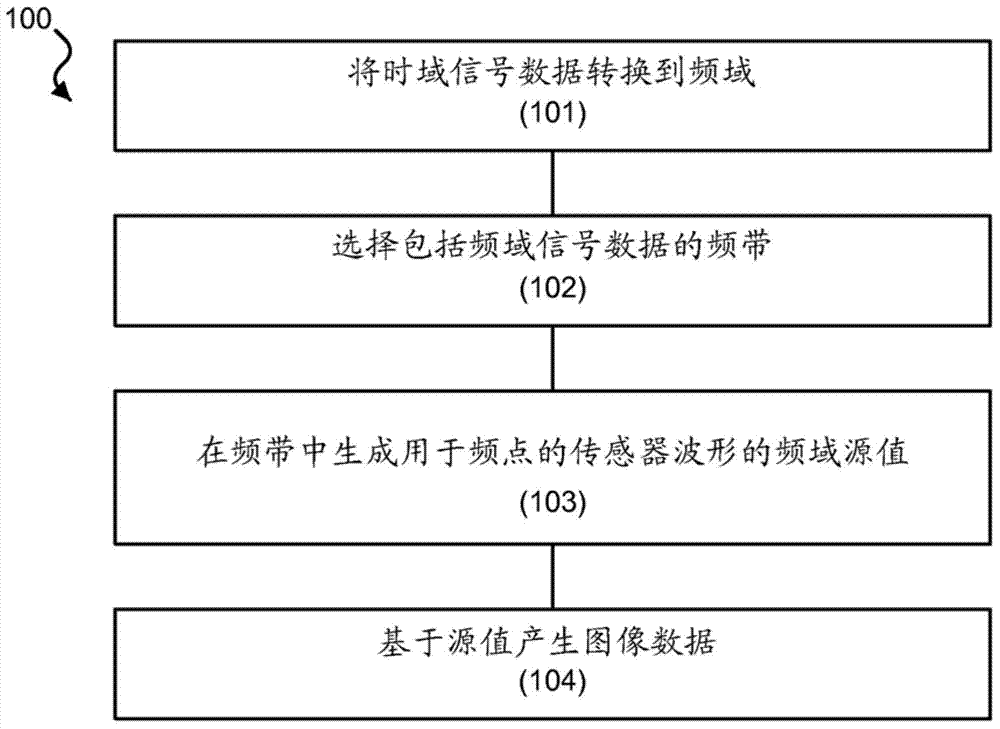
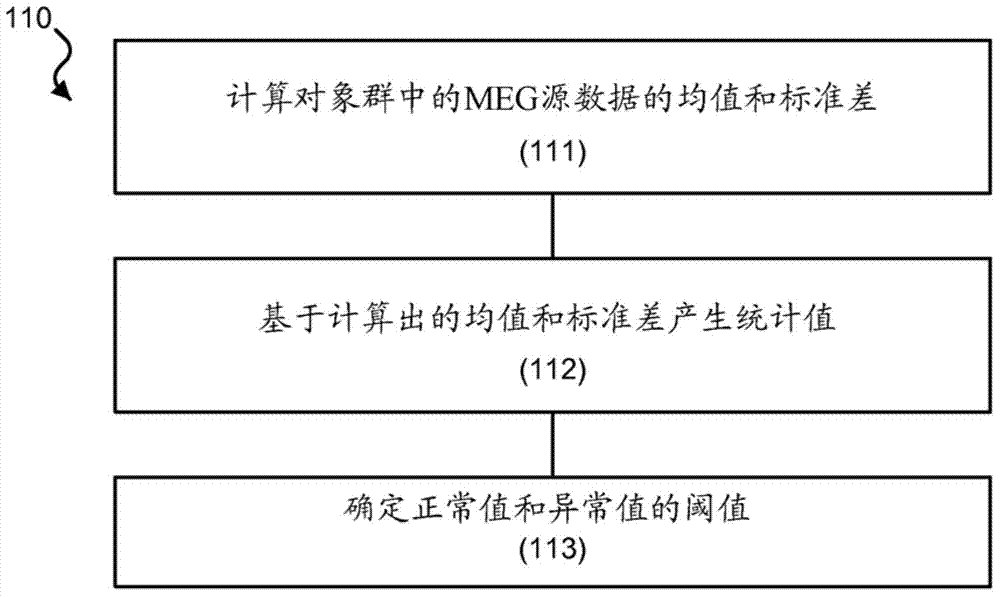
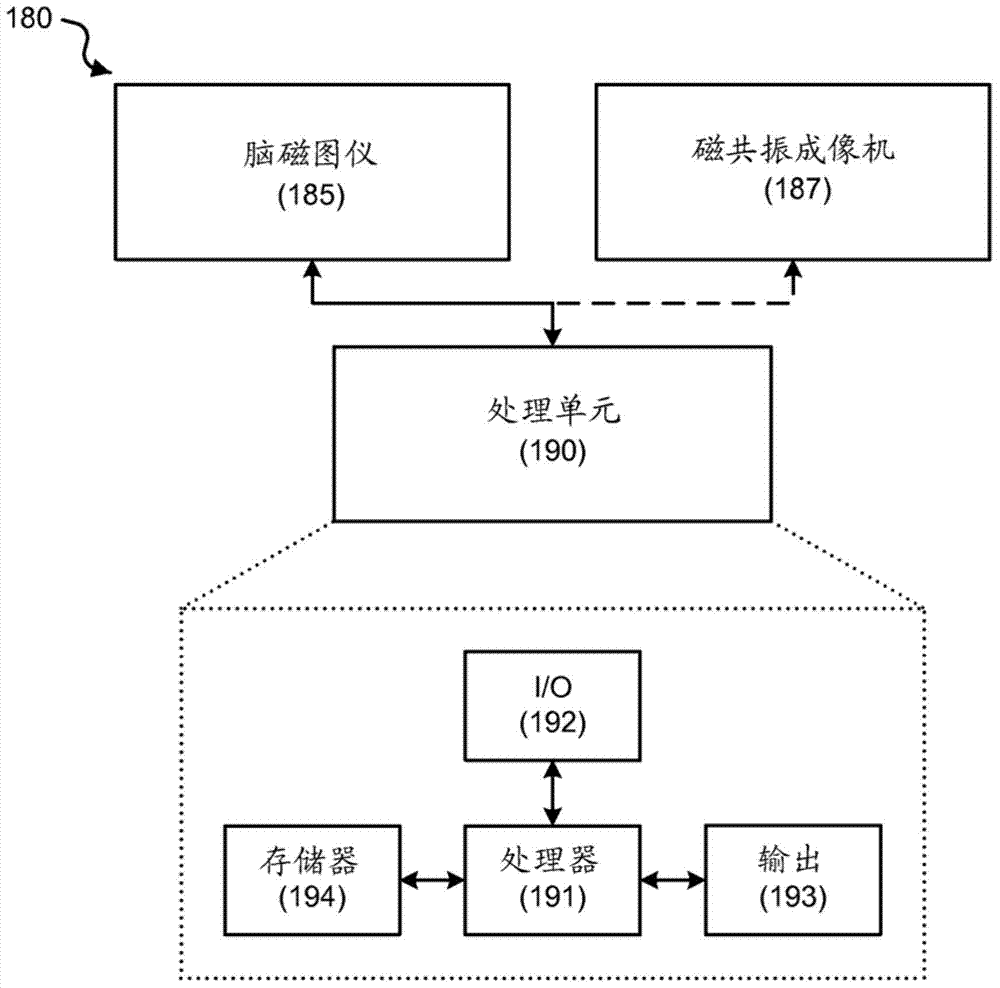
Magnetoencephalography source imaging
A magnetoencephalography and imaging technology, applied in the field of imaging technology, can solve problems such as inability to diagnose neuron damage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0023] Magnetoencephalography (MEG) is a technique used to map brain activity by recording the magnetic fields generated by electrical currents within cells in the brain. For example, synchronous electrical currents generated by neuronal cells can generate magnetic fields. For example, these magnetic signals can arise from the net effect of ionic currents flowing between neurons (e.g., during synaptic conduction), which can be modeled as electric dipoles, e.g., with position, orientation and amplitude currents and other non-dipole current sources that generate magnetic signals. Magnetic fields generated by neurons exhibit amplitudes on the order of femto-Tesla (fT), e.g., 10 for cortical activity. 1 fT and 10 for human alpha rhythm 3 fT. These neuronal magnetic signals can be detected by sensitive magnetometers. However, these neuronal magnetic signals are relatively weak compared to the typical ambient magnetic noise of the external body environment (which can be, for exa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com