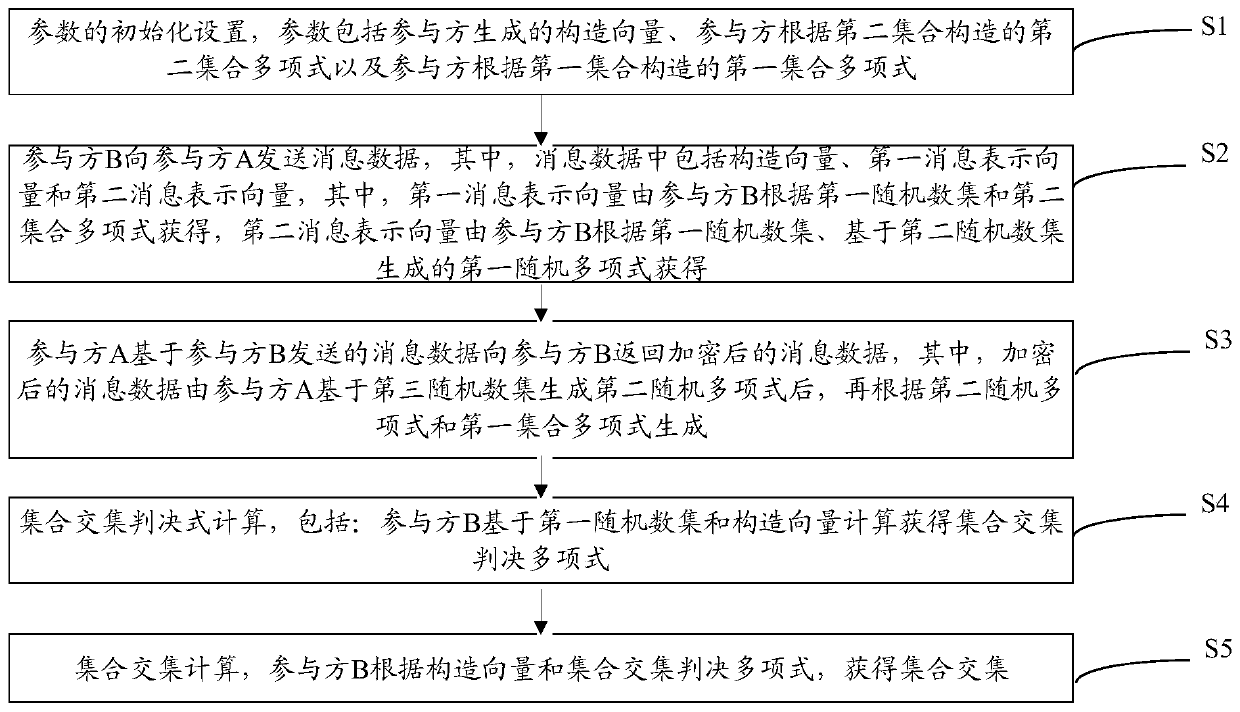
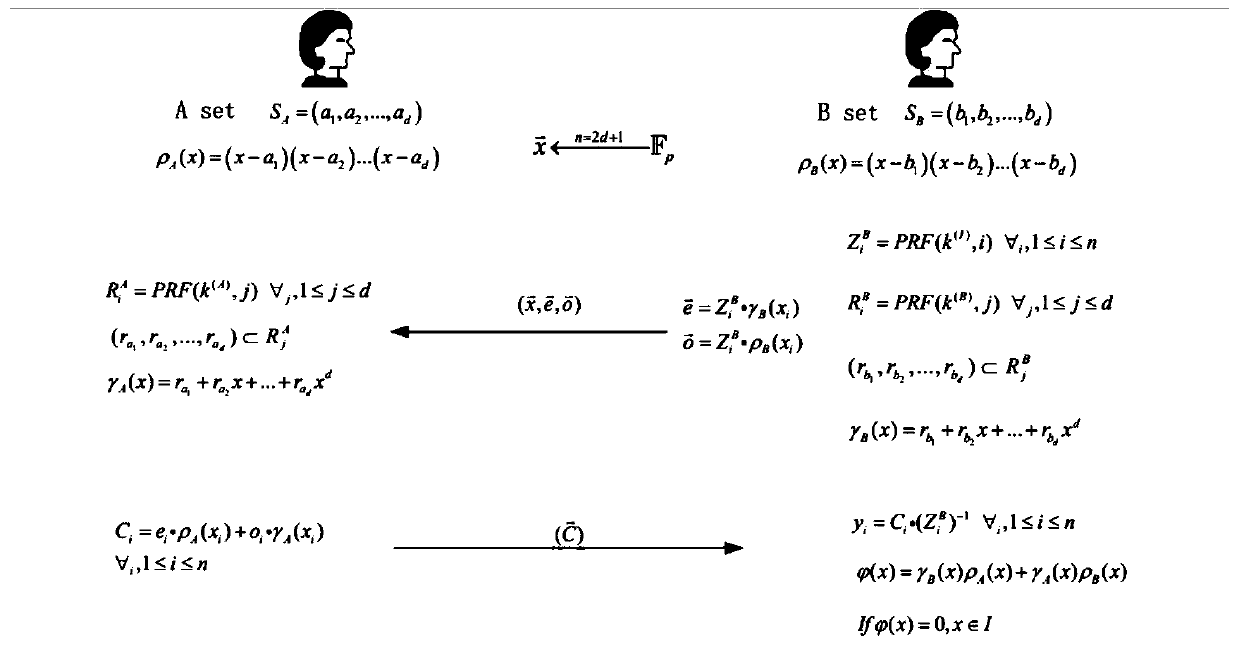
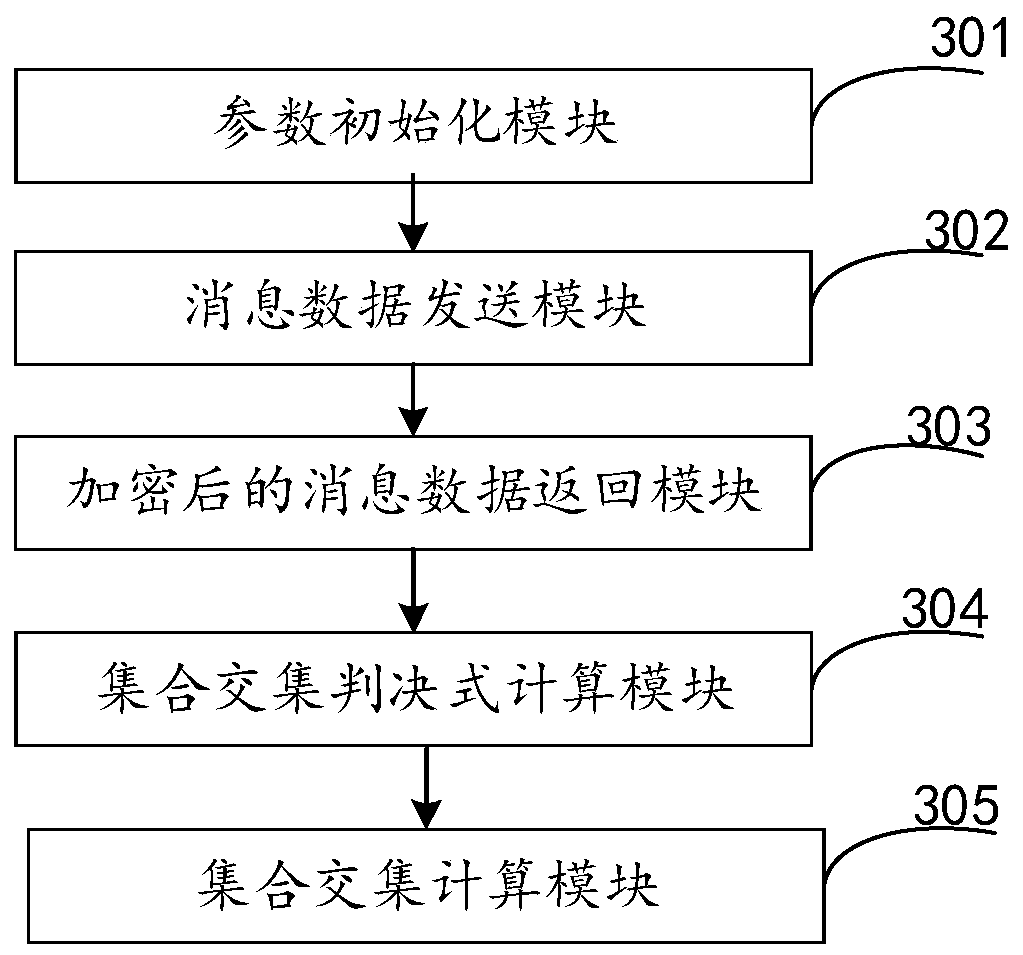
A privacy protection set intersection calculation method and system based on polynomial representation
The invention discloses a privacy protection set intersection calculation method and system based on polynomial representation. According to the intersection calculation method provided by the invention, two participants (a caller B and a responder A) contain the sets of the own attributes and are not acquired by the other party, and the two participants obtain a set intersection through secure multi-party calculation, so that the common attributes of the two parties are acquired. The method specifically comprises the following steps that firstly, a participant and a participant initialize; apolynomial formed by combining the calling party with the random number encrypts the attribute set of the calling party and sends the encrypted attribute set to the responder A; the responder A receives a polynomial formed by the data information and the random numbers, encrypts the data of the two parties of the participant again and sends the data to the responder A; and an intersection set is obtaind through the calculation of two secure parties. The privacy protection set intersection calculation method based on polynomial representation can be used for the multi-party data security communication by utilizing the properties of the polynomial, so that the technical effect of improving the cracking difficulty and safety is achieved.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for predicting instantaneous cutting force of milling based on maximum cutting force
InactiveCN106682281AAccurate predictionDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLower limitMilling cutter
The invention discloses a method for predicting instantaneous cutting force of milling based on maximum cutting force, aiming at solving the technical problem that an existing instantaneous cutting force prediction method fails to predict the instantaneous cutting force and instantaneous maximum cutting force of milling accurately. The technical scheme includes that the method includes firstly, determining an