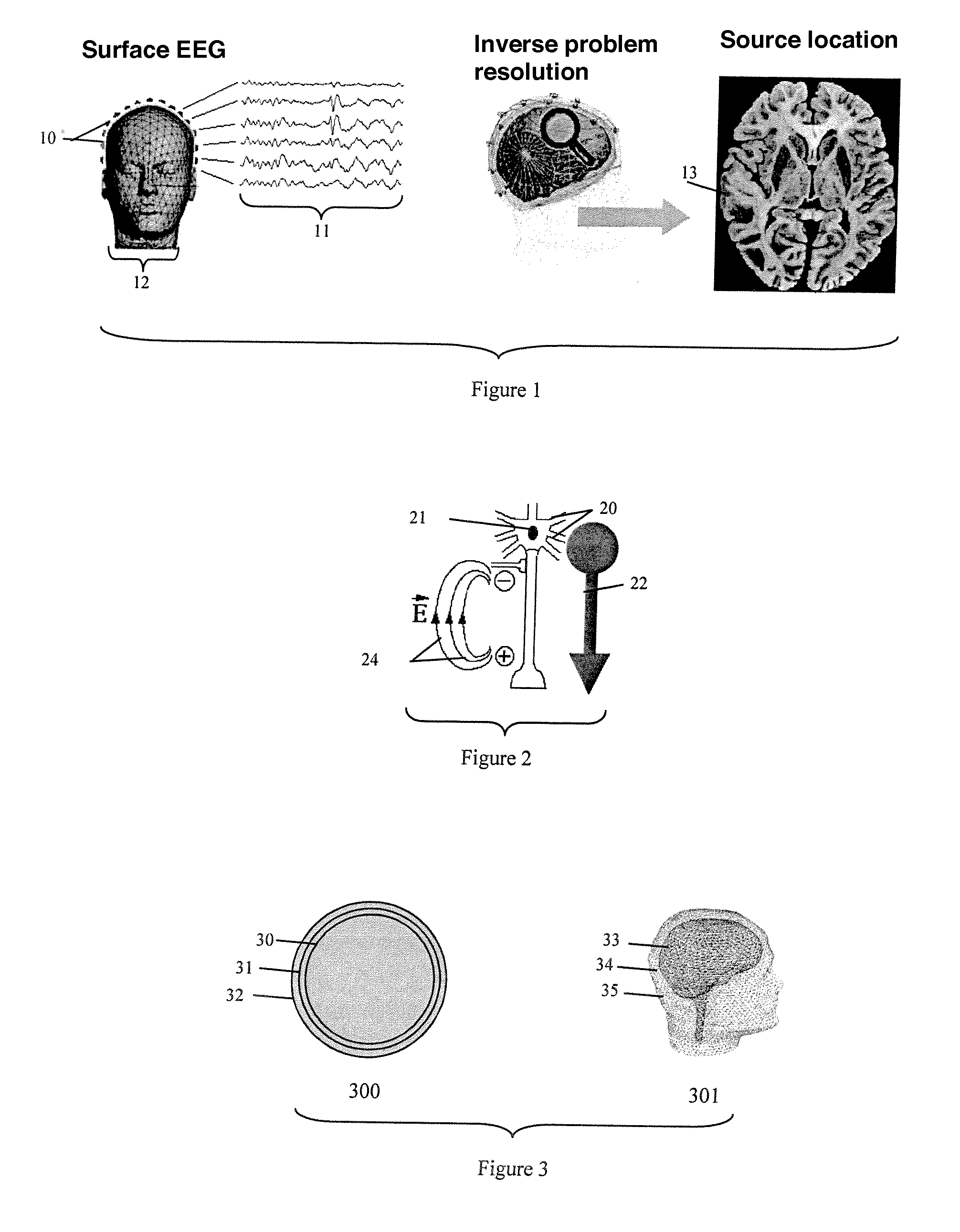
Patents
Literature
45 results about "Magnetoencephalography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
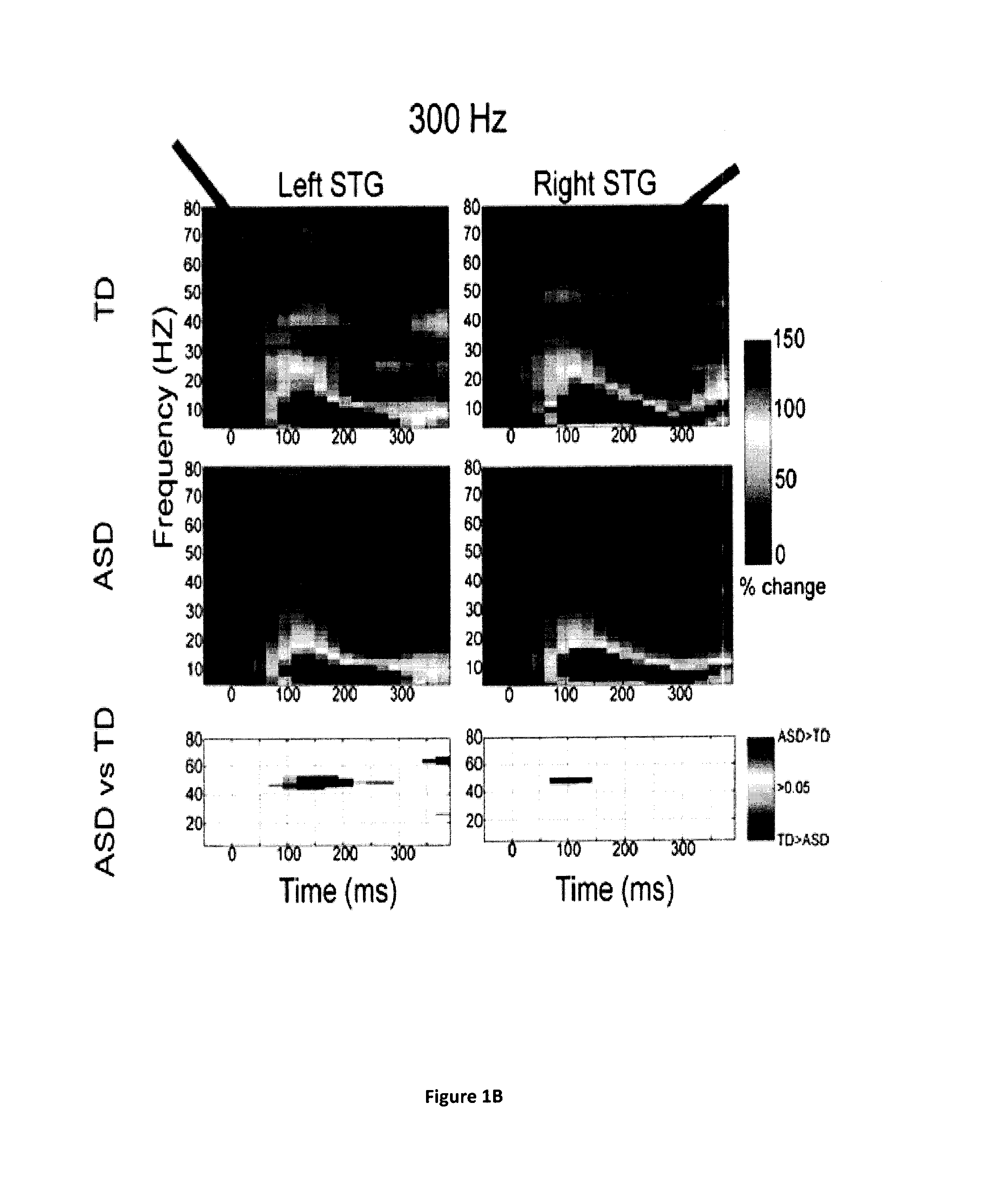
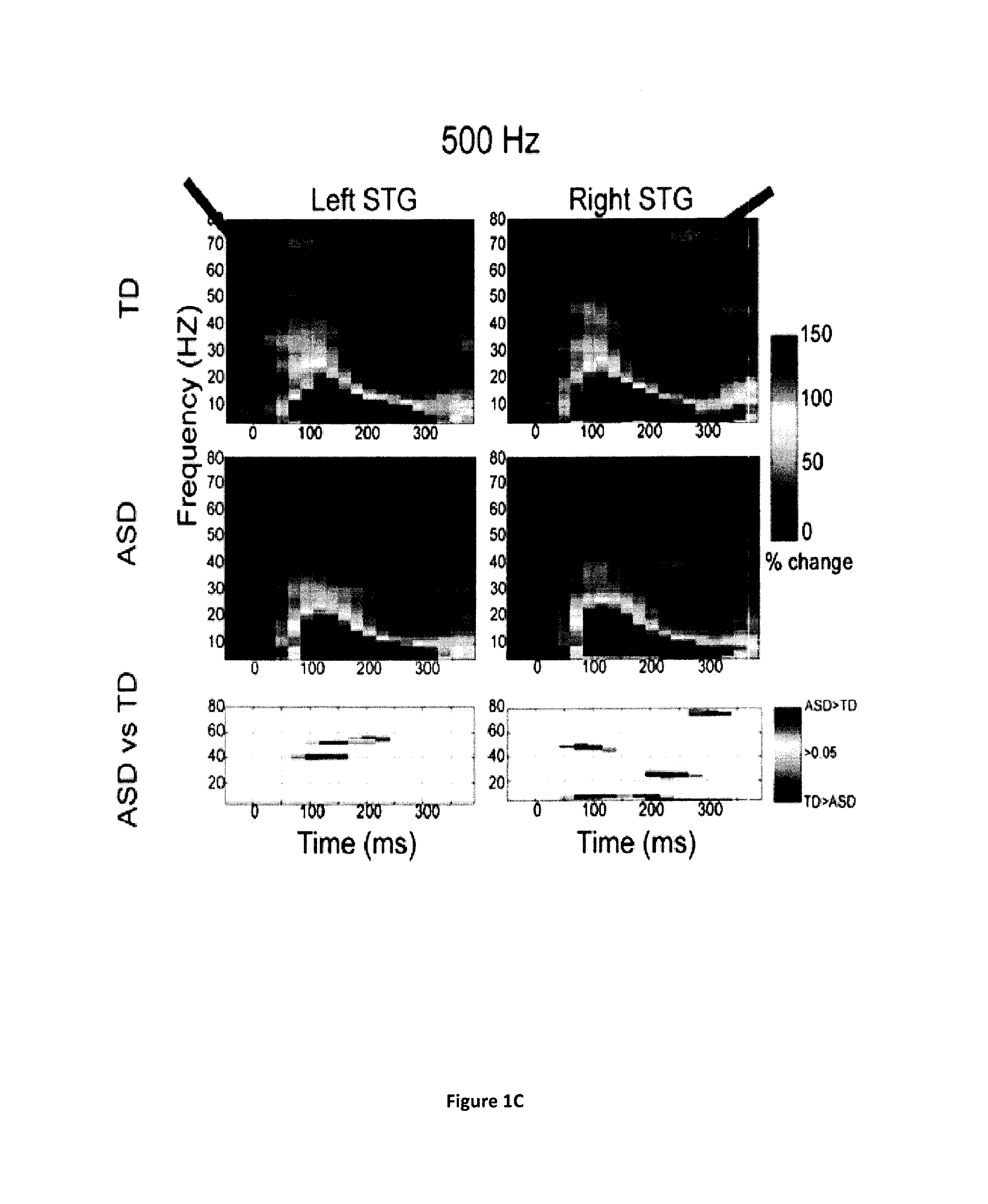
<ul><li>Normal results are shown by the map of neuronal activities created by MEG and MRI that show no irregularities in the electrical signals.</li><li>Abnormal signals may infer the reason for seizures and give an indication on whether a surgery is required.</li></ul>
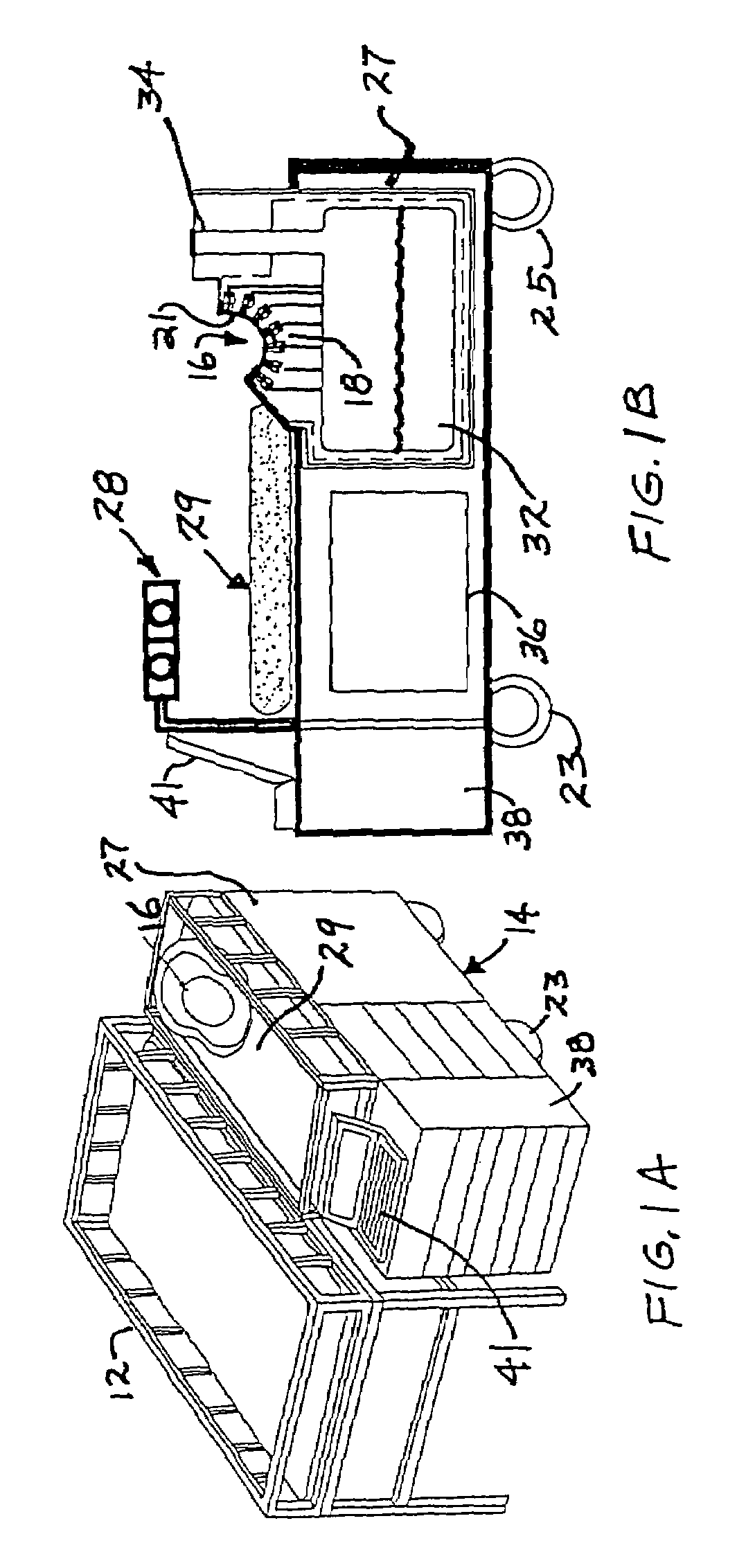
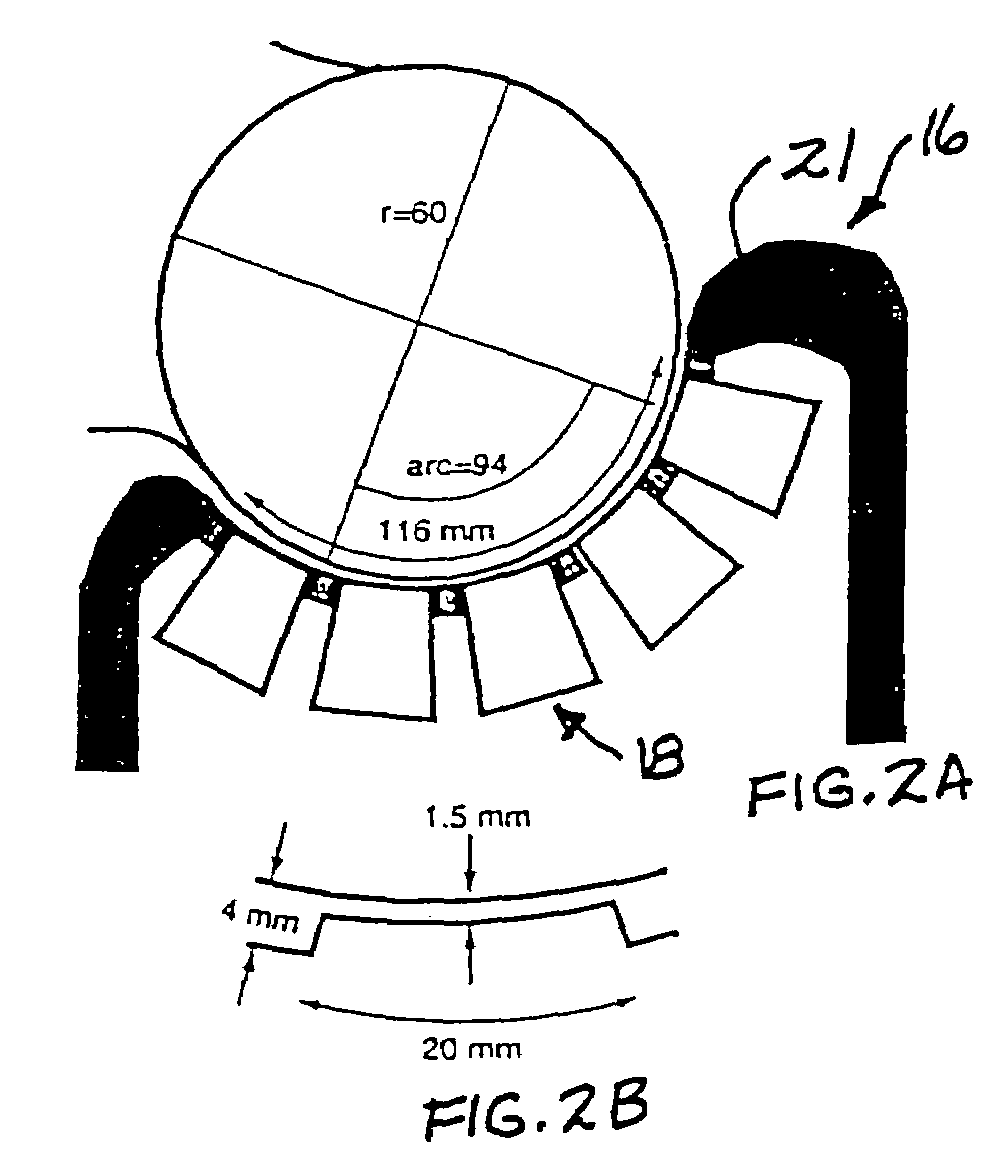
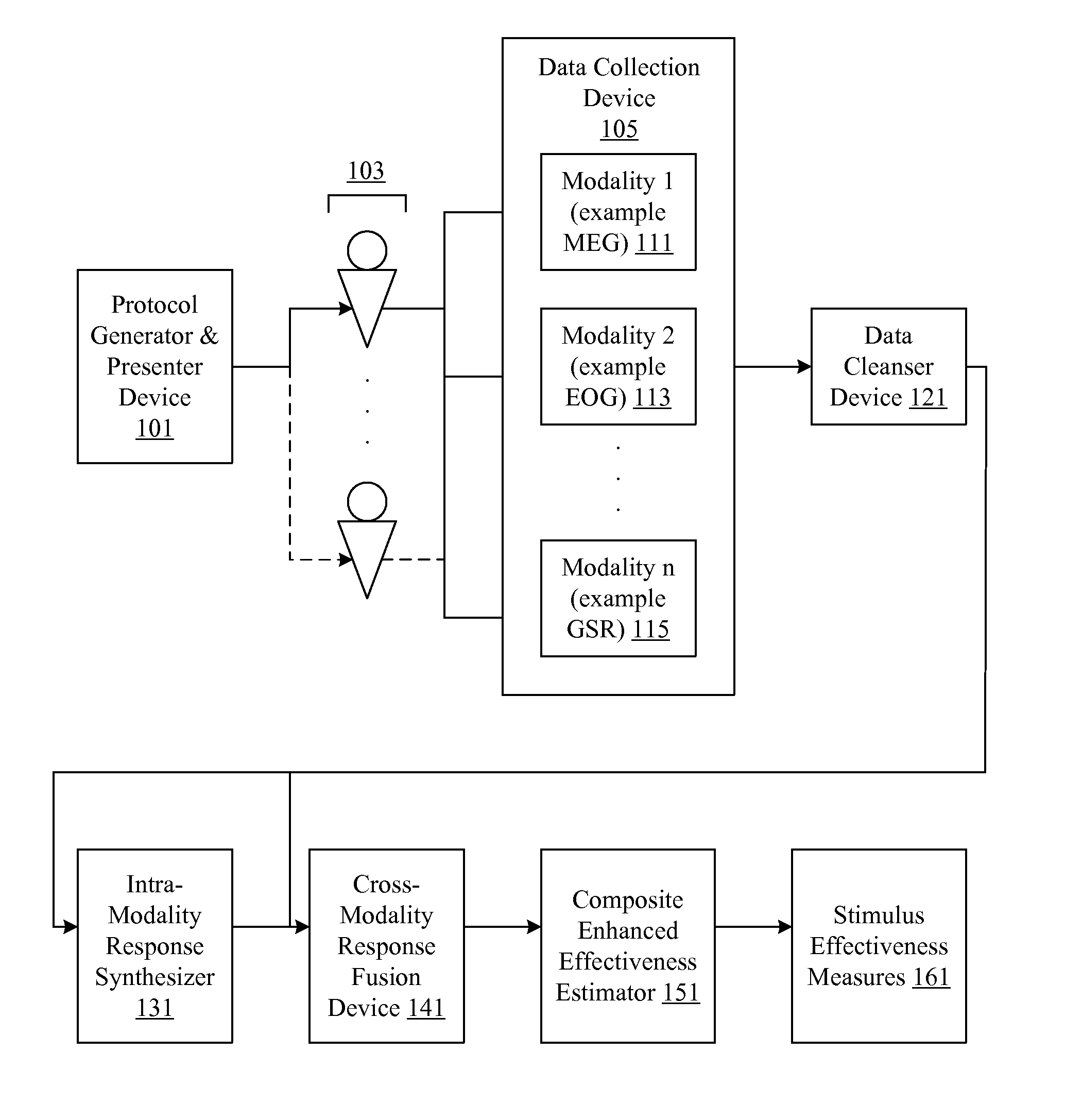
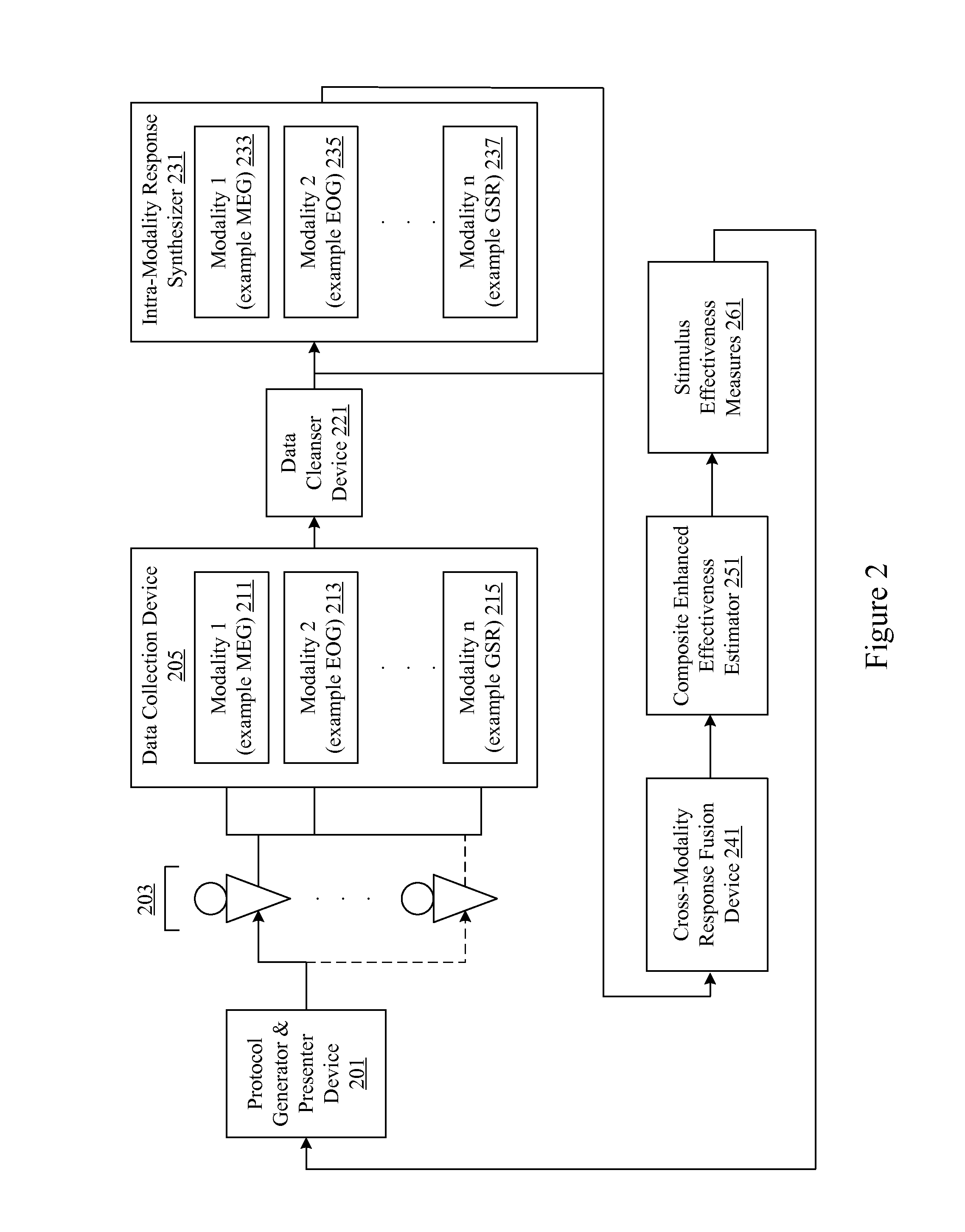
Analysis of marketing and entertainment effectiveness using magnetoencephalography
ActiveUS20090082643A1Analogue secracy/subscription systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringDiagnostic Radiology ModalityCross modality
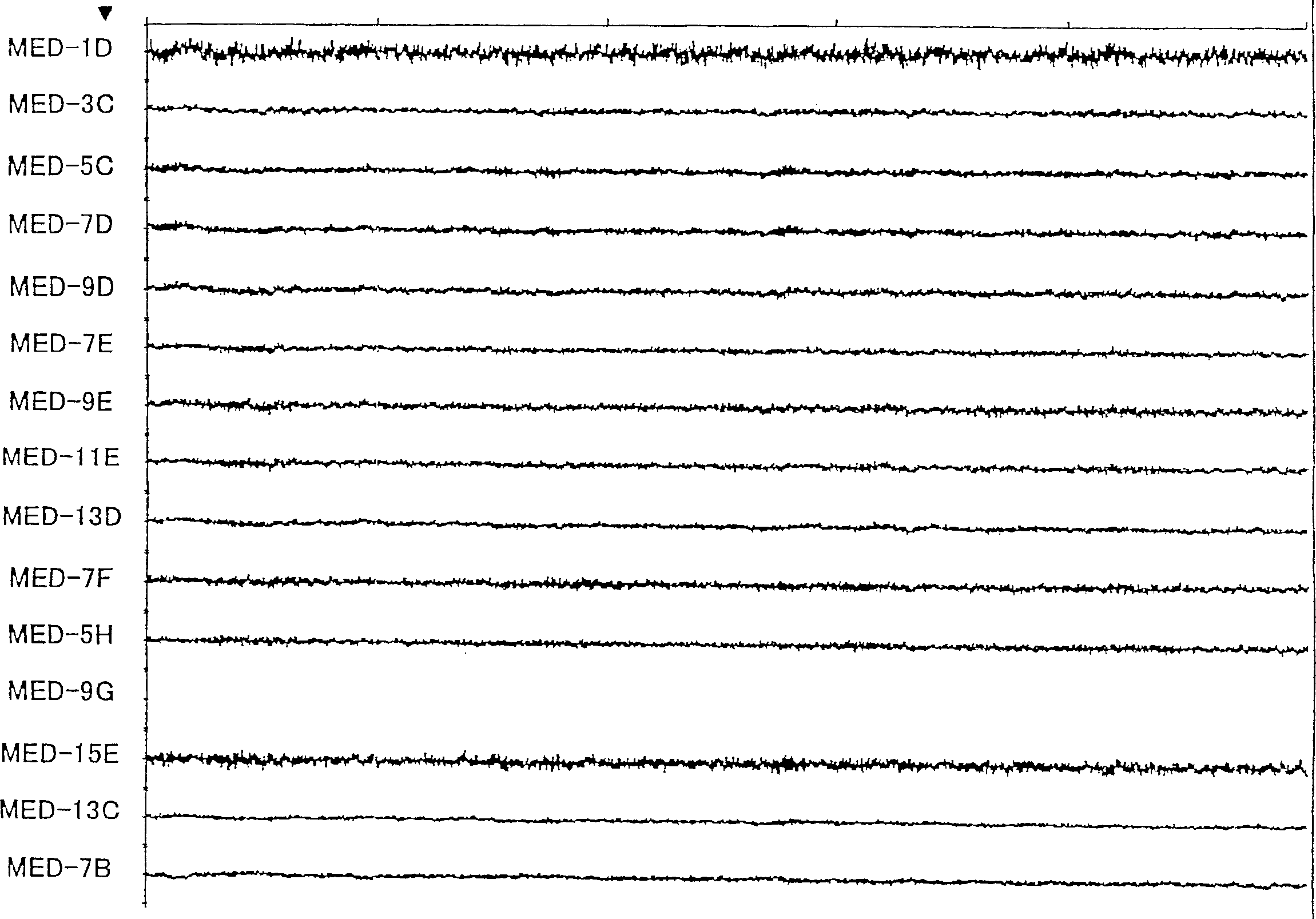
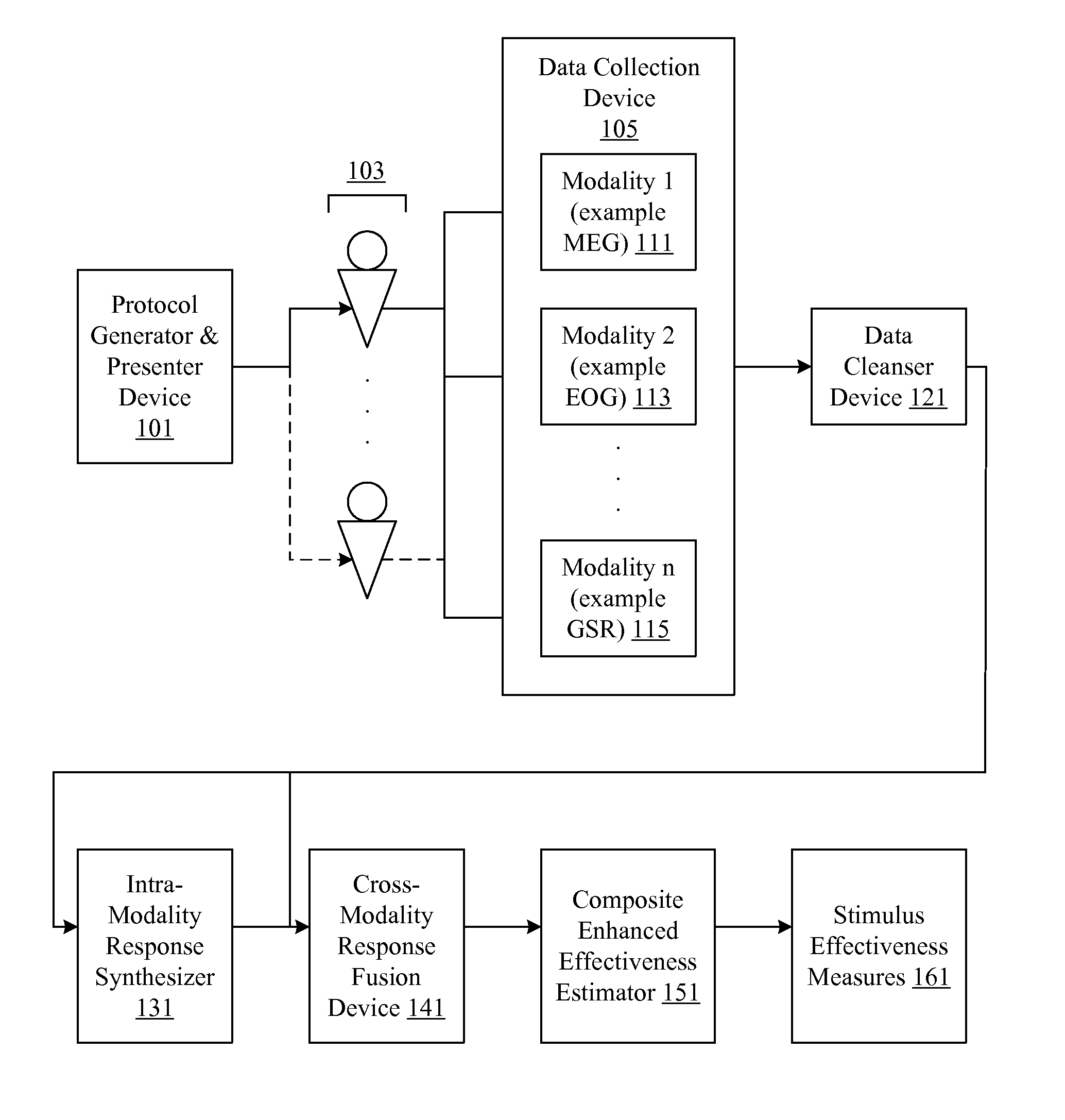
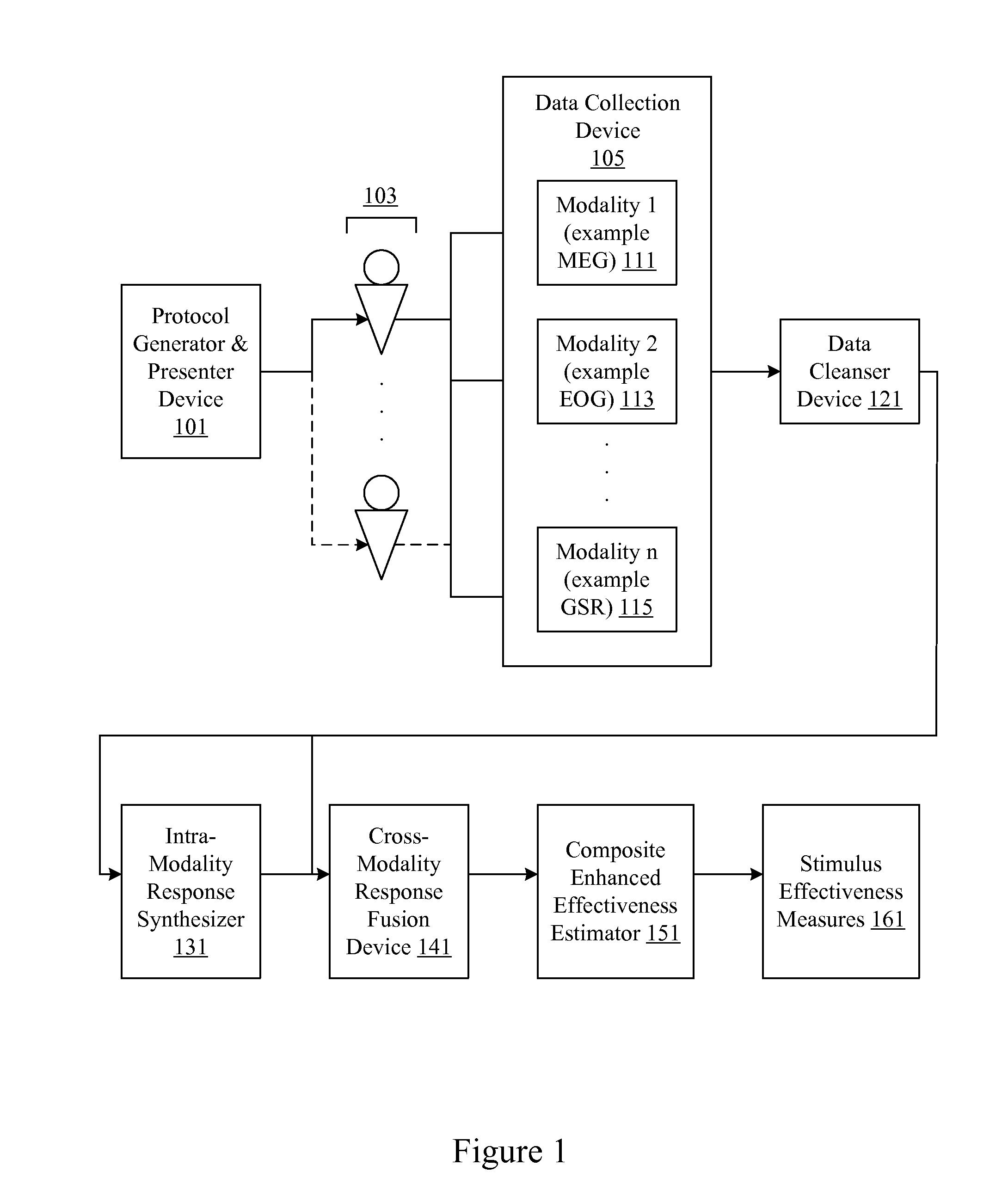
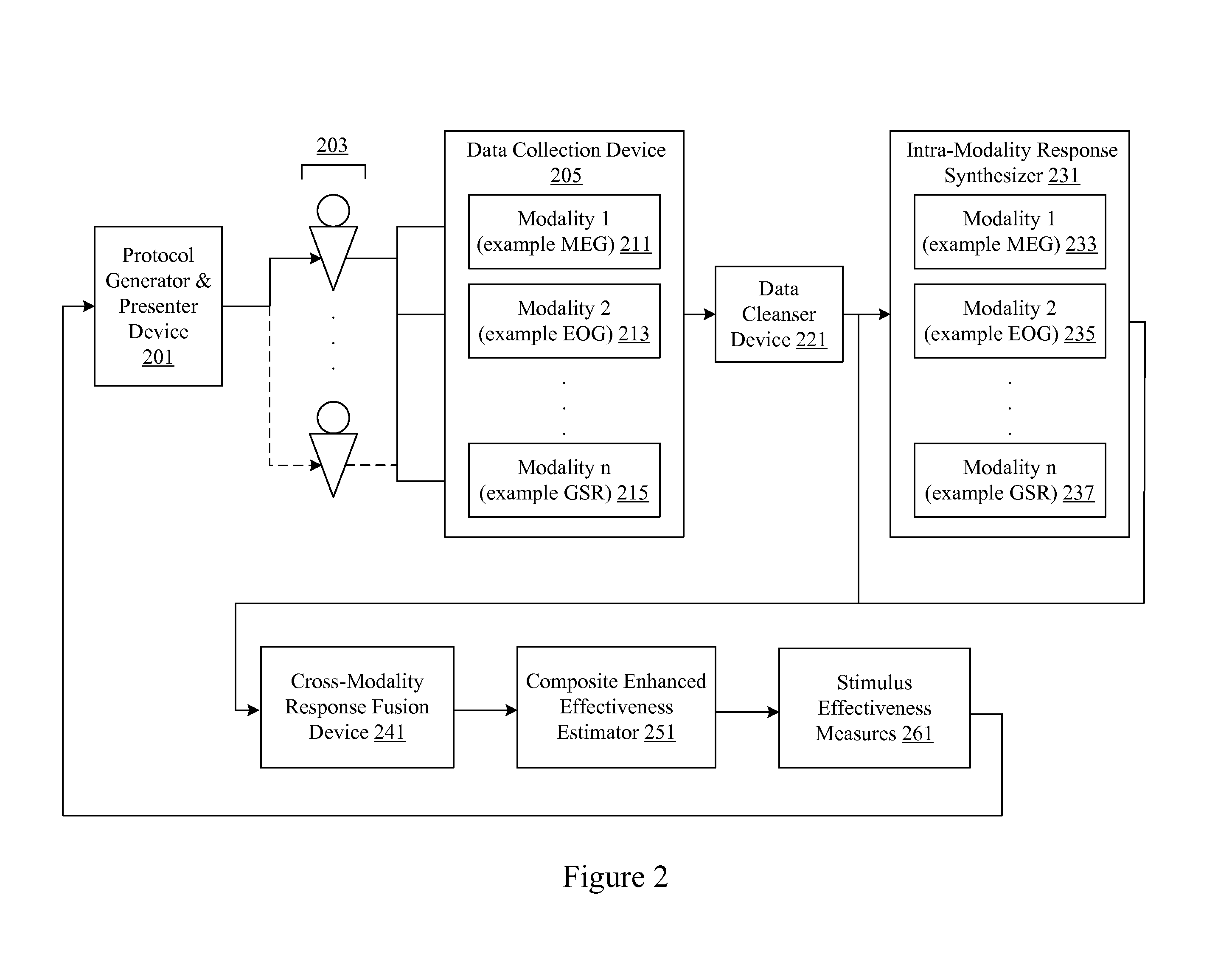
Central nervous system, autonomic nervous system, and effector data is measured and analyzed to determine the effectiveness of marketing and entertainment stimuli. A data collection mechanism including multiple modalities such as Magnetoencephalography (MEG), Electrooculography (EOG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), etc., collects response data from subjects exposed to marketing and entertainment stimuli. A data cleanser mechanism filters the response data. The response data is enhanced using intra-modality response synthesis and / or a cross-modality response synthesis.