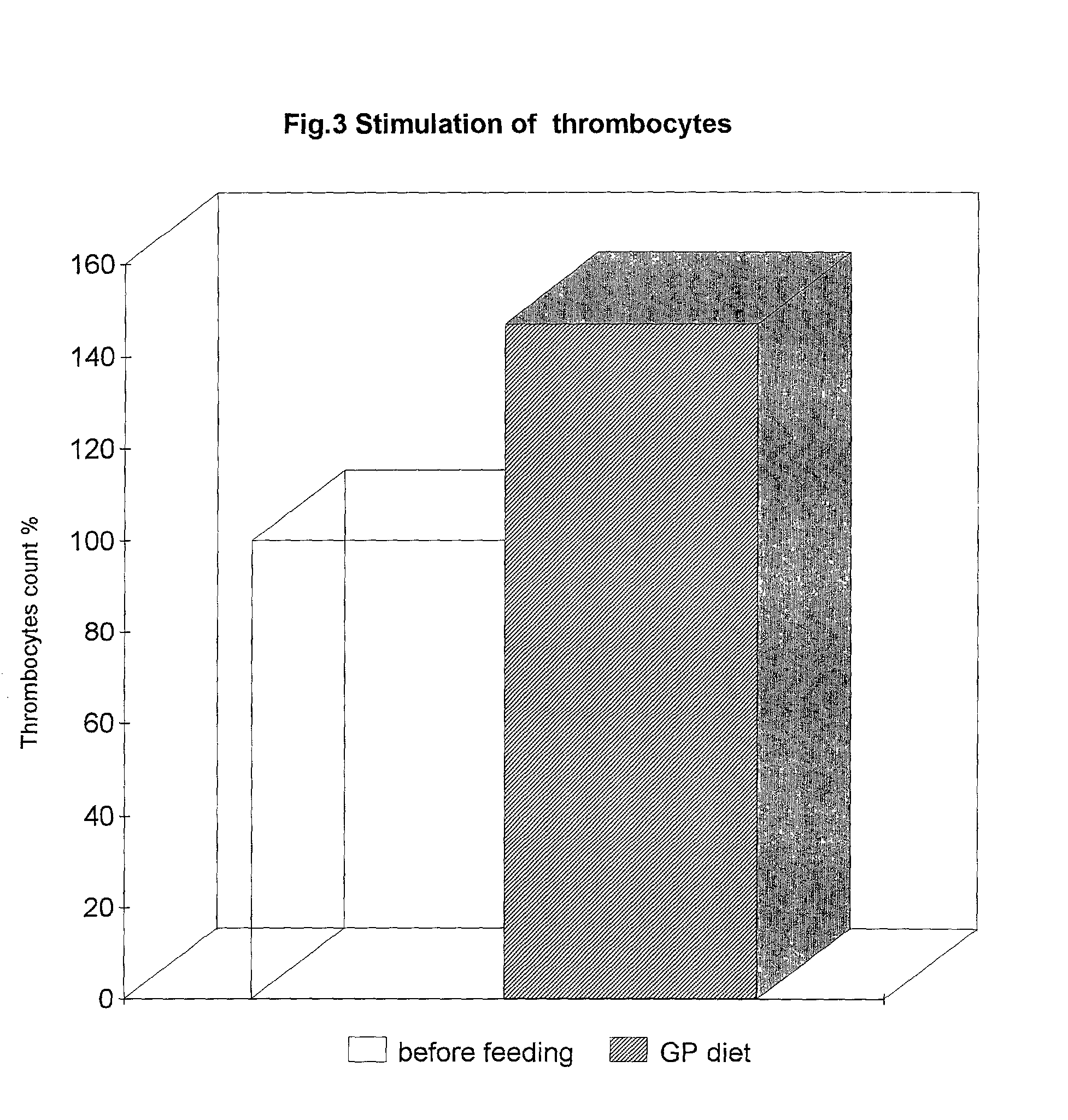
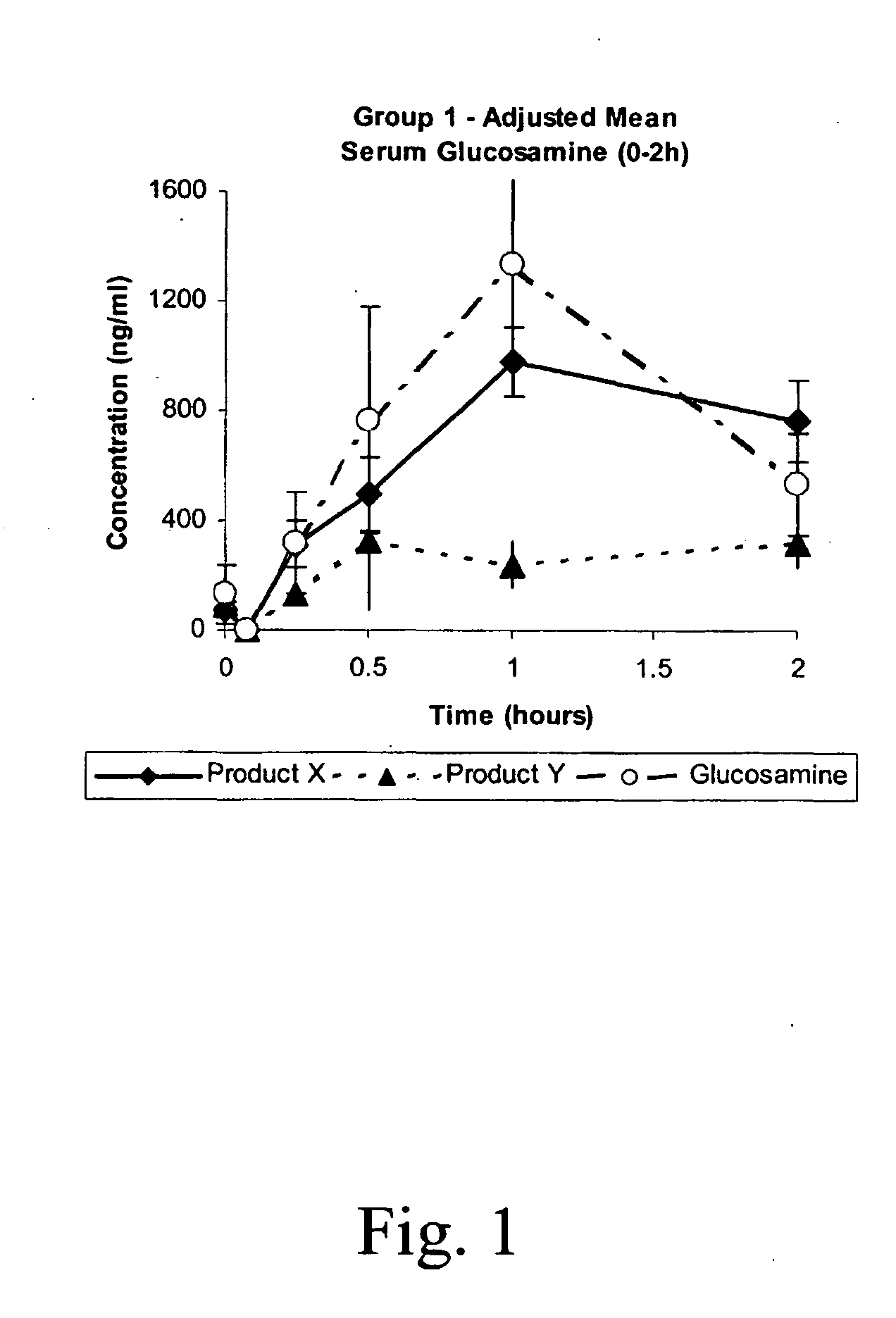
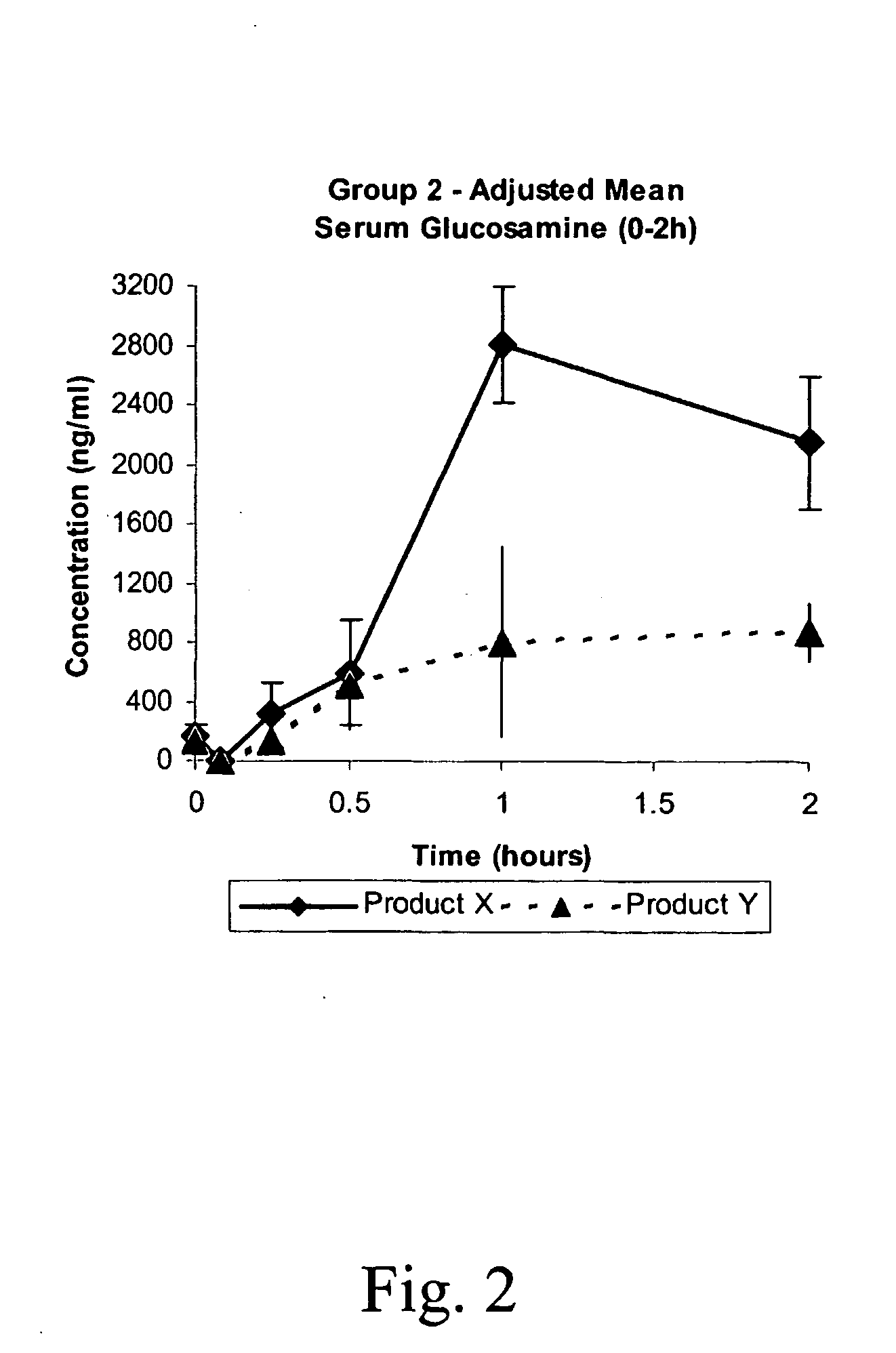
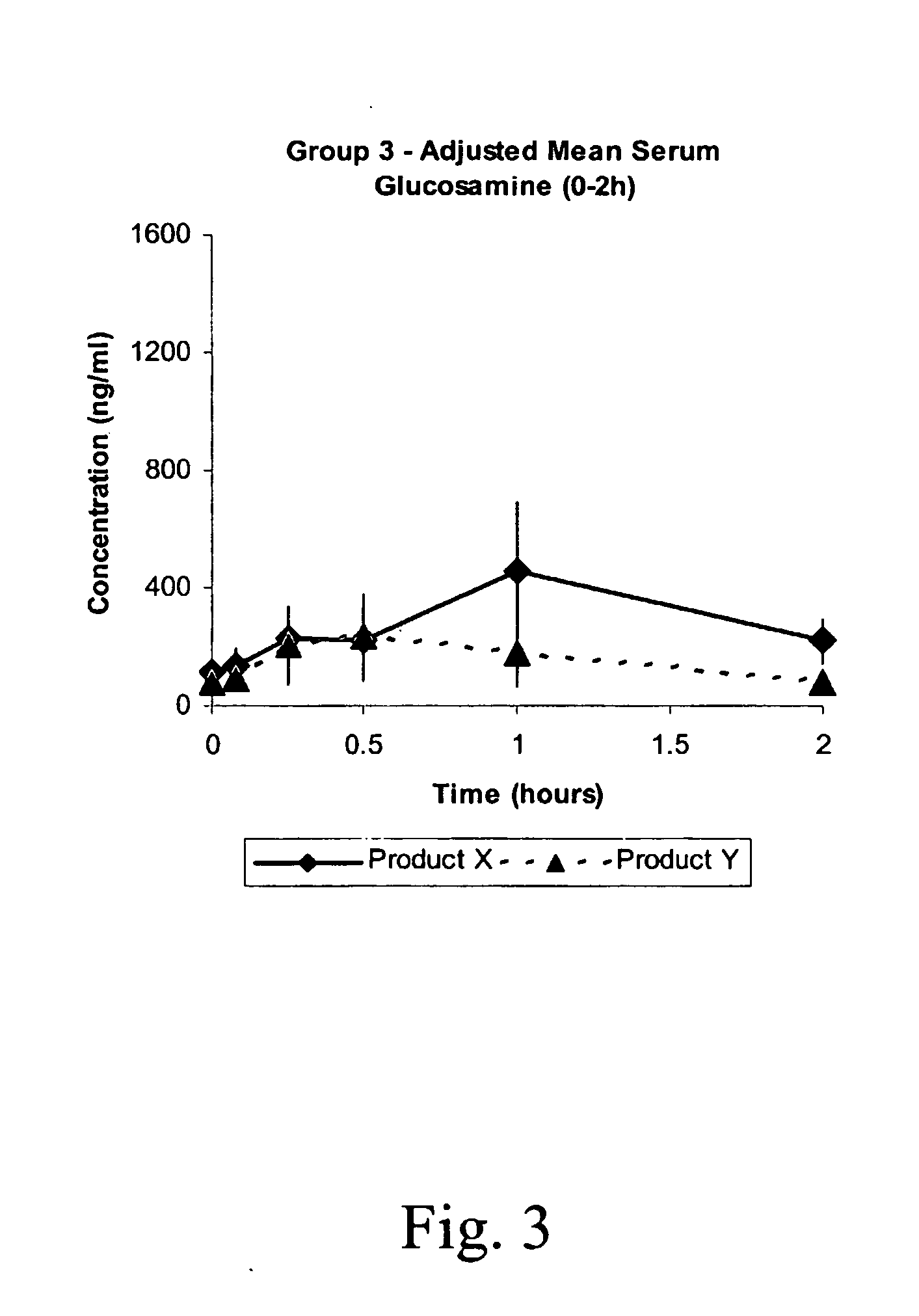
Patents
Literature
107 results about "N acetyl glucosamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Dietary regimen of nutritional supplements for relief of symptoms of arthritis
InactiveUS6136795AReduce inflammationPermits healingBiocideAcidic food ingredientsDocosahexaenoic acidRegimen
This invention is directed to a dietary regimen and a unique combination of nutritional supplements and a method. More specifically, this invention is directed to a unique combination of nutritional supplements which provides symptomatic relief from arthritis. The unique combination of nutritional supplements of this invention is believed to function by both increasing the available (effective blood level) of anti-inflammatory agents and promotion of the healing / regenerative process in the effected