upper limit and a lower limit of a cutting contact angle and cutting conditions of a jth cutter tooth of a milling cutter, and constructing a prediction equation of the instantaneous cutting force of milling with respect to cutting force parameters; obtaining the maximum cutting force under different cutting conditions through cutting experiments, and solving the cutting force coefficients so as to construct a cubic polynomial of the cutting force coefficients with respect to the cutting parameters; substituting the cubic polynomial of the cutting force coefficients into the prediction equation of the instantaneous cutting force of milling so as to obtain a prediction model of the instantaneous cutting force of milling. The method for predicting the instantaneous cutting force of milling based on the maximum cutting force has the advantage that the cubic polynomial is used for expressing complicated relations of the cutting force coefficients with respect to the cutting parameters, in which the cutting force coefficients are obtained by computing of the maximum instantaneous cutting force through the experiments, so that the instantaneous cutting force and the maximum instantaneous cutting force of milling can be predicted accurately.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Numerical control method
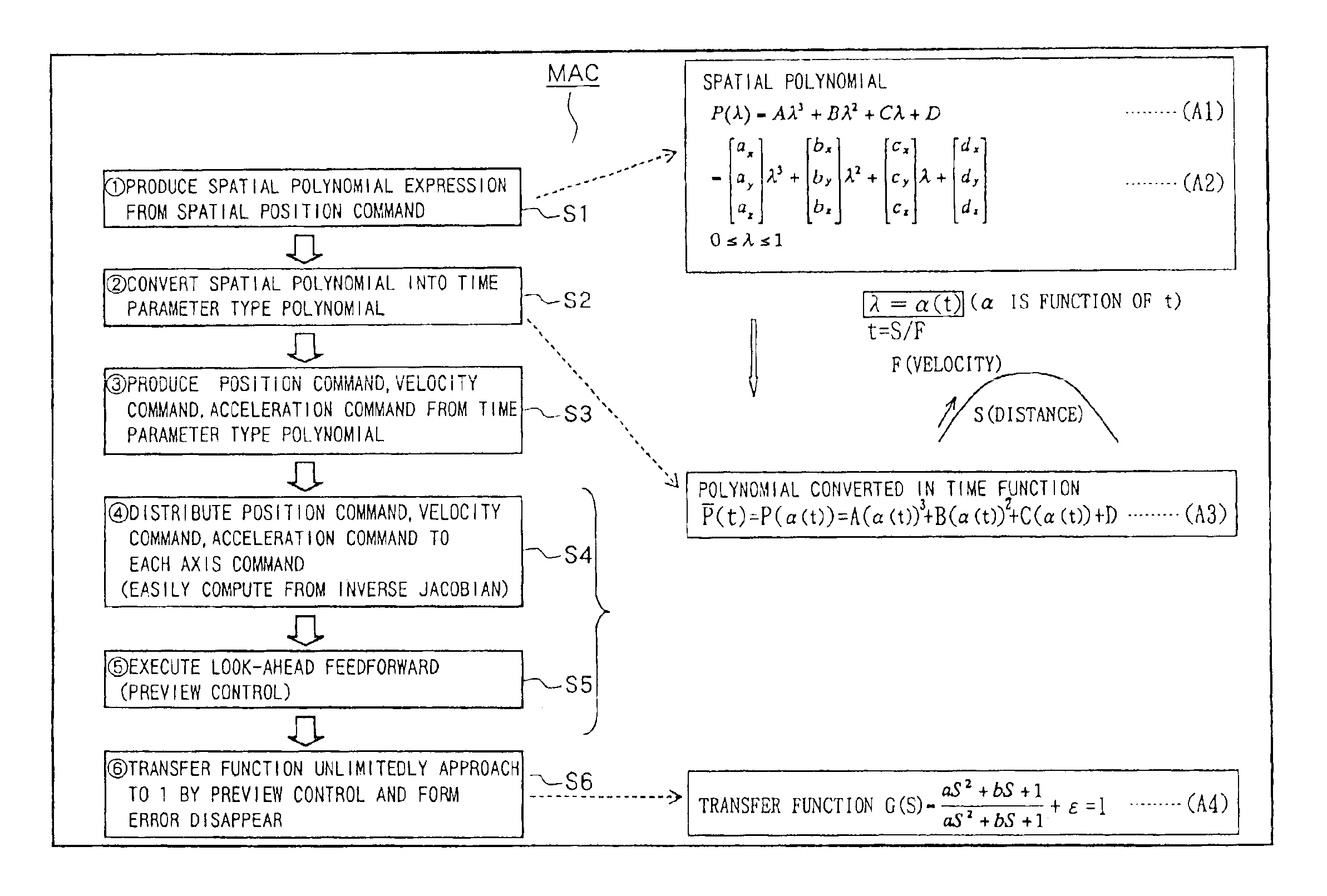
InactiveCN1357806ANo time lagMove preciselyComputer controlSimulator controlNumerical controlTime function
In a numerically controlled method of moving an object to be controlled along a predetermined locus, controlling control axes, the locus is made approximate to a spatial polynomial, a polynomial is converted into a polynomial as time function, the polynomial converted as time function is distributed to each control axis, control command in each control axis is produced on the basis of the polynomial distributed to each axis as time function, and the object to be controlled is moved along the locus, controlling each control axis on the basis of the control command. The velocity, the acceleration and the jerk of the object to be controlled can be easily obtained concerning each control axis in advance by differentiating the polynomial expressed by time function. The object to be controlled is controlled so as to move along the locus expressed by the polynomial, feeding irregularity or position shift is reduced and curved face machining at high accuracy is possible.
