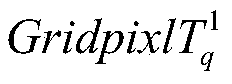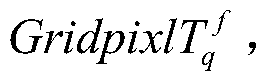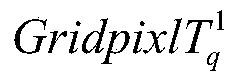Patents
Literature
67 results about "Nonlinear algorithms" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A novel approach to motion cueing, the “nonlinear algorithm” is introduced that combines features from both approaches. This algorithm is formulated by optimal control, and incorporates a new integrated perception model that includes both visual and vestibular sensation and the interaction between the stimuli.
High field magnetic resonance
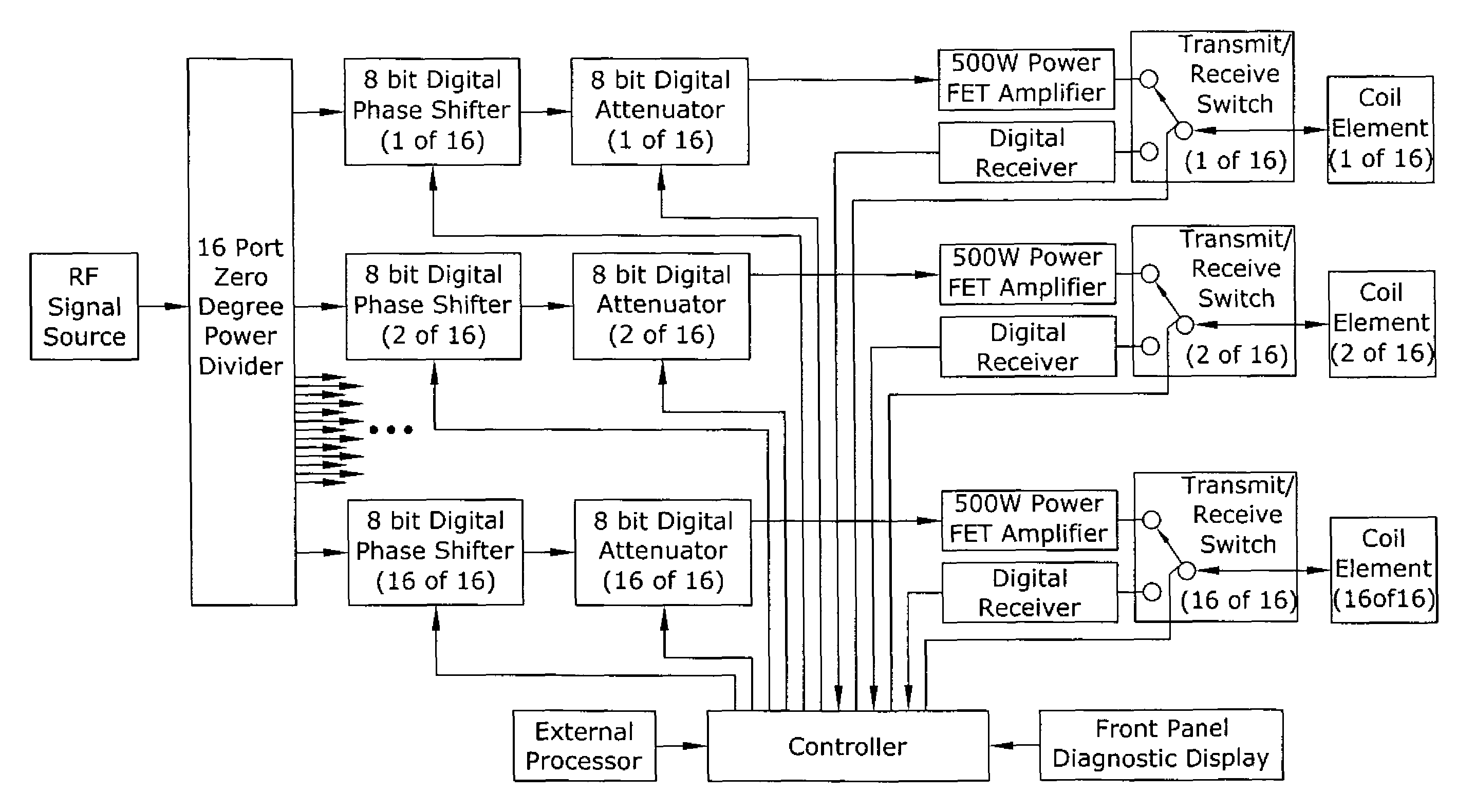
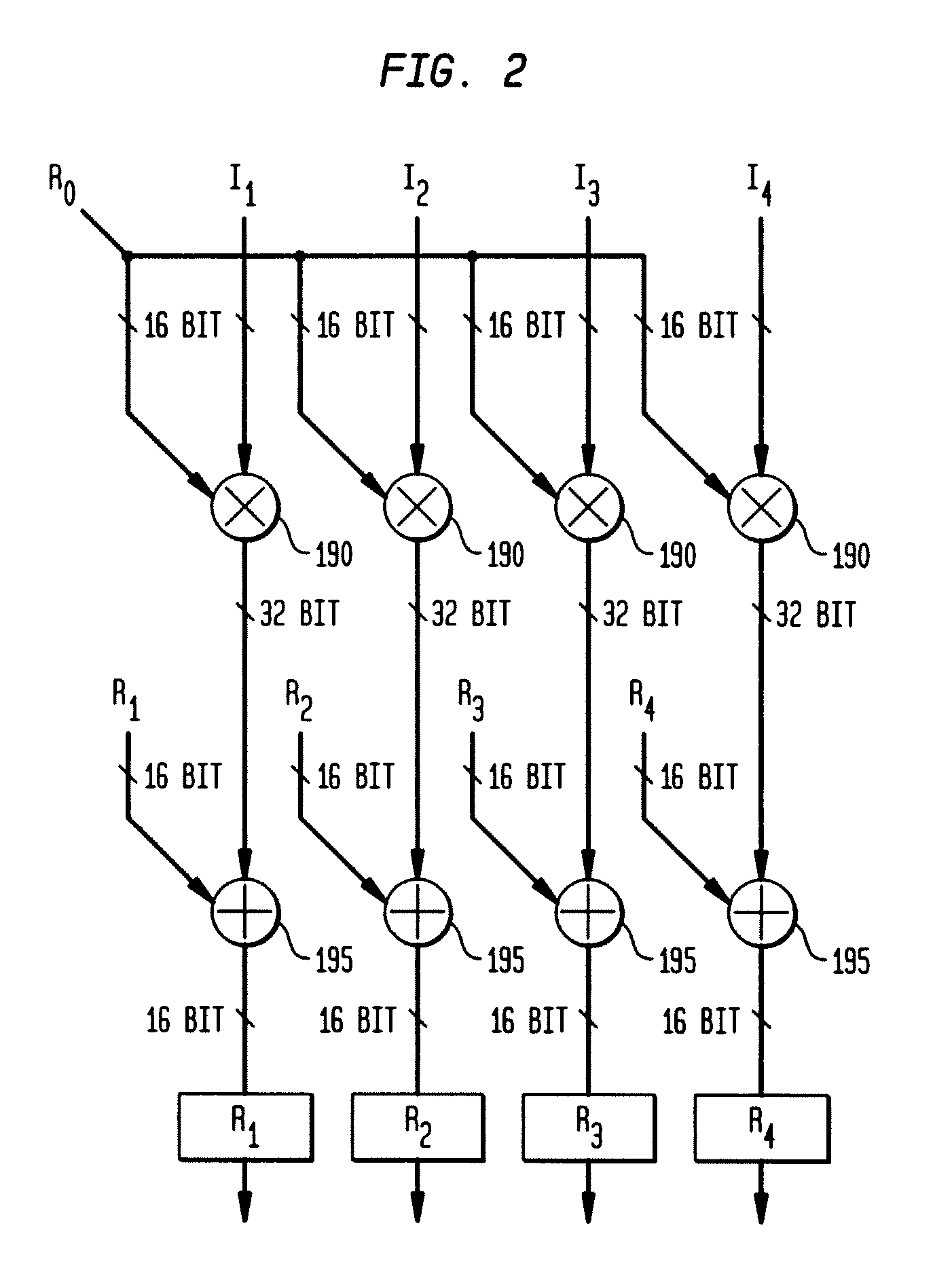
ActiveUS7800368B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionNonlinear algorithmsCurrent element
A magnetic resonance system is disclosed. The system includes a transceiver having a multichannel receiver and a multichannel transmitter, where each channel of the transmitter is configured for independent selection of frequency, phase, time, space, and magnitude, and each channel of the receiver is configured for independent selection of space, time, frequency, phase and gain. The system also includes a magnetic resonance coil having a plurality of current elements, with each element coupled in one to one relation with a channel of the receiver and a channel of the transmitter. The system further includes a processor coupled to the transceiver, such that the processor is configured to execute instructions to control a current in each element and to perform a non-linear algorithm to shim the coil.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
Non-invasive method and apparatus for determining a physiological parameter
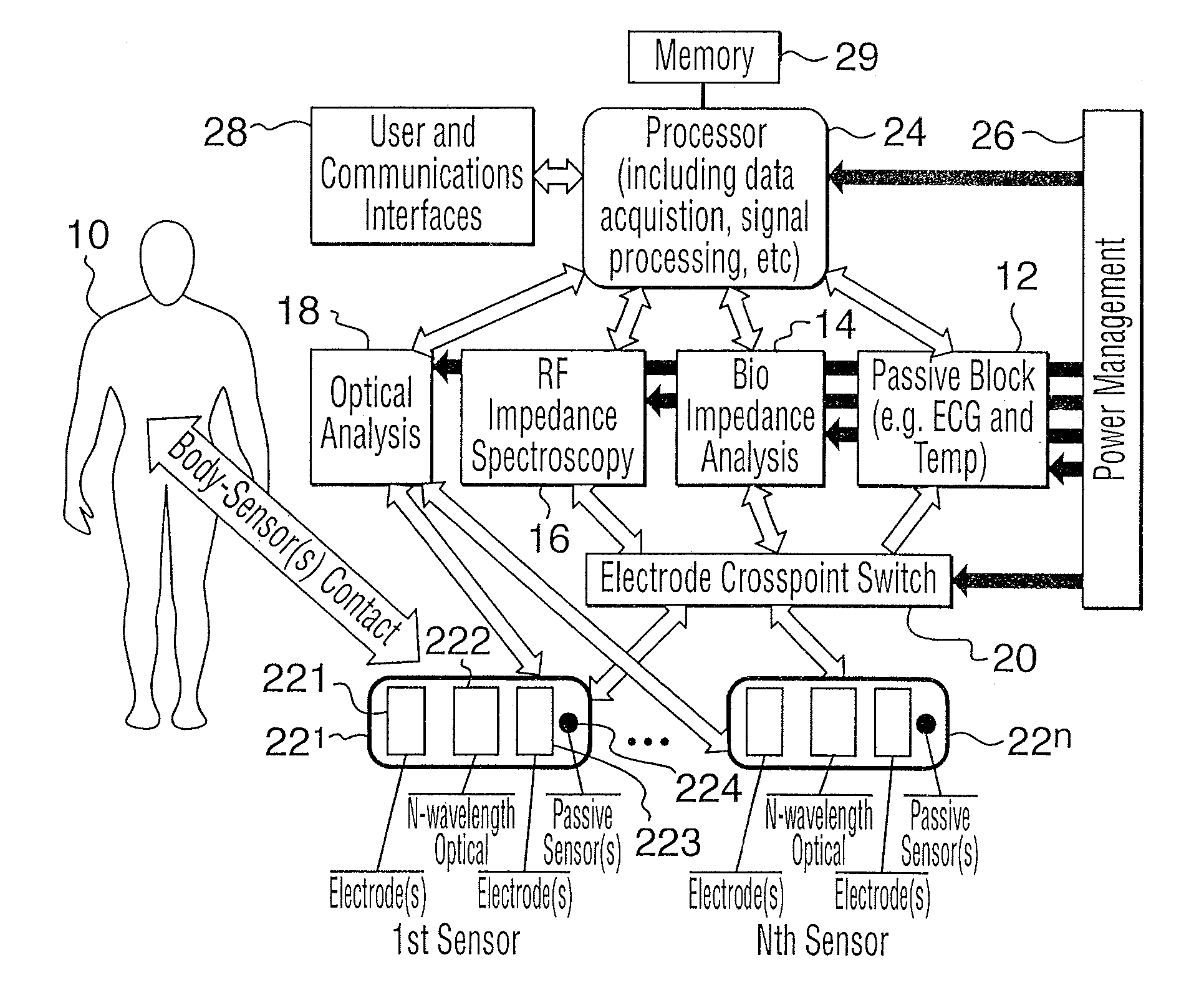
InactiveUS20100004517A1Accurate measurementThe result is accurateElectrotherapyElectrocardiographyMeasurement deviceNon invasive
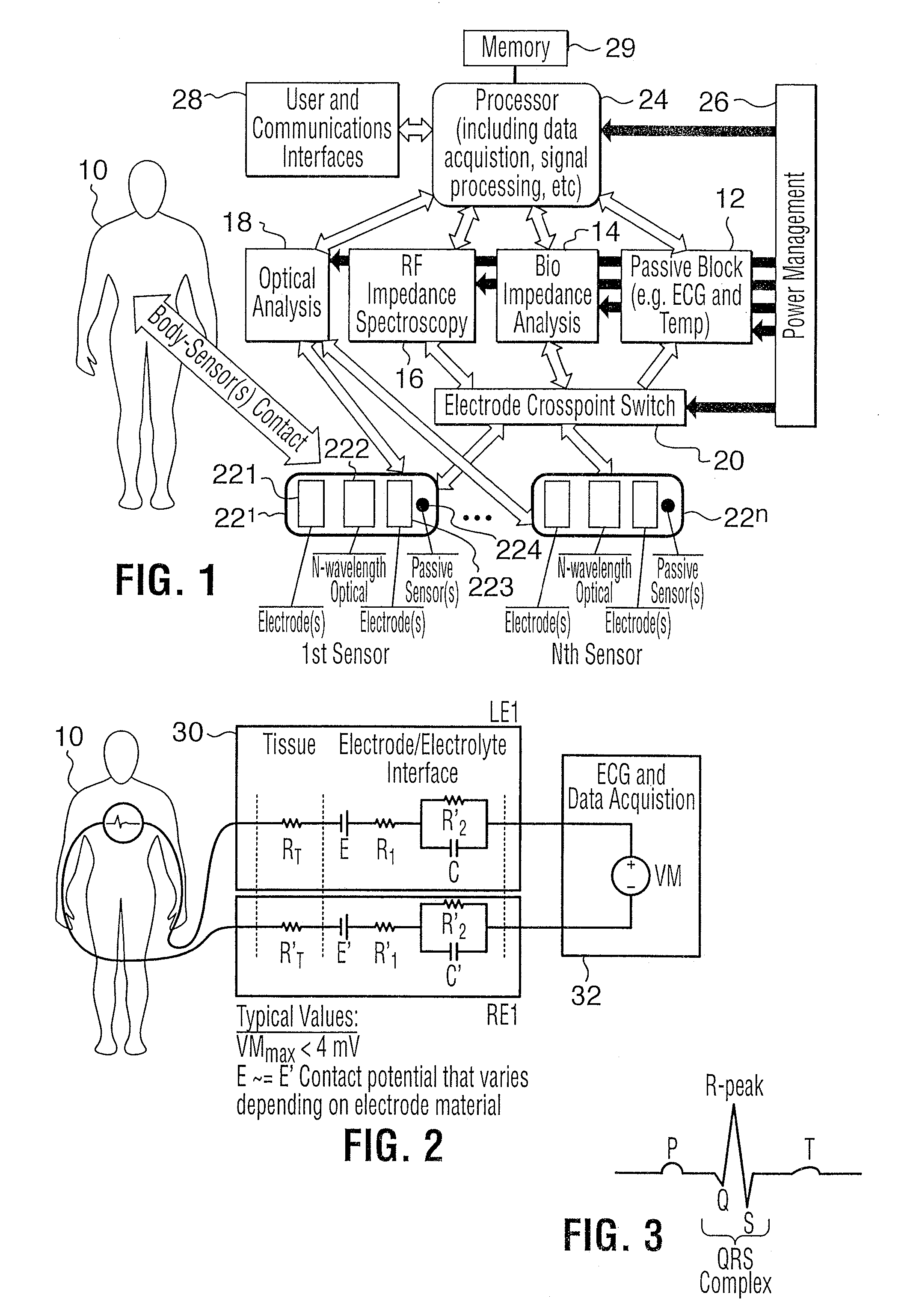
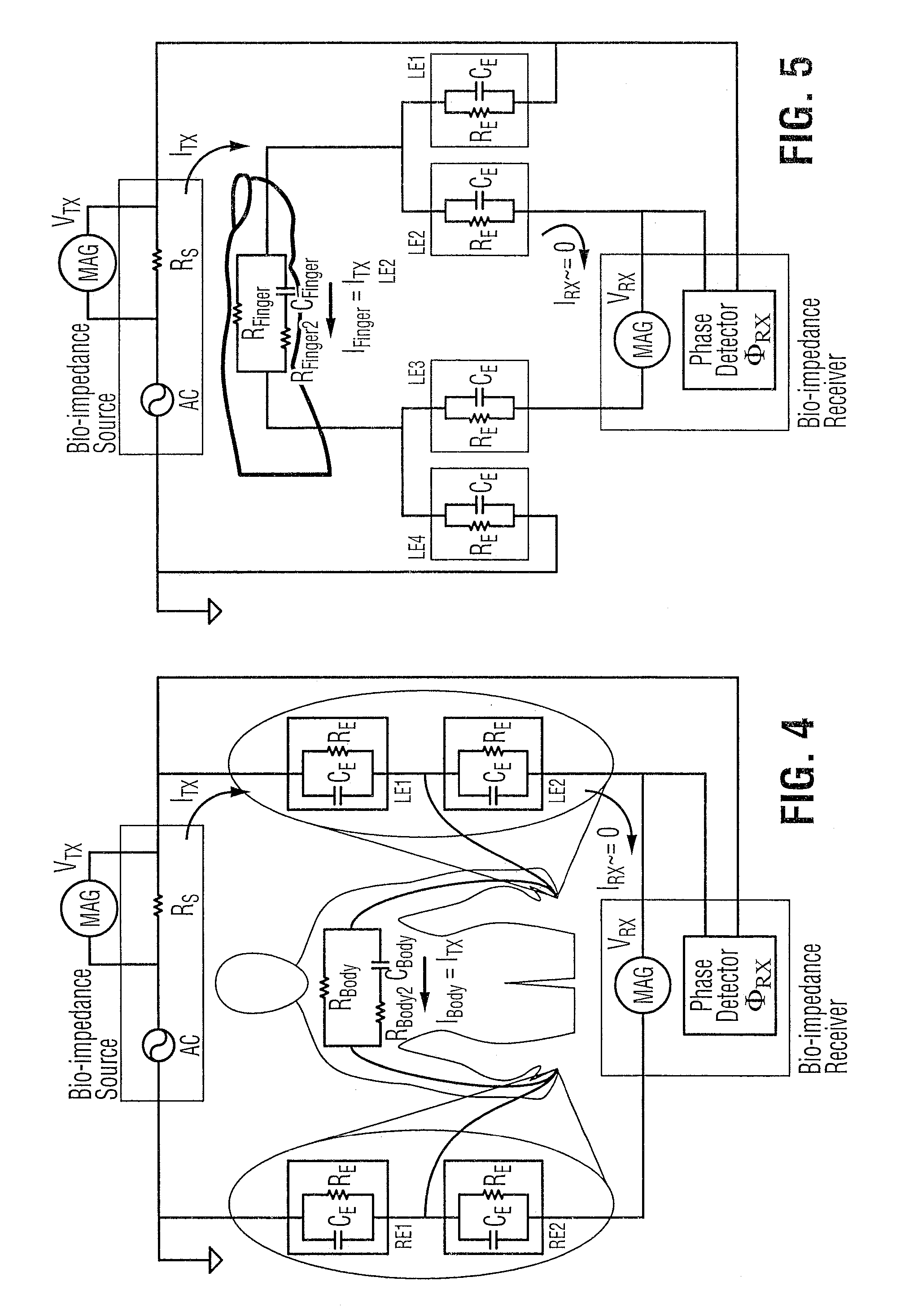
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for the non-invasive analysis of physiological attributes, such as heart rate, blood pressure, cardiac output, respiratory response, body composition, and blood chemistry analytes including glucose, lactate, hemoglobin, and oxygen saturation. Using a combination of multi-functioning disparate sensors, such as optical and electrical, improvements are made over existing physiological measurement devices and techniques. The special configuration of one or more multi-functional sensors is used to non-invasively measure multi-wavelength optical plus one or more of ECG, Bio-impedance, and RF-impedance spectroscopic data. This information is used to develop self-consistent, non-linear algorithm in order to derive the physiological attributes while compensating for various forms of interfering effects including motion artifacts, sensor attachment variability, device component variability, subject physical and physiology variability, and various interfering physiological attributes.
Owner:BIOPEAK CORP
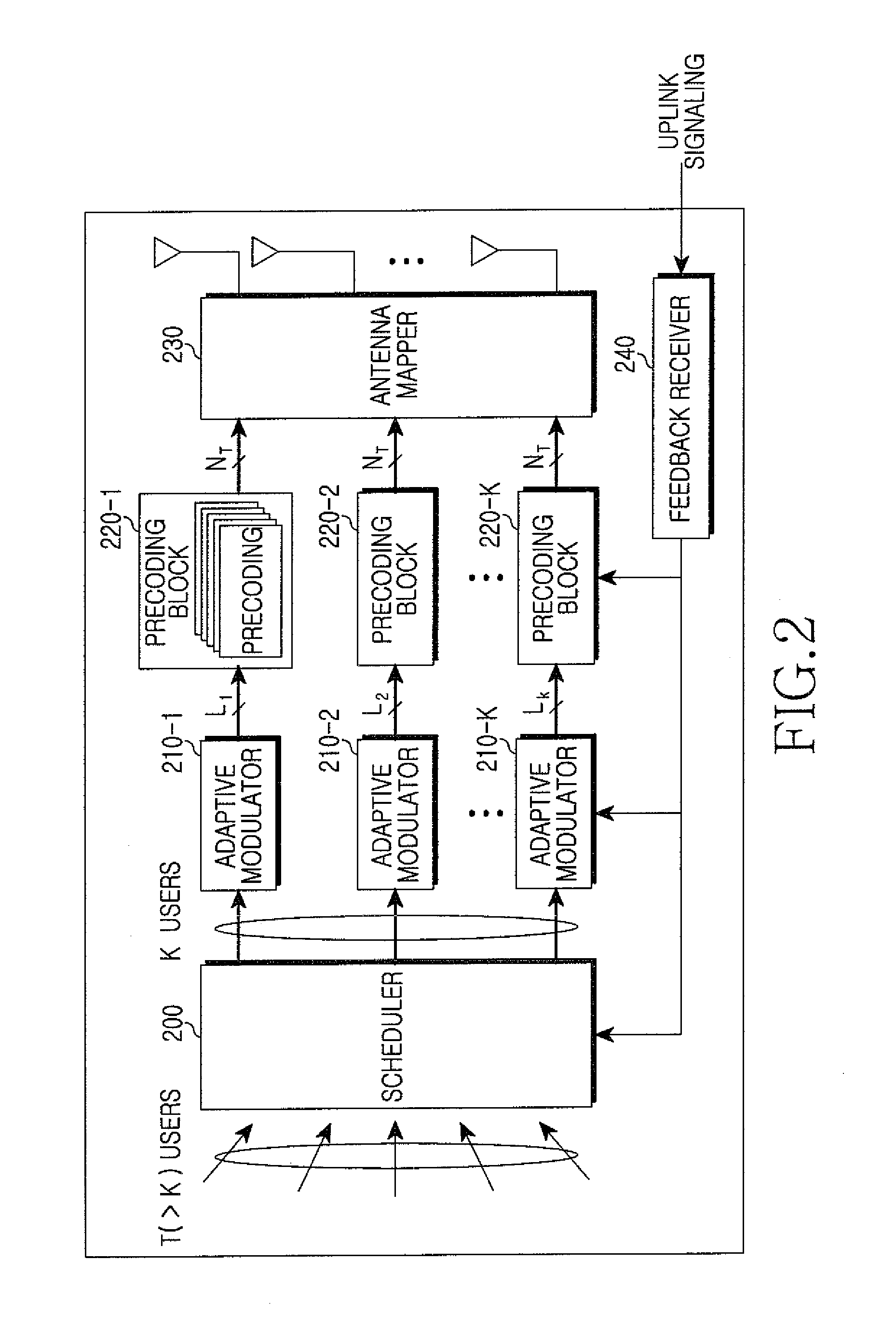
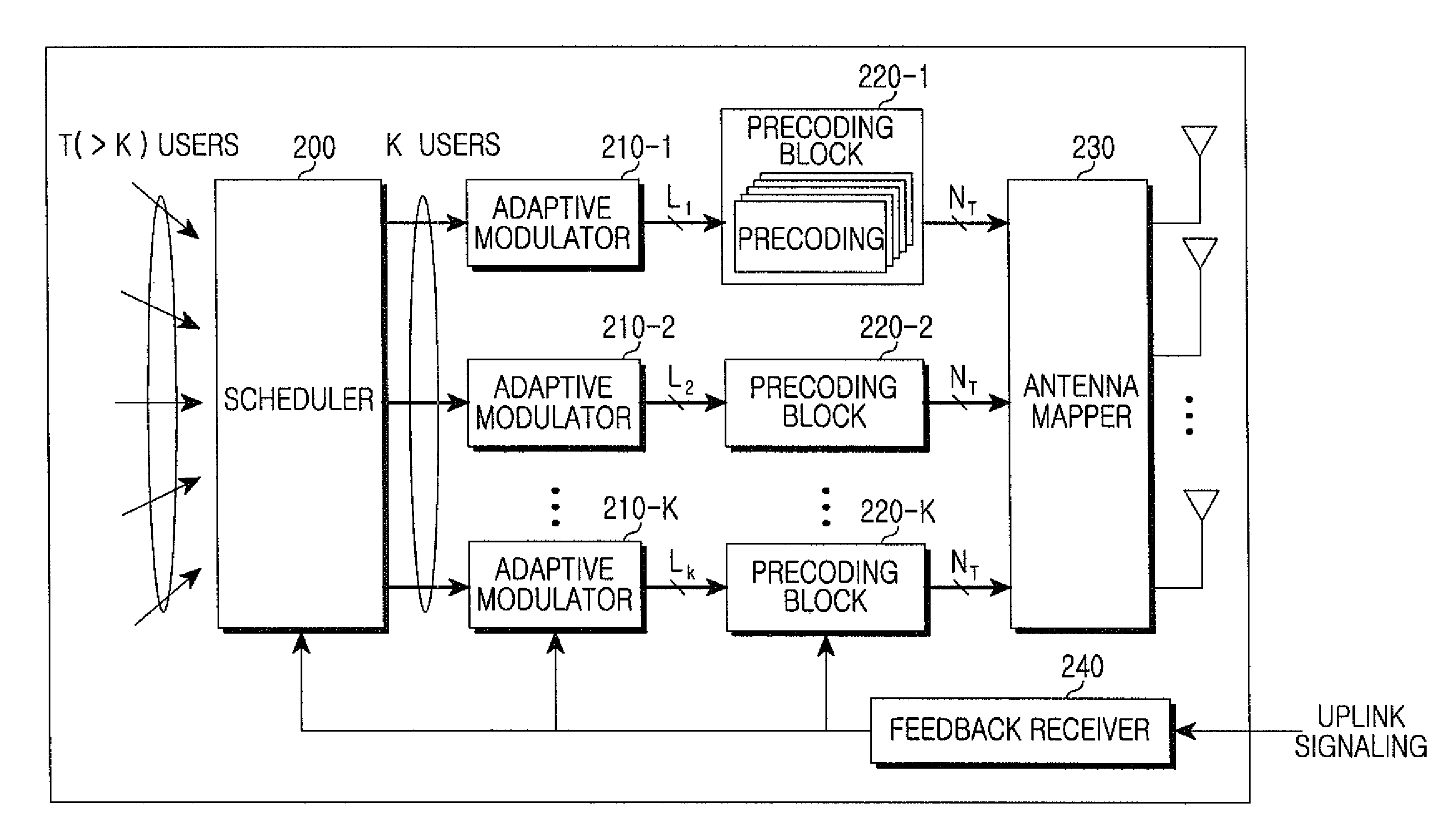
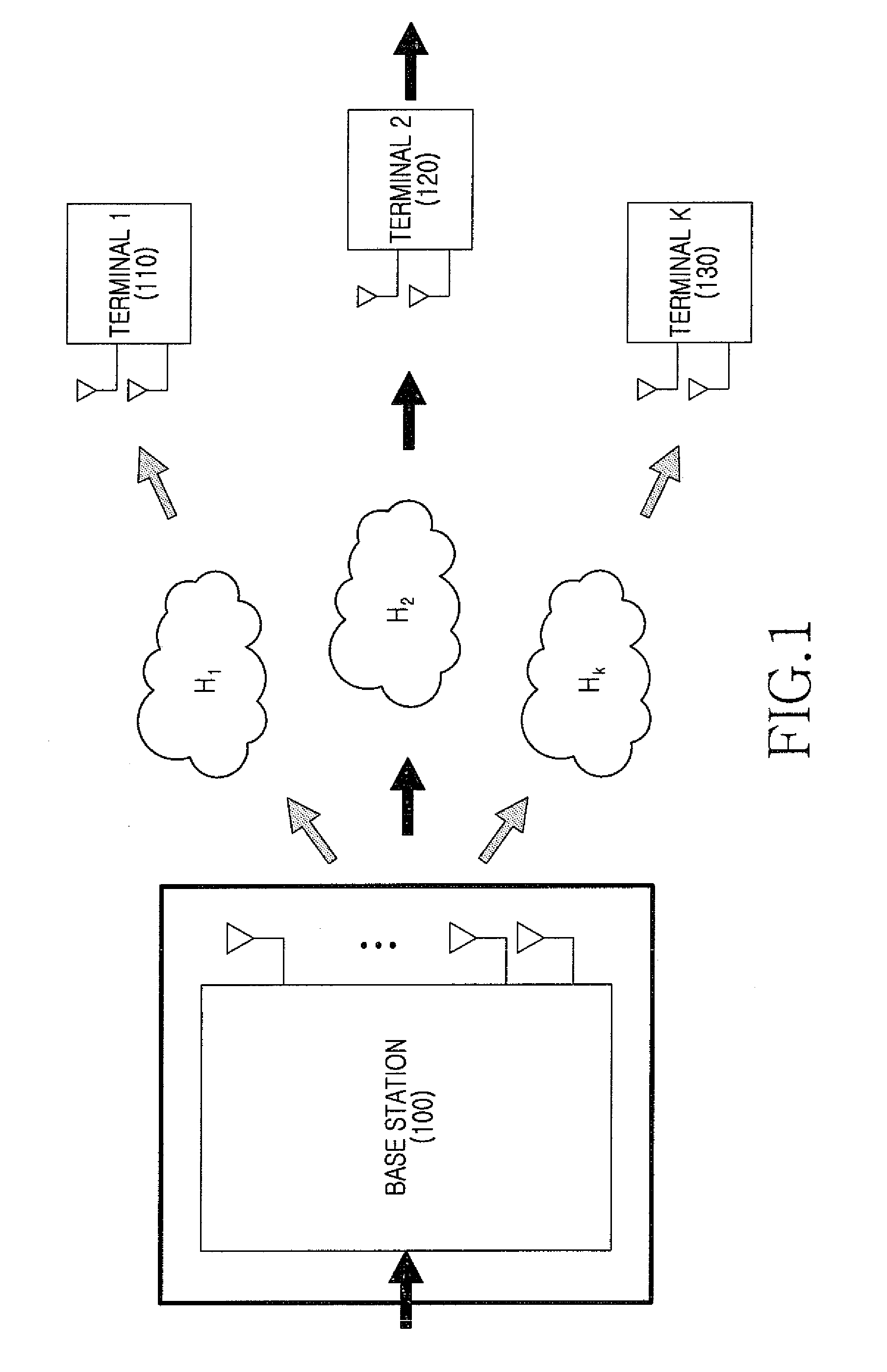
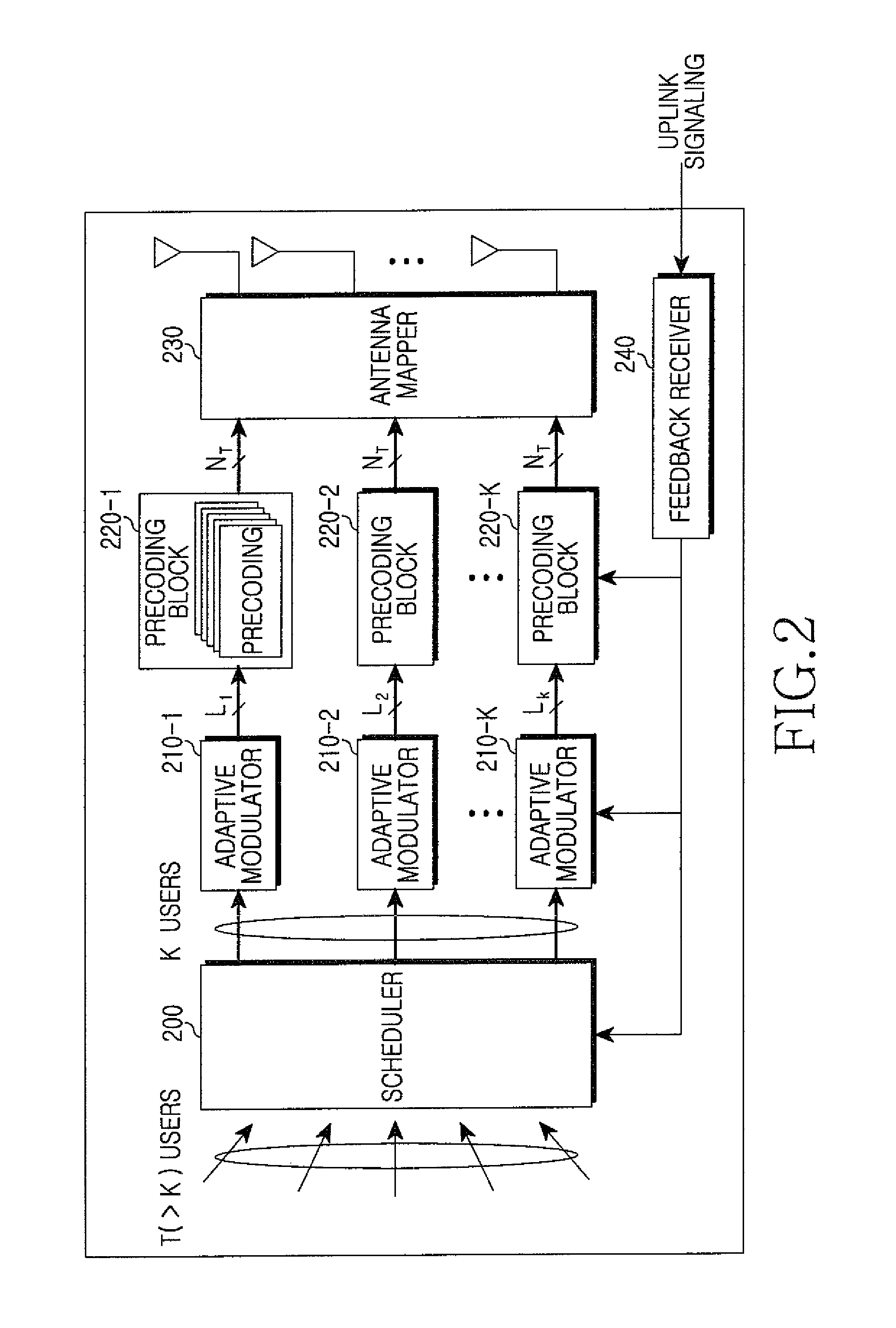
Precoder and precoding method in a multi-antenna system
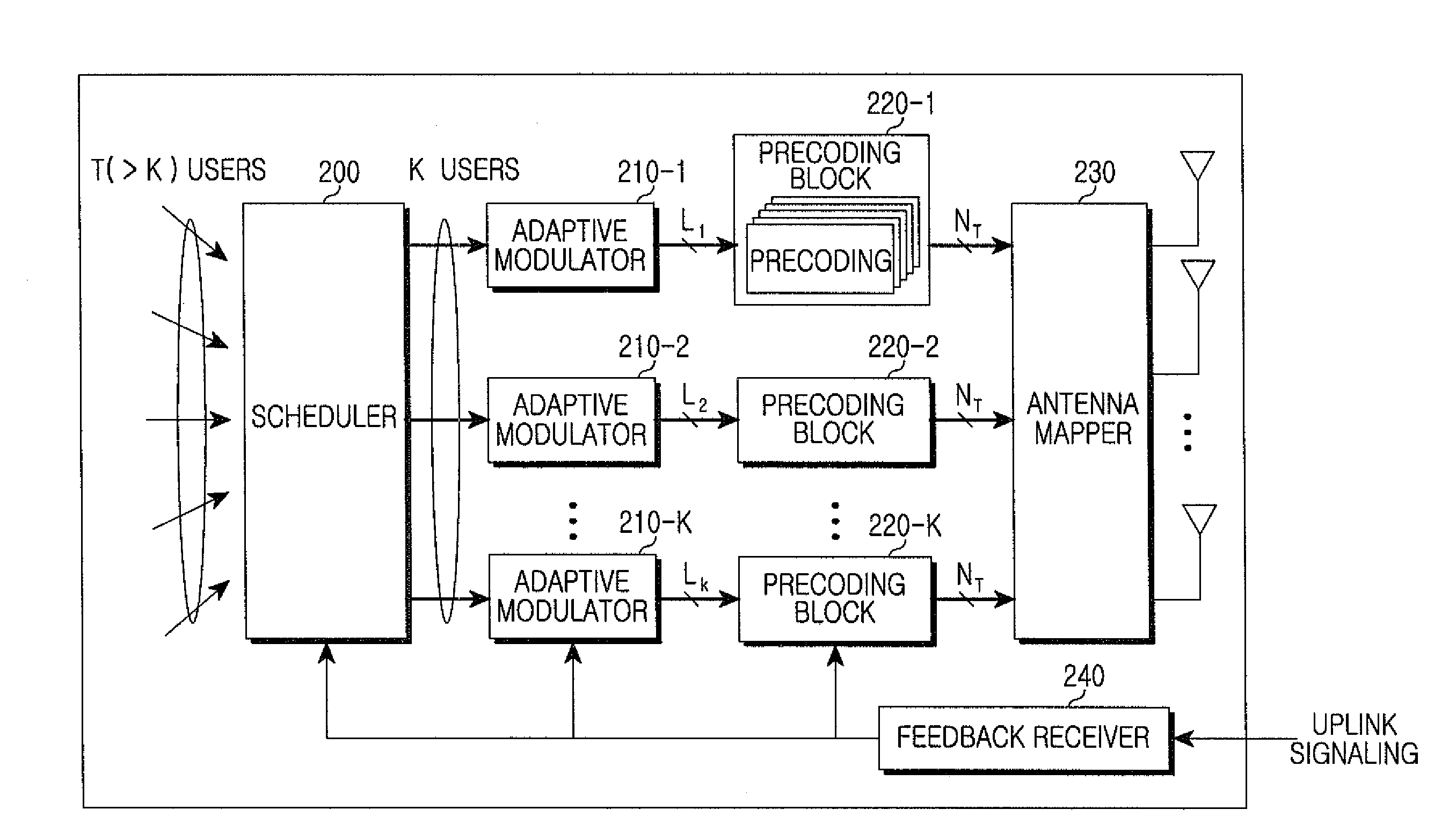
