Patents
Literature
46 results about "High field mri" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
High field magnetic resonance
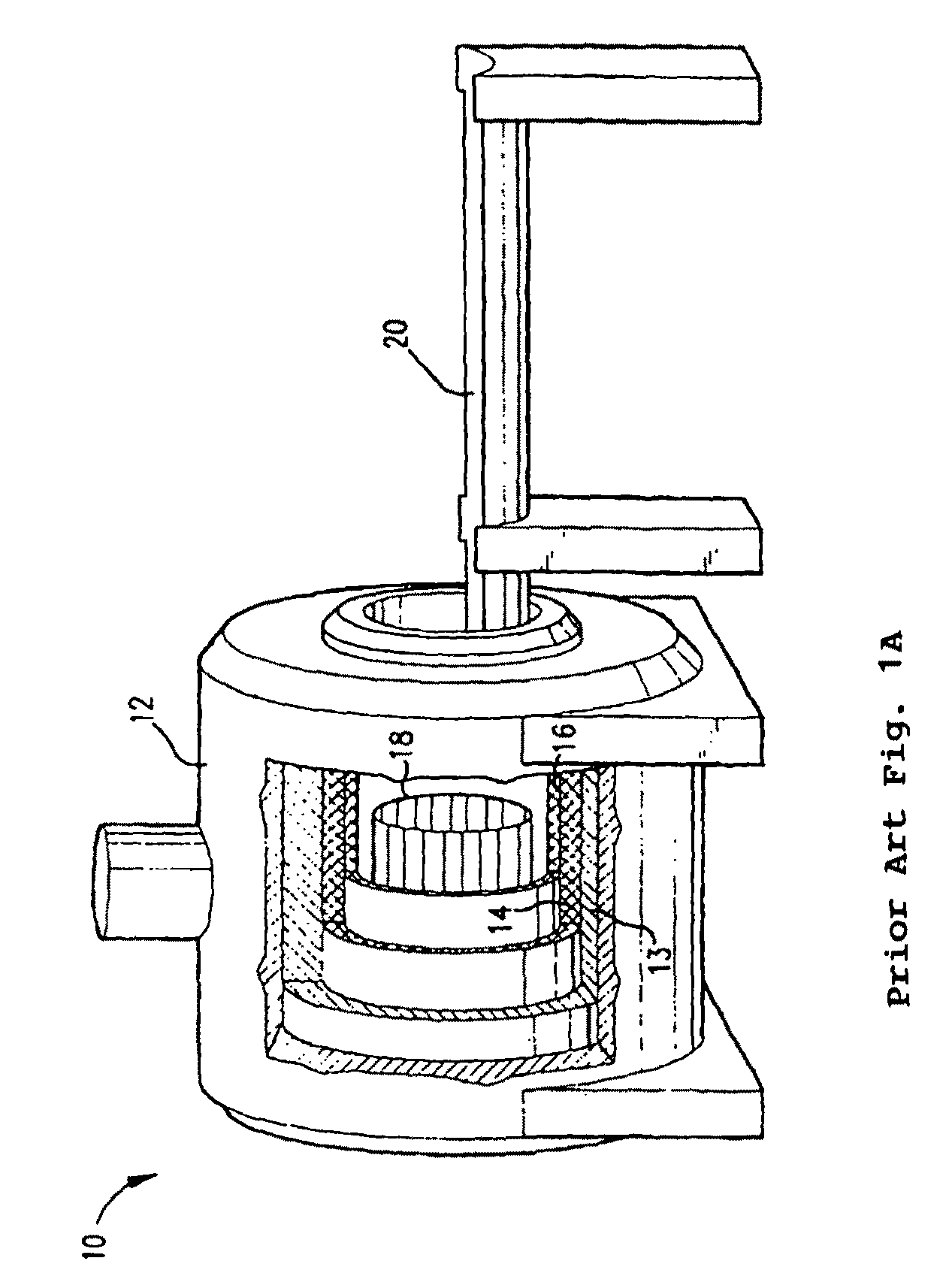
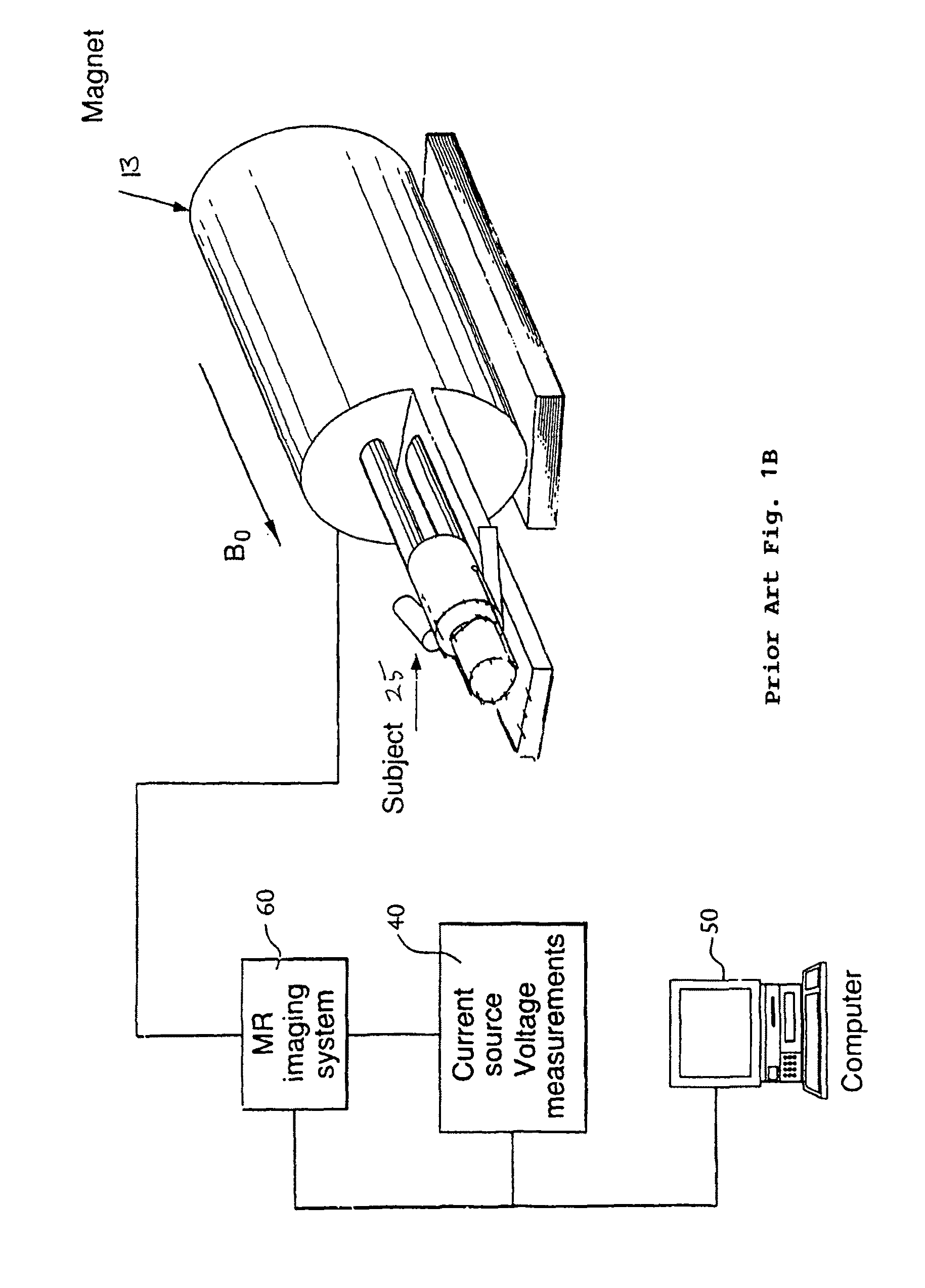
ActiveUS20080129298A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceResonanceHigh field mri
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
High field magnetic resonance
ActiveUS7800368B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNonlinear algorithmsCurrent element
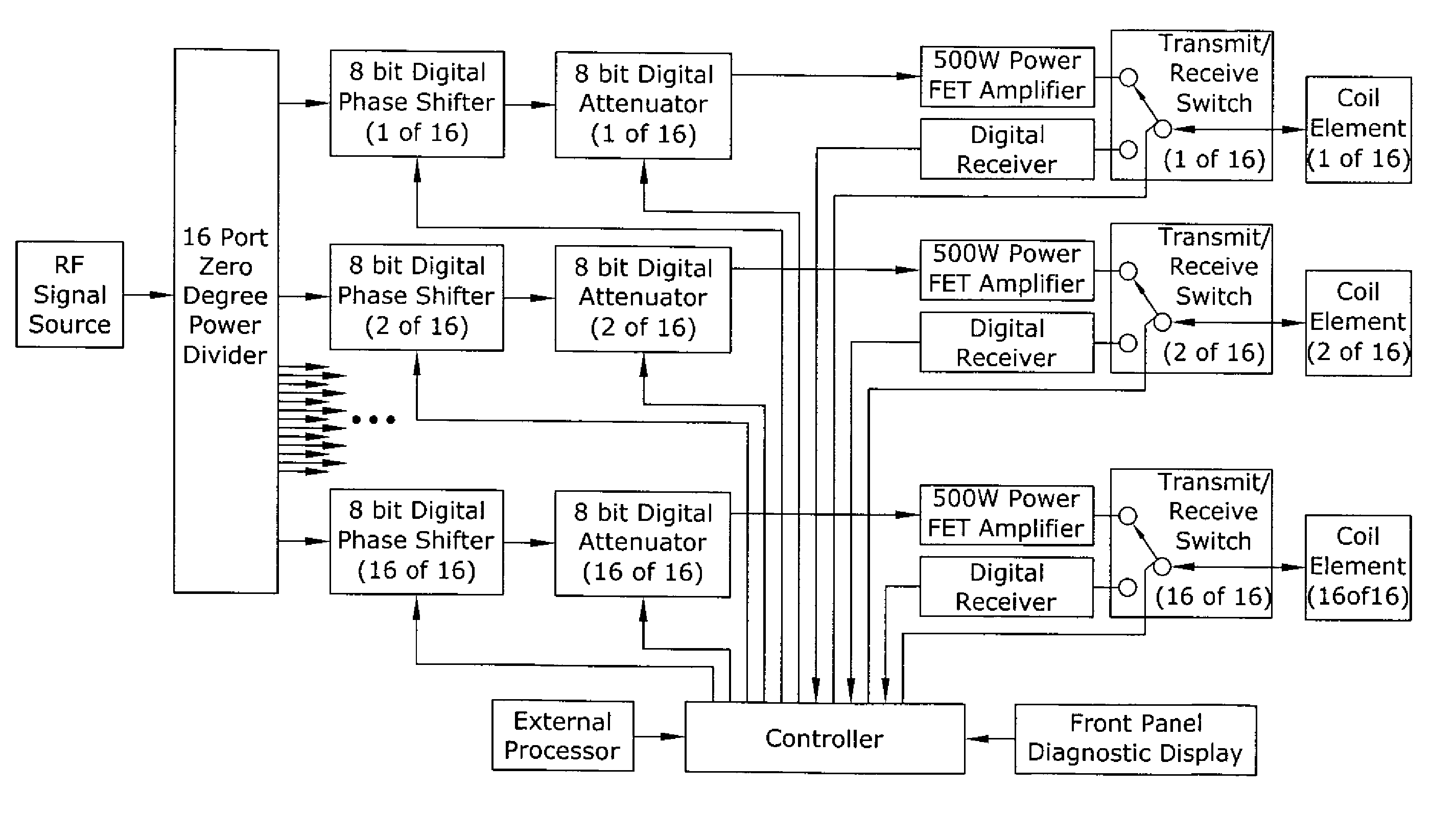
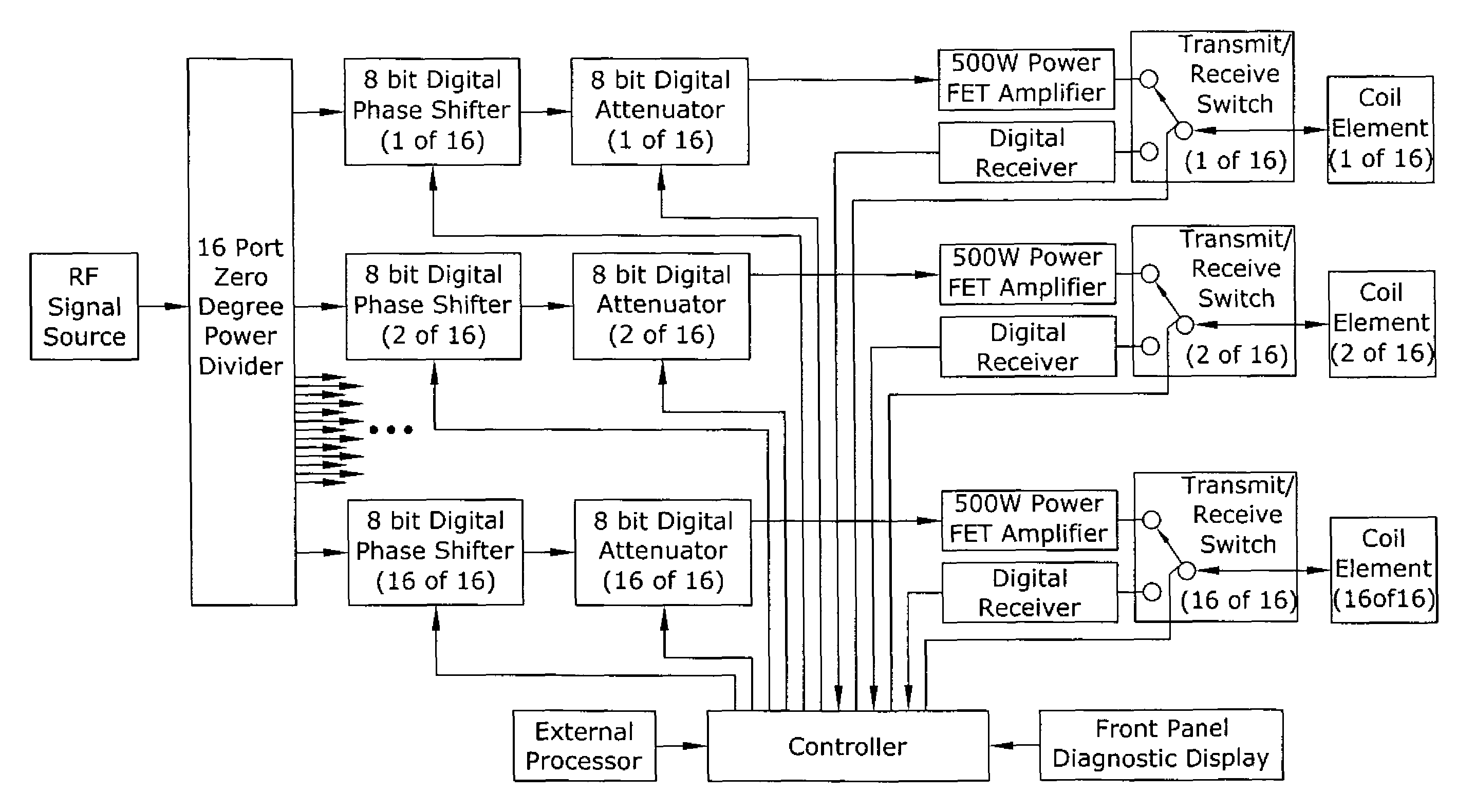
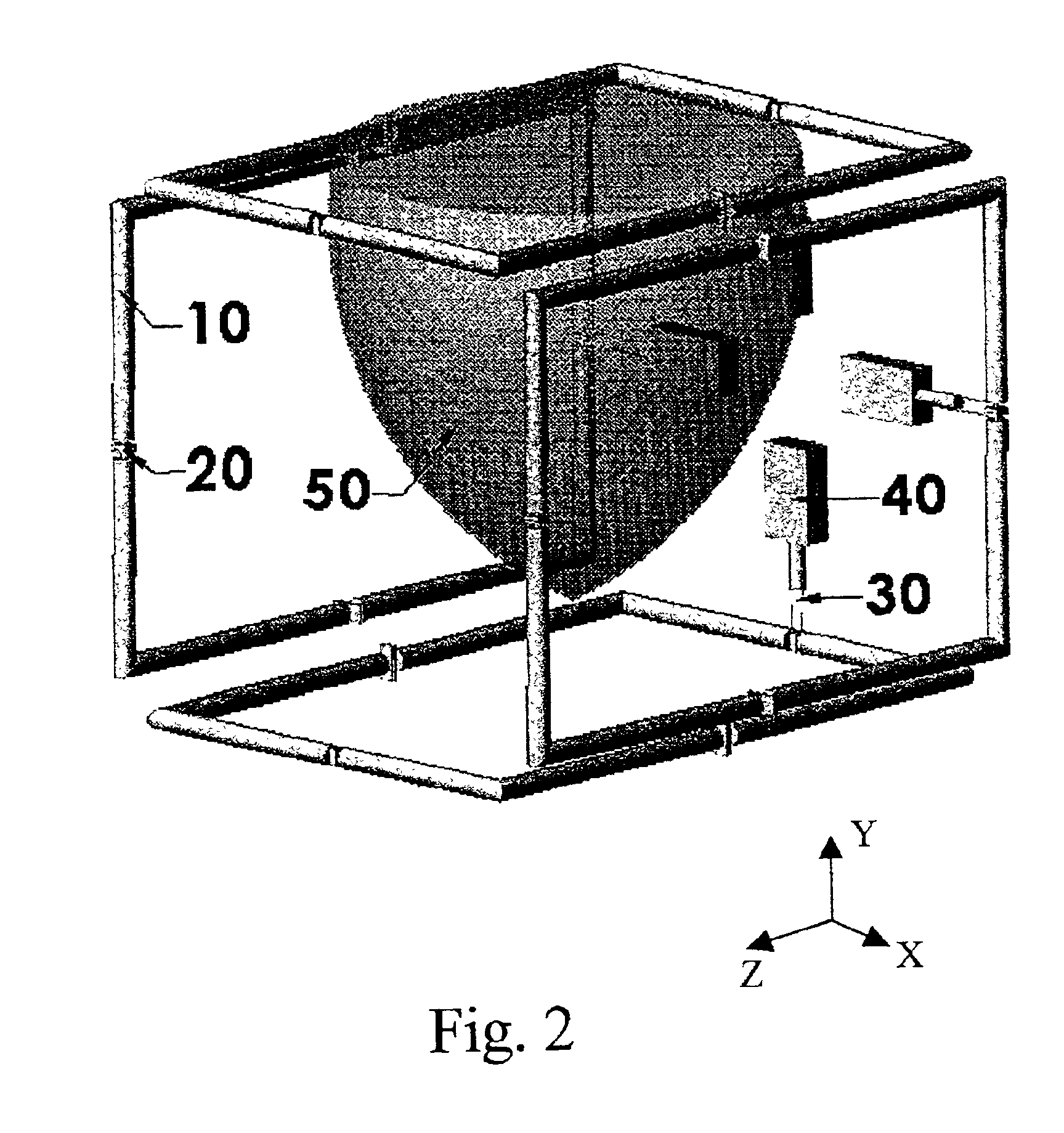
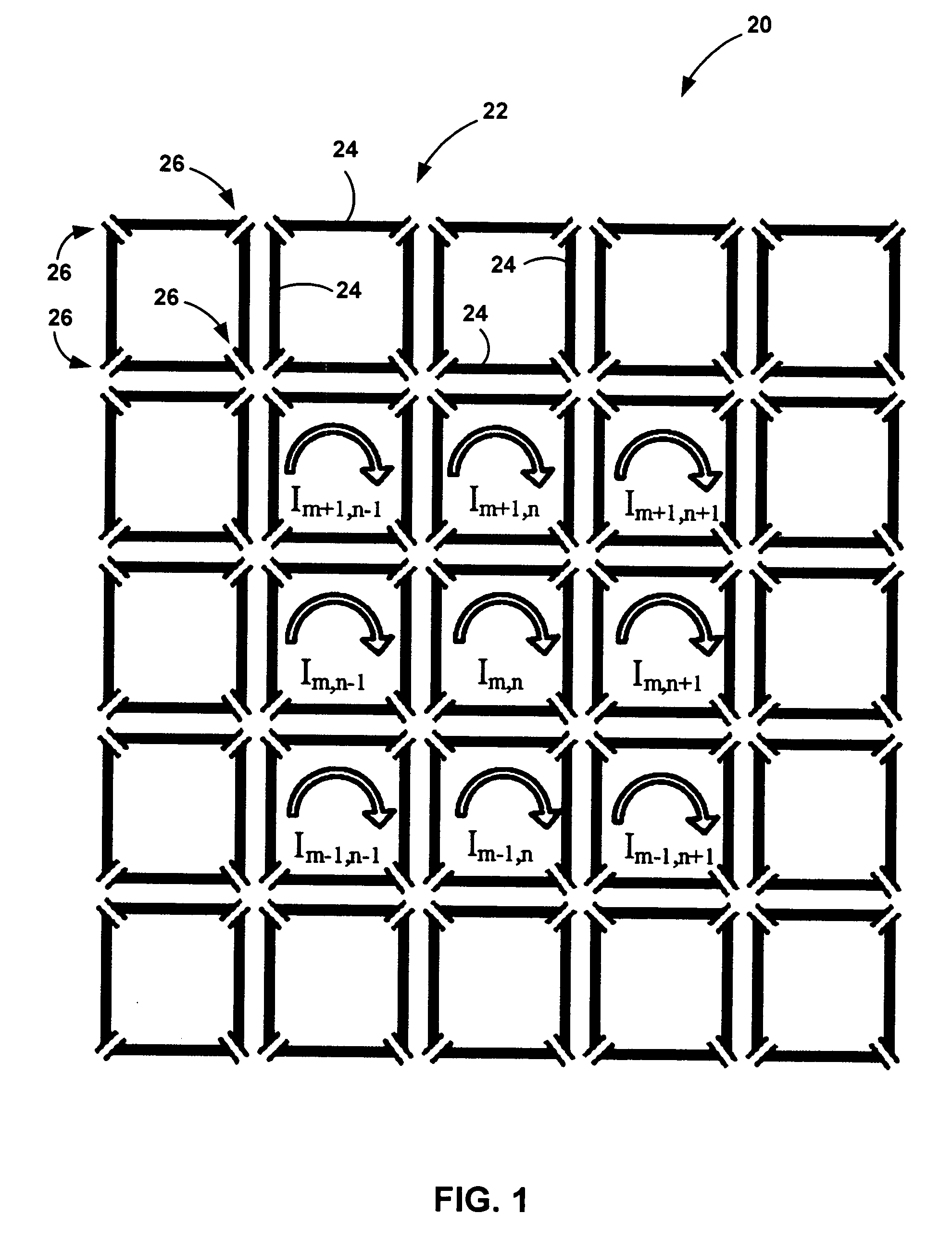
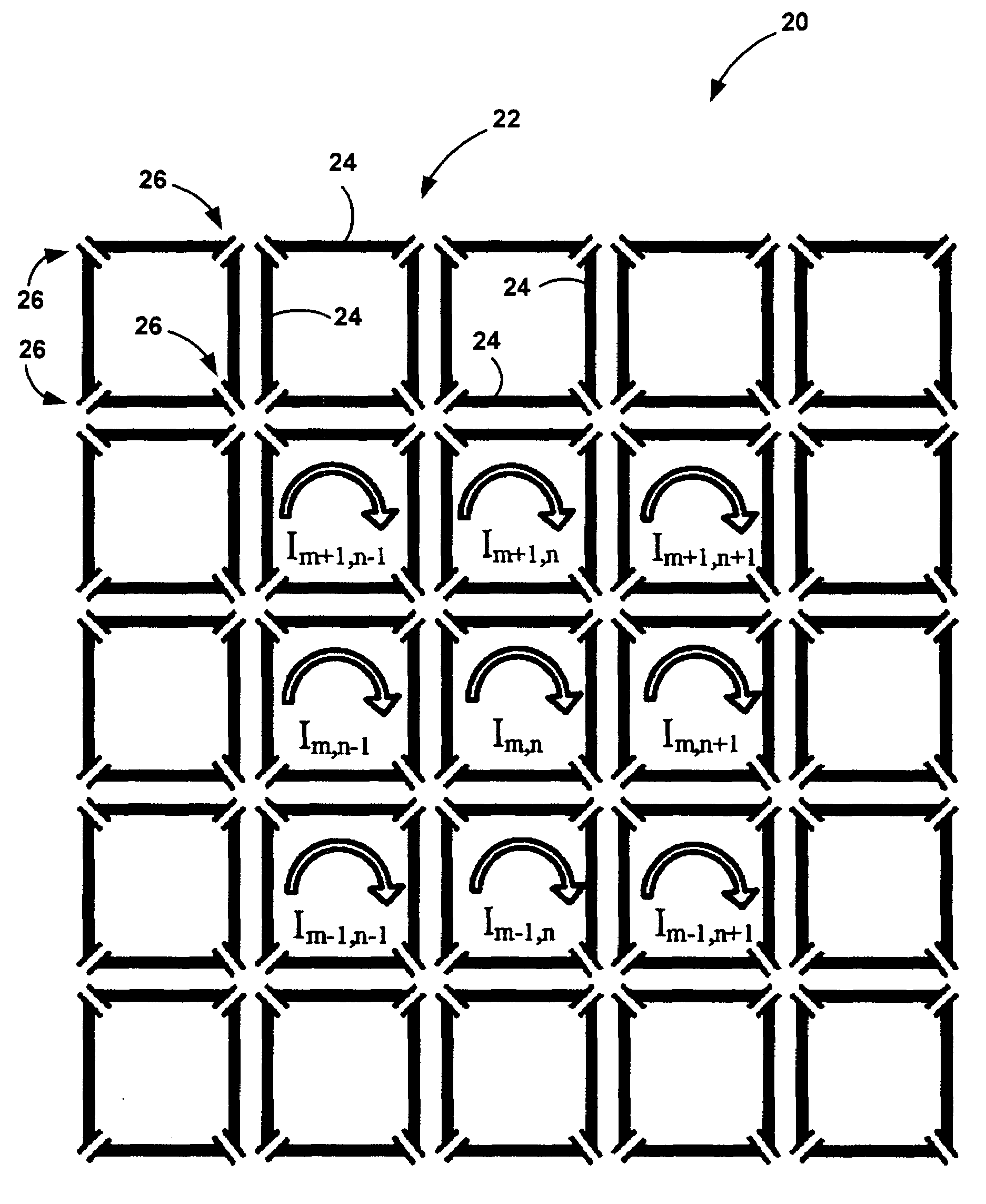
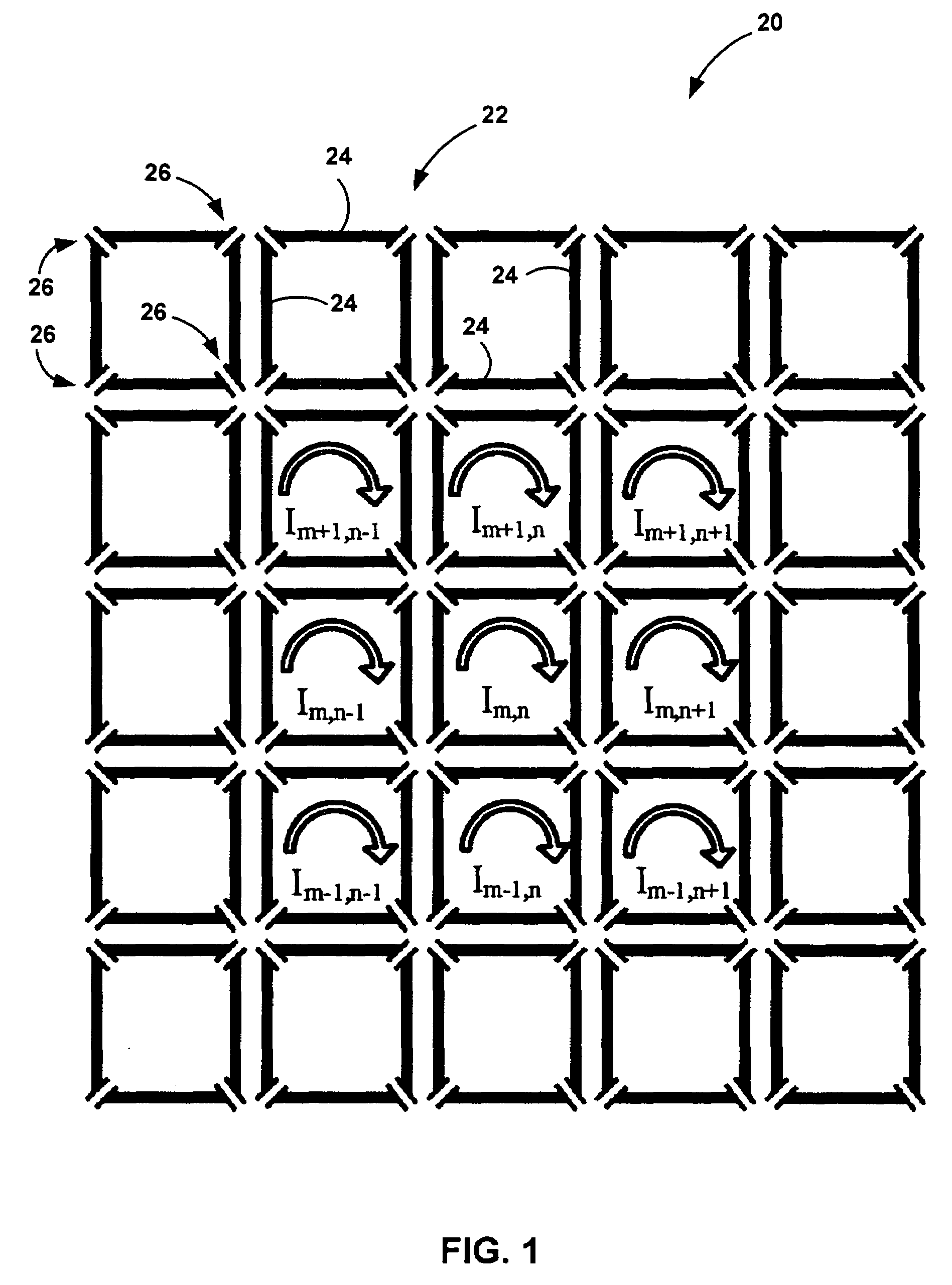
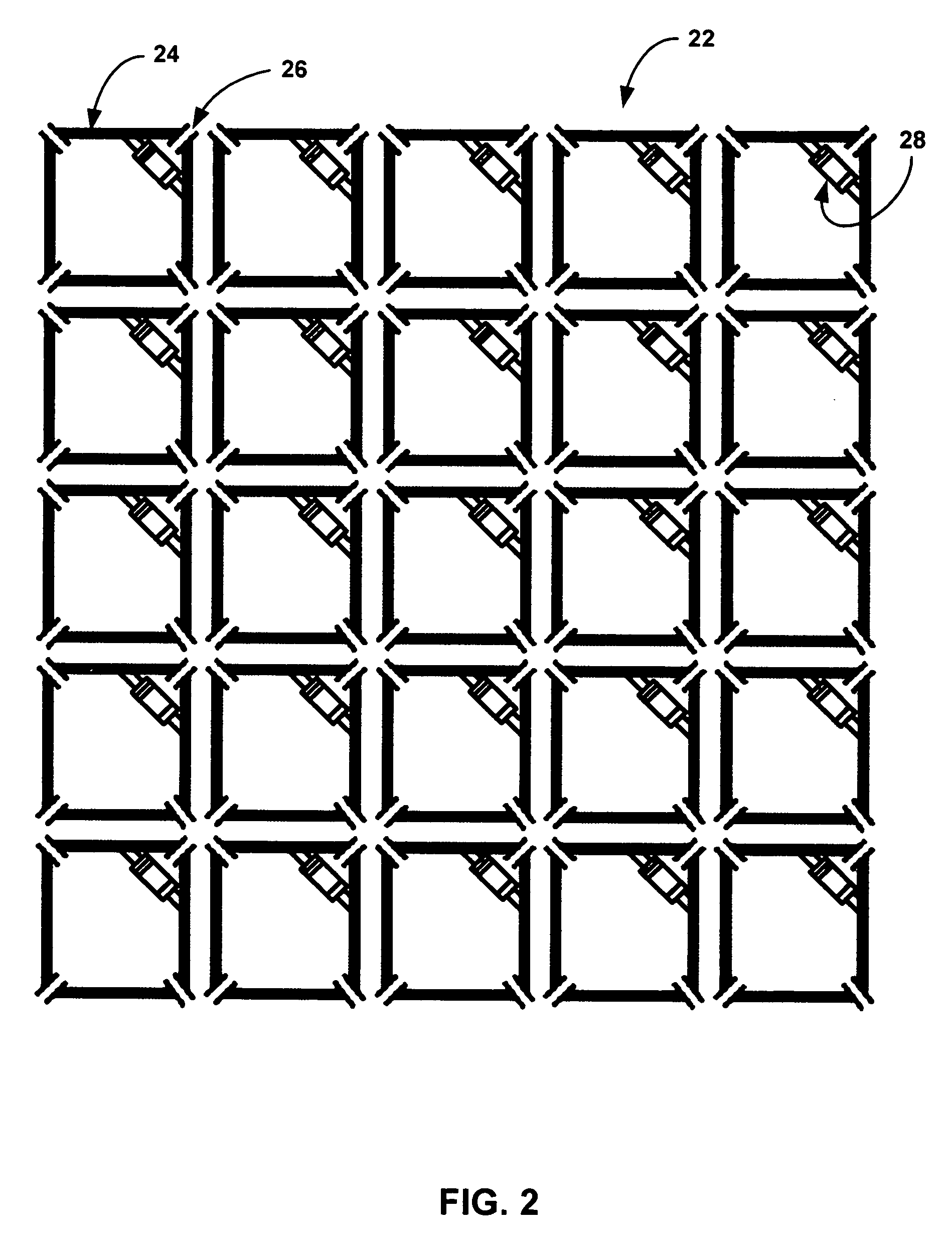
A magnetic resonance system is disclosed. The system includes a transceiver having a multichannel receiver and a multichannel transmitter, where each channel of the transmitter is configured for independent selection of frequency, phase, time, space, and magnitude, and each channel of the receiver is configured for independent selection of space, time, frequency, phase and gain. The system also includes a magnetic resonance coil having a plurality of current elements, with each element coupled in one to one relation with a channel of the receiver and a channel of the transmitter. The system further includes a processor coupled to the transceiver, such that the processor is configured to execute instructions to control a current in each element and to perform a non-linear algorithm to shim the coil.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
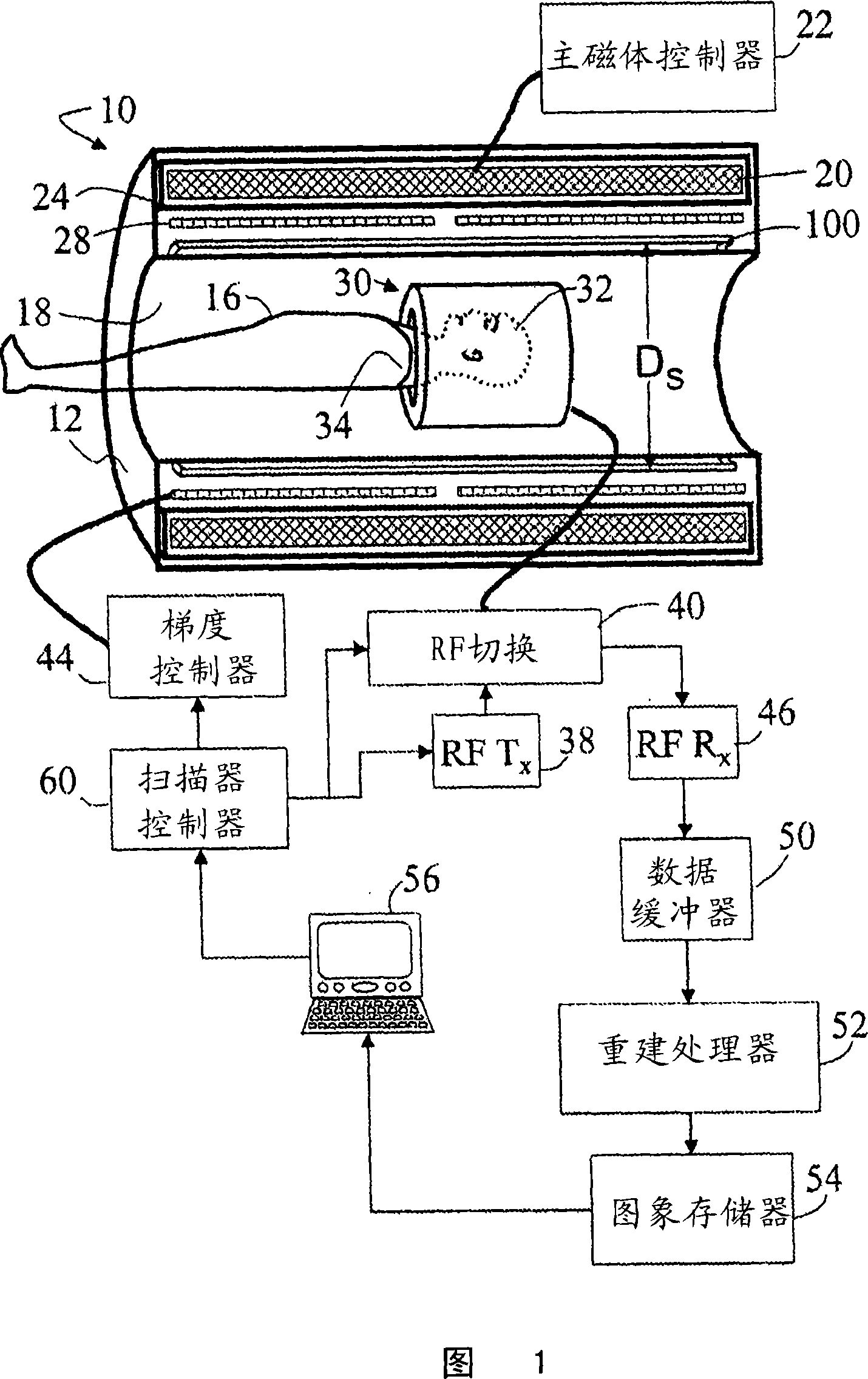
Breast biopsy and therapy system for magnetic resonance imagers
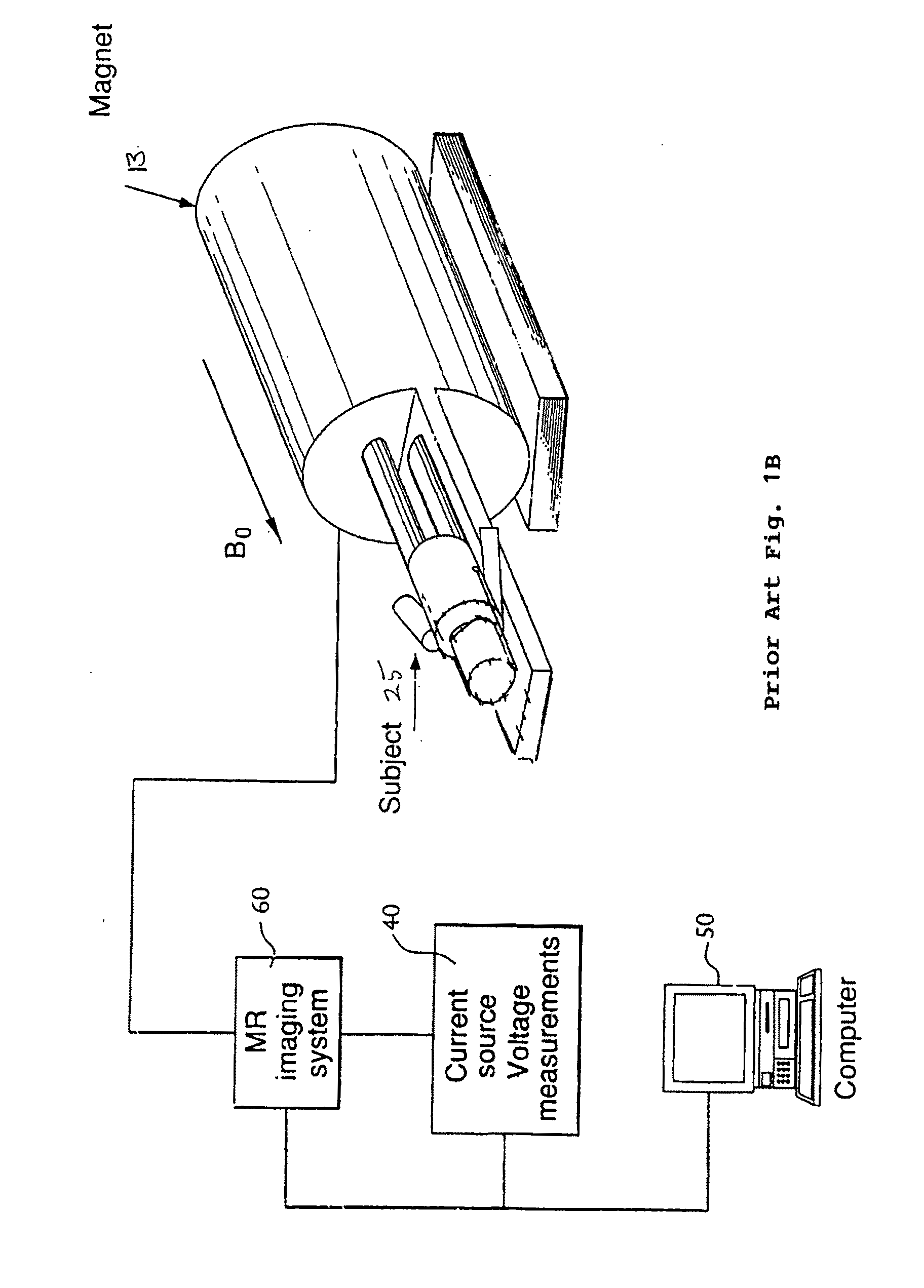
The present invention describes a device for performing breast biopsies and / or therapy within magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems. The apparatus includes a RF receiver antenna for magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. The RF coil includes openings in the front and side to provide access to the breast during the procedure. Compression plates are integrated into the breast coil which compress the breast either laterally or in the head / feet direction as required for optimal access to the breast. The apparatus includes a mechanical device for positioning interventional instruments in the breast such as biopsy or therapy instruments. The mechanical positioning devices position the instrument along the desired trajectory to the target site and insert the instrument into the breast while the patient remains inside the MRI scanner. Real time MR images may be acquired during instrument alignment and insertion to verify the trajectory. The mechanical positioning devices allow manipulation of instruments in any type of MRI scanner, including high field MRI systems with cylindrical magnets. The positioning devices provide a means to overcome limited access to the patient in MRI scanners. The positioning devices may be manually operated by means of gears, drive shafts, cables or other mechanical means. Or they may be electronically controlled by means of MR compatible motorized drive systems. The devices may be remotely controlled from outside the magnet for MRI systems that have limited access to the patient in the magnet. An interface between the electronically controlled drivers and the MRI scanner computer can provide robotic control of the instrument.
Owner:LAMPMAN DAVID A +1
Shim insert for high-field MRI magnets
InactiveUS20110260727A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHigh field mriOn demand
The present invention is a portable in-bore shim coil insert suitable for correcting high-degree and high-order magnetic field inhomogeneities over a limited examination zone in a magnetic resonance assembly operating above 3 T magnetic field strengths, wherein the magnetic resonance assembly includes at least a MRI magnet having an internal bore of known configuration and volume, at least one set of gradient coils, and an arrangement of radio frequency coils. The in-bore shim coil insert and corresponding method of use is able to produce higher degree and order shimming effects on-demand (i.e., the correction of at least some 3rd to 6th degree field terms or inhomogeneities) and will markedly improve the quality of in-vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy and / or imaging of any desired anatomic site, i.e., any or all of the various organs, tissues, and systems present in the body of a living subject.
Owner:PUNCHARD WILLIAM F B +3
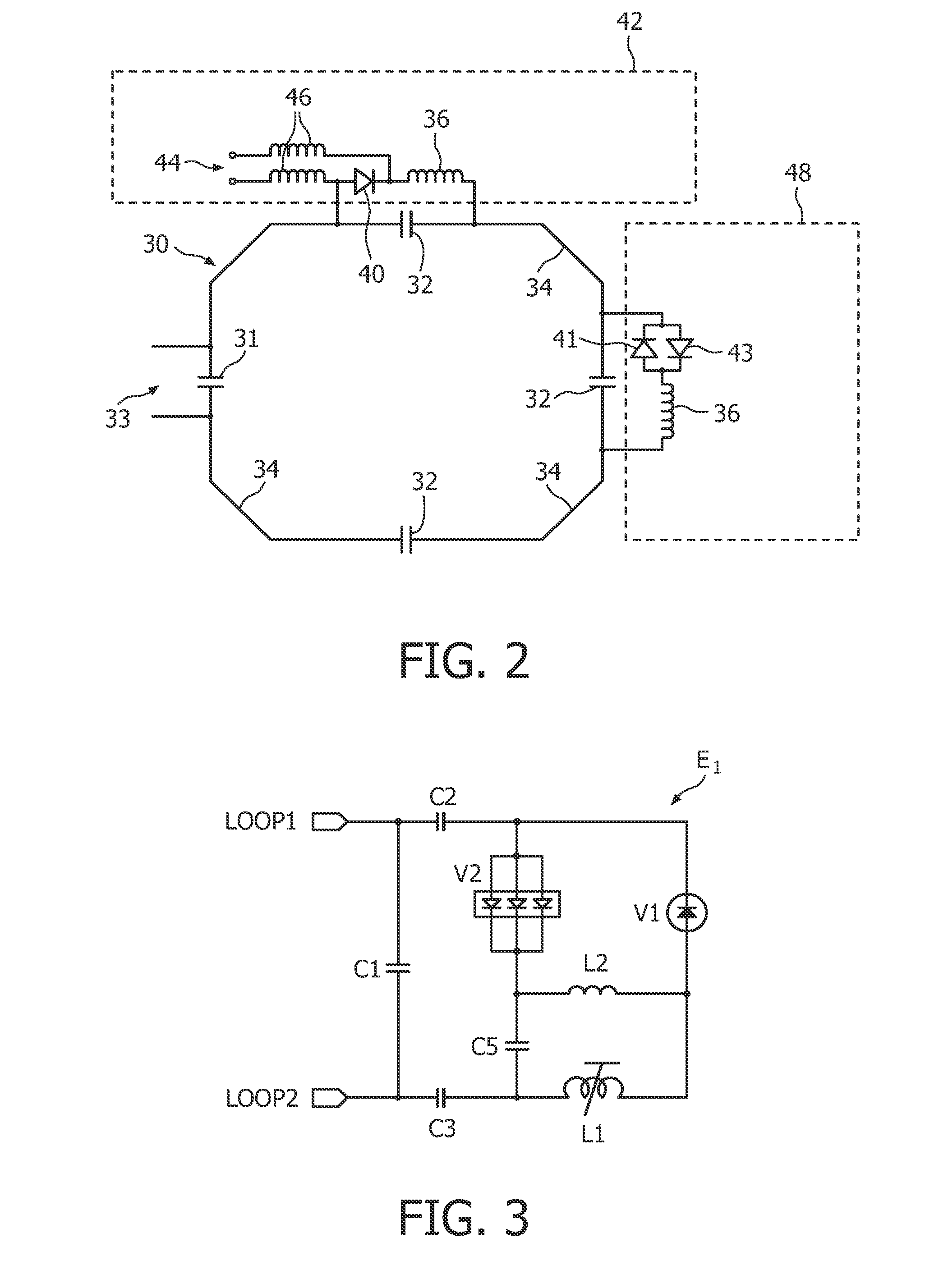
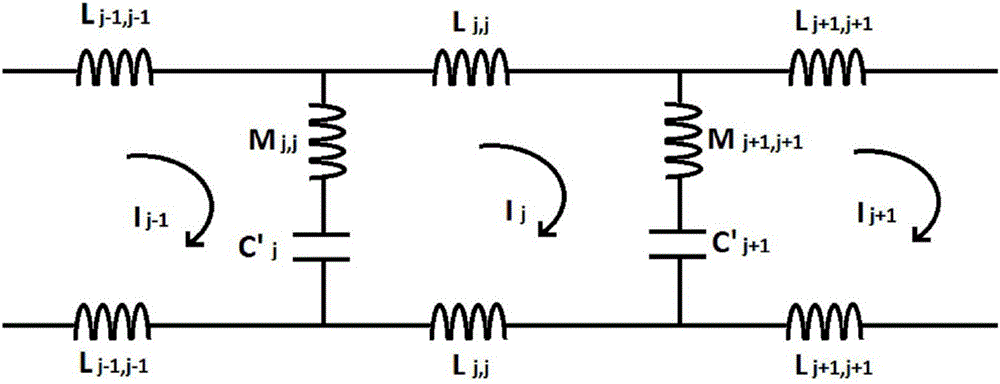
High-pass two-dimensional ladder network resonator
InactiveUS20060244448A1Suitable imageIncrease working frequencyMagnetic measurementsRecord carriers used with machinesHigh field mriParallel imaging