Owner:YAMAZAKI MAZAK KK
Serial finite field multiplier
ActiveUS6917218B2Computation using non-contact making devicesDigital computer detailsArray data structureTheoretical computer science
The present invention relates to a finite field multiplier used for implementing an encrypting algorithm circuit, thereby minimizing power consumption and circuit area in implementing the finite field multiplier with a LFSR (Linear Feedback Shift Register) structure. The Finite field multiplier of the present invention is an operator performing a modular operation on the multiplication result of two data represented on a polynomial basis in a Galois Field into an irreducible polynomial. The LFSR structure is a serial finite field multiplication structure, and has a merit over an array structure and a hybrid structure in application to systems that are limited in size and power due to its simplicity of circuits and also its capability of being implemented in a small size.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Method of manufacturing a mask blank substrate, method of manufacturing a mask blank, method of manufacturing a transfer mask, and method of manufacturing a semiconductor device
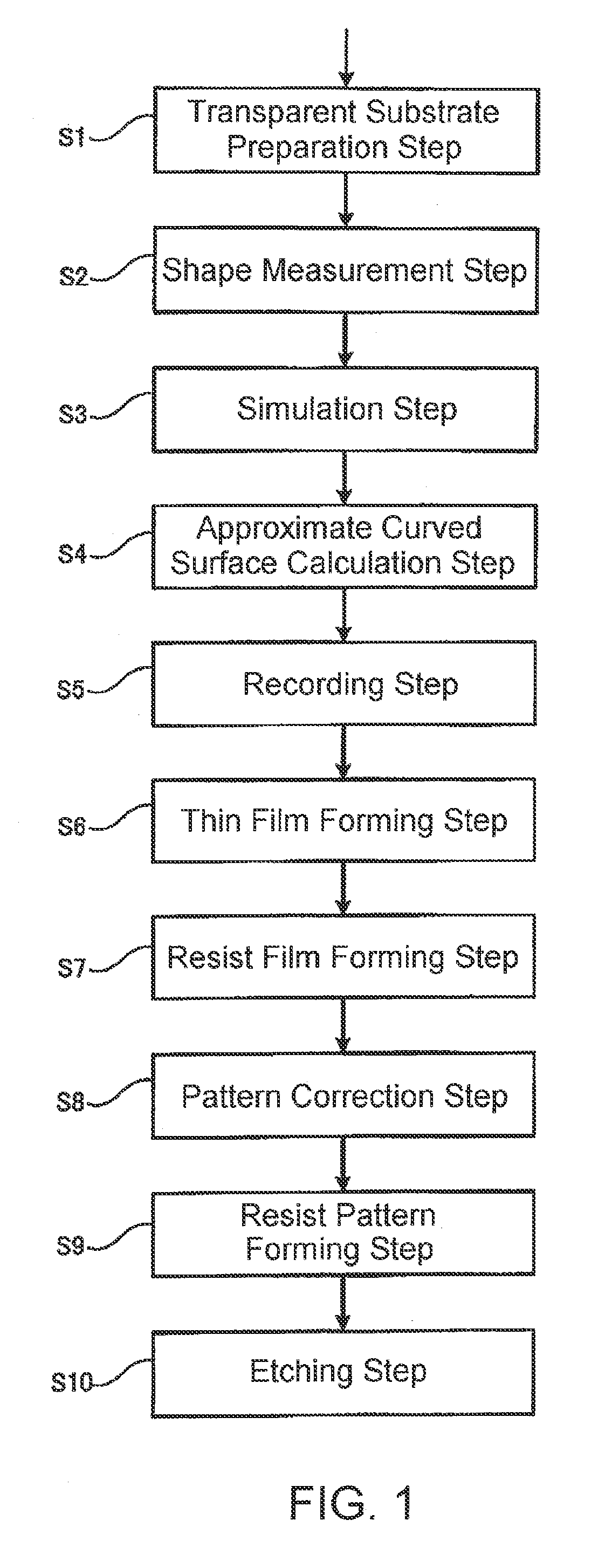
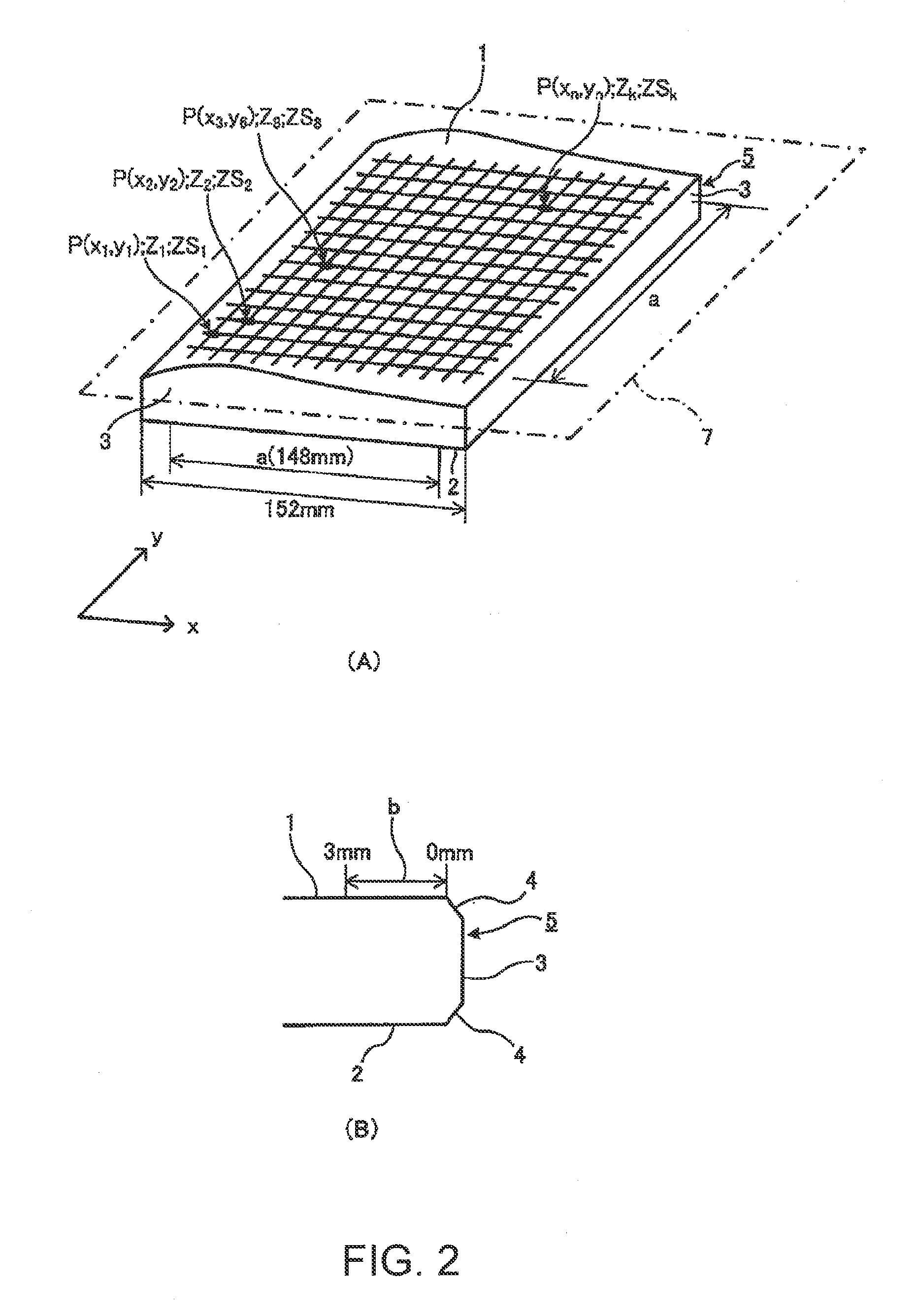
ActiveUS20130022900A1Easily and accurately calculationReduce computing timeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMeasurement pointEngineering
In a simulation step of simulating a surface configuration of a substrate which is used for a mask blank and which is set to an exposure apparatus, height information from a reference plane is derived from a plurality of measurement points on a main surface of the substrate. From the height information, a curved surface of fourth, fifth, or sixth order is approximated which is represented by a polynomial specified by a plurality of terms and coefficients of the terms. The coefficients are stored as coefficient information in association with the substrate.
Owner:HOYA CORP
