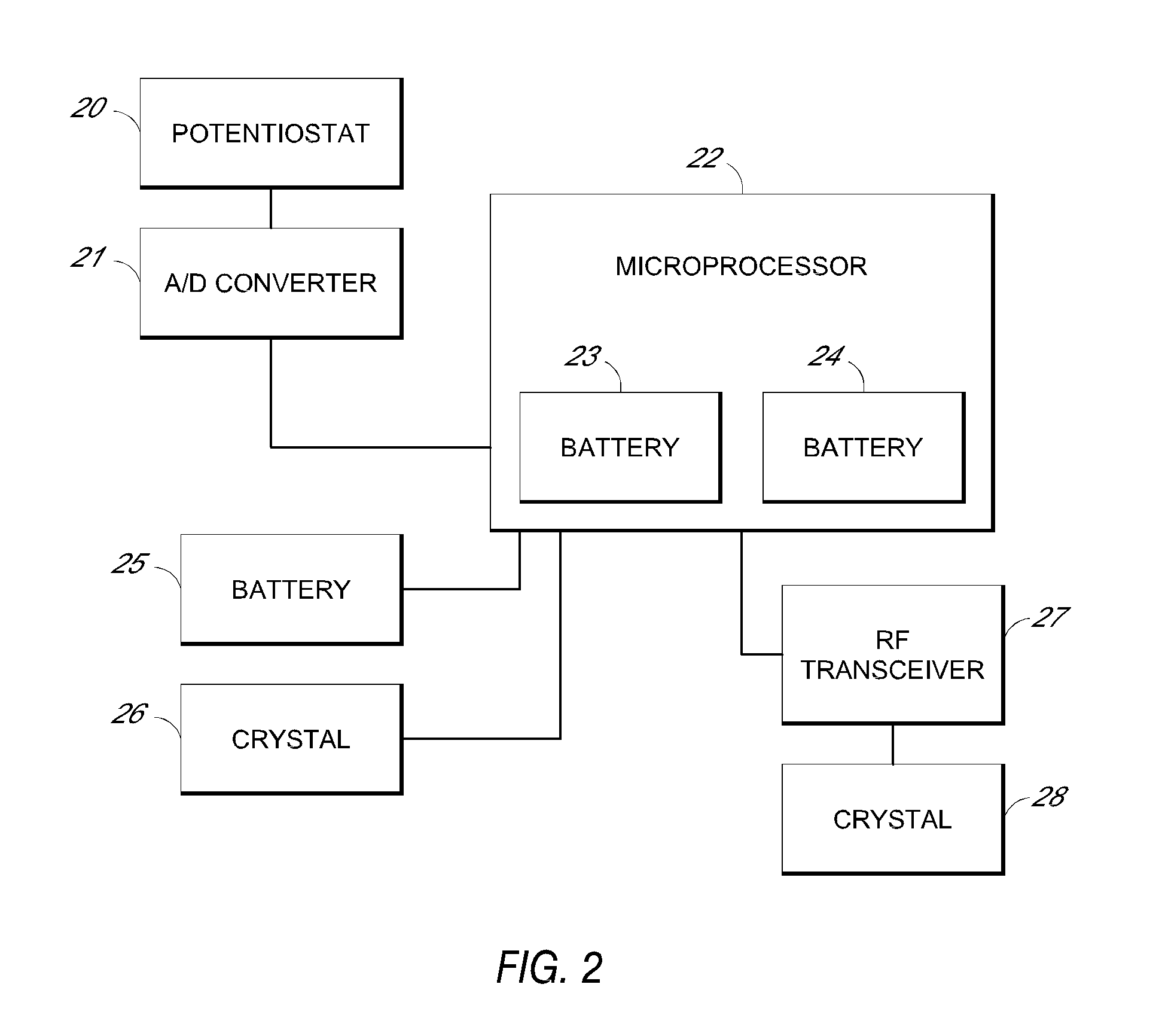
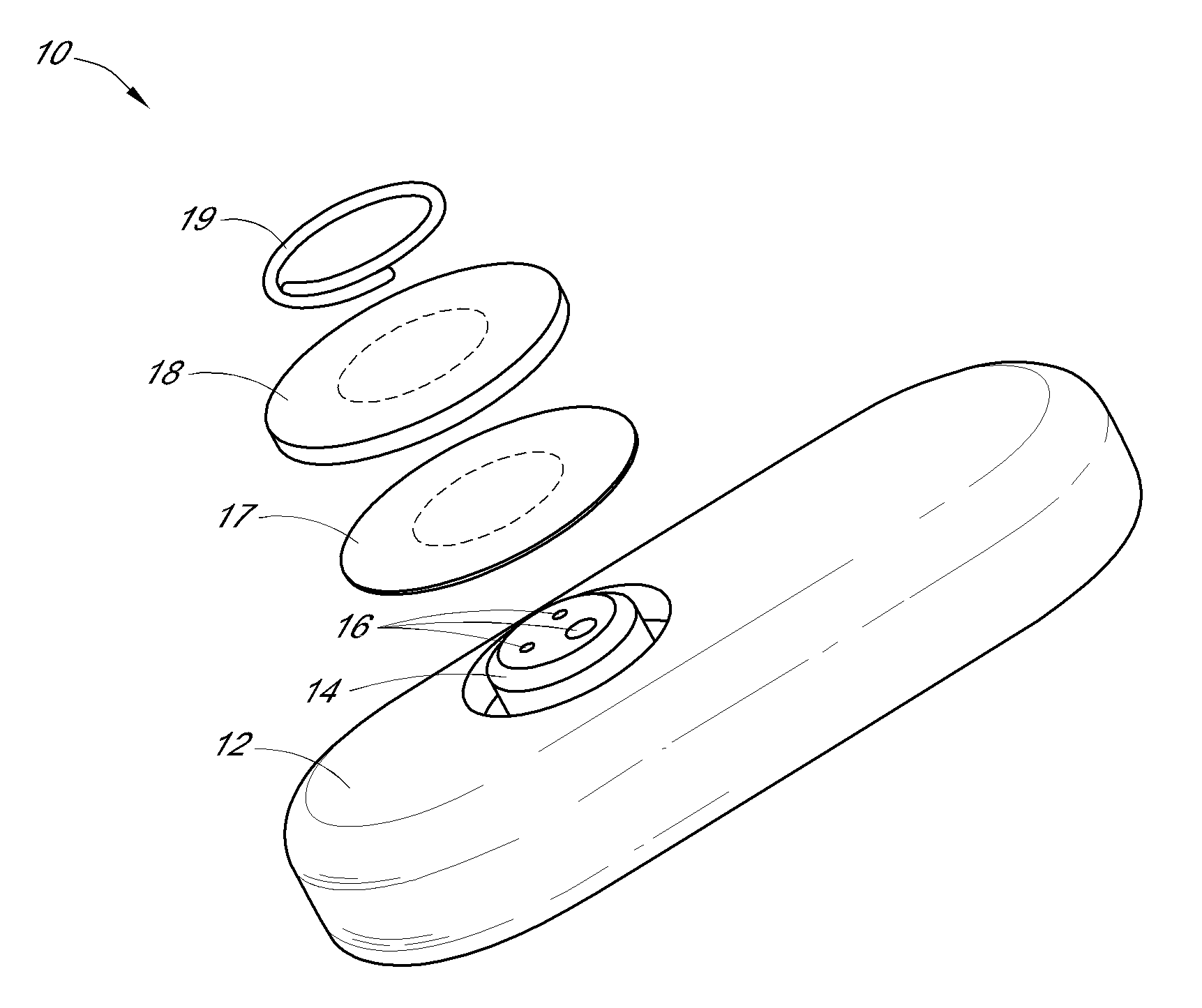
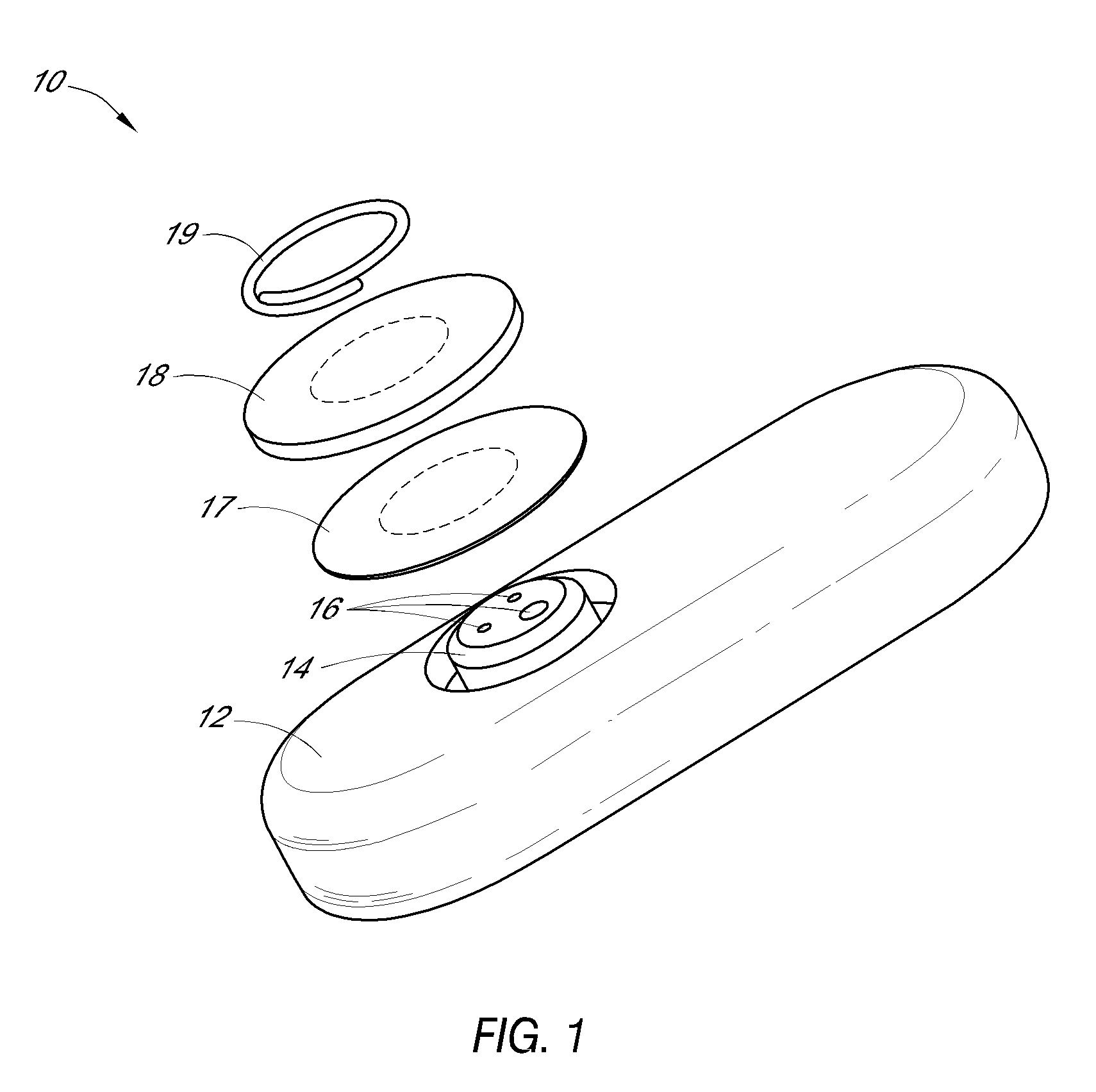
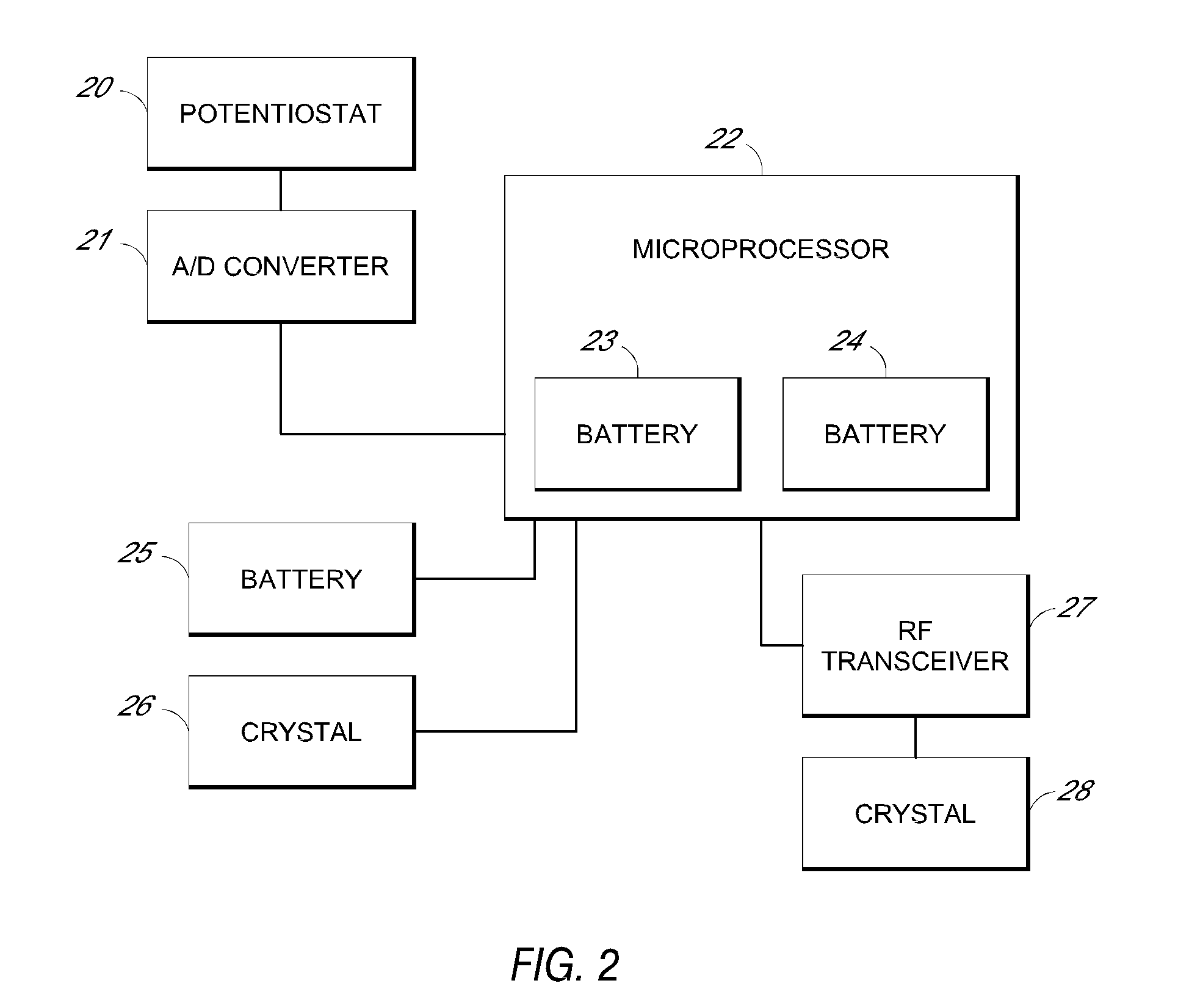
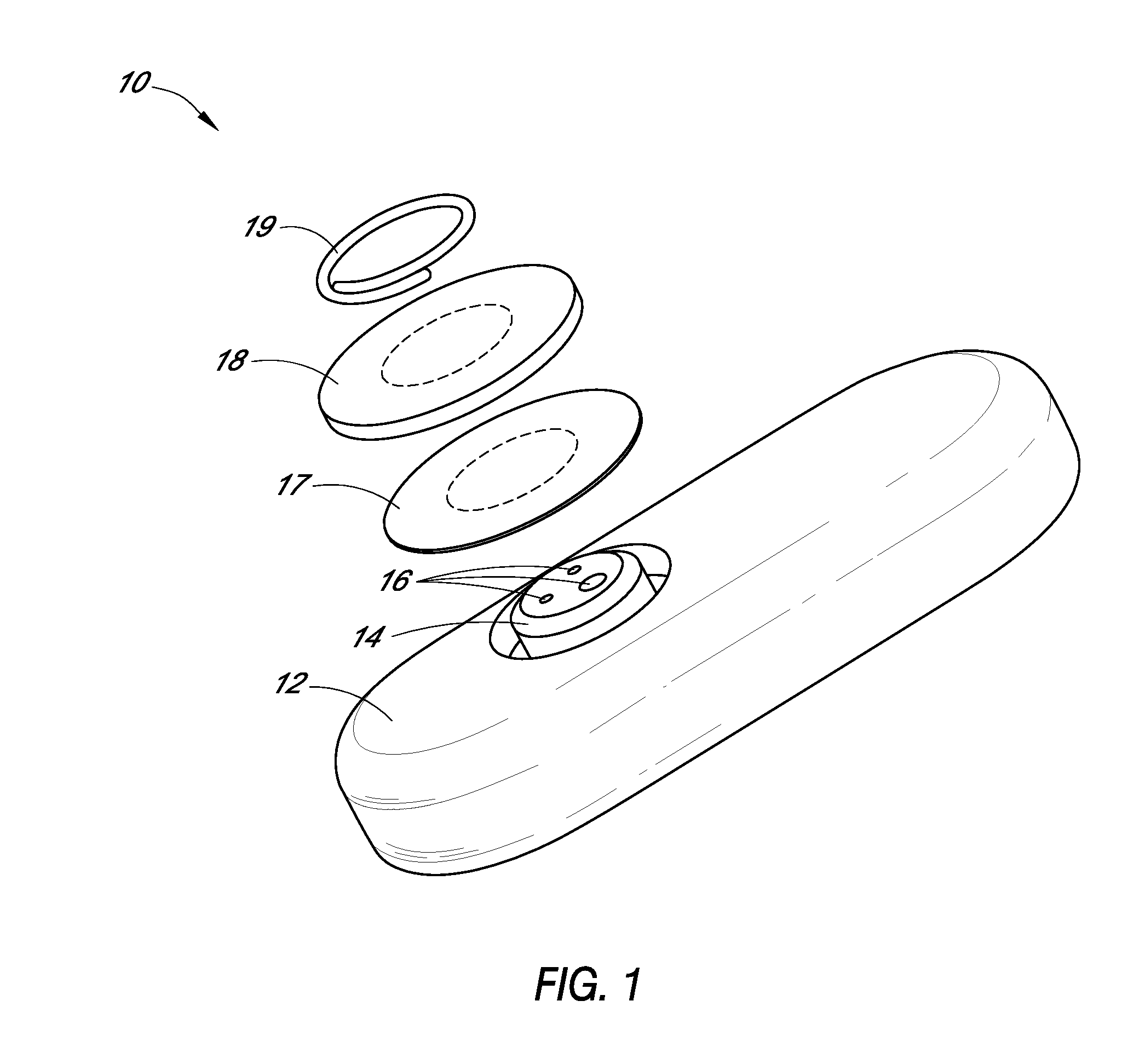
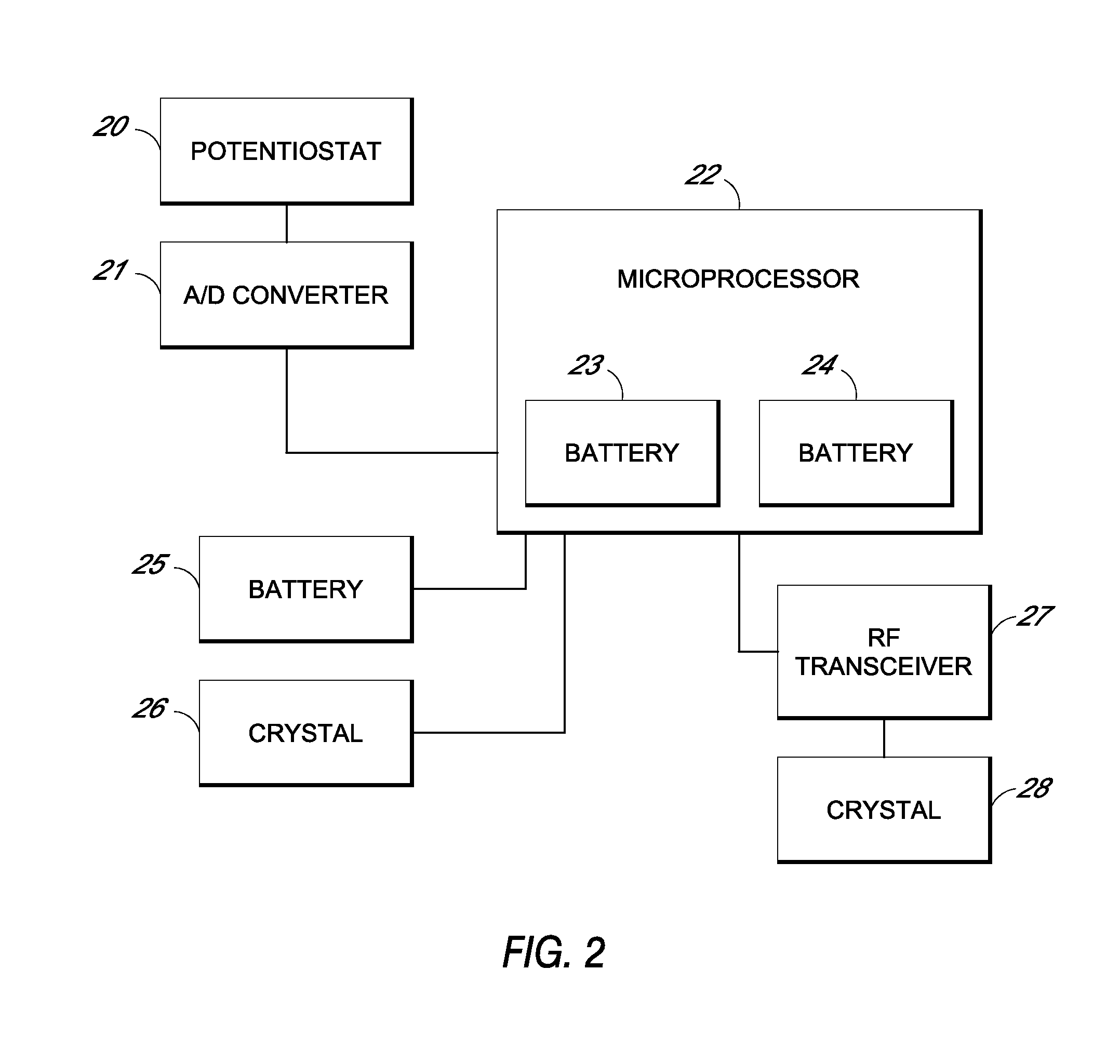
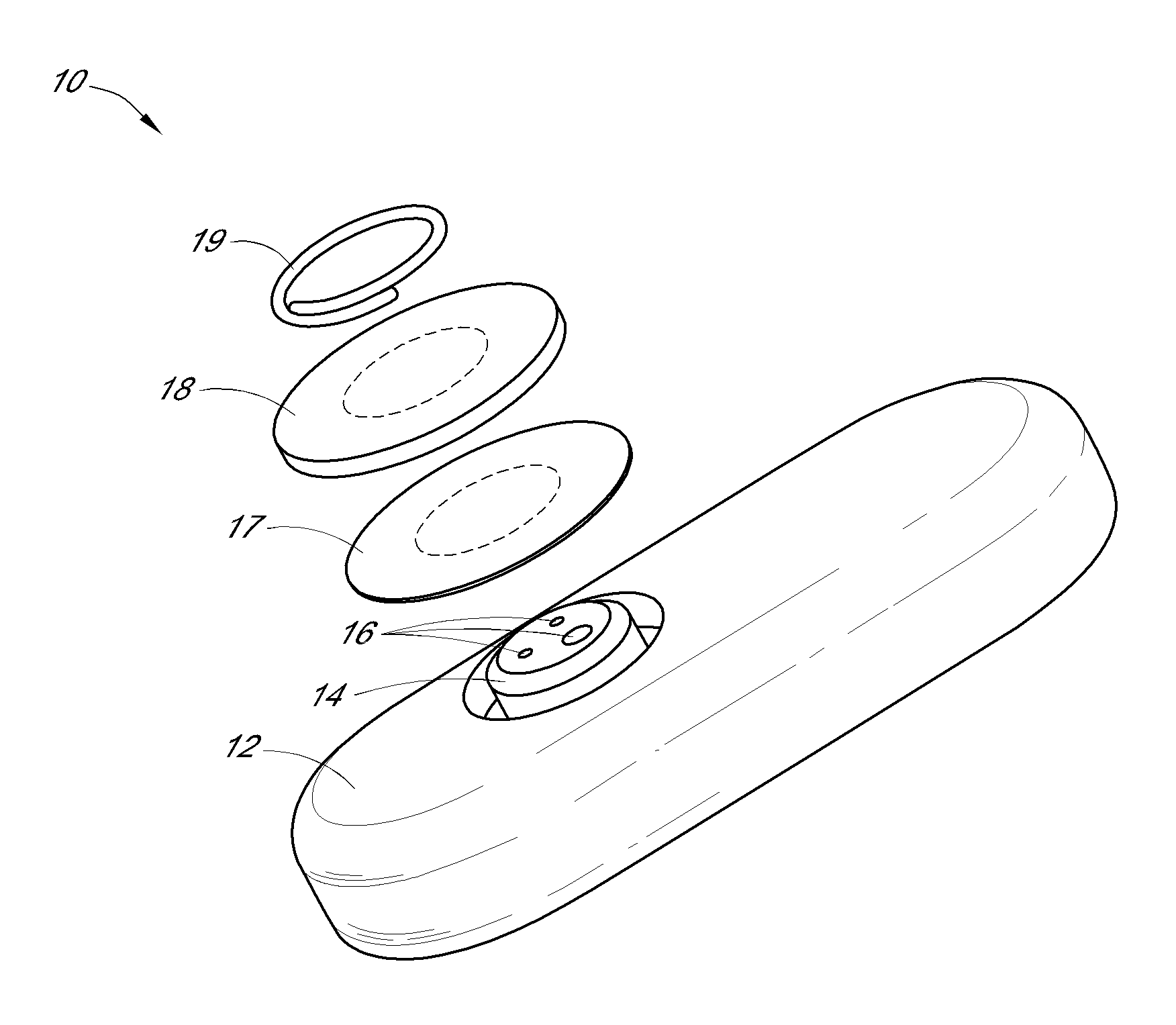
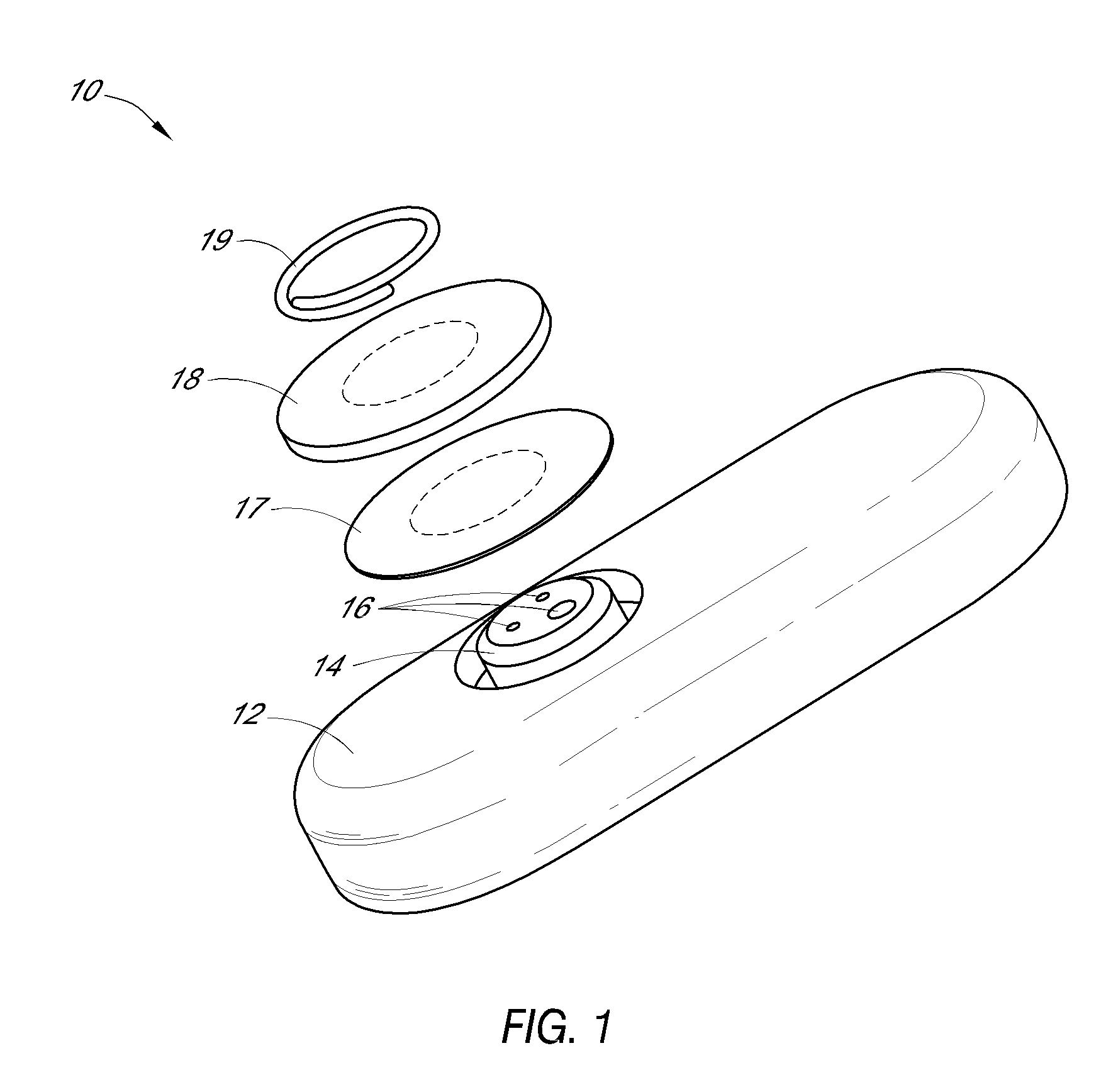
Patents
Literature
637 results about "Transducer calibration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
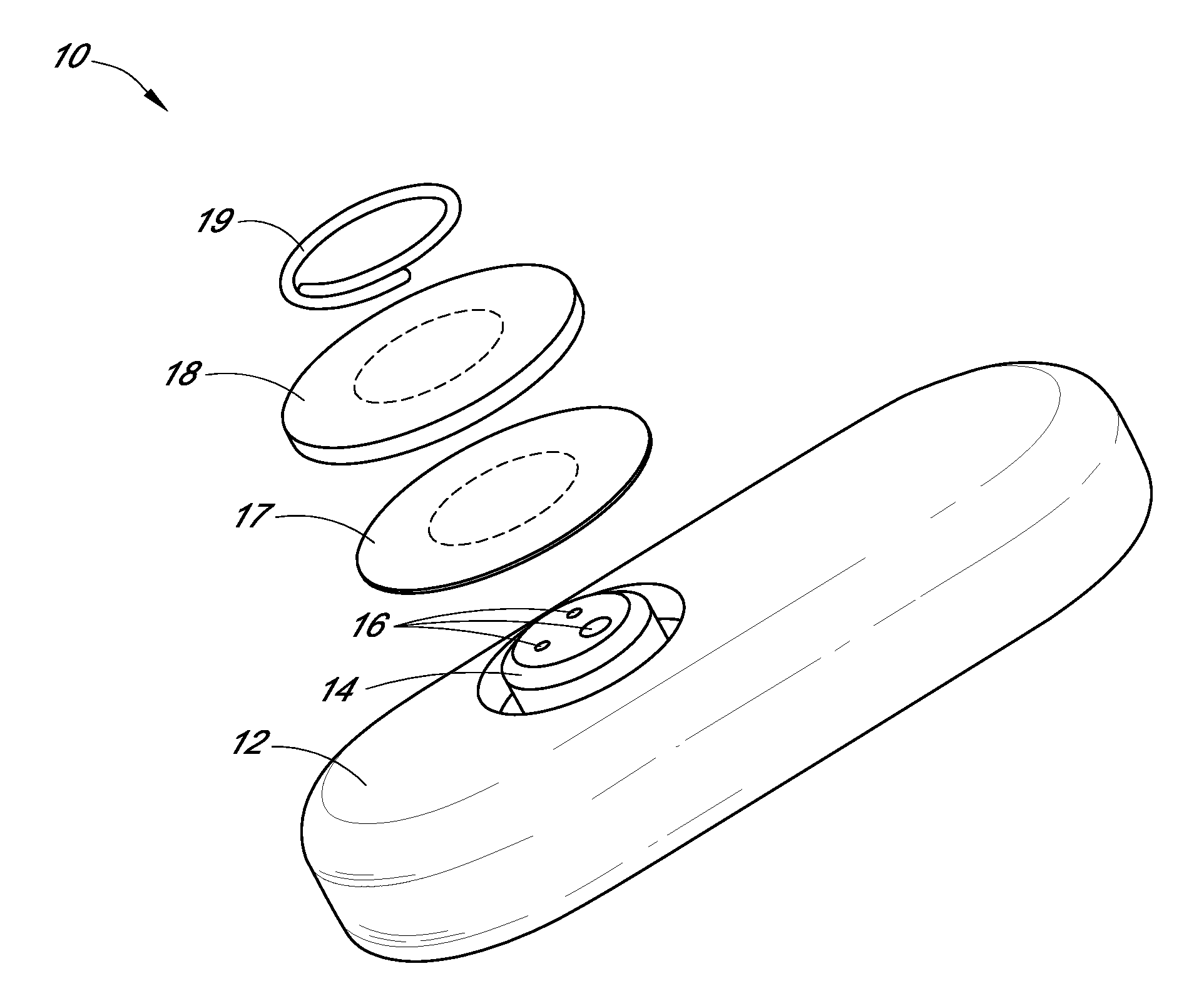
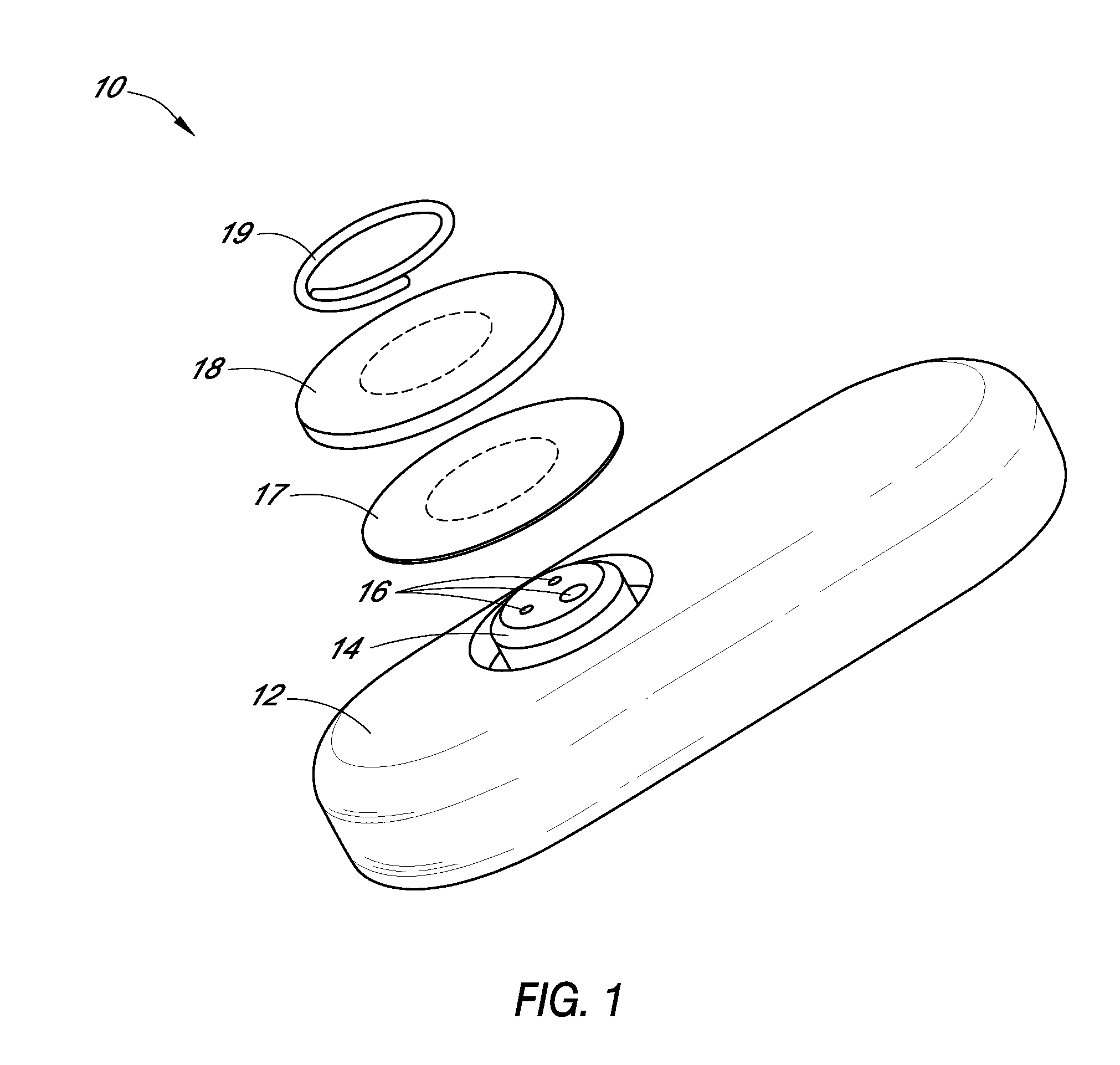
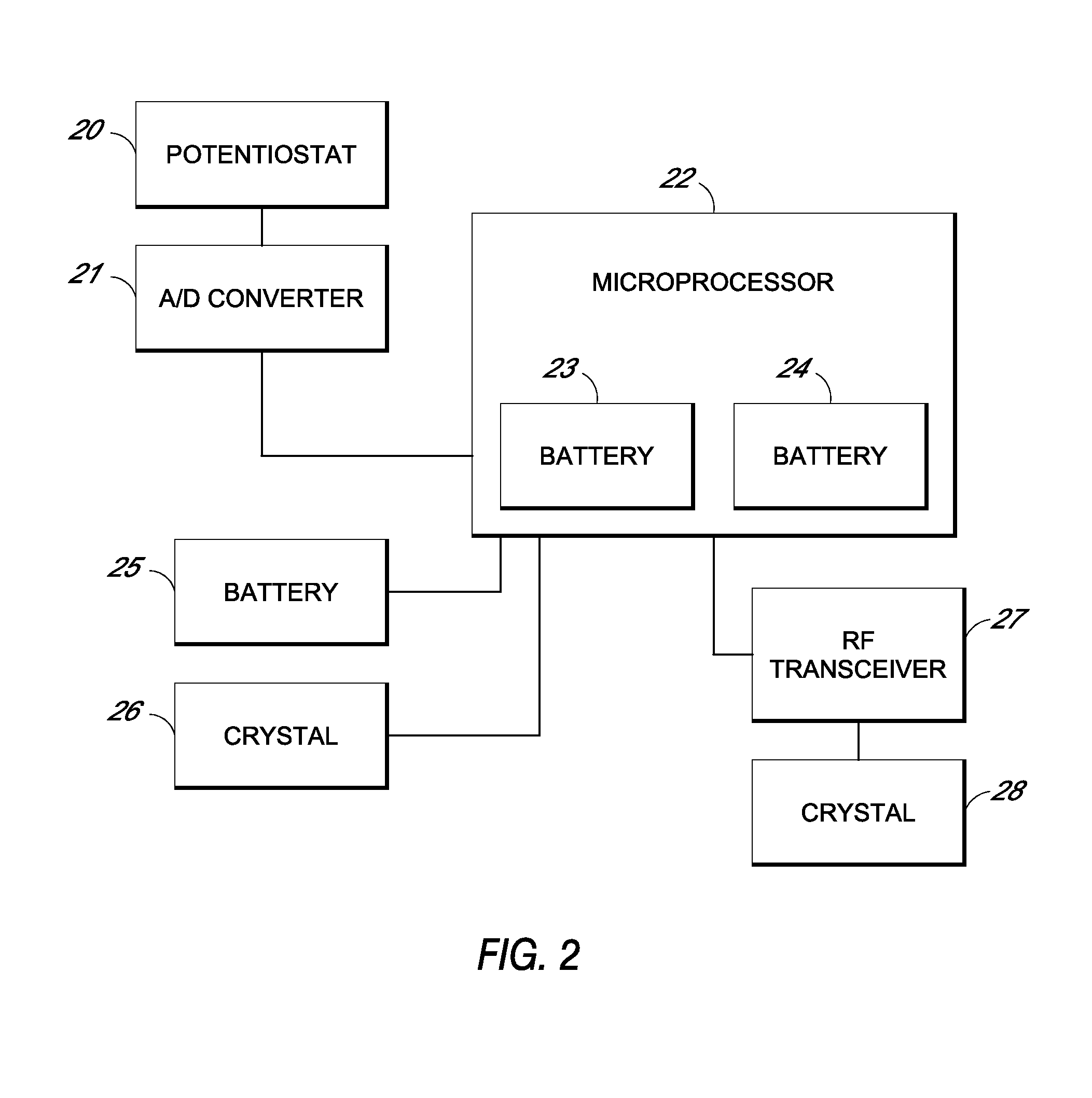
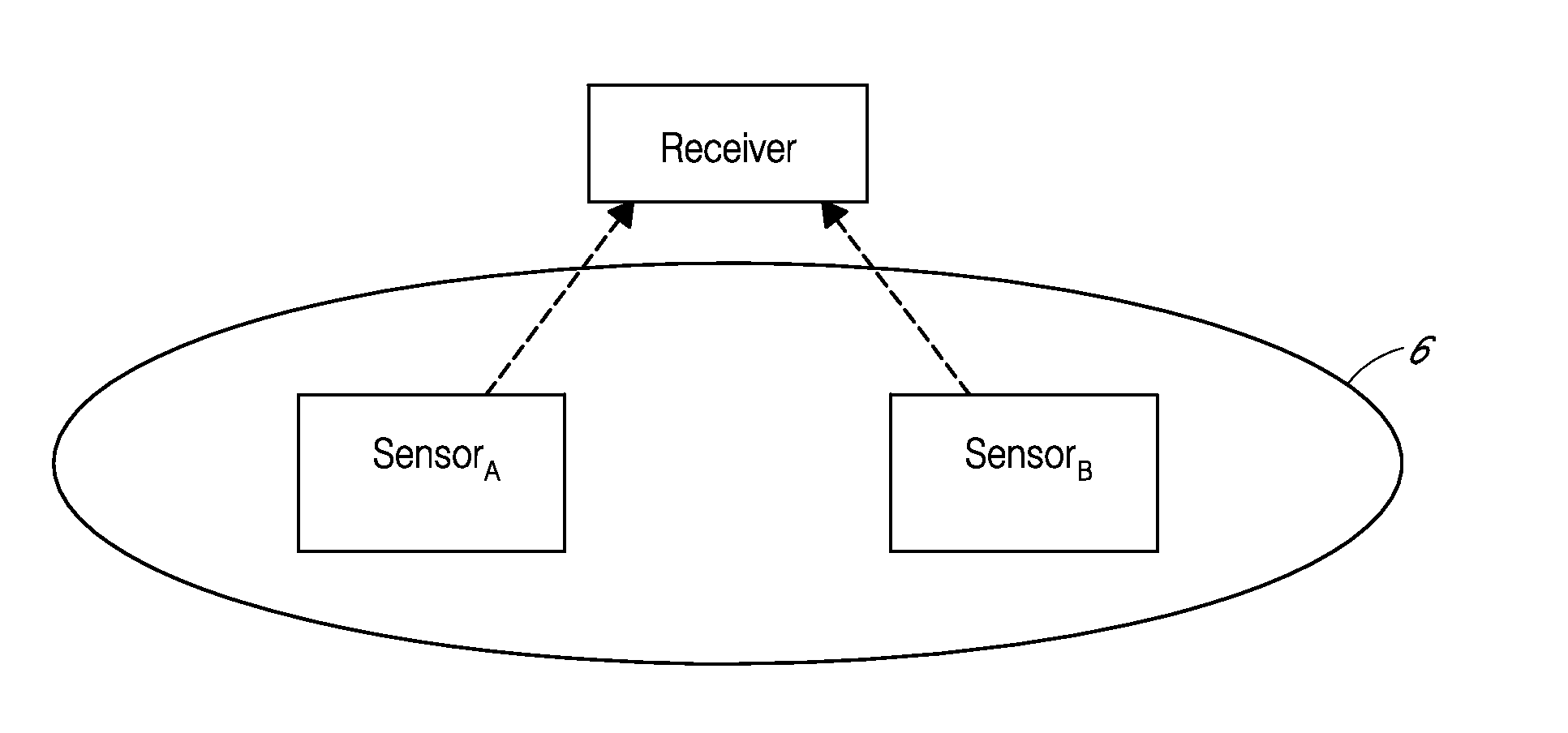
TRANSDUCER CALIBRATION. Transducers are test devices with an electrical output signal that is directly proportional to the force being applied. Calspan has the specialized equipment and knowledge to calibrate transducers used in crash testing, including: Accelerometers. Linear and Rotary Potentiometers.
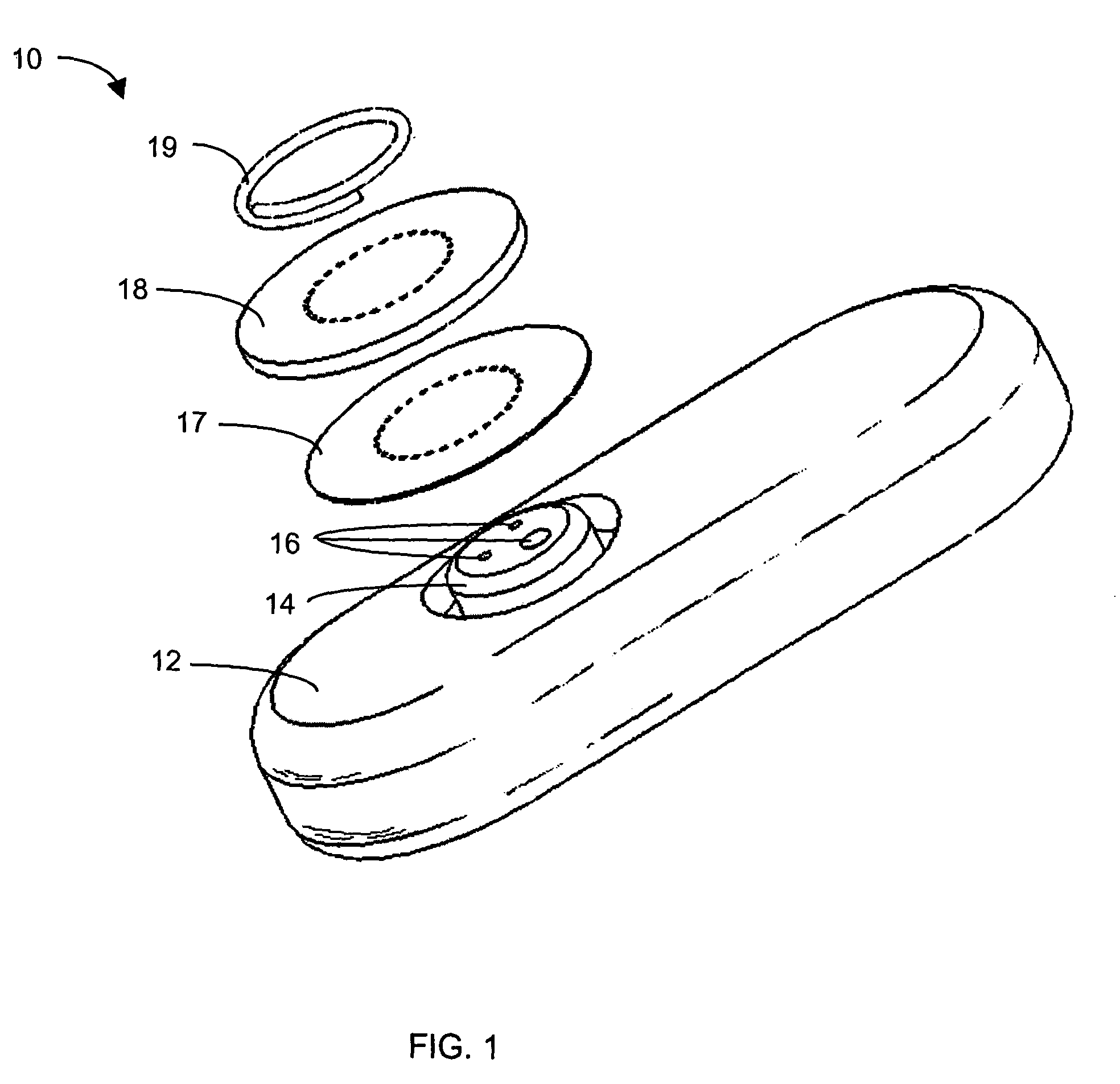
