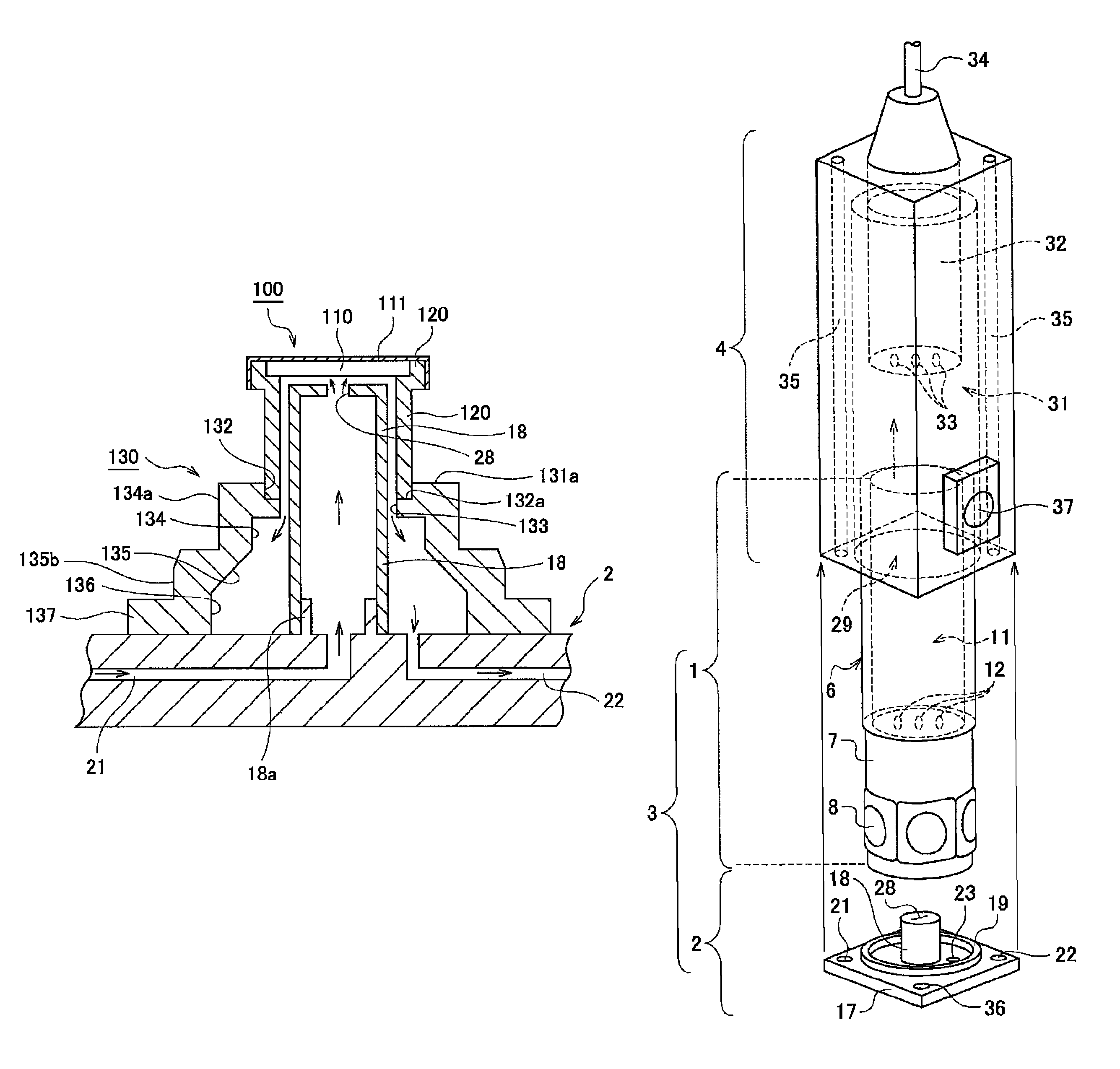
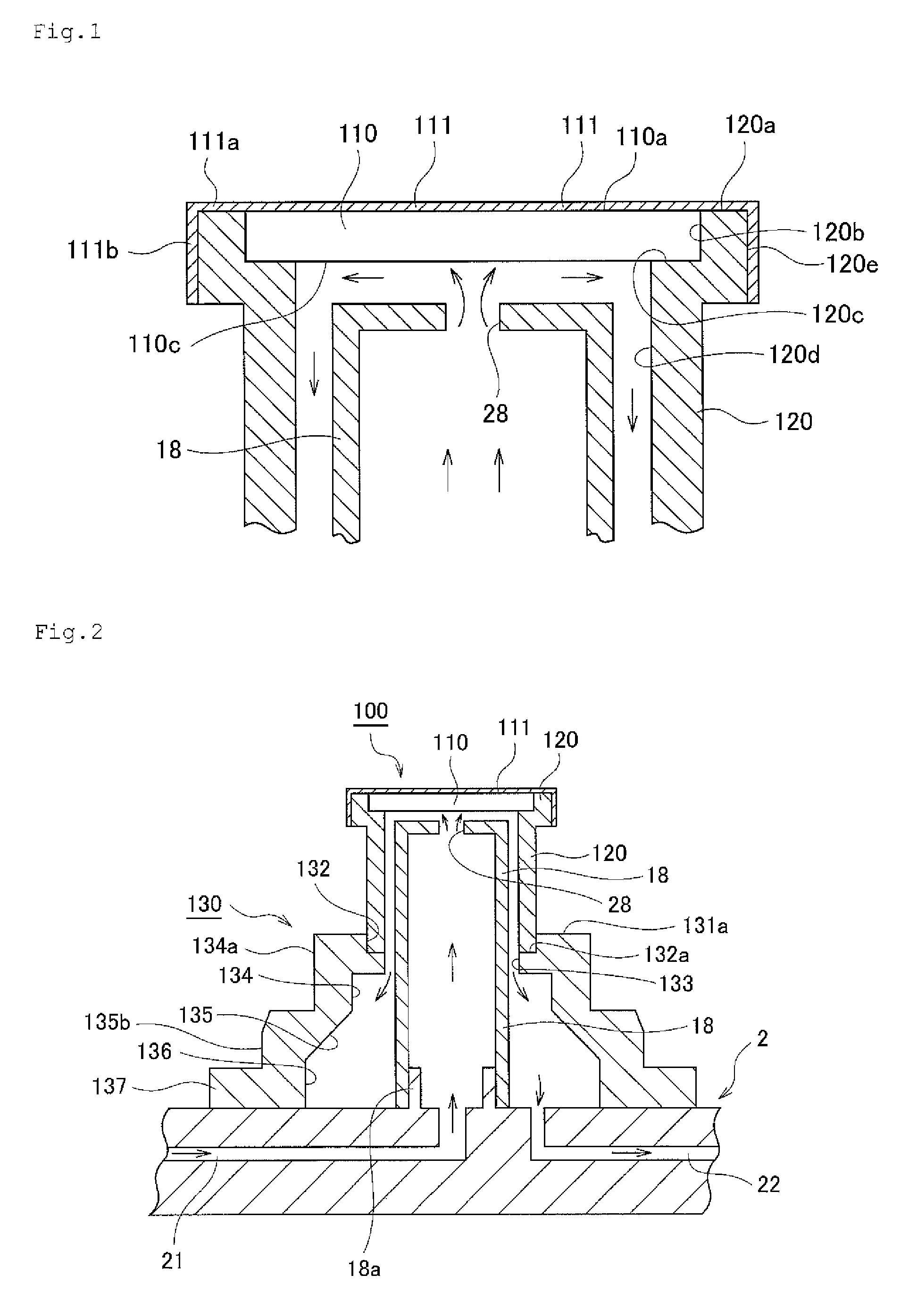
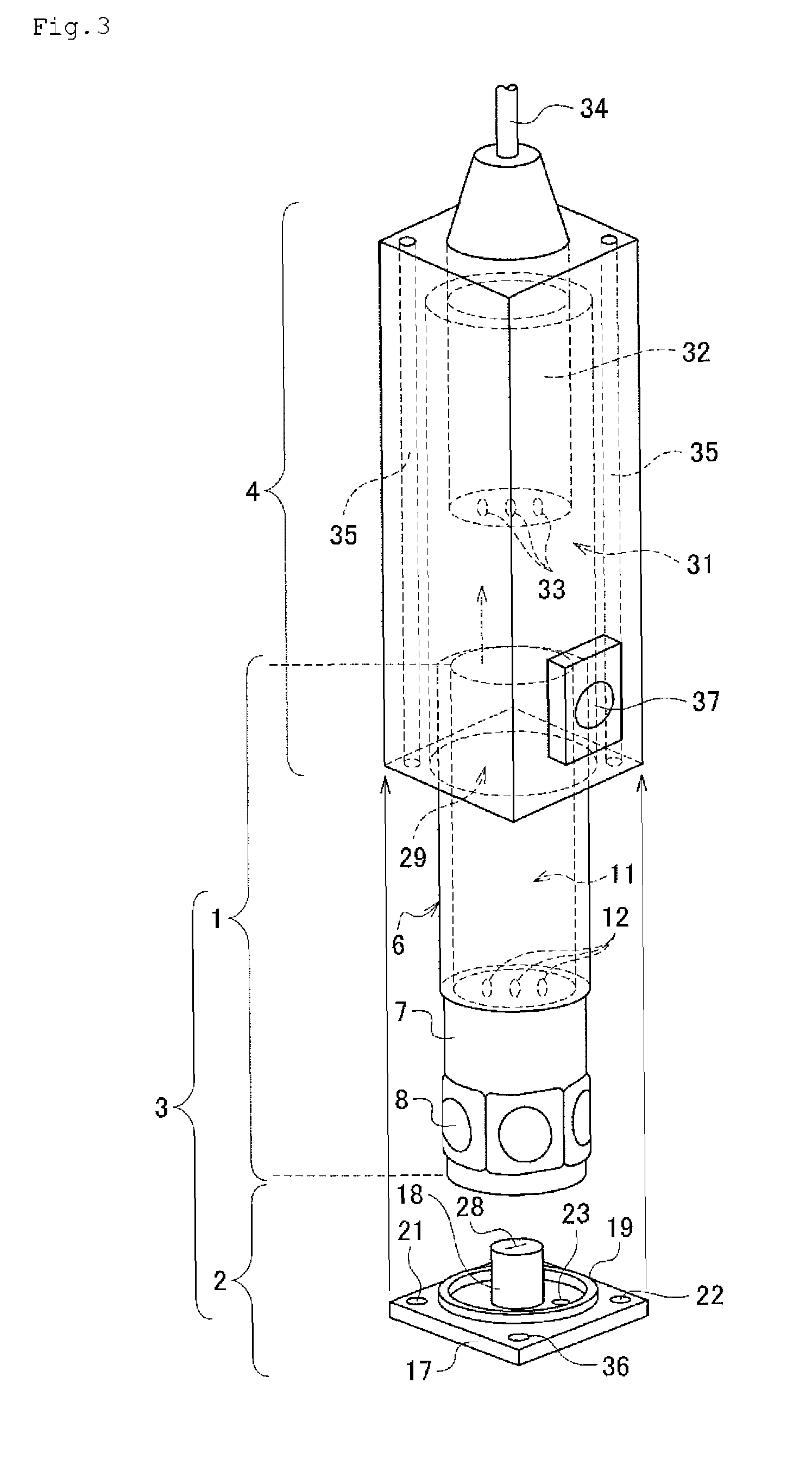
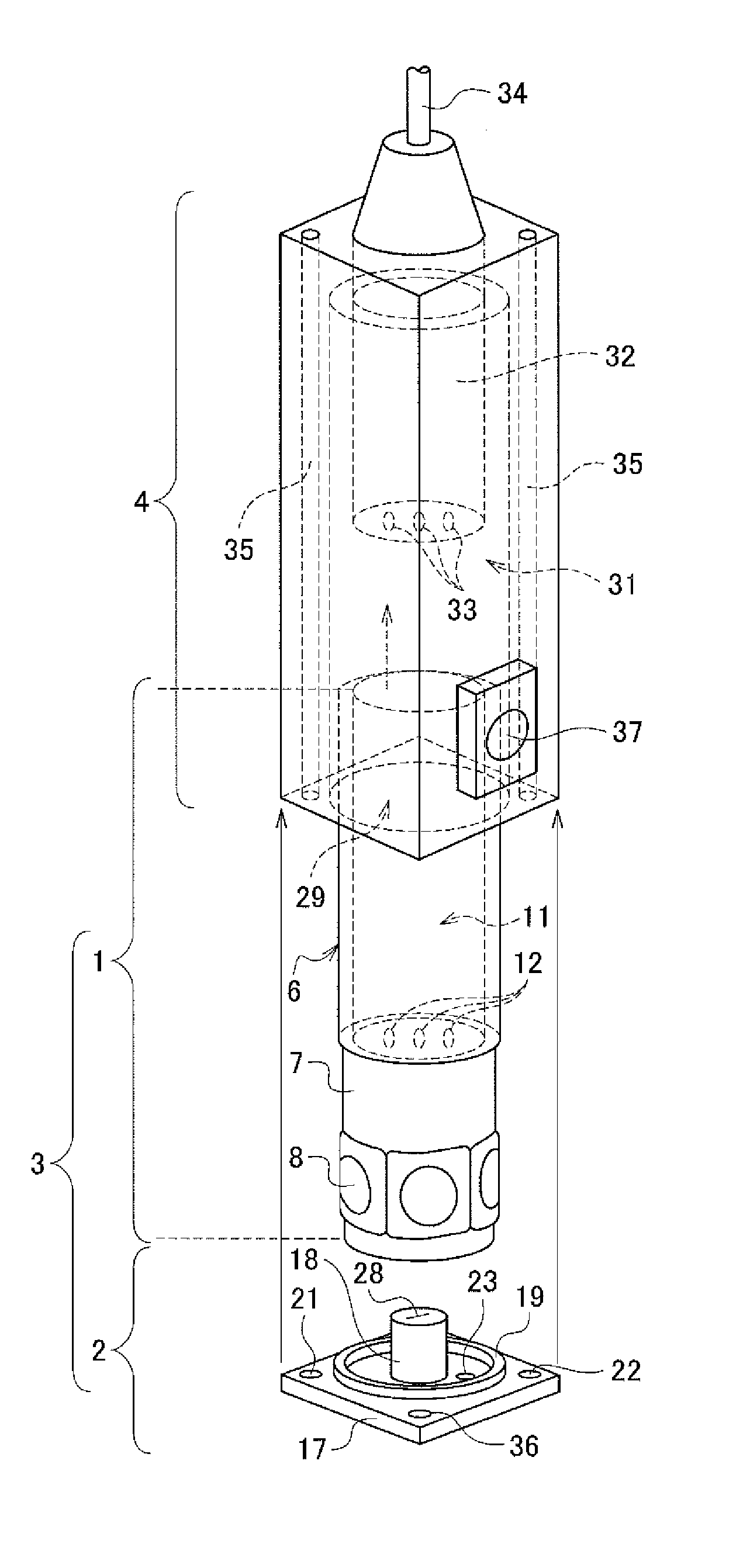
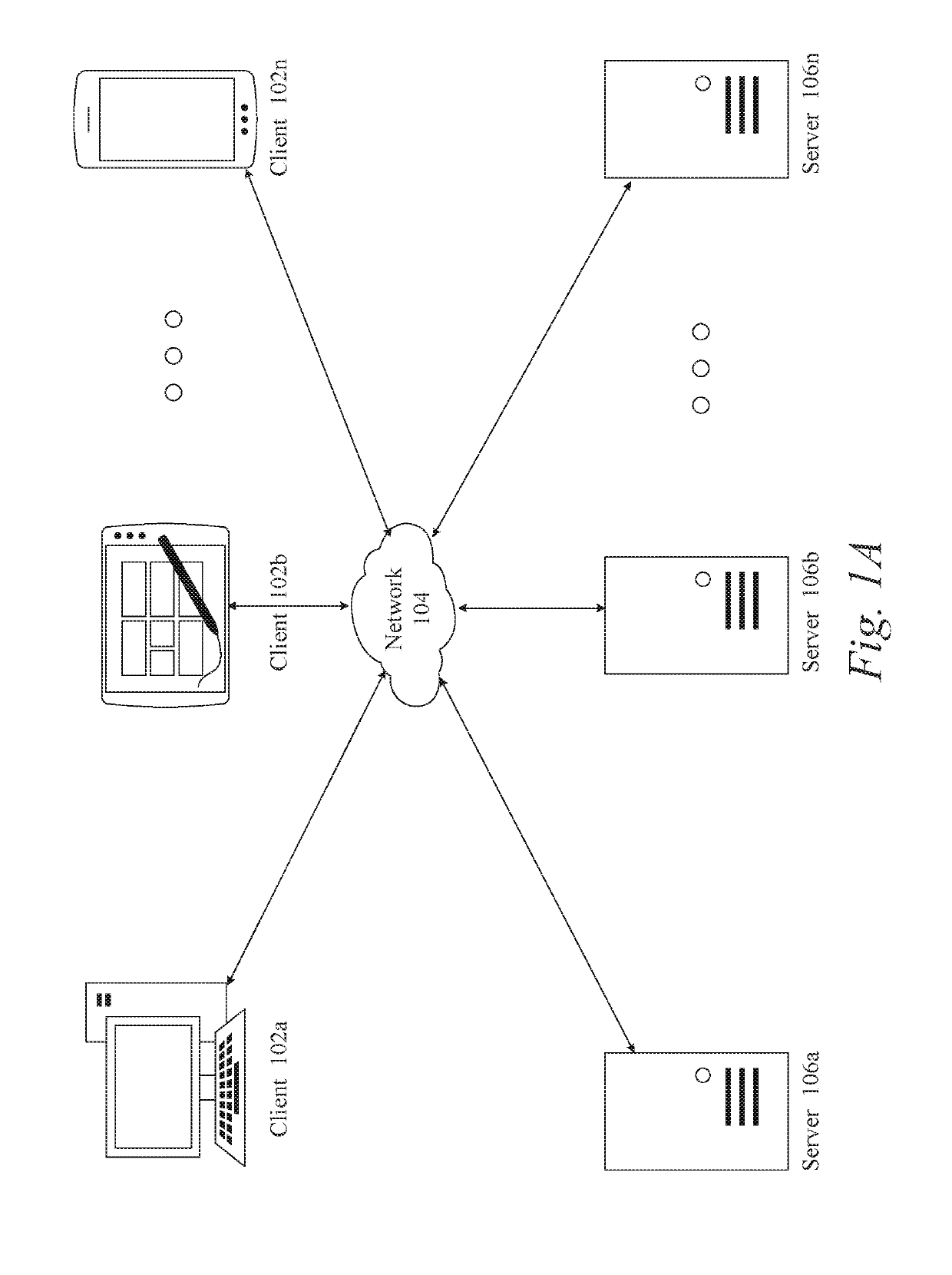
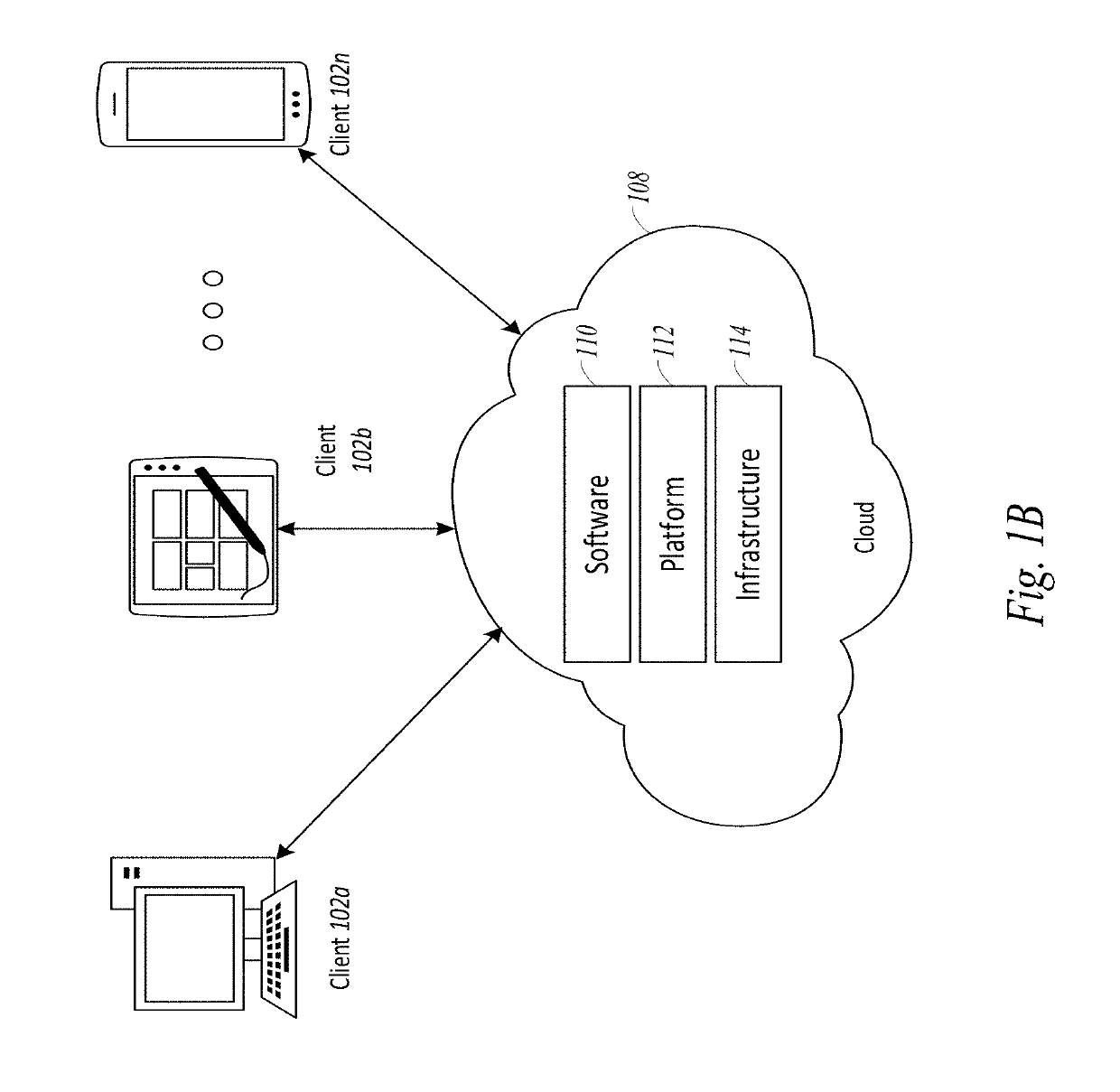
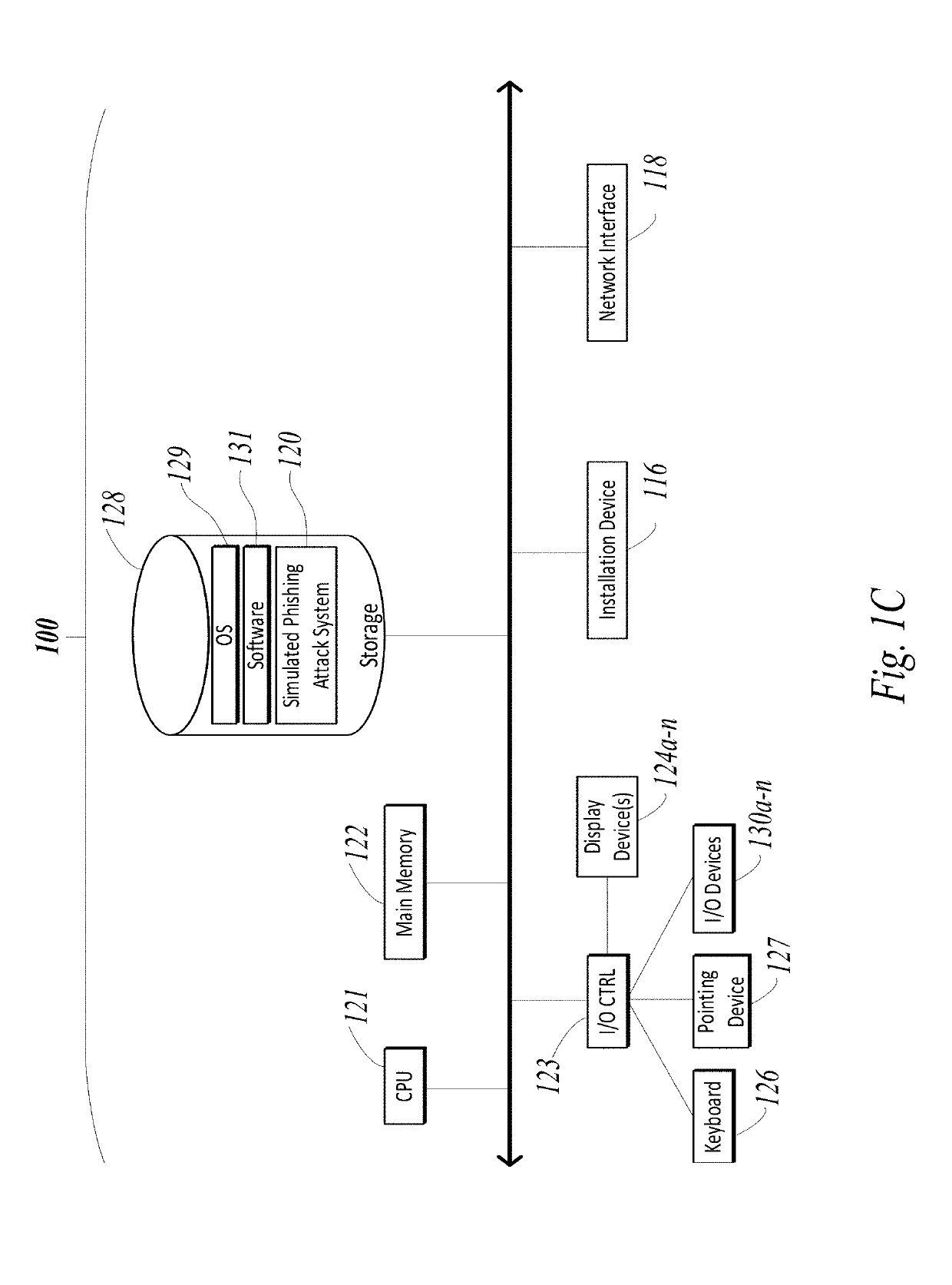
Patents
Literature
323results about How to "Same effect" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
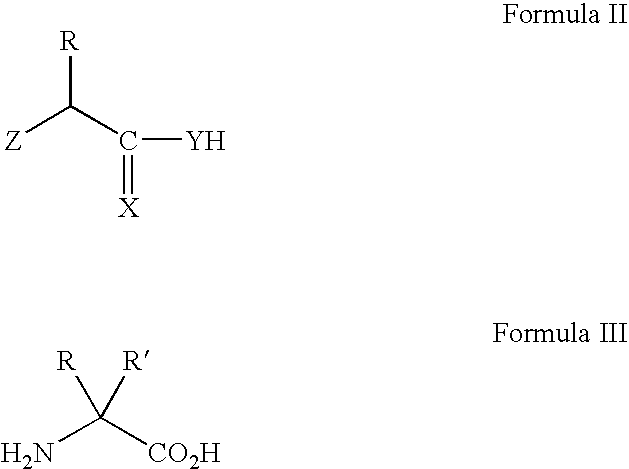
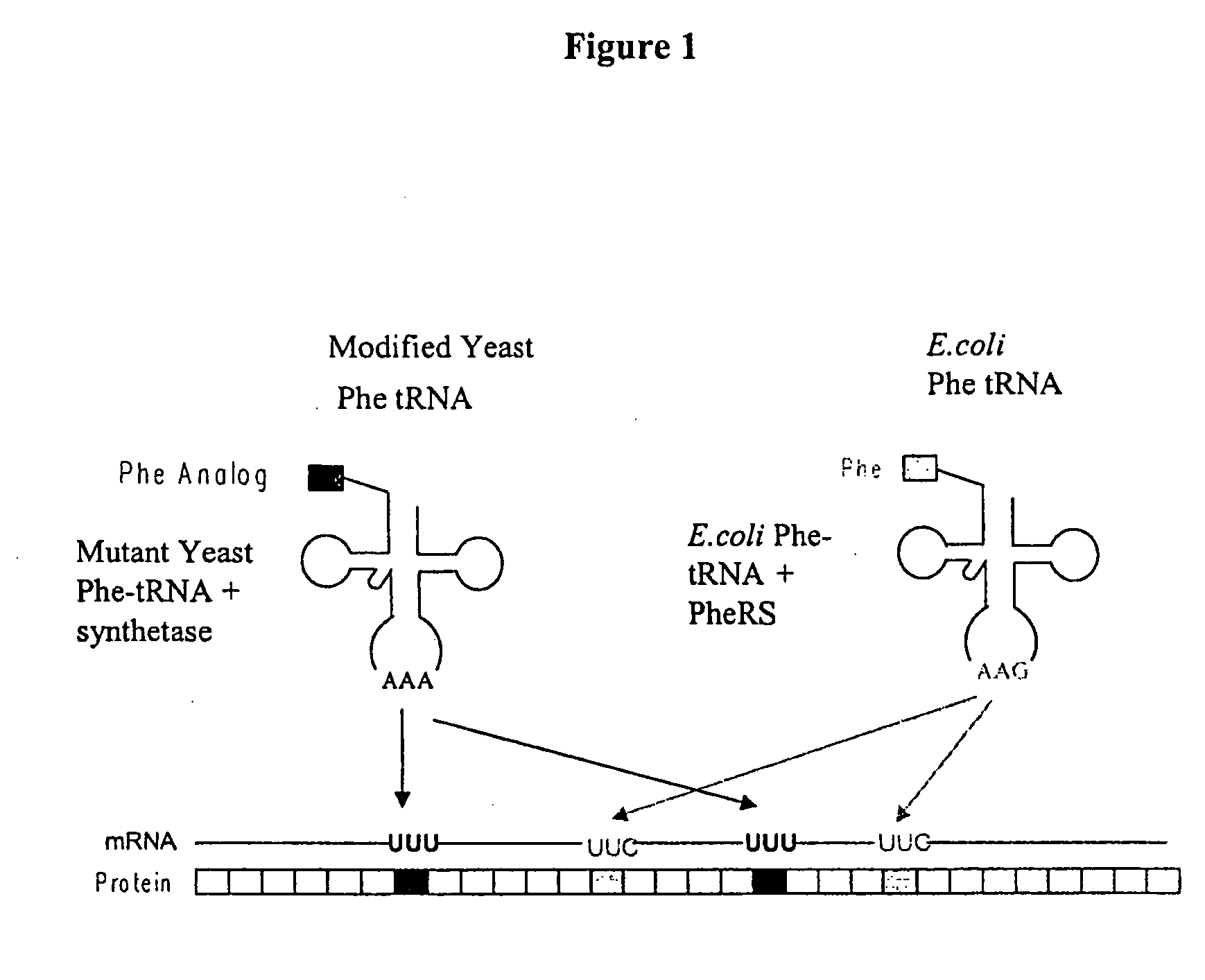
Modulating pH-sensitive binding using non-natural amino acids
InactiveUS20050260711A1Prolong half-life in vivoSame effectAnimal cellsSugar derivativesSide chainTumor antigen
The invention provides methods, systems and reagents for regulating pH-sensitive protein interaction by incorporating non-natural amino acids into the protein (e.g. an antibody, or its functional fragment, derivative, etc.). The invention also relates to specific uses in regulating pH-sensitive binding of antibodies to tumor site, by conferring enhanced tumor-specificity / selectivity. In that embodiment, the non-natural amino acids preferably have desirable side-chain pKa's, such that at below physiological pH (e.g. about pH 6.3-6.5) the non-natural amino acid confer enhanced binding to tumor antigens in acidic environments. Such non-natural amino acids can be incorporated by any suitable means, such as by utilizing a modified aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase to charge the nonstandard amino acid to a modified tRNA, which forms strict Watson-Crick base-pairing with a codon that normally forms wobble base-pairing with natural tRNAs (e.g. the degenerate codon orthogonal system.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Nutraceuticals or nutritional supplements and method of making
InactiveUS6949264B1Method is newPromote absorptionContainers for annular articlesConfectioneryControlled releaseMedicine
A method for producing a chewing gum with a controlled release active agent, as well as the chewing gum so produced, is obtained by physically modifying the release properties of the active agent, such as a nutraceutical or nutritional supplement, by coating and drying. The active agent is coated by encapsulation, partially coated by agglomeration, entrapped by absorption, or treated by multiple steps of encapsulation, agglomeration, and absorption. The coated active agent is preferably then co-dried and particle sized to produce a release-modified active agent for use in chewing gum. The active agent may also be used in a coating on a chewing gum product, as part of a rolling compound applied to the chewing gum product, or as a part of the liquid in a liquid-center chewing gum product.