A high-pass two-dimensional ladder network has been described for high-field MRI and credential applications. The next-to-highest eigenvalue of the network corresponds to a normal mode giving rise to B1 fields with good spatial homogeneity above the resonator plane. Other eigenvalues may also be used for specific imaging applications. In its most basic form, the ladder network is a collection of inductively coupled resonators where each element of the array is represented by at least one conducting strip having a self-inductance L, joined by a capacitor C at one or more points along each resonator. In the strong coupling limit of the inductively coupled high-pass two-dimensional ladder network resonator array, the array produces a high-frequency resonant mode that can be used to generate the traditional quadrature B1 field used in magnetic resonance imaging, and in the limit of weak or zero coupling reduces to a phased array suitable for parallel imaging applications.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
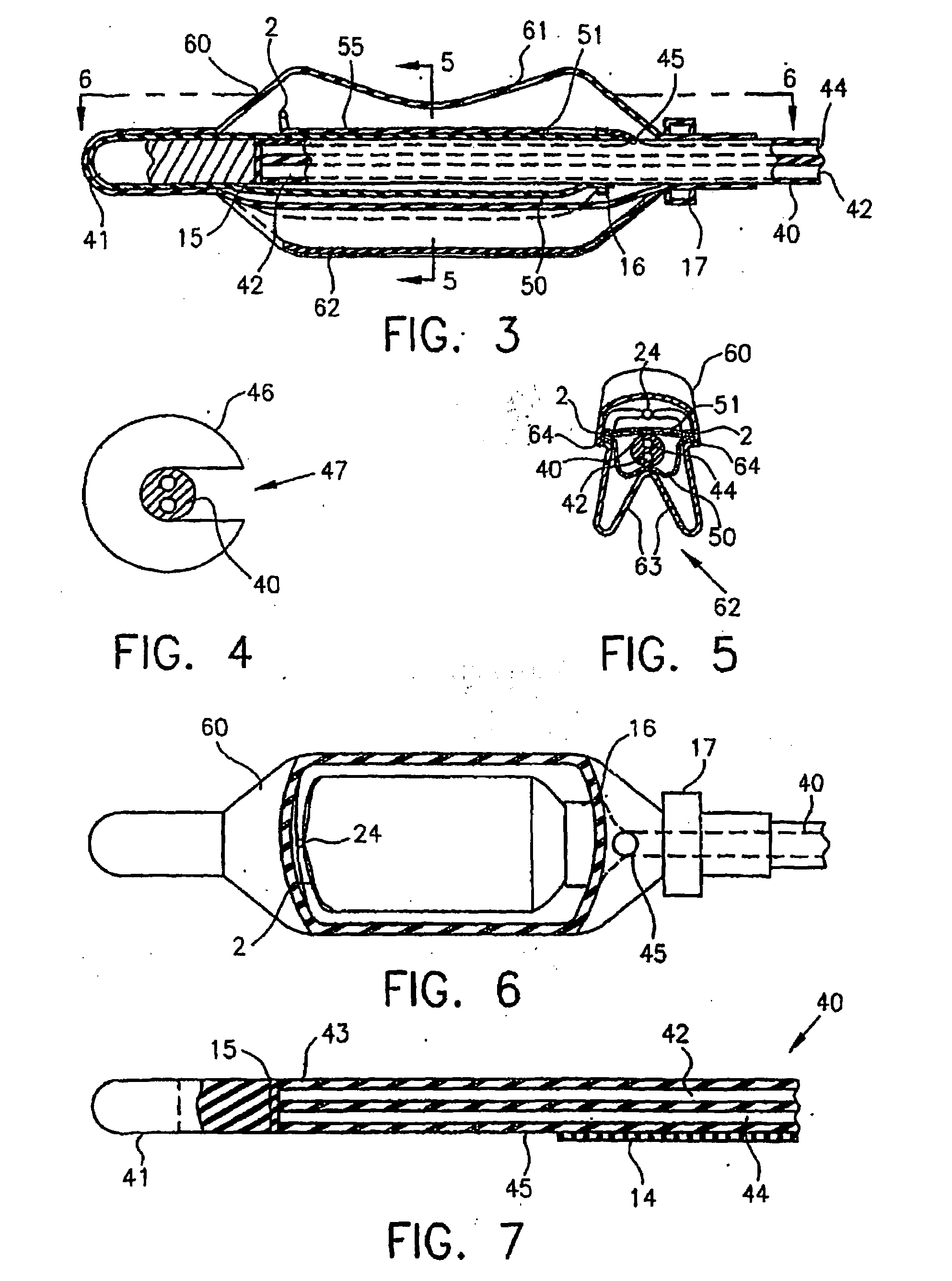
Intracavity probes and interfaces therefor for use in obtaining images and spectra of intracavity structures using high field magnetic resonance systems
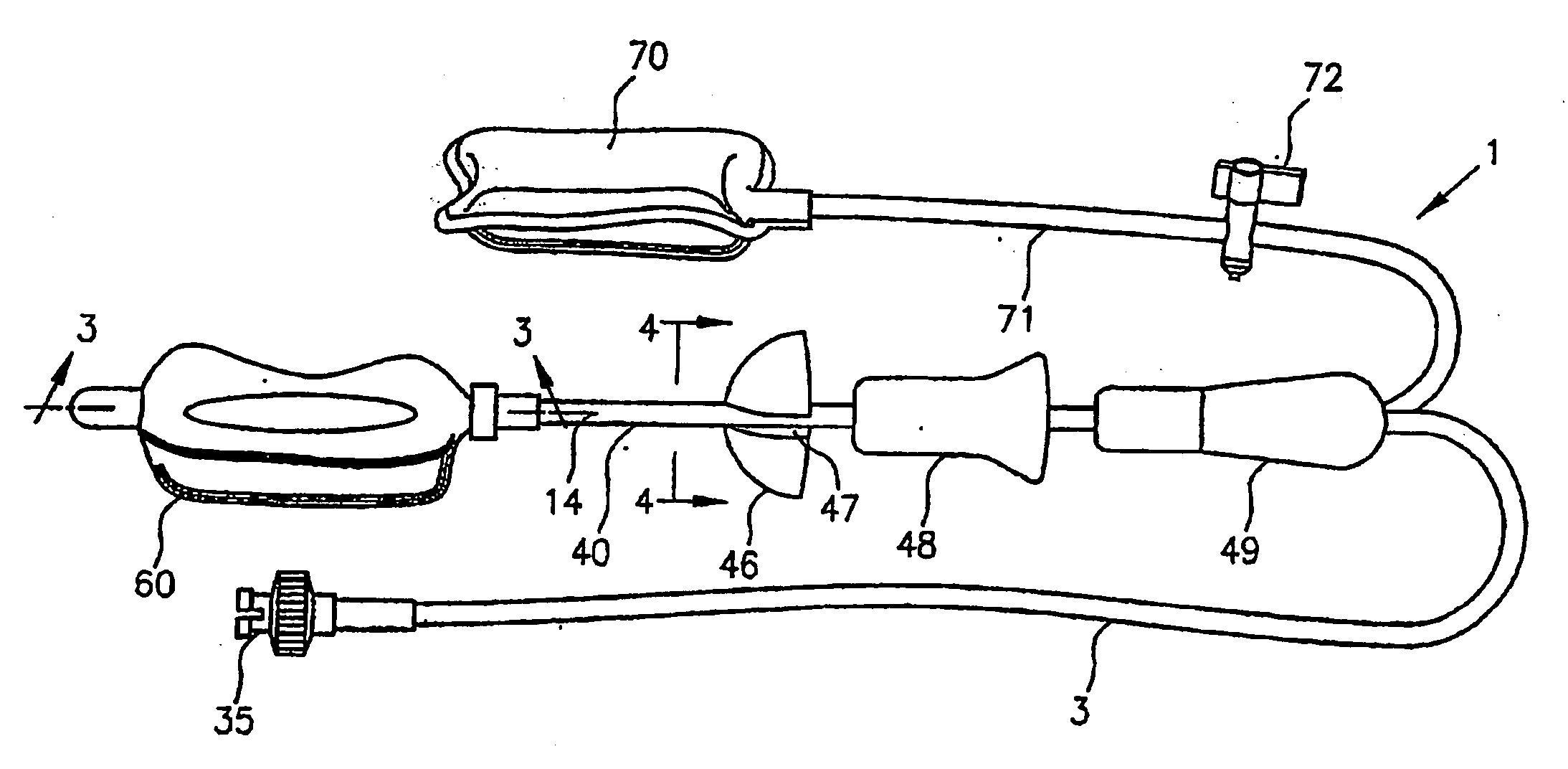
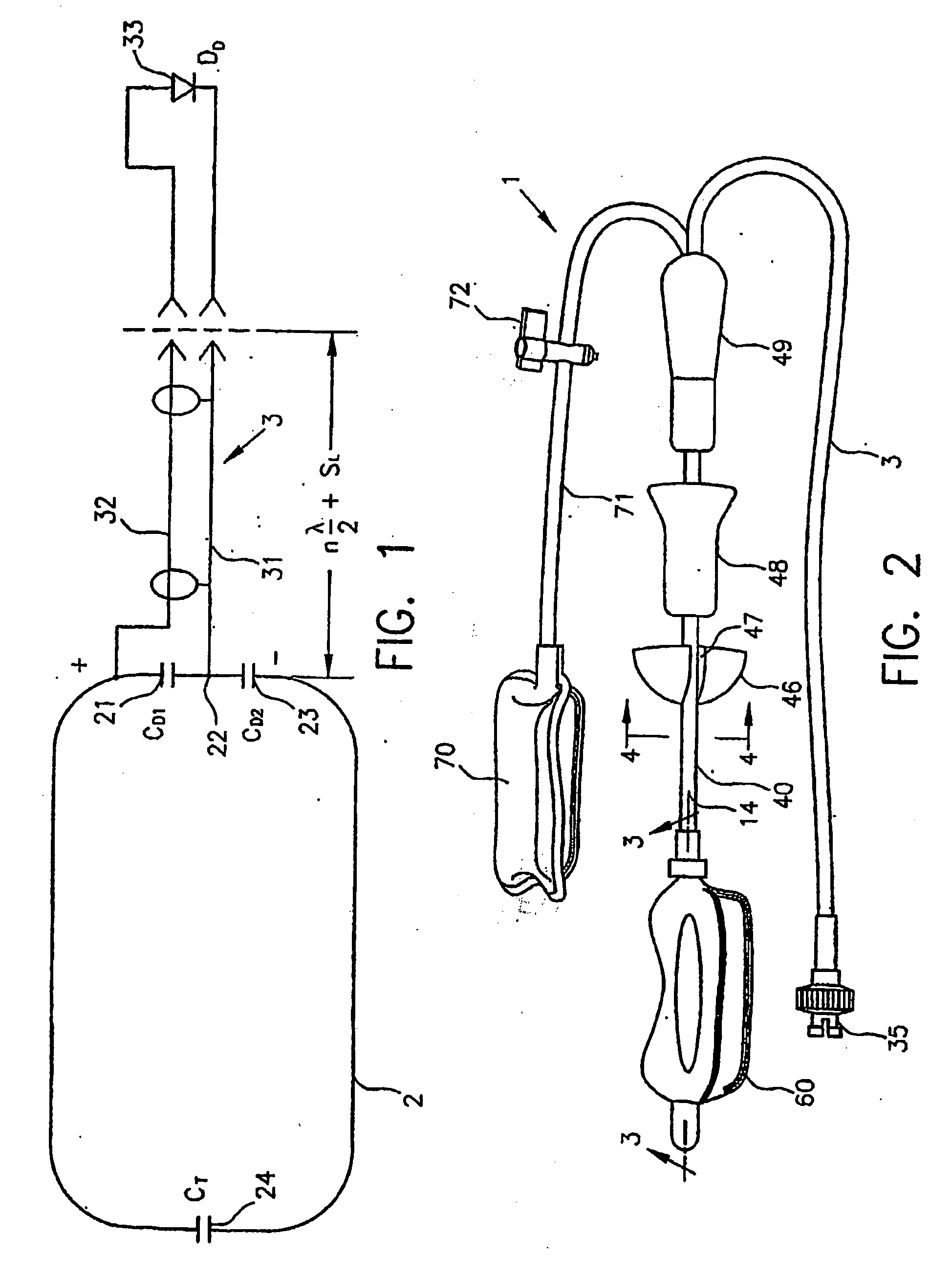
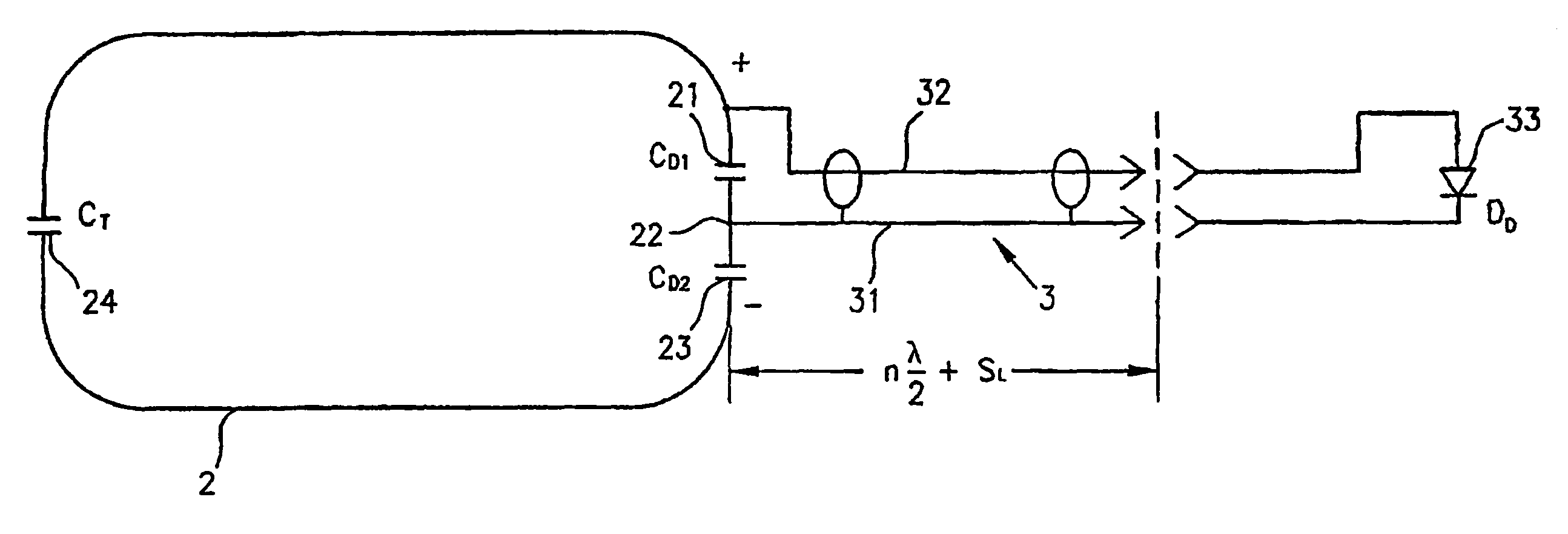
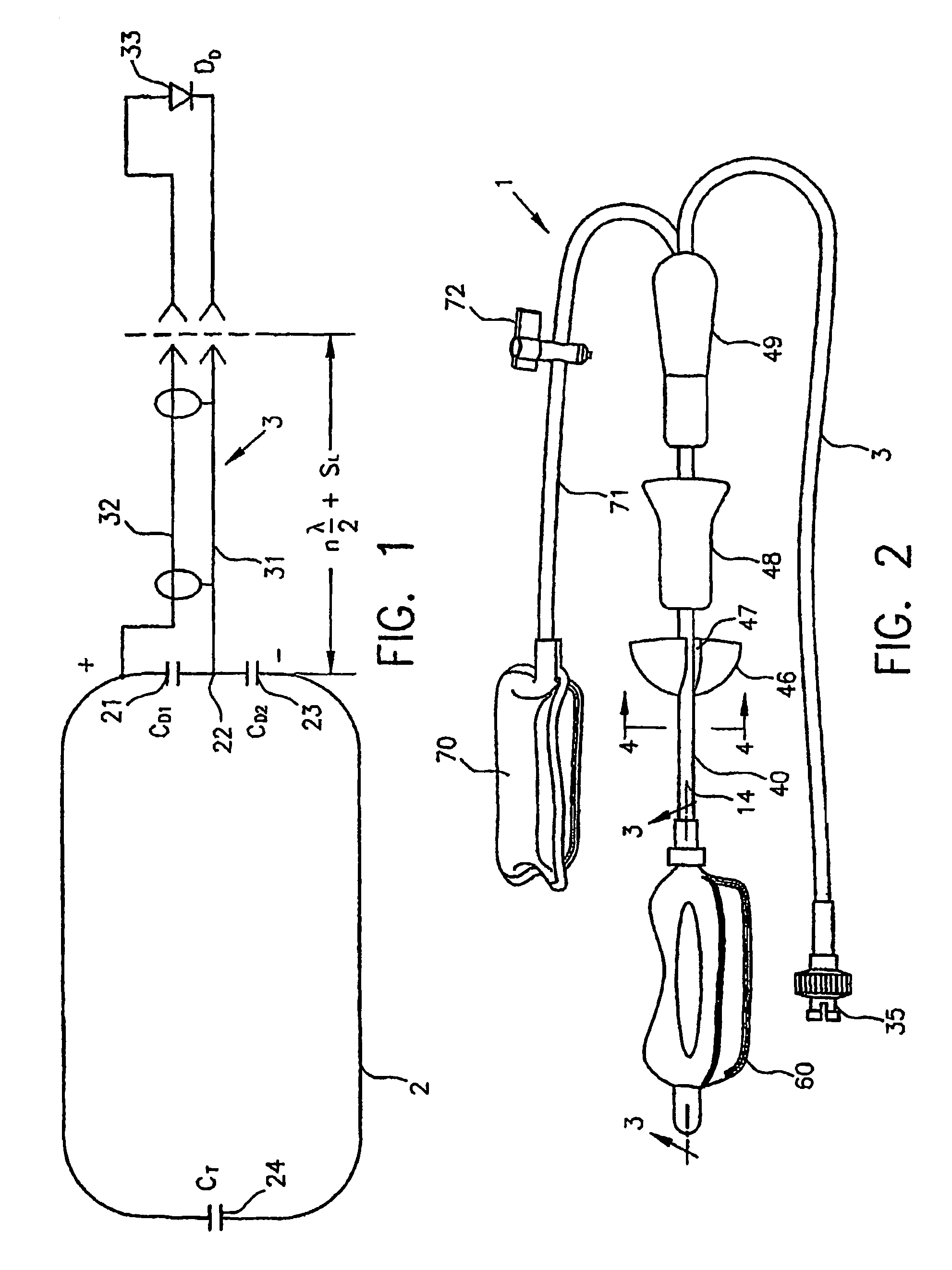
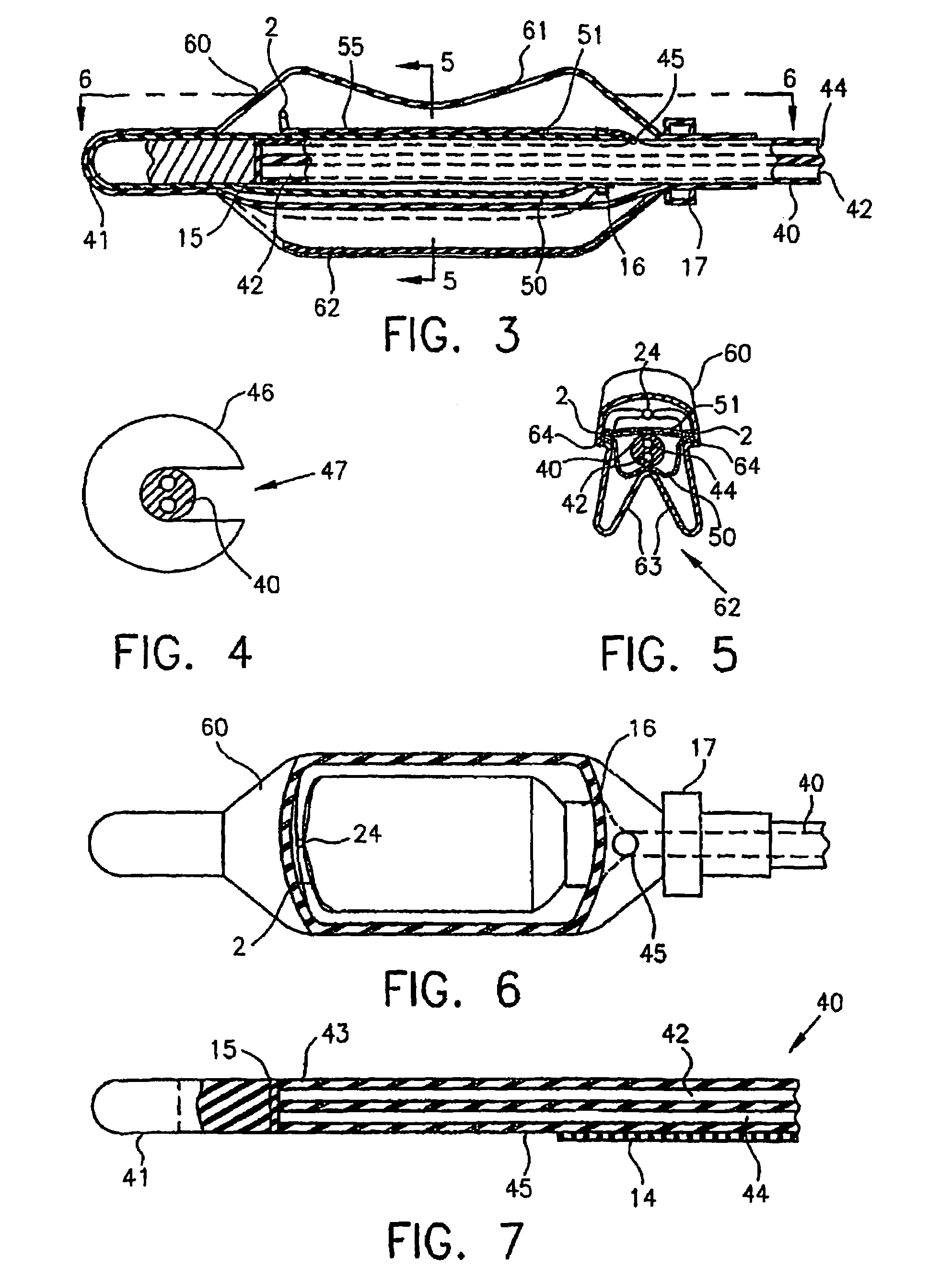
An intracavity probe for use with an MR system allows images or spectra of a region of interest within a cavity of a patient to be obtained. The probe includes a shaft, a balloon at one end thereof, and a coil loop within the balloon. The coil loop preferably includes two drive capacitors and a tuning capacitor, all of which in series. A junction node between the drive capacitors serves as a ground for electrically balancing the coil loop. Diametrically opposite the junction node, the tuning capacitor enables the coil loop to resonate at the operating frequency of the MR system. Across each drive capacitor is connected an output cable having an electrical length of SL+n(λ / 4). The output cables terminate in a plug that is used to connect the coil loop to an interface device for the intracavity probe.
Owner:DXTX MEDICAL INC
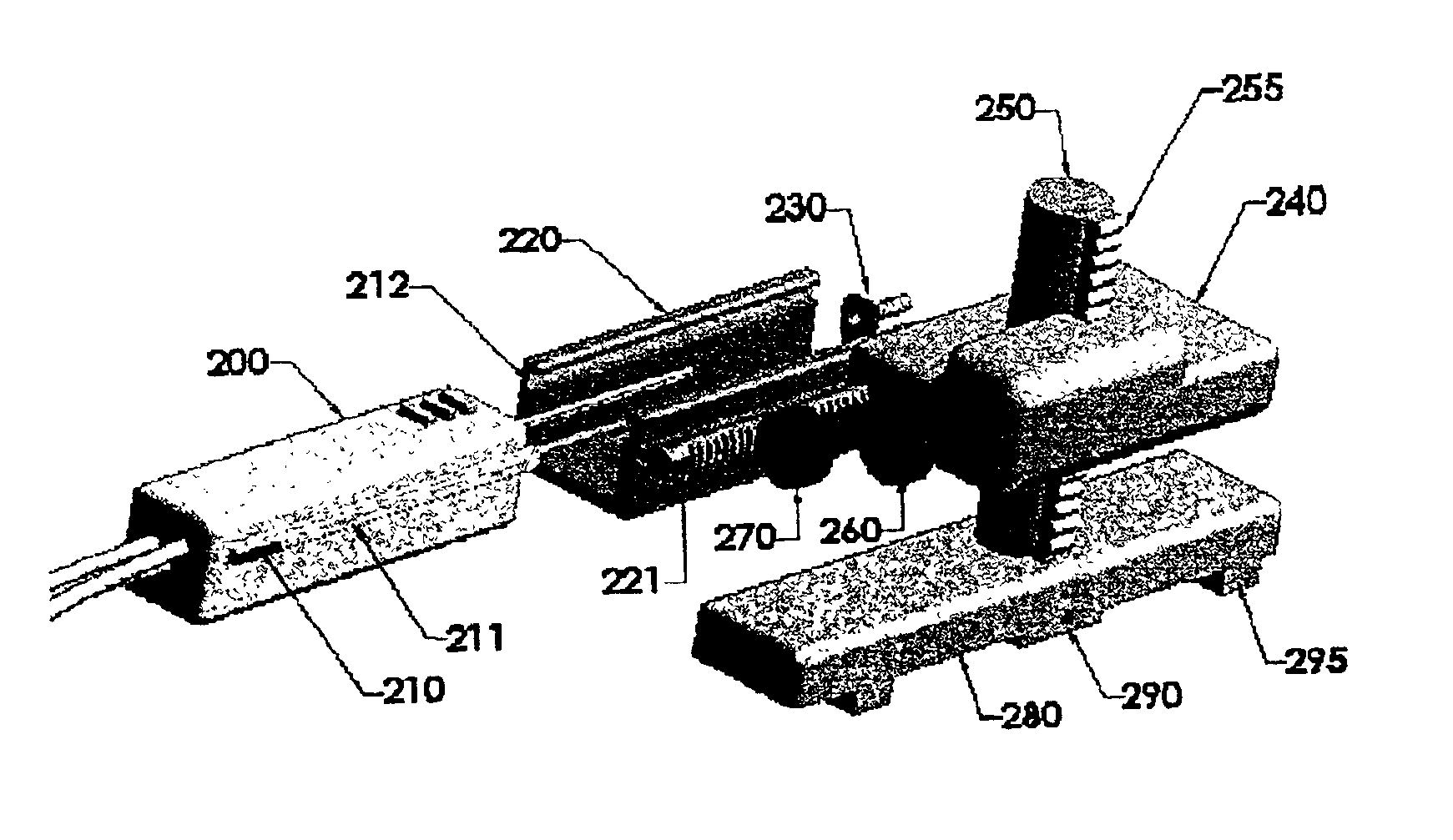
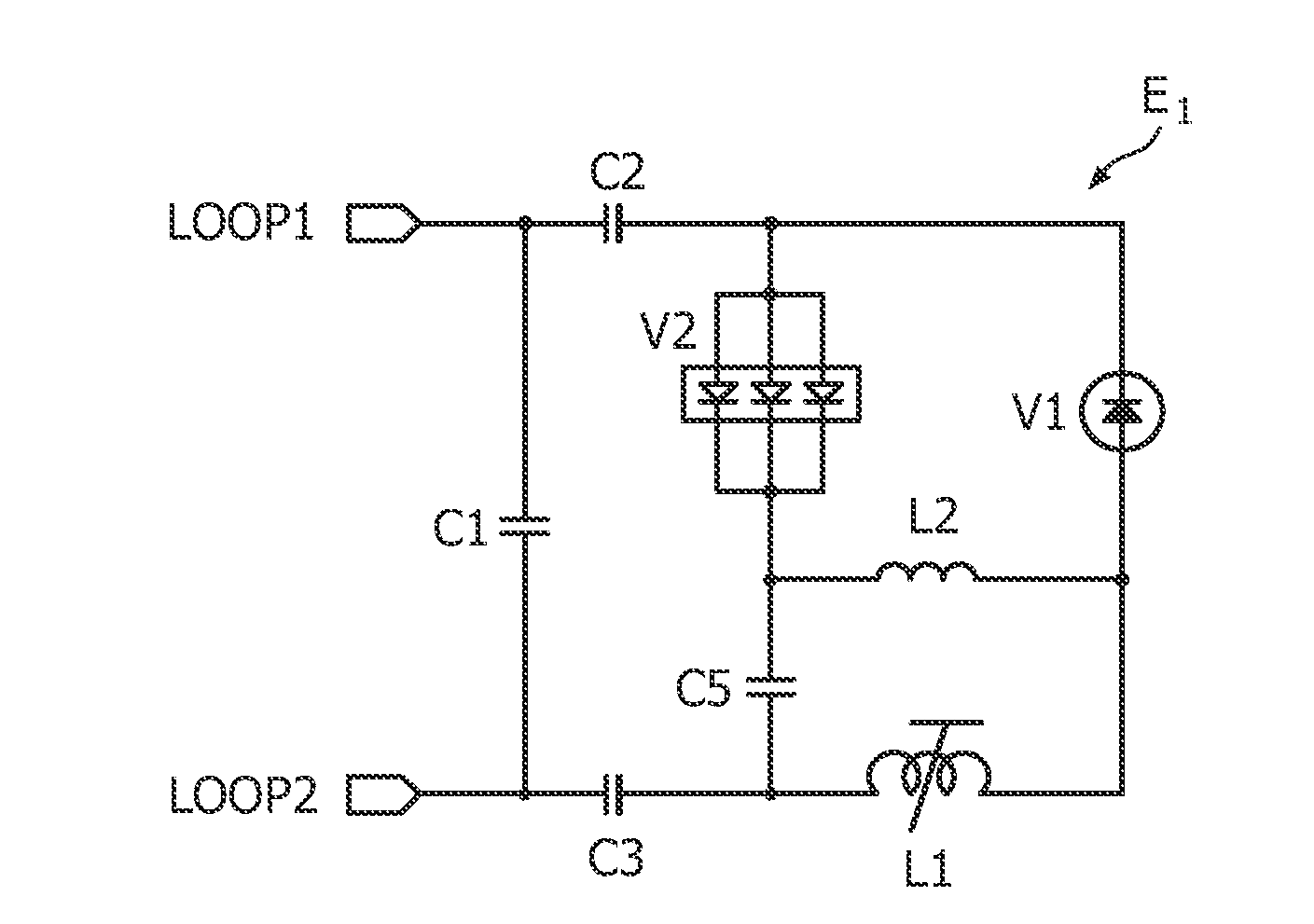
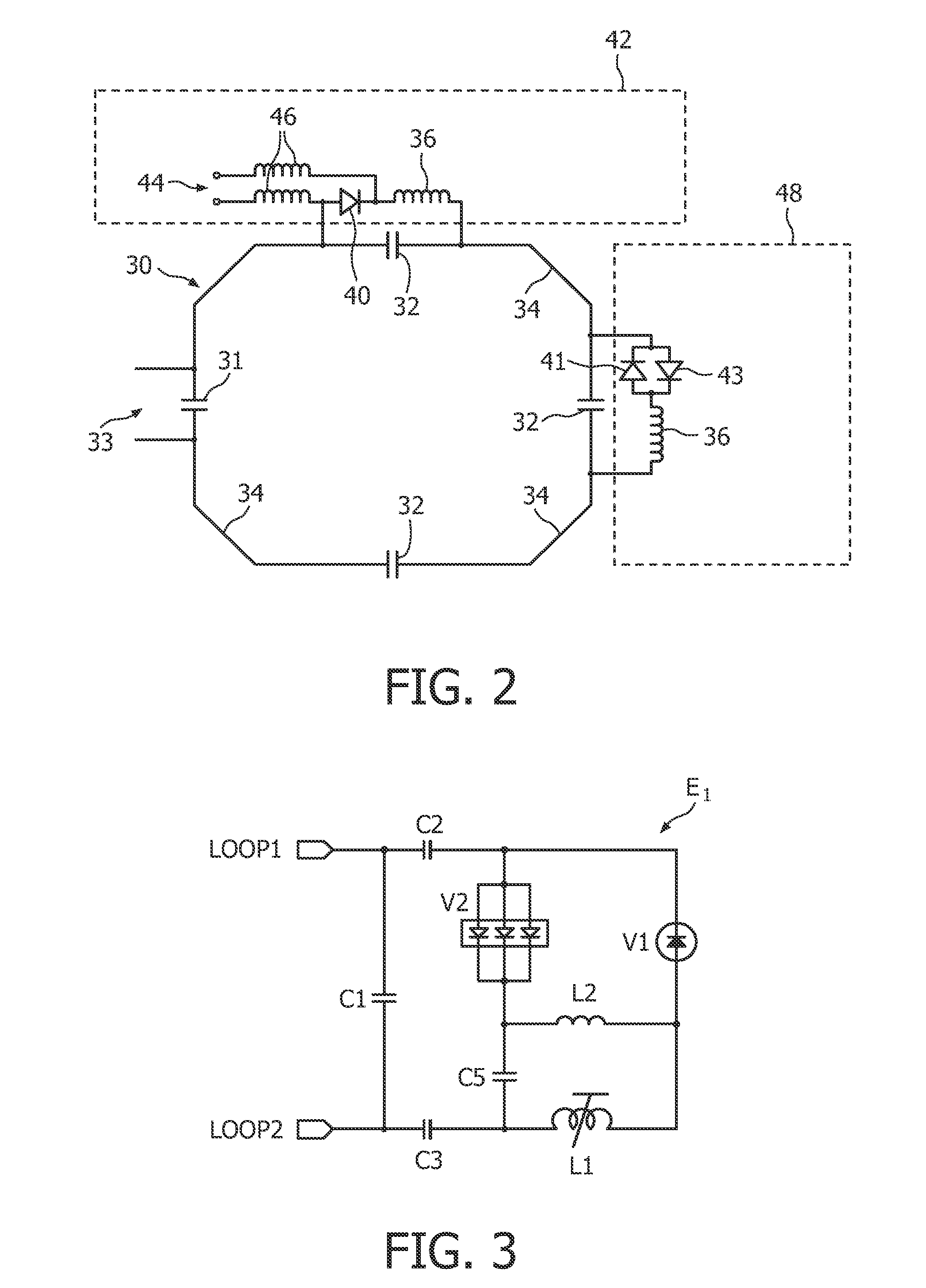
Detuning circuit and detuning method for an MRI system
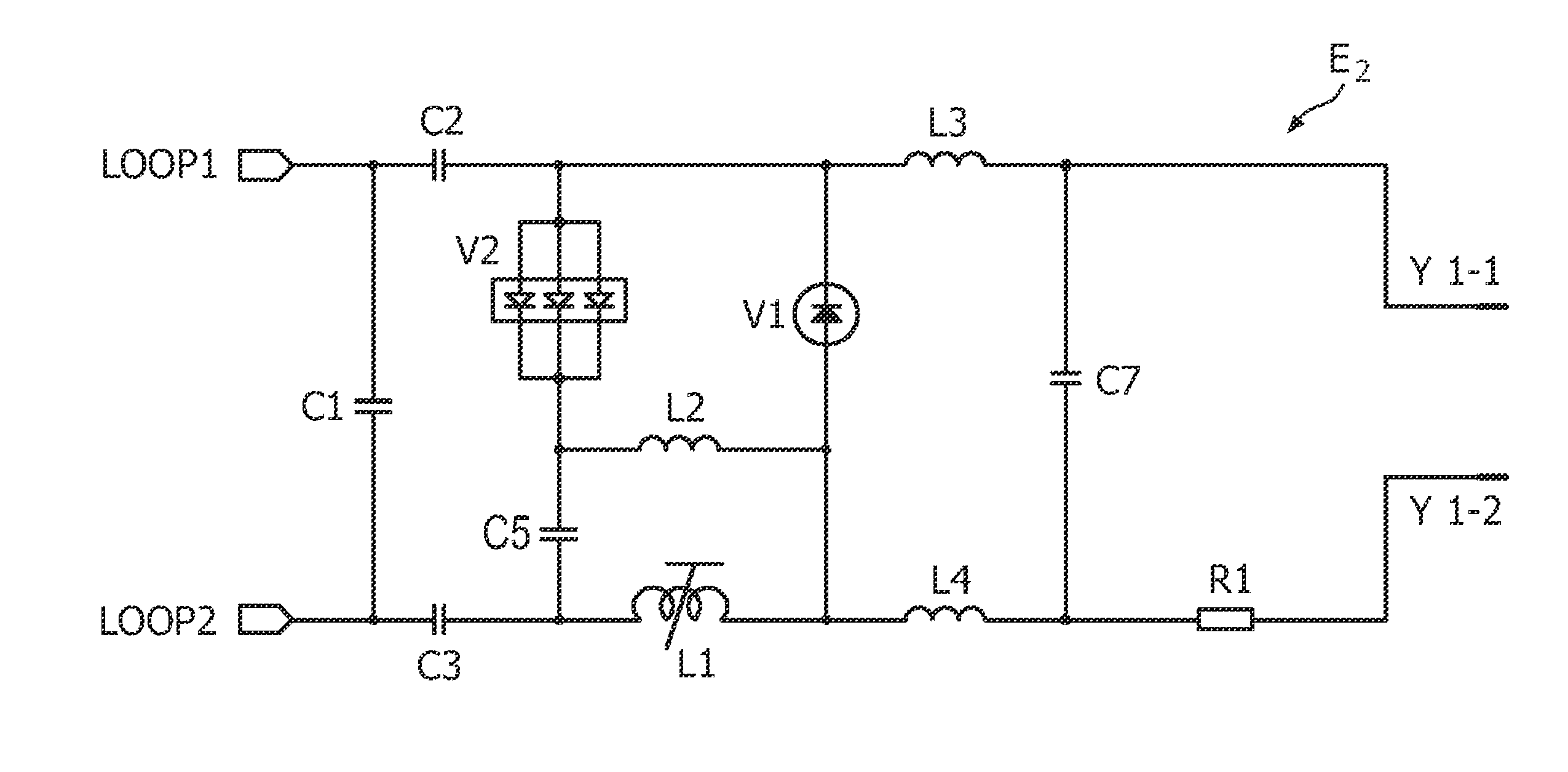
InactiveUS8013609B2Sufficient deliveryRobustMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionDc currentHigh field mri
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging system and a corresponding method having a transmit phase and a receive phase. Further, the present invention relates to a detuning circuit and a corresponding detuning method for detuning an RF receive coil during the transmit phase in such a magnetic resonance imaging system. In high-field MRI systems the transmit mode operating frequency is higher than normal high breakdown voltage rectifiers can handle when they are used to forward bias a passive detuning circuit PIN diode switch. The proposed circuit uses a current-limiting capacitor (C5) in series with a fast (e.g. schottky) rectifier diode (V2) with a reverse breakdown voltage of e.g. 20 volts and a fast reverse recovery time to generate a DC current. The rectifying circuit is isolated from the PIN diode (V1) with a relatively high-value inductor (L2), which ensures that no harmful transient current spikes can flow from the PIN diode anode to the rectifying circuit. The inductor (L2) still passes and maintains the DC current generated by the rectifying circuit through the PIN diode, thus enabling the robust forward-biasing of the PIN-diode during transmit mode. The use of a fast (and thus low-power) rectifier results in less dissipation on the detuning circuit, and helps in fulfilling the surface temperature limits posed on receiver coils.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Intracavity probes and interfaces therefor for use in obtaining images and spectra of intracavity structures using high field magnetic resonance systems
An intracavity probe for use with an MR system allows images or spectra of a region of interest within a cavity of a patient to be obtained. The probe includes a shaft, a balloon at one end thereof, and a coil loop within the balloon. The coil loop preferably includes two drive capacitors and a tuning capacitor, all of which in series. A junction node between the drive capacitors serves as a ground for electrically balancing the coil loop. Diametrically opposite the junction node, the tuning capacitor enables the coil loop to resonate at the operating frequency of the MR system. Across each drive capacitor is connected an output cable having an electrical length of SL+n(λ / 4). The output cables terminate in a plug that is used to connect the coil loop to an interface device for the intracavity probe.
Owner:DXTX MEDICAL INC
Shim insert for high-field MRI magnets
The present invention is a portable in-bore shim coil insert suitable for correcting high-degree and high-order magnetic field inhomogeneities over a limited examination zone in a magnetic resonance assembly operating above 3 T magnetic field strengths, wherein the magnetic resonance assembly includes at least a MRI magnet having an internal bore of known configuration and volume, at least one set of gradient coils, and an arrangement of radio frequency coils. The in-bore shim coil insert and corresponding method of use is able to produce higher degree and order shimming effects on-demand (i.e., the correction of at least some 3rd to 6th degree field terms or inhomogeneities) and will markedly improve the quality of in-vivo magnetic resonance spectroscopy and / or imaging of any desired anatomic site, i.e., any or all of the various organs, tissues, and systems present in the body of a living subject.
