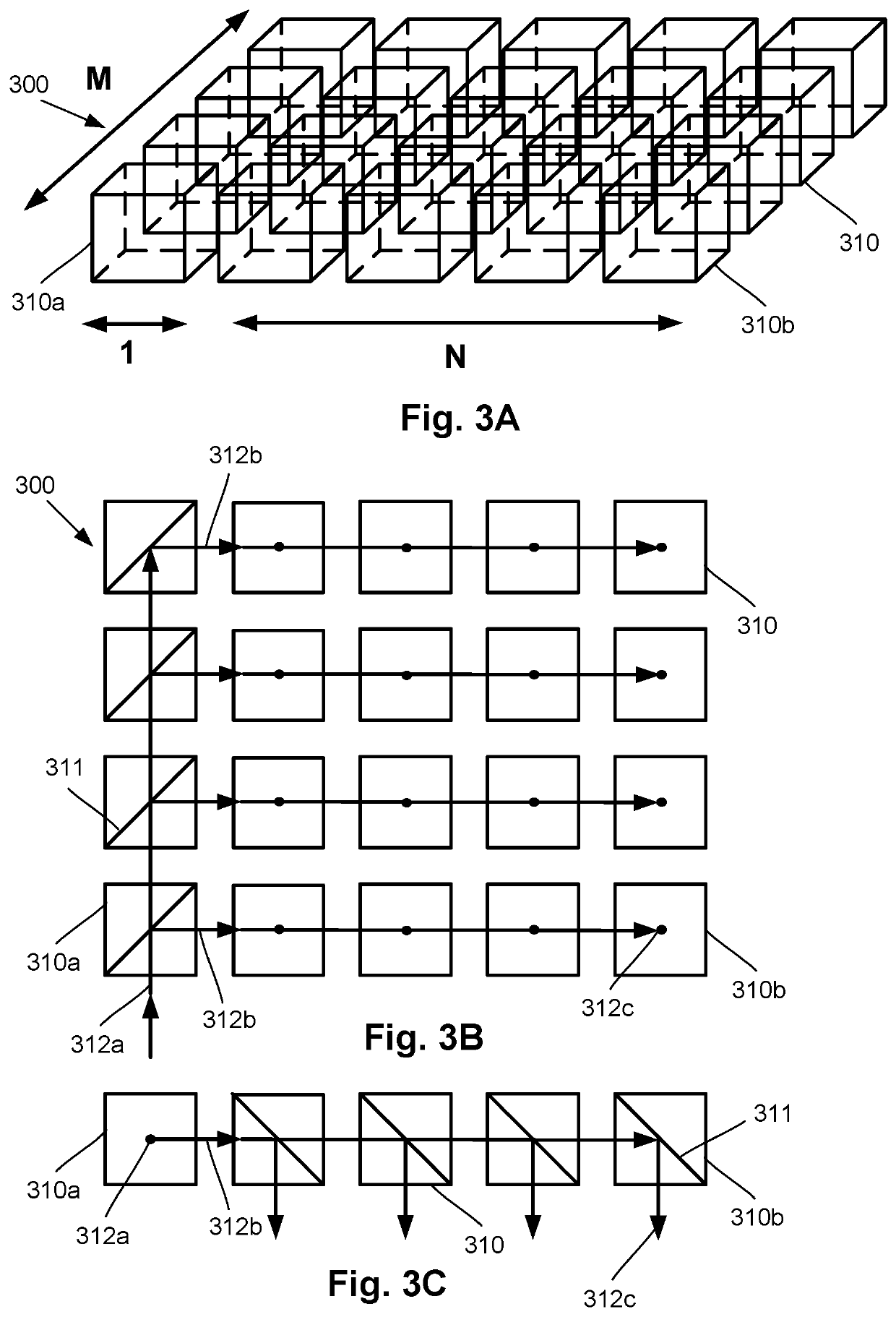
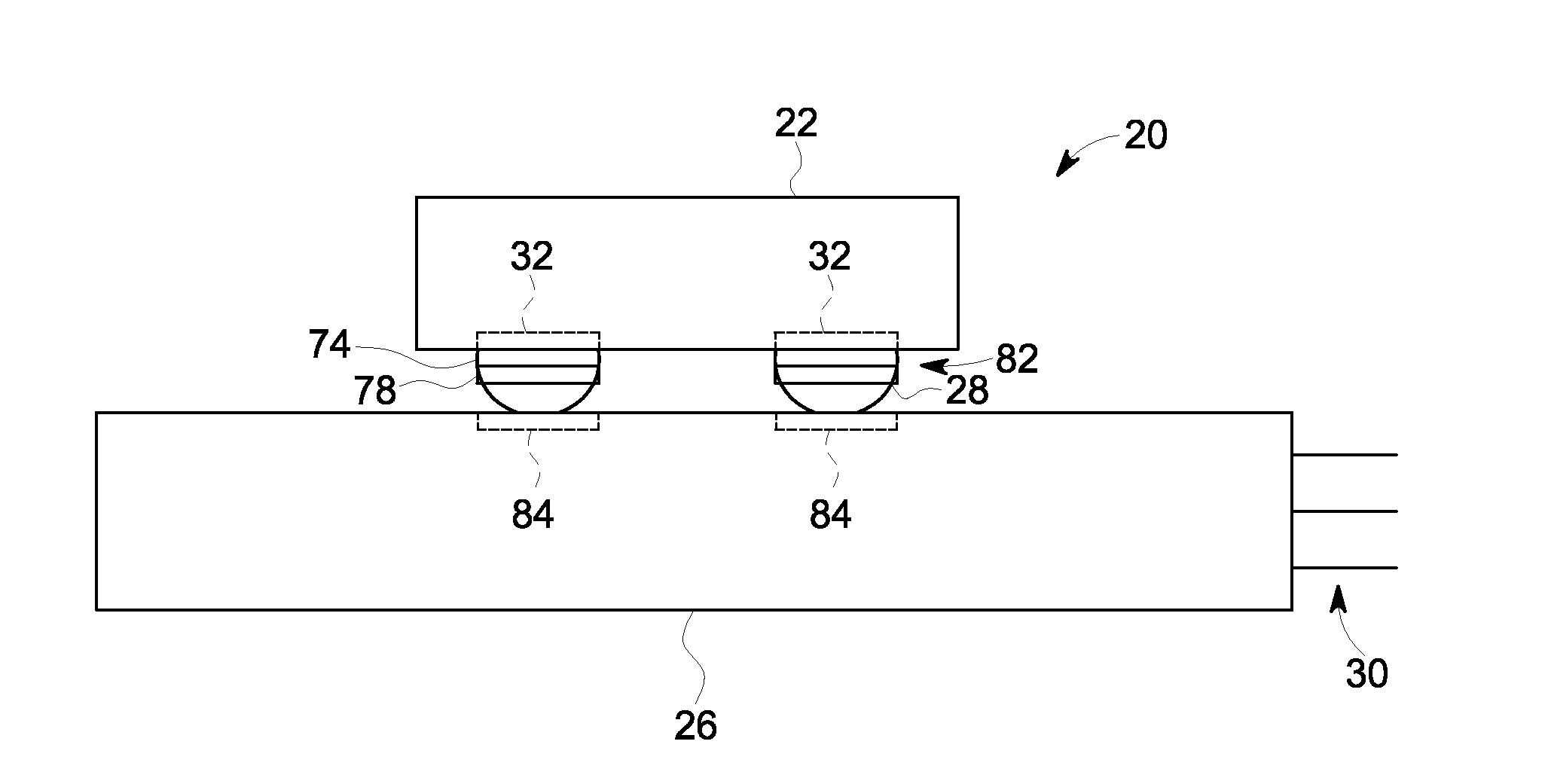
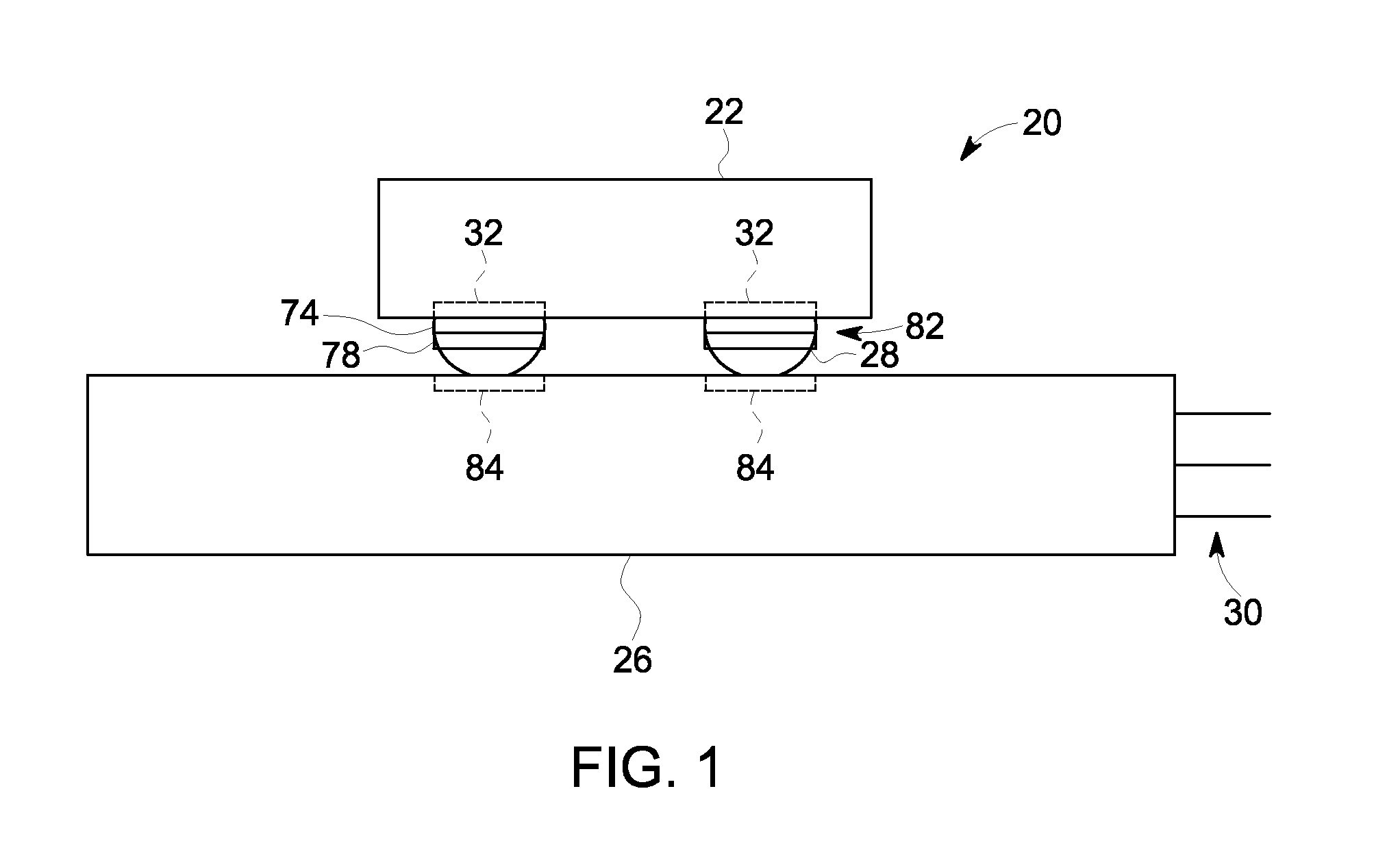
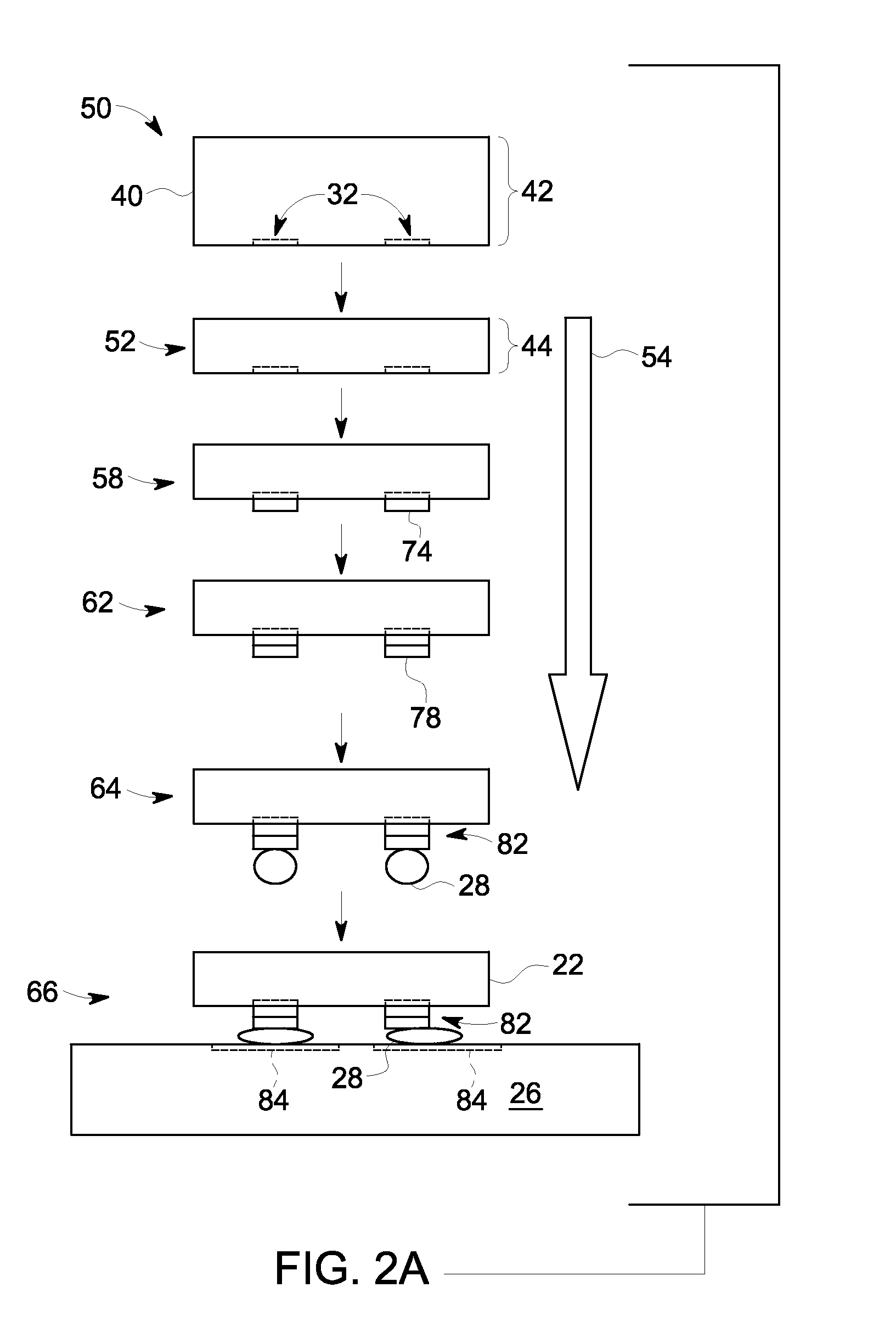
Patents
Literature
364results about "Magnetic sensor arrays" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
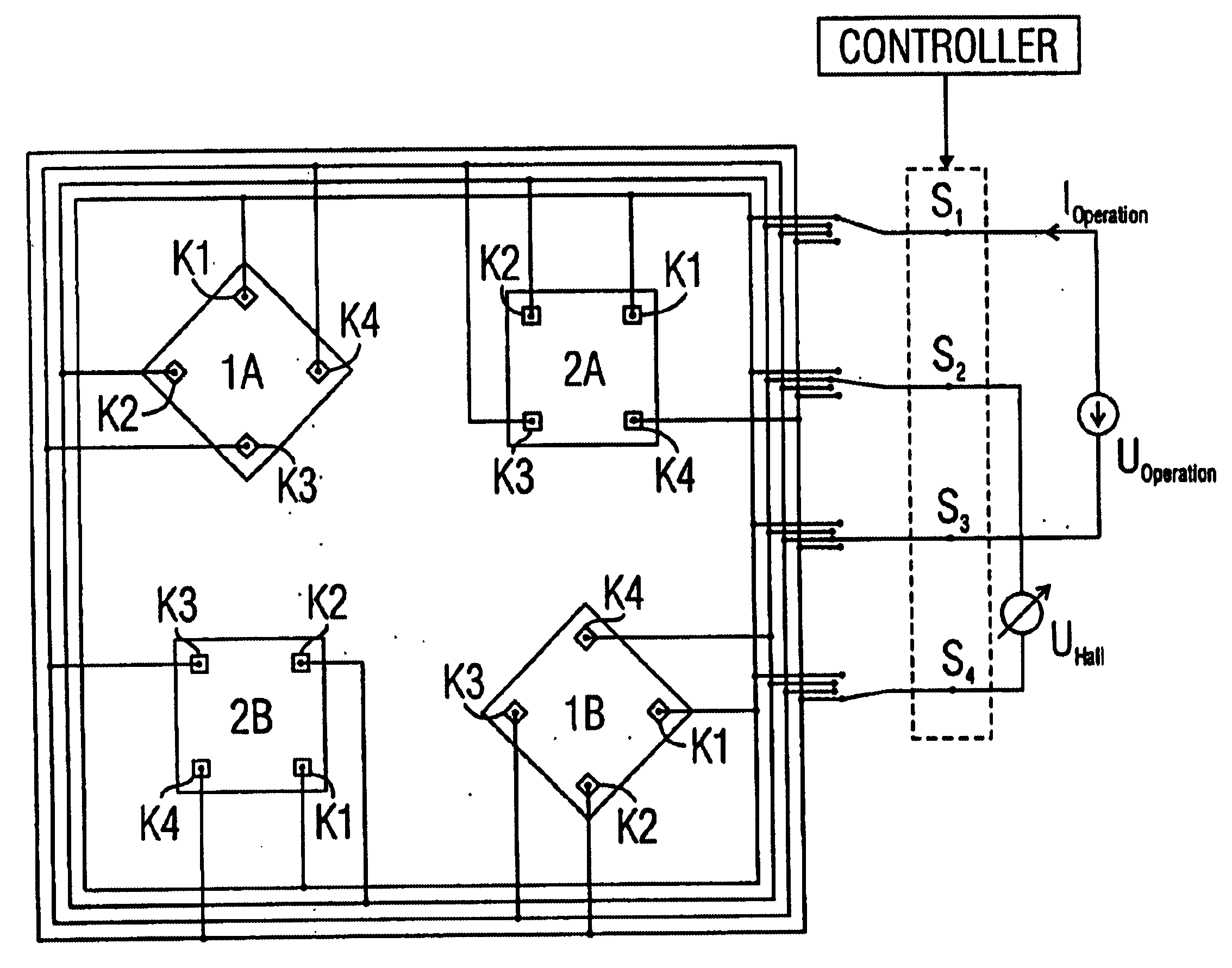
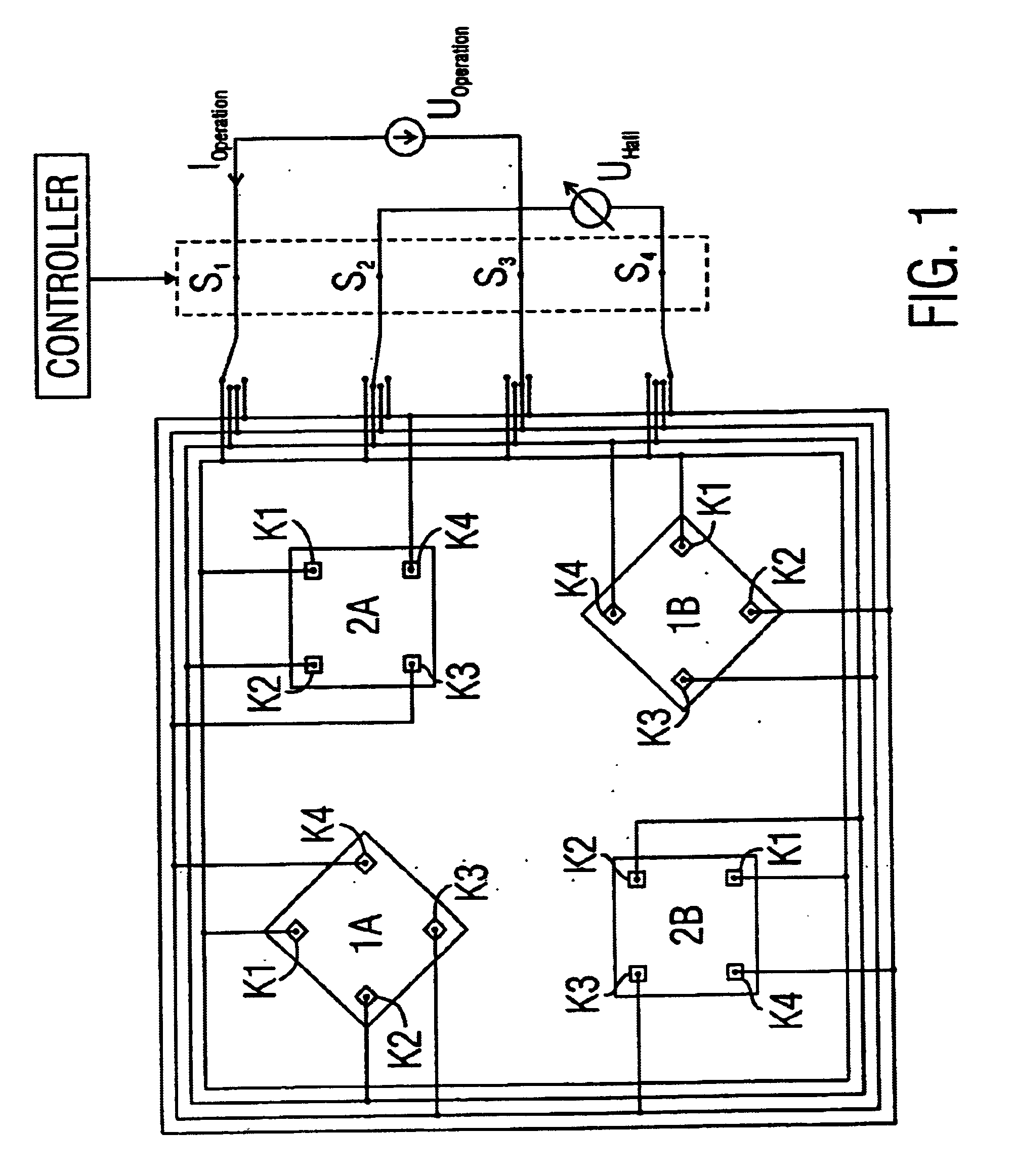
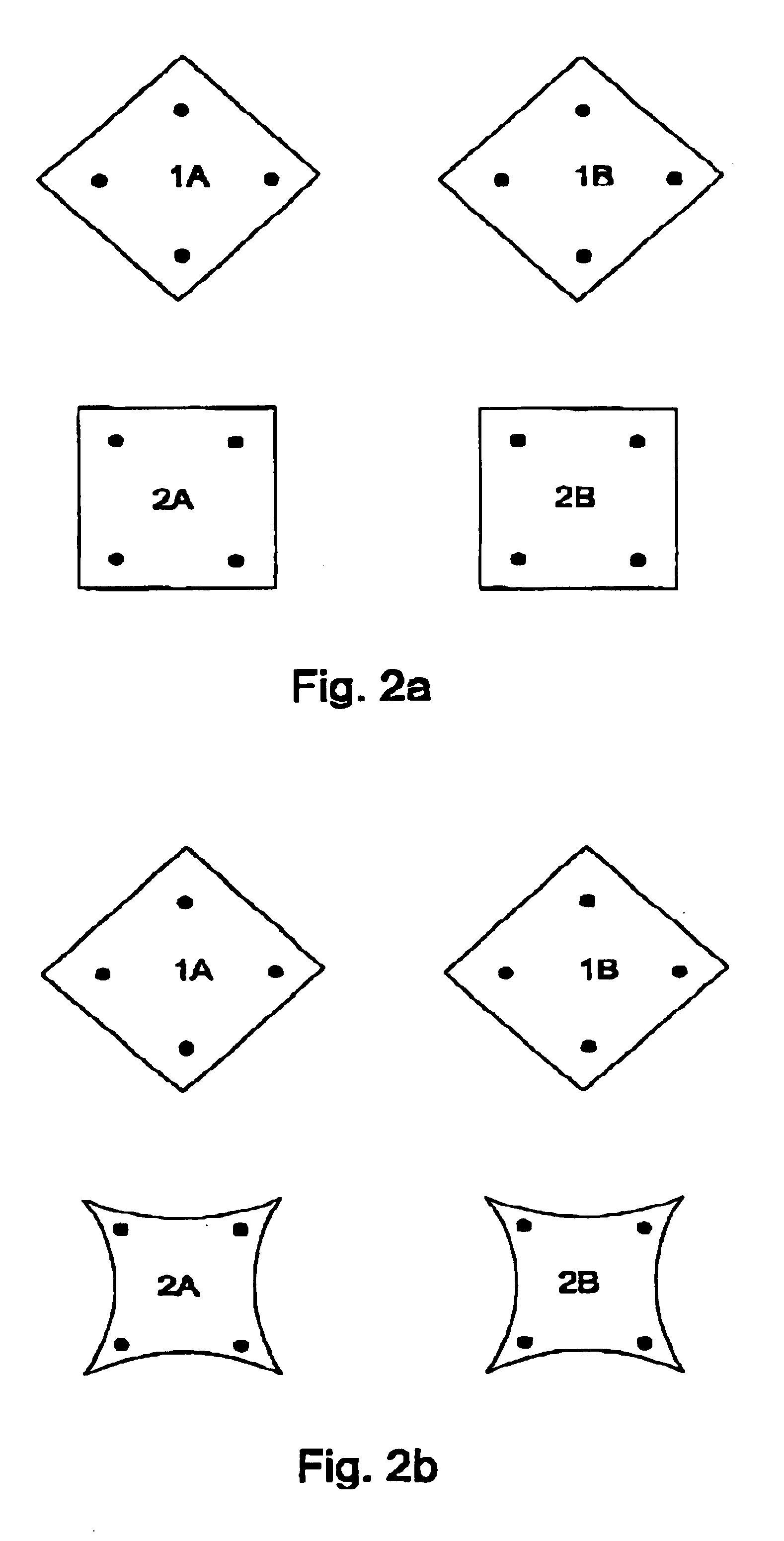
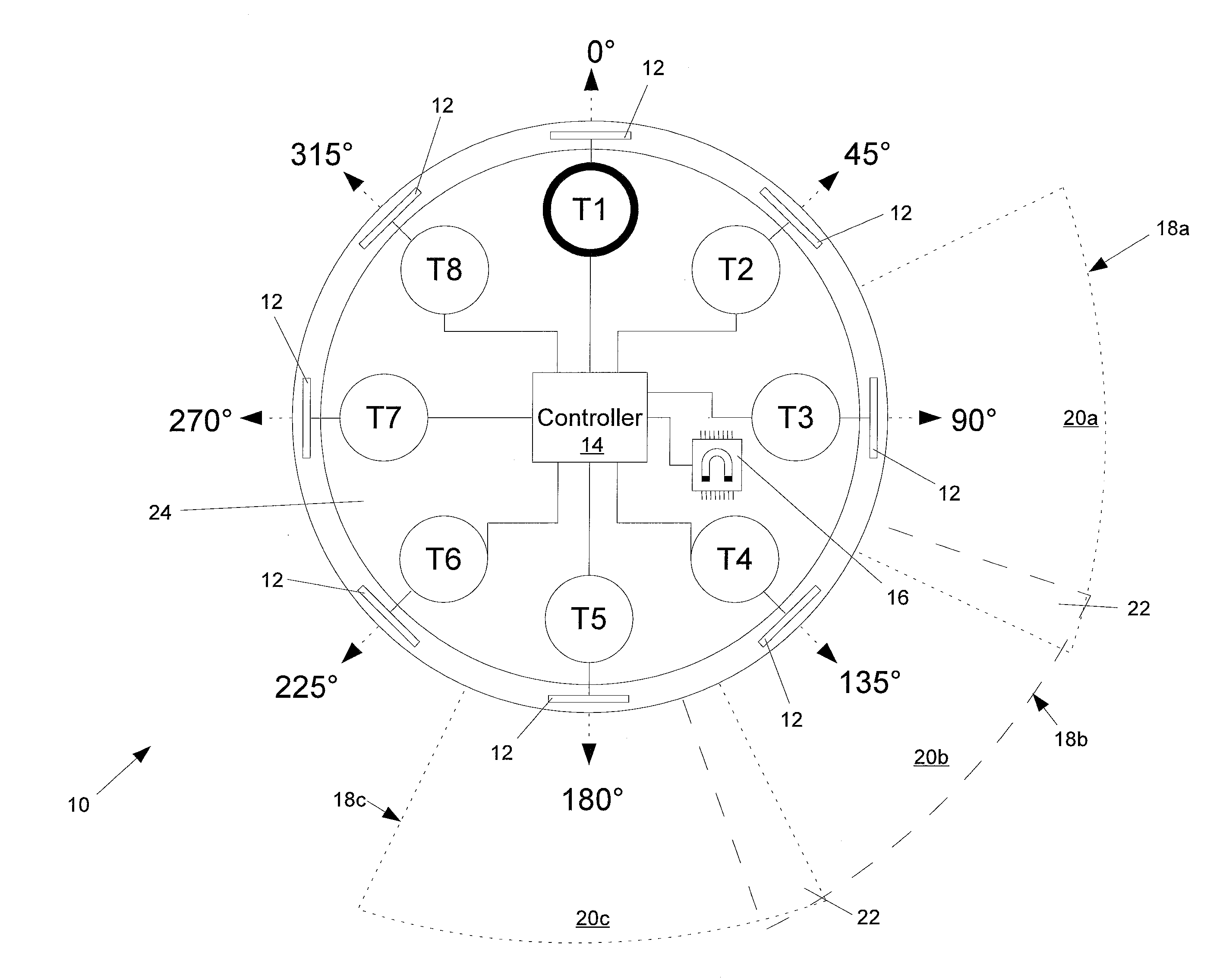
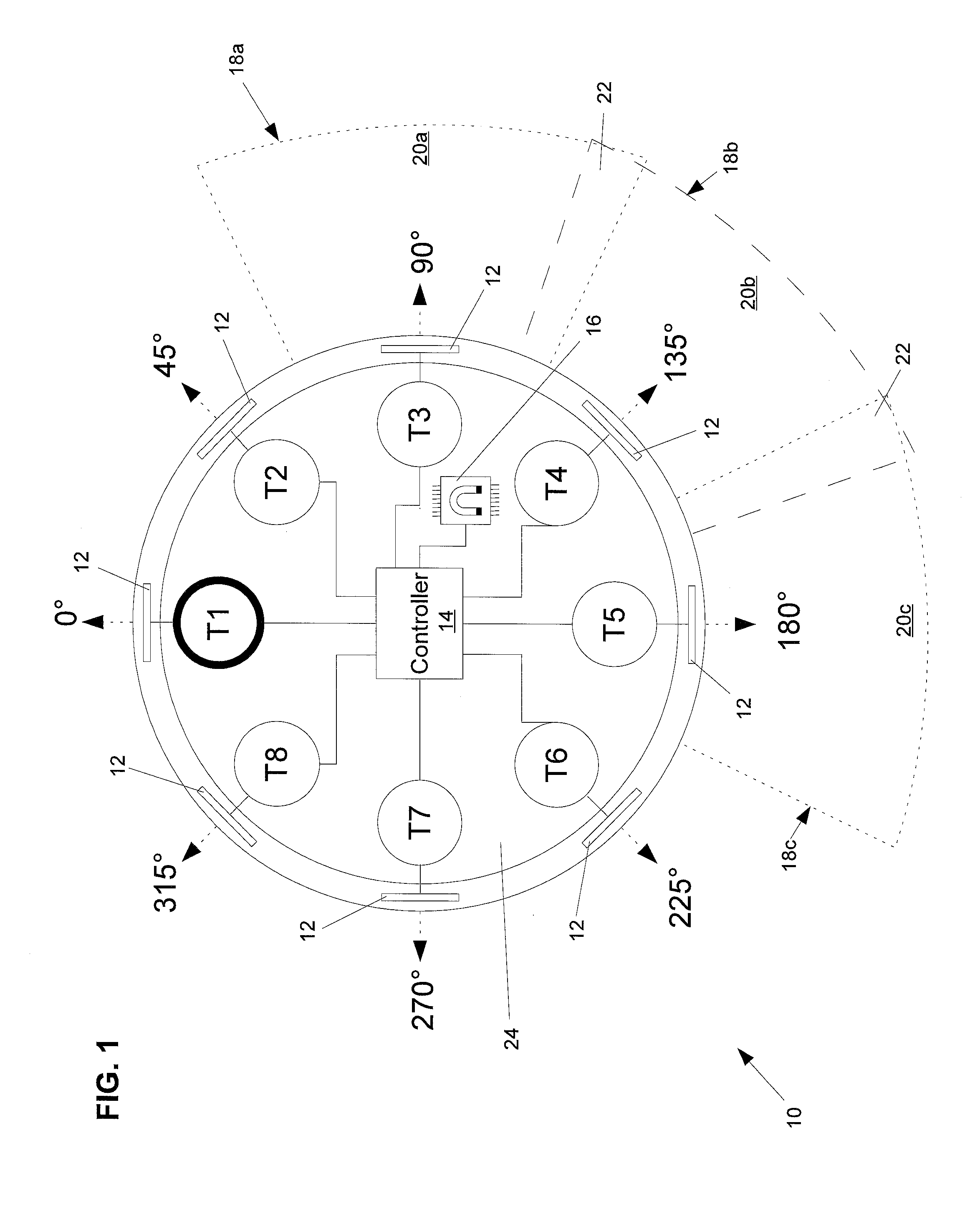
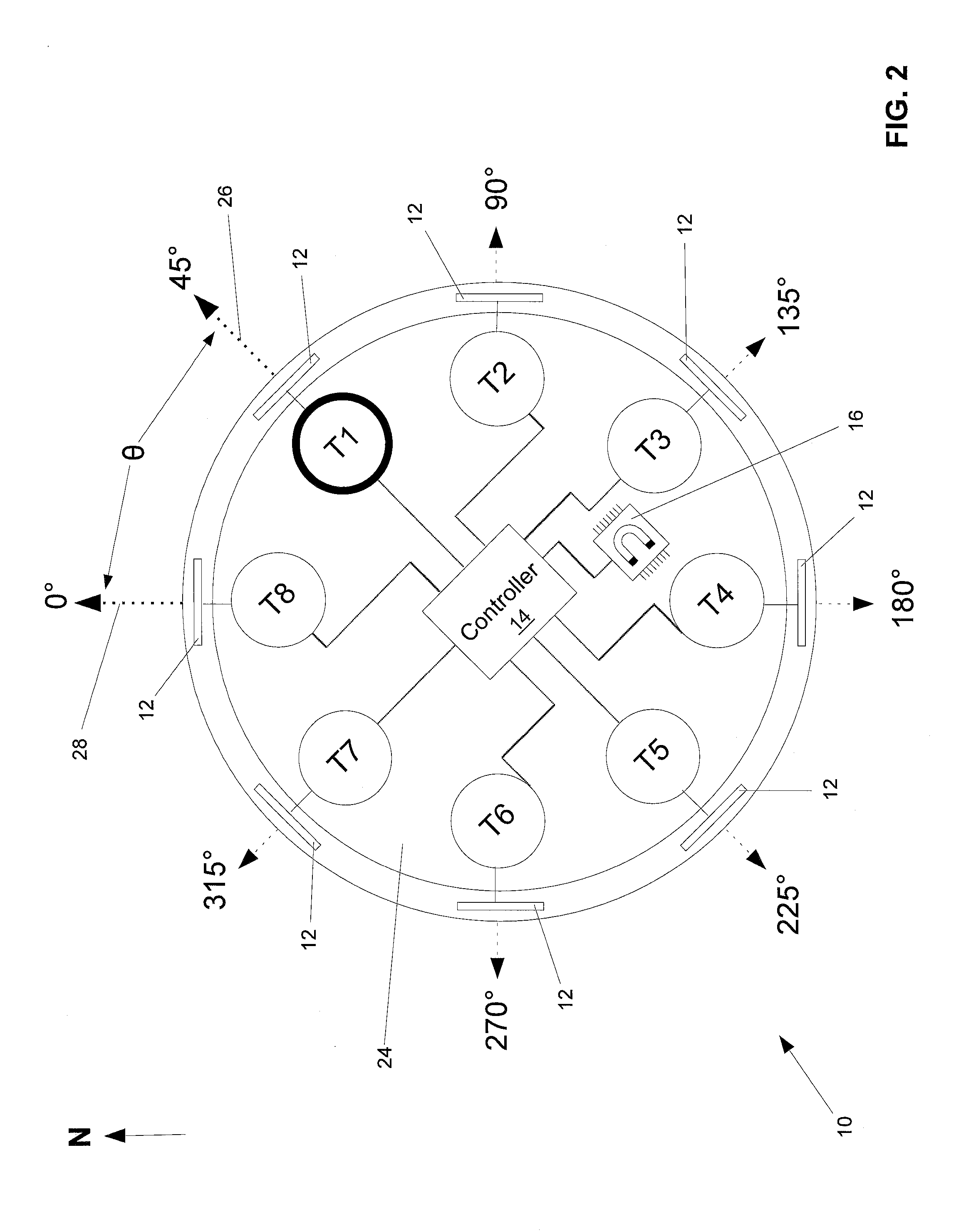
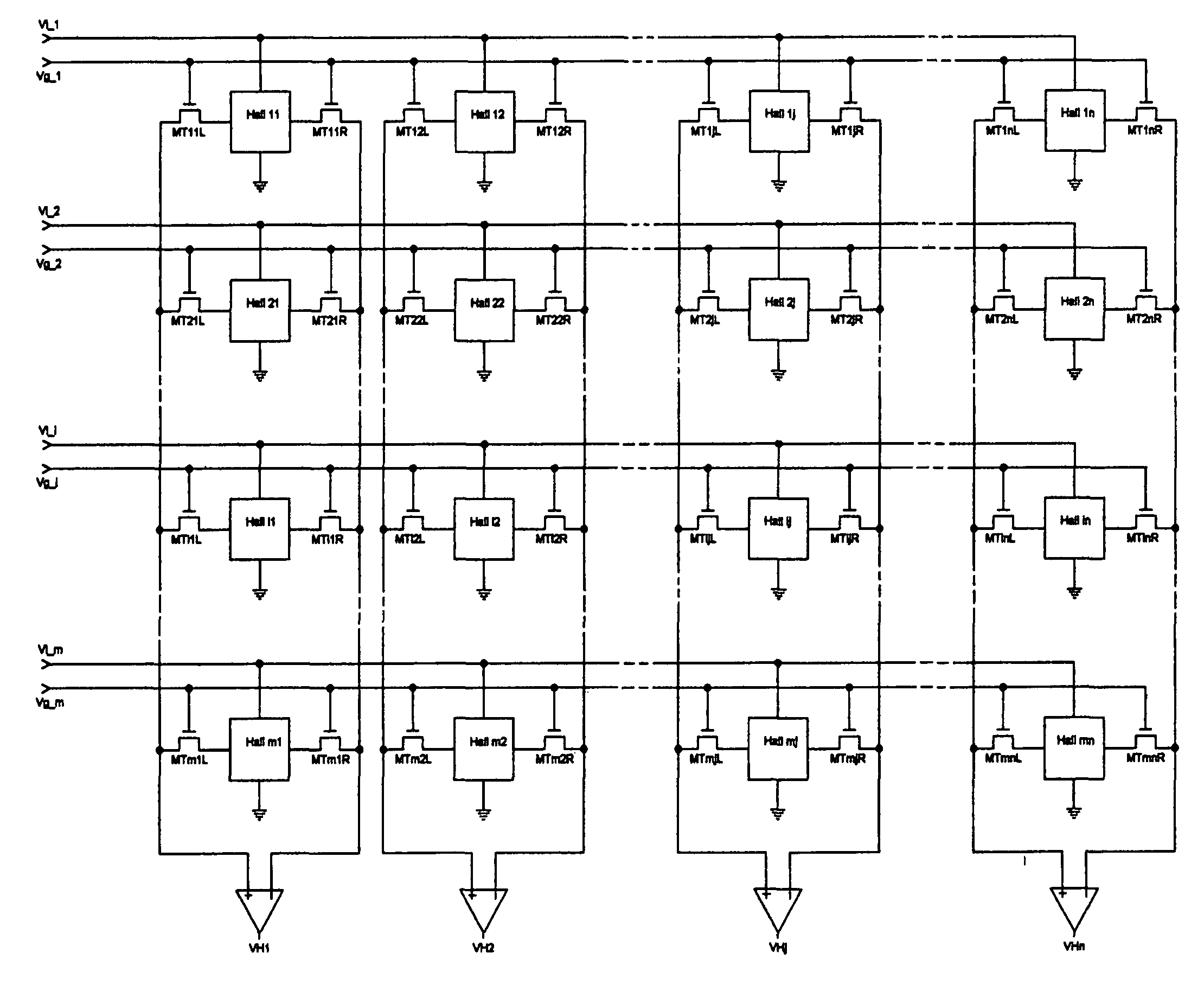
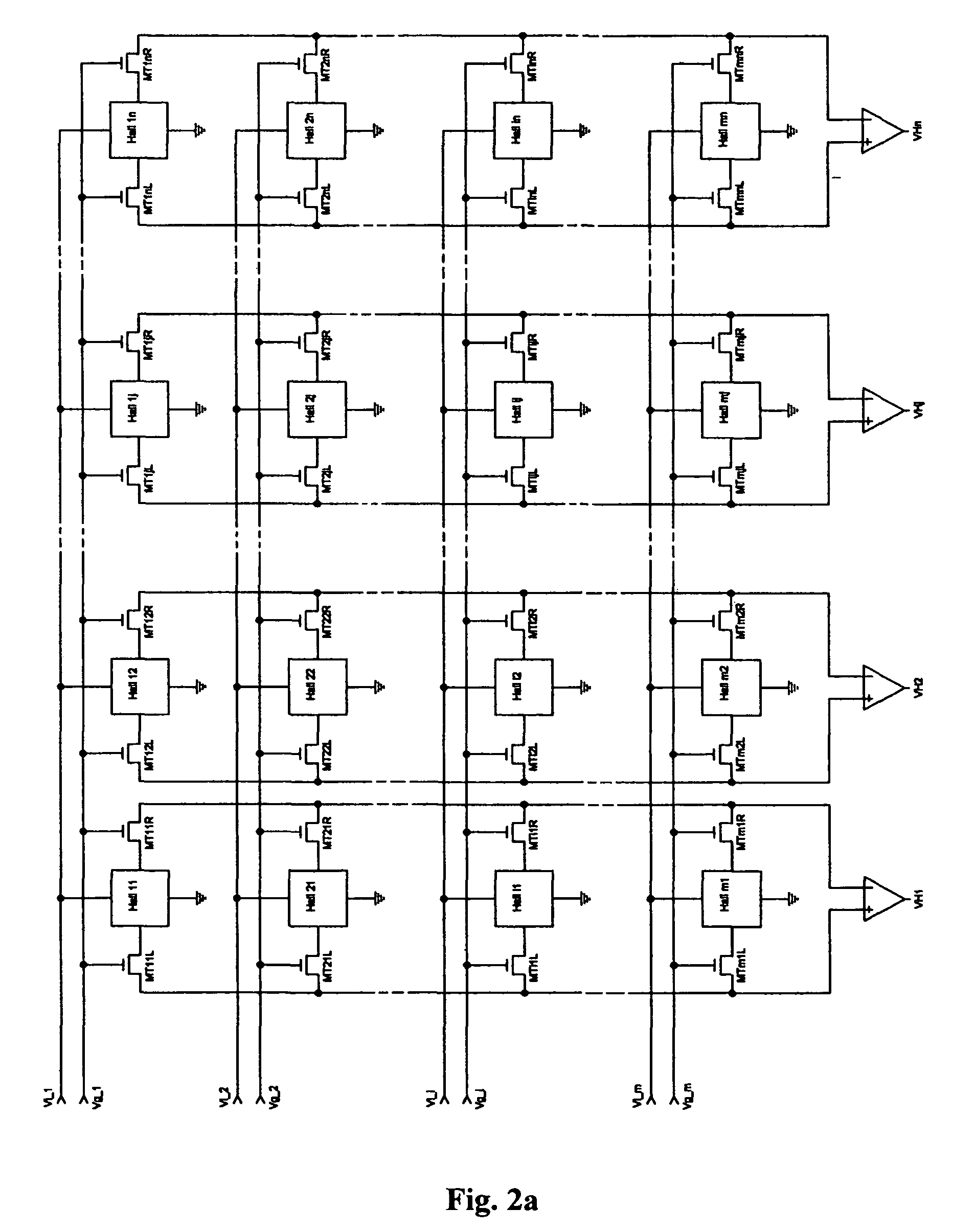
Hall sensor array for measuring a magnetic field with offset compensation
InactiveUS6768301B1Less complicated to manufactureReduce signalingSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSensor arrayVoltage source
A Hall sensor array for offset-compensated magnetic field measurement comprises a first and at least one additional pair of Hall sensor elements. Each Hall sensor element has four terminals, of which two act as power supply terminals for supplying an operating current and two act as measurement terminals for measuring a Hall voltage. Respective first supply terminals of each Hall sensor element are connected together and to a first terminal of a common voltage source and respective second supply terminals of each Hall sensor element are connected together and to a second terminal of the common voltage source so that the common voltage source supplies an operating current for the Hall sensor elements. The Hall sensor elements are operated in the spinning current mode so that the offset voltages of the Hall sensor elements approximately cancel one another out in a revolution so that the Hall signal contributions which actually depend on the magnetic field remain.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