Owner:WM WRIGLEY JR CO
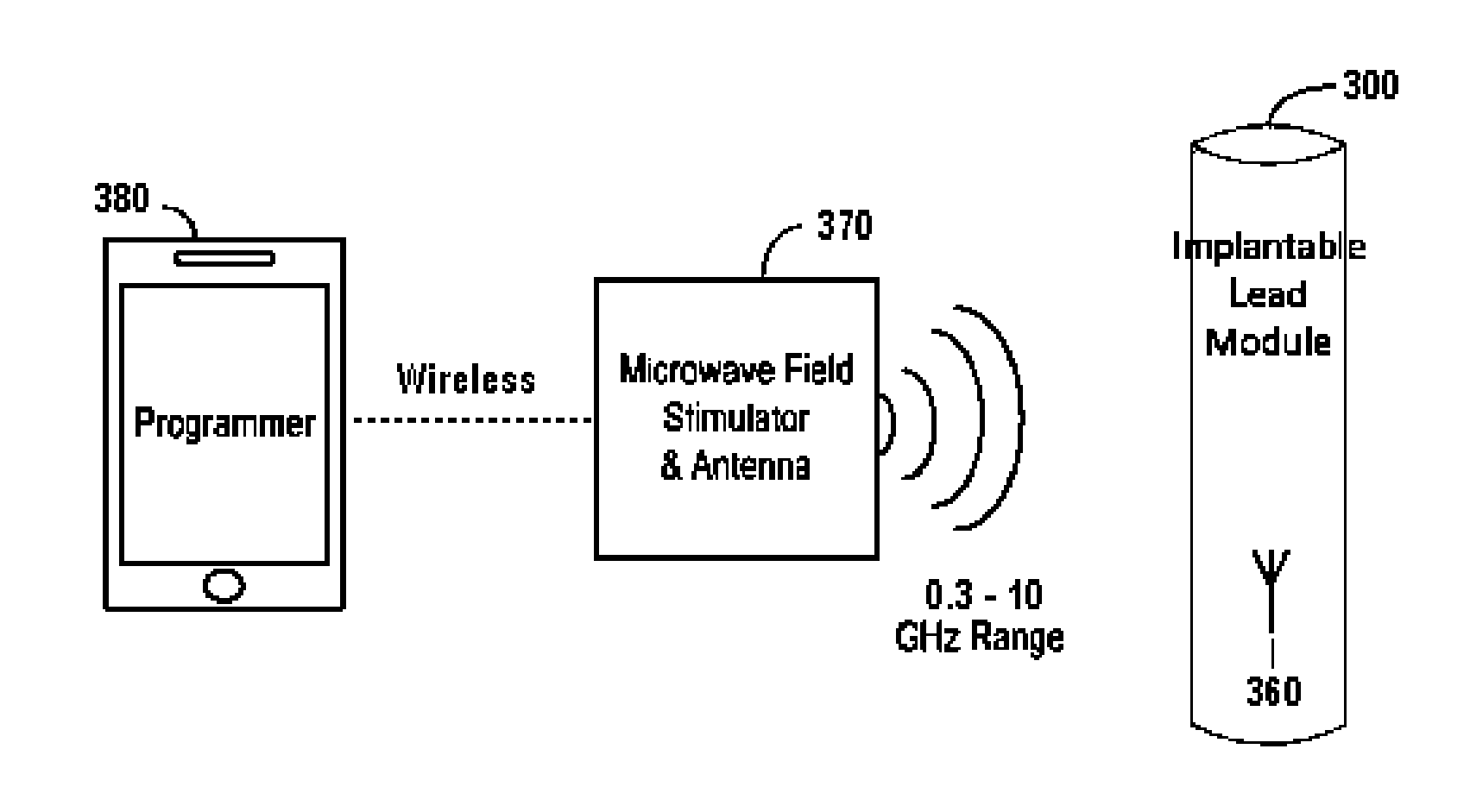
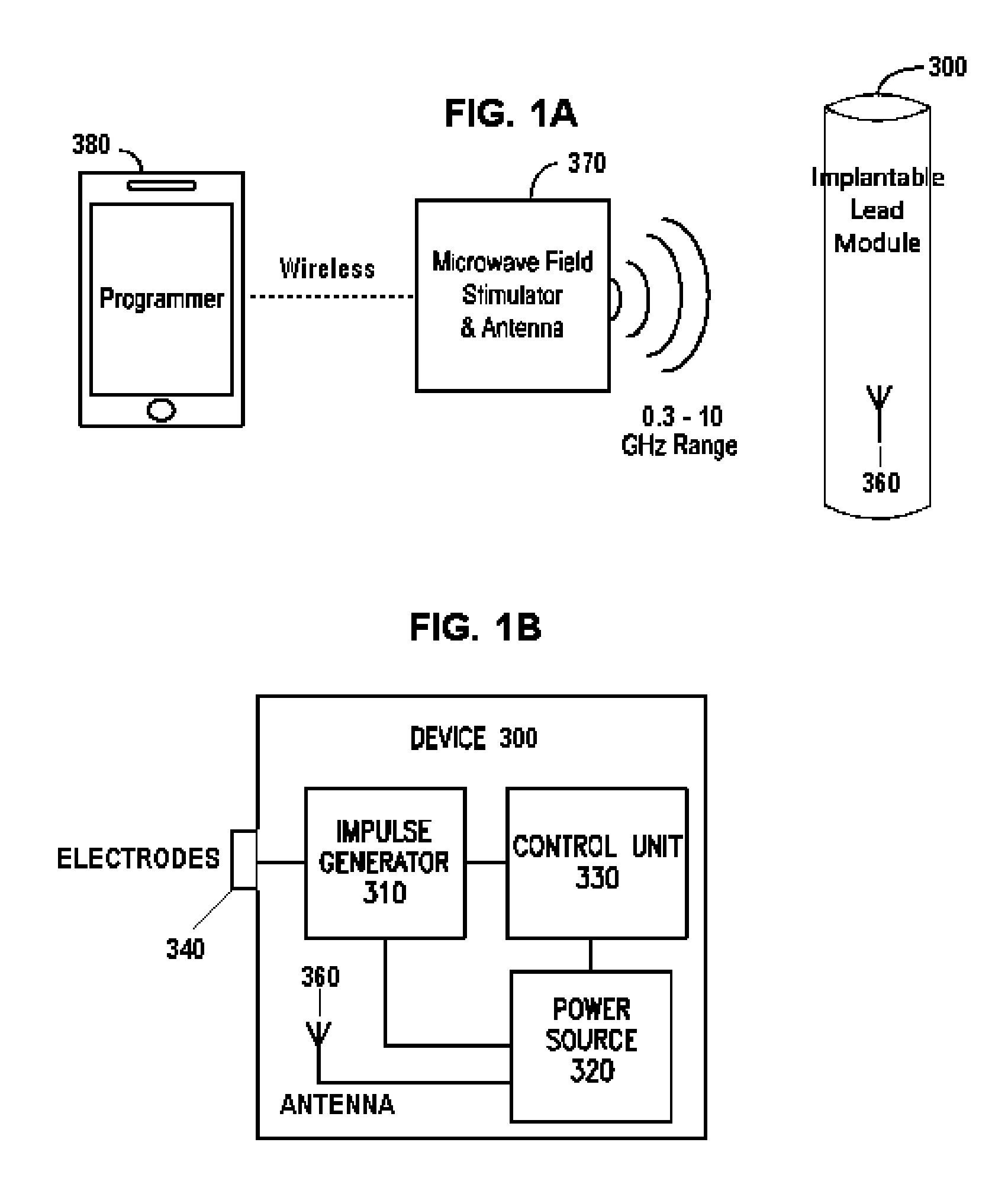
Nerve stimulator system
ActiveUS9205258B2Without sacrificing performanceSame effectImplantable neurostimulatorsArtificial respirationElectrical impulseElectromagnetic radiation
Owner:ELECTROCORE
System and method for detection and prevention of host intrusions and malicious payloads
InactiveUS20130347111A1Preventing executionSame effectMemory loss protectionError detection/correctionComputer hardwareComputer science
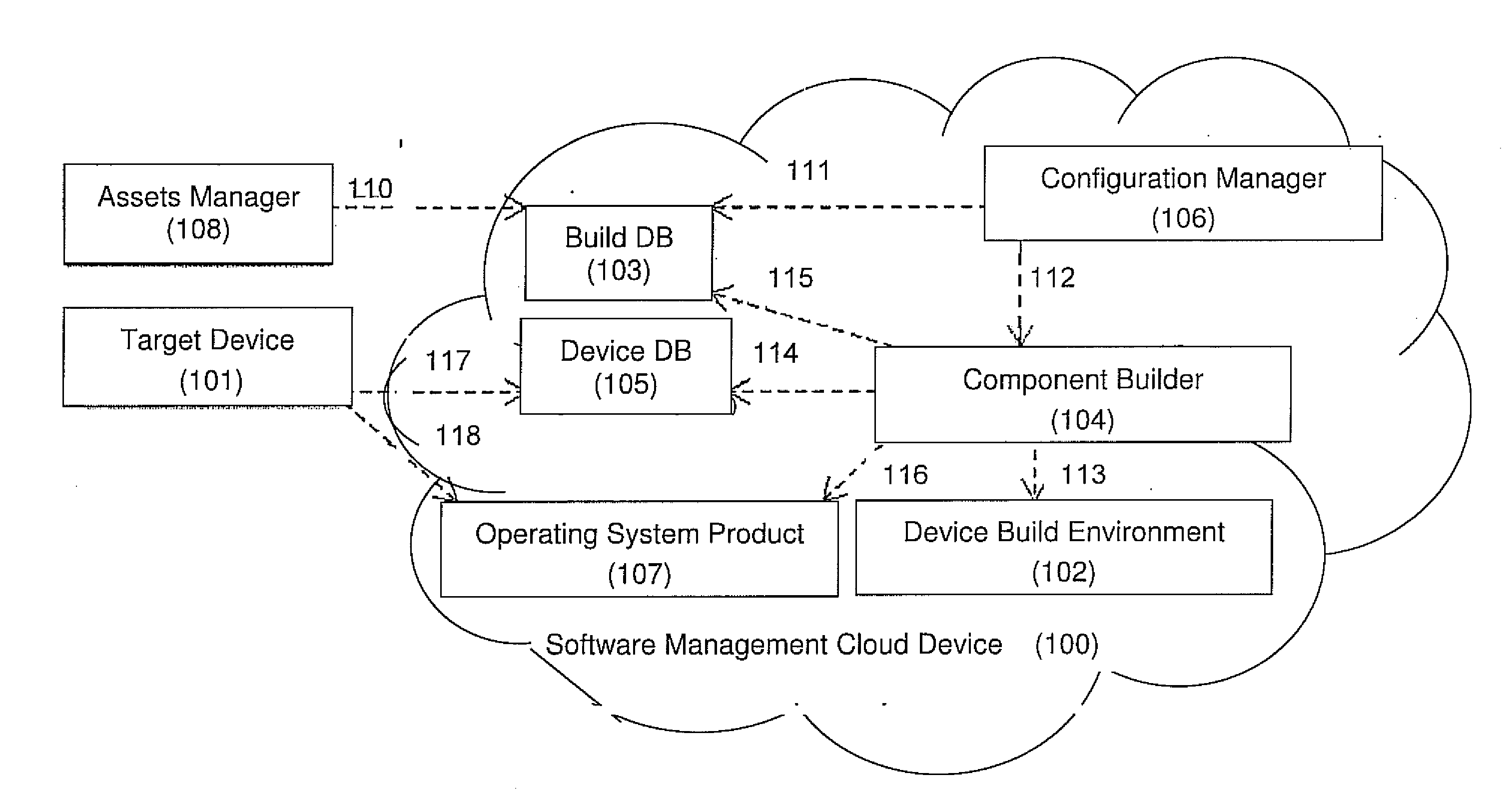
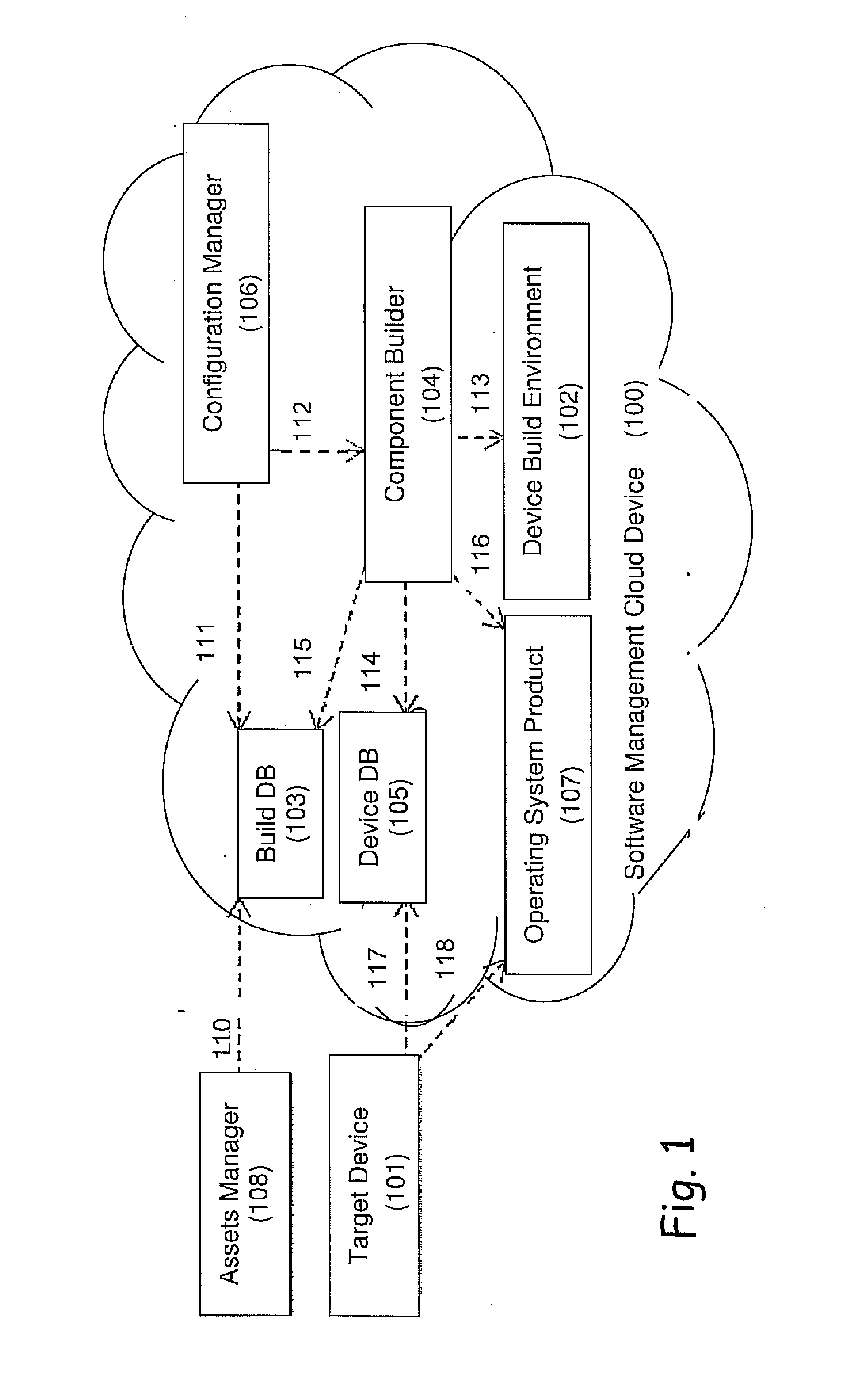
A computerized system for preventing host intrusions on a communication device. The device is wirelessly connected to a wireless communication network. The system includes a computer readable management software module configured to analyze malicious payloads. The management software module includes an asset manager module configured to assign updates to the communication device, a device database module configured to describe the communication device characteristics and a build database module configured to automate software builds of the communication device core operating system. The management software module also includes a component builder module configured to run a plurality of instruction sets to establish a build environment for the communication device according to the communication device characteristics, a configuration manager module configured to build the instruction sets and an operating system product module configured by the build database module as part of a build process triggered by the asset manager module.