Owner:PUNCHARD WILLIAM F B +3
Detuning circuit and detuning method for an MRI system
InactiveUS20100039113A1RobustLess dissipationElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceDc currentHigh field mri
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance imaging system and a corresponding method having a transmit phase and a receive phase. Further, the present invention relates to a detuning circuit and a corresponding detuning method for detuning an RF receive coil during the transmit phase in such a magnetic resonance imaging system. In high-field MRI systems the transmit mode operating frequency is higher than normal high breakdown voltage rectifiers can handle when they are used to forward bias a passive detuning circuit PIN diode switch. The proposed circuit uses a current-limiting capacitor (C5) in series with a fast (e.g. schottky) rectifier diode (V2) with a reverse breakdown voltage of e.g. 20 volts and a fast reverse recovery time to generate a DC current. The rectifying circuit is isolated from the PIN diode (V1) with a relatively high-value inductor (L2), which ensures that no harmful transient current spikes can flow from the PIN diode anode to the rectifying circuit. The inductor (L2) still passes and maintains the DC current generated by the rectifying circuit through the PIN diode, thus enabling the robust forward-biasing of the PIN-diode during transmit mode. The use of a fast (and thus low-power) rectifier results in less dissipation on the detuning circuit, and helps in fulfilling the surface temperature limits posed on receiver coils.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
High field magnetic resonance
ActiveUSRE47026E1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTransceiverCurrent element
A magnetic resonance system is disclosed. The system includes a transceiver having a multichannel receiver and a multichannel transmitter, where each channel of the transmitter is configured for independent selection of frequency, phase, time, space, and magnitude, and each channel of the receiver is configured for independent selection of space, time, frequency, phase and gain. The system also includes a magnetic resonance coil having a plurality of current elements, with each element coupled in one to one relation with a channel of the receiver and a channel of the transmitter. The system further includes a processor coupled to the transceiver, such that the processor is configured to execute instructions to control a current in each element and to perform a non-linear algorithm to shim the coil.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
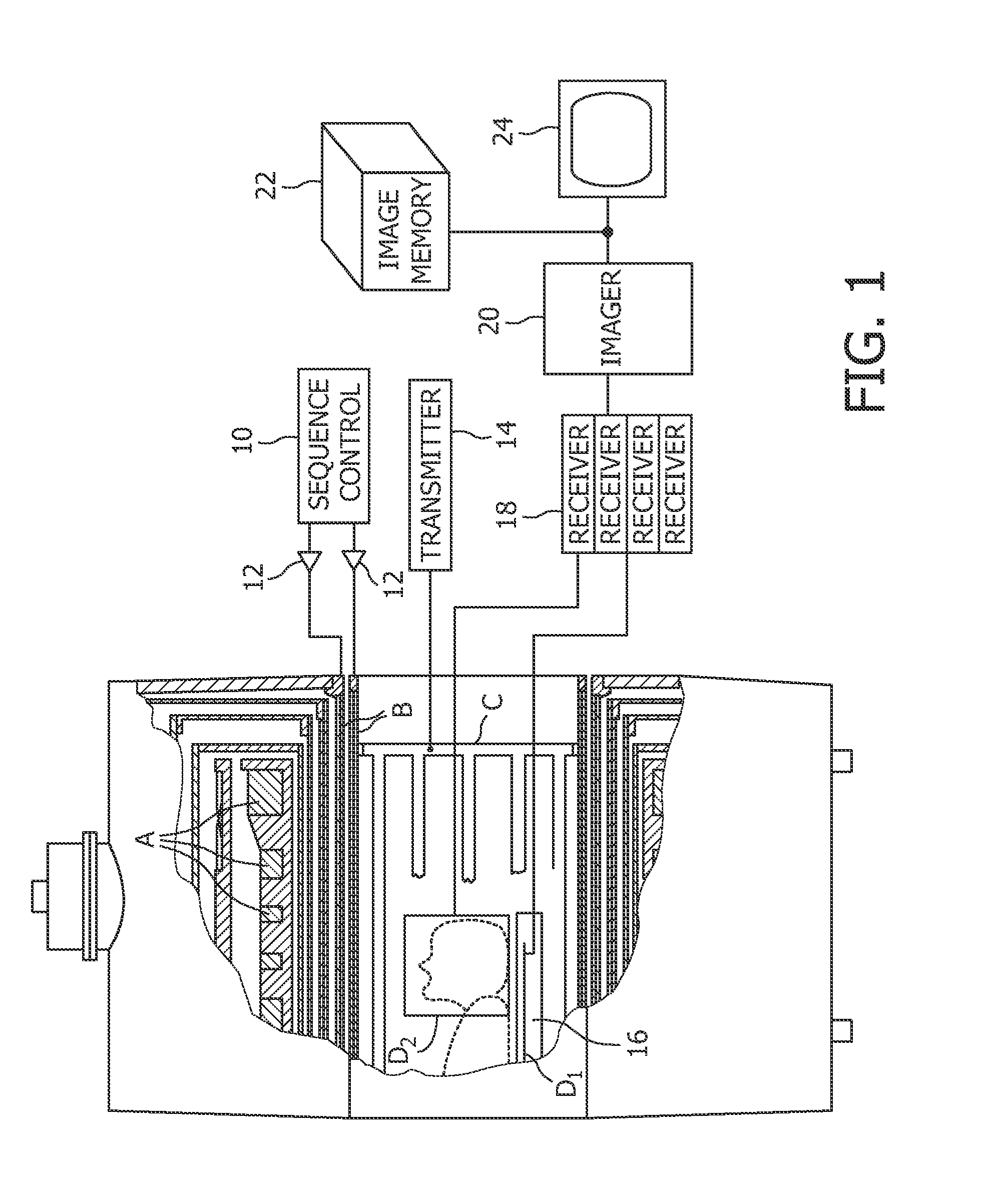
Method for obtaining electrical performance parameter distribution of human tissues by virtue of magnetic resonance tomography
ActiveCN103948389AIn line with the actual situationComply with electrical performance differencesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHuman bodyRectangular coordinates
The invention discloses a method for obtaining the electrical performance parameter distribution of human tissues by virtue of magnetic resonance tomography. The method comprises the following steps of a, measuring the human tissues to obtain a distribution map of three rectangular coordinate components Bx, By and Bz of a radio frequency magnetic field B in a space coordinate system by using high-field magnetic resonance equipment; b, substituting the distribution map of Bx, By and Bz into Formula I to obtain a complex characteristic gamma, wherein Formula I refers to the Specification; c, separating the real part and virtual part of the complex characteristic gamma to obtain the electrical conductivity and permittivity of the human tissues respectively. The method is high in result accuracy, electrical characteristic differences between different tissues and between health and lesion tissues can be calculated, electrical characteristic parameter differences of tissues in human bodies can be provided, and bases can be provided for clinical lesion diagnosis.
Owner:GUANGZHOU KOHEALA BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
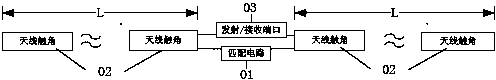
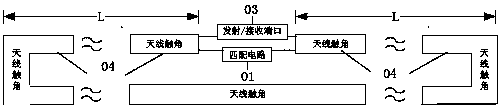
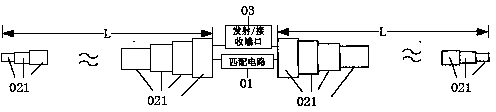
Electric dipole antenna and use method thereof
ActiveCN103915689AStable jobReduce lossRadiating elements structural formsAntenna feed intermediatesResonanceHigh field mri
The invention provides an electric dipole antenna which includes antenna feelers, and a match circuit and a transmission / reception port, both of which are connected with the antenna feelers. The lengths of the antenna feelers are adjusted through manual operation or an adjustment structure. The invention also provides a use method of the electric dipole antenna. The length of the electric dipole antenna can be adjusted so that the resonance frequency can be adjusted according to the difference of detection objects or difference of positions relative to the detection objects and thus the resonance frequency is at a work frequency. Therefore, a problem that an electric dipole antenna in the prior magnetic resonance system cannot be tuned or the tuning range is small and leads to extra loss is solved. Therefore, the electric dipole antenna is stable in work and applicable to clinical application of a high-field magnetic resonance system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