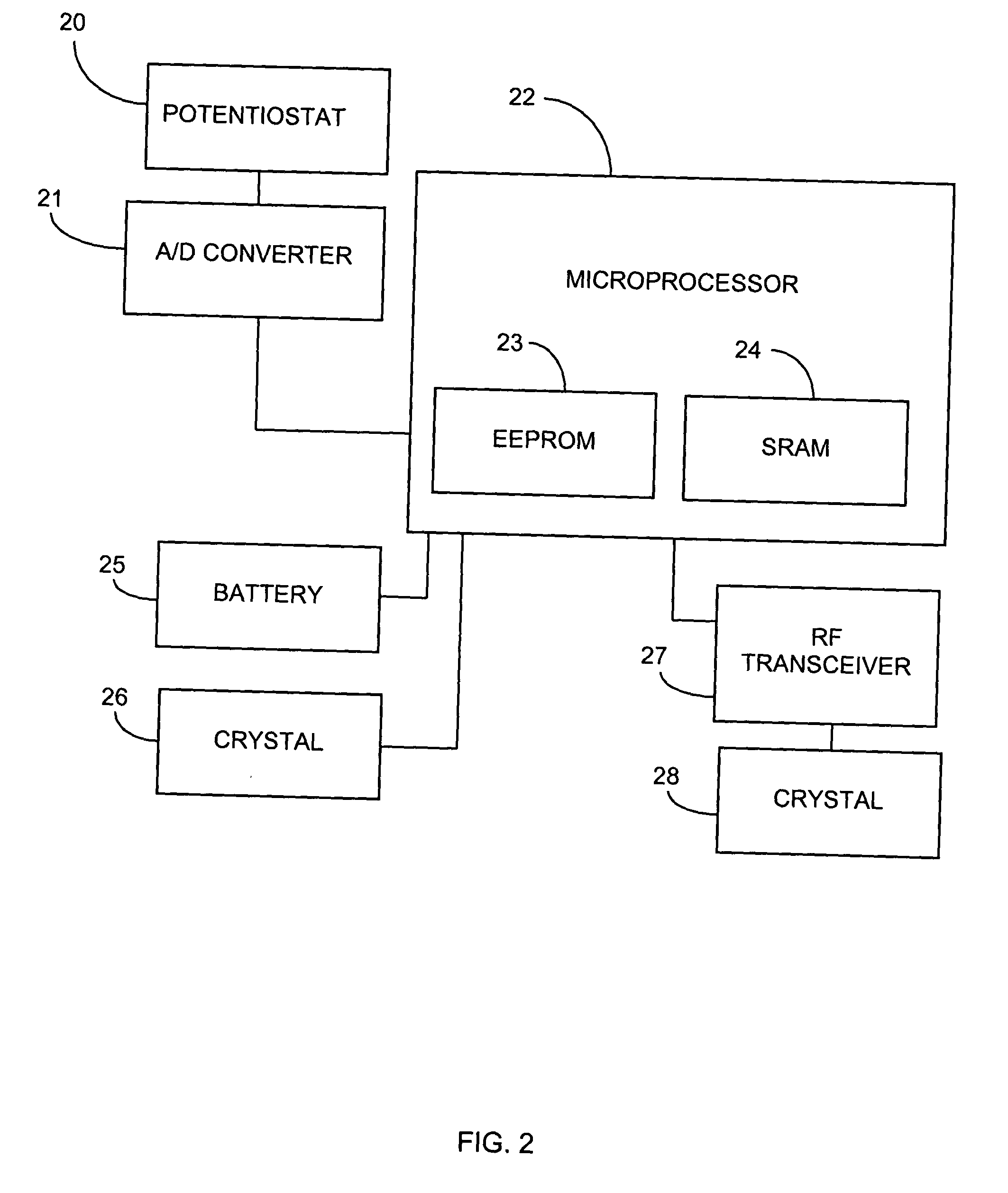
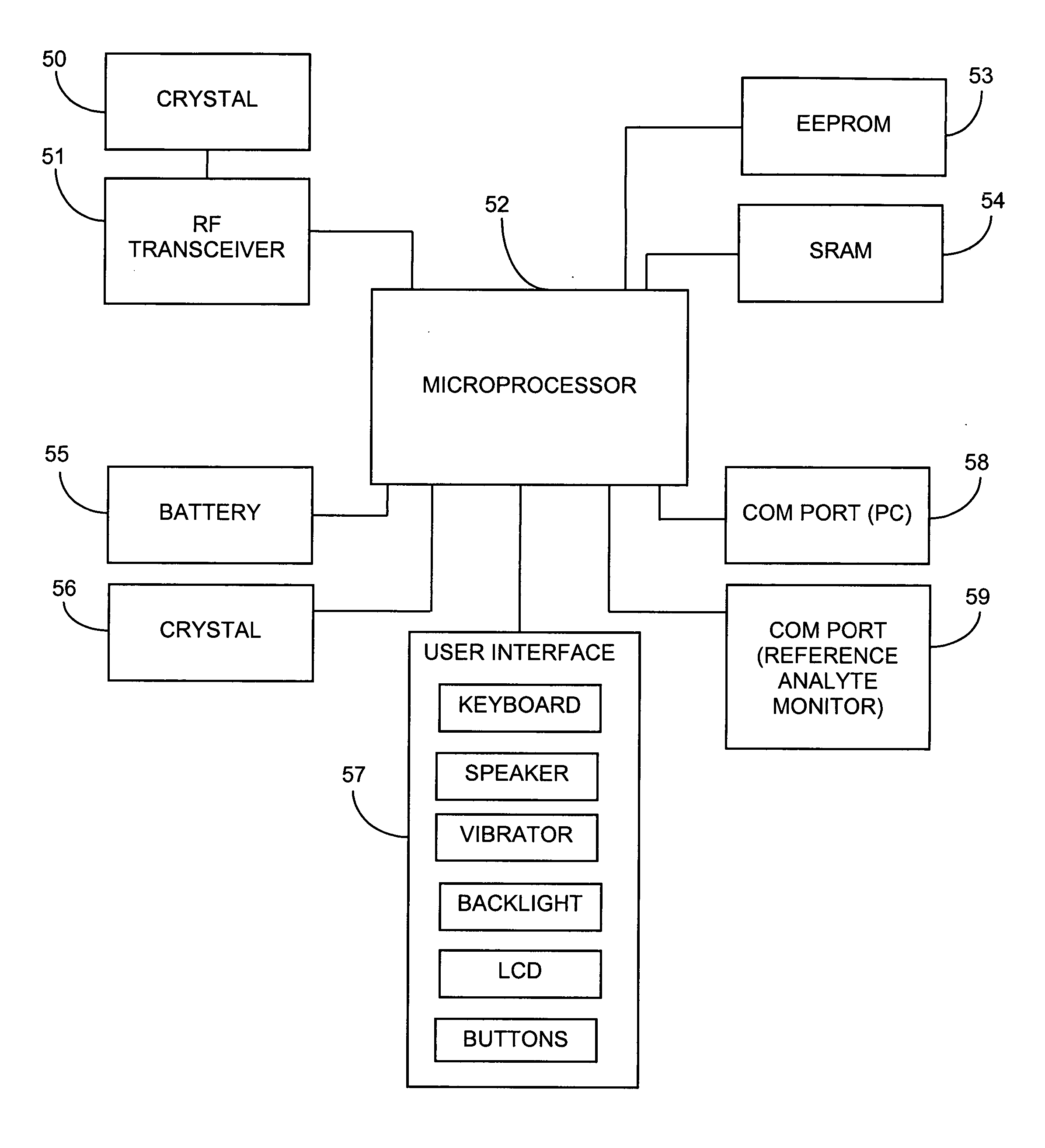
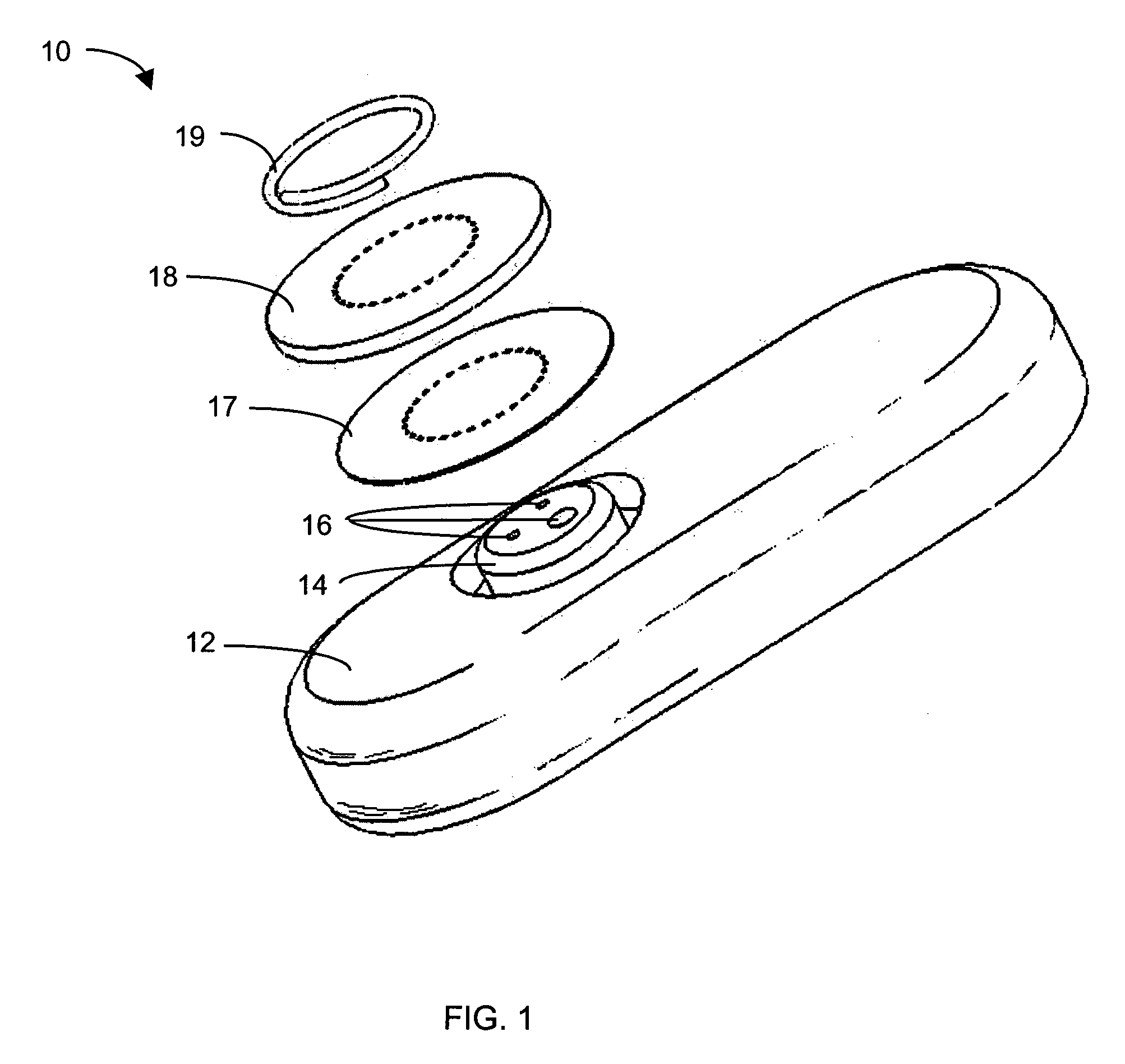
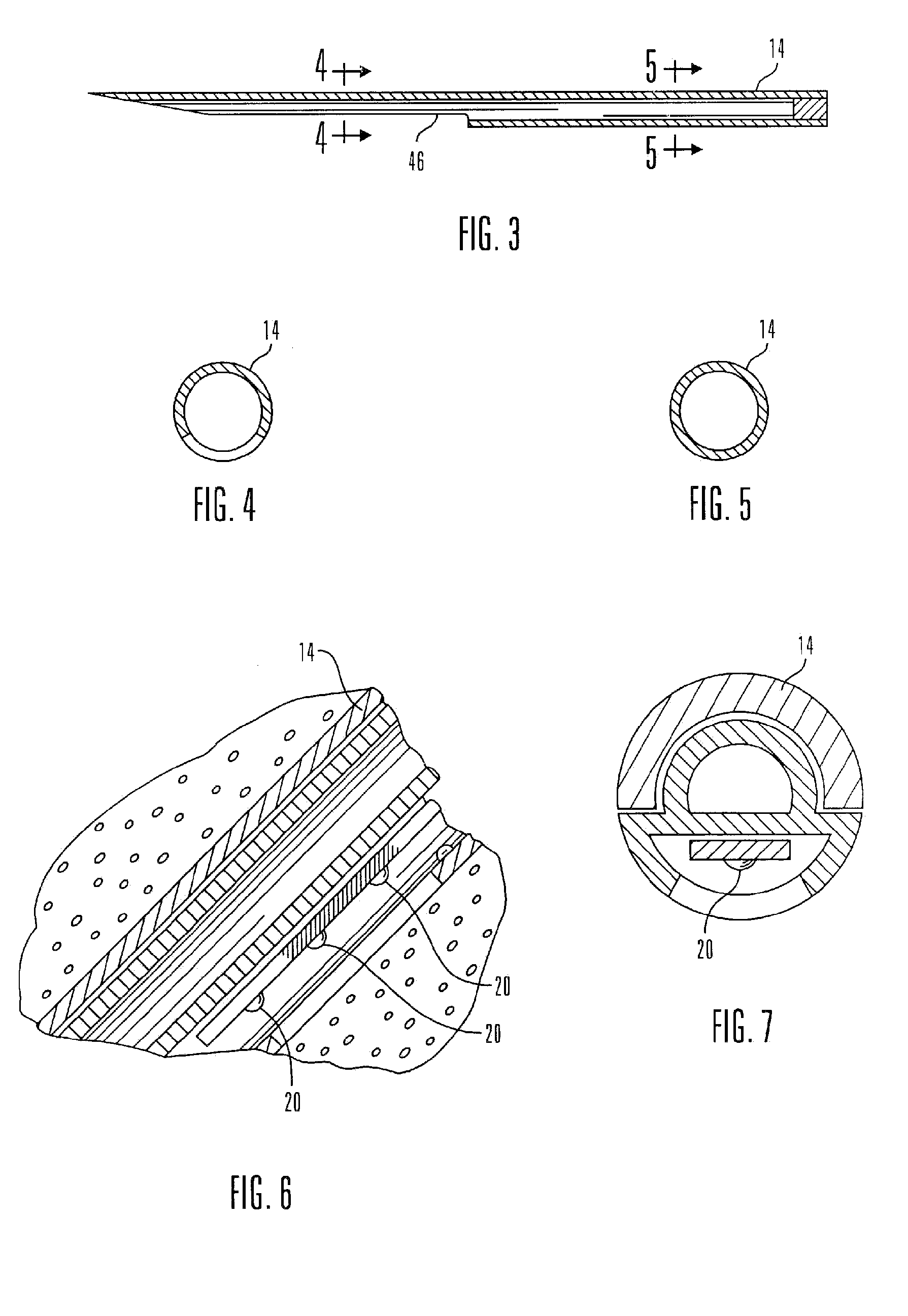
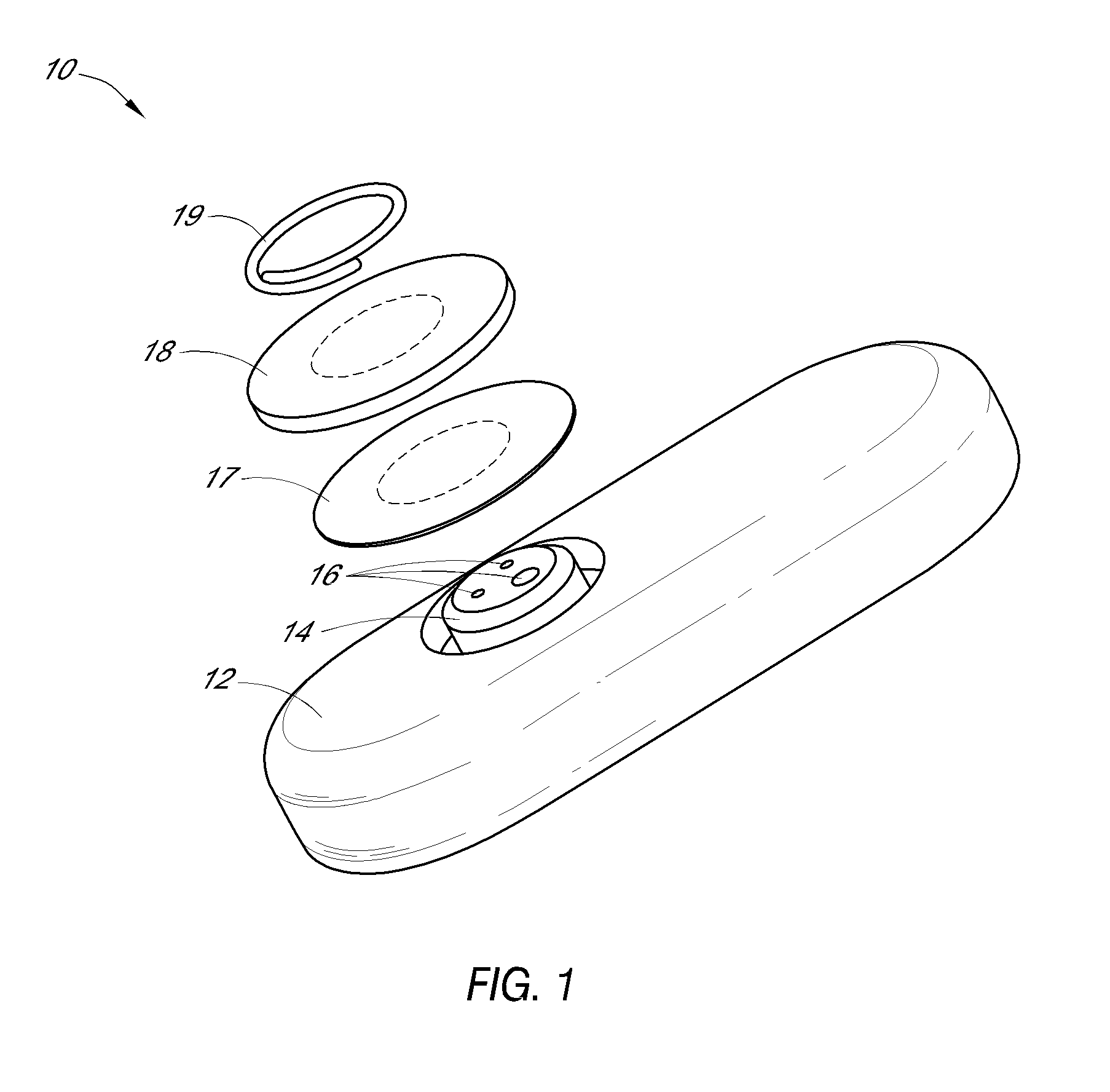
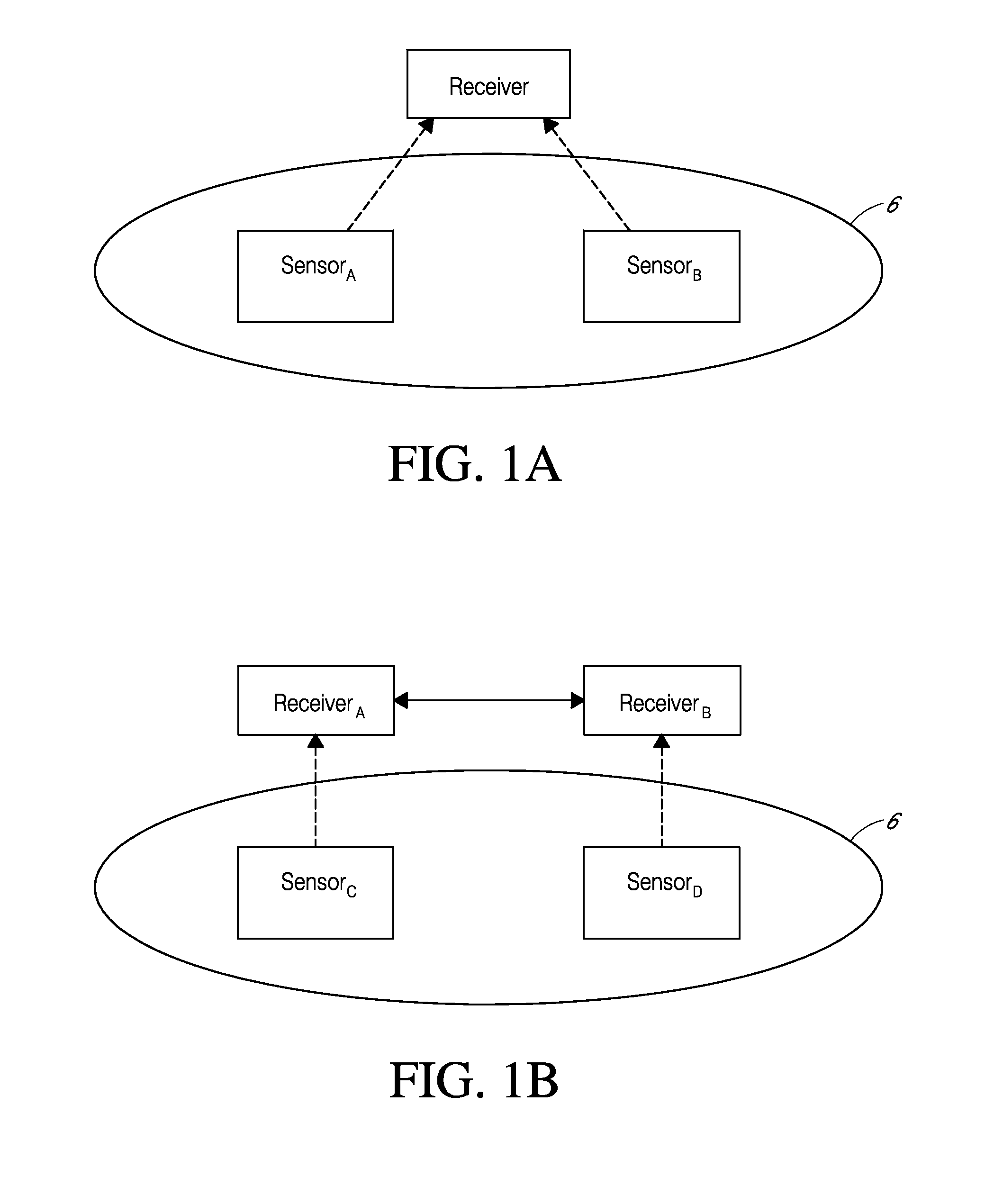
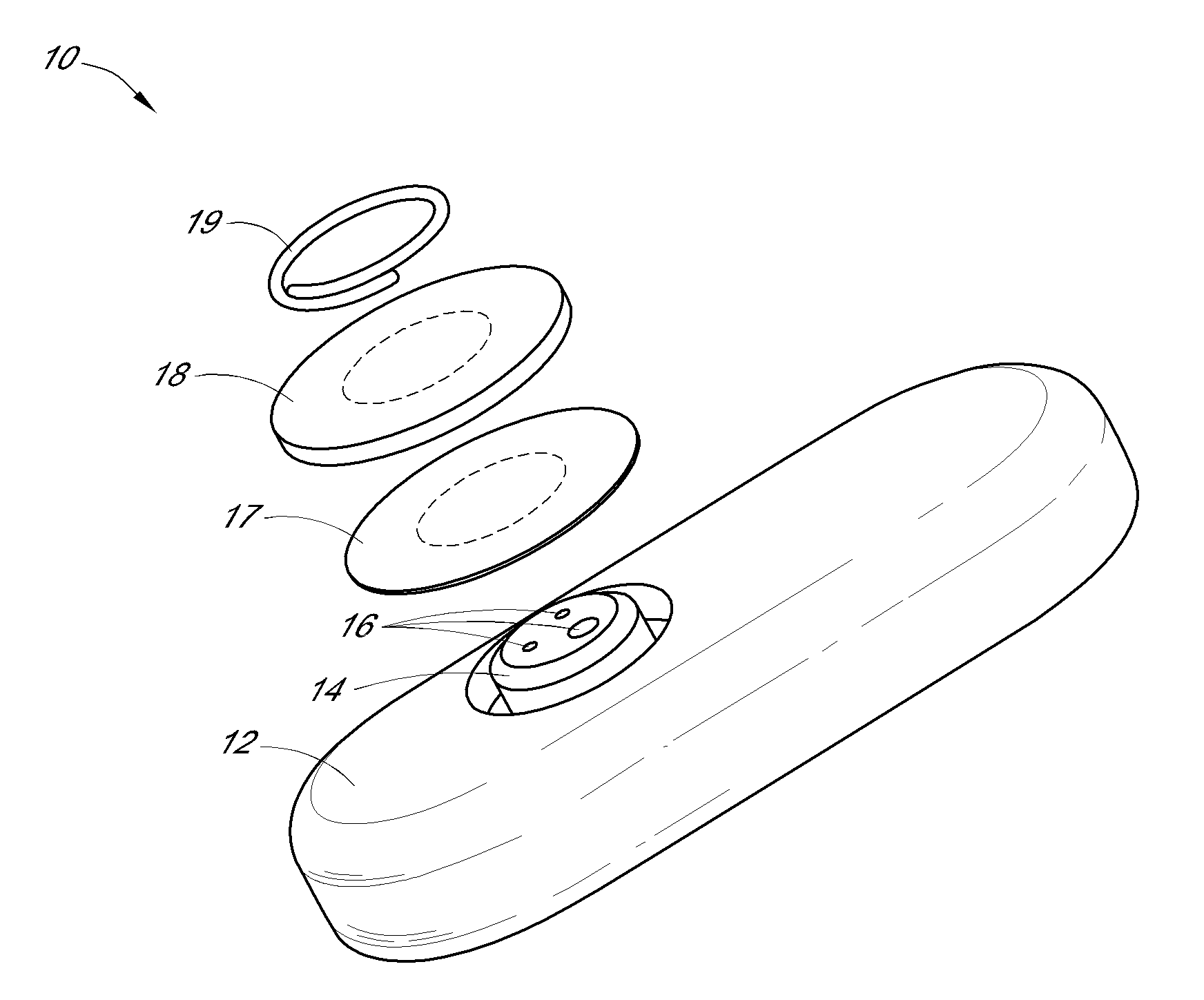
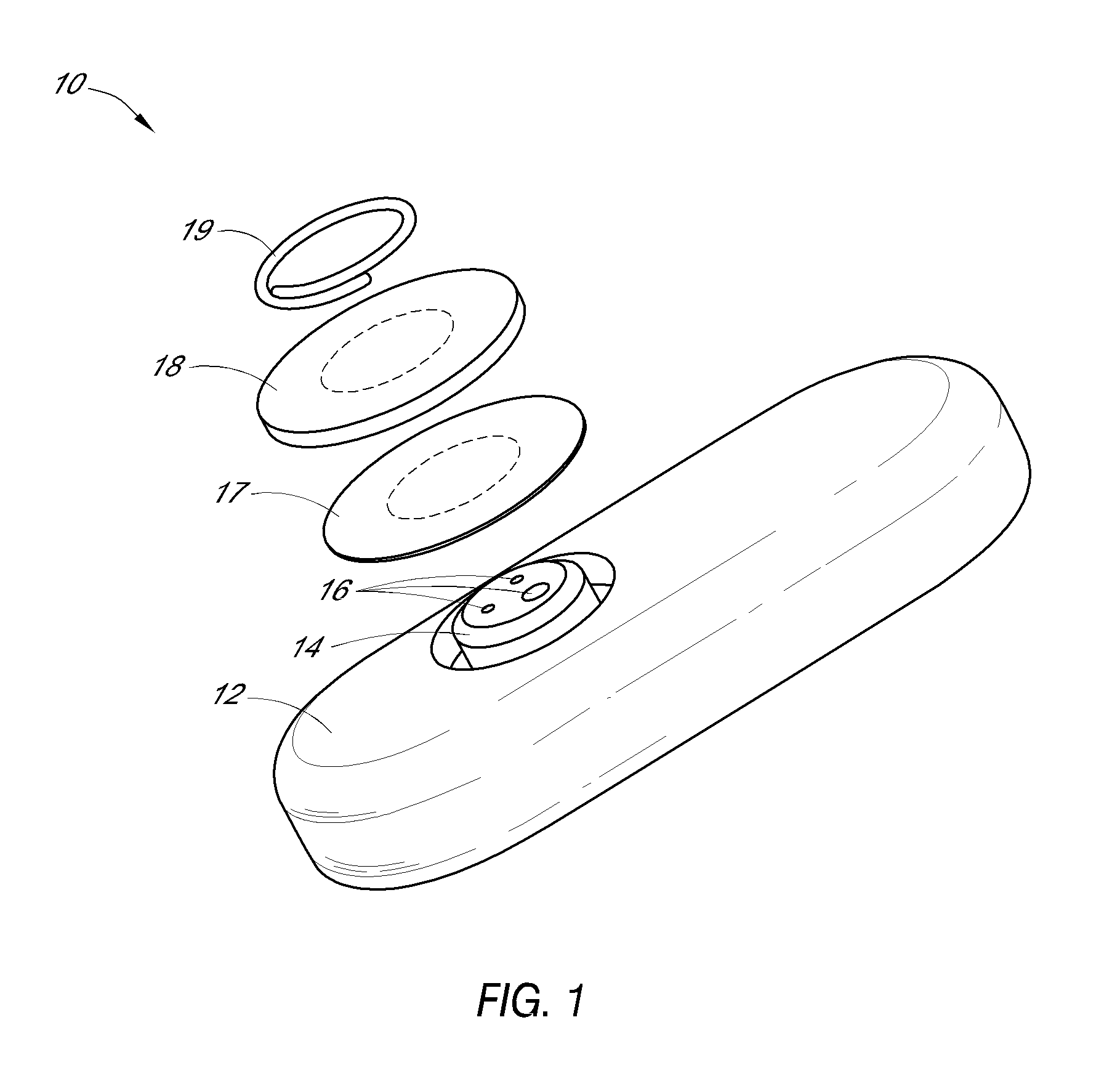
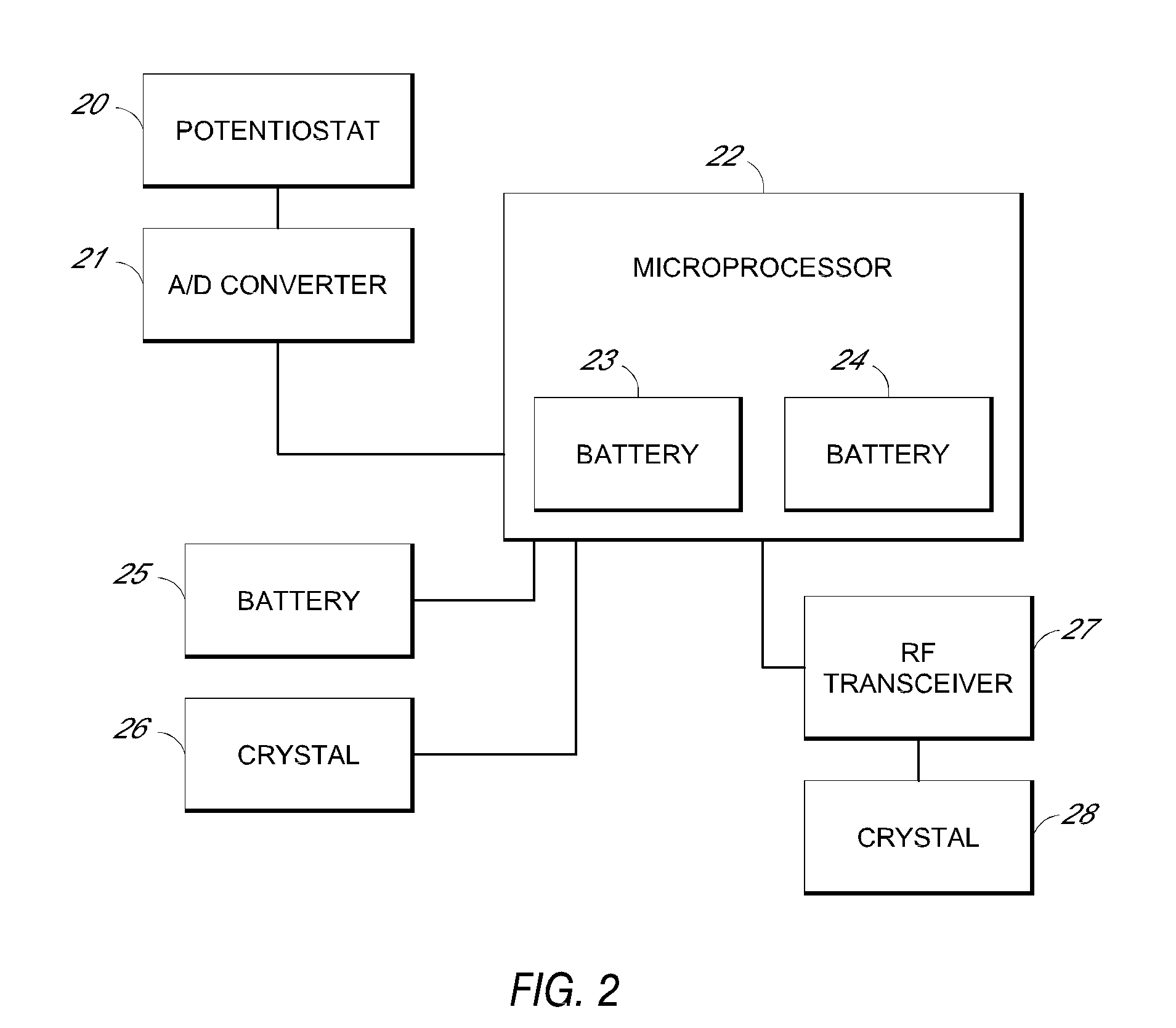
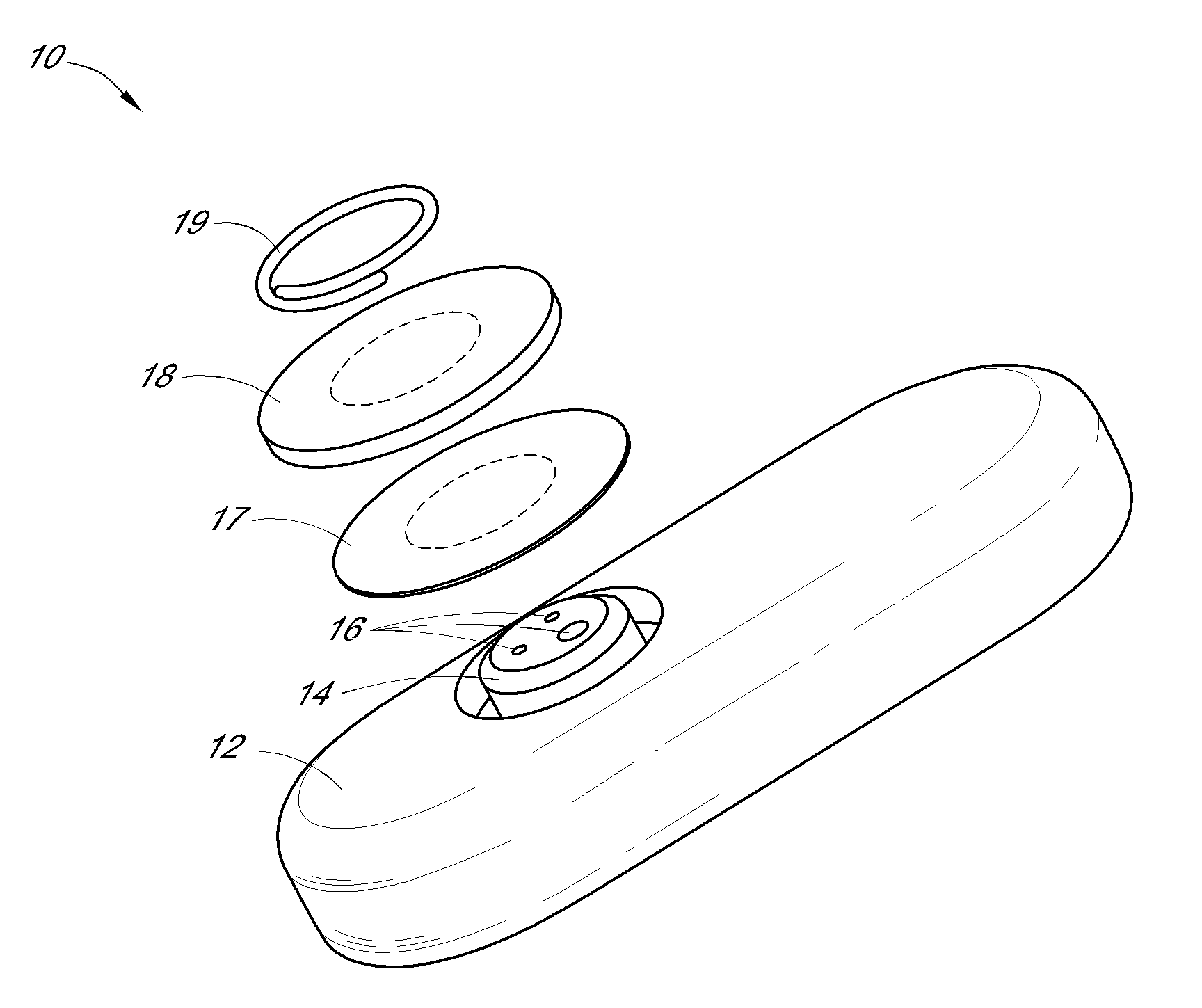
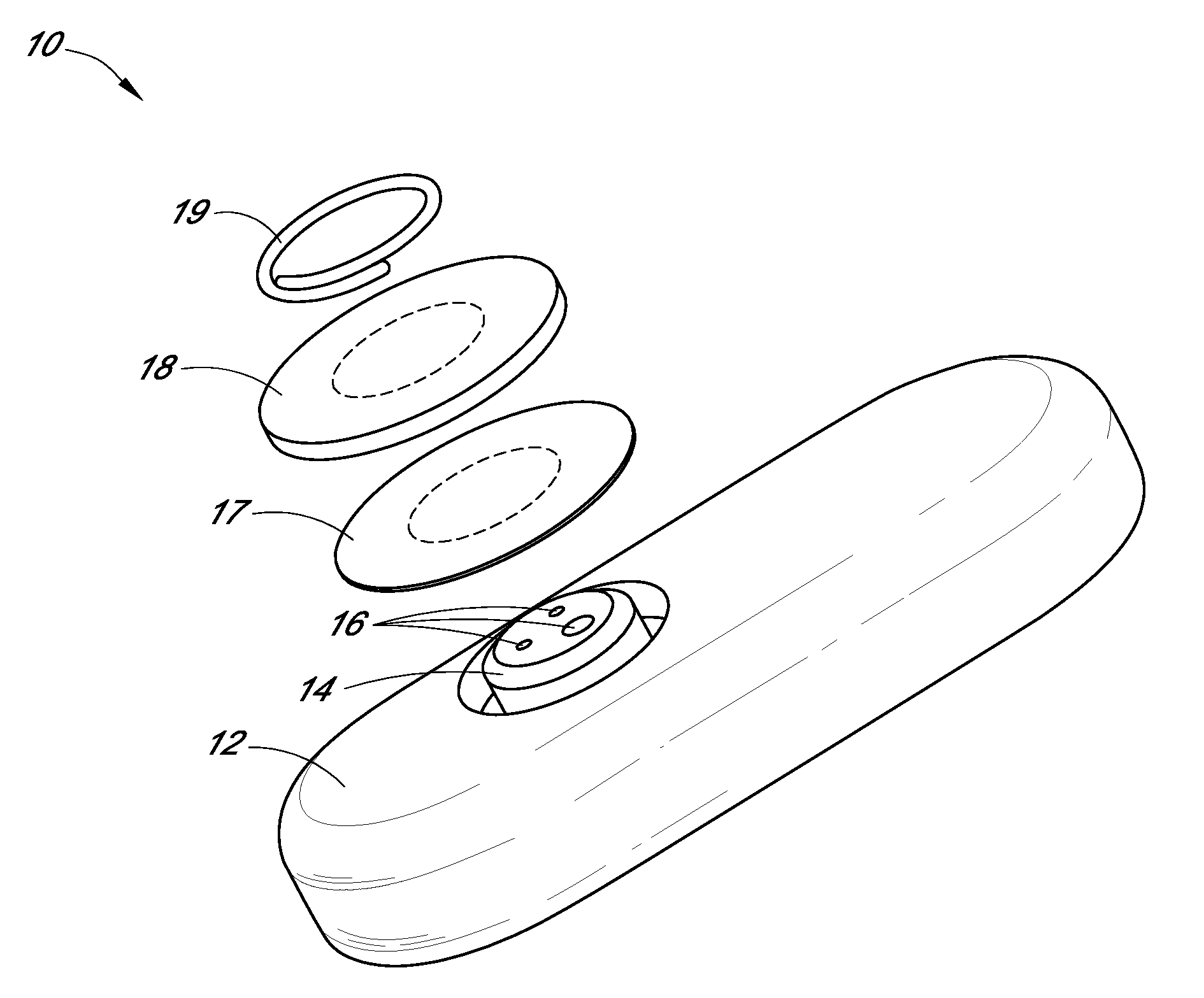
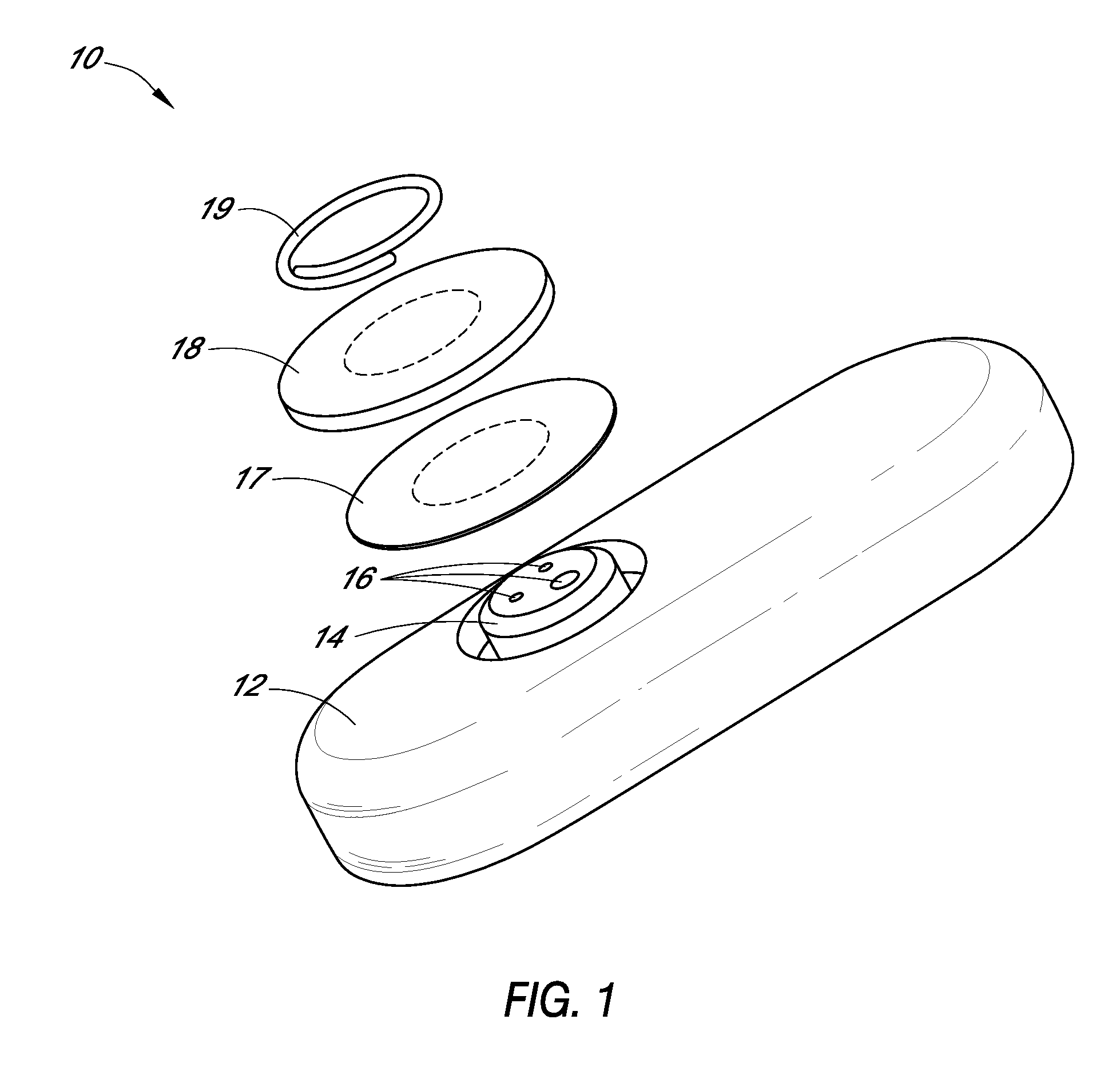
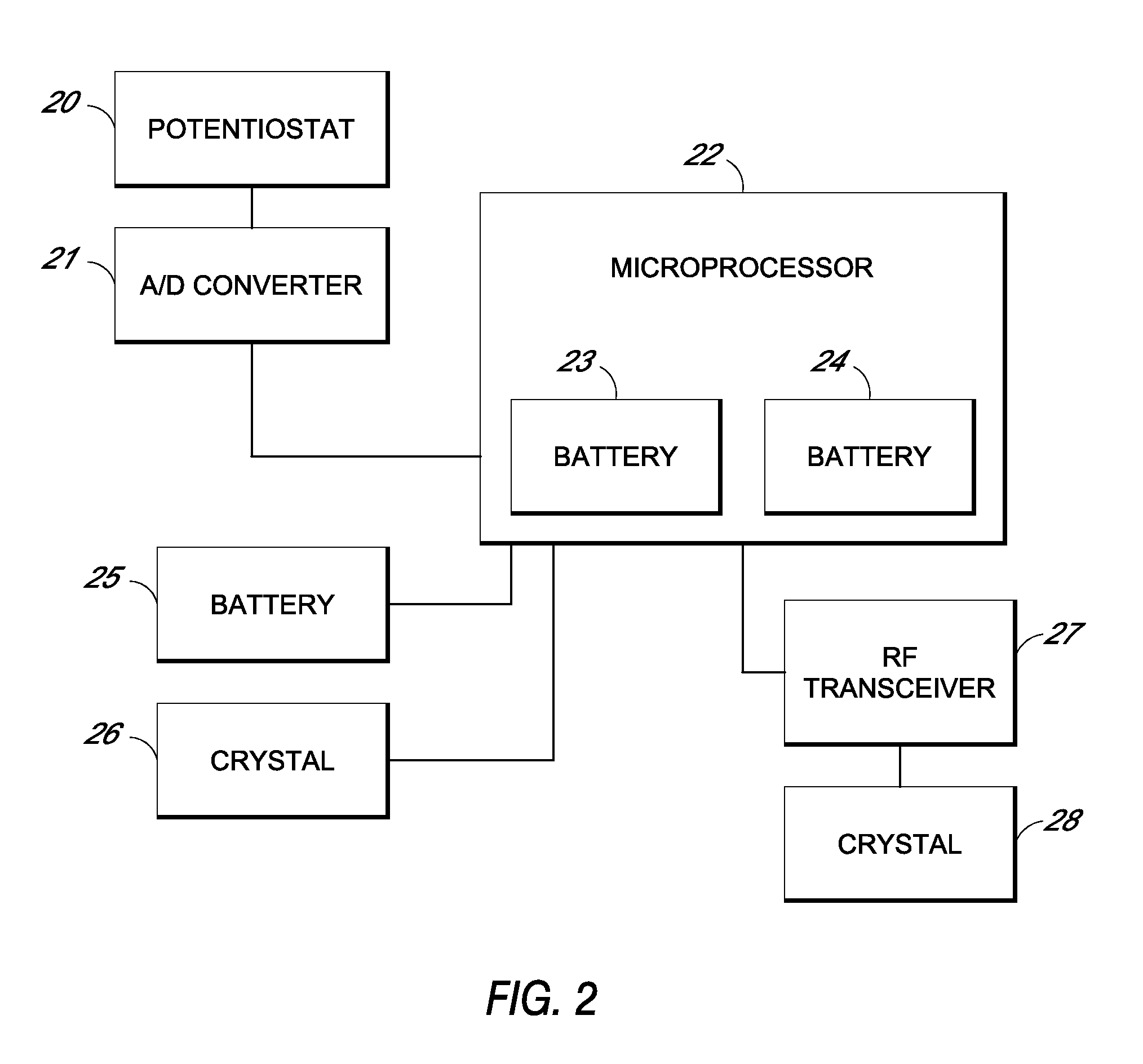
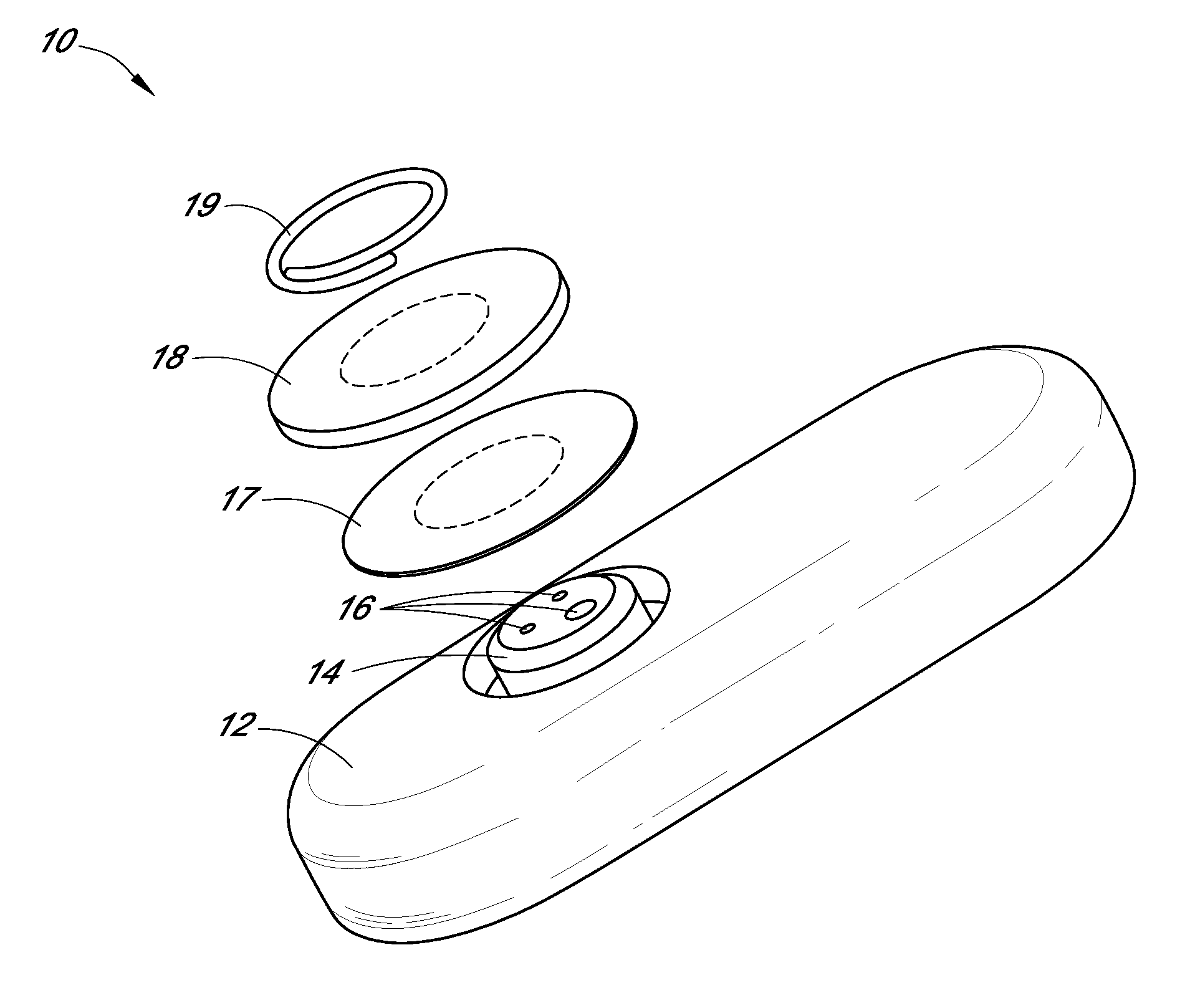
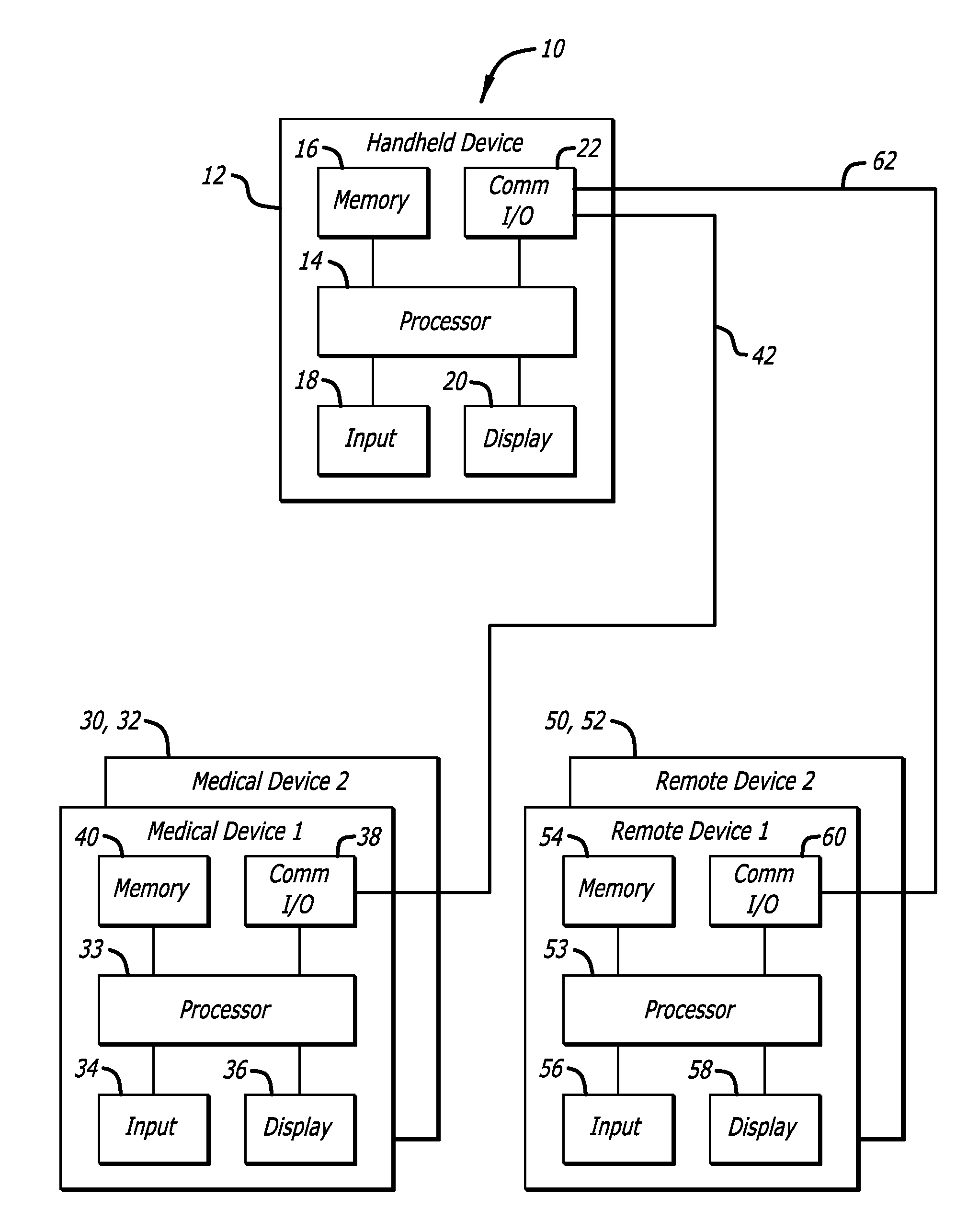
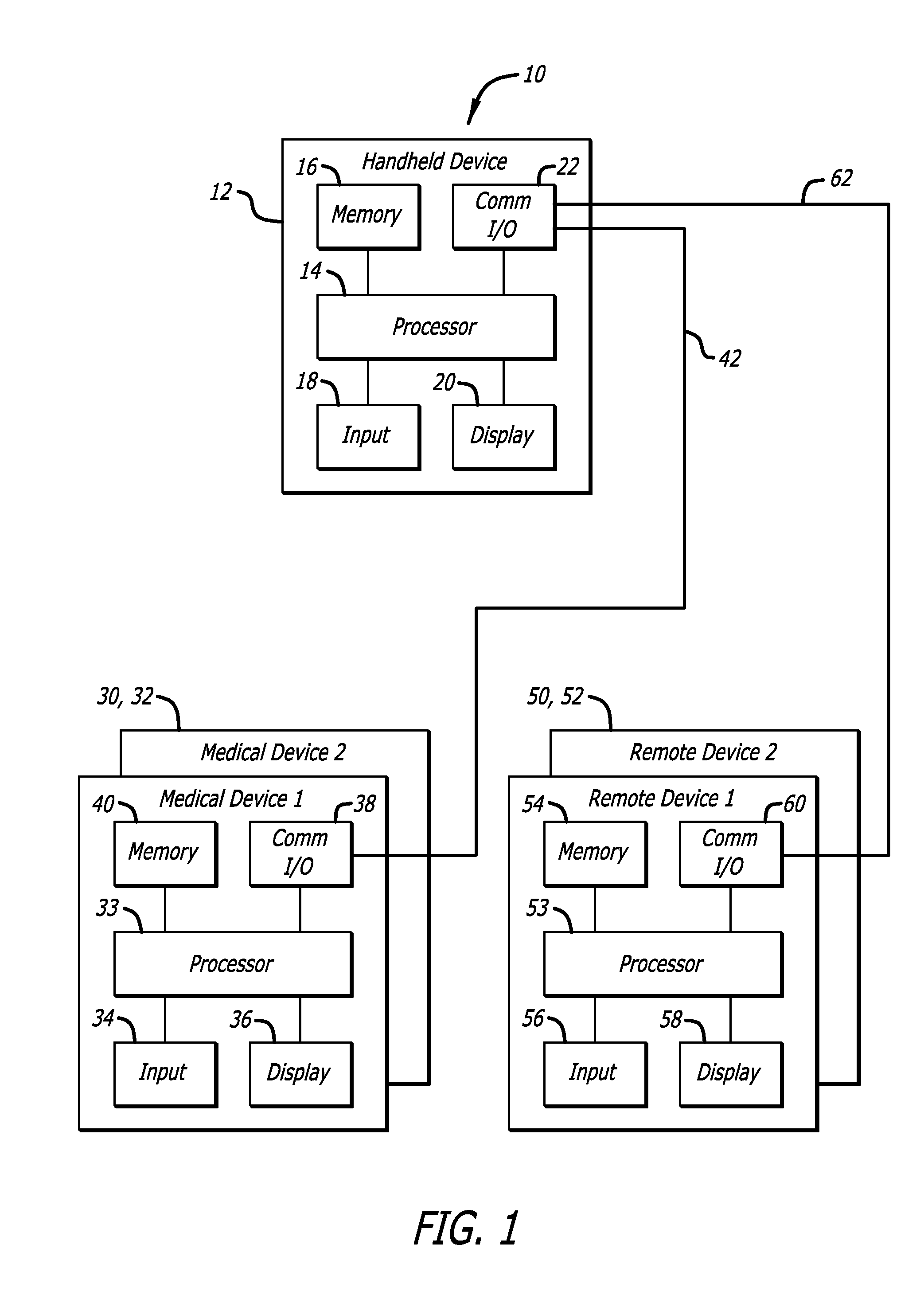
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
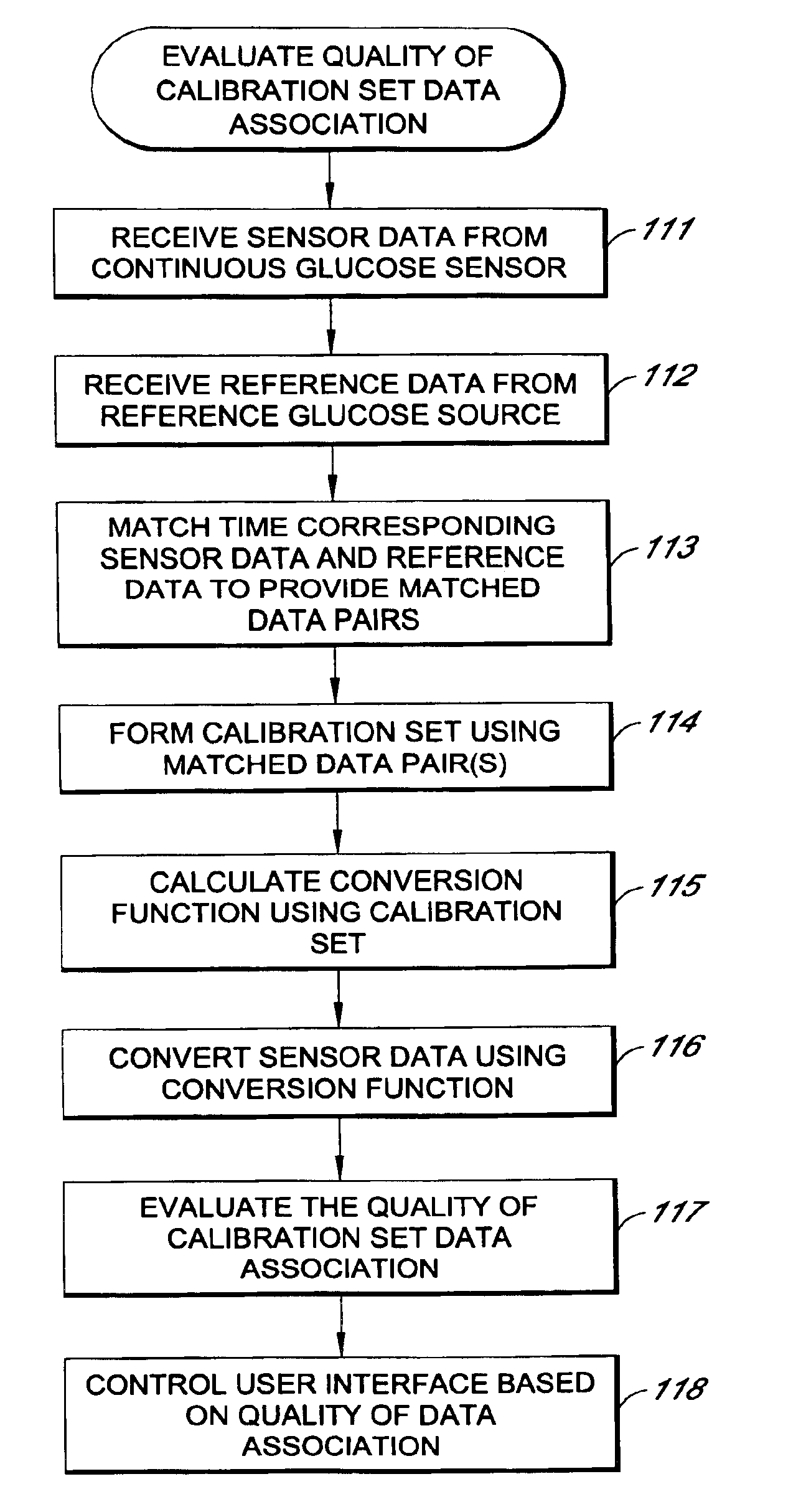
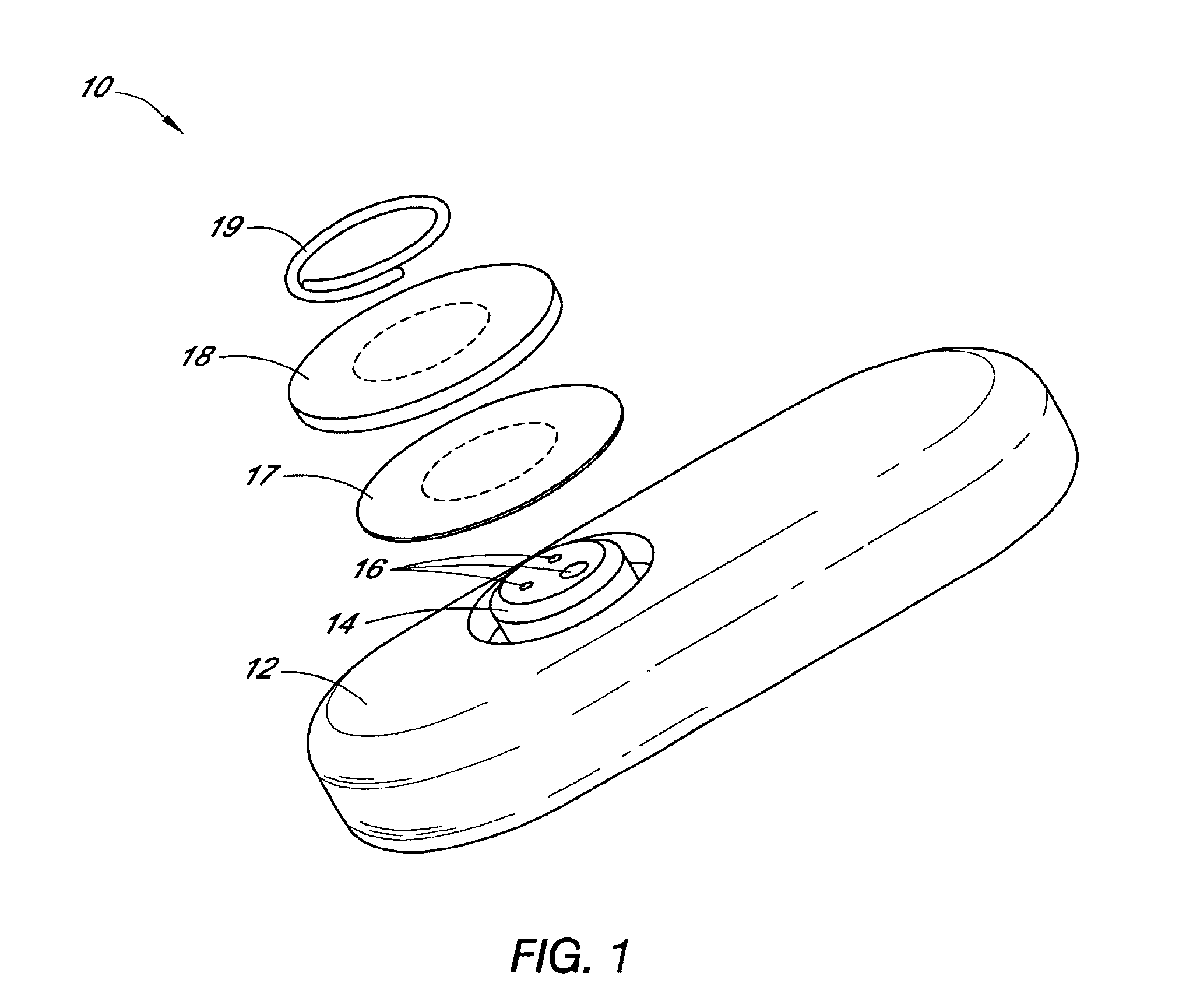
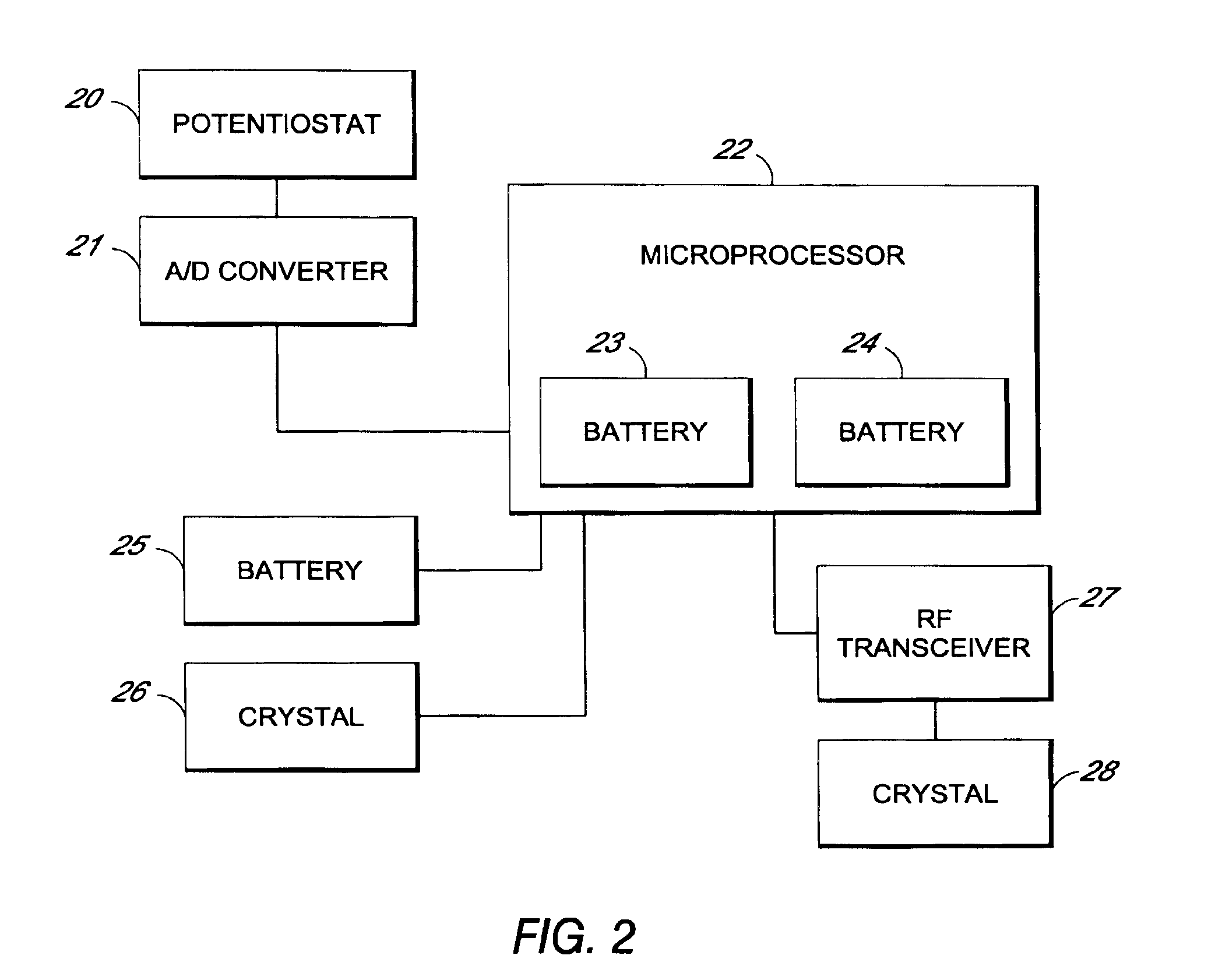
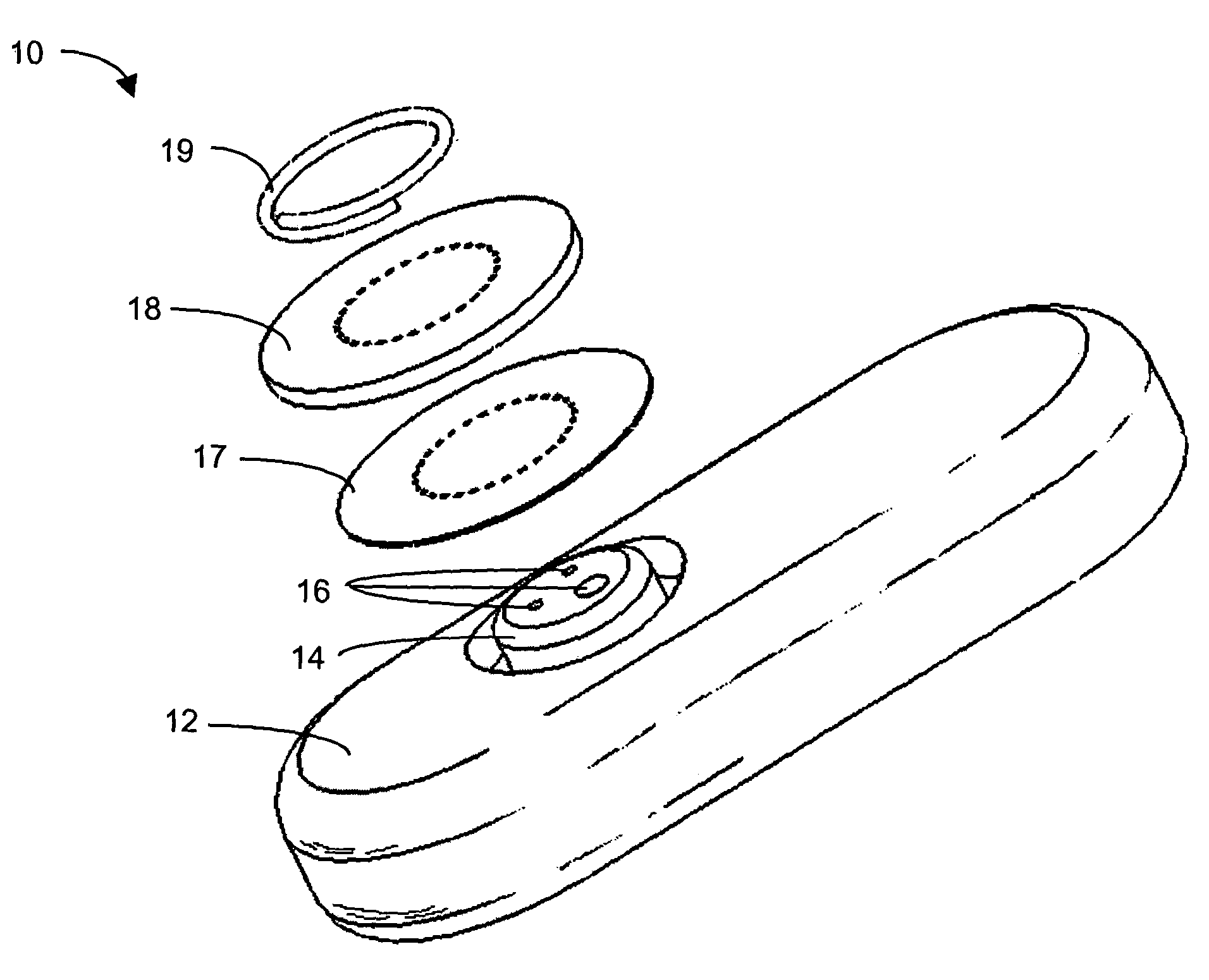
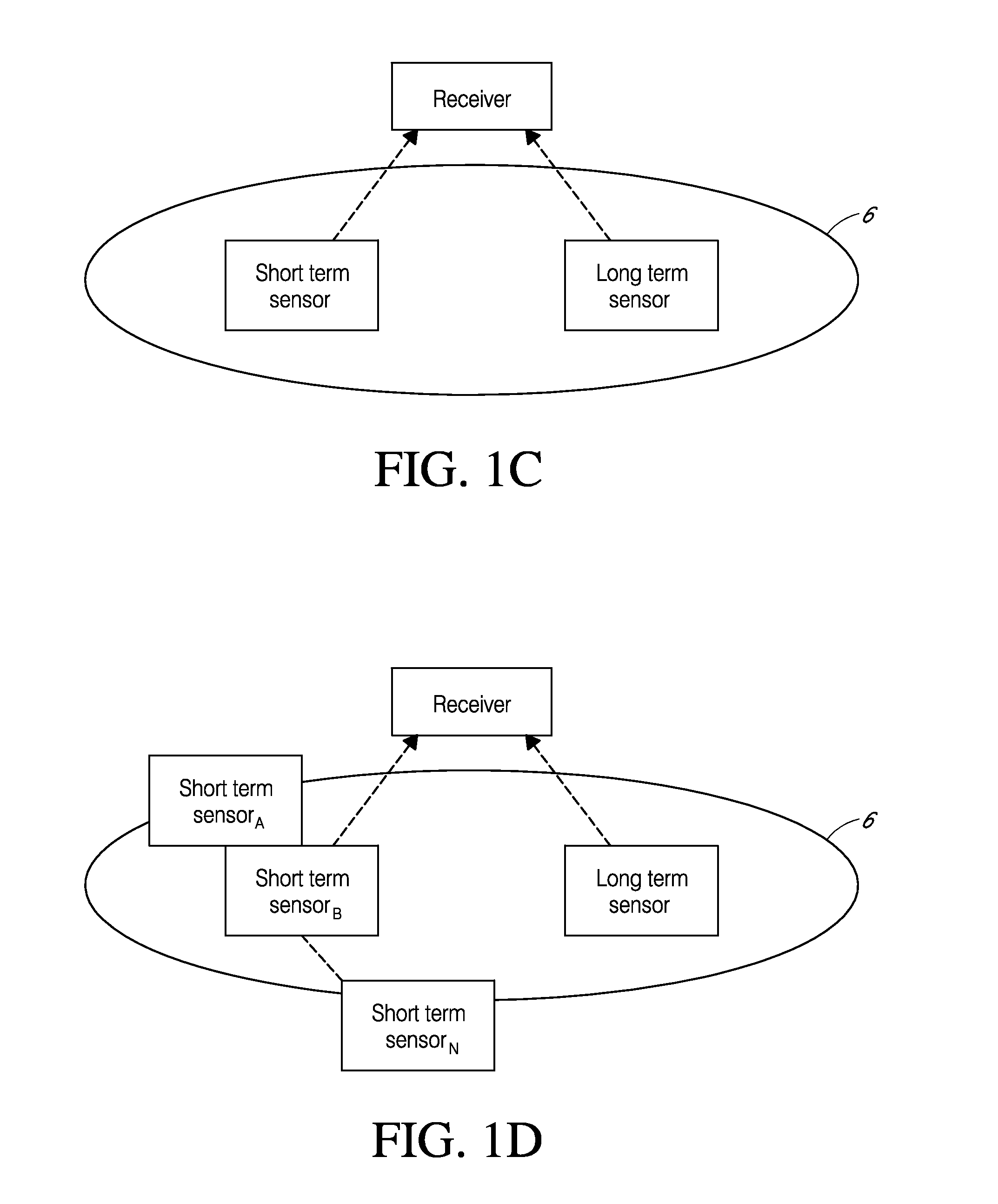
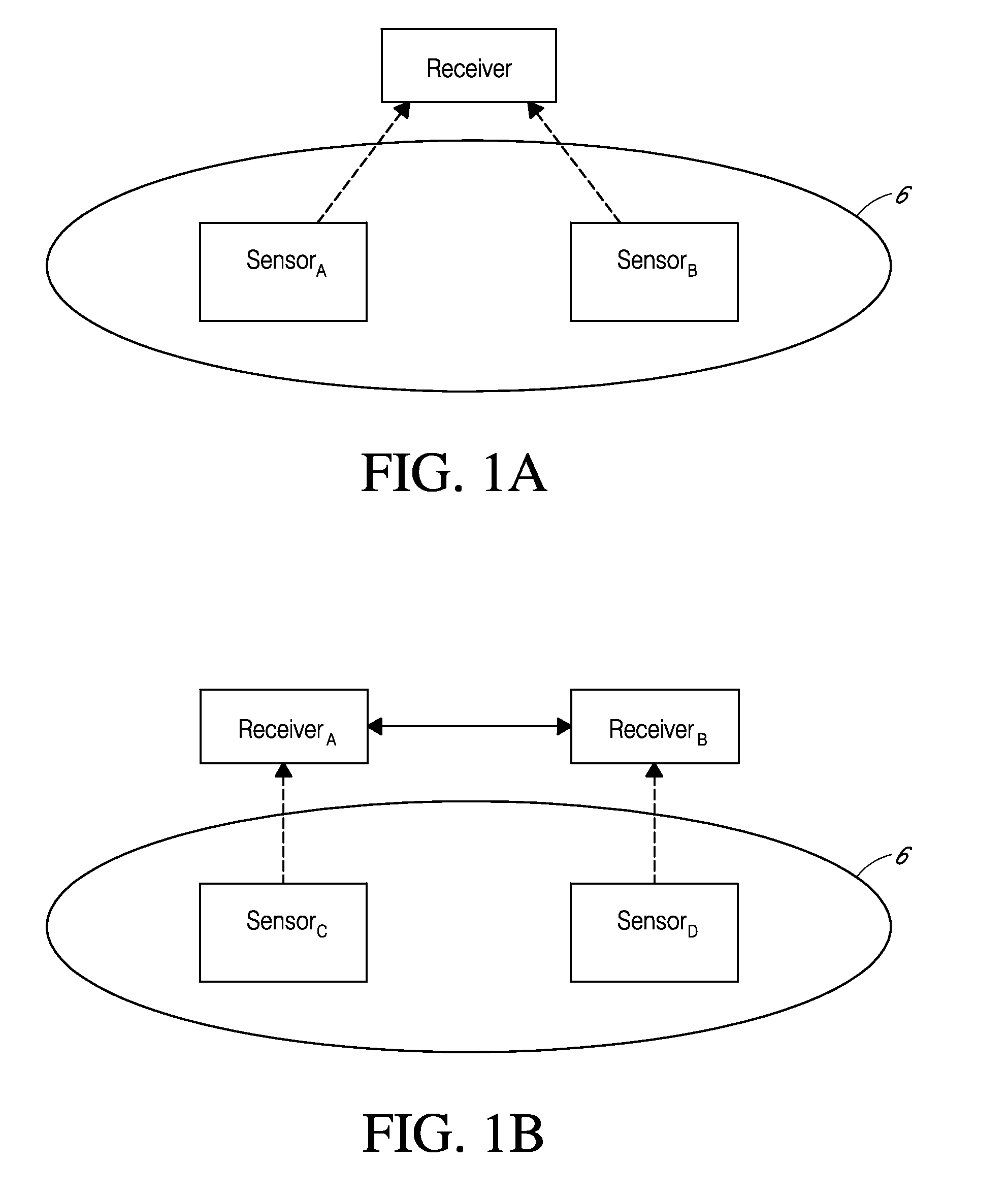
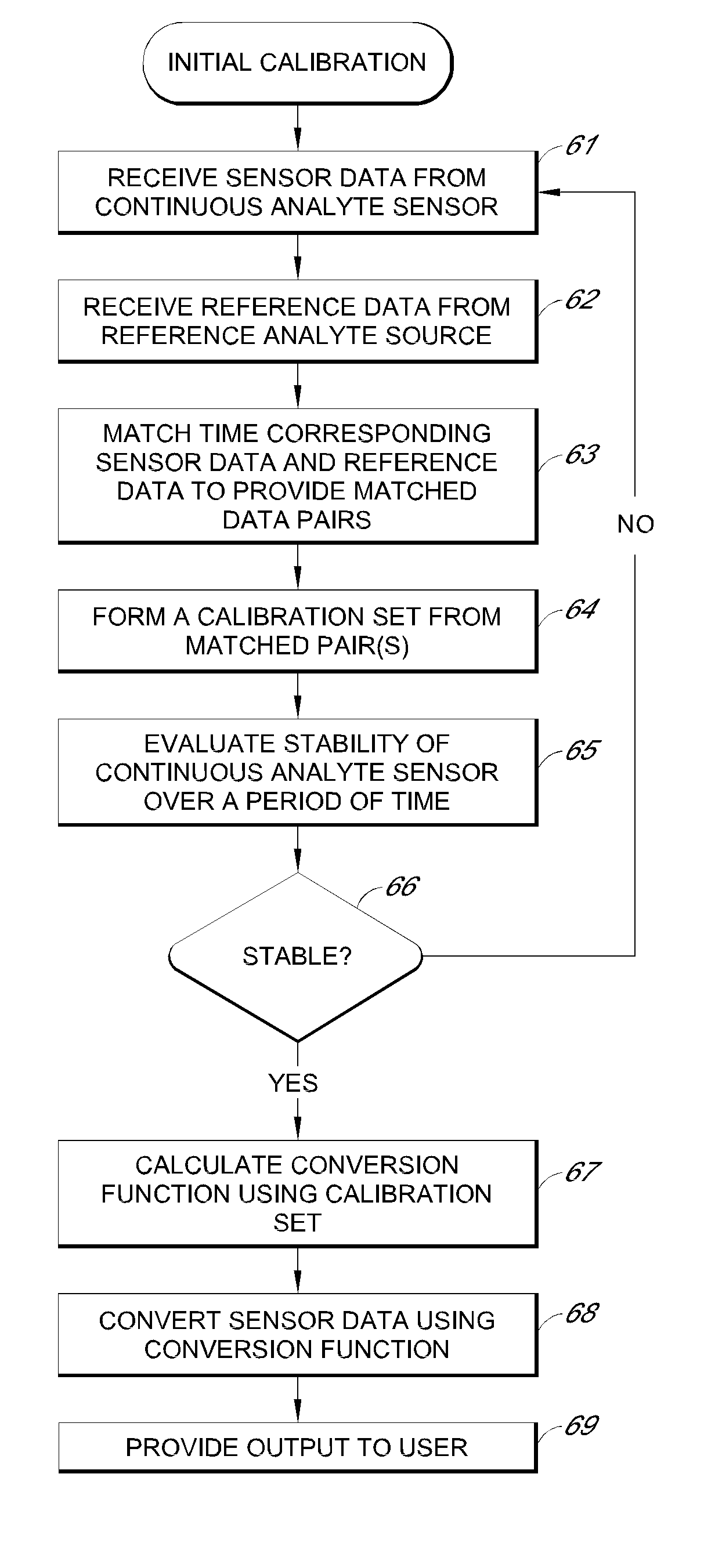
