Patents
Literature
267 results about "Adaptive computing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
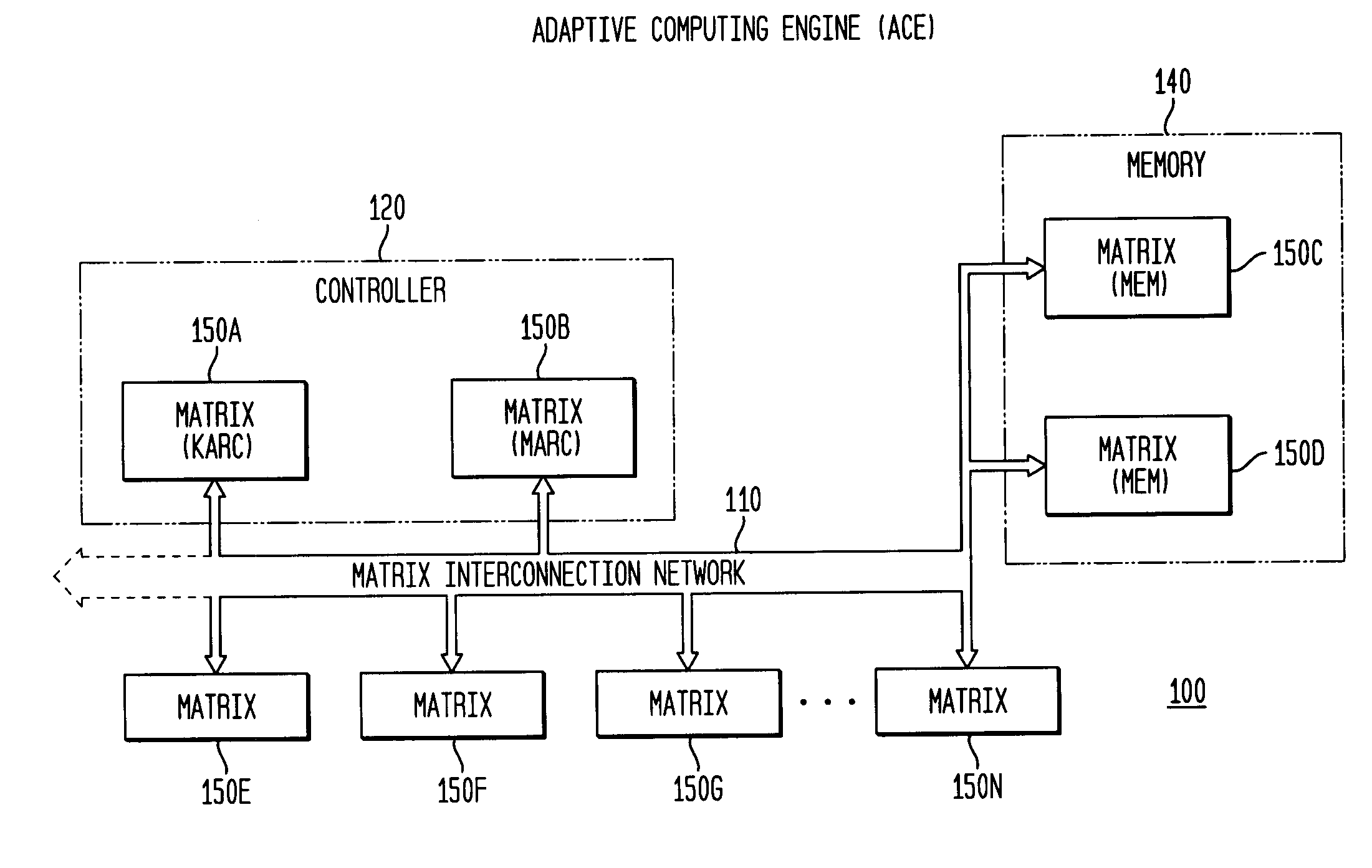
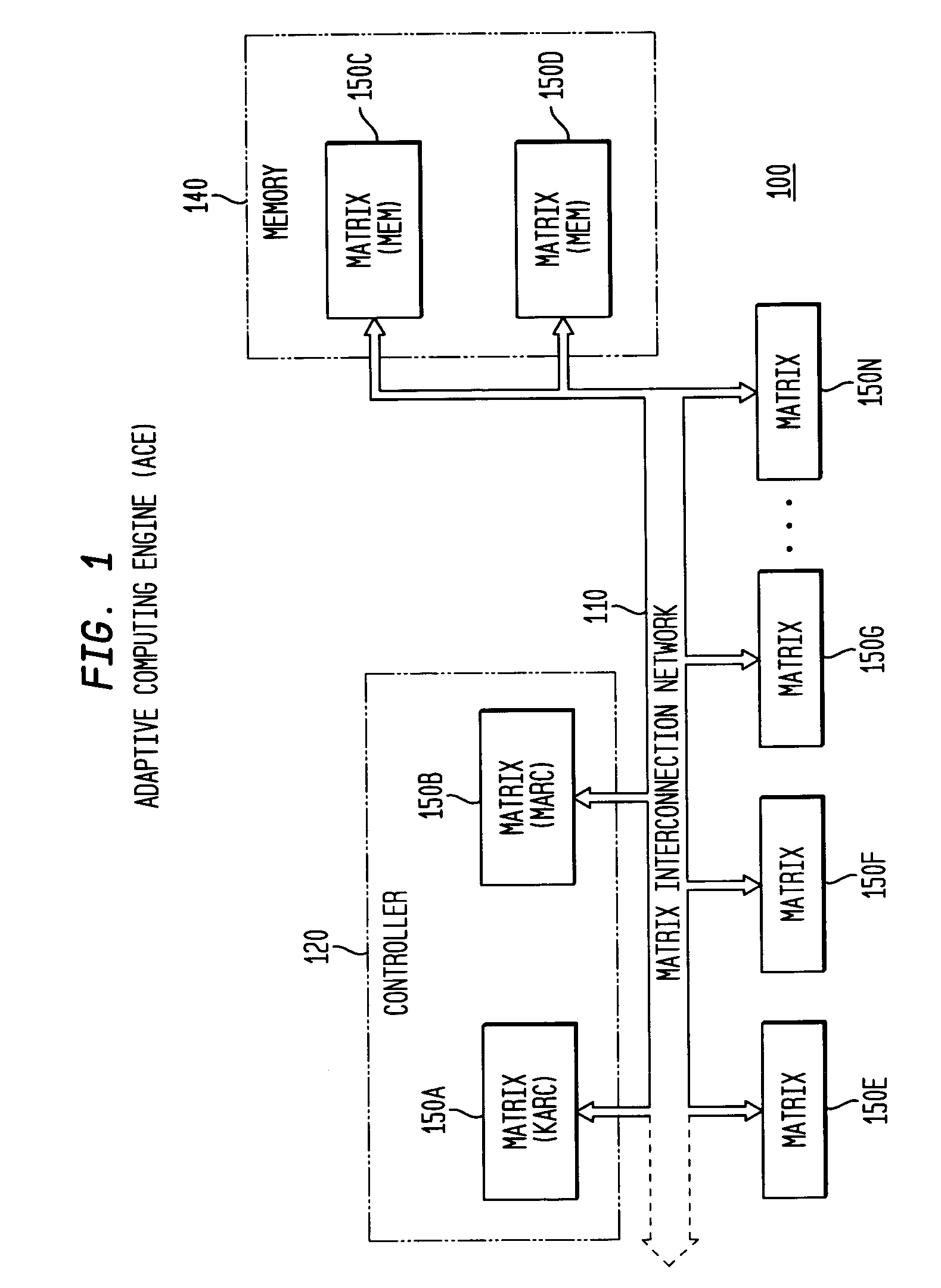
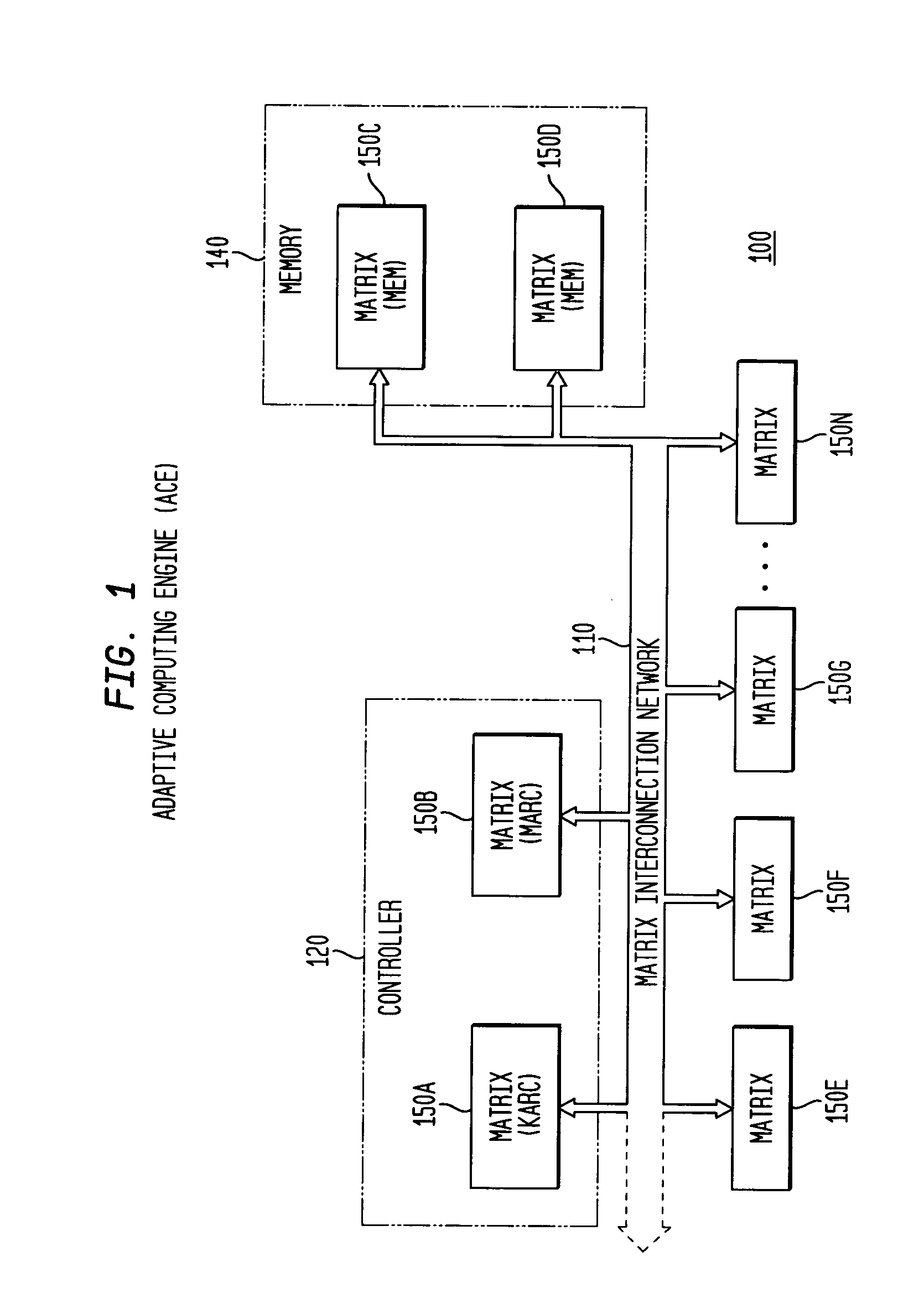
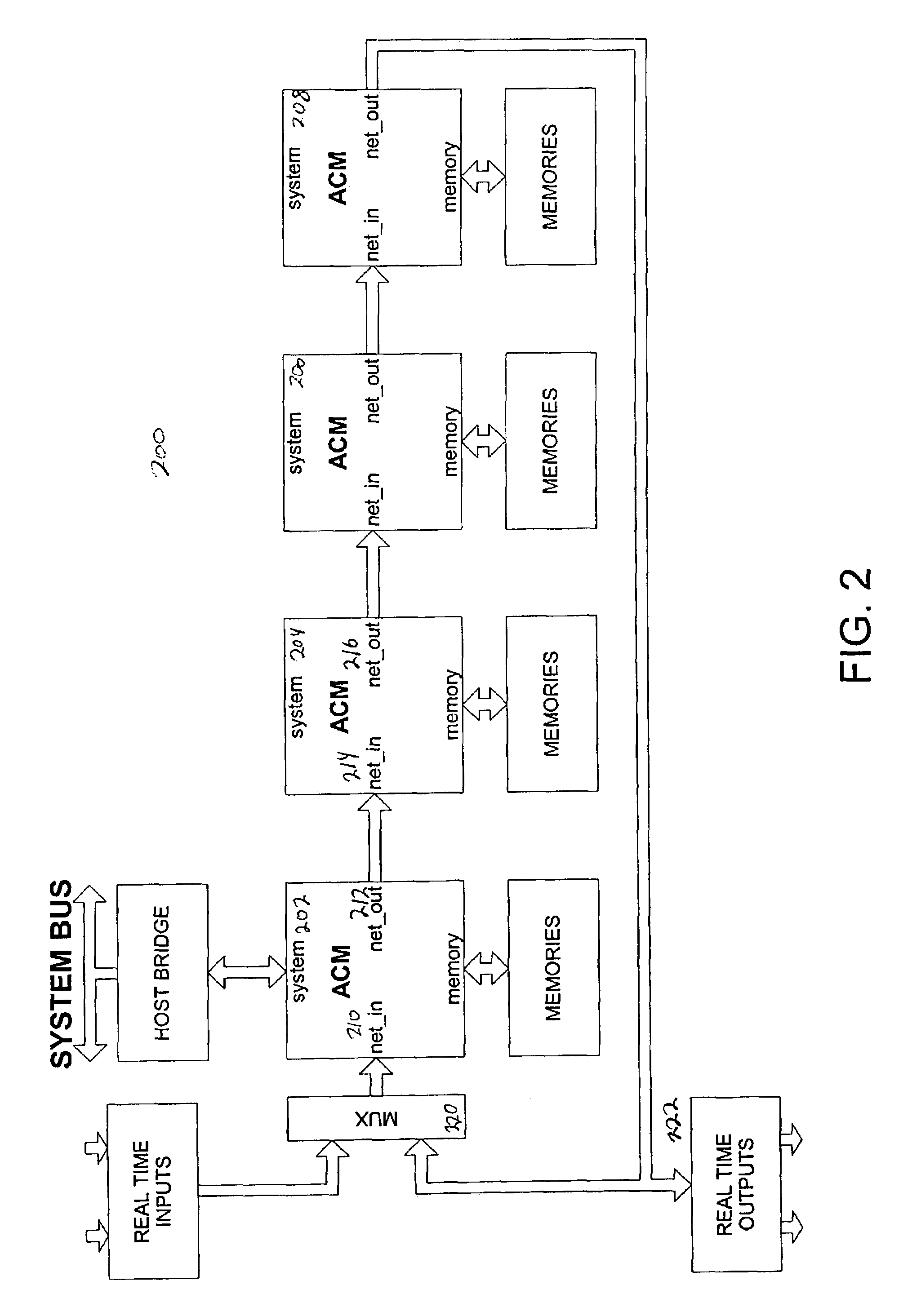
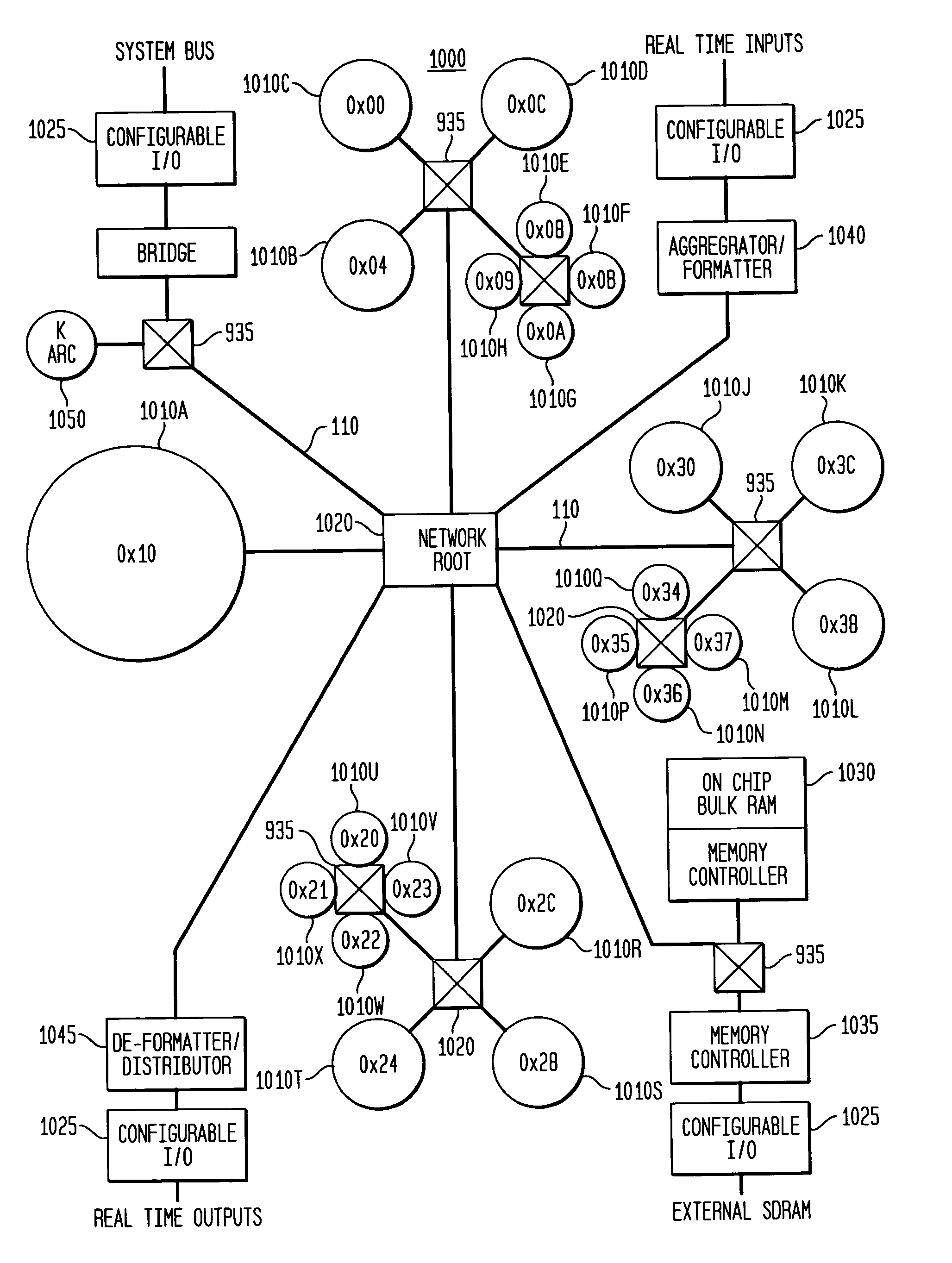
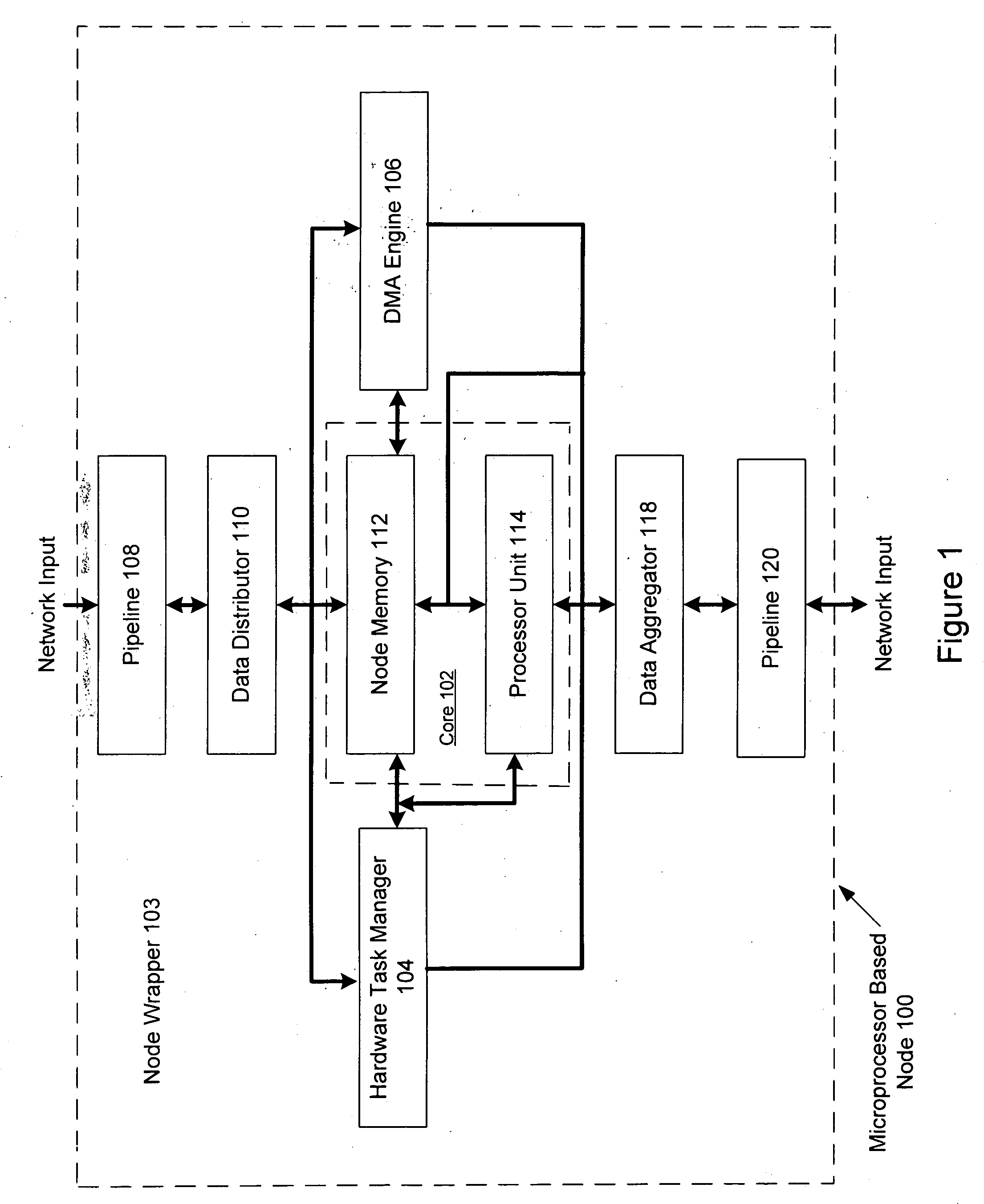
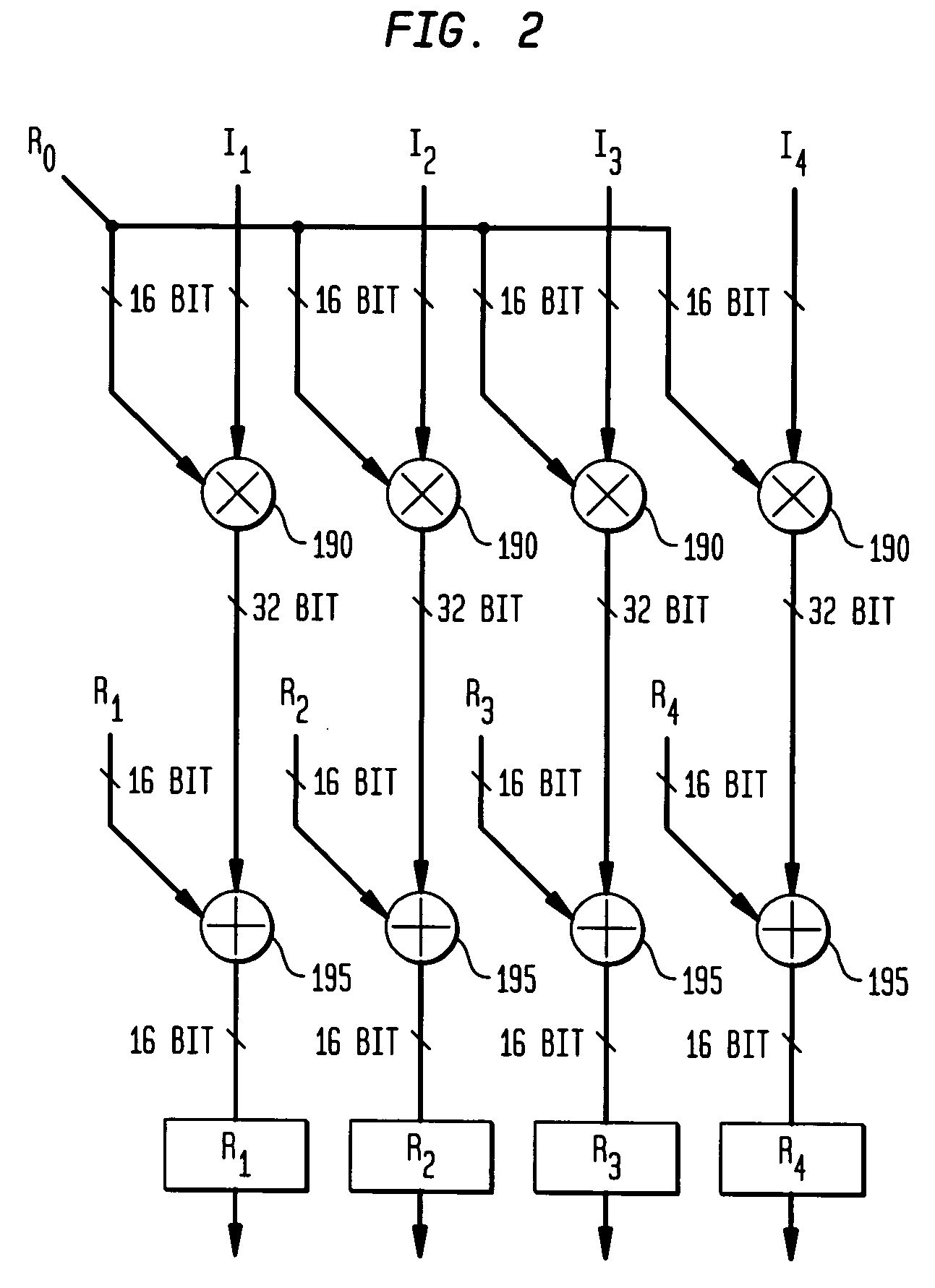
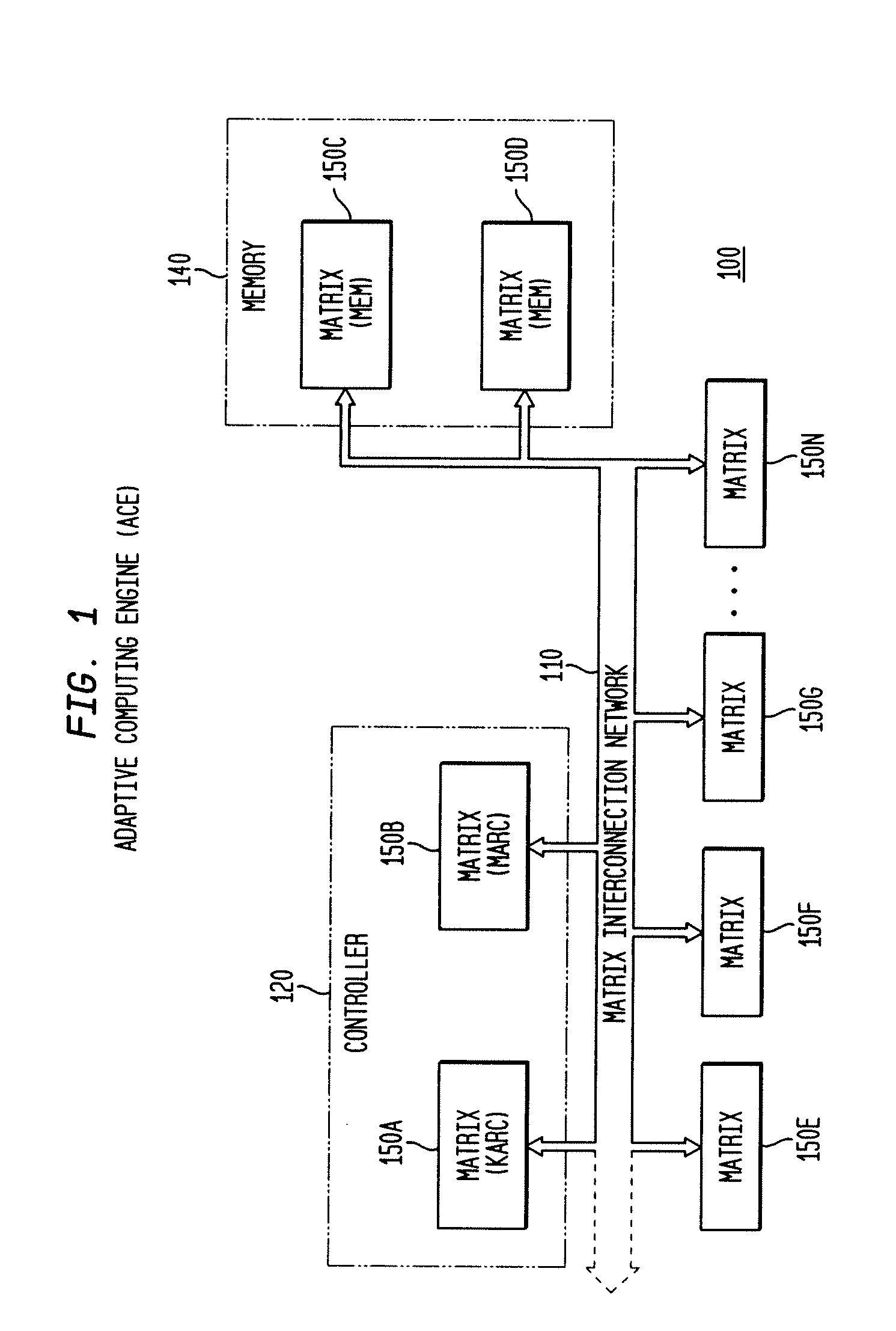
System, method and software for static and dynamic programming and configuration of an adaptive computing architecture
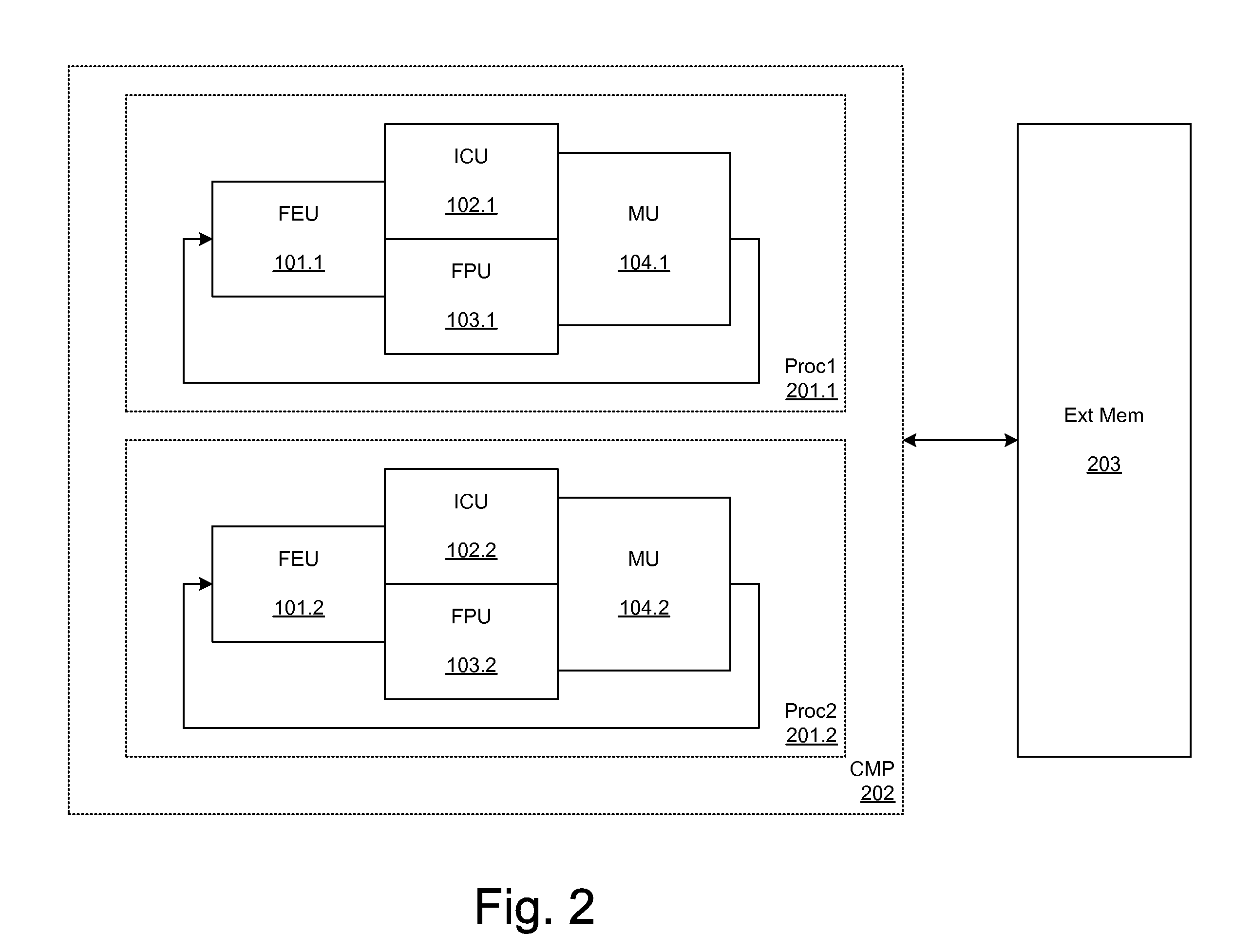
ActiveUS20050044344A1Architecture with single central processing unitSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectionSystems approaches
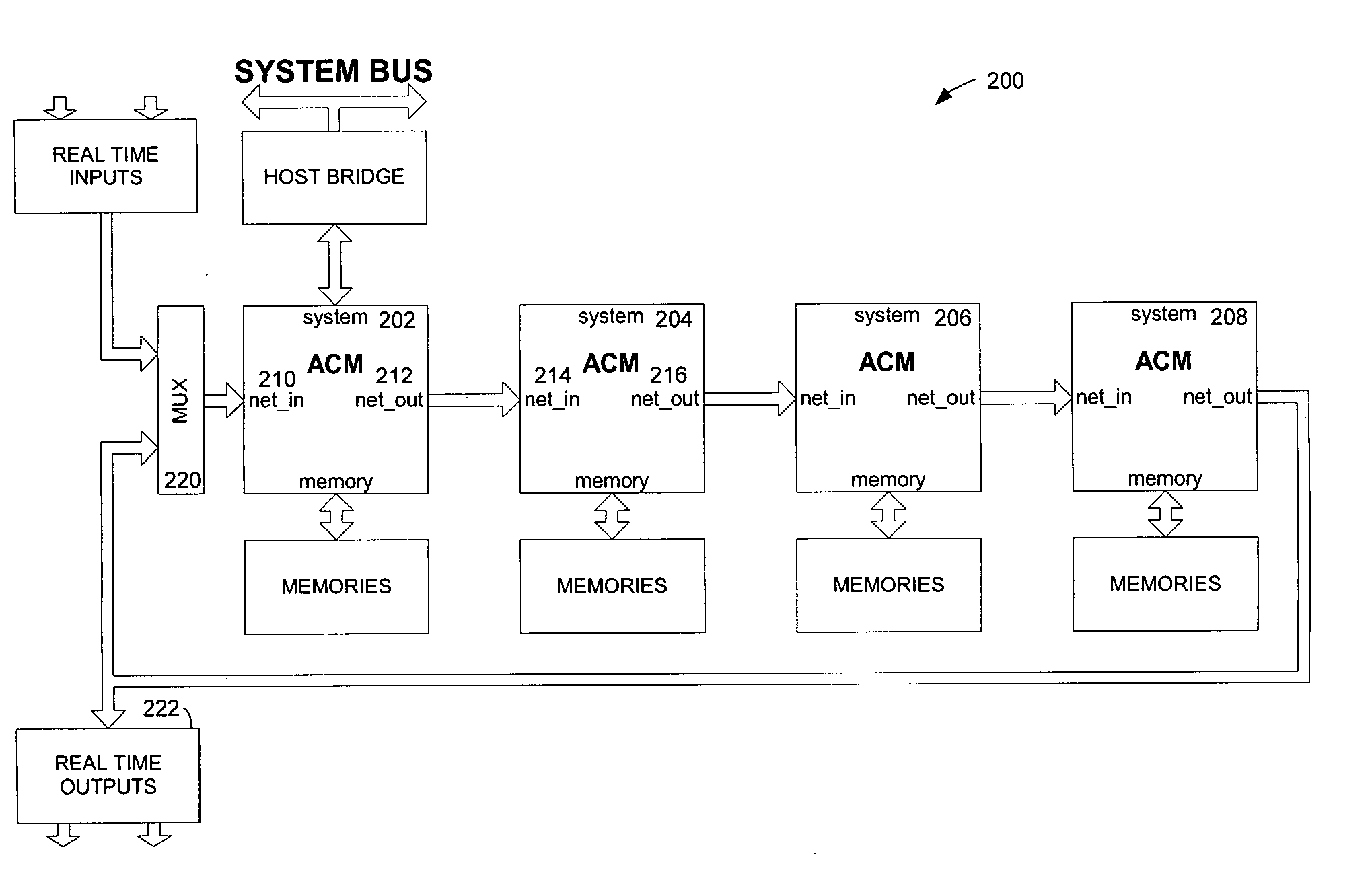
The present invention provides a system, method and software for programming and configuring an adaptive computing architecture or device. The invention utilizes program constructs which correspond to and map directly to the adaptive hardware having a plurality of reconfigurable nodes coupled through a reconfigurable matrix interconnection network. A first program construct corresponds to a selected node. A second program construct corresponds to an executable task of the selected node and includes one or more firing conditions capable of determining the commencement of the executable task of the selected node. A third program construct corresponds to at least one input port coupling the selected node to the matrix interconnect network for input data to be consumed by the executable task. A fourth program construct corresponds to at least one output port coupling the selected node to the matrix interconnect network for output data to be produced by the executable task;
Owner:CORNAMI INC
Asynchronous, independent and multiple process shared memory system in an adaptive computing architecture
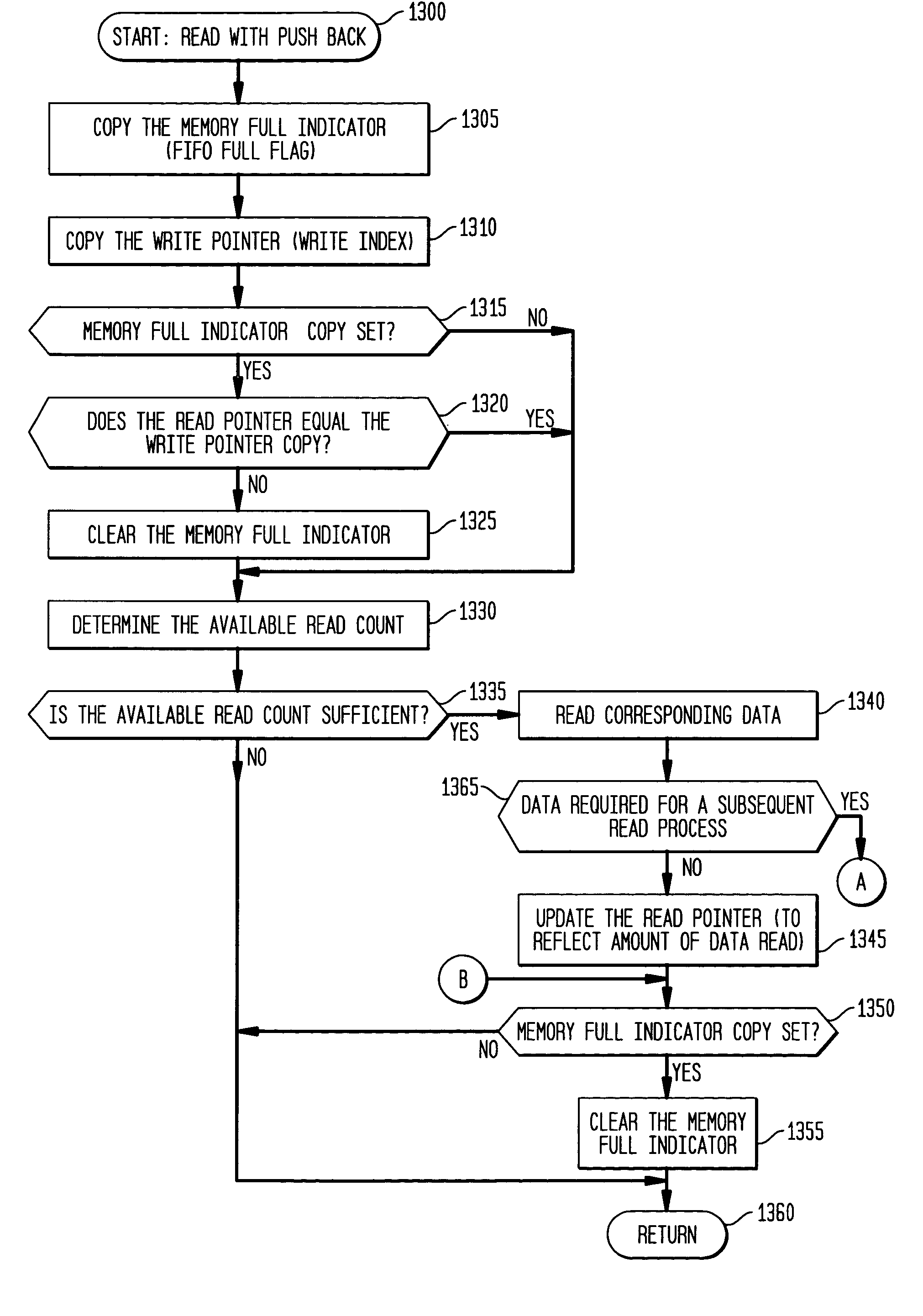
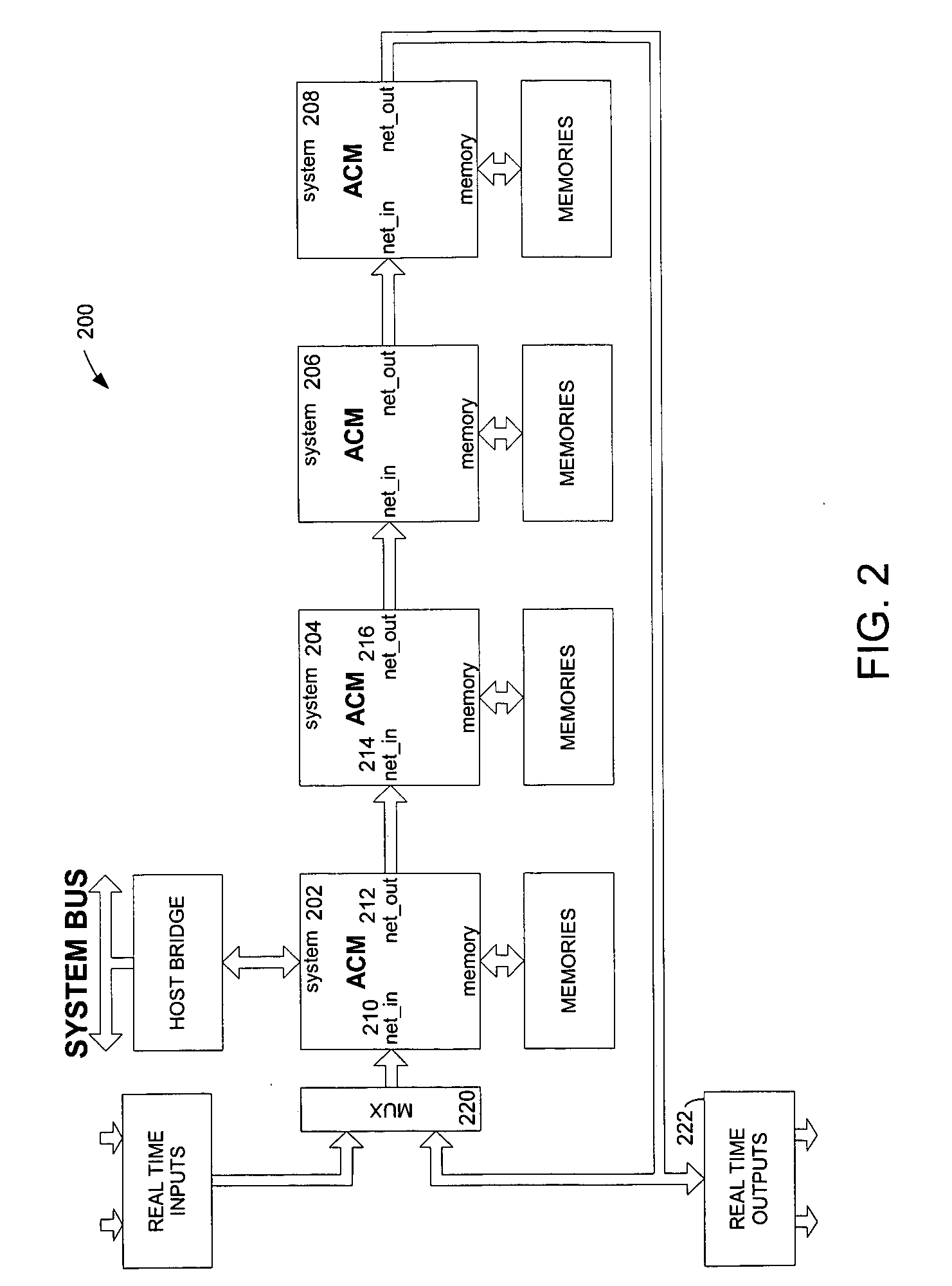
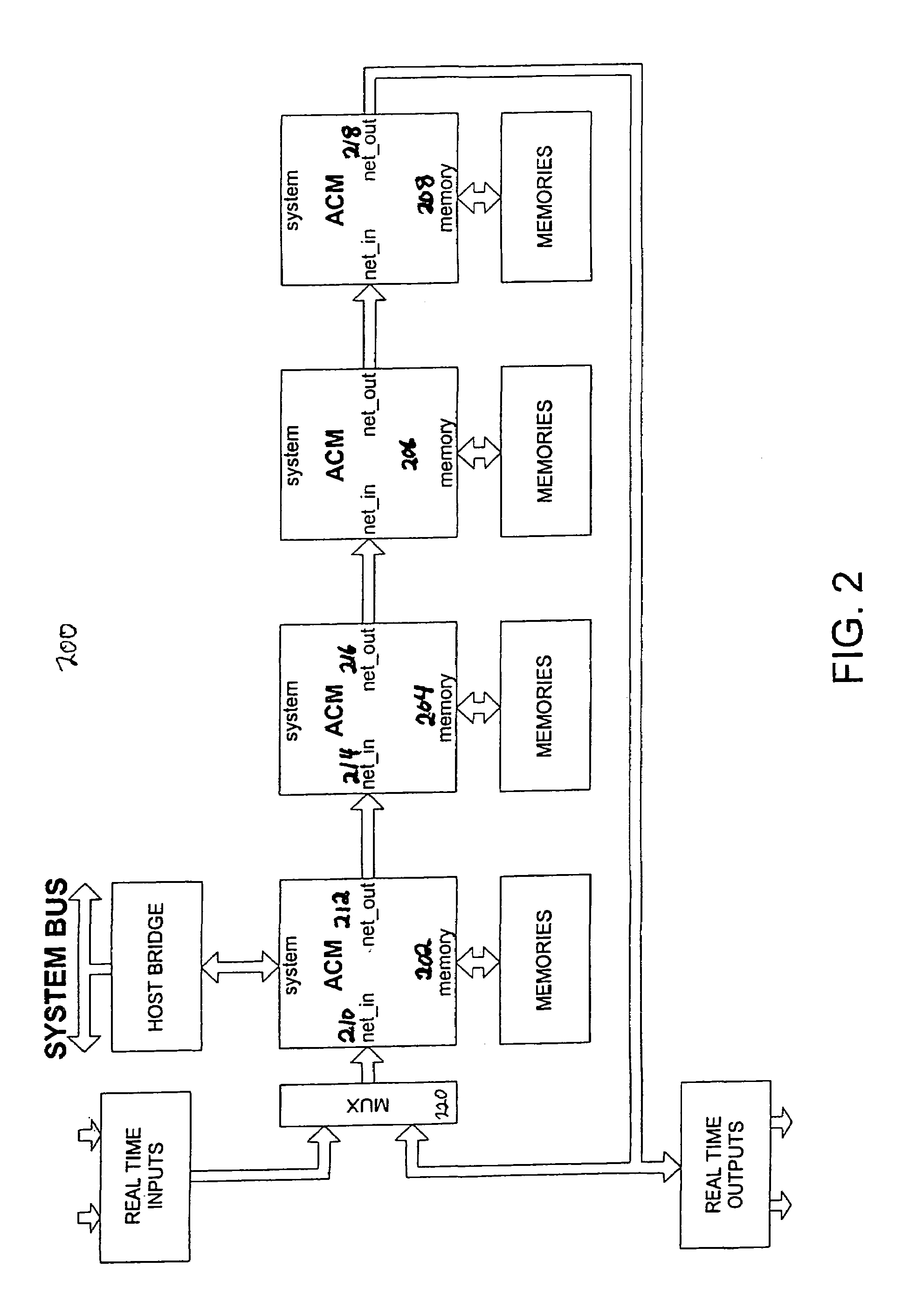
The present invention provides a system and method for implementation and use of a shared memory. The shared memory may be accessed both independently and asynchronously by one or more processes at corresponding nodes, allowing data to be streamed to multiple processes and nodes without regard to synchronization of the plurality of processes. The various nodes may be adaptive computing nodes, kernel or controller nodes, or one or more host processor nodes. The present invention maintains memory integrity, not allowing memory overruns, underruns, or deadlocks. The present invention also provides for “push back” after a memory read, for applications in which it is desirable to “unread” some elements previously read from the memory.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