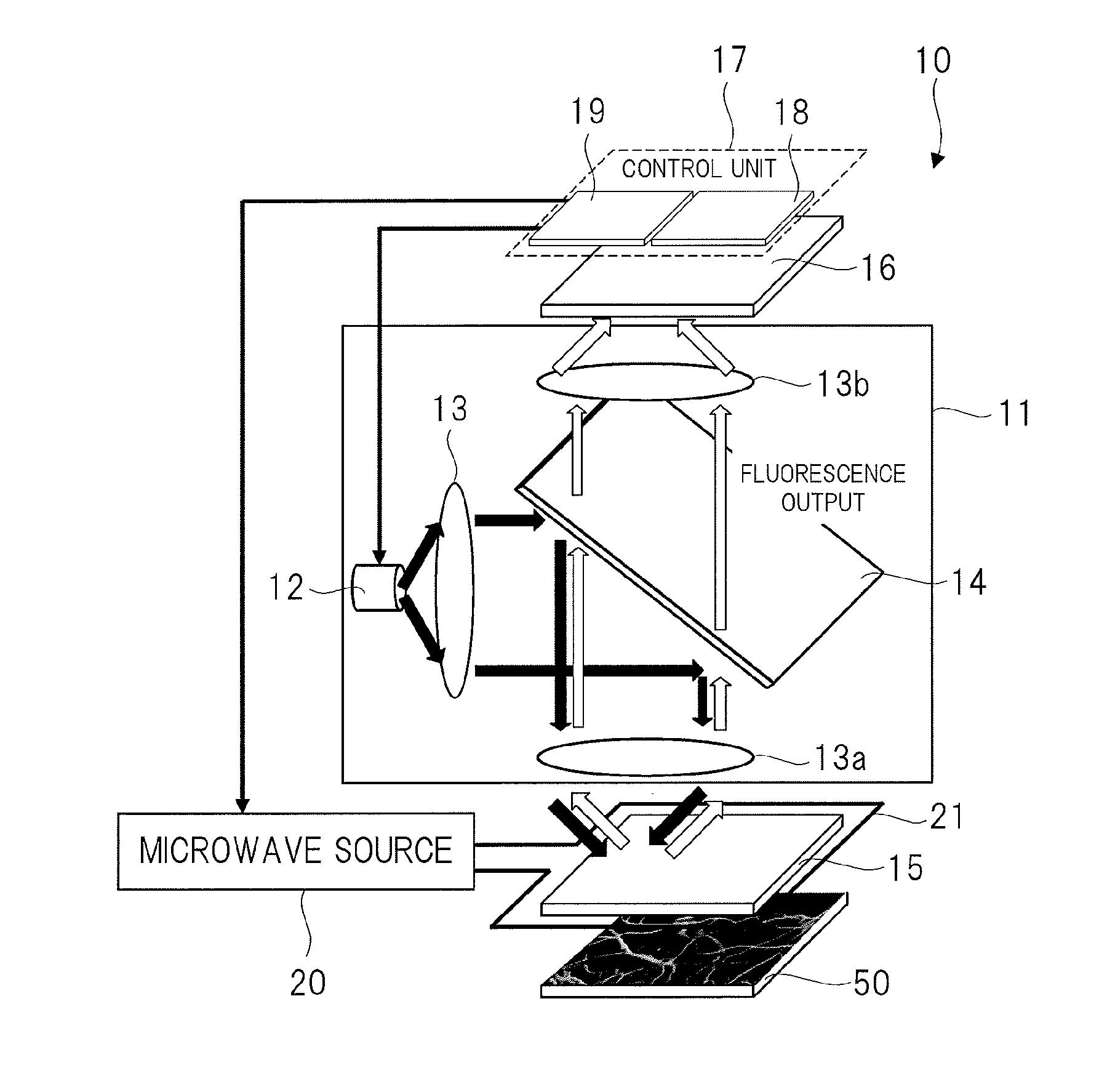
Magnetic measurement apparatus
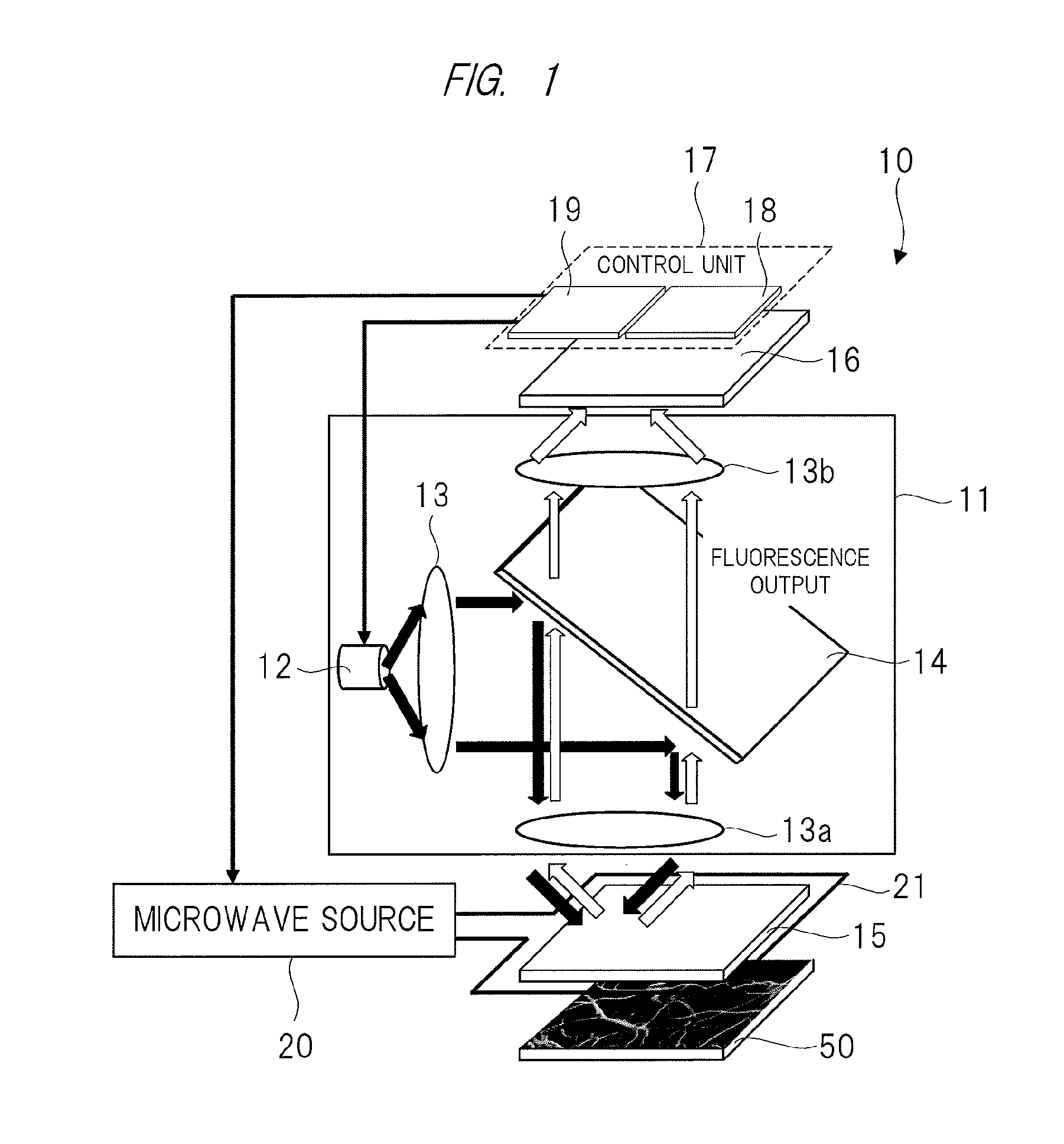
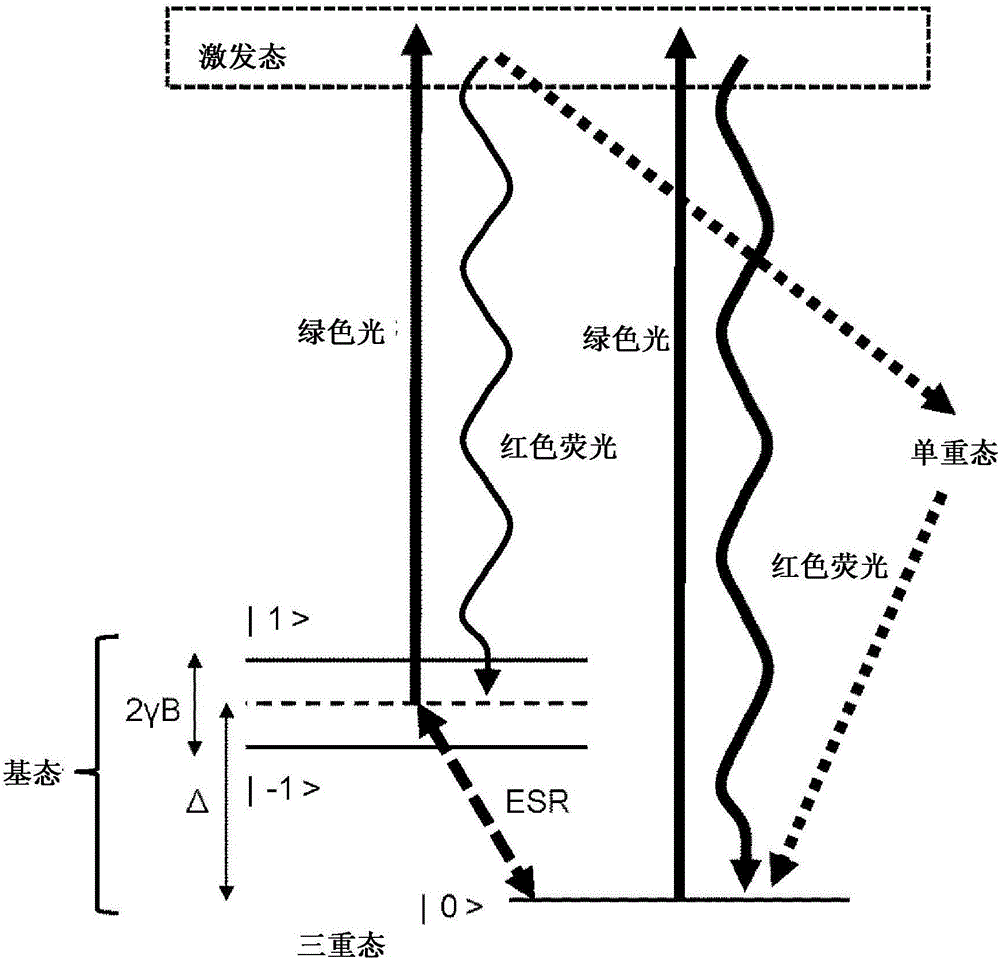
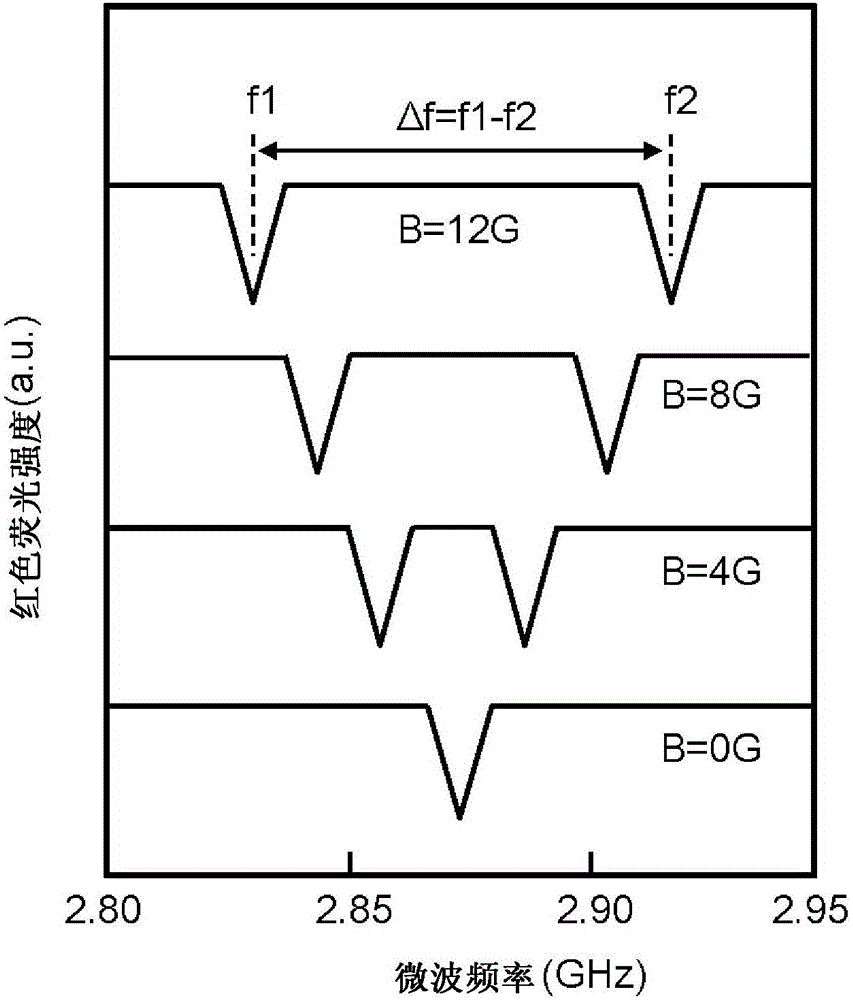
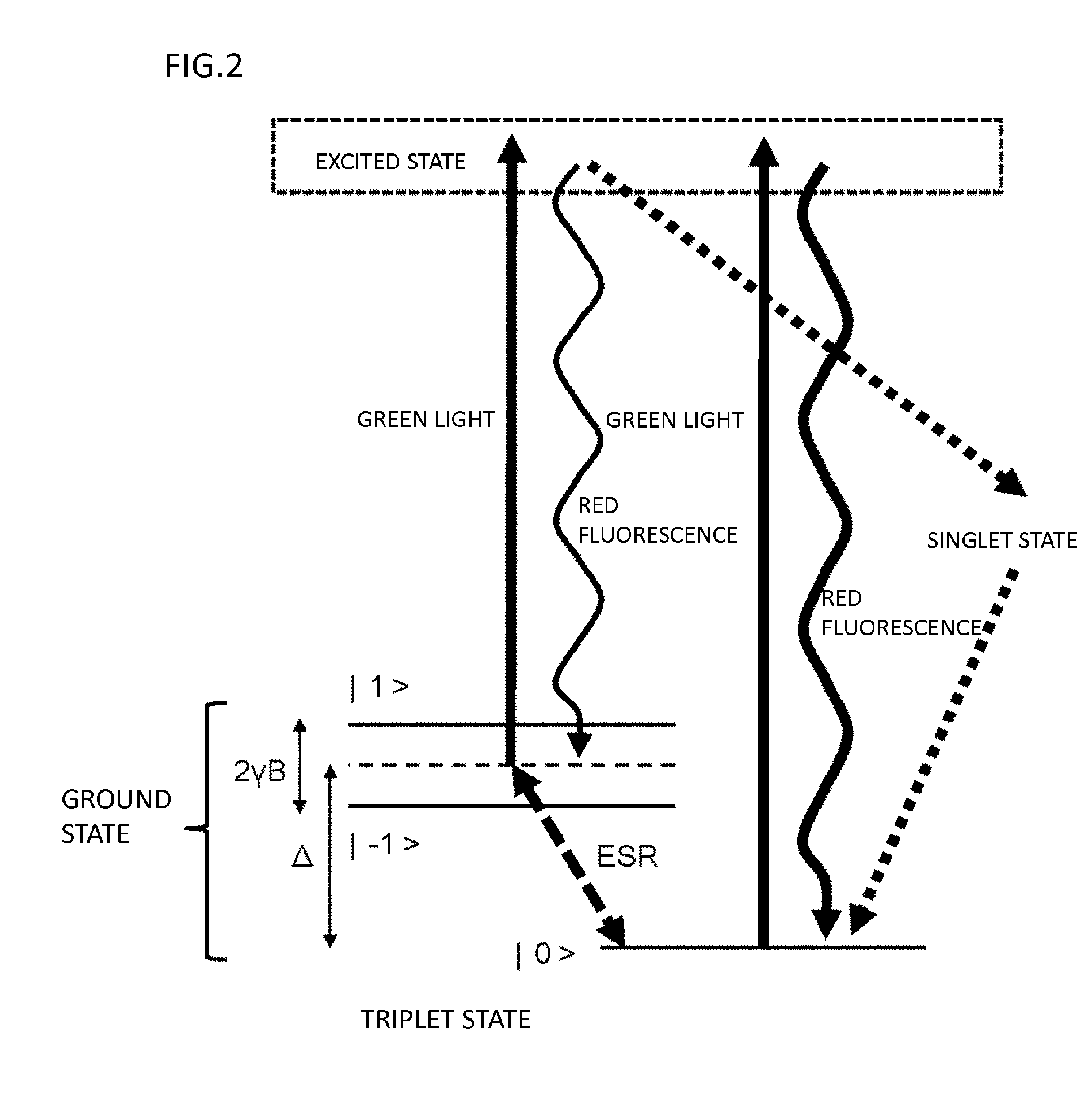
ActiveUS20150374250A1High measurement accuracyImprove detection accuracyPolycrystalline material growthDianostics using fluorescence emissionMagnetic measurementsDiamond crystal
High-accuracy magnetic measurement is performed by efficiently using nitrogen-vacancy pairs in all orientations. A magnetic measurement apparatus includes a diamond crystal and an image sensor. The diamond crystal has nitrogen-vacancy pairs. The image sensor detects the intensities of fluorescence generated by an exciting light applied to the diamond crystal by using a plurality of pixels. The nitrogen-vacancy pairs of the diamond crystal are made to one-to-one correspond to the pixels. The fluorescence generated by one nitrogen-vacancy pair is received by one pixel made to correspond to the nitrogen-vacancy pair.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Position-measuring device for fluidic cylinder-and-piston arrangements
InactiveUS7263781B2Easily integrated into cylinder profileEasy to adjustWalking sticksUsing electrical meansSensor arrayPiston
A position-measuring device for fluidic cylinder-and-piston arrangements having at least one Hall sensor, preferably arranged in the area of the cylinder wall, especially in a cylinder wall, and a magnetic region, arranged in the piston. At least one Hall sensor array has at least two Hall sensors spaced one from the other in the direction of movement of the piston. One coil is provided whose magnetic field permits the switching points of the Hall sensors to be adjusted in response to the coil current.
