Patents
Literature
69results about How to "Suitable image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
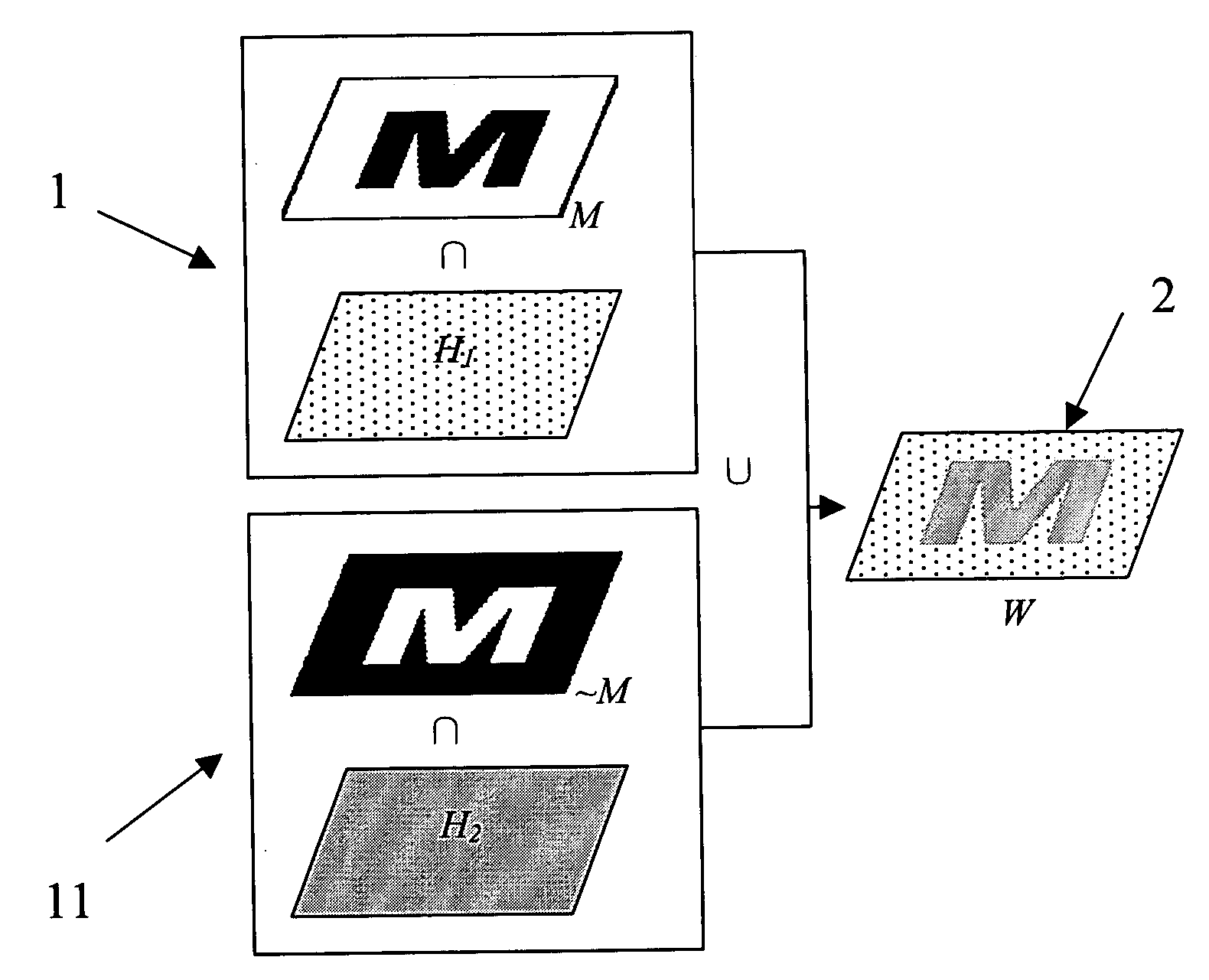
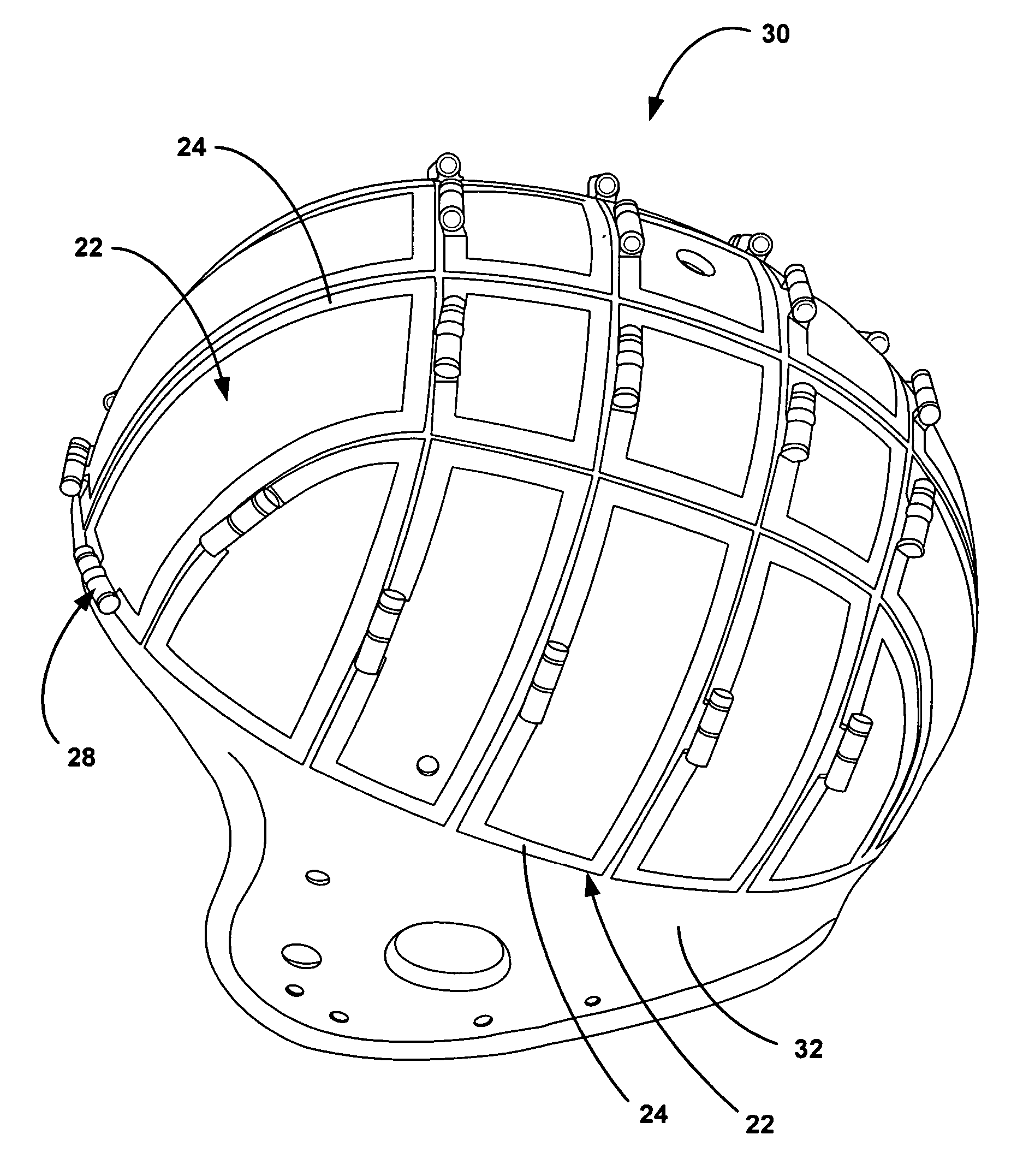
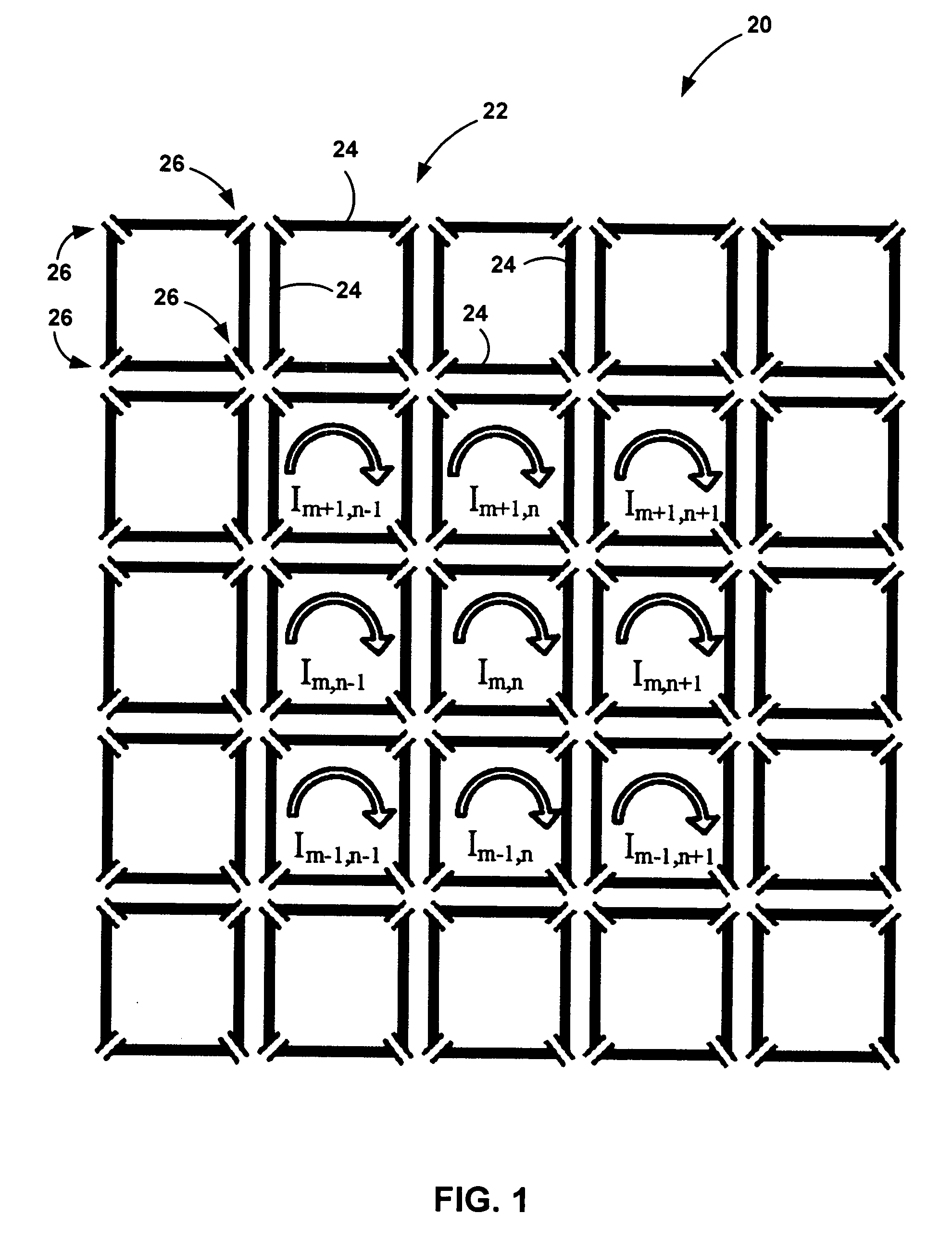
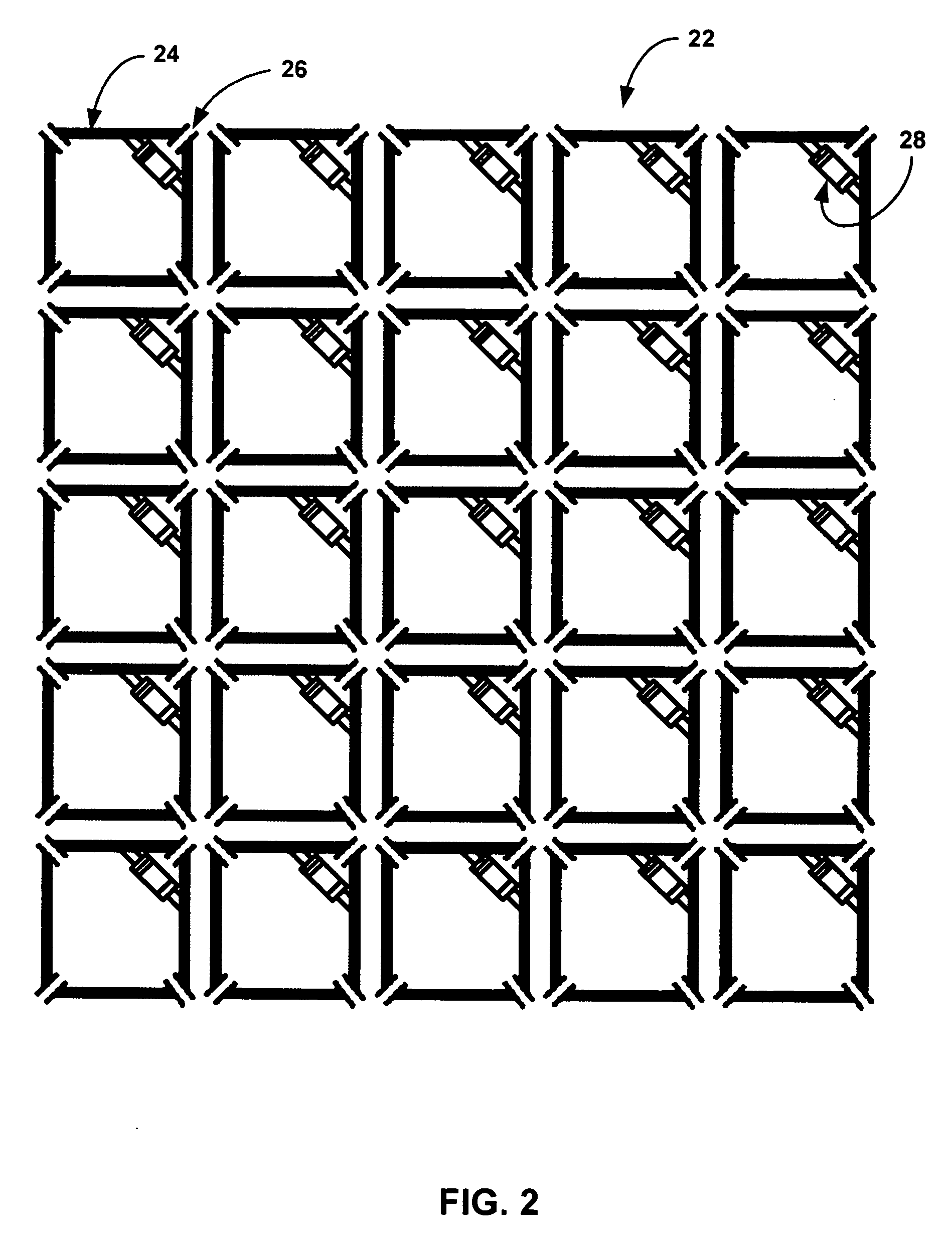
Method of watermark with hybrid halftone dots
ActiveUS20060170974A1Reducing invisibility effectEasy to produceVisual presentationPictoral communicationOptical scannersHue
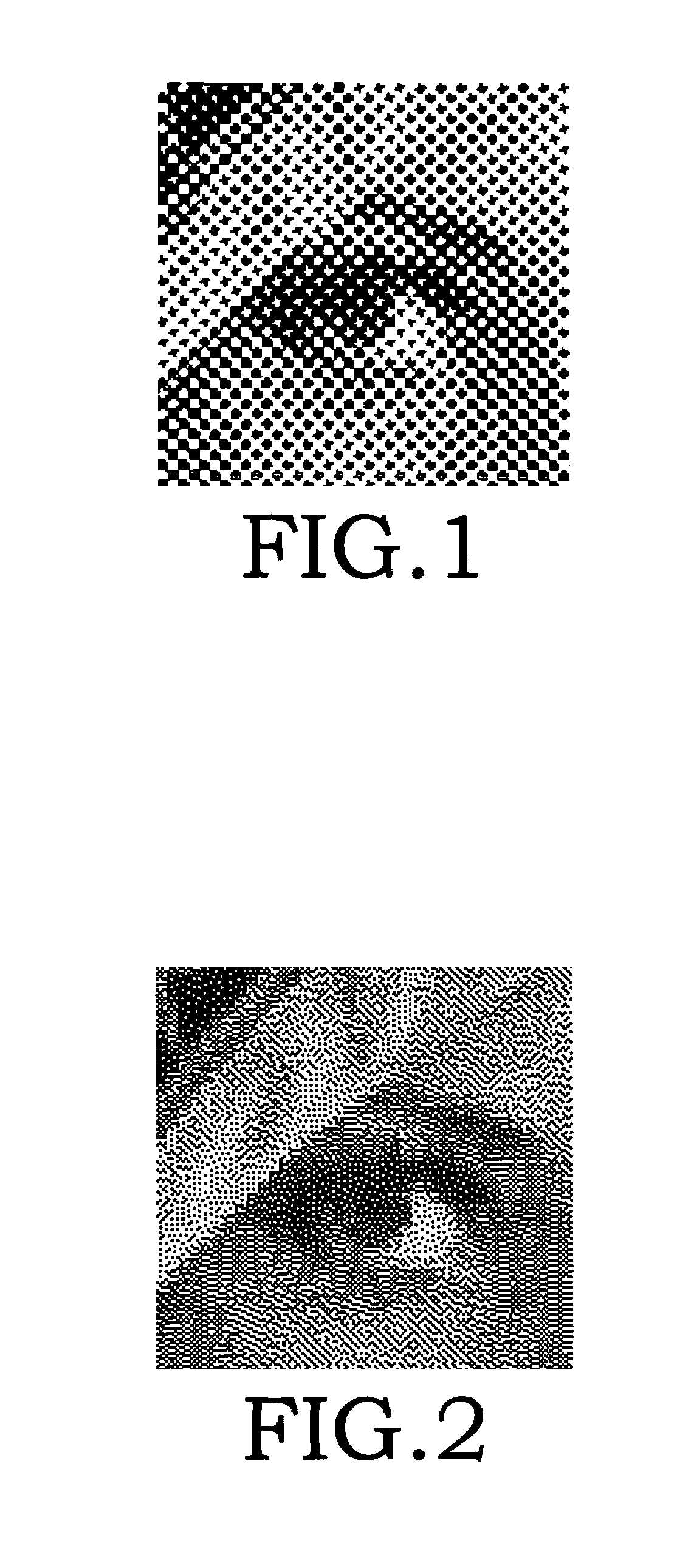
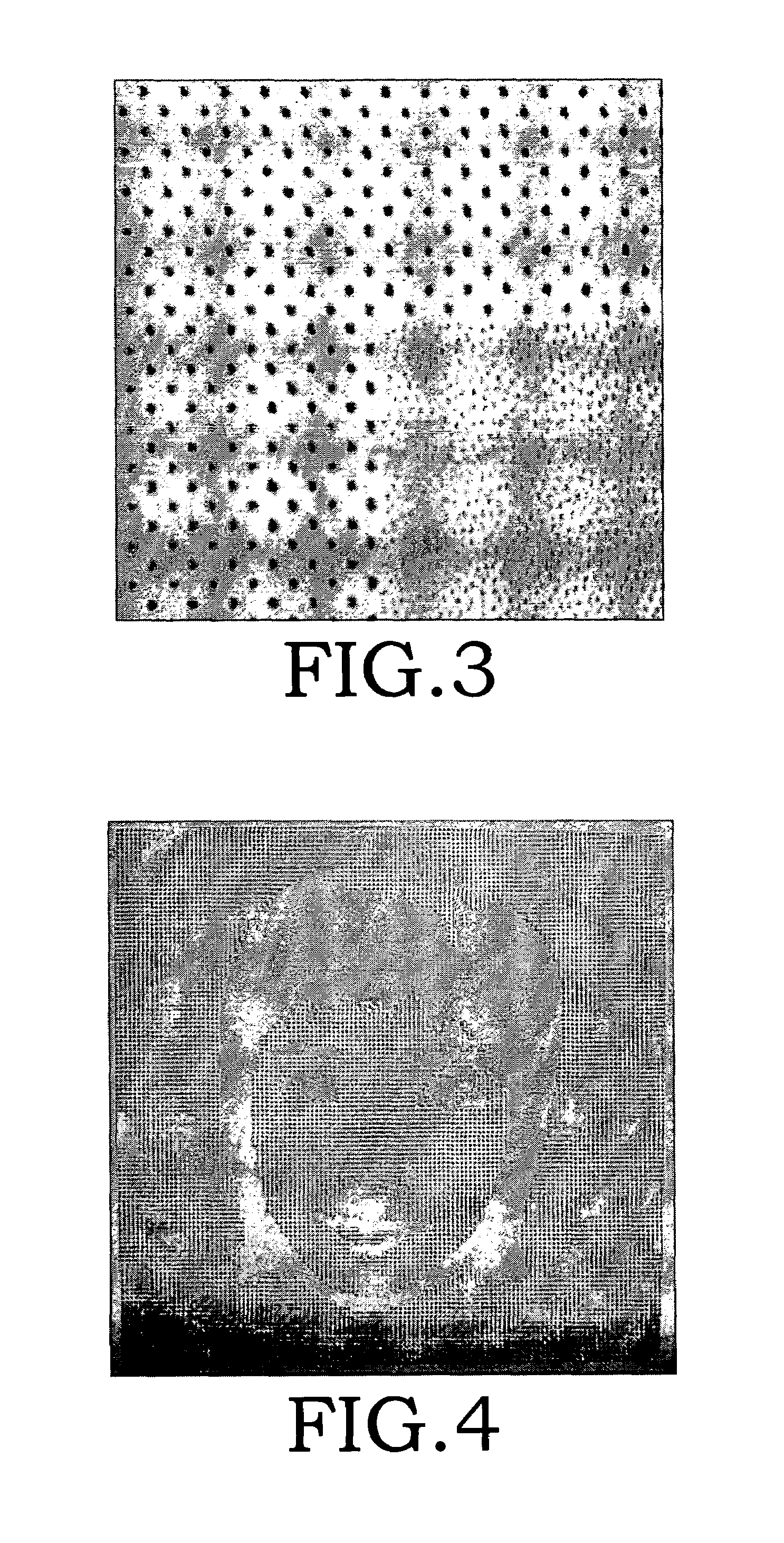
A method of watermark with hybrid halftone dots that is suitable for a printed shadow image. The watermark patterns that are composed of amplitude modulation (AM) and frequency modulation (FM) halftone dots (their concentration has been calibrated) cannot be perceived beyond a certain distance by the human eye. This is done through outputting the density calibration chart to choose the proper density parameters, which are applied to the manufacture process of the watermark with hybrid halftone dots. The hidden patterns of a watermark need to be pre-processed first, and thereby making the image blocks of AM and FM halftone dots to be combined smoothly. The copy machine, the lenticular lens and the optical scanner can detect the hidden watermark in the printed shadow image. Each secured document possesses a different serial number to achieve the document-version control.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
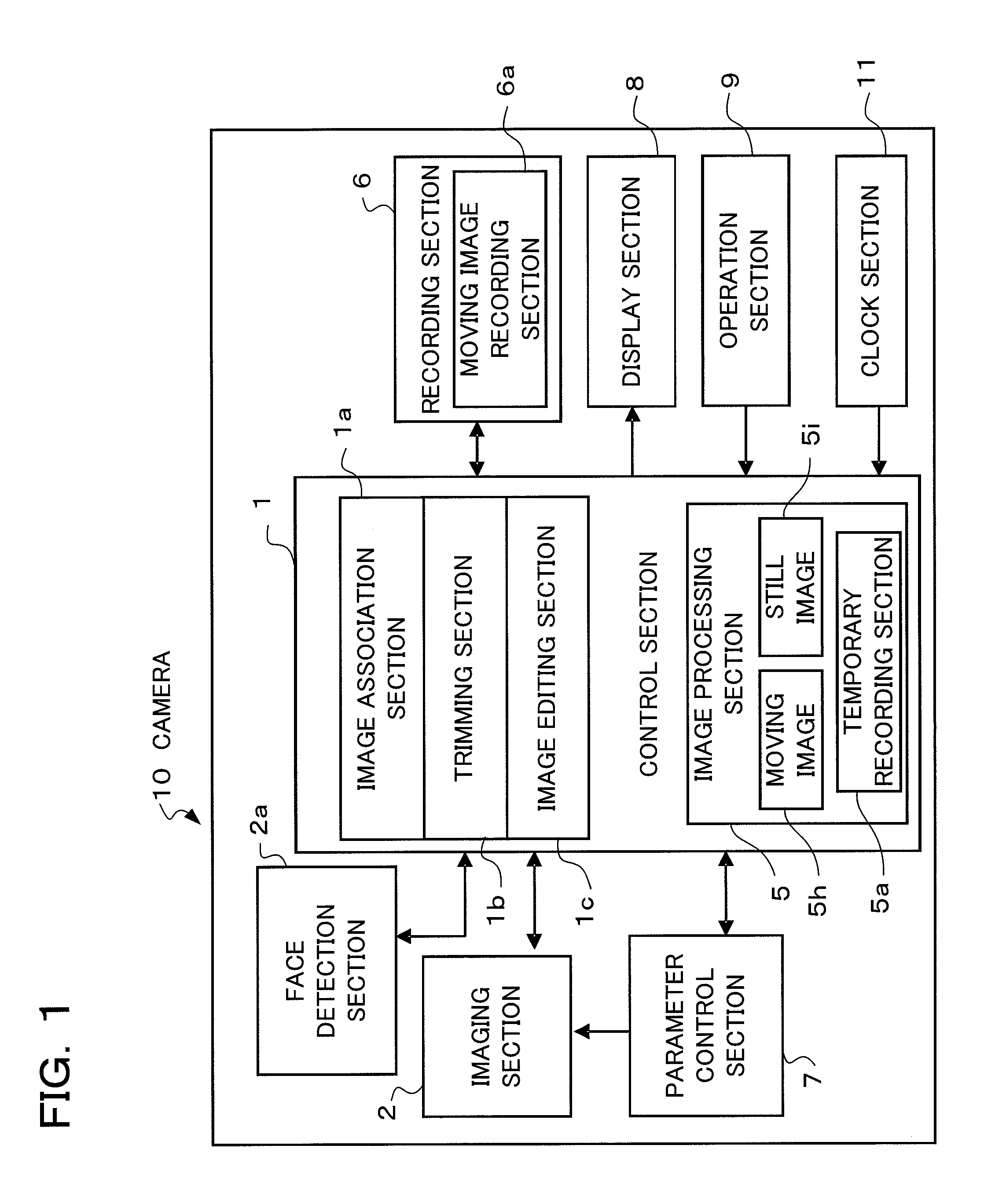
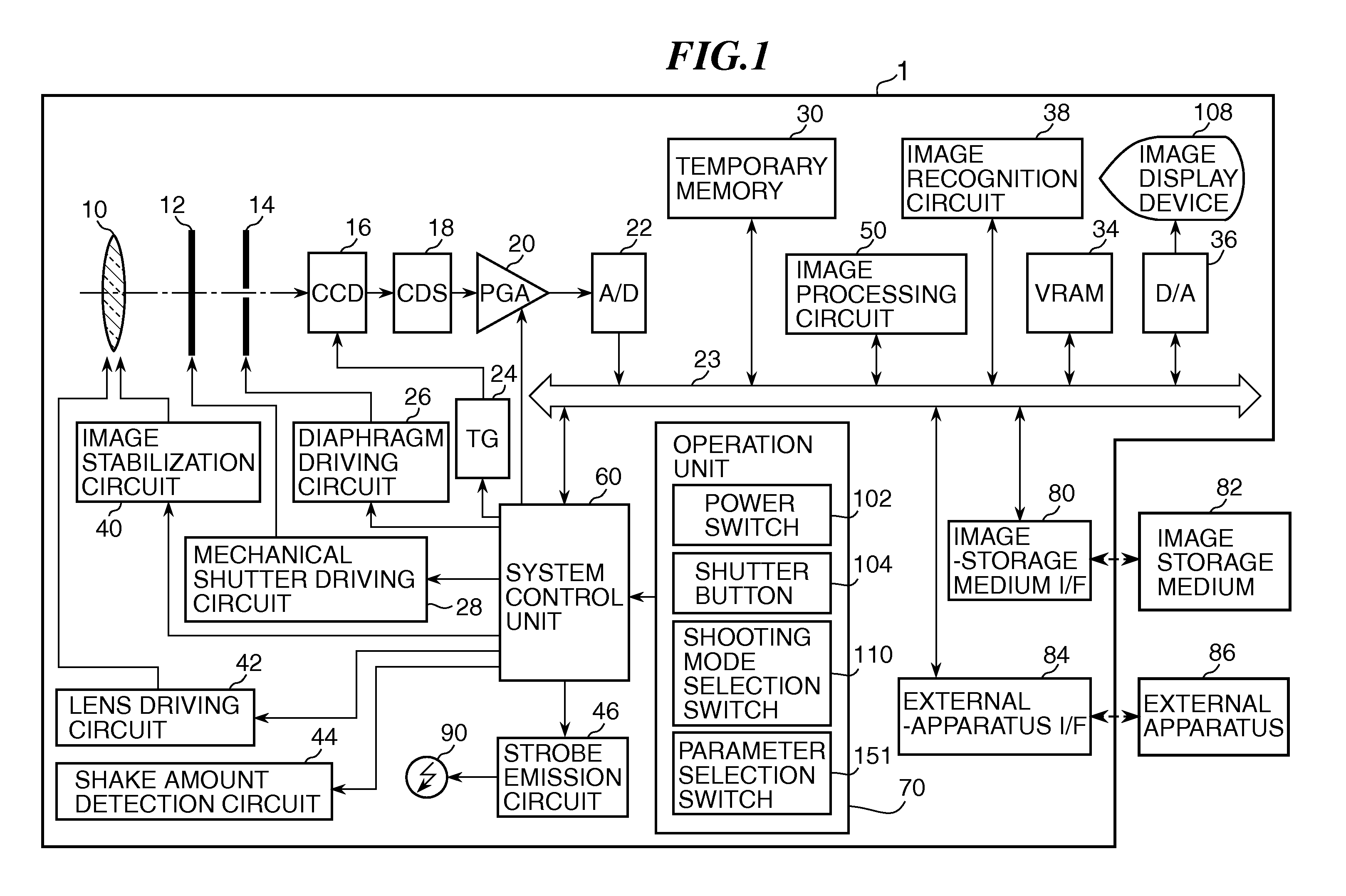
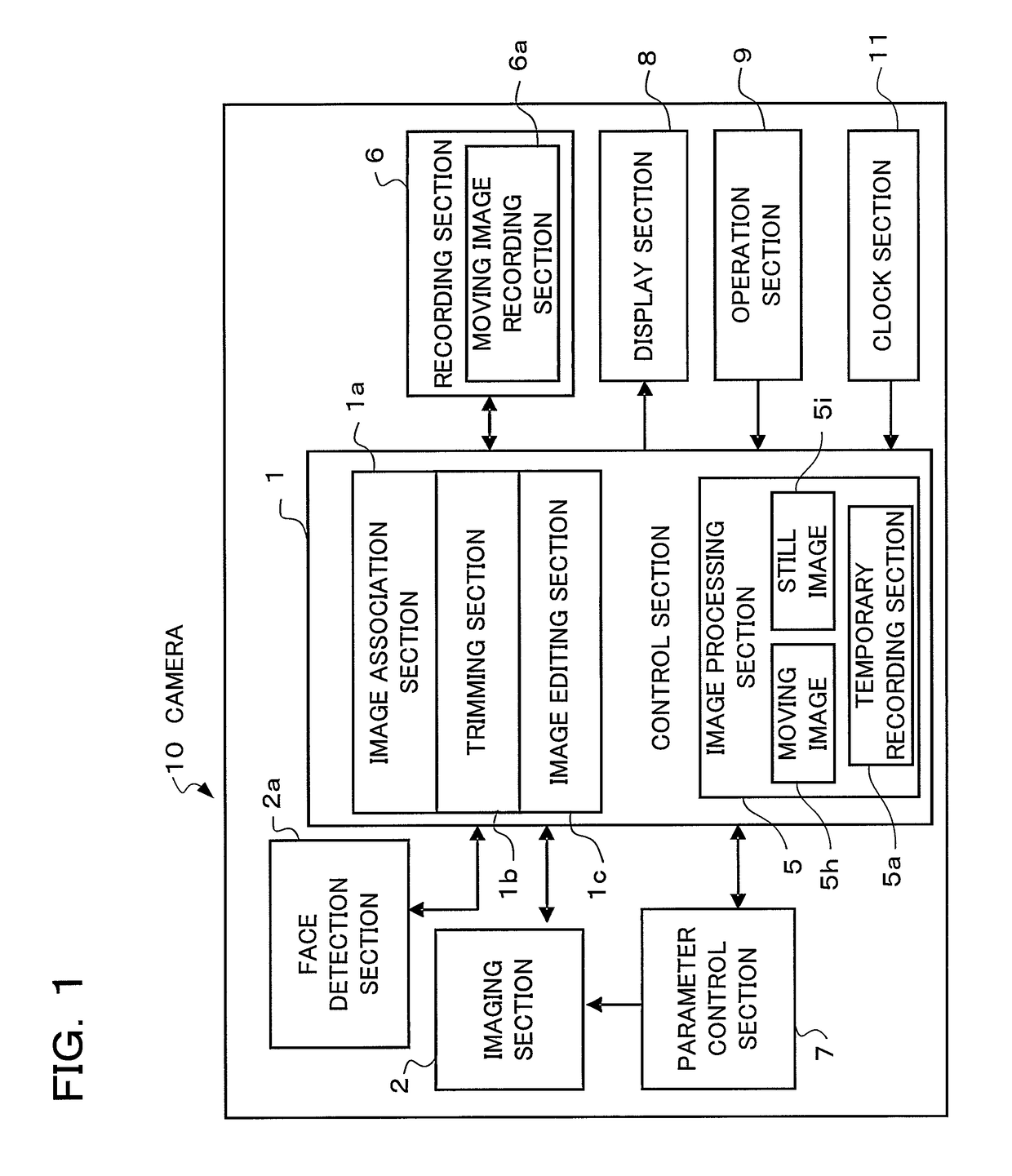
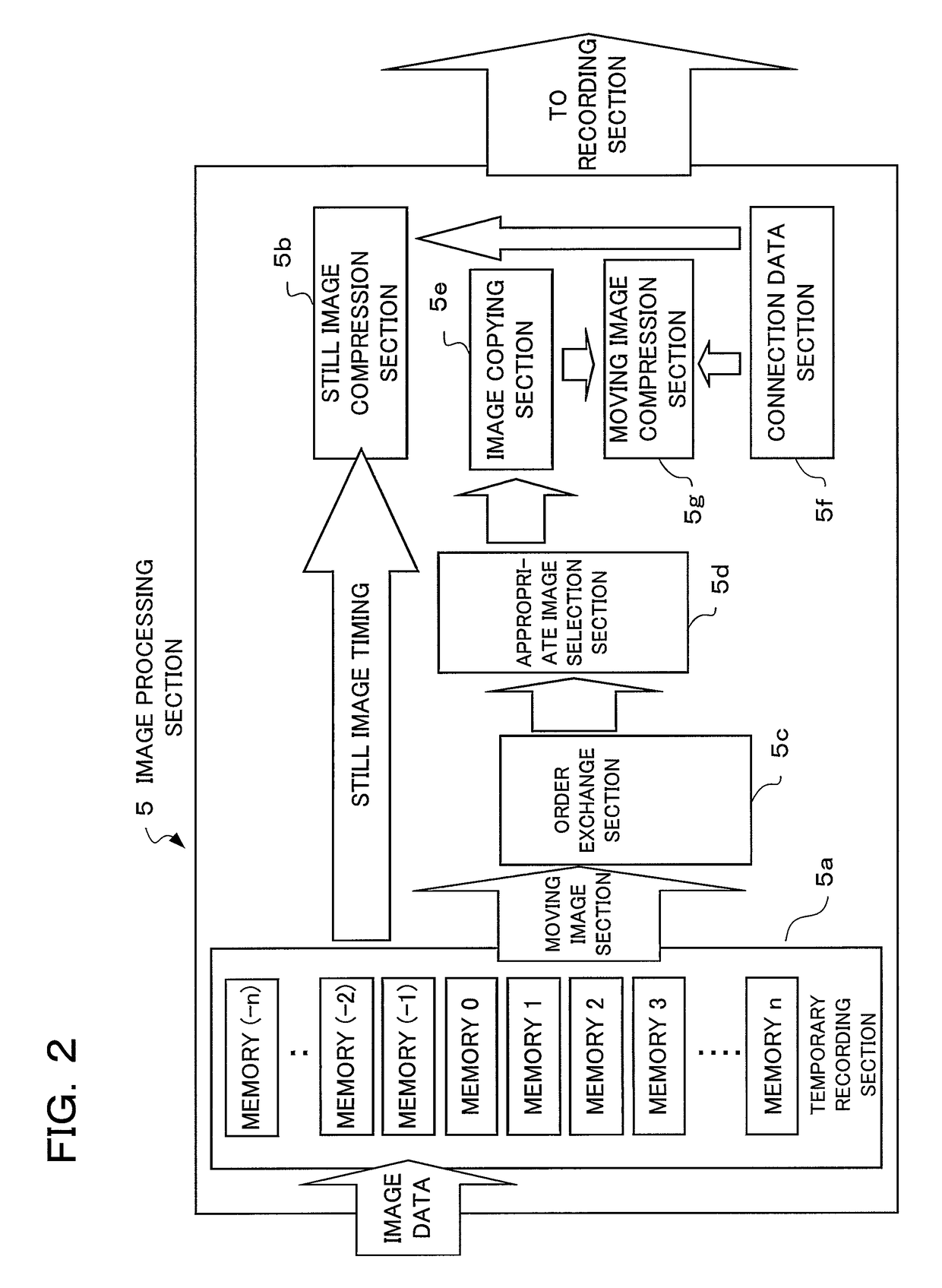
Camera and display control method of the same
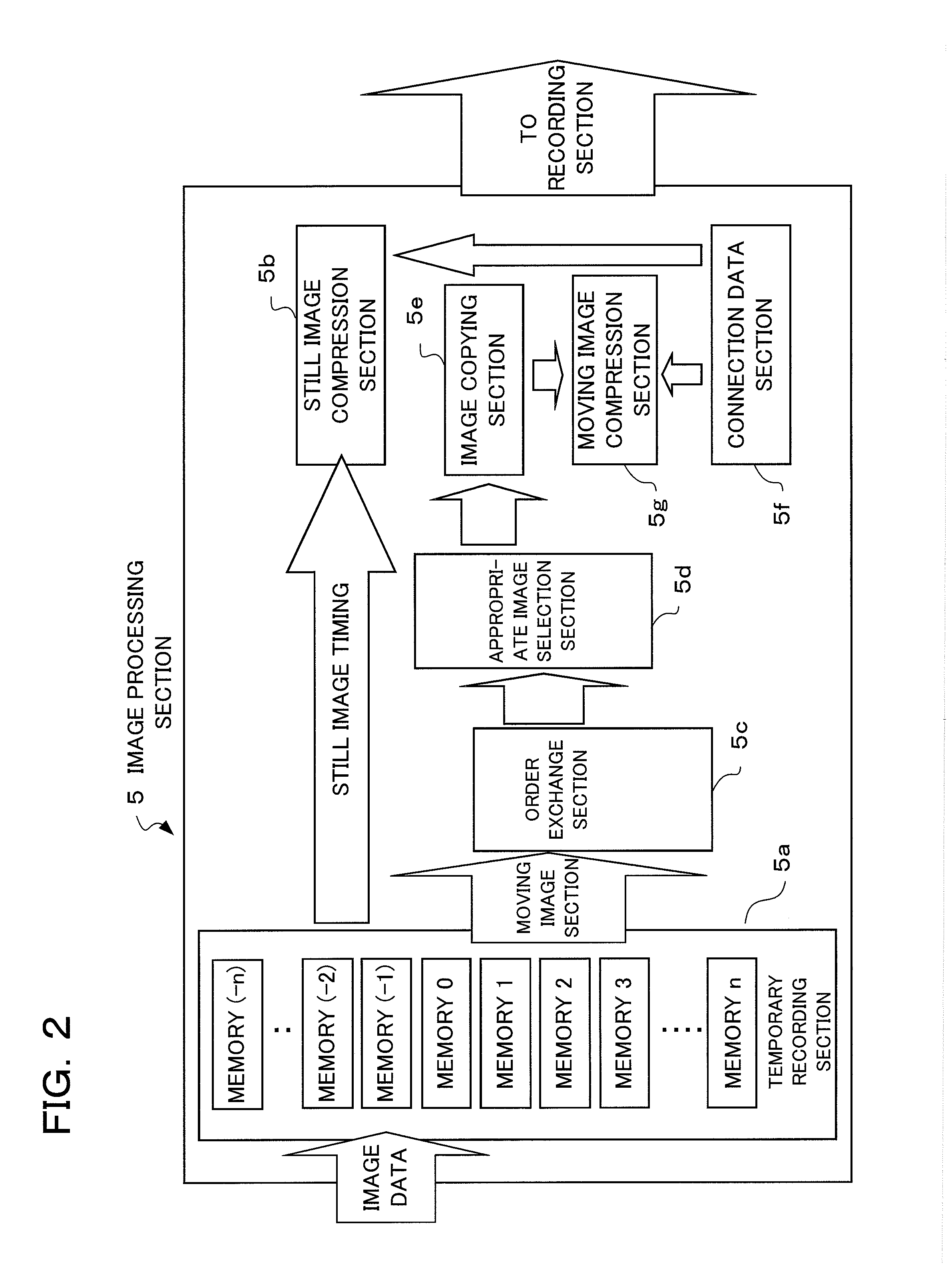
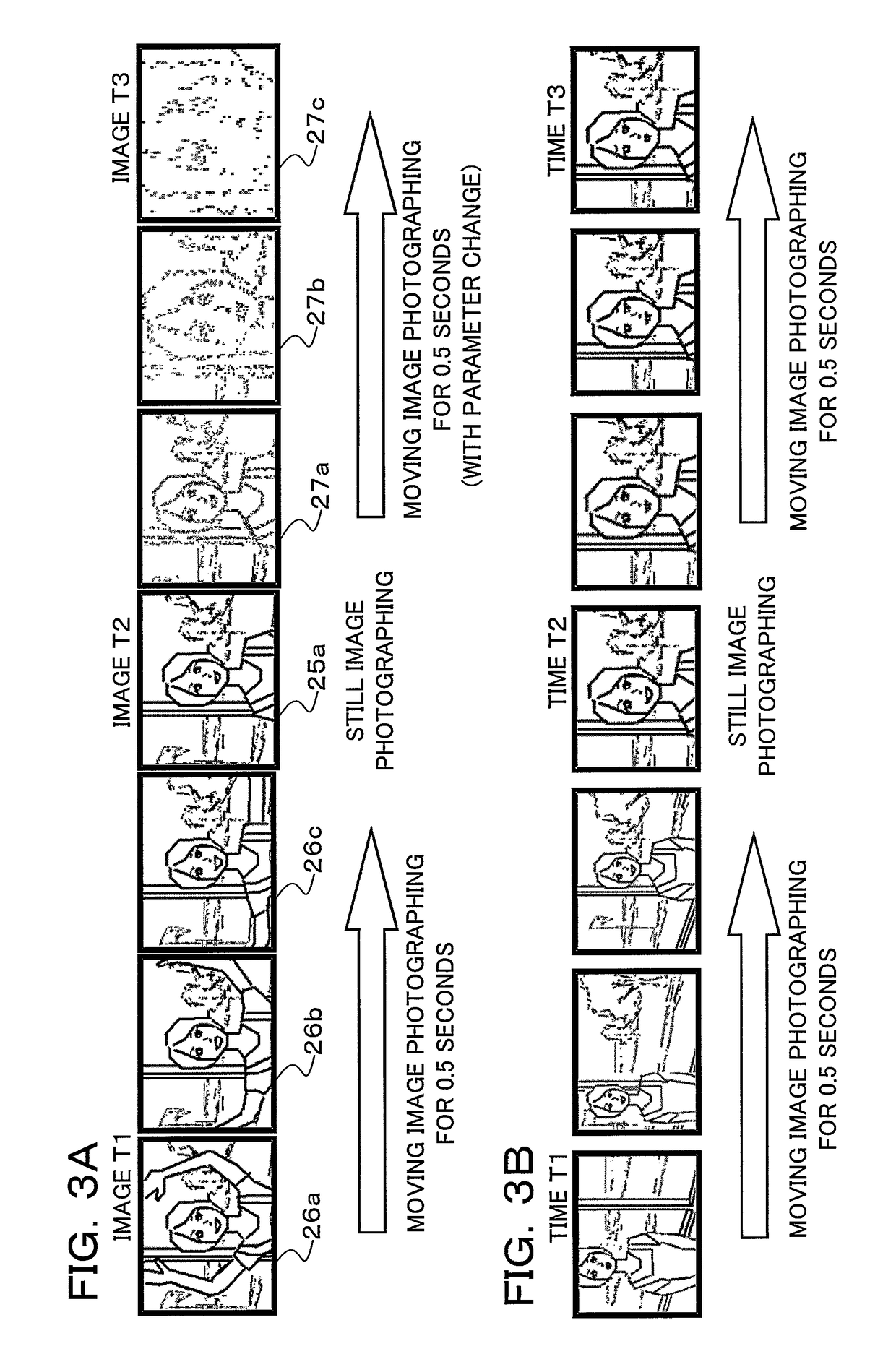
ActiveUS20110043651A1Suitable imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsThumbnail ImageImaging data
A camera according to the present invention comprises: an imaging section converting an object image into image data; a storage section storing still image data of a still image obtained by the imaging section, thumbnail image data of the still image, and moving image data of a moving image which has been photographed at timing at least either before or after photographing of the still image; a display section performing display of one or more thumbnail views according to the thumbnail image data; and a display control section, when one of the thumbnail views is designated in the thumbnail view display, performing display of the still image on the display section according to the still image data corresponding to the designated thumbnail view after having performed display of the moving image according to the moving image data corresponding to the designated thumbnail view stored in the storage section.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
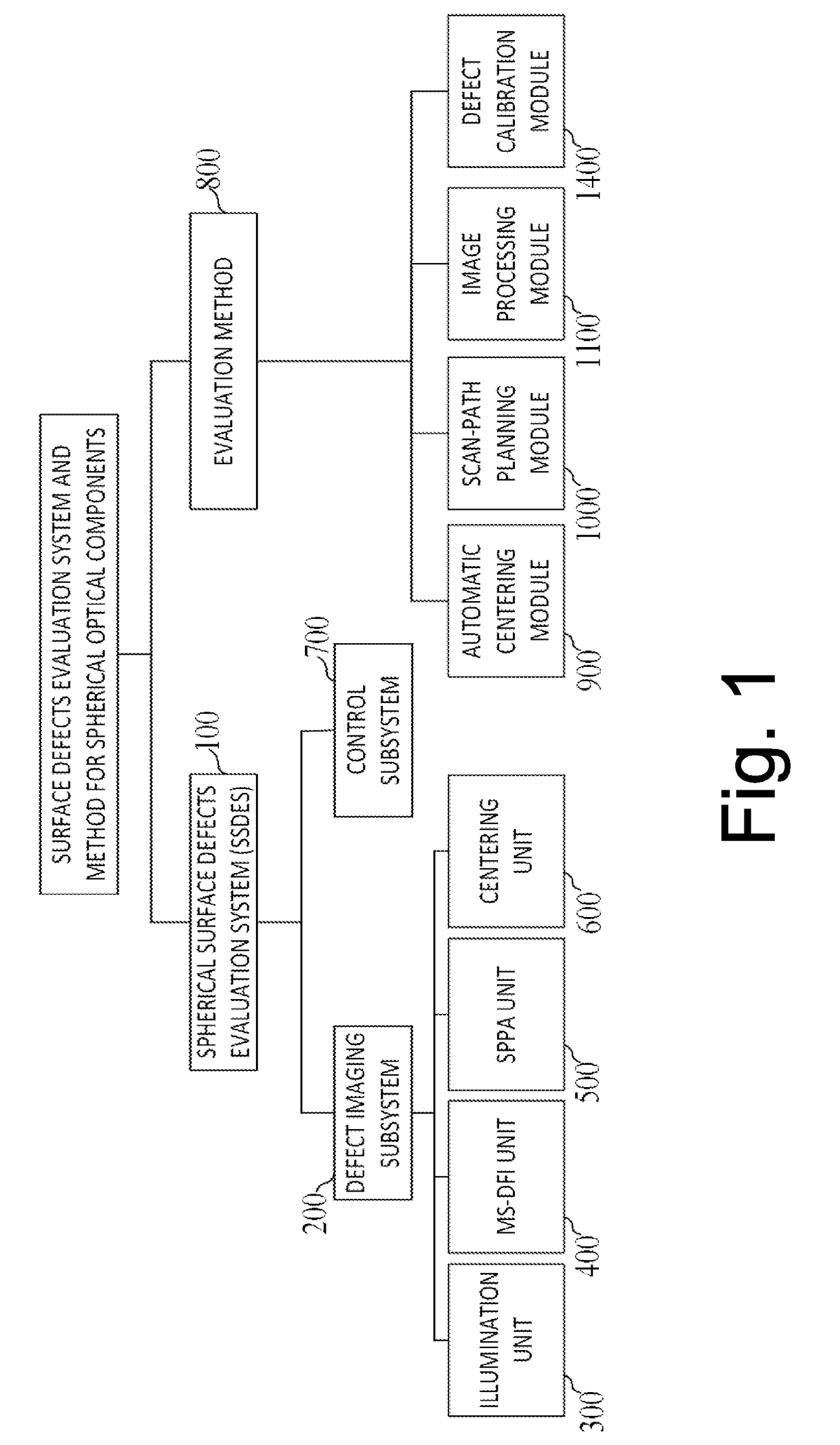