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
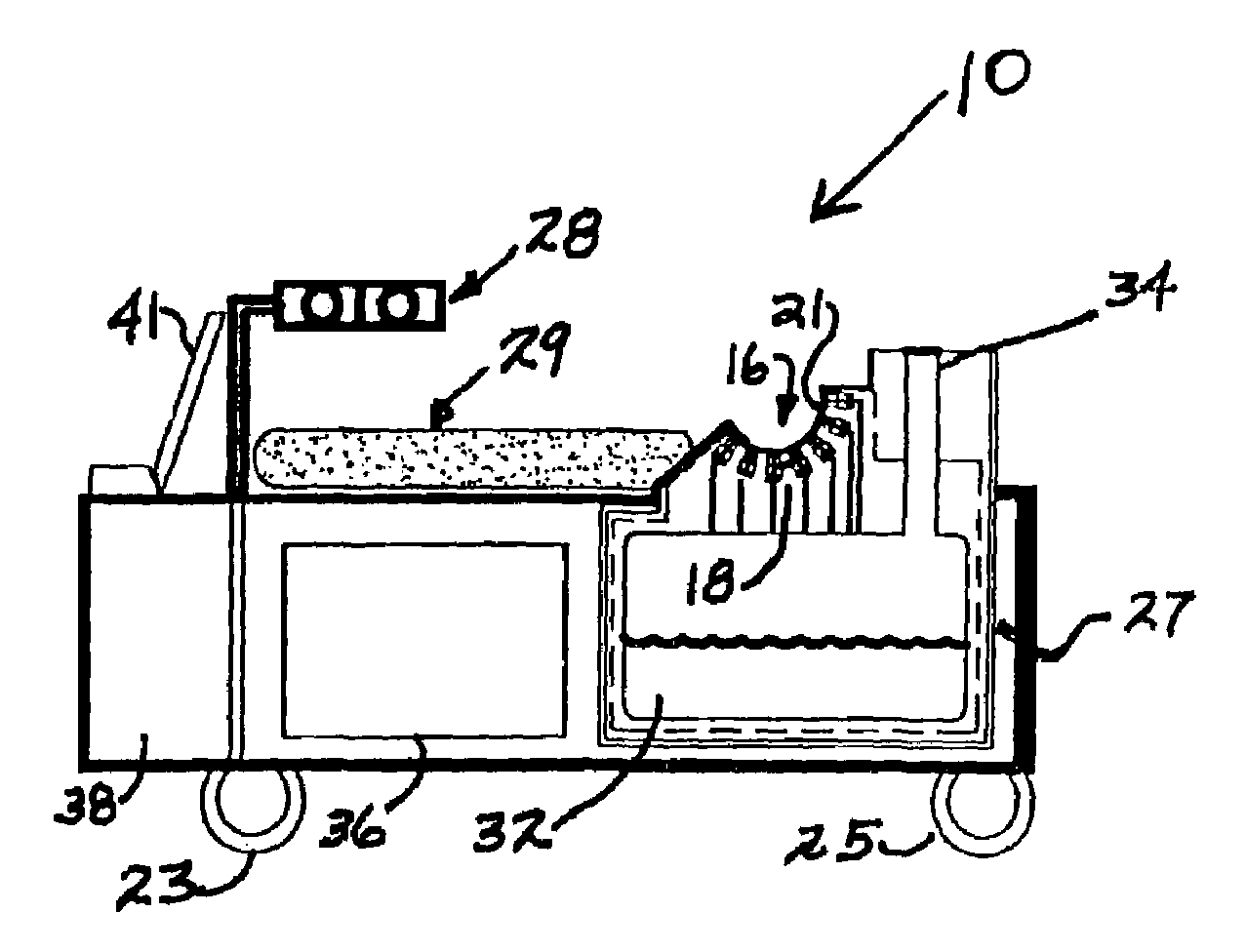
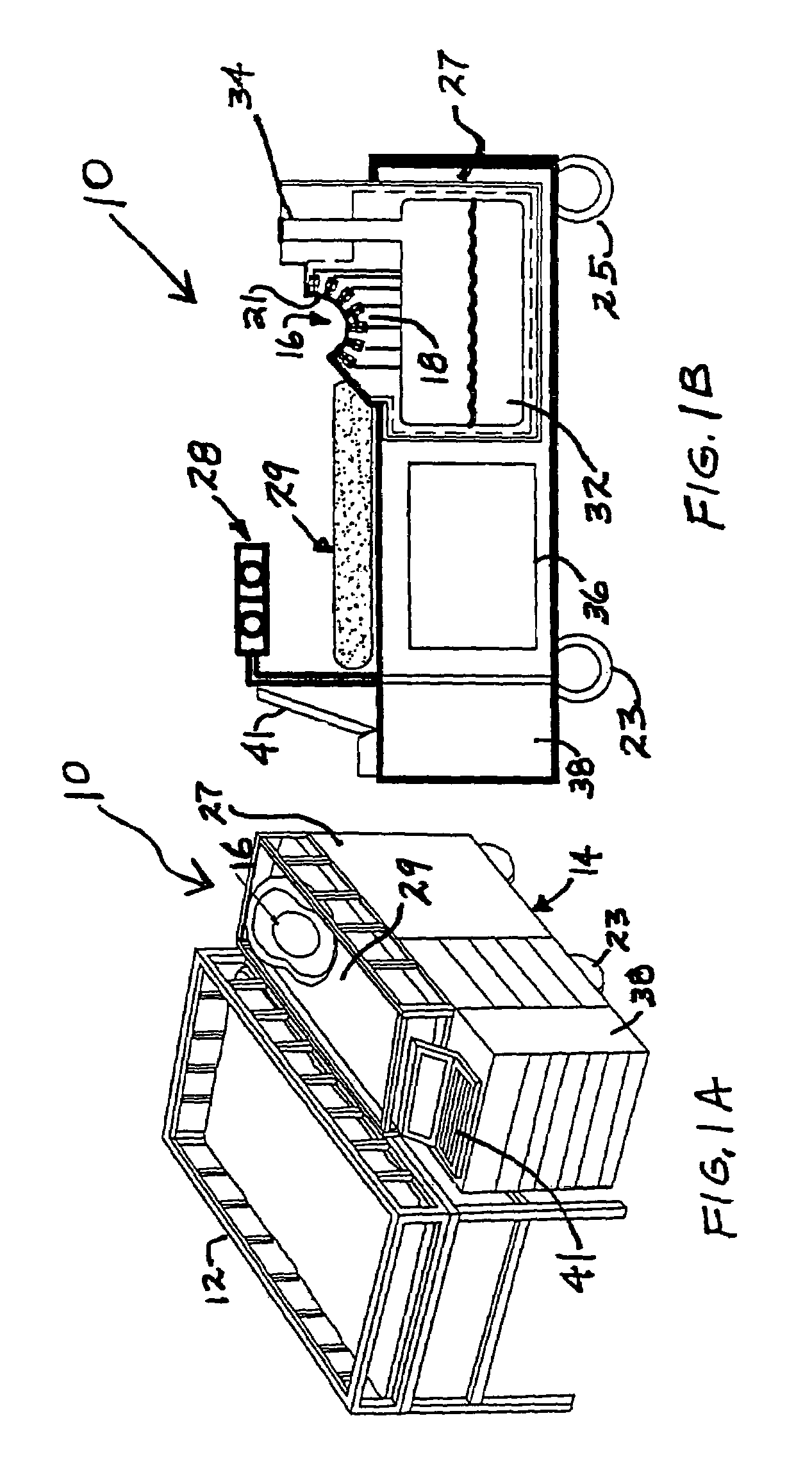
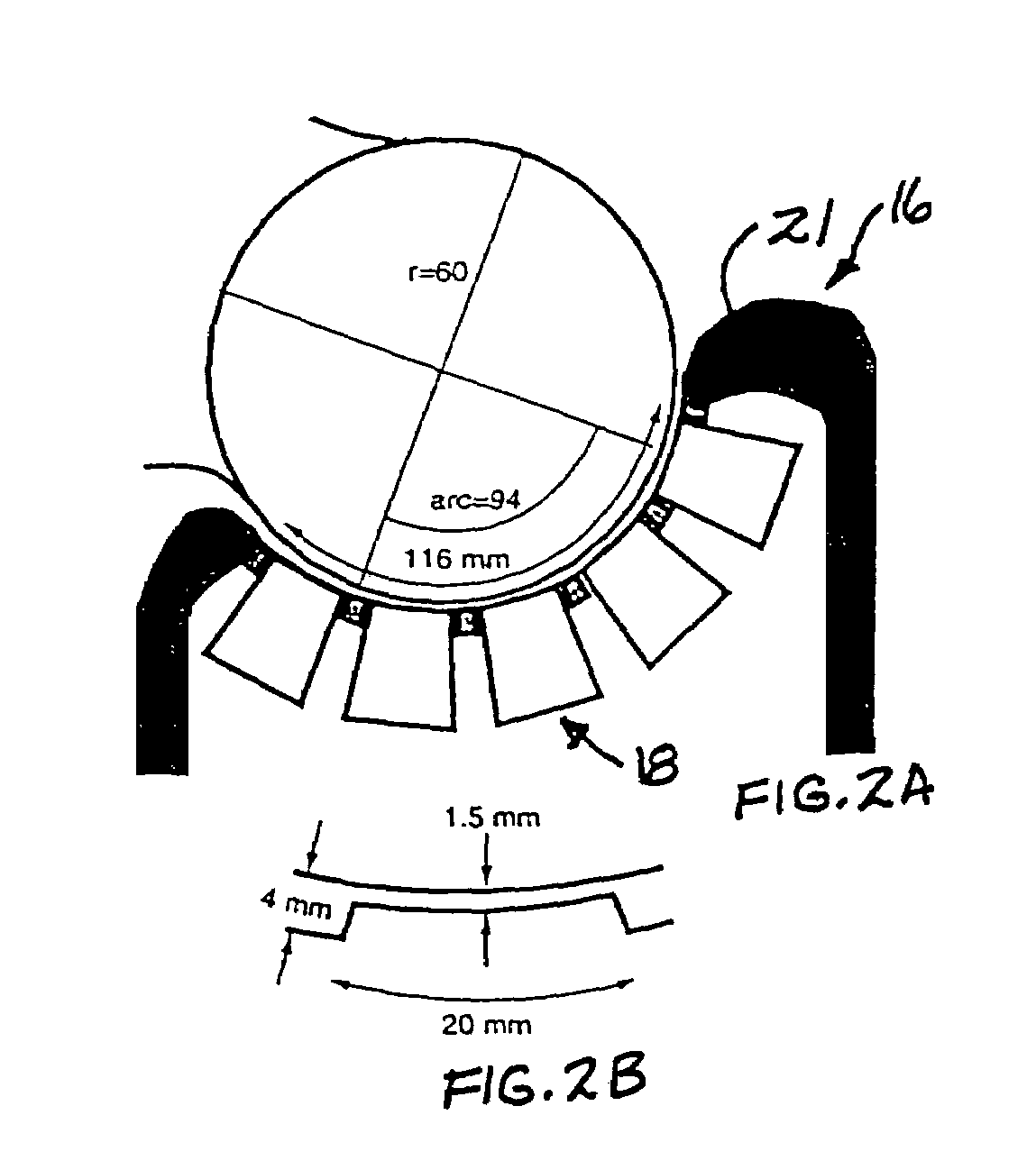
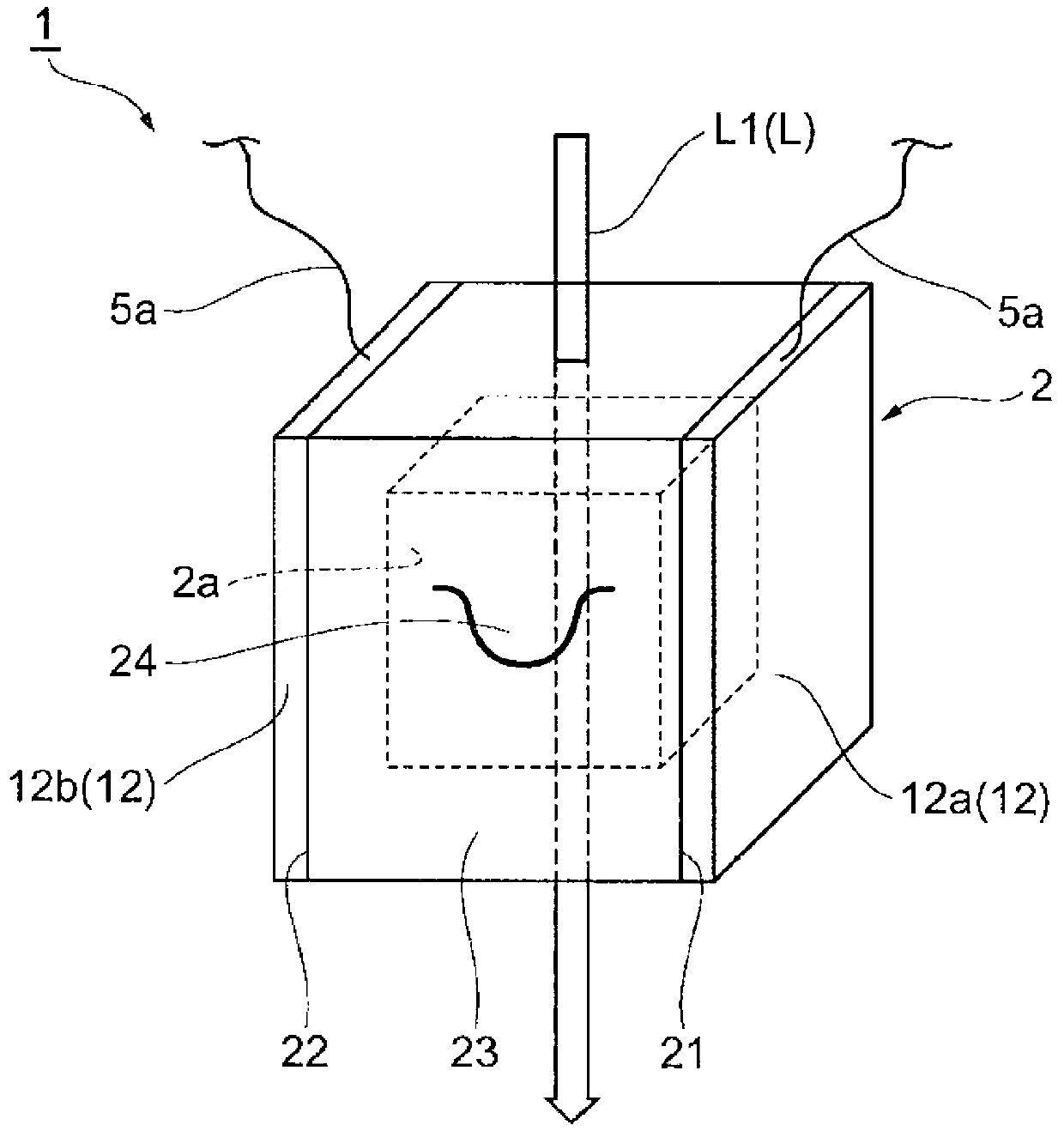
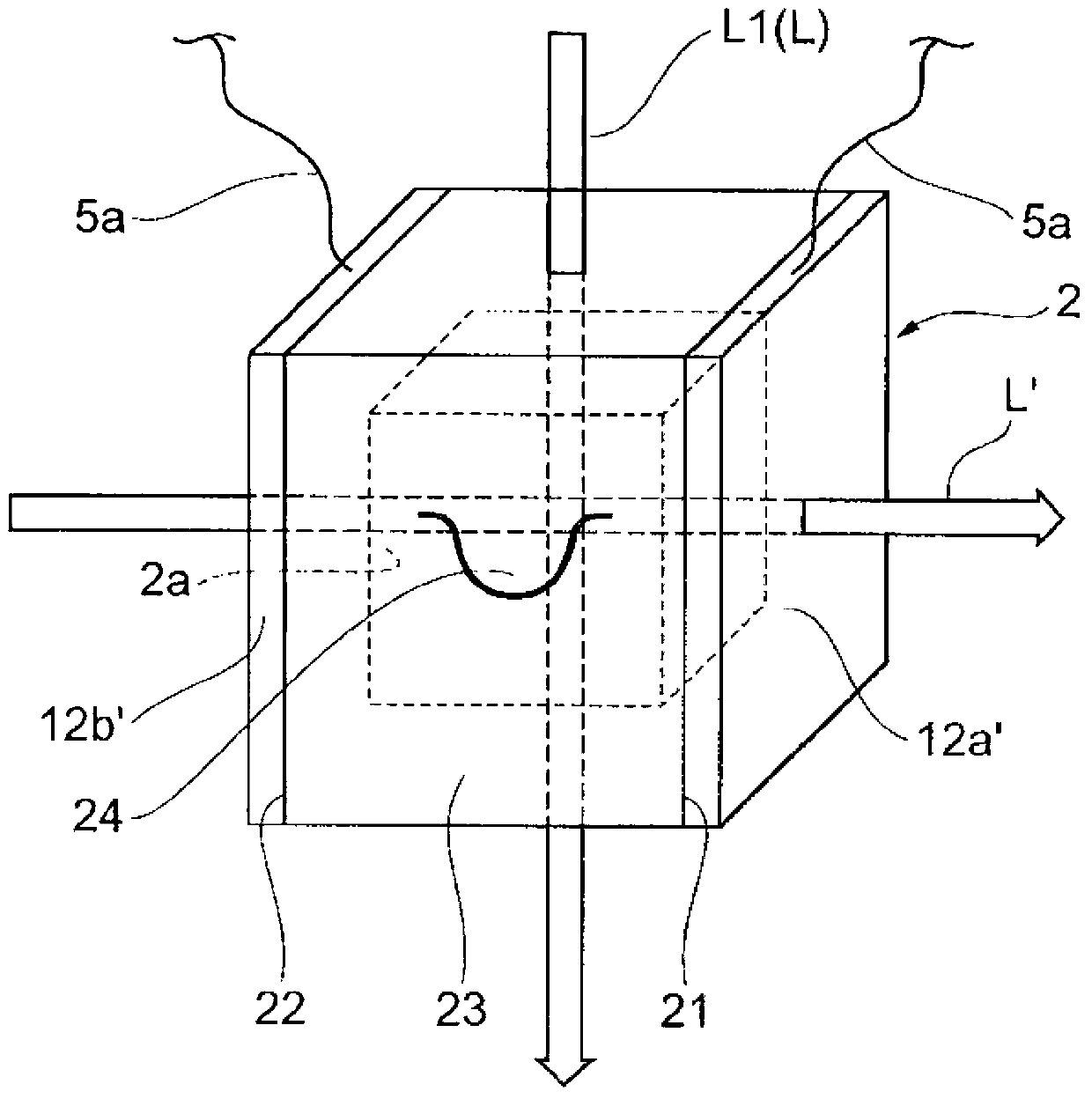
High-resolution magnetoencephalography system, components and method
InactiveUS7197352B2Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayMagnetoencephalography
Owner:TRISTAN TECH
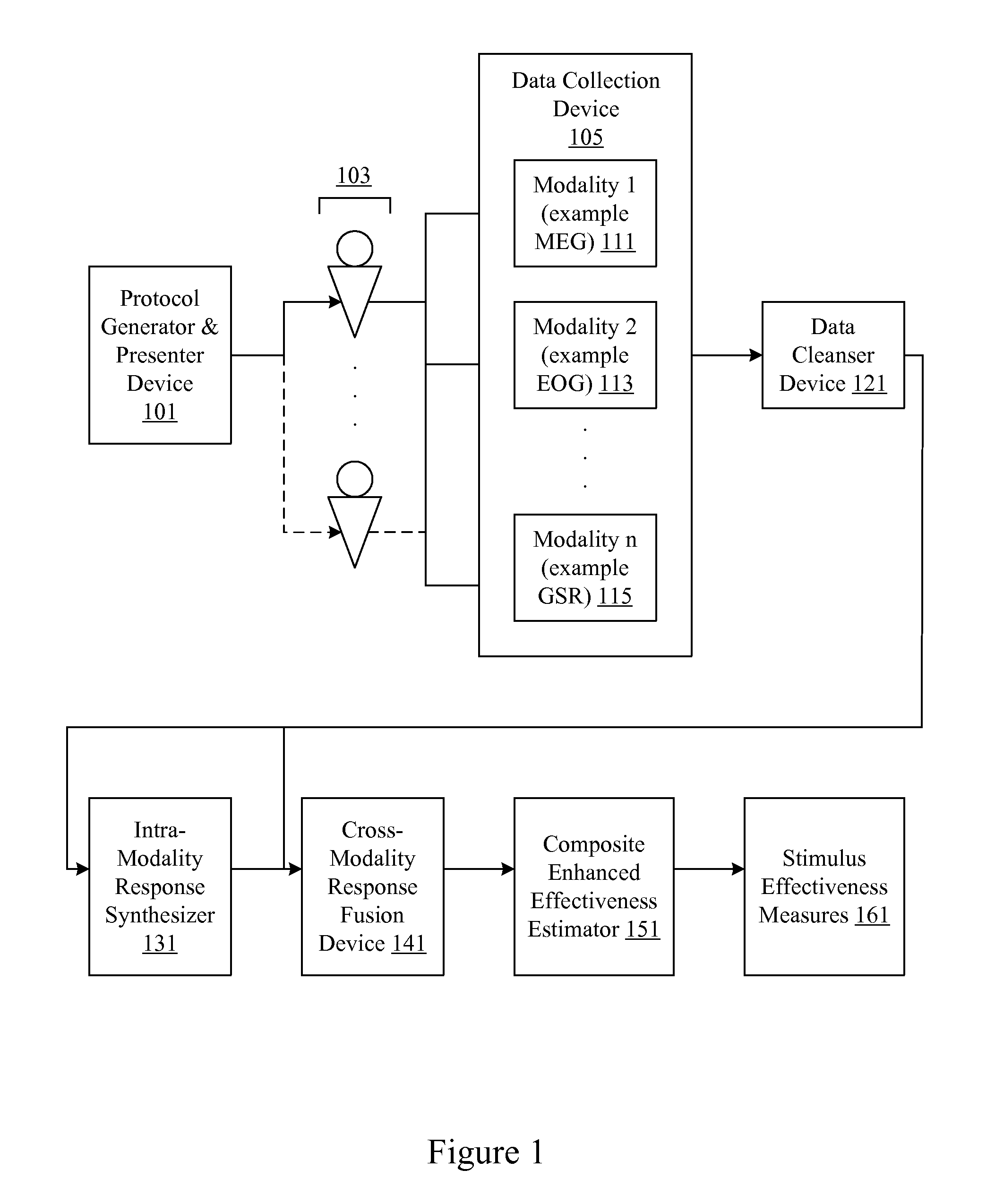
Analysis of marketing and entertainment effectiveness using magnetoencephalography
ActiveUS8494610B2Analogue secracy/subscription systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringCross modalityDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Central nervous system, autonomic nervous system, and effector data is measured and analyzed to determine the effectiveness of marketing and entertainment stimuli. A data collection mechanism including multiple modalities such as Magnetoencephalography (MEG), Electrooculography (EOG), Galvanic Skin Response (GSR), etc., collects response data from subjects exposed to marketing and entertainment stimuli. A data cleanser mechanism filters the response data. The response data is enhanced using intra-modality response synthesis and / or a cross-modality response synthesis.
