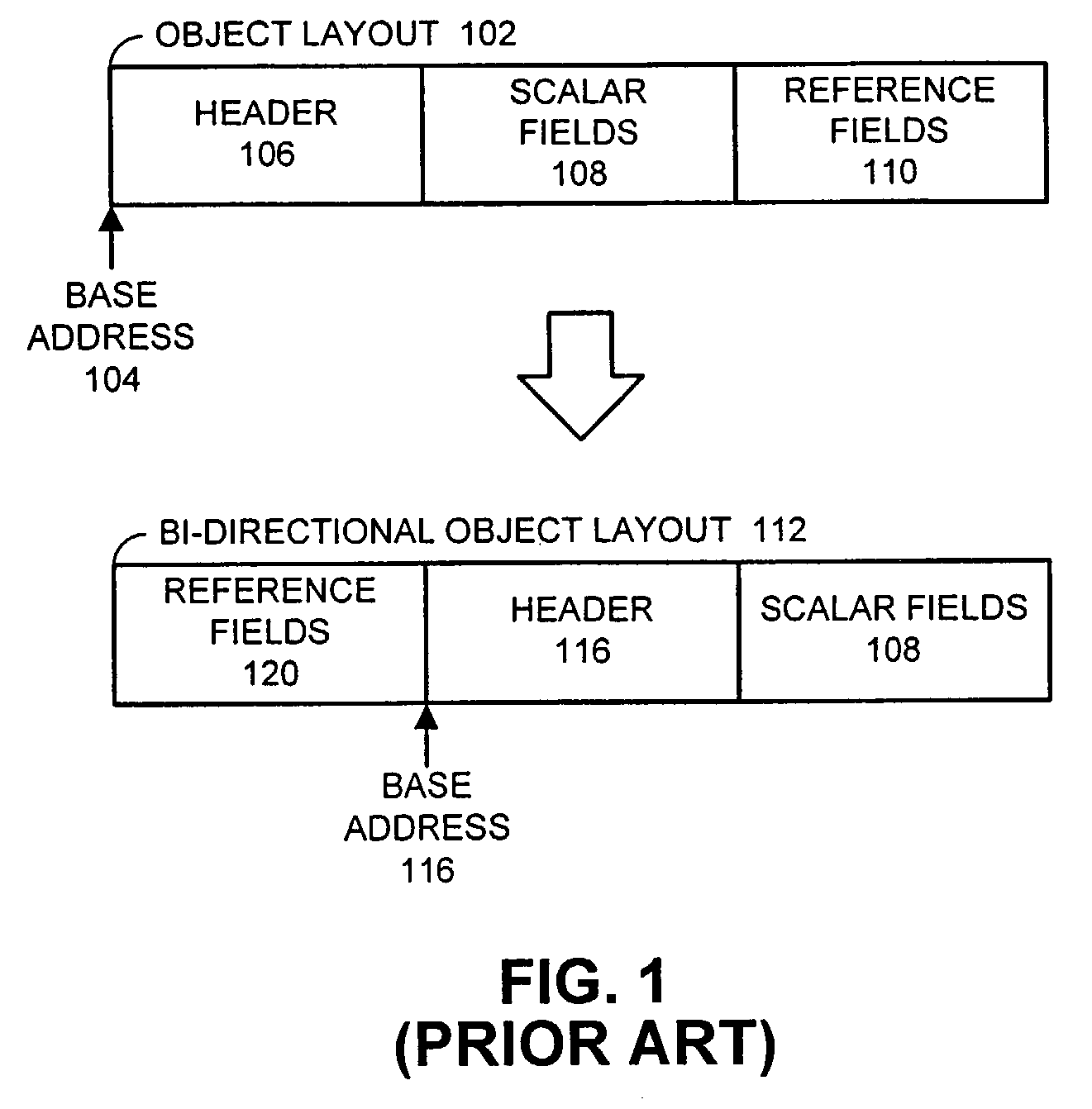
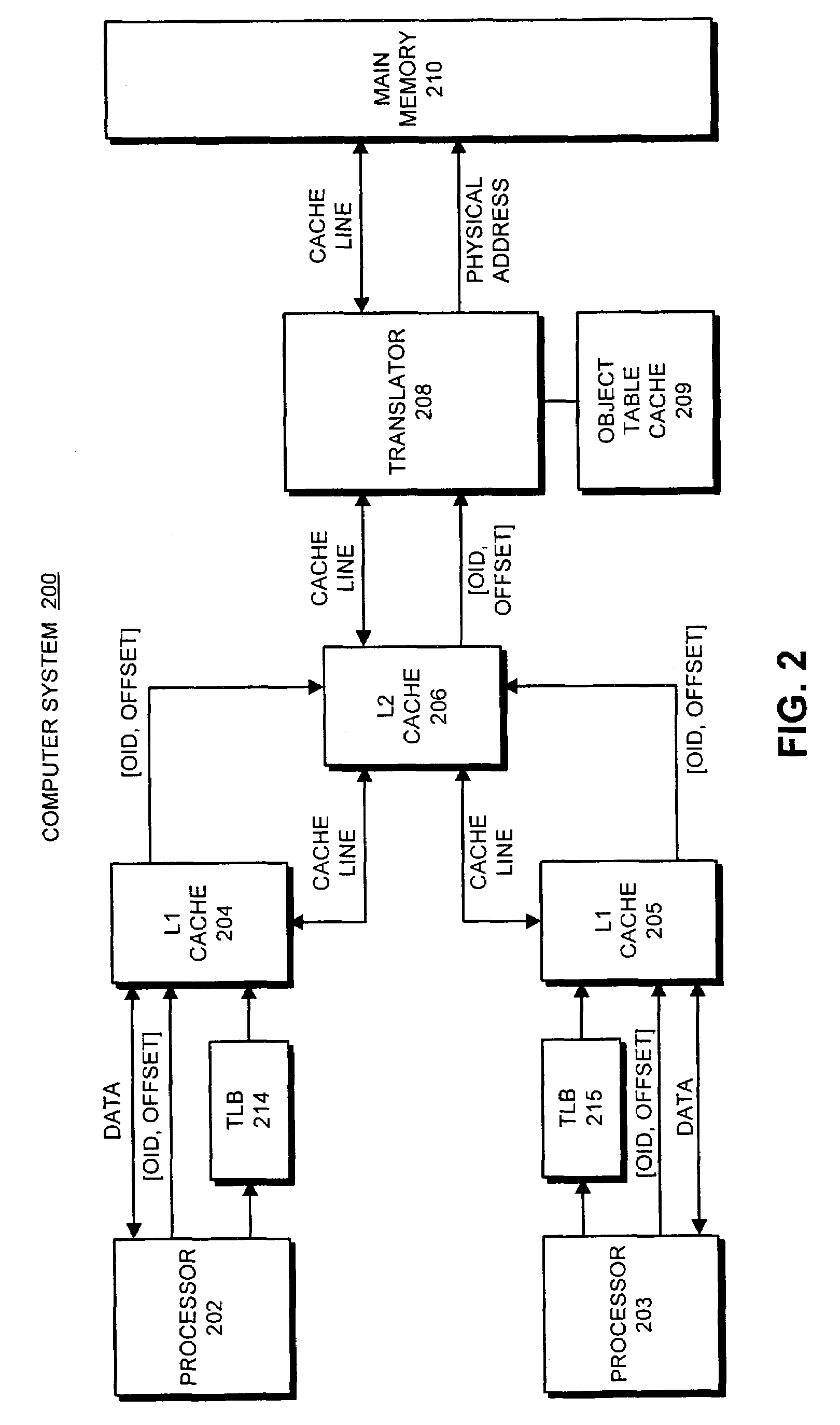
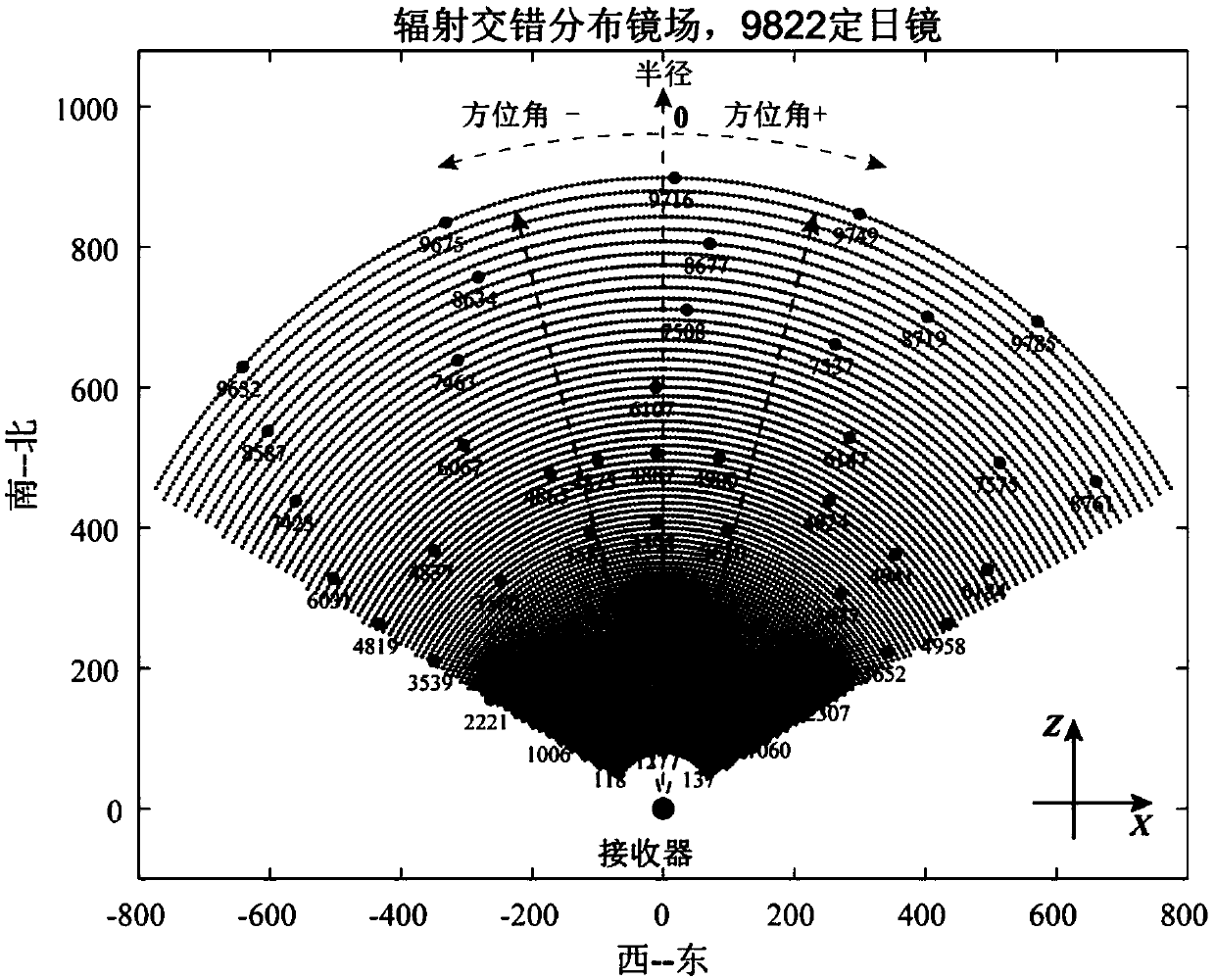
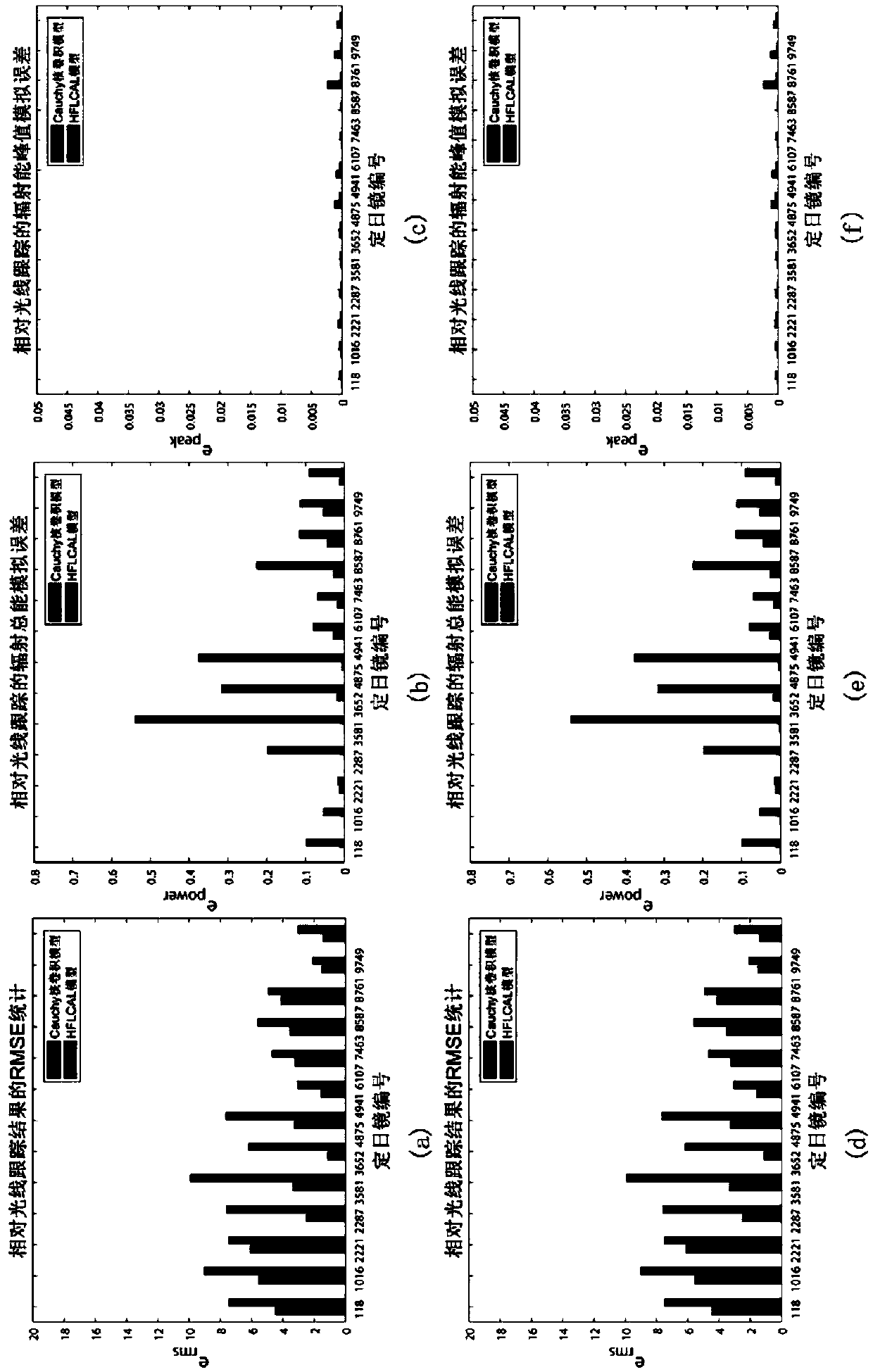
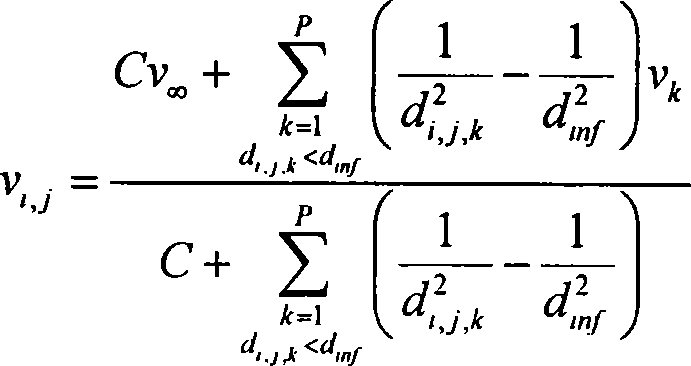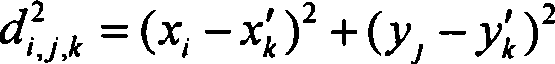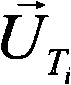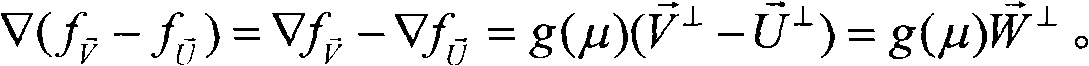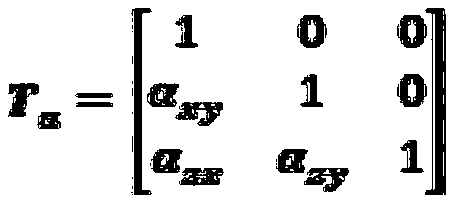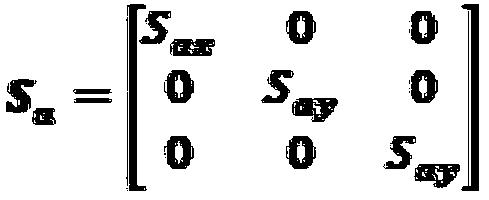Patents
Literature
60 results about "Scalar field" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics and physics, a scalar field associates a scalar value to every point in a space – possibly physical space. The scalar may either be a (dimensionless) mathematical number or a physical quantity. In a physical context, scalar fields are required to be independent of the choice of reference frame, meaning that any two observers using the same units will agree on the value of the scalar field at the same absolute point in space (or spacetime) regardless of their respective points of origin. Examples used in physics include the temperature distribution throughout space, the pressure distribution in a fluid, and spin-zero quantum fields, such as the Higgs field. These fields are the subject of scalar field theory.
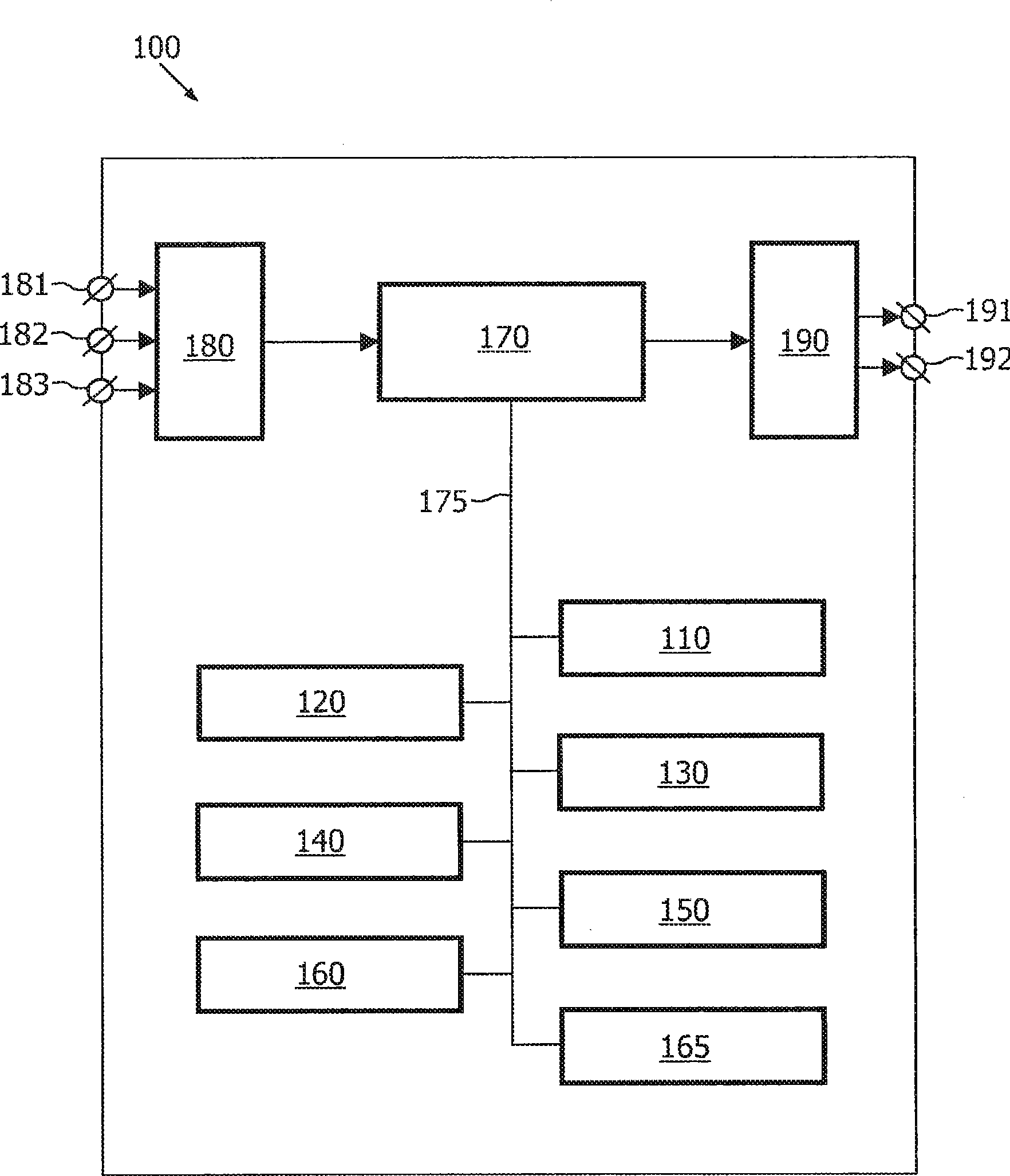
Variable resolution model based image segmentation
InactiveUS20090202150A1Effectively controlling smoothness of the computed model surface representedIncrease computational costImage enhancementImage analysisCoarse meshData set
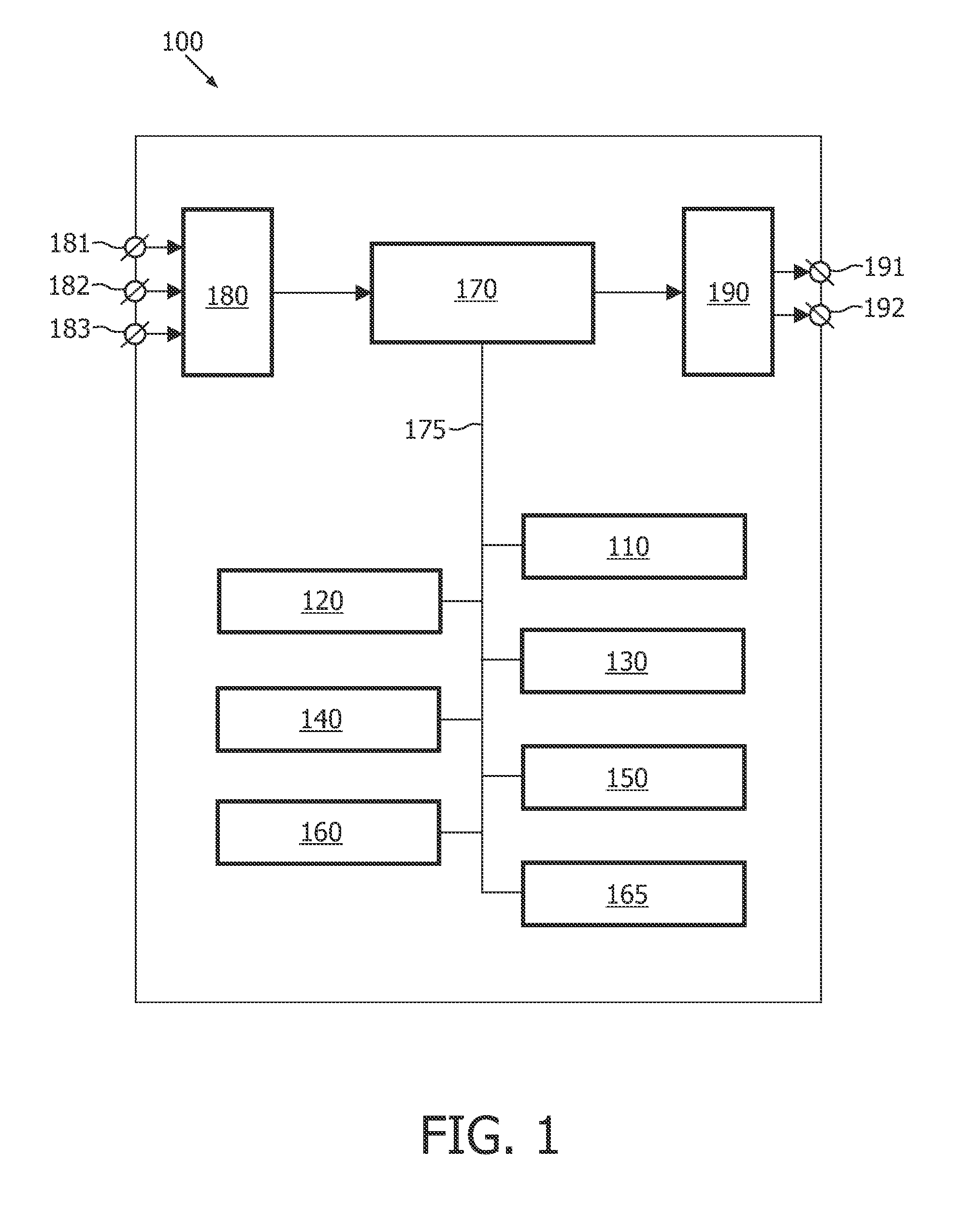
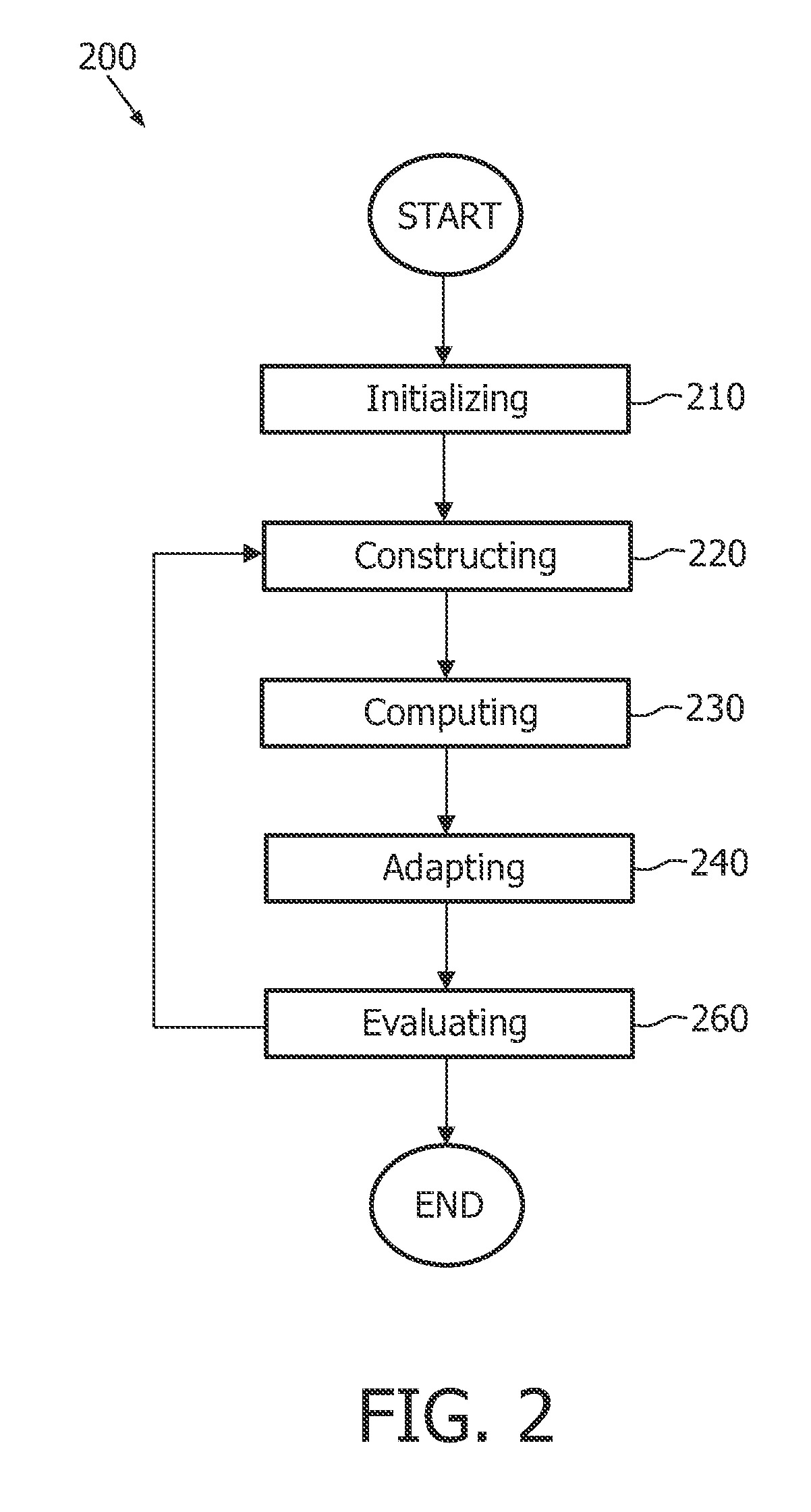