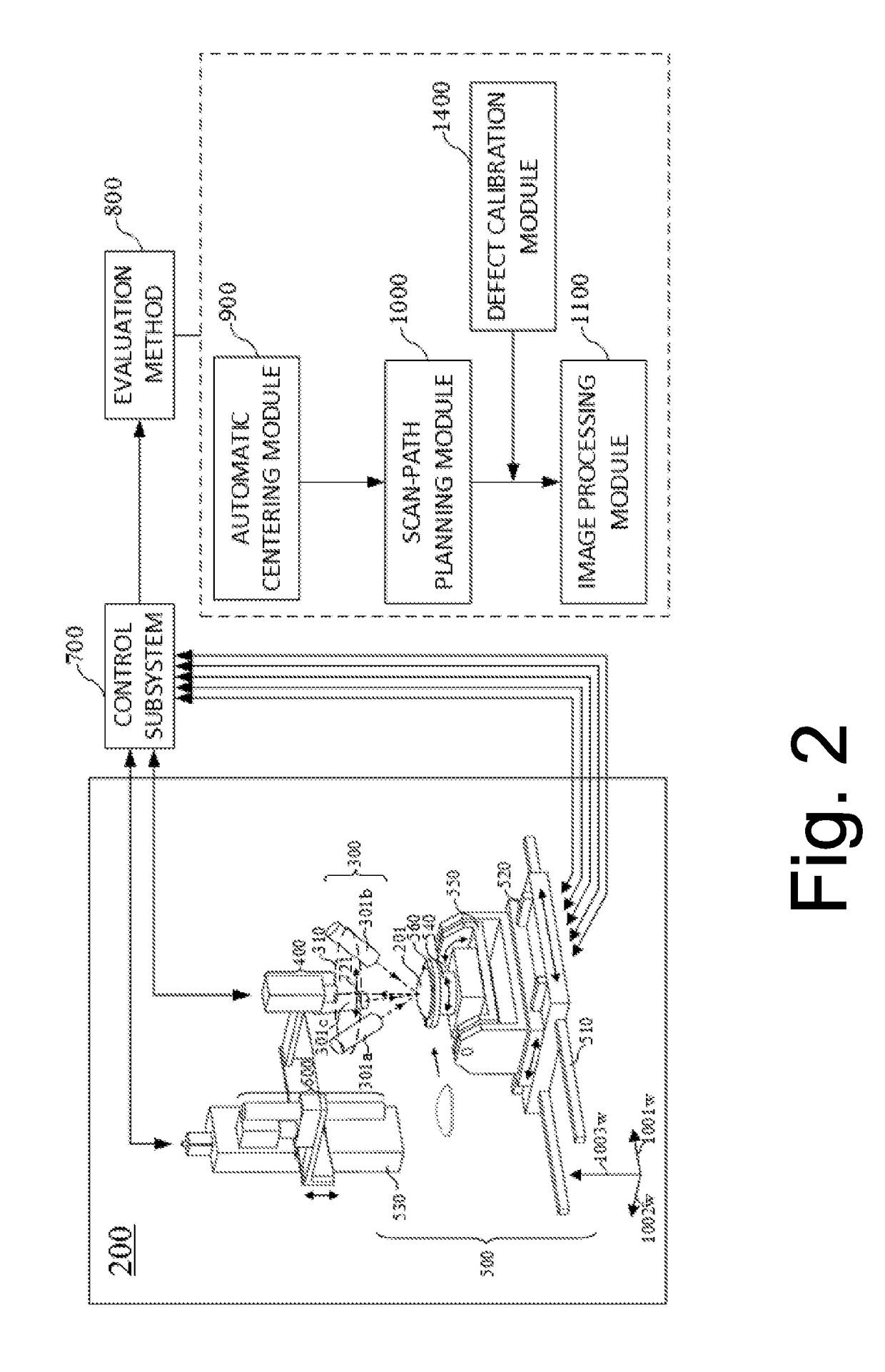
Surface defects evaluation system and method for spherical optical components
ActiveUS20170292916A1Easy to getSuitable imageOptically investigating flaws/contaminationFeature extractionImaging processing
A defects evaluation system and method are provided in the present invention. Based on the principle of the microscopic scattering dark-field imaging, the present invention implements a sub-aperture scanning for the surface of spherical optical components and then obtains surface defects information with image processing. Firstly, the present invention takes full advantage of the characteristic that the surface defects of spherical optical components can generate scattering light when an annular illumination beam irradiates on the surface, to implement the sub-aperture scanning and imaging that covers the entire spherical surface. Then, a series of procedures such as the global correction of sub-apertures, the 3D stitching, the 2D projection and the digital feature extraction are taken to inspect spherical surface defects. Finally, actual size and position information of defects are evaluated quantitatively with the defects calibration data. The present invention achieves the automatic quantitative evaluation for surface defects of spherical optical components, which considerably enhance the efficiency and precision of the inspection, avoiding the influence of subjectivity on the results. Eventually, reliable numerical basis for the use and process of spherical optical components is provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
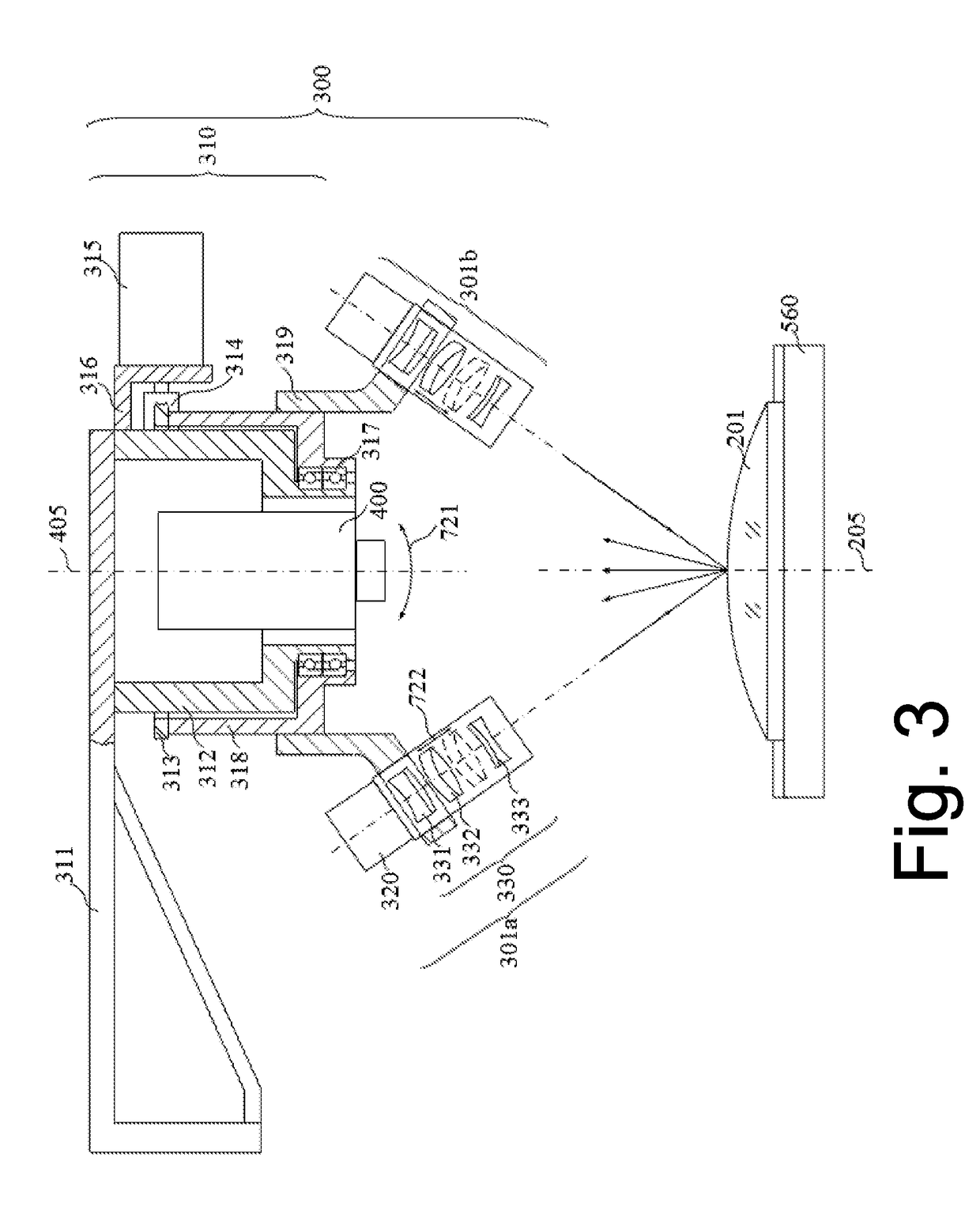
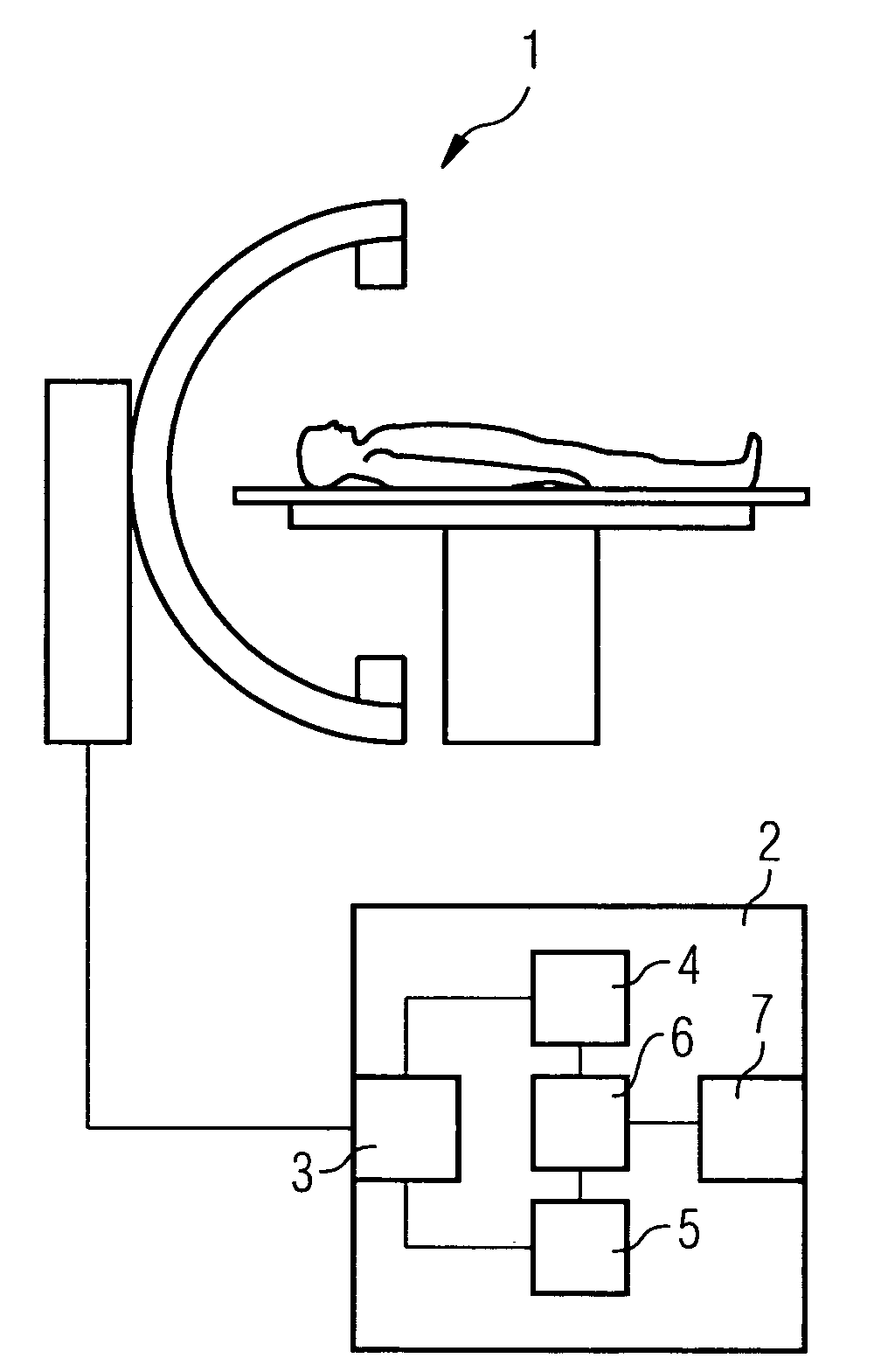
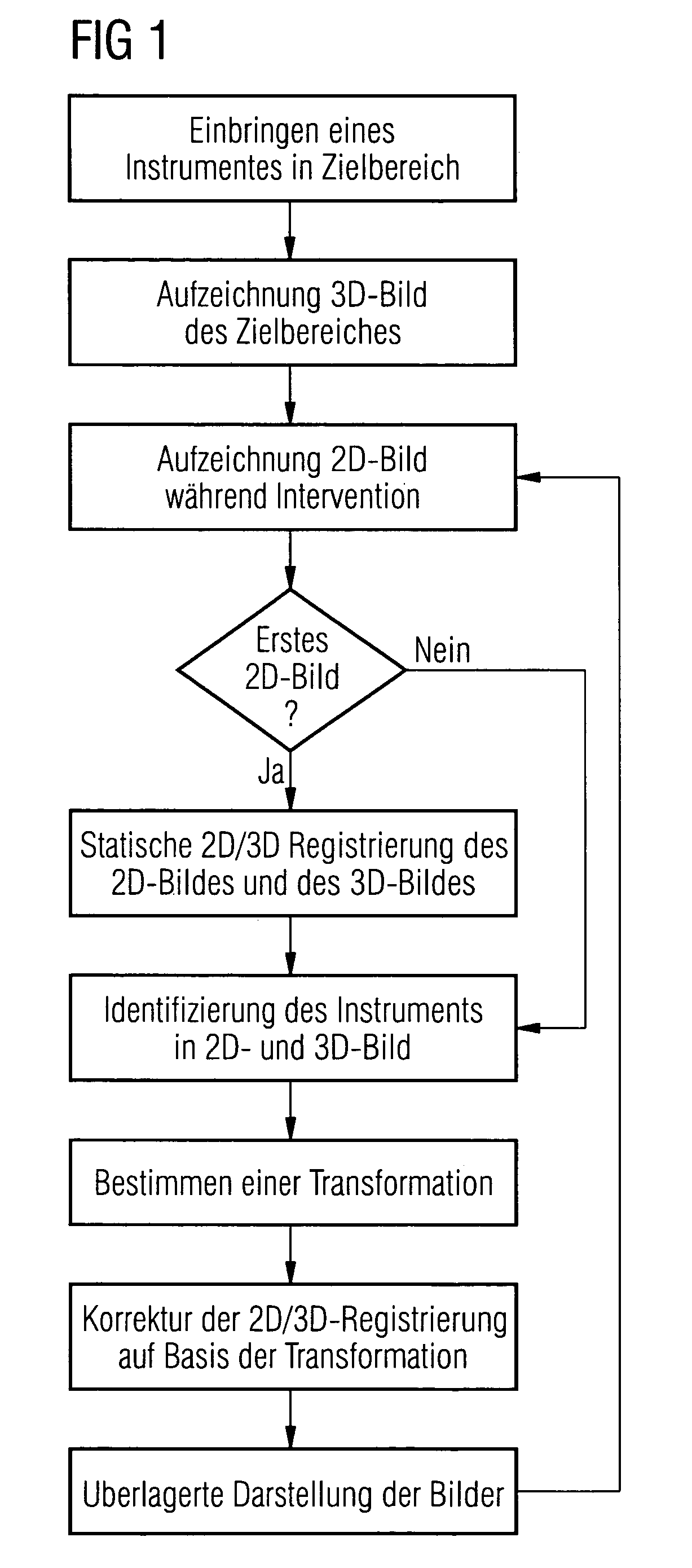
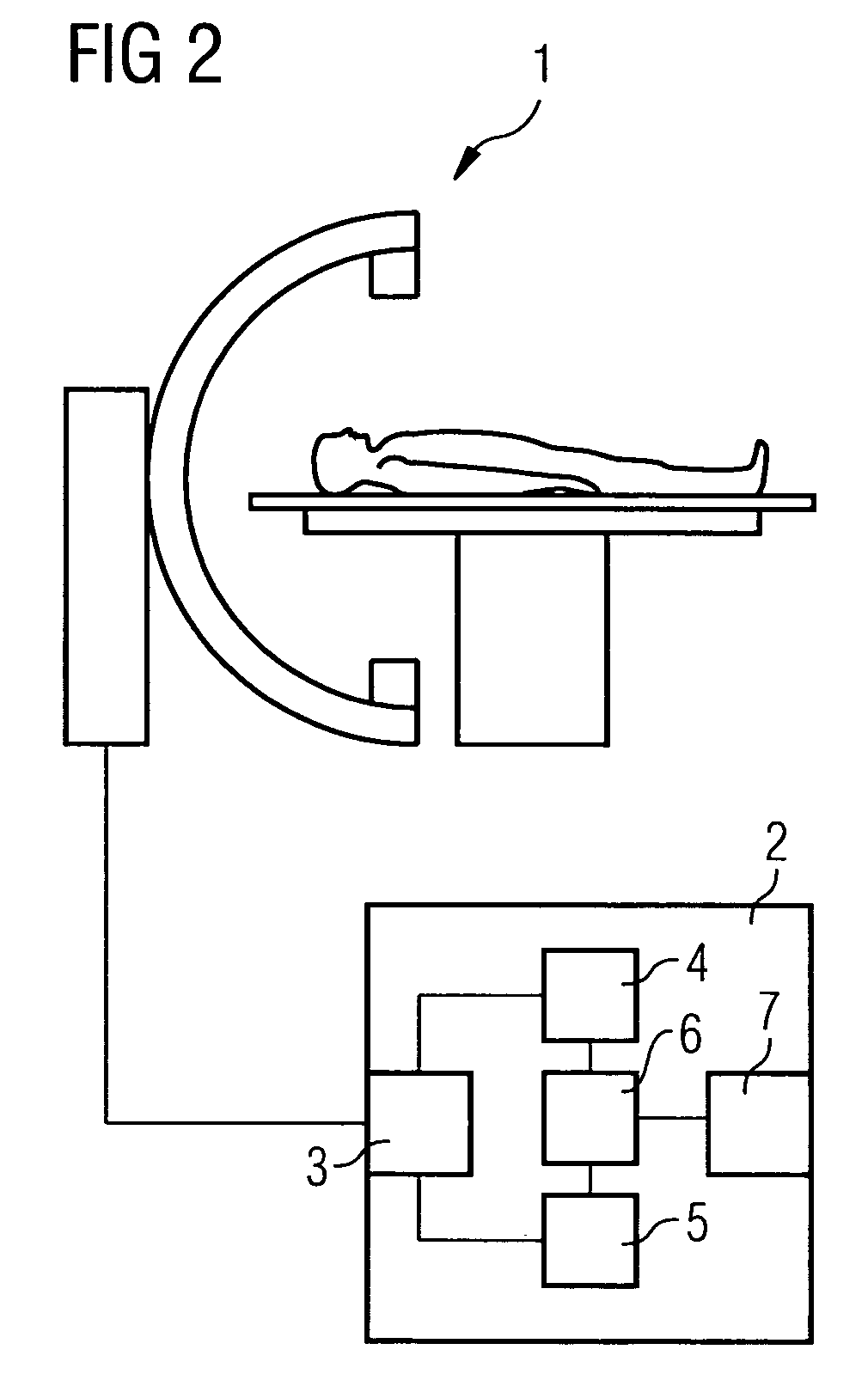
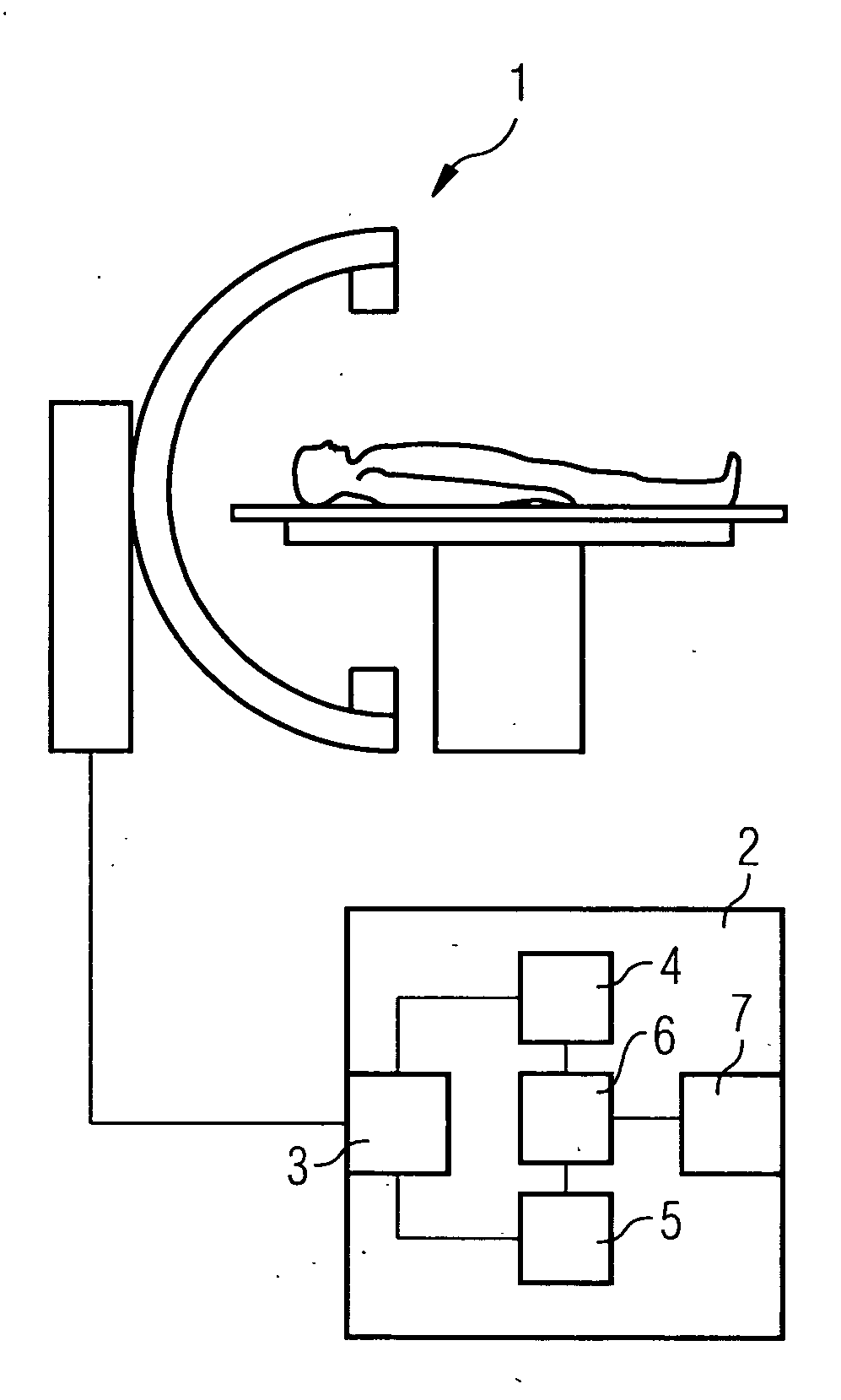
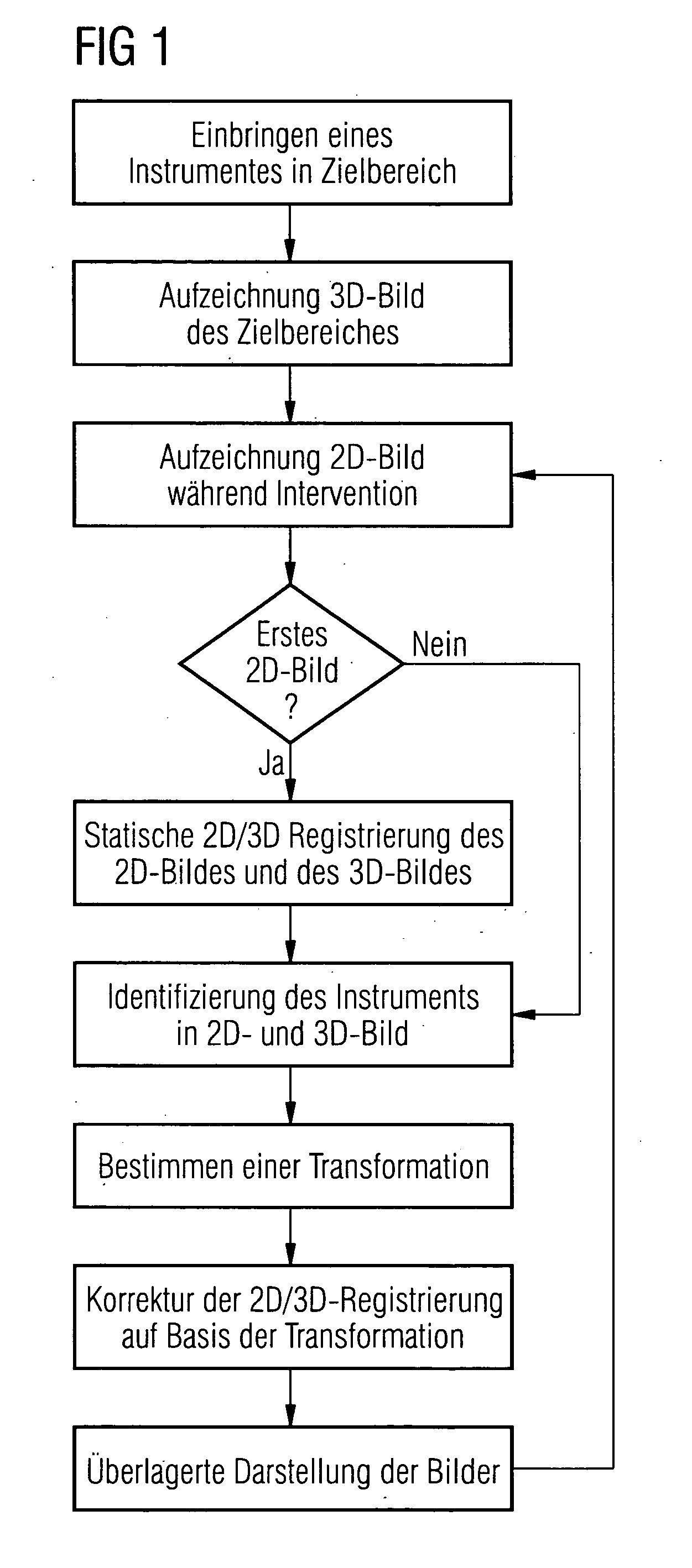
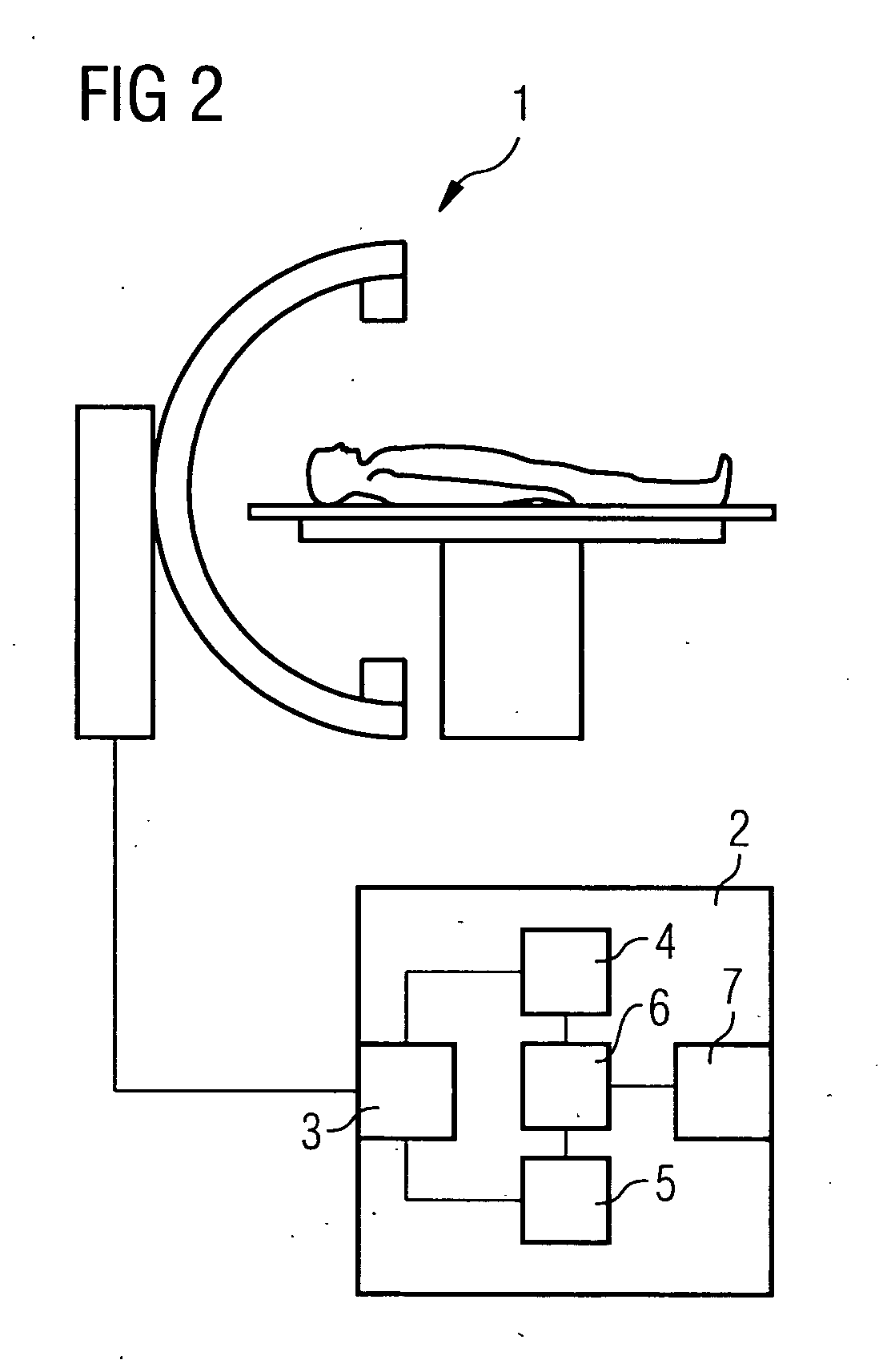
Method and device for correction motion in imaging during a medical intervention
ActiveUS7761135B2High target accuracySuitable imageImage enhancementImage analysisPresent methodFluoroscopic image
The present invention relates to a method and a device for correcting motion in imaging during a medical intervention, by which method a 3D tomographic image of a target area for the intervention is first recorded while there are one or more medical instruments in the target area that will remain there during the intervention. During the intervention 2D fluoroscopic images of the target area are recorded and registered with the 3D image. The registration is therein adjusted for each 2D fluoroscopic image in realtime based in each case on the one or more instruments. The 2D fluoroscopic images are then in each case visualized with representations, concurring in terms of perspective, of the 3D image. Virtually error-free overlaying of the 3D image with in each case one 2D fluoroscopic image can be implemented using the present method and associated device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