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
ActiveUS20050027463A1Material thermal conductivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalyteData system
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Pulse oximetry sensor adaptor
InactiveUS6993371B2Avoid complex processCost of very criticalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAudio power amplifierPulse oximetry
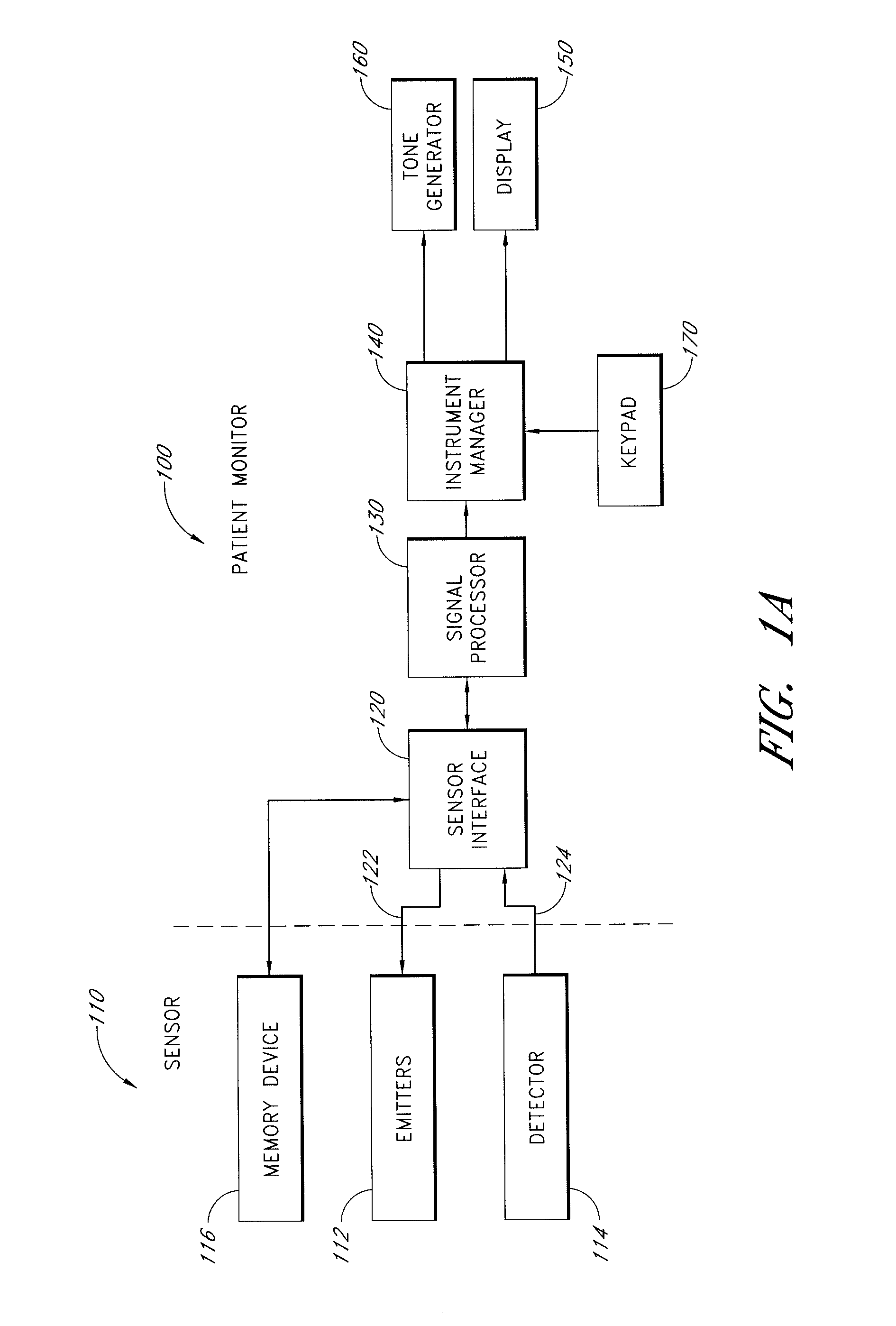
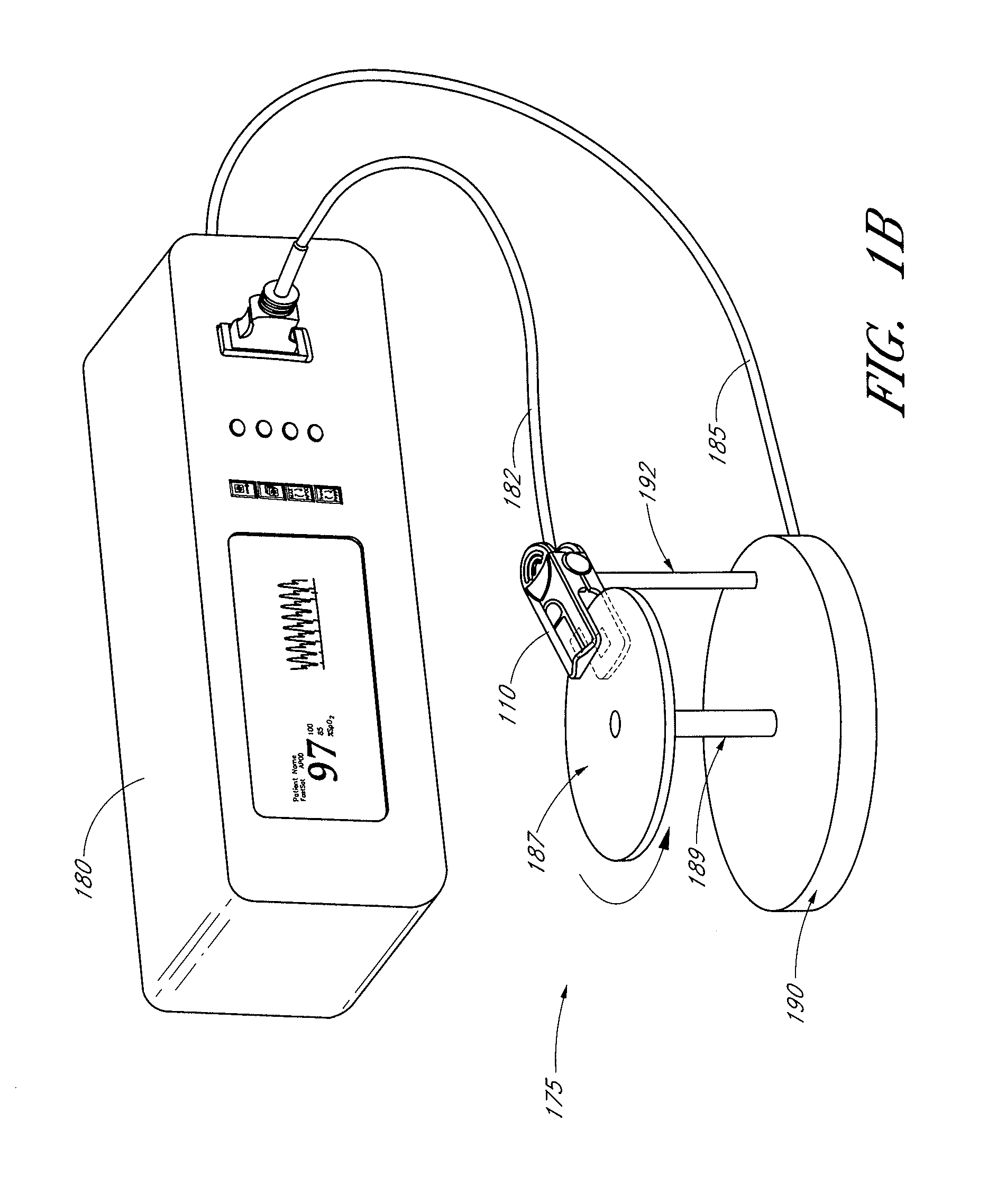
An adapter allows the interconnection of a sensor originating from one manufacturer to be coupled with conventionally incompatible monitors originating from other manufacturers to form a properly functioning pulse oximetry system. The adapter matches a sensor driver in a monitor to the current requirements and light source configuration of a sensor. The adapter also matches a sensor's light detector signal level to the dynamic range requirements of a monitor