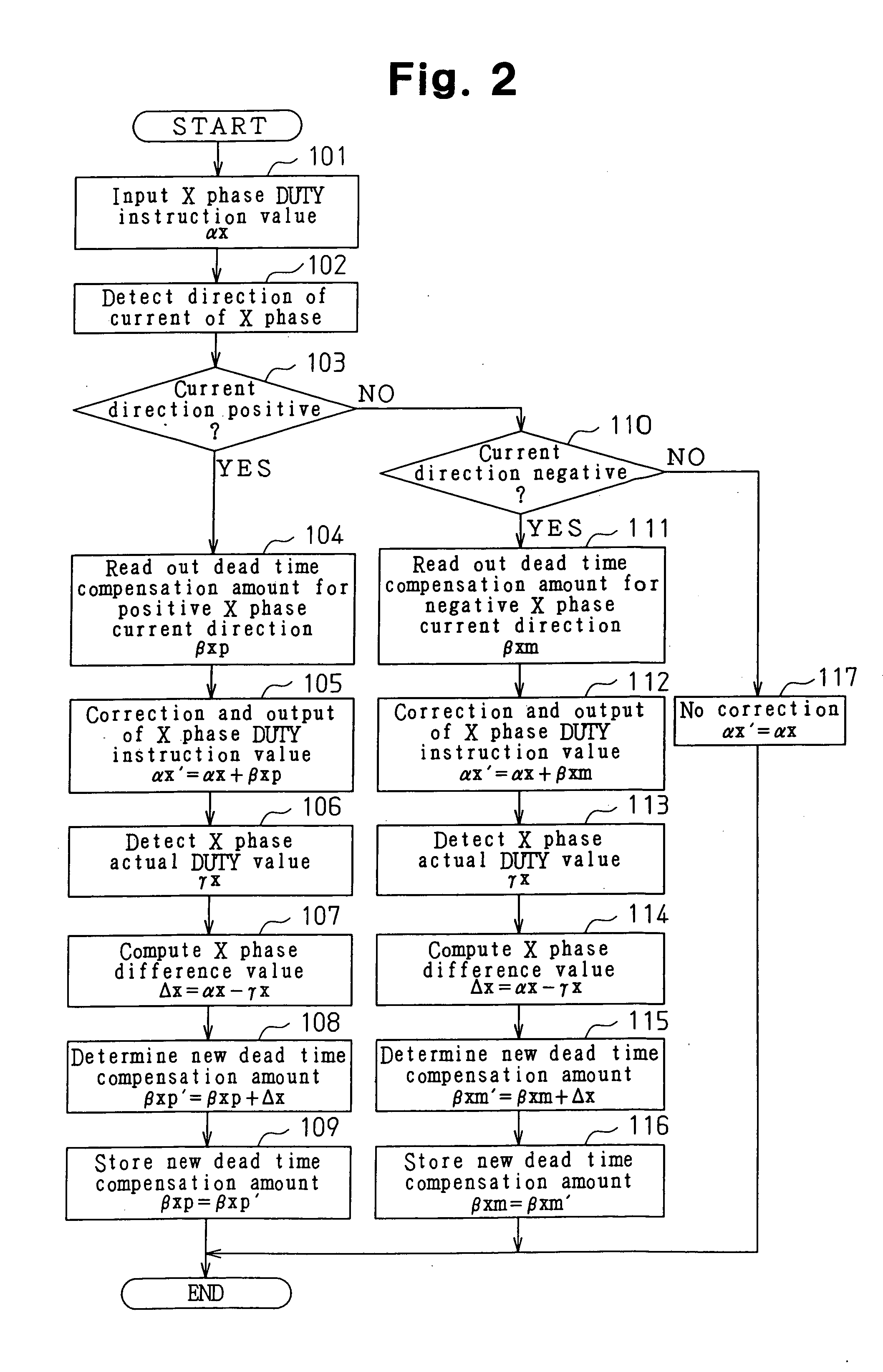
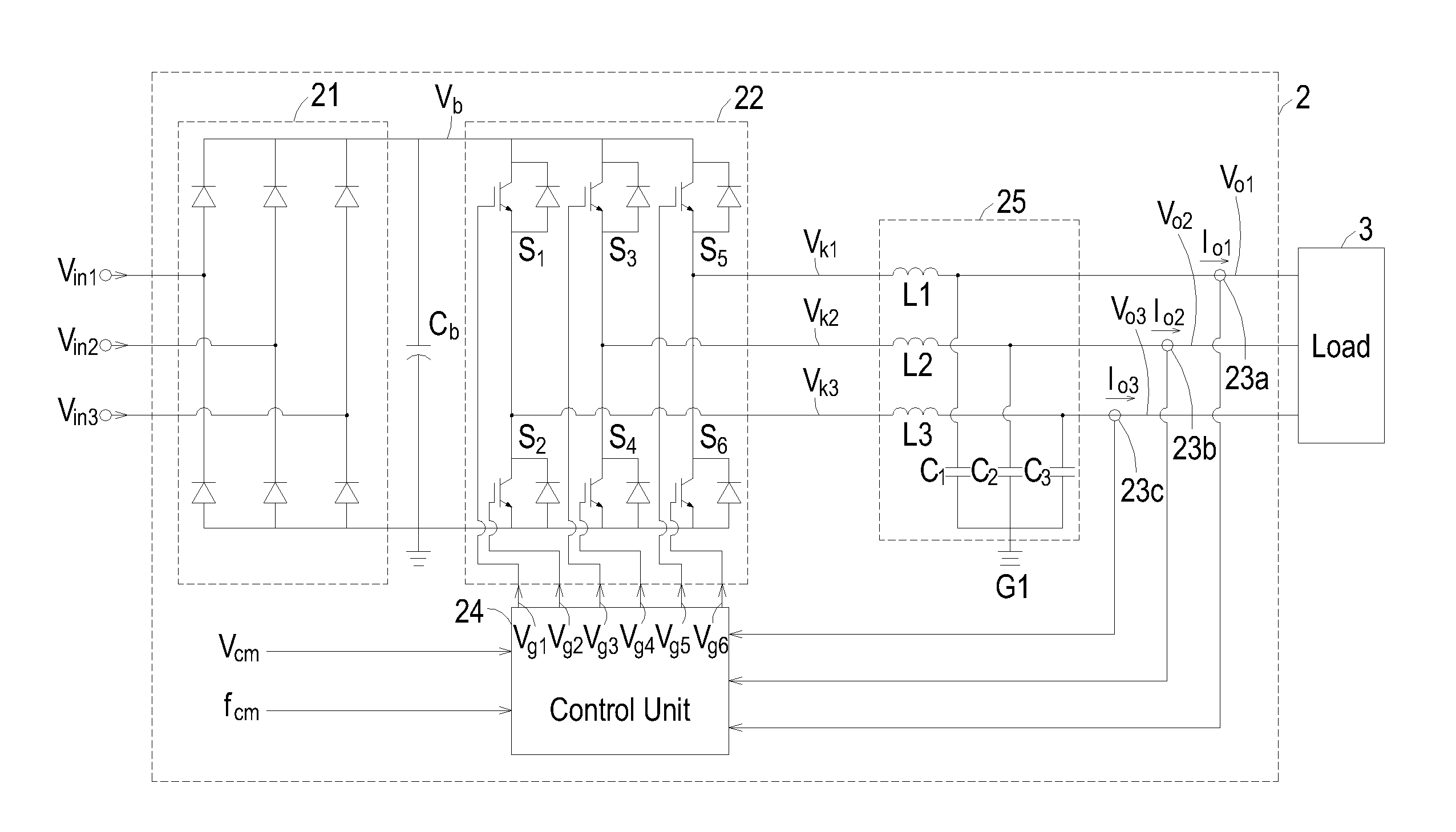
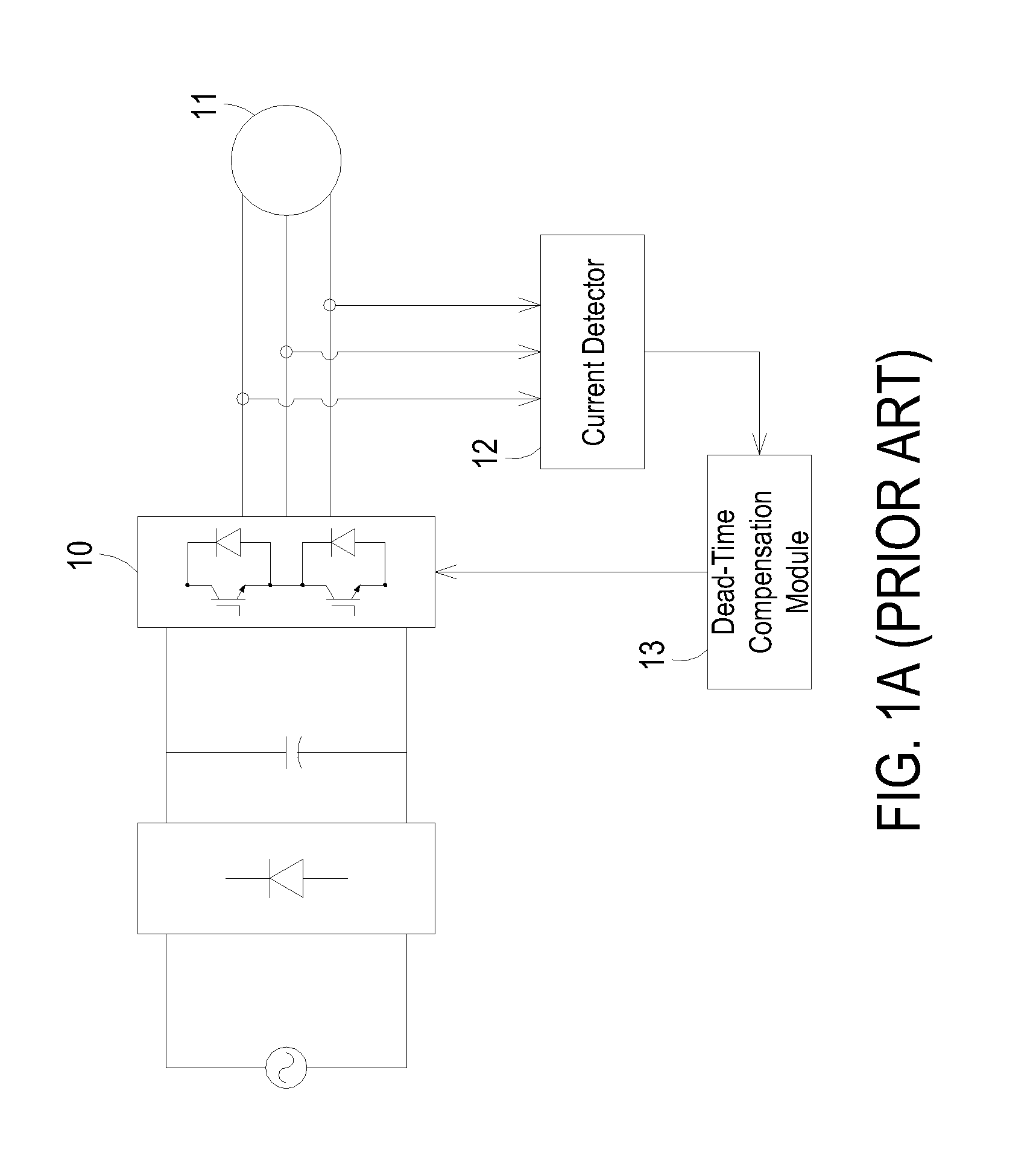
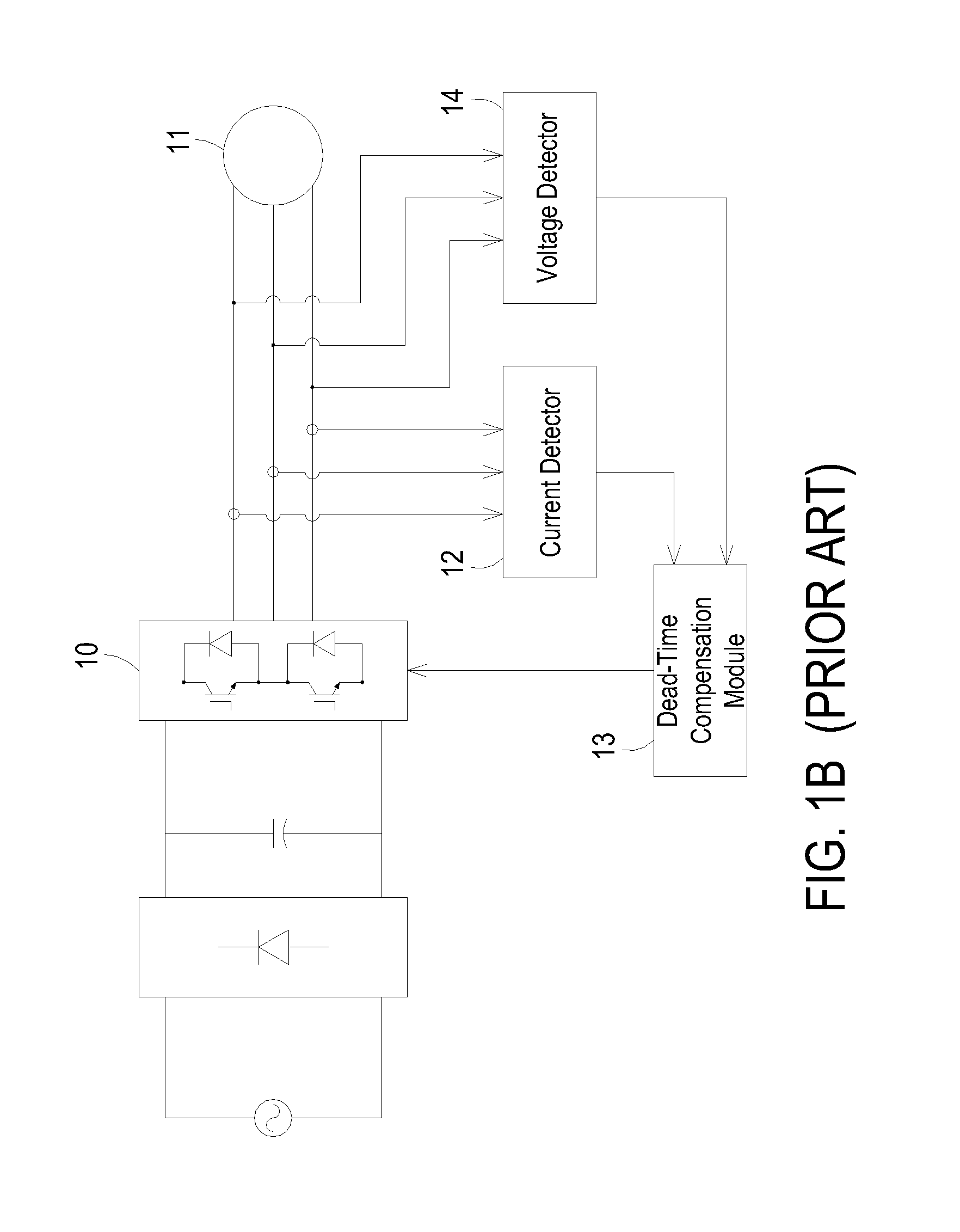
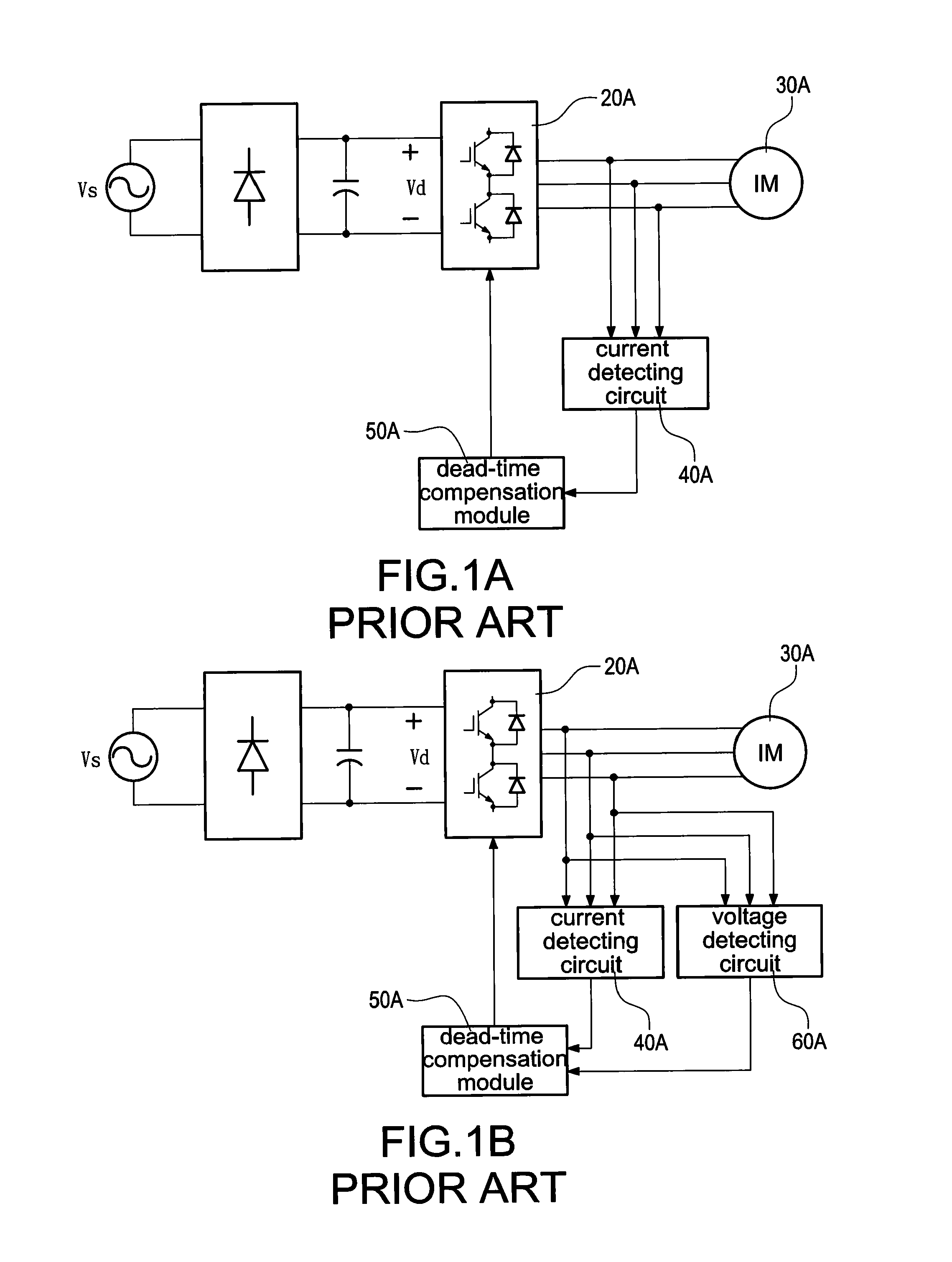
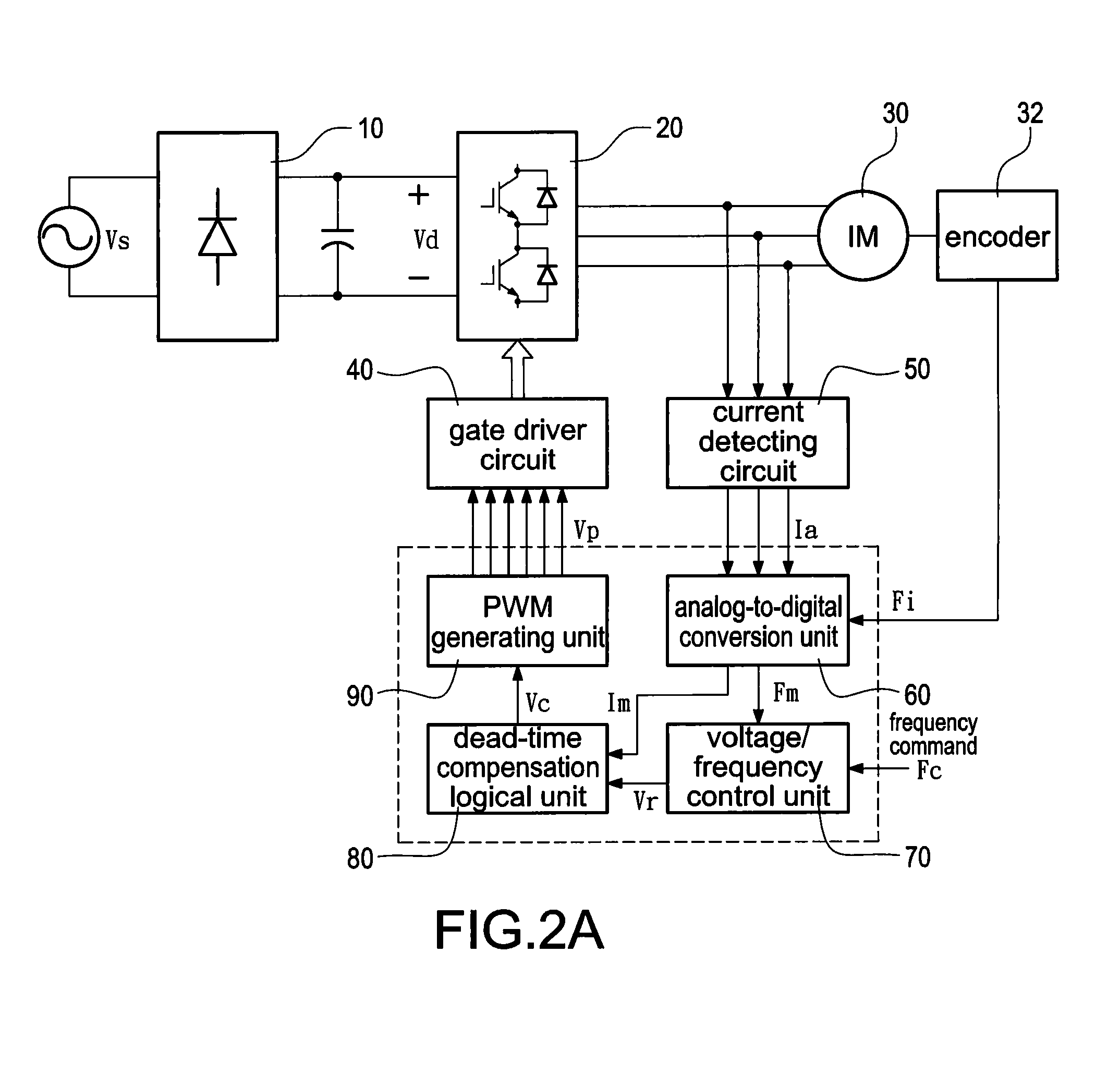
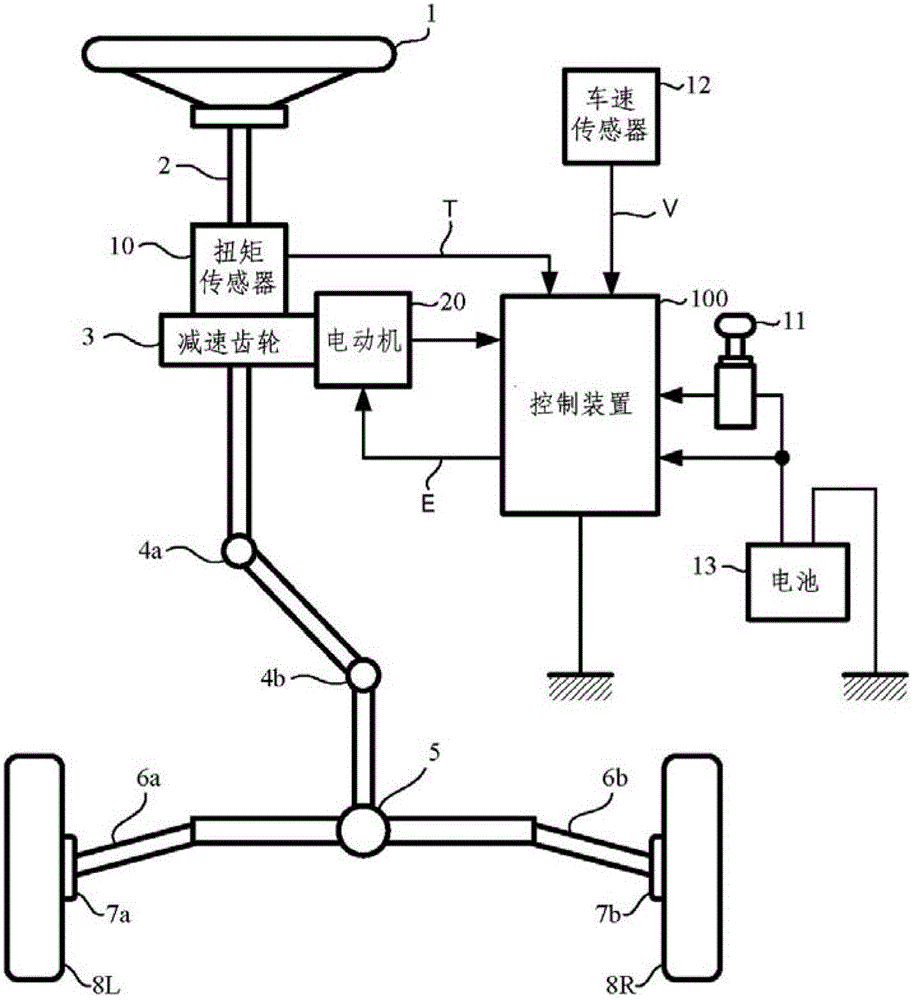
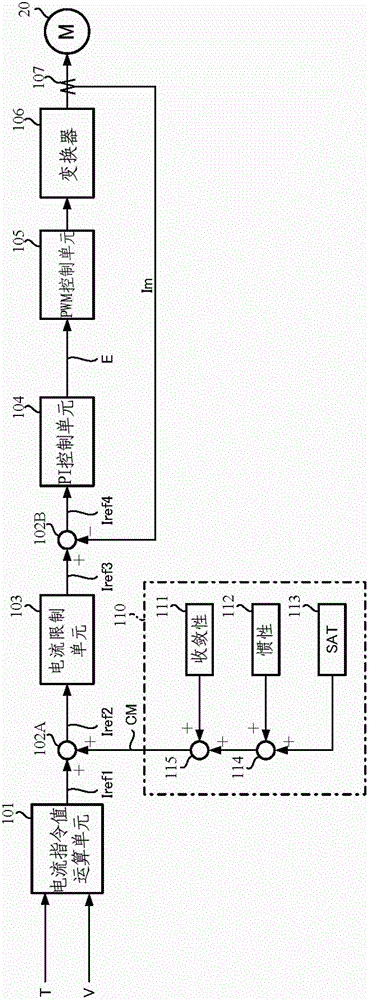
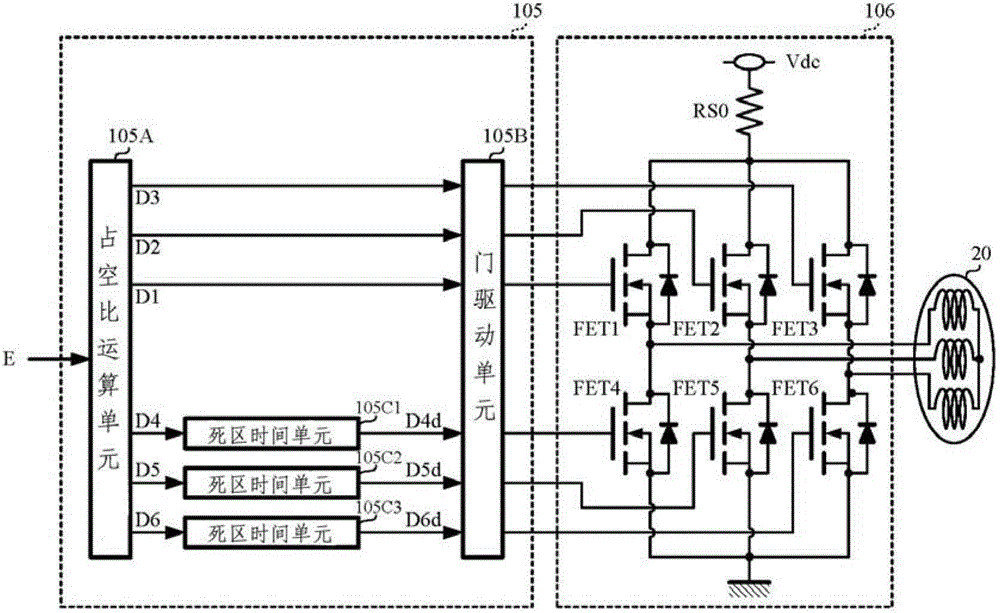
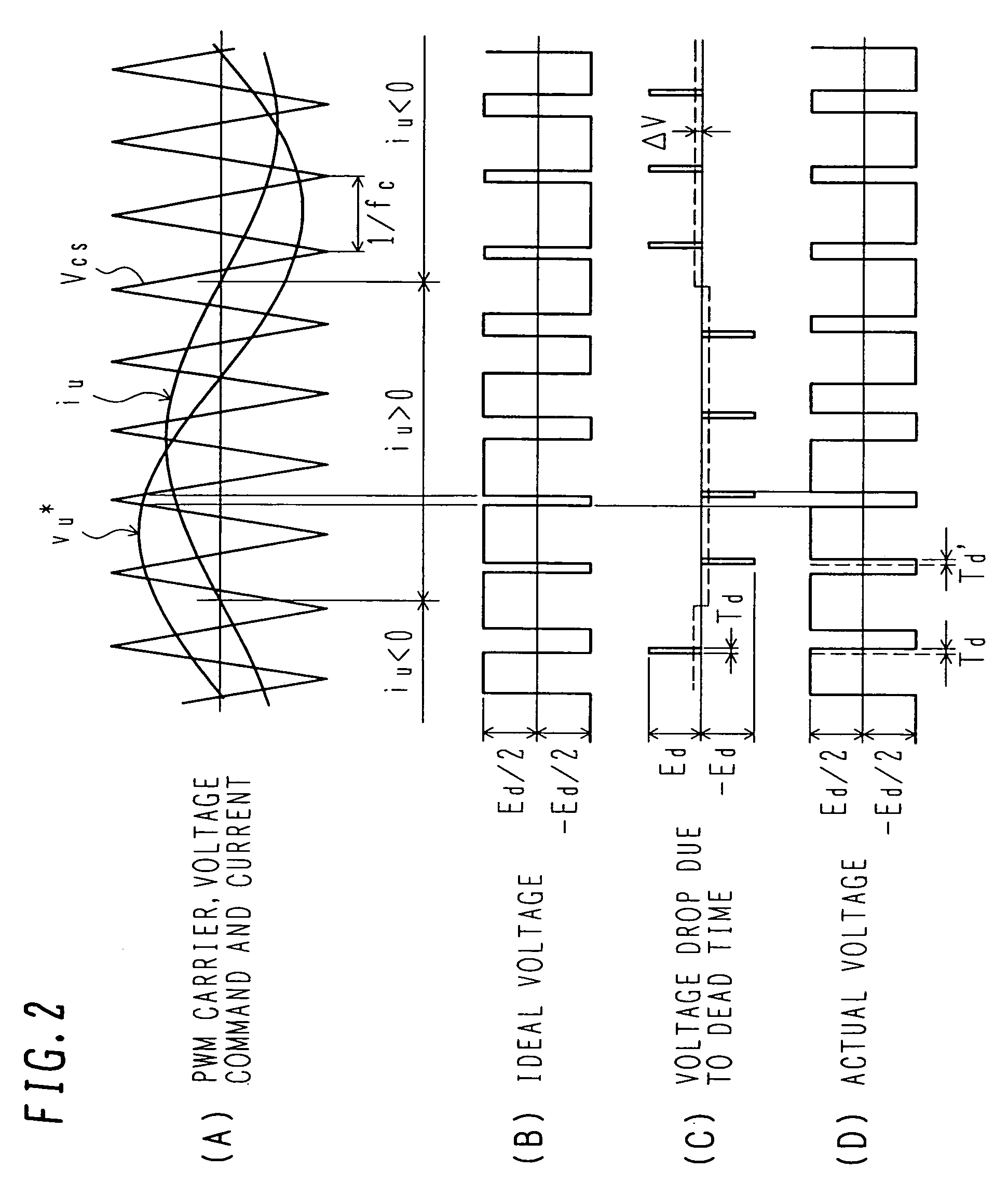
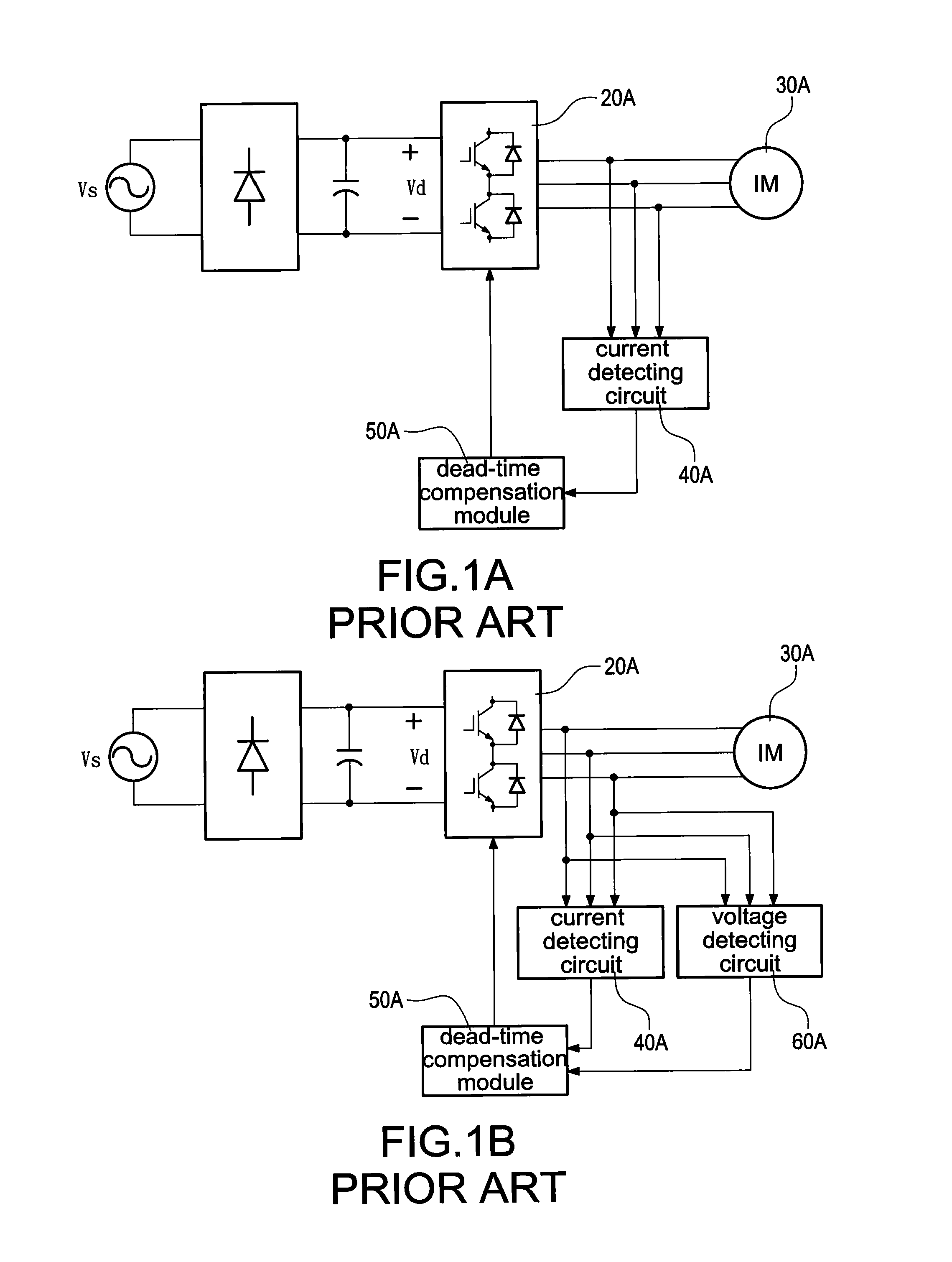
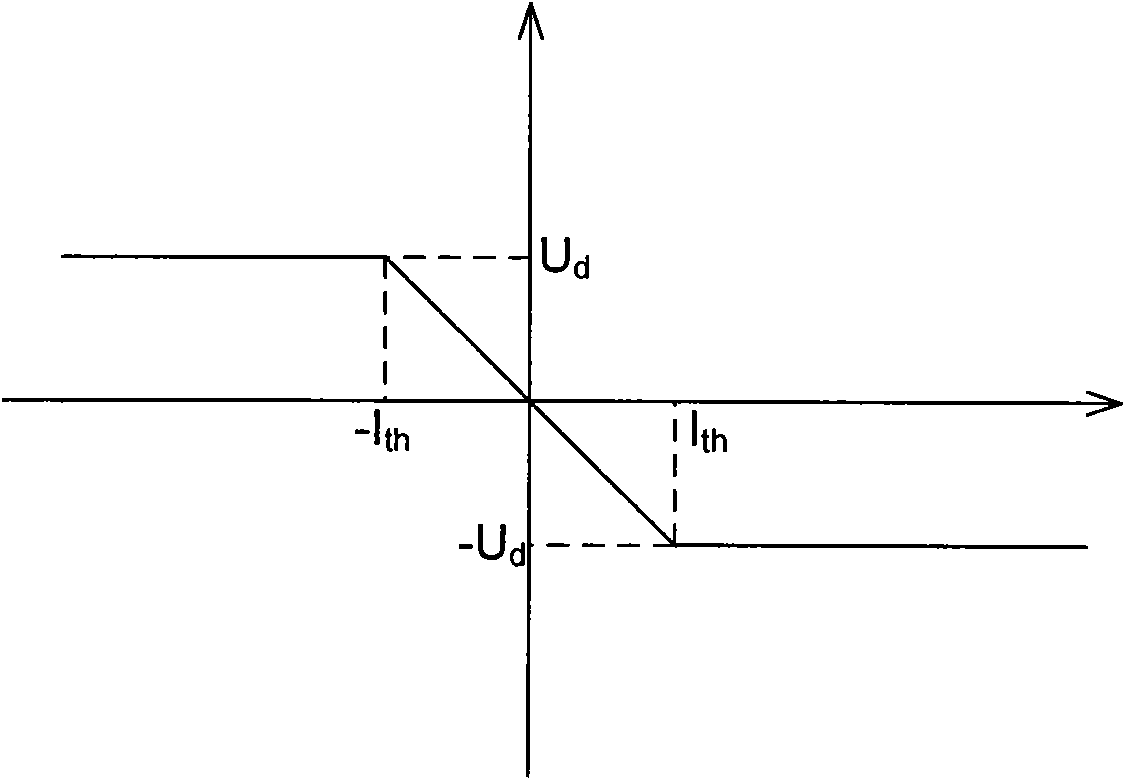
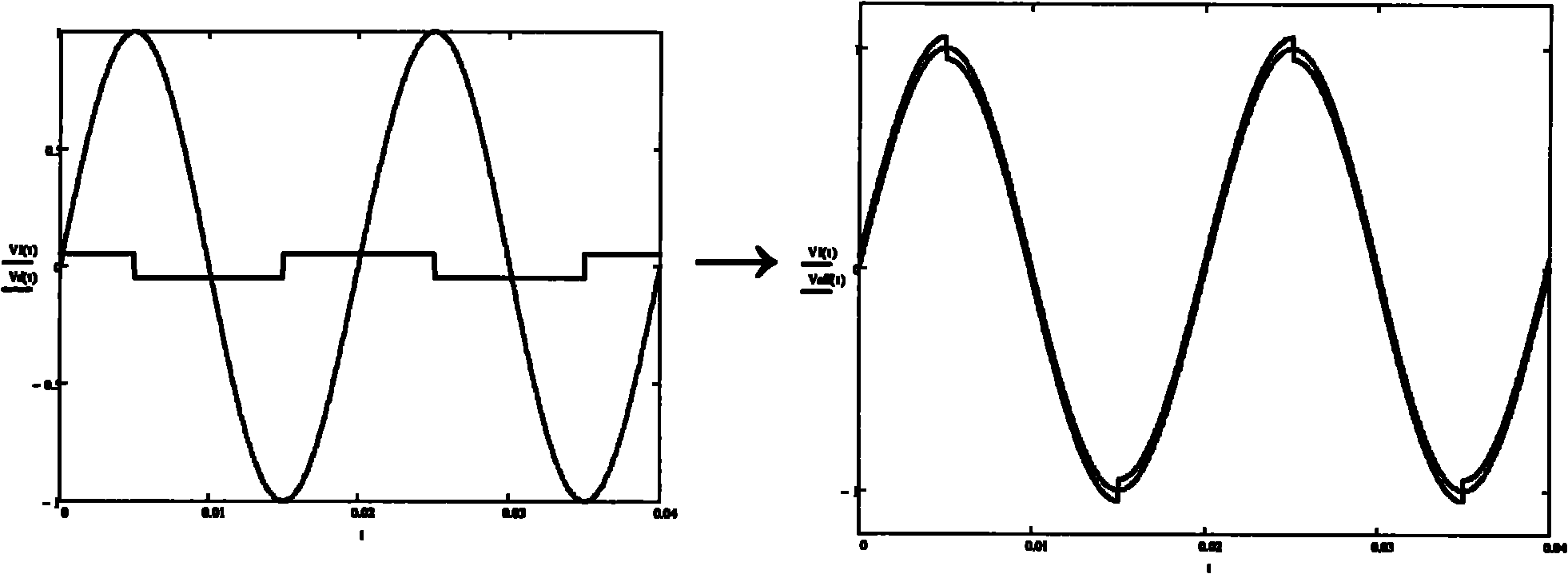
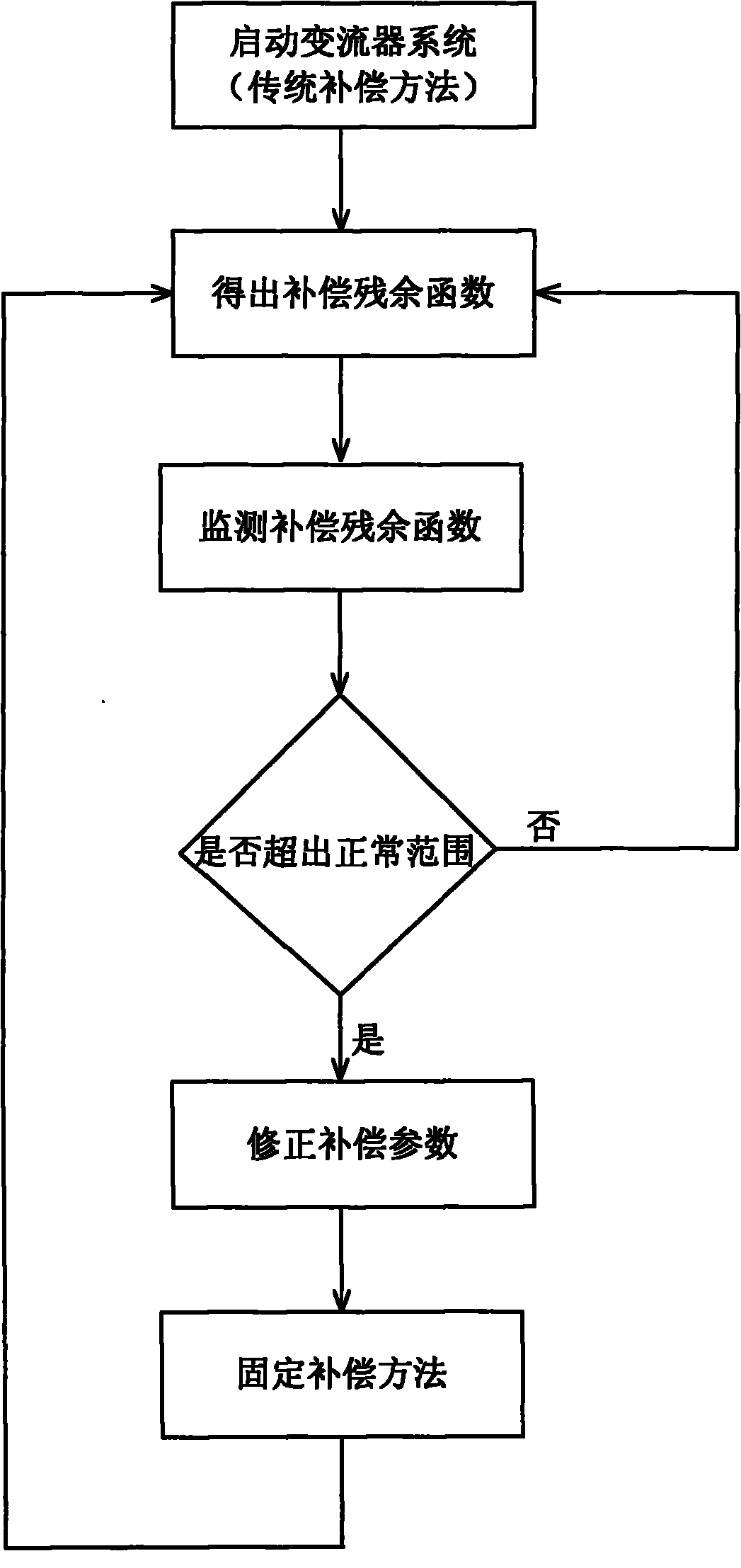
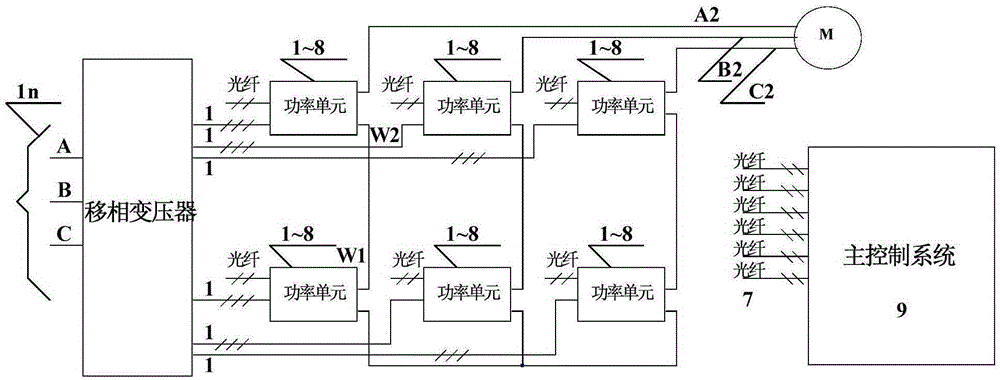
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Dead time compensation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
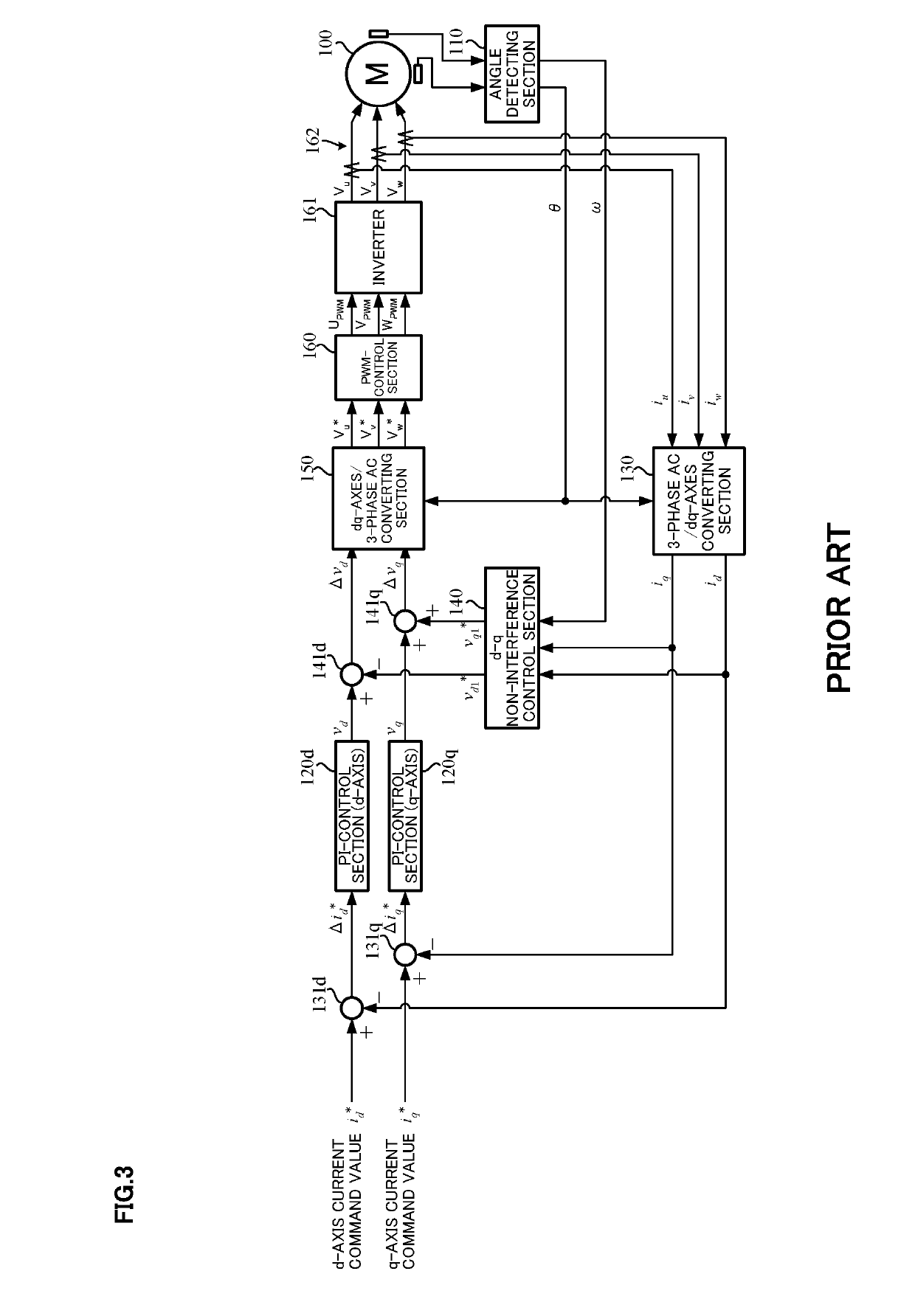
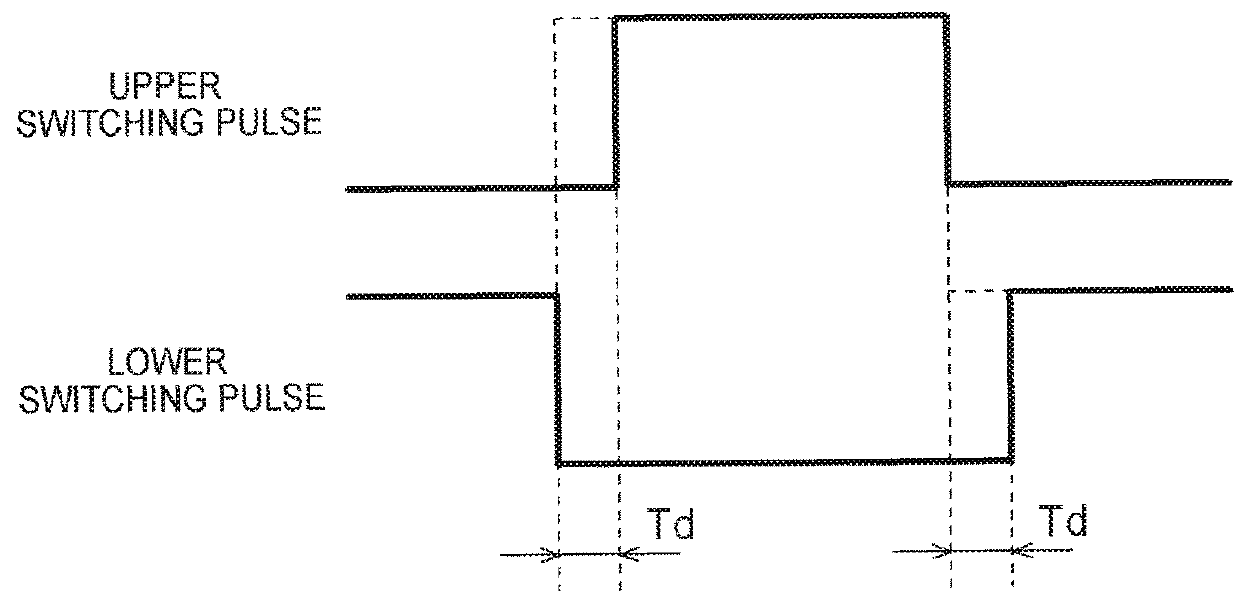
The dead time compensation can be adjusted on the Time Compensation tab of Axis1_ENC. It should theoretically be 3 cycles of the NC cycle time, although in practice 4 cycles are preferable.
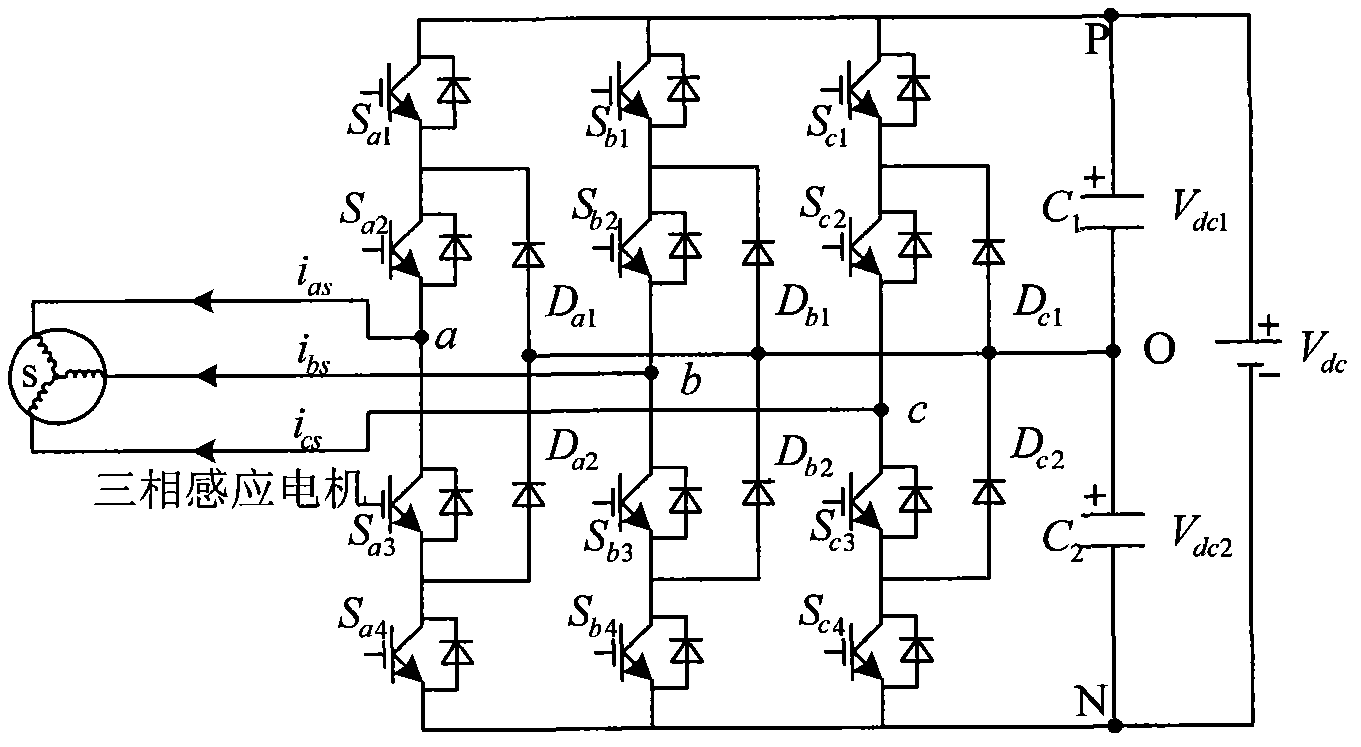
Three-level inverter dead time compensation control method
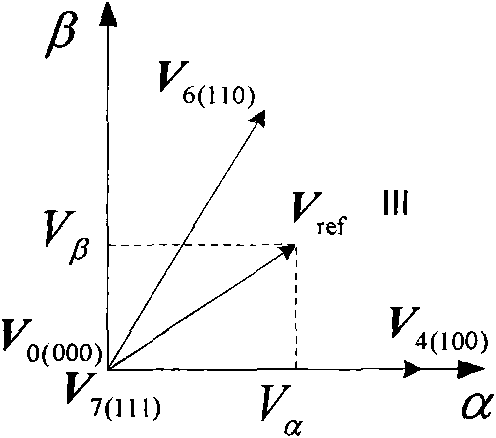
InactiveCN103236798AImproved output current waveformActual output line voltage risesAc-dc conversionThree levelVoltage vector
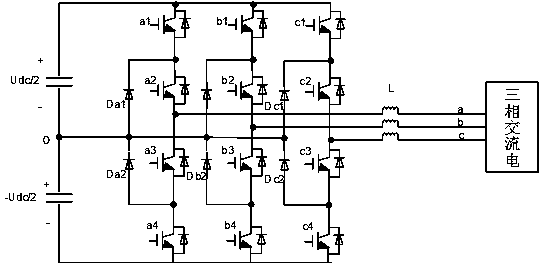
A three-level inverter dead time compensation control method is used for compensating the decrease of system performance caused by dead time. According to the topological structure of a three-phase three-level PWM (pulse width modulation) inverter, the method first sets corresponding dead time and determines the on-off delays of power elements in the inverter; the method then considers the tube voltage drops of the power transistors of the inverter and the tube voltage drops of clamping diodes of the inverter and calculates the common voltage expression of the output neutral point of the inverter; afterwards, according to the sector with three-phase current value and a reference voltage vector, the method determines the relational coefficient between voltage error caused by the tube voltage drops of the power transistors, the tube voltage drops of the clamping diodes and the on-off delays of the power transistors and current, and thereby the total dead time compensation time of each phase of the three-level PWM inverter is worked out. The method takes the dead time, the on-off delays of the power elements and the tube voltage drops into full consideration, solves the problem of voltage and current distortion caused by the dead time effect in the three-level inverter, and enhances system performance.
