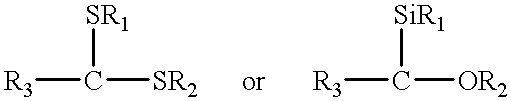Patents
Literature
891 results about "Micro electrode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
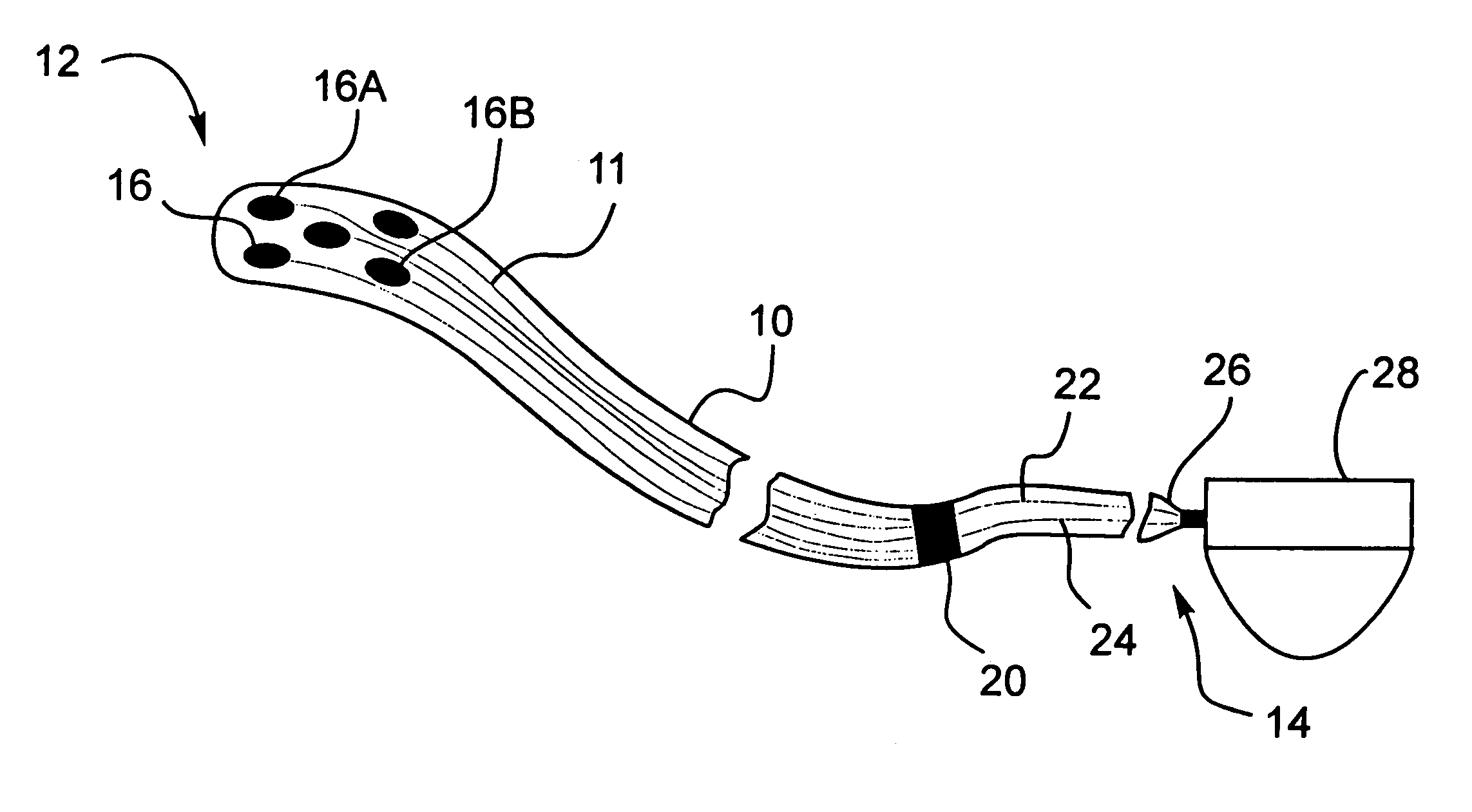
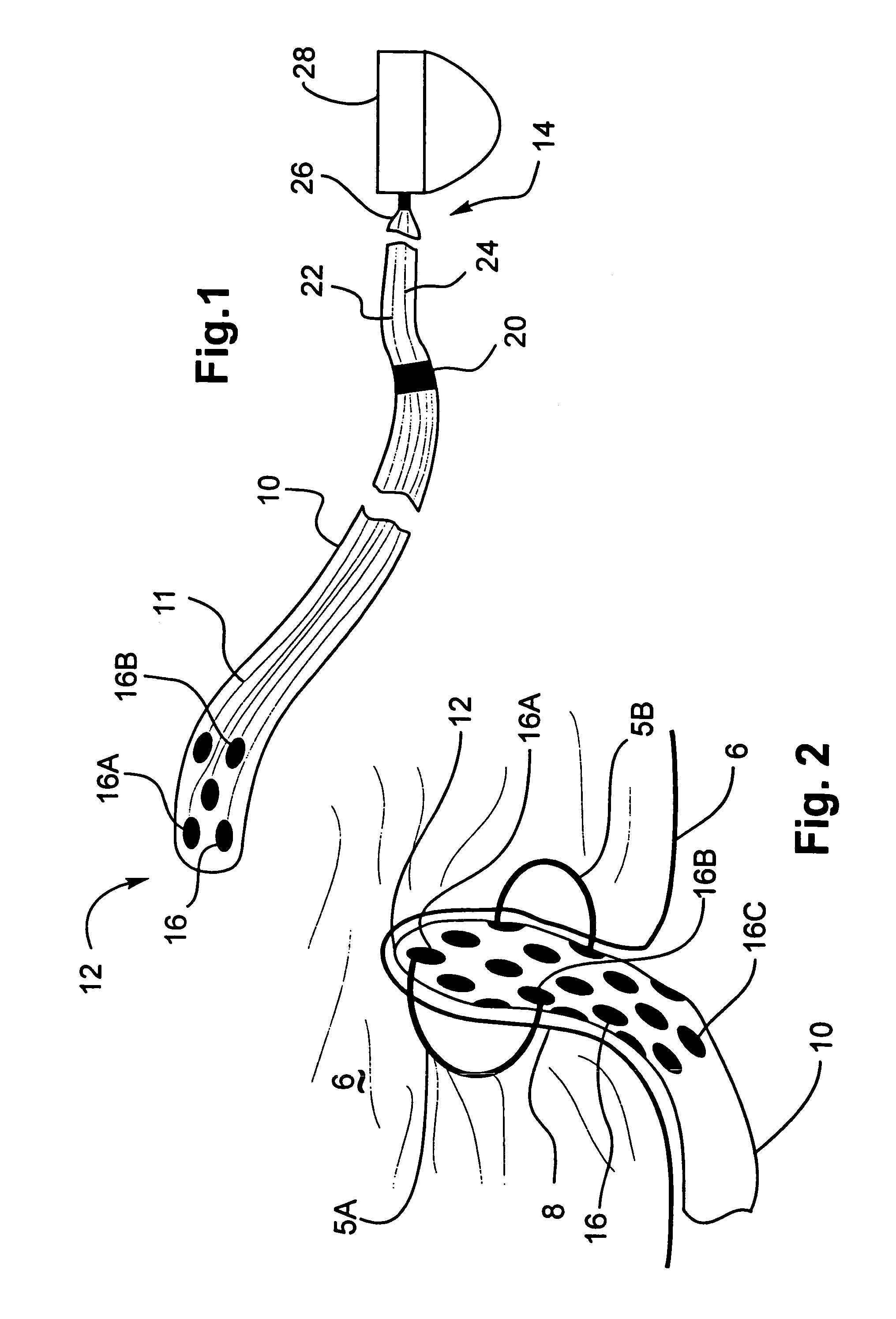
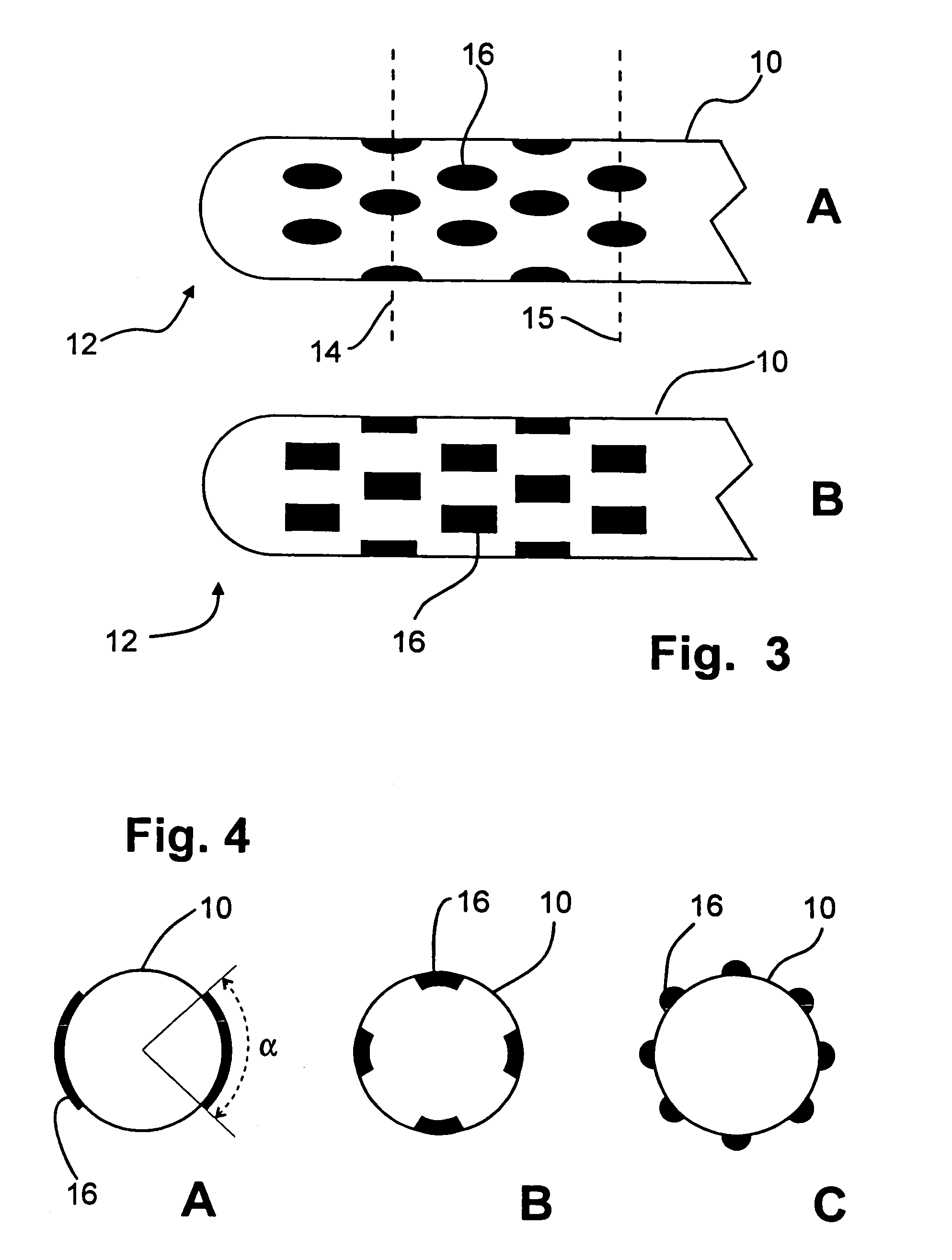
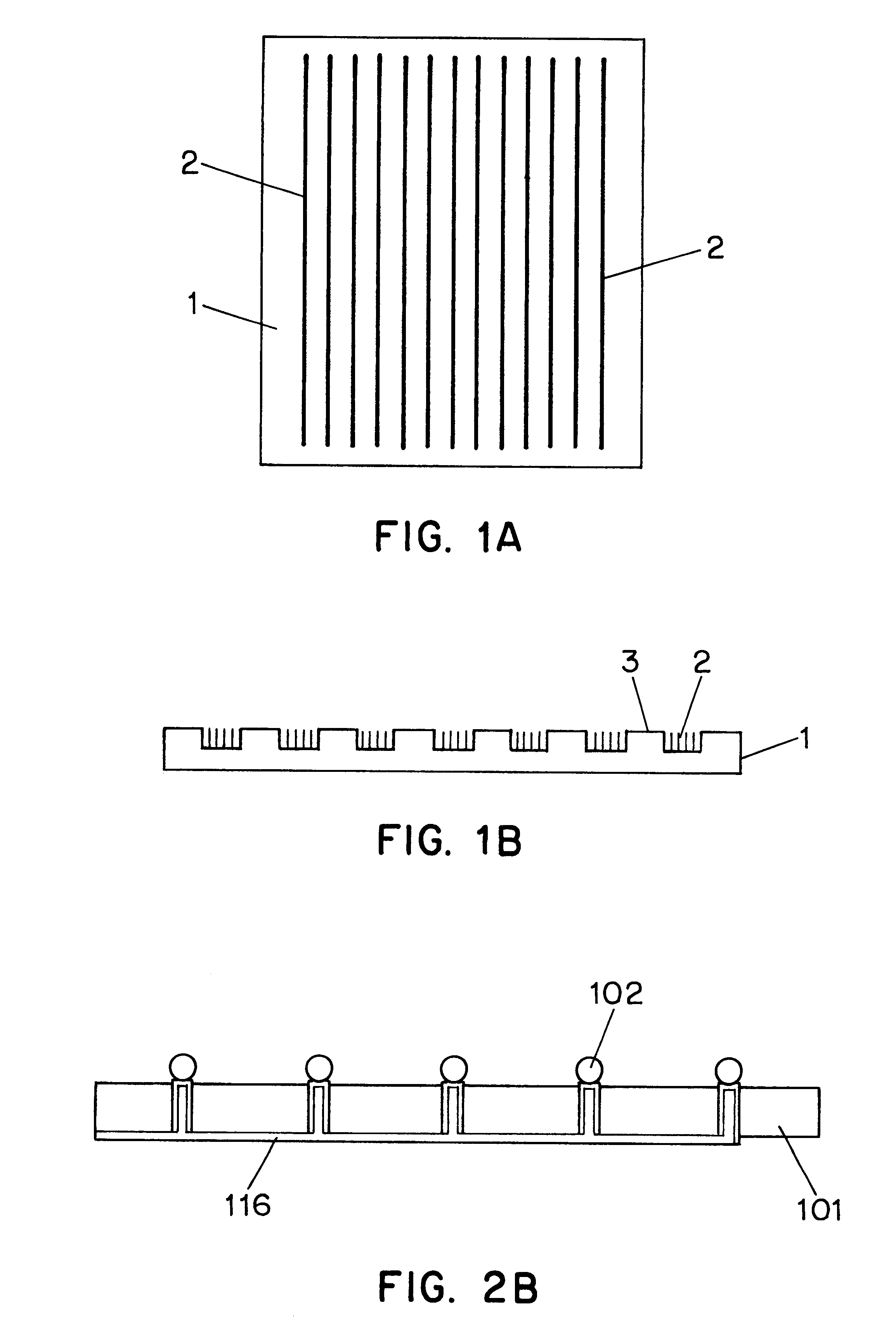
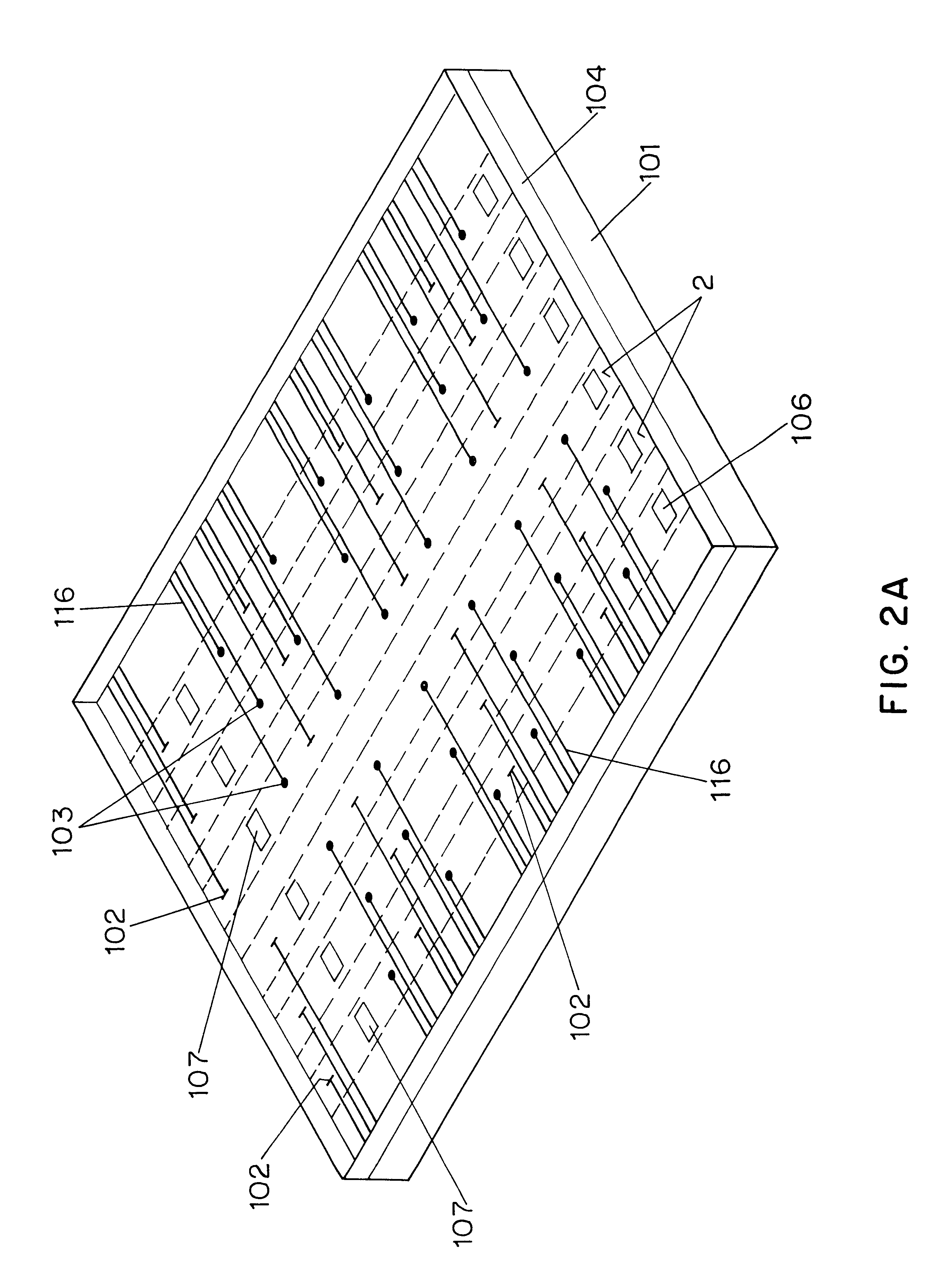
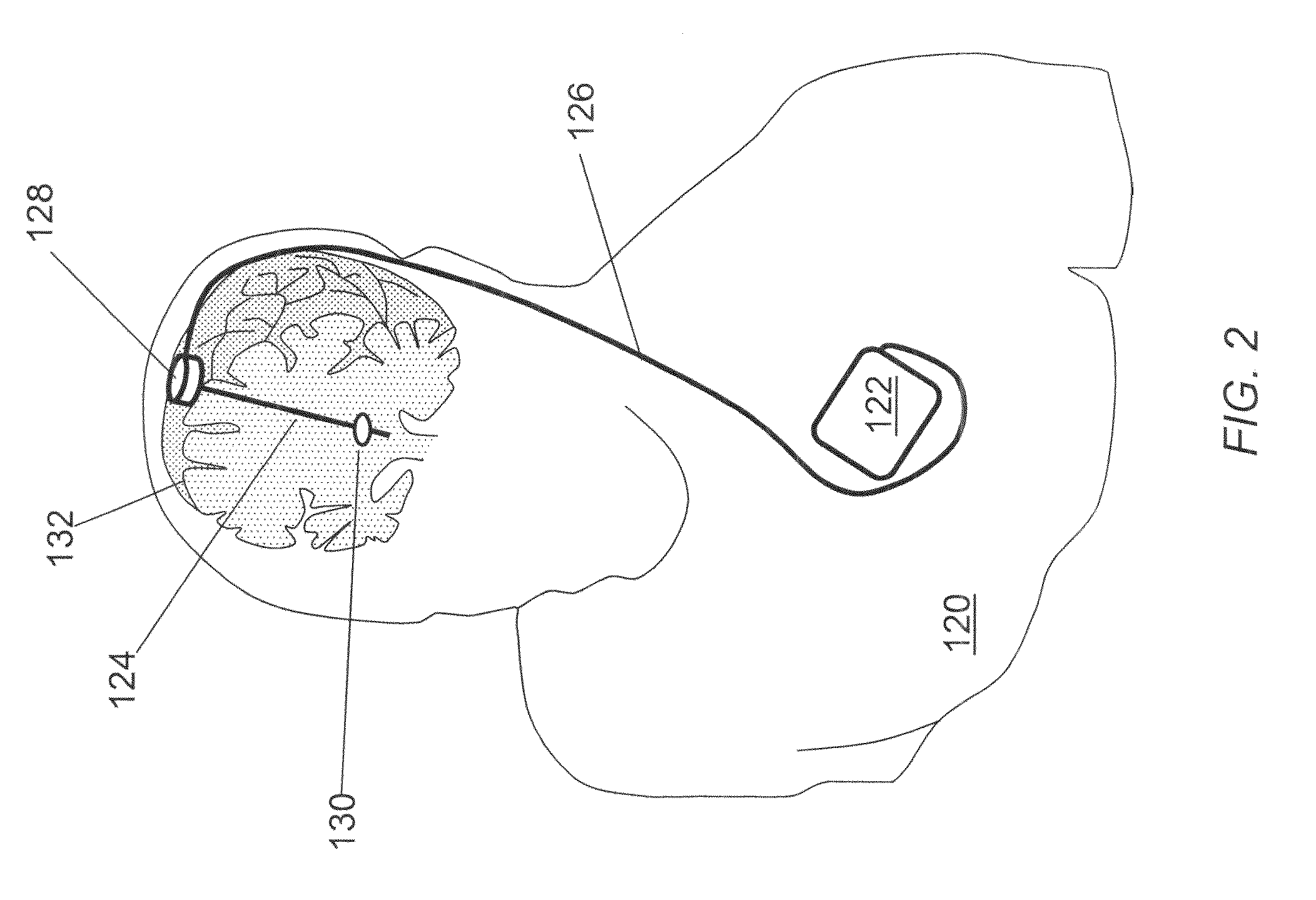
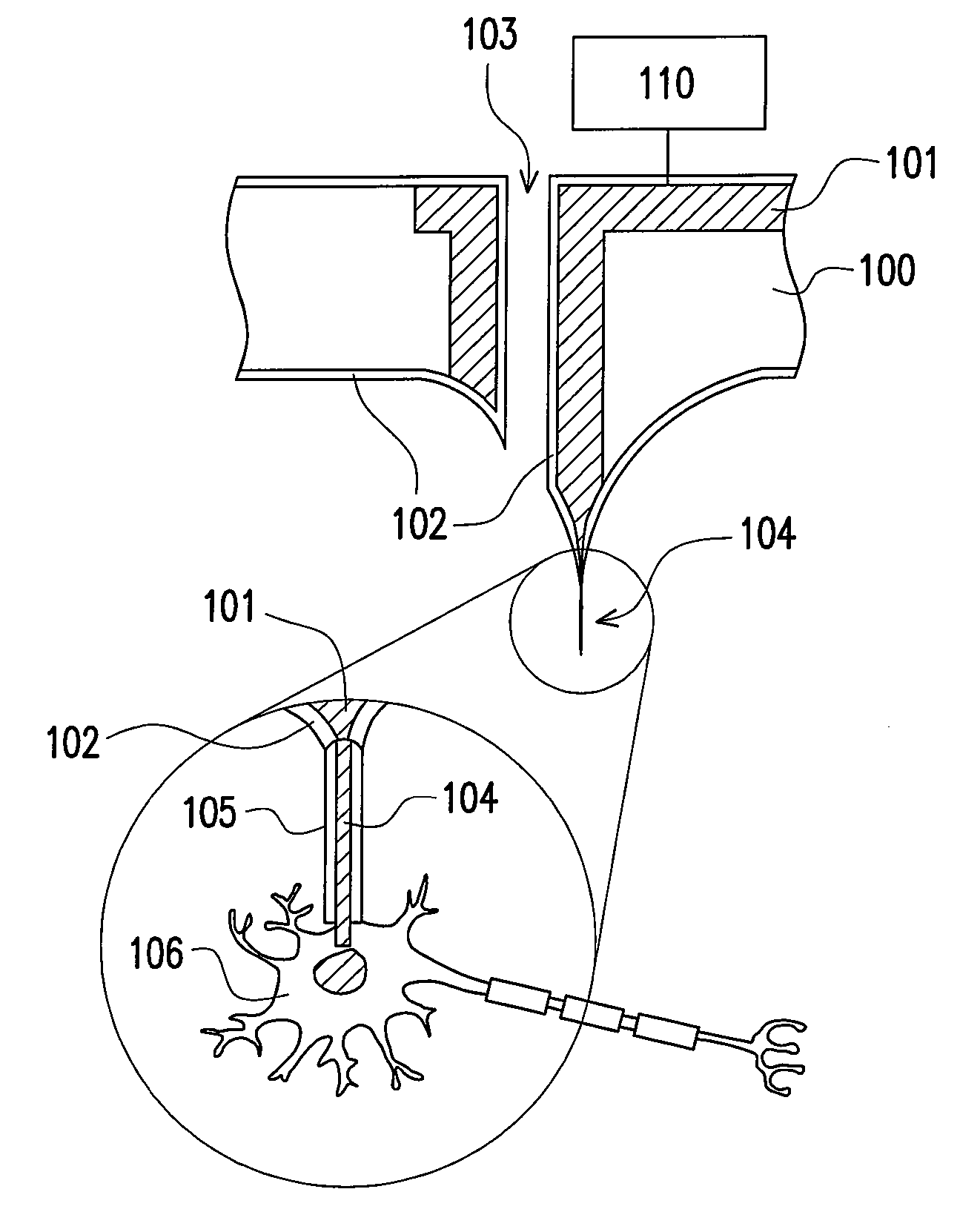
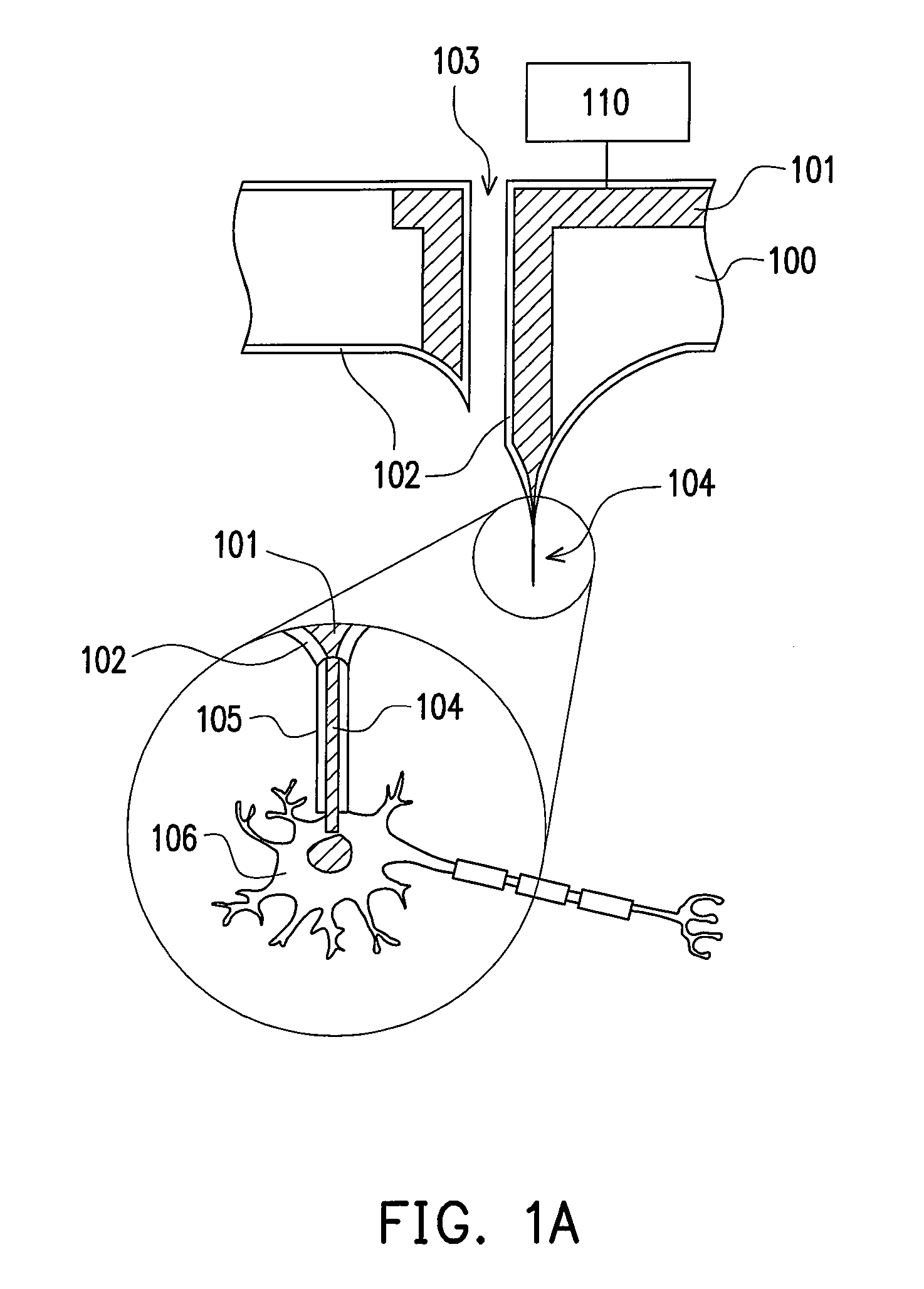
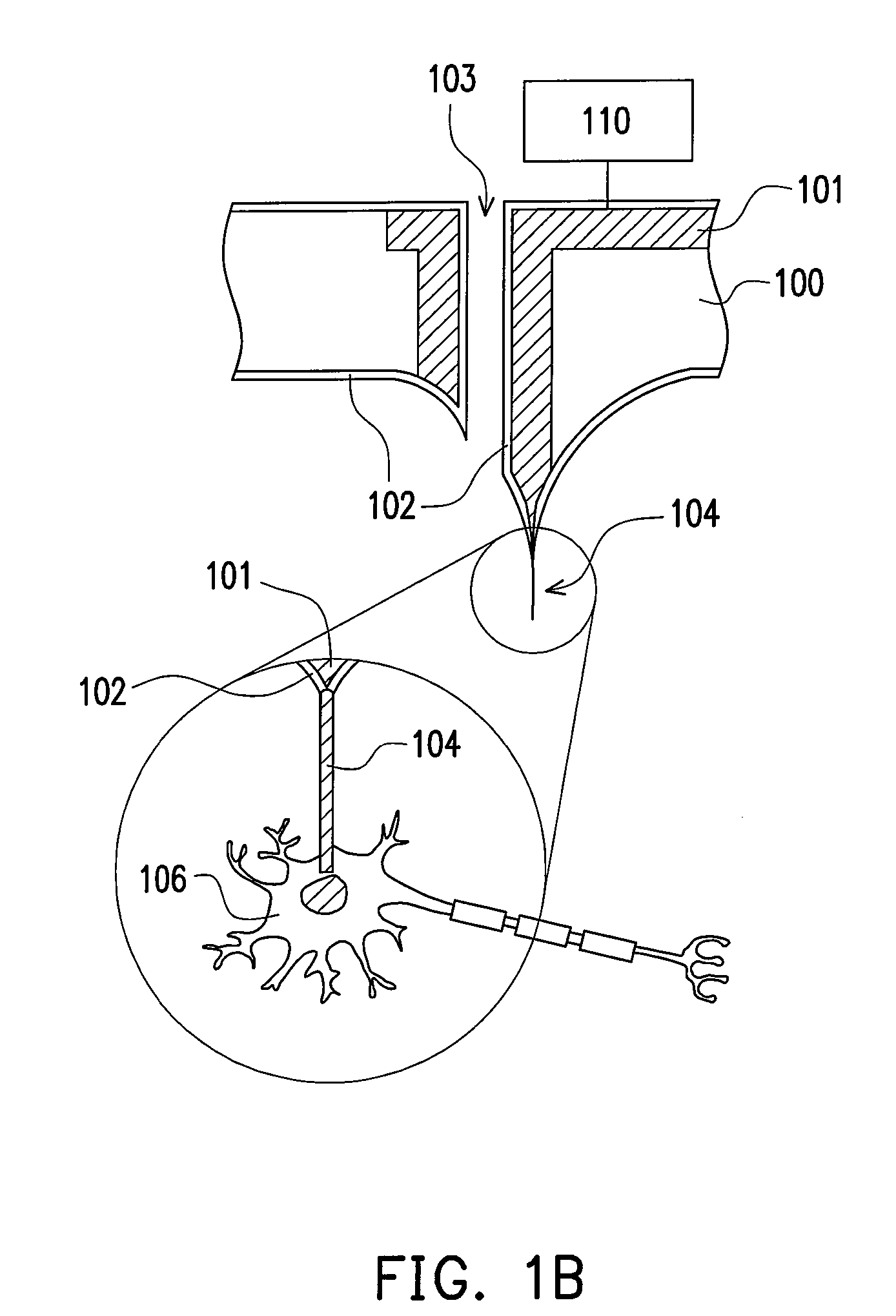
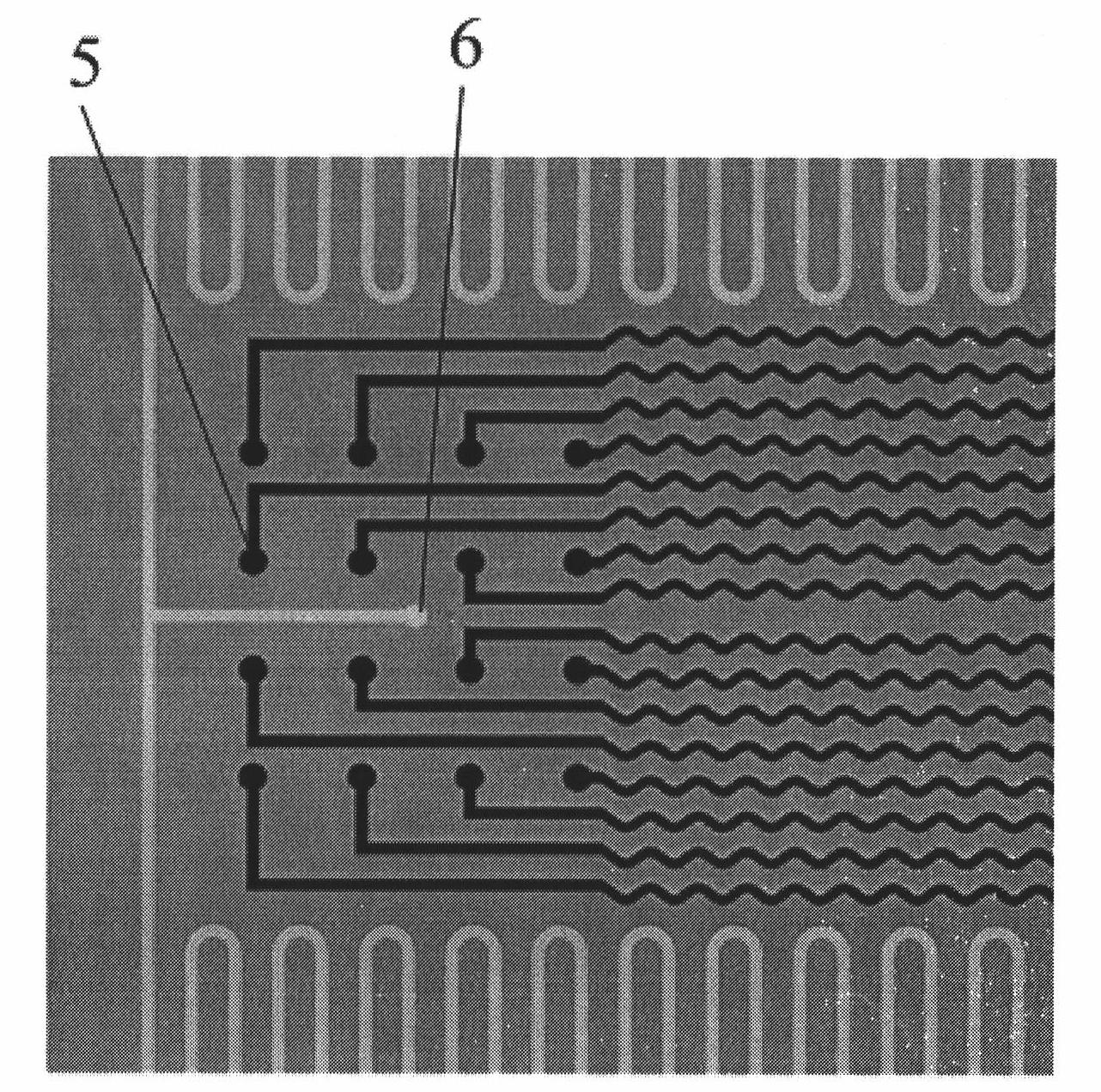
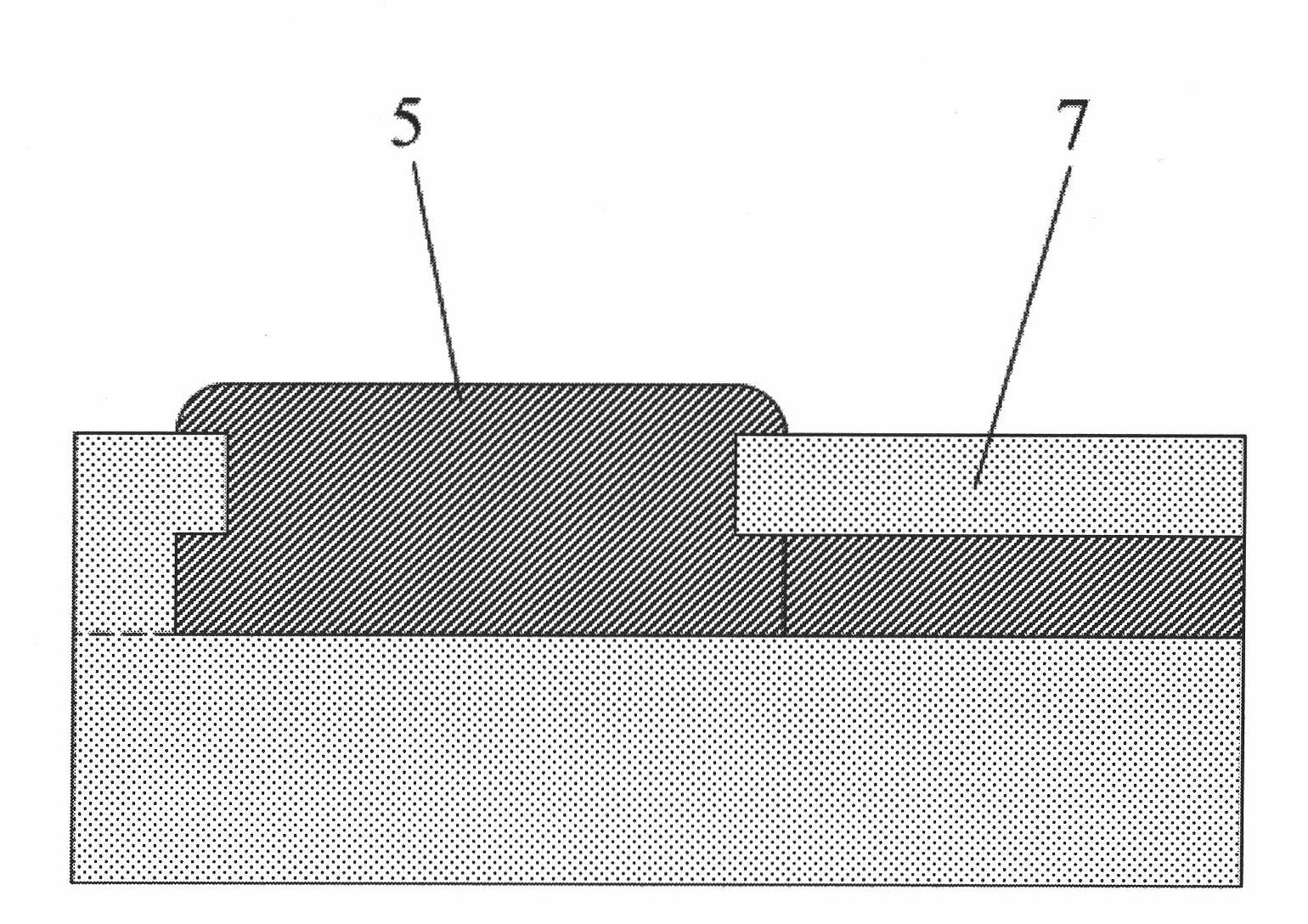
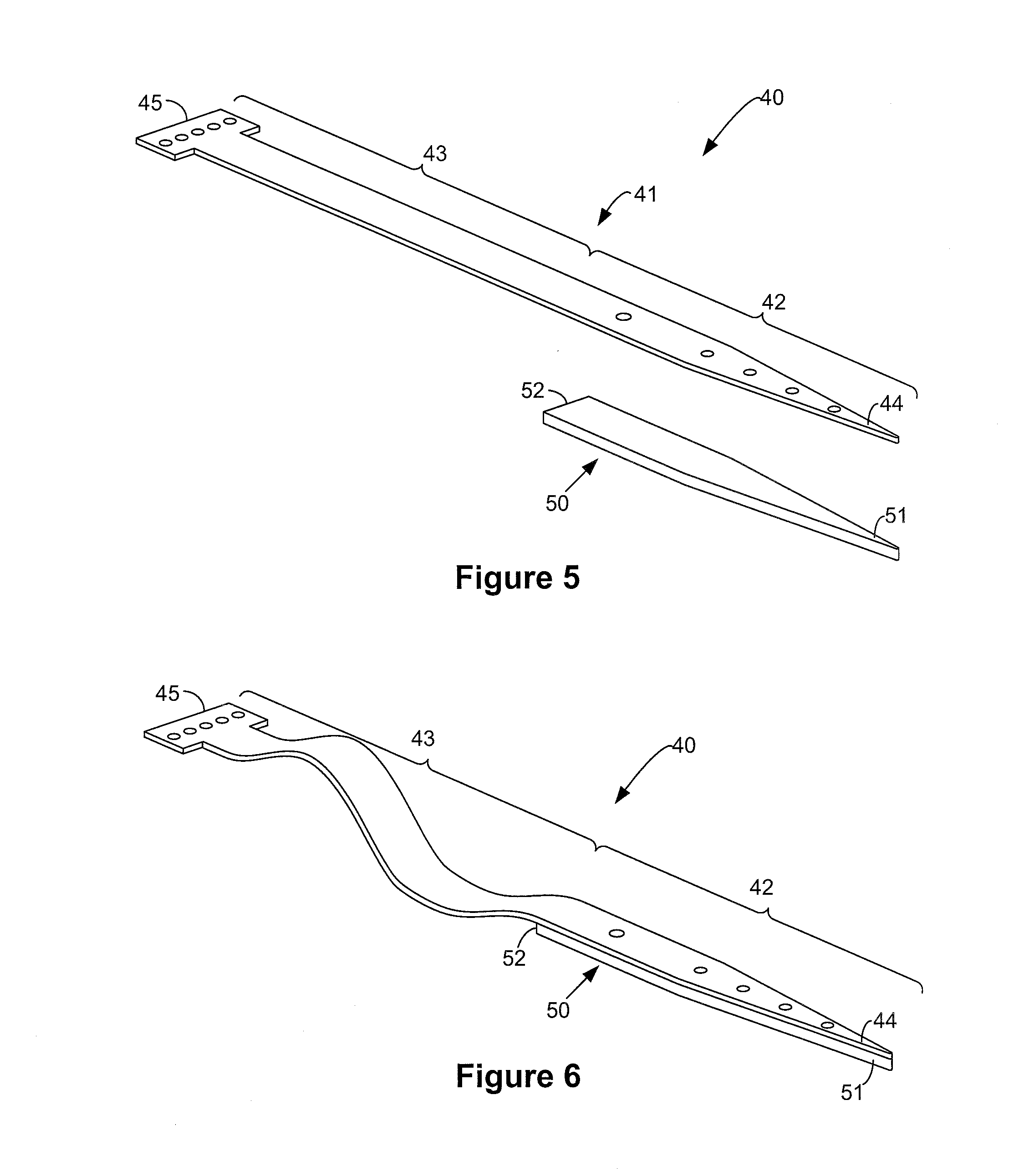
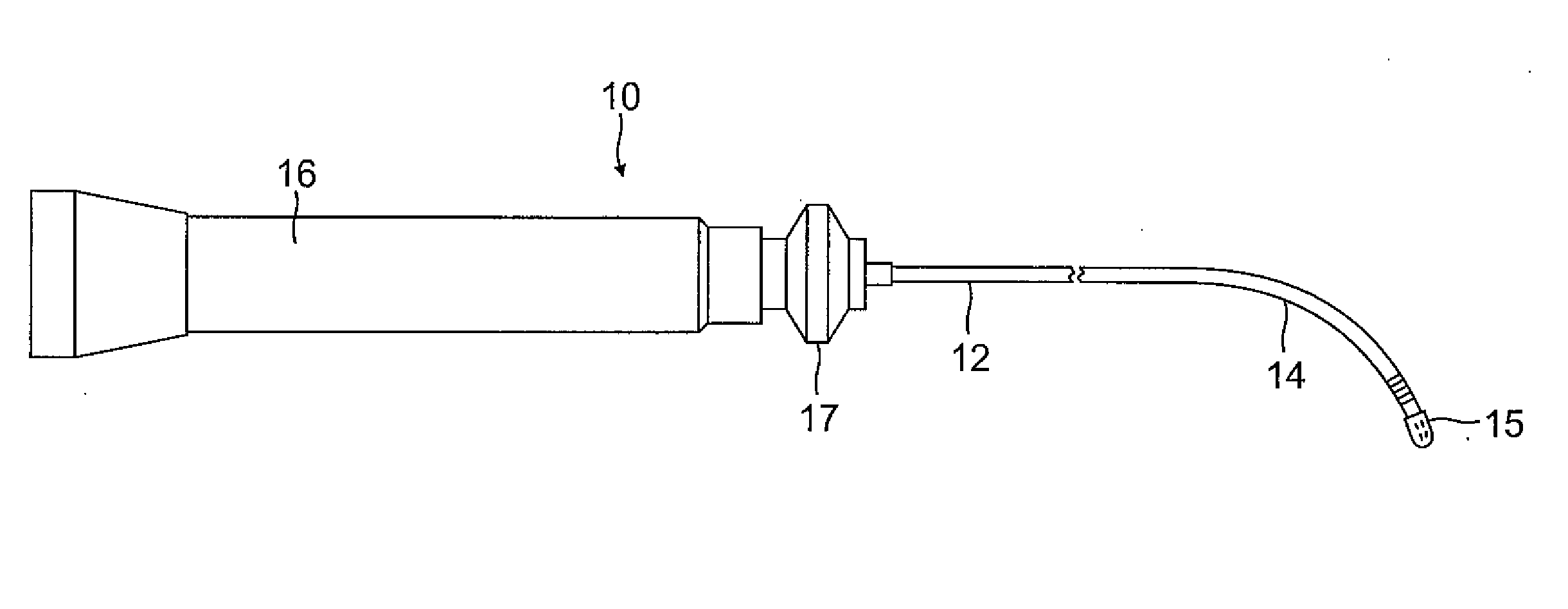
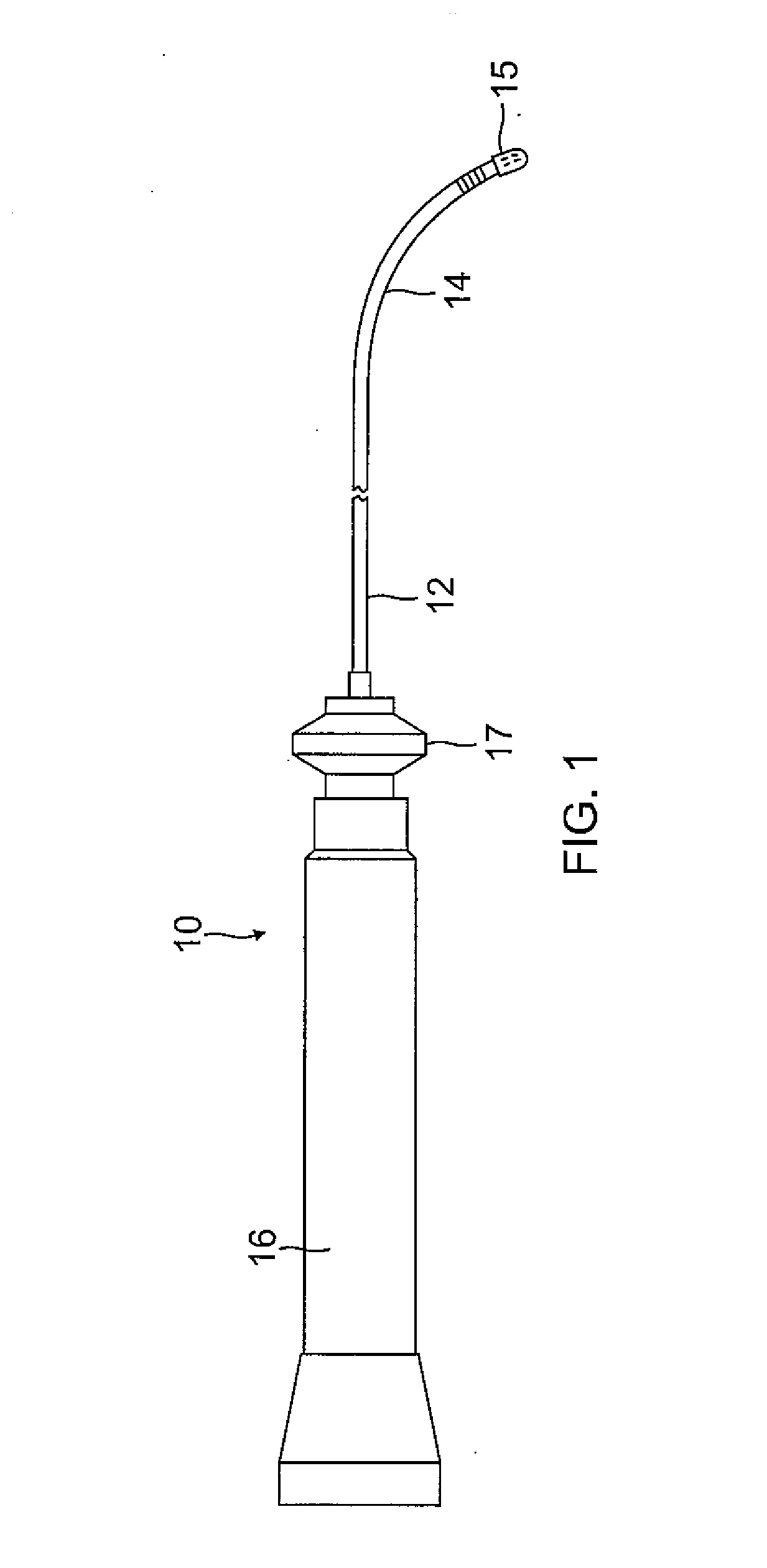
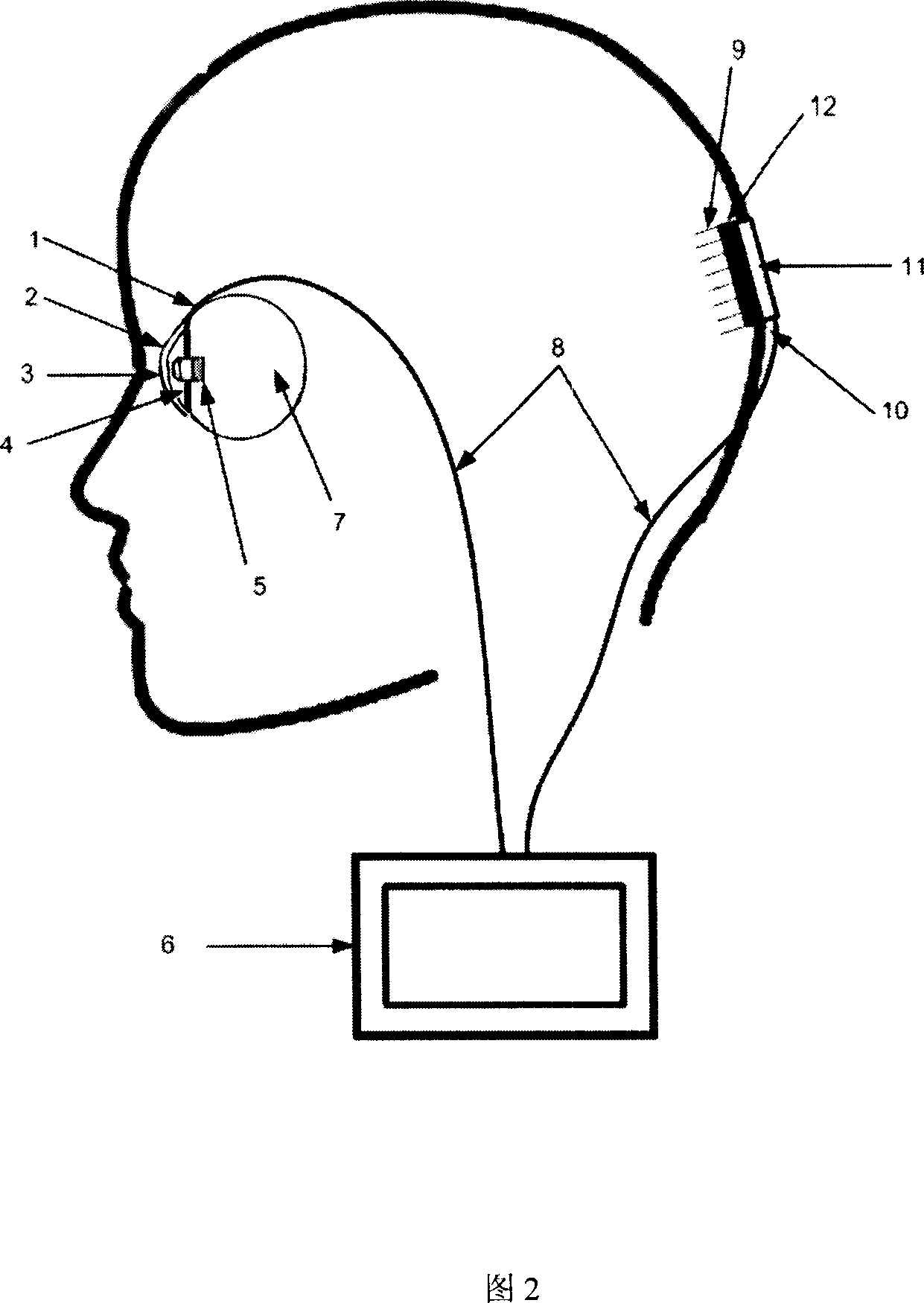
Medical implant device for electrostimulation using discrete micro-electrodes
InactiveUS7096070B1Good electrostimulationPromote resultsSurgeryInternal electrodesElectricityImplanted device
An improved medical implant device is provided which has a plurality of micro-electrodes. The use of a plurality of micro-electrodes allows a clinically effective electrical stimulation pathway to be selected once the implant is positioned within or adjacent to the tissue to be treated even if the implant is not optimally placed or located. Thus, in cases where the implant is not optimally placed, it is not necessary to remove the implant and then reposition it within or adjacent to the tissue to be treated, thereby reducing stress to the patient caused by additional surgery. Moreover, using the micro-electrodes of this invention, directional electrostimulation can be provided to the tissue to be treated. Implant devices with a plurality of micro-electrodes are provided which are especially adapted for use in reducing the frequency and / or severity of neurological tremors. Other implant devices having micro-electrodes are provided which are especially adapted for electrostimulation and / or electrical monitoring of endo-abdominal tissue or viscera.
