Patents
Literature
34 results about "Photoinhibition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photoinhibition is light-induced reduction in the photosynthetic capacity of a plant, alga, or cyanobacterium. Photosystem II (PSII) is more sensitive to light than the rest of the photosynthetic machinery, and most researchers define the term as light-induced damage to PSII. In living organisms, photoinhibited PSII centres are continuously repaired via degradation and synthesis of the D1 protein of the photosynthetic reaction center of PSII. Photoinhibition is also used in a wider sense, as dynamic photoinhibition, to describe all reactions that decrease the efficiency of photosynthesis when plants are exposed to light.
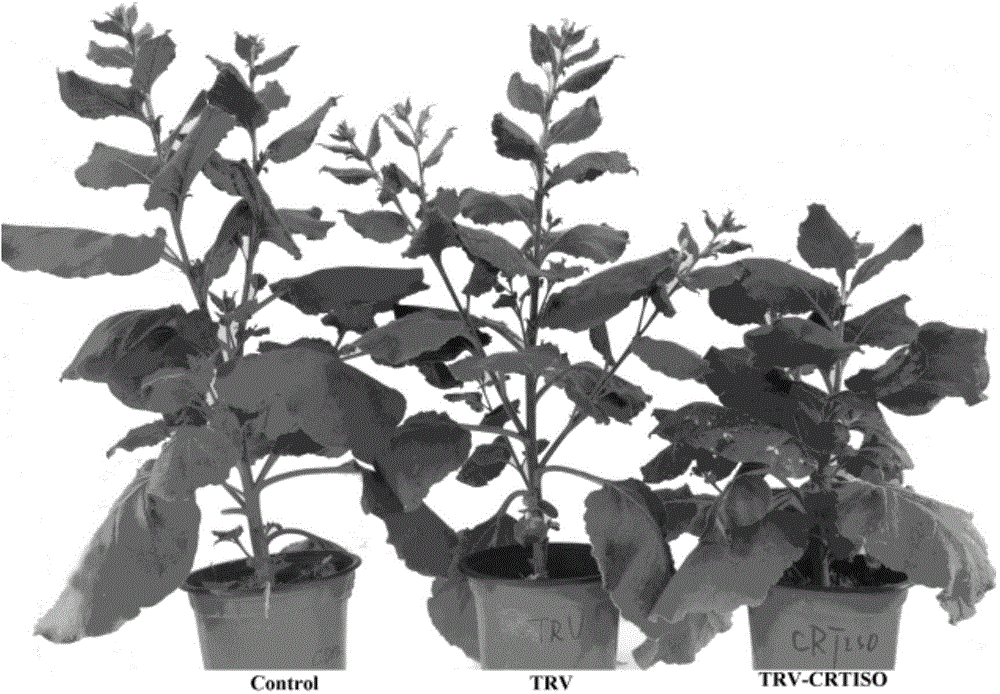
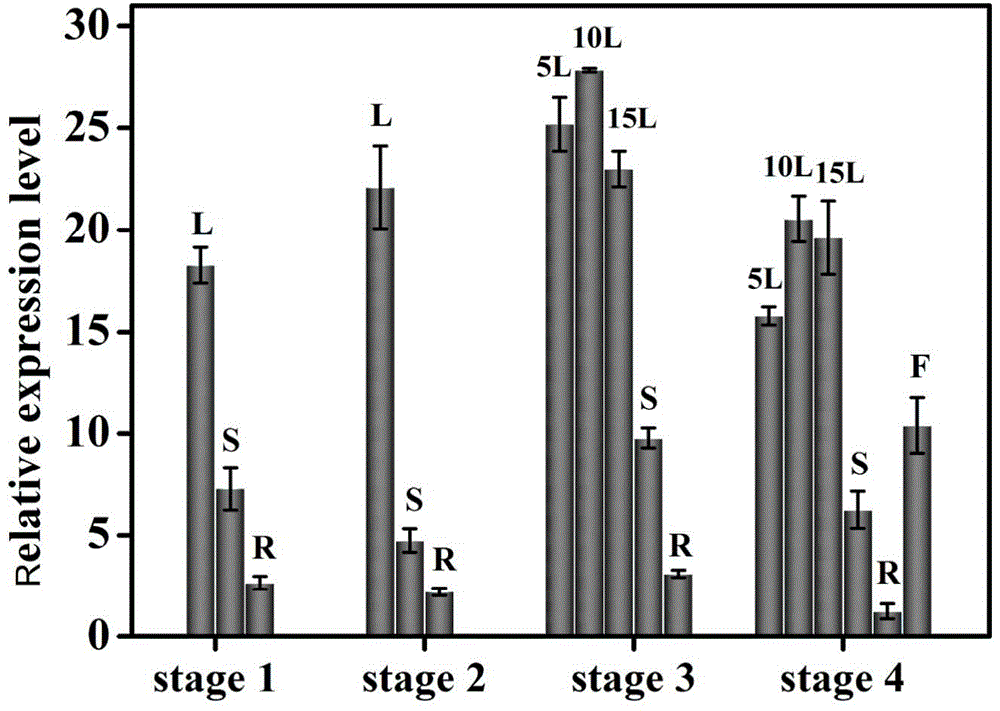
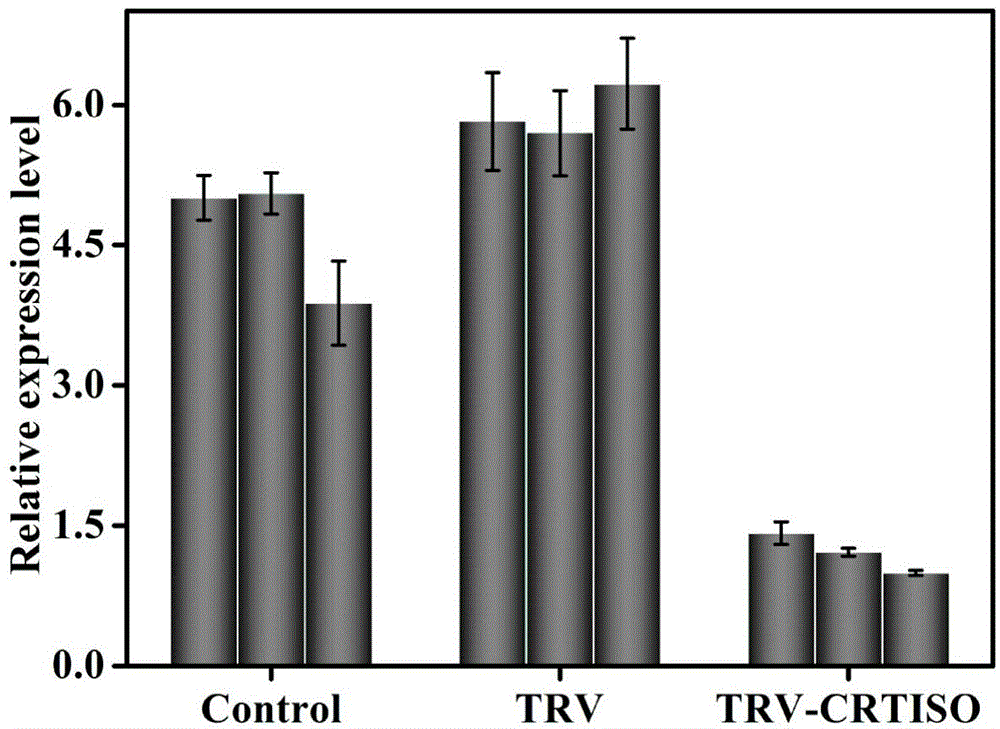
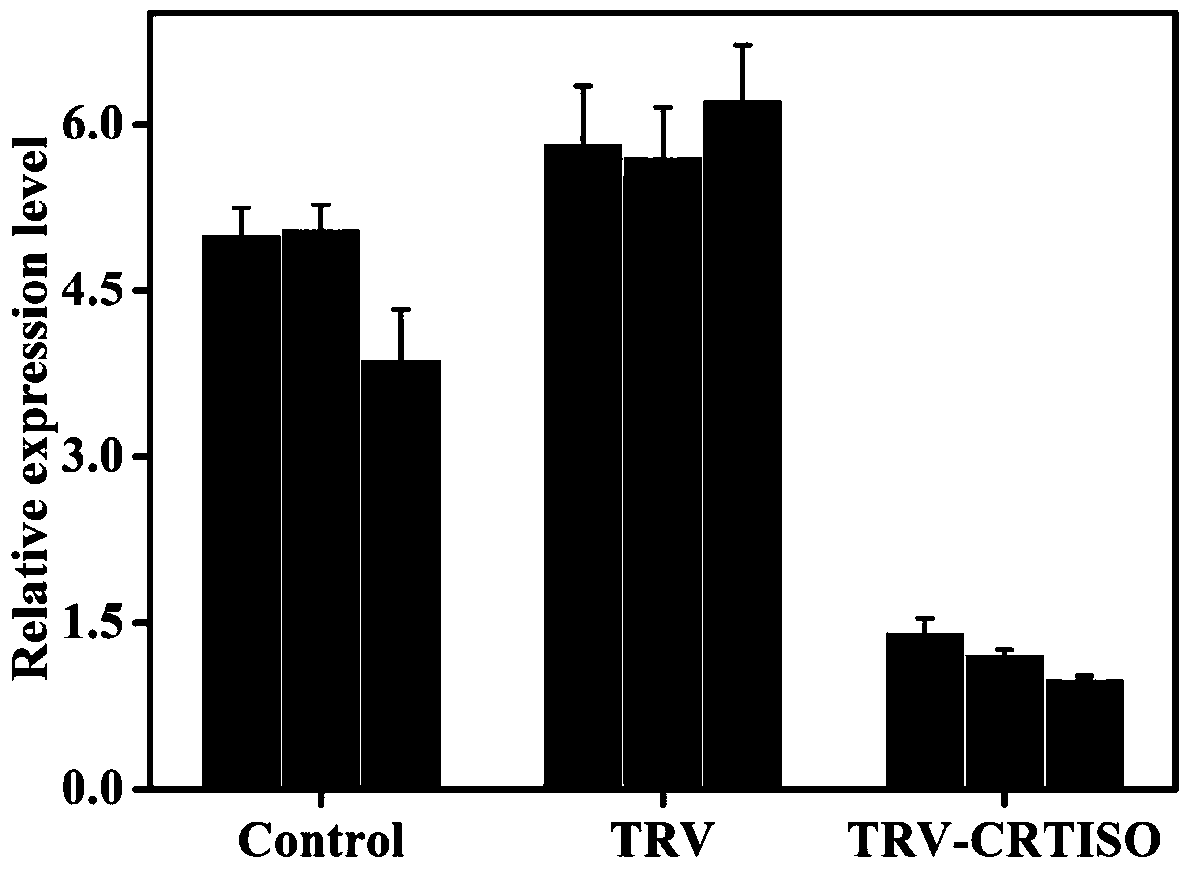
Tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene and is application
ActiveCN104152473AIncrease contentIncreased resistance to photoinhibitionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyBeta-Carotene
The invention discloses a tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene. The base sequence of the tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene is represented by SEQIDNO:1. In tobacco, a key carotenoid synthesis gene NtCRTISO is cloned, and the gene can be inhibited to effectively improve the carotenoid content of tobacco leaf and improve the photoinhibition resistance of tobacco plants. The invention discloses an important function of the CRTISO gene in tobacco in carotenoid synthesis. The CRTISO gene plays a great role in the regulation of the composition of carotenoid. A method for improving the content of carotenoid, especially beta-carotene, in the tobacco is searched, and a good theoretic guidance is provided for the improvement of the molecules of the plants.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Dual-beam super-resolution optical storage material read-write device and read-write method
ActiveCN108899053AResolve recordsSolve the problem of readingRecord information storageOptical beam guiding meansFluorescenceDual beam
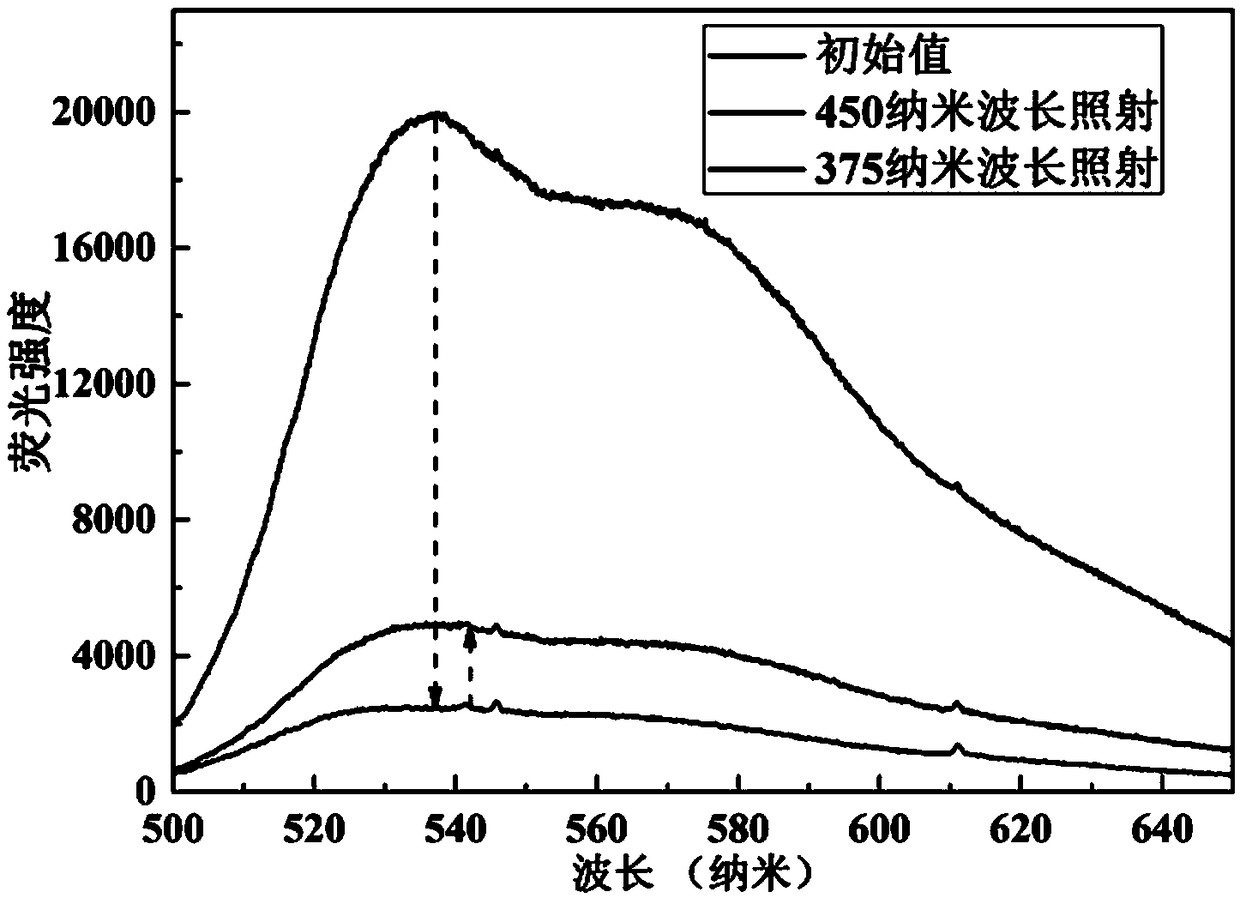
A dual-beam super-resolution optical storage material read-write device comprises an optical path and a computer; the optical path consists of a recording optical path, a reading-out optical path anda fluorescence collecting optical path. A read-write method is provided. The invention adopts pulsed light induction-continuous photoinhibition quenching recording mode, can quickly read information,solves the problem of recording and reading of materials simultaneously for the first time in the field of super-resolution optical storage, overcomes the erasing effect of photochromic materials in super-resolution recording, and obtains smaller recording spots and improve the storage density of optical discs.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
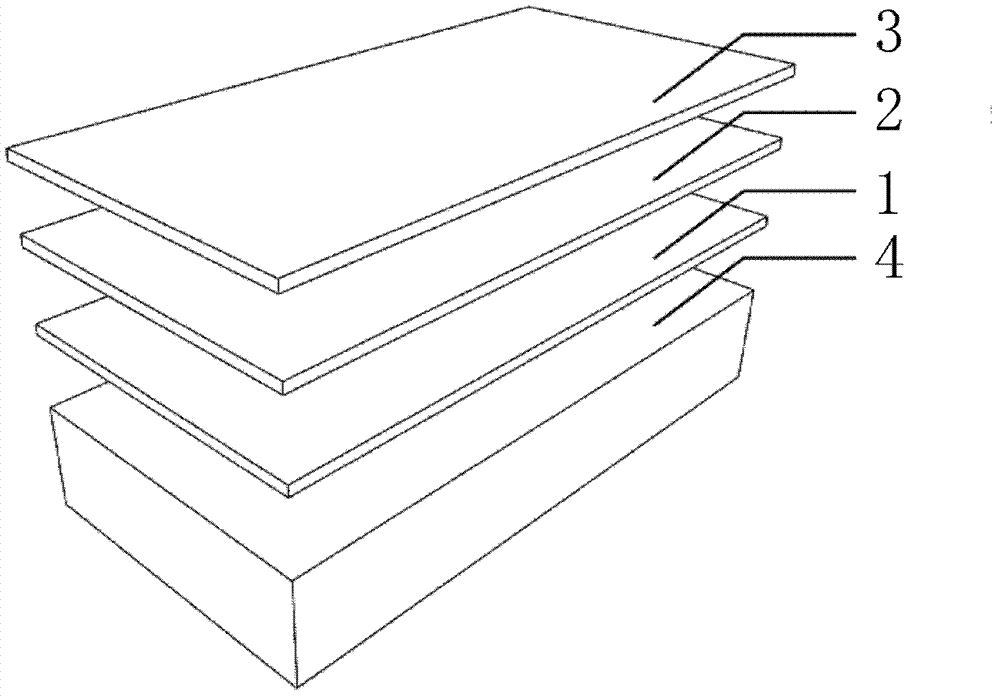
Non-toxic biological anti-fouling resistance reducing composite coating, preparation method for composite coating and anti-fouling resistance reducing treatment method for base material
InactiveCN102642356AReduce adverse effectsImprove efficiencyAntifouling/underwater paintsLuminescent paintsSurface layerPowder coating
The invention provides a non-toxic biological anti-fouling resistance reducing composite coating, which sequentially comprises a priming paint coating, a luminous powder coating and a protective coating. The protective coating is positioned on a surface layer, the priming paint coating is positioned on a bottom layer, the luminous powder coating is positioned between the protective coating and the priming paint coating, and the surface of the non-toxic biological anti-fouling resistance reducing composite coating is provided with a micron-sized pit structure. The invention further provides a preparation method for the composite coating and an anti-fouling resistance reducing treatment method for the surface of a base