Owner:NORTH CHINA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Dead-zone compensation method for voltage source inverter
InactiveCN101917158AZero Current Clamp Effect SuppressionClamp effect suppressionElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlVoltage vectorDead time
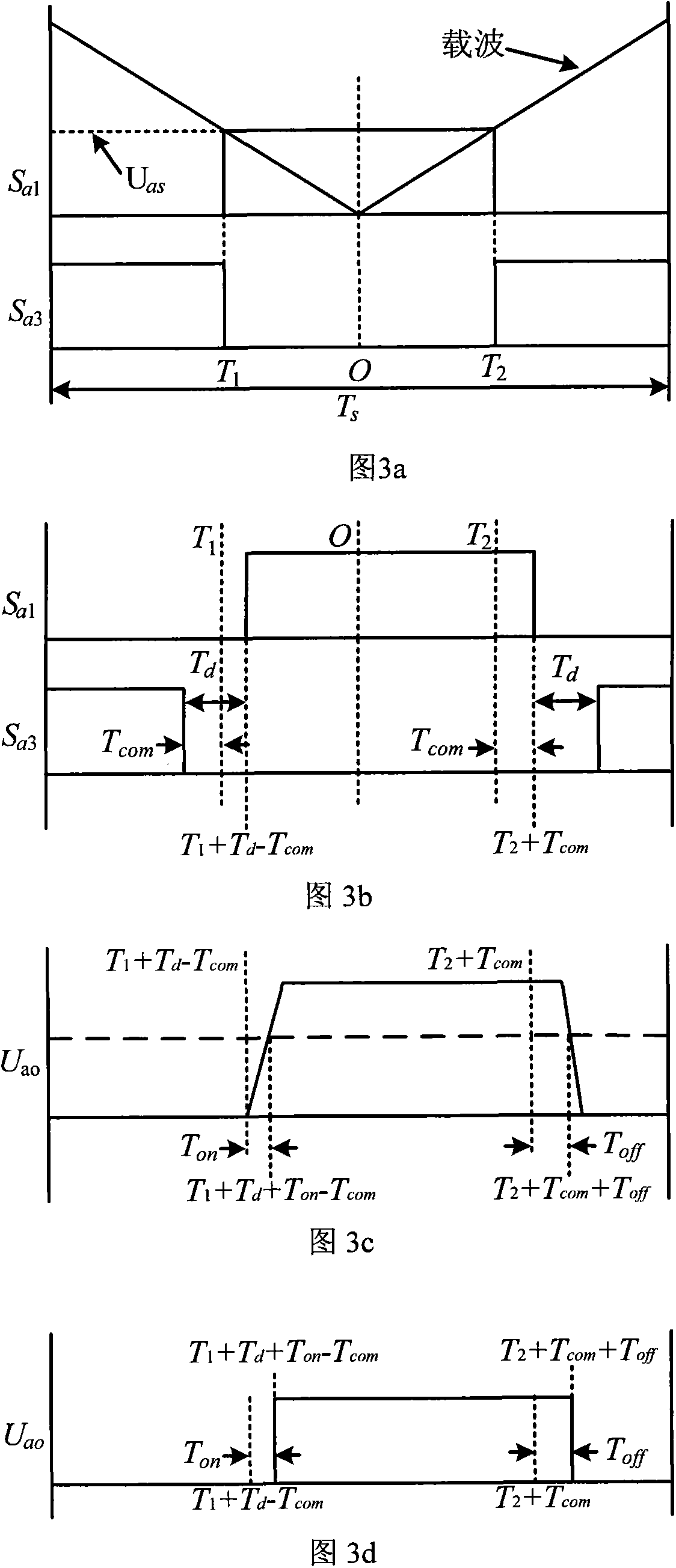
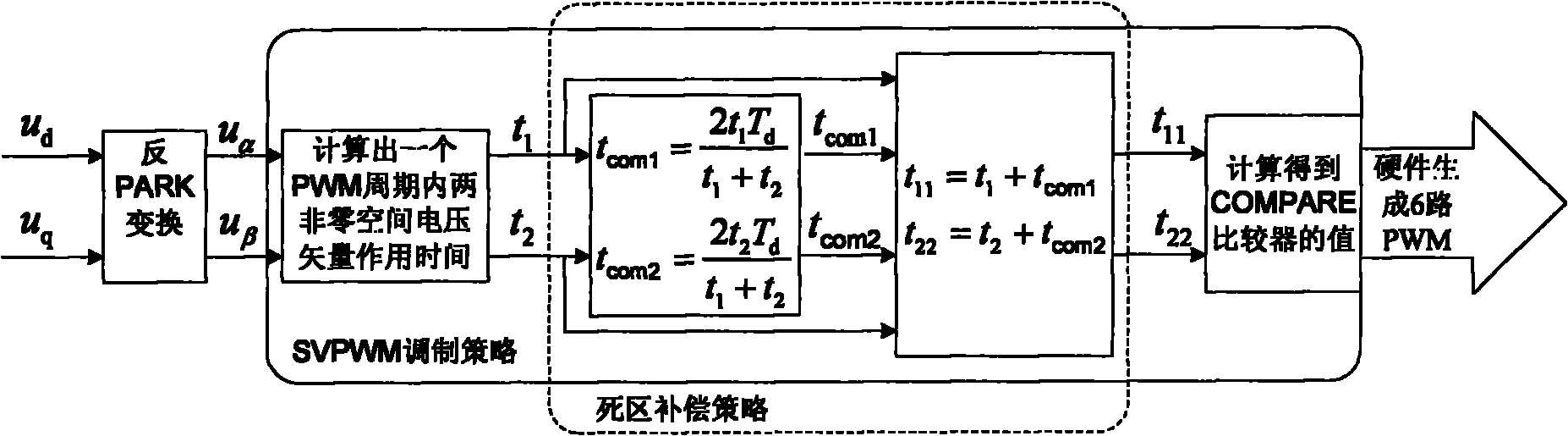
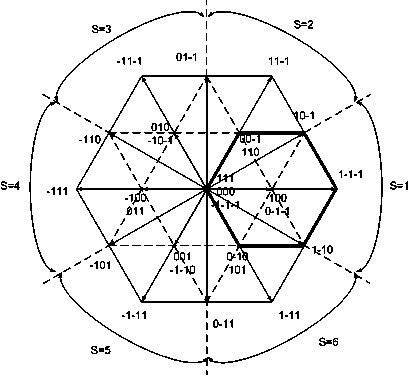
The invention relates to a dead-zone compensation method for a voltage source inverter. The method comprises the following steps of: performing dead-time compensation according to the acting time t1 and t2 of two non-zero base voltage vectors in a pulse-width modulation (PWM) period Ts and the practical dead time Td of the voltage source inverter based on the conventional space vector pulse width modulation (SVPWM) modulation strategy; adding two dead-time compensation time tcom1 and tcom2 and the acting time t1 and t2 of the two non-zero base voltage vectors to obtain new acting time t11 and t22 of the two non-zero base voltage vectors in the PWM period; and operating the new acting time t11 and t22 of the two non-zero base voltage vectors by using the SVPWM modulation strategy to generate a needed PWM pulse and finally realize deal-time compensation and zero-current clamping effect inhibition.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRICAL ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
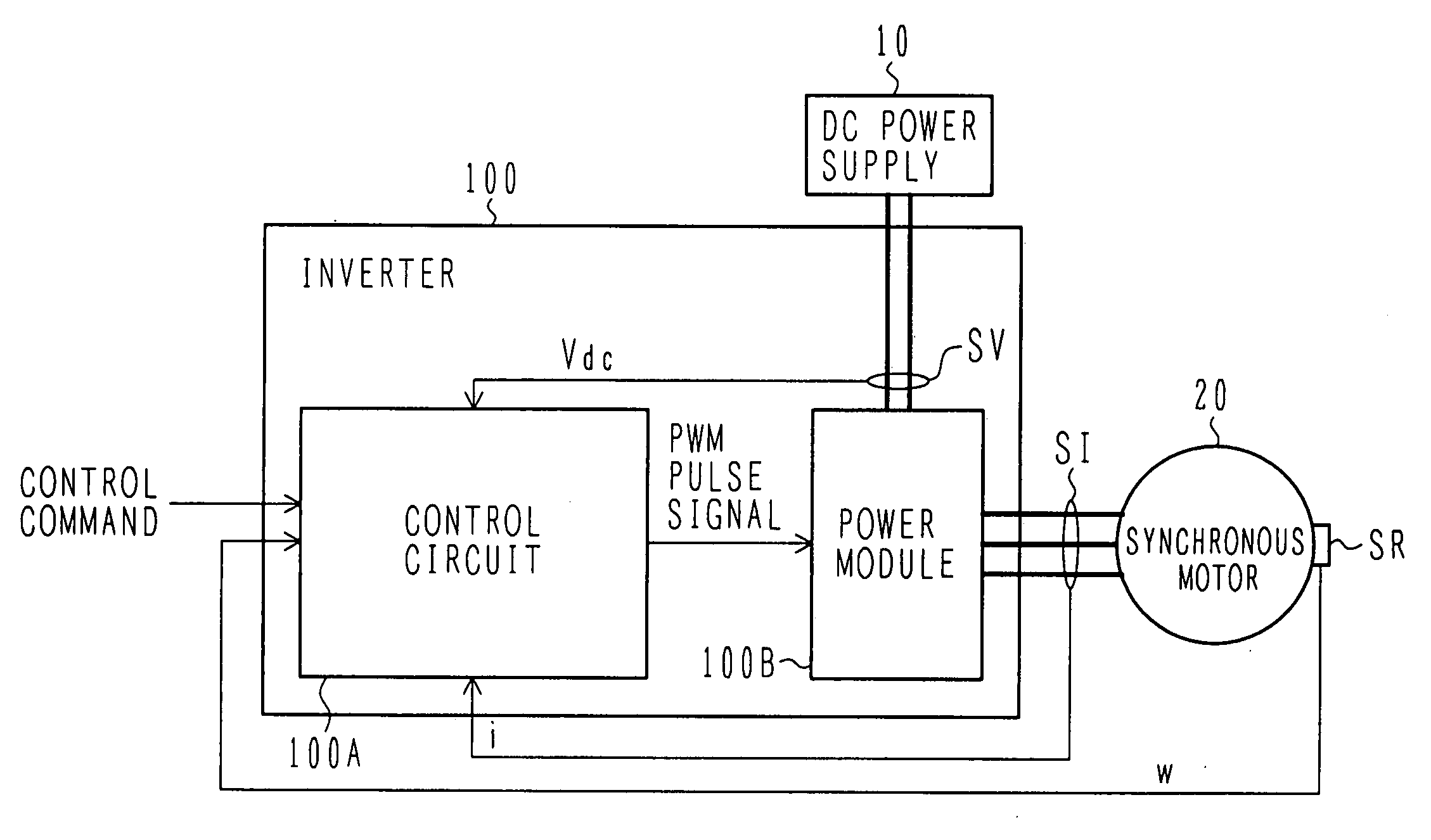
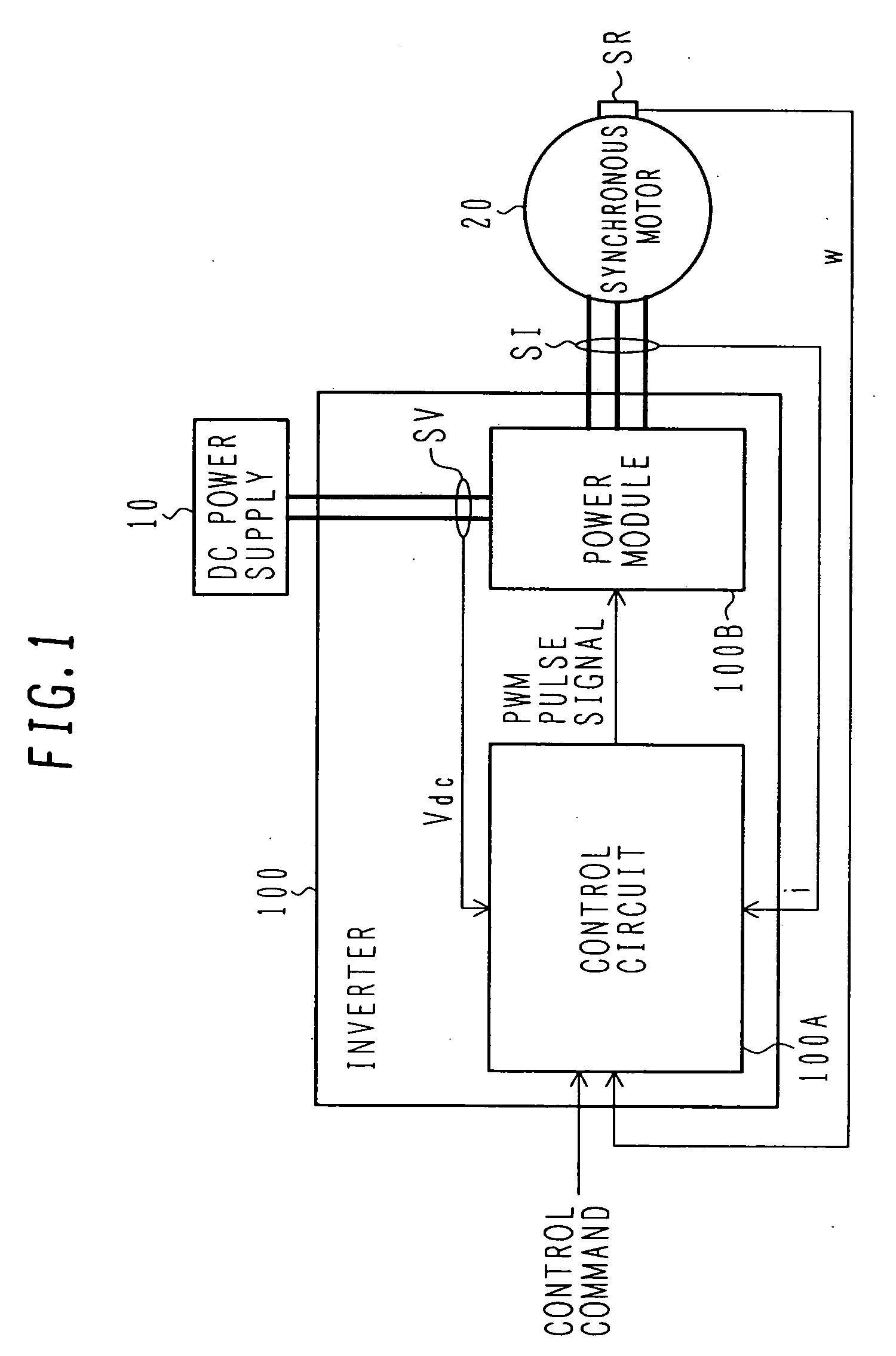
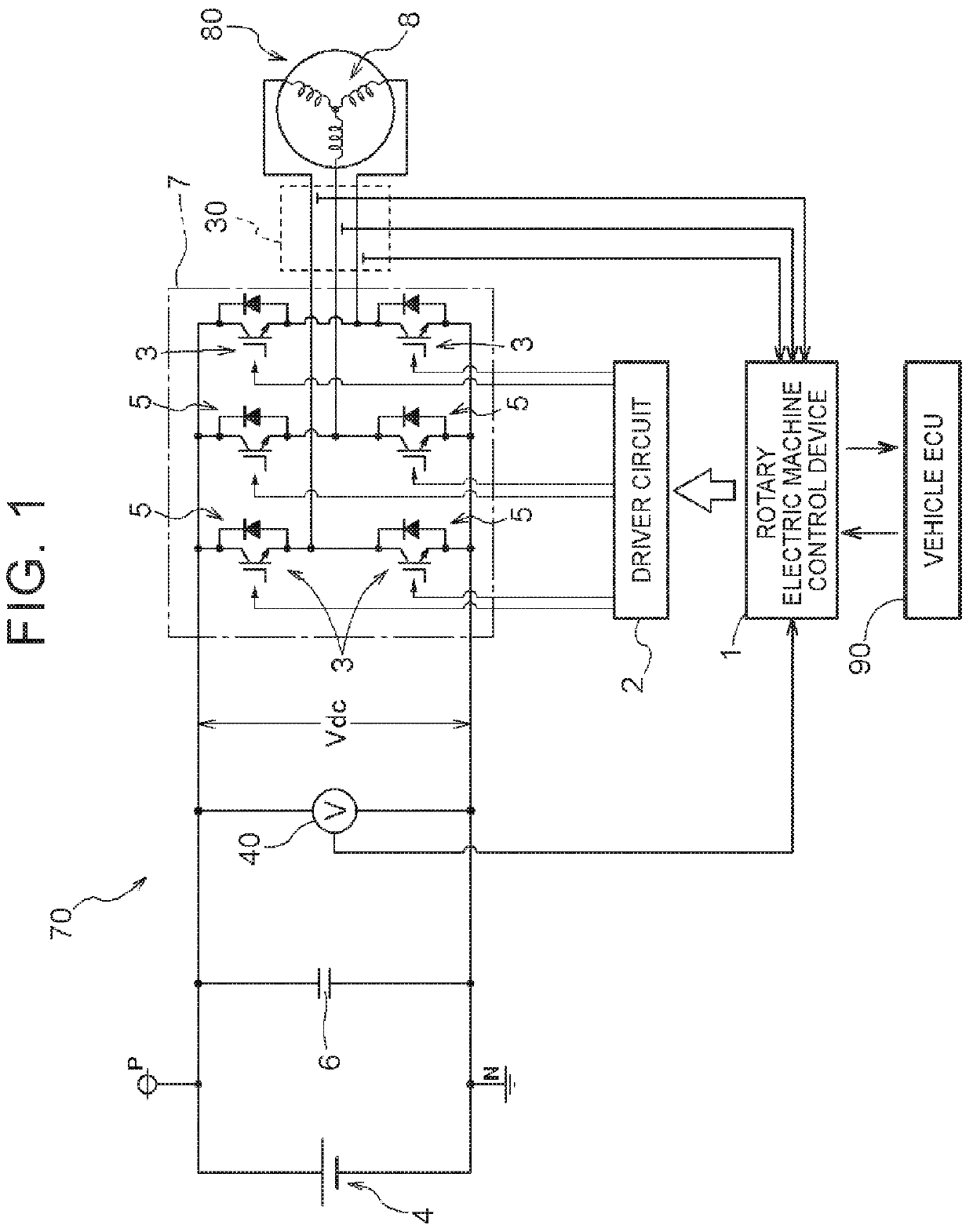
Electric power converter and motor driving system
InactiveUS20070176575A1Improve accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersEngineeringSwitching frequency
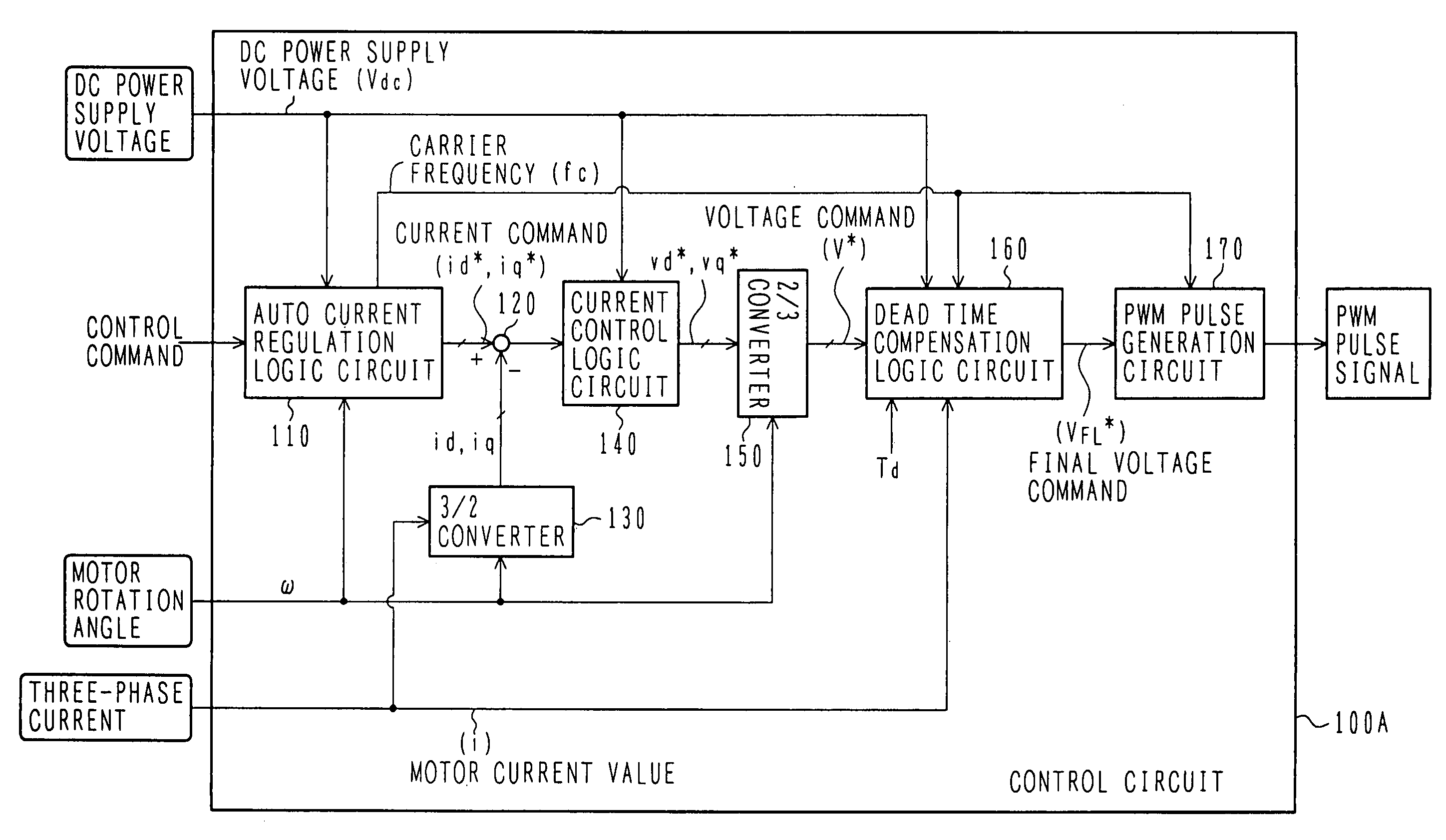
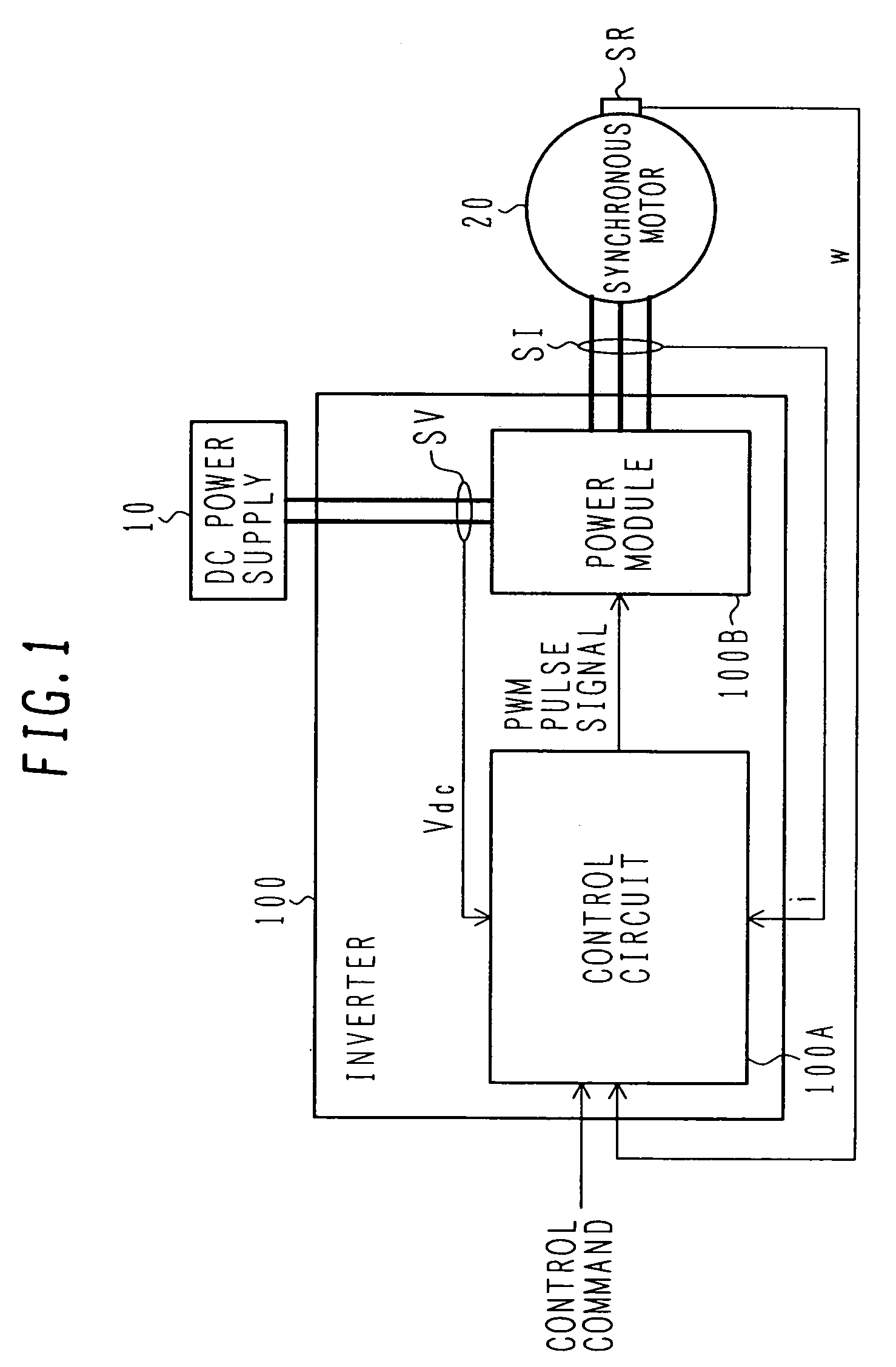
An electric power converter which has improved accuracy in compensation of a dead time. A motor driving system employing the electric power converter is also provided. A power module includes a plurality of switching devices connected in series and converts DC power to AC power. A control circuit produces a voltage command value in accordance with a control command inputted from the exterior, and produces gate signals to drive the switching devices of the power module corresponding to a final voltage command value which is obtained from the voltage command value with dead time compensation. A dead time compensation logic circuit calculates a final dead time compensation voltage based on a change rate of the voltage command value, a gain (dead time compensation voltage value), and a polarity of a current, the gain being calculated from a DC voltage value supplied to the electric power converter, a dead time, and a switching frequency.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
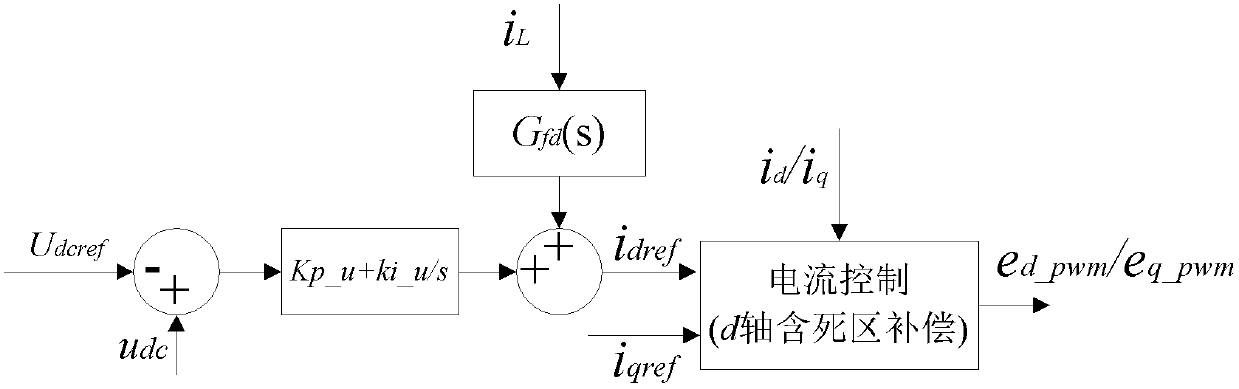
Improved method for controlling direct current (DC) bus voltage of two-stage converter
ActiveCN102710165AMinimizes impact on dynamic performanceFast outputAc-dc conversionMicrogridVoltage vector
The invention belongs to the technical field of control of converters in distributed generation and energy supply microgrid systems and relates to an improved method for controlling direct current (DC) bus voltage of a two-stage converter. The method has the following beneficial effects: on the basis of two-closed-loop control of the conventional DC bus voltage outer loop and the inverter output current inner loop, two auxiliary control methods, namely inverter dead-time compensation and dynamic power feedforward, are added, wherein the impacts of the error voltage vector caused by the dead-time effect on the dynamic performances of the current inner ring can be effectively eliminated through the inverter dead-time compensation; and the dynamic power feedforward is a first derivative element and can ensure the current reference of the current inner loop to track power output of the preceding DC / DC module in real time; and by adopting the two auxiliary control methods, DC bus voltage surge and fluctuation in the transient state of the two-stage converter can be effectively suppressed and the dynamic responses of the two-stage converter can be improved.
Owner:苏州钧灏电力有限公司
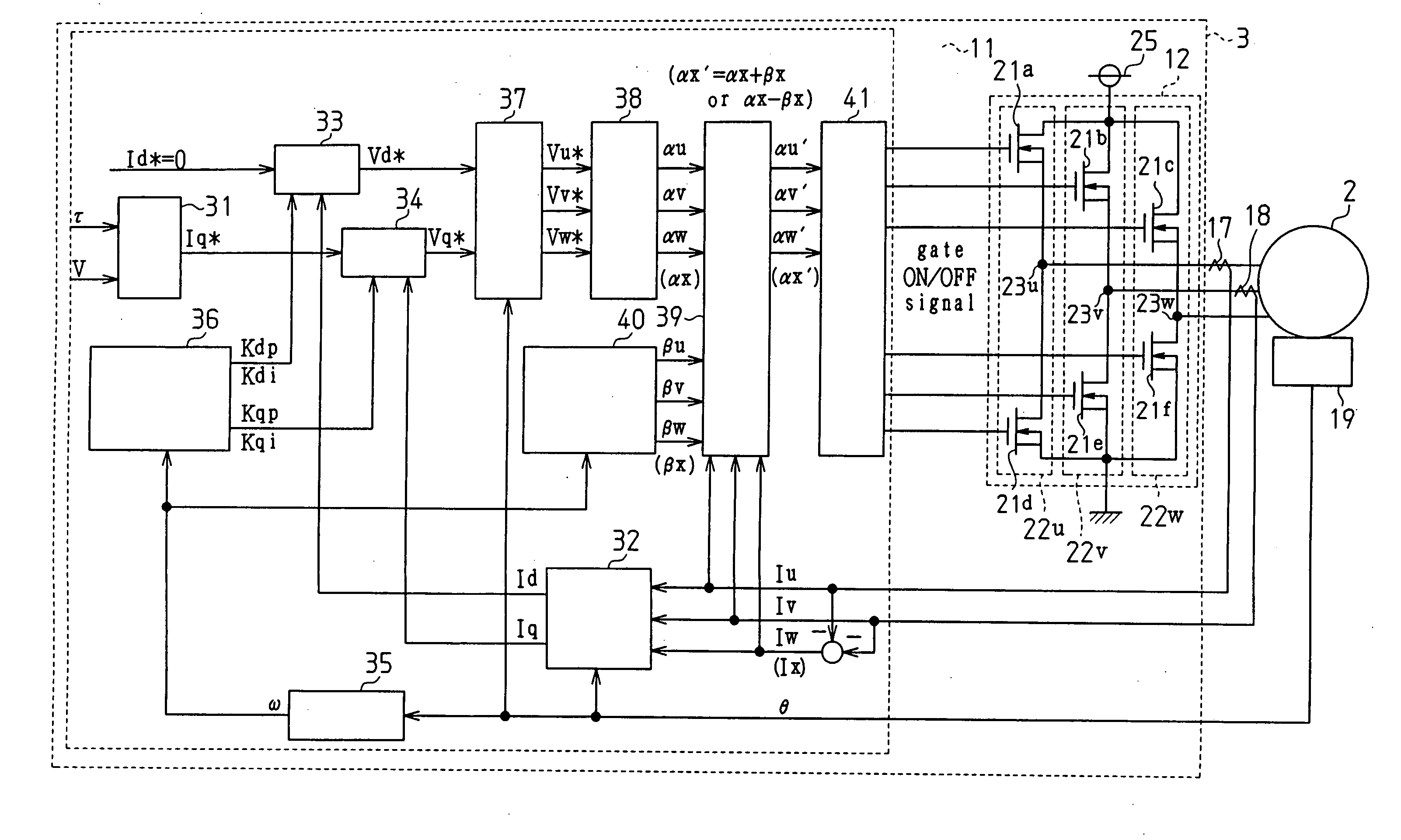
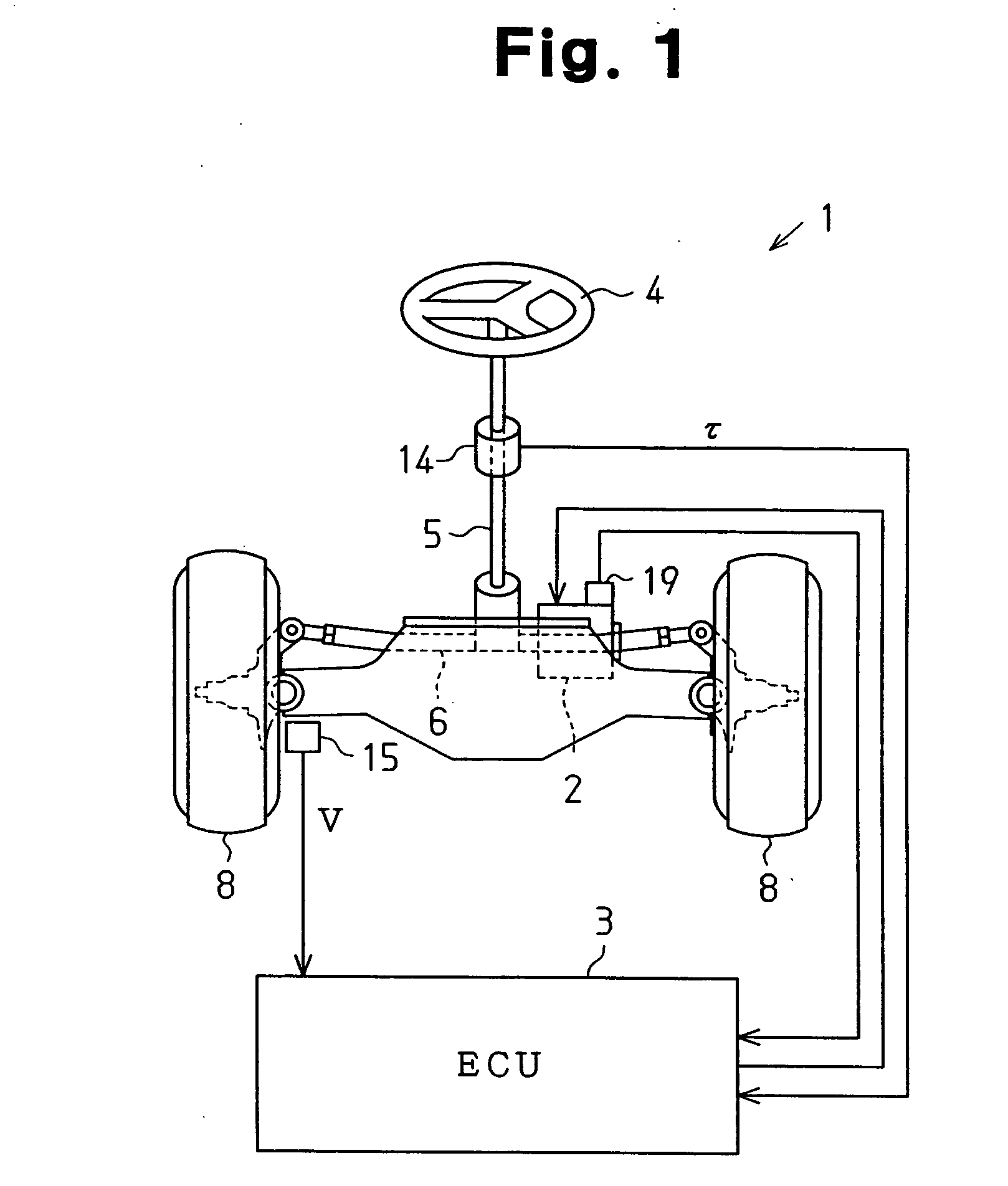
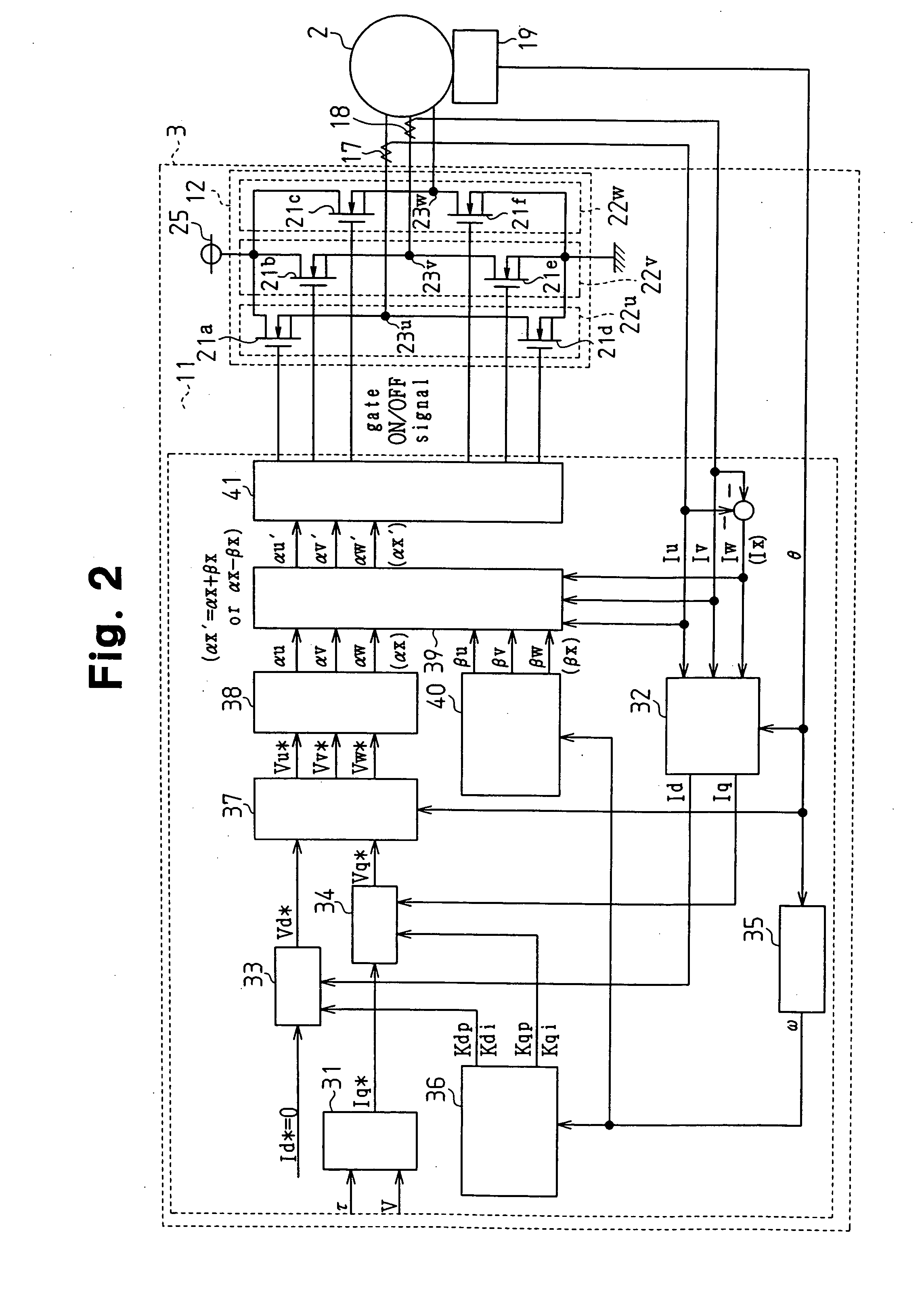
