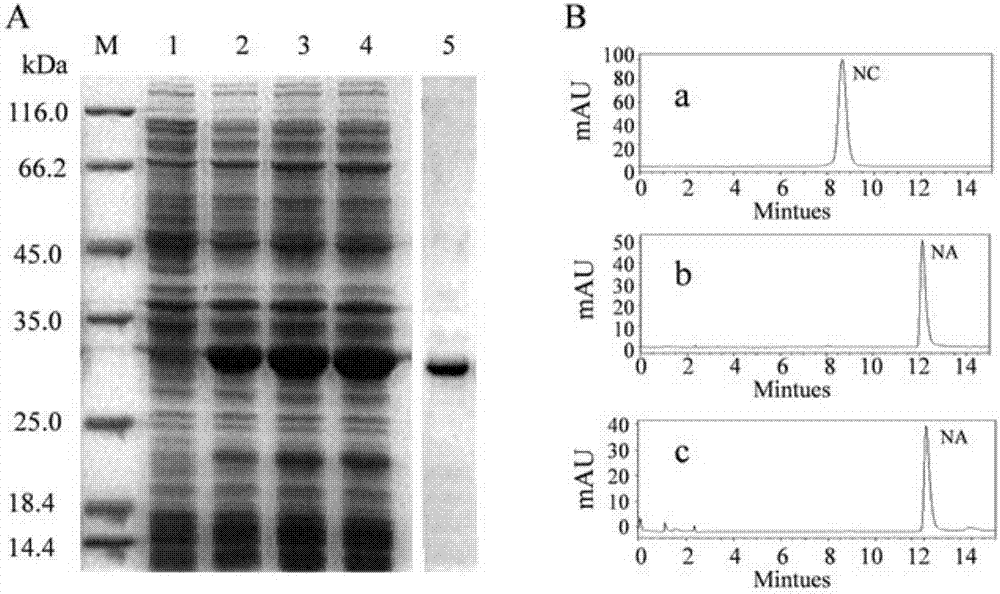
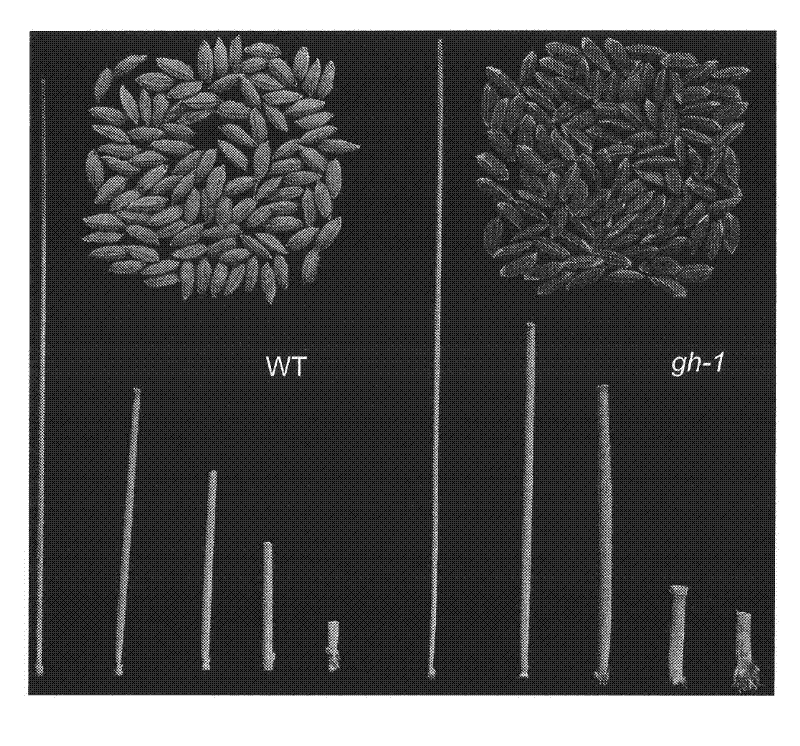
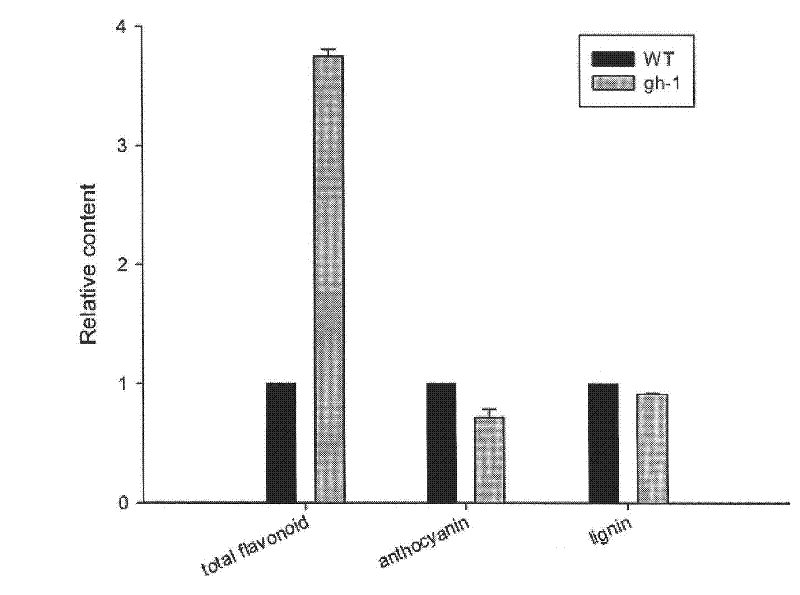
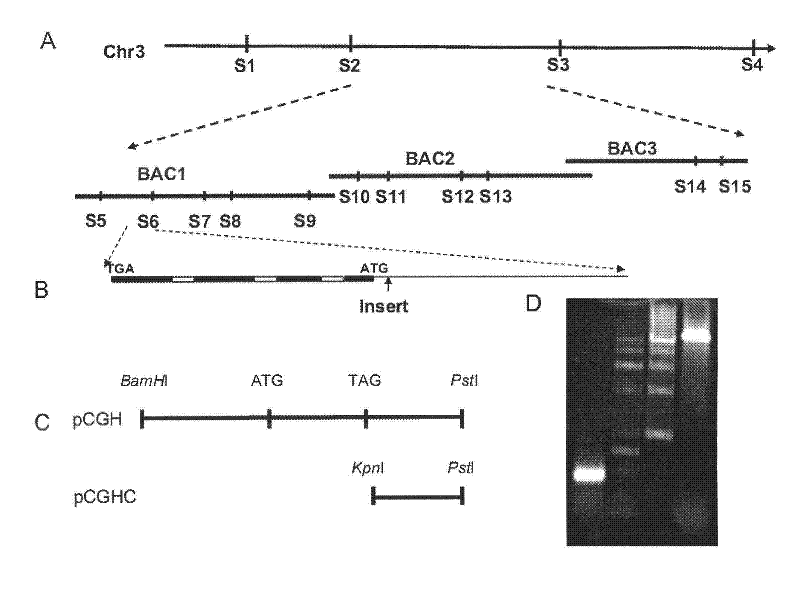
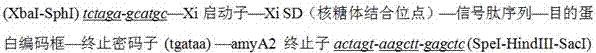Patents
Literature
140 results about "Isomerase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Isomerase Genes encode enzymes (Isomerases) that catalyze spatial or structural changes within a molecule by rearrangement or transfer of specific atoms or moieties to a new intramolecular location to form a new single product. The reactions do not involve a net change in the concentrations of compounds other than the substrate and the product. (NCI)
Novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103602627AEnhanced rate-limiting enzyme gene expressionPrevent backflowBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphate
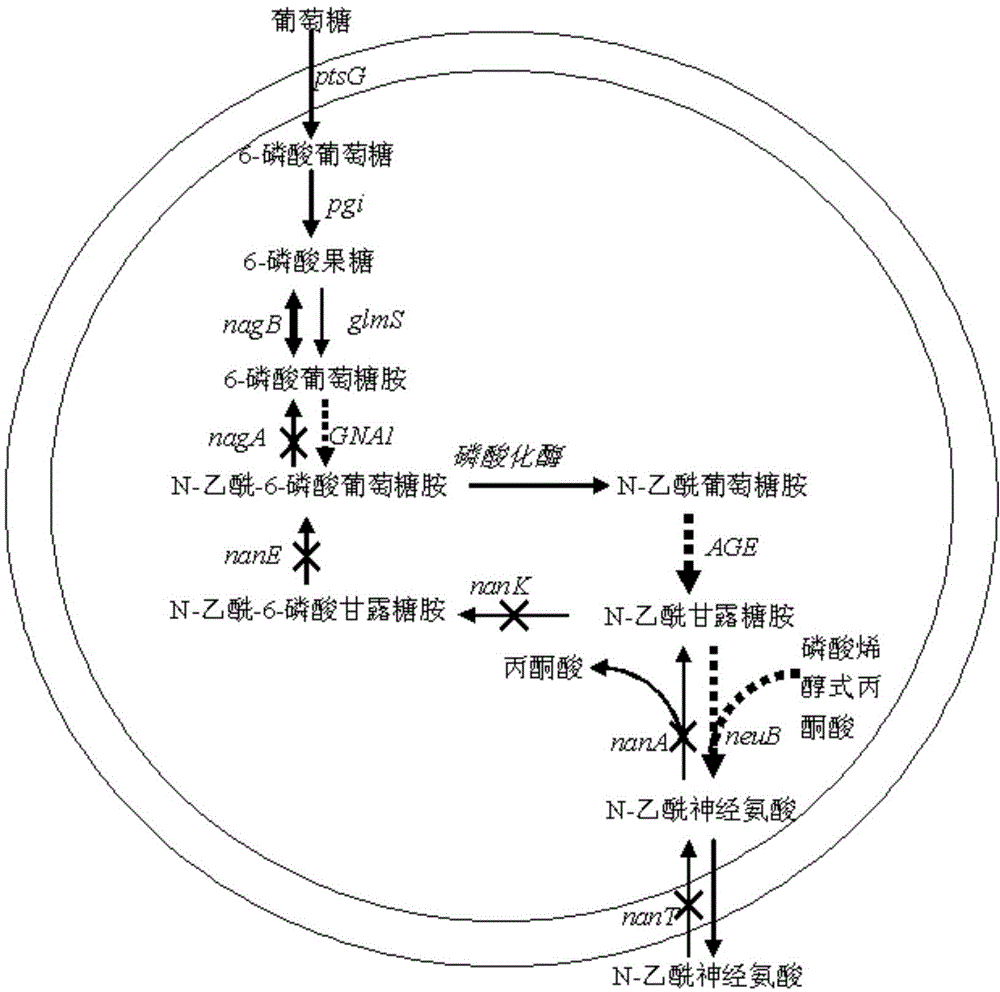
The invention discloses novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as a construction method and application thereof. The engineering bacterial is constructed by introducing an encoded 6-glucosamine phosphate acetylase gene, an N-acetyl glucosamine-2-isomerase gene and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene into escherichia coli to express, carrying out strengthened expression on 6-glucosamine phosphate deaminase gene contained in the escherichia coli per se and knocking off genes, for decomposing and utilizing enzyme in metabolic pathways, of the N-acetylneuraminic acid in the engineering bacteria. The engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention can be used for fermentation culture to synthesize the N-acetylneuraminic acid by using glucose or glycerinum as a substrate.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
High-yield N-acetylglucosamine metabolic engineering bacterium, as well construction method and applications thereof
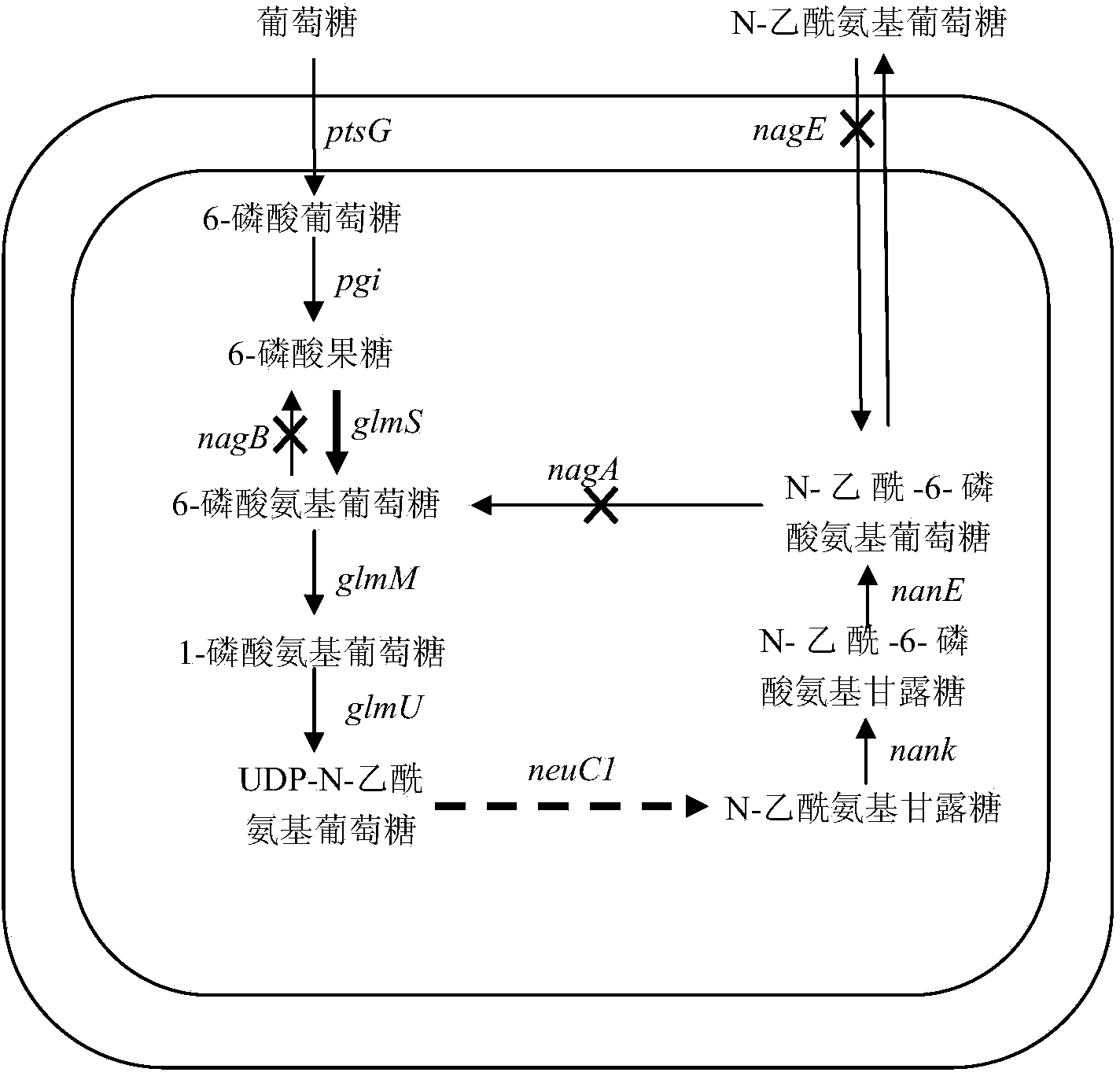
The invention discloses a high-yield N-acetylglucosamine metabolic engineering bacterium, as well a construction method and applications thereof. The engineering bacterium is a recombinant Escherichia coli by leading a coded UDP-N-acetylglucosamine epimerase gene and a coded 6-glucosamine phosphate synthetase gene into Escherichia coli for expression, and knocking out the gene N-acetylglucosamine in the Escherichia coli to decompose and utilize metabolic pathway enzyme; and the constructed engineering bacterium strain utilizes glucose as a substrate for fermenting and culturing and synthesizing the N-acetylglucosamine. The engineering bacterium is high in the fermenting level of synthesizing the N-acetylglucosamine by utilizing glucose, the accumulation of side products is less, and industrial production potential capability can be achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Process for preparing conjugated fatty acid