Owner:TRANSNEURONIX INC
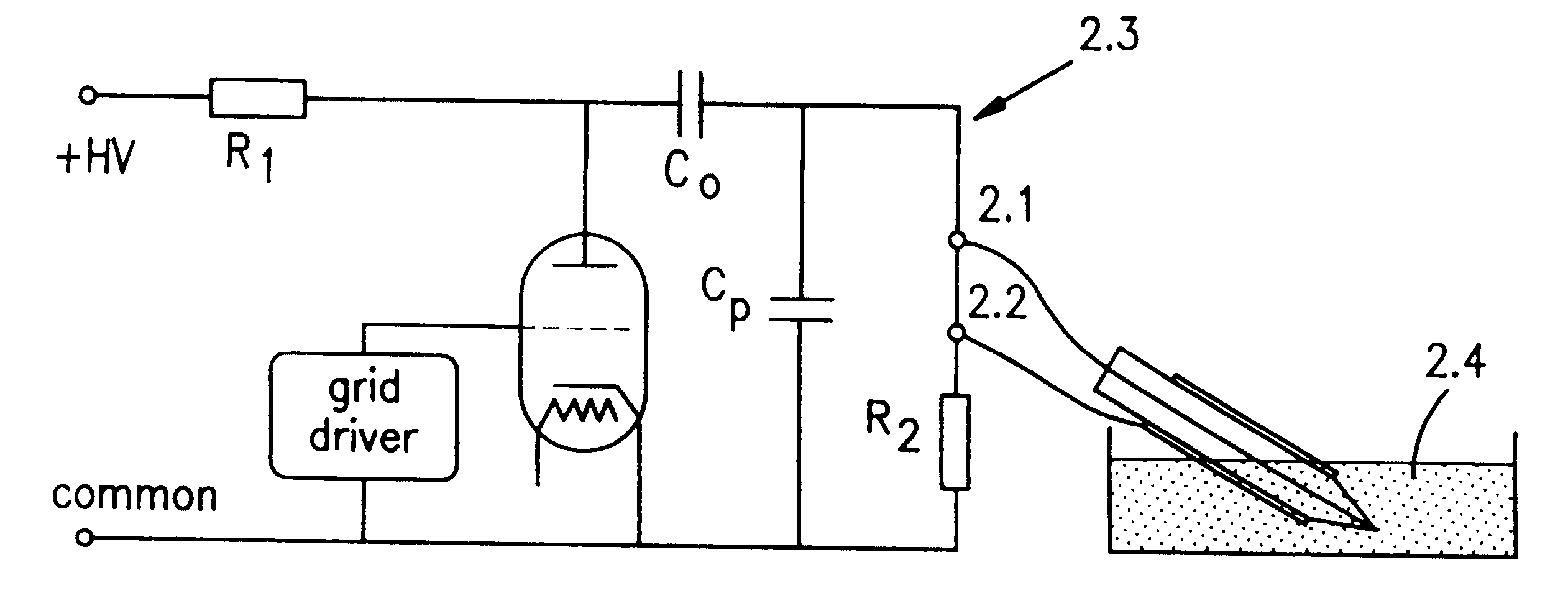
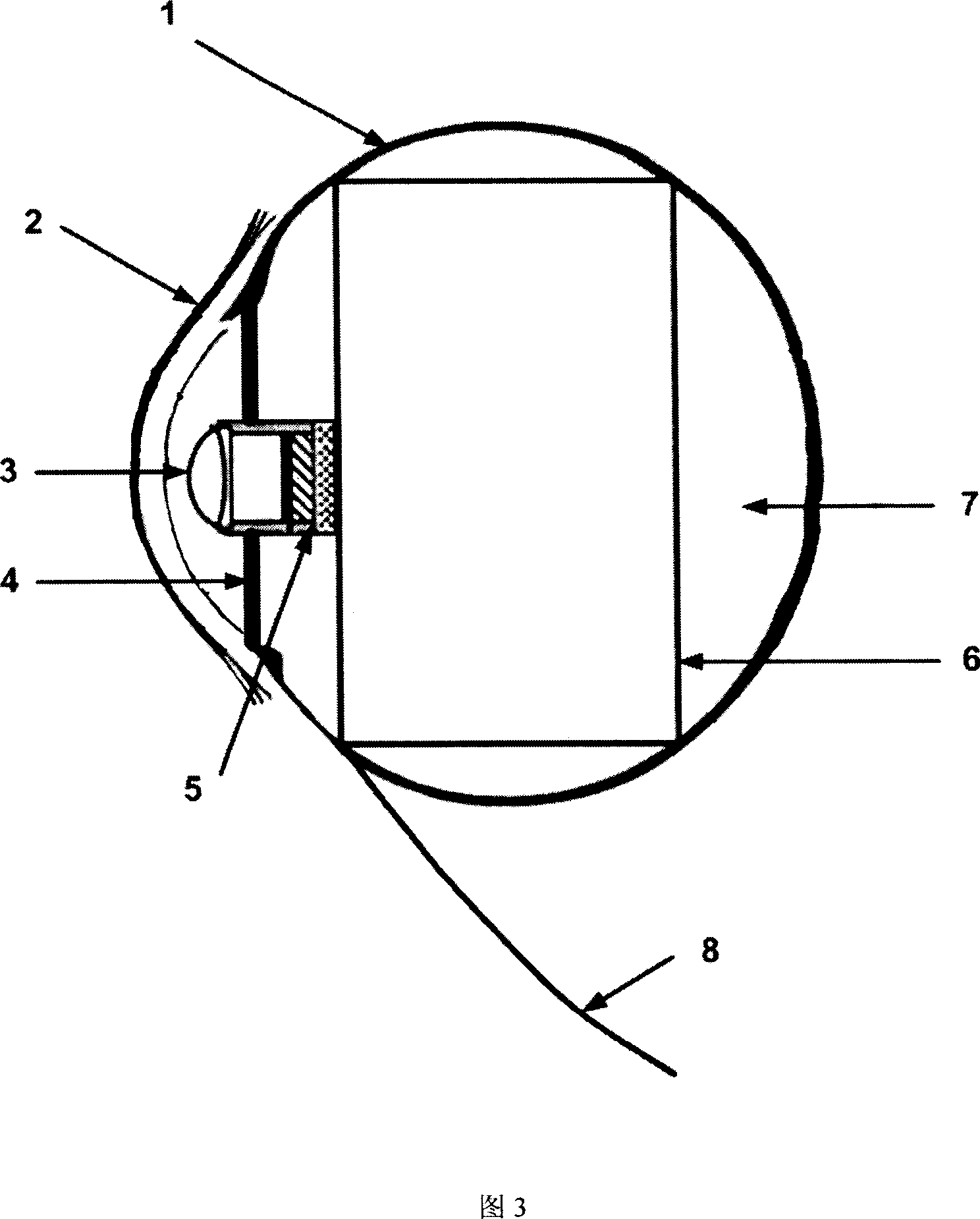
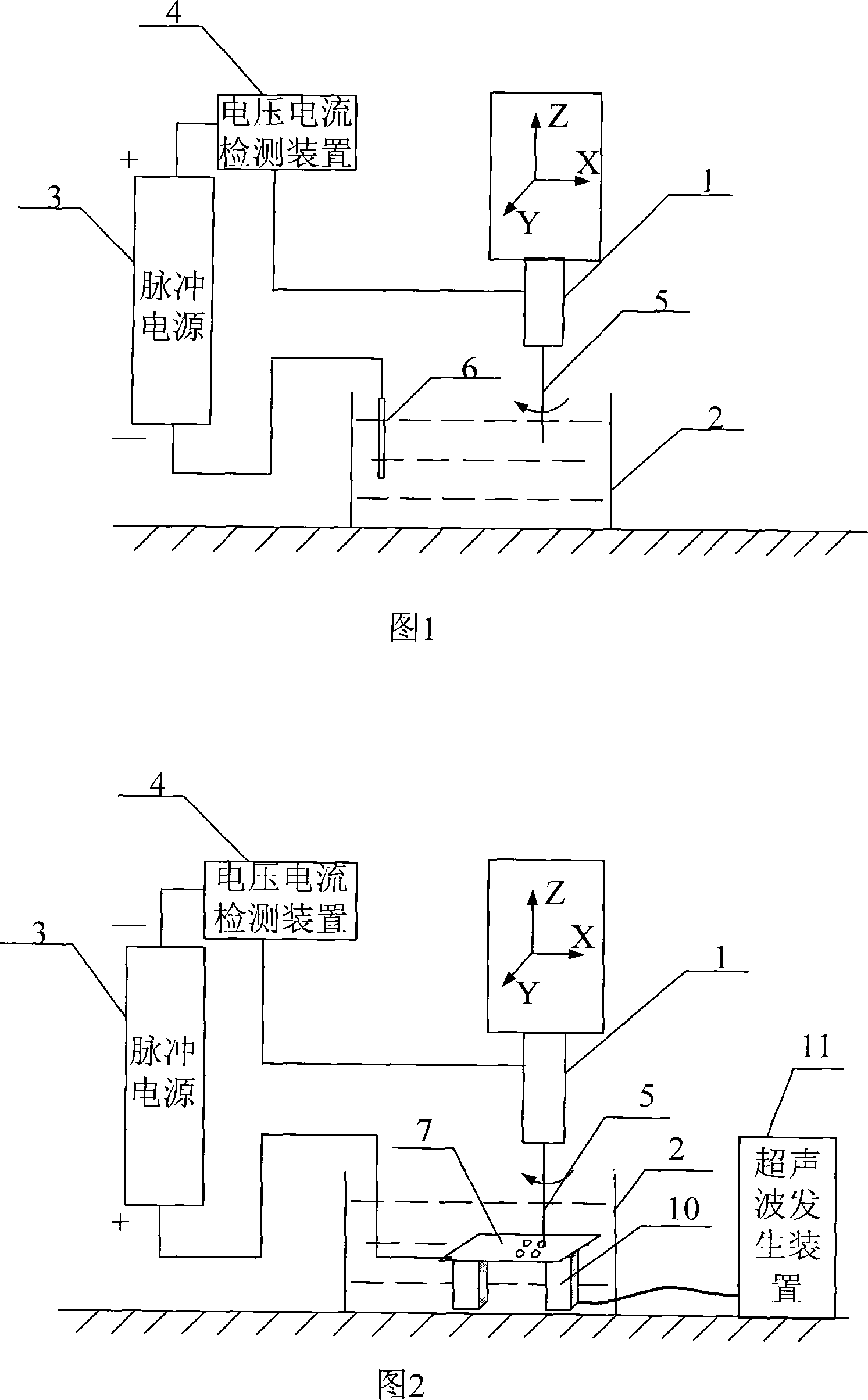
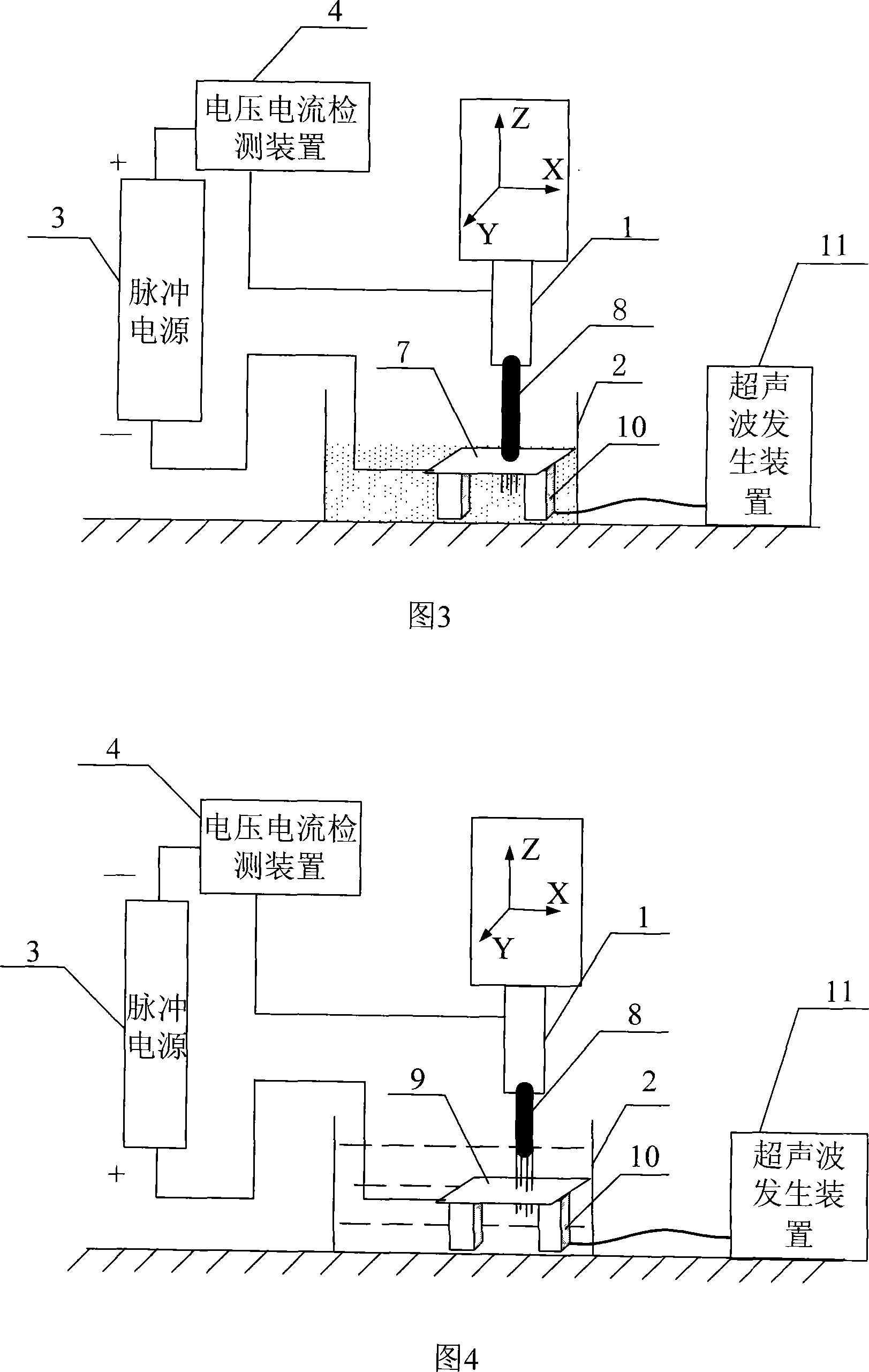
Method and a device for electro microsurgery in a physiological liquid environment
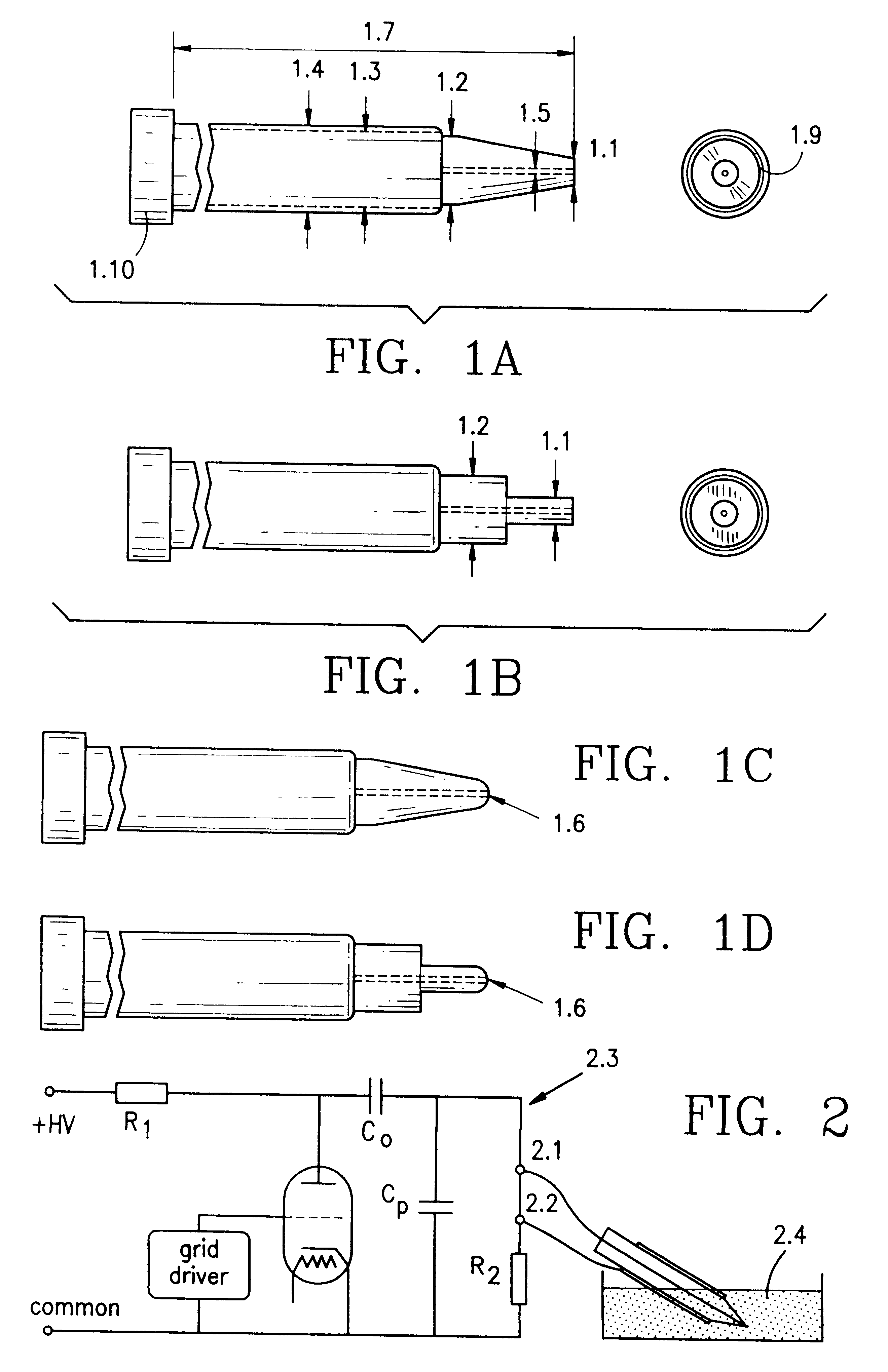
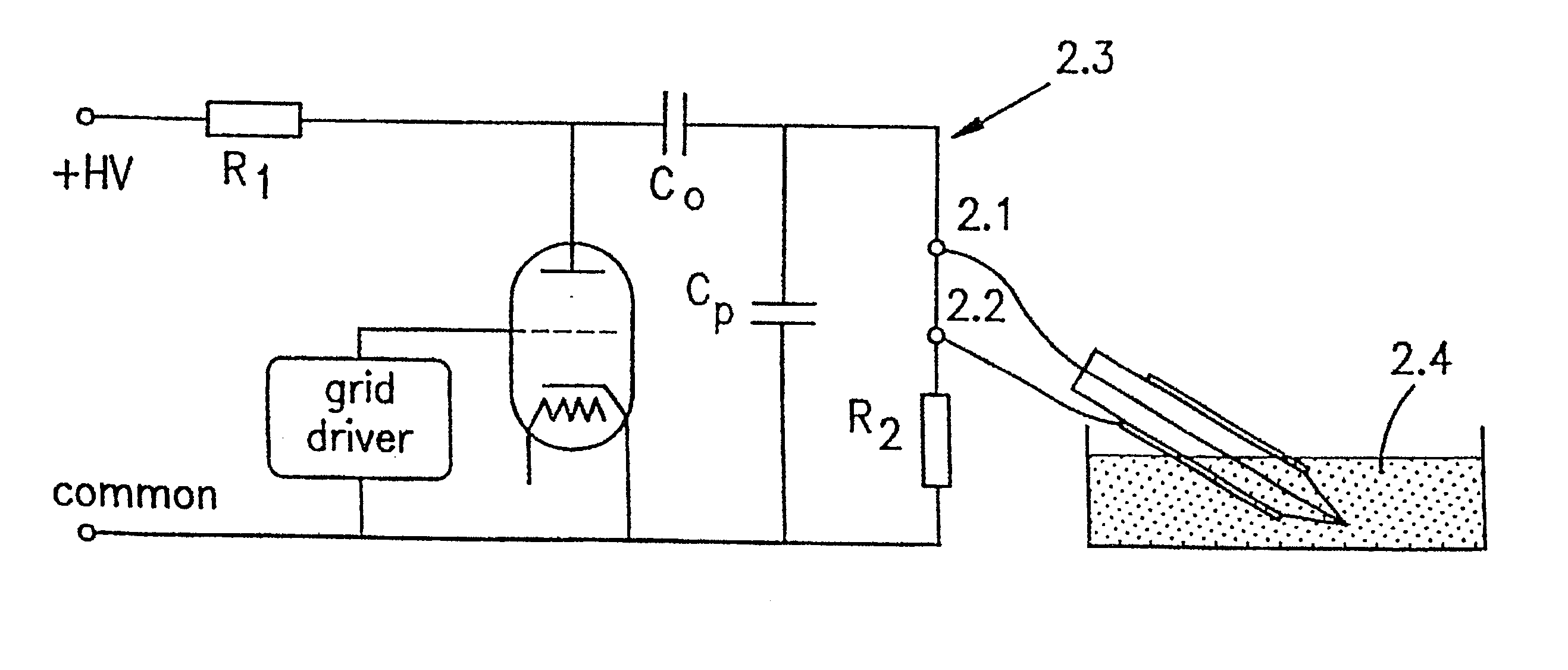
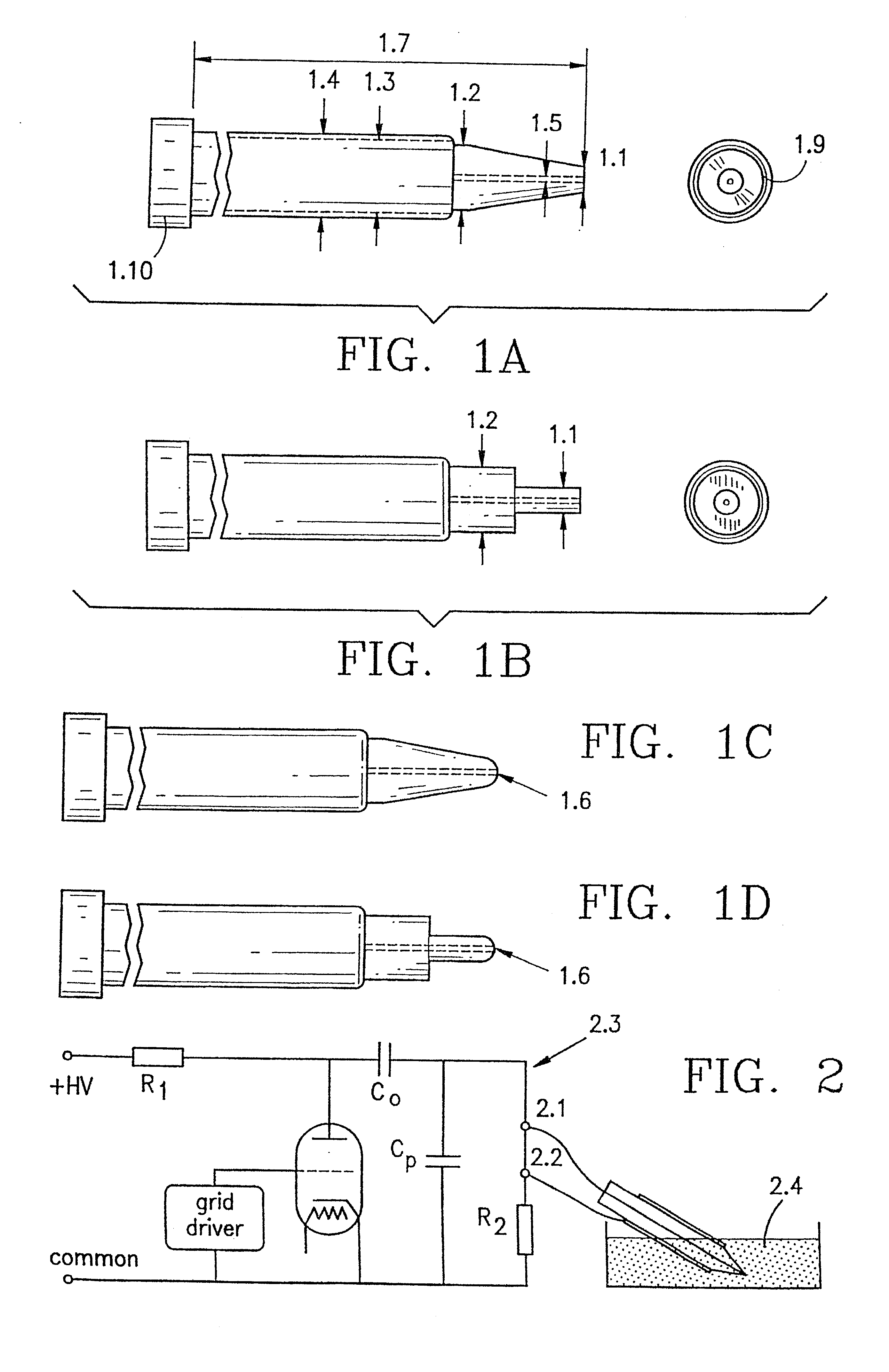
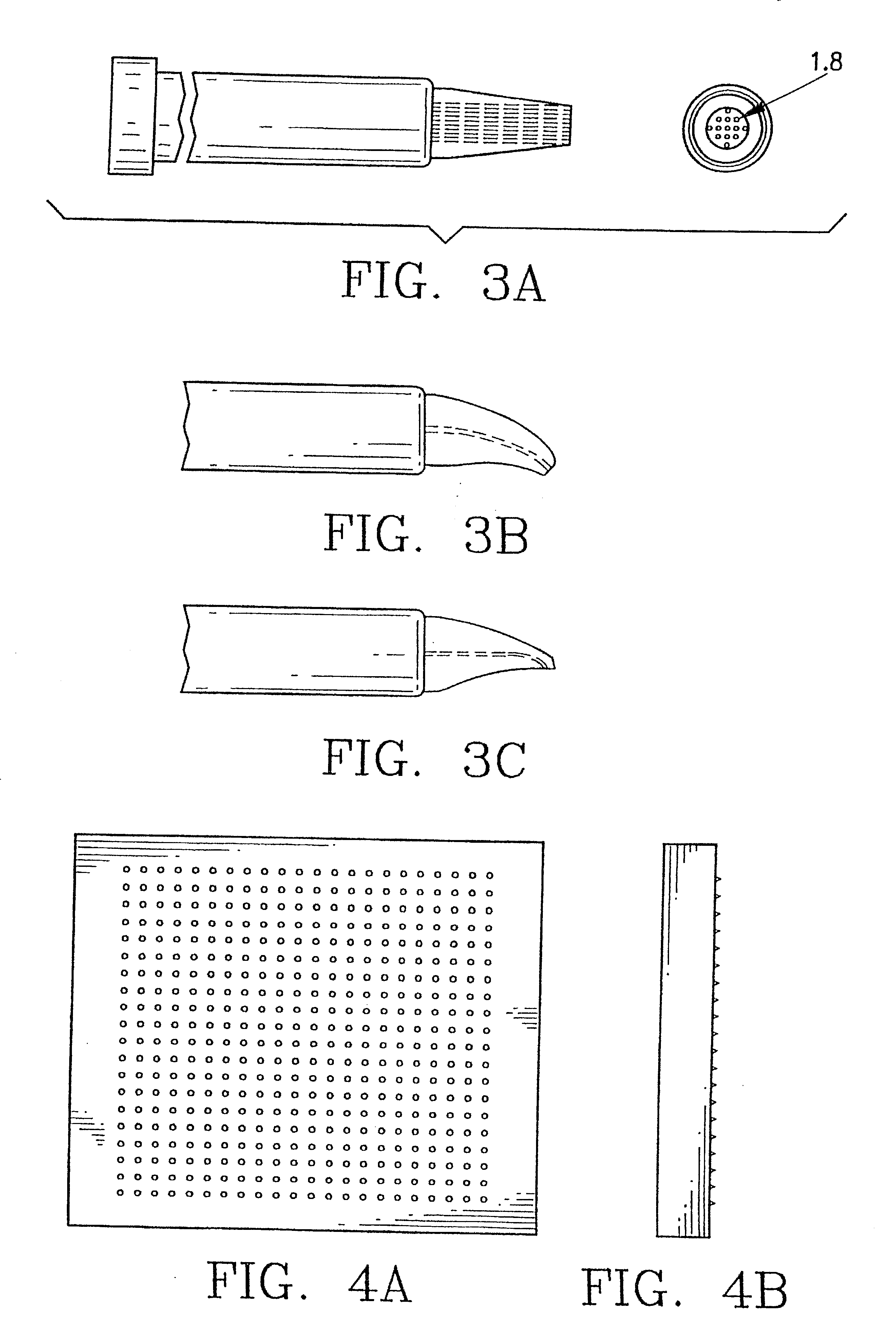
A method and device for electrical emulation of pulsed laser is disclosed. The device utilizes high voltage electrical discharges of sub-microsecond duration in a liquid medium to produce cavitation bubbles of sub-millimeter size for use in high speed precision cutting. Such bubbles are produced by a micro-electrode (1.6) having a central wire having a diameter of 1 microns to 100 microns embedded in an insulator. A coaxial electrode (1.9) surrounds the insulator, and may be spaced from the outer surface of the insulator to provide a path for removing tissue.
Owner:NANOPTICS
Flexible artificial retina devices
Owner:IRIDIUM MEDICAL TECH
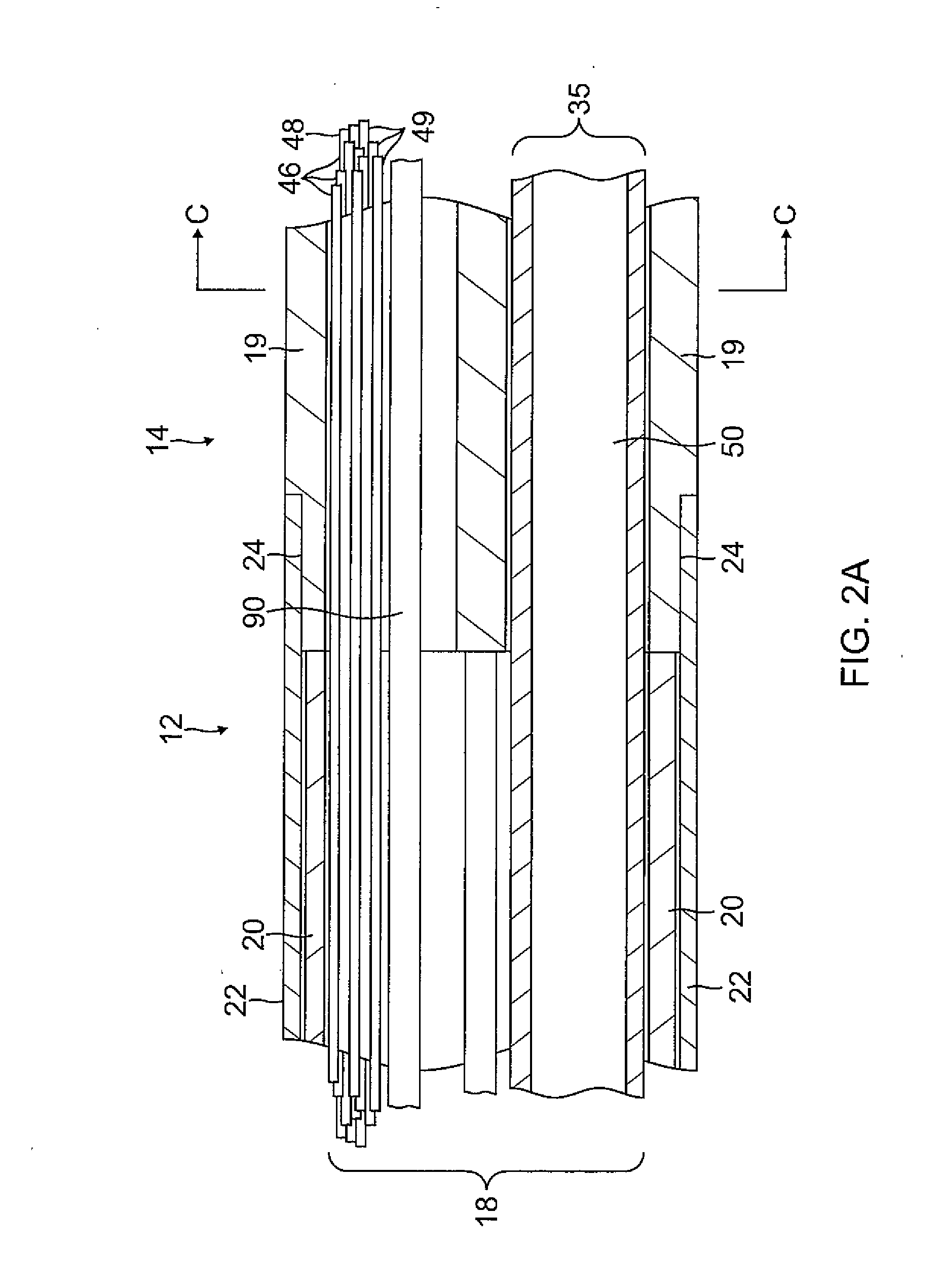
High resolution electrophysiology catheter
InactiveUS20150133914A1Improve fidelityImprove resolutionTransvascular endocardial electrodesCatheterMetallic electrodeMicroelectrode
An electrophysiology medical probes, which may be incorporated into a system and used to perform an electrophysiology procedure, is provided. The medical probe comprises an elongated member (e.g., a flexible elongated member), and a metallic electrode mounted to the distal end of the elongated member. In one embodiment, the metallic electrode is cylindrically shaped and comprises a rigid body. The medical probe further comprises a plurality of microelectrodes (e.g., at least four microelectrodes) embedded within, and electrically insulated from, the metallic electrode, and at least one wire connected to the metallic electrode and the microelectrodes.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Method and device for electro microsurgery in a physiological liquid environment