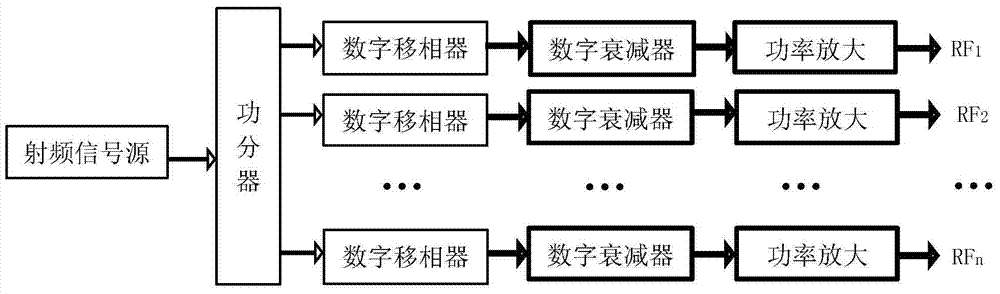
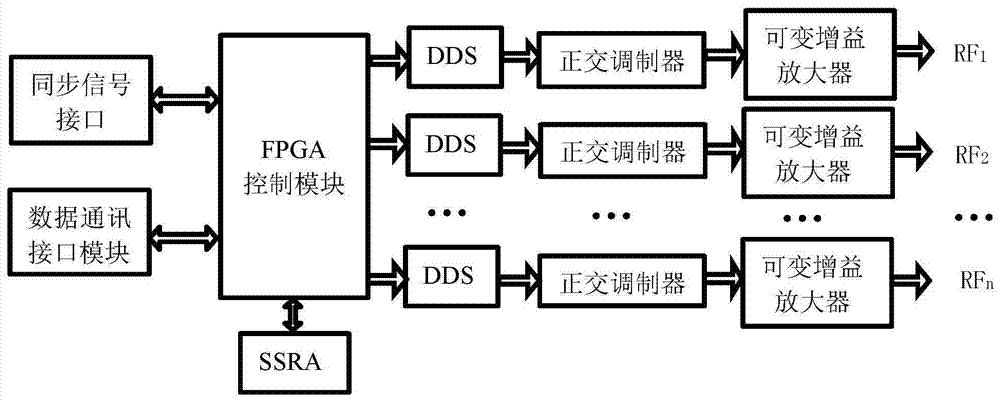
Multichannel magnetic resonance radio frequency transmission method and multichannel magnetic resonance radio frequency transmission device
ActiveCN106997033AReduce complexityLow costMeasurements using magnetic resonanceFpga implementationsHigh field mri
The invention discloses a multichannel magnetic resonance radio frequency transmission method and a multichannel magnetic resonance radio frequency transmission device. Firstly, a FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) is adopted to realize a DDS (Direct Digital Synthesizer) function and radio frequency waveform signal modulation; then, through an independent and high-performance DAC (Digital to Analog Converter) chip, multiple paths of radio frequency pulse signals with phase, frequency and amplitude adjustable independently can be outputted parallelly. Based on the FPGA and the DAC chip, the FPGA is used for realizing the DDS function and the radio frequency signal modulation on the multiple paths of signals, the multiple paths of radio frequency pulse signals with phase, frequency and amplitude adjustable independently can then be outputted parallelly through the high-performance DAC, a uniform radio frequency field is provided, and the quality of the high-field magnetic resonance signals is further improved. The problem that the existing technical scheme can not realize independent adjustment on each channel of signals can be solved effectively, and the complexity and the cost are reduced.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
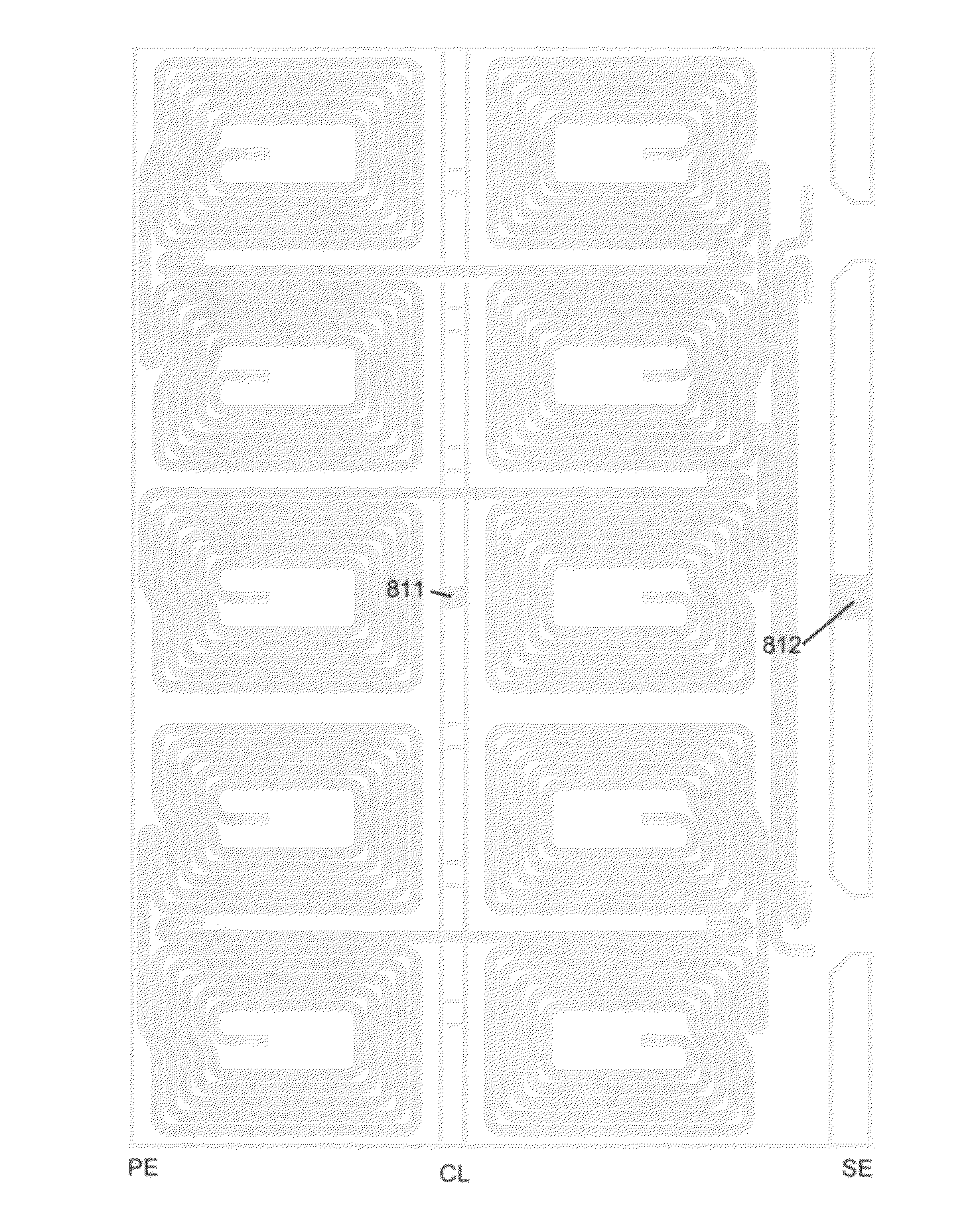
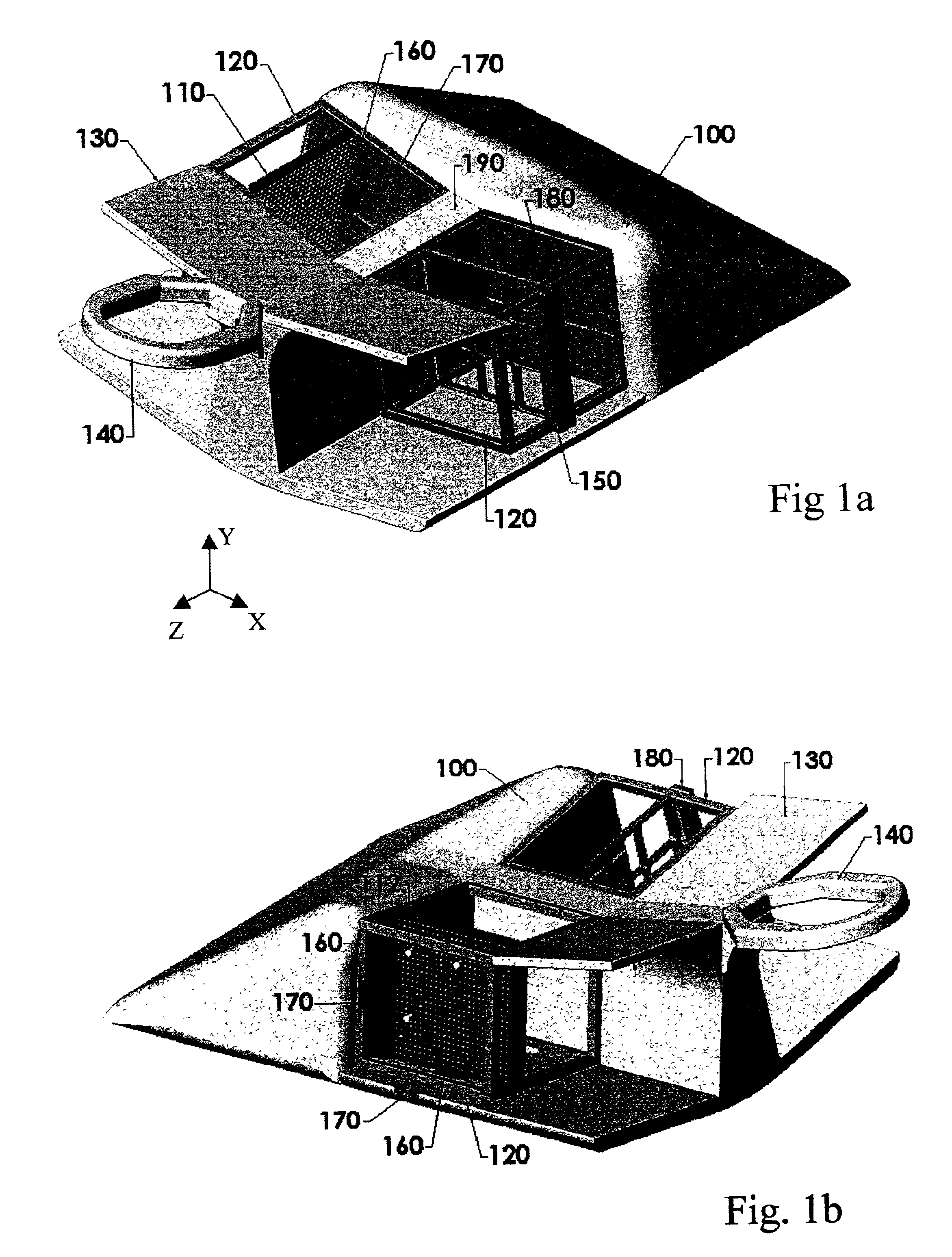
Electromagnetic shielding for high field MRI coils
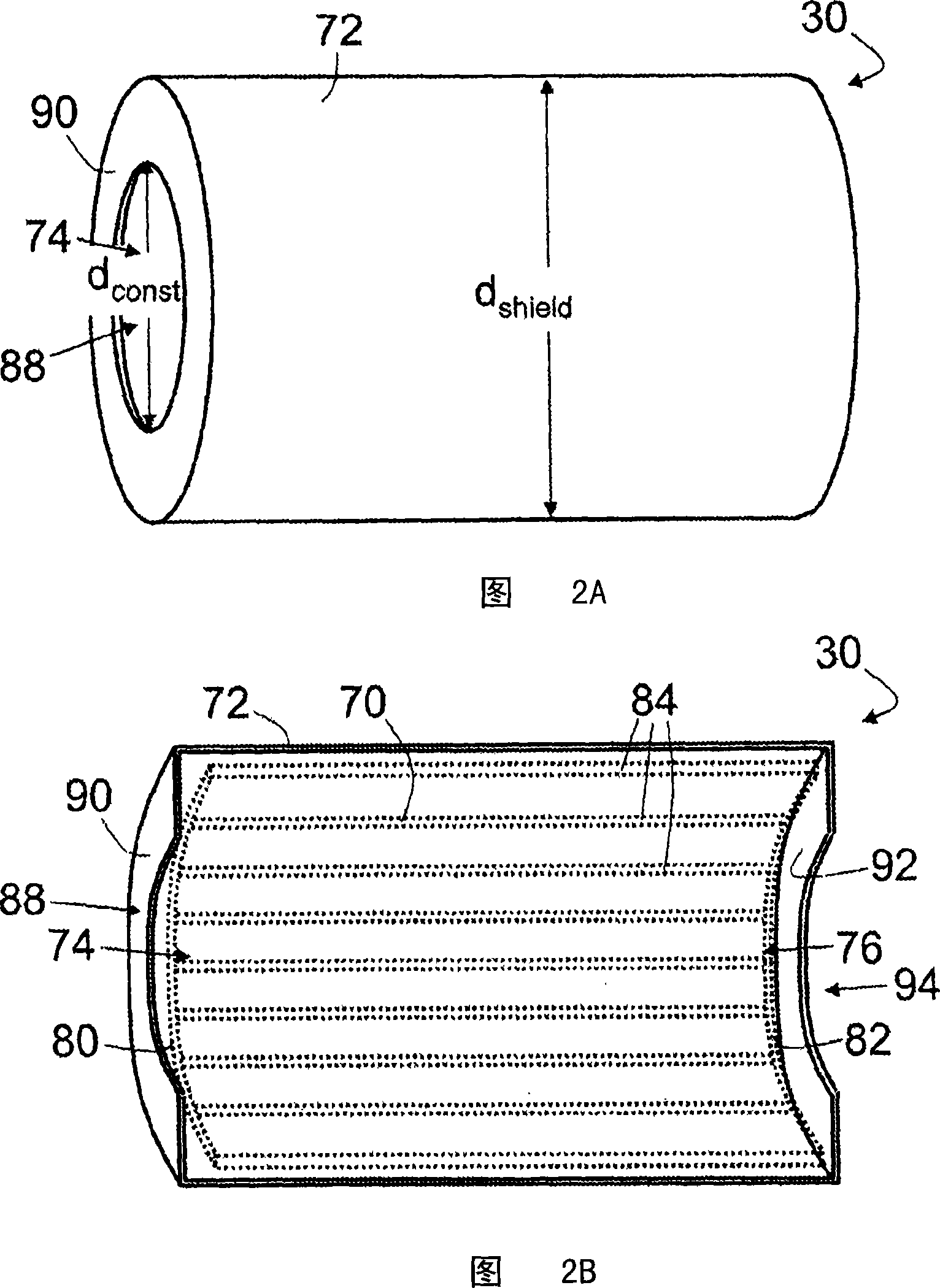
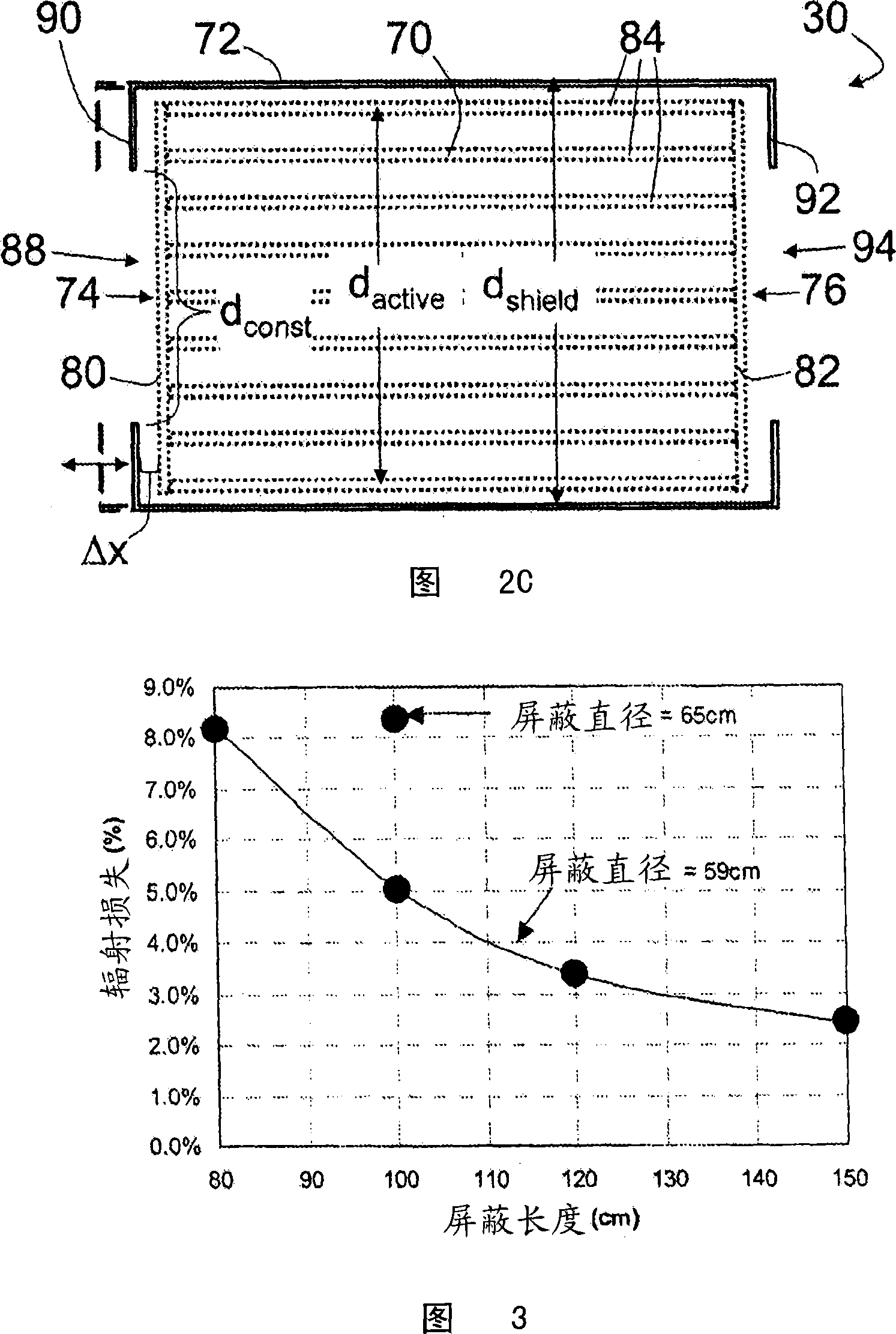
ActiveCN101171526AImprove efficiencyReduce radiation lossMagnetic measurementsHigh field mriEngineering
A radio frequency coil for magnetic resonance imaging includes an active coil member (70, 701, 170, 270) that defines an imaging volume. The active coil member has a first open end (74) with a first cross-sectional dimension (dactive). A shield coil member (72, 721, 722, 723, 724, 725, 172, 1722, 272) substantially surrounds the active coil member. The shield coil member has a constricted open end (88) arranged proximate to the first open end of the active coil member with a constricted cross-sectional dimension (dconst) that is less than the cross-sectional dimension (dShieid) of the shield coil member. In some embodiments, the radio frequency coil further includes an outer shield coil member (100) that is substantially larger than the shield coil member (72, 721, 722, 723, 724, 725, 172, 1722, 272), and surrounds both the active coil member and the shield coil member.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
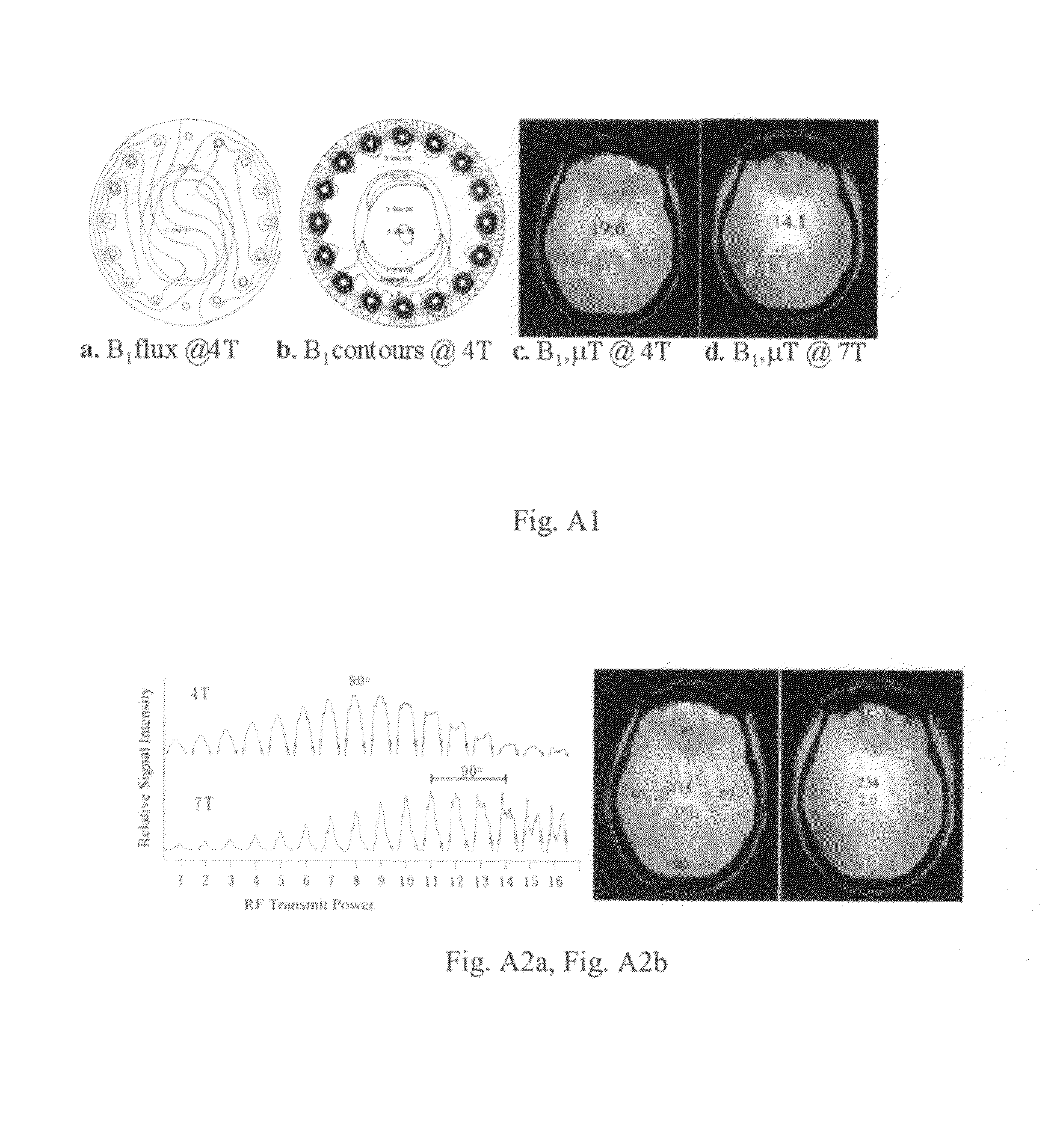
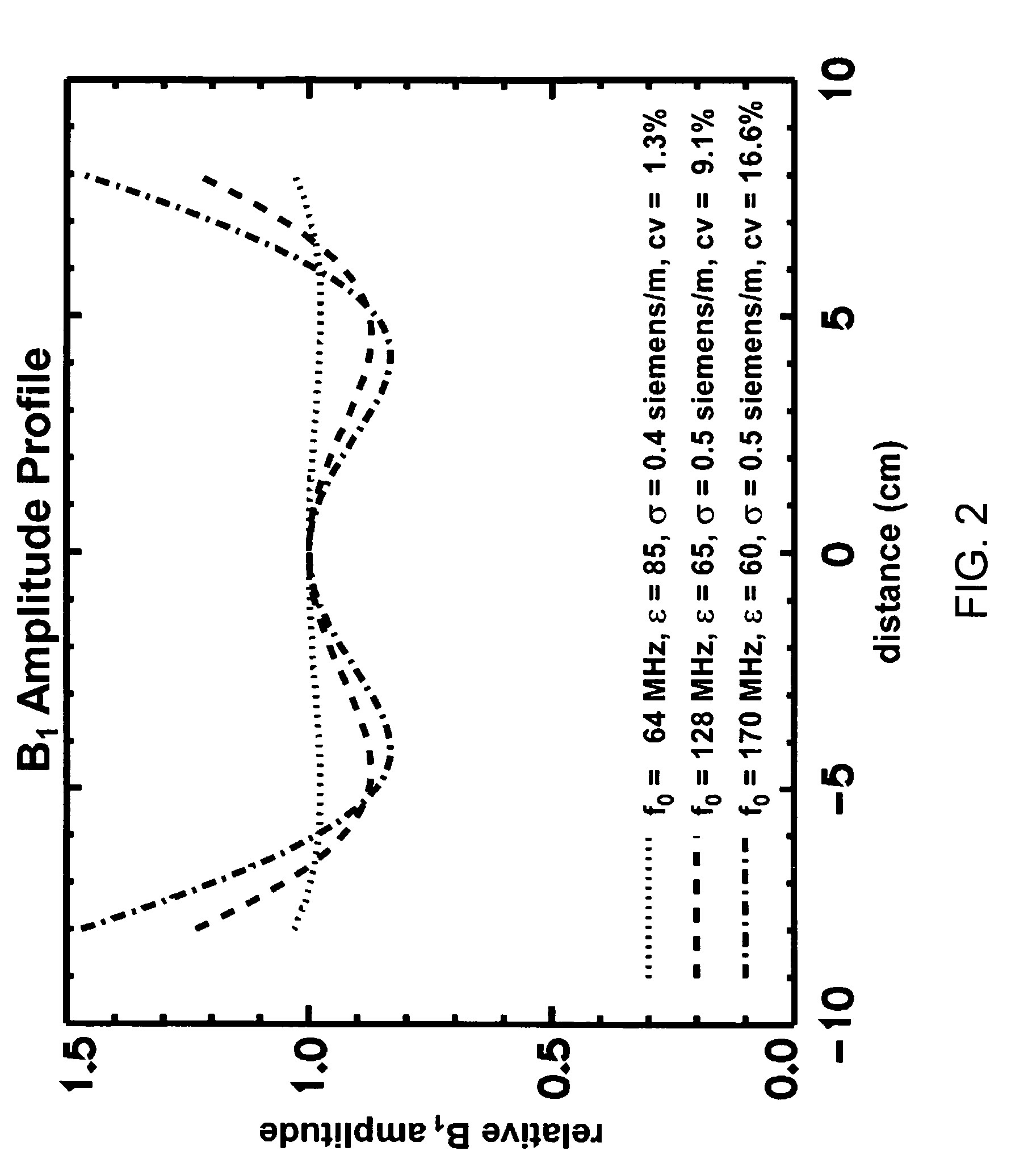
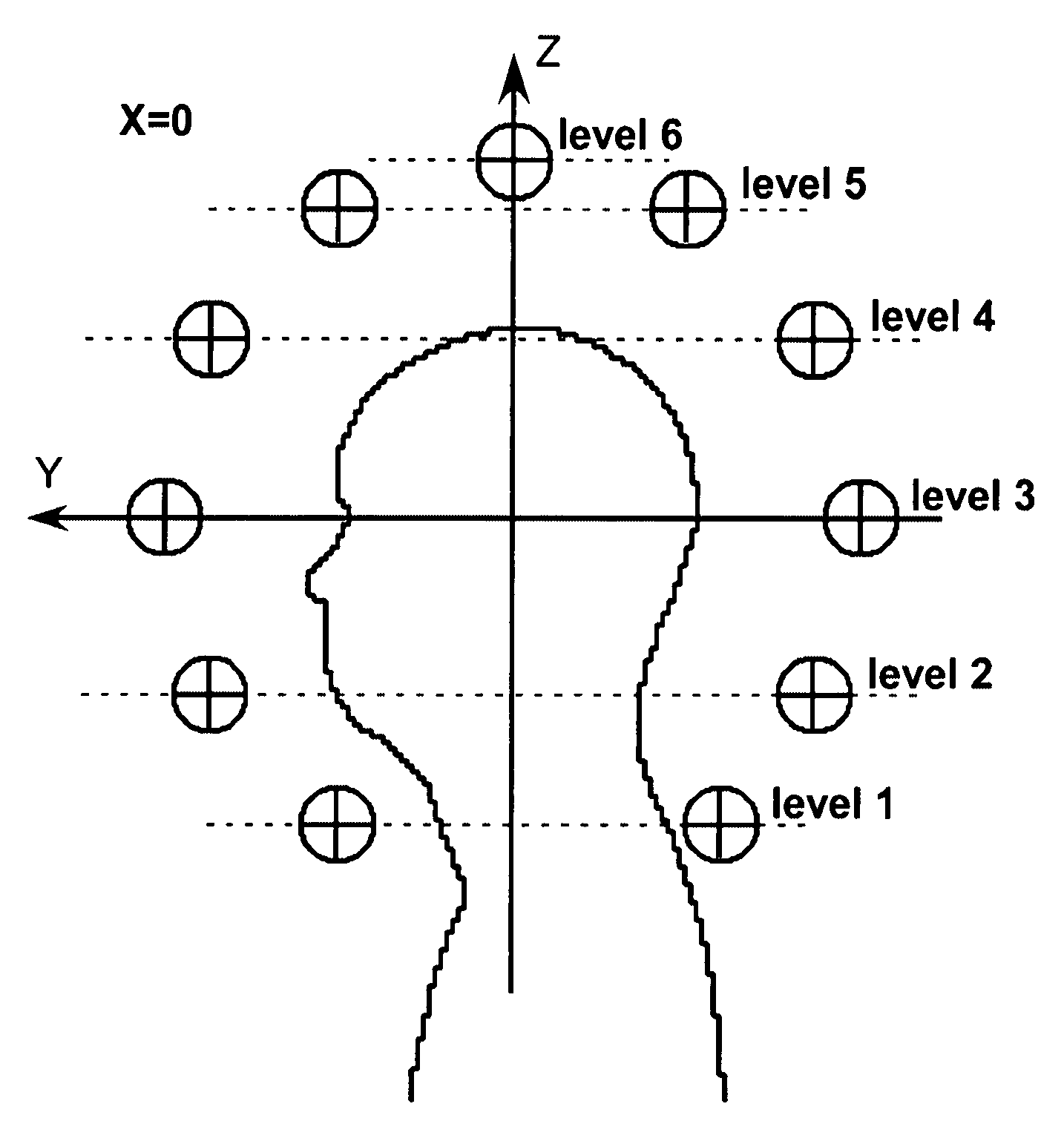
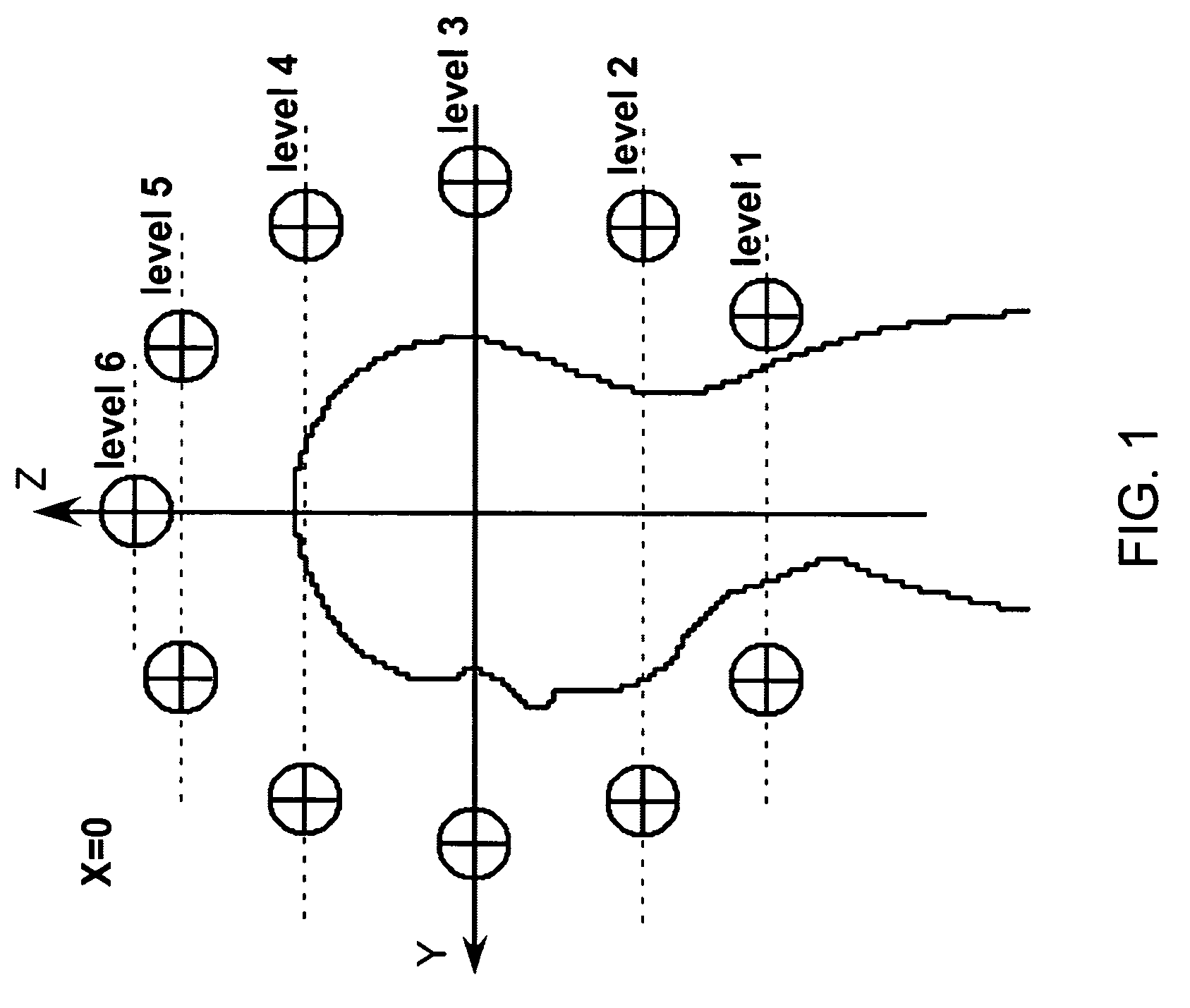
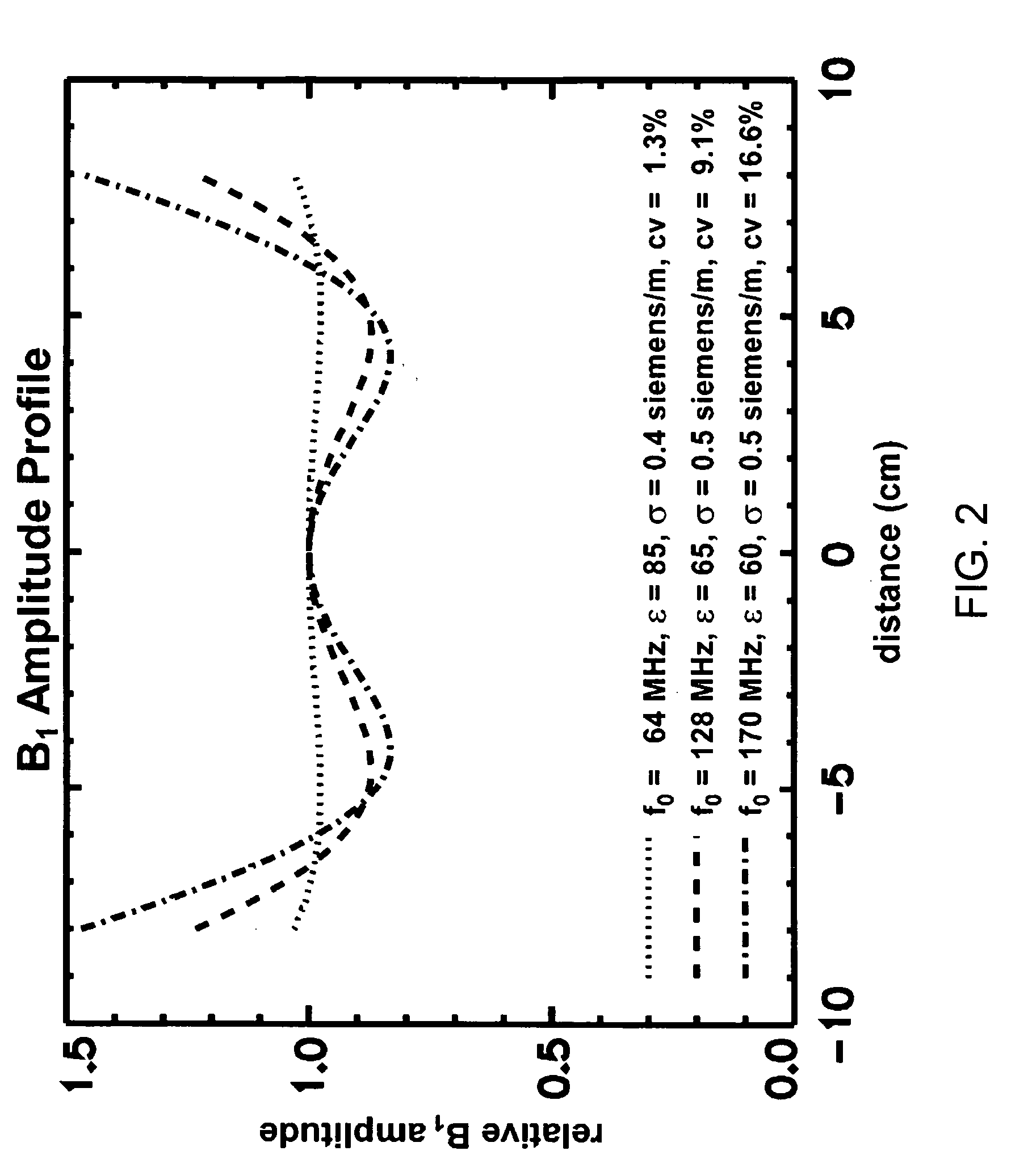
RF coil for a highly uniform B1 amplitude for high field MRI
InactiveUS7259562B2Improve homogeneityUniform magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringHigh field mriComposite element
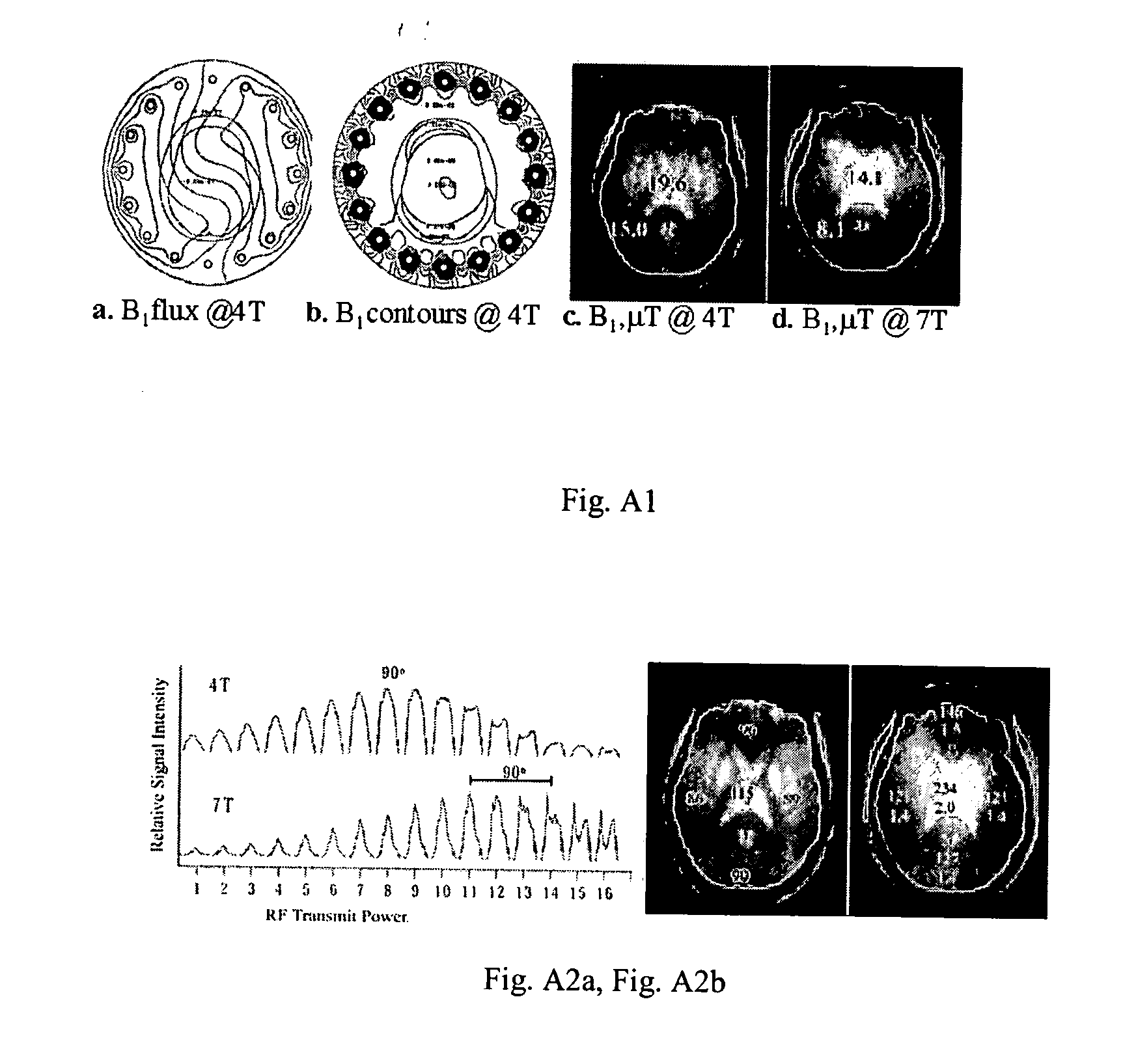
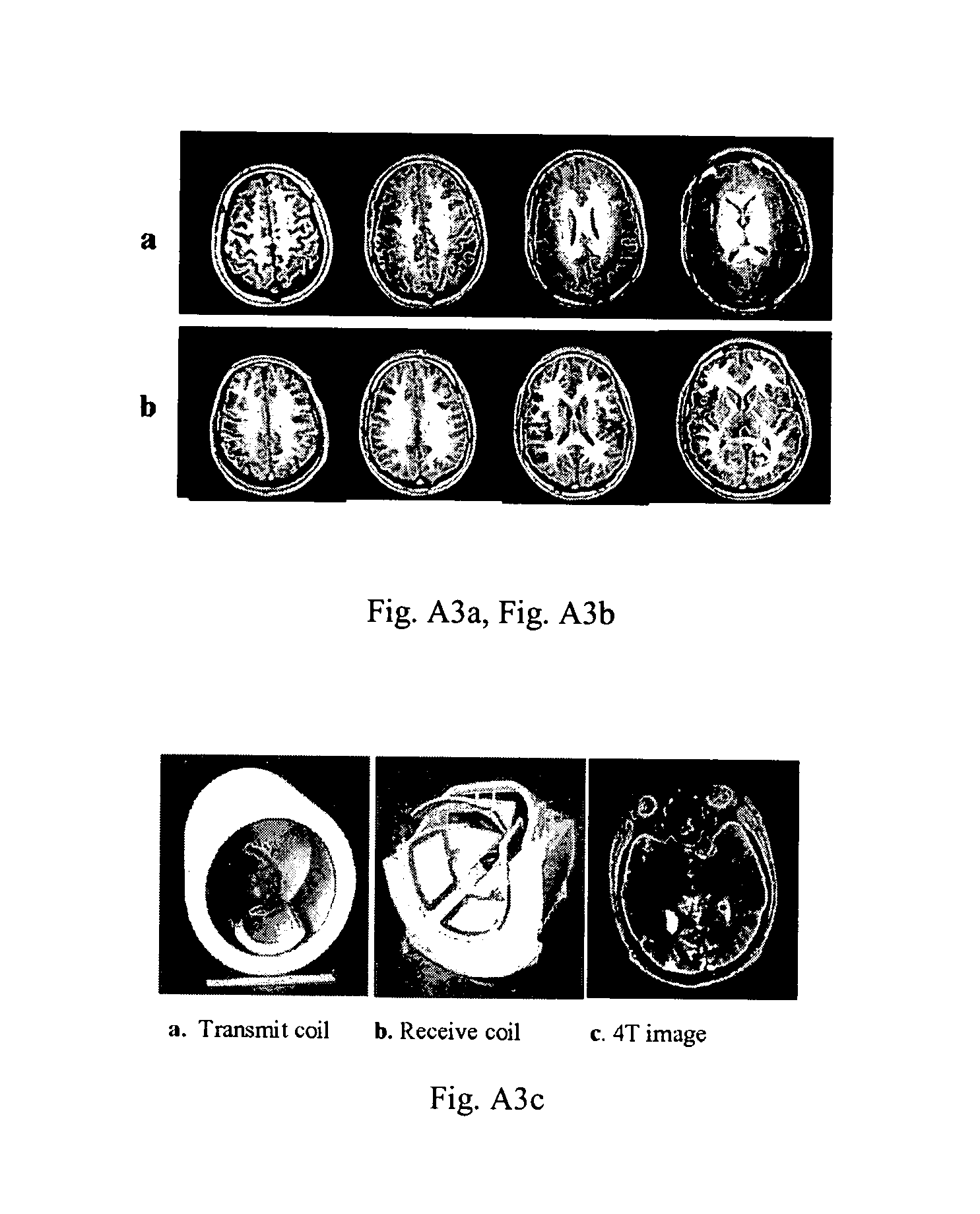
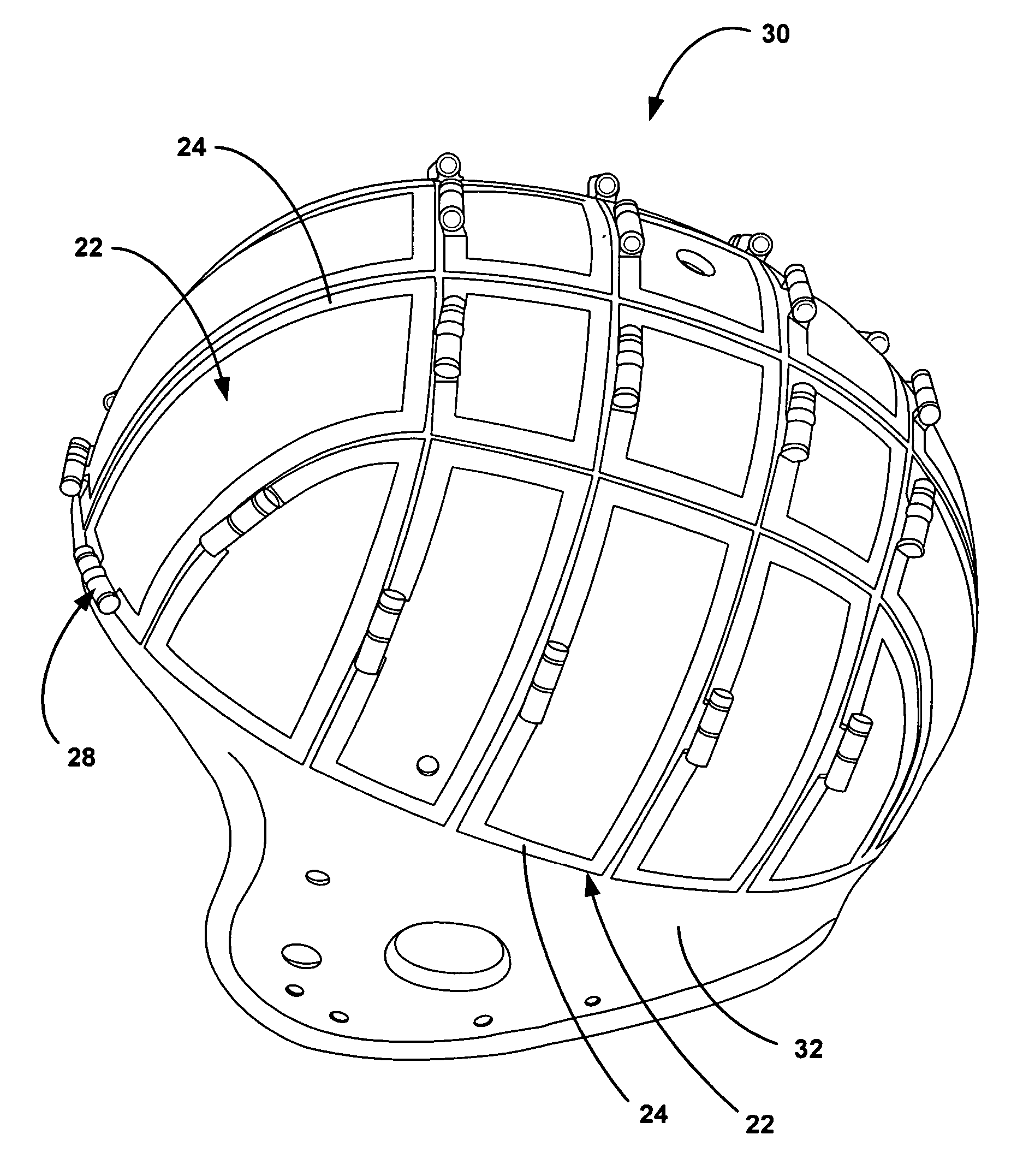
An array coil to achieve more uniform RF excitation for high field magnetic resonance imaging. In the preferred embodiment, the array coil has a plurality of transmit-composite elements distributed around the object to be imaged. A composite element comprises up to three current loops preferably orthogonal to each another. The array coil has the capability to shape the distribution of all three orthogonal components (x, y, and z) of the RF B1 field.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
RF coil for a highly uniform B1 amplitude for high field MRI
InactiveUS20060181277A1Improve homogeneityUniform magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringHigh field mriComposite element
An array coil to achieve more uniform RF excitation for high field magnetic resonance imaging. In the preferred embodiment, the array coil has a plurality of transmit-composite elements distributed around the object to be imaged. A composite element comprises up to three current loops preferably orthogonal to each another. The array coil has the capability to shape the distribution of all three orthogonal components (x, y, and z) of the RF B1 field.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
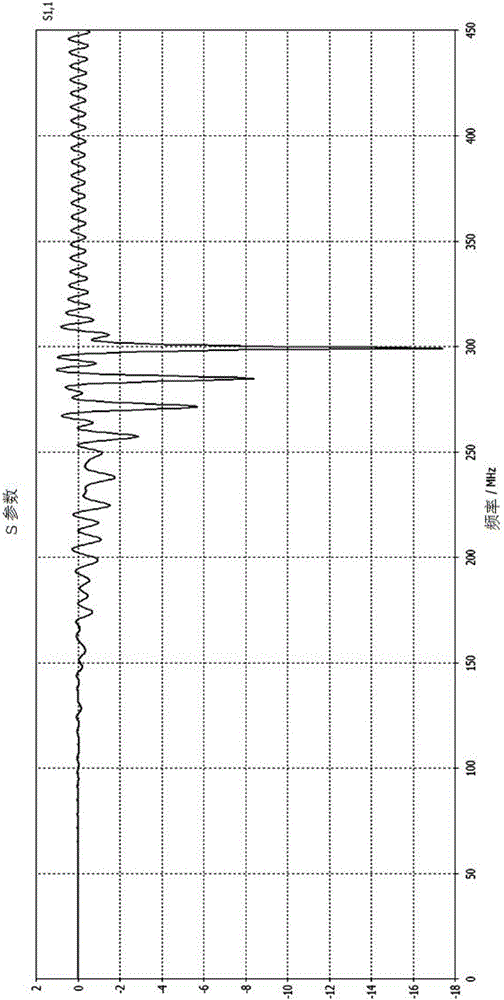
Metamaterial design method applied to high-field magnetic resonance radio frequency coil
InactiveCN106997412ACorrectly designedPractical designDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsResonanceHigh field mri