The invention provides a specific isomerase produced from lactic acid bacteria, wherein biological isomerization is employed for preparing conjugated aliphatic acid, the enzyme isomerizes 9c, 12c unsaturated fatty acid to form 9c, 11t conjugated aliphatic acid, such as 9c, 11t conjugated linolic acid, 9c, 11t conjugated linolenic acid. The invention also discloses the process for preparing conjugated aliphatic acid by conducting mutagenesis, modification, isomerase gene cloning to lactic acid bacteria, and various products of the prepared conjugated aliphatic acid and lactic acid bacteria product related with conjugated aliphatic acid.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
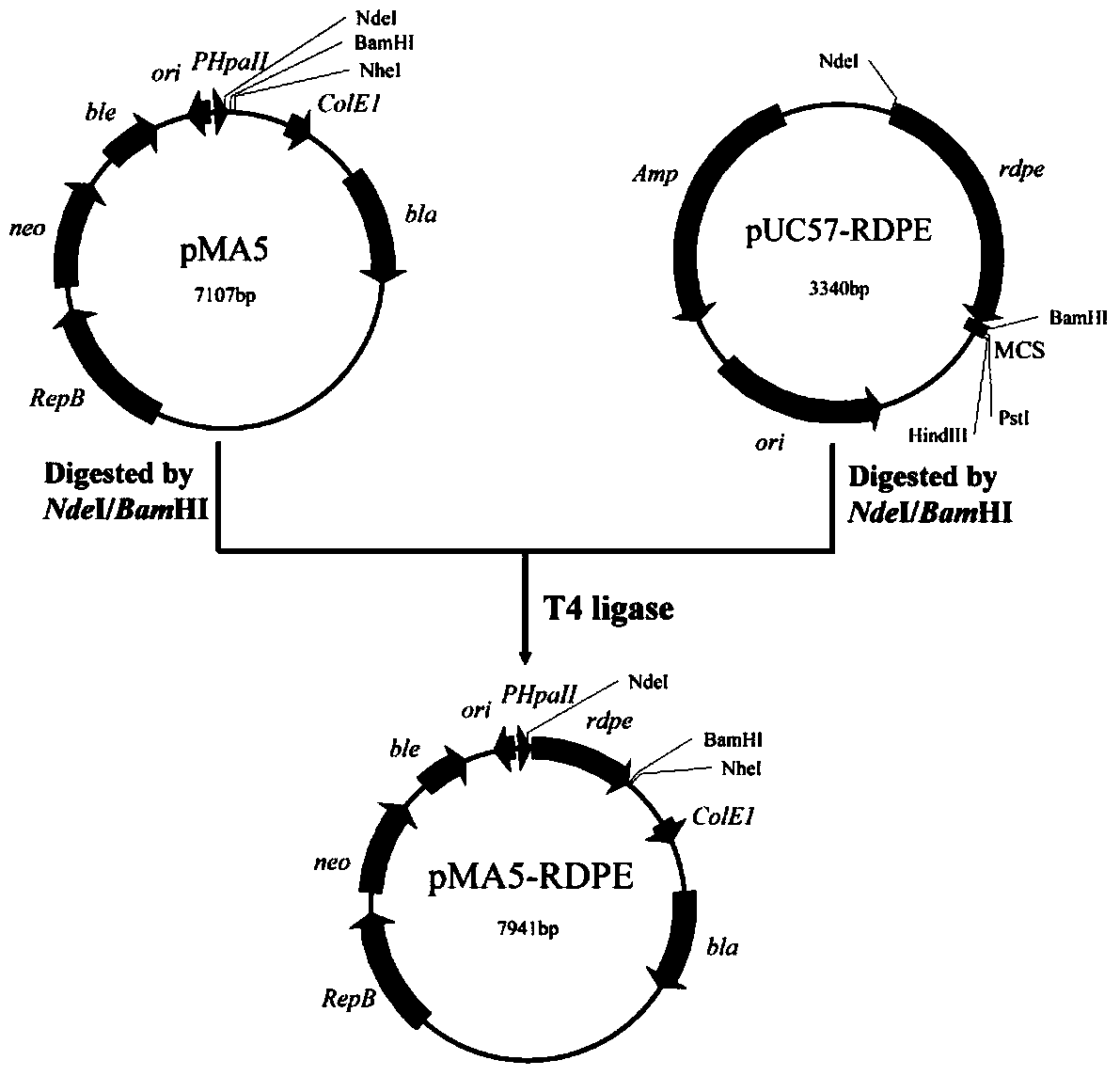
Genetic engineering strain capable of effectively secreting D-psicose 3-epimerase and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN105602879ASimple purification processLow production costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesPsicoseRumen
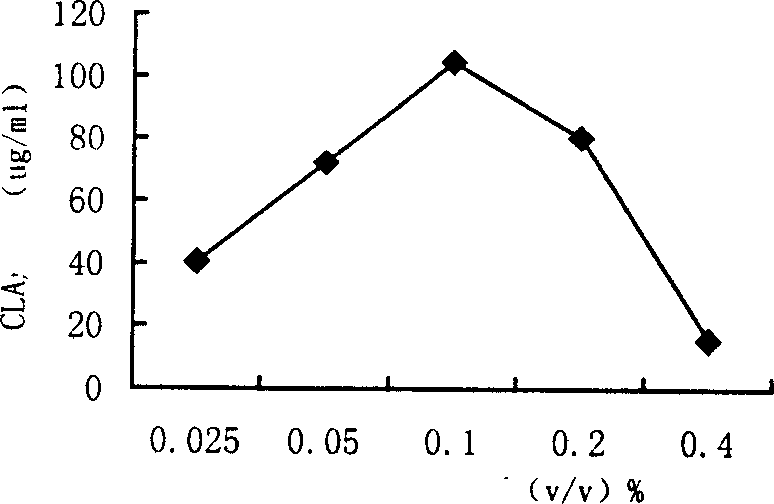
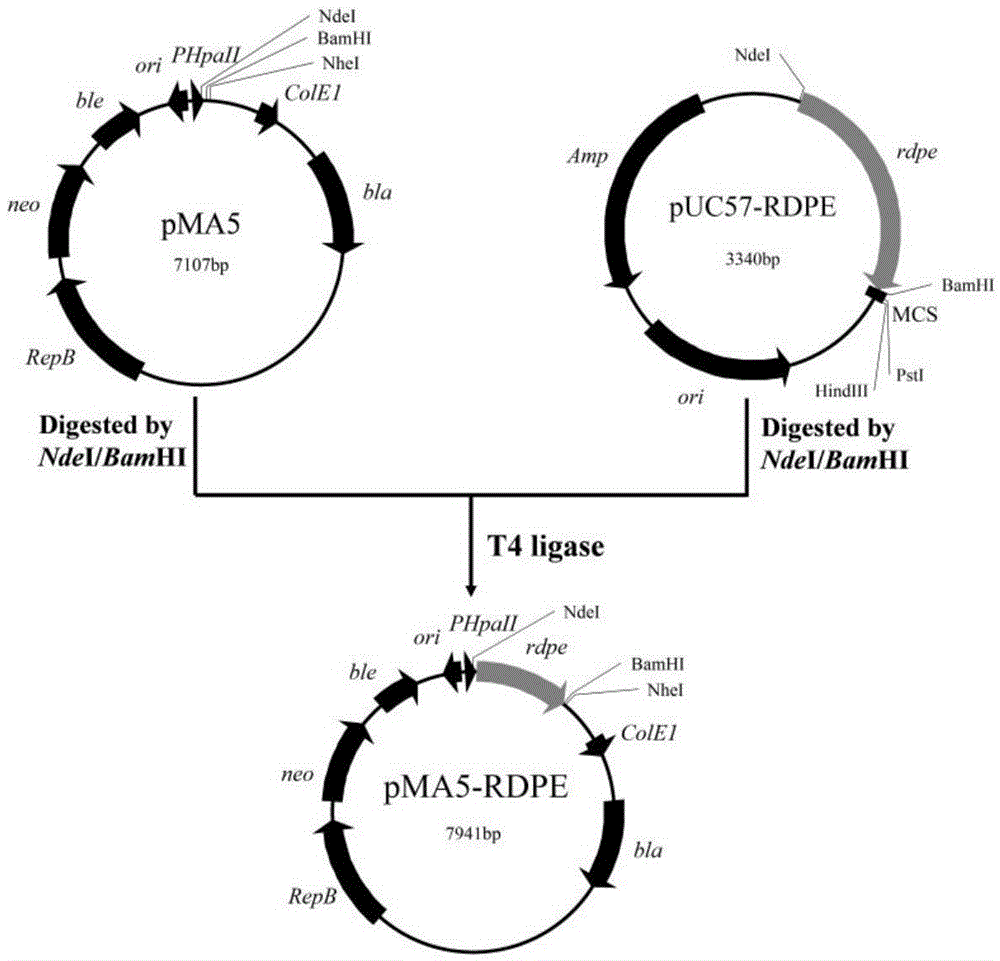
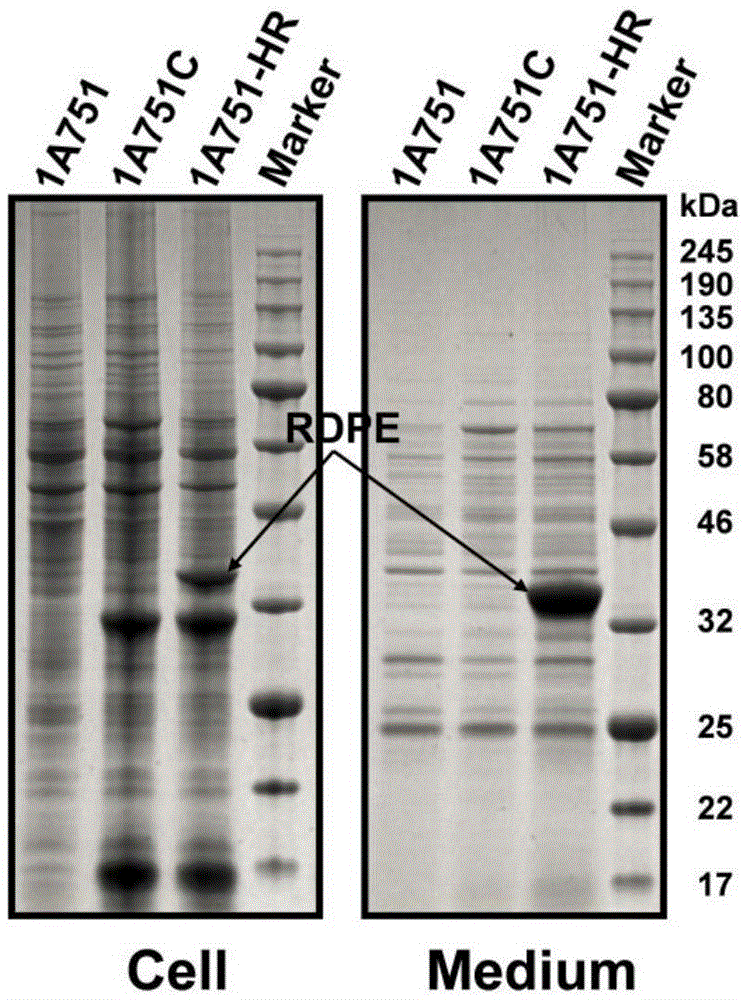
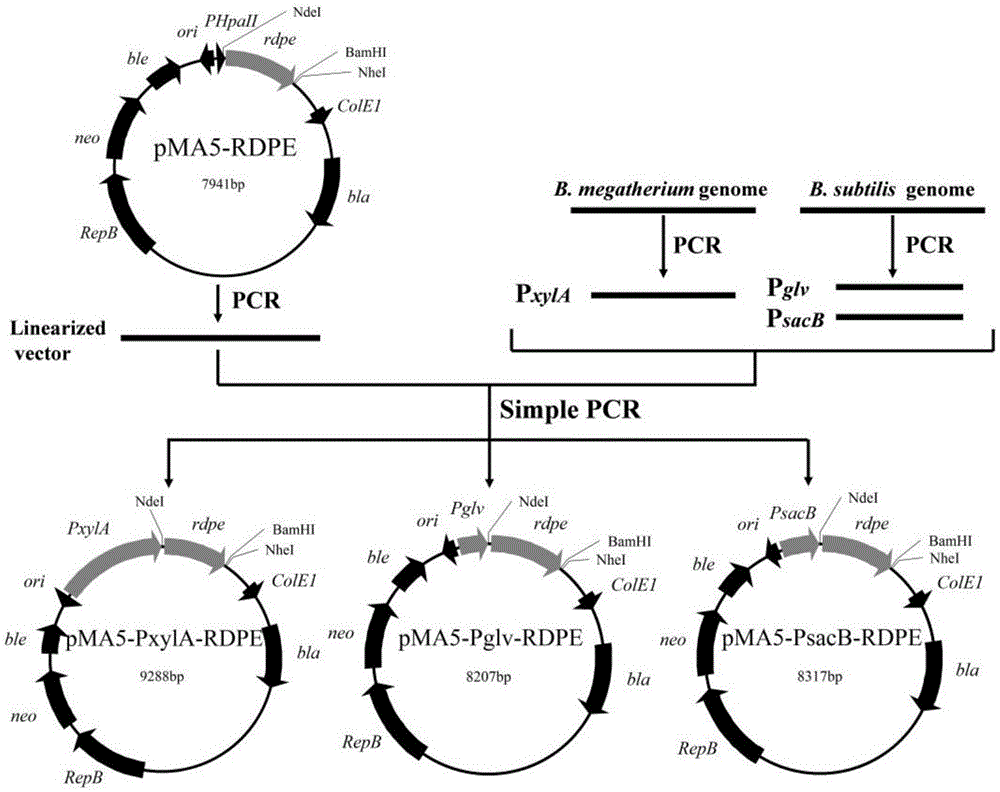
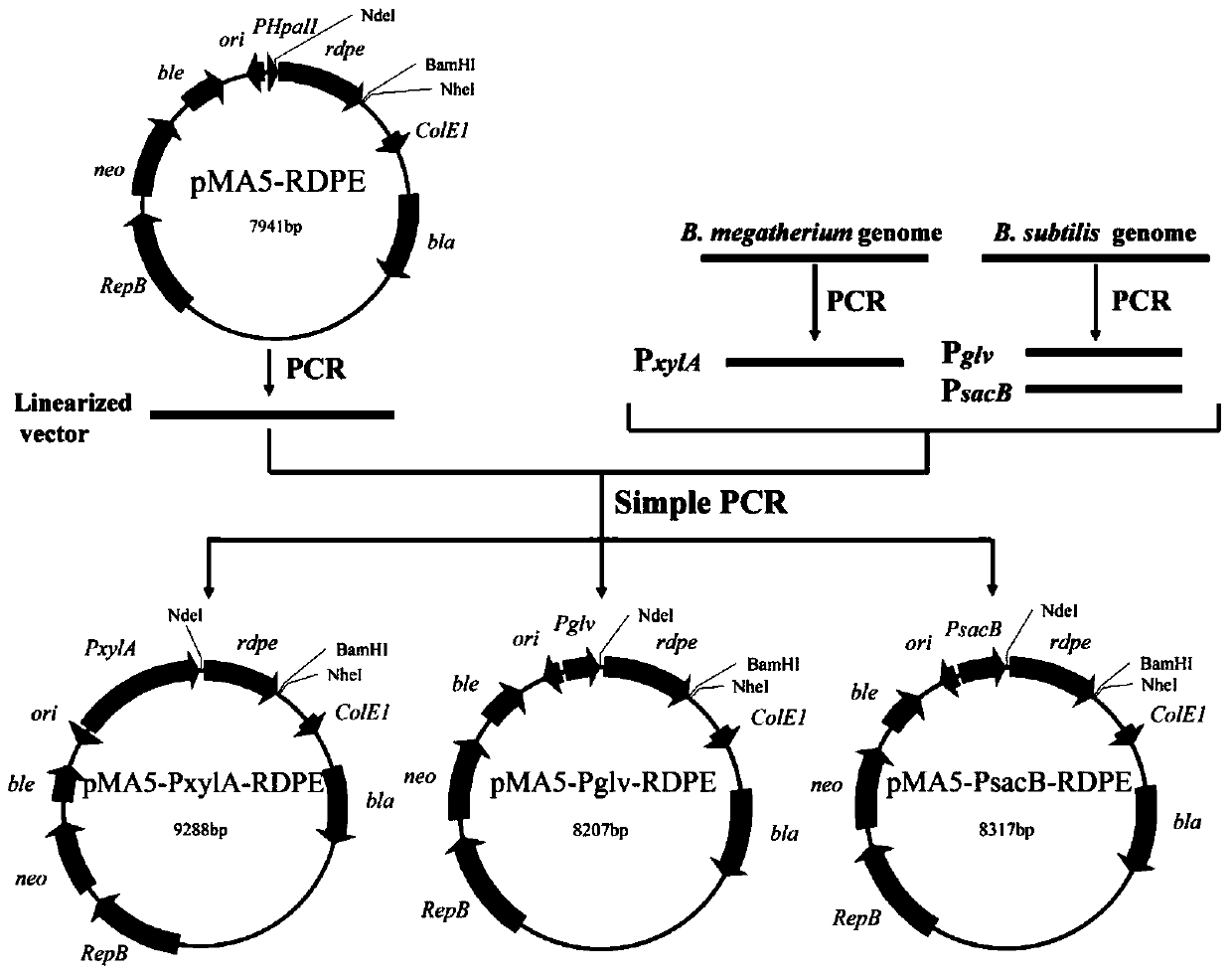
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a genetic engineering strain capable of effectively secreting D-psicose 3-epimerase and a construction method thereof. A D-psicose 3-epimerase gene rdpe from rumen bacterium Ruminococcus sp. 5_1_39B_FAA is obtained firstly, recombinant plasmid pMA5-RDPE construction and bacillus subtilis conversion are conducted, and then constitutive and secretive expression of RDPE in bacillus subtilis is achieved. By comparing three glucose-induced promoters, the optimal inducible promoter P[xylA] is obtained, and the RDPE secretion level is increased remarkably. By knocking out the xylose utilization gene xylAB (xylA and xylB), the xylose metabolism pathway of bacillus subtilis is blocked, the secretion amount of RDPE is further increased, and the optimal induced concentration of the inducer xylose is reduced to 0.5% from 4.0%. Finally, the engineered strain 1A751SD-XR is evaluated in a 7.5 L fermentation tank, and the RDPE secretion level can be as high as 95 U / mL and 2.6 g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Cloning, expression and application of eimeria tenella protein disulfide isomerase gene