High-pass two-dimensional ladder network resonator
InactiveUS20060244448A1Suitable imageIncrease working frequencyMagnetic measurementsRecord carriers used with machinesHigh field mriParallel imaging
A high-pass two-dimensional ladder network has been described for high-field MRI and credential applications. The next-to-highest eigenvalue of the network corresponds to a normal mode giving rise to B1 fields with good spatial homogeneity above the resonator plane. Other eigenvalues may also be used for specific imaging applications. In its most basic form, the ladder network is a collection of inductively coupled resonators where each element of the array is represented by at least one conducting strip having a self-inductance L, joined by a capacitor C at one or more points along each resonator. In the strong coupling limit of the inductively coupled high-pass two-dimensional ladder network resonator array, the array produces a high-frequency resonant mode that can be used to generate the traditional quadrature B1 field used in magnetic resonance imaging, and in the limit of weak or zero coupling reduces to a phased array suitable for parallel imaging applications.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Optical imaging probes
InactiveUS20110171136A1Reduce deliveryEnhance the imageNervous disorderSugar derivativesDiseaseDisease treatment
This invention relates to optical imaging probes and the use of such probes for diagnosing and monitoring disease, and disease treatment. The optical imaging probes of the current invention can be used to identify and characterize normal and diseased tissues with regards to altered metabolic activity.
Owner:VISEN MEDICAL INC
Method and apparatus for detecting an object within a dynamic scattering media
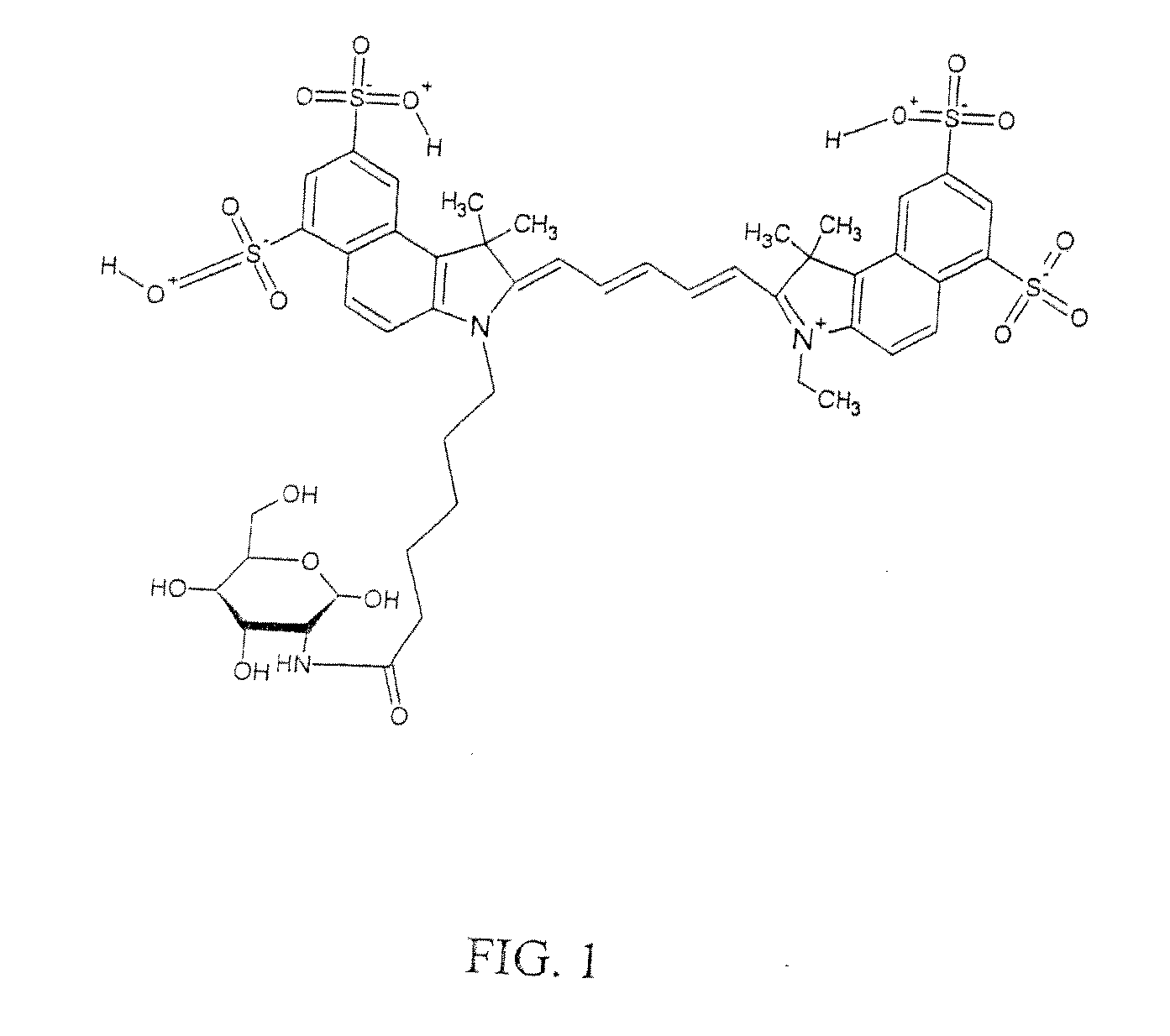
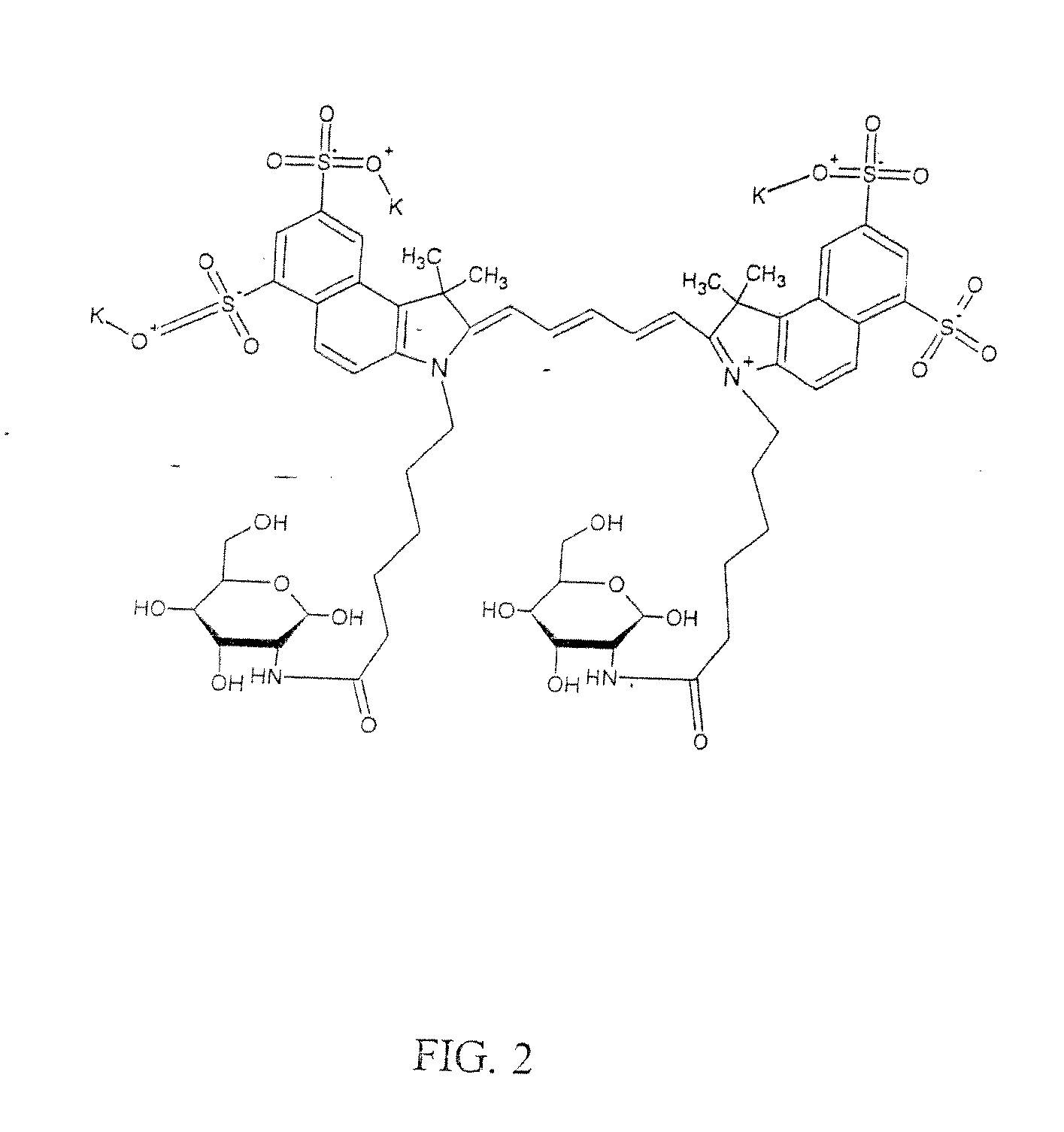
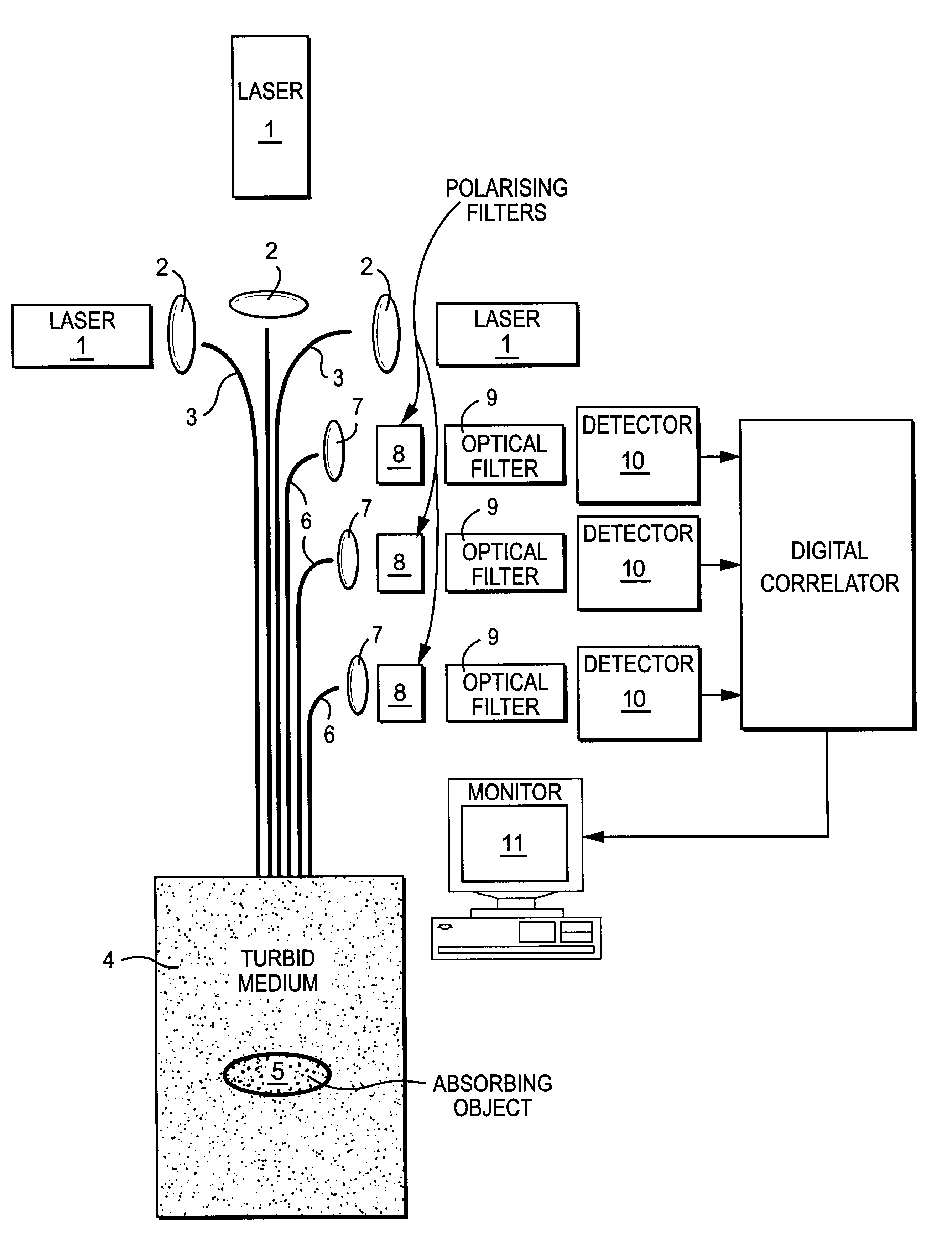
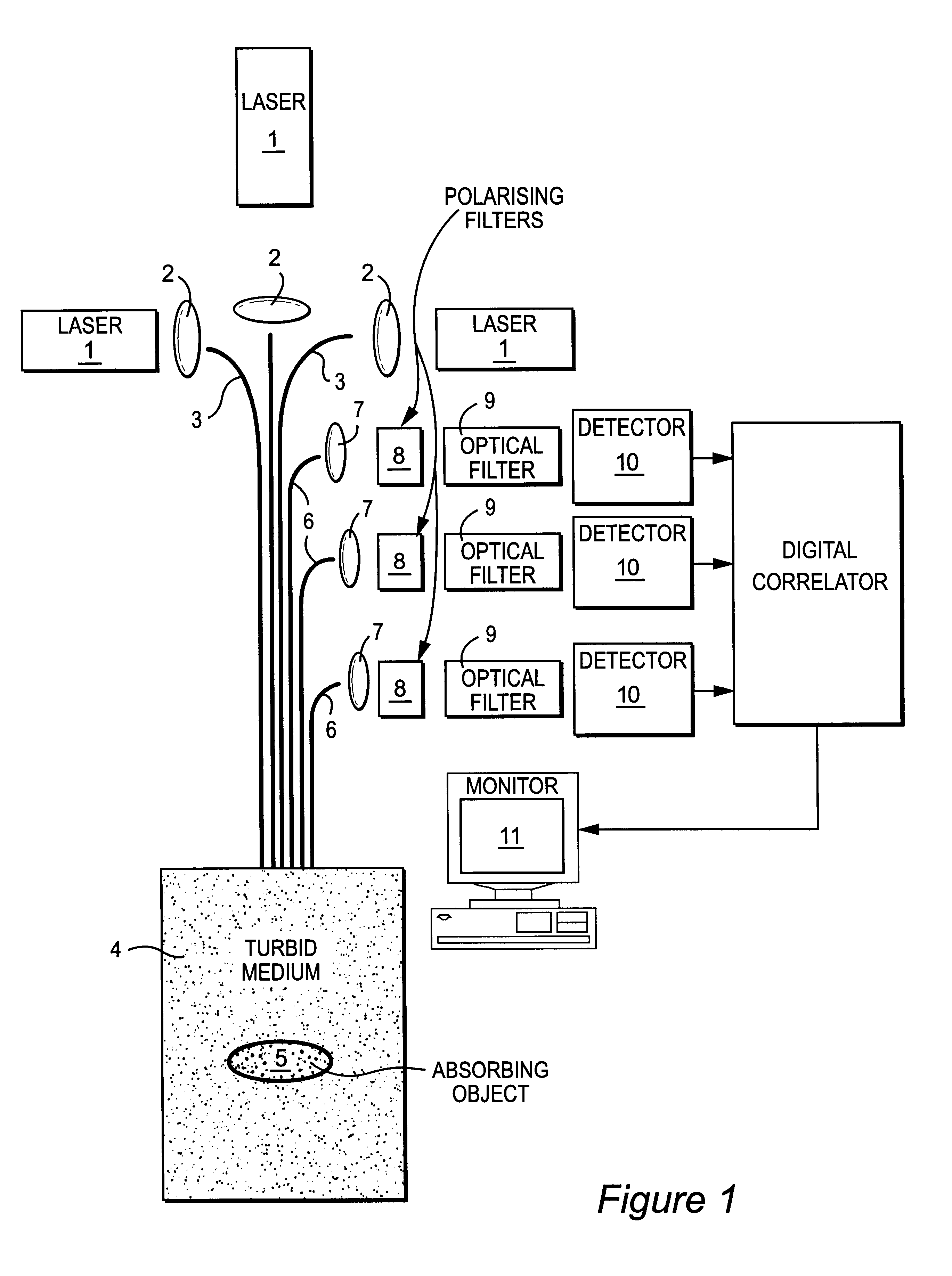
InactiveUS6754518B1Suitable imageIncrease opportunitiesSurgeryScattering properties measurementsTime domainWavelength
A method of detecting an object located within a dynamic scattering media, includes i) directing a continuous coherent light wave of predetermined wavelength into the media; ii) detecting dynamically scattered light emerging from the media; iii) correlating the detected light photons in the time or frequency domain; iv) determining the presence of an object from analysis of differences between the correlation and a correlation which would arise from photons scattered by the media only; and v) determining the approximate position of the object within the media from the analysis of the correlation and knowledge of the mean transport path of the light wave of predetermined wavelength within the media.