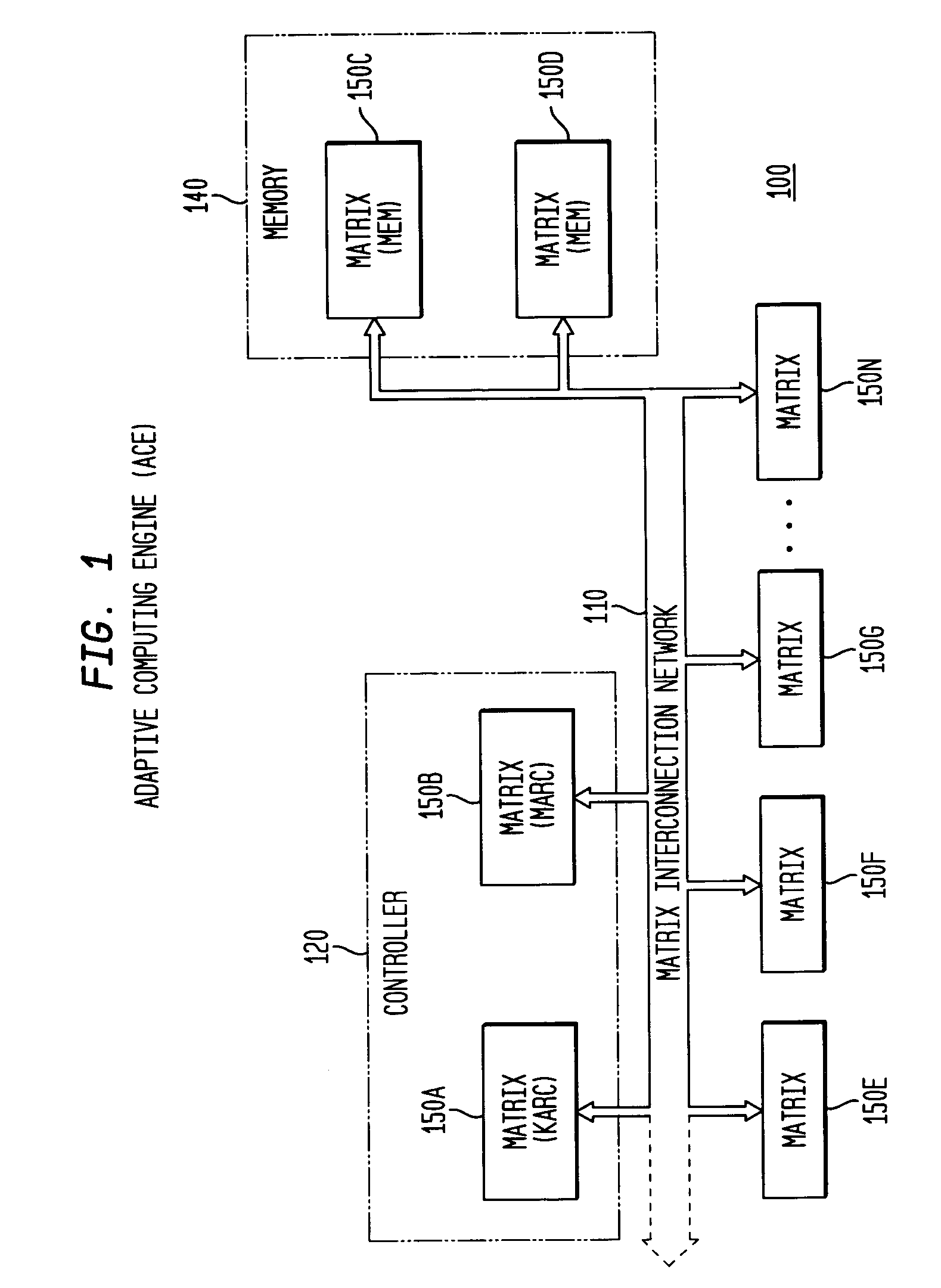
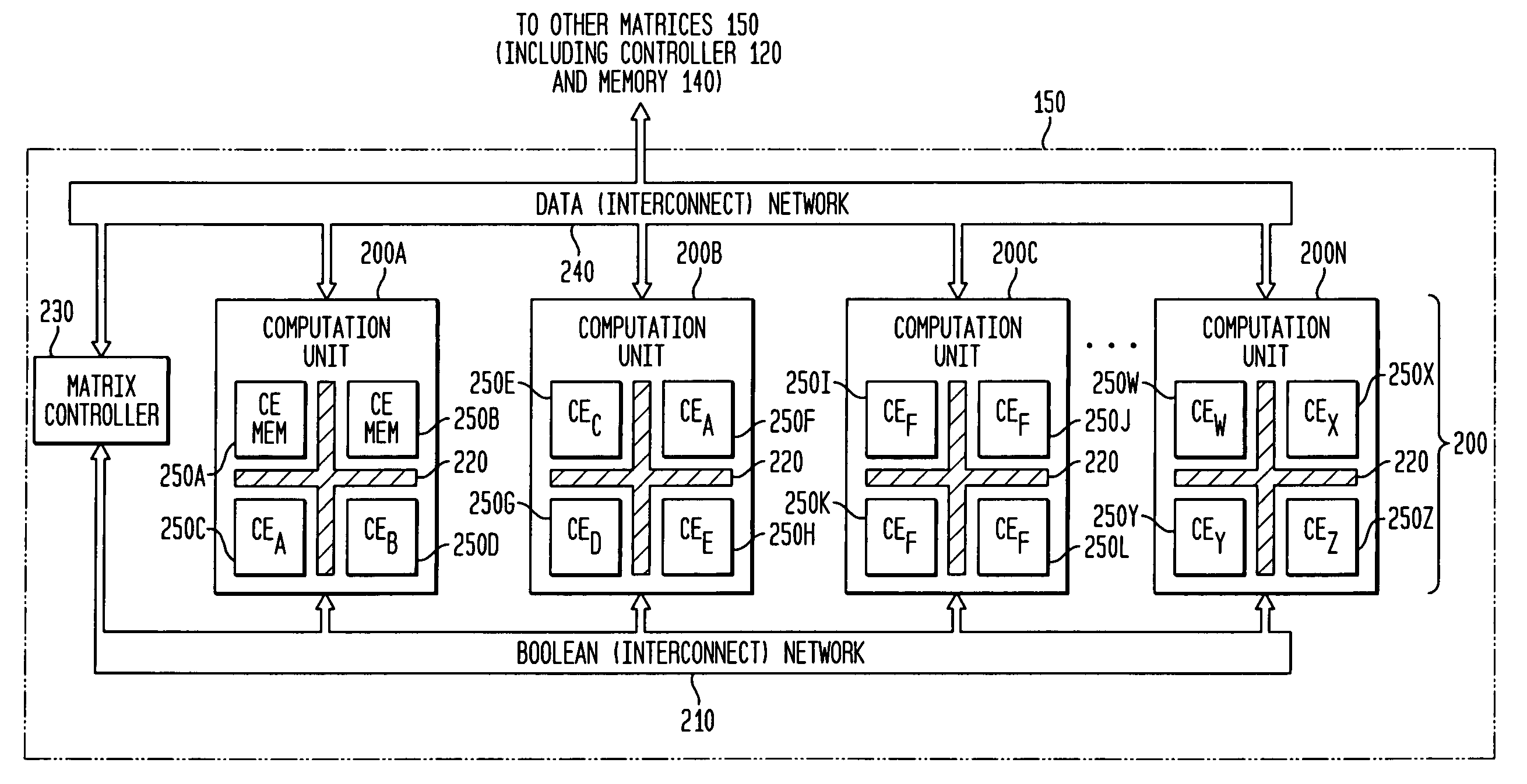
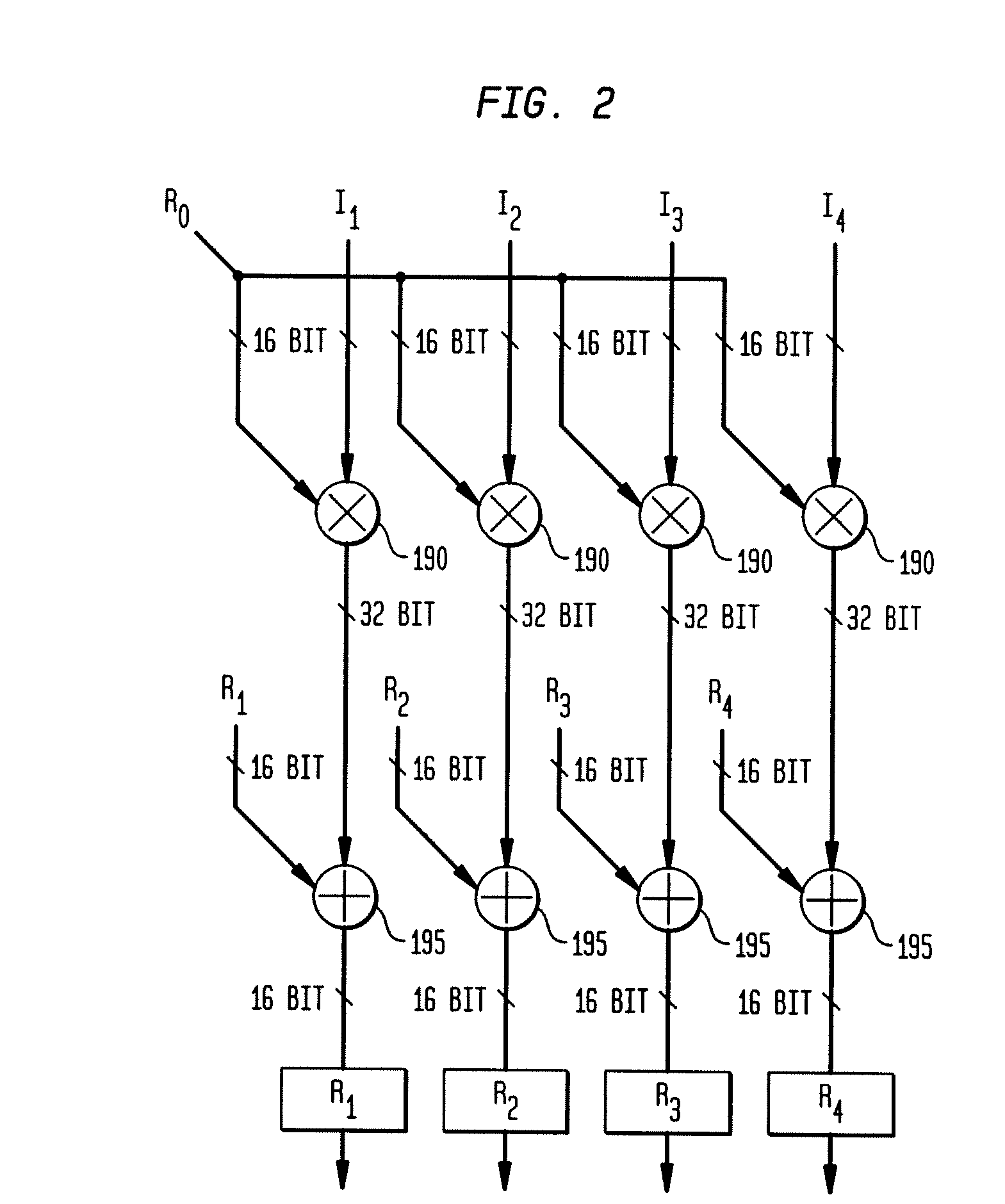
Adaptive computing ensemble microprocessor architecture
ActiveUS7389403B1Improve performanceImprove efficiencyEnergy efficient ICTGeneral purpose stored program computerExecution controlPower usage
An Adaptive Computing Ensemble (ACE) includes a plurality of flexible computation units as well as an execution controller to allocate the units to Computing Ensembles (CEs) and to assign threads to the CEs. The units may be any combination of ACE-enabled units, including instruction fetch and decode units, integer execution and pipeline control units, floating-point execution units, segmentation units, special-purpose units, reconfigurable units, and memory units. Some of the units may be replicated, e.g. there may be a plurality of integer execution and pipeline control units. Some of the units may be present in a plurality of implementations, varying by performance, power usage, or both. The execution controller dynamically alters the allocation of units to threads in response to changing performance and power consumption observed behaviors and requirements. The execution controller also dynamically alters performance and power characteristics of the ACE-enabled units, according to the observed behaviors and requirements.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
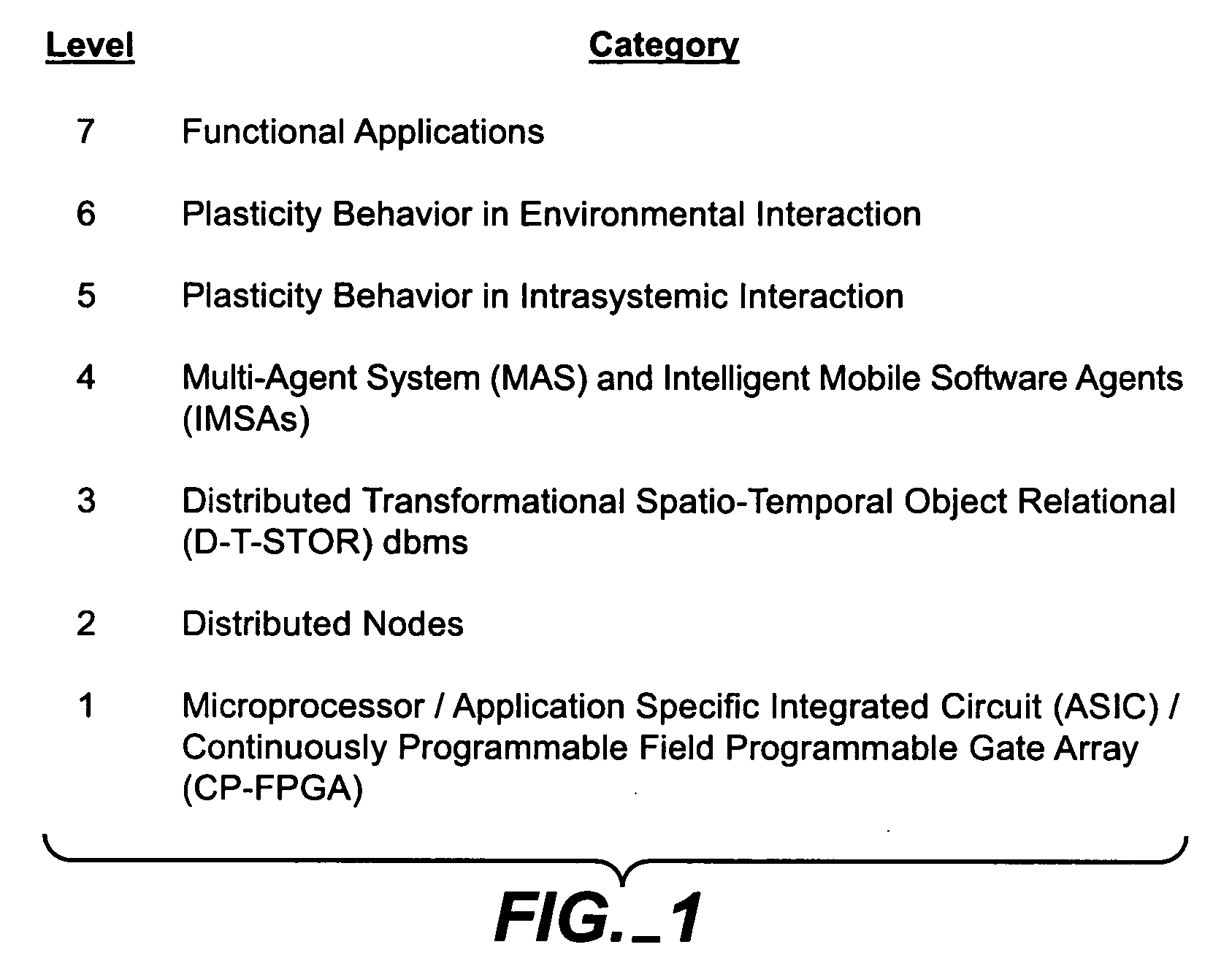
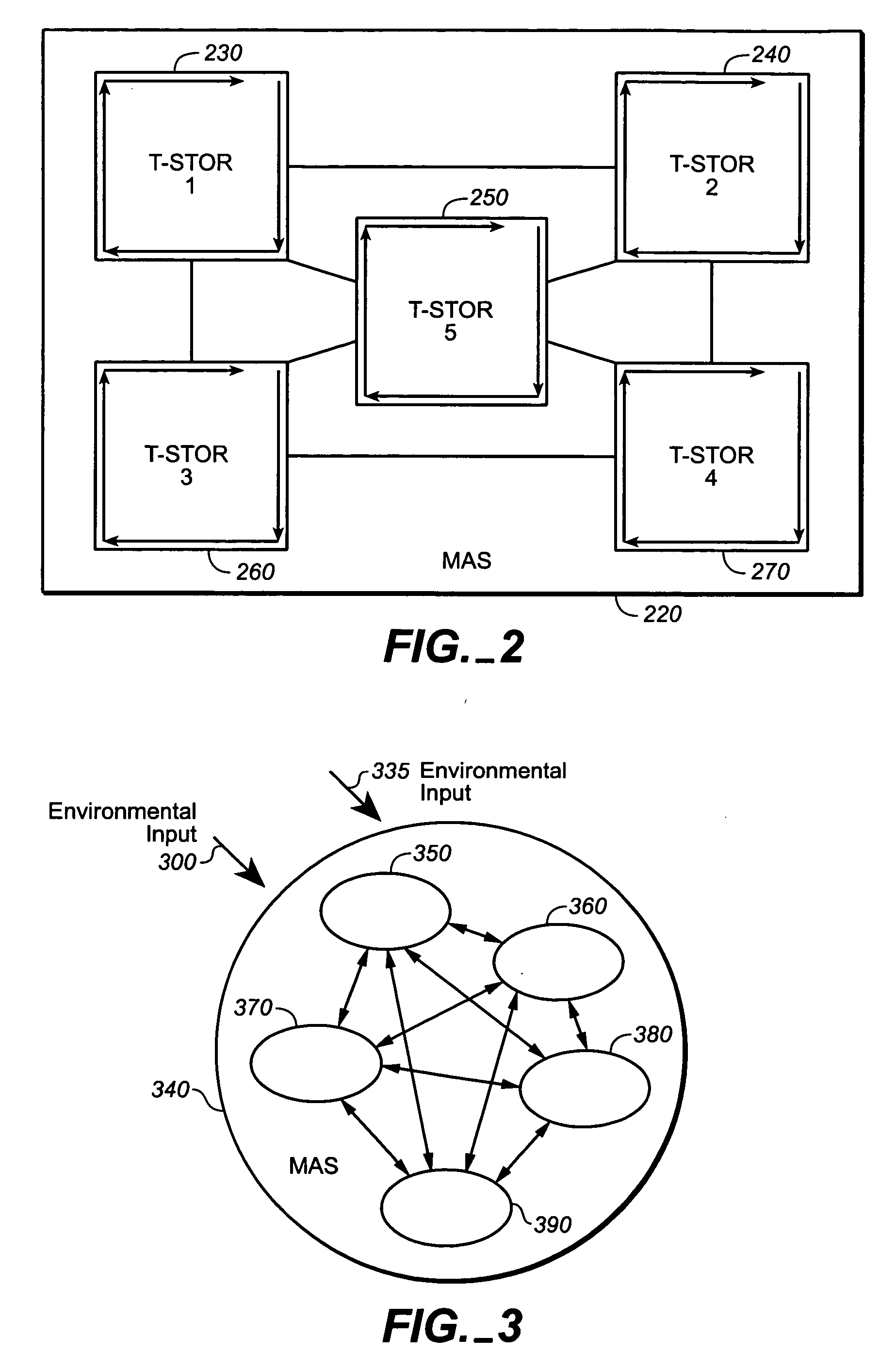
Dynamic adaptive distributed computer system
InactiveUS20050177593A1Most efficientOptimizes adaptive self-organizing operationDigital data processing detailsDigital computer detailsSearch analyticsComplex system
A system, methods and apparatus are described involving the self-organizing dynamics of networks of distributed computers. The system is comprised of complex networks of databases. The system presents a novel database architecture called the distributed transformational spatio-temporal object relational (T-STOR) database management system (dbms). Data is continuously input, analyzed, organized, reorganized and used for specific commercial and industrial applications. The system uses intelligent mobile software agents in a multi-agent system in order to learn, anticipate, and adapt and to perform numerous functions, including search, analysis, collaboration, negotiation, decision making and structural transformation. The system links together numerous complex systems involving distributed networks to present a novel model for dynamic adaptive computing systems, which includes plasticity of collective behavior and self-organizing behavior in intelligent system structures.