InactiveCN101418309AGenetic material ingredientsRecombinant DNA-technologyEscherichia coliEmoia loyaltiensis
The invention discloses an E.tenella protein disulfide linkage isomerase gene EtPDI (Clone ID is BW1-E06,and the Genbank accession number of is EF552214). The gene is connected with a procaryon expression vector pGEX-4T-2; a procaryon expression recombination plasmid pGEX-4T-EtPDI is constructed and is expressed in a colibacillus system; and most of the expressed recombining protein exists in a soluble form. The recombining protein 4T-EtPDI is purified to carry out SPS-PAGE and is transferred to a PVDF film; and antiserum of E.tenella oocyst oral immunized chicken is used as first resistance and goat anti-chicken IgG is used as second resistance to carry out Western-blot analysis, thereby indicating that the gene has certain antigen. The gene is used for preparing an anti-chicken coccidiosis drug and an anti-chicken coccidiosis vaccine.
Owner:SHANGHAI VETERINARY RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
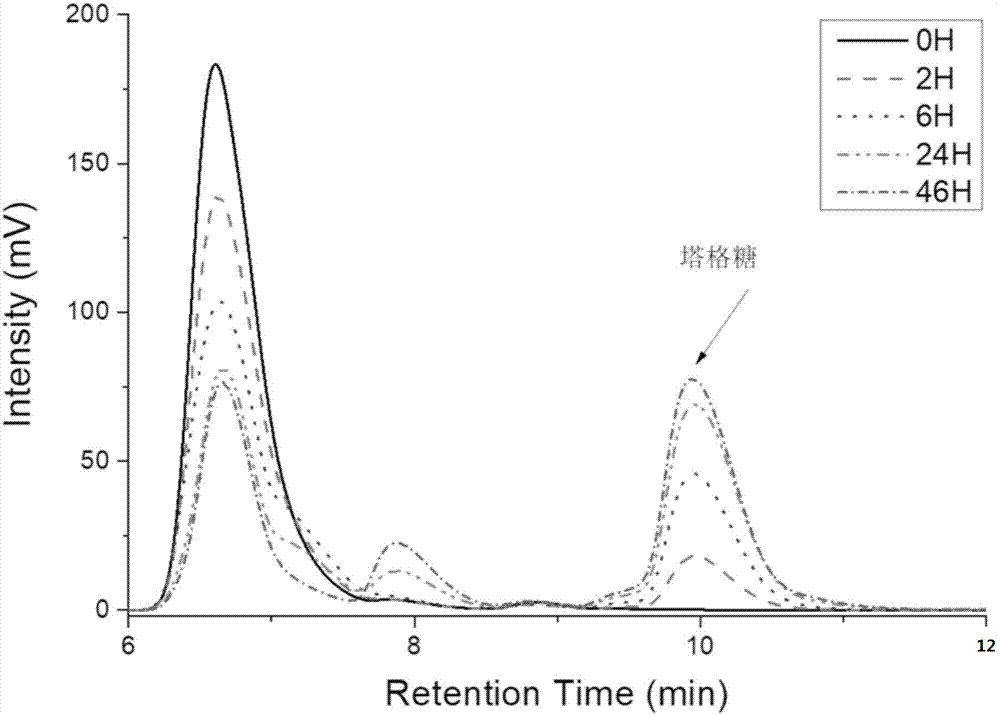
Method for preparing tagatose by using whole-cell catalysis
ActiveCN107988286AHigh yieldSuitable for large-scale productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationEscherichia coliTagatose
The invention discloses a method for preparing tagatose by using whole-cell catalysis. The method comprises the following steps of transferring plasmid containing an alpha-glucan phosphorylase gene (or cellulosic polysaccharide phosphorylase and cellobiose phosphorylase genes, or a sucrose phosphorylase gene), a phosphoglucomutase gene, a glucose phosphate isomerase gene, a 6-phosphate tagatose epimerase gene, and a 6-phosphate tagatose phosphatase gene into engineered escherichia coli, so as to obtain converted bacterial strain; inducing the converted bacterial strain to produce enzyme, and permeabilizing; mixing the permeabilized bacterial strain, establishing a whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction system with starch or starch derivative (or mixture of cellulase and cellulose or cellulose derivative, or sugarcane), and performing the whole-cell enzyme catalysis reaction, so as to obtain the tagatose. The method has the advantages that the tagatose is prepared by the whole-cell catalysis; the cost is low, the pollution is low, the yield rate is high, and the like; the method is suitable for preparing the tagatose in a scale way.
