Single-chip high-intensity magnetic field X-axis linear magneto-resistance sensor provided with calibration coil/reset coil
一种磁电阻传感器、磁电阻的技术,应用在磁性传感器领域,能够解决灵敏度差、传感器磁场变化率低、磁场灵敏度低等问题,达到保证测量的精度、提高效率的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
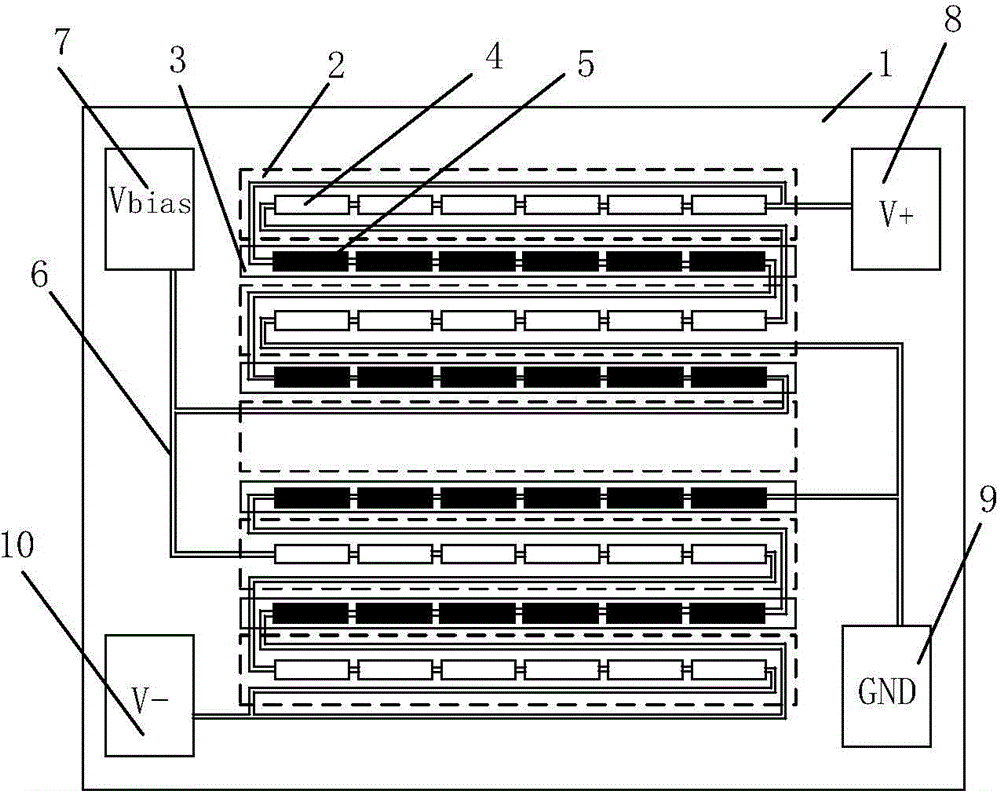
[0068] Figure 4 It is a structure and distribution diagram of a type one calibration coil 70, the calibration coil 70 is a planar coil, including a strip-shaped sensitive straight wire 101 and a reference straight wire 104 connected in series, the sensitive straight wire 101 has a width of Lx1, Its Y-axis center line is arranged along the sensitive magnetoresistive unit string 51, and each section of reference straight wire 104 includes two sub-straight wires 102 and 103, and the sub-straight wires 102 and 103 are connected in parallel and distributed symmetrically along the Y direction. Referring to both sides of the magnetoresistive sensing unit string 41 , the widths of the sub-straight wires 102 and 103 are both Lx2.
[0069] Figure 5-7 respectively Figure 4 Shown is a cross-sectional view of an X-axis magnetoresistive sensor comprising a type one calibration coil 70, wherein, Figure 5 Among them, the planar calibration coil is located on the substrate 1 and below t...