Owner:VICTORIA VNIVERSITY OF MANCHESTER THE
Use of transition metal compounds in imageable coatings
InactiveUS7270919B2Suitable imageEffective markingX-ray/infra-red processesPhotosensitive materialsChange colourMonomer
A process for forming an image on a substrate, which comprises coating the substrate with an amine of molybdenum, tungsten or vanadium that changes colour on heating or irradiation as an aqueous dispersion or suspension or as a solution in an organic solvent. Also described is a coated substrate, wherein the coating is a substantially visible light-transparent layer comprising an amine compound of molybdenum, tungsten or vanadium, and a solution of said amine compound and a thermoplastic polymer or a photo-polymerisable monomer.
Owner:DATALASE
Liquid crystal display panel and liquid crystal display thereof
ActiveUS20040217931A1Extend display timeHigh resolutionStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsLiquid-crystal displayEngineering
A liquid crystal display has a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix to be formed on a transparent insulating substrate. A first switching element formed in each pixel is a three-terminal TFT whose gate terminal is connected to the scanning line and two other terminals are respectively connected to a pixel electrode and a signal line. Furthermore, a second switching element formed in each pixel is a three-terminal TFT whose gate terminal is connected to a black selecting line and two other terminals are respectively connected to the pixel electrode and a common electrode.
Owner:HANNSTAR DISPLAY CORPORATION
Method and device for correction motion in imaging during a medical intervention
ActiveUS20070167721A1High target accuracySuitable imageImage enhancementImage analysisFluoroscopic imagePresent method
The present invention relates to a method and a device for correcting motion in imaging during a medical intervention, by which method a 3D tomographic image of a target area for the intervention is first recorded while there are one or more medical instruments in the target area that will remain there during the intervention. During the intervention 2D fluoroscopic images of the target area are recorded and registered with the 3D image. The registration is therein adjusted for each 2D fluoroscopic image in realtime based in each case on the one or more instruments. The 2D fluoroscopic images are then in each case visualized with representations, concurring in terms of perspective, of the 3D image. Virtually error-free overlaying of the 3D image with in each case one 2D fluoroscopic image can be implemented using the present method and associated device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
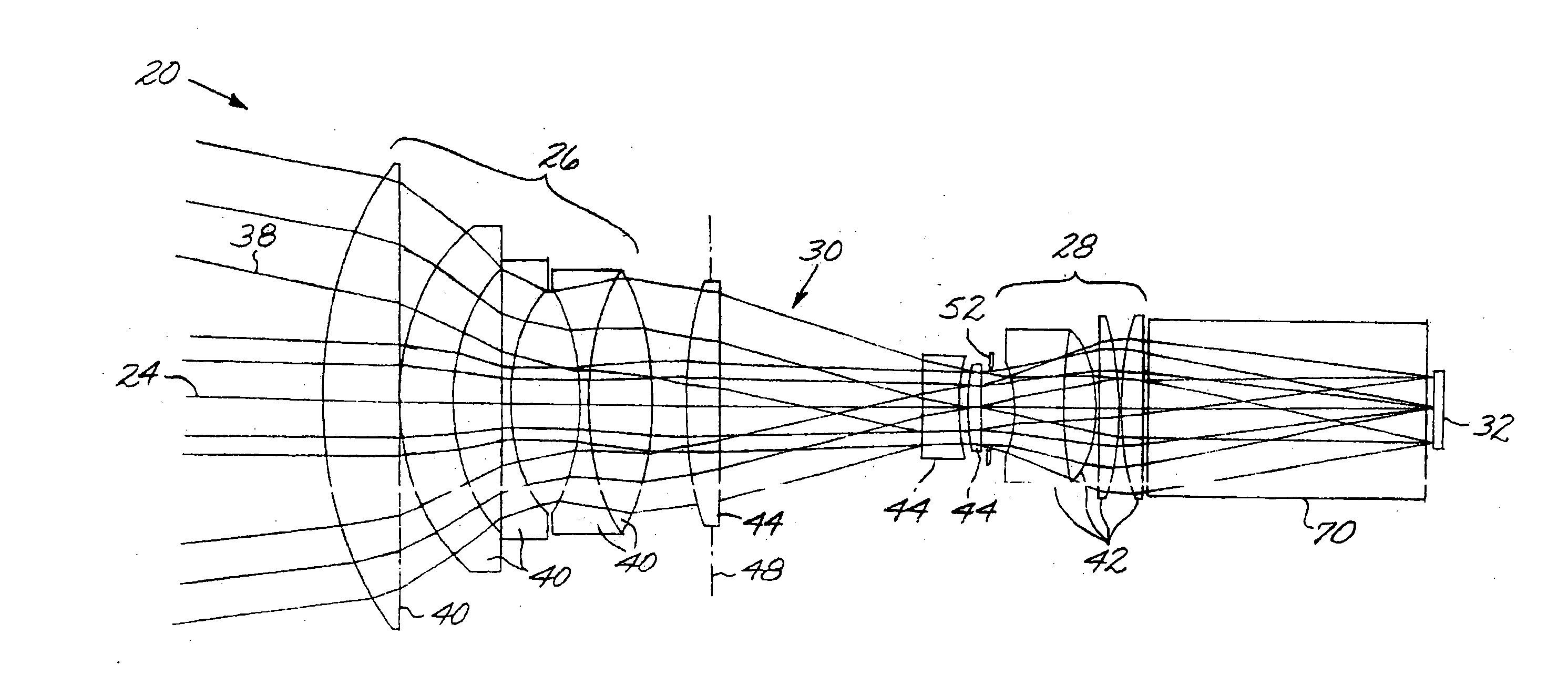
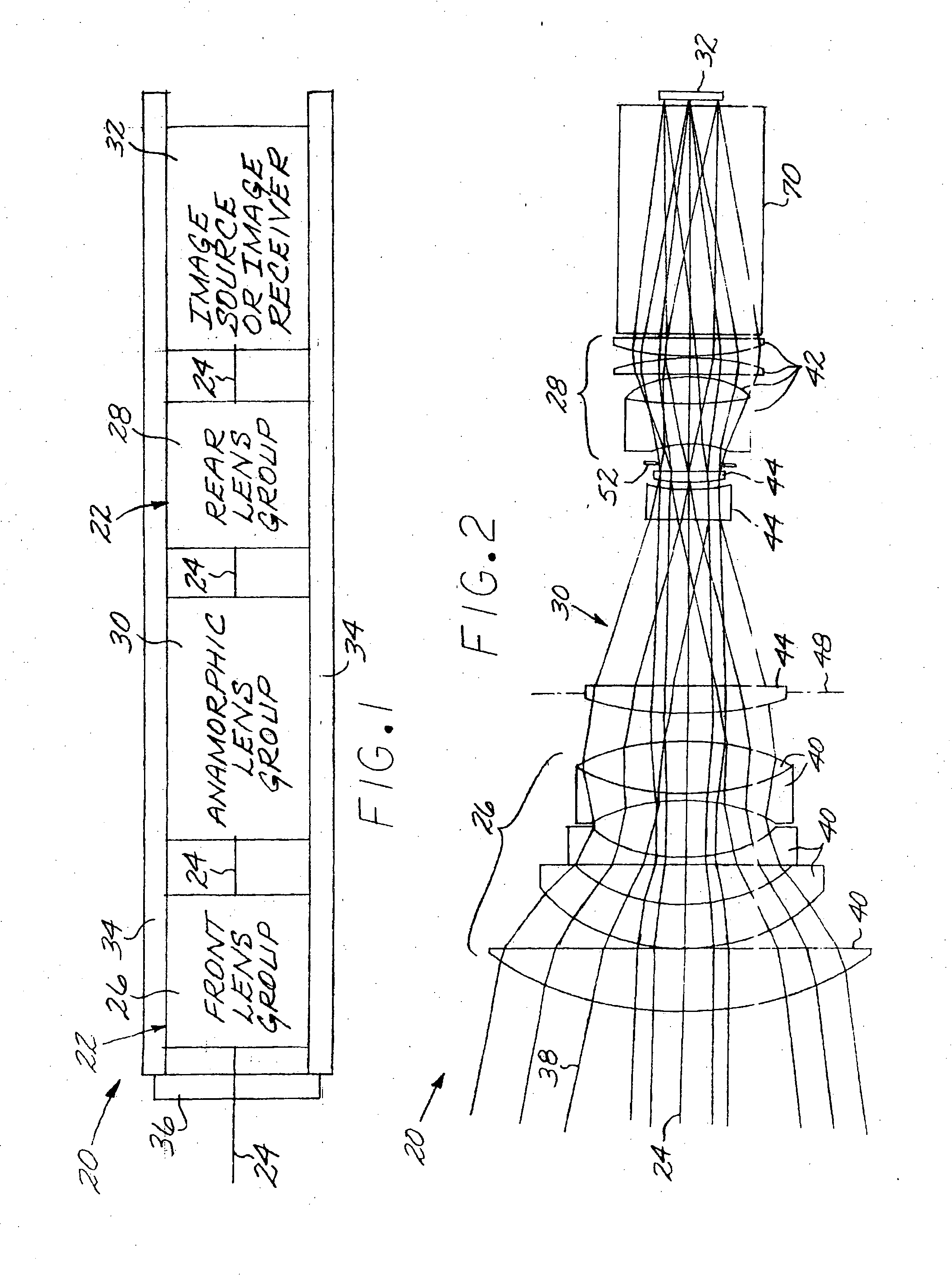
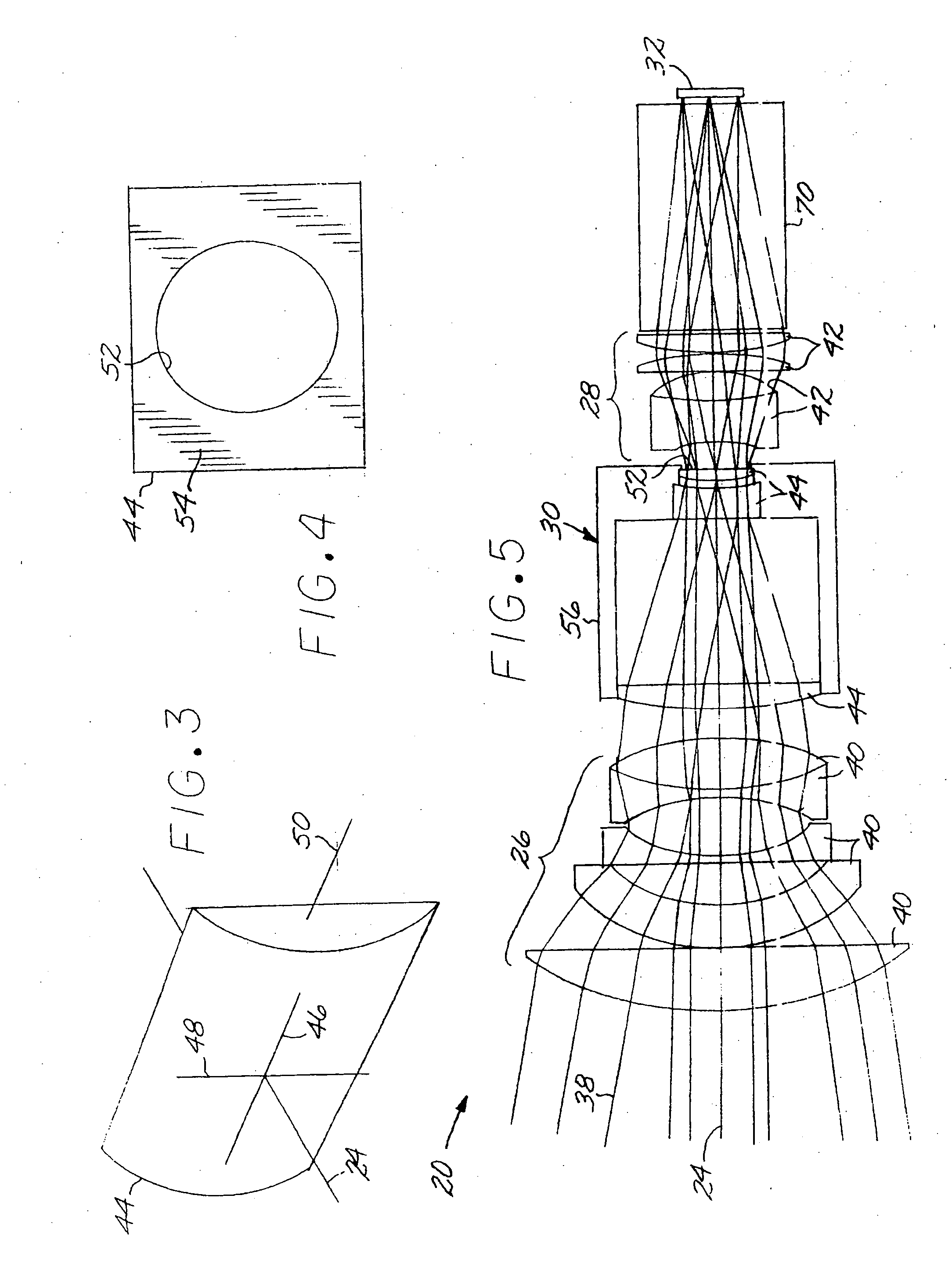
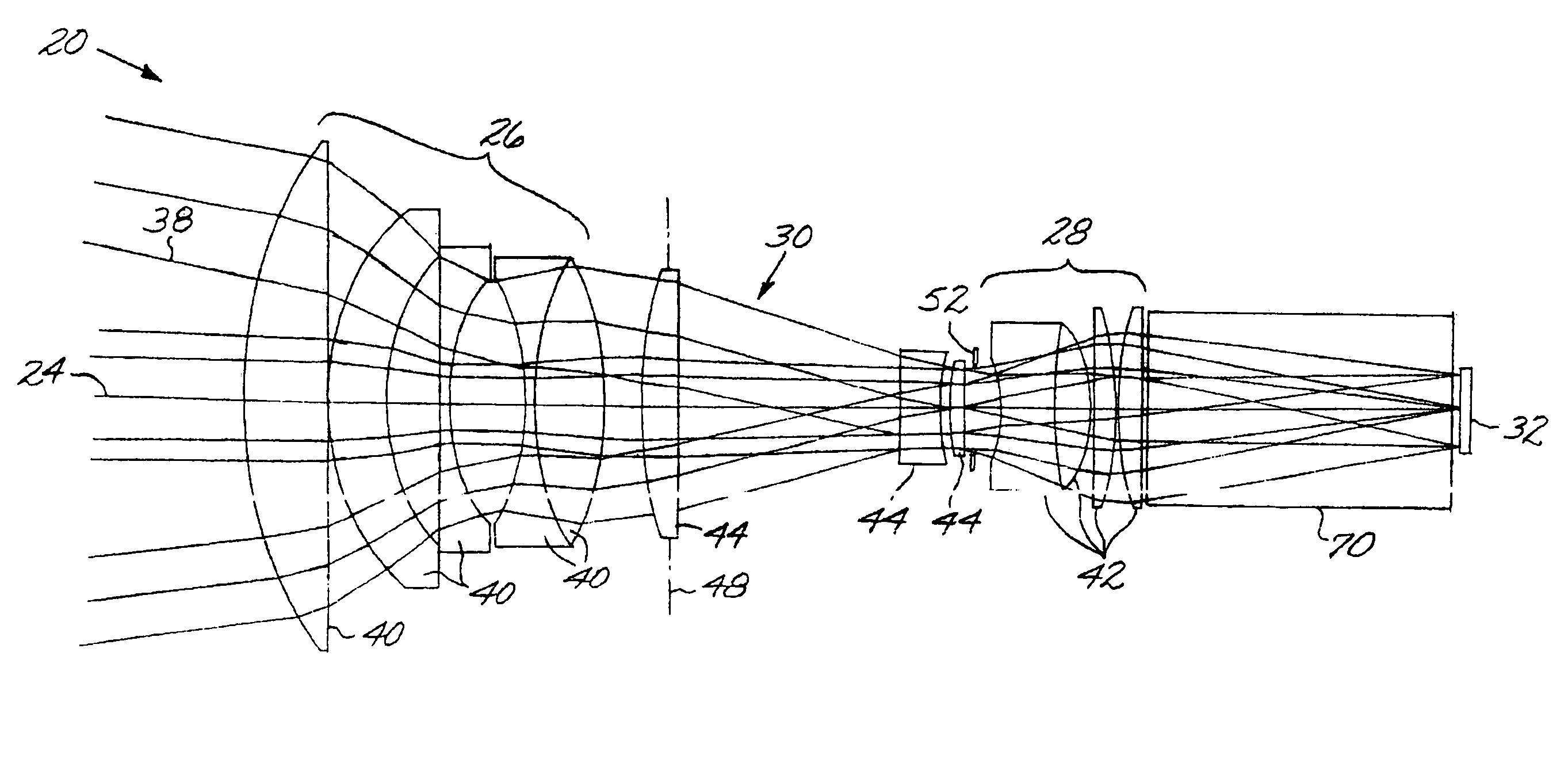
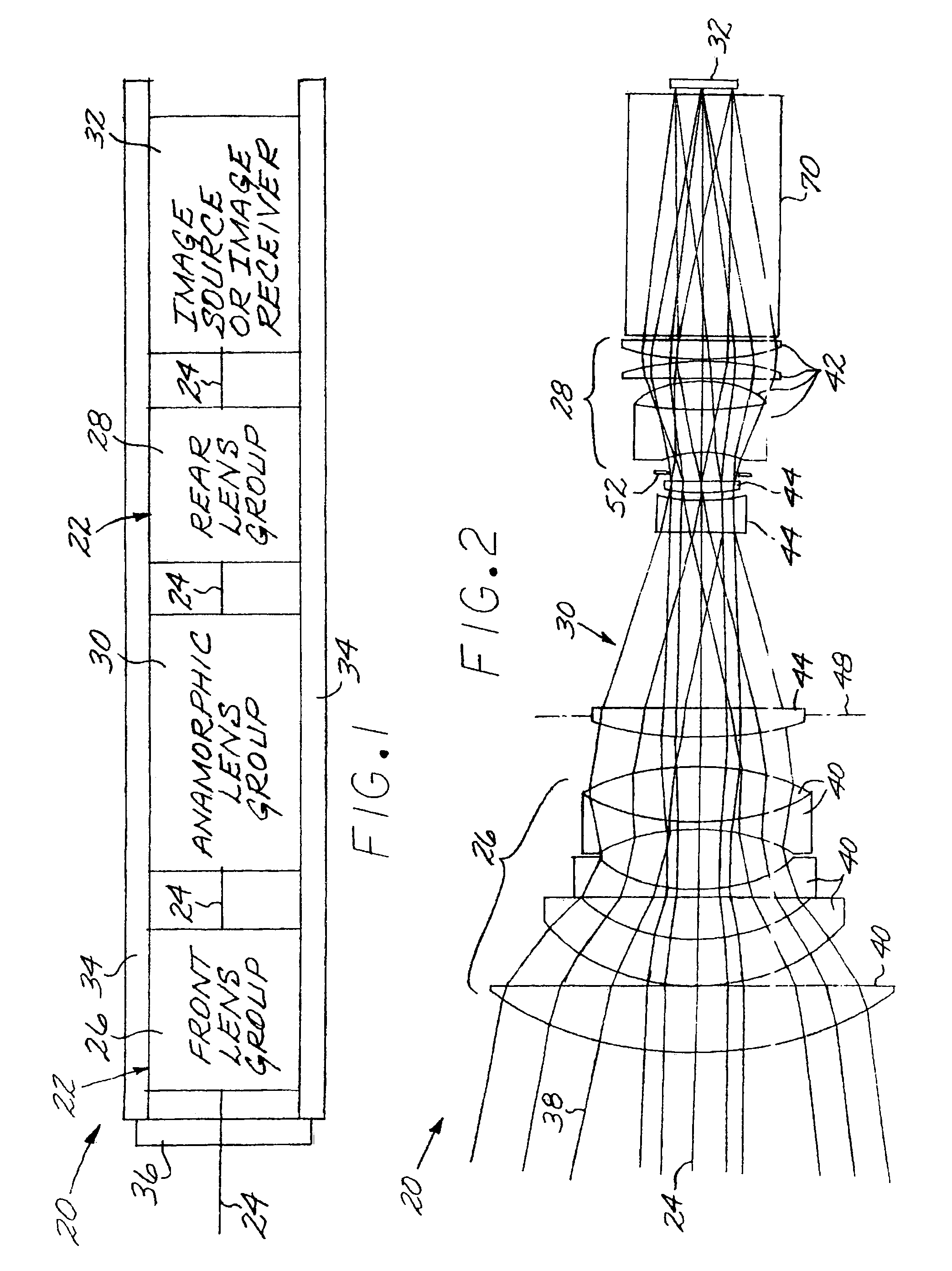
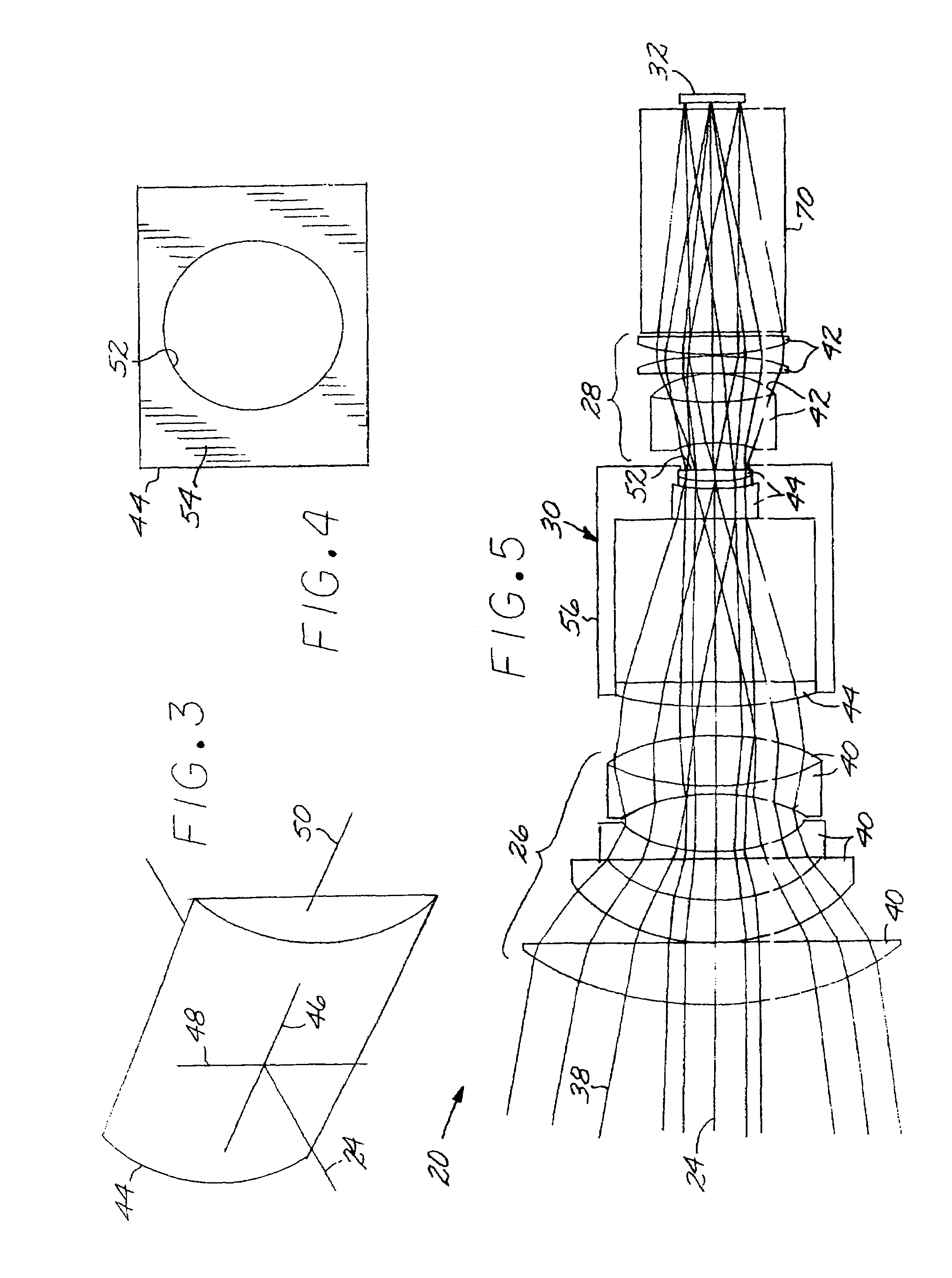
Optical system including an anamorphic lens
An optical system includes a primary lens group having a central beam path therethrough and including a front lens group and a rear lens group. An anamorphic lens group lies on the central beam path and is positioned between the front lens group and the rear lens group. The anamorphic lens group includes at least one optically powered anamorphic lens that has different enlargements of a light beam along different axes perpendicular to the central beam path. The anamorphic lens group may be mounted on structure that allows it to be removed from the central beam path. An image transceiver is either an image source that directs a light beam through the primary lens group and the anamorphic lens group, or is an image receiver that receives a light beam through the primary lens group and the anamorphic lens group.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
Optical system including an anamorphic lens
An optical system includes a primary lens group having a central beam path therethrough and including a front lens group and a rear lens group. An anamorphic lens group lies on the central beam path and is positioned between the front lens group and the rear lens group. The anamorphic lens group includes at least one optically powered anamorphic lens that has different enlargements of a light beam along different axes perpendicular to the central beam path. The anamorphic lens group may be mounted on structure that allows it to be removed from the central beam path. An image transceiver is either an image source that directs a light beam through the primary lens group and the anamorphic lens group, or is an image receiver that receives a light beam through the primary lens group and the anamorphic lens group.
Owner:RAYTHEON CANADA LTD
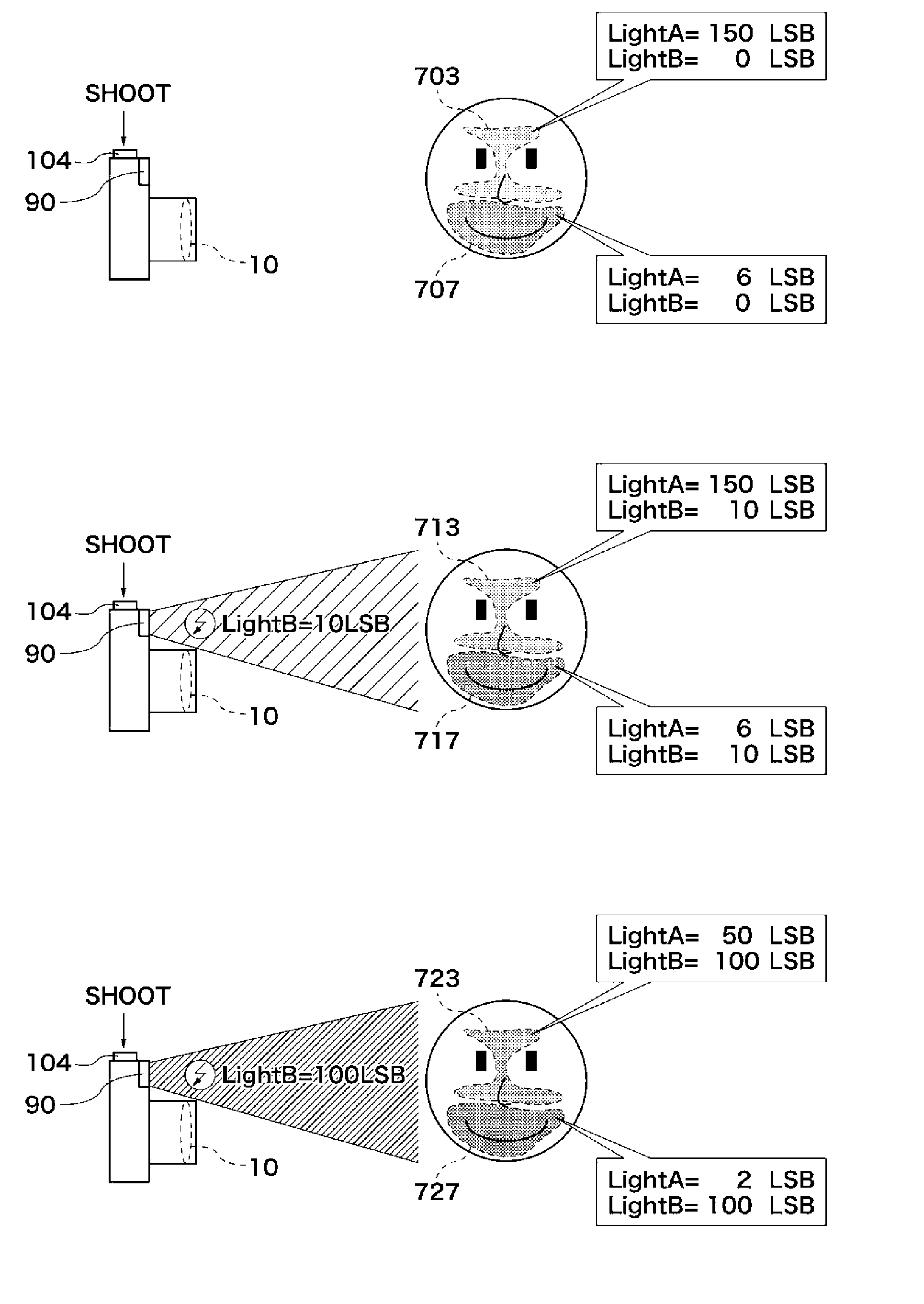
Image pickup apparatus and controlling method therefor
InactiveUS20110150451A1Suitable imageReducing variation in the color temperature of a subjectTelevision system detailsColor television detailsColor temperatureMaterials science
An image pickup apparatus that is capable of reducing variation in the color temperature of a subject in a taken image and capable of shooting a more suitable image. The image pickup apparatus can shoot with emitting a light emitting unit. A color temperature acquisition unit acquires information about a color temperature of a light illuminating a subject. An emission control unit controls emission of the light emitting unit. The emission control unit determines emission light amount of the light emitting unit based on a color temperature difference between a color temperature of an illumination light of the light emitting unit and a color temperature based on the information acquired by the color temperature information acquisition unit.