ActiveUS20080181285A1Reduce complexityImprove performanceDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingChannel state information
A precoder and a precoding method in a multiuser multi-antenna system are provided. The precoder includes a channel checker for determining a DownLink (DL) channel condition of terminals in a service coverage area, a pre-compensator for pre-compensating, for channel distortion, signals to be sent to the terminals when a nonlinear algorithm is selected based on the channel condition of the terminals, and an interference remover for canceling interference in a channel by multiplying the pre-compensated signals by inverse channels of the terminals, and for canceling interference between the terminals. Accordingly, the pre-equalization can be carried out without global channel state information, and an increase of the transmit power can be prevented in the permutation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
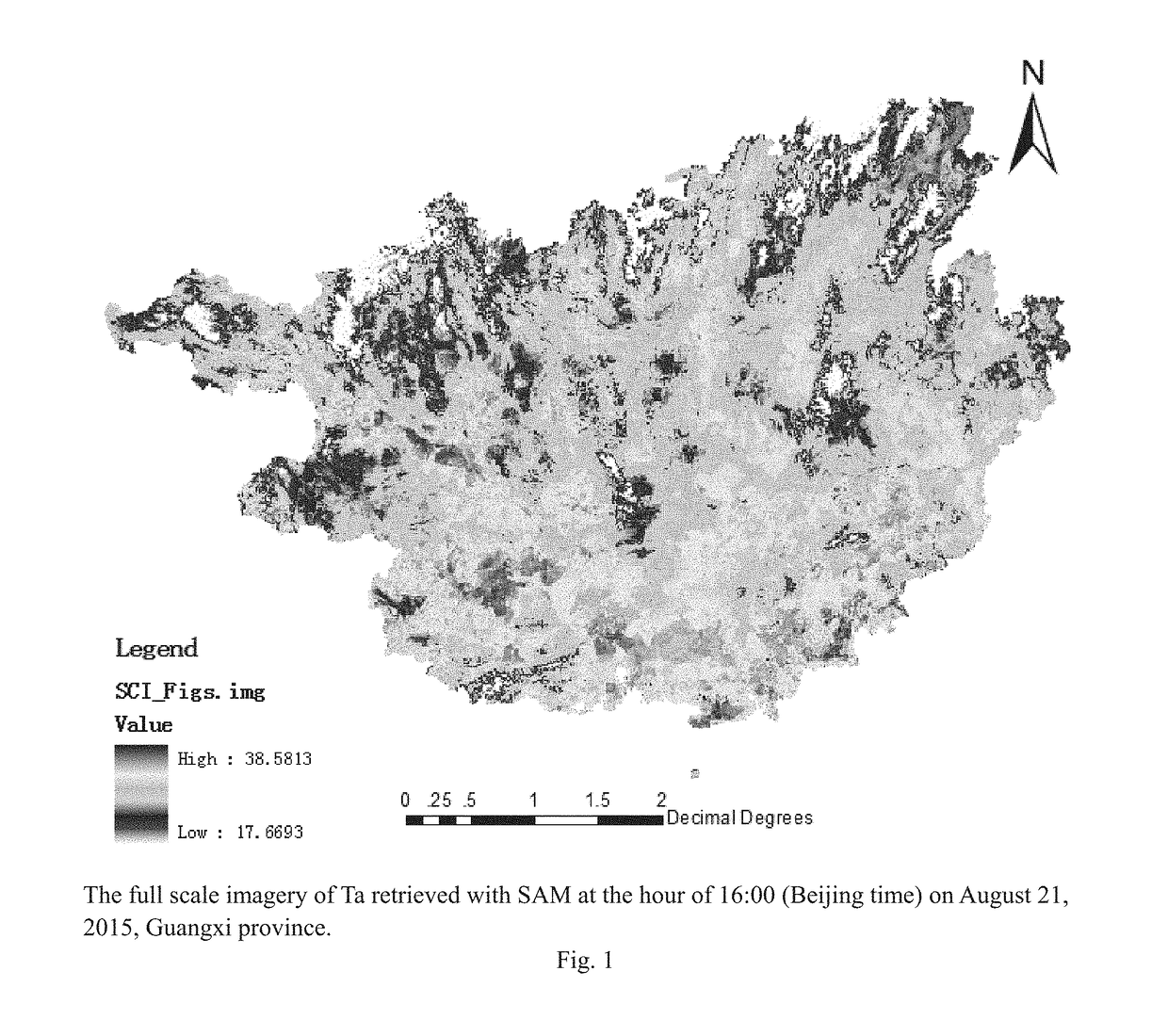
Novel nonlinear method for area-wide near surface air temperature precision retrieval
ActiveUS20190057171A1Improve retrieving accuracy and robustnessThermometer detailsKernel methodsNonlinear methodsNonlinear algorithms
A novel nonlinear method for area-wide near surface air temperature precision retrieval is described. The steps include: First, construct the 1st sub-model modelVEC1 to the f-th sub-model modelVECf. Establish and normalize raw data vectors of each gridded pixel sBlkVEC in the targeted area. Calculate the retrieved full maps (surfTf) of near surface air temperatures using each sub-model. Then, identify abnormal samples and define their near-range regions in surfTf Apply a selective arithmetic mean (SAM) approach to achieve precision temperature map surfT. And finally apply further modification to the pixels of surfT where pixlf∈badsurfTδf is true to all f=1, 2, 3, . . . .Using the super nonlinear algorithm, this invention provides a solution of retrieving near surface air temperature based on combinations of various factors (information fusion) to achieve satisfied prediction errors, which are independent of cloud levels and topographic characteristics. Specifically, the information fusion between space and ground surface enables reliable prediction of near surface air temperature maps overcoming the inference of cloud.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF METEOROLOGICAL DISASTER REDUCING RES +1
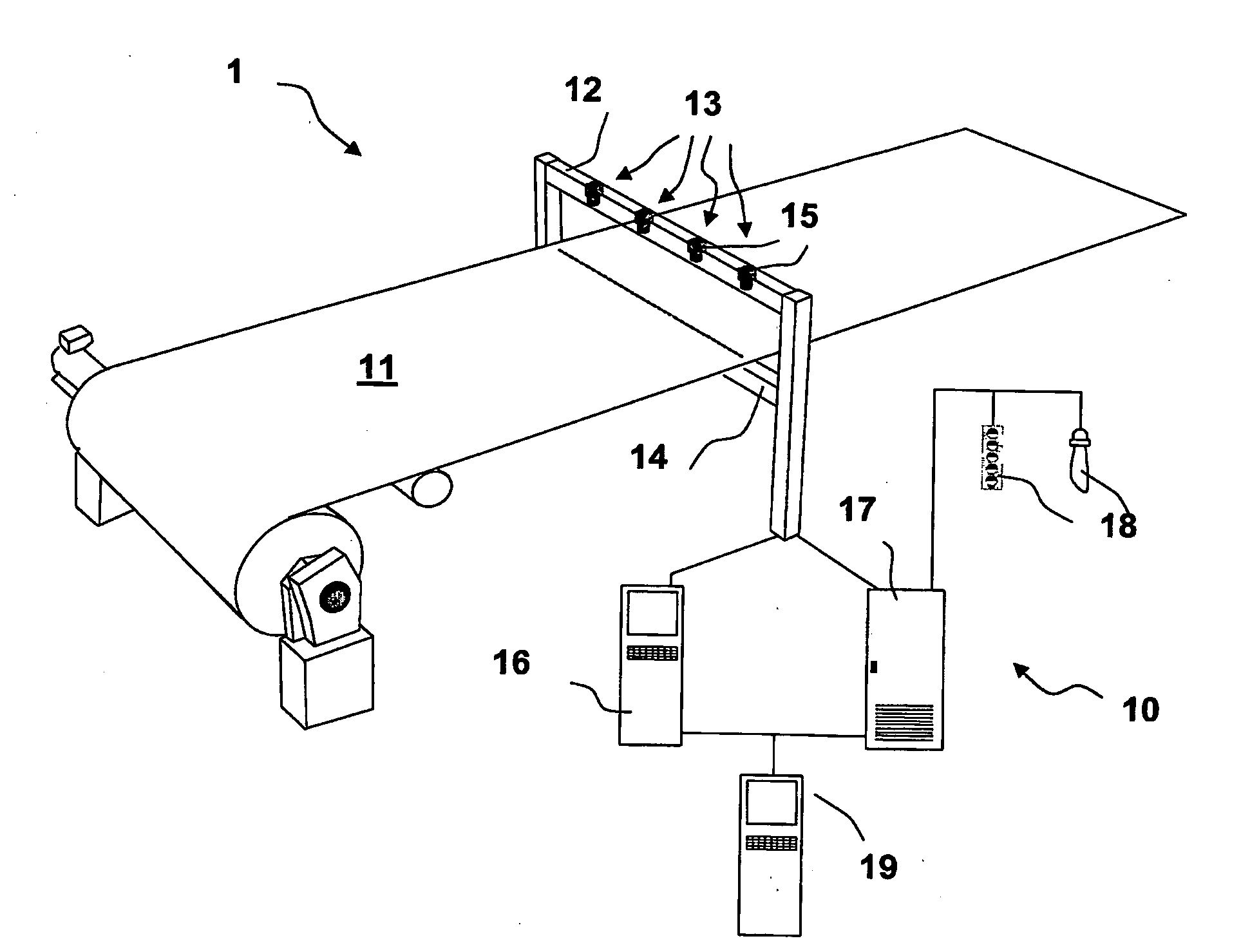
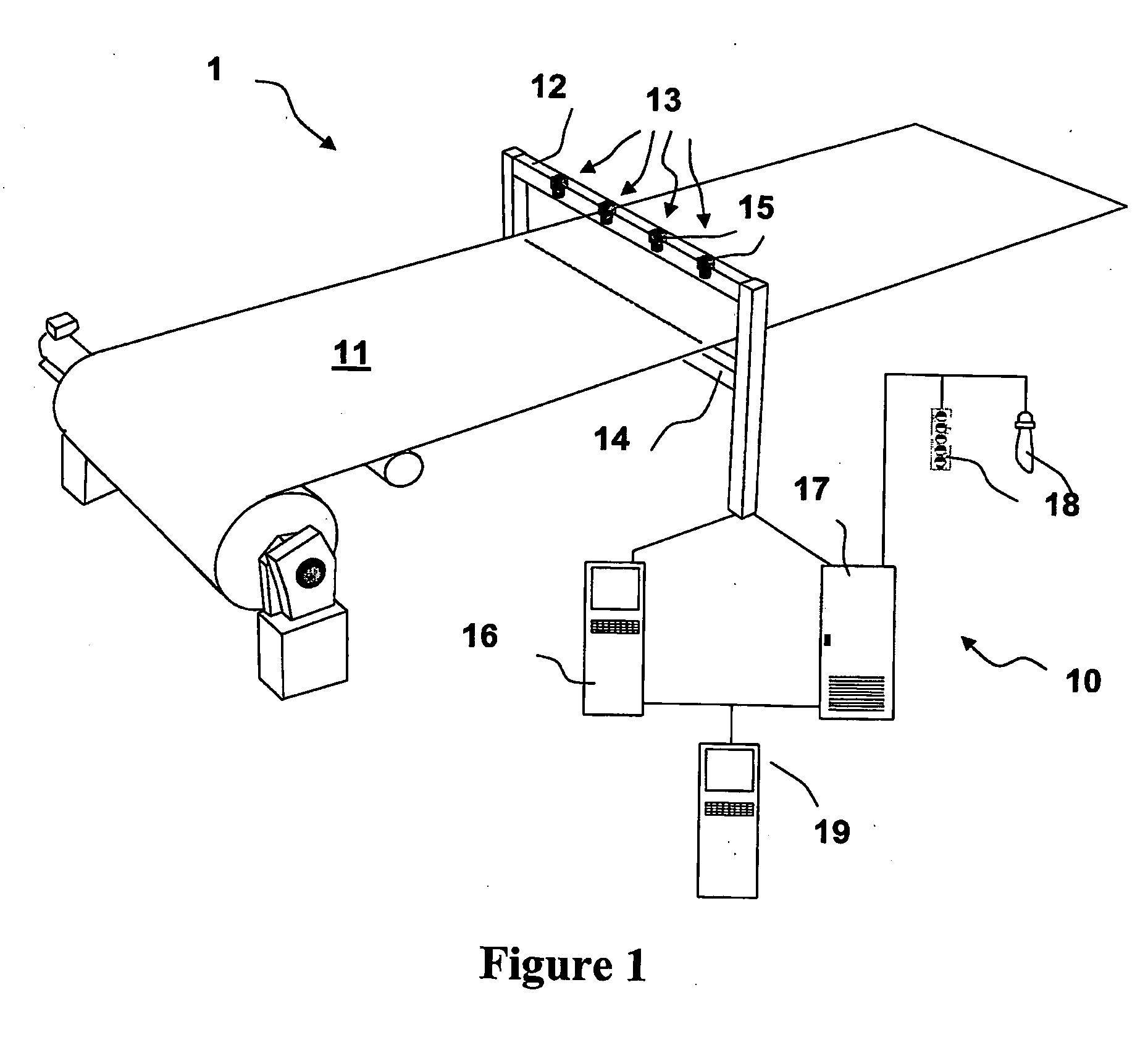
Method and Product for Detecting Abnormalities
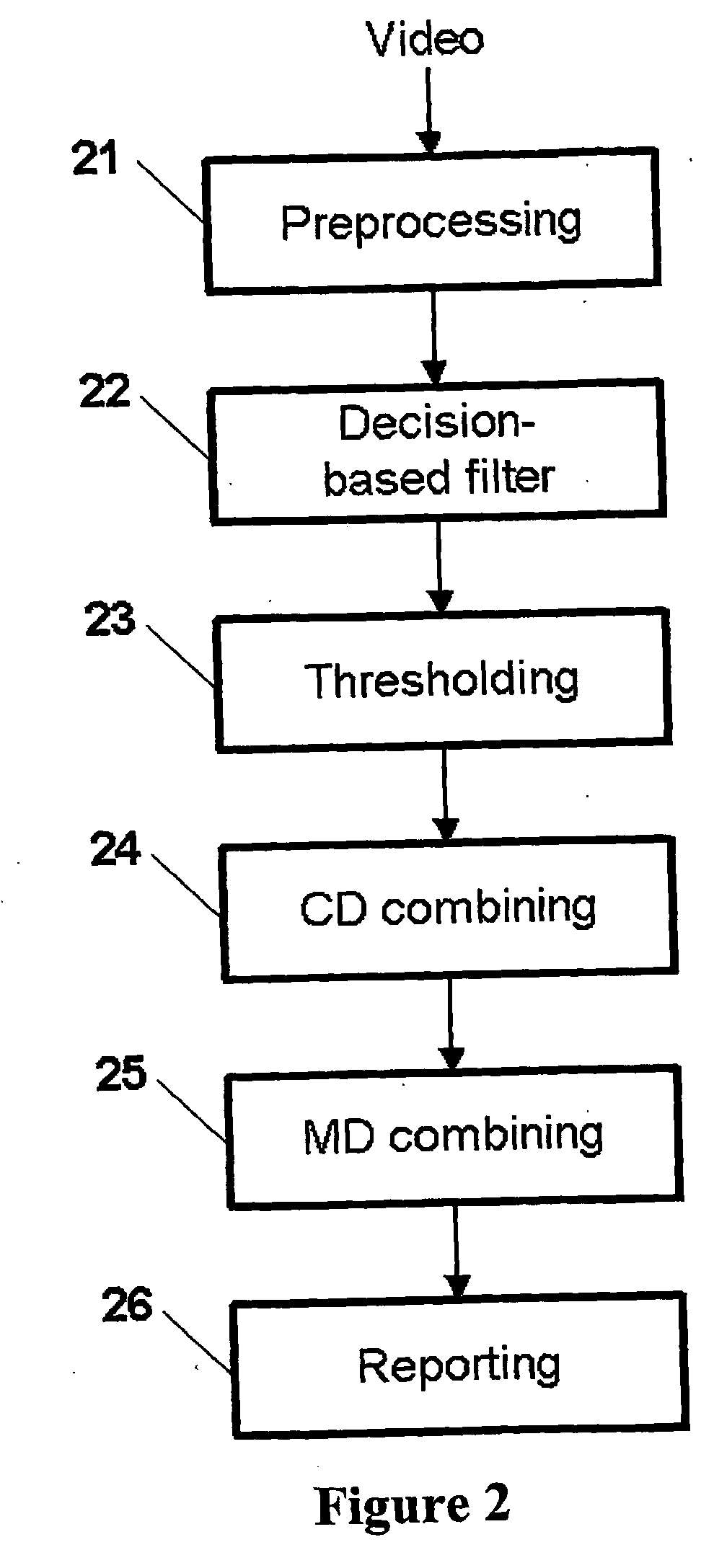
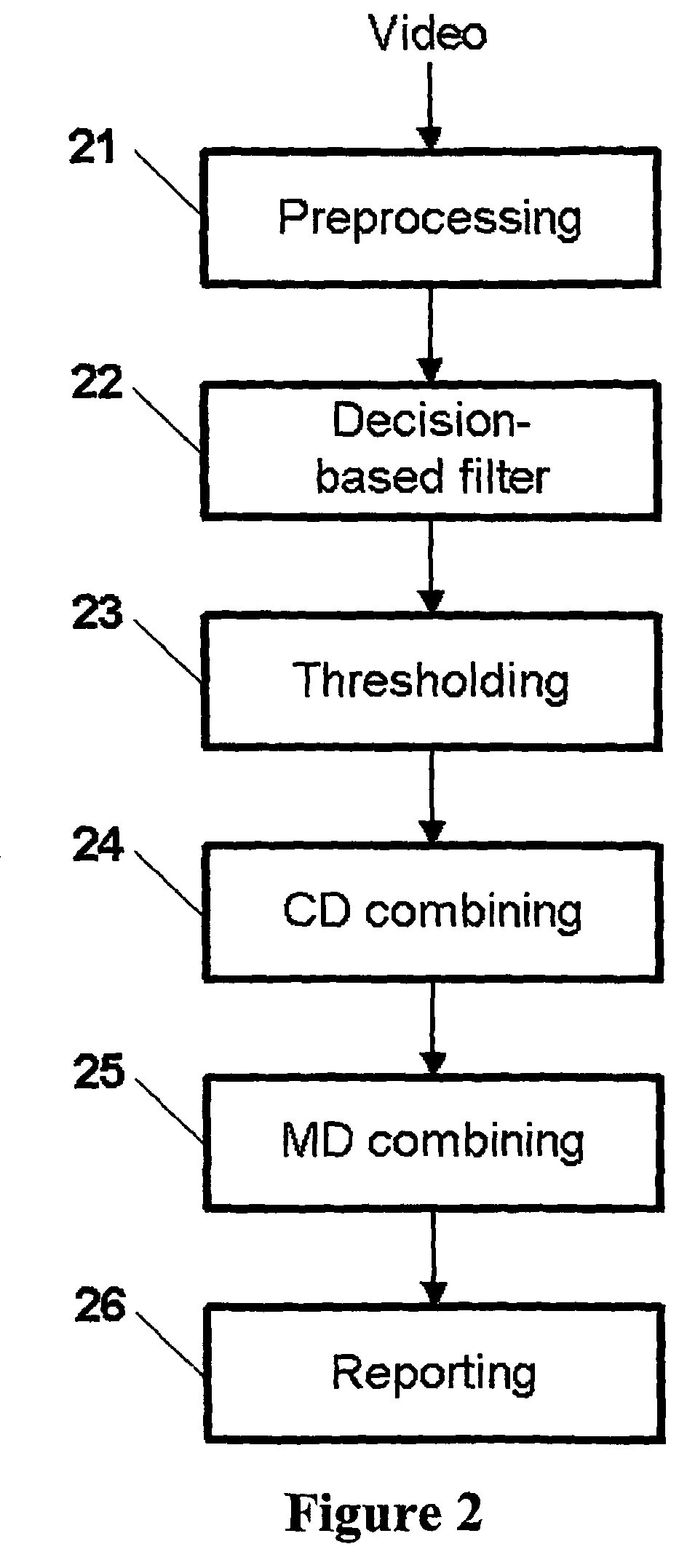
A new method for processing image data in order to detect abnormalities in a web is provided. The web is monitored by at least one camera, whereby an image comprising of plurality of pixels is generated. The data of the image is stored in a memory. Image data is filtered by a processor by creating a filtered image data by weighting the image data and at least one of earlier image data and earlier filtered image data; and combining the weighted image data and at least one of the weighted earlier image data and the weighted earlier filtered image data; and controlling filtering by at least one nonlinear algorithm; and thresholding the created filtered image data.