Owner:NORGREN GMBH
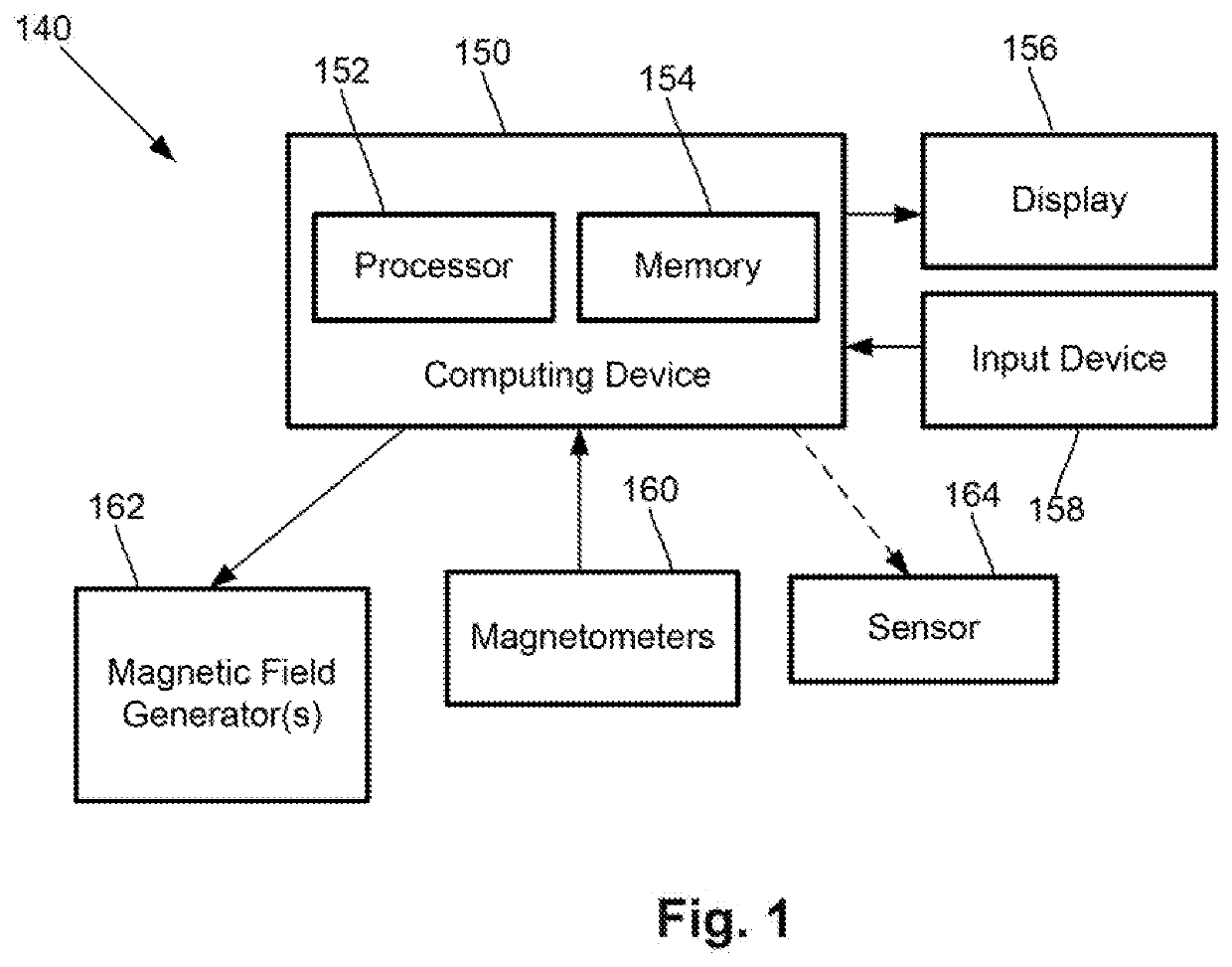
Magnetic field measurement systems and methods of making and using
InactiveUS20190391213A1Magnetic field offset compensationMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic tension forceCondensed matter physics
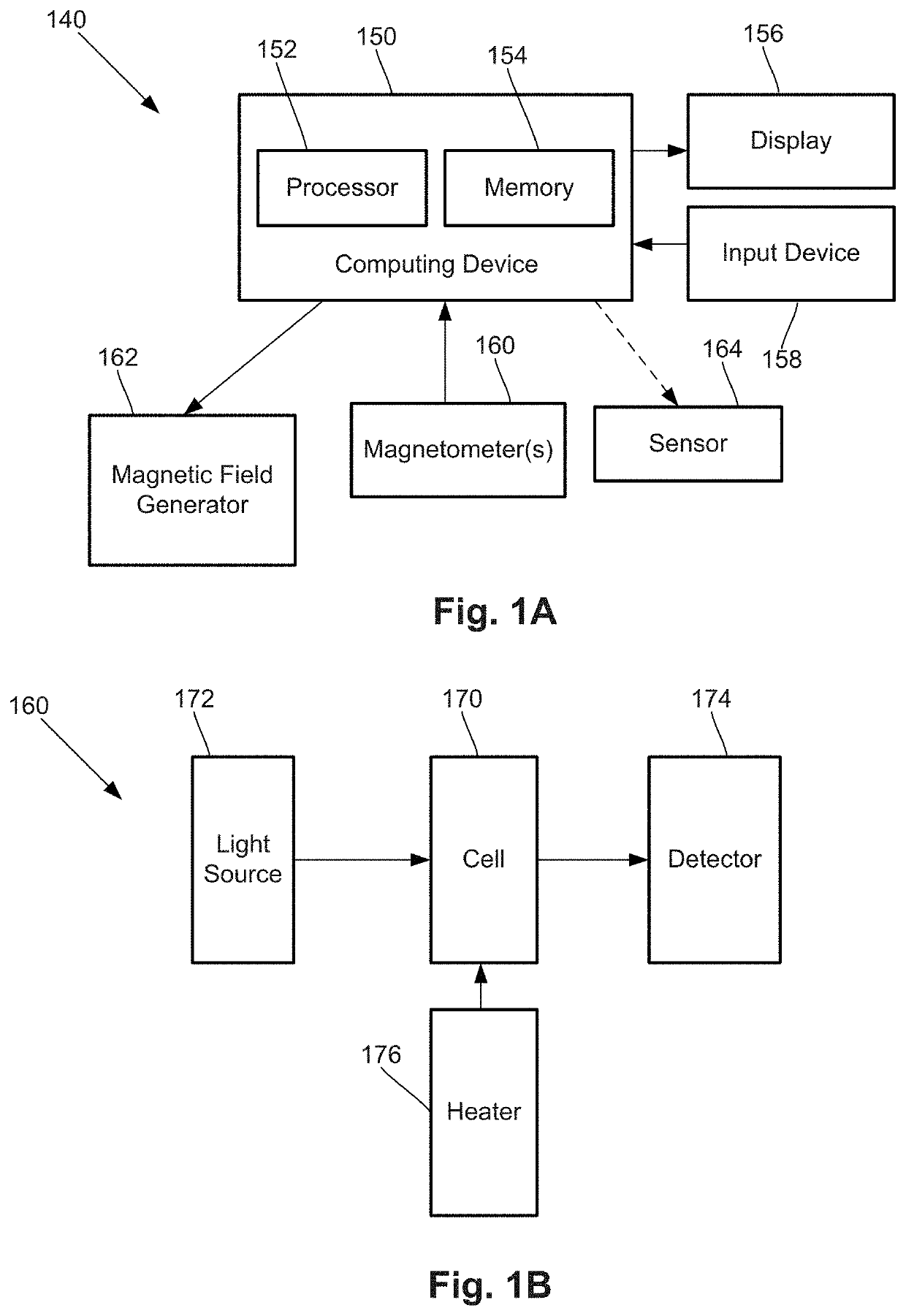
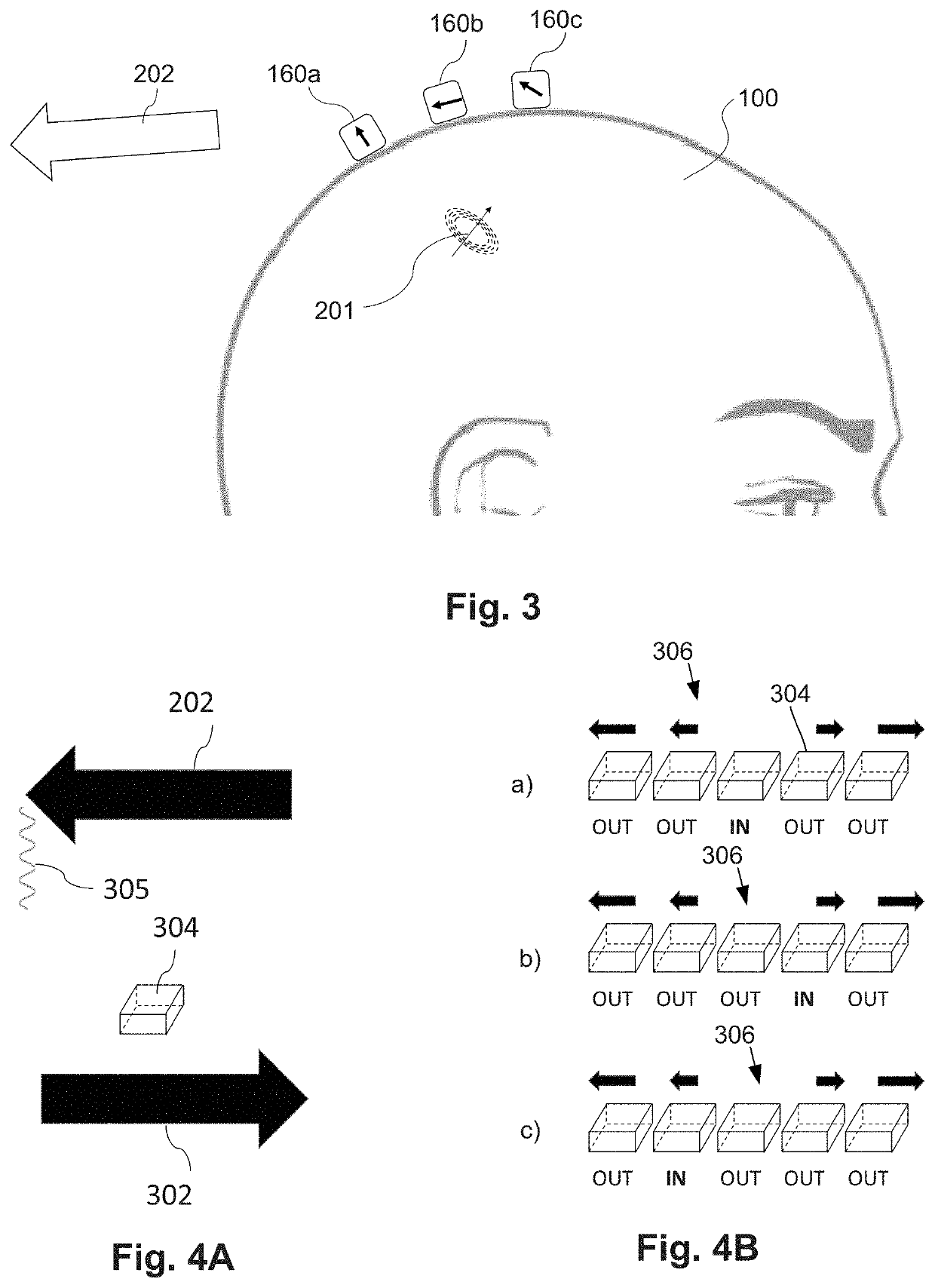
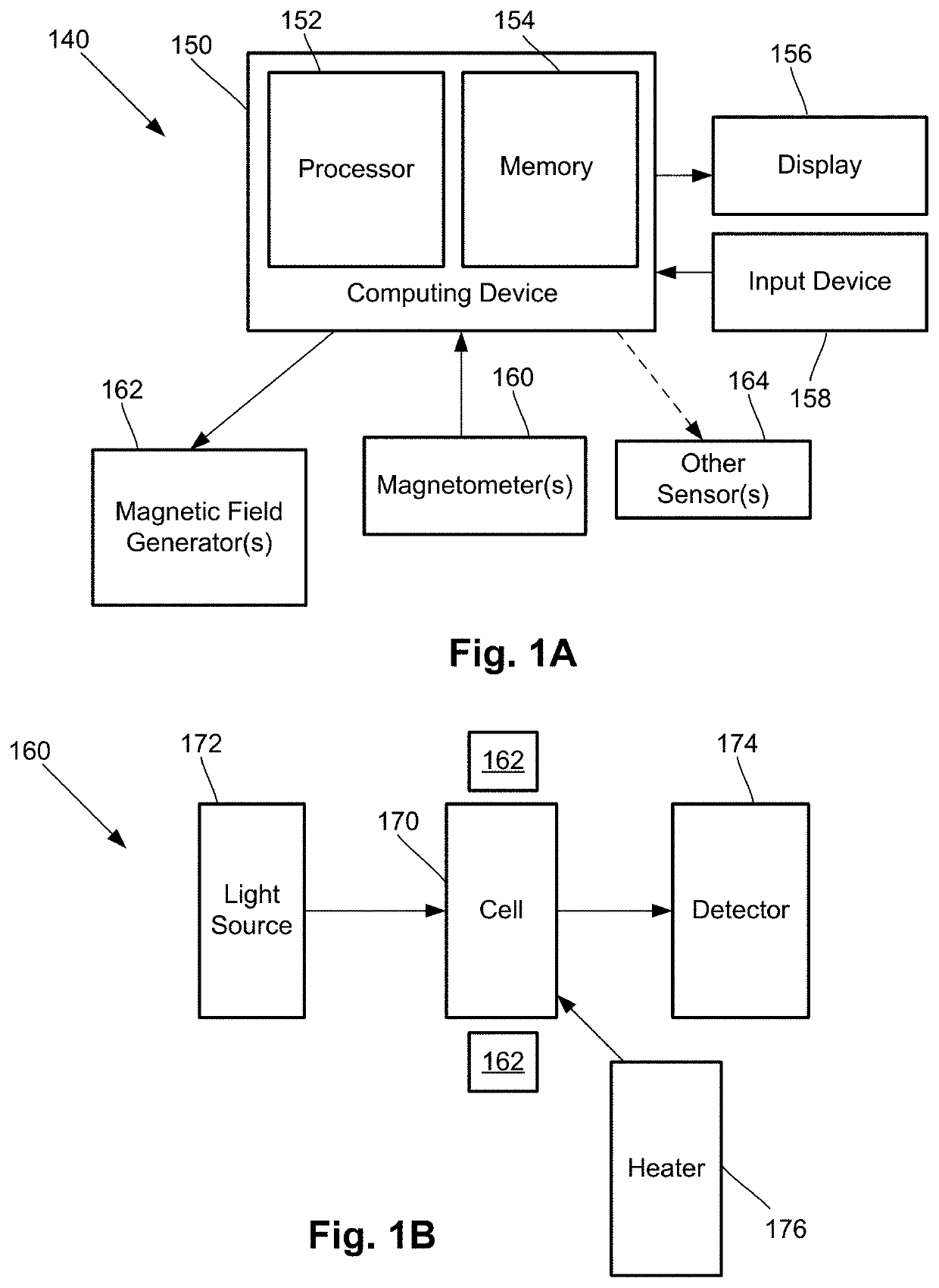
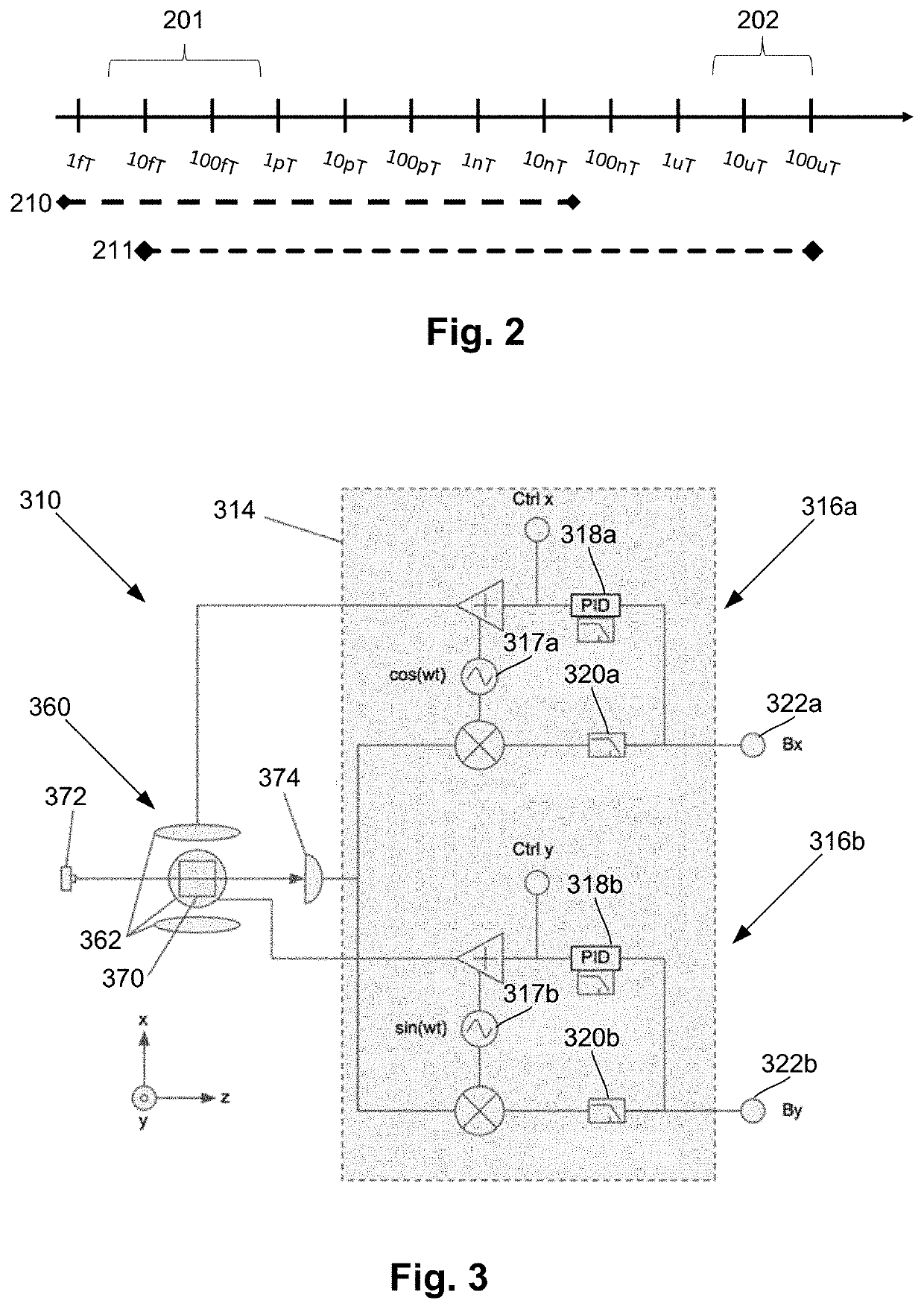
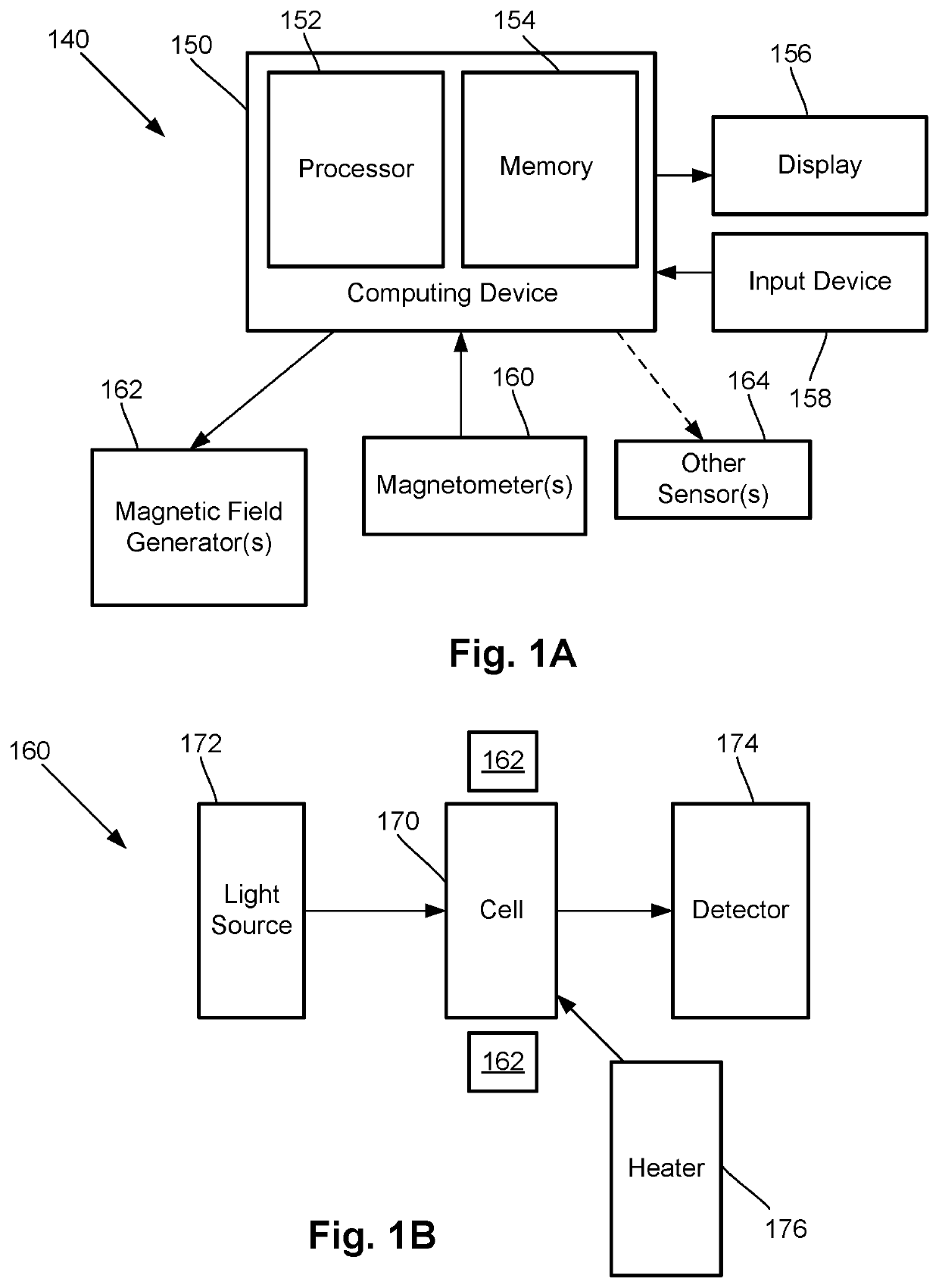
A magnetic field measurement system includes an array of magnetometers; at least one magnetic field generator with each of the at least one magnetic field generator configured to generate a first magnetic field at one or more of the magnetometers, wherein the generated first magnetic field combines with the ambient magnetic field to produce a directional magnetic field at the one or more of the magnetometers, where a magnitude and direction of the directional magnetic field is selectable using the at least one magnetic field generator; and a controller coupled to the magnetometers and the at least one magnetic field generator, the controller including a processor configured for receiving signals from the magnetometers, observing or measuring a magnetic field from the received signals, and controlling the at least one magnetic field generator to generate the first magnetic field and select the direction of the directional magnetic field.
