Patents
Literature
66 results about "Imaging ultrasound" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ultrasound imaging (sonography) uses high-frequency sound waves to view inside the body. Because ultrasound images are captured in real-time, they can also show movement of the body's internal organs as well as blood flowing through the blood vessels.
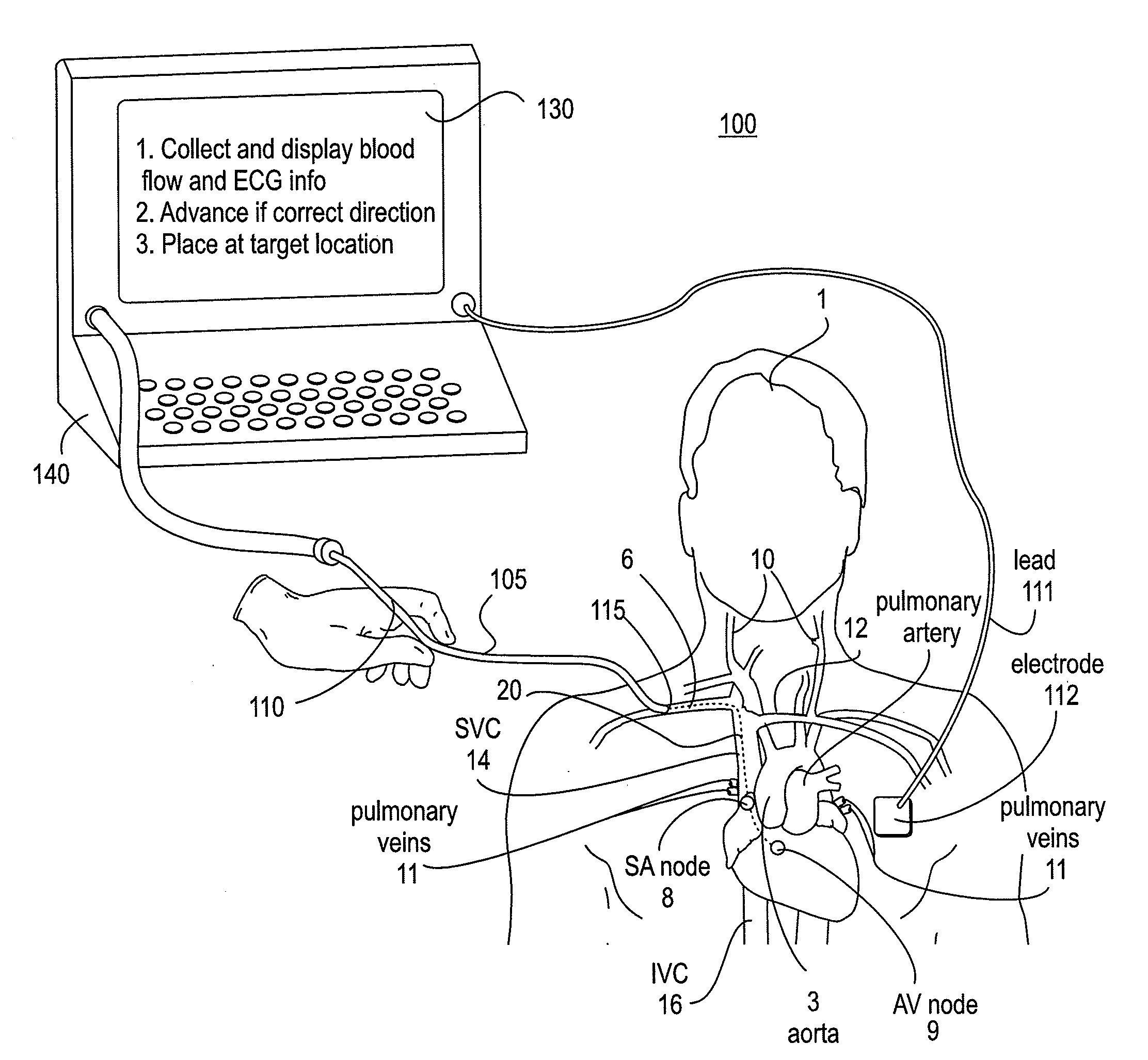
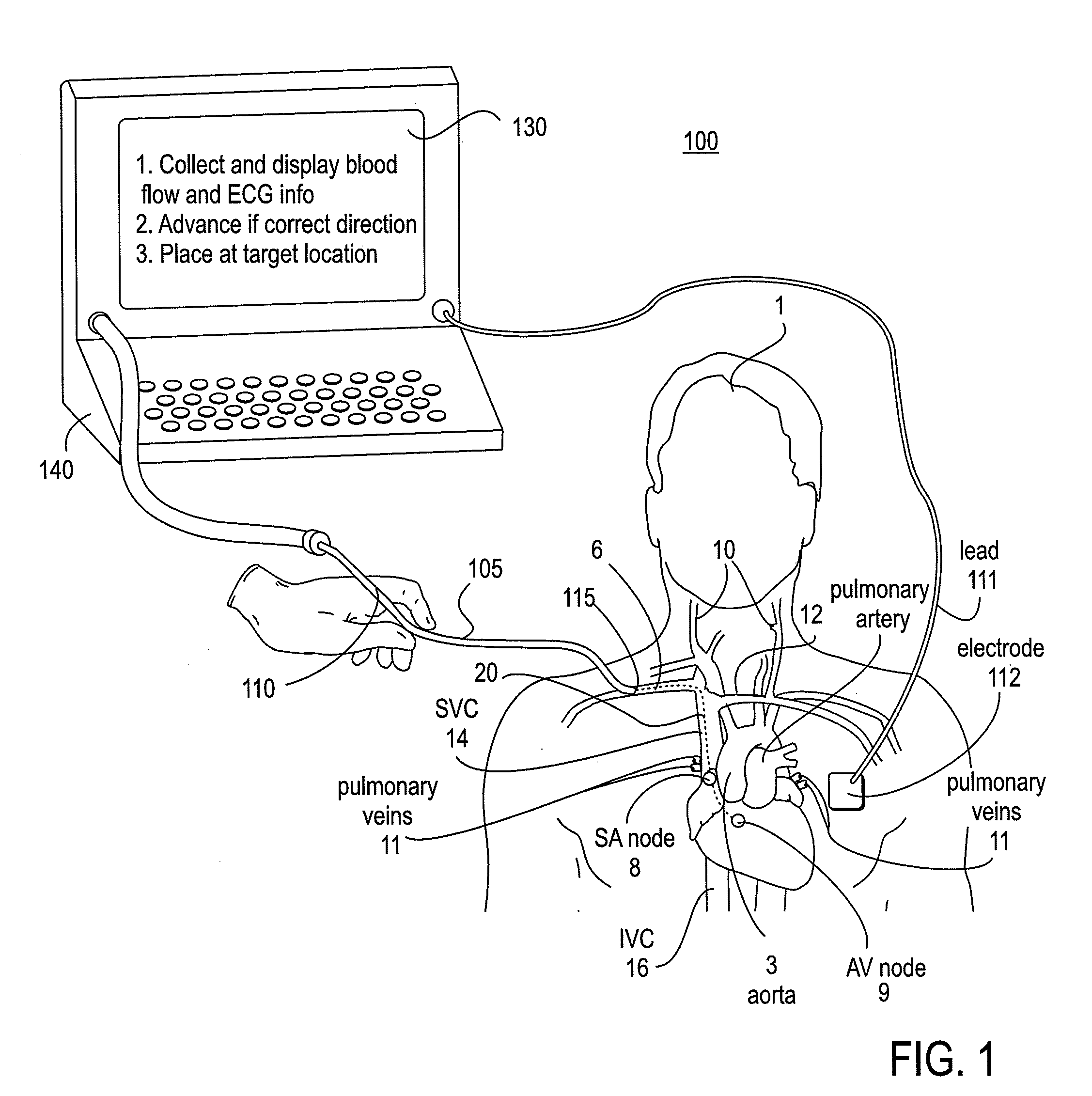
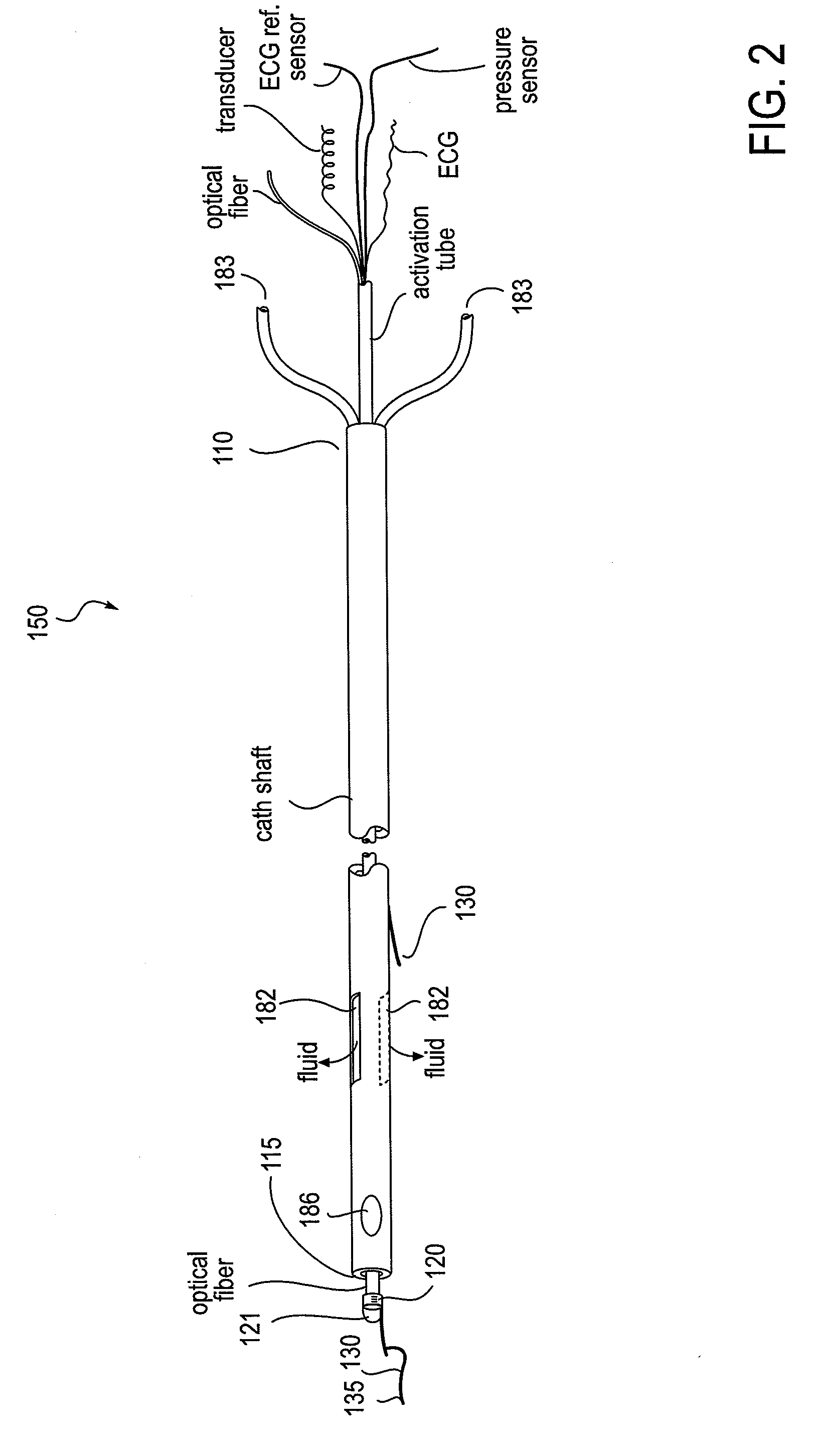
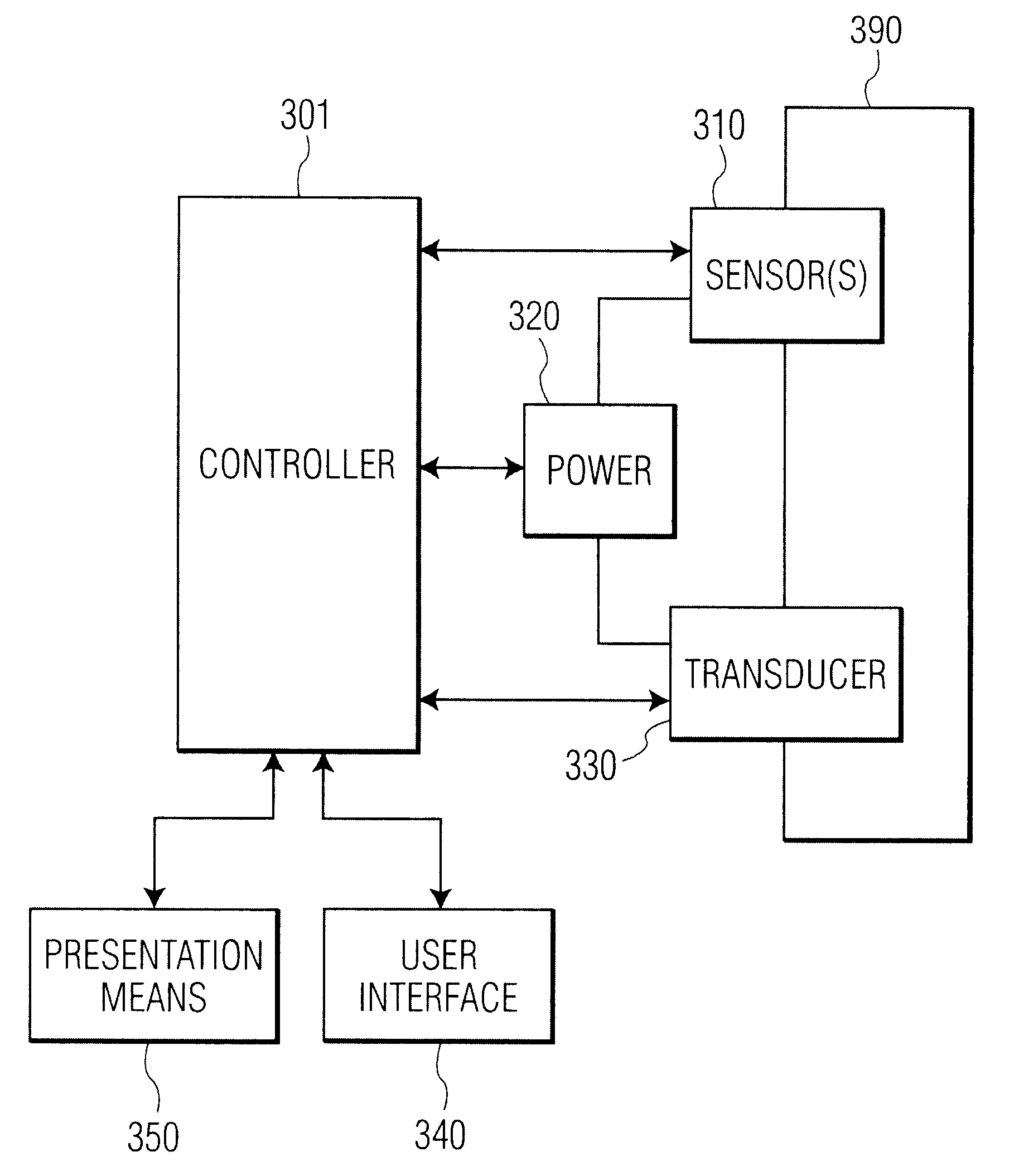
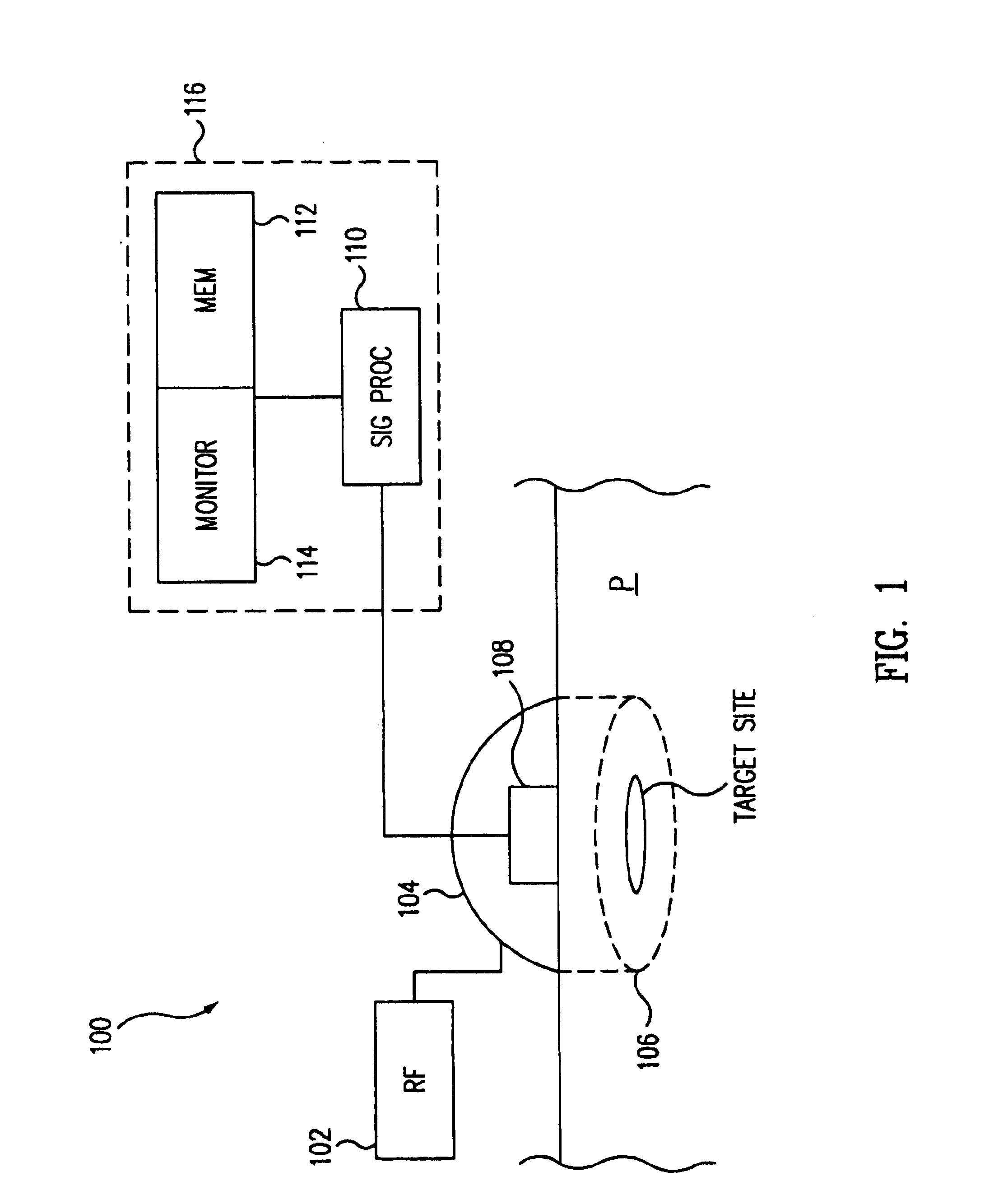
Apparatus and Method for Endovascular Device Guiding and Positioning Using Physiological Parameters
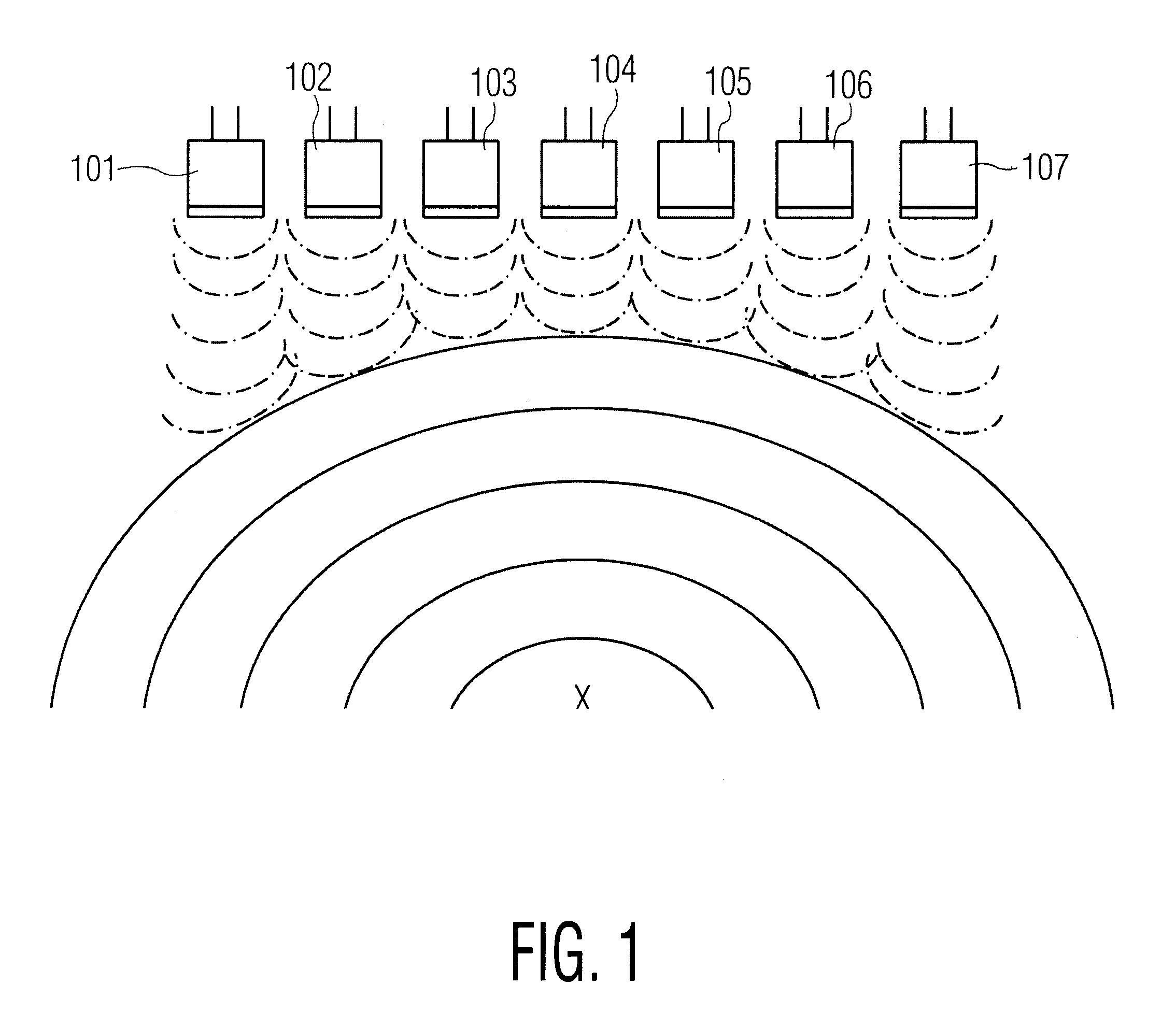
ActiveUS20090005675A1Improve accuracyImpede advancementStethoscopeHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesGuidance systemMedicine
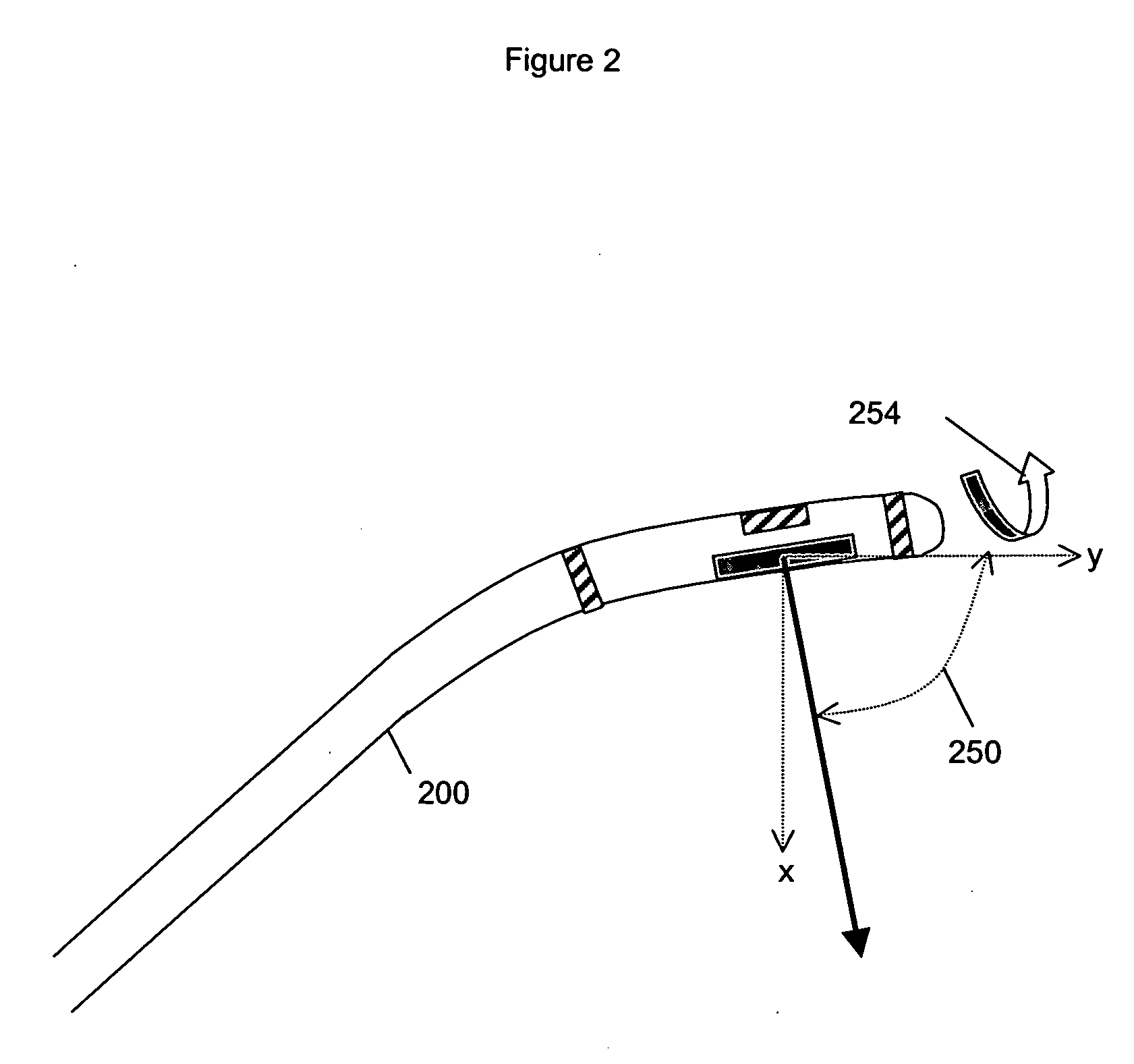
An endovascular access and guidance system has an elongate body with a proximal end and a distal end; a non-imaging ultrasound transducer on the elongate body configured to provide in vivo non-image based ultrasound information of the vasculature of the patient; an endovascular electrogram lead on the elongate body in a position that, when the elongate body is in the vasculature, the endovascular electrogram lead electrical sensing segment provides an in vivo electrogram signal of the patient; a processor configured to receive and process a signal from the non-imaging ultrasound transducer and a signal from the endovascular electrogram lead; and an output device configured to display a result of information processed by the processor. An endovascular device has an elongate body with a proximal end and a distal end; a non-imaging ultrasound transducer on the elongate body; and an endovascular electrogram lead on the elongate body in a position that, when the endovascular device is in the vasculature, the endovascular electrogram lead is in contact with blood. The method of positioning an endovascular device in the vasculature of a body is performed by advancing the endovascular device into the vasculature; transmitting a non-imaging ultrasound signal into the vasculature using a non-imaging ultrasound transducer on the endovascular device; receiving a reflected ultrasound signal with the non-imaging ultrasound transducer; detecting an endovascular electrogram signal with a sensor on the endovascular device; processing the reflected ultrasound signal received by the non-imaging ultrasound transducer and the endovascular electrogram signal detected by the sensor; and positioning the endovascular device based on the processing step.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Imaging ultrasound transducer temperature control system and method
InactiveUS6669638B1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsTemperature controlUltrasonic sensor
A system and method for controlling the heat of an ultrasonic transducer is disclosed. The presently preferred embodiments of the present invention control the temperature of the transducer face by changing the imaging modes of the system. In a preferred embodiment, feedback from temperature sensing elements placed in the transducer is used to determine when to switch from a higher power imaging mode to a lower power imaging mode. In another preferred embodiment, the system switches from a higher power imaging mode to a lower power imaging mode after a predetermined period of time has elapsed. In yet another preferred embodiment, the system switches to a "mixed" imaging mode, where the system cycles rapidly between a higher power imaging mode and a lower power imaging mode, and the resulting data is combined to form a single image.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for localizing an ultrasound catheter
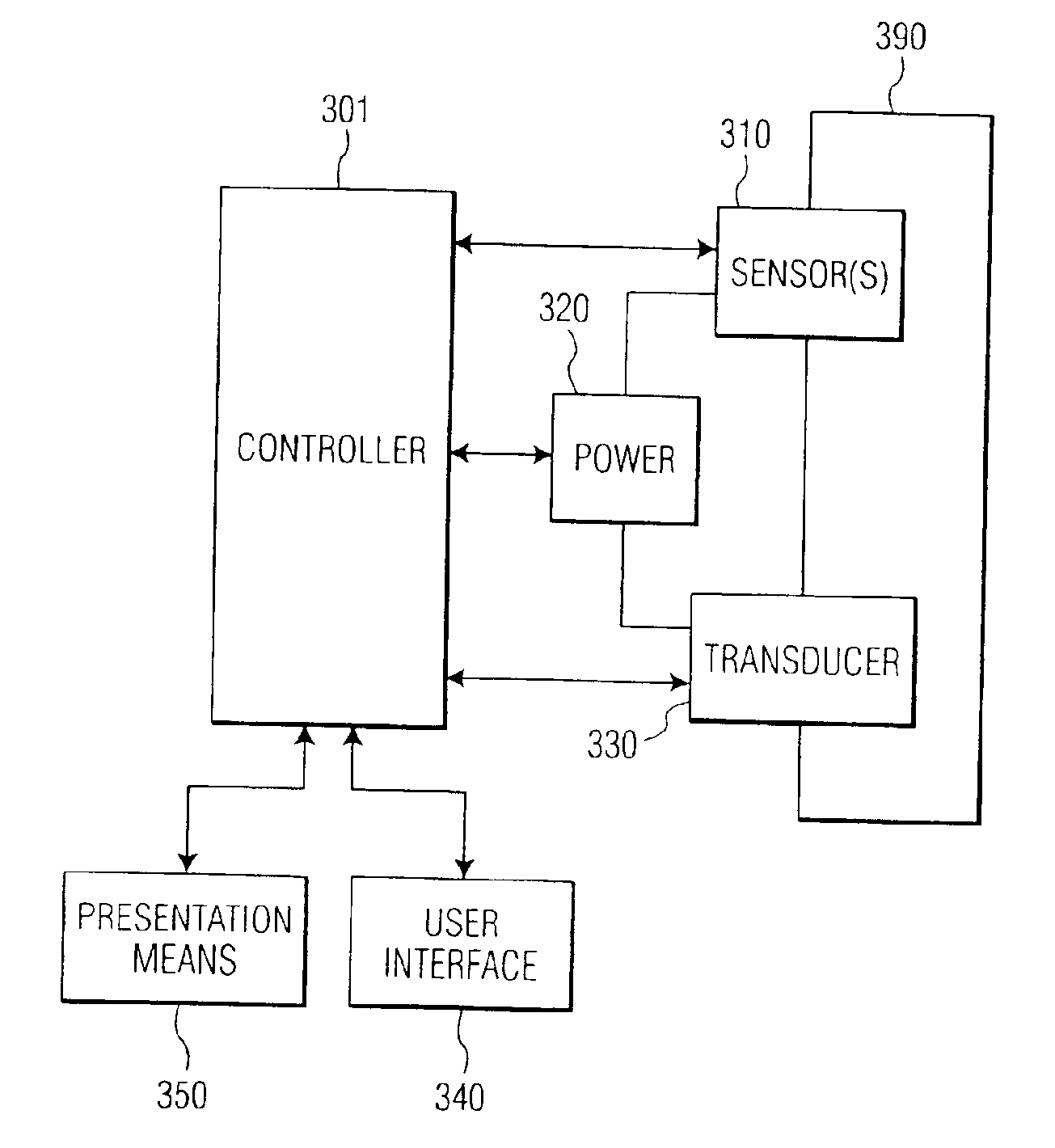
An imaging system is provided with an ultrasound catheter and a controller coupled to the ultrasound catheter. The catheter includes a localizer sensor configured to generate positional information for the ultrasound catheter, and an imaging ultrasound sensor having a restricted field of view. The controller co-registers images from the imaging ultrasound sensor with positional information from the localizer sensor.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
Imaging ultrasound transducer temperature control system and method using feedback
InactiveUS6905466B2Reduce the temperatureReduce temperatureUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationOperational system
A system and method for controlling the heat of an ultrasonic transducer is disclosed. In the presently preferred embodiments, the system and method controls the temperature of the transducer by changing operating system parameters based on feedback from temperature sensing elements placed in the transducer. The chosen mutable system parameters may be preset by the construction of the ultrasonic system, under the control of the ultrasonic system user, or a combination of the two. In several exemplary embodiments, the one or more mutable system parameters are altered by an amount proportionate to the difference between the current temperature and a preferred operating temperature. In another exemplary embodiment, the system switches to a lower power imaging mode when the temperature feedback indicates a threshold temperature has been reached.