Owner:NIELSEN CONSUMER LLC
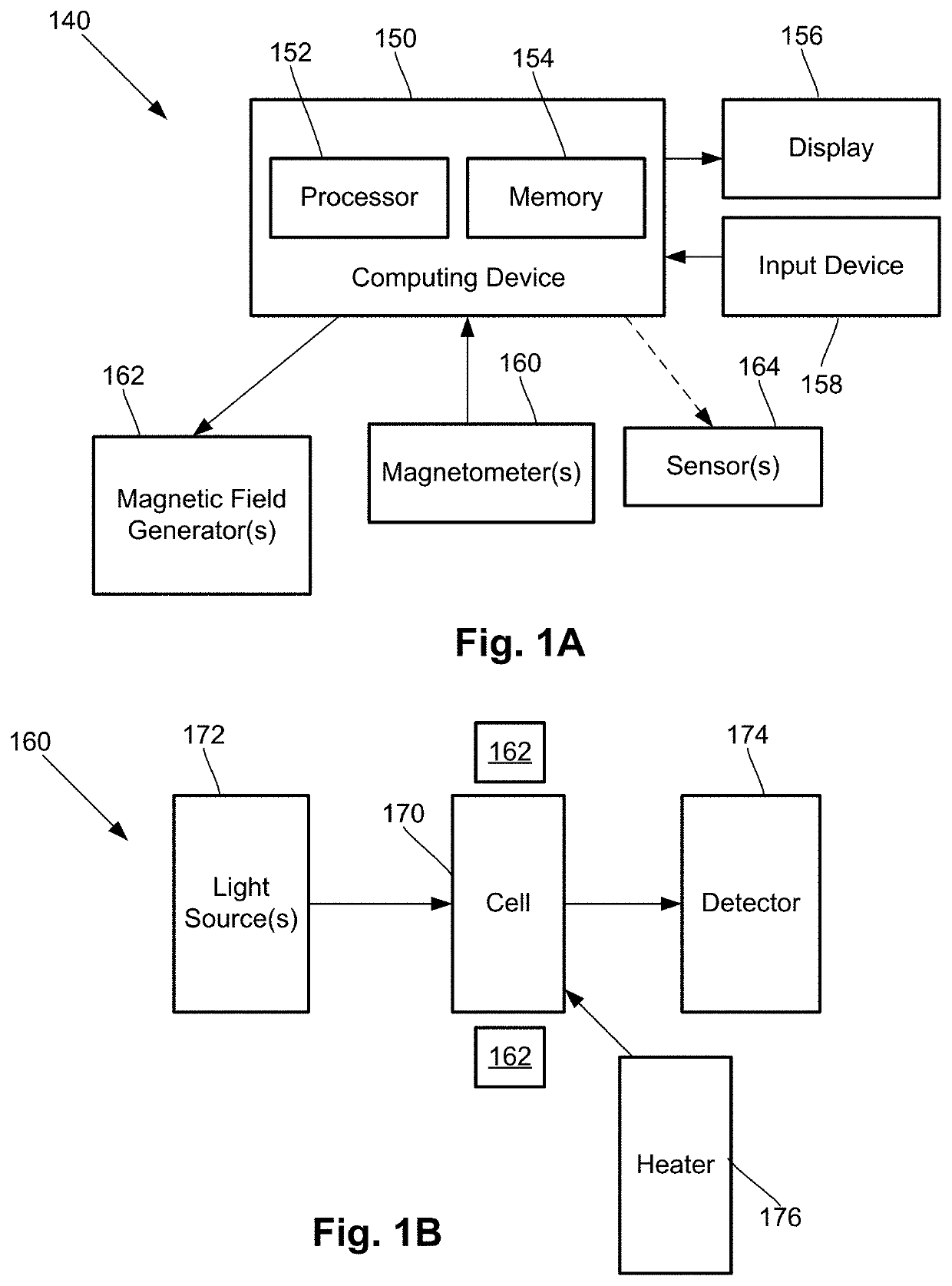
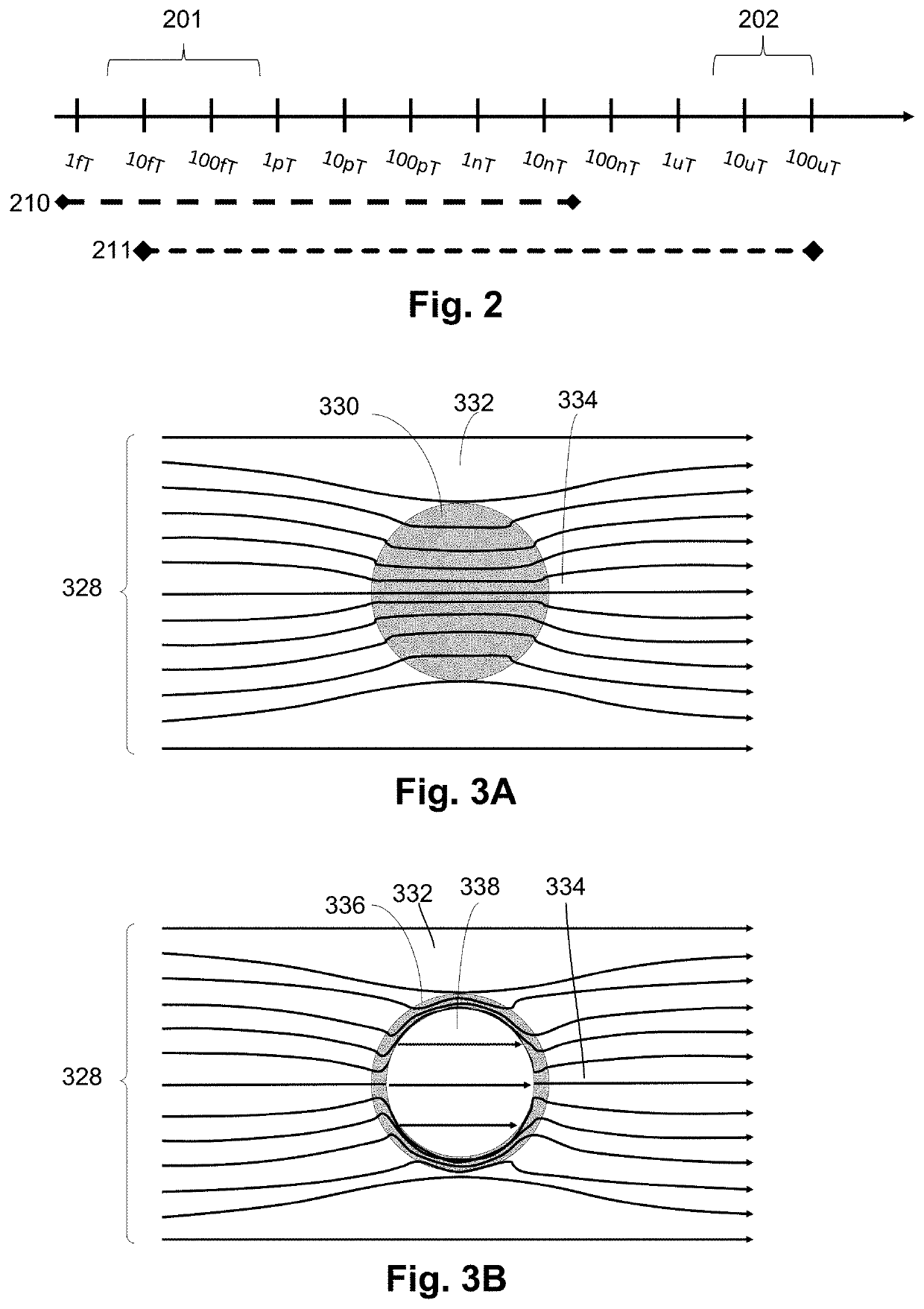
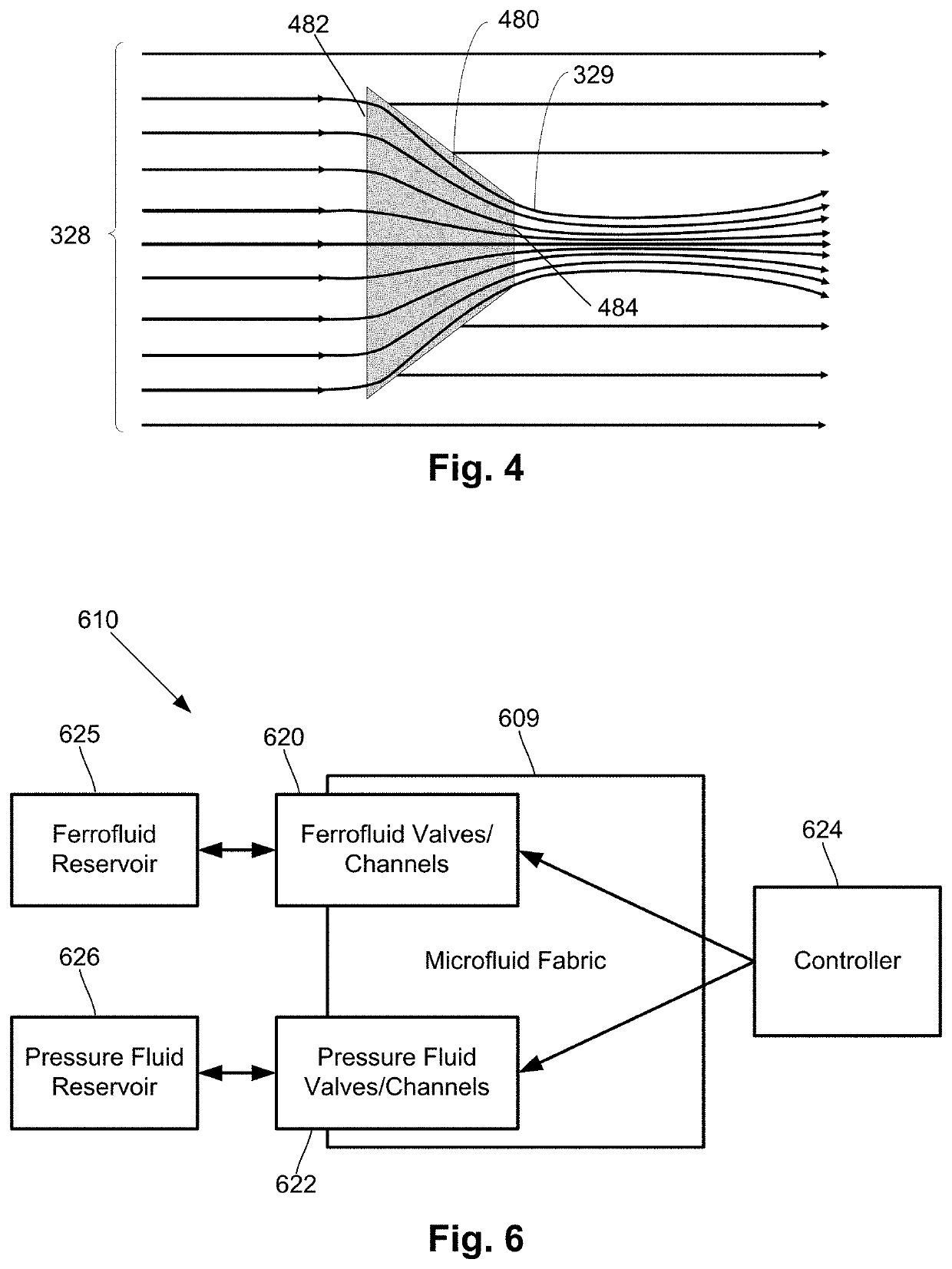
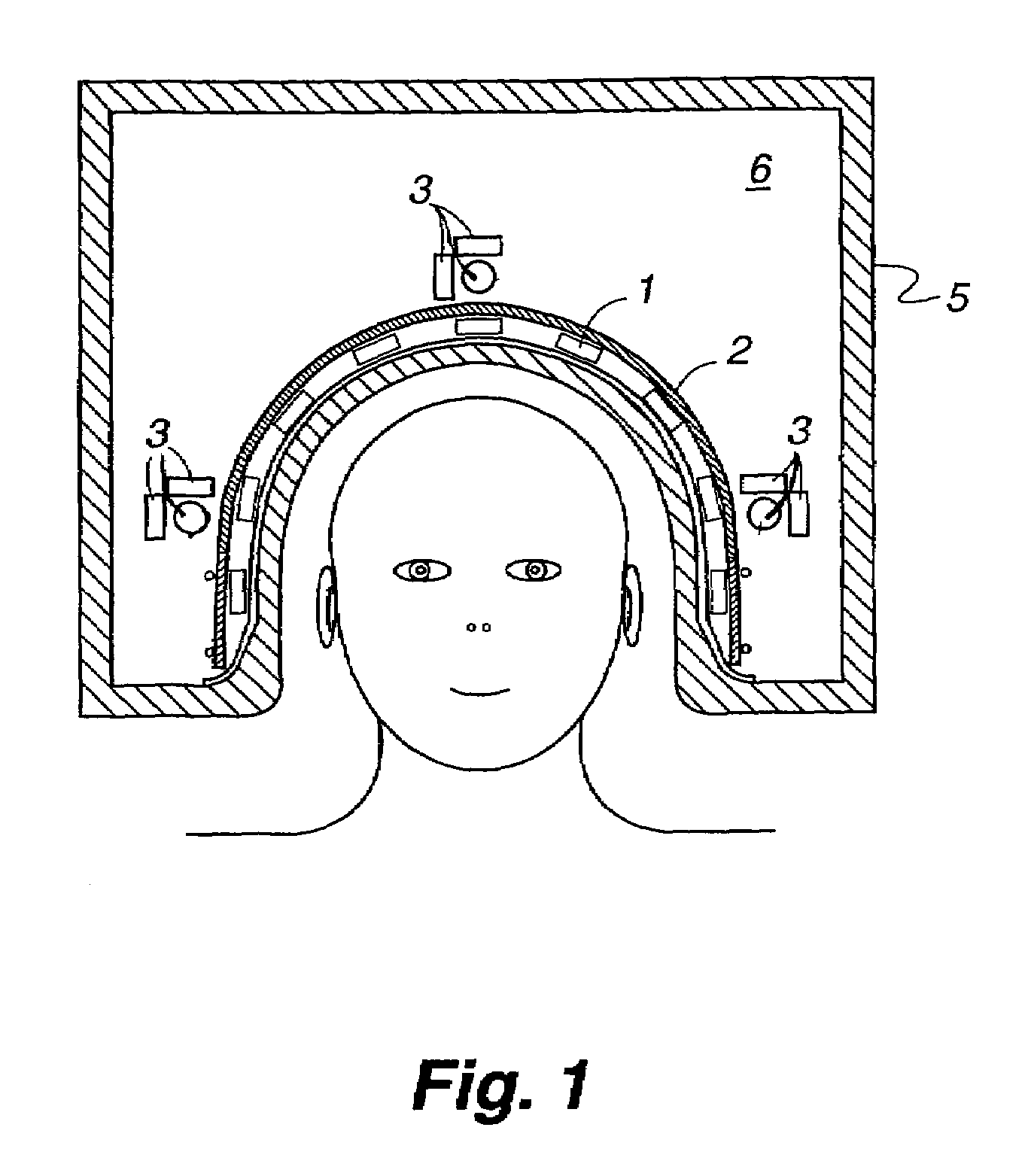
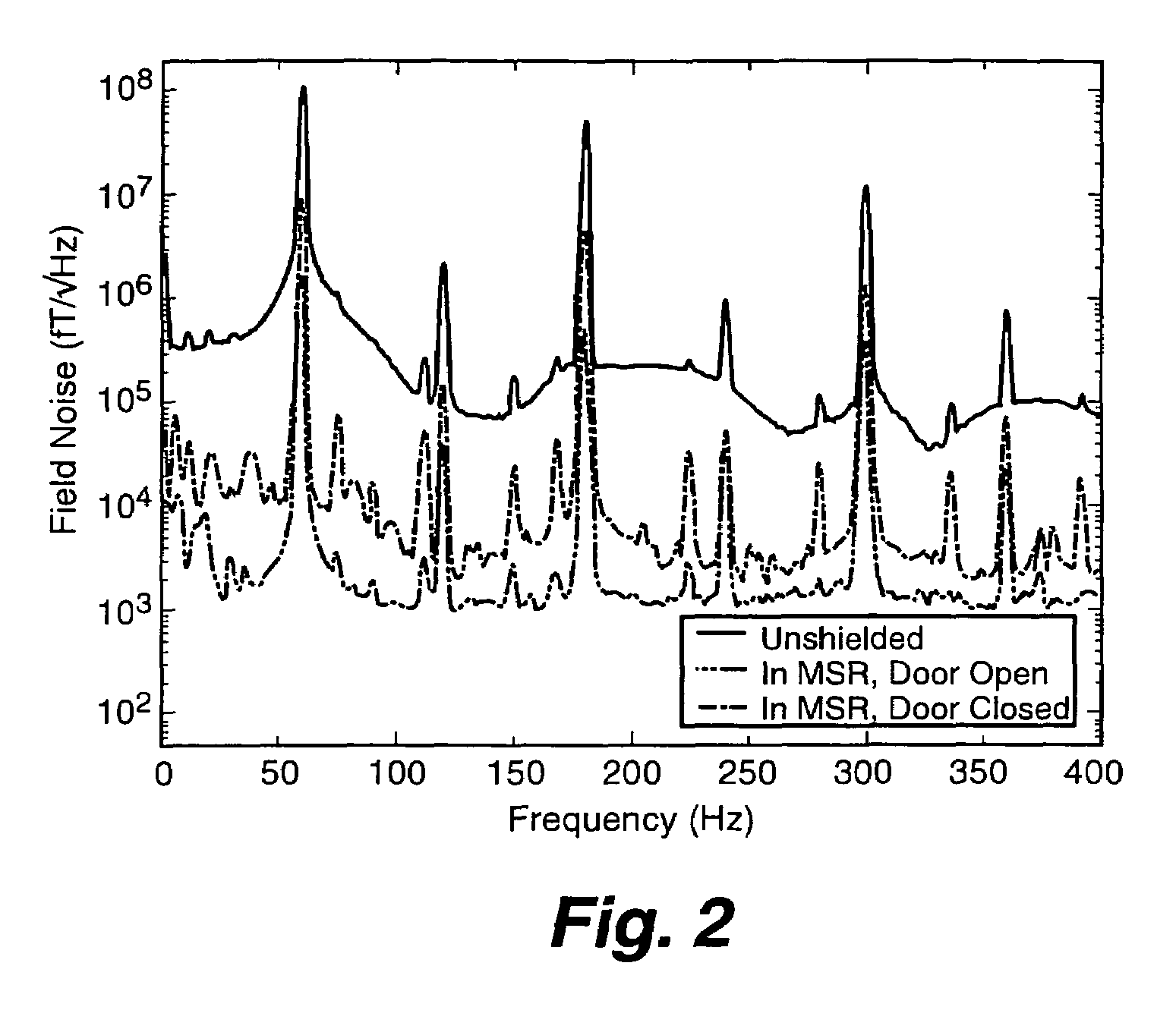
Dynamic magnetic shielding and beamforming using ferrofluid for compact magnetoencephalography (MEG)
ActiveUS20200088811A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesMagnetoencephalographyMagnetic shield
A magnetic field measurement system can include at least one magnetometer; and a ferrofluid shield disposed at least partially around the at least one magnetometer. For example, the ferrofluid shield can include a microfluid fabric and a ferrofluid disposed in or flowable into the microfluid fabric. As another example, the ferrofluid shield can include a ferrofluid and a controller configured to alter an arrangement of the ferrofluid within the ferrofluid shield.
Owner:HI LLC
Analysis of brain patterns using temporal measures
ActiveUS20080091118A1Low costImprove throughputElectroencephalographyMedical simulationBrain pathologiesAlgorithm
A set of brain data representing a time series of neurophysiologic activity acquired by spatially distributed sensors arranged to detect neural signaling of a brain (such as by the use of magnetoencephalography) is obtained. The set of brain data is processed to obtain a dynamic brain model based on a set of statistically-independent temporal measures, such as partial cross correlations, among groupings of different time series within the set of brain data. The dynamic brain model represents interactions between neural populations of the brain occurring close in time, such as with zero lag, for example. The dynamic brain model can be analyzed to obtain the neurophysiologic assessment of the brain. Data processing techniques may be used to assess structural or neurochemical brain pathologies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF MINNESOTA
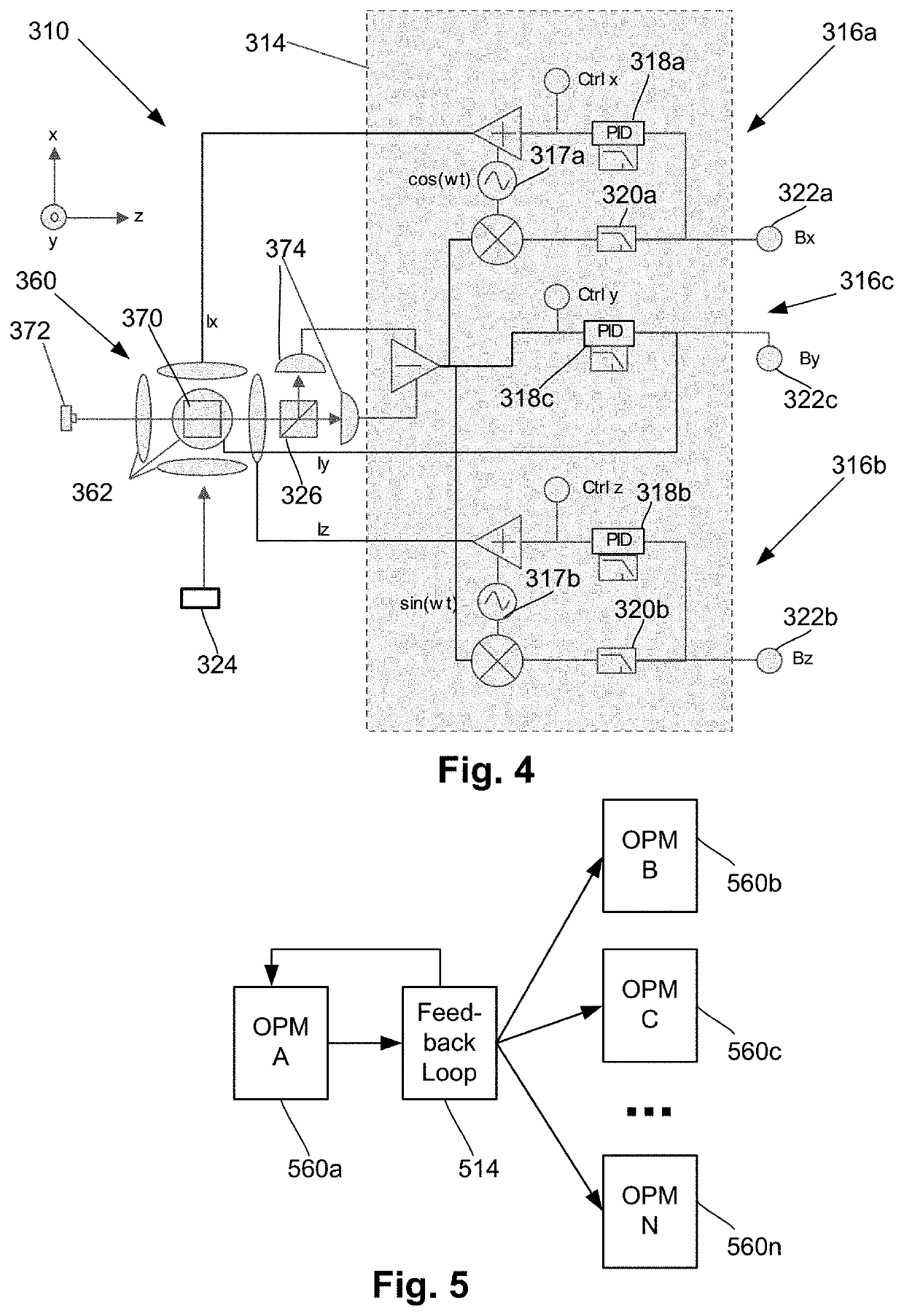
Neural feedback loop filters for enhanced dynamic range magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems and methods
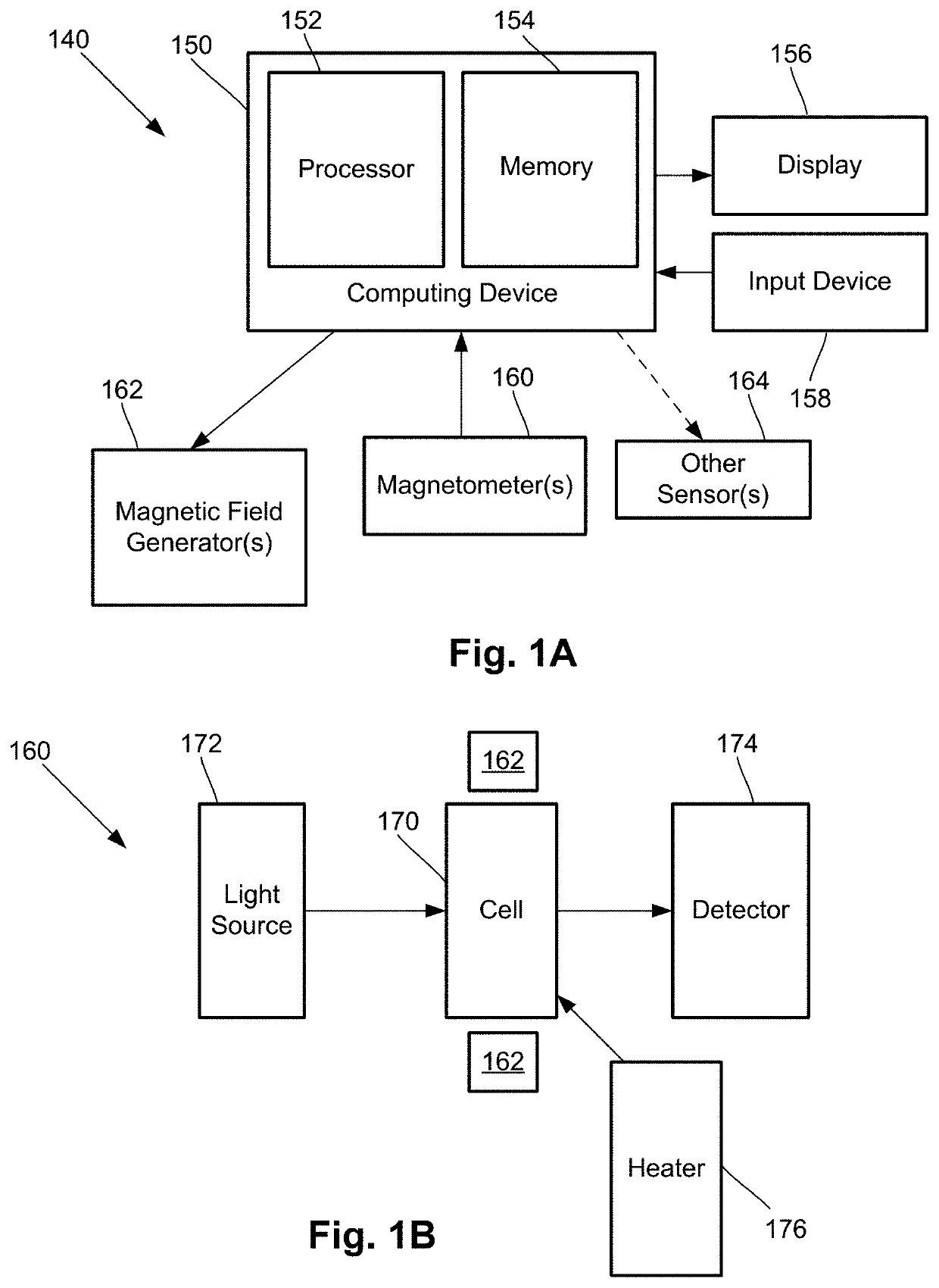
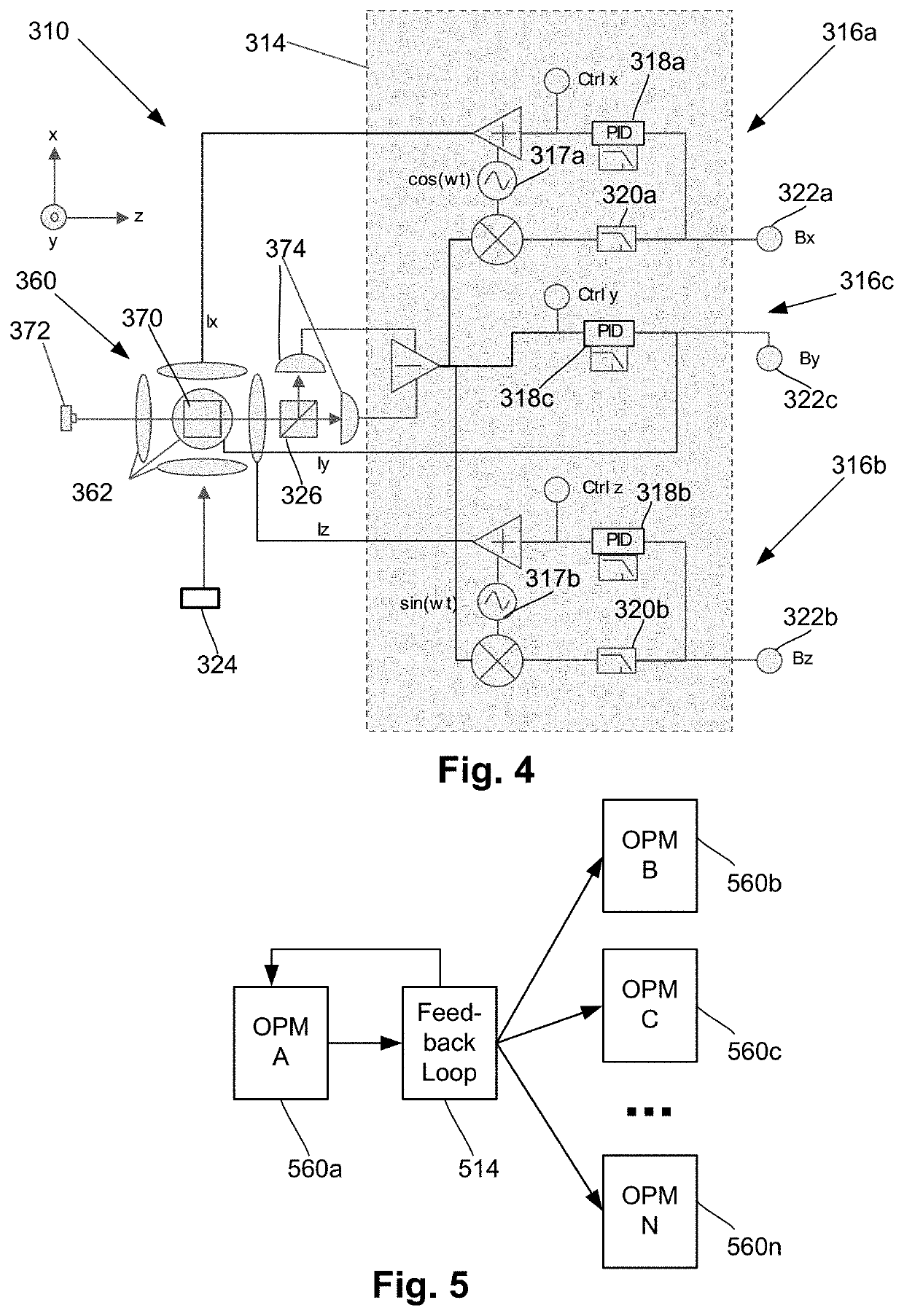
ActiveUS20200256929A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringLow-pass filterSoftware engineering
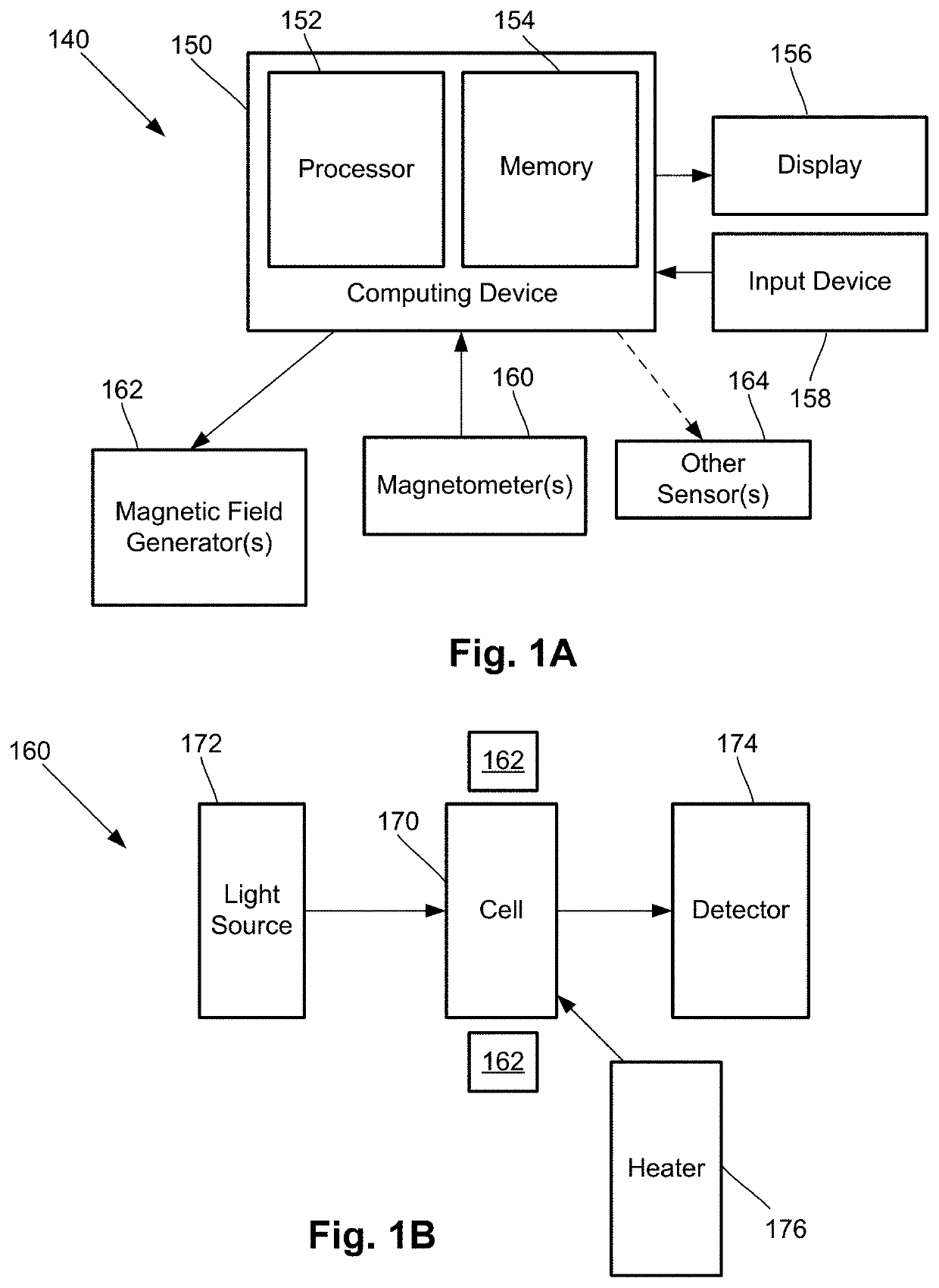
One embodiment is a magnetic field measurement system that includes at least one magnetometer having a vapor cell, a light source to direct light through the vapor cell, and a detector to receive light directed through the vapor cell; at least one magnetic field generator disposed adjacent the vapor cell; and a feedback circuit coupled to the at least one magnetic field generator and the detector of the at least one magnetometer. The feedback circuit includes at least one feedback loop that includes a first low pass filter with a first cutoff frequency. The feedback circuit is configured to compensate for magnetic field variations having a frequency lower than the first cutoff frequency. The first low pass filter rejects magnetic field variations having a frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and provides the rejected magnetic field variations for measurement as an output of the feedback circuit.