Owner:CANON KK
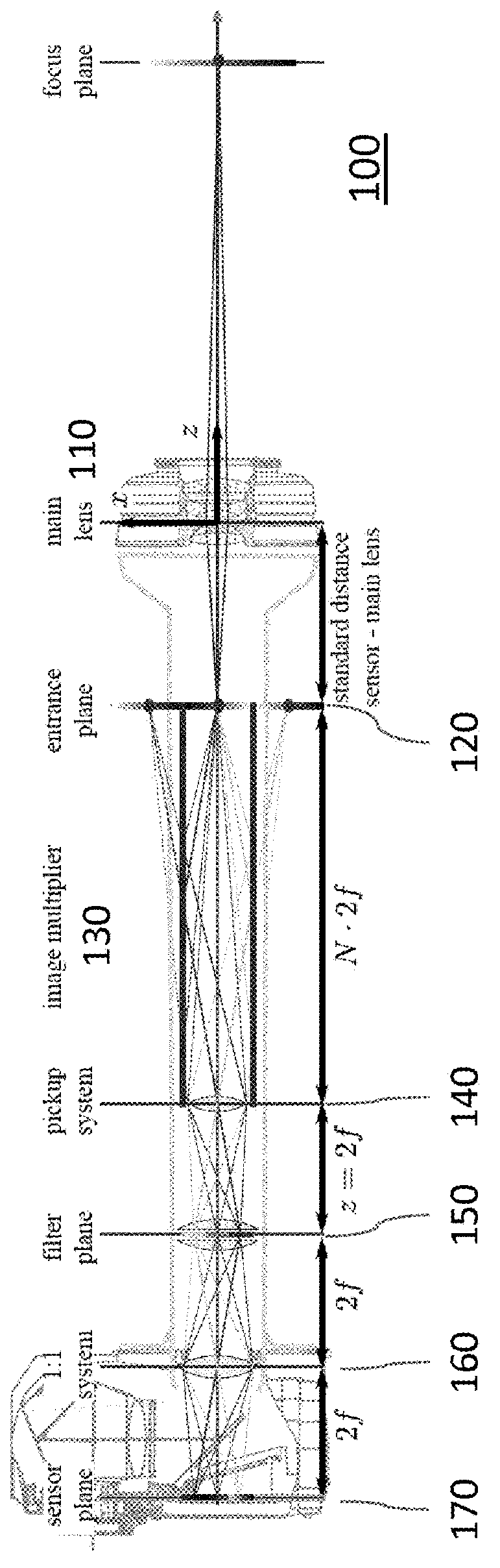
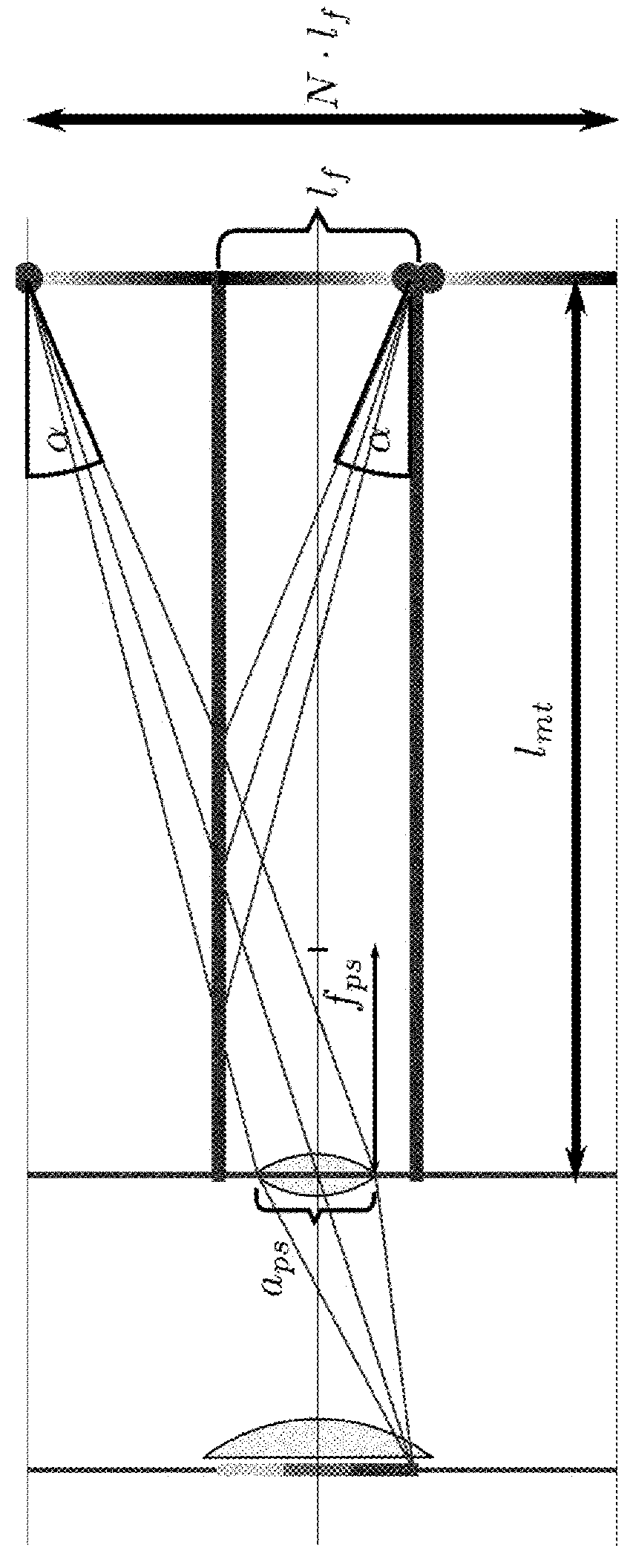
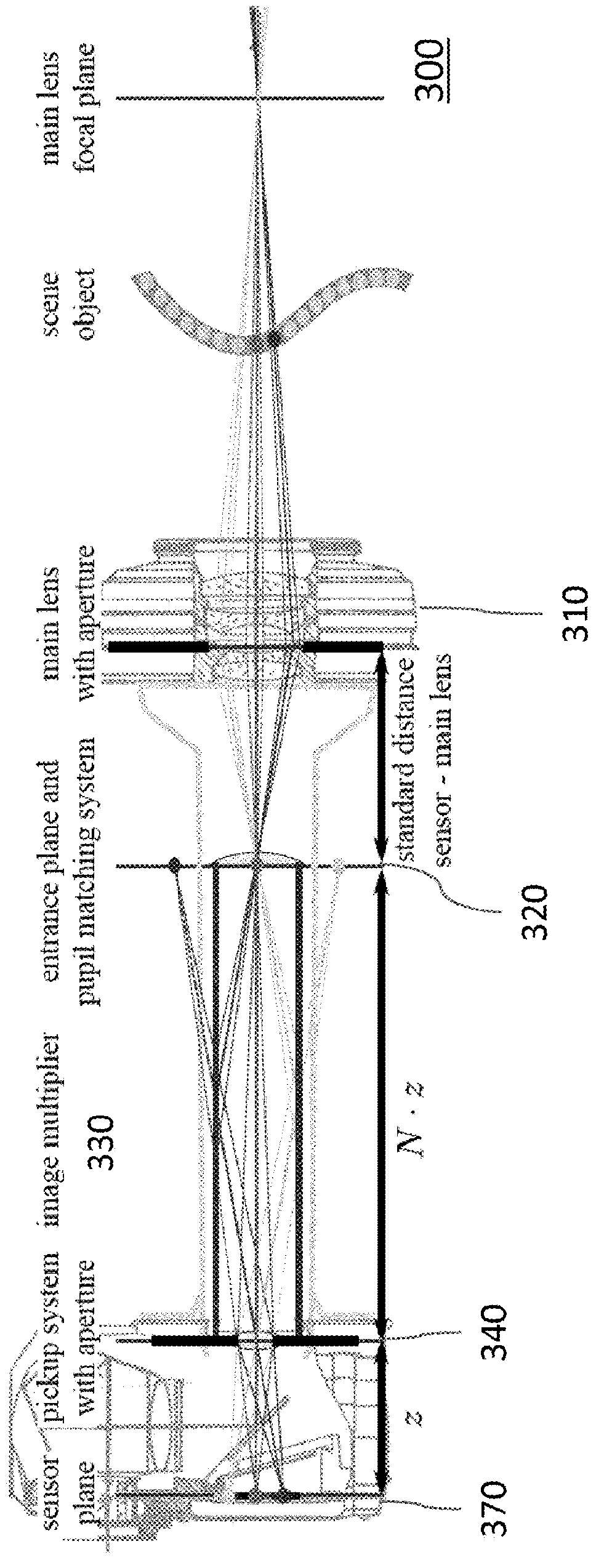
Plenoptic imaging device
ActiveUS20160057407A1Wide-spread adoption of plenoptic imaging by usersAvoid necessityTelevision system detailsPrismsImaging equipmentOptical image
A plenoptic imaging device according to the invention comprises an image multiplier (130) for obtaining a multitude of optical images of an object or scene and a pick-up system (140) for imaging at least some of the multitude of images to a common image sensor (170) during the same exposure of the sensor.
Owner:KLENS GMBH
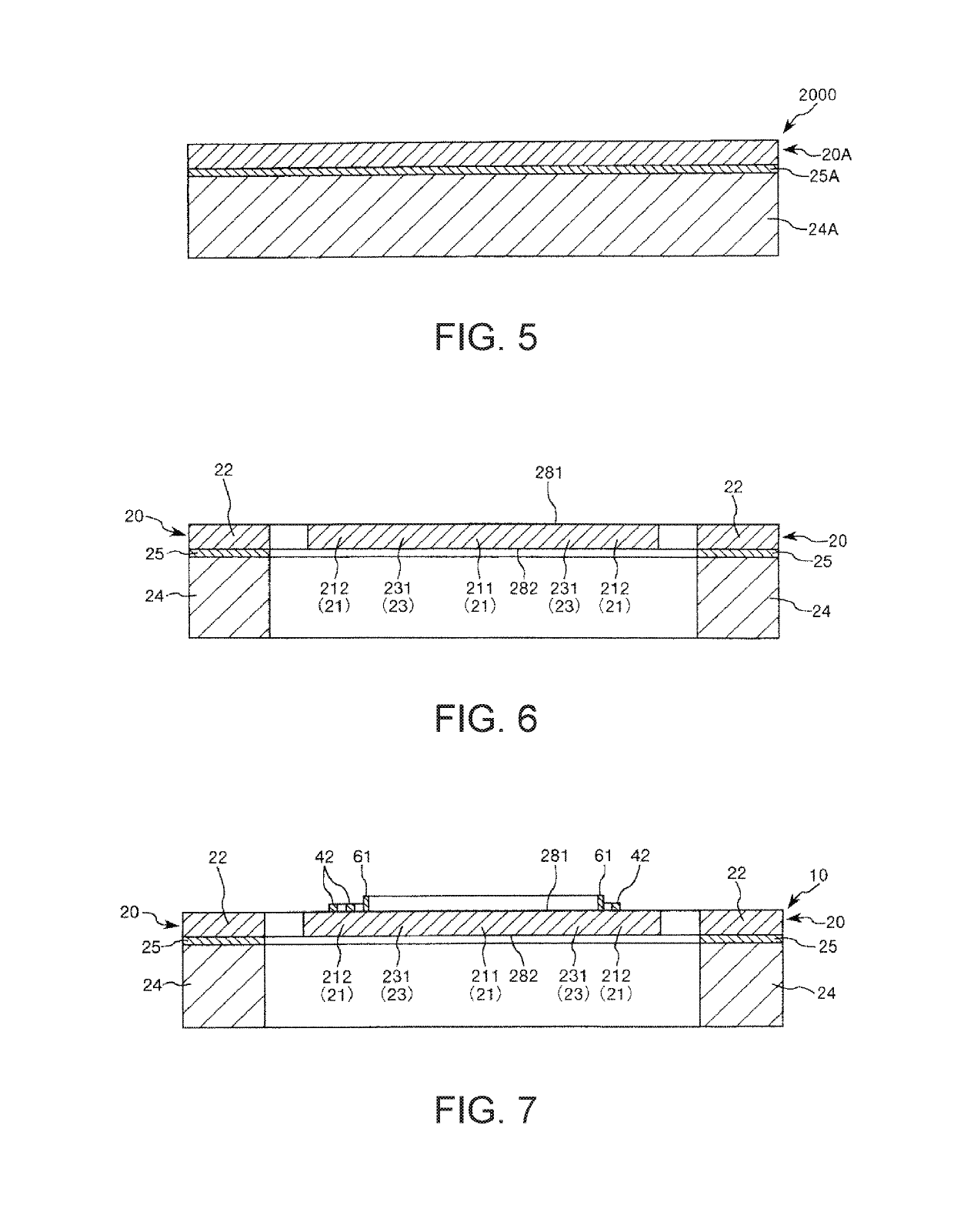
Method of watermark with hybrid halftone dots
ActiveUS7554699B2Improve stealth performanceImprove practicalityVisual presentationPictoral communicationOptical scannersLenticular lens
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Member for optical scanner, optical scanner, method of manufacturing optical scanner, image display device, and head-mounted display
A member for an optical scanner includes: a functional portion including a movable portion, a shaft portion oscillatably supporting the movable portion, and a support portion supporting the shaft portion; a wiring line provided on the movable portion; and a structure provided on the functional portion and thicker than the wiring line; the wiring line and the structure are provided on a first major surface of the functional portion.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
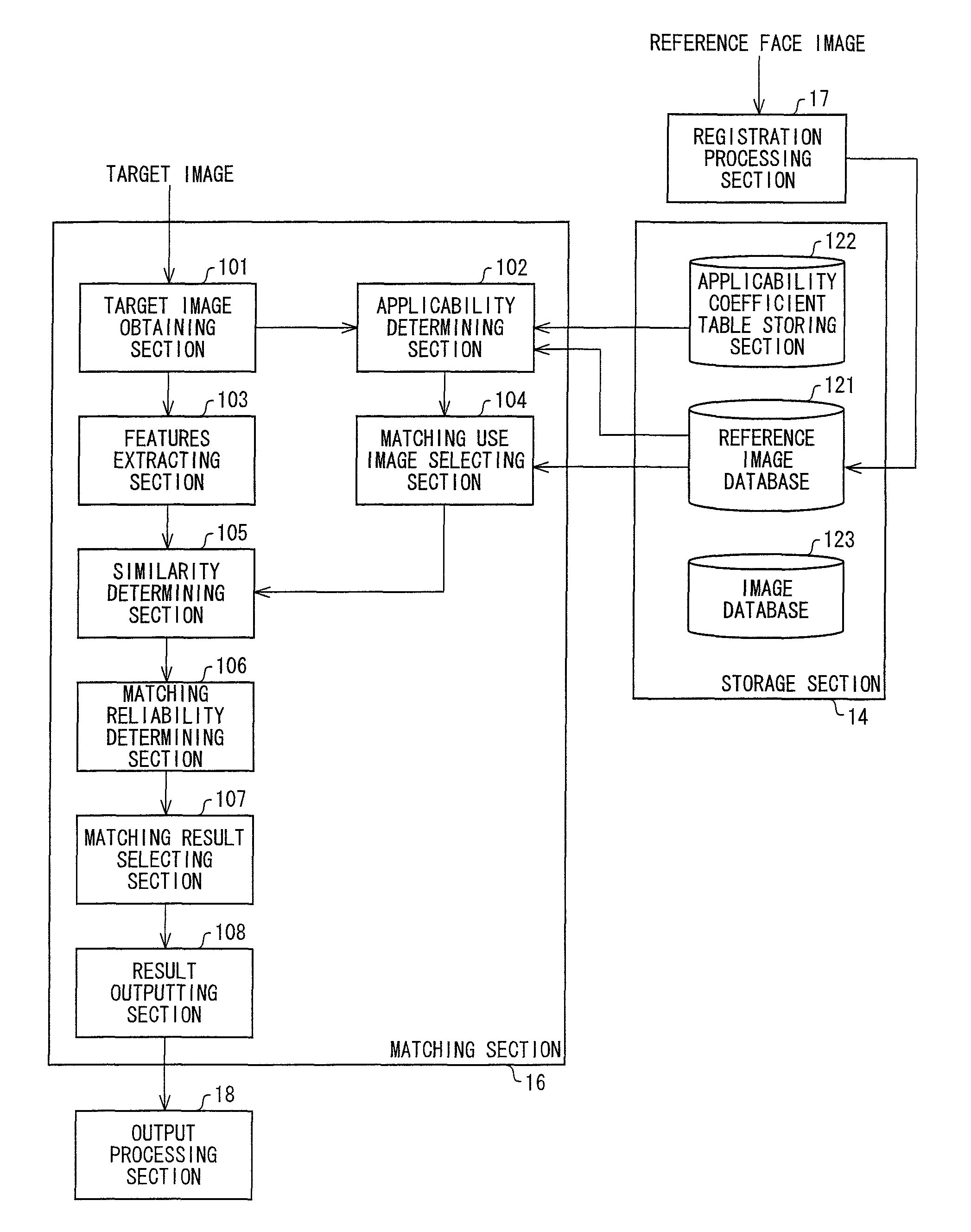
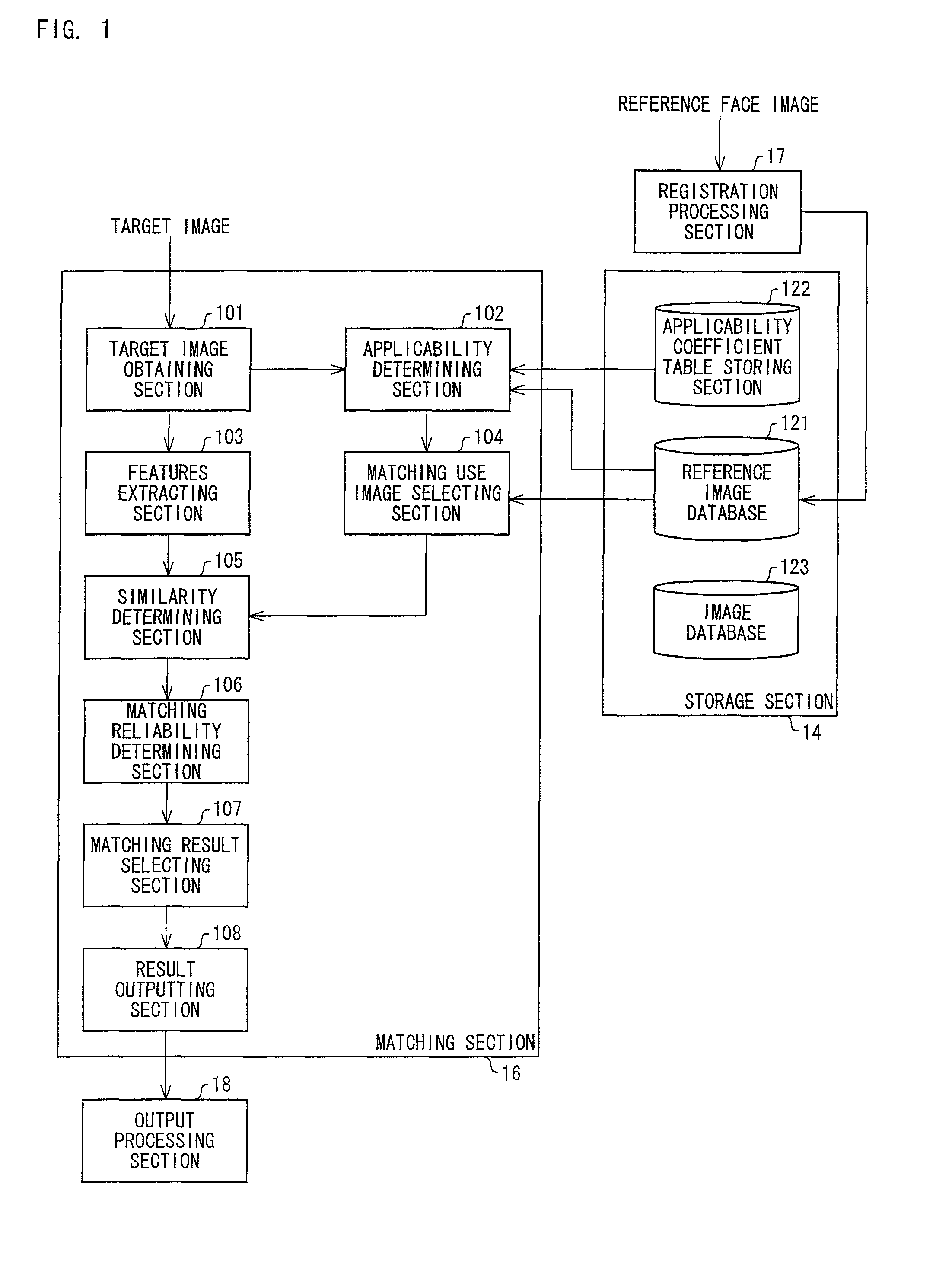
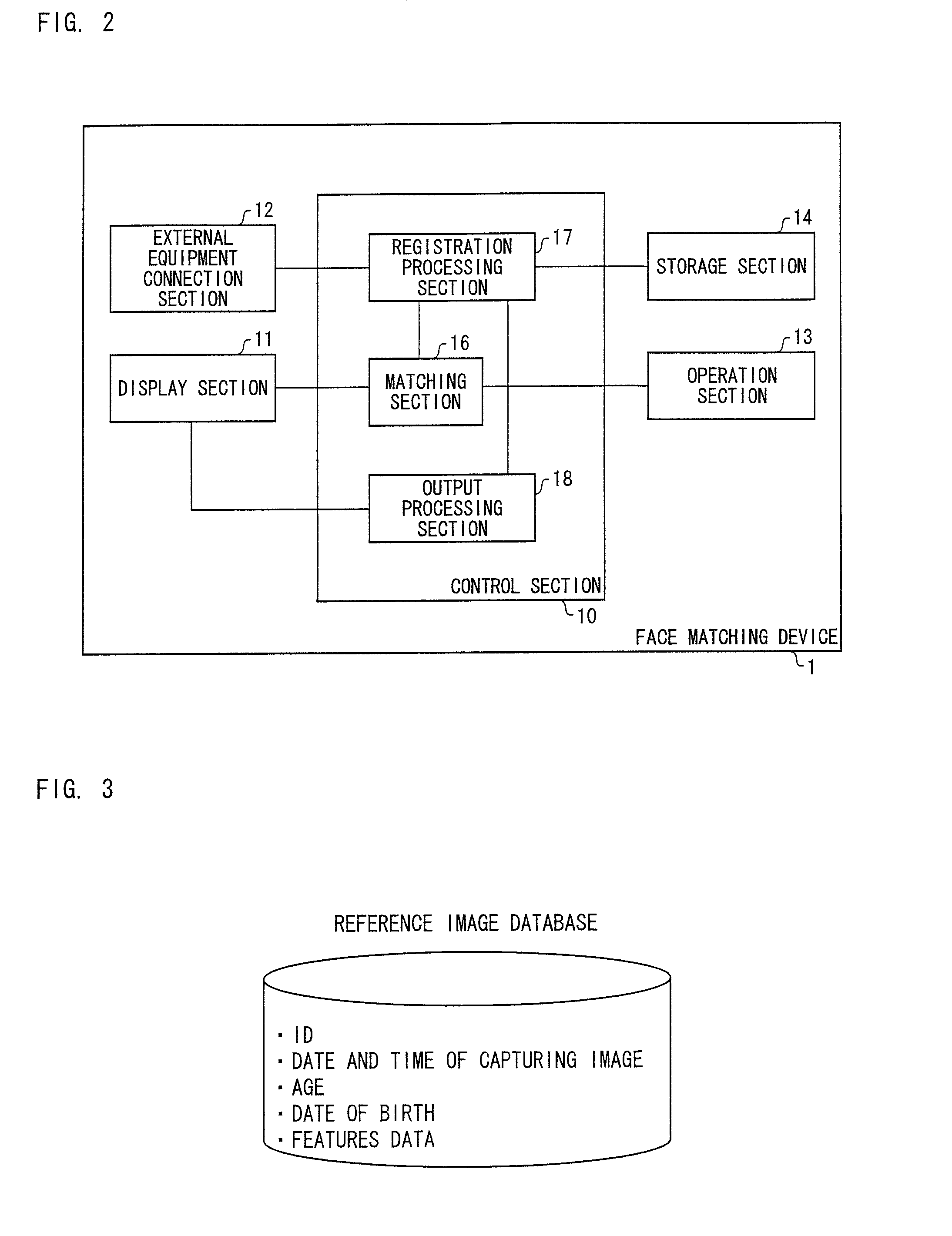
Face matching device, electronic device, face matching device control method, and face matching device control program
ActiveUS8396264B2Suitable imageExact matchImage analysisDigital data information retrievalPattern recognitionReference image
Owner:ORMON CORP
Autofocus method using liquid lens
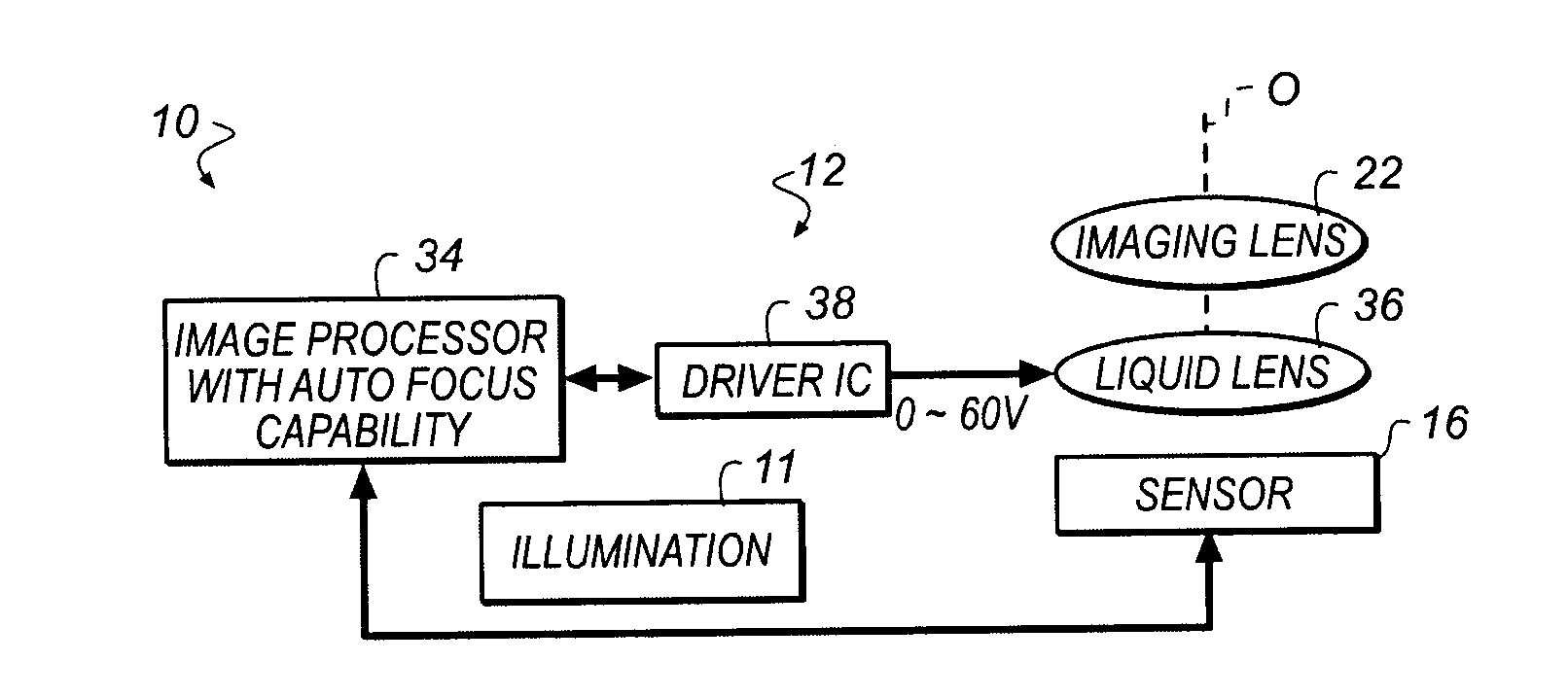
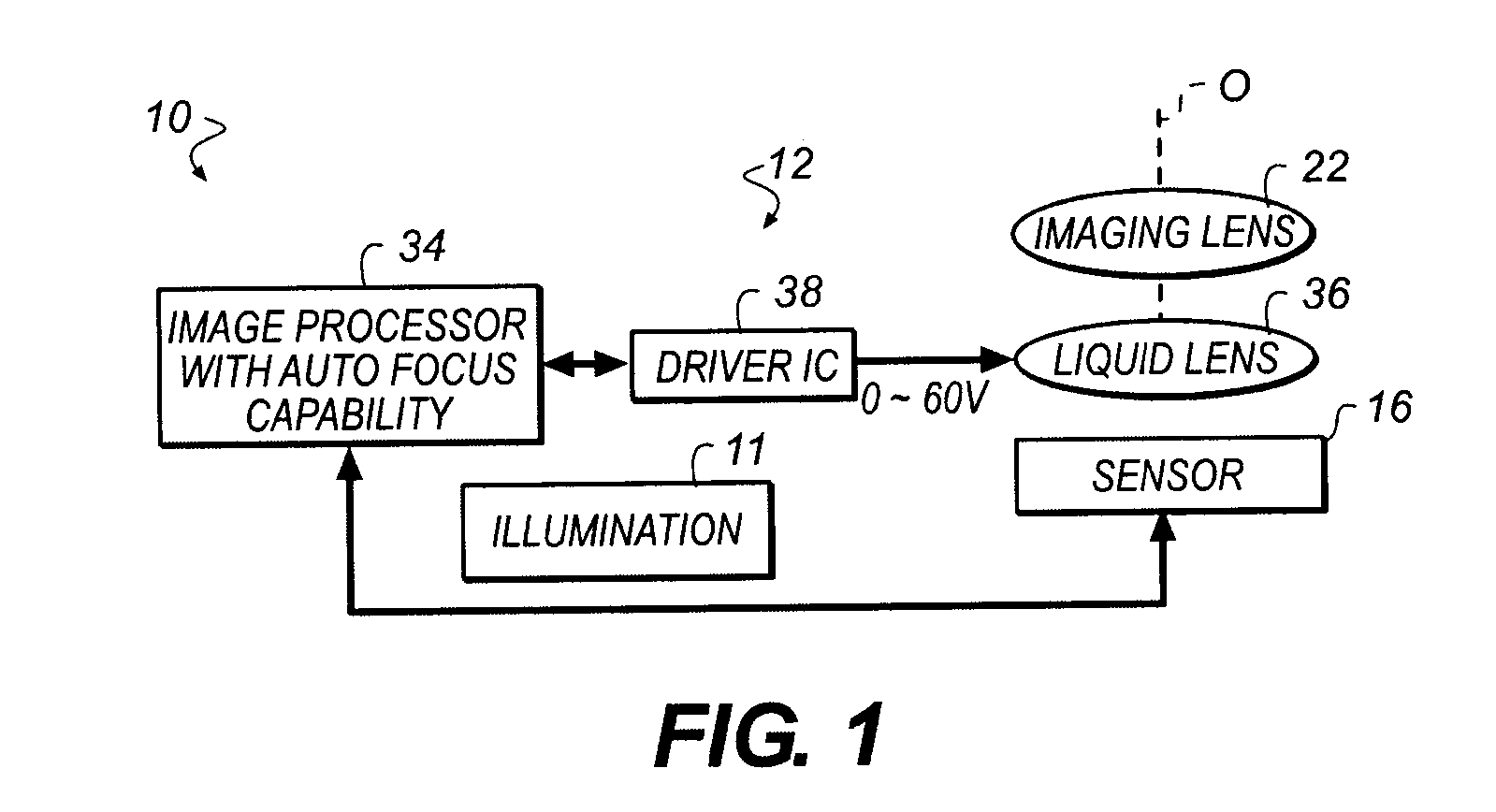
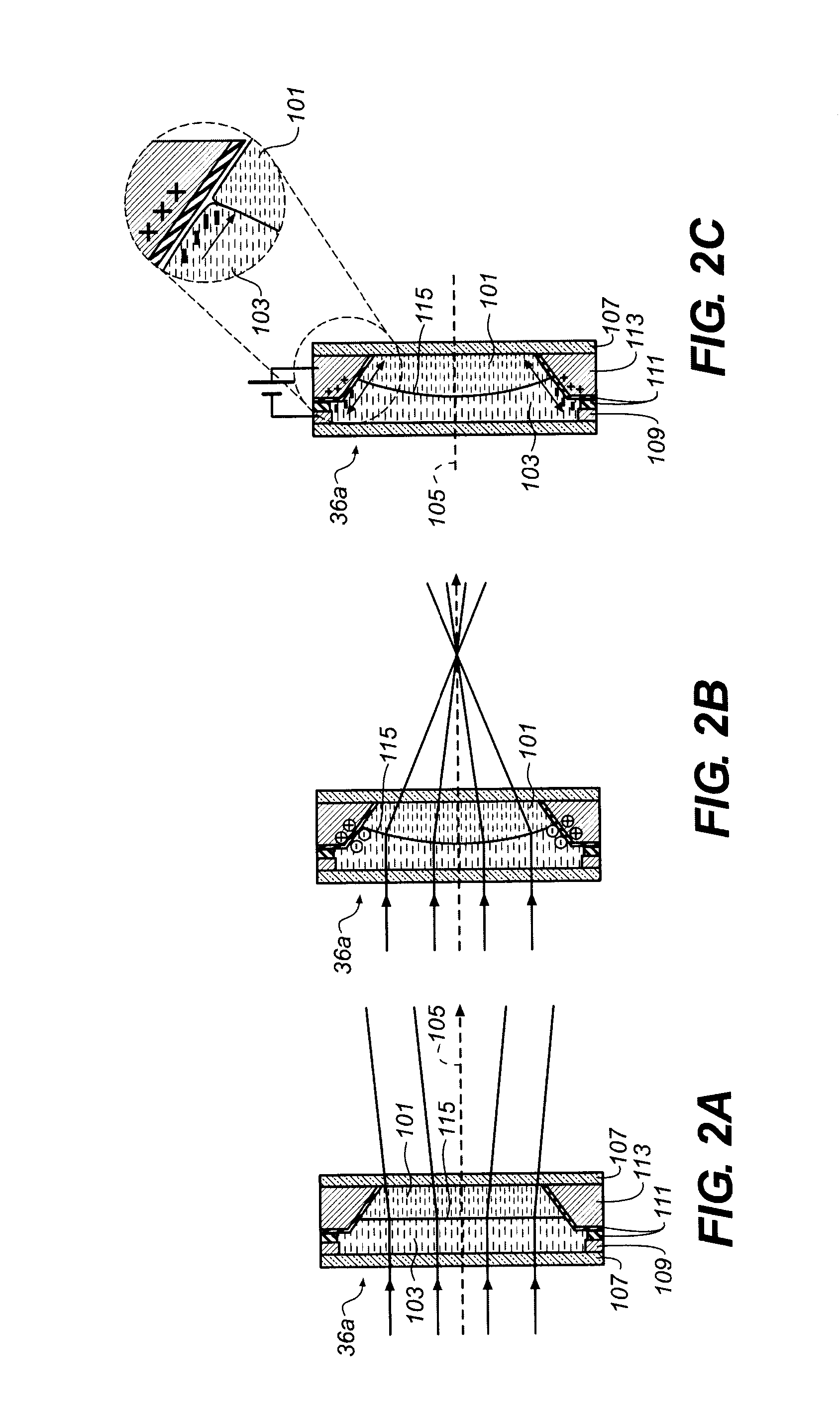
ActiveUS20140002626A1Suitable imageProjector focusing arrangementEndoscopesCamera lensFocal position
An autofocus method for an intra-oral camera modulates the focus of a liquid lens in a cycle that has at least first, second, and third focus positions and obtains an image at each focus position, measuring focus of the obtained image. The position of the liquid lens is adjusted according to the measured focus. Steps of modulating the focus of the liquid lens in the cycle with at least first, second, and third focus positions, and obtaining the image at each focus position and measuring focus of the obtained image are repeated.