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Imaging ultrasound transducer temperature control system and method using feedback
InactiveUS20040073113A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSonificationOperational system
A system and method for controlling the heat of an ultrasonic transducer is disclosed. In the presently preferred embodiments, the system and method controls the temperature of the transducer by changing operating system parameters based on feedback from temperature sensing elements placed in the transducer. The chosen mutable system parameters may be preset by the construction of the ultrasonic system, under the control of the ultrasonic system user, or a combination of the two. In several exemplary embodiments, the one or more mutable system parameters are altered by an amount proportionate to the difference between the current temperature and a preferred operating temperature. In another exemplary embodiment, the system switches to a lower power imaging mode when the temperature feedback indicates a threshold temperature has been reached.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
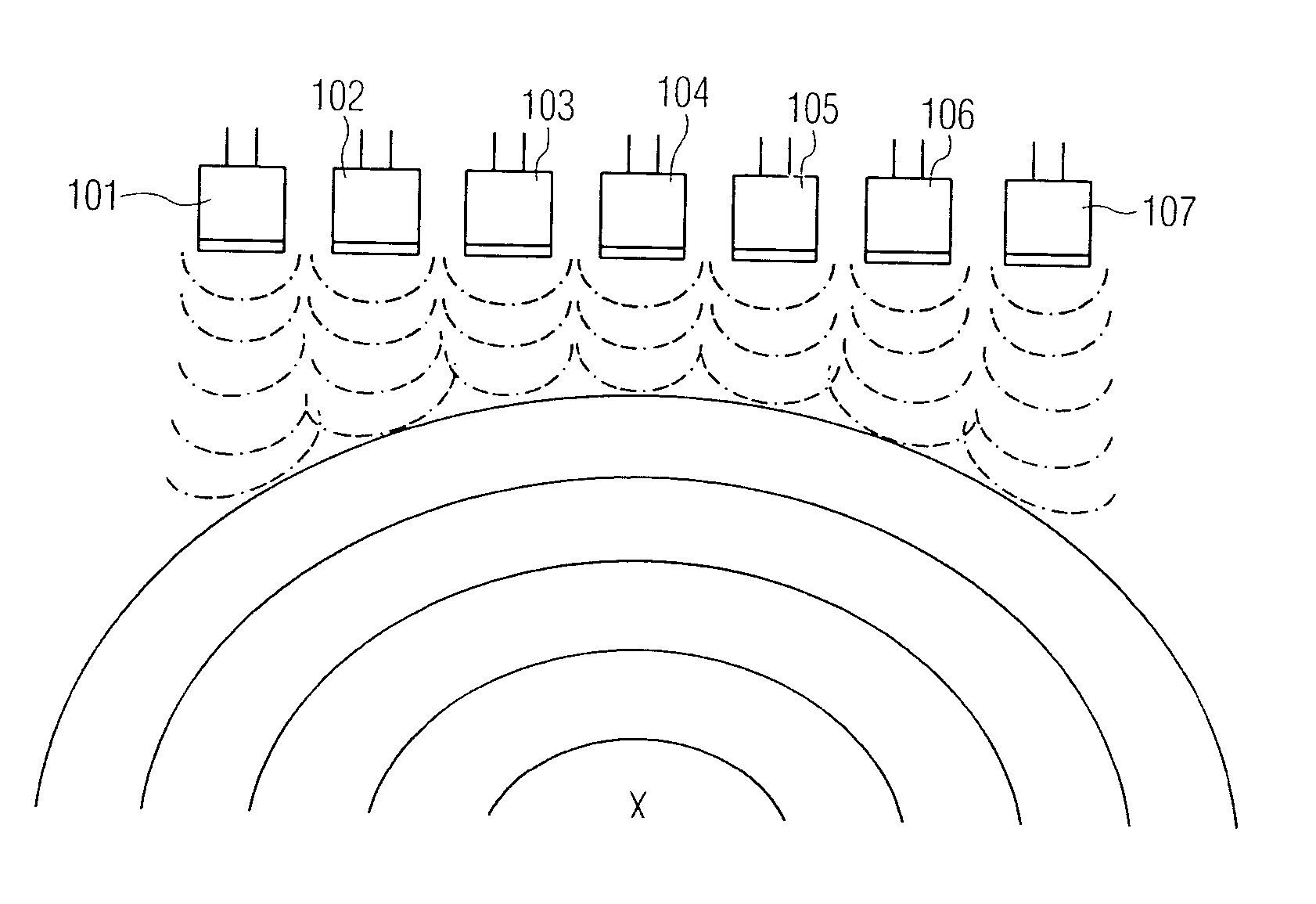
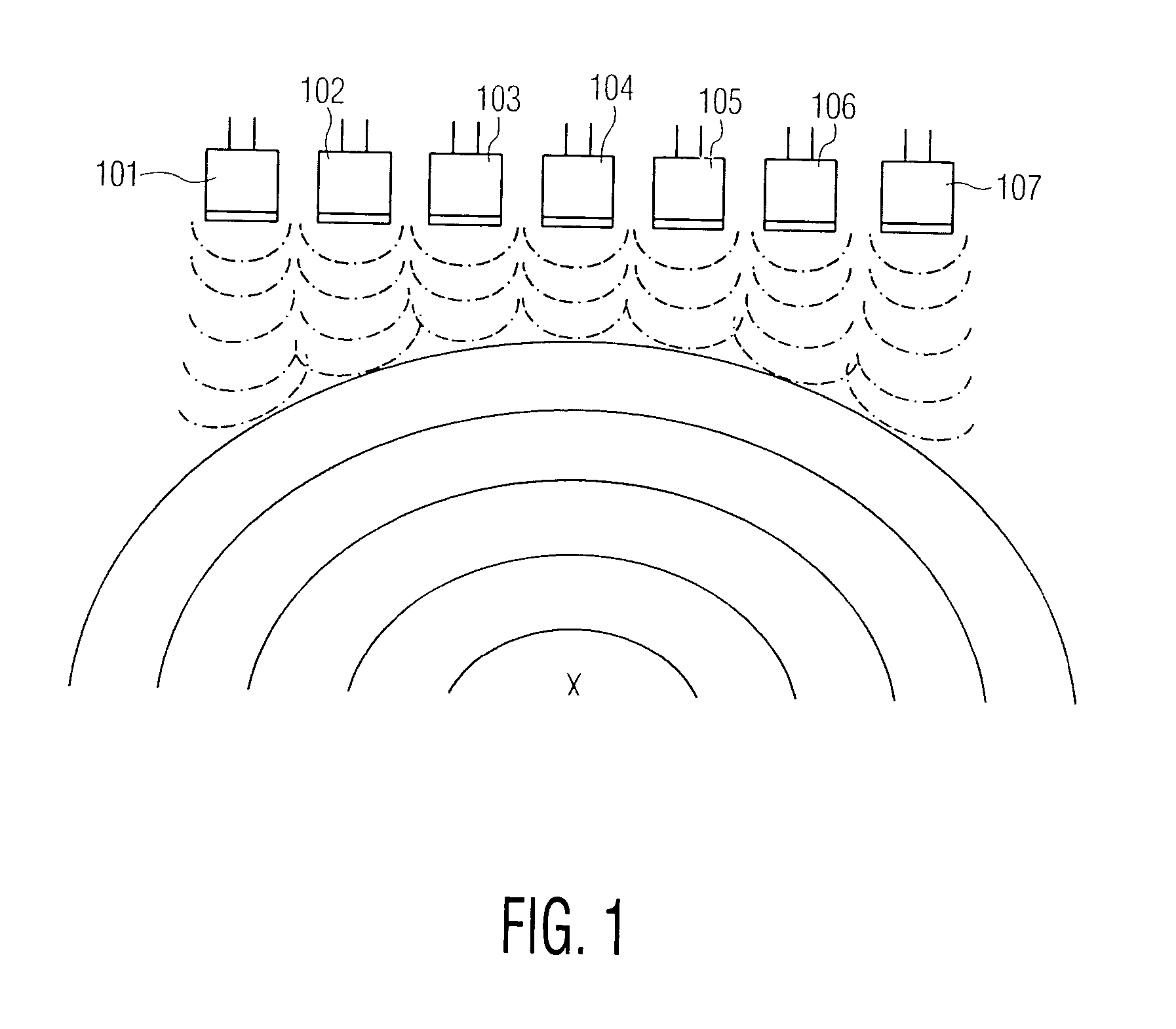
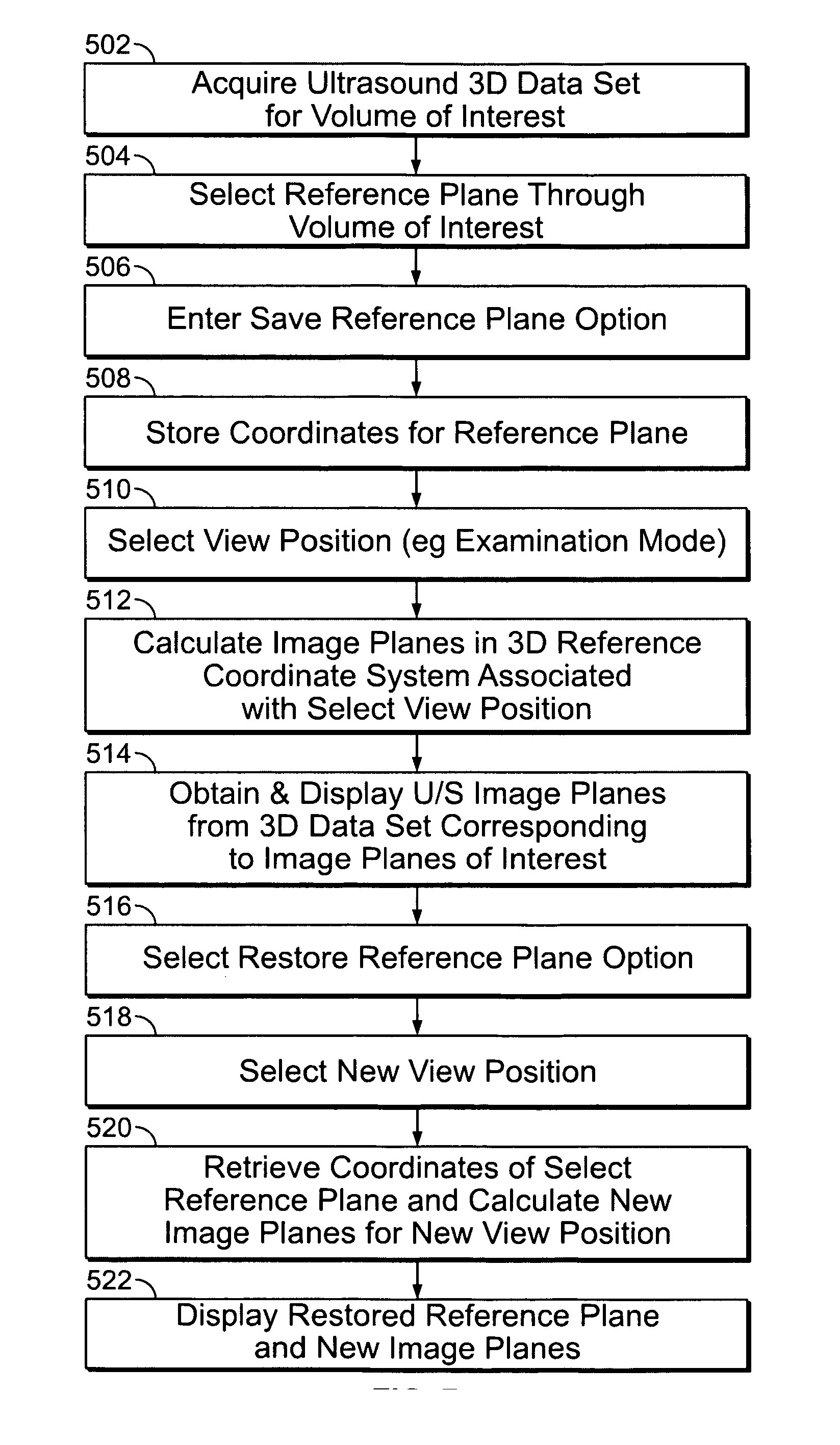
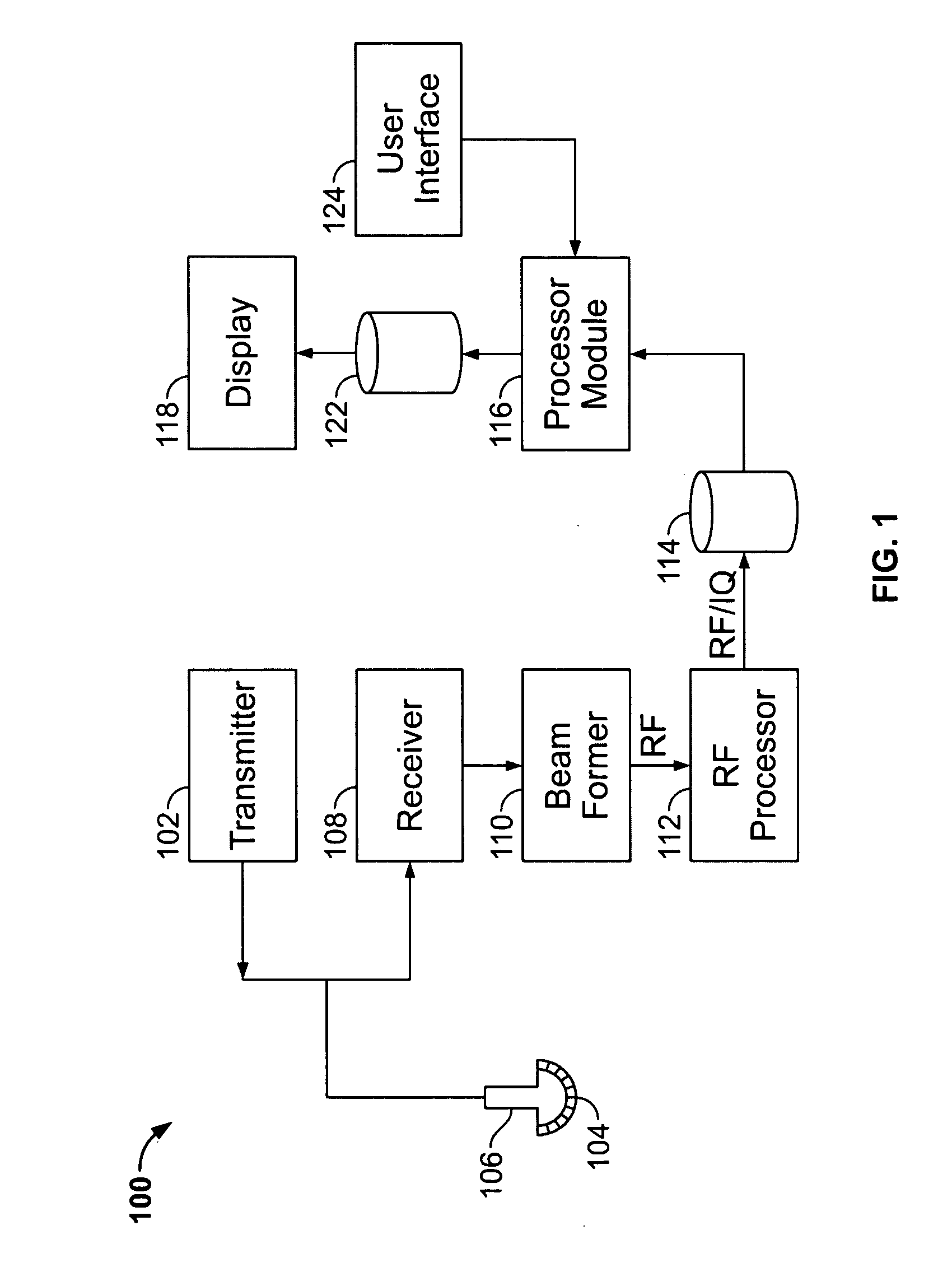
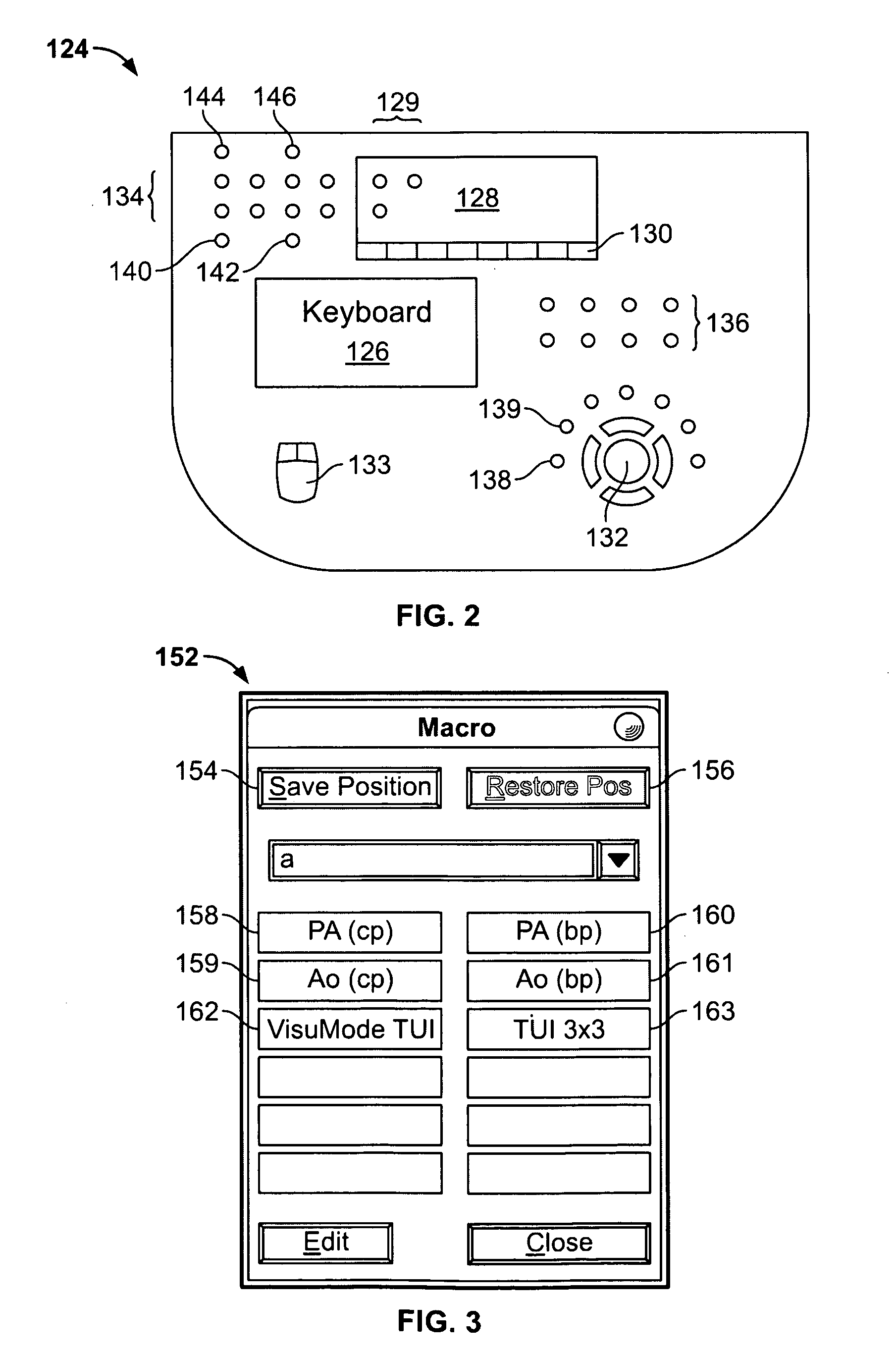
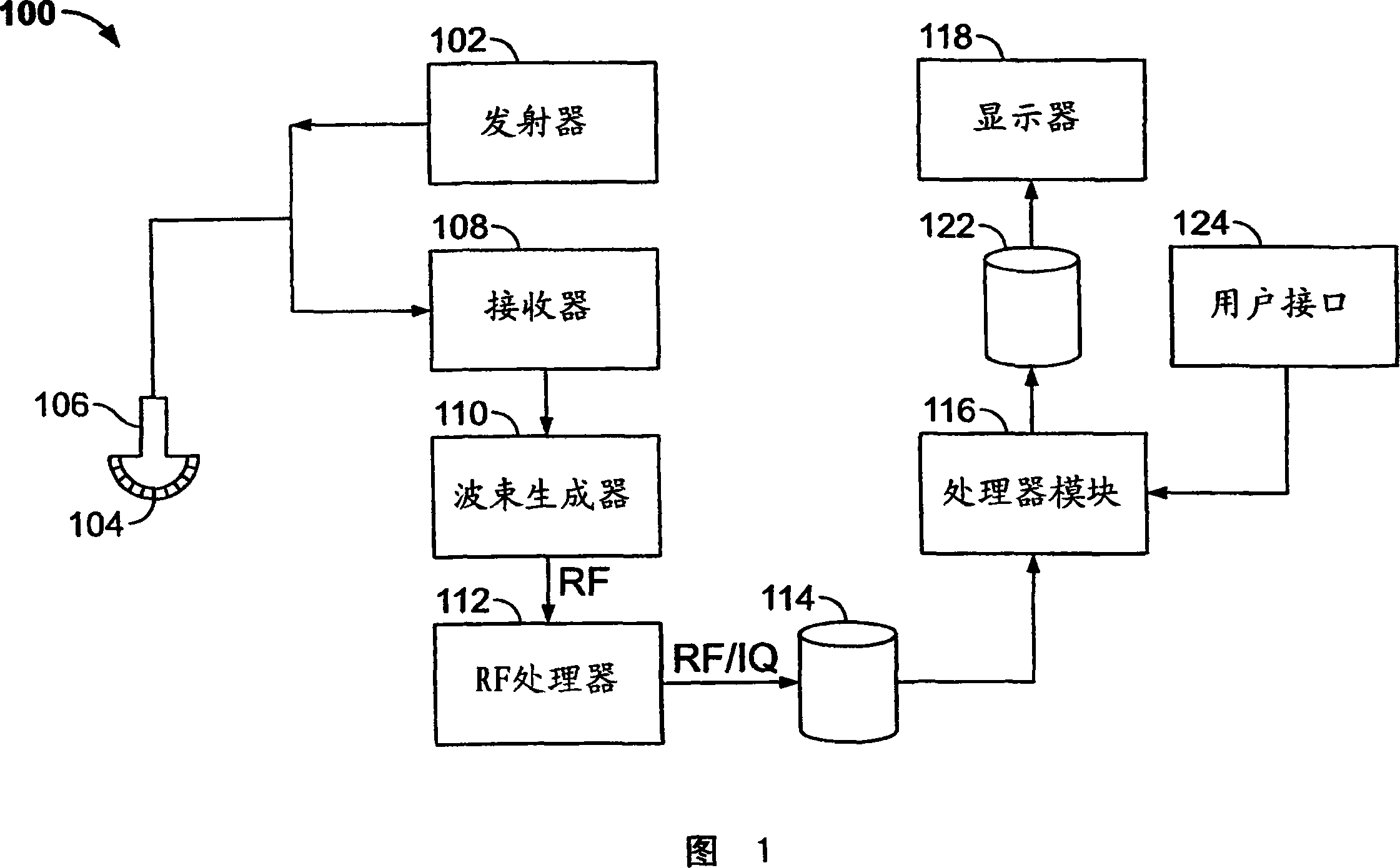
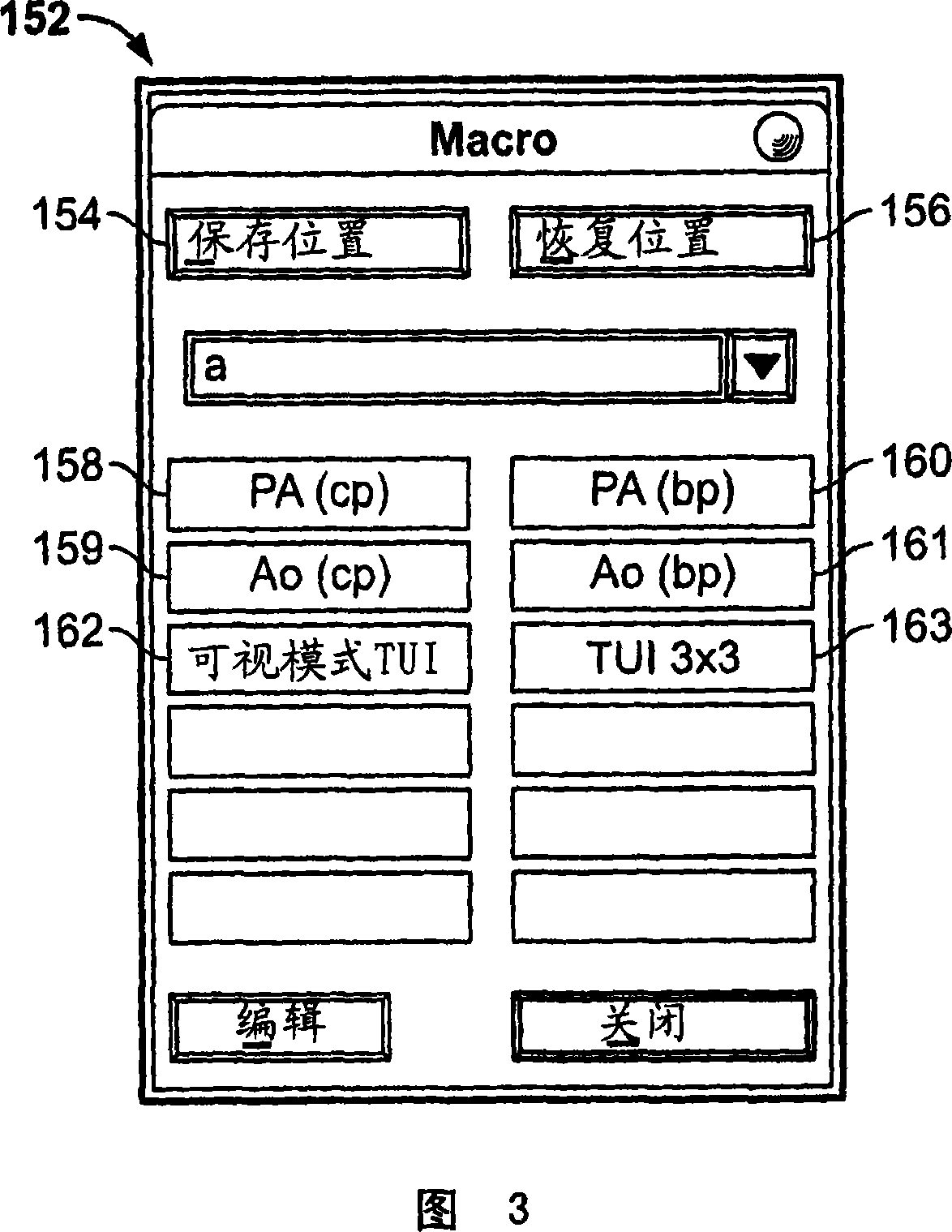
User interface for automatic multi-plane imaging ultrasound system
InactiveUS20070255139A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCharacter and pattern recognitionData setSonification
A diagnostic ultrasound system is provided for automatically displaying multiple planes from a 3-D ultrasound data set. The system comprises a user interface for designating a reference plane, wherein the user interface provides a safe view position option and a restore reference plane option. A processor module maps the reference plane into a 3D ultrasound data set and automatically calculates image planes based on the reference plane for a current view position and a prior view position. A display is provided to selectively display the image planes associated with the current and prior reference planes. Memory stores the prior reference plane in response to selection of the save reference plane option, while the display switches from display of the current reference plane to restore the prior reference plane in response to selection of the restore reference plane option. Optionally, the memory may store coordinates in connection with the current and prior reference planes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for localizing an ultrasound catheter
An imaging system is provided with an ultrasound catheter and a controller coupled to the ultrasound catheter. The catheter includes a localizer sensor configured to generate positional information for the ultrasound catheter, and an imaging ultrasound sensor having a restricted field of view. The controller co-registers images from the imaging ultrasound sensor with positional information from the localizer sensor.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL ATRIAL FIBRILLATION DIV