The invention relates to the field of electromagnetic metamaterials. In order to designed metamaterials to be more accurate and practical, the invention provides a metamaterial design method applied to a high-field magnetic resonance radio frequency coil. The design method can comprise the following steps that: the electromagnetic field simulation of a metamaterial periodic structure: using electromagnetic field simulation software to carry out structure design on the metamaterial periodic structure to enable the S parameter of the metamaterial to achieve magnetic resonance working frequency; the extraction of effective magnetic permeability: according to a simulated S21 parameter result, extracting the effective magnetic permeability of the metamaterial; and the manufacture of the real object of the metamaterial: manufacturing the designed metamaterial. The design method which is put forward by the invention has the main advantages: a simulation result is highly matched with the S21 measurement result of the manufactured real object of the metamaterial; a practically applied metamaterial size is taken as a simulation structure, a simulation result is more reliable, and therefore, the design method is more practical in a magnetic resonance field.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
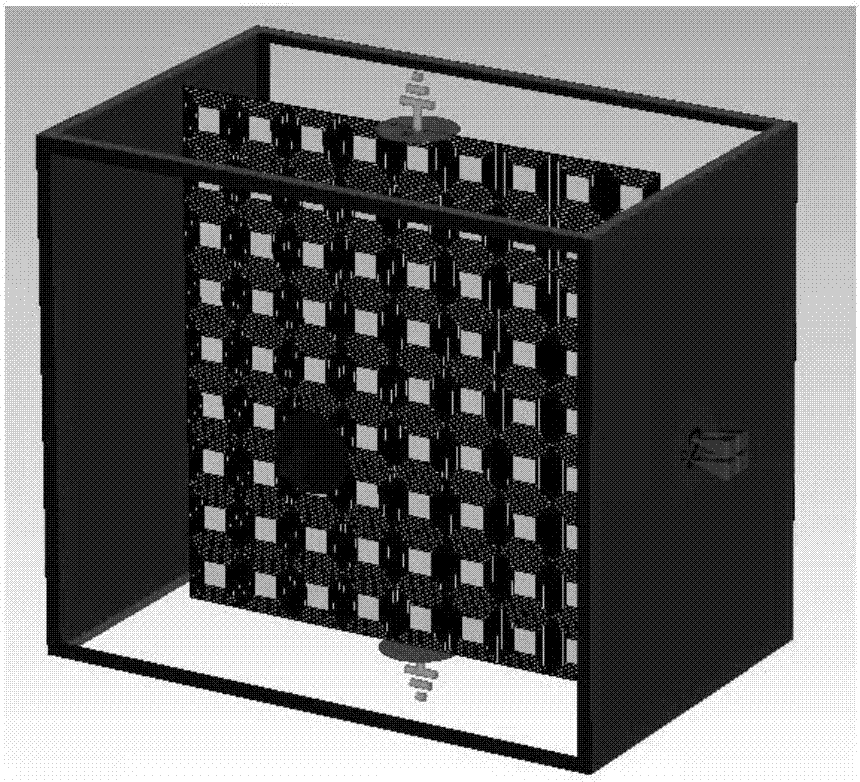
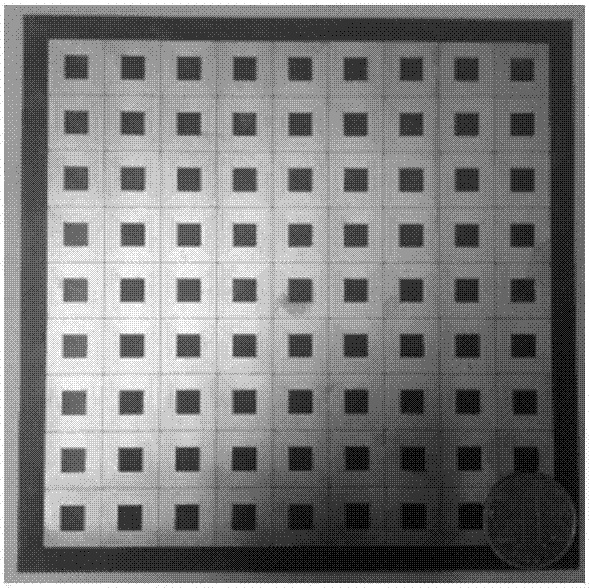
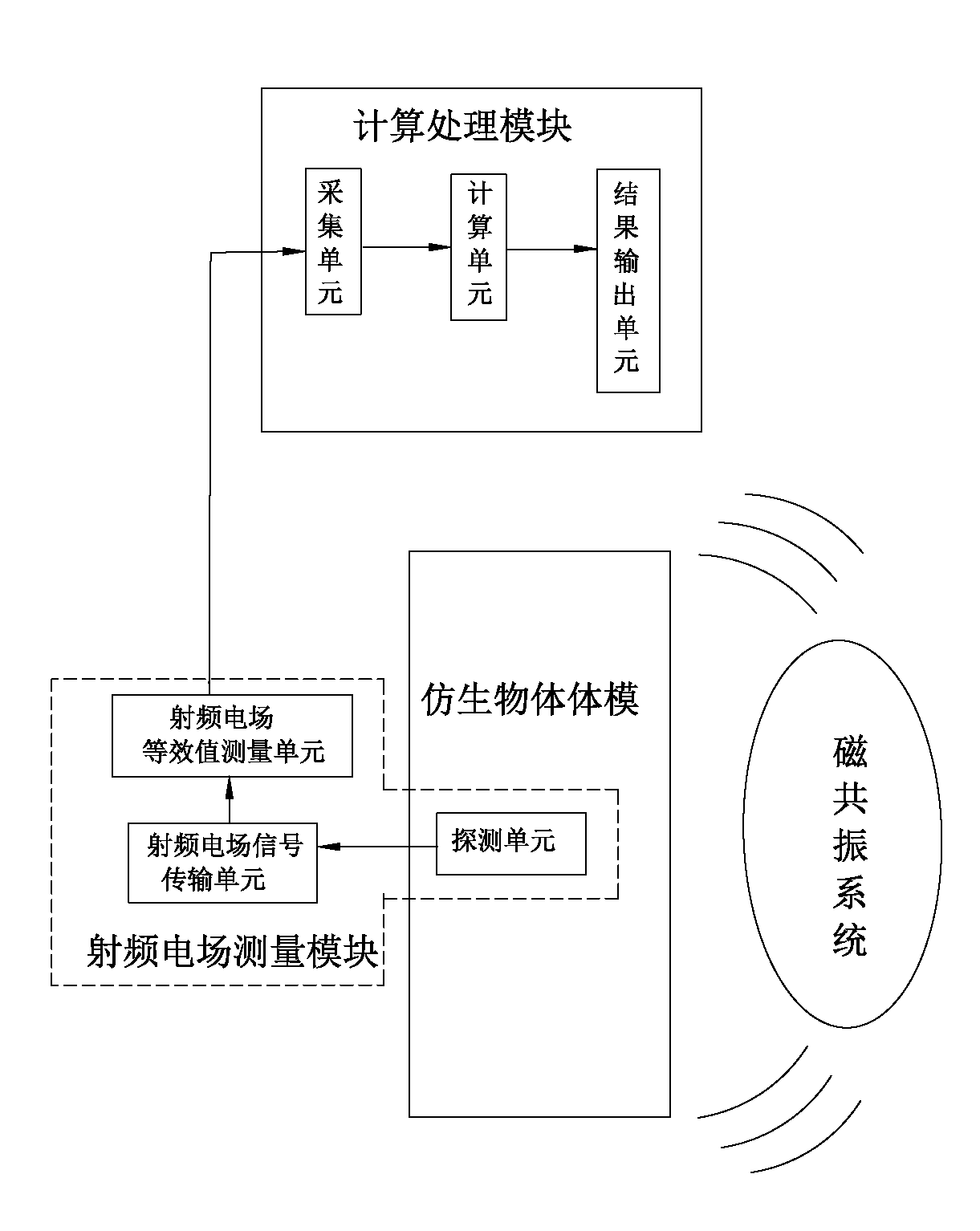
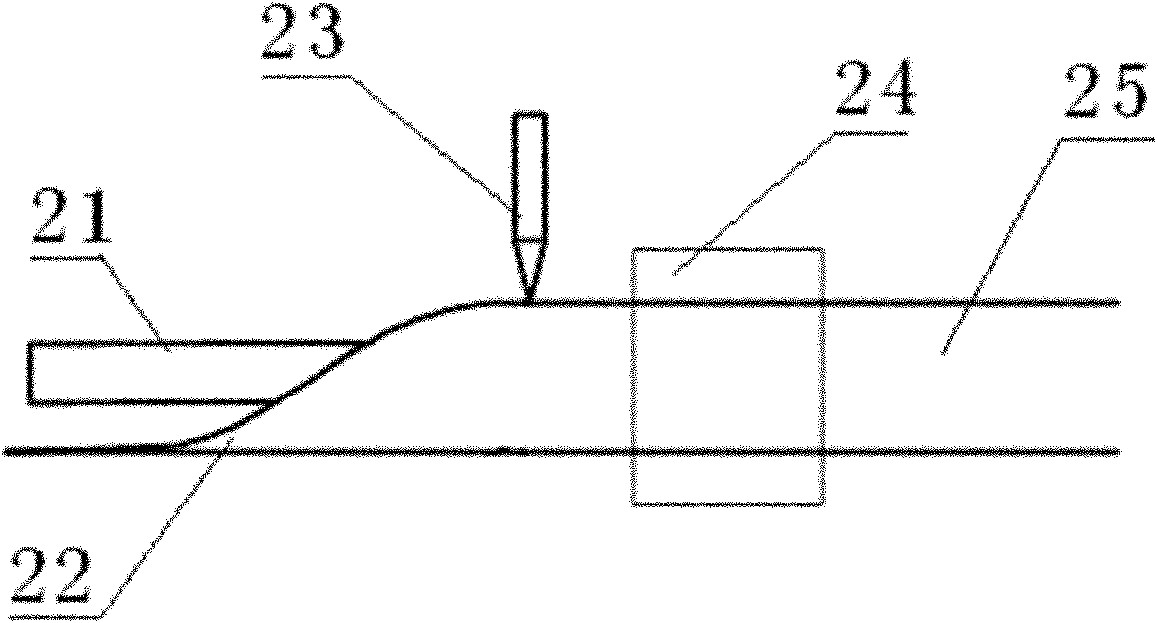
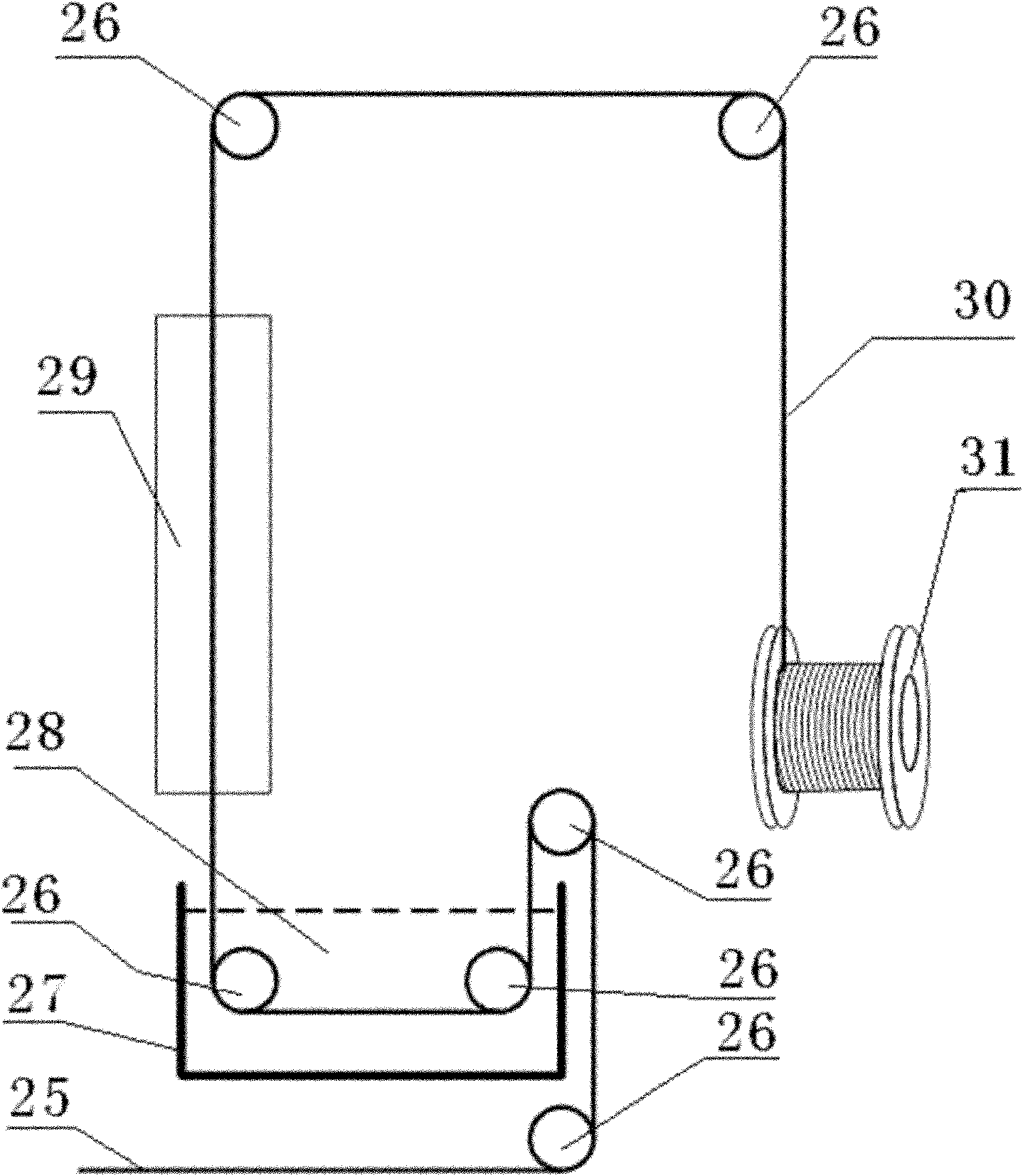
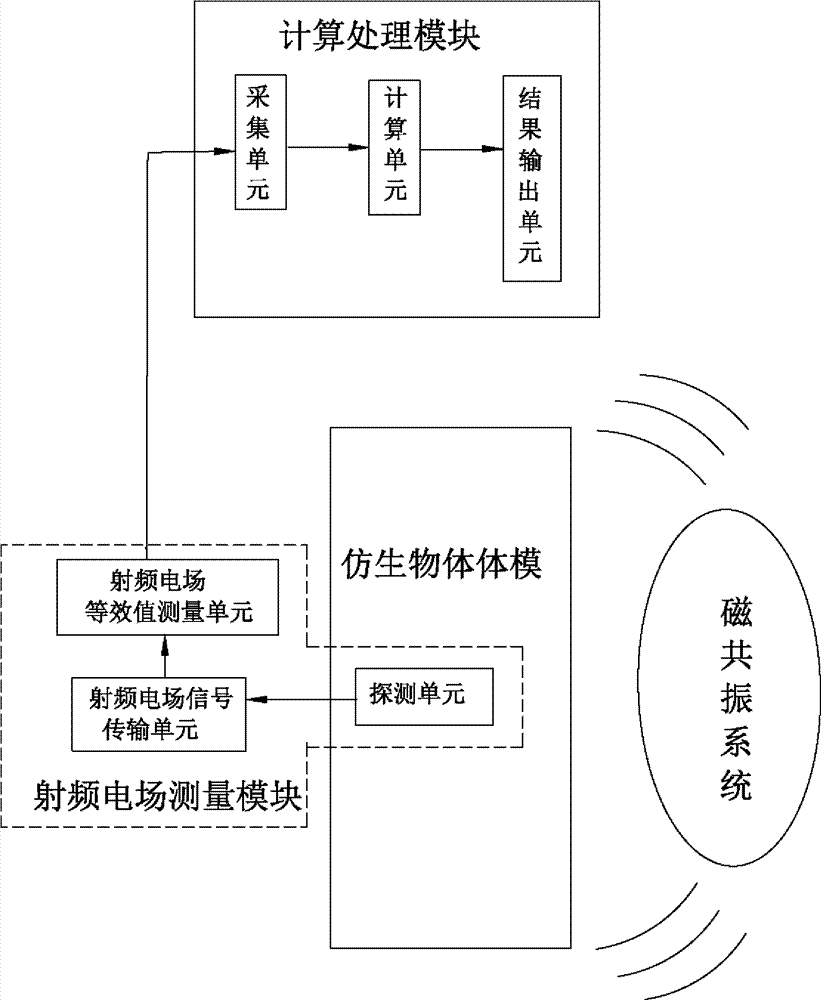
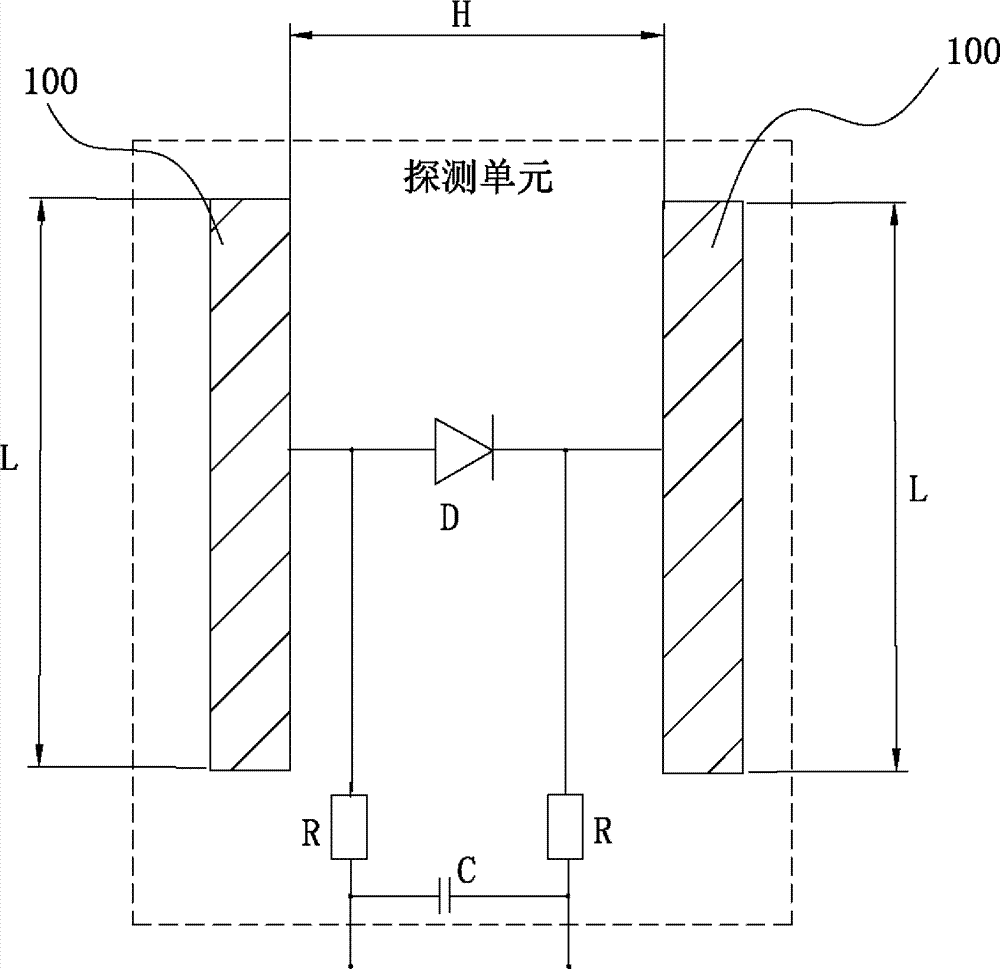
High-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system, high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing method and magnetic resonance system
The invention discloses a high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system, a high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model method and a magnetic resonance system with the high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system. The high-field-magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system comprises a radio frequency electric field measuring module, a bionic object body model and a computation processing module, the bionic object body model is positioned in a working area of the magnetic resonance system, the radio frequency electric field measuring module detects a radio frequency electric field of a target portion of the bionic object body model and obtains an equivalent value of the radio frequency electric field of the target portion, and the processing module computes to obtain a magnetic resonance scanning radio frequency Local SAR (specific absorption rate) value of the target portion according to the obtained equivalent value of the radio frequency electric field measuring module and a dielectric parameter of the target portion of a bionic object body model system. By means of comparing a Local SAR1 value obtained by the high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system with a Local SAR2 value automatically obtained by the magnetic resonance system via bionic object body model scanning, the Local SAR2 value given by the magnetic resonance system is verified, and accordingly the safety of magnetic resonance scanning is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
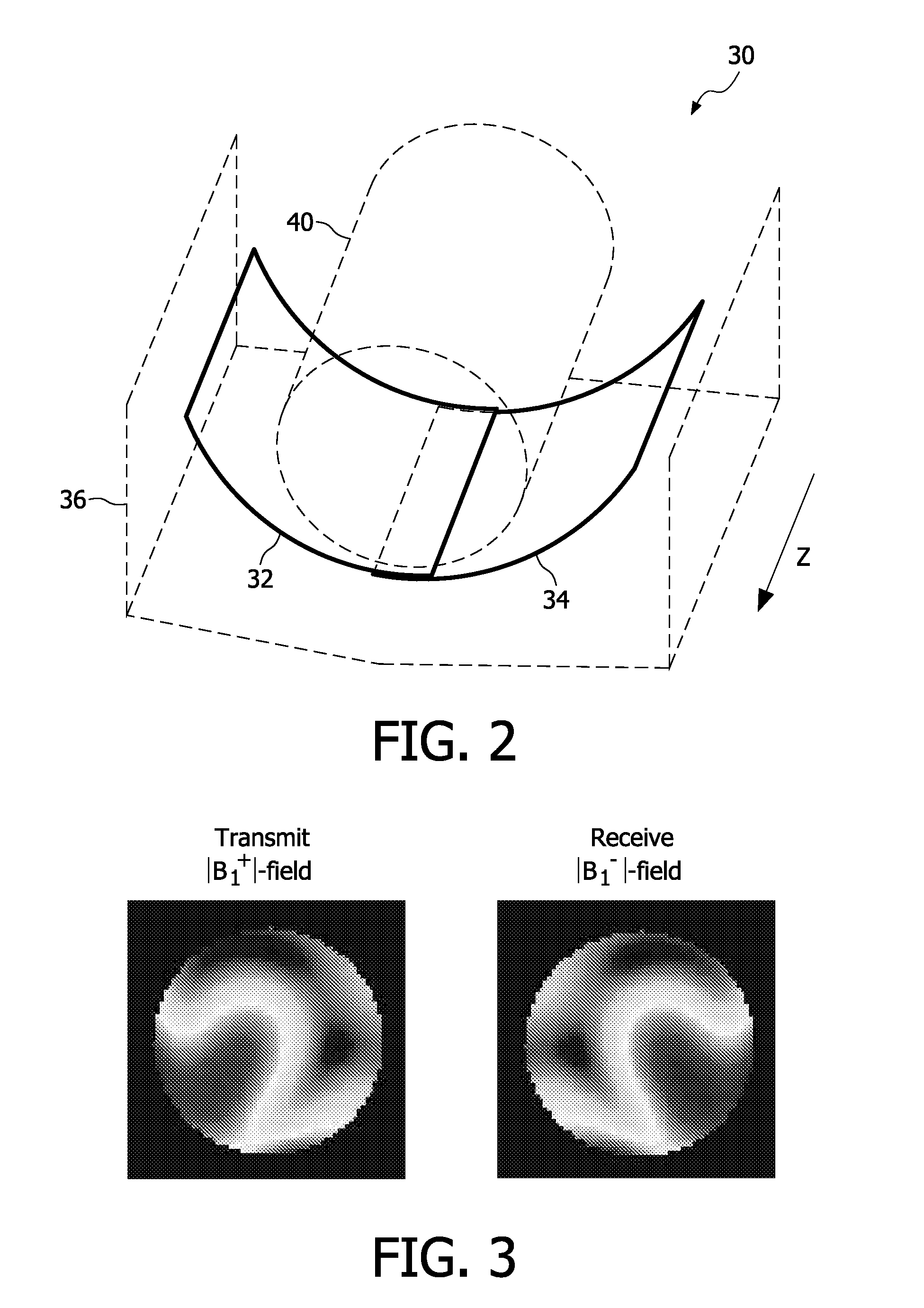
Transmit/receive coil for ultra-high field MRI
ActiveUS20110115483A1Improve correspondenceImproved magnetic resonanceElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using NMRHigh field mriTransmission channel
A magnetic resonance coil comprises a first set of coil elements (54, 56, 80) operatively connectable with a transmit channel (66, 74) to couple with a transmit region of sensitivity for a selected load at a magnetic field strength greater than 3 Tesla, and a second set of coil elements (52, 54, 82) operatively connectable with a receive channel (66, 74) to couple with a receive region of sensitivity for the selected load at the magnetic field strength greater than 3 Tesla. The first set of coil elements is arranged proximate to but not surrounding the transmit region of sensitivity, and the second set of coil elements is arranged proximate to but not surrounding the receive region of sensitivity. The first set of coil elements and the second set of coil elements having at least one coil element (52, 56) not in common. The first and second sets of coil elements define transmit and receive regions of sensitivity for the selected load at the magnetic field strength greater than 3 Tesla that are substantially similar.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
High-pass two-dimensional ladder network resonator
InactiveUS7642781B2Suitable imageIncrease working frequencyMagnetic measurementsRecord carriers used with machinesHigh field mriParallel imaging
A high-pass two-dimensional ladder network has been described for high-field MRI and credential applications. The next-to-highest eigenvalue of the network corresponds to a normal mode giving rise to B1 fields with good spatial homogeneity above the resonator plane. Other eigenvalues may also be used for specific imaging applications. In its most basic form, the ladder network is a collection of inductively coupled resonators where each element of the array is represented by at least one conducting strip having a self-inductance L, joined by a capacitor C at one or more points along each resonator. In the strong coupling limit of the inductively coupled high-pass two-dimensional ladder network resonator array, the array produces a high-frequency resonant mode that can be used to generate the traditional quadrature B1 field used in magnetic resonance imaging, and in the limit of weak or zero coupling reduces to a phased array suitable for parallel imaging applications.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