Owner:HI LLC
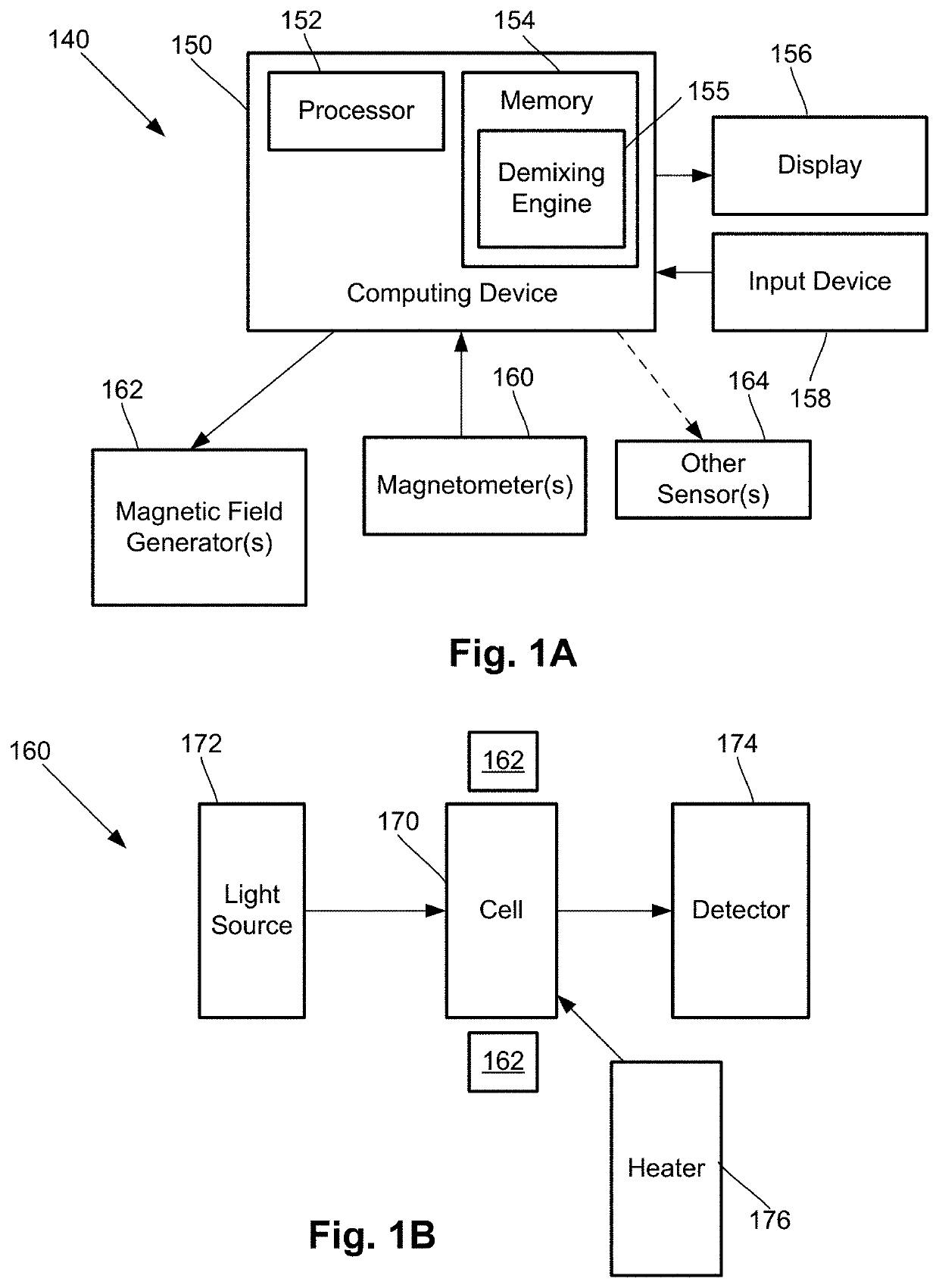
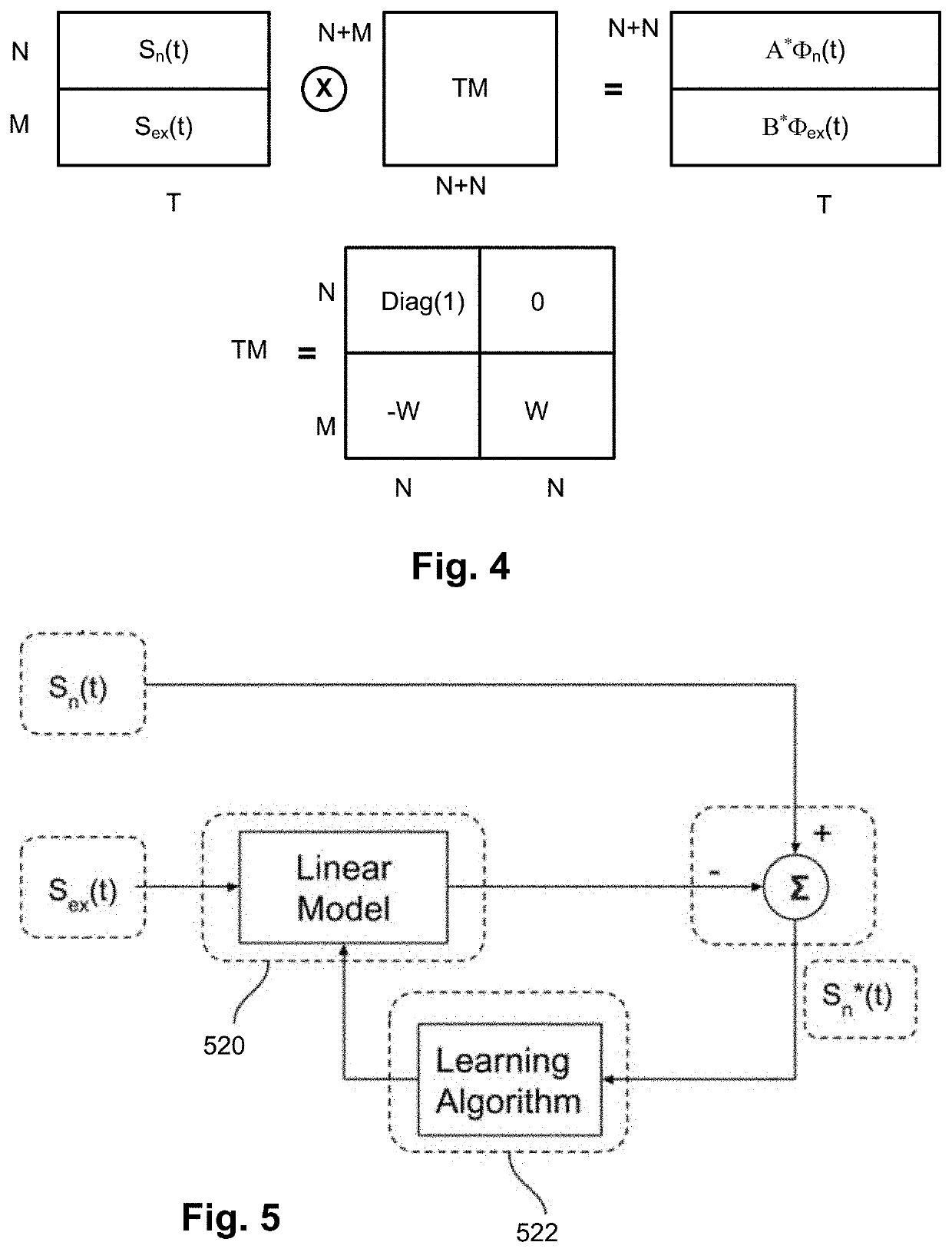
Systems and methods for suppression of interferences in magnetoencephalography (MEG) and other magnetometer measurements
InactiveUS20200334559A1Magnetic field offset compensationDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetoencephalographyComputational physics
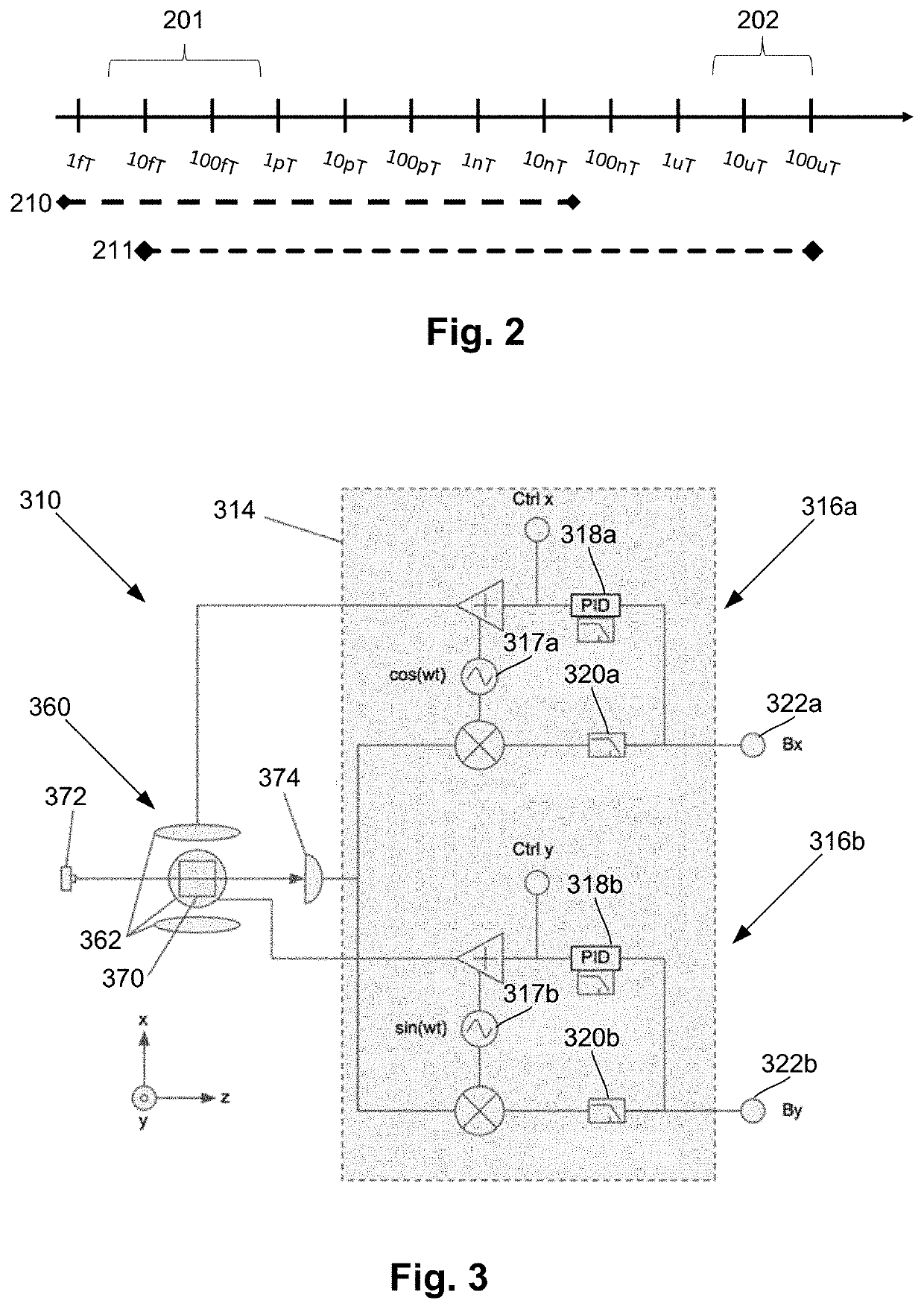
A magnetic field measurement system, non-transitory computer-readable medium or method can include instructions for, or performance of, actions including receiving output of multiple first magnetic field sensors and multiple second magnetic field sensors; and demixing, using the output of the first and second magnetic field sensors, at least one signal from at least one target source from signals from other magnetic field sources. The demixing may be performed using a model in which the output of the first magnetic field sensors includes the at least one signal from the at least one target source and that the output of the second magnetic field sensors does not include the at least one signal from the at least one target source.
Owner:HI LLC
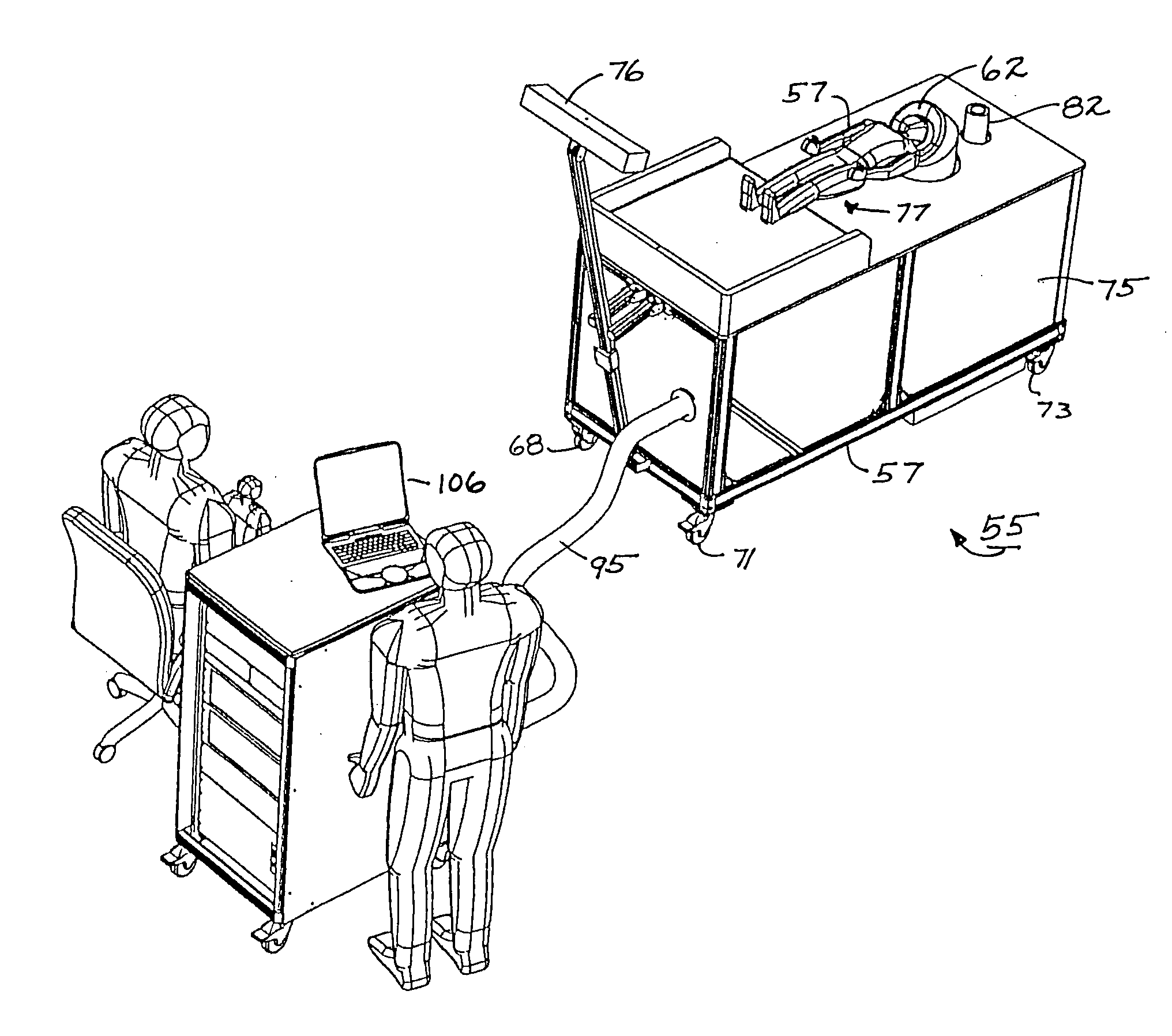
High-resolution magnetoencephalography system and method
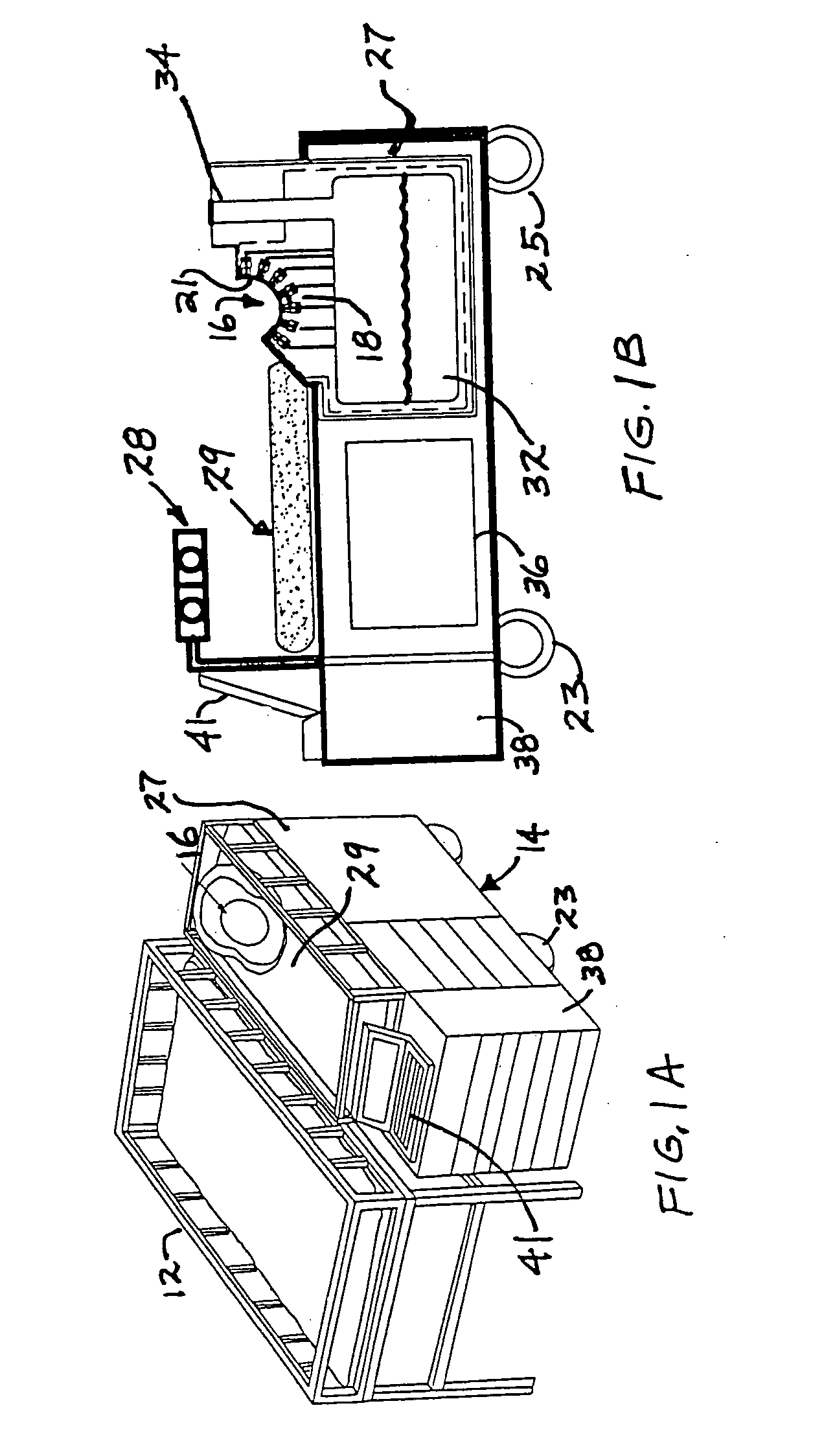
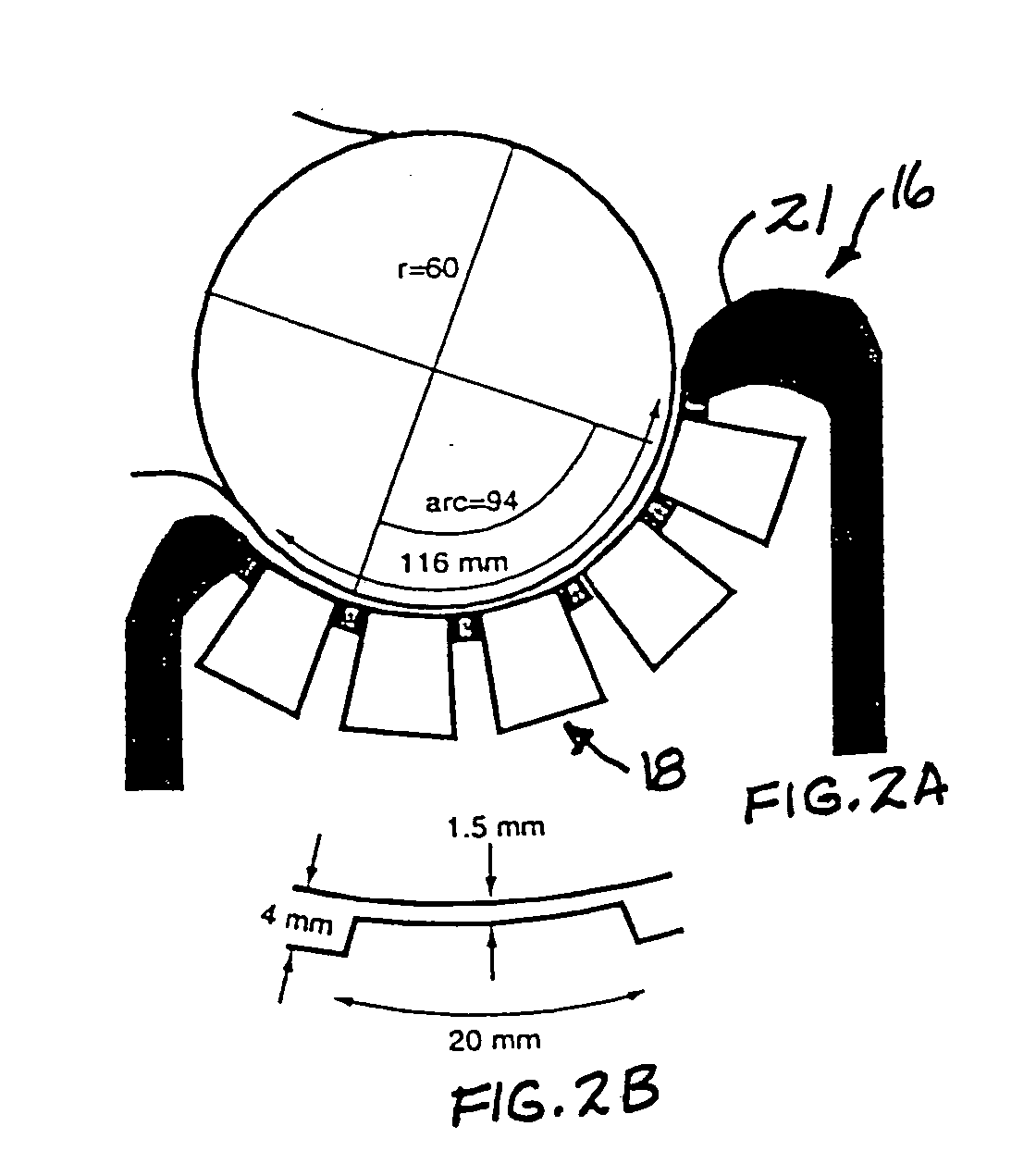
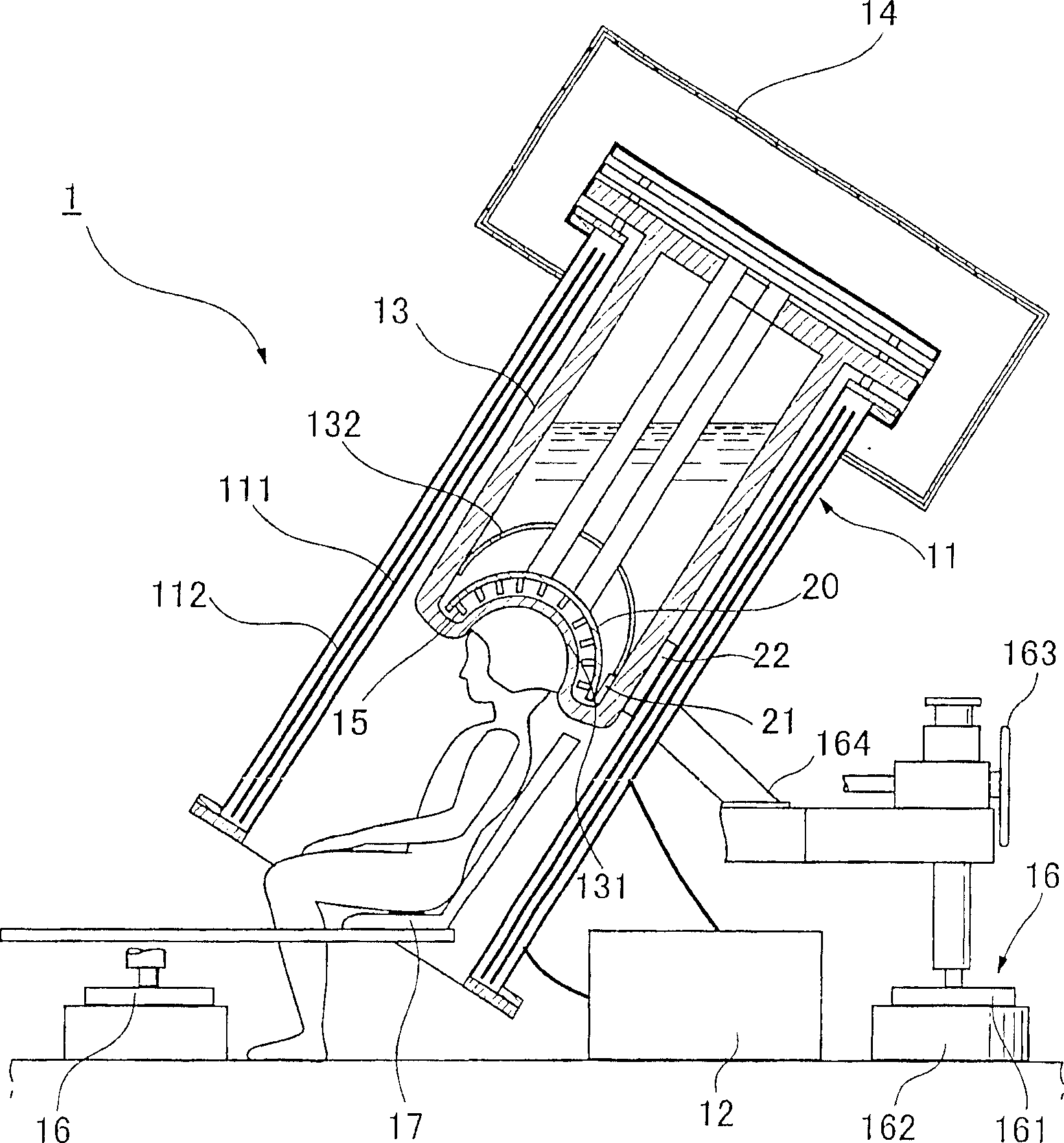
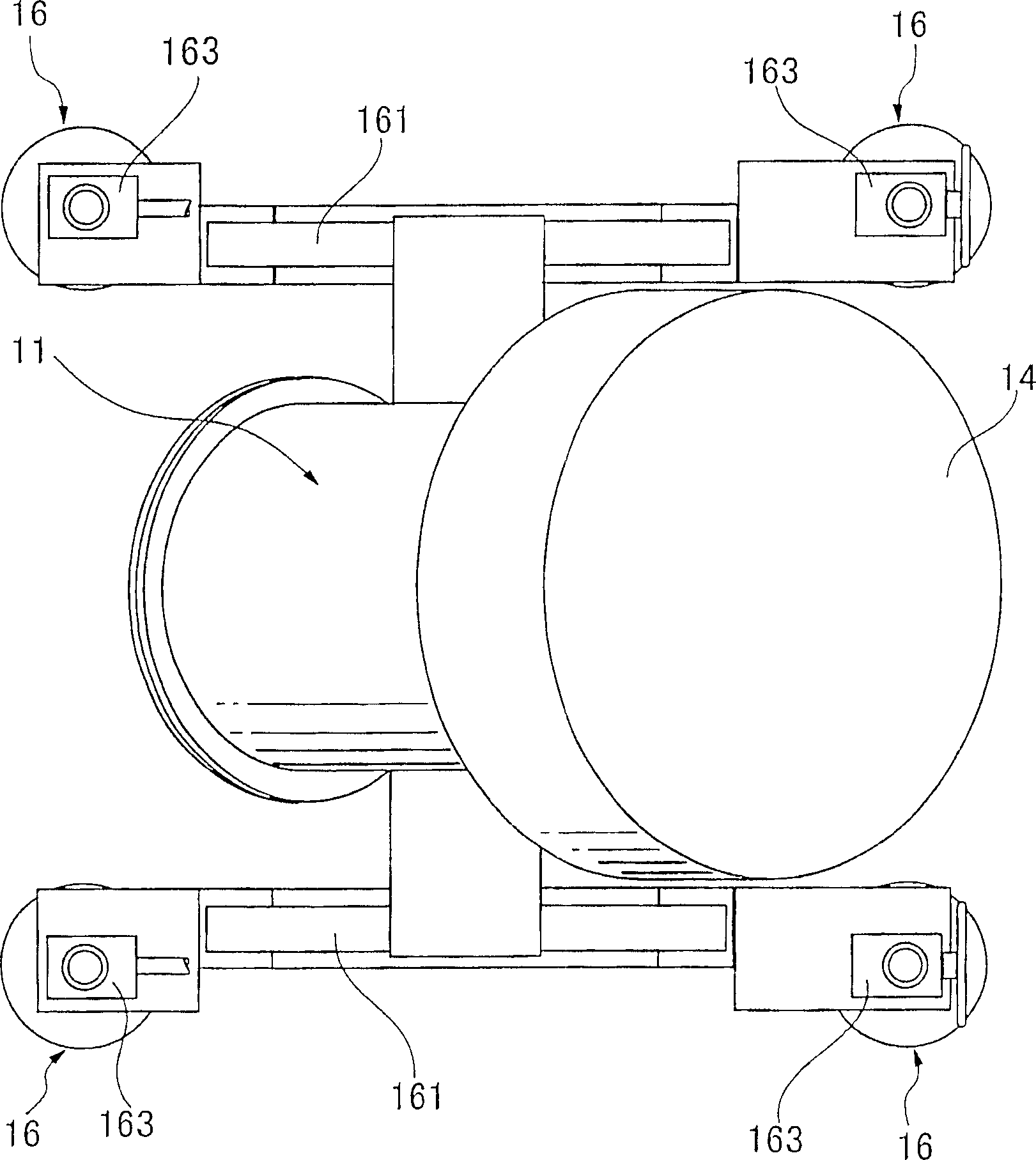
According to certain embodiments of the present invention, there is provided a magnetoencephalography and method employing a portable cart having a SQUID dewar mounted in an inverted manner thereon, and having a headrest assembly mounted on the cart for supporting the head of a patient and forming a portion of the dewar. The headrest assembly includes an array of magnetic sensors of the SQUID dewar for responding to electrical activity of the brain of the head.