Motor controller and electric power steering apparatus
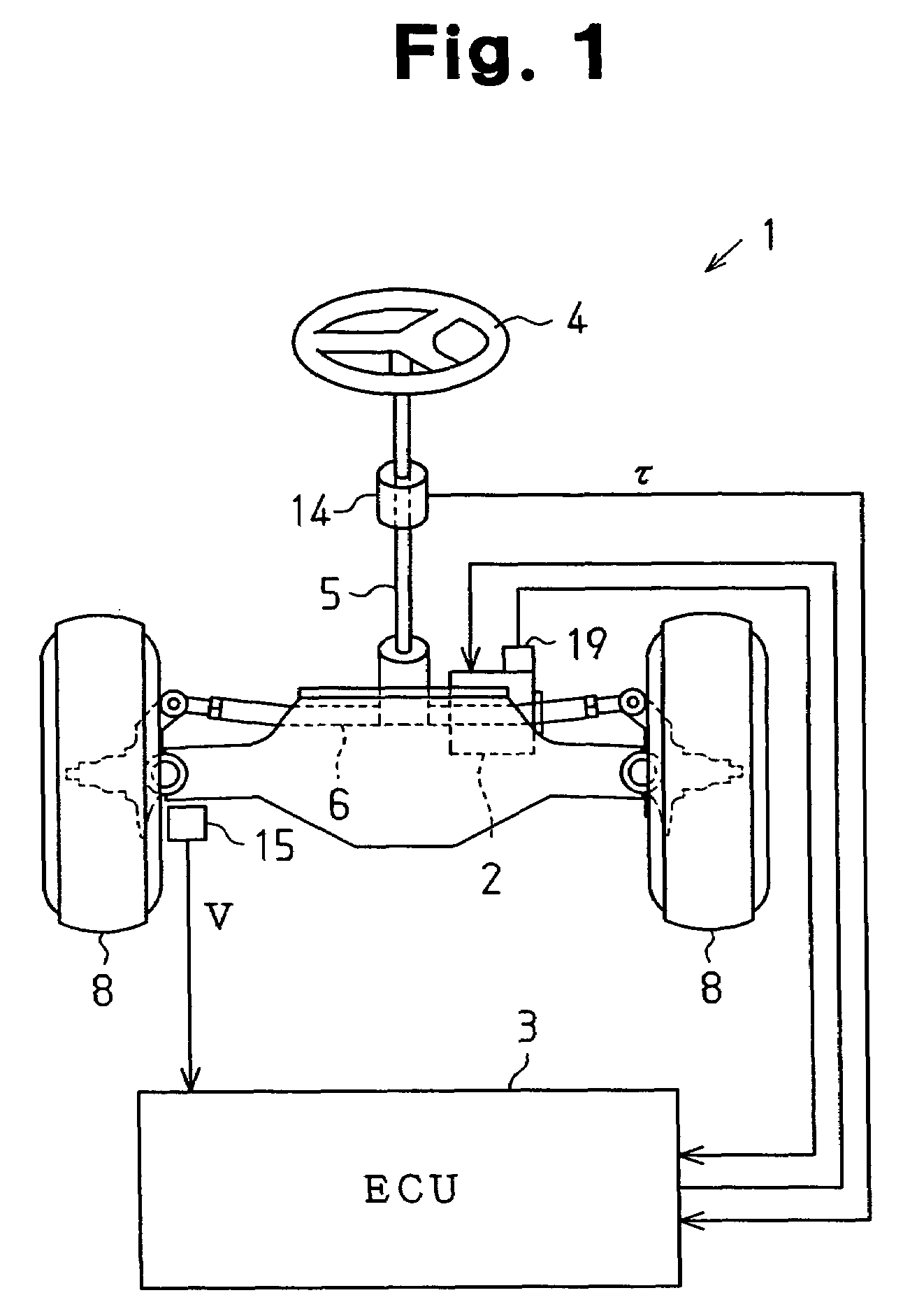
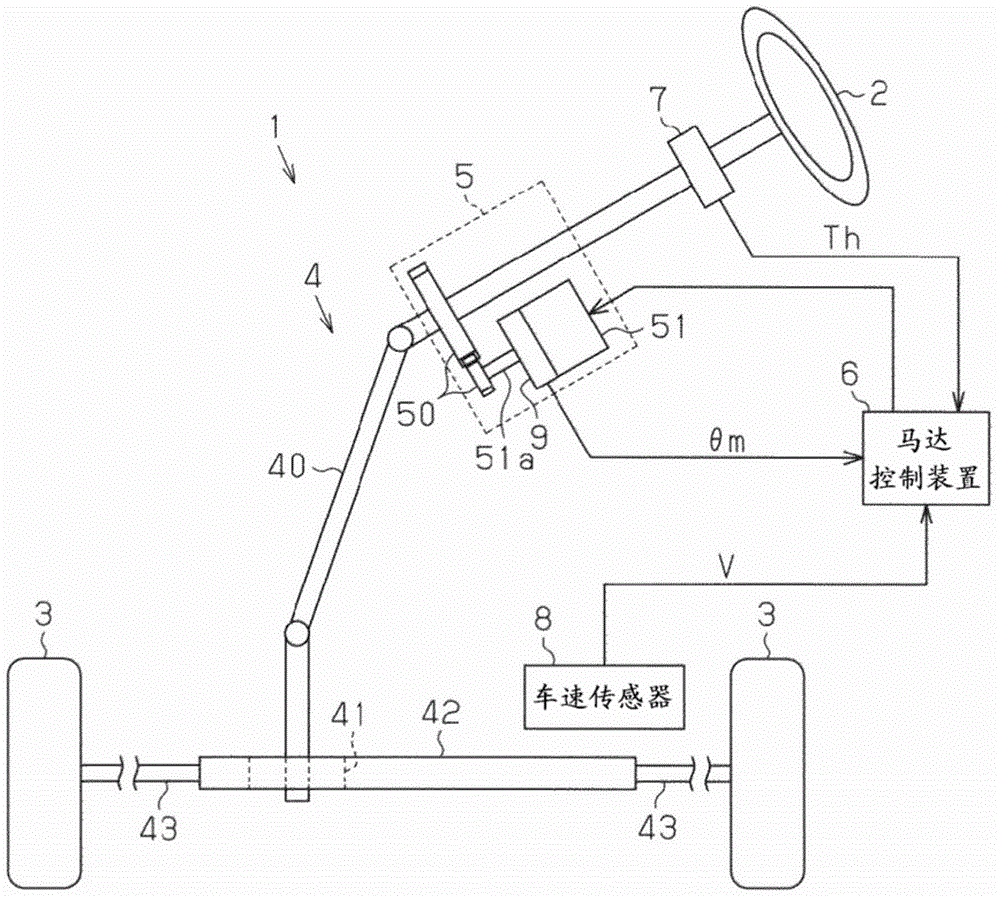
ActiveUS20060049784A1Accurate compensationAC motor controlDC motor speed/torque controlBrushless motorsElectric power steering
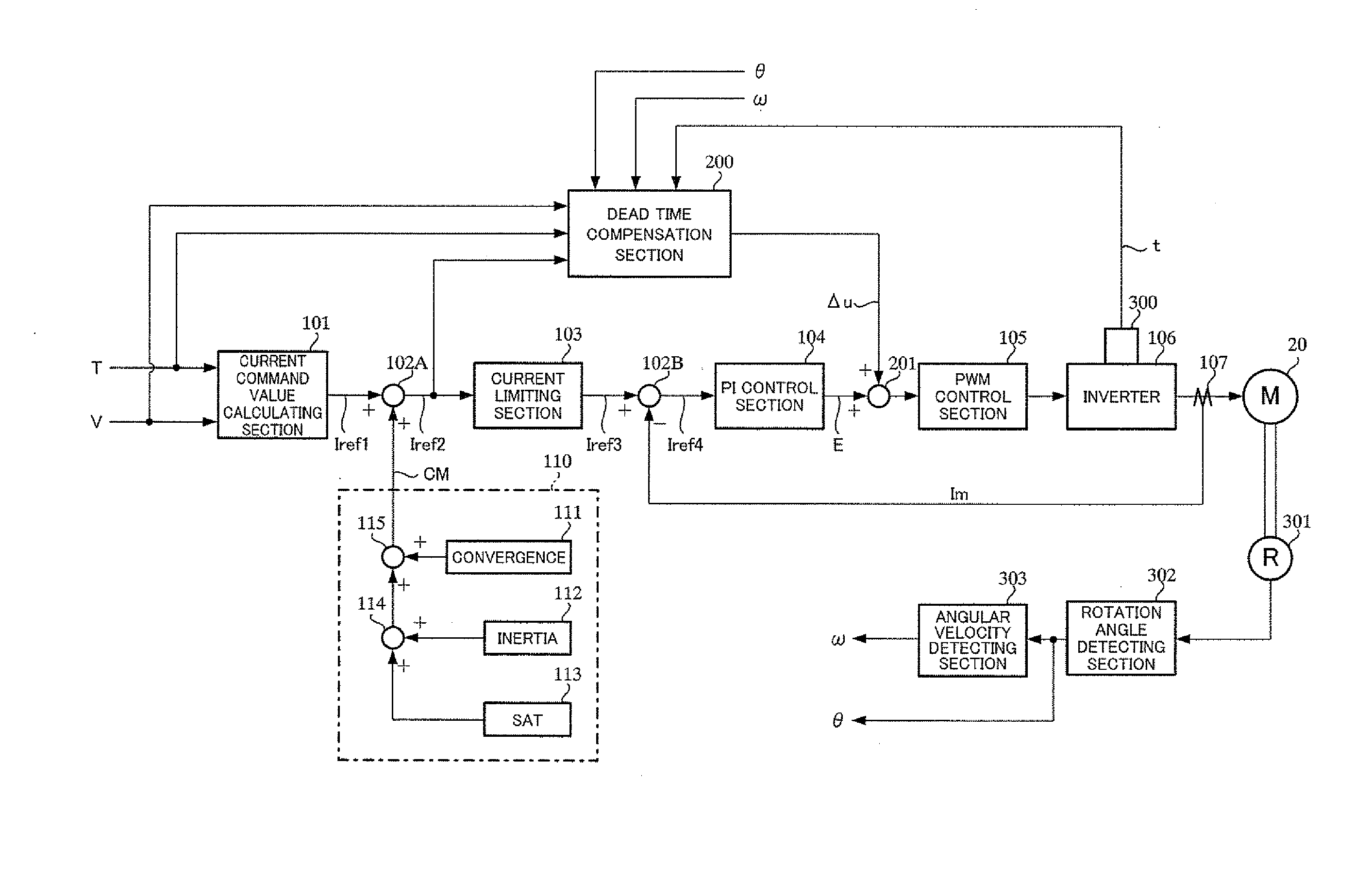
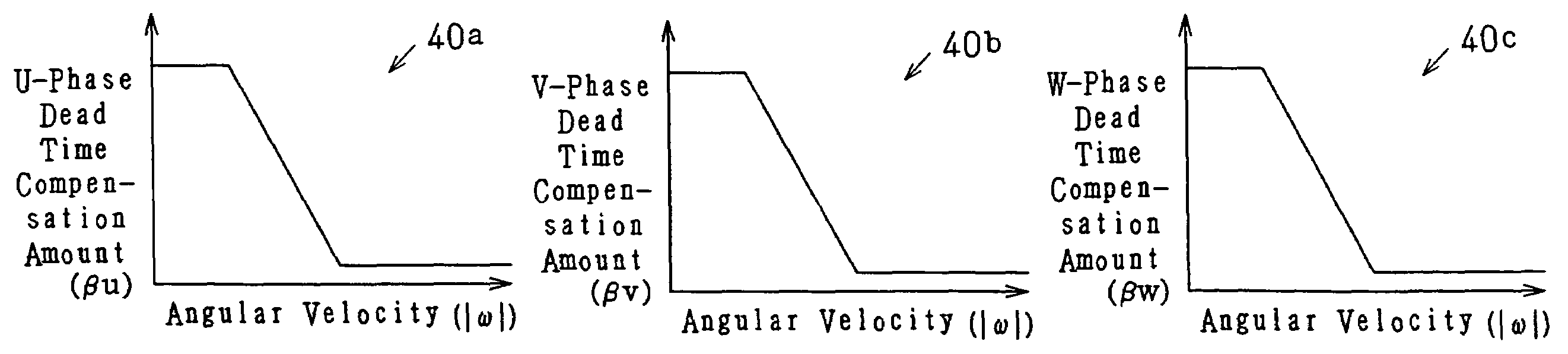
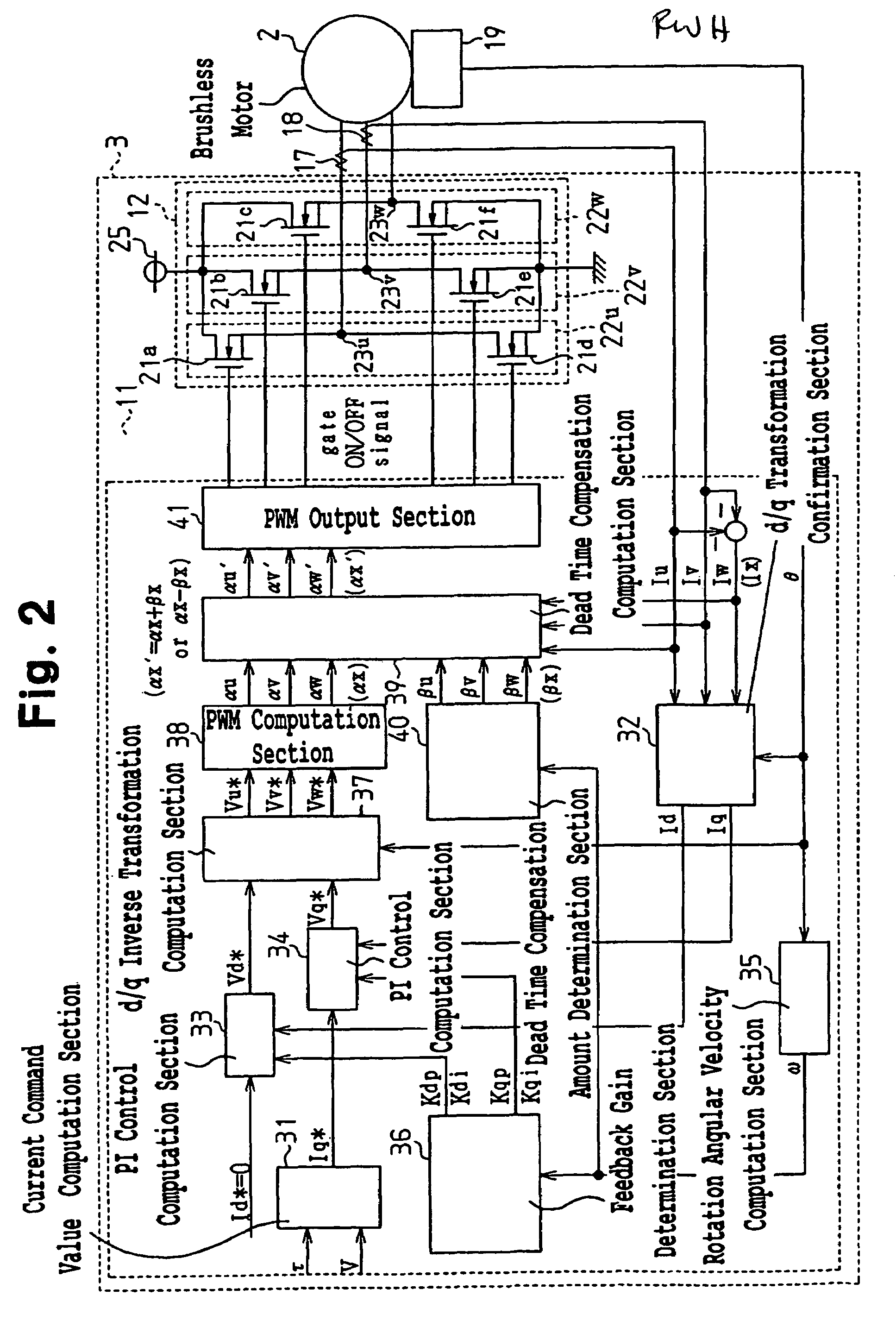
A microcomputer includes a rotation angular velocity computation section, a feedback gain determination section, and a dead time compensation amount determination section. The rotation angular velocity determination section computes the rotation angular velocity of a brushless motor. Based on the rotation angular velocity, the feedback gain determination section determines feedback gains. The dead time compensation amount determination section determines a dead time compensation amount. The greater the absolute value of the rotation angular velocity, that is, the higher the rotation speed of the brushless motor, the greater the feedback gains determined by the feedback gain determination section become, and the higher the responsivity of the feedback gains becomes. The greater the absolute value of the rotation angular velocity, the smaller the dead time compensation amount determined by the dead time compensation amount determination section becomes.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD +2
Motor controller
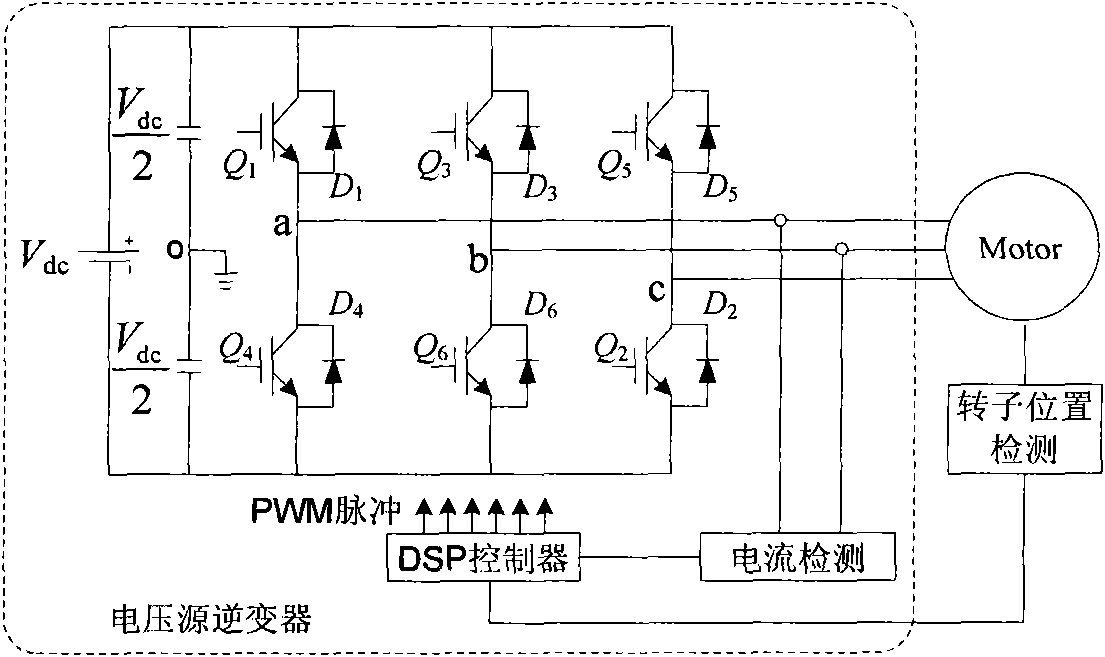
InactiveUS7102322B2Highly accurate compensation without delaySingle-phase induction motor startersTorque ripple controlMicrocomputerDead time compensation
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD +2
Driver having dead-time compensation function
ActiveUS20130063059A1Reduce manufacturing costMotor/generator/converter stoppersSynchronous motors startersDead timeDead time compensation
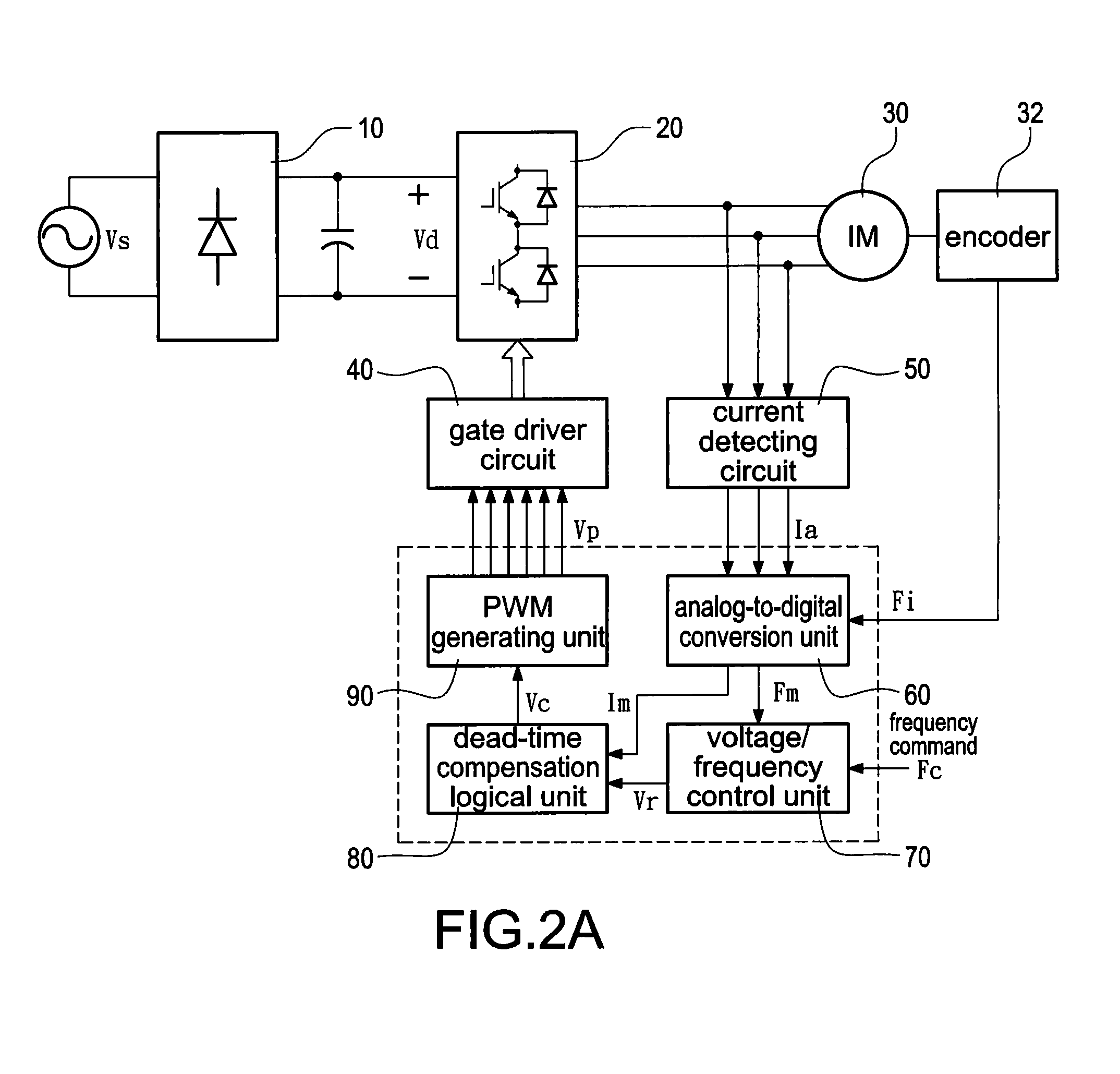
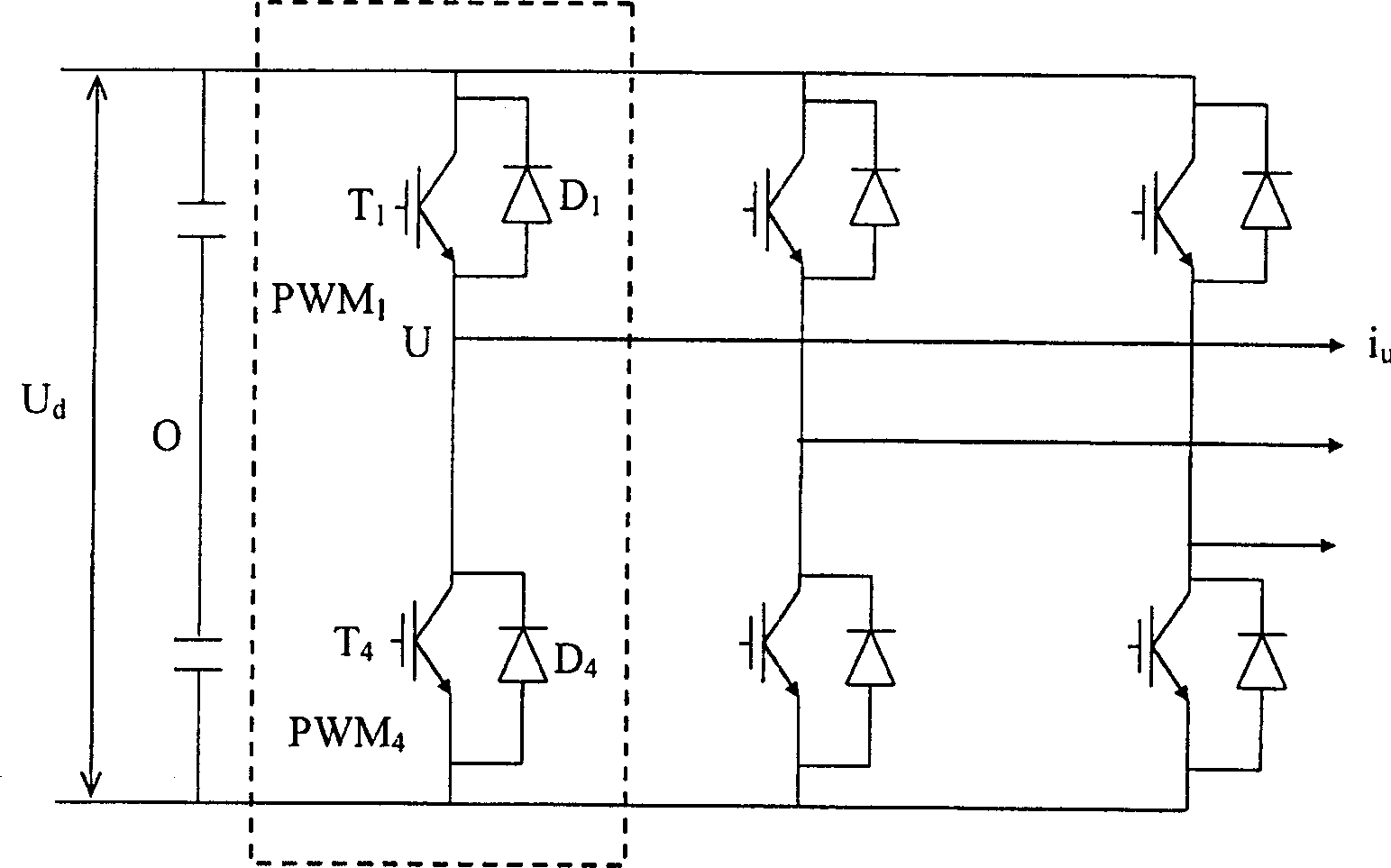
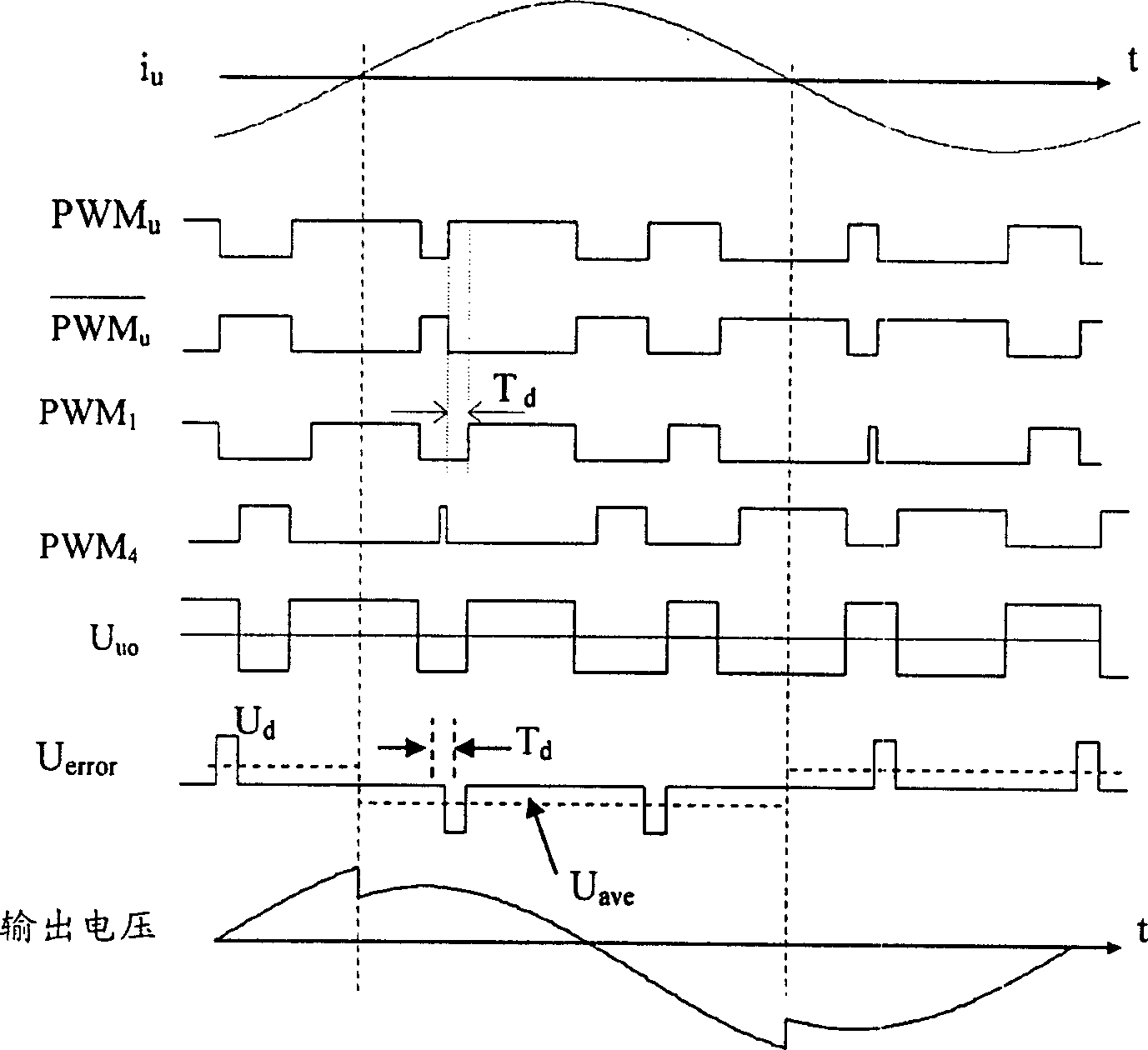
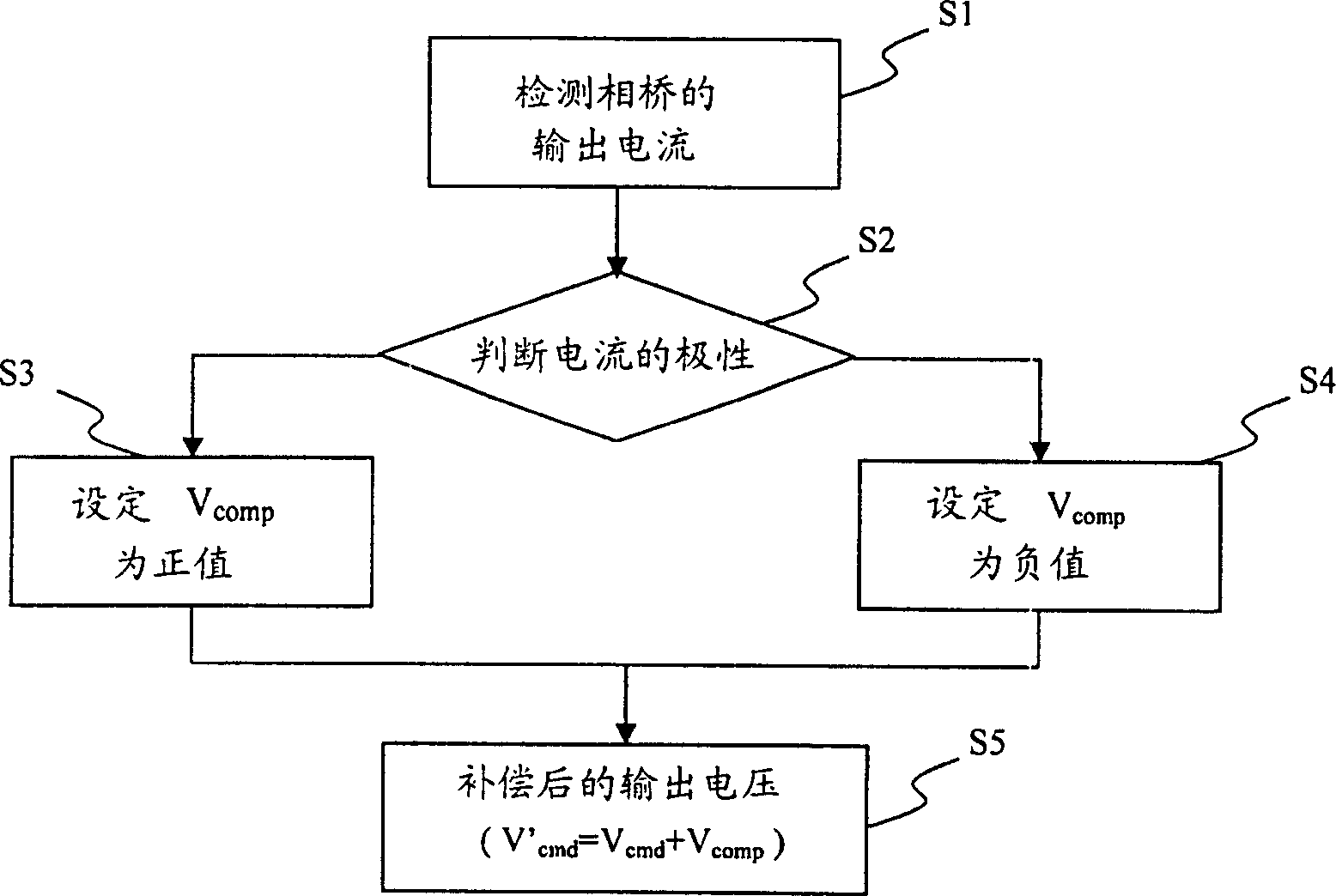
Proposed is a driver having dead-time compensation function. The driver having dead-time compensation function generates an output voltage according to a voltage command and a frequency command. The driver includes an inverter, an output current detector and a control unit. The inverter receives a DC voltage and operates with a pulse width modulation mode so that the driver outputs the output voltage and an output current. The output current detector detects the current value of the output current to generate a output current detecting signal. The control unit outputs a switching control signal to inverter according to the voltage command and the frequency command. The control unit corrects a reference command according to dead-time and the output current detecting signal related to the output current so that amplitude and waveform smoothness of the output voltage and the output current are compensated.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Output current distortion compensating apparatus in inverter
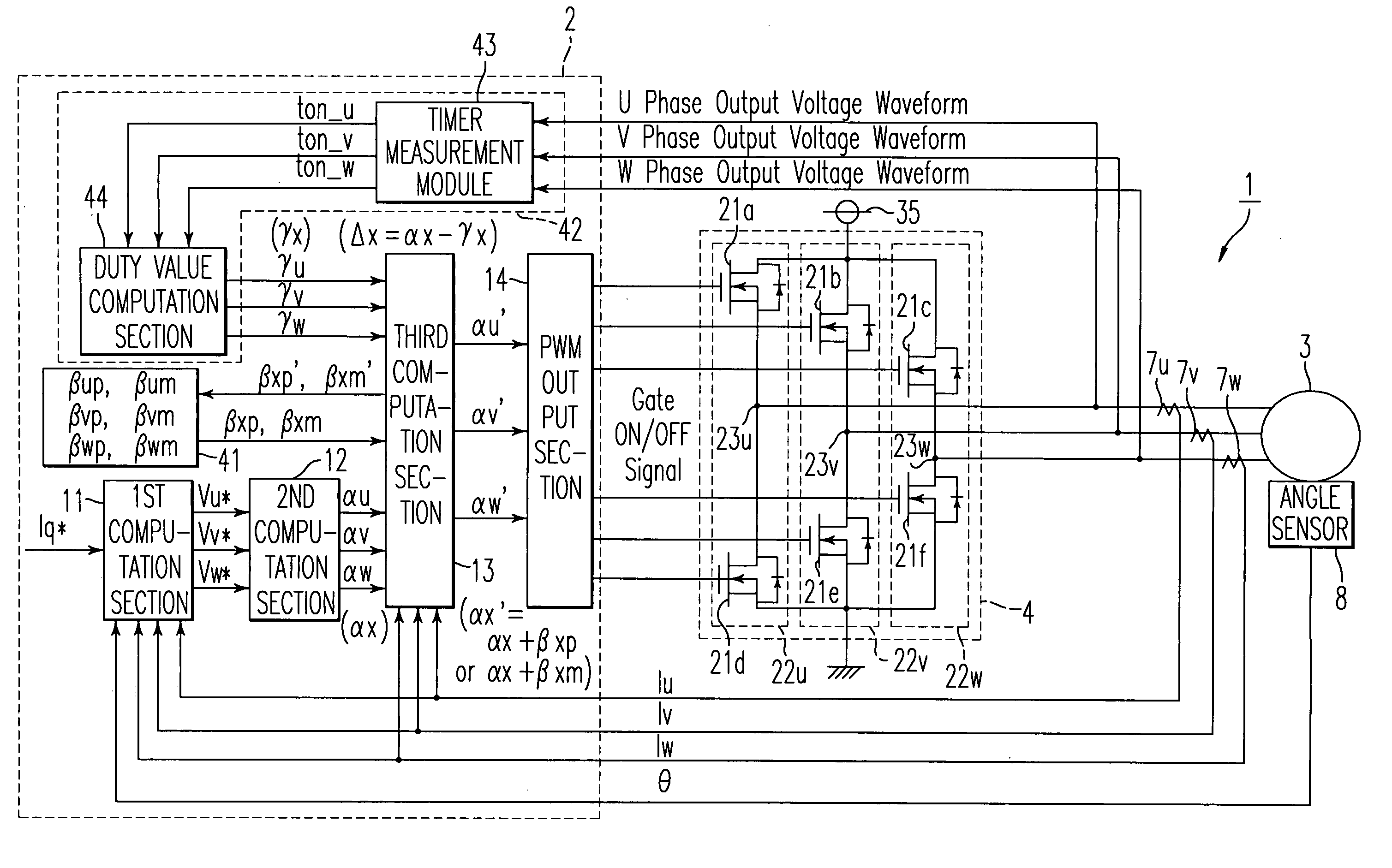
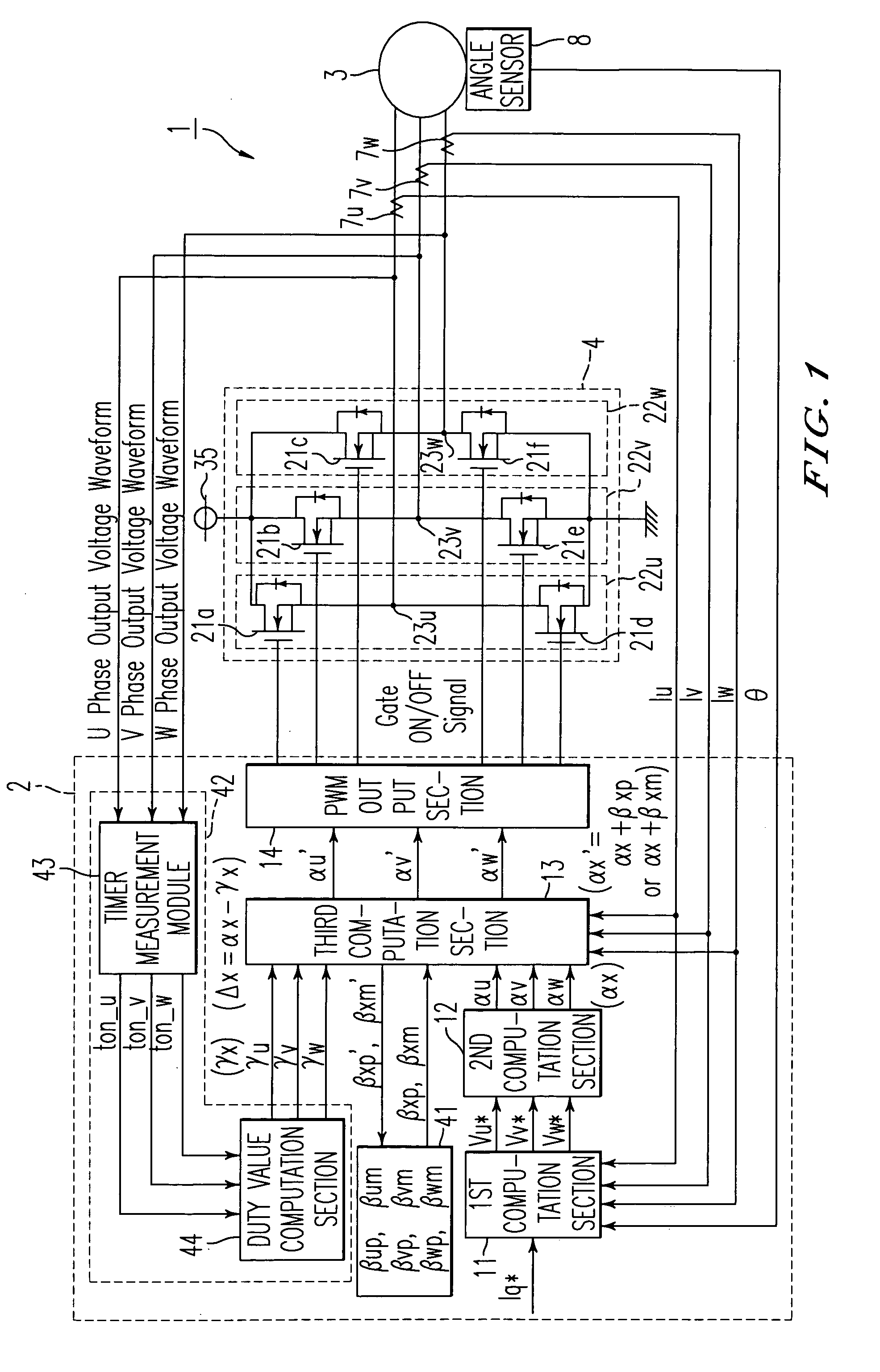
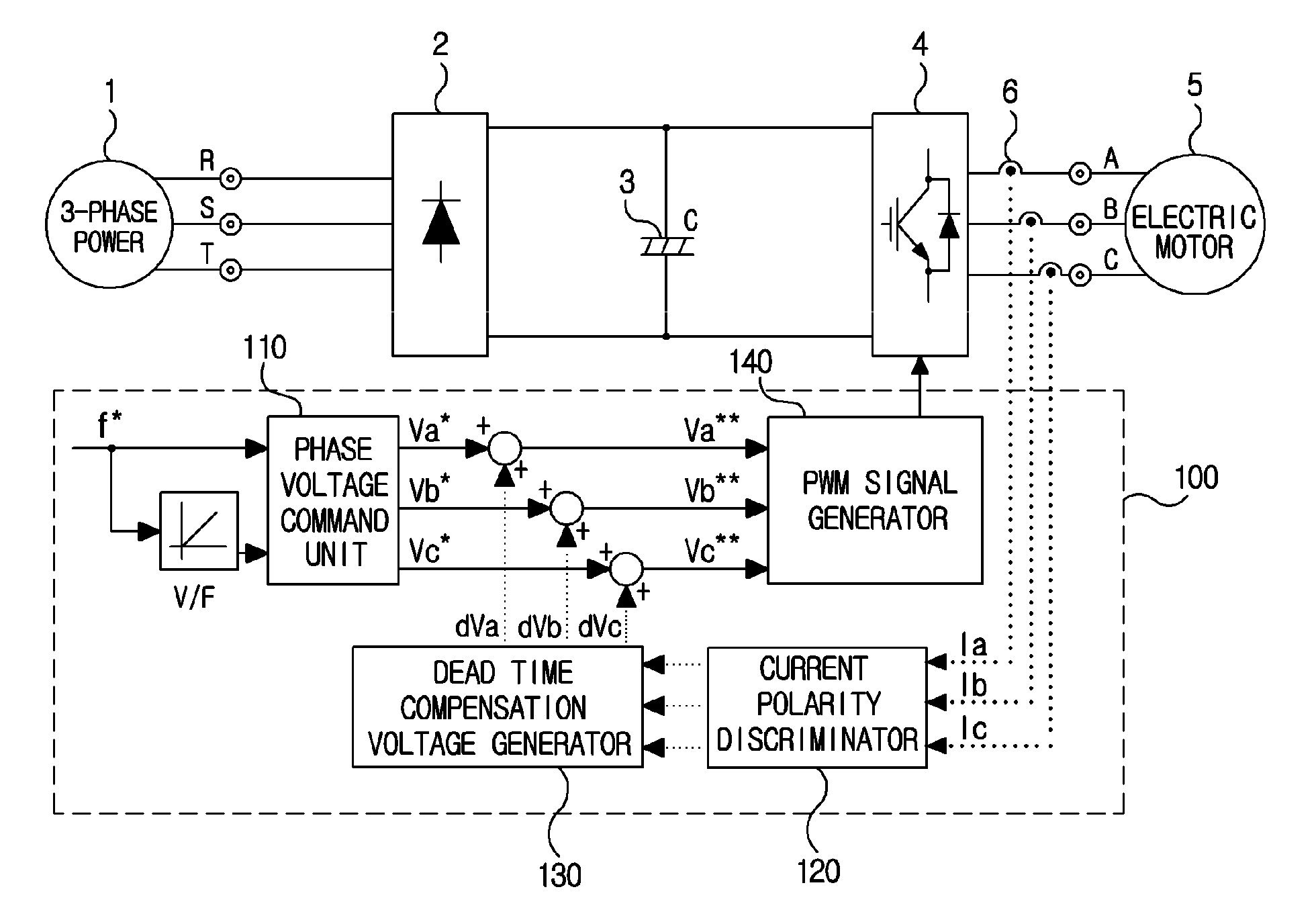
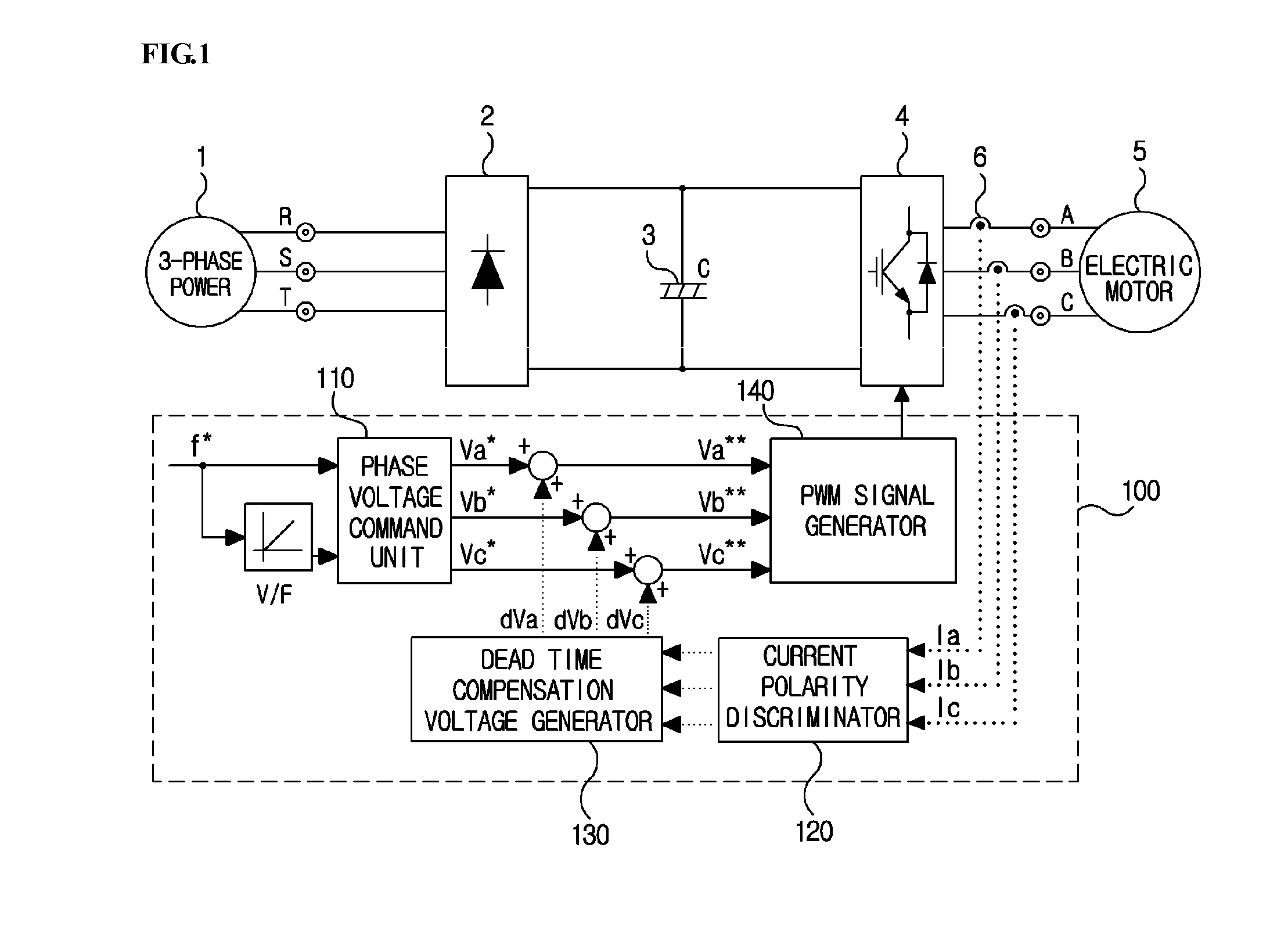
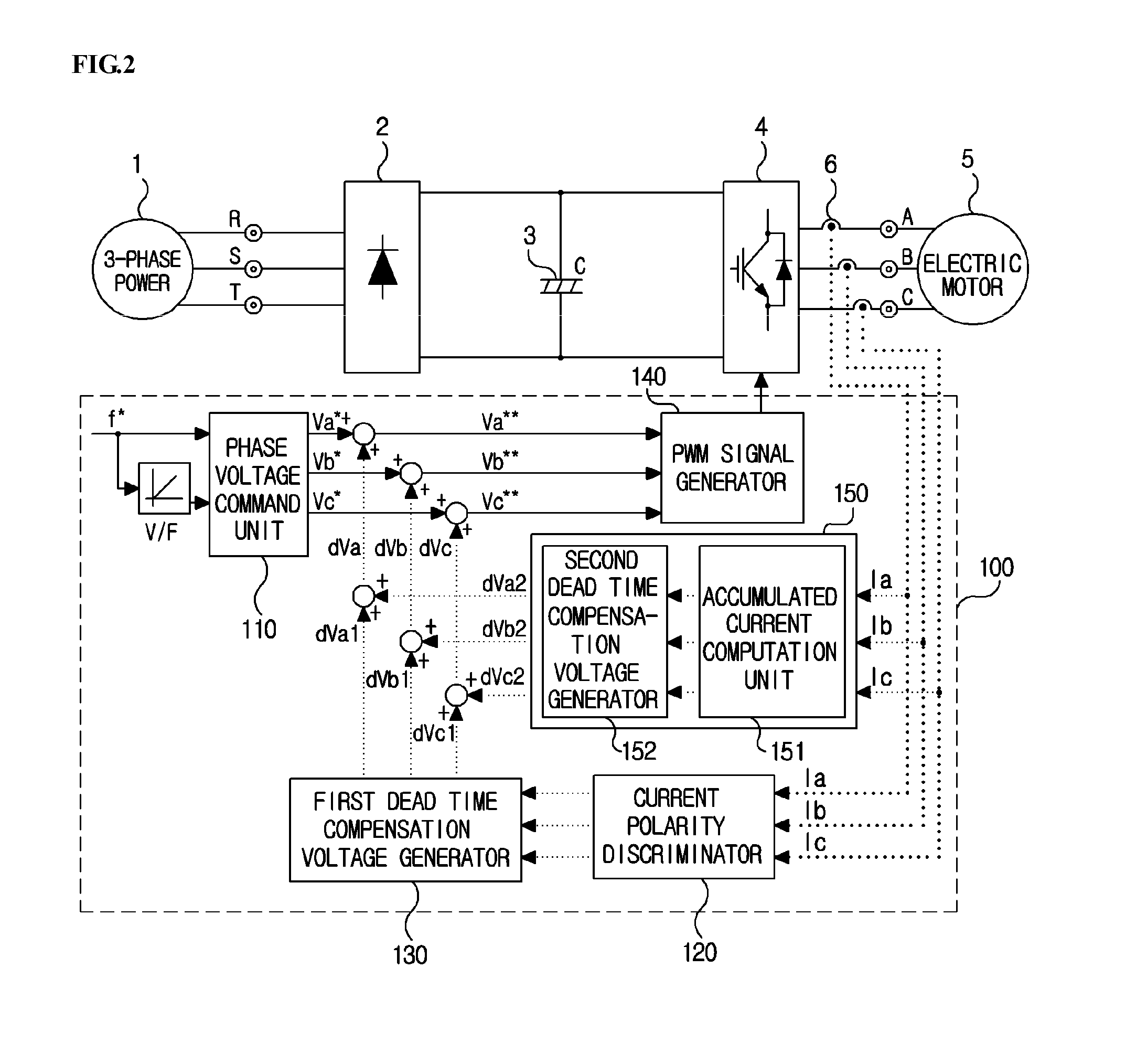
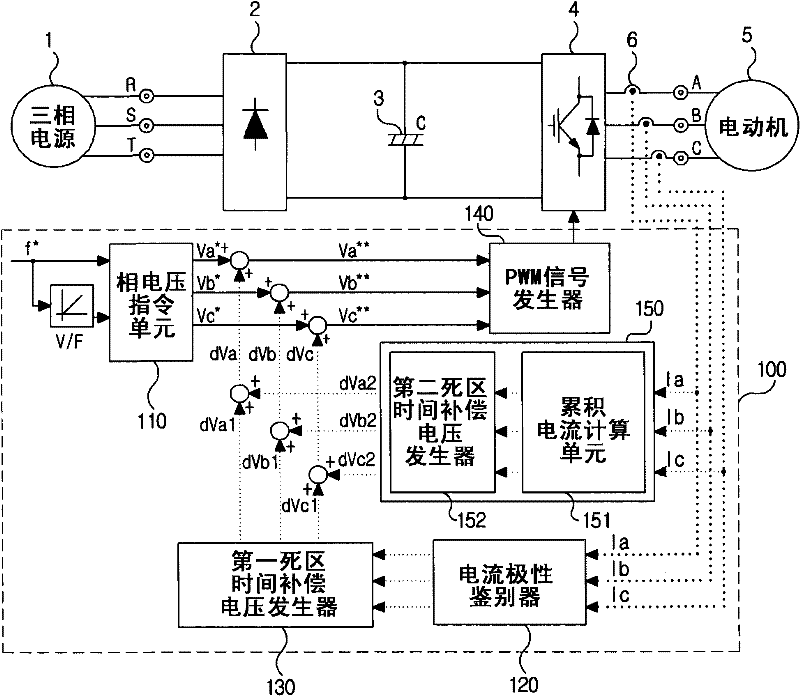
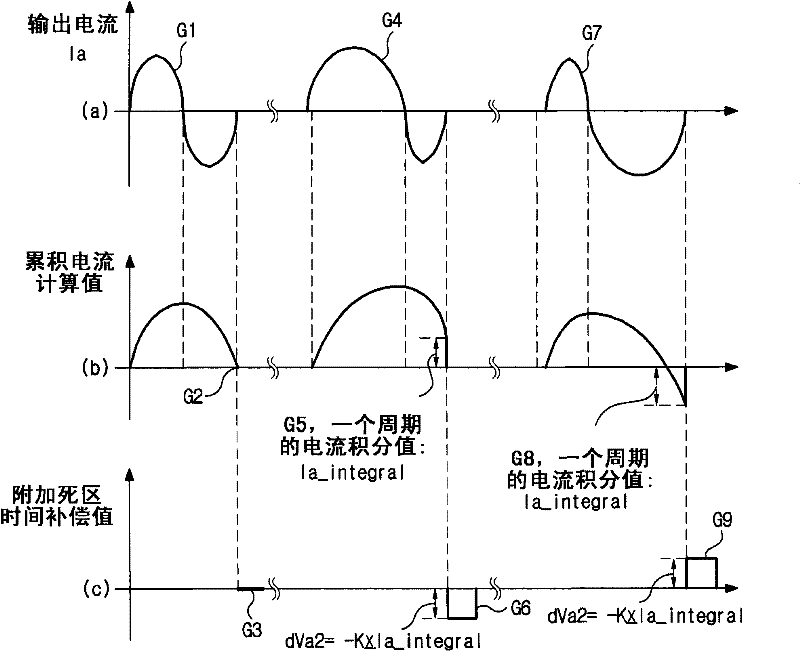
ActiveUS20110273914A1Reduce imbalanceDead time errorAC motor controlDc-ac conversion without reversalPower inverterVoltage generator
An output current distortion compensating apparatus in an inverter is disclosed, the inverter including an inverter controller generating a PWM signal for controlling a PWM voltage generator, wherein the inverter controller includes a first dead time compensation voltage generator generating a compensation voltage based on an output current polarity of each phase in the inverter, and a second dead time compensation voltage generator generating a compensation voltage based on an output current waveform of each phase in the inverter, and wherein a first dead time compensation voltage outputted from the first dead time compensation voltage generator and a second dead time compensation voltage outputted from the second dead time compensation voltage generator are added to generate a final dead time compensation voltage, thereby preventing occurrence of hunting phenomenon in which a current is greatly fluctuated.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