Owner:CARESTREAM DENTAL TECH TOPCO LTD
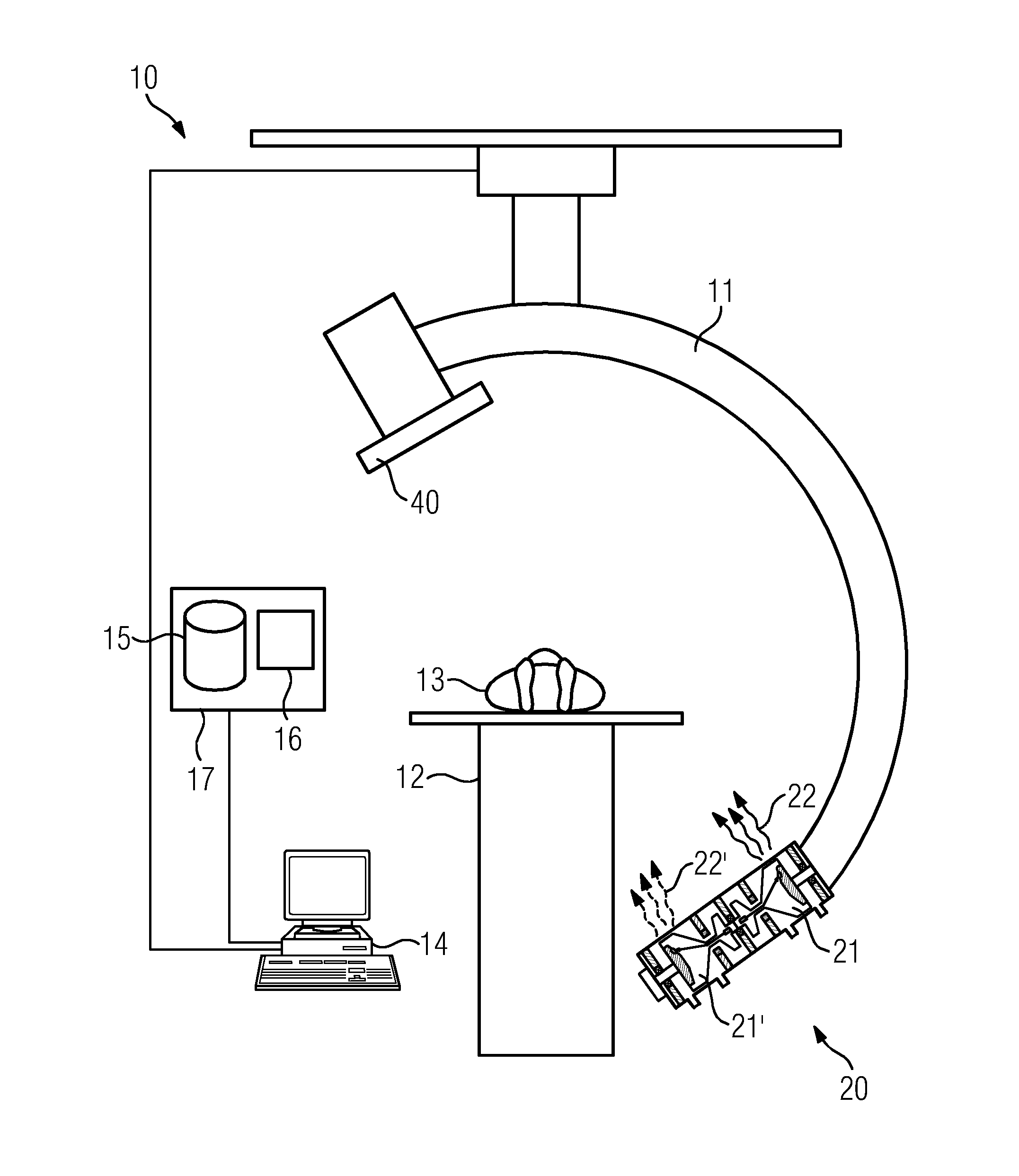
Method and system unit for stereoscopic x-ray imaging
ActiveUS8908826B2Quality improvementCompact and low-cost structureX-ray/infra-red processesRadiation diagnostic clinical applicationsSoft x rayShortest distance
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Poly(peptide) as a chelator: methods of manufacture and uses
InactiveUS20060246005A1Prolonged targeting potentialGood water solubilityIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsImaging agentMethod of images
Novel compositions for imaging that include (a) a polypeptide that includes two or more consecutive amino acids that will function to non-covalently bind valent metal ions and (2) a valent metal ion chelated to at least one of the two consecutive amino acids, are disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of imaging using these novel compositions, such as methods of imaging a tumor within a subject. Methods of synthesizing an imaging agent and kits for preparing an imaging agent are also disclosed. Methods for determining the effectiveness of a candidate substance as an imaging agent that involve conjugating or chelating the candidate substance with a polypeptide that includes two or more consecutive amino acids that will function to non-covalently bind valent metal ions.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Multifunctional infrared-emitting composites
ActiveUS20140193331A1Highly useful luminescenceLow cytotoxicityCompounds screening/testingPowder deliveryRare-earth elementMedicine
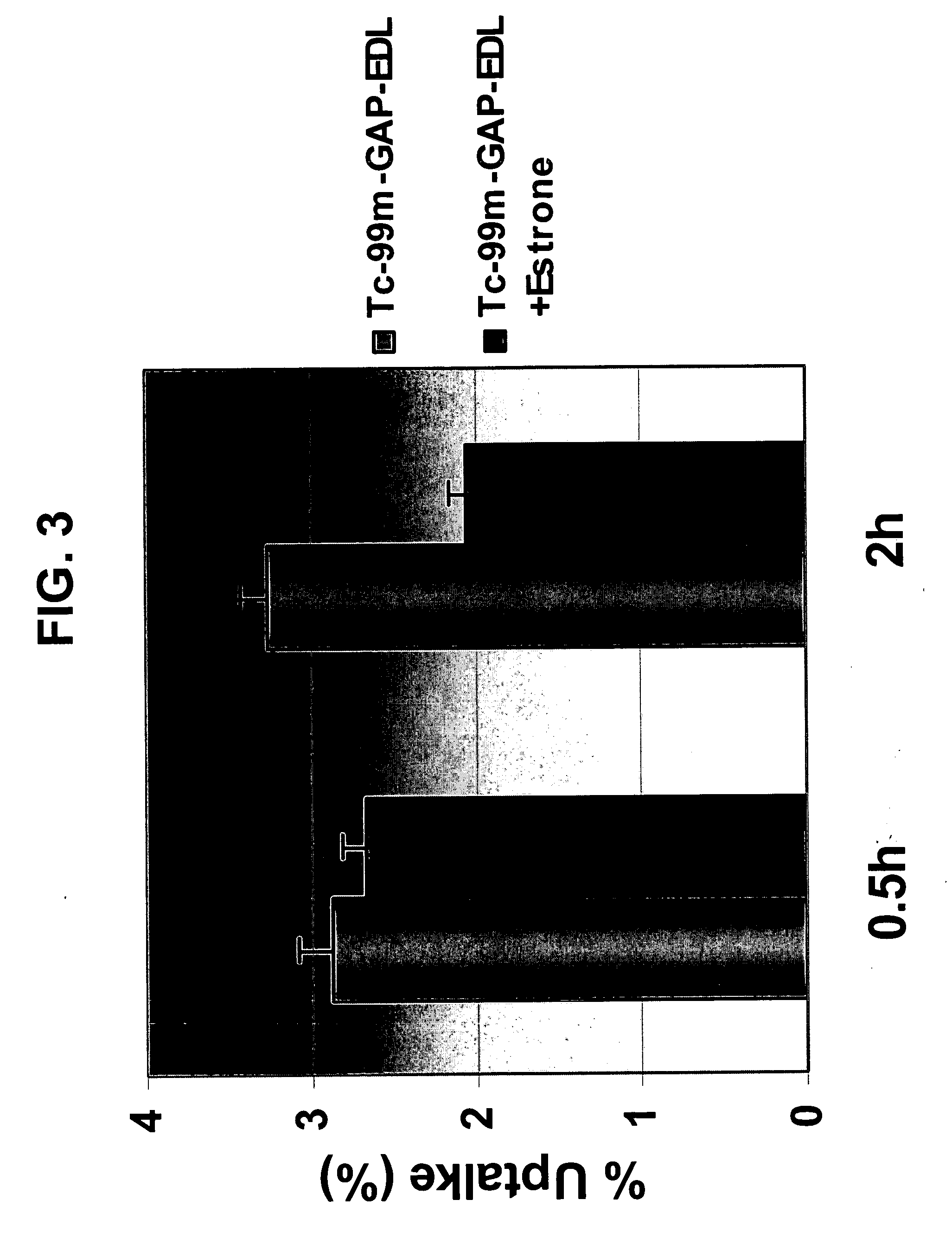
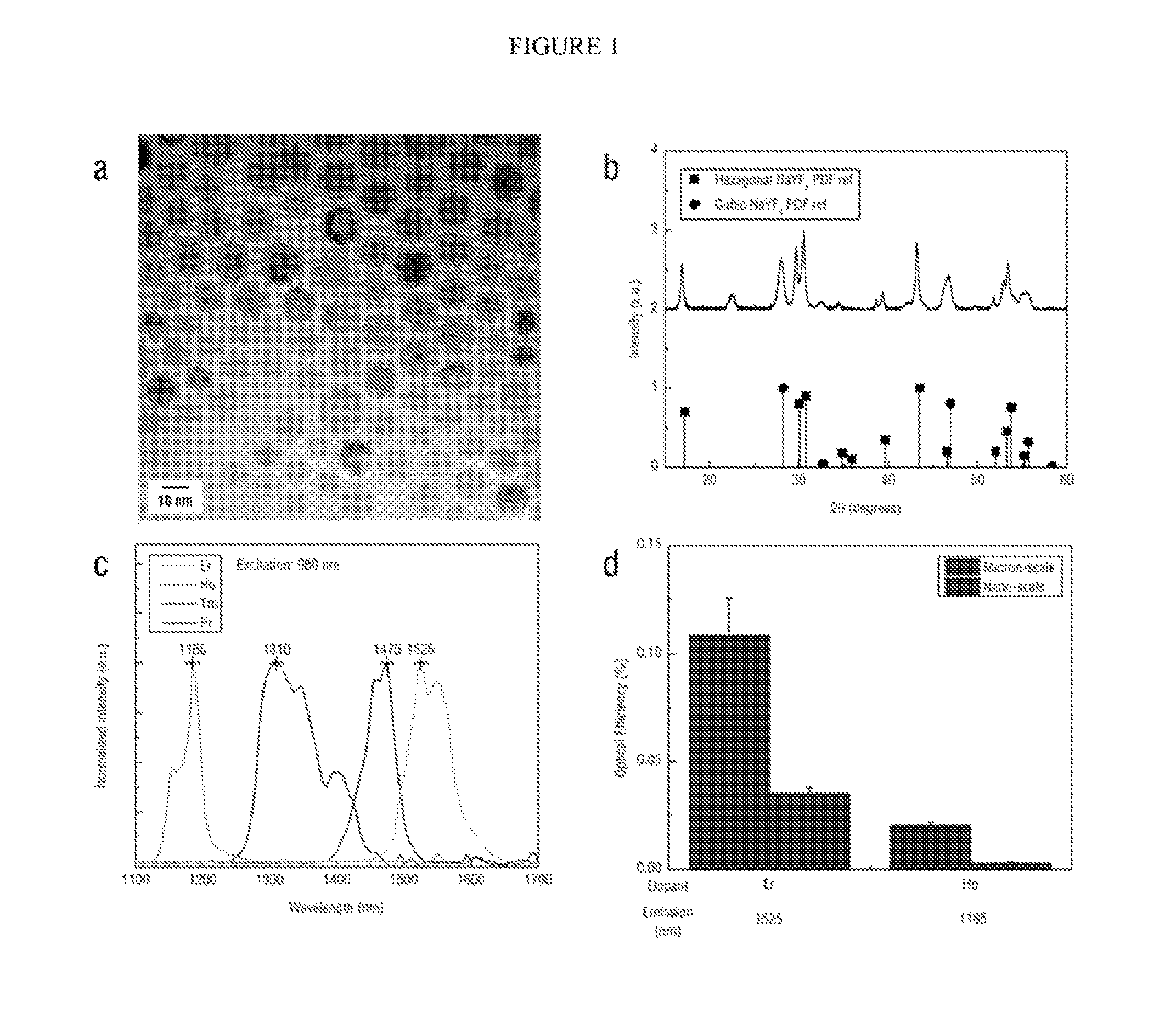
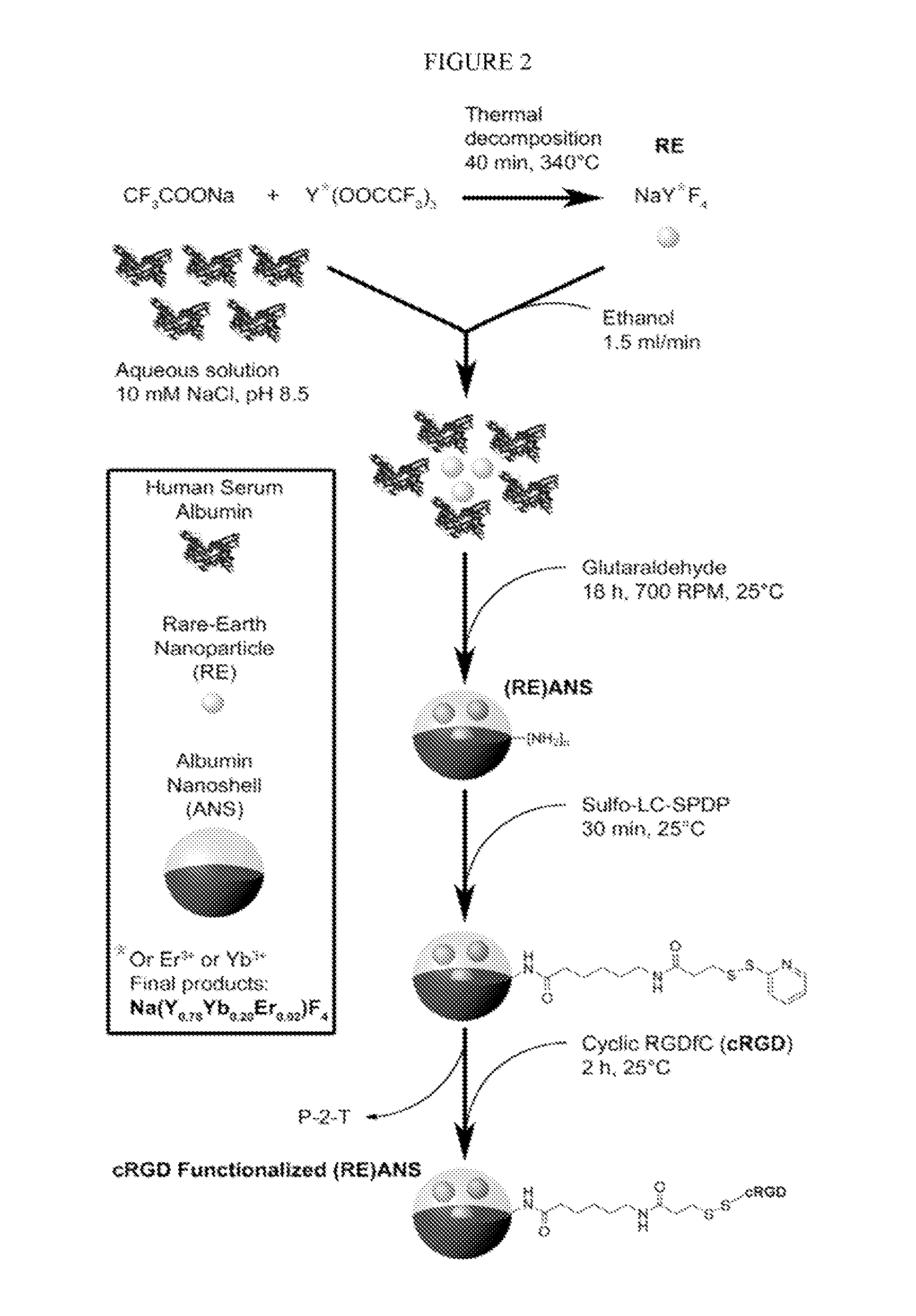
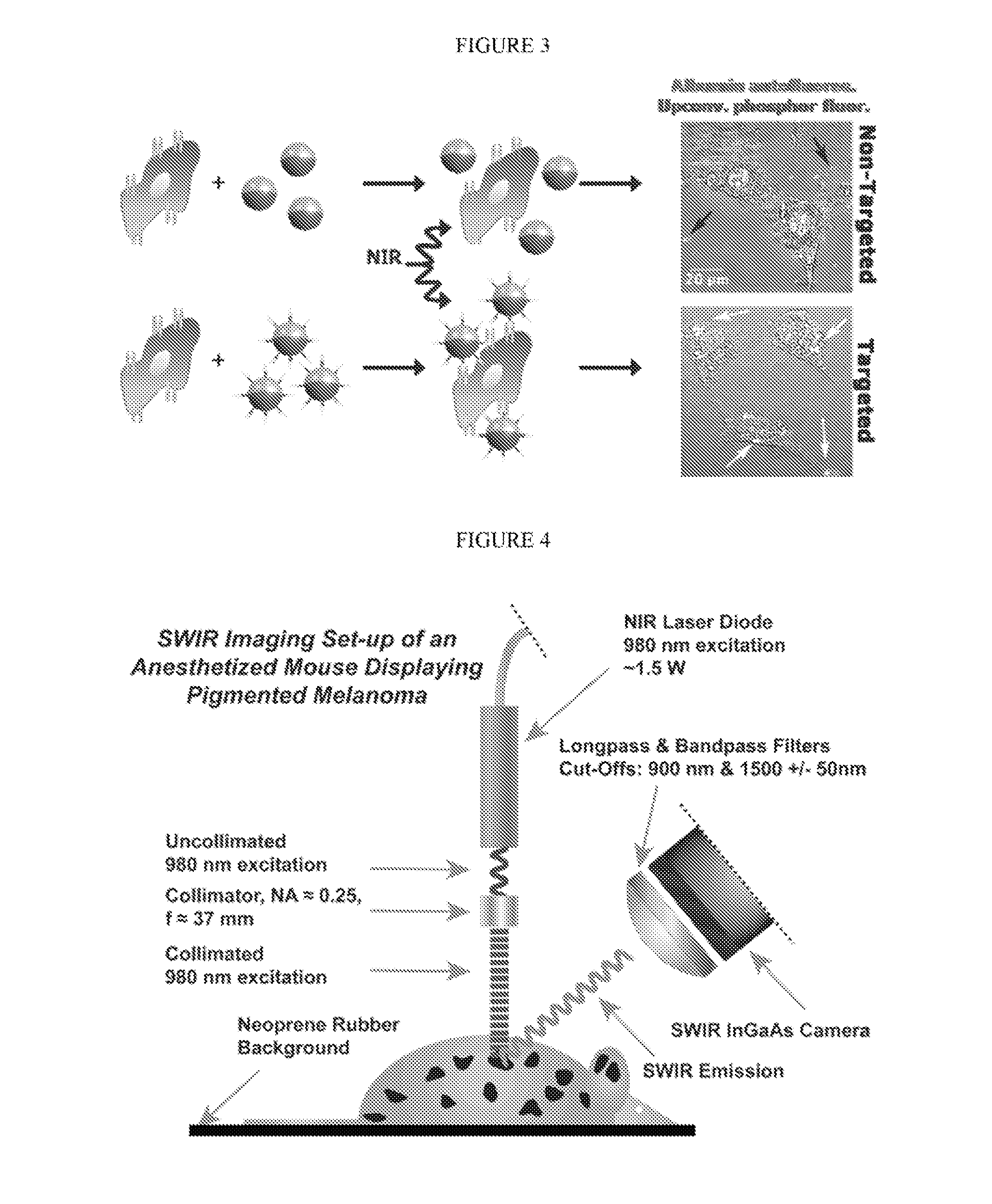
Disclosed is a method of non-invasive infrared imaging, comprising (a) administering a composition containing infrared-emitting particles which contain rare earth elements that emit in the short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) spectrum, where the particles are encapsulated with a biocompatible matrix to form downconverting encapsulated particles; and (b) irradiating with infrared radiation, where both excitation and emission spectra of the encapsulated particles are in the infrared region. Analogous methods of image-guided biomedical intervention, and drug tracking and delivery are also disclosed. Also disclosed is a composition for biomedical applications, containing infrared-emitting particles which contain rare earth-elements that emit in the short-wavelength infrared (SWIR) spectrum, where the particles are encapsulated with a biocompatible matrix to form downconverting encapsulated particles.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
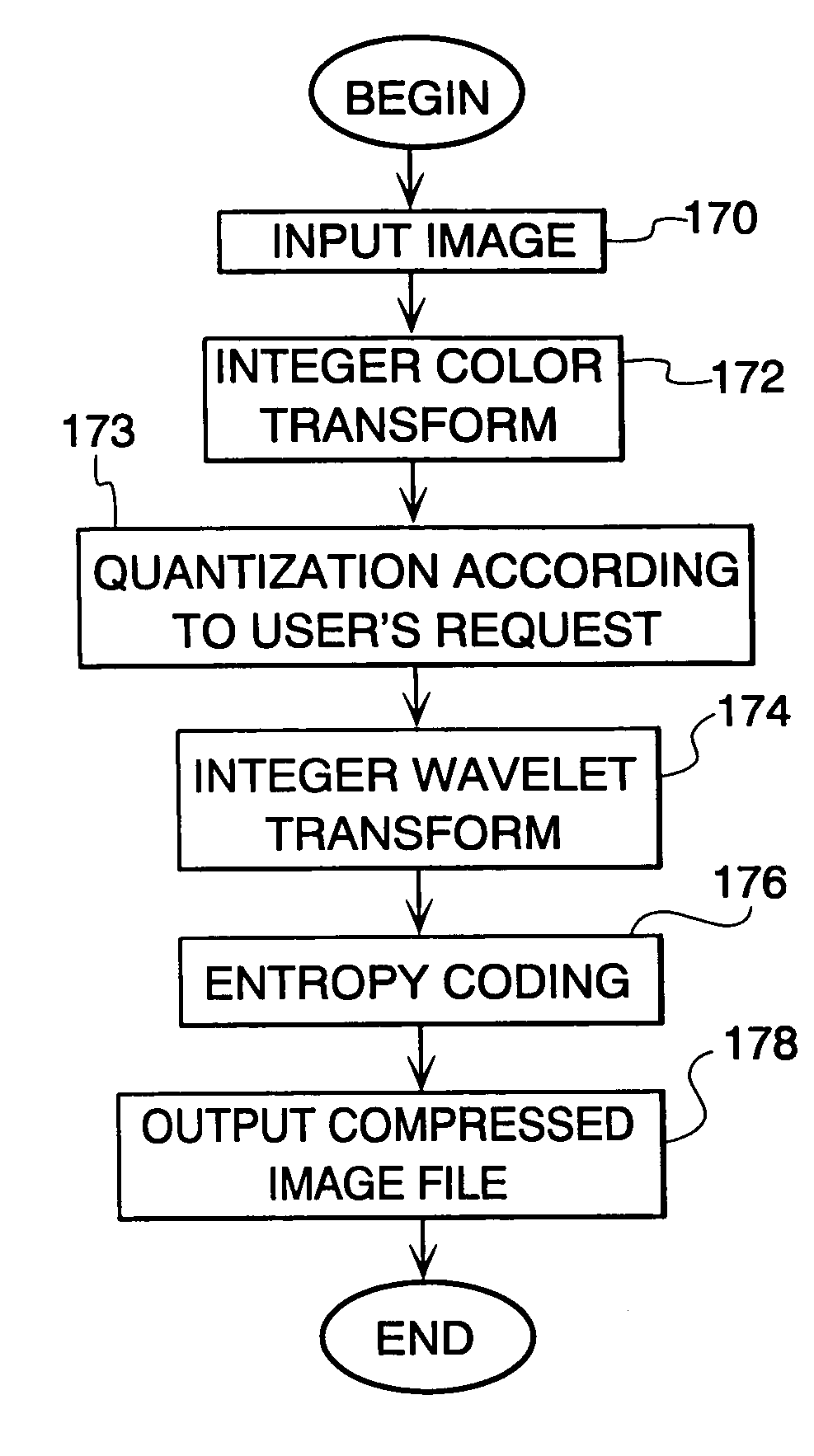
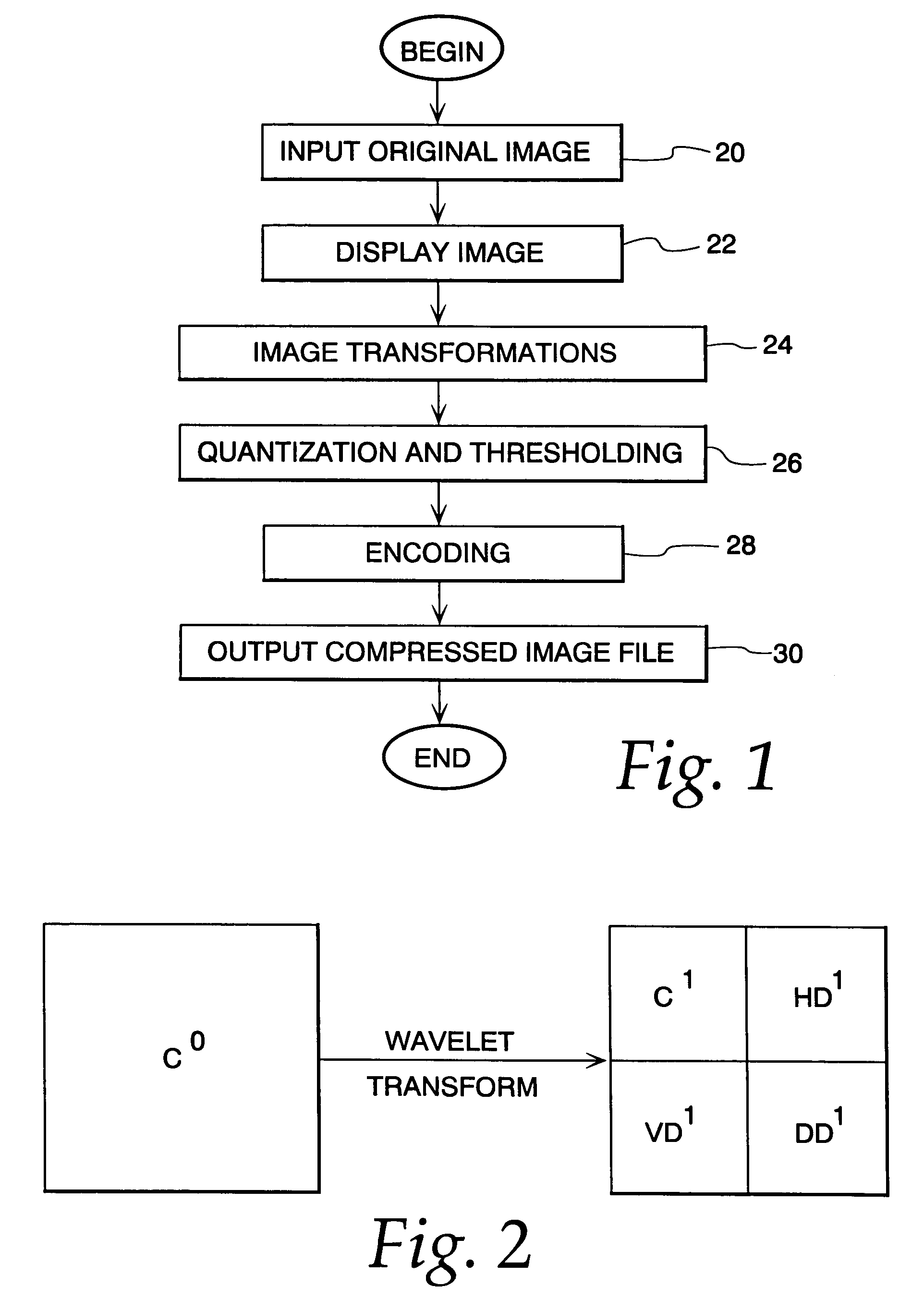
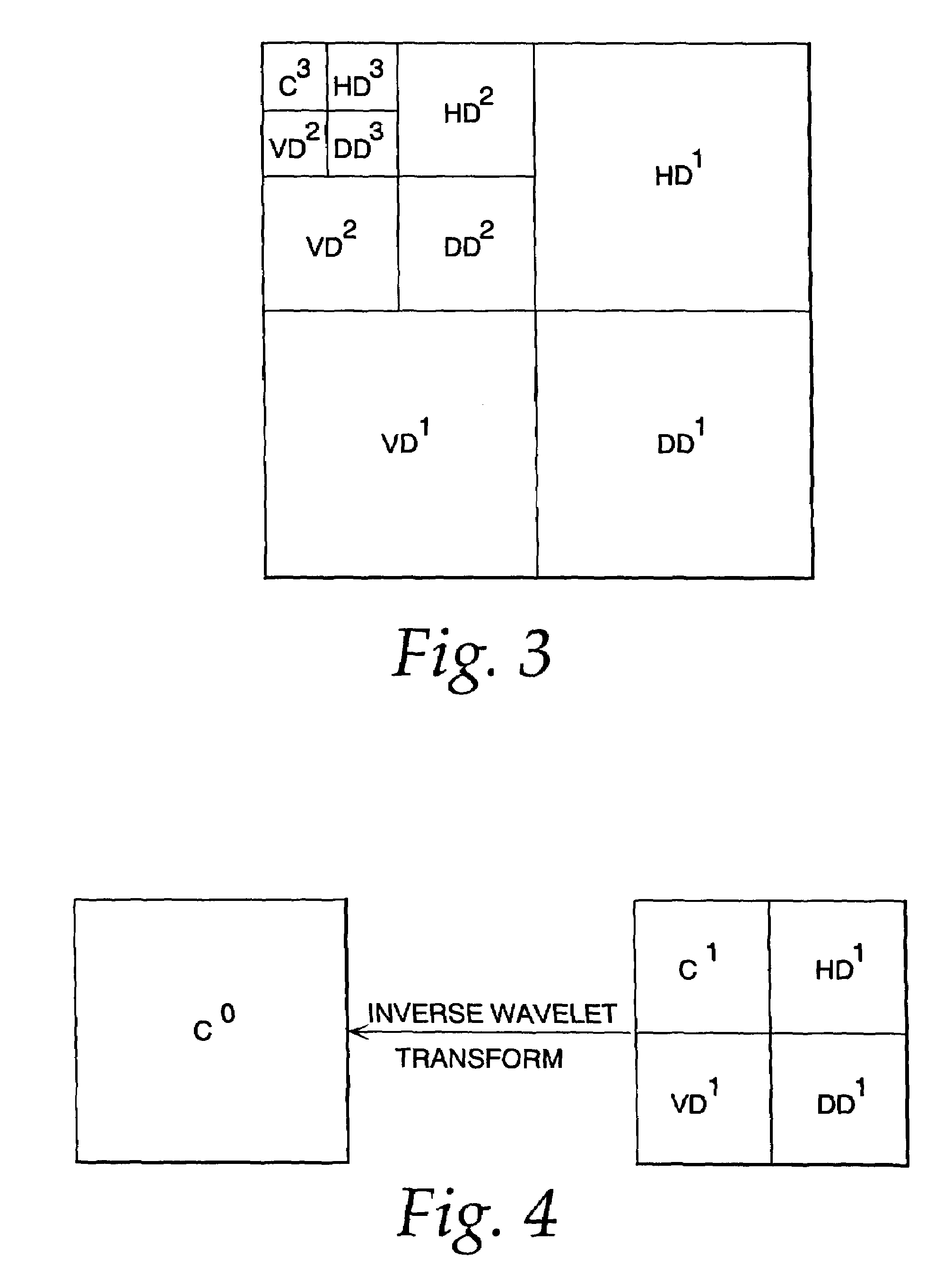
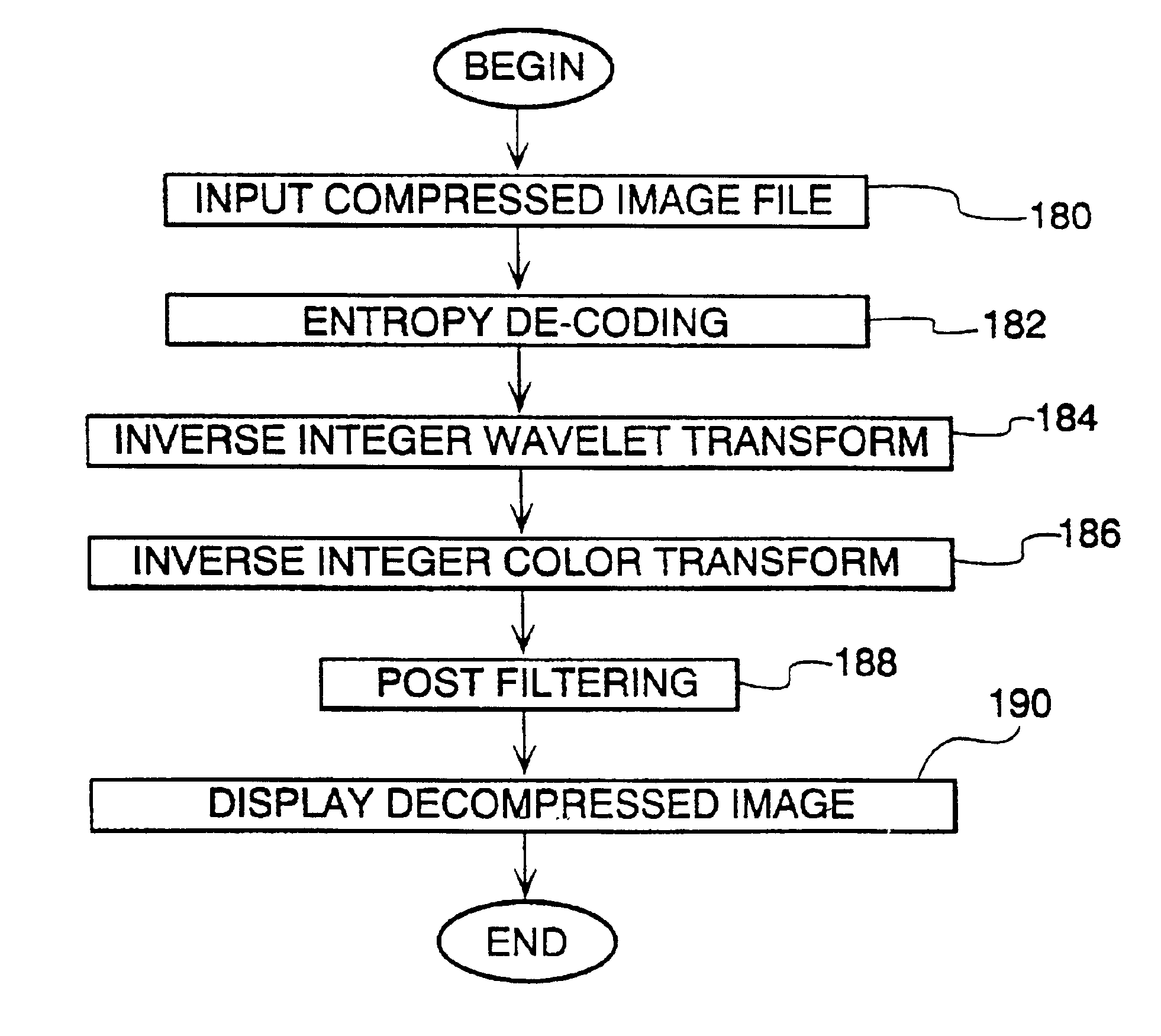
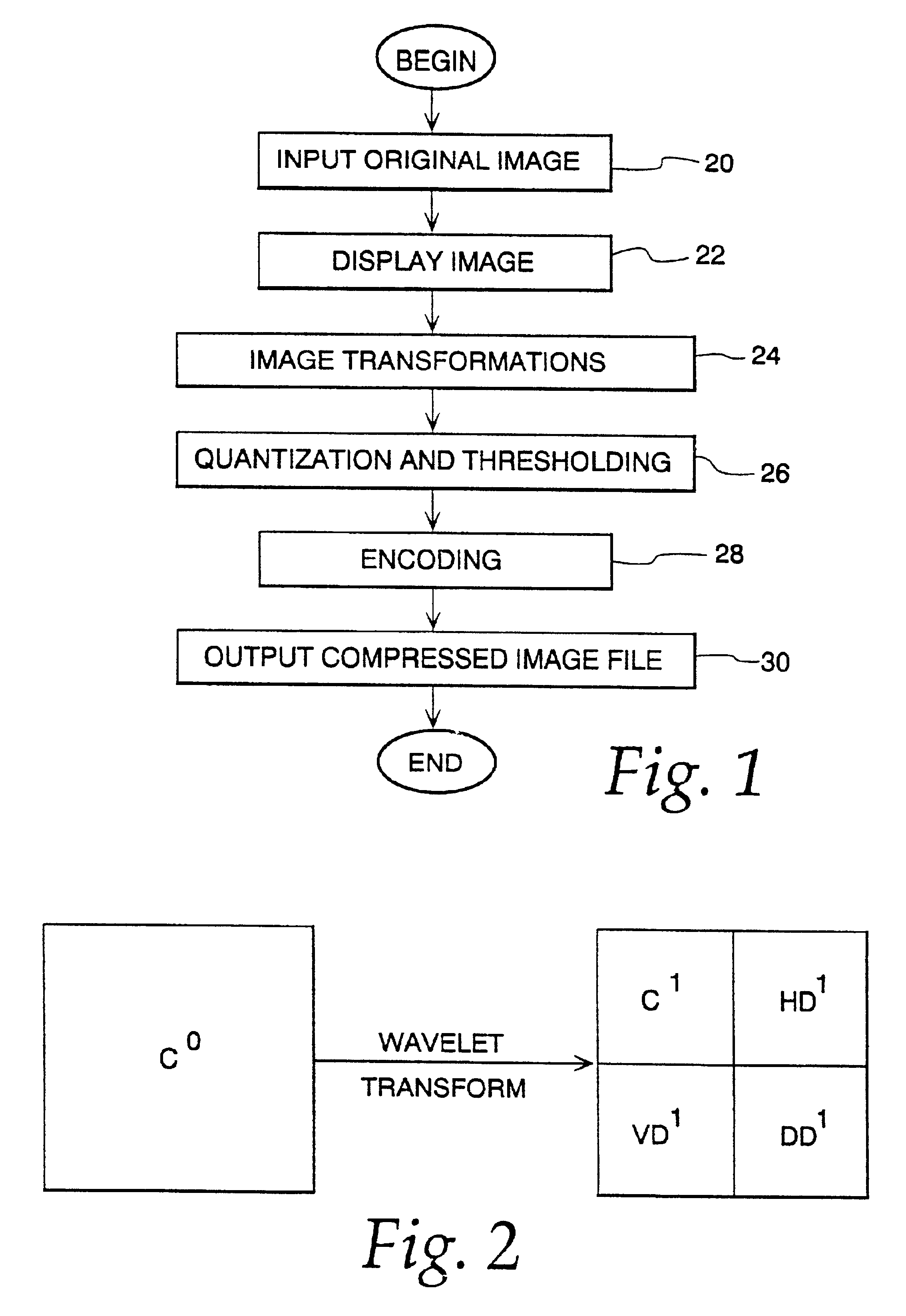
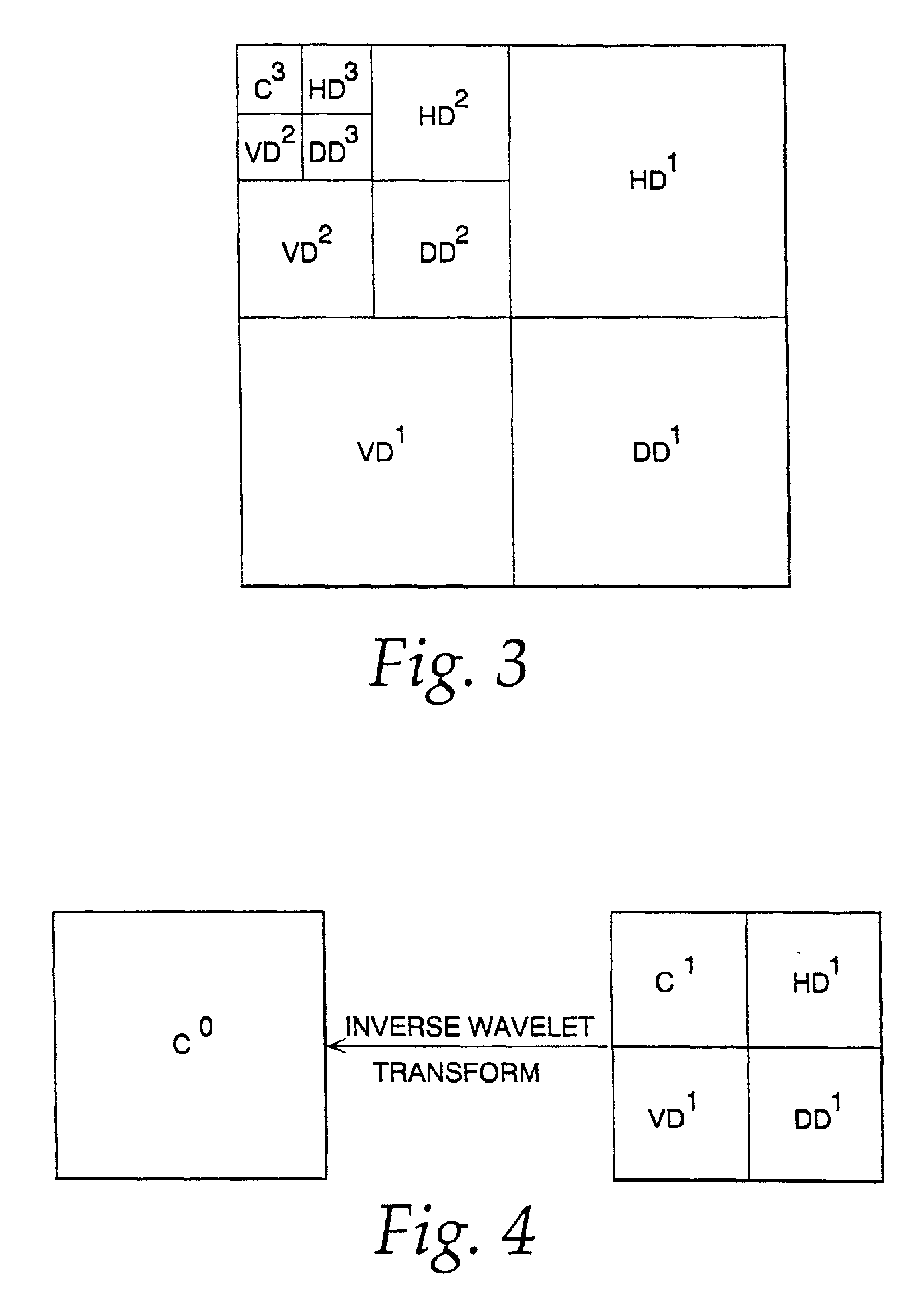
Image compression and decompression based on an integer wavelet transform using a lifting scheme and a correction method
InactiveUS7003168B1Significant loss of accuracyReduced computing resourceColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionColor imageImage compression
A wavelet-based image compression system and method are presented. Compression is accomplished by performing a wavelet transformation of an input digital image. The resulting wavelet coefficients are compared to a threshold value. Coefficients falling below the threshold are discarded. The remaining coefficients are quantized. The quantized coefficients are then compressed using an entropy encoding technique, such as arithmetic, run length, or Huffman encoding, or a combination of Huffman and run length encoding. The wavelet transform can be an integer wavelet transform derived using a lifting scheme or correction method, while the quantization scheme can be sub-band oriented. Input color image pixels can be reduced using a color table. In addition, color pixels can be transformed between color spaces prior to wavelet transformation.
