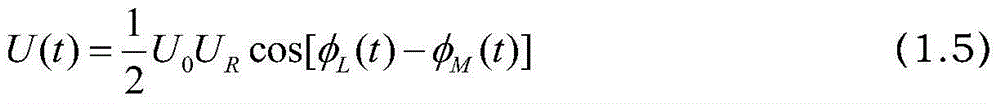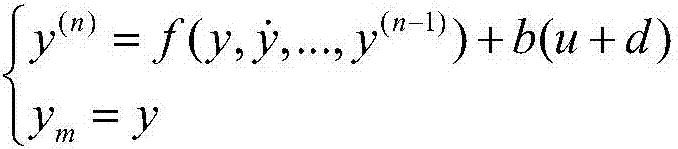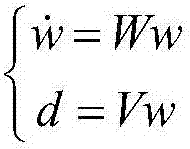Patents
Literature
562results about How to "Achieve compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
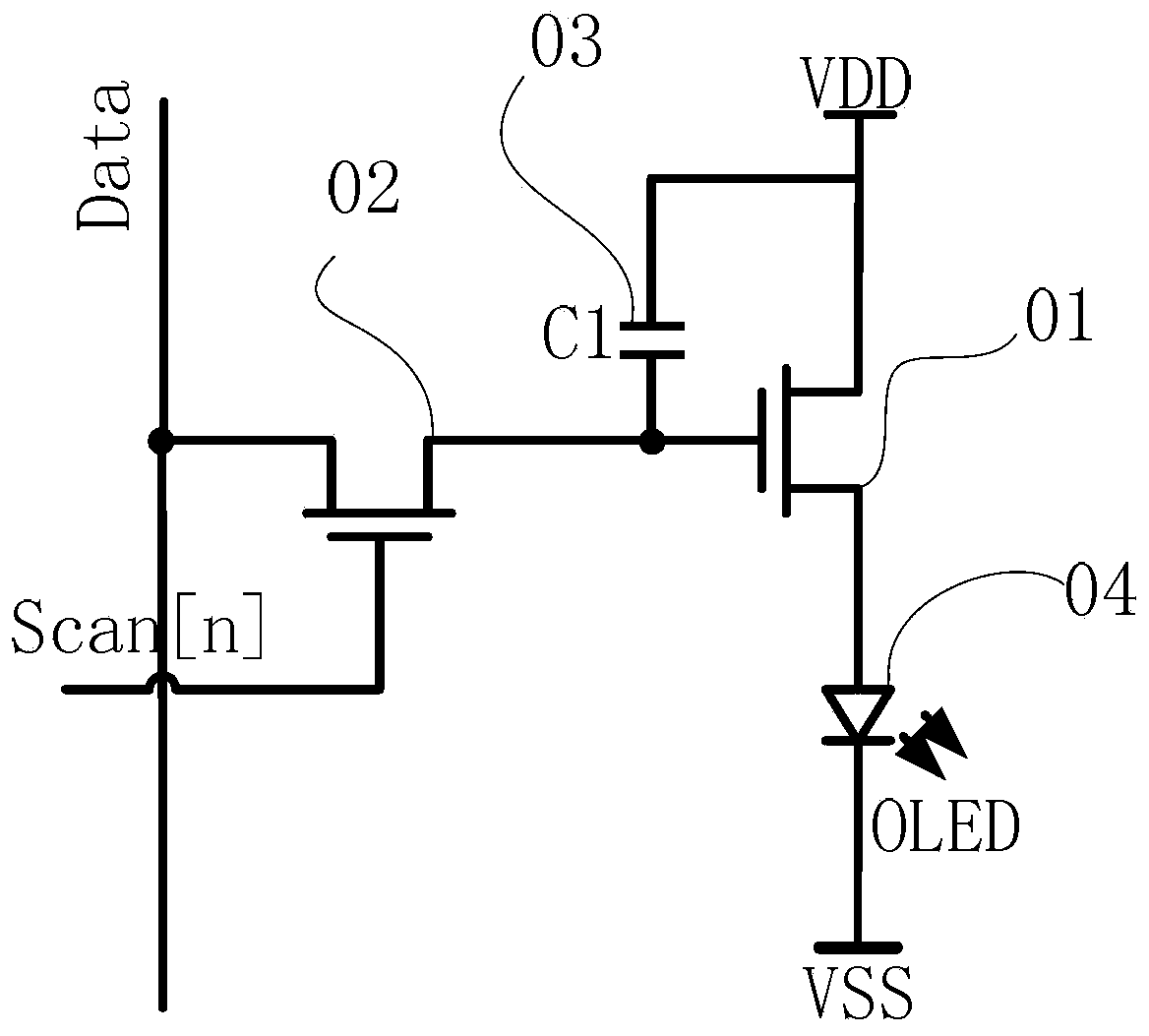
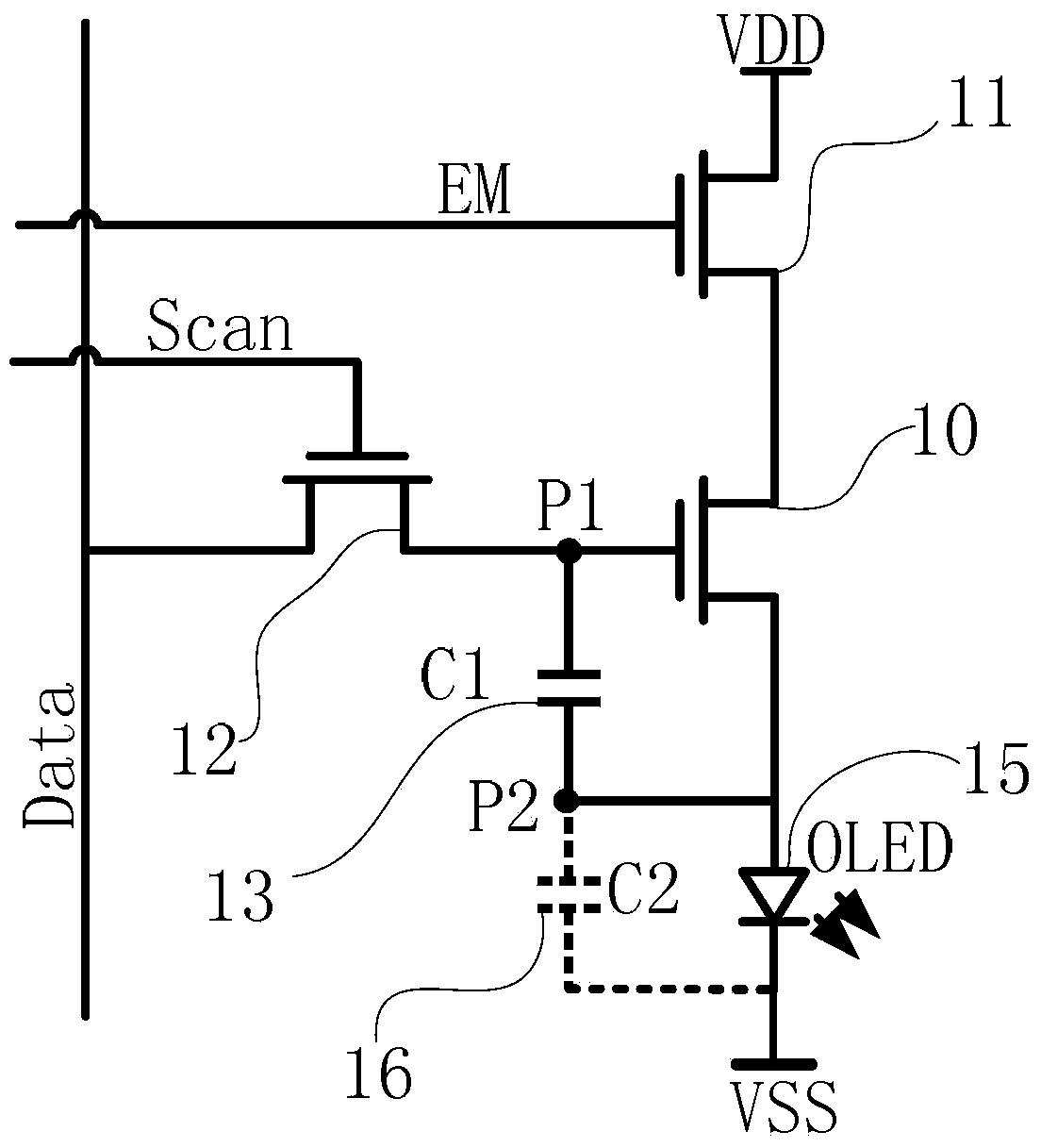
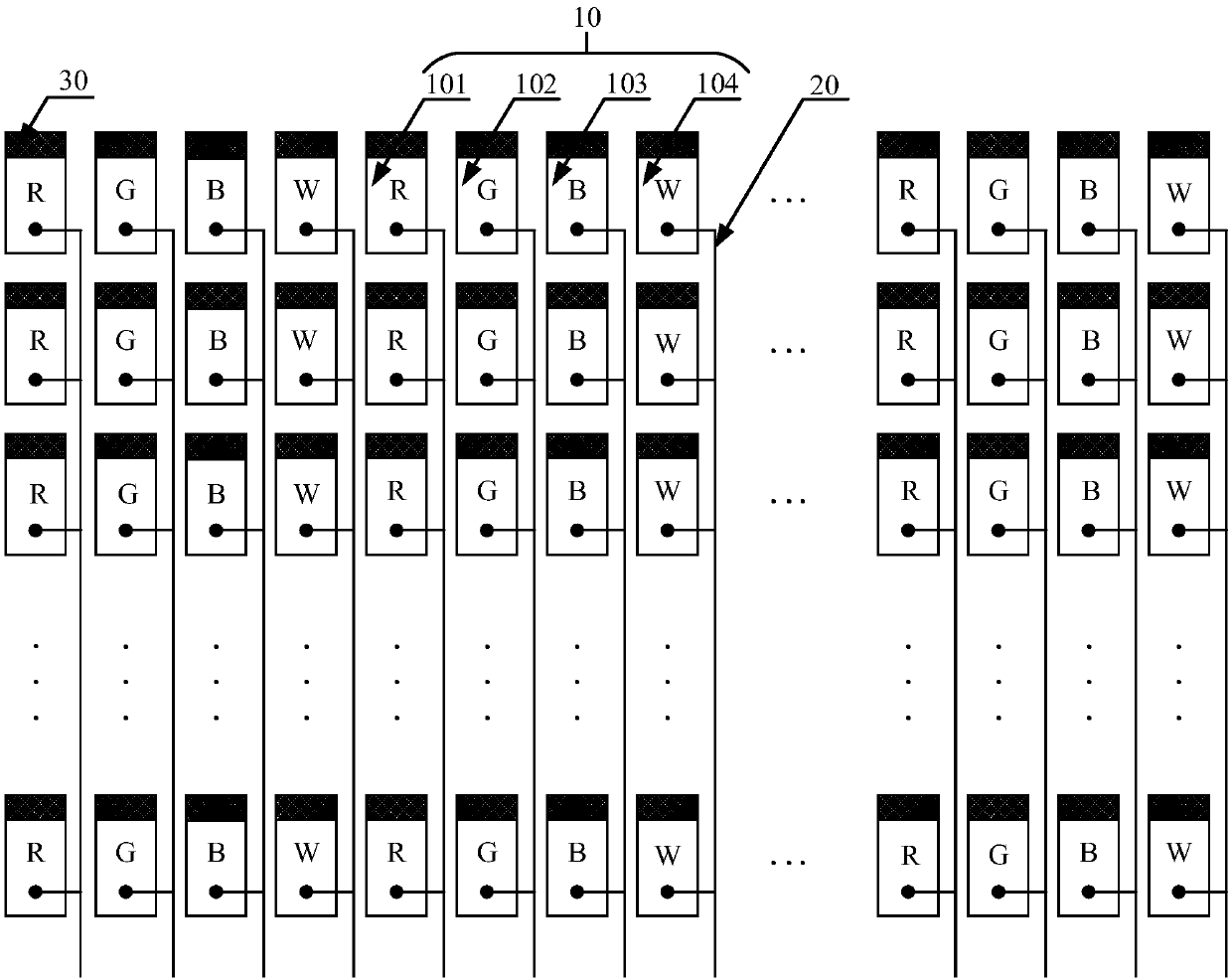
Display device and pixel circuit thereof
ActiveCN103440840ASolve uneven displayAchieve compensationStatic indicating devicesCapacitanceControl line
Disclosed are a display device and a pixel circuit of the display device. According to a first switch transistor, in a threshold value compensation phase, signals provided by a power source control line and a light-emitting control line are responded to. The first switch transistor is switched on, and threshold value voltage information of a driving transistor is stored in a connecting node of a second electrode of the driving transistor and a light-emitting component. According to a second switch transistor, in a data writing-in phase, the first switch transistor is switched off, the second switch transistor is switched on by responding to a signal provided by a scanning line, and a data voltage provided by a data line is stored at a connecting node of the first end of a storage capacitor and a control electrode of the driving transistor. The compensation of threshold value voltage drifting of a TFT device and the light-emitting component is achieved, and the problem of uneven display caused by the threshold value voltage drifting of the driving transistor and the threshold value voltage of the light-emitting component is solved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
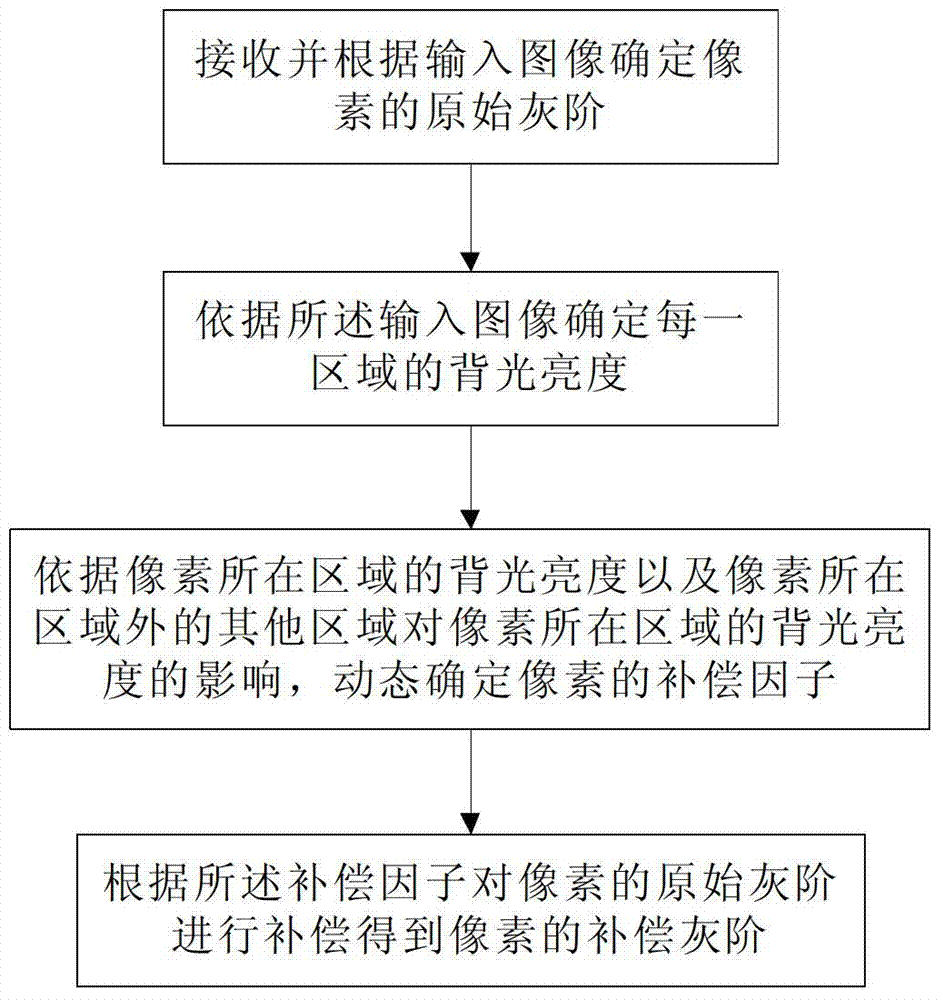
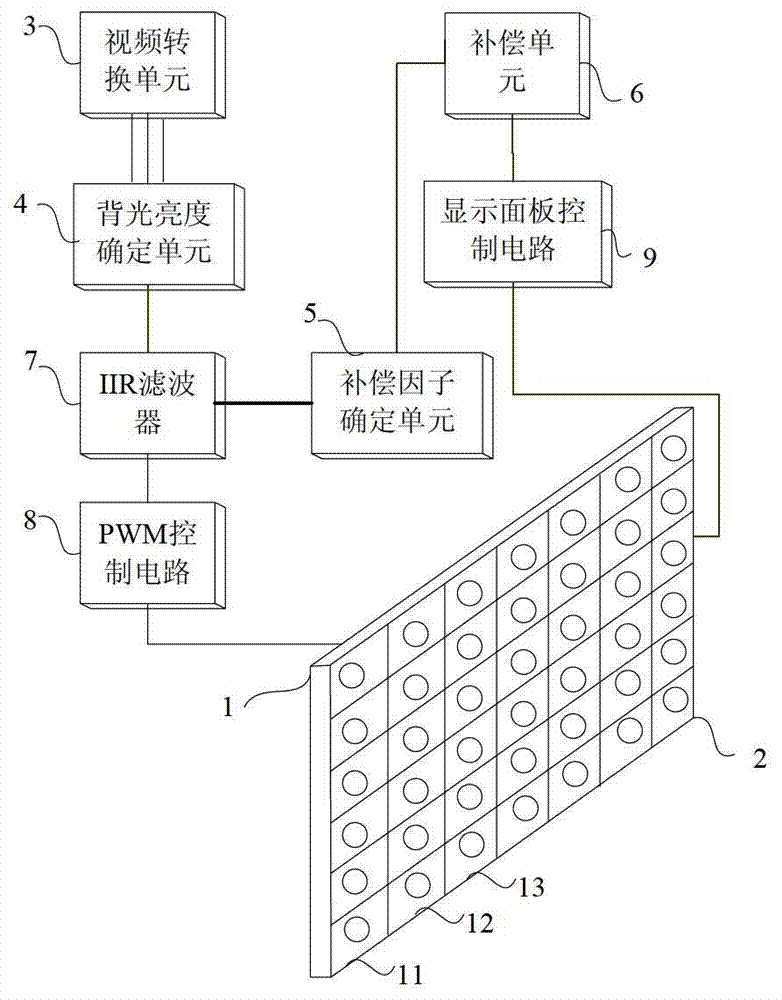
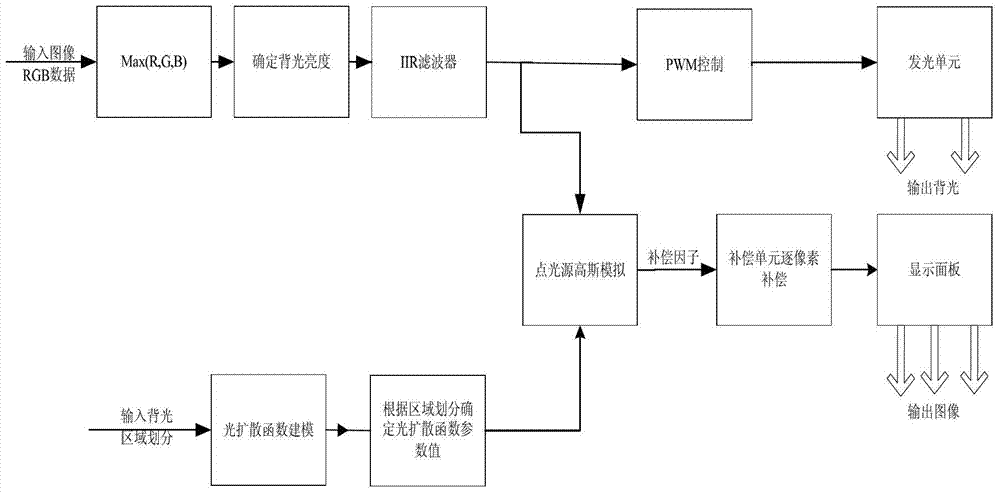
Direct type backlight luminance compensation method and display device
ActiveCN103295553AImprove the display effectSmall distortionStatic indicating devicesElectric light circuit arrangementDisplay deviceComputer science
The invention discloses a direct type backlight luminance compensation method and a display device, and is designed for solving the problems that image distortion is large after luminance compensation in the existing direct type backlight luminance compensation methods. The direct type backlight luminance compensation method includes: receiving and confirming original gray scale of pixel (i,j) according to input images; confirming backlight brightness of each area according to the input images; dynamically confirming compensating factors fcom (i,j) according to backlight brightness in pixel (i,j) area and influence on backlight brightness from other areas outside the pixel (i,j) area to the pixel (i,j) area; compensating original gray scale of pixel (i,j) according to the compensating factors fcom (i,j) to acquire compensating gray scale of pixel (i,j), wherein, i is taken as line number of pixel, and j is taken as column number of pixel. The direct type backlight luminance compensation method and the display device have the advantages that image distortion is small, data volume is small and the like after luminance compensation.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
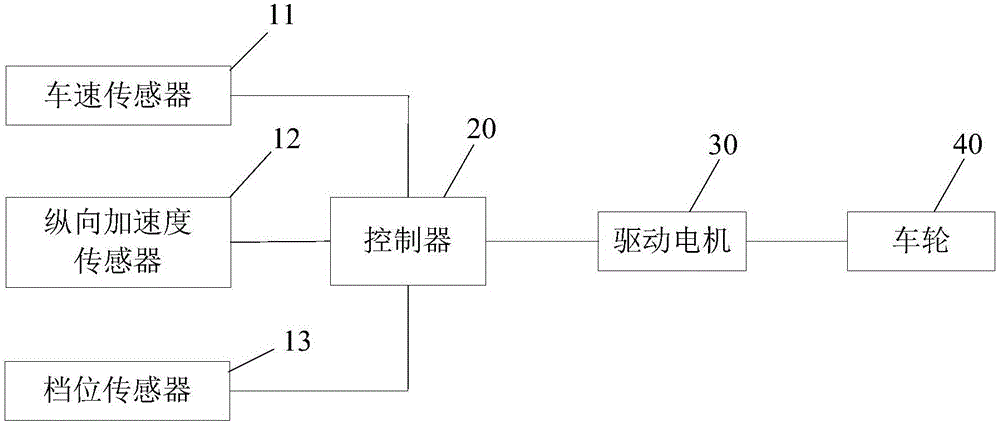
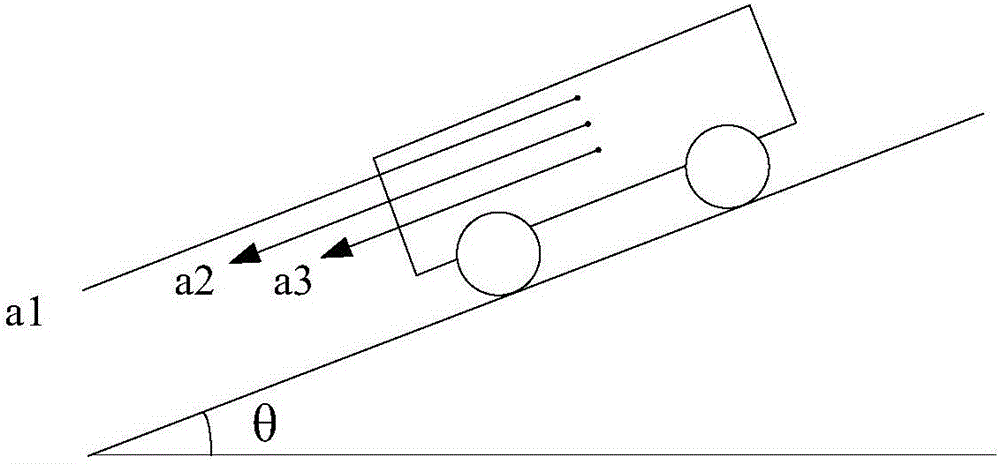
Control method and control system for worming torque of electric automobile and electric automobile
ActiveCN106428011ASame acceleration performanceImprove comfortVehicle condition input parametersControl systemElectric machinery