Owner:TRISTAN TECH
Noise cancellation in magnetoencephalography and electroencephalography with isolated reference sensors
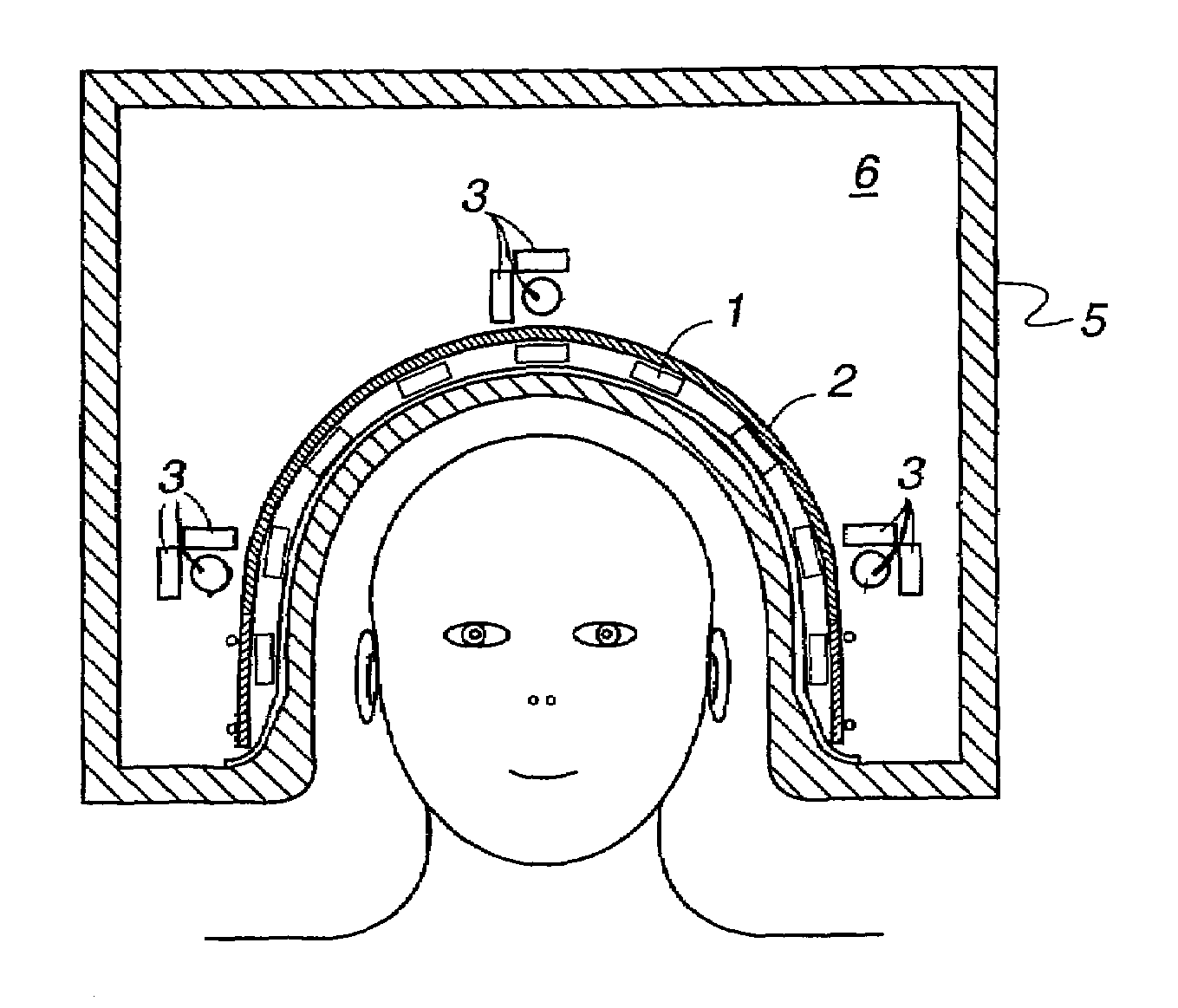
An apparatus measures electromagnetic signals from a weak signal source. A plurality of primary sensors is placed in functional proximity to the weak signal source with an electromagnetic field isolation surface arranged adjacent the primary sensors and between the weak signal source and sources of ambient noise. A plurality of reference sensors is placed adjacent the electromagnetic field isolation surface and arranged between the electromagnetic isolation surface and sources of ambient noise.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
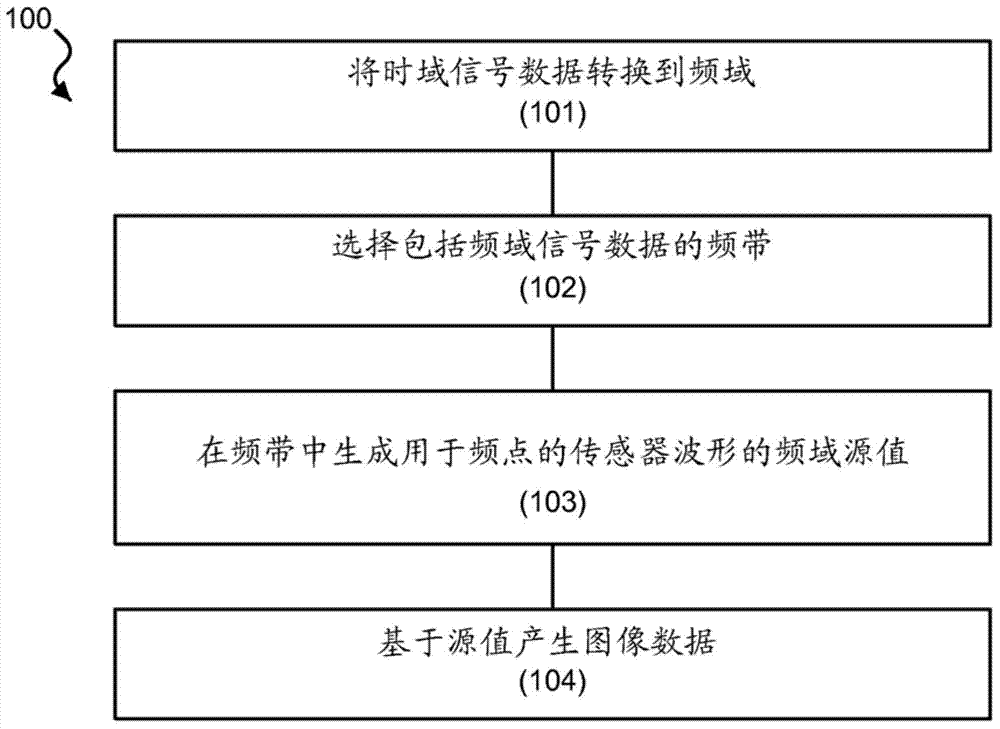
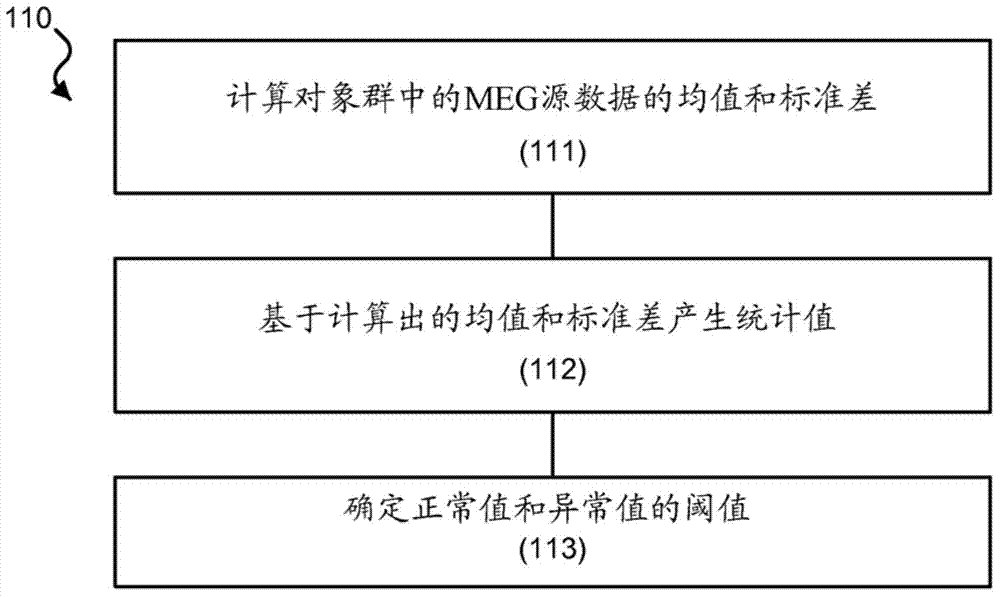
Magnetoencephalography source imaging
InactiveCN103717129AMagnetic measurementsMedical automated diagnosisMagnetoencephalographySource imaging
Techniques, devices and systems are disclosed for magnetoencephalography (MEG) source imaging. In one aspect, a method includes selecting signal data associated with one or more frequency bands from a spectrum of the signal data in the frequency domain, in which the signal data represents magnetic signals emitted by a brain of a subject and detected by a plurality of sensors outside the brain, defining locations of sources within the brain that generate the magnetic signals, in which the number of locations of the sources is selected to be greater than the number of sensors, and generating a source value of signal power based on the selected signal data corresponding to a respective location of the locations at the one or more frequencies.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
High-resolution magnetoencephalography system, components and method
InactiveUS20040254443A1Magnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensor arrayMagnetoencephalography
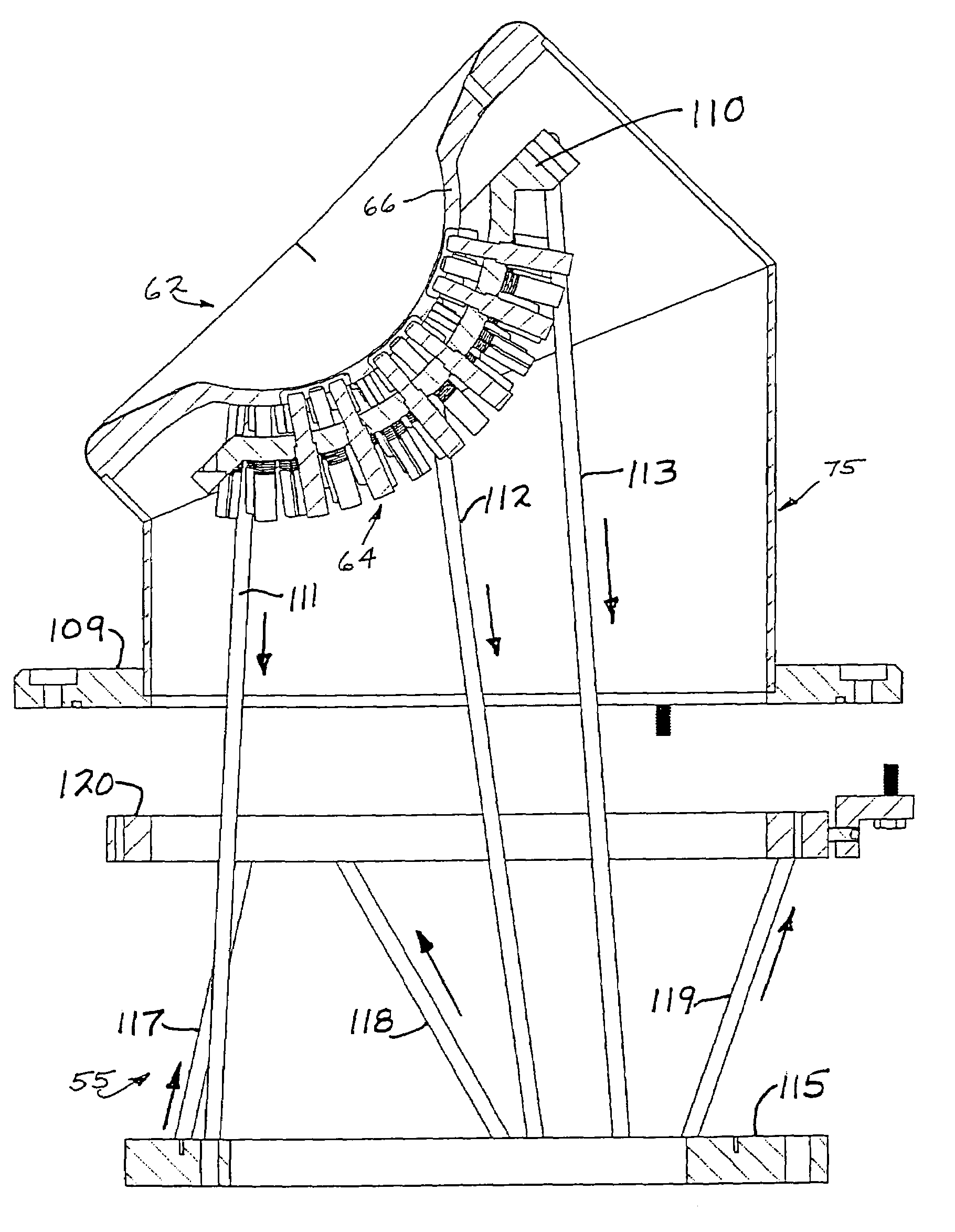
According to certain embodiments of the present invention, there is provided a mounting arrangement for a magnetoencephalography (MEG) system headrest assembly forming a portion of a SQUID dewar and having a fixed headrest and an array of sensors, wherein a sensor array plate positions the sensors relative to the headset. A plurality of first rods interconnecting the array plate and the movable mounting member. A plurality of second rods are fixed at one of their ends relative to the dewar and are connected at their opposite ends to the movable mounting member. Each one of the first and second rods is composed of material expandable and contractible with changes in temperature, whereby the movable mounting member tends to be moved in one direction toward or away from the sensor array plate, and tends to be moved in an opposite direction away from or toward the array plate, resulting in temperature changes affecting the first and second rods, so that the sensor array plate and its sensors maintain a substantially constant spacing between the sensors and the headrest with changes in temperature. A plurality of second rods are fixed at one of their ends relative to the dewar and are connected at their opposite Each one o the rods is composed of material expandible and contractable with changes in temperature, whereby the movable mounting member tends to be moved in one direction toward or away from the sensor array plate, and tends to be moved in an opposite direction away from or toward the array plate resulting in temperature changes affecting the first and second rods, so that the sensor array plate and its sensors maintain a substantially constant spacing between the sensors and and headrest with changes in temperature.
Owner:TRISTAN TECH
High-resolution magnetoencephalography system and method
Owner:TRISTAN TECH
Methods and apparatuses for 3D imaging in magnetoencephalography and magnetocardiography
InactiveUS20110313274A1Improve accuracyEffective informationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetocardiographyReconstruction problem
This invention discloses methods and apparatuses for 3D imaging in Magnetoencephalography (MEG), Magnetocardiography (MCG), and electrical activity in any biological tissue such as neural / muscle tissue. This invention is based on Field Paradigm founded on the principle that the field intensity distribution in a 3D volume space uniquely determines the 3D density distribution of the field emission source and vice versa. Electrical neural / muscle activity in any biological tissue results in an electrical current pattern that produces a magnetic field. This magnetic field is measured in a 3D volume space that extends in all directions including substantially along the radial direction from the center of the object being imaged. Further, magnetic field intensity is measured at each point along three mutually perpendicular directions. This measured data captures all the available information and facilitates a computationally efficient closed-form solution to the 3D image reconstruction problem without the use of heuristic assumptions. This is unlike prior art where measurements are made only on a surface at a nearly constant radial distance from the center of the target object, and along a single direction. Therefore necessary, useful, and available data is ignored and not measured in prior art. Consequently, prior art does not provide a closed-form solution to the 3D image reconstruction problem and it uses heuristic assumptions. The methods and apparatuses of the present invention reconstruct a 3D image of the neural / muscle electrical current pattern in MEG, MCG, and related areas, by processing image data in either the original spatial domain or the Fourier domain.
Owner:SUBBARAO MURALIDHARA
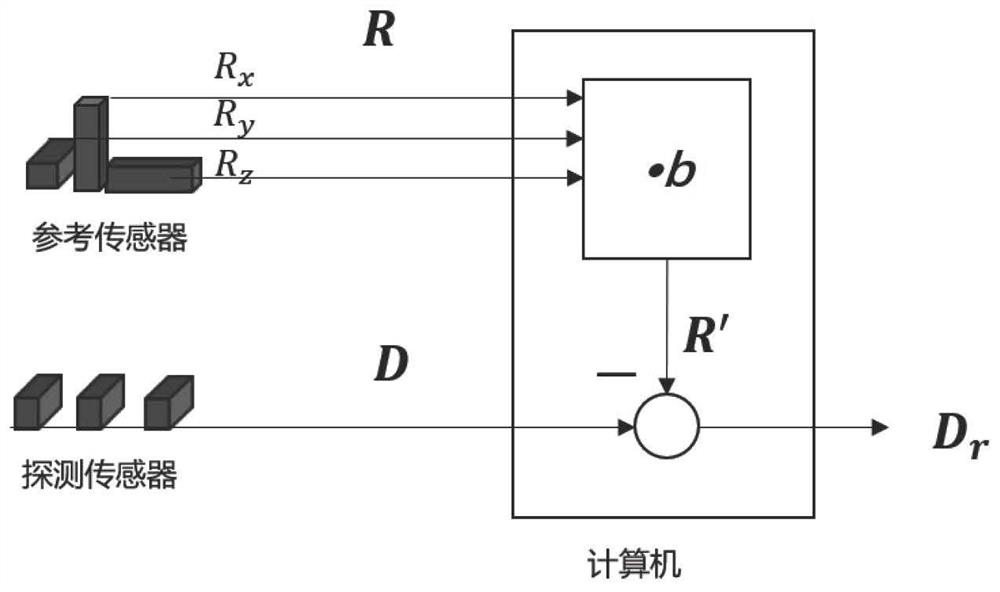
Multi-dimensional parameter identification method and device: application to the location and reconstruction of deep electrical activities by means of surface observations
InactiveUS20090093964A1Easy to openGood estimateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityMagnetoencephalography
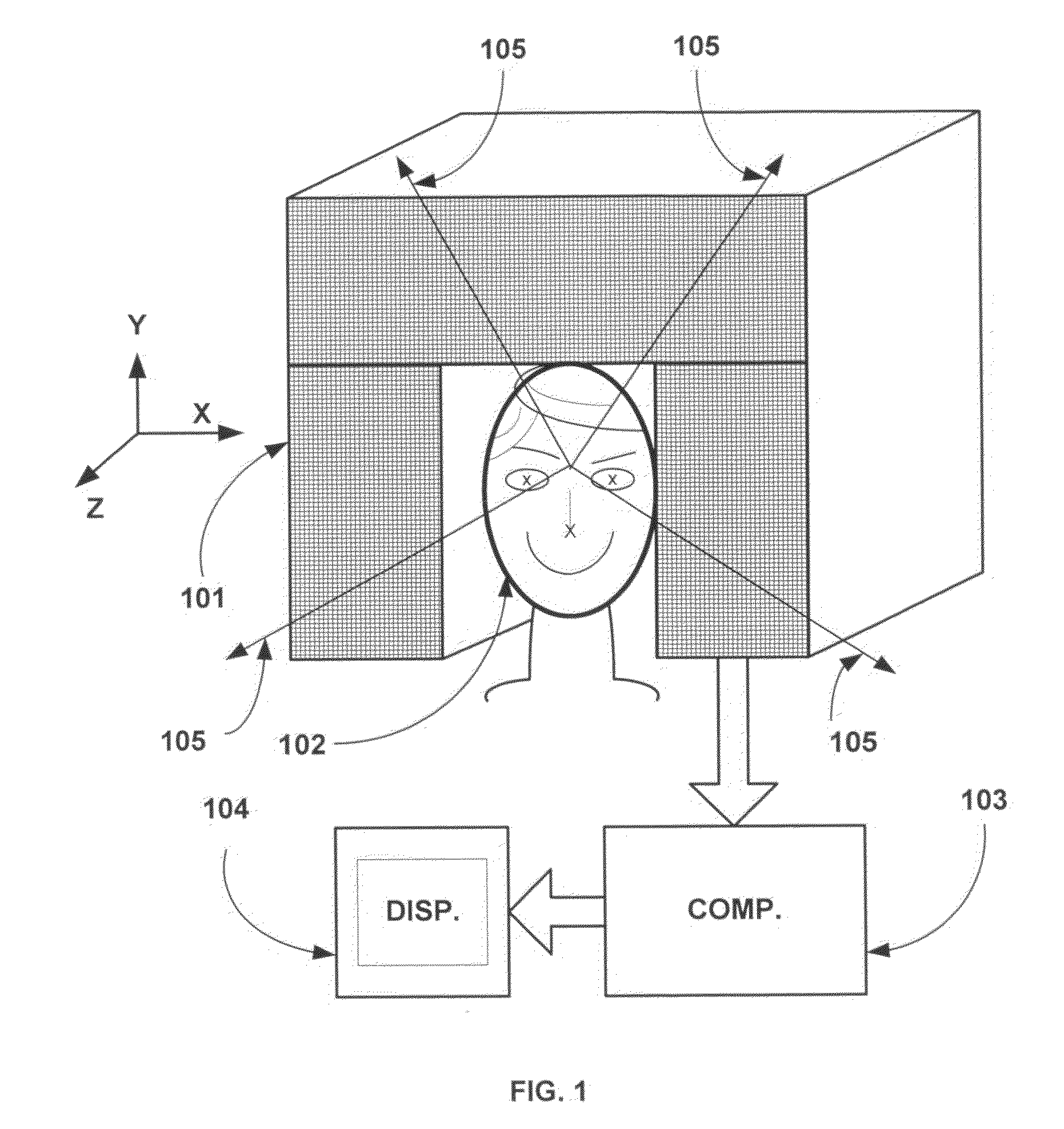
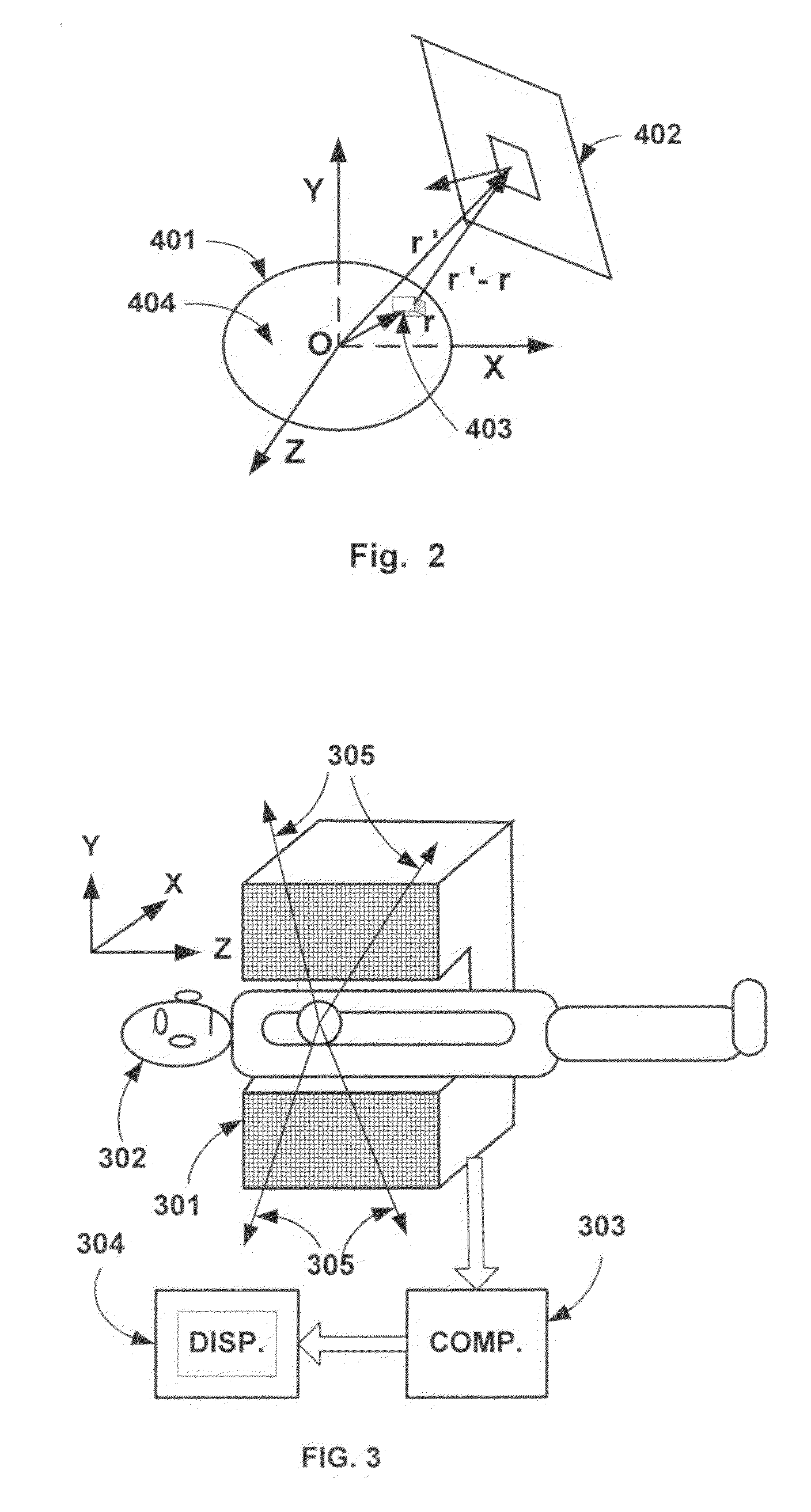
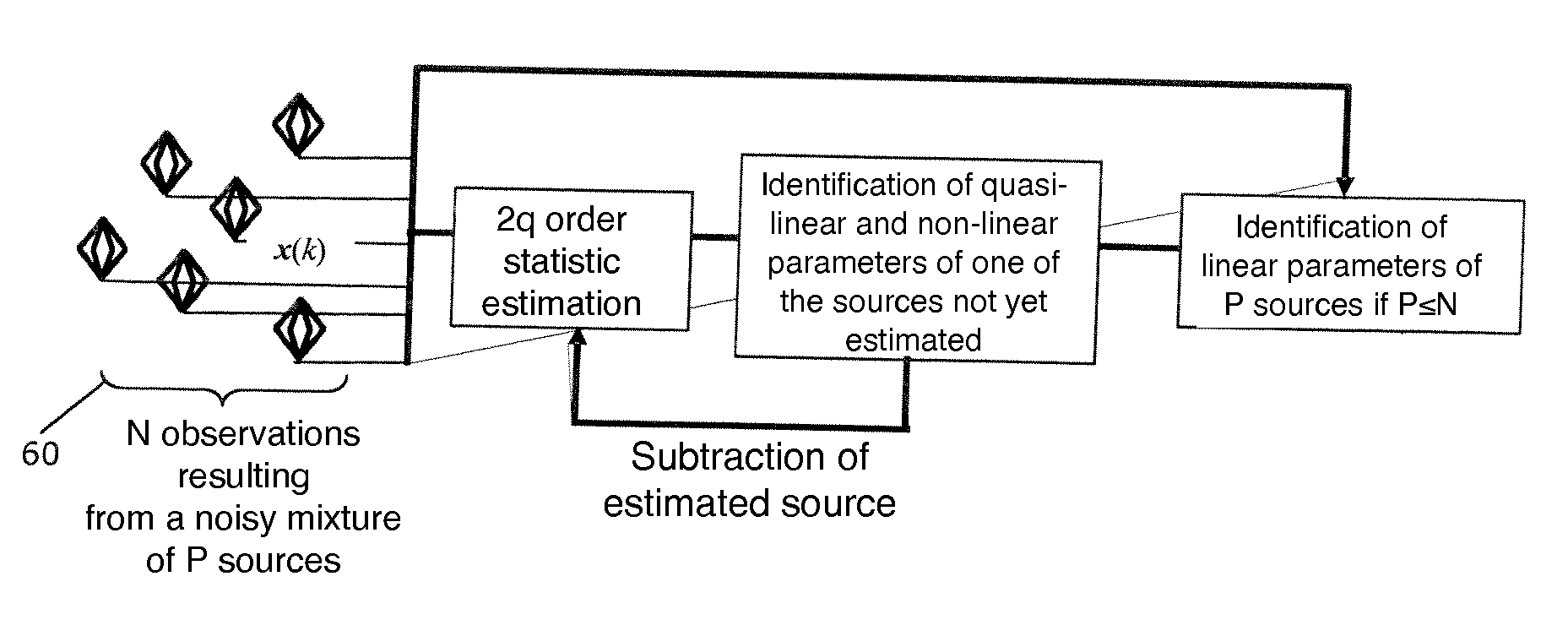
A method is provided for identifying multidimensional parameters of a plurality of P>1 sources of interest present in a predetermined multidimensional conductive environment by a plurality of observations (60) in a finite number of N≧1. The method includes using i) a factorisation of a problem matrix formulation, ii) the creation of a virtual network of the order 2q (q>1) sensors by using cumulants of order 2q from observations and iii) the concept of an extended deflation of order 2q taking into consideration the presence of potentially (but not entirely) correlated sources. The method and device can be used for electroencephalograpy, magnetoencephalography, geophysics and seismology.