material. According to the non-toxic biological anti-fouling resistance reducing composite coating prepared by the preparation method, as luminous powder is capable of illuminating environments, attachment of marine organisms is reduced by means of the photoinhibition effect. On one hand, the luminous powder is non-toxic and radiation-free, and negative effects on the environments are decreased. On the other hand, as the surface of the composite coating is provided with the micron-sized pit structure, the flow field of a near wall can be changed, resistance reduction is realized and coupled with an anti-fouling method, and anti-fouling and resistance reducing functions are realized.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Methods of making a deflection member
A method for manufacturing a deflection member is disclosed. The method may include the step of incorporating a monomer, a photoinitiator system, a photoinhibitor, and / or a reinforcing member. A further step includes blending the monomer, photoinitiator, and / or photoinhibitor to form a blended photopolymer resin. Further steps may be emitting a first wavelength and emitting a second wavelength. A further step may be polymerizing the monomer to form a resinous framework comprising protuberance locked-on to the reinforcing member.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
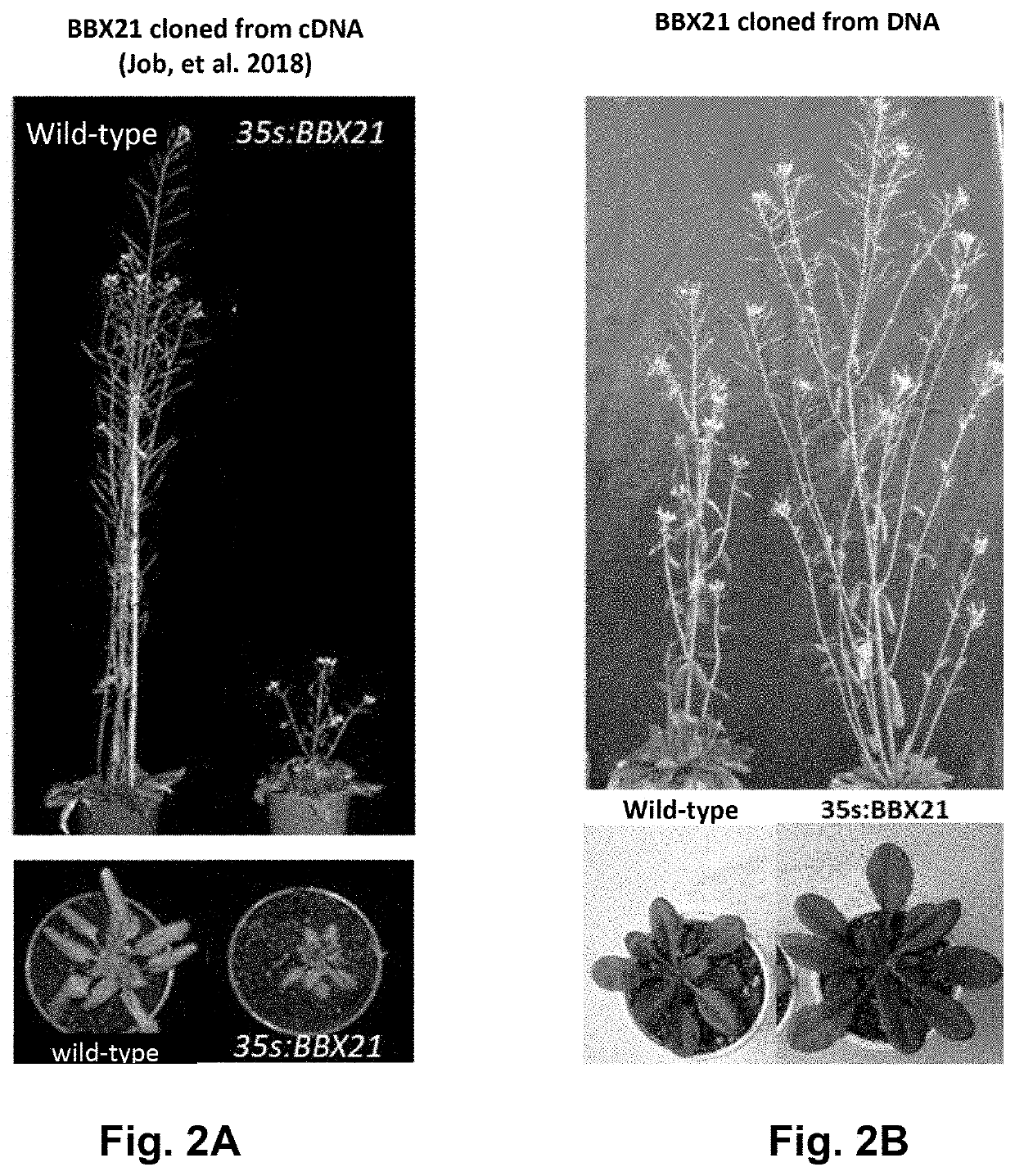
Polynucleotide construct for improving agricultural characteristics in crop plants
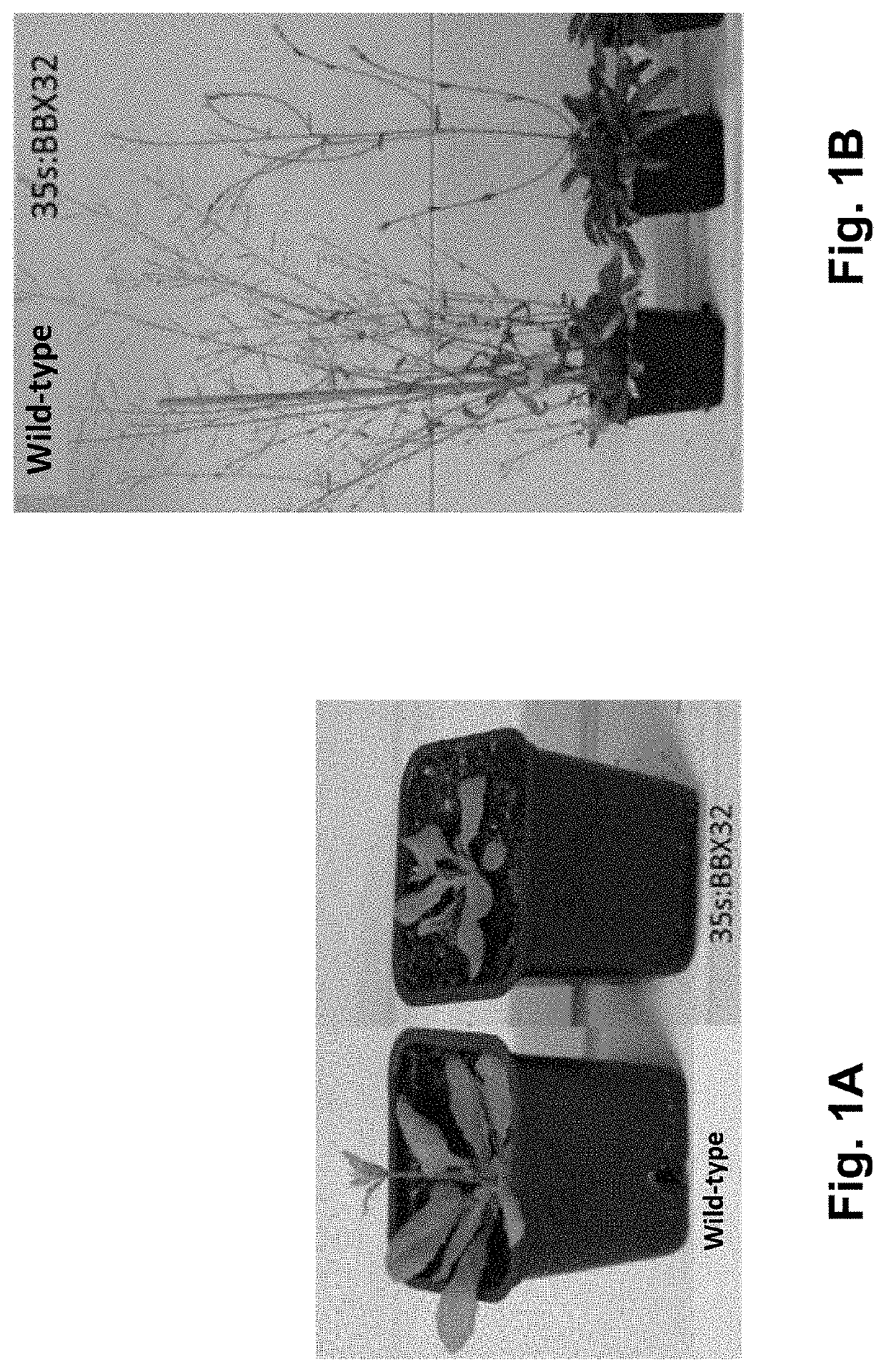
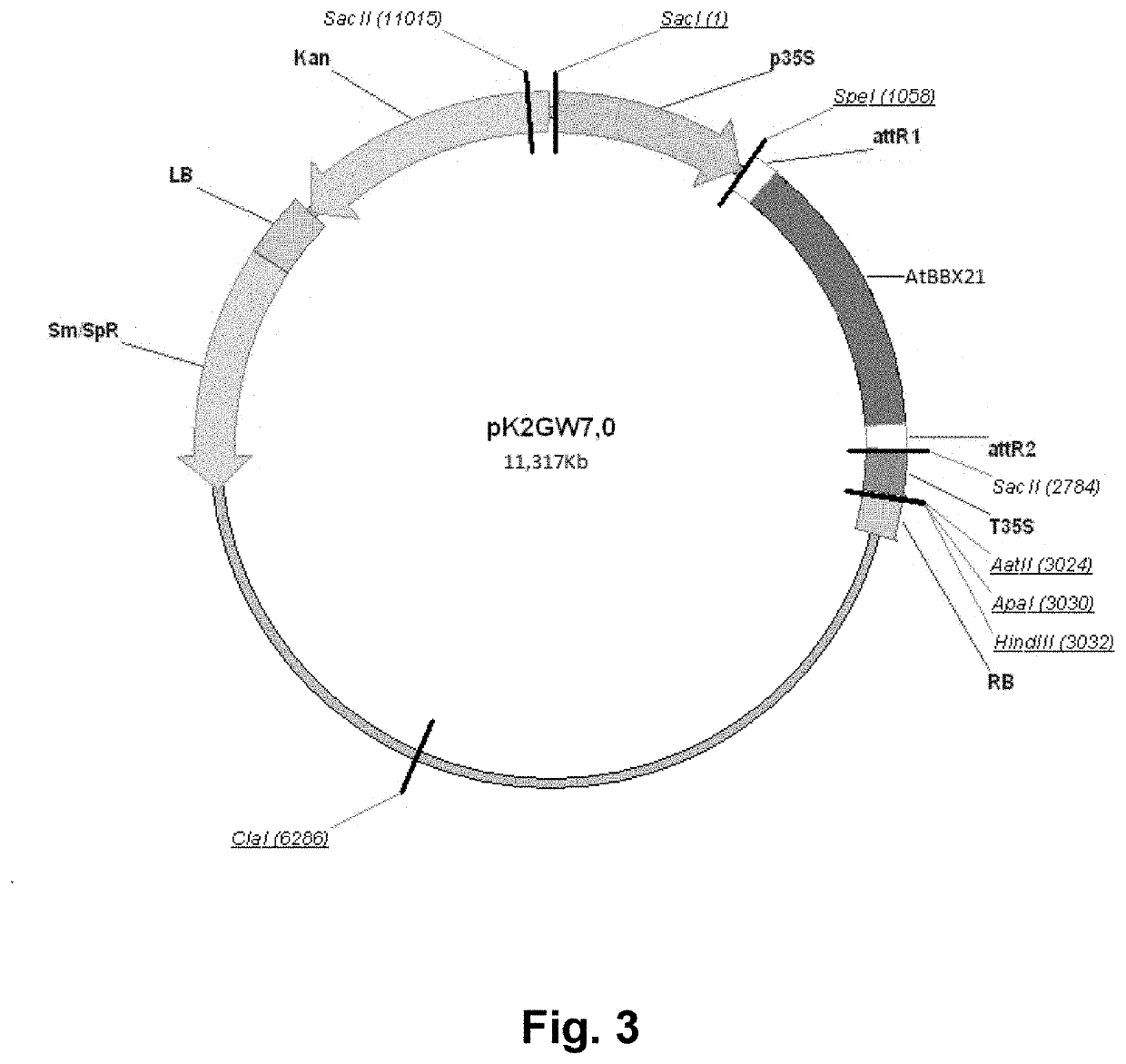
ActiveUS20200299711A1Increase photosynthetic rateHigh yieldClimate change adaptationPlant peptidesBiotechnologyWater-use efficiency
The present invention generally relates to the field of genetic engineering and obtaining transgenic traits for agronomic applications. More specifically, the present invention relates to a specific transgenic event in agricultural crops that improves plant characteristics. Yet more specifically, the invention relates to a polynucleotide construct comprising a gene from Arabidopsis thaliana. In particular, the polynucleotide construct of the invention comprises the gene AtBBX21 which encodes a B-box protein from Arabidopsis thaliana. The transgenic event of the invention increases green and seed yield, reduces photoinhibition, improves water use efficiency, increases tuber and chlorophyll production and improves photosynthetic rates, among others. The polynucleotide construct of the invention comprises a sequence depicted as SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also provides a transgenic plant transformed with said polynucleotide construct, wherein said plant exhibits improved characteristics. In a particularly preferred embodiment, the transgenic plant is a potato (Solanum tuberosum) plant that overexpresses a gene from Arabidopsis thaliana, wherein said potato plant exhibits improved characteristics.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET +1
Arachis hypogaca violaxanthin de-epoxidase (AhVDE) gene and coding protein and application thereof
InactiveCN103695444AImproved deepoxidation stateSpeed up heat dissipationOxidoreductasesFermentationNicotiana tabacumNucleotide
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, and particularly relates to an arachis hypogaca violaxanthin de-epoxidase (AhVDE) gene. A nucleotide sequence is shown by the sequence 1 in a sequence table. An amino acid sequence of the AhVDE gene is shown by the sequence 2 in the sequence table. The invention also discloses an application of the AhVDE gene in a protective photosynthesis mechanism. The AhVDE gene is transfected to tobacco to obtain a transgenic plant; under the stress of excess luminous energy, the transgenic plant has higher NPQ and de-epoxidation state of xanthophyll cycle than a wild plant, thereby indicating that the over-expression of AhVDE changes the relative content of xanthophyll cycle components and leads to the change of the de-epoxidation state under the condition of excess luminous energy, and the heat dissipation capacity of xanthophyll cycle is enhanced. The capacity of the transgenic plant for dissipating the excess luminous energy is enhanced, so that the PSII excitation energy pressure is reduced, the photoinhibition degree of PSII and PSI under the stress of excess luminous energy is relieved, and the photosynthesis mechanism is protected finally.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