The invention discloses a control method and a control system for a worming torque of an electric automobile. The control method comprises the following steps: acquiring a basic part T1 of the worming torque according to a vehicle speed u look-up table; calculating a gravity acceleration component a3 of a vehicle according to a longitudinal acceleration a1 and a travel acceleration a2 of the vehicle; calculating a gradient resistance compensation part initial value T2' of the worming torque according to a complete vehicle mass m, the gravity acceleration component a3 and a tire rolling radius R; attenuating the obtained gradient resistance compensation part initial value T2' of the worming torque with increase of the vehicle speed according to a current vehicle speed u, thereby obtaining a gradient resistance compensation part T2 of the worming torque; adding the basic part T1 of the worming torque with the gradient resistance compensation part T2 of the worming torque to obtain a total worming torque T; and controlling a driving motor to output the total worming torque T to enable the vehicle to worm. The control method and the control system take a road grade into consideration to achieve compensation of gradient resistance, thereby enabling the vehicle to have same acceleration performance and good comfort no matter traveling uphill, downhill or on a level road.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GEELY HLDG GRP CO LTD +1
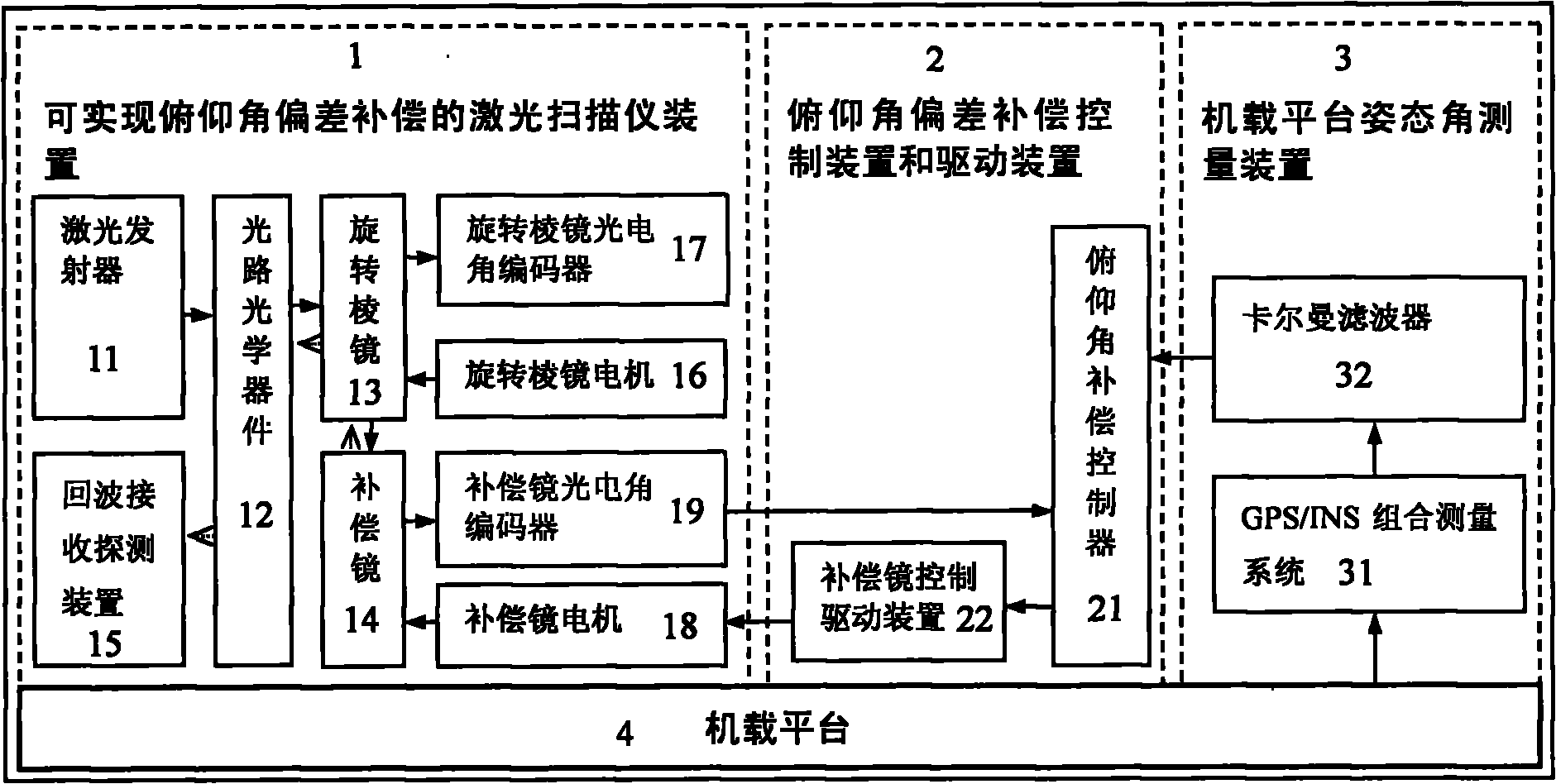
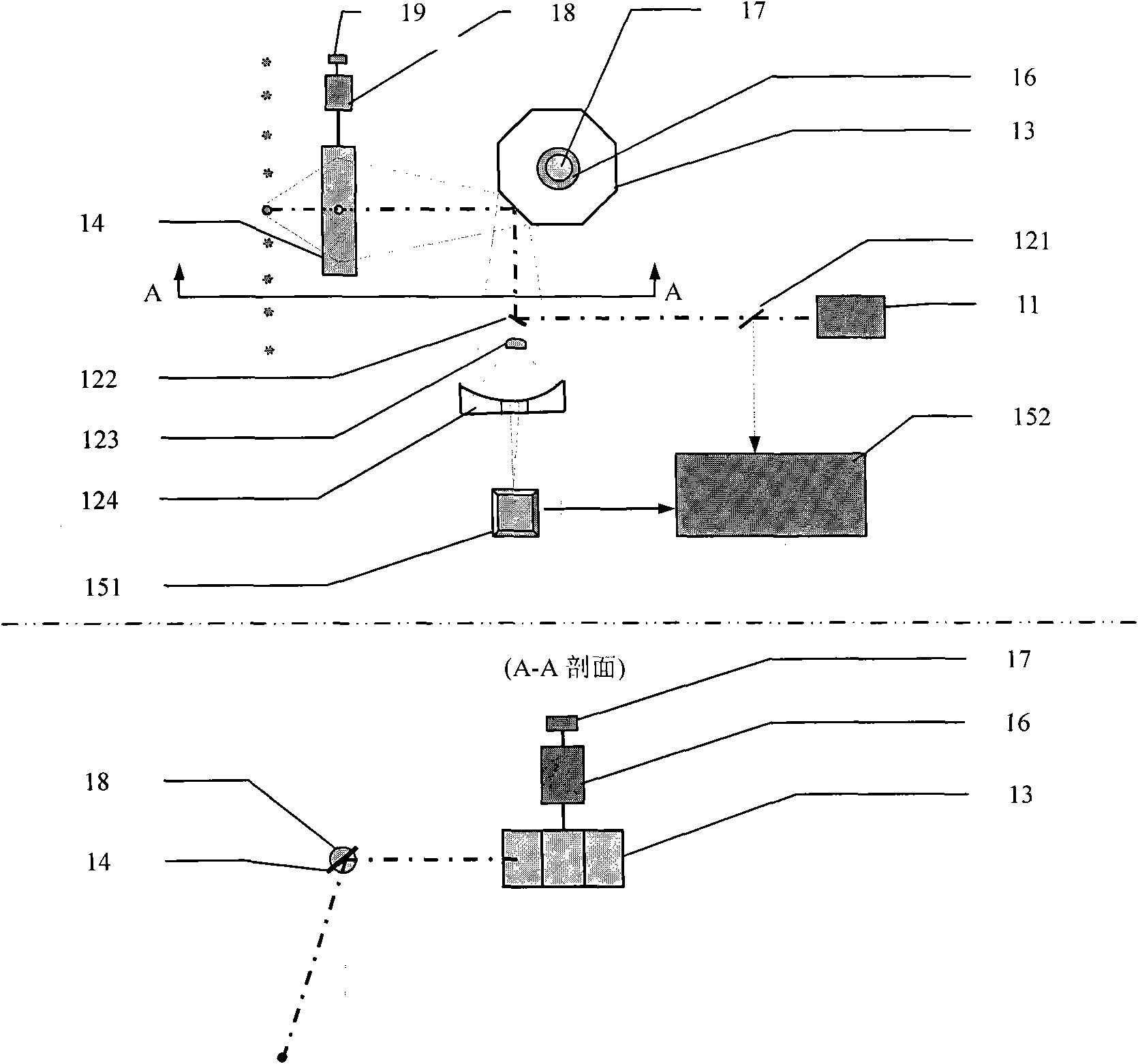
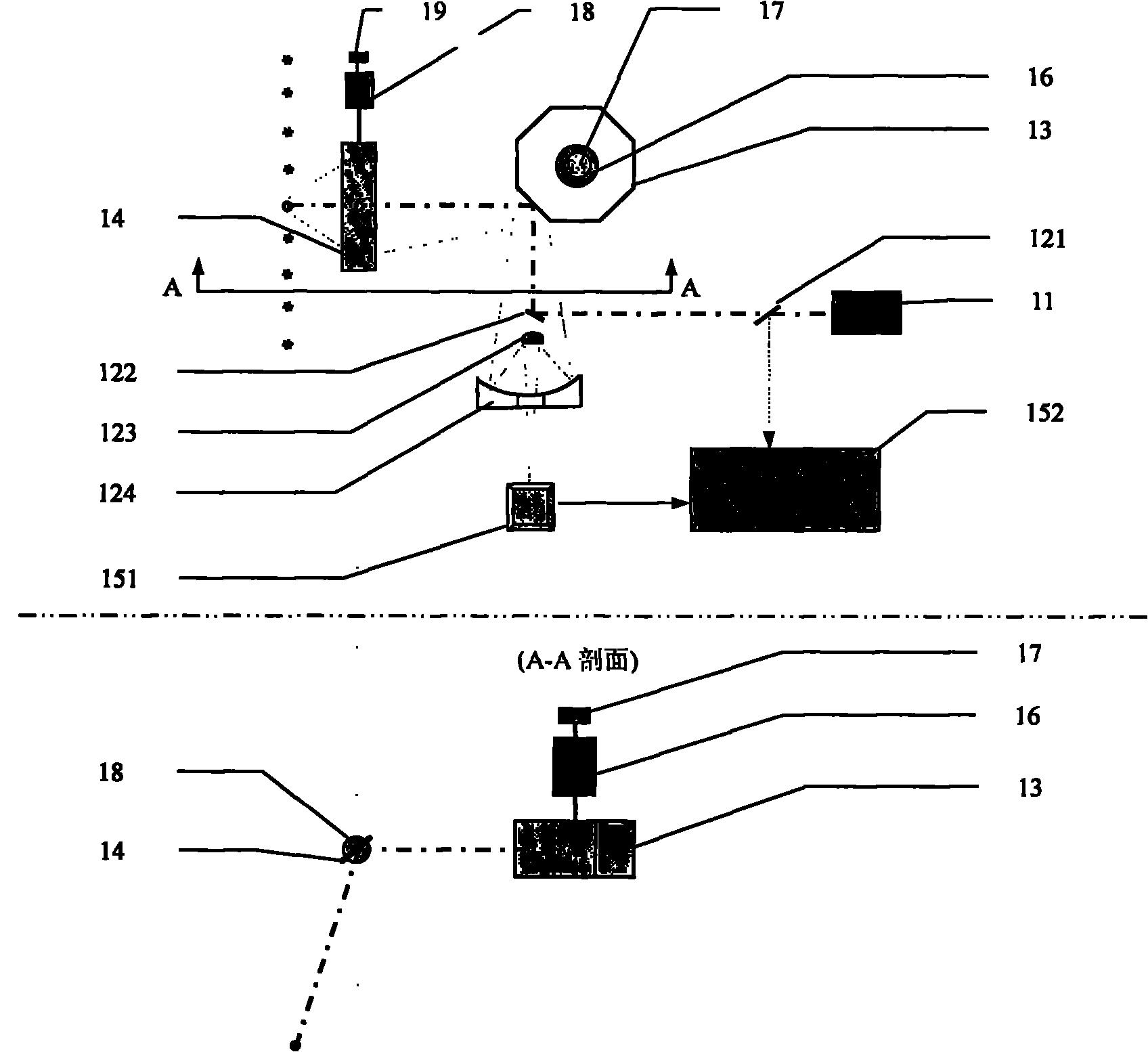
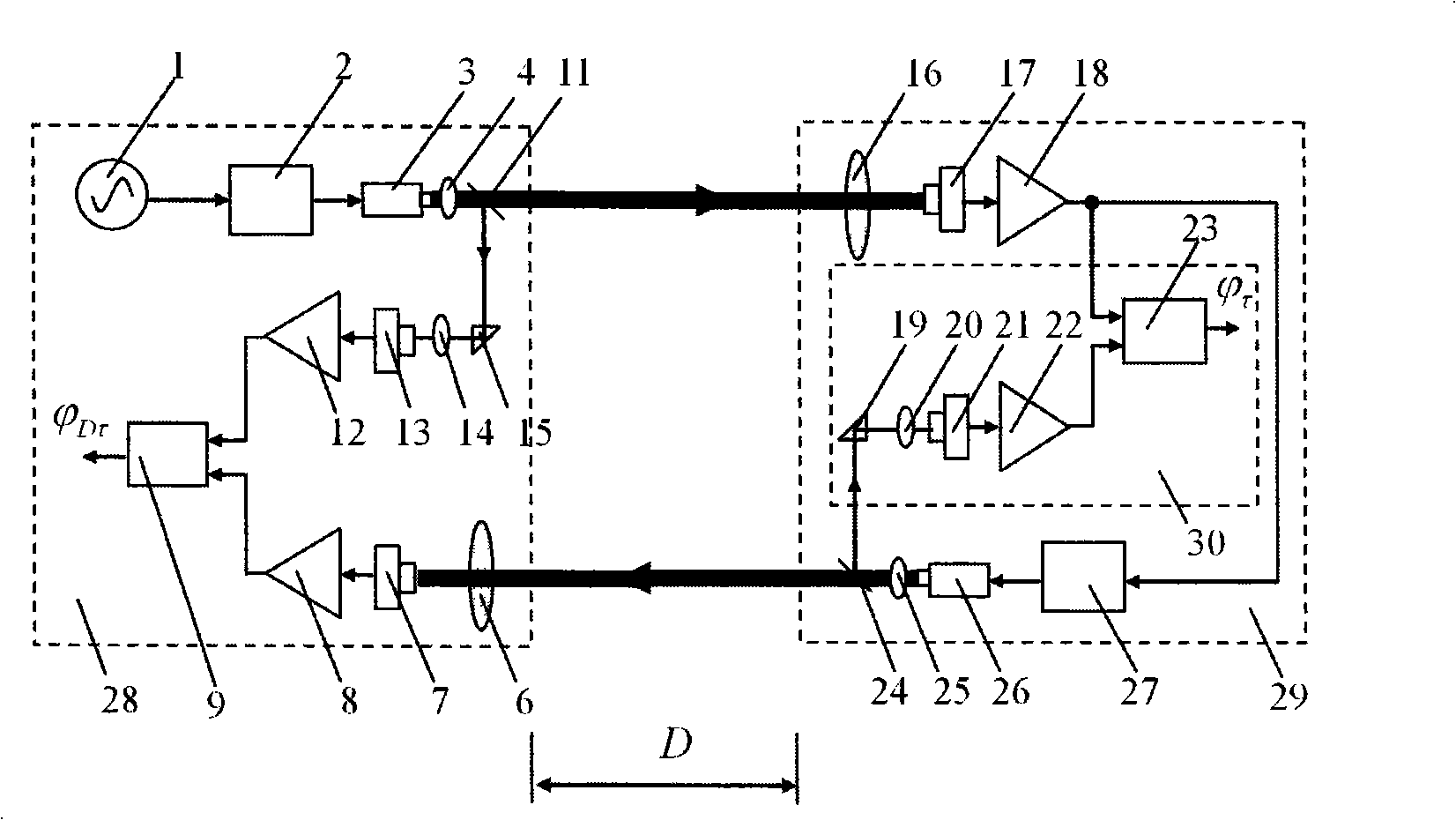
Airborne laser radar pitch angle deviation real-time compensation method and device
InactiveCN101865996AAchieve compensationReduce size and massElectromagnetic wave reradiationPhysicsMeasurement device
The invention discloses an airborne laser radar pitch angle deviation real-time compensation method and an airborne laser radar pitch angle deviation real-time compensation device. The device comprises a laser scanner device capable of realizing pitch angle deviation compensation, a pitch angle compensation controller and driving device, a GPS / INS combined measurement device, wherein the laser scanner device capable of realizing the pitch angle deviation compensation comprises a laser scanning transmitting and receiving system, a scanning prism, a compensation mirror, a photoelectric axial angle encoder and a compensation mirror motor; the GPS / INS combined measurement device acquires the attitude angle (pitch angle, rolling angle and yaw angle) deviation of a airborne platform and provides the acquired attitude angle deviation to the pitch angle compensation controller and driving device; and the pitch angle compensation controller and driving device controls the motor of the compensation mirror by using a compensation signal, receives a feedback signal from the compensation mirror photoelectric angle encoder, completes the closed-loop control of the pitch angle deviation compensation mirror and realizes the real-time high-accuracy compensation of the pitch angle deviation of an airborne laser radar.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
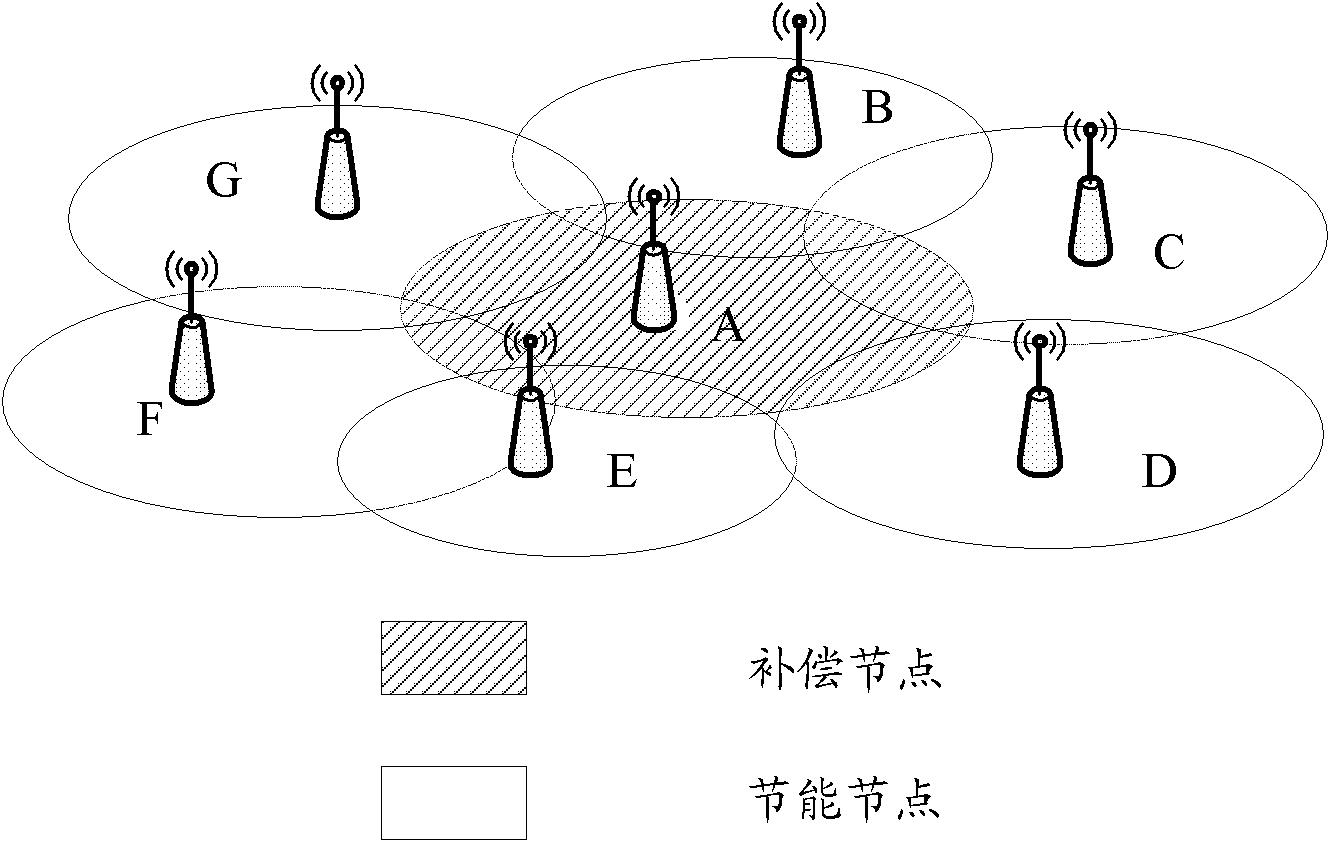
Compensating method and device and recovering method and device of overlay area
InactiveCN102065448ARealize energy savingAchieve compensationPower managementEnergy efficient ICTEngineering
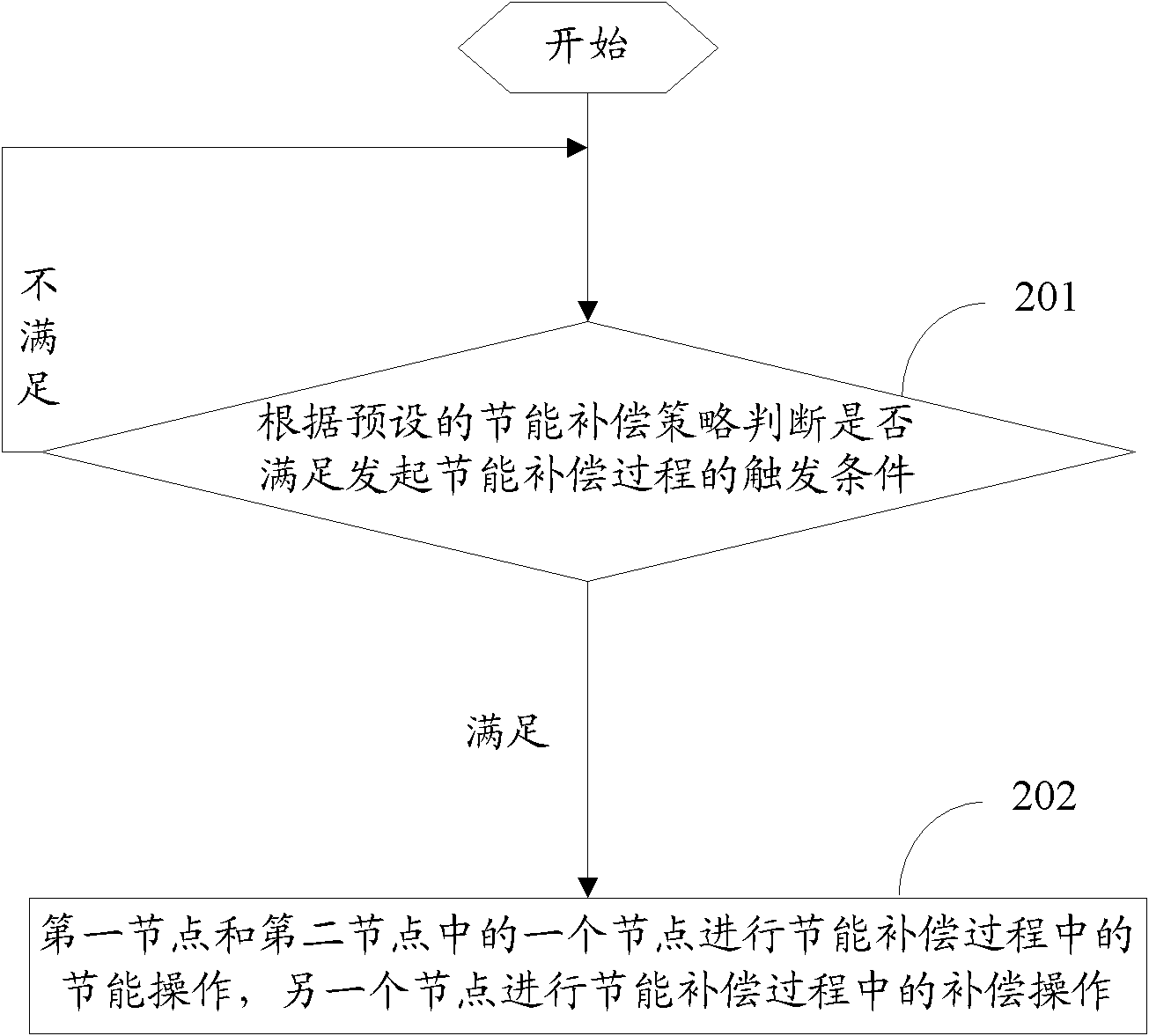
The invention discloses a compensating method and a recovering method of an overlay area, which are used for realizing the energy saving and the compensation between nodes. The overlay compensating method comprises the following steps of: judging whether a toggle condition for starting an energy saving compensating process is met according to a preset energy saving compensating strategy; when the toggle condition for starting the energy saving compensating process is met, carrying out energy saving operation in the energy saving compensating process by one of a first node and a second node, and carrying out compensating operation in the energy saving compensating process by the other node, wherein the first node is a compensating node, the second node is an energy saving node, or the first node is the energy saving node, and the second node is the compensating node. The invention also discloses a device for implementing the compensating method and a device for implementing the recovering method.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD +1