A method and device for electrical emulation of pulsed laser is disclosed. The device utilizes high voltage electrical discharges of sub-microsecond duration in a liquid medium to produce cavitation bubbles of sub-millimeter size for use in high speed precision cutting. Such bubbles are produced by a micro-electrode (1.6) having a central wire having a diameter of 1 microns to 100 microns embedded in an insulator. A coaxial electrode (1.9) surrounds the insulator, and may be spaced from the outer surface of insulator to provide a path for removing tissue.
Owner:NANOPTICS
Micro-electrophoresis chip for moving and separating nucleic acids and other charged molecules
A microelectrophoresis chip comprises a substrate in which there are formed one or more channels, one channel for each sample to be evaluated. The channels extend for the length of the chip, a distance of generally around 1 cm, and are about 1 to 10 mum wide and 1 to 10 mum in depth. The channels are filled with a homogeneous separation matrix which acts as an obstacle to the electrophoretic migration of the charged molecules. Microelectrodes disposed in the channels are used to induce an electric filed within the homogeneous separation medium. When a voltage is applied across two or more of the microelectrodes, the charged molecules are induced to move and separate according to the electric field density, the type of solvent film, and the charge, shape and size of the charged molecule. The chip may further comprise detectors, such as light polarization detectors, fluorescence emission detectors, biosensors, electrochemical sensors or other microcomponents which may include sites for enzymatic or chemical manipulation of the moved or separated charged molecules.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE DIAGNOSTICS INC +1