Owner:UNIV DE RENNES I
Location method for dynamic neuromagnetic source
ActiveCN105212895ARealize reverse estimation solutionDynamic positioning is faster and more preciseImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringTime domainMagnetoencephalography
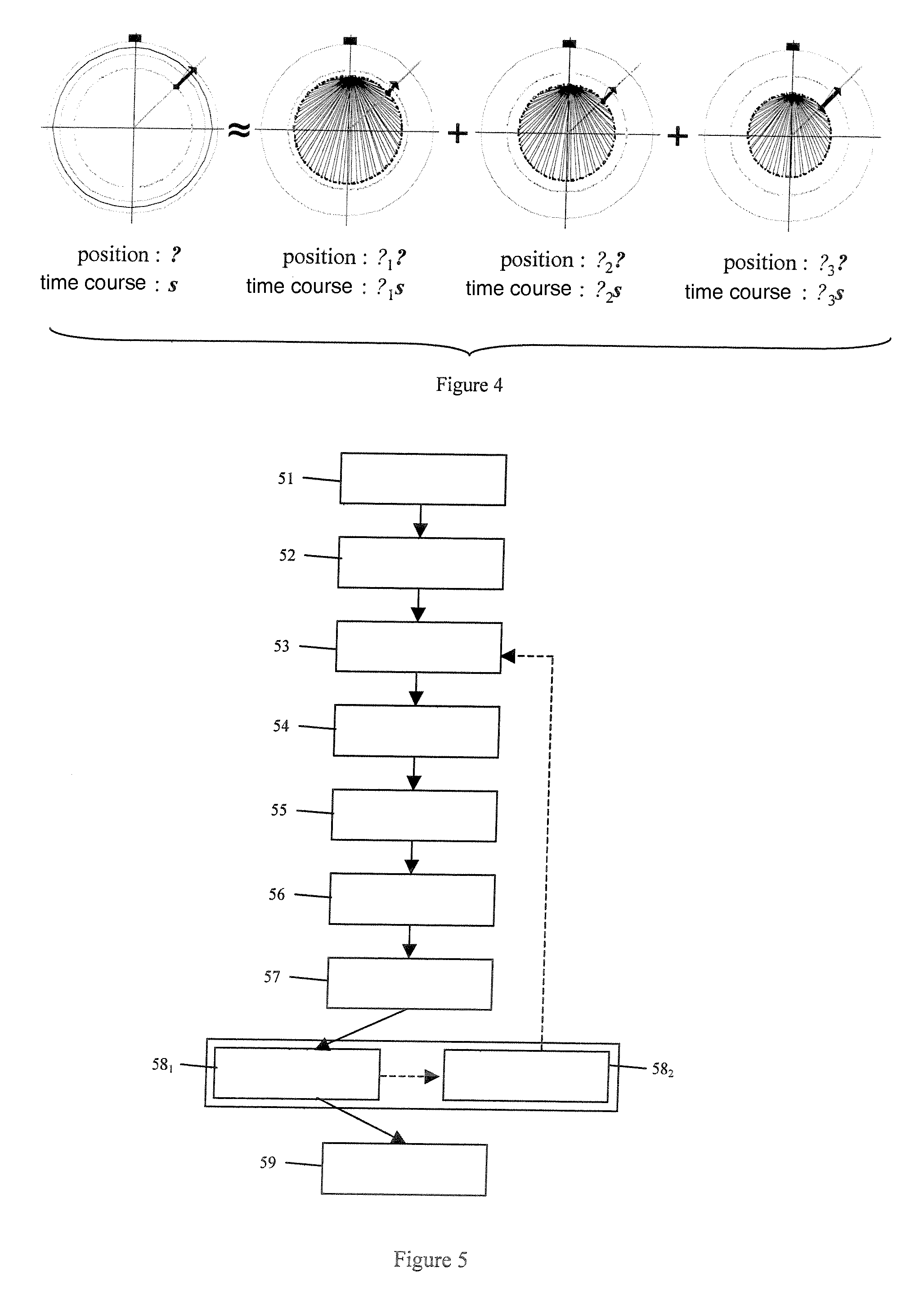
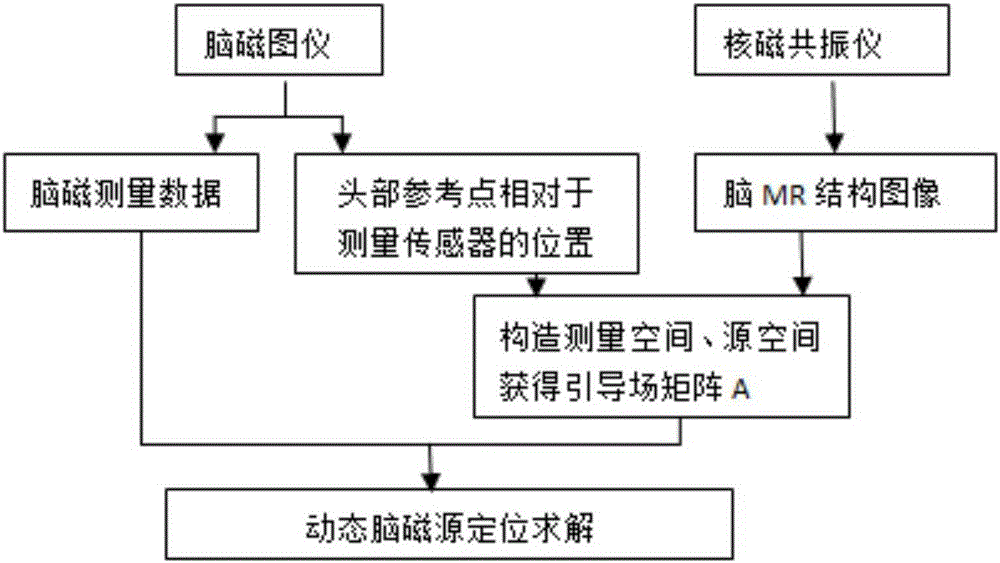
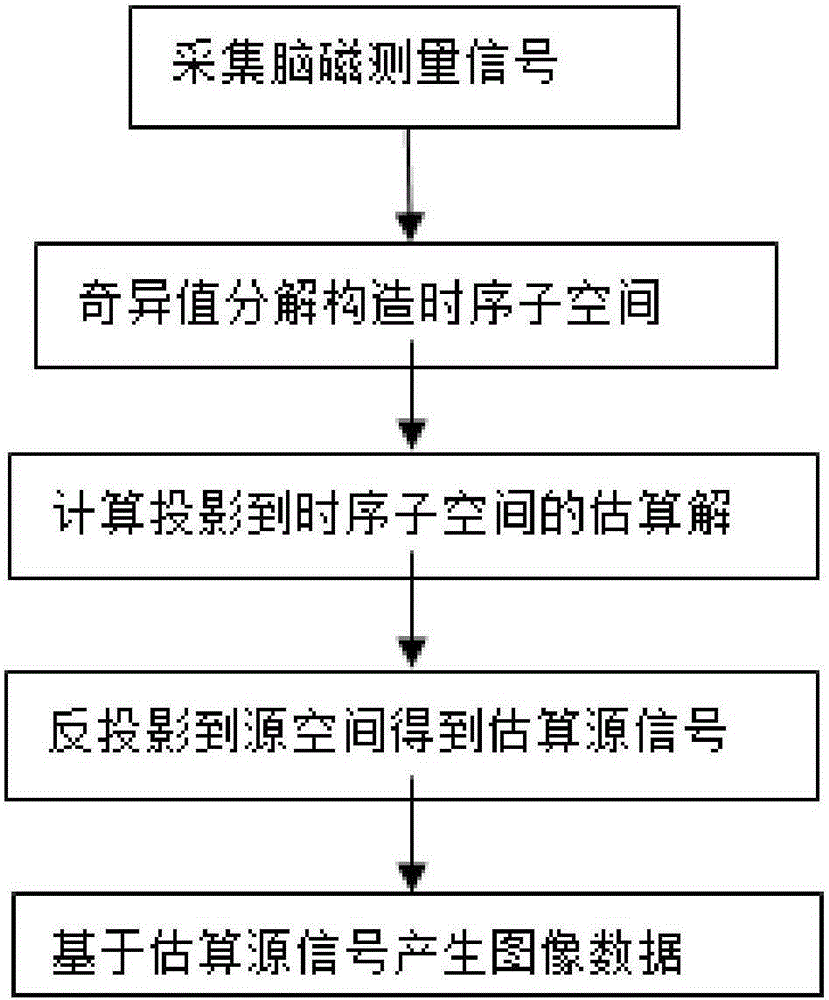
The invention discloses a location method for a dynamic neuromagnetic source. The location method comprises following steps: collecting a brain MR structure image and a magnetoencephalography MEG signal B and setting measurement space; setting space where a source signal is formed in the cerebral cortex as source space; determining the space-shifting relation between measurement space and source space and further determining the relation between an MEG signal B and a source signal matrix X, constructing subspace for the time domain, projecting the MEG signal B and the source signal matrix X to the subspace for the time domain, solving in order to obtain a source signal X, and extracting position information of the source signal X and intensity information thereof so that a location process for the dynamic neuromagnetic source is finished. The location method for the dynamic neuromagnetic source has following beneficial effects: the technical problem that the dynamic neuromagnetic source is not easily positioned is solved; and especially the technical problem that a transmitting process for a mutant neuromagnetic source signal is not easily studied is also solved.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
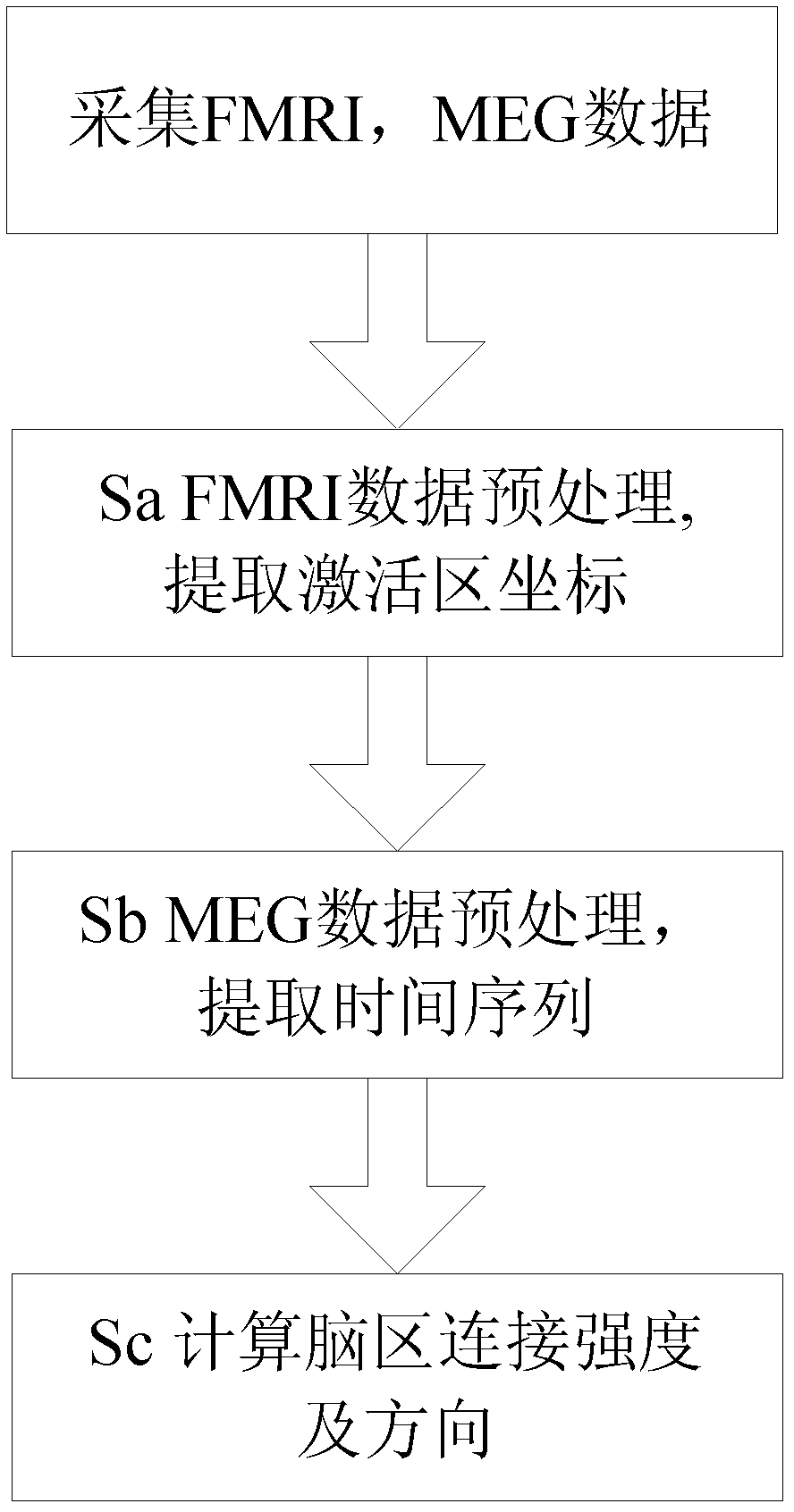
Encephalic region causal connection detection method combining functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI) and magnetoencephalography (MEG)
InactiveCN102496159AComplete and accurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisMagnetoencephalographyComputer vision
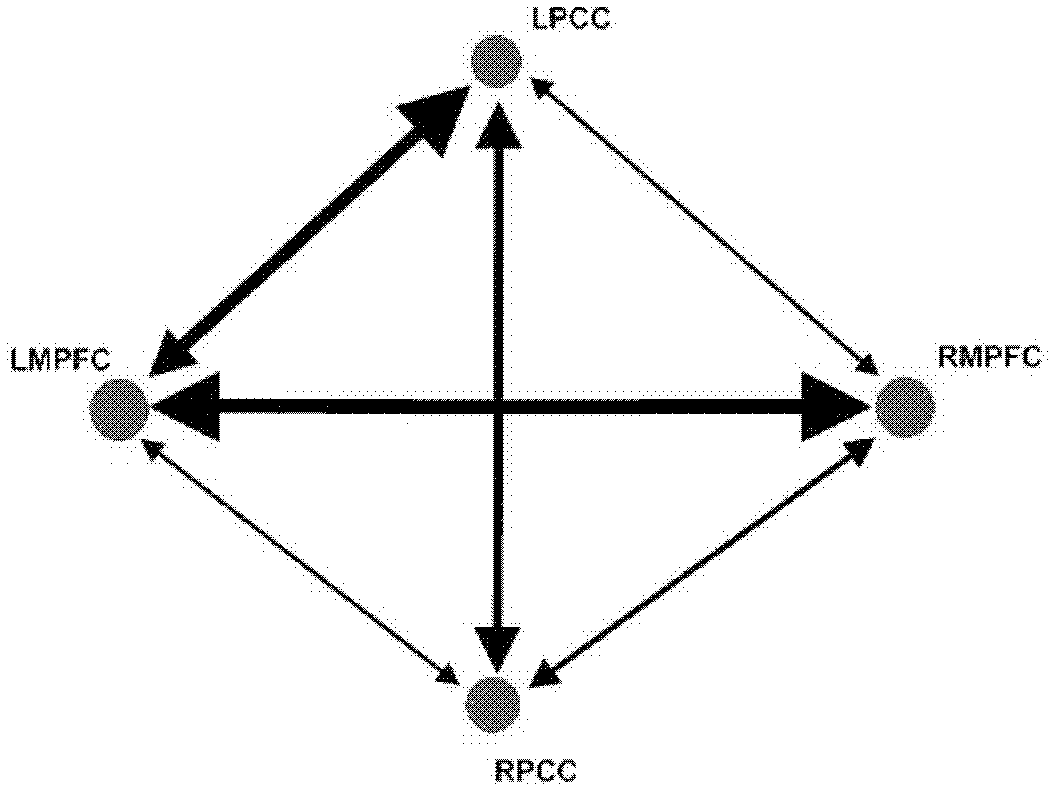
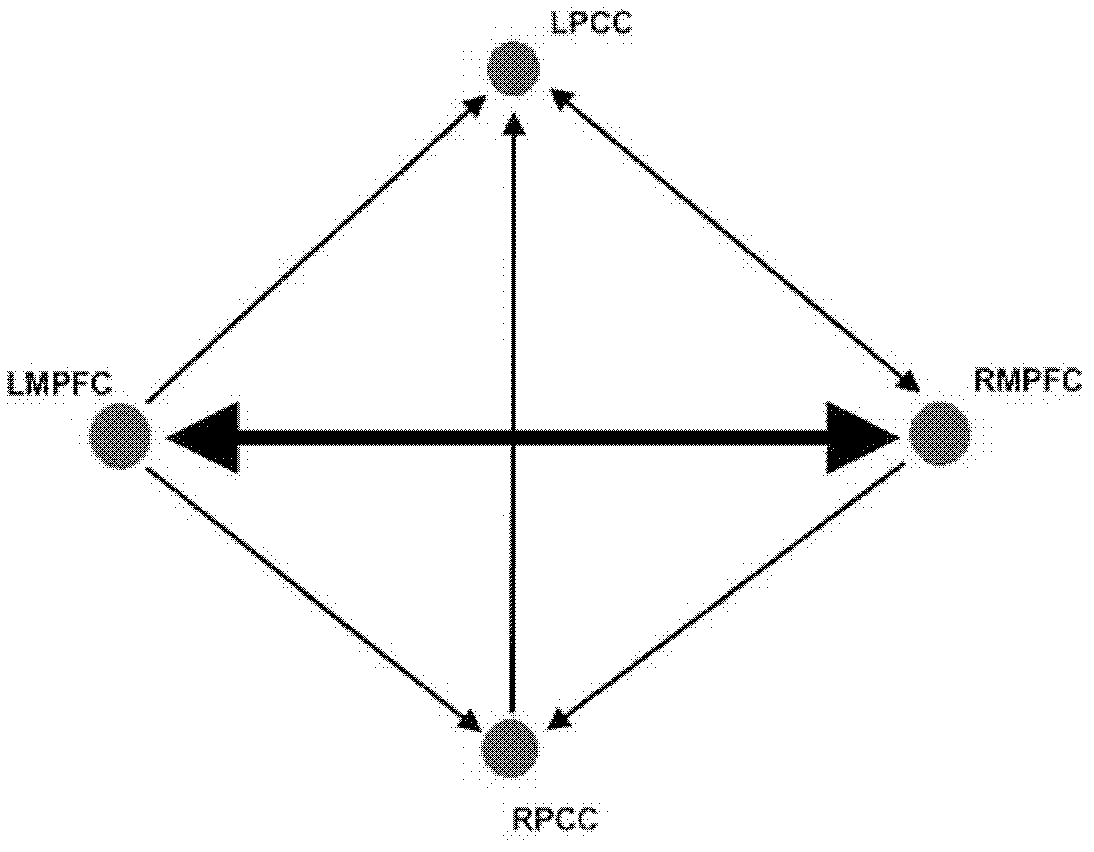
The invention relates to an encephalic region causal connection detection method combining functional magnetic resonance imaging (FMRI) and magnetoencephalography (MEG), which comprises the following steps that: firstly, a coordinate of an active region is extracted from a FMRI image after the data preprocessing; secondly, an encephalic region time sequence of a corresponding position region is extracted from an MEG data after being preprocessed on the basis of the extracted FMRI active region coordinate; and thirdly, the causal connection strength and direction between every two adjacent encephalic regions are calculated according to the extracted MEG encephalic region time sequence, and an oriented network image is used for displaying a remarkable connection. The method is a valid encephalic region causal connection detection method combining two imaging modes such as FMRI and MEG, so the encephalic region causal connection can be more complete and more accurate to detect compared to the detection method by only utilizing the FMRI image.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
EEG (Electroencephalograph) electrode cap
ActiveCN104382594AEasy to fixExtended service lifeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHigh densityMedicine
The invention relates to an EEG (Electroencephalograph) electrode cap. The EEG electrode cap comprises a cap body, electrodes and leading wires, wherein each electrode comprises a fixing ring, an electrode slice and a bonding sealant; a cavity of which two ends are opened and are communicated is formed in the middle part of each fixing ring, each cavity is internally provided with an electrode slice locating platform, and the electrode slices are arranged on the electrode slice locating platforms; one side of each electrode slice is fixed with the inner wall of the cavity of the corresponding fixing ring through the bonding sealant, and the other side of each electrode slice is combined with a conductive adhesive in a conductive adhesive chamber; fixing grooves are formed in the outer cylindrical surfaces of the fixing rings, and the fixing grooves are used for fixing the electrodes with the cap body; conductive adhesive filling holes which are communicated with the conductive adhesive chamber are formed in the bonding sealant after the bonding sealant is solidified; the electrode slices are connected with the leading wires penetrating through leading wire holes in the fixing rings. The EEG electrode cap disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the electrode slices and the fixing rings are integrally designed, and skin pretreatment, adhesive filling and adhesive supplementation can be conveniently carried out; the locating is convenient and reliable, the EEG electrode cap is tightly attached to the scalp, the wearing is comfortable, and the EEG electrode cap is particularly suitable for EEG measurement under the environment of high density, long sleep process, MEG (Magnetoencephalography) and nuclear magnetism.