Owner:SOLOMON NEAL
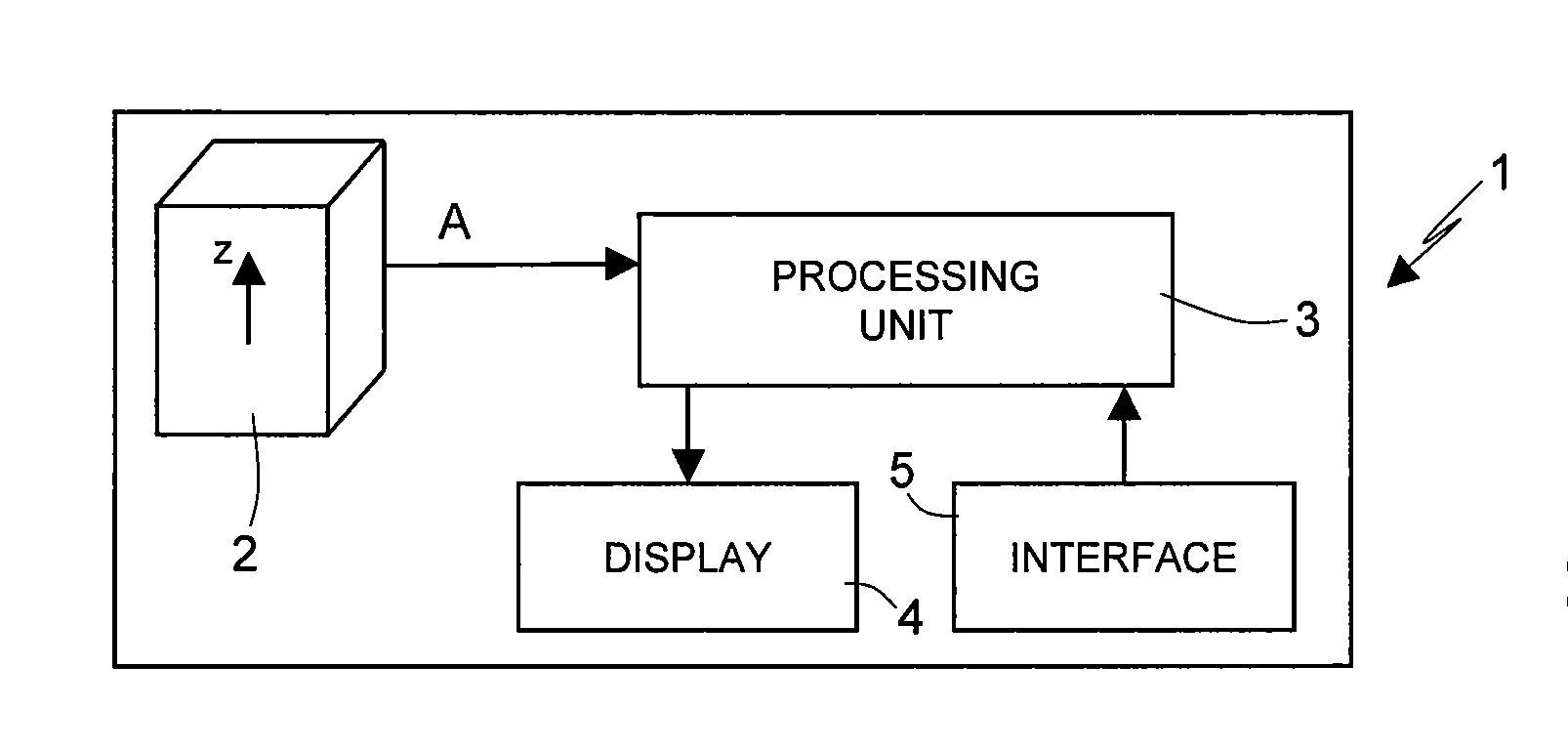
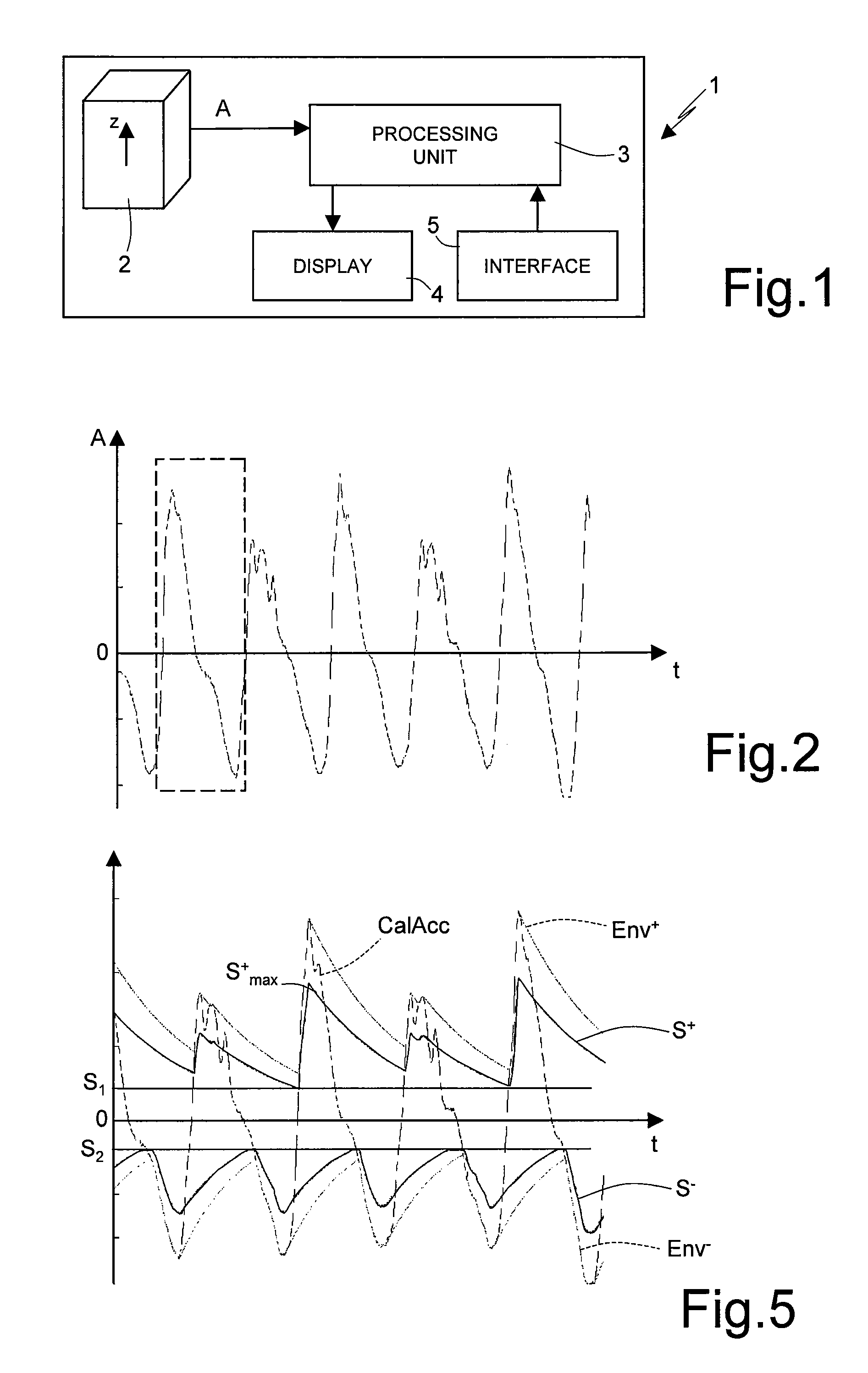
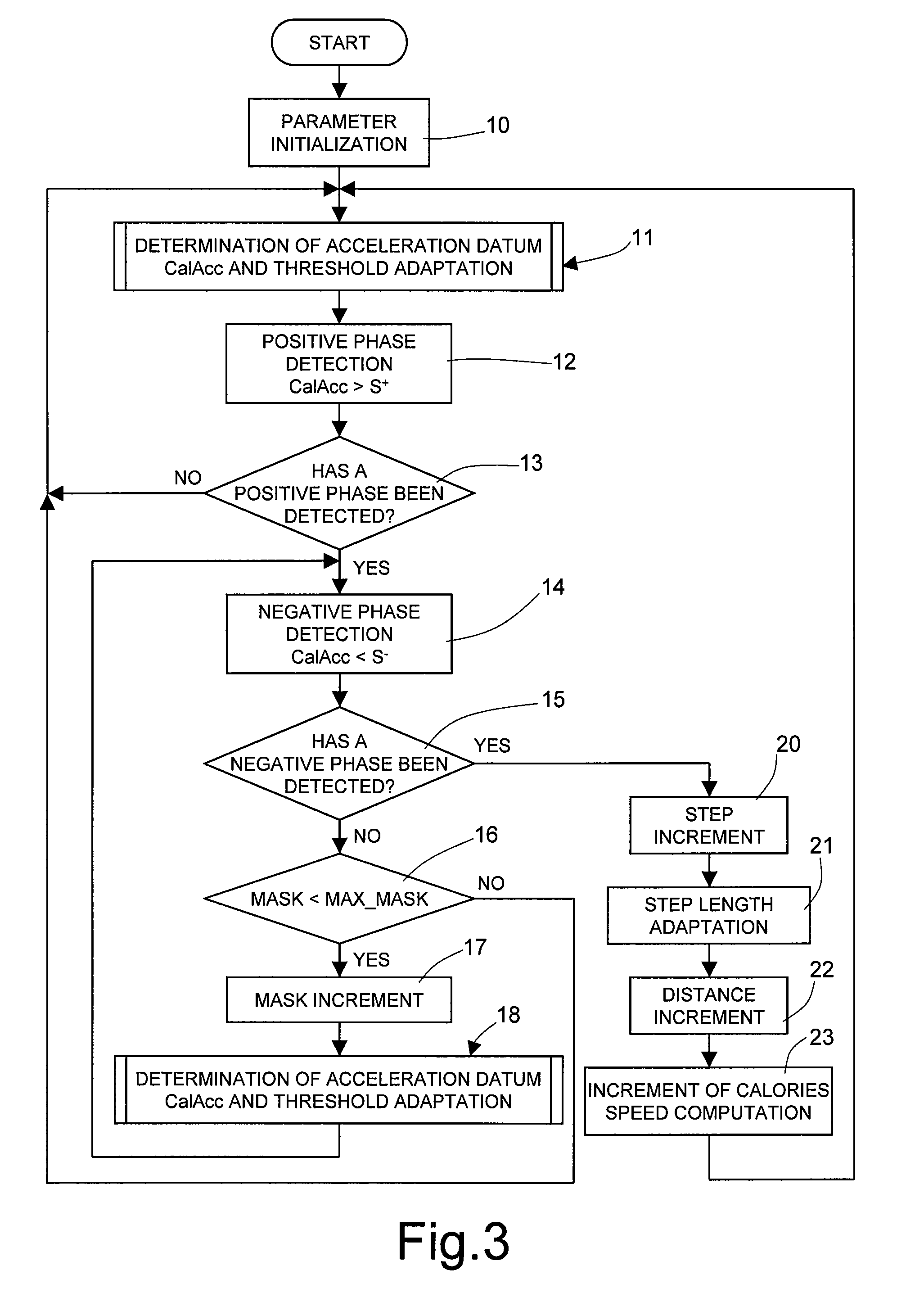
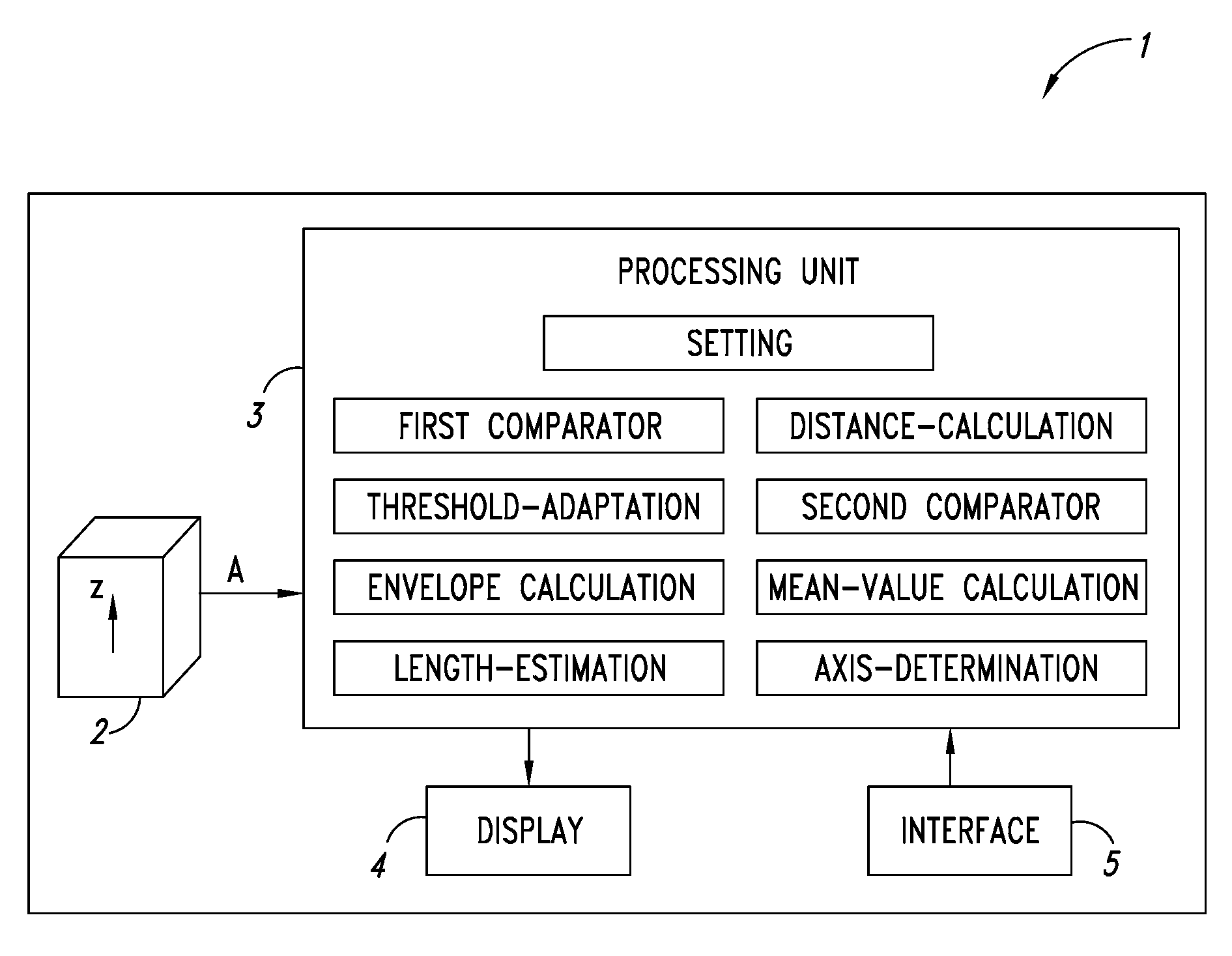
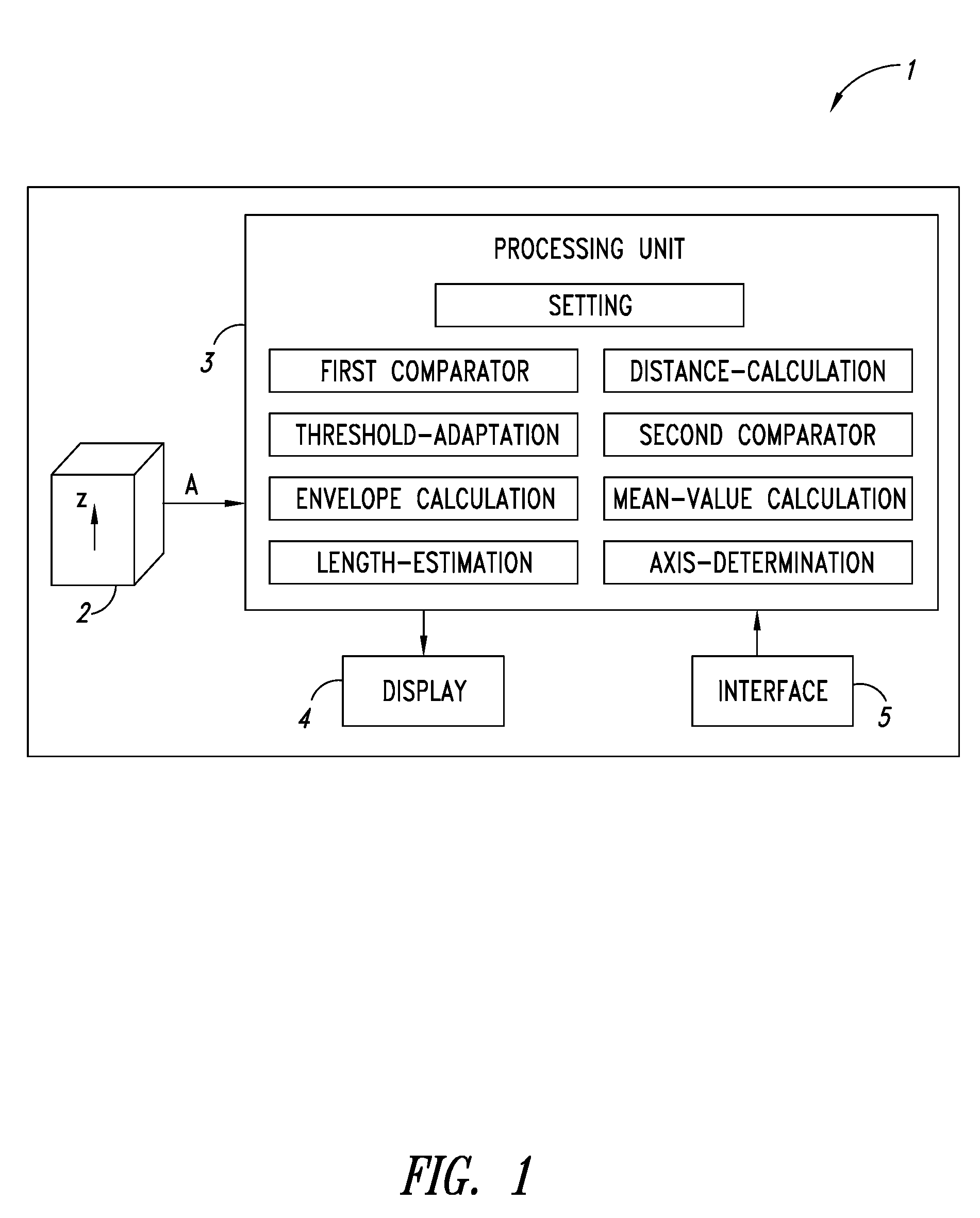
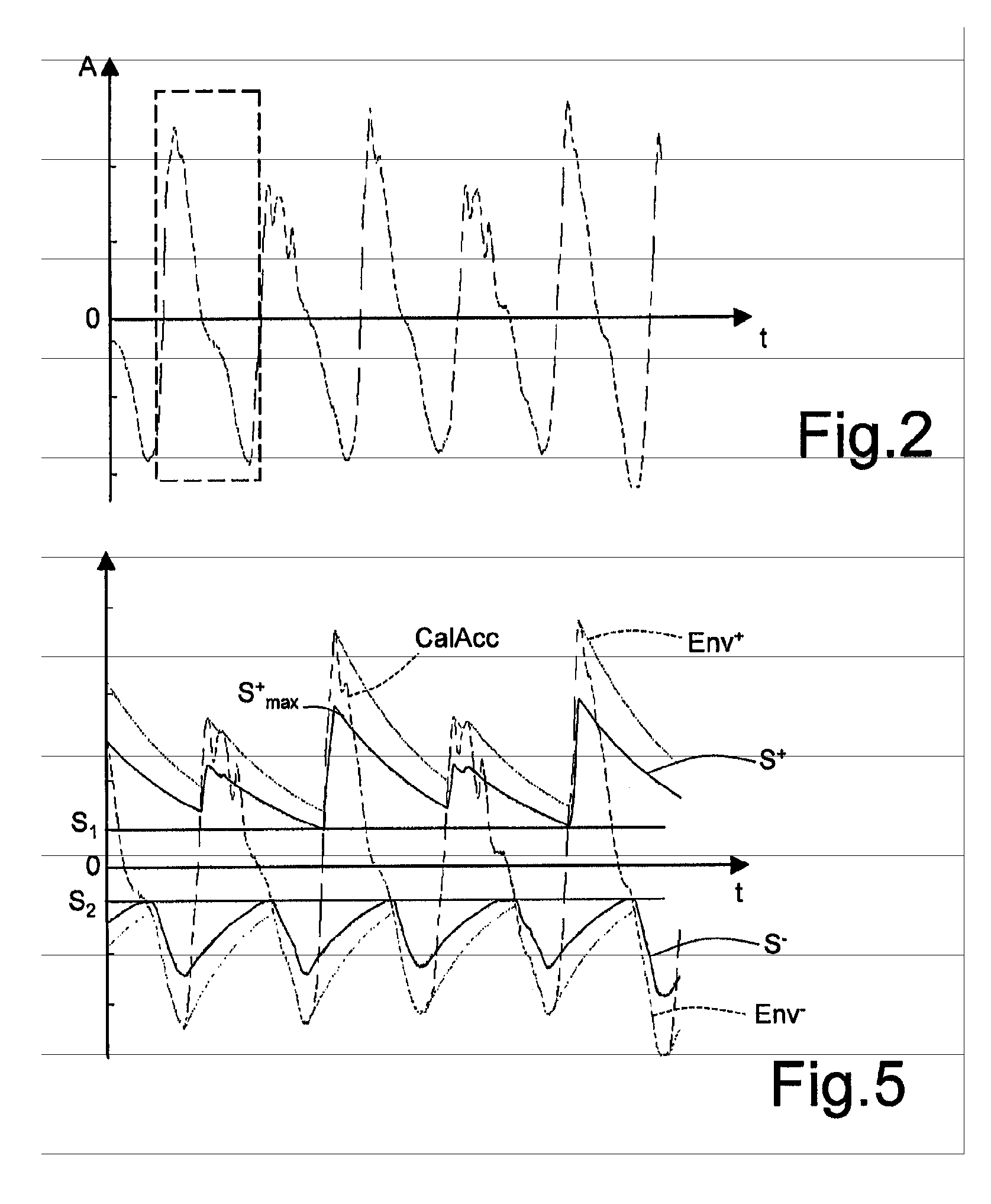
Pedometer device and step detection method using an algorithm for self-adaptive computation of acceleration thresholds
ActiveUS20070143068A1Overcome disadvantagesOvercome problemsDigital computer detailsMechanical clearance measurementsAccelerometerProcessing element
In a pedometer device for detecting and counting steps of a user on foot, an accelerometer sensor detects a vertical acceleration generated during the step. A processing unit, connected to the accelerometer sensor, processes an acceleration signal relating to the acceleration in order to detect the occurrence of a step, and in particular compares the acceleration signal with a first reference threshold. The processing unit automatically adapts the first reference threshold as a function of the acceleration signal. In particular, the processing unit modifies the first reference threshold as a function of an envelope of the amplitude of the acceleration signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
Pedometer device and step detection method using an algorithm for self-adaptive computation of acceleration thresholds
ActiveUS7463997B2Digital computer detailsMechanical clearance measurementsAccelerometerSelf adaptive
In a pedometer device for detecting and counting steps of a user on foot, an accelerometer sensor detects a vertical acceleration generated during the step. A processing unit, connected to the accelerometer sensor, processes an acceleration signal relating to the acceleration in order to detect the occurrence of a step, and in particular compares the acceleration signal with a first reference threshold. The processing unit automatically adapts the first reference threshold as a function of the acceleration signal. In particular, the processing unit modifies the first reference threshold as a function of an envelope of the amplitude of the acceleration signal.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS SRL
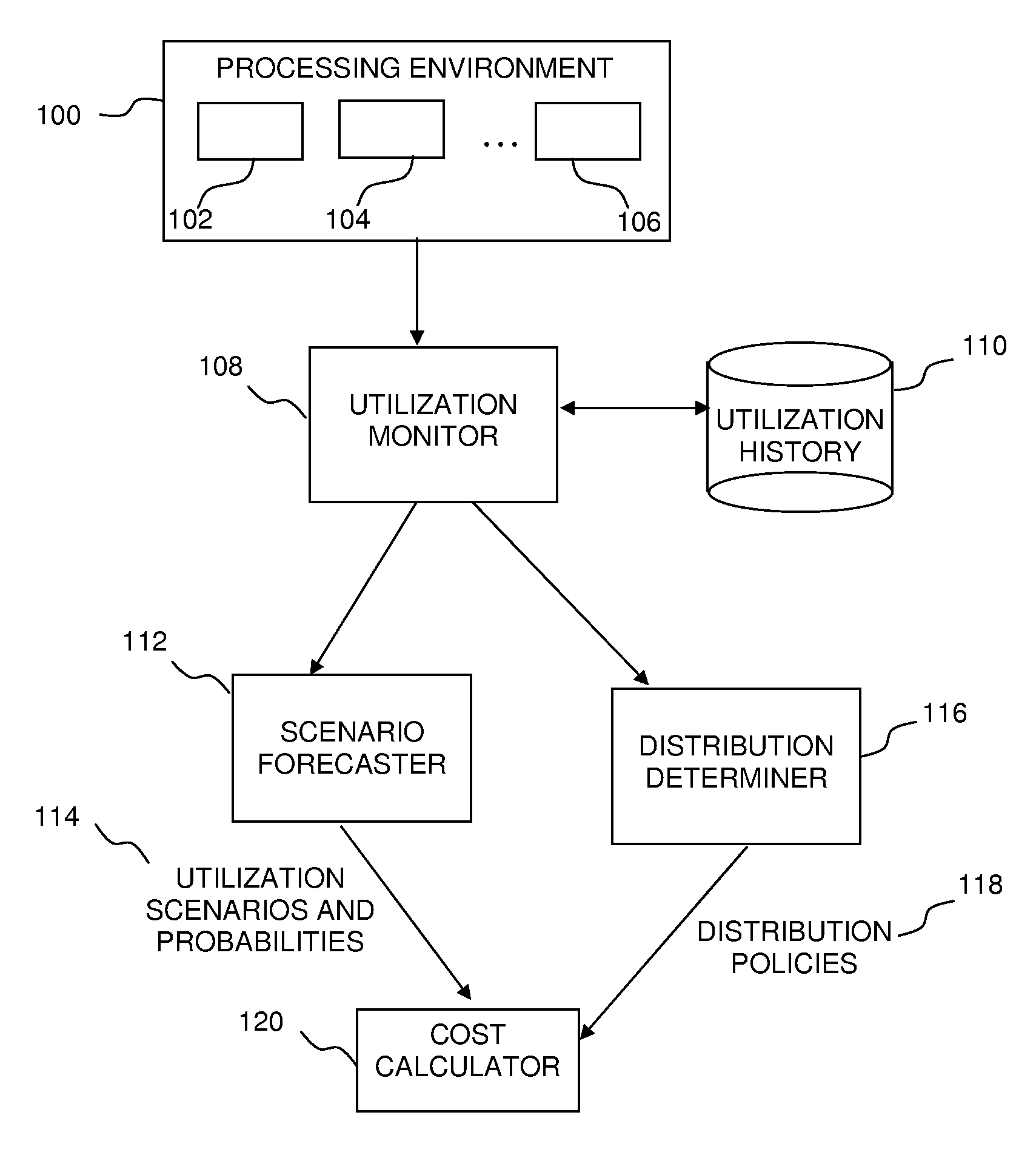
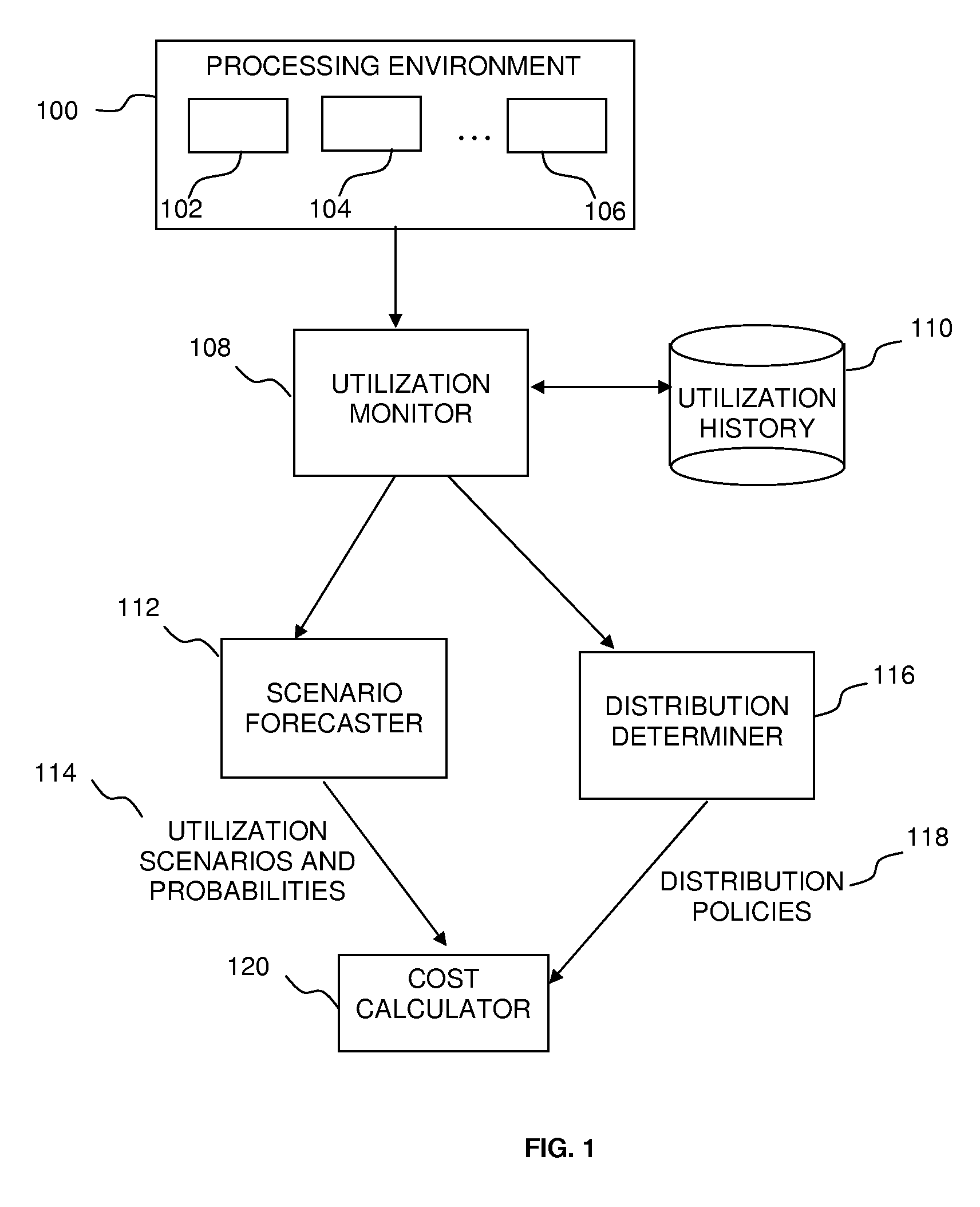
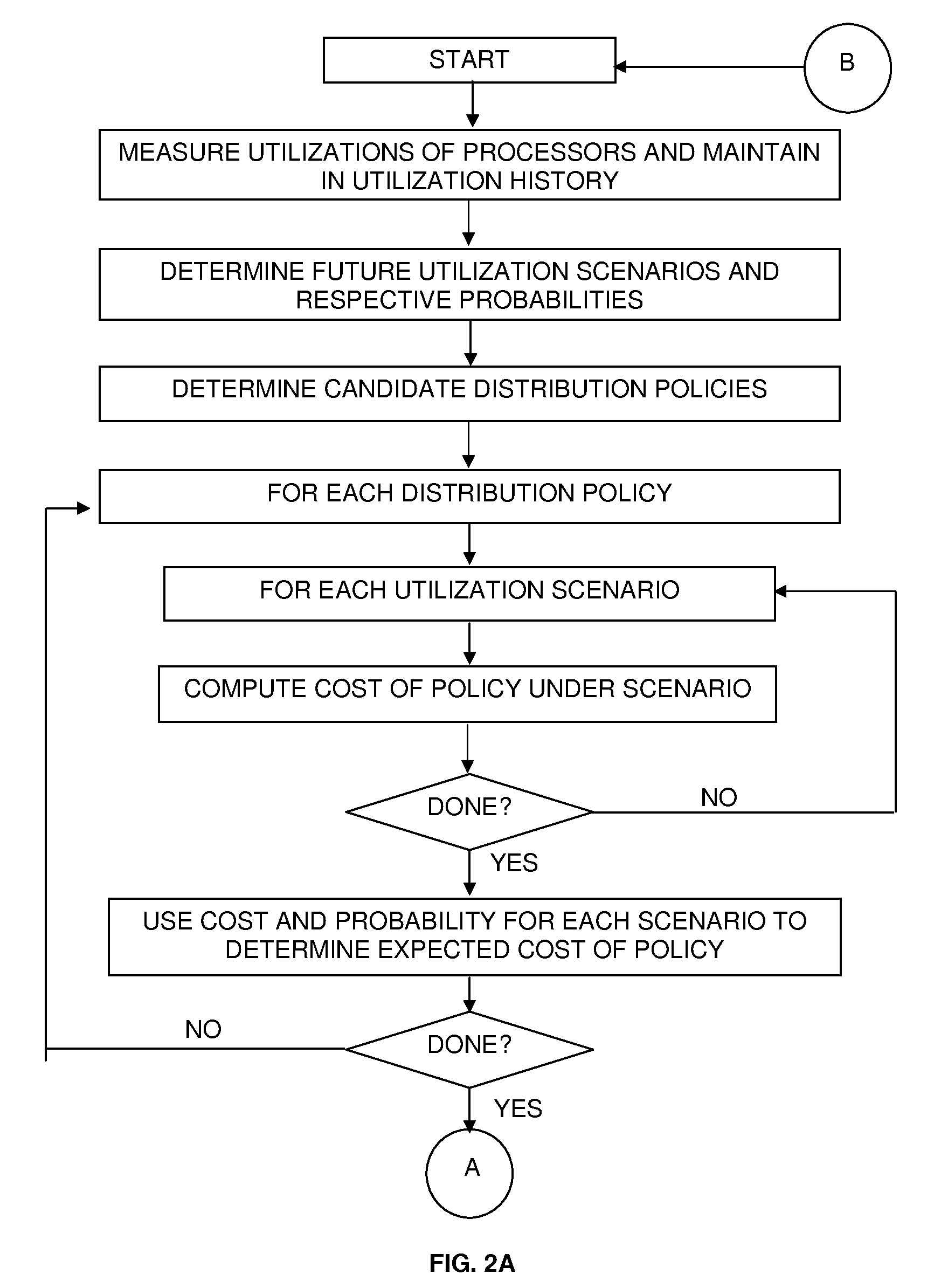
Adaptive Computing Using Probabilistic Measurements
InactiveUS20100250642A1Error detection/correctionData resettingAdaptive computingReal-time computing
Determining a configuration of a computer system for performing an operation, by determining an expected performance of a computer system based on at least one possible usage scenario given a current configuration of the computer system according to a current set of system parameters, determining an expected performance of the computer system based on at least one possible usage scenario given at least one candidate configuration of the computer system according to at least one candidate set of system parameters, and configuring the computer system according to whichever of the sets of system parameters that has a more favorable expected performance as determined in accordance with predefined criteria.
Owner:IBM CORP
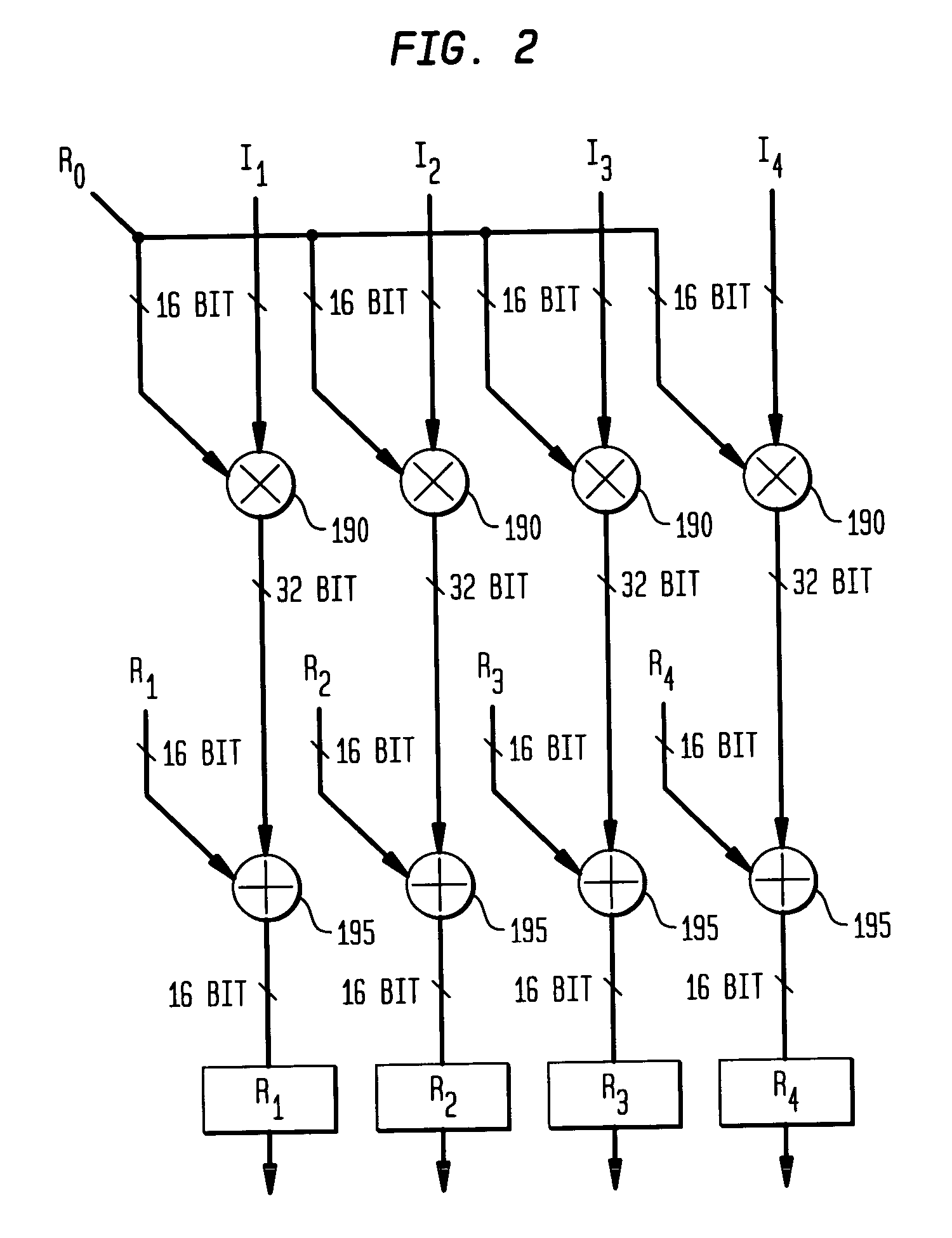
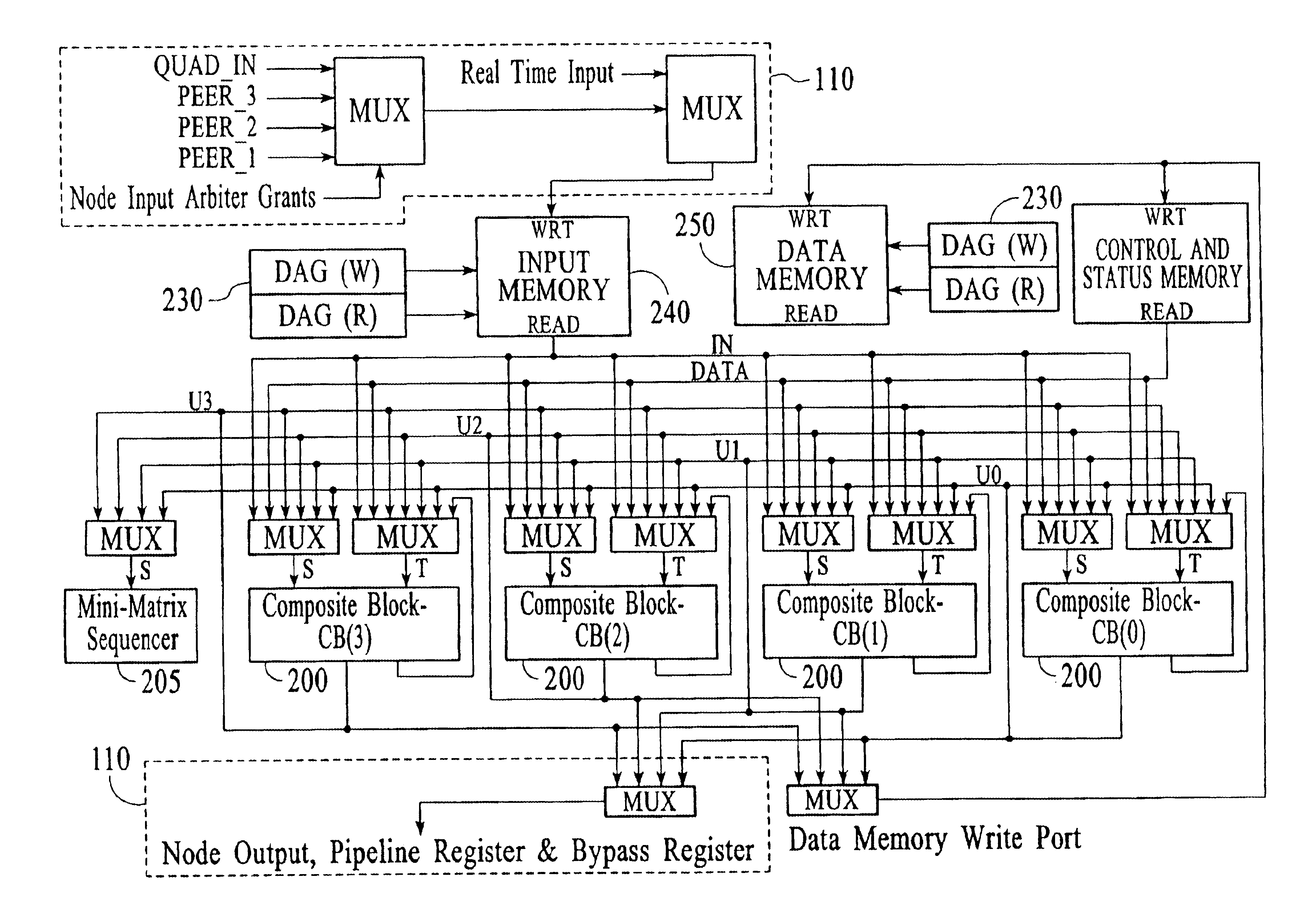
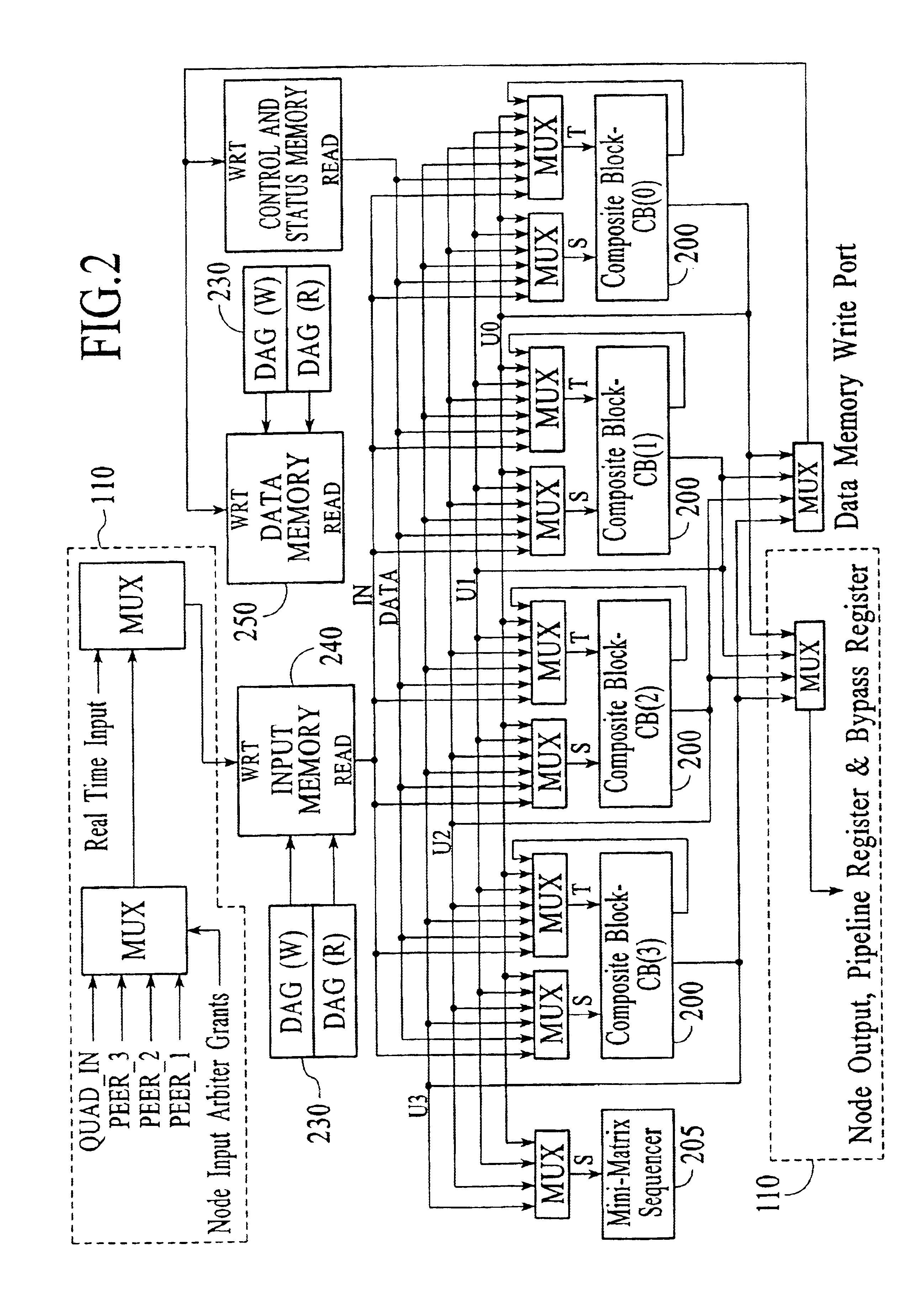
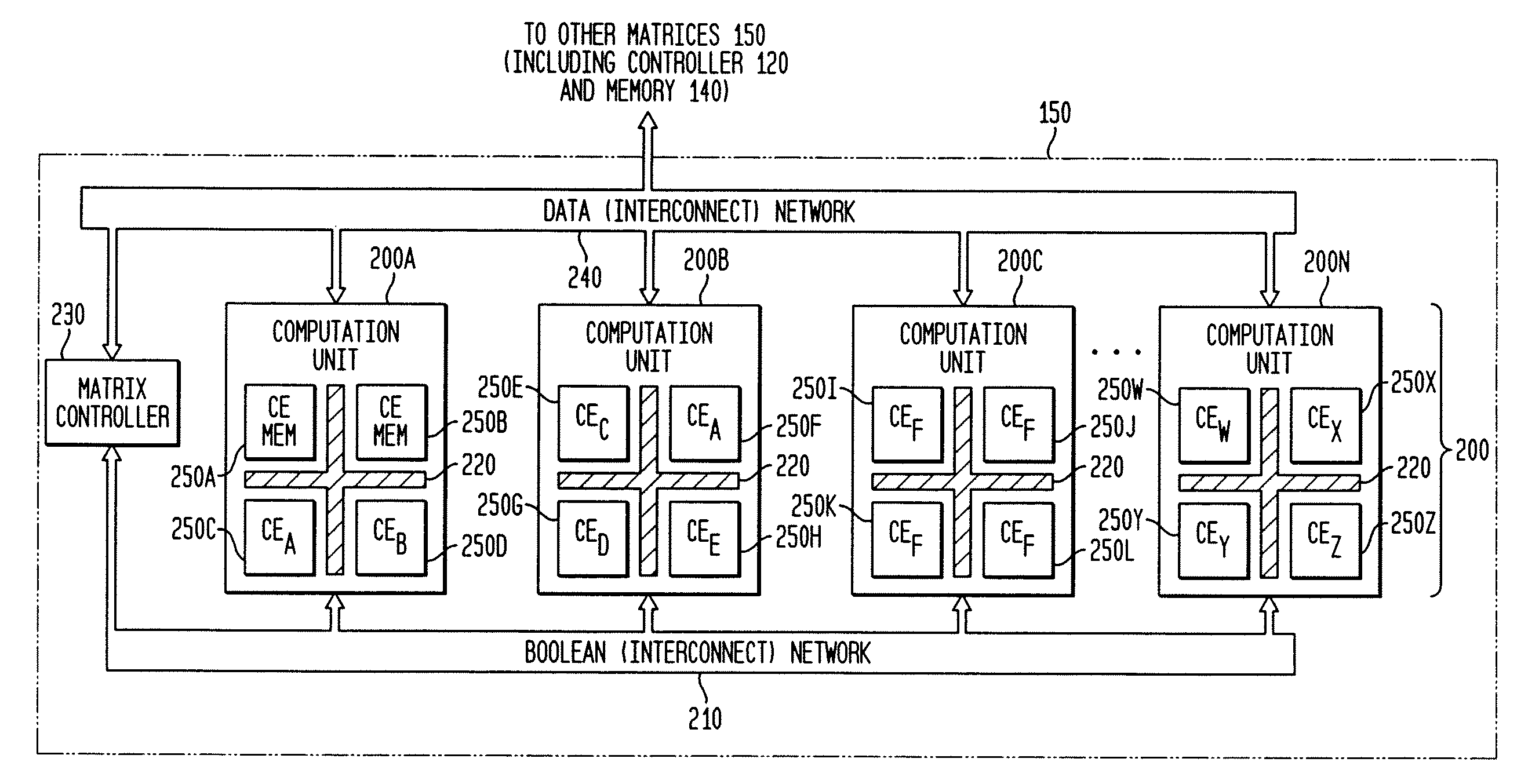
Adaptive computing engine with dataflow graph based sequencing in reconfigurable mini-matrices of composite functional blocks
InactiveUS6874079B2Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsNext instruction address formationDigital signal processingParallel computing
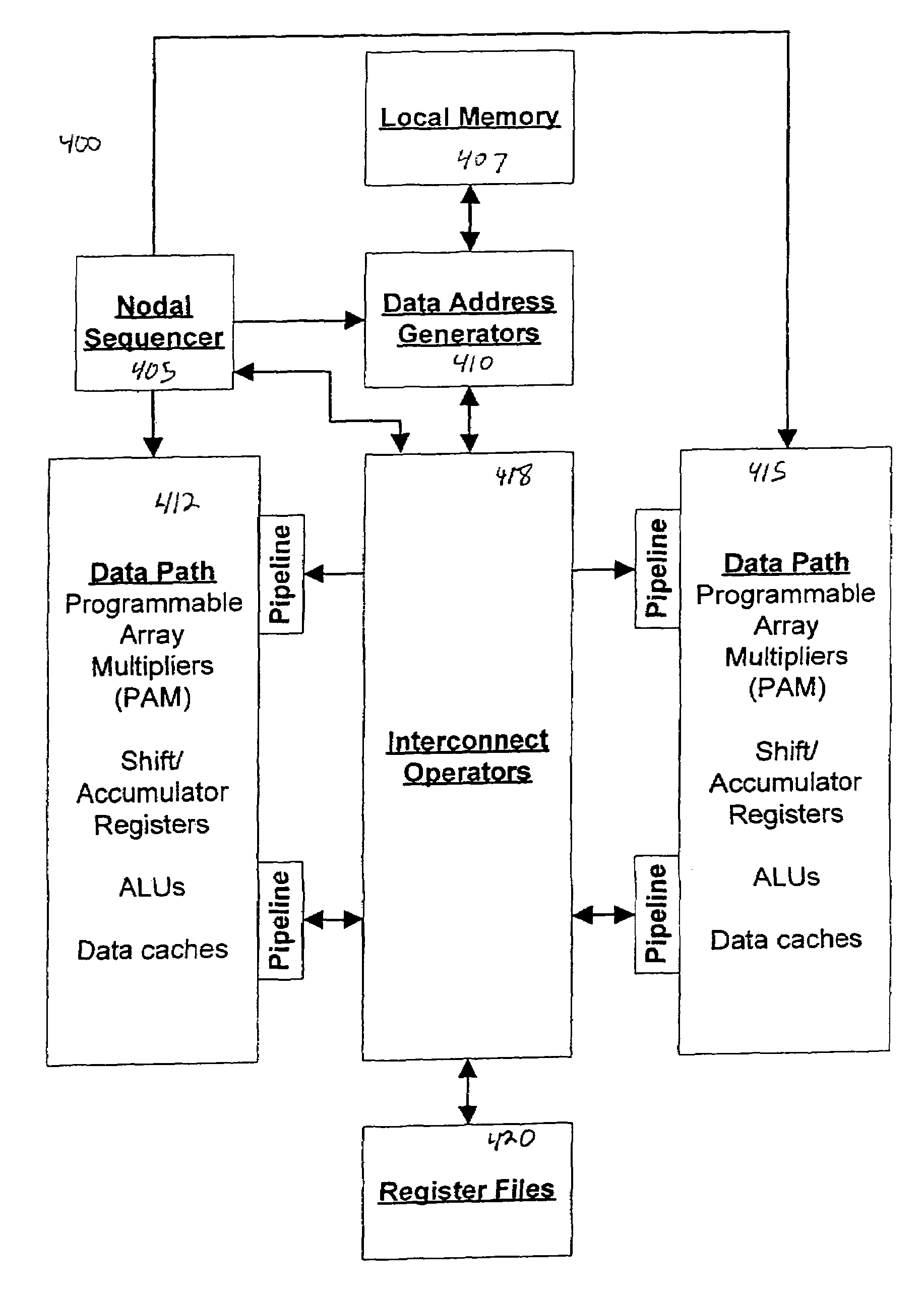
Aspects of a method and system for digital signal processing within an adaptive computing engine are described. These aspects include a mini-matrix, the mini-matrix comprising a set of composite blocks, each composite block capable of executing a predetermined set of instructions. A sequencer is included for controlling the set of composite blocks and directing instructions among the set of composite blocks based on a data-flow graph. Further, a data network is included and transmits data to and from the set of composite blocks and to the sequencer, while a status network routes status word data resulting from instruction execution in the set of composite blocks. With the present invention, an effective combination of hardware resources is provided in a manner that provides multi-bit digital signal processing capabilities for an embedded system environment, particularly in an implementation of an adaptive computing engine. These and other advantages will become readily apparent from the following detailed description and accompanying drawings.