Owner:ZIMPERIUM INC
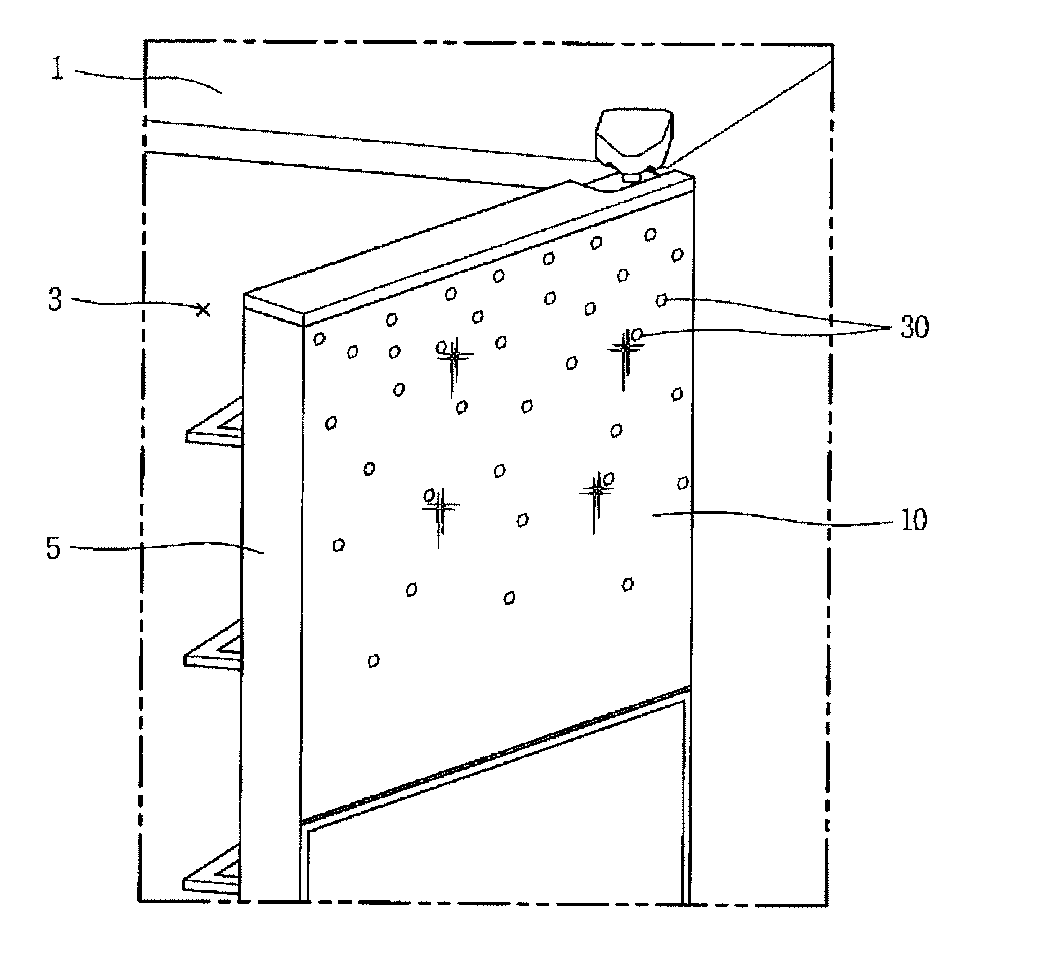
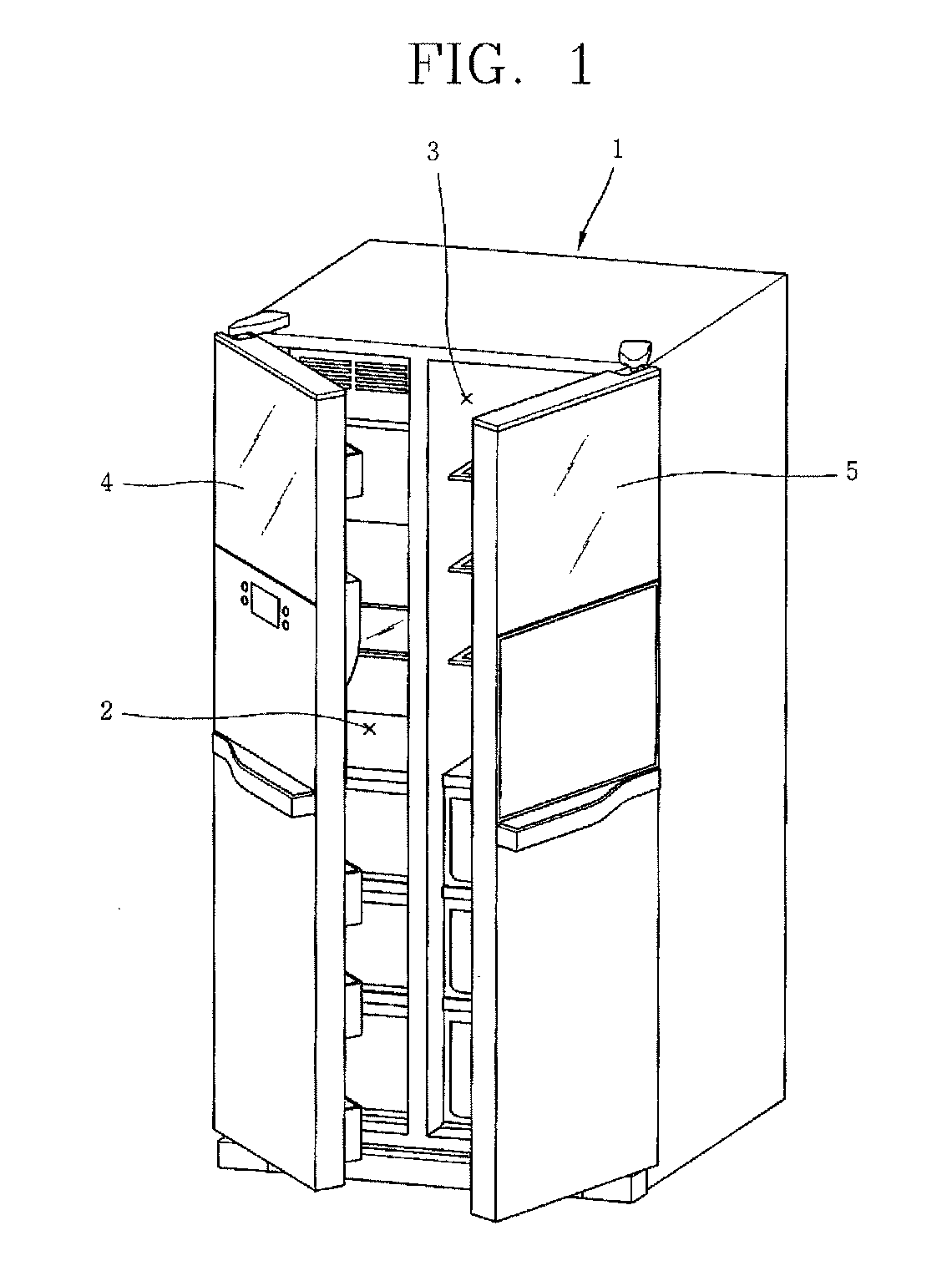
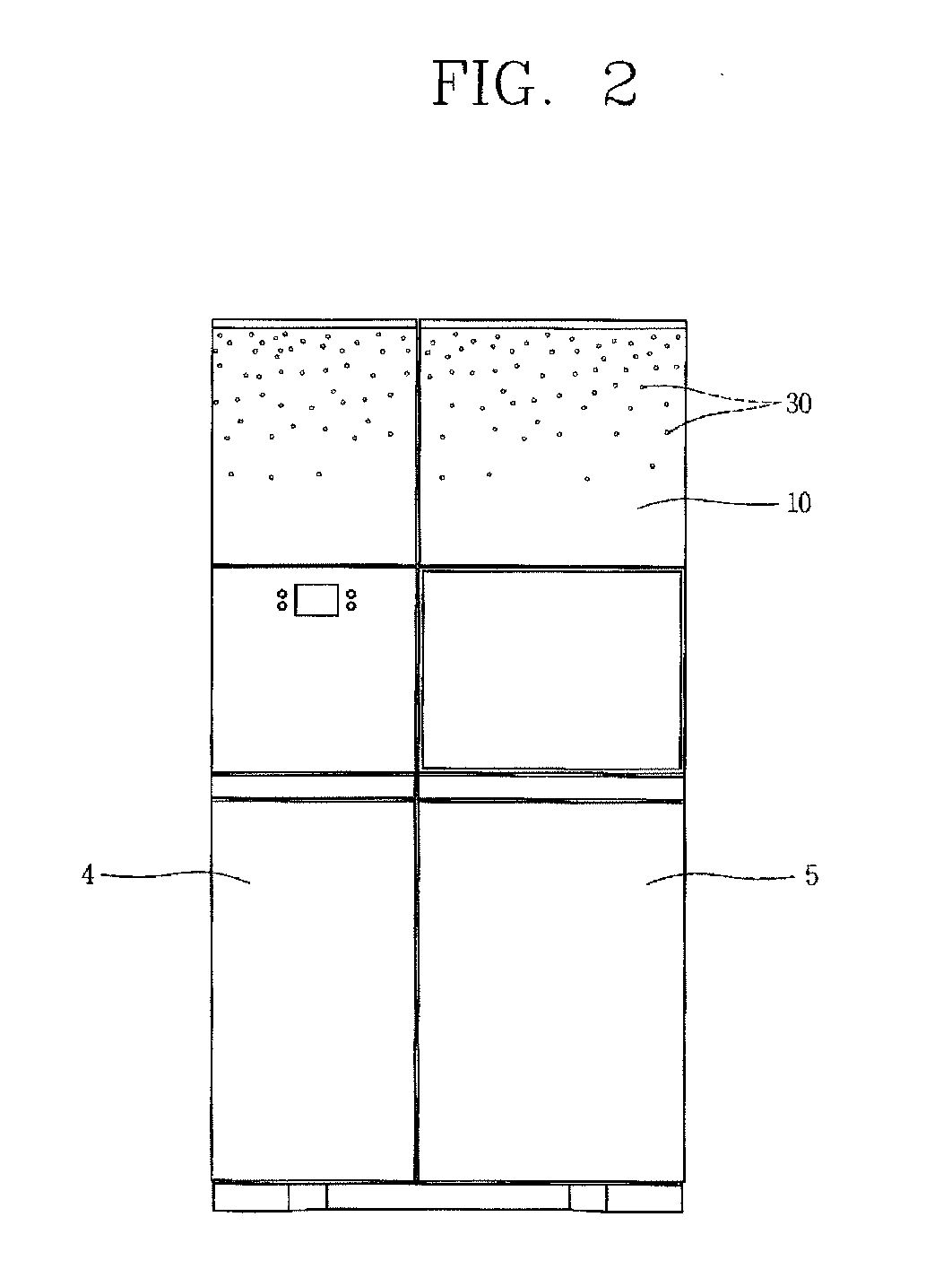
Decorative panel and refrigerator having the same
ActiveUS20100295425A1Reduce material costsSame effectFurnace componentsLighting elementsEngineeringRefrigerated temperature
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS INC
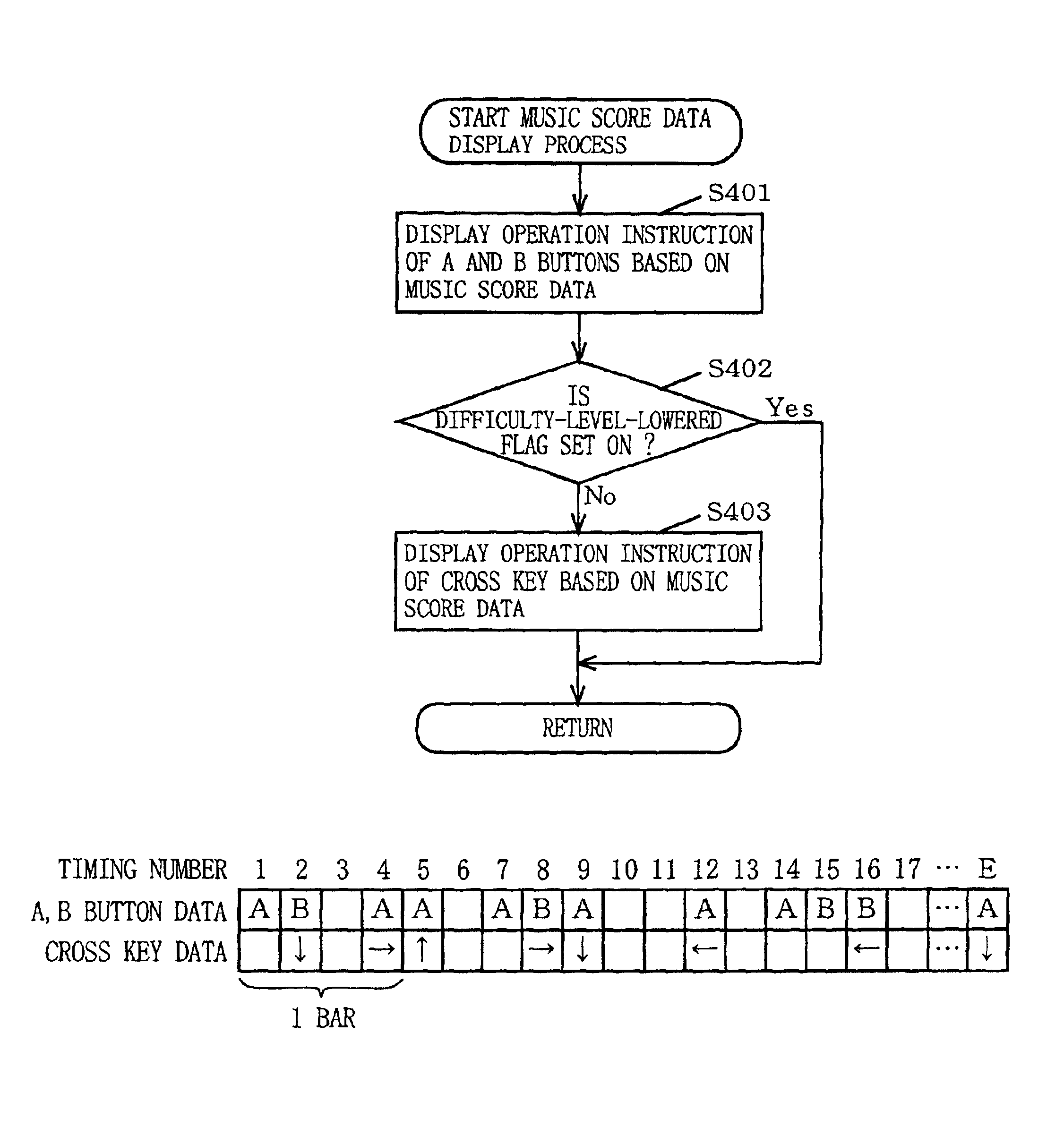
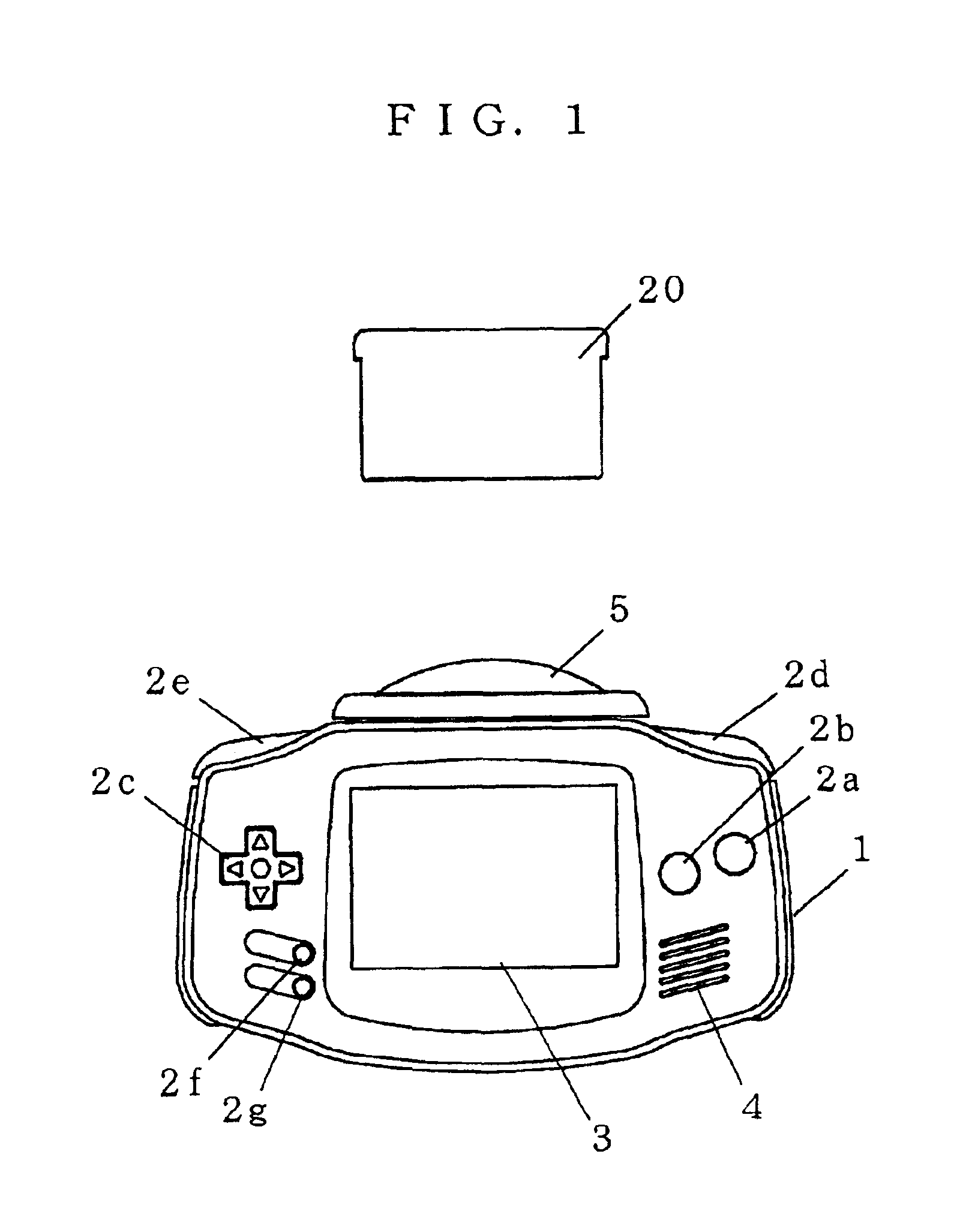
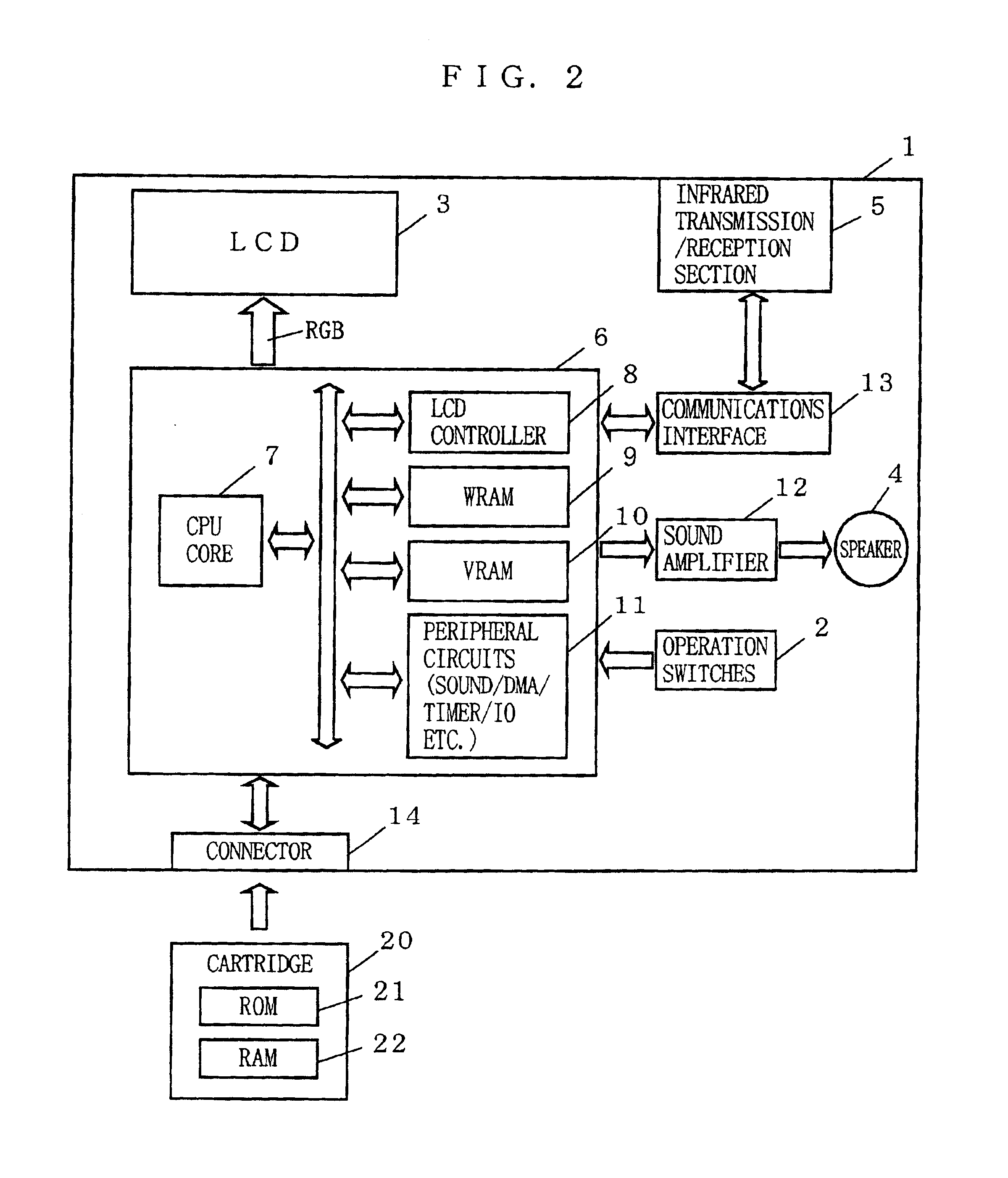
Game machine and program therefor
InactiveUS6913536B2Convenient and consistent game playSame effectVideo gamesSpecial data processing applicationsSimulationGame based
Game machines automatically change the difficulty level of the game operation in the middle of the game based on an evaluation made on a player's game operation. A game machine determines, at least in terms of timing and type, whether the player's inputted button operation matches with the button operation designated by the game. If there is a match, the game machine determines it as an operation success. If not, the game machine determines it as an operation error. Based on the degree of operation success or operation error, the game machine dynamically changes the difficulty level of the game operation in the middle of the game.
Owner:NINTENDO CO LTD
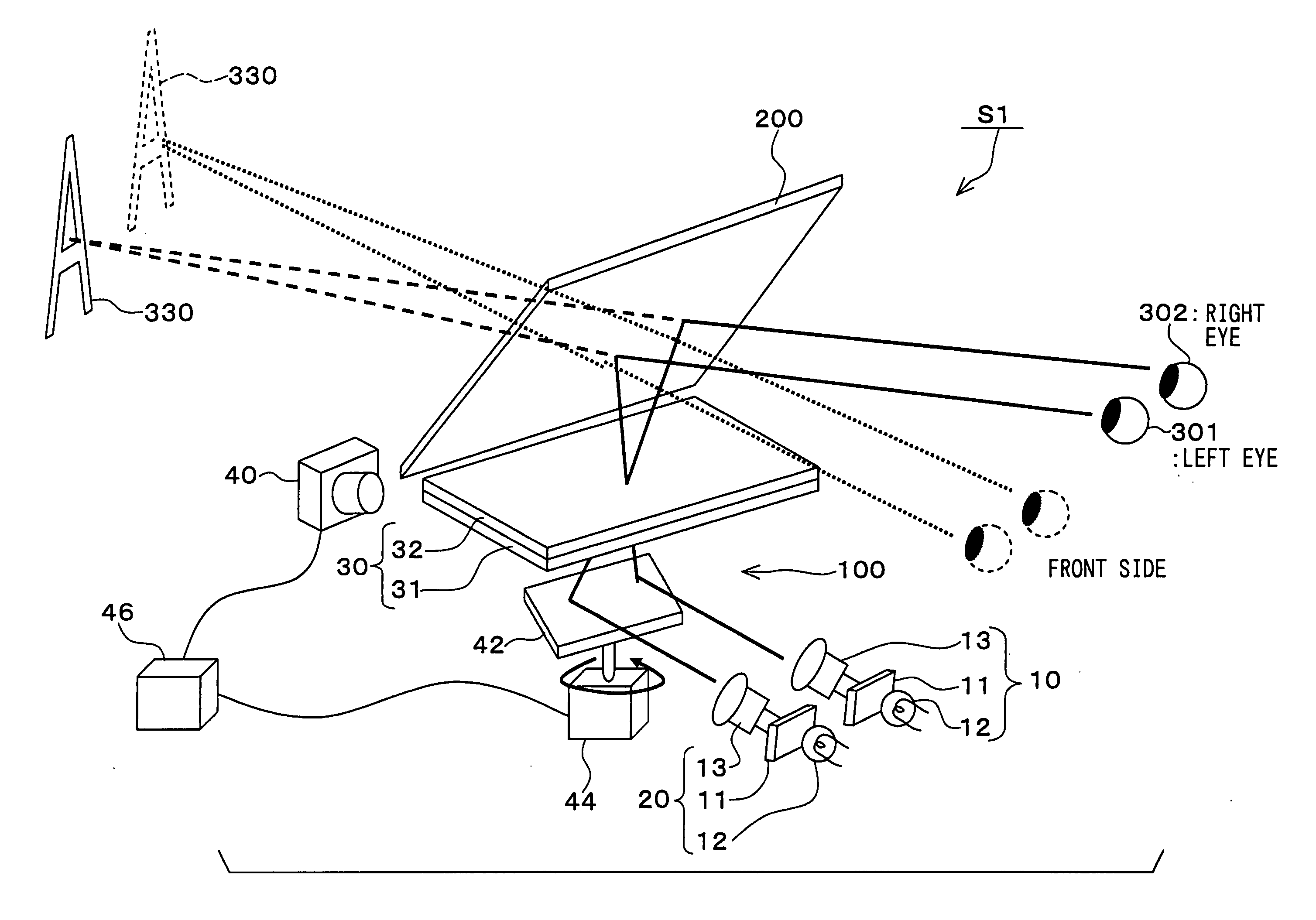
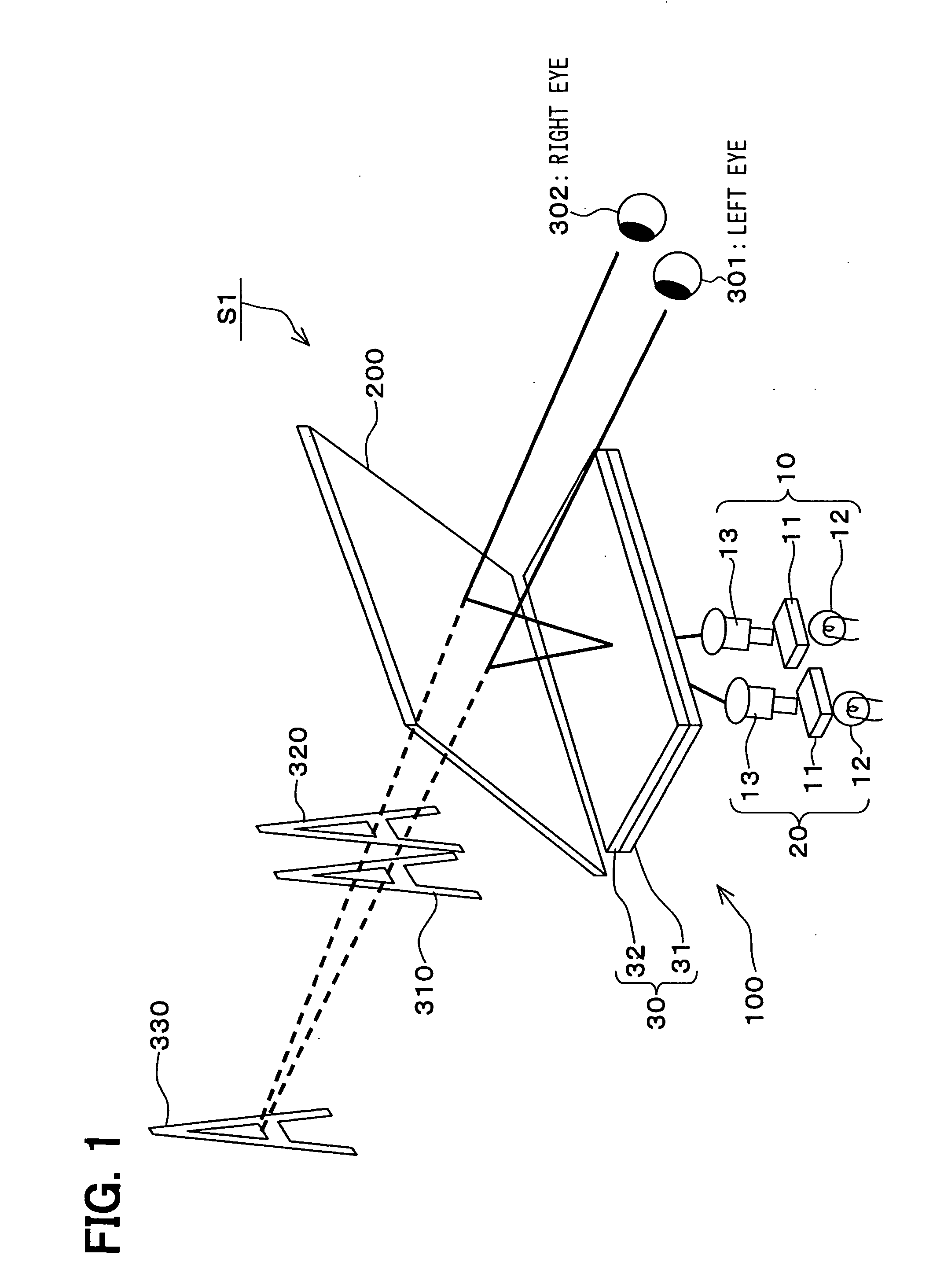
Virtual image display apparatus
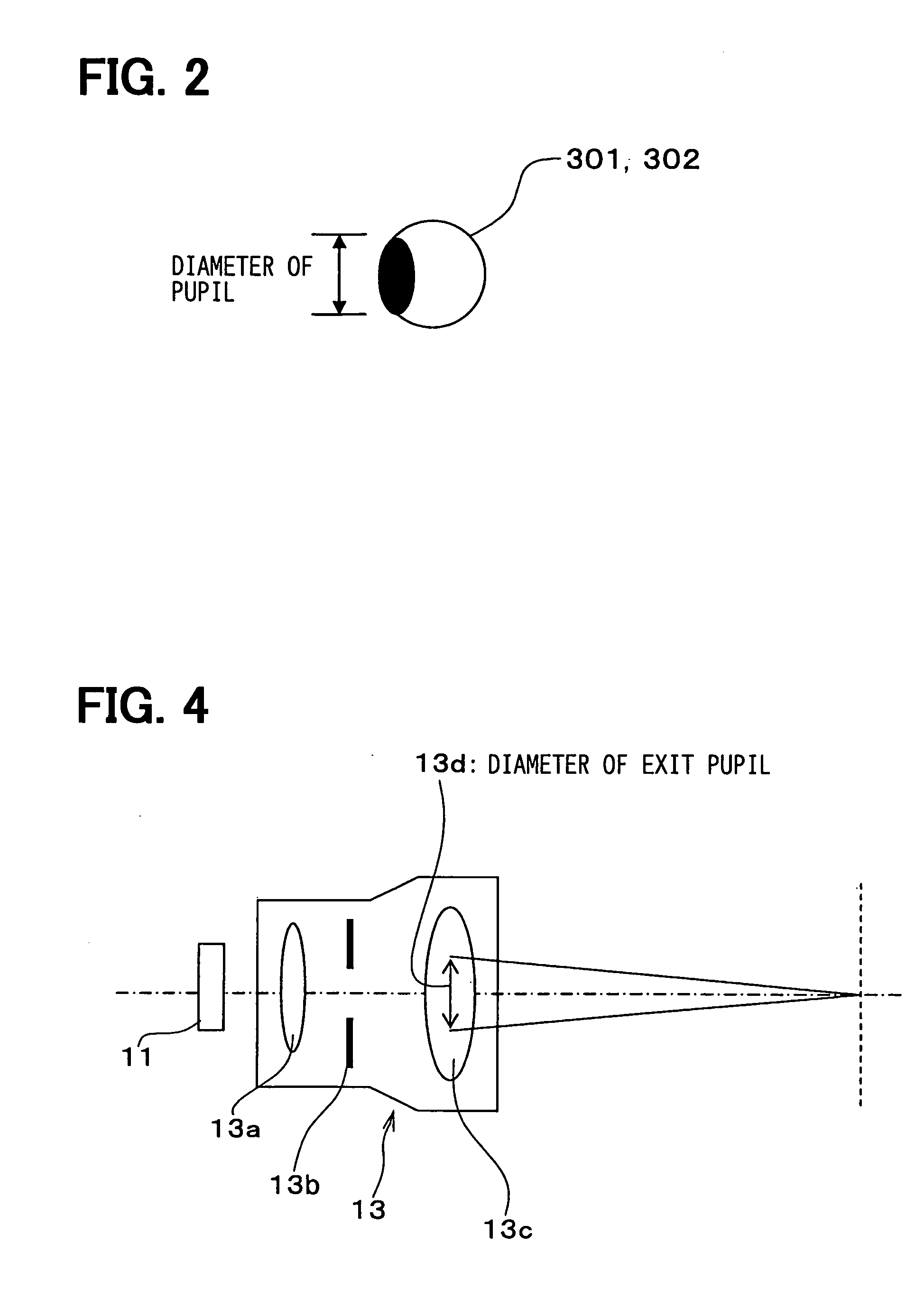
InactiveUS20050052617A1Simple structureQuality improvementProjectorsVehicle componentsDisplay deviceProjection system
A virtual image display apparatus comprises a pair of optical projection systems, each having a display device, a light source and a projection lens. The images formed on the display device are projected to an image location optical system, which comprises a light collecting lens and an optical diffusion device. The light rays from the optical projection systems are reflected at a translucent reflecting means, so that the light rays are respectively collected at right and left eyes of an observing person. As a result, the images can be recognized by the person as a virtual image in the distance. Since the optical diffusion device diffuses the light rays, in such a way that the light rays to one of observing eyes may not reach the other observing eye, so that the image information of the respective light rays can be recognized by the observing person, without causing a cross-talk.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Organic electroluminescent element and organic electroluminescent display device
InactiveUS20070024168A1Easily adjustLight quantityIncadescent screens/filtersDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceAnode
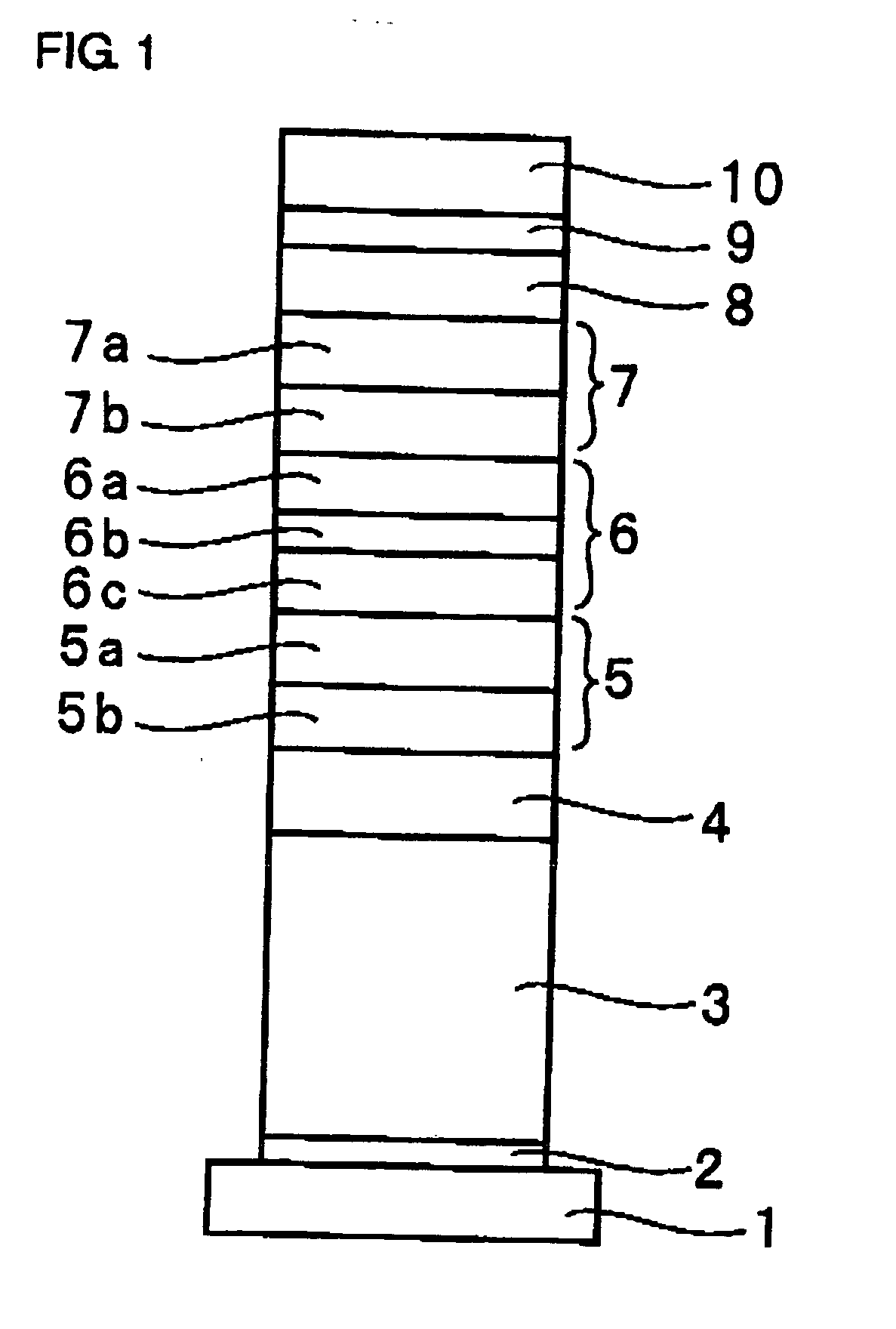
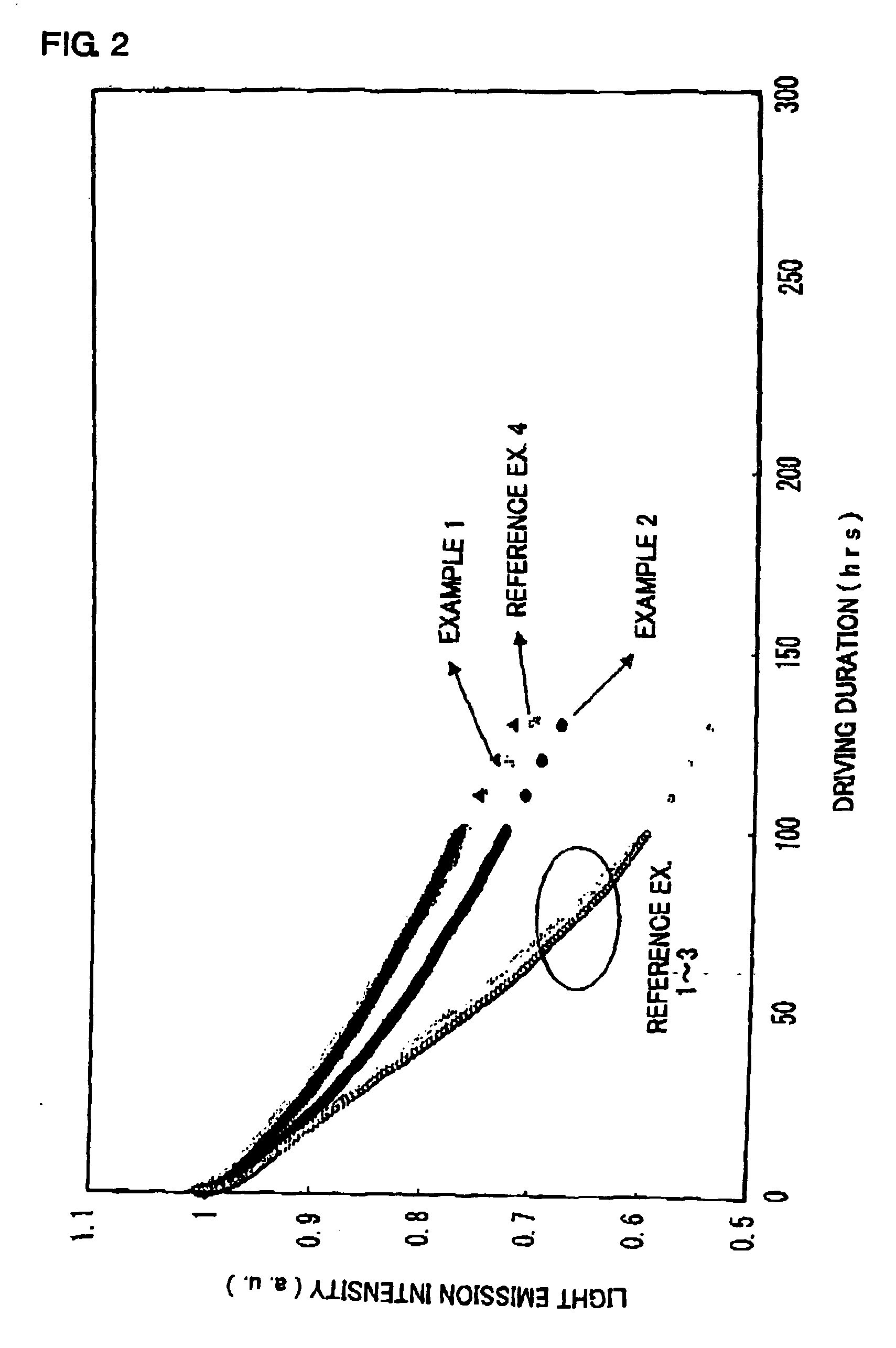
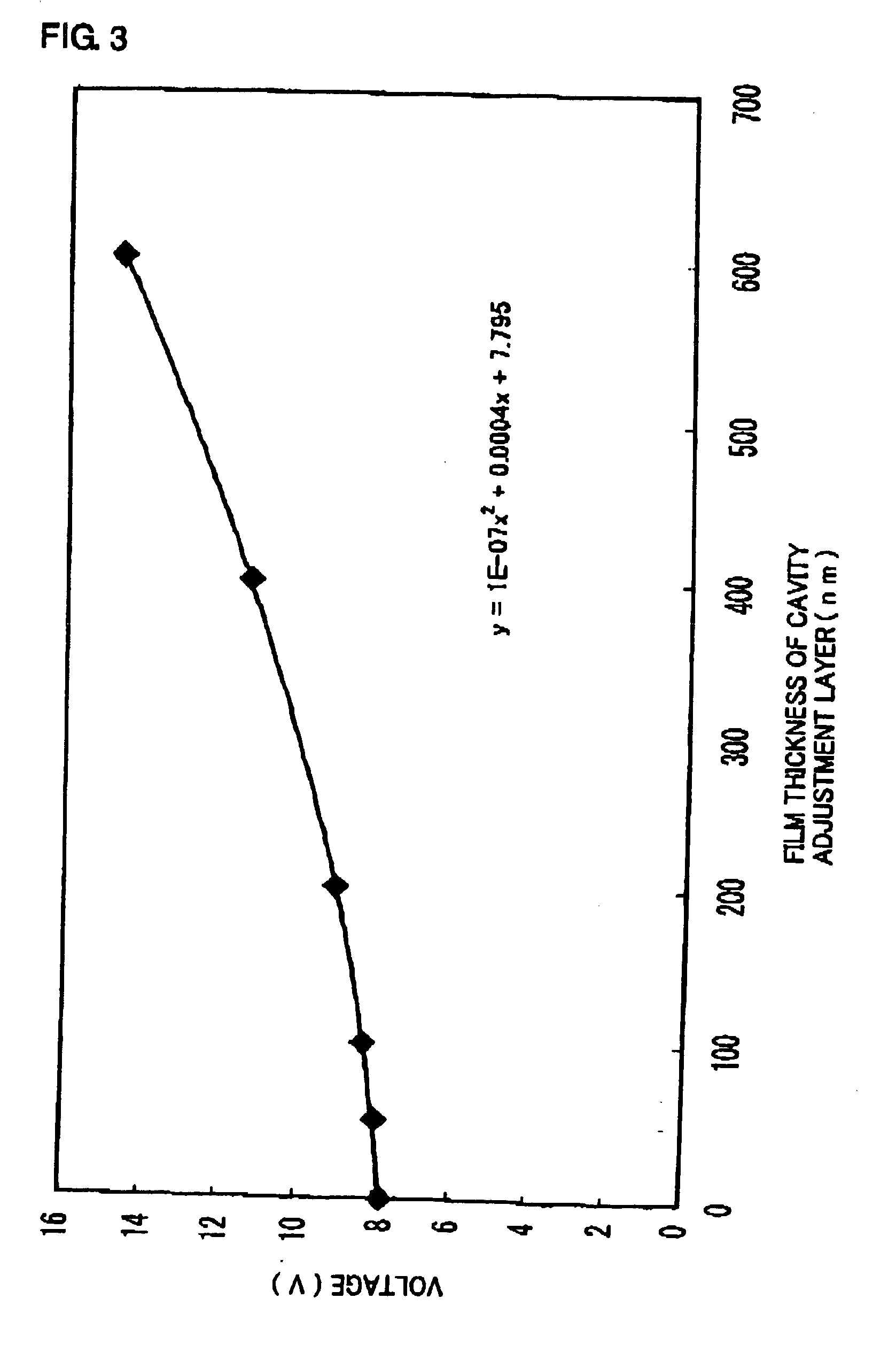
The invention provides an organic electroluminescent element comprising a cathode, an anode, a plurality of light emitting units layered and arranged between the cathode and the anode via an intermediate unit, a cavity adjustment layer formed between the light emitting unit nearest to the anode and the anode, and an electron extracting layer formed adjacently to the cavity adjustment layer in the light emitting unit side and is characterized in that the film thickness of the cavity adjustment layer is adjusted to adjust the optical distance from the light emitting position of each light emitting unit to the anode.
Owner:SANYO ELECTRIC CO LTD
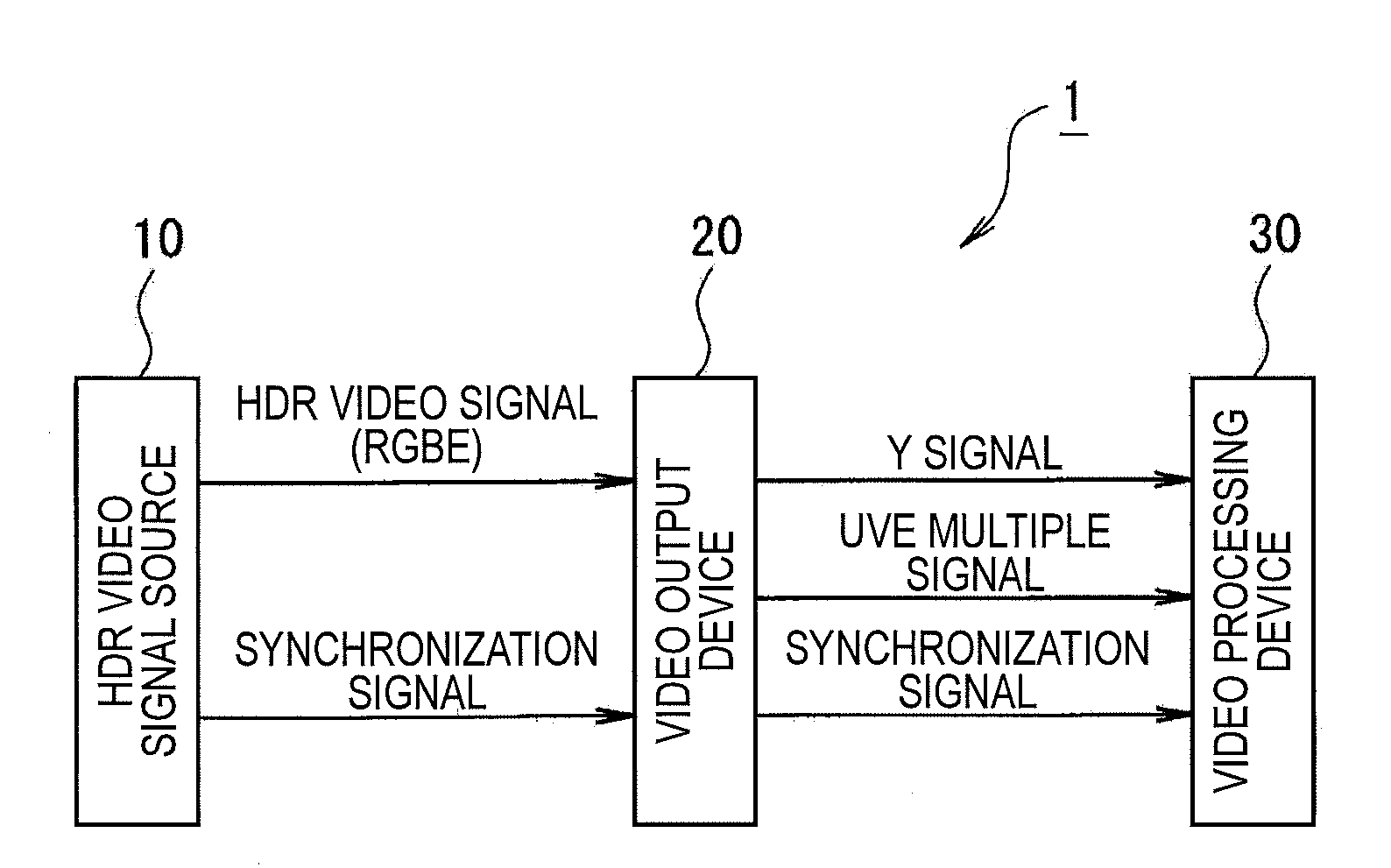
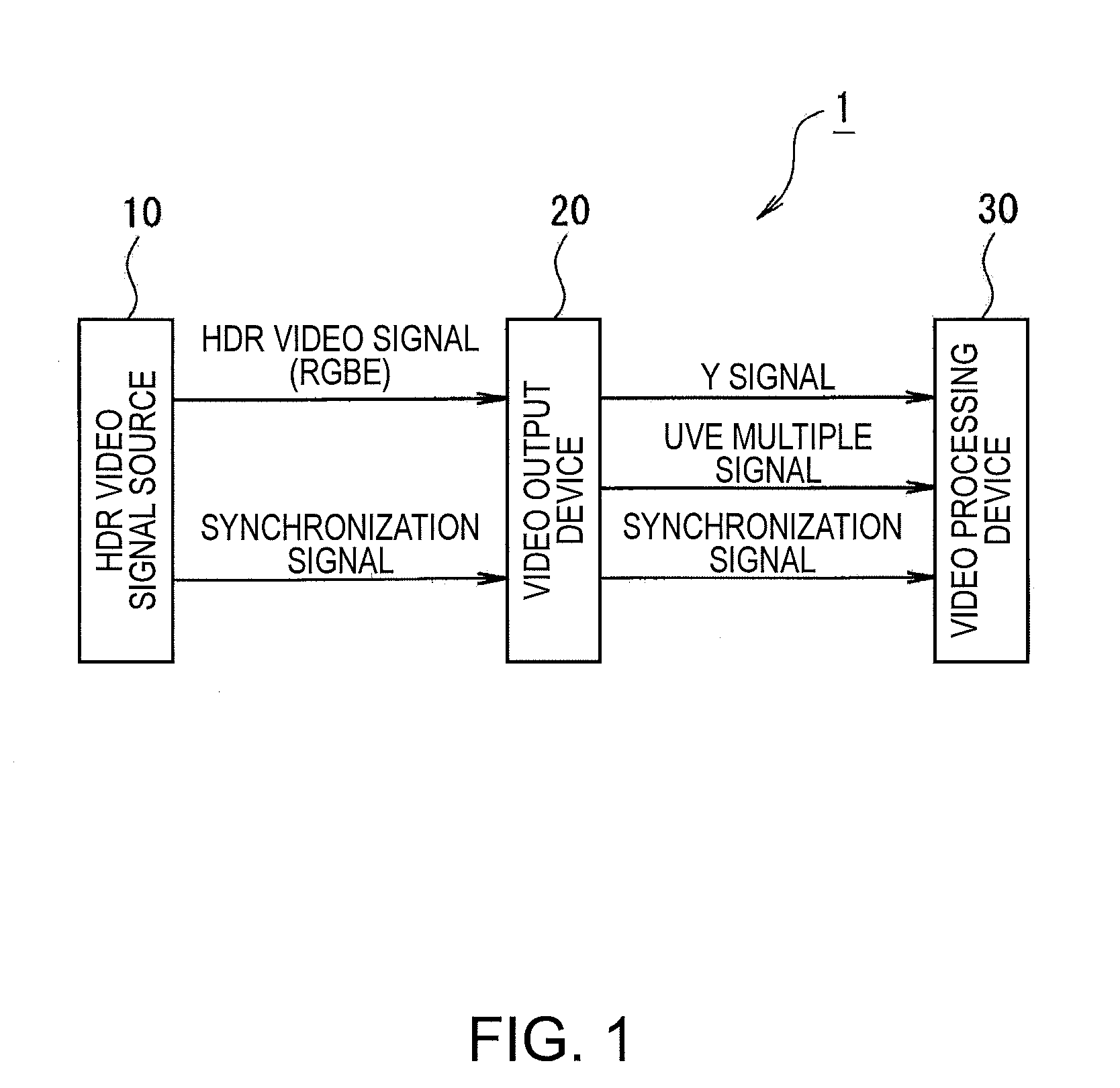
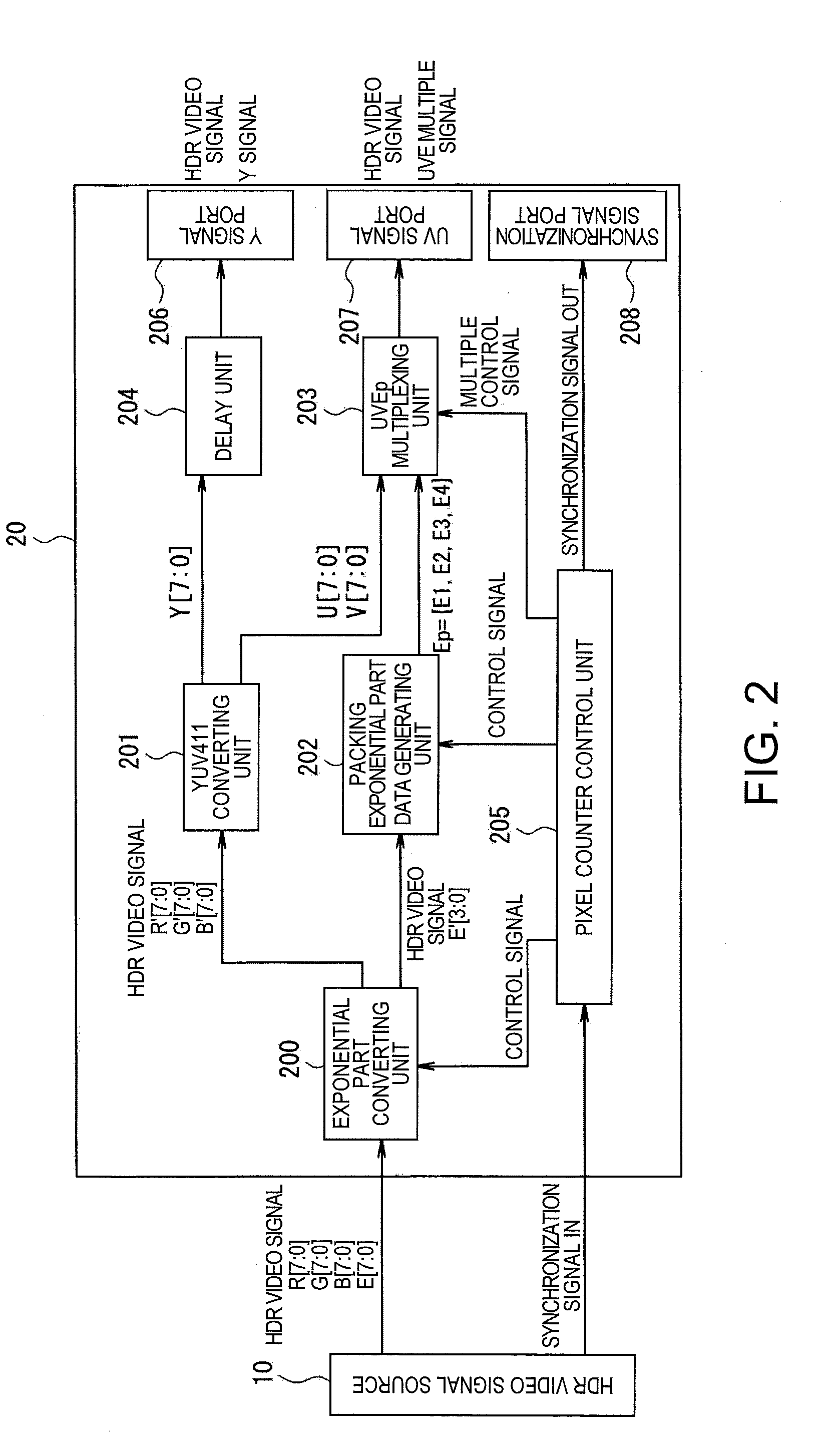
Video output device, video output method, video output program, video processing system, video processing device, video processing method, and video processing program
InactiveUS20080198266A1Same effectSame operationTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsMultiplexingComputer graphics (images)
A video output device which converts image data into a YUV system video signal composed of a brightness signal Y and a chrominance signal UV and outputs the video signal obtained by the conversion through a predetermined interface is disclosed. The video output device includes: a mantissa part converting unit which, with respect to first image data composed of pixel data in which a pixel value is expressed by a floating point format in which a mantissa part has N bits (N is a natural number of 2 or more), a cardinal number is X (X is a natural number of 2 or more) and an exponential part has M bits (M is a natural number of 2 or more), converts mantissa part data of the pixel data configuring the first image data into the YUV system video signal; a multiplexing unit which multiplexes exponential part data of the pixel data configuring the first image data to the chrominance signal UV of the YUV system video signal; and a video signal output unit which outputs the YUV system video signal including the brightness signal Y and the chrominance signal UV obtained by multiplexing the exponential part data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