Owner:WUHAN GREENTEK
Wearable type portable quantum magnetoencephalography system and method
InactiveCN109567784ARealize acquisitionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetoencephalographyQuantum detector
The invention discloses a wearable type portable quantum magnetoencephalography system and method. The wearable type portable quantum magnetoencephalography system comprises a magnetoencephalographiccap, fixed slots, limiting clamping sleeves and quantum detectors, wherein the magnetoencephalographic cap is a rubber cap which is made of a flexible material and has flexibility; the magnetoencephalographic cap is provided with a plurality of fixed slots which are uniformly arrayed; one limiting clamping sleeve is arranged at the periphery of each fixed slot; each quantum detector is fixedly mounted on the corresponding limiting clamping sleeve; a detection end of each quantum detector extends into the corresponding fixed slot. The quantum detectors are used for replacing traditional ultrasonic equipment and a detection array is formed into a wearable form, so that portable acquisition of magnetoencephalographic signals is realized and the system has a wide application prospect in clinical and scientific researches. The magnetoencephalographic cap with certain flexibility is matched with the fixed slots with the matched size to from the detection array which can extend and retract toa certain extent; the wearable type portable quantum magnetoencephalography system is applicable to almost people by just designing the magnetoencephalographic caps with different sizes.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
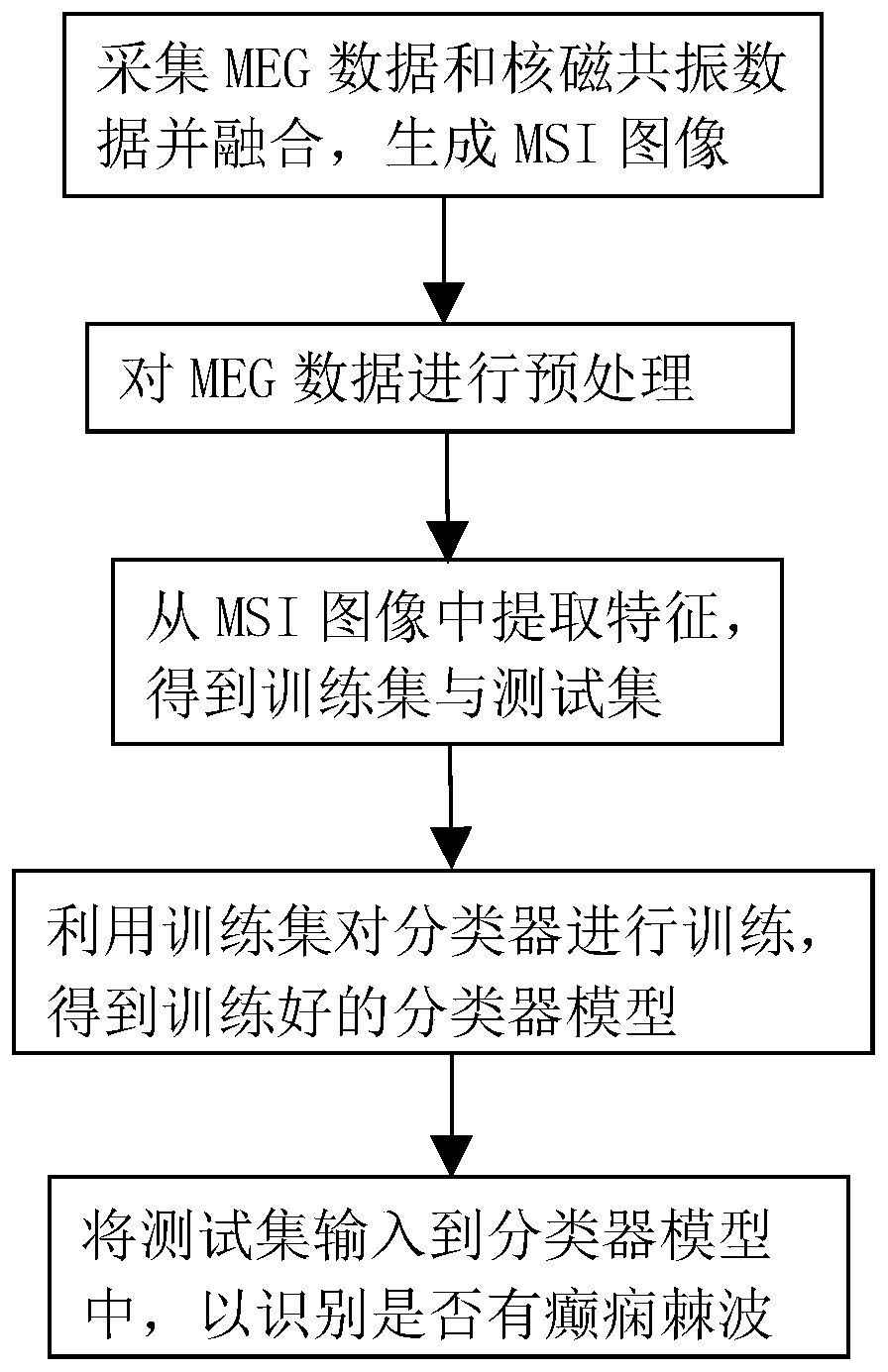
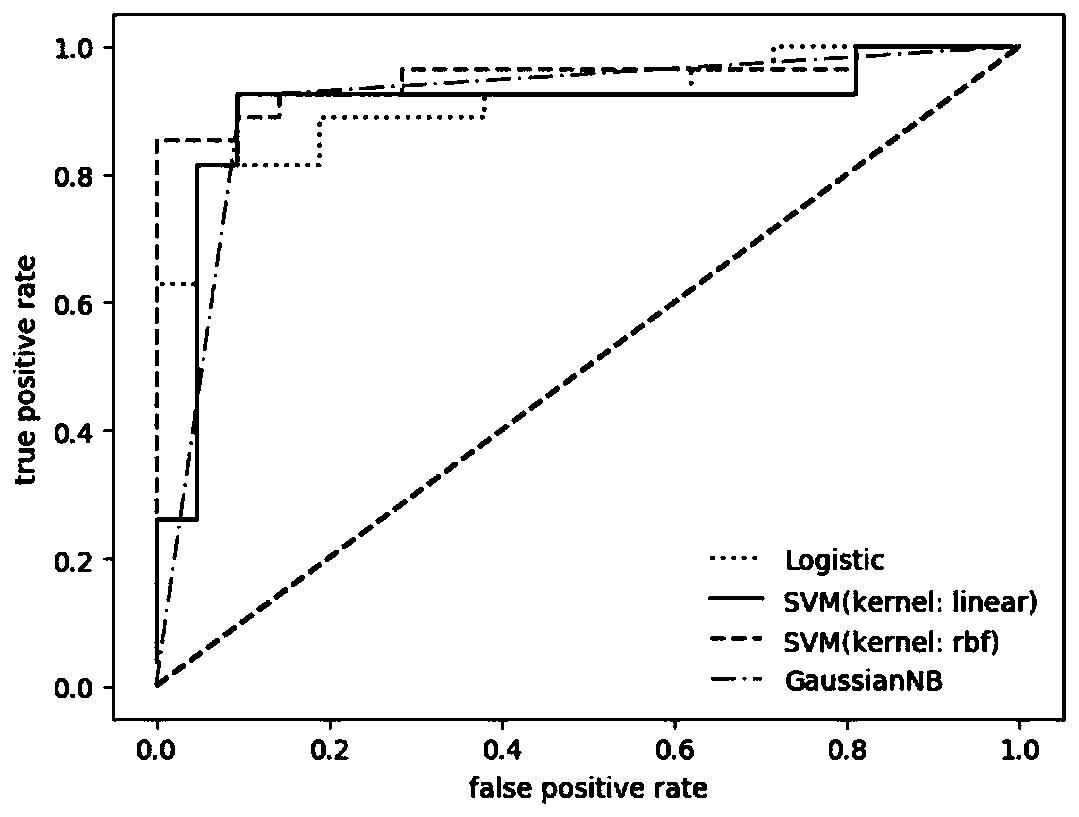
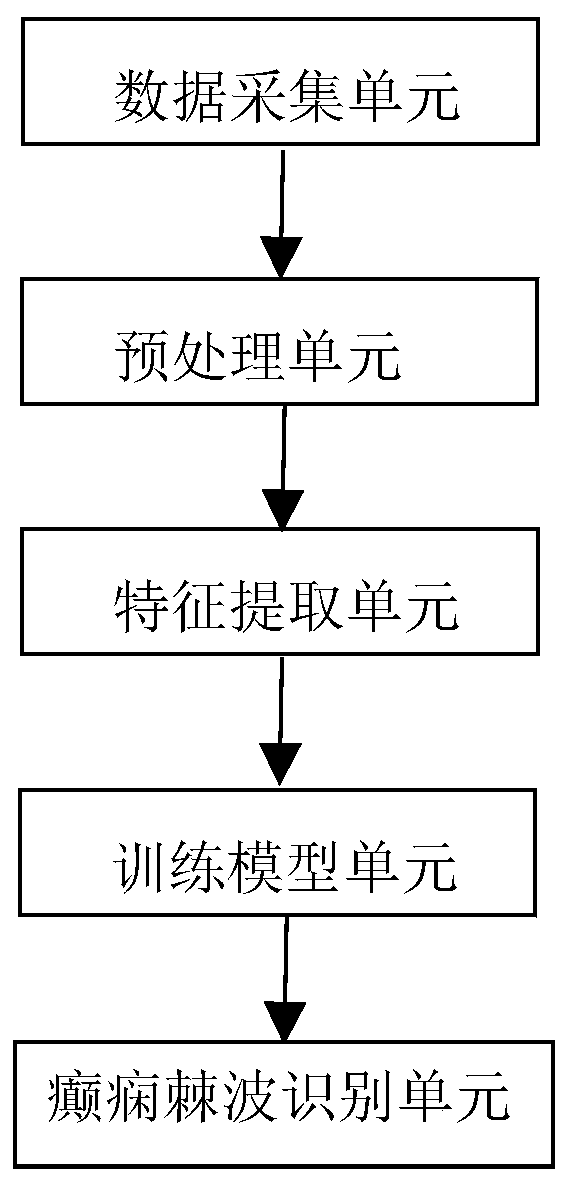
Magnetoencephalography epileptic spike wave recognition method and system
ActiveCN109700463AReduce labor intensityReduce missed detection rateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFeature vectorData set
The invention relates to a magnetoencephalography epileptic spike wave recognition method and system. The method comprises the following steps of dividing MEG data into spike wave data and non-spike wave data, and pretreating the MEG data to respectively obtain the spike wave data and the non-spike wave data, of which the N segment phases are the same in length; performing analytical treatment onthe obtained segments of data, performing extraction to obtain characteristic vectors of various segments of data to form a sample dataset, and dividing the sample dataset into a training set and a test set; training a radial primary kernel function support vector machine classifier through the training set to obtain a trained classifier model; and inputting the test set to the classifier model torecognize whether epileptic spike waves exist or not. Automatic recognition of epilepsy brain magnetic signals can timely judge the condition of the patients, wherein the judgment accuracy rate can achieve 93.8%, the labor intensity of doctors is reduced, the detection accuracy rate is increased, and the omission factor and the false positive rate are reduced. The magnetoencephalography epilepticspike wave recognition method and system have important significance clinically.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Magnetoencephalography biomarkers of gaba-b agonist drug activity in autism spectrum disorders
ActiveUS20160022207A1Improve response delayReduce delaysDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsClinical psychologyAgonist drugs
Owner:THE CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF PHILADELPHIA
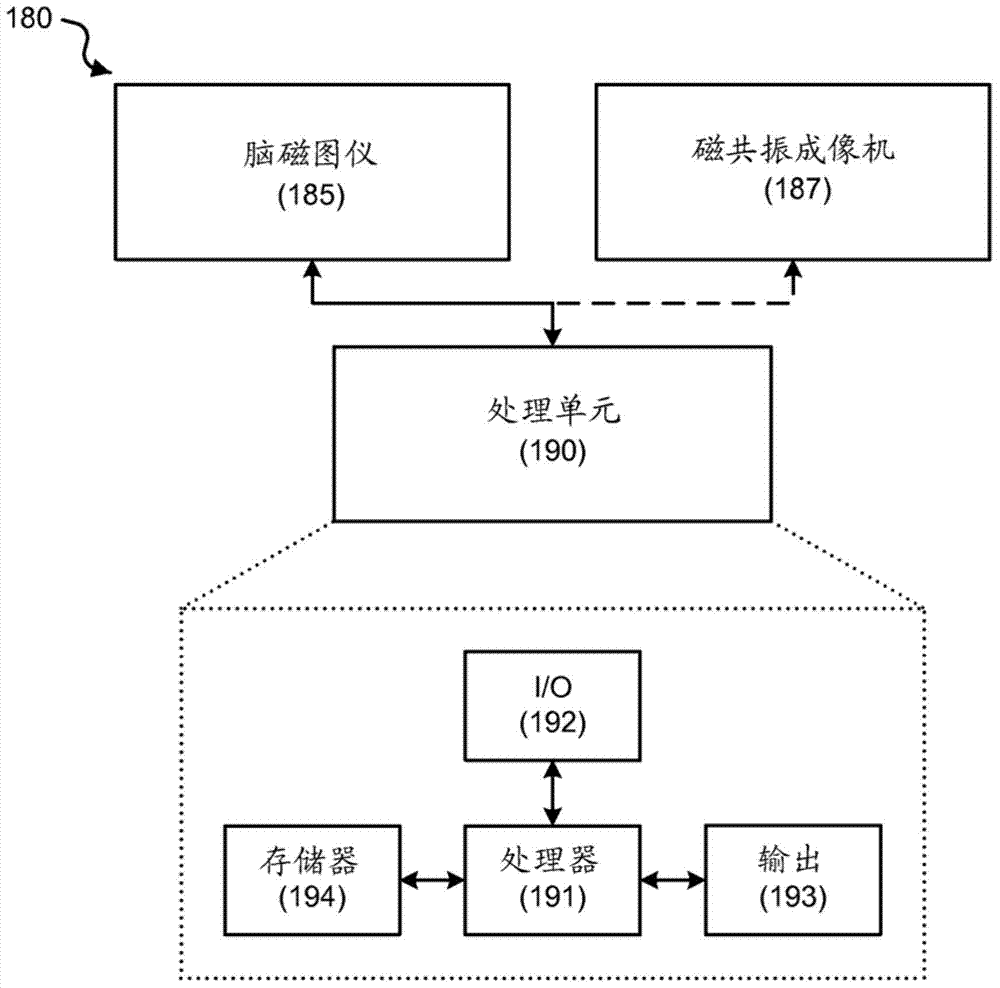
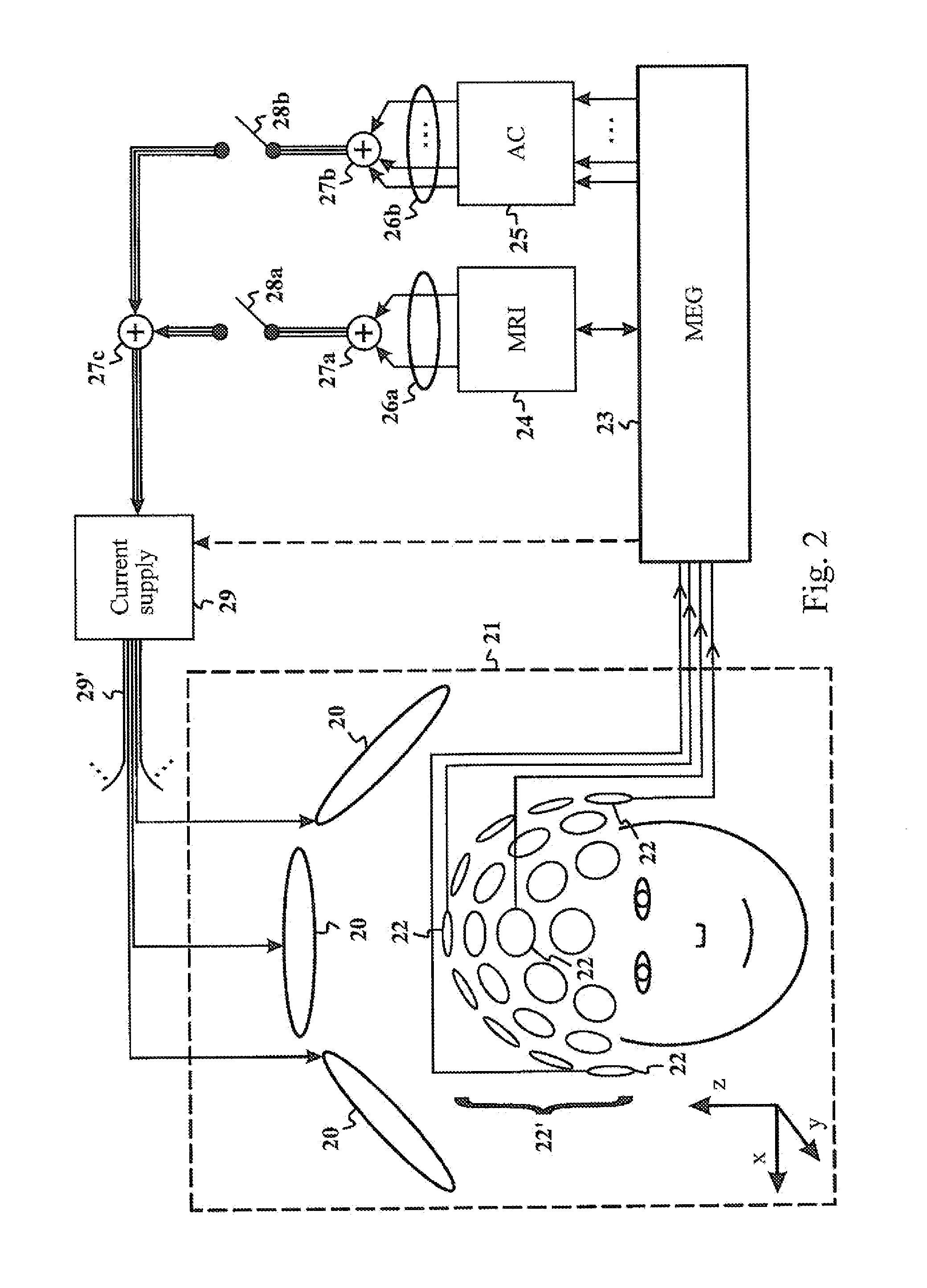
Method for designing coil systems for generation of magnetic fields of desired geometry, a magnetic resonance imaging or magnetoencephalography apparatus with a coil assembly and a computer program
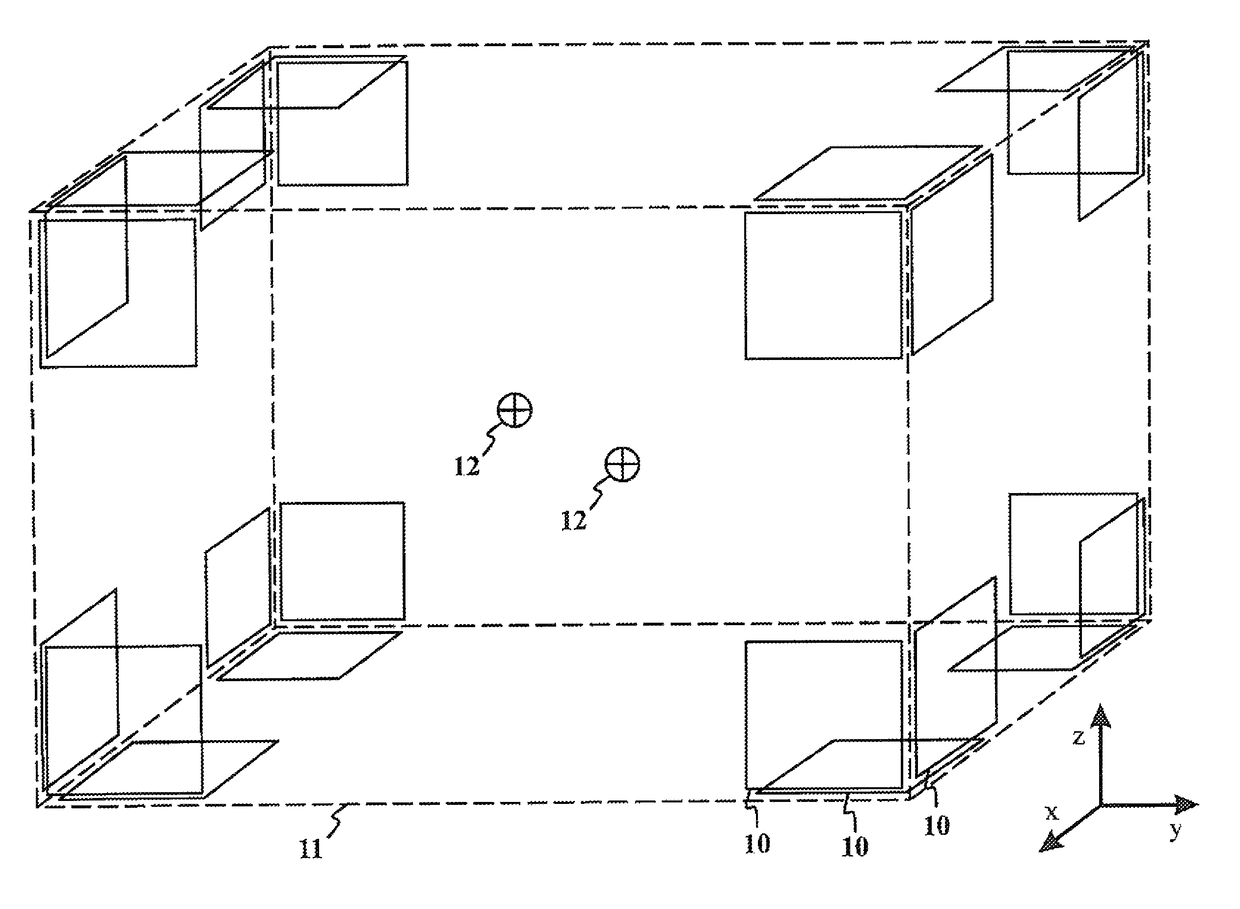
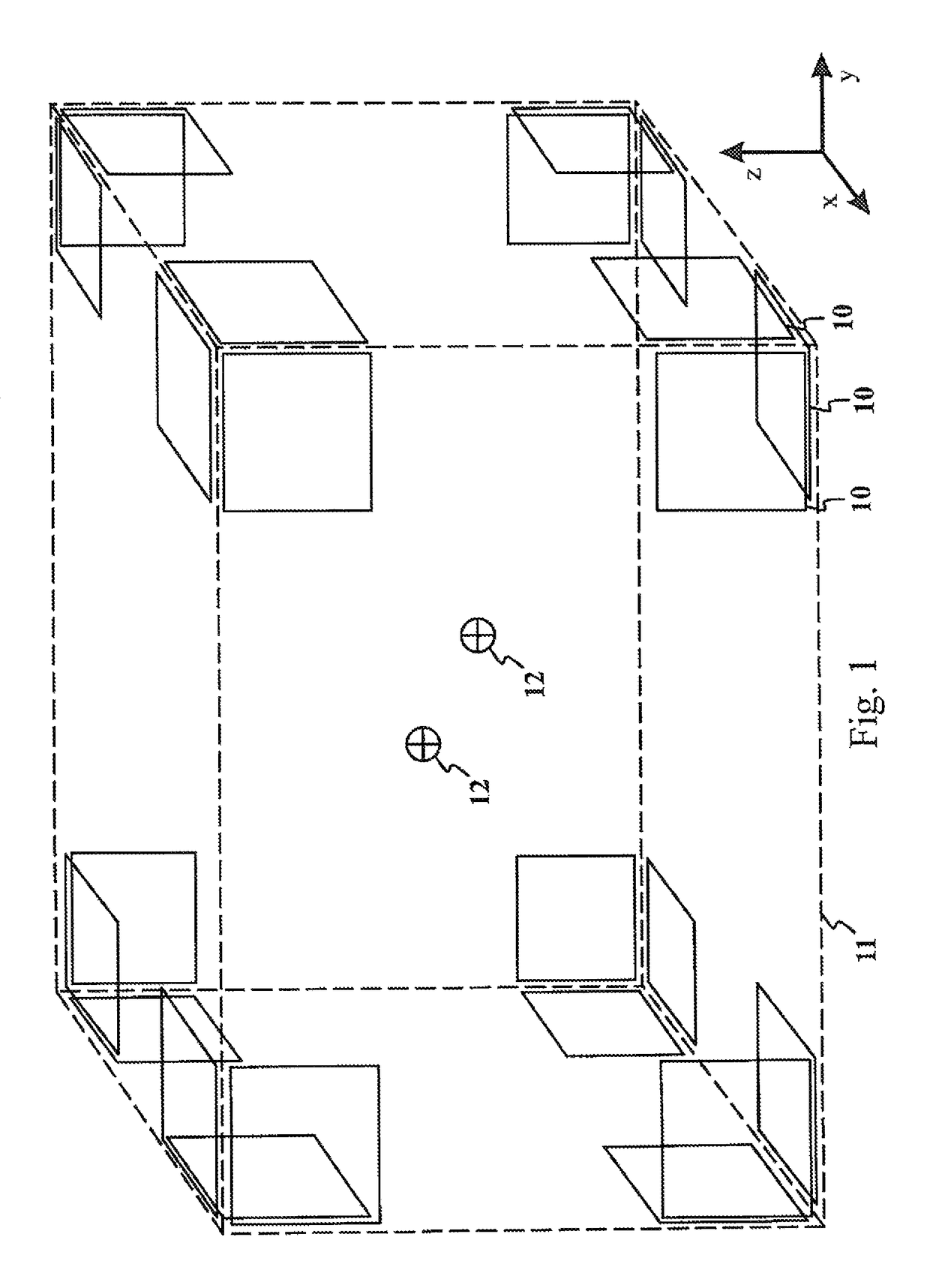
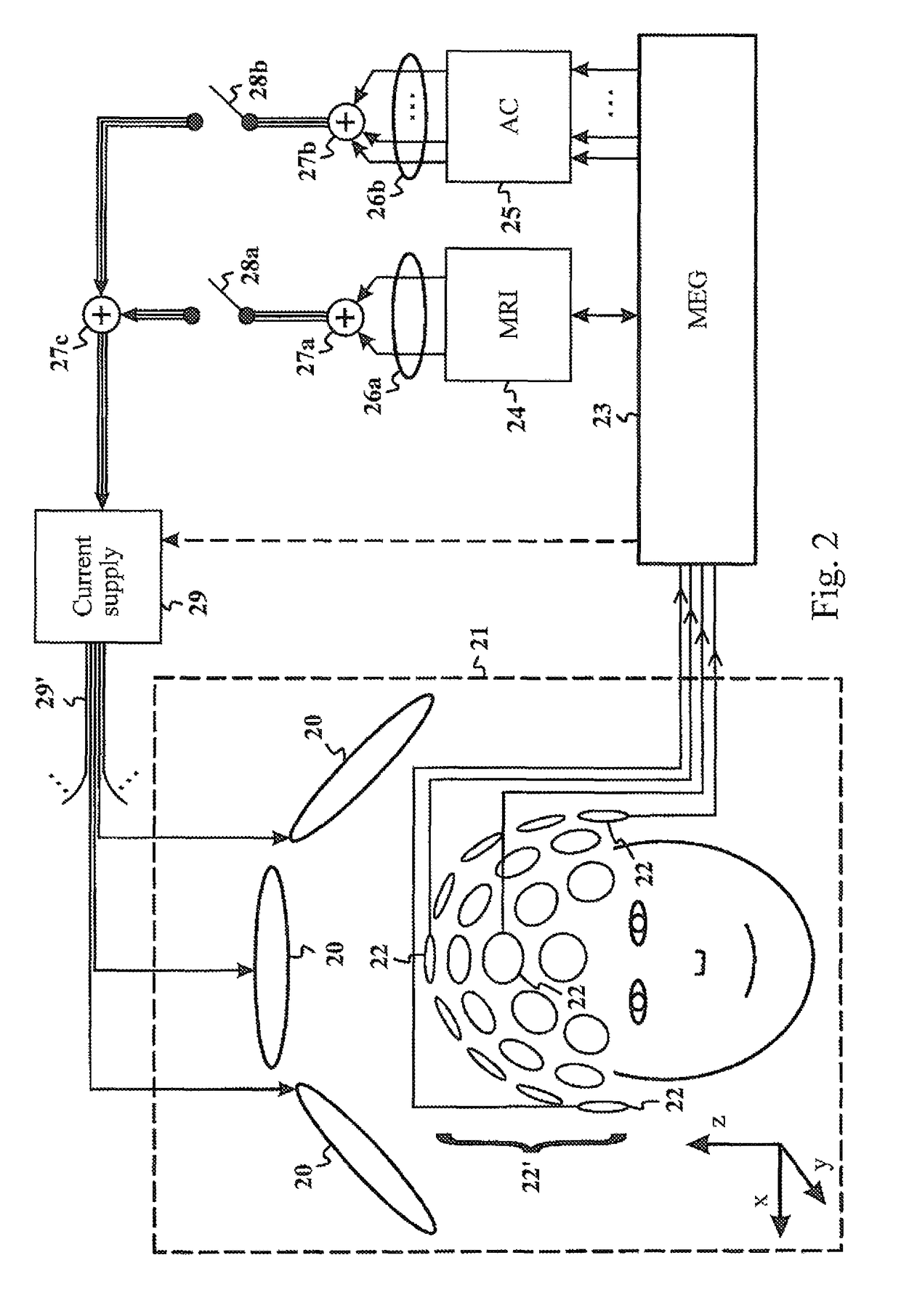
ActiveUS20130197838A1CouplingMinimize couplingResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase anglePrincipal component analysisMagnetoencephalography
The present invention introduces a method, apparatus and computer program for magnetic resonance imaging or magnetoencephalography applications in order to control currents of a coil assembly (20), and thus achieving desired magnetic fields precisely in the measuring volume (21). The approach is an algebraic method where a field vector is generated for the test currents of each coil (20). Vector and matrix algebra is applied and a linear set of equations is formed. Field components and their derivatives up to the desired order can be taken into account. Principal component analysis or independent component analysis can be applied for determination of the dominant external interference components. By checking the condition value for the matrix (33, 45), it is possible to investigate whether a reasonable solution of currents for desired magnetic fields is possible to achieve. Finally, solved currents can be installed into a current supply unit (29) feeding the coils of the assembly (20). The invention can be applied as an active compensation feature for different interference shapes in the MEG application (25), or for the precise creation of the fields and gradients in the MRI application (24).
Owner:MEGIN OY
Quantum magnetoencephalography system and method based on magnetic shielding cylinder
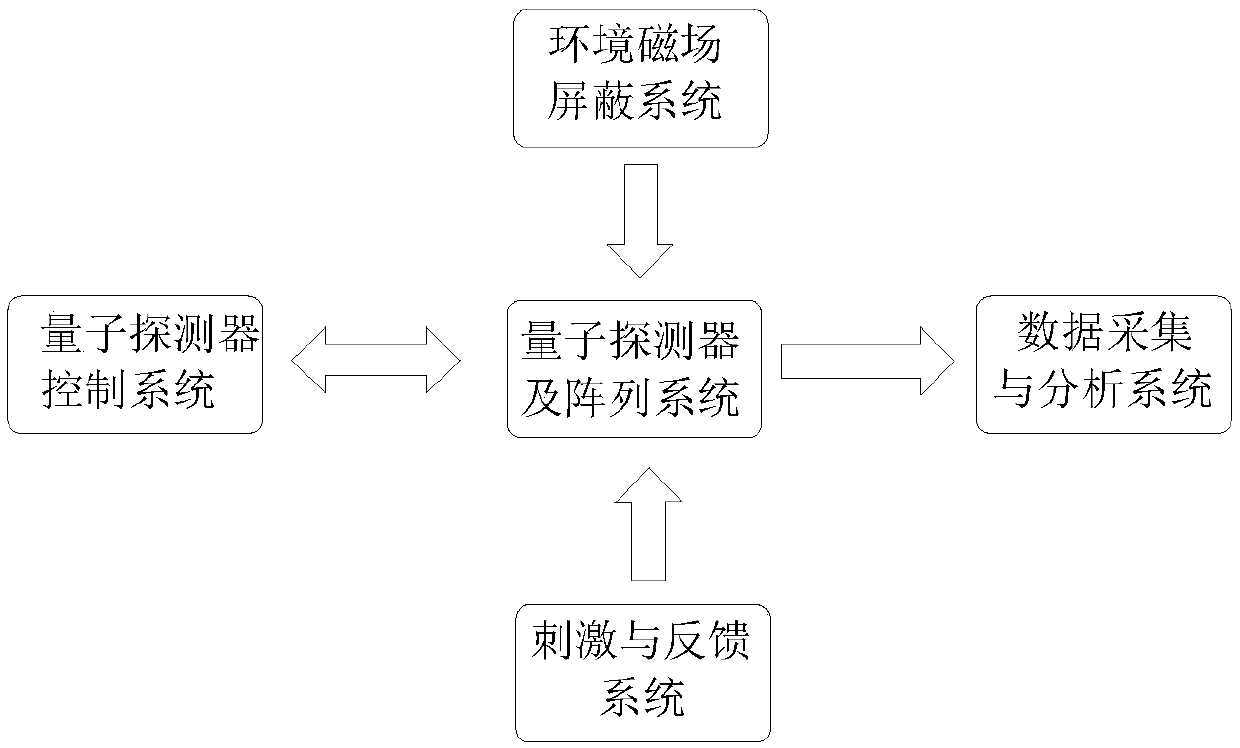
InactiveCN109567785AReduce operating costsAvoid lostDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOperational costsControl system
The invention discloses a quantum magnetoencephalography system and method based on a magnetic shielding cylinder. The system comprises a quantum detector and array system, an environmental magnetic field shielding system, a quantum detector control system, a data acquisition and analysis system, and a stimulation and feedback system, wherein the quantum detector and array system are bidirectionally connected with the quantum detector control system through signals; the quantum detector control system and the stimulation and feedback system are connected with the data acquisition and analysissystem through signals; and the quantum detector and array system is externally provided with the environmental magnetic field shielding system. The quantum magnetoencephalography system and method disclosed by the invention have the technical effects that the operating cost is low; a detection array can be flexibly changed for matching the contour of an individual head, so that the detection efficiency is increased; meanwhile, the system and device can be extended to high-efficiency signal detection of people at different ages; the extra loss of brain magnetic signals is avoided in the spatial distance, and the absolute signal strength is improved; and the magnetic shielding cylinder is used for replacing a shielded room necessary for traditional magnetoencephalography, so that the performance of magnetic shielding is significantly improved while the cost is saved.