Owner:CORNAMI INC
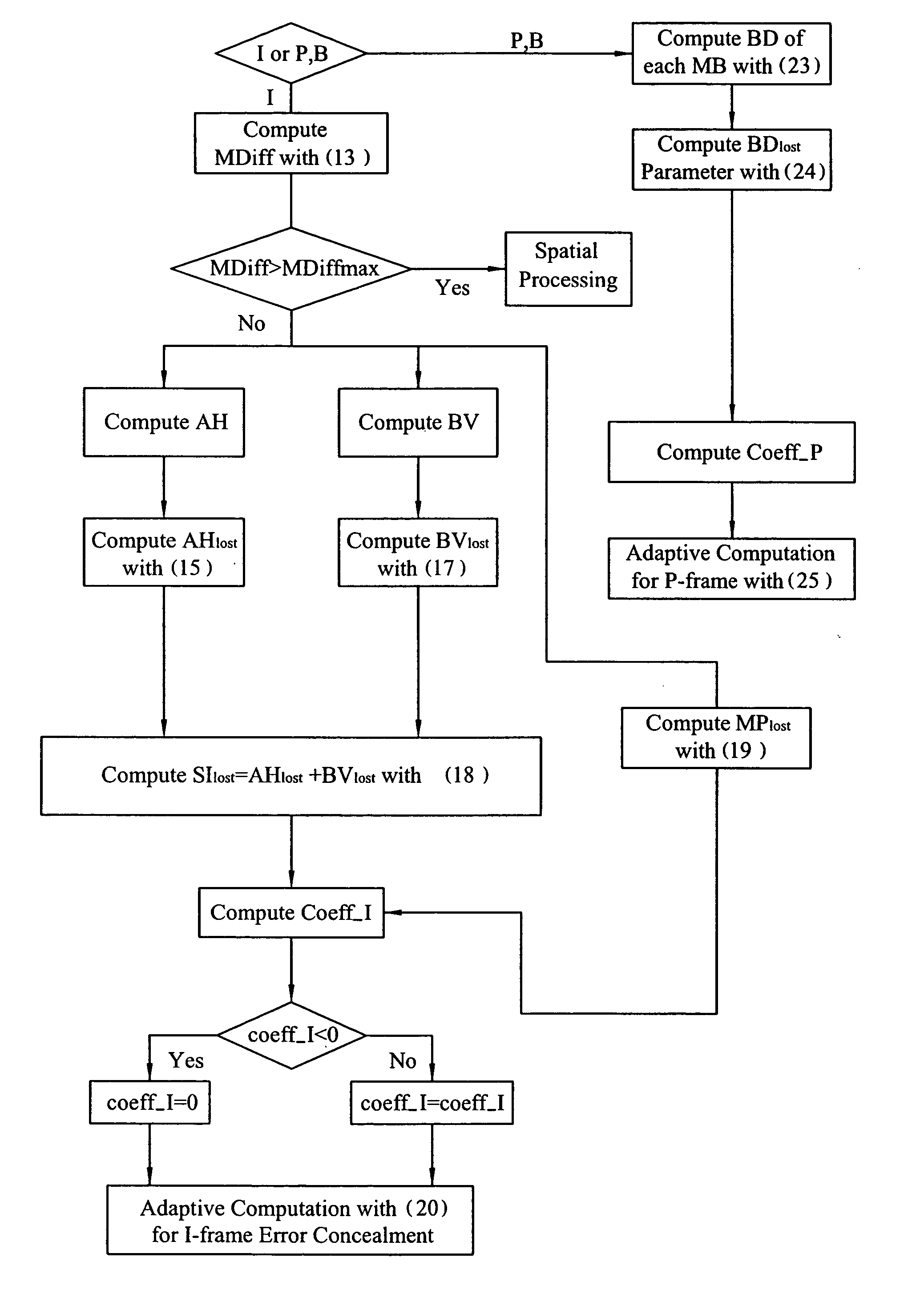
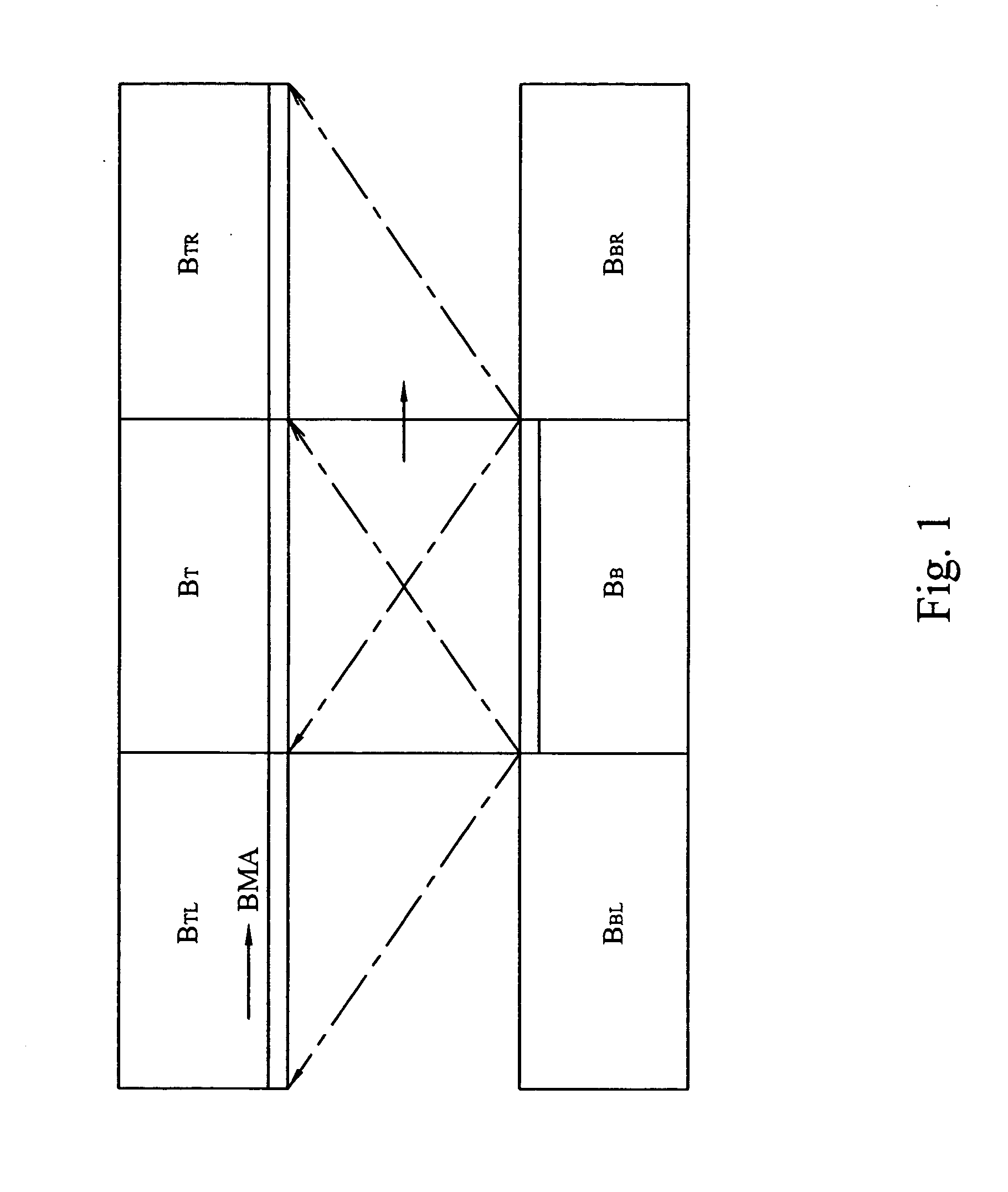
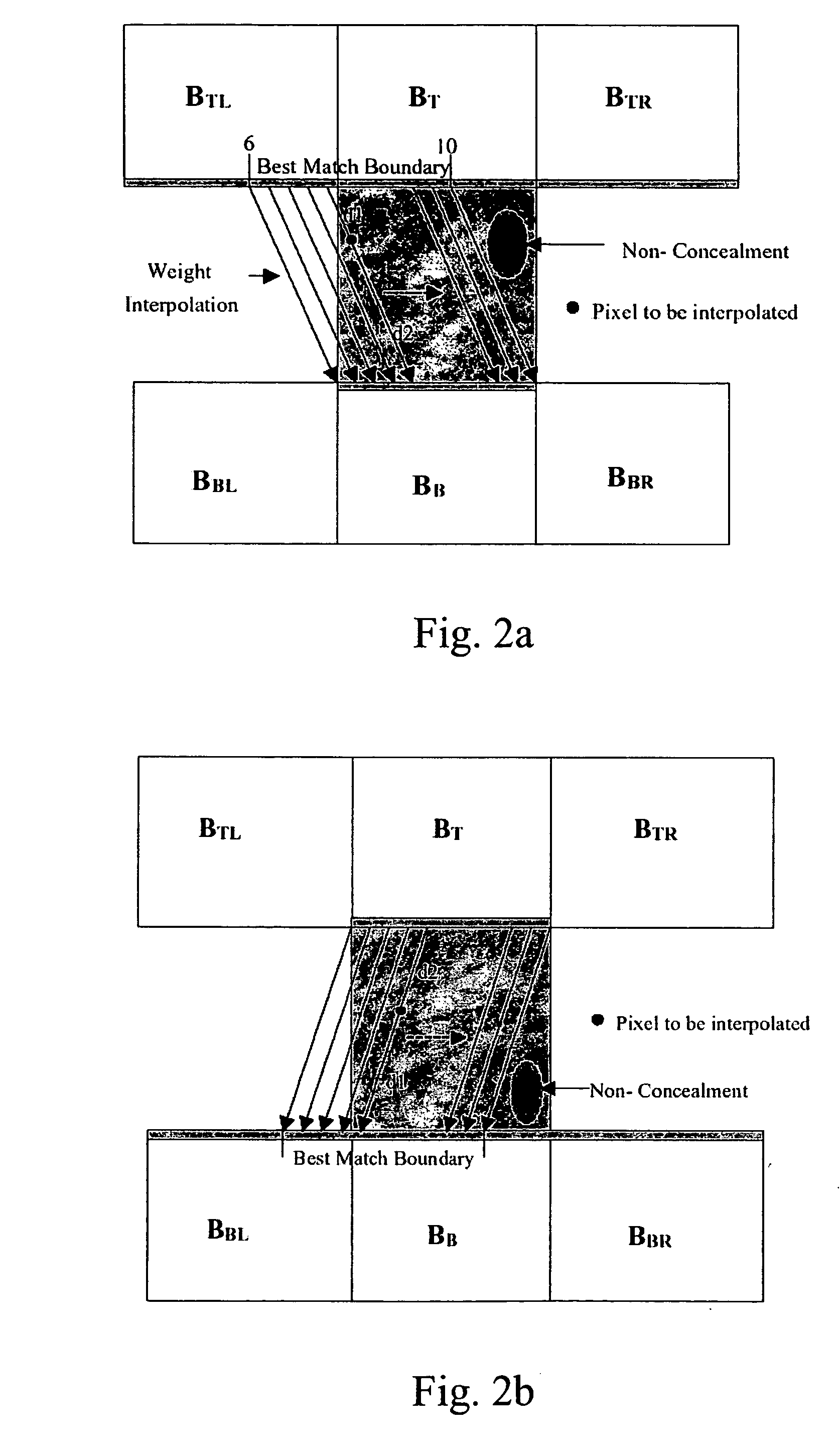
Apparatus and method for error concealment
InactiveUS20060062304A1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionError concealmentTime data
The present invention provides an apparatus and a method for error concealment. The control core receives an input signal and identifies an error macro-block in a column of slice of a frame and a frame type of the frame. The parameter computation module receives a plurality of DCT coefficients and temporal data to derive at least a coefficient for the weighting in an adaptive computation for the frame. The temporal compensation module computes the temporal data to obtain a result of the temporal compensation. The spatial processing module computes spatial data to obtain a result of the spatial processing. The adaptive processing module proceeds the adaptive computation with the coefficient for the weighting derived by the parameter computation module, the result of the temporal compensation and the result of the spatial processing, and generates a result of the adaptive processing. The spatial processing may be a bilinear interpolation or a spatial interpolation.
Owner:NAT KAOHSLUNG FIRST UNIV OF SCI & TECH
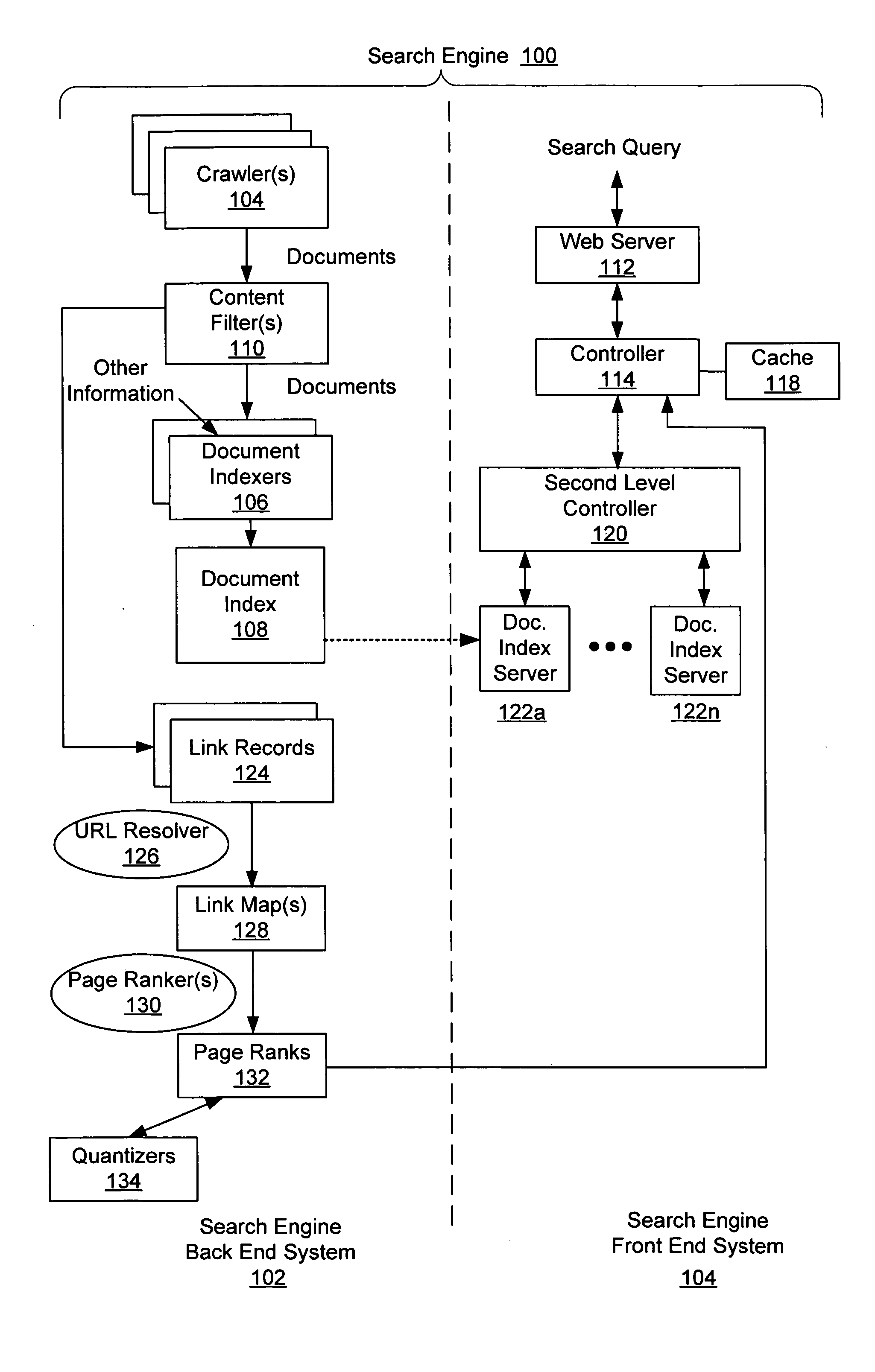
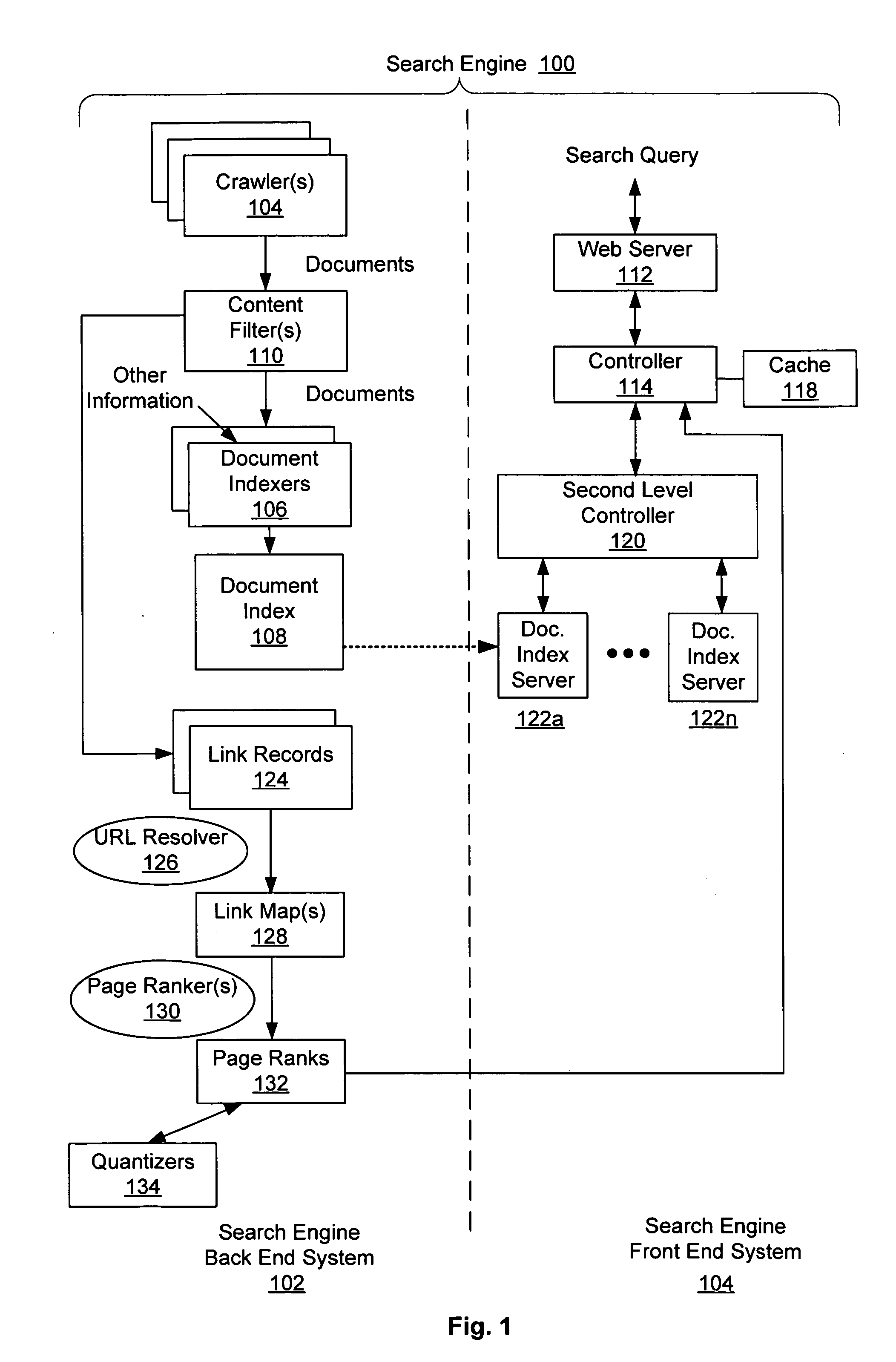
Adaptive computation of ranking
ActiveUS20050027685A1Reduce computing costData processing applicationsWeb data indexingPaper documentDocument preparation
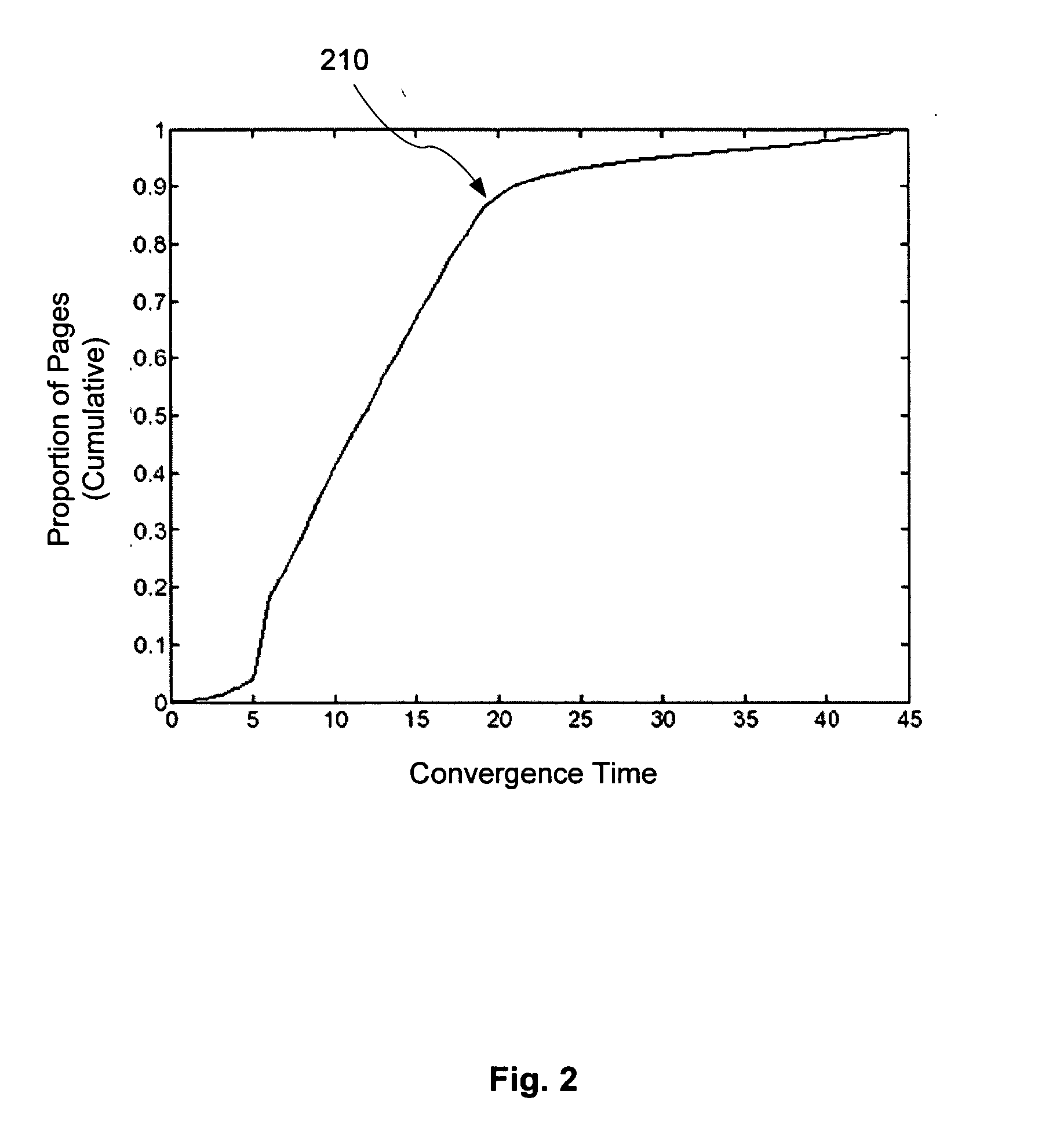
A system and method is disclosed in which a ranking function for a set of document rank values is iteratively solved with respect to a set of linked documents until a first stability condition is satisfied. After such condition is satisfied, some of the ranks will have converged. The ranking function is modified to take into account these converged ranks so as to reduce the ranking function's computation cost. The modified ranking function is then solved until a second stability condition is satisfied. After such condition is satisfied more of the ranks will have converged. The ranking function is again modified and process continues until complete.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Asynchronous, independent and multiple process shared memory system in an adaptive computing architecture
The present invention provides a system and method for implementation and use of a shared memory. The shared memory may be accessed both independently and asynchronously by one or more processes at corresponding nodes, allowing data to be streamed to multiple processes and nodes without regard to synchronization of the plurality of processes. The various nodes may be adaptive computing nodes, kernel or controller nodes, or one or more host processor nodes. The present invention maintains memory integrity, not allowing memory overruns, underruns, or deadlocks. The present invention also provides for “push back” after a memory read, for applications in which it is desirable to “unread” some elements previously read from the memory.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
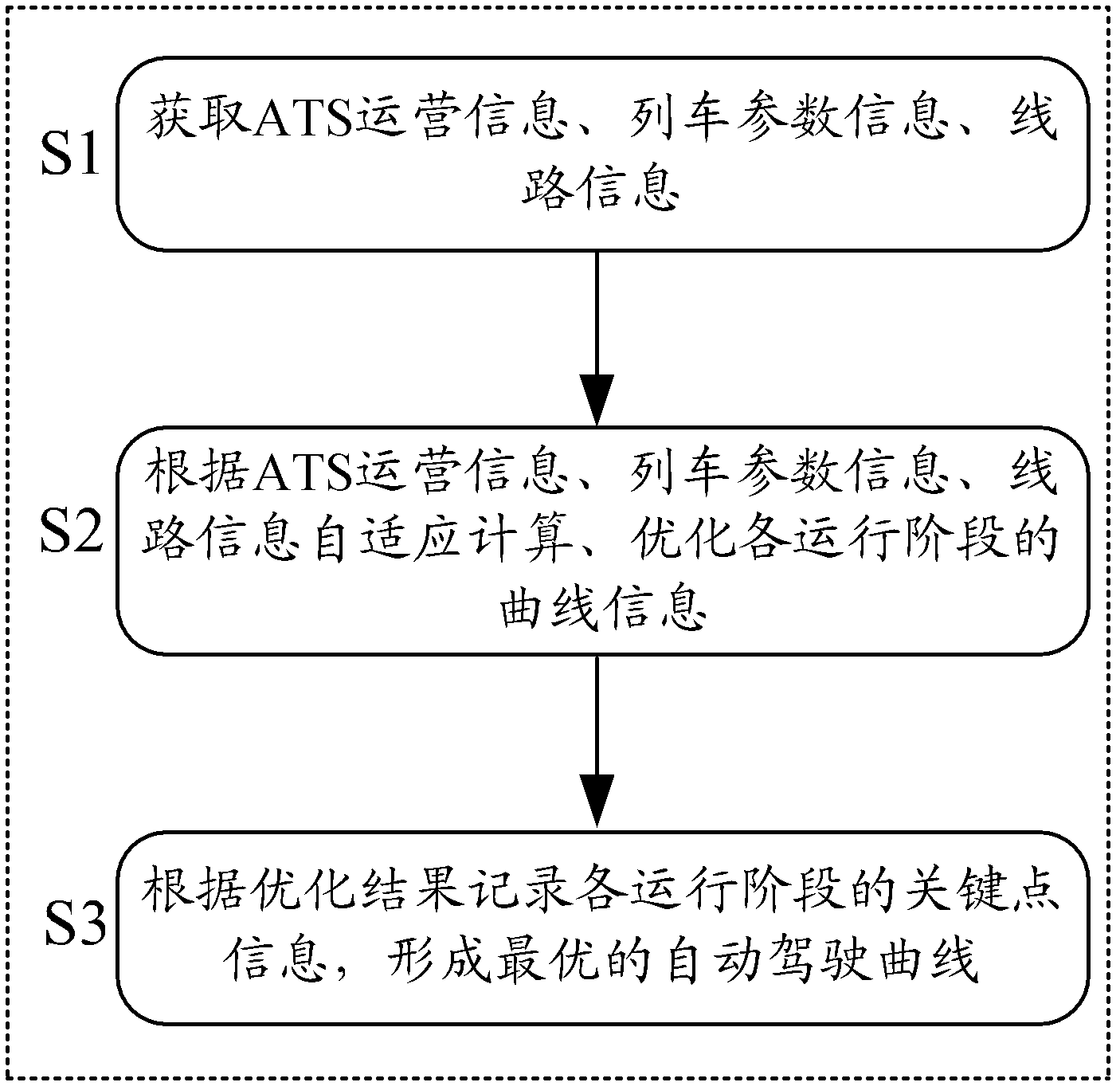
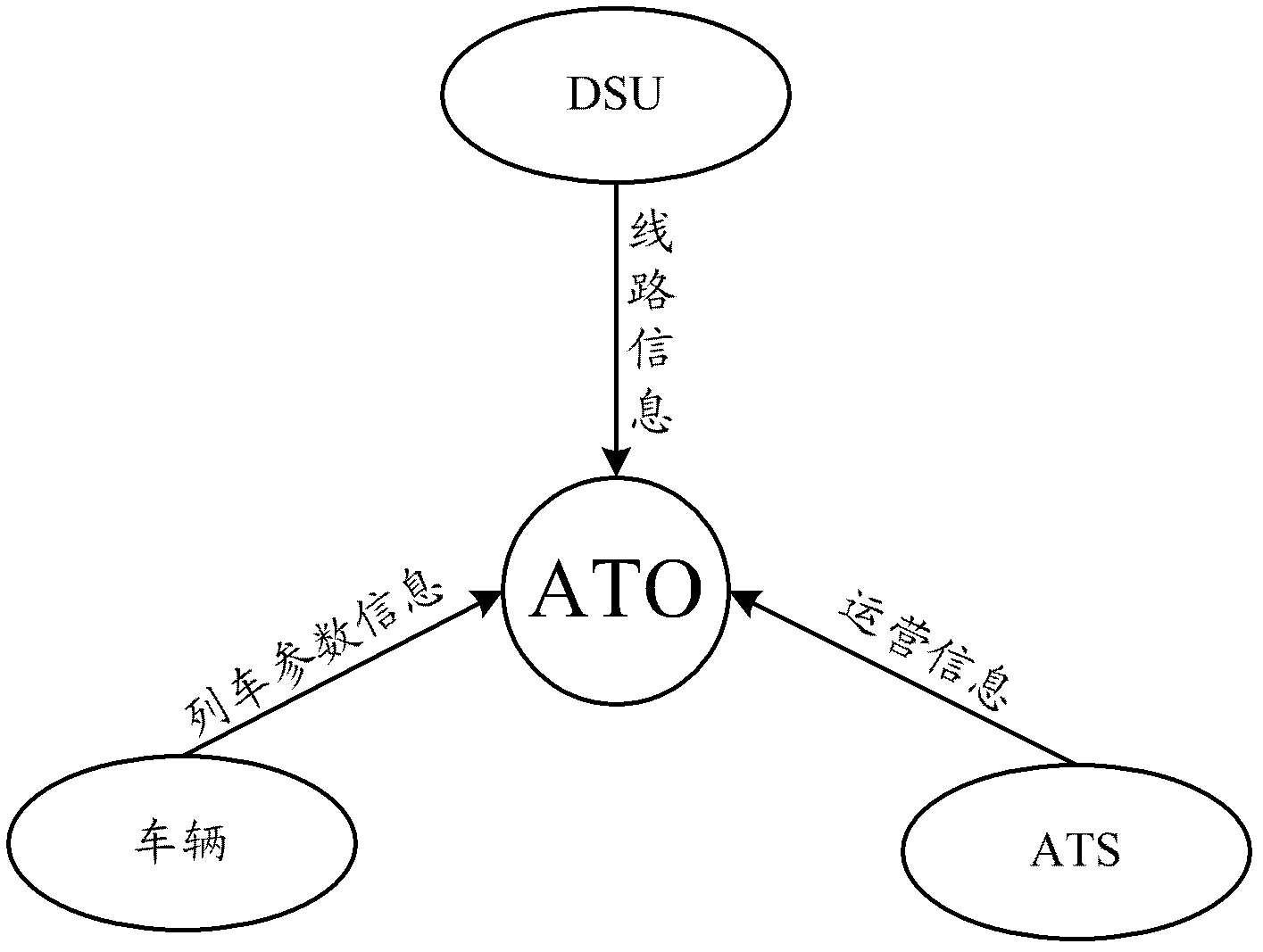
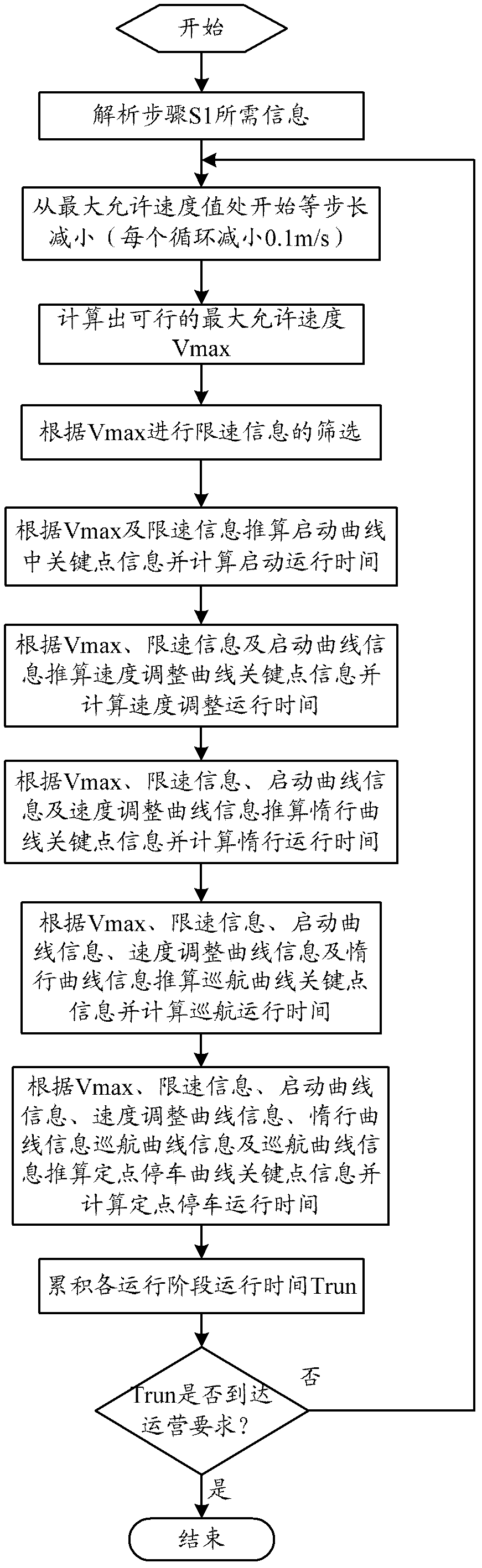
Method for achieve automatic driving curve generation between stations during operation by automatic train driving system
InactiveCN102442323AOptimally run the automatic driving curveRun on timeLocomotivesWork performanceMonitoring system
The present invention relates to a method for achieve automatic driving curve generation between stations during operation by an automatic train driving system. The method comprises that: the system real timely acquires operation information of an automatic train monitoring system, train parameter information and track information of a track database; the driving curve information at each operation stage between the stations is real timely and adaptively calculated; the key point information at each operation stage between the stations is extracted and recorded according to the driving curve information; the best automatic driving curve of the train between the stations during the operation is real timely generated. With adopting the method for achieve the automatic driving curve generation between the stations during the operation by the automatic train driving system, a plurality of disadvantages of the train in the automatic driving process are effectively overcome; the advantages of higher comfort, good energy saving effect, high parking precision, easy adjustment, stable and reliable work performance, and wide application range are provided; the purposes of punctual operation, energy saving operation, high comfort operation, safe and smooth operation of the train are achieved, and the operation requirements of the CBTC system are completely met.