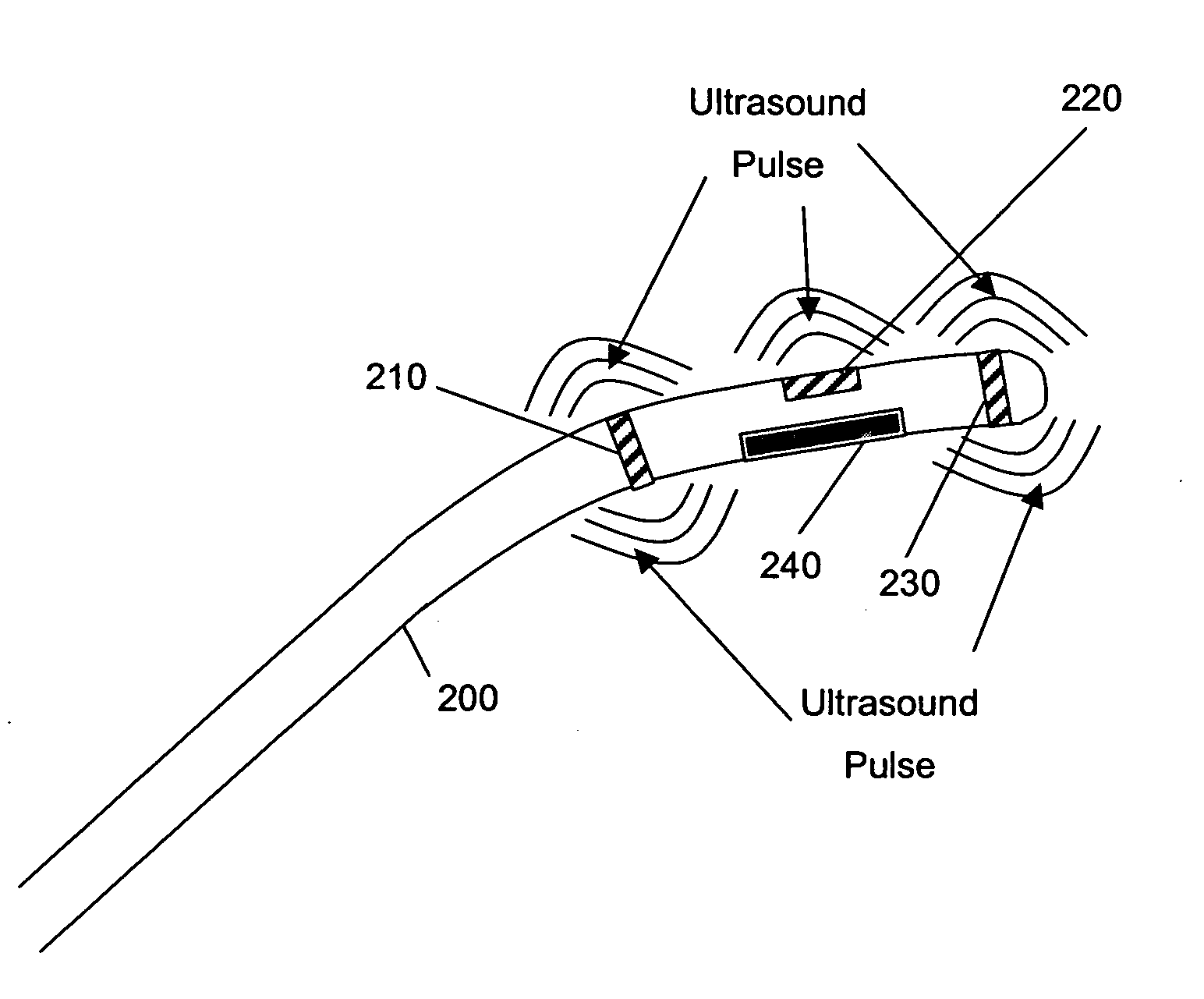
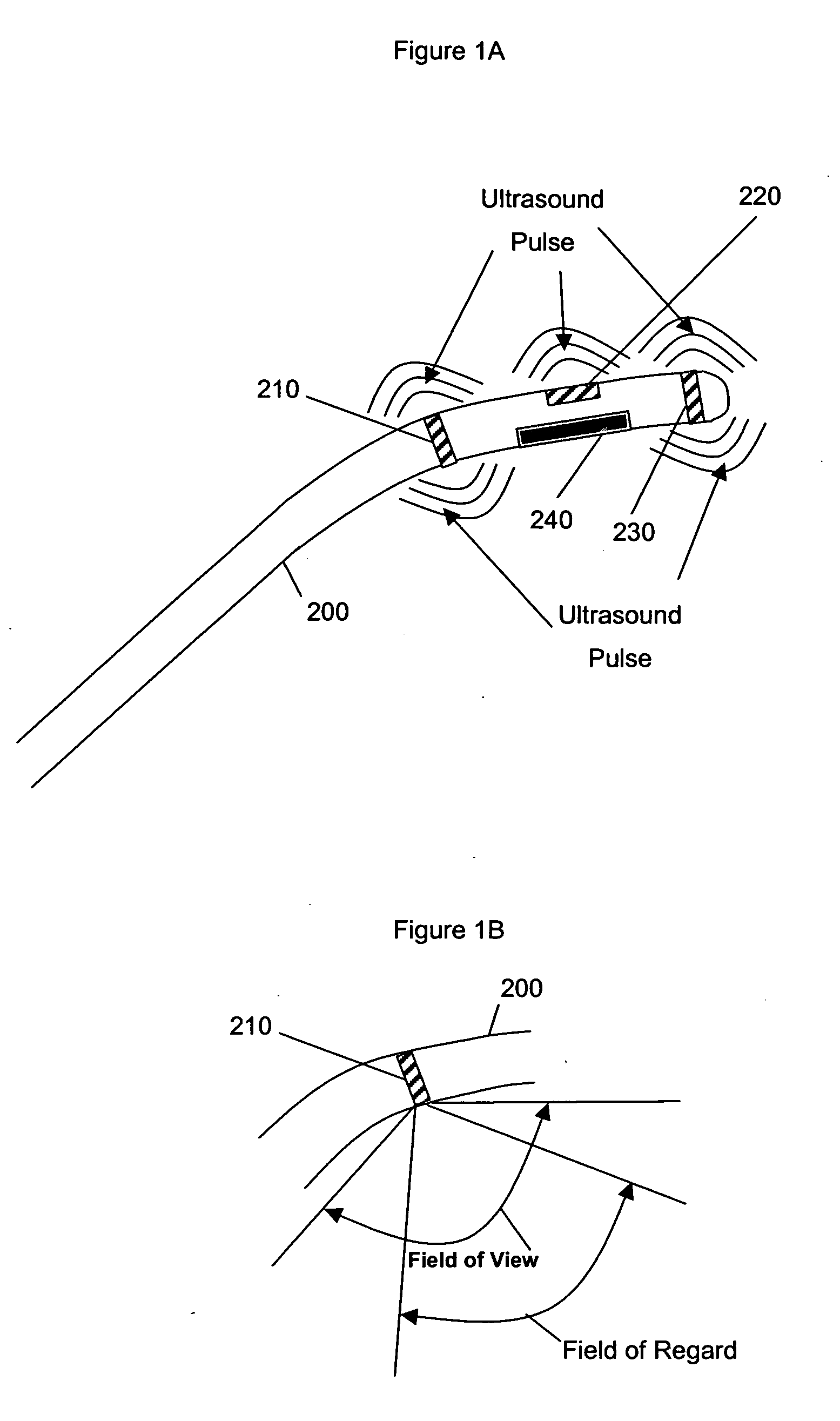
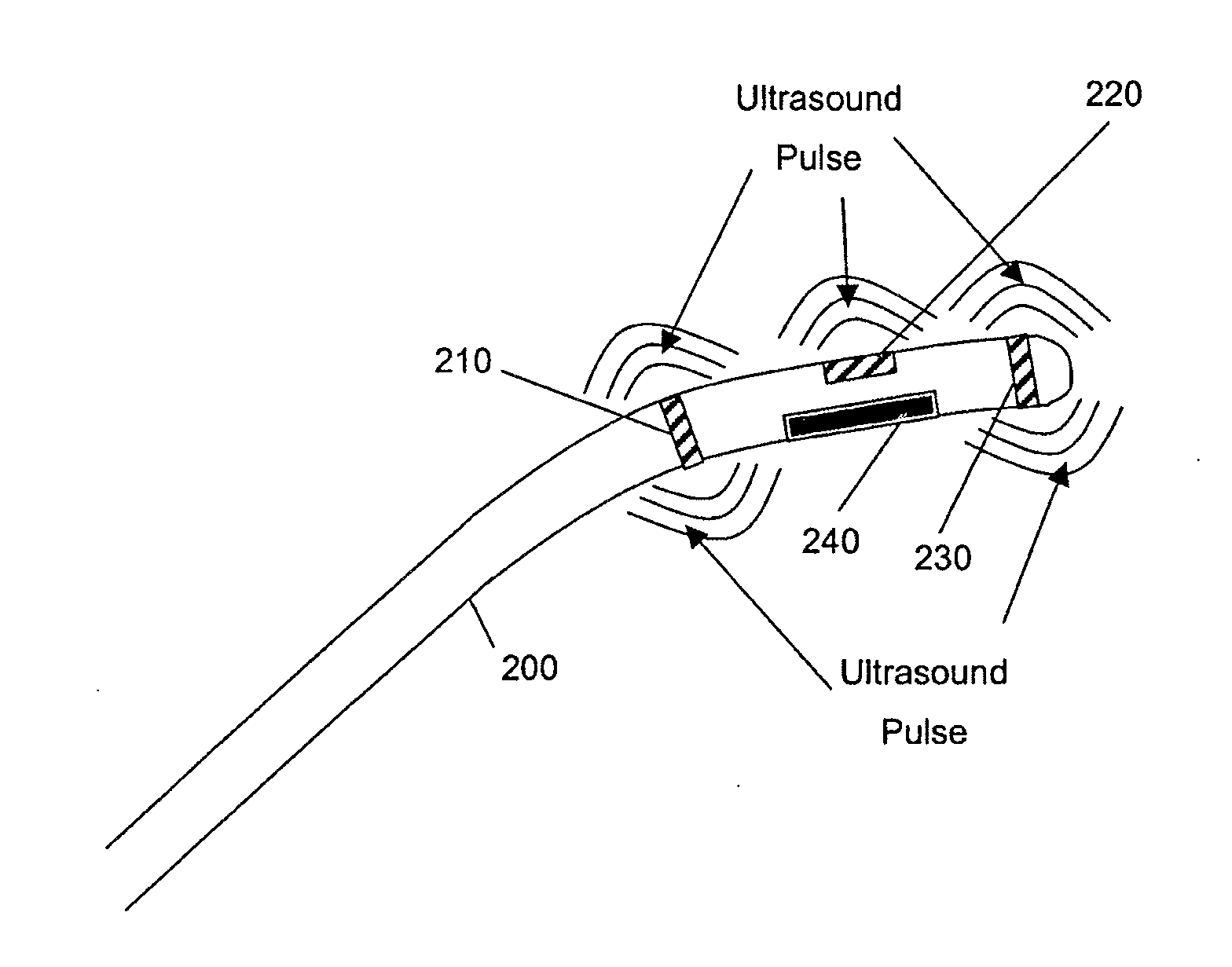
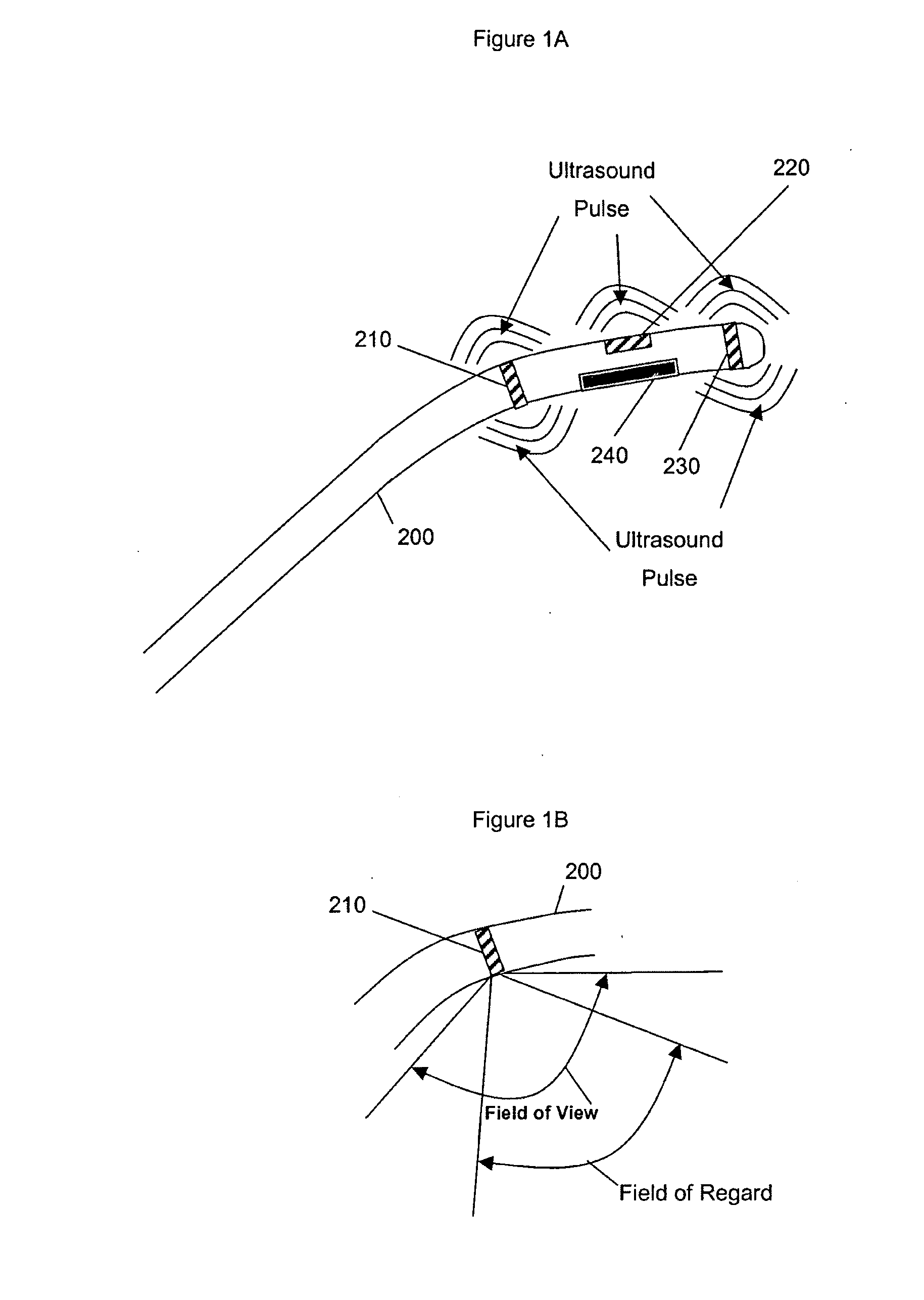
Method for monitoring of medical treatment using pulse-echo ultrasound
InactiveUS7846096B2Improve accuracyOvercome limitationsSurgical needlesChiropractic devicesUltrasound imagingSonification
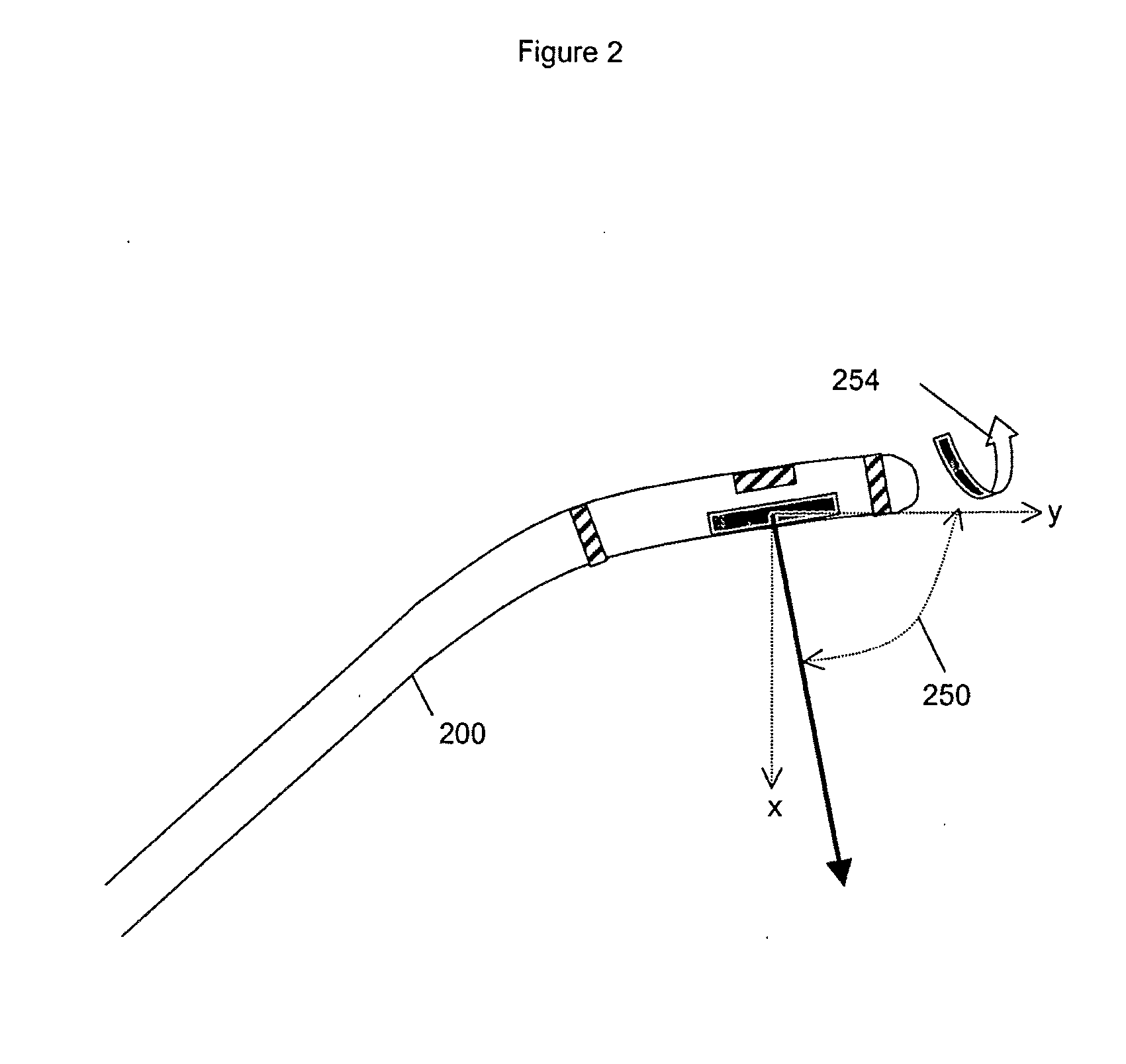
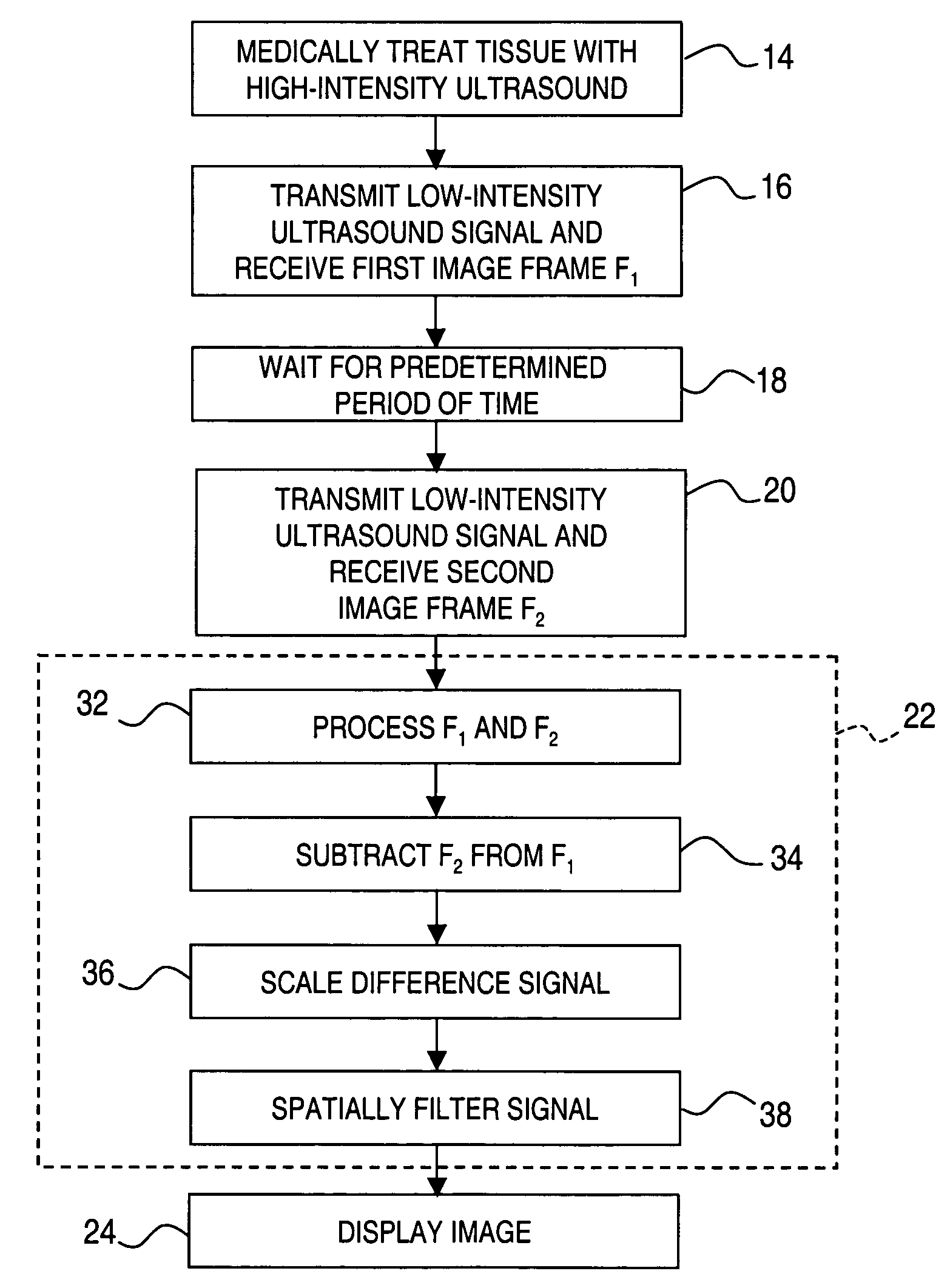
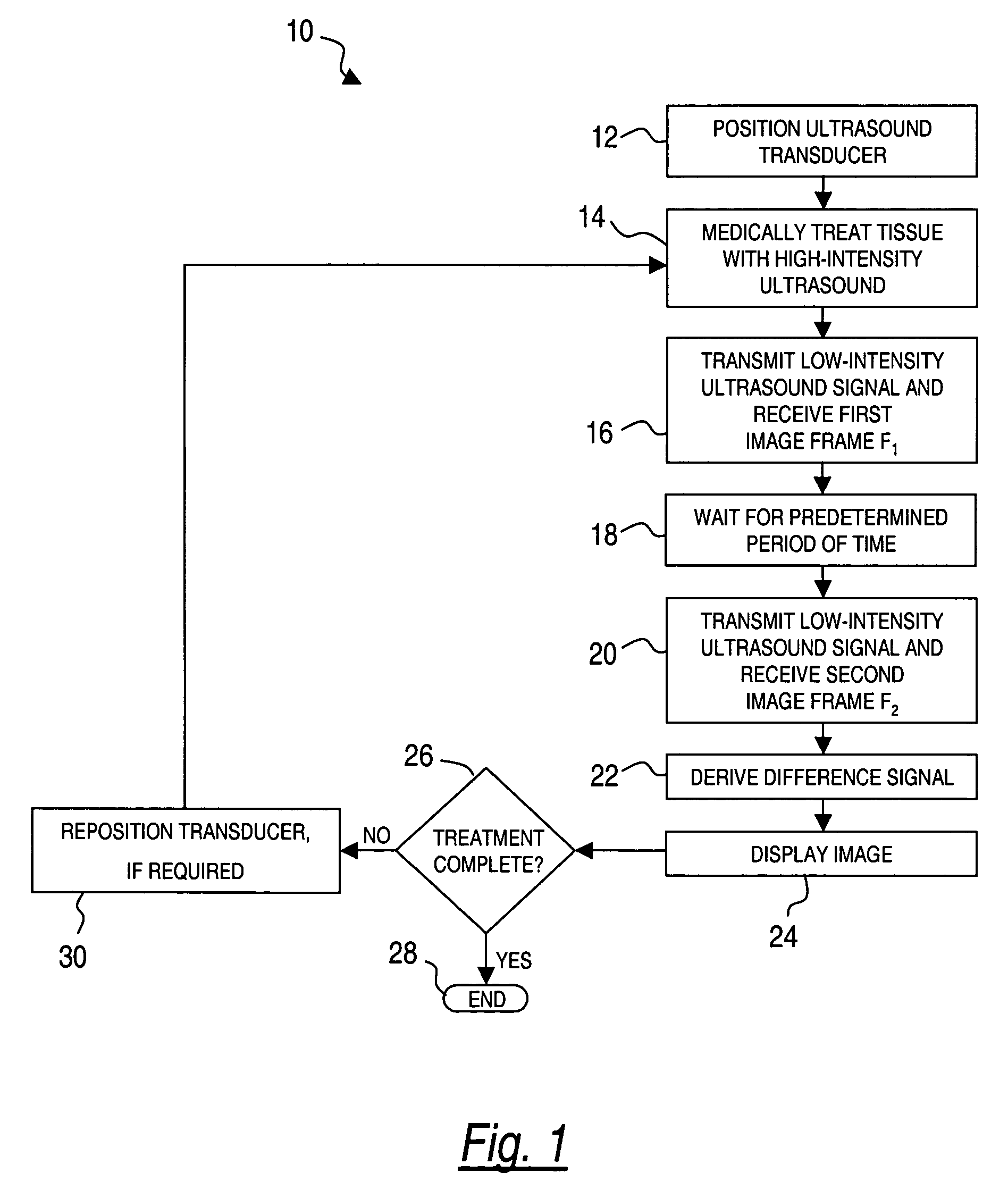
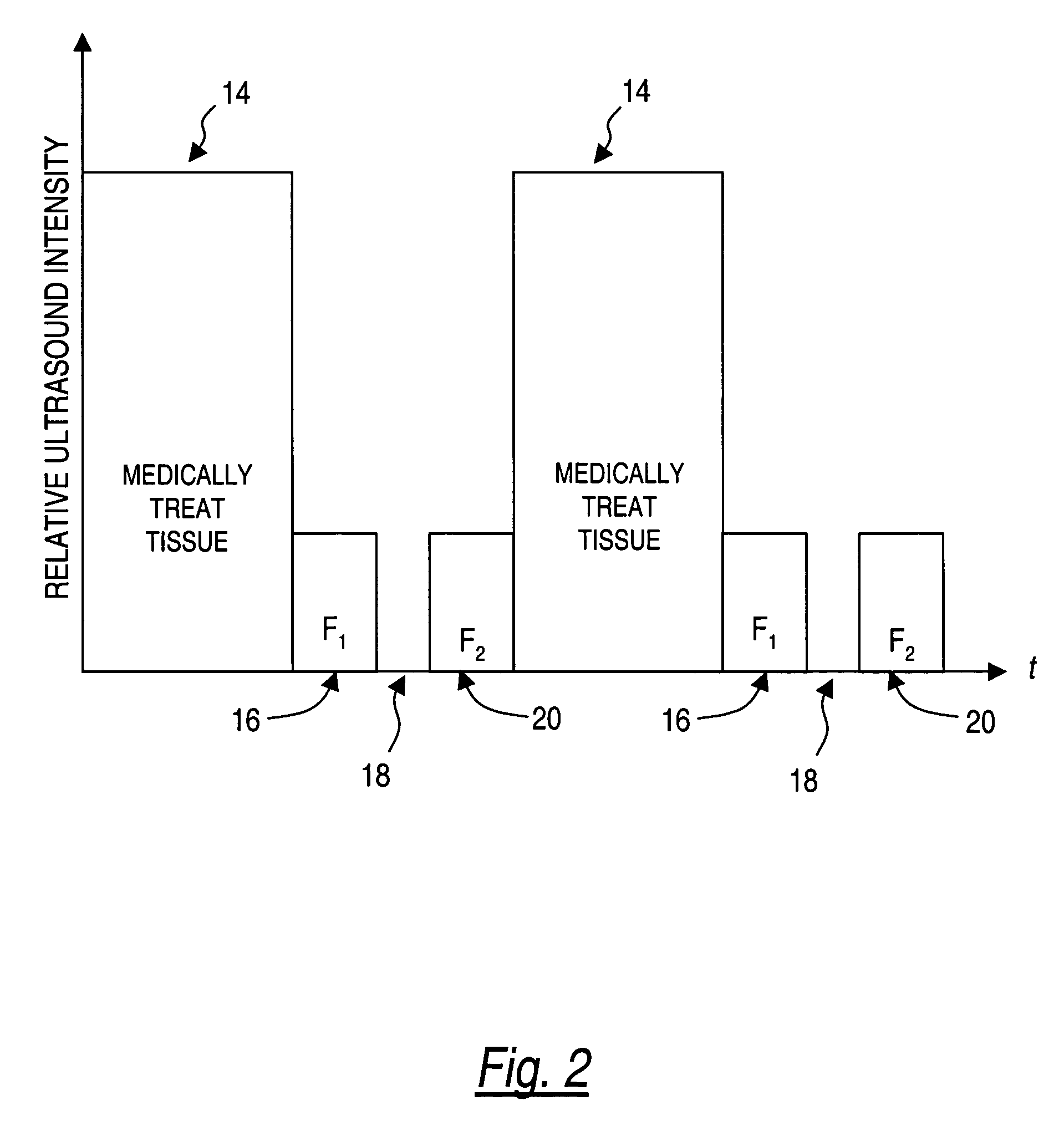
A method for ultrasound imaging of anatomical tissue. A first signal is received from a first imaging ultrasound wave which has been reflected from a location in the anatomical tissue during a first time period. A second signal is received from a second imaging ultrasound wave which has been reflected from the location in the anatomical tissue during a later second time period, following a discrete medical treatment. The second signal is subtracted from the first signal to form a difference signal. The difference signal may be scaled, spatially filtered, then used to generate an indication, the indication showing the effect of the medical treatment in the location in the anatomical tissue.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
Ultrasound treatment and imaging system
InactiveUS20050102009A1Ultrasound therapyOrgan movement/changes detectionSubcutaneous adipose tissueConnective tissue fiber
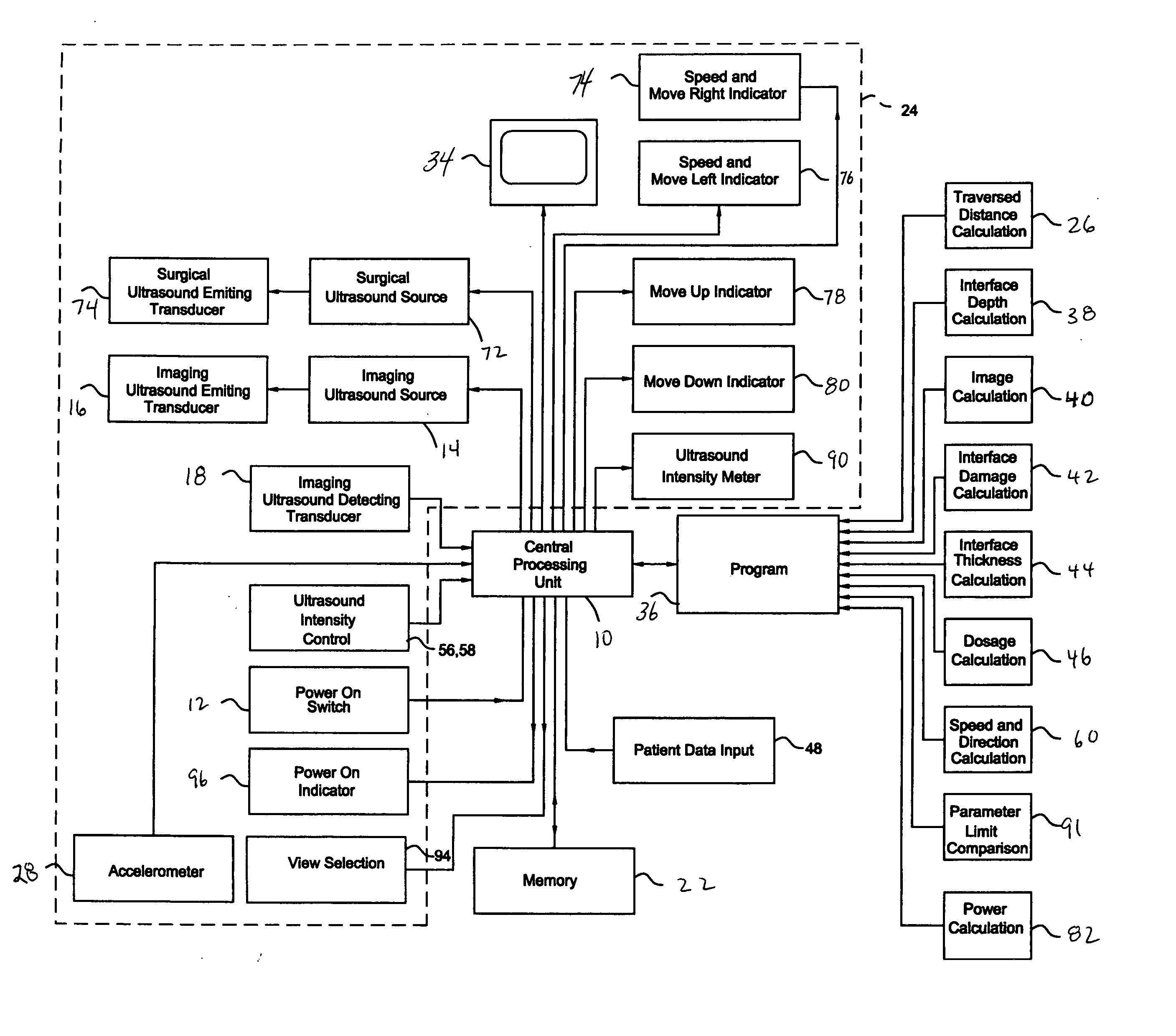
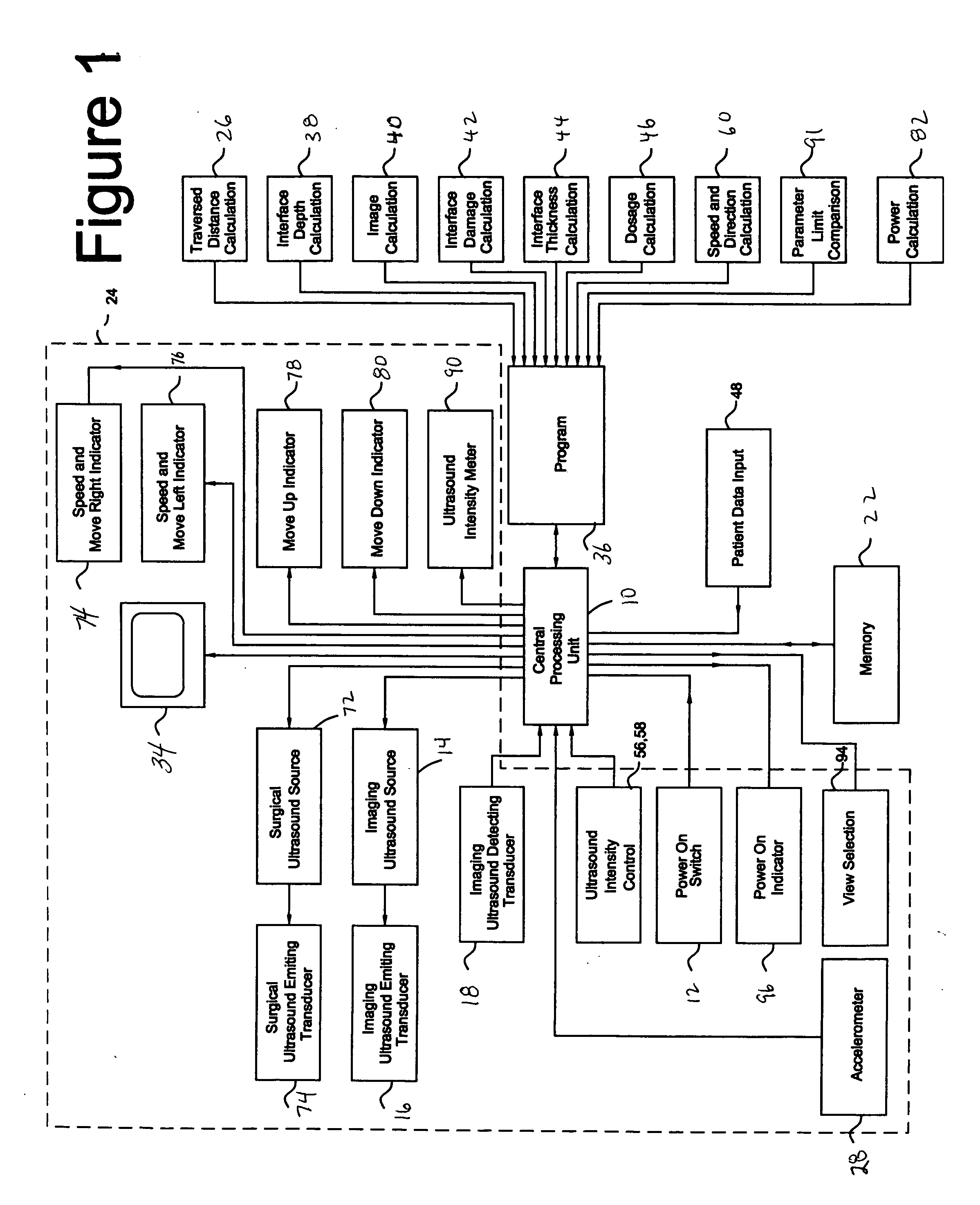
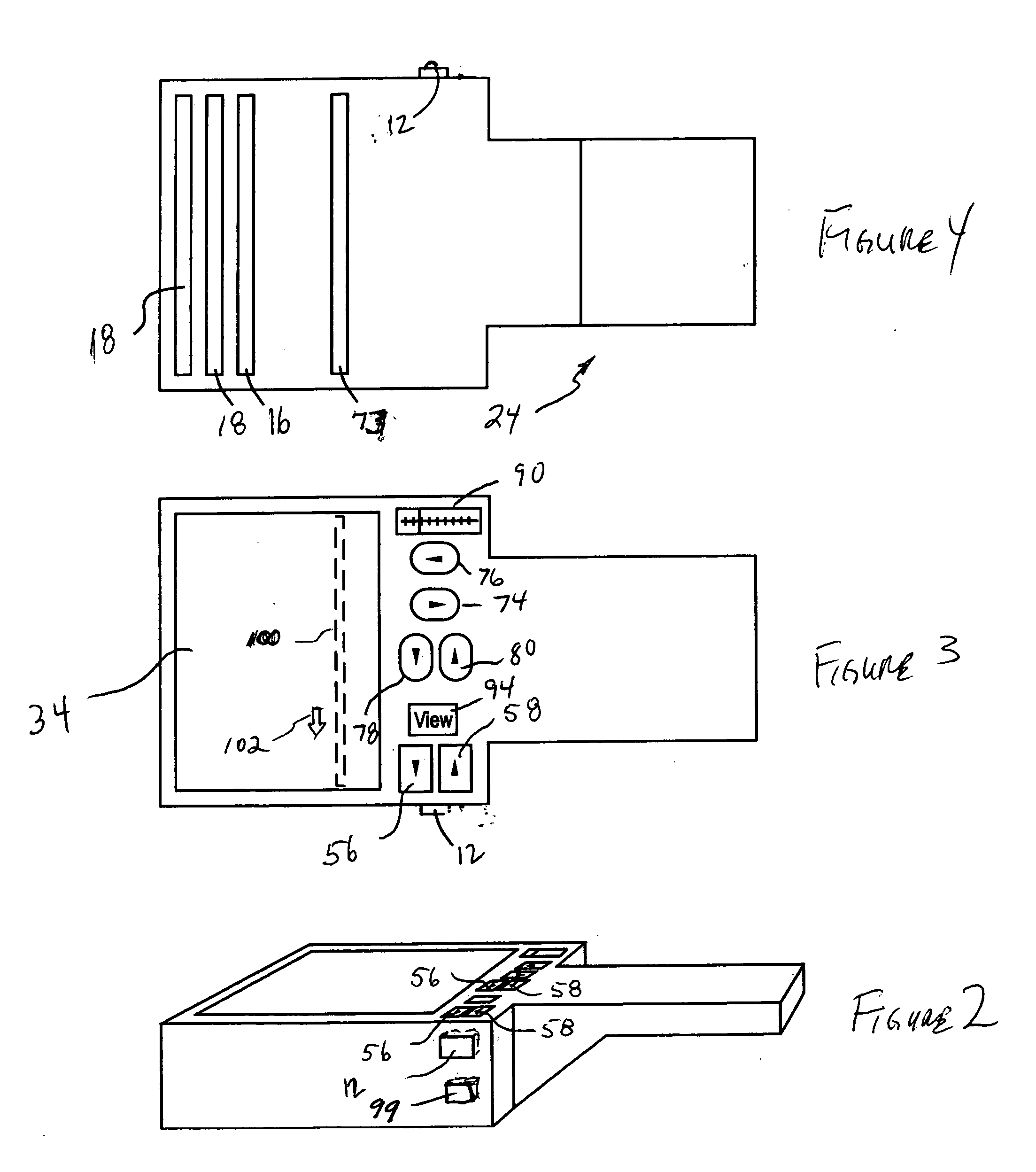
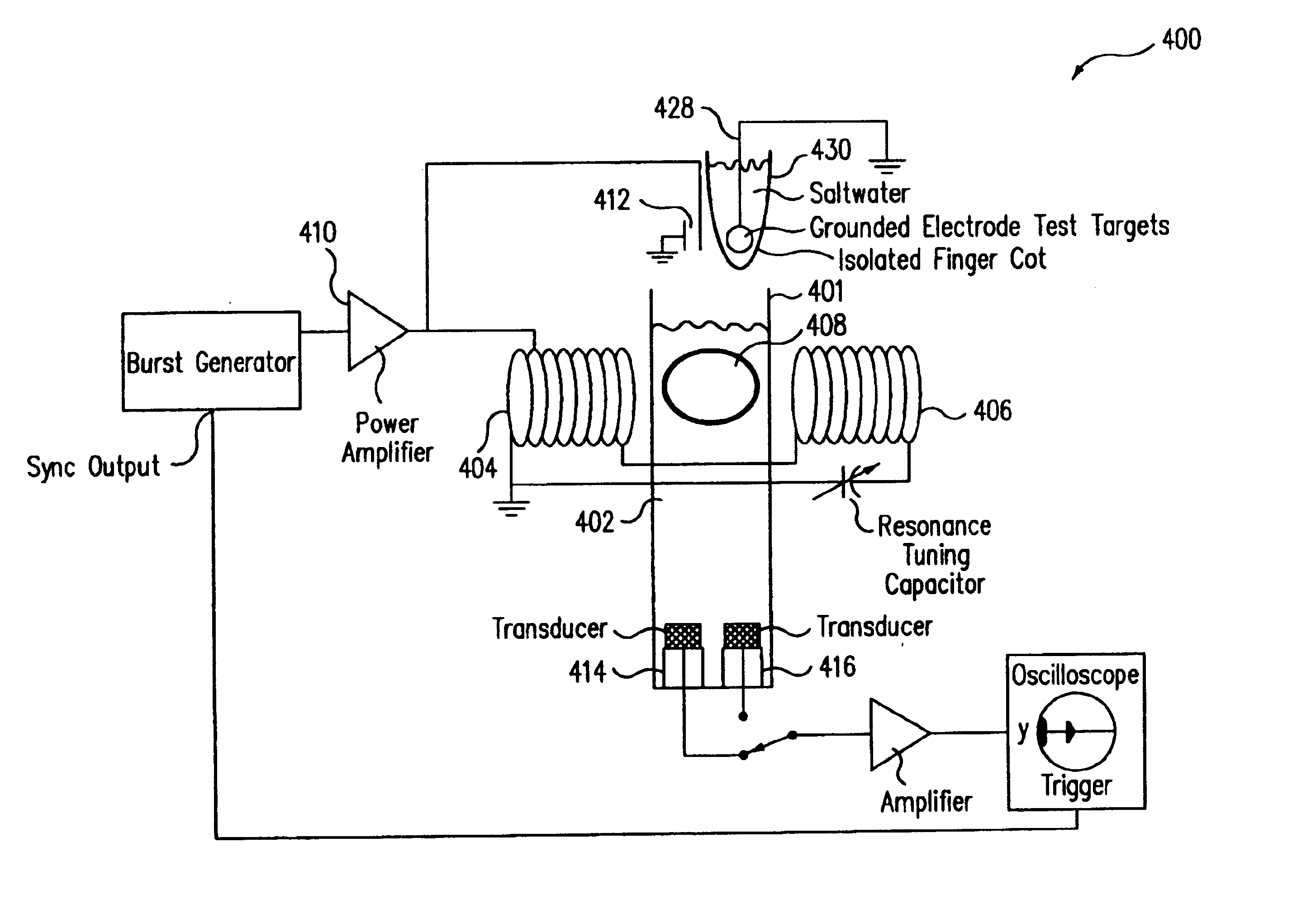
Apparatus for treating cellulite under the surface of the skin comprising a surgical ultrasonic energy source is disclosed. An ultrasonic energy transmitting surface is driven by a surgical ultrasonic energy source. The ultrasonic energy transmitting surface is configured to concentrate ultrasonic energy in the layer of connective tissue lying at the interface between the dermis and the subcutaneous adipose tissue. The surgical ultrasonic energy source is of sufficient power to cause disruption of the layer of connective tissue lying at the interface between the dermis and the subcutaneous adipose tissue during a dosage period. An imaging ultrasonic energy transmitting surface is driven by the imaging ultrasonic energy source. An imaging ultrasonic energy detector is coupled to receive the reflected output of the imaging ultrasonic energy transmitting surface. A computing device is coupled to the output of the imaging ultrasonic energy detector. A program resident in the computing device configures the computing device to generate an image of tissues under the surface of the skin of a patient. A display for displaying the image of tissues under the surface of the skin of the patient provides the person implementing the treatment with first and second images. The first image is a before ultrasound treatment three dimensional or other image and the second image is an after ultrasound treatment image of the tissue is treated. An applicator housing is configured to be held by the hand of an individual, the imaging ultrasonic energy detector is mounted on the applicator housing.