Owner:HI LLC
Magnetic field measurement system and method of using variable dynamic range optical magnetometers
ActiveUS20200025844A1Improve dynamic rangeReduce in quantityMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic sensor arraysEngineeringComputational physics
A magnetic field measurement system includes an array of magnetometers; at least one magnetic field generator configured to generate a compensation field across the array of magnetometers; and a controller coupled to the magnetometers and the at least one magnetic field generator and configured for adjusting a dynamic range and sensitivity of the array by adjusting a spatial variation of the compensation field to alter which of the magnetometers of the array operate in a measurement mode. Another magnetic field measurement system utilizes at least one magnetometer instead of the array. The controller is configured for adjusting a dynamic range and sensitivity of the array by adjusting a spatial variation of the compensation field to alter which of multiple domains within the at least one magnetometer operate in the measurement mode
Owner:HI LLC
Multiple dimension position sensor
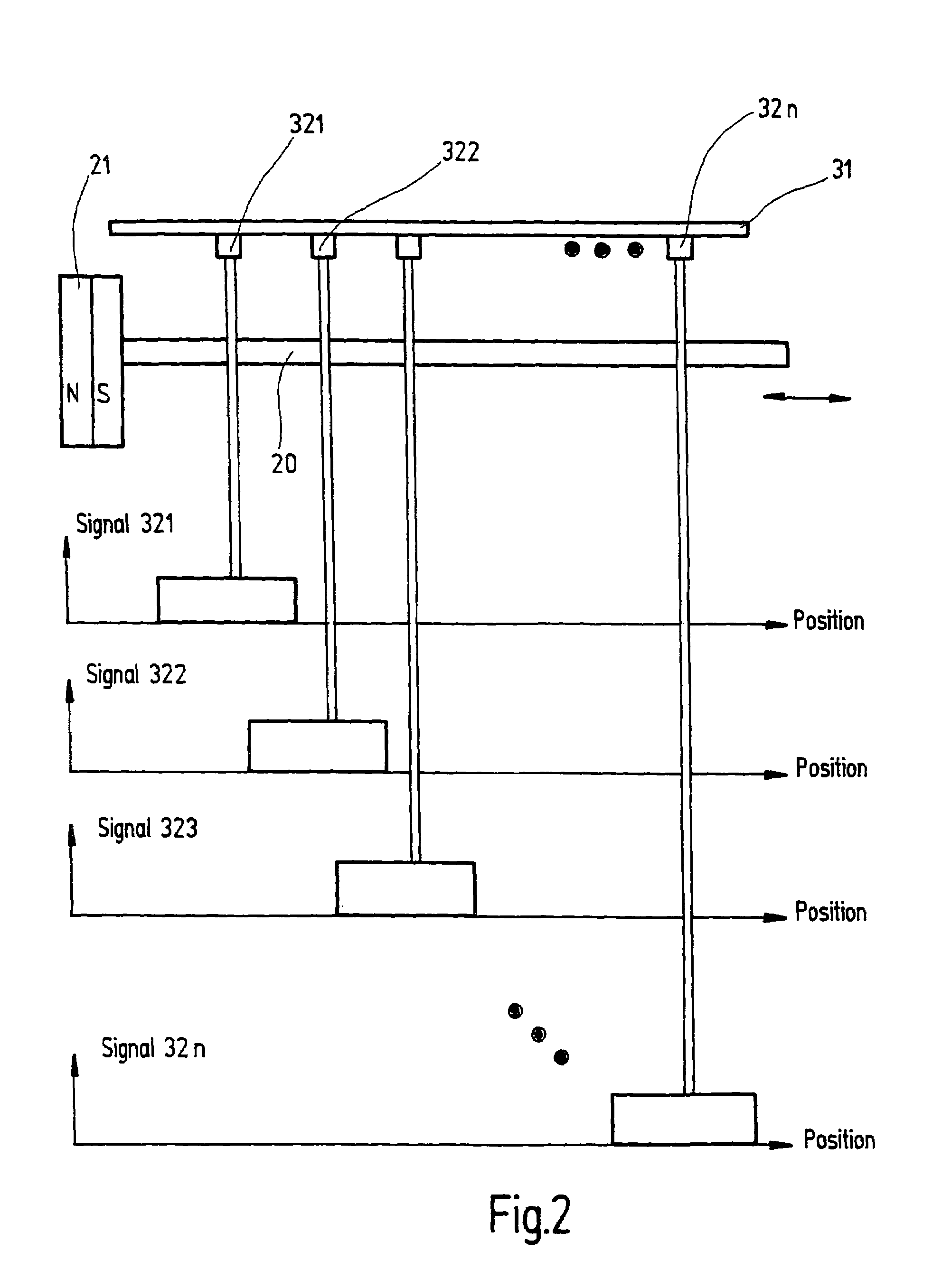
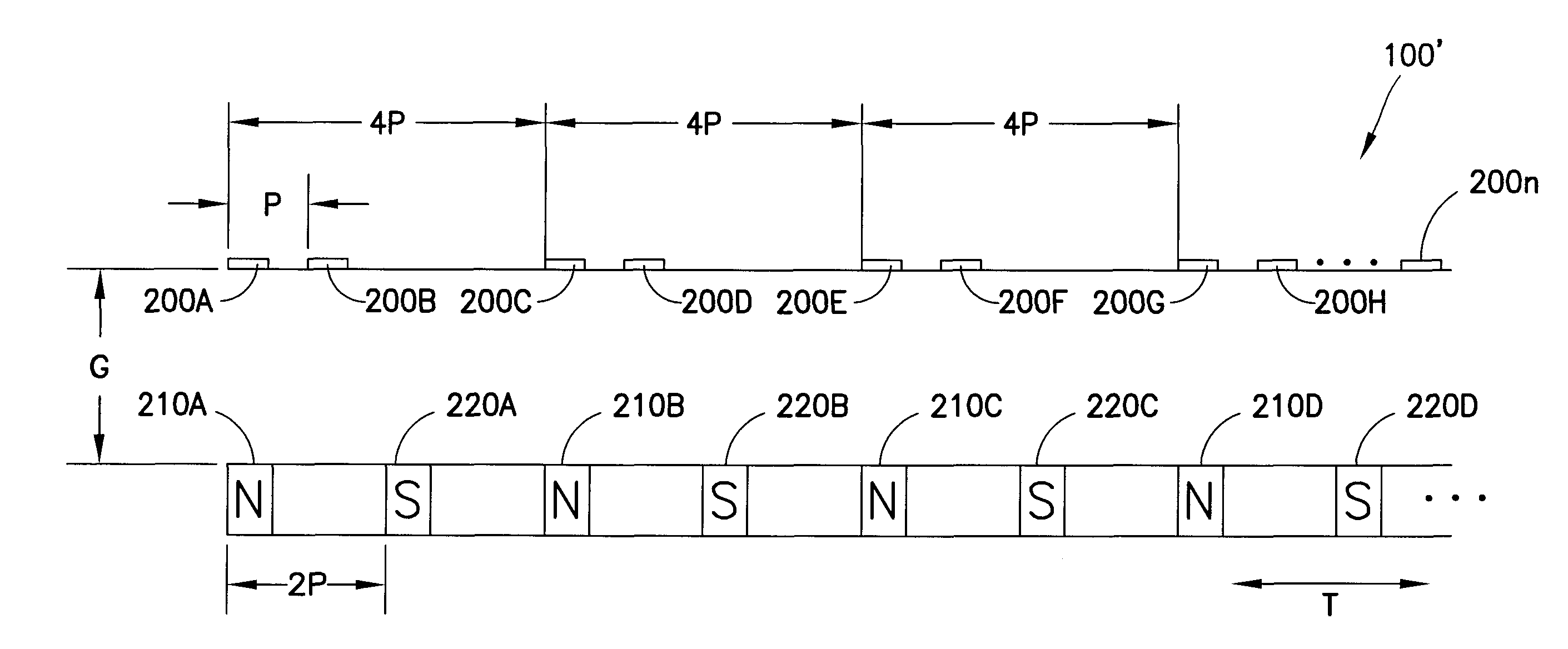
ActiveUS8129984B2Electric/magnetic position measurementsSolid-state devicesMeasurement deviceEngineering
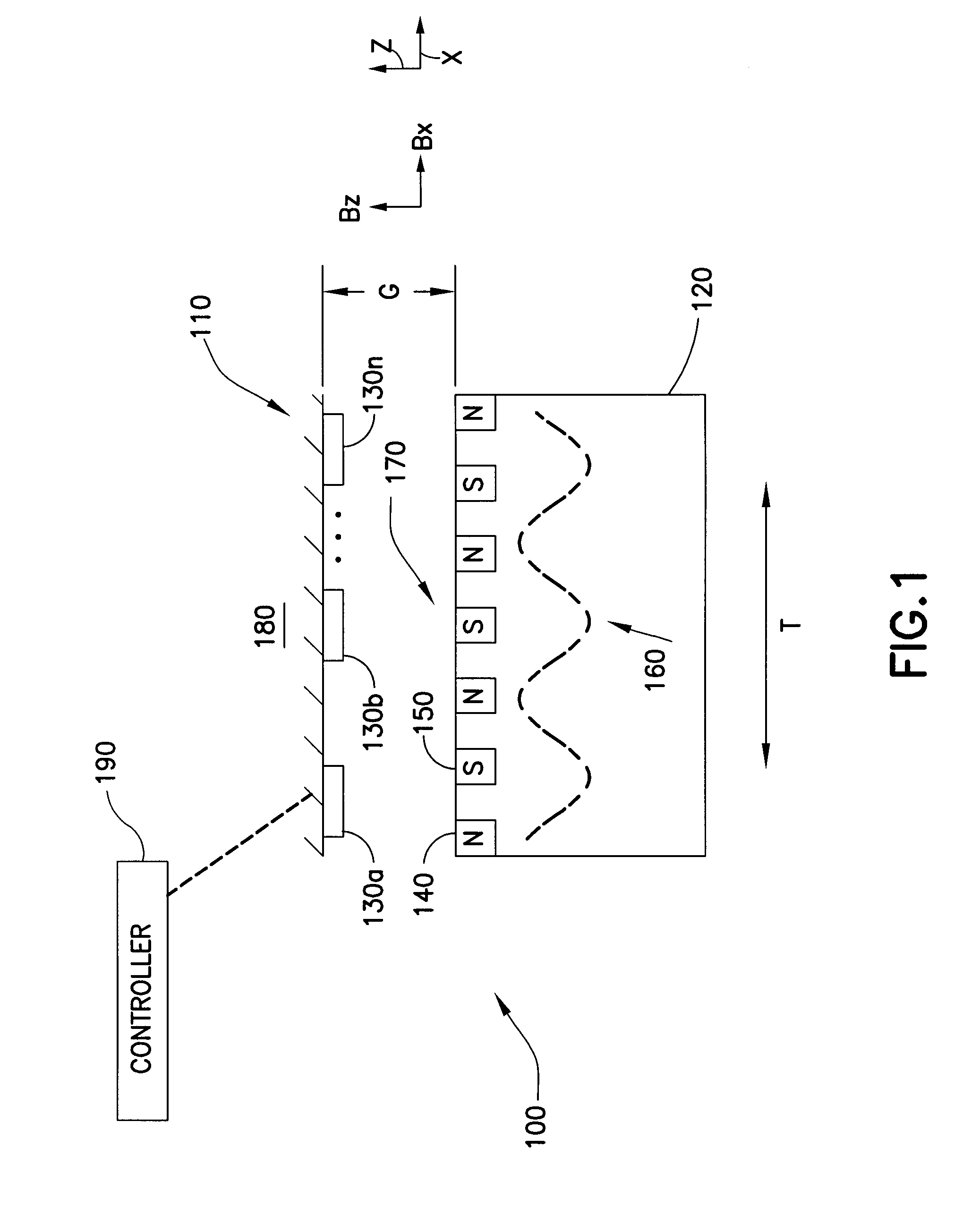
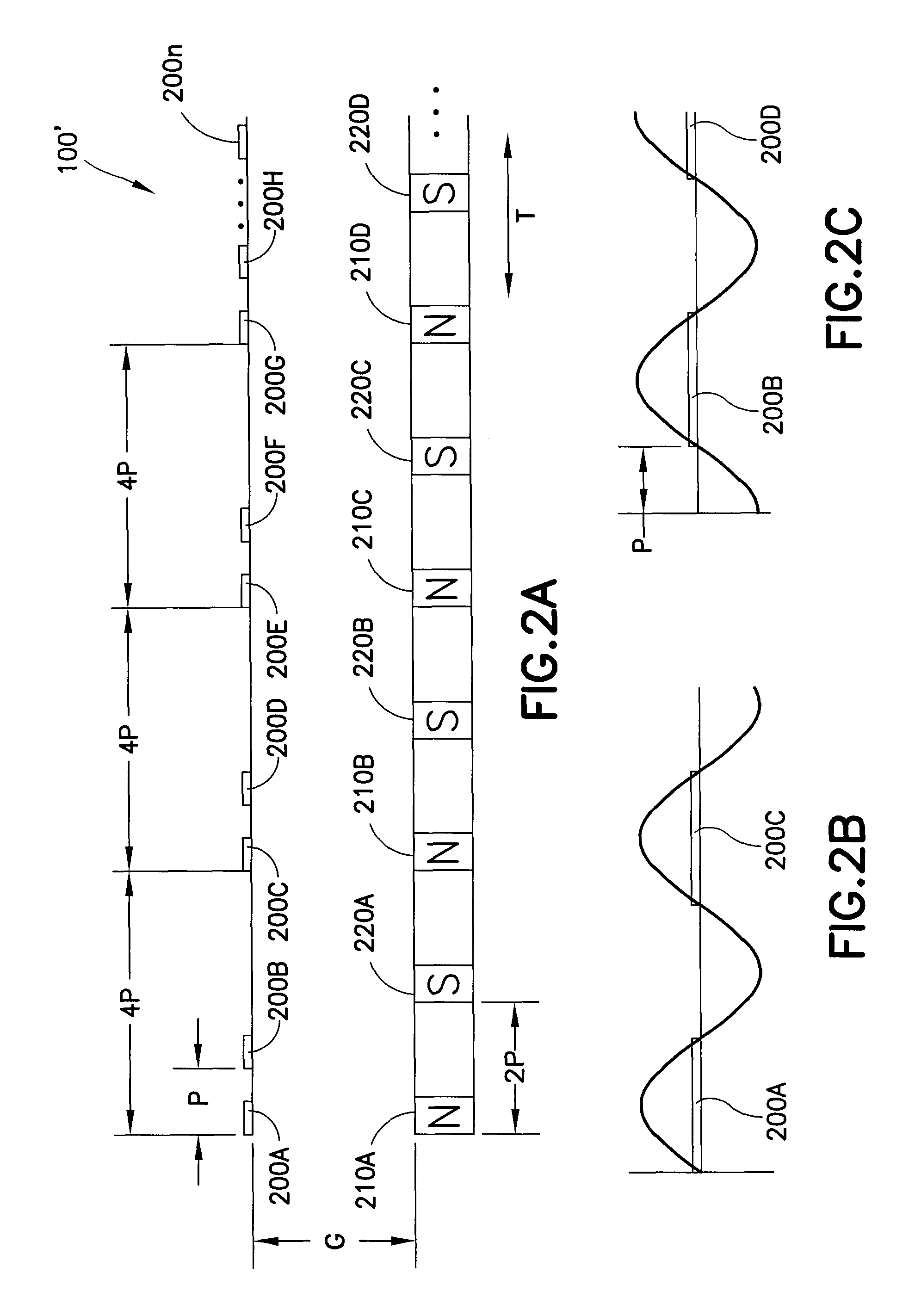
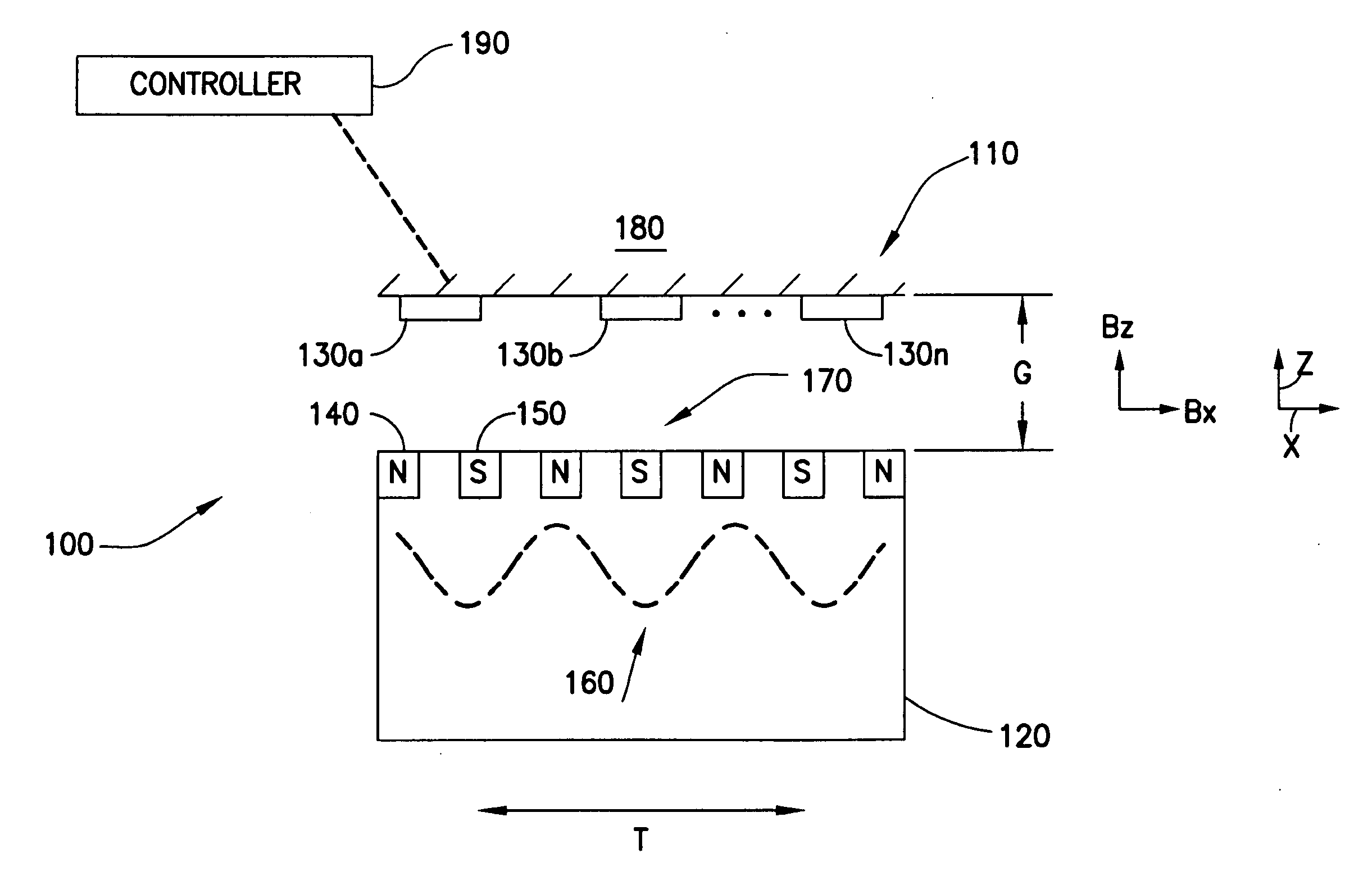
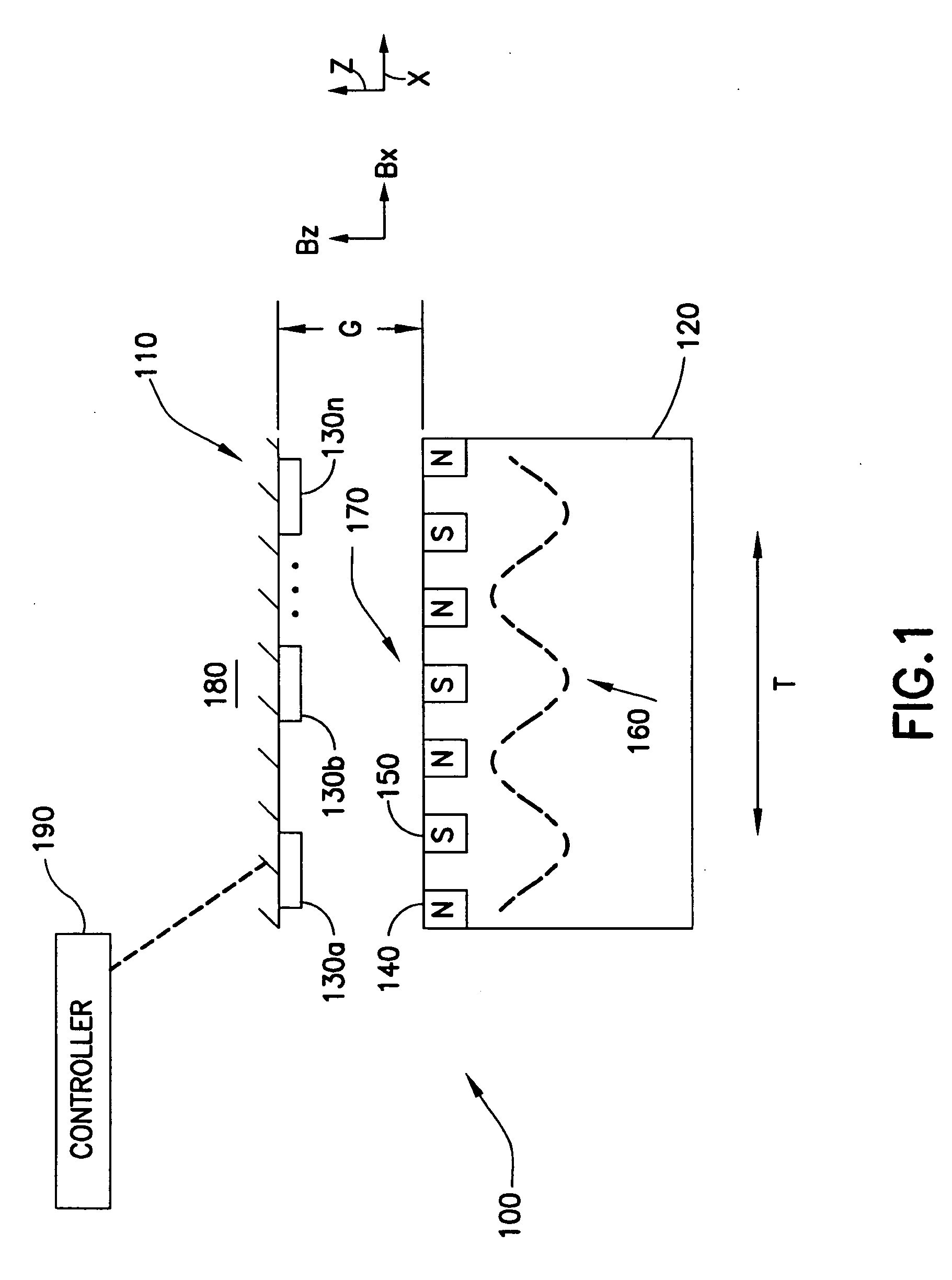
An apparatus including a controller, a workpiece transport in communication with the controller having a movable portion and a transport path, and a multi-dimensional position measurement device including at least one field generating platen attached to the movable portion and at least one sensor group positioned along the transport path and in communication with the controller, the field generating platen is configured for position measurement and propelling the movable portion, each sensor in the at least one sensor group is configured to provide but one output signal along a single axis corresponding to a sensed field generated by the at least one field generating platen and the controller is configured calculate a multi-dimensional position of the movable portion based on the but one output signal of at least one of the sensors in the at least one sensor group, the multi-dimensional position including a planar position and a gap measurement.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
Multiple dimension position sensor
ActiveUS20090224750A1Solid-state devicesElectric/magnetic position measurementsMeasurement deviceEngineering
An apparatus including a controller, a workpiece transport in communication with the controller having a movable portion and a transport path, and a multi-dimensional position measurement device including at least one field generating platen attached to the movable portion and at least one sensor group positioned along the transport path and in communication with the controller, the field generating platen is configured for position measurement and propelling the movable portion, each sensor in the at least one sensor group is configured to provide but one output signal along a single axis corresponding to a sensed field generated by the at least one field generating platen and the controller is configured calculate a multi-dimensional position of the movable portion based on the but one output signal of at least one of the sensors in the at least one sensor group, the multi-dimensional position including a planar position and a gap measurement.