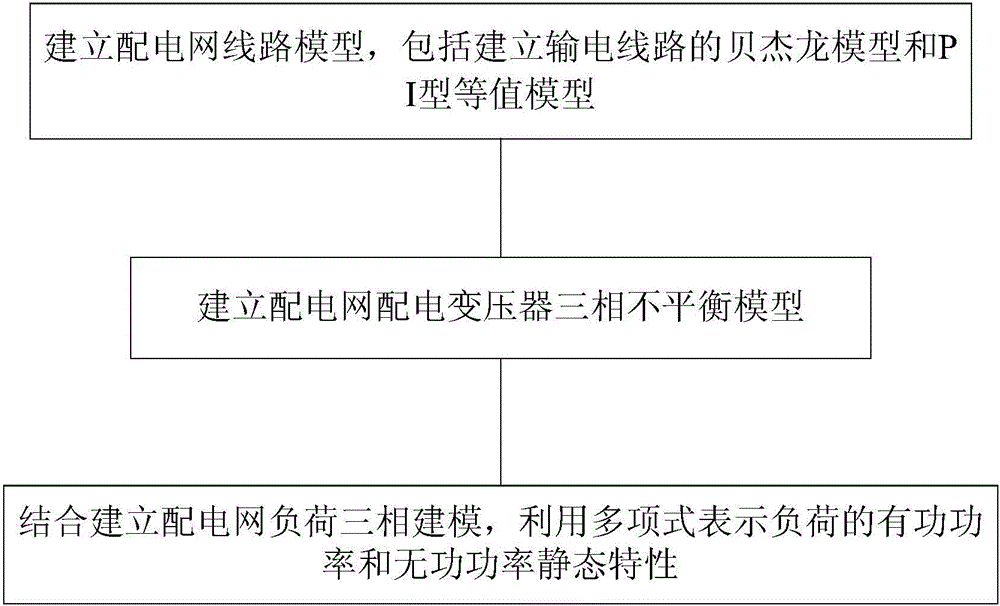
Three-phase modeling method for distribution network
InactiveCN106056479AData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsDistribution transformerSimulation
The invention discloses a three-phase modeling method for a distribution network, comprising the steps of: (1) establishing distribution network line models including a Bergeron model and a PI equivalent model of a transmission line; (2) establishing a three-phase balance model of a distribution transformer of the distribution network; and (3) expressing the static characteristics of active power and reactive power of a load by using a polynomial in combination with three-phase modeling for establishing the load of the distribution network. The three-phase modeling method for the distribution network provides a theoretical basis for three-phase model establishment and parameter setting of equipment in an intelligent distribution network management system, and provides a theoretical foundation for on-line three-phase asymmetrical load flow analysis.
Owner:NARI TECH CO LTD +2
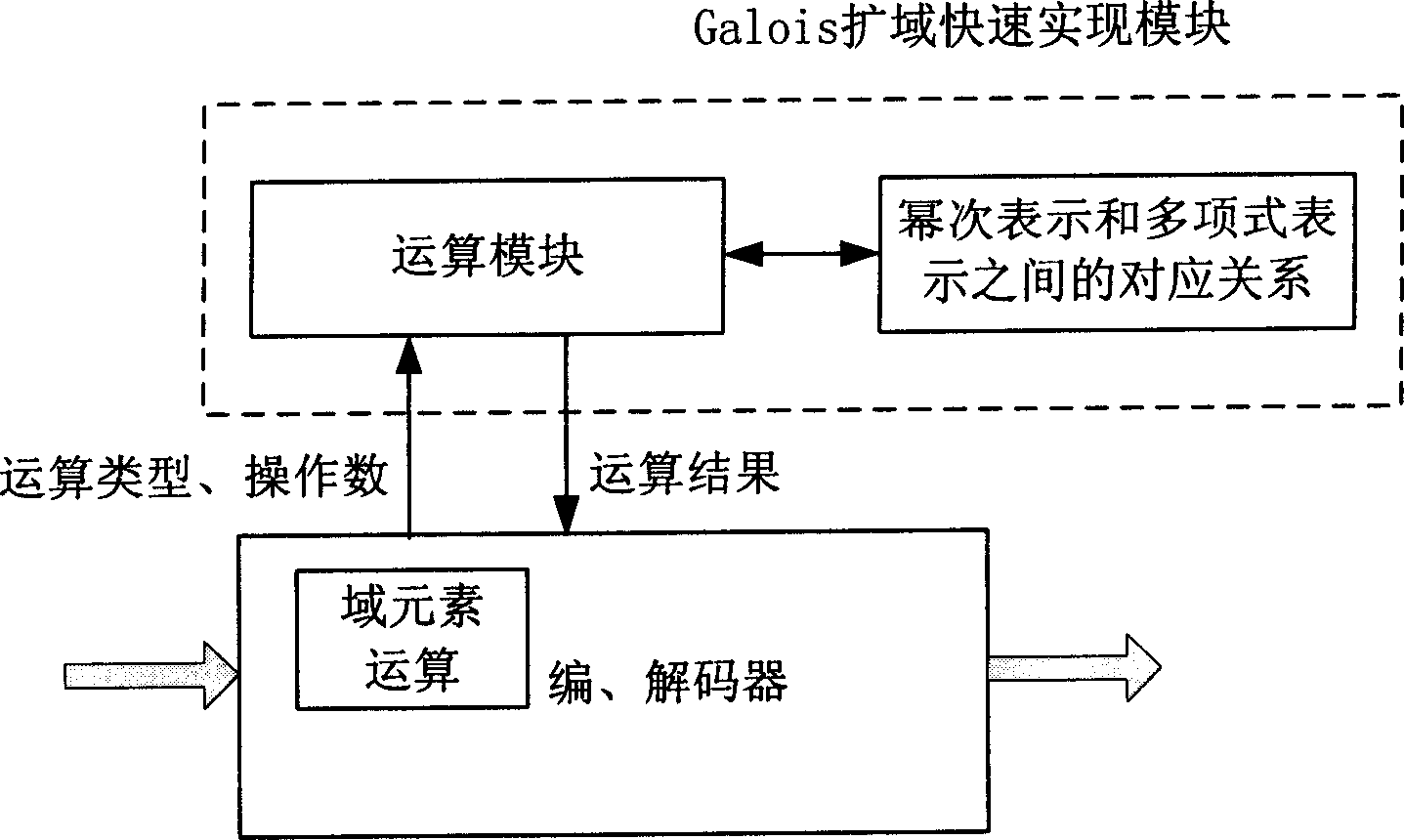
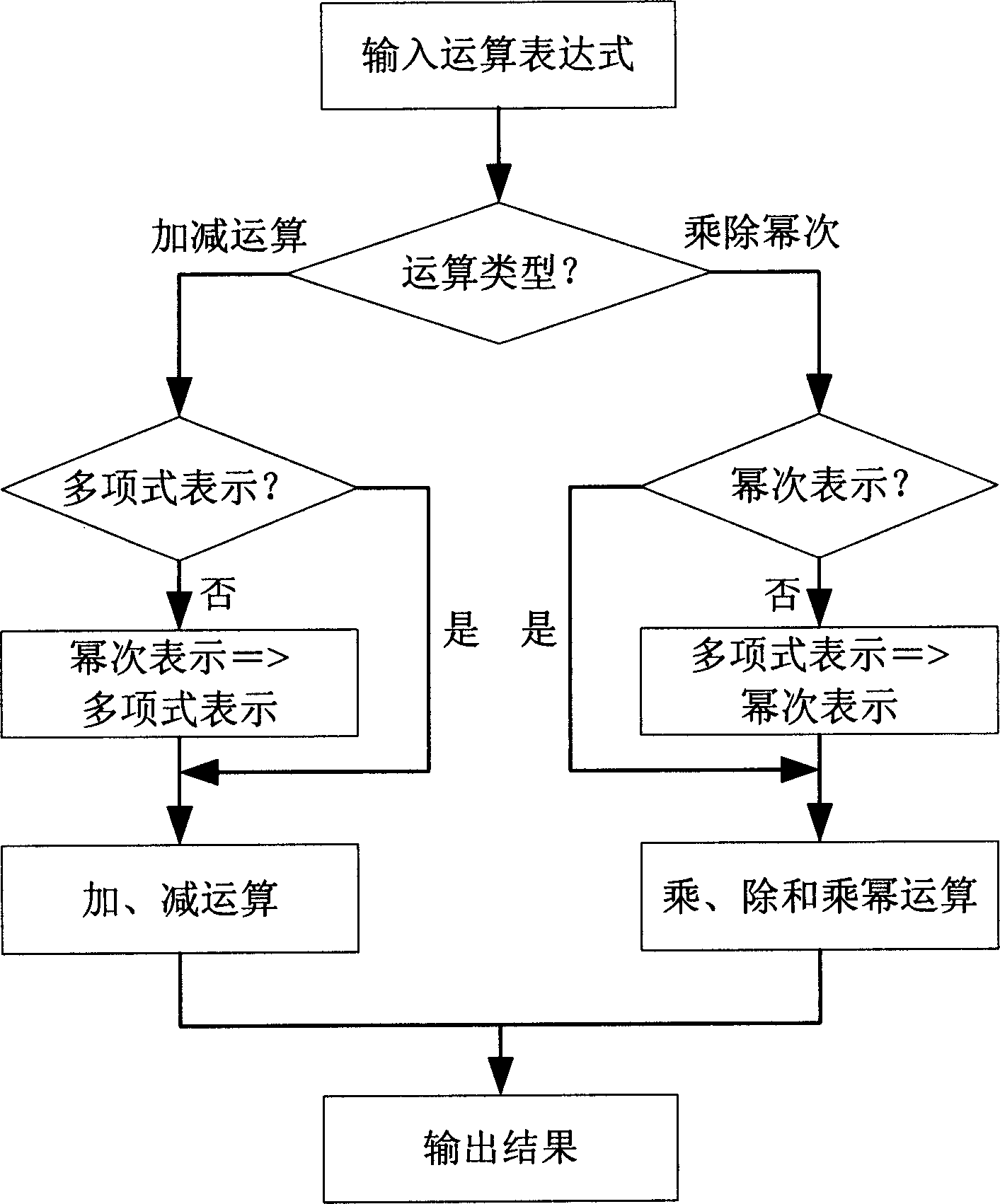
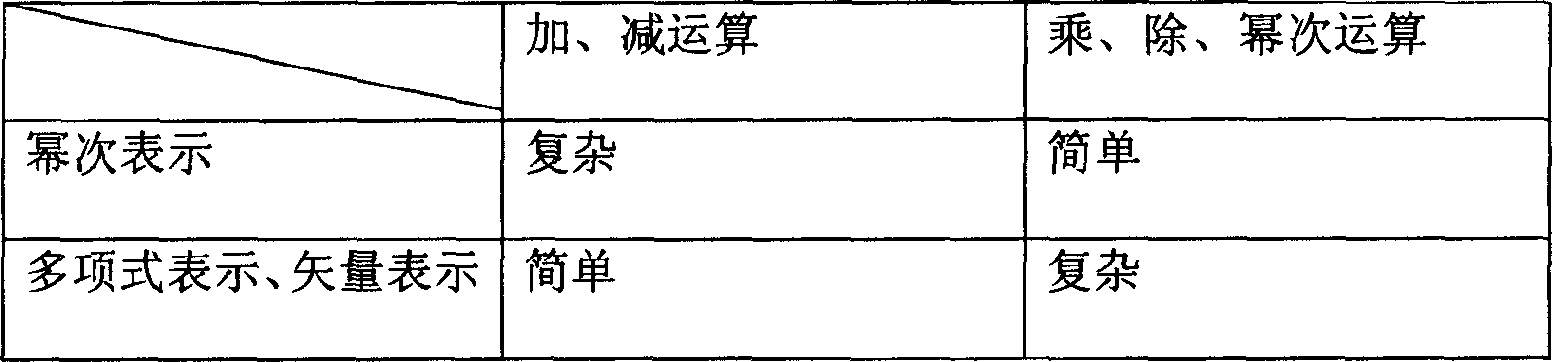
Method for rapid realizing Galois domain-extending operation in BCII coding
InactiveCN1777043ASpeed up conversion operationsFast operationCode conversionCyclic codesOperandPolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checks
The method establishes coincidence relation of each element between exponent denotation and polynomial denotation. Operation of extension field is carried out according to following steps: inputting operation expression to be carried out Galois operation of extension field; determining types of Galois operation of extension field in operation expression; determining express mode of operand in operation expression; based on the said types, carrying out relevant conversion for express mode of operand according to coincidence relation of elements built through query; carrying out corresponding operation for converted operand; finally, outputting result of Galois operation of extension field. Implementing hybrid operation through two kinds of denotation for Galois element of extension field, the invention raises operational speed for encoding and decoding BCH, and lowers complexity of software for implementing Galois operation of extension field.