Three-level inverter dead time compensation control method
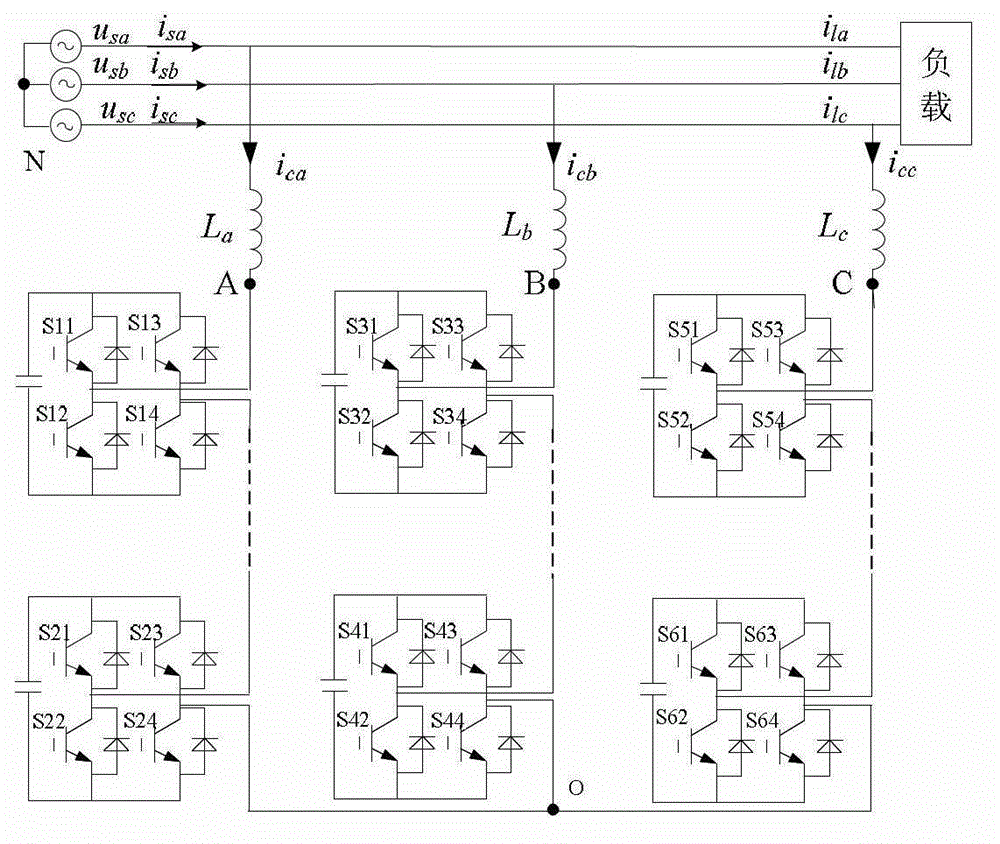
InactiveCN103236798AImproved output current waveformActual output line voltage risesAc-dc conversionThree levelVoltage vector
A three-level inverter dead time compensation control method is used for compensating the decrease of system performance caused by dead time. According to the topological structure of a three-phase three-level PWM (pulse width modulation) inverter, the method first sets corresponding dead time and determines the on-off delays of power elements in the inverter; the method then considers the tube voltage drops of the power transistors of the inverter and the tube voltage drops of clamping diodes of the inverter and calculates the common voltage expression of the output neutral point of the inverter; afterwards, according to the sector with three-phase current value and a reference voltage vector, the method determines the relational coefficient between voltage error caused by the tube voltage drops of the power transistors, the tube voltage drops of the clamping diodes and the on-off delays of the power transistors and current, and thereby the total dead time compensation time of each phase of the three-level PWM inverter is worked out. The method takes the dead time, the on-off delays of the power elements and the tube voltage drops into full consideration, solves the problem of voltage and current distortion caused by the dead time effect in the three-level inverter, and enhances system performance.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Reactive power compensation device based on novel modular multilevel topology and control method thereof
InactiveCN104934989ASolve the three-phase unbalance problemAchieve compensationPolyphase network asymmetry elimination/reductionReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationEngineeringAlternating current
A reactive power compensation device based on novel modular multilevel topology and a control method thereof relate to a high-voltage and large-power reactive power compensation device. In the prior art, compensation in a high-voltage and large-power field is limited and an inhibiting ability to circulation is insufficient. The invention aims at solving the above problems. A three-phase alternating-current power supply, a resistance-inductance load, a MMC converter, a signal detection circuit, a control circuit and a driving circuit are included. The MMC converter comprises three bridge arms which share a same structure and are connected in parallel. Each bridge arm comprises an upper bridge arm and a lower bridge arm which are symmetrical about a middle point of the bridge arm and are connected in series. Each upper bridge arm comprises a resistor, an inductor, several half-bridge units and an H bridge unit which are connected in series. The inductor of each upper bridge arm and an inductor of each lower bridge arm are connected in series. The middle points of the three bridge arms of the converter are connected in parallel between the three-phase alternating-current power supply and the load through a lead. By using the device and the method in the invention, power-grid reactive power can be compensated; a three-phase imbalance problem of a system is solved; effects of supporting a power grid voltage and inhibiting the circulation are achieved.