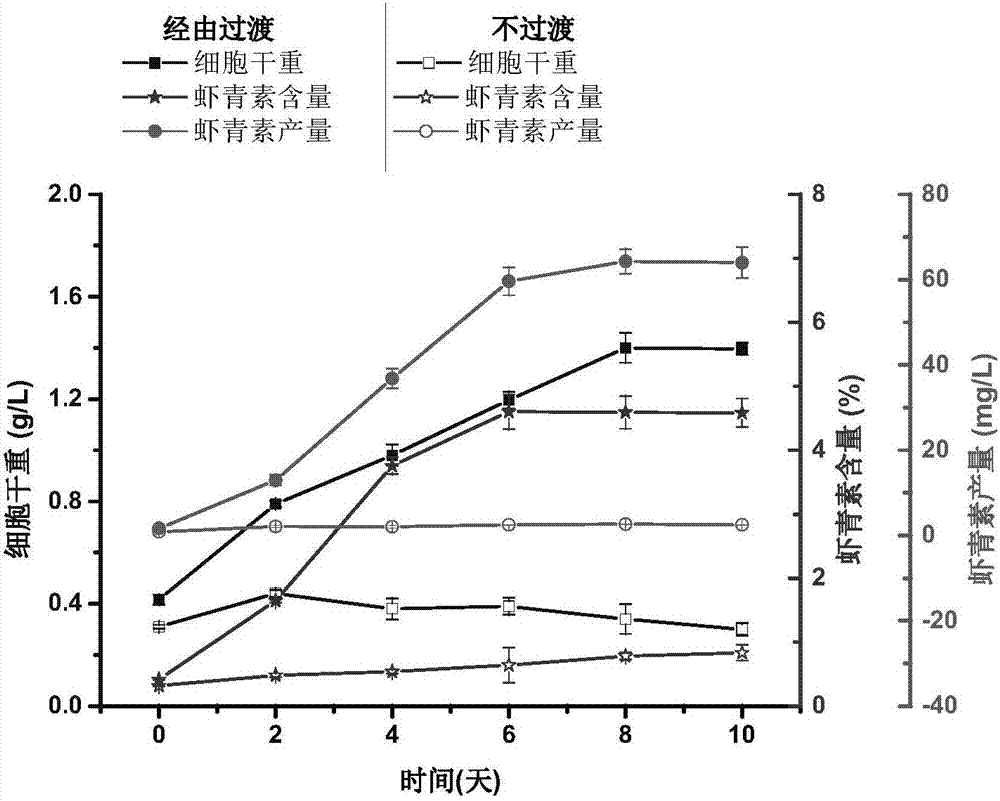
Method for avoiding microalgae photoinhibition and improving astaxanthin yield
ActiveCN107189946AVarious meansSolve the problem of large-scale industrializationUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesAstaxanthinFishery
The invention relates to a new method for avoiding microalgae photoinhibition and improving astaxanthin yield in the culture process of microalgae. In general, a two-stage method is adopted to cultivate the microalgae to produce astaxanthin, wherein on the first stage, massive reproduction of cells and accumulation of biomass are achieved in a heterotrophic, autotrophic or mixotrophic culture mode, and on the second stage, accumulation of the astaxanthin in the cells are achieved in methods, such as light stress assisted with nutrition stress. However, when the microalgae is transformed from the firsts stage to the second stage, phenomenons, such as light stress usually occur, and accordingly the astaxanthin yield is seriously influenced. Therefore, multiple methods are adopted to control culture conditions in a transformation process, such as medium components controlling, sunshading, weak light transition, initial inoculated density improving, gradual dilution and outdoor inoculated time adjusting so that cell conditions can be adjusted and the cells can improve the ability to resist a strong light; therefore, thelight stress problem of the microalgae under the strong light is solved completely, the efficiency of the microalgae for producing the astaxanthin is improved greatly, and low cost, high efficiency and large-scale cultivation of the microalgae for producing the astaxanthin are achieved.
Owner:云南保山泽元藻业健康科技有限公司
Application of OsGP3 gene in improving photoinhibition resistance of rice
The invention discloses application of an OsGP3 gene is improving photoinhibition resistance of rice, and belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering. According to the invention, a vector constructed through RNAi interference technology is imported into the rice, so that the expression of the OsGP3 gene in the rice is inhibited, and subsequently the functional expression of the OsGP3 gene in a rice plant is researched. A result obtained by comparing with a wild type plant shows that the wild type plant is significantly higher than a transformed plant in NPQ value, showing that the OsGP3 gene plays an important role in photoprotection of the rice; and the OsGP3 gene can be integrated into rice genome through transgenic means, so that the capacity of the rice in consuming excess light energy is enhanced and the effects on protecting the rice and improving crop yield are achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
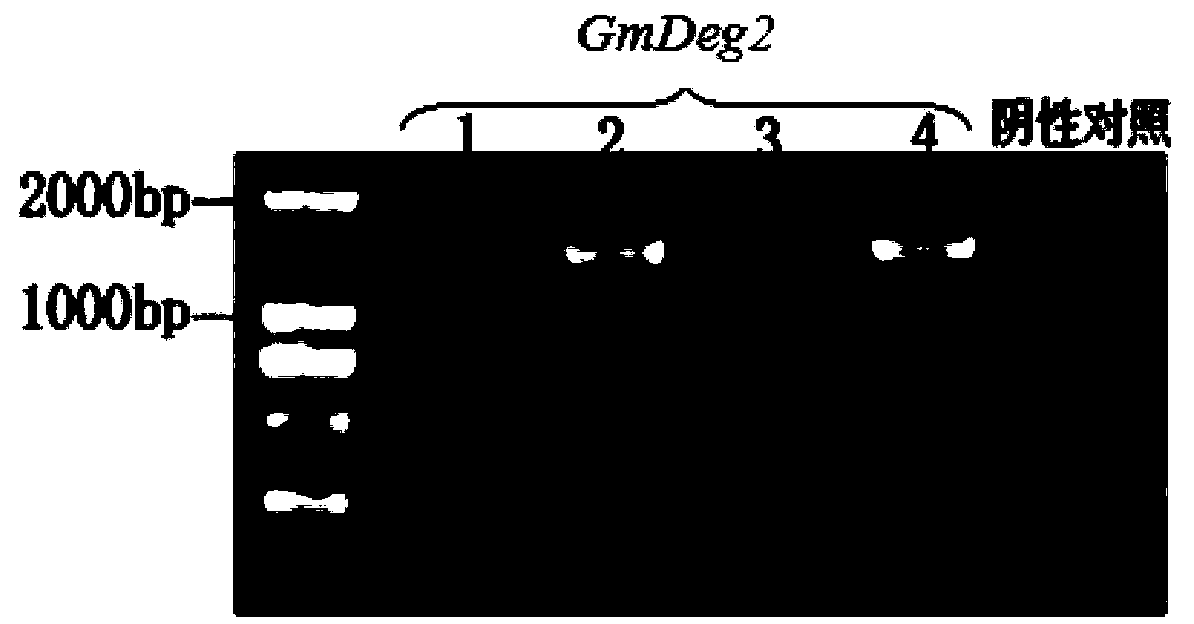
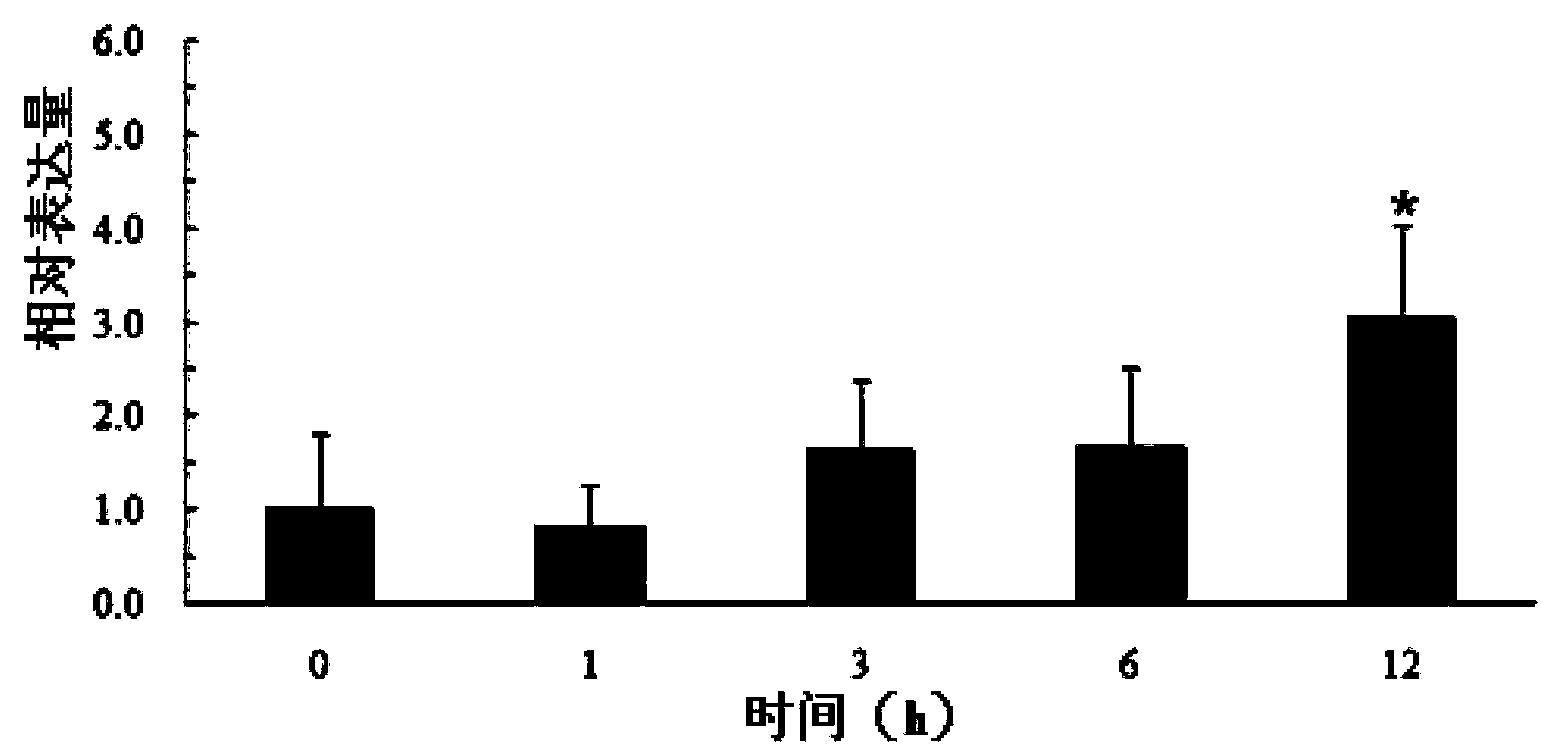
Soybean photosynthesis related gene GmDeg2 and application thereof
ActiveCN102994532ASubstrate requirements are highRegulates protease activityHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyPlant cell
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and discloses a soybean photosynthesis related gene GmDeg2 and an application thereof. The soybean photosynthesis related gene GmDeg2 has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 1; protein coded by the gene has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. By using any vector which can guiding expression of exogenous genes in a plant, the GmDeg2 gene of the invention can be introduced into a plant cell so as to obtain a transgenic plant with improved photoinhibition resistance. The gene of the invention has important significance on soybean photoinhibition resistance, especially on cultivation of soybean varieties with high photosynthetic efficiency.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for relieving photoinhibition of haematococcus pluvialis
