Geosynchronous orbit synthetic aperture radar velocity spatial variability compensating method
A technology of synthetic aperture radar and geosynchronous orbit, applied in the direction of radio wave reflection/re-radiation, using re-radiation, measuring devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
[0180] In this example, the relevant parameters are as follows:
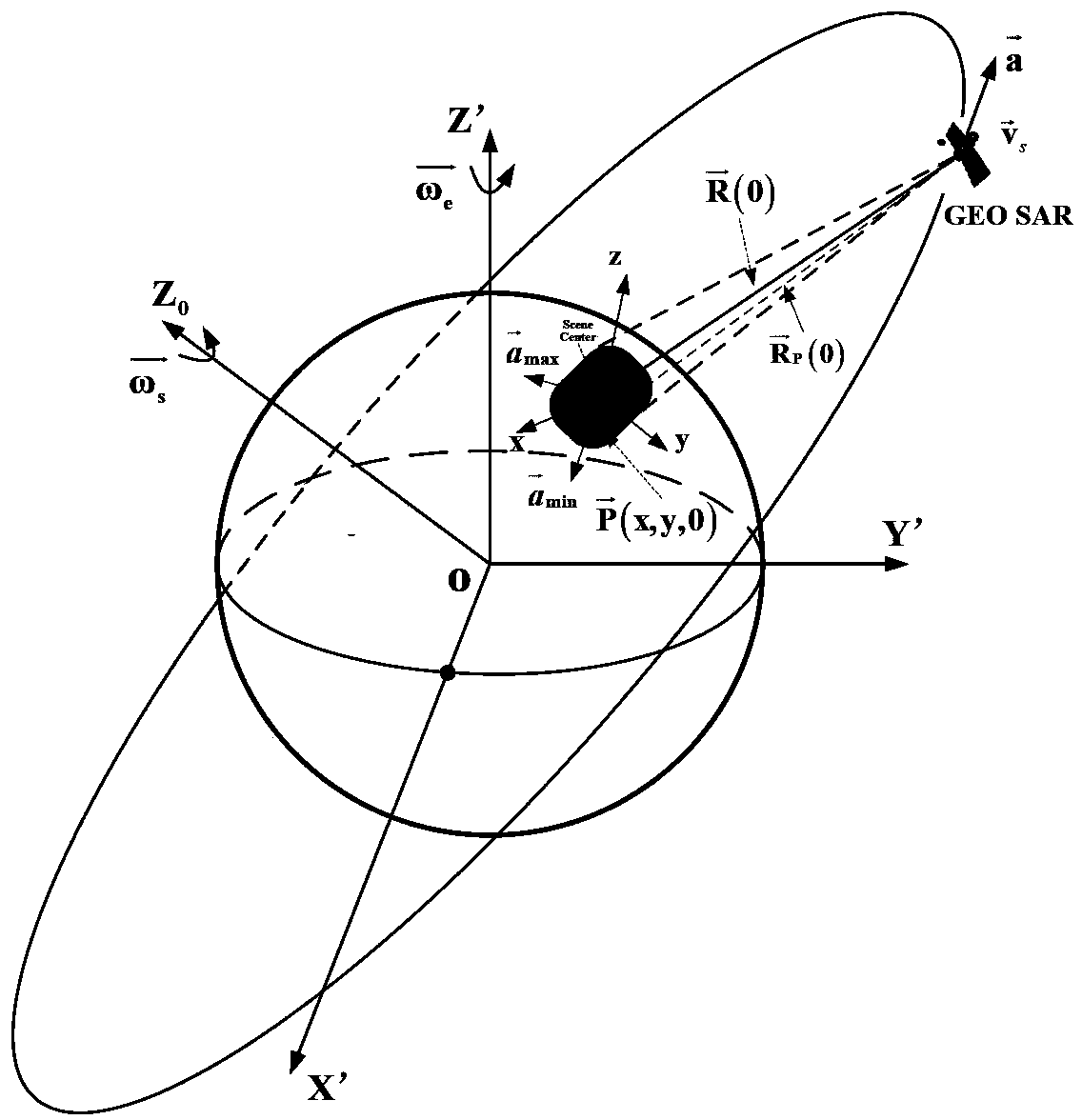
[0181] Orbital semi-major axis: 42164.17Km, orbital inclination: 53°, orbital eccentricity: 0.07, argument of perigee: 270°; right ascension of ascending node: 265°, antenna size: 30m, frequency band: L band (0.24m wavelength), Sampling rate: 18MHz, bandwidth 20MHz, pulse repetition frequency PRF: 200.