Micro-circuit system with array of functionalized micro-electrodes
InactiveUS6203758B1Immobilised enzymesSequential/parallel process reactionsCombinatorial chemistryElectron
A micro-circuit for performing analyses of multimolecular interactions and for performing molecular syntheses, comprising: (a) a support; (b) at least one micro-electrode attached to the support, the micro-electrode being selectively electronically activated and the micro-electrode having a protective layer which is removable; (c) a binding entity for attachment to the at least one micro-electrode, the binding entity being capable of attachment to at least one micro-electrode when the protective layer has been removed; and (d) a power source being operatively connected to at least one micro-electrode for electronically activating at least one micro-electrode. The micro-circuit of the present invention also includes embodiments featuring a micro-circuit reader for detecting the interaction of the binding entity to a complementary probe, as well as methods for making and using the micro-circuit of the present invention.
Owner:BEN GURION UNIVERSITY OF THE NEGEV
Micro-current Iontophoretic Percutaneous Absorptive Patch
A self-contained, conveniently disposable percutaneous absorptive patch of the present invention utilizes, in a novel ways, the existing percutaneous absorptive principles to delivering topical medications quickly, painlessly, and effectively through the skin barrier. The absorptive principles include the epidermal microcuts / micro-needles, permeation enhancers, and micro-current iontophoresis. Most importantly, the transdermal absorptive patch of the present invention introduces a novel incorporation of self-producing micro-electrical currents and micro-electrodes into the existing conventional iontophoretic principle.