Owner:NO 32 RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
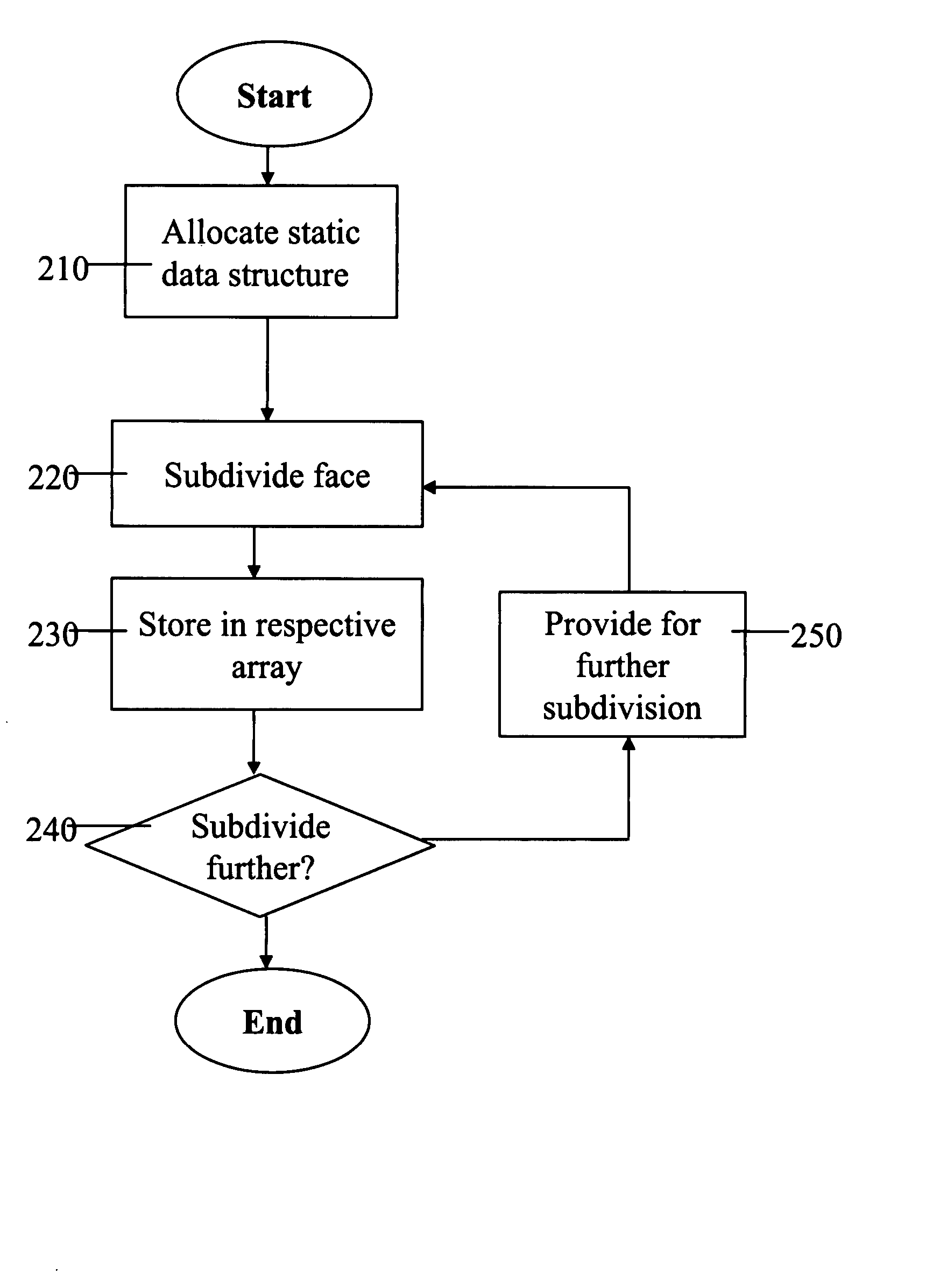
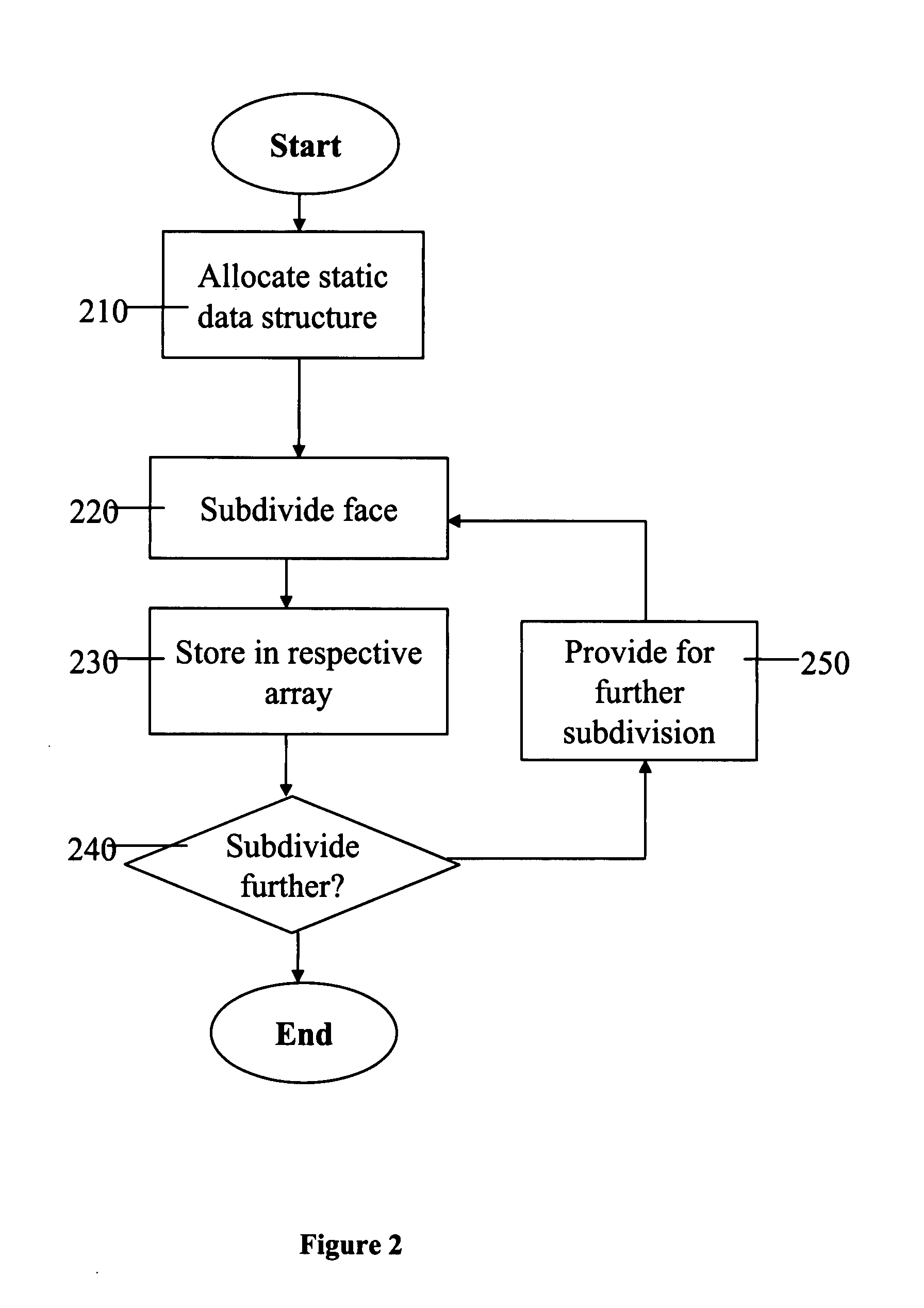
Adaptive computation of subdivision surfaces
A method for the computation of a subdivision surface from a base mesh of coarse faces which requires no dynamic allocations is performed as follows. First, a static data structure is allocated. The static data structure includes a hierarchy of data arrays, where each of the data arrays is for storing control mesh data for a single coarse face at a respective subdivision level. The size of each of the data arrays is determined by the respective subdivision level. A subdivision algorithm is then applied to each of the base mesh coarse faces in turn. During the subdivision of a single coarse face, the resulting data for each subdivision level is stored in the respective data array. The static data structure may store further data for each subdivision level respectively, such as a tag for each of the sub-faces at the given level. The subdivision may be applied adaptively, by applying level-of-detail control information at intermediate subdivision levels.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
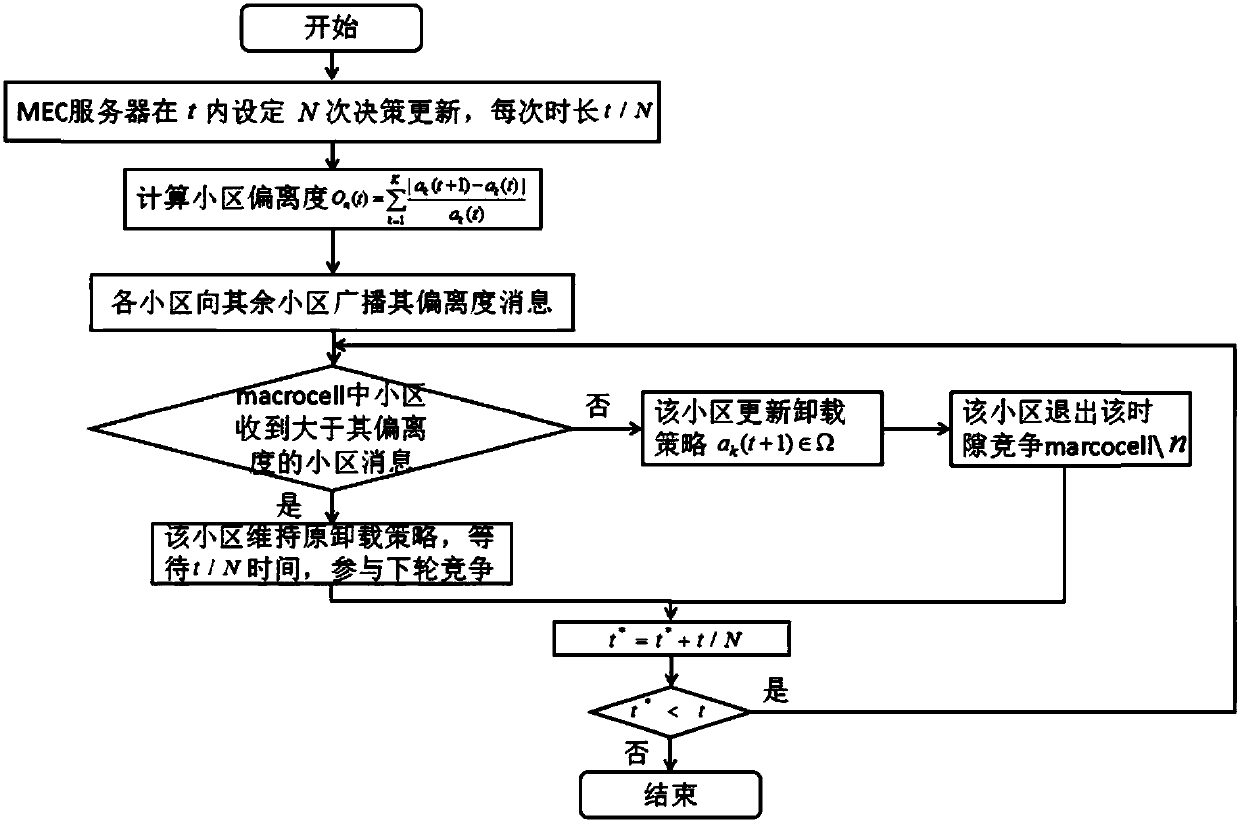
Distributed uplink unloading strategy for mobile edge computing
The invention discloses a distributed uplink unloading strategy for mobile edge computing. The invention obtains an adaptive computing unloading strategy based on the Lyapunov theory and a proposed deviation degree update decision algorithm DUDA. The strategy comprises two main aspects: first, obtaining an optimal unloading decision set of users in Small Cells based on the Lyapunov theory on the premise of ensuring the system stability and minimized overhead; and secondly, proposing the DUDA to decide an unloading decision update sequence of the Small Cells in each time slot according to the deviation degree; and in the distributed uplink unloading strategy disclosed by the invention, it is considered that a user terminal has partial task unloading capability, that is, the tasks of a single users can be subdivided, a part of tasks are selected for local calculation according to specific application requirements and available resources with the target of minimizing the system overhead,and the remaining tasks are unloaded to an edge server of a Macro Cell in the HetNet scene. According to the distributed uplink unloading strategy disclosed by the invention, the system stability andthe optimal overhead are ensured by determining a drift penalty function, and an optimal unloading strategy set of users in the Small Cell under the condition is obtained.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF STATE GRID ZHEJIANG ELECTRIC POWER COMAPNY +2
Adaptive computer sequencing of actions
InactiveUS20090172671A1Multiprogramming arrangementsVisual/graphical programmingCompletion StatusAlgorithm
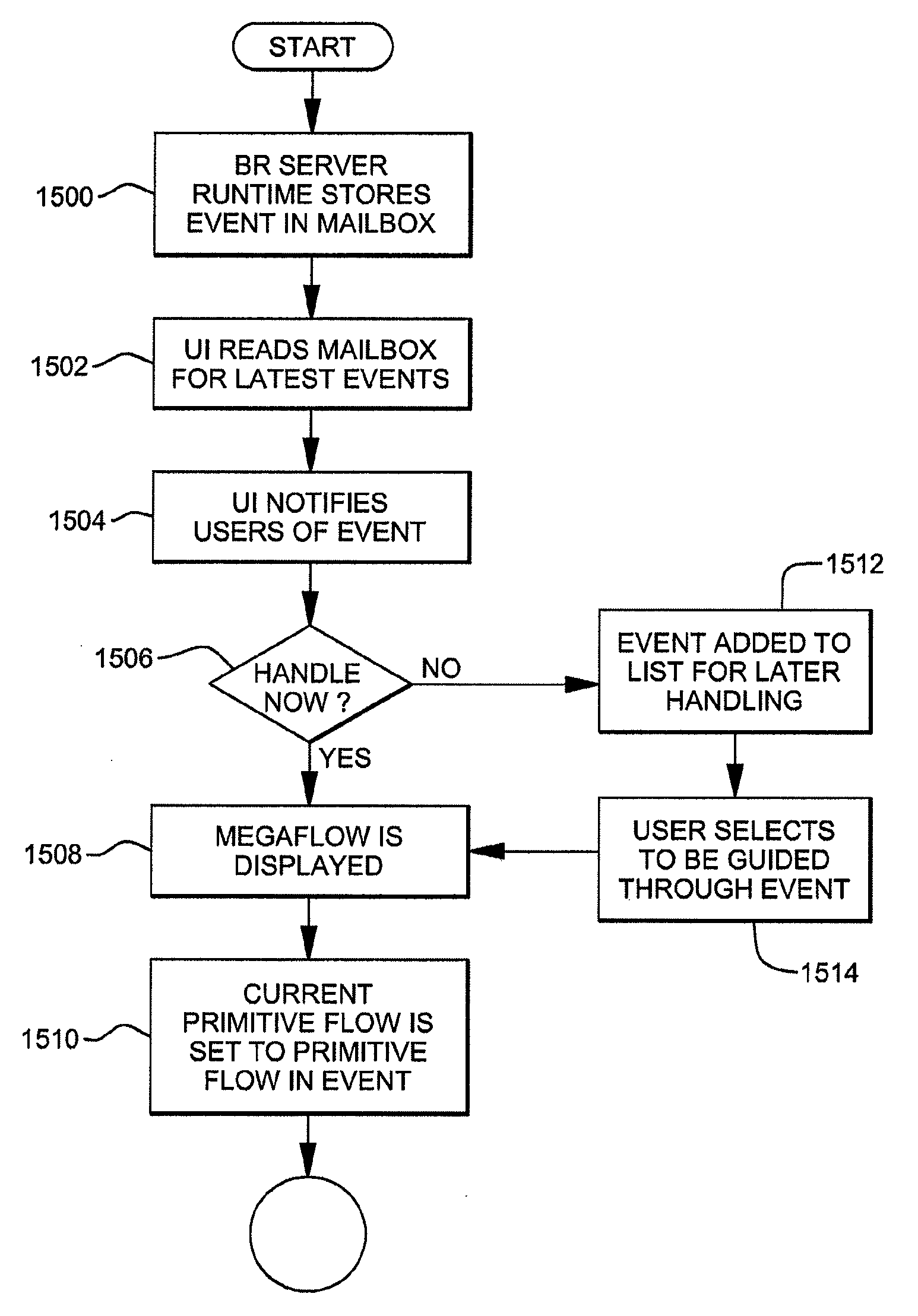
A recommended sequence of tasks to complete a complex task is programmatically defined. The recommended sequence is adaptive in that the sequence can be altered based on the completion status of one or more of the tasks.
Owner:IBM CORP
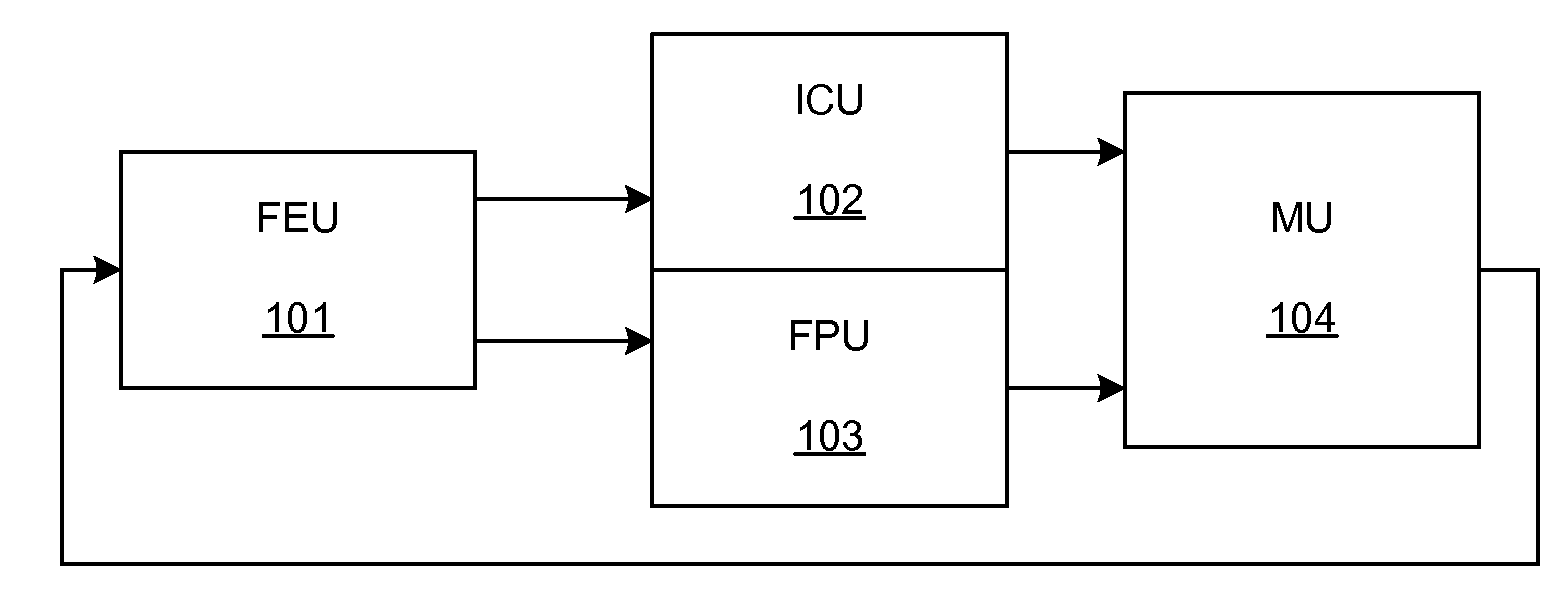
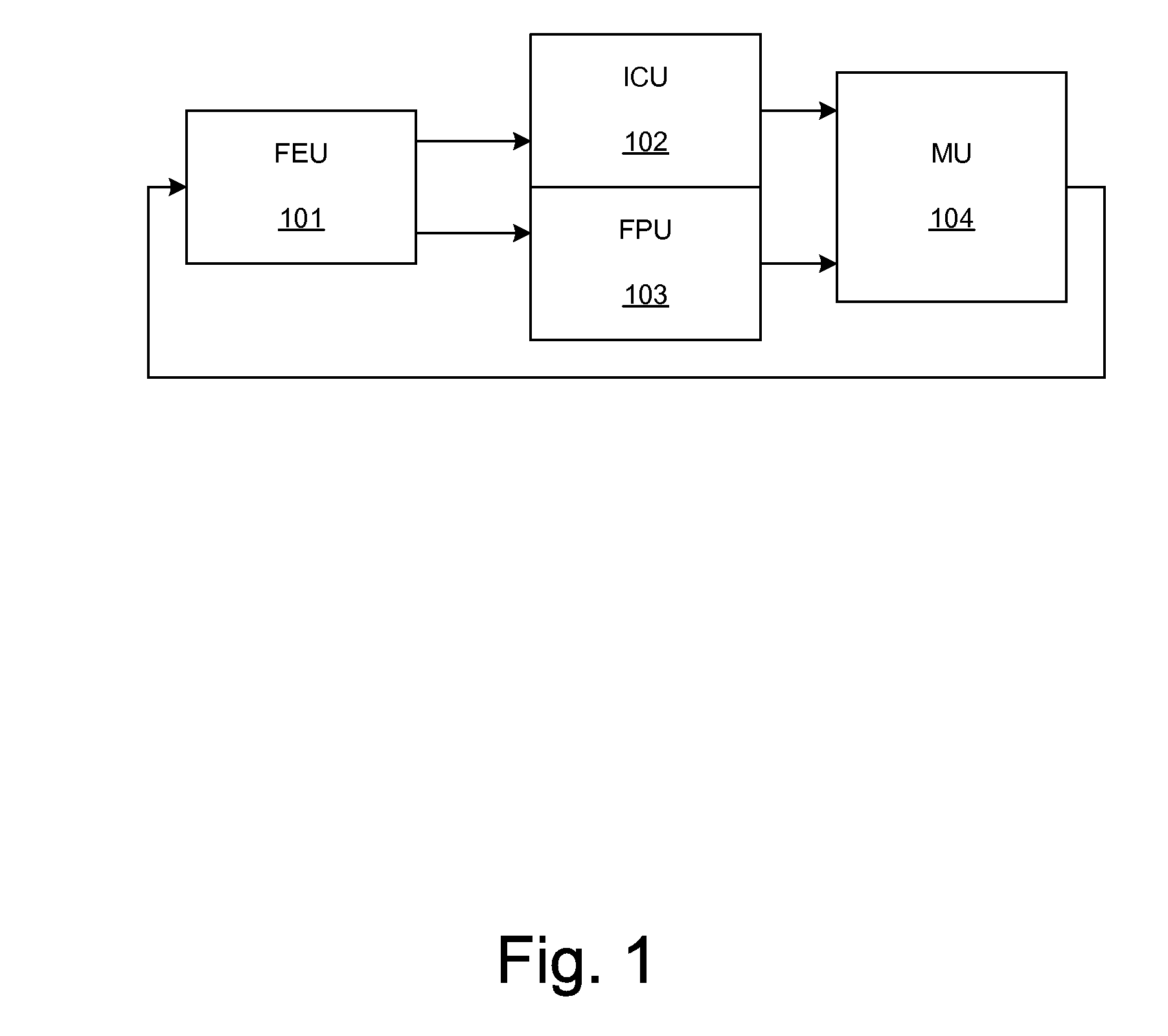
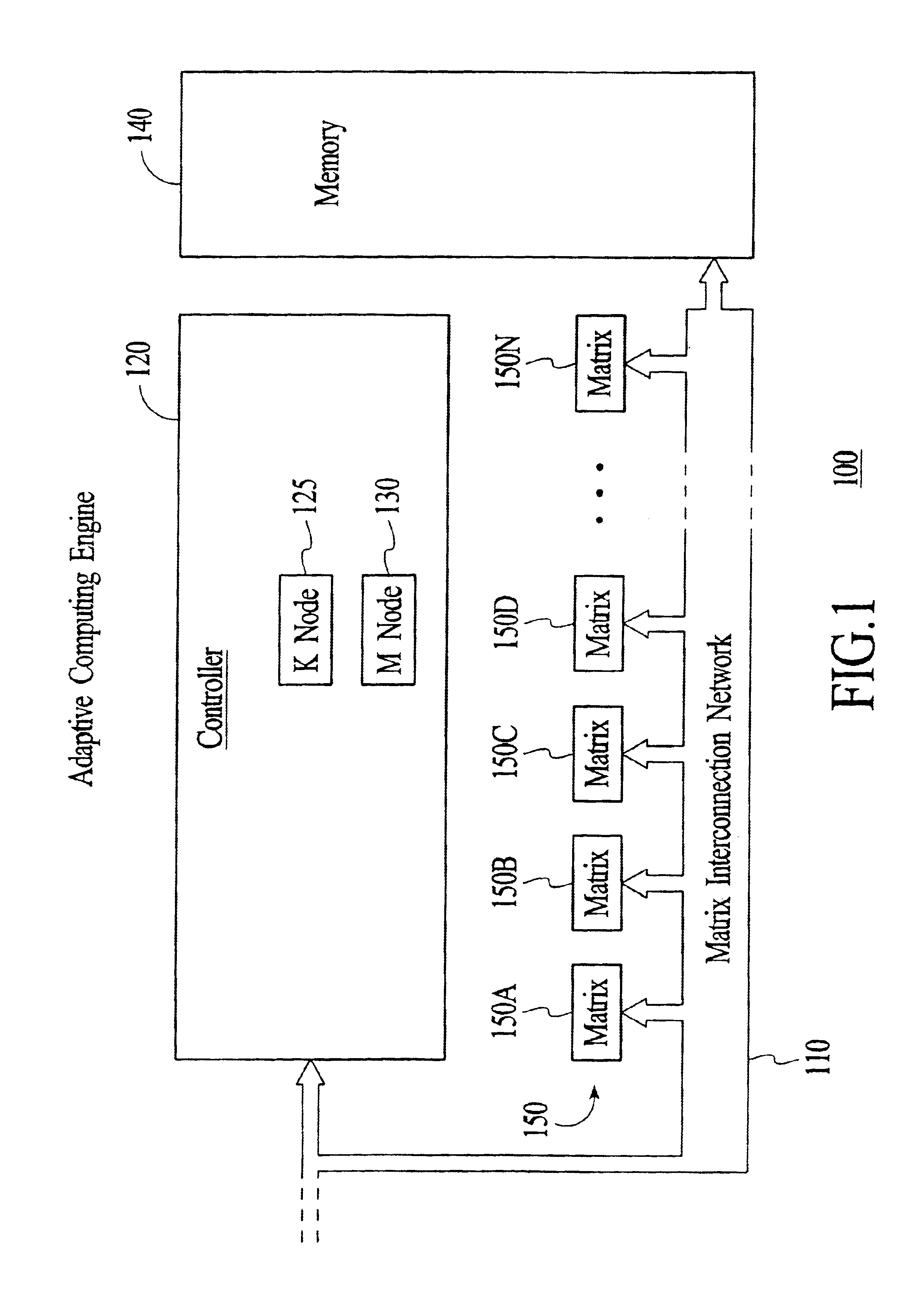
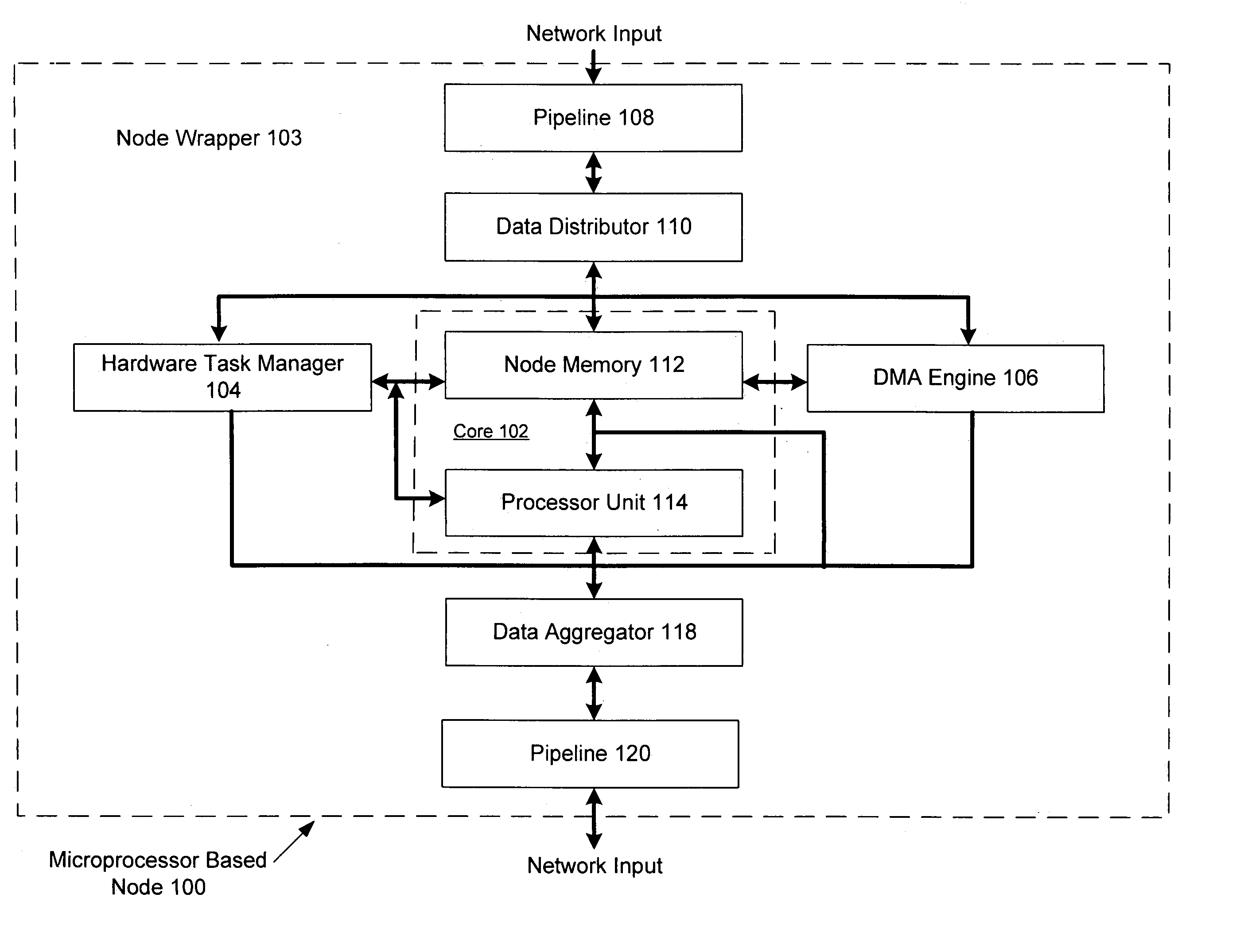
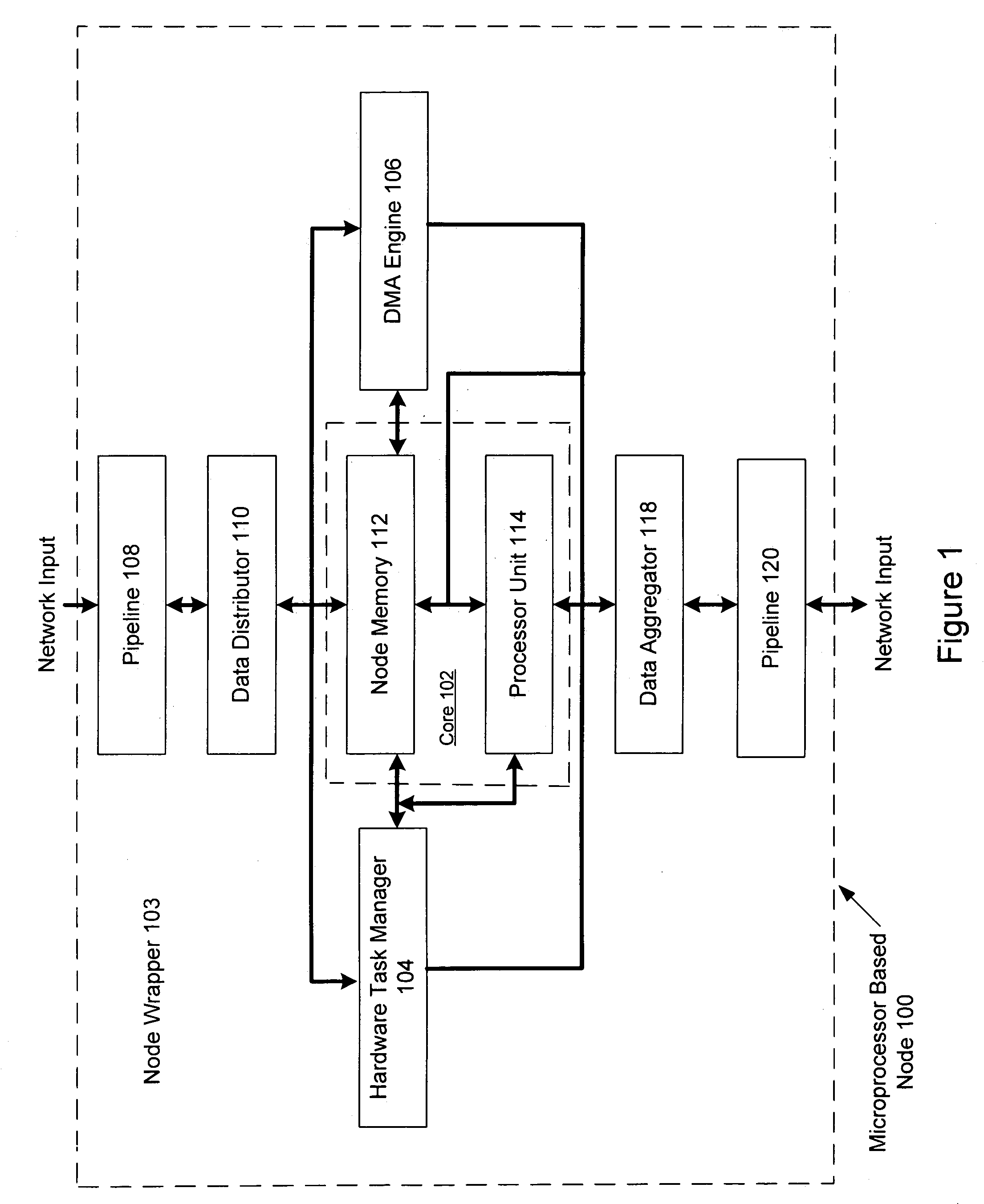
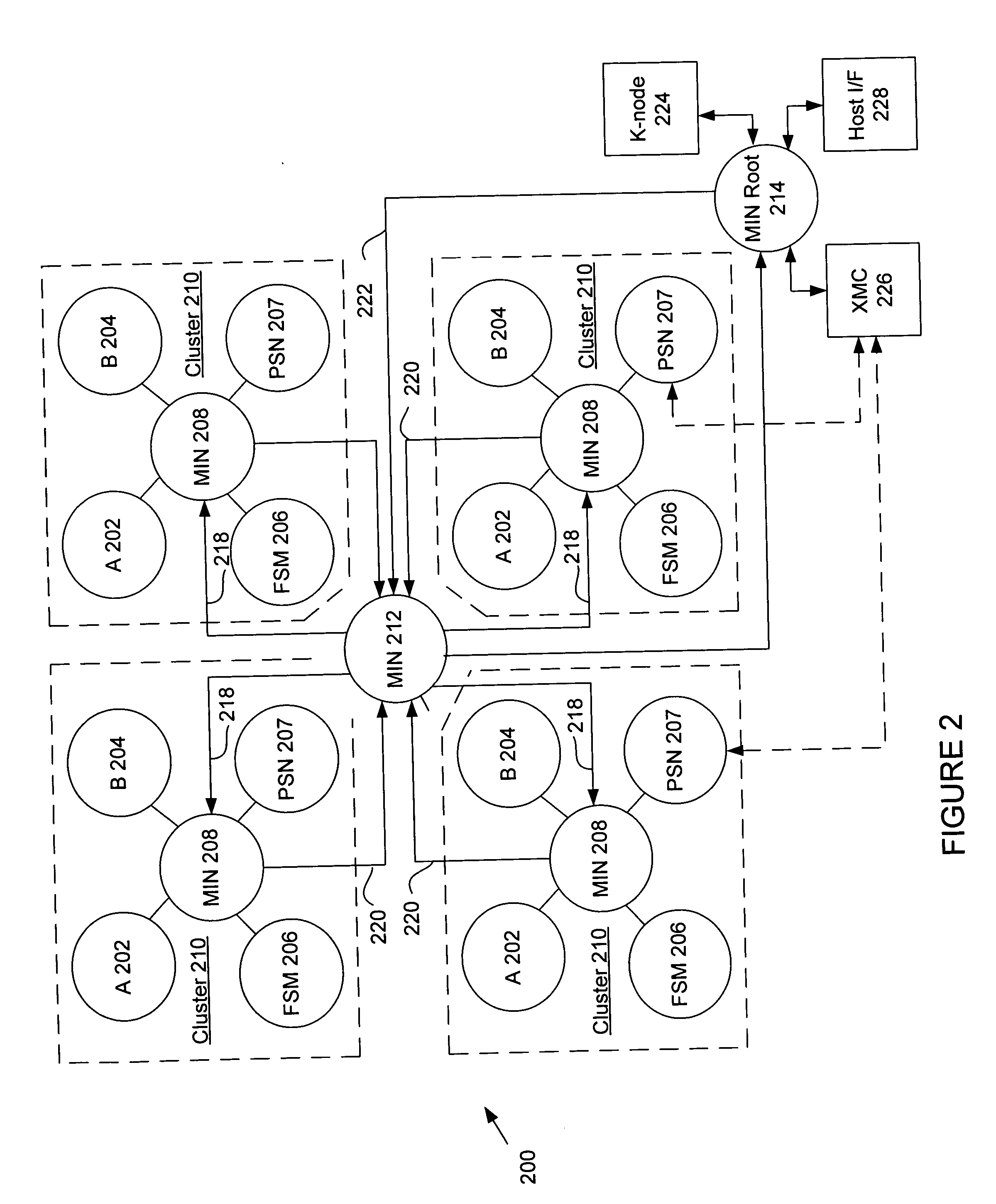
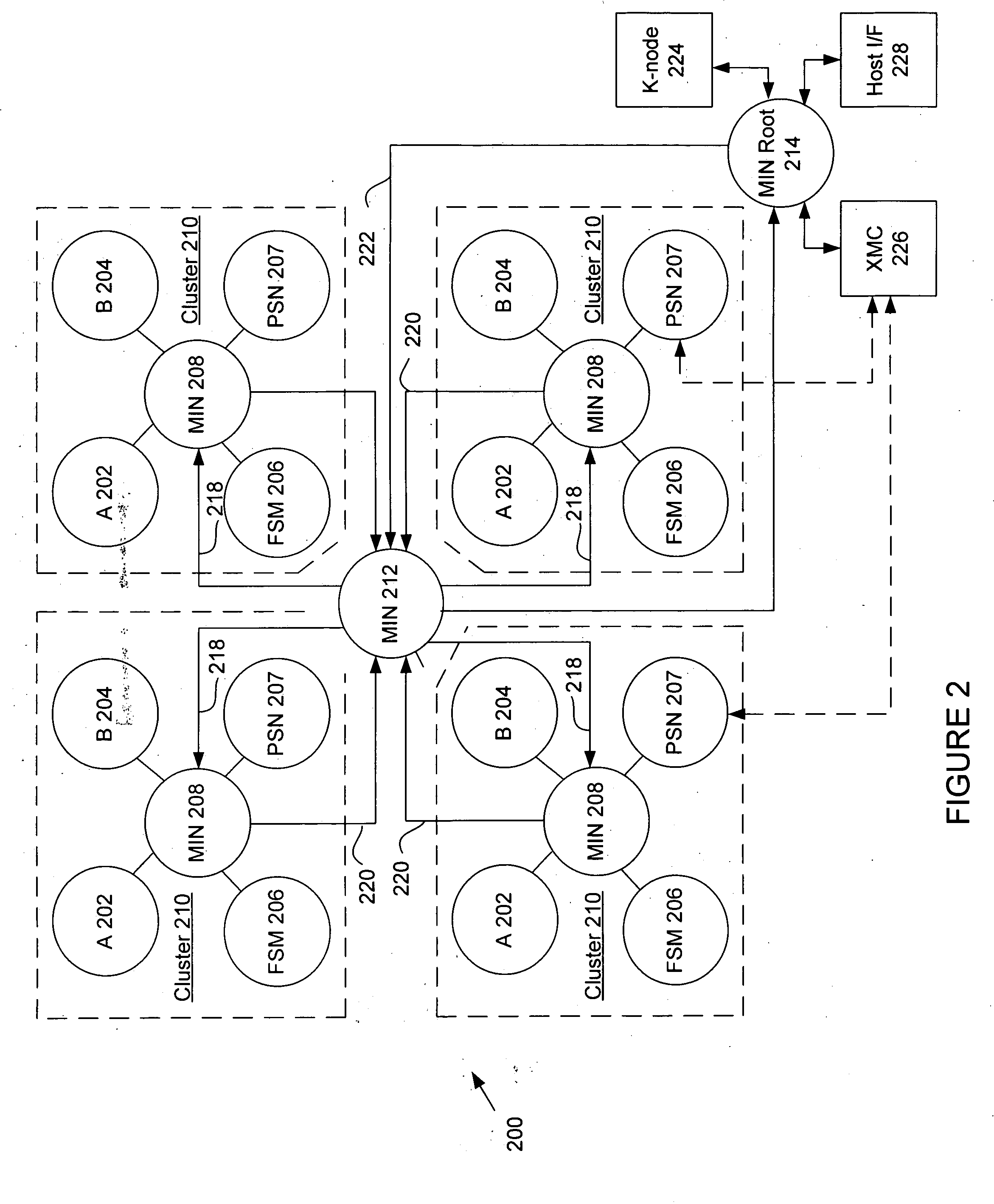
System and method using embedded microprocessor as a node in an adaptable computing machine
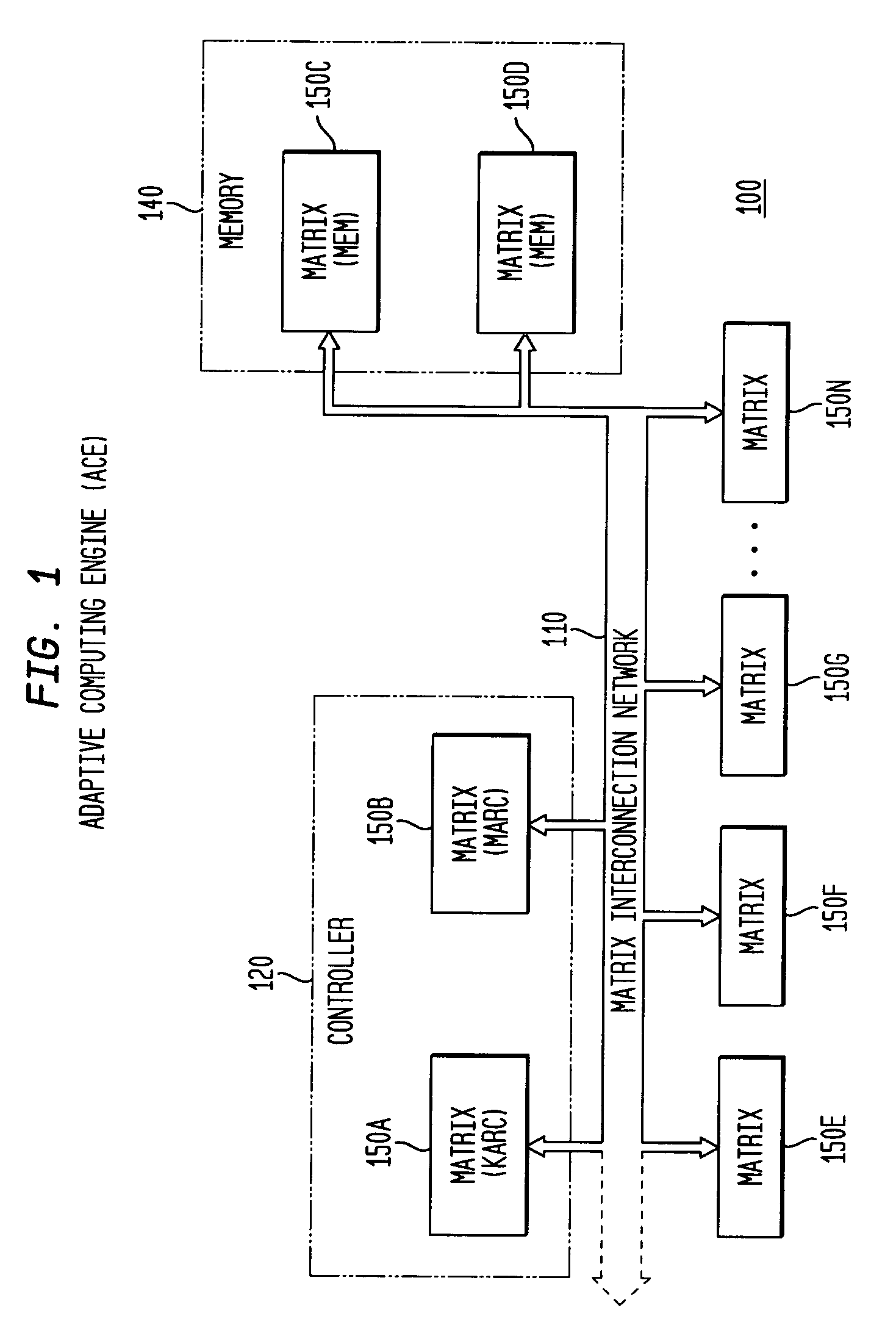
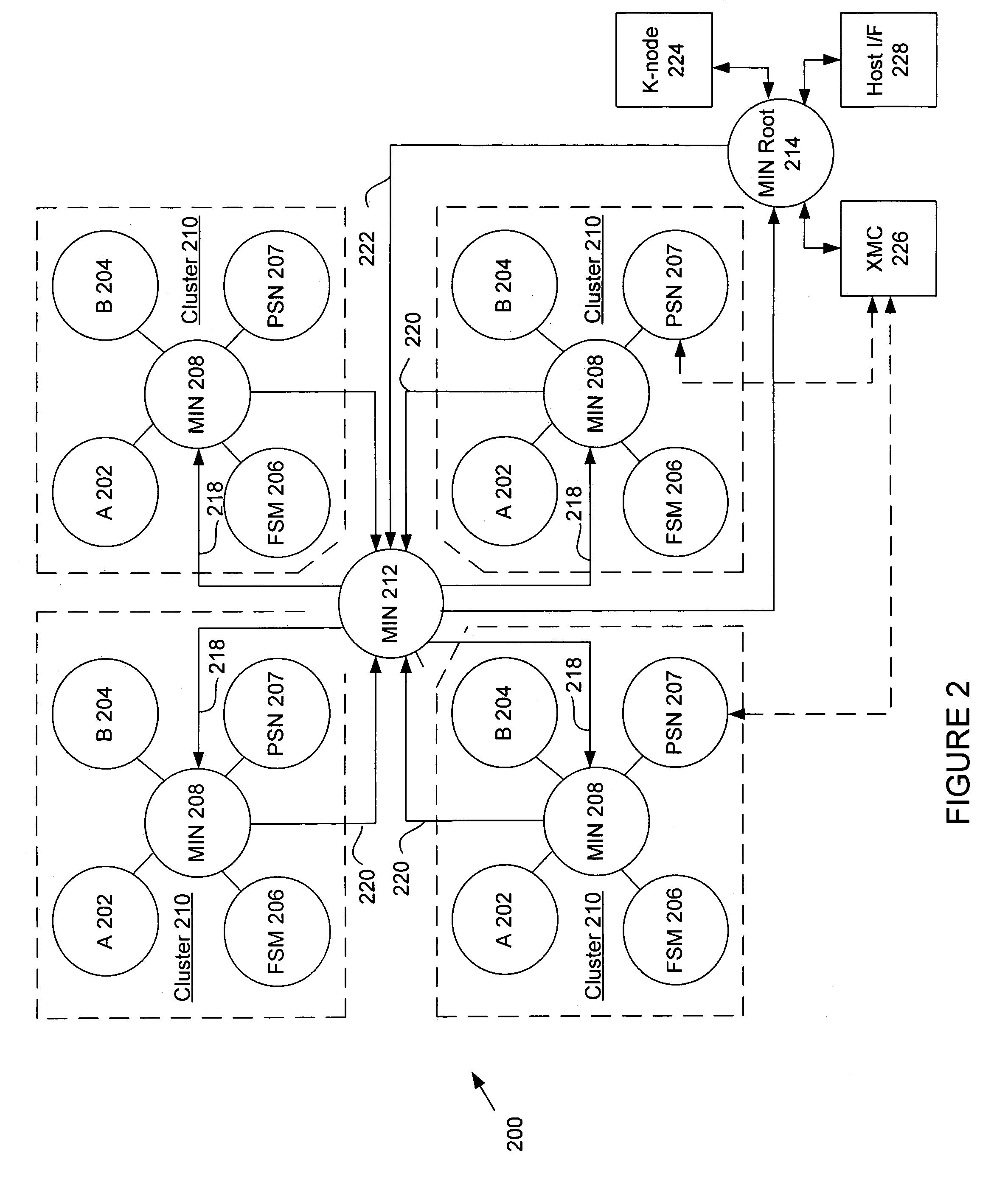
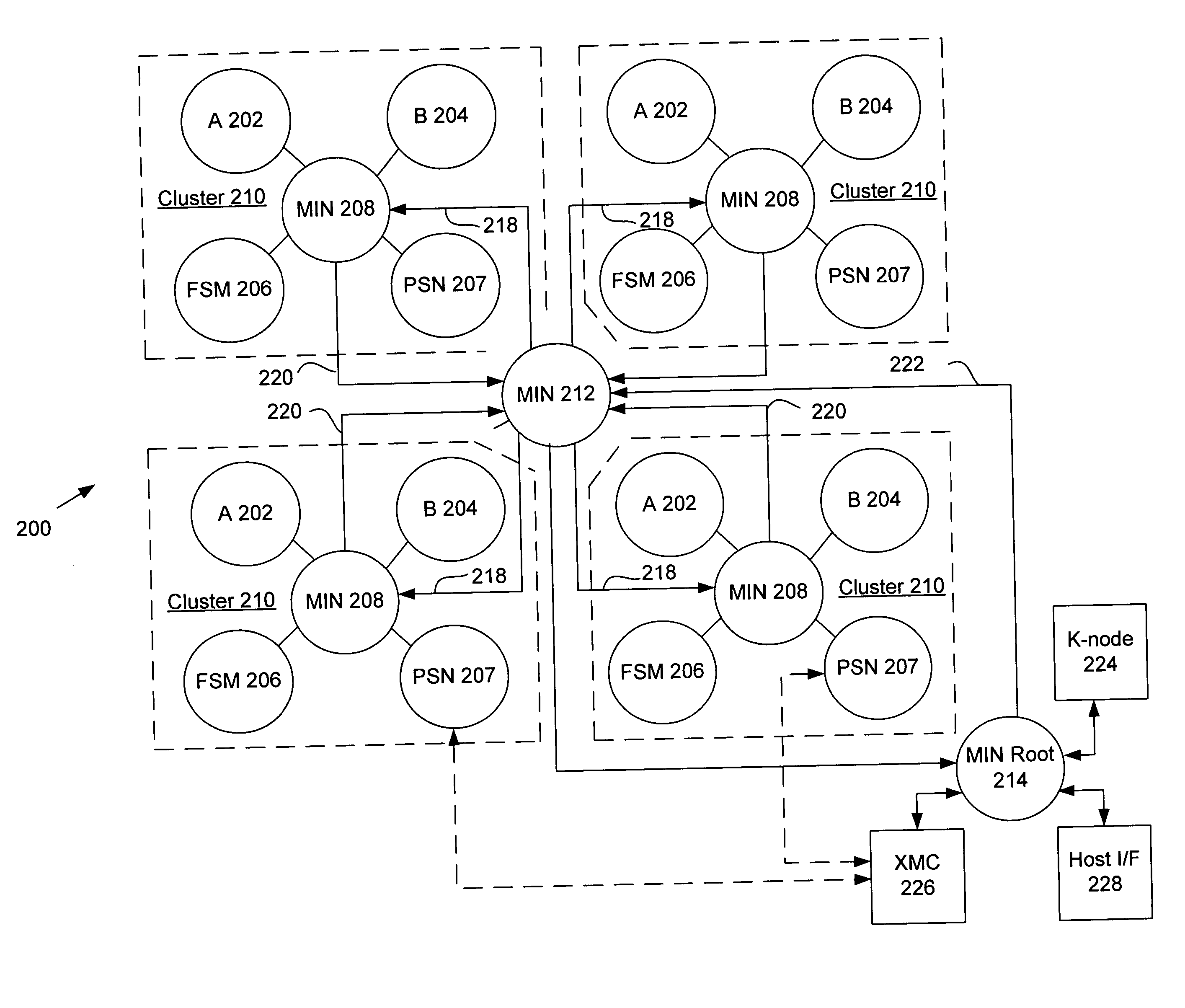
ActiveUS7194598B2Easy to useInherent adaptabilitySingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsMultiple digital computer combinationsGeneral purposeFinite-state machine