ActiveCN108504619AAlleviate photoinhibition problemsLow priceUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBetaxanthinsGlycerol
The invention belongs to the technical field of microalgae organisms, and particularly relates to a method for relieving photoinhibition of haematococcus pluvialis. Haematococcus pluvialis cells are transferred to strong light for light inducing after being cultured to reach a platform period, a small-molecular organic matter (glycerol or natrium aceticum) is added to a culture system, photoinhibition of algae cells is relieved, and the accumulation of astaxanthin in the culture process is promoted. By adding the small-molecular organic matter (glycerol or natrium aceticum) during transferringin the culture stage one time or multiple times, the capacity of haematococcus pluvialis of resisting strong light is enhanced, the problem that photoinhibition happens to haematococcus pluvialis under the strong light, so cell density is lowered is sufficiently solved, and the production efficiency of astaxanthin by the haematococcus pluvialis is improved.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method for alleviating the photoinhibition of Haematococcus pluvialis
ActiveCN108504619BAlleviate photoinhibition problemsLow priceUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesSodium acetateGlycerol
The invention belongs to the field of microalgae biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for alleviating the photoinhibition of Haematococcus pluvialis. When the culture of Haematococcus pluvialis cells reaches the plateau stage, when the light is transferred to strong light for light induction, small molecule organic matter glycerol or sodium acetate is added to the culture system, thereby reducing the photoinhibition of algal cells and promoting the production of astaxanthin during the culture process. accumulation. The present invention enhances the ability of Haematococcus pluvialls to resist strong light by adding small molecular organic matter (glycerol or sodium acetate) one or more times during the transition of the cultivation stage, and fully overcomes the strong light resistance of Haematococcus pluvialls. The occurrence of photoinhibition leads to a decrease in cell density, which in turn increases the production efficiency of astaxanthin in Haematococcus pluvialis.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
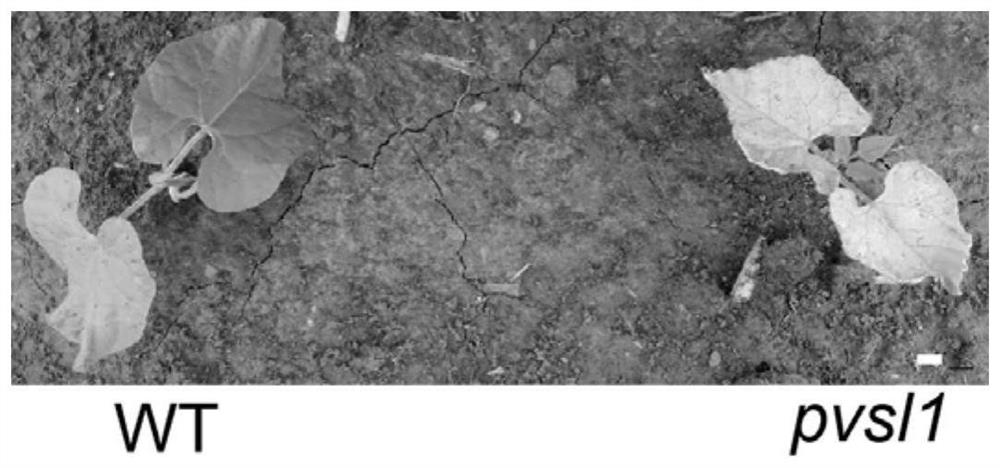
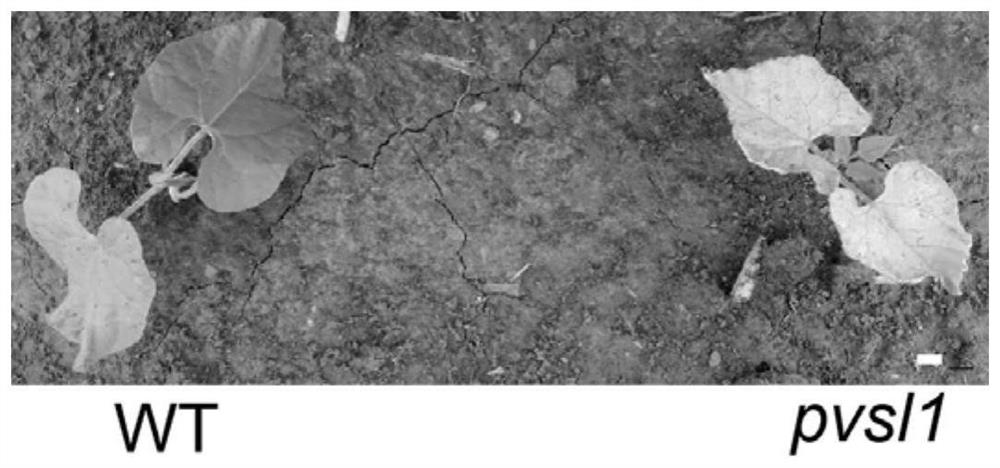
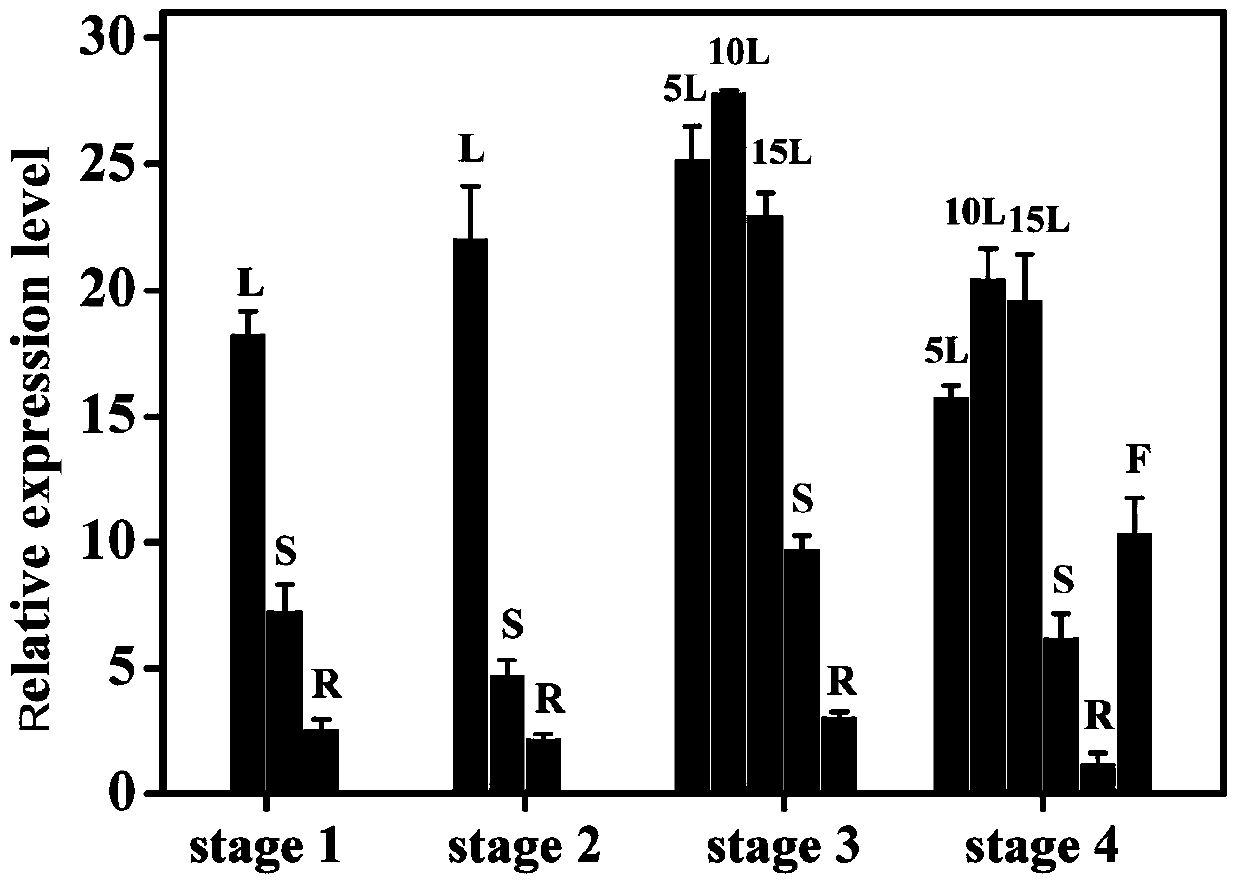
Phaseolus vulgaris metalloproteinase PvFtsH2 gene as well as encoding protein and application thereof
ActiveCN112359050AIncrease productionReduce chlorophyll contentHydrolasesFermentationMetalloprotease GeneNucleotide
The invention discloses a phaseolus vulgaris metalloproteinase PvFtsH2 gene as well as an encoded protein and application thereof, relates to the field of gene engineering, and particularly relates toa plant metalloproteinase PvFtsH2 gene as well as an encoded protein and the application thereof. The invention provides a kidney bean FtsH metalloproteinase PvFtsH2 gene as well as an encoding protein and application thereof. A nucleotide sequence of the PvFtsH2 gene is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1 in a sequence table. The amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is shown as SEQ ID NO: 2. Phytophysiology and molecular biology methods prove that the PvFtsH2 gene plays a role in the photoinhibition response process, and mutation of the gene causes reduction of the FV / FM value, reduction of the chlorophyll content and D1 protein accumulation under the photoinhibition condition. The method has important application value in the aspect of increasing the yield of kidney beans by improving the lightenergy utilization rate.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Antioxidation-related genes of wheat as well as coding proteins thereof and application thereof