Owner:VOLT KEVIN
Electropolymerization molecular imprinting technology-based double-parameter composite micro-sensor and preparation thereof
Relating to sensors and molecular imprinting technologies, the invention discloses an electropolymerization molecular imprinting technology-based double-parameter composite micro-sensor and a preparation thereof. According to the invention, three electrochemical microelectrode systems are integrated on a same chip, and each electrochemical microelectrode system has its independent micro-electrochemical reaction pool. Through encapsulation by a sealant, the integrated chip can form an open composite measurement pool containing three electrochemical microelectrode systems. In the micro-reaction pool of each electrochemical microelectrode system, by injecting a solution from the outside, a molecular imprinting procedure containing in situ polymerization and ultrasonic elution of template molecules can be implemented separately, thus obtaining a molecularly imprinted sensor. The left and right microelectrode systems of the composite micro-sensor respectively recognize two corresponding molecules due to different molecularly imprinted sensitive membranes, and the electrochemical microelectrode system positioned in the middle is used as a differential detection reference so as to deduct background signals and environmental effects of a test system. The composite micro-sensor provided in the invention can recognize two molecules simultaneously.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
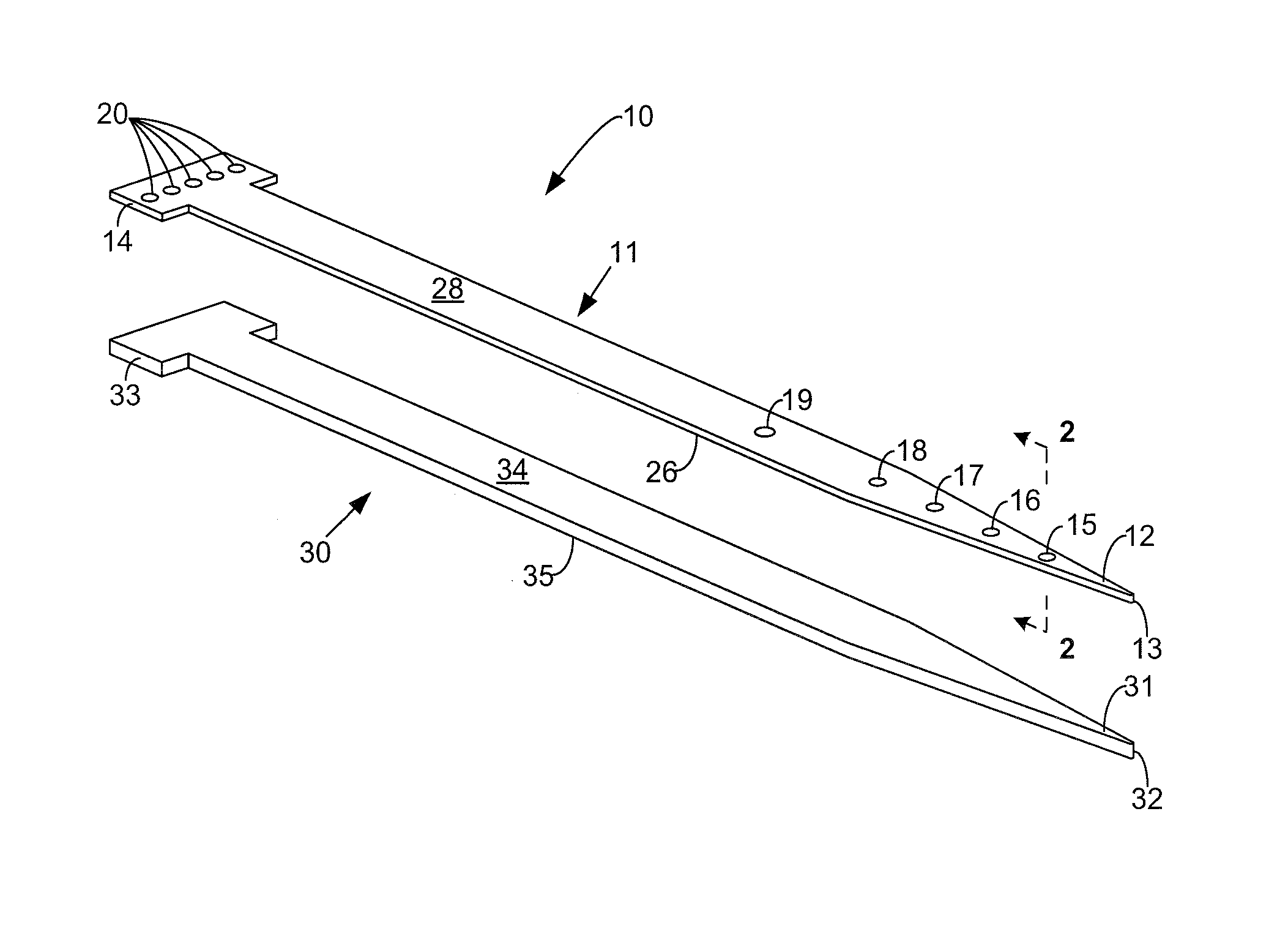
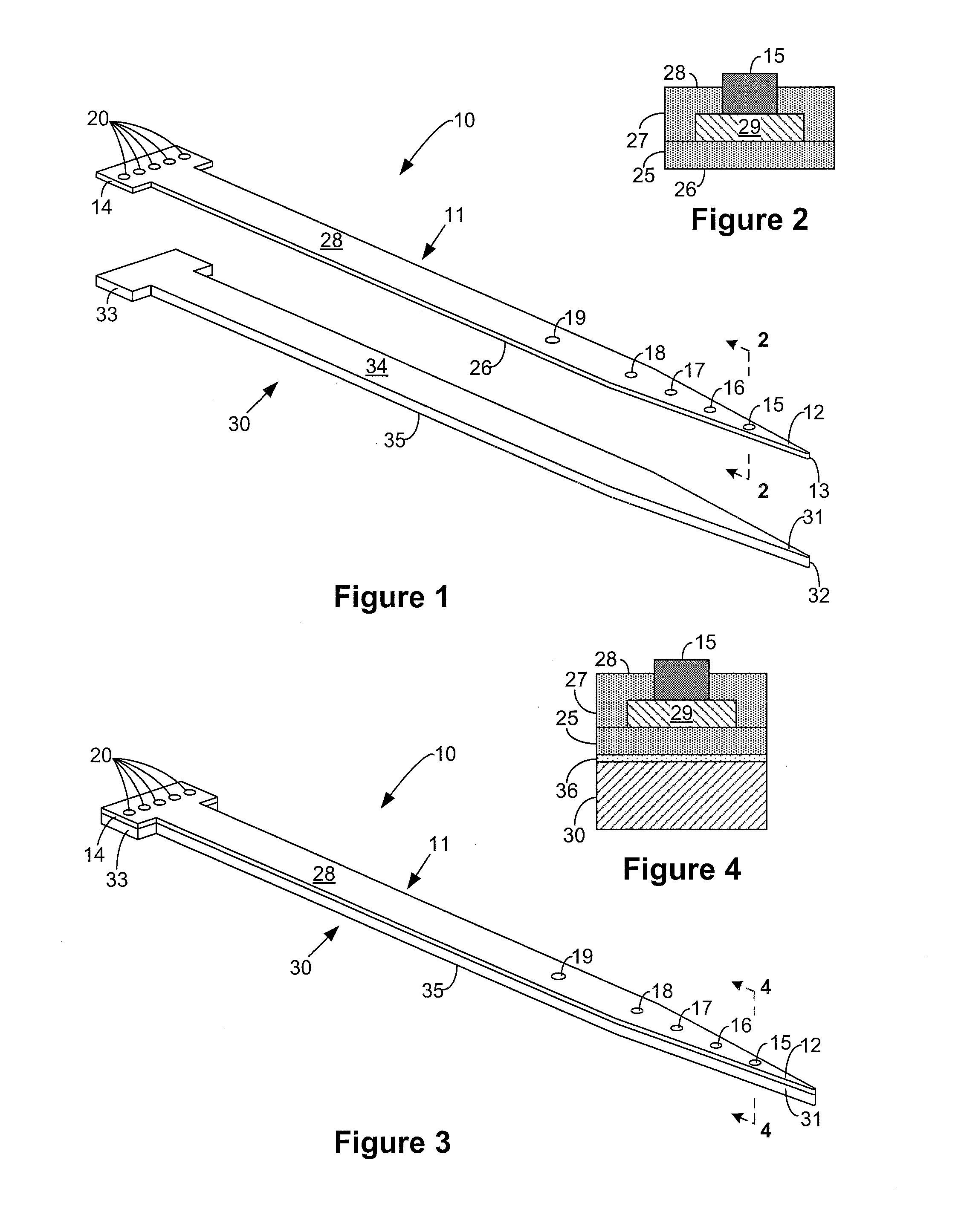
Microfabricated neurostimulation device
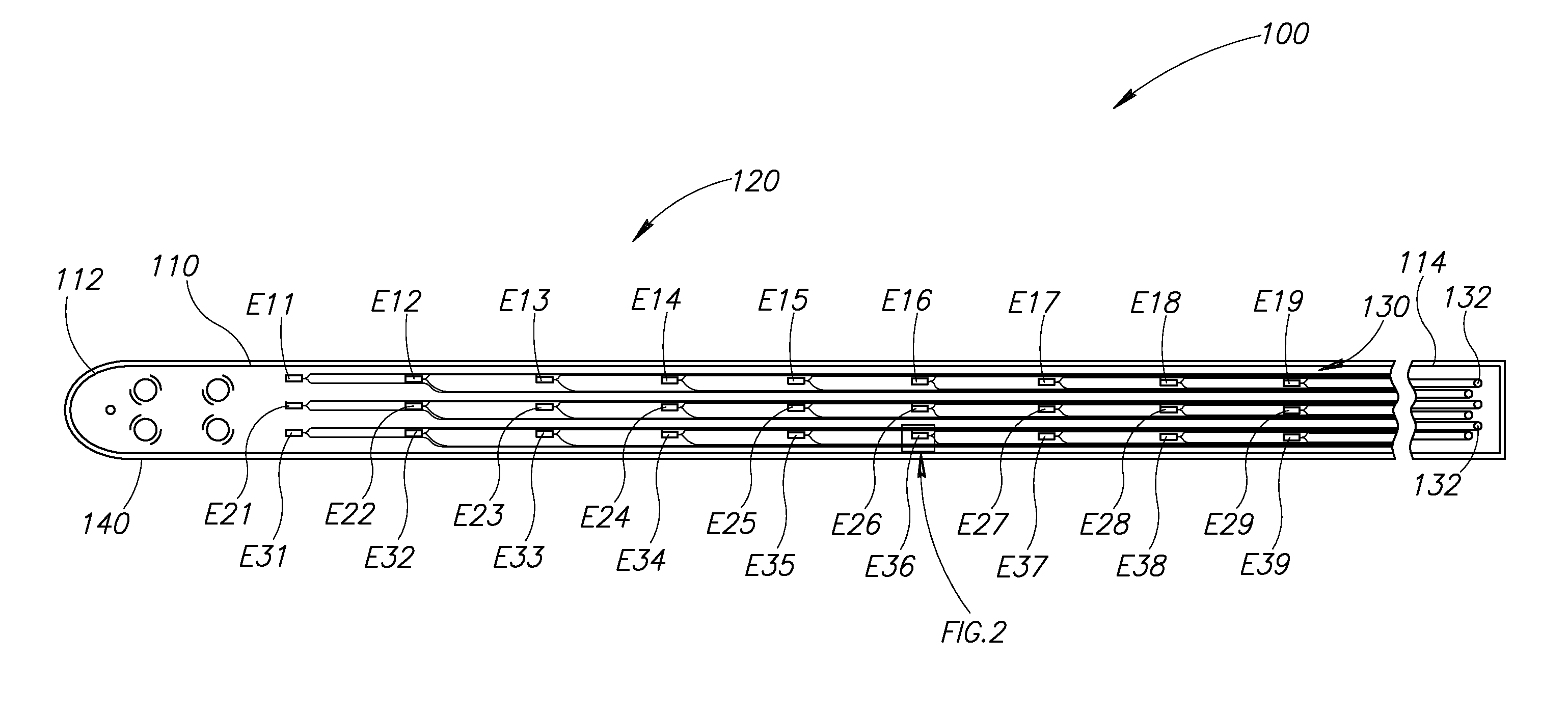
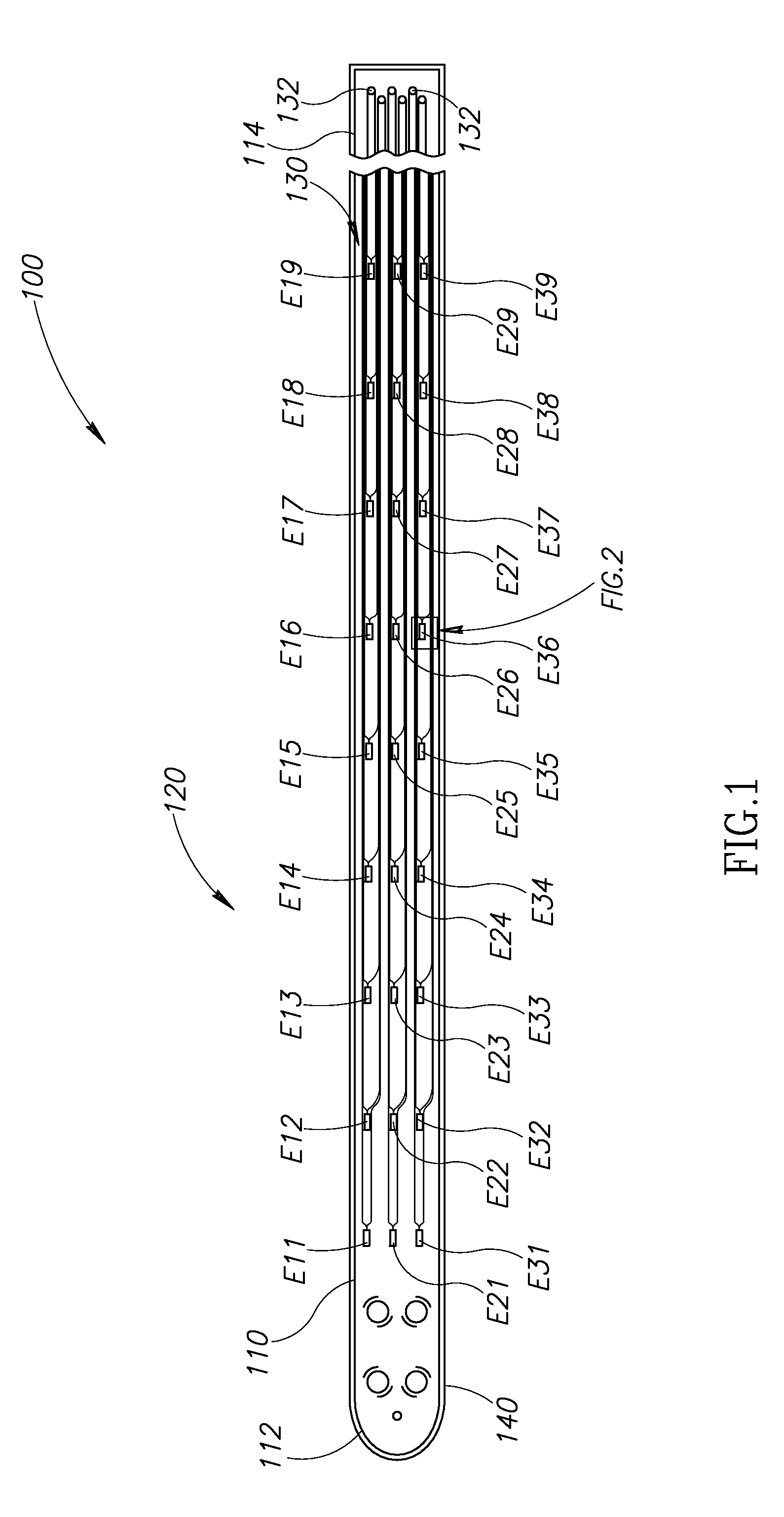
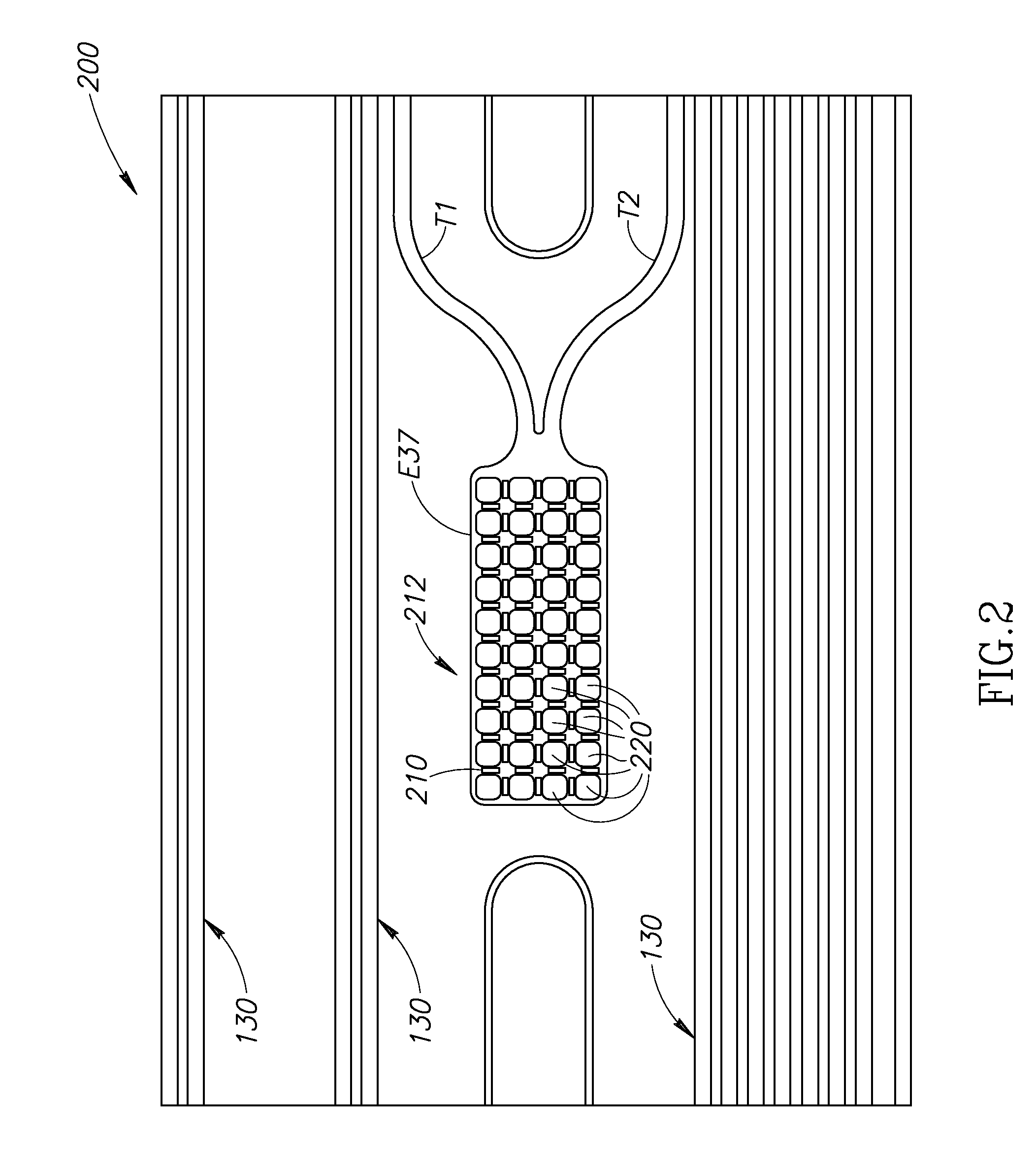
Described herein are microelectrode array devices, and methods of fabrication and use of the same, to provide highly localized and efficient electrical stimulation of a neurological target. The device includes multiple microelectrode elements arranged along an elongated probe shaft. The microelectrode elements are dimensioned and shaped so as to target individual neurons, groups of neurons, and neural tissue as may be located in an animal nervous system, such as deep within a human brain. Beneficially, the neurological probe can be used to facilitate location of the neurological target and remain implanted for long-term monitoring and / or stimulation.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
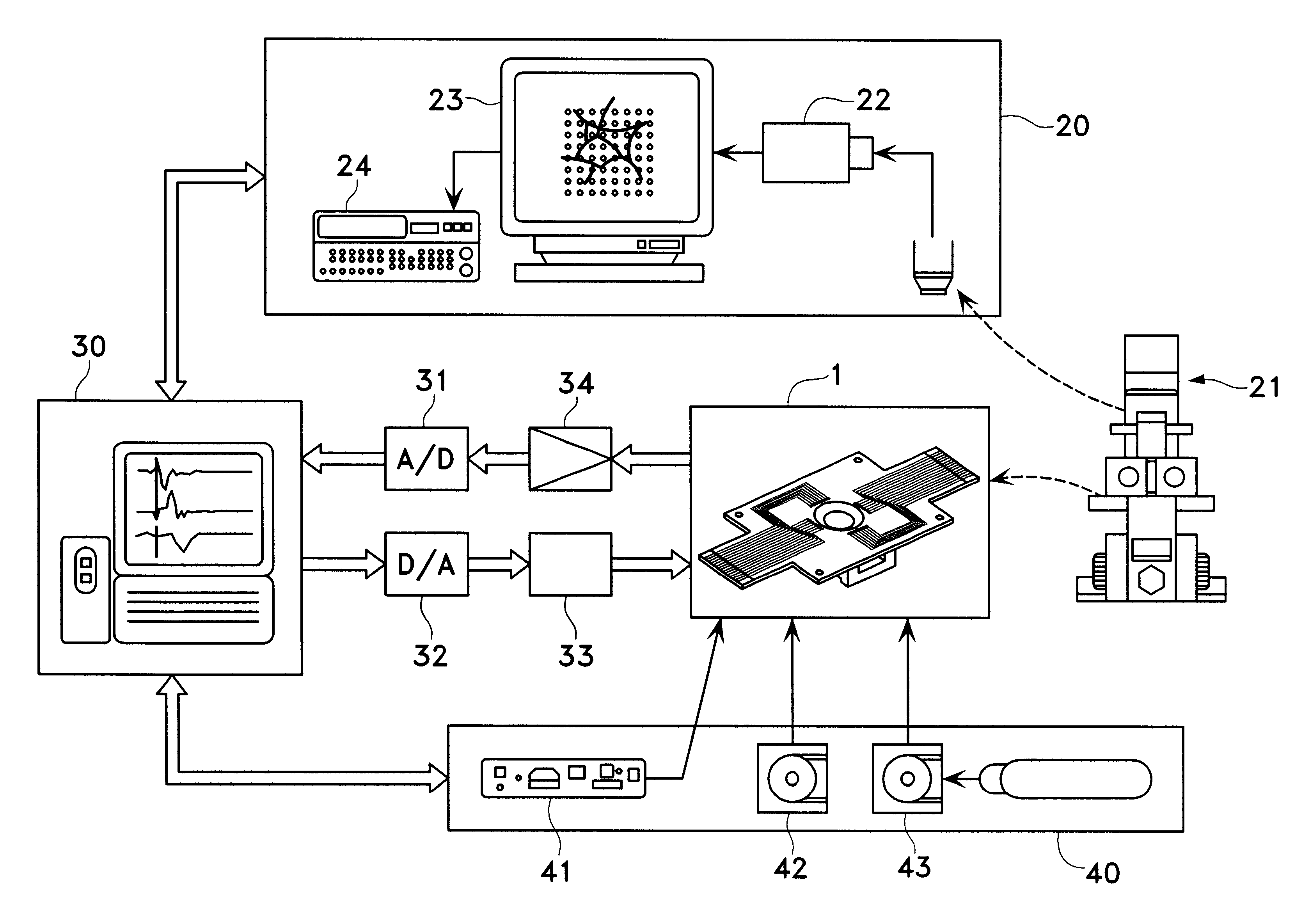
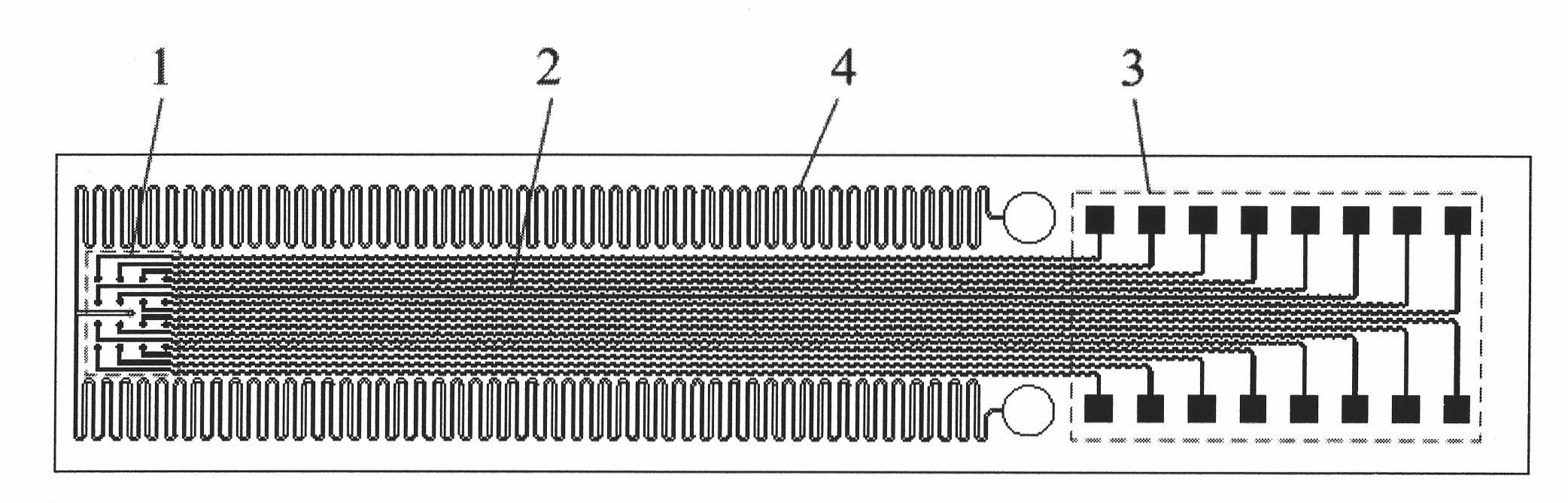
Cell potential measurement apparatus having a plurality of microelectrodes
InactiveUSRE38323E1Precise positioningReduce surface resistanceBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMeasurement devicePotential change
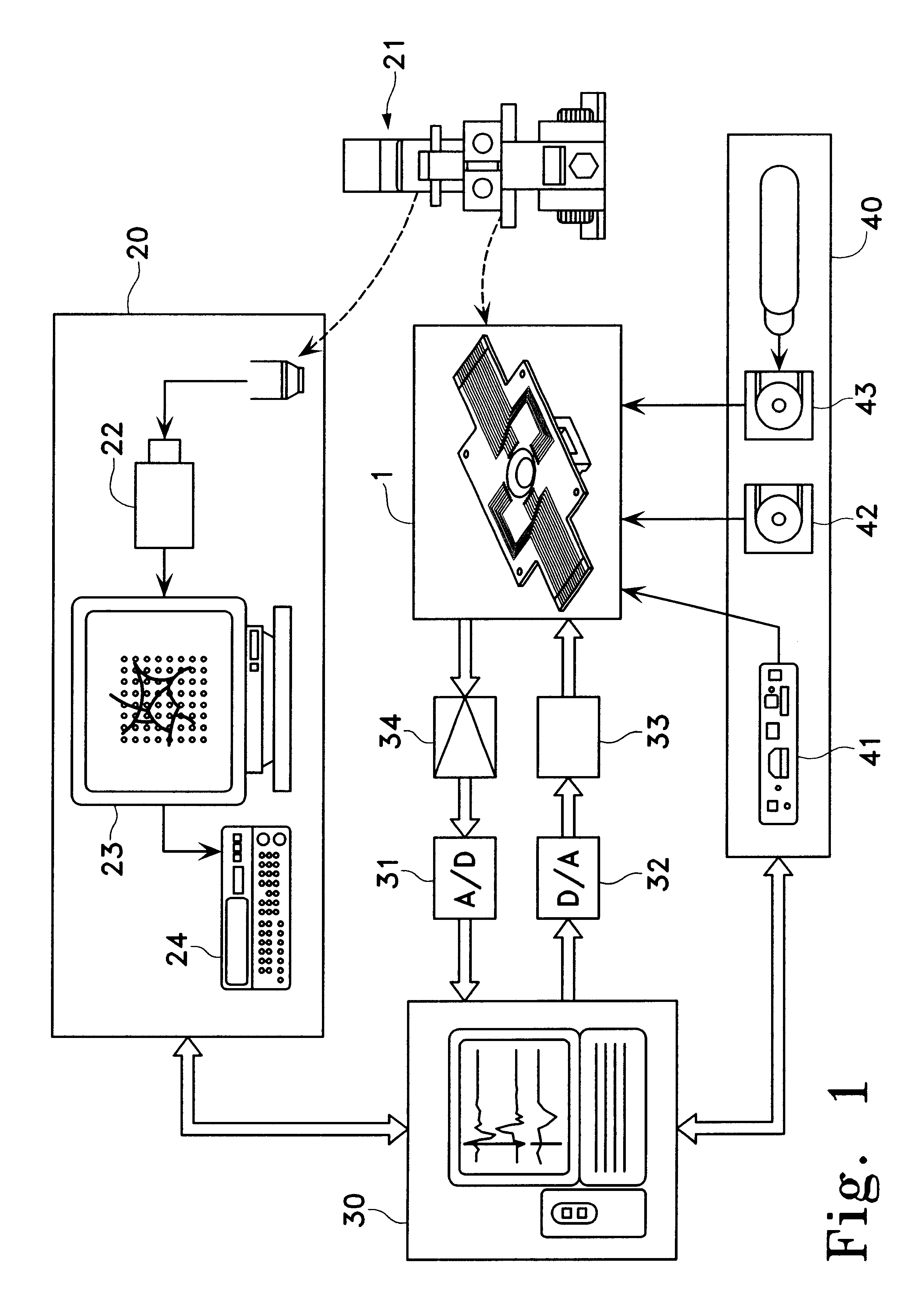
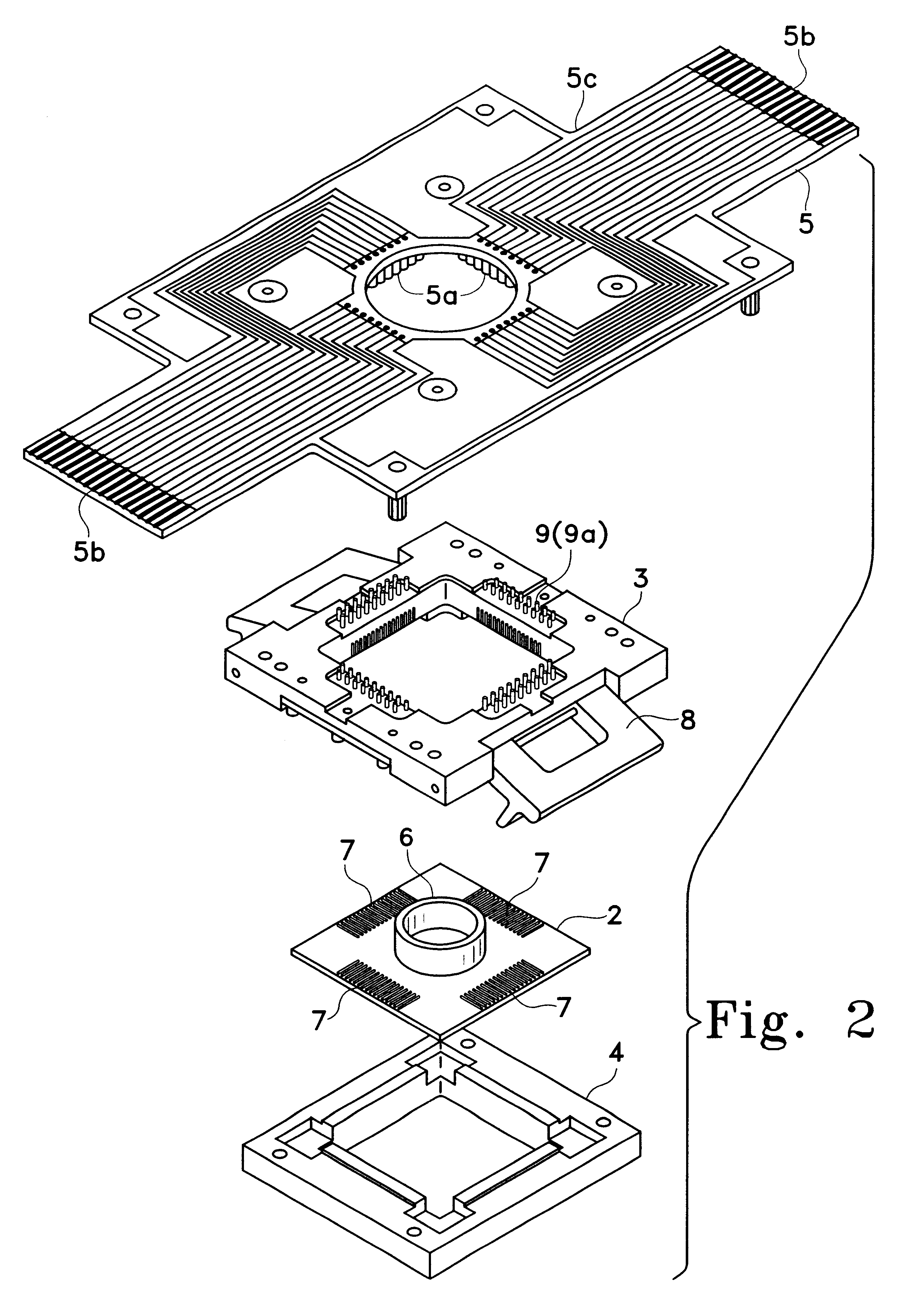
A cell potential measurement apparatus, which uses a planar electrode enabling a multi-point simultaneous measurement of potential change arising from cell activities, is provided which can conduct measurements accurately and efficiently as well as can improve convenience of arranging measurement results. According to the configuration of the cell potential measurement apparatus of this invention, it includes an integrated cell holding instrument 1, which includes a planar electrode provided with a plurality of microelectrodes arranged in a matrix form on the surface of a substrate, a cell holding part for placing cells thereon, drawer patterns from the microelectrodes, and electric contact points for outside connections; an optical observation means 20 for optical observations of cells; a stimulation signal supply means 30 to be connected to the cell holding instrument for providing electric stimulation to the cells; and a signal processing means 30 to be connected to the cell holding instrument for processing an output signal arising from electric physiological activities of the cells. It is preferable that a cell culturing means 40 is also provided for maintaining a culture atmosphere of the cells placed on the integrated cell holding instrument.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
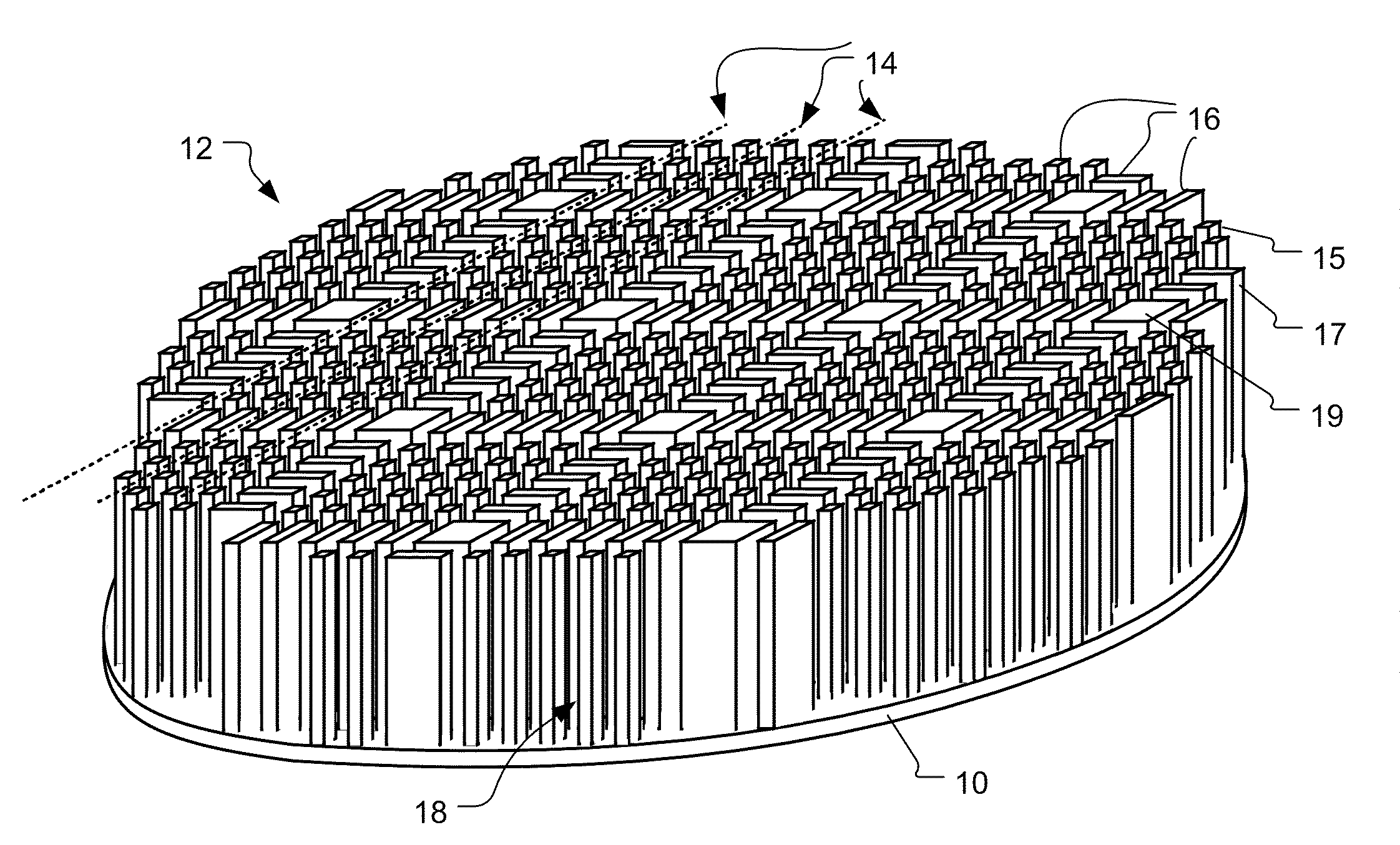
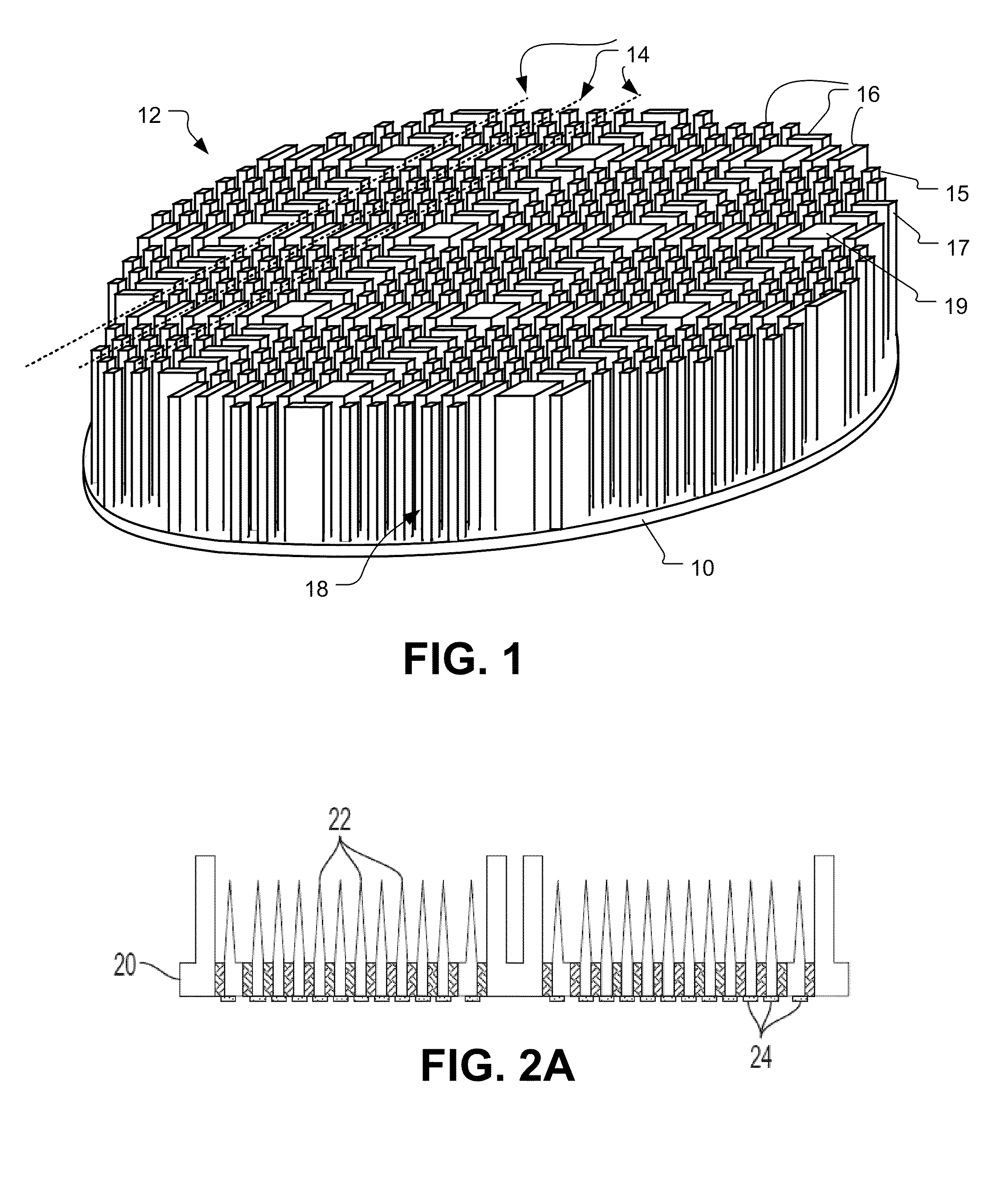
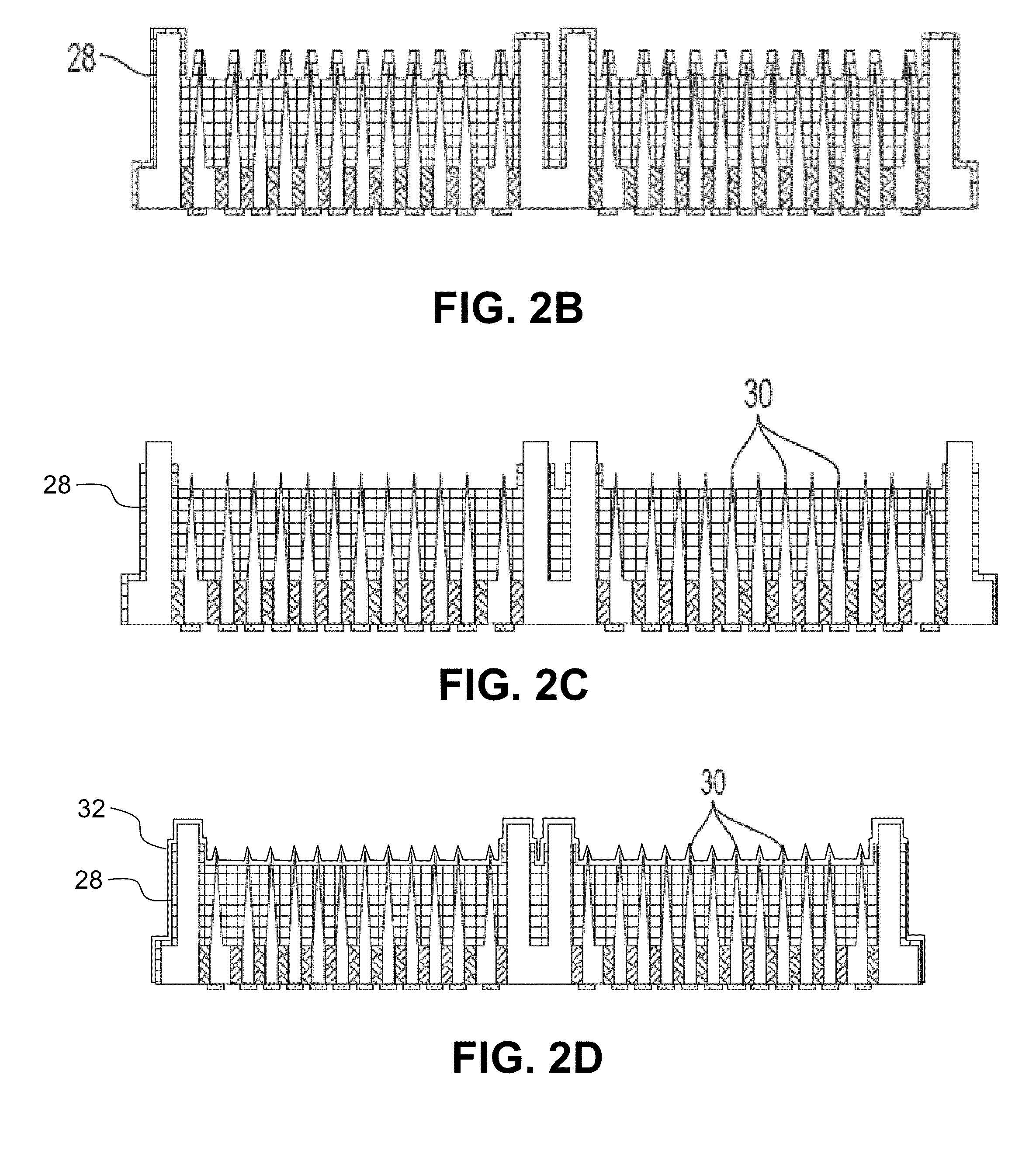