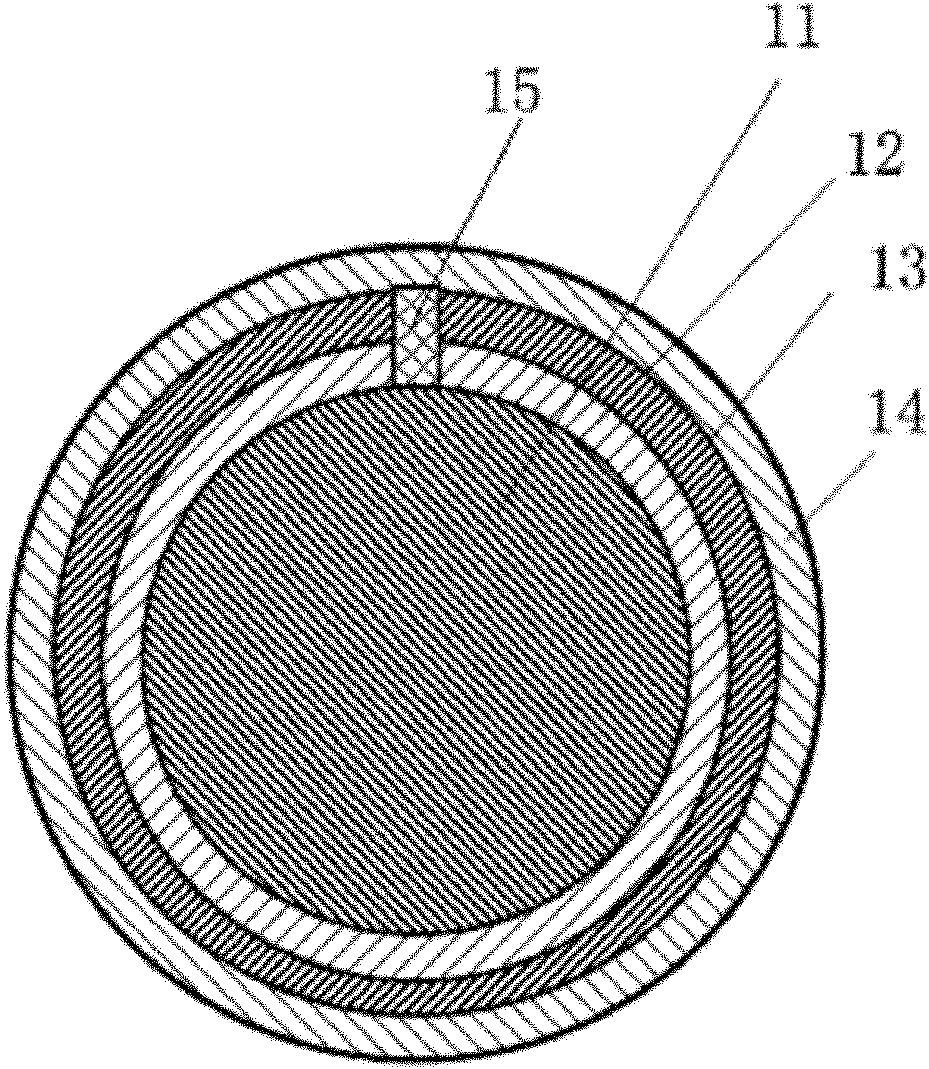
NbTi/YBCO (yttrium barium copper oxide) composite superconducting wire with circular section
InactiveCN102097180AImprove dynamic stabilityHigh superconducting filling rateSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSuperconductor devicesYttrium barium copper oxideElectrical conductor
The invention discloses an NbTi / YBCO (yttrium barium copper oxide) composite superconducting wire with circular section, belonging to the field of superconducting materials. The composite superconducting wire is characterized in that a low temperature superconducting wire with circular section is covered by a stable layer; the stable layer is covered by a high temperature superconducting substrate layer through rolling; Ag solders are used for soldering the high temperature superconducting substrate layer in the rolled gaps of the high temperature superconducting substrate layer and forming an Ag soldered joint; a high temperature superconductor coating is coated on the outer surface of the high temperature superconducting substrate layer; the low temperature superconducting wire and the stable layer are NbTi / Cu low temperature composite superconducting wires; and the high temperature superconducting substrate layer and the high temperature superconductor coating are respectively made of Ni-W alloy tapes and high temperature superconducting material YBCO. The composite superconducting wire has the following beneficial effects: a YBCO high temperature superconducting coating conductor and the NbTi / Cu low temperature composite superconducting wires are combined; by utilizing the characteristic that the n value of the YBCO high temperature superconducting material is much less than the n value of the low temperature superconducting material NbTi and the characteristic of high superconductor critical temperature, rise of the whole voltage of the low / high temperature composite superconducting wires can be suppressed and temperature rise of the composite superconducting wire can be reduced; and compared with the traditional low / high temperature superconducting magnets, the superconducting magnet operates more stably, has higher efficiency and is safer, and is applied to high-field MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) magnets, MRI magnets and the like.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
High-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system, high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing method and magnetic resonance system
The invention discloses a high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system, a high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model method and a magnetic resonance system with the high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system. The high-field-magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system comprises a radio frequency electric field measuring module, a bionic object body model and a computation processing module, the bionic object body model is positioned in a working area of the magnetic resonance system, the radio frequency electric field measuring module detects a radio frequency electric field of a target portion of the bionic object body model and obtains an equivalent value of the radio frequency electric field of the target portion, and the processing module computes to obtain a magnetic resonance scanning radio frequency Local SAR (specific absorption rate) value of the target portion according to the obtained equivalent value of the radio frequency electric field measuring module and a dielectric parameter of the target portion of a bionic object body model system. By means of comparing a Local SAR1 value obtained by the high-field magnetic resonance scanning safety testing body model system with a Local SAR2 value automatically obtained by the magnetic resonance system via bionic object body model scanning, the Local SAR2 value given by the magnetic resonance system is verified, and accordingly the safety of magnetic resonance scanning is guaranteed.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
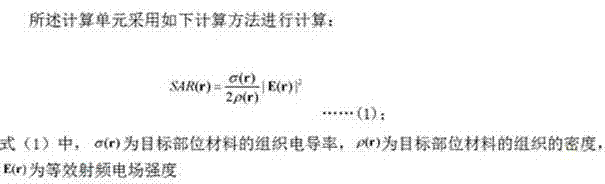
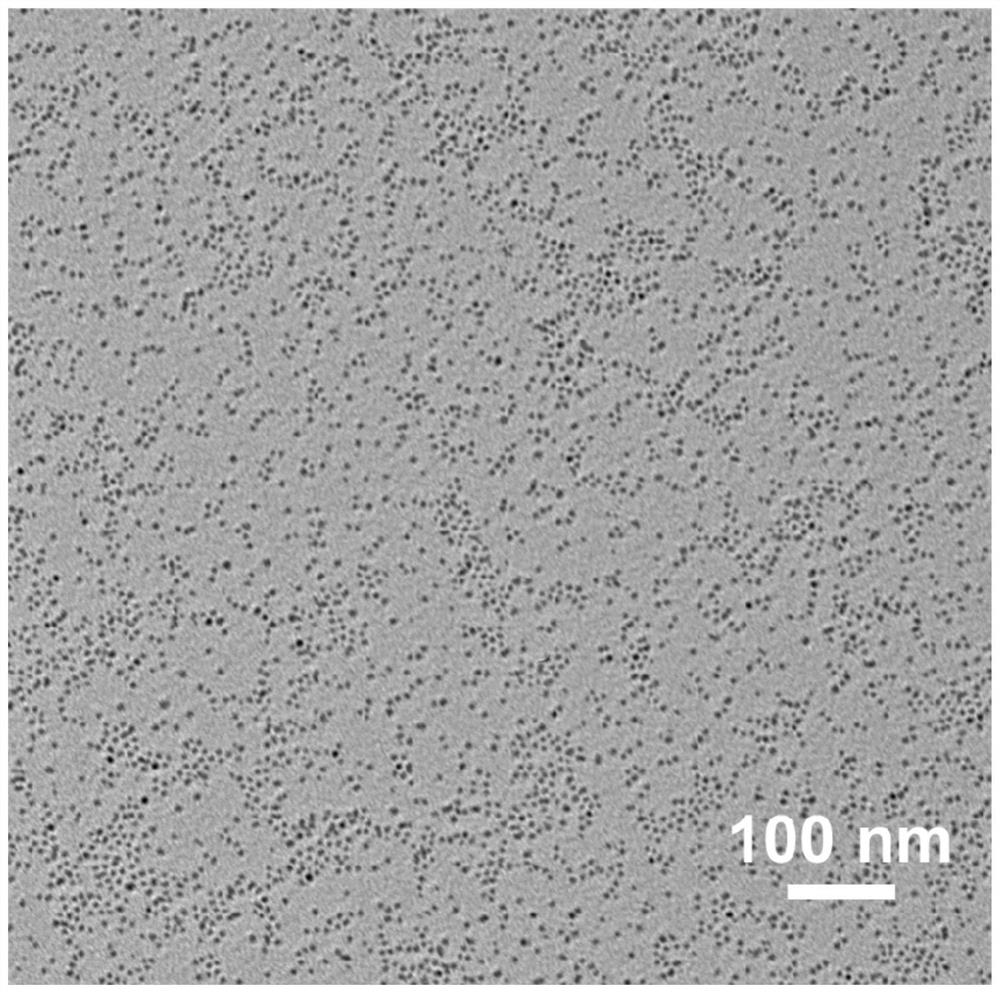
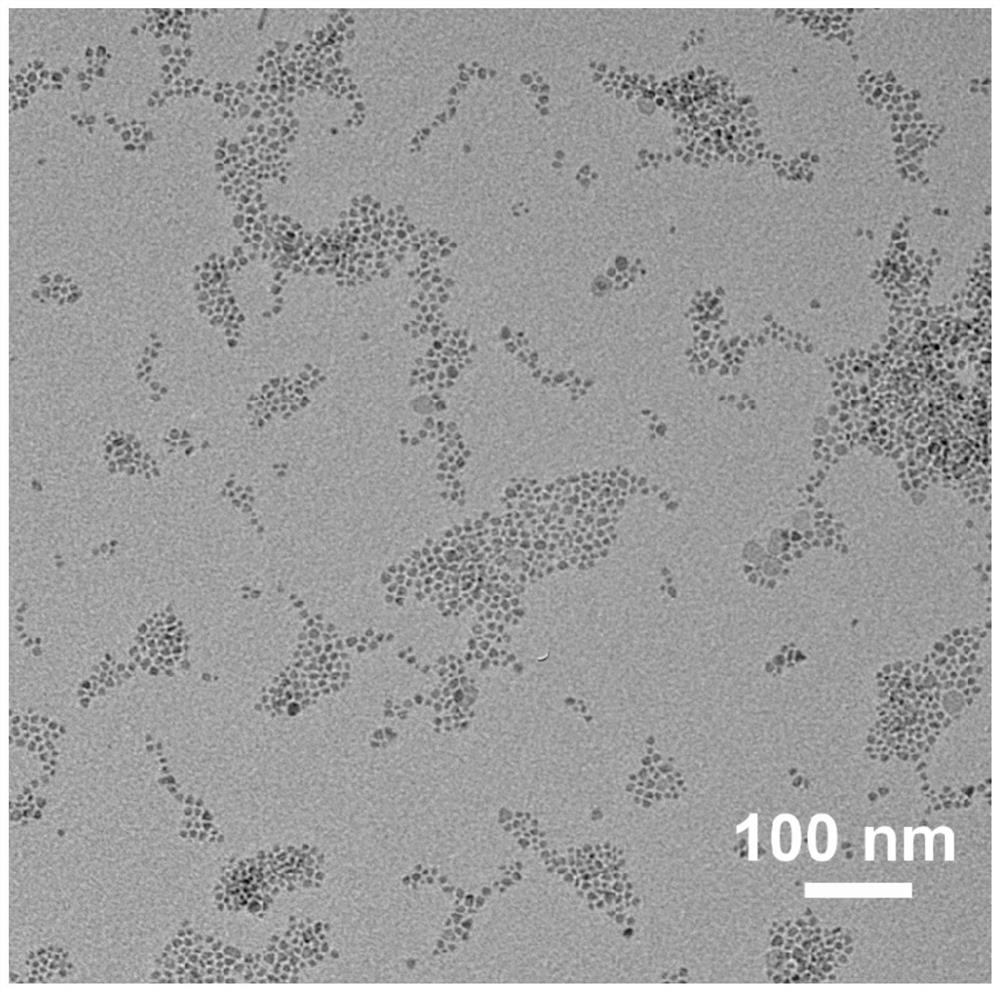
T1-T2 bimodal ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance contrast agent as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112274657AGood ultra-high field magnetic resonance imaging effectAccurate permeabilityMaterial nanotechnologyNanomagnetismHigh field mriMagnetite Nanoparticles