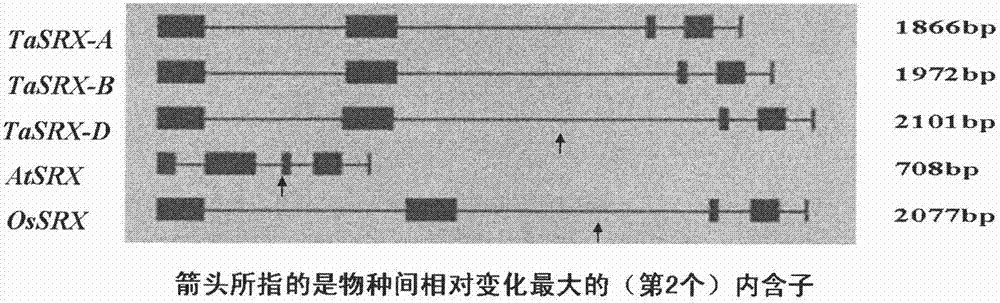
The invention discloses antioxidation-related genes TaSRX-A, TaSRX-B and TaSRX-D of wheat as well as coding proteins and application thereof. The invention also discloses the application of the genes and the coding proteins thereof in regulating the antioxidation function of plants or protecting a photosynthetic system from photoinhibition and photoxidation function. The genes have the advantagesof being capable of clearing away active oxygen in a light stress condition, protecting the photosynthetic system, enhancing the capabilities of resisting photoinhibition and photoxidation of the plants and further increasing the biomass of the plants. The genes and the coding proteins thereof disclosed by the invention have an important theoretical significance and a practical significance for researching light stress resisting mechanisms of common wheat and increasing the output of the common wheat and other important crops and have wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
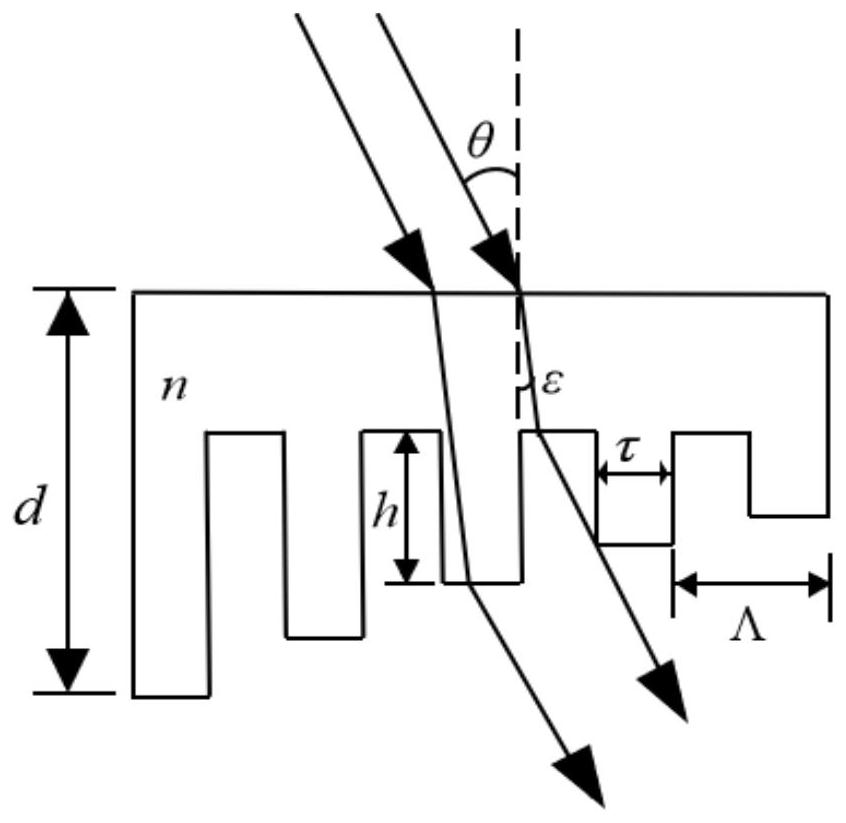
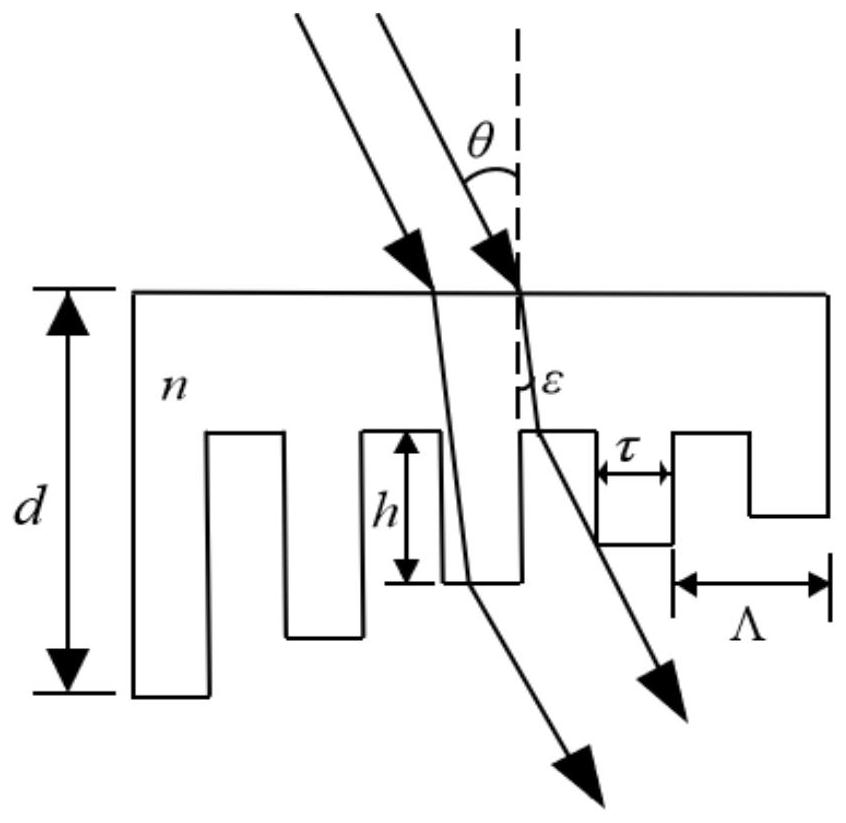
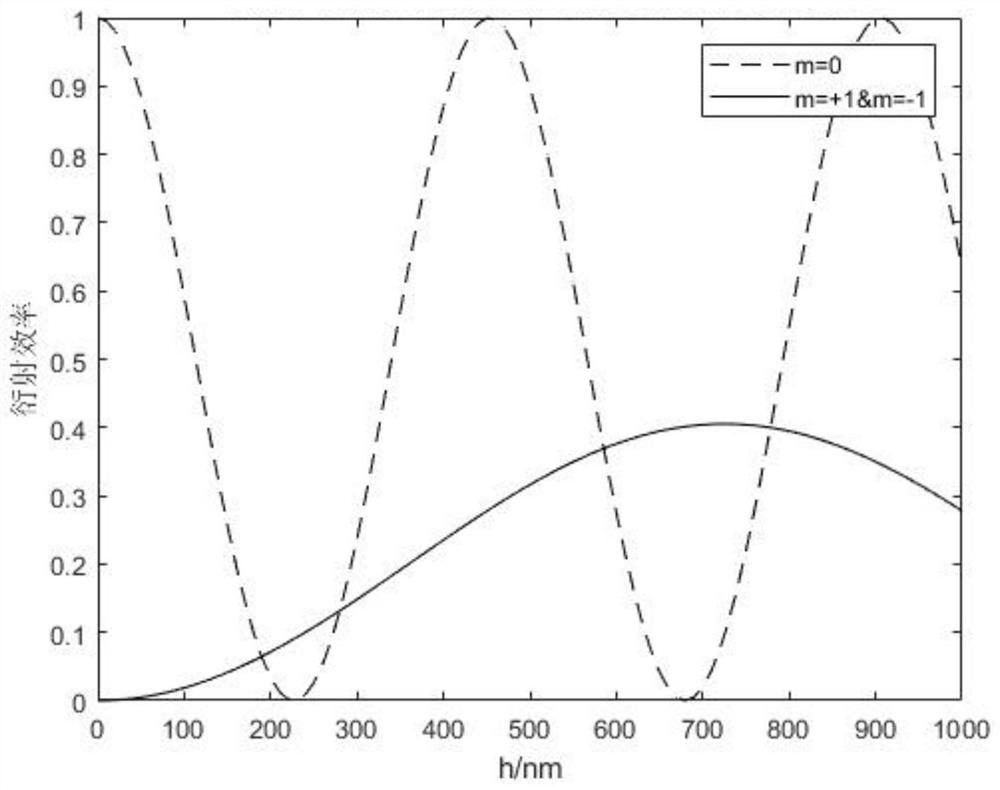
Preparation method of grating with continuously changing diffraction efficiency
ActiveCN111880254AImprove imaging effectImprove information transmission abilityDiffraction gratingsOptical waveguide light guideContinuous lightSpectral bands
The invention discloses a preparation method of a grating with continuously changing diffraction efficiency, which comprises the following steps of: adopting a first beam of light and a second beam oflight of which spectral bands are not overlapped with each other, forming interference light after the first beam of light is interfered, and forming light with continuous light intensity change in space by the second beam of light; irradiating interference light and light with continuous light intensity change in space to the photosensitive material at the same time, and obtaining a grating withcontinuously-changed diffraction efficiency; wherein the light-sensitive material is a light-cured material, the light-sensitive material is cured by interference light, and the light-inhibited light-sensitive material with continuous light intensity change in space is cured; or the photosensitive material is a material with photoinduced refractive index change. The preparation method provided bythe invention is obtained by directly exposing the photosensitive material, and mainly aims at the defect of poor uniformity of the emergent light beams of the existing optical system based on the waveguide grating coupler, so that the emergent light beams with uniformly distributed light intensity can be obtained; therefore, the imaging capability, the information transmission capability and other performances of the optical system are effectively improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
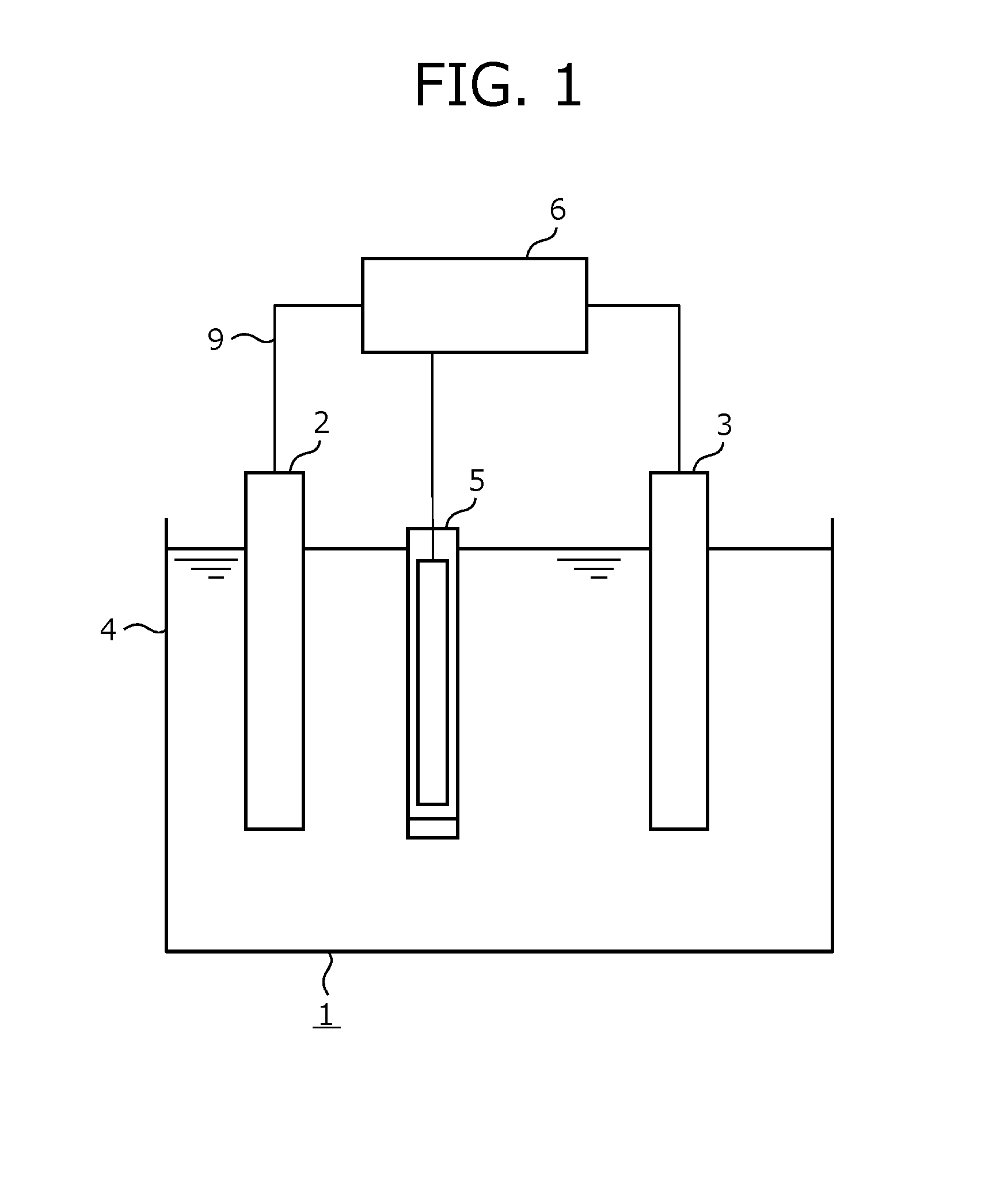
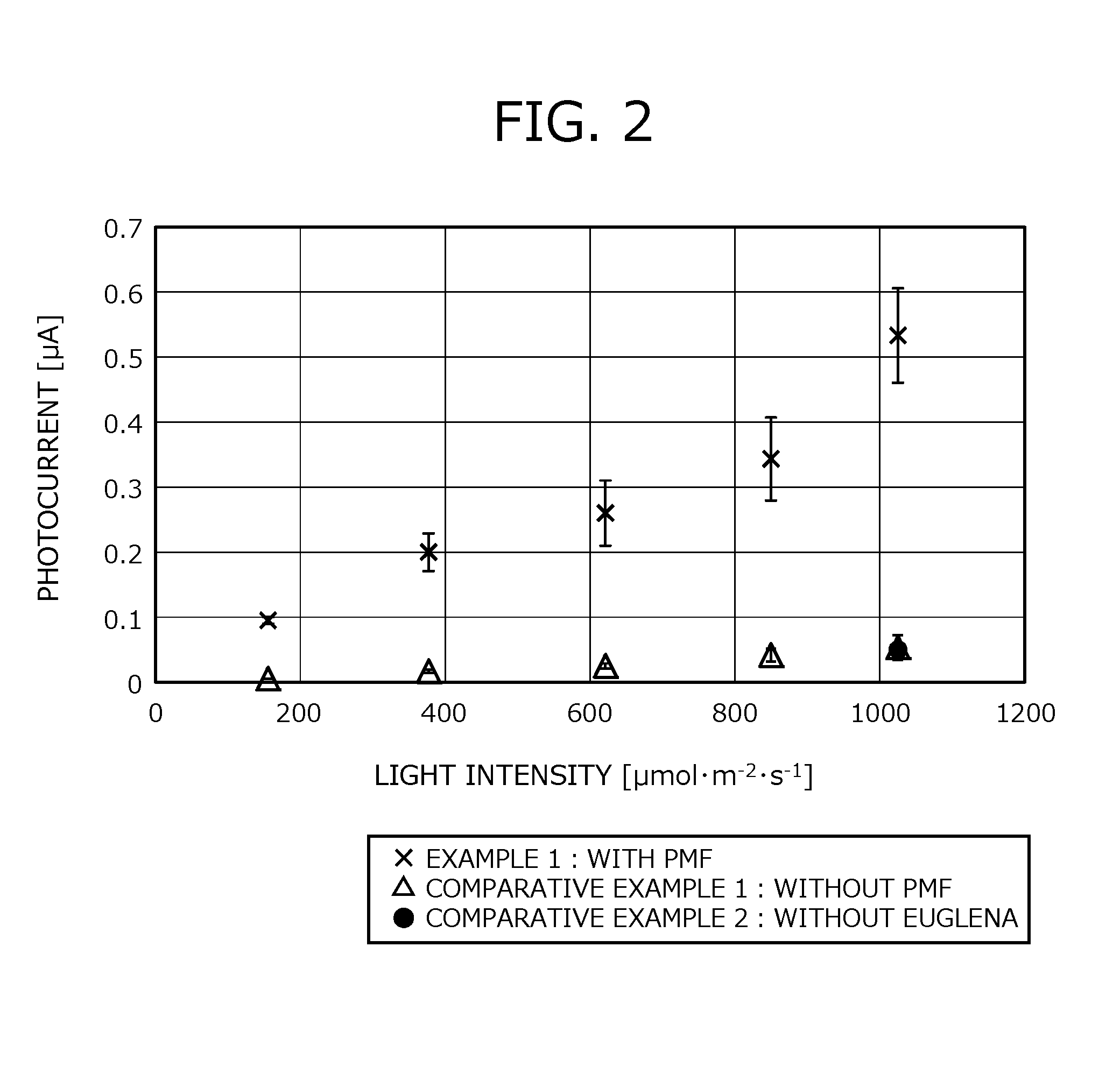
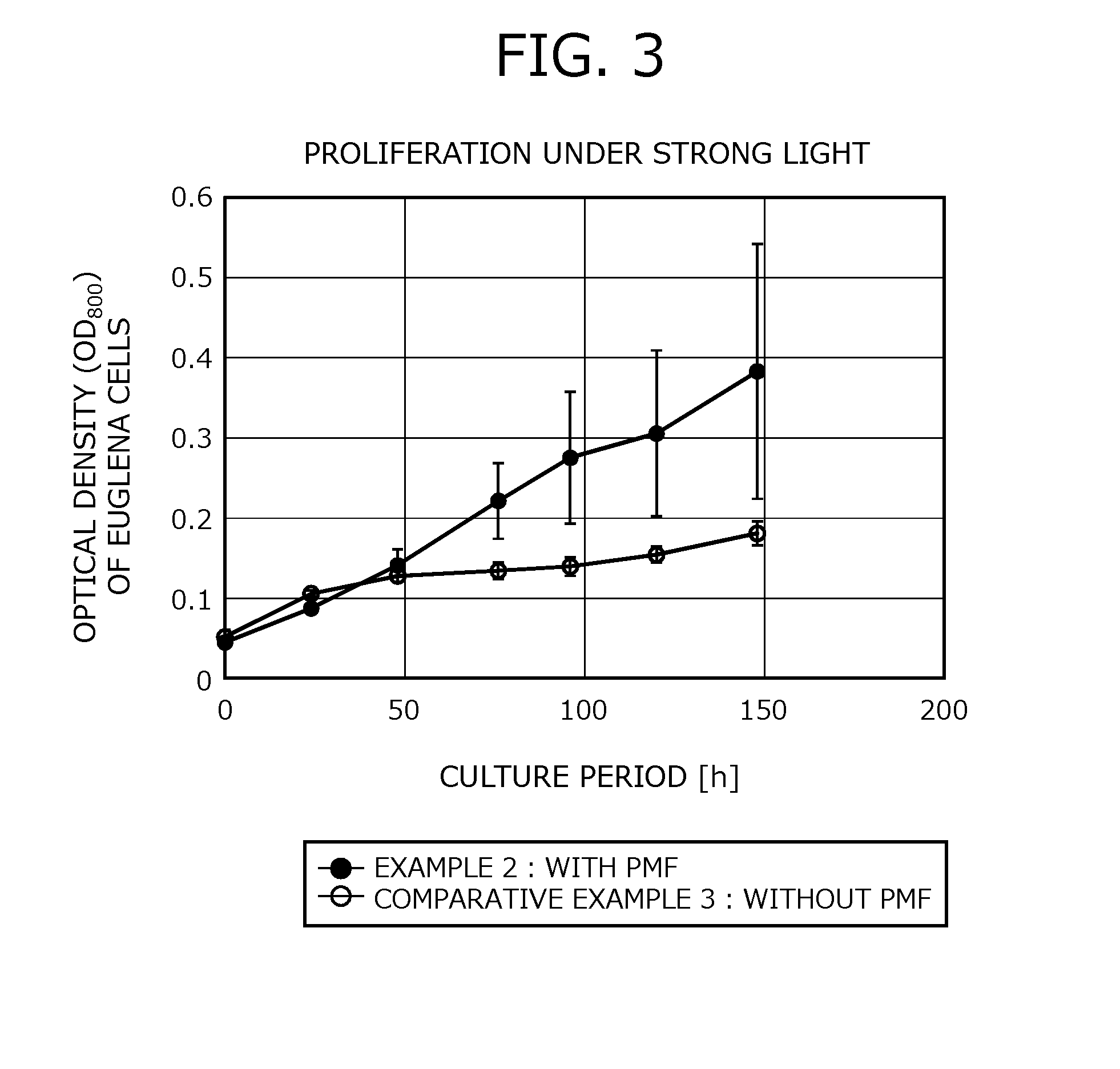
Medium and method for culturing euglena and method for reducing photoinhibition in euglena
InactiveUS20160281077A1Reduce photoinhibitionIncrease productionUnicellular algaeWaste based fuelCell membraneOrganism
A medium for culturing Euglena includes a cell membrane-permeable electron mediator that includes a biocompatible moiety and a redox-active moiety. A method for culturing Euglena includes culturing Euglena in a medium including a cell membrane-permeable electron mediator that includes a biocompatible moiety and a redox-active moiety. The medium is placed in a fermenter system that includes a device for extracting electrons from the medium. A method for reducing photoinhibition in Euglena includes electrochemically culturing Euglena in a medium including a cell membrane-permeable electron mediator that includes a biocompatible moiety and a redox-active moiety. The medium is placed in a fermenter system that includes a device for extracting electrons from the medium.