Owner:BOOKS AUTOMATION US LLC
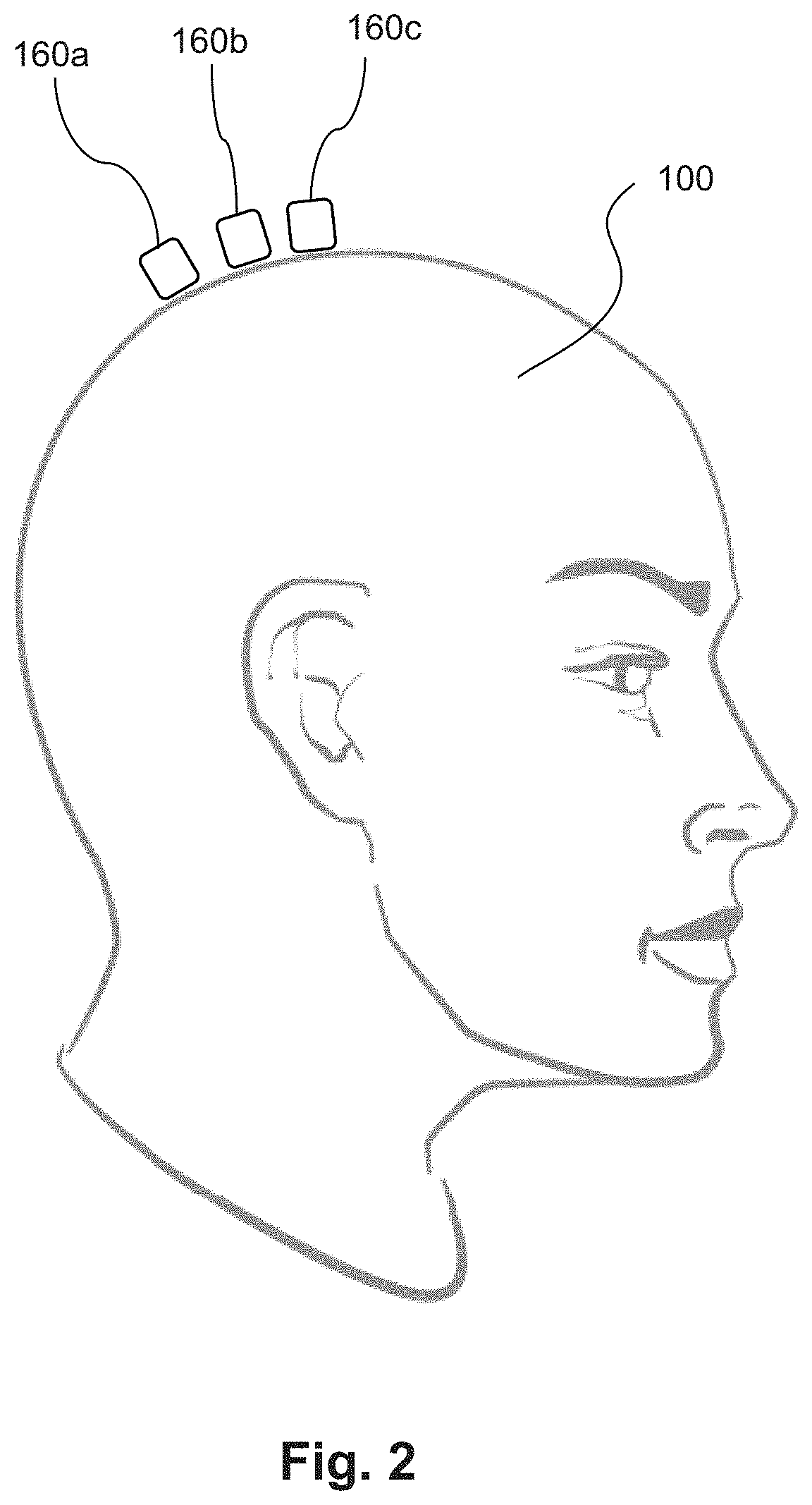
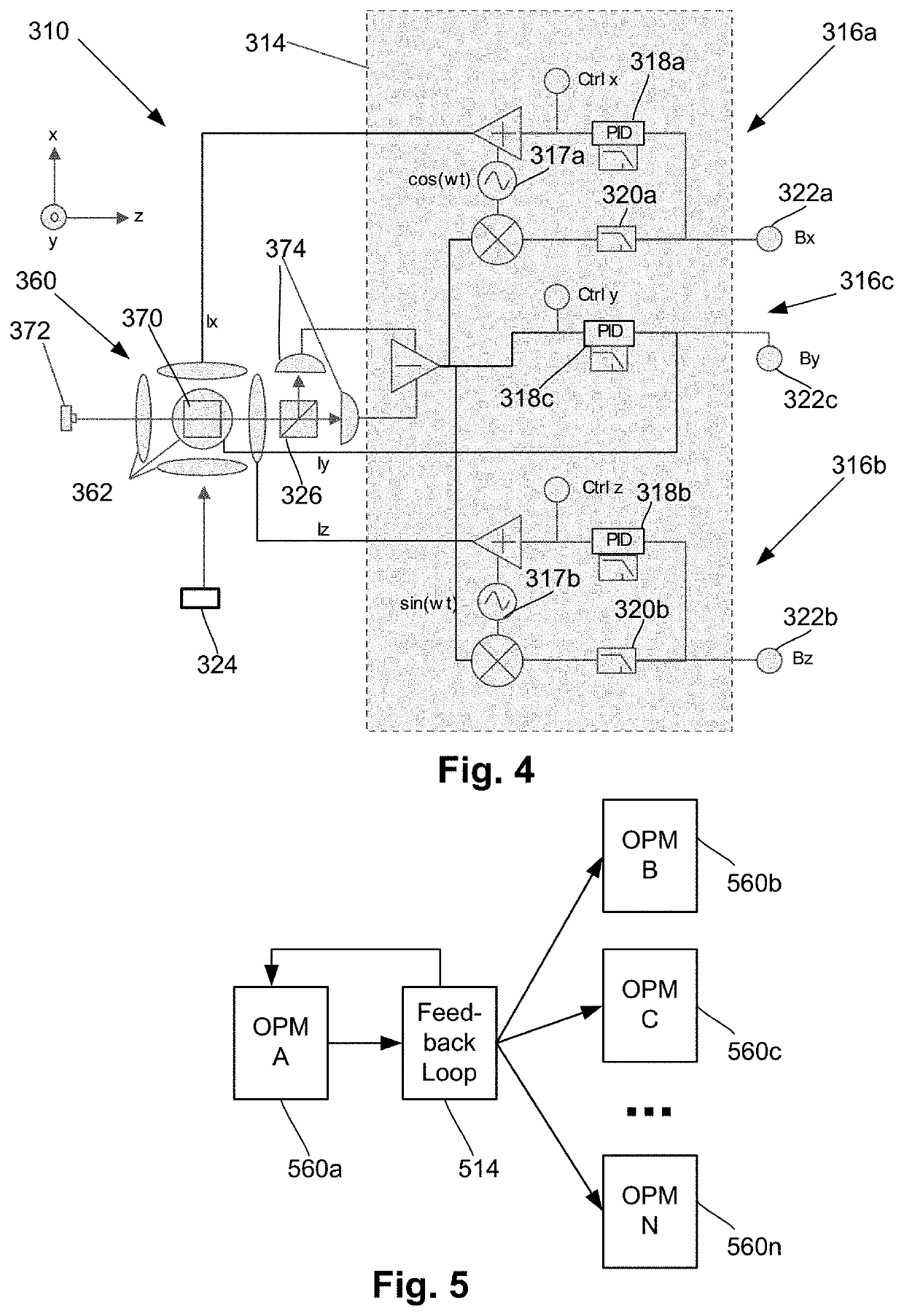
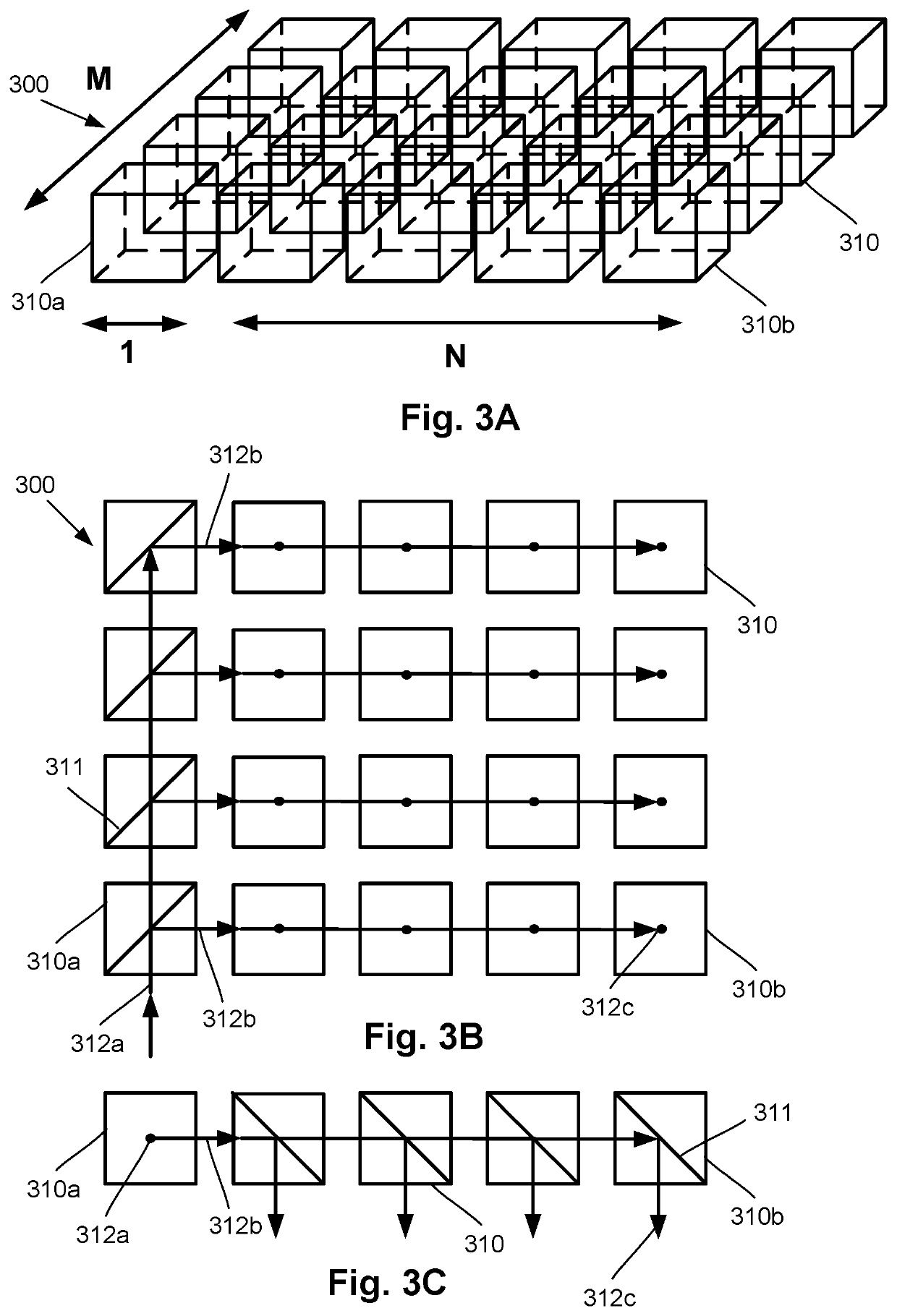
Integrated magnetometer arrays for magnetoencephalography (MEG) detection systems and methods
ActiveUS20200309873A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringWaferingEngineering
An array of optically pumped magnetometers includes a vapor cell arrangement having a wafer defining one or more cavities and alkali metal atoms disposed in the cavities to provide an alkali metal vapor; an array of light sources, each of the light sources arranged to illuminate a different portion of the one or more cavities of the vapor cell arrangement with light; at least one mirror arranged to reflect the light from the array of light sources after the light passes through the one or more cavities of the vapor cell arrangement; and an array of detectors to receive light reflected by the at least one mirror, wherein each of the detectors is arranged to receive light originating from one of the light sources.
Owner:HI LLC
Neural feedback loop filters for enhanced dynamic range magnetoencephalography (MEG) systems and methods
ActiveUS20200256929A1Analysis using optical pumpingDiagnostic recording/measuringLow-pass filterSoftware engineering
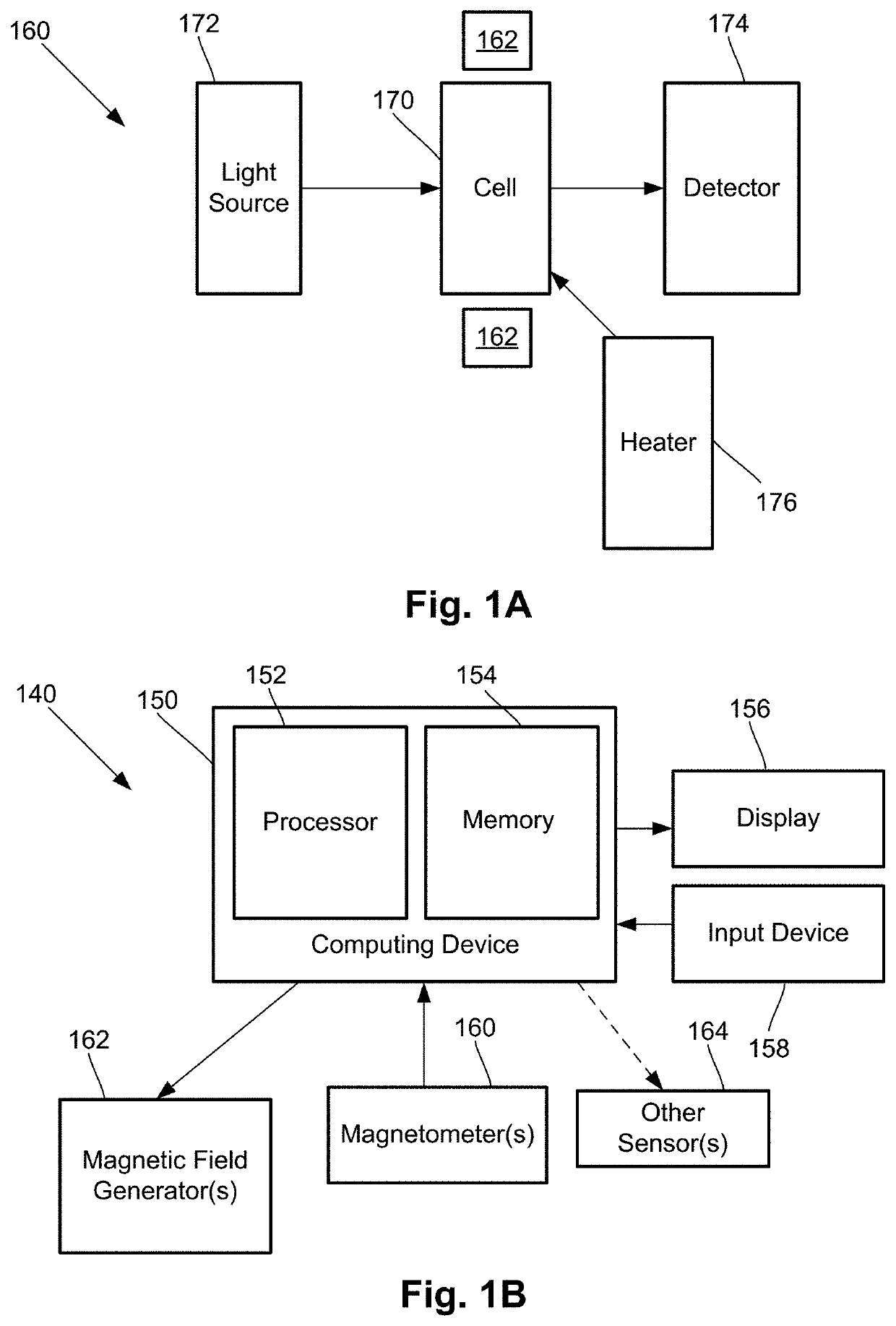
One embodiment is a magnetic field measurement system that includes at least one magnetometer having a vapor cell, a light source to direct light through the vapor cell, and a detector to receive light directed through the vapor cell; at least one magnetic field generator disposed adjacent the vapor cell; and a feedback circuit coupled to the at least one magnetic field generator and the detector of the at least one magnetometer. The feedback circuit includes at least one feedback loop that includes a first low pass filter with a first cutoff frequency. The feedback circuit is configured to compensate for magnetic field variations having a frequency lower than the first cutoff frequency. The first low pass filter rejects magnetic field variations having a frequency higher than the first cutoff frequency and provides the rejected magnetic field variations for measurement as an output of the feedback circuit.
Owner:HI LLC
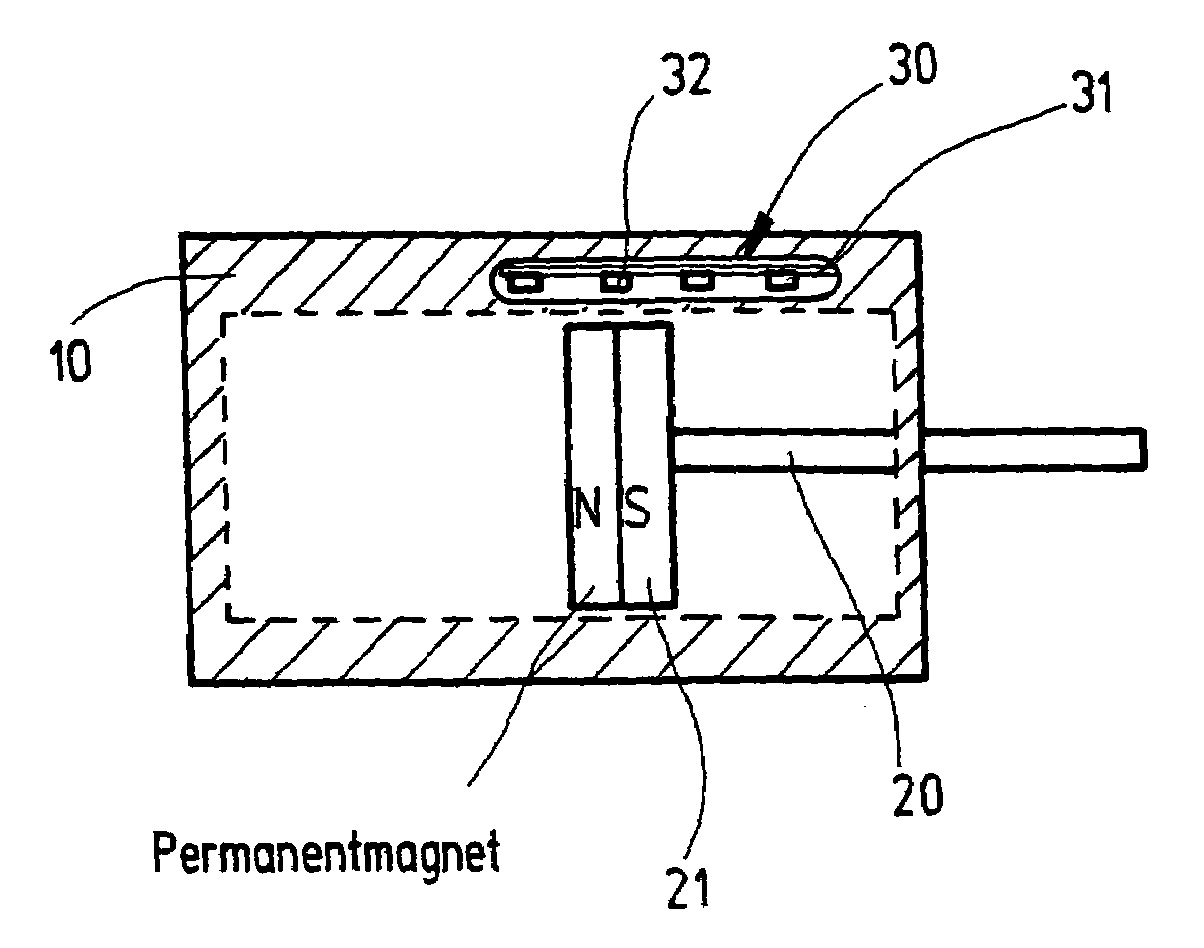
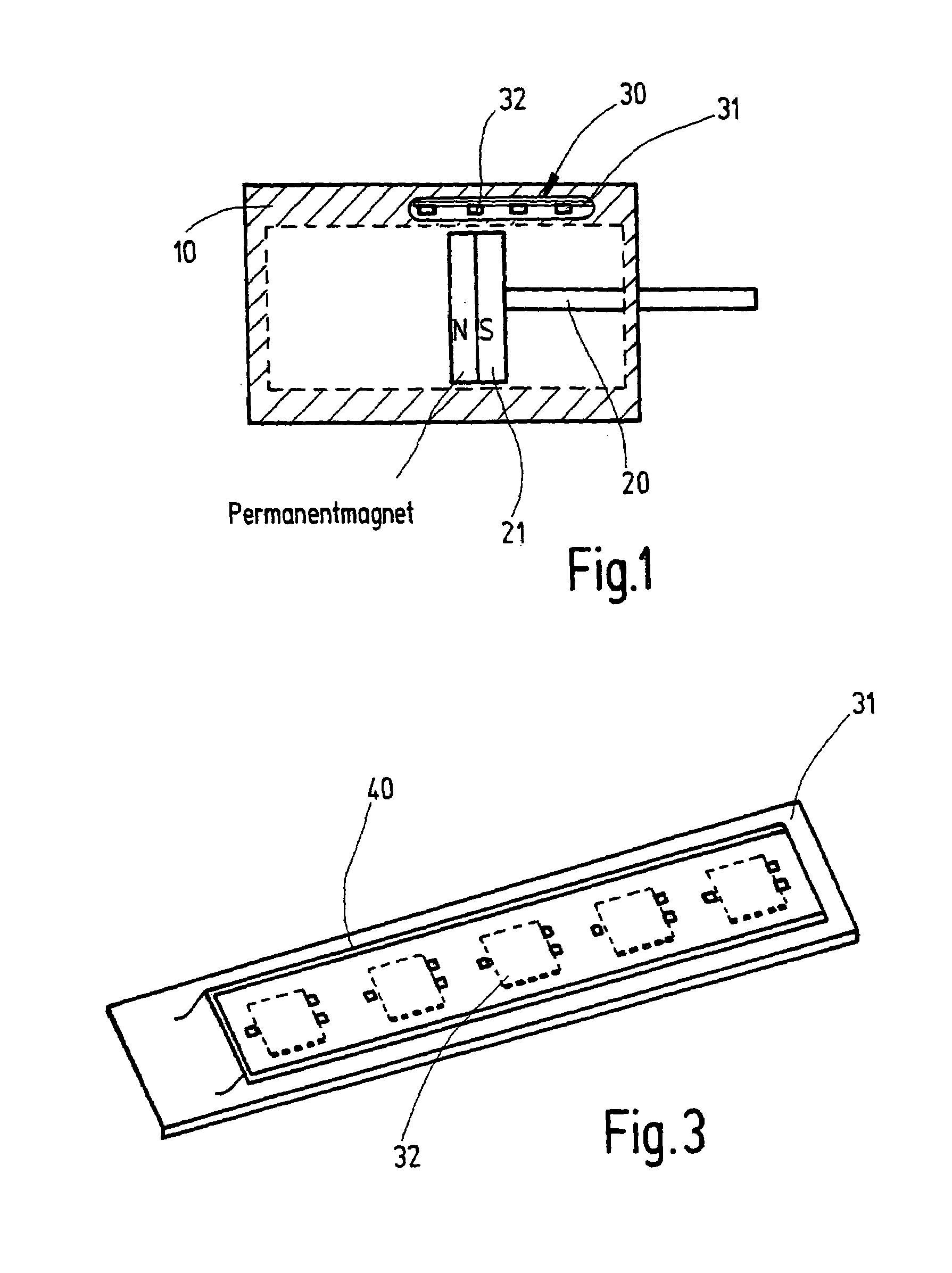
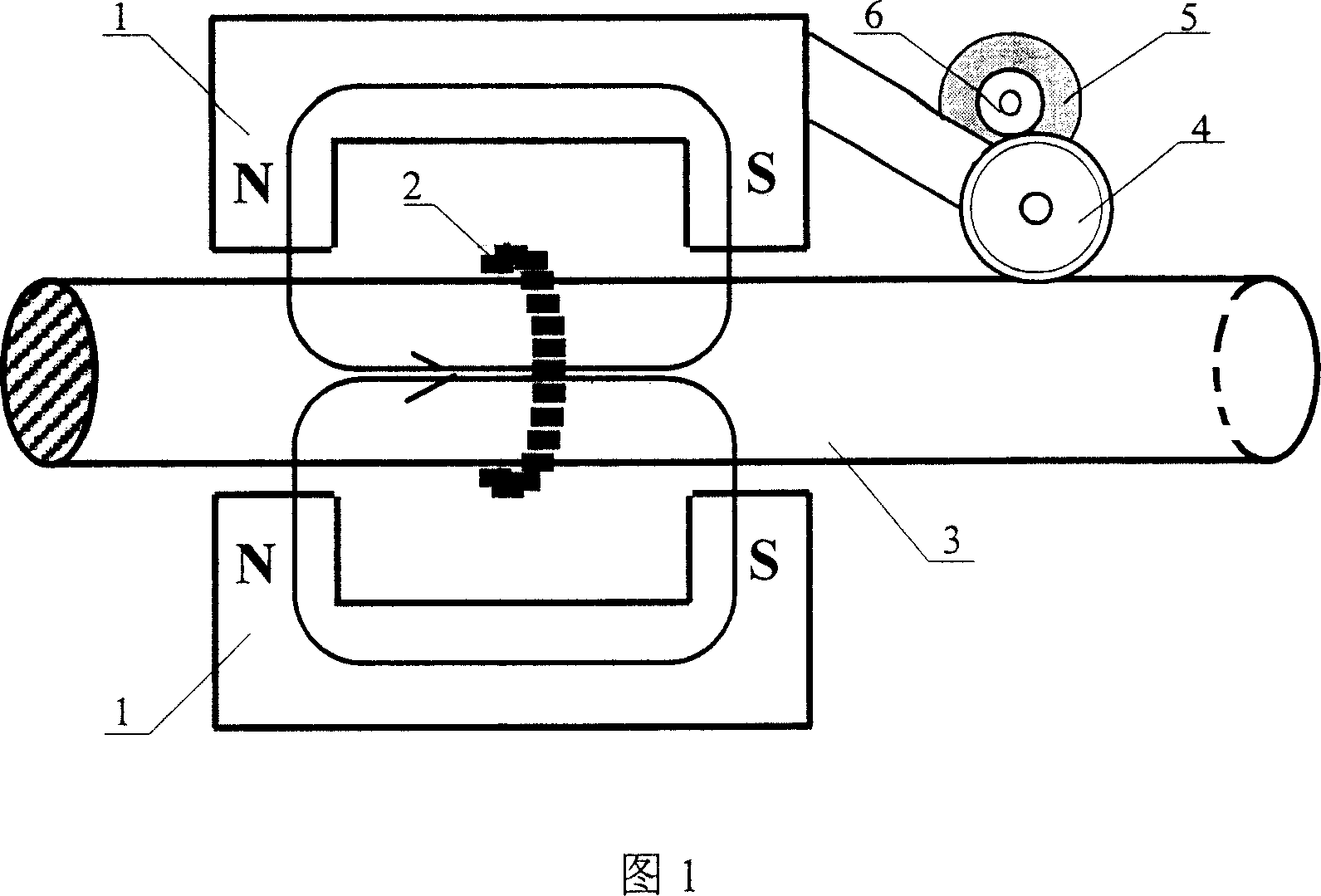
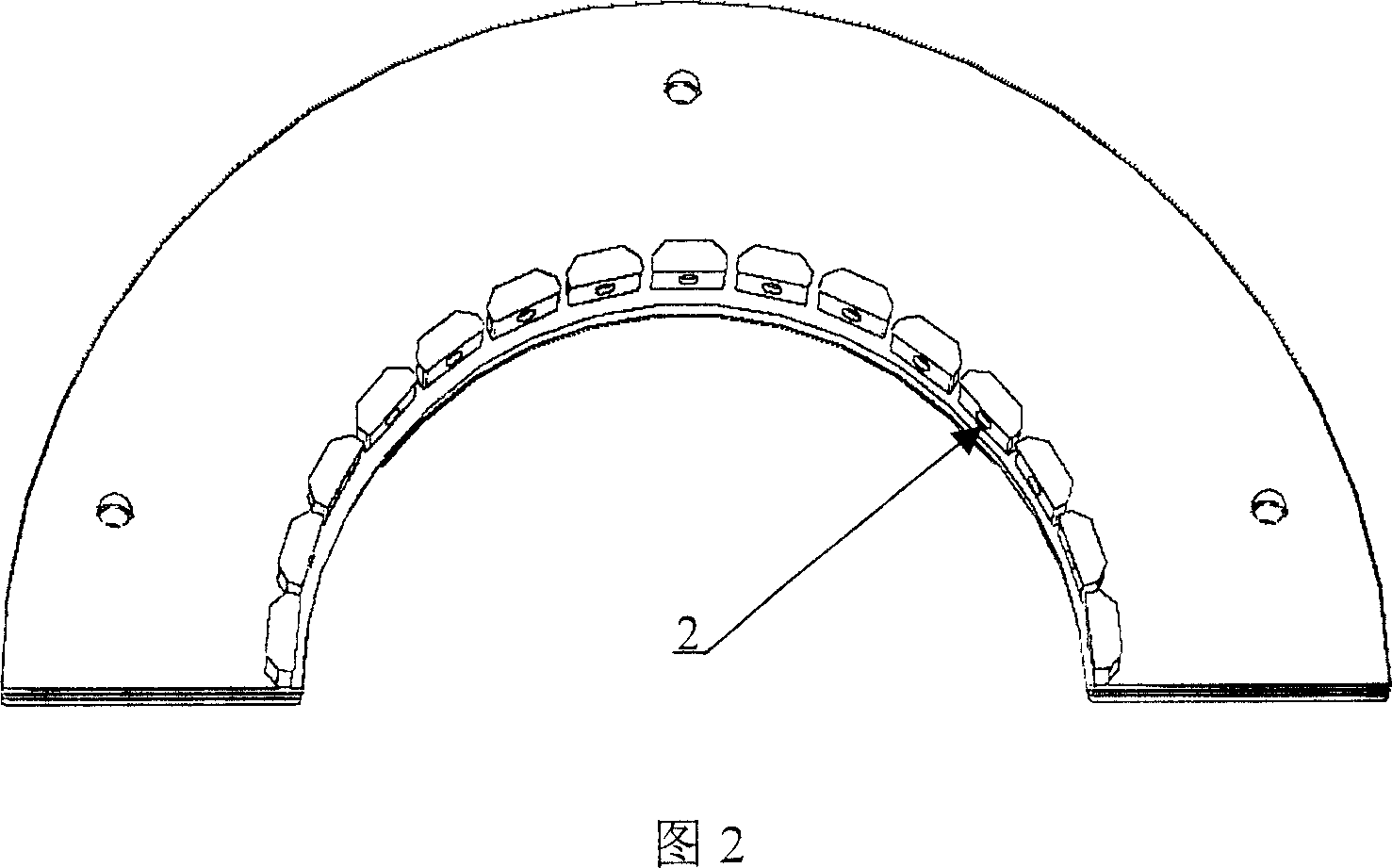
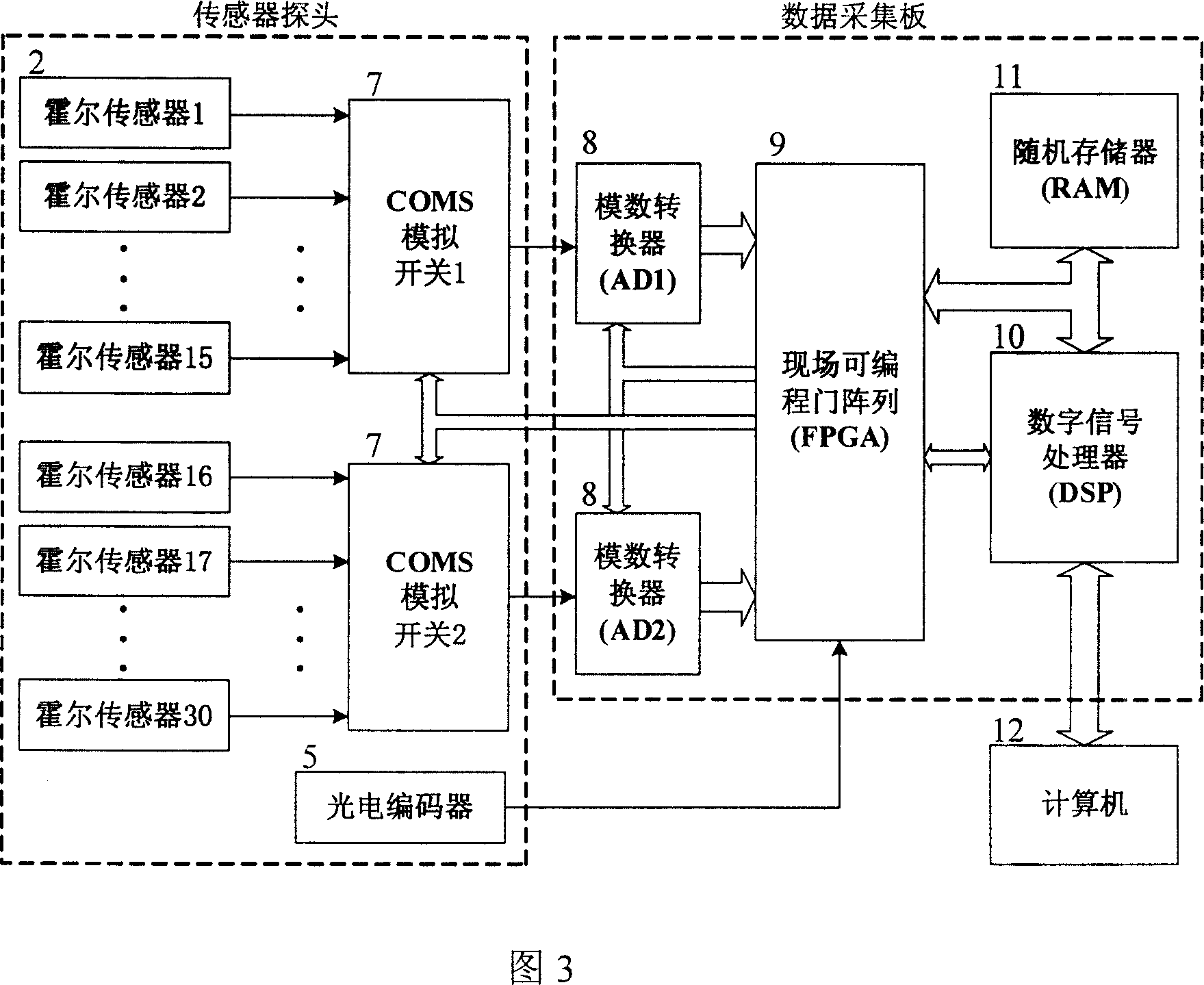
Hall sensor array based steel ropes nondestructive examination method and device
InactiveCN1928543AHigh precisionEliminate the wave componentMagnetic sensor arraysMaterial magnetic variablesSensor arrayTrapping
The wire rope detection method based on 3D leakage magnetic field comprises: acquiring the defect sample magnetic leakage signal by Hall sensor array; eliminating trough by an adaptive space trapping filter; taking normalization and K-L transformation to extract feature and train NN, and detecting the real defect by the network. The corresponding detection device comprises: a sensor probe included a permanent magnet excitation part and an analog switch and a photoelectric encoder, a data acquirement processor, and a computer. This invention can provide full defect signal and improve detection precision.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
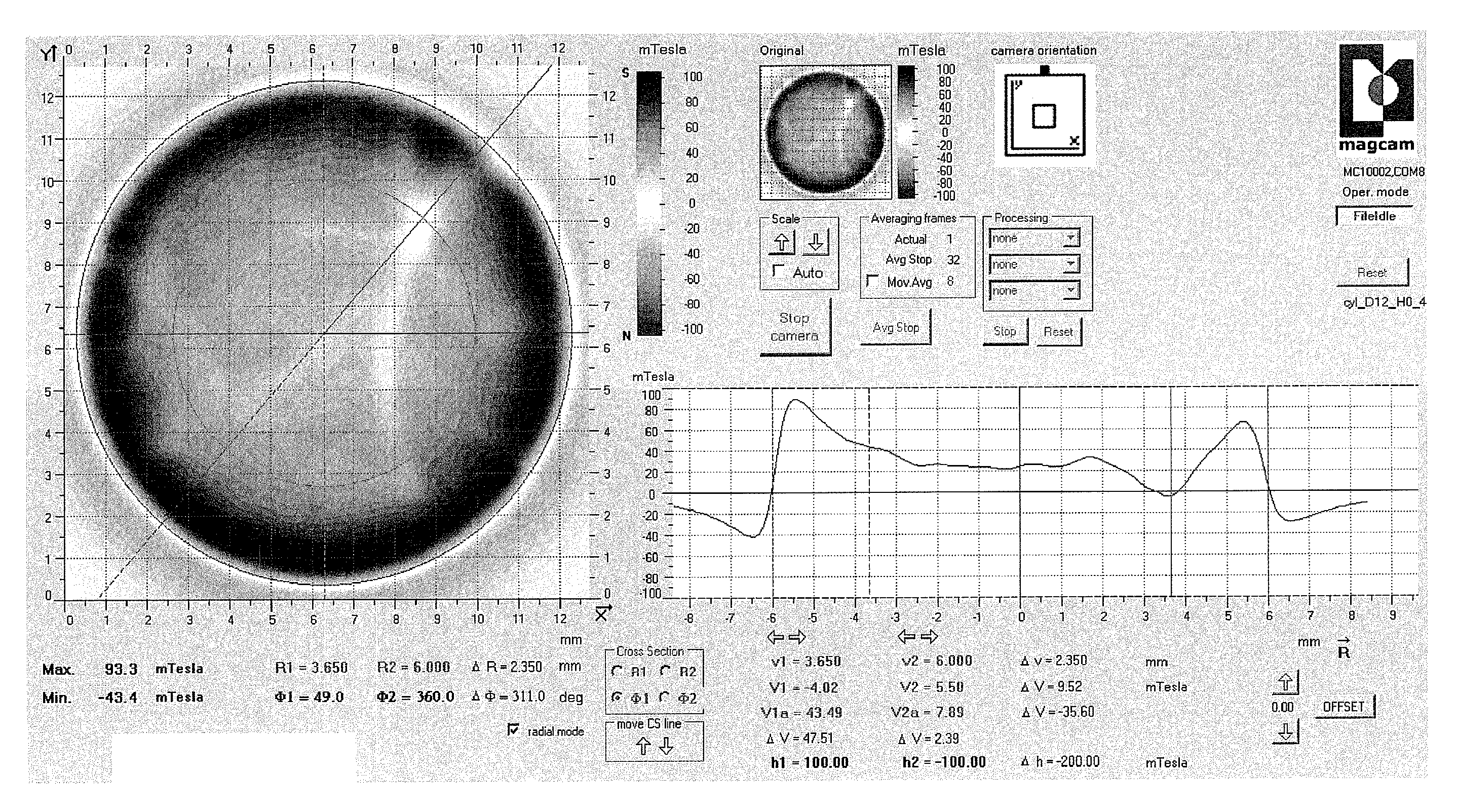