Owner:天工生物科技(天津)有限公司
Tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene and is application
ActiveCN104152473AIncrease contentIncreased resistance to photoinhibitionGenetic engineeringFermentationBiotechnologyBeta-Carotene
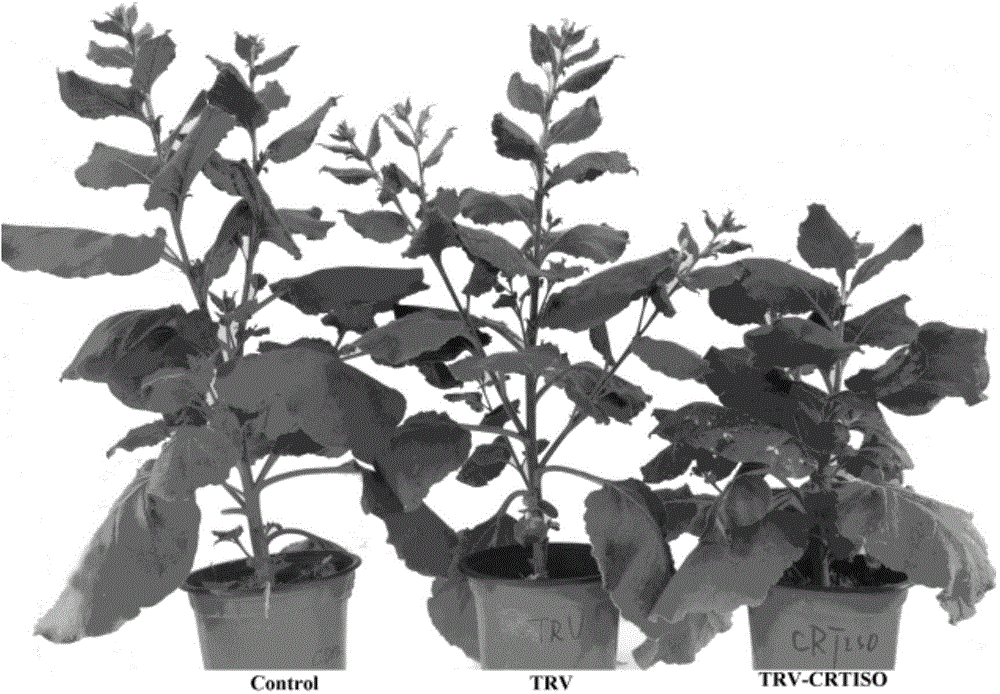
The invention discloses a tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene. The base sequence of the tobacco carotenoid isomerase gene is represented by SEQIDNO:1. In tobacco, a key carotenoid synthesis gene NtCRTISO is cloned, and the gene can be inhibited to effectively improve the carotenoid content of tobacco leaf and improve the photoinhibition resistance of tobacco plants. The invention discloses an important function of the CRTISO gene in tobacco in carotenoid synthesis. The CRTISO gene plays a great role in the regulation of the composition of carotenoid. A method for improving the content of carotenoid, especially beta-carotene, in the tobacco is searched, and a good theoretic guidance is provided for the improvement of the molecules of the plants.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
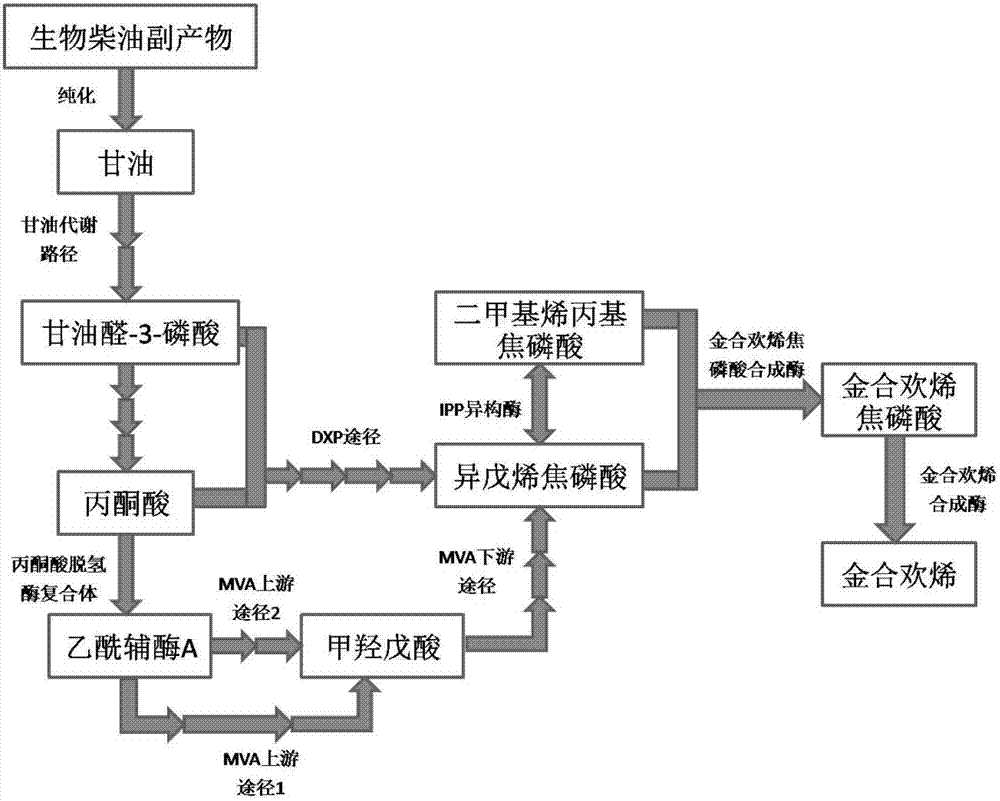
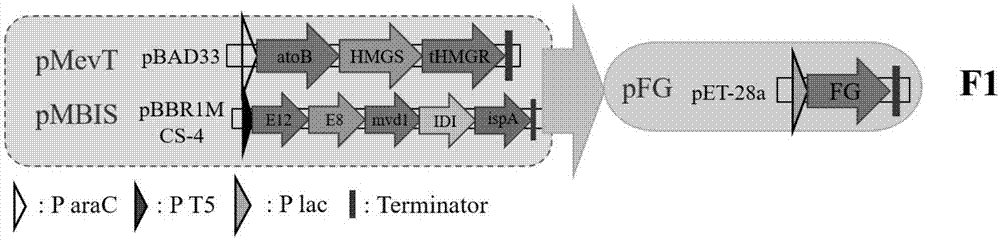
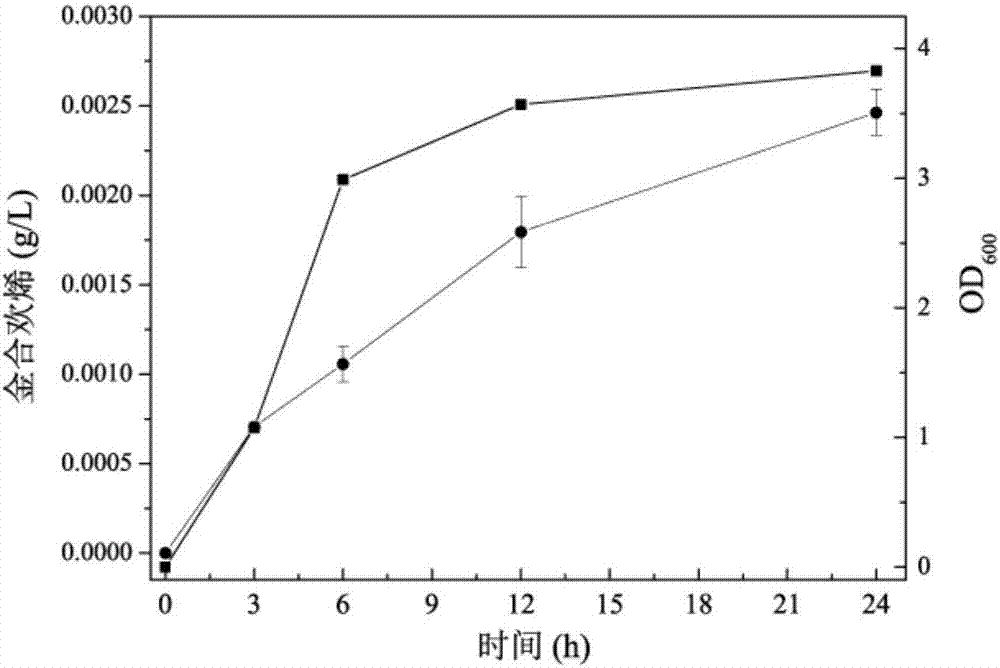
Method for preparing farnesene by using biodiesel by-product
ActiveCN107418978ABroaden raw material selectionConducive to sustainable large-scale productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiodieselIsopentenyl pyrophosphate
The invention discloses a method for preparing farnesene by using a biodiesel by-product. The method comprises the steps of purification of the biodiesel by-product, wherein the purity of the purified glycerin reaches 63.8% (w / w), building of a recombinant host cell for preparing farnesene from the purified glycerin as the raw material, wherein the recombinant host cell comprises related genes in a mevalonate pathway or deoxymutulose-5-hexose monophosphate pathway, an isopentene pyrophosphate isomerase gene, a farnesene isopentenyl pyrophosphate synthetase gene and a farnesene synthetase gene. The method also comprises fermentation of the purified glycerin as the raw material in the recombinant host cell to prepare the farnesene, wherein the concentration of the obtained farnesene is 0.025g / L; and optimum construction of the recombinant host cell capable of improving the yield of the farnesene by employing the purified glycerin as the raw material, wherein the concentration of the obtained farnesene reaches 2.9g / L, and the concentration is improved by 115 times in comparison with that before optimization.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
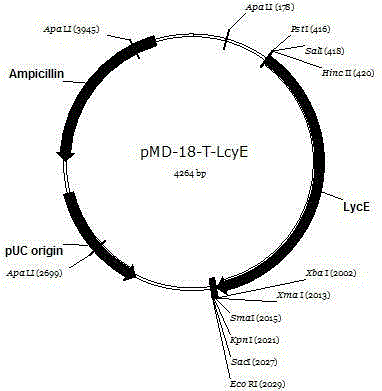
Wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene and recombinant vector comprising gene
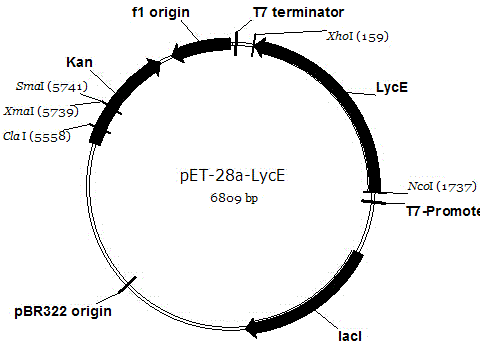
The invention relates to a wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene and a recombinant vector comprising the gene. The gene is selected from one of the following nucleotide sequences: 1) a nucleotide sequence shown in a sequence SEQ ID NO.1; and 2) a homologous sequence or an allelic gene thereof and a derivative nucleotide sequence thereof in which 70% of one or more nucleotides are added, replaced, inserted or deleted in the nucleotide sequence shown in the sequence SEQ ID NO. 1. By extracting the total RNA of fresh wolfberry leaves, a wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene Lm LcyE is cloned by using a 3'RACE technology, and an obtained complete genome sequence is 1569. An escherichia coli expression vector pET28a-LmLcyE is constructed, the enzymatic activity of cloned wolfberry isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase gene Lm LcyE encoding is identified by using an escherichia coli heterologous expression system, and the wolfberry lycopene epsilon-cyclase gene Lm LcyE can catalyze lycopene for cyclizing the lycopene into delta carotene, so that metabolism flows downstream, thereby improving the content of alpha-carotenoid.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as construction and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN113817658AIncrease production intensityIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering, and particularly relates to a genetically engineered bacterium for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid through xylose induction. Escherichia coli is used as a starting strain, an N-acetylglucosamine synthesis pathway is integrated on a genome, an N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene bAGE and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene neuB from collar algae are introduced, an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis pathway is constructed, and a key gene nano ATEK of a catabolism pathway of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is knocked out. Meanwhile, metabolic pathways of precursor substances required by synthesis of the N-acetylneuraminic acid are subjected to multi-copy reinforcement, part of bypass metabolic pathways are knocked out, key enzyme genes for producing GlcNAc and Neu5Ac are optimized according to different copy numbers, the optimal proportion of the key enzyme genes is finally determined, and the high-yield strain of the N-acetylneuraminic acid is obtained. The highest yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach 28g / L, the highest production intensity can reach 0.67 g / (L*h) which is the highest value reported at present, and the N-acetylneuraminic acid has important industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
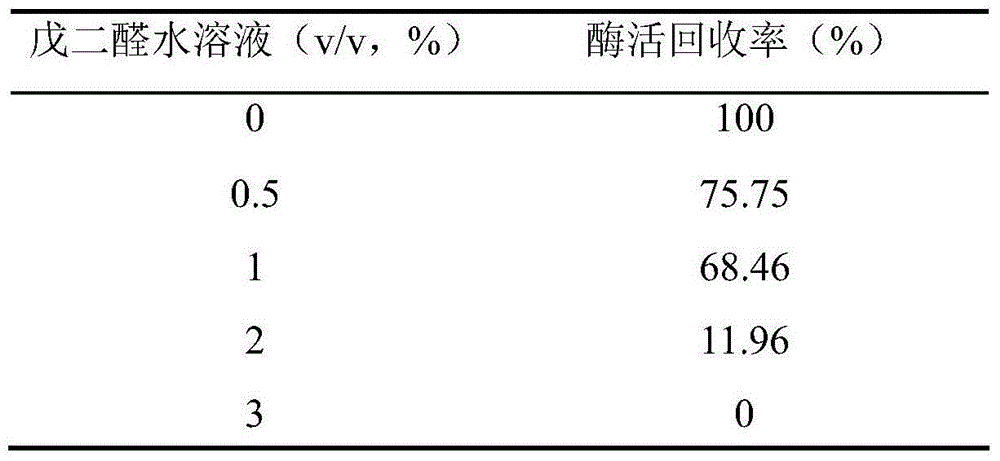
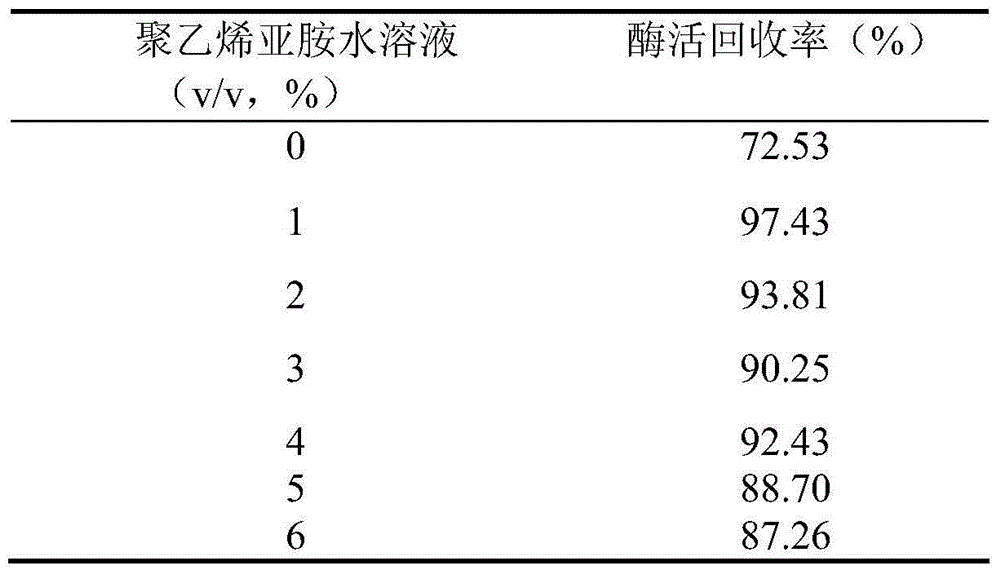
Immobilization method for cells containing glucose isomerase
ActiveCN104962546AImmobilization method is simpleMeet the use requirementsMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesEscherichia coliGenetic engineering
The invention discloses an immobilization method for cells containing glucose isomerase. The immobilization method comprises the following steps of adding wet bacteria obtained by performing fermented culture on a recombinant genetic engineering strain containing glucose isomerase genes in buffer liquor so as to obtain bacterial suspension; adding a carrier in the bacterial suspension; uniformly stirring the bacterial suspension; adding polyethyleneimine and glutaraldehyde to perform crosslinking; filtering the bacterial suspension after performing stirring crosslinking on the bacterial suspension for 1-2 hours at the temperature of 0-30 DEG C; washing filter cakes by using distilled water; extruding the filter cakes into long strips by using an axial extruder; airing the long strips at room temperature; and smashing the long strips into granules so as to obtain immobilized glucose isomerase cells containing the glucose isomerase. The immobilization method has the advantages that the cost of an immobilization material is low, the method is easy to operate and high in mechanical strength, the immobilization material is stable at high temperature, prepared recombinant escherichia coli whole cells for producing the glucose isomerase in an immobilization manner can be used for catalyzing D-glucose to produce D-fructose at high temperature, the conversion rate is 54% at the temperature of 85 DEG C, after being repeatedly used ten times, the cells still have enzyme activity which is higher than 90%, and the industrial application prospect is high.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