Embodiment 2
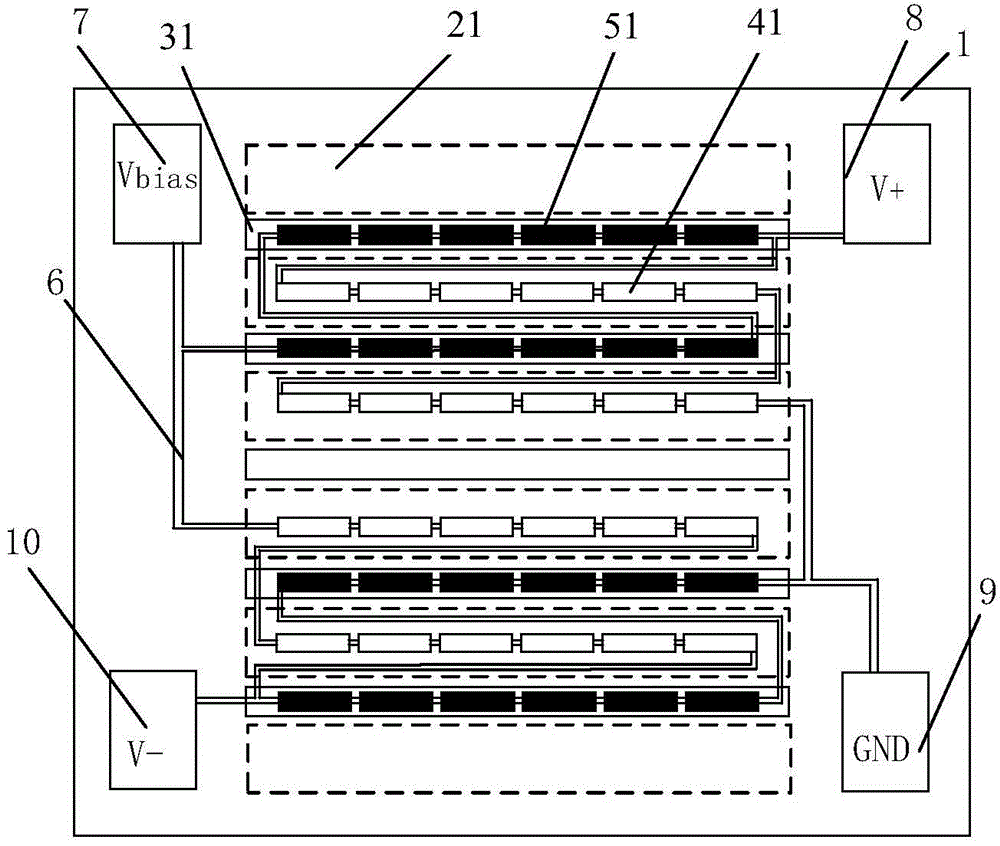
[0078] Figure 14 It is a structural diagram of the type two planar calibration coil 80 on a single-chip X-axis linear magnetoresistive sensor with a high-intensity magnetic field. The type two planar calibration coil 80 includes two straight wires, that is, a reference straight wire 105 and a sensitive straight wire 106, respectively located in the shield The gap between the shield 21 and the attenuator 31, and the reference straight wire 105 has a wider width and is located on the side close to the shield 21, and the sensitive straight wire 106 is narrower and is located on the side near the attenuator 31, and The sensitive straight wire 106 and the reference straight wire 105 are connected in series.
[0079] Figure 15 It is a cross-sectional view of a type two planar calibration coil 80 on a single-chip X-axis linear magnetoresistive sensor with a high-intensity magnetic field. Wherein, the reference straight wire 105 and the sensitive straight wire 106 are located at t...
Embodiment 3
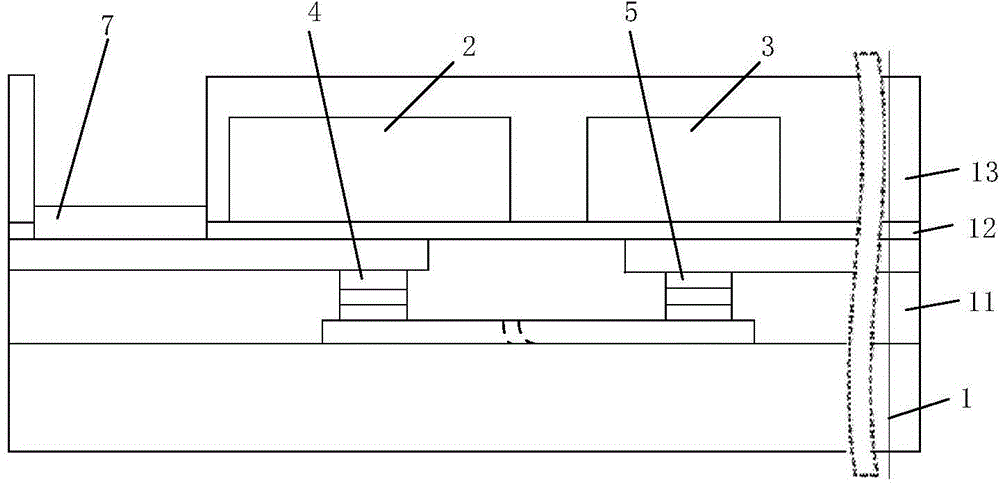
[0083] Figure 19 It is a distribution diagram of the type three-plane calibration coil 81 on the high-intensity magnetic field single-chip X-axis magnetoresistive sensor. The type three-plane calibration coil 81 includes a sensitive straight wire 107 and a reference straight wire 108, both of which are connected in series, wherein the reference straight wire The wire 108 corresponds to the shield 21, the sensitive straight wire 107 corresponds to the attenuator 31, and the reference straight wire 108 and the sensitive straight wire 107 are elongated, which are respectively connected to the attenuator. 31 coincides with the Y-axis centerline of the shield 21, and the width of the sensitive straight wire 107 is smaller than the width of the reference straight wire 108.
[0084] Figure 20 It is a cross-sectional view of the type three-plane calibration coil 81 on the high-intensity magnetic field single-chip X-axis magnetoresistive sensor, and the reference straight wire 108 a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com