preamplifier. Further, the adapter provides compatible sensor calibration, sensor type and security information to a monitor. The adapter may have a self-contained power source or it may derive power from the monitor, allowing both passive and active adapter components. The adapter is particular suited as an adapter cable, replacing a conventional patient cable or sensor cable as the interconnection between a sensor to a monitor in a pulse oximetry system.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Non-invasive sensor calibration device
ActiveUS8418524B2Reliable timeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansOptically investigating flaws/contaminationNon invasiveAcoustics
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data for sensor calibration
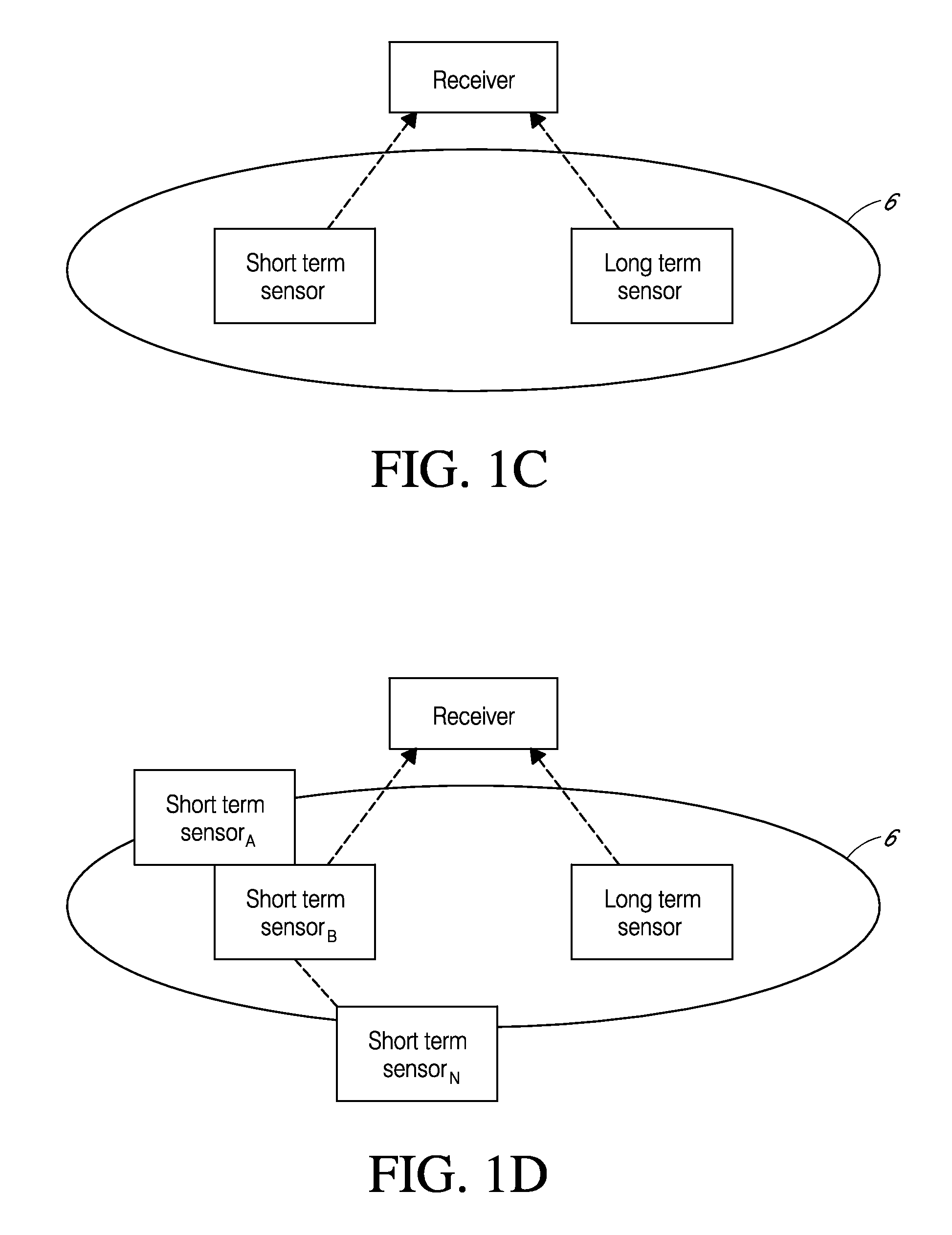