Owner:UPLOAD TECH
Image compression using an interger reversible wavelet transform with a property of precision preservation
InactiveUS6904175B2Without significant loss of accuracyCompression is selectivePicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningColor imageImage compression
A wavelet-based image compression system and method are presented. Compression is accomplished by performing a wavelet transformation of an input digital image. The resulting wavelet coefficients are compared to a threshold value. Coefficients falling below the threshold are discarded. The remaining coefficients are quantized. The quantized coefficients are then compressed using an entropy encoding technique, such as arithmetic, run length, or Huffman encoding, or a combination of Huffman and run length encoding. The wavelet transform can be an integer wavelet transform derived using a lifting scheme or correction method, while the quantization scheme can be sub-band oriented. Input color image pixels can be reduced using a color table. In addition, color pixels can be transformed between color spaces prior to wavelet transformation.
Owner:UPLOAD TECH
Camera and display control method of the same
ActiveUS8471944B2Suitable imageTelevision system detailsColor television detailsDisplay deviceThumbnail Image
A camera according to the present invention comprises: an imaging section converting an object image into image data; a storage section storing still image data of a still image obtained by the imaging section, thumbnail image data of the still image, and moving image data of a moving image which has been photographed at timing at least either before or after photographing of the still image; a display section performing display of one or more thumbnail views according to the thumbnail image data; and a display control section, when one of the thumbnail views is designated in the thumbnail view display, performing display of the still image on the display section according to the still image data corresponding to the designated thumbnail view after having performed display of the moving image according to the moving image data corresponding to the designated thumbnail view stored in the storage section.
Owner:OM DIGITAL SOLUTIONS CORP
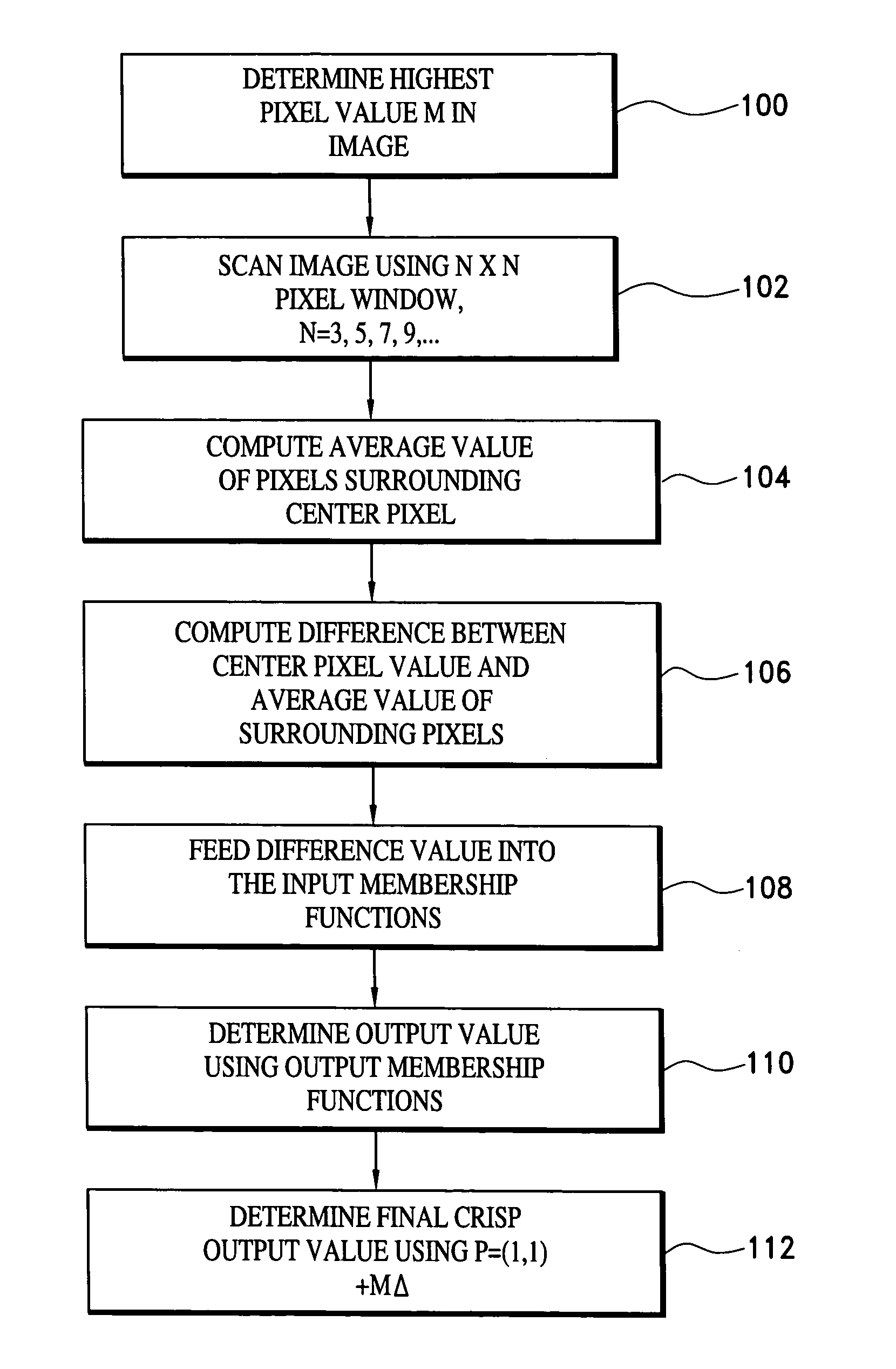
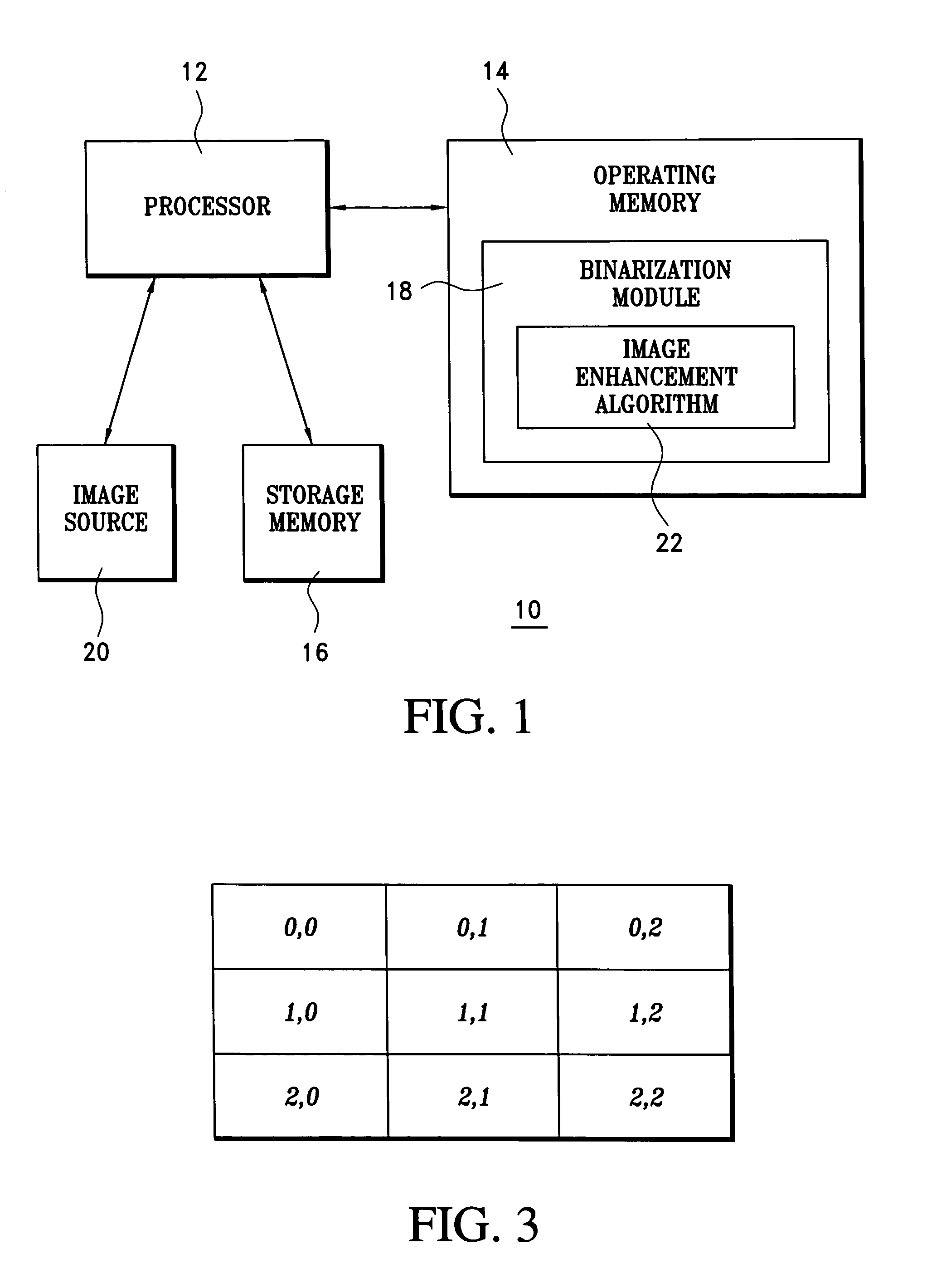
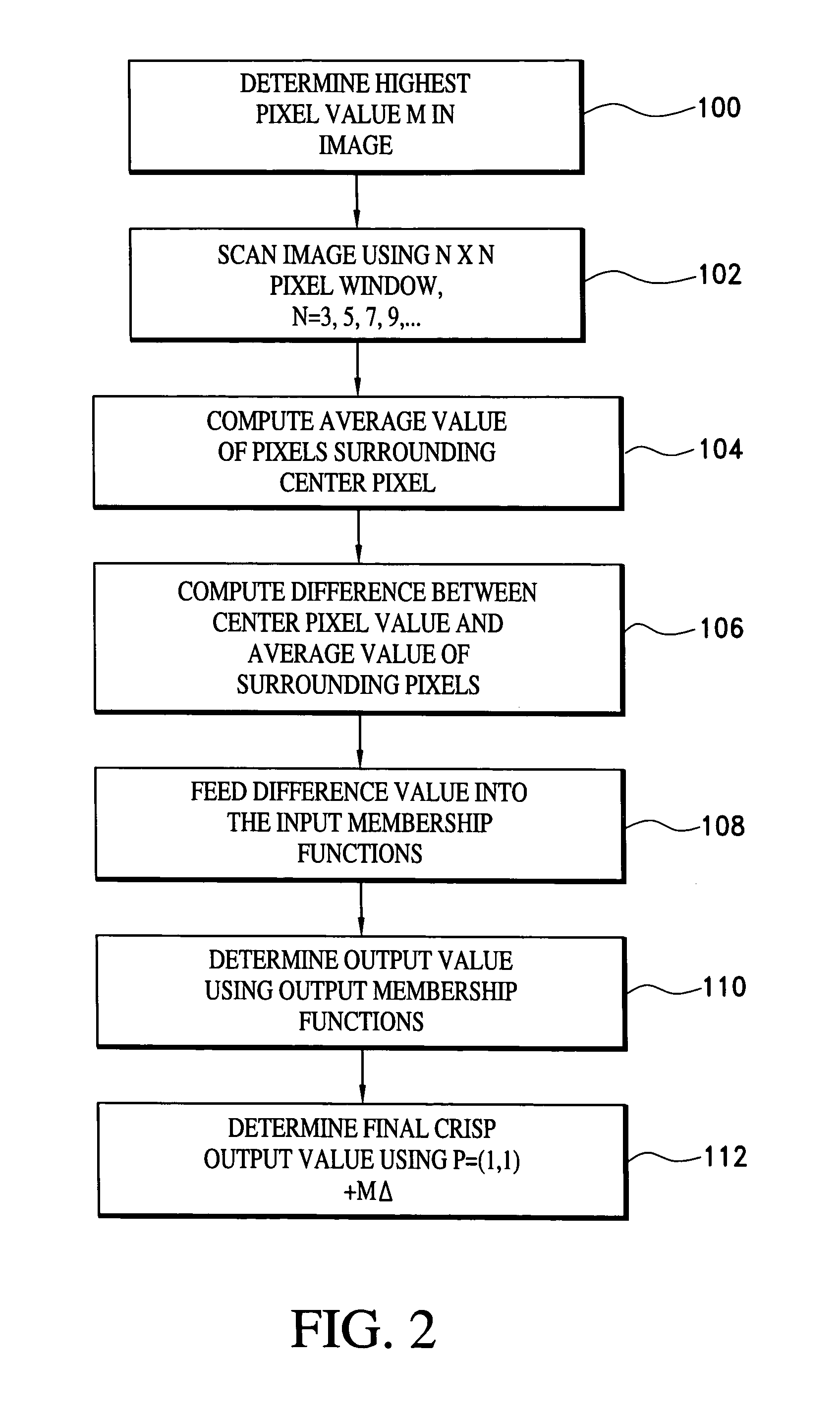
Image processing for binarization enhancement via fuzzy reasoning
InactiveUS7496237B1Increase contentEnhances poor-qualityCharacter recognitionPictoral communicationPattern recognitionImaging processing
A technique for enhancing a gray-scale image to improve conversions of the image to binary employs fuzzy reasoning. In the technique, pixels in the image are analyzed by comparing the pixel's gray scale value, which is indicative of its relative brightness, to the values of pixels immediately surrounding the selected pixel. The degree to which each pixel in the image differs in value from the values of surrounding pixels is employed as the variable in a fuzzy reasoning-based analysis that determines an appropriate amount by which the selected pixel's value should be adjusted to reduce vagueness and ambiguity in the image and improve retention of information during binarization of the enhanced gray-scale image.