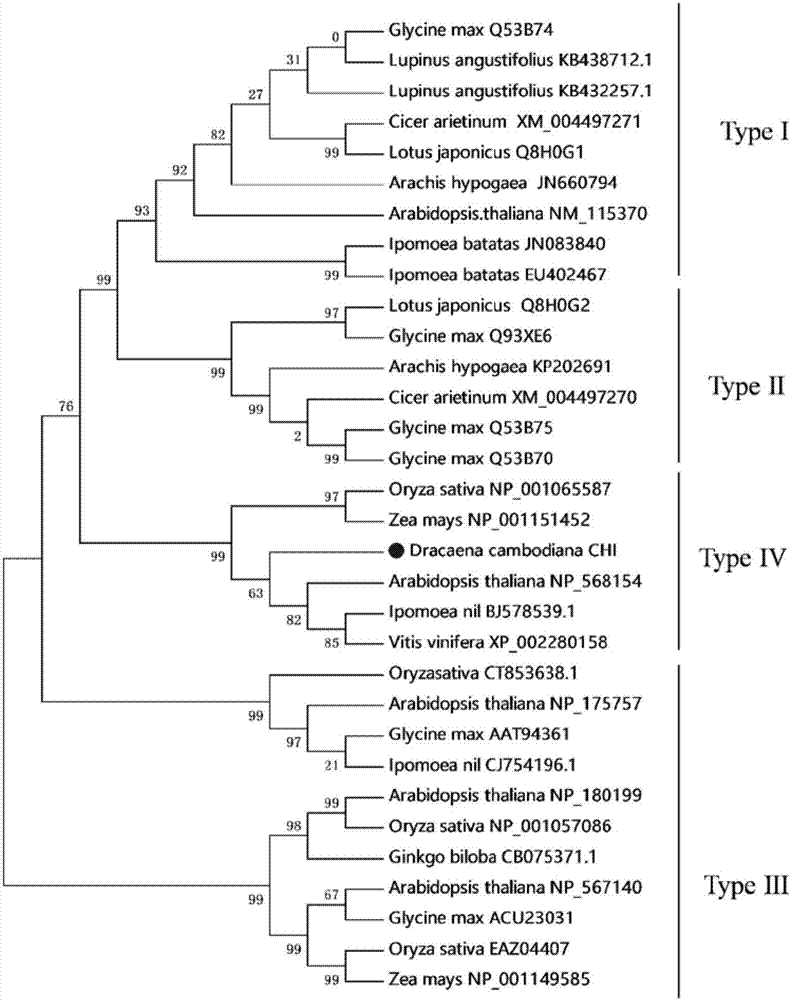
Dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1, encoding gene thereof and application
InactiveCN107190016AIncrease productionHigh economic valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1, an encoding gene thereof and an application. The nucleotide sequence of the gene comprises: (a) a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; or (b) a nucleotide sequence formed by substituting, deleting and / or increasing one or a plurality of proteins expressing the same function of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; or (c) a nucleotide sequence with 90% or more homologous proteins expressing the same function of the nucleotide sequence (a) or (b). The amino acid sequence of the dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, or is an amino acid sequence formed by substituting, deleting or increasing one or a plurality of amino acids of SEQ ID NO: 2 and has the same function. The dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1 gene is obtained by cloning for the first time, the obtained DcCHIL1 proteins have chalcone isomerase activity, the gene is transferred into dracaena cambodiana by biotechnology, so that dracaena cambodiana flavone accumulation and the yield of dragon's blood can be improved, and the gene has a wide application prospect and great economic values.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Protein used for controlling anthocyanidin content, coding gene thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN102477092AHigh in anthocyaninsHigh nutritional valueViruses/bacteriophagesPlant peptidesOrganic chemistryChalcone isomerase
The invention discloses a protein used for controlling the content of anthocyanidin, a coding gene thereof, and an application thereof. The invention discloses a paddy rice chalcone isomerase (CHI), a coding gene thereof, and an application thereof. The protein is represented by the following (1) or (2): (1) a protein composed of an amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence list; (2) a protein with a same activity as that of the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2, wherein the protein is derived from the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2 through substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues. The paddy rice CHI gene provided by the invention can be used as a molecular marker and assists in paddy rice seed breeding. The paddy rice CHI gene also has an important value on the study of reasonable utilization of rice hulls.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Engineered Escherichia coli and method of synthesis of catalyzing fumaric acid from maleic acid in presence of Engineered Escherichia coli
InactiveCN106222122AImprove expression efficiencyHigh densityBacteriaCis-trans-isomerasesFumaraseEscherichia coli
The invention relates to engineered Escherichia coli capable of high-yield production of fumaric acid; specifically, fumarase coded genes fumA and fumC of Escherichia coli are knocked off, and maleic cis-trans isomerase gene from Serratia marcescens is converted to obtain the engineered Escherichia coli. The invention also discloses a method of synthesis of catalyzing fumaric acid from maleic acid by using the engineered Escherichia coli. The method includes culturing the engineered Escherichia coli by fermenting, subjecting the engineered Escherichia coli to high-density inductive expression when OD600 reaches 40-80, and applying the obtained fermentation broth to biochemical catalysis of maleic acid in presence of Engineered Escherichia coli to obtain fumaric acid. The genes fumA and fumC in the Escherichia coli are knocked off by using Red homologous recombination, a metabolic pathway of its fumaric acid to L-malic acid is cut off, the maleic cis-trans isomerase from Serratia marcescens is then expressed, and the obtained genetically-engineered Escherichia coli can efficiently convert maleic matrix to synthesize high-purity fumaric acid, there is nearly no L-malic acid byproduct synthesized, and basis is provided for the industrialized production of fumaric acid by whole-cell process catalysis of maleic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Glucose isomerase and gene, mutant, engineering bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN104745563AIncrease productionSolve the problem of low optimum reaction temperatureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses a glucose isomerase, an encoding gene, a recombinant vector, a genetically engineered bacteria and a mutant thereof and an application of the glucose isomerase and the mutant thereof in preparation of D-fructose for catalyzing D-glucose isomerization. A recombinant escherichia coli capable of efficiently expressing high-temperature resistant glucose isomerase, provided by the invention, solves the problem of low optimal reaction temperature of a common glucose isomerase, is applied to production of the glucose isomerase and has the advantages of high yield, simple process and convenient industrial application; the strain can be directly used for the high fructose syrup production without cell disruption; after finishing fermentation, the total enzyme activity for D-fructose at the temperature of 90 DEG C is 414.3U / g, the conversion rate of D-fructose is 55.4%, the remnant enzyme activity at the temperature of 90 DEG C after storage for 24h is 68% and the equilibrium of reaction is shortened to 1.5h; a good technical support for the large-scale production of the high fructose syrup and for the use of high fructose syrup as an important food additive can be provided.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
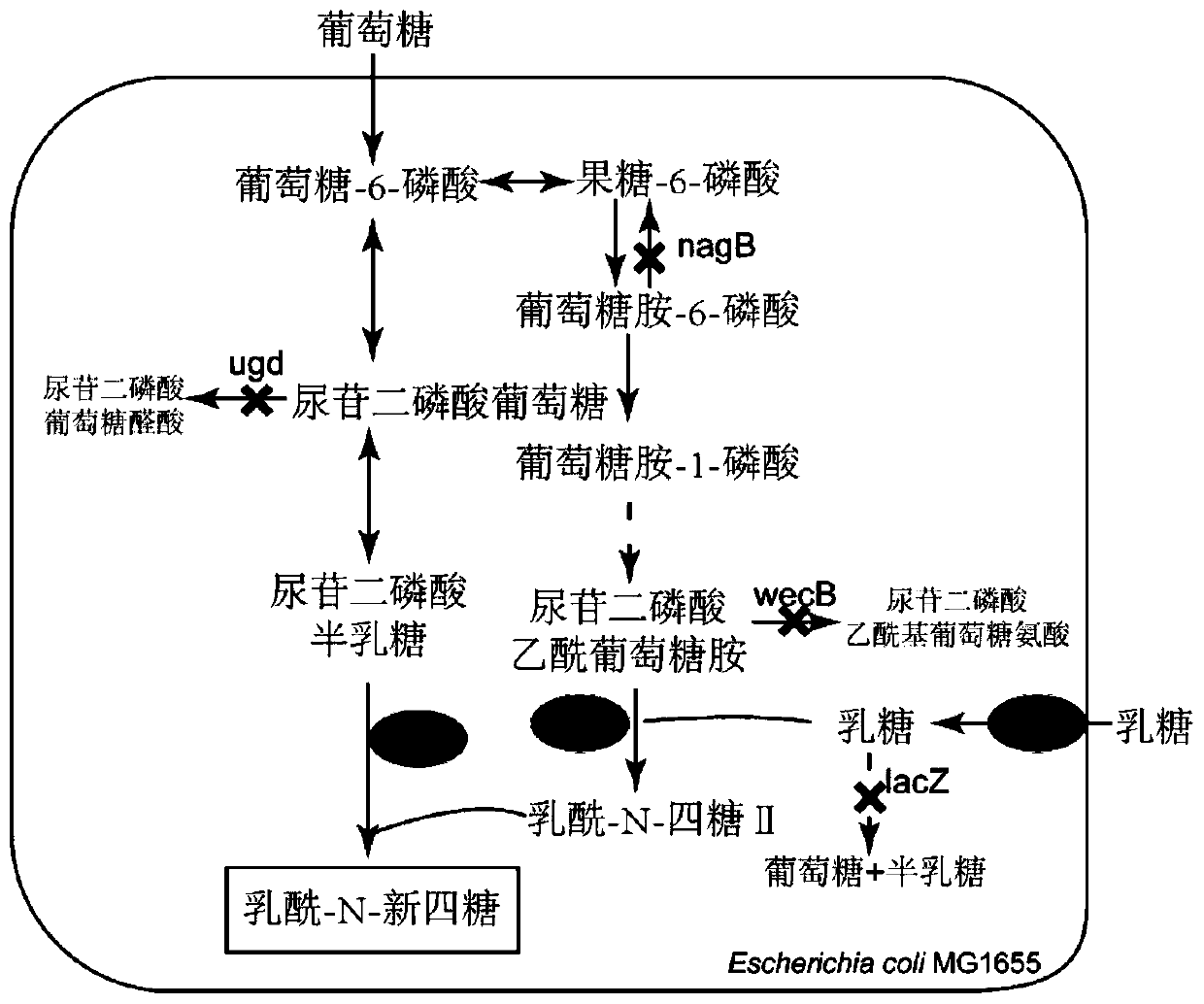
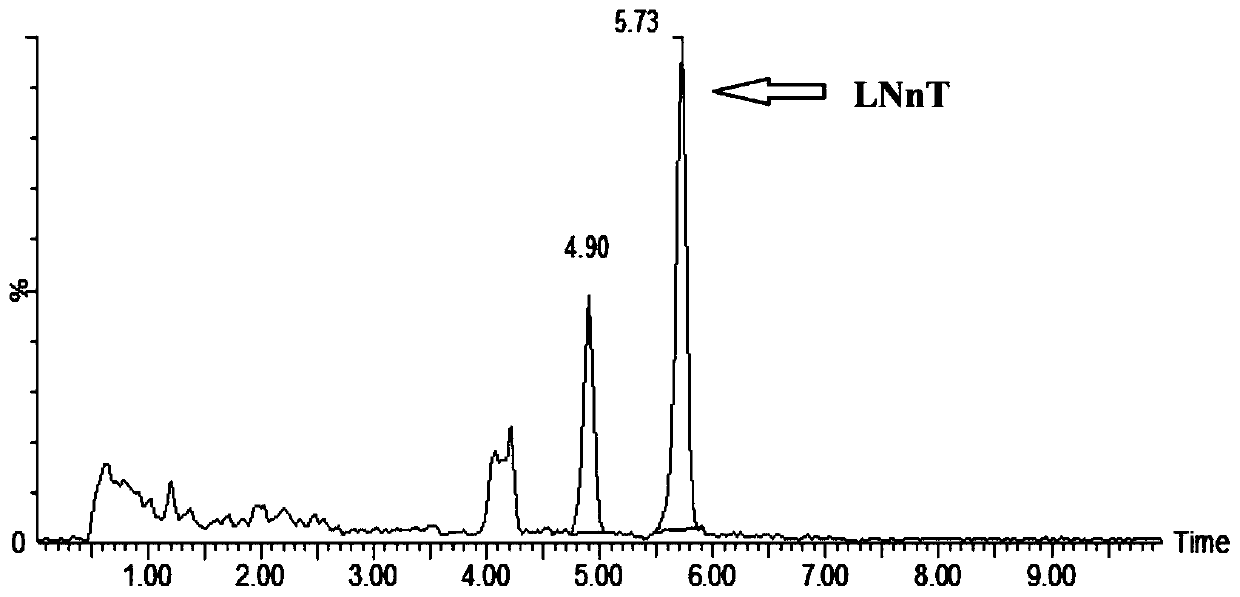
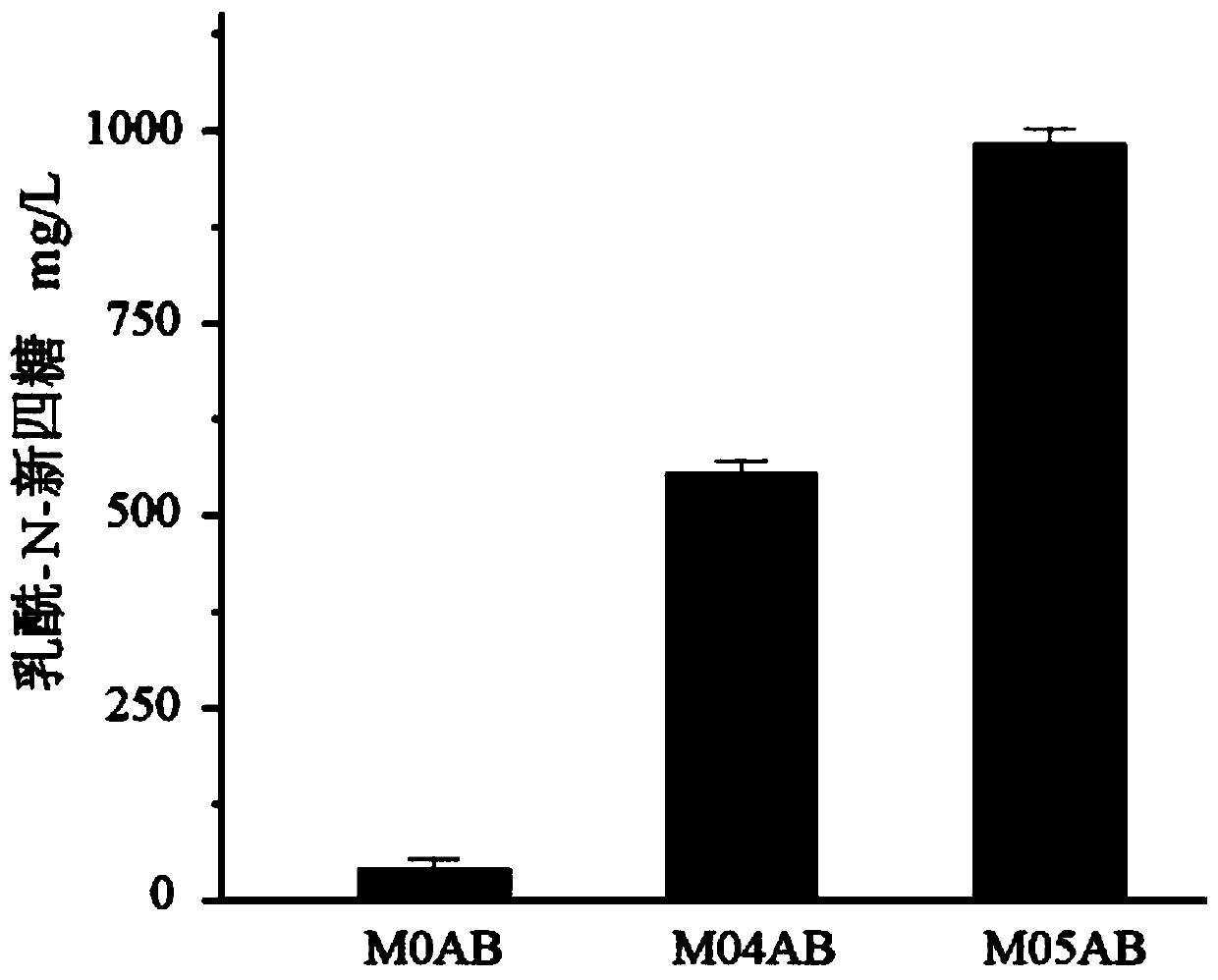
Recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing lactoyl N-neotetraose and construction method and application of recombinant escherichia coli