Owner:HARBIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
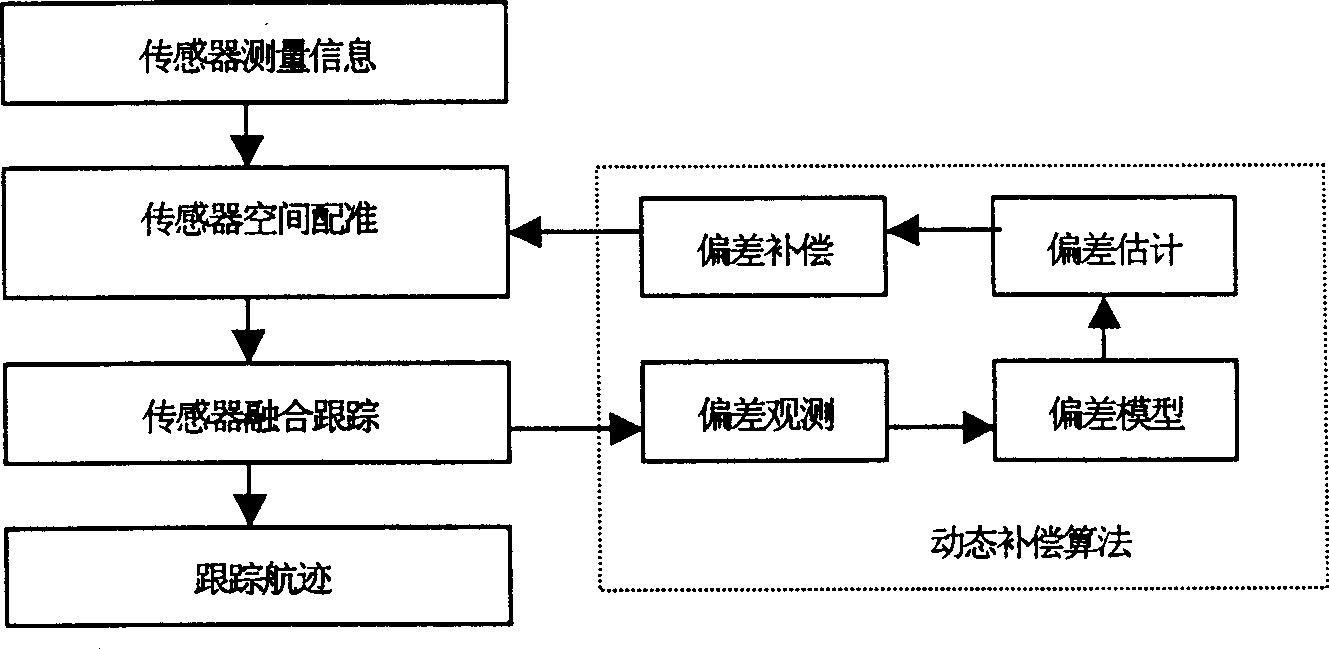
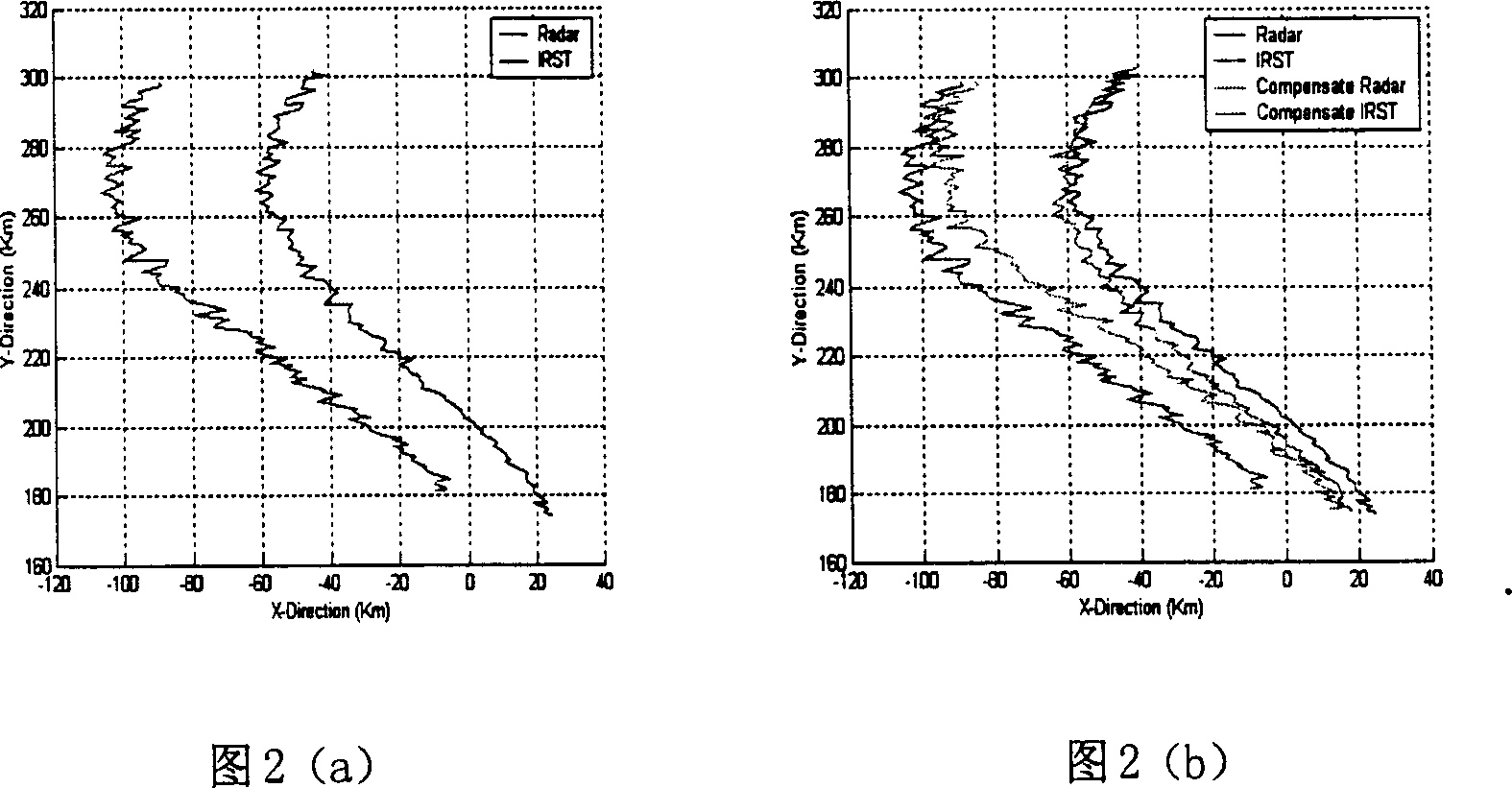
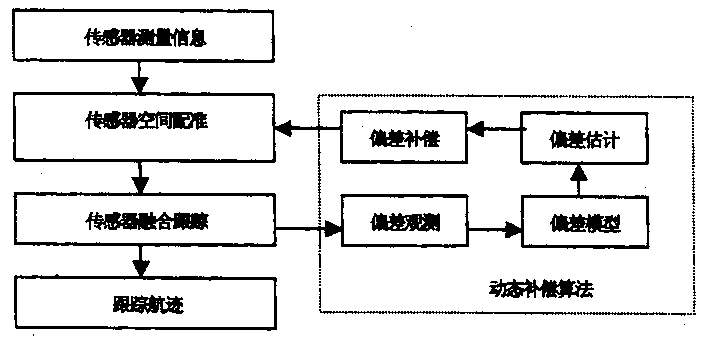
Registration deviation on line compensation method of multisensor grafting tracing system
InactiveCN1479081ARealize online estimationAchieve compensationInstruments for road network navigationWave based measurement systemsProbability estimationMultiple sensor
An in-line compensation method for the match error of multiple sensors integrated tracking system features that the maximal probability estimation method is used to determine the initial error, extracting the system error by use of the information measured by sensors, and the filtered tracking information, and performing in-line compensation.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
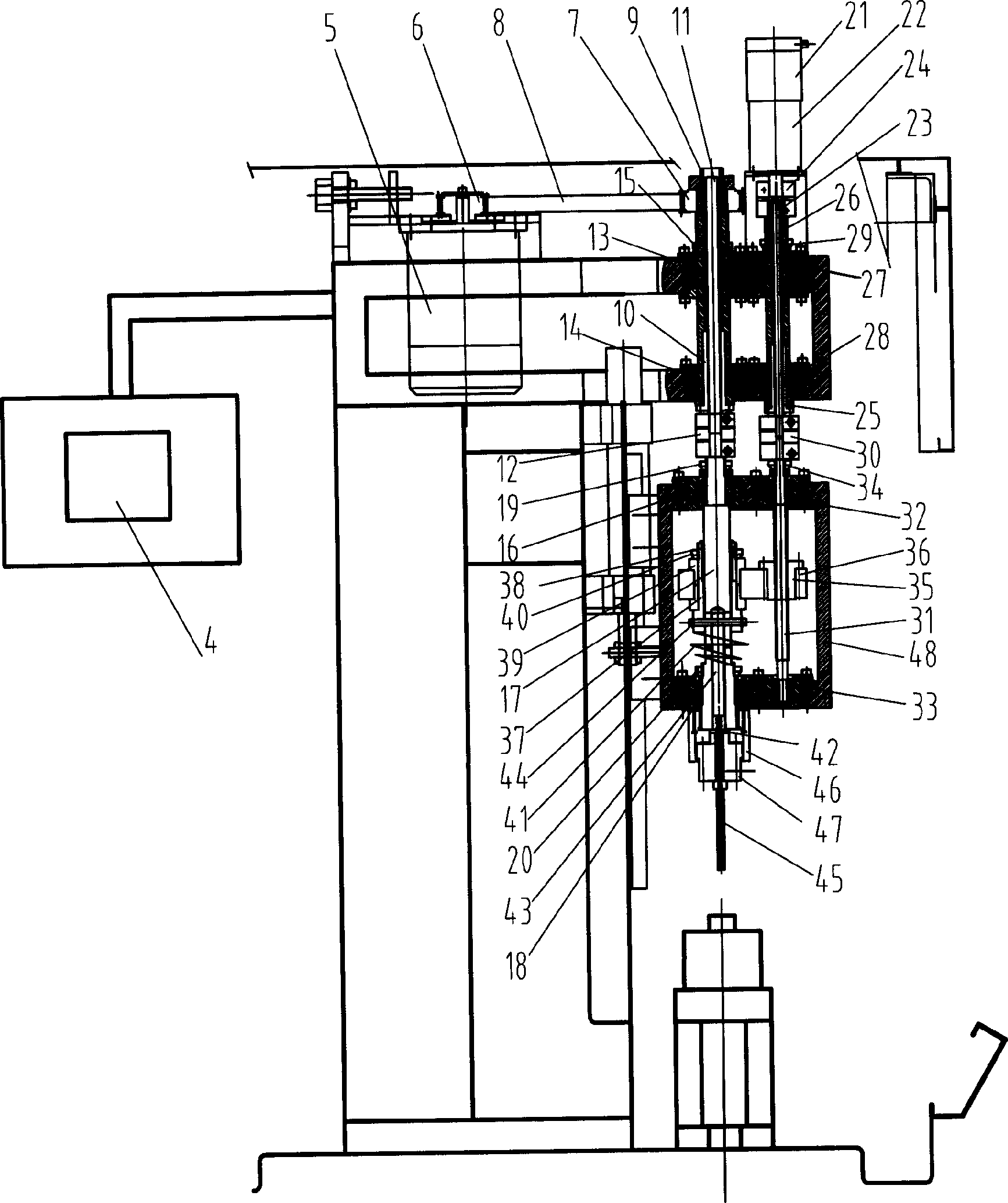
Digital control vertical high precision honing machine
InactiveCN1654167AConvenient real-time operation and monitoringEasy to operateAutomatic grinding controlHoning machinesProcessing accuracyReciprocating motion
The numerically controlled vertical high precision honing machine in the field of mechanical technology includes main shaft driving mechanism of vertical honing head, radial micro feeding mechanism of honing strip, high speed smooth honing head reciprocating mechanism, and digital control system. The connection mode includes vertical setting of the main shaft driving mechanism of vertical honing head and the radial micro feeding mechanism of honing strip on the honing machine bed, connection between the main shaft driving mechanism of vertical honing head and the radial micro feeding mechanism of honing strip via the feeding sleeve, and the connection of the high speed smooth honing head reciprocating mechanism to the main shaft driving mechanism of vertical honing head and the radial micro feeding mechanism of honing strip via bearing. The present invention has the advantages of simple structure, reasonable layout, high stability and reliability, etc.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV +1
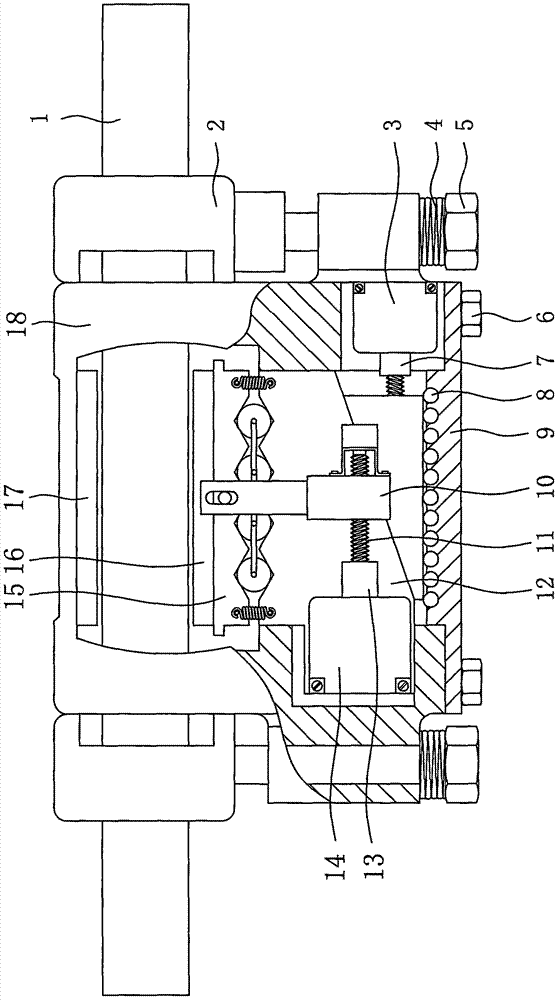
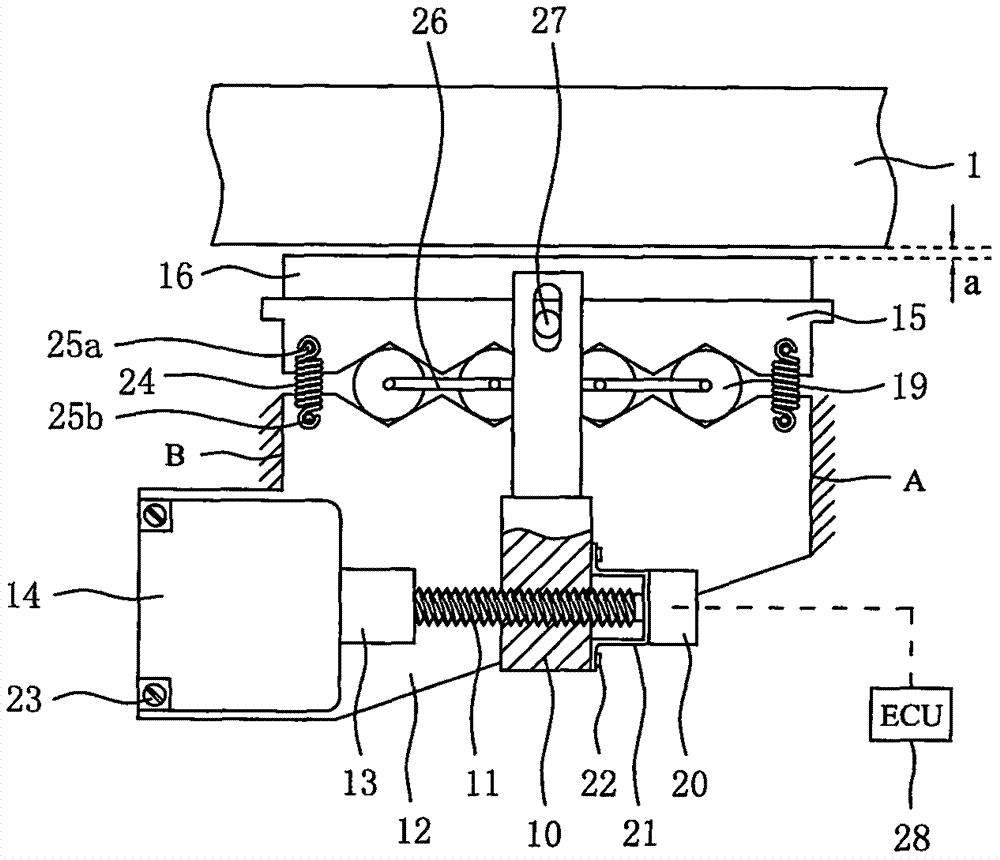
Self-force-increasing type electronic-mechanic brake for automobile
InactiveCN107035790AAchieve compensationGuaranteed constancyAxially engaging brakesBrake actuating mechanismsAuto regulationMotor drive
The invention discloses a self-force-increasing type electronic-mechanic brake for an automobile. An upper friction plate and a lower friction plate are arranged at the two sides of a brake disc. The upper friction plate is fixedly mounted on a brake caliper body. The brake caliper body is mounted on a brake caliper bracket through guiding rods and can move axially on the guiding rods. A dust cover is arranged between the brake caliper body and each guiding rod. A first motor is fixed to a lower wedge block through first screws. The first motor is connected with a first threaded rod through a first coupling. The first threaded rod is in transmission connection with a push rod through a thread. In the braking process, the first motor drives the first threaded rod to rotate, the first threaded rod pushes the push rod to move in the horizontal direction, and furthermore, the push rod pushes an upper wedge block to move in the horizontal direction and the vertical direction; normal brake clearances are eliminated; and the lower friction plate is in contact with the brake disc, and braking is achieved. The self-force-increasing type electronic-mechanic brake for the automobile has the self-force-increasing function; the input torque of each motor can be greatly reduced; and meanwhile, the self-force-increasing type electronic-mechanic brake has the function that the clearance can be adjusted automatically, and wear of the friction plates is compensated.
Owner:JINHUA VOCATIONAL TECH COLLEGE
Automatic compensation device of phase noise of Raman laser system based on closed loop feedback and method thereof
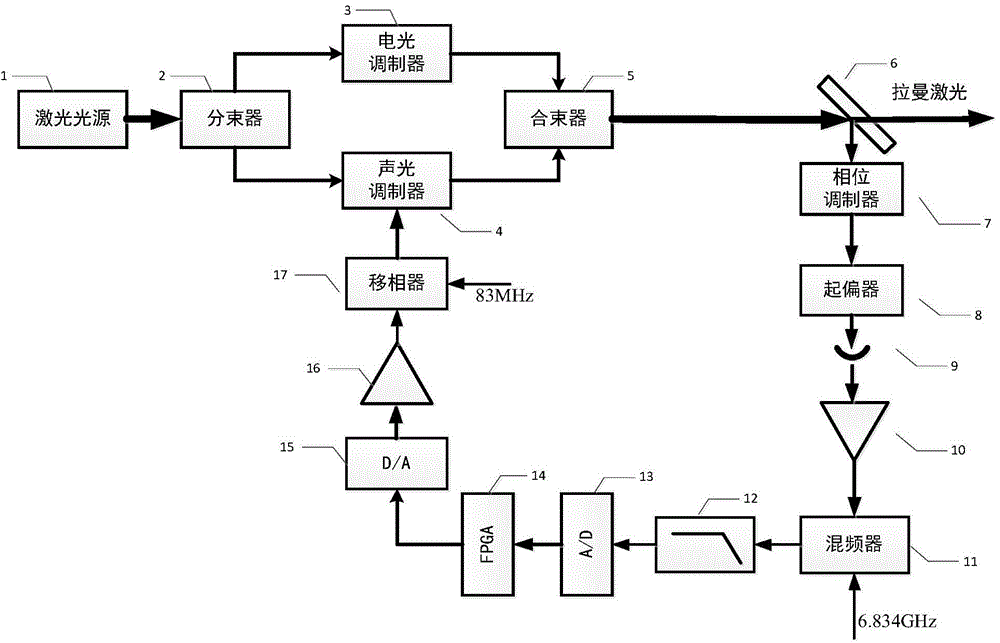
InactiveCN104682187ARealize regulationAchieve compensationLaser using scattering effectsLow noisePhase noise
The invention discloses an automatic compensation device of a phase noise of a Raman laser system based on closed loop feedback and a method thereof. The device comprises a laser source, a beam splitter, an electrooptical modulator, an acoustic optical modulator, a beam combiner, a half-transparent half-reflecting mirror, a phase modulator, a polarizer, a photoelectric detector, a low noise microwave amplifier, a frequency mixer, a low pass filter, an analog-digital converter, an FPGA, a digital-to-analog converter, a low frequency amplifier and a phase shifter. The automatic compensation device and method provided by the invention are capable of automatically adjusting and compensating a phase difference in the Raman laser system and reducing the phase noise caused by the vibration of a light path of the Raman laser system. By adopting the circuit control mode, the advantages of integration, modularization and easy debugging of a control system are achieved.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Three-phase high-voltage cascading mixing power compensator and control method thereof
InactiveCN103151783AMake up for harmonic compensation defectsReduce capacityReactive power adjustment/elimination/compensationReactive power compensationPower qualityLow voltage
The invention discloses a three-phase high-voltage cascading mixing power compensator and a control method thereof. In order to compensate higher harmonic current, a single-phase active filter is connected on an input filter inductance of the three-phase high-voltage cascading mixing power compensator in parallel, since majority of basic wave voltages are born by a cascading multi-electrical-level PWM (pulse-width modulation) current transformer, the basic wave on the filter inductance is extremely small, a low-voltage high-frequency switch appliance can be adopted for the active filter to realize the compensation of high harmonic current; and meanwhile an LC (logic controller) single-tuning filter is connected onto the cascading multi-electrical-level PWM current transformer in parallel, a low-impedance passageway is provided for high harmonic current, and the harmonic compensation capability of the active filter is improved. According to the compensator and the control method thereof, comprehensive compensation on reactive power and harmonics can be realized, and the electrical energy quality of a high-voltage power distribution network is greatly improved.