Owner:NASA
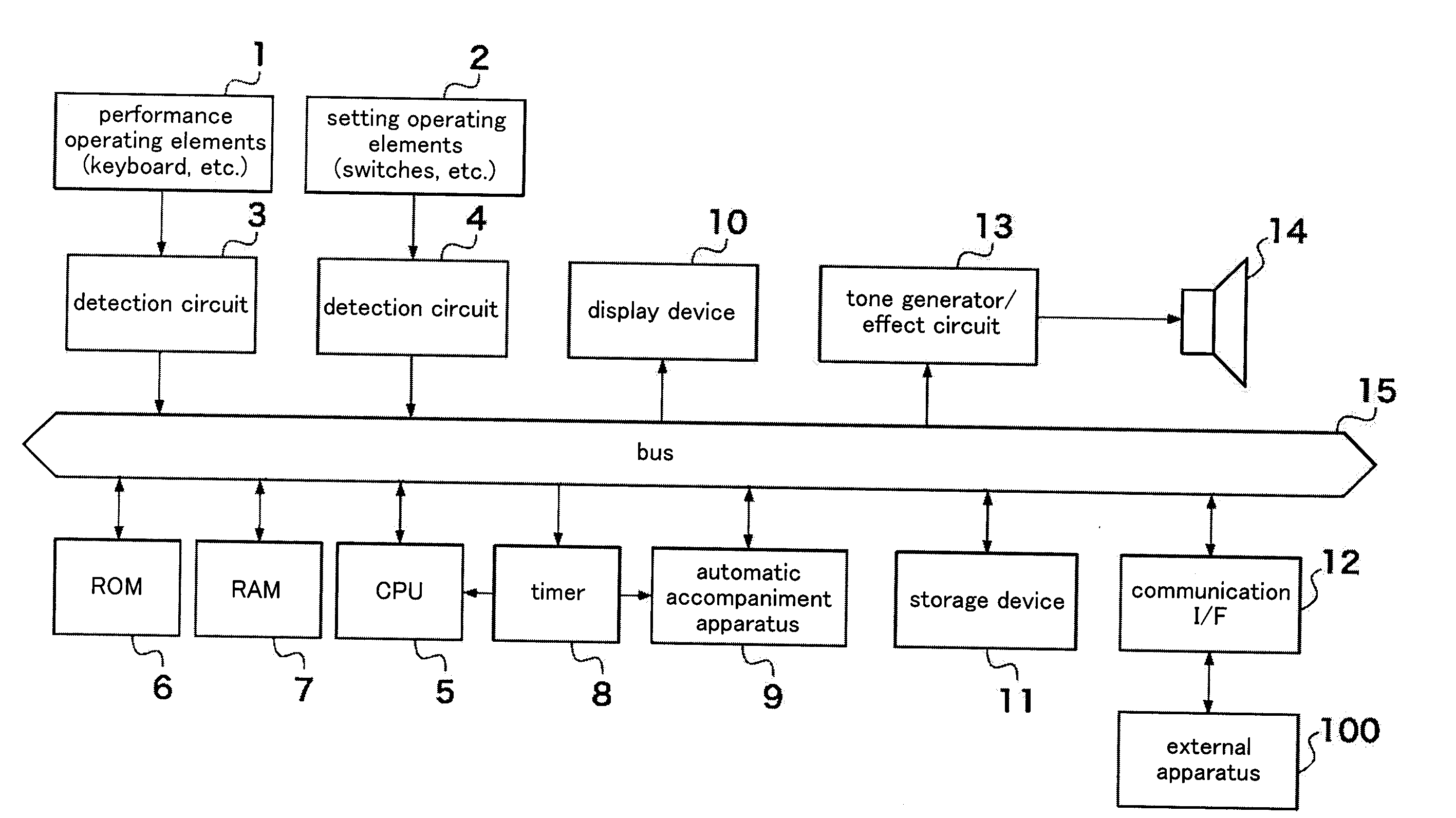
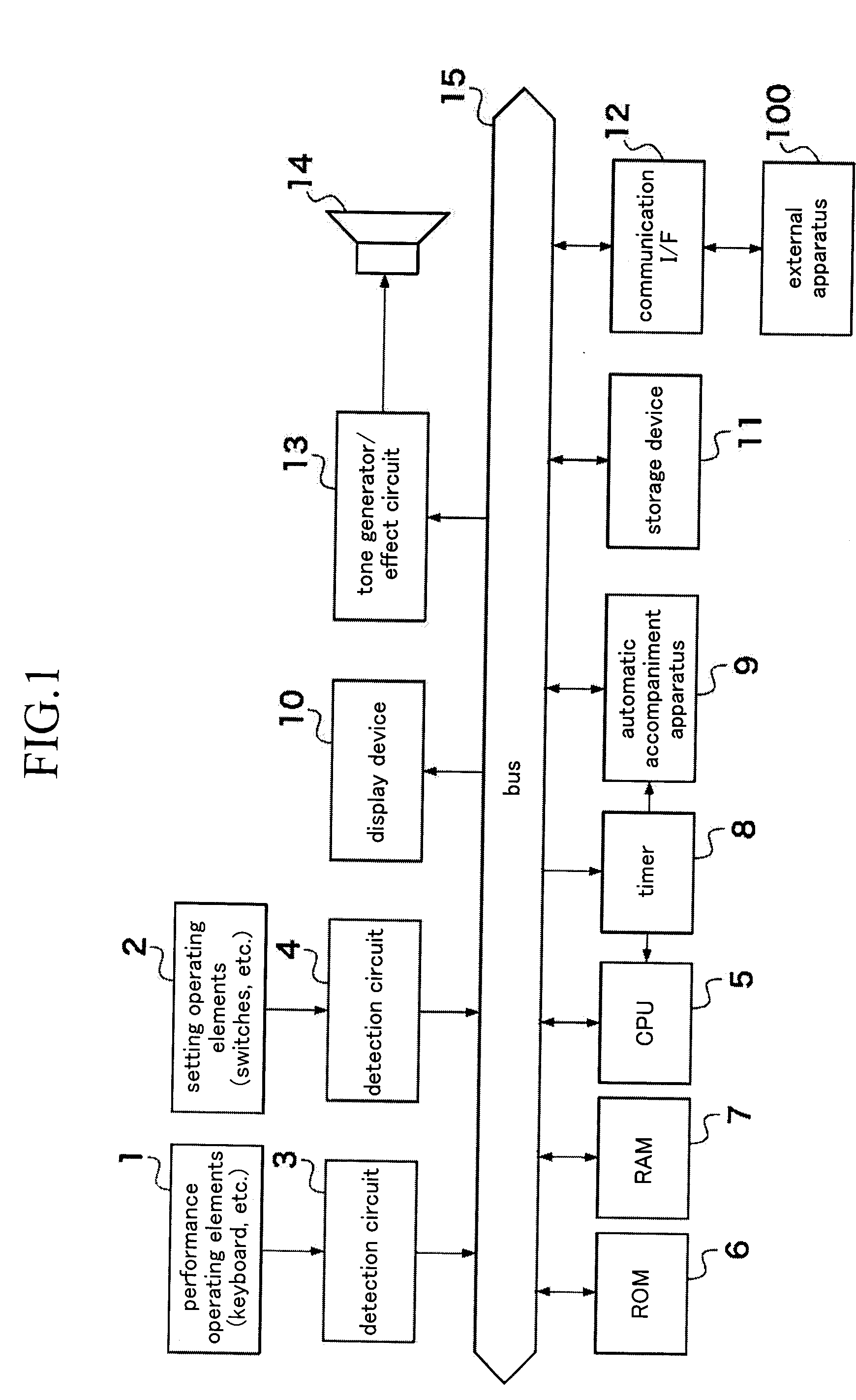
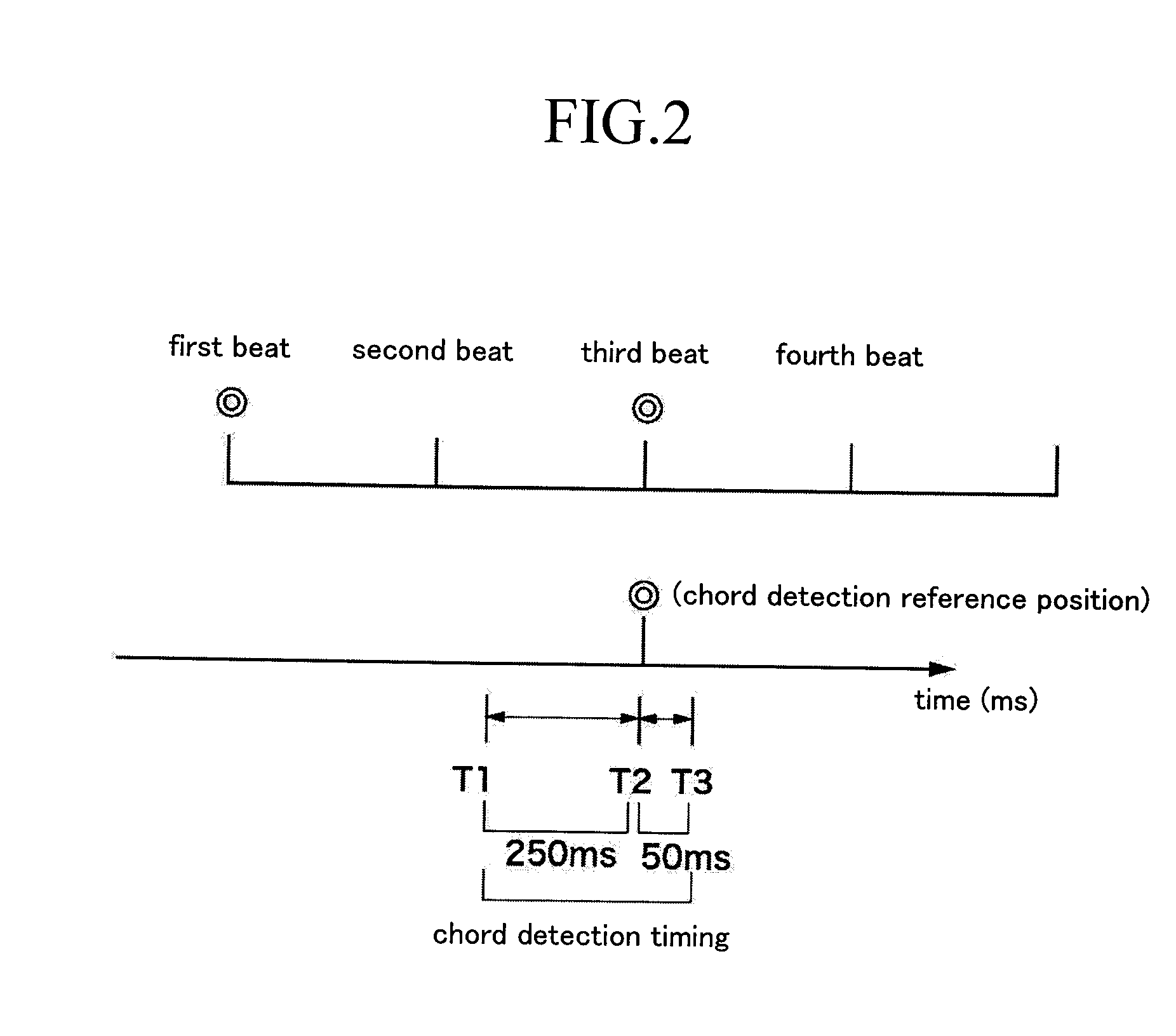
Apparatus and method for detecting chord
InactiveUS20140238220A1Takes effortEasy to detectElectrophonic musical instrumentsSpeech recognition
Owner:YAMAHA CORP
Biological Imaging Device
ActiveUS20110096967A1Reduce astigmatismSuitable imageOptical radiation measurementTelevision system detailsCamera lensTwo dimensional detector
Optical waveguide paths to observe a sample on a sample holder from a plurality of directions while guiding an image of light in each direction which is emitted out of the sample toward a direction of a two dimensional detector via a main imaging lens include an optical waveguide path which never receives the light directly from the sample. The optical waveguide path which never receives the light directly from the sample forms an image of the sample within a substantial focus range of the main imaging lens, and includes optical elements arranged such that a light beam after formation of the image proceeds toward a direction of the main imaging lens. Optical elements on at least one optical waveguide path are those for forming real images. Therefore, the main imaging lens images the sample and those real images in block on the two dimensional detector.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Solid-state image-capturing device and method for driving solid-state image-capturing device
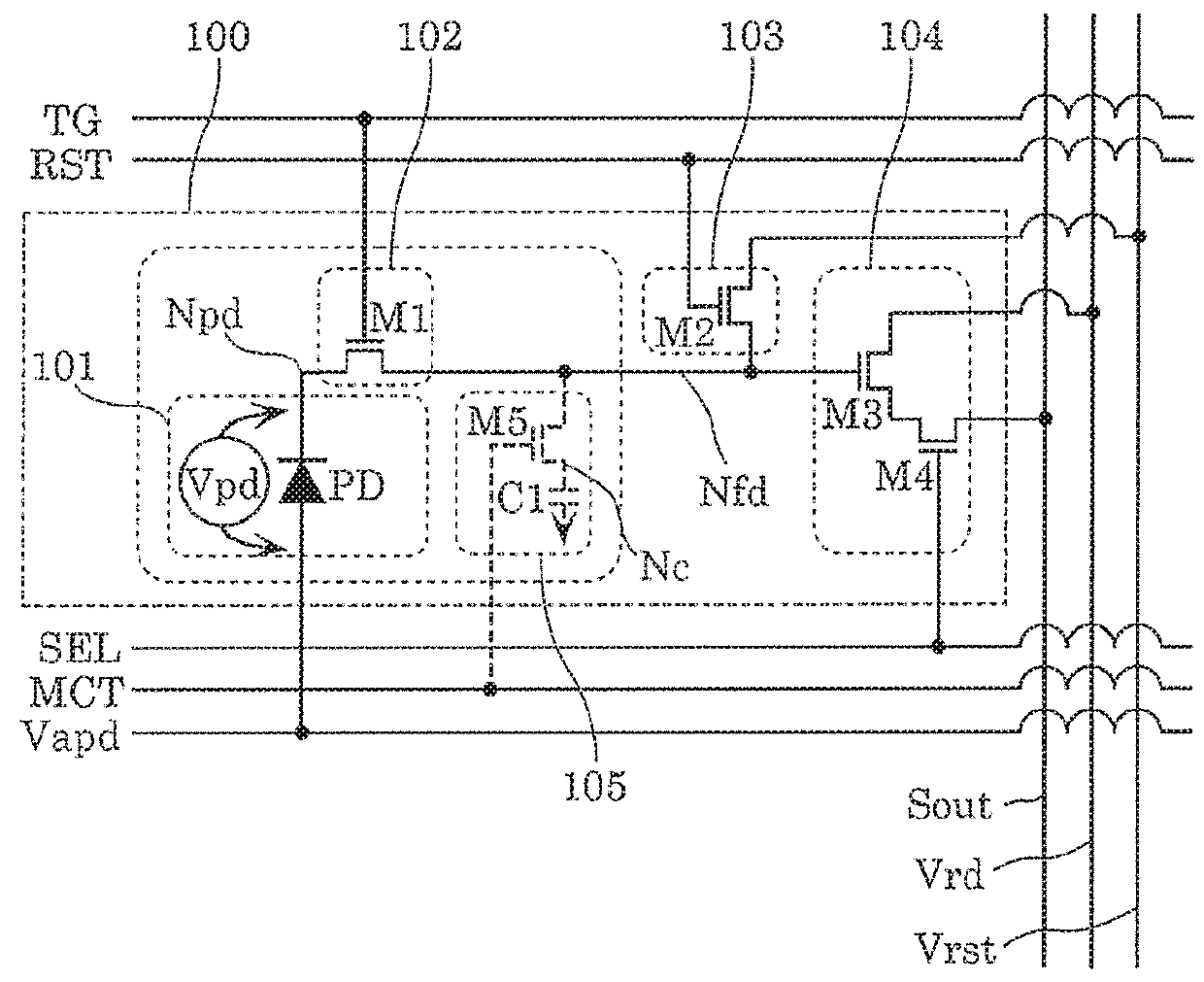
ActiveUS20180278877A1Reduction in frame rate can be suppressedTime can be eliminatedTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityControl signal
A solid-state image-capturing device includes a pixel array including a plurality of pixel circuits arranged in rows and columns. Each pixel circuit includes: a photoelectric conversion element that generates an electric charge through photoelectric conversion between a bias terminal and a first node, and amplifies the electric charge according to a bias voltage applied via the bias terminal and the first node; a transfer circuit that electrically connects the first node to a second node according to a first control signal; a reset circuit that applies a reset voltage to the second node according to a second control signal; an output circuit that reads out a voltage of the second node according to a third control signal; and an analog memory that is electrically connected to the second node according to a fourth control signal.
Owner:PANASONIC INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY MANAGEMENT CO LTD
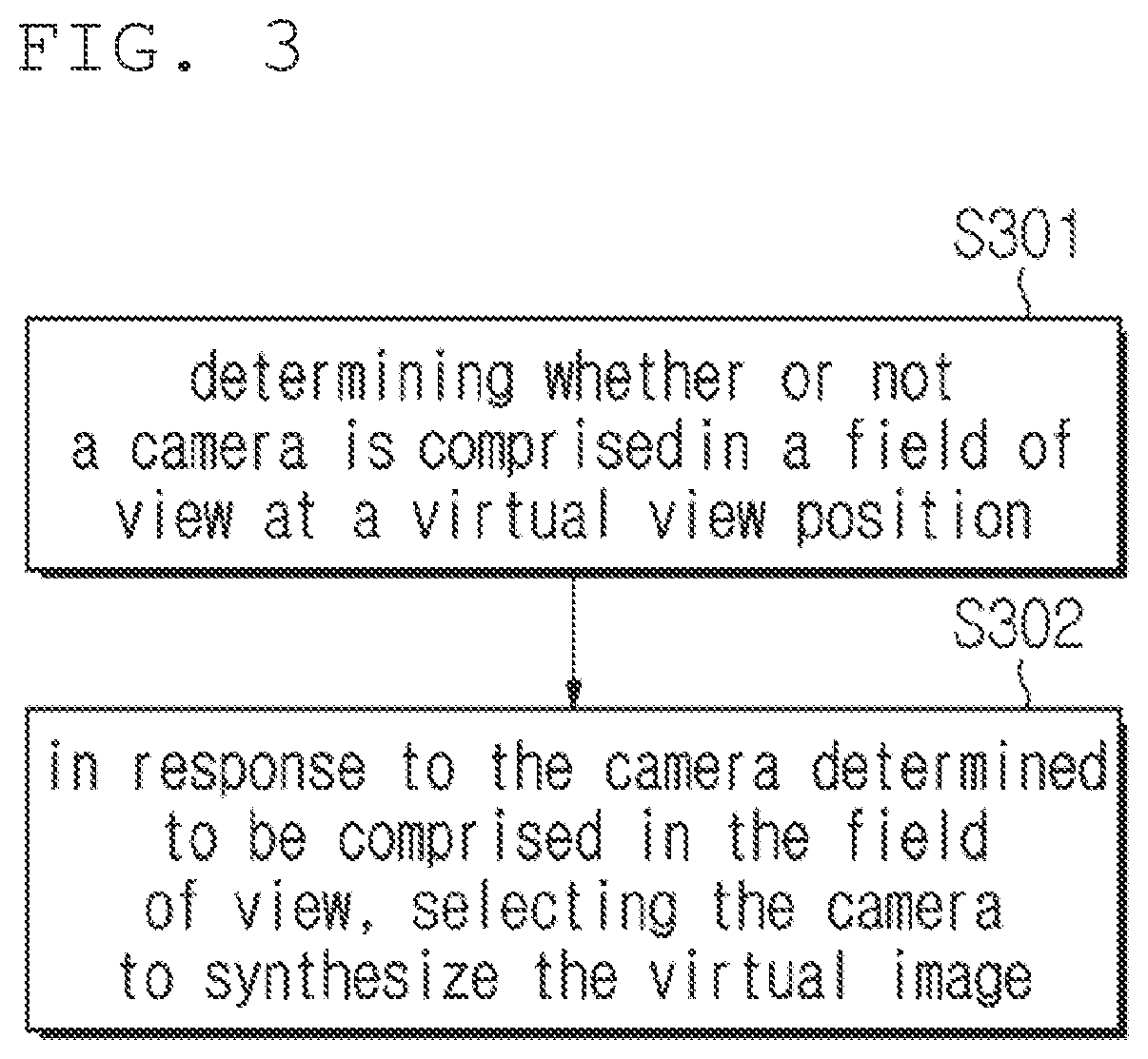
Apparatus and method for selecting camera providing input images to synthesize virtual view images
The present disclosure provides an apparatus and a method for selecting camera providing input images to synthesize virtual view images. According to the present disclosure, A method of selecting a camera providing an input image to synthesize a virtual view image, the method may comprise, for a camera providing an input image, determining whether or not the camera is comprised in a field of view (FoV) at a virtual view position and in response to the camera determined to be comprised in the field of view, selecting the camera to synthesize the virtual image, wherein the determining determines, by way of comparison, whether or not a direction from the virtual view position to a position of the camera is in the FoV at the virtual view position.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
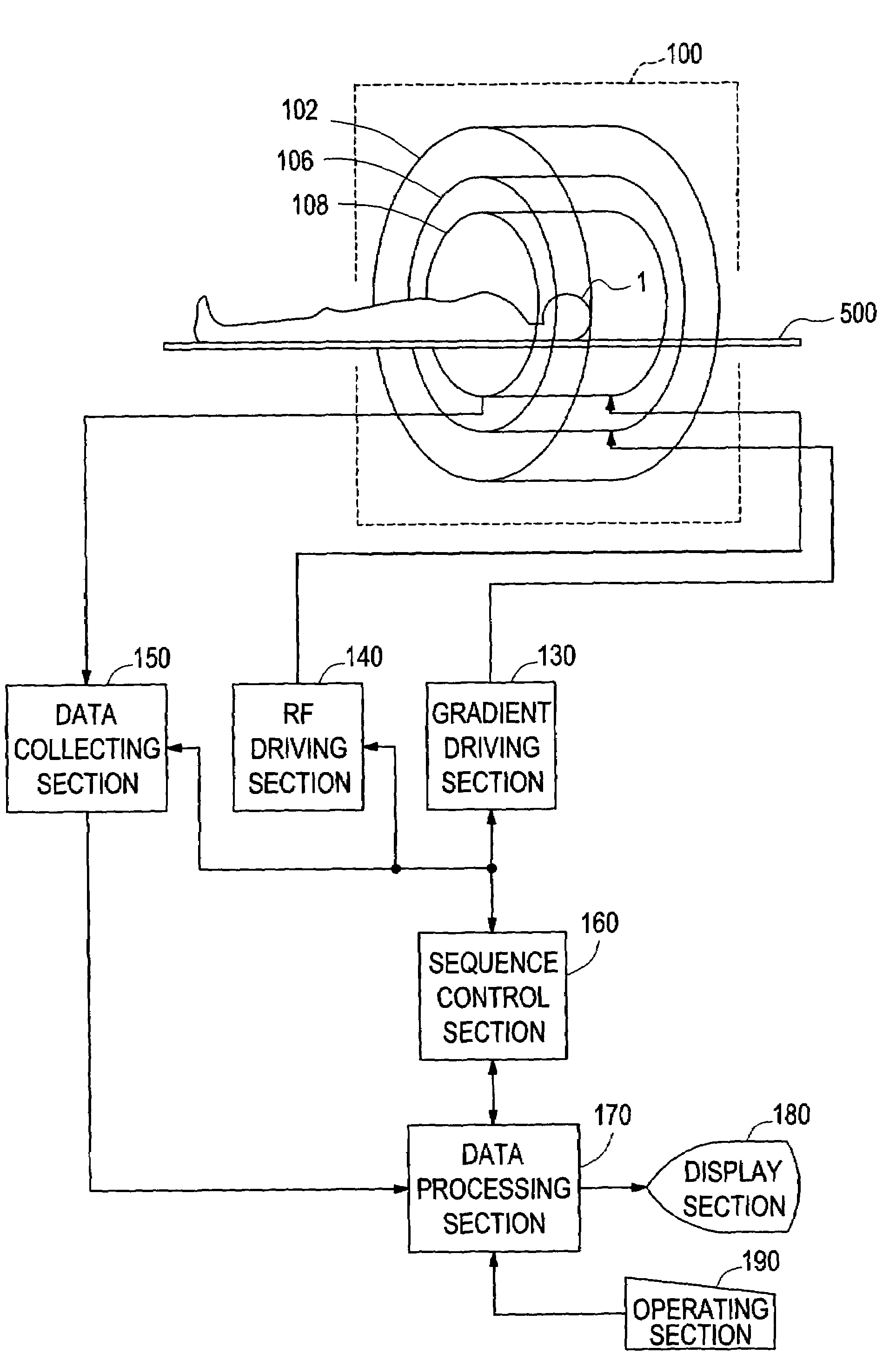
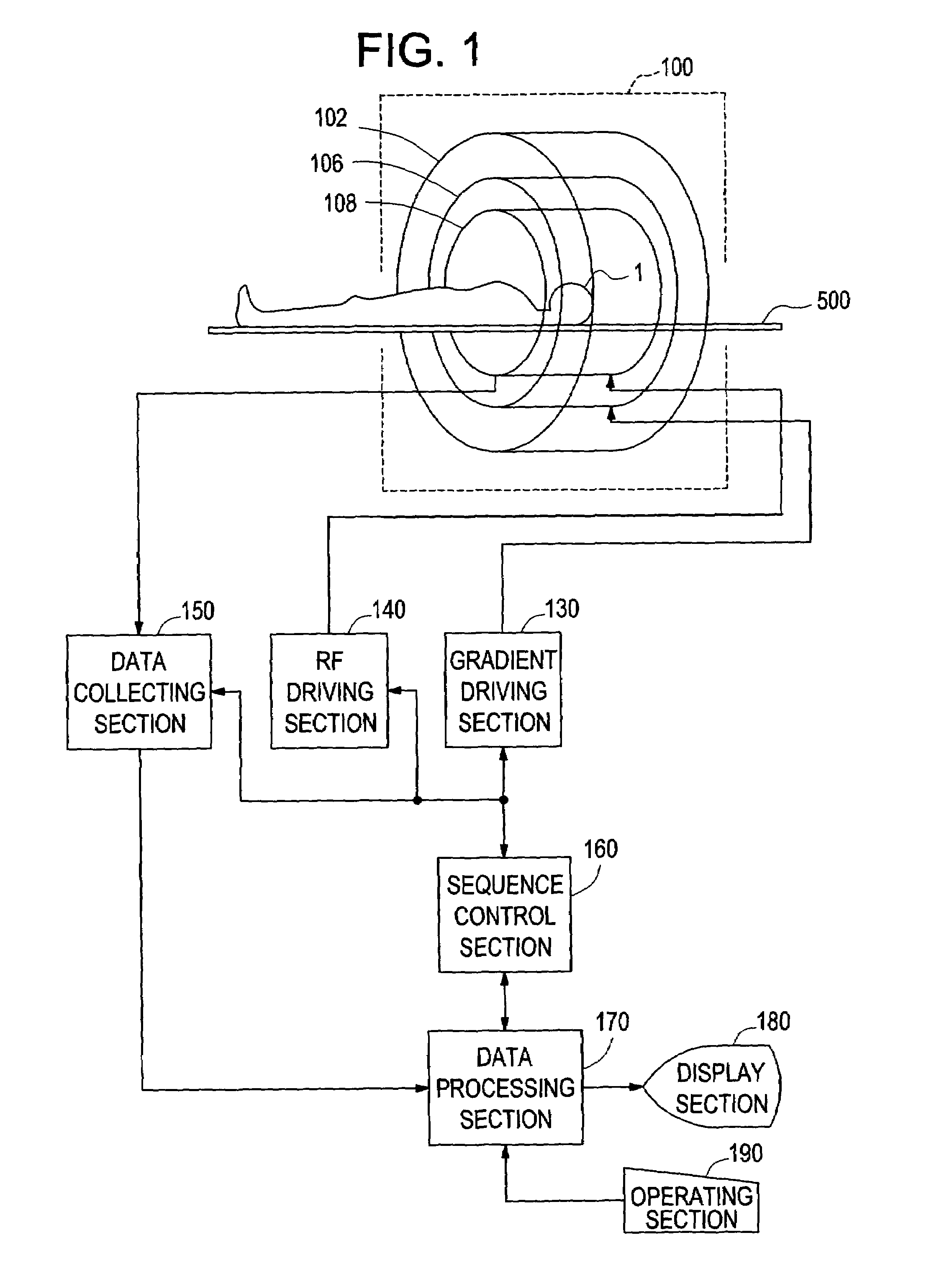
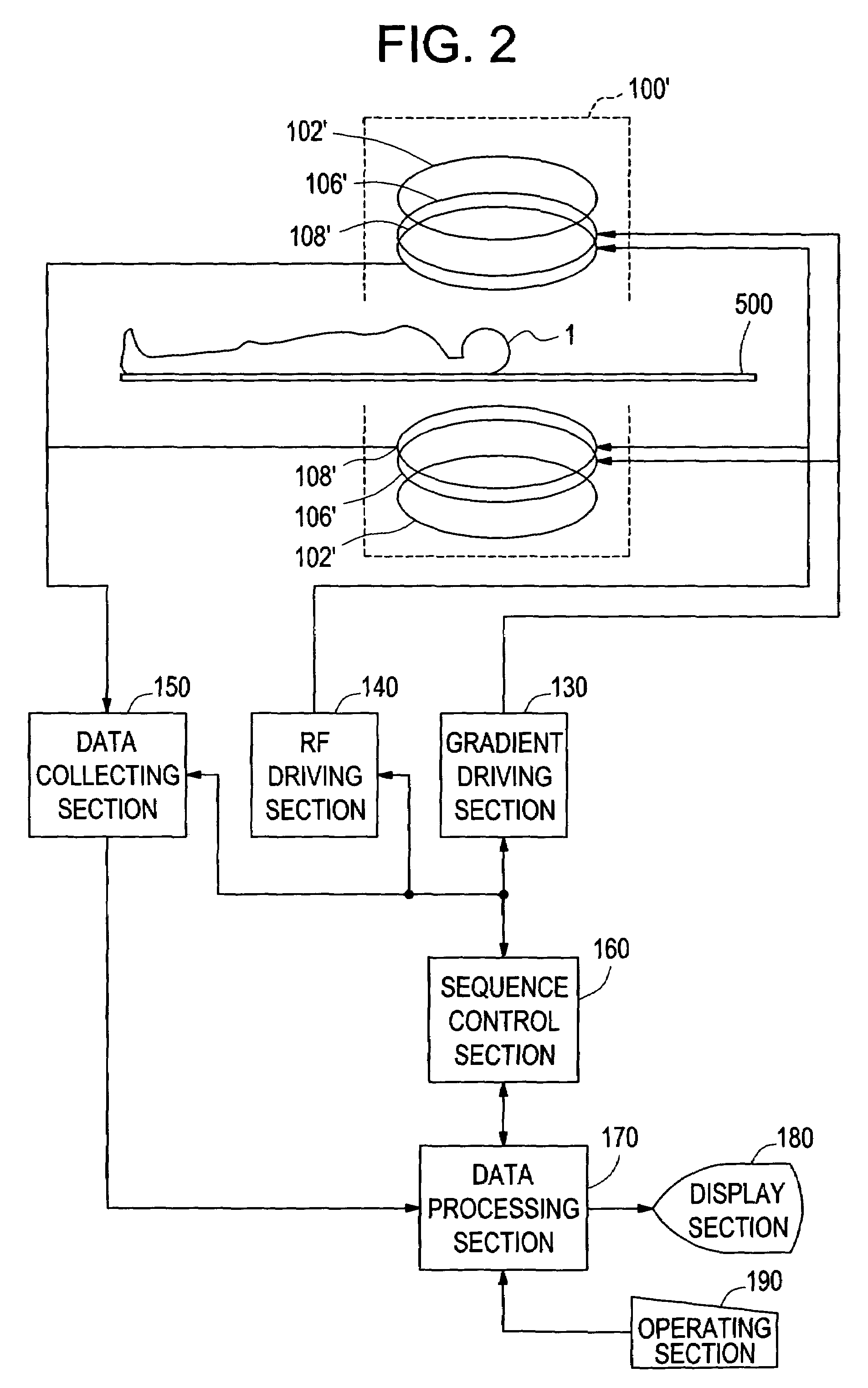
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
InactiveUS7336986B2Shorten the timeSuitable imageSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringPhase differenceSpins
An apparatus includes acquiring means for acquiring echo data of a plurality of views in which a phase difference between water and fat is 2π / m with spins within a subject brought to the SSFP state and repeating the acquisition for k=0 through M−1 with a step difference in a phase of an RF pulse of 2π·k / M; transforming means for conducting Fourier transformation on the echo data based on the phase step difference; separating means for separating water data and fat data respectively in F(0) term and F(1) term of the Fourier-transformed data using the phase difference between water and fat; adding means for obtaining a sum of absolute values of at least the water data or fat data in the F(0) term and F(1) term; and image producing means for producing an image based on the sum data.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com