Owner:EUGLENA
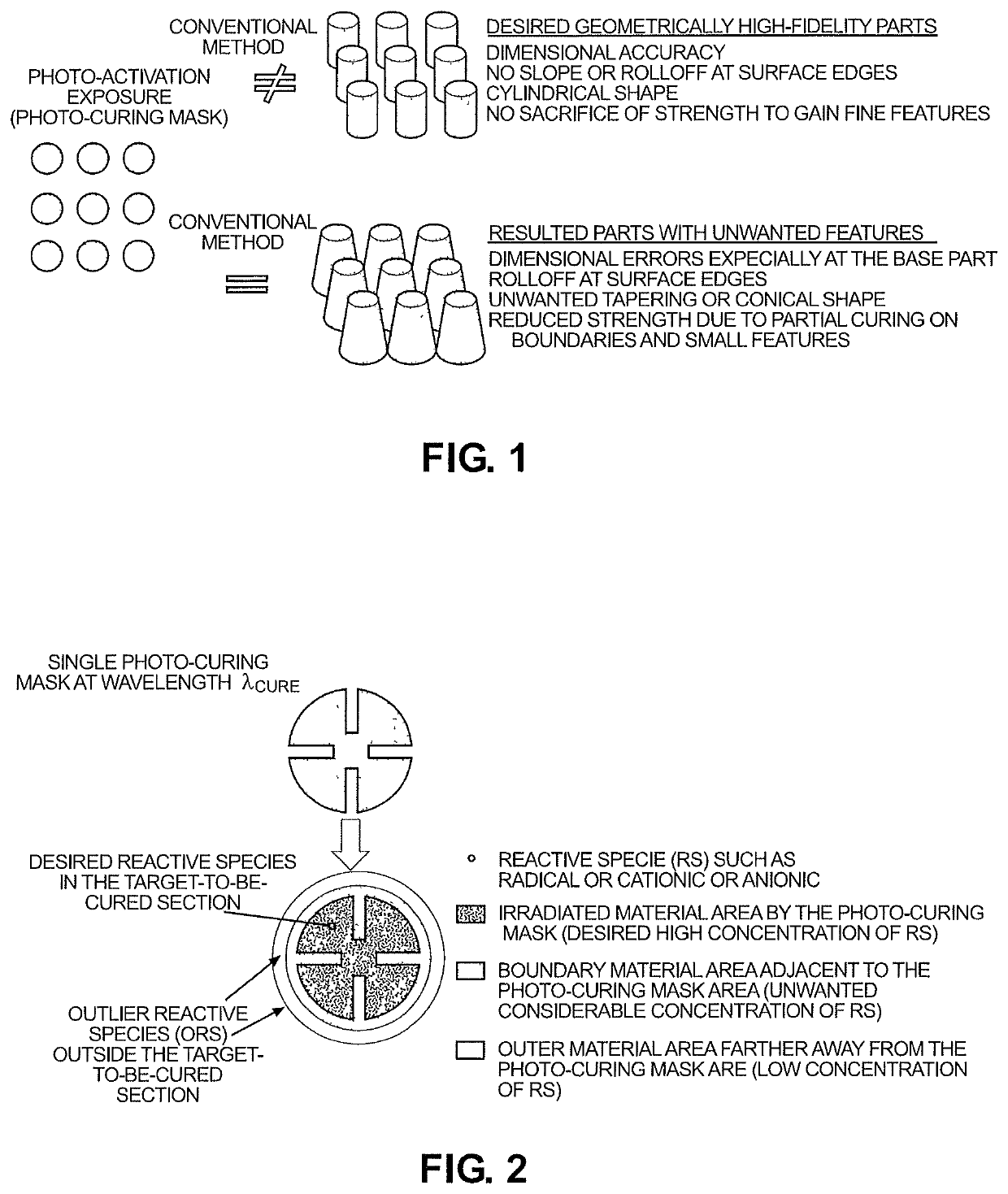
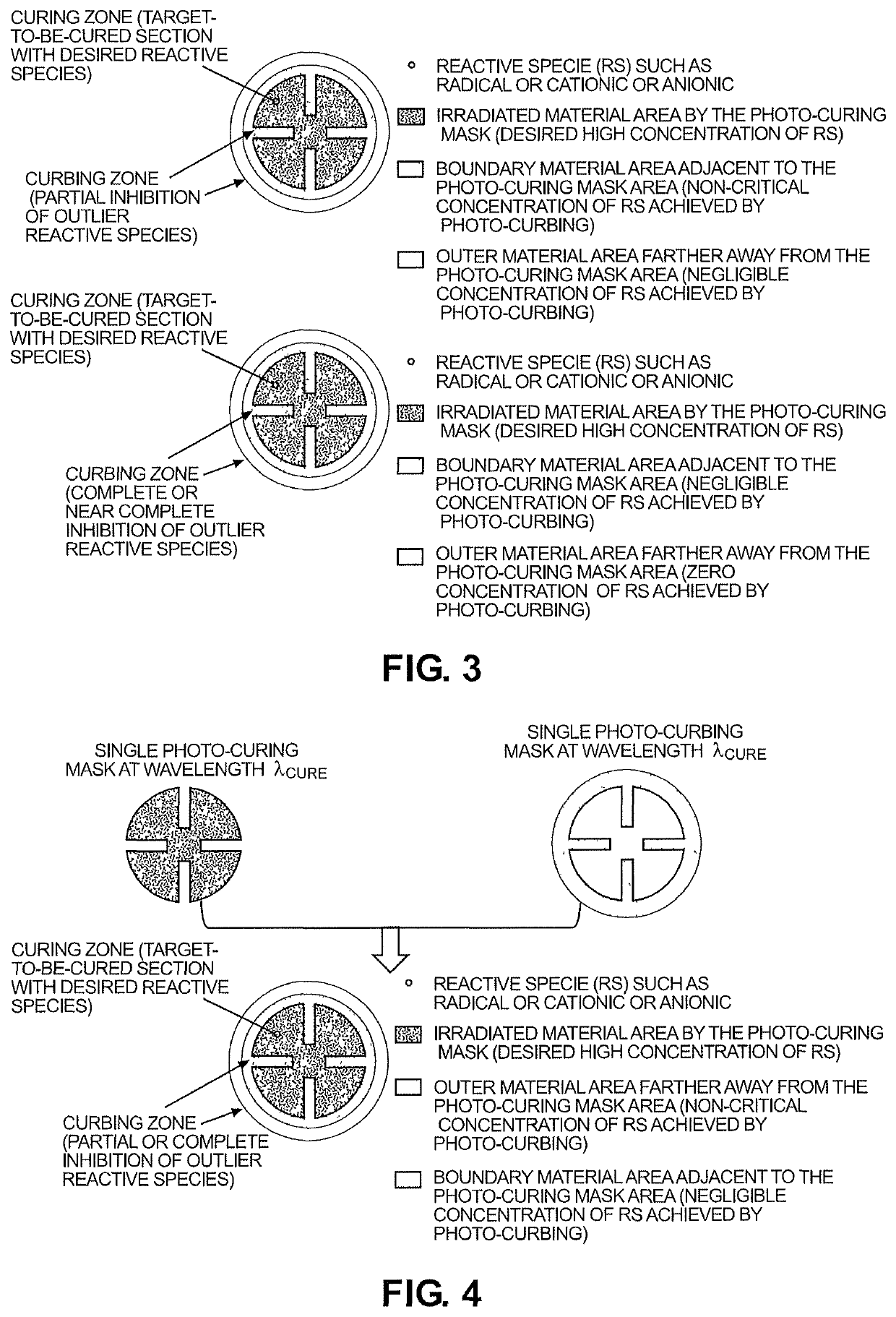
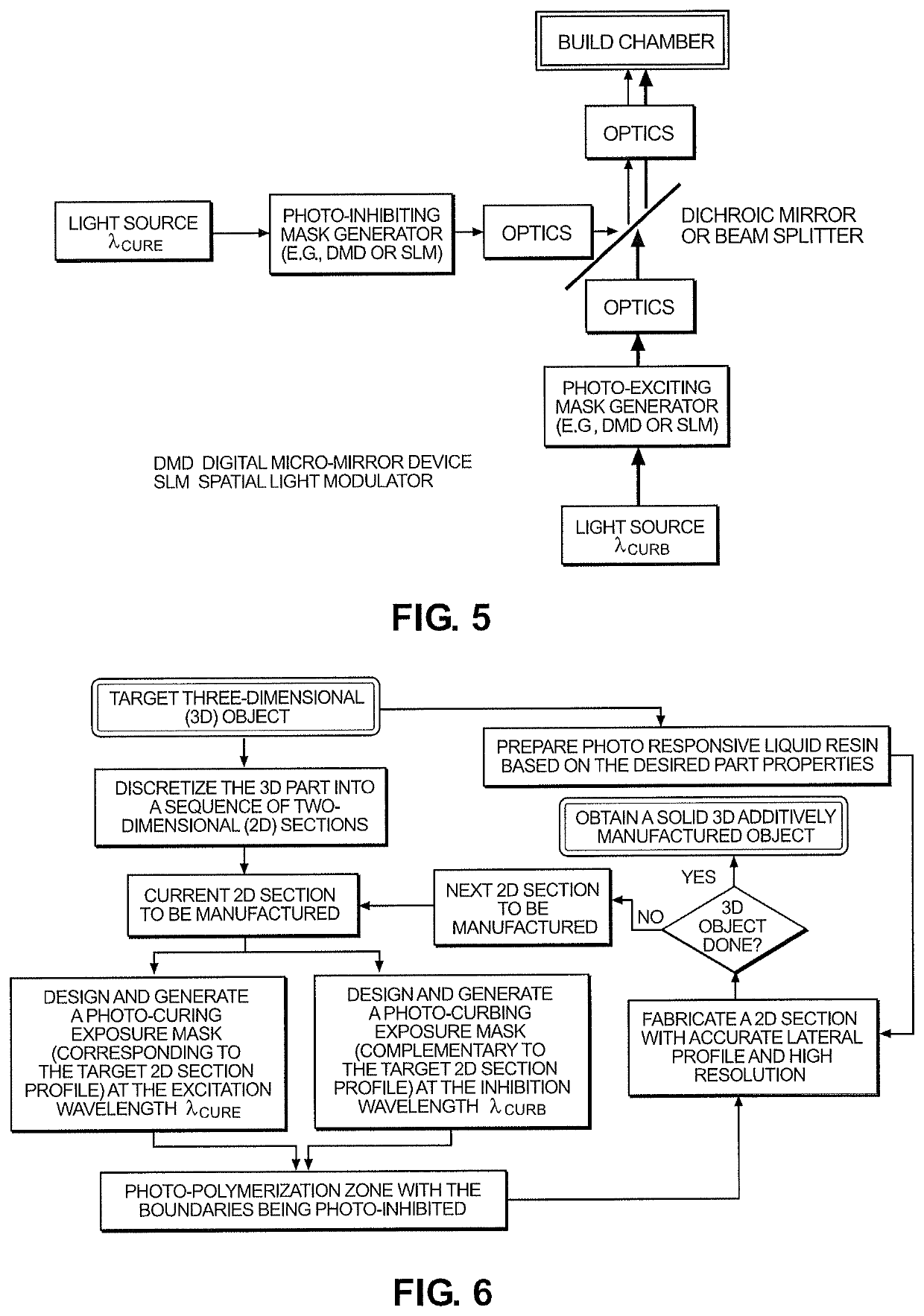
Systems and methods for photopolymerization based additive manufacturing enabled by multiple-wavelength irradiations
PendingUS20220143906A1High resolutionManufacturing platforms/substrates3D object support structuresBeam splitterDual wavelength
A system for single photon absorption based vat photopolymerization additive manufacturing with photoinhibition induced curb and photoexcitation induced cure (SPA2CurbCure), comprising: a build chamber; a two-wavelength projection irradiation unit delivering a patterned photo-curbing exposure mask and a patterned photo-curing exposure mask, respectively, to create a curing legion of initiating chemicals surrounded by a distribution of inhibiting species; wherein a curing light beam comprising light having a first wavelength and a curbing light beam comprising light having a second wavelength from the irradiation unit are manipulated into adjacent complementary exposures, combined by a dichroic beam splitter and collimated into a target resin material in the build chamber.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Antioxidation-related genes of wheat as well as coding proteins thereof and application thereof
The invention discloses antioxidation-related genes TaSRX-A, TaSRX-B and TaSRX-D of wheat as well as coding proteins and application thereof. The invention also discloses the application of the genes and the coding proteins thereof in regulating the antioxidation function of plants or protecting a photosynthetic system from photoinhibition and photoxidation function. The genes have the advantagesof being capable of clearing away active oxygen in a light stress condition, protecting the photosynthetic system, enhancing the capabilities of resisting photoinhibition and photoxidation of the plants and further increasing the biomass of the plants. The genes and the coding proteins thereof disclosed by the invention have an important theoretical significance and a practical significance for researching light stress resisting mechanisms of common wheat and increasing the output of the common wheat and other important crops and have wide application prospects.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A method to avoid photoinhibition of microalgae to improve astaxanthin production
ActiveCN107189946BIncrease productionVarious meansUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAstaxanthin
Owner:云南保山泽元藻业健康科技有限公司
Tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene and its application
ActiveCN104152473BIncrease contentIncreased resistance to photoinhibitionGenetic engineeringFermentationAgricultural scienceBeta-Carotene
The invention discloses a tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene. The base sequence of the tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene is represented by SEQIDNO:1. In tobacco, a key carotenoid synthesis gene NtCRTISO is cloned, and the gene can be inhibited to effectively improve the carotenoid content of tobacco leaf and improve the photoinhibition resistance of tobacco plants. The invention discloses an important function of the CRTISO gene in tobacco in carotenoid synthesis. The CRTISO gene plays a great role in the regulation of the composition of carotenoid. A method for improving the content of carotenoid, especially beta-carotene, in the tobacco is searched, and a good theoretic guidance is provided for the improvement of the molecules of the plants.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Bean metalloprotease pvftsh2 gene and its encoded protein and application
ActiveCN112359050BIncrease productionReduce chlorophyll contentHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyMetalloprotease Gene
The bean metalloprotease PvFtsH2 gene and its encoded protein and application relate to the field of genetic engineering, in particular to a plant metalloprotease PvFtsH2 gene and its encoded protein and application. The invention provides a bean FtsH metalloprotease PvFtsH2 gene, its encoded protein and application. The nucleotide sequence of the PvFtsH2 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence listing. The amino acid sequence of the encoded protein is shown in SEQ ID NO:2. The present invention confirms that the PvFtsH2 gene plays a role in the light-inhibition response process through plant physiology and molecular biology methods, and the mutation of the gene leads to F under light-inhibition conditions. V / F M The value decreased, the chlorophyll content decreased, and the D1 protein accumulated. The invention has important application value in increasing the yield of kidney beans by improving the utilization rate of light energy.