Owner:马伏军
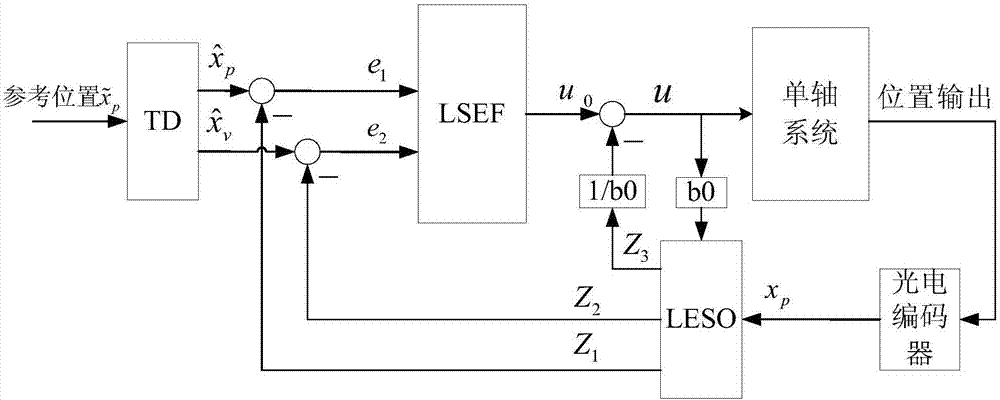
Nonlinear system active disturbance rejection control method based on interference observer
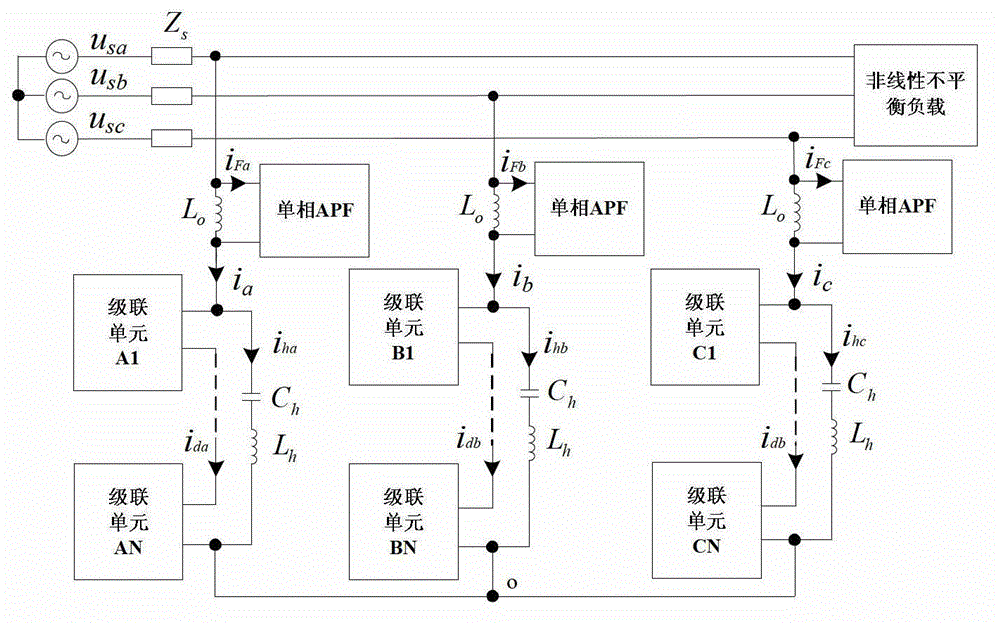
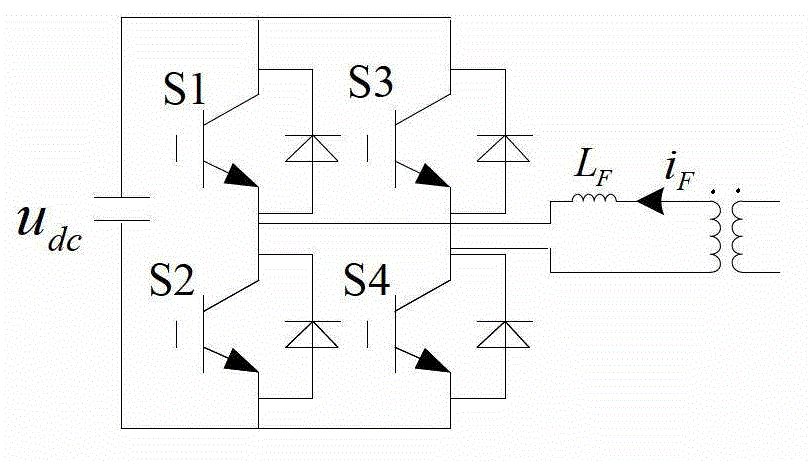
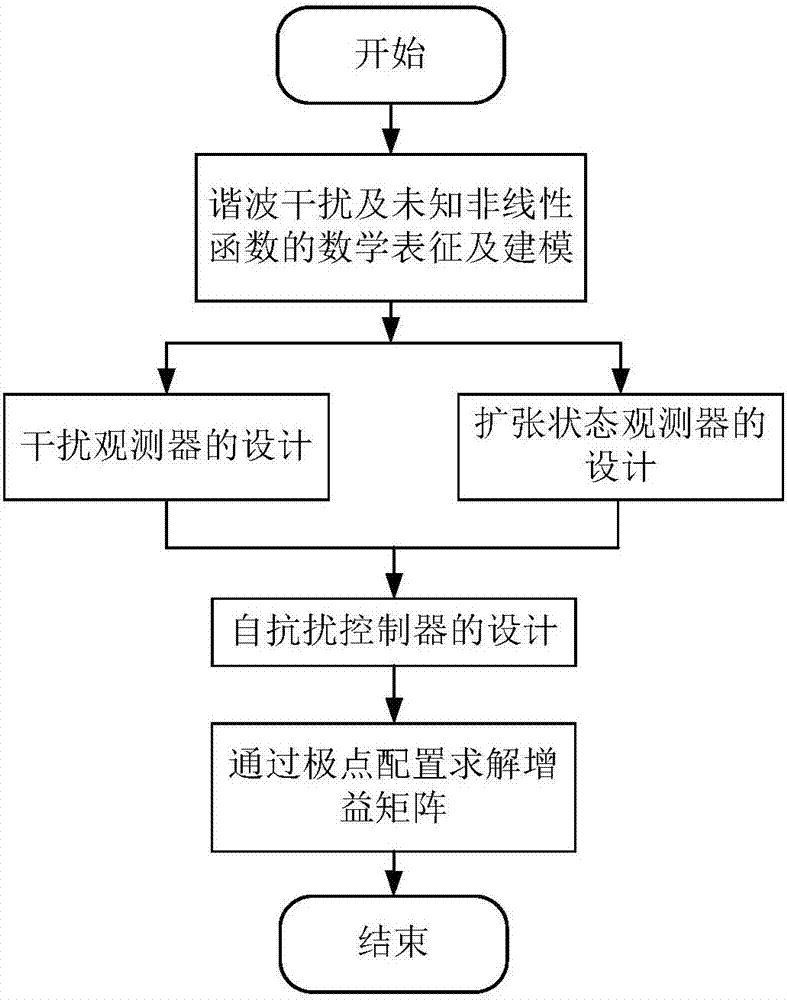
ActiveCN107168071AAchieving Simultaneous EstimationAchieve compensationAdaptive controlInterference resistanceHarmonic
The invention relates to a nonlinear system active disturbance rejection control method based on an interference observer, targeting a nonlinear single-input and single-output system containing an unknown nonlinear function and harmonic wave interference. The nonlinear system active disturbance rejection control method based on an interference observer comprises steps of performing mathematic representation on the harmonic wave interference and the nonlinear function, establishing an external model of the harmonic wave interference, designing an interference observer and an extended state observer on the basis of control input and measurement output information, completing estimation on the harmonic wave interference, the unknown non-linear function and a system state, designing an active disturbance controller according to the output of the interference observer and the extended state observer and completing gain solving of the observer and the controller on the basis of a separation theorem and a pole arrangement theory. The nonlinear system active disturbance rejection control method based on the interference observer has advantages of high interference resistance and high control accuracy and can be used for high accuracy control containing the interference and the unknown non-linear system.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
LCD
InactiveCN101256327AAchieve compensationAchieve preparationStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesCapacitanceLiquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a liquid crystal display, each pixel of an array substrate comprising a storage capacitance. A data line metal layer compensation block is inserted between a pixel electrode of the storage capacitance and a common electrode and connected with the pixel electrode by a contact hole and fully covered by the pixel electrode. The area of the data line metal layer compensation block is smaller along with the distance to the scanning line of the array substrate is farther. The liquid crystal display effectively increases the storage capacitance by reducing the distance between the two metal electrodes without increasing the overlap area. Because the data line metal layer compensation block is fully covered by the pixel electrode layer, there is no problem of contraposition accuracy between the two layers, namely the difference of delta Vp of two sides of the panel is finely compensated to realize the low flash of the display panel.
Owner:上海广电光电子有限公司
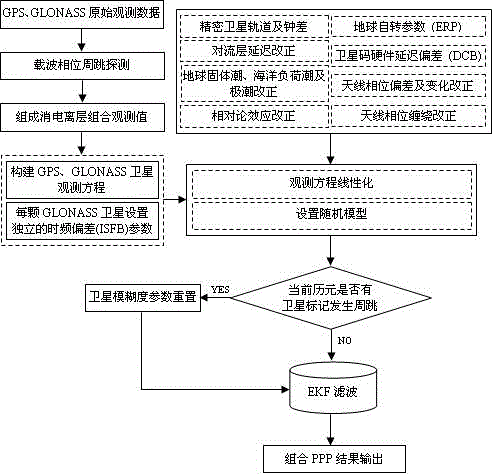
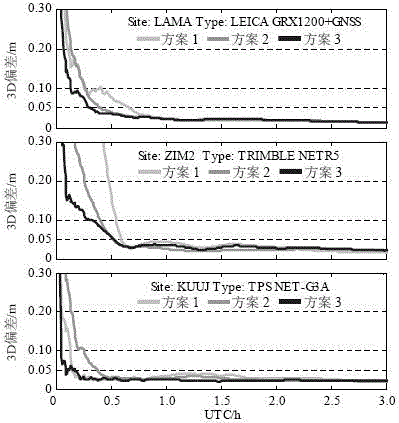
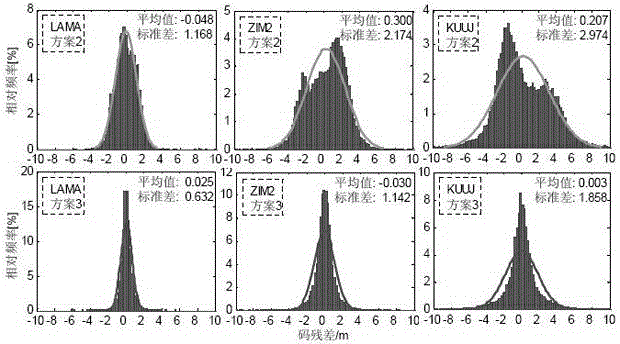
Method for improving convergence speed of combined precise point positioning of GPS (Global Position System) and GLONASS
ActiveCN104597465AAchieve compensationGood effectSatellite radio beaconingEngineeringGlobal Positioning System
The invention discloses a method for improving a convergence speed of combined precision single-point positioning (PPP) of a GPS (Global Position System) and a GLONASS. A plurality of independent 'time frequency bias' parameters are introduced into a function model to make up the defect in the prior art that GLONASS code inter-frequency bias is ignored in a modeling process; the convergence speed of the combined PPP of the GPS and the GLONASS is remarkably improved under the condition of not losing positioning precision. With the adoption of the method disclosed by the invention, a random model of GLONASS and GPS equal weight can be used for obtaining a code pseudo-range observation value when the PPP is combined, so that the defect that the weight ratio is determined by experiences in the prior art is avoided.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
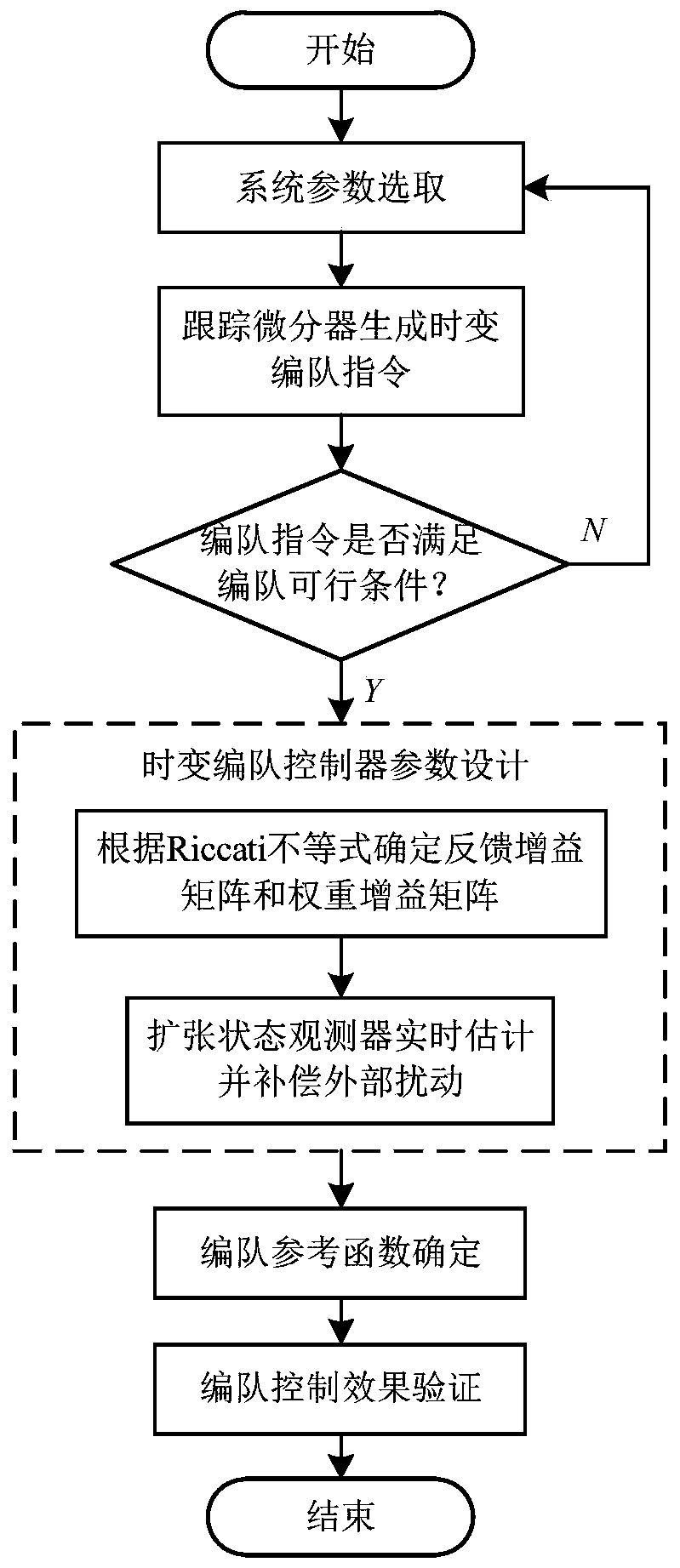
Multi-agent fully-distributed active disturbance rejection time-varying formation control method
ActiveCN110597061AReduce the risk of jitterHelps smooth changesAdaptive controlDifferentiatorMulti-agent system
The invention discloses a multi-agent fully-distributed active disturbance rejection time-varying formation control method. The multi-agent fully-distributed active disturbance rejection time-varyingformation control method is based on a multi-agent system which is composed of N autonomous second-order isomorphic agents. The multi-agent fully-distributed active disturbance rejection time-varyingformation control method uses an active disturbance rejection control idea for reference, and comprises the steps of: firstly, constructing an active disturbance rejection time-varying formation controller and an action weight self-adaptive updating law based on a self-adaptive control and error feedback control strategy according to interaction weights and formation state errors of the agents; adopting an extended state observer to determine disturbance compensation; adopting a tracking differentiator to generate a time-varying formation instruction; further providing a completely distributedcontrol gain design method; and finally providing the multi-agent fully-distributed active disturbance rejection time-varying formation control method. The multi-agent fully-distributed active disturbance rejection time-varying formation control method realizes the effect of how to implement active disturbance rejection time-varying formation control on the multi-agent system affected by externaldisturbance in a completely distributed manner, so that the multi-agent system has disturbance suppression robustness while realizing time-varying formation.
Owner:ROCKET FORCE UNIV OF ENG
Active collaboration type phase laser distance measuring method and apparatus
ActiveCN101349757AImprove signal-to-noise ratioLow powerElectromagnetic wave reradiationLaser rangingUltrasound attenuation
The invention belongs to the laser ranging technical field, which arranges an active cooperation target end device at an object in a laser ranging process, wherein the active cooperation target device amplifies and reflects the laser signal of a ranging end to the ranging end, the ranging end receives the optical signal from the active cooperation target end device to realize the cooperation between the active cooperation target end device and the ranging end to complete the ranging process. The invention changes the prior single beam roundtrip measurement mode into a double beam single-pass cooperation measurement method to change the attenuation mode of the reflected light energy of the measurement system from the fourth power attenuation function of the ranged distance in the prior art to second power attenuation function, thereby improving the reflected light energy and the signal noise ratio of the system, improving ranging effect along with the increase of distance and realizing remote high accuracy measurement under low laser emission power and optical receiving aperture. The inventive device is composed of a ranging end device and an active cooperation end device having same optical and electric structures with the ranging end device.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
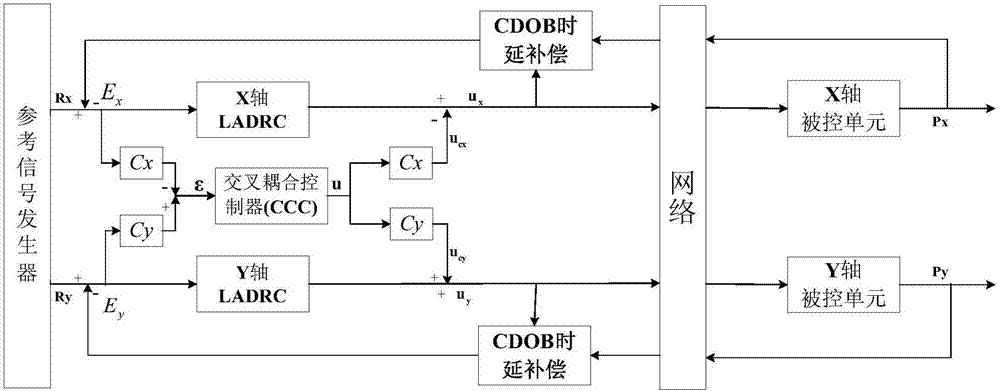
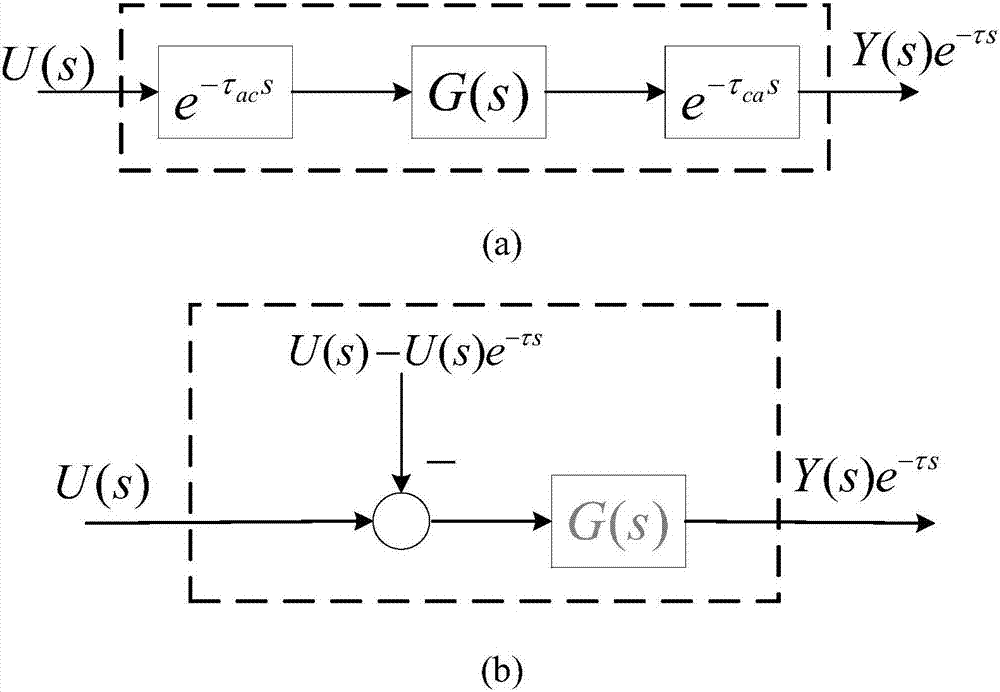
Communication-jamming-observer-based cross coupling control method of networked multi-axis motion control system
InactiveCN107085373AStrong anti-disturbanceAchieve compensationAdaptive controlActive disturbance rejection controlEngineering
The invention relates to a communication-jamming-observer-based cross coupling control method of a networked multi-axis motion control system. According to the method, for single-axis track tracking control, a linear auto disturbance rejection controller is used for realizing the good tracking system of the single-axis track tracking control and the good anti-disturbance capability for uncertainty of the system model. In order to prevent uncertainty being equal to the system disturbance and being caused by network delay, the method employs a communication jamming observer having the delay estimation and compensation functions, thereby realizing real-time estimation and compensation for uncertainty caused by the single-axis network induced delay. And for a multi-axis coordination motion control track contour model in the networked multi-axis motion control system, a contour error model of the system at the current time is calculated; and according to the obtained contour error, a PID-based contour error compensation controller is designed to realize compensation controlling on the system contour track.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
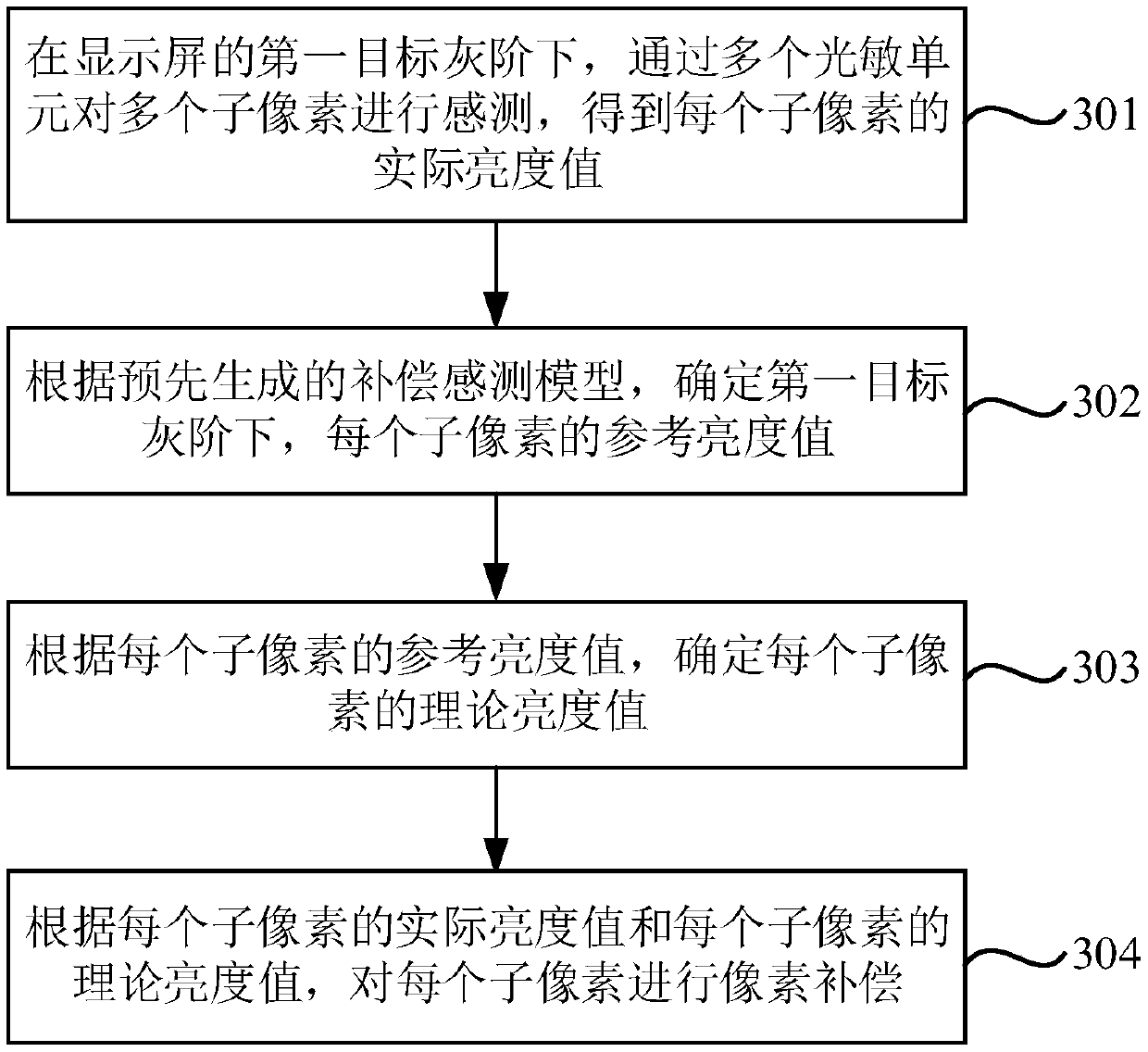
Pixel compensation method and device, storage medium, and display screen
ActiveCN109523955AImprove uniformityPixel Compensation ImplementationCathode-ray tube indicatorsBrightness perceptionCompensation methods