Owner:ABB OY
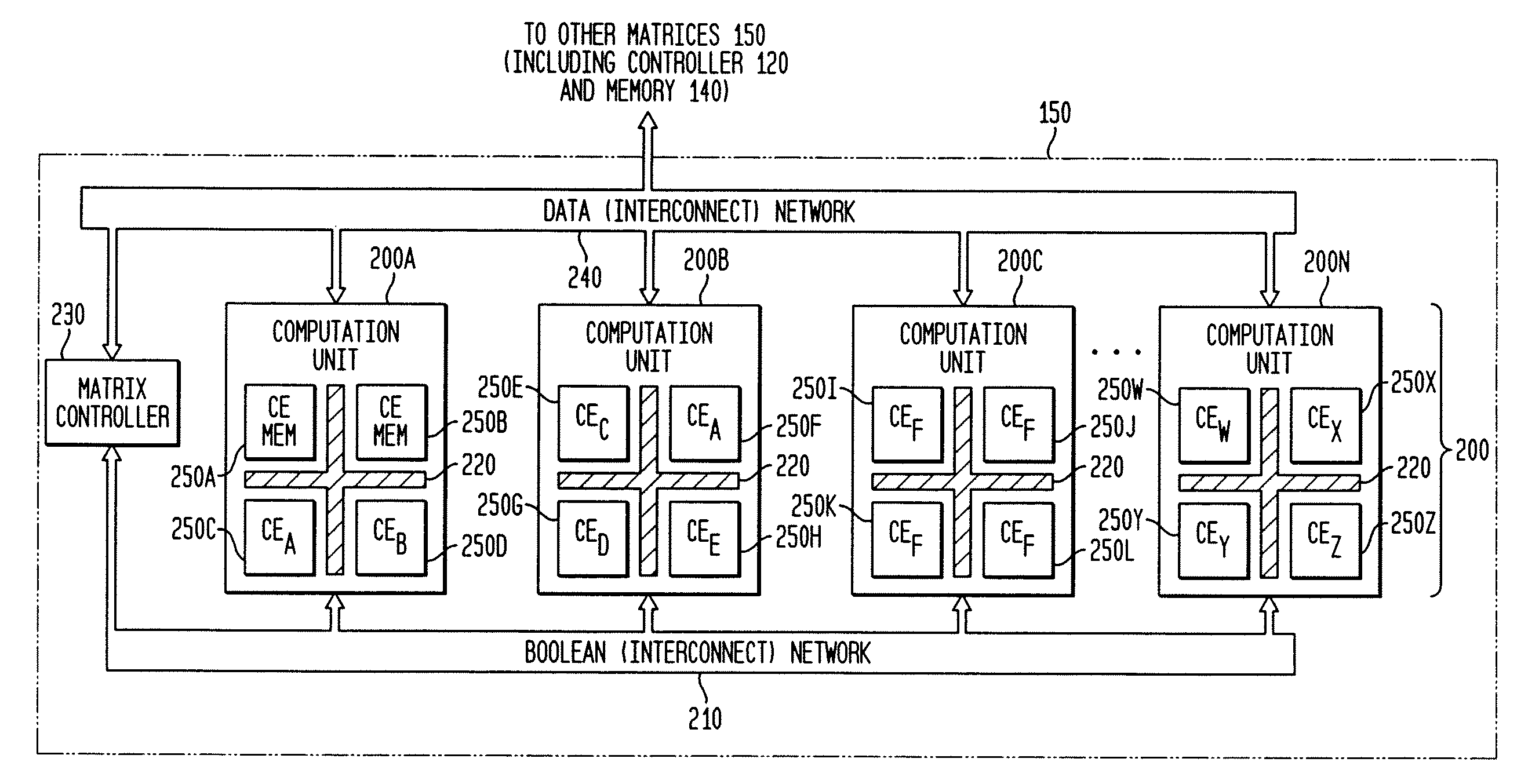
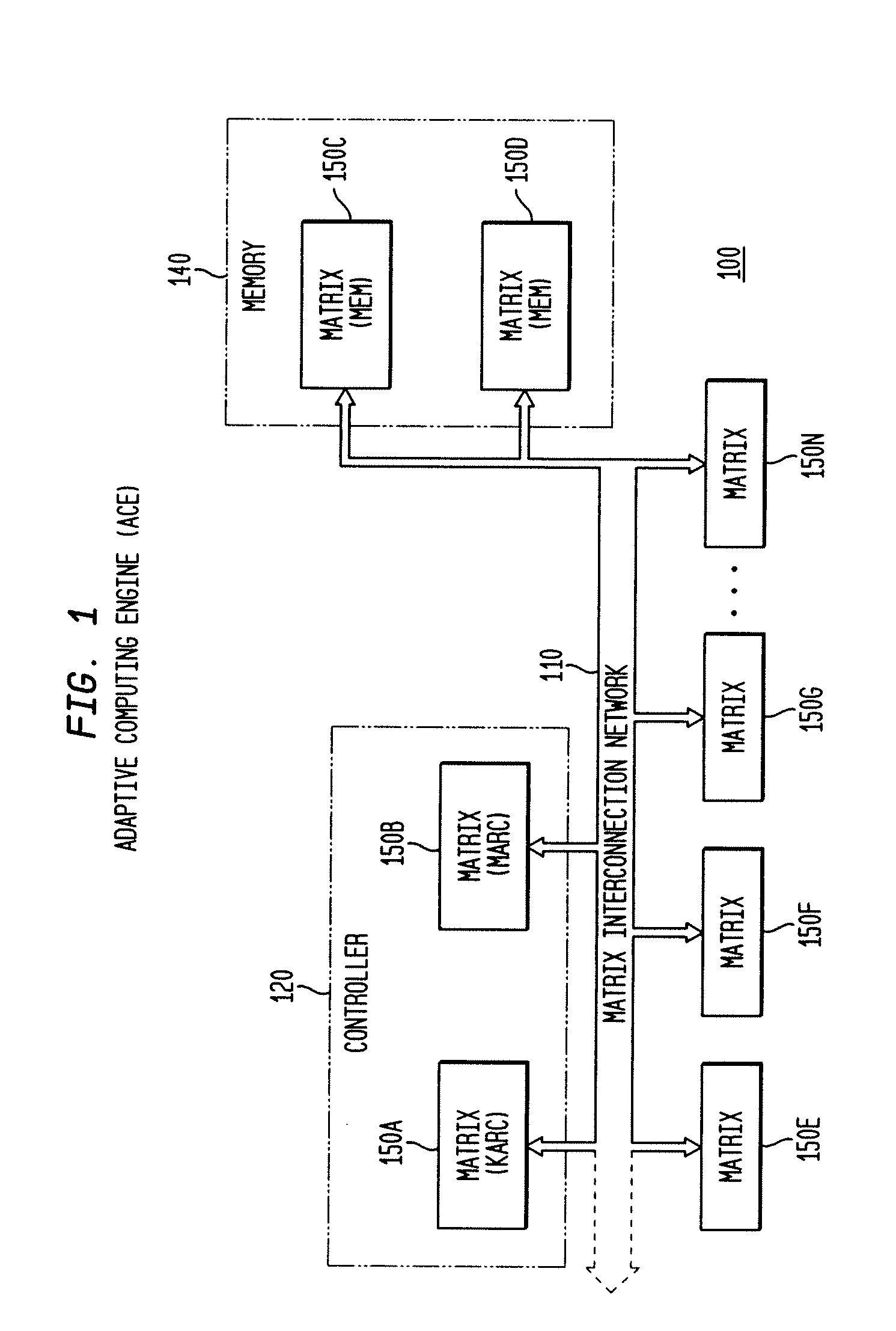
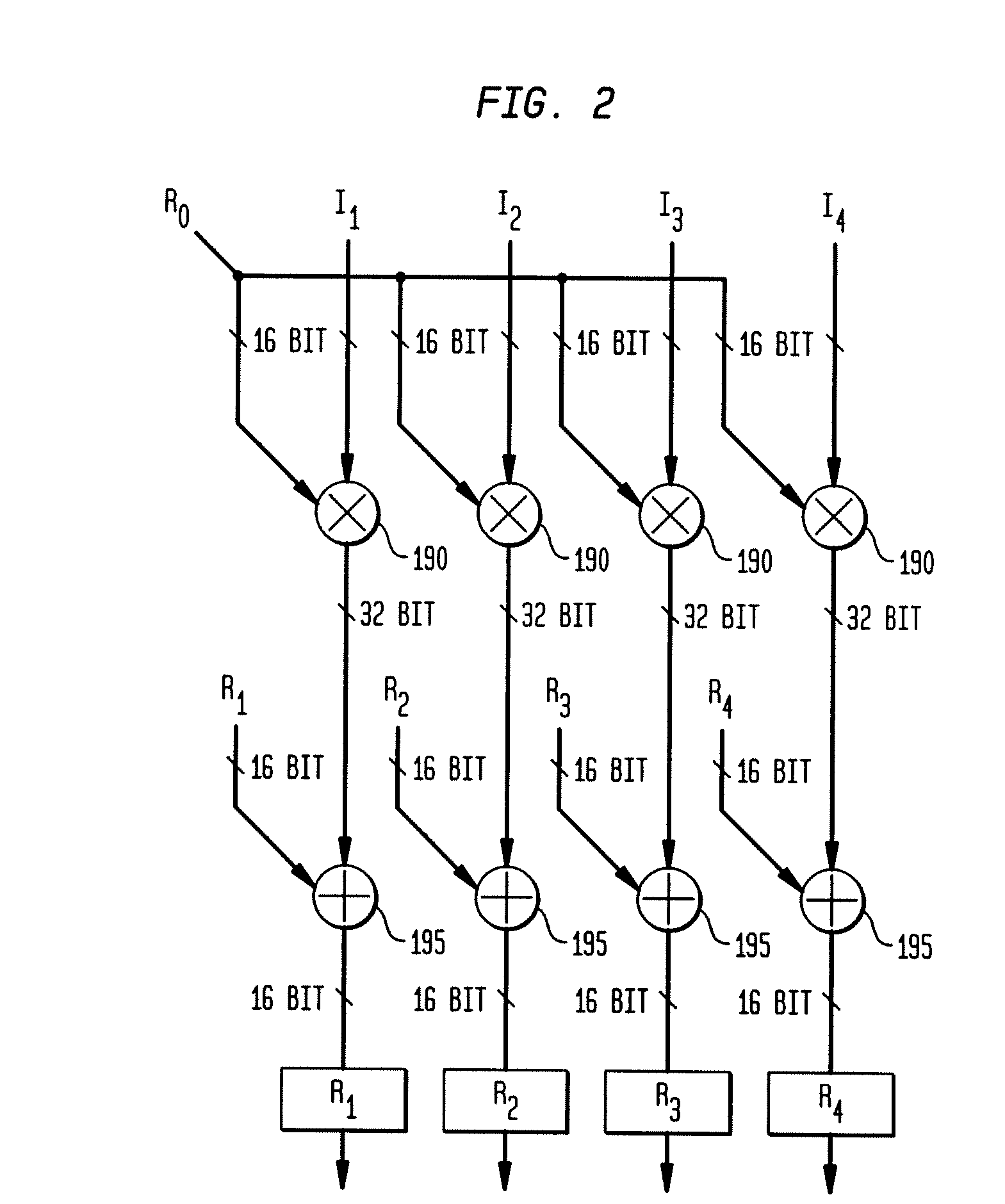
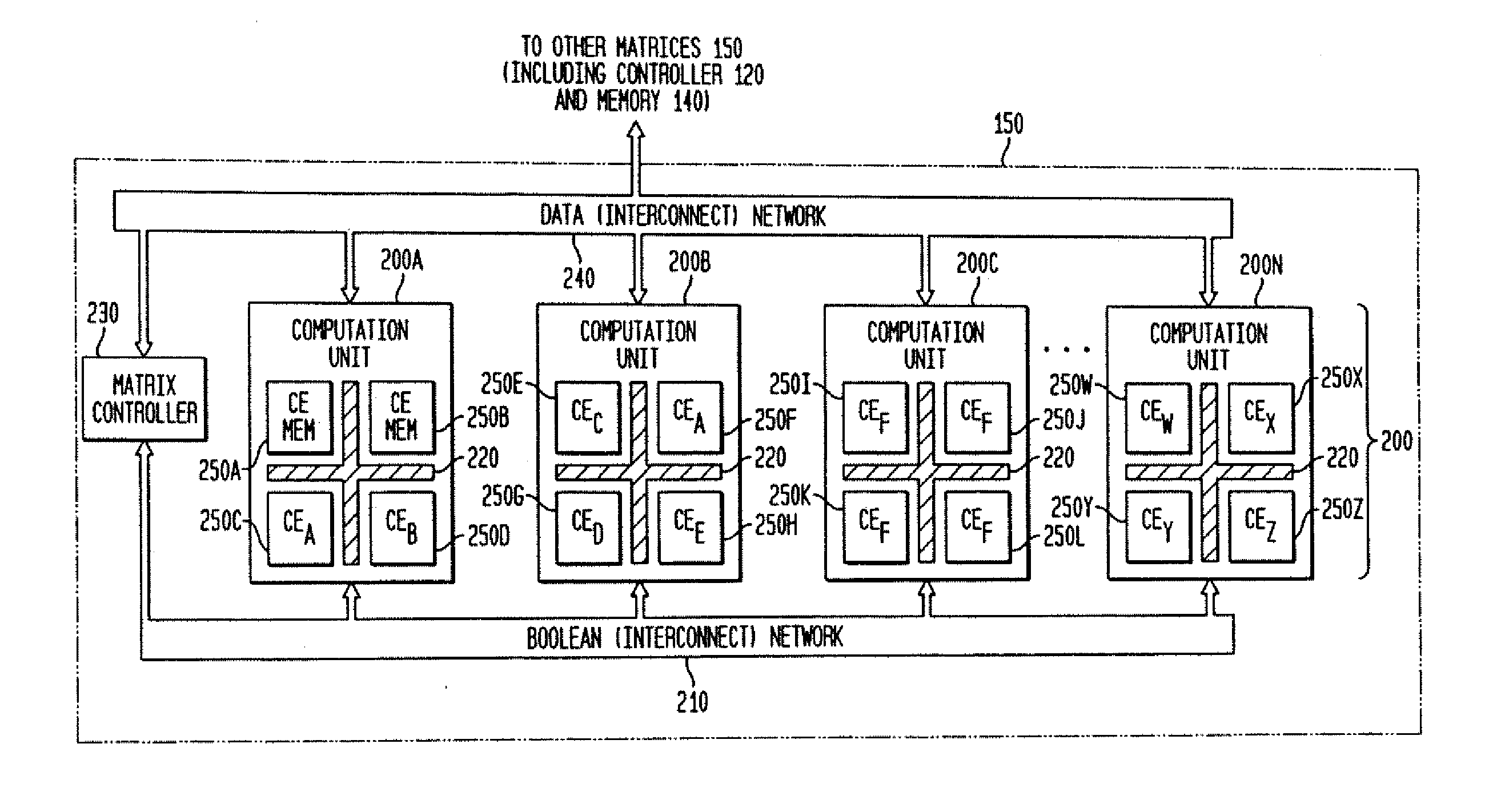
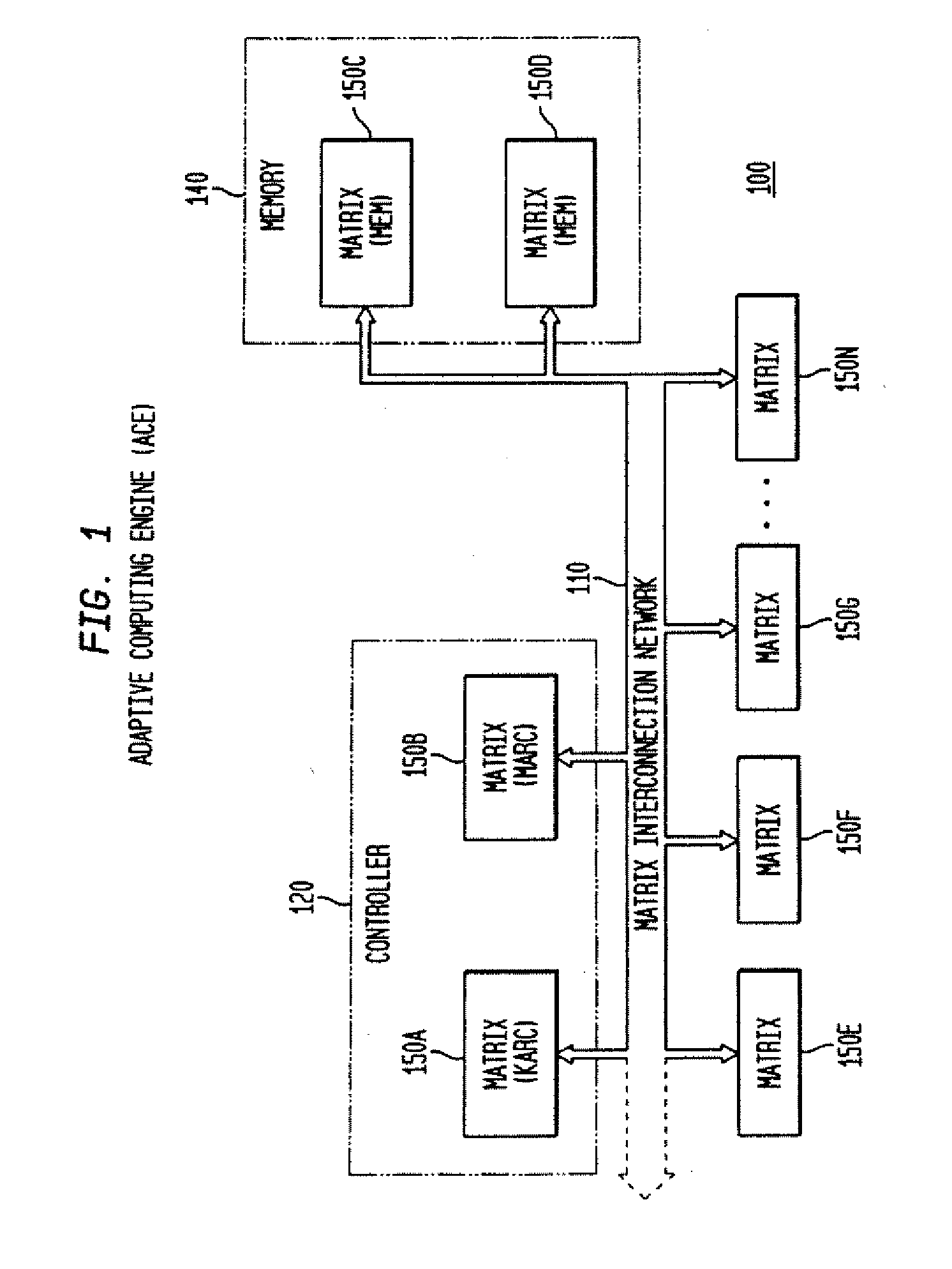
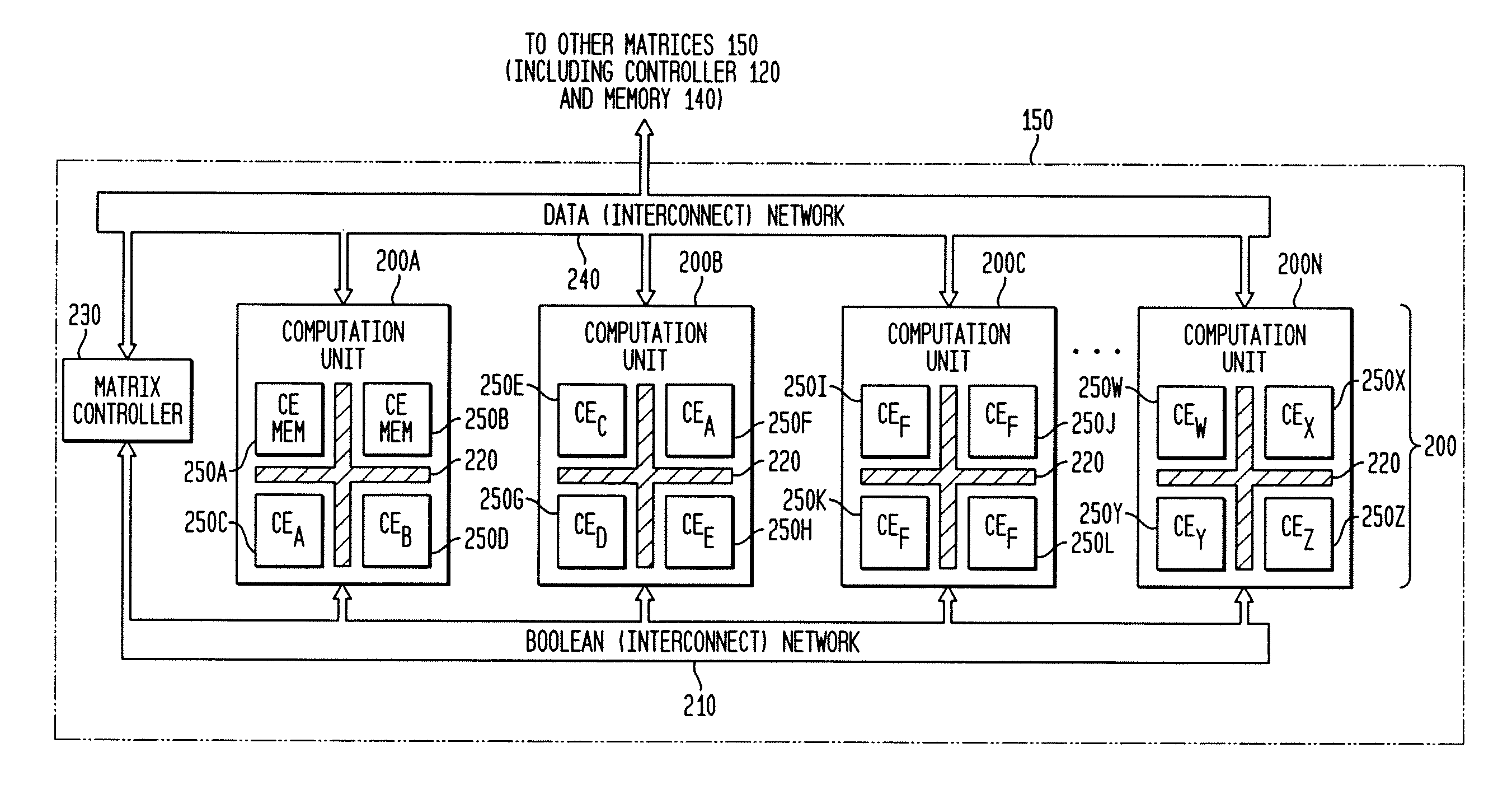
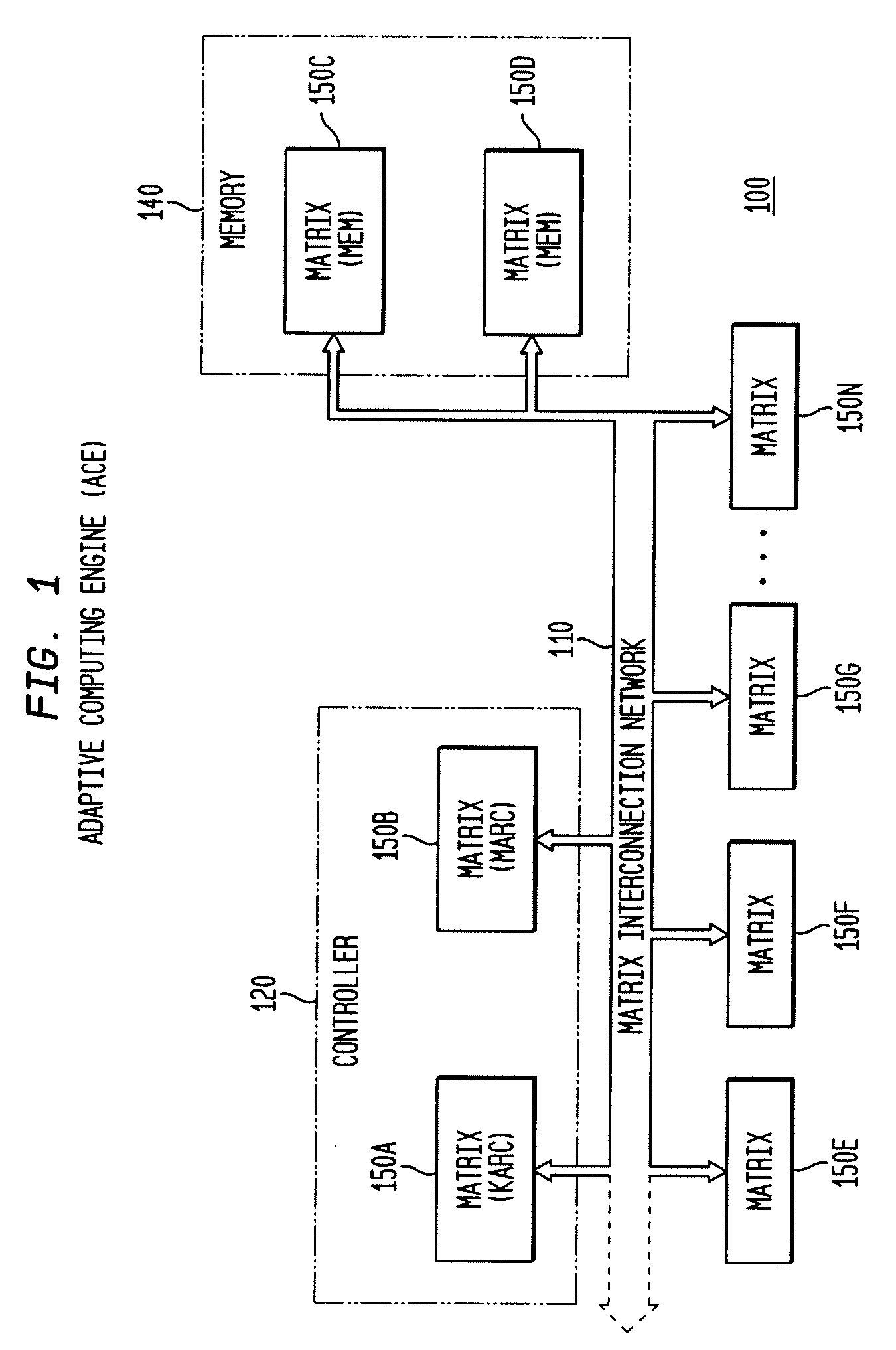
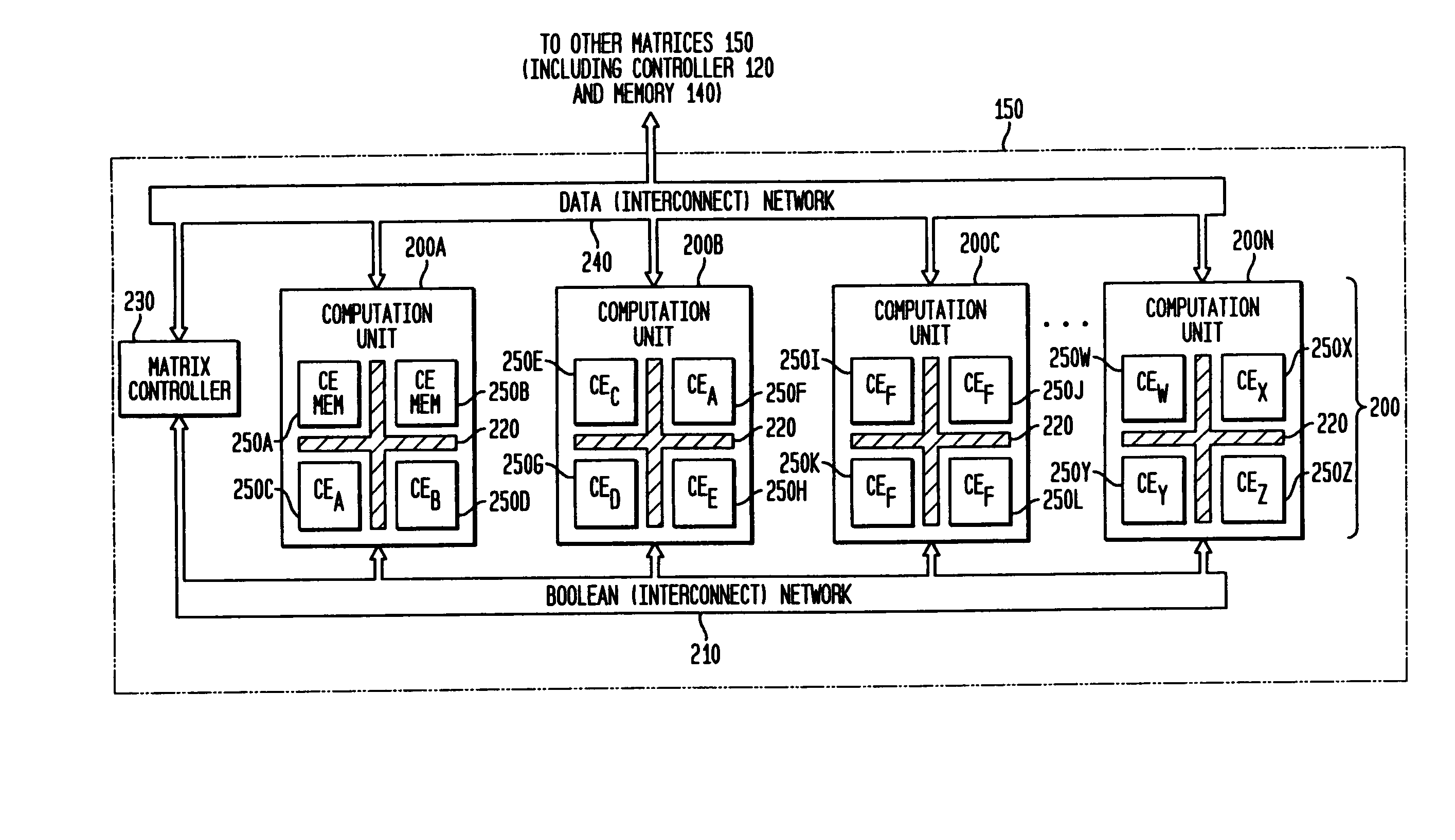
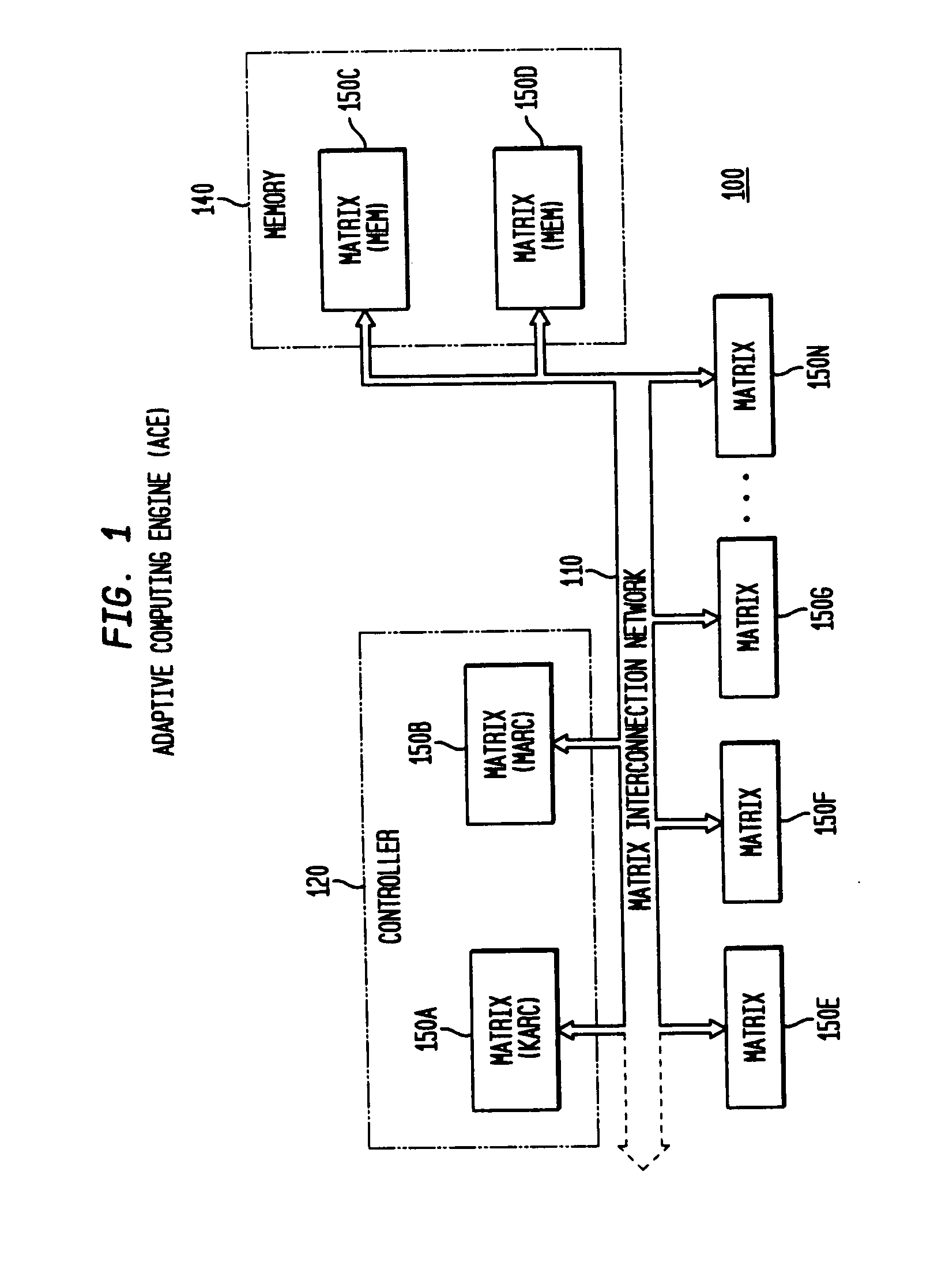
Adaptive integrated circuitry with heterogeneous and reconfigurable matrices of diverse and adaptive computational units having fixed, application specific computational elements
InactiveUS20090037691A1Minimizing potential disadvantageIncrease speedEnergy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsHand heldFinite-state machine
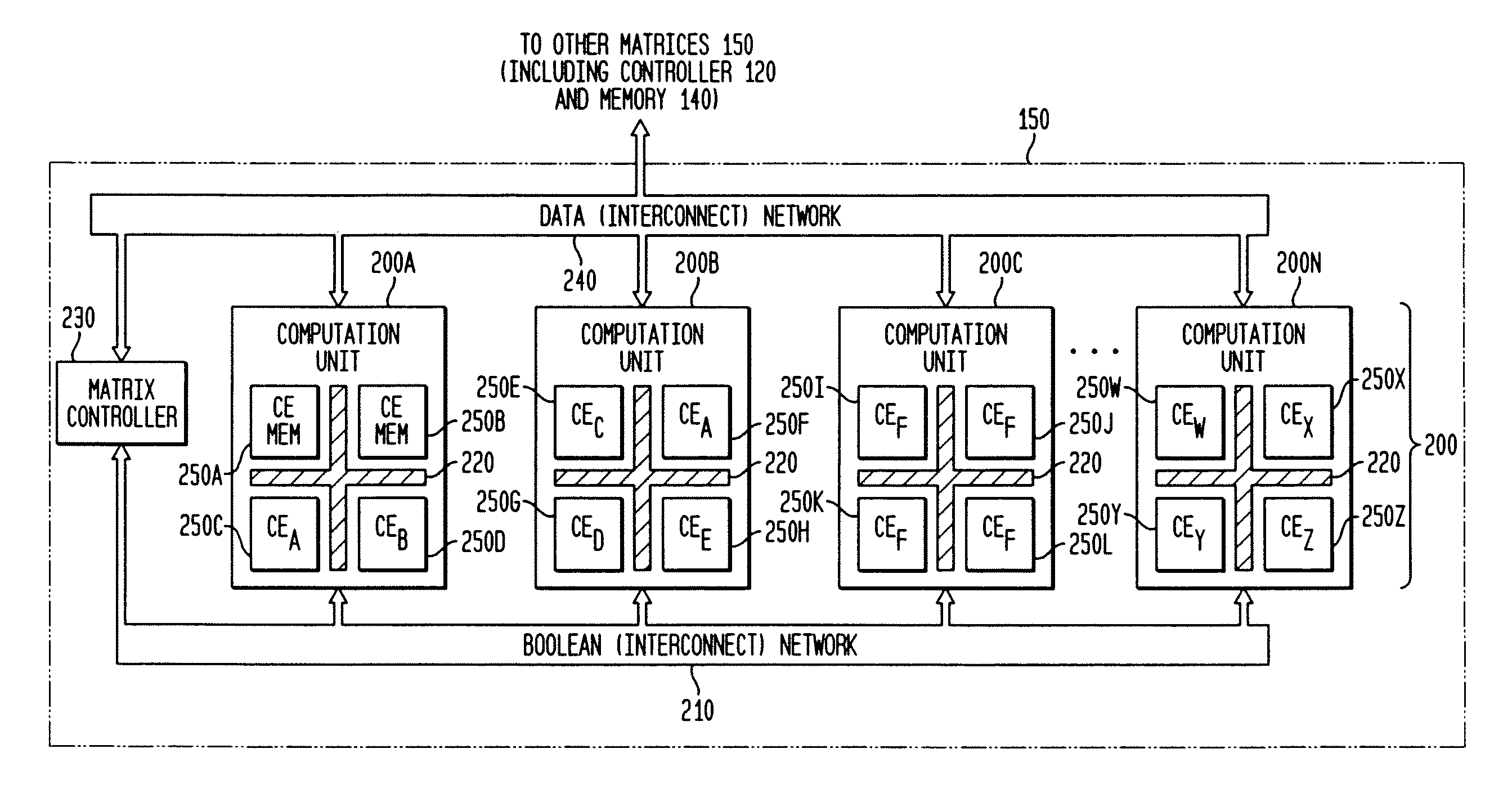
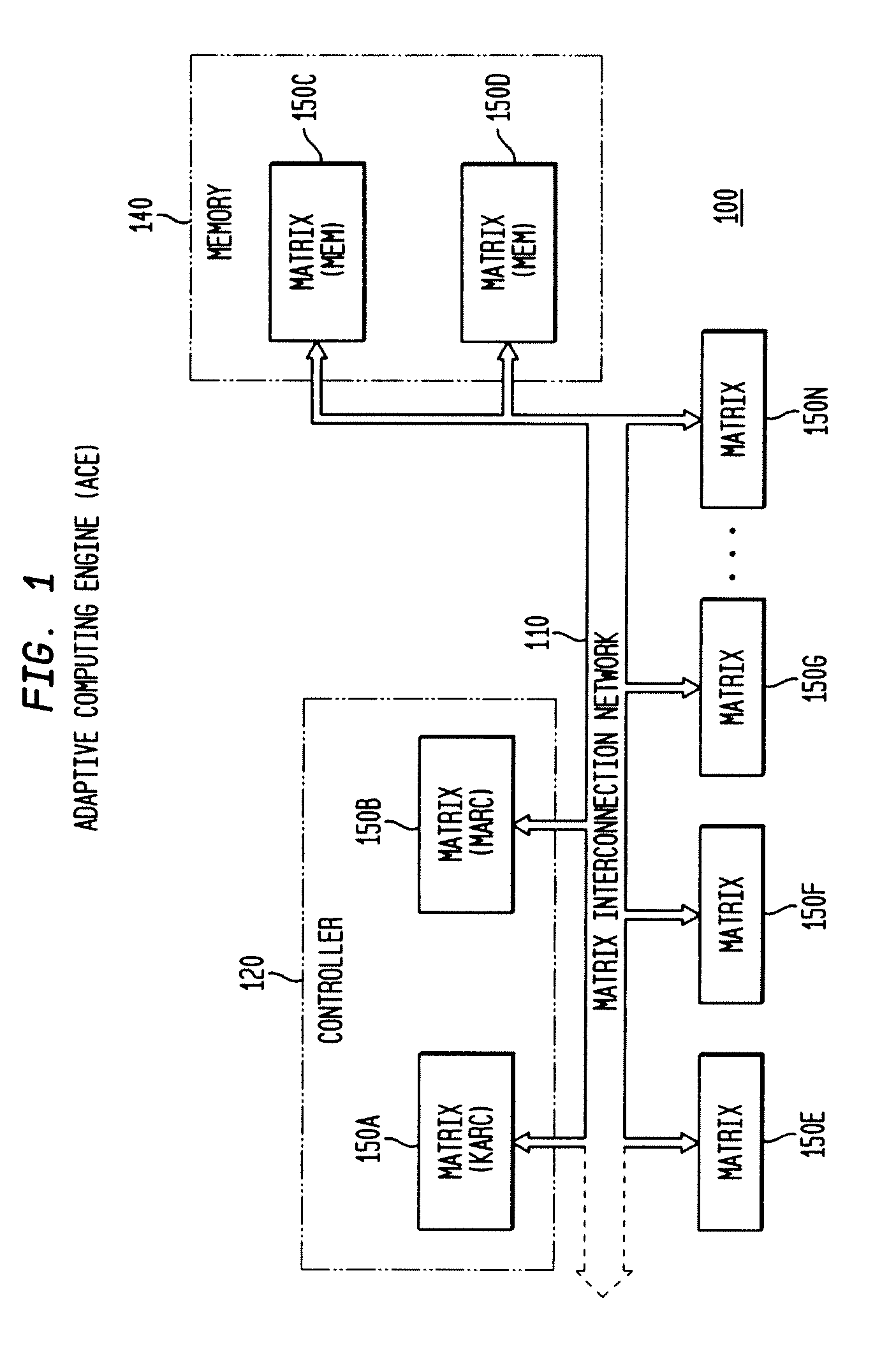
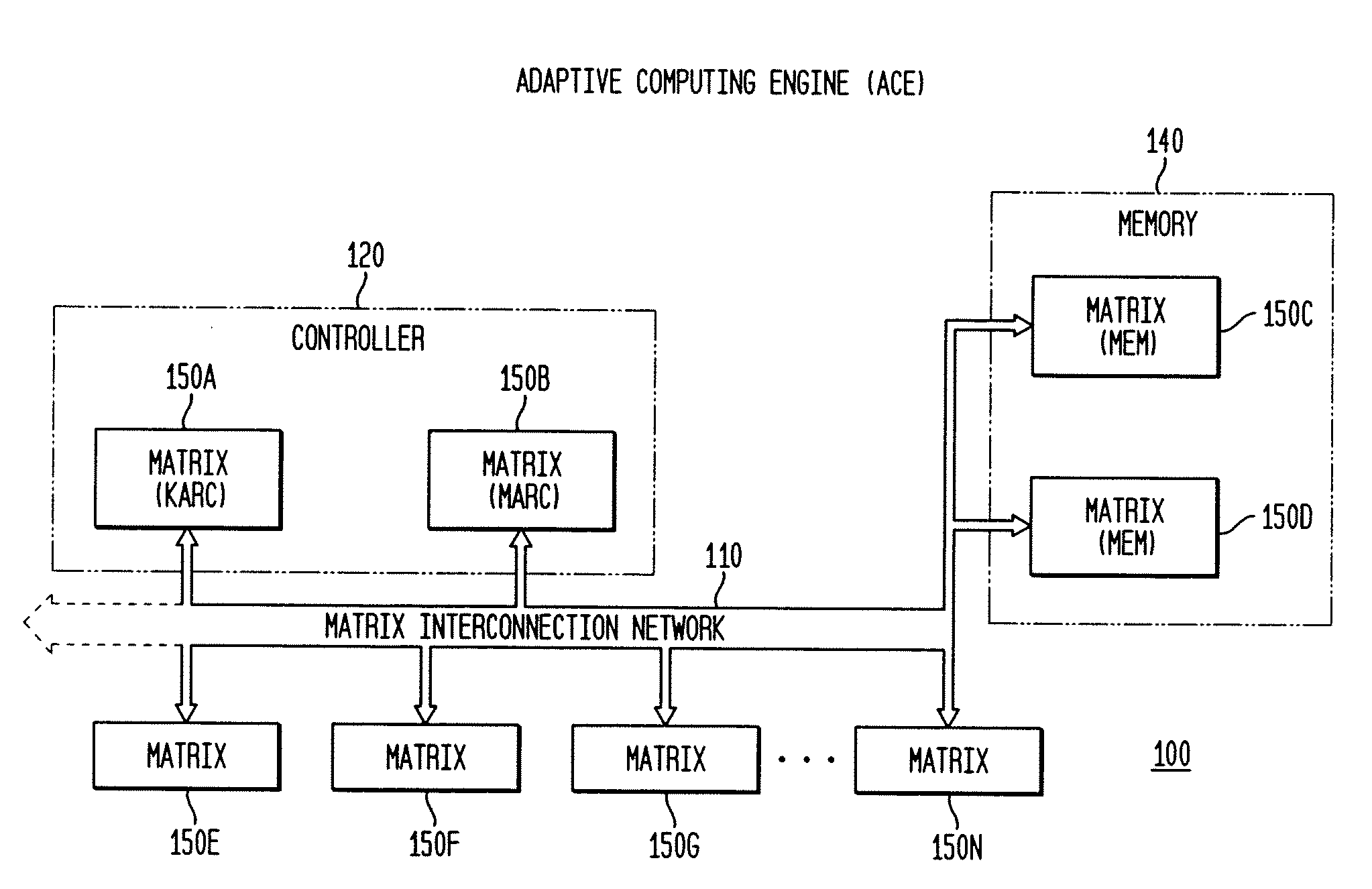
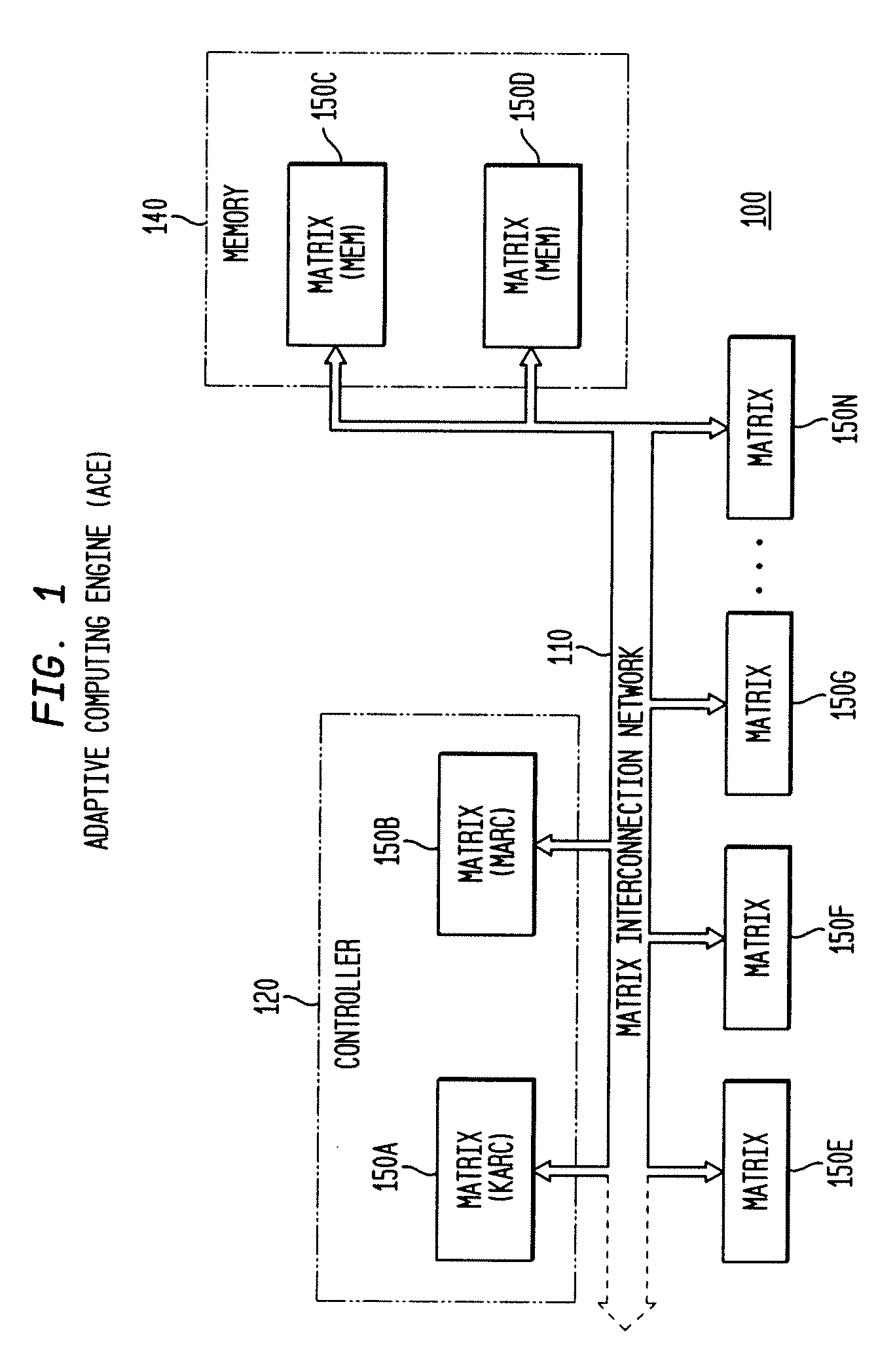
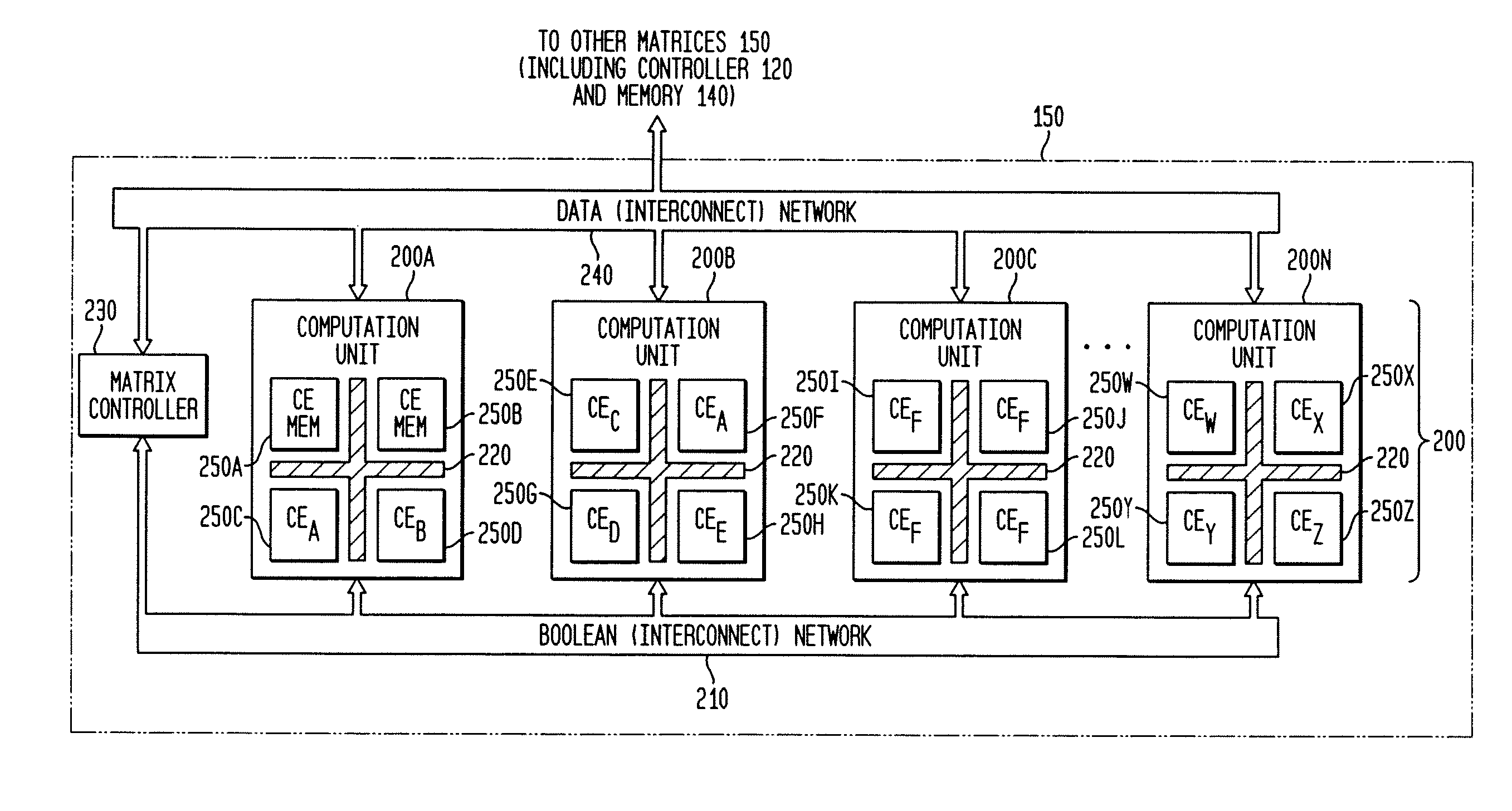
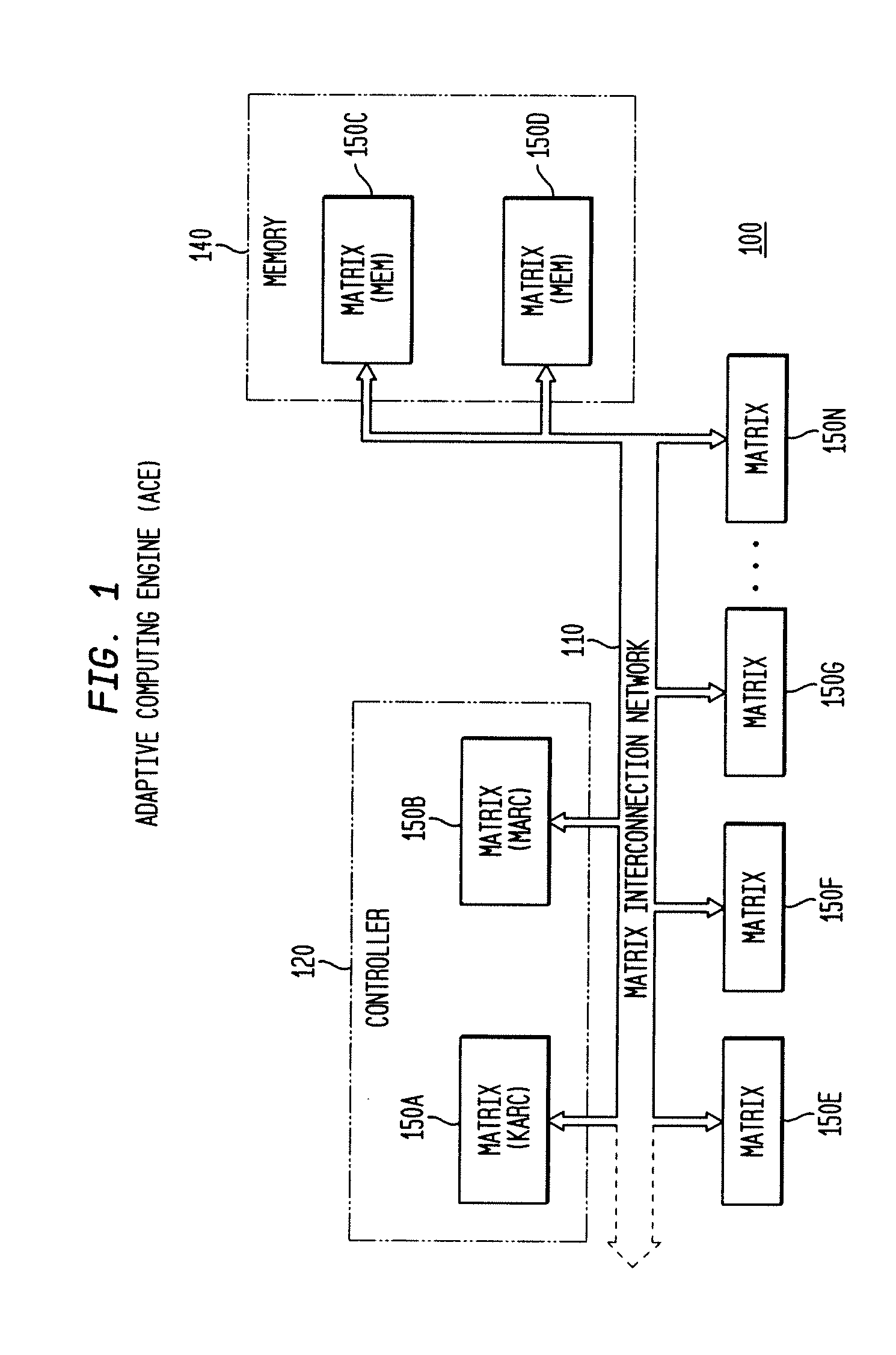
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The preferred IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
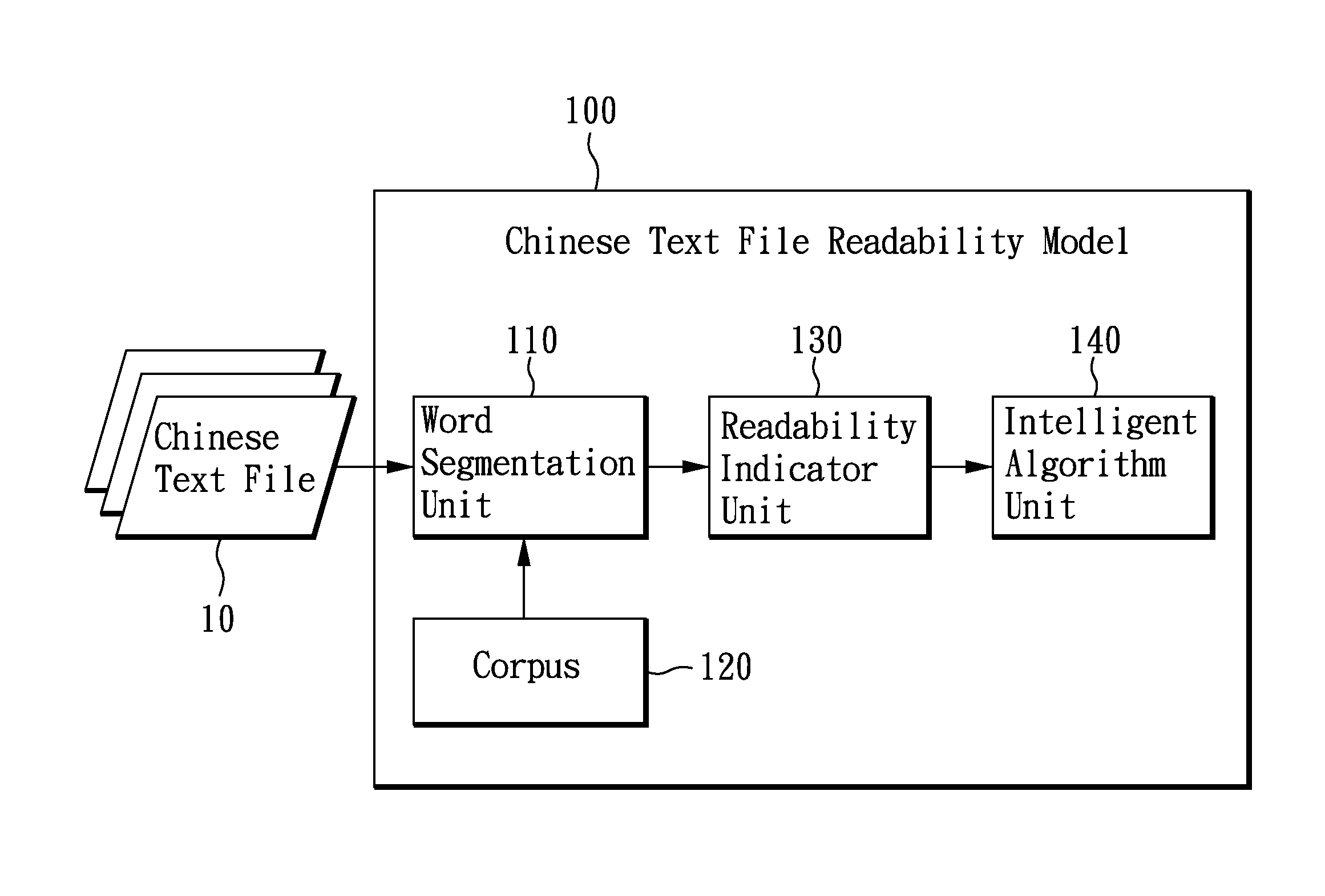
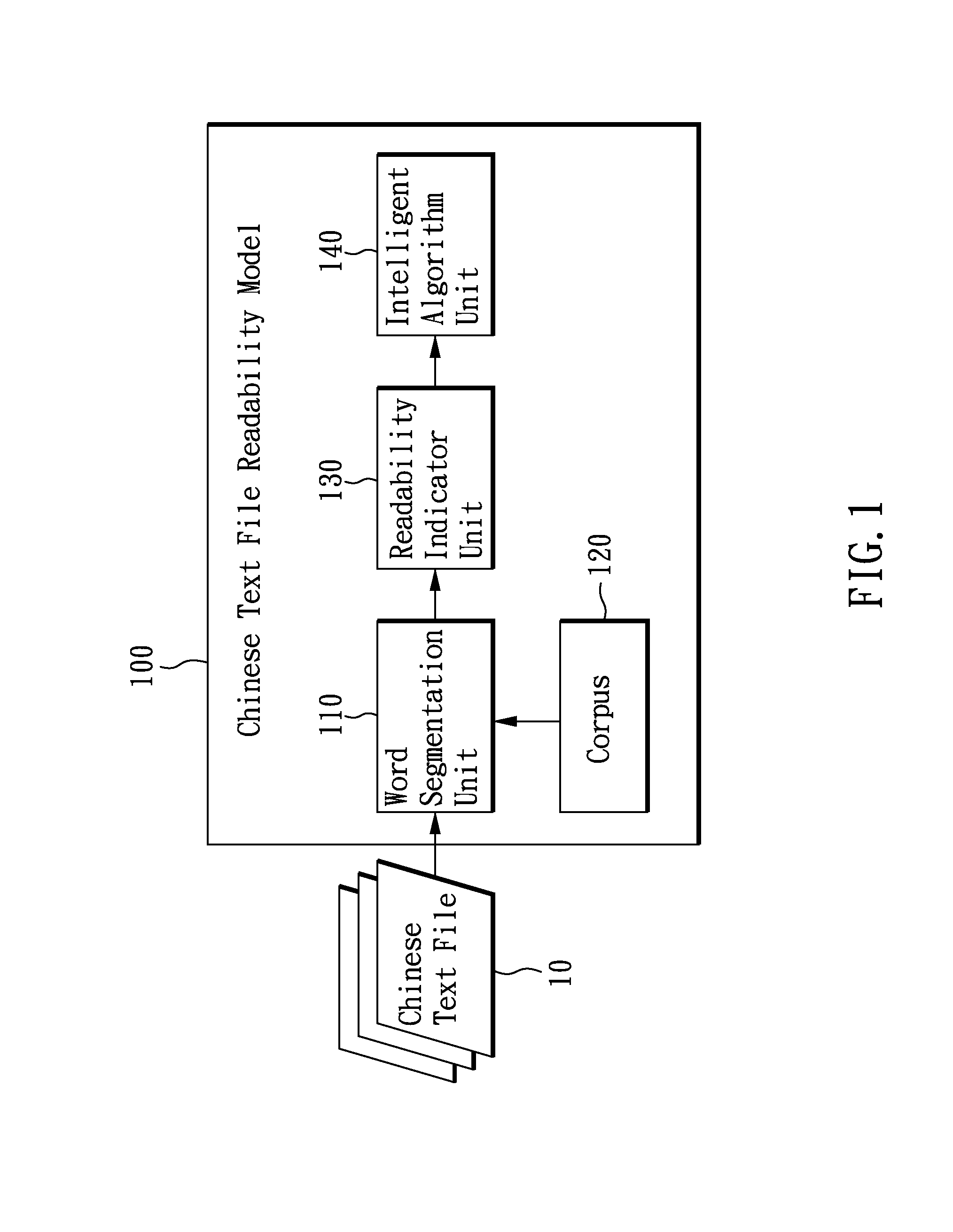
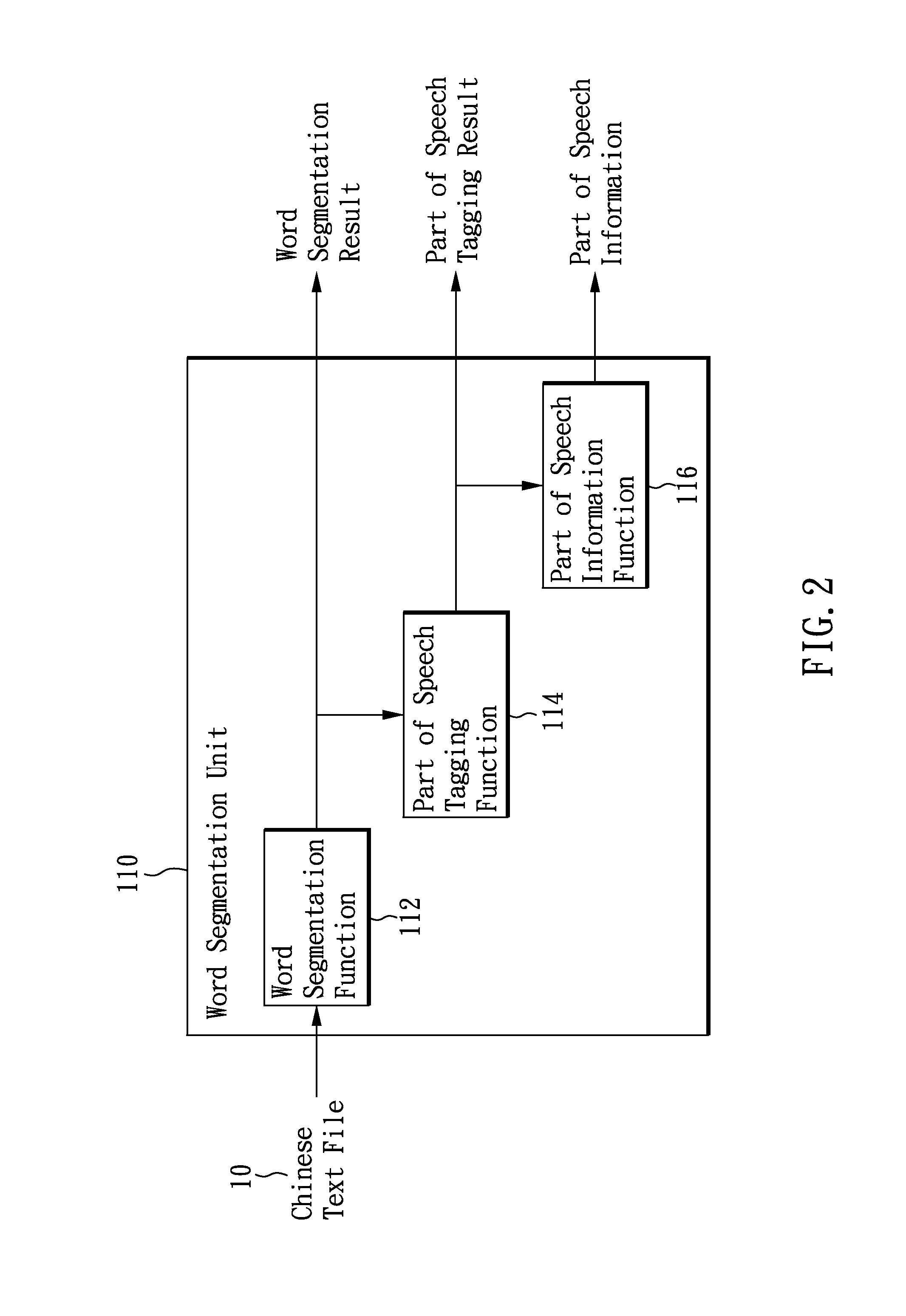
System and Method Using Data Reduction Approach and Nonlinear Algorithm to Construct Chinese Readability Model
InactiveUS20140012569A1Natural language translationSpecial data processing applicationsPart of speechNonlinear algorithms
The invention constructs Chinese readability model with data reduction and smart / advanced artificial intelligence algorithm. The model contains 1) a word segmentation which segments words and tags the part of speech of the words. 2) a readability indicator unit which analyzes readability features based the segmented words segmentation and part of speech tagging; and 3) an evolution algorithm unit, which construct a Chinese text readability model using data reduction approach and smart / advanced artificial intelligence algorithm. The present invention assesses the readability of Chinese texts, based on a small amount of Chinese text, and identifies the adequate readers.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Precoder and precoding method in a multi-antenna system
ActiveUS8204142B2Canceling interference among terminalsReduce complexityDiversity/multi-antenna systemsError prevention/detection by diversity receptionPrecodingChannel state information
A precoder and a precoding method in a multiuser multi-antenna system are provided. The precoder includes a channel checker for determining a DownLink (DL) channel condition of terminals in a service coverage area, a pre-compensator for pre-compensating, for channel distortion, signals to be sent to the terminals when a nonlinear algorithm is selected based on the channel condition of the terminals, and an interference remover for canceling interference in a channel by multiplying the pre-compensated signals by inverse channels of the terminals, and for canceling interference between the terminals. Accordingly, the pre-equalization can be carried out without global channel state information, and an increase of the transmit power can be prevented in the permutation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Method and apparatus for reducing peak average power ratio of multi-carrier system