Dead-time compensation apparatus of pwm inverter and method thereof
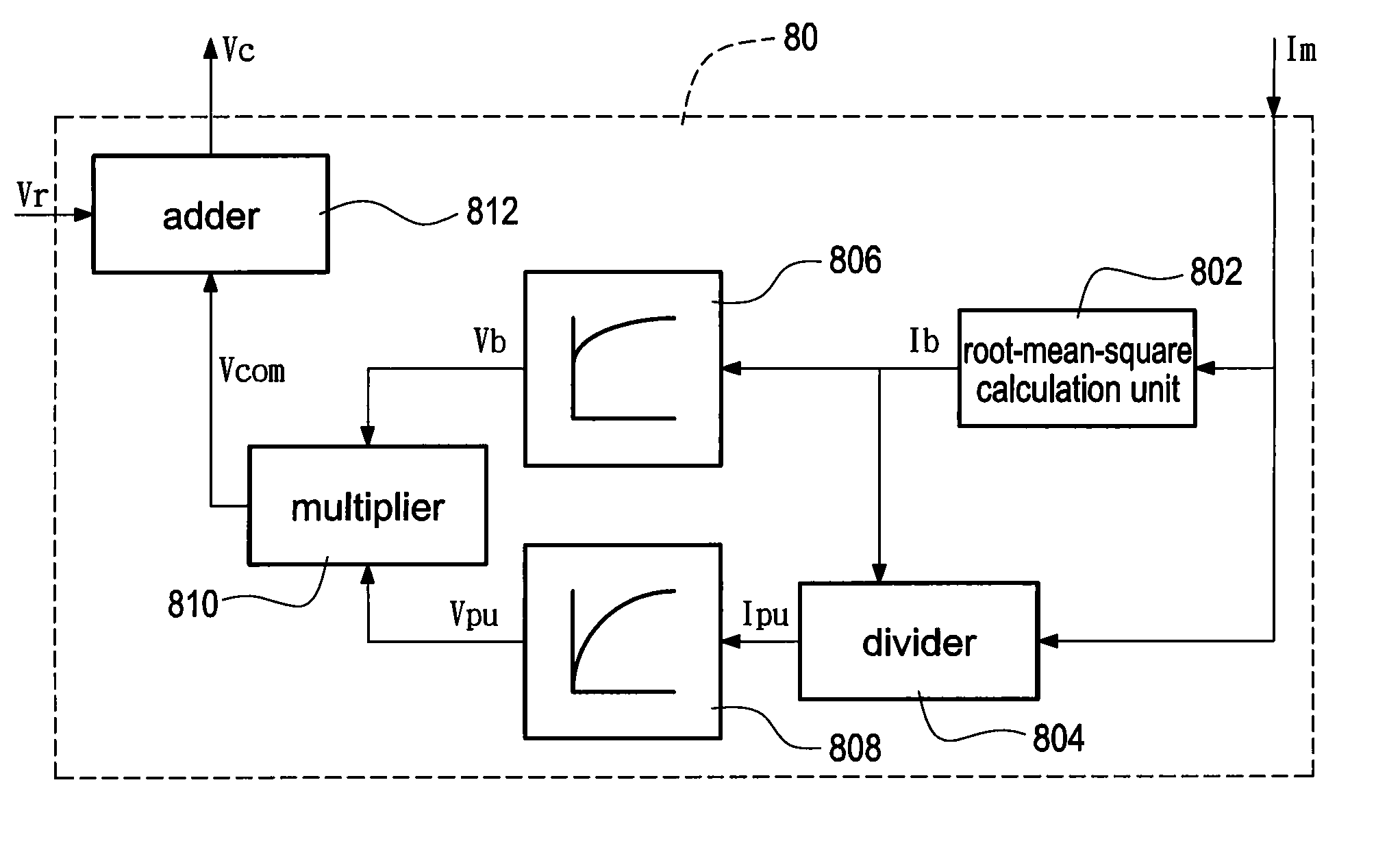
ActiveUS20110156632A1Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersTime responseLow speed
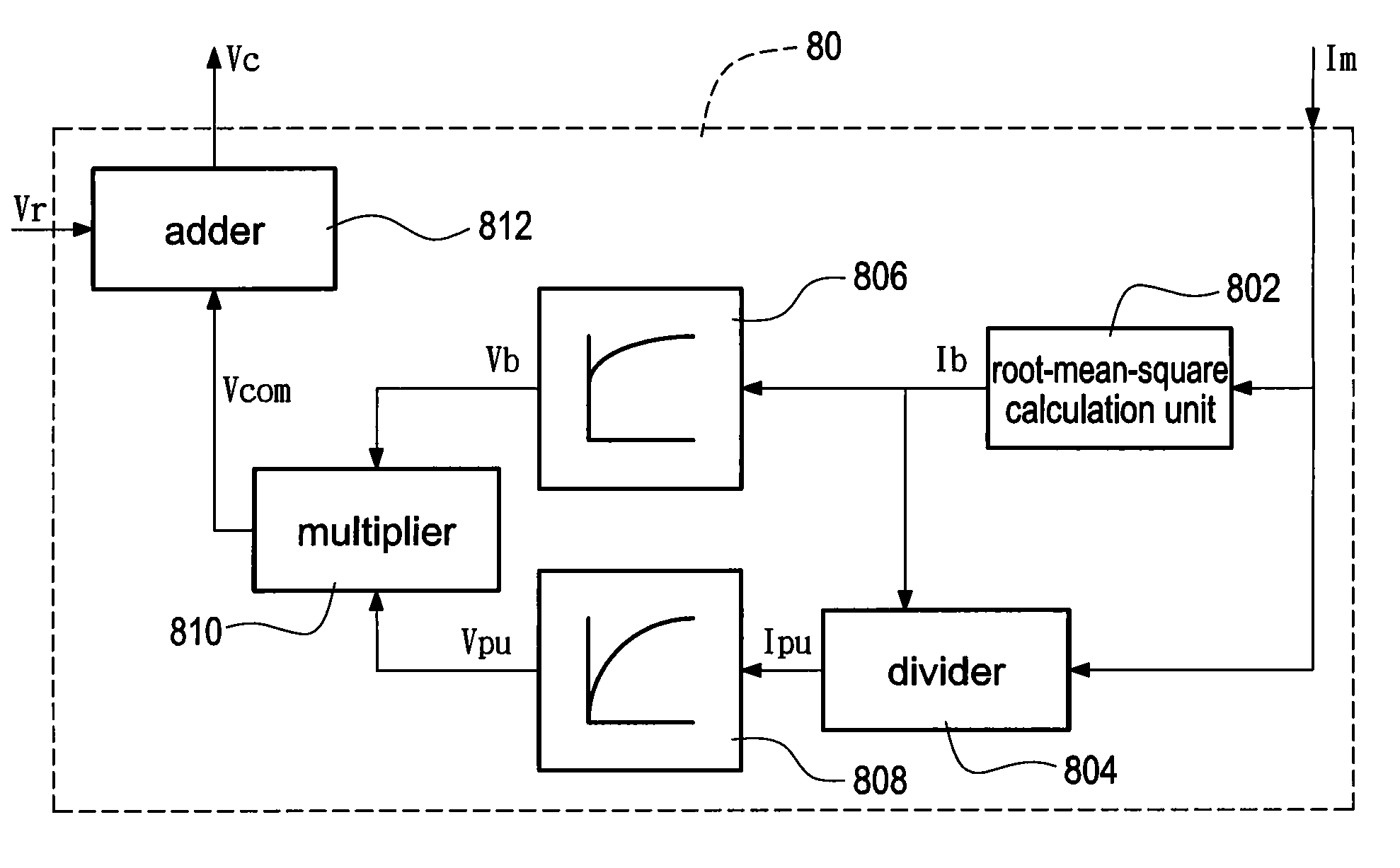
A dead-time compensation method is applied to a PWM inverter, which is provided to drive an induction motor using a constant V / f control. The method first calculates a root-mean-square current of the output instantaneous current of the inverter. Afterward, a lookup table of the root-mean-square current is used to obtain a dead-time compensation base voltage and a dead-time compensation per-unit voltage. Finally, the dead-time compensation base voltage is multiplied by the dead-time compensation per-unit voltage to produce a dead-time compensation voltage of the PWM inverter. Accordingly, the method reduces complexity of converting the current to the voltage to reach a faster real-time response. Furthermore, a more accurate dead-time compensation voltage is obtained without increasing hardware costs and the efficiency of operating the induction motor is improved at low speed and light load condition.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Apparatus for controlling electric power steering apparatus
ActiveCN102985311ASmall distortionLess dead time compensationSteering linkagesAutomatic steering controlElectric power steeringArithmetic processing unit
Owner:NSK LTD
Dead-time compensation method for electric drives
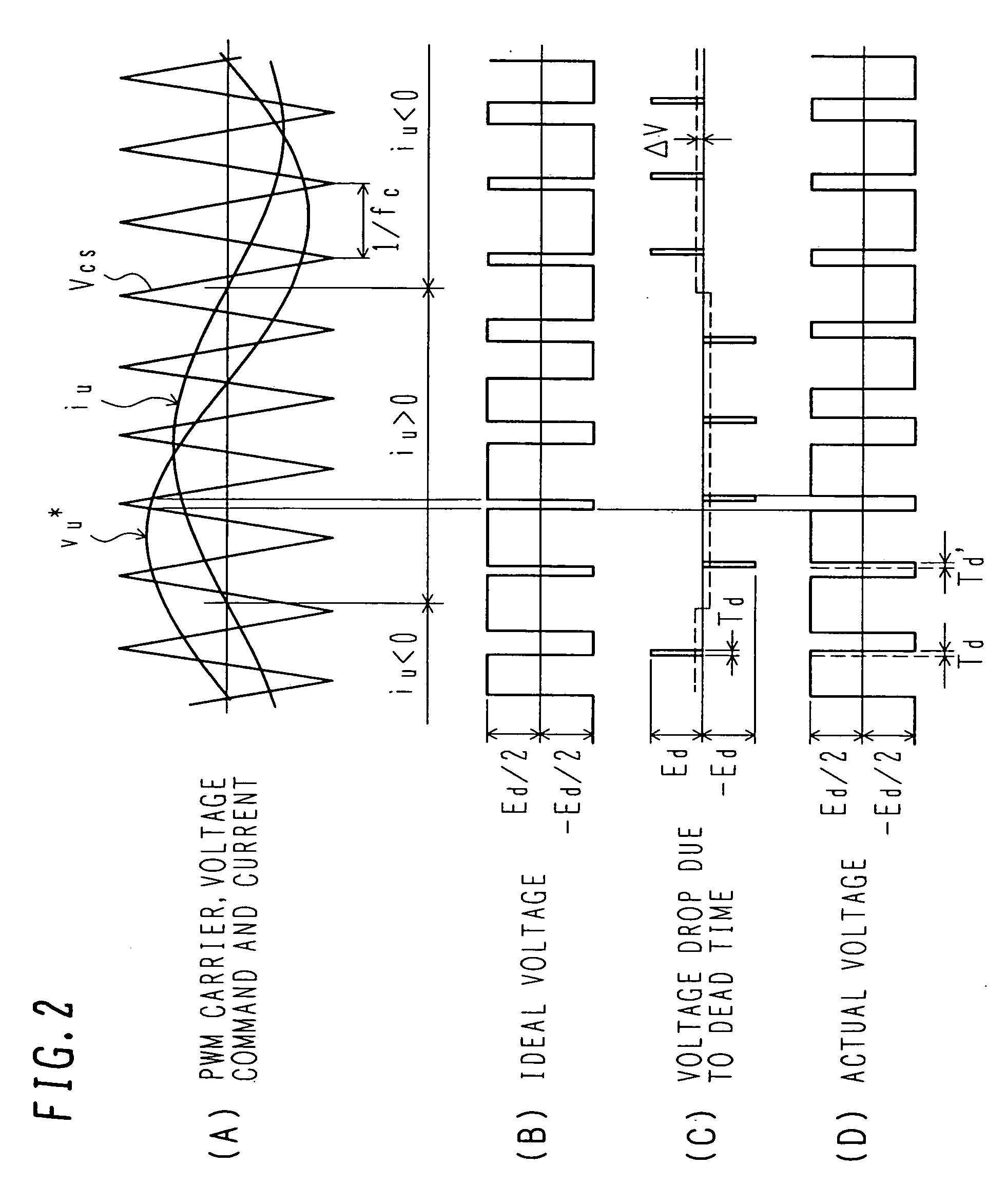
InactiveUS7286375B1Dead time compensationConversion with intermediate conversion to dcEmergency protective circuit arrangementsElectricityDead time
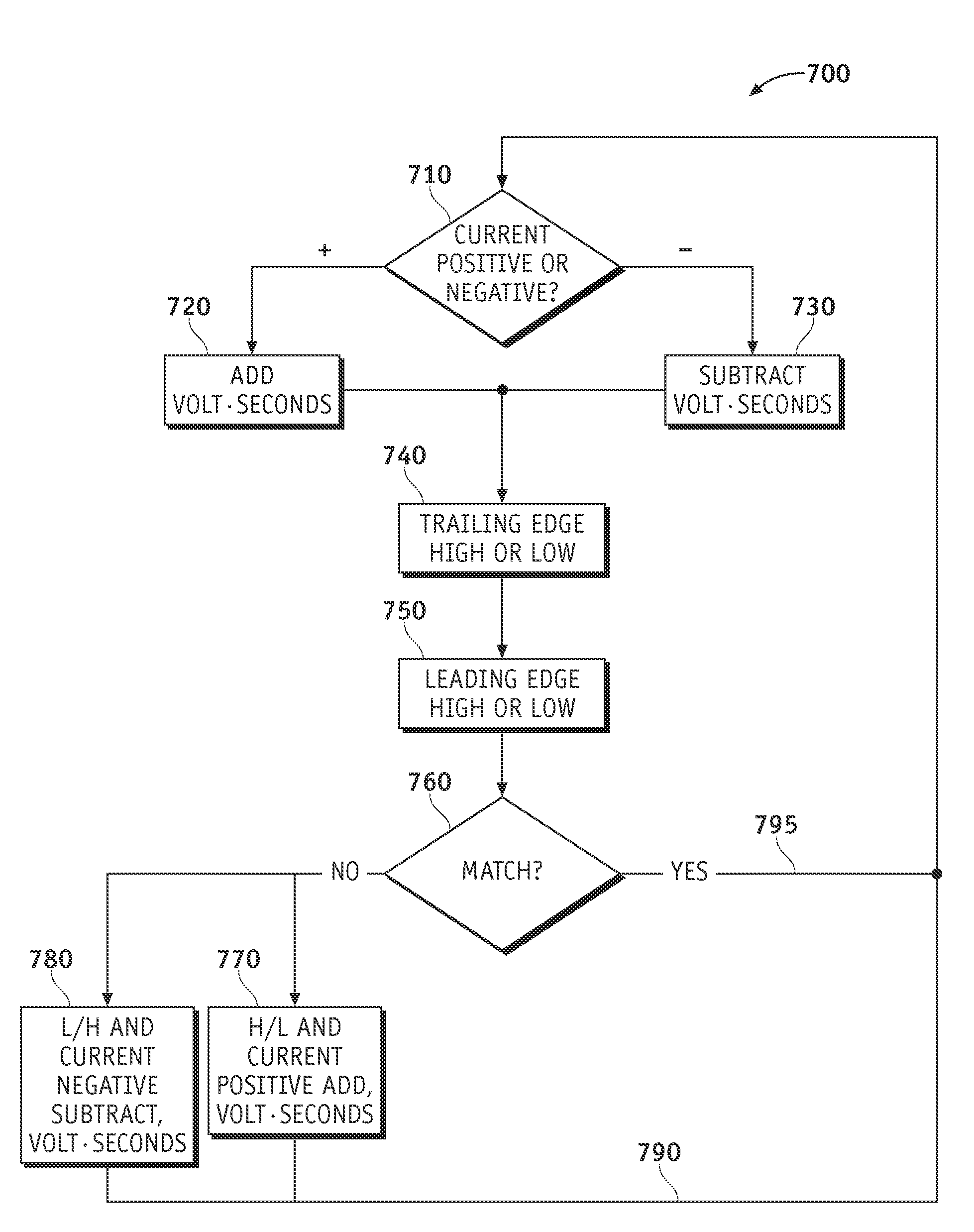
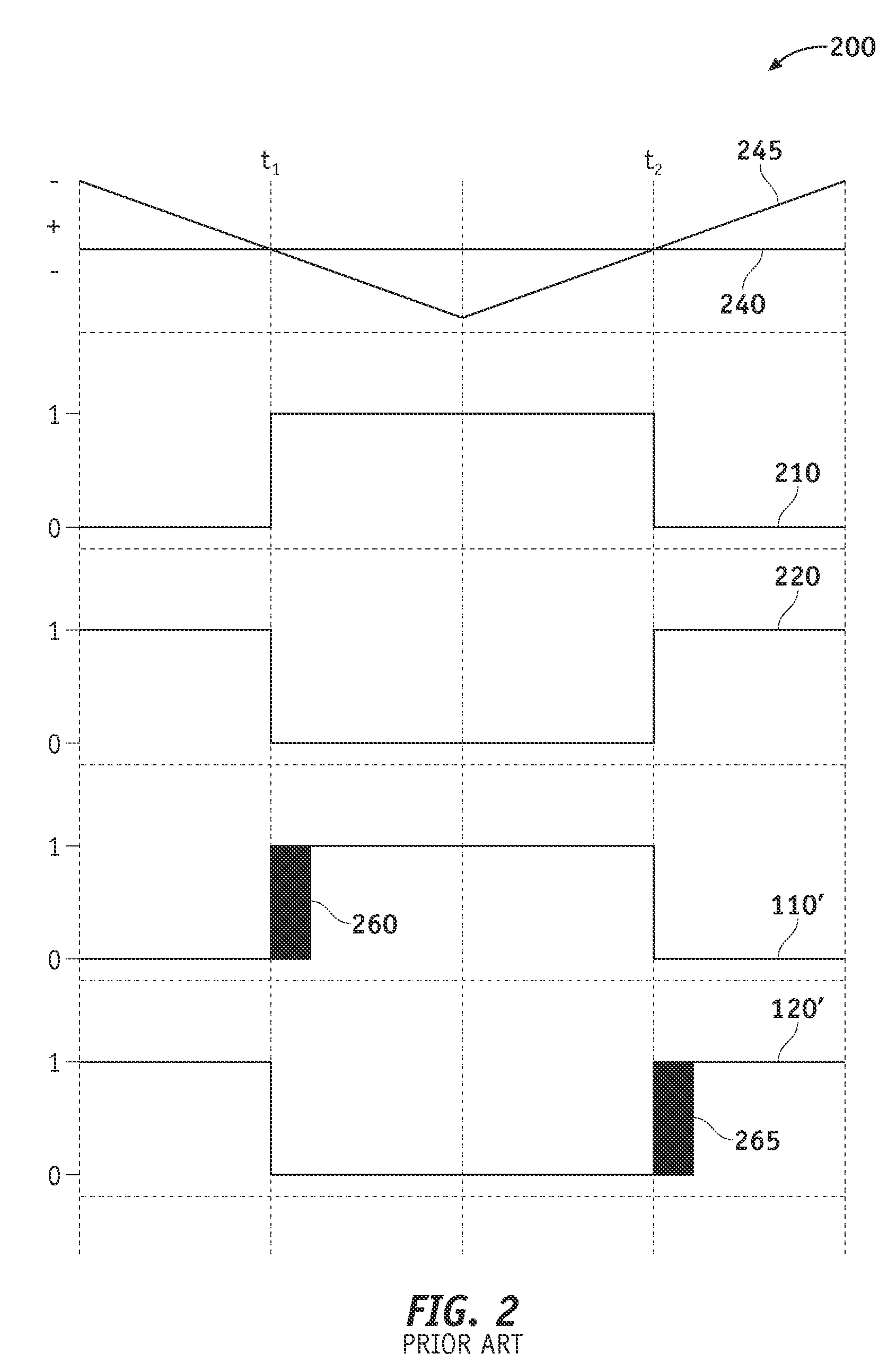
Methods and apparatus are provided for compensating for a deviation in voltage output of a phase leg inverter when dead-time periods are inserted to prevent shoot-through failures. The method includes determining a pulse width for an input signal to the inverter such that the inverter voltage output is a desired amount. The pulse width is based on the non-inverted or inverted pulse sequences of two carrier signals and the polarity of current through the inverter. An amount of pulse width is added to the input signal when the current is positive, and an amount of pulse width is subtracted from the input signal when the current is negative. An additional amount of pulse width is added to or subtracted from the input signal depending on whether the carrier signal sequence changes from a non-inverted signal to an inverted signal or changes from an inverted signal to a non-inverted signal, respectively.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Current loop control system based FPGA, and servo device
InactiveCN105932925AIncrease refresh rateReduced execution timeElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsCurrent loop controlVoltage vector
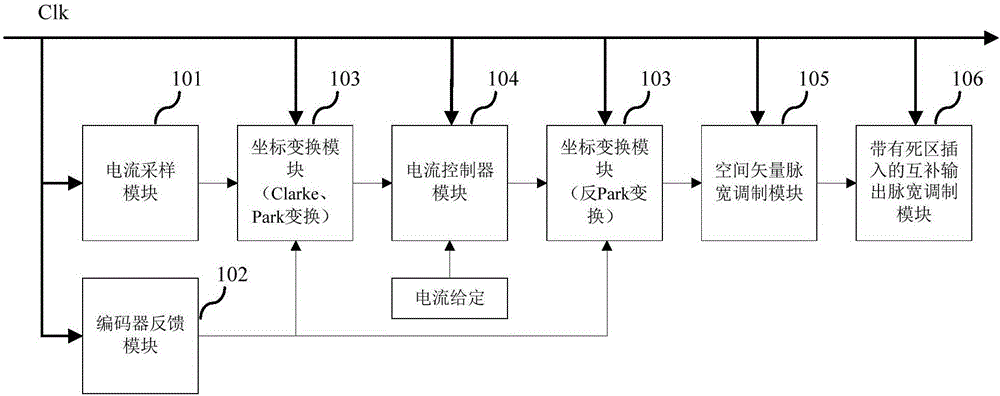
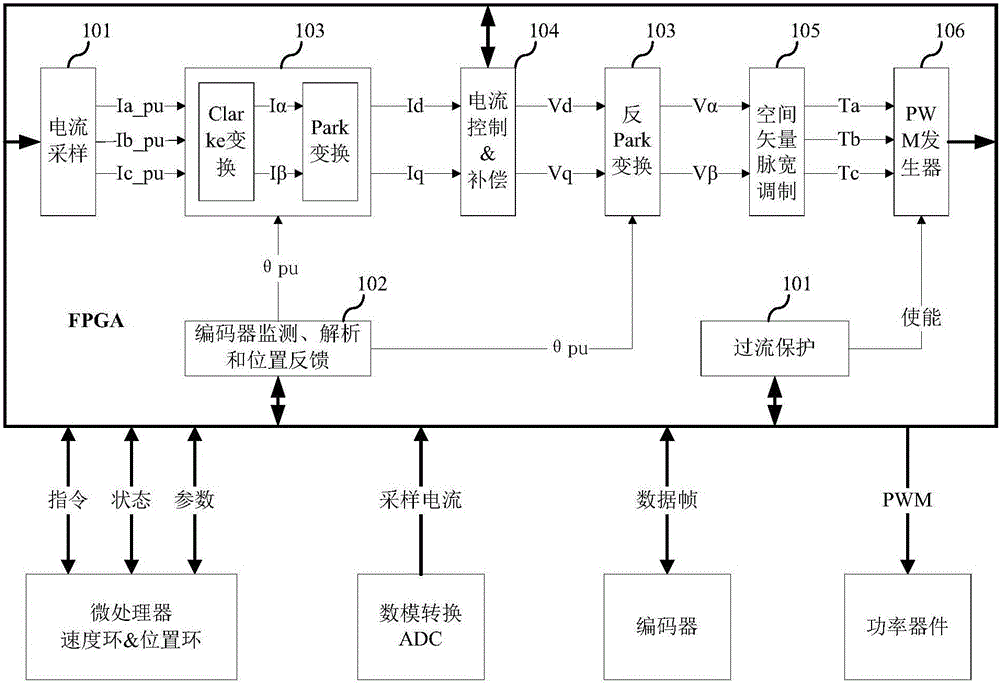
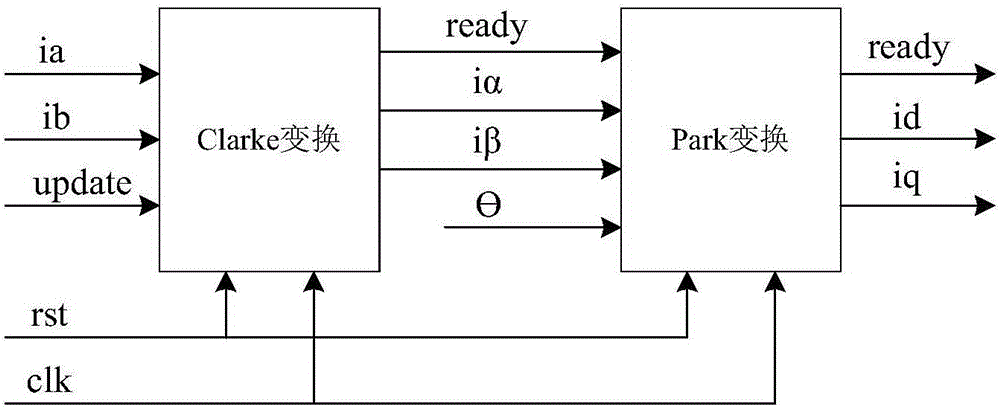
The invention relates to the technical field of alternating current servo vector control, and discloses a current loop control system based on an FPGA, and a servo device. According to the system and the device, through adoption of current loop control based on an FPGA hardware logic parallel processing mode, a current given quantity and signals sent by a current sampling module are input into a current controller module for PID calculation and decoupling compensation processing, a voltage vector reference value under a rotating coordinate system is output; a voltage vector reference value under a static coordinate system is output according to a rotor angle value output by an encoder feedback module and the output voltage vector reference value under the rotating coordinate system; a space vector pulse width modulation module converts the voltage vector reference value under the static coordinate system into three-way effective duty cycles; a complementary output pulse width modulation module with dead zone insertion converts the three-way effective duty cycles into six-way pulse width modulation square signals after dead-time compensation. Through adoption of the system and the device, the current loop control time is reduced, and the current loop bandwidth is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI STEP ELECTRIC +1