The invention relates to a pixel compensation method and device, a storage medium and a display screen, and belongs to the technical field of display. The method includes the steps: sensing a plurality of sub-pixels by using a plurality of photosensitive cells at a first target gray scale of the display screen to obtain an actual brightness value of each sub-pixel; determining a reference luminance value of each sub-pixel at the first target gray scale according to a pre-generated compensation sensing model, wherein the compensation sensing model is used to record the correspondence relation between the target gray scale and theoretical pixel data, and the theoretical pixel data includes the reference luminance value of each sub-pixel; determining the theoretical luminance value of each sub-pixel according to the reference luminance value of each sub-pixel; and performing pixel compensation for each sub-pixel according to the actual luminance value of each sub-pixel and the theoreticalluminance value of each sub-pixel. The method realizes the compensation for the pixel aging of the display screen, and improves the uniformity of an image displayed on the display screen. The methodis used to compensate for the display screen.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD
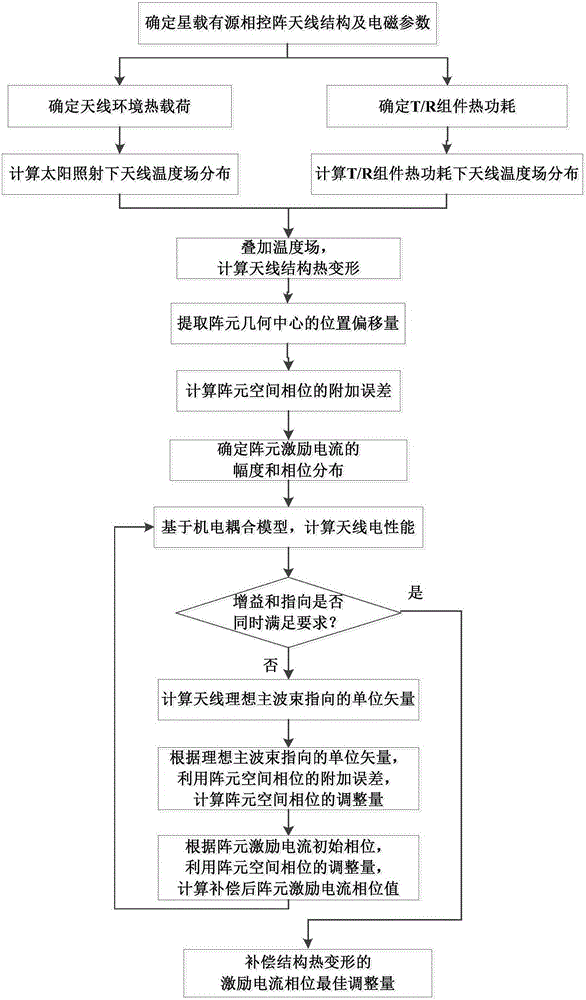
Gain-and-direction-orientated structure thermal deformation compensation method for satellite-borne active phase control array antenna
ActiveCN105742817AAchieve compensationReduce structural complexityAntennasPhase currentsThermal deformation
The invention discloses a gain-and-direction-orientated structure thermal deformation compensation method for a satellite-borne active phase control array antenna. The method comprises the steps of determining structural parameters, material attributes and electromagnetic parameters of the antenna; determining antenna environment thermal load; calculating antenna temperature field distribution under sunshine; determining T / R assembly thermal power consumption; calculating antenna temperature field distribution under the T / R assembly thermal power consumption; performing temperature field superposition and calculating the thermal deformation of the antenna structure; extracting position offset in the array element geometric center; calculating the additional error of the array element space phase; determining the amplitude and phase distribution of array element excitation current; calculating the electrical performance of the antenna; judging whether gain and direction are both satisfied simultaneously or not; and calculating the antenna ideal main beam directed unit vector, the adjusting amount of the array element space phase, and the phase current of the compensated array element excitation current. The compensation method provided by the invention is combined with a phase adjusting method, so that the electrical performance compensation to the deformed satellite-borne active phase control array antenna is realized; the problem of antenna electrical performance degradation caused by structural thermal deformation is solved; and the normal operation of the antenna can be ensured.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Dead zone compensation method for space vector pulse width modulation output based on equivalent vector effect
ActiveCN101964597AImprove the effectIncrease or decrease duration of actionElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhysicsDead band
The invention discloses a dead zone compensation method for space vector pulse width modulation output based on equivalent vector effect which can effectively avoid output voltage distortion, and is characterized by simple algorithm and strong universality in order to solve the problem that the dead zone compensation method is complicated when space vector pulse width modulation output is employed in the prior art. The compensation method takes the dead zone effect equivalent to the effect of a basic space vector through judging the current direction of each bridge-arm switch device of an inverter and offsets the dead zone effect through increasing or decreasing the non-zero basic space vector action time of a sector area where the modulation vector stays to efficiently realize the dead zone compensation for the space vector pulse width modulation output so as to greatly improve the low-speed control effects.
Owner:东元总合科技(杭州)有限公司
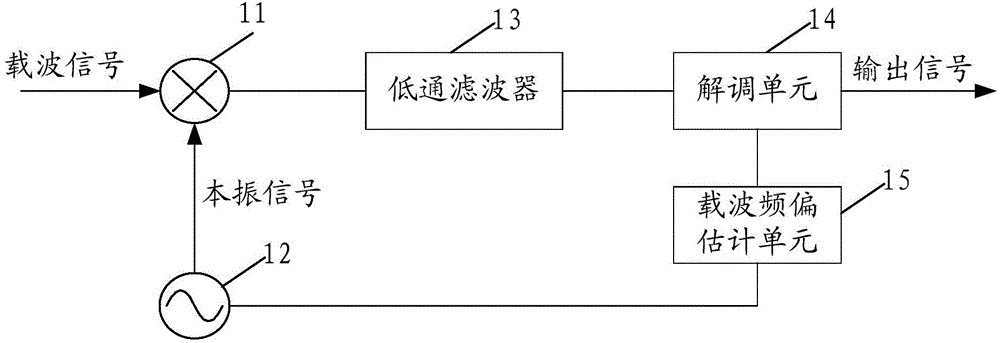
Carrier wave frequency offset compensation method, apparatus and receiving system
ActiveCN105337916AEasy to implementImprove compatibilityMulti-frequency code systemsMultiple carrier systemsLocal oscillator signalLow-pass filter
A carrier wave frequency offset compensation method, an apparatus and a receiving system are disclosed. The carrier wave frequency offset compensation method comprises the following steps of aiming at each sweeping frequency point in a sweeping frequency scope, calculating a signal intensity indication value of a receiving signal respectively, wherein the sweeping frequency point is used for adjusting a frequency of a receiving-end local oscillator signal; based on the signal intensity indication value and a frequency value of each corresponding sweeping frequency point, determining an estimation value of the carrier wave frequency offset; based on the estimation value of the carrier wave frequency offset, adjusting the frequency of the local oscillator signal so as to realize compensation to the carrier wave frequency offset. Further, through a fine compensation method of the carrier wave frequency offset, the fine compensation is performed on the carrier wave frequency offset after the compensation. Under the condition that the carrier wave frequency offset is large, estimation and compensation can be performed on the carrier wave frequency offset effectively. Under a small bandwidth work mode of a low pass filter, the large carrier wave frequency offset can be compensated. Receiver performance is increased and simultaneously a carrier wave frequency offset compensation scope can be effectively expanded.
Owner:SHANGHAI EASTSOFT MICROELECTRONICS
Optical fibre grating wavelength demodulating method
A method for demodulating grating wavelength of optical fibre includes using wideband optical source and a pair of optical fibre connected in series with one as reference and the other as measurement, measuring return power of this pair of optical fibre to obtain reflecting wavelength variation of reference fibre to measurement fibre for achieving wavelength modulation.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
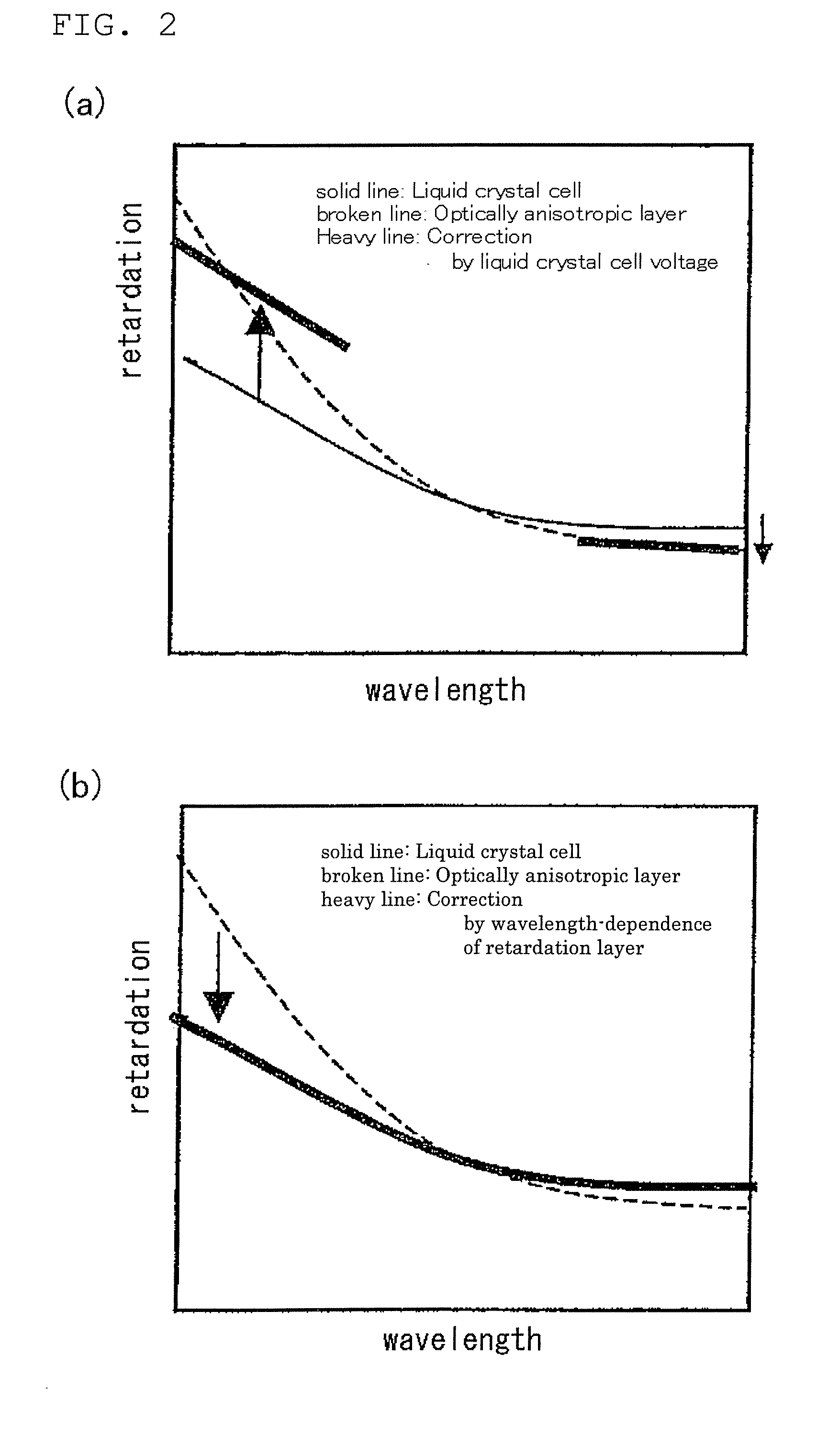
Optical Compensation Film, Method of Producing the Same, and Polarizing Plate and Liquid Crystal Display Device Using the Same
ActiveUS20080113112A1Achieve compensationGood colorLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsLiquid crystallineColor shift
A liquid crystal display showing a high contrast and reduced in color shift depending on the viewing angle is provided.The liquid crystal display device comprises a liquid crystal cell having a retardation value Re1(400) at 400 nm and a retardation value Re1(550) at 500 nm in the black state; and at least one layer of optically anisotropic layer formed of a composition comprising at least one species of liquid crystalline compound, having a retardations value Re2(400) at 400 nm and a retardation value Re2(550) at 550 nm,wherein Re2(400) and Re2(550) of said optically anisotropic layer, and retardations values Re1(400) and Re1(550) satisfy the relational expression (1) below:0.9≦α2 / α1≦1.1 Relational Expression (1)where, α1=Re1(400) / Re1(550) and α2=Re2(400) / Re2(550).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
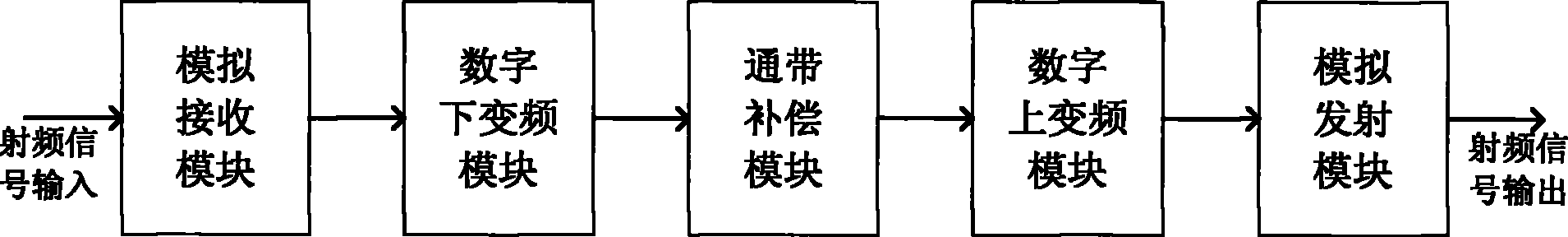
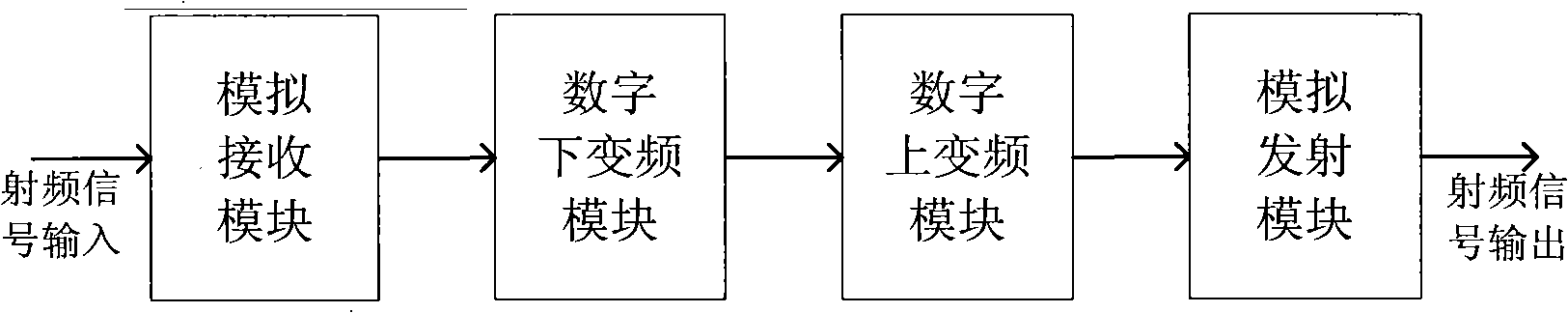
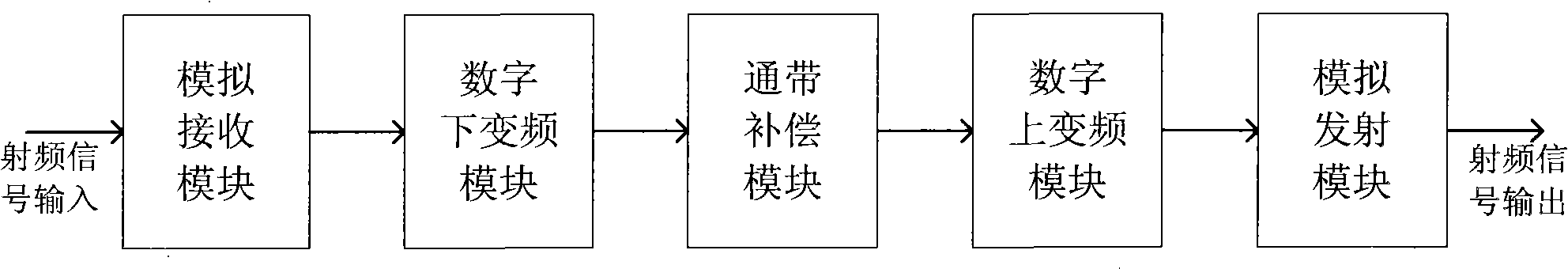
Digital communication system and method for improving flatness in signal band thereof
ActiveCN101815054ASmall fluctuationImprove flatnessMulti-frequency code systemsDigital signal processingCarrier signal
The invention relates to the field of digital signal processing of wireless communication and provides a digital communication system, which comprises an analog receiving module which carries out analog filtering and analog down-conversion processing on radio frequency signals, a digital down-conversion module which carries out decimation filtering processing on digital signals, a pass band compensation module which carries out fluctuating compensation on signals in pass bands, a digital up-conversion module which carries out interpolation filtering and up-conversion frequency mixing processing on the digital signals and an analog launching module which carries out analog filtering and analog up-conversion processing on the radio frequency signals. The invention also provides a method for improving flatness in a signal band in the digital communication system. A frequency domain compensation coefficient is obtained by the digital filtering processing in the frequency domain, namely testing the fluctuation characteristics of the system, and frequency domain filtering processing is carried out on the frequency domain signals according to the frequency domain compensation coefficient, thus realizing fluctuation correction and compensation in the signal band and improving the flatness in each carrier signal pass band in a digital repeater system.