Methods for Wafer Scale Processing of Needle Array Devices
InactiveUS20090301994A1Avoid lack of depthHead electrodesDecorative surface effectsResistHigh volume manufacturing
Methods of fabricating needle arrays on a wafer scale include etching a wafer of columns and needles and coating the same with an electrically insulating material and exposing electrically conductive tips. This process can benefit from using a slow spin speed to distribute resist material across the wafer before etching and using a carrier wafer to support singulated arrays to allow full coverage of upper array surfaces with electrically insulating materials. These processes allow for efficient high volume production of high count microelectrode arrays with a high repeatability and accuracy.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Cell potential measuring electrode and measuring apparatus using the same
InactiveUSRE37977E1Simple manufacturing processCost benefitImmobilised enzymesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMicroelectrodeBattery cell
This invention relates to a low impedance cell potential measuring electrode assembly typically having a number of microelectrodes on an insulating substrate and having a wall enclosing the region including the microelectrodes. The device is capable of measuring electrophysiological activities of a monitored sample using the microelectrodes while cultivating those cells or tissues in the in the region of the microelectrodes. The invention utilizes independent reference electrodes to lower the impedance of the overall system and to therefore lower the noise often inherent in the measured data. Optimally the microelectrodes are enclosed by a physical wall used for controlling the atmosphere around the monitored sample.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Nano-material electrode modification based electrochemical integrated digital micro-fluidic chip
InactiveCN103170383ASolve bottlenecksEnhanced electrochemical detection capabilitiesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansLaboratory glasswaresAutomatic controlEngineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of micro-fluidic analysis chips, and concretely relates to a nano-material electrode modification based electrochemical integrated digital micro-fluidic chip. The electrochemical integrated digital micro-fluidic chip treats a digital micro-fluidic chip as a base and integrates an electrochemical-sensing micro-electrode, an electrochemical electrode is embedded in the control electrode of the digital micro-fluidic chip, and all the electrodes are positioned in a same plane of the chip. The nano-material modification of the electrochemical sensing electrode is realized through the micro-fluidic automatic control in order to enhance the electrochemical sensing capability of the micro-fluidic chip. The nano-material electrode modification based electrochemical integrated digital micro-fluidic chip has the advantages of novel design, high integration level, convenient making, high automation degree, strong detection capability, realization of the micro-scale, rapid and sensitive detection, and substantial widening of the application ranges of the electrochemical sensing and digital micro-fluidic fields.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Multifunctional nano-probe interface structure for neural prostheses and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveUS20080140195A1Accurately and regionally stimulateEasy to combineSpinal electrodesHead electrodesNeural cellIsolation layer
A novel multifunctional nano-probe interface is proposed for applications in neural stimulation and detecting. The nano-probe interface structure consists of a carbon nanotube coated with a thin isolation layer, a micro-electrode substrate array, and a controller IC for neural cell recording and stimulation. The micro-electrode substrate array contains wires connecting the carbon nanotube with the controller IC, as well as microfluidic channels for supplying neural tissues with essential nutrition and medicine. The carbon nanotube is disposed on the micro-electrode substrate array made by silicon, coated with a thin isolation layer around thereof, and employed as a nano-probe for neural recording and stimulation.