The invention relates to system (100) for segmenting an image dataset based on a deformable model for modeling an object in the image dataset, utilizing a coarse mesh for adapting to the image dataset and a fine mesh for extracting detailed information from the image dataset, the system comprising an initialization unit (110) for initializing the coarse mesh in an image dataset space, a construction unit (120) for constructing the fine mesh in the image dataset space based on the initialized coarse mesh, a computation unit (130) for computing an internal force field on the coarse mesh and an external force field on the coarse mesh, wherein the external force is computed based on the constructed fine mesh and the scalar field of intensities, and an adaptation unit (140) for adapting the coarse mesh to the object in the image dataset, using the computed internal force field and the computed external force field, thereby segmenting the image dataset. Since only the coarse mesh is adapted to the image dataset, keeping the modeled object surface smooth does not require a smoothing of the surface over large neighboring areas, and therefore the adaptation of the coarse mesh is much faster than the adaptation of the fine mesh. Advantageously, the proposed technique can be easily integrated into existing frameworks of model-based image segmentation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
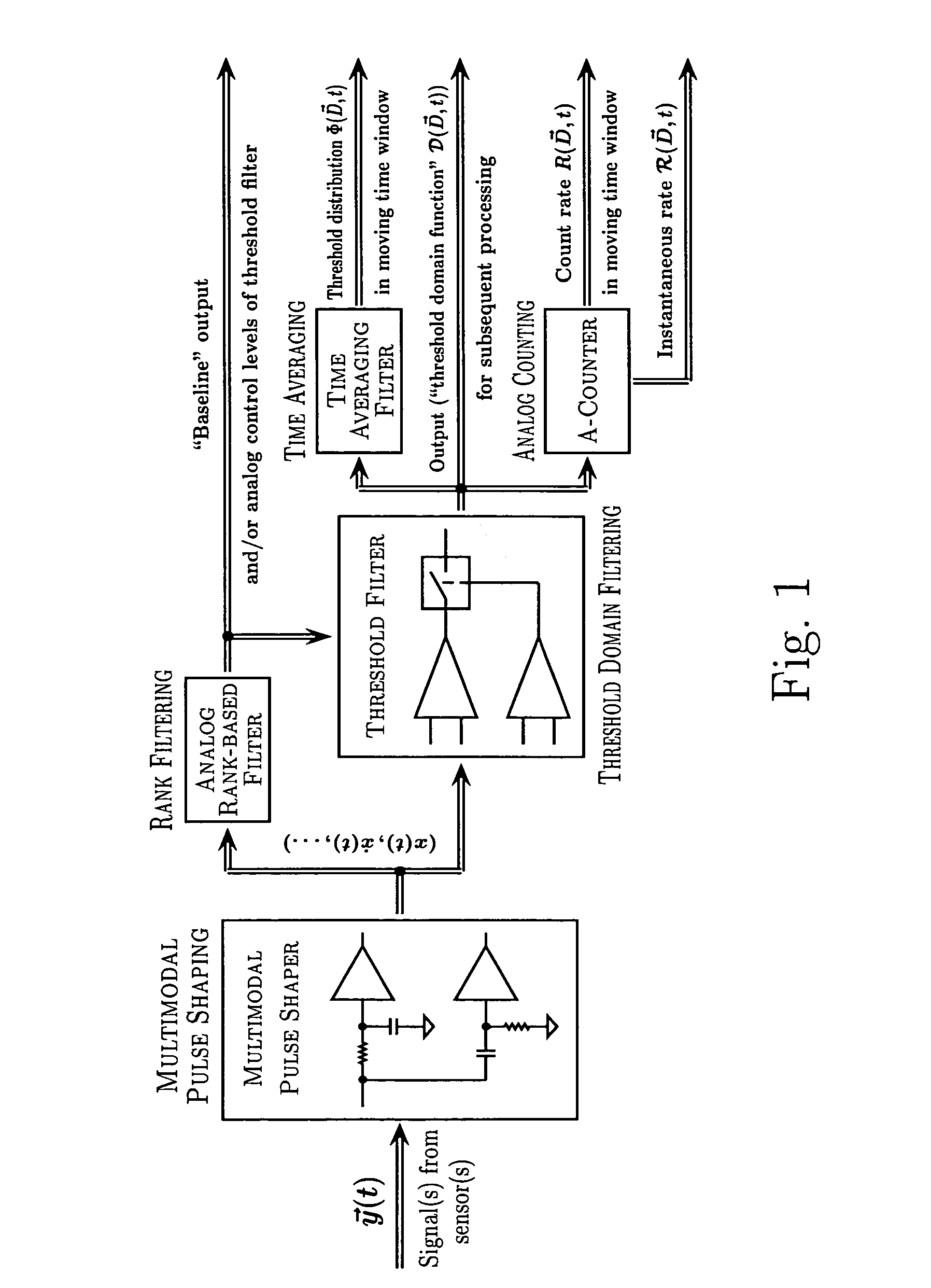
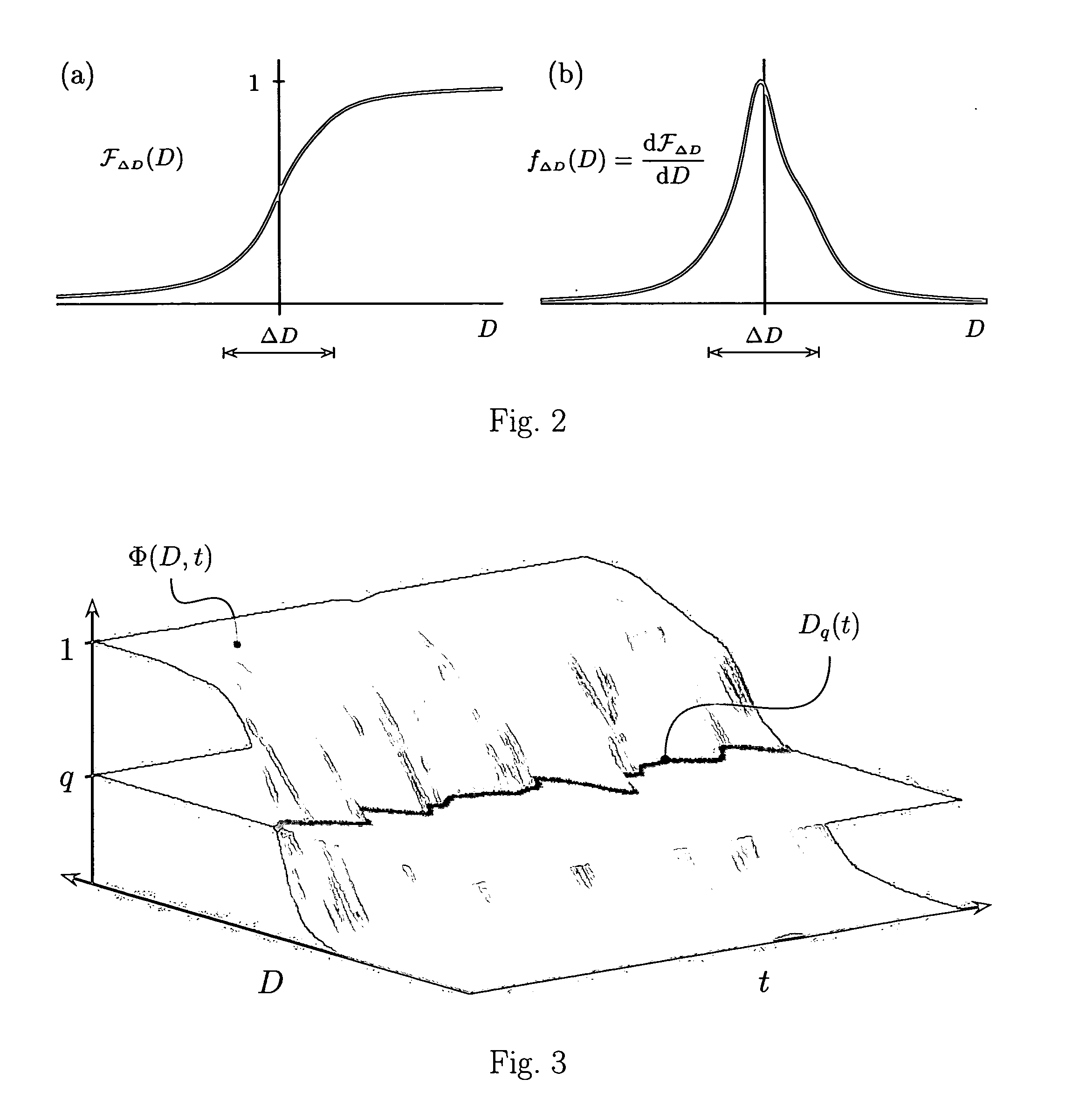
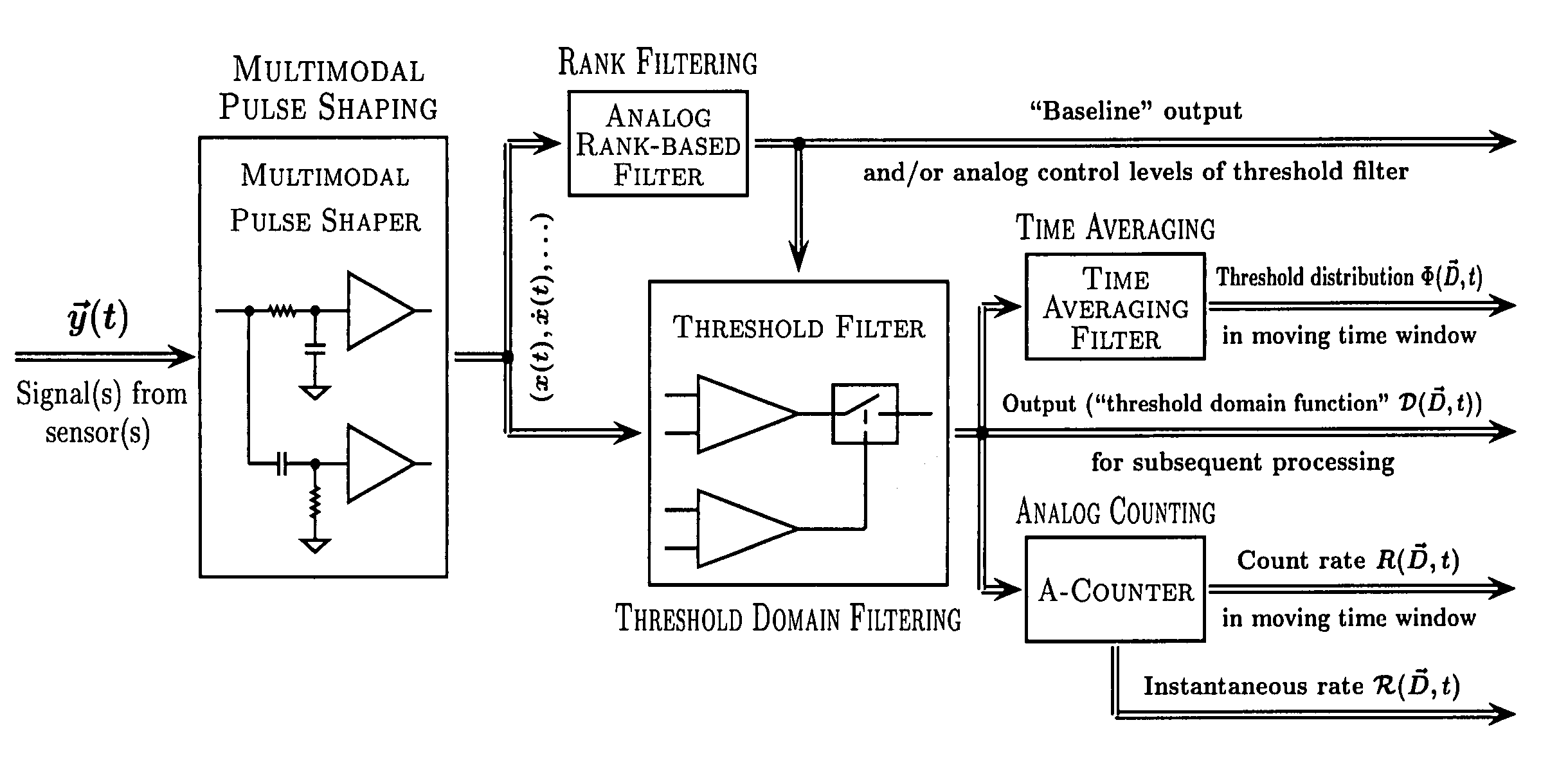
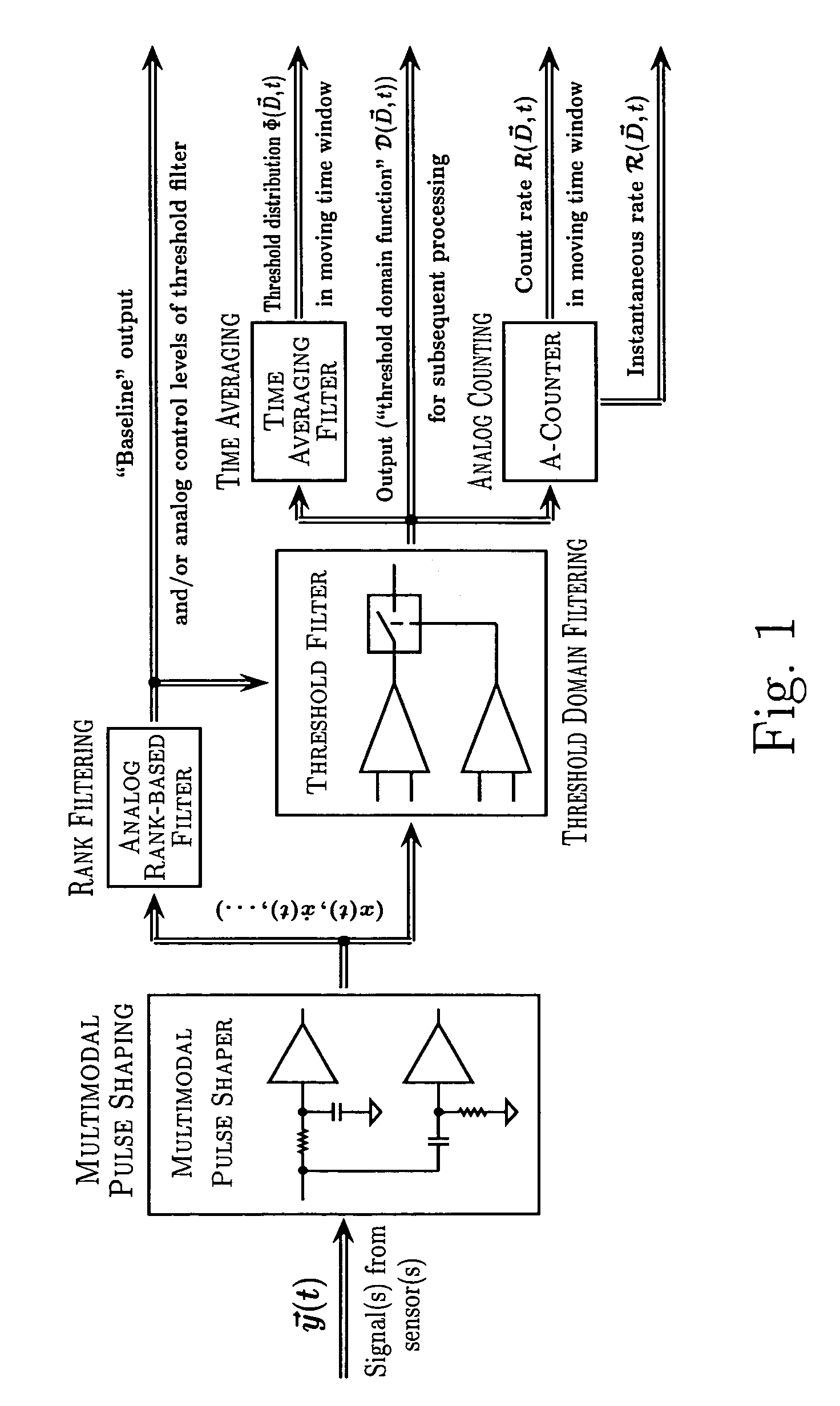
Method and apparatus for adaptive real-time signal conditioning, processing, analysis, quantification, comparison, and control
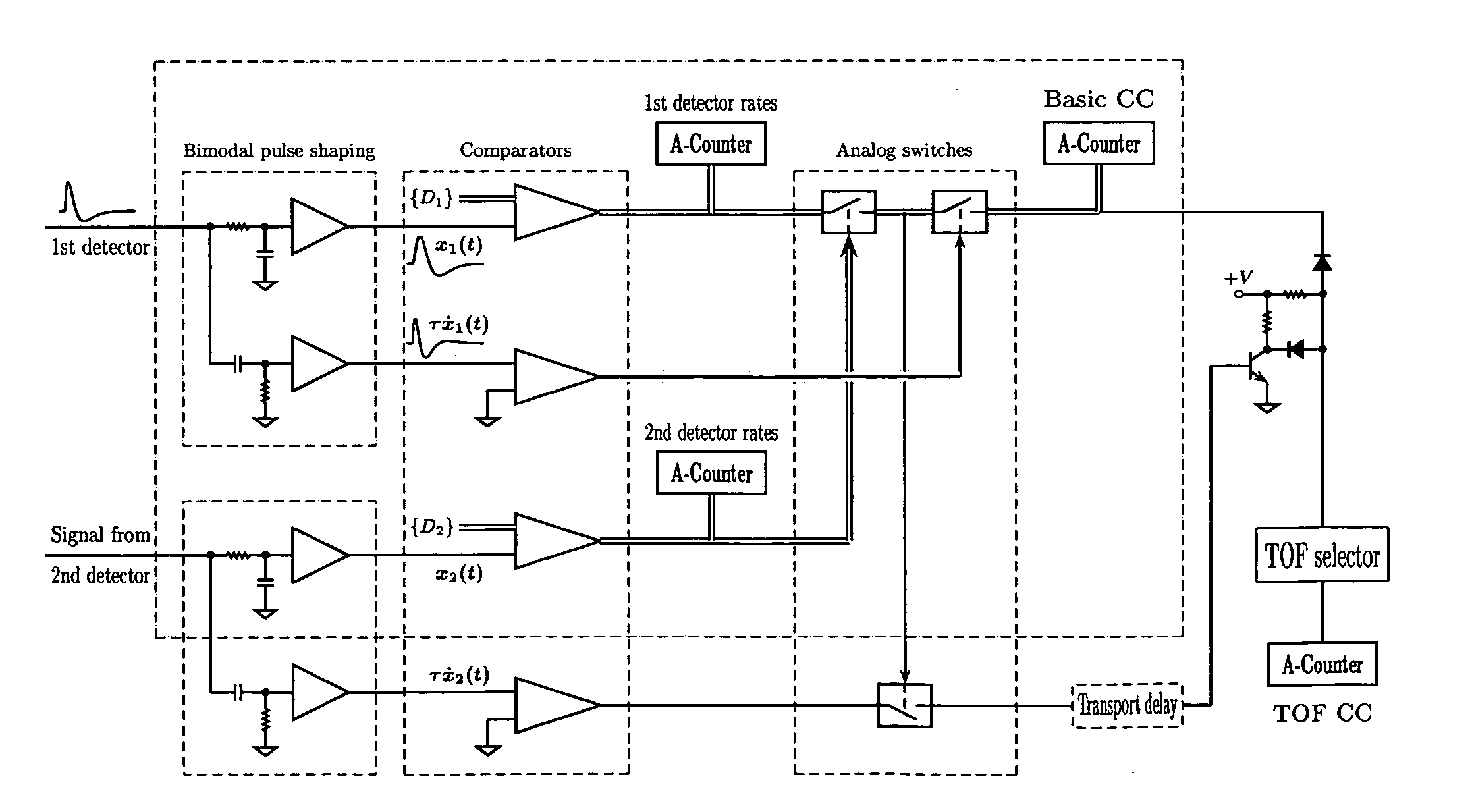
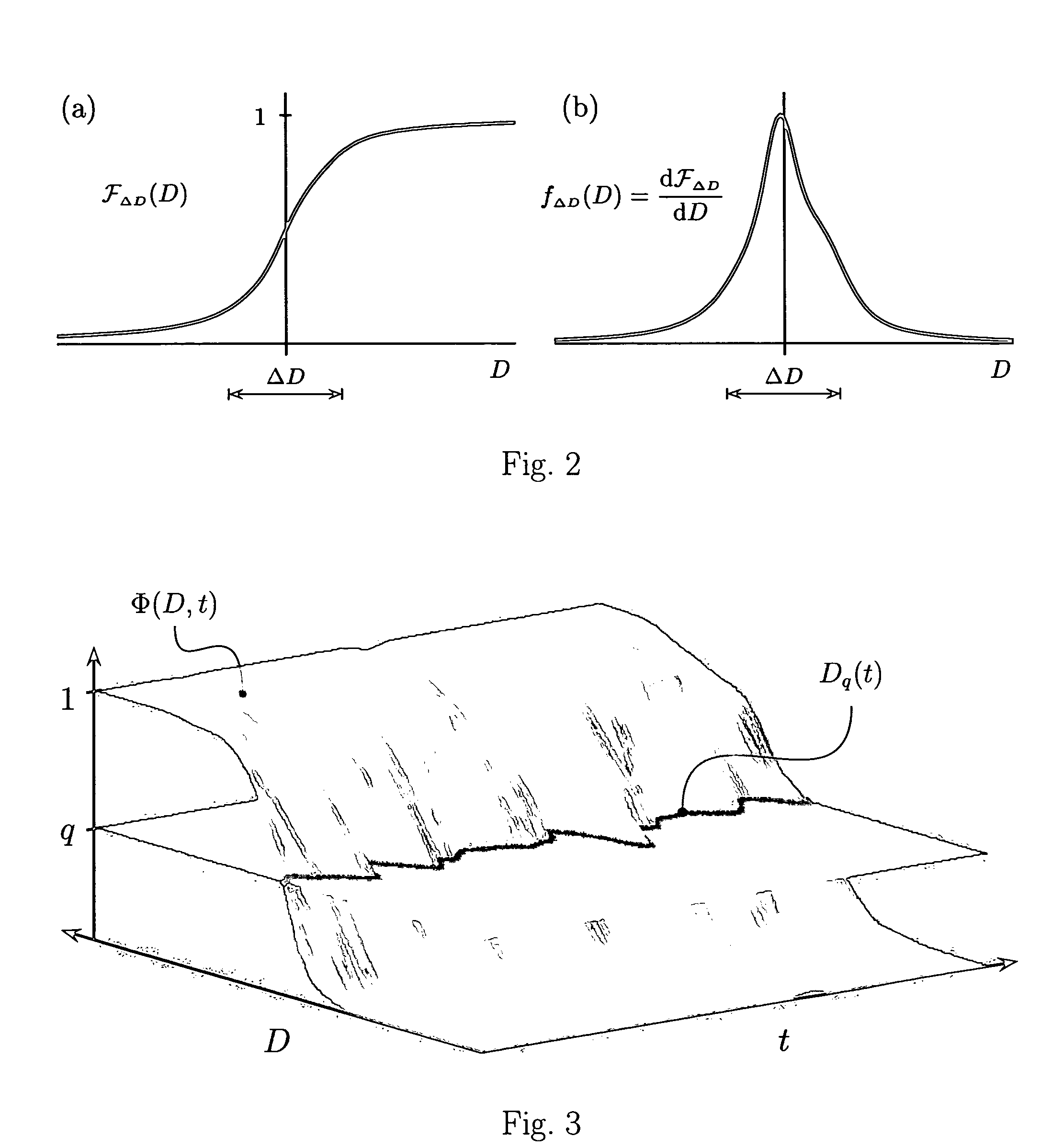
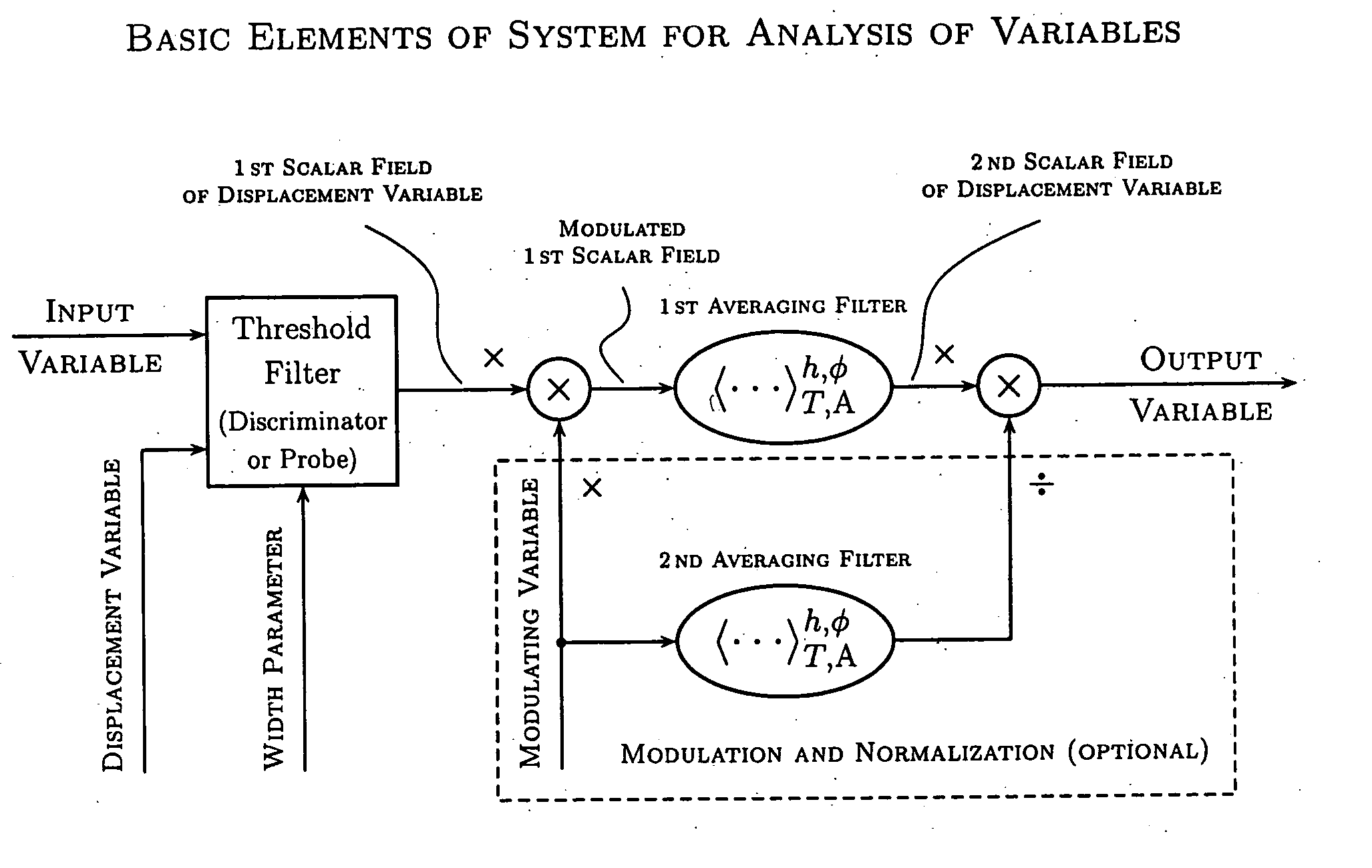
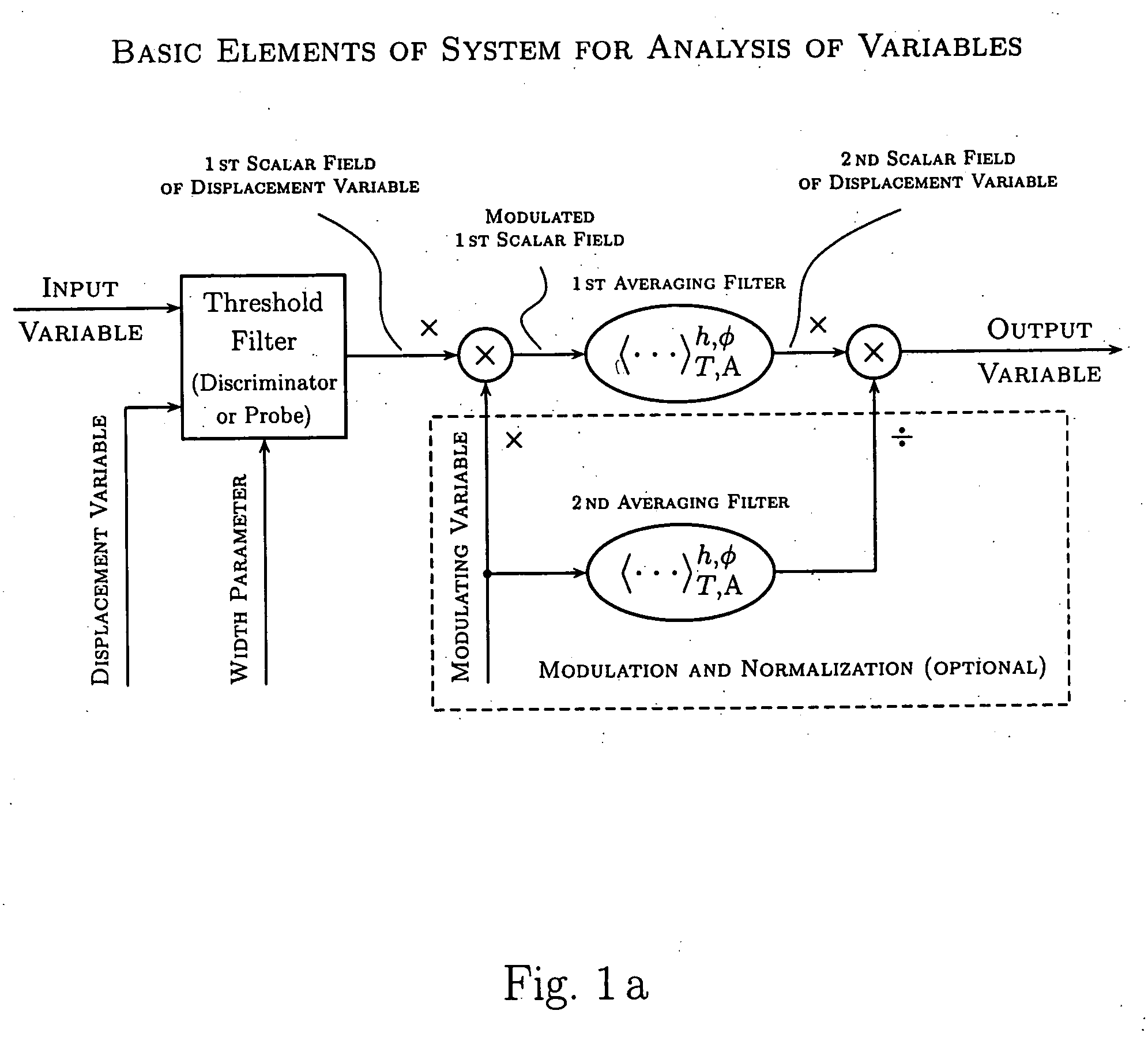
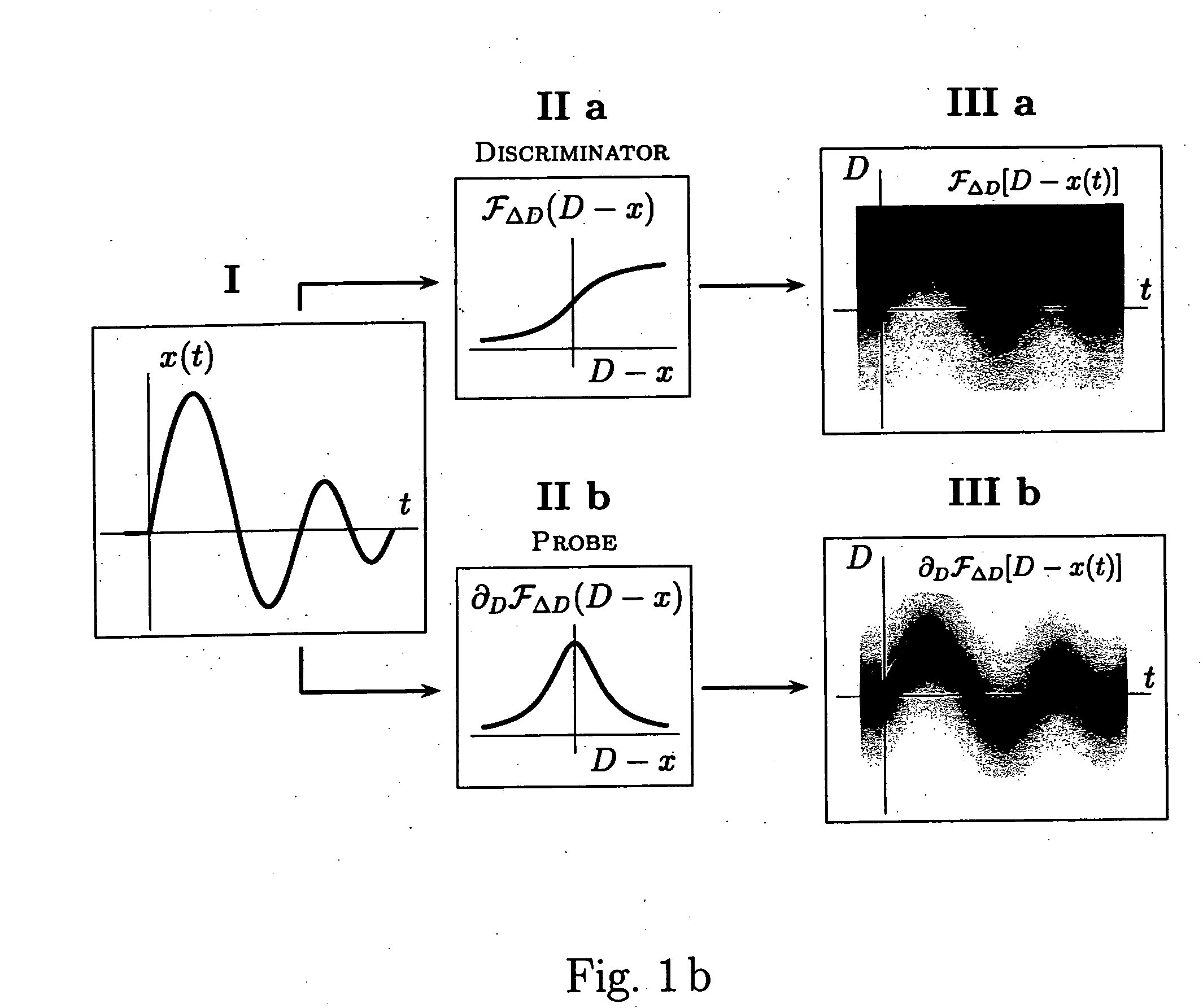
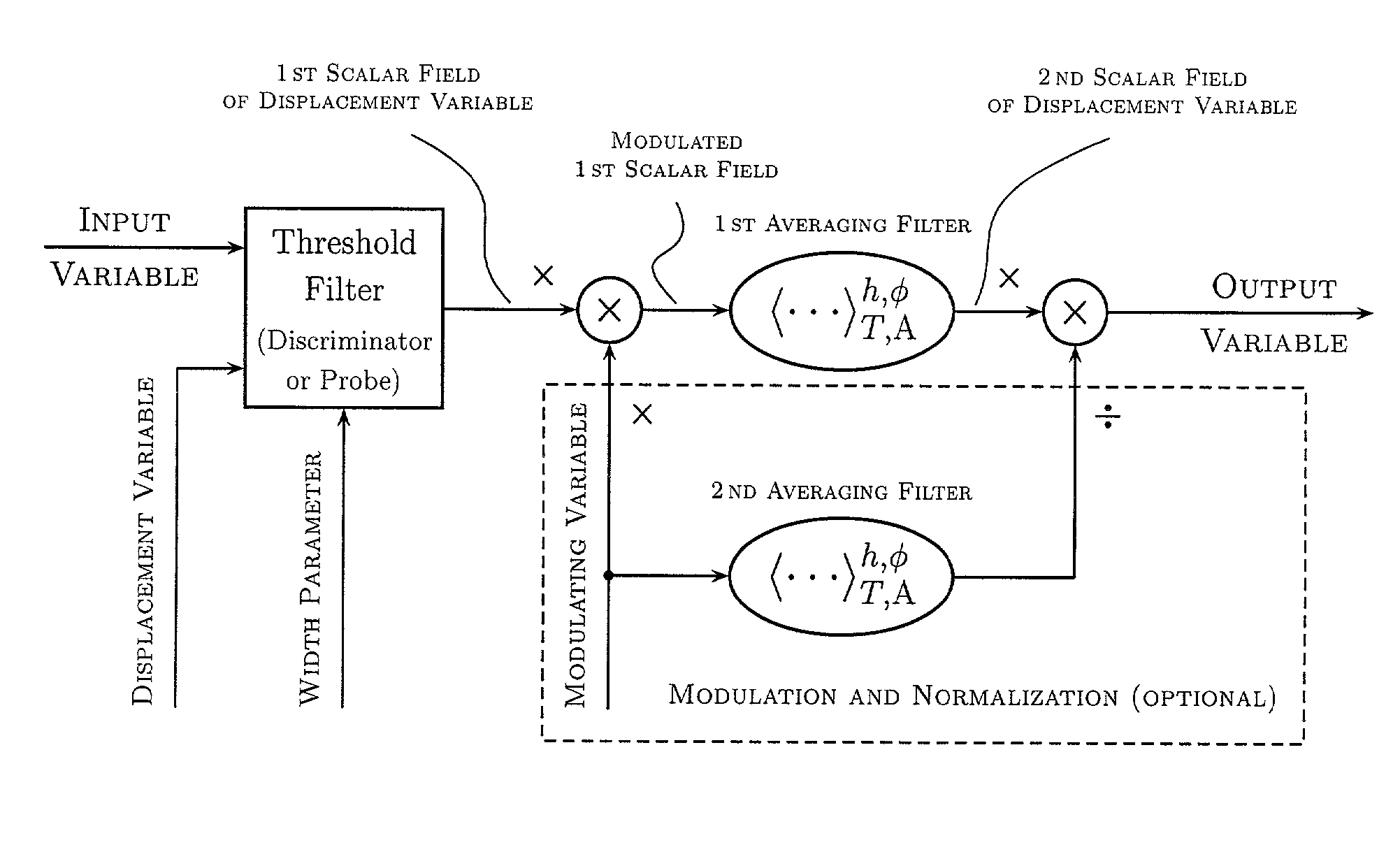
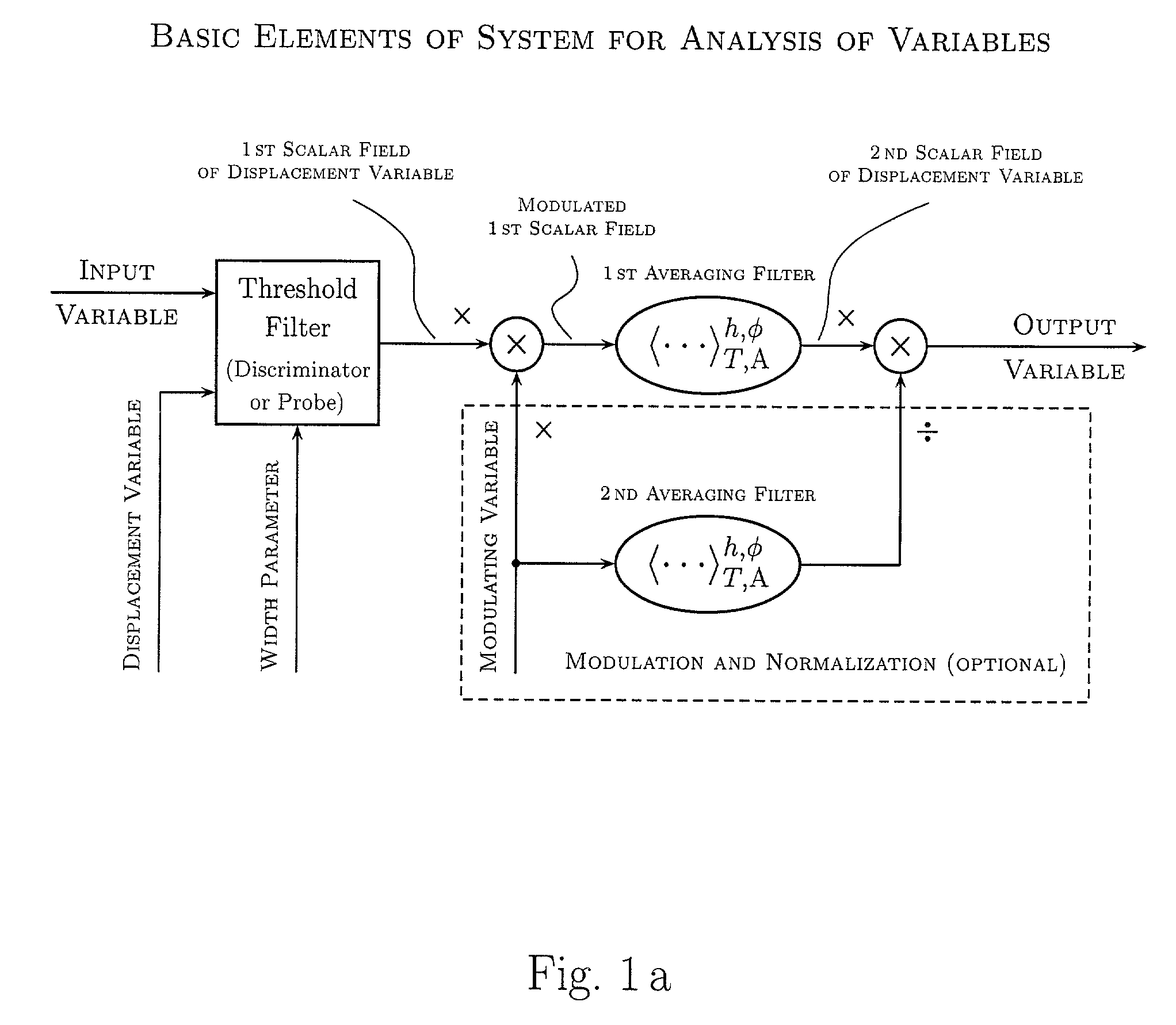