The invention relates to a T1-T2 bimodal ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance contrast agent. The contrast agent comprises magnetic nanoparticles, a water-soluble ligand modifying the surfaces of the magnetic nanoparticles, and a water-soluble polymer modified the surfaces of the magnetic nanoparticles through chemical coupling. The contrast agent has a good ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance imaging effect in vivo, and the tumor vascular permeability can be accurately evaluated with high sensitivity through T1-T2 bimodal magnetic resonance imaging. The invention further relates to a preparationmethod of the T1-T2 bimodal ultrahigh-field magnetic resonance contrast agent and application of the contrast agent in preparation of magnetic resonance nano contrast agents. The contrast agent has the advantages of controllable reaction conditions of the preparation method, uniform product size, good morphology, high product biosafety and good clinical conversion possibility.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
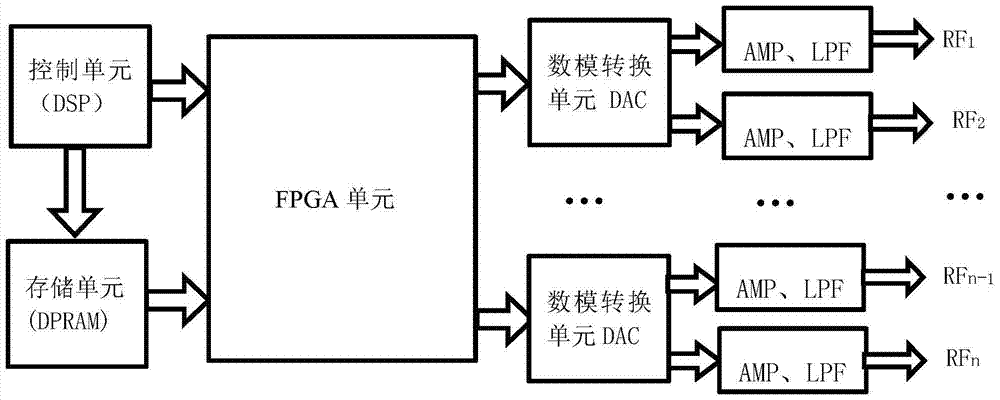
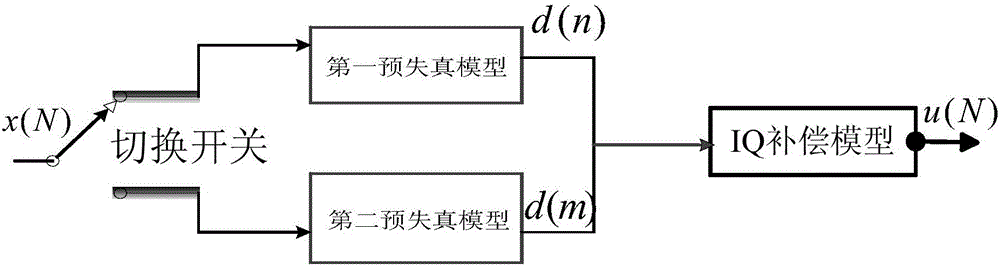
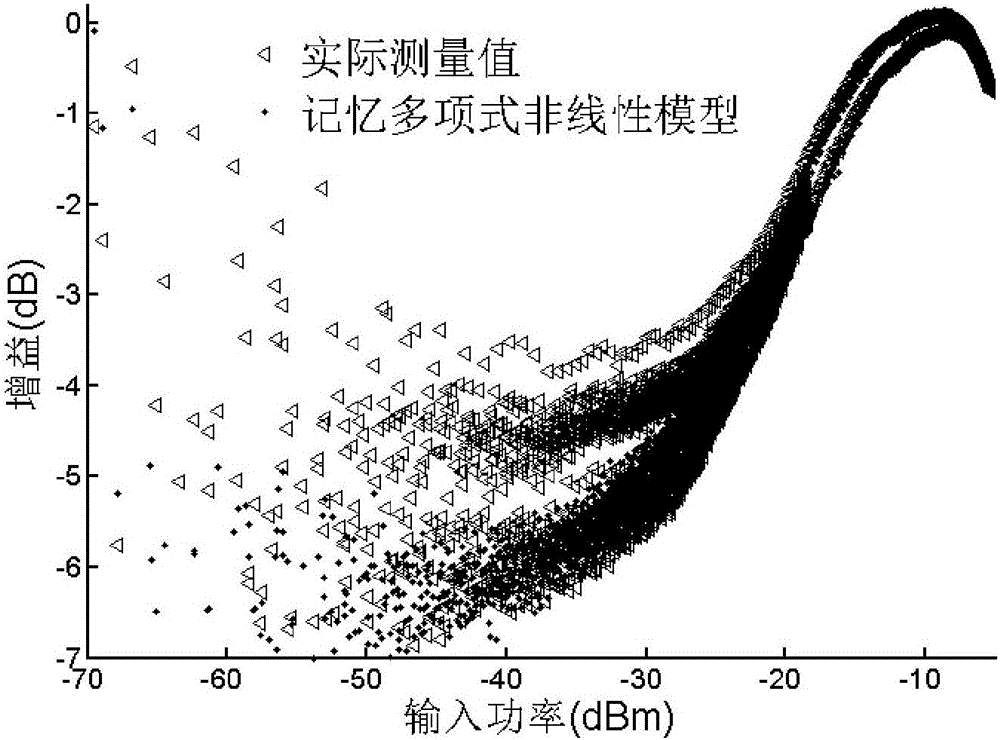
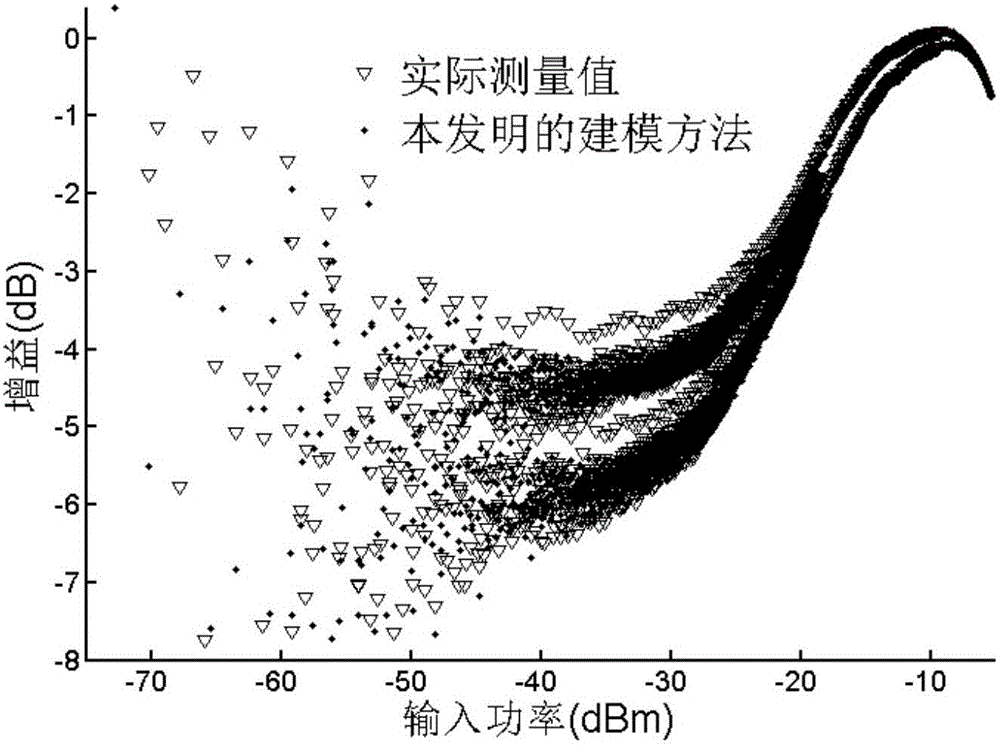
Digital pre-distorter for high-field MRI high-power radio frequency power amplifier
ActiveCN105978501AHigh pre-distortion accuracyAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionNonlinear distortionHigh field mri
The invention discloses a digital pre-distorter for a high-field MRI high-power radio-frequency power amplifier. The digital pre-distorter comprises a first pre-distortion model, a second pre-distortion model, an IQ compensation model and a switching switch. The first pre-distortion model is used for carrying out pre-distortion on a first segment of an original baseband data sequence. The second pre-distortion model is used for carrying out pre-distortion on a second segment of the original baseband data sequence. The first segment of the original baseband data sequence is the sequence composed of data starting from a first piece of original baseband data to the original baseband data with the maximum module value in the original baseband data, wherein the original baseband data is extracted at the input end of the high-field MRI high-power radio-frequency power amplifier. The second segment of the original baseband data sequence is the sequence composed of the residual original baseband data of the original baseband data sequence except the first segment of the original baseband data sequence. The digital pre-distorter has the advantages that the nonlinear distortion resulting from the self cause of the radio-frequency power amplifier and the linear distortion resulting from IQ defects can be compensated, and the pre-distortion precision is high.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Transmit/receive coil for ultra-high field MRI
ActiveUS8441259B2Improve correspondenceImprove performanceMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionHigh field mriTransmission channel
A magnetic resonance coil comprises a first set of coil elements (54, 56, 80) operatively connectable with a transmit channel (66, 74) to couple with a transmit region of sensitivity for a selected load at a magnetic field strength greater than 3 Tesla, and a second set of coil elements (52, 54, 82) operatively connectable with a receive channel (66, 74) to couple with a receive region of sensitivity for the selected load at the magnetic field strength greater than 3 Tesla. The first set of coil elements is arranged proximate to but not surrounding the transmit region of sensitivity, and the second set of coil elements is arranged proximate to but not surrounding the receive region of sensitivity. The first set of coil elements and the second set of coil elements having at least one coil element (52, 56) not in common. The first and second sets of coil elements define transmit and receive regions of sensitivity for the selected load at the magnetic field strength greater than 3 Tesla that are substantially similar.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
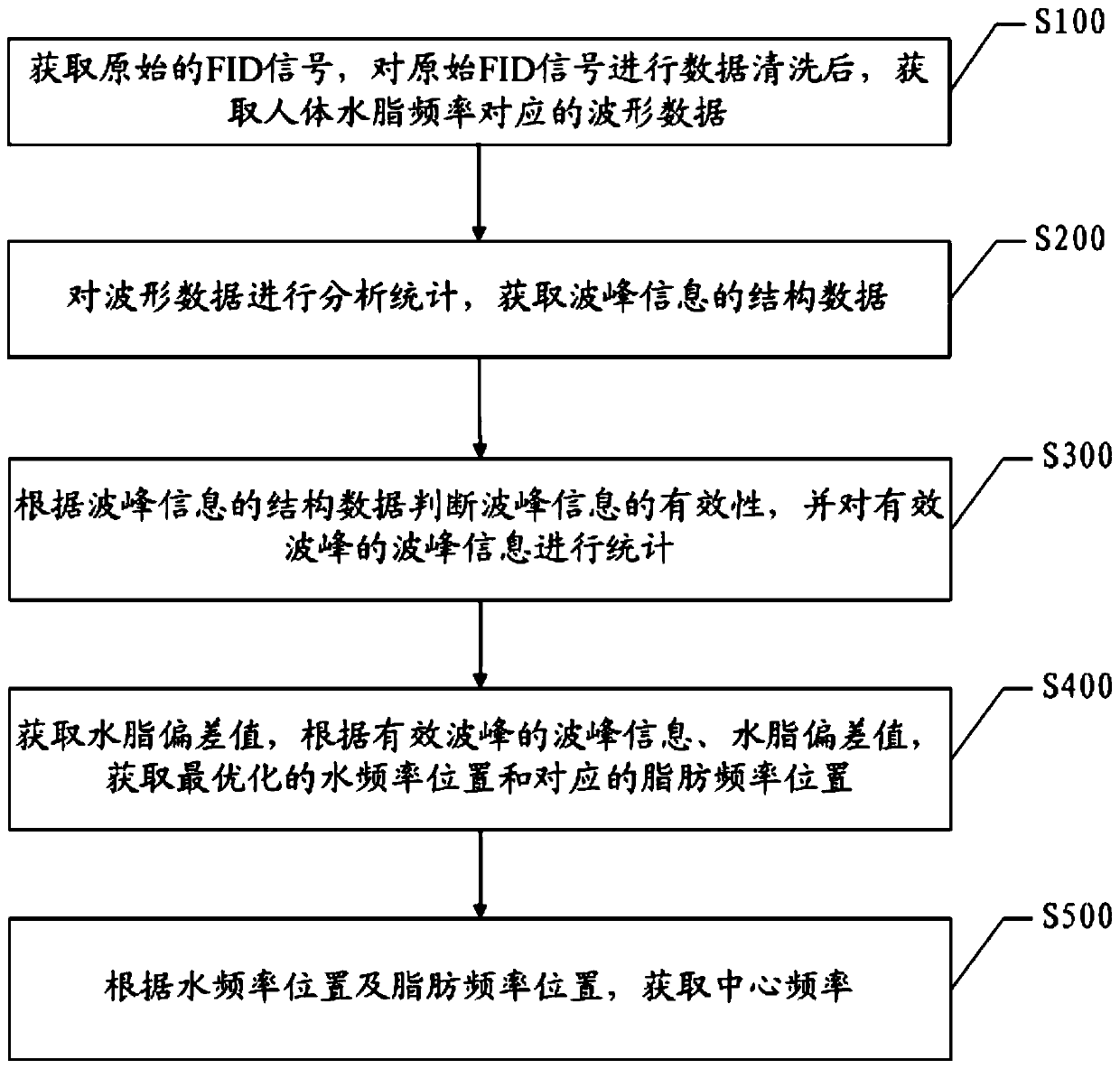
Superconducting high-field magnetic resonance center frequency calculation method and system
PendingCN111460934AOptimal water frequency positionOptimize water frequency positionCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsHigh field mriSilica gel
The embodiment of the invention discloses a superconducting high-field magnetic resonance center frequency calculation method and system, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining an original FIDsignal, carrying out the data cleaning of the original FID signal, and obtaining waveform data corresponding to the water and fat frequency of a human body; analyzing and counting the waveform data toobtain structural data of the wave crest information; judging the validity of the wave crest information according to the structure data of the wave crest information, and counting the wave crest information of the valid wave crest; acquiring a water-fat deviation value, and acquiring an optimal water frequency position and a corresponding fat frequency position according to the peak informationof the effective peak and the water-fat deviation value; and acquiring a center frequency according to the water frequency position and the fat frequency position. According to the embodiment of the invention, the accurate water frequency position can be automatically and quickly found, and the optimal water frequency position can be analyzed and calculated when interference signals such as signals generated by silica gel fillers, a plurality of fat frequencies and differences of different channels exist.
Owner:SHENZHEN BASDA MEDICAL APP
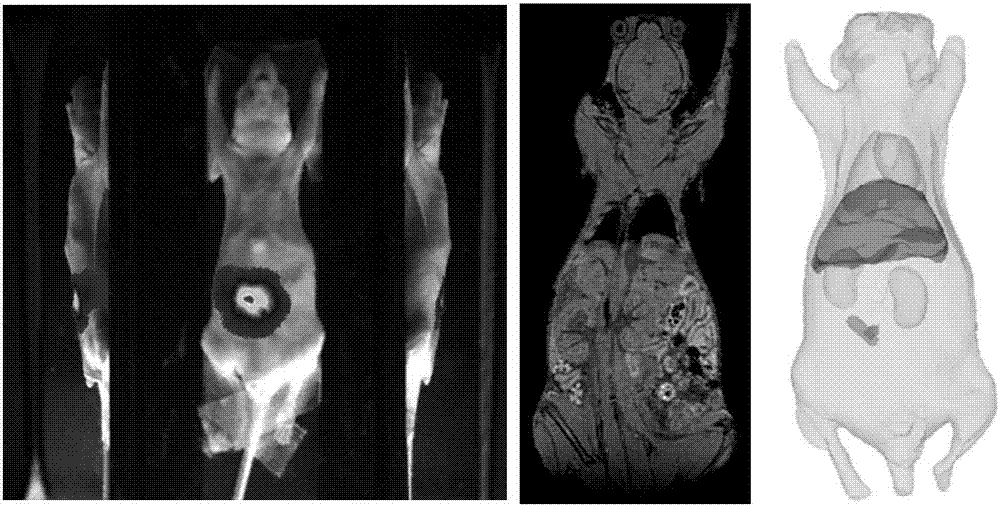