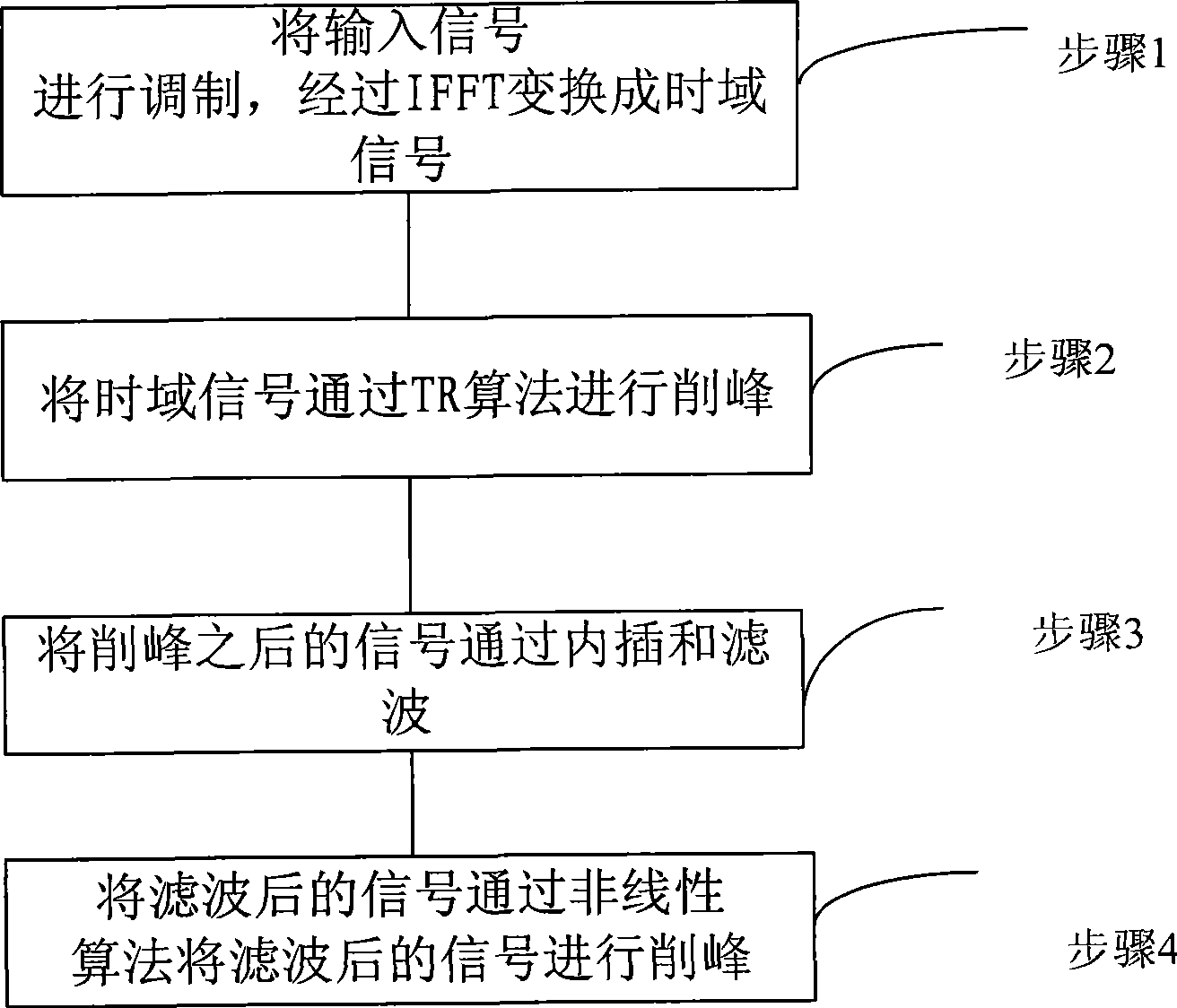
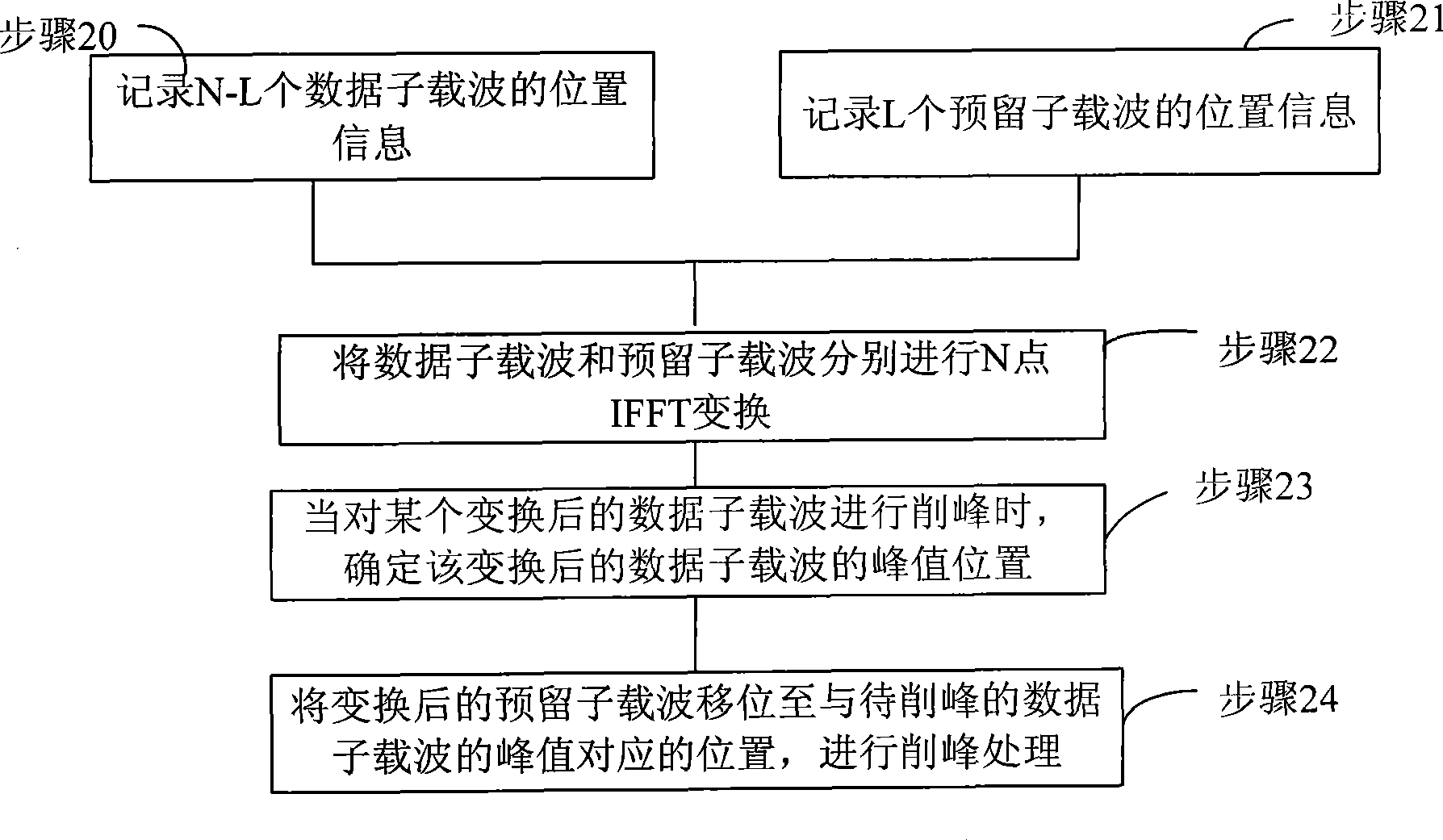
InactiveCN101414994AReduce complexityReduce regeneration peakMulti-frequency code systemsTime domainNonlinear algorithms
The invention provides a method used for reducing peak-to-average power ratio of a multi-carrier system, comprising the steps as follows: firstly, input signals are modulated and converted into time domain signals; subsequently, peak clipping is carried out on the time domain signal by a TR algorithm; subsequently, the peak-clipped signals are interpolated and filtrated; furthermore, peak clipping is carried out on the filtrated signals by a nonlinear algorithm. The invention also provides a device used for reducing the peak-to-average power ratio of a multi-carrier system, comprising a first peak clipping device which is used for clipping the peak of the input time domain signals by the TR algorithm, and a radio frequency remote module which is connected with the first peak clipping module and is used for carrying out interpolation and filtration on the peak-clipped signals, and a second peak clipping module which is connected with the radio frequency remote module and is used for clipping peak of the filtrated signals by the nonlinear algorithm. The method and the device can effectively reduce the regeneration peak which affects the system performance little owning to extremely small possibility of the regeneration peak.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
Method and system for managing hardware resources to implement system functions using an adaptive computing architecture
InactiveUS7752419B1Minimizing potential disadvantageIncrease speedEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingFinite-state machineHand held
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The exemplary IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications. In an exemplary embodiment, some or all of the computational elements are alternately configured to implement two or more functions.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
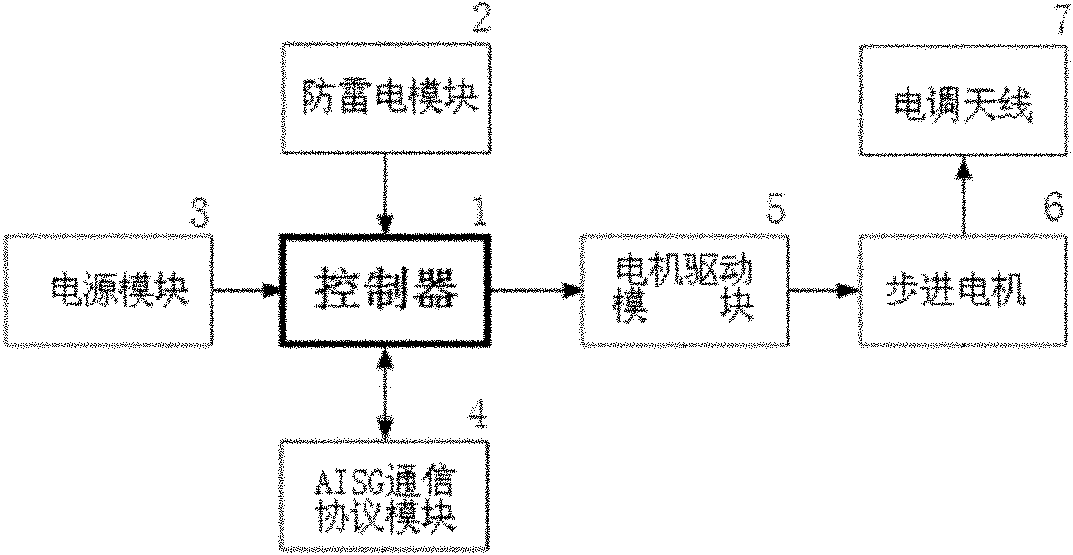
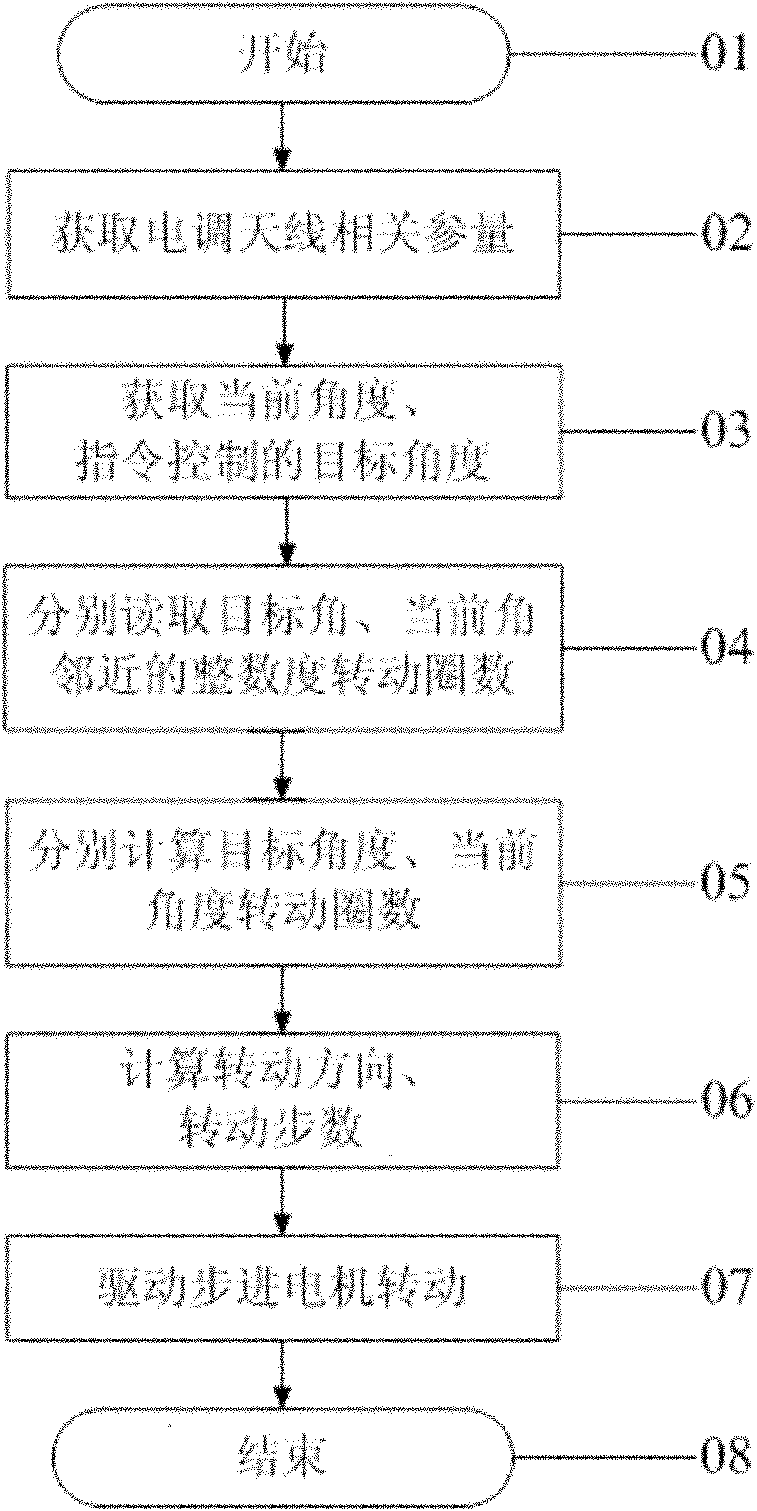
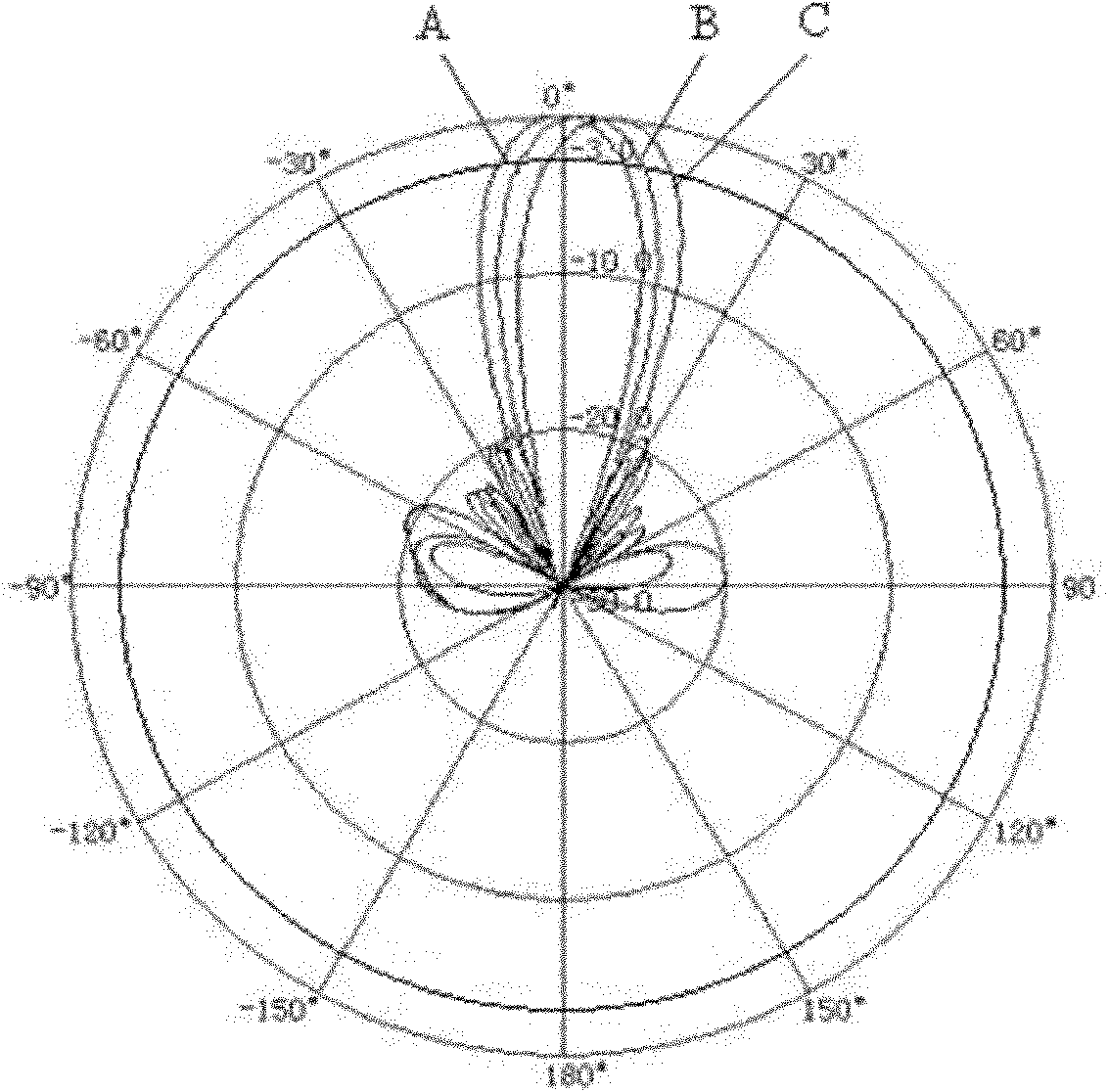
Nonlinear algorithm for controlling downtilt angles of electrically-adjustable antenna
ActiveCN102064388AEasy to controlPrecise adjustment of electric downtilt angleAntennasElectricityNonlinear algorithms