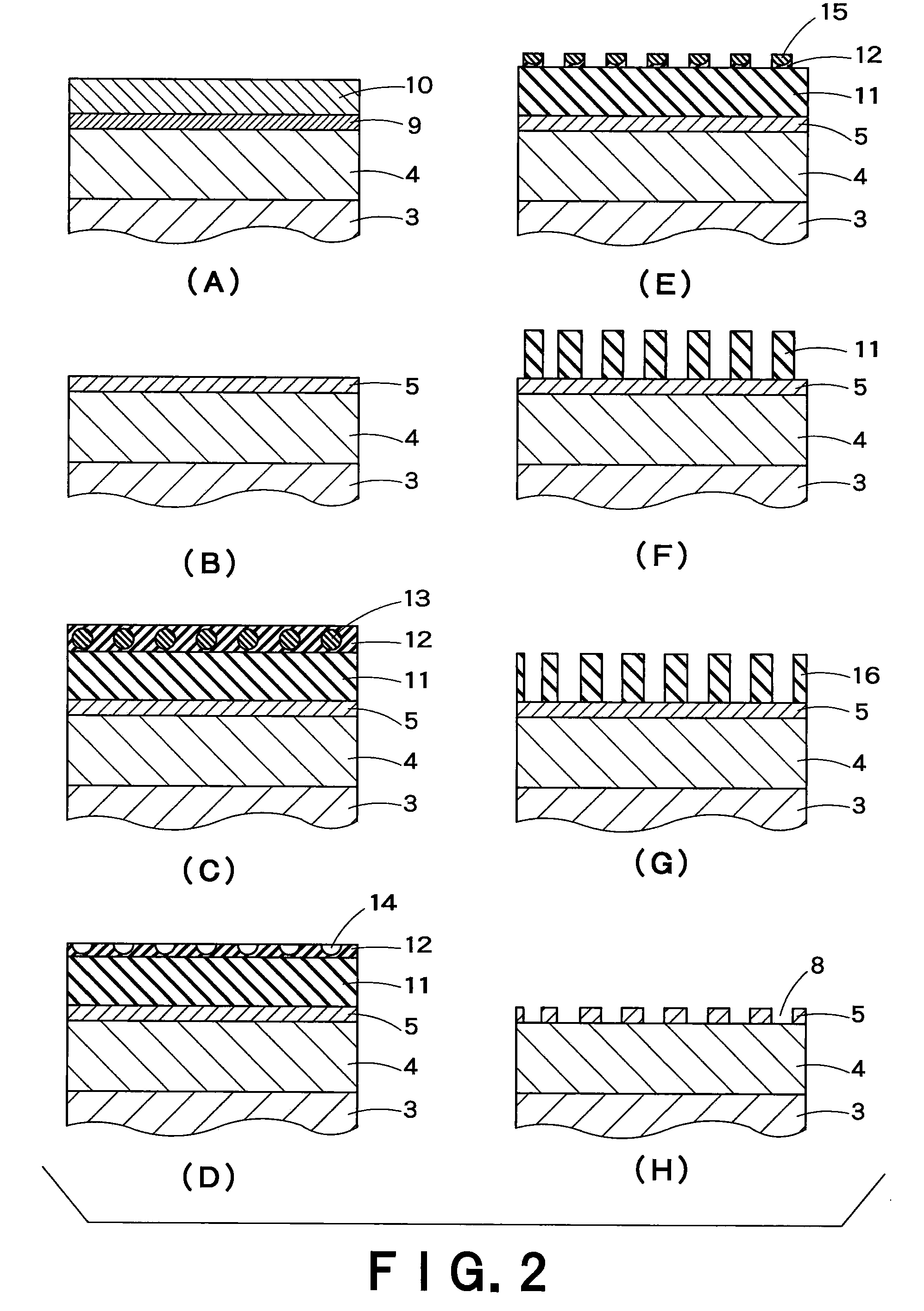
Light-transmitting metal electrode having hyperfine structure and process for preparation thereof
ActiveUS20090079322A1Shape is not particularly restrictedImprove efficiencyConductive layers on insulating-supportsControl electrodesAverage diameterMaterials science
The present invention provides a metal electrode transparent to light. The metal electrode comprises a transparent substrate and a metal electrode layer composed of a metal part and plural openings. The metal electrode layer continues without breaks, and 90% or more of the metal part continues linearly without breaks by the openings in a straight length of not more than ⅓ of the visible wavelength to use in 380 nm to 780 nm. The openings have an average diameter in the range of not less than 10 nm and not more than ⅓ of the wavelength of incident light, and the pitches between the centers of the openings are not less than the average diameter and not more than ½ of the wavelength of incident light. The metal electrode layer has a thickness in the range of not less than 10 nm and not more than 200 nm.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Semiconductor light-emitting element and process for production thereof
InactiveUS20090242925A1Difficult to manufactureSuitable for manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOhmOhmic contact
The present invention provides a semiconductor light-emitting element comprising an electrode part excellent in ohmic contact and capable of emitting light from the whole surface. An electrode layer placed on the light-extraction side comprises a metal part and plural openings. The metal part is so continuous that any pair of point-positions in the part is continuously connected without breaks, and the metal part in 95% or more of the whole area continues linearly without breaks by the openings in a straight distance of not more than ⅓ of the wavelength of light emitted from an active layer. The average opening diameter is of 10 nm to ⅓ of the wavelength of emitted light. The electrode layer has a thickness of 10 nm to 200 nm, and is in good ohmic contact with a semiconductor layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Game performing method, storage medium, game apparatus, data signal and program
ActiveUS20040058730A1Easy to operateImprove perceptionCathode-ray tube indicatorsVideo gamesData signalAutomotive engineering
Owner:BANDAI NAMCO ENTERTAINMENT INC
Target for X-ray generator, method of manufacturing the same and X-ray generator
ActiveUS9020101B2Improve thermal conductivityAvoid damageCathode ray tubes/electron beam tubesX-ray tube electrodesElectricityThermal contact
There is provided a target for an X-ray generator, including: a holder part made of an electrically conductive material and having an opening part; a diamond plate air-tightly joined to the holder part so as to close the opening part; a thin film target provided on a surface of the diamond plate, with its outer peripheral part extending to the holder part to be electrically connected to the holder part, wherein the holder part is configured to be electrically connected to a power supply of the X-ray generator, and the diamond plate is incorporated into the X-ray generator with one side disposed in a vacuum atmosphere where the thin film target is formed, and an opposite side thereto disposed at a side where the diamond plate is brought into thermal contact with a refrigerant and cooled.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
Target for x-ray generator, method of manufacturing the same and x-ray generator
ActiveUS20130259207A1Improve thermal conductivitySame thermal effectX-ray tube electrodesVacuum evaporation coatingConductive materialsThermal contact
There is provided a target for an X-ray generator, including: a holder part made of an electrically conductive material and having an opening part; a diamond plate air-tightly joined to the holder part so as to close the opening part; a thin film target provided on a surface of the diamond plate, with its outer peripheral part extending to the holder part to be electrically connected to the holder part, wherein the holder part is configured to be electrically connected to a power supply of the X-ray generator, and the diamond plate is incorporated into the X-ray generator with one side disposed in a vacuum atmosphere where the thin film target is formed, and an opposite side thereto disposed at a side where the diamond plate is brought into thermal contact with a refrigerant and cooled.