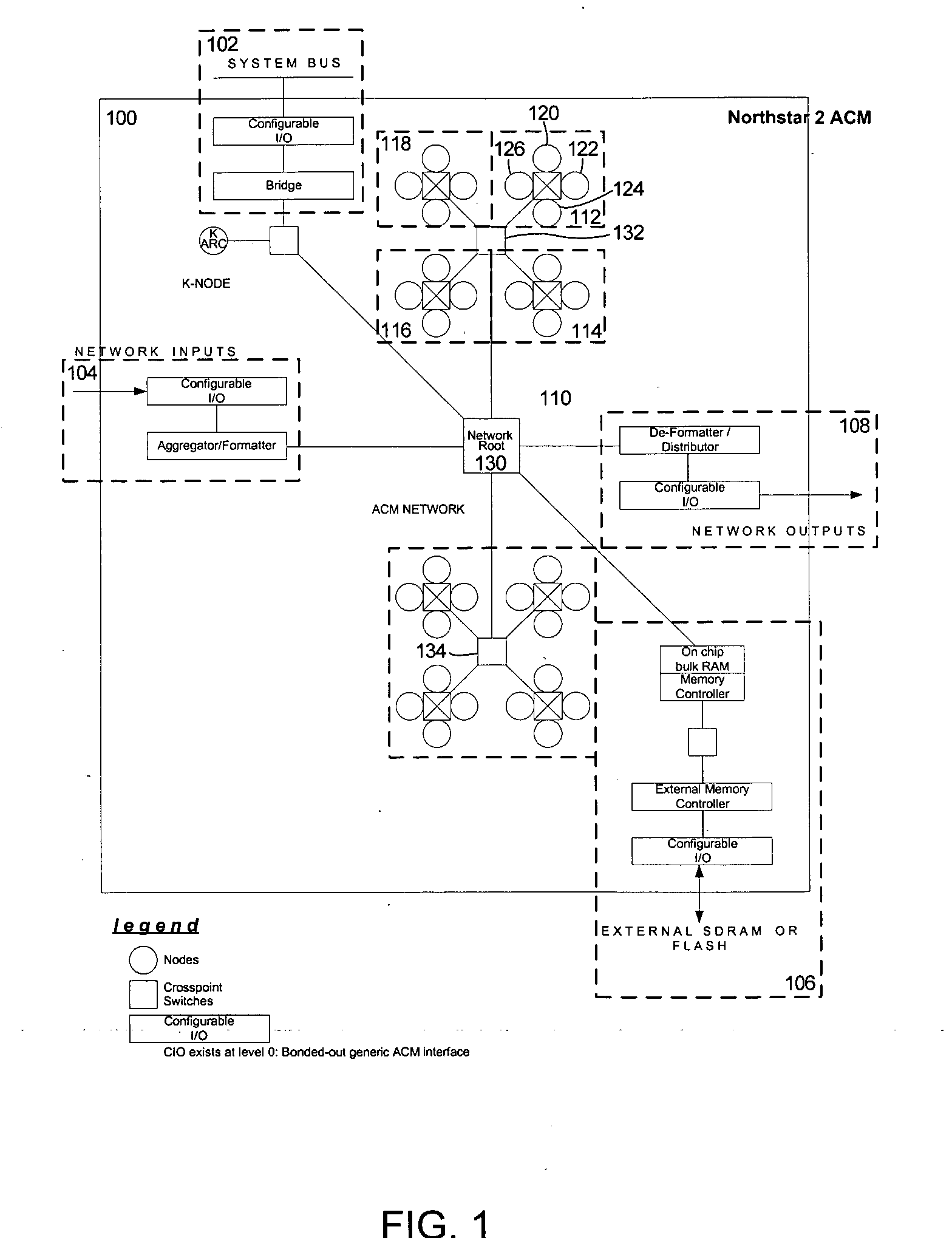
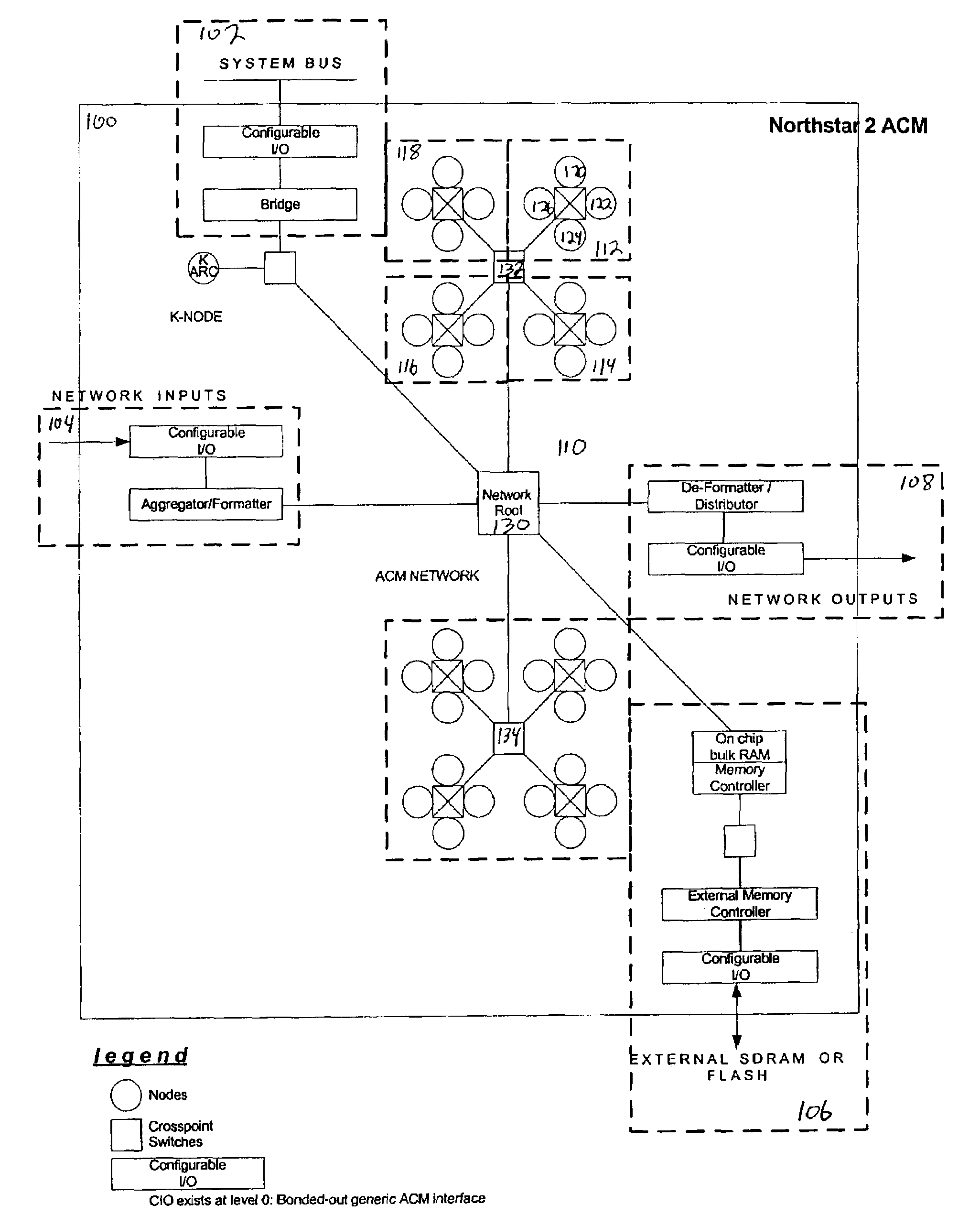
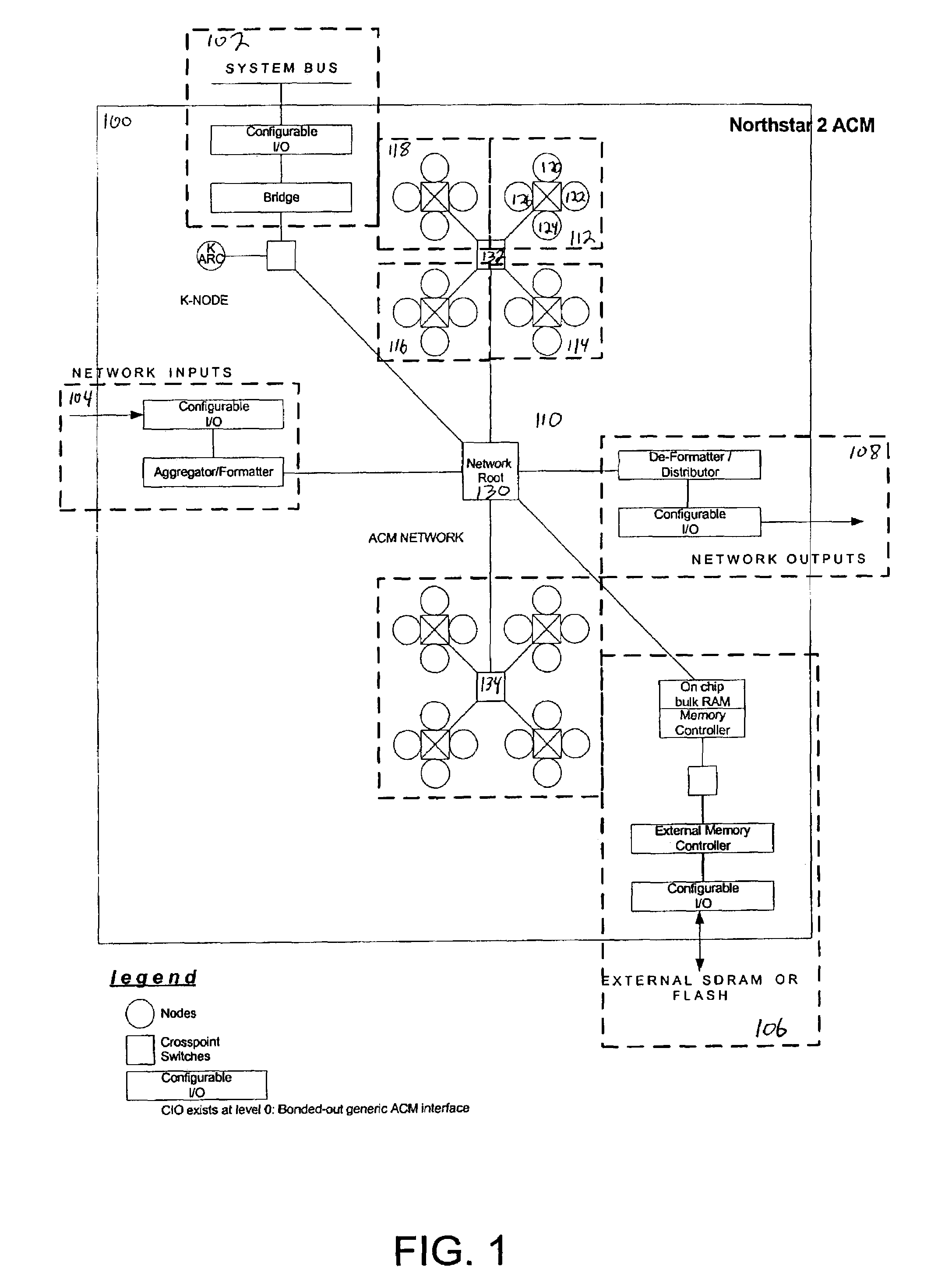
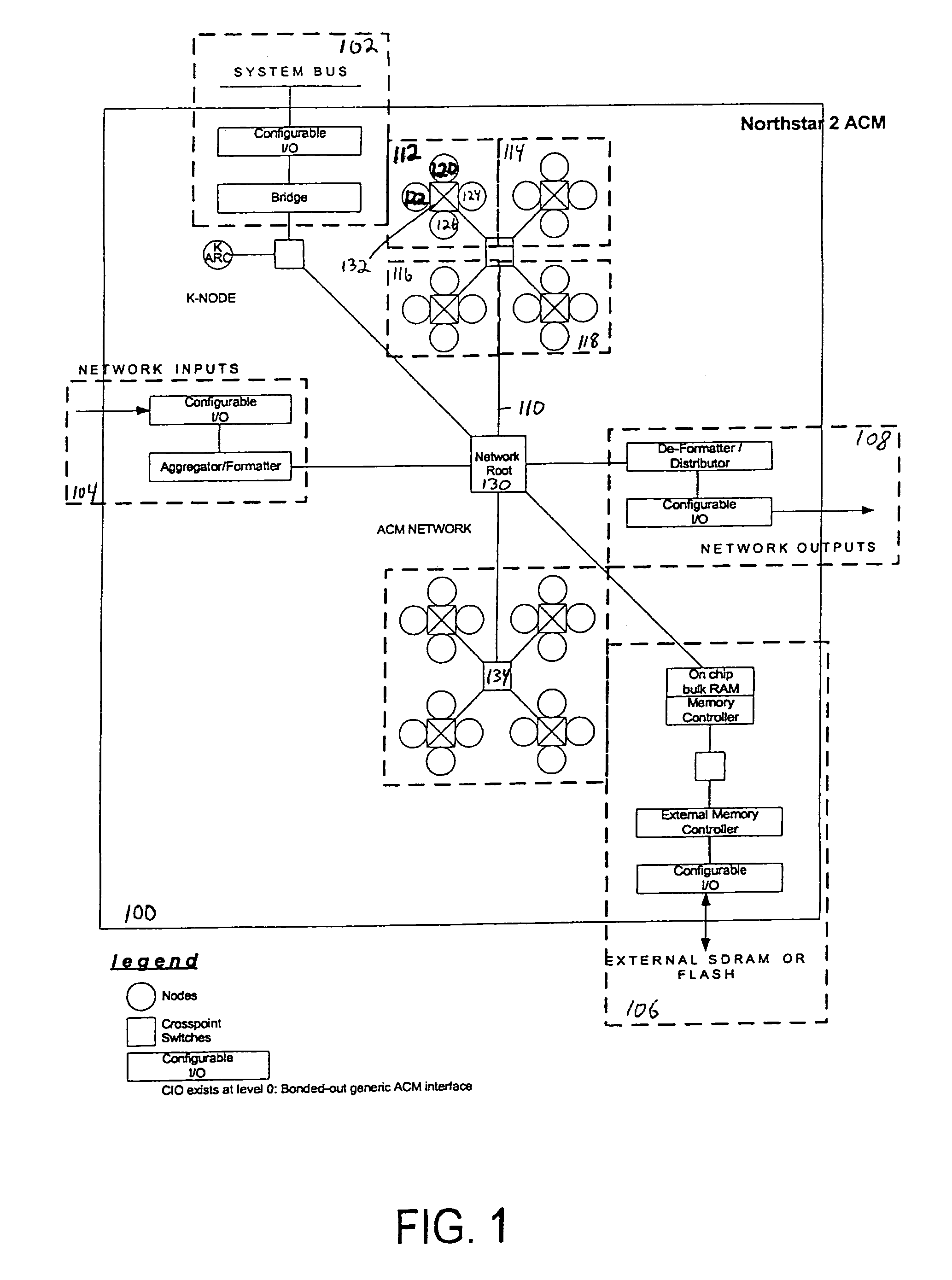
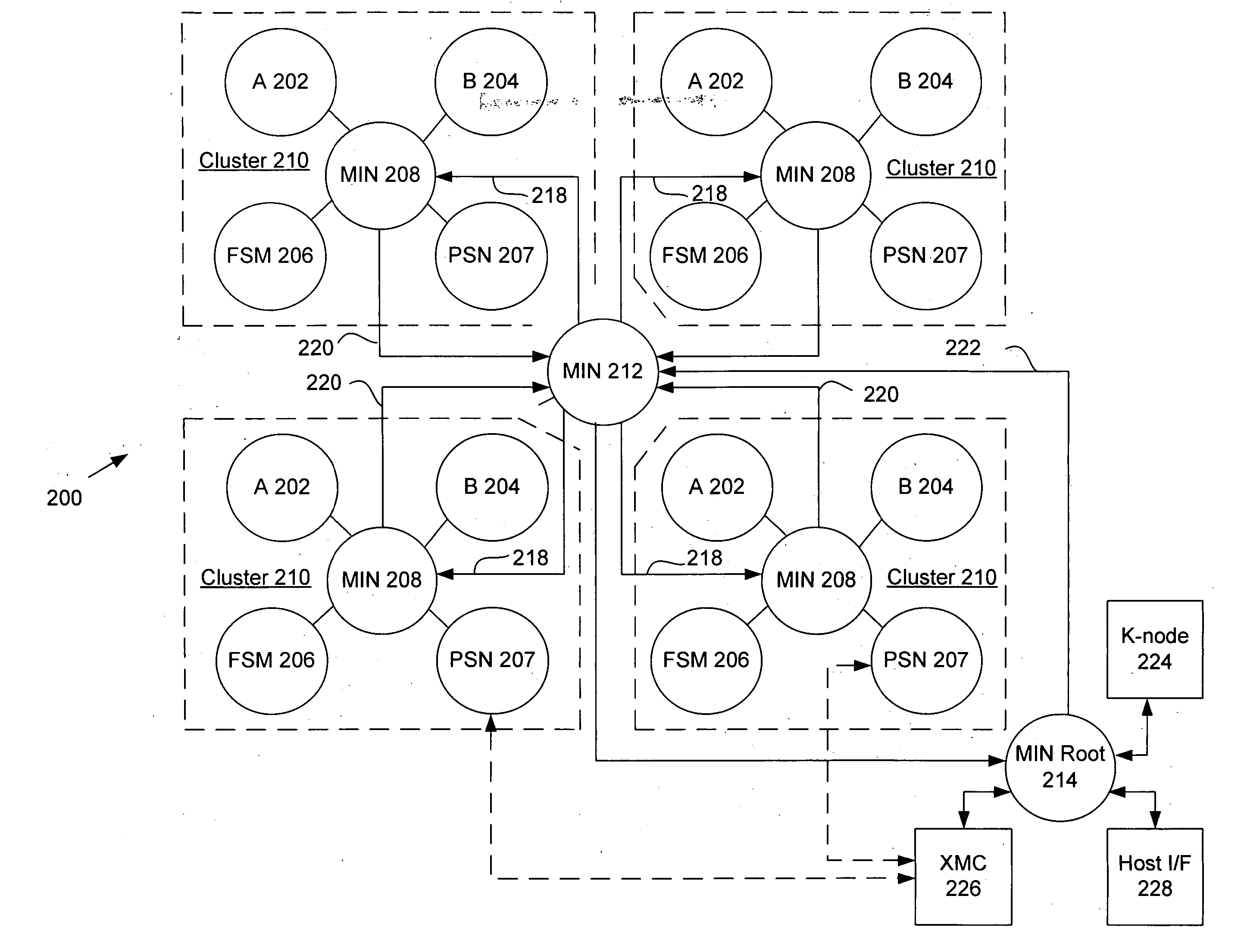
The present invention provides an adaptive computing engine (ACE) that includes processing nodes having different capabilities such as arithmetic nodes, bit-manipulation nodes, finite state machine nodes, input / output nodes and a programmable scalar node (PSN). In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a common architecture is adaptable to function in either a kernel node, or k-node, or as general purpose RISC node. The k-node acts as a system controller responsible for adapting other nodes to perform selected functions. As a RISC node, the PSN is configured to perform computationally intensive applications such as signal processing. The present invention further provides an interconnection scheme so that a plurality of ACE devices operates under the control of a single k-node.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
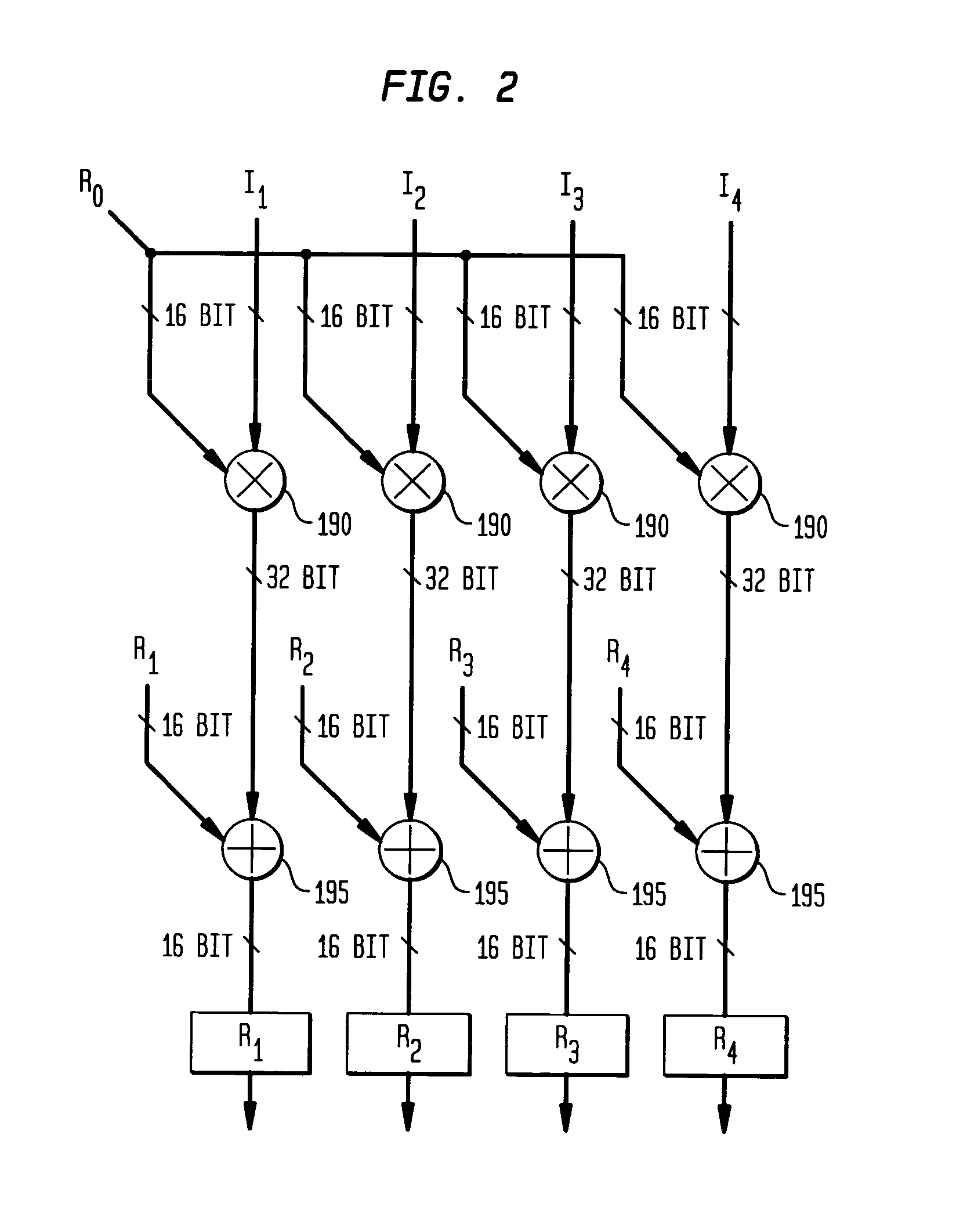
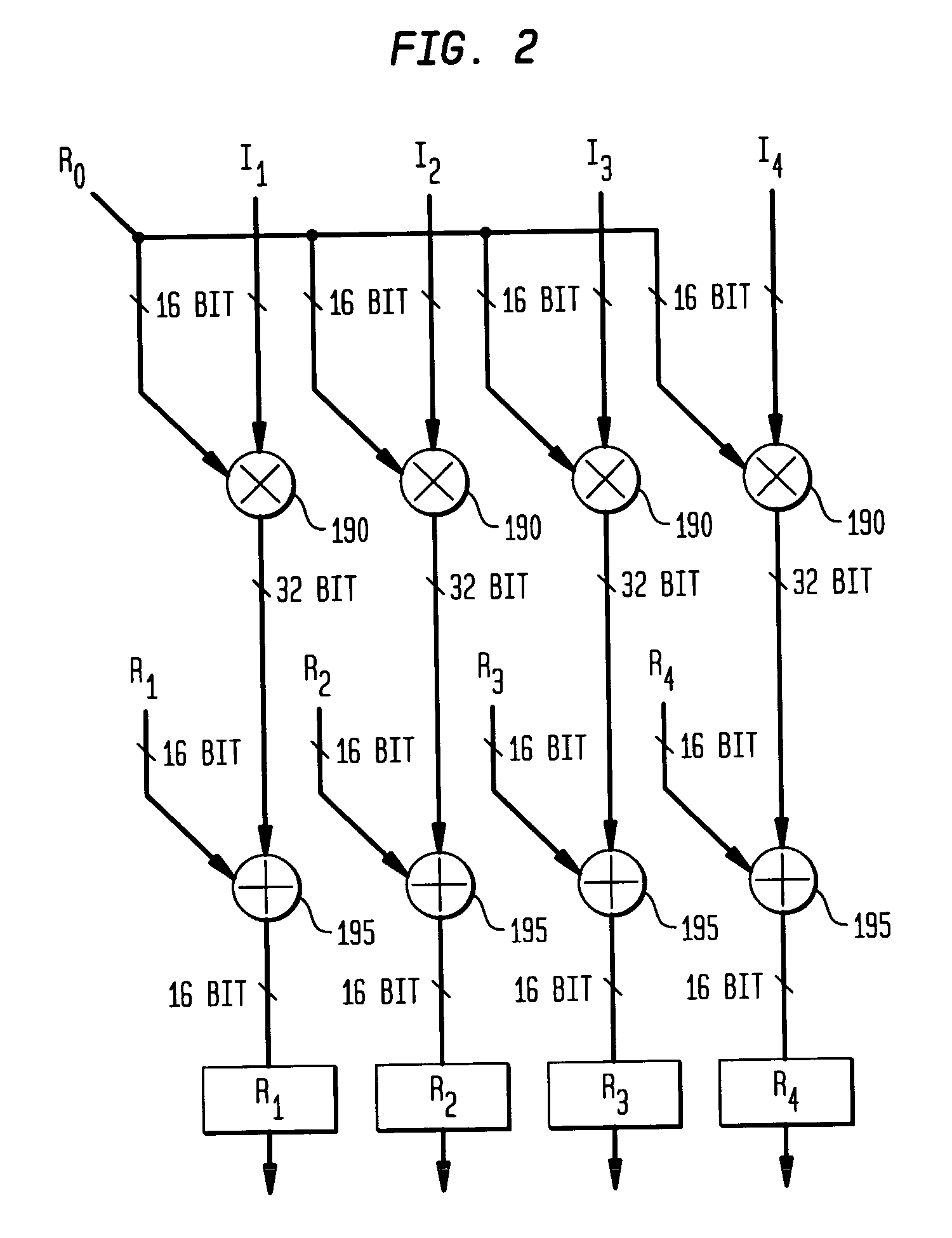
Arithmetic node including general digital signal processing functions for an adaptive computing machine
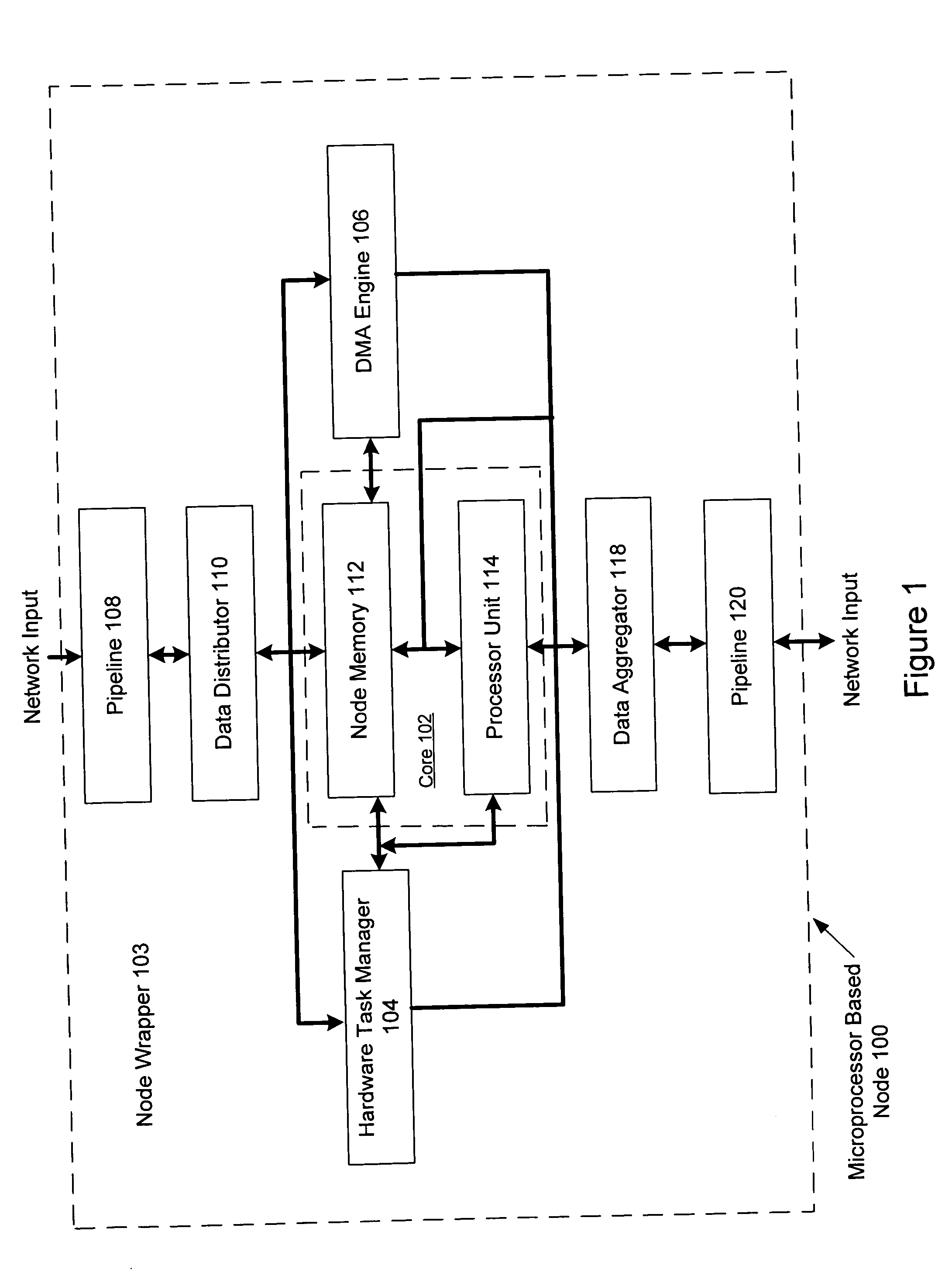
ActiveUS20060015701A1Single instruction multiple data multiprocessorsElectric digital data processingDigital signal processingInterconnection
An apparatus for processing operations in an adaptive computing environment is provided. The adaptive computing environment including at least one processing node. A node includes a memory configured to receive and store data. The data is received from a programmable interconnection network and stored. The node also includes an execution unit configured to perform a signal processing operation. The operation is performed using data retrieved from the memory and an output result is generated. The output result may be used for further computations or sent directly to the programmable interconnection network for transfer to another processing node in the adaptive computing environment.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
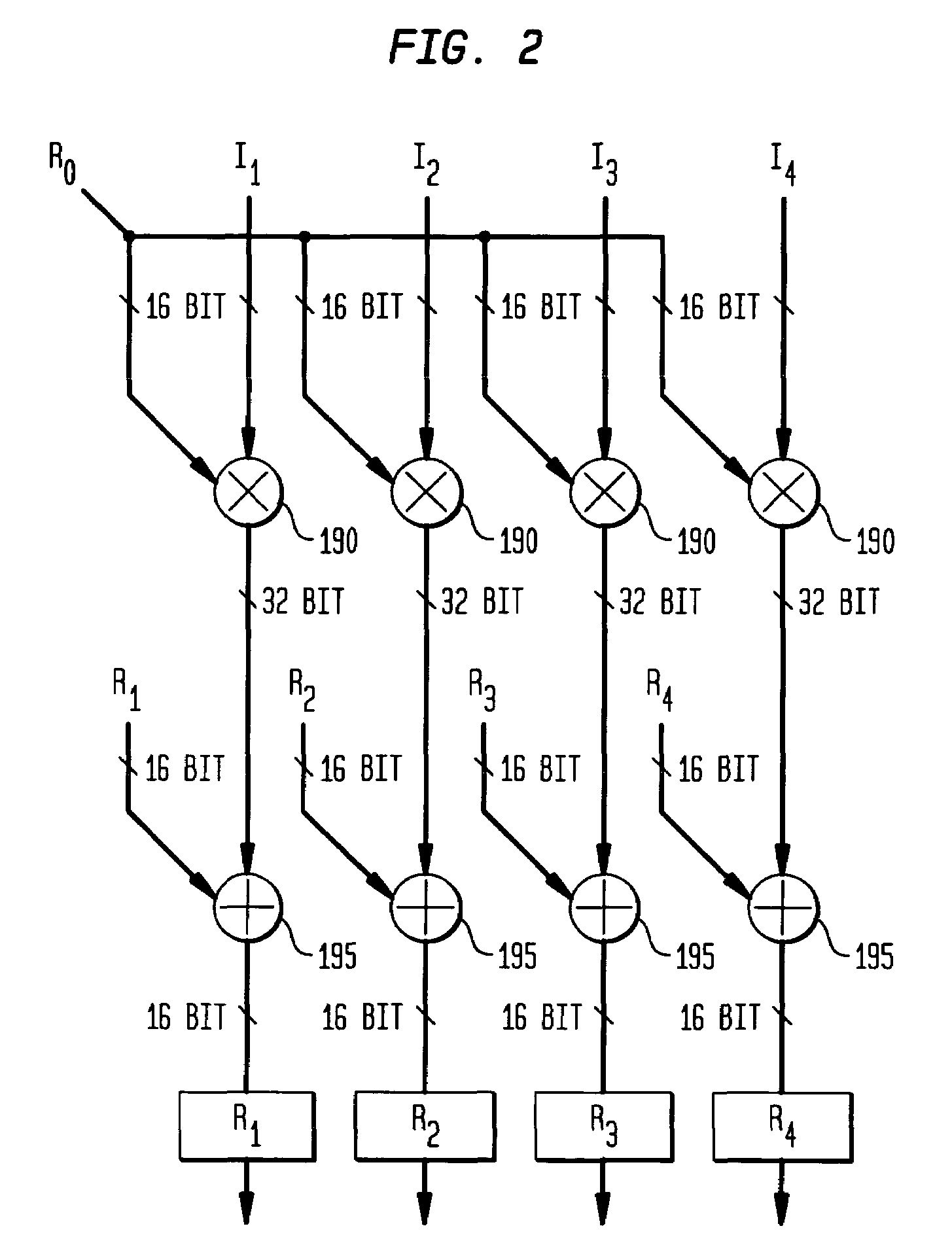
Reconfigurable filter node for an adaptive computing machine
A reconfigurable filter node including an input data memory adapted to store a plurality of input data values, a filter coefficient memory adapted to store a plurality of filter coefficient values, and a plurality of computational units adapted to simultaneously compute filter data values. Filter data values are the outputs of a filter in response to input data values or a second plurality of filter coefficients to be used in subsequent filter data value computations. First and second input data registers load successive input data values input data memory or from adjacent computational units. Each computational unit comprises a pre-adder adapted to output either the sum two input data values stored in the computational unit or alternately to output a single input data value, and a multiply-and-accumulate unit adapted to multiply the output of the pre-adder by a filter coefficient and accumulate the result.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
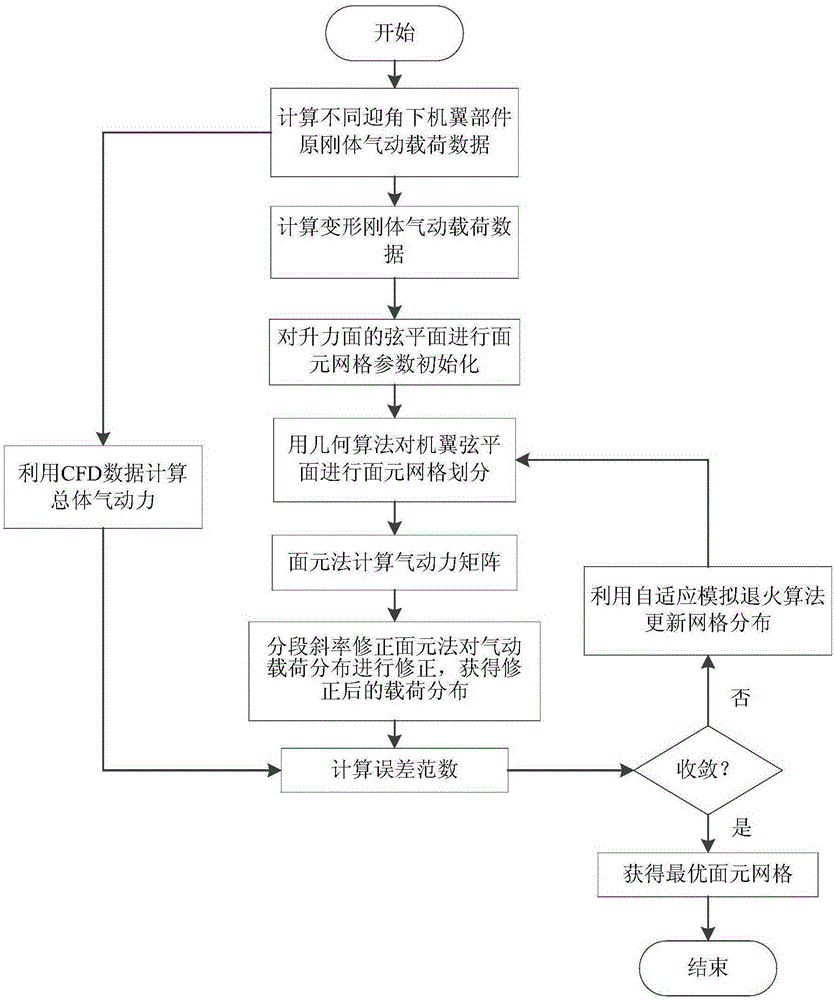
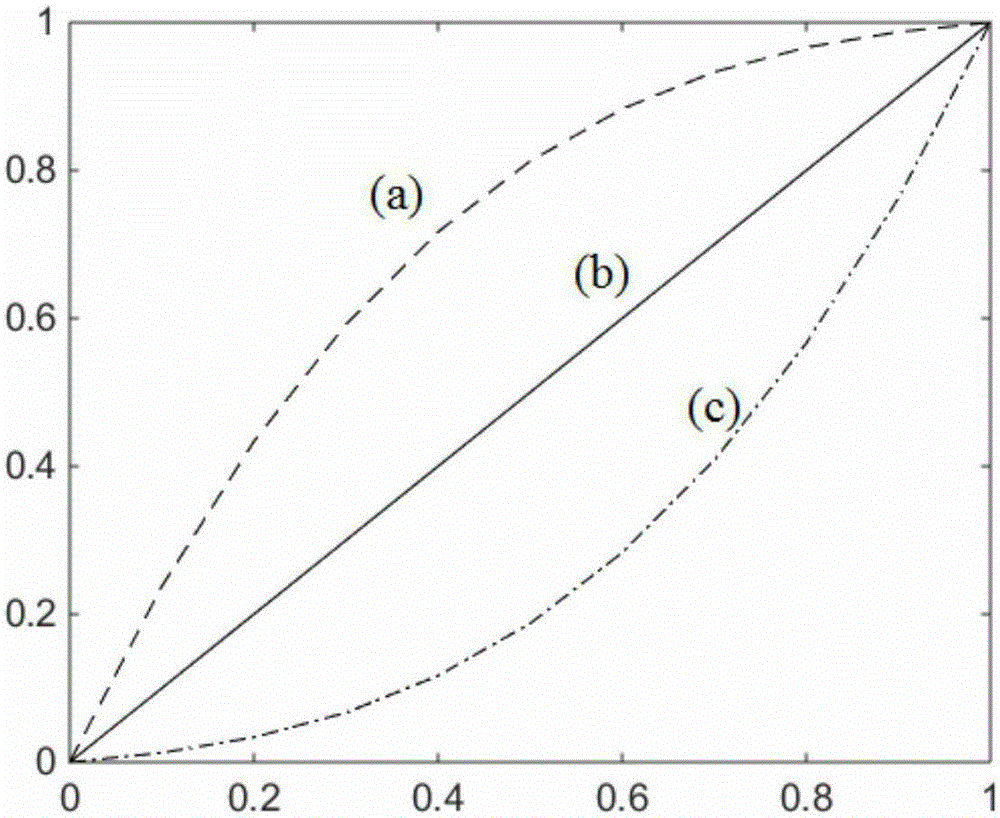
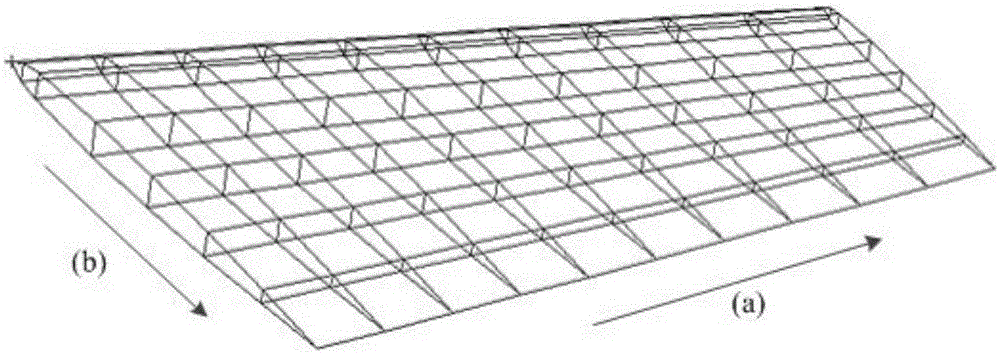
Surface element correction and grid beforehand self-adaption calculation method
ActiveCN105183996AImprove computing efficiencyHigh precisionSpecial data processing applications3D modellingAdaptive simulated annealingCorrection method