Owner:VIMICRO CORP
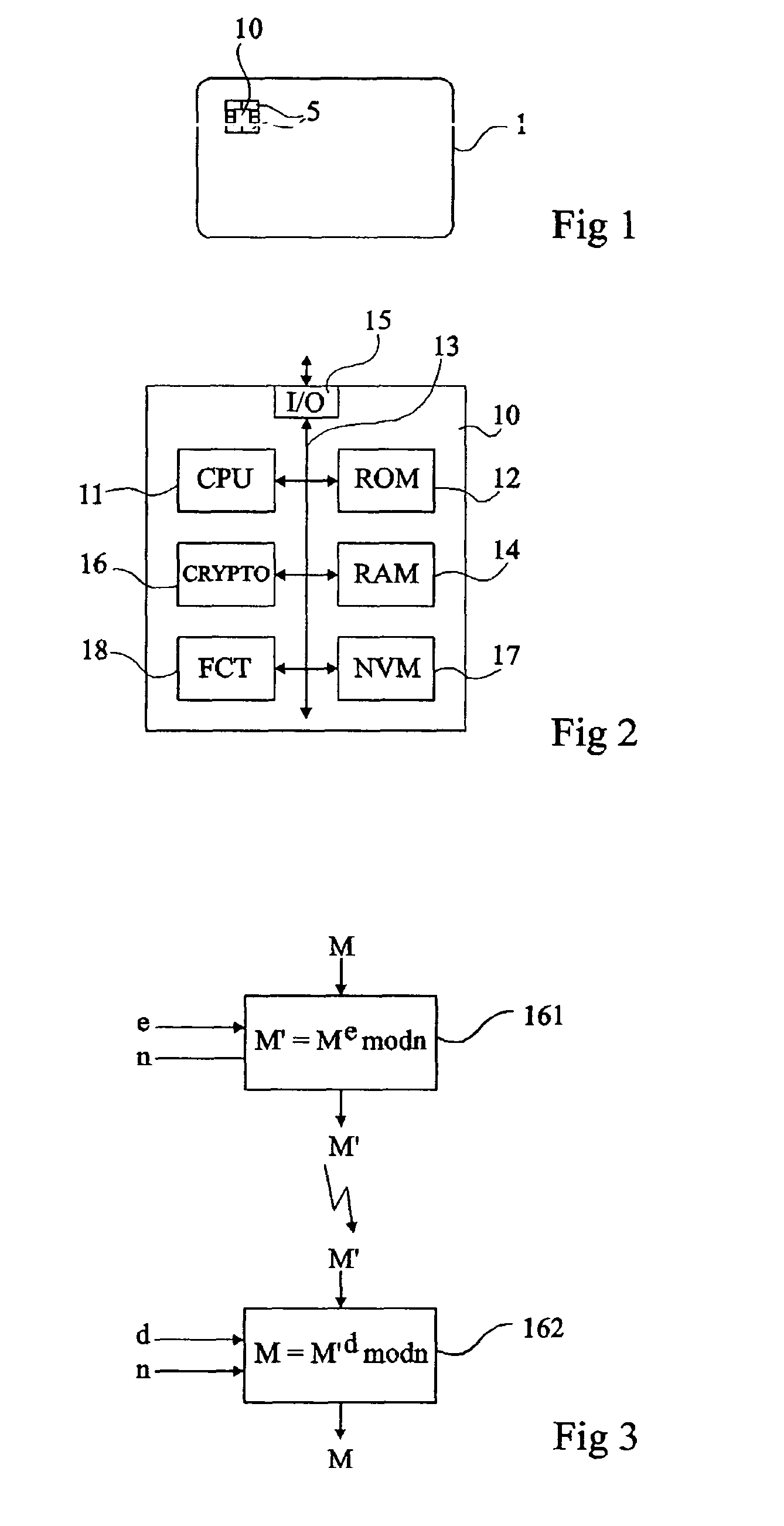
Protection of a calculation performed by an integrated circuit
ActiveUS9313027B2Not adversely affect the rapidity of execution of the calculationsPublic key for secure communicationCryptographic attack countermeasuresPolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checksComputer science
Owner:PROTON WORLD INT
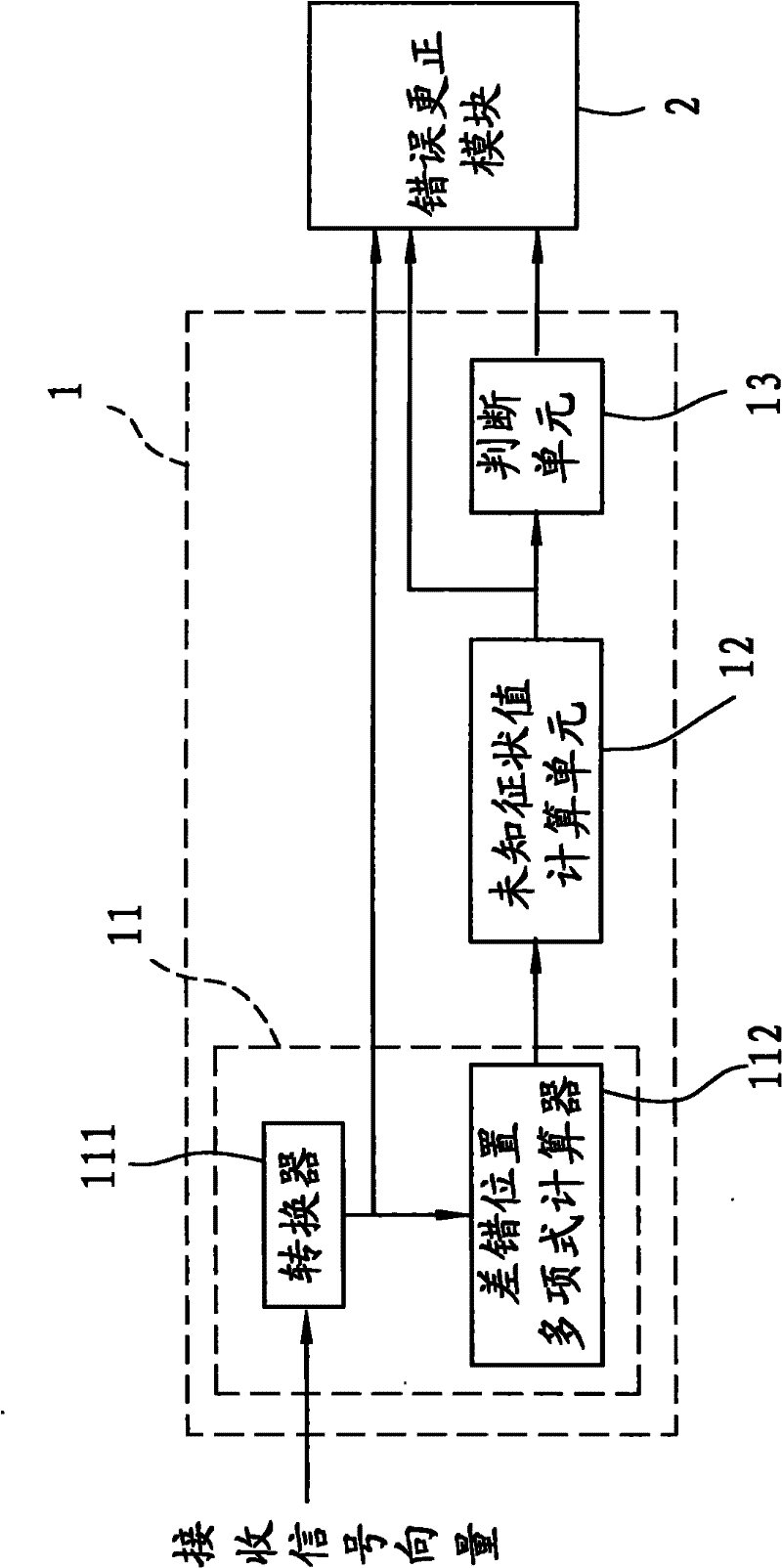
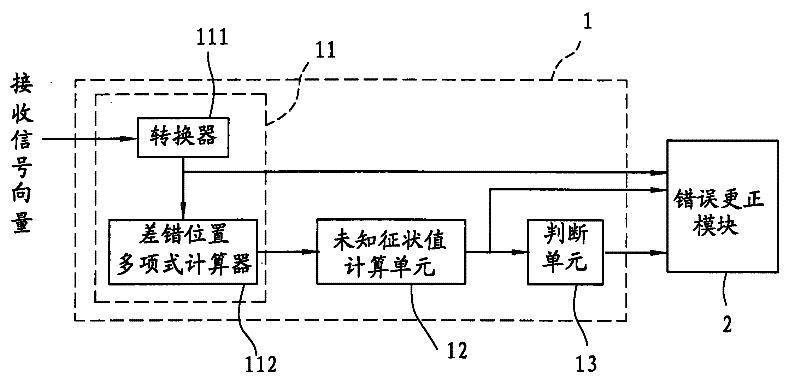
Error detection decoding module and error detection correction device
InactiveCN102263607AAccelerate computing speedEasy to detectCorrect operation testingPattern recognitionTarget signal
The invention relates to an error detection decoding module. The error detection decoding module is used for receiving a received signal vector transmitted by a noise channel, wherein the received signal vector comprises an error vector signal which can be represented by an erasure-locator polynomial. The error detection decoding module comprises a known symptom sign value computing unit, an unknown symptom sign value computing unit and a judgment unit, wherein the known symptom sign value computing unit obtains a target signal vector with a plurality of known symptom sign values according to the received signal vector, and computes the erasure-locator polynomial according to the known symptom sign values; the unknown symptom sign value computing unit computes a plurality of unknown symptom sign values according to the erasure-locator polynomial and the known symptom sign values; and the judgment unit outputs a detection result signal according to a symptom sign set formed by the known and unknown symptom sign values.
Owner:I-SHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for realizing digital signal processor non-linear function quick and fixed-point operation
InactiveCN101055564AReduce computational complexityAvoid computational complexityComplex mathematical operationsDigital signal processingFloating point