Owner:COSTANTINO PETER
Electromagnetic-acoustic imaging
InactiveUS6974415B2Significant differenceImaging of tissue conductivity properties is especially convenientUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using tomographySignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Sonification
Ultrasound induced by RF irradiation within FDA exposure limits is produced with sufficient signal-to-noise ratio to allow acquisition of sub-millimeter resolution images within practical time frames.
Owner:EMERSON JANE F +3
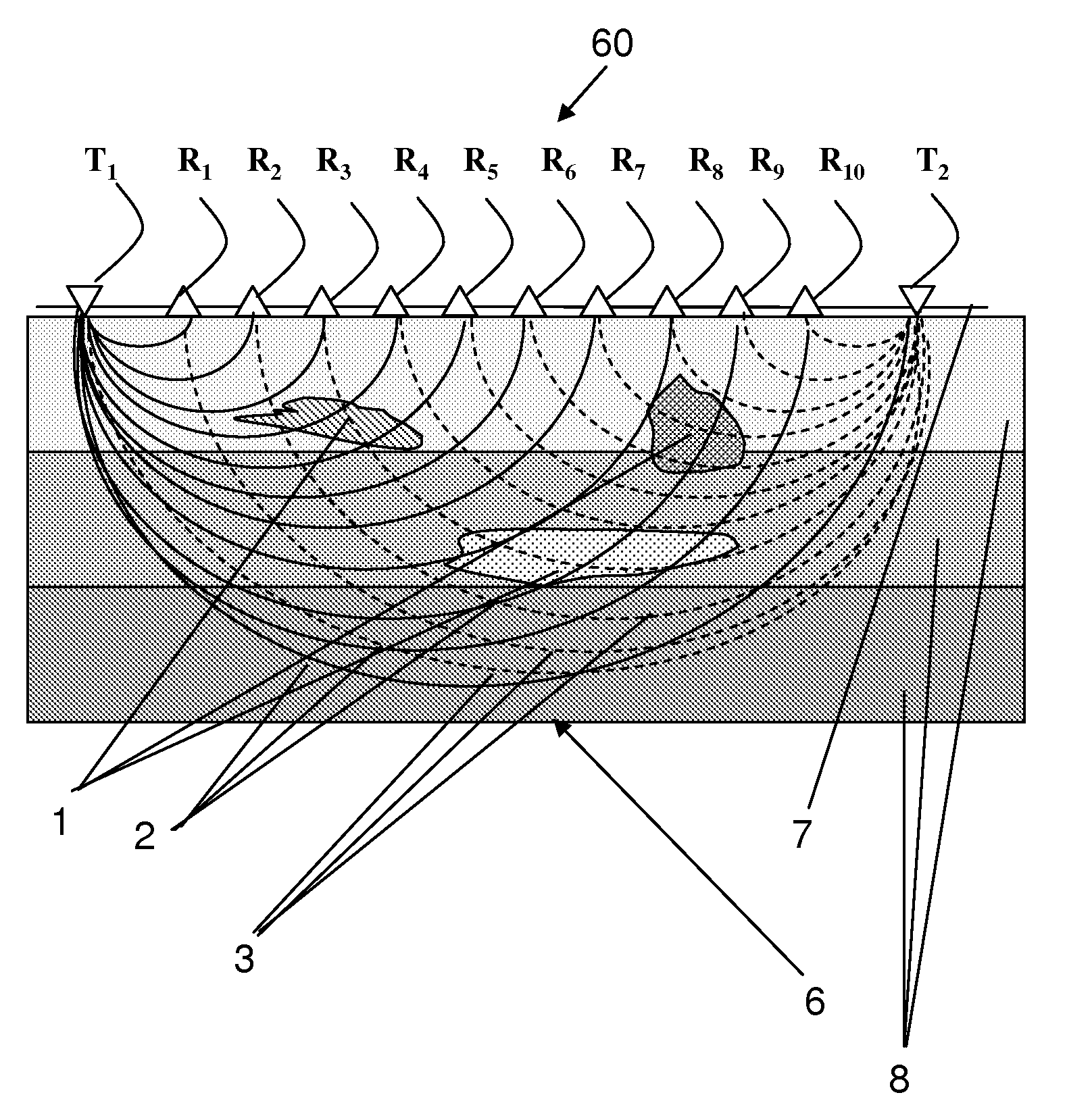
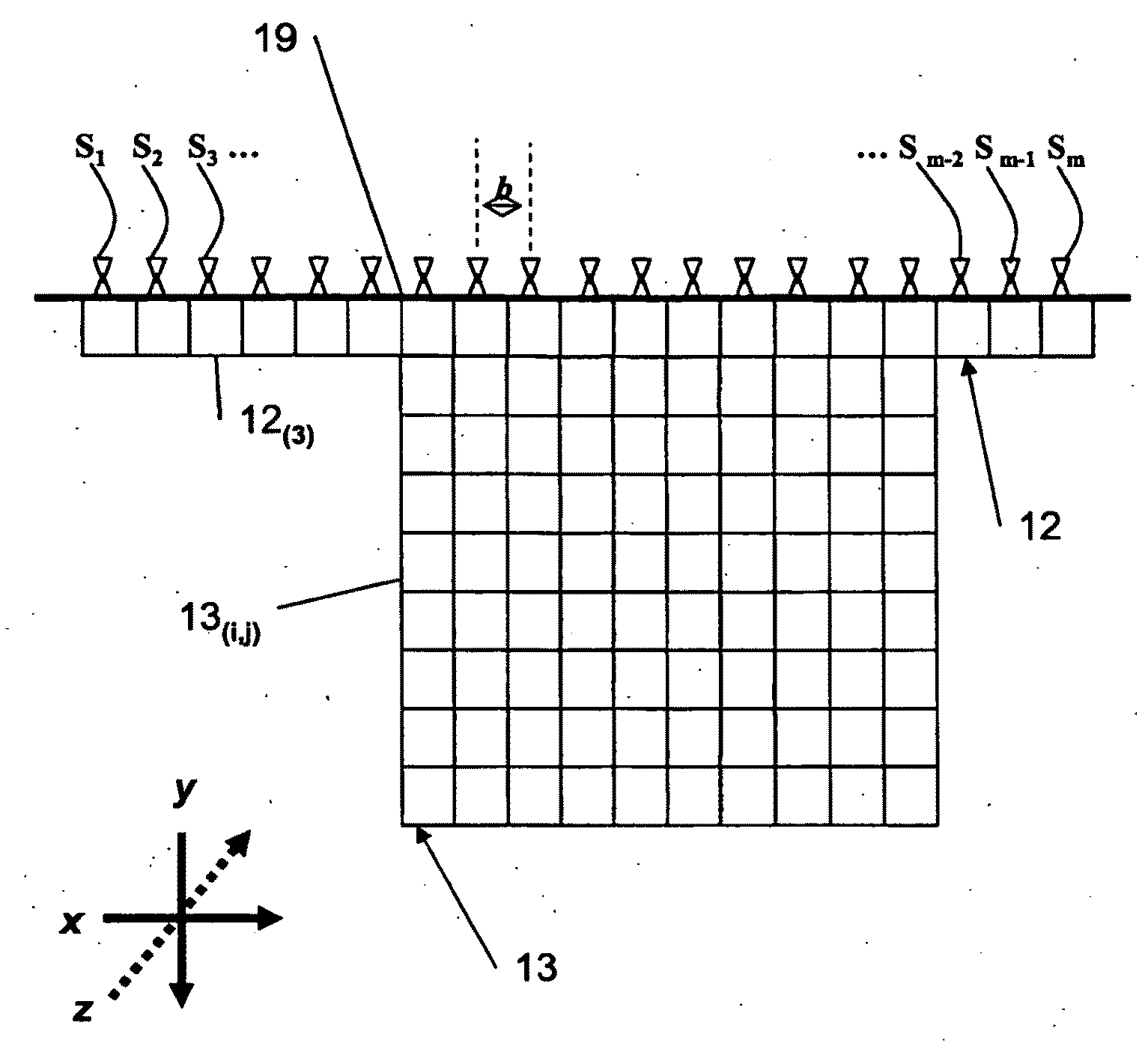
3-d quantitative-imaging ultrasonic method for bone inspections and device for its implementation
InactiveUS20110112404A1Enabling useUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsPorositySonification
The invention is a differential 3D Quantitative-Imaging Ultrasonic Tomography method for inspecting a layered system that is comprised of a heterogeneous object embedded in a volume of space that comprises layers having an acoustic impedance gradient between the layers providing non-linear beams travels. A transducer grid is attached to the surface of the layered system in a unilateral manner. By sequentially changing the distance between transmitter and receiver the fastest travel times of the ultrasonic oscillations are measured. A differential approach provides from the data the longitudinal wave velocities values for each elementary volume that make up an inspected volume. These values are used to construct two and three-dimensional maps of the longitudinal wave velocity values distribution in the inspected volume and the porosity values distribution in the heterogeneous object. By applying statistical treatment to the obtained data the longitudinal wave velocity in the inspected material matrix part is estimated.
Owner:GOUREVITCH ALLA
Intrauterine ultrasound and method for use
InactiveUS20070161905A1High resolutionSuitable imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterMedical imagingImaging ultrasound
A method and apparatus for medical imaging is described. The apparatus applies specifically to accessing and targeting tissue in a small cavity or tightly enclosed space. The medical imaging apparatus or device uses ultrasound waves with elements that act as both a transmitter and receiver in order to image body tissues. The ultrasound is an array or plurality of arrays that may be arranged on the tip on a probe or catheter for insertion into a patient's body.
Owner:GYNESONICS
Micromanipulator control arm for therapeutic and imaging ultrasound transducers
ActiveUS20110054315A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyTherapeutic DevicesControl arm
A medical imaging and therapy device is provided that may include any of a number of features. One feature of the device is that it can image a target tissue volume and apply ultrasound energy to the target tissue volume. In some embodiments, the medical imaging and therapy device is configured controllably apply ultrasound energy into the prostate by maintaining a cavitational bubble cloud generated by an ultrasound therapy system within an image of the prostate generated by an imaging system. The medical imaging and therapy device can be used in therapeutic applications such as Histotripsy, Lithotripsy, and HIFU, for example. Methods associated with use of the medical imaging and therapy device are also covered.
Owner:HISTOSONICS +1
Ultrasonic treatment equipment
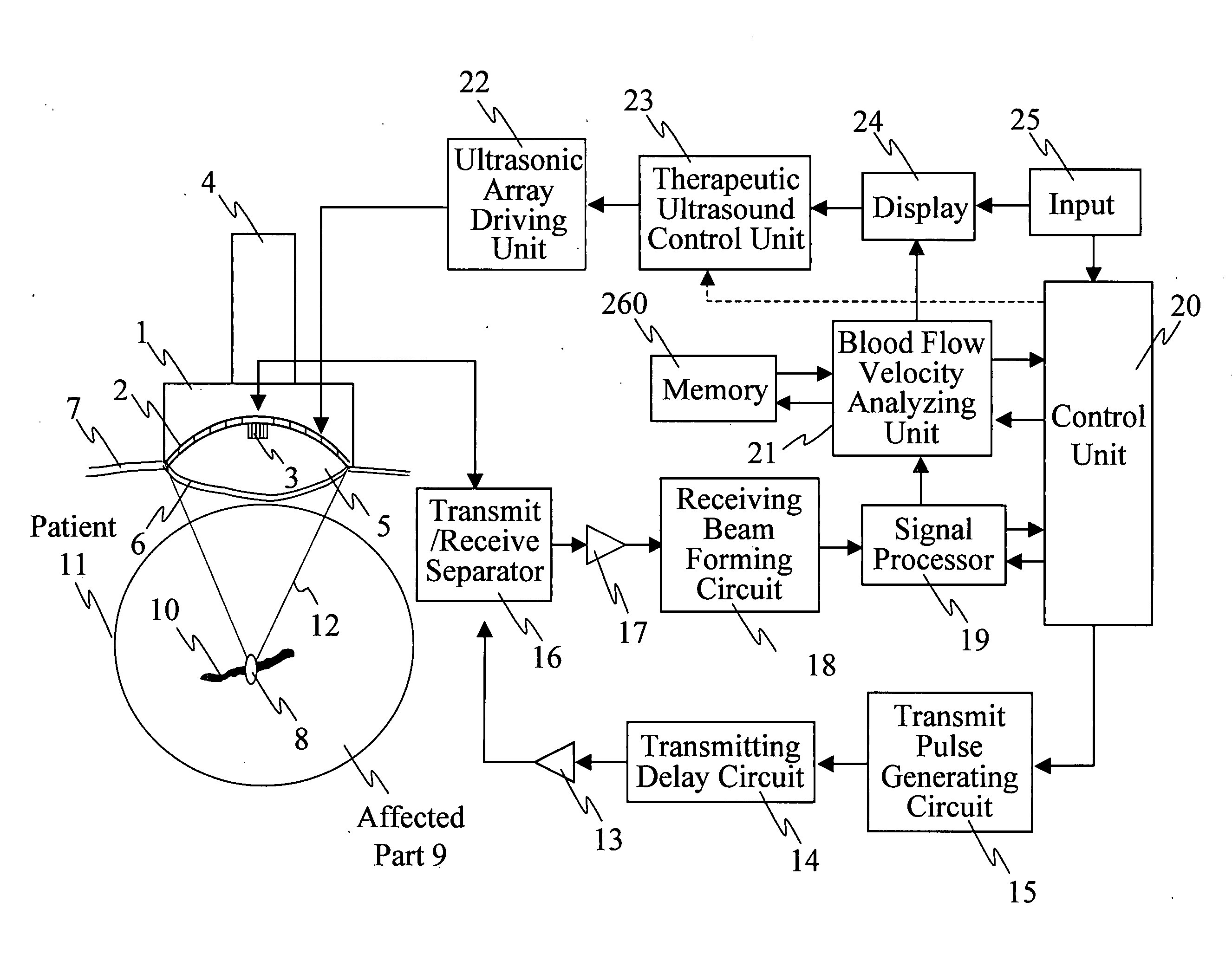
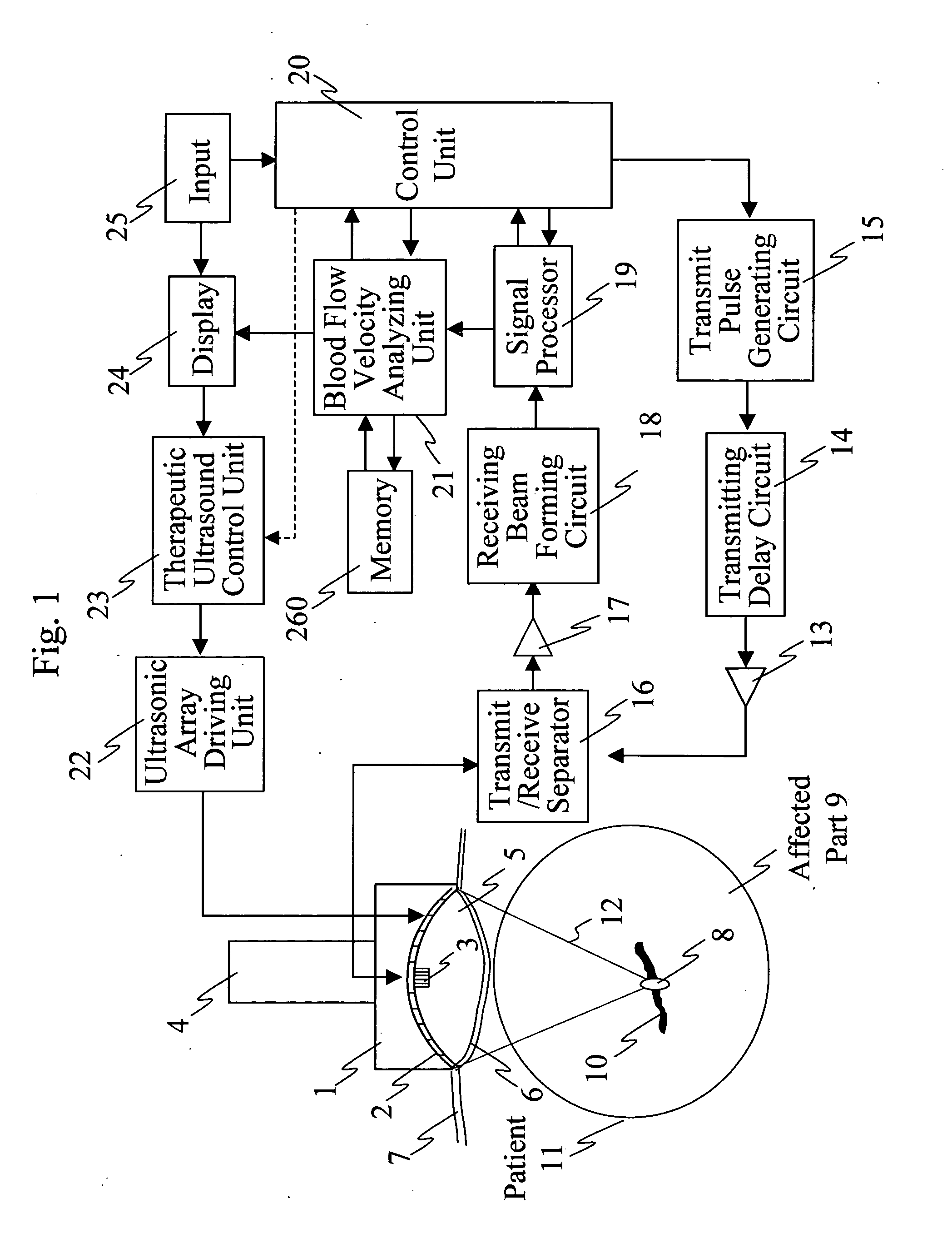
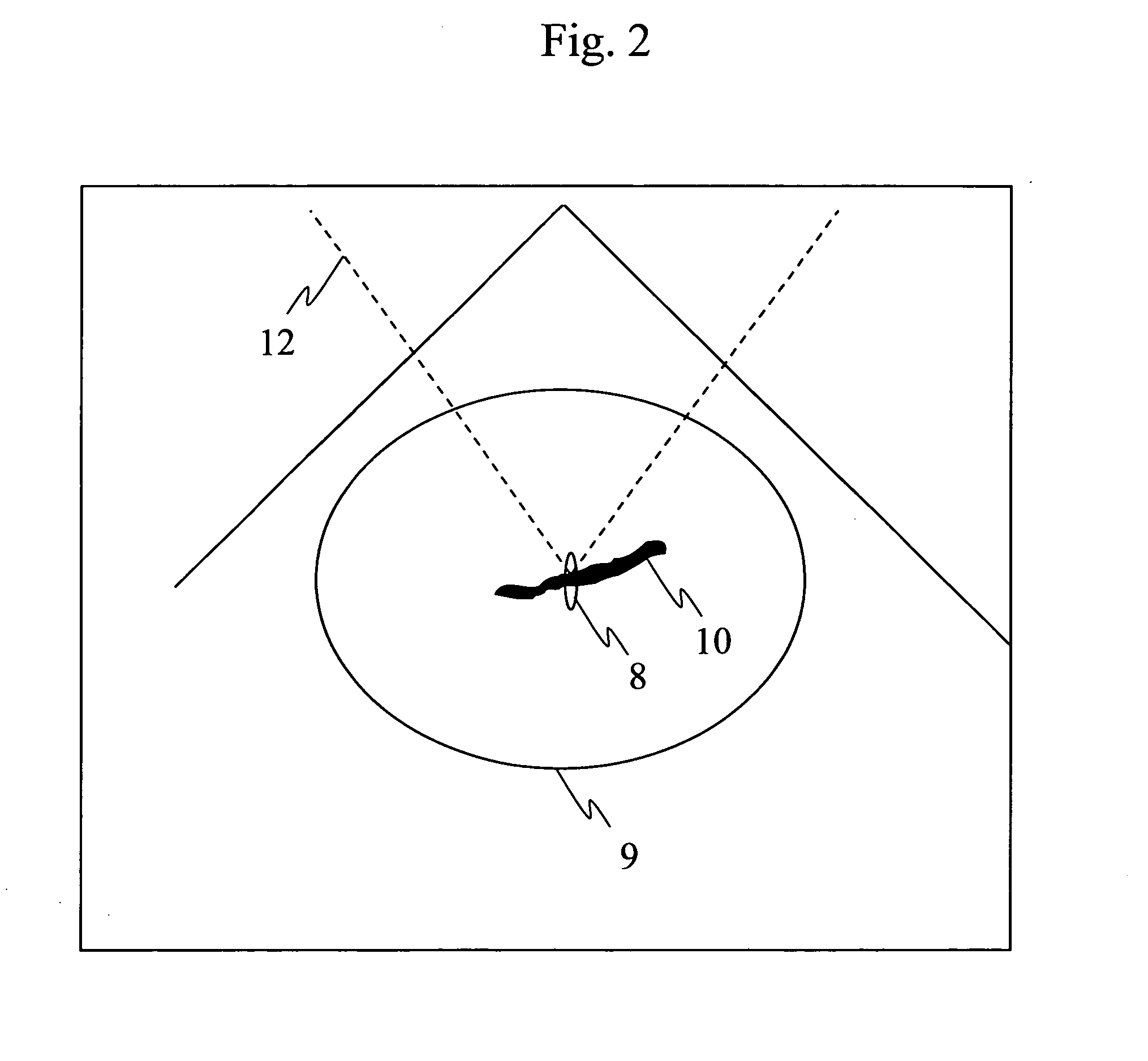
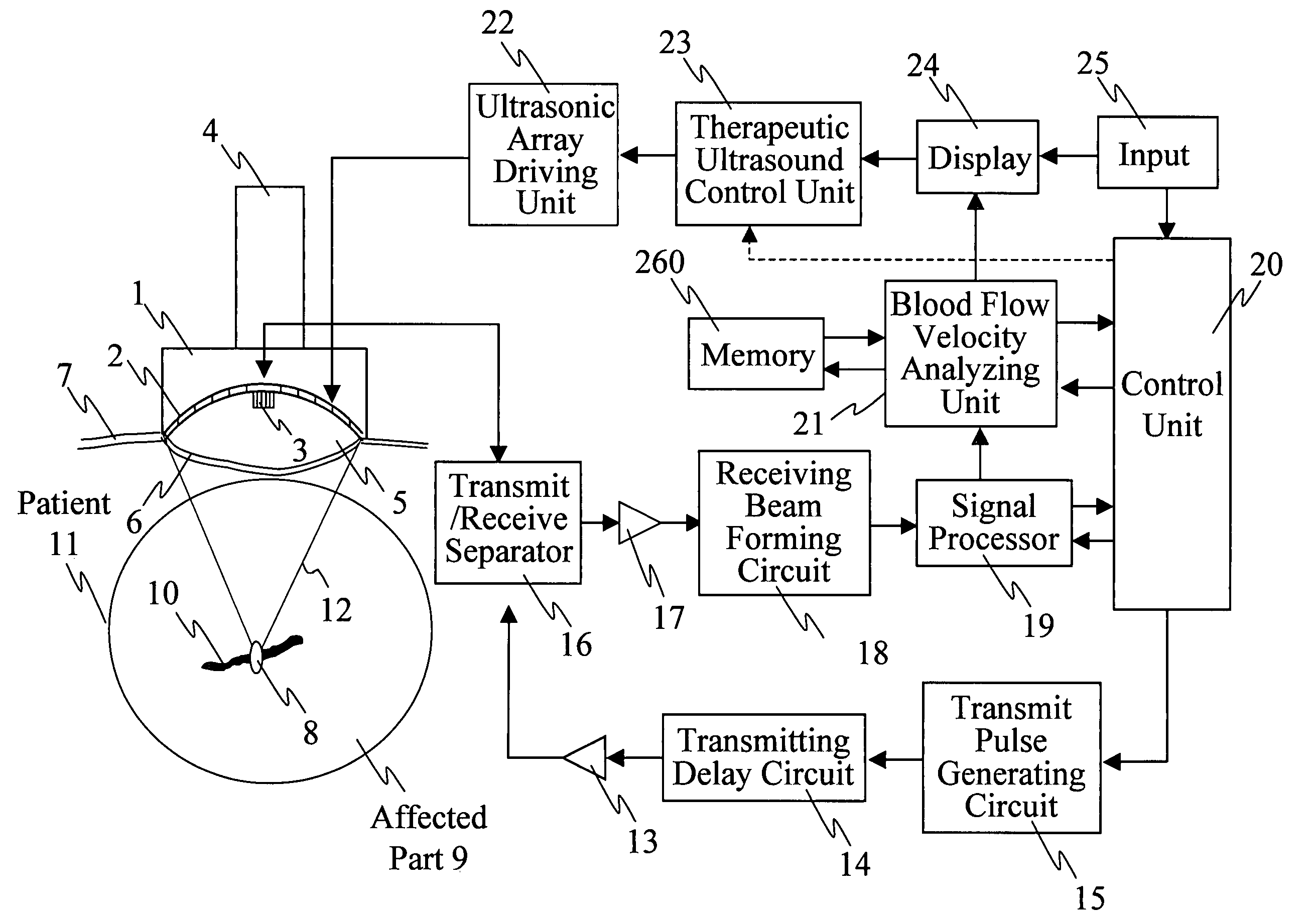
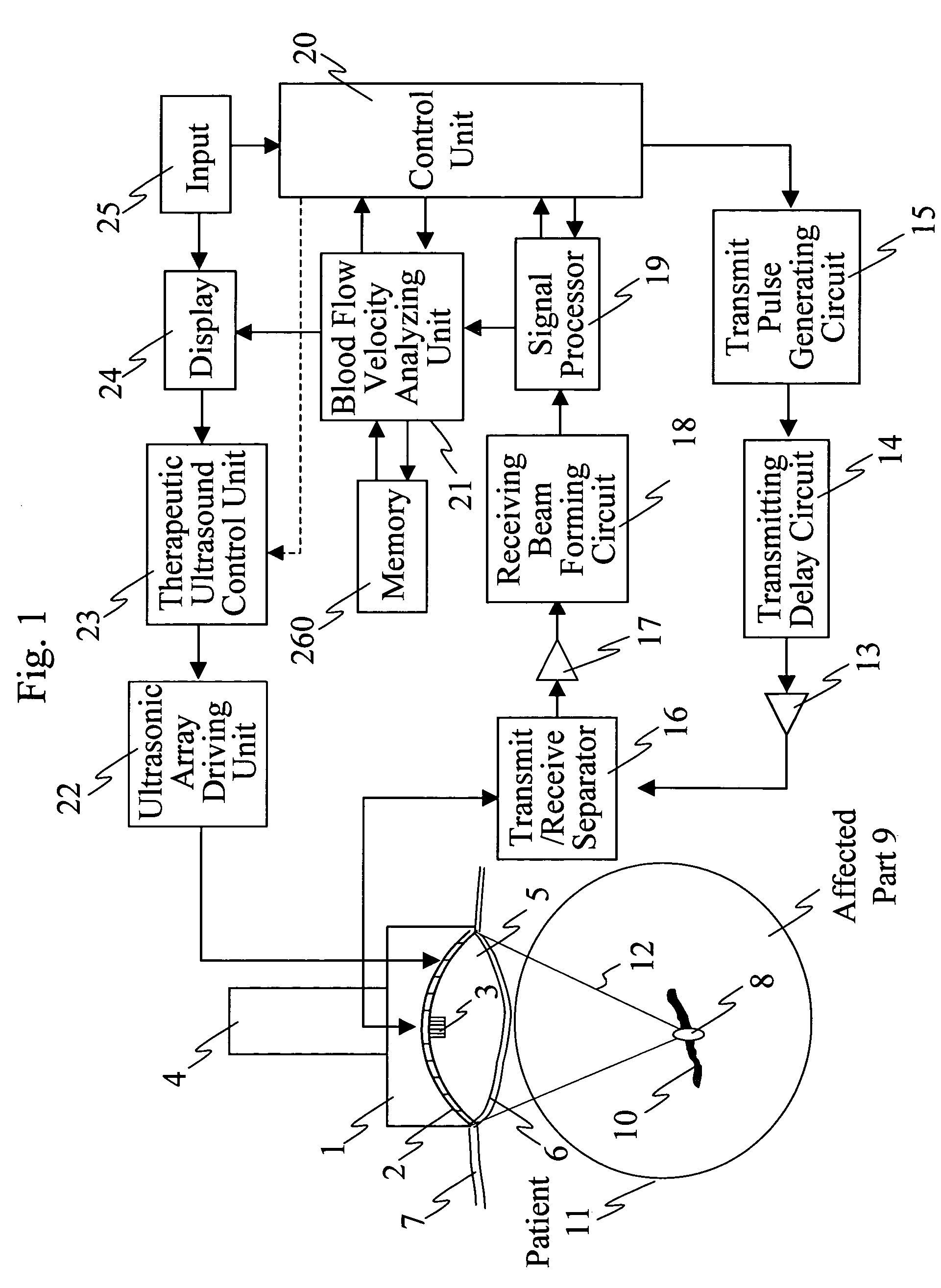
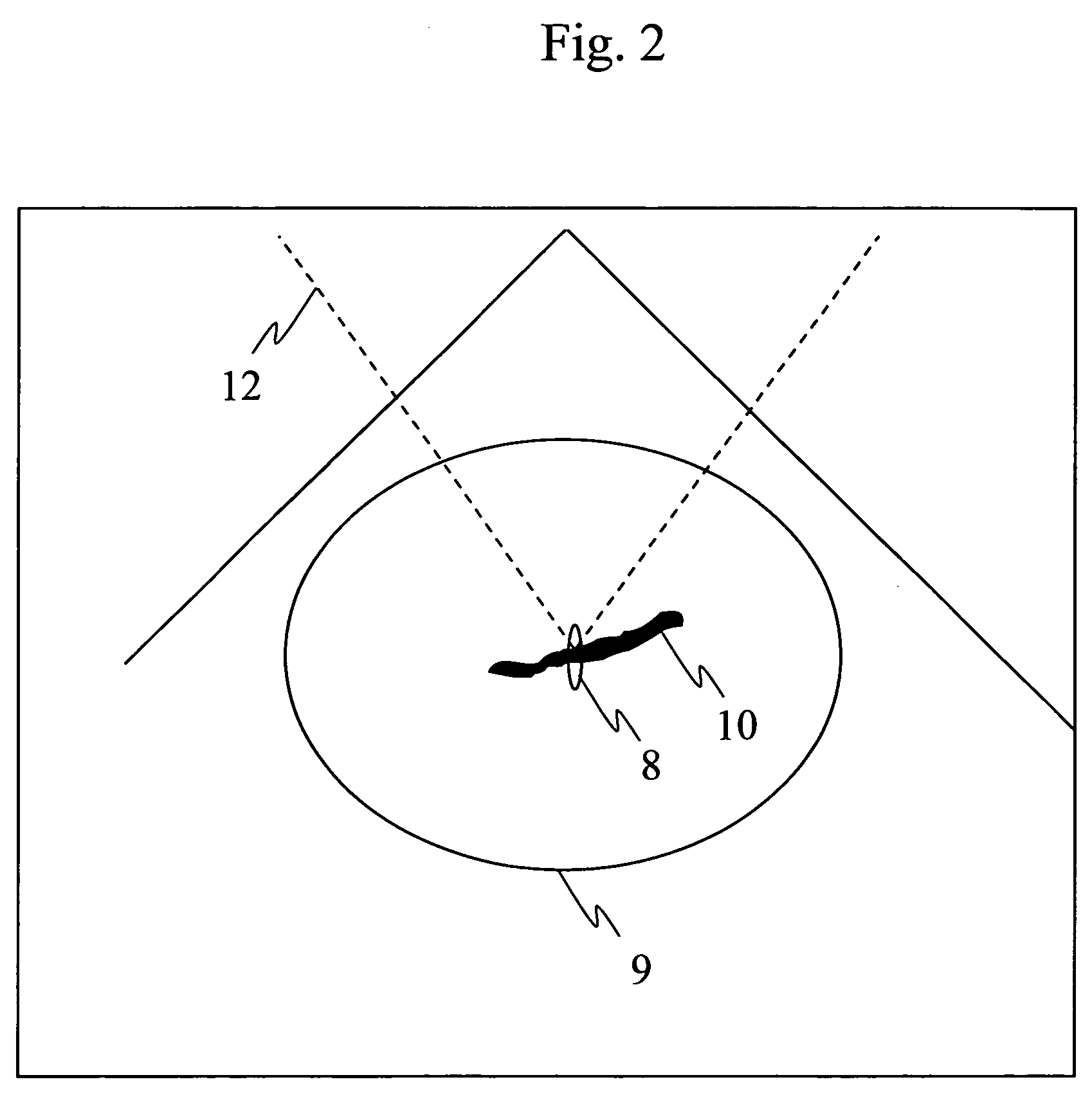
InactiveUS20070161897A1Accurate exposureEasy to shrinkUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasonic sensorMedicine
Ultrasonic treatment equipment is provided which repeats therapeutic ultrasound exposure while measuring a degree of vessel constriction on a therapeutic ultrasound exposure basis. This equipment includes: a therapeutic ultrasonic transducer 2 which exposes a blood vessel of an affected part to a focused therapeutic ultrasonic wave for a specified period of exposure time; an imaging ultrasonic probe 3 which images an ultrasound tomographic image of the affected part; a display unit 24 which displays the ultrasound tomographic image; means 21 for detecting a blood flow signal from a signal received by the imaging ultrasonic probe and determining the blood flow velocity of the blood vessels of the affected part; means 21 for calculating a rate of change in blood flow velocity during the exposure to the therapeutic ultrasonic wave or before and after the exposure to the therapeutic ultrasonic wave; and means 23 for controlling exposure conditions of the therapeutic ultrasonic wave on the basis of the rate of change in blood flow velocity, and thereby controlling the therapeutic ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
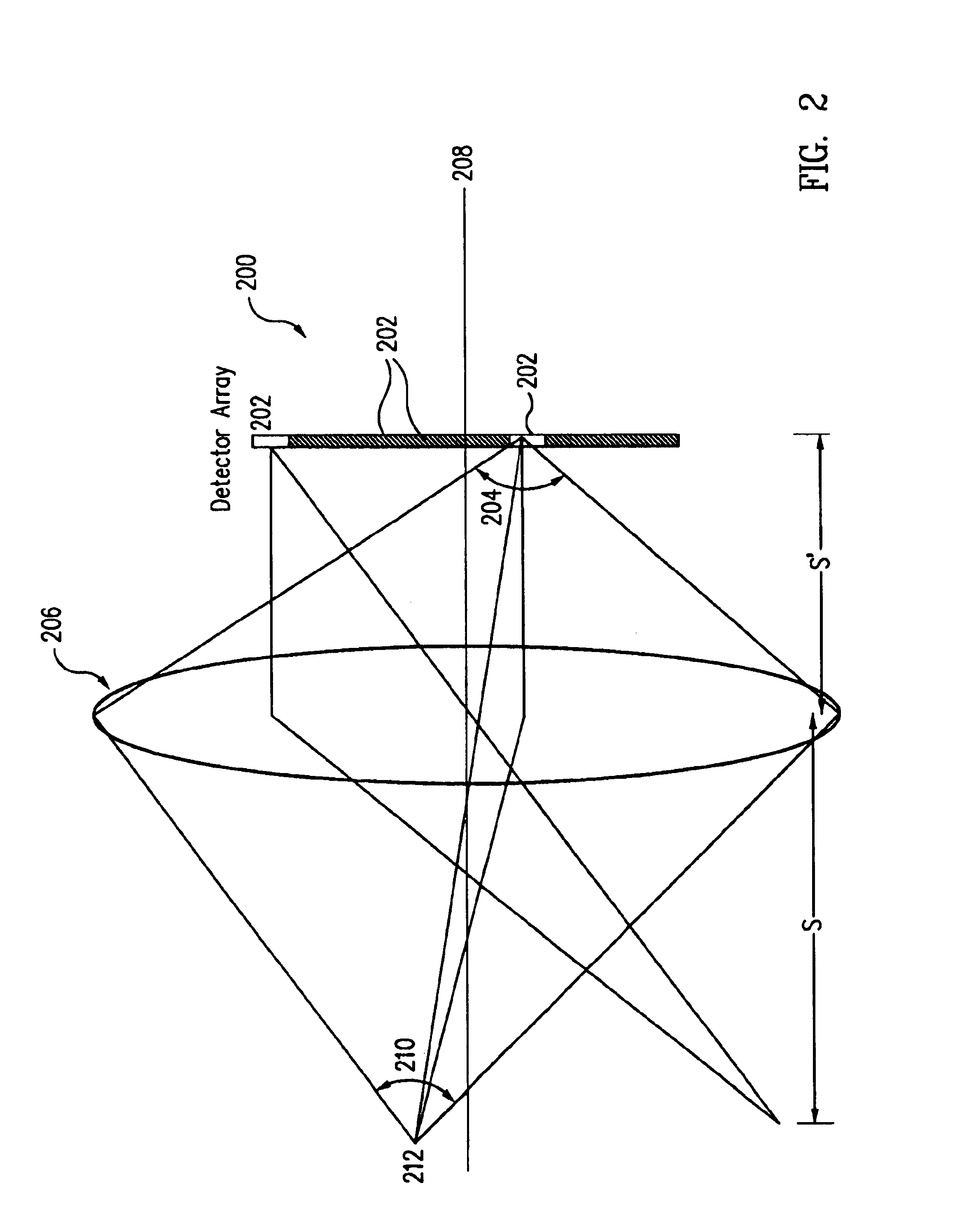
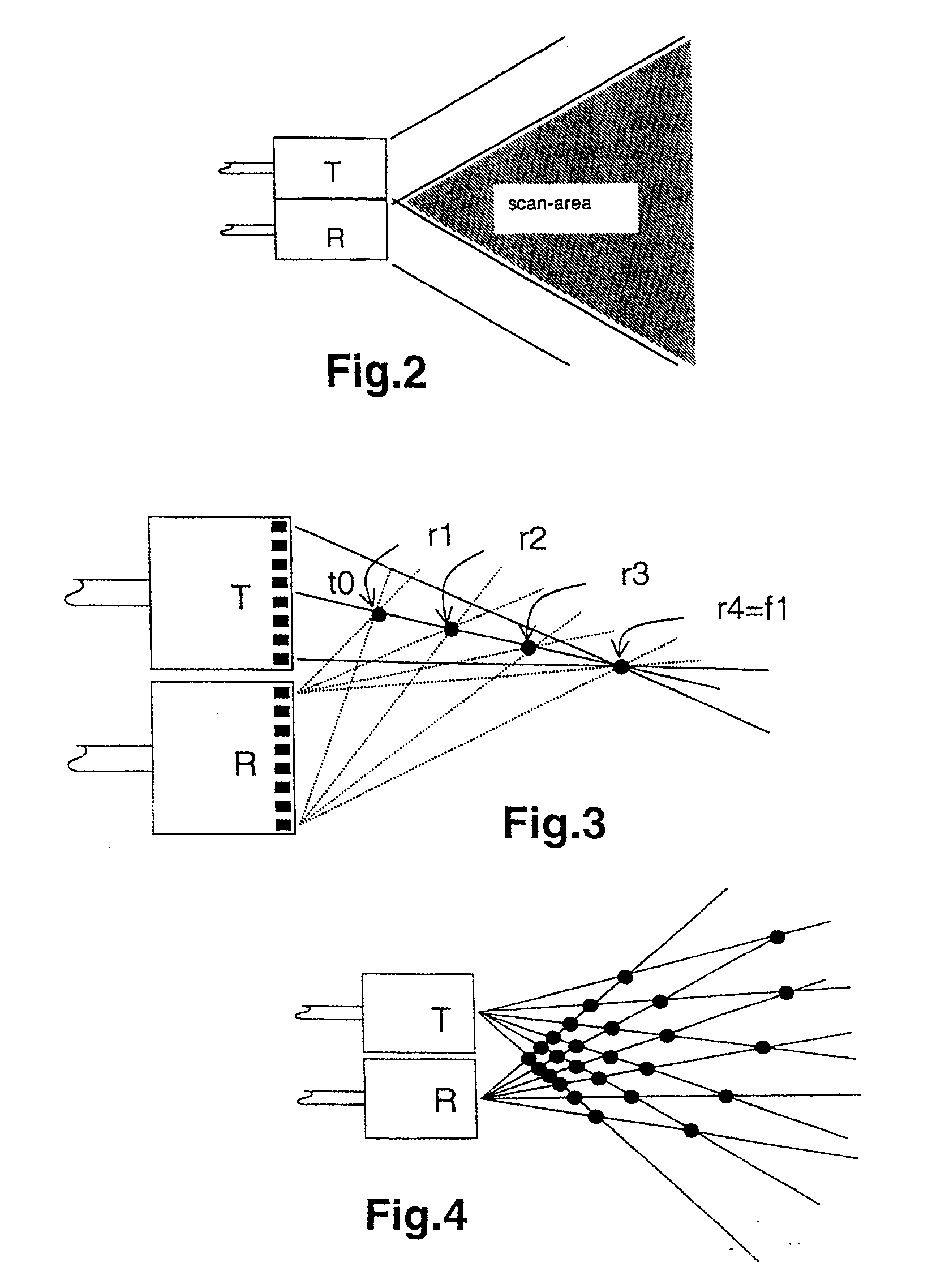
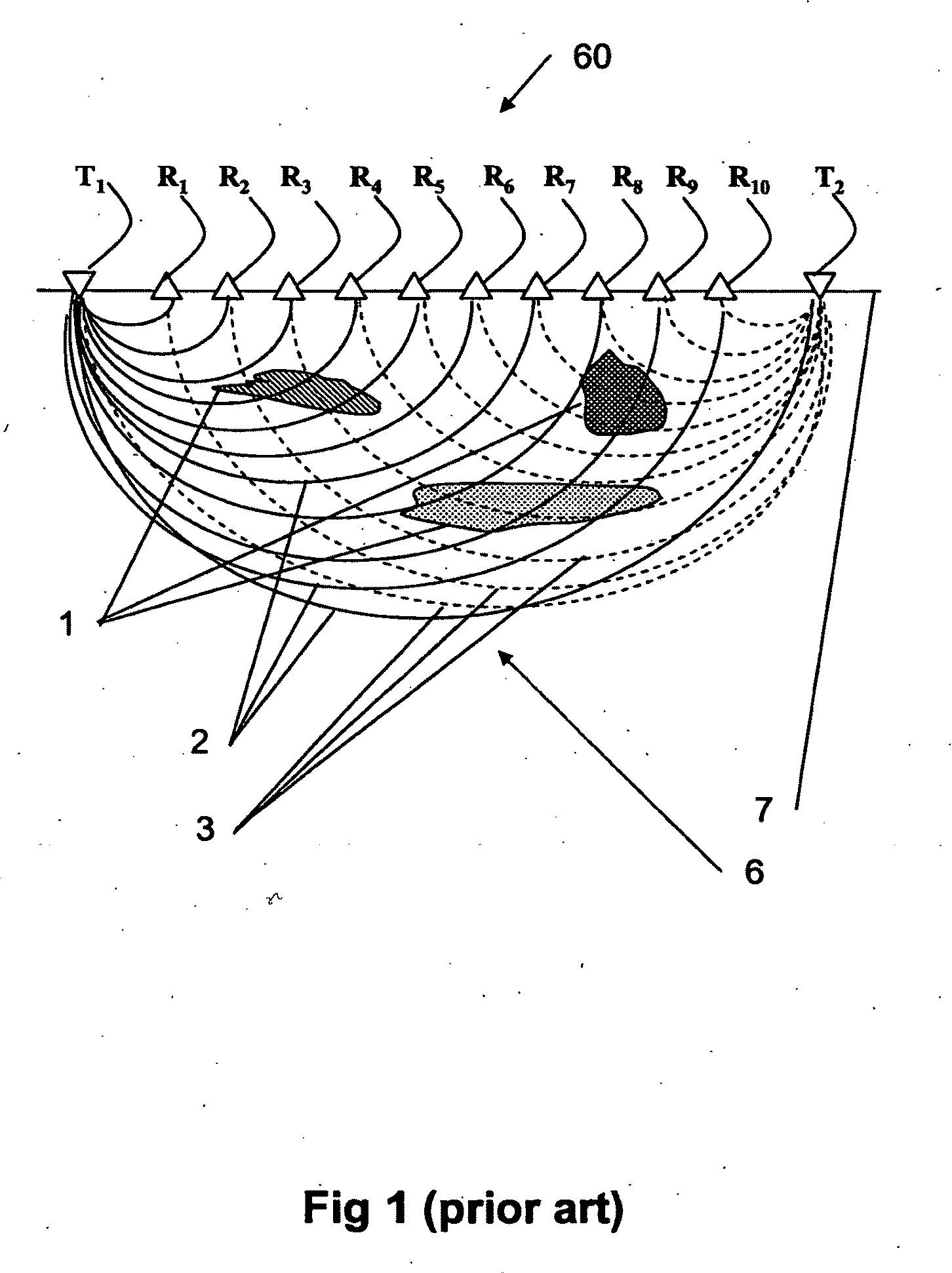
Ultrasound system and ultrasound diagnostic apparatus for imaging scatterers in a medium