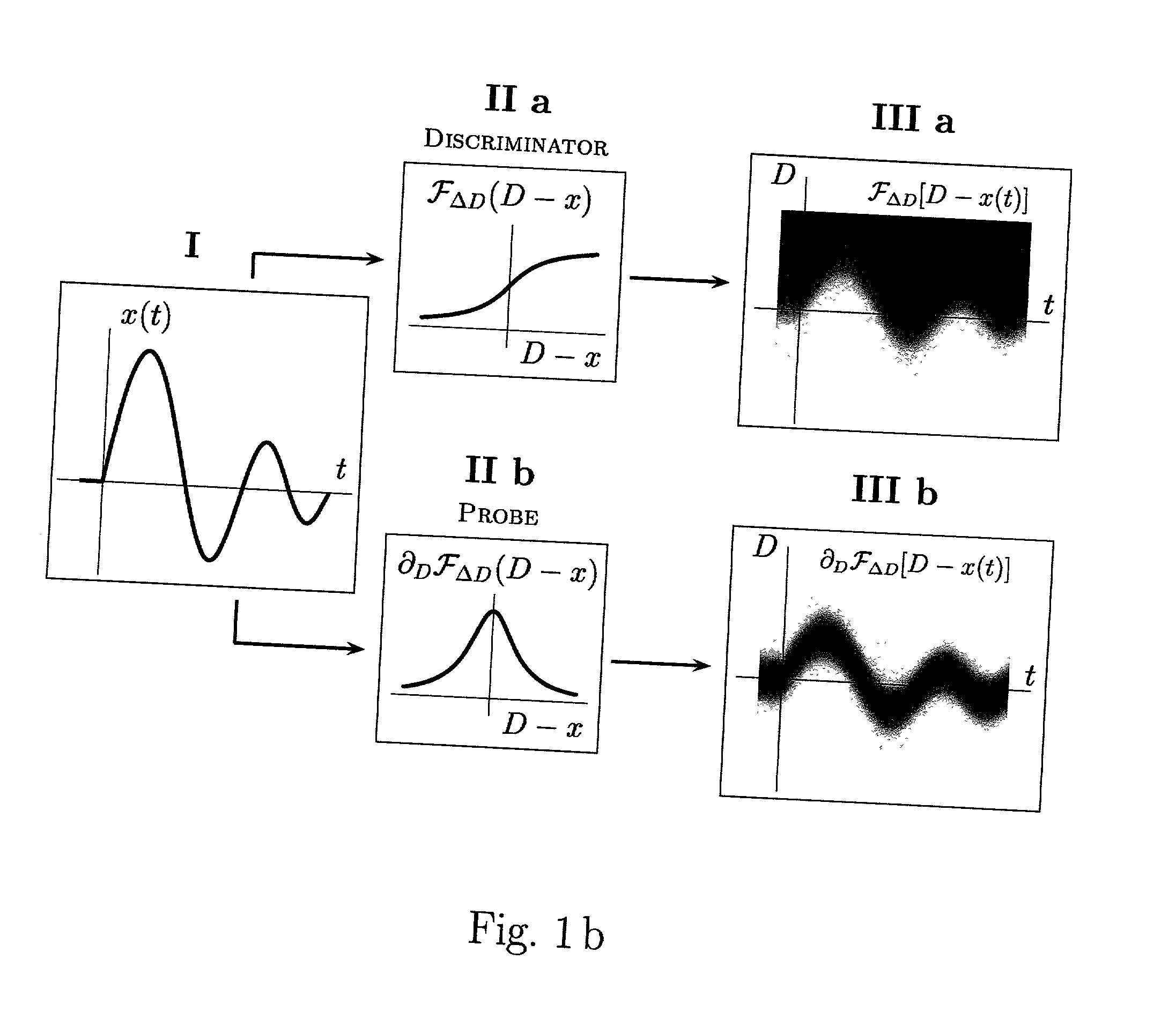
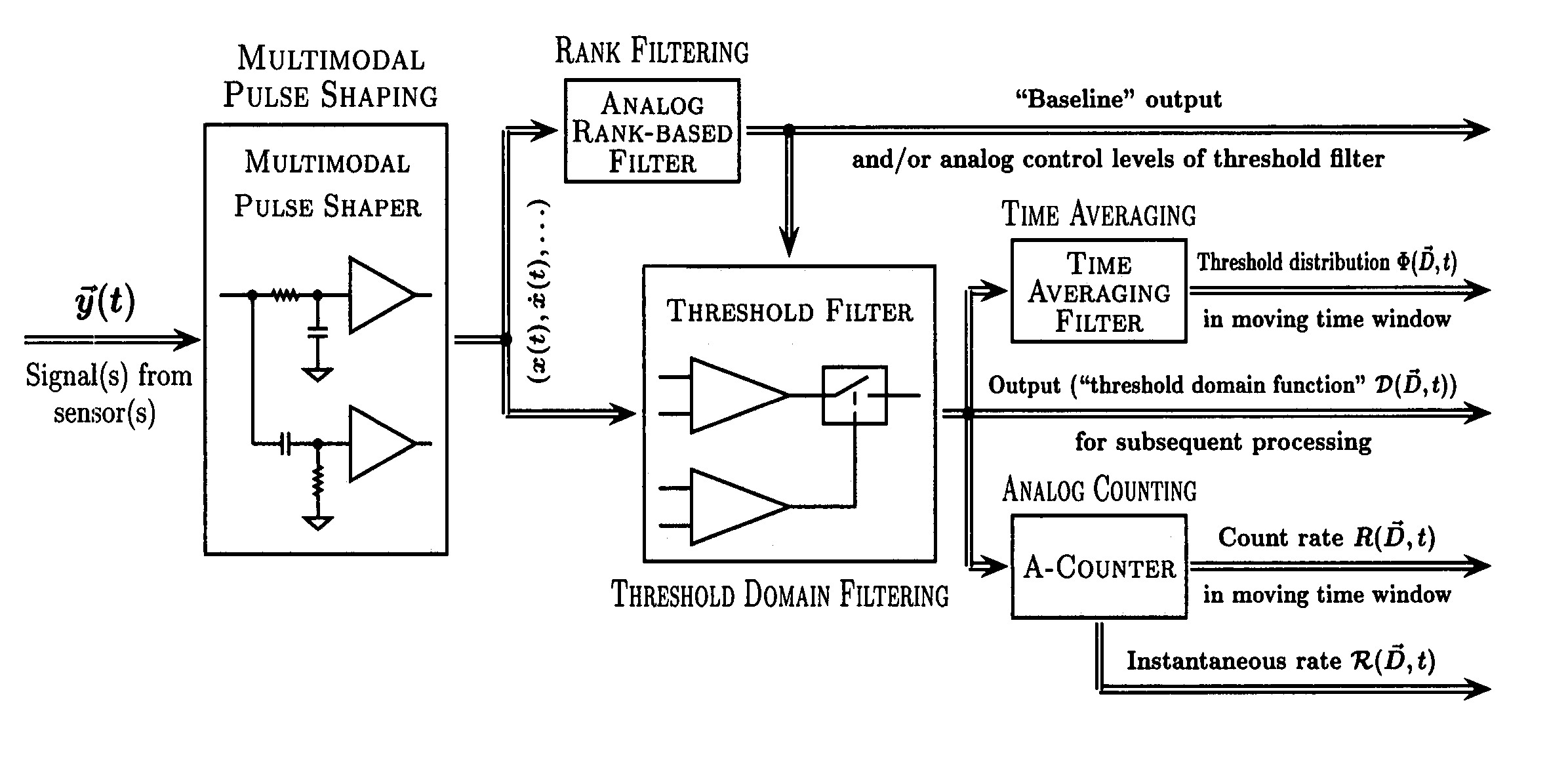
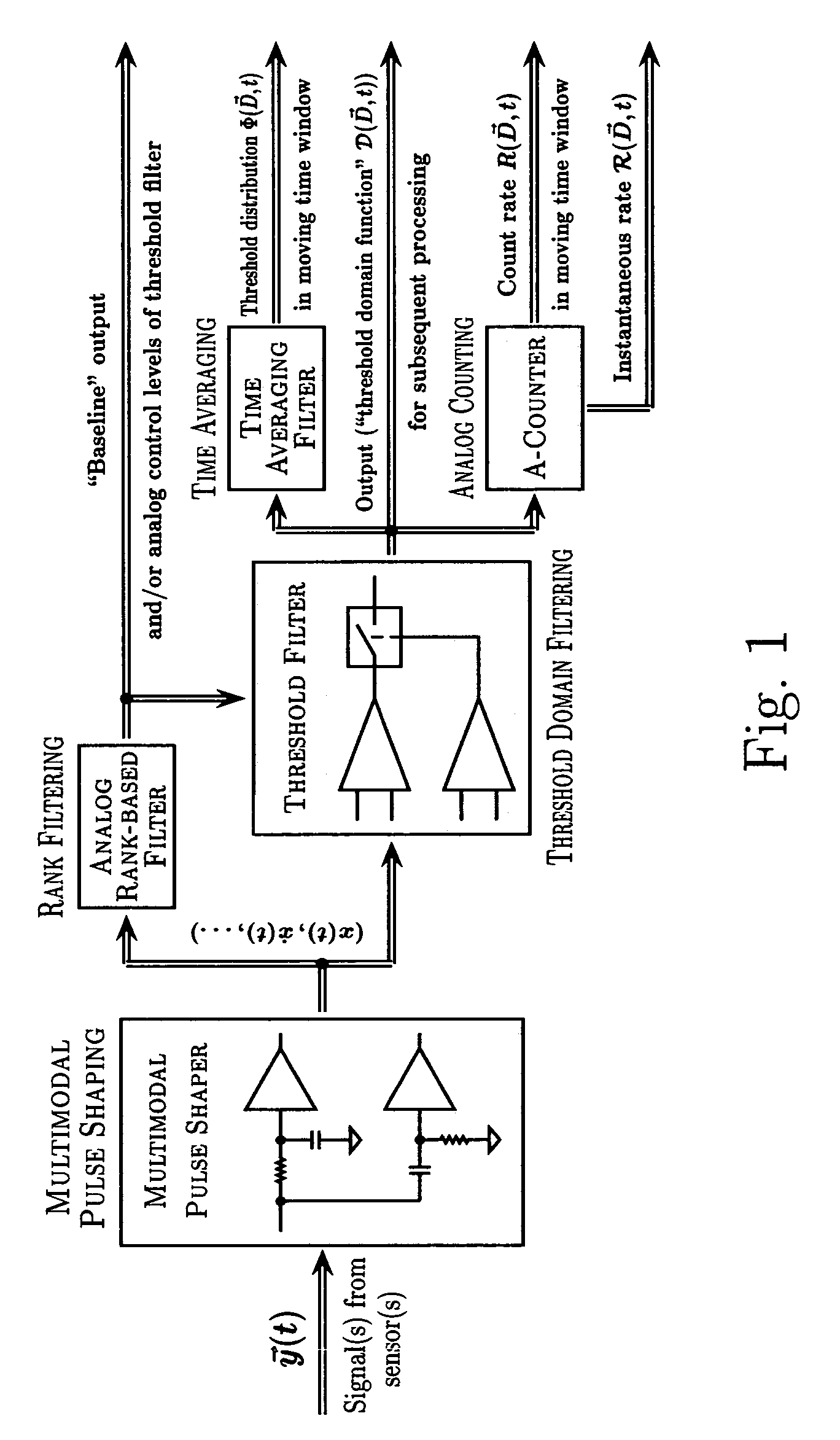
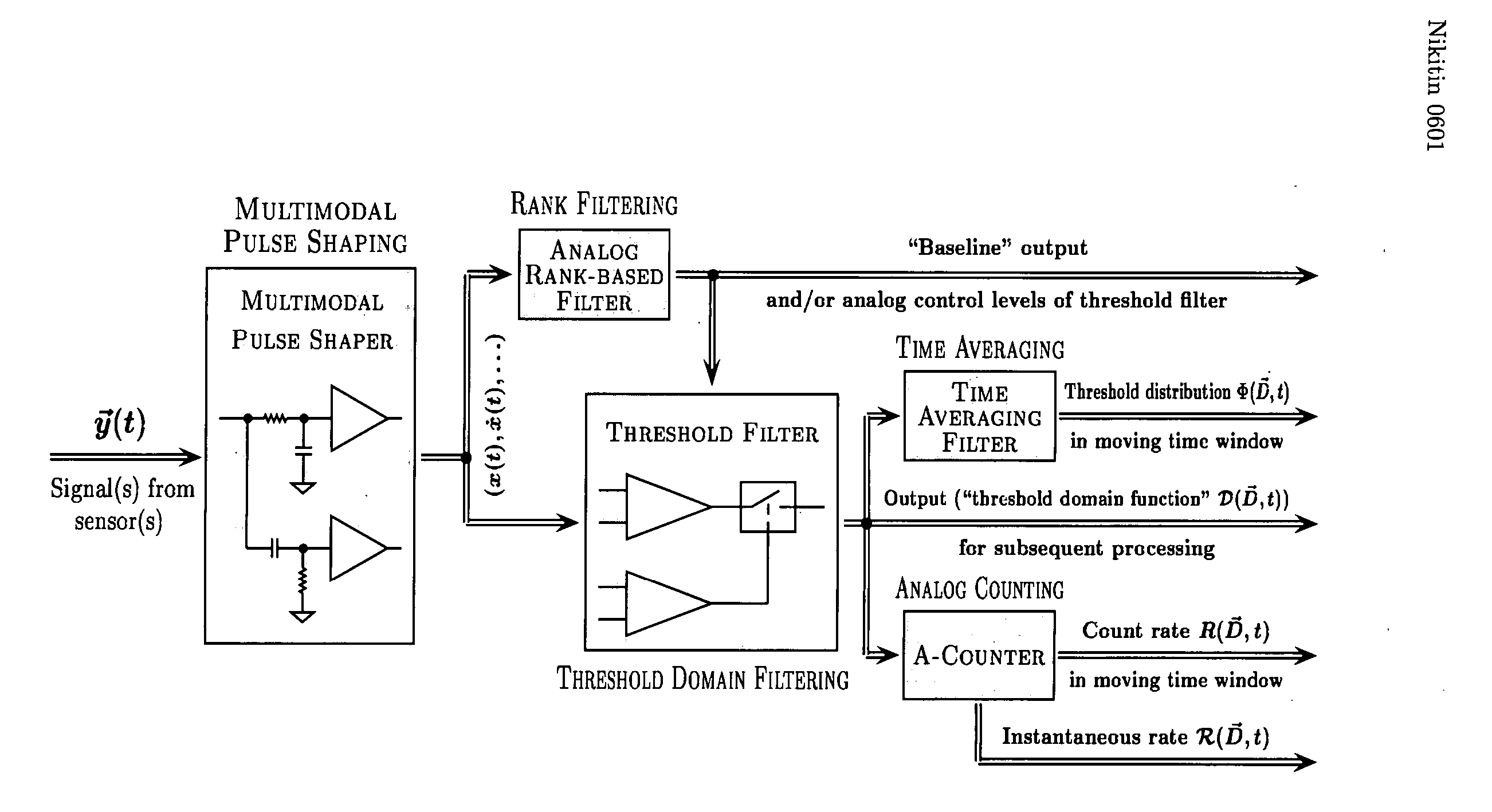
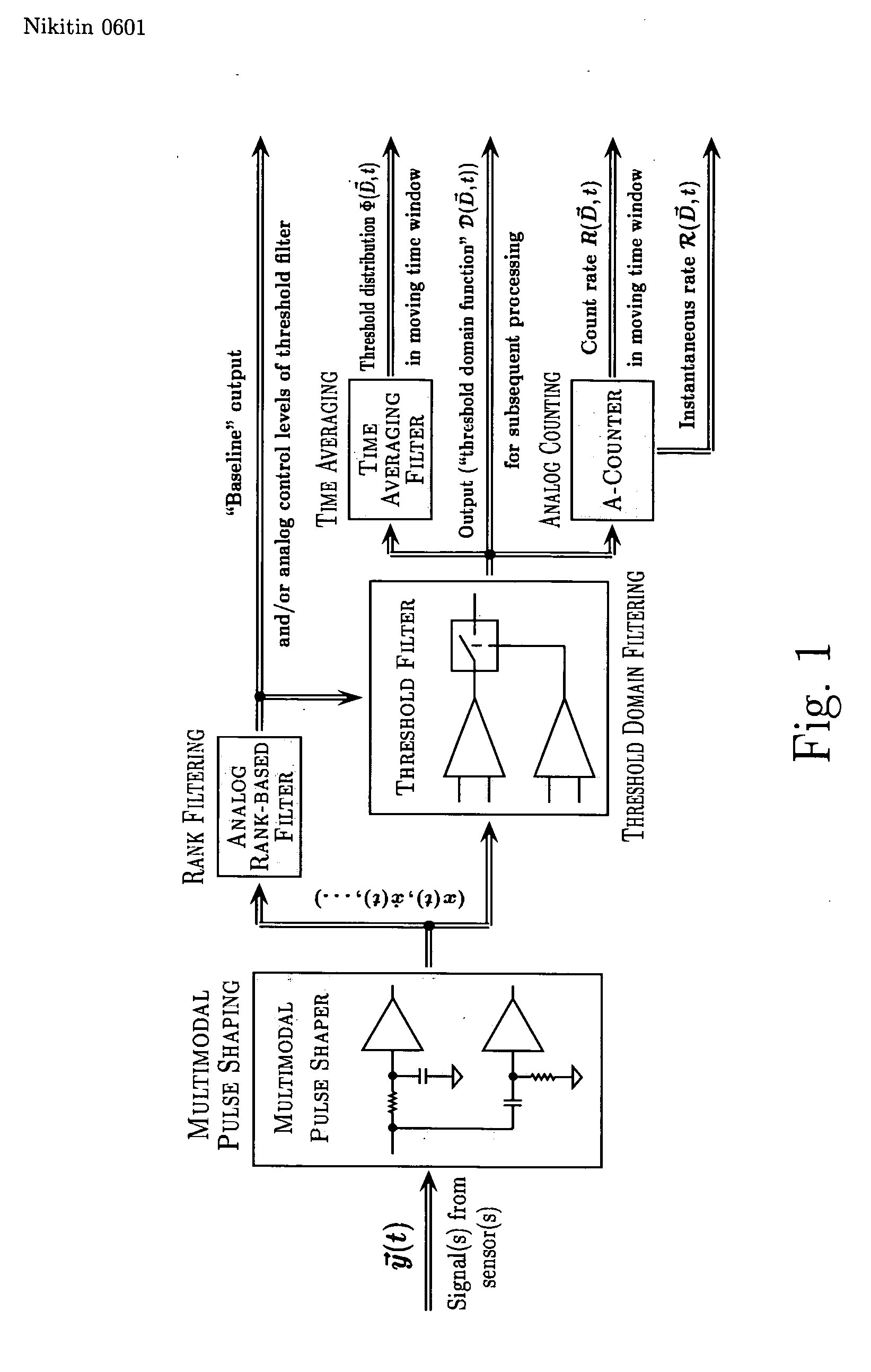
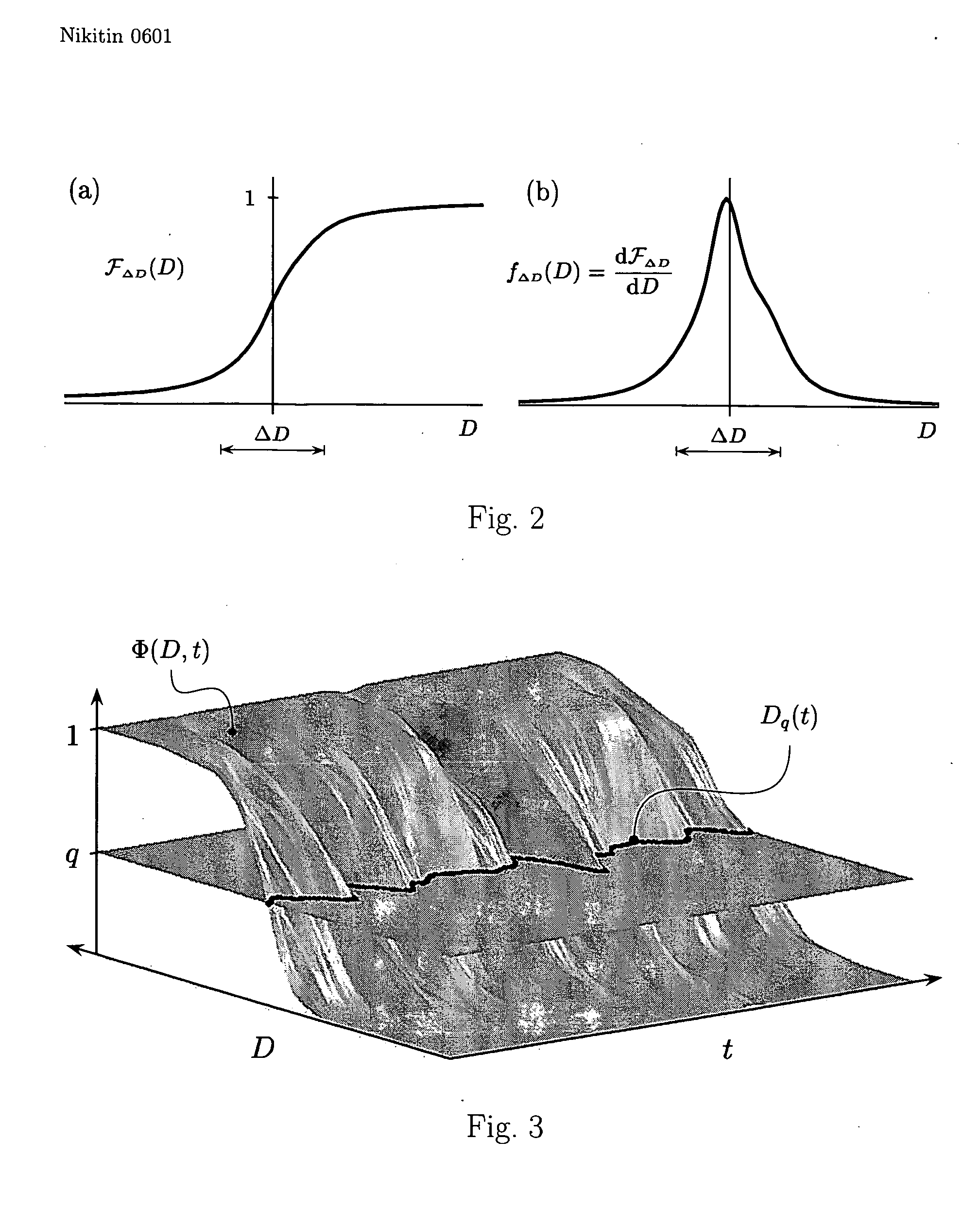
Various components of the present invention are collectively designated as Adaptive Real-Time Embodiments for Multivariate Investigation of Signals (ARTEMIS). It is a method, processes, and apparatus for measurement and analysis of variables of different type and origin. In this invention, different features of a variable can be quantified either locally as individual events, or on an arbitrary spatio-temporal scale as scalar fields in properly chosen threshold space. The method proposed herein overcomes limitations of the prior art by directly processing the data in real-time in the analog domain, identifying the events of interest so that continuous digitization and digital processing is not required, performing direct, noise-resistant measurements of salient signal characteristics, and outputting a signal proportional to these characteristics that can be digitized without the need for high-speed front-end sampling. The application areas of ARTEMIS are numerous, e.g., it can be used for adaptive content-sentient real-time signal conditioning, processing, analysis, quantification, comparison, and control, and for detection, quantification, and prediction of changes in signals, and can be deployed in automatic and autonomous measurement, information, and control systems. ARTEMIS can be implemented through various physical means in continuous action machines as well as through digital means or computer calculations. Particular embodiments of the invention include various analog as well as digital devices, computer programs, and simulation tools.