The invention discloses a nonlinear algorithm for controlling downtilt angles of an electrically-adjustable antenna, relating to the technical field of base station antenna. Based on a remote control system for the electrically-adjustable antenna, the invention is characterized in that the algorithm set in a controller of the control system comprises the following steps of: 1, storing parameters associated with various modes of the electrically-adjustable antennae which are regarded as controlled objects as well as the number of adjusting rotation of each downtilt angle of various modes of the electrically-adjustable antennae in relation to zero reference; 2, when information of an order for the adjustment of the electrically-adjustable antennae is received, determining, according to the information, the type of the electrically-adjustable antennae to be adjusted and the associated parameters of the controlled electrically-adjustable antennae; and 3, adjusting target downtilt angles of the electrically-adjustable antennae by determining adjusting rotation direction and rotation quantity based on the angle adjusting rotation parameters of the controlled electrically-adjustable antennae and on the current downtilt angle. The algorithm is convenient in use, high in adjustment precision and is suitable for remotely adjusting the electric downtilt angles of various types of the electrically-adjustable antennae in mobile communication.
Owner:WUHAN HONGXIN TELECOMM TECH CO LTD
Method and system for managing hardware resources to implement system functions using an adaptive computing architecture
InactiveUS20100293356A1Effectively and efficiently combinesEffectively and efficiently and maximizesEnergy efficient ICTArchitecture with single central processing unitFinite-state machineHand held
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The exemplary IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications. In an exemplary embodiment, some or all of the computational elements are alternately configured to implement two or more functions.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Nonlinear techniques for pressure vector acoustic sensor array synthesis
InactiveUS7274622B1Narrow acoustic beam widthMulti-channel direction findingAcoustic wave reradiationSensor arrayNonlinear algorithms
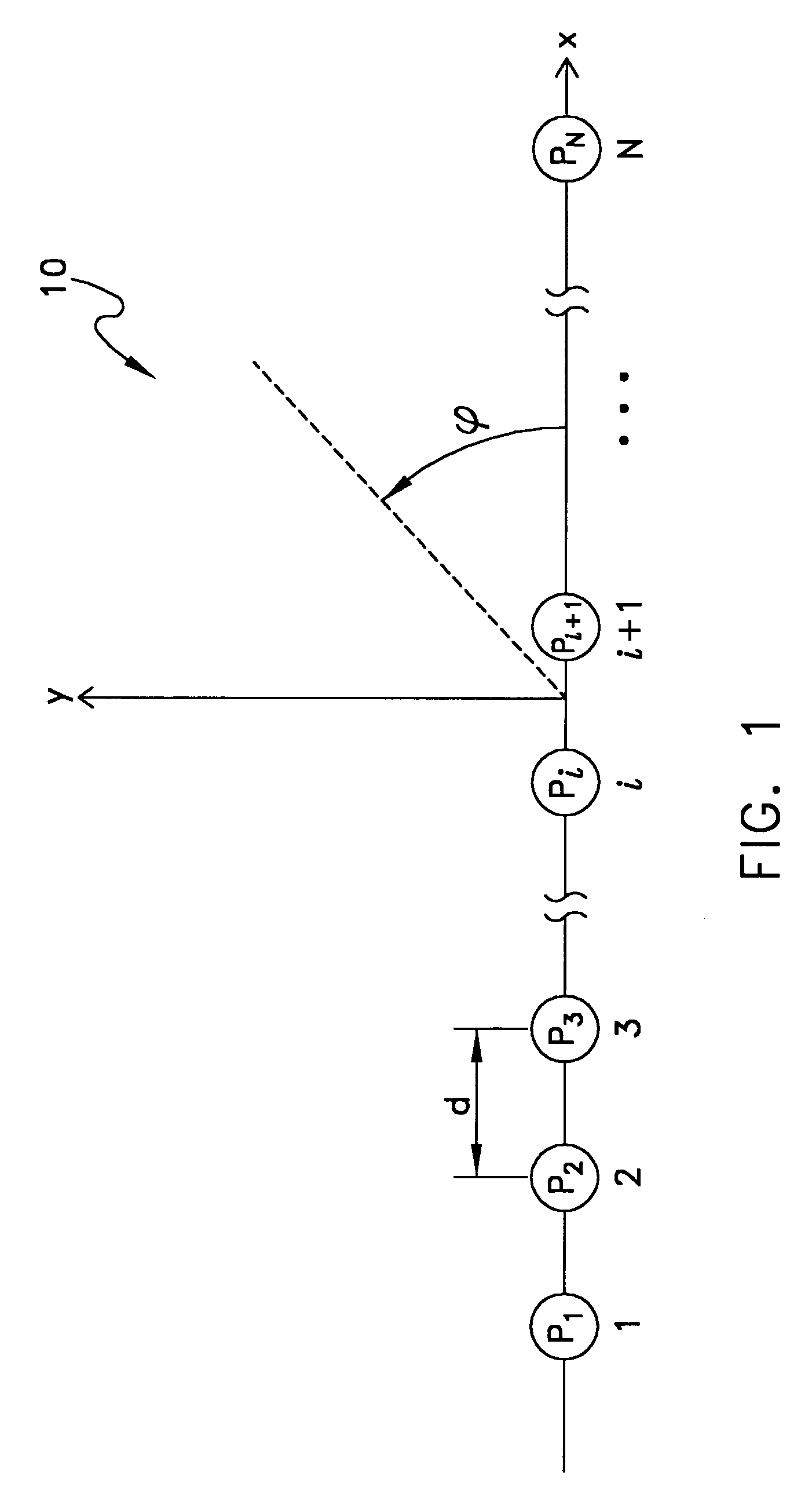
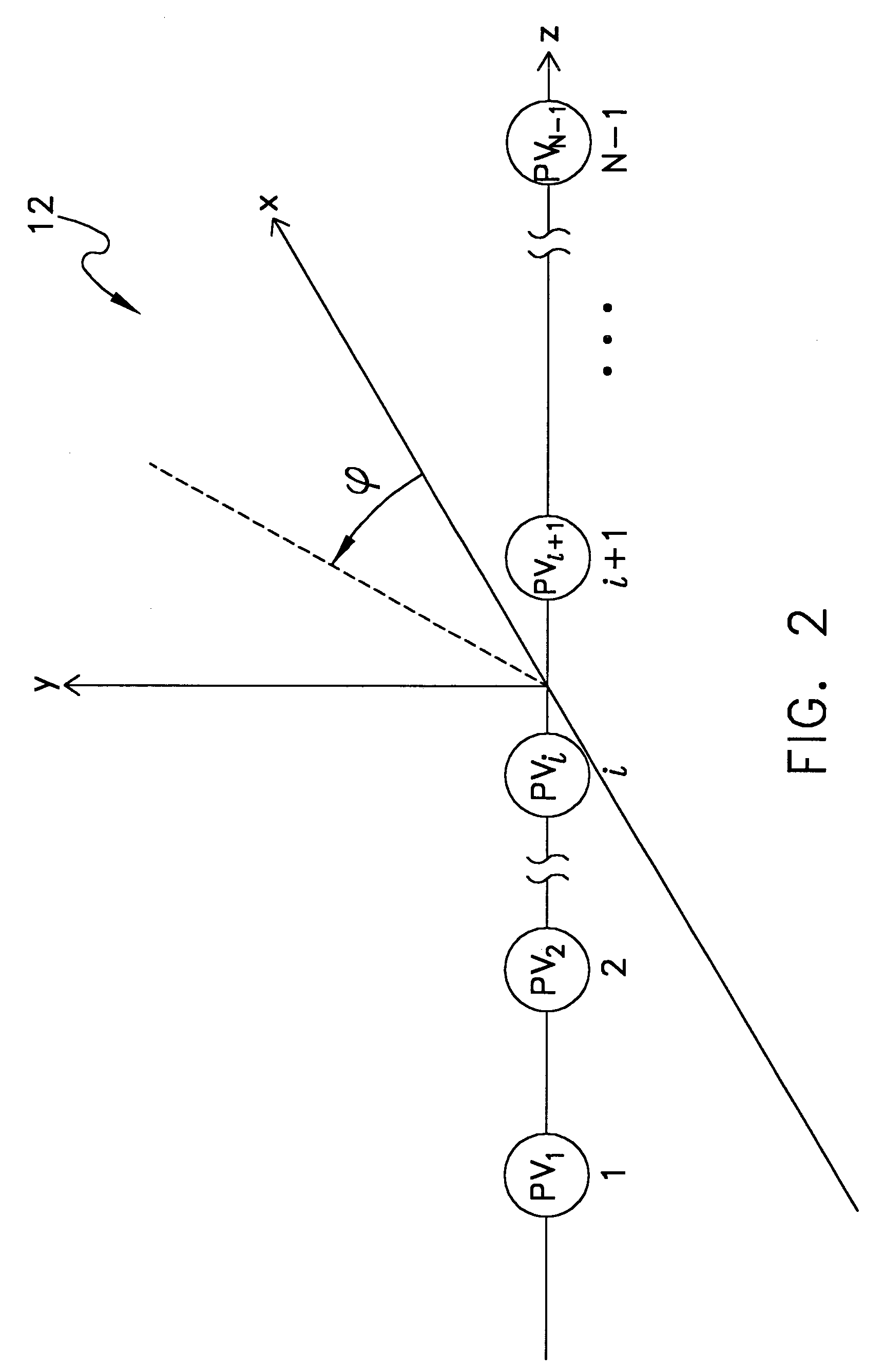
The present invention presents a method for use with an acoustic sensor array comprised of a number of pressure-vector sensors capable of sensing the acoustic scalar field and acoustic vector field of an acoustic wave. The method is a signal processing technique that utilizes nonlinear processing of pressure-vector sensor signals in the acoustic sensor array. The method involves the steps of receiving the sensor output values, processing the output values using a non-linear algorithm to create a mathematical series of values, transforming the series, applying weighting to the series and performing a summation of the values in the series to calculate the array directivity response. The array directivity response can then be further processed where the array is part of a sonar system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