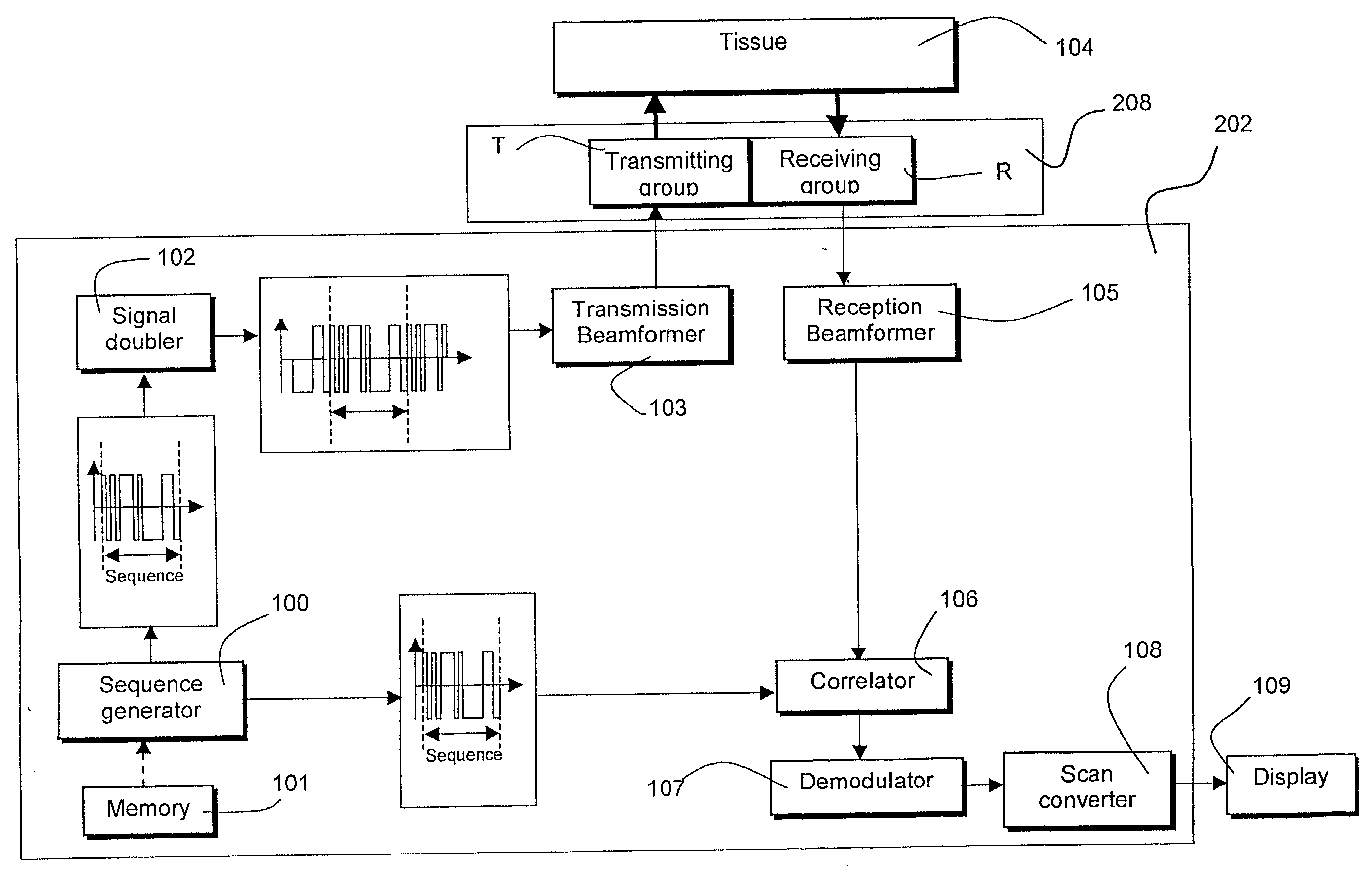
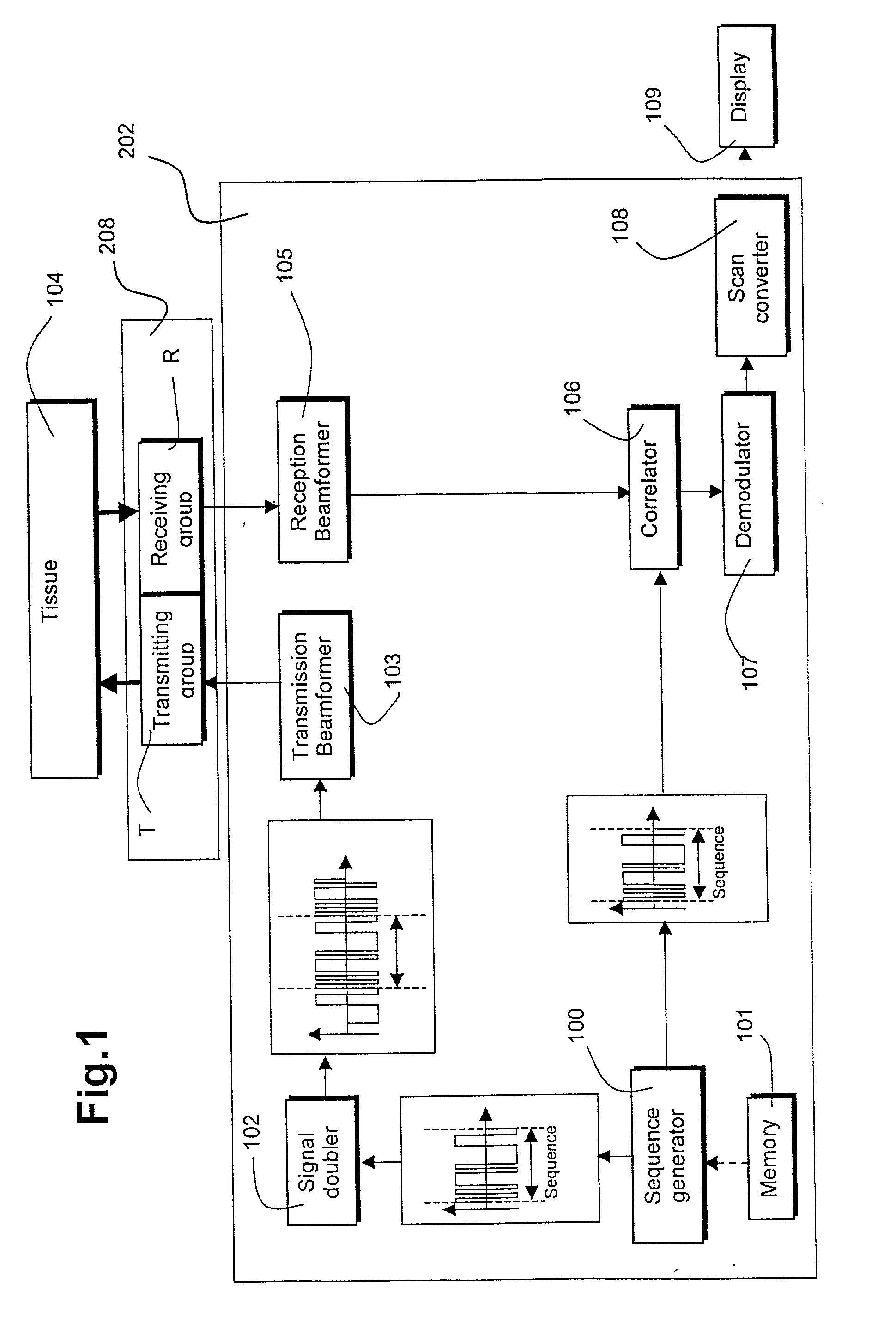
InactiveUS20020049381A1Processing detected response signalHeart/pulse rate measurement devicesUltrasound imagingSonification
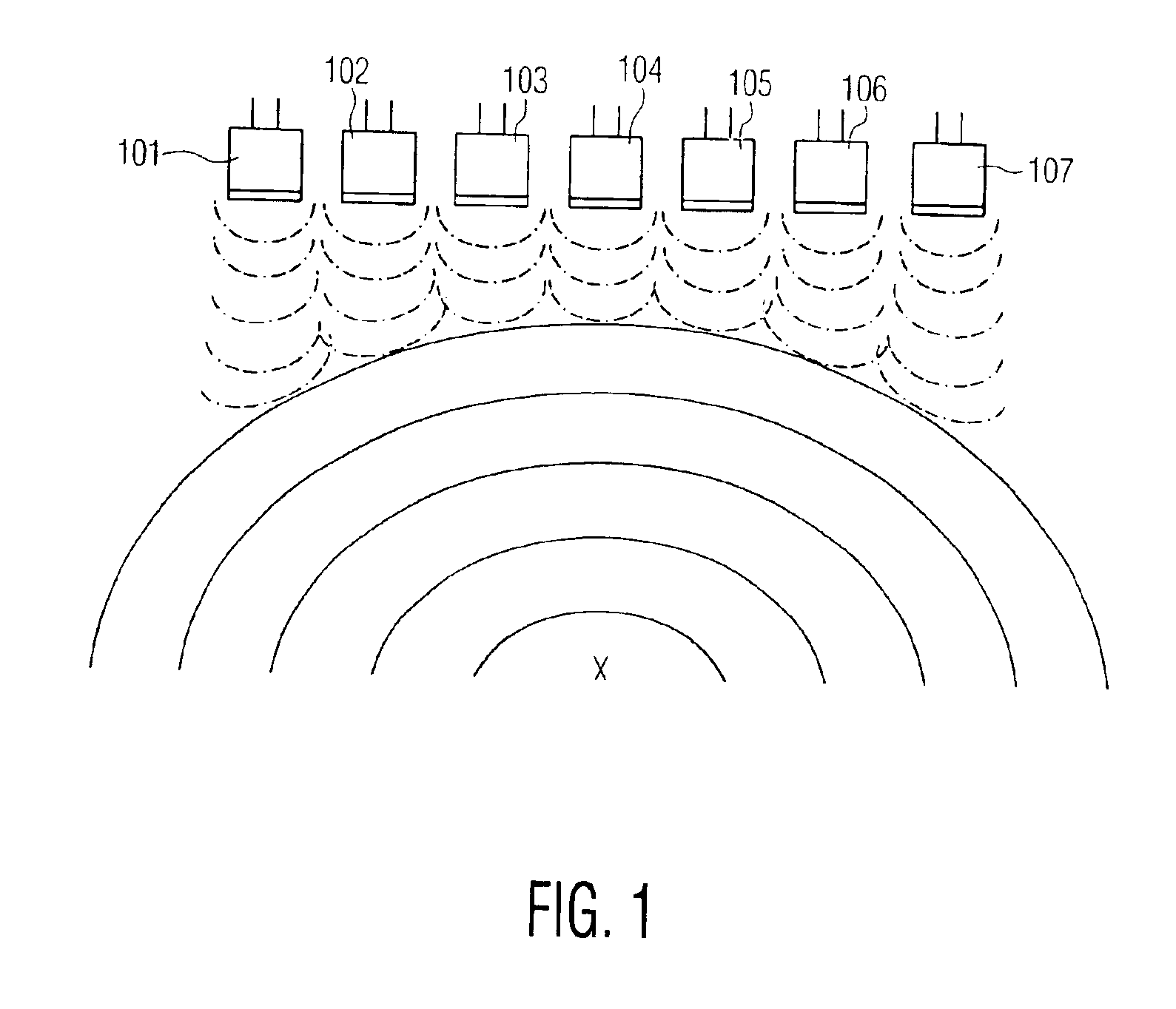
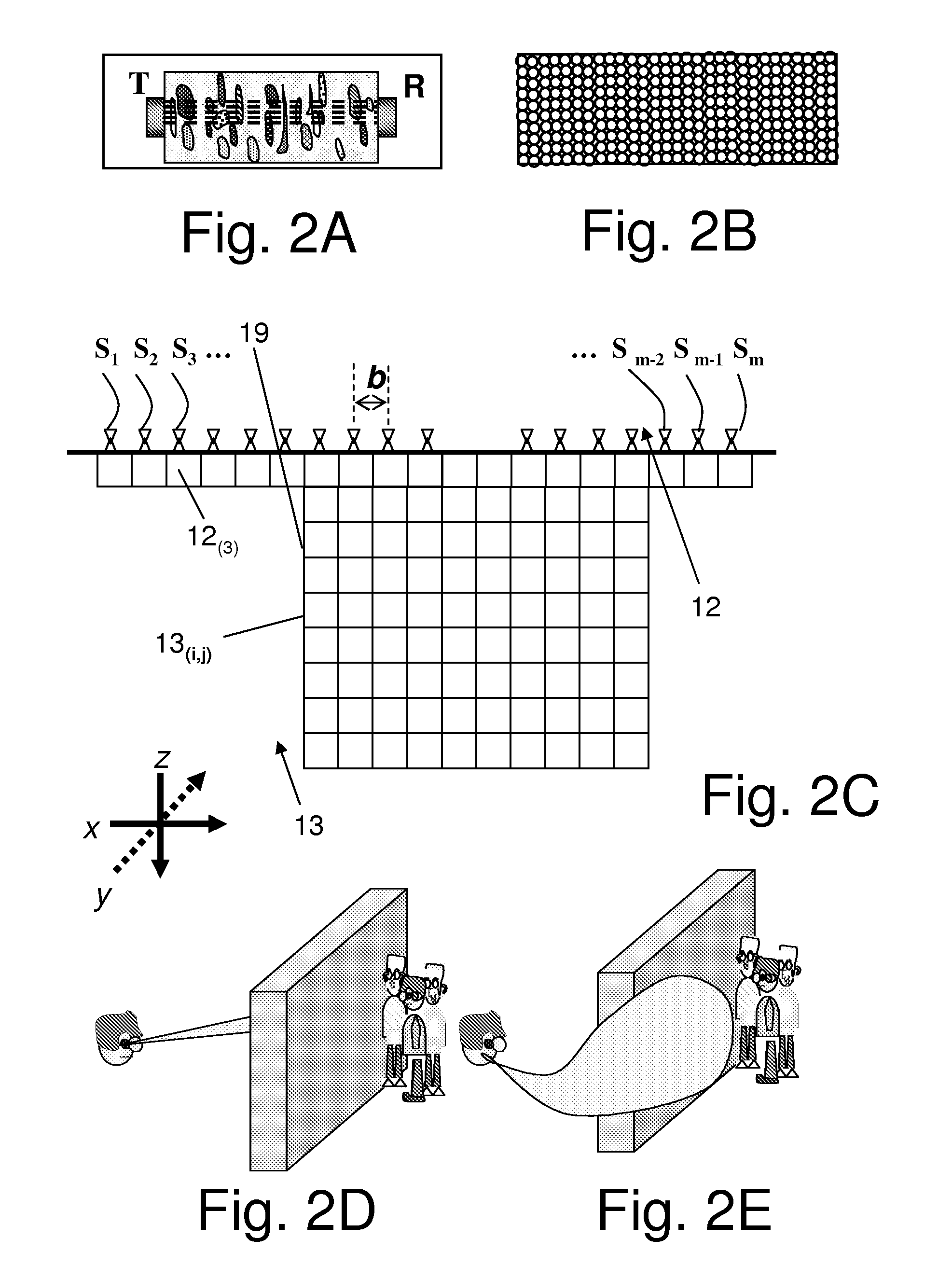
An ultrasound imaging system for imaging ultrasound scatterers, comprising a probe (208) for transmitting ultrasound waves and detecting ultrasound echoes reflected by said ultrasound scatterers, wherein said probe comprises a first group of transducer elements, labeled transmitting group (T), to transmit ultrasound waves, and a distinct second group of transducer elements, labeled receiving group (R), to detect ultrasound echoes reflected by said ultrasound scatterers. The system also comprises a processing system (202) comprising transmission and reception means, coupled to said probe (208), for providing coded signal to said transmitting group (T) and receiving signals from said receiving group (R) respectively; transmission beam-forming means (103) for focussing the ultrasound waves on a focus line, reception beam-forming means (105) for forming beam-summed received signals from signals received from the focus line and processing means for processing said beam-summed received signals to form decoded signals so as; and means for displaying an image (109) that is a function of said decoded signals.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
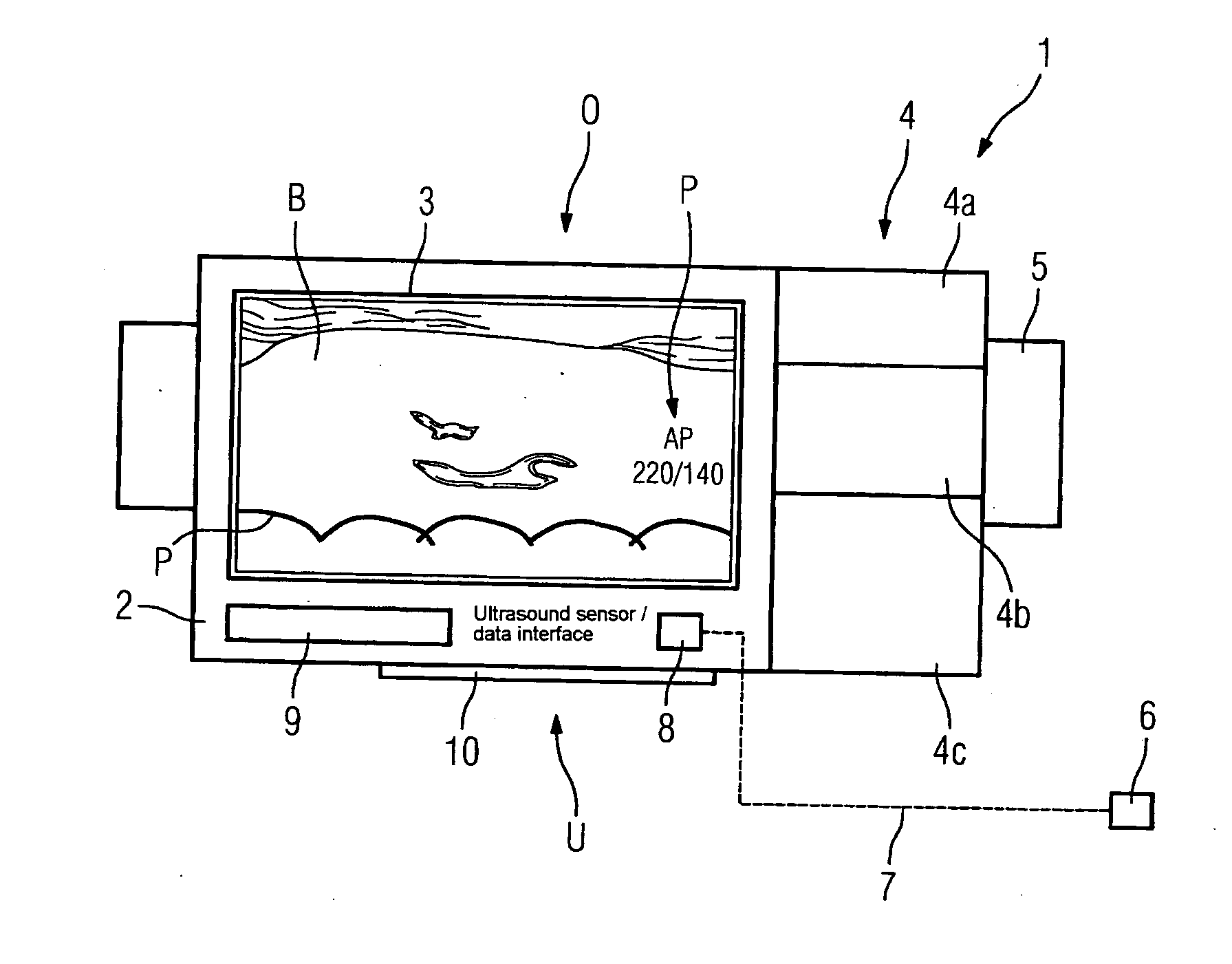
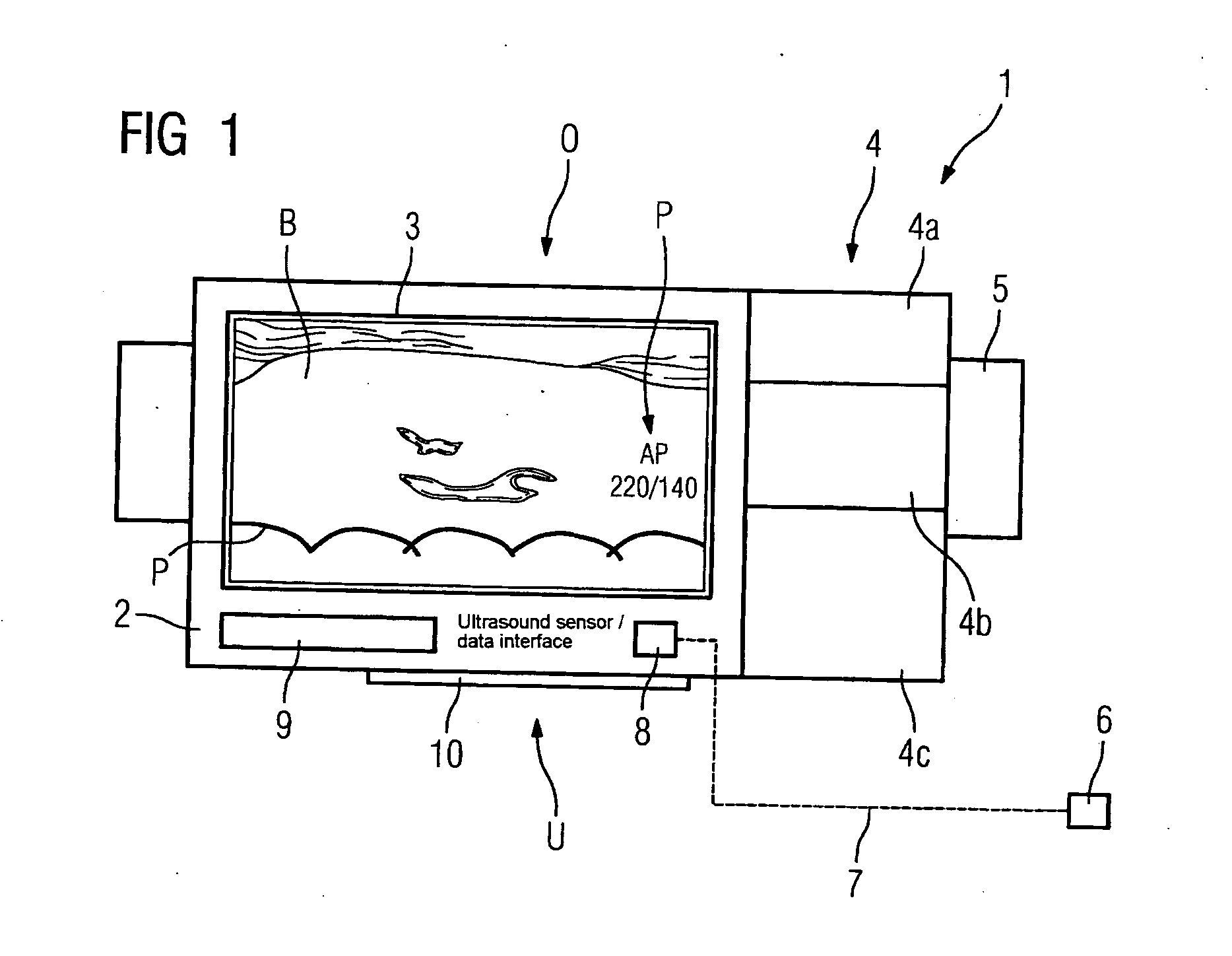
Mobile defibrillator
InactiveUS20070038256A1Reduce adverse effectsFast supplyOrgan movement/changes detectionHeart defibrillatorsIrregular heart rhythmMedicine
The invention relates to a mobile defibrillator which has a housing. In order to improve the diagnostic reliability, particularly in the case of irregular heart rhythms and myocardial infarctions, provision is additionally made for an imaging ultrasound device to be provided in or on the housing.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
User interface for automatic multi-plane imaging ultrasound system
InactiveCN101061962AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCathode-ray tube indicatorsData setSonification
A diagnostic ultrasound system is provided for automatically displaying multiple planes from a 3-D ultrasound data set. The system comprises a user interface for designating a reference plane, wherein the user interface provides a safe view position option and a restore reference plane option. A processor module maps the reference plane into a 3D ultrasound data set and automatically calculates image planes based on the reference plane for a current view position and a prior view position. A display is provided to selectively display the image planes associated with the current and prior reference planes. Memory stores the prior reference plane in response to selection of the save reference plane option, while the display switches from display of the current reference plane to restore the prior reference plane in response to selection of the restore reference plane option. Optionally, the memory may store coordinates in connection with the current and prior reference planes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and device for an imaging ultrasonic inspection of a three-dimensional workpiece
ActiveUS20100064811A1High measuringHigh evaluation speedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesNon destructiveSonification
A method for an imaging ultrasonic inspection of a three-dimensional workpiece, in which ultrasonic waves are coupled into the workpiece with at least one ultrasonic transducer and ultrasonic waves reflected within the workpiece are received by ultrasonic transducers and converted into ultrasonic signals forming the basis of the non-destructive imaging ultrasonic inspection.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Ultrasonic treatment equipment
InactiveUS7699779B2Small amount of blood flowRepeat exposureUltrasound therapyBlood flow measurement devicesUltrasonic sensorImaging ultrasound
Ultrasonic treatment equipment is provided which repeats therapeutic ultrasound exposure while measuring a degree of vessel constriction on a therapeutic ultrasound exposure basis. This equipment includes: a therapeutic ultrasonic transducer 2 which exposes a blood vessel of an affected part to a focused therapeutic ultrasonic wave for a specified period of exposure time; an imaging ultrasonic probe 3 which images an ultrasound tomographic image of the affected part; a display unit 24 which displays the ultrasound tomographic image; means 21 for detecting a blood flow signal from a signal received by the imaging ultrasonic probe and determining the blood flow velocity of the blood vessels of the affected part; means 21 for calculating a rate of change in blood flow velocity during the exposure to the therapeutic ultrasonic wave or before and after the exposure to the therapeutic ultrasonic wave; and means 23 for controlling exposure conditions of the therapeutic ultrasonic wave on the basis of the rate of change in blood flow velocity, and thereby controlling the therapeutic ultrasonic transducer.