The invention discloses a method for implementing a rapid fixed-point operation of nonlinear function in the digital signal processor. When a digital sound video signal is coded by the digital signal processor, the method carries out the fixed-point calculation for the nonlinear function which is included in the digital sound video signal,firstly the nonlinear function is developped according to Taylor formula, and former n items is reserved to produce the approximate to Maclaurin expansion according to operational precision; then the polynomial in the former step is represented the rapid algorithm form of Qin Jiu Shao polynomial; finally, each item of Qin Jiu Shao polynomial is calibrated using DSP designated implementation method, and takes part in the calculation after calibration. The invention leaves out the switchbetween the fixed-points and floating-point before or after the calculation of nonlinear function, accordingly the operational efficiency is greatly improved; the invention, different with look-up table, reduces the cost of harware without occupying big memory.
Owner:CENT ACADEME OF SVA GROUP
Method of manufacturing crystal oscillator and the crystal oscillator manufactured by the method
InactiveCN1945965AGenerator stabilizationOscillations generatorsPolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checksVoltage control
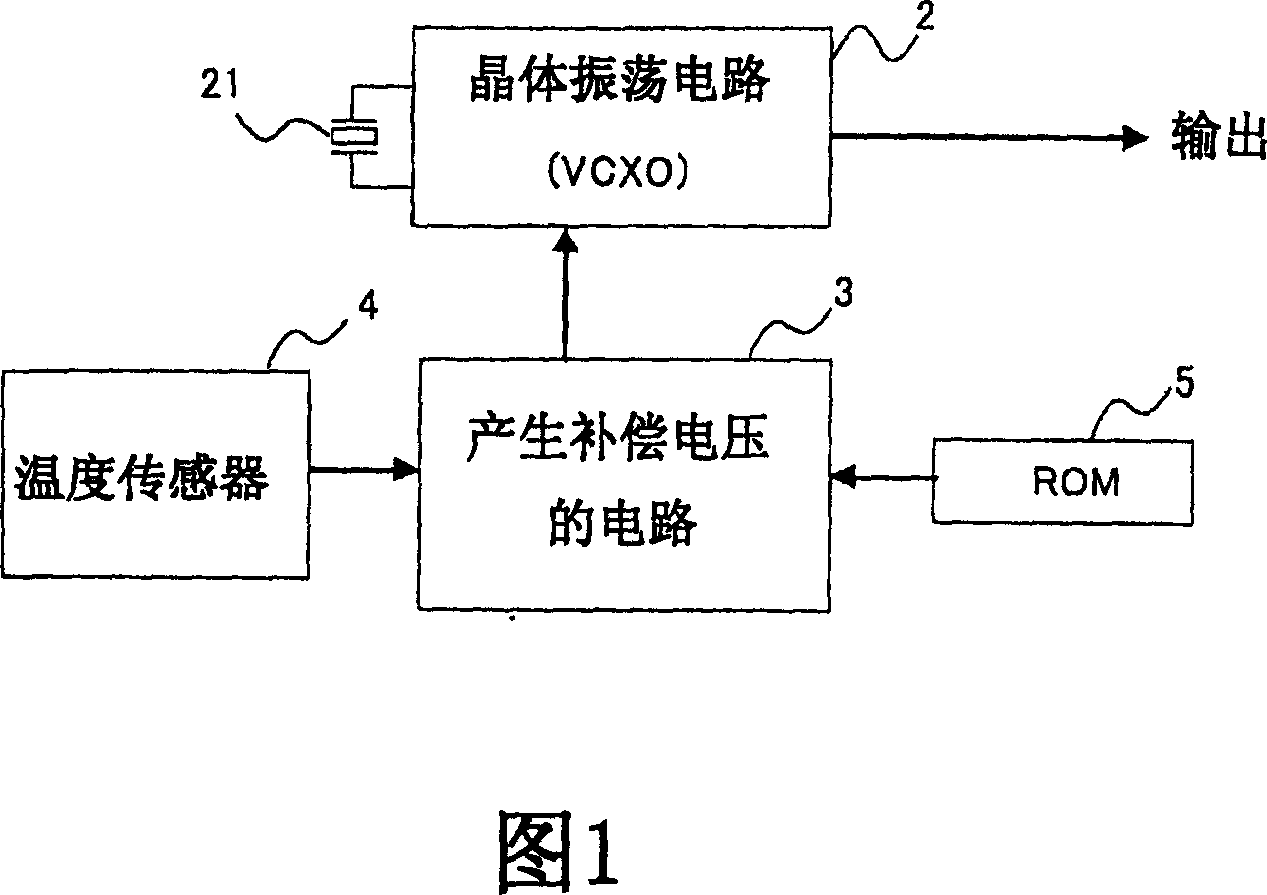
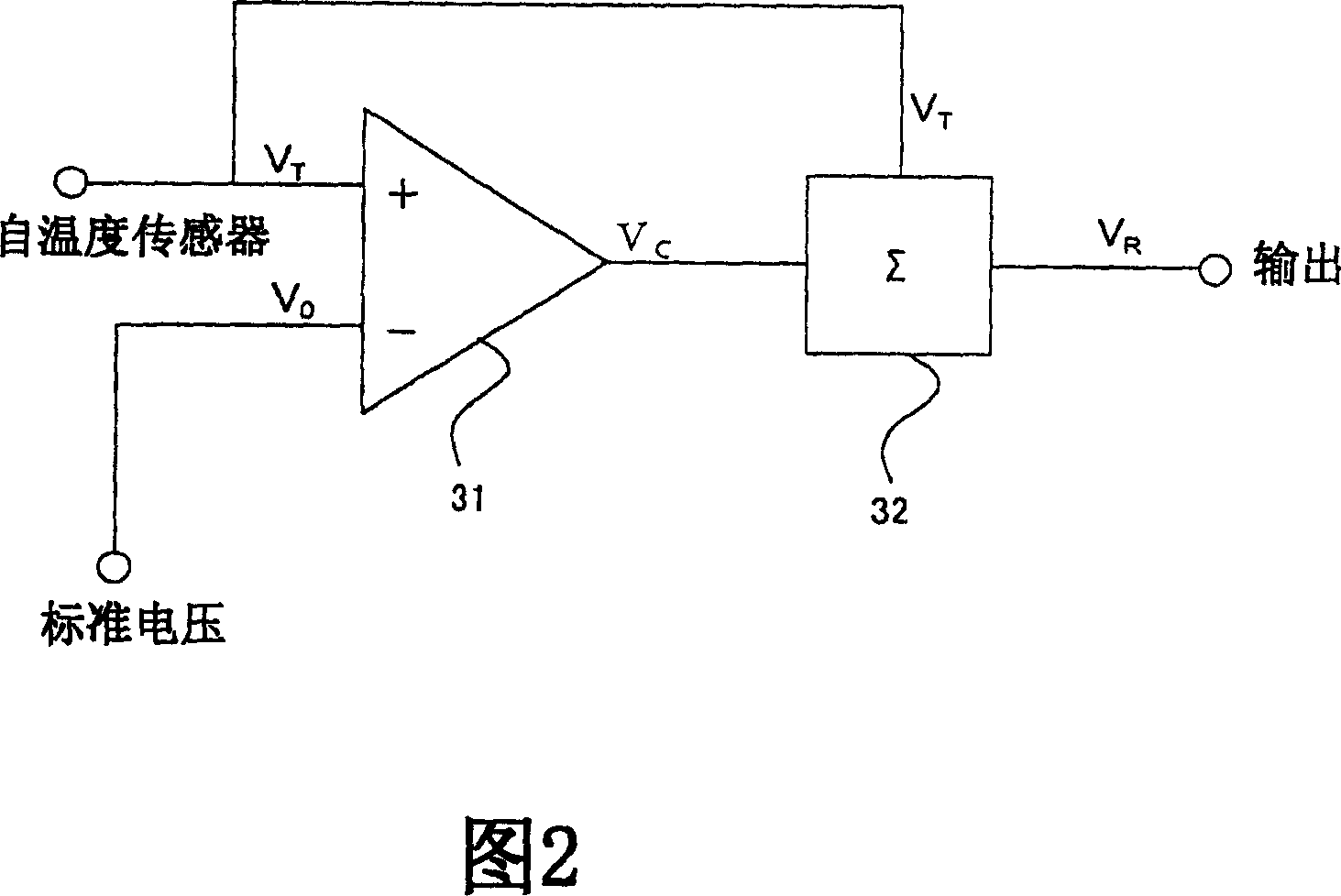
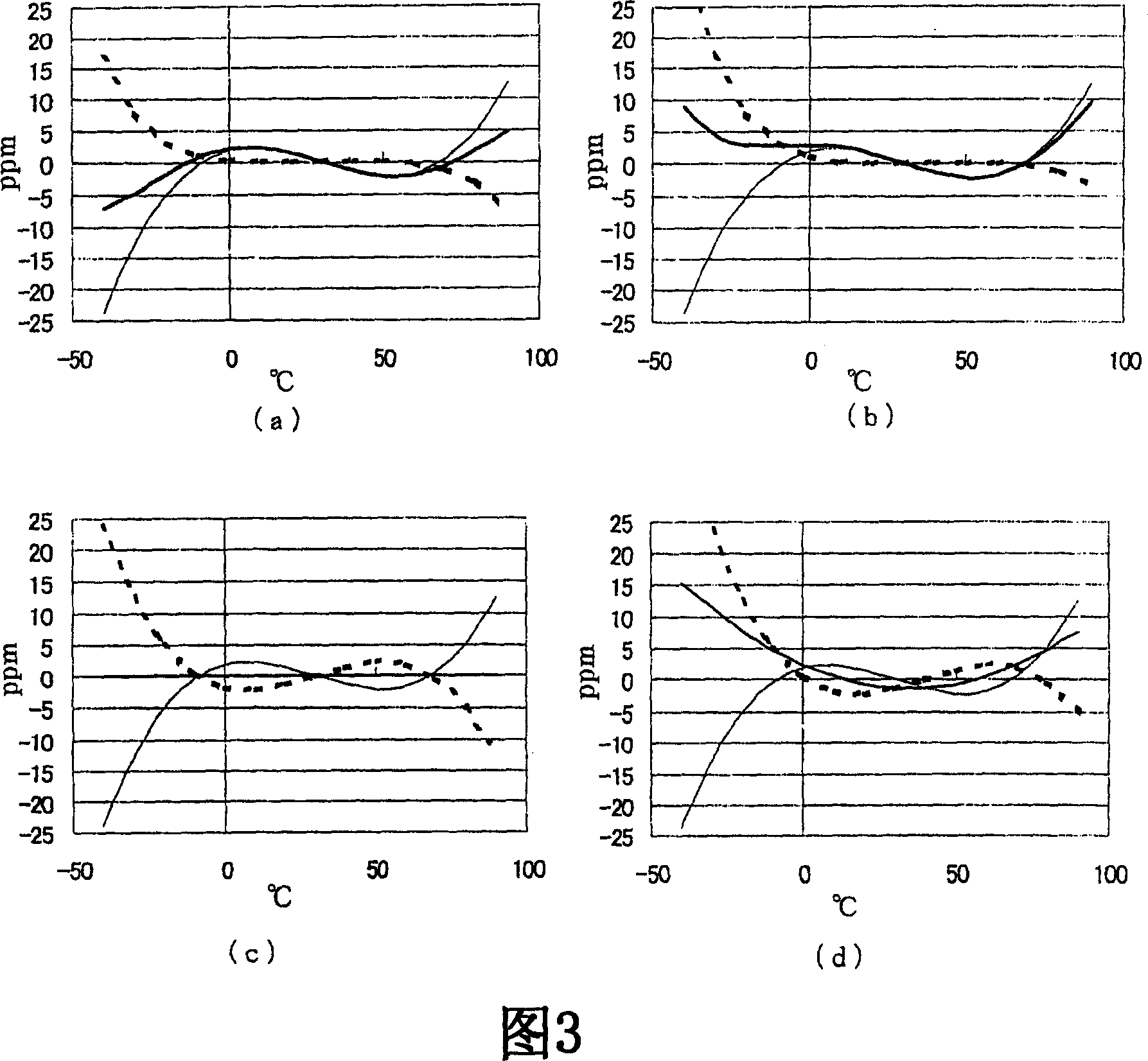
The method of manufacturing a crystal oscillator that is compensated for temperature with low-cost, and a crystal oscillator that is compensated for temperature by the method is disclosed. A plurality of crystal oscillators are manufactured by preparing a compensation circuit that generates a common compensation voltage in accordance with a predetermined compensation curve expressed by a quintic polynomial of an ambient temperature; and manufacturing each of the plurality of crystal oscillators by integrating the compensation circuit with a voltage controlled oscillation circuit including a crystal resonator, the common compensation voltage generated by the compensation circuit being supplied to the voltage controlled oscillation circuit so that the temperature characteristic of the crystal resonator is compensated.