Arrangement and method for characterizing magnetic systems
ActiveUS20120209546A1Improve fitEasy to analyzeComputation using non-denominational number representationElectrical measurementsQuality controlCondensed matter physics
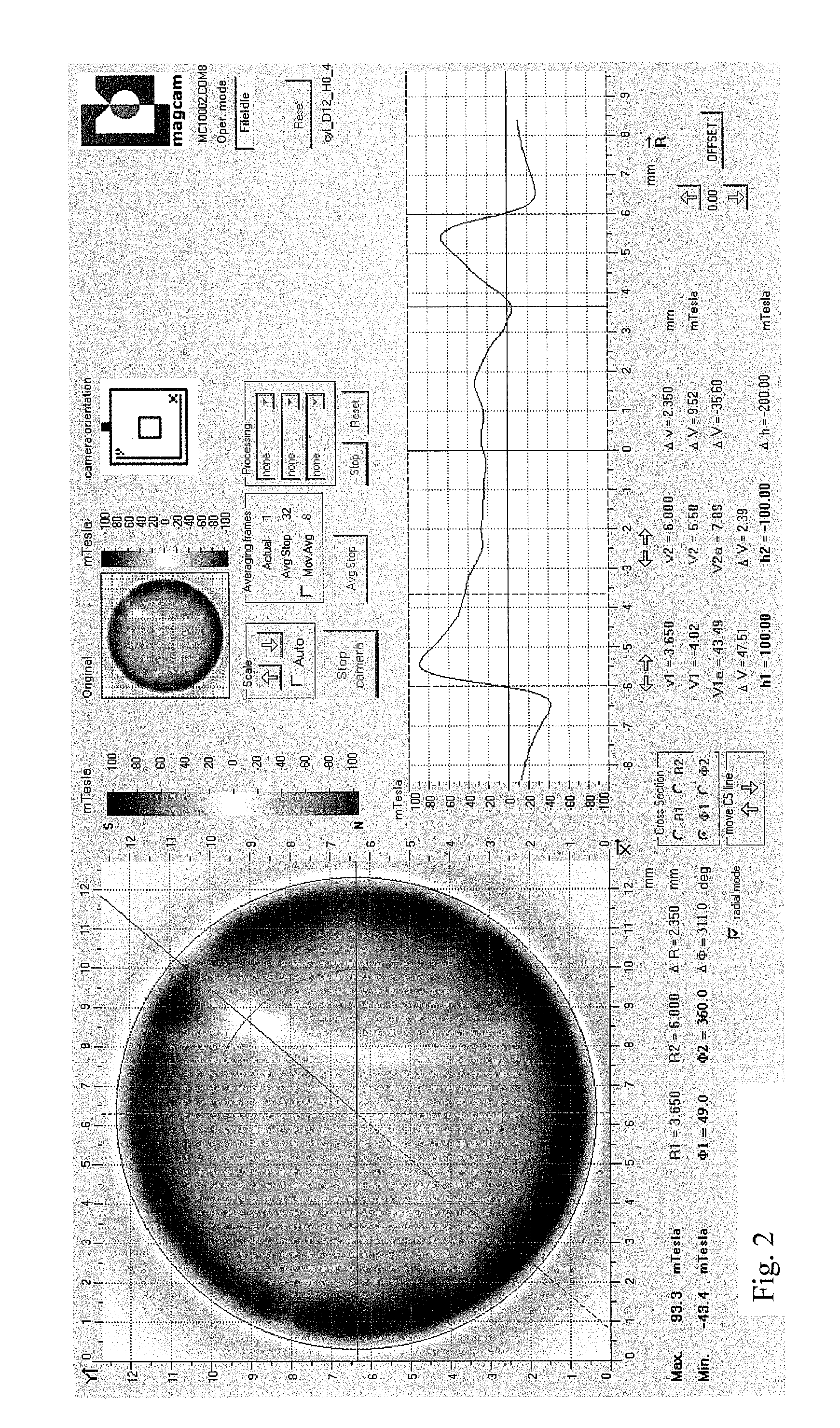
The present invention relates to a new method for characterizing magnets, magnetic assemblies (combinations of magnets) and magnetic materials. In what follows, these will be called under the common term ‘magnetic systems’. The method is based on obtaining quantitative properties of the magnetic system by combining magnetic field measurement data and theoretical modeling or simulation data. The input parameters of the theoretical model are optimized using an optimization method in order to obtain a best fit to the measured data. In this method, the present invention involves precalculating magnetic field distributions prior to the optimization execution in order to considerably speed up the process. Combining this advanced data processing with fast magnetic field mapping using e.g. a magnetic field camera, allows real-time measurement and data analysis of magnetic systems for applications in e.g. quality control of such magnetic systems.
Owner:MAGCAM
Wireless array device and system for managing wireless arrays having magnetometers
A wireless array for providing access to a network is provided. The wireless array includes at least two transceivers in signal communication with a client. A magnetometer of the wireless array provides orientation information relating to an orientation of the wireless array relative to a magnetic field. A controller of the wireless array is in signal communication with the transceivers and the magnetometer. The controller manages the communications exchanged via the transceivers and receives the orientation information provided by the magnetometer.
Owner:CAMBIUM NETWORKS
Angular position sensor
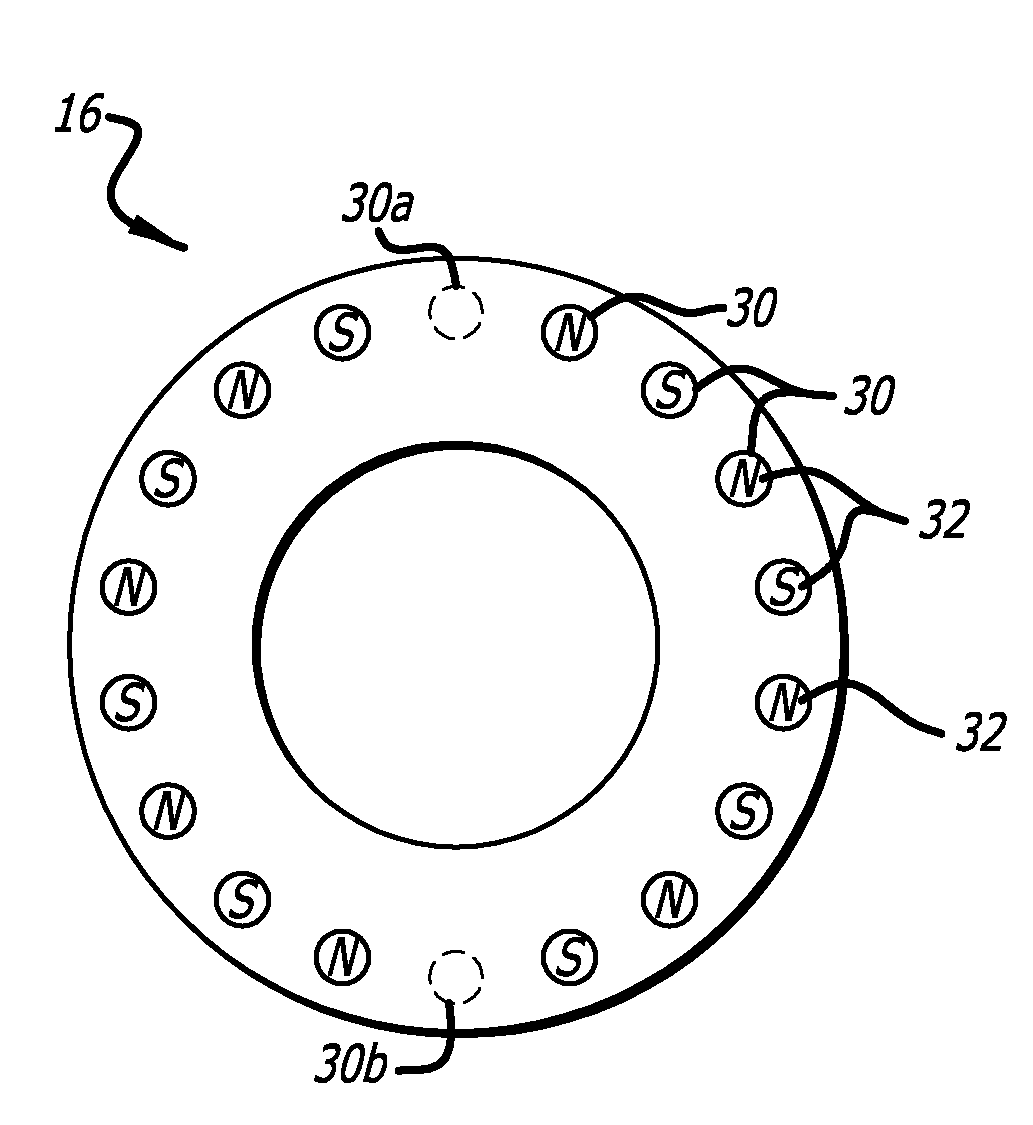
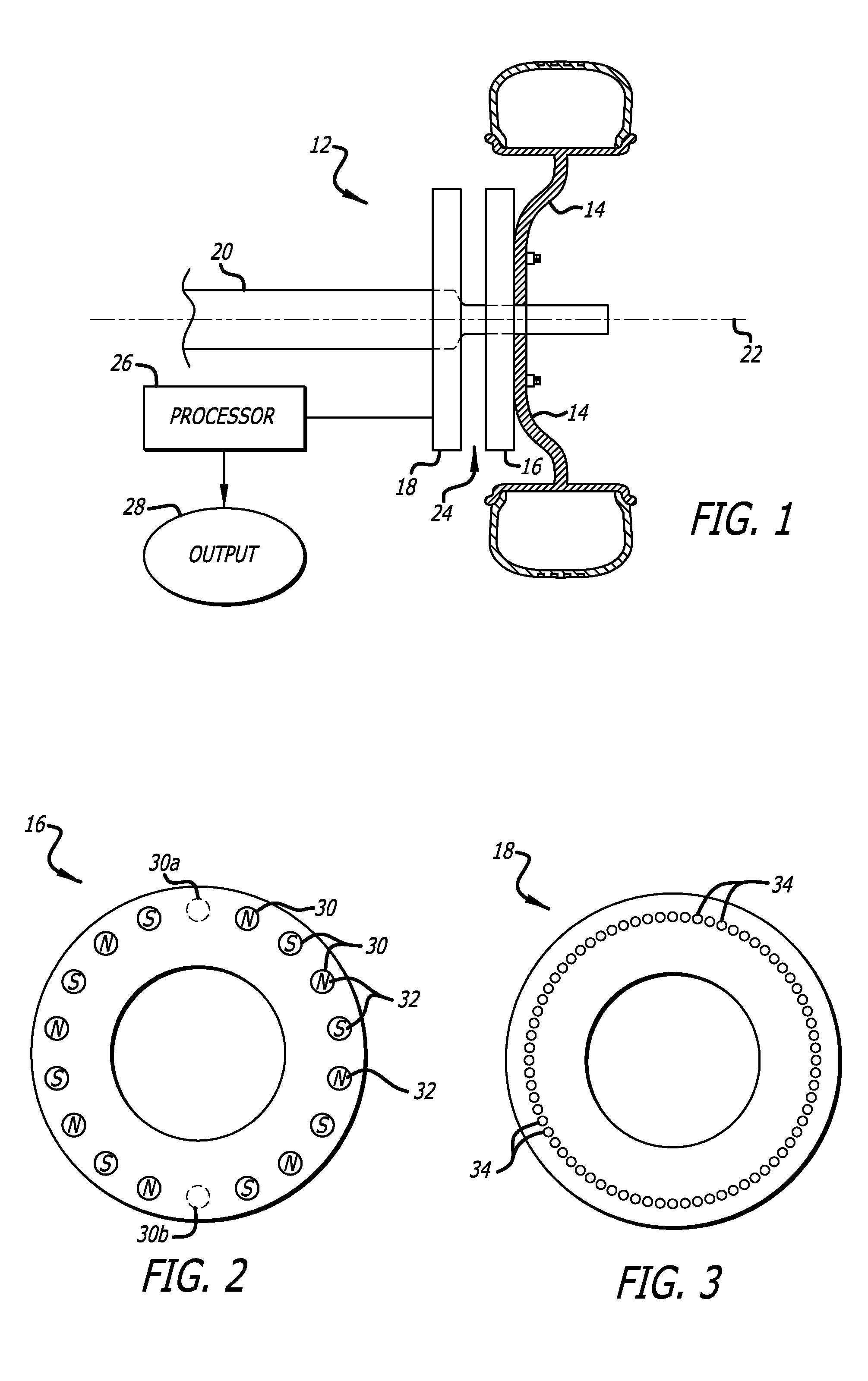
ActiveCN101707879AAccurately determineLinear/angular speed measurementMagnetic sensor arraysAngular velocityPosition sensor
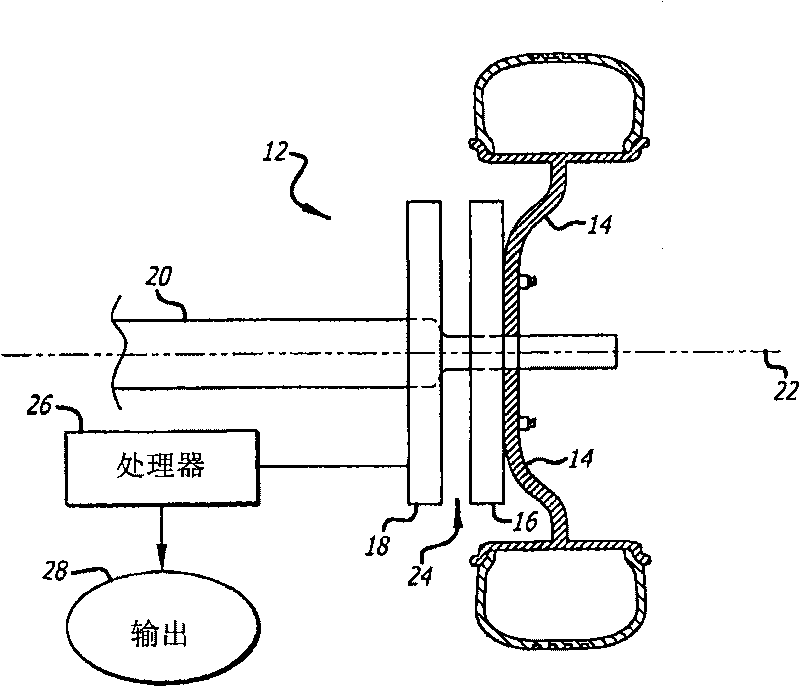
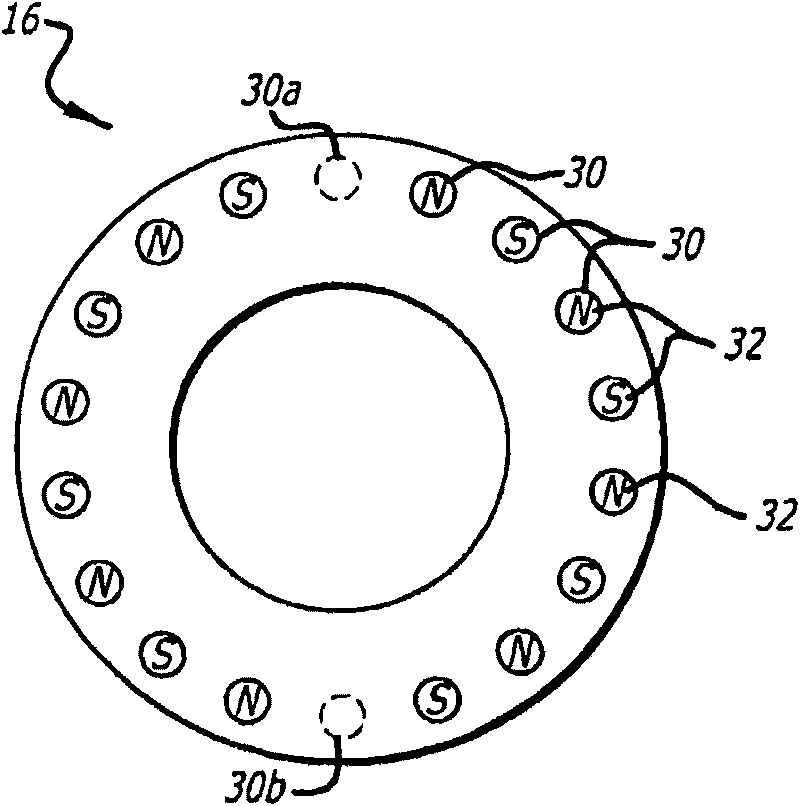
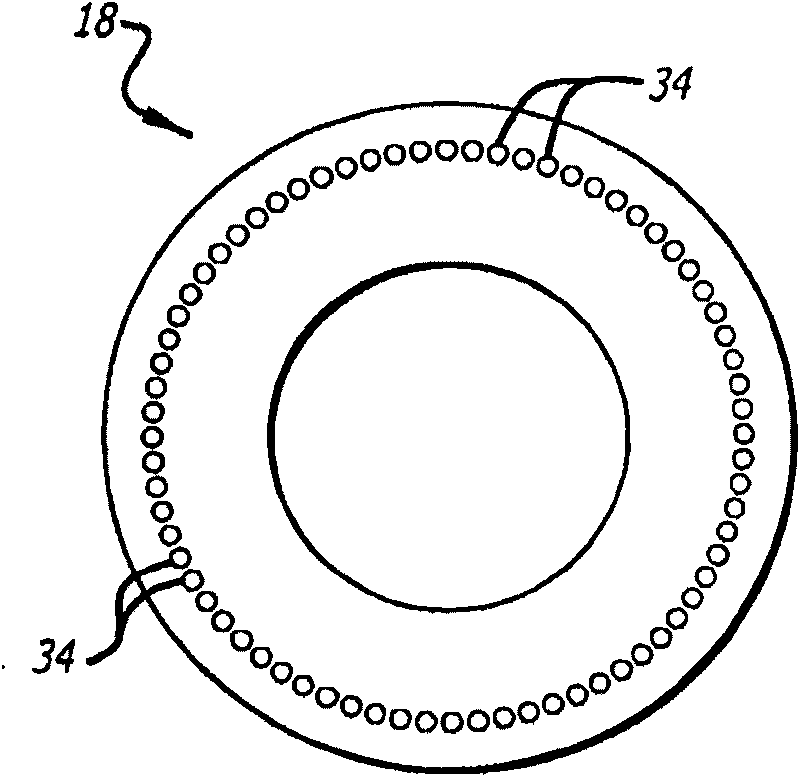
An angular position sensor (24) and method that relies on a stationary- circular array of Hall sensors (18) and a rotatable circular array of magnets (16) arranged about a common axis (22). A periodic and simultaneous reading of all of the Hall sensor outputs is used to determine angular velocity.
Owner:HYDRO AIRE AEROSPACE CORP
Methods and systems using molecular glue for covalent bonding of solid substrates
ActiveUS20200123416A1Group 4/14 element organic compoundsAdhesive processes with adhesive heatingPolymer scienceMoiety
A method for bonding together two substrates includes providing a molecular glue including glue molecules, each of the glue molecules having at least two —O—Si or —O—Al moieties; reacting a surface of a first substrate with the molecular glue to attach the glue molecules to the surface of the first substrate by at least one of the —O—Si or —O—Al moieties; and reacting a surface of a second substrate with the molecular glue to attach the glue molecules to the surface of the second substrate by at least another one of the —O—Si or —O—Al moieties. The method can be used for a variety of applications including manufacturing a vapor cell.