Owner:HITACHI LTD +1
Mobile defibrillator
InactiveUS8038617B2Quick and reliable diagnosisElectrotherapyOrgan movement/changes detectionIrregular heart rhythmMedicine
The invention relates to a mobile defibrillator which has a housing. In order to improve the diagnostic reliability, particularly in the case of irregular heart rhythms and myocardial infarctions, provision is additionally made for an imaging ultrasound device to be provided in or on the housing.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
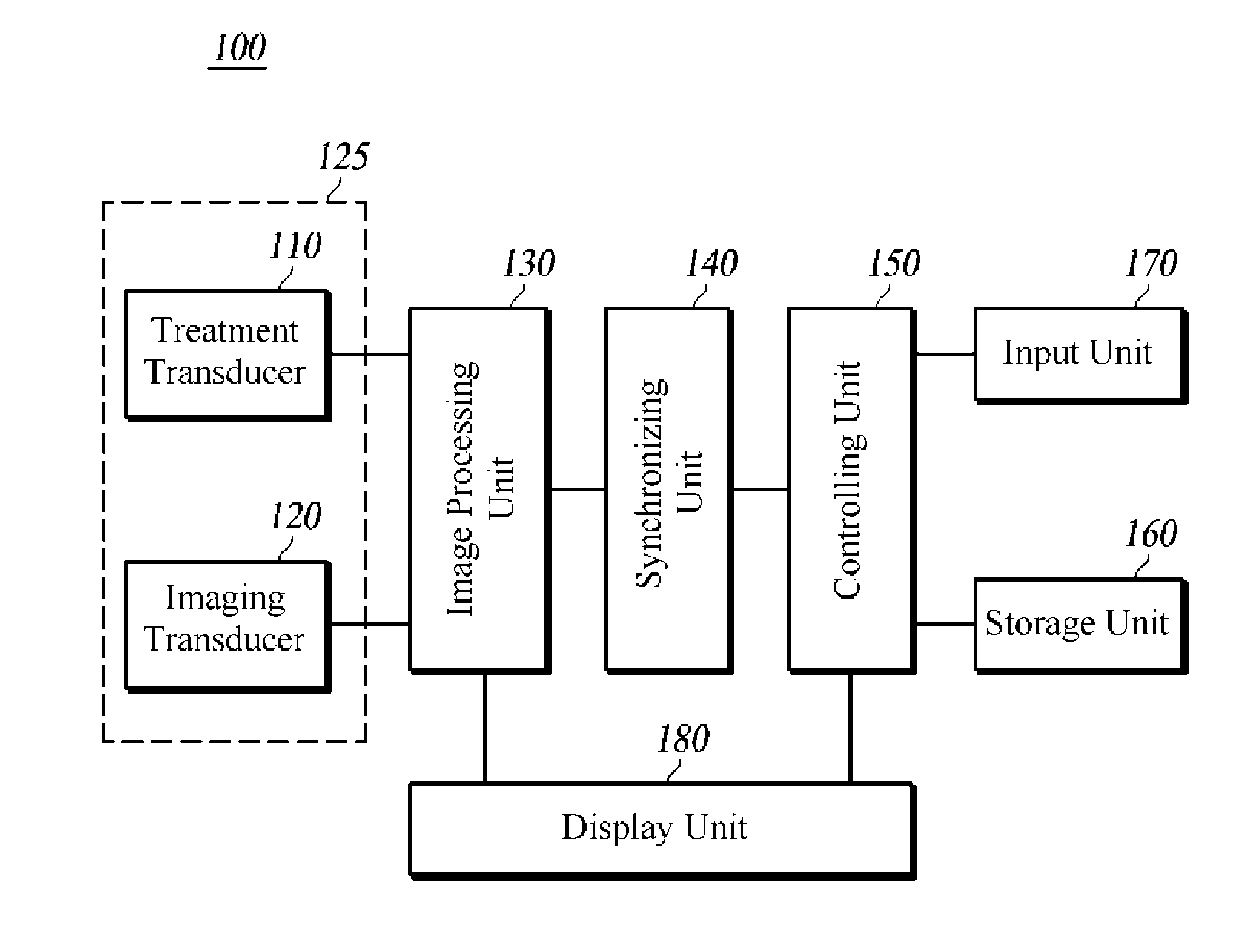
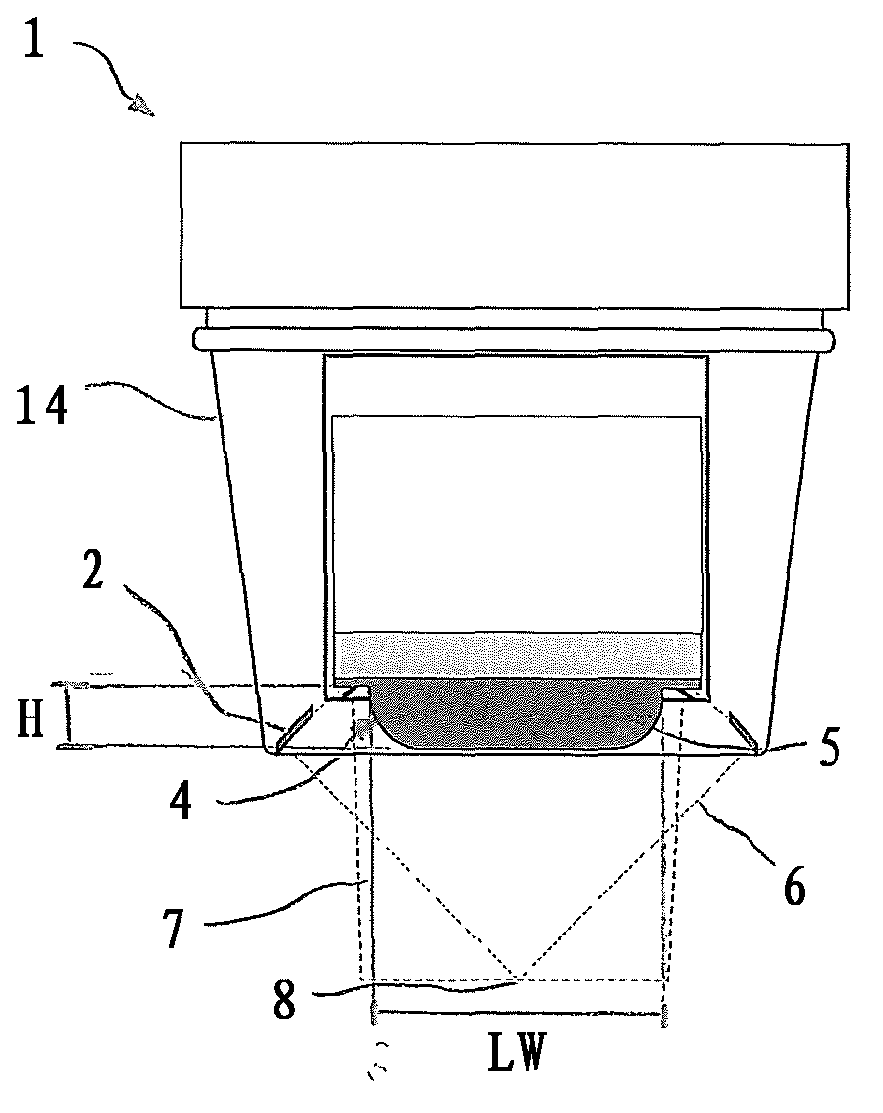
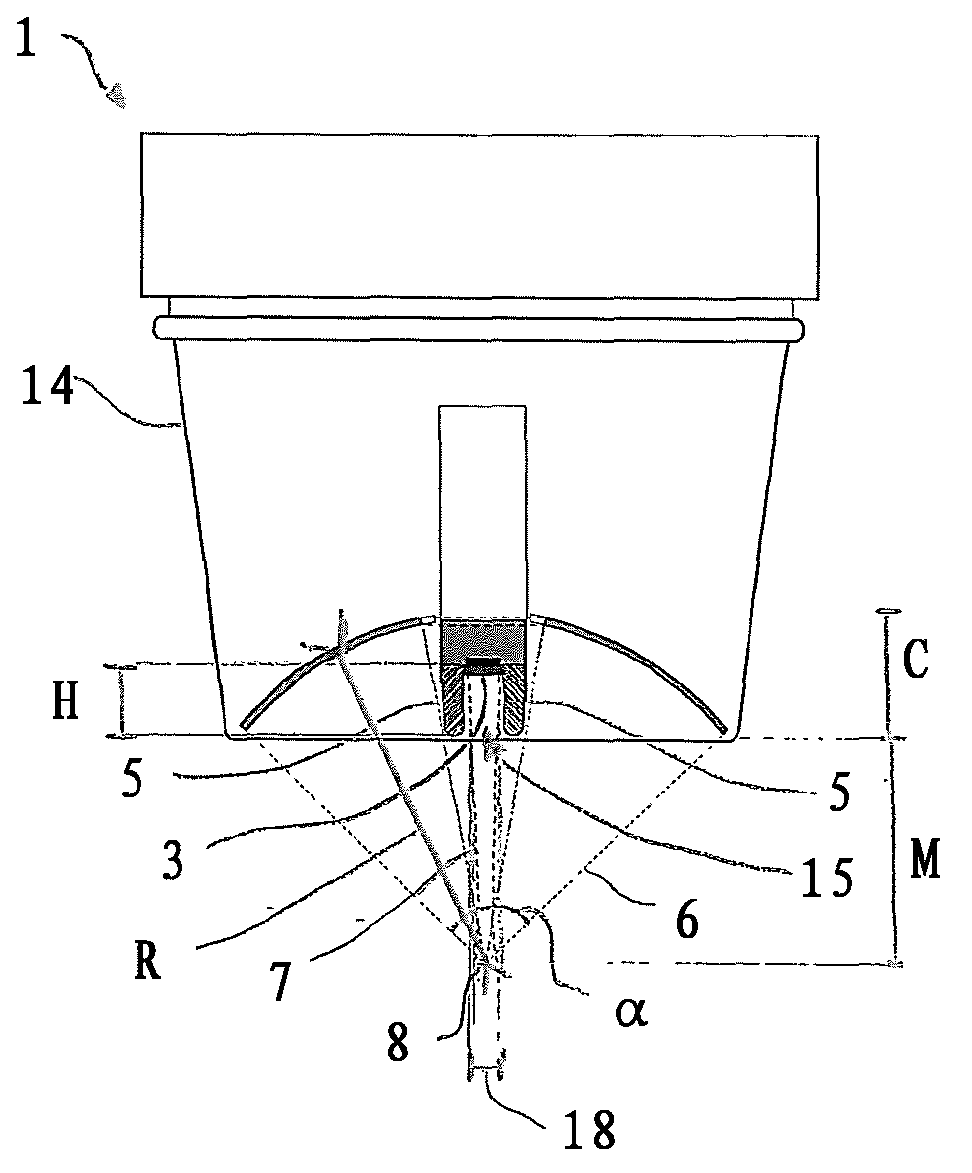
Method for confirming location of focal point, and ultrasonic medical apparatus therefor
InactiveUS20160007960A1Material analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSurgerySonificationImaging ultrasound
A method and an ultrasound medical apparatus for confirming a focal point of a high-intensity focused ultrasound are disclosed. A method of confirming a focal point, for pre-targeting a location of a high-intensity ultrasound by synchronizing the high-intensity ultrasound and an imaging ultrasound and using a reflected signal of the synchronized imaging ultrasound and high-intensity ultrasound from a focal point to which the ultrasounds are transmitted, and an ultrasound medical apparatus for implementing the method are provided.
Owner:ALPINION MEDICAL SYST
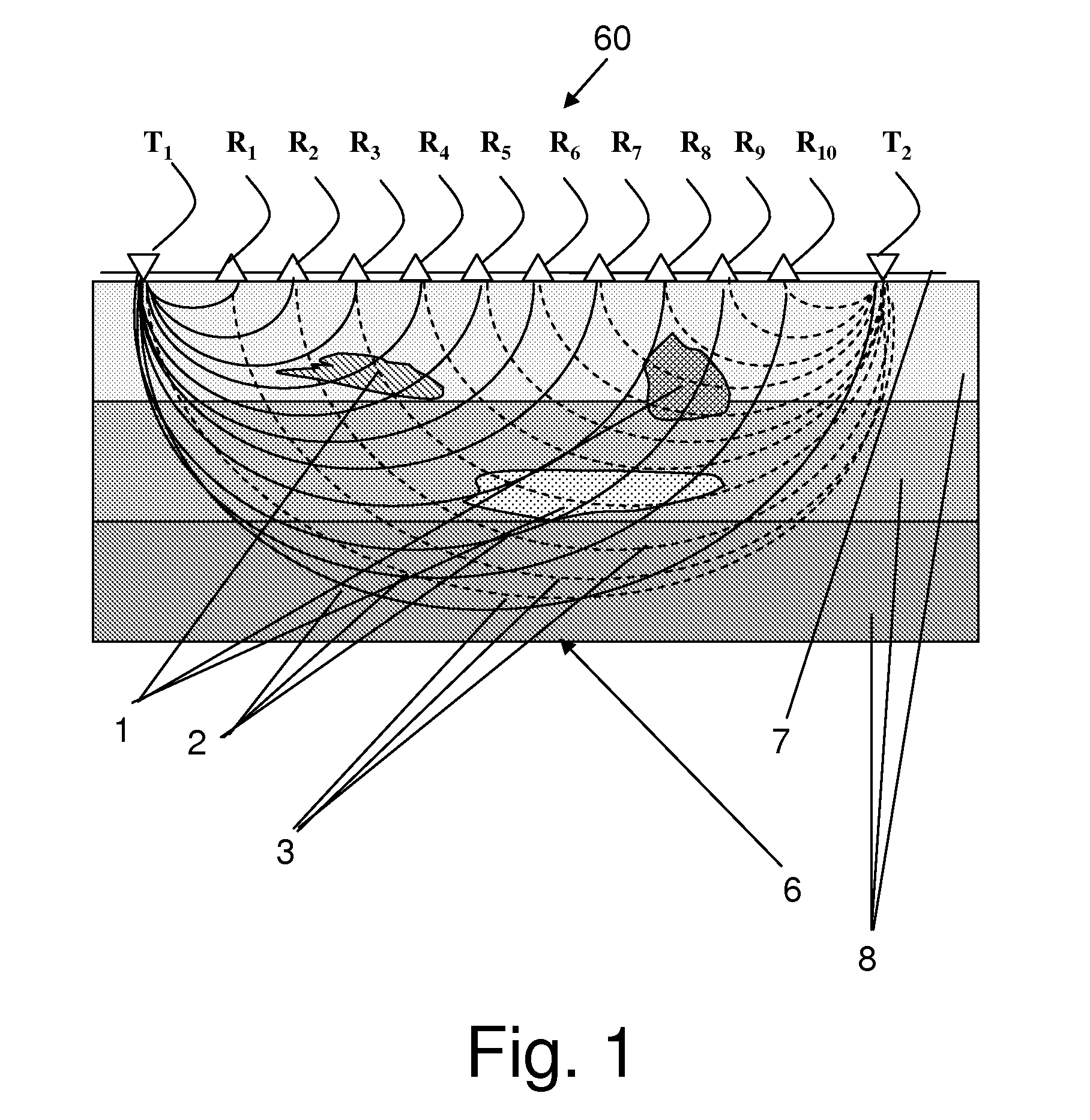
3D quantitative-imaging ultrasonic method for bone inspections and device for its implementation
InactiveUS20100185089A1Reliable diagnosisQuality andUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsHealth-index calculationSonificationArrival time
The Ultrasonic Tomographical method and system is provided using measurements of time of flight low frequency acoustic waves. Differences in first signal arrival times from plurality of known transmitters' locations to plurality of known receivers' location are used, wherein the transmitters and receivers are at an angle to the surface of the observed object. 3D mapping of the acoustic propagation speed is reconstructed, revealing anatomical details and physiological properties.
Owner:GOUREVITCH ALLA
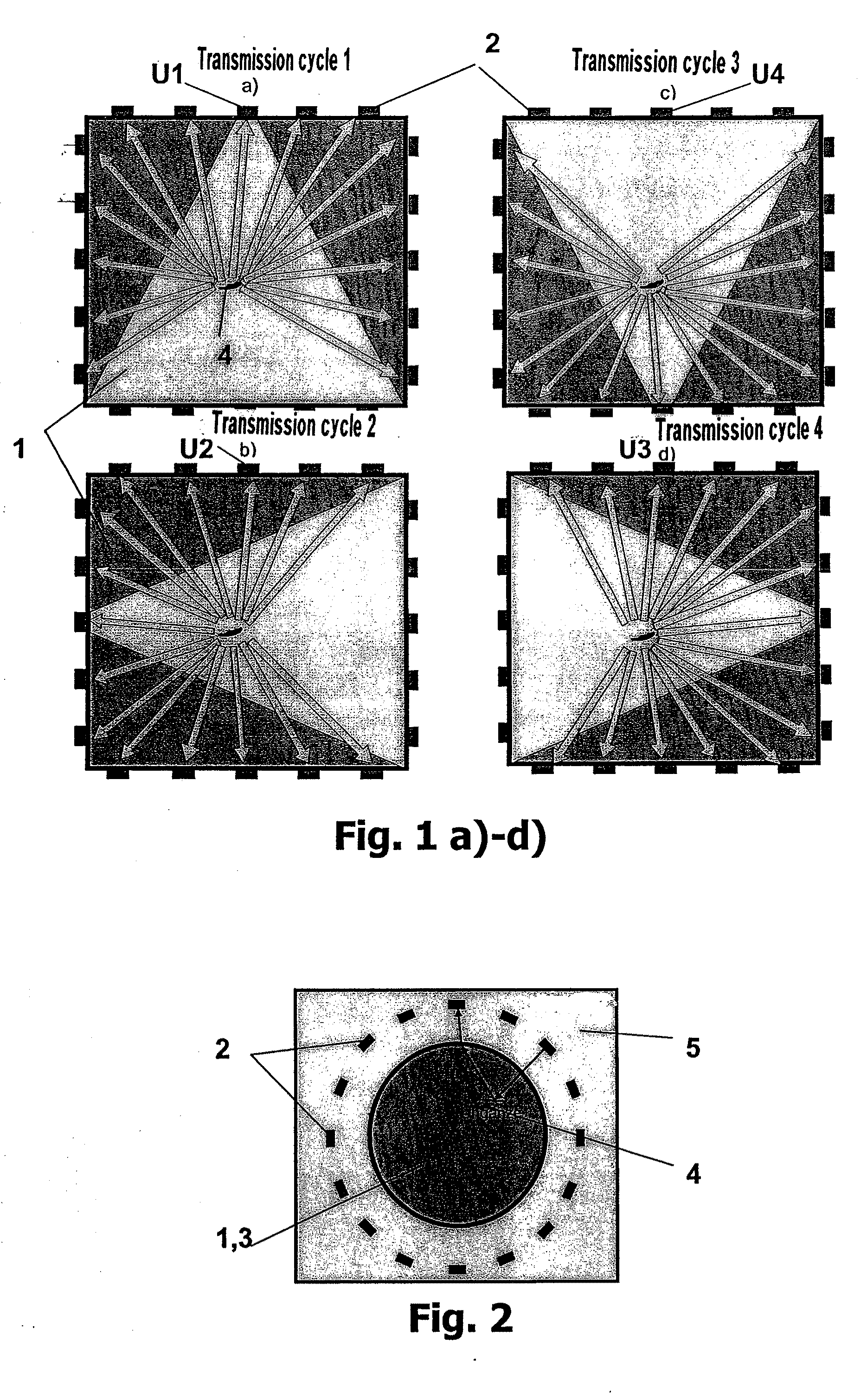
Lentis three-dimensional imaging ultrasonography and appropriative ultrasonic probe array
The invention discloses a human eye lens 3D imaging ultrasonic scanning method and a special ultrasonic probe array. A data processing unit controls scanning to the ultrasonic probe array formed by a plurality of ultrasonic probes regularly arranged on a probe bracket, scans transmitting signal one by one and processes the echoed signals on the other ultrasonic probes in the ultrasonic scanning array to acquire a lens 3D image. The lens 3D imaging ultrasonic scanning method can not only acquire a 3D solid image and has the biggest advantage that as no anesthetization is needed on the eyeballs of a person to be detected when the ultrasonic probe array ultrasonically scans the human eyes, the invention can utilize a principle that the lens of the two eyes are carrying out the same regulation simultaneously when the human eyes watch an object normally to directly observe the diopter adjustment changes of the curves in front of and behind the lens and observe the function of how to adjust the lens with ciliary muscle in real time with full range; thereby providing an effective technical means for researching the adjusting mechanism of eyes.