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V
Method and apparatus for adaptive real-time signal conditioning, processing, analysis, quantification, comparison, and control
Various components of the present invention are collectively designated as Adaptive Real-Time Embodiments for Multivariate Investigation of Signals (ARTEMIS). It is a method, processes, and apparatus for measurement and analysis of variables of different type and origin. In this invention, different features of a variable can be quantified either locally as individual events, or on an arbitrary spatio-temporal scale as scalar fields in properly chosen threshold space. The method proposed herein overcomes limitations of the prior art by directly processing the data in real-time in the analog domain, identifying the events of interest so that continuous digitization and digital processing is not required, performing direct, noise-resistant measurements of salient signal characteristics, and outputting a signal proportional to these characteristics that can be digitized without the need for high-speed front-end sampling. The application areas of ARTEMIS are numerous, e.g., it can be used for adaptive content-sentient real-time signal conditioning, processing, analysis, quantification, comparison, and control, and for detection, quantification, and prediction of changes in signals, and can be deployed in automatic and autonomous measurement, information, and control systems. ARTEMIS can be implemented through various physical means in continuous action machines as well as through digital means or computer calculations. Particular embodiments of the invention include various analog as well as digital devices, computer programs, and simulation tools.
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V
Method and apparatus for analysis of variables
InactiveUS20040158592A1Simple and clear interpretationImprove applicabilityImage enhancementSpeech analysisVolumetric Mass DensityVector field
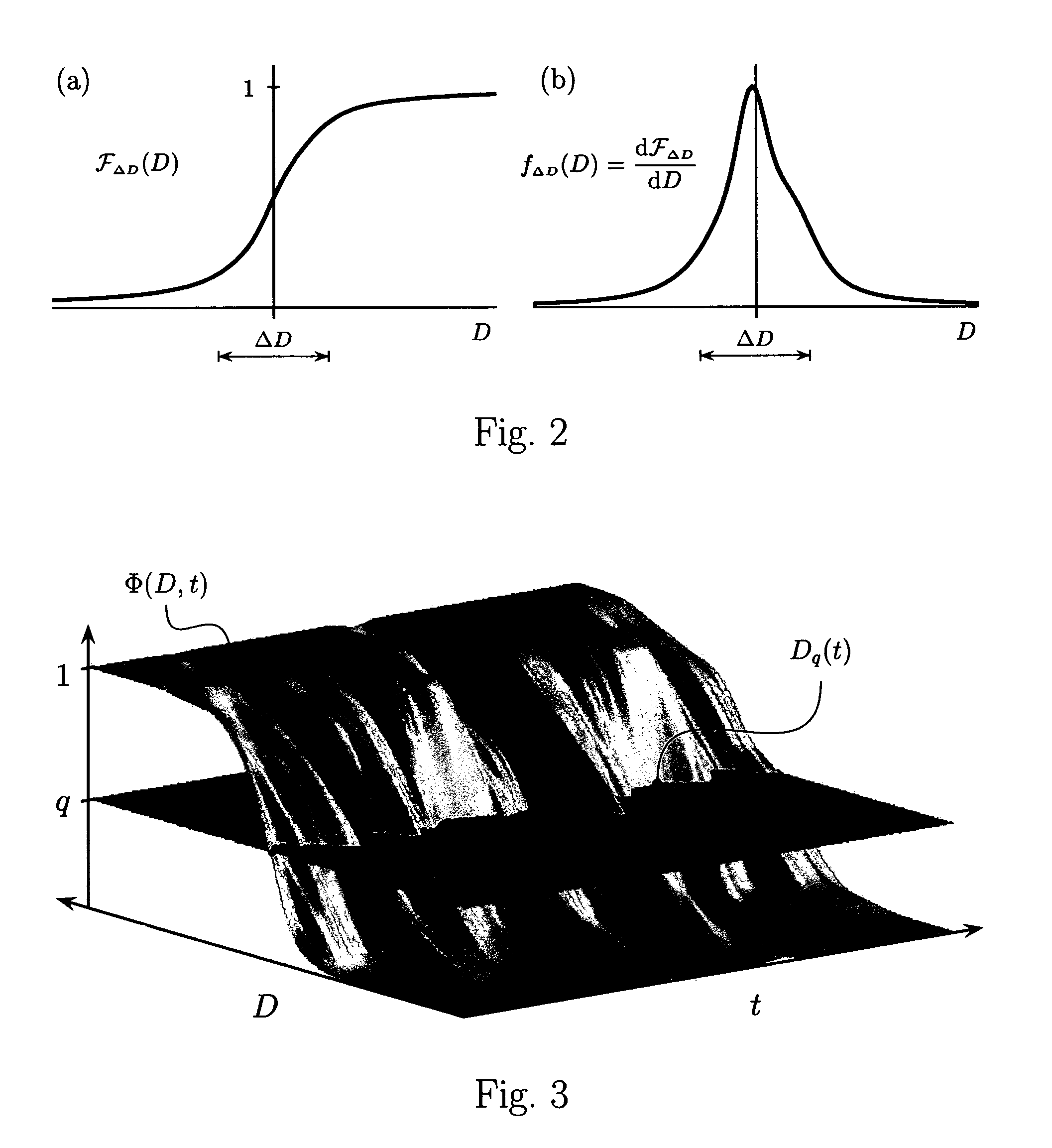
Various components of the present invention are collectively designated as Analysis of Variables Through Analog Representation (AVATAR). It is a method, processes, and apparatus for measurement and analysis of variables of different type and origin. AVATAR offers an analog solution to those problems of the analysis of variables which are normally handled by digital means. The invention allows (a) the improved perception of the measurements through geometrical analogies, (b) effective solutions of the existing computational problems of the order statistic methods, and (c) extended applicability of these methods to analysis of variables. The invention employs transformation of discrete or continuous variables into normalized continuous scalar fields, that is, into objects with mathematical properties of density and / or cumulative distribution functions. In addition to dependence on the displacement coordinates (thresholds), these objects can also depend on other parameters, including spatial coordinates (e.g., if the incoming variables are themselves scalar or vector fields), and / or time (if the variables depend on time). Moreover, this transformation of the measured variables may be implemented with respect to any reference variable. Thus, the values of the reference variable provide a common unit, or standard, for measuring and comparison of variables of different natures, for assessment of mutual dependence of these variables, and for evaluation of changes in the variables and their dependence with time. The invention enables, on a consistent general basis, a variety of new techniques for analysis of variables, which can be implemented through various physical means in continuous action machines as well as through digital means or computer calculations. Several of the elements of these new techniques do have digital counterparts, such as some rank order techniques in digital signal and image processing. However, this invention significantly extends the scope and applicability of these techniques and enables their analog implementation. The invention also introduces a wide range of signal analysis tools which do not exist, and cannot be defined, in the digital domain. In addition, by the present invention, all existing techniques for statistical processing of data, and for studying probability fluxes, are made applicable to analysis of any variable.
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V +1
Method and apparatus for analysis of variables
ActiveUS20050165879A1Improve applicabilityMore opportunityImage enhancementComputing operations for integration/differentiationPattern perceptionVector field
Various components of the present invention are collectively designated as Analysis of Variables Through Analog Representation (AVATAR). It is a method, processes, and apparatus for measurement and analysis of variables of different type and origin. AVATAR offers an analog solution to those problems of the analysis of variables which are normally handled by digital means. The invention allows (a) the improved perception of the measurements through geometrical analogies, (b) effective solutions of the existing computational problems of the order statistic methods, and (c) extended applicability of these methods to analysis of variables. The invention employs transformation of discrete or continuous variables into normalized continuous scalar fields, that is, into objects with mathematical properties of density and / or cumulative distribution functions. In addition to dependence on the displacement coordinates (thresholds), these objects can also depend on other parameters, including spatial coordinates (e.g., if the incoming variables are themselves scalar or vector fields), and / or time (if the variables depend on time). Moreover, this transformation of the measured variables may be implemented with respect to any reference variable. Thus, the values of the reference variable provide a common unit, or standard, for measuring and comparison of variables of different natures, for assessment of mutual dependence of these variables, and for evaluation of changes in the variables and their dependence with time. The invention enables, on a consistent general basis, a variety of new techniques for analysis of variables, which can be implemented through various physical means in continuous action machines as well as through digital means or computer calculations. Several of the elements of these new techniques do have digital counterparts, such as some rank order techniques in digital signal and image processing. However, this invention significantly extends the scope and applicability of these techniques and enables their analog implementation. The invention also introduces a wide range of signal analysis tools which do not exist, and cannot be defined, in the digital domain. In addition, by the present invention, all existing techniques for statistical processing of data, and for studying probability fluxes, are made applicable to analysis of any variable.
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V +1
Method and system for displaying a relational abstraction of a data store
InactiveUS20050021538A1Minimizes learning curveQuickly and easily understandDigital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsScalar fieldData storing
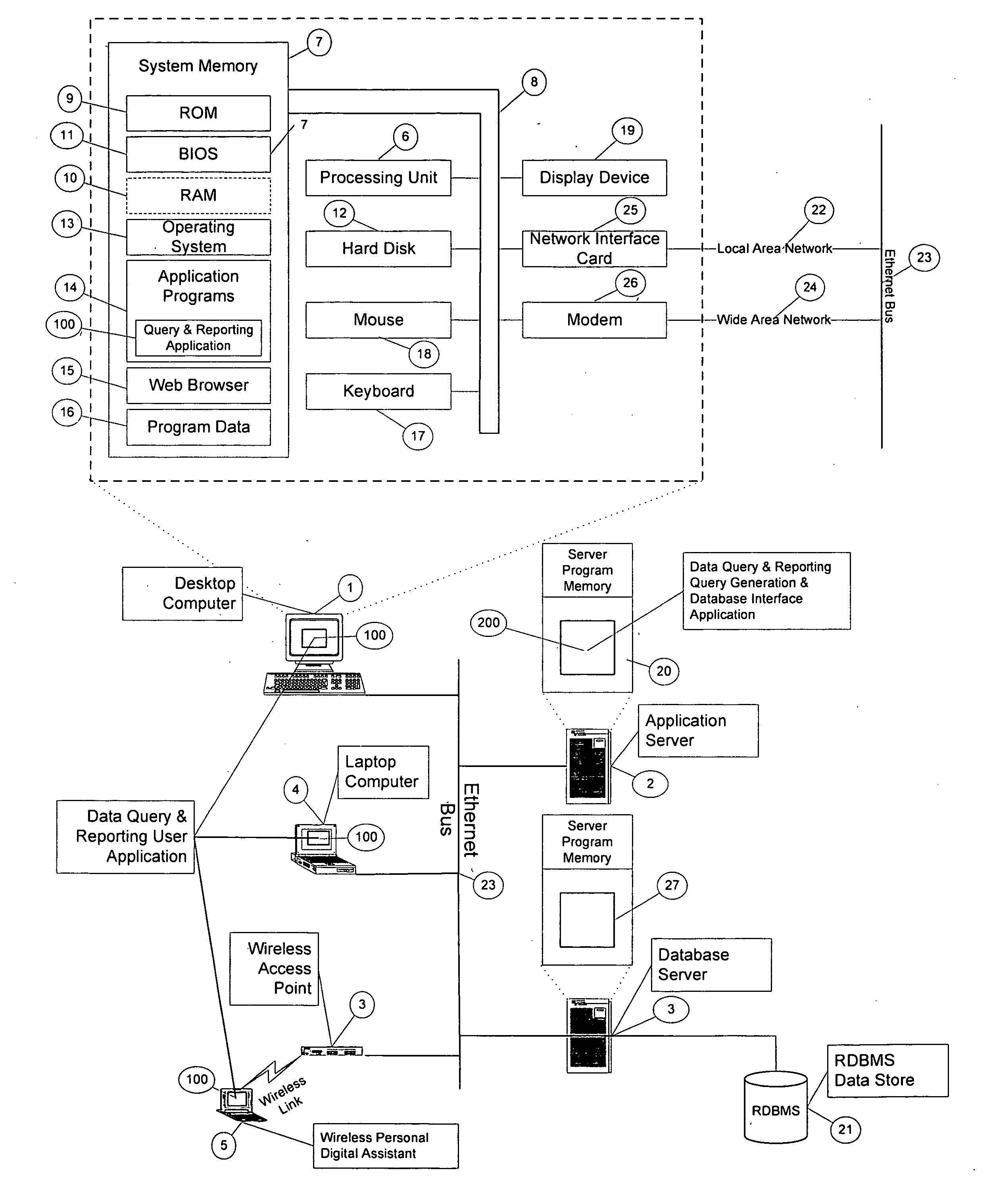