The invention relates to a surface element correction and grid beforehand self-adaption calculation method. According to the method, segmented linearizing correction is carried out on a low-order surface element method with multiple groups of CFD aerodynamic force load data under different attack angles, and distribution of surface element calculation grids is optimized by adopting a self-adaption simulated annealing algorithm. By means of self-adaption optimization of the surface element grids, the accuracy of the surface element correction method is improved, and the defect that a traditional surface element correction method depends on grid distribution is overcome. When the optimized grids are applied to the surface element correction method, the advantage of high calculation efficiency of the surface element method is kept, the accuracy of overall wing stress close to the CFD data can be ensured, and the accuracy and efficiency in the aeroelasticity optimal iteration design process are effectively improved. The accuracy error between the obtained aerodynamic load data and CFD calculation results is within 2% and effectively extends to the non-linear segment in which aerodynamic loads change along with the attack angle, and the aerodynamic load calculation efficiency in the changing process of structural rigidity parameters is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
System, method and software for static and dynamic programming and configuration of an adaptive computing architecture
ActiveUS7200837B2Architecture with single central processing unitSpecial data processing applicationsInterconnectionSelf adaptive
The present invention provides a system, method and software for programming and configuring an adaptive computing architecture or device. The invention utilizes program constructs which correspond to and map directly to the adaptive hardware having a plurality of reconfigurable nodes coupled through a reconfigurable matrix interconnection network. A first program construct corresponds to a selected node. A second program construct corresponds to an executable task of the selected node and includes one or more firing conditions capable of determining the commencement of the executable task of the selected node. A third program construct corresponds to at least one input port coupling the selected node to the matrix interconnect network for input data to be consumed by the executable task. A fourth program construct corresponds to at least one output port coupling the selected node to the matrix interconnect network for output data to be produced by the executable task.
Owner:CORNAMI INC
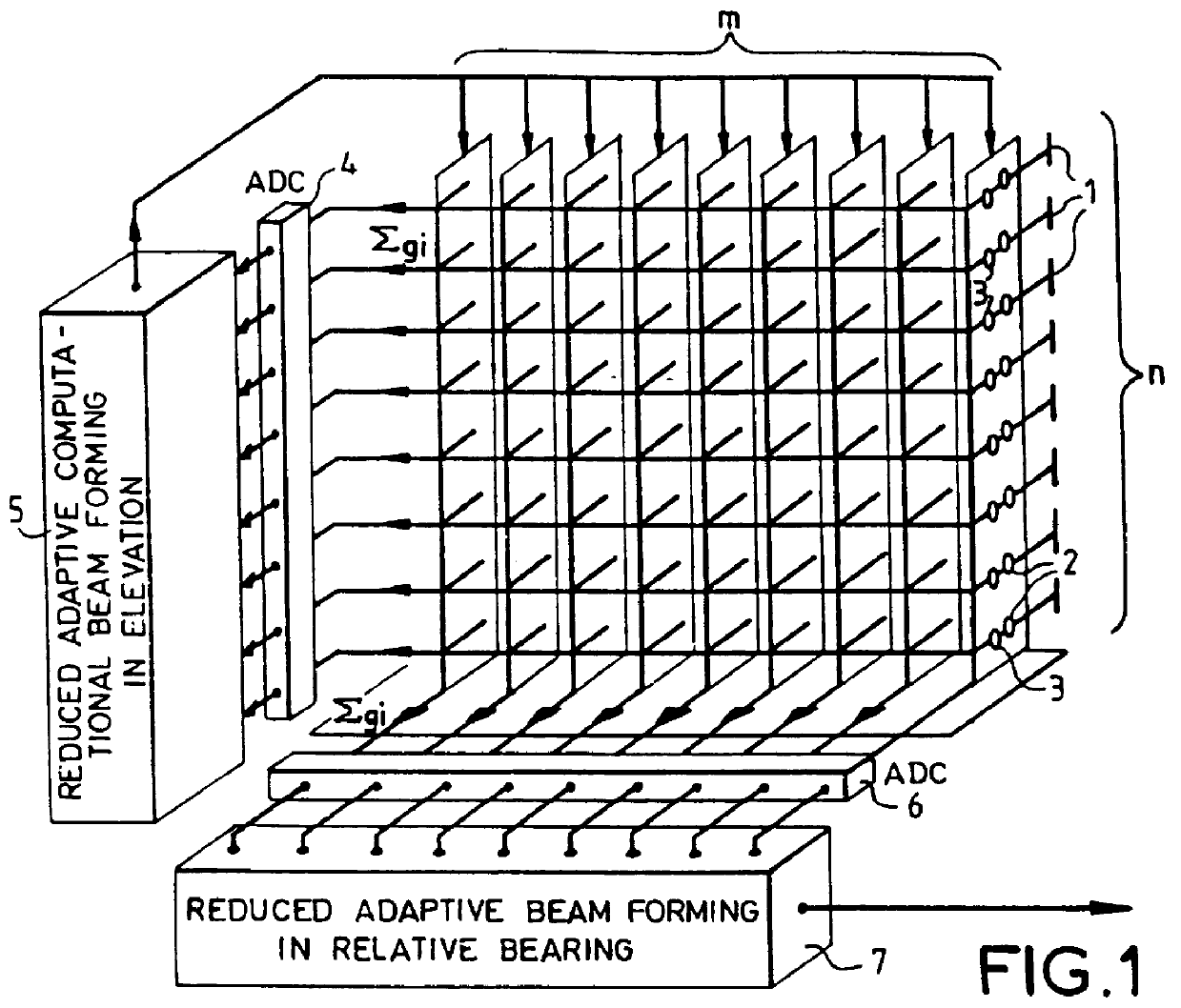
Anti-jamming array antenna
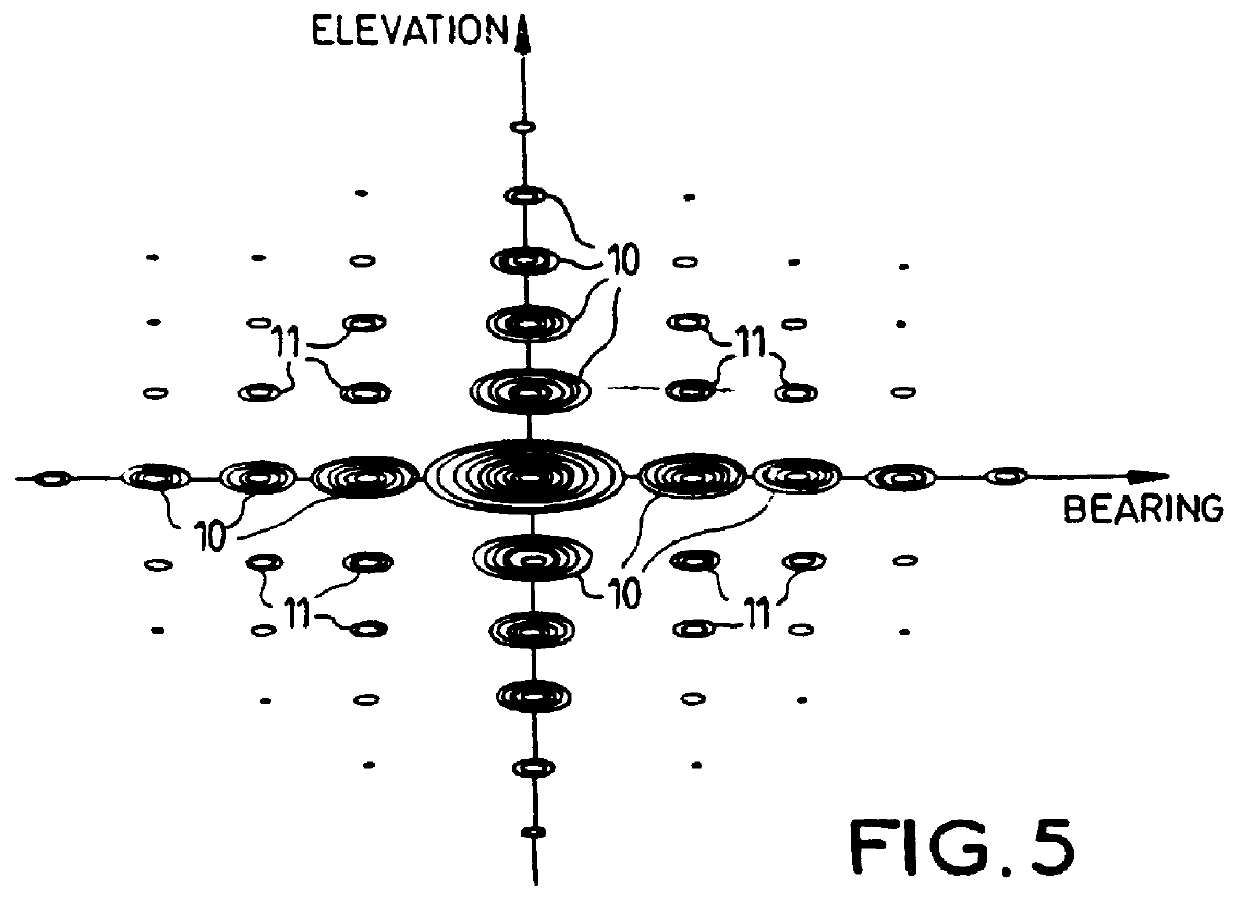
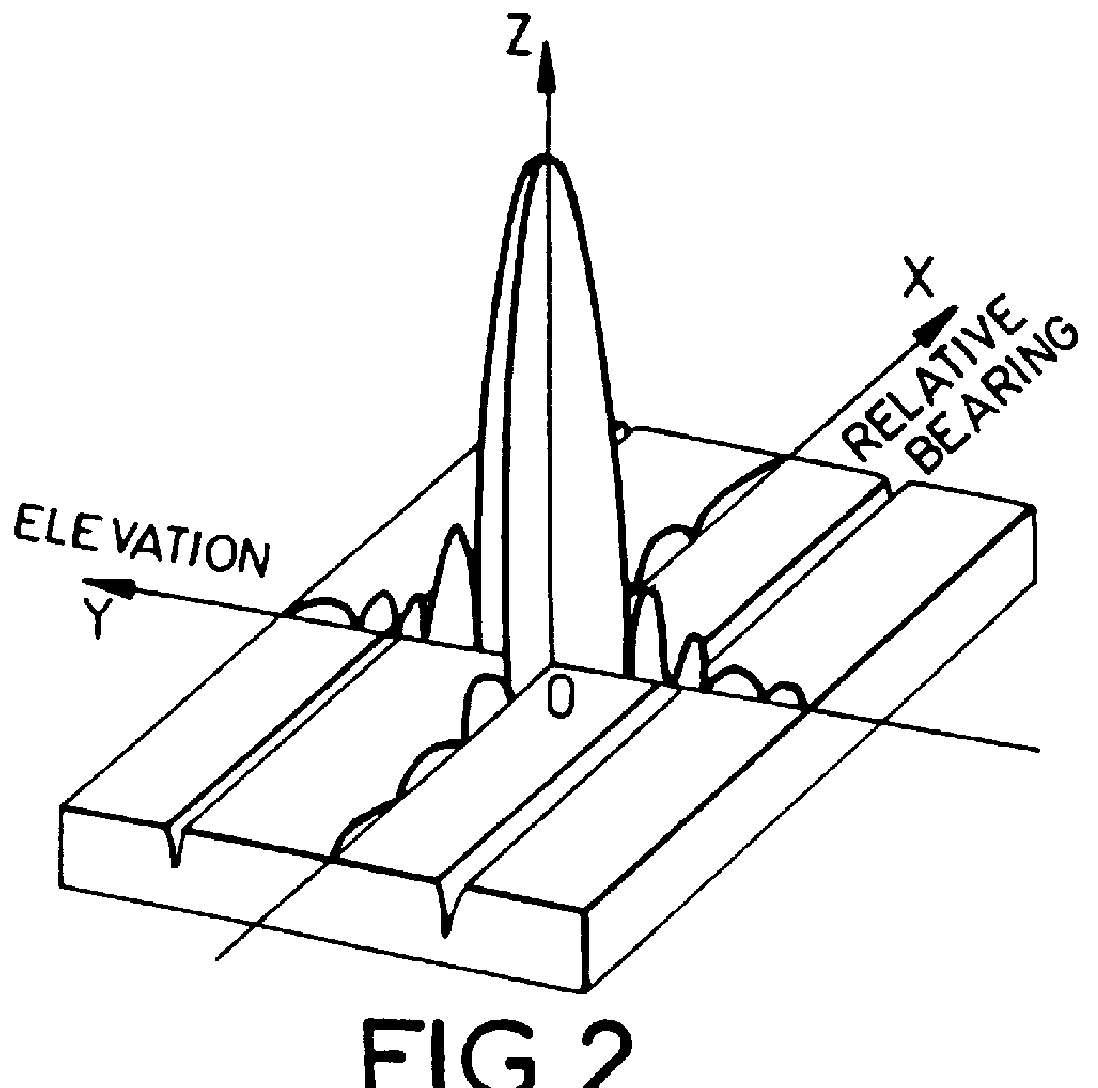
InactiveUS6124828AReduce processing loadRadio wave direction/deviation determination systemsCommunication jammingAnti jammingPhase shifted
This array antenna with anti-jamming in reception for radioelectrical or ultrasound waves is provided with radiating elements fitted out individually or in groups with amplitude-controlled and phase-controlled passive or active modules enabling aiming at transmission as well as at reception by analog beam-forming. It possesses a reception anti-jamming circuit carrying out successively two reduced, adaptive computational beam-forming operations, one in elevation which is performed on a grouping, in horizontal alignments, of the reception signals of the radiating elements and working on the reception signals by modifying the settings of the controlled modules and the other in relative bearing, performed on a grouping, in vertical alignments, of the signals of the radiating elements that which it phase-shifts and adds up to form a reception channel for the total antenna. The reception anti-jamming thus obtained has performance characteristics comparable to those that would result from a full adaptive beam-forming operation. At the same time, it requires a far smaller volume of processing.