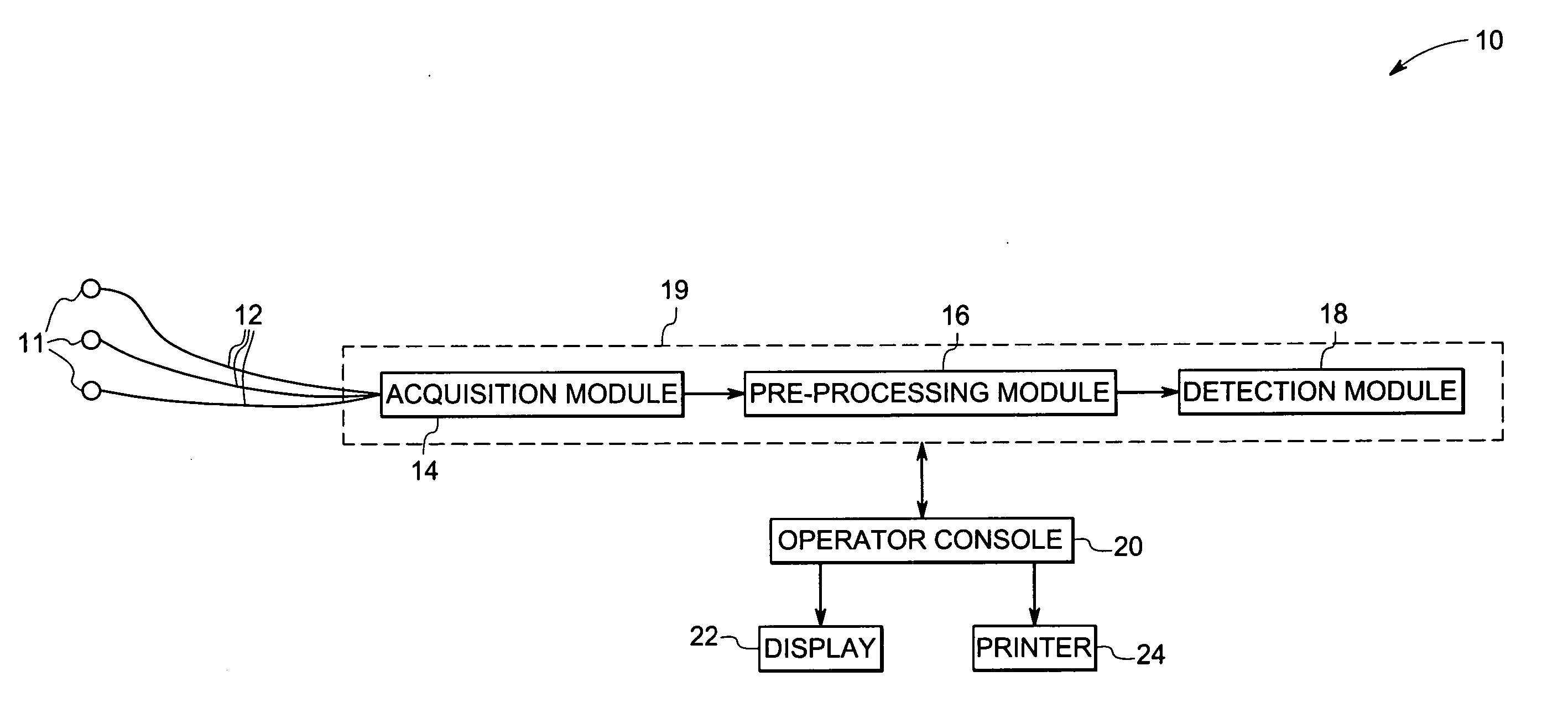
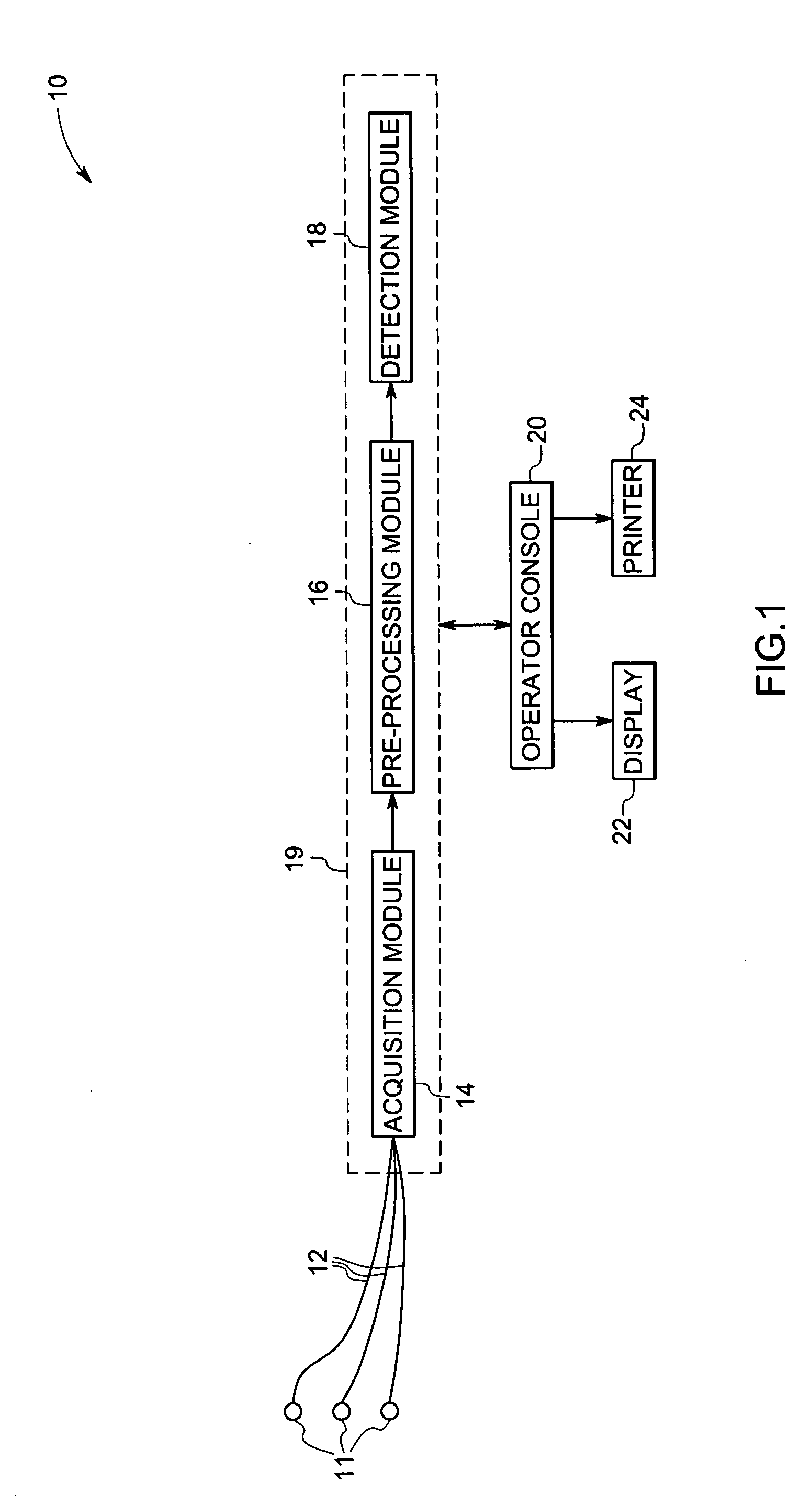
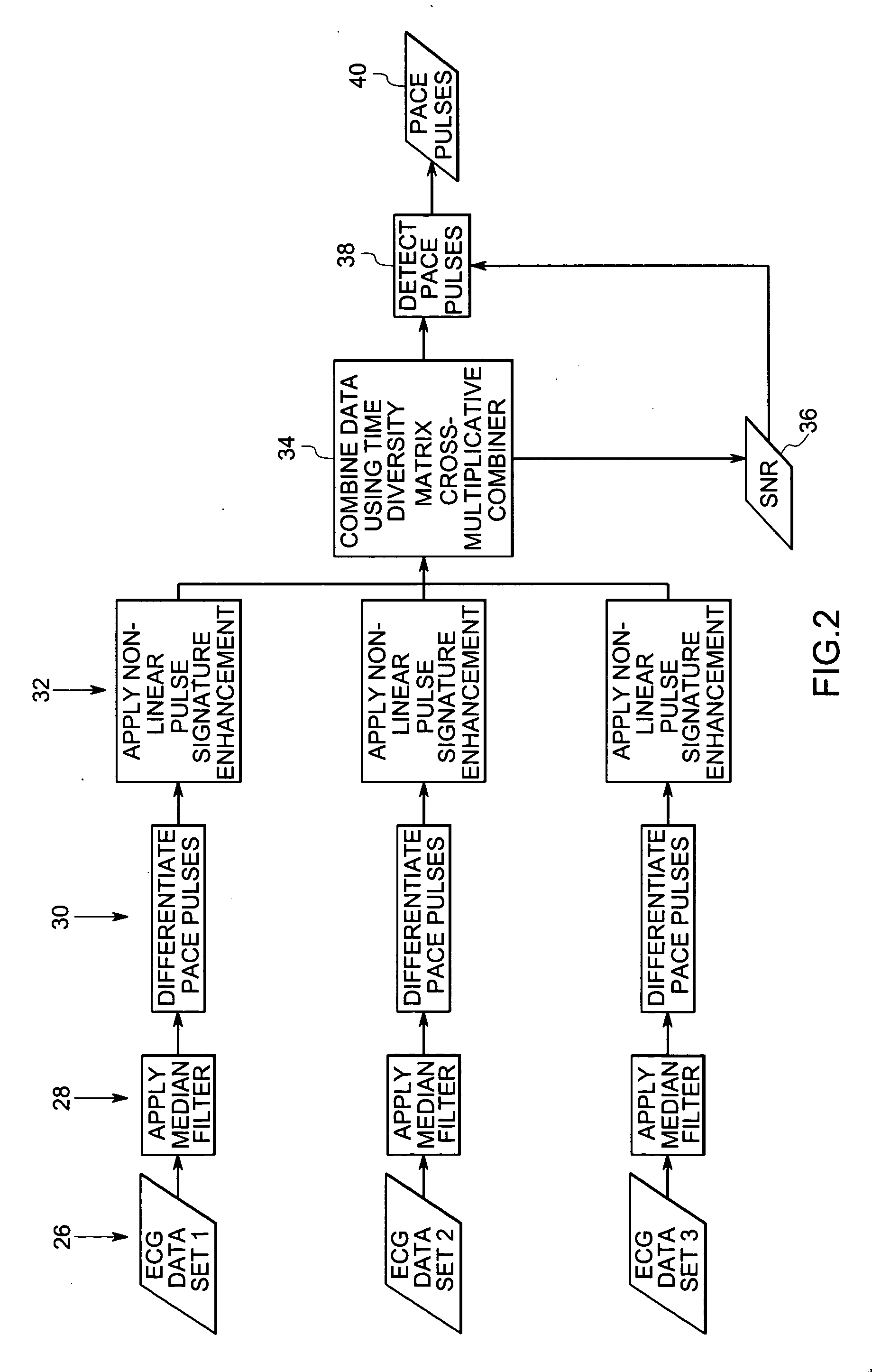
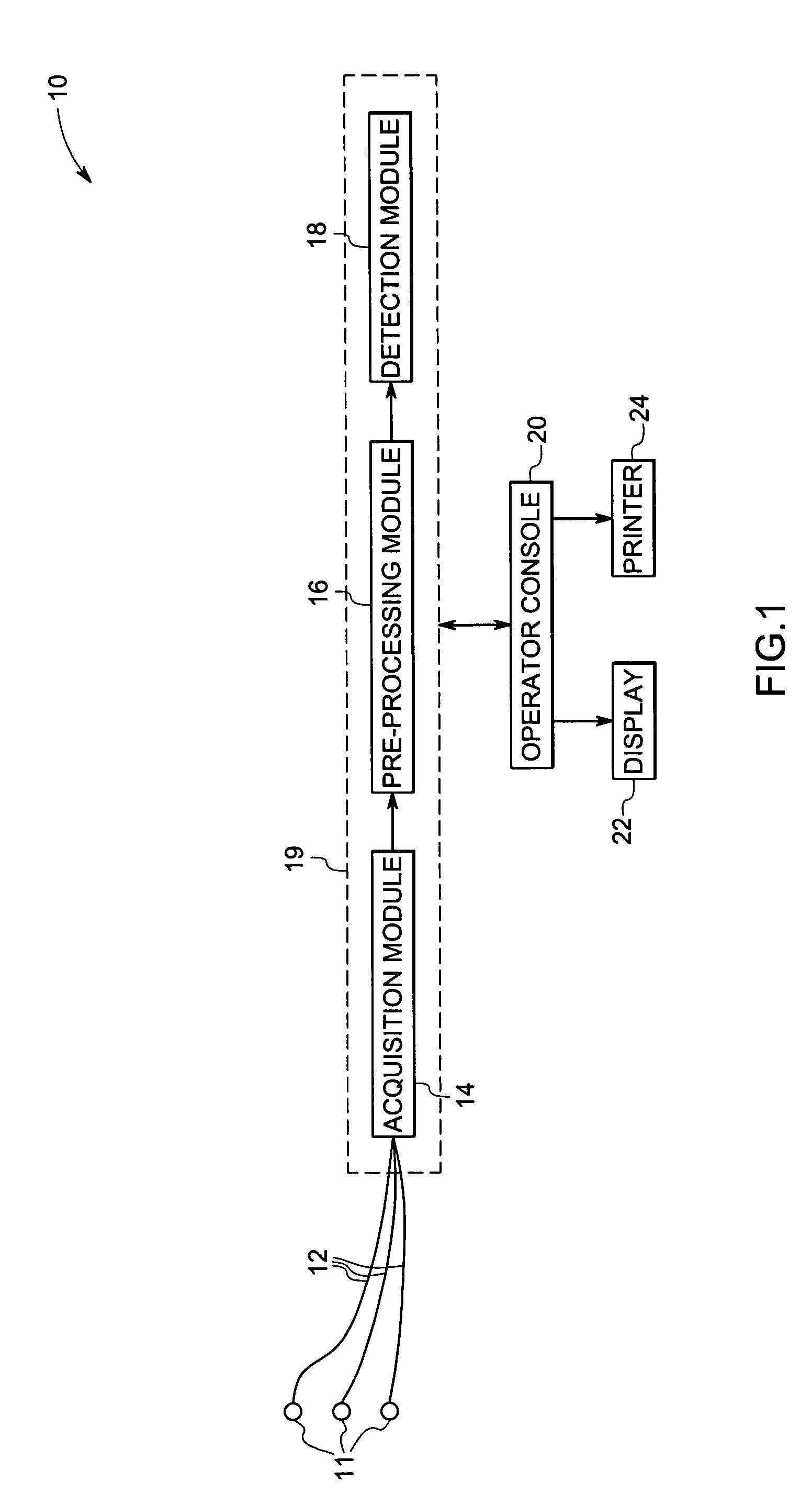
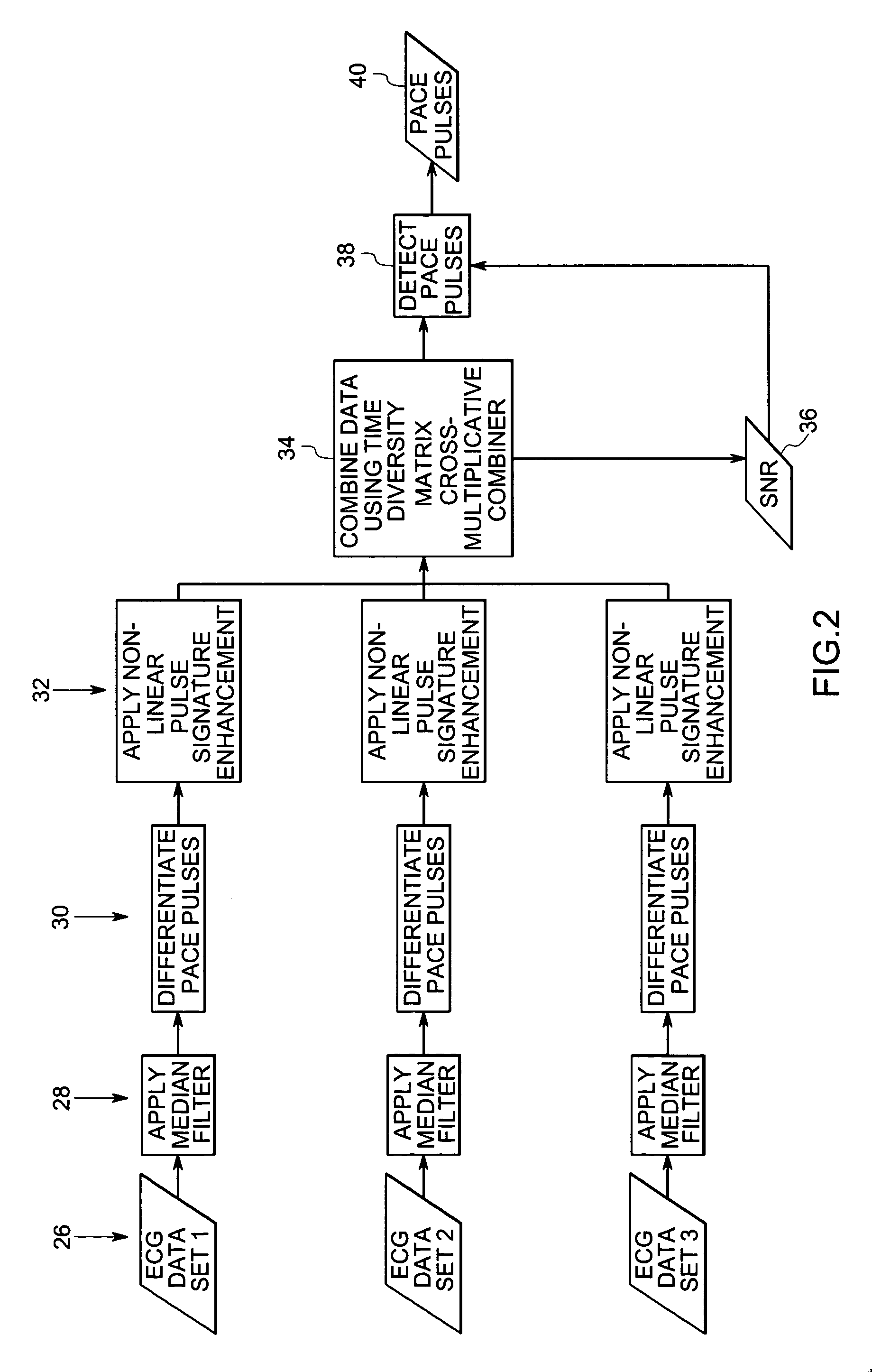
Method and system for detecting pace pulses
The present technique provides for the detection of pace pulses in electrocardiogram data. The technique provides for processing one or more sets of electrocardiogram data via a non-linear algorithm. Furthermore, the technique provides for detecting one or more pace pulses in the one or more sets of electrocardiogram data via a non-linear detection algorithm. Systems and computer programs that afford functionality of the type defined by this method are also provided by the present technique.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
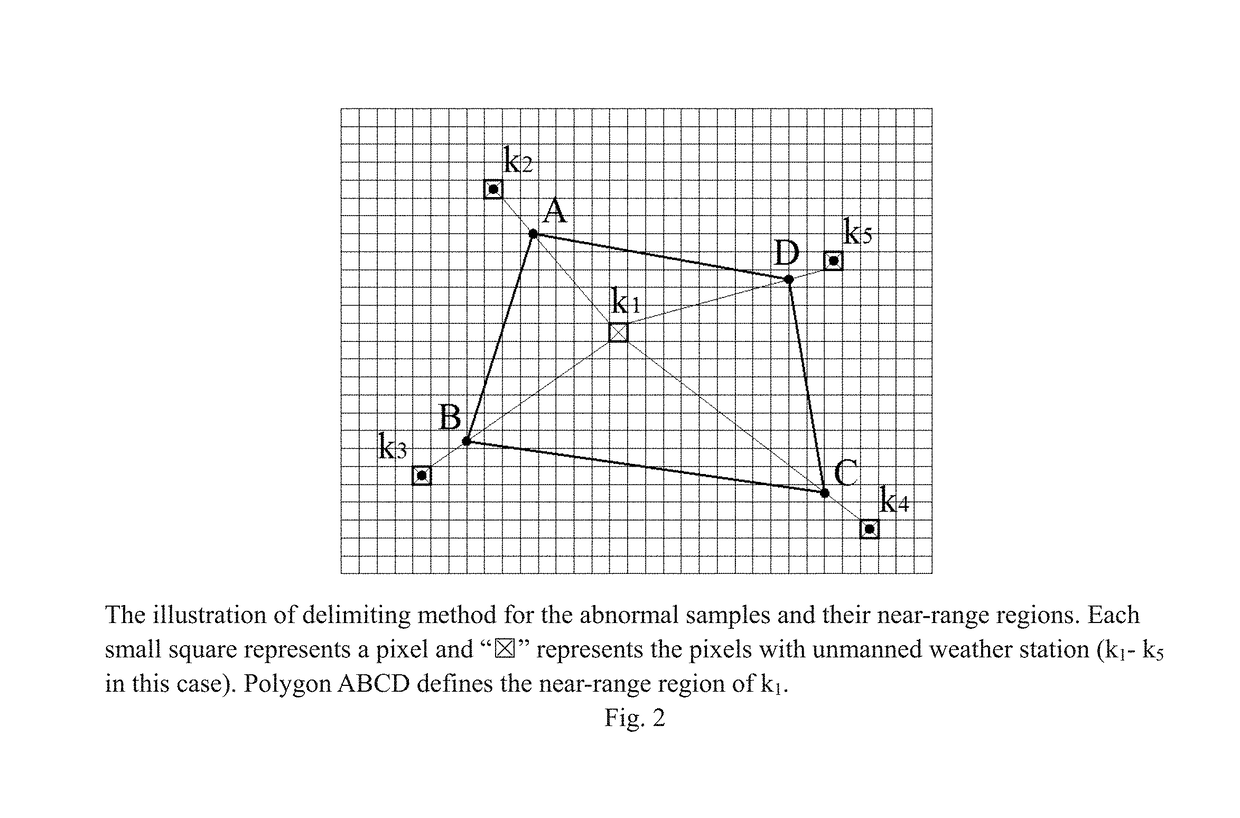
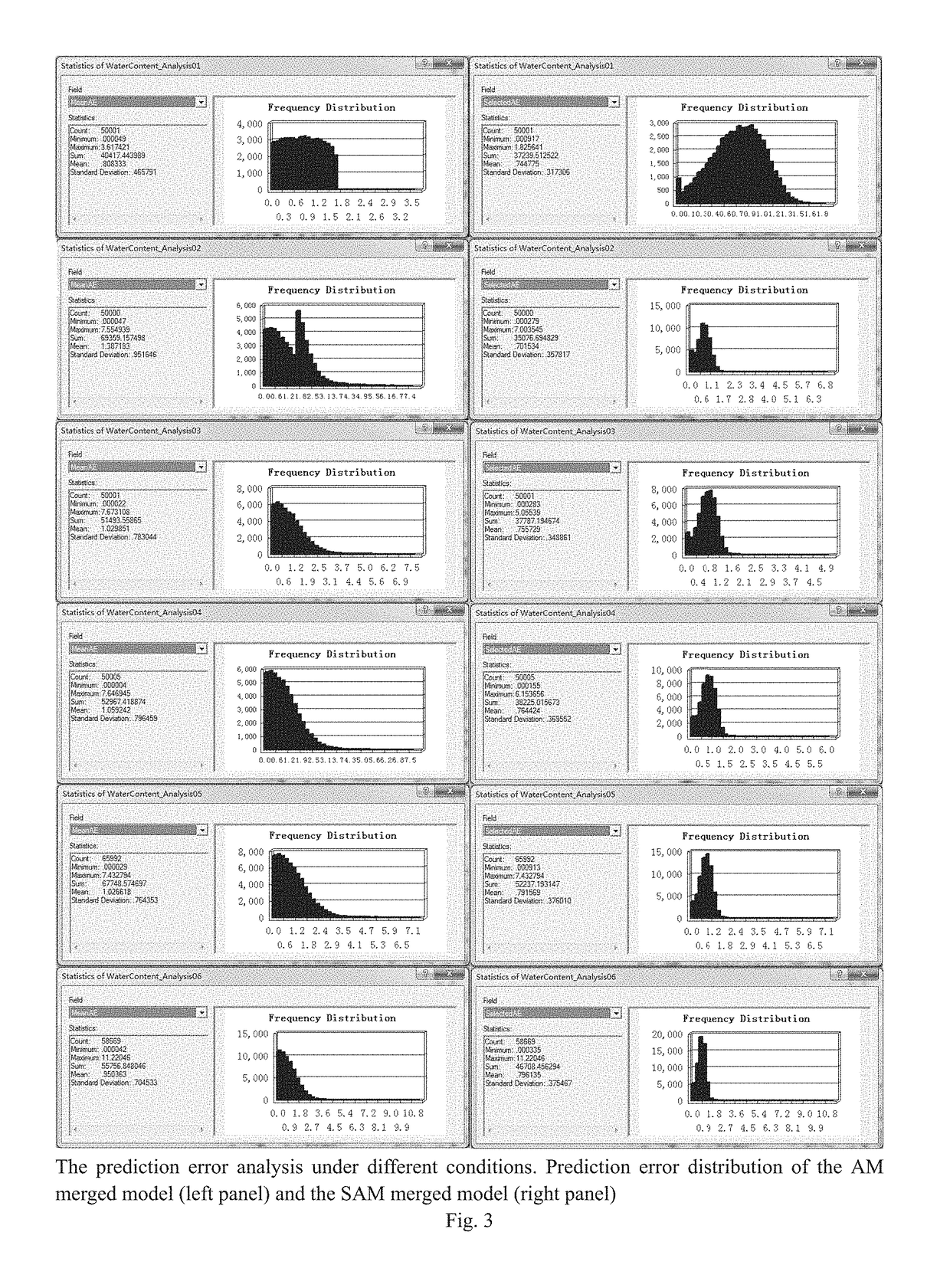
Near-surface air temperature inversion method
ActiveCN104657935AAvoid interferenceImplement combined applicationImage data processing detailsTerrainOriginal data
The invention discloses a near-surface air temperature inversion method comprising the following steps: establishing an original data record set of an unmanned weather station; constructing a first sub-pattern learning set and a first sub-pattern validation set; and acquiring a second sub-pattern to a fth sub-pattern, performing near-surface air temperature inversion to acquire a near-surface air temperature inversion image map of a target zone, and performing error correction to acquire a corrected near-surface air temperature inversion image map. According to the near-surface air temperature inversion method disclosed by the invention, the near-surface air temperature inversion is performed by collecting actually-measured air temperature of the unmanned weather station, collecting meteorological satellite data, DEM data and astronomy and calendar rules and also adopting a super nonlinear algorithm, and the near-surface air temperature inversion image map is then calculated by using a high-performance computer. Results show that the near-surface air temperature inversion method disclosed by the invention is relatively high in pattern accuracy, high in result reliability and strong in generalization ability, and ensures that the interferences of clouds, terrains and the like can be overcome; and a constructed CPU+GPU heterogeneously-cooperative parallel computer ensures that the computation speed can be increased by more than 1000 times, so that the near-surface air temperature inversion method is convenient for large-area application and computing capacity expansion.