Owner:NORTHEAST INST OF GEOGRAPHY & AGRIECOLOGY C A S
Device for detecting contamination with photosynthesis inhibitor and method for detecting contamination with photosynthesis inhibitor
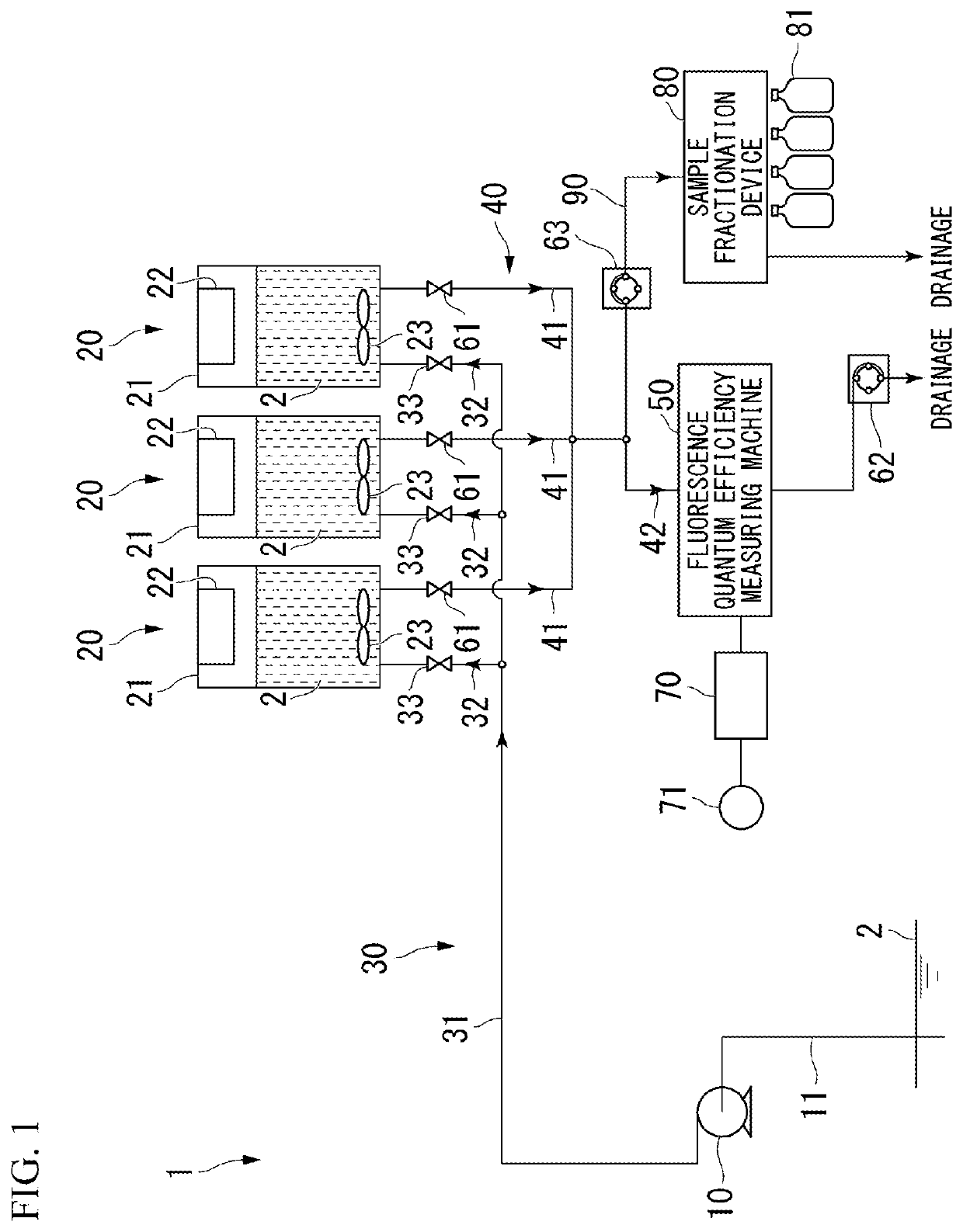
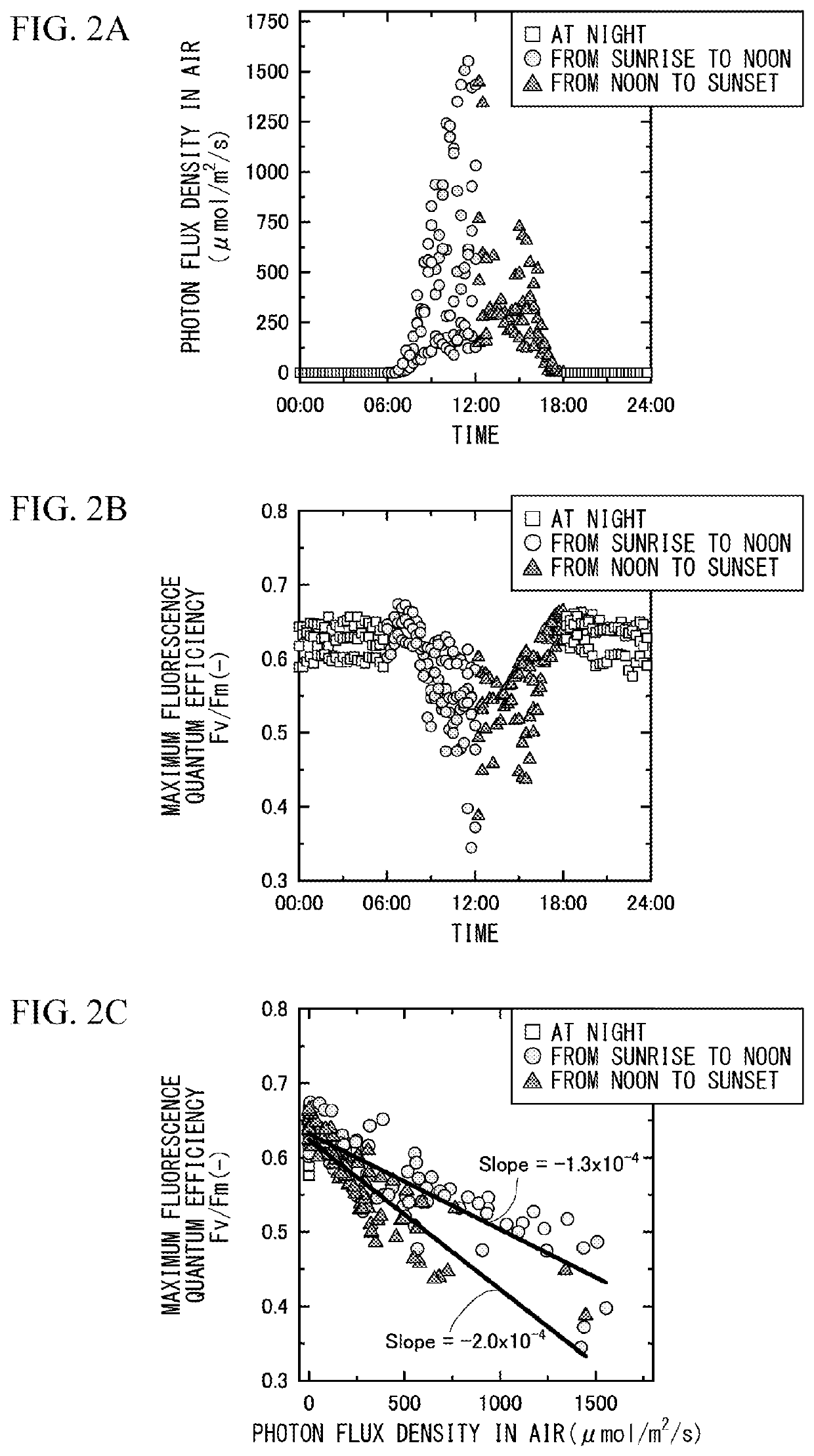
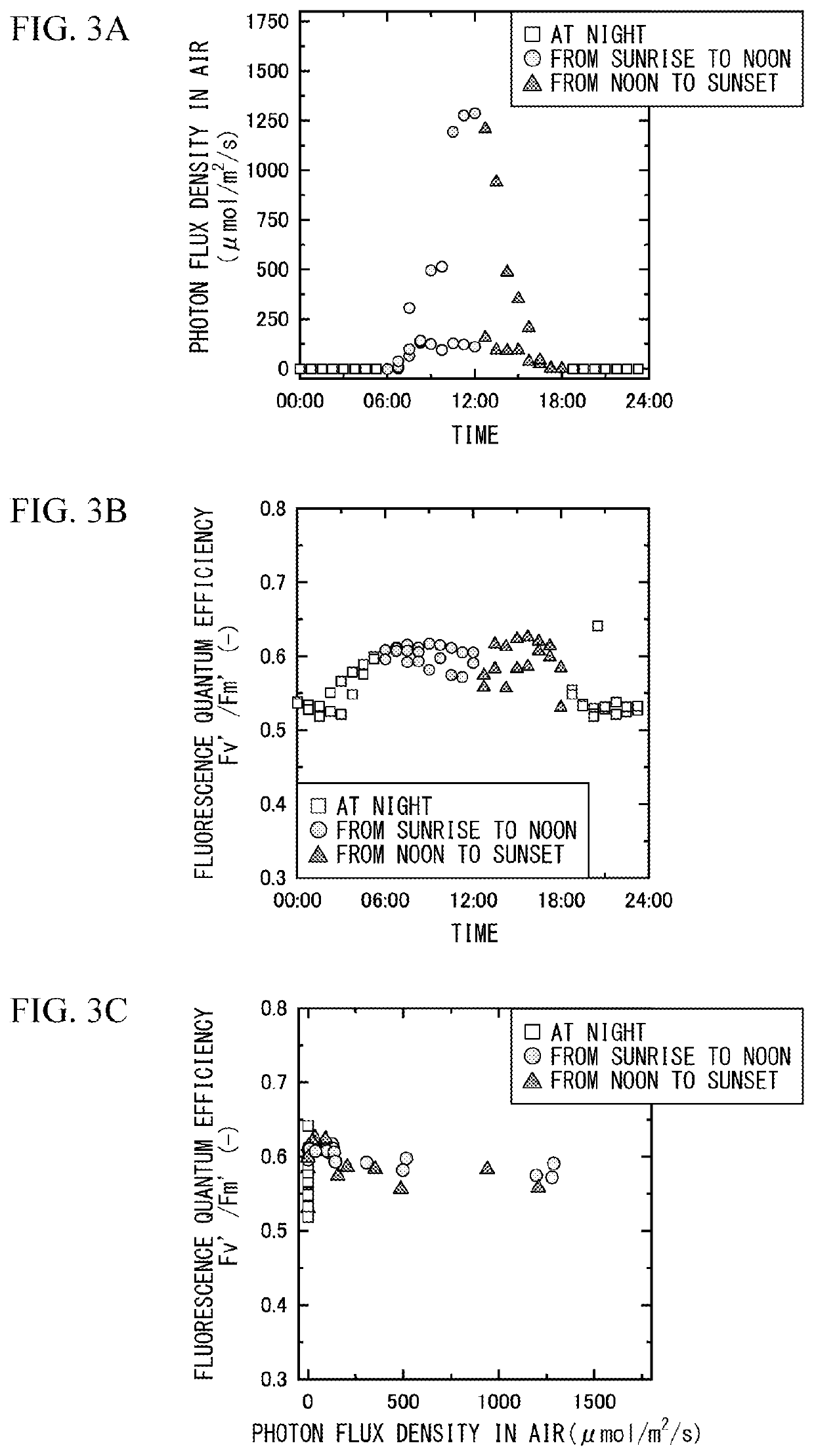
PendingUS20220163450A1Simple methodSeawater treatmentWithdrawing sample devicesQuantum efficiencyPhoto irradiation
The present invention provides a device (1) for detecting contamination with a photosynthesis inhibitor, the device including a collection device (10) configured to collect a test liquid, a light-blocking pretreatment tank (21) configured to store the test liquid (2) collected by the collection device in a state of containing phytoplankton, a stirring device configured to maintain a floating state of the phytoplankton in the test liquid stored in the pretreatment tank, an irradiation light source configured to irradiate the phytoplankton in the test liquid stored in the pretreatment tank with weak light having an underwater photon flux density that does not cause photoinhibition, a drainage conduit (40) configured to allow the test liquid discharged from the pretreatment tank to flow thereinto, and a fluorescence quantum efficiency measuring machine (50) provided for the drainage conduit and configured to measure a fluorescence quantum efficiency of the phytoplankton in the test liquid discharged from the pretreatment tank, and a method for detecting contamination with a photosynthesis inhibitor, the method including a liquid supply step, a storing and weak-light irradiation step, and a fluorescence quantum efficiency measurement step.
Owner:NAT INST FOR ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES +1
Organic devices for the photoinhibition of excitable cells
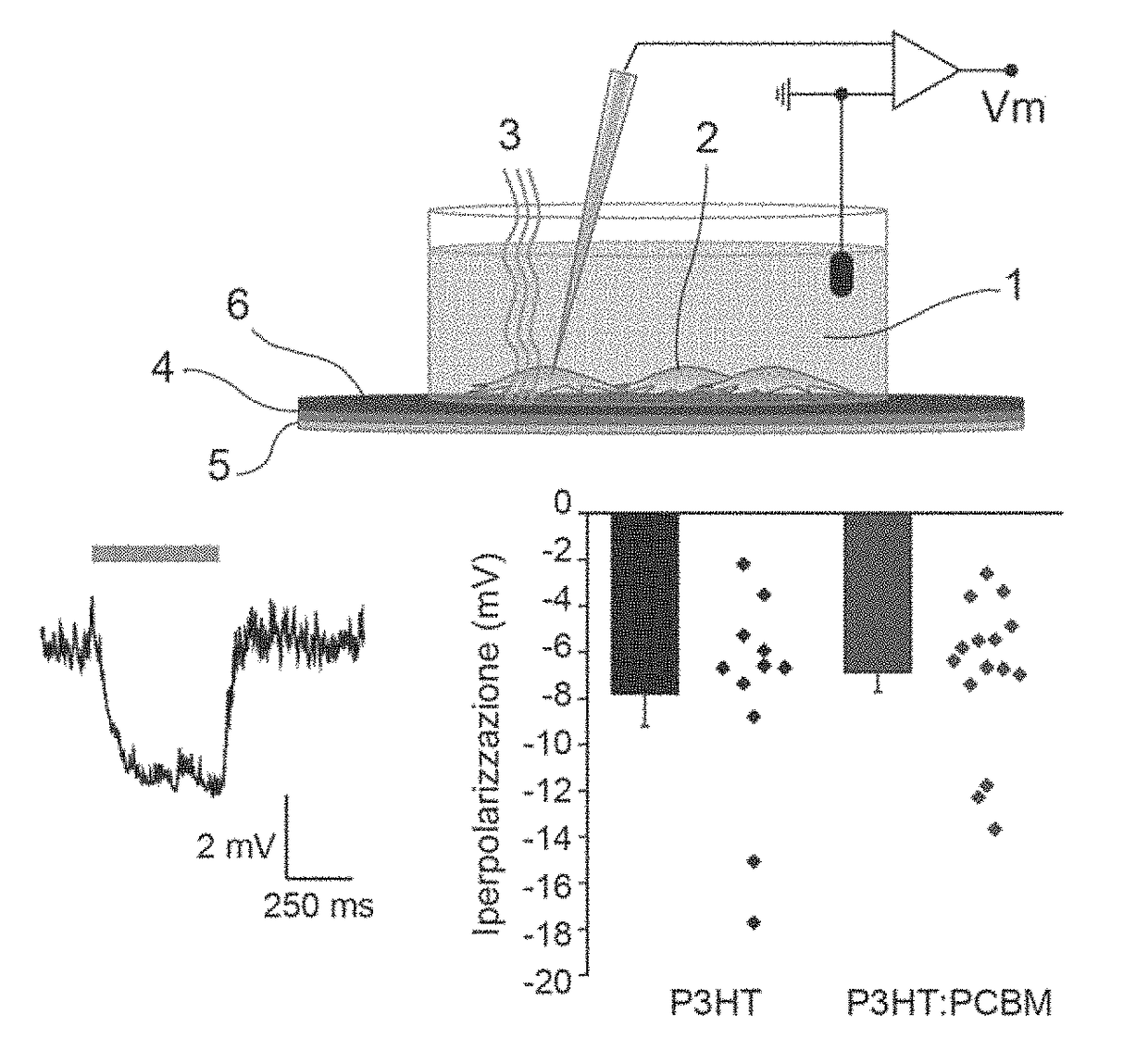
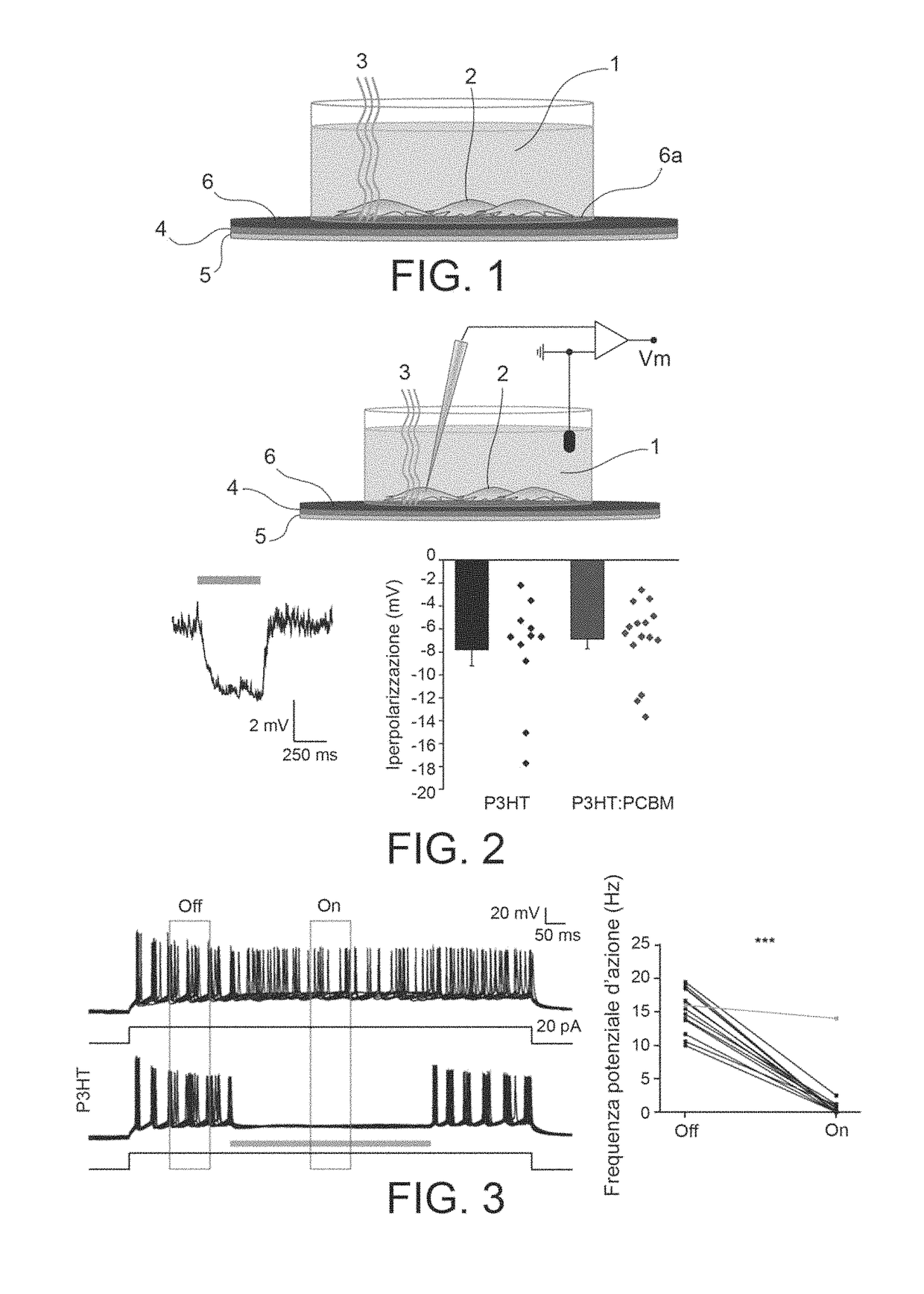
ActiveUS9938518B2Electrical/wave energy microorganism treatmentCoatingsExcitable cellPhotoinhibition
Devices are provided for inhibiting the electrical activity of an excitable cell through the application of a pulse of light which includes a substrate and a photoreactive film both of non-conducting material and laid directly on one another, in which the photoreactive film includes a layer of semiconductor polymer material and has an interface surface which can be placed in contact with an excitable cell and an electrolyte solution. After absorbing light, when placed in contact with the excitable cell and the electrolyte solution, the photoreactive film produces a potential difference across this interface surface which is capable of giving rise to hyperpolarization of the membrane of the excitable cell. Methods of inhibiting the electrical activity of excitable cells using such devices are also provided.