Owner:RIGAKU CORP
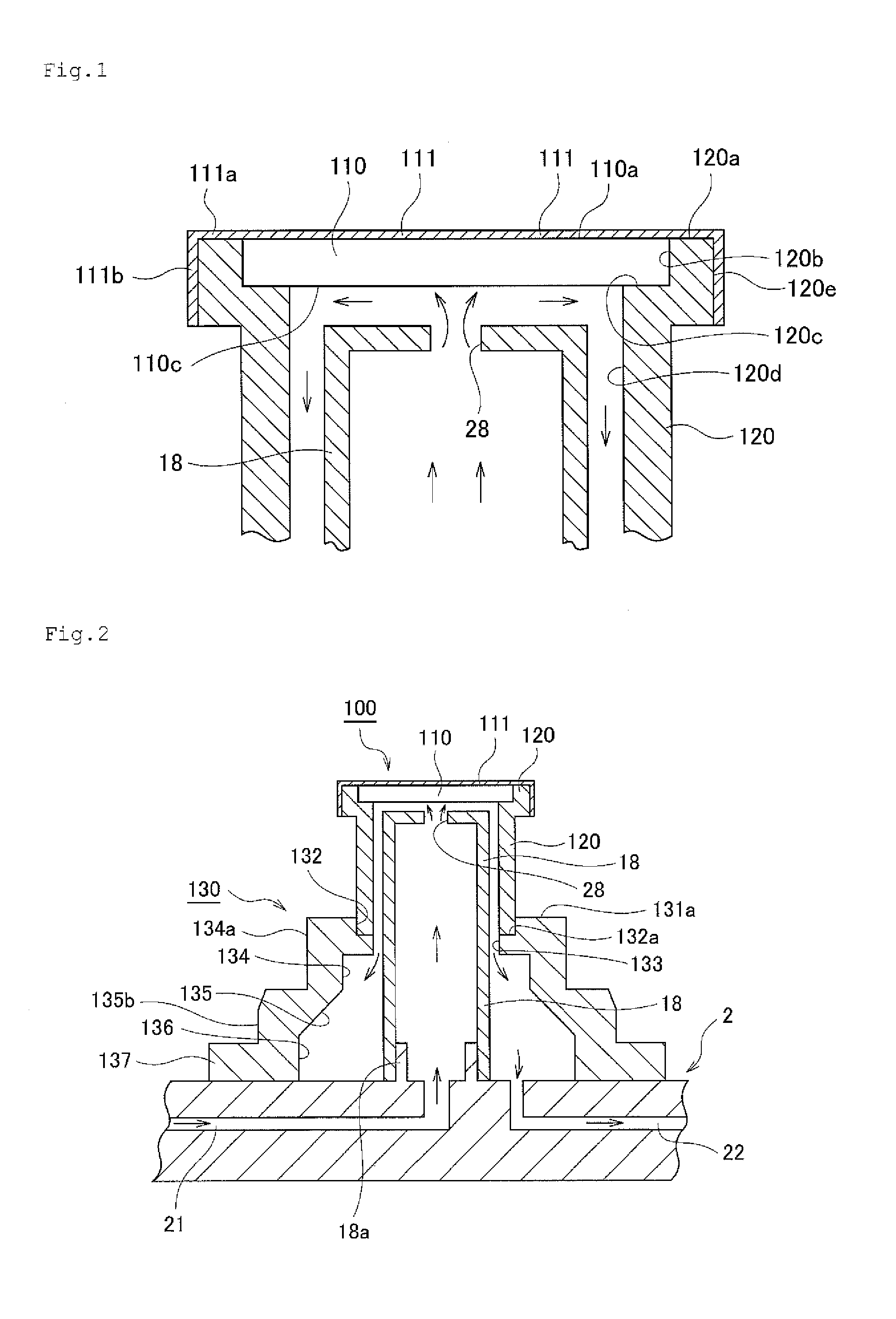
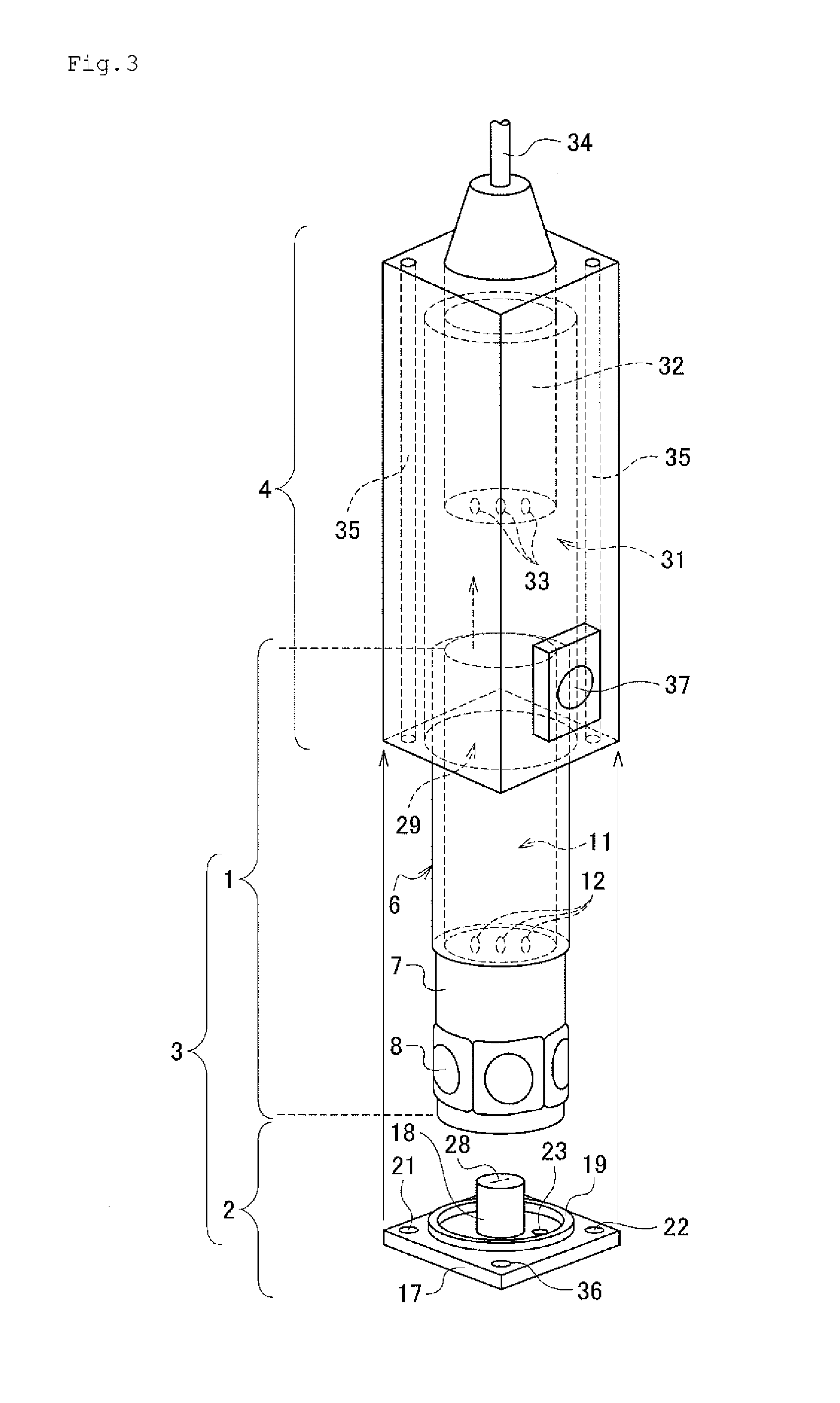
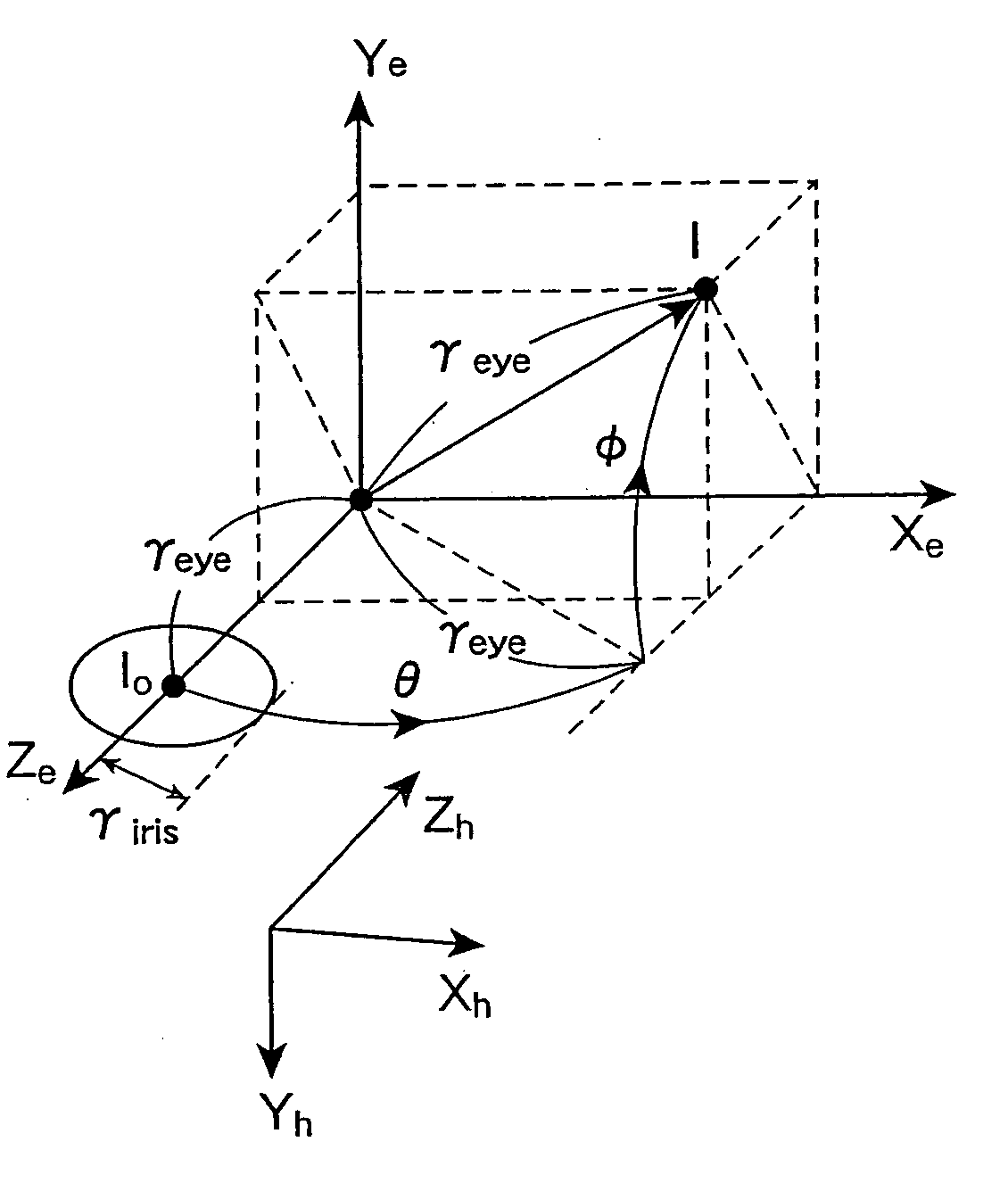
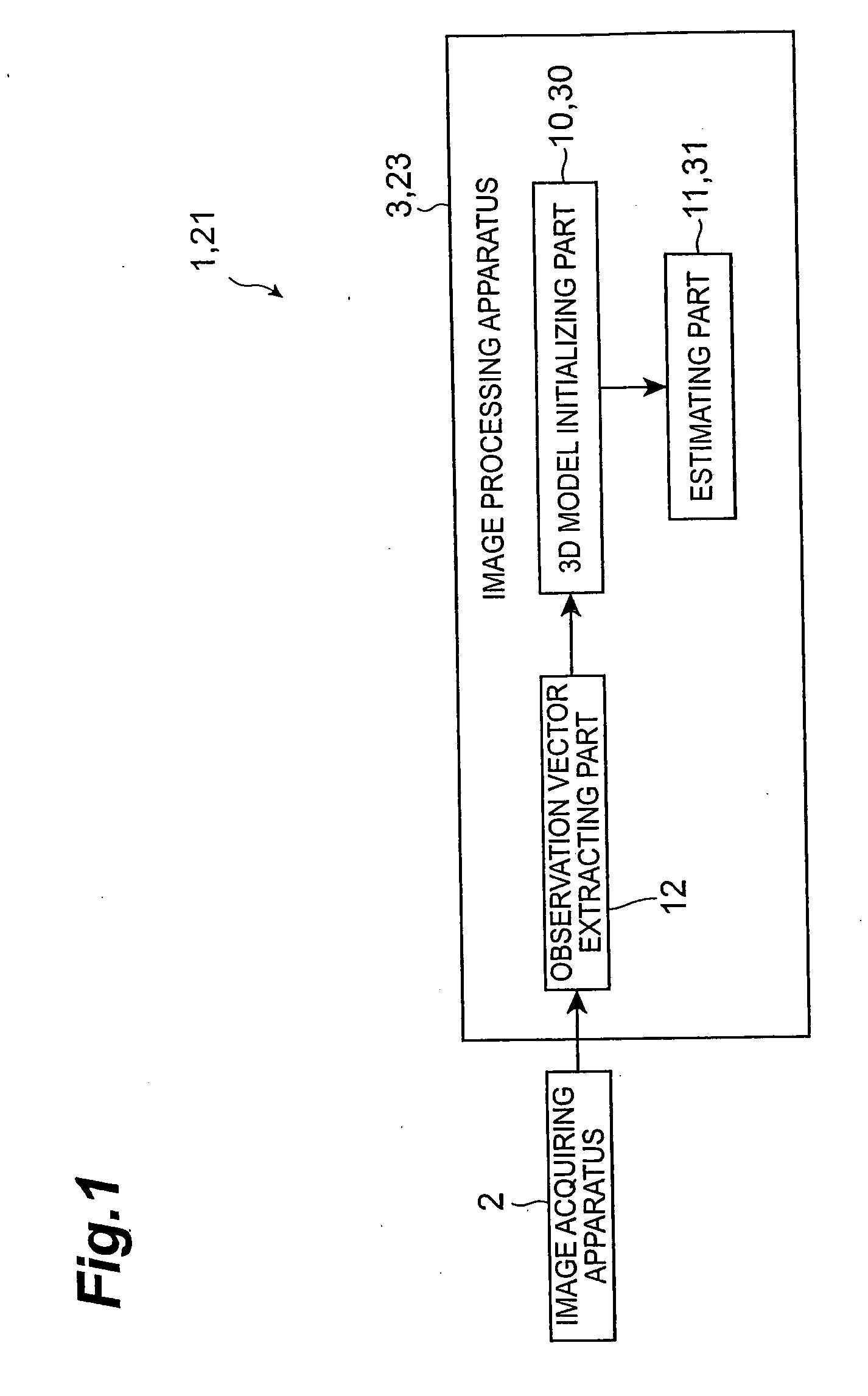
Image processing apparatus, image processing method, image processing program, and recording medium
InactiveUS20070052698A1Same effectAccurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingObject motion
An image processing apparatus is an apparatus for determining a gaze from a motion picture of a face taken by a monocular camera, and is configured to define a 3D structure of a center of a pupil on the facial picture by a static parameter and a dynamic parameter, and to determine the gaze by estimating the static parameter and the dynamic parameter. Another image processing apparatus is an apparatus for determining a motion of a 3D object from a motion picture thereof taken by a monocular camera, and is configured to define a 3D structure of the 3D object on the picture by a rigid parameter and a non-rigid parameter, and to determine the motion of the 3D object by estimating the rigid parameter and the non-rigid parameter.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Spring dendrobe flowering period control method
InactiveCN1555691AImprove viewing valueNo change in shape and colorPlant phenotype modificationAbscisic acidCataphyll
A method for regulating the blossoming period of spring dendrobium nobile featues that after the blades of its pseudobulb are fully developed, the mixed solution containing paclobutrazol and abscisic acid is sprayed onto the surface of blades for promoting the pseudobulb to become rope, and after 10-15 days, the solution containing thidiazuron is sprayed on the surface of its leaf for inducing the generation of flower buds.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Semiconductor light-emitting element and process for production thereof
InactiveUS8101964B2Improve efficiencyReduced scattering effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOhmic contactLength wave
The present invention provides a semiconductor light-emitting element comprising an electrode part excellent in ohmic contact and capable of emitting light from the whole surface. An electrode layer placed on the light-extraction side comprises a metal part and plural openings. The metal part is so continuous that any pair of point-positions in the part is continuously connected without breaks, and the metal part in 95% or more of the whole area continues linearly without breaks by the openings in a straight distance of not more than ⅓ of the wavelength of light emitted from an active layer. The average opening diameter is of 10 nm to ⅓ of the wavelength of emitted light. The electrode layer has a thickness of 10 nm to 200 nm, and is in good ohmic contact with a semiconductor layer.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
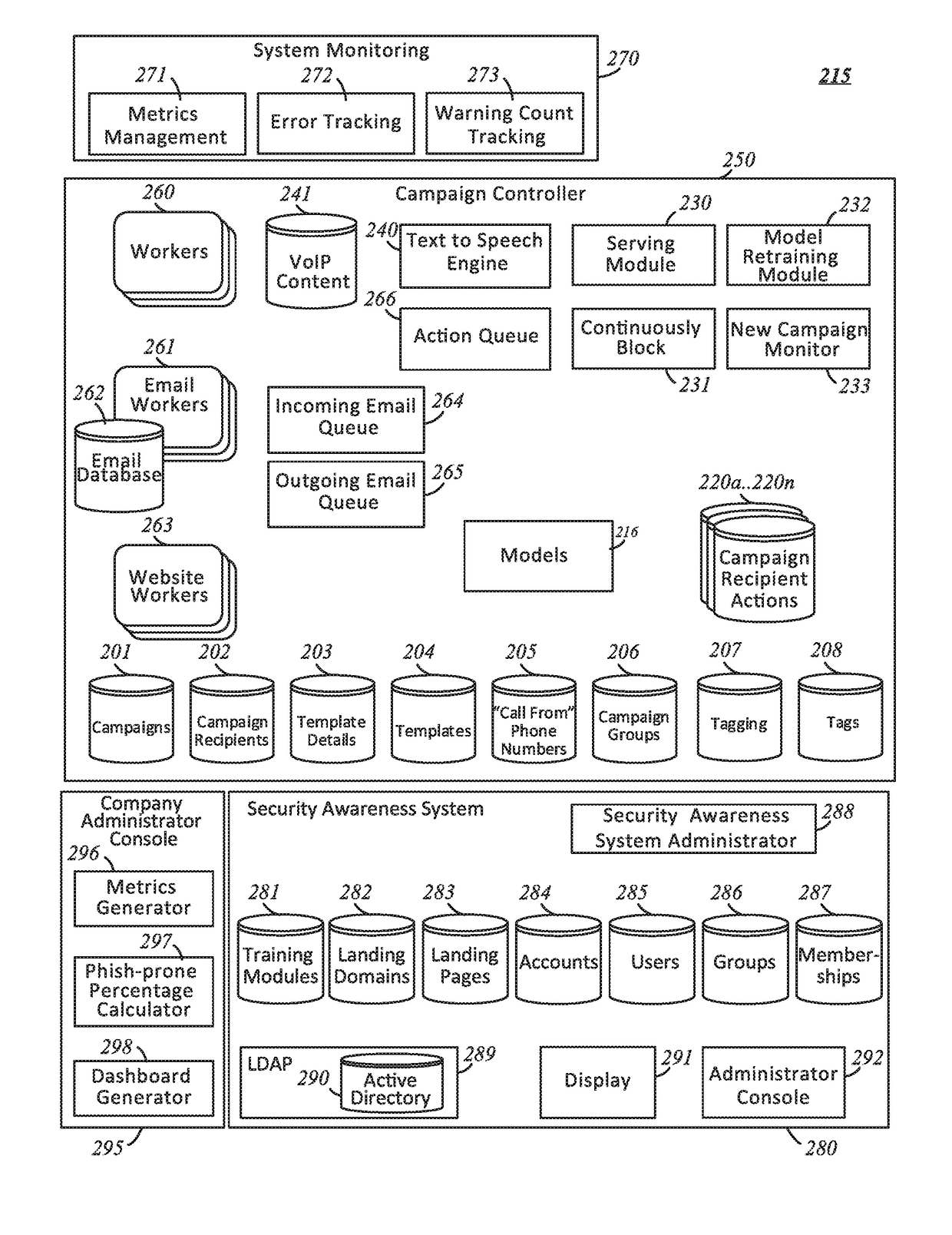
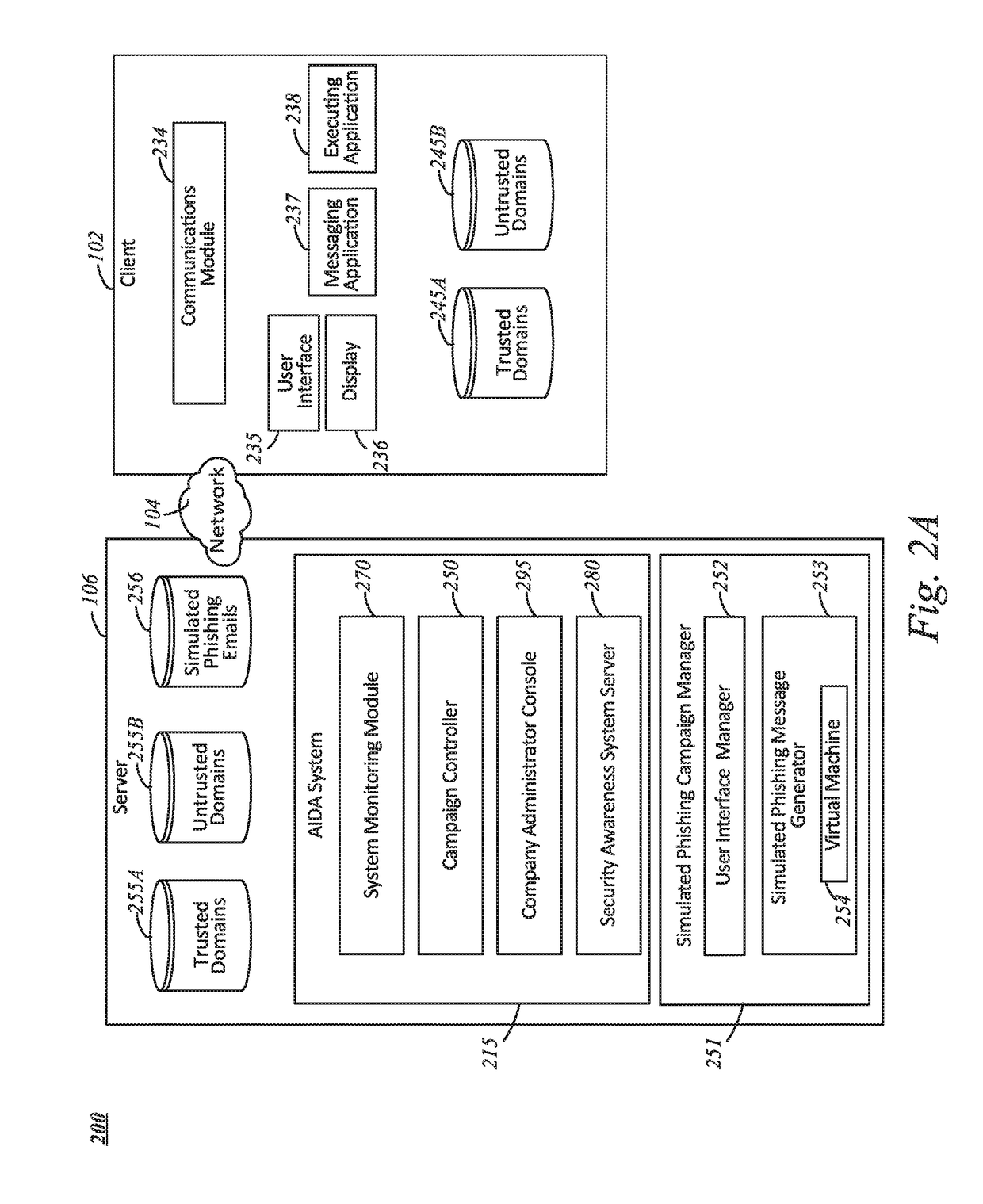
Systems and methods for aida based second chance
ActiveUS20190173919A1Avoid actionSame effectArtificial lifePlatform integrity maintainanceDevice MonitorA domain
Methods and systems are described in which a system provides a user interface to confirm whether to review or take an action associated with an untrusted email. A driver on a device monitors the startup of any processes. Responsive to monitoring, the driver detects an application process that was created that indicates than an application was launched, and notifies a user console about the creation of the application process. The user console determines if the application process is of significance, if so, it injects a monitor library into the process. Once injected into the process, the monitor library detects if the application process receives an action of a user to access a domain that is not identified as trusted. The monitor library notifies the user console of the user's URL-access request.