Owner:HI LLC
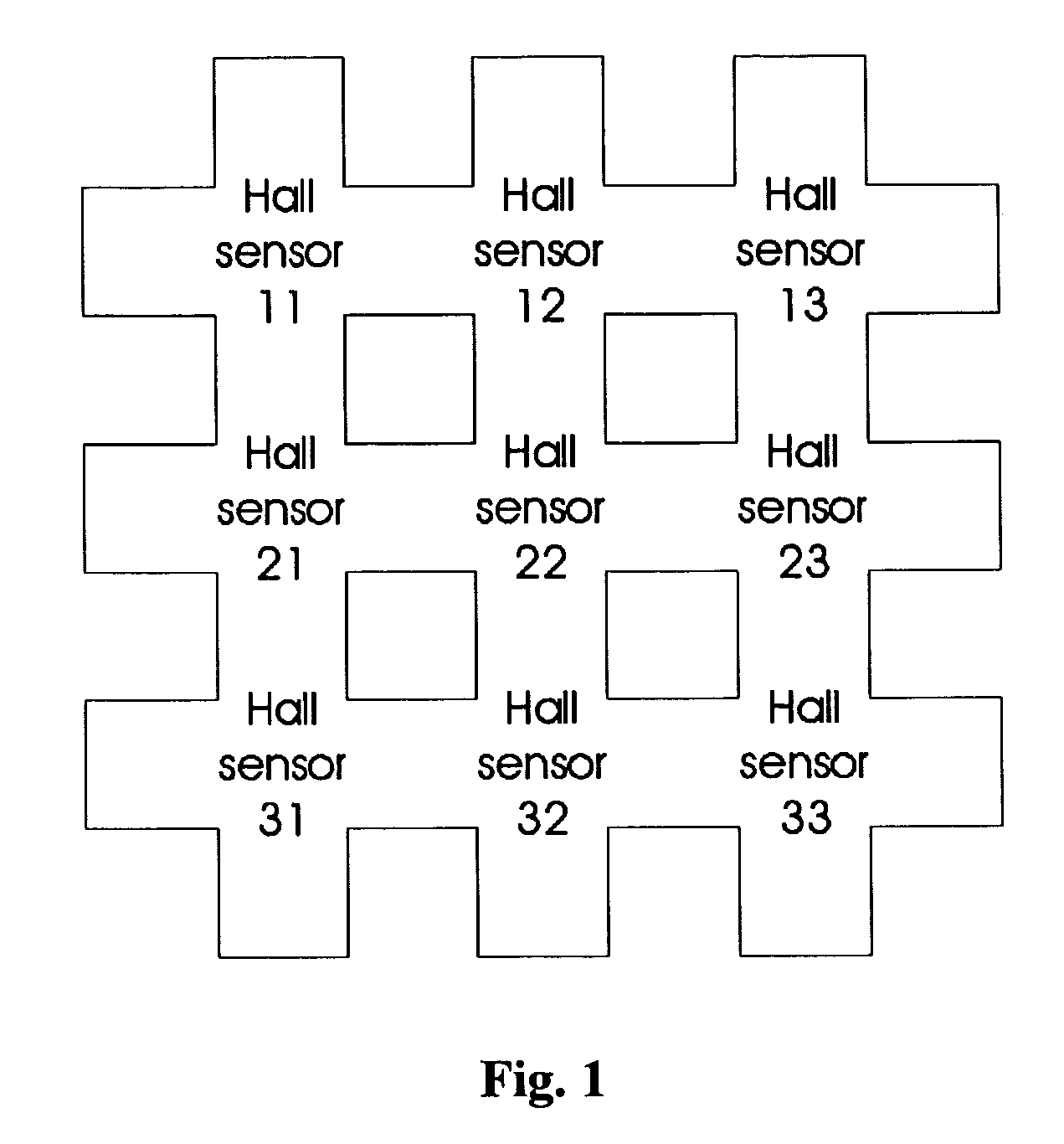
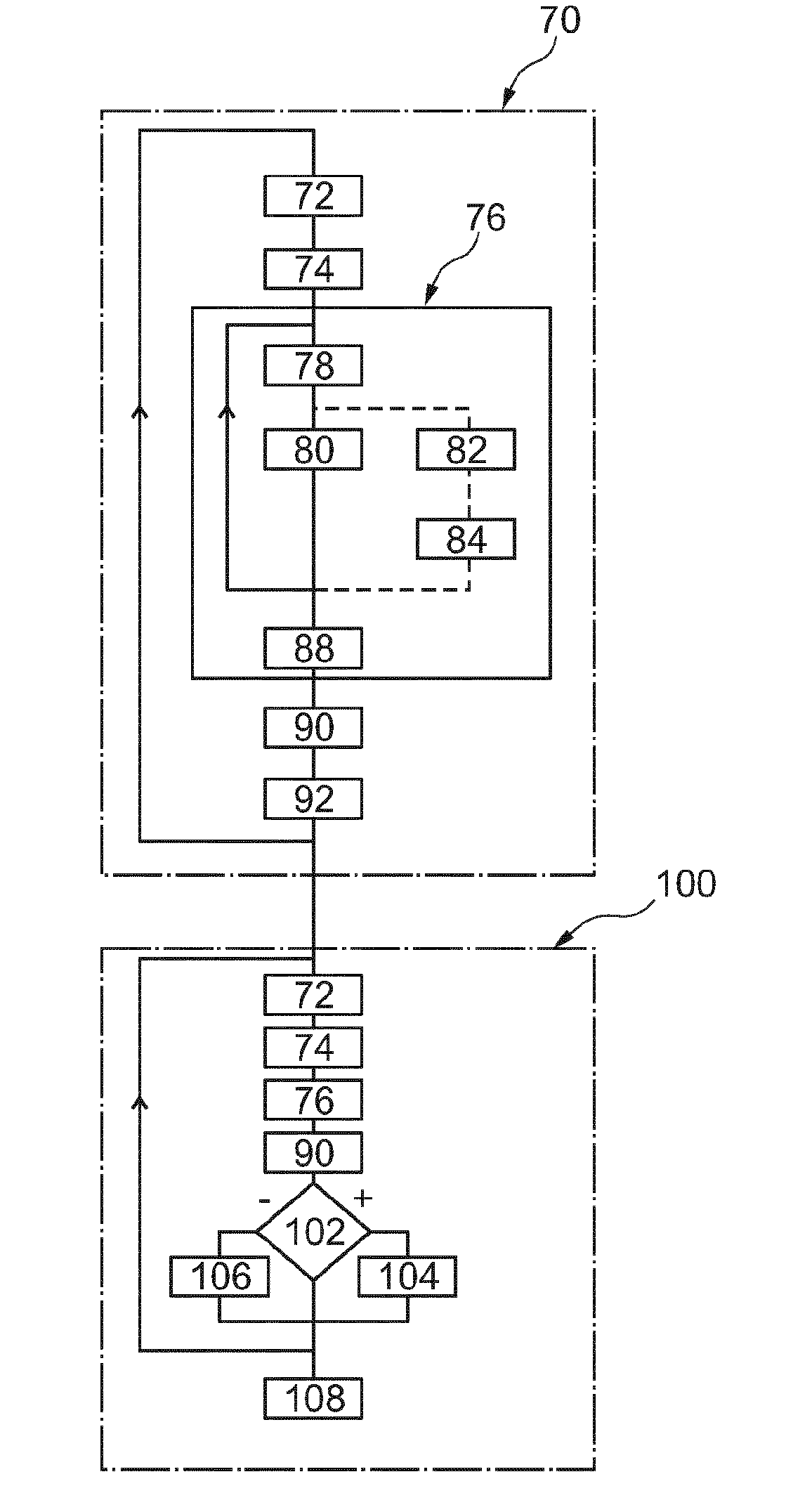
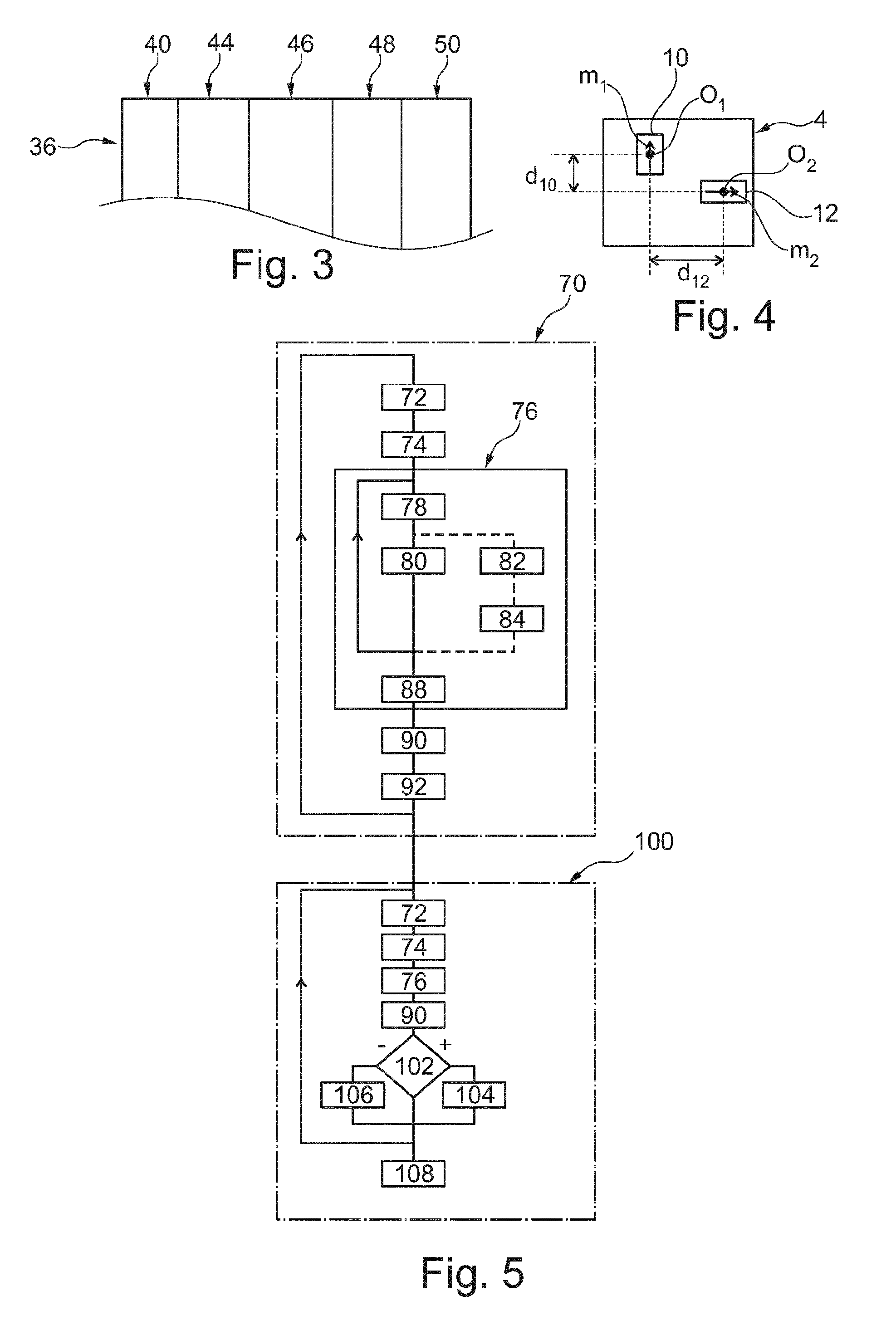
Method and apparatus for detecting spatially varying and time-dependent magnetic fields
ActiveUS7902820B2Avoid leakage currentImprove gate breakdown voltageSolid-state devicesMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesSensor arrayLocal field
Certain inventive aspects provide local field imaging with high spatial, time and field resolution by using an array of Hall effect sensors that can be individually read out. The design combines semiconductor Hall sensors and switches that isolate the addressed Hall sensor from the rest of the array. The compact design allows for large and very dense Hall sensor arrays that can be read out in a straightforward way.
Owner:MAGCAM
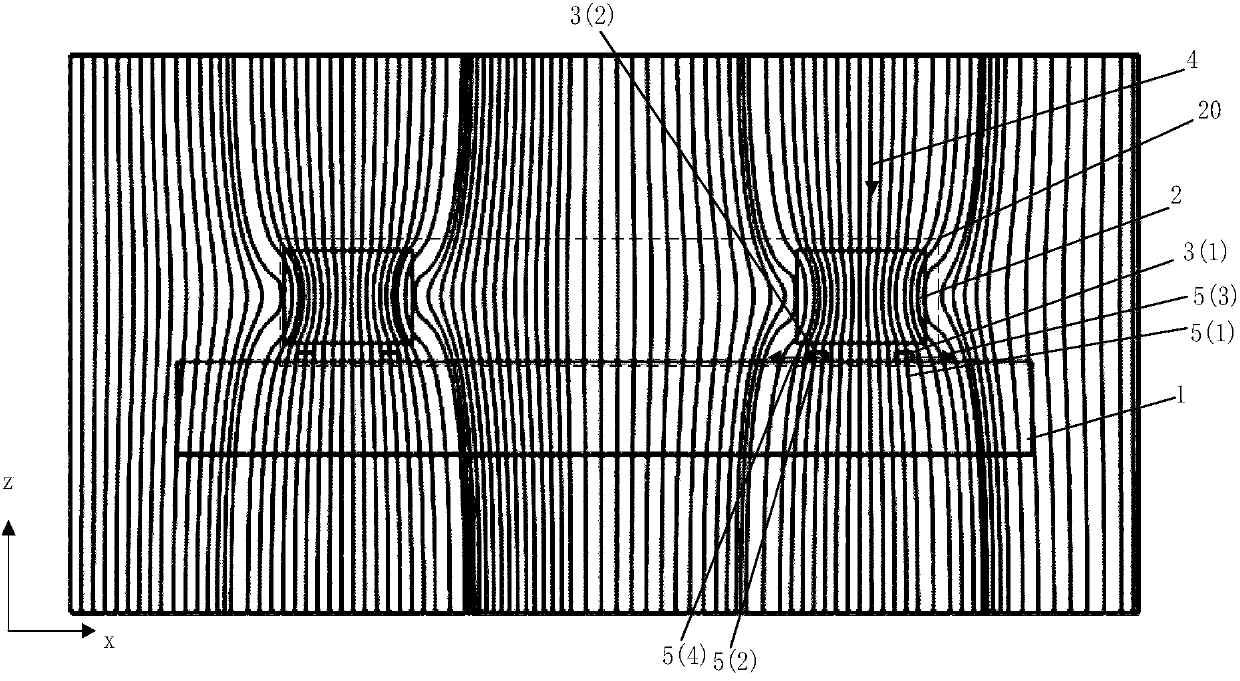
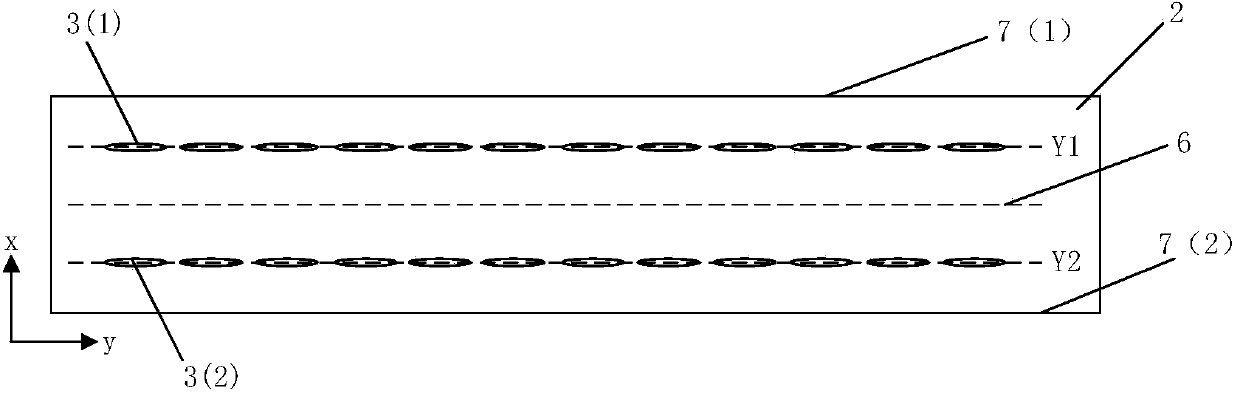
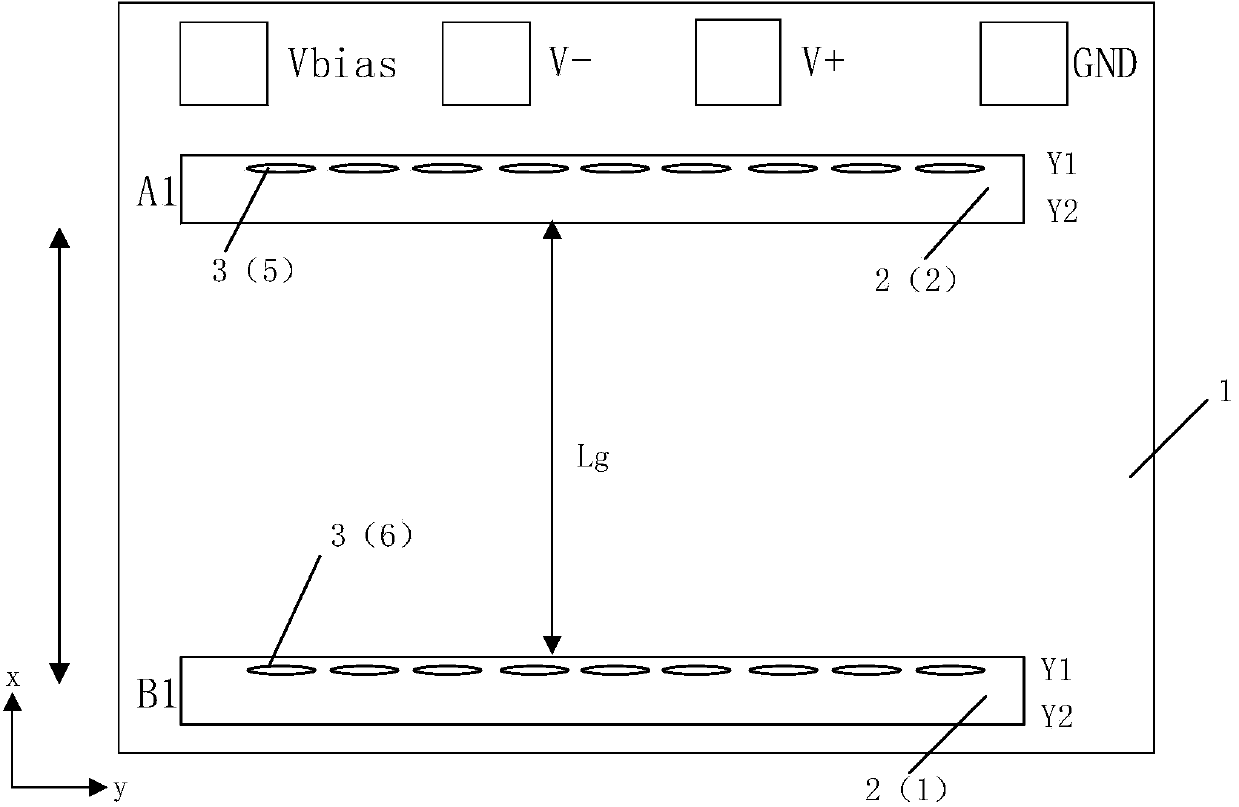
Magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip
ActiveCN103995240ASmall sizeReduce power consumptionMagnetic field measurement using flux-gate principleMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesMagnetic field gradientElectrical resistance and conductance
The invention discloses a magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip which is used for detecting the gradients of components of a Z-axis magnetic field generated by magnetic media in the X-Y plane so as to conduct magnetic imaging on the magnetic media. The magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip comprises a Si substrate, two or two groups of sets containing a plurality of flux leaders and magnetic resistance sensing units which are electrically connected, wherein the distance between the sets is Lg. The magnetic resistance sensing units are located on the Si substrate and located above or below the edges of the flux leaders, the components of the Z-axis magnetic field are converted into the mode that the components of the Z-axis magnetic field are parallel to the surface of the Si substrate and in the direction of the sensitive axes of the magnetic resistance sensing units, and the magnetic resistance sensing units are electrically connected into a half-bridge or whole-bridge gradient meter, wherein the distance between opposite bridge arms is Lg. The sensor chip can be used together with a PCB, a PCB and back magnetor a PBC and back magnet and packaging shell. According to the magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip, measurement of the Z-axis magnetic field gradient is achieved by using plane sensitive magnetic resistance sensors, and the magnetic resistance Z-axis gradient sensor chip has the advantages of being small in size and low in power consumption, having higher magnetic field sensitivity than a Hall sensor and the like.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
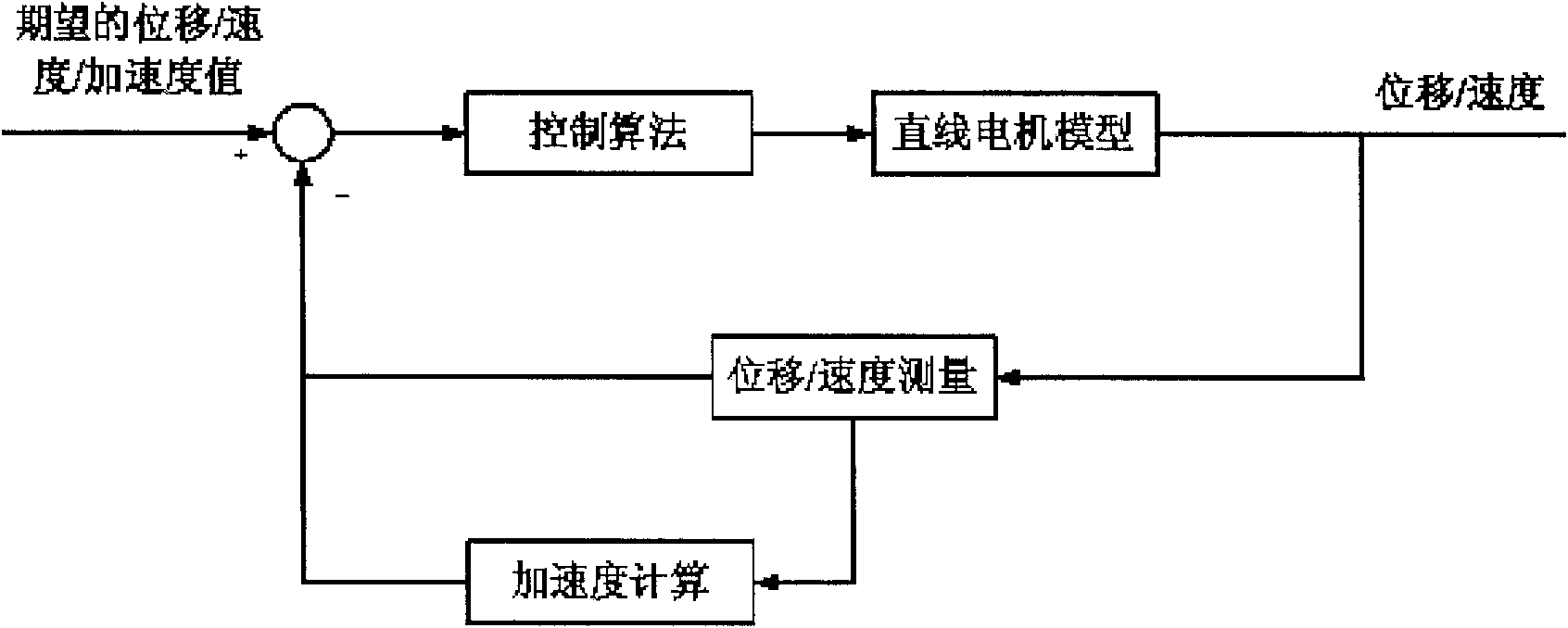
Linear motor motion control method based on fixed-step speed measurement
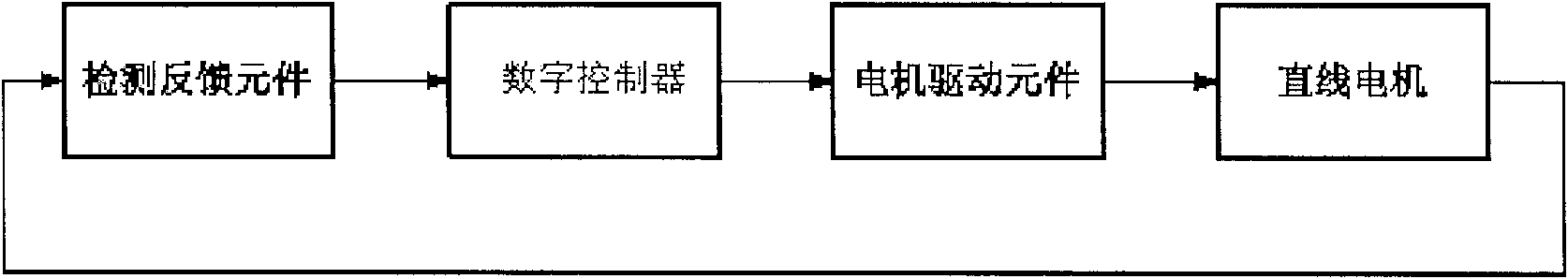
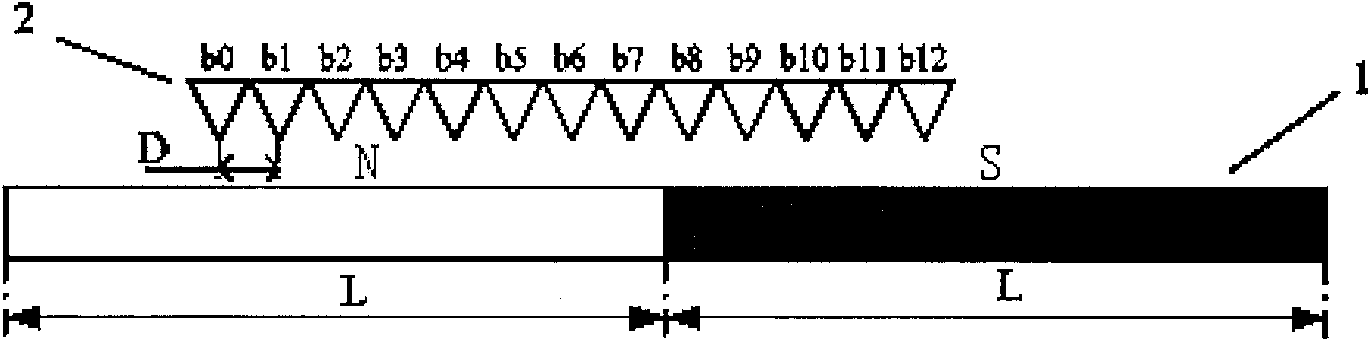
ActiveCN101841295ARealize motion controlSolve positioning controlDynamo-electric converter controlMagnetic sensor arraysSensor arrayLow speed
The invention discloses a linear motor motion control method based on fixed-step speed measurement. Equidistantly arranged Hall switch sensor arrays are used for conducting the position measurement and the speed measurement of the rotor of a linear motor and implementing back-and-forth motion control by stages. The control sequentially comprises a high-speed constant speed stage, a speed reduction stage, a low-speed constant speed stage and a boundary guidance stage. Position PID control, acceleration PID control, speed PID control and position PD control are respectively implemented in each of the four stages. Since the method is based on a simple measurement device and the motion control of the linear motor with variable load capacity can be realized, the invention has the advantages that no grating precise measurement mechanism is required, the problem that the millimeter-scale linear motor positioning control cannot be realized on the dependence of Hall switch sensors only in the prior art is solved, and the cost and the complexity of the system are reduced.