Owner:THOMSON CSF SA
System and method using embedded microprocessor as a node in an adaptable computing machine
ActiveUS20040143724A1Improve performanceReduce power consumptionArchitecture with single central processing unitSpecific program execution arrangementsGeneral purposeFinite-state machine
The present invention provides an adaptive computing engine (ACE) that includes processing nodes having different capabilities such as arithmetic nodes, bit-manipulation nodes, finite state machine nodes, input / output nodes and a programmable scalar node (PSN). In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a common architecture is adaptable to function in either a kernel node, or k-node, or as general purpose RISC node. The k-node acts as a system controller responsible for adapting other nodes to perform selected functions. As a RISC node, the PSN is configured to perform computationally intensive applications such as signal processing.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
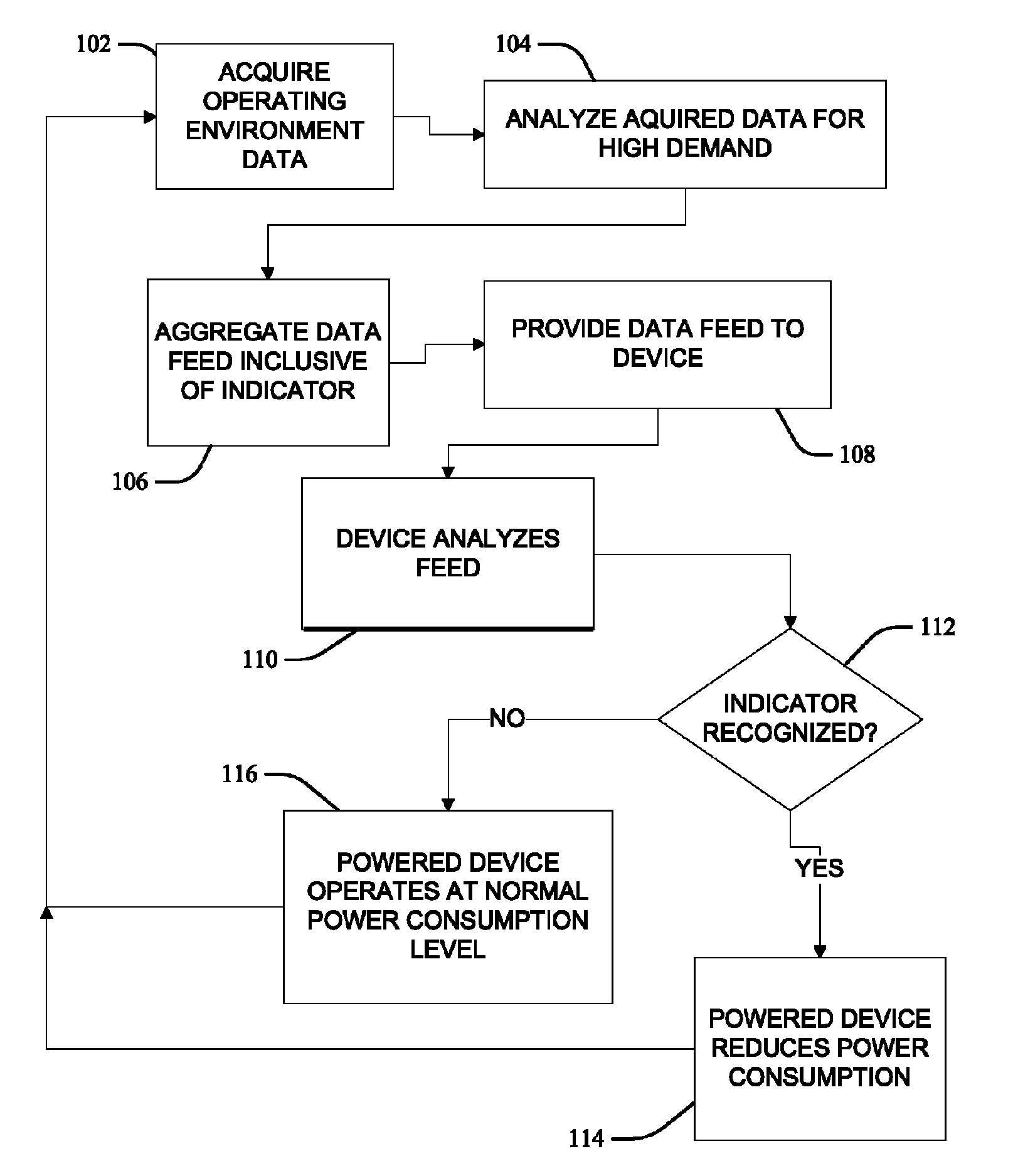
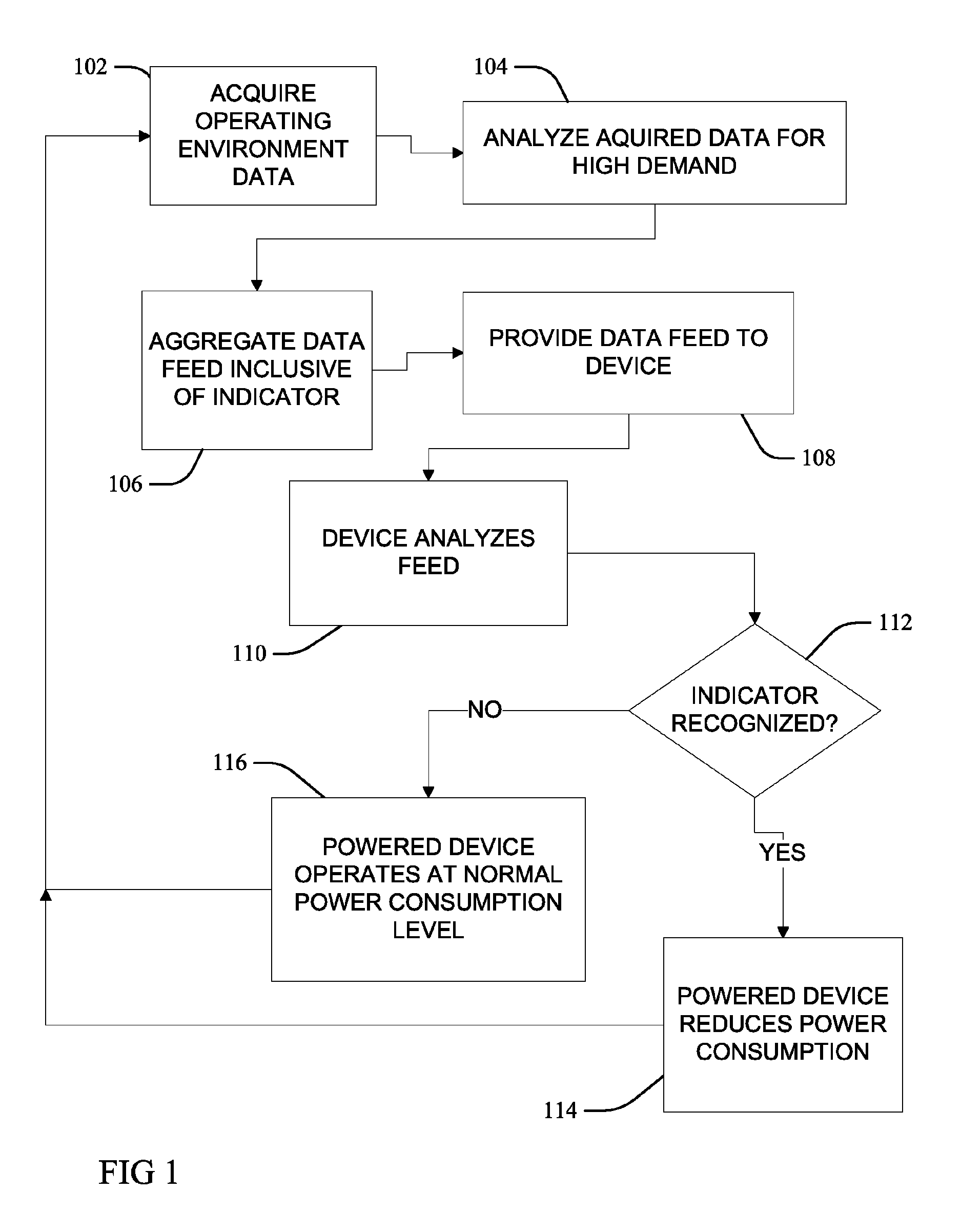
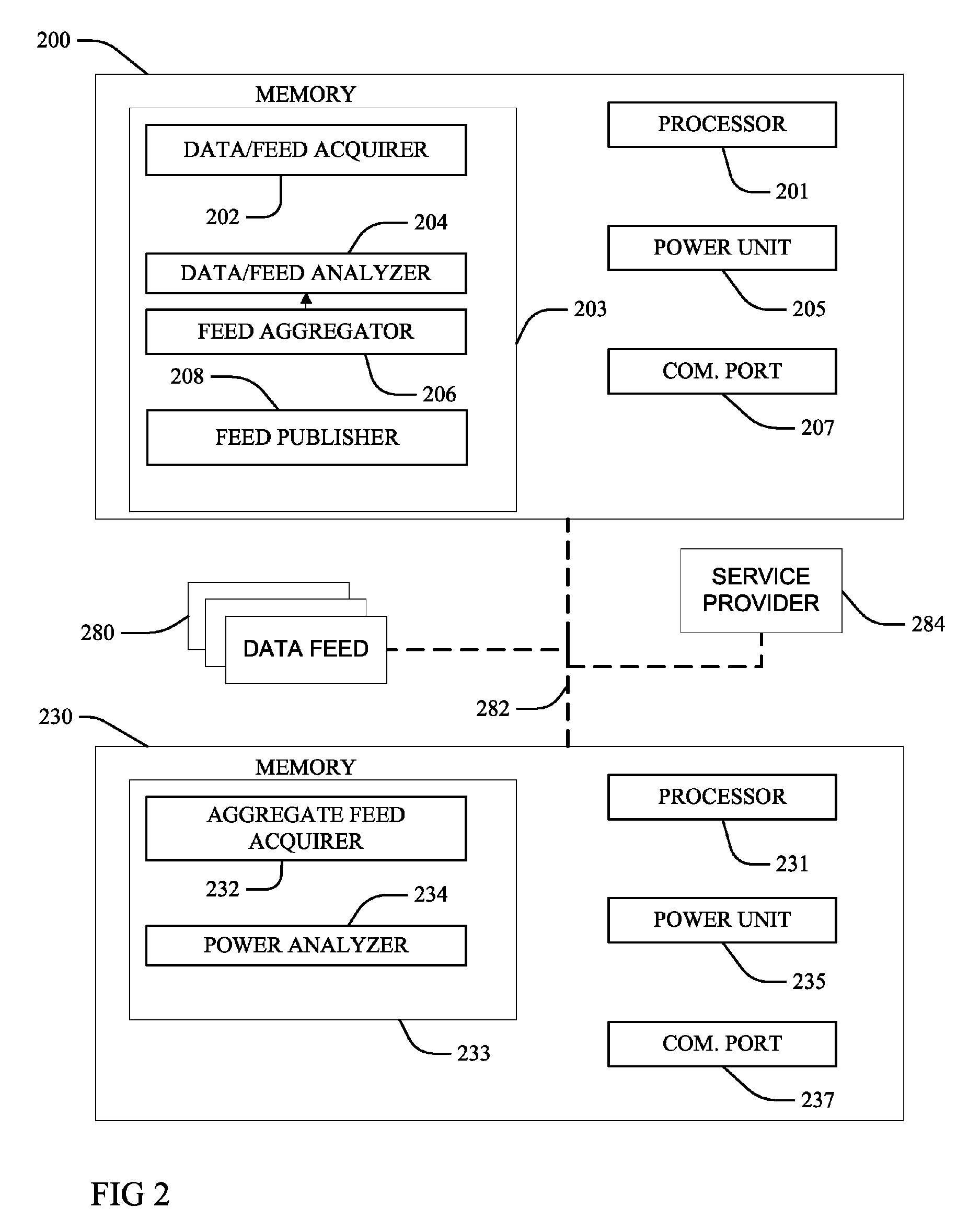
Adaptive computing responsive to environmental conditions
ActiveUS8291243B2Reduce the amount requiredIncrease powerPower network operation systems integrationVolume/mass flow measurementElectric power systemProgrammable logic device
Methods, including service methods, articles of manufacture, systems, articles and programmable devices are provided for adapting the power consumption of a computational device in response to environmental conditions. Operating environmental condition data relevant to the generation of electric power is acquired from an operating environment feed and analyzed to determine a high electric power demand indication. If the analyzing determines a high electric power demand indication, then a computational device automatically reduces an amount of electric power consumption.
Owner:GRAPHITE CHARGING CO LLC
Cache for instruction set architecture using indexes to achieve compression
ActiveUS7194605B2Register arrangementsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInstruction setStore instruction
A method for compressing a set of instructions in an adaptive computing machine includes identifying frequently executed instructions, inserting an explicit caching instruction associating the identified instructions with an index value in the set of instructions before the identified instructions and replacing at least one instance of the frequently executed instructions subsequent to the explicit caching instruction with a compressed instruction referencing the index value. One or more instructions can be identified for compression, including groups of consecutive or non-consecutive instructions. The explicit caching instruction directs a node in an adaptive computing machine to store instructions in an instruction storage unit in association with an index value. Instructions stored in the storage unit are retrievable with reference to the index value. The compressed instruction may include one or more references to index values, and can include a sequence of index values indicating the sequence of execution of the associated instructions.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
System and method using embedded microprocessor as a node in an adaptable computing machine
ActiveUS20050166033A1Increase the number ofHigh speed communicationSingle instruction multiple data multiprocessorsElectric digital data processingGeneral purposeParallel computing
The present invention provides an adaptive computing engine (ACE) that includes processing nodes having different capabilities such as arithmetic nodes, bit-manipulation nodes, finite state machine nodes, input / output nodes and a programmable scalar node (PSN). In accordance with one embodiment of the present invention, a common architecture is adaptable to function in either a kernel node, or k-node, or as general purpose RISC node. The k-node acts as a system controller responsible for adapting other nodes to perform selected functions. As a RISC node, the PSN is configured to perform computationally intensive applications such as signal processing. The present invention further provides an interconnection scheme so that a plurality of ACE devices operates under the control of a single k-node.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
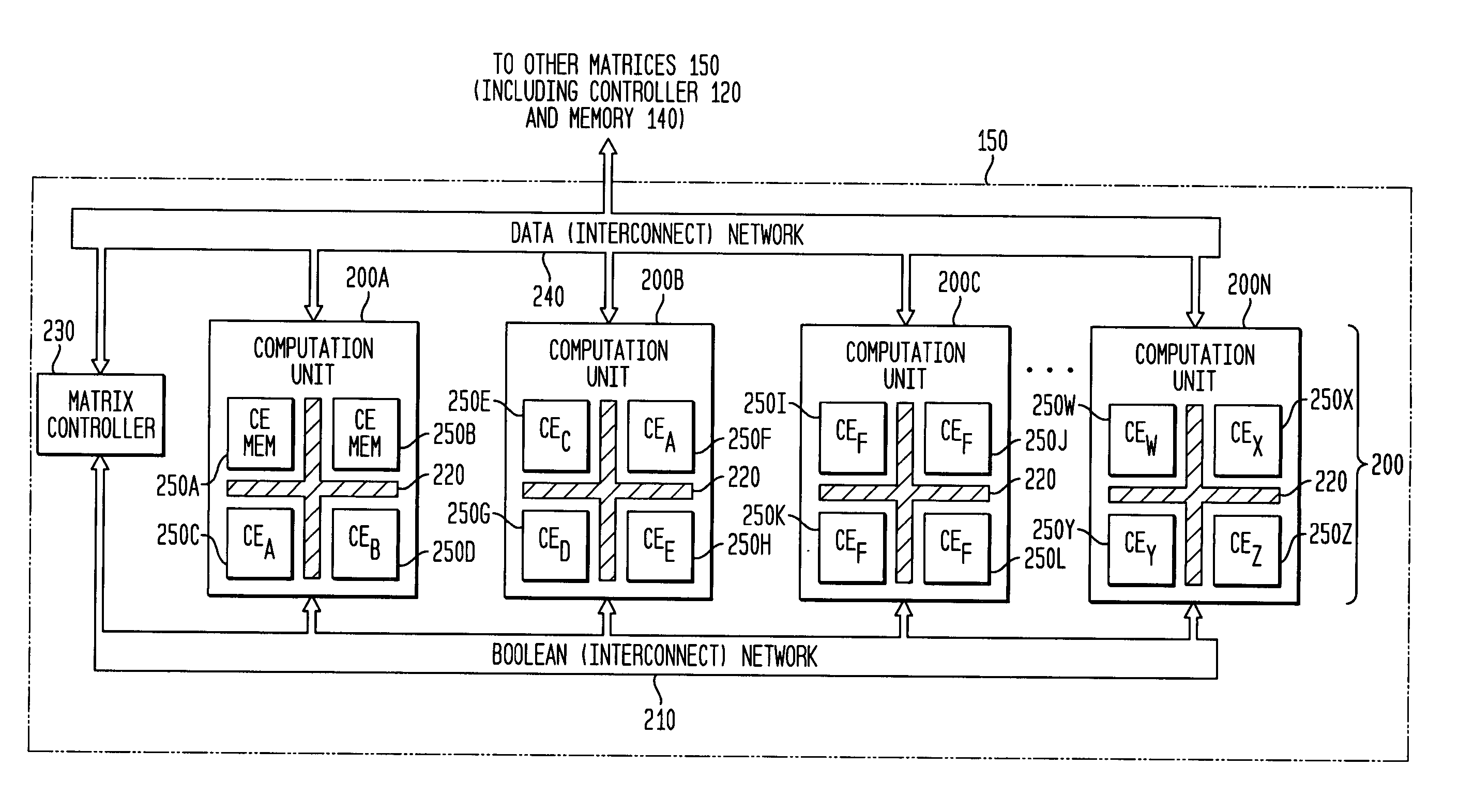
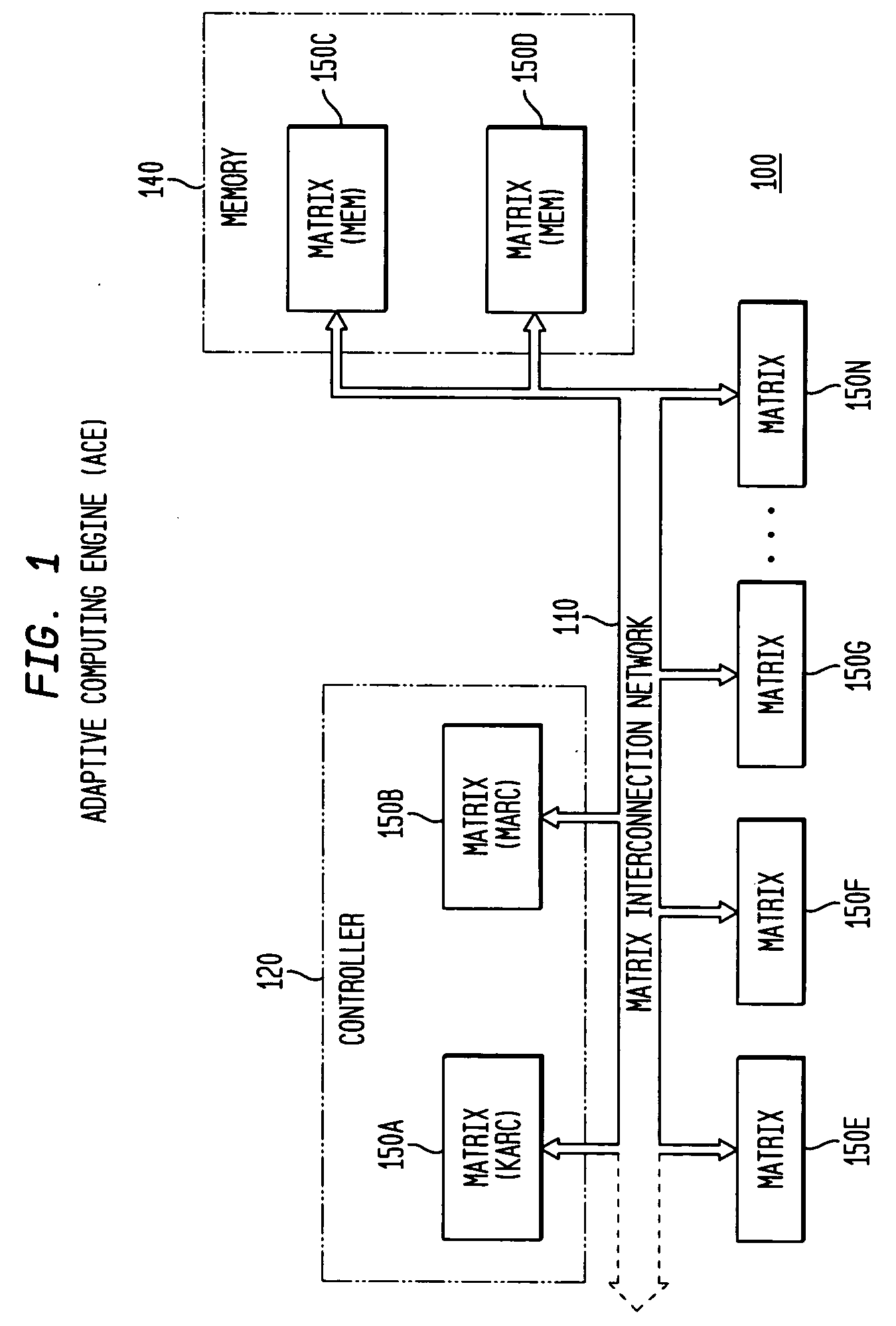
Adaptive integrated circuitry with heterogeneous and reconfigurable matrices of diverse and adaptive computational units having fixed, application specific computational elements
InactiveUS20050091472A1Minimizing potential disadvantageIncrease speedEnergy efficient ICTEnergy efficient computingLinear algorithmAdaptive computing
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The preferred IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
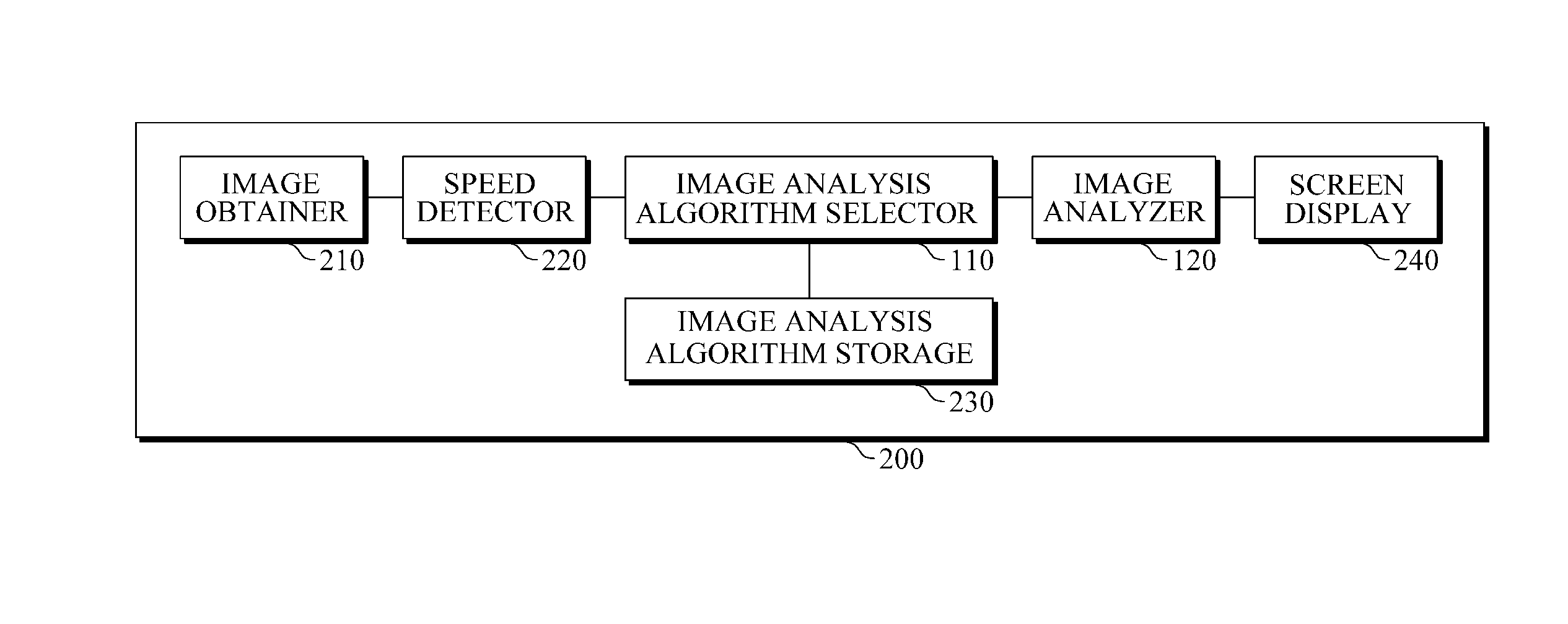
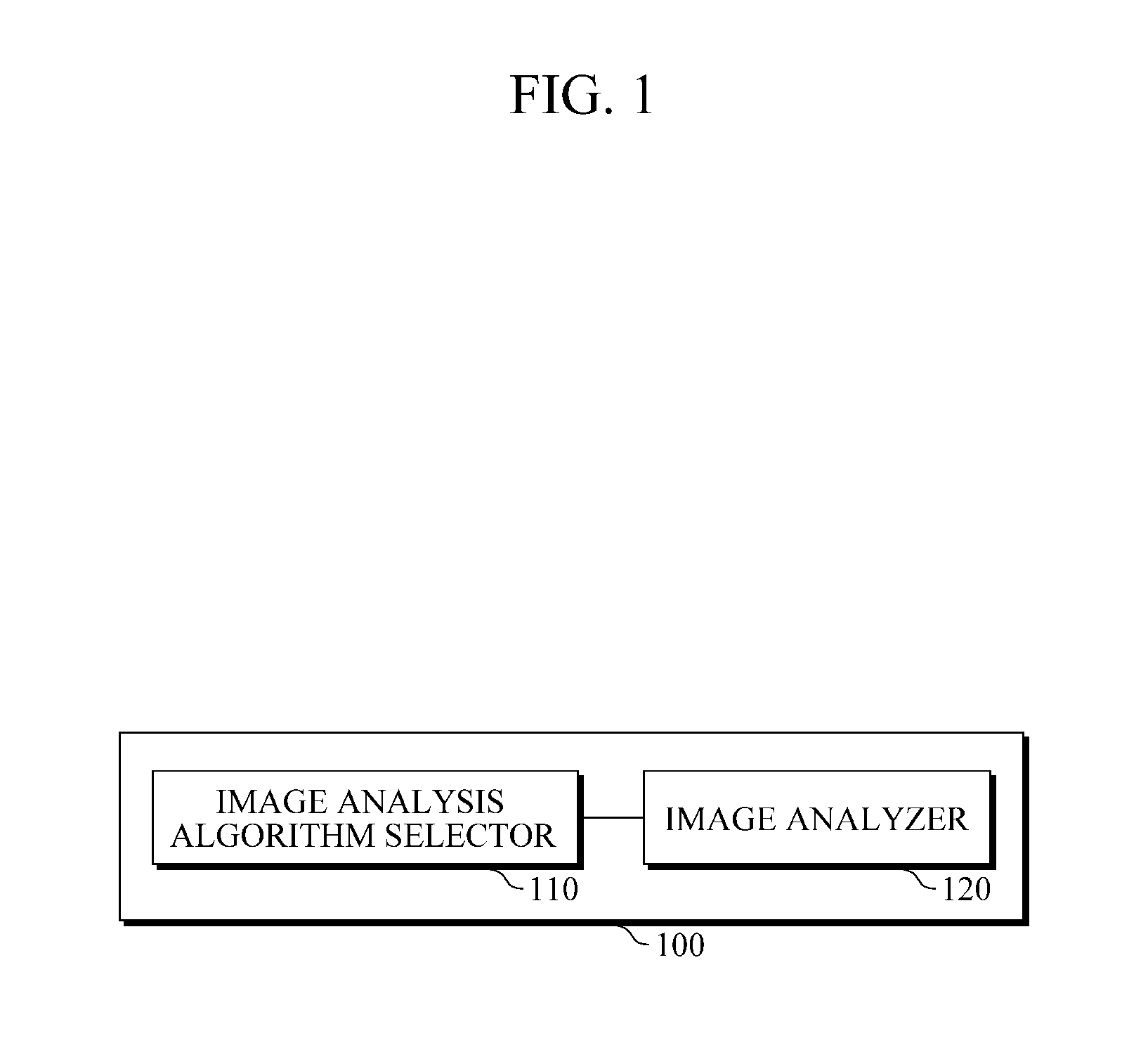
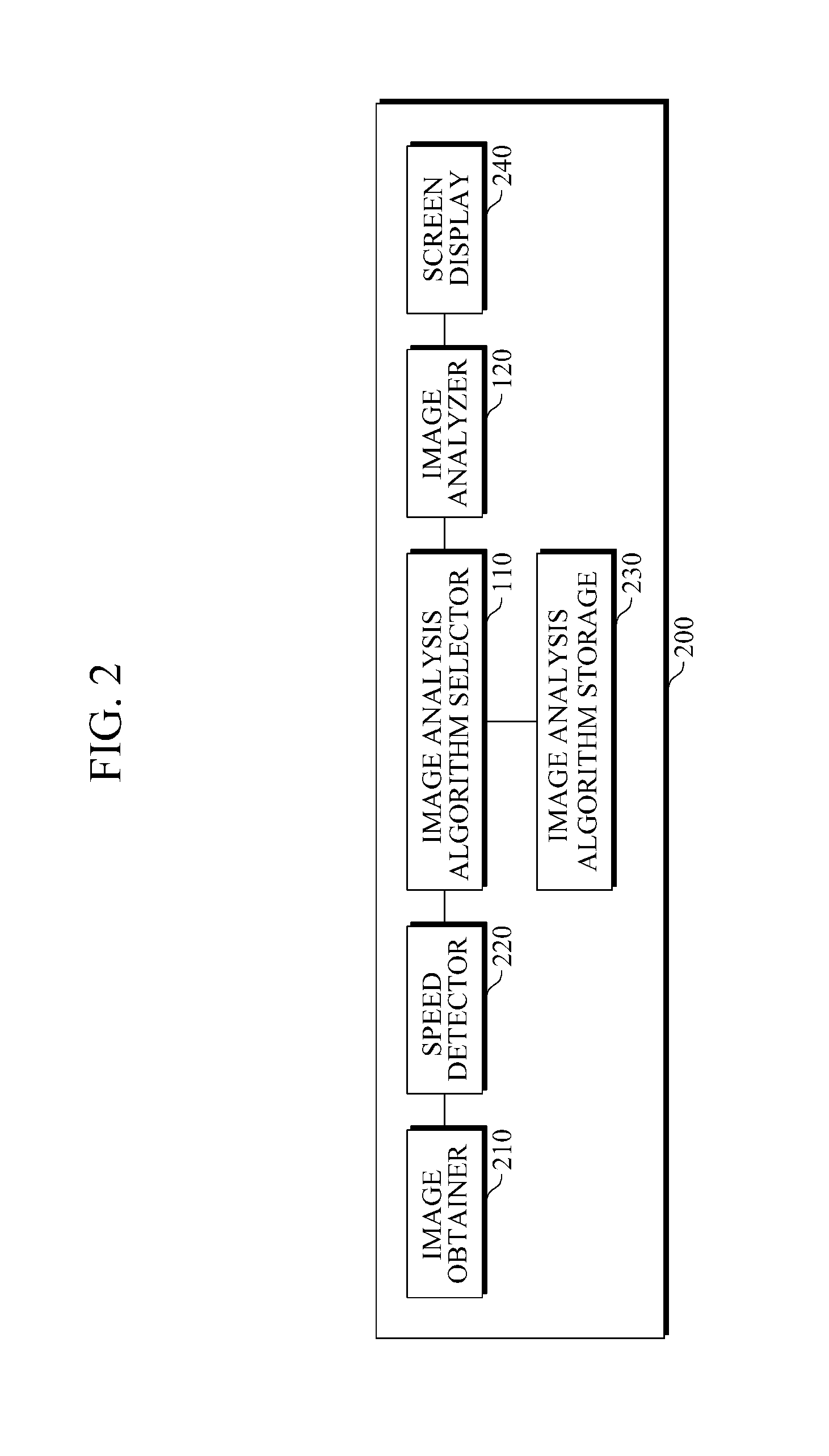
Apparatus and method for adaptive computer-aided diagnosis
InactiveUS20160048737A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementPattern recognitionImage resolution
An apparatus and method for adaptive computer-aided diagnosis (CAD) are provided. The adaptive CAD apparatus includes an image analysis algorithm selector configured to select an image analysis algorithm based on a speed of a probe or a resolution of a current image frame obtained by the probe; and an image analyzer configured to detect and classify a region of interest (ROI) in the current image frame using the selected image analysis algorithm.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Adaptive integrated circuitry with heterogeneous and reconfigurable matrices of diverse and adaptive computational units having fixed, application specific computational elements
InactiveUS20090037691A1Minimizing potential disadvantageIncrease speedEnergy efficient ICTProgram control using stored programsHand heldFinite-state machine
The present invention concerns a new category of integrated circuitry and a new methodology for adaptive or reconfigurable computing. The preferred IC embodiment includes a plurality of heterogeneous computational elements coupled to an interconnection network. The plurality of heterogeneous computational elements include corresponding computational elements having fixed and differing architectures, such as fixed architectures for different functions such as memory, addition, multiplication, complex multiplication, subtraction, configuration, reconfiguration, control, input, output, and field programmability. In response to configuration information, the interconnection network is operative in real-time to configure and reconfigure the plurality of heterogeneous computational elements for a plurality of different functional modes, including linear algorithmic operations, non-linear algorithmic operations, finite state machine operations, memory operations, and bit-level manipulations. The various fixed architectures are selected to comparatively minimize power consumption and increase performance of the adaptive computing integrated circuit, particularly suitable for mobile, hand-held or other battery-powered computing applications.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
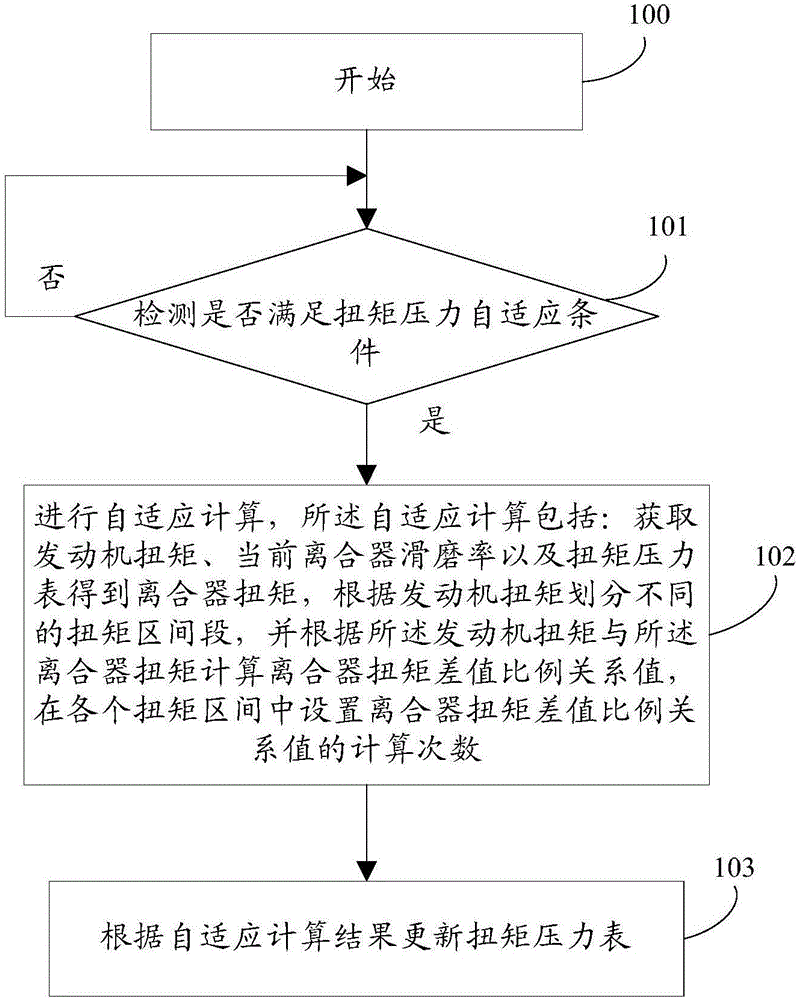
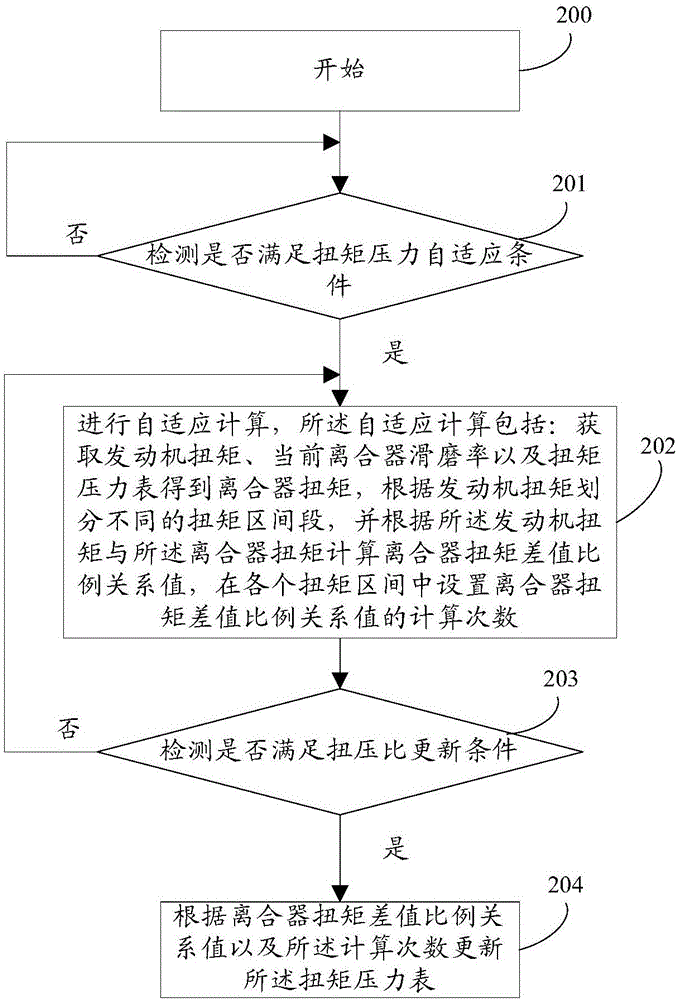
Clutch torque and pressure self-adaptive method and system
The invention relates to the technical field of transmission control, in particular to a clutch torque and pressure self-adaptive method and system The method comprises the following steps: detecting whether to meet the torque and pressure self-adaptive conditions or not; if YES, performing self-adaptive calculation, wherein the self-adaptive calculation comprises the steps of obtaining engine torque, obtaining current clutch grinding rate, obtaining clutch torque through the engine torque, the current clutch grinding rate and a torque and pressure gauge, dividing different torque intervals according to the engine torque, calculating a clutch torque difference proportional relationship value according to the engine torque and the clutch torque, and setting the frequency of calculation on the clutch torque difference proportional relationship value in the various torque intervals; updating the torque and pressure gauge according to self-adaptive calculation results. Through the clutch torque and pressure self-adaptive method and system provided by the invention, the accuracy and the precision of clutch torque transmission are ensured.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
Cellular nerve network with genetic algorithm (GACNN)-based multisource image fusion method
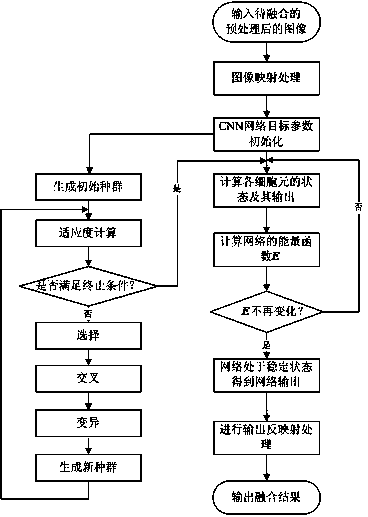
ActiveCN103971329AImprove accuracyEasy to observeGeometric image transformationGenetic modelsFeature extractionNerve network
The invention discloses a cellular nerve network with genetic algorithm (GACNN)-based multisource image fusion method, belonging to the field of multisource mage fusion. According to the GACNN-based multisource image fusion method, the multisource image in the same scene can output fusion images with better effect by taking a CNN system as a framework and combining genetic algorithm self-adaptive computing network template parameters, thus facilitating the follow-up processing of image information, and providing more useful and more efficient information for the aspects of feature extraction, image recognition, human decision and the like; the accuracy of the fusion image can be effectively improved while the fusion result can be fast obtained, thus facilitating the observation of human eyes and machine detection, and being convenient for analysis and practical application.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com