joints, thus, producing unexpected and lasting symptomatic relief from the debilitating effects of both osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. The essential nutritional supplements of the dietary regimen of this invention are as follows: (a) gamma linolenic acid (unrefined), hereinafter "GLA"(b) a mixture of eicosapentaenoic acid and docosahexaneoic acid, hereinafter collectively "EPA"(c) a mixture of chondroitin sulfate, N-acetyl glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine sulfate and manganese aspartate, hereinafter collectively "CHONDROX"The regimen is adjusted based upon the weight of the individual, and once symptomatic relief is achieved, the individual remains essentially free from the debilitating effects of arthritis so as long the daily regimen is faithfully followed.
Owner:IRWIN NATURALS 4HEALTH INC +1
Combined energy and topical composition application for regulating the condition of mammalian skin
InactiveUS20080031833A1Improve the situationEasy to superviseCosmetic preparationsBiocidePersonal careSalicylic acid
Method for regulating the condition of mammalian skin comprising the steps of applying a first personal care composition to an area of skin where regulation is desired, wherein the first personal care composition comprises at least one skin care active selected from the group consisting of niacinamide, salicylic acid, peptides, N-acetyl glucosamine, panthenol, butylated hydroxytoluene, N-acyl amino acid compounds, hexamidine, green tea, ascorbyl glucoside, hexanediol, pentanediol, a skin lightening agent, a heat shock protein potentiator, and mixtures thereof, and delivering energy to the area of skin by contacting the skin with an energy delivery device for a treatment period of at least 2½ minutes, wherein the energy delivery device comprises a skin-contacting surface that is controllably heatable to a temperature of from 37° C. to 50° C.