Owner:湖南天安门业科技有限公司
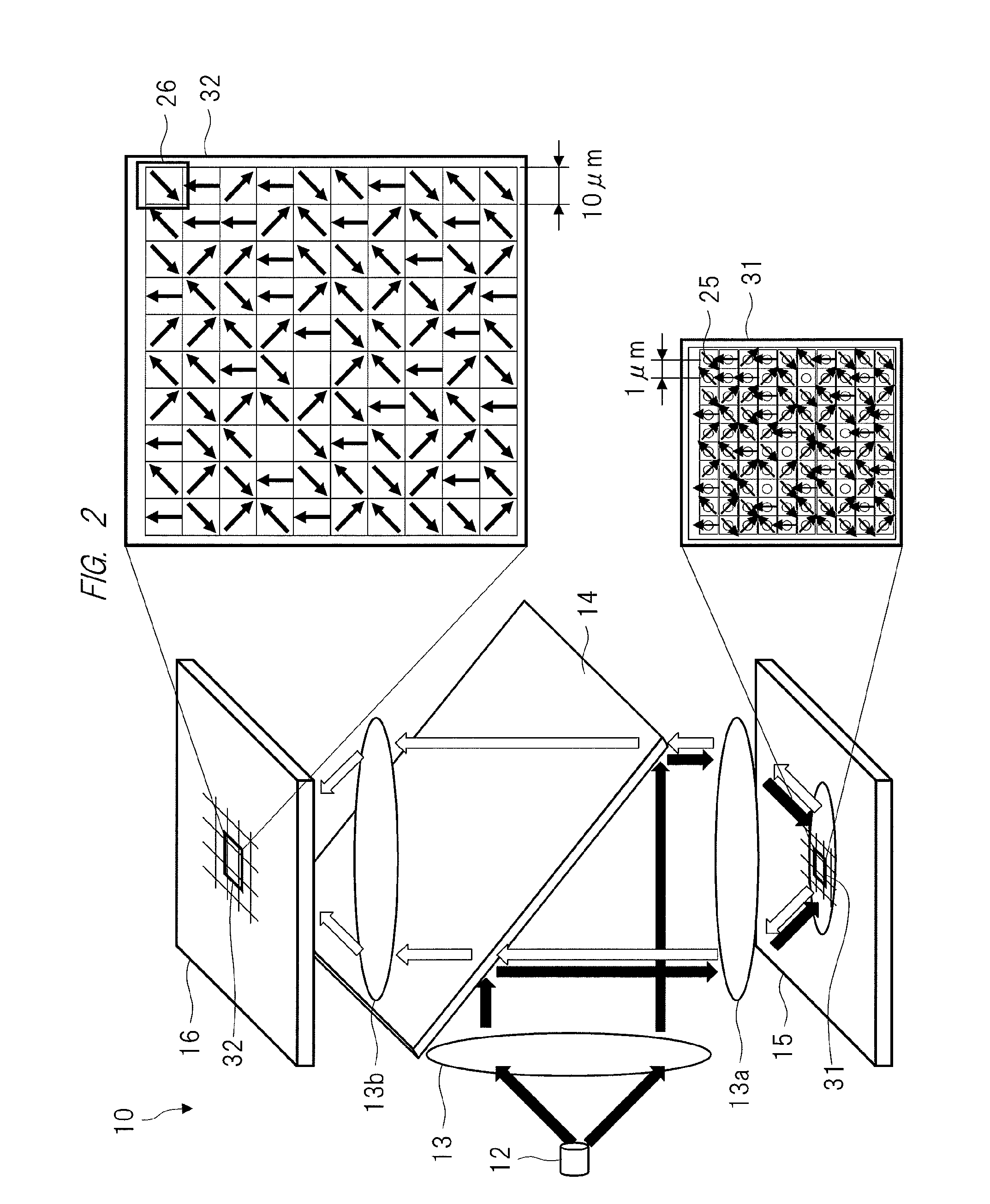
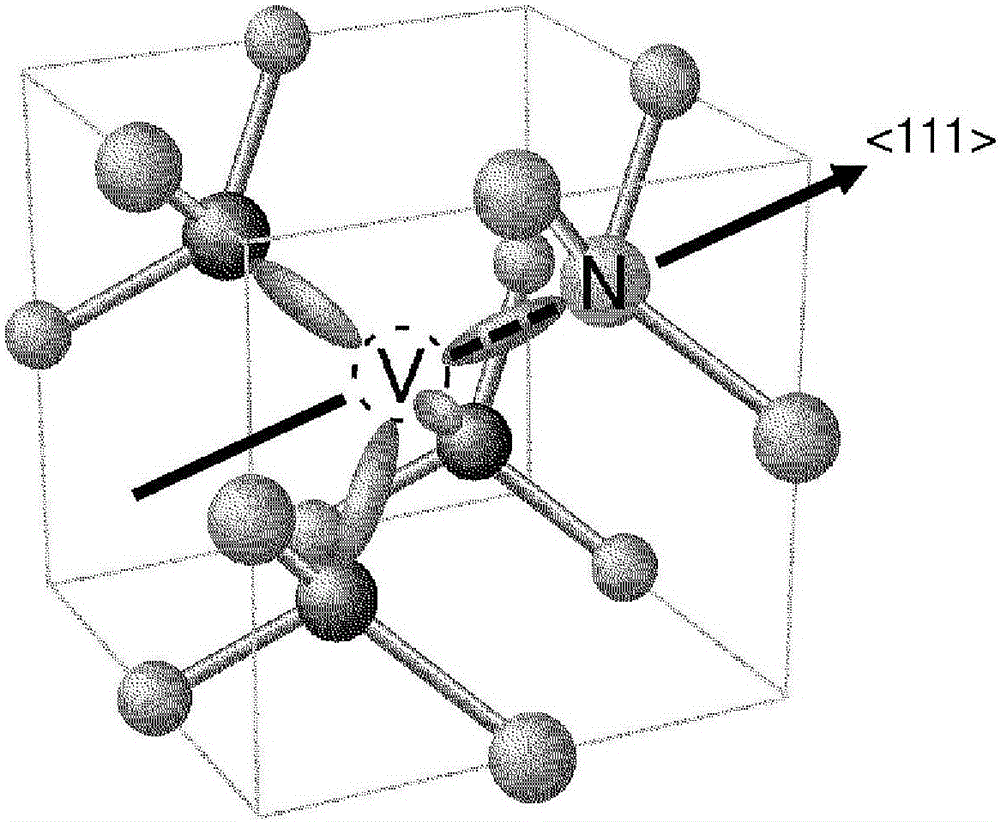
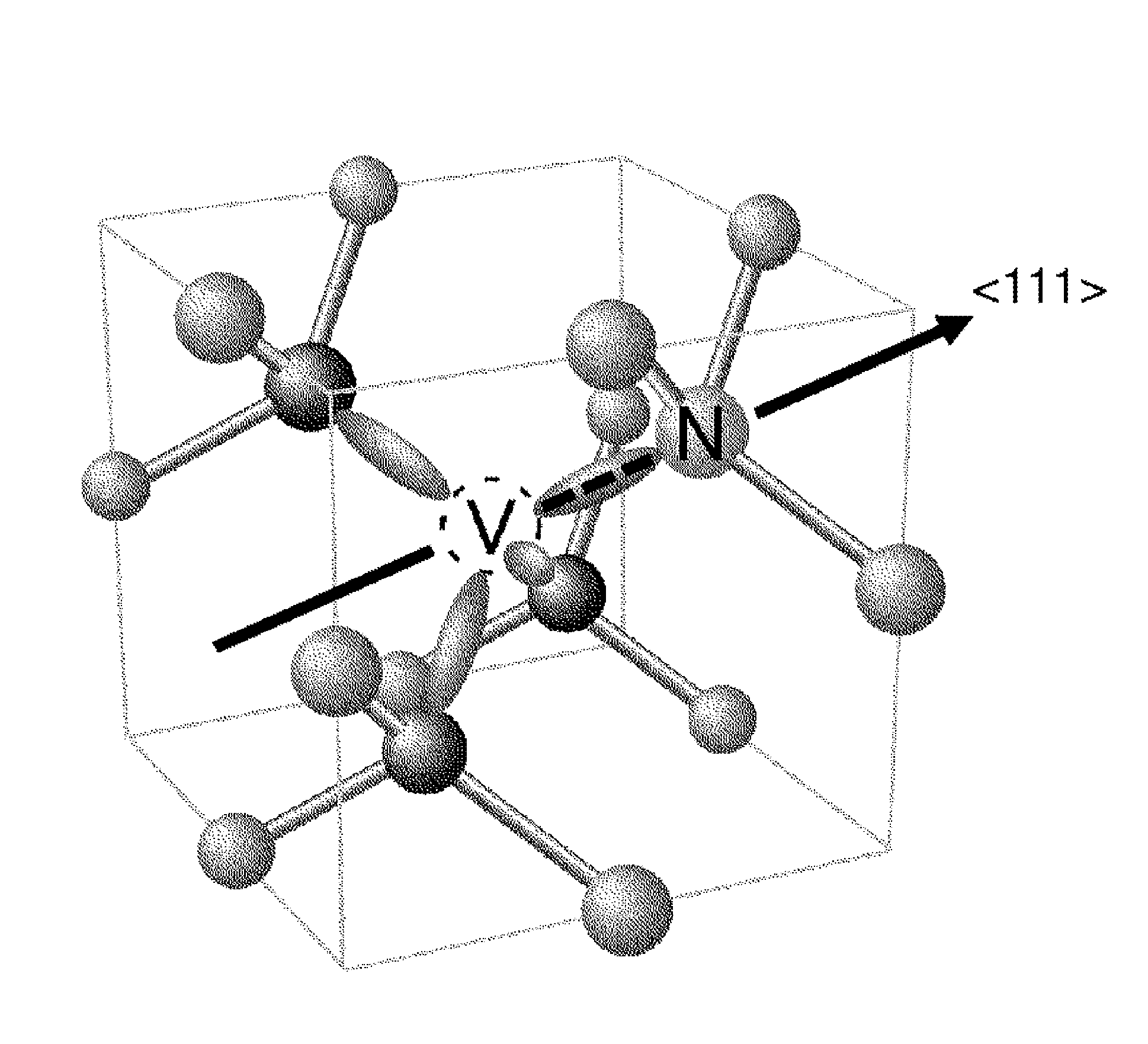
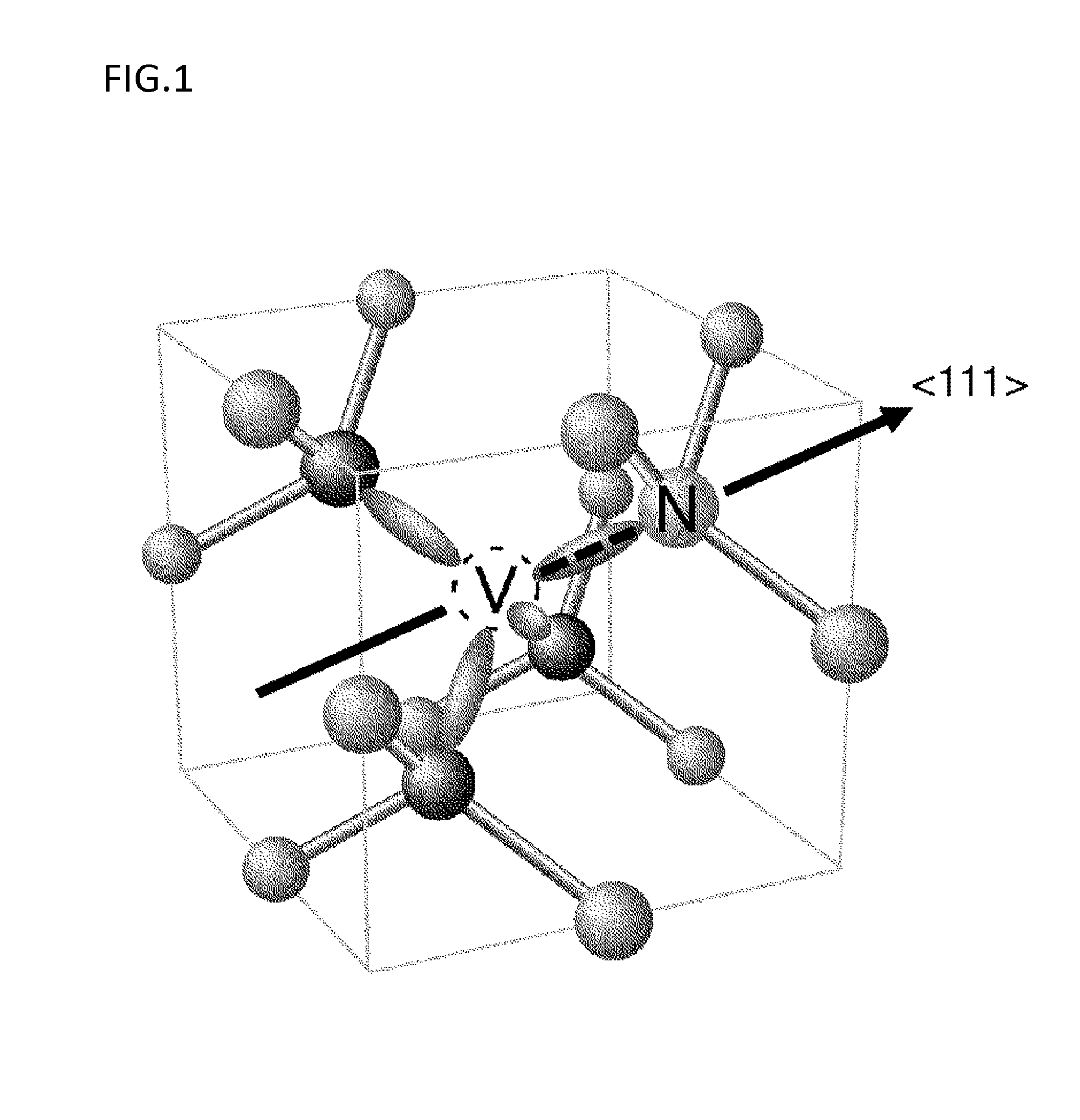
Diamond crystal, diamond element, magnetic sensor, magnetic measurement device, and method for manufacturing sensor array
ActiveCN106414818AIncrease contrastPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSensor arrayMagnetic measurements
Provided is a technique for making two-dimensional magnetic measurement with high sensitivity possible at normal temperature in the atmosphere. The diamond crystal pertaining to the present invention is characterized by having an NV region including a complex (NV center) of nitrogen substituted for a carbon atom and a vacancy adjacent to the nitrogen on or near the surface thereof, the NV region having a donor concentration equal to or greater than the concentration of the NV center, or the crystal in the NV region being the (111) face or a face having an off angle no more than + / -10 degrees of the (111) face, and the principal axis of the NV center being a < 111 > axis orthogonal to the (111) face. Through such a diamond crystal, substantially 100% of the NV center can be placed in a negatively charged state (NV-), the spin state of the NV- center can be aligned in one direction, and ODMR signal peaks also become sharp. Through the sensor array pertaining to the present invention, the NV center generated in the diamond crystal can be maintained in the negatively charged state (NV-).
Owner:THE JAPAN SCI & TECH AGENCY +1
Diamond crystal, diamond devices, magnetic sensor, magnetic sensor system, and method for manufacturing sensor array
ActiveUS20160334474A1Increase contrastSharp peakPolycrystalline material growthFrom chemically reactive gasesSensor arrayDiamond crystal
A diamond crystal according to the present invention has an NV region containing a complex (NV center) of nitrogen substituted with a carbon atom and a vacancy located adjacent to the nitrogen, on a surface or in the vicinity of the surface, wherein the NV region has a donor concentration equal to or higher than the concentration of the NV centers, or a crystal of the NV region is a {111} face or a face having an off-angle that is ±10 degrees or less against the {111} face, and a principal axis of the NV center is a <111> axis that is perpendicular to the {111} face. Such a diamond crystal enables almost 100% of the NV center to be a state (NV−) of having a negative electric charge, and spin states of the NV− centers to be aligned in one direction.
Owner:JAPAN SCI & TECH CORP +1
Methods and systems for homogenous optically-pumped vapor cell array assembly from discrete vapor cells
ActiveUS20210139742A1Easy to insertReduce widthApparatus using atomic clocksManufacture of electrical instrumentsEngineeringBiology
A method of making an array of vapor cells for an array of magnetometers includes providing a plurality of separate vapor cell elements, each vapor cell element including at least one vapor cell; arranging the vapor cell elements in an alignment jig to produce a selected arrangement of the vapor cells; attaching at least one alignment-maintaining film onto the vapor cell elements in the alignment jig; transferring the vapor cells elements and the at least one alignment-maintaining film from the alignment jig to a mold; injecting a bonding material into the mold and between the vapor cell elements to bond the vapor cell elements in the selected arrangement; removing the at least one alignment maintaining film from the vapor cell elements; and removing the bonded vapor cells elements in the selected arrangement from the mold to provide the array of vapor.
Owner:HI LLC
Systems and methods having an optical magnetometer array with beam splitters
ActiveUS10996293B2Magnetic field offset compensationDiagnostic recording/measuringBeam splitterMedicine
An array of optically pumped magnetometers includes an array of vapor cells; and an array of beam splitters. The array of beam splitters is arranged into columns, including a first column, and rows. Each row and each column includes at least two of the beam splitters. The array of beam splitters is configured to receive light into the first column of the array and to distribute that light from the first column into each of the rows and to distribute the light from each of the rows into a plurality of individual light beams directed toward the vapor cells.
Owner:HI LLC
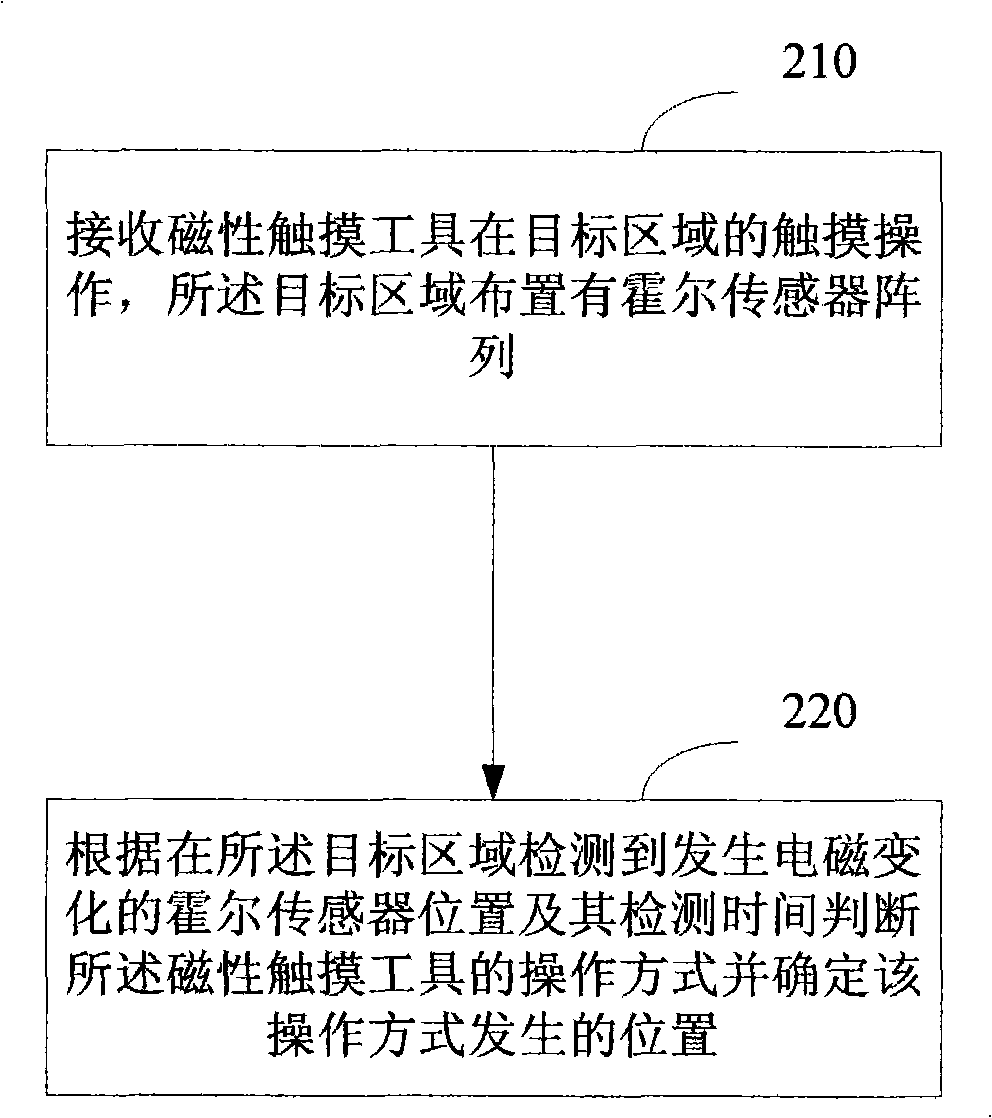
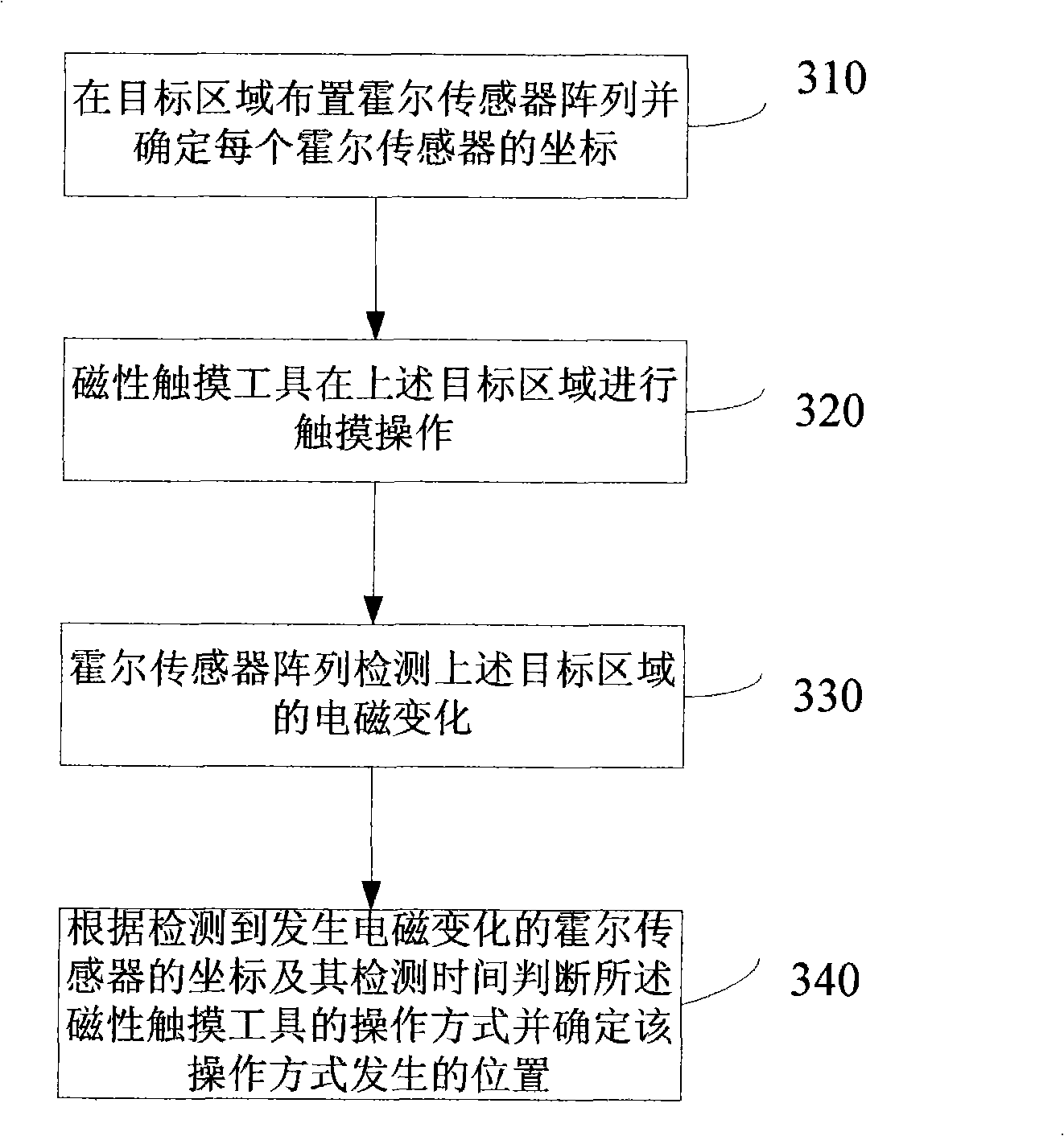
Touch detection method, apparatus and system
InactiveCN101403954ARealize detectionAvoid the influence of human factors and even environmental factorsMagnetic sensor arraysInput/output processes for data processingSensor arrayTouchpad
The invention discloses a touch detection method, a device and a system thereof, belonging to the touch detection technical field. The method includes: touch operation of a magnetic touch tool in a target area in which a hall sensor array is arranged is received; the operation mode of the magnetic touch tool is judged according to the position of the detected hall sensor, electromagnetism of which is changed, in the target area and the detection time, and the occurring position of the operation mode is determined. The device comprises a touch receiving module and a touch detecting module. The system comprises a touchpad and a magnetic touch tool which is used for touching the touchpad; wherein, the touchpad consists of a touch receiving module and a touch detecting module. The invention realizes the detection on touch by the hall sensor array and avoids the influence of man-induced factor caused by using touch tools such as fingers, and the like, and even the environment factor, thus improving the detection precision.
Owner:HUAWEI DEVICE (SHENZHEN) CO LTD
Systems and methods having an optical magnetometer array with beam splitters
ActiveUS20210041513A1Magnetic field offset compensationDiagnostic recording/measuringBeam splitterMedicine
An array of optically pumped magnetometers includes an array of vapor cells; and an array of beam splitters. The array of beam splitters is arranged into columns, including a first column, and rows. Each row and each column includes at least two of the beam splitters. The array of beam splitters is configured to receive light into the first column of the array and to distribute that light from the first column into each of the rows and to distribute the light from each of the rows into a plurality of individual light beams directed toward the vapor cells.
Owner:HI LLC
Sensor assembly for use in medical position and orientation tracking
ActiveUS20140005517A1Magnetic-field-controlled resistorsSolid-state devicesMagnetic reluctanceEngineering
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC
Angular position sensor
ActiveUS8169214B2Accurate dataSolid-state devicesAcceleration measurementAngular degreesAngular velocity
Owner:HYDRO AIRE AEROSPACE CORP
Single bridge magnetic field sensor
ActiveUS20170059668A1Lower the volumeMagnetic sensor arraysConverting sensor outputElectricityElectrical connection
A single bridge magnetic field sensor includes a fluxguide mounted to a surface of a substrate. A bridge unit includes first, second, third, and fourth magnetoresistive elements mounted around the fluxguide and mounted on the surface of the substrate. A switching circuit is electrically connected to two voltage inputs, two grounding terminals, two voltage output terminals, and the four magnetoresistive elements. The switching circuit can proceed with circuit switching according to a magnetic field in each axis direction to be measured, thereby changing electrical connection between the voltage inputs, the grounding terminals, the voltage output terminals, and the four magnetoresistive elements. A measuring unit is electrically connected to the two voltage output terminals and the four magnetoresistive elements. The magnetoresistances of the four magnetoresistive elements measured by the measuring unit and output voltages of the voltage output terminals can be used to obtain a magnetic field measurement result.
Owner:NAT TAIWAN UNIV
Sensor device
ActiveUS20150198678A1Cost-effectiveHigh failure safetyMagnetic sensor packagingMagnetic field measurement using galvano-magnetic devicesElectricityElectrical conductor
A sensor device having a first housing with a first semiconductor body and a plurality of metallic terminal contacts for electrical contacting of a first sensor, and a second housing with a second semiconductor body with a plurality of metallic terminal contacts for electrical contacting of a second sensor. A section of the plurality of terminal contacts penetrates the second housing on the face side and the second semiconductor body is arranged with a back surface on a front side of the second metal substrate. The two housings form a module, whereby the two housings are connected form-fittingly to one another in the shape of a stack by a fixing device in a way in which the bottom side of the first housing is joined to the bottom side of the second housing and the plurality of terminal contacts of the two housings point in the same direction.
Owner:TDK MICRONAS GMBH
Method for automatic recognition of a mobile magnetic object
ActiveUS20150301216A1Increase the number ofReliable methodMagnetic sensor arraysElectric/magnetic detectionErrors and residualsMagnetic dipole
An automatic recognition method includes the calculation of an error representative of the difference between an estimate of the values of the magnetometer measurements when the positions, orientations and amplitudes of the magnetic moments of the P dipoles are equal to those determined, and the values of the magnetometer measurements taken. There is the selection of another system of equations linking each measurement of a triaxial magnetometer to the position, orientation and amplitude of the magnetic moment of P′ magnetic dipoles. The method includes the calculation of at least one distinctive feature of the object presented from the position, orientation, or amplitude of the magnetic moment of each dipole determined with the system of equations that minimizes the error calculated. The method includes the recognition of the magnetic object presented if the calculated distinctive features correspond to those of a known object, otherwise the lack of recognition of this object.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
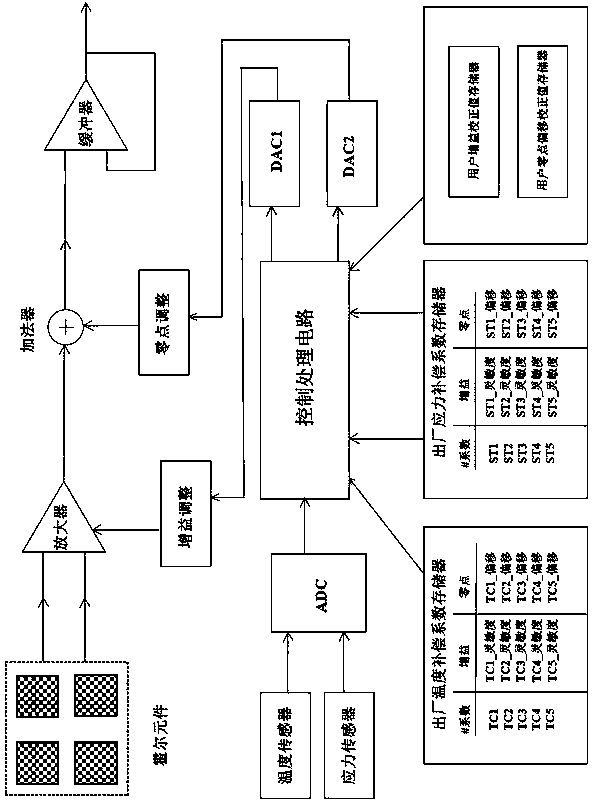
Compensation circuit for sensitivity and zero temperature drift in Hall sensor integrated chip and compensation method thereof
ActiveCN110542870AImprove performance indicatorsAchieve compensationMagnetic sensor arraysGain correctionAnalog-to-digital converter
The invention discloses a compensation circuit for sensitivity and zero temperature drift in a Hall sensor integrated chip. The compensation circuit comprises an Hall sensing element, an amplifier, anadder, a buffer, a gain adjustment module, a zero adjustment module, a temperature sensor, a stress sensor, an ADC (analog-to-digital converter), a control processing circuit, a first DAC, a second DAC, a factory temperature compensation coefficient memory, a factory stress compensation coefficient memory, a user gain correction value memory and a user zero offset correction value memory. Correspondingly, the invention also provides a compensation method of the compensation circuit for sensitivity and zero temperature drift in the Hall sensor integrated chip. According to the compensation circuit and the compensation method, the sensitivity and zero-point temperature drift compensation precision is greatly improved, the performance index of the sensor is improved, and requirements of customers for sensitivity and zero-point temperature compensation in the production or use process of the sensor are met; and the method not only realizes temperature compensation of the sensitivity, butalso realizes compensation of zero-point temperature drift, and can quickly respond to change of an external magnetic field.
Owner:NINGBO CRRC TIMES TRANSDUCER TECH CO LTD
Single-chip high-intensity magnetic field X-axis linear magneto-resistance sensor provided with calibration coil/reset coil
ActiveCN104698409ACalibrate the size of the magnetic field for precise adjustmentImprove measurement efficiencyMagnetic field offset compensationMagnetic sensor arraysElectrical resistance and conductancePower flow
A single-chip high-intensity magnetic field X-axis linear magneto-resistance sensor provided with a calibration coil / reset coil comprises a high-intensity magnetic field single-chip reference bridge type X-axis resistance sensor and the calibration coil / reset coil, wherein the calibration coil is a planar coil, the reset coil is a planar or three-dimensional coil, the planar calibration coil and the planar reset coil can be located above a substrate and under a magneto-resistance sensing unit, between the magneto-resistance sensing unit and a soft magnetic flux guider, above the soft magnetic flux guider or at the gap position, the soft magnetic flux guider and the magneto-resistance sensing unit are winded with the three-dimensional rest coil, and the calibration coil and the reset coil respectively produce calibration magnetic fields parallel to pinning layer direction and even reset magnetic fields in free layer direction at the position of a magneto-resistance unit. Calibration and magnetic-state reset of the single-chip X-axis linear magneto-resistance sensor can be achieved by controlling the current of the calibration coil / reset coil, and the single-chip high-intensity magnetic field X-axis linear magneto-resistance sensor ahs the advantages of being efficient, quick to use and convenient to operate.
Owner:MULTIDIMENSION TECH CO LTD
Popular searches
Galvano-magnetic hall-effect devices Semiconductor devices Sensors Magnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devices Single crystal growth details Diagnostics using fluorescence emission Fluid-pressure actuators Altering/correcting law of variation Metal working apparatus Converting sensor output electrically/magnetically
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com