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli for synthesizing lactoyl N-neotetraose and a construction method and application of the recombinant escherichia coli. The recombinant escherichia coli are obtained by knocking out a beta-galactosidase lacZ gene, a glucosamine-6-phosphodeaminase nagB gene, a UDP-acetylglucosamine epitope isomerase wecB gene and a UDP-glucose dehydrogenase ugd gene in the host genome of escherichia coli and overexpressing a lactose transportase lacY gene, beta-1, 3-N-glucosaminidase lgtA gene and a beta-1, 4 galactosyltransferase lgtB gene on the genome. The yield of lactoyl-N-neotetraose synthesized by recombinant escherichia coli reaches 985 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for further metabolic engineering transformation of escherichia coli to produce lactoyl-N-neotetraose.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Thermostability transformation of maleic acid cis-trans isomerase and application thereof
ActiveCN106636052AImprove thermal stabilityIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHalf-lifeWild type
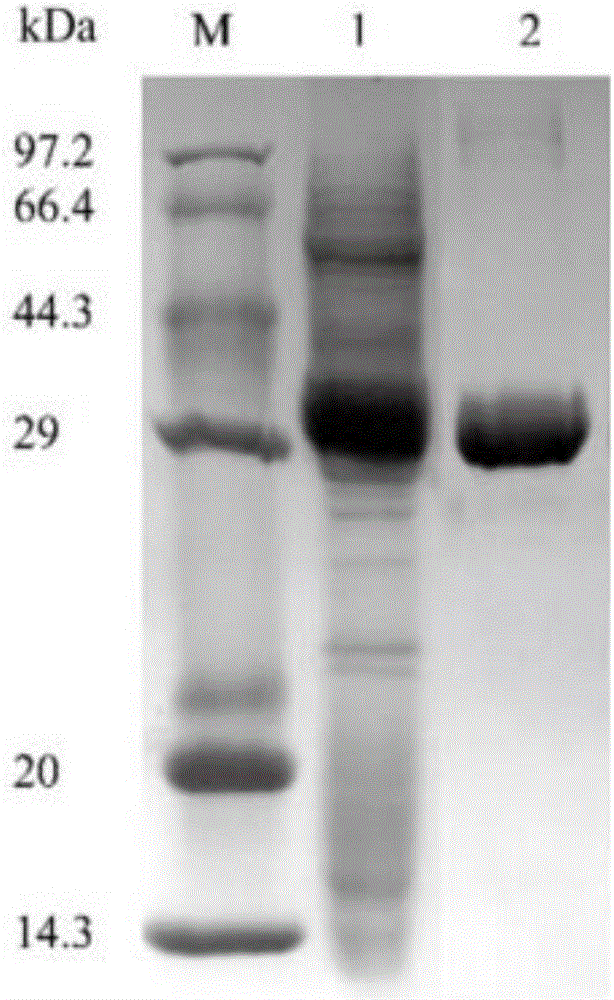
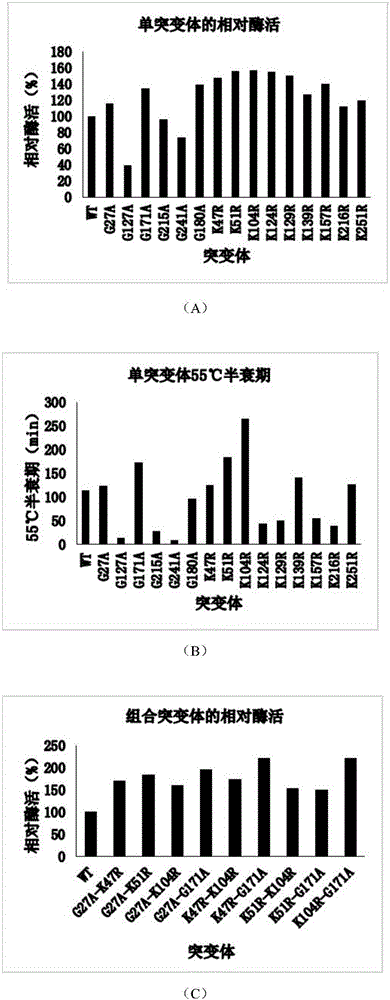
The invention discloses thermostability transformation of maleic acid cis-trans isomerase and application thereof, and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The maleic acid cis-trans isomerase gene maiA from serratia marcescens is subjected to thermostability transformation by a semi-rational design method. Compared with the wild maleic acid cis-trans isomerase, the obtained mutant has the advantages that the half-life period of the mutant G27A-G171A at 55 DEG C is 2.9 times of that of the wild type, and the enzyme activity is 1.96 times of that of the wild type; the half-life period of the mutant G27A-K104R is 4.18 times of the wild type at 55 DEG C, and the enzyme activity is 1.59 times of that of the wild type.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Phophomannose isomerase gene and its coded protein and use
The invention discloses a gene and its protein of phosphomannose isomerase, and its application. The purpose is that providing a gene and its protein of phoshomannose isomerase, and applying the gene and protein in selecting trans-genic plant. The gene has one of nucleotide sequences as follow: 1) the SEQ ID NO: 1 DNA sequence in sequence table; 2) coding the DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in the sequence table; 3) the nucleotide sequence that can hybrid with restrict DNA sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1 in the sequence table at high strict condition. Mannose has no harm for human and animal, degradation-liable in environment and selected marker system has the advantages of product yield safety, the selecting regent price is cheap, the selecting procedure is simplicity and the selected marker system don't impact the metabolism balance of transformation plant, the trans-genic plant grow vigorous, significance effect selection. The selected marker system has potential and extensive application outlook in trans-genic plant study and its market process; it may be the leading selected marker system in plant transformation.
Owner:龙域集团有限公司
Chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, method for constructing same and application of chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium
ActiveCN109486734AHigh molecular weightGood yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood additiveUridine diphosphate
The invention discloses a chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, a method for constructing the same and application of the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. Chondroitin synthetase genes and UDP (uridine diphosphate)-glucosamine isomerase genes are transferred into corynebacterium glutamicum to obtain the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium. The chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, the method and the application have the advantages that the corynebacterium glutamicum is used as a host for the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, is a GRAS (generally recognized as safe) strain affirmed by the Food and Drug Administration of the America, does not secreteoptional endotoxin or exotoxin, is safe and can be applied to producing amino acid or food additives and the like for a long term, and chondroitin produced by the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium is high in molecular weight and good in yield; the chondroitin yield of preferable recombinant bacteria of the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium can reach 3.7 g / L, chondroitin products with high molecular weights can be produced by the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium, and accordingly the chondroitin producing genetic engineering bacterium has anexcellent industrial prospect and can be effectively applied to medicines and health protection.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
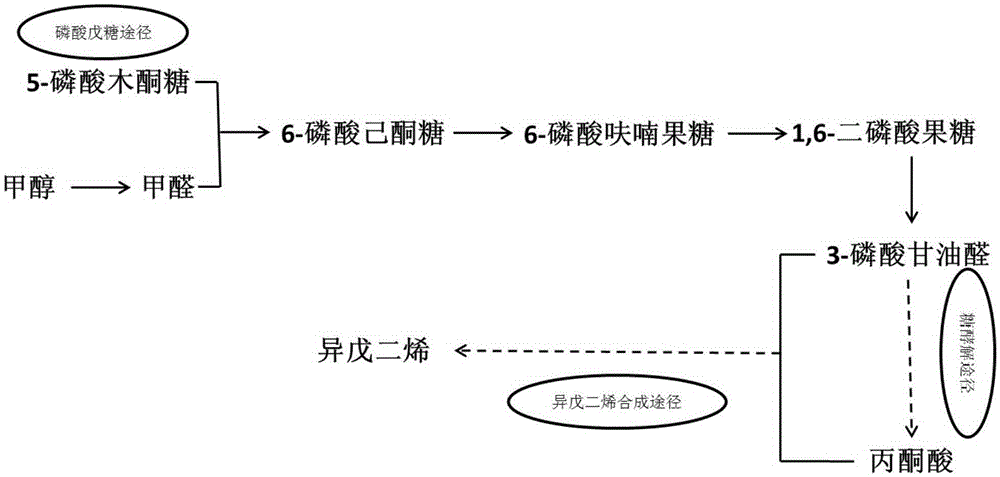
Escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria for preparing isoprene through catalytic methanol and preparation method and application of escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria
The invention discloses escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria for preparing isoprene through catalytic methanol and a preparation method and application of the escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. The escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria have the isoprene synthesizing approach, and meanwhile methanol dehydrogenase gene MDH, 3-hexulose-6-P synthase gene RmpA, 3-hexulose-6-P isomerase gene RmpB and methanol dehydrogenase activated protein gene Act are overexpressed. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a method and application method for establishing the escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria. The escherichia coli genetically engineered bacteria can biologically synthesize isoprene with methanol as the substrate and has the advantages of being high in conversion efficiency, low in production cost and the like; the conversion rate of methanol-isoprene can reach 21.83%.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for synthesizing lacto-N-neotetraose based on balanced UDP-sugar supply and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN109825465AIncrease productionEfficient synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlutamineTransferase Gene
The invention discloses a method for synthesizing lacto-N-neotetraose based on balanced UDP-sugar supply. Recombinant bacillus subtilis is obtained by integrating two beta-1,4-galactosyltransferases,integrating a glucose-6-phosphate isomerase gene, a glutamine-fructose-6-phosphate aminotransferase gene, a UTP-glucose-1-phosphate uridyl transferase gene and a UDP-glucose-epimerase gene, knocking out a UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase gene and exogenously expressing a beta-1,3-N-glucosamine transferase gene on a genome of a host bacterium bacillus subtilis 168 delta amyE: P43-lacY, P43-lgtB and PxylA-comK. The recombinant bacillus subtilis synthesizes the lacto-N-neotetraose, and the yield on a shake flask can reach 1800 mg / L, and the efficient synthesis of the lacto-N-tetraose is achieved.