Owner:SCHOOL OF OPHTHALMOLOGY & OPTOMETRY WENZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
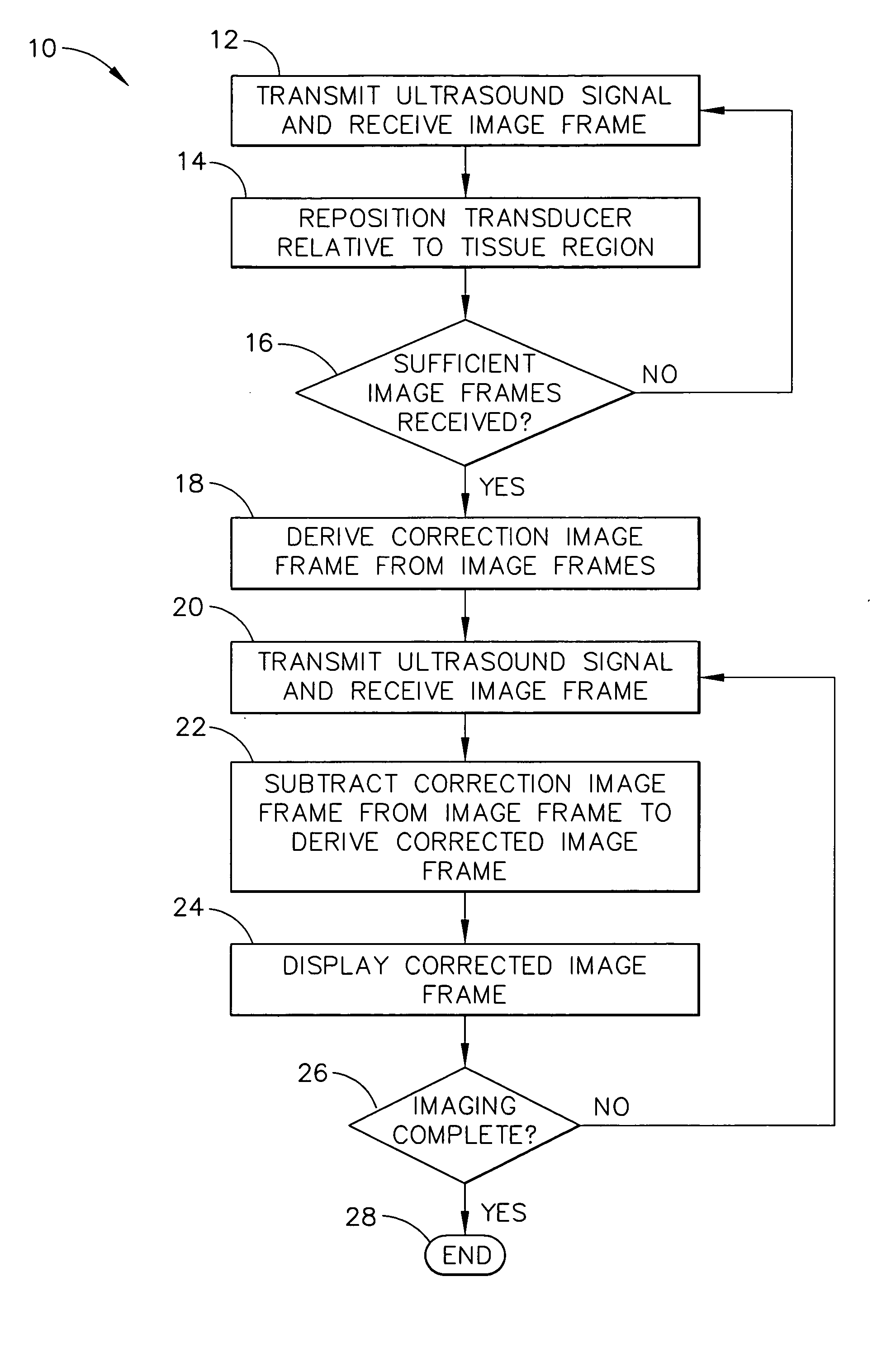
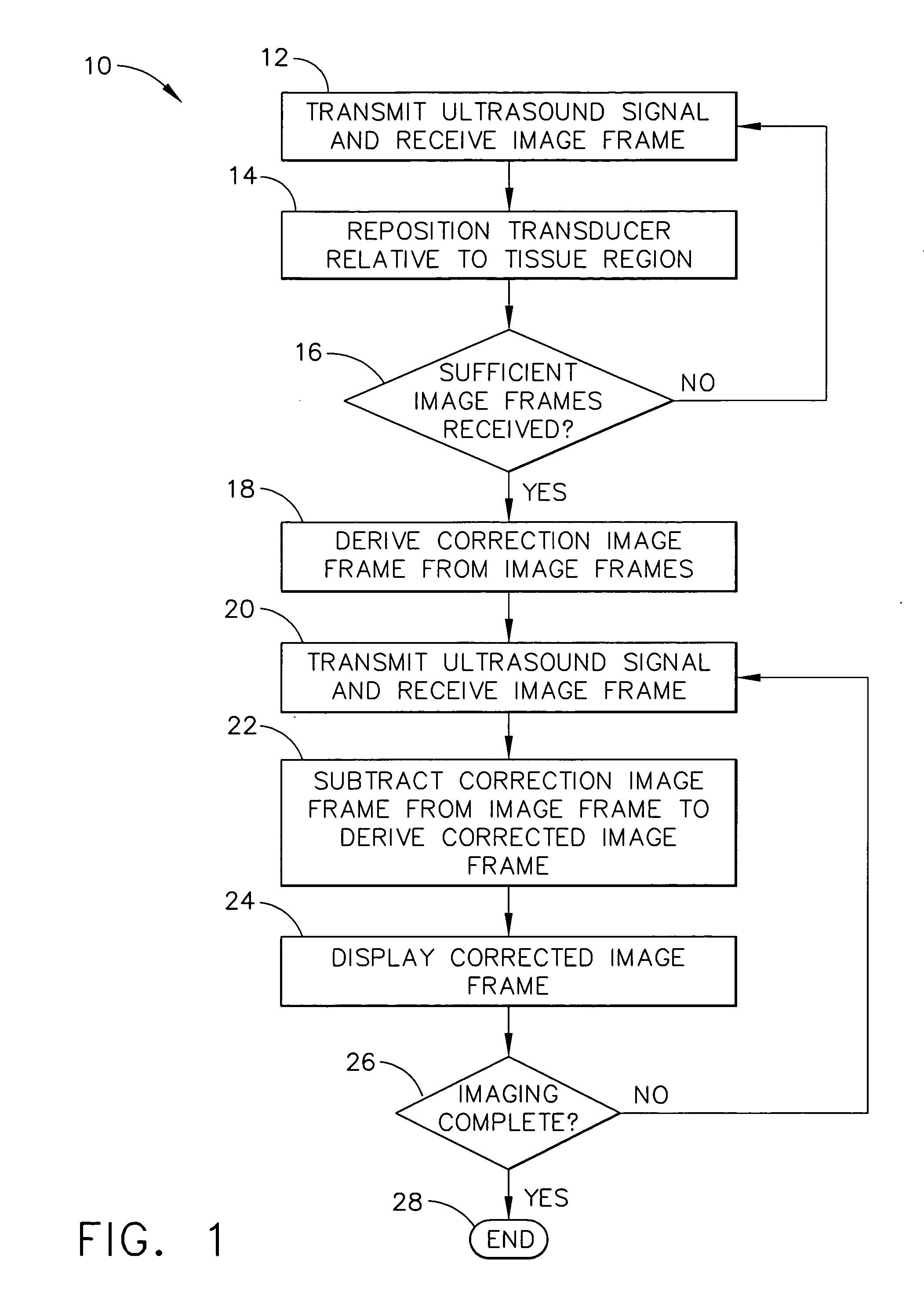
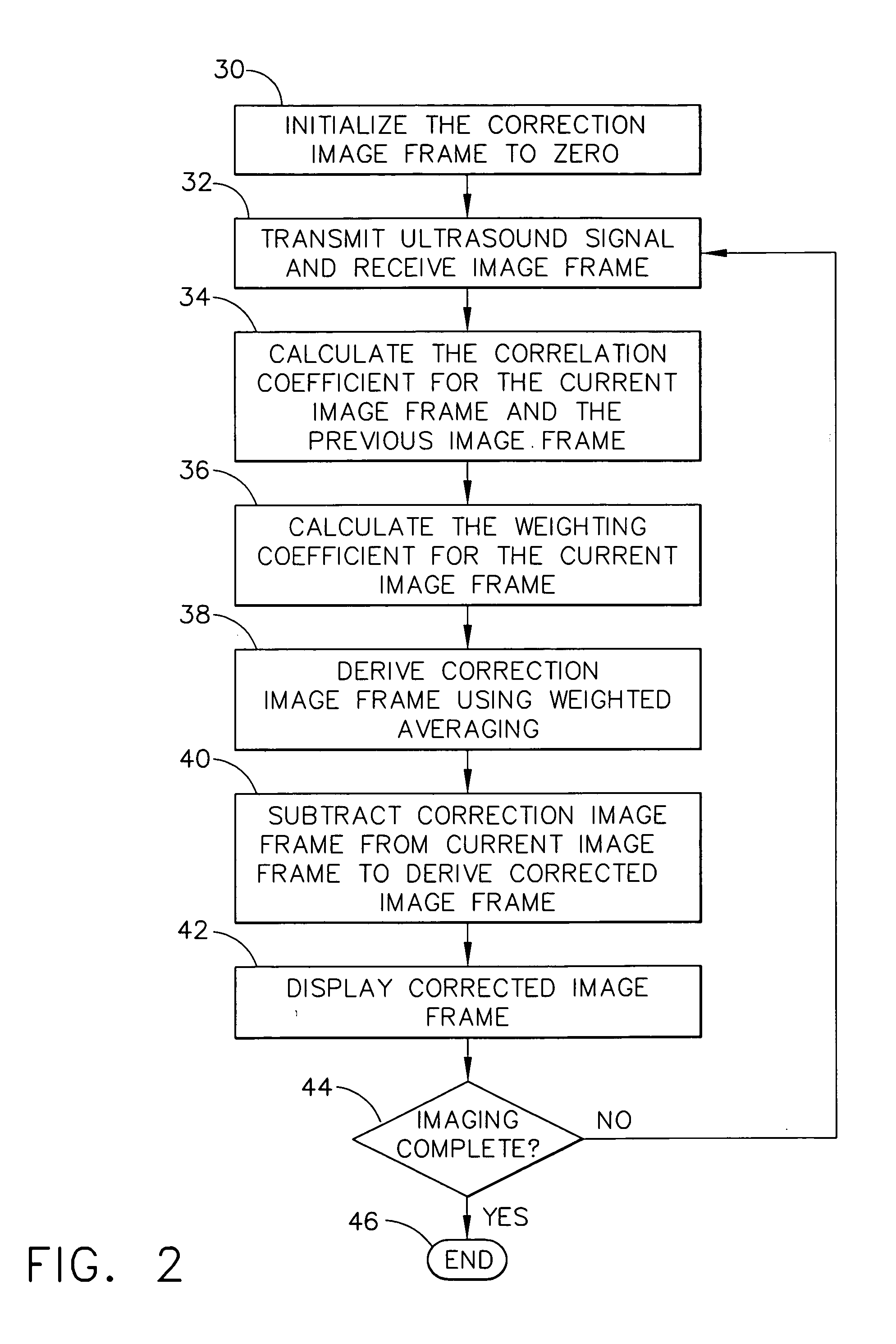
Method for reducing electronic artifacts in ultrasound imaging
InactiveUS20050240105A1Reduce artifactsWave based measurement systemsSurgeryUltrasound imagingSonification
A method for reducing electronic artifacts in ultrasound images of anatomical tissue. At least two calibration signals are received from imaging ultrasound waves that have been reflected from different regions in anatomical tissue. A correction signal is derived from the calibration signals. The correction signal is subtracted from a signal to derive a corrected signal. An image generated from the corrected signal is then displayed. The correction signal may be derived using weighted averaging and may be updated upon receipt of additional signals. The correction signal may be initialized to zero periodically, in response to a change in the system, or at the direction of the operator.
Owner:ETHICON ENDO SURGERY INC
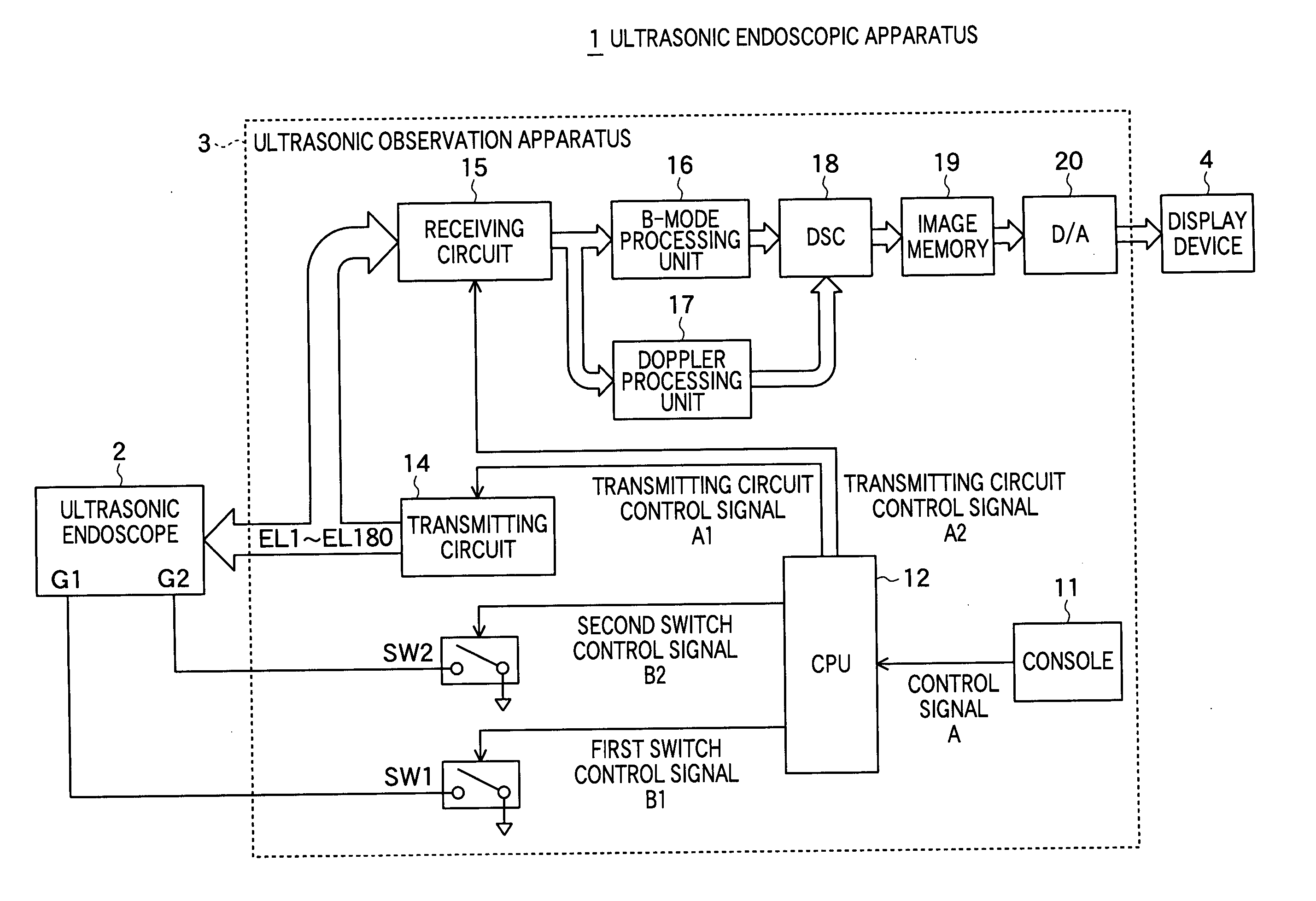
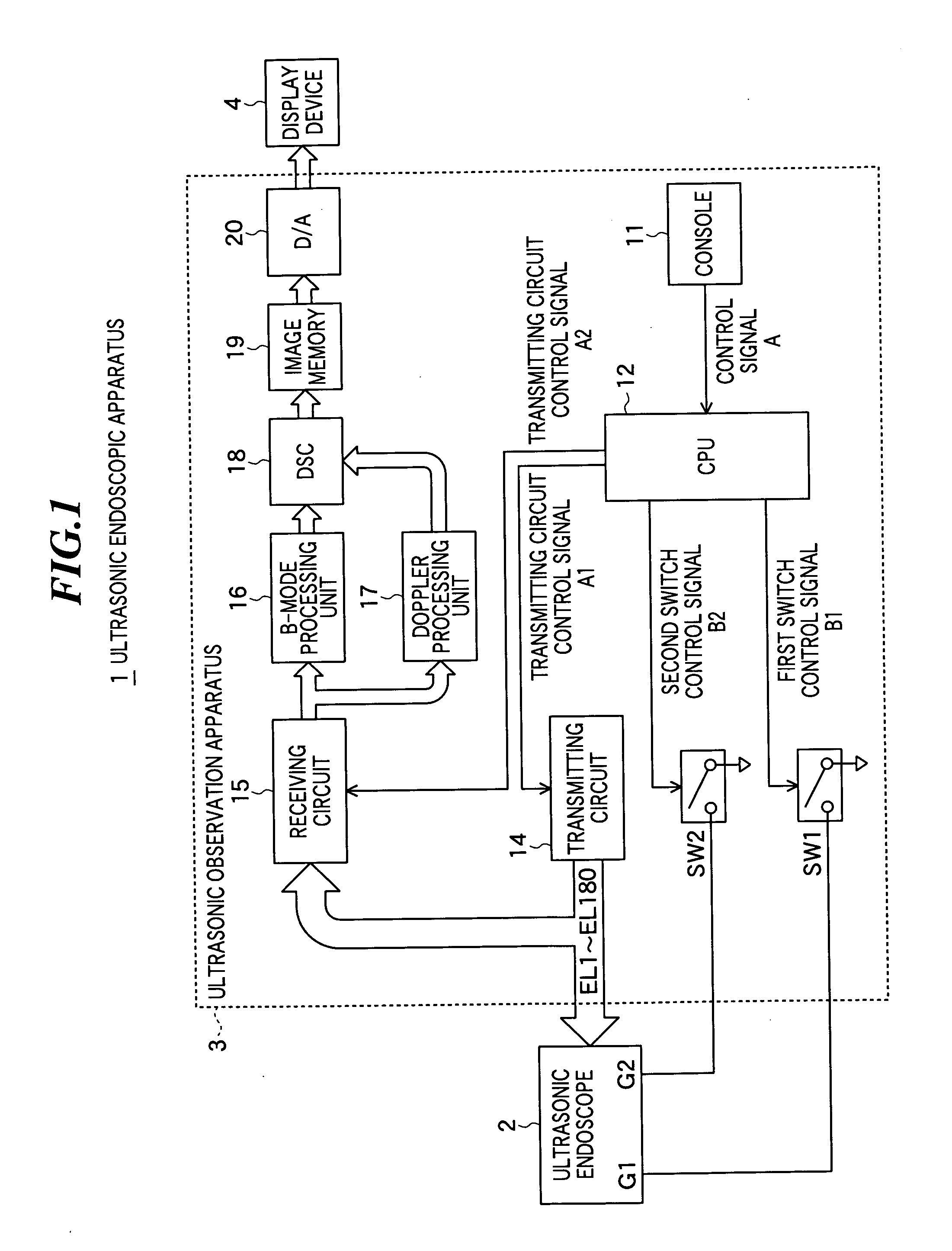
Ultrasonic endoscope and ultrasonic endoscopic apparatus
InactiveUS20060058679A1Increase frame rateQuality imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationUltrasonic beam
In an ultrasonic endoscope capable of being inserted into a body of a patient and imaging ultrasonic tomographic images, a frame rate in electronic radial scanning operation is improved. The ultrasonic endoscope includes: an ultrasonic transducer unit including plural ultrasonic transducers, each having a first electrode and a second electrode, for transmitting and receiving ultrasonic waves; a plurality of first interconnections each connected to the first electrodes of predetermined ultrasonic transducers; and a plurality of second interconnections each connected to the second electrodes of ultrasonic transducers having the first electrodes not connected to each other; wherein the ultrasonic transducer unit performs scanning operation by simultaneously transmitting the same number of ultrasonic beams in each of plural angle regions when selectively supplied with drive signals via the plurality of first interconnections and the plurality of second interconnections.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP +1
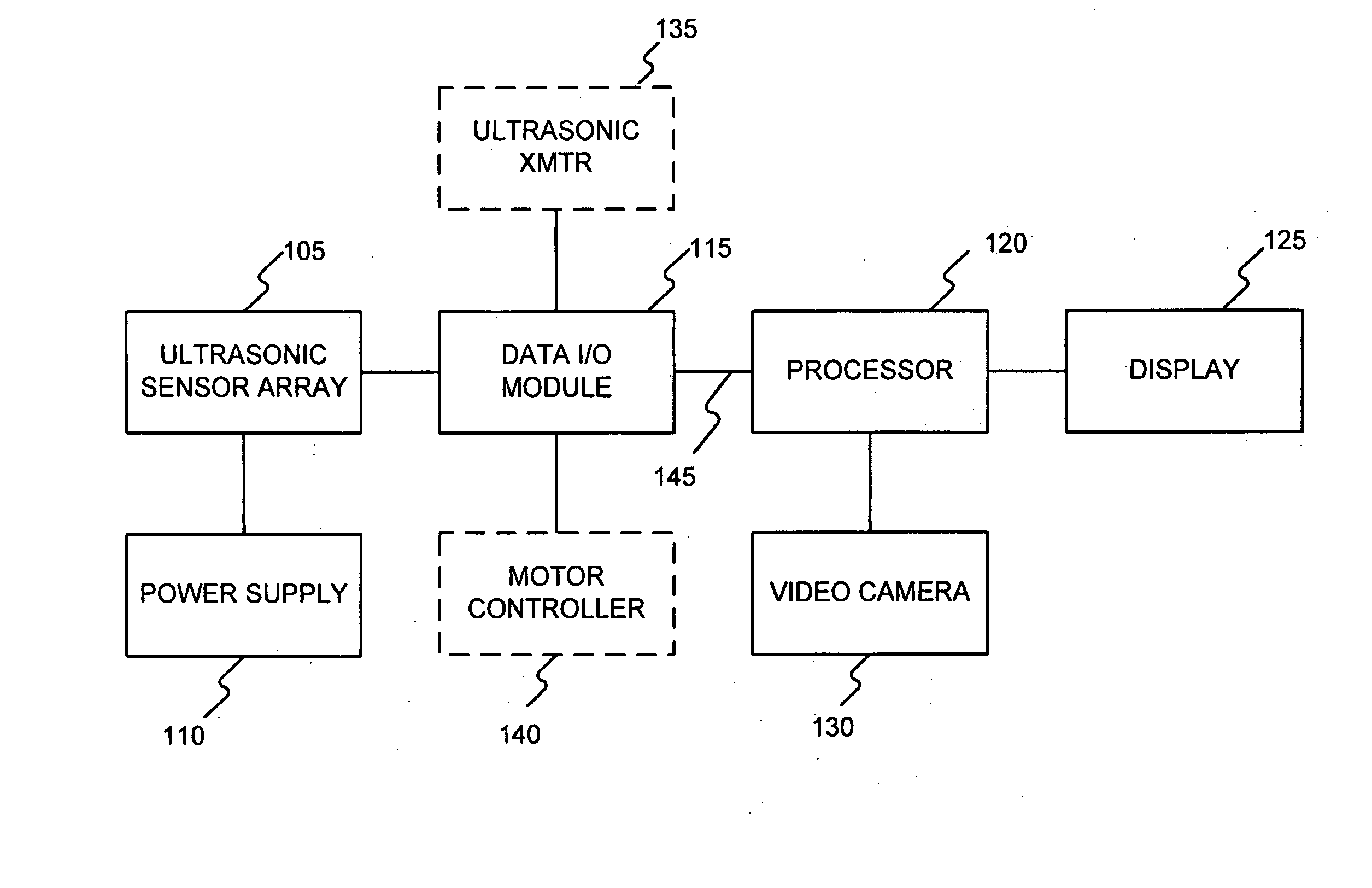
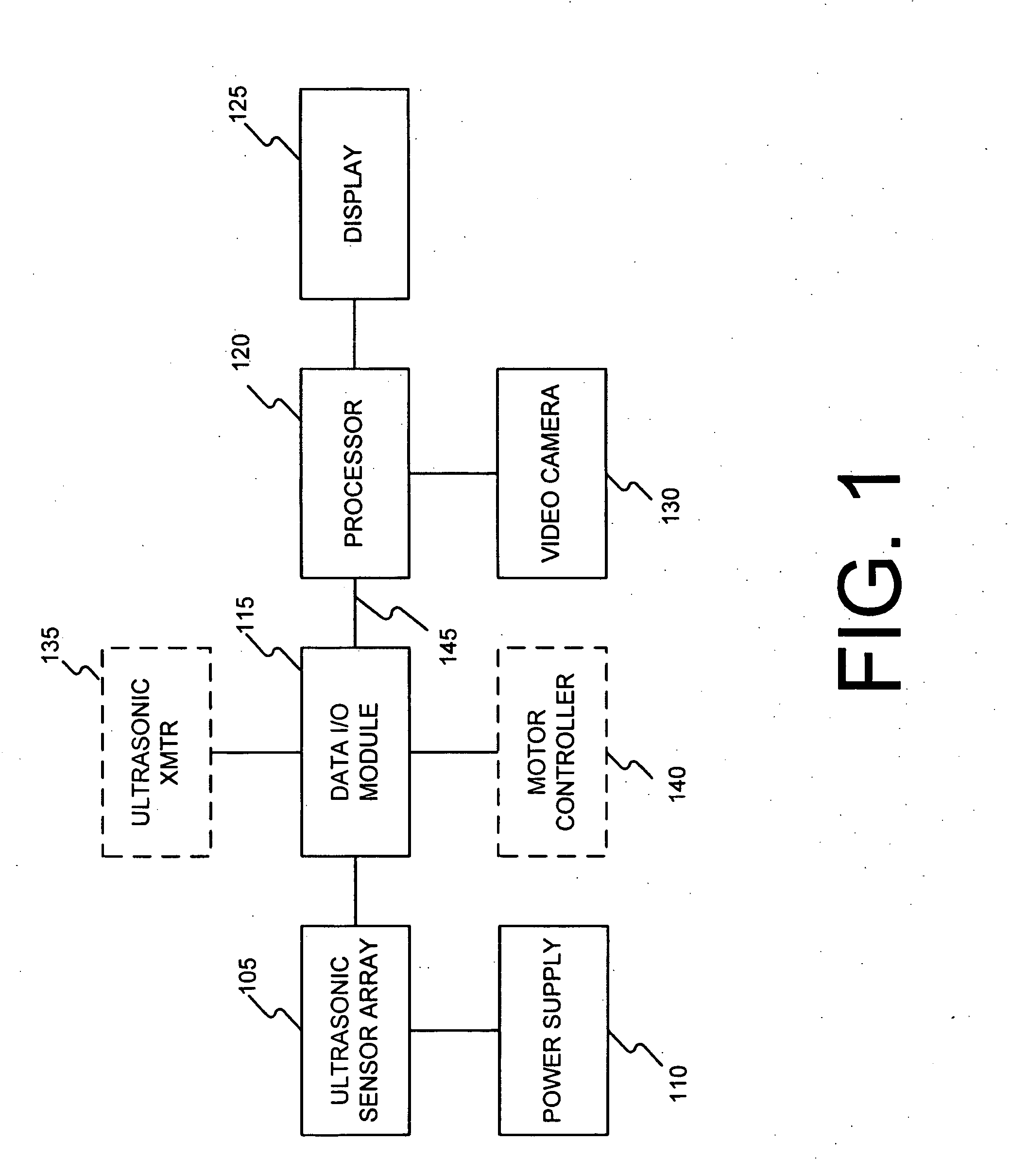
System and method for ultrasonic detection and imaging
InactiveUS20070238993A1Easy to testVibration measurement in solidsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSonificationUltrasonic testing
Systems and Methods are disclosed for the detection and imaging of ultrasonic energy. Embodiments of the invention utilize an array of ultrasonic sensors where data from each of the sensors are processed by RMS-to-DC conversion. In addition, embodiments of the invention output a contour map based on detected ultrasonic energy and blend at least one feature of the contour map with a feature of a visible image so that a blended image can be displayed to an operator. Furthermore, embodiments of the invention provide a system and method for repositioning an array of ultrasonic sensors with respect to target area or Unit Under Test (UUT) to facilitate a thorough and repeatable test.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
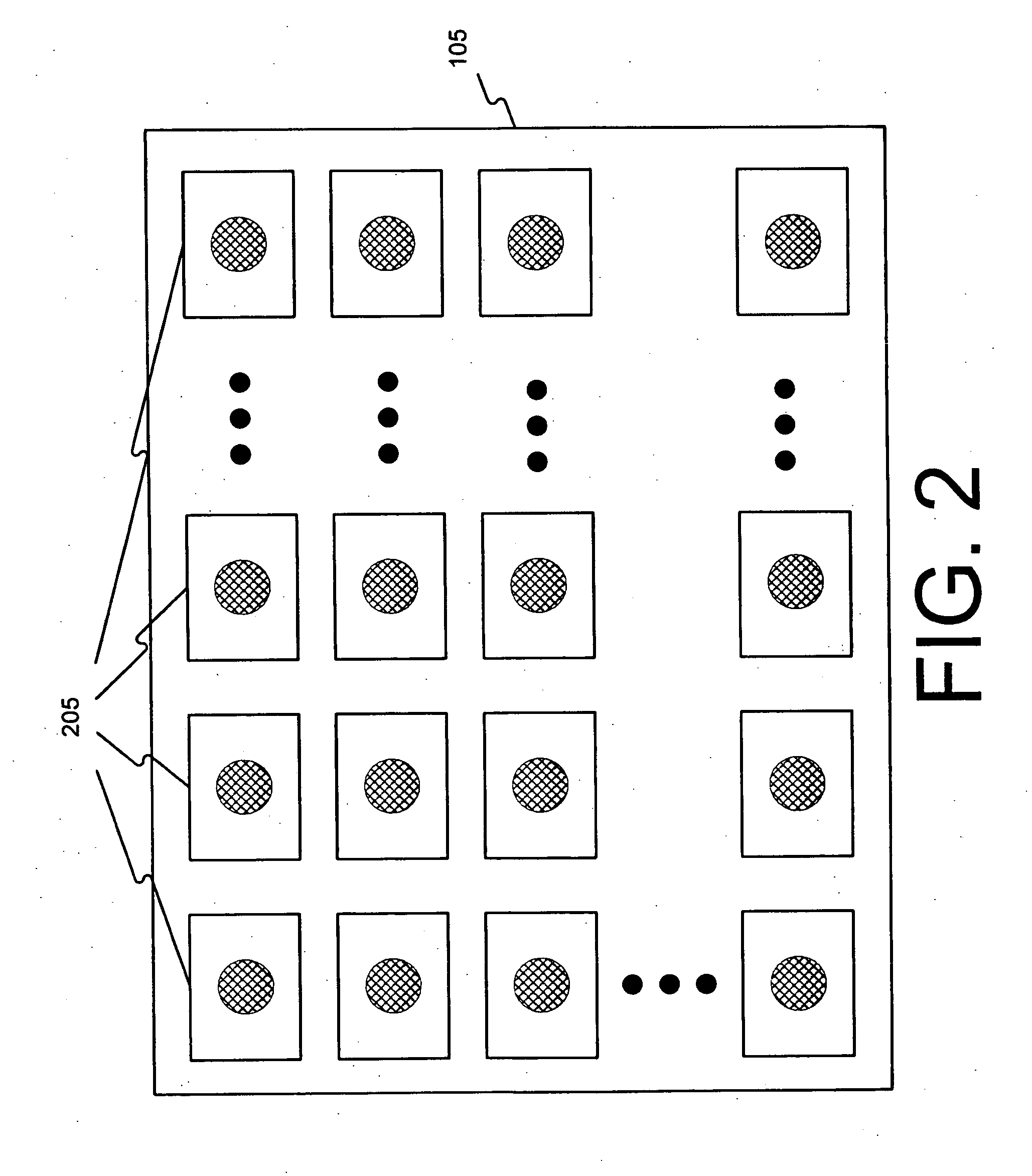
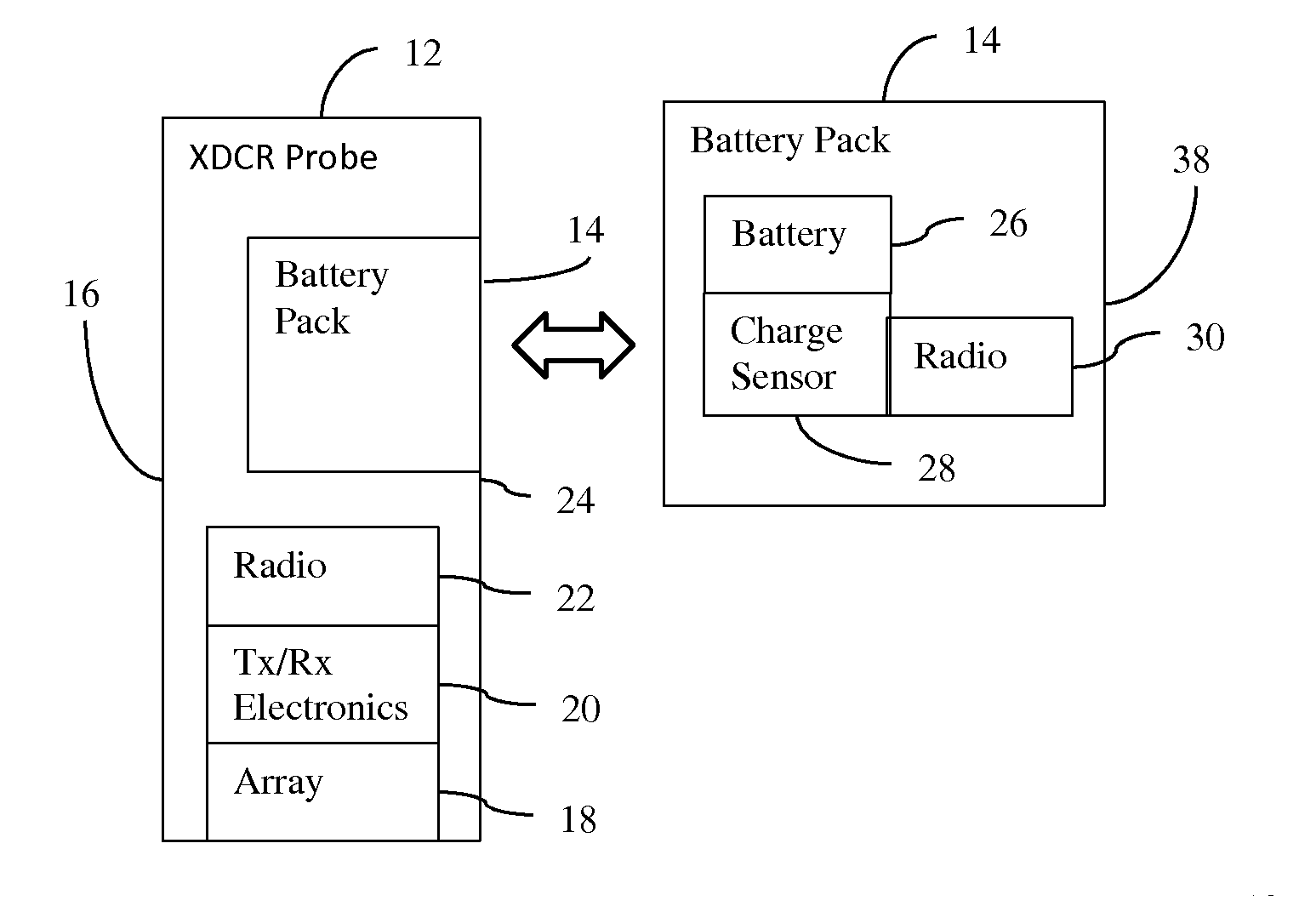
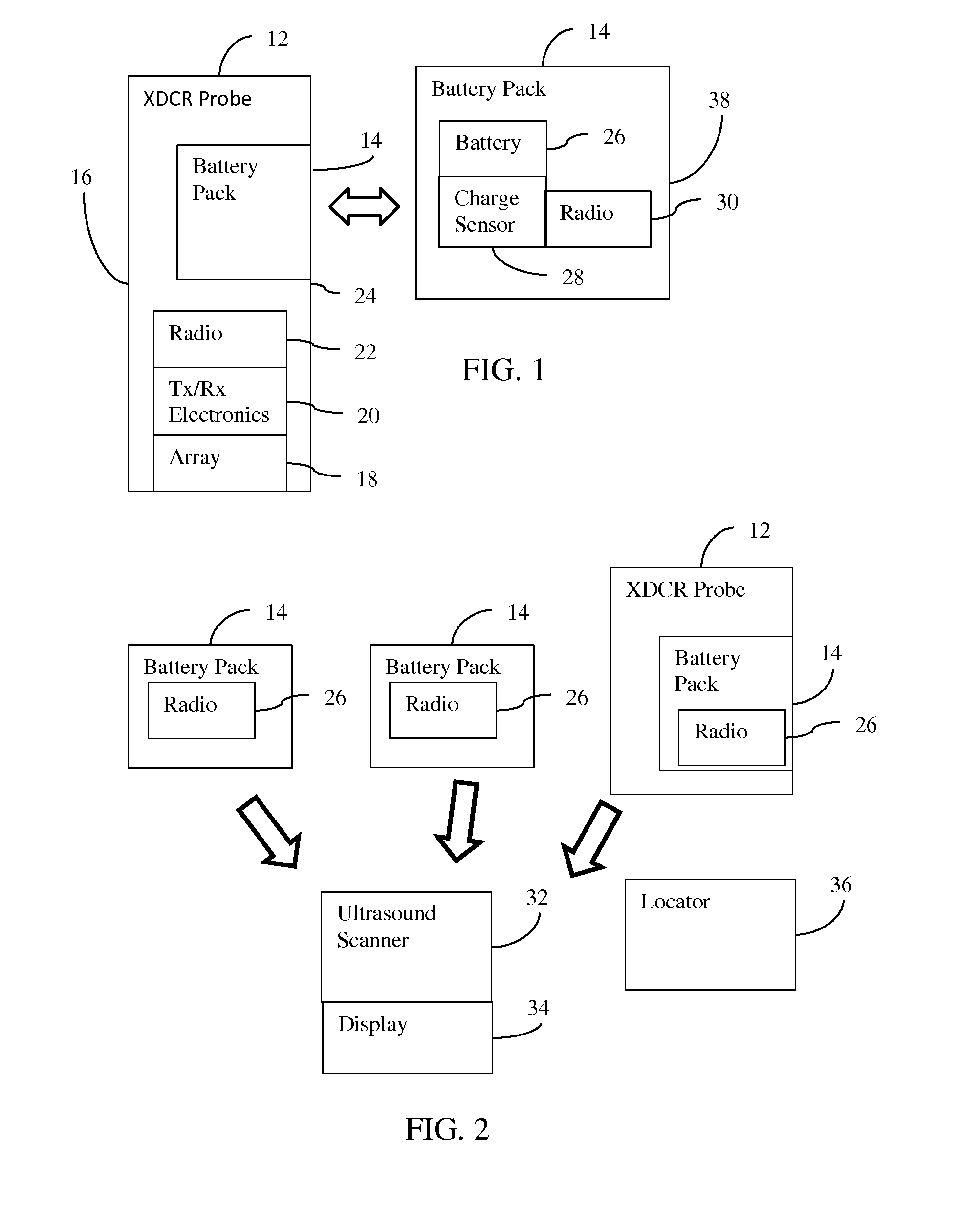