A method and system for displaying a relational abstraction data store are disclosed. A relational abstraction of a data store is defined, the definition including a plurality of views, scalar or aggregate fields associated with the views, and relations between the views. The fields and relations associated with views are displayed and related to a base view through a sequence of relations. The fields displayed are constrained based upon the sequence of relations from the base view. Scalar fields are displayed where the sequence of relations does not contain a to-many relation. Aggregate fields are displayed where the sequence of relations contains at least one to-many relation. Distinct aggregate fields are displayed where the relation path sequence contains a to-many relation followed by a many-to-one relation. A field may be displayed with additional information indicating how, or whether, the fields may be used. The display of fields may be constrained in predetermined ways. The display of relations may be displayed with additional information about the nature of the relations and the sequence of the relation path. Fields and relations may be displayed using a hierarchical means of display such as in trees structures or lists, or may be displayed using a natural language description.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
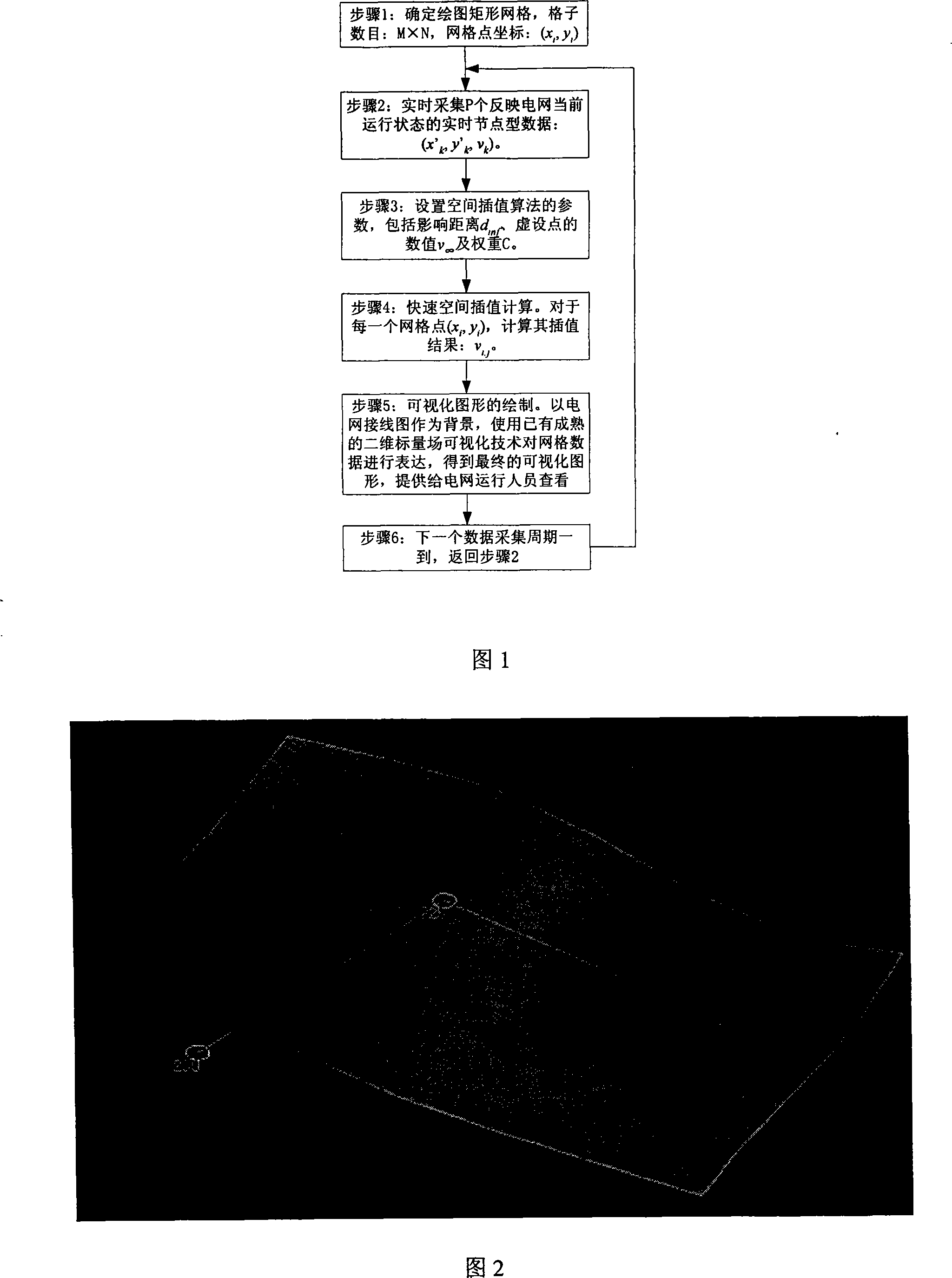
Three-dimensional visualization method for power system real time node data base on rapid space interpolation
InactiveCN101231631AImprove visual effectsImprove practicalitySpecial data processing applications3D-image renderingNODALElectric power system
The invention relates to a power system real time nodal data three-dimensional visualization method which is based on the fast spatial interpolation, and belongs to the power system three-dimensional visualization techniology field. The method comprises the following steps that: the scale of rectangular grids is determined and drawn; the nodal data in a power network are collected; the parameters of the spatial interpolation algorithm are set; the calculation is carried out through the fast spatial interpolation algorithm; for each grid point (xi, yj), the interpolation result (vi, j) is calculated, the power network wiring diagram is taken as the background, and the two-dimensional scalar field visualization technology is used to express grid data (xi, yj, vi, j), so as to obtain the visual graphic of the real time nodal data, which is used to carry out the real time safety economy monitoring to the power network; while ensuring the rapidity, the invention remarkably improves the visual effect and the practicability of the three-dimensional visual graphic through introducing a dummy average point and modifying the weight coefficient.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method and apparatus for adaptive real-time signal conditioning, processing, analysis, quantification, comparision, and control
ActiveUS7107306B2Reduce noiseSimple designComputing operations for integration/differentiationRecognisation of pattern in signalsScalar fieldSignal conditioning
Various components of the present invention are collectively designated as Adaptive Real-Time Embodiments for Multivariate Investigation of Signals (ARTEMIS). It is a method, processes, and apparatus for measurement and analysis of variables of different type and origin. In this invention, different features of a variable can be quantified either locally as individual events, or on an arbitrary spatio-temporal scale as scalar fields in properly chosen threshold space. The method proposed herein overcomes limitations of the prior art by directly processing the data in real-time in the analog domain, identifying the events of interest so that continuous digitization and digital processing is not required, performing direct, noise-resistant measurements of salient signal characteristics, and outputting a signal proportional to these characteristics that can be digitized without the need for high-speed front-end sampling.The application areas of ARTEMIS are numerous, e.g., it can be used for adaptive content-sentient real-time signal conditioning, processing, analysis, quantification, comparison, and control, and for detection, quantification, and prediction of changes in signals, and can be deployed in automatic and autonomous measurement, information, and control systems. ARTEMIS can be implemented through various physical means in continuous action machines as well as through digital means or computer calculations. Particular embodiments of the invention include various analog as well as digital devices, computer programs, and simulation tools.
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V
Nonlinear techniques for pressure vector acoustic sensor array synthesis
InactiveUS7274622B1Narrow acoustic beam widthMulti-channel direction findingAcoustic wave reradiationSensor arrayNonlinear algorithms
The present invention presents a method for use with an acoustic sensor array comprised of a number of pressure-vector sensors capable of sensing the acoustic scalar field and acoustic vector field of an acoustic wave. The method is a signal processing technique that utilizes nonlinear processing of pressure-vector sensor signals in the acoustic sensor array. The method involves the steps of receiving the sensor output values, processing the output values using a non-linear algorithm to create a mathematical series of values, transforming the series, applying weighting to the series and performing a summation of the values in the series to calculate the array directivity response. The array directivity response can then be further processed where the array is part of a sonar system.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
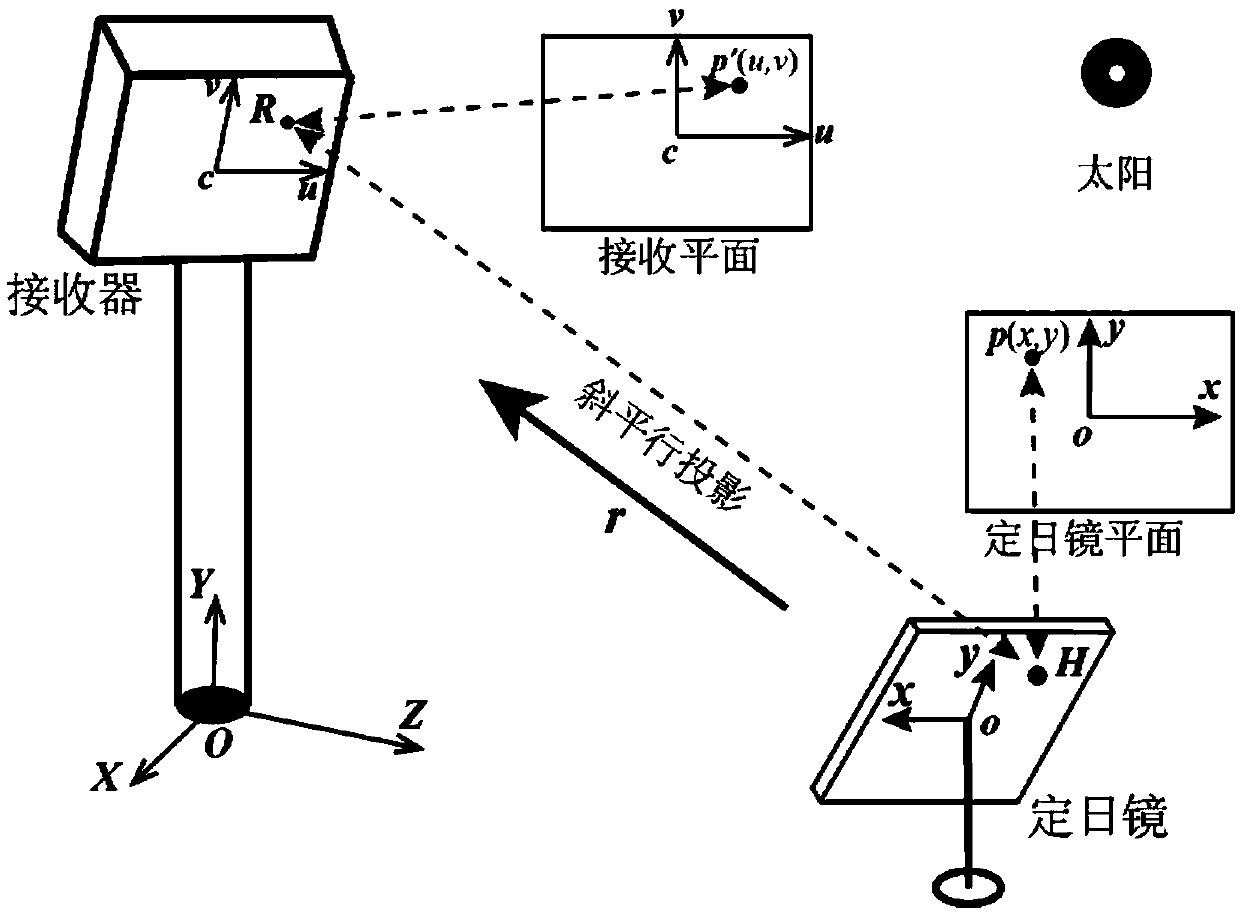
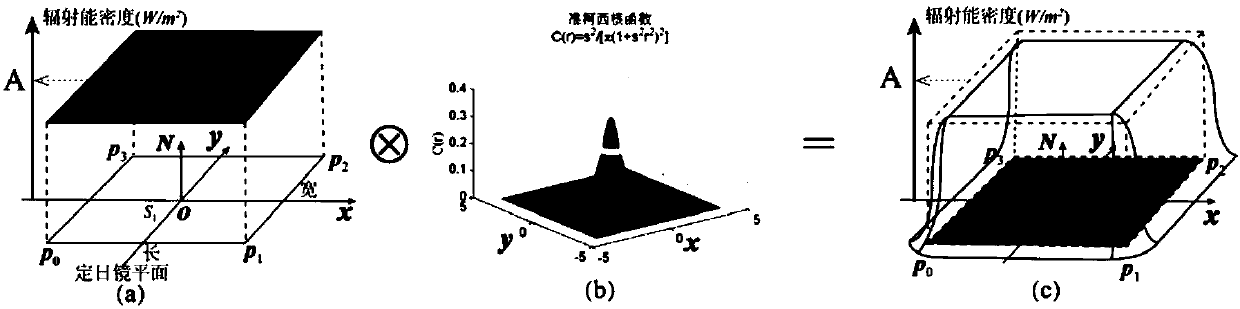
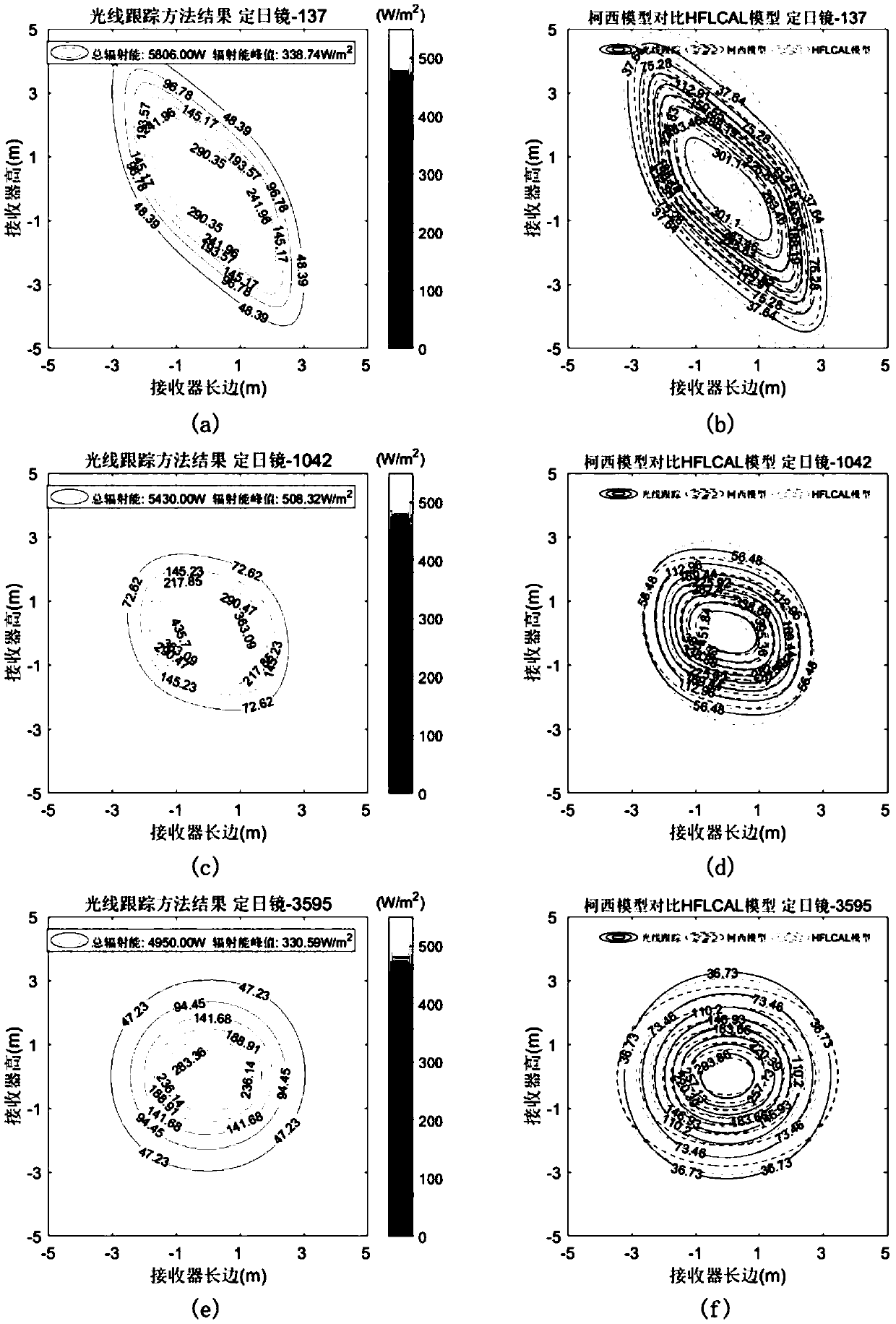
A method for simulating radiation energy density distribution of light spots in tower type solar thermal power generation
ActiveCN109670248AHigh precisionQuick calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLight spotPower generation system
The invention discloses a method for simulating radiation energy density distribution of light spots in tower type solar thermal power generation, which relates to the technical field of tower type solar thermal power generation system simulation and comprises the following steps of (1) extracting an effective reflection area on the surface of a heliostat under the condition of considering the influence of shadow and shielding; (2) deducing and establishing an analytical model of a virtual radiation energy density distribution scalar field function defined under a heliostat local coordinate system; (3) obliquely projecting the virtual radiation energy density distribution scalar field function to a receiving plane in parallel along the reflection direction of a heliostat to complete modeling of radiation energy density distribution received on a receiver. According to the method, factors such as the sunlight direction, the radiation energy distribution of the solar surface, the position, the size and the rotation of the heliostat, the micro surface of the heliostat and shadow and shielding are considered, and experiment and comparison results show that compared with an existing analysis method, the analysis model provided by the invention is higher in precision and can be quickly calculated.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
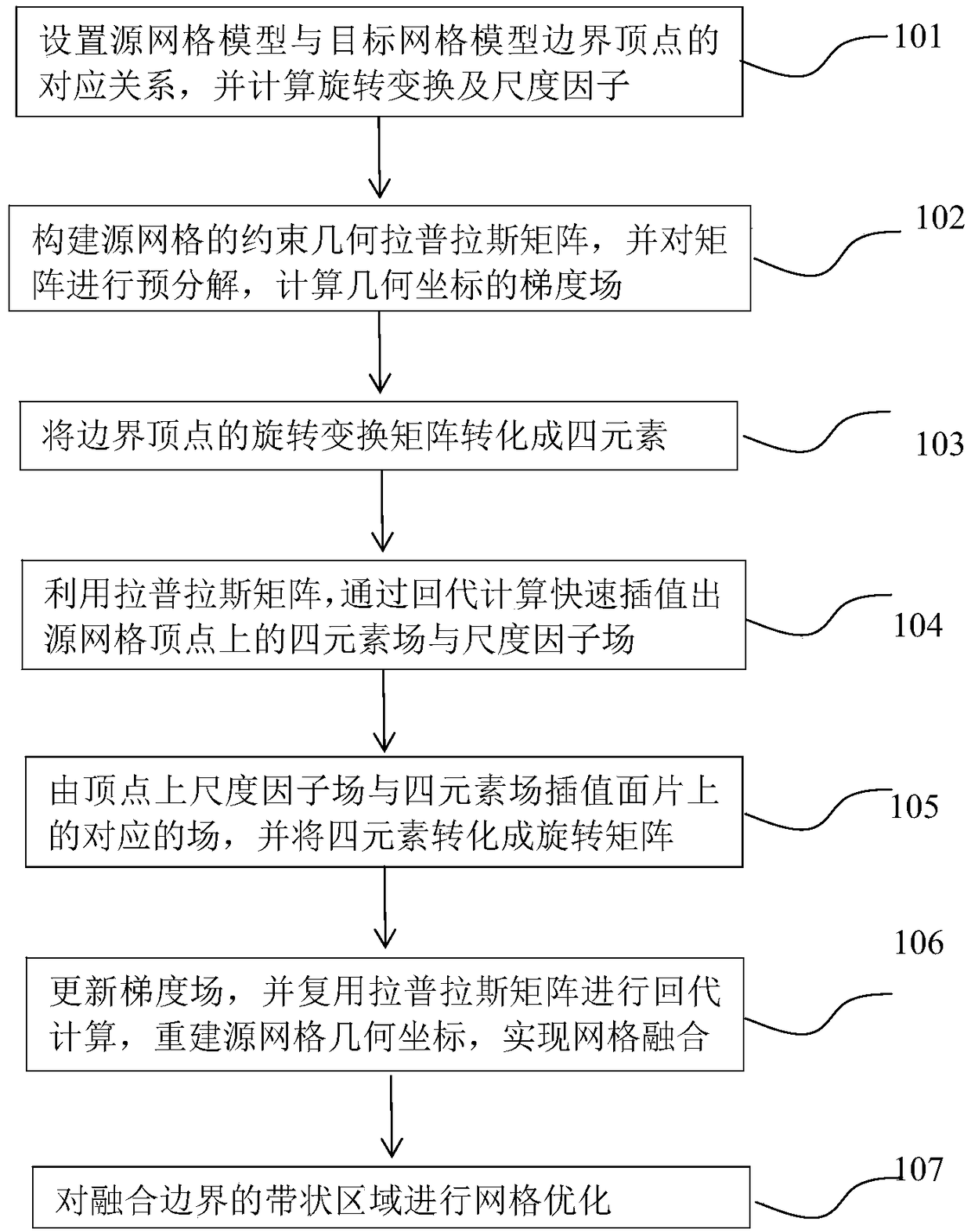
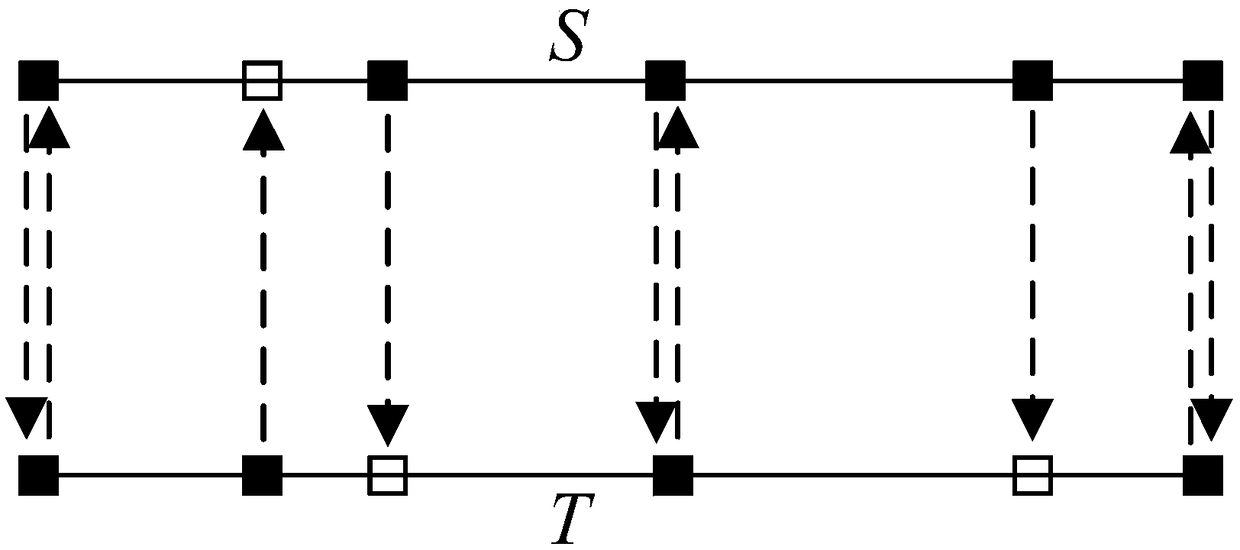
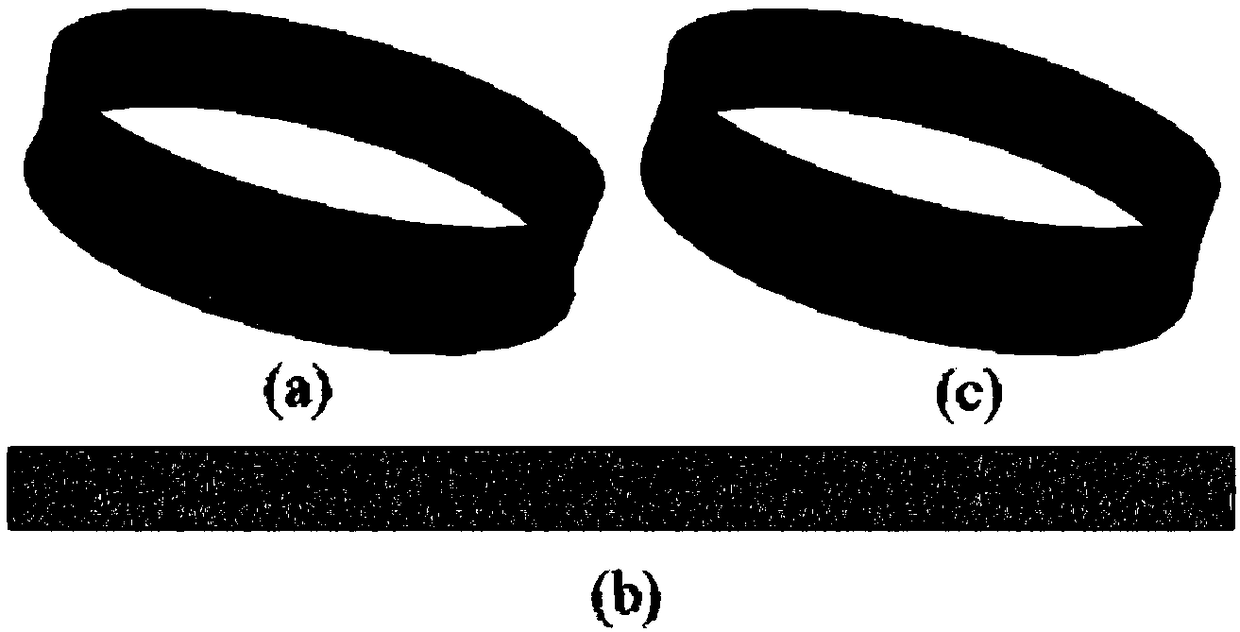
An efficient mesh fusion method based on reusable Laplace matrix