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data are disclosed, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. The sensor can be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. Reference data resulting from benchtop testing an analyte sensor prior to its insertion can be used to provide initial calibration of the sensor data. Reference data from a short term continuous analyte sensor implanted in a user can be used to initially calibrate or update sensor data from a long term continuous analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
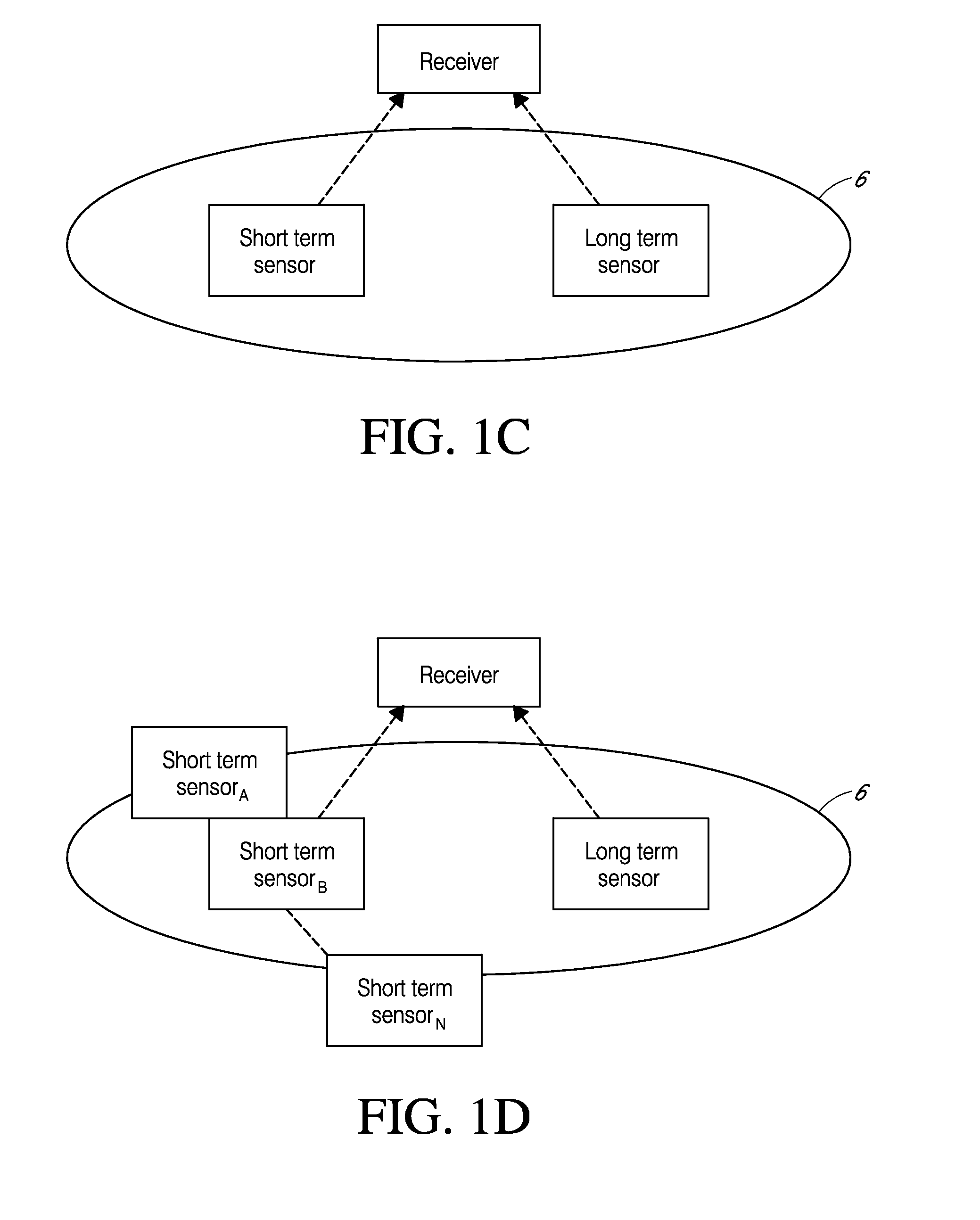
Method Of Manufacturing An Auto-Calibrating Sensor
InactiveUS20080114228A1Shorten the timeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansCatheterAnalyteEngineering
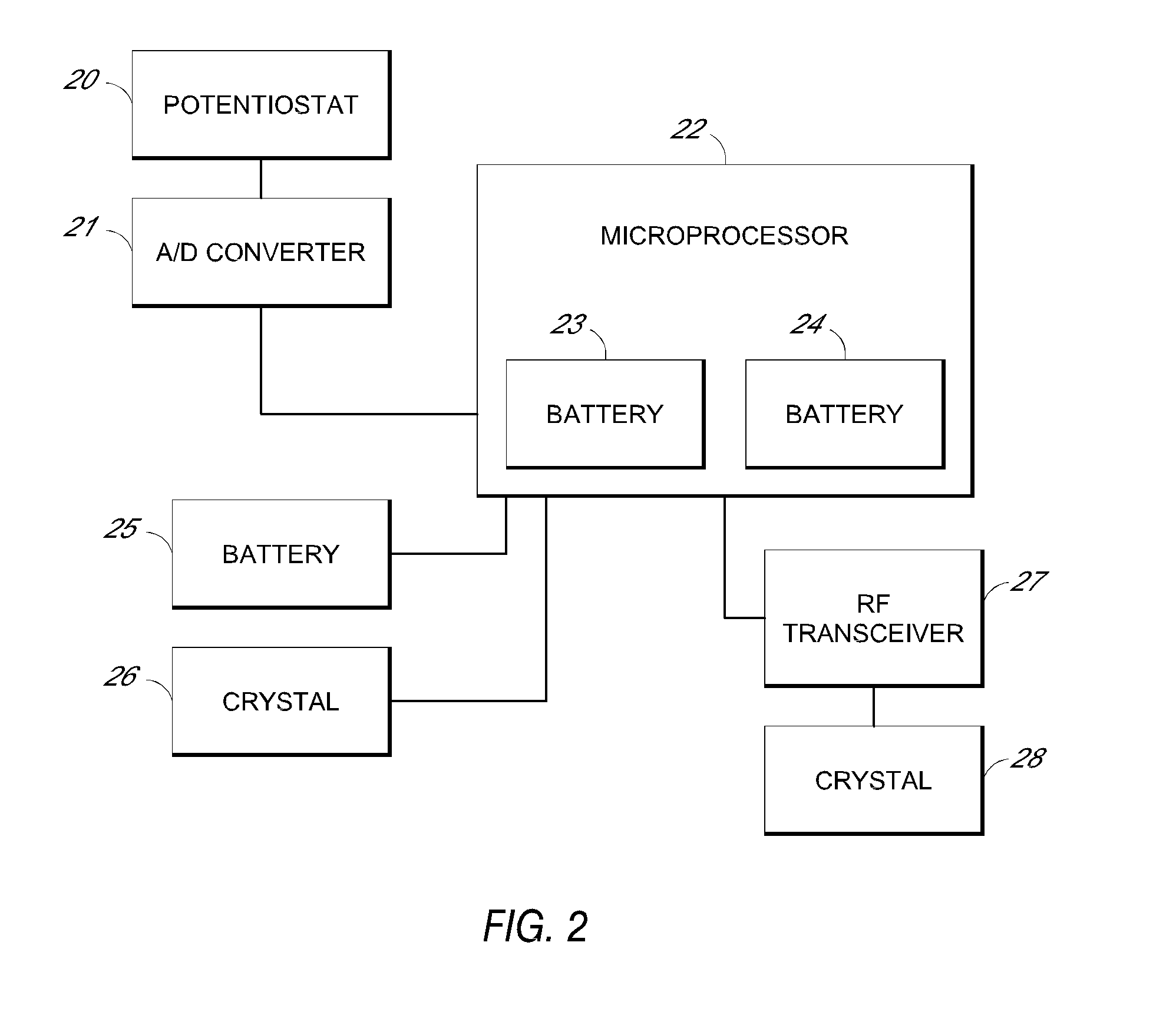
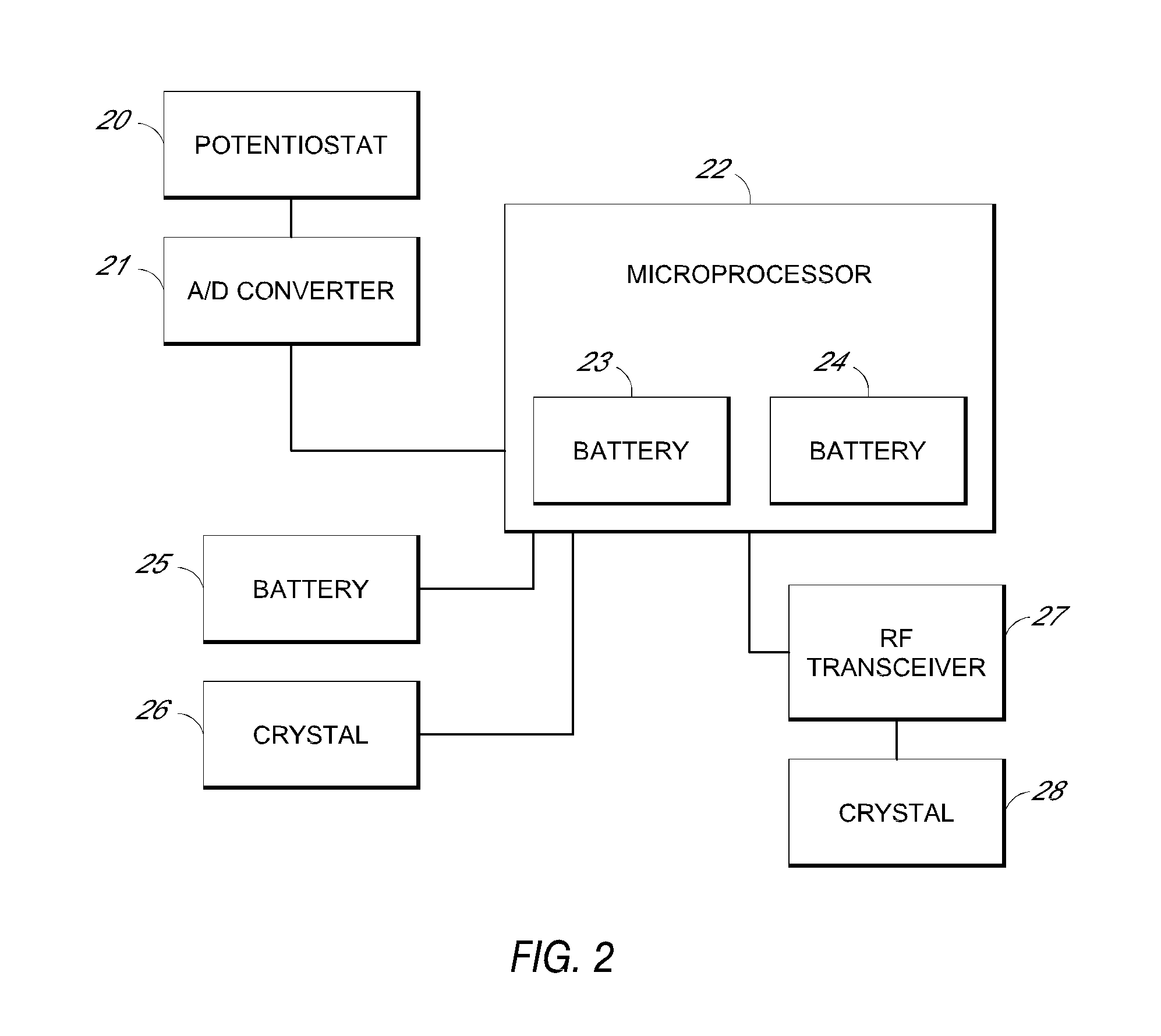
The invention concerns a sensor that, when exposed to a fluid, develops a measurable characteristic that is a function of the level of an analyte in the fluid and of a calibration quantity of the sensor. A calibration quantity is some physical, chemical or other inherent property that the sensor possesses that affects its response to the analyte. The sensor includes an RFID tag that receives, stores and conveys information representing the calibration quantity. The wireless device is incorporated into or attached to the sensor during the manufacturing process and before the sensor is calibrated. The wireless device can be written wirelessly once the calibration has been done. This does not involve any additional handling of the sensor and can be done once the sensor has been placed into a protective enclosure. Because of this, the process of wirelessly transmitting the calibration information to the wireless device does not alter any pre-existing calibration quantities and neither does it introduce any new calibration quantities, thus preserving the calibration of the sensor even though the sensor has been wirelessly modified to carry information representing its calibration quantity.