Owner:GUANGXI INST OF METEOROLOGICAL DISASTER REDUCING RES +1
Abdominal organ dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging method based on compressed sensing
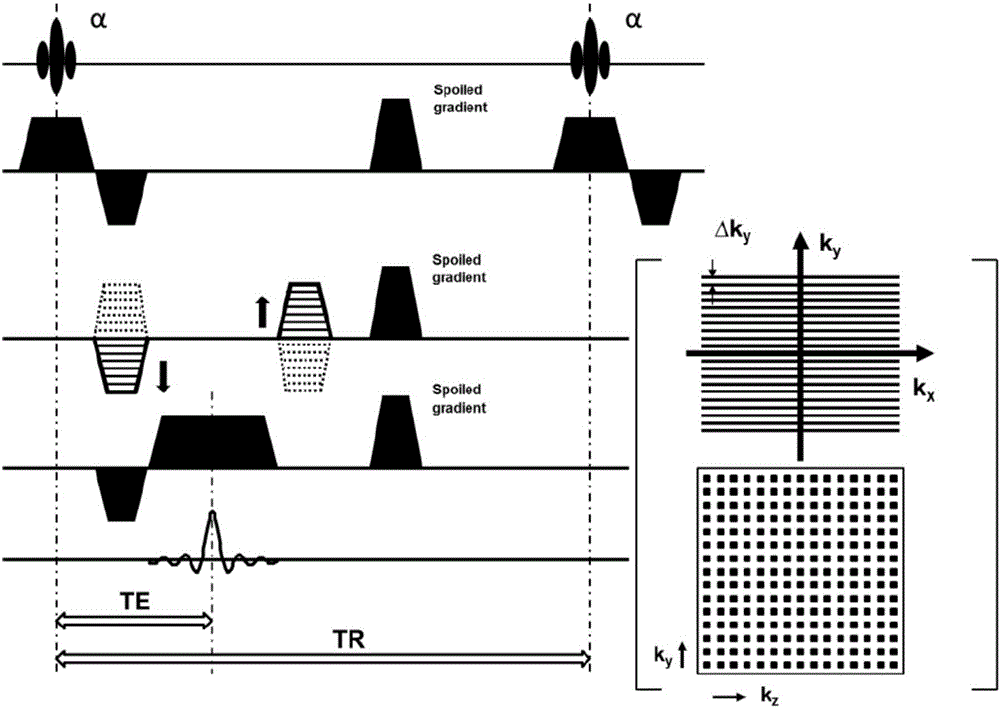
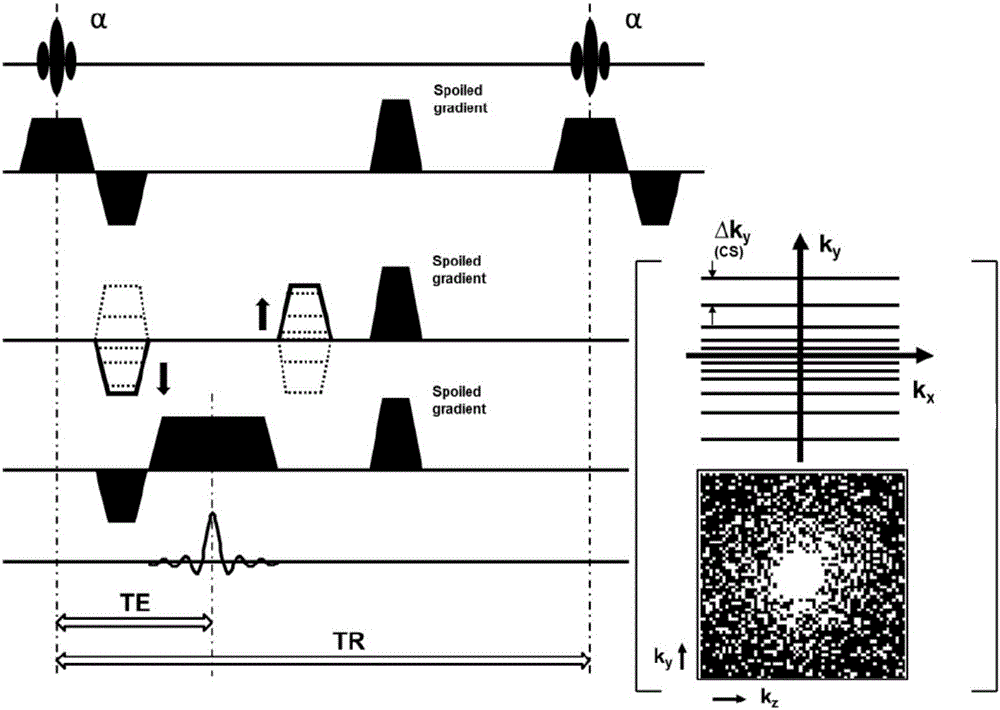
ActiveCN105005012AImprove time resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringDynamic contrastPhase Code
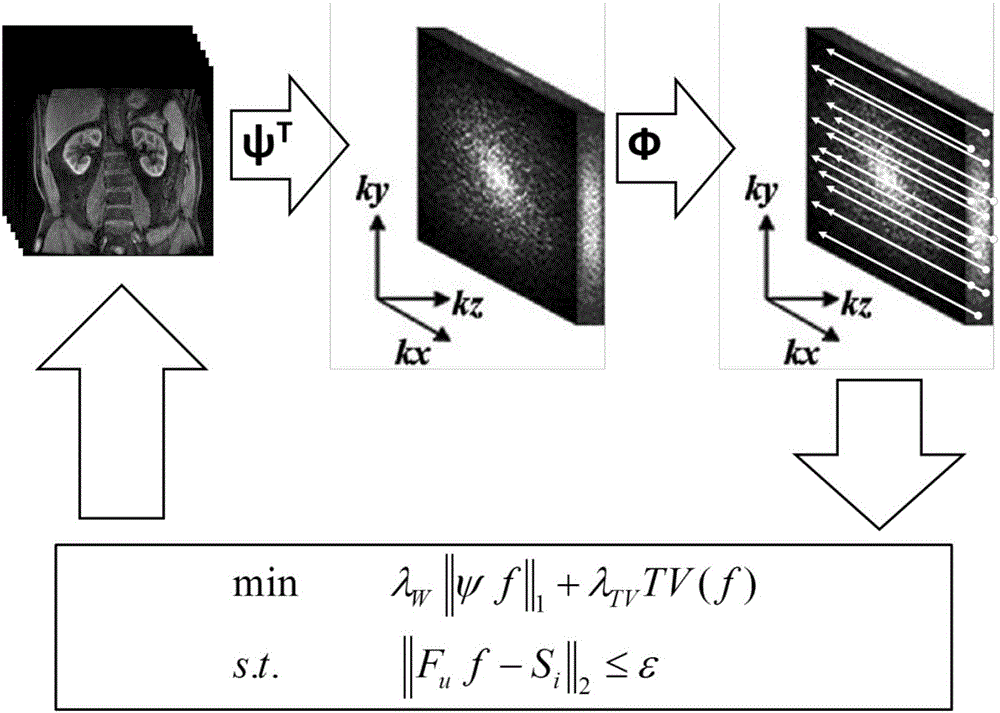
The invention relates to an abdominal organ dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging method based on compressed sensing. The method concretely includes the steps: 1), a magnetic resonance imaging pulse sequence includes a three dimensional gradient echo excitation pulse, a space coding gradient and a signal relaxation sequence, the three of which are explained respectively as follows: 1.1) setting parameters of a radio frequency excitation pulse of a three dimensional gradient echo sequence; 1.2) optimizing a choose-layer phase coding kz and an inner-layer phase coding ky respectively, that is to say, carrying out sub-sampling according to a CS theory, the frequency coding direction kx being fully sampling; and 1.3) applying spoiled gradient to an x gradient direction, a y gradient direction and a z gradient direction in terms of the signal relaxation sequence; 2) a magnetic resonance imaging system carries out compressed sampling of k-space data of all phases of DCE-MRI scanning for an abdominal organ on the basis of a CS optimized magnetic resonance imaging pulse sequence, and obtains original sampling data of a time sequence; and 3) CS reconstruction of the original sampling data is conducted, that is to say, a DICOM image of the abdominal organ is reconstructed and obtained on the basis of a non-linear algorithm with a minimized 1<1> normal form. The method can be widely applied to abdominal organ dynamic contrast enhanced magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
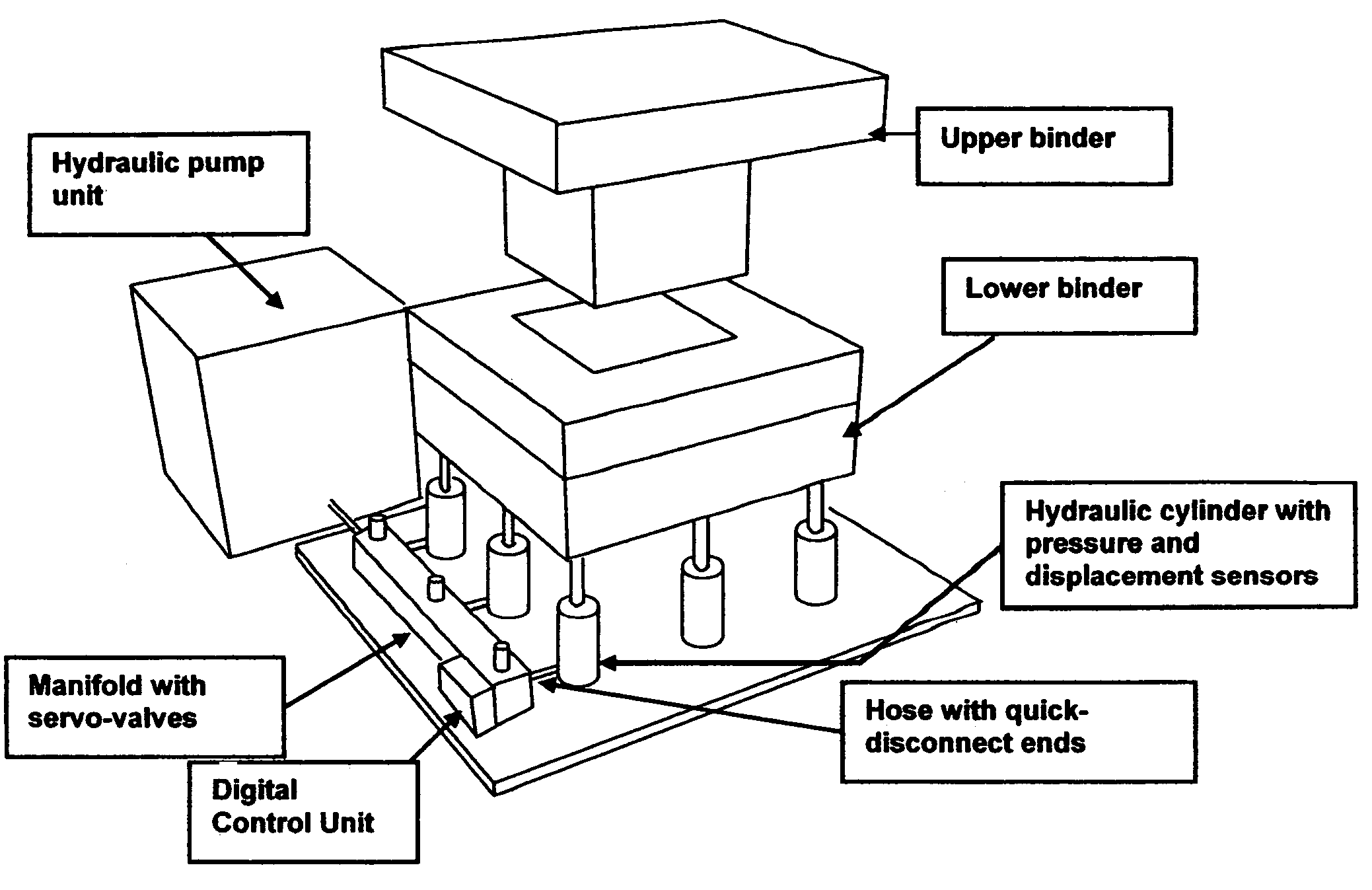
Reconfigurable variable blank-holder force system and method for sheet metal stamping
InactiveUS7257460B2Easy transitionImprove processing efficiencySpecial data processing applicationsPressesEngineeringActuator
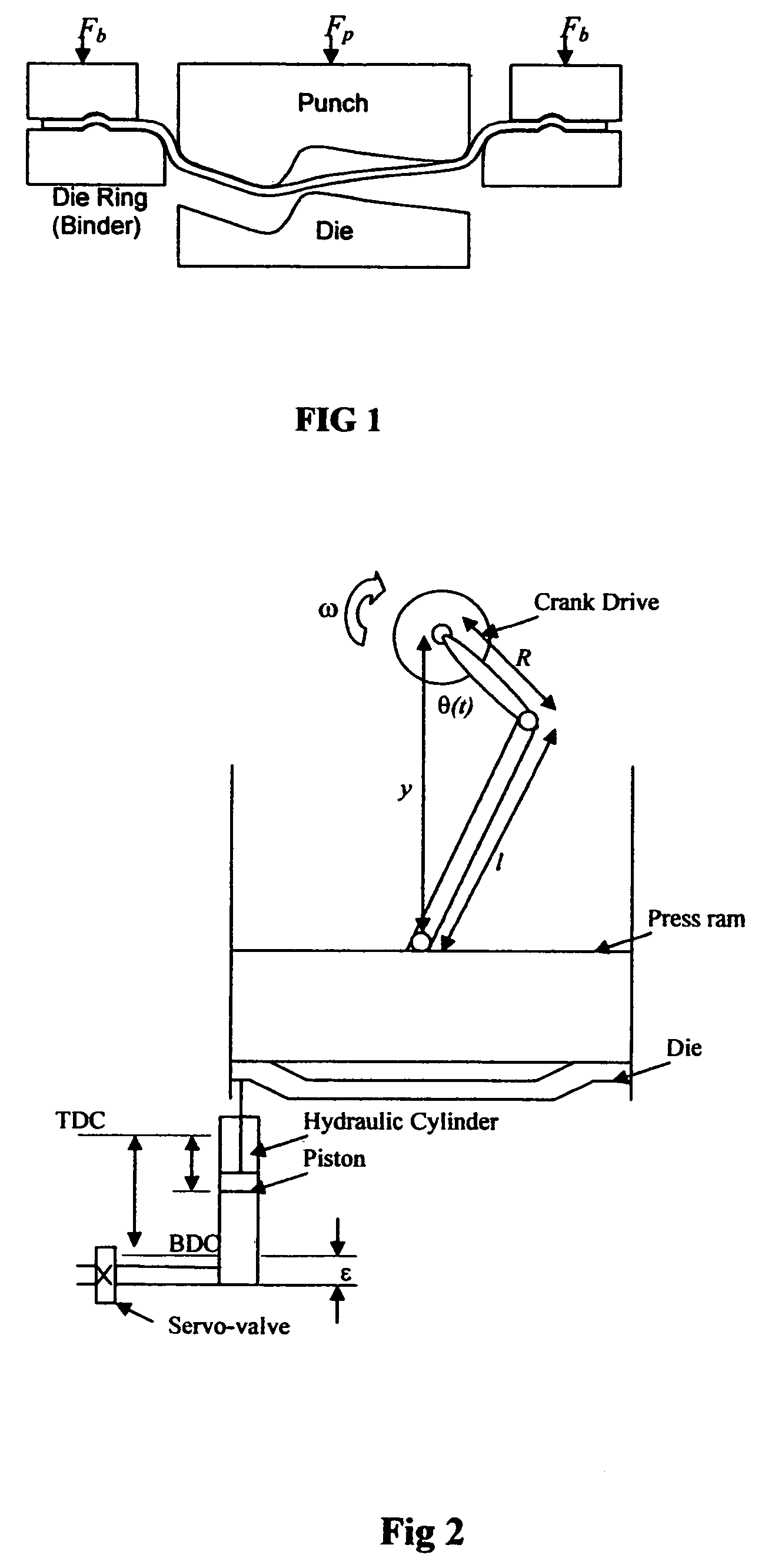
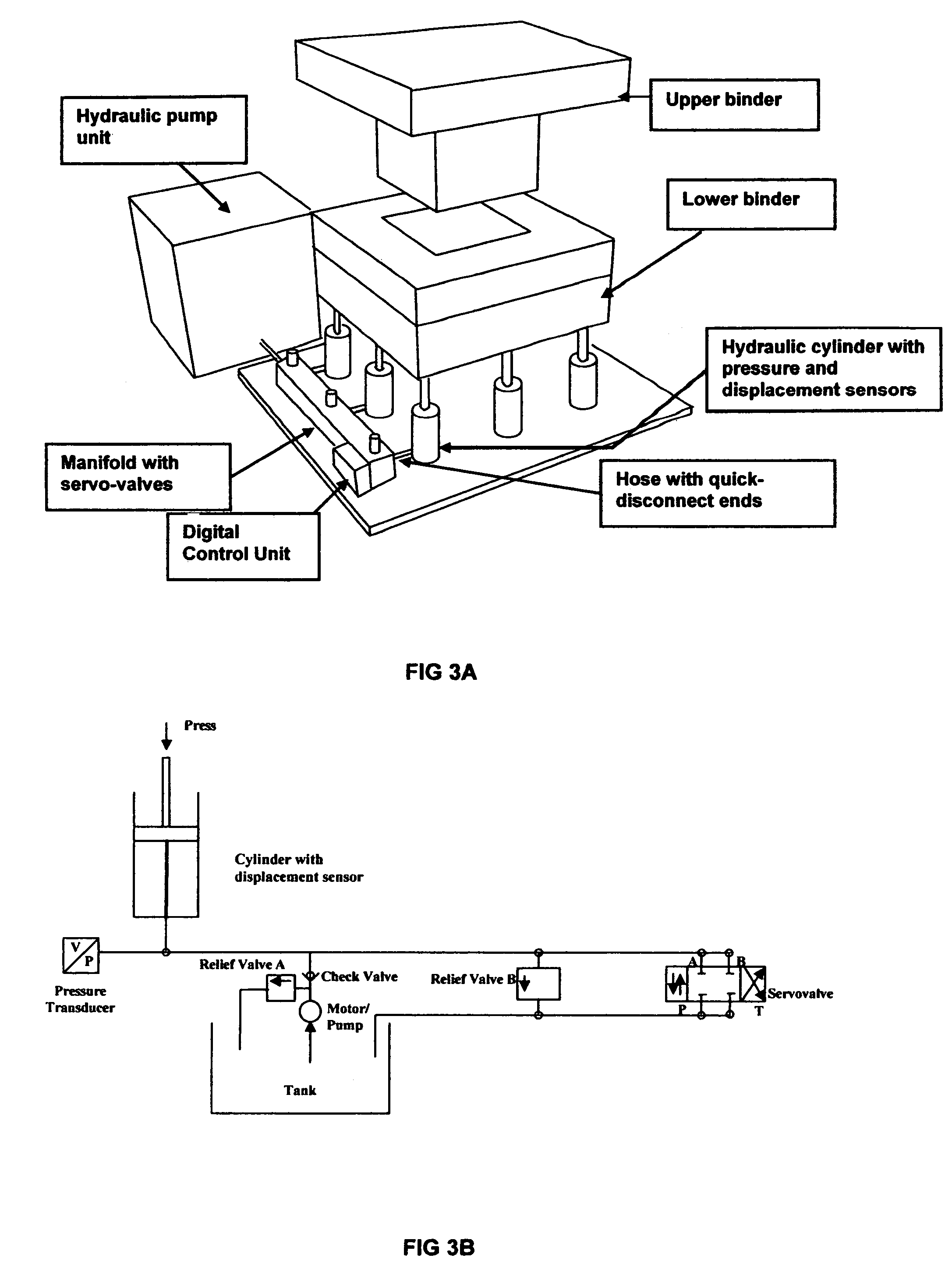
A reconfigurable variable blank-holder force system (and method) for producing sheet metal stampings comprises a portable hydraulic unit, controlled by a digital control system and a knowledge-based expert system to enable reconfigurability and an easy transition from the try-out stage to production. The knowledge-base has a hierarchical structure and includes stored information about part geometry, material properties and press parameters. The expert system enables an operator to determine optimal blank-holder forces, and to fine-tune through a graphical interface unit. The optimal blank-holder forces are generated by hydraulic force actuators, using a controller running a nonlinear algorithm that accounts for valve nonlinearities, variable flow-rate and numbers of operational cylinders. The portable hydraulic unit preferably comprises hydraulic cylinders with quick disconnect hoses, a manifold, servo-valves and a pump unit. A structured method to utilize this system to produce sheet metal stampings is also described. An article embodying the method is included.
Owner:VENUGOPAL RAVINDER +2
Method and product for detecting abnormalities
A new method for processing image data in order to detect abnormalities in a web is provided. The web is monitored by at least one camera, whereby an image comprising of plurality of pixels is generated. The data of the image is stored in a memory. Image data is filtered by a processor by creating a filtered image data by weighting the image data and at least one of earlier image data and earlier filtered image data; and combining the weighted image data and at least one of the weighted earlier image data and the weighted earlier filtered image data; and controlling filtering by at least one nonlinear algorithm; and thresholding the created filtered image data.
Owner:ABB OY
Three-dimensional electromagnetic imaging method based on contrast source inversion algorithm
InactiveCN102854499AQuality improvementImprove practicalityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionHigh resolution imagingEarth surface
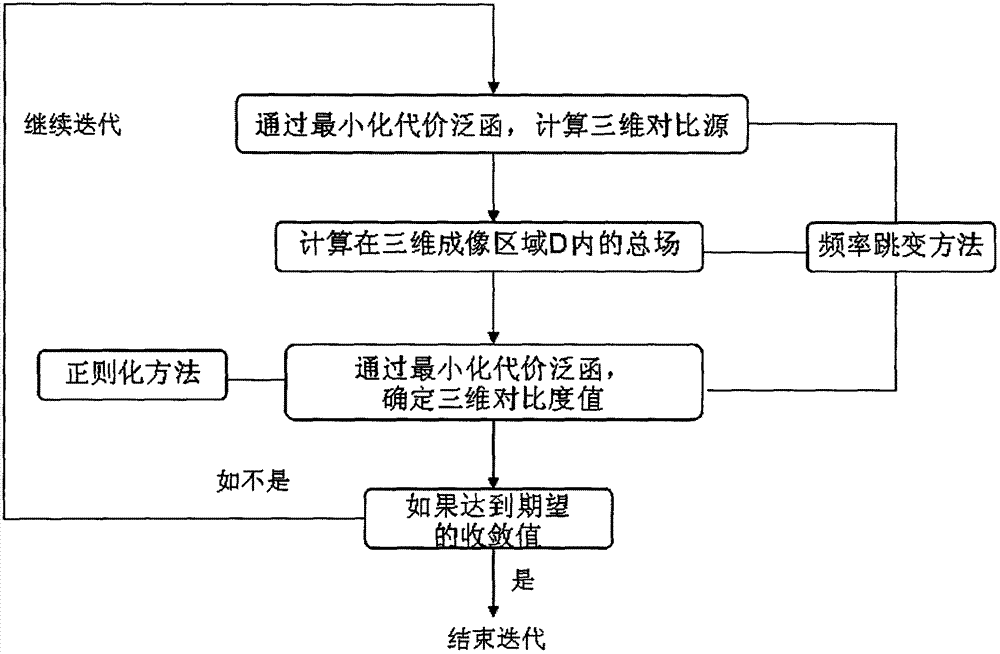
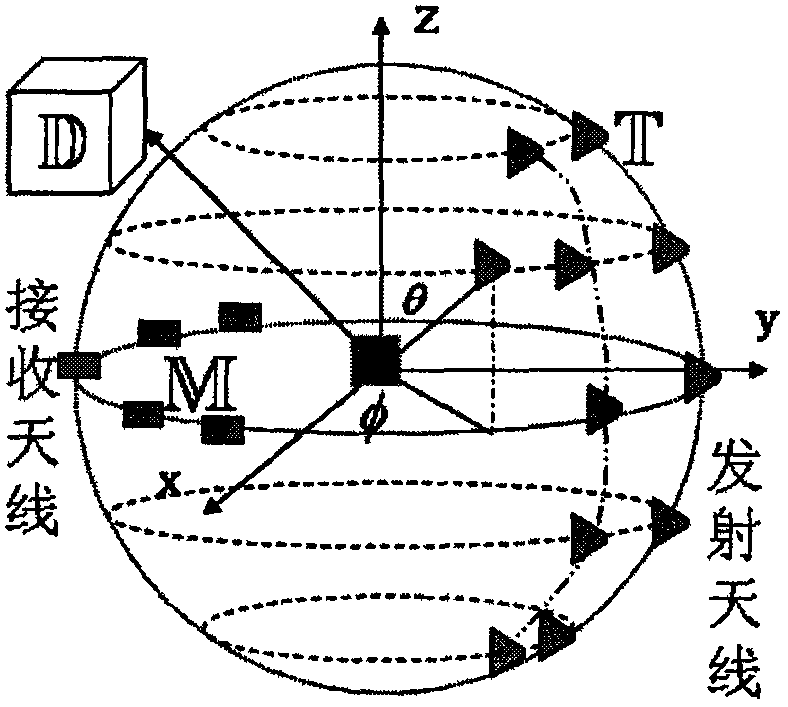
An application of three-dimensional imaging to the field of practical engineering such as nondestructive inspection, medical imaging, ground surface detection, geophysical exploration and the like is of great potential. As approximate treatment is adopted in a linear imaging algorithm, a reconstructed image is limited in precision and accuracy; and while in a non-linear algorithm such as a contrast source inversion (CSI) algorithm, position, shape and material parameters of an image such as an interested target can be gradually improved in an iteration process, and an image most similar to the interested target is reconstructed at last. The invention discloses a nonlinear imaging method for multi-frequency multi-transceiver three-dimensional electromagnetic actual measurement data based on the contrast source inversion algorithm combining a frequency hopping method with a regularization method. As forward calculation is not needed, a calculation amount for calculating a three-dimensional dyadic green function operator and a conjugate operator of the function operator in the iteration process is controllable, and a reconstruction result proves that the method can be widely applied to the field of practical applications with requirements of high-precision and high-resolution imaging due to precision and feasibility of an application to three-dimensional electromagnetic imaging.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Communication-free hopping code generation method of access control system
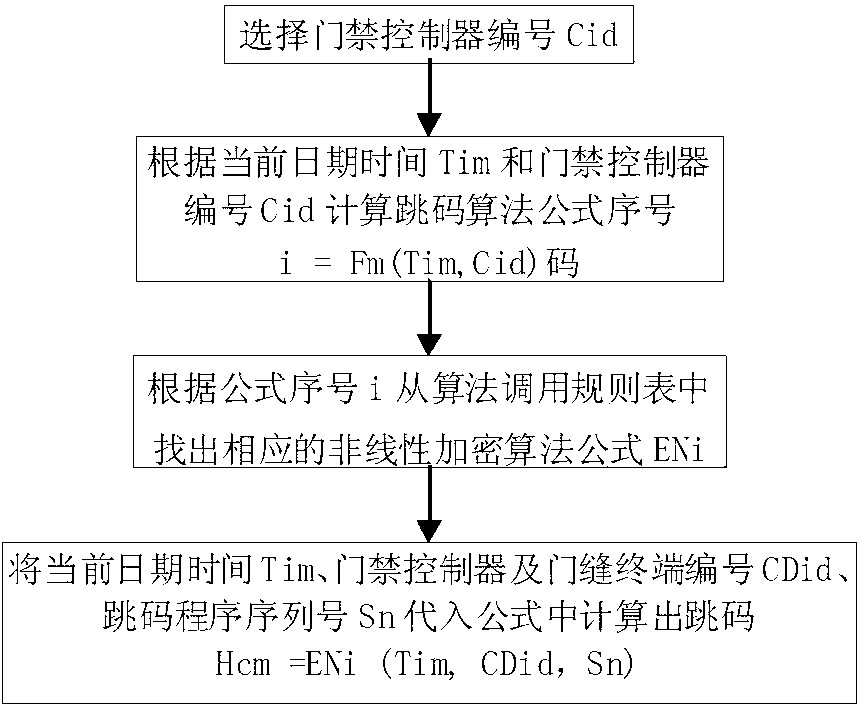
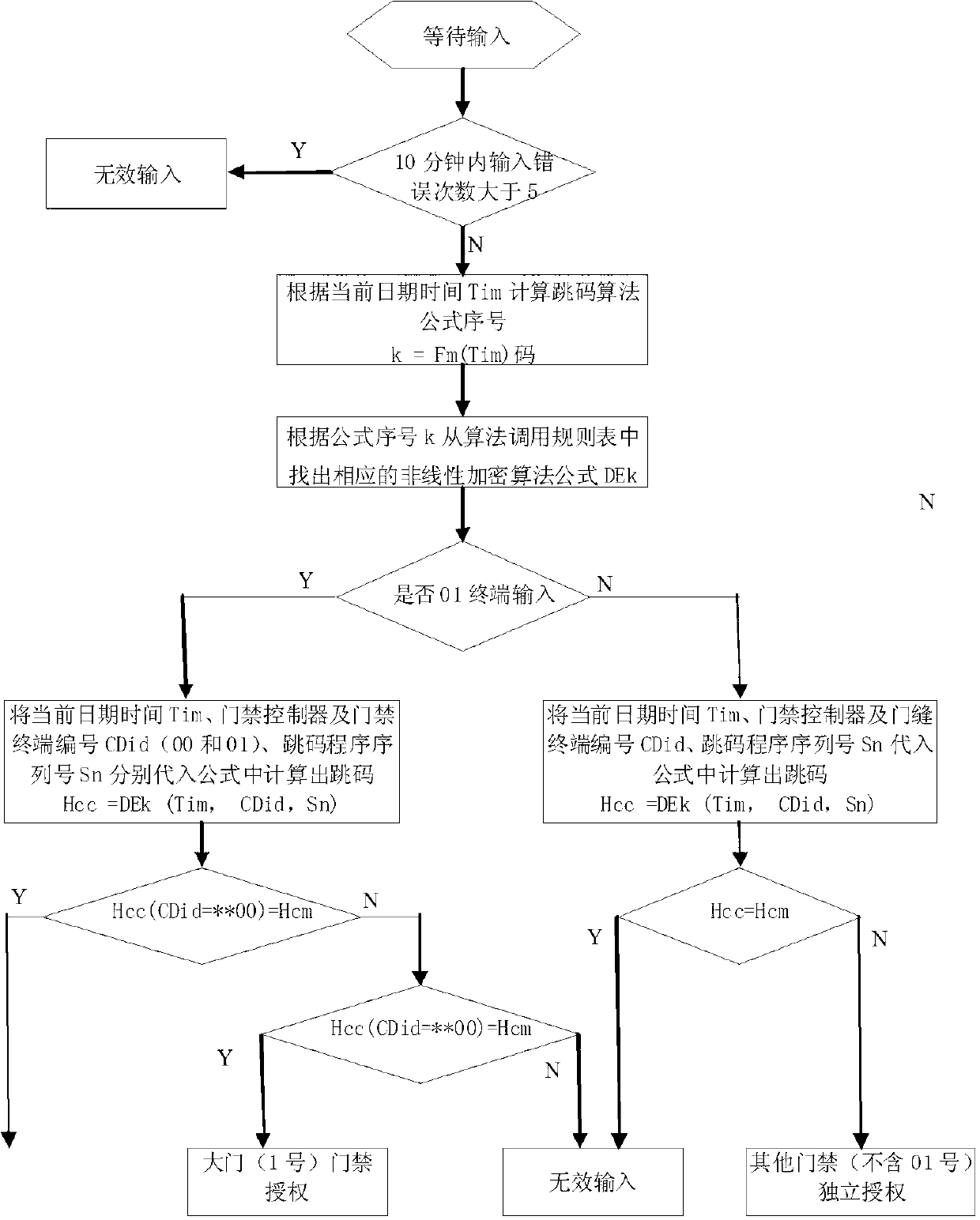
InactiveCN103136830AAchieve decryptionImplement the encryption functionIndividual entry/exit registersComputer hardwareNonlinear algorithms
The invention discloses a communication-free hopping code generation method of an access control system. A hopping code generation system comprises a hopping code terminal and access controllers, one hopping code terminal corresponds to a plurality of access controllers, each access controller controls one access terminal or a plurality of access terminals, wherein a hopping code generating program is mounted in the hopping code terminal, the hopping code generating program is provided with a set of nonlinear algorithms for generating hopping codes and an encryption algorithm calling rule list corresponding to the access controllers, and the algorithms of each access controller at different time intervals are different. A decryption program of the access controllers is provided with a decryption algorithm calling rule list corresponding to the hopping code terminal and a set of decryption nonlinear algorithms, wherein an algorithm at each time interval is the same as the algorithm of the hopping code terminal. According to the communication-free hopping code generation method of the access control system, a corresponding access control terminal is authorized according to a comparison result, no communication link is arranged between the hopping code terminal and the access controllers, and thus non-repeating codes in different time of the access controllers are achieved.
Owner:国网江苏省电力有限公司金湖县供电分公司 +3
Method and system for detecting pace pulses
The present technique provides for the detection of pace pulses in electrocardiogram data. The technique provides for processing one or more sets of electrocardiogram data via a non-linear algorithm. Furthermore, the technique provides for detecting one or more pace pulses in the one or more sets of electrocardiogram data via a non-linear detection algorithm. Systems and computer programs that afford functionality of the type defined by this method are also provided by the present technique.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
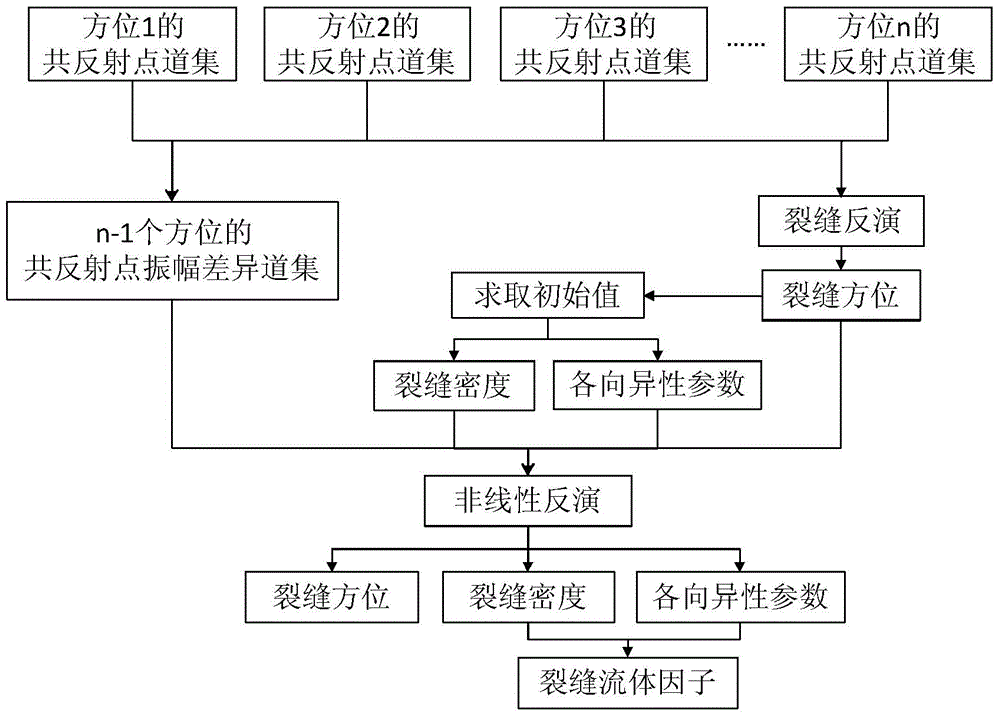
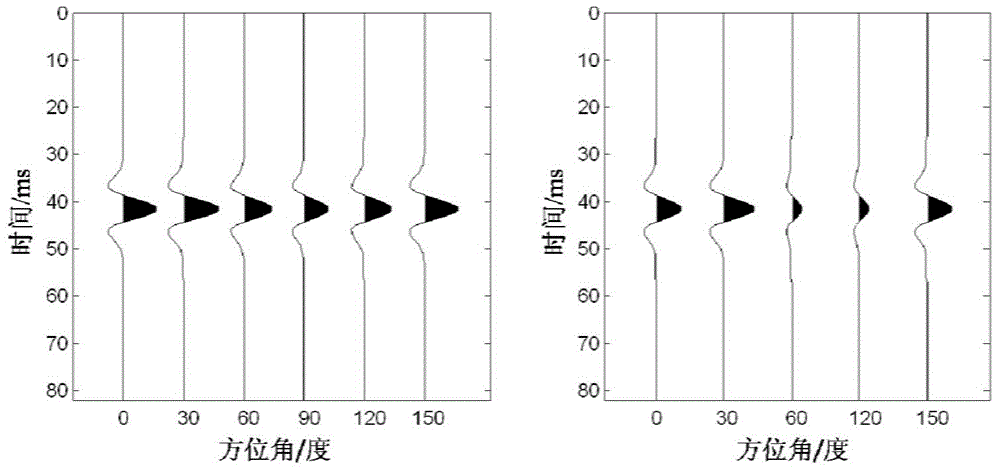
Crack based on non-linear algorithm and method for identifying fluid in crack
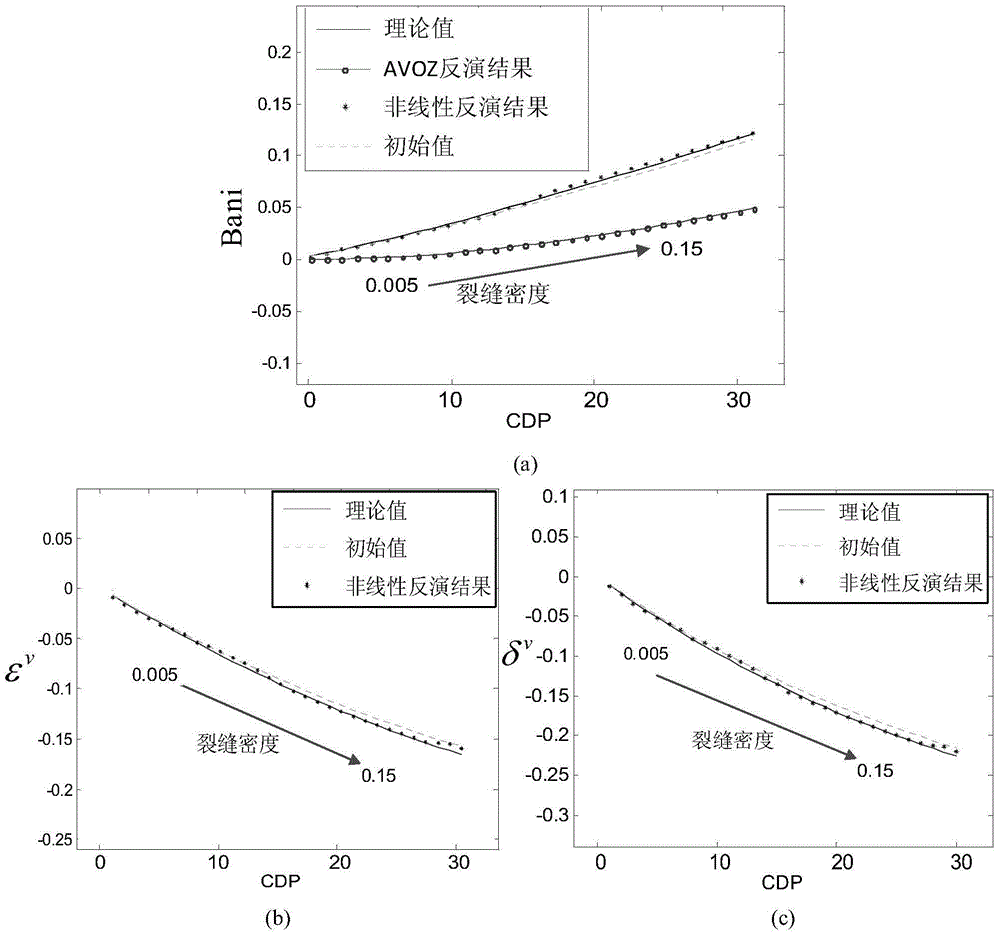
InactiveCN104018826ADetailed descriptionExplain feasibilityBorehole/well accessoriesNonlinear algorithmsParticle swarm algorithm
The invention provides a crack based on a non-linear algorithm and a method for identifying fluid in the crack. The method provided by the invention is based on a trinomial Ruger reflection coefficient equation, and a non-linear equation containing a third member (sin<2>[theta]tan<2>[theta] member) of the Ruger equation and Thomsen anisotropic parameters are deduced out by a different position subtraction method. A non-linear algorithm-particle swarm algorithm is utilized for solving out the crack density, the Thomsen anisotropic parameters and the like from the deduced equation. A crack fluid indicating factor expression is deduced by utilizing the solved crack density and the Thomsen anisotropic parameters. In actual application, the crack density obtained on the basis of the provided non-linear equation is much closer to a theoretical value than the crack density obtained through conventional linear AVOZ inversion; anisotropic parameter values of the inversion are very close to the theoretical value; the crack fluid indicating factor obtained by using the solution of the non-linear equation is used for perfectly identifying the types of the crack fluid; and the feasibility of the method is sufficiently shown.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (BEIJING)
Adaptive integrated circuitry with heterogeneous and reconfigurable matrices of diverse and adaptive computational units having fixed, application specific computational elements
InactiveUS20090037692A1Effectively and efficiently combinesEffectively and efficiently and maximizesEnergy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsHand heldFinite-state machine
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The preferred IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
Adaptive integrated circuitry with heterogeneous and reconfigurable matrices of diverse and adaptive computational units having fixed, application specific computational elements
InactiveUS20090037693A1Minimizing potential disadvantageIncrease speedEnergy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsHand heldFinite-state machine
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The preferred IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
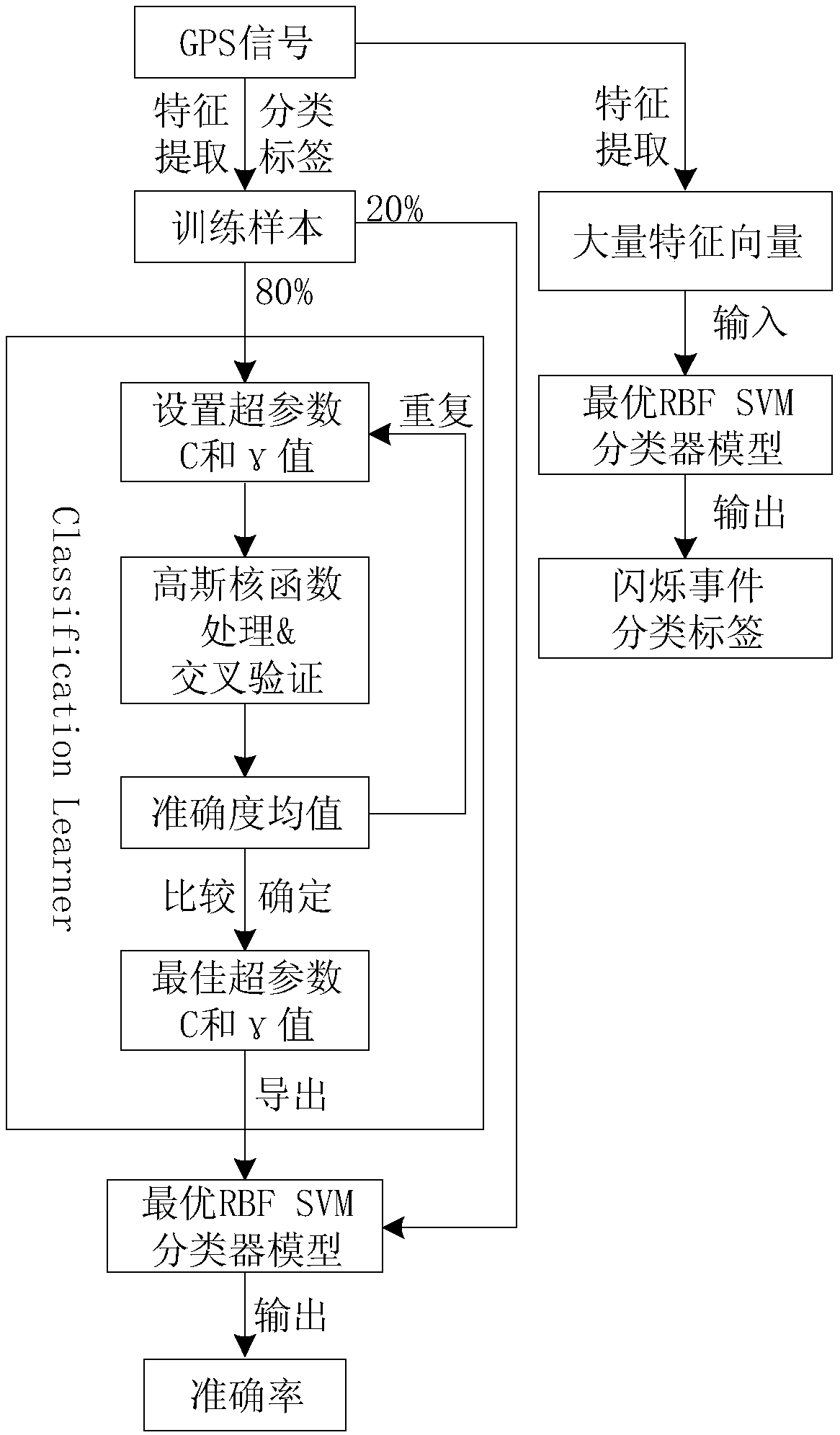
An ionospheric phase scintillation detection method based on nonlinear SVM algorithm
ActiveCN109508730AImprove performanceImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmSvm classifier
The invention provides an ionospheric phase scintillation detection method based on a nonlinear SVM algorithm, The method uses nonlinear SVM algorithm in machine learning to judge the phase flicker ofthe detected signal. The purpose of SVM algorithm is to find a super-flat surface sample with certain characteristics and classify it, and then apply it to new samples. In this proces, Firstly, the received GPS signal is processed by high-pass filter and the maximum value and average value of the phase scintillation index are calculated. Take it as a learning sample to label the corresponding blinking event, and set the label to 1 or 1, indicate that that phase flicker event occurs or does not occur, then the samples are input into the nonlinear SVM classifier for learning, When the new phasescintillation event eigenvector enters the SVM classifier, it will automatically classify the new phase scintillation event. The detection method can classify a large number of scintillation events at the same time, and the use of nonlinear SVM algorithm improves the accuracy of the classification model.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Adaptive integrated circuitry with heterogeneous and reconfigurable matrices of diverse and adaptive computational units having fixed, application specific computational elements
InactiveUS20100161940A1Effectively and efficiently combinesEffectively and efficiently and maximizesEnergy efficient ICTProgram control using wired connectionsFinite-state machineHand held
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The preferred IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications.