InactiveCN109410335AImprove efficiencyReach the speed of real-time response3D-image rendering3D modellingTime responseScalar field
The invention discloses an efficient mesh fusion method based on a reusable Laplace matrix. The method includes: setting the correspondence between the boundary vertices of the source mesh model and the target mesh model, calculating the local transformation from the boundary vertices of the source mesh to the boundary vertices of the corresponding target mesh, using Laplace operator to calculatethe rotation field and the scale factor field, reusing Laplace matrix to reconstruct the geometric coordinates, and so on. In this method, the interpolation problems of geometric fusion, rotating field and scale factor field are transformed into Laplacian (Poisson) equations, and only one Cholesky decomposition and multiple iterations are needed to obtain eight scalar fields, which is two orders of magnitude faster than the traditional geodesic-based interpolation method. This method can not only obtain the results comparable to the traditional Poisson fusion method, but also significantly improve the efficiency and achieve the speed of real-time response.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV
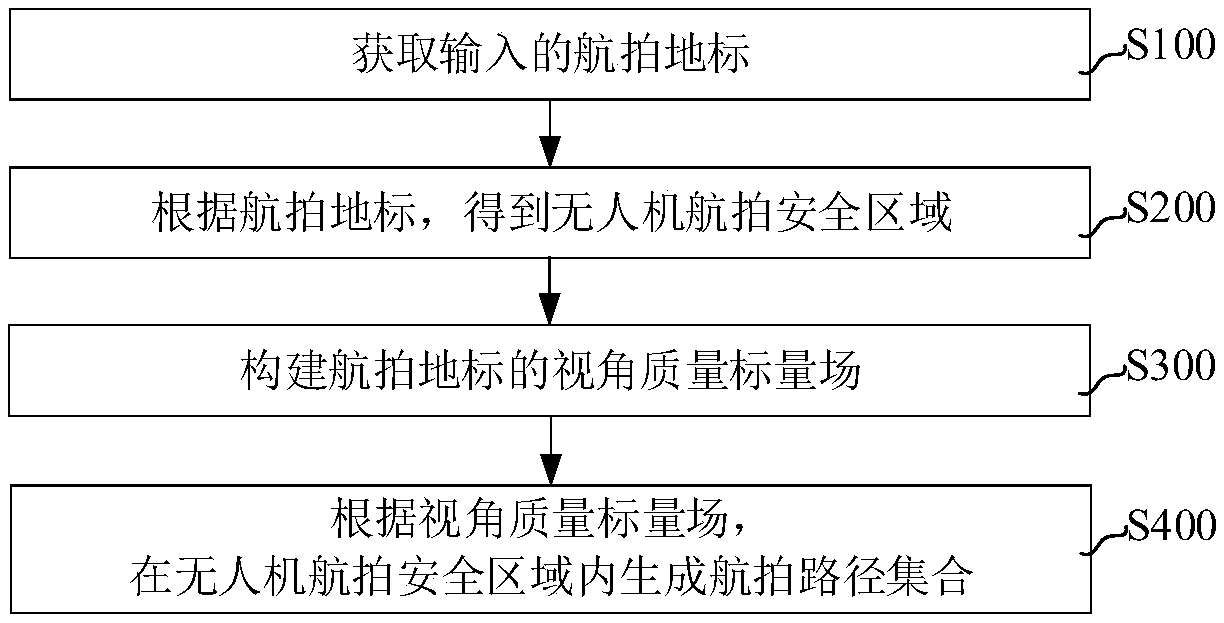
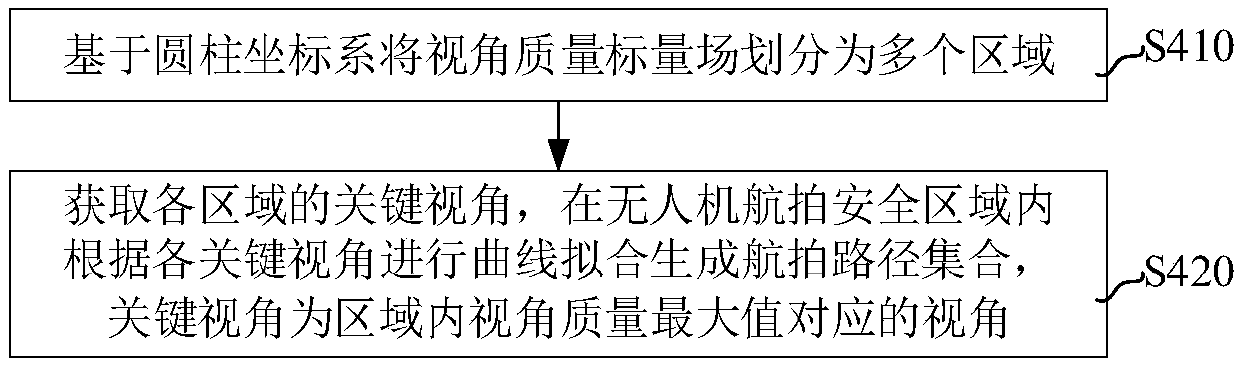
Aerial photographing path generating method and device for unmanned aerial vehicle, computer equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN108981706ARealize automatic generationReduce workloadNavigational calculation instrumentsPicture interpretationScalar fieldUncrewed vehicle
The invention relates to an aerial photographing path generating method and device for an unmanned aerial vehicle, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining an input aerial photographing landmark; obtaining an aerial photographing safety area of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the aerial photographing landmark; constructing a view angle quality scalar field of the aerial photographing landmark, and generating an aerial photographing path set in the aerial photographing safety area of the unmanned aerial vehicle according to the view angle quality scalar field. The aerial photographing path generating method and device can be adopted to realize automatically generating the aerial photographing path, so that user workload and working difficulty coefficient can be greatly reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Method and apparatus for adaptive real-time signal conditioning, processing, analysis, quantification, comparison, and control
InactiveUS20060253512A1Reduce noiseSimple designComputing operations for integration/differentiationRecognisation of pattern in signalsTime signalDigitization
Owner:NIKITIN ALEXEI V
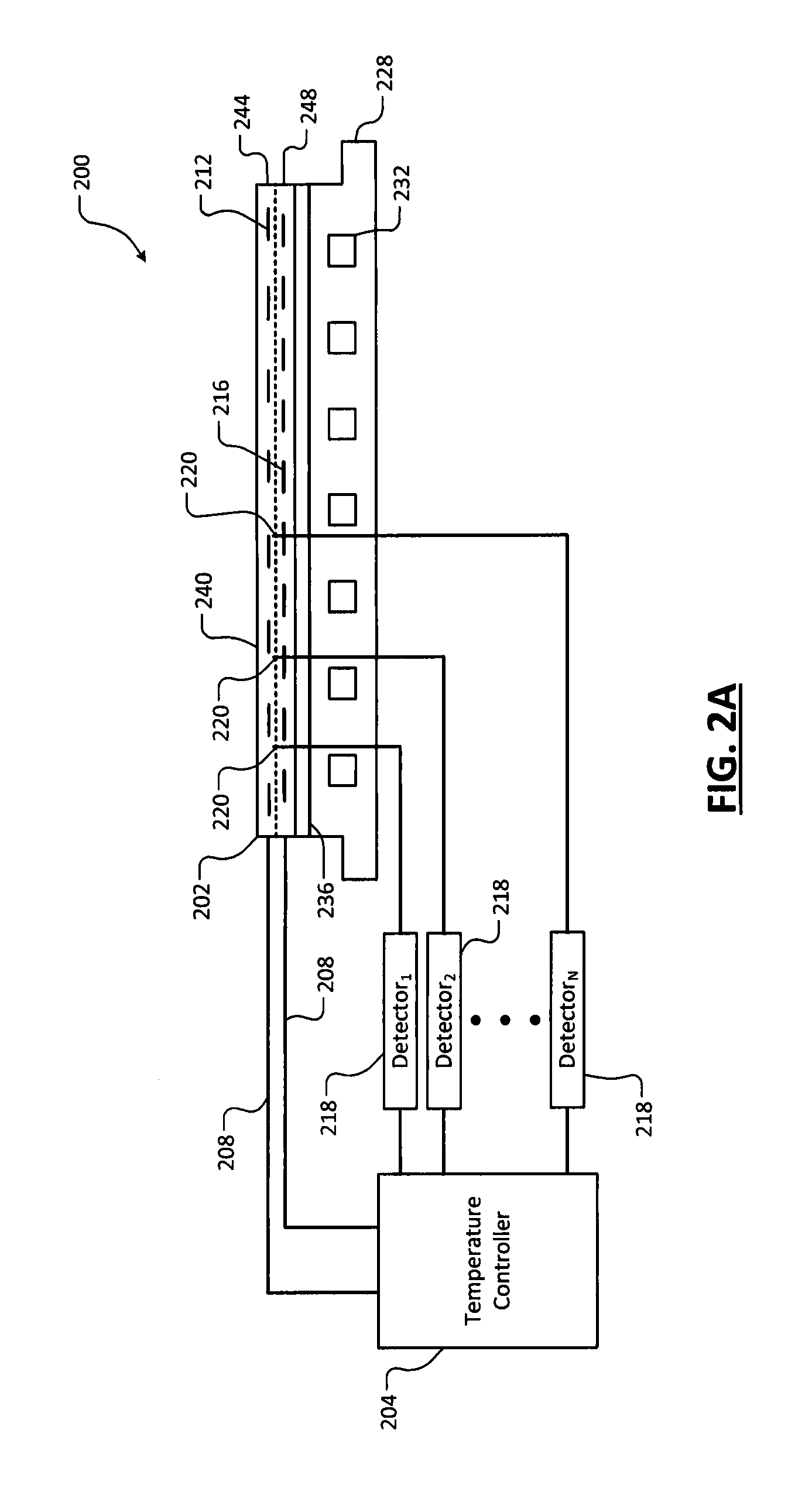
Systems and methods for calibrating scalar field contribution values for a limited number of sensors including a temperature value of an electrostatic chuck and estimating temperature distribution profiles based on calibrated values
ActiveUS20160370795A1Thermometers using mean/integrated valuesSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementScalar fieldEngineering
A system including a controller, an interface, and a calibration controller. The controller is configured to (i) select a set of fields, and (ii) based on the set of fields, supply control effort to first actuators in zones of a chamber. The interface is configured to receive feedback signals from sensors. The feedback signals are indicative of fields respectively of the zones. The controller is configured to adjust an amount of control effort supplied to the actuators based on the fields. The calibration controller is configured to, based on the fields, generate calibration values for each of the sensors. The calibration values for each of the sensors are indicative of field contributions corresponding respectively to the actuators.
Owner:LAM RES CORP
Volume data non-photorealistic rendering method based on GPU (graphic processing unit) acceleration
ActiveCN103366395AGood non-realistic effectDraws well and realistically3D-image renderingEnergy minimizationScalar field
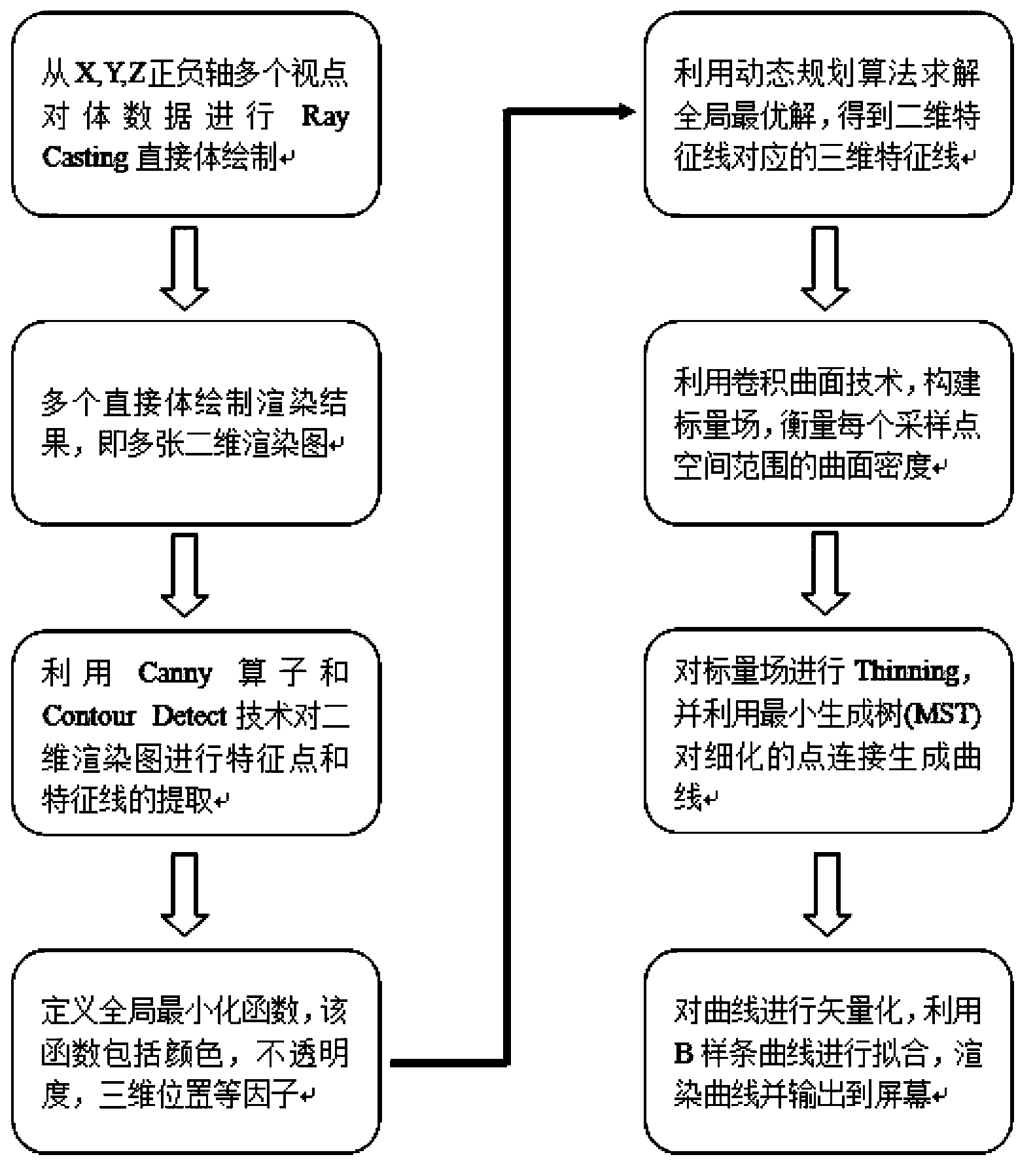
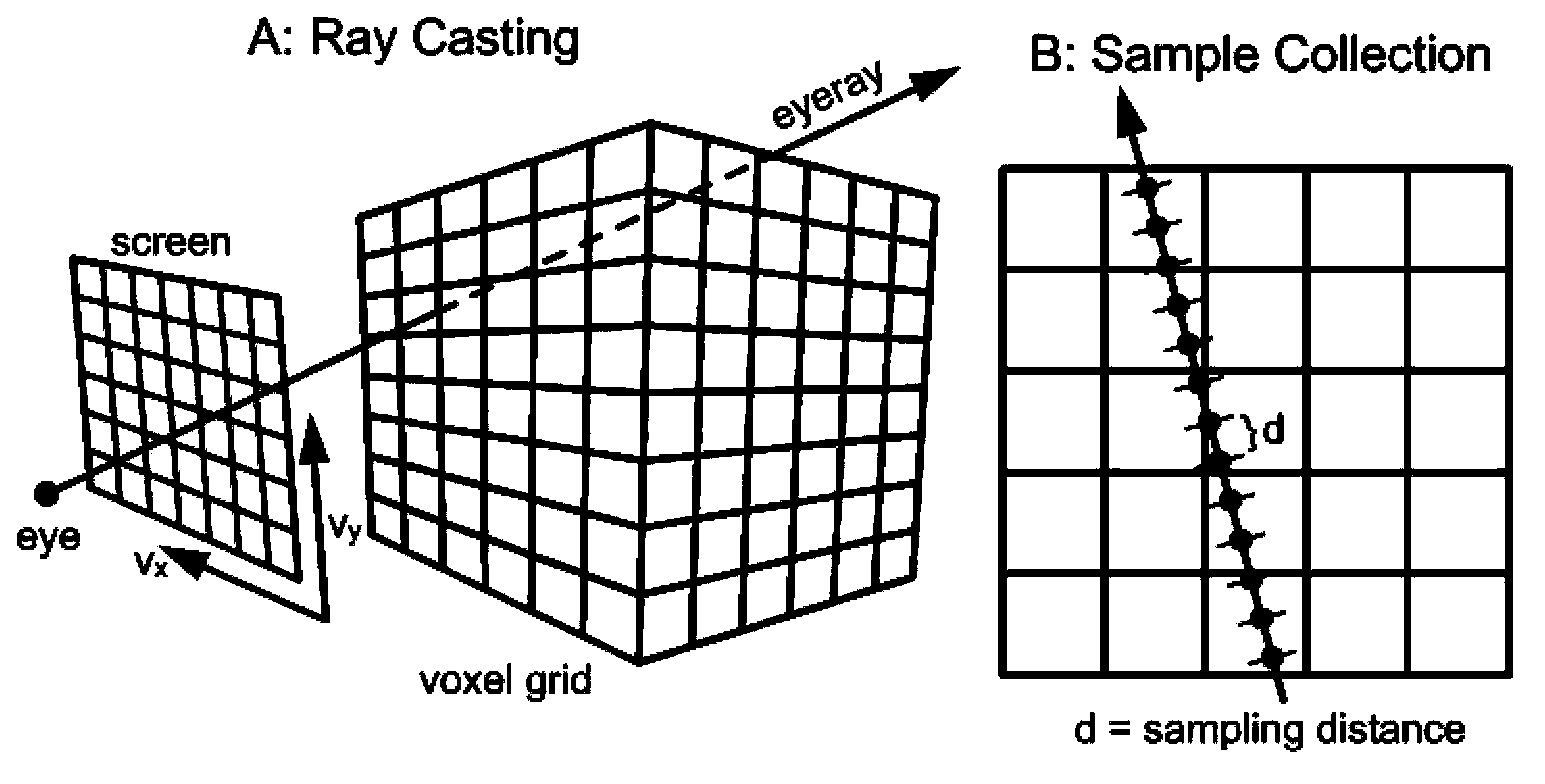
The invention relates to a volume data non-photorealistic rendering method based on GPU (graphic processing unit) acceleration. The method comprises the following steps of carrying out the direct volume rendering for medical volume data under multiple viewpoints, acquiring a plurality of rendering results, extracting a characteristic line for the two-dimensional rendering result, defining a global energy miniaturization rule, calculating a three-dimensional characteristic line, utilizing a convolution surface method to define a scalar field, clustering the three-dimensional characteristic line, utilizing a B-type curve to fit the line, and completing the stylized rendering. By utilizing the powerful calculation capacity of the GPU, the rendering speed and efficiency can be greatly improved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
User controlled method for generating highly structured triangular meshes
The invention discloses a novel user controlled method for generating highly structured triangular meshes, comprising the following steps: (1) generating corresponding characteristic constraint and a density field on an input mesh model according to user requirements, and generating a corresponding field of direction according to the characteristic constraint and the user requirements; (2) constructing three scalar fields on the input mesh model, wherein the direction of contour lines of each scalar field is in accordance with that of the field of direction in step (1), the geodesic distance between adjacent contour lines of each scalar field is 1 / mu on the input mesh model, and mu represents the density field in step (1); and (3) extracting the contour lines of each scalar field, and forming the triangular meshes by intersecting the extracted contour lines. The invention has the beneficial effects that the highly structured triangular meshes can be generated; optimized singular point distribution can be automatically obtained; and edge direction, sampling density, characteristics alignment and the like of the mesh are directly controlled by the user, and at the same time, facet quality is maintained.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SENSETIME TECH DEV CO LTD
Atmospheric feature detection using Langrangian scalar integration
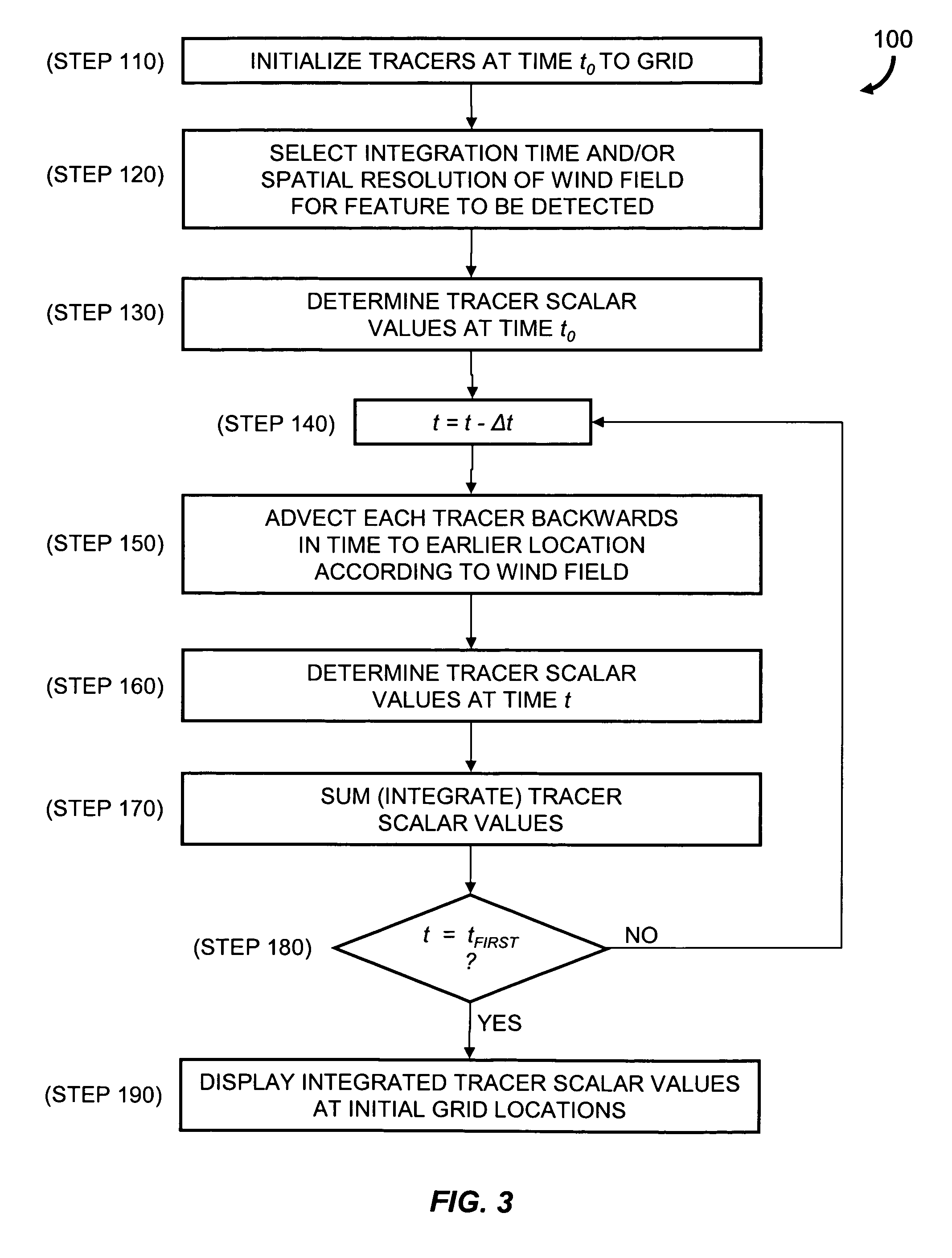
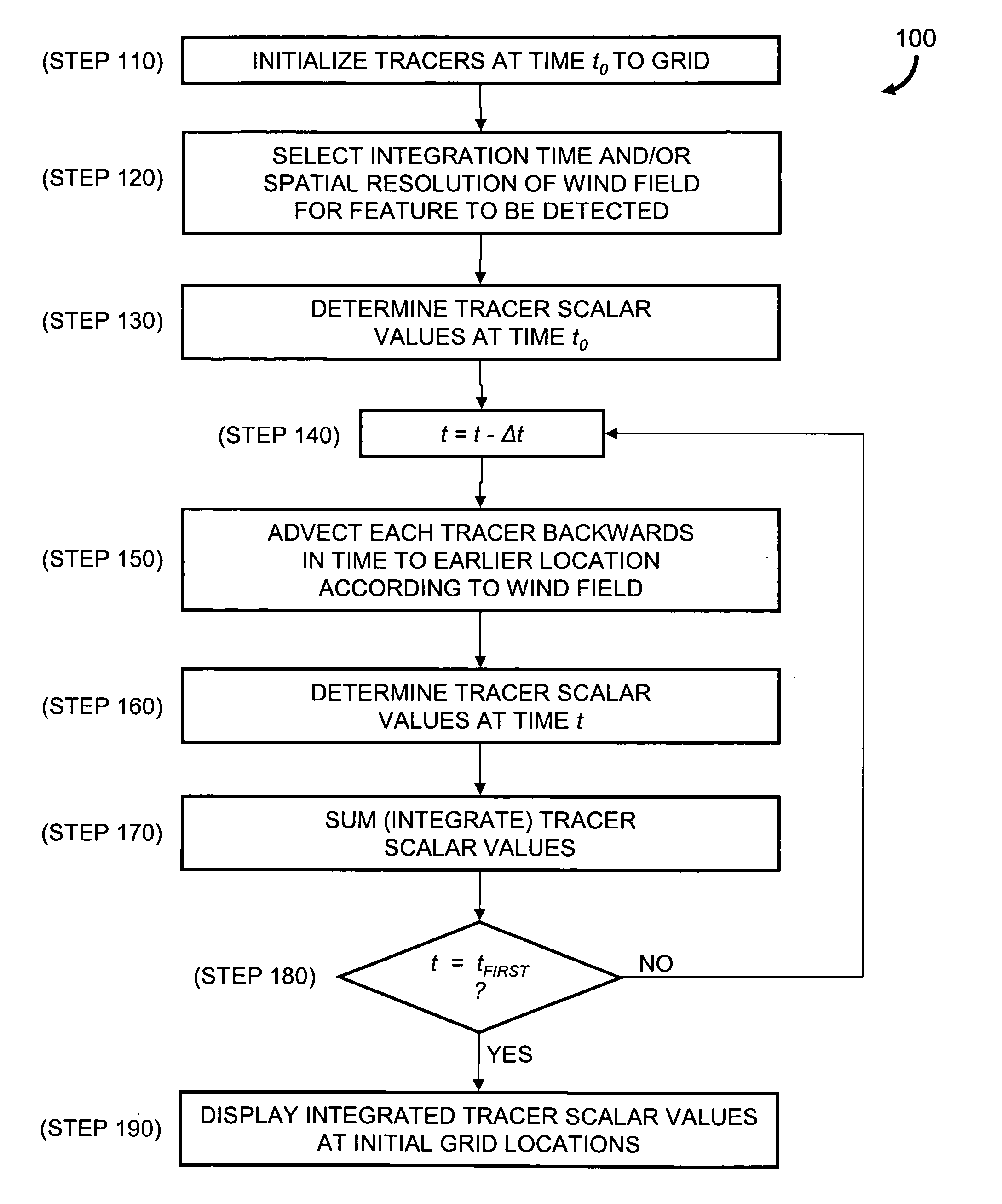
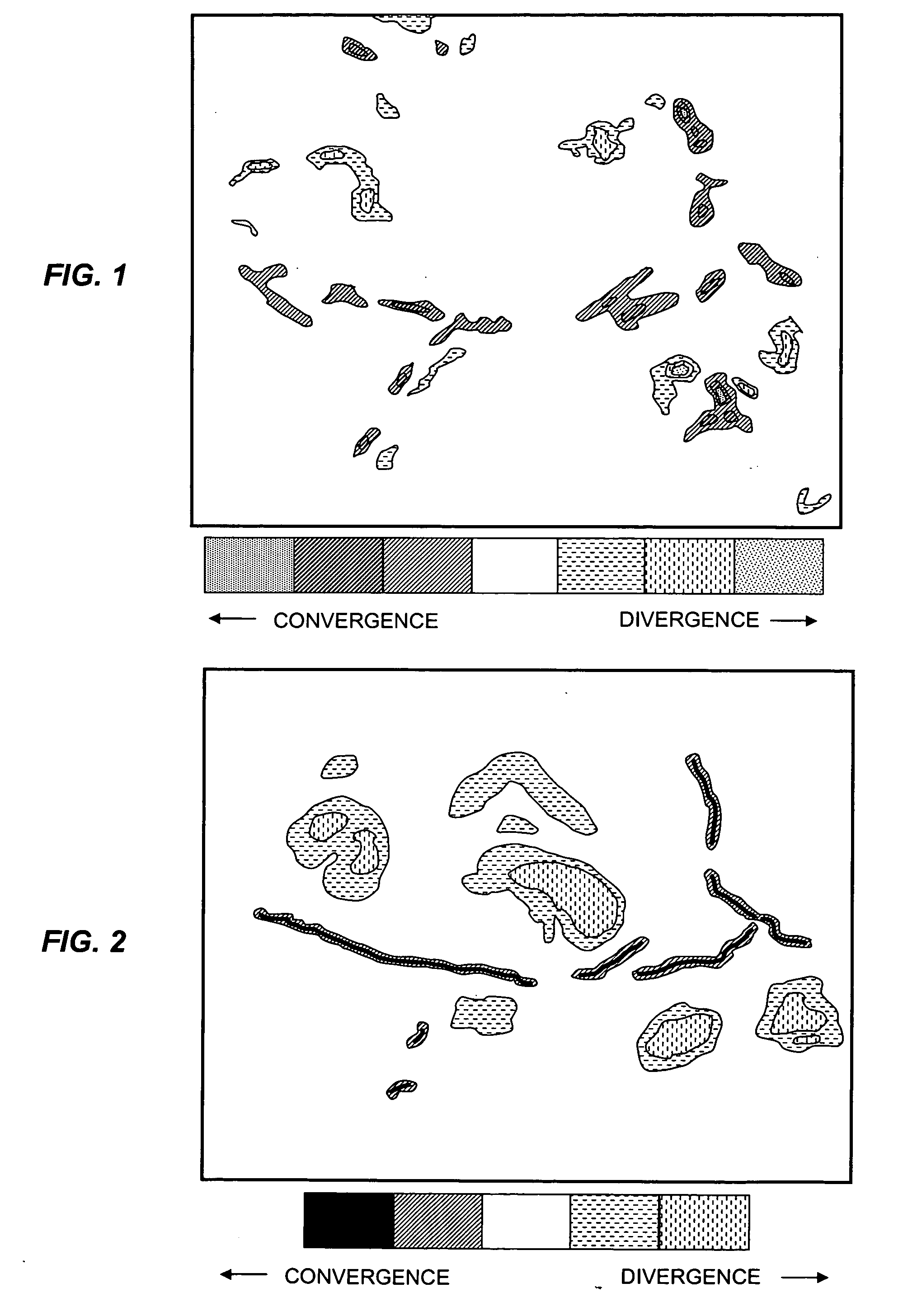
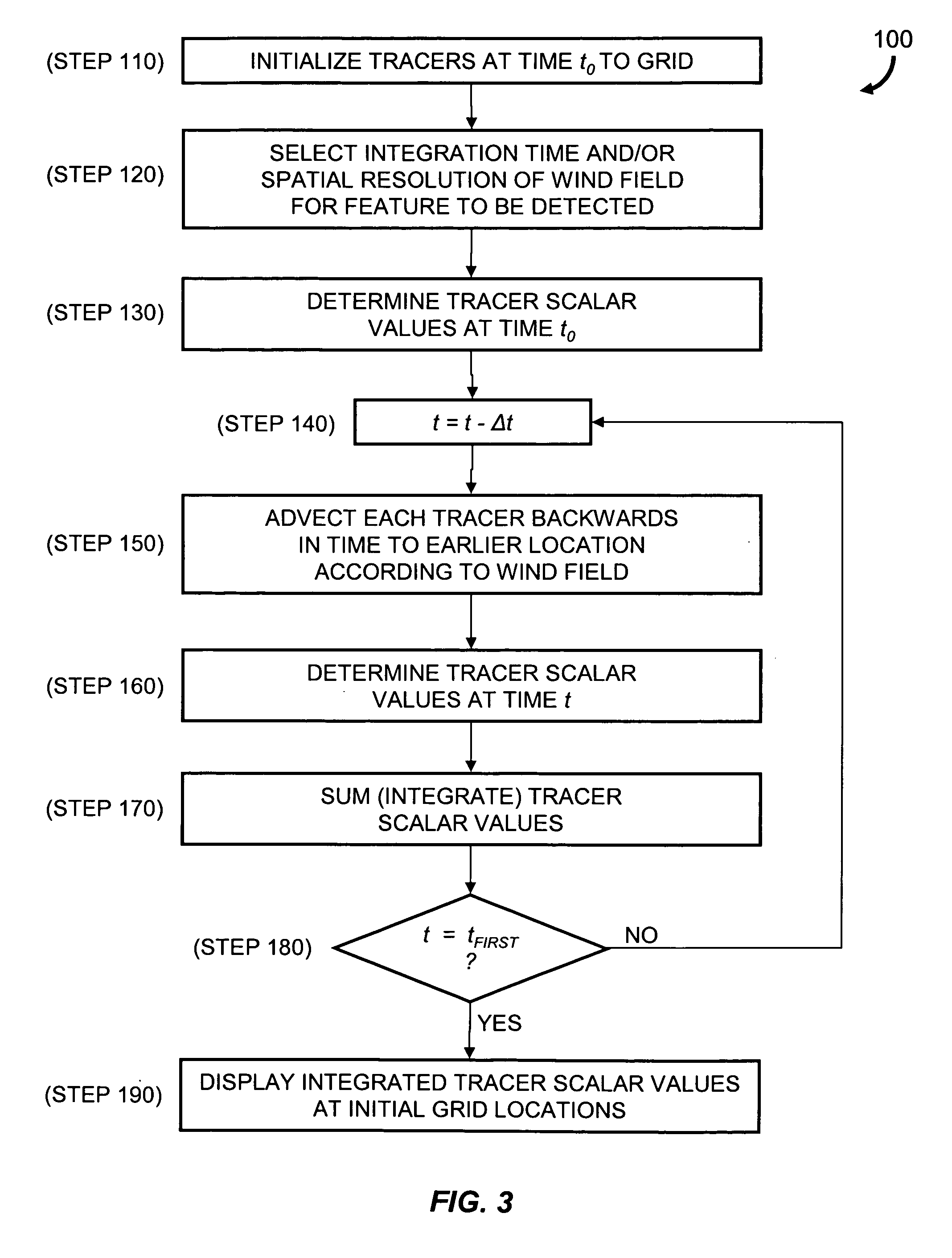
InactiveUS7472021B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear monitoringCharacteristic typeScalar field
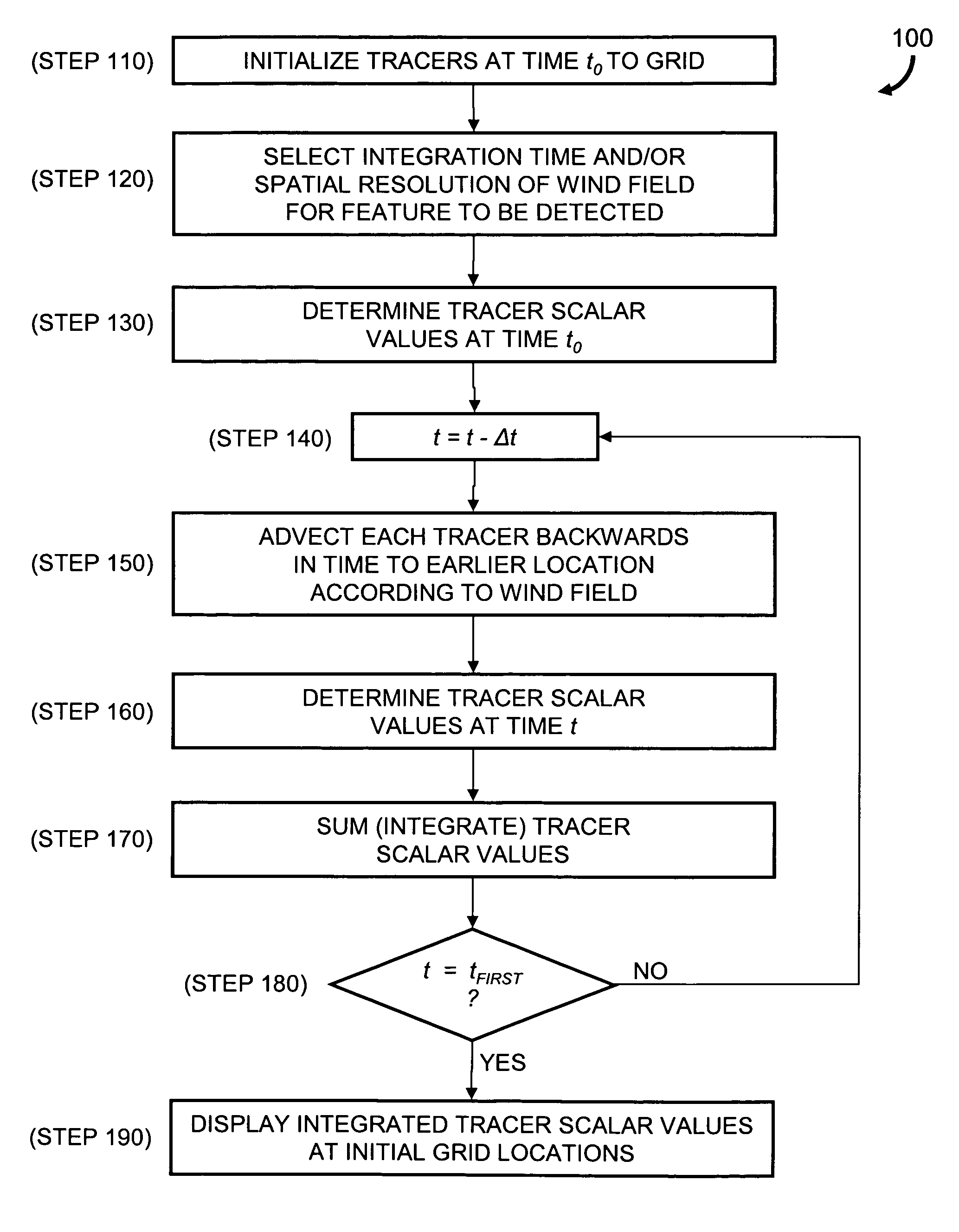
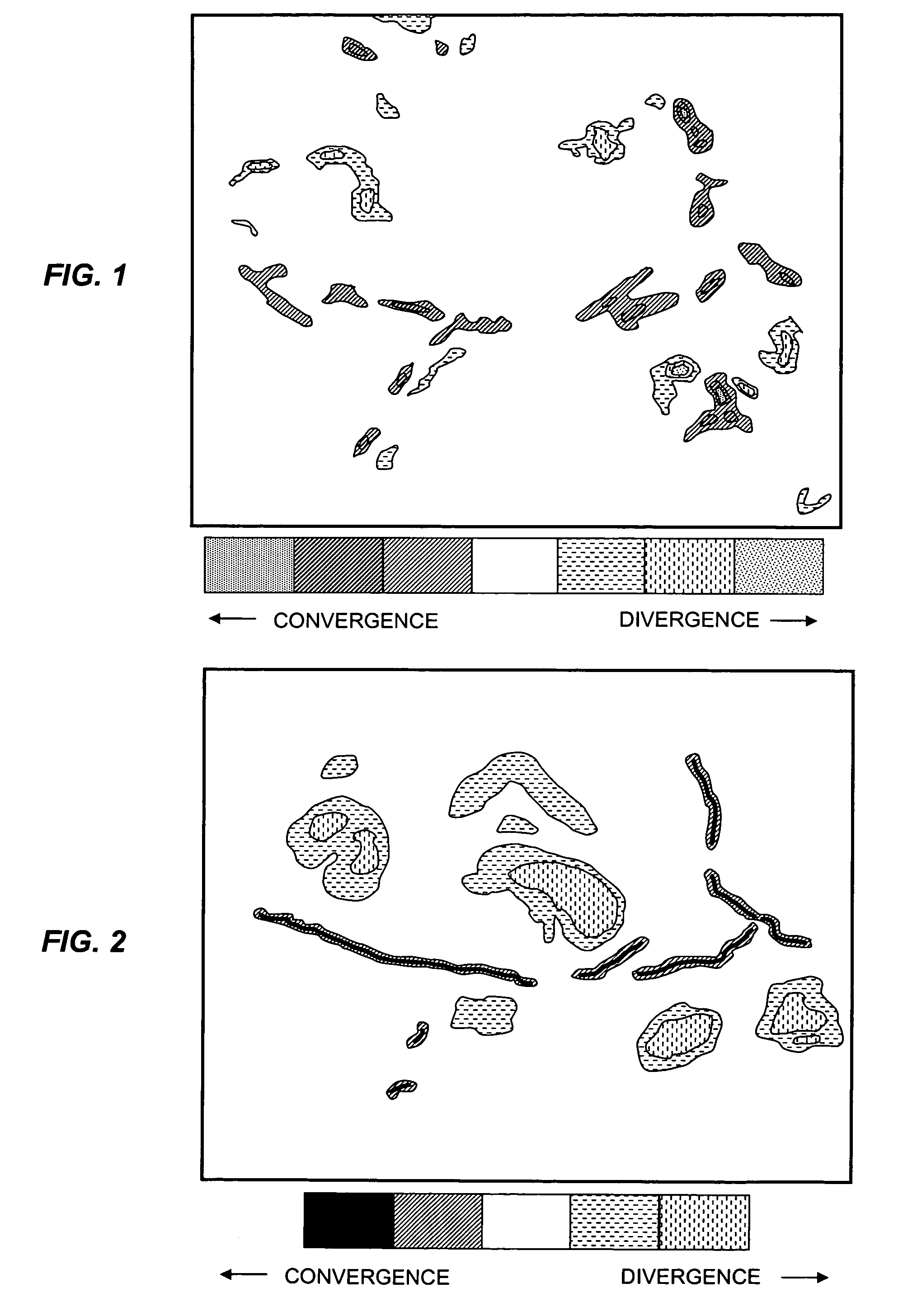
Described are a method and a system for detecting an atmospheric feature. A value of a meteorological scalar field at an initial time is determined for a set of tracers. Each tracer is initialized at a first tracer location. An integration time is selected according to a coherence time of a type of the feature to be detected. Alternatively, or in combination with the selected integration time, a spatial resolution of the wind field is selected according to a spatial scale of the type of feature to be detected. Each tracer is advected to a second tracer location at an earlier time according to the integration time and the wind field. A value of the meteorological scalar field at the earlier time and second tracer location is determined for each tracer and summed with the value at the first location to generate an integrated value of the meteorological scalar field.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