Owner:KNOWBE4 INC
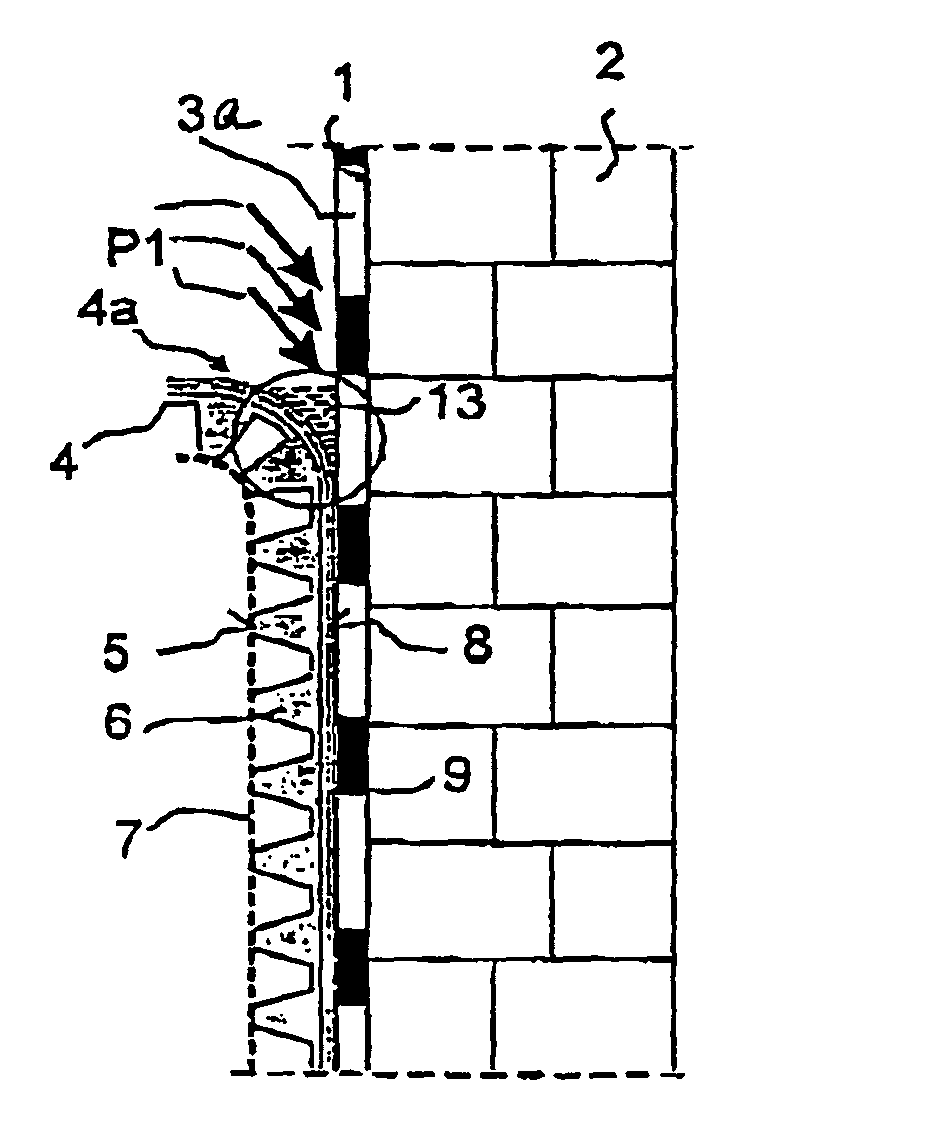
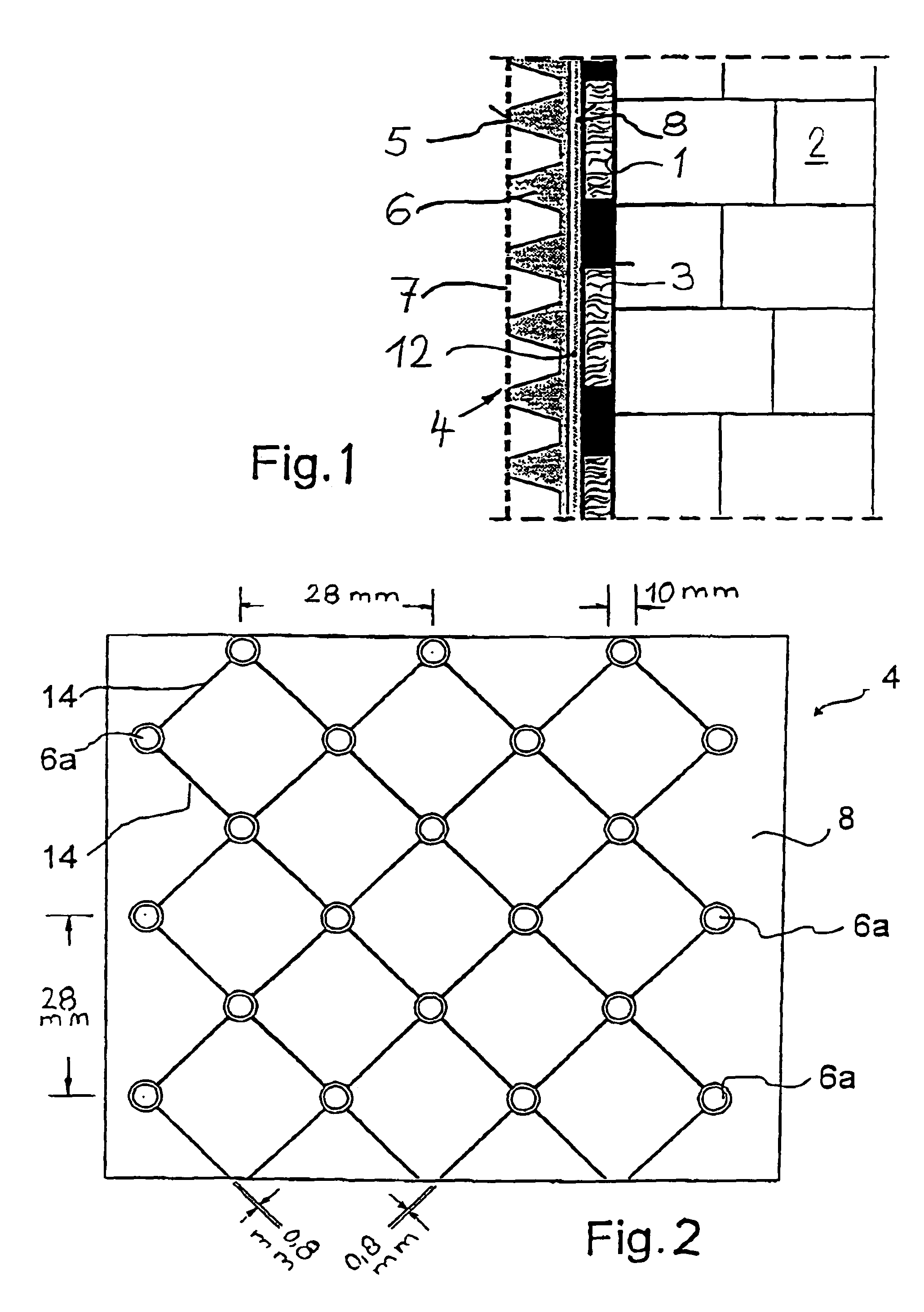
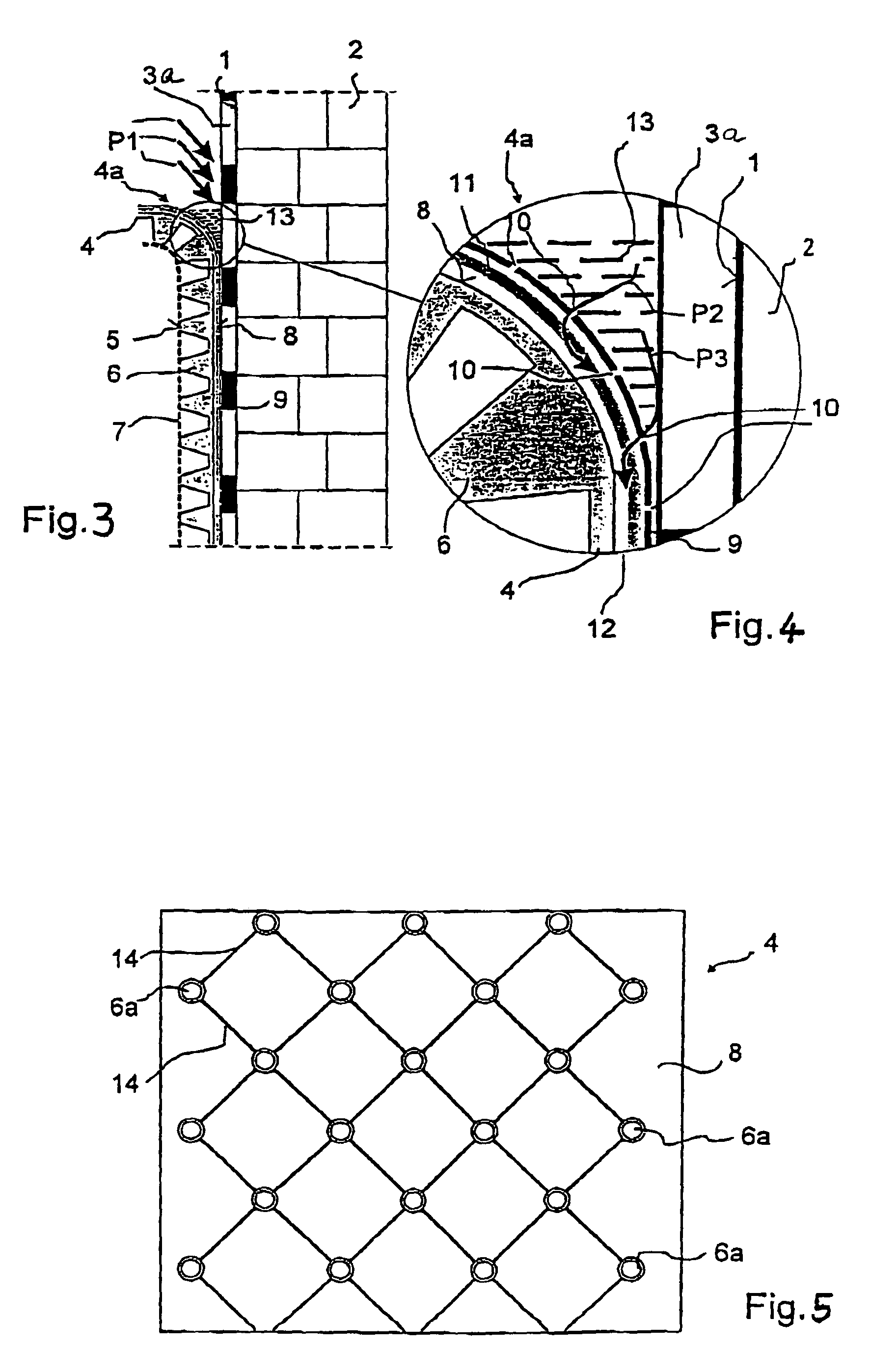
Membrane for the protection of buildings
InactiveUS7698858B2Same protective effectAvoid collectingHuman health protectionCeilingsMembrane configurationChemistry
Owner:EWALD DORKEN
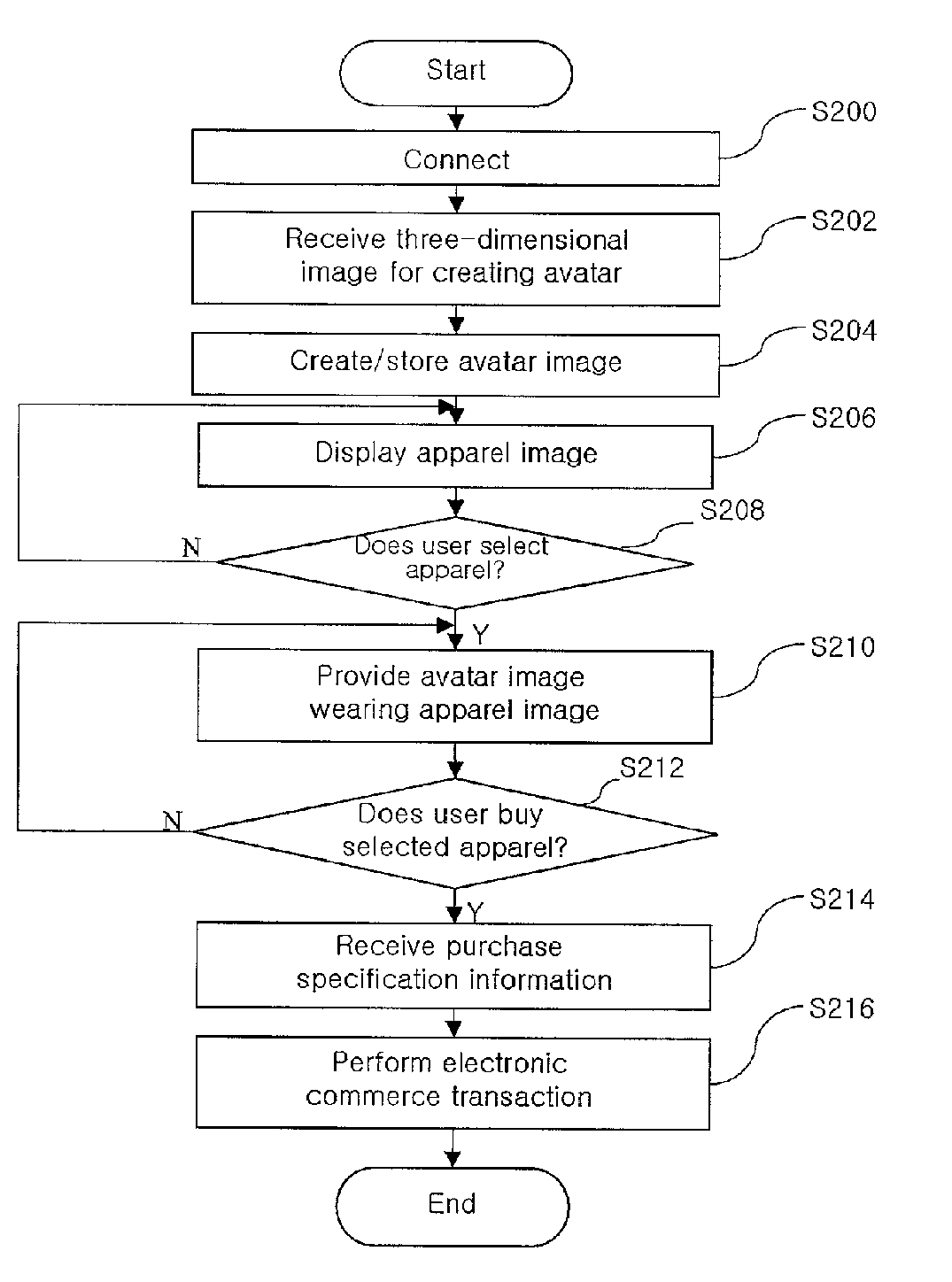
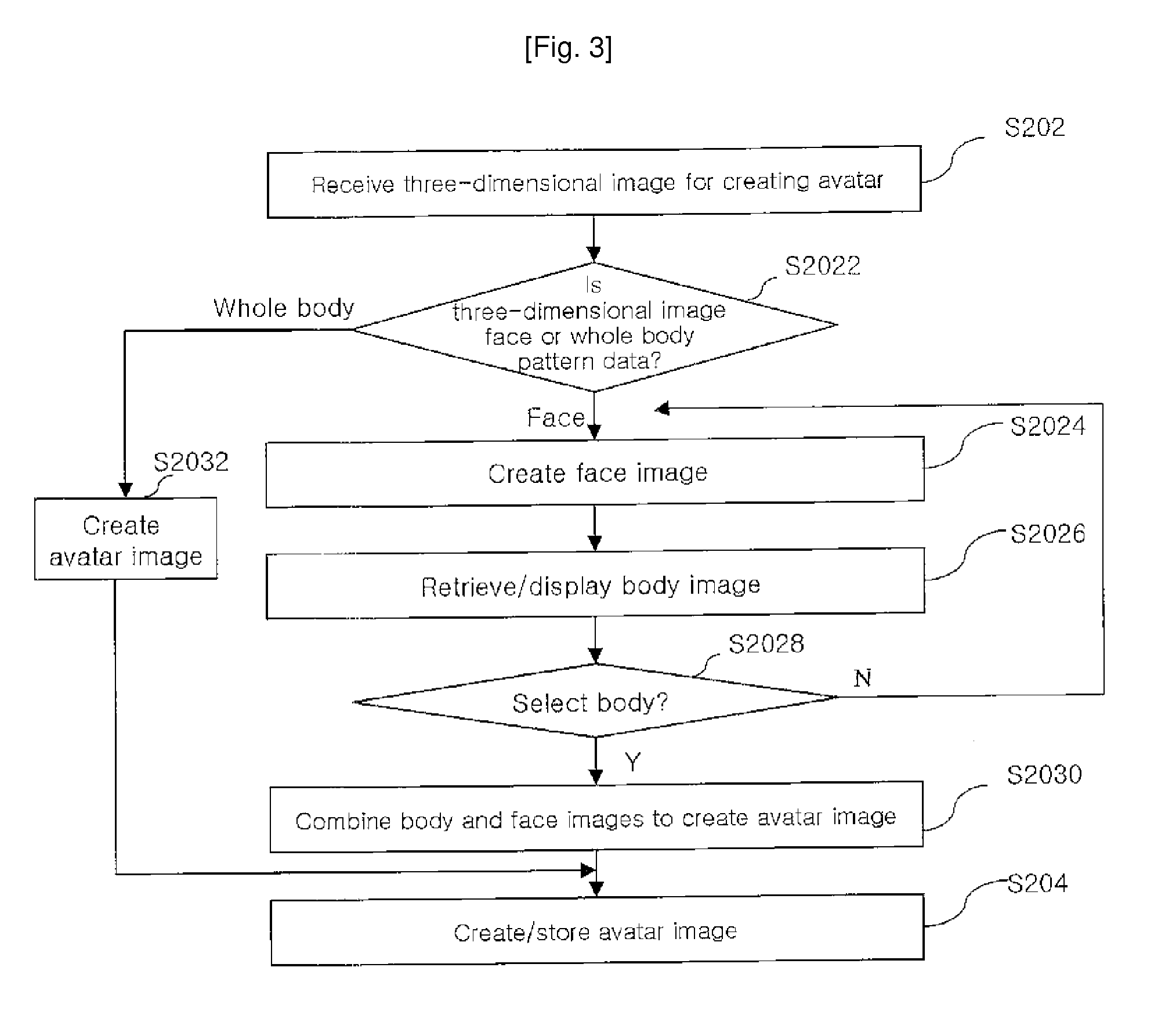
Electronic Commerce System for the Digital Fashion Using an Avatar Based on a User and Method for Operating the Same
InactiveUS20080249897A1Increase the number of timesSame effectMarketingInput/output processes for data processingReceiptE-commerce
A shopping-mall system utilizing user-based avatars comprises a terminal for transmitting user's three-dimensional image data through a wired or wireless communication network and then selecting any one of items provided through the wired or wireless communication network to receive an avatar image wearing the selected item and to transmit purchase specification information for purchasing the selected item. An avatar creation server receives the three-dimensional image data from the terminal and then creates an avatar image. A three-dimensional shopping-mall server puts any one item selected among a plurality of items stored therein on the avatar image created by the avatar creation server to provide the terminal with the avatar image wearing the item, and then performs an electronic commerce transaction with the terminal on the receipt of the purchase specification information of the selected item.
Owner:SKC C
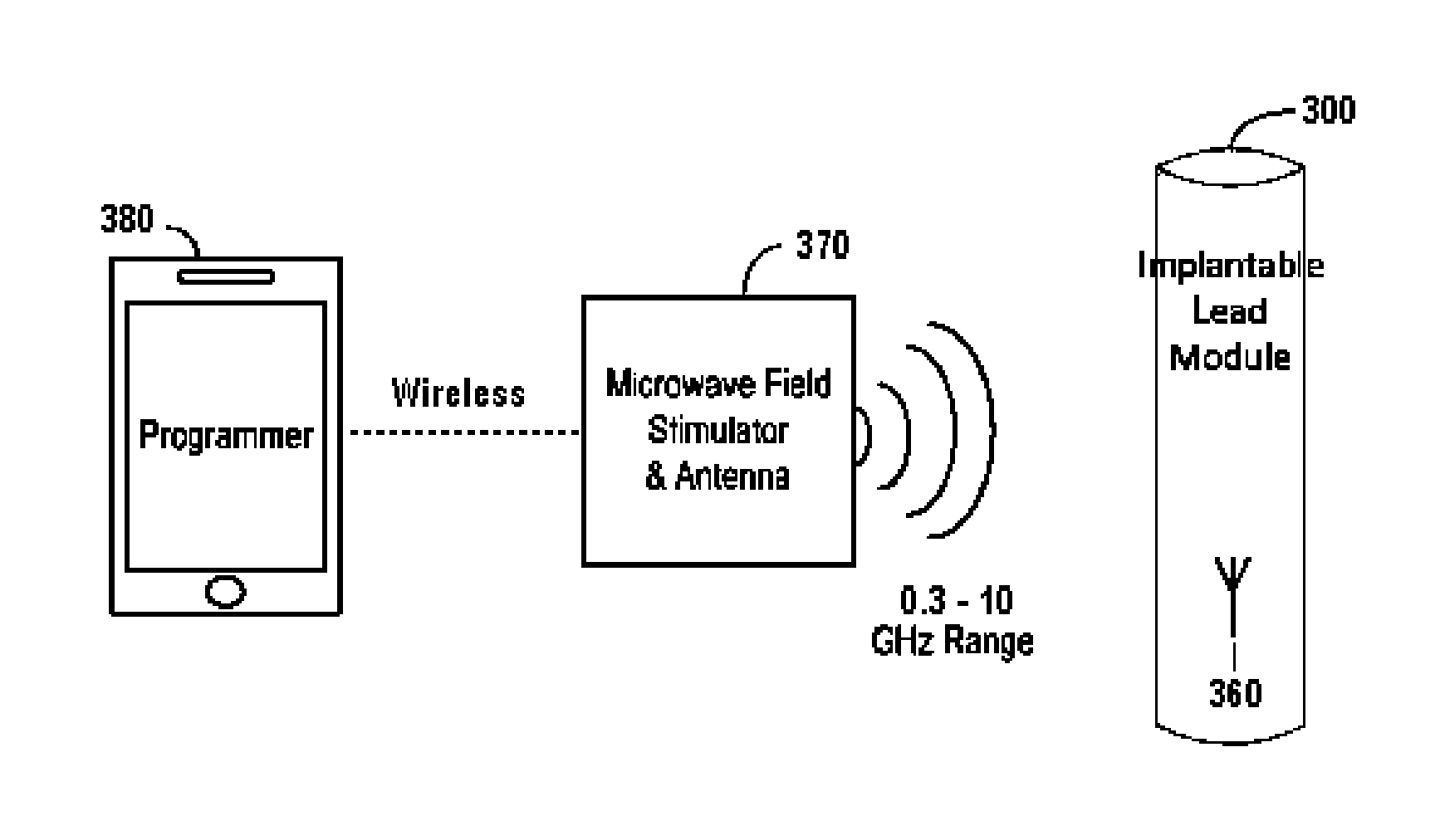
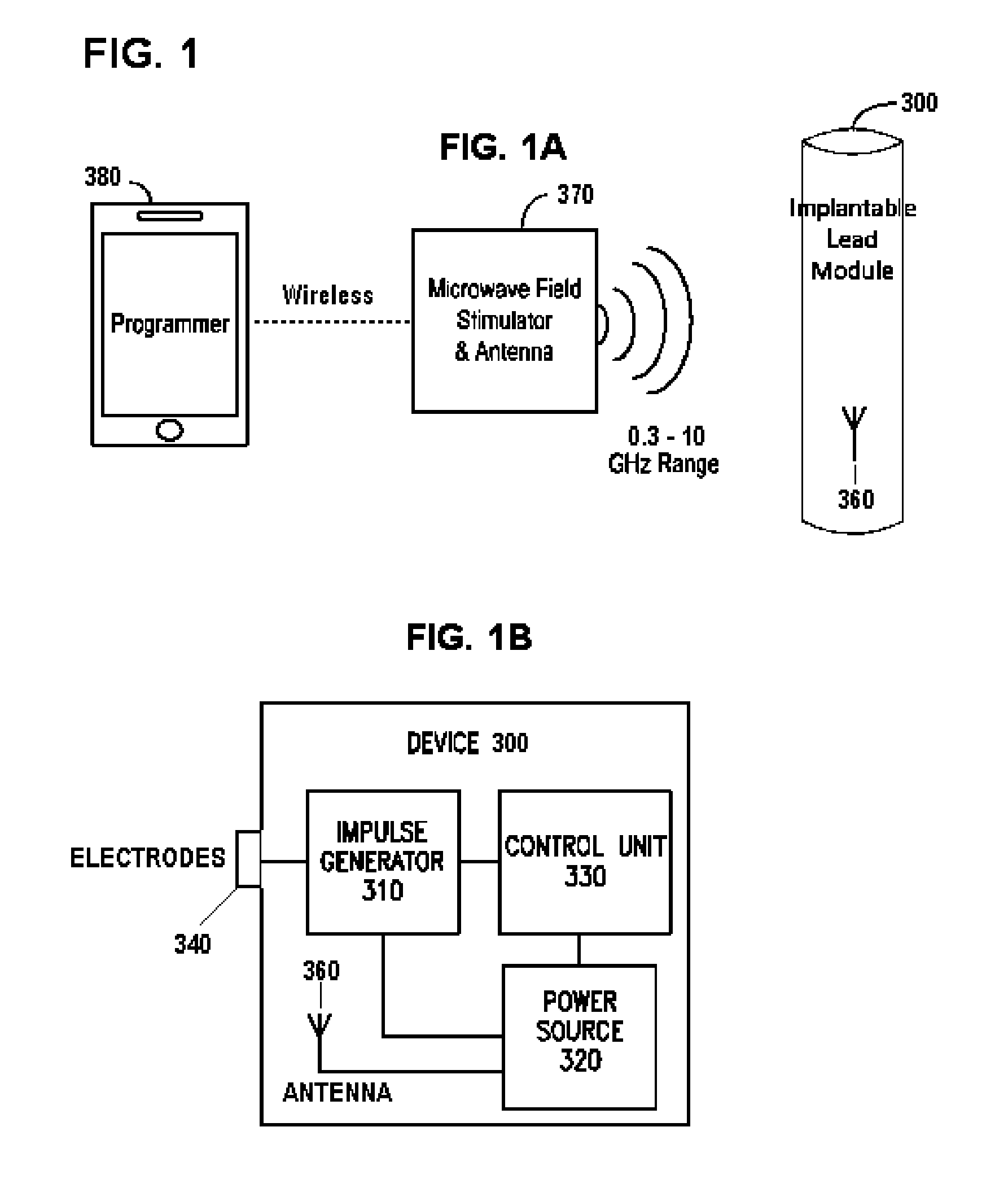
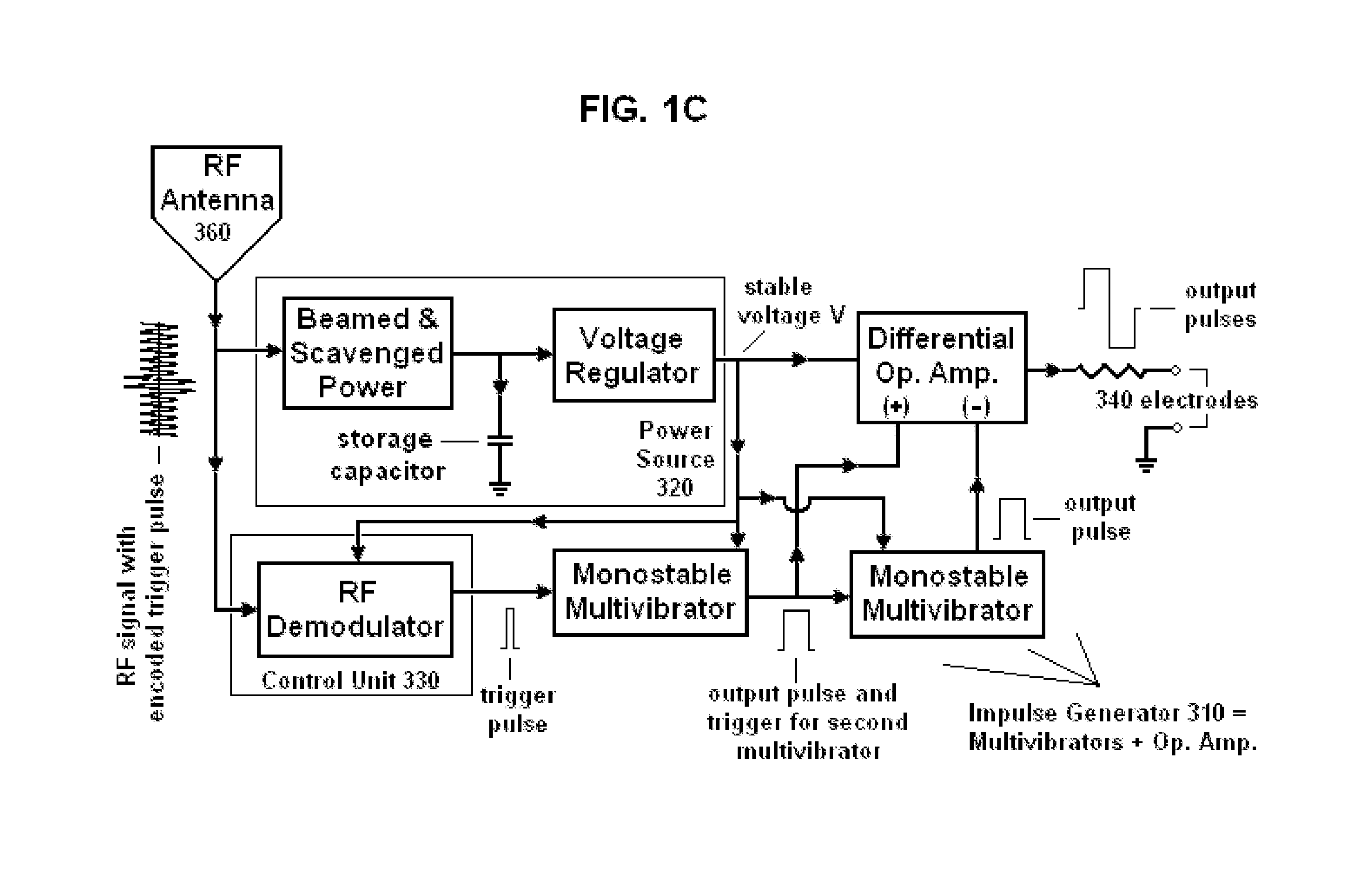
Nerve stimulator system
ActiveUS20150127068A1Without sacrificing performanceSame effectImplantable neurostimulatorsArtificial respirationElectrical impulseElectromagnetic radiation
Devices, systems and methods for applying electrical impulse(s) to one or more selected nerves are described. An electrical stimulator is introduced through a to a target location within, adjacent to, or in close proximity with, the carotid sheath. The stimulator has an antenna that allows it to be powered solely by far-field or approximately plane wave electromagnetic radiation, having frequencies in the range of 0.3 to 10 GHz. Electrical impulses are applied through the stimulator to a vagus nerve to stimulate, block or otherwise modulate activity of the nerve and treat the patient's condition. The stimulator uses an adjustable number of fixed voltage (or fixed current) pulses with fixed duration to elicit desired changes in nerve response, the timing of which are controlled by an external power transmitter and controller.