Owner:THE PROCTER & GAMBLE COMPANY
Novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103602627AEnhanced rate-limiting enzyme gene expressionPrevent backflowBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphate
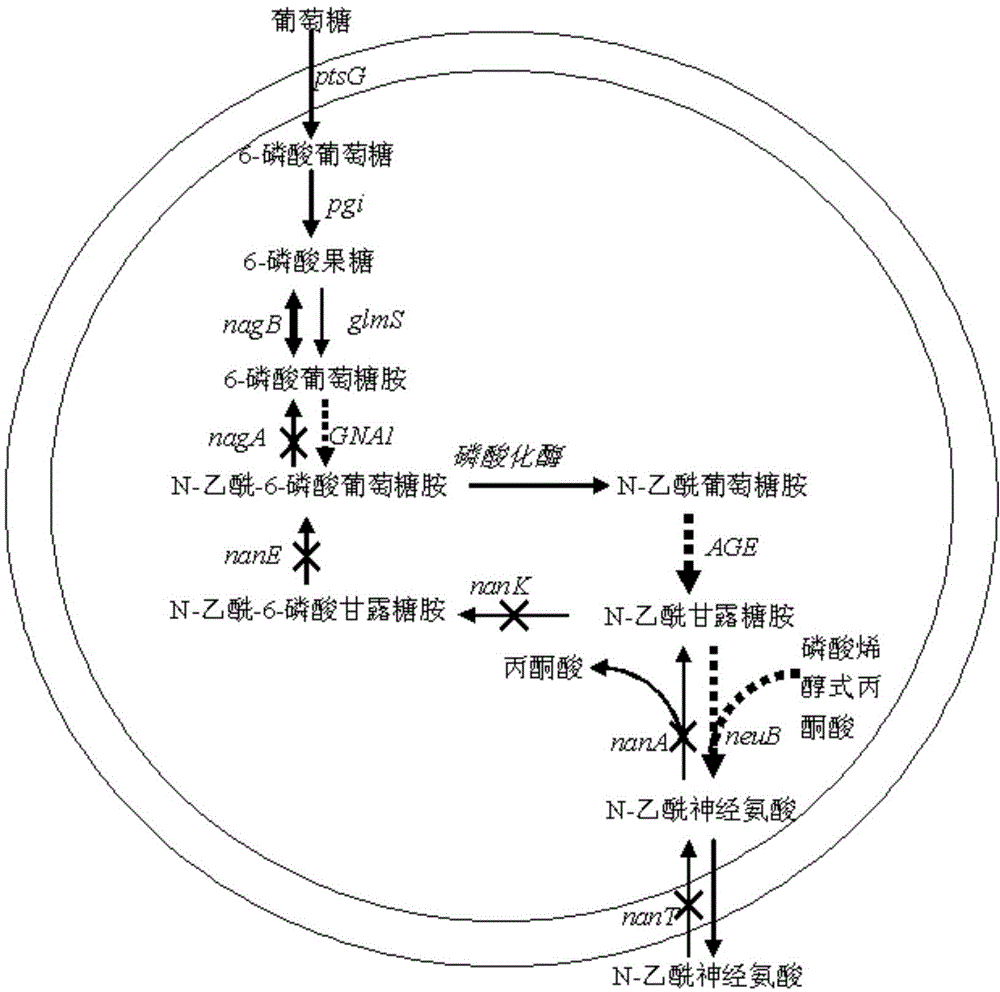
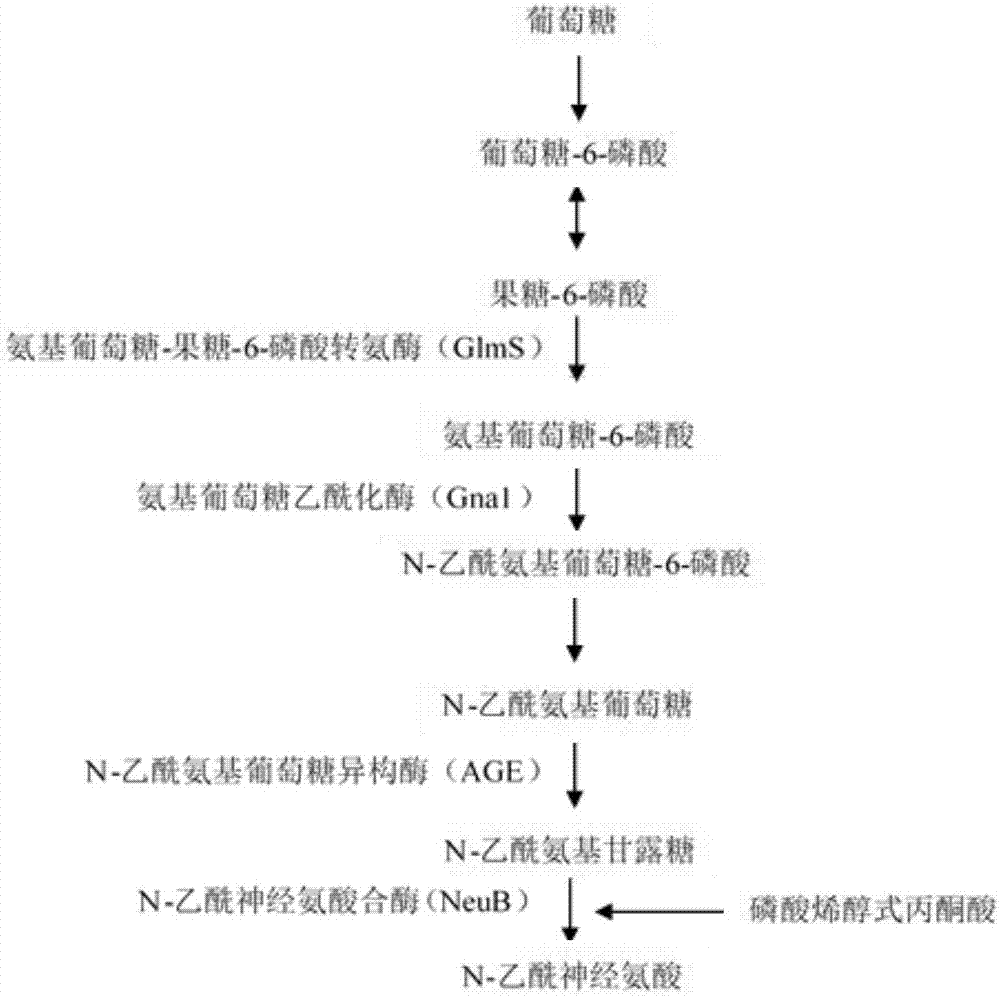
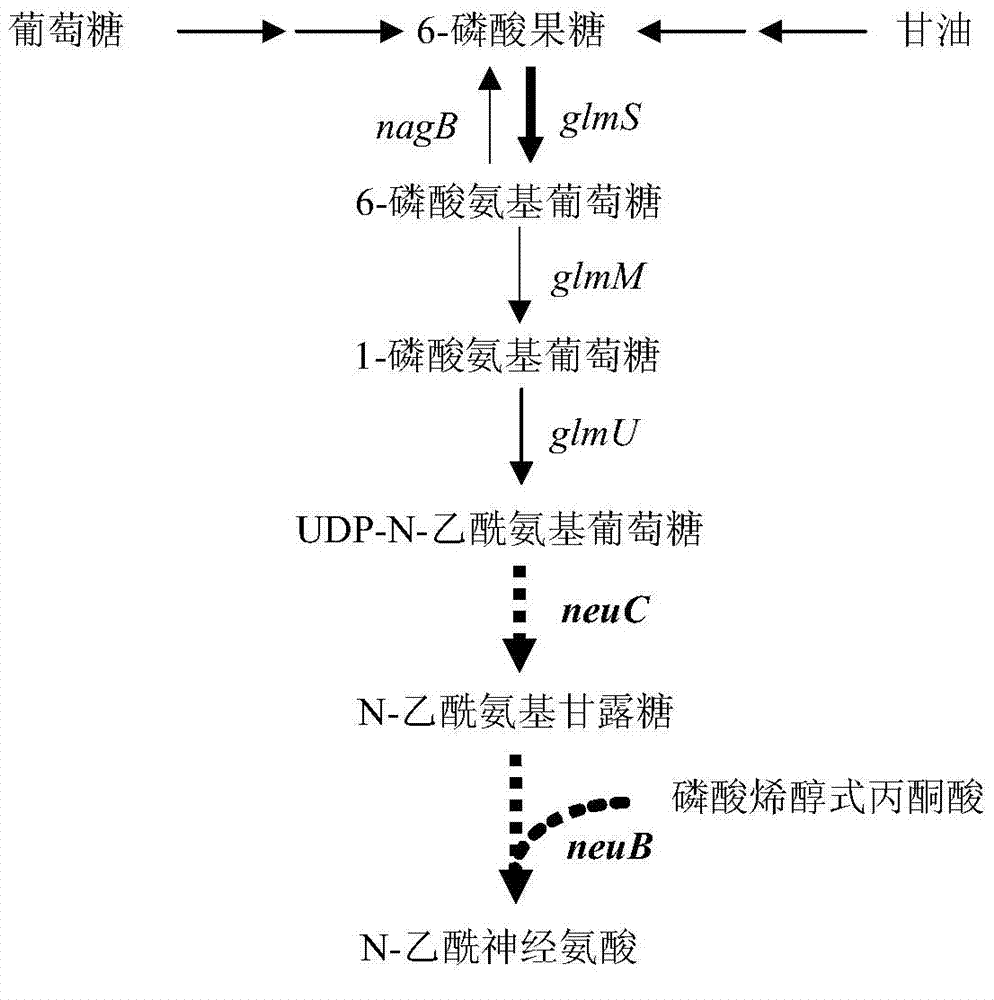
The invention discloses novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as a construction method and application thereof. The engineering bacterial is constructed by introducing an encoded 6-glucosamine phosphate acetylase gene, an N-acetyl