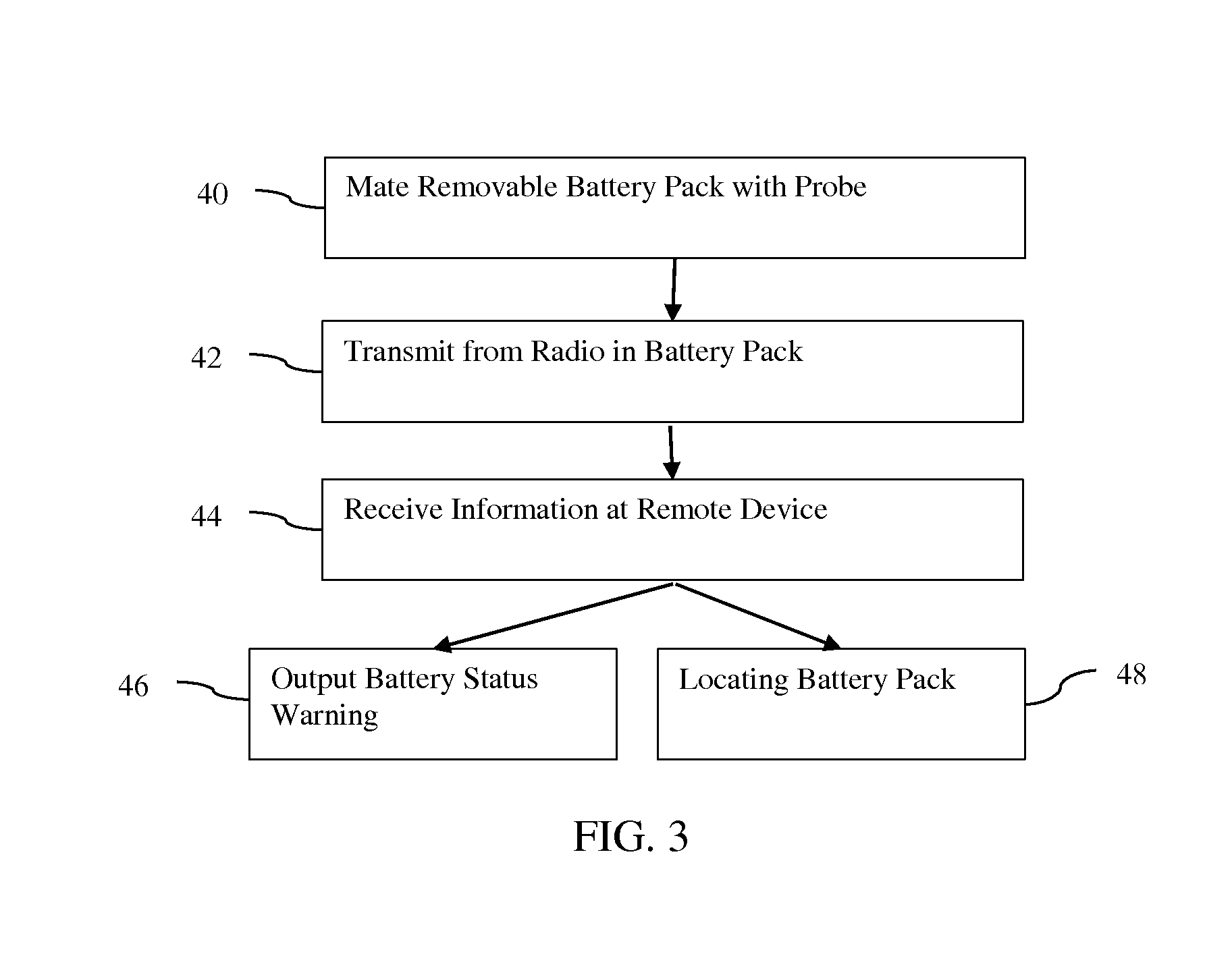
Medical diagnostic imaging ultrasound probe battery pack radio
InactiveUS20160317131A1Non-electrical signal transmission systemsCatheterUltrasound imagingUltrasonic sensor
In an ultrasound imaging system, a wireless radio is included as part of a removable battery pack. The charge, signals used for locating the battery, and other information may be wirelessly communicated from the battery pack even when not connected with an ultrasound transducer probe. Queries, configuration data and other information may be communicated from the ultrasound system or locator device to the probe battery and its circuitry. The same radio may be used by the ultrasound transducer probe when connected. Alternatively, a different radio is used by the probe.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
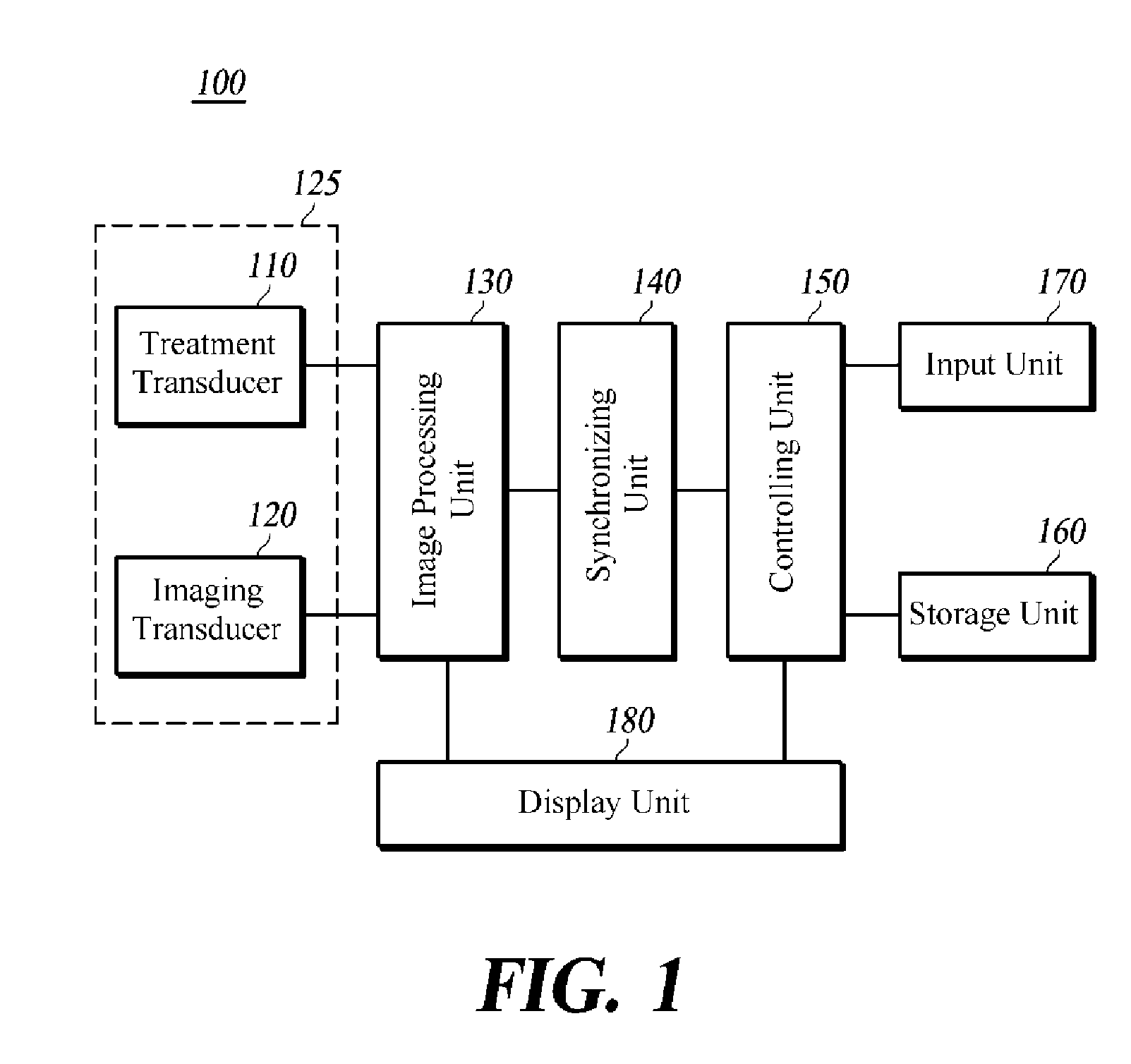
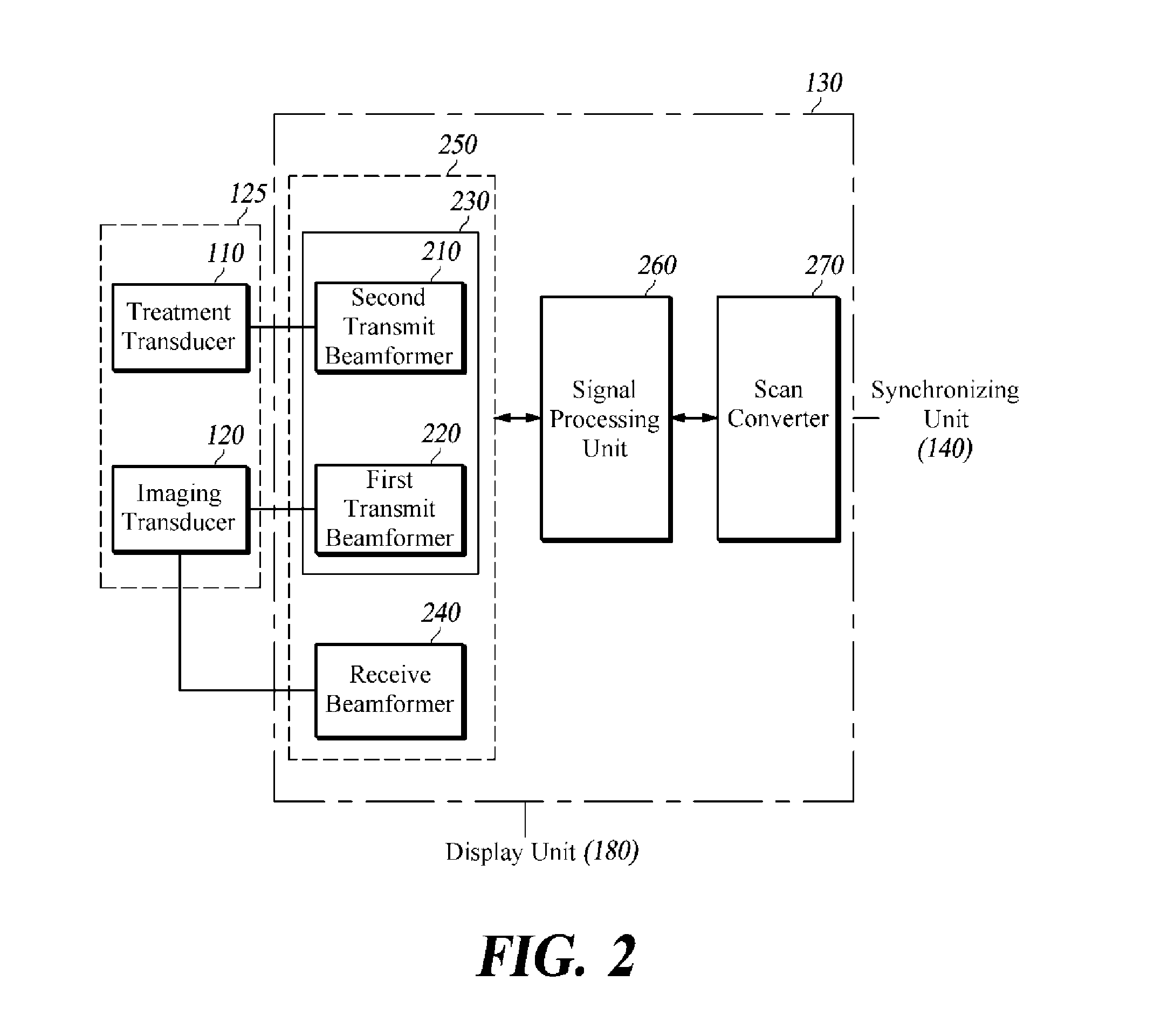
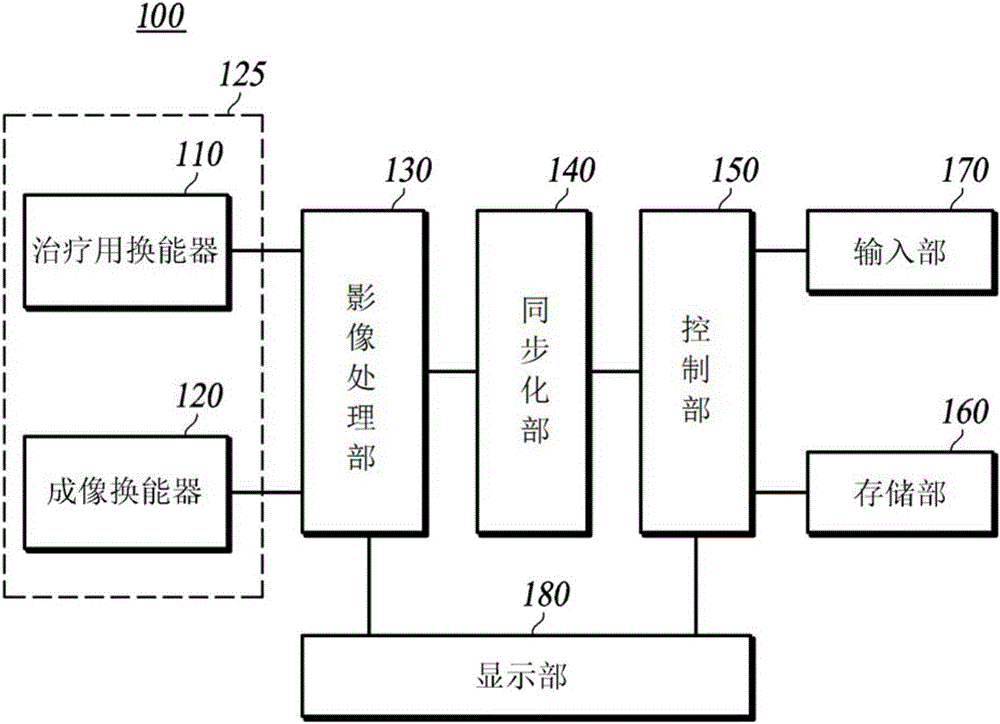
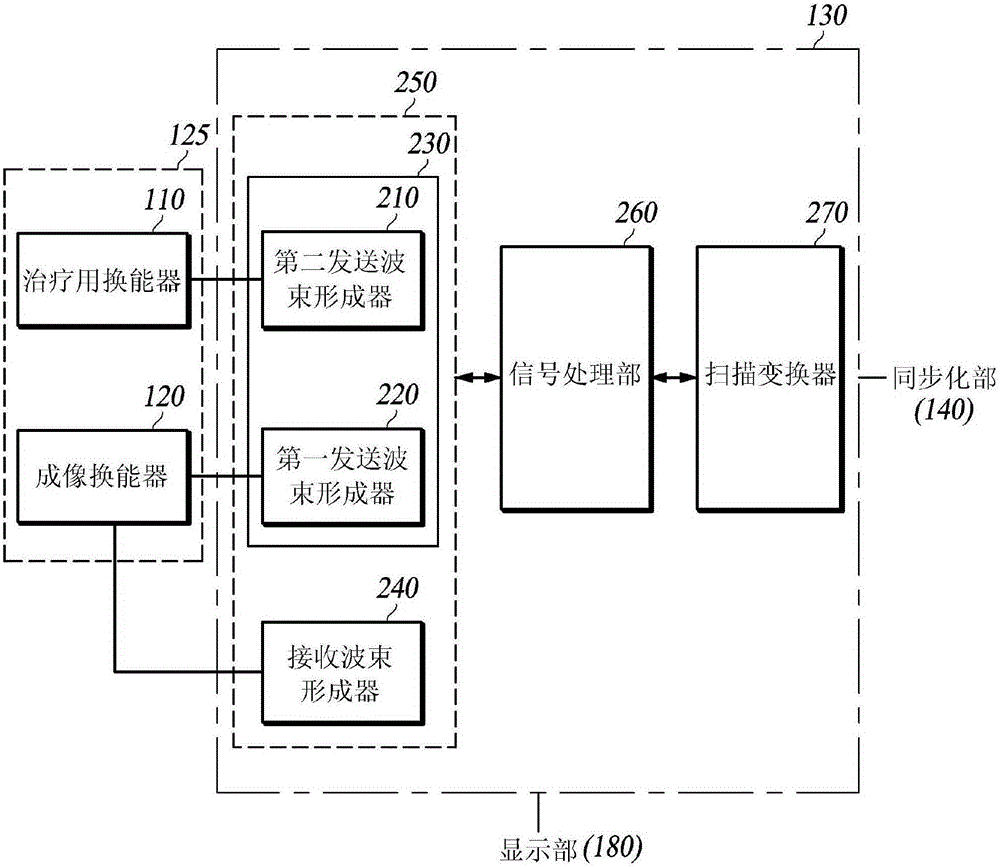
Combined therapy and imaging ultrasound apparatus
InactiveUS20050182326A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapySonificationHigh-intensity focused ultrasound
An ultrasound imaging and treatment system including: a diffraction grating transducer; and, a signal source electrically coupled to the diffraction grating transducer and operative: in a first mode to provide a wide-band excitation signal to the diffraction grating transducer to operate the diffraction grating transducer in an imaging manner; and in a second mode to provide a narrow-band excitation signal to the diffraction grating transducer to operate the diffraction grating transducer in a high intensity focused ultrasound insonifying manner.
Owner:DVX LLC
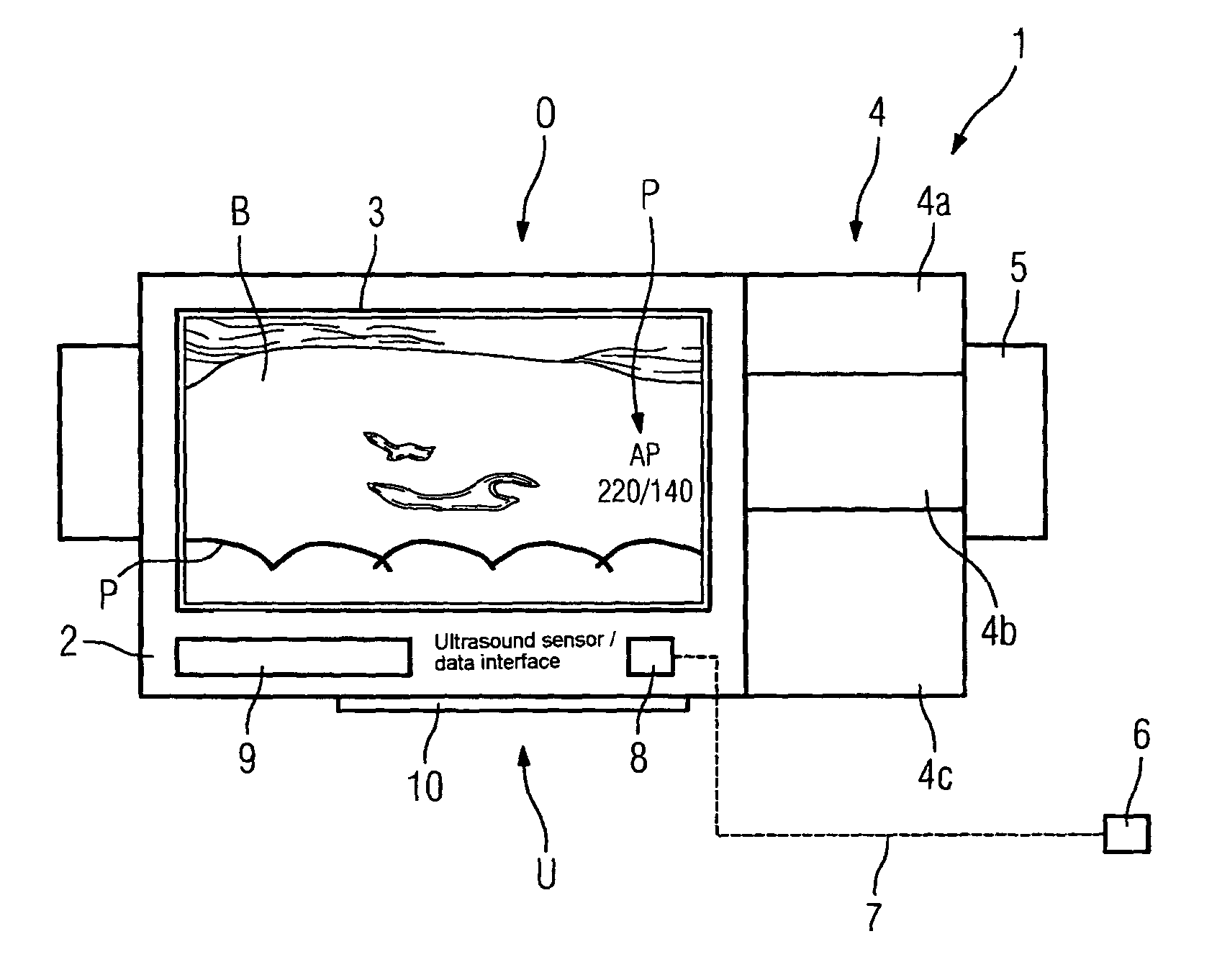
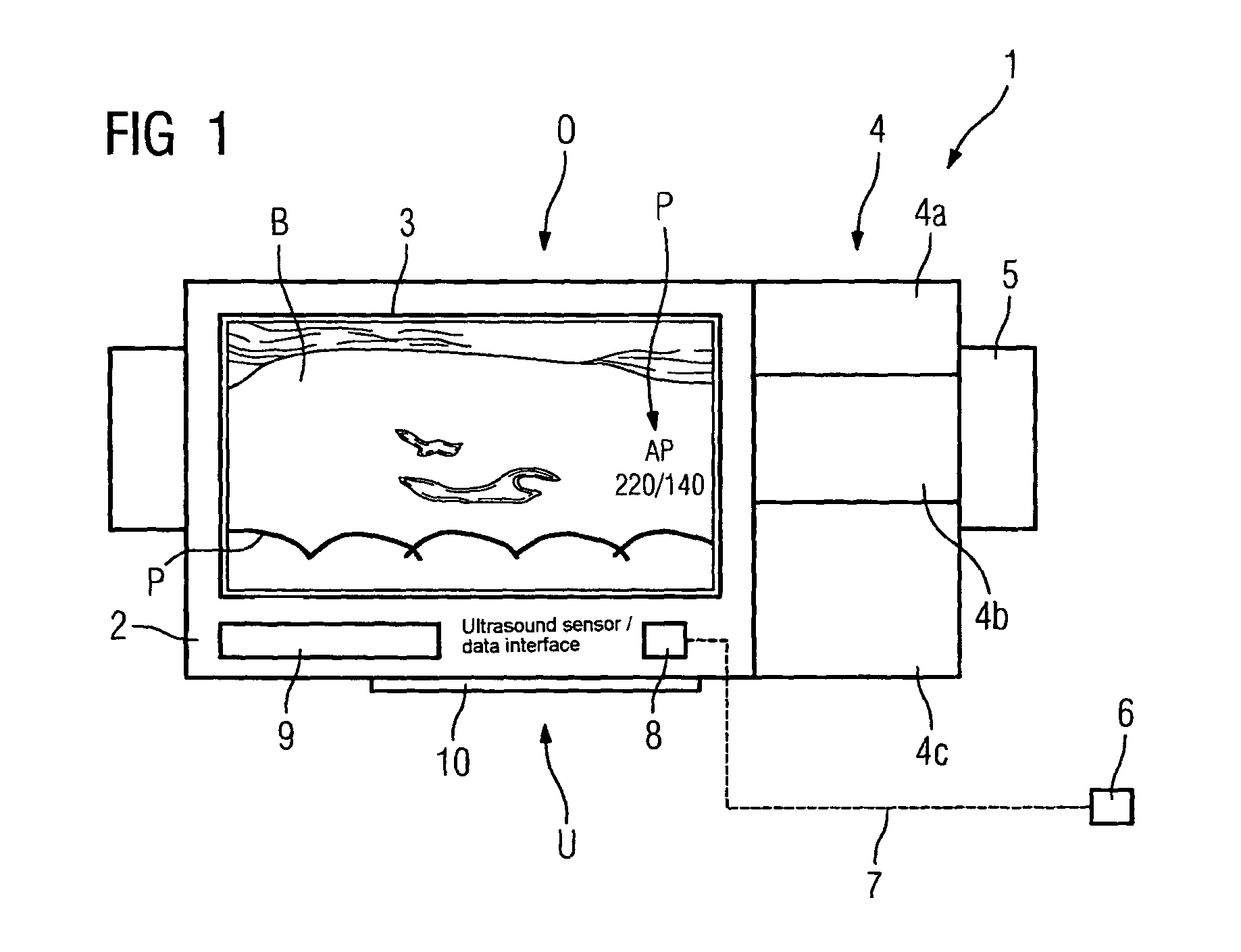
Ultrasound probe head comprising an imaging transducer with a shielding element
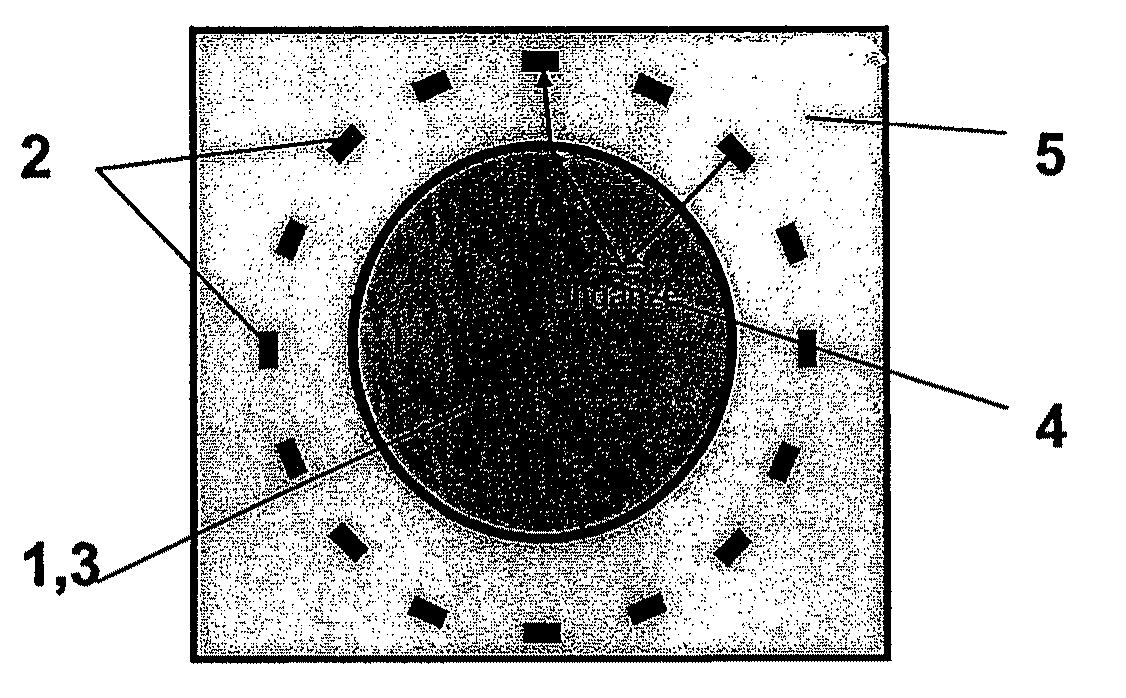
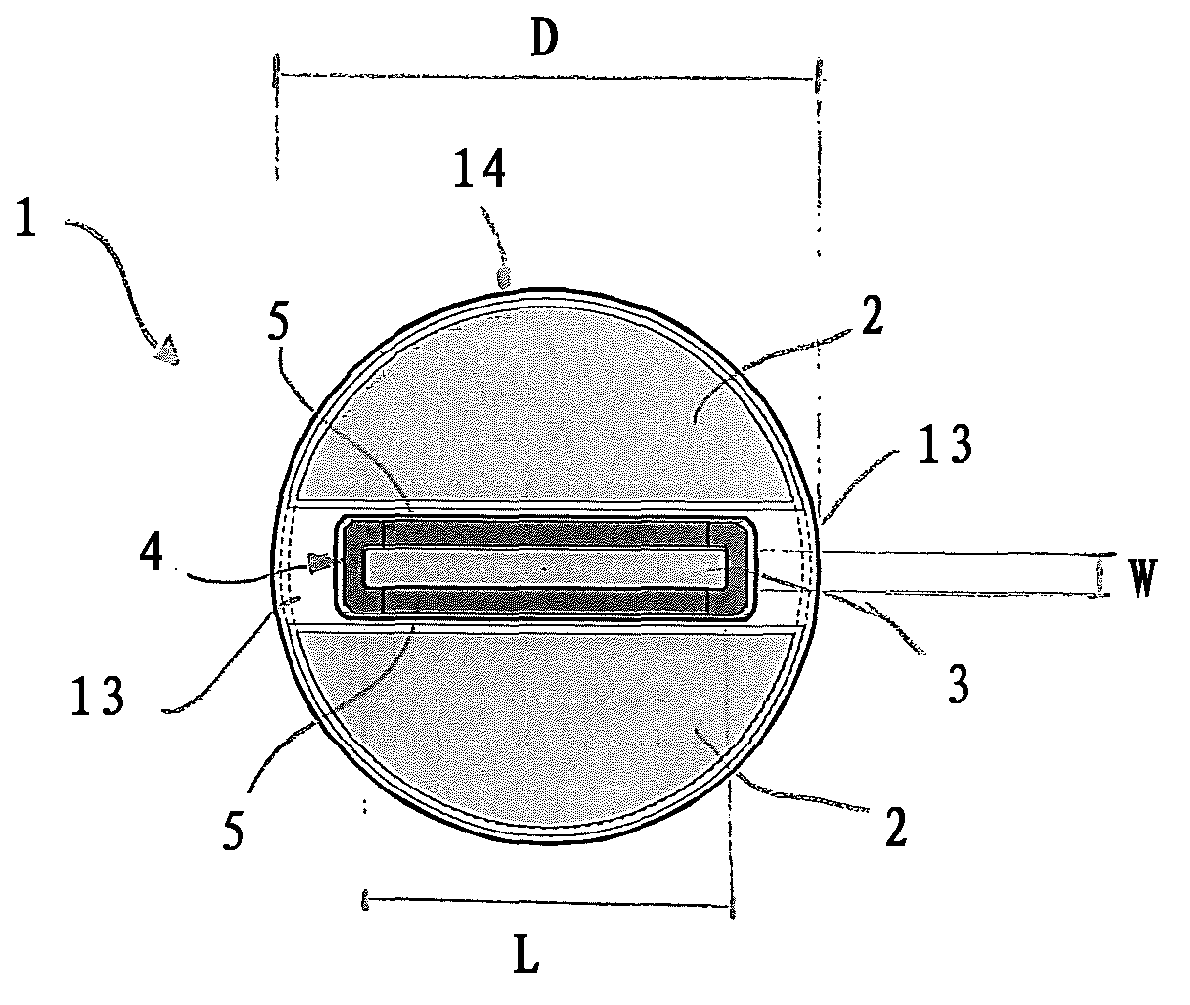
ActiveCN102939131AReduce risk of damageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyRadiologyImaging ultrasound
The present invention relates to an ultrasound probe head (1), especially for HIFU treatment, comprising a treatment ultrasound transducer (2) and an imaging ultrasound transducer (3). The imaging transducer (3) comprises a shield element (4) configured such that most of the energy of ultrasound waves (10) reflected in the direction of the imaging transducer (3) are held back by said shield element (4). The shield element (4) is configured in such a way as not to interfere with the emission of the imaging ultrasound waves (7).
Owner:THERACLION
Method for confirming location of focal point, and ultrasonic medical apparatus therefor
InactiveCN105188847AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyImaging ultrasoundHigh intensity
Provided are a method and an ultrasonic medical apparatus for confirming the location of a focal point of high-intensity focused ultrasonic waves. Provided are a method for confirming the location of a focal point and an ultrasonic medical apparatus therefor, the method synchronizing the point in time at which high-intensity ultrasonic waves and imaging ultrasonic waves are generated, and, as a result, pre-targeting the location of the high-intensity ultrasonic waves by means of reflected signals at the focal point to which the synchronized imaging and high-intensity ultrasonic waves are transmitted.
Owner:ALPINION MEDICAL SYST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com