Owner:ELECTROCORE
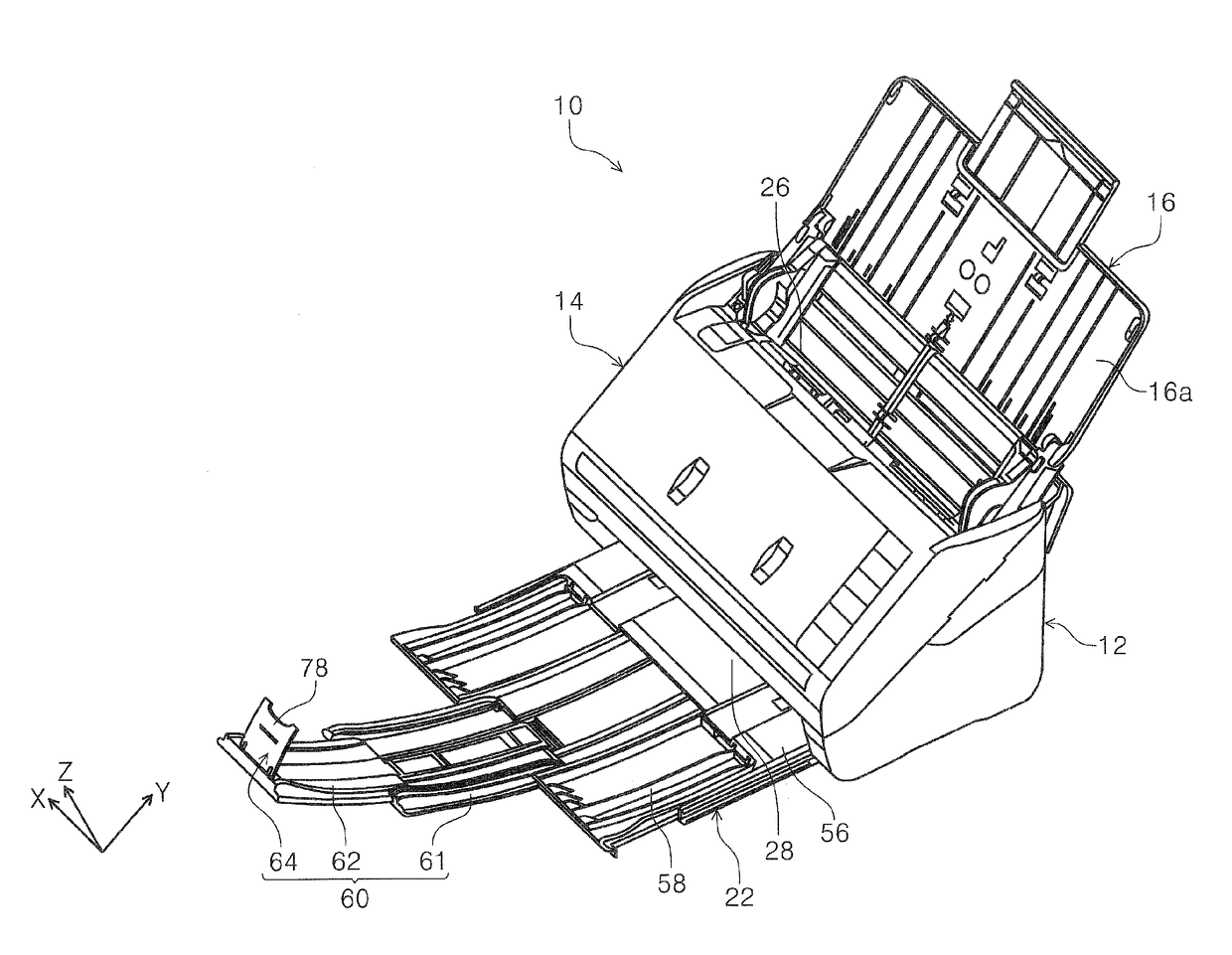
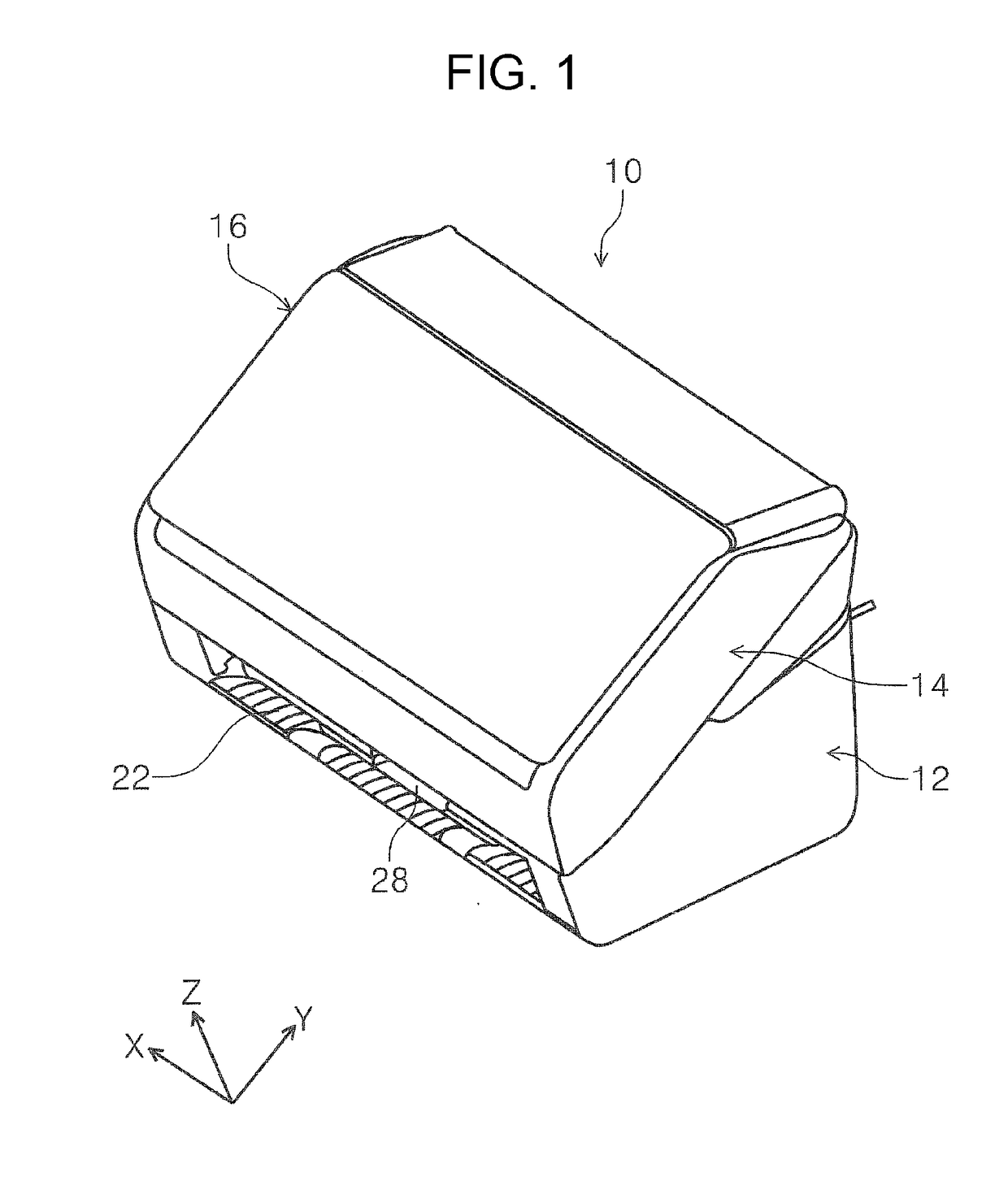
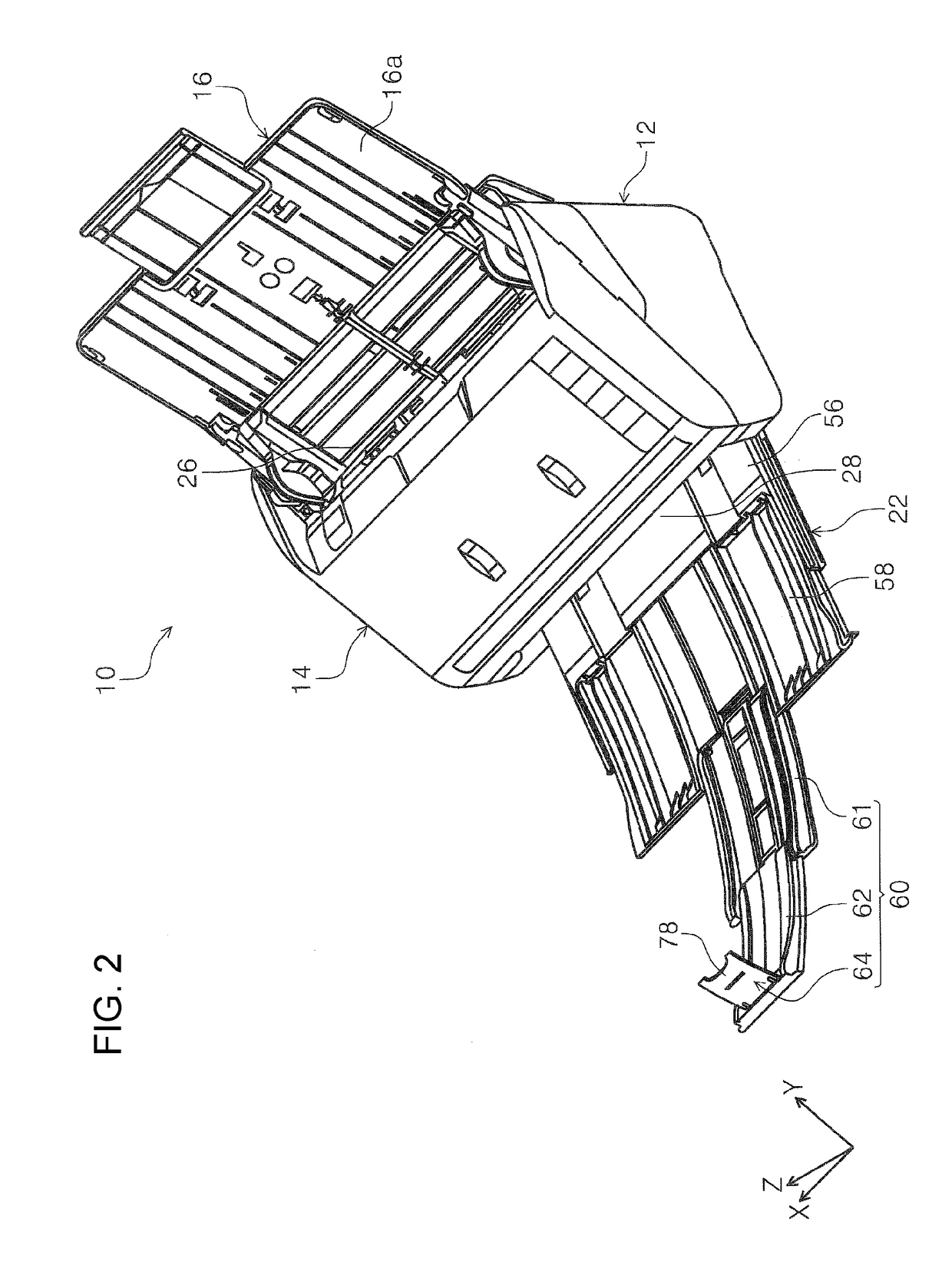
Medium discharging device and image reading apparatus
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Electronic manual display apparatus
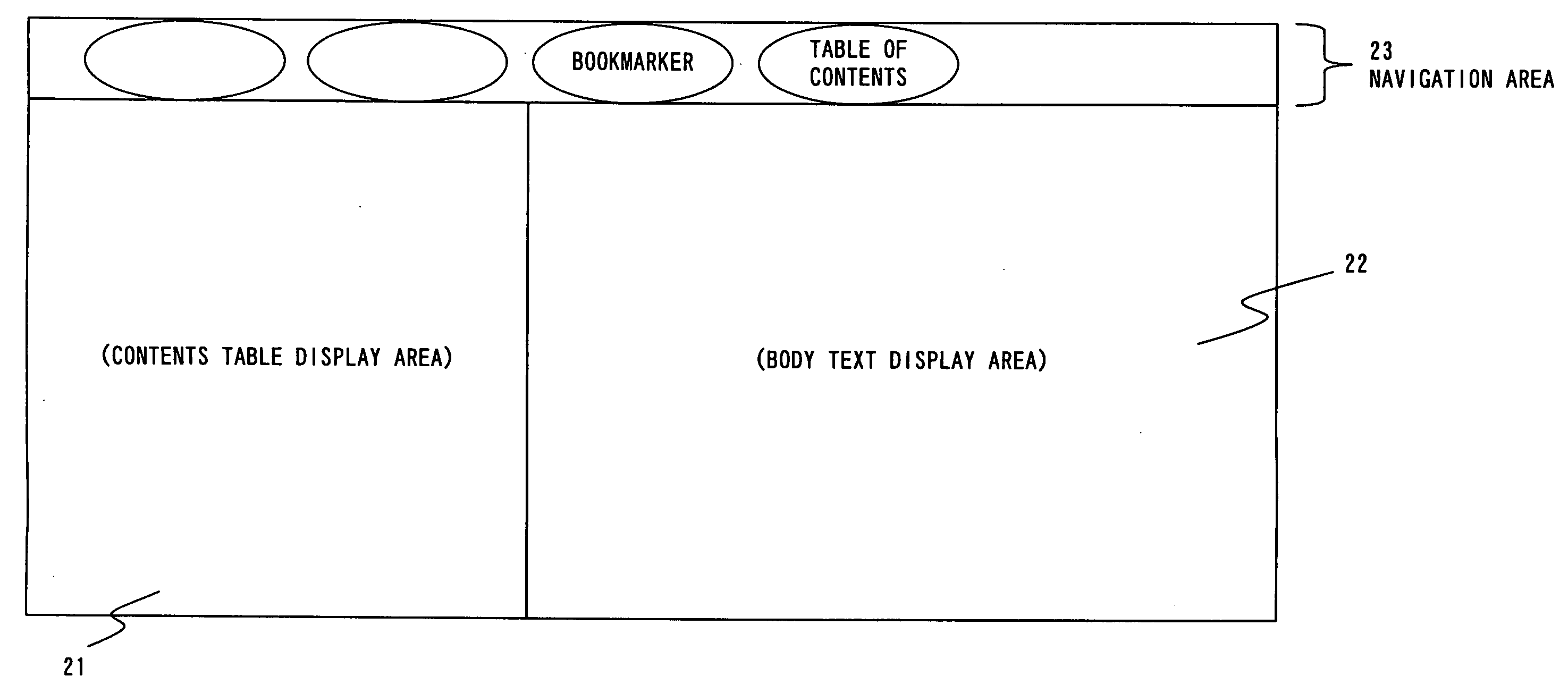
InactiveUS20060224942A1Improve convenienceQuick identificationDigital data processing detailsNatural language data processingDocument preparationDocumentation
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
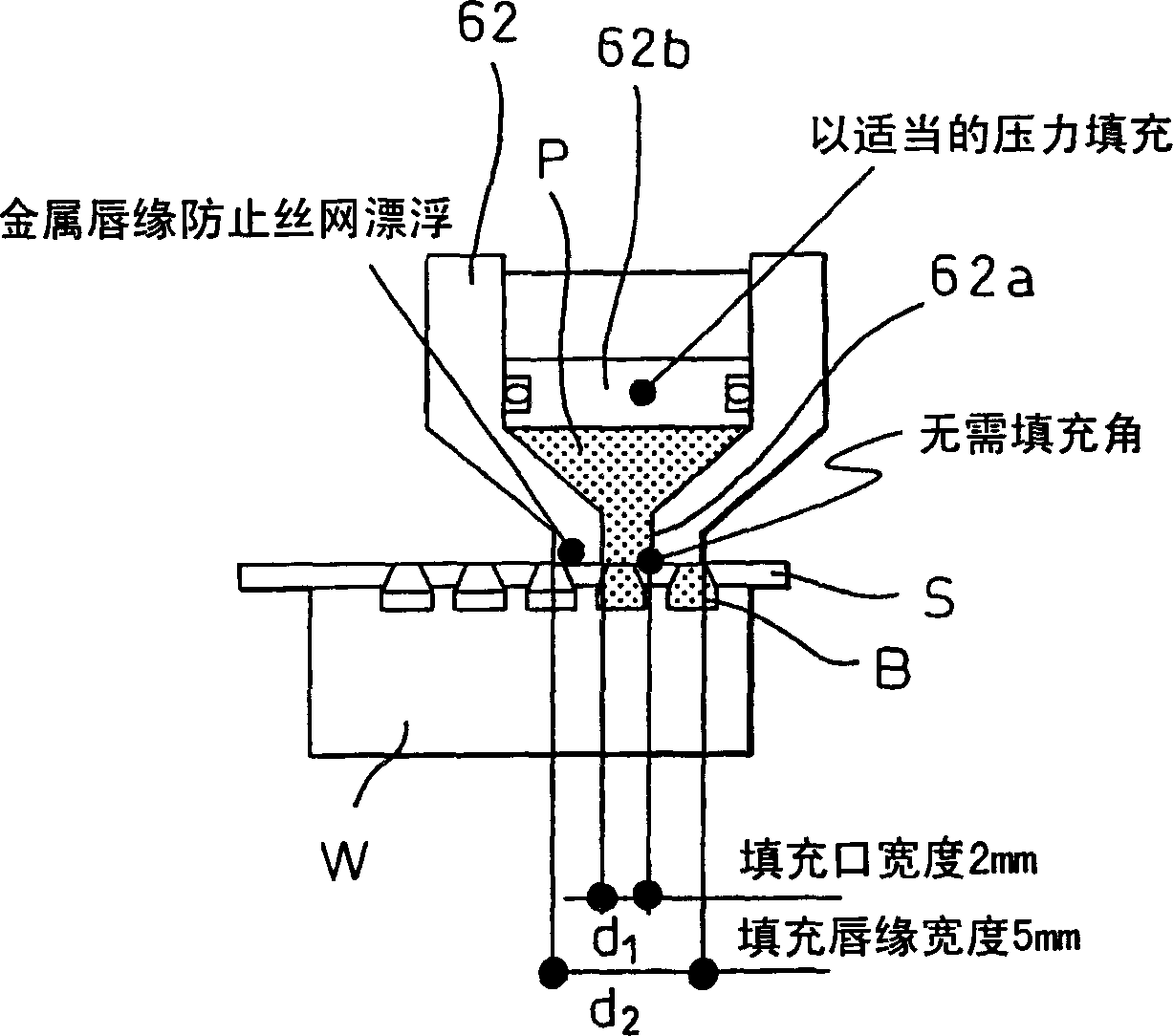
Screen printing machine and printing method thereof
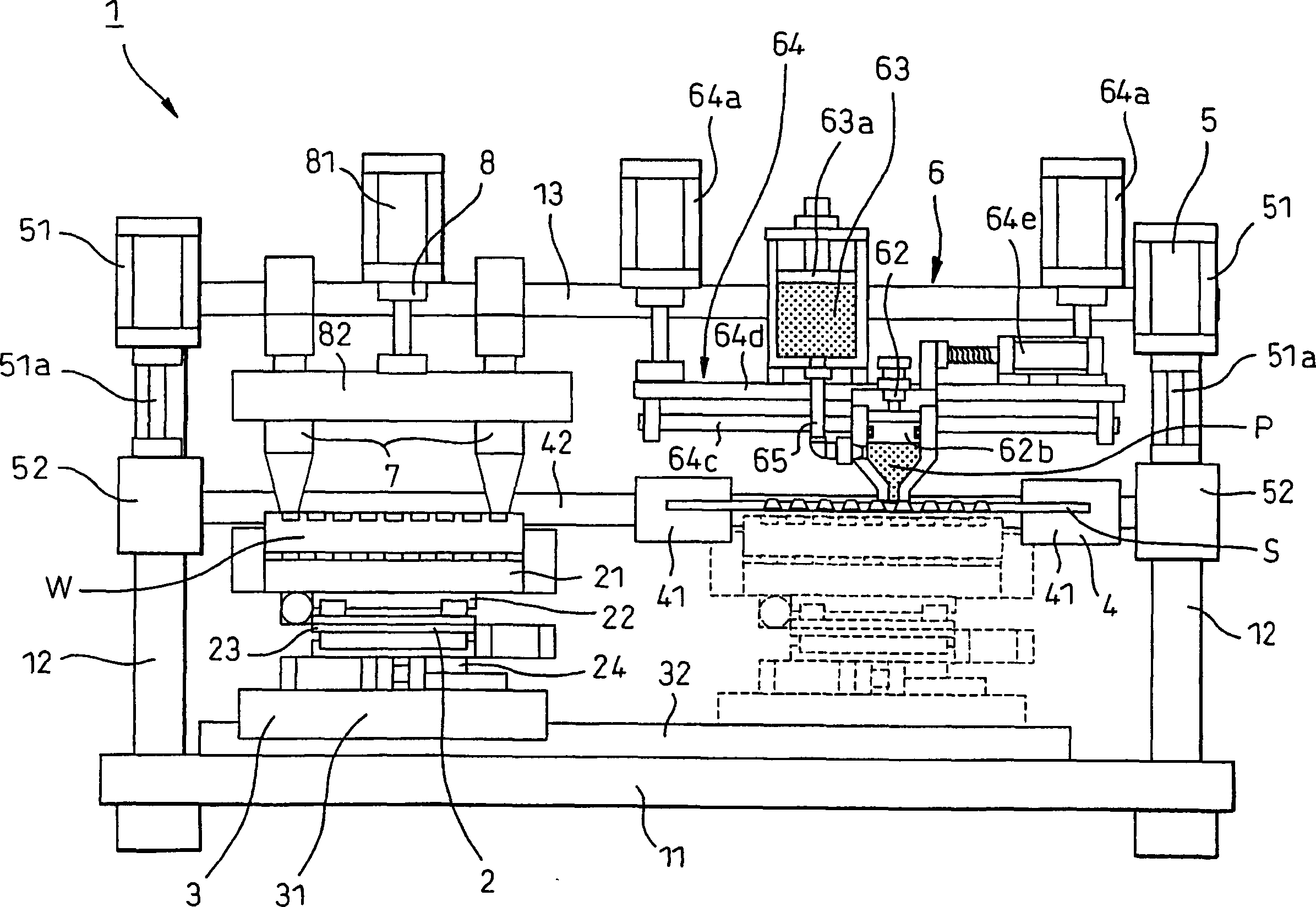
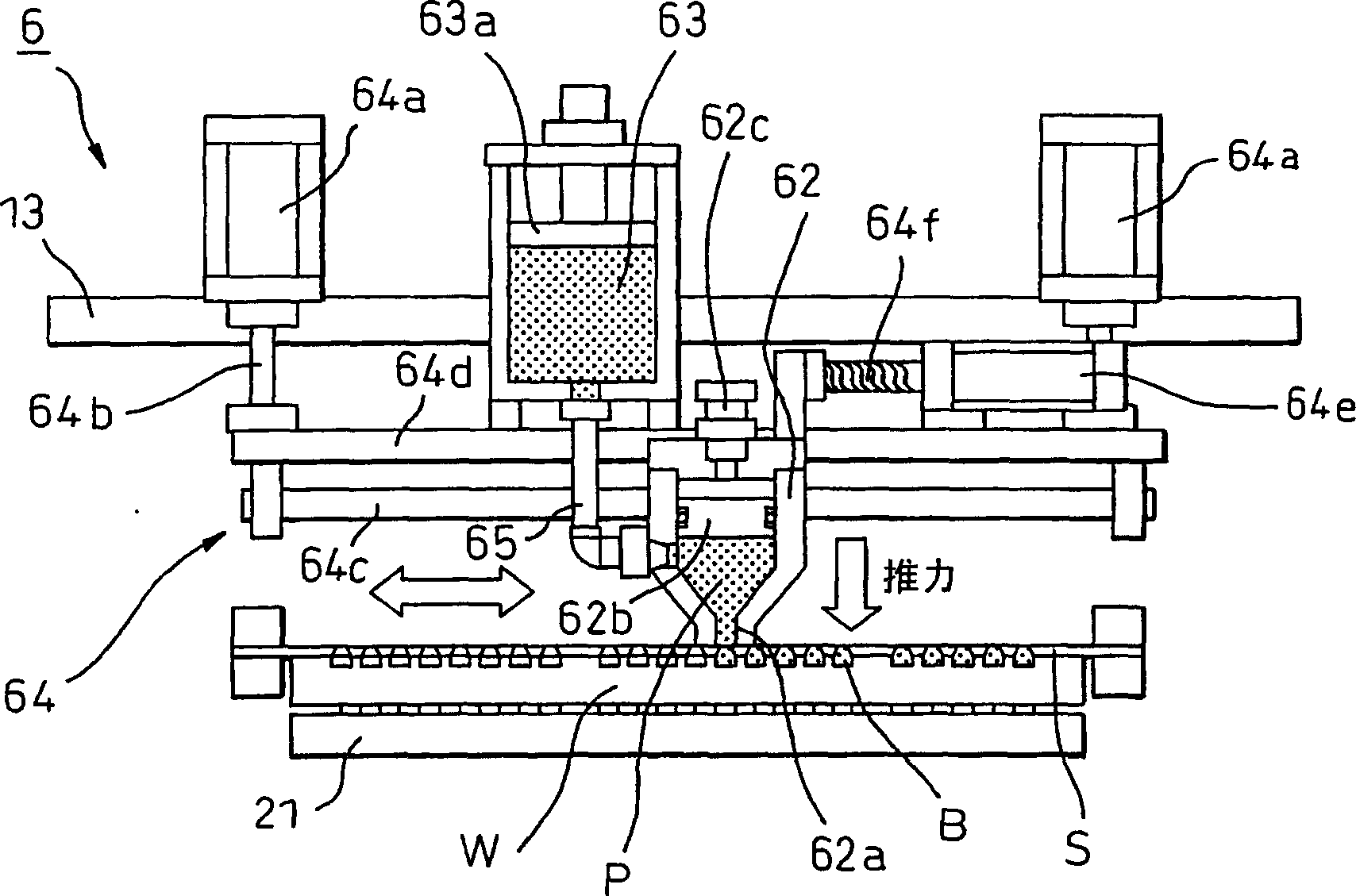
InactiveCN1796109AClose contactSame effectScreen printersConductive pattern formationEngineeringPrinting press
A printing mechanism (6) of a screen printer (1) for printing a paste (P) through a screen (S) onto a workpiece (W) at a printing position comprising: contacting the screen at a distal end A filling nozzle (62), a filling head (62) into which paste consumed during printing is filled, and a feed box (63) for supplying paste into the filling head. There is an extrusion mechanism (62b, 63a) in each of the filling head and the feed box, and the extrusion pressure of the paste to the screen mask can be controlled. The printing mechanism also includes a filling head support mechanism (64), which can support the filling head in such a way that the filling head can move up and down, and can also adjust the thrust of the filling head on the screen.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Magnetic encoder
InactiveUS20050007226A1Strong magnetic characteristicEasy to handleRolling contact bearingsBearing assemblyMagnetic tension forceAdhesive
A magnetic encoder for use in a vehicle axle for generating pulse code by magnetic force. A magnetic ring is attached with an adhesive to a reinforcing ring fixed on the vehicle axle and then S and N poles are alternately magnetized thereon in a circumferential manner. Further the edge of the reinforcing ring is folded to fix the magnetic ring by caulking into the reinforcing ring.