Owner:BRIGHT DAIRY & FOOD
Glucose isomerase genes, encoding enzymes, vectors and engineering bacteria and application
InactiveCN104293759AIncrease productionEfficient expression resistant to high yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention discloses glucose isomerase genes, encoding enzymes, recombinant vectors and genetic engineering bacteria and application of glucose isomerase gene engineering bacteria in aspects of preparation of D-fructose by virtue of catalysis of D-glucose isomerization. According to the recombinant Escherichia coli for efficiently expressing high-temperature-resistant glucose isomerase, the problem that general glucose isomerase is low in optimal reaction temperature is solved; the glucose isomerase produced by using the strain has the advantages of high yield, simple process, convenient industrial application and the like, the strain can be directly used for producing high fructose syrup, and cell disruption is not needed; and moreover, after fermentation is ended, the total enzyme activity of D-glucose reaches 715U / L under the condition of 85 DEG C, and the conversion rate of the D-fructose is 55 percent, so that a good technical support is provided for performing large-scale production of the high fructose syrup and taking the high fructose syrup as an important food additive.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH +1
Glucose isomerase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN102443578ASolve technical problemsSignificant technological progressMicroorganism based processesIsomerasesBiotechnologyHalf-life
The invention discloses a glucose isomerase mutant and application thereof, belonging to the technical field of enzyme genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, a high temperature glucose isomerase gene (NCBI coding: CP000088) is obtained from total DNA of thermobifida fusca, and after site-directed mutagenesis, high efficiency expression of the glucose isomerase gene with a high conversion rate is realized, with the plasmid pT7-7 or a vector that can express glucose isomerase as an expression vector and E. coli BL21 (DE3) or a bacterial strain that can express glucose isomerase as an expression host; the glucose isomerase gene has altogether 1158 nucleotide and encodes 385 amino acids; expression plasmid is constructed in the invention, glucose isomerase is expressed through conversion of bacteria or yeast, and an obtained recombinase mutant has activity of glucose isomerase and has a conversion rate of 60% at a temperature of 70 DEG C, 7% higher than the conversion rate of a parent; optimum temperature of the recombinant glucose isomerase is 80 DEG C, an optimum pH is 10, and the half life of the recombinant glucose isomerase at a temperature of 70 DEG C is no less than 30 h. The recombinant glucose isomerase is particularly applicable to production of F55 high-fructose syrup in the industry of foodstuffs.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
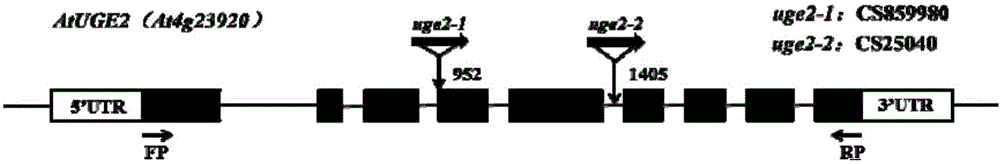
Application of arabidopsis thaliana gene At-UGE2, overexpression mutant strain and deletion mutant strain in plant character adjustment
The invention provides application of arabidopsis thaliana UDP-glucose 4-isomerase gene At-UGE2, an overexpression mutant strain 35S:UGE2 and a deletion mutant strain uge2 in adjustment of plant yield correlated characters, adversity resistance characters and the like. The function of biological synthesis and conversion of the UDP-glucose and UDP-galactose, which are catalyzed by UDP-glucose 4-isomerase, in adjustment of plant growth and development as well as adversity stress response is disclosed, a high-quality gene is provided for plant variety improvement, a new method and a new mechanism for improving plant yield characters and adversity resistance abilities are explained, and important economic significance and application value are achieved.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF BOTANY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Safflower chalcone isomerase (CHI) gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103820478AEasy to synthesizeReduce flavonoid contentGenetic engineeringFermentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidTransgene
The invention discloses a safflower chalcone isomerase (CHI) gene. The RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of safflower pedals is reversely transcribed into a cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid), the cDNA is used as a template to carry out 3' and 5' race cloning, the 3' and 5' end sequences of the safflower CHI gene are respectively obtained, a safflower CHI sequence is obtained through splicing of the 3' and 5' end sequences, the whole gene length is 1161bp, and the length of an opening reading frame is 654bp. The safflower CHI gene is named ct-(i)CHI( / i), and the result of the sequence comparison and analysis of the safflower CHI gene on ncbi (National Center for Biotechnology Information) shows that the homology of the gene with a dutchmanspipe root CHI gene reaches 82%. Experiments show that the synthesis of flavone can be promoted by the over-expression ct-(i)CHI( / i) gene, the flavone content can be lowered after the ct-(i)CHI( / i) gene is inhibited, and the safflower CHI gene has wide prospects in the aspect of cultivating high-content flavonoids transgenic plants.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
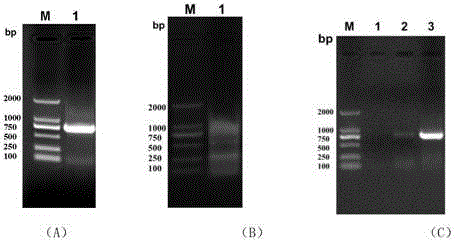
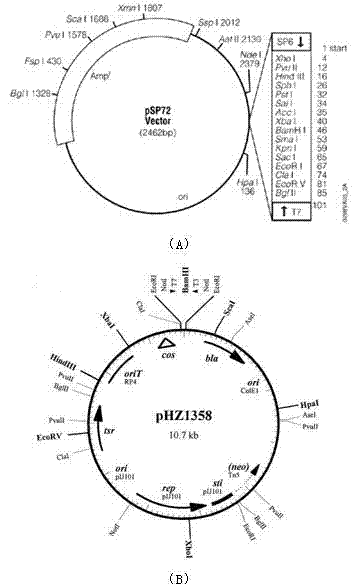
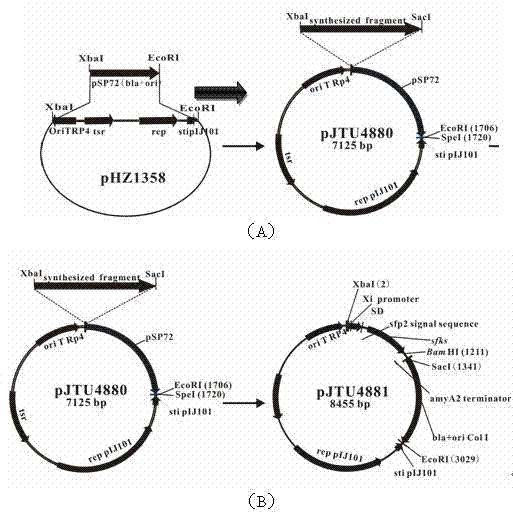
Construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids and production method for keratinase
InactiveCN102533833AIncrease productionHydrolasesVector-based foreign material introductionAmylaseSrc family kinase