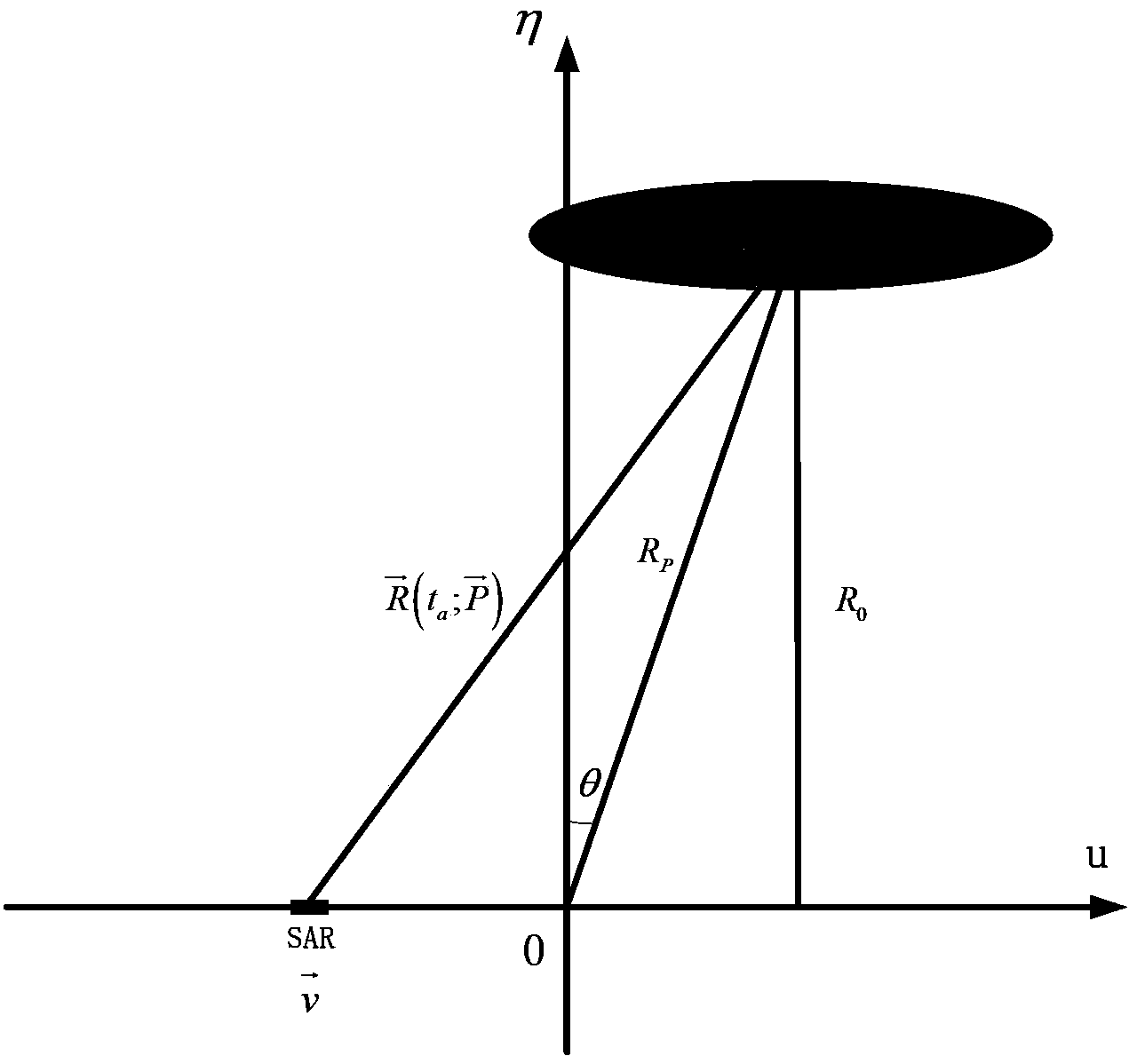
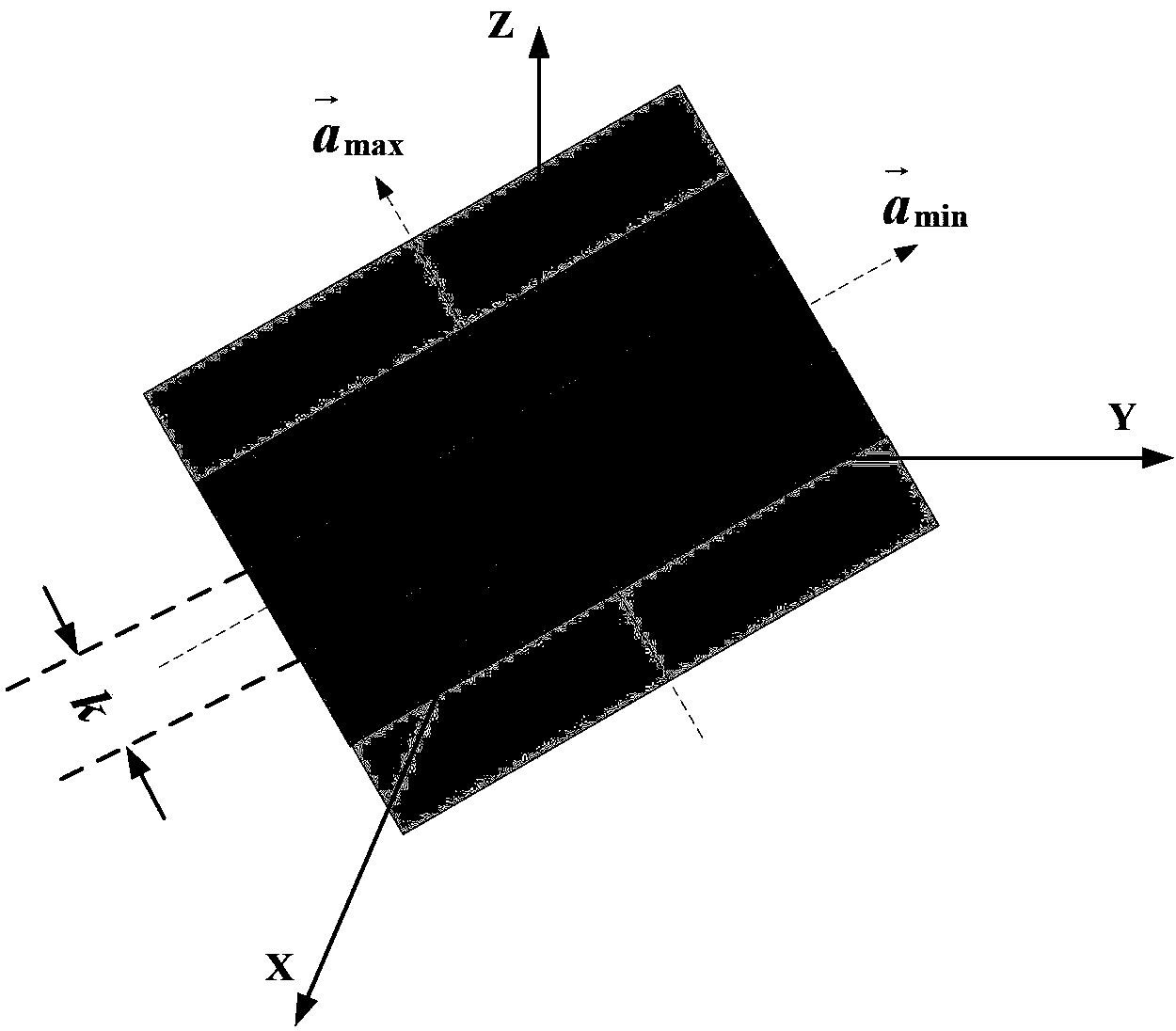
[0182] We substitute the relevant parameters into equations (36), (37) and (38) respectively to find k bound-RCM =1.34×10 14 Km,k bound-SRC =4.9×10 4 Km,k bound-a = 3.14Km. Therefore we choose k bound =k bound-a =3.14Km as the value of k, such as image 3 Shown is the division result of the final compensation area.
[0183] Figure 5 The imaging results of the lattice target of the traditional SRC algorithm and the improved SRC algorithm of the present invention are shown. It can be seen that the traditional SRC algorithm does not compensate for the spatial variability of the velocity, resulting in the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com