Owner:LIFESCAN IP HLDG LLC
Modified Sensor Calibration Algorithm
ActiveUS20090112478A1Reduce weightQuick changeTesting/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsData integrityGlucose polymers
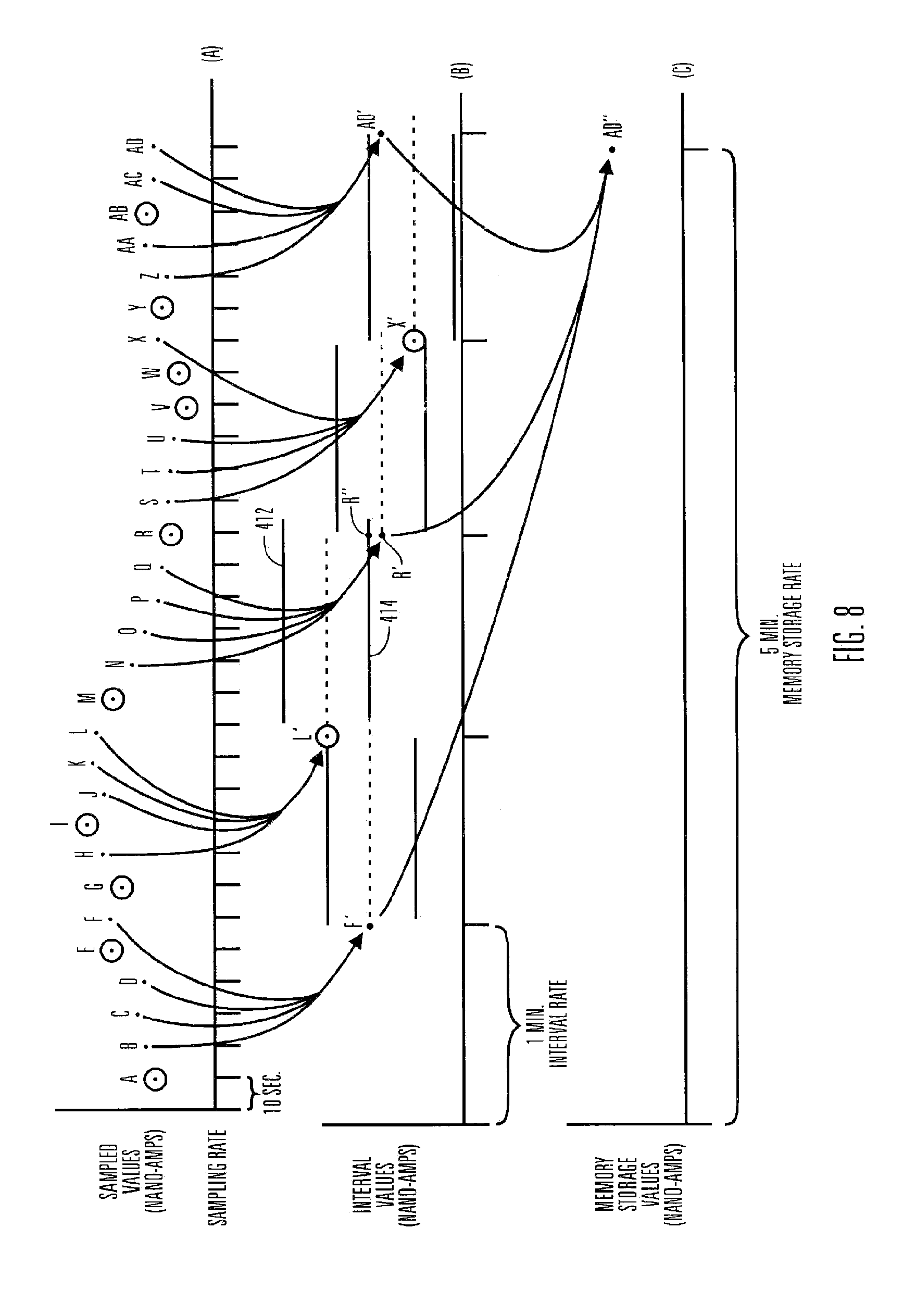
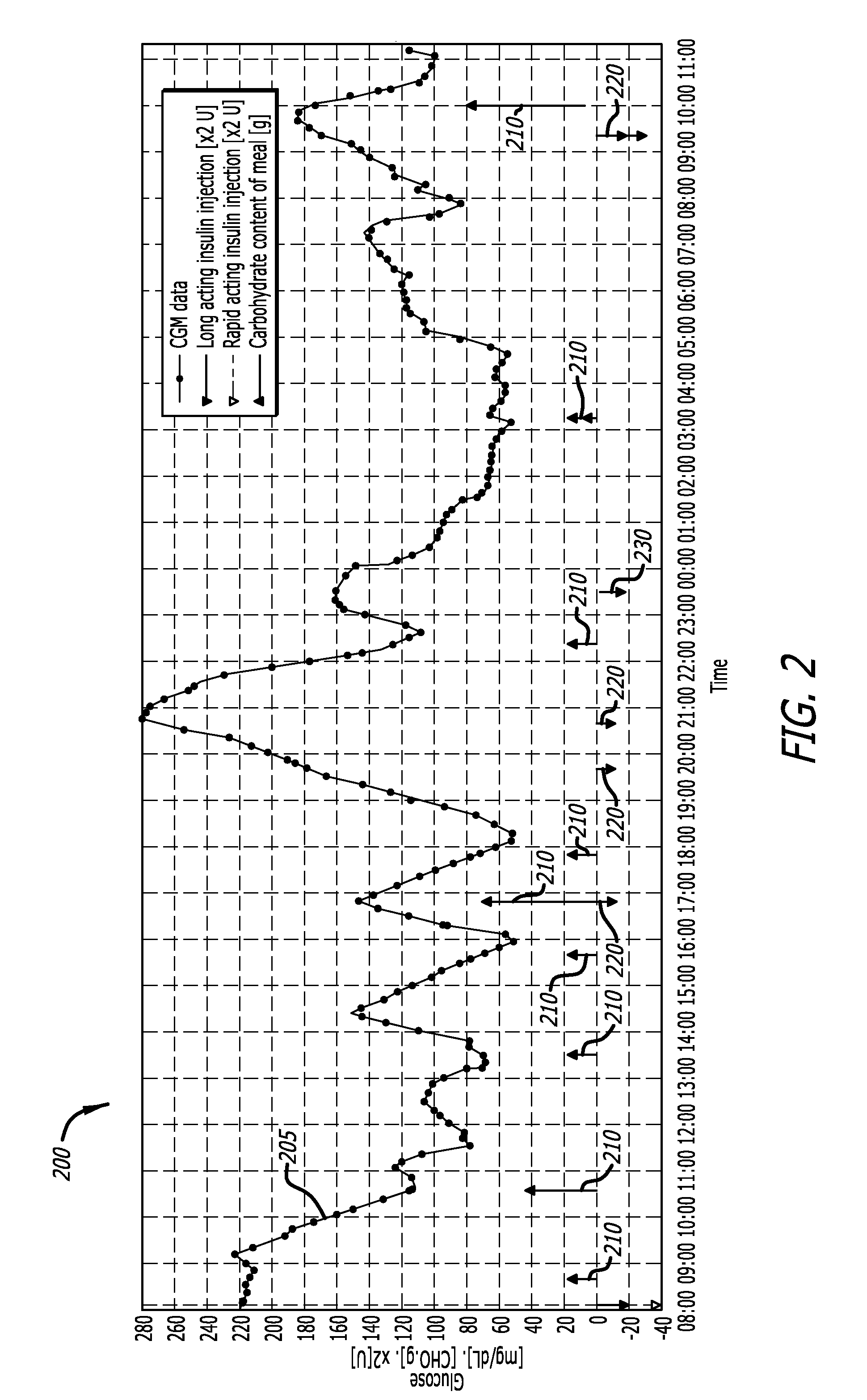
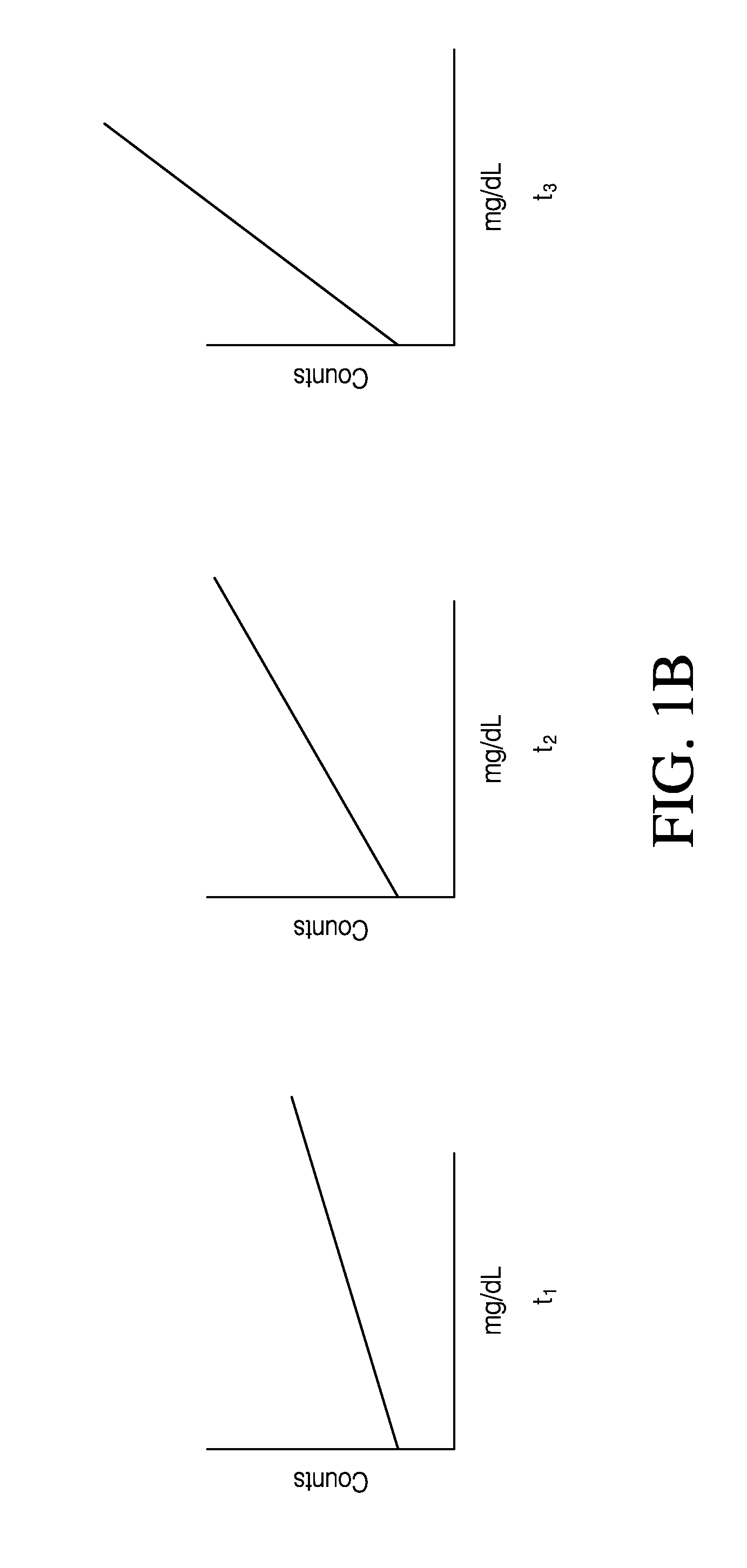
A method of calibrating glucose monitor data includes collecting the glucose monitor data over a period of time at predetermined intervals, obtaining reference glucose values from a reference source that temporally correspond with the glucose monitor data obtained at the predetermined intervals, calculating the calibration characteristics using the reference glucose values and corresponding glucose monitor data to regress the obtained glucose monitor data, and calibrating the obtained glucose monitor data using the calibration characteristics. In additional embodiments, calculation of the calibration characteristics includes linear regression and, in particular embodiments, least squares linear regression. Alternatively, calculation of the calibration characteristics includes non-linear regression. Data integrity may be verified and the data may be filtered. Further, calibration techniques may be modified during a fast rate of change in the patient's blood glucose level to increase sensor accuracy.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
InactiveUS20110231140A1Testing/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAnalyteData system
Owner:DEXCOM INC
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
ActiveUS20110231142A1Testing/calibration apparatusSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsAnalyteData system
Owner:DEXCOM INC
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data for sensor calibration
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data are disclosed, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. The sensor can be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. Reference data resulting from benchtop testing an analyte sensor prior to its insertion can be used to provide initial calibration of the sensor data. Reference data from a short term continuous analyte sensor implanted in a user can be used to initially calibrate or update sensor data from a long term continuous analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Advanced analyte sensor calibration and error detection
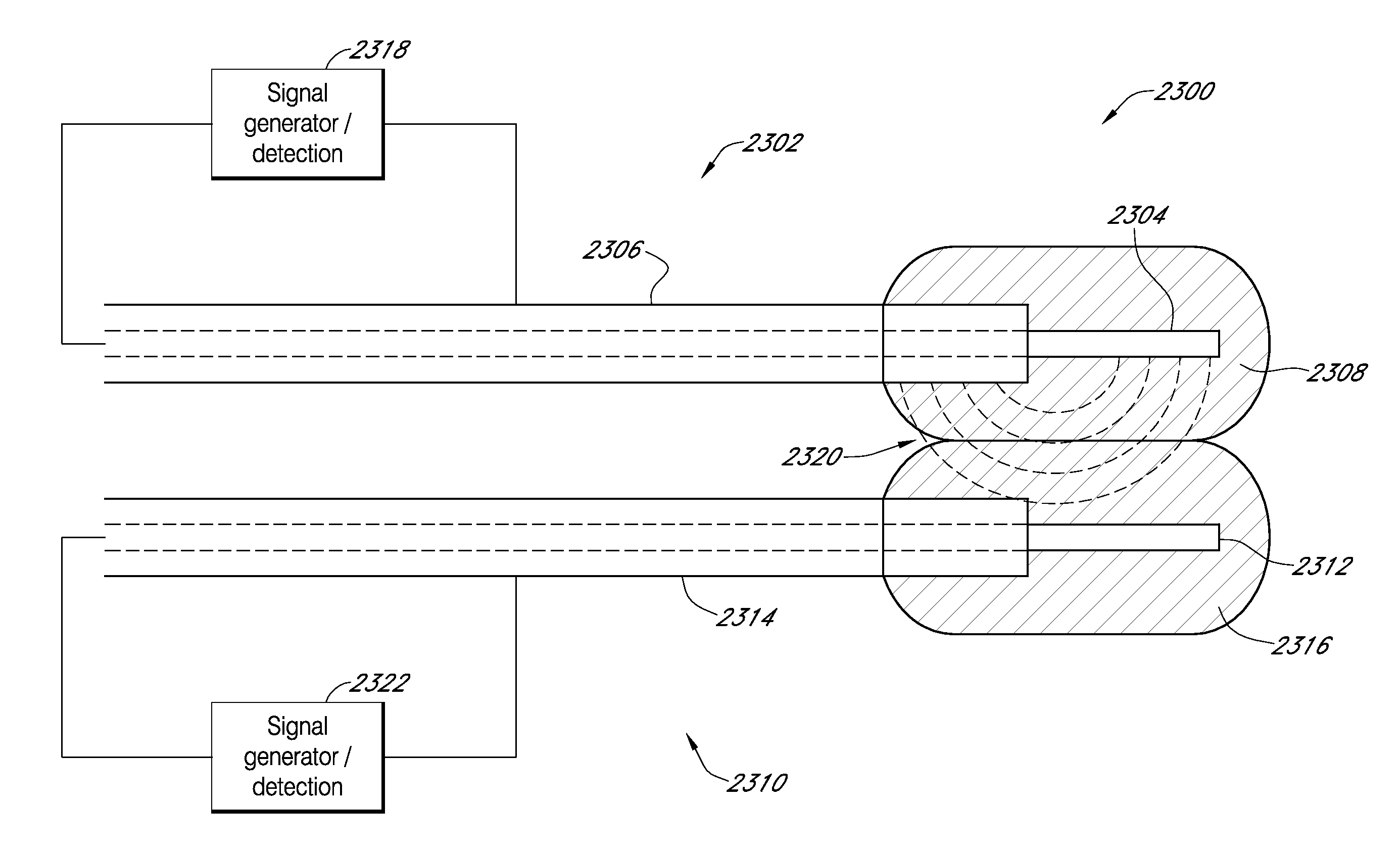
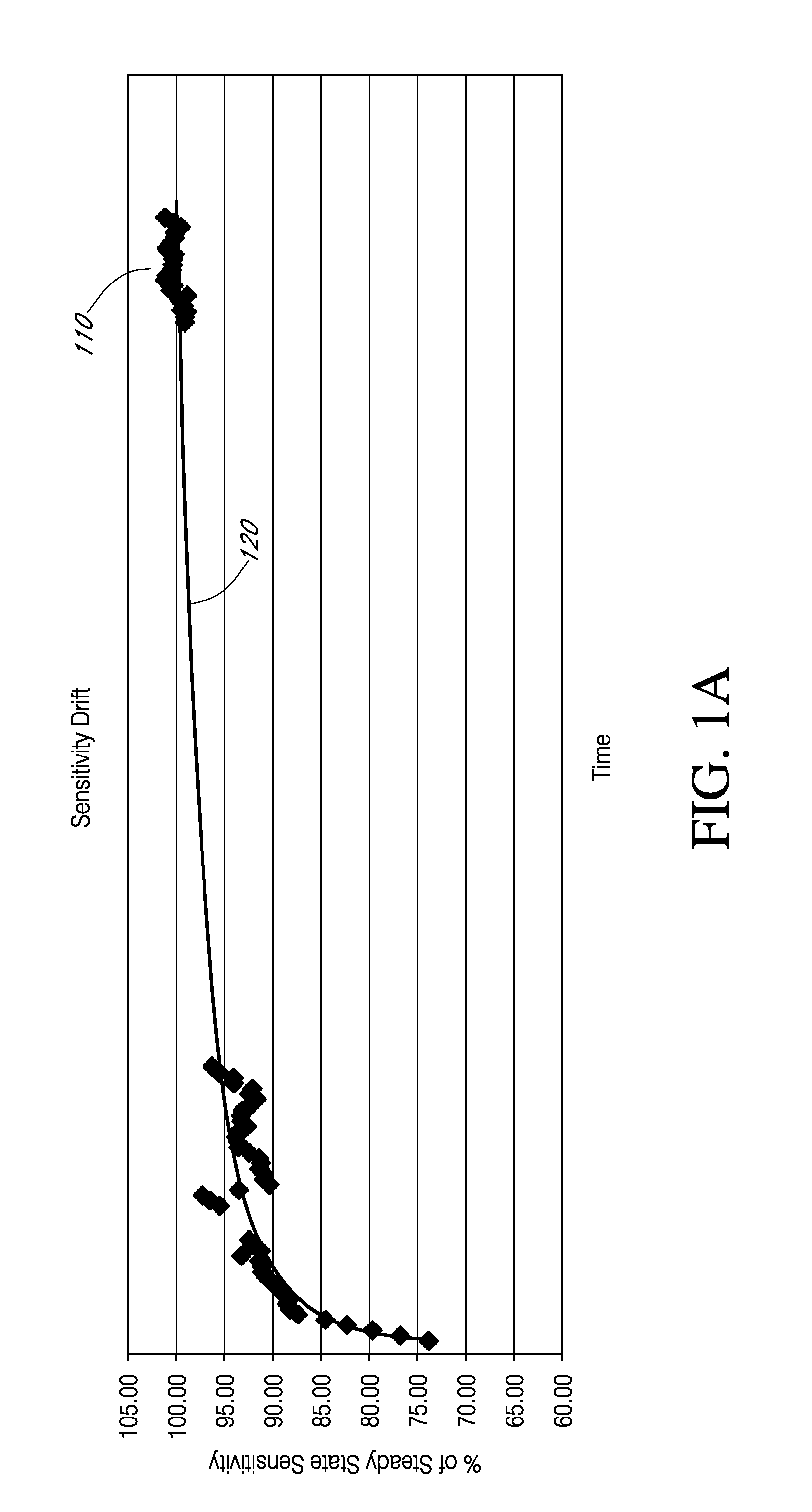
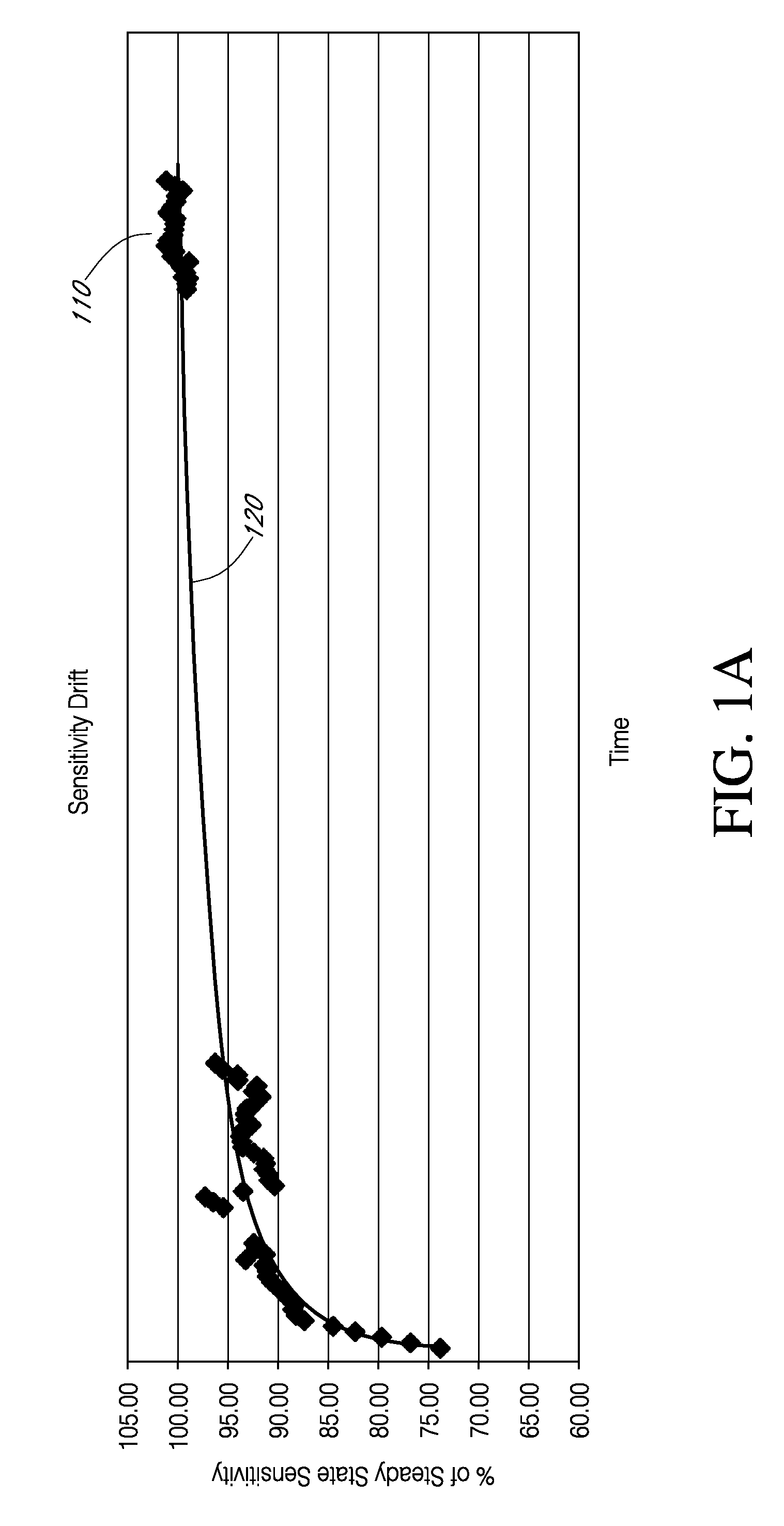
Systems and methods for processing sensor data and self-calibration are provided. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided which are capable of calibrating a continuous analyte sensor based on an initial sensitivity, and then continuously performing self-calibration without using, or with reduced use of, reference measurements. In certain embodiments, a sensitivity of the analyte sensor is determined by applying an estimative algorithm that is a function of certain parameters. Also described herein are systems and methods for determining a property of an analyte sensor using a stimulus signal. The sensor property can be used to compensate sensor data for sensitivity drift, or determine another property associated with the sensor, such as temperature, sensor membrane damage, moisture ingress in sensor electronics, and scaling factors.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
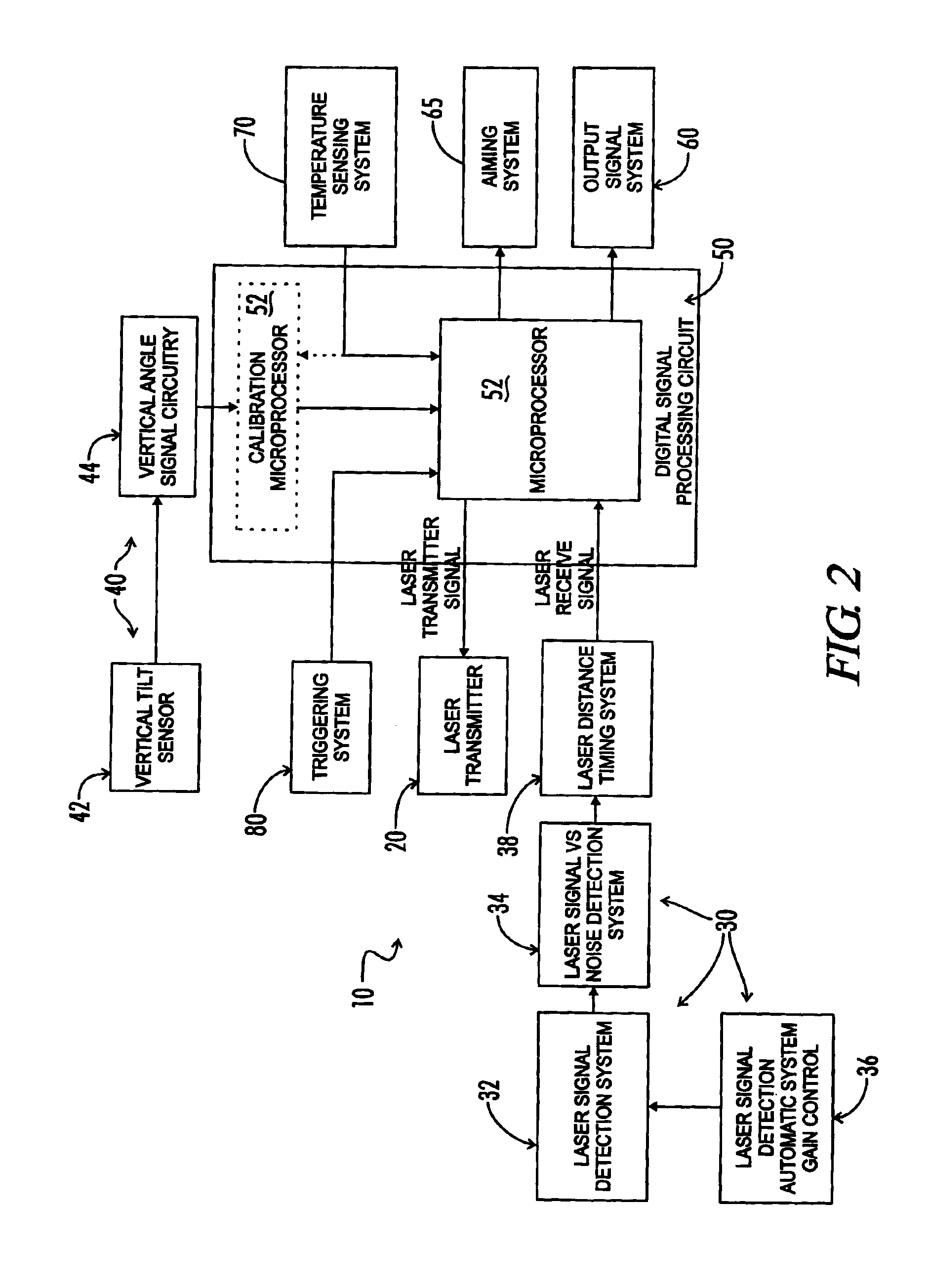
Tilt-compensated laser rangefinder
InactiveUS6873406B1Minimize impactError minimizationAngle measurementOptical rangefindersDigital signal processingInternal temperature
The present invention is a laser ranging device that incorporates an internal tilt sensor, an internal temperature sensor, and an internal pressure sensor. The tilt sensor is used to measure the target's vertical angle relative to the horizontal reference plane. Digital signal processing circuitry controls the firing of the laser pulse, calculation of time-of-flight range, measurement of the vertical angle of the tilt sensor, measurement of ambient temperature and storage of tilt sensor and temperature sensor calibration data. The digital signal processing circuitry then provides the user temperature corrected ballistic ranging information, including horizontal range. Additionally, an automatic gain control system minimizes the effects of target to target variance in reflectivity and its associated errors. It is also an object of this invention to electronically minimize errors in the measurement of a vertical angle caused by housing vibration and by temperature variance errors.