Owner:KAWASAKI MICROELECTRONICS
Roll stand for rolling a product, in particular made of metal
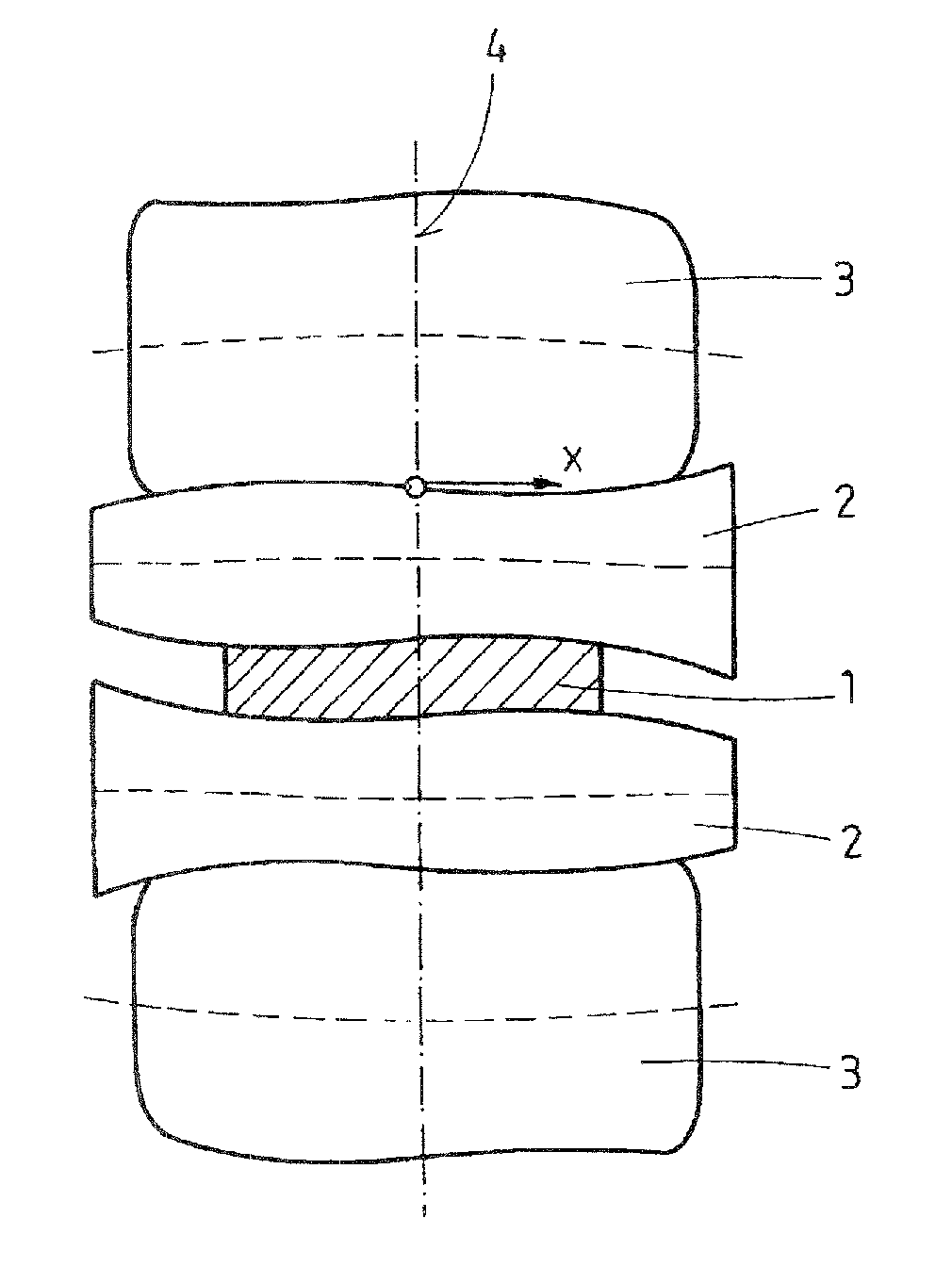
ActiveUS9180503B2Metal rolling stand detailsRollsEngineeringPolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checks
The invention relates to a roll stand for rolling a product, in particular made of metal, comprising a pair of first rollers contacted by a pair of second rollers supporting the first rollers, wherein the first roller and the second rollers have an asymmetrical radius curve (CVC grind) relative to a center plane, wherein the radius curve of the first rollers is represented by a polynomial of the third or fifth order. In order to design the wedging of a second roller supporting a first roller such that optimal operating conditions are set, the invention proposes that the radius curve of the second roller is given by a polynomial of the third or fifth order, wherein special relationships are prescribed for the ratios between the coefficients.
Owner:SMS GRP GMBH
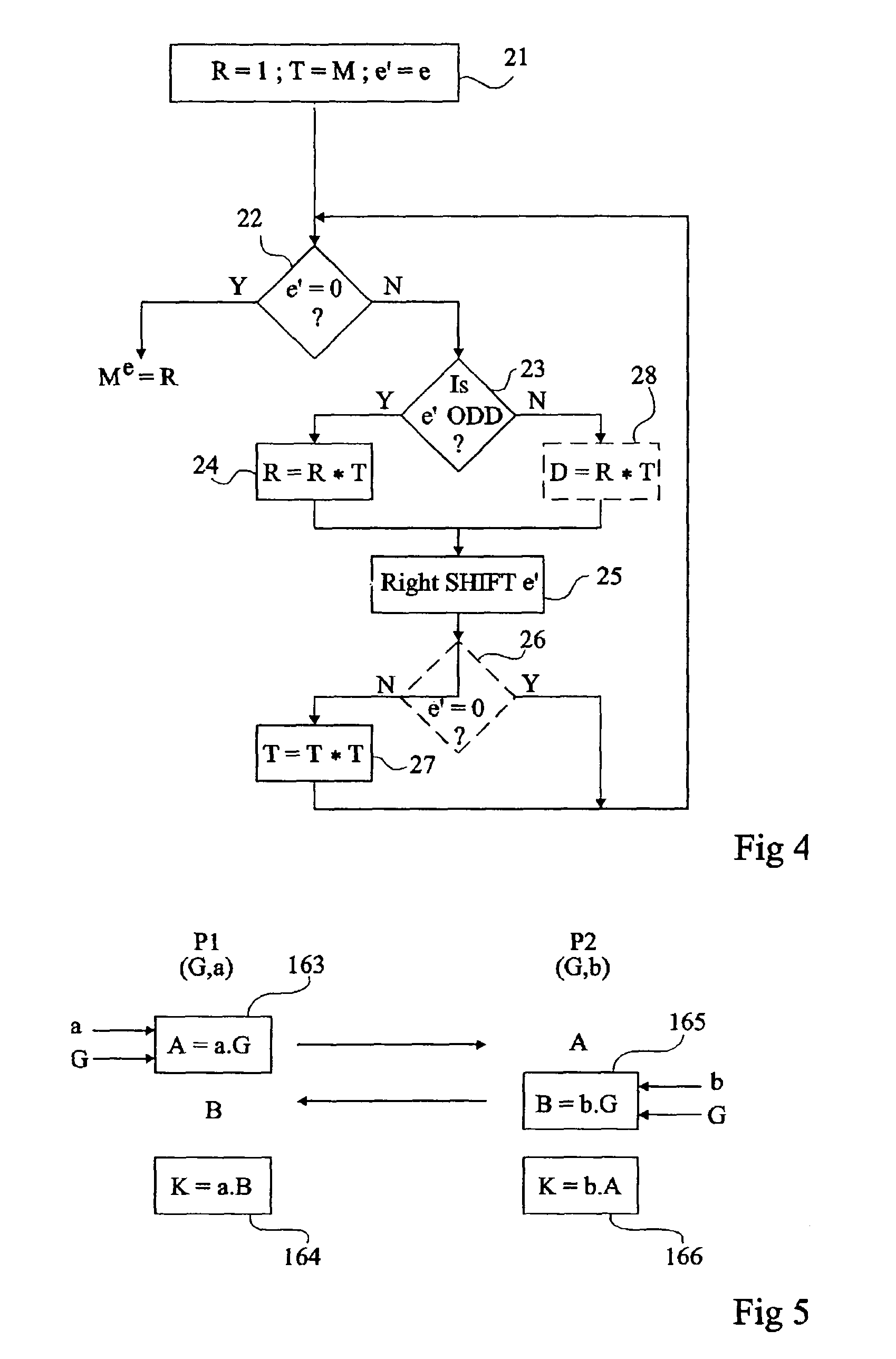
Detection of a disturbance in a calculation performed by an integrated circuit
ActiveUS8150029B2Prevent exploitationNot adversely affect the rapidity of execution of the calculationsUser identity/authority verificationComputer security arrangementsPolynomial representations of cyclic redundancy checksComputer science
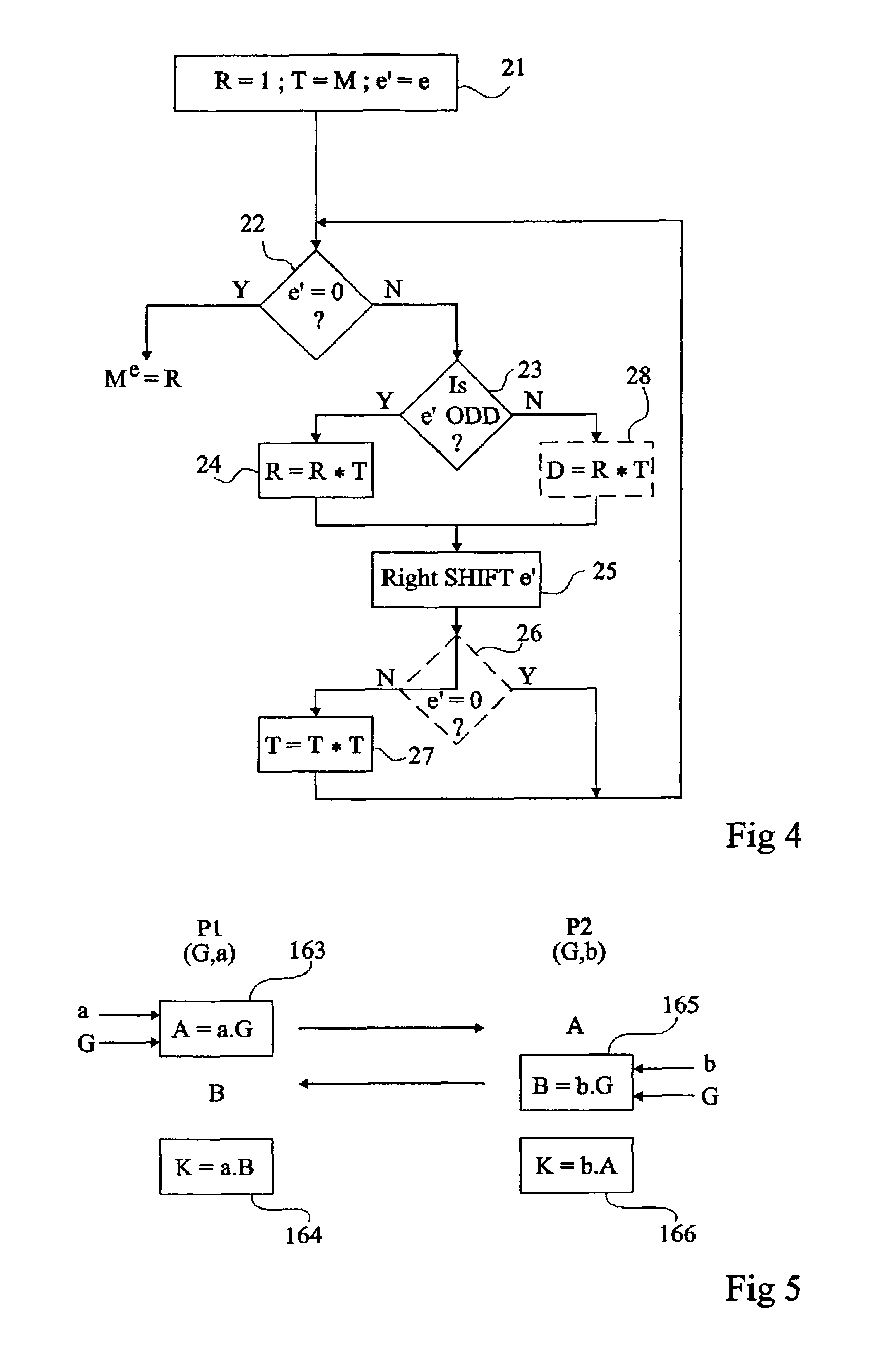
A method for detecting a disturbance of a calculation, by an electronic circuit, of a result of an integral number of applications of an internal composition law on elements of an abelian group, by successive iterations of different steps according to the even or odd character of a current coefficient of a polynomial representation of said integral number, the degree of which determines the number of iterations, each iteration including: in case of an odd current coefficient, updating at least one first variable intended to contain the result at the end of the calculation; and in case of an even current coefficient, of updating a second variable and a comparison of this second variable with an expected value.