Control device for electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20130066524A1Improve performanceTotal current dropSteering initiationsDigital data processing detailsElectric power steeringDead time compensation
A control apparatus for an electric power steering apparatus, including a dead time characteristic section that calculates a dead time characteristic value; a steering status determining section that determines a steering status; a gain section that varies a gain of the dead time characteristic value in accordance with a determination of the steering status; a polarity determining section that switches polarity determining methods in accordance with the determination of the steering status and determines a polarity on the basis of a detected current of a motor, a current command value or a model current; a temperature sensor that detects a temperature of an inverter; a dead time temperature correction value calculating section that calculates a dead time temperature correction value corresponding to the temperature; and a calculation processing section that calculates and processes the dead time temperature correction value with respect to a dead time compensation value with polarity based on an output of the gain section and outputs a dead time compensation value.
Owner:NSK LTD
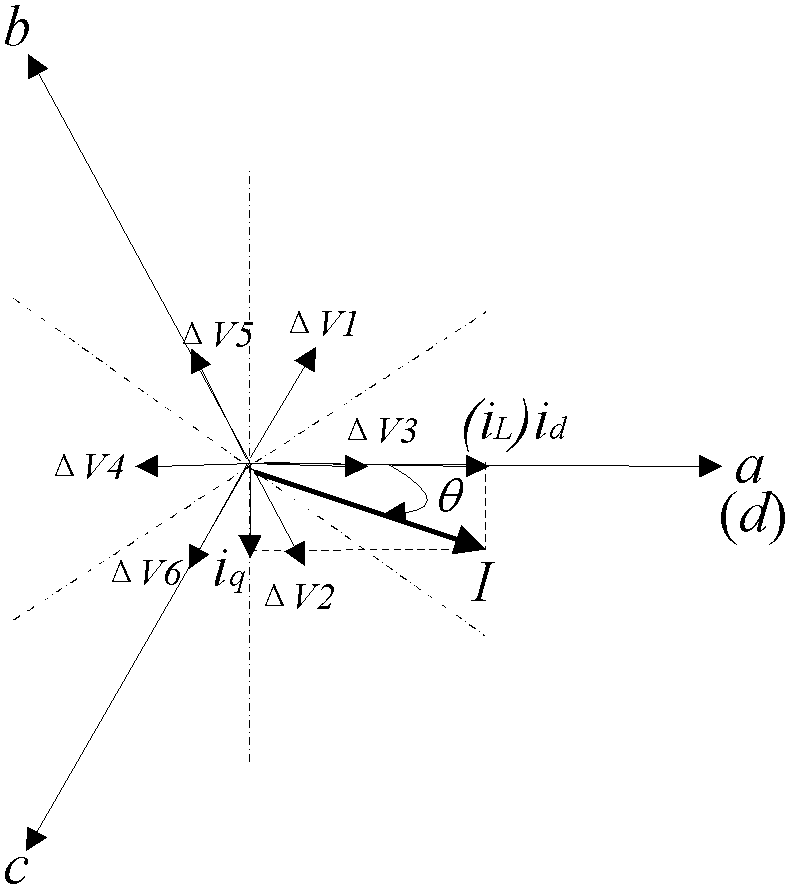
Vector controlled "dead-time effect" compensation method for permanent magnet synchronous motor
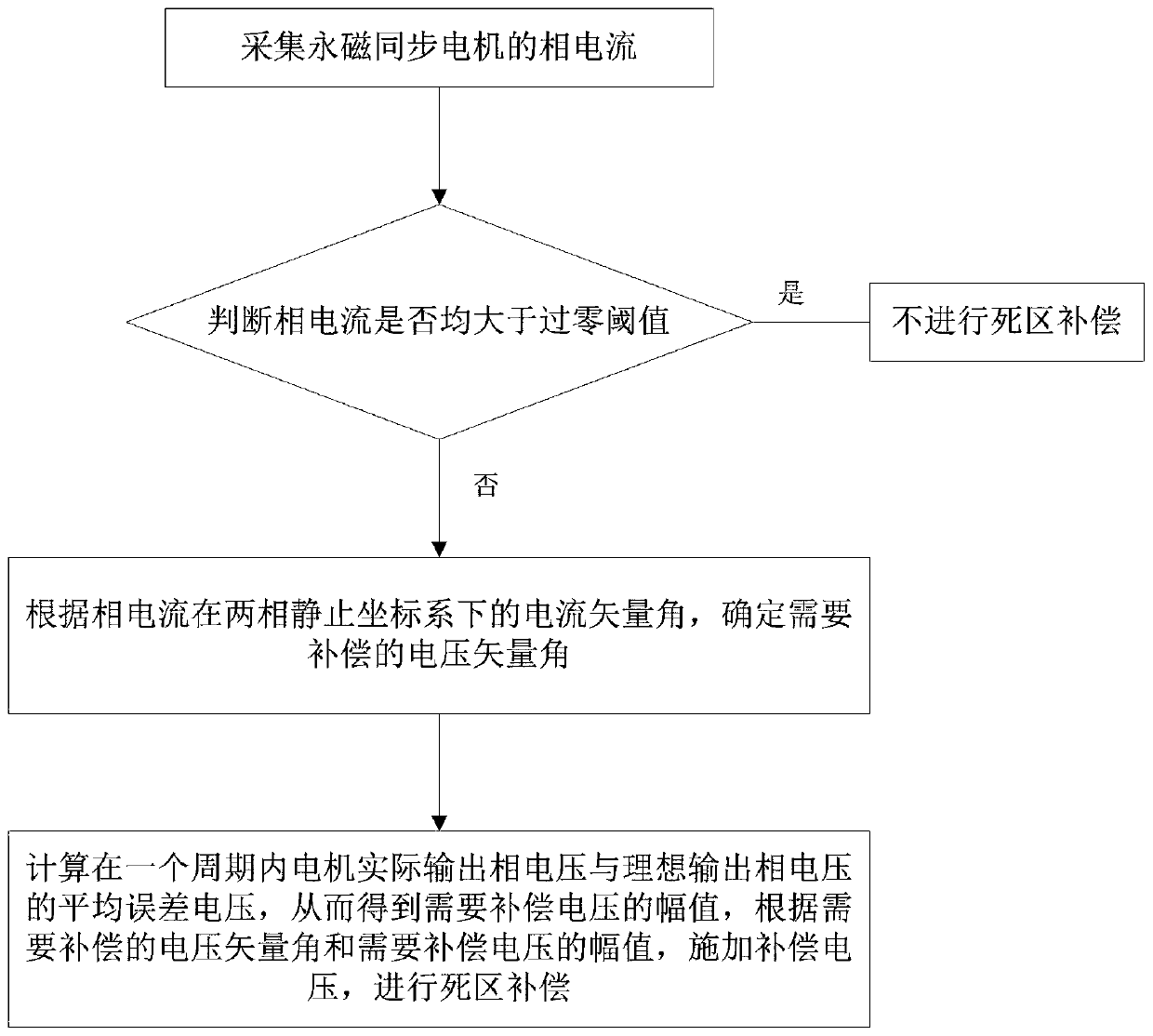
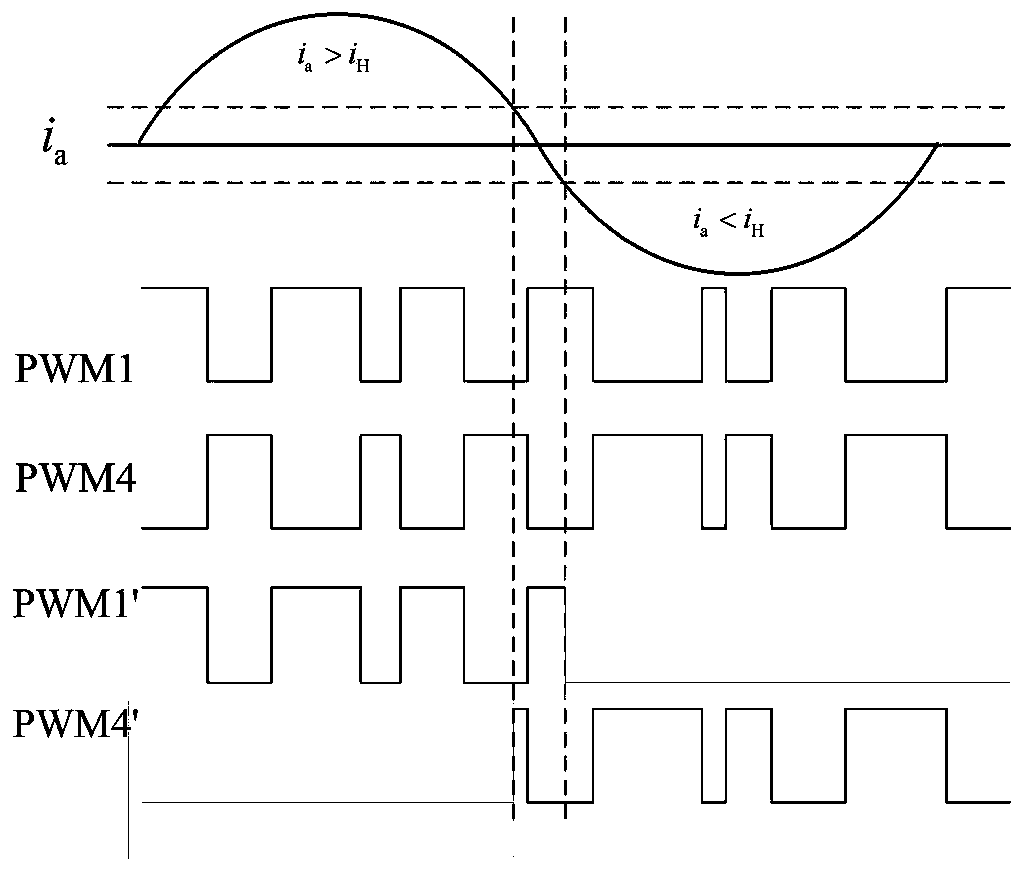
InactiveCN110071669ALow costPrevent false compensationElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlPhase currentsDead time
The invention relates to a vector controlled "dead-time effect" compensation method for a permanent magnet synchronous motor, and belongs to the technical field of permanent magnet synchronous motors,and solves the problems in the prior art such as compensation effect dependent on the accuracy of the motor model, need for additional hardware, complicated calculation and compensation by mistakes.The vector controlled "dead-time effect" compensation method for permanent magnet synchronous motor comprises the following steps: collecting phase currents ia, ib, ic of the permanent magnet synchronous motor; respectively comparing |ia|, |ib| or |ic| with a zero-cross threshold iH, if |ia|, |ib| or |ic| is less than or equal to the zero-cross threshold iH, performing the dead time compensation;otherwise, not performing the dead time compensation. The dead time compensation comprises steps of determining a voltage vector angle that needs to be compensated; calculating an average error voltage of the output phase voltages in a cycle, thereby obtaining the amplitude of the voltage to be compensated, applying a compensation voltage according to the voltage vector angle to be compensated andthe amplitude of the voltage to be compensated for performing a dead time compensation, so as to the accurate and fast dead time compensation.
Owner:BEIJING MECHANICAL EQUIP INST
Motor controller and electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS7126304B2Accurate compensationAC motor controlSynchronous motors startersElectric power steeringBrushless motors
A microcomputer includes a rotation angular velocity computation section, a feedback gain determination section, and a dead time compensation amount determination section. The rotation angular velocity determination section computes the rotation angular velocity of a brushless motor. Based on the rotation angular velocity, the feedback gain determination section determines feedback gains. The dead time compensation amount determination section determines a dead time compensation amount. The greater the absolute value of the rotation angular velocity, that is, the higher the rotation speed of the brushless motor, the greater the feedback gains determined by the feedback gain determination section become, and the higher the responsivity of the feedback gains becomes. The greater the absolute value of the rotation angular velocity, the smaller the dead time compensation amount determined by the dead time compensation amount determination section becomes.