Owner:UCHIYAMA MFG
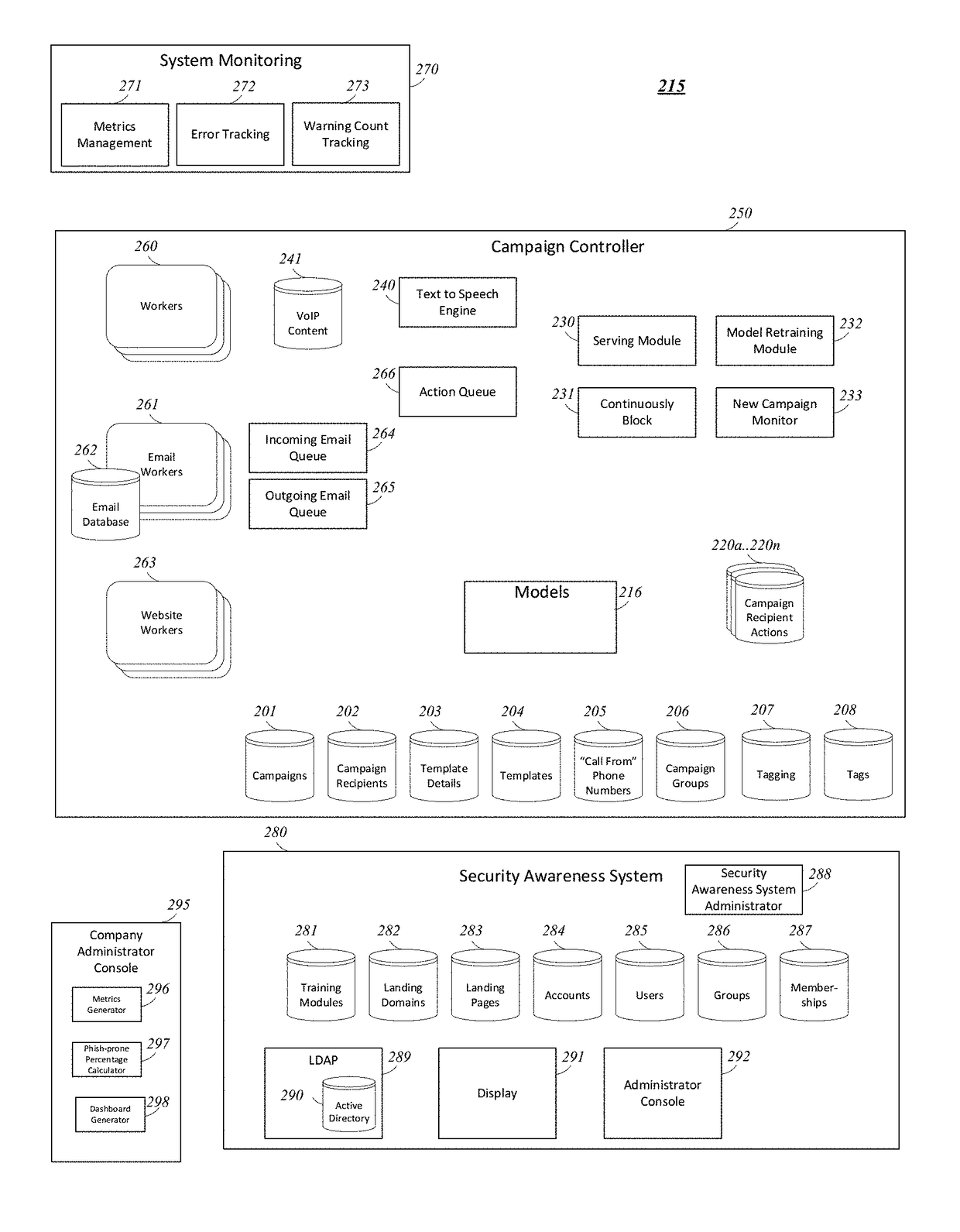
Systems and methods for an artificial intelligence driven smart template
ActiveUS20180159889A1Avoid actionSame effectWeb data indexingDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringPhishing
The present disclosure describes systems and methods for determining a subsequent action of a simulated phishing campaign. A campaign controller identifies a starting action for a simulated phishing campaign directed to a user of a plurality of users. The simulated phishing campaign includes a plurality of actions, one or more of the plurality of actions to be determined during execution of the simulated phishing campaign The campaign controller responsive to the starting action, communicates a simulated phishing communication to one or more devices of a user. The campaign controller determines a subsequent action of the plurality of actions of the simulated phishing campaign based at least on one of a response to the simulated phishing communication received by the campaign controller or a lack of response within a predetermined time period and initiating, responsive to the determination, the subsequent action of the simulated phishing campaign.
Owner:KNOWBE4 INC
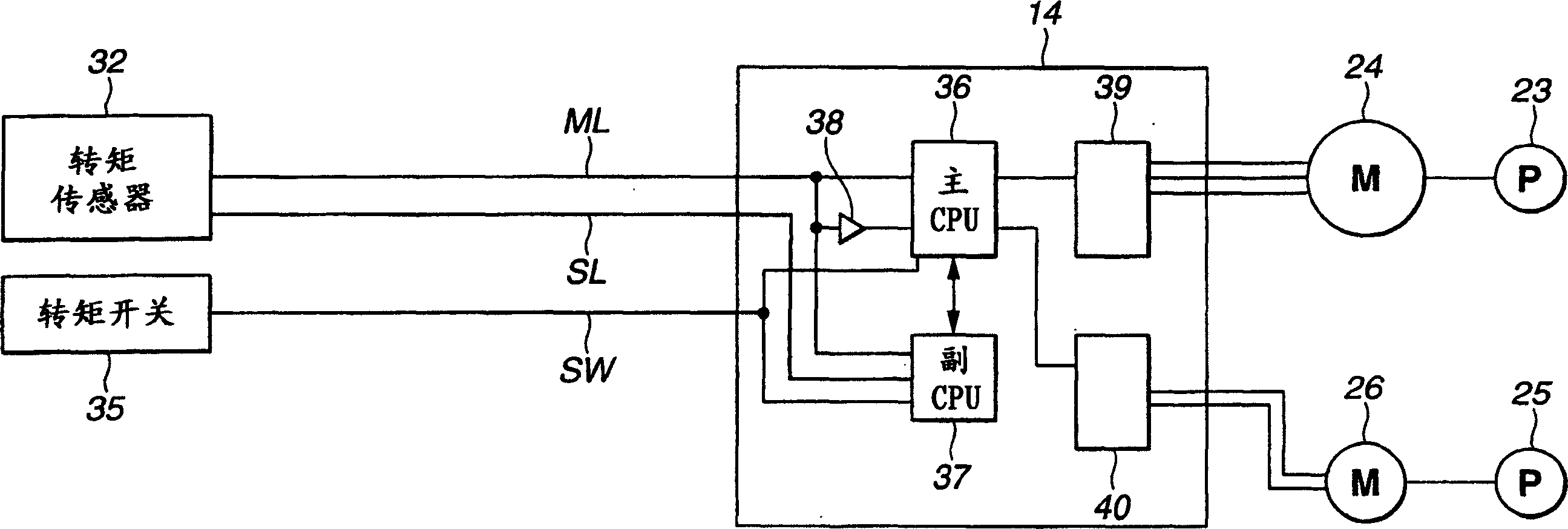
Power steering device and method of controlling the power steering device
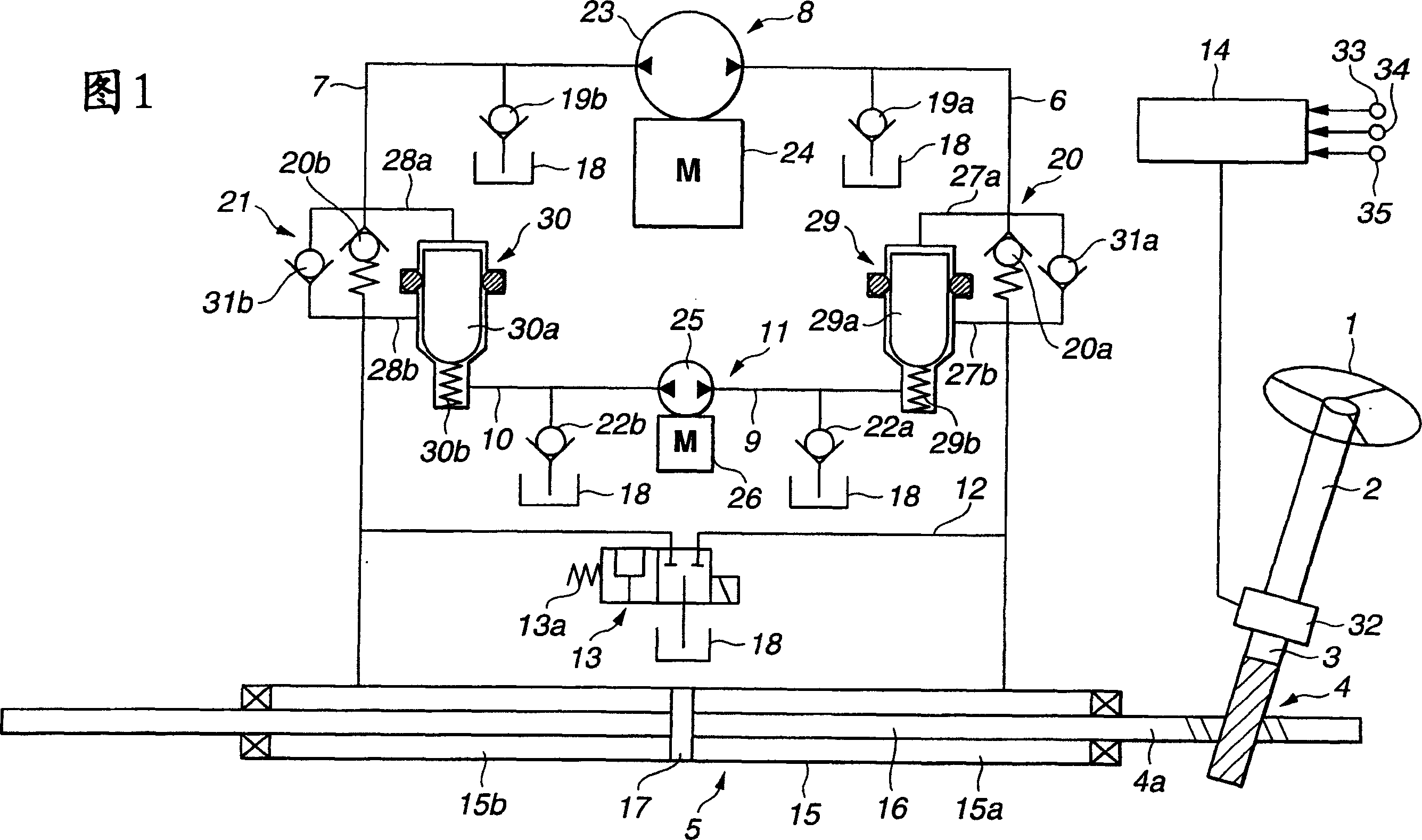
InactiveCN1835861AReduce manipulative strengthAchieve smooth transition controlSteering linkagesFluid steeringDriver/operatorPower steering
A power steering device, comprising a hydraulic power cylinder (5) assisting the steering force of a rack and pinion mechanism (4) and a first hydraulic pressure supply mechanism (8) having a first trochoid pump (23) and a first electric motor (24) selectively supplying hydraulic pressure to both hydraulic pressure chambers (15a) and (15b) through first and second passages (6) and (7). When the first hydraulic pressure supply mechanism fails, a second hydraulic pressure supply mechanism (11) selectively supplies working hydraulic pressure to both hydraulic pressure chambers through third and fourth passages (9) and (10) according to instruction signals from a control unit (14). Since a steering assist force is actively given to the rack and pinion mechanism (4) by the second hydraulic pressure supply mechanism (11), a steering wheel operating force given by a driver can be reduced.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Systems and methods for an artificial intelligence driven smart template
ActiveUS20180159888A1Avoid actionSame effectWeb data indexingDesign optimisation/simulationEngineeringPhishing
The present disclosure describes systems and methods for using a template for a simulated phishing campaign, A database includes a plurality of templates for simulated phishing campaigns, each template of the plurality of templates identifying a list of a plurality of types of simulated phishing communications and at least a portion of content for the simulated phishing communications. A campaign controller selects a template from the plurality of templates for a simulated phishing campaign directed to a user of a plurality of users; and communicates, to one or more devices of the user a first type of simulated phishing communication of the plurality of types of simulated phishing communications with at least the portion of content identified by the template.
Owner:KNOWBE4 INC
Dynamic fin comprising coupled fin sections
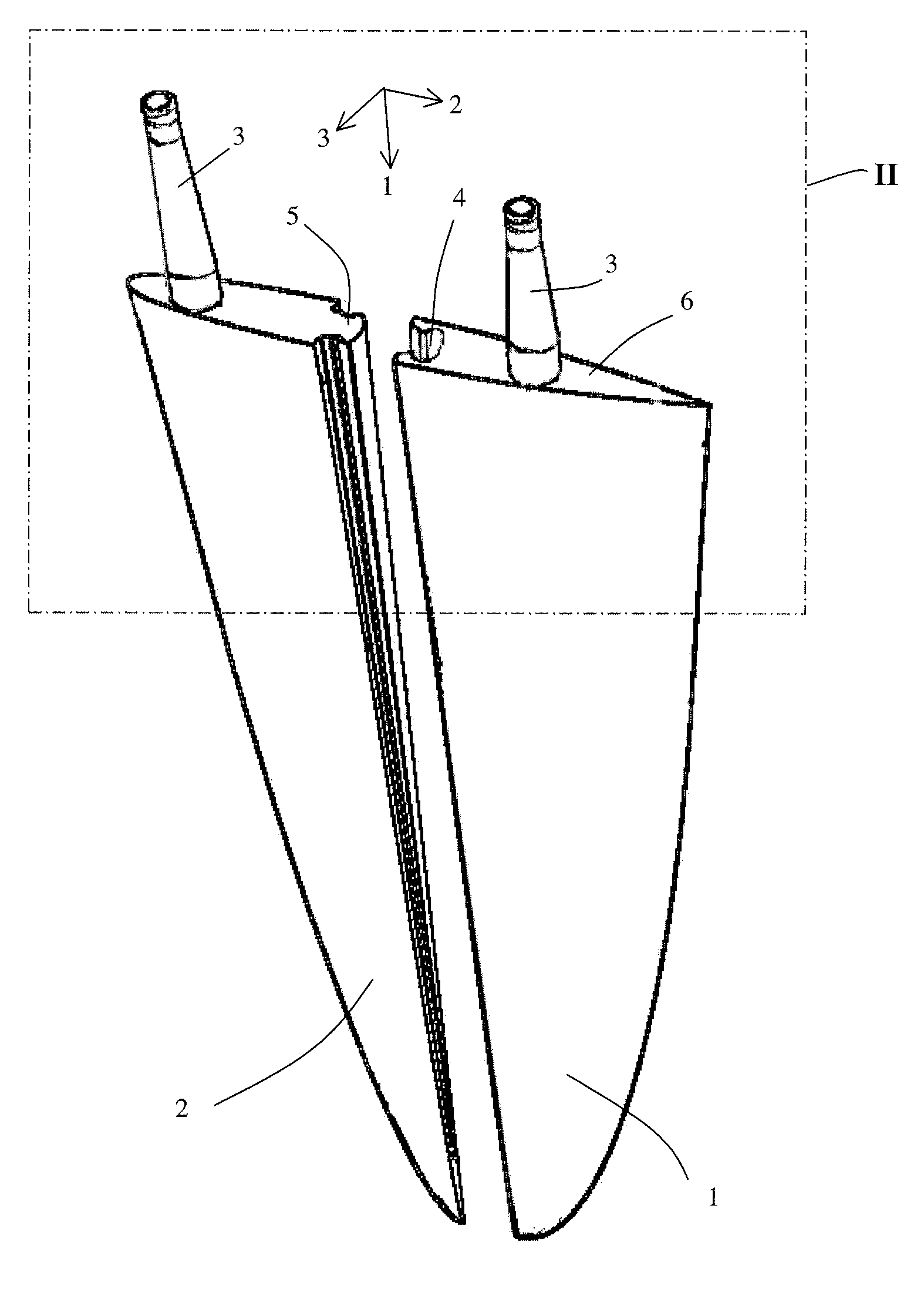
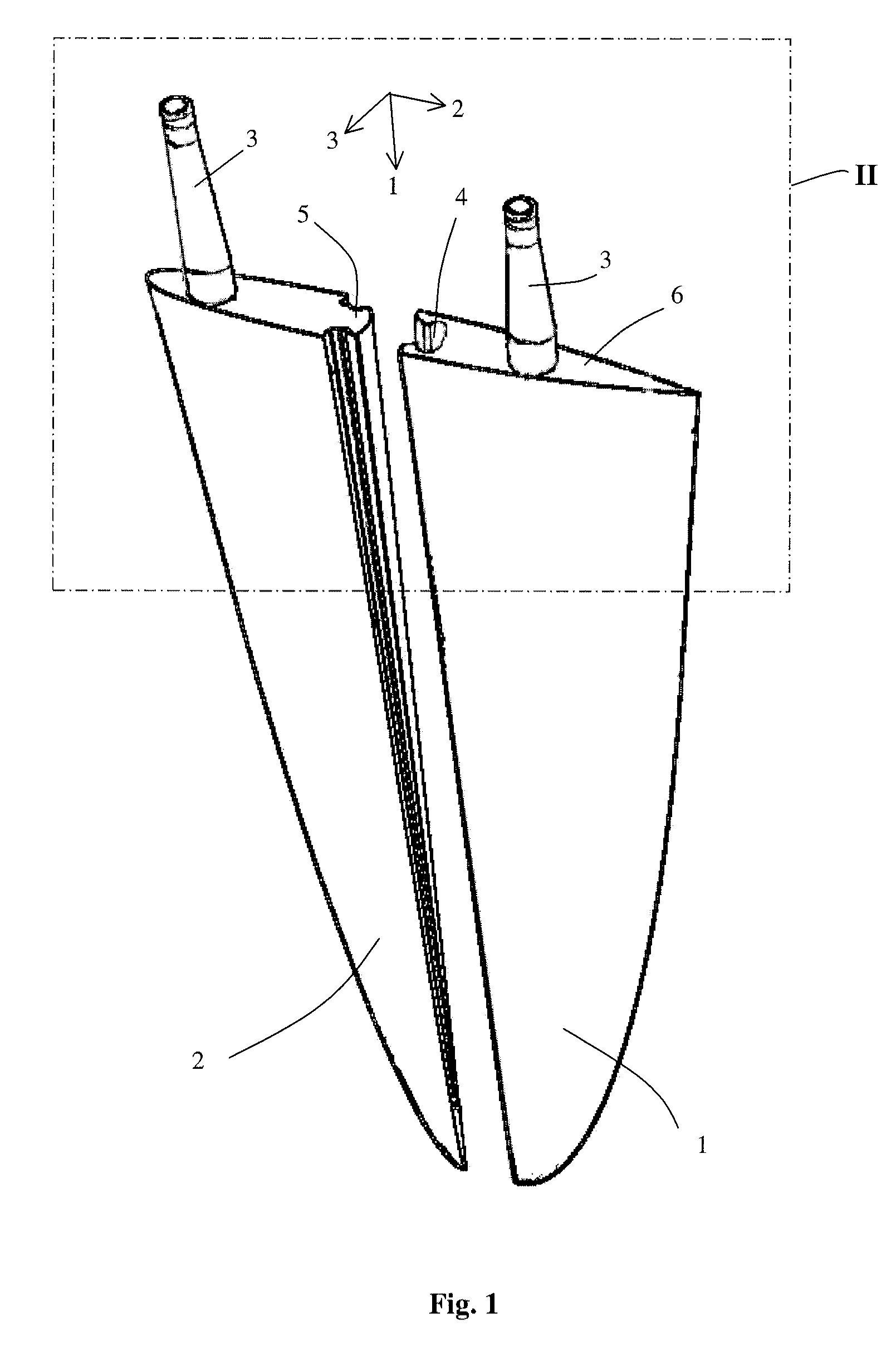
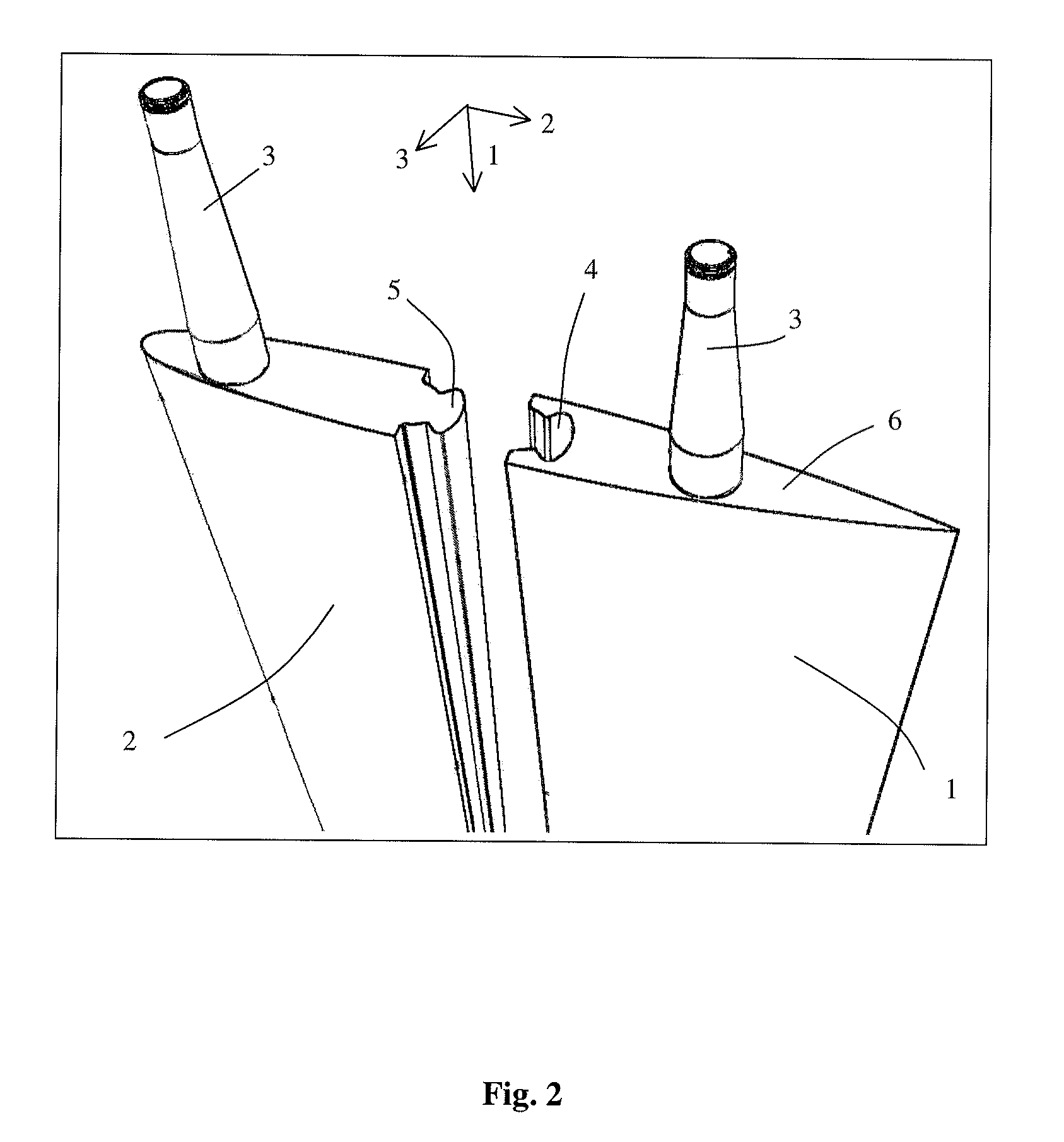
InactiveUS20110061579A1Improves hydro and aerodynamic propertySame effectPropellersWater sport boardsRotational axisCoupling
A dynamic or aerodynamic fin comprising at least two parallel arranged fin sections. At least one fin section comprises a rotational axis for installing the fin section by a rotation shaft. An end stop is provided for stopping the rotational movement of the fin section to define an extreme position. In the extreme position the fin sections provide a substantially cambered shape to the fin. The dynamic fin is improved in that it comprises a pair of coupling elements. A first fin section is coupled to a second adjacent fin section by a pair of a first and second coupling elements. The first coupling element is complementary to the second coupling element. The first coupling element is part of, preferably integral, with the first fin section and the second coupling element is part of, preferably integral, with the second fin section.
Owner:VAN GELDER KLAAS BOUDEWIJN
Systems and methods for artificial model building techniques
ActiveUS10009375B1Avoid actionSame effectPlatform integrity maintainanceTransmissionHyperlinkRequest - action
Embodiments disclosed describe a security awareness system may adaptively learn the best design of a simulated phishing campaign to get a user to perform the requested actions, such as clicking a hyperlink or opening a file. In some implementations, the system may adapt an ongoing campaign based on user's responses to messages in the campaign, along with the system's learned awareness. The learning process implemented by the security awareness system can be trained by observing the behavior of other users in the same company, other users in the same industry, other users that share similar attributes, all other users of the system, or users that have user attributes that match criteria set by the system, or that match attributes of a subset of other users in the system.
Owner:KNOWBE4 INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com