Owner:PROTON WORLD INT
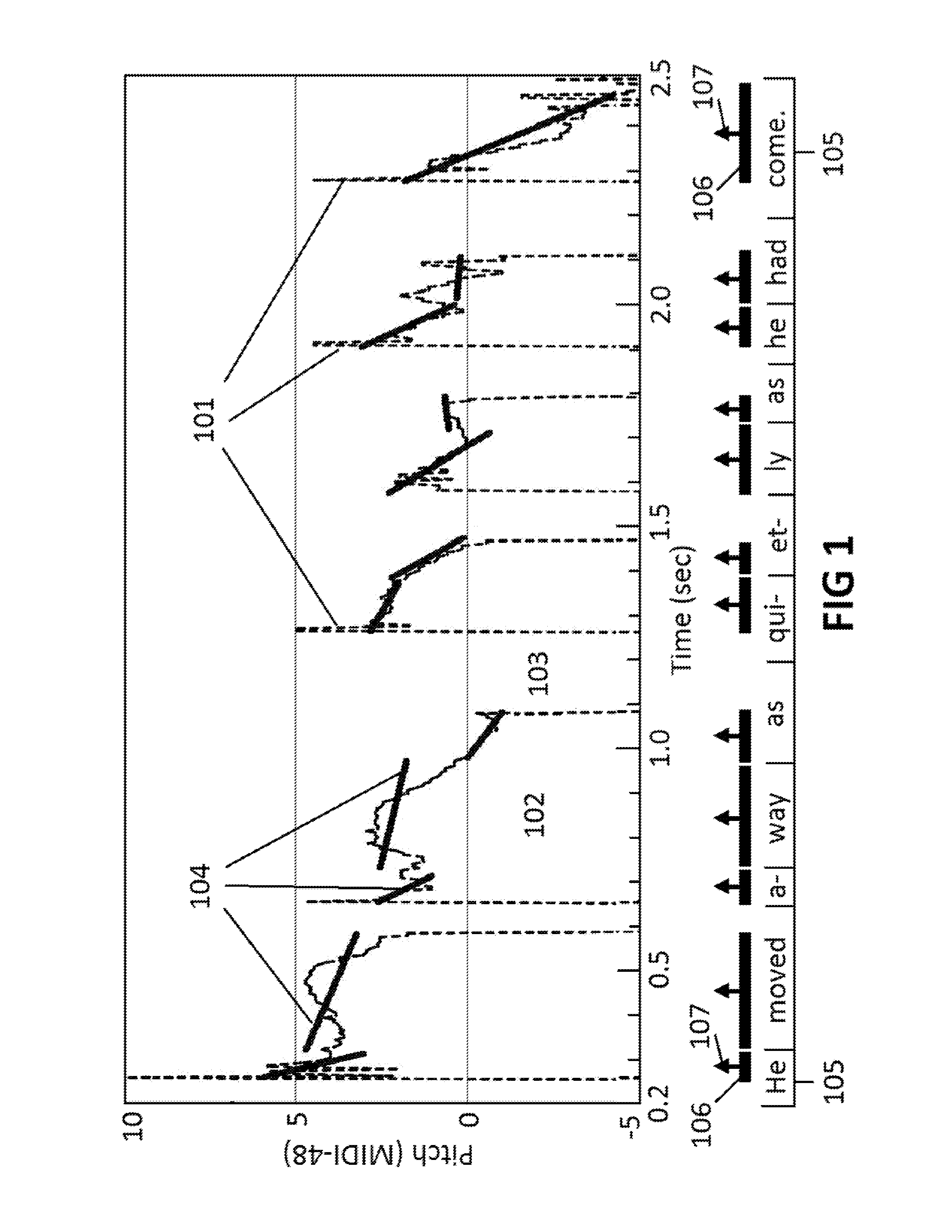
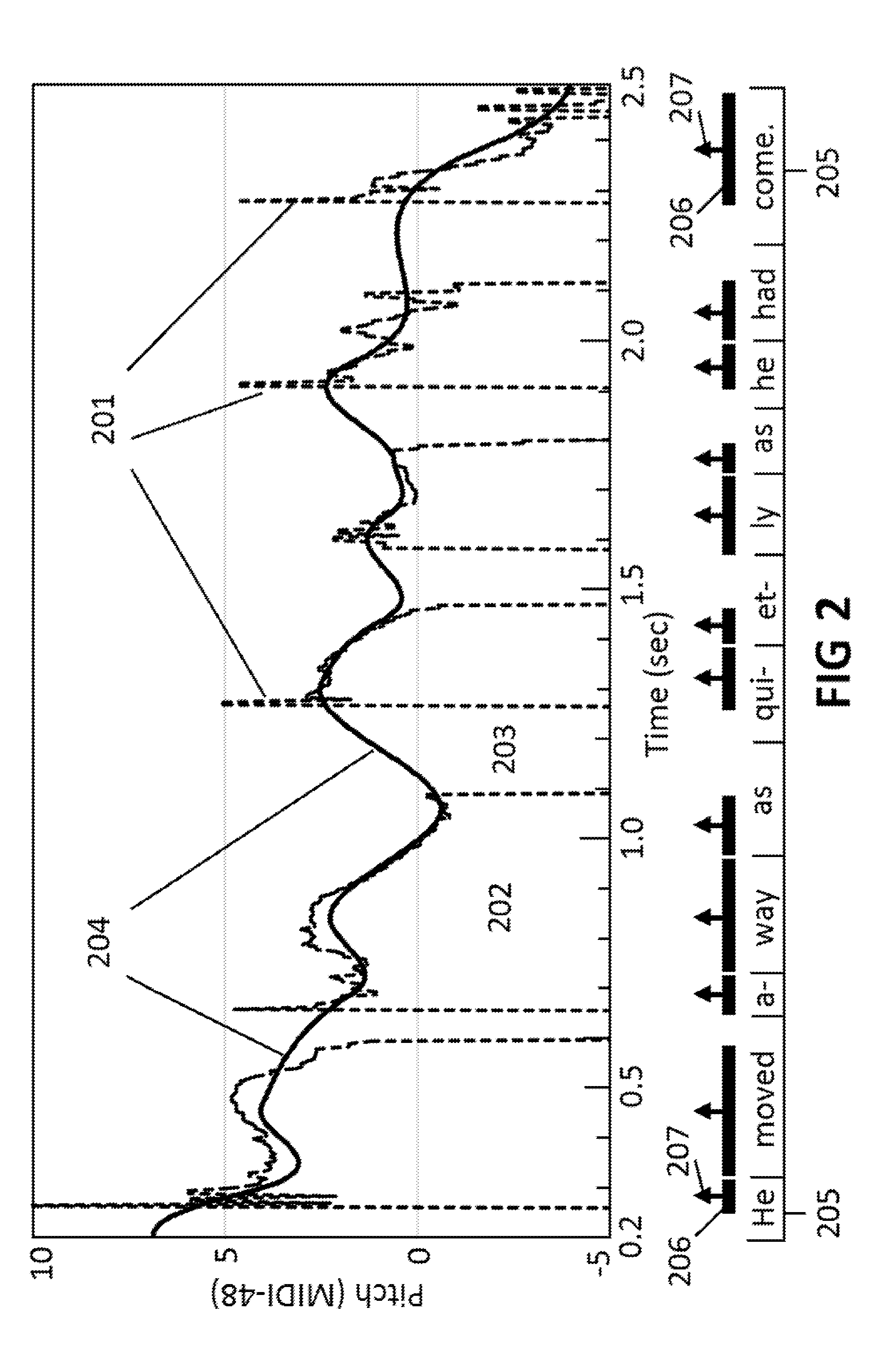
Prosody generation using syllable-centered polynomial representation of pitch contours
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
Shimming method for correcting inhomogeinity of a static magnetic field generated by a magnet of a nuclear magnetic resonance machine
ActiveUS20150276911A1Simple processMaximize rangeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonanceHarmonic
A shimming method for correcting inhomogeneity of a static magnetic field generated by a magnet of a nuclear magnetic resonance imaging machine includes: measuring the magnetic field at a plurality of points over a reference surface; generating a polynomial that solves Laplace's equation with boundary conditions given on the reference surface, the polynomial representing the magnetic field on the reference surface and having a plurality of harmonic terms, each associated with a coefficient; determining the coefficients from the field sampling values; defining a grid for positioning a plurality of correction elements and relating it to the field structure; and calculating the position and magnitude parameters of the correction elements, such that the correction elements affect the coefficients of the magnetic field to obtain the desired field characteristics, wherein the reference surface is a superquadric surface, such that the magnetic field is corrected in a volume delimited by the superquadric surface.
Owner:ESAOTE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com