ISO-surface tesselation of a volumetric description
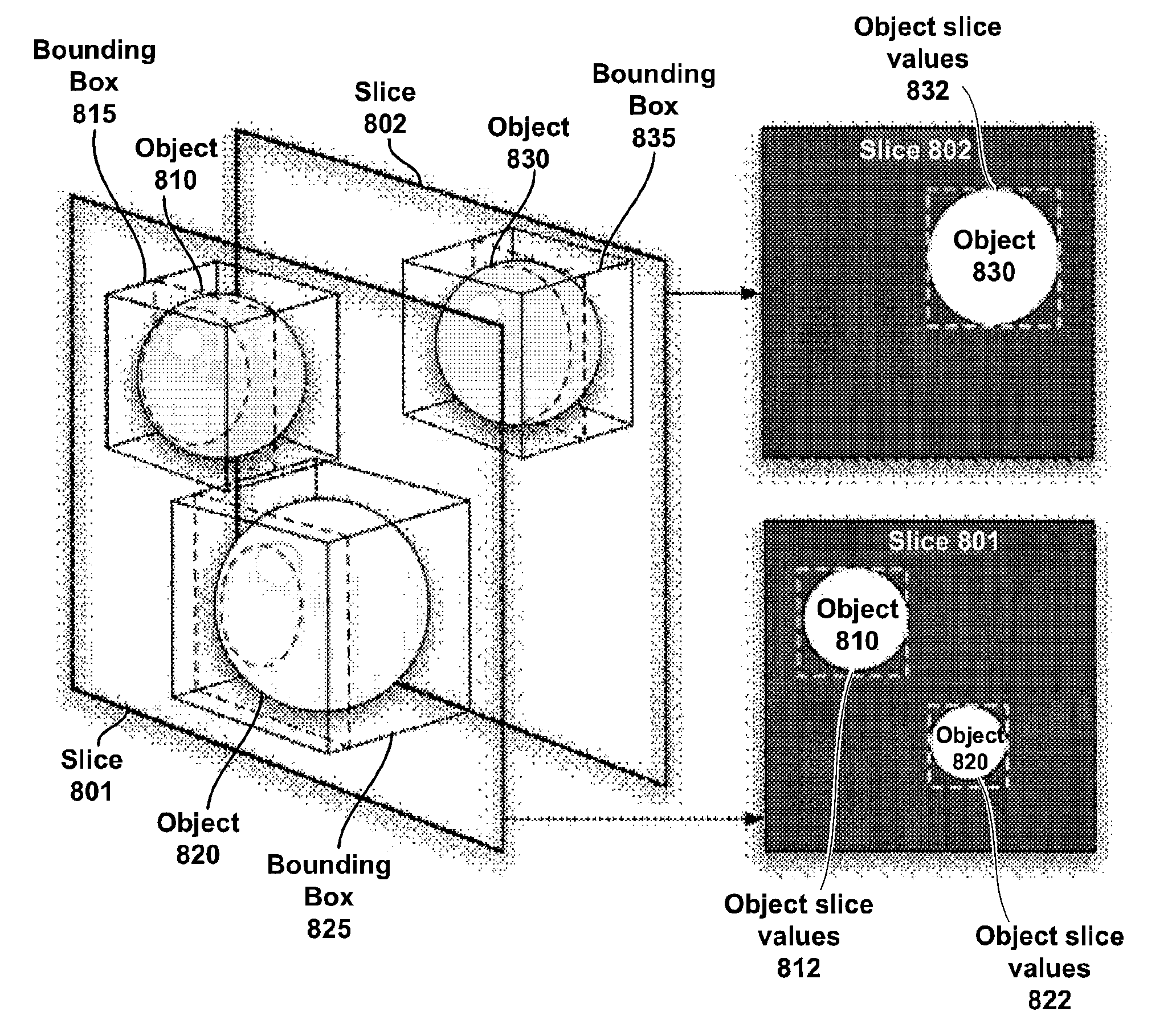
ActiveUS7724254B1Avoid redundant calculationsReduce needCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsScalar fieldRender Target
A multi-threaded graphics processor is configured to generate a tessellated iso-surface from a volumetric description using slices of values that are stored in render targets. The volumetric description can be a complex mathematic equation, a sum of metaballs, a pre-computed scalar field represented as a 3D volume texture, or a rendered volume. Slices are aligned along an axis and spaced before being intersected with the volume to determine iso-surface intersections for the x, y, and z axes. The intersections are stored in render targets and are processed by a shader program to produce a tessellated iso-surface.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
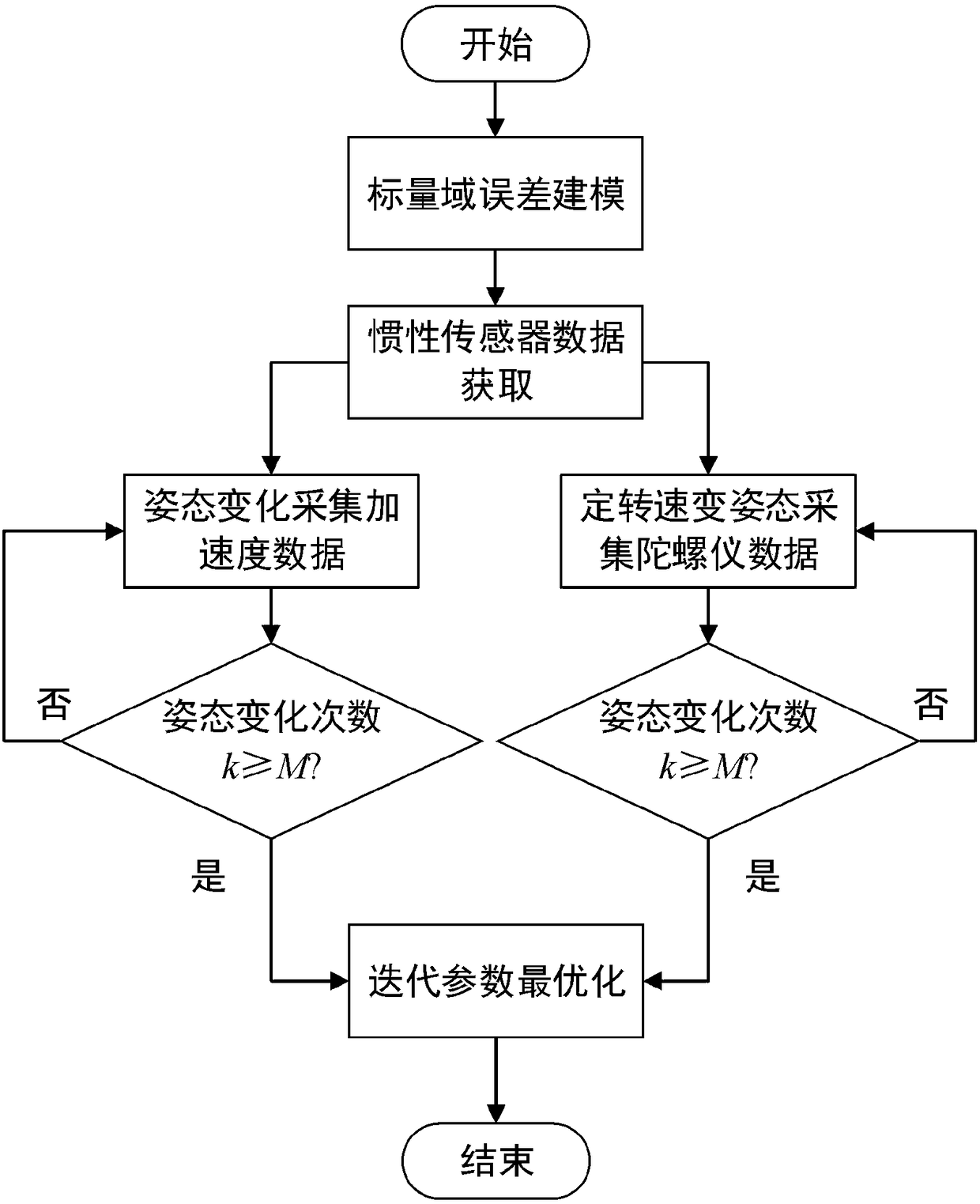
Calibration method of scalar domain MEMS inertial system
The invention relates to a calibration method of a scalar domain MEMS inertial system, and solves the problem of a simplification of an error parameter calibration of a MEMS inertial system. The method mainly comprises the following steps: Step 1, establishing a table to quantify a sensor error model of the MEMS inertial system; Step 2, performing a carrier flipping motion, collecting several position data, and completing effective data acquisition calibrated by a MEMS accelerometer; Step 3, performing a carrier speed motion, changing carrier orientation, and completing date acquisition calibrated by a MEMS gyroscope; Step 4, using an iterative optimization algorithm to realize error parameter estimation; Step 5, if k = M which is the number of calibration posture changes in the scalar field, outputting the estimated error parameter , and completing the calibration process; if k < M, indicating that the calibration process is not completed, repeating the steps 2 to 5 above until the calibration process ends.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
Atmospheric feature detection using Lagrangian scalar integration
InactiveUS20070118290A1Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceNuclear monitoringCharacteristic typeScalar field
Described are a method and a system for detecting an atmospheric feature. A value of a meteorological scalar field at an initial time is determined for a set of tracers. Each tracer is initialized at a first tracer location. An integration time is selected according to a coherence time of a type of the feature to be detected. Alternatively, or in combination with the selected integration time, a spatial resolution of the wind field is selected according to a spatial scale of the type of feature to be detected. Each tracer is advected to a second tracer location at an earlier time according to the integration time and the wind field. A value of the meteorological scalar field at the earlier time and second tracer location is determined for each tracer and summed with the value at the first location to generate an integrated value of the meteorological scalar field.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Algorithm and a method for characterizing surfaces with fractal nature
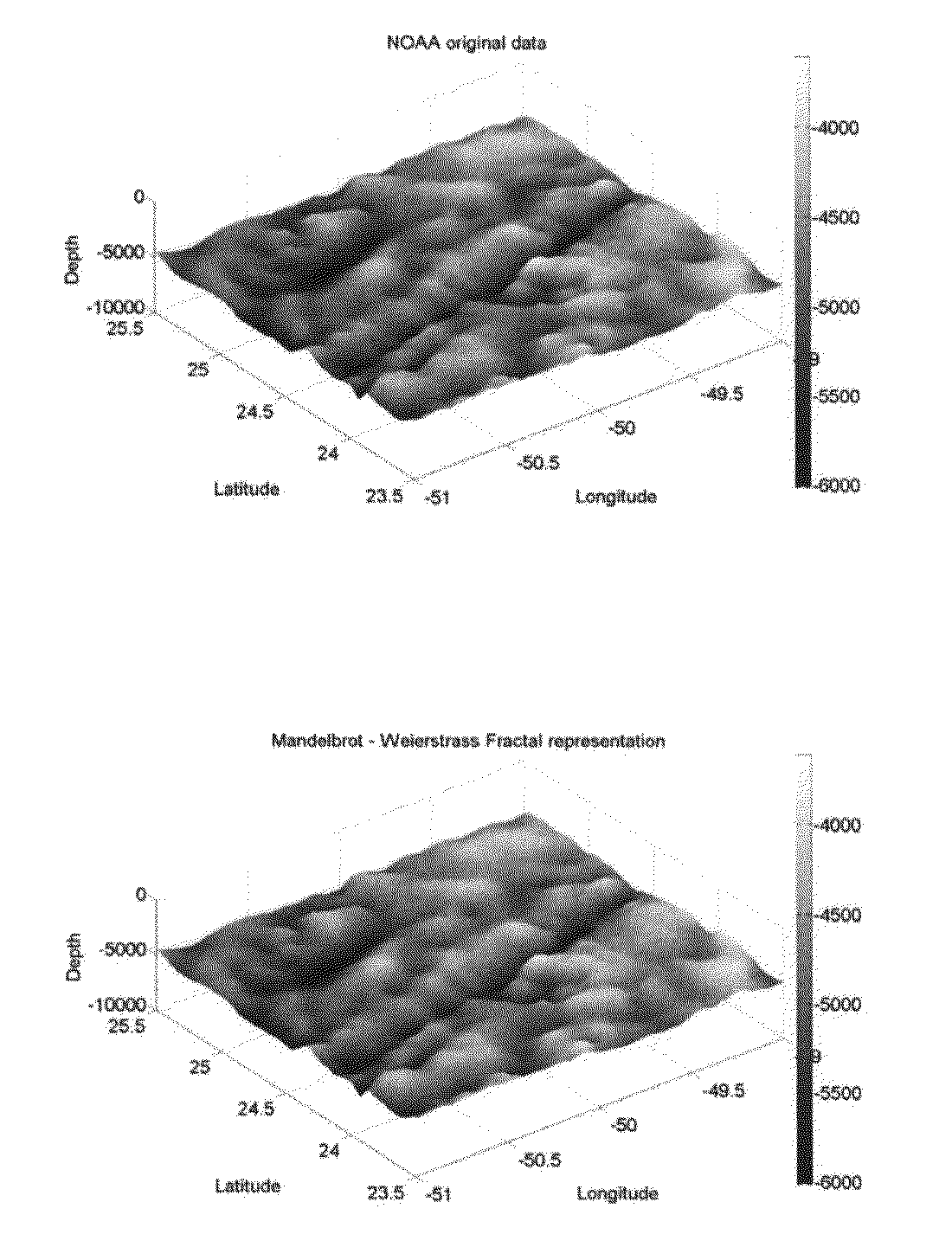
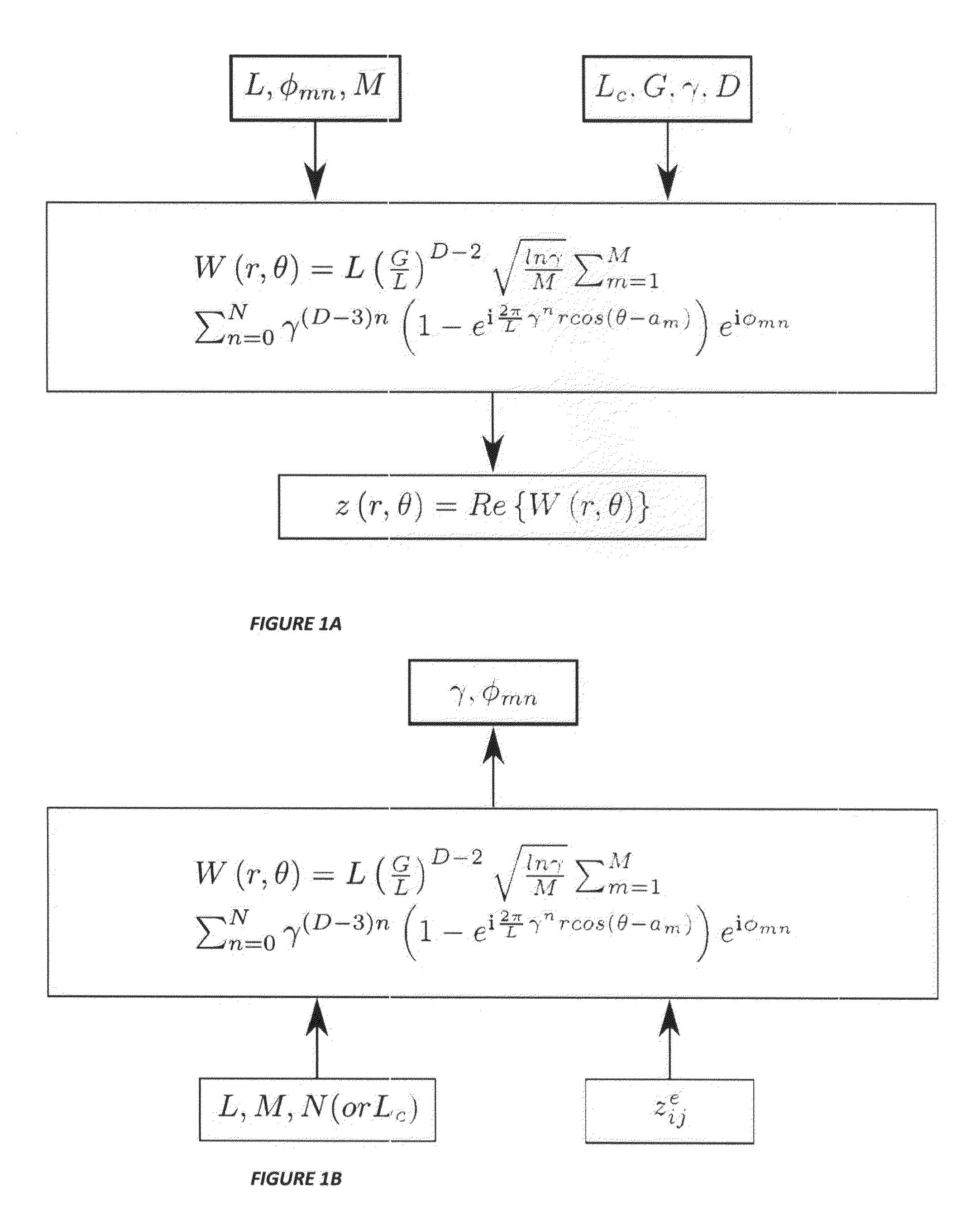
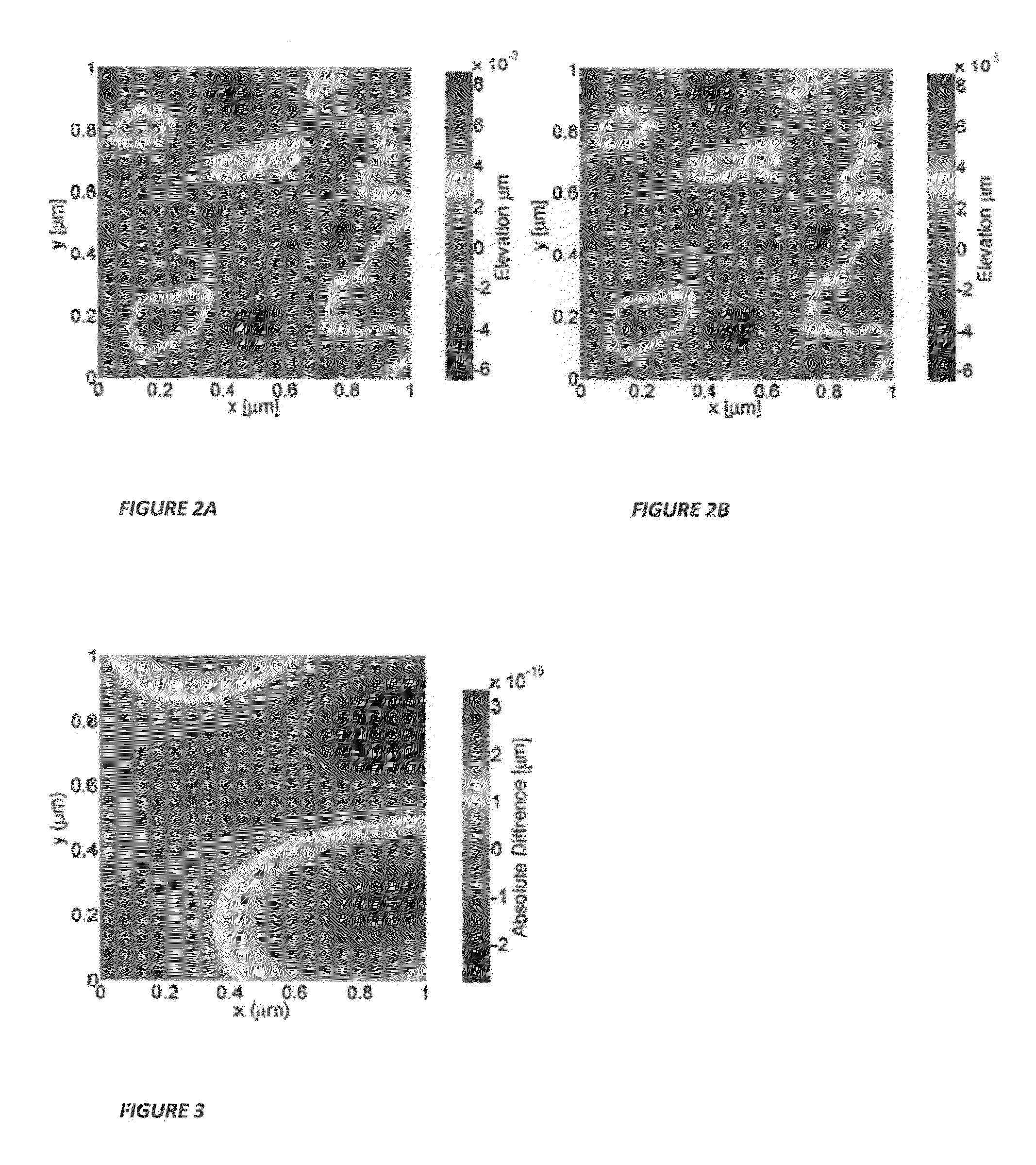
A computer implemented method for directly determining parameters defining a Weierstrass-Mandelbrot (W-M) analytical representation of a rough surface scalar field with fractal character, embedded in a three dimensional space, utilizing pre-existing measured elevation data of a rough surface in the form of a discrete collection of data describing a scalar field at distinct spatial coordinates, is carried out by applying an inverse algorithm to the elevation data to thereby determine the parameters that define the analytical and continuous W-M representation of the rough surface. The invention provides a comprehensive approach for identifying all parameters of the W-M function including the phases and the density of the frequencies that must greater than 1. This enables the infinite-resolution analytical representation of any surface or density array through the W-M fractal function.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
Tooth jaw semi-automatic accurate segmentation algorithm based on a depressed sensing harmonious scalar field
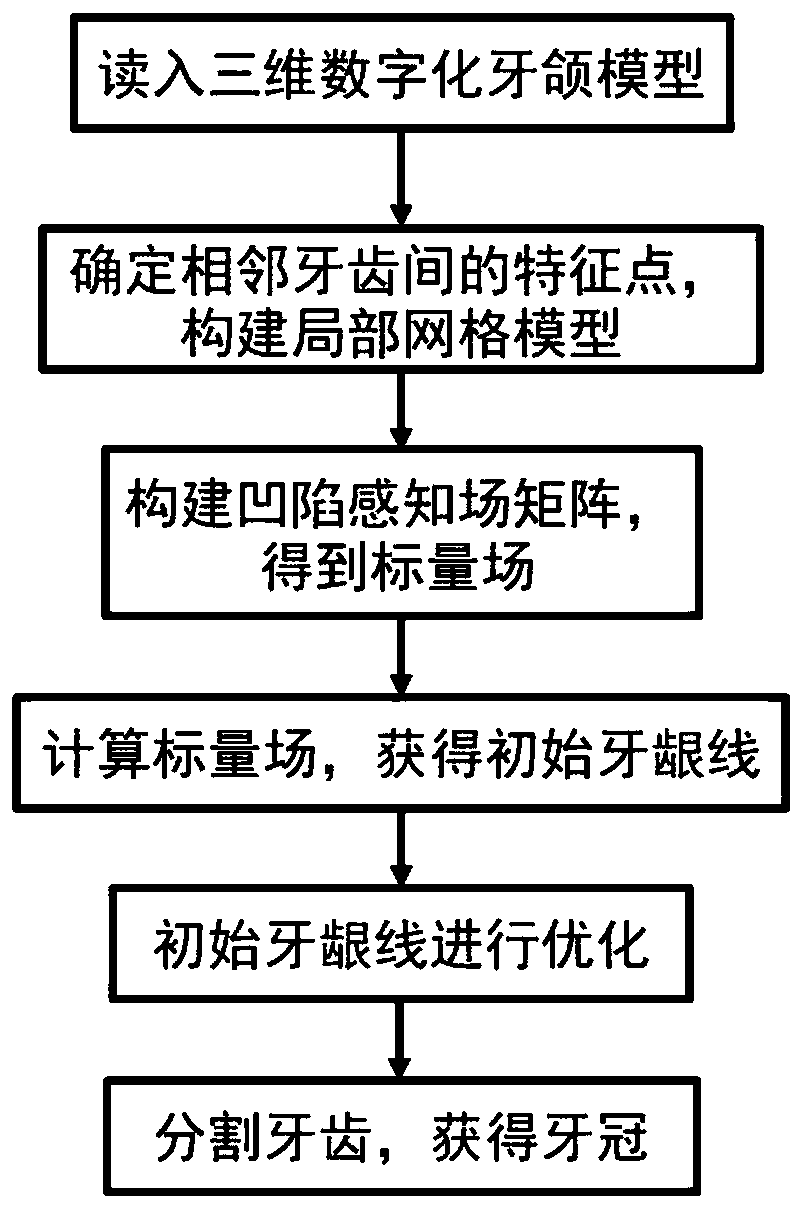
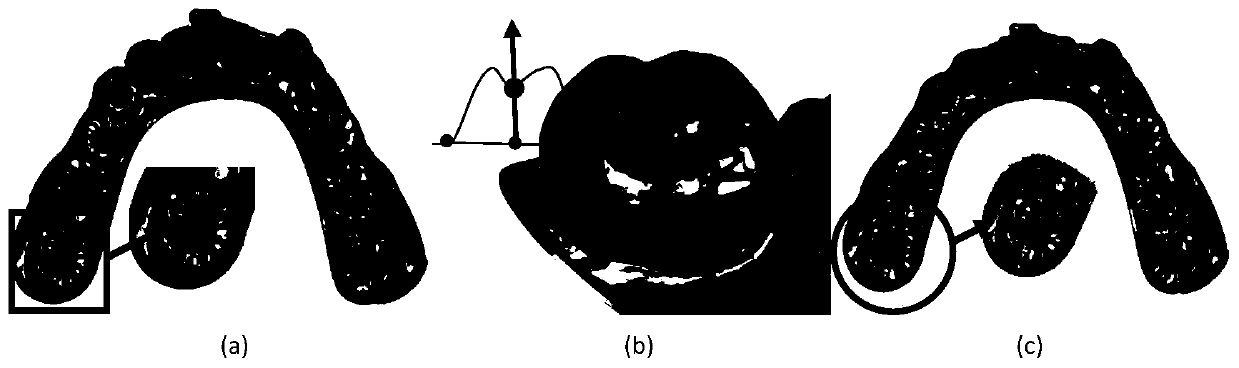
ActiveCN109993751AAccurate extractionReduce interactionImage enhancementImage analysisSplit linesScalar field
The invention discloses a tooth jaw semi-automatic accurate segmentation algorithm based on a depressed sensing harmonious scalar field, and the algorithm mainly comprises the following steps: firstly, manually picking up a point in a slit between every two adjacent teeth, building a local depressed sensing harmonious field matrix through the picked points at the two sides of each tooth, and calculating the harmonious scalar field of a local area of a model; secondly, obtaining a series of contour lines on the local grid, and selecting an optimal contour line as a tooth segmentation line by utilizing a voting mechanism; and finally, optimizing the segmentation lines by using a heuristic feature line extraction algorithm to obtain accurate gingival lines so as to realize accurate segmentation of the teeth. By adopting the algorithm, accurate segmentation of teeth can be realized, subsequent excessive manual interaction is not needed, the automation degree is high, the comprehensive extraction time is short, and the actual requirements can be met.
Owner:CHANGSHU INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
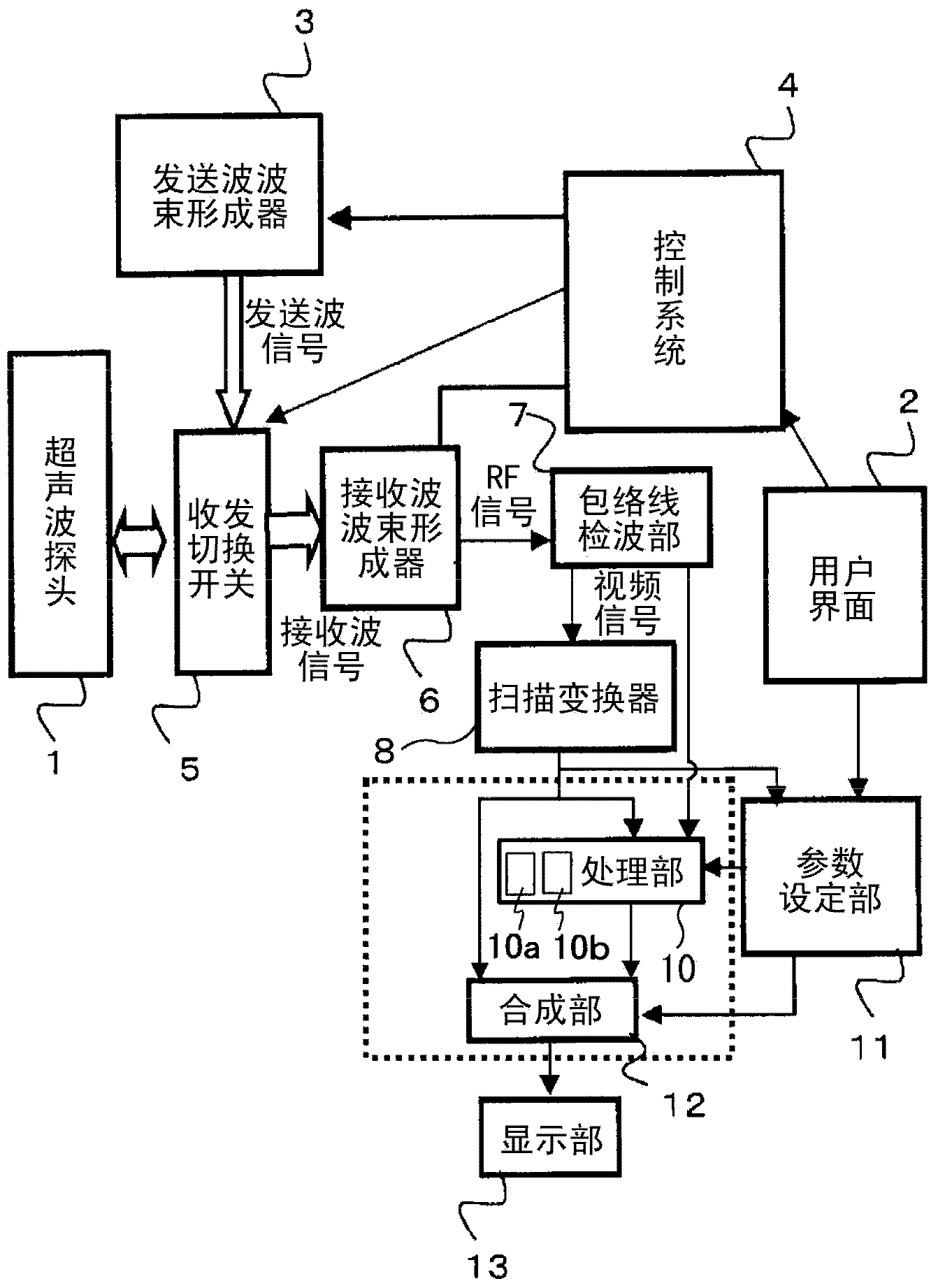
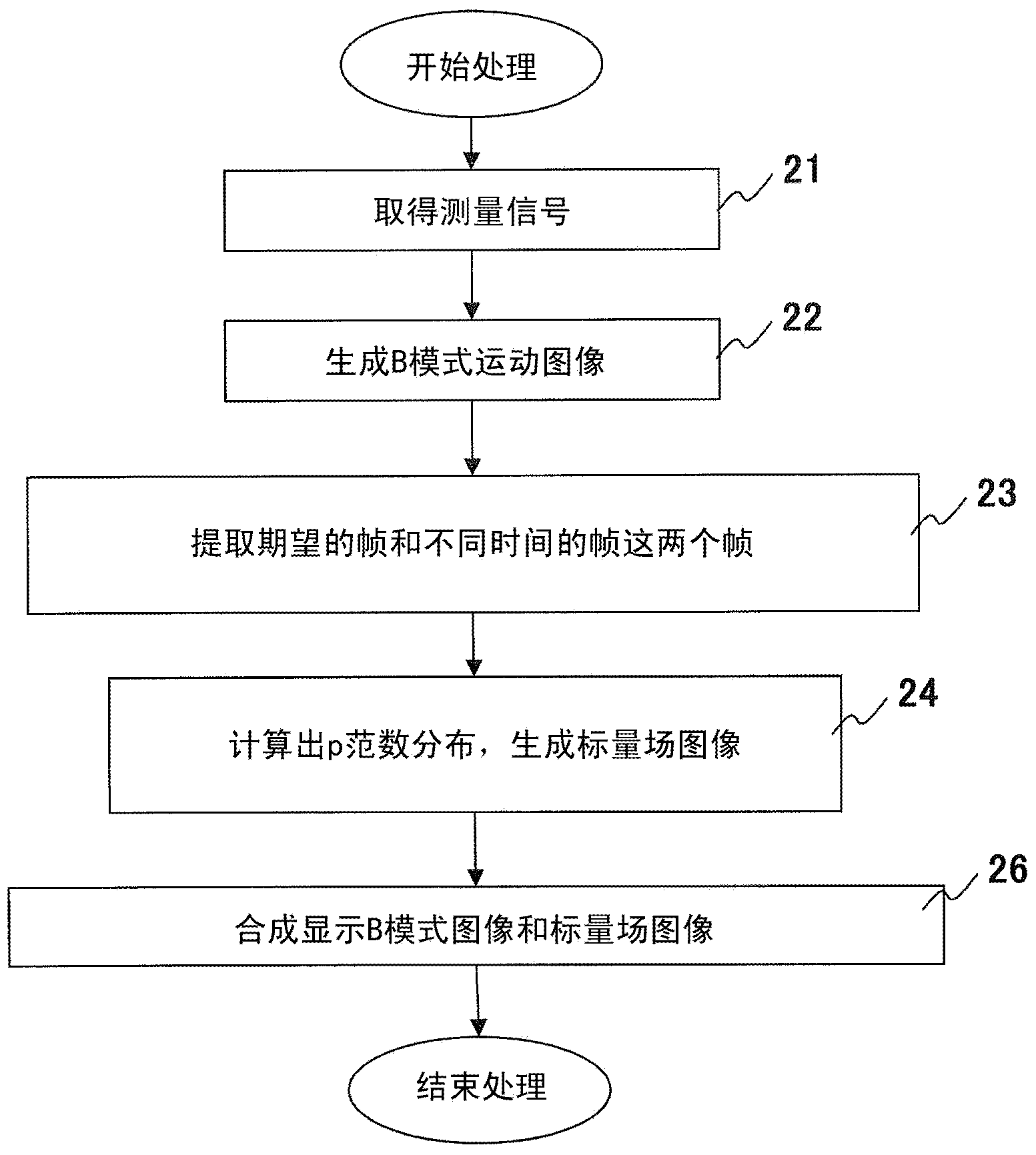
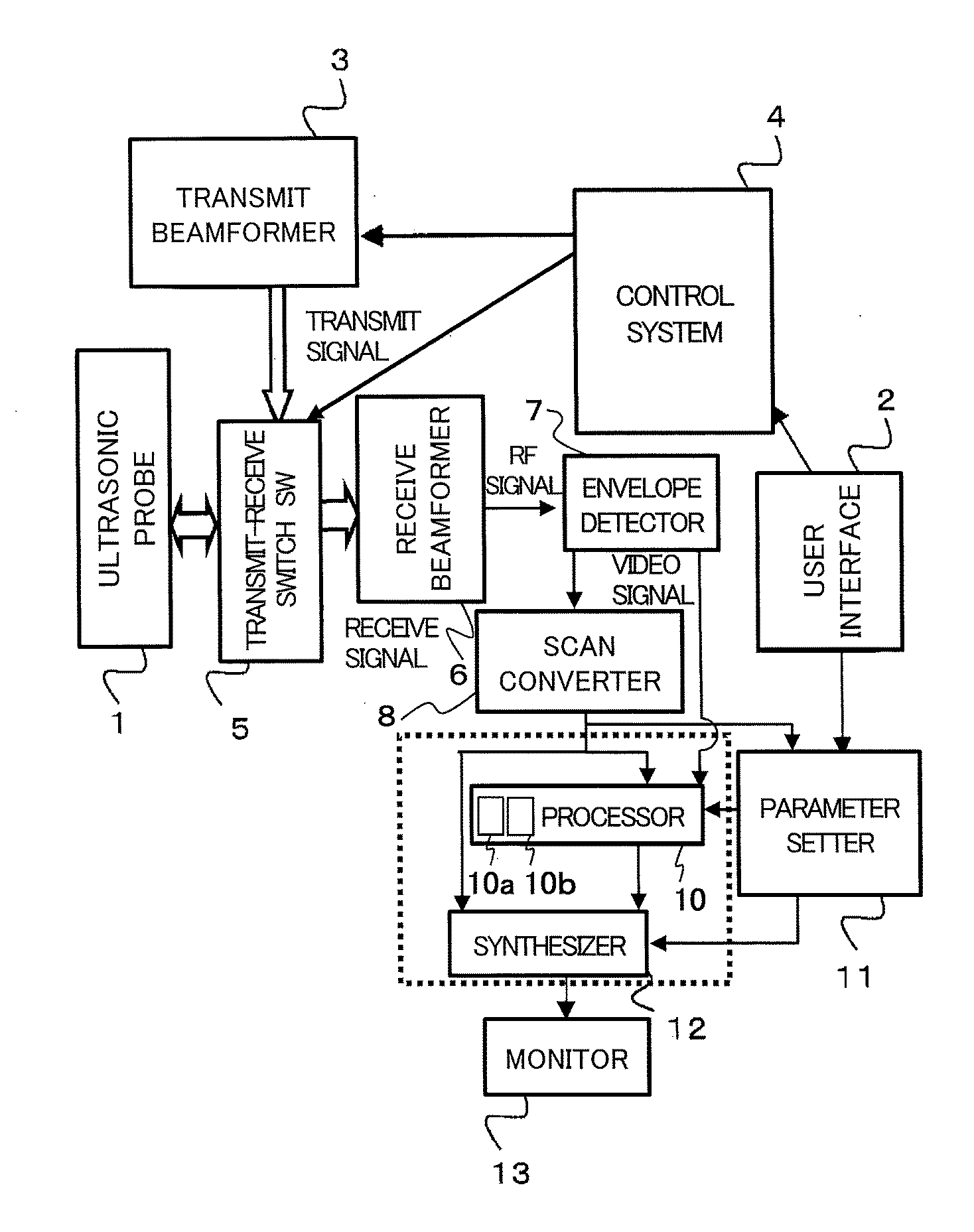
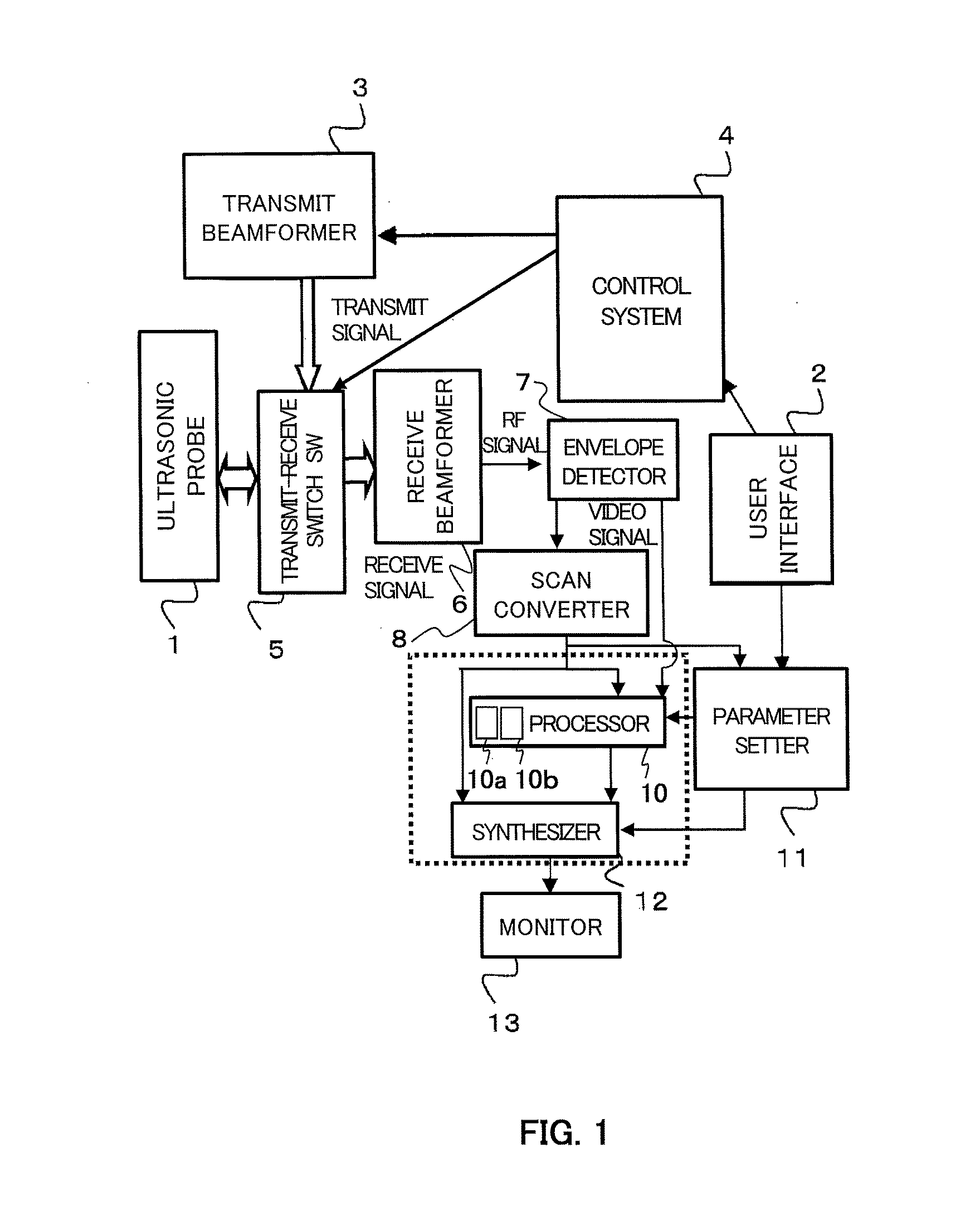
Ultrasound imaging apparatus, ultrasound imaging method and ultrasound imaging program
InactiveCN103906473AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsUltrasound imagingScalar field
Owner:HITACHI LTD
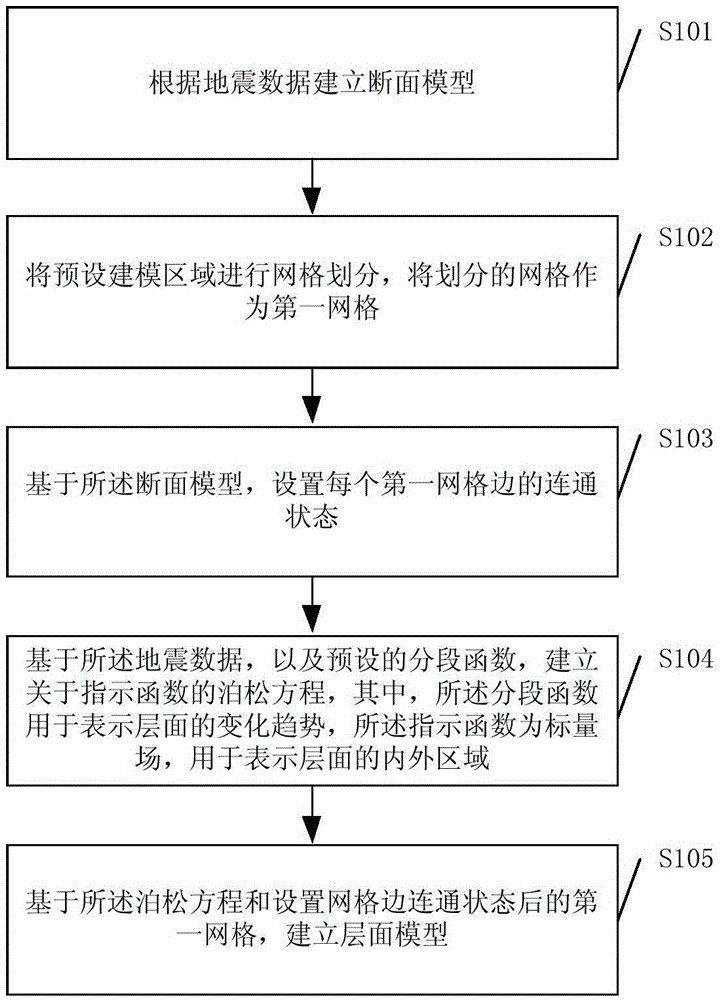
Bedding surface model establishment method
ActiveCN105487116AEfficiently buildImprove adaptabilitySeismic signal processingScalar fieldComputer science
An embodiment of the invention discloses a bedding surface model establishment method. The method comprises: according to seismic data, establishing a sectional model; performing grid division on a preset modeling region, using the divided grids as first grids; based on the sectional model, setting communication state of each first grid edge; based on the seismic data, and a preset piecewise function, establishing a poisson equation relative to an indicator function, wherein the piecewise function is used for representing variation trend of a bedding surface, and the indicator function is a scalar field and used for representing inner and outer regions of the bedding surface; and based on the poisson equation and the first grids whose grid communication states are set, establishing a bedding surface model. The method can be suitable to be used in conditions that normal faults and / or reverse faults exist, and the method can improve establishing efficiency of the bedding surface model.