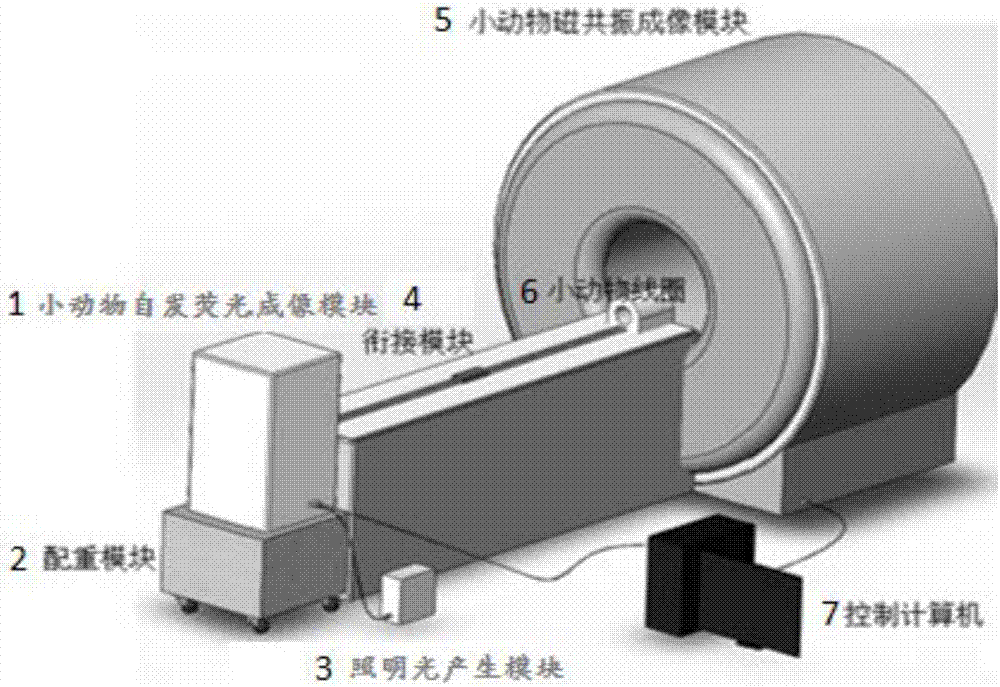
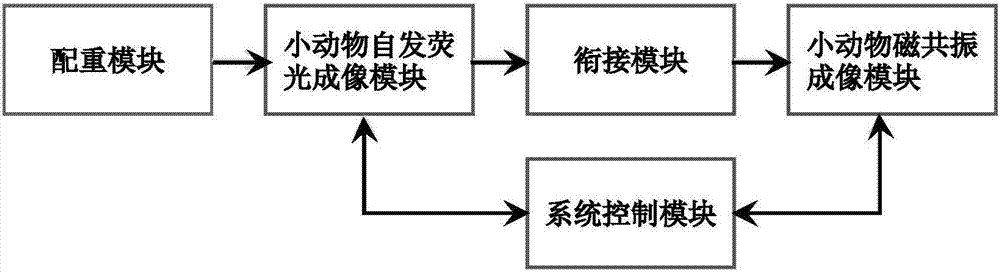
Spontaneous fluorescence and magnetic resonance bimodal molecular fusion small animal imaging system and method
InactiveCN107080538ASolve the problem of inhomogeneityIncrease the amount of data availableImage enhancementImage analysisLymphatic SpreadFluorescence
The invention relates to a spontaneous fluorescence and magnetic resonance bimodal molecular fusion small animal imaging system and a spontaneous fluorescence and magnetic resonance bimodal molecular fusion small animal imaging method. The spontaneous fluorescence and magnetic resonance bimodal molecular fusion small animal imaging system comprises a magnetic resonance small animal imaging module, a spontaneous fluorescence small animal imaging module, a jointing module and a system control module, wherein the magnetic resonance small animal imaging module comprises a magnetic resonance examination bed; the spontaneous fluorescence small animal imaging module is placed at the tail end of the magnetic resonance examination bed; the spontaneous fluorescence small animal imaging module detects optical signals through a CCD; the jointing module achieves one-stop information acquisition of a small animal between the spontaneous fluorescence imaging module and the magnetic resonance imaging module; the system control module is used for controlling the spontaneous fluorescence small animal imaging module, the magnetic resonance small animal imaging module and the jointing module and processing the acquired magnetic resonance and fluorescence data. Through the system and the method,spontaneous fluorescence and high-field magnetic resonance bimodal imaging is adopted to provide effective molecular imaging methods for detecting abnormality in cellular and molecular levels during lesion, exploring occurrence, development and metastasis of a tumor, monitoring a therapeutic process, evaluating the therapeutic effect of a medicine and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
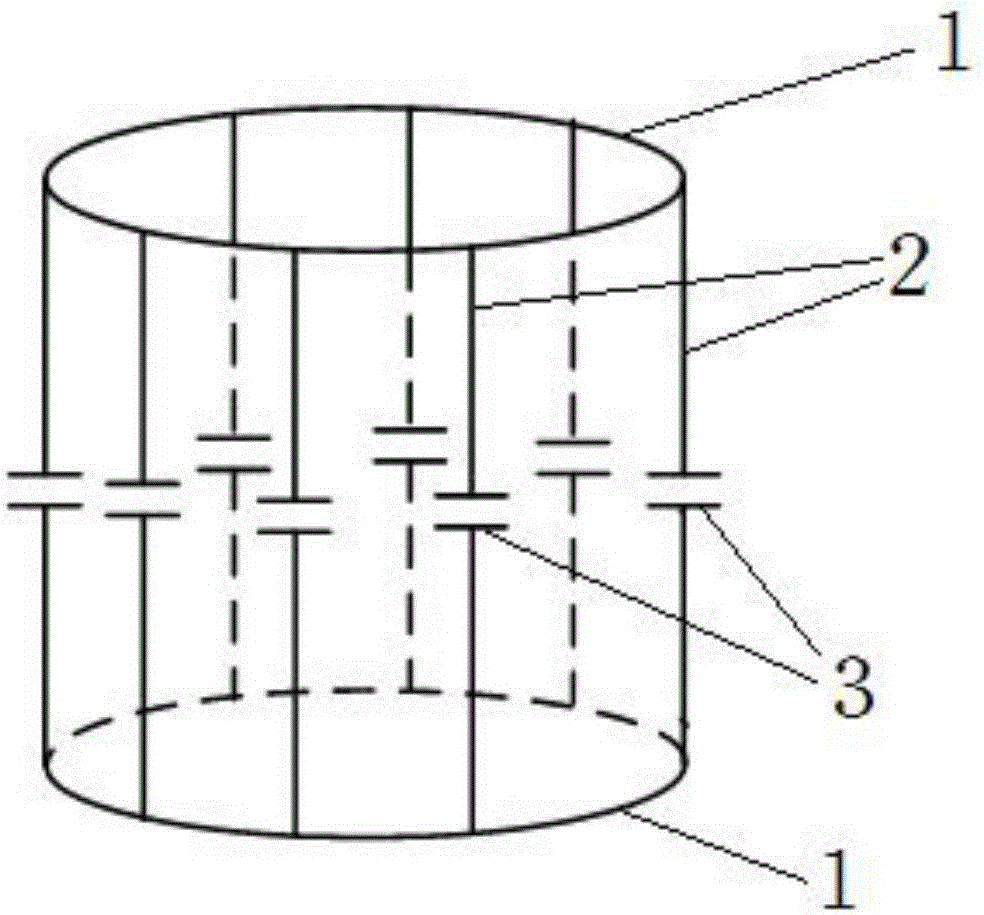
High-field MRI birdcage coil
InactiveCN105891750AHigh-resolutionImprove performance parametersMeasurements using magnetic resonanceHigh field mriMetallic materials
The invention discloses a high-field MRI birdcage coil. The high-field MRI birdcage coil comprises two metal rings with the same structures, wherein the metal rings are respectively located at the upper end and the lower end; the two metal rings are connected with each other via a plurality of cylindrical channels made of a metal material in a vertical direction; the cylindrical channels are used for equally dividing the metal ring at the upper end and the metal ring at the lower end into a plurality of parts; each cylindrical channel is divided into an upper part and a lower part from the middle; the upper and lower parts of each cylindrical channel are electrically connected with each other via a capacitor device. The high-field MRI birdcage coil also comprises an outer metal cover; the outer metal cover is covered on the outer side of the metal rings and the cylindrical channels, has a shielding effect and is formed by a radio frequency coil wound to be cylindrical. The high-field MRI birdcage coil is good in parameter performance; an eight-channel birdcage coil is provided for a high-field (7T) magnetic resonance imaging system; the resolution ratio of generated images is improved; the requirements on imaging of a magnetic resonance technique at present can be met.
Owner:HEILONGJIANG UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
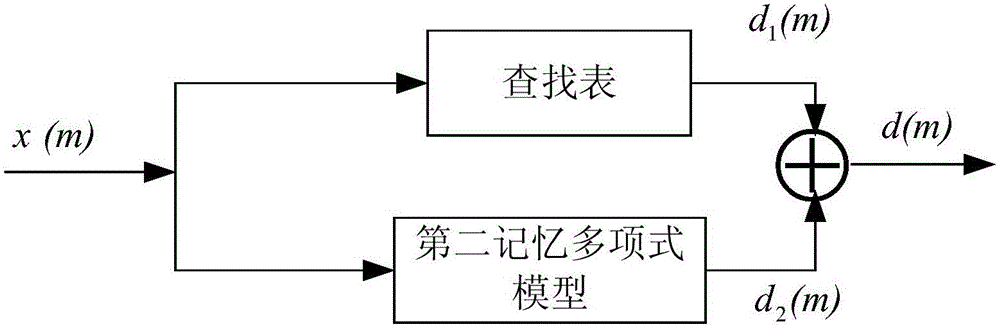
Nonlinear modeling method for high-field MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) high-power RF (Radio Frequency) power amplifier
ActiveCN105956291AAccurate trackingSpecial data processing applicationsNonlinear modelHigh field mri
The invention discloses a nonlinear modeling method for a high-field MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) high-power RF (Radio Frequency) power amplifier. The nonlinear modeling method comprises the steps of: segmenting an acquired original baseband data sequence and distorted baseband data sequence, training a first nonlinear model by using a first segment of original baseband data sequence as input data and using a first segment of distorted baseband data sequence as output data, obtaining model parameters of the first nonlinear model, training a second nonlinear model by using a second segment of original baseband data sequence as input data and using a second segment of distorted baseband data sequence as output data, obtaining model parameters of the second nonlinear model, and giving the model parameters of the first nonlinear model to the first nonlinear model to obtain a first sub-model; giving the model parameters of the second nonlinear model to the second nonlinear model to obtain a second sub-model; and verifying accuracy of the first sub-model and the second sub-model. The nonlinear modeling method has the advantages that a nonlinear model of the high-field MRI high-power RF (Radio Frequency) power amplifier can be accurately established, and nonlinear characteristics of the high-field MRI high-power RF (Radio Frequency) power amplifier are accurately tracked.
Owner:NANYANG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com