Owner:FOND INST ITAL DI TECH +1
Peanut Violaxanthin Decycloxygenase Gene, Its Encoded Protein and Its Application
InactiveCN103695444BImproved deepoxidation stateSpeed up heat dissipationOxidoreductasesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology, in particular to a peanut violaxanthin decycloxygenase gene, the nucleotide sequence of which is shown in sequence 1 in the sequence list. The amino acid sequence of peanut violaxanthin decycloxygenase gene, the amino acid sequence is shown in sequence 2 in the sequence list. Application of peanut violaxanthin decycloxygenase in protecting photosynthetic apparatus. The peanut violaxanthin decycloxygenase gene was transfected into tobacco to obtain transgenic plants. Under excess light energy stress, the transgenic plants had higher NPQ and deepoxidation status of lutein cycle than wild-type plants, indicating that Under the condition of excess light energy, AhVDE The overexpression of lutein changes the relative content of lutein cycle components, which leads to the change of deepoxidation state and improves the heat dissipation capacity of lutein cycle. The enhanced ability of transgenic plants to dissipate excess light energy reduces the pressure of PSII excitation energy, thereby reducing the degree of photoinhibition of PSII and PSI under excess light energy stress, and finally protecting the photosynthetic apparatus.
Owner:BIOTECH RES CENT SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Soybean photosynthesis related gene GmDeg2 and application thereof
ActiveCN102994532BSubstrate requirements are highRegulates protease activityHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyPlant cell
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for inhibiting growth of harmful blue algae by utilizing colored light
PendingCN112624254AGrowth inhibitionEnhanced advantageWater/sewage treatment by irradiationSpecific water treatment objectivesFluorescent lightColored light
The invention discloses a method for inhibiting growth of harmful blue algae by utilizing colored light. Blue fluorescent lamps are erected on the water surface and arranged on the water area side by side in parallel, and meanwhile it is ensured that the whole underwater light environment is within a certain wavelength range. When harmful blue algae are not massively propagated in spring and early summer, the advantages of green algae are enhanced. The method provided by the invention is low in implementation cost, remarkable in effect, simple to operate and easy to popularize.
Owner:江苏中鹏环保集团有限公司
A high-sensitivity coronagraph stray light detection device
ActiveCN111060289BHigh sensitivityHigh detection sensitivityTesting optical propertiesOptical radiationPhoton counting detector
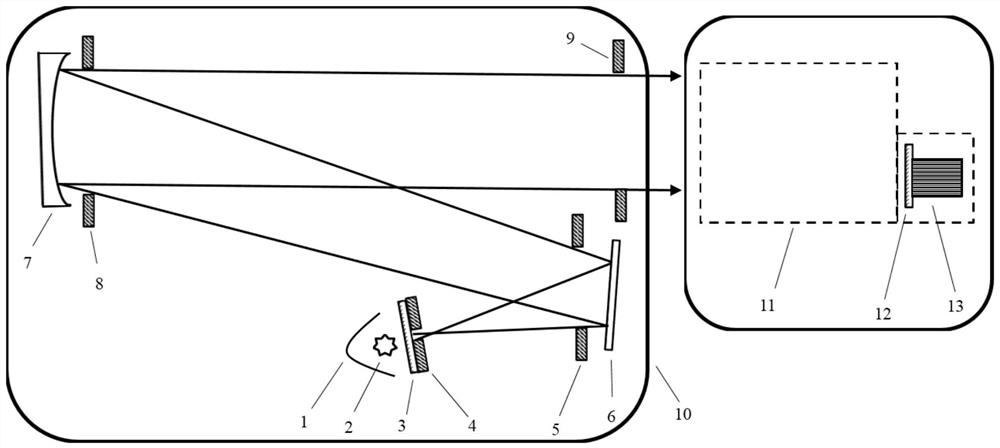
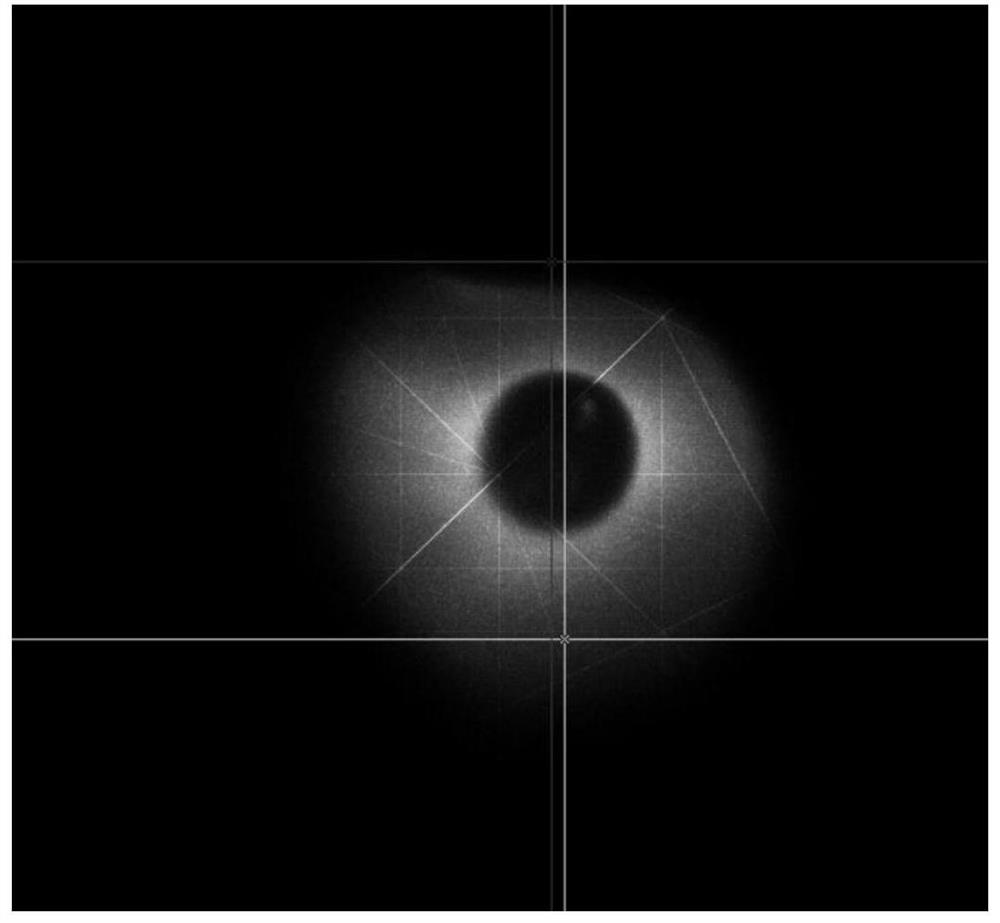
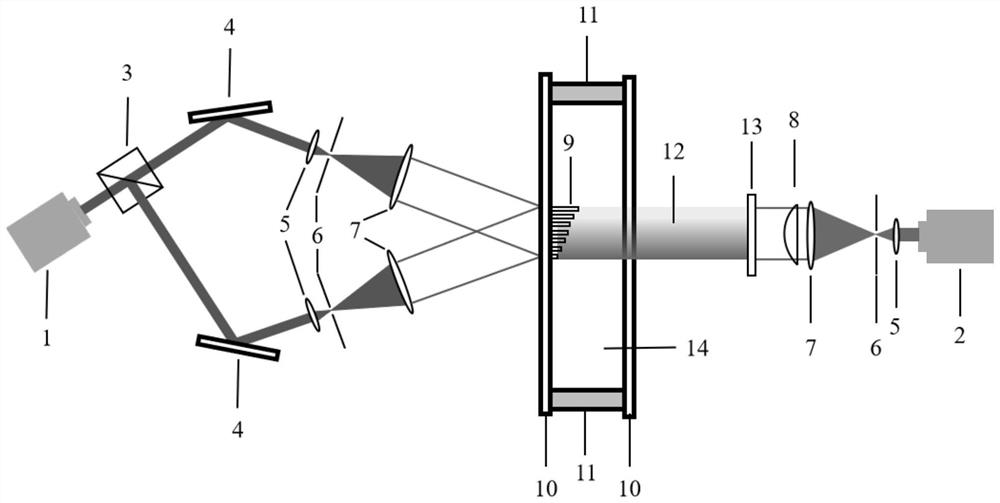
The invention provides a high-sensitivity coronagraph stray light detection device, which relates to the field of observation and detection of astronomical targets. The optical filter is arranged between the coronagraph to be tested and the single-photon counting detector, and the single-photon counting detector is arranged on the focal plane of the coronagraph to be tested; The simulated sunlight enters the coronagraph to be tested, the band-pass filter performs wavelength selection for the band to be tested, and the single photon counting imaging detector detects the stray light brightness and solar surface brightness of the coronagraph to be tested. The invention can realize the detection of the coronagraph stray light suppression ability by separately measuring the solar surface radiation and the coronagraph stray light radiation, and overcomes the inability to use solar radiation directly to coronagraph stray light suppression in low altitude areas due to the influence of atmospheric scattering. Difficulties in the detection of photoinhibition capacity.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF OPTICS FINE MECHANICS & PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A preparation method of a grating with continuously changing diffraction efficiency
ActiveCN111880254BImprove imaging effectImprove information transmission abilityDiffraction gratingsOptical waveguide light guideContinuous lightSpectral bands
The invention discloses a preparation method of a grating with continuously changing diffraction efficiency: the first beam and the second beam of light with two spectral bands that do not overlap with each other are used, the first beam of light is interfered to form interference light, and the second beam of light Form light with continuous light intensity changes in space; irradiate the interference light and the light with continuous light intensity changes in space on the photosensitive material at the same time, and obtain a grating with continuous change in diffraction efficiency; The material is cured, and the light with continuous light intensity changes in space inhibits the curing of the photosensitive material; or the photosensitive material is a material whose refractive index changes due to light. The preparation method provided by the present invention is directly obtained by exposing the photosensitive material, mainly aiming at the disadvantage of poor uniformity of the outgoing beam of the existing optical system based on the waveguide grating coupler, and can obtain the outgoing beam with uniform light intensity distribution, thereby Effectively improve the imaging capability and information transmission capability of the optical system.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Soybean photosynthesis related gene GmDeg1 and applications thereof
InactiveCN102978225ARegulatory activityIncreased resistance to photoinhibitionHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyPlant cell
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a soybean photosynthesis related gene GmDeg1 and applications thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the soybean photosynthesis related gene GmDeg1 is shown as SEQ ID NO. 1, and the amino acid sequence of coded proteins is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. By using a carrier which can guide an exogenous gene to be expressed in a plant, the gene GmDeg1 disclosed by the invention is guided into plant cells, so that a transgenic plant with an improved photoinhibition resistance capacity can be obtained. The gene disclosed by the invention has an anti-photoinhibition effect on soybeans, and especially has a great significance on cultivating high-photosynthetic-efficiency soybean varieties.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of light resistant core-shell type water-based acrylic ester type resin paint and coating agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a light resistant core-shell type water-based acrylic ester type resin paint and coating agent. The following raw materials in proportion by weight: water, emulsifying agents and methacrylic acid are added into a 500ml flask with three necks; the temperature is raised to 40 to 50 DEG C; stirring is performed for 30min; monomers A are added; emulsification is performed for 30 to 40min; the temperature is raised to 70 DEG C; backflow water starts to be introduced; after the temperature is raised to 80 DEG C, heat insulation is performed for 2h; 0.2to 0.4g of initiators (6g of water is used for dissolution) are dropwise added; the dropwise adding time lasts 30 to 70 min; after the dropwise addition is completed, reaction is performed for 2h; core layer emulsion is obtained; the monomers B and 0.2 to 0.5g of initiators (6g of water is used for dissolution) are dropwise added into the obtained core layer emulsion at the same time, and the dropwise adding time lasts 40 min; after the dropwise addition is completed, heat insulation is performed for 85 to 95 DEG C; stirring reaction is performed for 1 to 2h; at the temperature, 0.4g of emulsifying agents and 0.1 to 0.3g of cross-linking agents and photoinhibition fixatives are added; the reaction is performed for 40min; ammonium hydroxide is added for regulating the pH value to 7 to 8; the light resistant core-shell type water-based acrylic ester type resin paint and coating agent. The obtained paint and coating agent has high light resistant performance.
Owner:段瑶瑶
Non-toxic biological anti-fouling resistance reducing composite coating, preparation method for composite coating and anti-fouling resistance reducing treatment method for base material
InactiveCN102642356BReduce adverse effectsImprove efficiencyAntifouling/underwater paintsLuminescent paintsSurface layerPowder coating
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com