Owner:BC P INC CHINA NAT PETROLEUM CORP +1
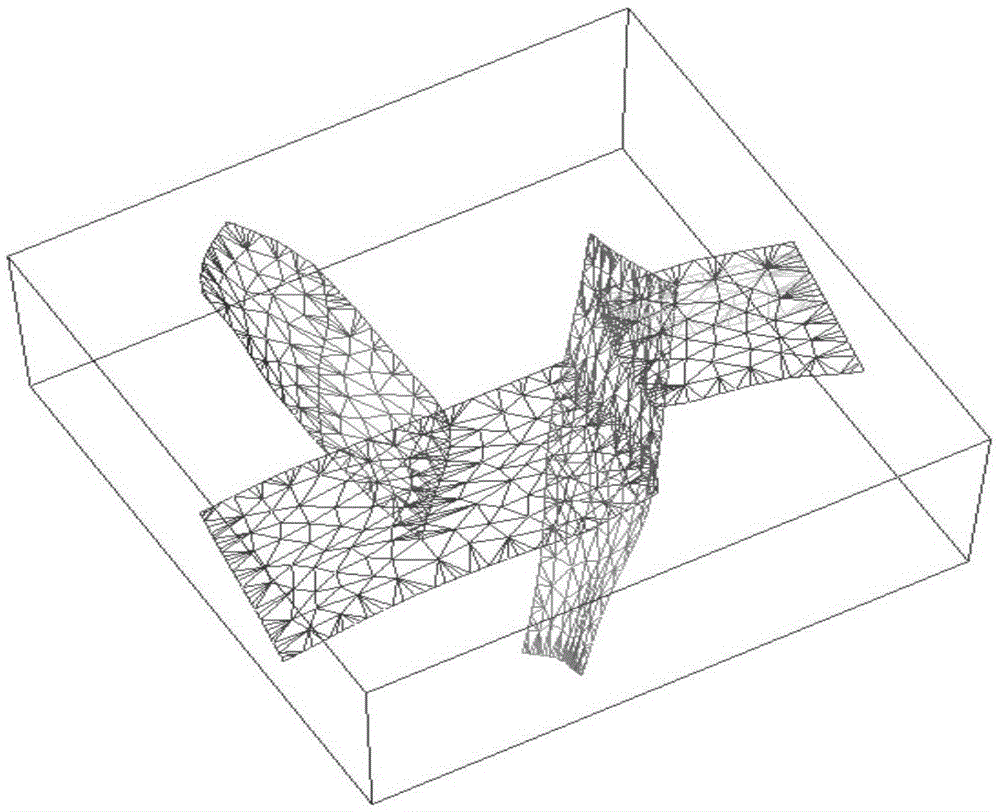
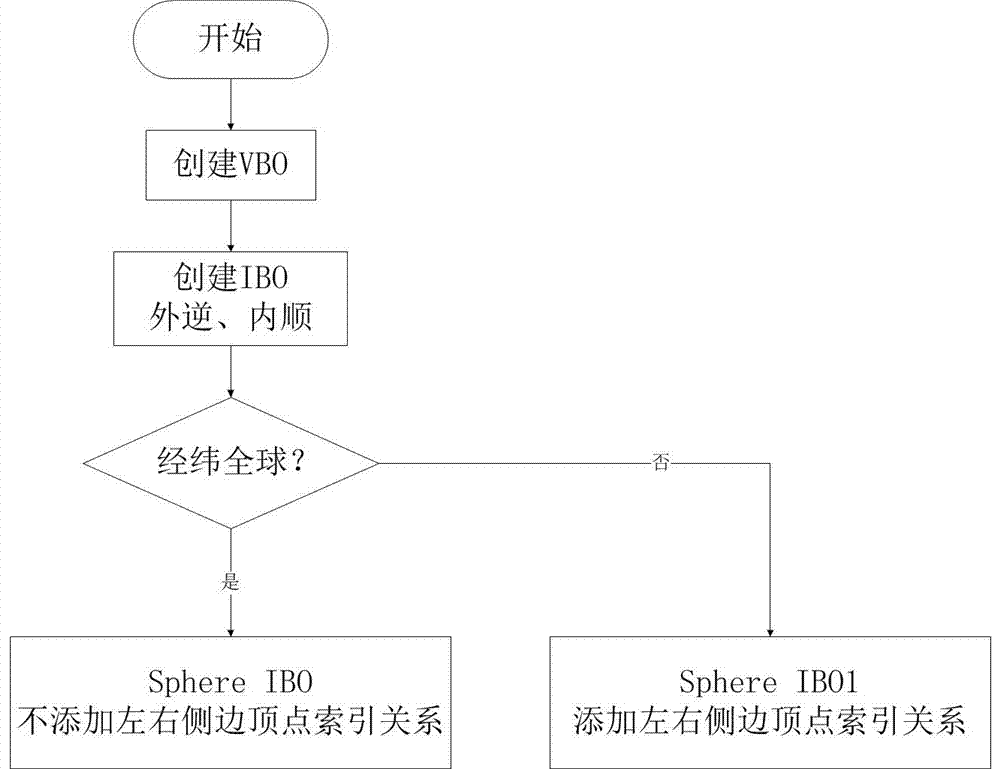
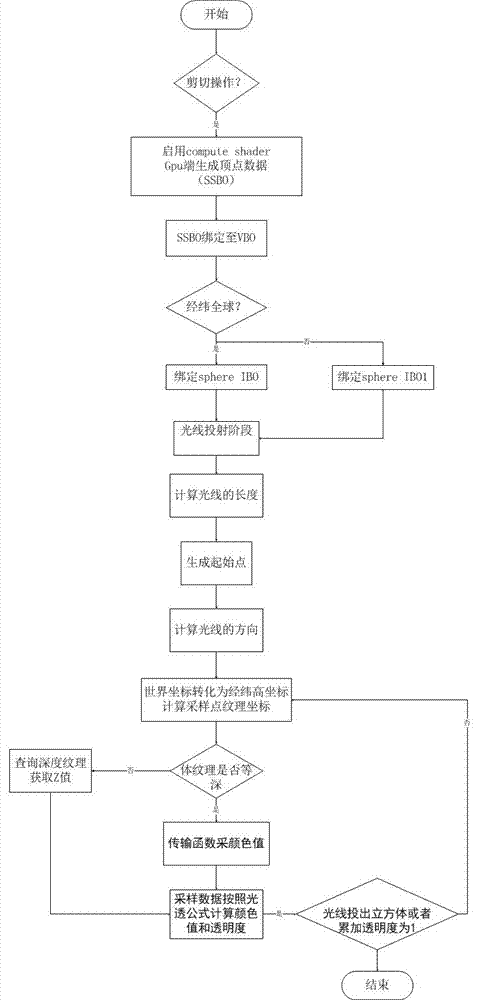
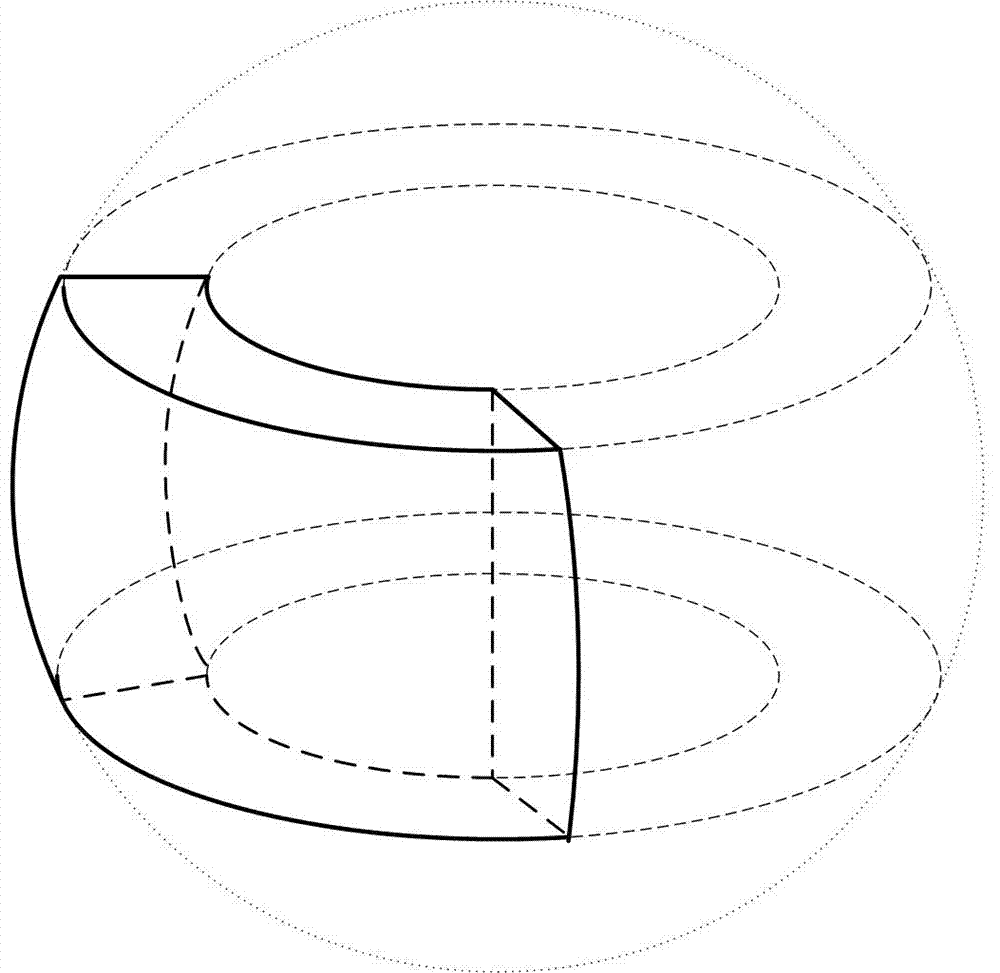
Spherical body drawing method capable of supporting real-time cutting operation
InactiveCN107507264AAccurate samplingAvoid drawing delaysGeographical information databasesSpecial data processing applicationsComputer graphics (images)Scalar field
The invention relates to a marine scalar field body drawing method capable of supporting a real-time cutting operation based on an earth spherical shell model. The method specifically comprises the steps of establishing a spherical shell agent geometric body in global and local cases respectively, and creating two index objects; obtaining data real-time longitude, latitude and depth ranges according to a cutting operation, calculating vertex coordinates in real time by using a calculation shader on a GPU; starting a depth test, and generating a front surface and a rear surface of light projection; and realizing a light projection algorithm based on the earth spherical shell model on the GPU by adopting a shader language GLSL. Coordinate transformation is performed during the process of light projection, a path of light projection is converted from world coordinates into longitude, latitude and depth coordinates. The spherical body drawing method calculates the vertex coordinates in real time at the GPU terminal by using the calculation shader, can support a real-time cutting operation of the marine water data and has a good visualization effect for marine scalar field data with different longitude, latitude and depth ranges.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
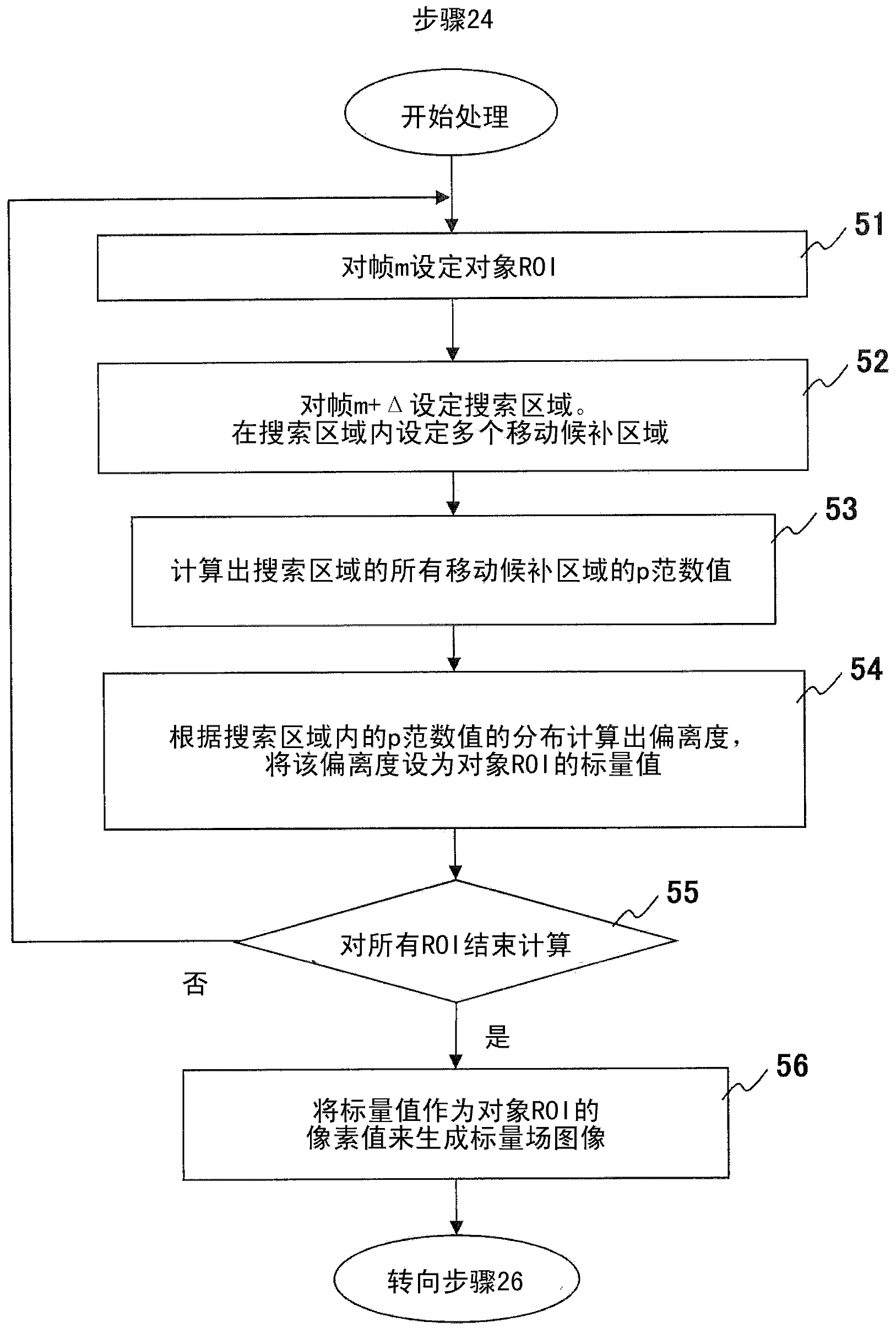
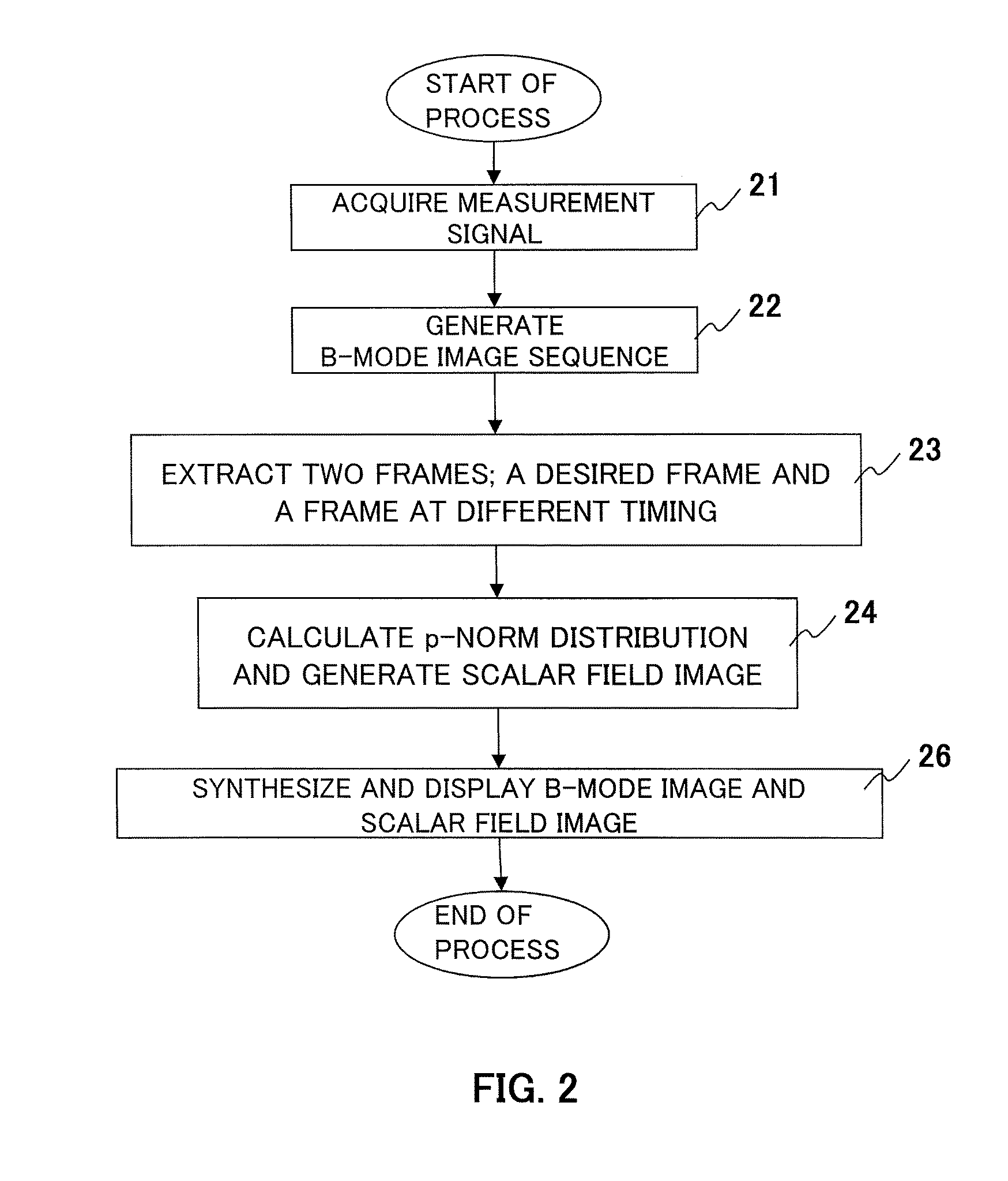
Ultrasound imaging apparatus, ultrasound imaging method and ultrasound imaging program
InactiveUS20160213353A1Wave based measurement systemsHealth-index calculationUltrasound imagingSonification
The present invention is to provide an ultrasound imaging apparatus which generates a scalar field image directly without obtaining a motion vector, so as to make tissue boundaries discernible.A received signal is processed to generate images of two or more frames, two frames are selected from the images, multiple regions of interest are set in one frame, and in the other frame, search regions each wider than the region of interest are set respectively for the multiple regions of interest. In the search region, multiple candidate regions each in a size corresponding to the region of interest are provided. Then, a norm is obtained between a pixel value of the region of interest and a pixel value of the candidate region, for each of the multiple candidate regions, thereby obtaining a norm distribution within the search region. An image is generated assuming a value representing the state of the norm distribution as a pixel value of the region of interest that is associated with the search region.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
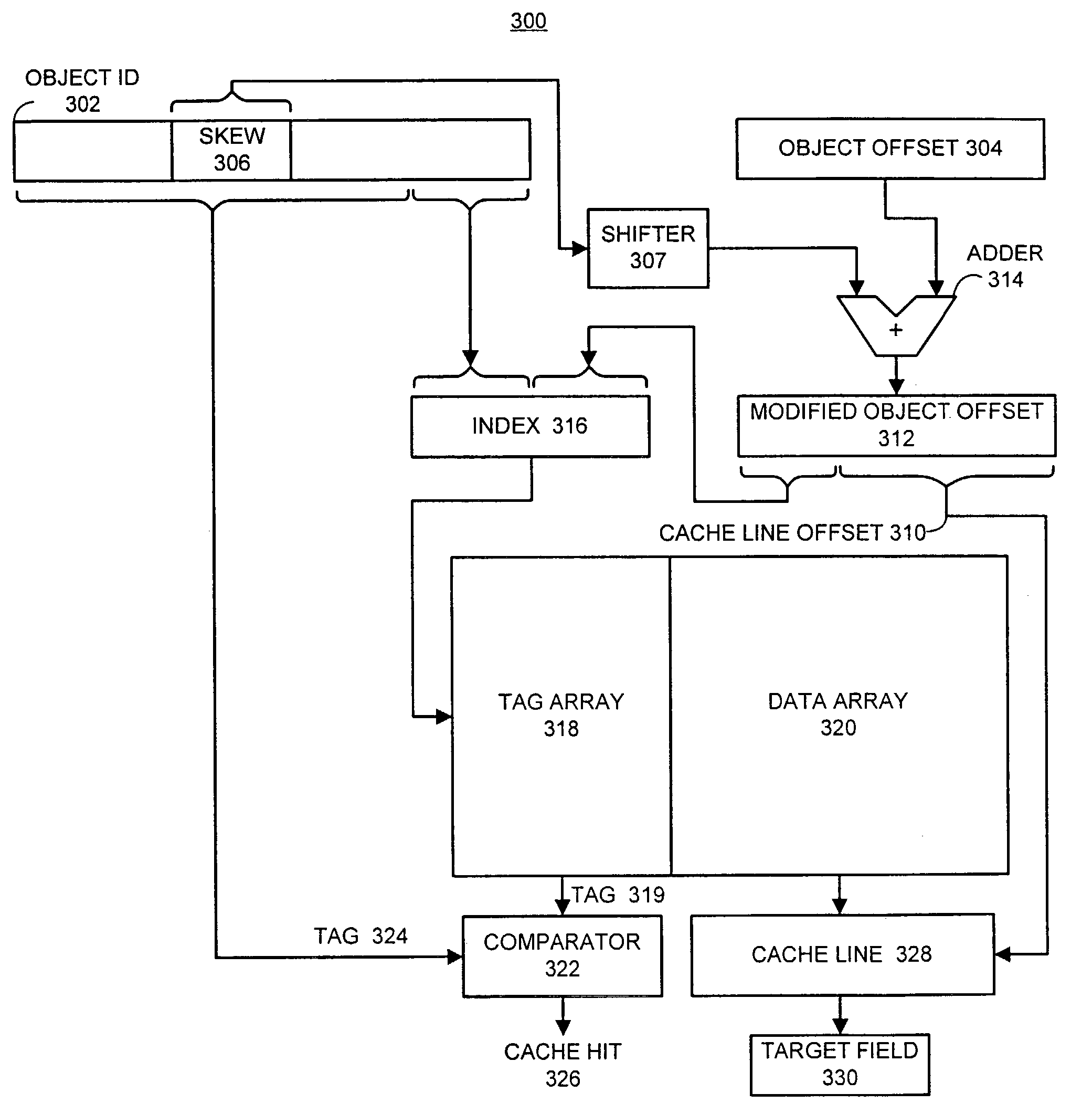
Method and apparatus for skewing a bi-directional object layout to improve cache performance
ActiveUS7246141B2Good cache behaviorFacilitates skewing a bi-directional object layoutData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationReference fieldScalar field
One embodiment of the present invention facilitates skewing a bi-directional object layout to provide good cache behavior. During operation, the system receives a request to access an object. This request includes an object identifier and an object offset that specifies the offset of a target field within the object, wherein the object has a bi-directional layout that locates scalar fields at positive offsets and reference fields at negative offsets, so that a reference field can be immediately identified from its object offset. Next, the system determines a skew value for a cache line containing the object, wherein data within the cache line is shifted based upon the skew value, so that reference fields with small negative offsets are likely to be located in the same cache line as scalar fields with small positive offsets. Next, the system uses the skew value in accessing the object.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
An optimization method for radiation energy light spot analysis model parameters
ActiveCN109697315AHigh precisionQuick calculationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsLight spotModel parameters
The invention discloses an optimization method for radiation energy light spot analysis model parameters. The optimization method comprises the following steps: (1) establishing a virtual radiation energy density scalar field on a heliostat; (2) projecting the radiation energy on a receiving surface through oblique parallel projection to obtain a final radiation energy distribution result; (3) obtaining a virtual radiation energy density distribution function on a heliostat coordinate system; (4) setting a global measurement index root-mean-square error; (5) optimizing the parameter s by adopting a weighted objective function; (6) minimizing the indexes in the steps (4) and (5) within a preset requirement, and solving to obtain the value of the optimized parameter s. Compared with an existing analysis method, the method is higher in precision and can be used for quickly calculating, and the problems that an analysis model for simulating radiation energy density light spots reflected bya heliostat is low in precision simulation precision and parameters are difficult to determine in the past are solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Variable resolution model based image segmentation
InactiveCN101479763AGuaranteed smoothnessReduce computing costImage enhancementImage analysisData setCoarse mesh
The invention relates to system (100) for segmenting an image dataset based on a deformable model for modeling an object in the image dataset, utilizing a coarse mesh for adapting to the image dataset and a fine mesh for extracting detailed information from the image dataset, the system comprising an initialization unit (110) for initializing the coarse mesh in an image dataset space, a construction unit (120) for constructing the fine mesh in the image dataset space based on the initialized coarse mesh, a computation unit (130) for computing an internal force field on the coarse mesh and an external force field on the coarse mesh, wherein the external force is computed based on the constructed fine mesh and the scalar field of intensities, and an adaptation unit (140) for adapting the coarse mesh to the object in the image dataset, using the computed internal force field and the computed external force field, thereby segmenting the image dataset. Since only the coarse mesh is adapted to the image dataset, keeping the modeled object surface smooth does not require a smoothing of the surface over large neighboring areas, and therefore the adaptation of the coarse mesh is much faster than the adaptation of the fine mesh. Advantageously, the proposed technique can be easily integrated into existing frameworks of model-based image segmentation.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Dynamic layering rendering expression method of two-dimensional scalar field on electronic map
InactiveCN102938230AIngenious ideaImprove processing efficiencyMaps/plans/chartsSurface layerScalar field
The invention relates to a dynamic layering rendering expression method of a two-dimensional scalar field on an electronic map. Aiming at a boundary polygon collection with complicated space nested relationship, a thought that a hollow ring is formed by double boundaries is used, and a vector plane extracting method is provided according to parity judgment nested relationship containing polygon. The method can complete extraction of a layering vector plane of field data (raster data) rapidly at one time and returns the layering vector plane to a foreground program of the electronic map so as to perform rendering of surface layers at different regions. Compared with a traditional method, the method is rapid in computation speed, can extract all vector planes at different regions in the field data at one time, and solves the problem that a traditional electronic map or a Web geographic information system (GIS) is poor in timeliness and dynamics caused by large data volume and slow layering conversion in rendering of grid data. When the dynamic layering rendering expression method is used for superimposed display with other map layers, transparent or semitransparent coloring effect can be shown well.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com