glucosamine-2-isomerase gene and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene into escherichia coli to express, carrying out strengthened expression on 6-glucosamine phosphate deaminase gene contained in the escherichia coli per se and knocking off genes, for decomposing and utilizing enzyme in metabolic pathways, of the N-acetylneuraminic acid in the engineering bacteria. The engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention can be used for fermentation culture to synthesize the N-acetylneuraminic acid by using glucose or glycerinum as a substrate.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Modified antibody, antibody-conjugate and process for the preparation thereof
ActiveUS20150258210A1Reduced potencyDamage bindingImmunoglobulins against growth factorsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFucosylationAntibody conjugate
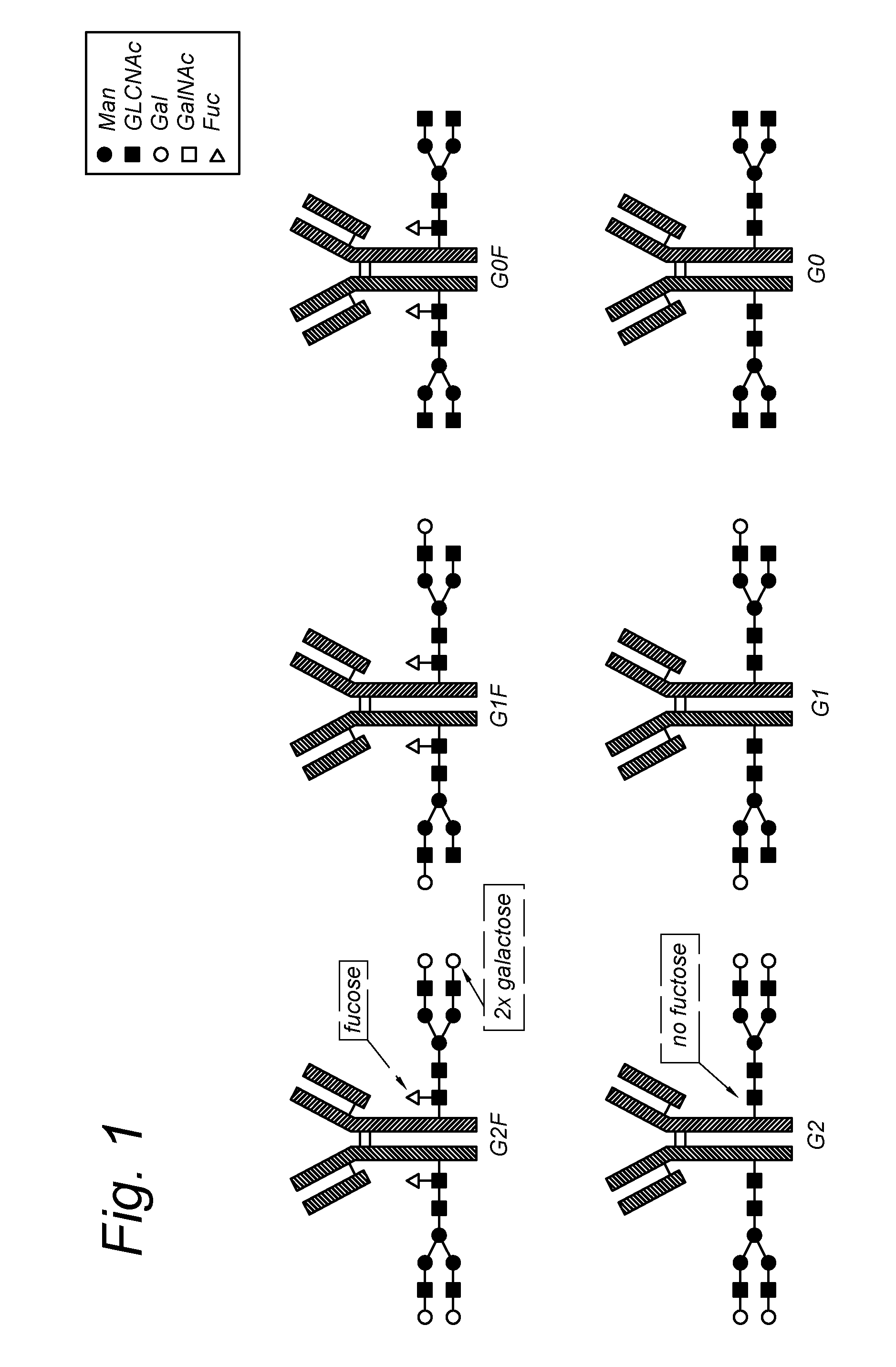
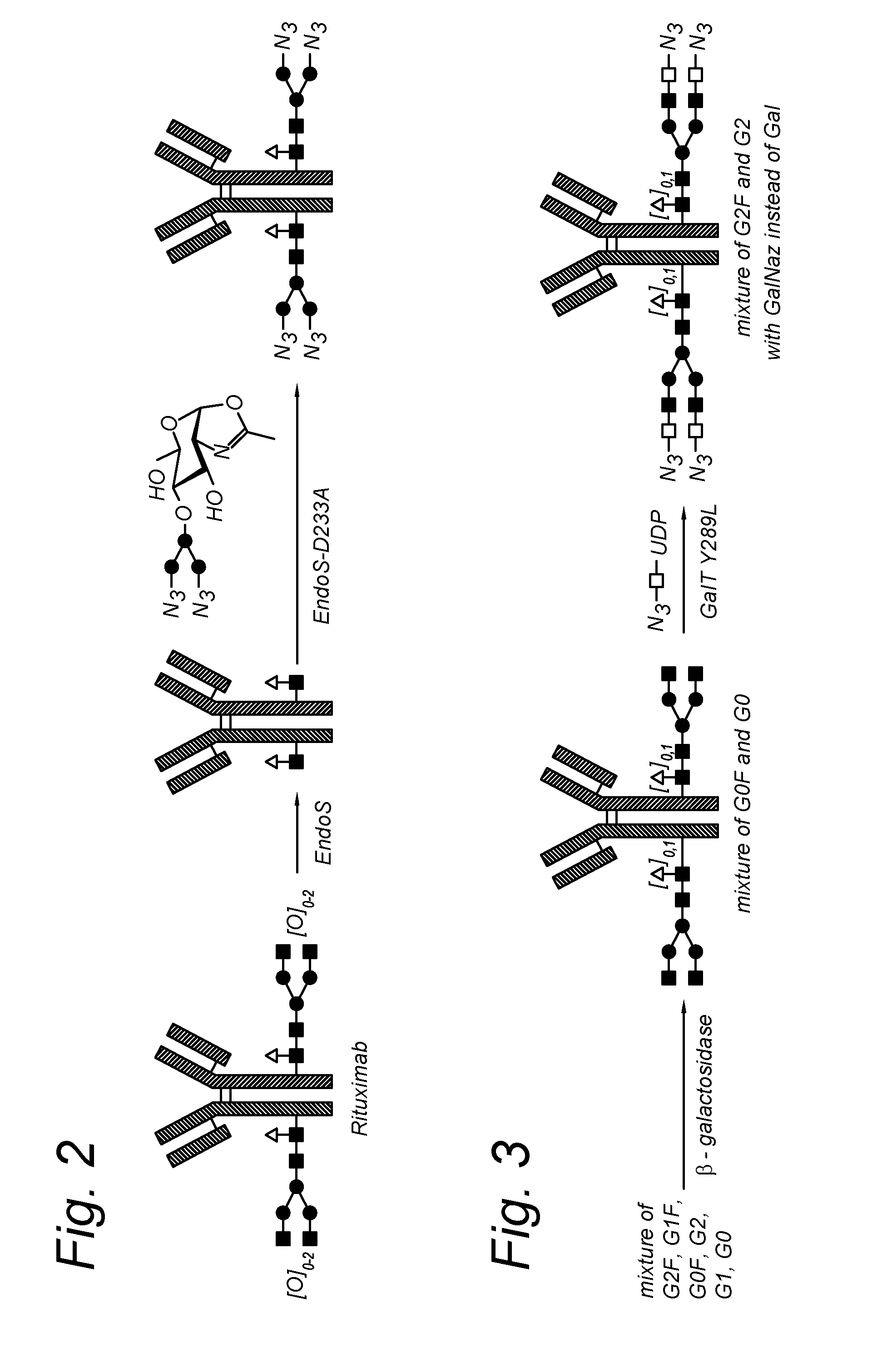
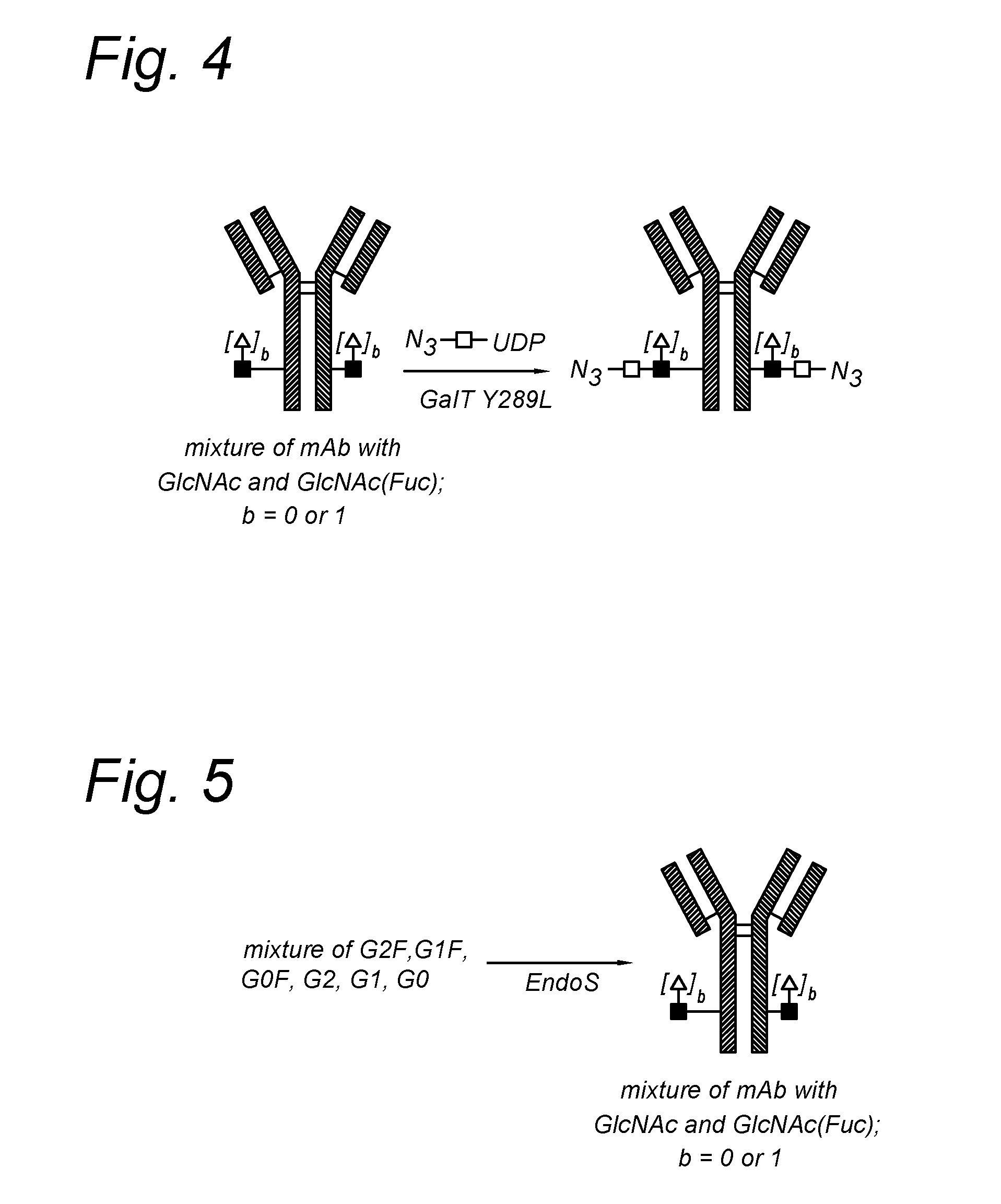
The present invention relates to an antibody comprising a GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent, wherein S(A)x is a sugar derivative comprising x functional groups A wherein A is independently