Owner:COMBA TELECOM SYST CHINA LTD
Geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar velocity spatial variability compensating method
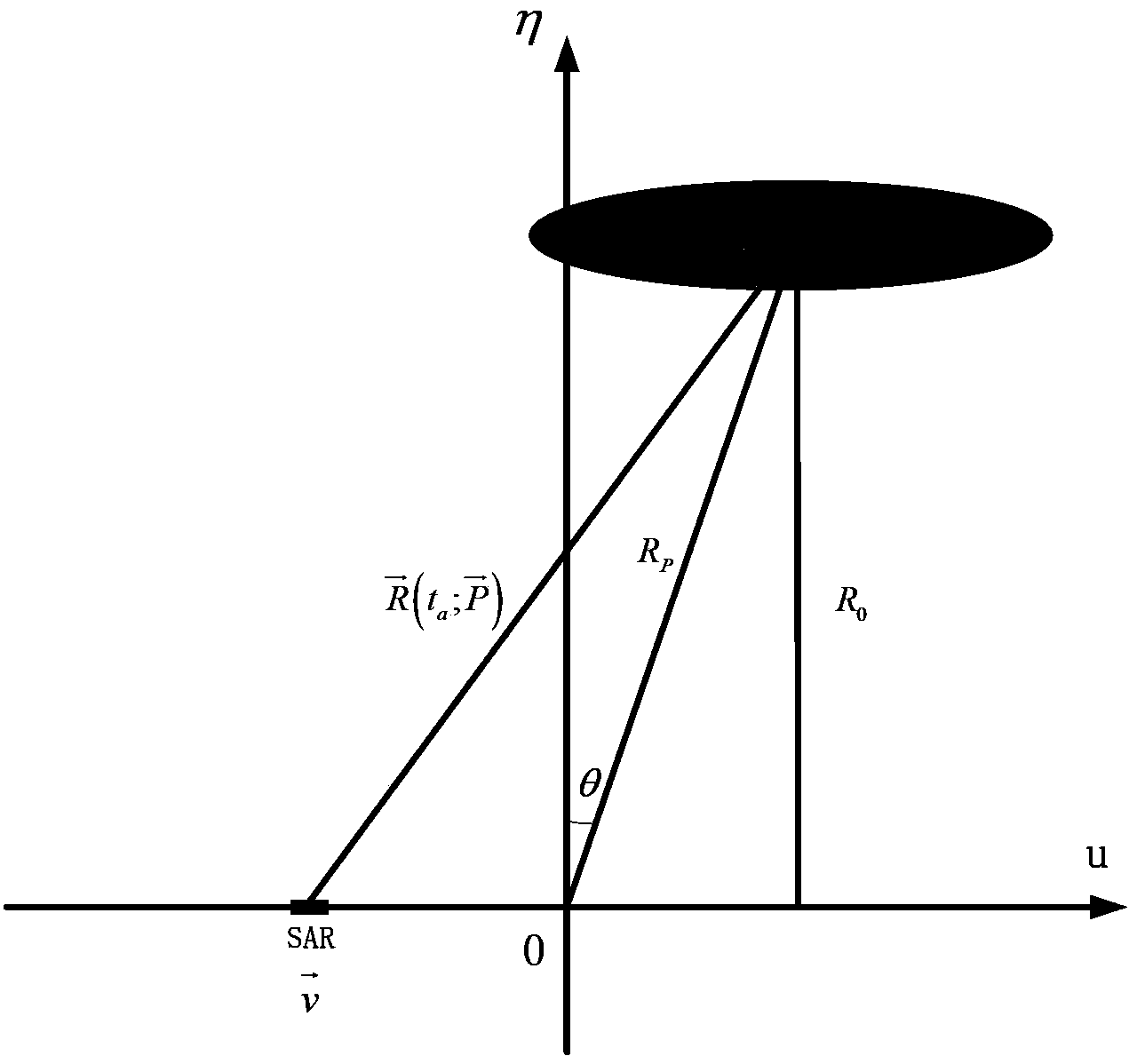
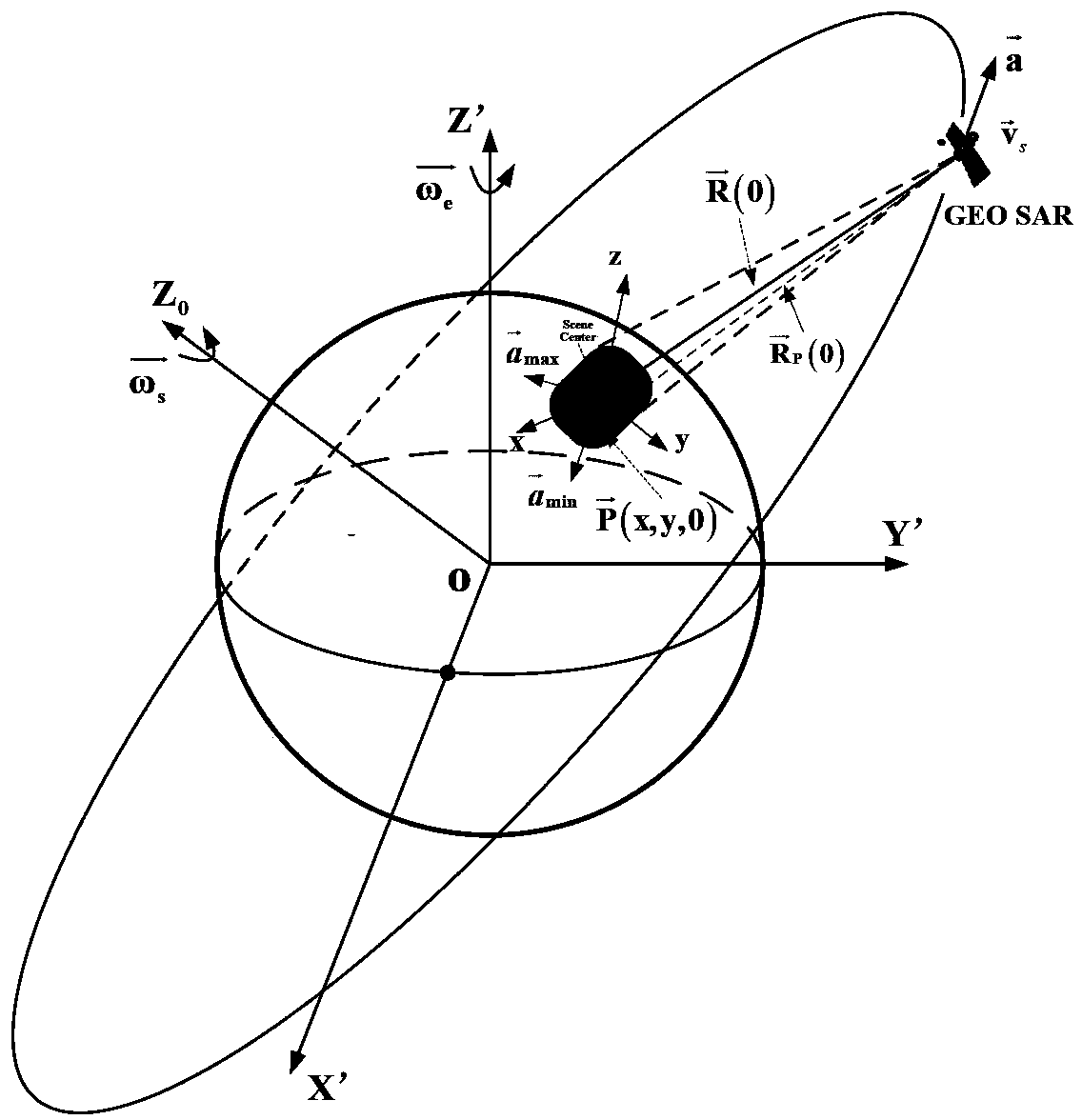
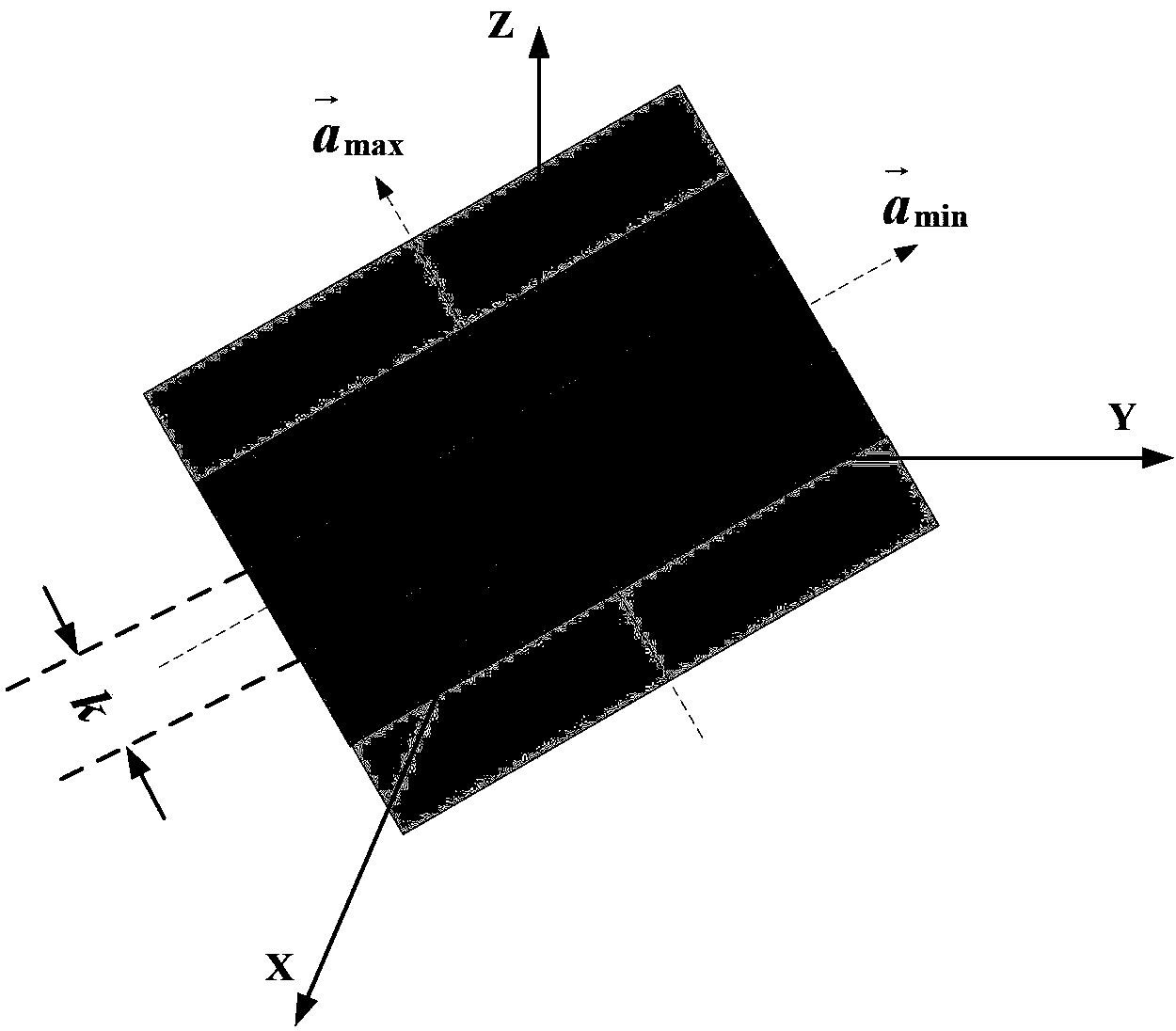
InactiveCN103364782AImplement focus processingSolved - speed space variation compensation problemRadio wave reradiation/reflectionSynthetic aperture radarClassical mechanics
The invention discloses a geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar velocity spatial variability compensating method. According to the method, the velocity spatial variability is compensated through self-adaptive phase compensation processing, so that a core problem, i.e. a velocity spatial variability compensation problem, of geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar (GEO SAR) large-scale scene imaging is solved, the GEO SAR large-scale scene imaging focusing processing of arbitrary position is realized, and a good effect is obtained.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
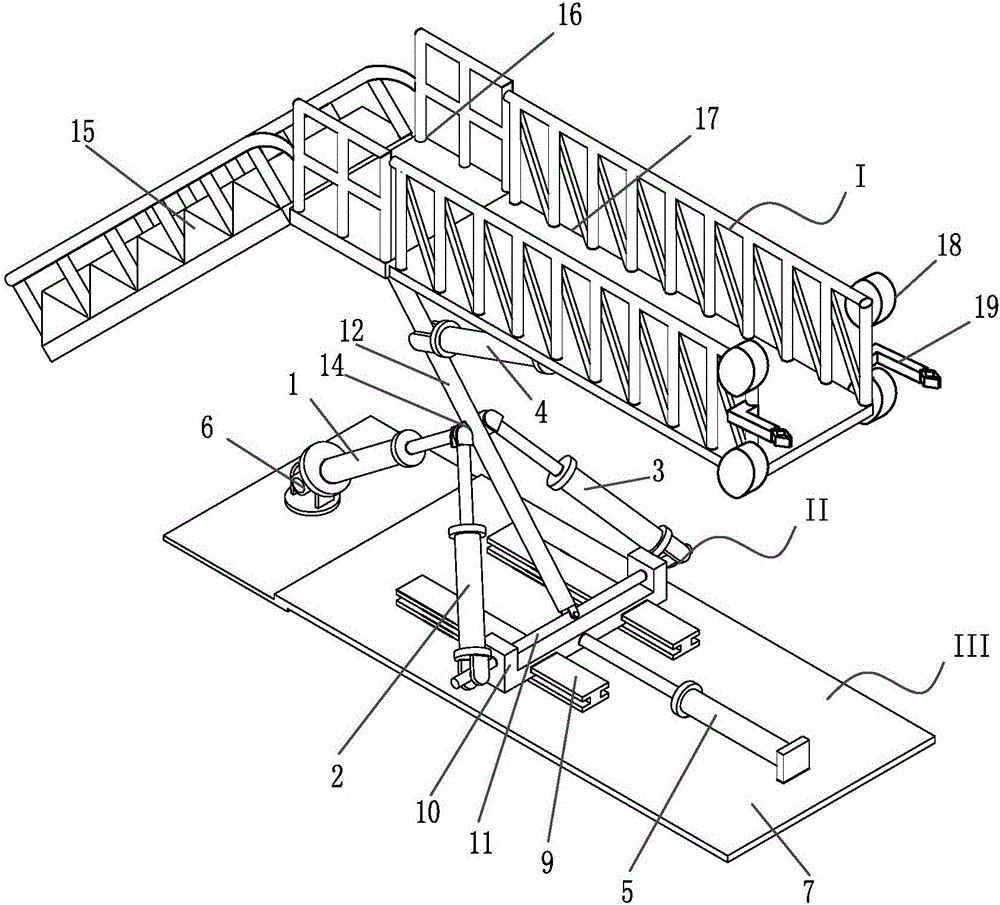
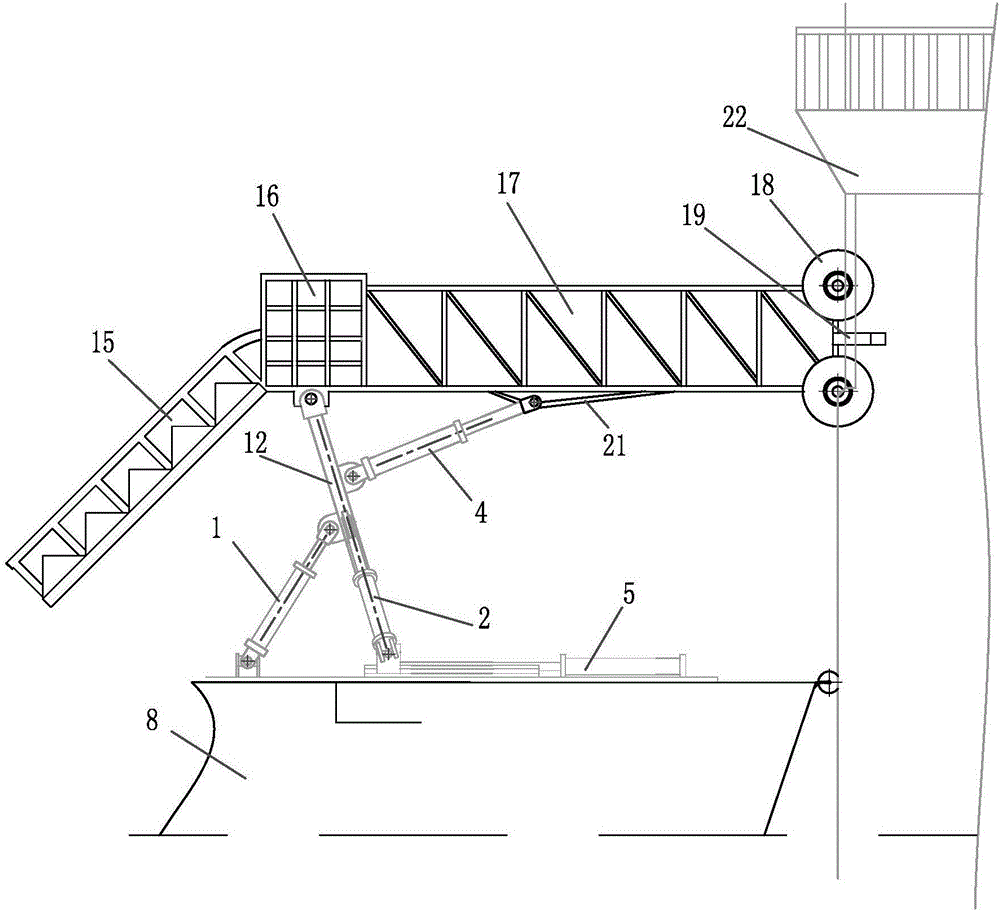
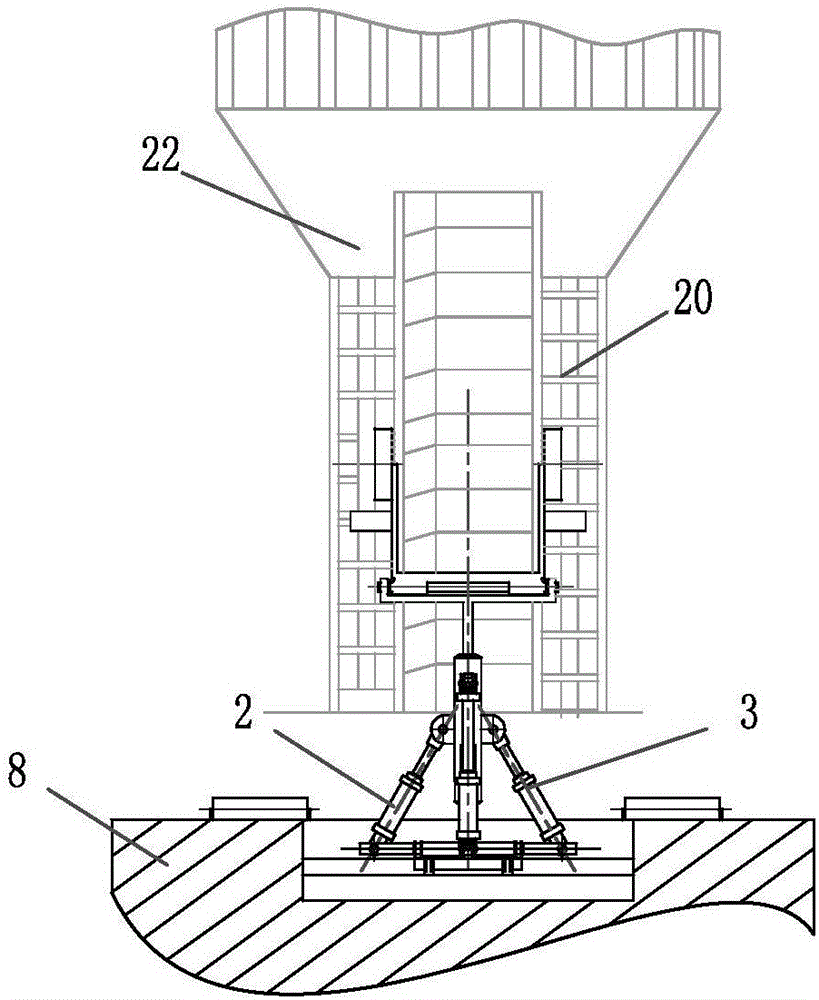
Wave compensating device for ascending operation of high-rise pile cap
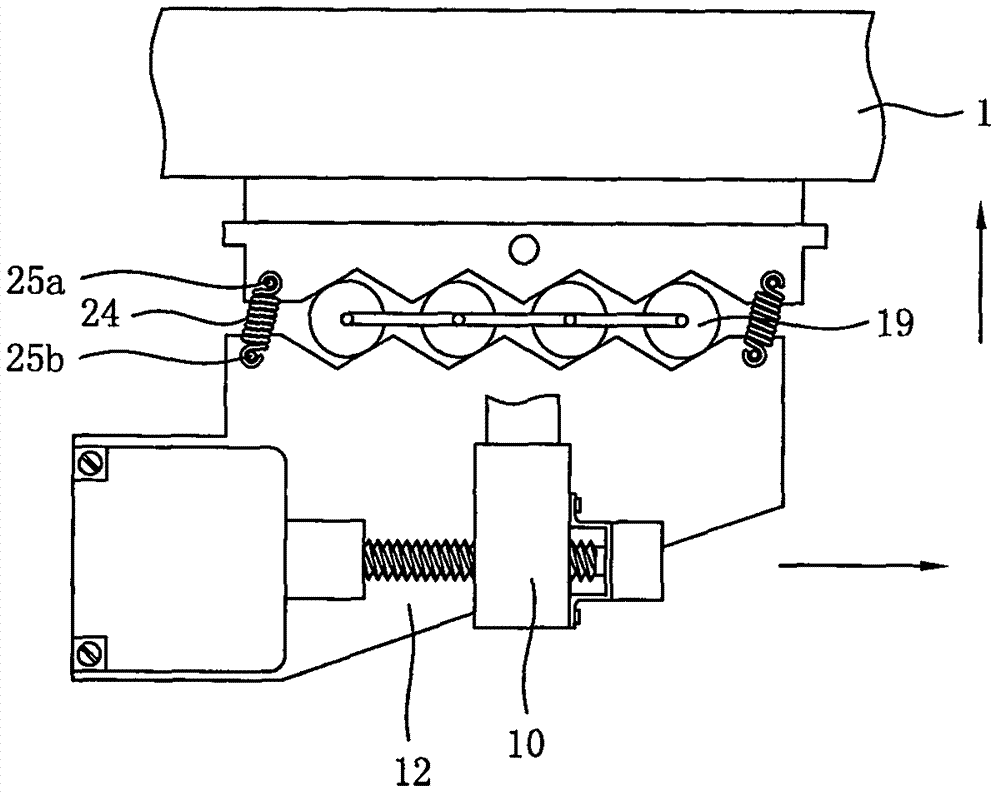
ActiveCN106828789AMotion compensationCompensate for coupled motionCargo handling apparatusVessel partsHydraulic cylinderElectricity
The invention discloses a wave compensating device for ascending operation of a high-rise pile cap, and belongs to the technical field of basic maintenance work of offshore wind piles. The wave compensating device comprises a horizontal ladder part, a hydraulic drive compensation mechanism and a base mechanism, wherein the hydraulic drive compensation mechanism is arranged on the base mechanism; the horizontal ladder part is arranged on the hydraulic drive compensation mechanism; the hydraulic drive compensation mechanism drives the horizontal ladder part to move; and the base mechanism is arranged on a bearing hull. The wave compensating device is driven by a hydraulic device to control a hydraulic cylinder to stretch and contract; and when a ship carries out three-degree-of-freedom motion of rolling, pitching and heaving, effective compensation is achieved, so that a worker more safely passes a horizontal ladder. Feedback control is adopted by the wave compensating device for ascending operation of the high-rise pile cap, so that the wave compensating device is strong in anti-jamming capability, good in adaptability, high in compensation accuracy and stable in compensation performance.