Owner:QST HLDG L L C
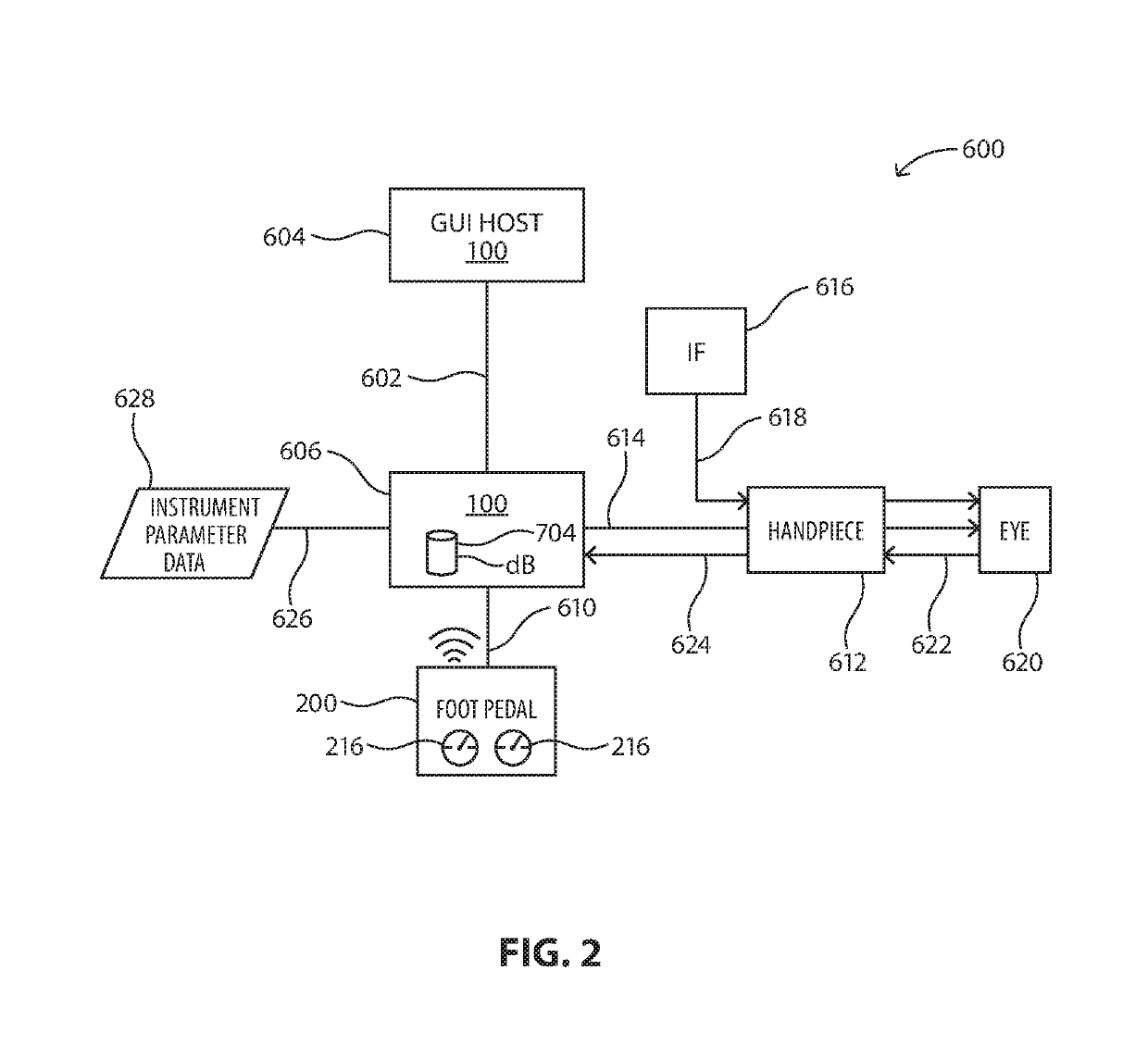
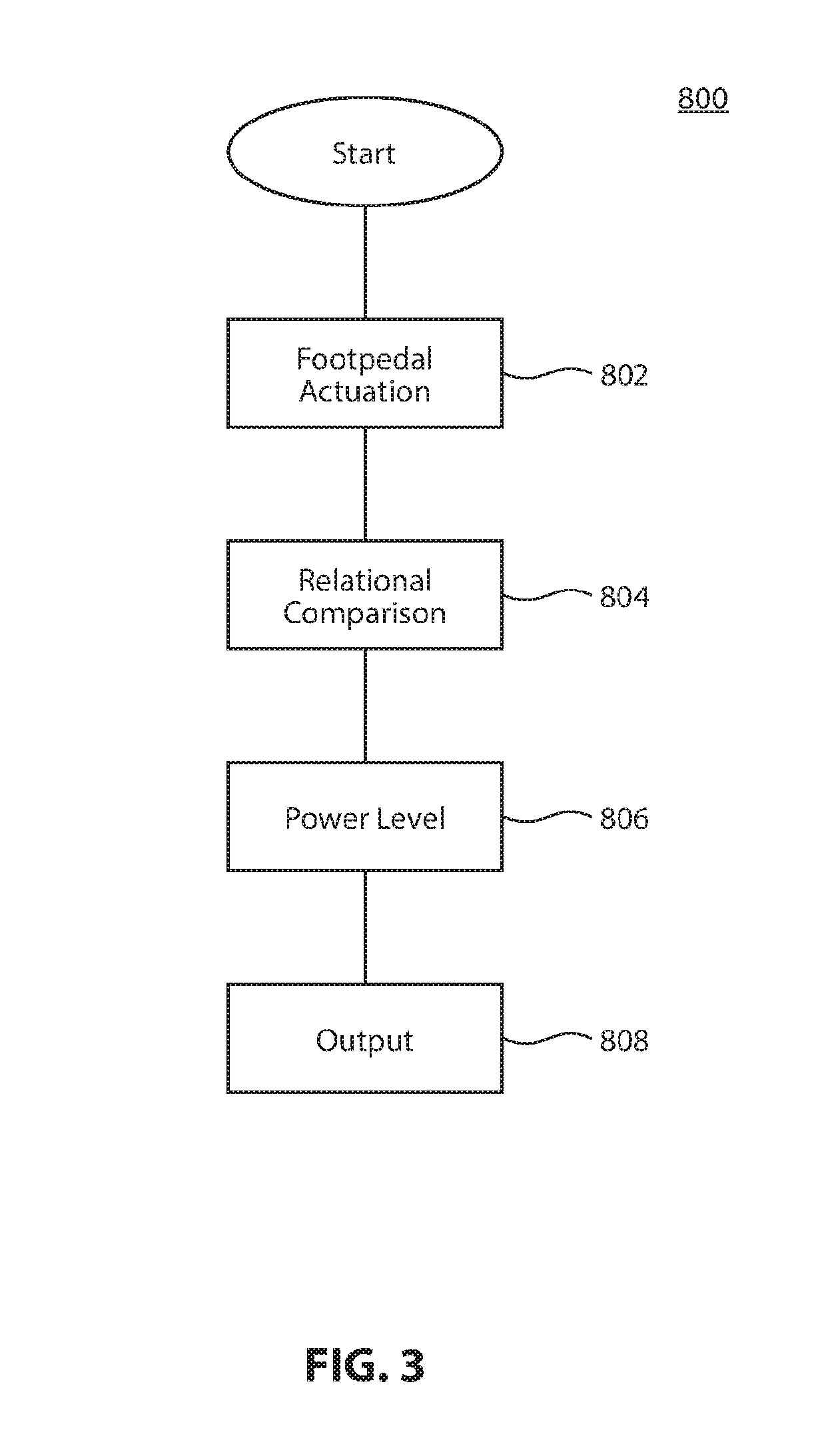
Apparatus, system and method of ultrasonic power delivery in a surgical system
The disclosed apparatus, system and method may include at least a phacoemulsification surgical console having a customizable non-linear custom phacoemulsification mode. The apparatus, system and method may include an ultrasonic delivery tip; a foot pedal; and non-transitory computing code resident on a computing memory associated with a computing processor which, when executed by the processor, causes to be executed the steps of: receiving a percentage actuation of the foot pedal; calculating, including from a non-linear algorithm, a percentage actuation for the ultrasonic delivery tip corresponded to the received percentage foot pedal actuation; and dictating the calculated percentage actuation for the ultrasonic delivery tip actuation to the ultrasonic delivery tip.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON SURGICAL VISION INC
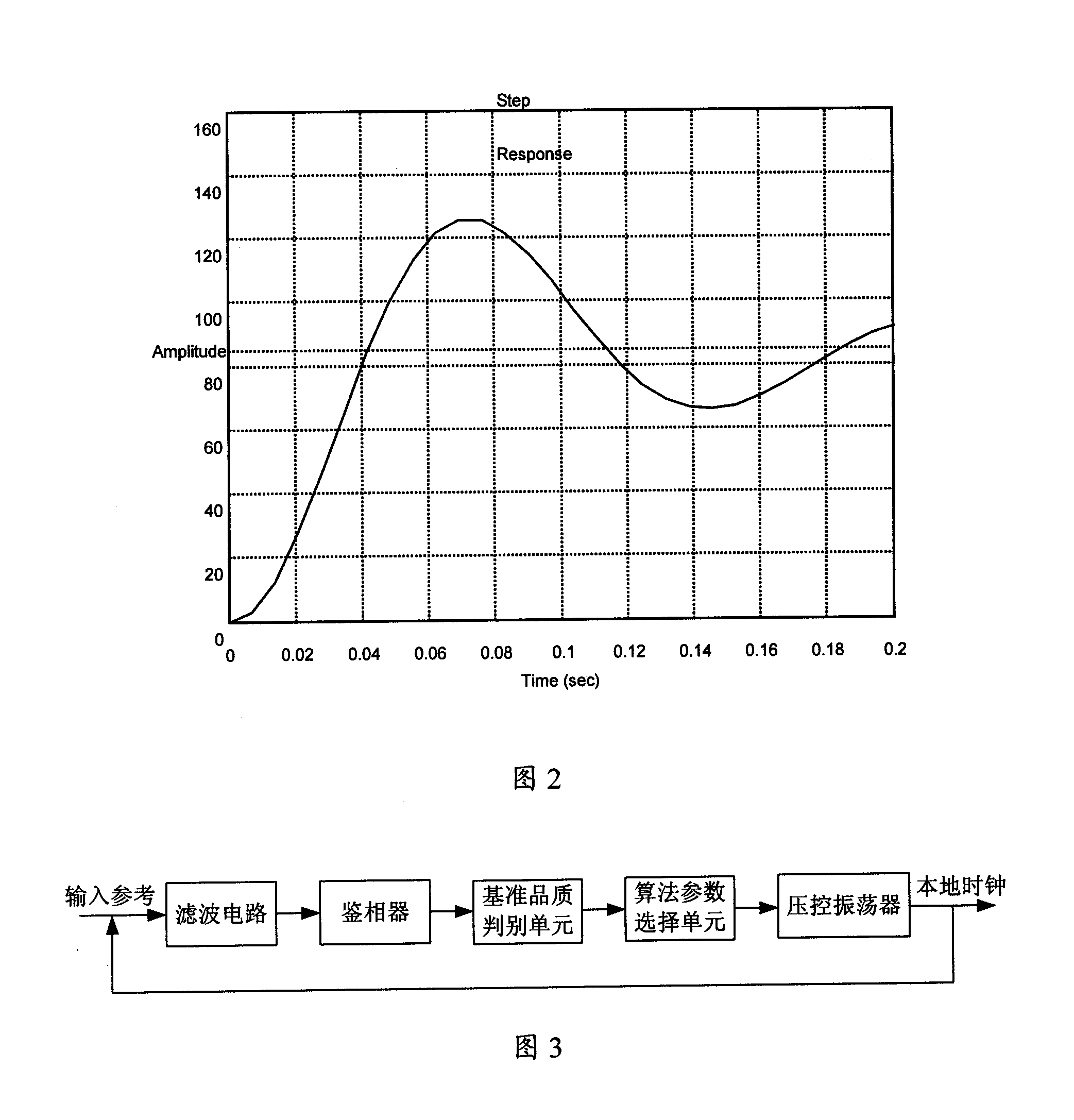
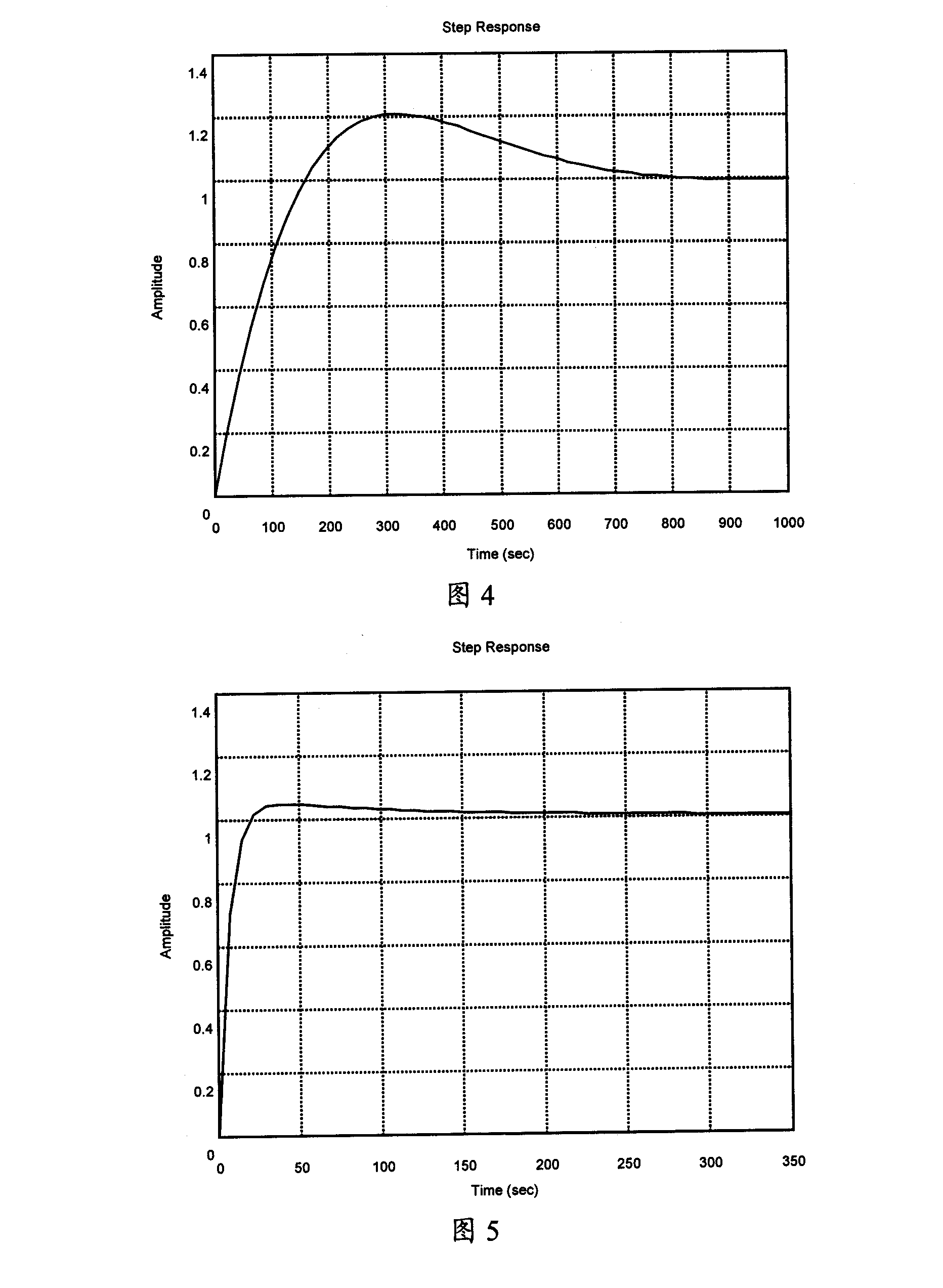
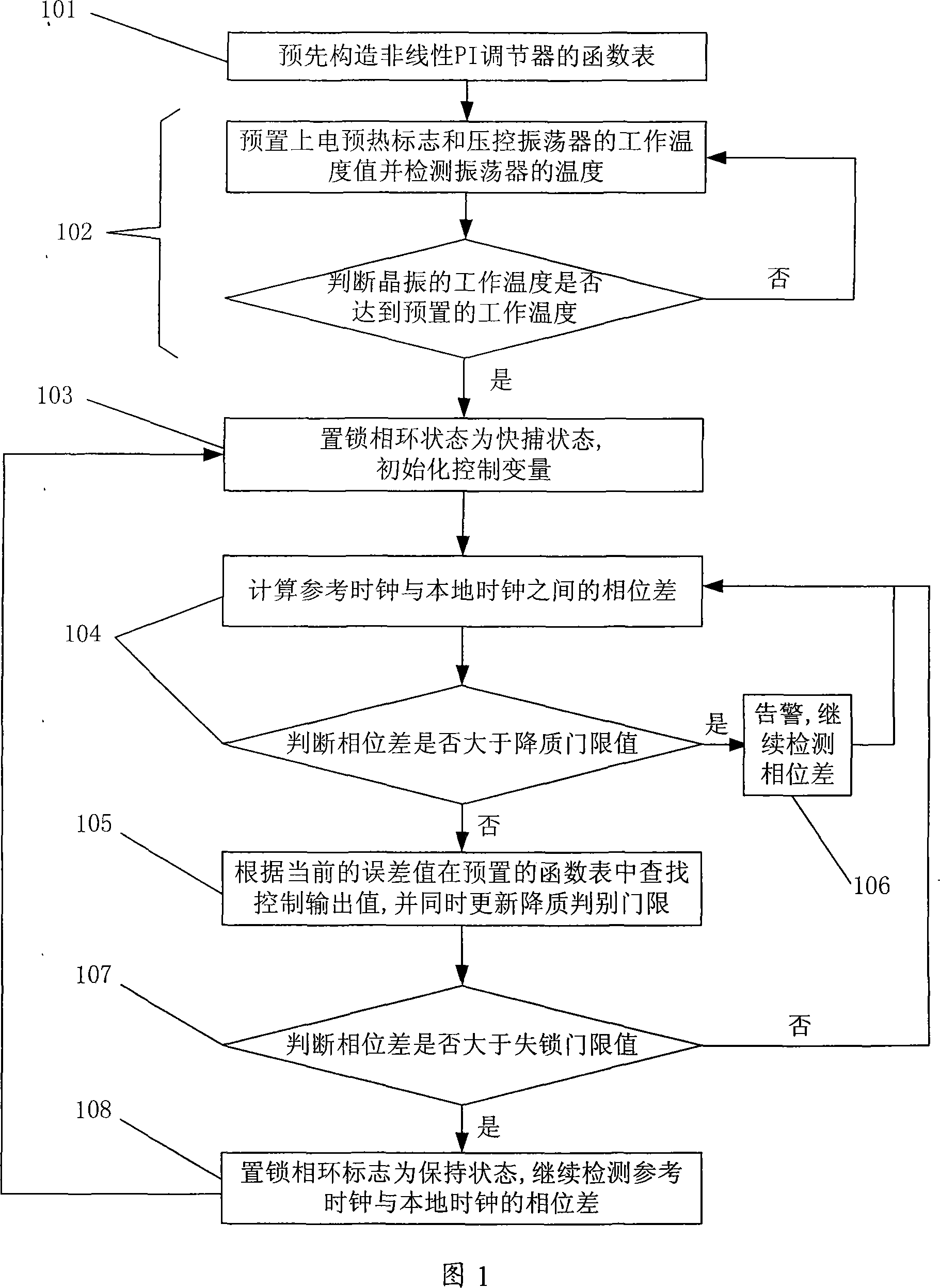
Nonlinear parameter regulating phase-locked loop method and device
InactiveCN101174940AImprove dynamic response performanceSmooth changeSynchronising arrangementPhase differencePhase-locked loop
The present invention provides a method and a device for regulating the phase-locked loop with non-linear parameter; the present invention is used for realizing the clock synchronization between the local clock and the network clock; the method comprises that the function list of a non-linear PI regulator is prefabricated and the function calculation data list is stored in a non-volatile memory in advance; the phase difference between the reference clock and the local output clock is detected cyclically. The gain parameter of the present PI control link obtained by the data list stored in advance is consulted according to the phase difference and the parameter is substituted into the PI control link to calculate the controlling quantity. The method and the device of the present invention, by presetting the non-linear algorithm parameter list, obtains the gain parameter value of the PI control link at every phase error point; the anti-interference capability is greatly increased compared with the original one; the dynamic response capability of the phase-locked loop is promoted, the regulating time and the overshoot are further reduced; moreover, the robust property of the phase-locked loop is enhanced.
Owner:ZTE CORP
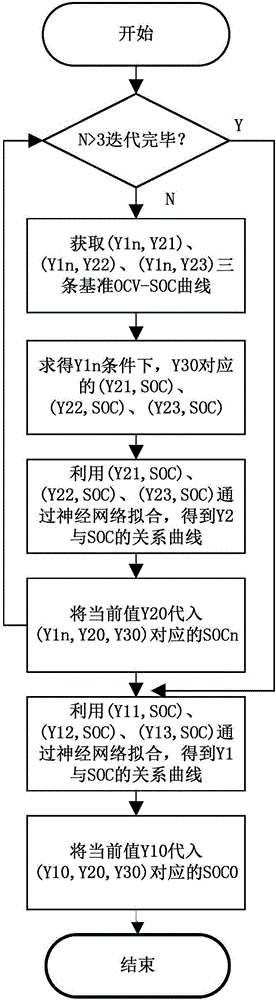
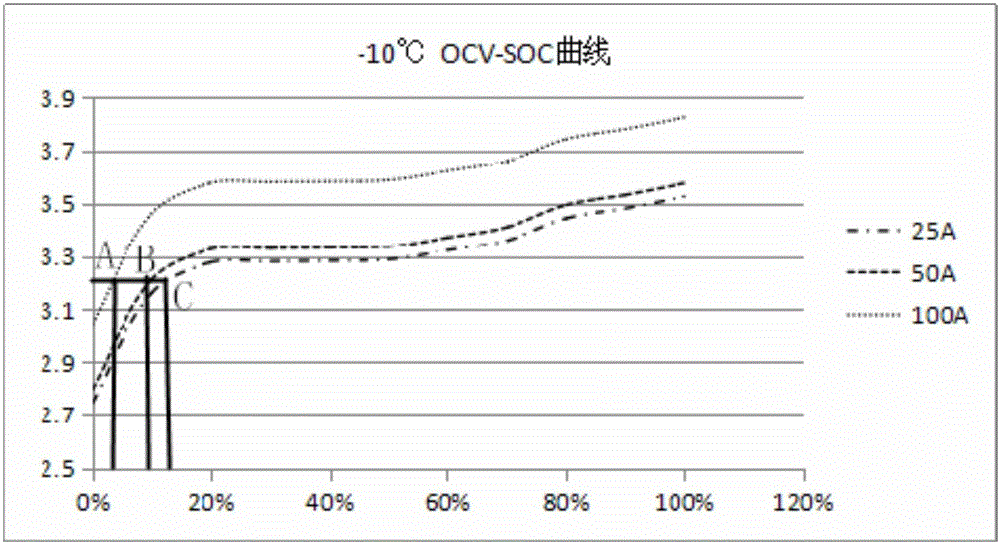
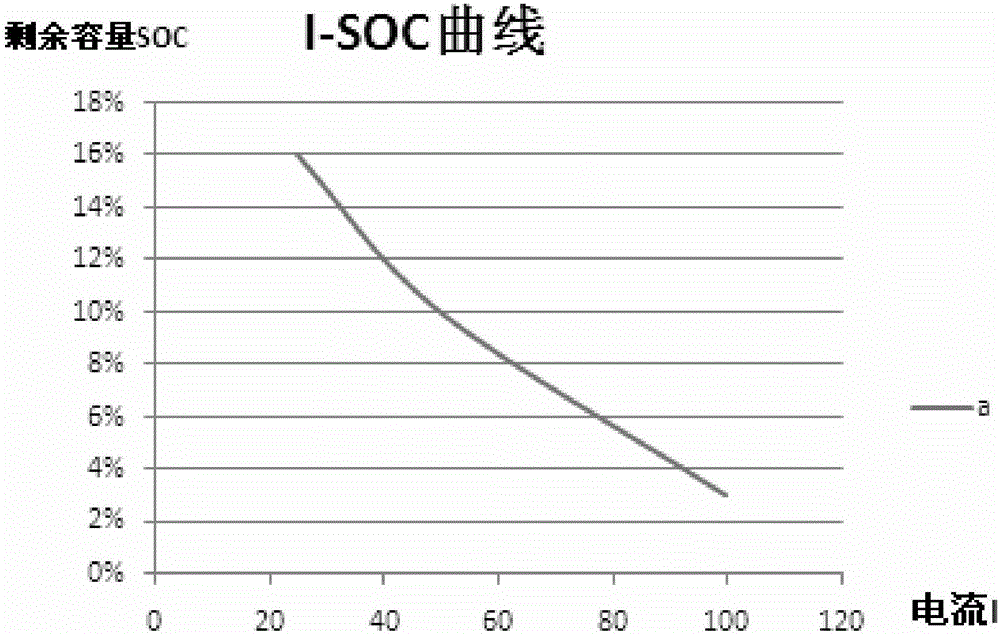
OCV-SOC curve real-time online prediction method and device
The present invention provides an OCV-SOC curve real-time online prediction method. The method includes the following steps that: the OCV-SOC curve of a battery when a certain influence factor is constant and the other influence factors are variable is obtained, and the obtained curve is adopted as a reference OCV-SOC curve, an influence factor value in the curve is set to a reference influence factor value; all influence factor values under the current state of the battery are obtained; and the reference OCV-SOC curve is fitted through a nonlinear algorithm under corresponding influence factors according to the obtained current influence factor values, so that the SOC value of the battery under the current state can be obtained, With the OCV-SOC curve real-time online prediction method adopted, similarity between a predicted OCV-SOC curve and an actually tested OCV-SOC curve can be improved.
Owner:WASION GROUP HLDG
Adaptive integrated circuitry with heterogeneous and reconfigurable matrices of diverse and adaptive computational units having fixed, application specific computational elements
InactiveUS20080098095A1Effectively and efficiently combinesEffectively and efficiently and maximizesEnergy efficient ICTArchitecture with single central processing unitNonlinear algorithmsFinite-state machine
The present invention provides an adaptive integrated circuit. The various embodiments include a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations.
Owner:ALTERA CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com