Owner:TOYODA MASCH WORKS LTD +2
Motor control device and electric power steering device
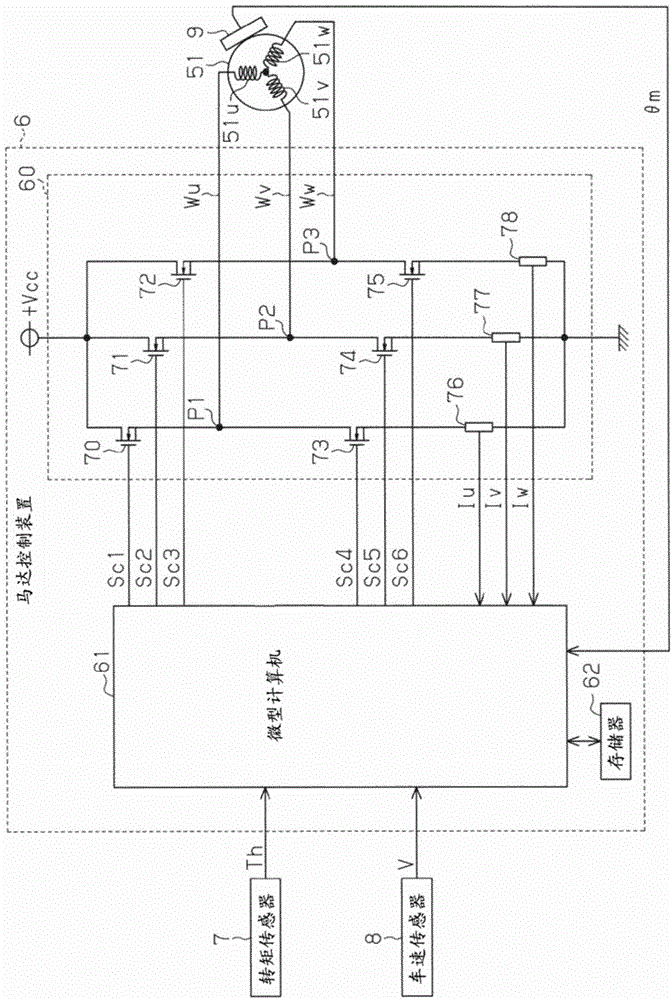
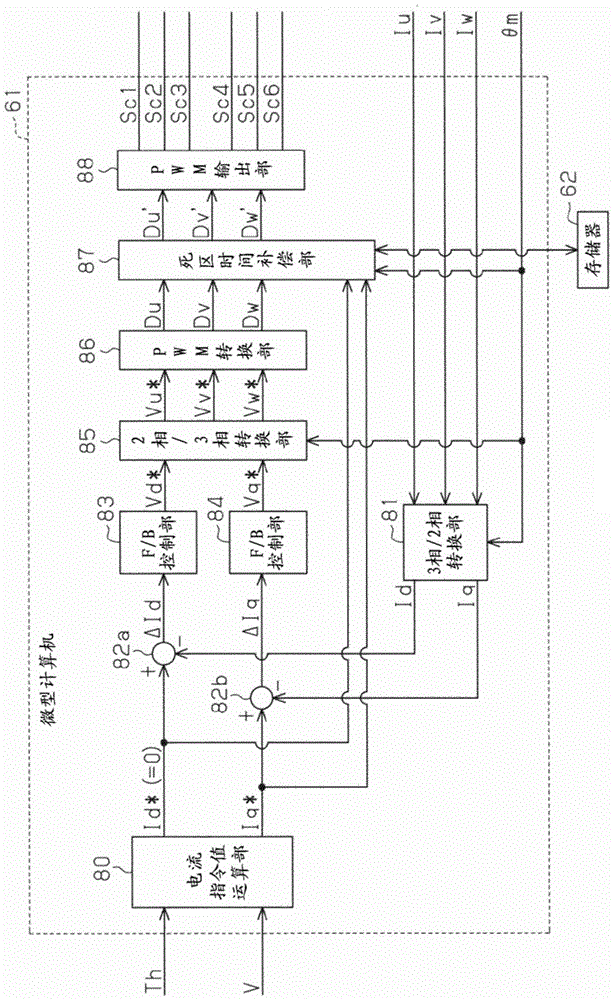
ActiveCN104901601ASuppress abnormal noiseSuppress discomfortSpeed controllerVector control systemsMicrocomputerElectric power steering
A motor control device includes a motor drive circuit and a microcomputer that controls the drive circuit. The microcomputer generates a control signal on the basis of duty command values Du, Dv, and Dw to control the drive circuit. The microcomputer includes a dead time compensation section 87 that corrects the duty command values Du, Dv, and Dw on the basis of dead time compensation values Ddu, Ddv, and Ddw. The dead time compensation section 87 includes a basic compensation value computation section 92 that computes a basic compensation value Dd as a fundamental value of the dead time compensation values Ddu, Ddv, and Ddw, and a filter section 93 that performs a filtering process corresponding to a low-pass filter on the basic compensation value Dd. The dead time compensation section 87 sets the dead time compensation values Ddu, Ddv, and Ddw on the basis of an output value ± from the filter section 93.
Owner:JTEKT CORP
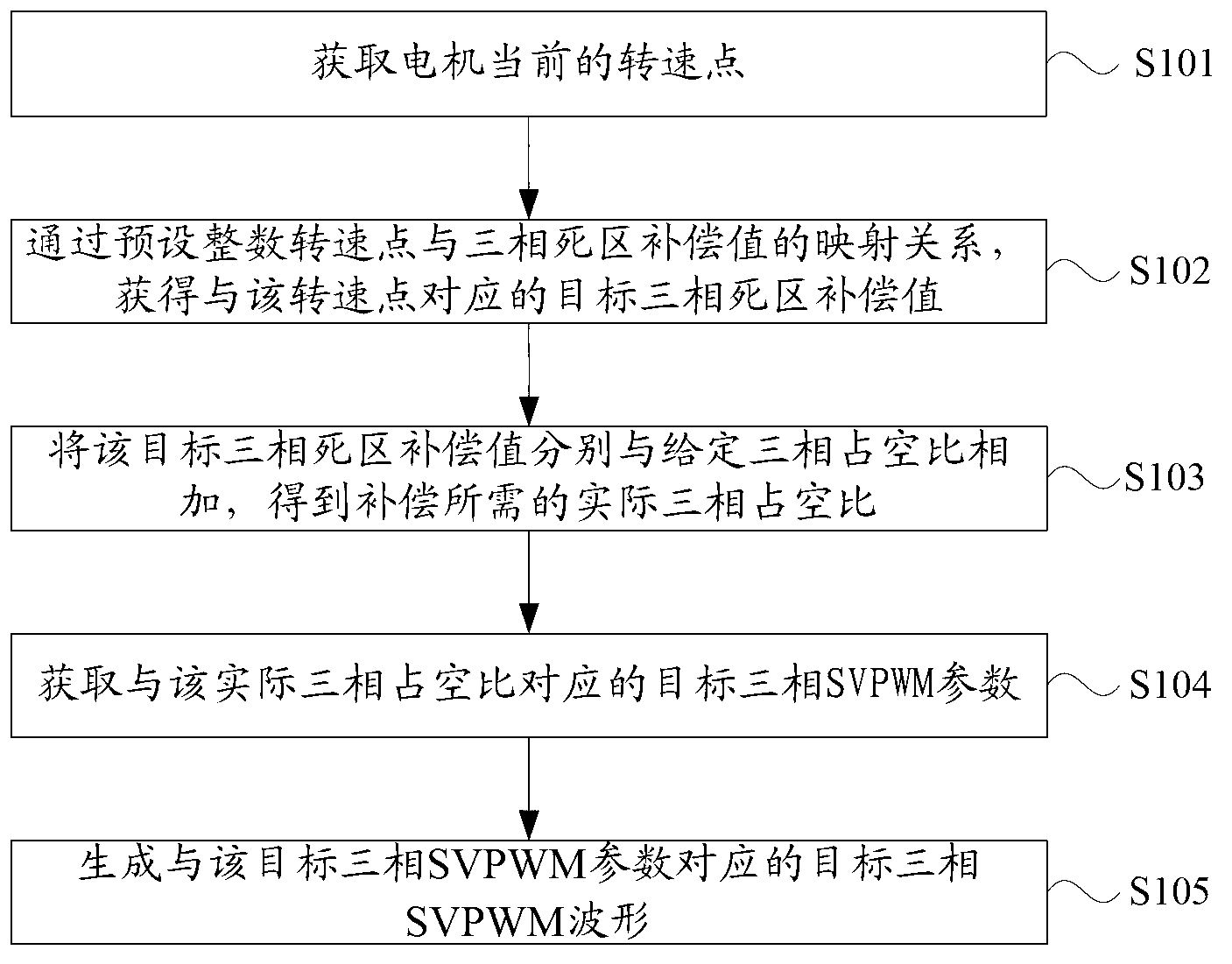
Dead time effect compensation method and device
ActiveCN103078589AImprove control efficiencyAC motor controlAc-dc conversionDead time compensationThree-phase
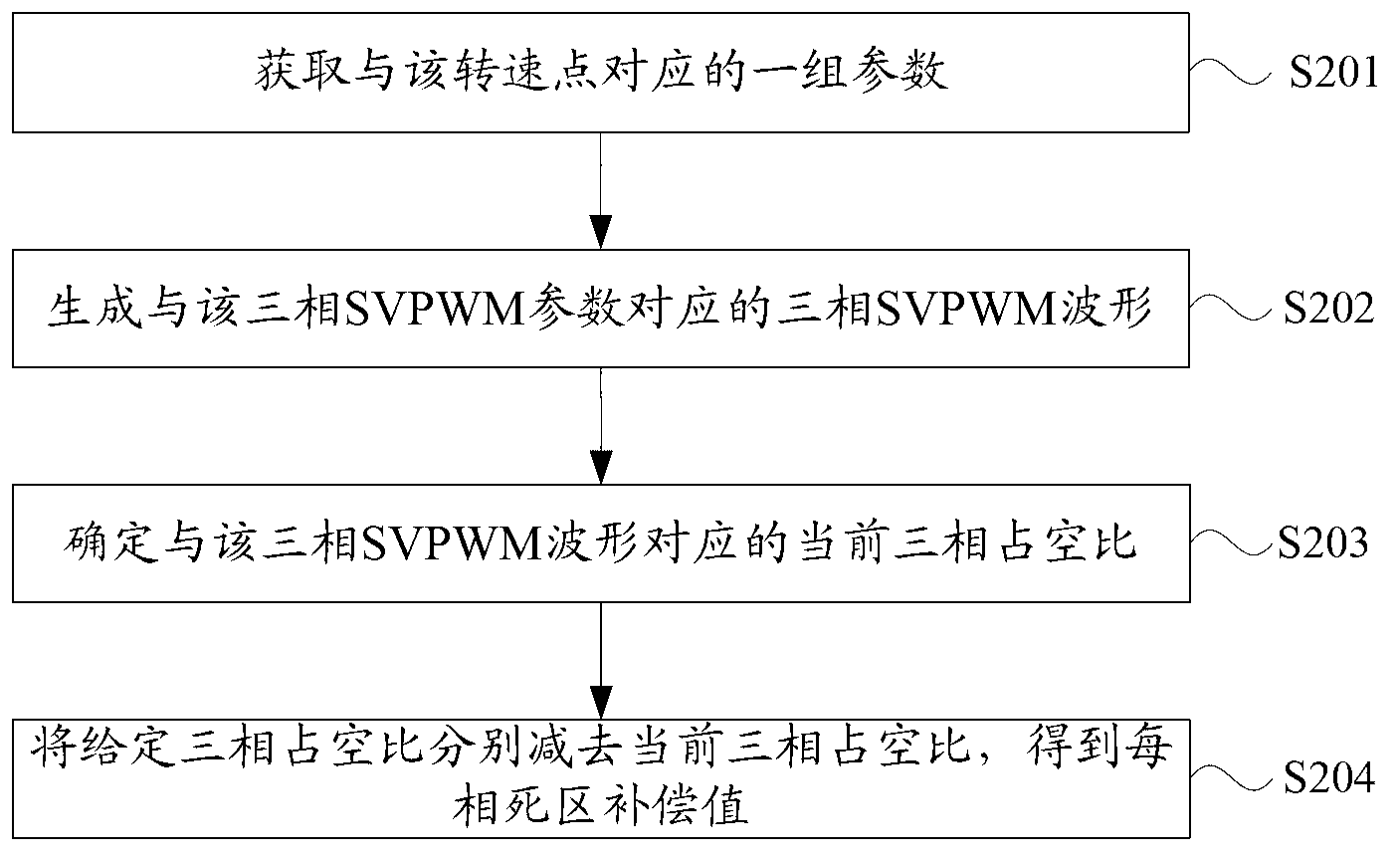
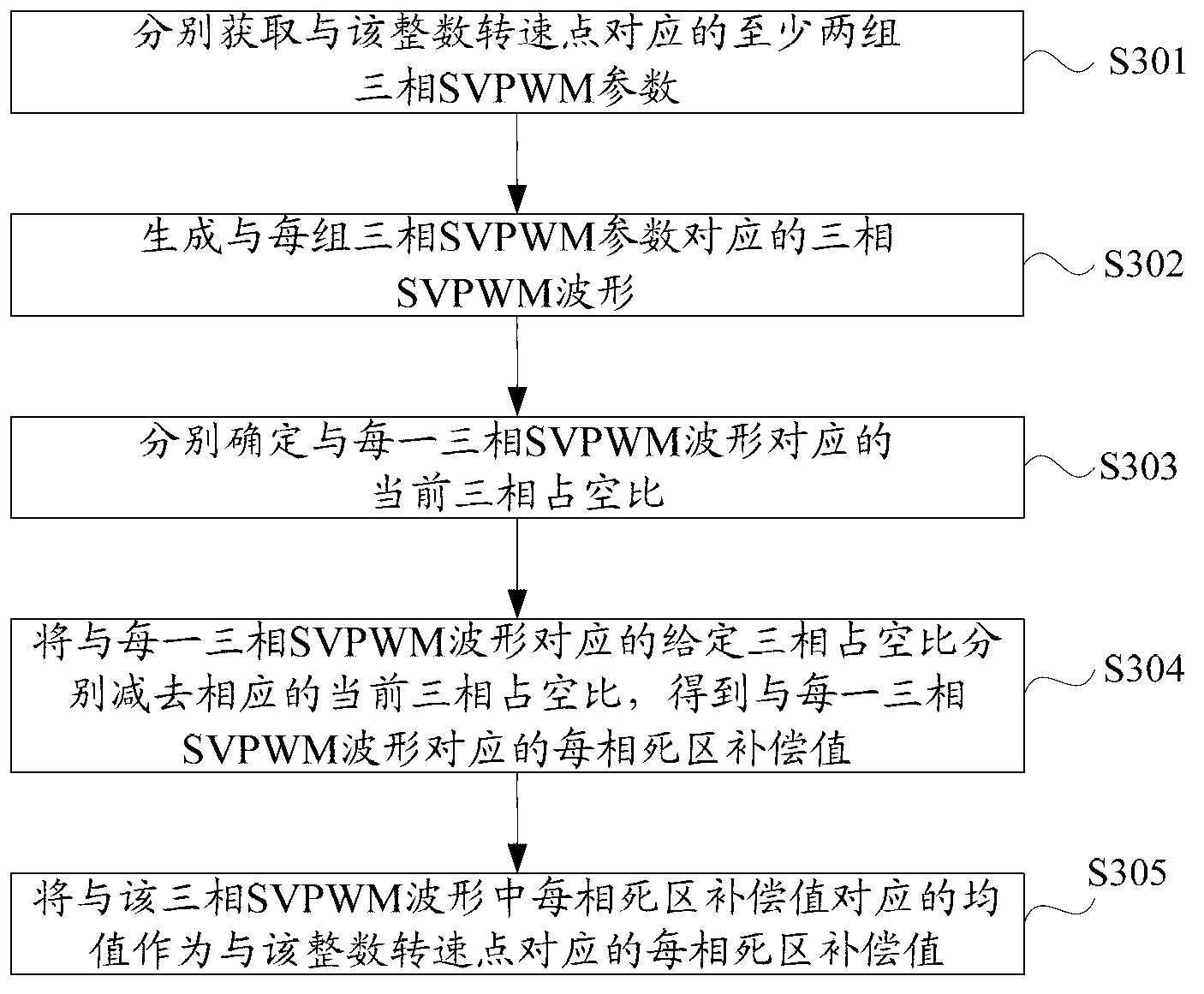
The invention discloses a dead time effect compensation method and a dead-time effect compensation device. The method comprises the following steps of: presetting a mapping relation between an integer rotating speed point and a three-phase dead time compensation value to obtain a target three-phase dead time compensation value which corresponds to a current rotating speed point; adding the target three-phase dead time compensation value with a given three-phase duty ratio to obtain a practical three-phase duty ratio needed by compensation; and further obtaining a target three-phase SVPWM (Space Vector Pulse Width Modulation) parameter which corresponds to the practical three-phase duty ratio to generate a target three-phase SVPWM waveform so as to finish compensation for the three-phase SVPWM waveform under the rotating speed point. According to the method and the device, the problem that the current three-phase duty ratio of the three-phase inverter circuit output waveform of a motor controller is lower than the given three-phase duty ratio due to the presence of the dead time is solved, and the control efficiency of the motor controller is further increased.
Owner:深蓝汽车科技有限公司
Electric power converter and motor driving system
InactiveUS7541769B2Improve accuracyElectronic commutation motor controlMotor/generator/converter stoppersSwitching frequencyDc voltage
An electric power converter which has improved accuracy in compensation of a dead time. A motor driving system employing the electric power converter is also provided. A power module includes a plurality of switching devices connected in series and converts DC power to AC power. A control circuit produces a voltage command value in accordance with a control command inputted from the exterior, and produces gate signals to drive the switching devices of the power module corresponding to a final voltage command value which is obtained from the voltage command value with dead time compensation. A dead time compensation logic circuit calculates a final dead time compensation voltage based on a change rate of the voltage command value, a gain (dead time compensation voltage value), and a polarity of a current, the gain being calculated from a DC voltage value supplied to the electric power converter, a dead time, and a switching frequency.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Dead-time compensation apparatus of PWM inverter and method thereof
ActiveUS8084986B2Single-phase induction motor startersMotor/generator/converter stoppersTime responseLow speed
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Dead-time compensation method and device of inverter
ActiveCN105450060AReduce the possibility of distortionAccurate compensationDc-ac conversion without reversalPower qualityDead time
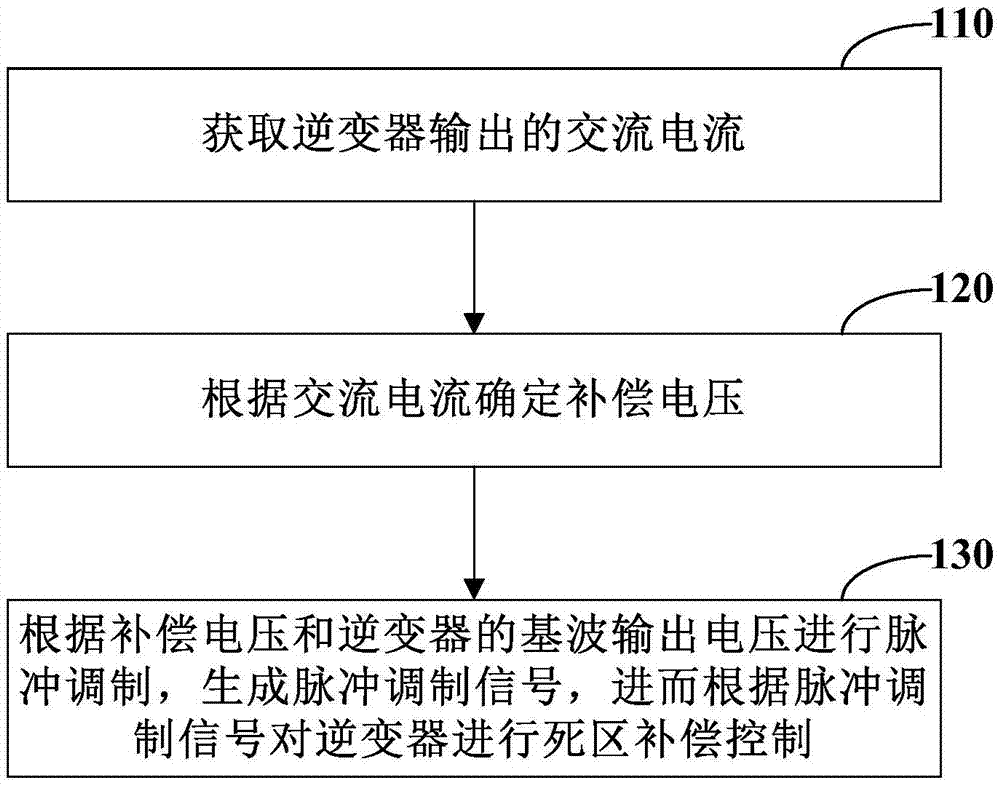
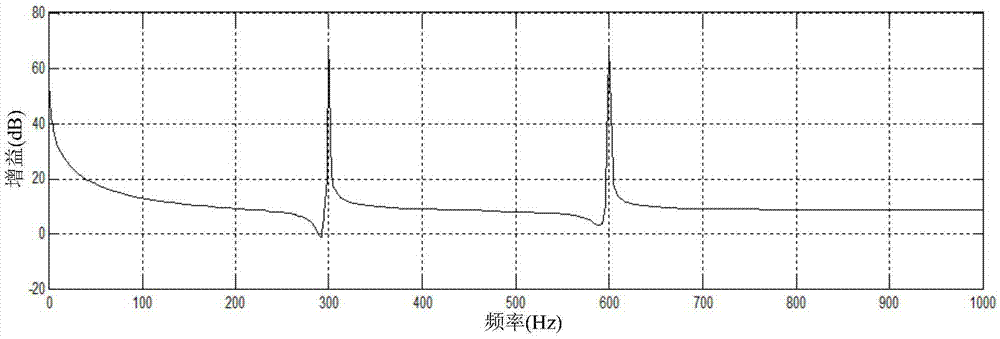
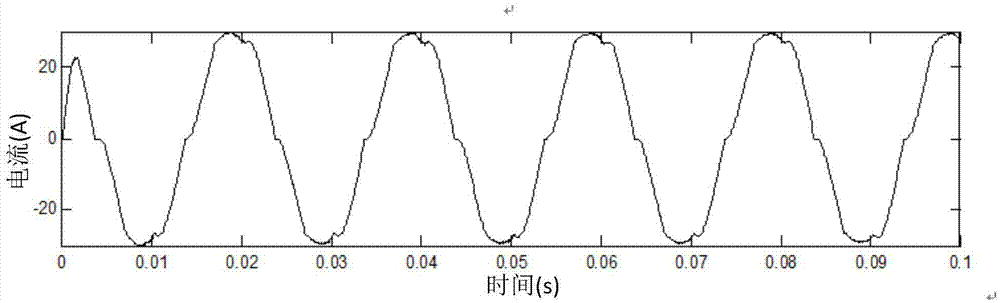
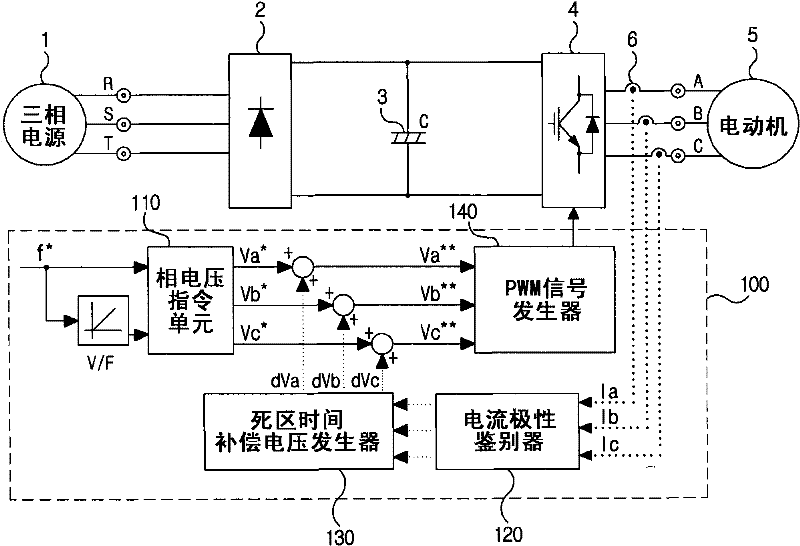
The embodiment of the invention provides a dead-time compensation method and device of an inverter. The dead-time compensation method of the inverter comprises the following steps of acquiring AC current output from the inverter; determining compensation voltage according to the AC current; carrying out pulse modulation and generating a pulse modulation signal according to the compensation voltage and fundamental wave output voltage of the inverter; and carrying out dead-time compensation control on the inverter according to the pulse modulation signal. Through the dead-time compensation method and device of the inverter, provided by the invention, the dead-time voltage is accurately and dynamically compensated, the distortion probability of the output current of the inverter is reduced, and the electric energy quality is enhanced.
Owner:BEIJING ETECHWIN ELECTRIC
Output current distortion compensating apparatus in inverter
InactiveCN102237848AAvoid Oscillating PhenomenaDead time compensation error reductionAC motor controlDc-ac conversion without reversalVoltage generatorFrequency changer
An output current distortion compensating apparatus in an inverter is disclosed, the inverter including an inverter controller generating a PWM signal for controlling a PWM voltage generator, wherein the inverter controller includes a first dead time compensation voltage generator generating a compensation voltage based on an output current polarity of each phase in the inverter, and a second dead time compensation voltage generator generating a compensation voltage based on an output current waveform of each phase in the inverter, and wherein a first dead time compensation voltage outputted from the first dead time compensation voltage generator and a second dead time compensation voltage outputted from the second dead time compensation voltage generator are added to generate a final dead time compensation voltage, thereby preventing occurrence of hunting phenomenon in which a current is greatly fluctuated.
Owner:LSIS CO LTD
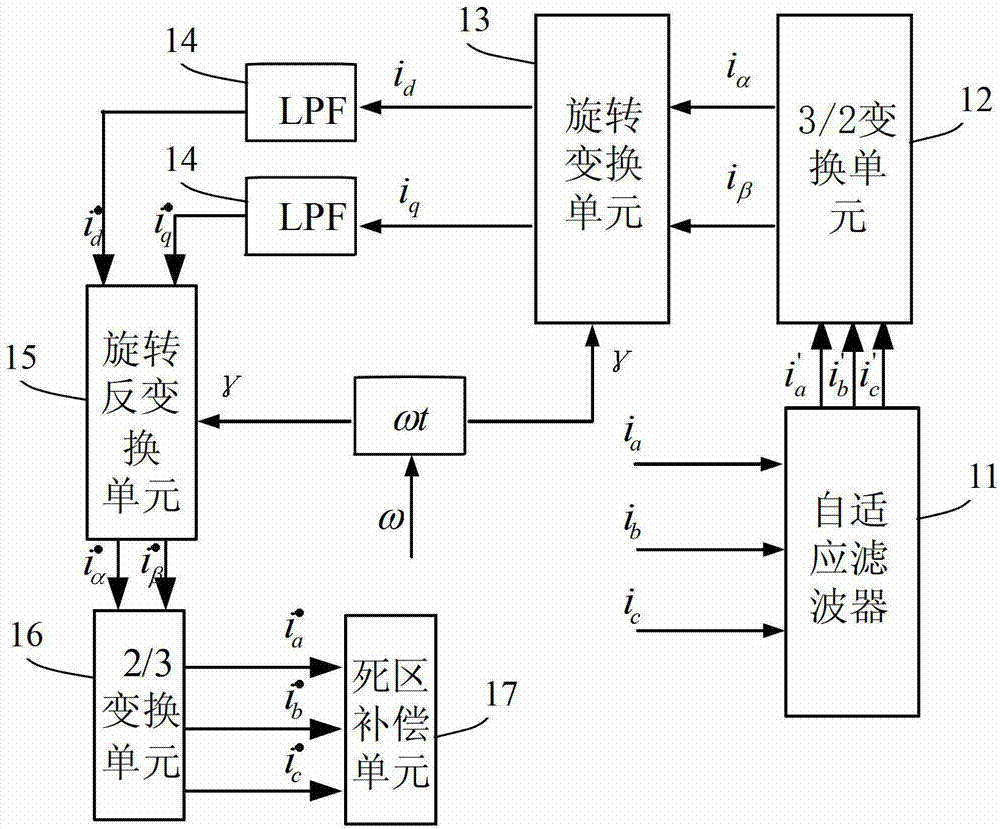
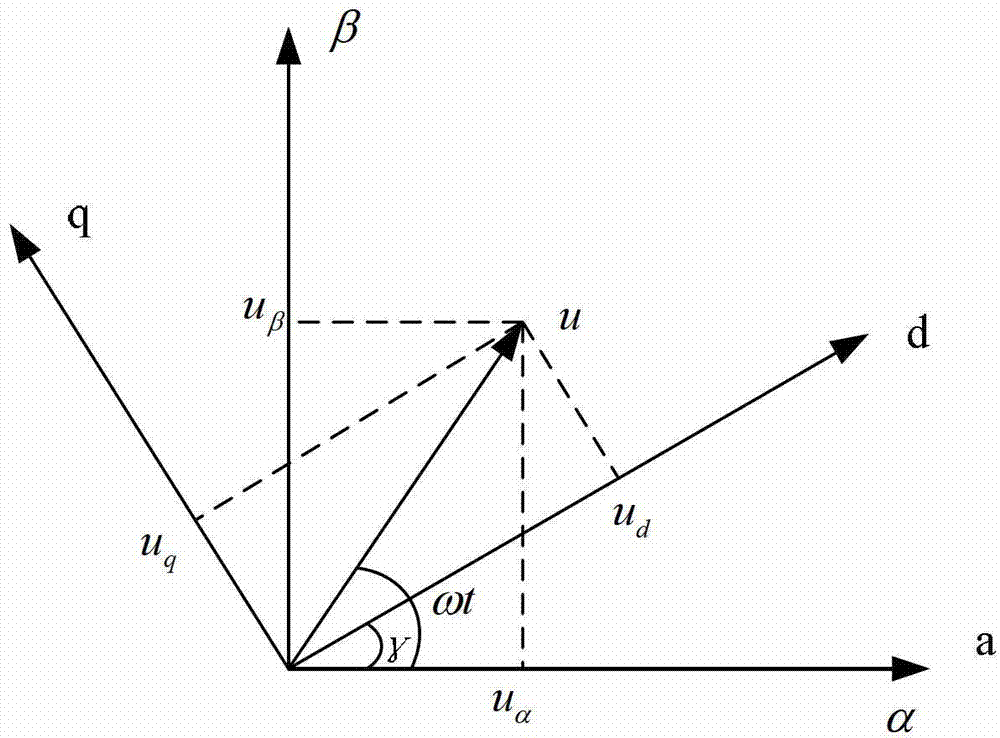
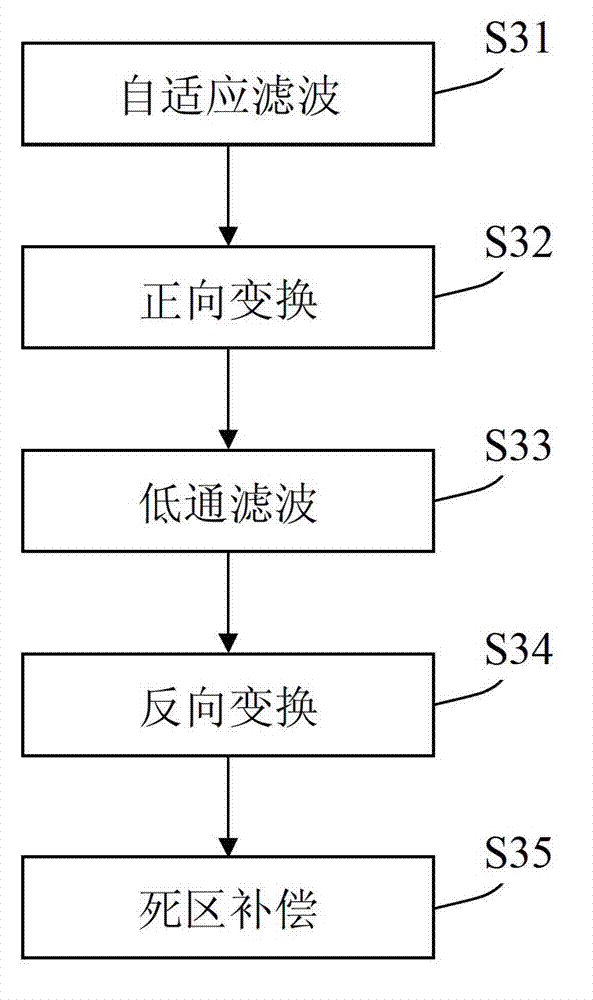
Dead-time compensation system and method
ActiveCN102931902AAvoid failureOvercoming detectionElectronic commutation motor controlVector control systemsAdaptive filterDead time compensation
The invention provides a dead-time compensation system which comprises a current sampling unit, an adaptive filter, a forward conversion unit, a low-pass filter, a reverse conversion unit and a dead-time compensation unit, wherein the adaptive filter is used for adaptively filtering each of sampled three phases of current to obtain a three-phase current forecast value; the forward conversion unit is used for executing 3 / 2 conversion and rotary conversion on the three-phase current forecast value; the low-pass filter is used for performing low-pass filtration; the reverse conversion unit is used for performing rotary reverse conversion and 2 / 3 conversion; and the dead time compensation unit is used for performing dead-time compensation according to the current subjected to 2 / 3 conversion. The invention also provides a corresponding dead-time compensation method. According to the invention, the adaptive filter can filter the sampled three phases of current, thereby overcoming an error between a detected value and a real value, which is caused by current detection delay and further avoiding failure of dead-time compensation caused by inaccurate detected current value.
