Vision prosthesis device based on optical-disc micro-electrode array
A micro-electrode array and visual prosthesis technology, applied in the field of medical devices, can solve the problems of not solving the efficiency and practicality of electrical nerve stimulation, not taking into account the fixing method of the electrode array, and the small number of electrodes in the stimulating electrode array, etc. Biocompatibility, restoration of visual function, low risk effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings: this embodiment is implemented on the premise of the technical solution of the present invention, and detailed implementation methods and specific operating procedures are provided, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the following the described embodiment.
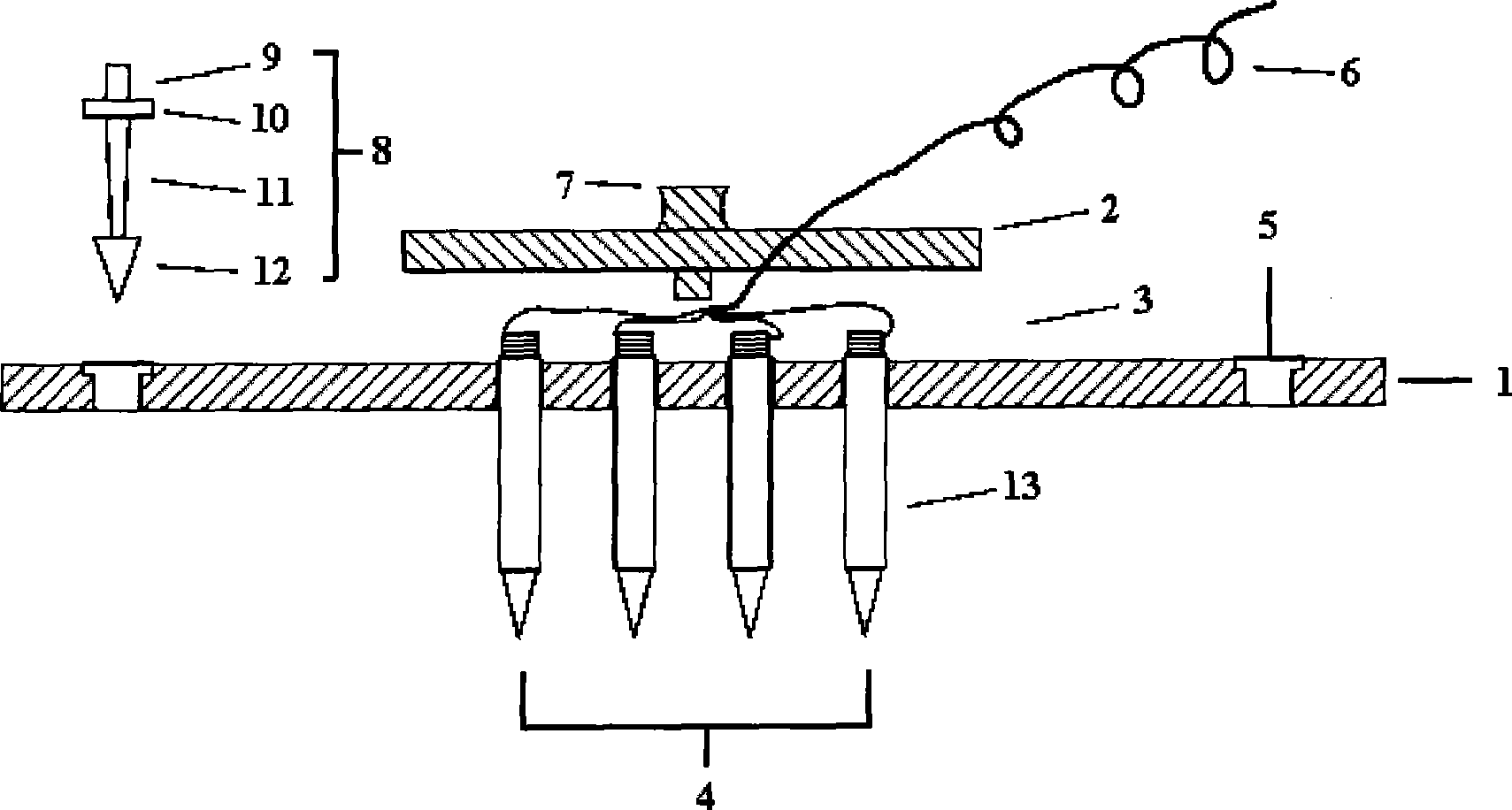
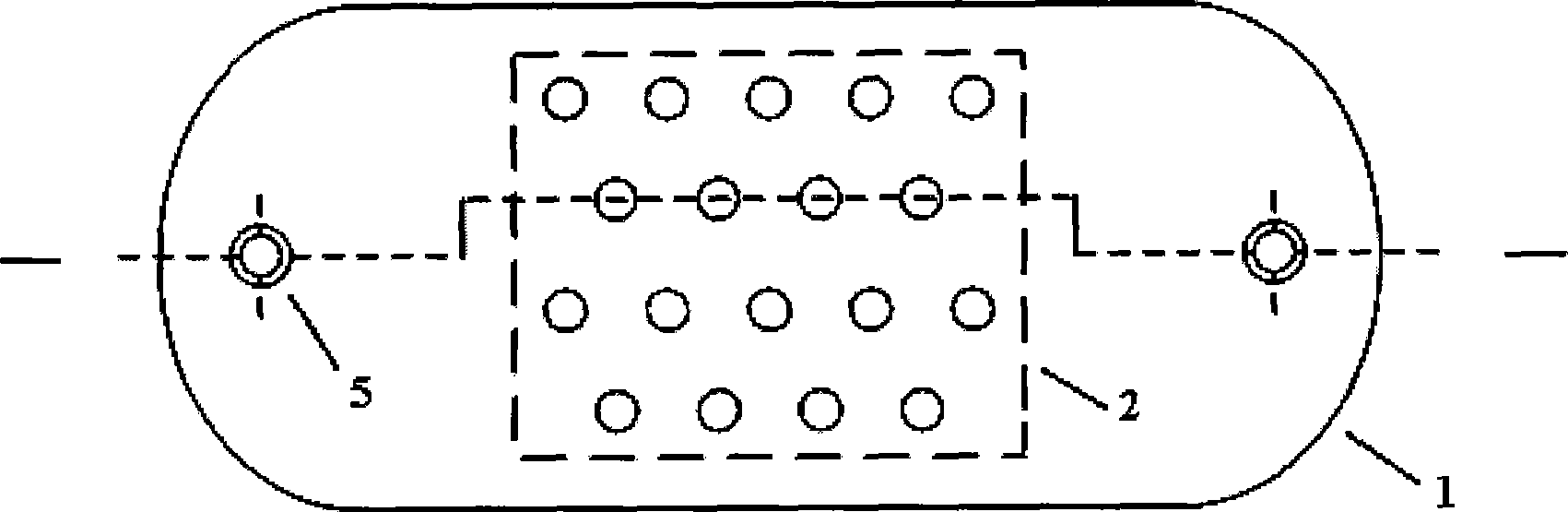
[0032] Such as figure 1 , figure 2As shown, this embodiment includes: a microelectrode array substrate 1, a cover plate 2, a microelectrode array 4, electrode wires 6 and retinal pins 8, wherein,
[0033] The two ends of the microelectrode array substrate 1 are respectively provided with a retinal pin via hole 5, and the middle position is provided with 18 electrode via holes, and the retinal pin 8 passes through the retinal pin via hole to fix the micromotor array base 1 on the optic disk 15 of the retina, The microelectrode array 4 is composed of 18 electrode wir...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com