Owner:OPTI LOGIC CORP
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM
Safety features for integrated insulin delivery system
ActiveUS20100298765A1Preventing hypoglycemiaLimited hyperglycemiaDrug and medicationsMedical devicesGlucose sensorsHypoglycemia
Safety features are applied to an integrated insulin delivery system to enhance safety while accounting for glucose sensor bias and calibration errors. One safety feature includes comparisons of calibrations of the sensor to nominal sensitivity and taking action, such as limiting insulin delivery or taking a further calibration of the sensor. In another feature, an automatic resumption of a basal delivery rate is programmed into the delivery device to avoid the possibility of complete loss of delivery of insulin in the event that communication with the delivery device is disrupted. Other features include steps taken to avoid hypoglycemia in the event that the sensor is negatively biased.
Owner:ABBOTT DIABETES CARE INC
Advanced analyte sensor calibration and error detection
ActiveUS20120265035A1Material analysis by electric/magnetic meansMaterial analysis by optical meansAnalyteContinuous analysis
Systems and methods for processing sensor data and self-calibration are provided. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided which are capable of calibrating a continuous analyte sensor based on an initial sensitivity, and then continuously performing self-calibration without using, or with reduced use of, reference measurements. In certain embodiments, a sensitivity of the analyte sensor is determined by applying an estimative algorithm that is a function of certain parameters. Also described herein are systems and methods for determining a property of an analyte sensor using a stimulus signal. The sensor property can be used to compensate sensor data for sensitivity drift, or determine another property associated with the sensor, such as temperature, sensor membrane damage, moisture ingress in sensor electronics, and scaling factors.
Owner:DEXCOM
System and methods for processing analyte sensor data
Systems and methods for processing sensor analyte data, including initiating calibration, updating calibration, evaluating clinical acceptability of reference and sensor analyte data, and evaluating the quality of sensor calibration. During initial calibration, the analyte sensor data is evaluated over a period of time to determine stability of the sensor. The sensor may be calibrated using a calibration set of one or more matched sensor and reference analyte data pairs. The calibration may be updated after evaluating the calibration set for best calibration based on inclusion criteria with newly received reference analyte data. Fail-safe mechanisms are provided based on clinical acceptability of reference and analyte data and quality of sensor calibration. Algorithms provide for optimized prospective and retrospective analysis of estimated blood analyte data from an analyte sensor.
Owner:DEXCOM INC
Advanced analyte sensor calibration and error detection
Systems and methods for processing sensor data and self-calibration are provided. In some embodiments, systems and methods are provided which are capable of calibrating a continuous analyte sensor based on an initial sensitivity, and then continuously performing self-calibration without using, or with reduced use of, reference measurements. In certain embodiments, a sensitivity of the analyte sensor is determined by applying an estimative algorithm that is a function of certain parameters. Also described herein are systems and methods for determining a property of an analyte sensor using a stimulus signal. The sensor property can be used to compensate sensor data for sensitivity drift, or determine another property associated with the sensor, such as temperature, sensor membrane damage, moisture ingress in sensor electronics, and scaling factors.
Owner:DEXCOM
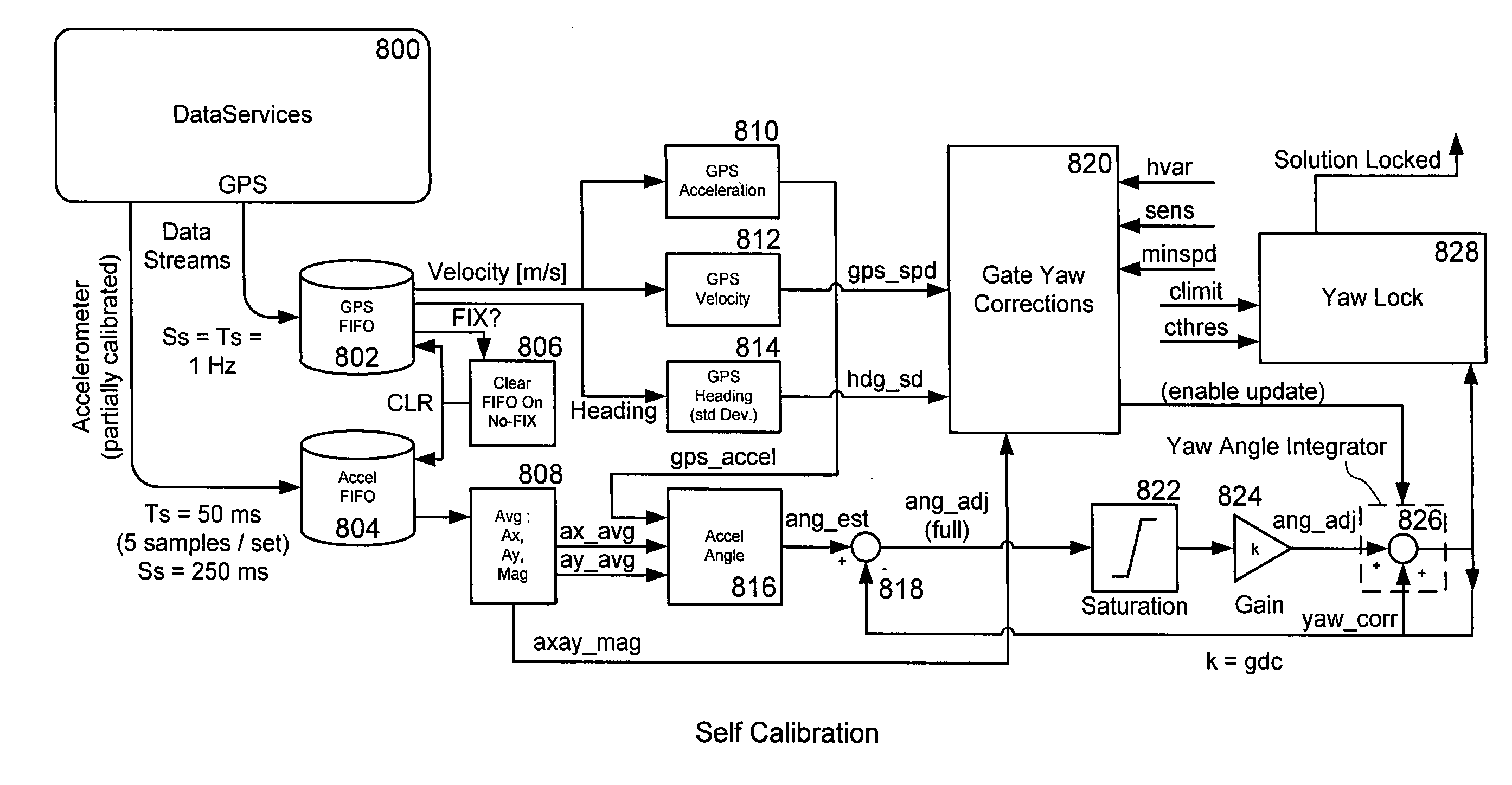
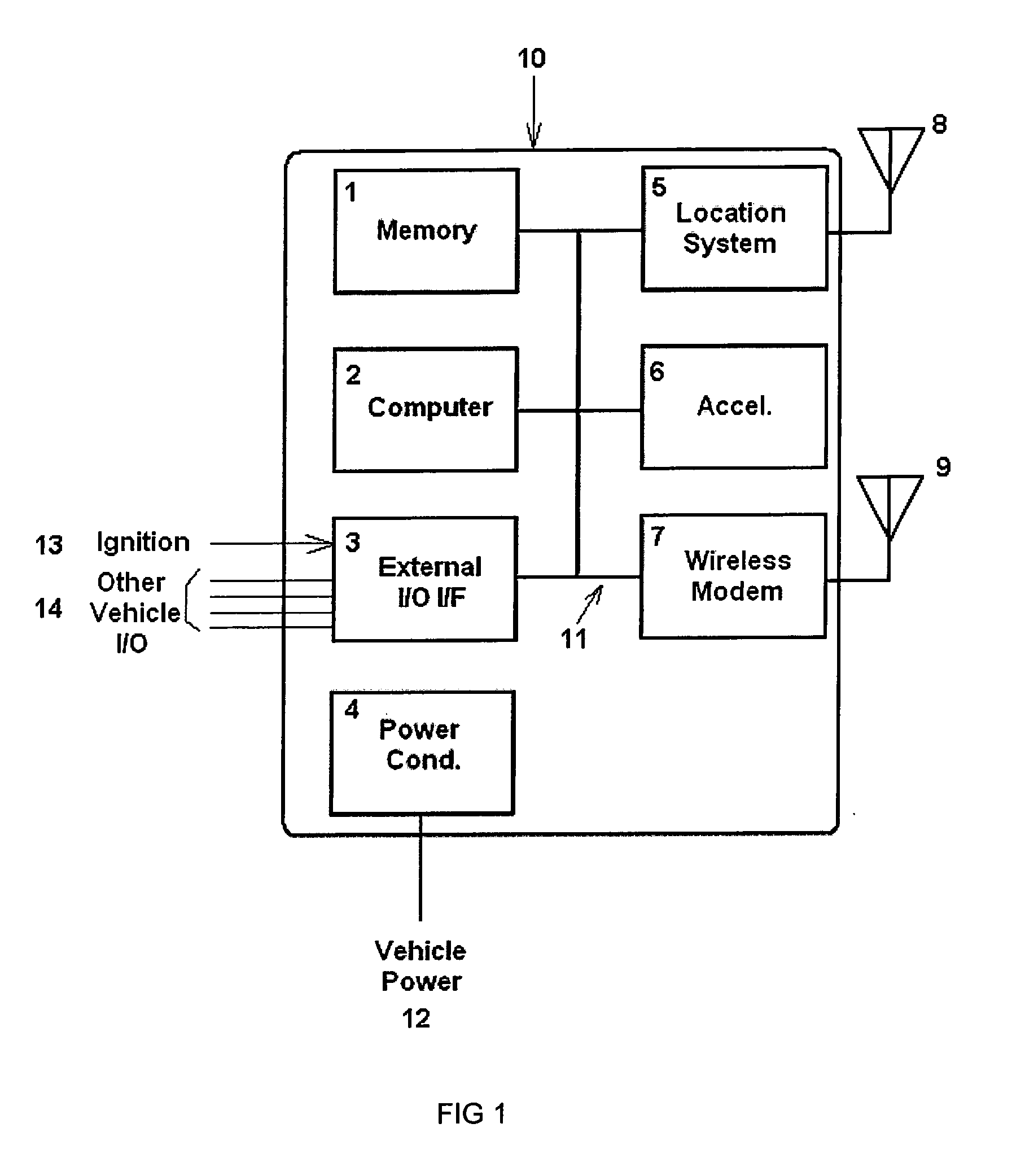
Vehicle sensor caliration for determining vehicle dynamics
ActiveUS20110202225A1Increase probabilityVehicle testingRegistering/indicating working of vehiclesVehicle dynamicsAccelerometer
An accelerometer sensor equipped device uses GPS and known alignment data to determine the alignment of the accelerometer sub-system when the vehicle is stationary and in motion. The alignment data is determined from known surface information, measured GPS velocity, and measured GPS Heading.
Owner:GEOTAB
Integrated force sensitive lens and software
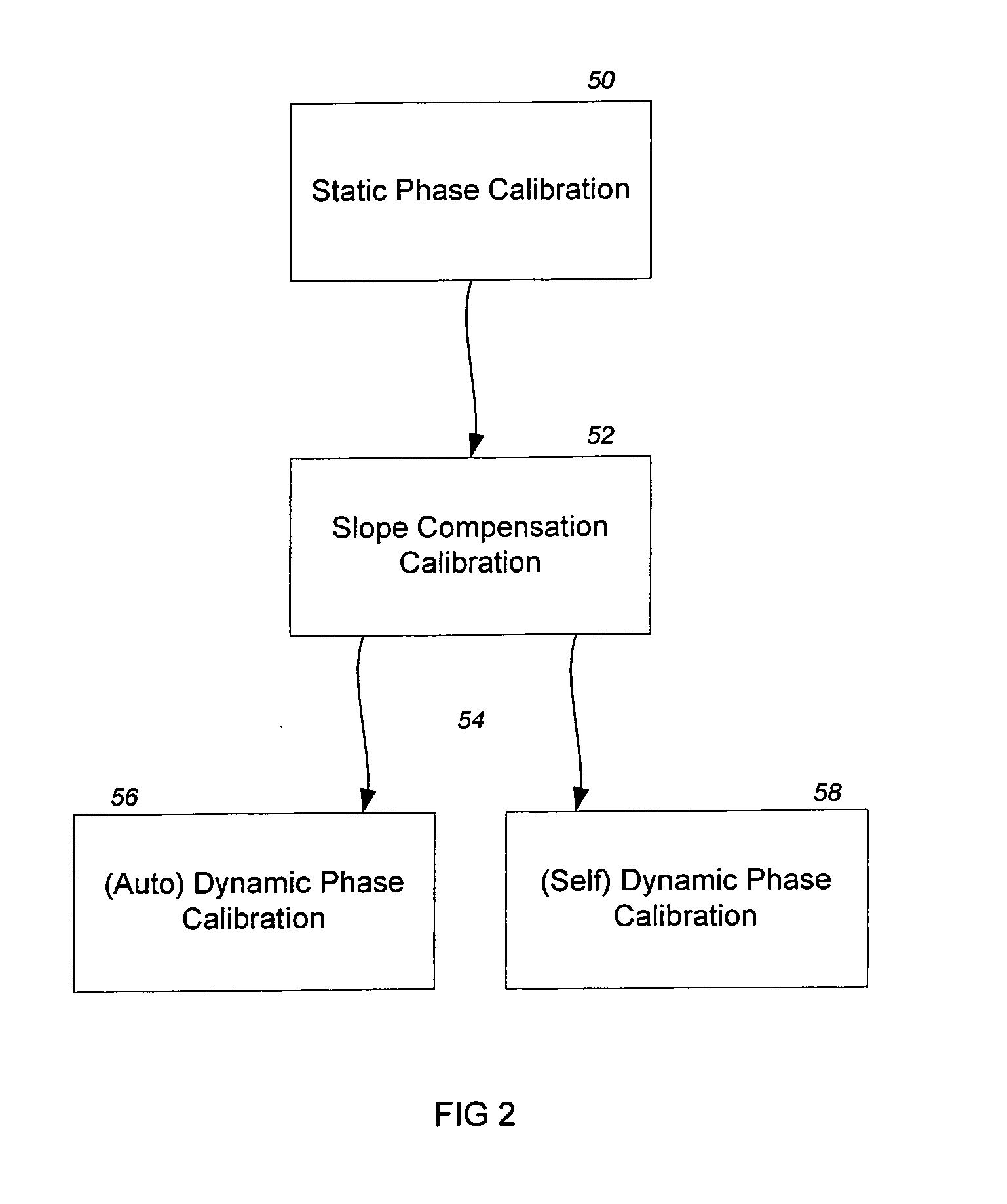
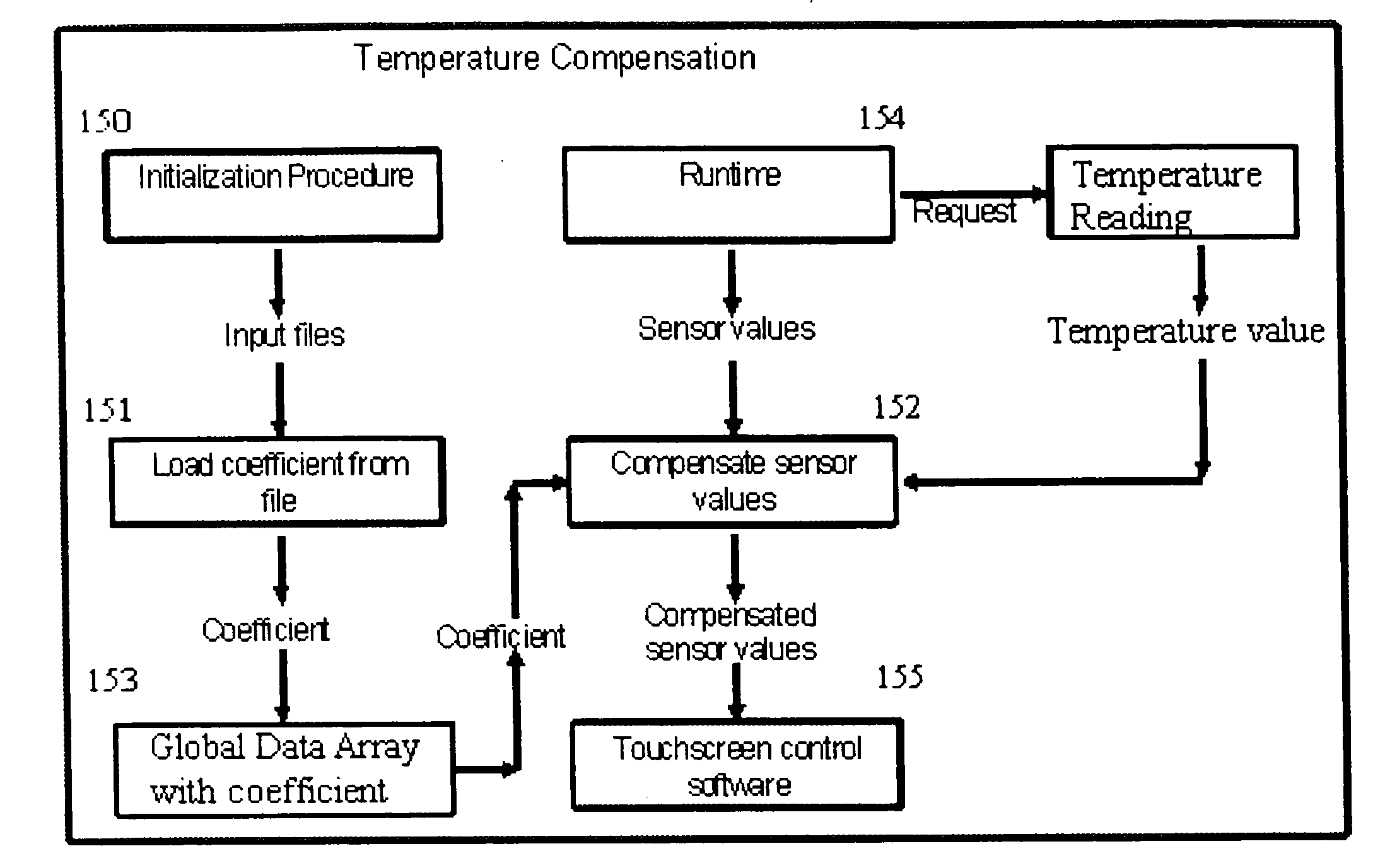
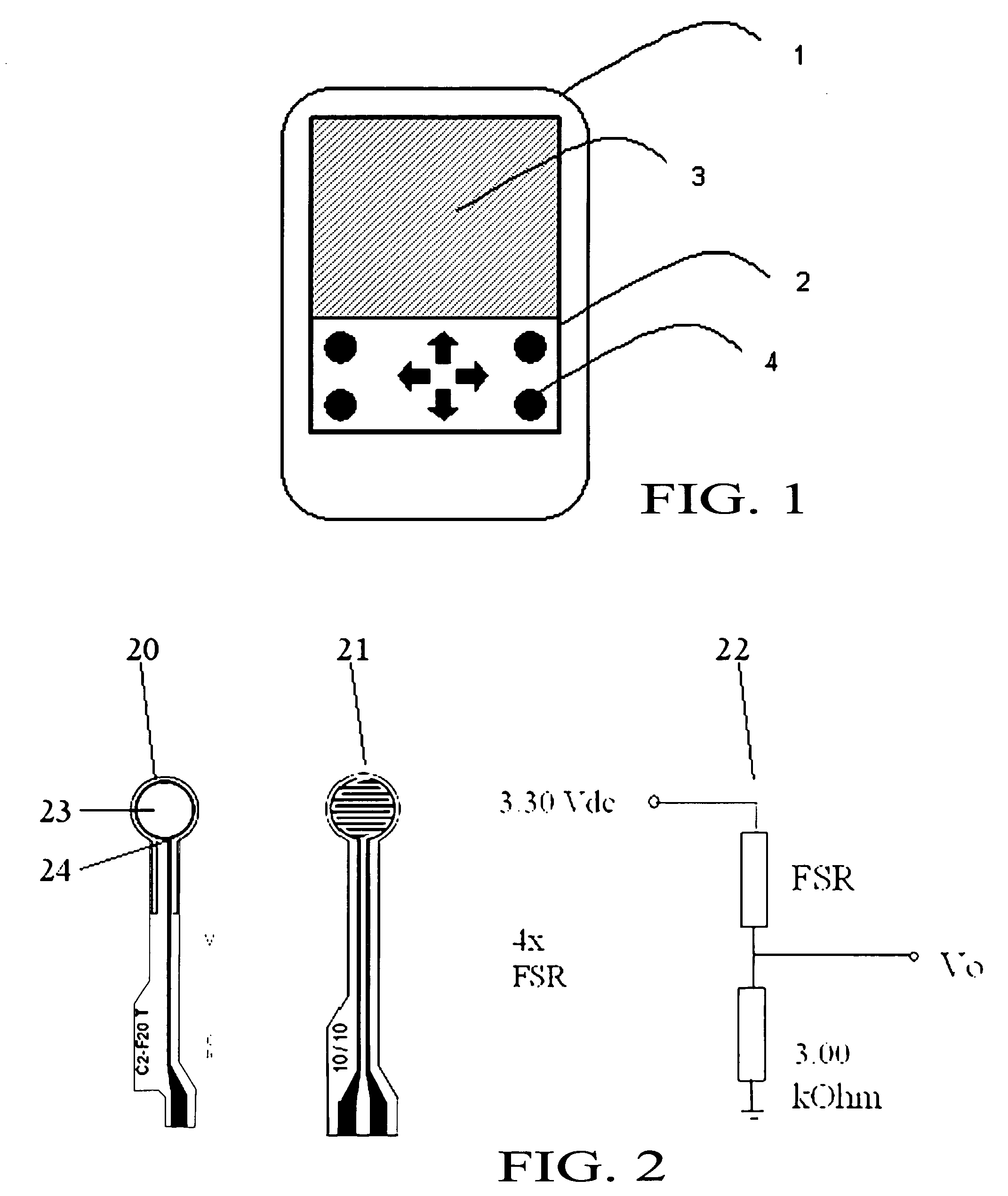
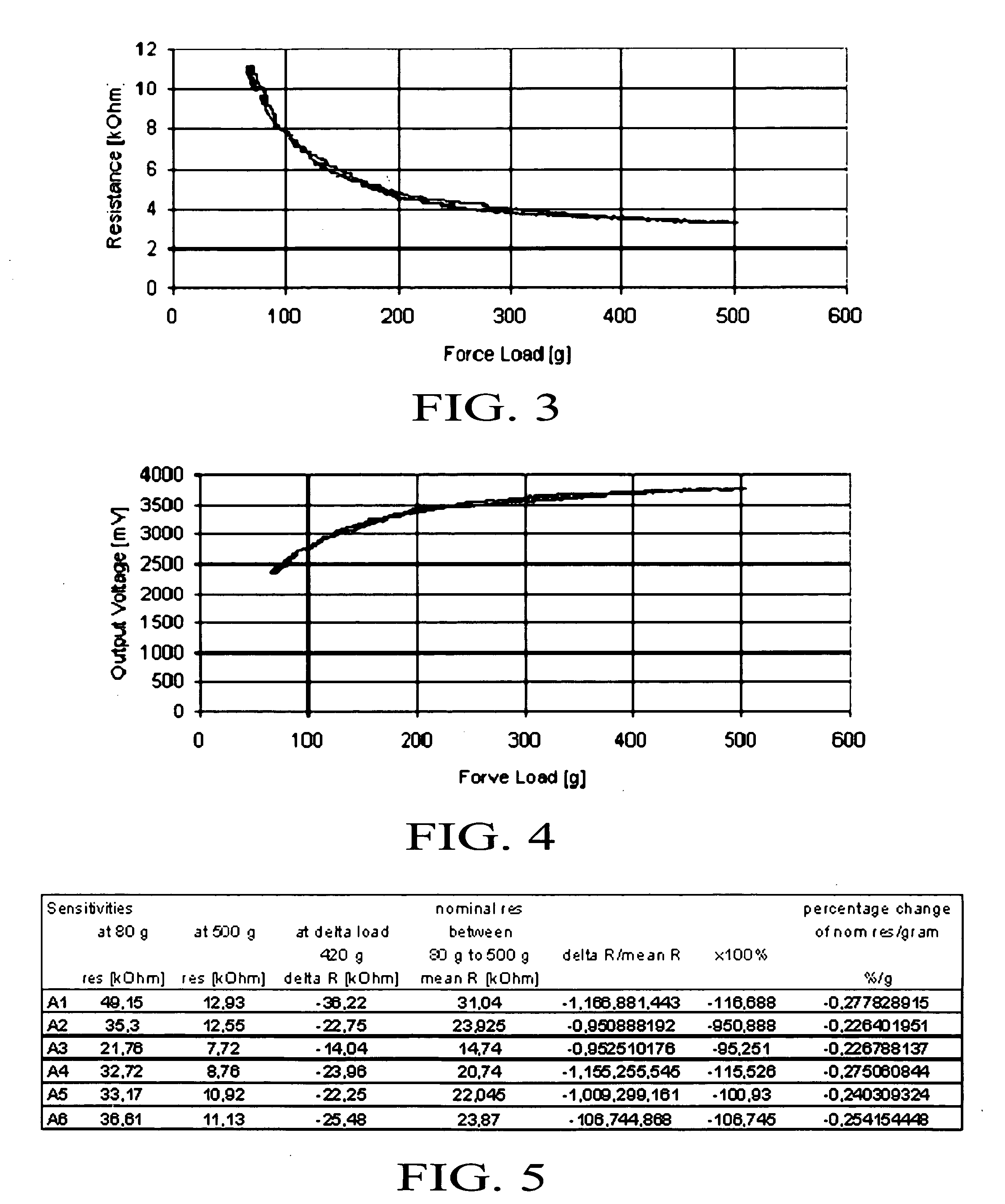
ActiveUS20090066673A1Low costElectrical measurementsTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesCamera lensTouchscreen
A software compensation method that allows a touch sensitive display to be built using low-cost FSR force sensors The compensation method comprises an array of functional compensation modules including filtering, voltage conversion, temperature compensation, humidity compensation, sensor calibration, sensor reading linearization, auto calibration, positioning determination and finally end-user and mechanical calibration. The array of compensation modules can bring system accuracy from a non-compensated average positioning error in the 25% to 50% range, down to aN end-user acceptable range of 0% to 5%. The increased positioning accuracy makes it possible to use FSRs as opposed to traditional piezoresistive based touch screen sensors.
Owner:APPLE INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com