Owner:SUZHOU INOVANCE TECH CO LTD
System and method for low speed control of polyphase ac machine
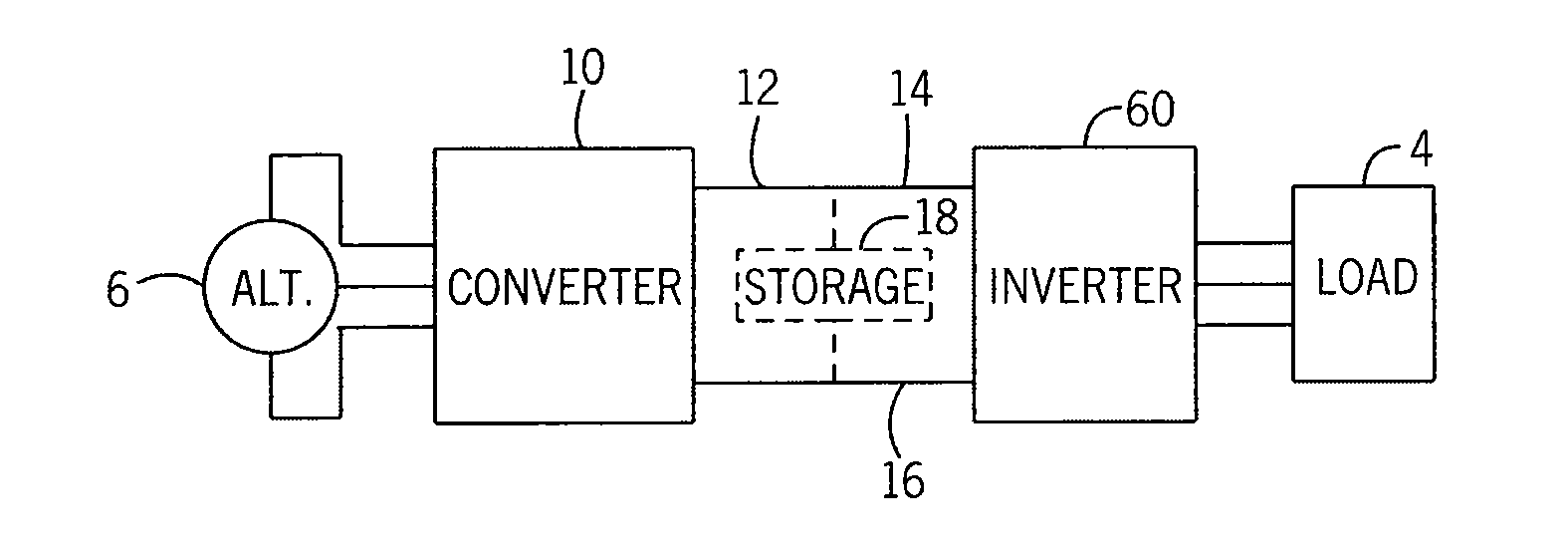
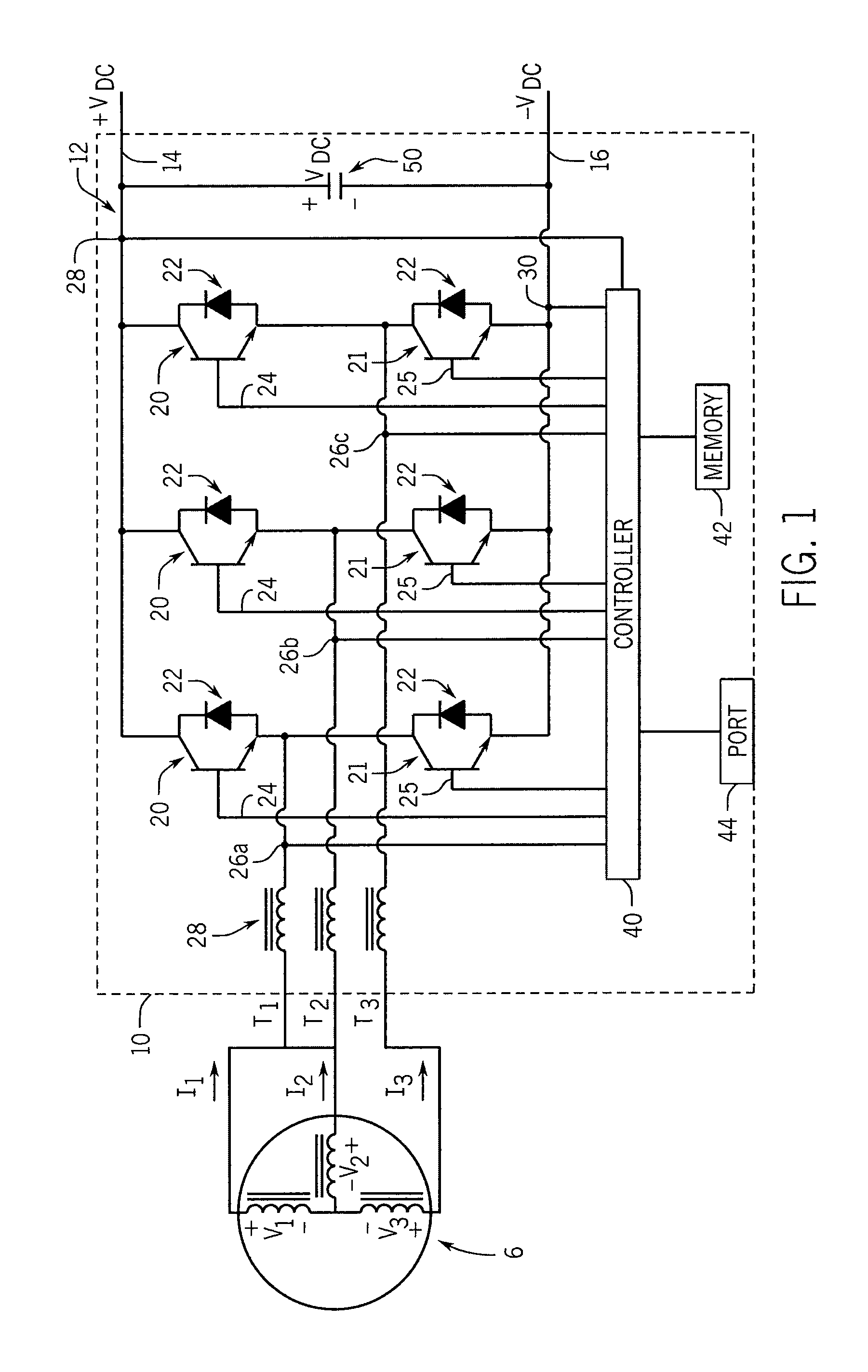
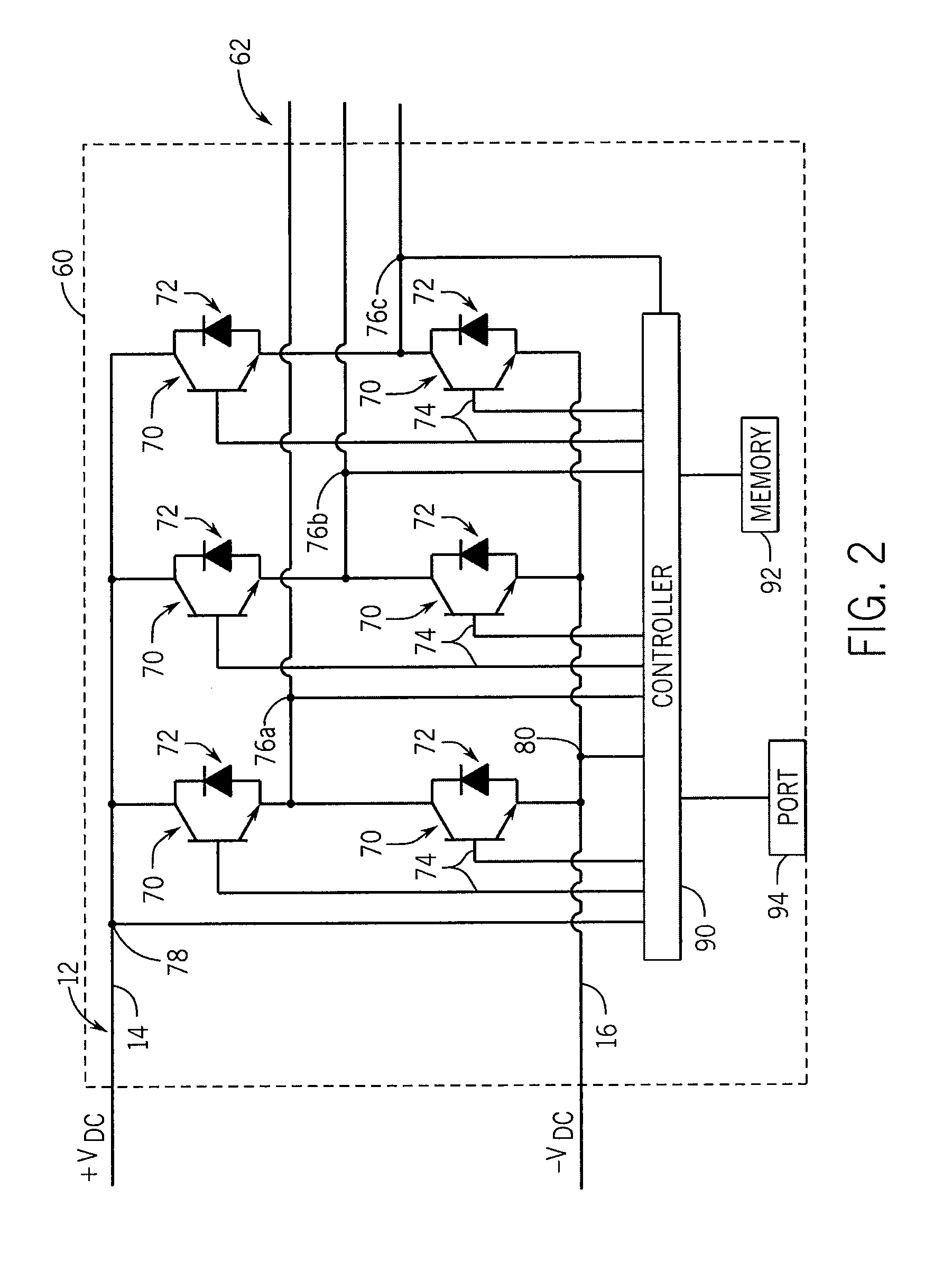
InactiveUS20130155730A1Maximize efficiencyEasy to operateMaterial nanotechnologyHeavy metal active ingredientsLow speedTotal harmonic distortion
A power converter configured to improve power capture in a wind turbine during low wind speed operation is disclosed. The power converter converts the power generated by the alternator of the wind turbine into a suitable AC current for delivery to a utility grid or to an electric load independent of the utility grid. The power converter is configured to operate in multiple operating modes, utilizing both synchronous and non-synchronous control methods, to extend the operating range of the power converter. During non-synchronous operation, the power converter utilizes a modulation routine that may either vary the dead-time compensation period during a constant modulation period or vary the modulation period with a constant on-time. A seamless transfer between non-synchronous and synchronous control methods with low total harmonic distortion (THD) improves the range of power generation for wind generators.
Owner:ENSYNC
Method for compensating dead time of converter based on distortion function
ActiveCN102013829AImprove steady-state characteristicsReduce low frequency harmonic componentsAc-dc conversionDead time compensationControl system
The invention discloses a novel method for compensating dead time of a converter, which is applied to universal voltage source converters. In the method, a distortion function correction step is increased on the basis of the normal method for compensating the dead time compensation. In the method, voltage feedback is used as a reference, and a dead time effect distortion function is corrected fora plurality of periods, so that the accuracy for dead time compensation can be effectively improved and the output quality of the converter is improved. The method is easy to implement and does not cause obvious disturbance to a converter control system.
Owner:WUXI SILENT ELECTRIC SYST SES TECH CO LTD +1
Intelligent power unit for high-power converter device and control method
ActiveCN105391310ASuitable for all-round controlLow costAc-dc conversionAc-ac conversionMicrocontrollerEngineering
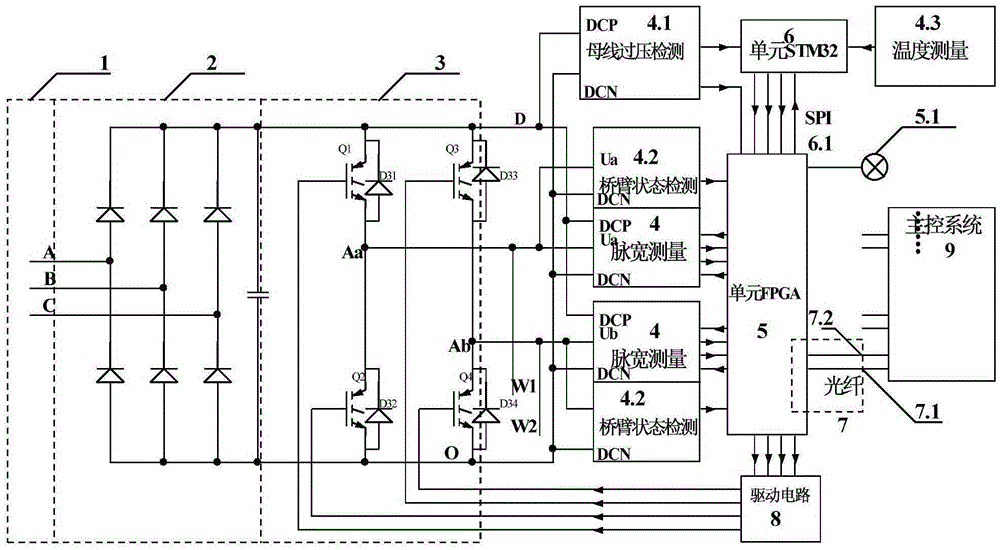
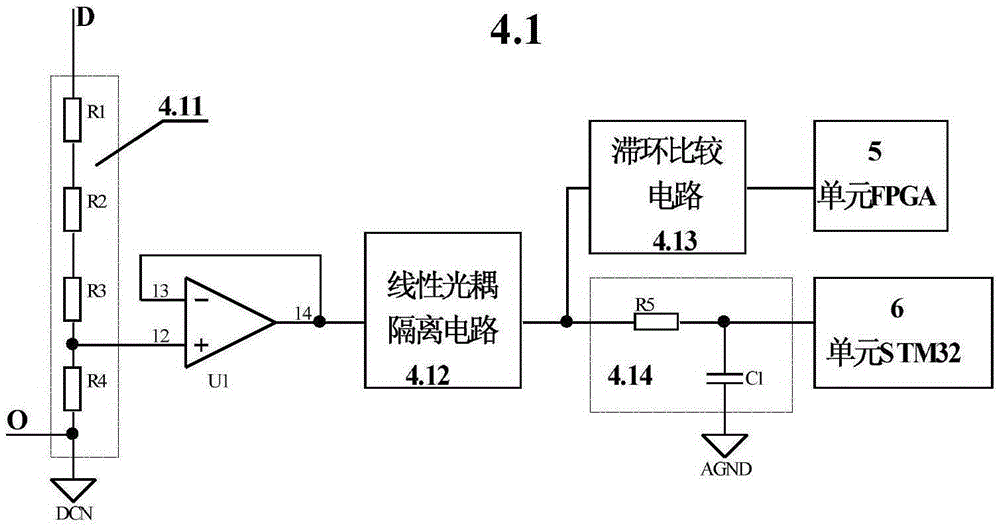
The invention relates to an intelligent power unit for a high-power converter device and a control method, used for a high-voltage frequency converter and a photovoltaic inverter. The frequency converter is formed by a plurality of power units, each phase of which is arranged in multiple layers, in series; each power unit is provided with a unit field programmable logic array FPGA and a single chip microcomputer unit STM32; the unit field programmable logic array FPGA and the single chip microcomputer unit STM32 are connected through a serial interface SPI; bus over-voltage detection, temperature measurement, bridge arm open-circuit and short-circuit state detection having flash lamp indication, pulse wide measurement and the like are connected to the inlet of the FPGA; the outlet is connected to a driving circuit; a main control system comprises a central data controller and a layer controller on the same mainboard; bidirectional transmission between the main control system and the FPGA is realized through two optical fibres; the two have communication state detection; transmission is carried out according to a specified time sequence; therefore, the anti-interference performance is high; the real-time performance of fault response is ensured; dead-time compensation in pulse width measurement is carried out according to the real waveform; the compensation precision is the highest; a variable-frequency motor is constant in waveform and steady in torque; a test result shows that: the communication speed is high; the synchronization performance is good; the reliability is high; performances are comprehensively optimized and intelligentized; the cost is low; and the intelligent power unit is used for the driving power supply of the variable-frequency motor and the power supply of the photovoltaic inverter.
Owner:四川中大华瑞能源技术有限公司
Electric power steering apparatus
ActiveUS20190256128A1Control distortionResponsibility of controlTorque ripple controlAC motor controlPhase currentsBrushless motors
An electric power steering apparatus of a vector control system converts calculated dq-axes current command values into 3-phase duty command values, driving-controls a 3-phase brushless motor by an inverter of a PWM control, and applies an assist torque to a steering system of a vehicle, wherein compensation signs of 3-phase current model command values in which the dq-axes current command values are converted into a 3-phase current command value model are estimated, wherein a dead time compensation amount is calculated based on an inverter-applying voltage, and wherein dead time compensation is performed by adding dead time compensation values that are 2-phase values converted from 3-phase values in which the compensation signs are multiplied with the dead time compensation amount, to dq-axes voltage command values, or by adding 3-phase dead time compensation values to 3-phase voltage command values.
Owner:NSK LTD
Method and apparatus for adaptive compensation of dead time for inverter and converter
InactiveCN1467907AImprove performanceImprove stabilityAc-dc conversionDead timeDead time compensation
The invention relates to the compensation of dead time effect in electronic appliances such as inverters or converters having one or more legs with two complementary switches. The invented method mainly includes following steps providing an initial pulse width modulated (PWM) reference, providing a bias current and detecting the bias current crossing points, providing a dead time compensation signal which is adjusted responsive to the crossing points, and adding the dead time compensation signal to the PWM reference. Hence an adaptive compensation is accomplished independent of types of switching elements and load conditions. A high reliable circuit with low cost is further included as a preferred embodiment of bias current crossing points detection.
Owner:DELTA ELECTRONICS INC
Vector controller based on software dead-time compensation
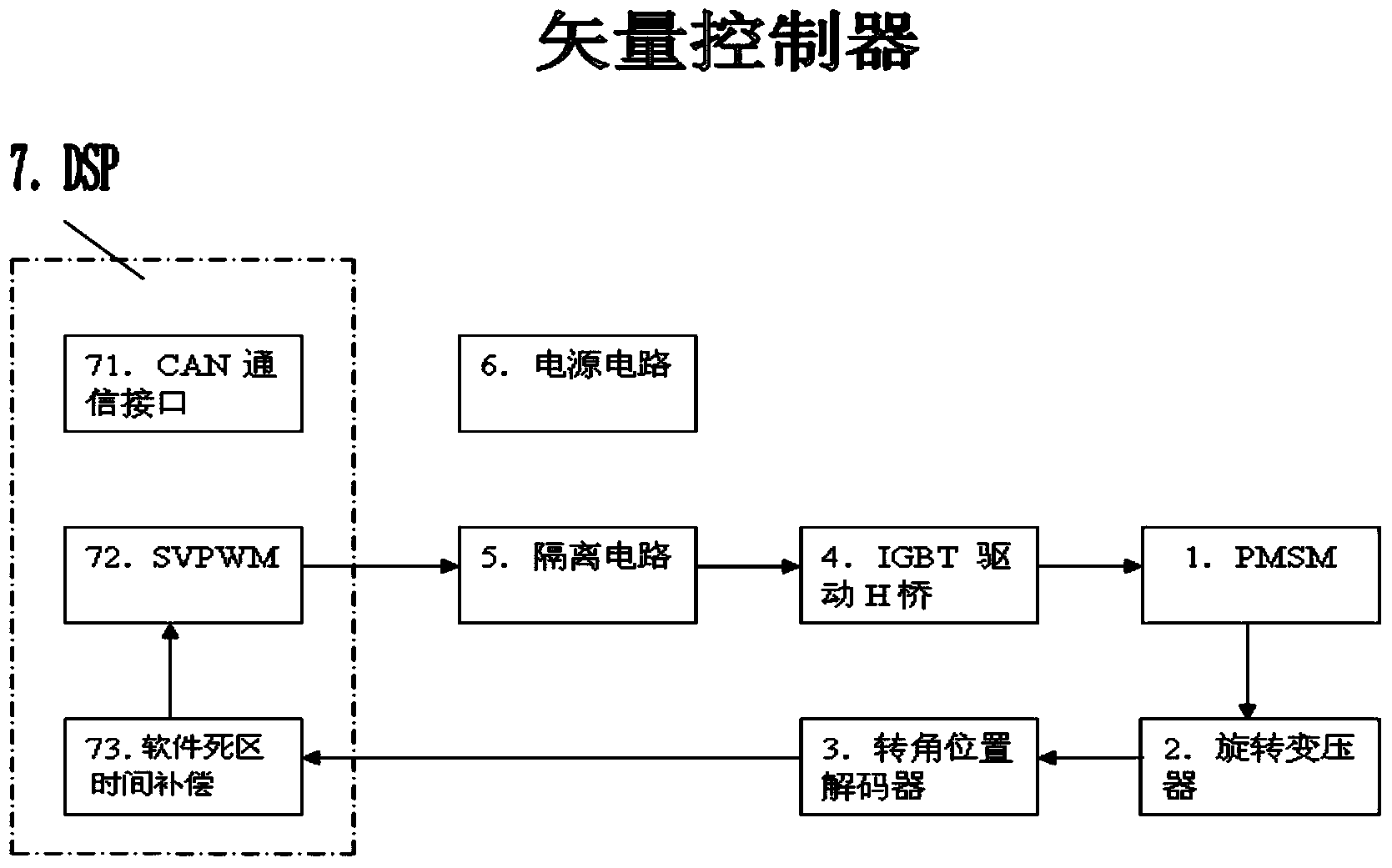
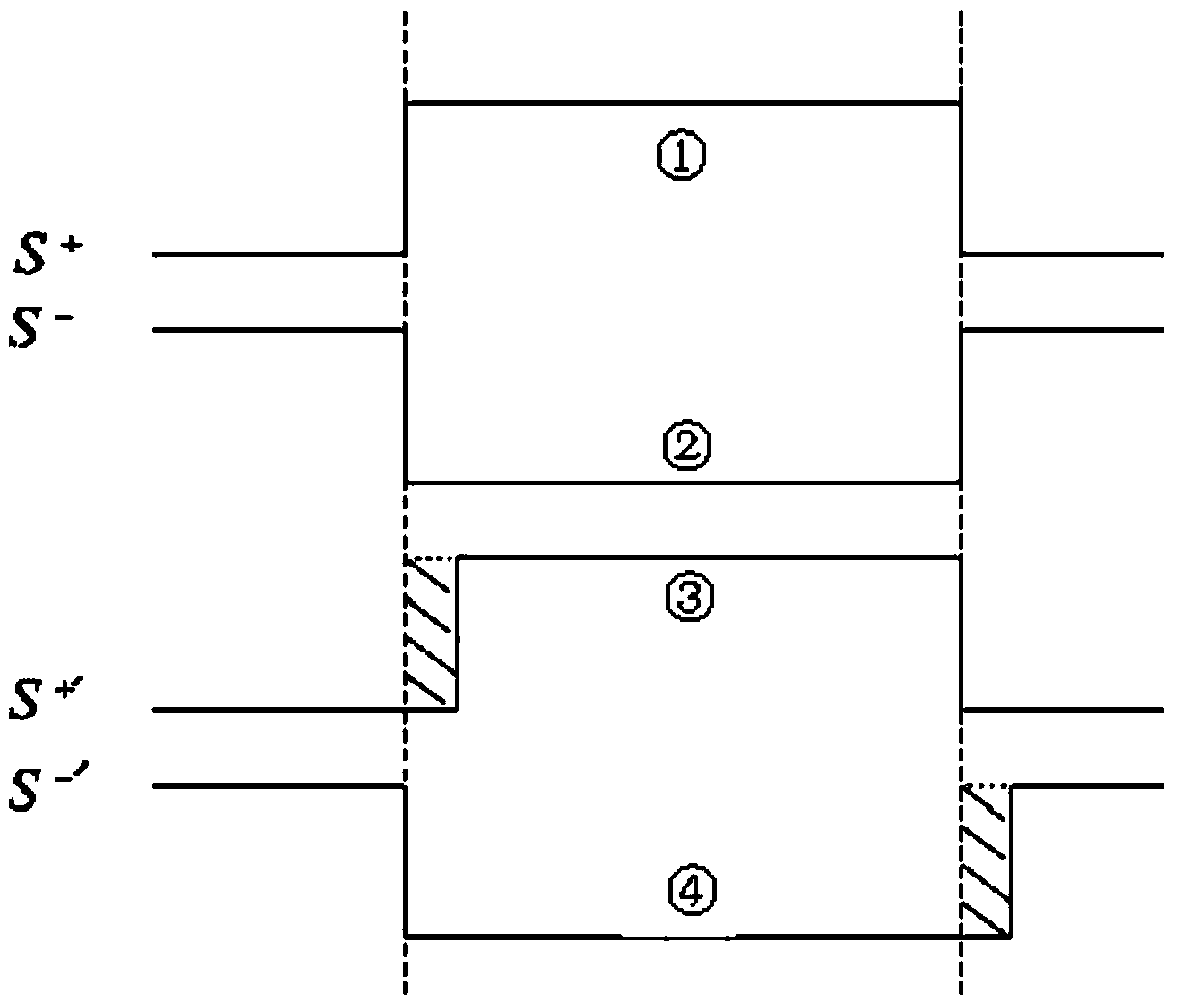
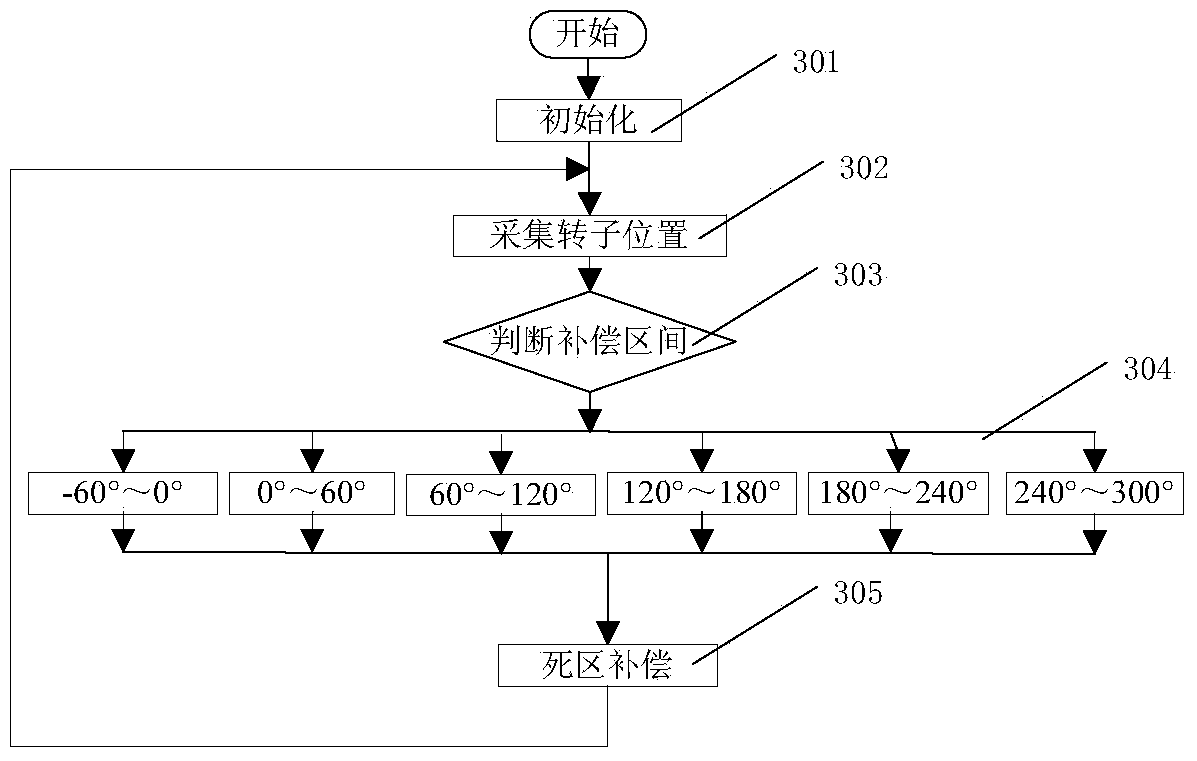
ActiveCN103872960AGuaranteed uptimeImprove stabilityElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlDigital signal processingVoltage vector
The invention discloses a vector controller based on software dead-time compensation. The vector controller based on software dead-time compensation comprises a digital signal processor (DSP), a permanent magnet synchronous motor (PMSM), a rotary transformer, a corner position decoder and an IGBT driving H-bridge. The DSP comprises a space voltage vector pulse width modulator (SVPWM). The IGBT driving H-bridge is connected with the PMSM. The rotary transformer is connected with the corner position decoder and the PMSM. The DSP is connected with the corner position decoder. The software dead-time compensation algorithm is used for compensating for the switch-on time and the switch-off time of the SVPWM. A drive signal generated by the SVPWM controls the switch-on and switch-off of the IGBT driving H-bridge, so that the PMSM is driven. According to the vector controller based on software dead-time compensation, the dead-time compensation function is achieved based on the corner position, detected in real time, of a motor rotor, waveform distortion of the current output by a motor controller is reduced, and the stability and reliability of motor control are improved.
Owner:哈尔滨通联客车有限公司
Rotary electric machine control device
ActiveUS9998052B2Reduce errorsAccurate detectionMotor control for very low speedsVector control systemsLower limitDead time compensation
The magnetic pole position of a rotary electric machine is electrically derived accurately by reducing a voltage error due to a dead time while suppressing the influence on the operation efficiency of the rotary electric machine. A control device performs dead-time compensation, and performs current feedback control in a d-q-axis vector coordinate system using a magnetic pole position computed on the basis of an induced voltage produced by rotation of a rotor or on the basis of a response component to a high-frequency observation signal applied to the rotary electric machine. In the case where the rotary electric machine is controlled by deciding current commands Id*, Iq* in the d-q-axis vector coordinate system, the rotary electric machine control device controls the rotary electric machine such that the magnitude of an armature current Ia becomes equal to or more than a lower-limit current Ia_min prescribed in advance.
Owner:AISIN AW CO LTD
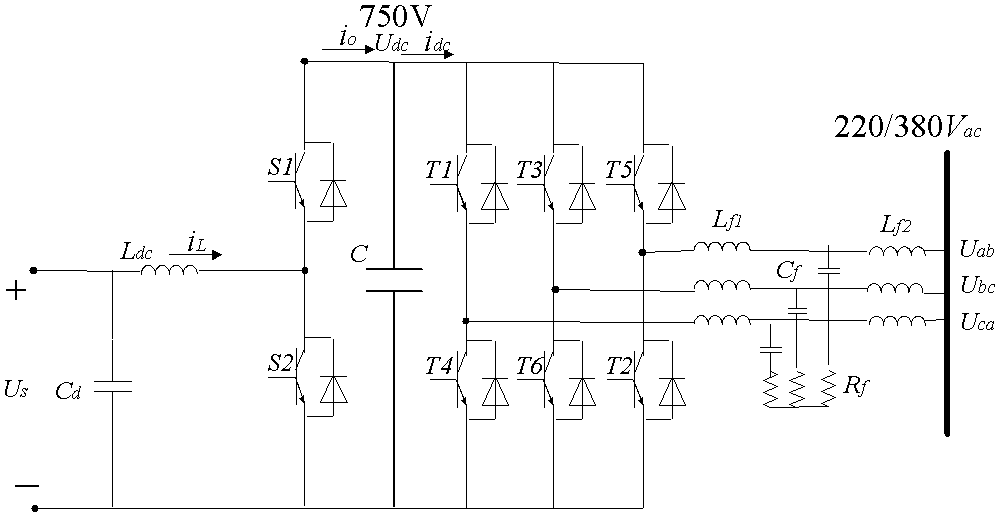
Dead-time compensation method for NPC-based three-level SVPMW (space vector pulse width modulation) rectifier
The invention discloses a dead-time compensation method for an NPC-based three-level SVPMW (space vector pulse width modulation) rectifier. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, computing the general expression of a dead-time-free reconstitution voltage impulse by not considering tube voltage drop and the general expression of a dead-time reconstitution voltage impulse by considering the tube voltage drop to obtain a general expression of reconstitution voltage impulse compensation amount; then, selecting the general expression of the reconstitution voltage impulse compensation amount, which corresponds to three-phase voltage, according to the directions of all phase current and the timing sequence states of all phase voltages to work out voltage compensation amount; finally, feeding back the worked out voltage compensation amount to a reference voltage vector before being reconstituted, and performing compensation. According to the dead-time compensation method disclosed by the invention, by adopting a novel compensation amount selection method, the compensation amount is computed during a voltage reconstitution process, and compensation participated control is performed on the reference voltage vector; dead time and the tube voltage drop are fully considered, and therefore voltage and current distortion problem generated by the dead-time effect in the NPC-based rectifier is solved, and the system performance is improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com