The invention relates to a construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids and a production method for keratinase. The construction method for streptomycete expression plasmids includes the following steps: a promoter Xi of actinoplanes missouriensis xylose isomerase and a terminator of streptomycete avermitilis amylase are sleeved, and the promoter-shine-dalgarno (SD) sequence comes from 90 to 269bp of an actinoplanes missouriensis xylose isomerase gene; a cloned src family kinases (sfks) gene is inserted in a construction expression frame structure of a synthetic Xi promoter-SD-amyA2 terminator fragment, and then a conventional method is used for constructing the streptomycete expression plasmids. The production method for keratinase includes: leading the streptomycete expression plasmids into an expression host of streptomycete lividans TK24 through conjugal transfer, performing recombinant expression and generating the keratinase. Specific activity of a crude enzyme solution is 1700 U / mg after expression of the expression plasmids in the streptomycete lividans TK24 and is improved by 50 times compared with specific activity of starting strain streptomycete fradiae varieties S-221, and yield of the keratinase is much higher than starting strains after the expression.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
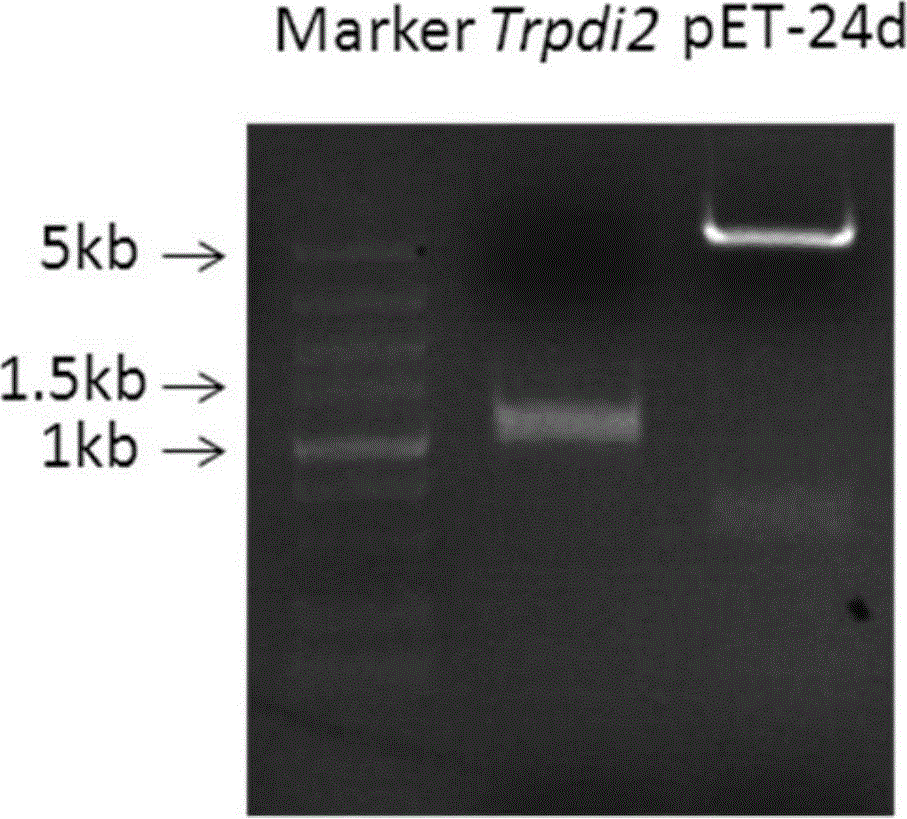
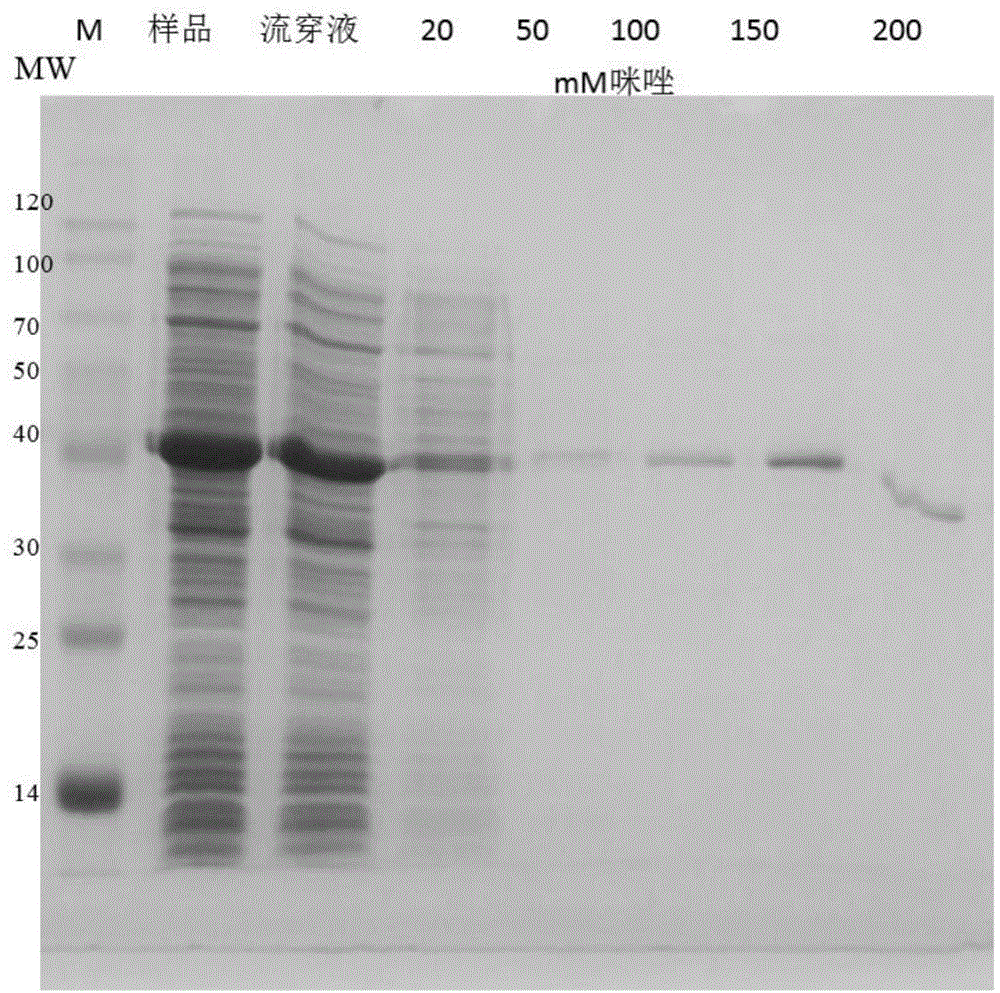
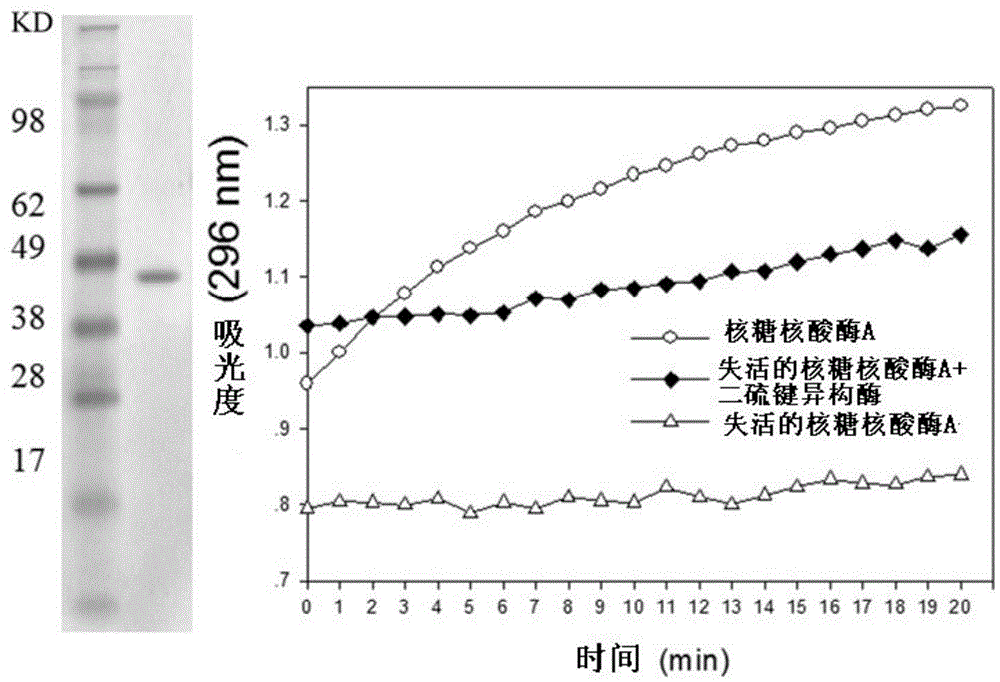
Disulfide bond isomerase gene Trpdi2 from Trichoderma reesei and application thereof
InactiveCN104694560AActivity recovery or maintenanceIncrease productionIsomerasesFermentationBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a disulfide bond isomerase gene Trpdi2 from Trichoderma reesei and application thereof. The disulfide bond isomerase gene separated from Trichoderma reesei has a polynucleotide sequence of (a) (b) or (c): (a) a polynucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID No.1; (b) a polynucleotide sequence complementary with the polynucleotide sequence in (a) according to the principle of complementary base pairing; and (c) a cDNA sequence of the polynucleotide sequence (a)shown in the SEQ ID NO.1 or (b) polynucleotide sequence: a polynucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The invention also obtains disulfide isomerase the from the encoding of the disulfide bond isomerase gene separated from the Trichoderma reesei and verifies the application of disulfide isomerase.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
A genetically engineered strain for efficiently secreting d-psicose 3-epimerase, its construction method and its application
ActiveCN105602879BSimple purification processLow production costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBio engineeringRumen
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and particularly relates to a genetic engineering strain capable of effectively secreting D-psicose 3-epimerase and a construction method thereof. A D-psicose 3-epimerase gene rdpe from rumen bacterium Ruminococcus sp. 5_1_39B_FAA is obtained firstly, recombinant plasmid pMA5-RDPE construction and bacillus subtilis conversion are conducted, and then constitutive and secretive expression of RDPE in bacillus subtilis is achieved. By comparing three glucose-induced promoters, the optimal inducible promoter P[xylA] is obtained, and the RDPE secretion level is increased remarkably. By knocking out the xylose utilization gene xylAB (xylA and xylB), the xylose metabolism pathway of bacillus subtilis is blocked, the secretion amount of RDPE is further increased, and the optimal induced concentration of the inducer xylose is reduced to 0.5% from 4.0%. Finally, the engineered strain 1A751SD-XR is evaluated in a 7.5 L fermentation tank, and the RDPE secretion level can be as high as 95 U / mL and 2.6 g / L.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
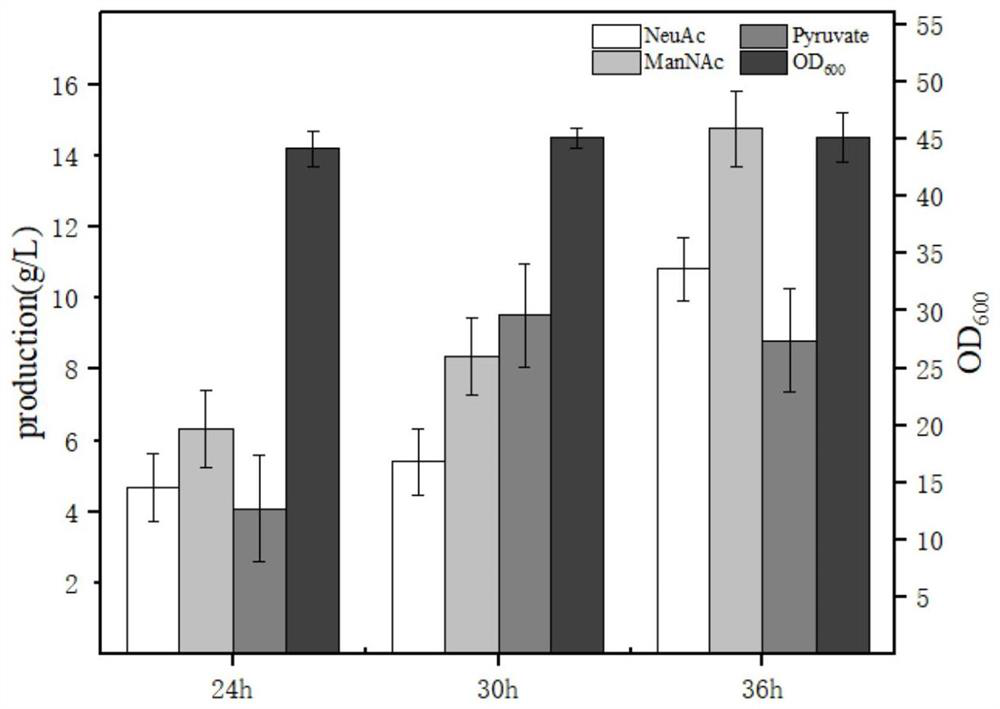
Engineering strain for xylose-induced production of N-acetylneuraminic acid and application of engineering strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering and particularly relates to construction and application of a genetic engineering strain for xylose-induced production of N-acetylneuraminic acid. According to the construction and the application, a N-acetylglucosamine synthesis way is integrated with a genome, a N-acetylglucosamine 2-epimerase gene bAGE and a N-acetylneuraminicacid lyase gene shNAL are introduced, a N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is constructed, and a key gene nanTEK of a catabolism way of the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is knocked out. Meanwhile, metabolic ways of precursor substances required for synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid are subjected to multicopy strengthening, and part of bypath metabolic ways are subjected to knockout, so that the N-acetylneuraminic acid high yielding strain is obtained. In case of shake-flask fermentation for 36h, the yield of the N-acetylneuraminic acid can reach 10.8g / L to the maximum, the production intensity can reach 0.3g / (L*h) which is the maximum value reported at present, and thus, the engineering strain has an important industrial application value.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
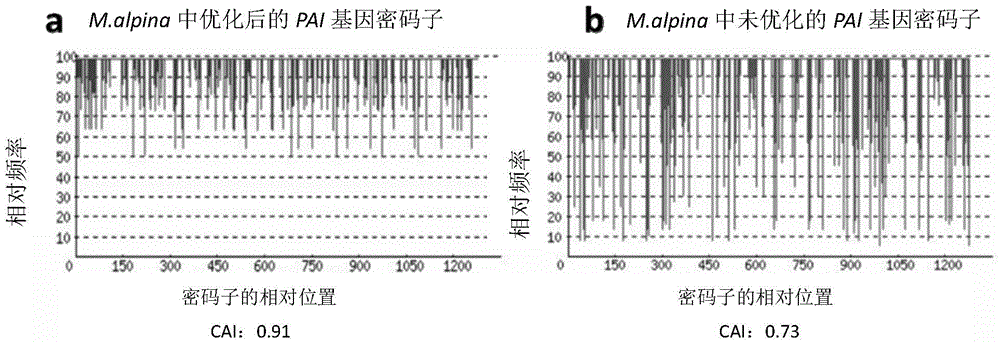
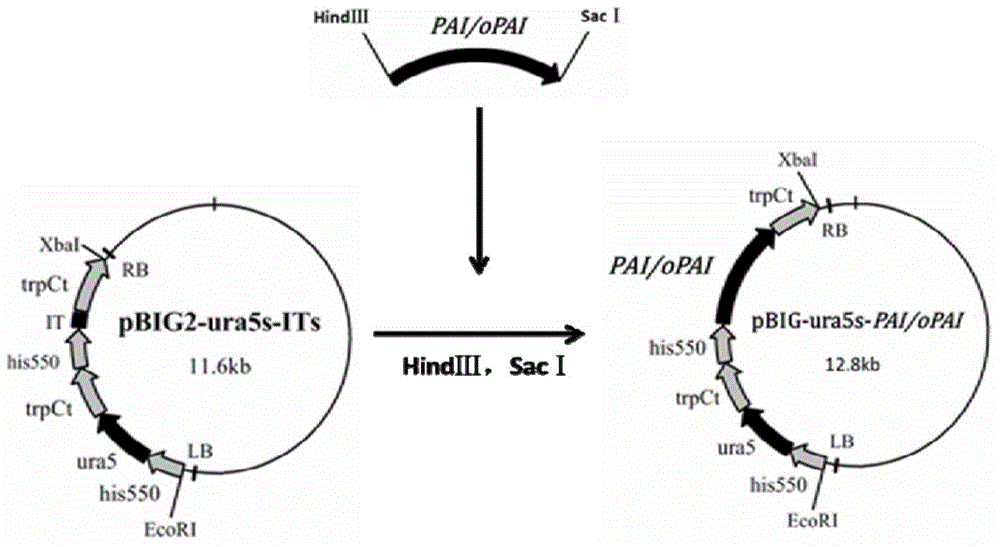
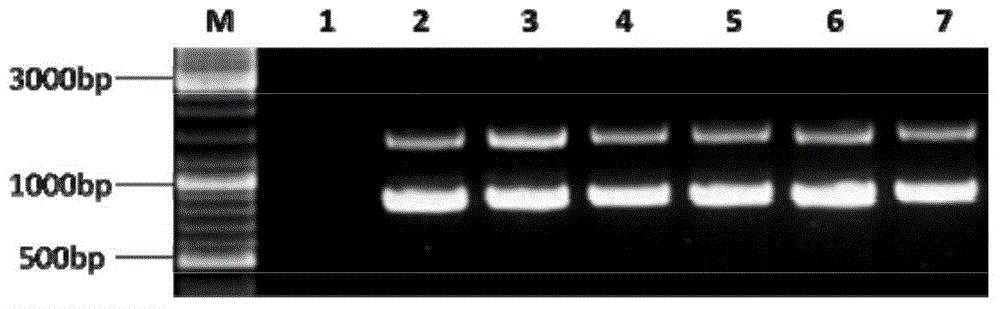
Recombinant mortierella alpina strain for heterologous expression of linoleic acid isomerase gene and construction method thereof
The invention provides recombinant mortierella alpina oPAI for heterologous expression of linoleic acid isomerase gene from propionibacterium acnes and provides a method for constructing a recombinant mortierella alpina strain for heterologous expression of linoleic acid isomerase gene from propionibacterium acnes, and the invention further provides a use of the recombinant mortierella alpina strain for producing fatty acid, namely biological synthesizing conjugated linoleic acid. With mortierella alpina uracil auxotroph strain MAU1 as a material, a recombinant strain for heterologous expression of linoleic acid isomerase gene from propionibacterium acnes is successfully constructed, and a target product conjugated linoleic acid is detected in the recombinant strain added with long-chain acyl-coenzyme A for synthesizing an enzyme inhibitor.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com