Owner:NATIONAL TSING HUA UNIVERSITY
PDMS-based flexible implanted neural microelectrode and manufacturing method
ActiveCN101912666AGood biocompatibilityIncrease elasticityInternal electrodesMedical devicesBiocompatibility TestingMicroelectrode
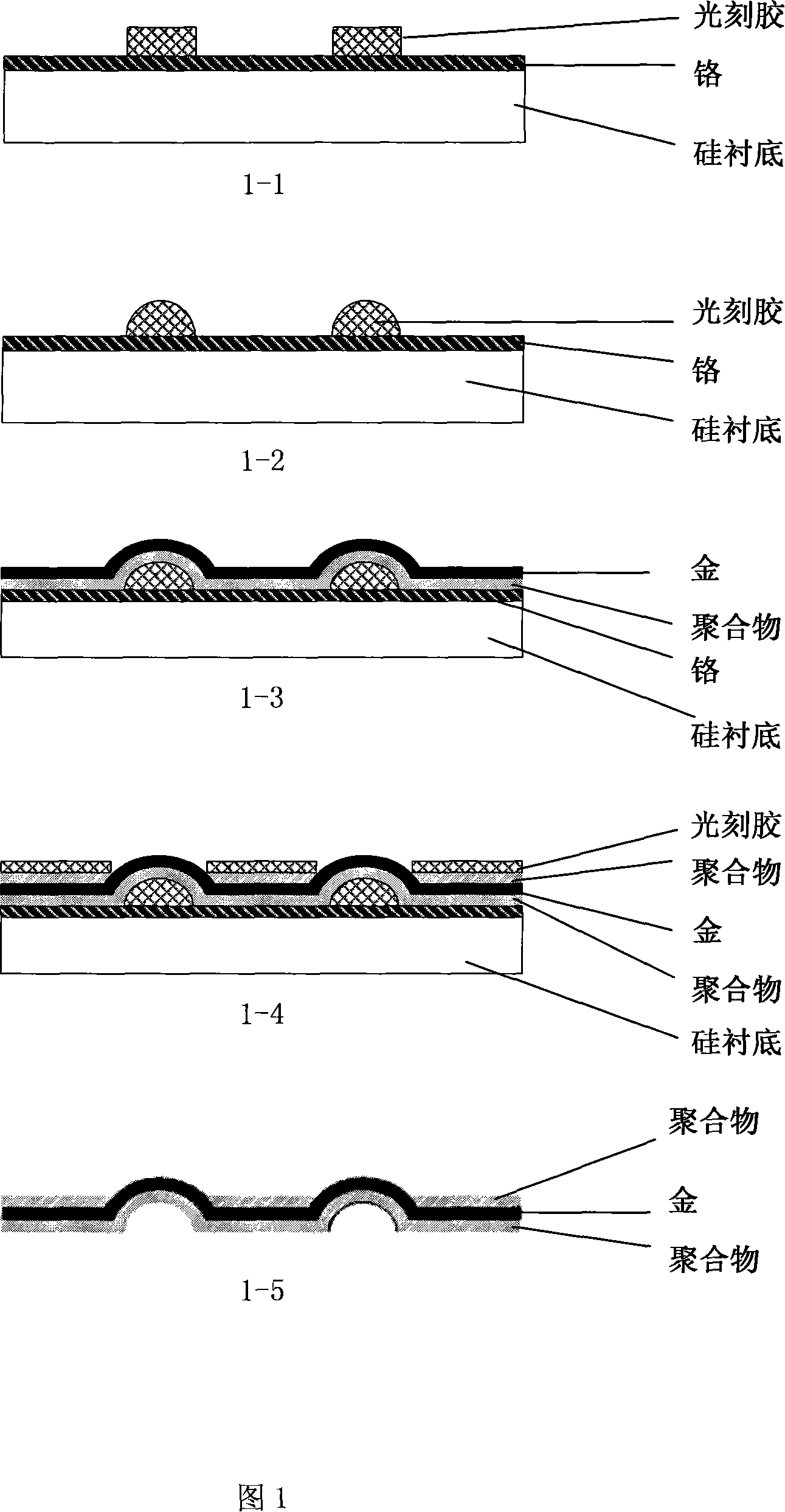
The invention discloses a polydimethylsiloxane-based (PDMS) flexible implanted neural microelectrode and a manufacturing method. The electrode is characterized in that the PDMS with high biocompatibility and mechanical elasticity is used as a substrate material for the neural microelectrode, wherein the implanted flexible neural microelectrode which comprises an electrode site region, a connecting line region, a welding spot region and a micro-pipeline region is formed by electroplating technology, PDMS injection molding technology and bonding technology; the electrode site, the connecting line and the welding spot are structurally formed of an electroplated metal layer, so that the tensile resistance and the reliability of the metal structure of the PDMS microelectrode are enhanced; and the micro-pipeline integrated on the electrode can be used for pouring a curable liquid material which contains medicament or nerve growth factor, so that the operability of the operation implantation of the PDMS neutral microelectrode and the biocompatibility after the implantation are improved. Meanwhile, the preparation method of the PDMS microelectrode provided by the invention has the characteristics of simple process, low cost and standard batch manufacturing.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF MICROSYSTEM & INFORMATION TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Rigid spine reinforced polymer microelectrode array probe and method of fabrication
ActiveUS8738110B2Increased buckling strengthReduce riskLine/current collector detailsInternal electrodesTitaniumMicroelectrode
A rigid spine-reinforced microelectrode array probe and fabrication method. The probe includes a flexible elongated probe body with conductive lines enclosed within a polymeric material. The conductive lines connect microelectrodes found near an insertion end of the probe to respective leads at a connector end of the probe. The probe also includes a rigid spine, such as made from titanium, fixedly attached to the probe body to structurally reinforce the probe body and enable the typically flexible probe body to penetrate and be inserted into tissue, such as neural tissue. By attaching or otherwise fabricating the rigid spine to connect to only an insertion section of the probe body, an integrally connected cable section of the probe body may remain flexible.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
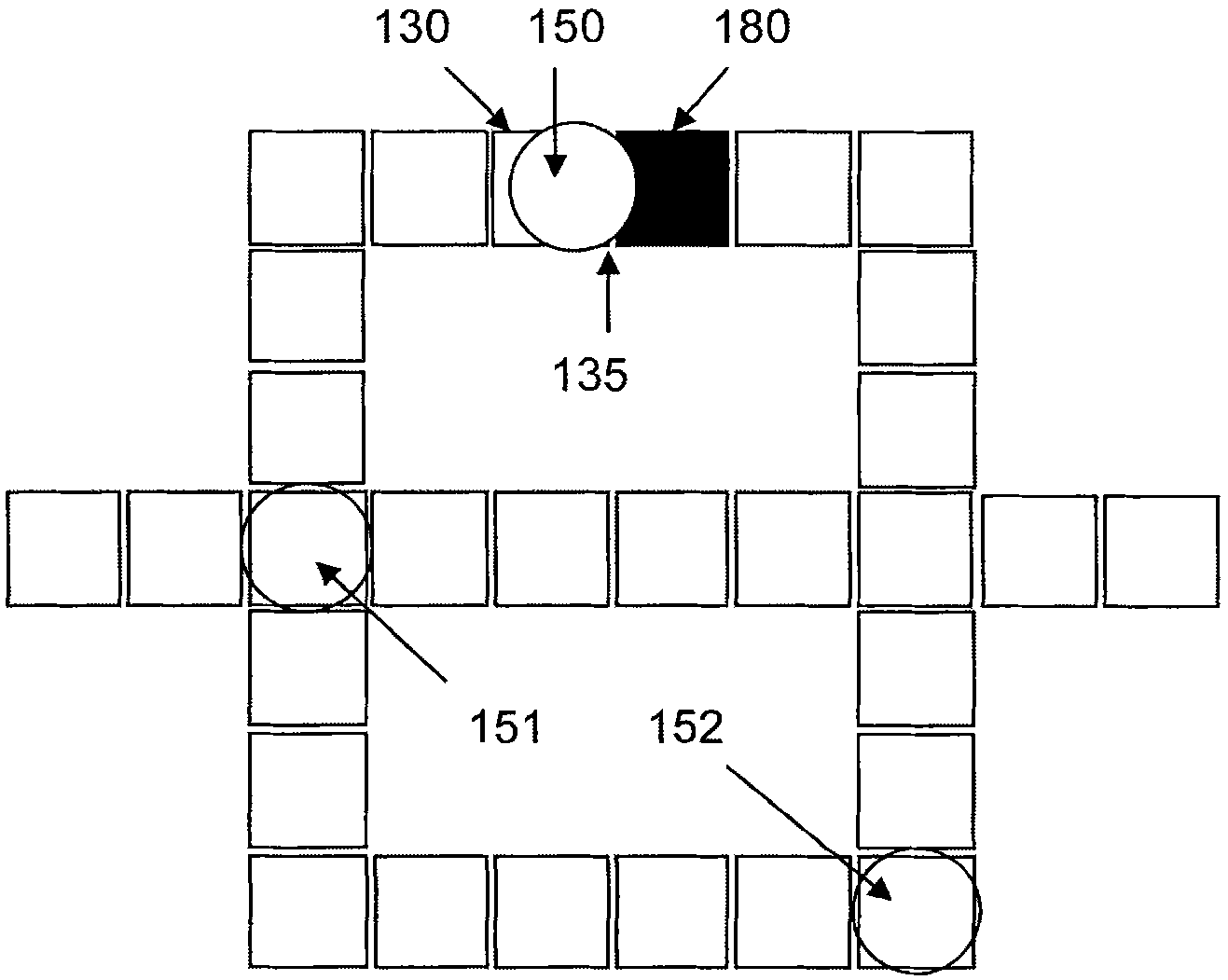
Microelectrode array architecture
InactiveCN102671724ALaboratory glasswaresSpecial data processing applicationsSystems managementField-programmability
The invention discloses a microelectrode array architecture, concretely a device of the microelectrode array architecture, comprising: (a) a bottom plate comprising an array of multiple microelectrodes disposed on a top surface of a substrate covered by a dielectric layer; wherein each of the microelectrode is coupled to at least one grounding elements of a grounding mechanism, wherein a hydrophobic layer is disposed on the top of the dielectric layer and the grounding elements to make hydrophobic surfaces with the droplets; (b) a field programmability mechanism for programming a group of configured-electrodes to generate microfluidic components and layouts with selected shapes and sizes; and, (c) a system management unit, comprising: a droplet manipulation unit; and a system control unit.
Owner:王崇智 +3
Flexible retina salient point micro-electrode chip and production method thereof
InactiveCN101380257AAchieve preparationReduce heat damageEye treatmentBiocompatibility TestingMicroelectromechanical systems
The invention discloses a flexible retina emboss micro-electrode chip in the technical field of a micro-electronic-mechanical-system and a manufacture method thereof. In the method, parylene C is used as a flexible substrate and an insulating material for preparing a micro-electrode array which is formed by the arrangement of a plurality of micro-electrode sensing elements; simultaneously, an electrode lead and a lead welding point are manufactured to form the flexible retina emboss micro-electrode chip which is planted into the retina part of a human eye, can realize the safe and effective contact with the neuron of the retina, effectively reduce the stimulation to a pulse current, reduce the inserting damage to a biological tissue caused by the planting of the micro-electrode and can improve the effect of electric simulating and neural signal recording, thereby better recovering the visual function. In the invention, the parylene C is used as the substrate of a flexible electrode; the excellent electric insulating performance and mechanical performance thereof can improve the biocompatibility of the micro-electrode chip to a larger extent and have good stability for a long period. In the invention, an MEMS technique is adopted, thus realizing the integration of a functional unit and the flexible substrate of the micro-electrode.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Implanted flexible neural microelectrode comb, and preparation method and implanting method thereof
ActiveCN106667475AReduce implant areaImprove mechanical stabilityDecorative surface effectsPrinted circuit aspectsShape changeInsulation layer
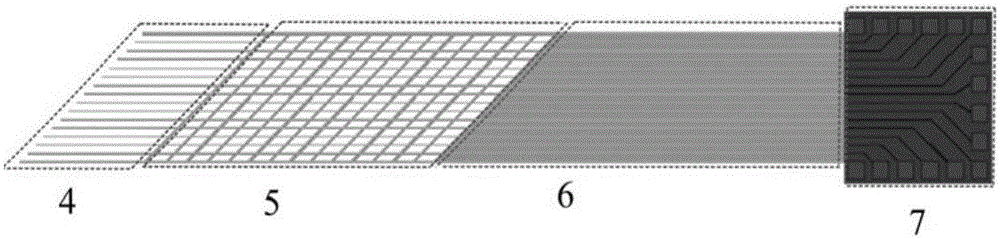
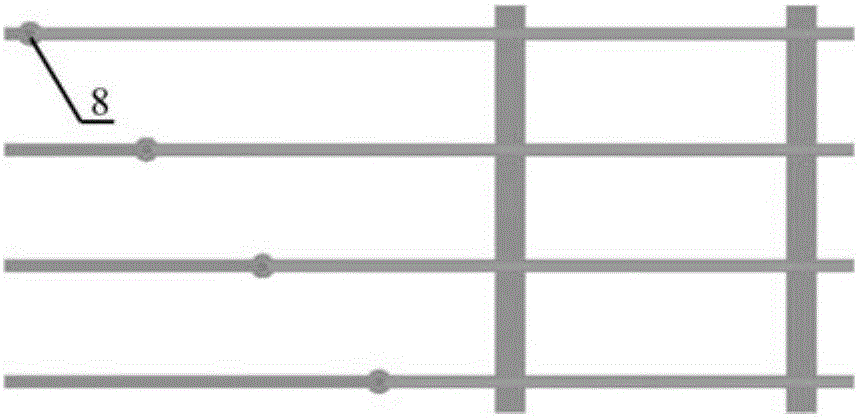
The invention provides an implanted flexible neural microelectrode comb, and a preparation method and an implanting method thereof. The flexible neural microelectrode comb is mainly composed of a flexible substrate layer, a flexible insulation layer and a metal connection wire layer arranged between the flexible substrate layer and the flexible insulation layer; the flexible neural microelectrode comb comprises a comb-like structure, a grid structure, a solid structure and a welding pad connected in sequence; electrode sites are arranged on the comb-like structure; welding points are arranged on the welding pad; the metal connection wire layer is composed of metal connection wires connecting the electrode sites and the welding points; and the flexible insulation layer is arranged on the surfaces of the electrode sites and the welding points. The flexible neural microelectrode comb prepared according to the method provided by the invention has a wire-grid-plane gradual changing structure, and thus is improved in mechanical stability during a shape changing process. The mechanical property of the implanted flexible neural microelectrode comb is matched with a brain tissue, the implanting areas is small, an inflammatory response of the brain is avoided, and electroencephalogram signals can be stably tracked and measured in a multi-point manner for a long time.
Owner:BEIJING BCIFLEX MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
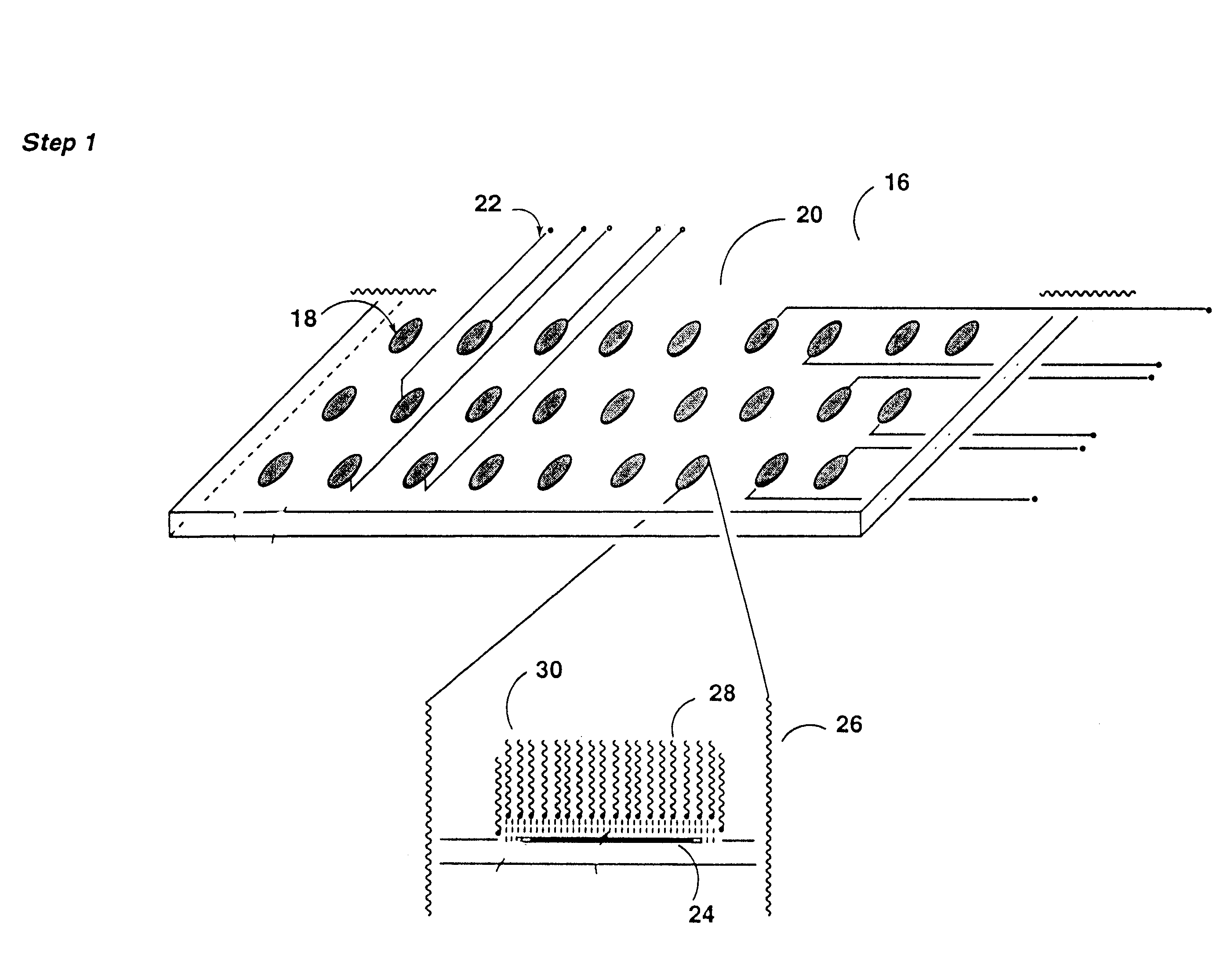
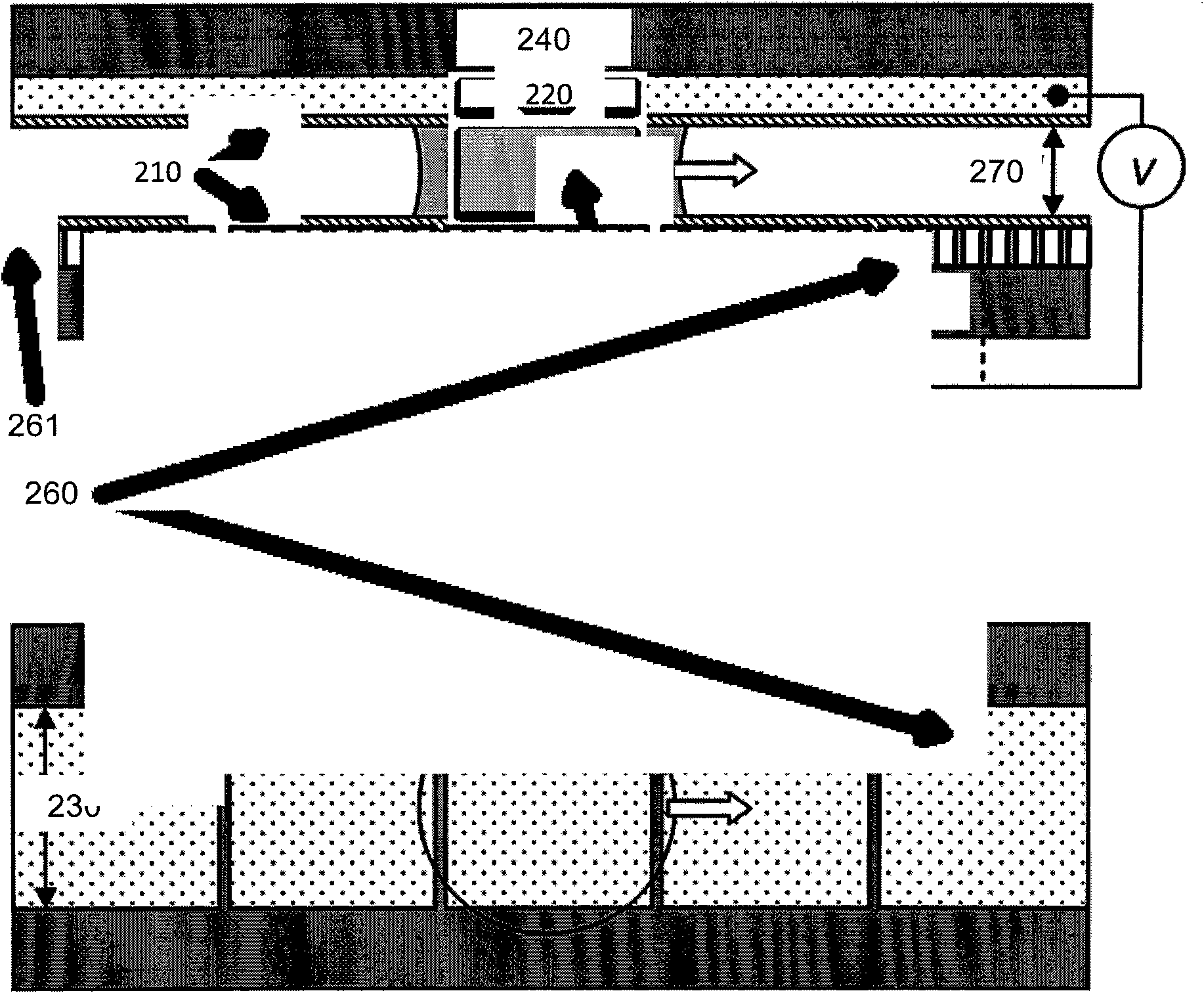
High throughput functional genomics
InactiveUS20030065452A1High impedance sealReduce lateral flowMaterial nanotechnologyMicrobiological testing/measurementGenomicsBiotechnology
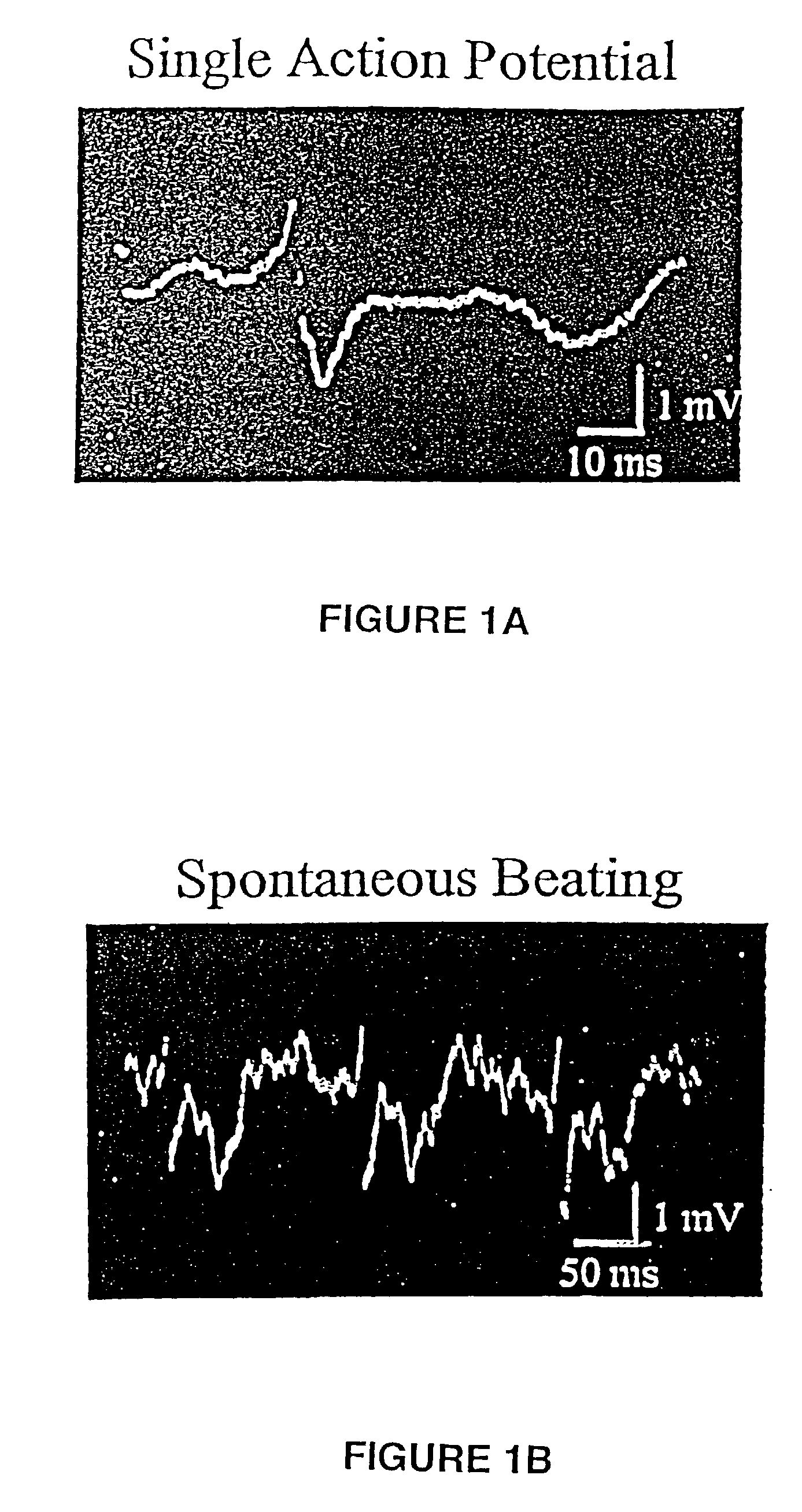
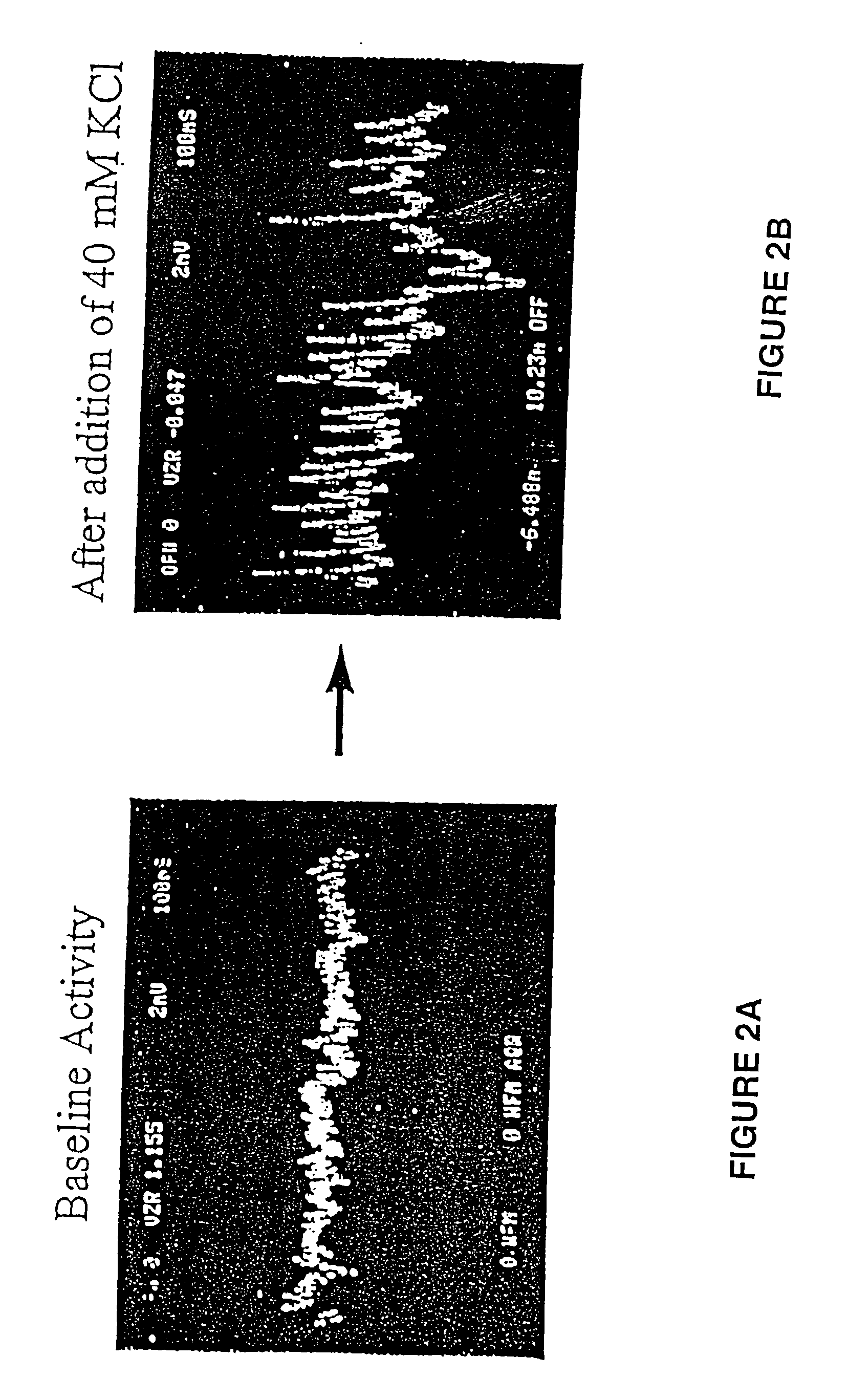
This invention focuses on the marriage of solid-state electronics and neuronal function to create a new high-throughput electrophysiological assay to determine a compound's acute and chronic effect on cellular function. Electronics, surface chemistry, biotechnology, and fundamental neuroscience are integrated to provide an assay where the reporter element is an array of electrically active cells. This innovative technology can be applied to neurotoxicity, and to screening compounds from combinatorial chemistry, gene function analysis, and basic neuroscience applications. The system of the invention analyzes how the action potential is interrupted by drugs or toxins. Differences in the action potentials are due to individual toxins acting on different biochemical pathways, which in turn affects different ion channels, thereby changing the peak shape of the action potential differently for each toxin. Algorithms to analyze the action potential peak shape differences are used to indicate the pathway(s) affected by the presence of a new drug or compound; from that, aspects of its function in that cell are deduced. This observation can be exploited to determine the functional category of biochemical action of an unknown compound. An important aspect of the invention is surface chemistry that permits establishment of a high impedance seal between cell and a metal microelectrode. This seal recreates the interface that enables functional patch-clamp electrophysiology with glass micropipettes, and allows extracellular electrophysiology on a microelectrode array. Thus, the invention teaches the feasibility of using living cells as diagnostics for high throughput real-time assays of cell function.
Owner:HICKMAN JAMES J
Microelectrode, applications thereof and method of manufacturing
InactiveUS8010208B2Prevent penetrationSpinal electrodesHead electrodesMicroelectrodeMaterials science
An electrode device is disclosed. The electrode device comprises an electrically conductive core of micrometric size coated by at least one electrically isolating layer. The electrically conductive core comprises a substrate coated by at least one metallic layer having a nanometric pattern thereon and being at least partially exposed at a tip of the electrically conductive core.
Owner:NANO BIOSENSORS
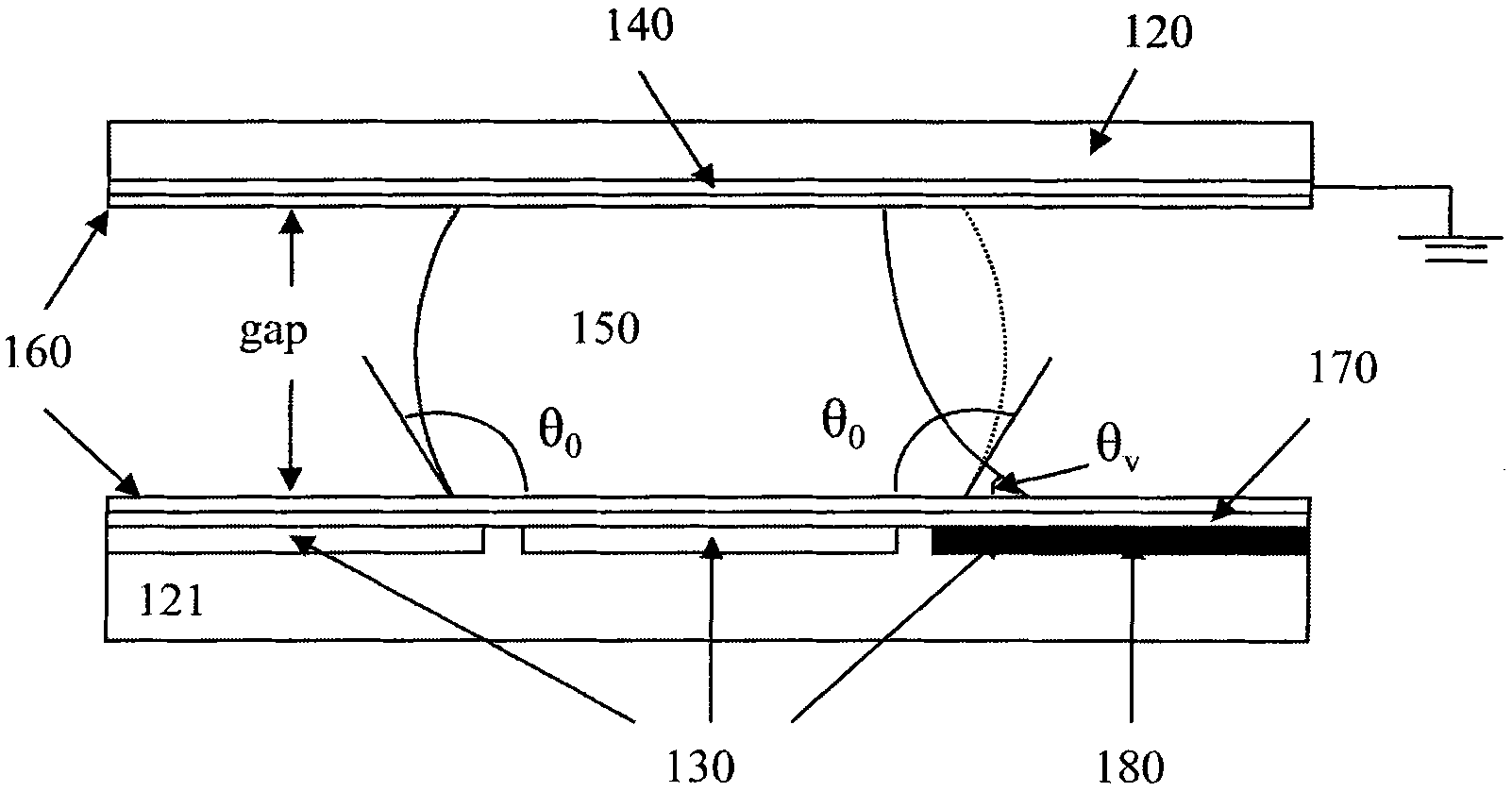