Owner:BEIJING QUANMAG HEALTHCARE CO LTD
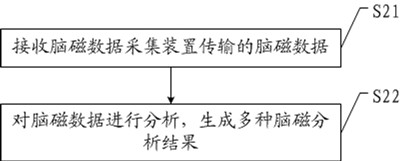
Magnetoencephalography data acquisition and analysis method and system
InactiveCN113827246AAvoid defectsEasy to useDiagnostic signal processingHealth-index calculationMagnetoencephalographyData acquisition
The invention provides a magnetoencephalography data acquisition and analysis method and system, and relates to the technical field of medicine. The magnetoencephalography data acquisition and analysis method is applied to the magnetoencephalography data acquisition and analysis system based on an atom magnetometer, wherein the system comprises a stimulation generation device, a magnetoencephalography data acquisition device and a magnetoencephalography data analysis device; the magnetoencephalography data acquisition device is connected with the magnetoencephalography data analysis device; and the stimulation generation device and the magnetoencephalography data acquisition device both act on a subject. The method comprises the steps that the magnetoencephalography data acquisition device acquires magnetoencephalography data generated by the subject under stimulation of the stimulation generation device, and the magnetoencephalography data analysis device receives the magnetoencephalography data transmitted by the magnetoencephalography data acquisition device and analyzes the magnetoencephalography data to generate various brain magnetic analysis results. The complete magnetoencephalography analysis method and system can be provided for the atom magnetometer, and experiment and clinical analysis are facilitated.
Owner:HANGZHOU INNOVATION RES INST OF BEIJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Magnetoencephalography device and method of using the same
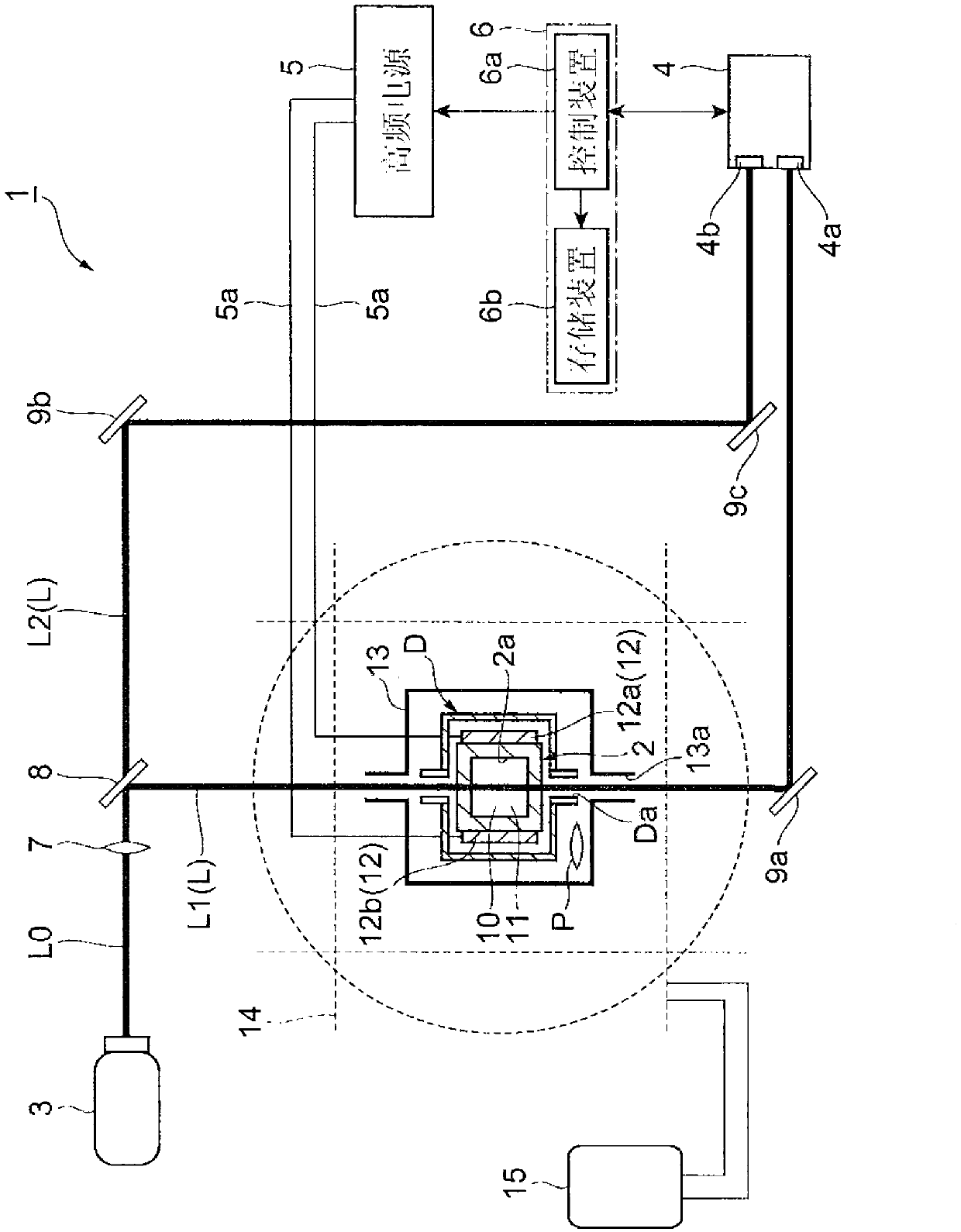
InactiveCN1735376AAvoid captureMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesDiagnostic recording/measuringLow noiseElectrical conductor
It is possible to provide a magnetoencephalography device having a low noise and a high sensitivity. When installing on a floor the magnetoencephalography device using a high-temperature superconductor magnetic shield device, anti-vibration means is provided to eliminate generation of a noise and to eliminate relative movement between the high-temperature superconductor magnetic shield and an SQUID fluxmeter. Even if an inevitable small vibration is caused, the fluctuation component detected by the SQUID fluxmeter is not generated from static magnetism trapped.
Owner:NAT INST OF INFORMATION & COMM TECH
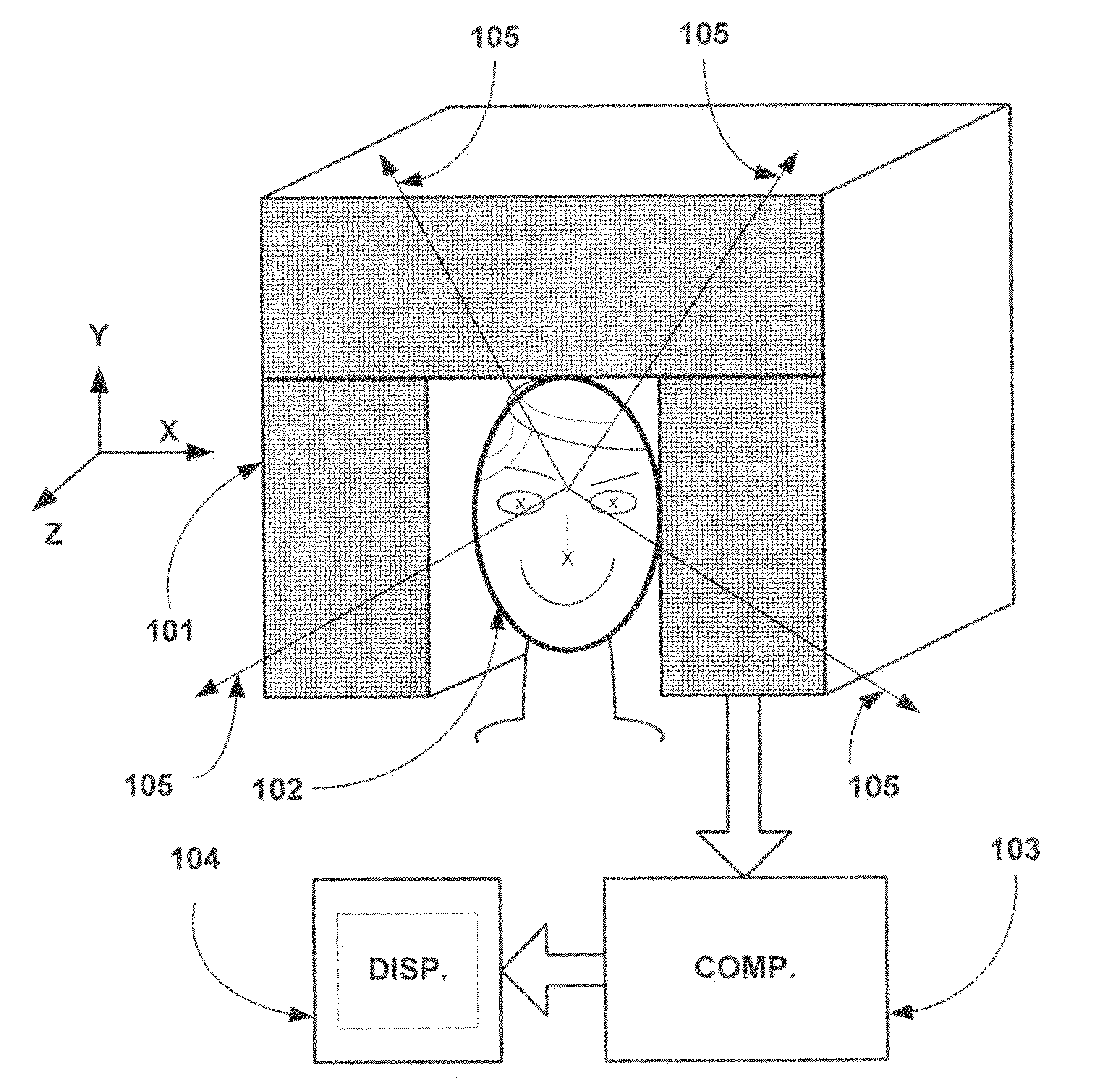
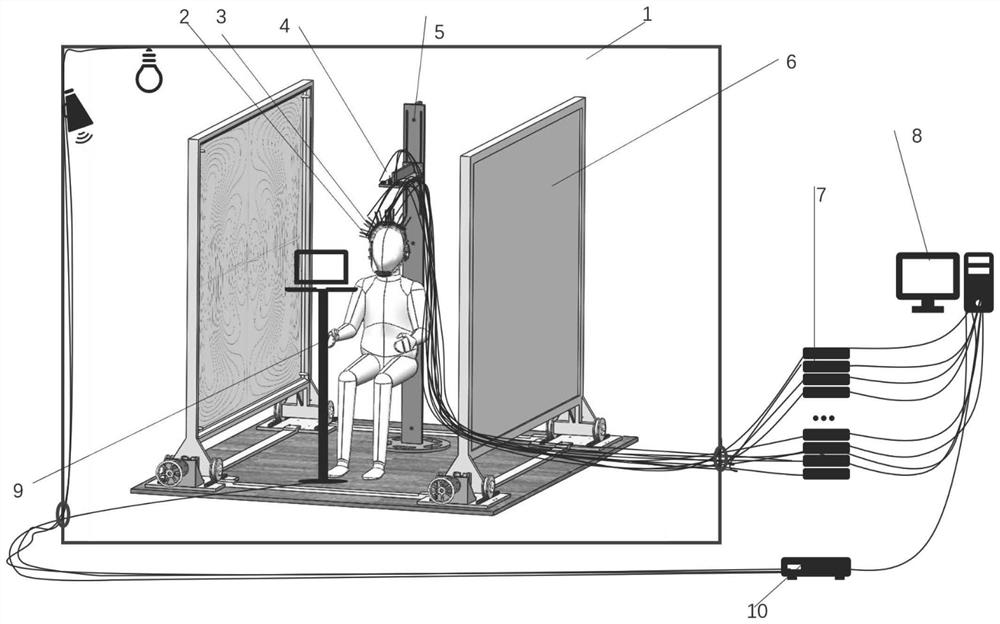
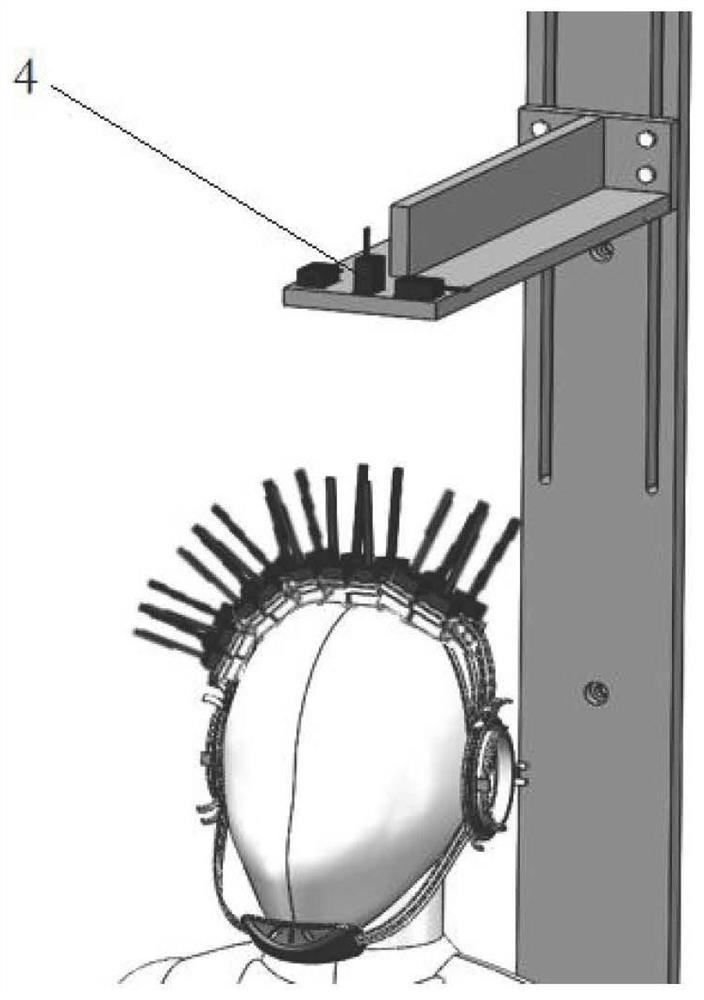
Method for drawing up data which can be used to assess cognitive or sensomotor capabilities or capacities of people subjected to a test
In order to draw up data which can be used to assess the cognitive or sensomotor capabilities or capacities of people subjected to a test, measuring samples collected by measuring methods known per se (e.g. magnetoencephalography or electro-encephalography) and representing the cerebral activities of the test person, are recorded in a synchronized manner with a sequence of different test situations which the test person faces. Relevant changes in activity are traced and localized from the recorded measuring samples. Groups are then formed based upon the locality of the relevant activity changes, each of the groups containing activity changes of a pre-determined cerebral region. The groups are interrelated and data describing the relation between the groups of relevant activity changes is prepared for the assessment, for example visualized or acoustically presented with experimentally determined limiting values or comparison data.
Owner:AMIDZIC OGNJEN
Method for designing coil systems for generation of magnetic fields of desired geometry, a magnetic resonance imaging or magnetoencephalography apparatus with a coil assembly and a computer program
ActiveUS9977764B2CouplingMinimize couplingResistance/reactance/impedenceVoltage-current phase anglePrincipal component analysisMagnetoencephalography
The present invention introduces a method, apparatus and computer program for magnetic resonance imaging or magnetoencephalography applications in order to control currents of a coil assembly (20), and thus achieving desired magnetic fields precisely in the measuring volume (21). The approach is an algebraic method where a field vector is generated for the test currents of each coil (20). Vector and matrix algebra is applied and a linear set of equations is formed. Field components and their derivatives up to the desired order can be taken into account. Principal component analysis or independent component analysis can be applied for determination of the dominant external interference components. By checking the condition value for the matrix (33, 45), it is possible to investigate whether a reasonable solution of currents for desired magnetic fields is possible to achieve. Finally, solved currents can be installed into a current supply unit (29) feeding the coils of the assembly (20). The invention can be applied as an active compensation feature for different interference shapes in the MEG application (25), or for the precise creation of the fields and gradients in the MRI application (24).
Owner:MEGIN OY
Optically pumped magnetometer, magnetoencephalography meter, and MRI device
InactiveCN103314305AHeating evenlyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsHeat resistanceOptical pumping
The present invention provides an optically pumped magnetometer, a magnetoencephalography meter, and an MRI device. The optically pumped magnetometer is used for measuring a magnetic field of a subject of interest by utilizing optical pumping, and comprises: a non-magnetic cell in which at least an alkali metal is encapsulated and which has light transmissivity and heat resistance; a laser beam emission unit which emits a laser beam toward the cell to achieve the optical pumping of at least the alkali metal; a detection unit which receives the transmitted laser beam that has been transmitted through the cell and which detects a detection signal associated with the magnetic field; and a high-frequency voltage application unit which applies a high-frequency voltage to a pair of application sections arranged in the cell and which heats the cell by dielectric heating.
Owner:SUMITOMO HEAVY IND LTD
Wearable magnetoencephalography instrument environmental noise suppression system and method
PendingCN113768505AEnvironmental noise suppressionHigh strengthDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSensor arrayEnvironmental noise
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetoencephalography detection, and provides a wearable magnetoencephalography instrument environmental noise suppression system and method. The system comprises a magnetic shielding room, a magnetoencephalography measuring cap, an atomic magnetometer detection sensor array and an atomic magnetometer reference sensor array, wherein a testee wears the magnetoencephalography measuring cap on the head and is placed in the magnetic shielding room, the atomic magnetometer detection sensor array is arranged in the magnetoencephalography measuring cap, and the atomic magnetometer reference sensor array is arranged above the head of the testee. The system is simpler in structure, light and flexible. In addition, according to the wearable magnetoencephalography instrument environmental noise suppression method, gradient arrangement configuration does not need to be carried out on each atomic magnetometer detection sensor, on the basis that the configuration of the detection sensors on the original flexible measuring cap is kept unchanged, the intensity of magnetoencephalography signals can be kept not attenuated, the environmental noise of the shielding room can be effectively suppressed, and the signal-to-noise ratio of the magnetoencephalography signals is improved.
Owner:JIHUA LAB
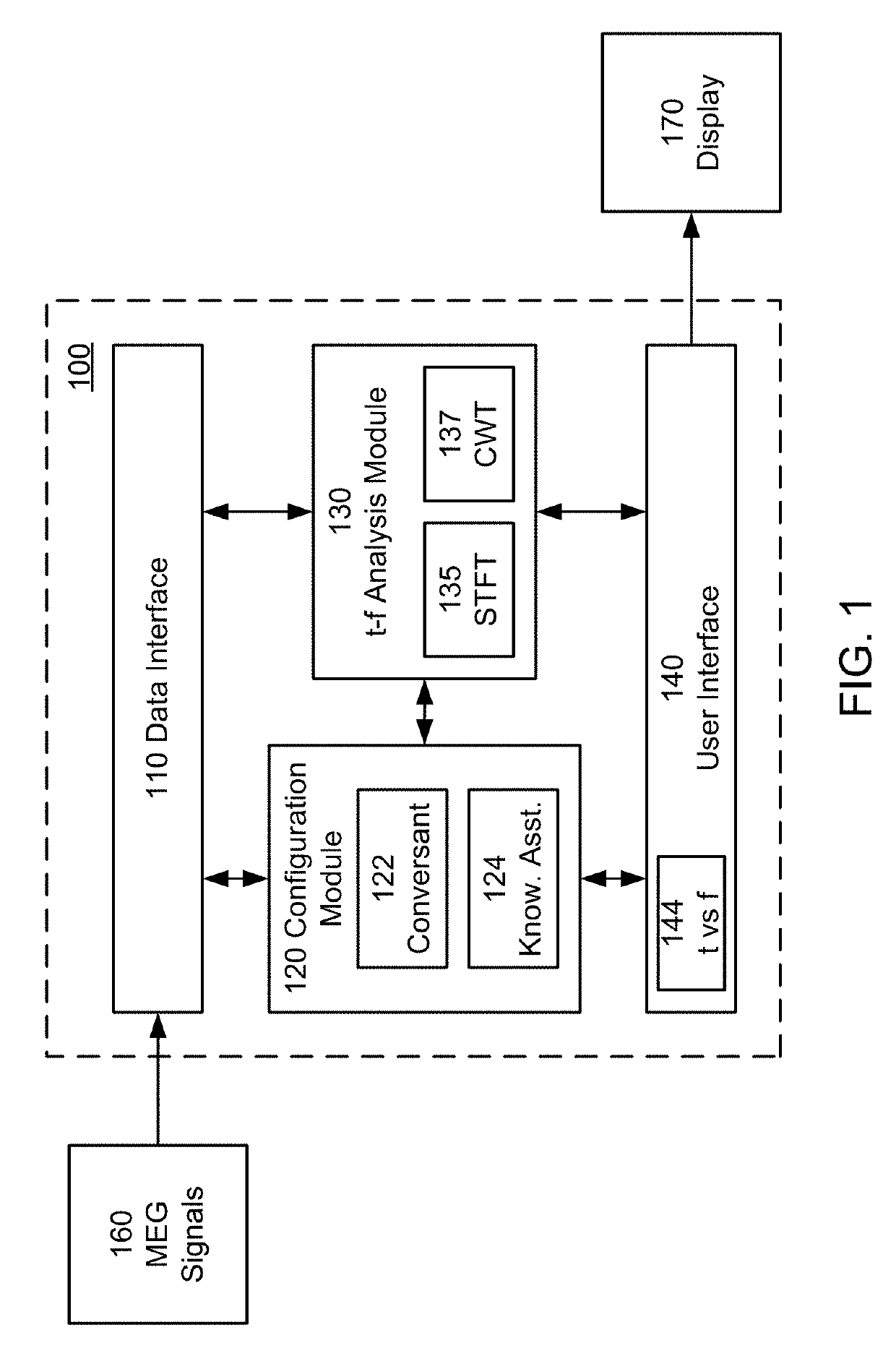
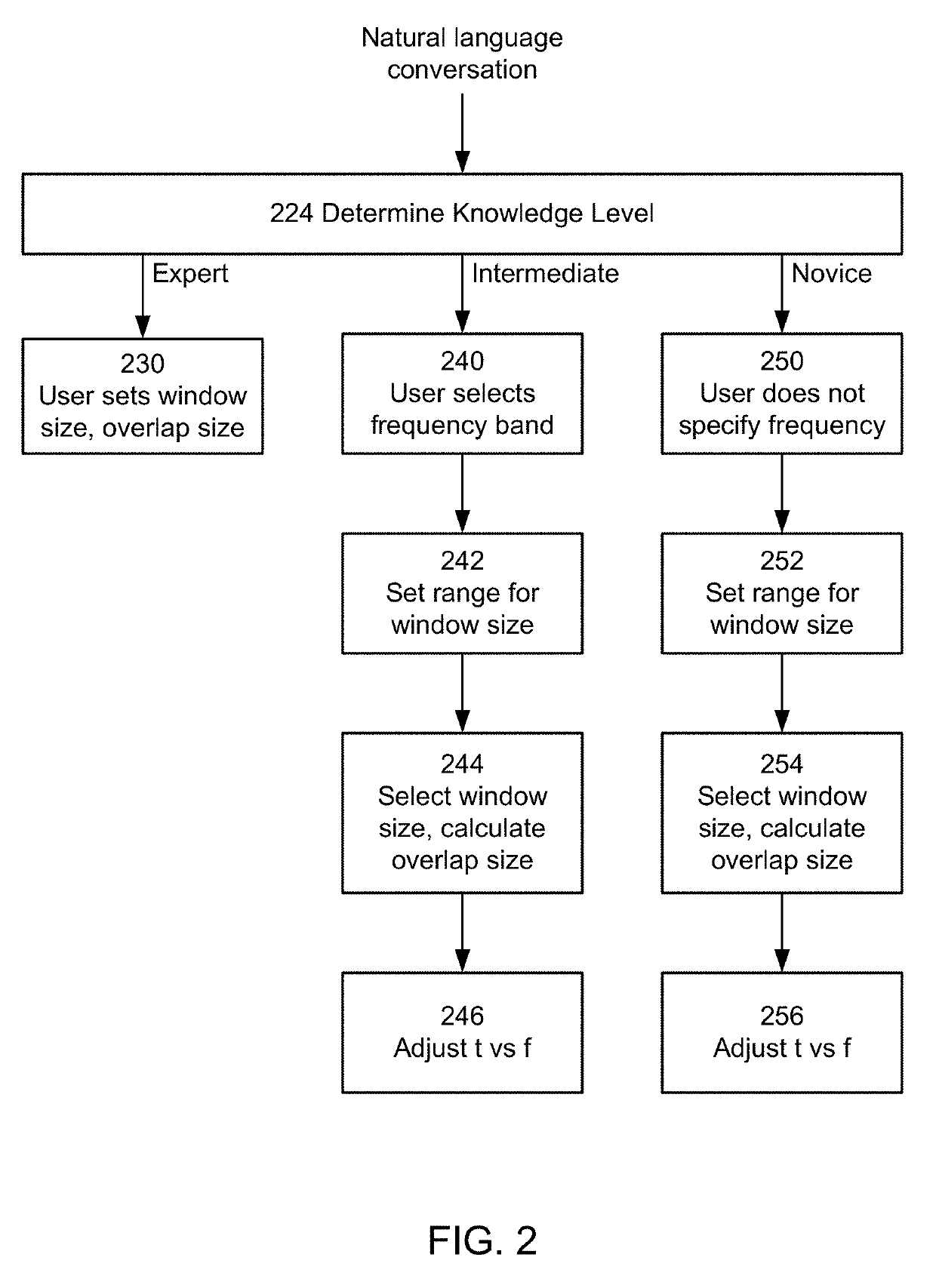
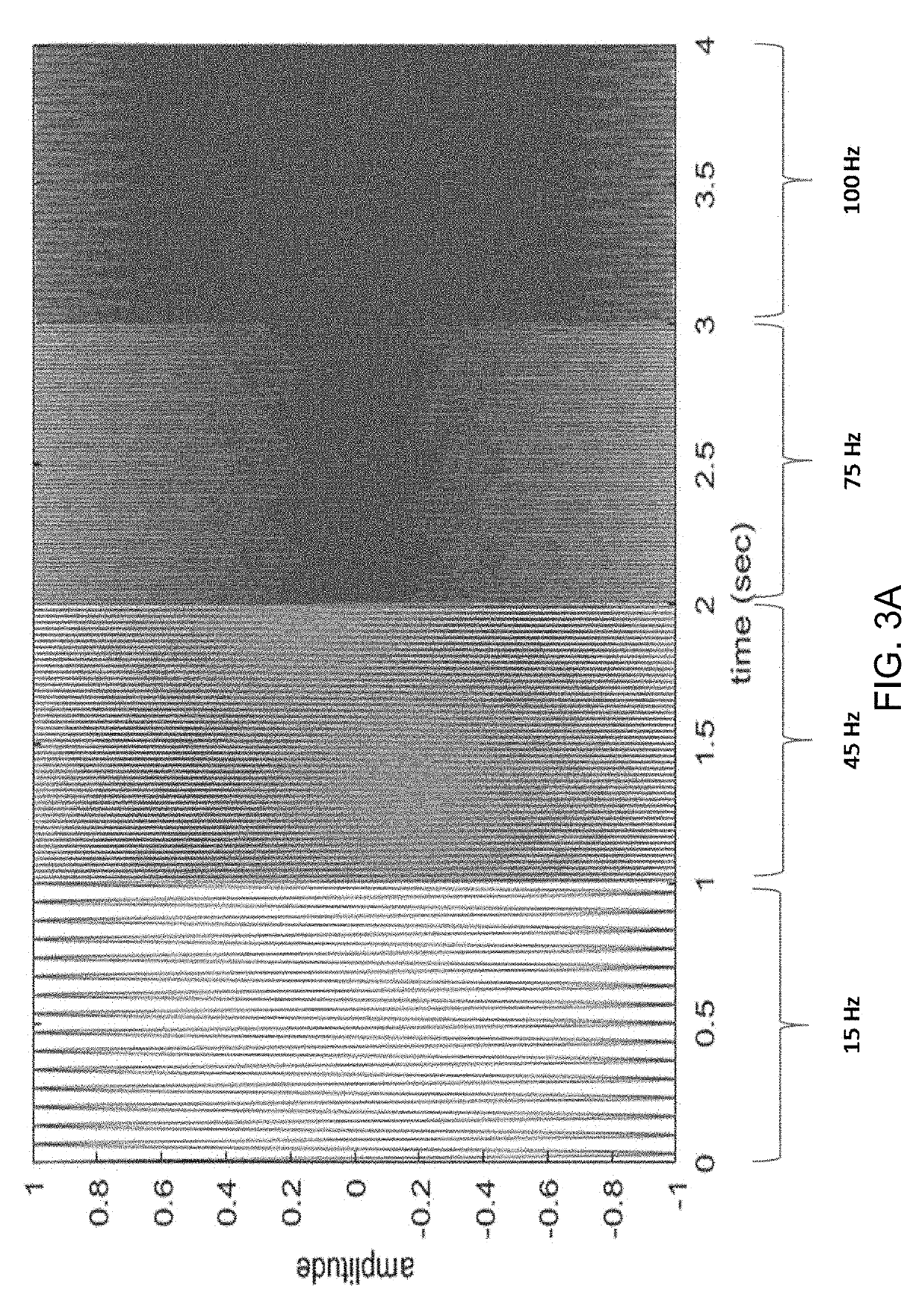
Intelligent parameterization of time-frequency analysis of encephalography signals
ActiveUS20190274567A1Overcome limitationsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImage resolutionTime–frequency analysis
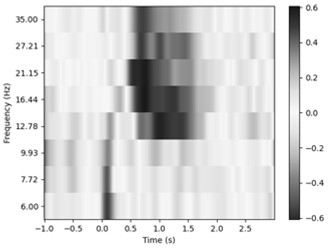
A system assists users in time and frequency analysis of magnetoencephalography (MEG) signals. In one aspect, a system includes an analysis module, a configuration module and a user interface. The analysis module performs a time and frequency analysis of the MEG signal, for example a short time Fourier transform (STFT) or a continuous wavelet transform (CWT) analysis. The analysis is parameterized by a parameter set that affects the time and frequency resolution of the analysis, for example window size and overlap size for STFT or center frequency and decay parameter for CWT. The configuration module automatically determines or assists the user to determine correct values for the parameter set.
Owner:RICOH KK
Neural feedback loop filters for enhanced dynamic range magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems and methods
ActiveUS11022658B2Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringLow-pass filterSoftware engineering
One embodiment is a magnetic field measurement system that includes at least one magnetometer having a vapor cell, a light source to direct light through the vapor cell, and a detector to receive light directed through the vapor cell; at least one magnetic field generator disposed adjacent the vapor cell; and a feedback circuit coupled to the at least one magnetic field generator and the detector of the at least one magnetometer. The feedback circuit includes at least one feedback loop that includes a first low pass filter with a first cutoff frequency. The feedback circuit is configured to compensate for magnetic field variations having a frequency lower than the first cutoff frequency. The first low pass filter rejects magnetic field variations having a frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and provides the rejected magnetic field variations for measurement as an output of the feedback circuit.
Owner:HI LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com