Owner:JIANGSU HANTONG SHIP HEAVY IND
Error calibration compensation method of accelerometers in MEMS-IMU under dynamic environment
ActiveCN103323625AAchieve compensationTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesAccelerometerSky
The invention discloses an error calibration compensation method of three axial accelerometers in an MEMS-IMU under the dynamic environment. The error calibration compensation method includes the steps of enabling an outer frame of a rotary table to operate in a speed mode, then enabling the Z axis to return to the zero position, enabling an inner frame of the rotary table to operate in a sine mode, changing installation of the IMU, respectively enabling the direction of a sensitive shaft of the X-axis accelerometer and the direction of a sensitive shaft of the Y-axis accelerometer to be parallel to the sky direction, enabling the accelerometers to sense the dynamic accelerated speeds and the dynamic angle speeds in the operating mode same as that of the Z-axis accelerometer, recording the output data of the three axial accelerometers, carrying out analysis and processing, and obtaining the installing errors, the calibration coefficients and the zero wanders of the three axial accelerometers in the MEMS-IMU and influence factors of the dynamic angle speeds on the accelerometers. The error calibration compensation method is simple and easy to implement, obviously improves the accuracy of an MEMS-IMU system, and is particularly suitable for systems with low-cost and low-accuracy MEMS accelerometers.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
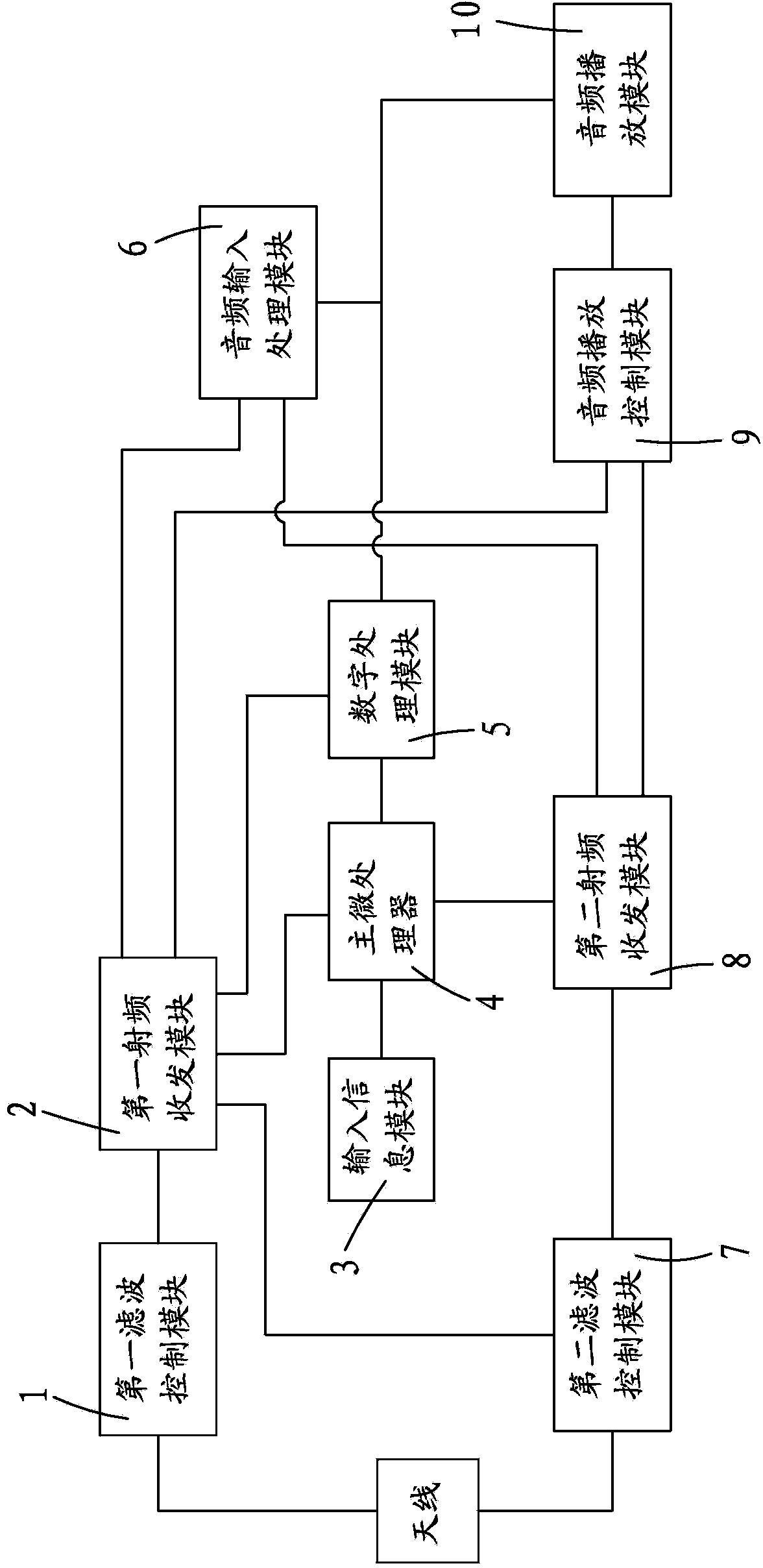
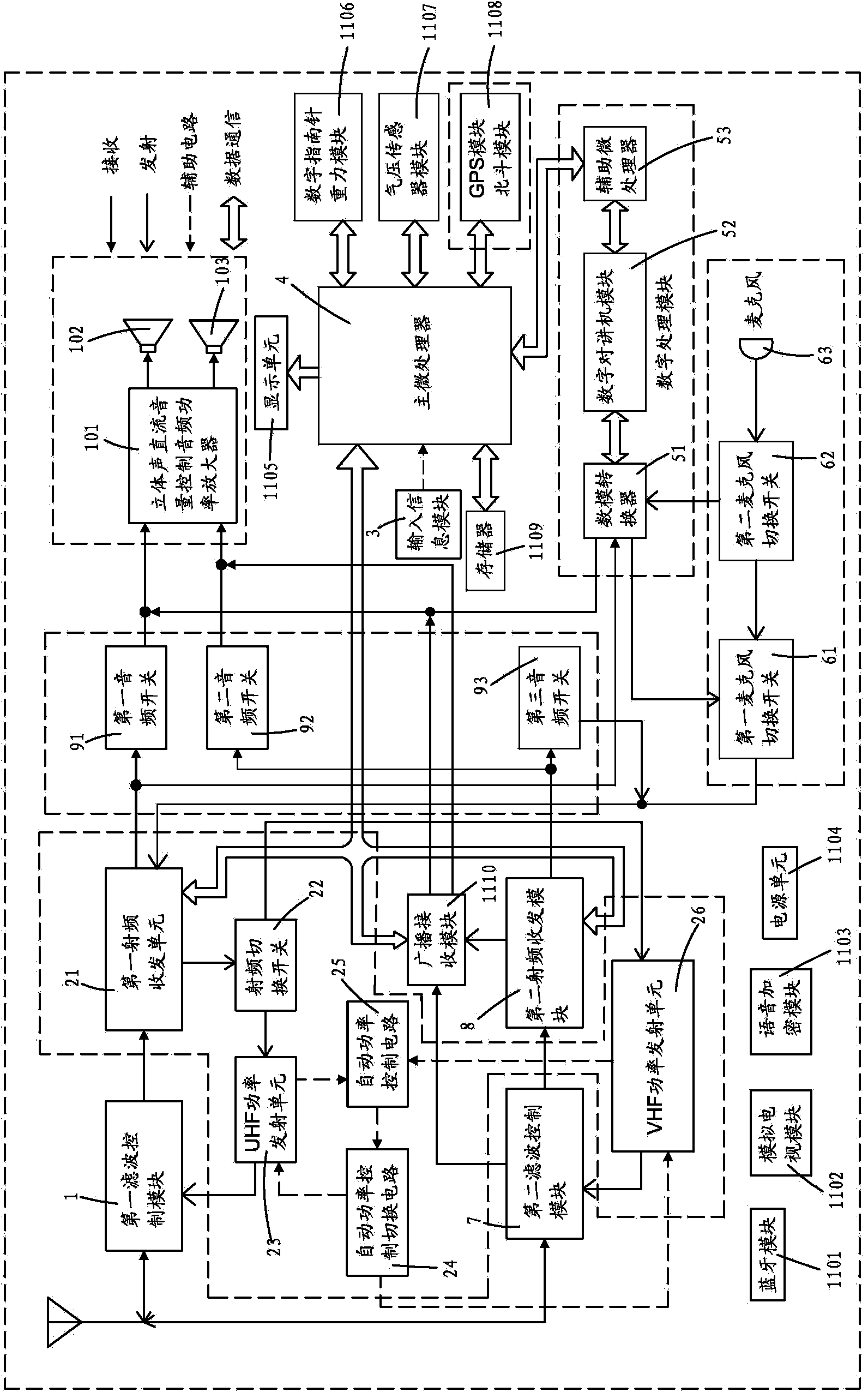
Multimedia interphone capable of receiving analog and digital signals in multiple frequency bands simultaneously
ActiveCN103595437AAchieve compensationAchieve protectionTransmissionStations for two-party-line systemsAnalog signalBroadcasting
The invention provides a multimedia interphone capable of receiving analog and digital signals in multiple frequency bands simultaneously. The interphone comprises a first filtering control module, a first radio frequency receiving and dispatching module, a second filtering control module, a second radio frequency receiving and dispatching module, an audio input processing module, an audio broadcasting control module, an audio broadcasting module, an input information module, a main microprocessor and a digital processing module. The interphone can simultaneously receive two different frequency points of two random frequency bands including a UHF band and a VHF band, a VHF band and UHF band, a UHF band and a UHF band, and a VHF band and a VHF band, and can receive the digital and analog signals at the same time.
Owner:QIXIANG ELECTRON SCI & TECH
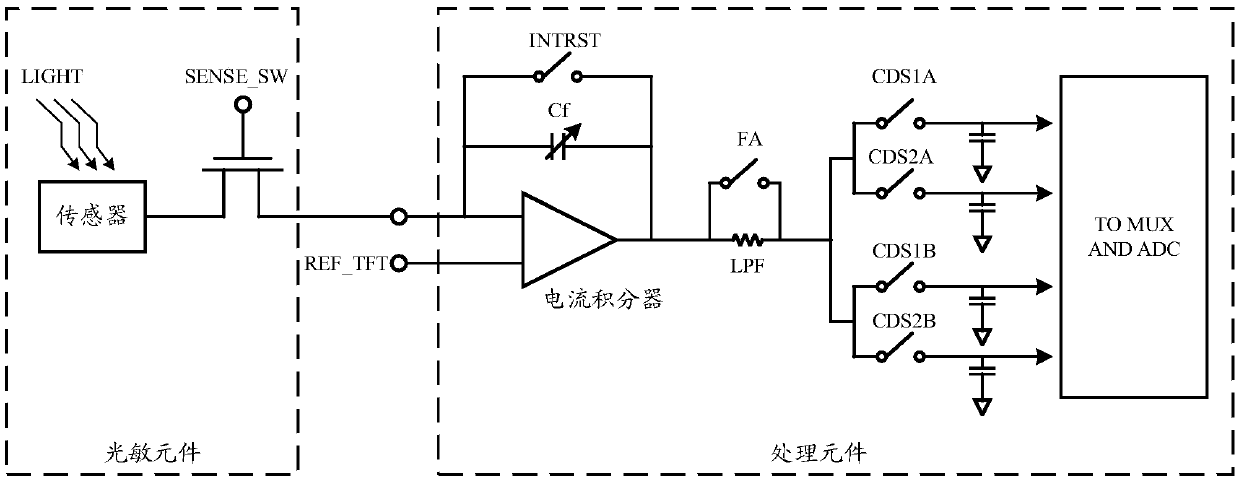
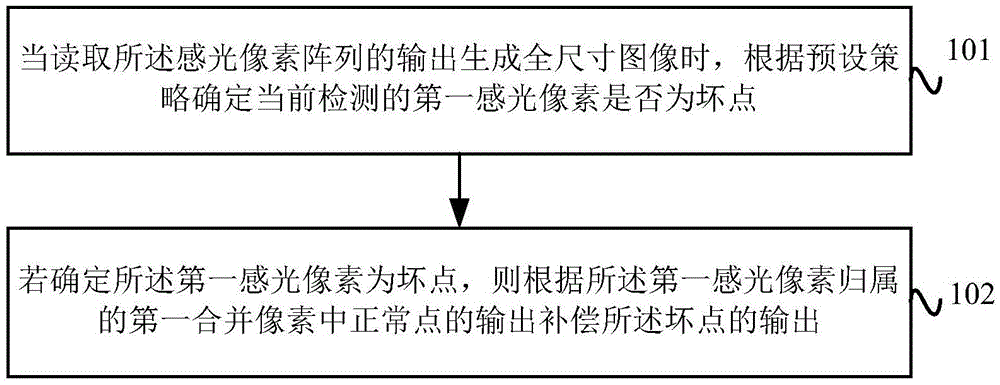
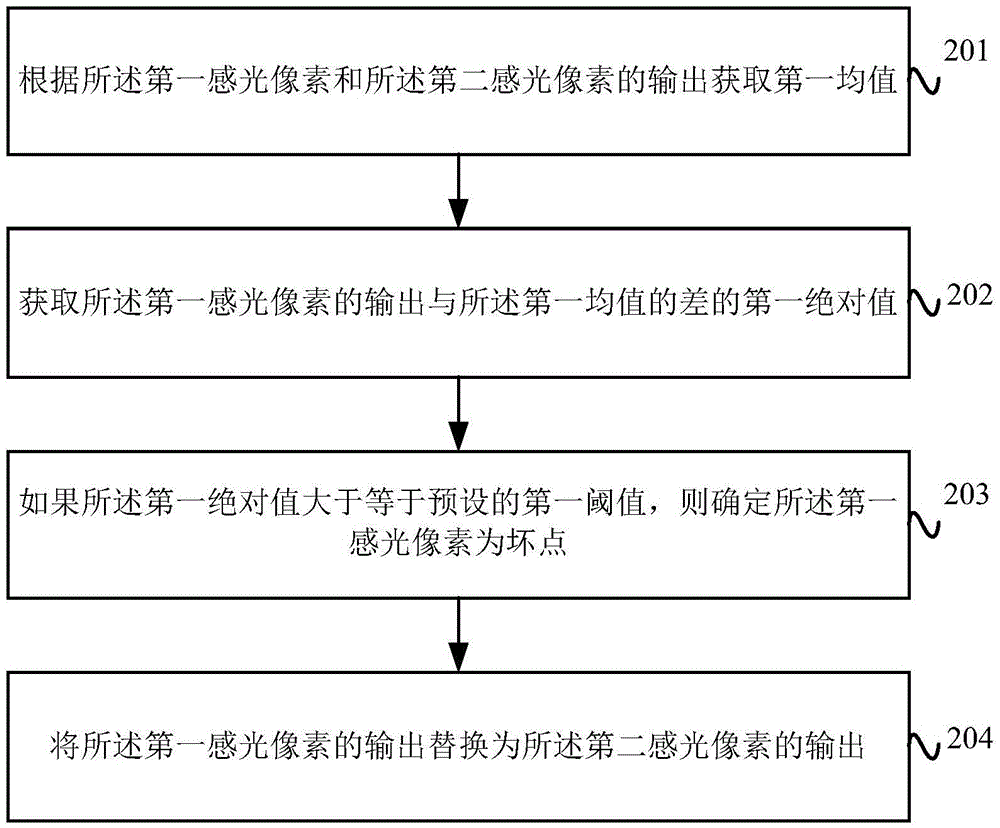
Image defective pixel compensation method and device and terminal device
ActiveCN105611196AImprove quality and clarityRealize detection and compensationTelevision system detailsColor television detailsPixel arrayDefective pixel
The invention provides an image defective pixel compensation method and device and a terminal device.A pre-provided image sensor comprises a photosensitive pixel array and an optical filter arranged on the photosensitive pixel array; the optical filter comprises a filter unit array; and each filter pixel covers m*n photosensitive pixels, thus forming a combined pixel, wherein the m*n is more than 1. The method comprises the following steps of when the output of the photosensitive pixel array is read to form a full size image, detecting whether a currently detected first photosensitive pixel is a defective pixel or not according to a preset strategy; and if it is determined that the first photosensitive pixel is the defective pixel, compensating the output of the defective pixel according to the outputs of the normal pixels in the first combined pixel to which the first photosensitive pixel belongs. The defective pixel on the image sensor can be detected and compensated; and the quality and the definition of the output image can be improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG OPPO MOBILE TELECOMM CORP LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com