Catheter with irrigated tip electrode with porous substrate and high density surface micro-electrodes
ActiveUS20160184008A1Irrigate evenlyCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringPorous substrateElectrical connection
A catheter has a multifunctional “virtual” tip electrode with a porous substrate and a multitude of surface microelectrodes. The surface microelectrodes are in close proximity to each other and in a variety of configurations so as to sense tissue for highly localized intracardiac signal detection, and high density local electrograms and mapping. The porous substrate allows for flow of conductive fluid for ablating tissue. The surface microelectrodes can be formed via a metallization process that allows for any shape or size and close proximity, and the fluid “weeping” from the porous substrate provides more uniform irrigation in the form of a thin layer of saline. The delivery of RF power to the catheter tip is based on the principle of “virtual electrode,” where the conductive saline flowing through the porous tip acts as the electrical connection between the tip electrode and the heart surface. The substrate and the surface electrodes are constructed of MRI compatible materials so that the physician can conduct lesion assessment in real time during an ablation procedure. The surface electrodes include noble metals, including, for example, platinum, gold and combinations thereof.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER (ISRAEL) LTD
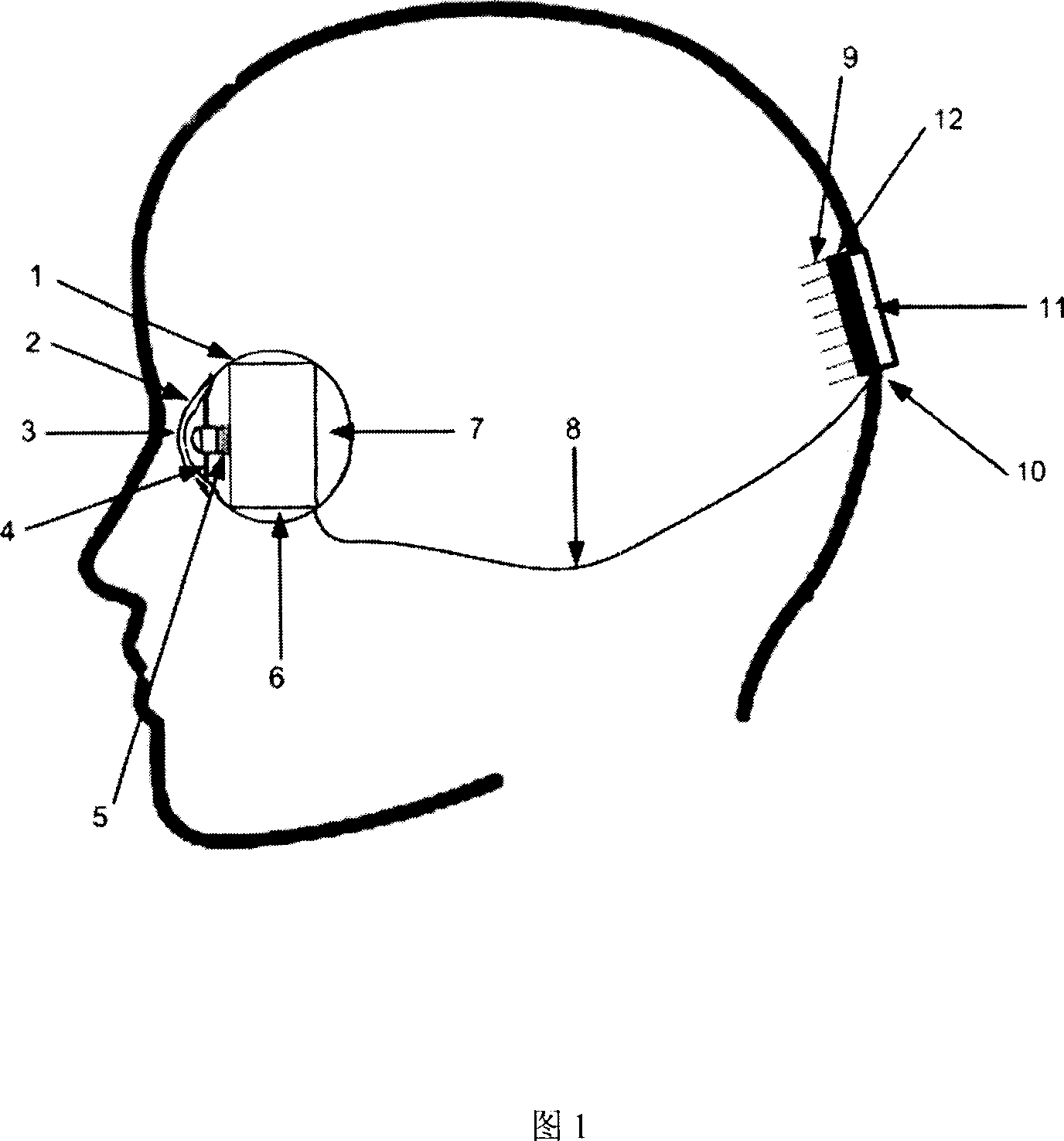
Implantable vision prosthesis
ActiveCN1961850AAvoid in vitro installationRelieve stressEye implantsInternal electrodesOcular prosthesisEngineering
The invention relates to a vision artificial element as medical tool, wherein it comprises that micro camera false eye and needle micro electrode array which can be planted into orbit; said micro camera false eye comprises solar energy battery board or charge device, micro optical lens group, photoelectric converter, signal processing converter, false eye base, and false eye sheet; the solar-energy battery board or charge device, micro optical lens group, photoelectric converter and signal processing converter are packed into false eye base; the signal processing converter is outside the false eye base; the micro camera false eye is planted into the orbit; the needle micro electrode array comprises base, micro electrode, inner wire, interface base, fixing hole, wire, and fixing plate; the fixing plate is fixed on the skull; the micro electrode via the drill hole of skull enters into vision layer; the vision electric signal via wire is transmitted into micro electrode array. The invention can improve the spatial accuracy of false eye.
Owner:上海华实投资有限公司
Three-dimensional flexible nervus and preparation method
ActiveCN101172184AIncrease current output capabilityIncrease surface areaPrecision positioning equipmentDecorative surface effectsDiseaseEngineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional flexible neural microelectrode and a manufacturing method thereof. The microelectrode uses a flexible polymer as a base material, and performs progressive electroplating through a circular pattern design of a metal seed layer to form smooth three-dimensional convex features. The electrode site structure can not only ensure good contact between the electrode site and the nerve cells, but also avoid damage to the nerve tissue caused by the sharp edges and corners of the raised electrode sites in the existing three-dimensional neural microelectrode. In addition, through the composite electroplating process in the electroplating process, that is, nano-scale dispersants are added to the electroplating solution to form a submicron-scale microporous structure on the surface of the electrode, increasing the surface area of the electrode site, thereby enhancing the current output capability of the electrode and ensuring the nerve. Effective stimulation of microelectrodes under the constraints of biosafety conditions. The three-dimensional flexible neural microelectrode provided by the invention can be widely used in the fields of neurological disease treatment, neurological rehabilitation, neurobiological basic research and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI NEURO XESS TECH CO LTD
Method for preparing ball-shaped bump biological microelectrode array
InactiveCN101149559ASimple processEasy to operateSemi-permeable membranesEye implantsLacquerRetinal Prosthesis
This invention discloses a sort of method that it uses the light-sensitive lacquer hot-melt method to prepare the roundness heave biologic micro-electrode array. It uses the light-sensitive lacquer technique to prepare the heave cylindrical light-sensitive lacquer, and it adopts the hot-melt circumfluence light-sensitive lacquer to form the roundness salient point. A bed of polymer which is covered in the underlay is used for the protecting material of the bottom of the device, and the presented in figures forms the metal electrode point and the lead, and then that it covers the polymer to be the protecting material of the top of the device. The presented in figures reveals the electrode point and the weld point, and it gets the needed roundness heave smooth micro-electrode array. The cost of the invention is low, also the technical process is simple, and it has the upper irritant effect. It is used for the preparation of the biologic micro-electrode array which has the nerve-cell stimulation of the retina prosthesis and so on.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Parylene-based microelectrode array implant for spinal cord stimulation
ActiveUS20140316503A1Spinal electrodesConductive layers on insulating-supportsImplantable ElectrodesMicroelectrode
An implantable electrode array assembly configured to apply electrical stimulation to the spinal cord. A substantially electrically nonconductive layer of the device has a first portion positionable alongside the spinal cord that includes a plurality of first openings. The layer has a second portion that includes a plurality of second openings. Electrodes and traces are positioned inside a peripheral portion of a body portion of the device and alongside the layer. At least one of the first openings is adjacent each of the electrodes to provide a pathway through which the electrode may provide electrical stimulation to the spinal cord. At least one of the second openings is adjacent each of the traces to provide a pathway through which the trace may receive electrical stimulation. At least one trace is connected to each electrode and configured to conduct electrical stimulation received by the trace(s) to the electrode.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH +2
Combinational processing method for micro-array axle hole
The invention relates to the micro matrix shaft hole combination machining method with the combination of electrochemical machining, electrical spark machining, and hypersonic recombination, to solve the difficulties of un-assured precision, low machining efficiency, and complex shape hard to machining. It makes single micro electrode through electrochemical machining, machining micro matrix master hole on the flat electrodes, making micro matrix shaft through electrical spark machining and complex supersonic vibration, and using micro matrix shaft and electrochemical machining to make the micro matrix shaft hole. It has high machining precision, high in efficiency and convenient.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for detecting or assaying target substance by utilizing oxygen electrode
InactiveUS6410251B2Low costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAntigenRedox
A method for detecting or assaying one constituting member in a specific binding pair, for example, the antigen in an antigen / antibody pair, by utilizing specific binding such as binding between an antigen and an antibody, together with redox reaction for detecting a label, wherein an oxygen micro-electrode with a sensing surface area of 1 mm2 or less is used; and an apparatus to which the method is applicable. According to the method and by using the apparatus, redox reaction for assaying the label can be completed in such a short time as several minutes. Therefore, an inexpensive disposable apparatus for household use can be realized.
Owner:TOYOTA CENT RES & DEV LAB INC
Field-programmable lab-on-a-chip based on microelectrode array architecture
InactiveCN102671722AEasy to solveExcellent time to marketLaboratory glasswaresFluid controllersLab-on-a-chipField-programmability
The invention discloses a field-programmable lab-on-a-chip based on microelectrode array architecture, concretely a system related to filed-programmable lab-on-chip (FPLOC) microfluidic operations, fabrications, and programming based on microelectrode array architecture. The FPLOC device by employing a microelectrode array interface may include the following: (a) a bottom plate comprising an array of multiple microelectrodes disposed on a top surface of a substrate covered by a dielectric layer; wherein each of the microelectrode is coupled to at least one grounding elements of a grounding mechanism, wherein a hydrophobic layer is disposed on the top of the dielectric layer and the grounding elements to make hydrophobic surfaces with the droplets; (b) a field programmability mechanism for programming a group of configured-electrodes to generate microfluidic components and layouts with selected shapes and sizes; and, (c) a FPLOC functional block, comprising: I / O ports; a sample preparation unit; a droplet manipulation unit; a detection unit; and a system control unit.
Owner:王崇智 +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com