selected from the group consisting of an azido group, a keto group and an alkynyl group and x is 1, 2, 3 or 4, wherein said GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent is bonded to the antibody via CI of the N-acetylglucosamine of said GlcNAc-S(A)x substituent, and wherein said N-acetylglucosamine is optionally fucosylated. The invention also relates to an antibody-conjugate, in particular to an antibody-conjugate according to the Formula (20) or (20b), wherein AB is an antibody, S is a sugar or a sugar derivative, D is a molecule of interest, and wherein said N-acetylglucosamine is optionally fucosylated (b is 0 or 1). The invention further relates to a process for the preparation of a modified antibody, to a process for the preparation of an antibody-conjugate, and to said antibody-conjugate for use as a medicament. In addition, the invention relates to a kit of parts comprising an azide-modified antibody and a linker-conjugate, wherein said linker-conjugate comprises a (hetero)cycloalkynyl group and one or more molecules of interest.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
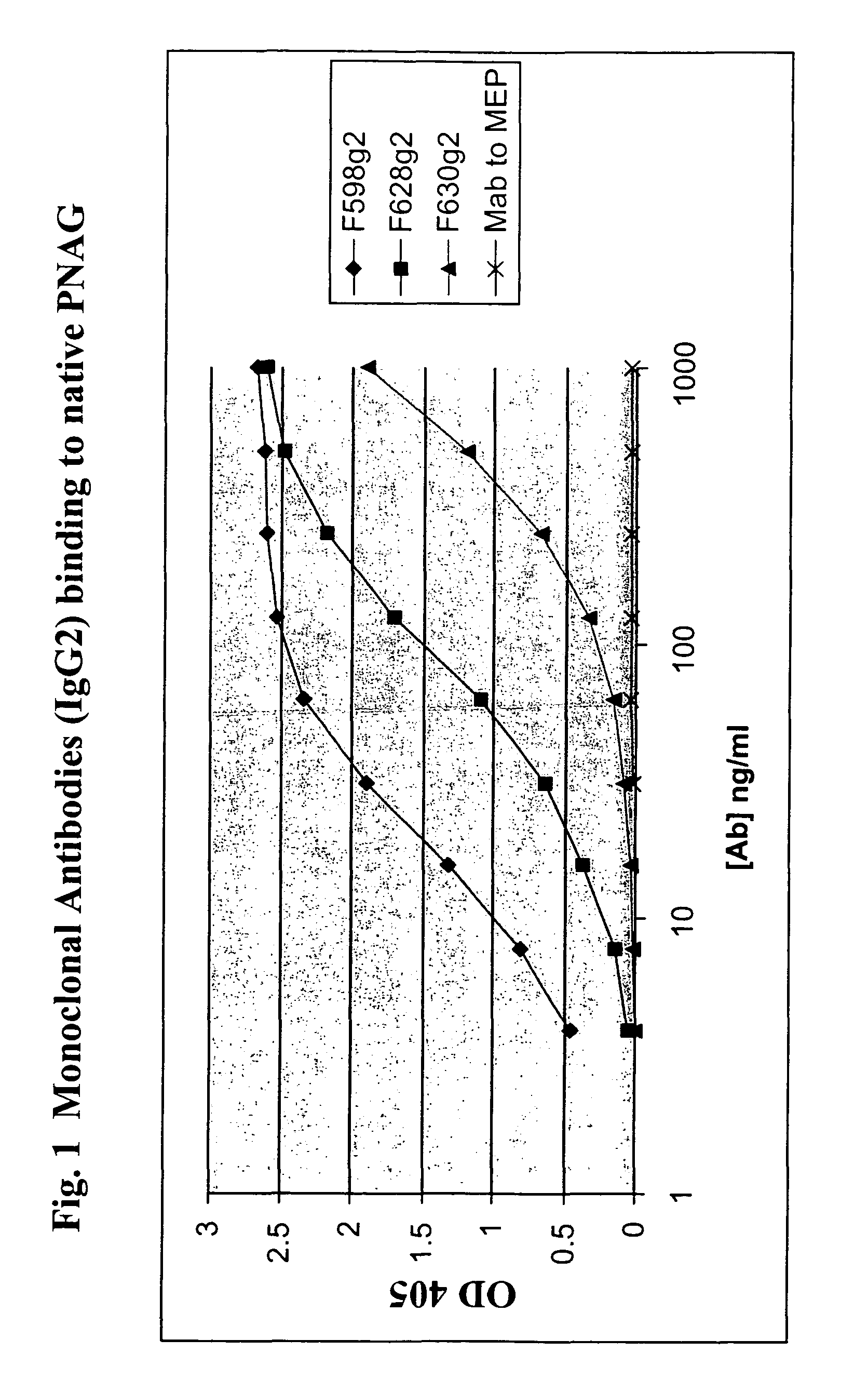
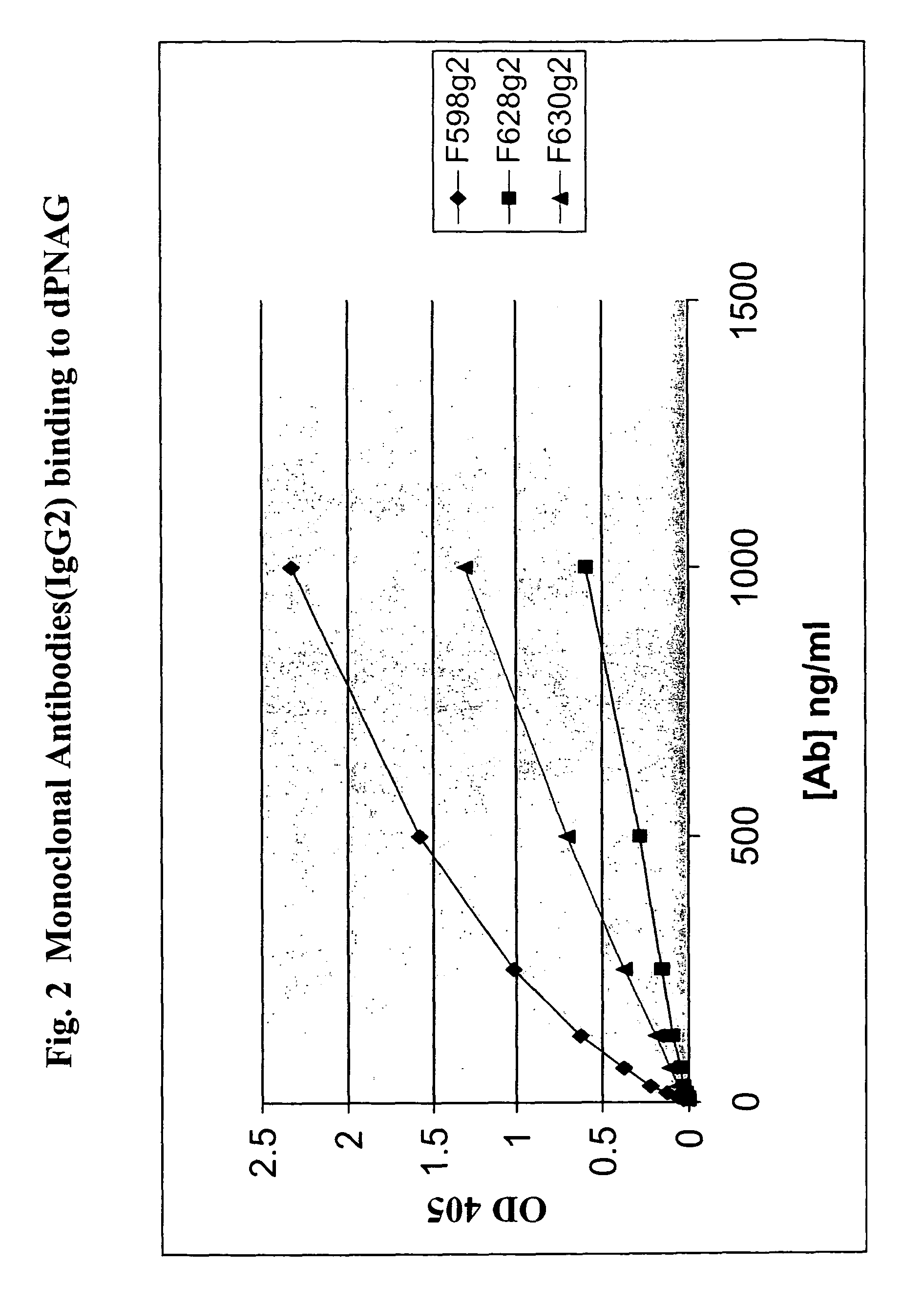
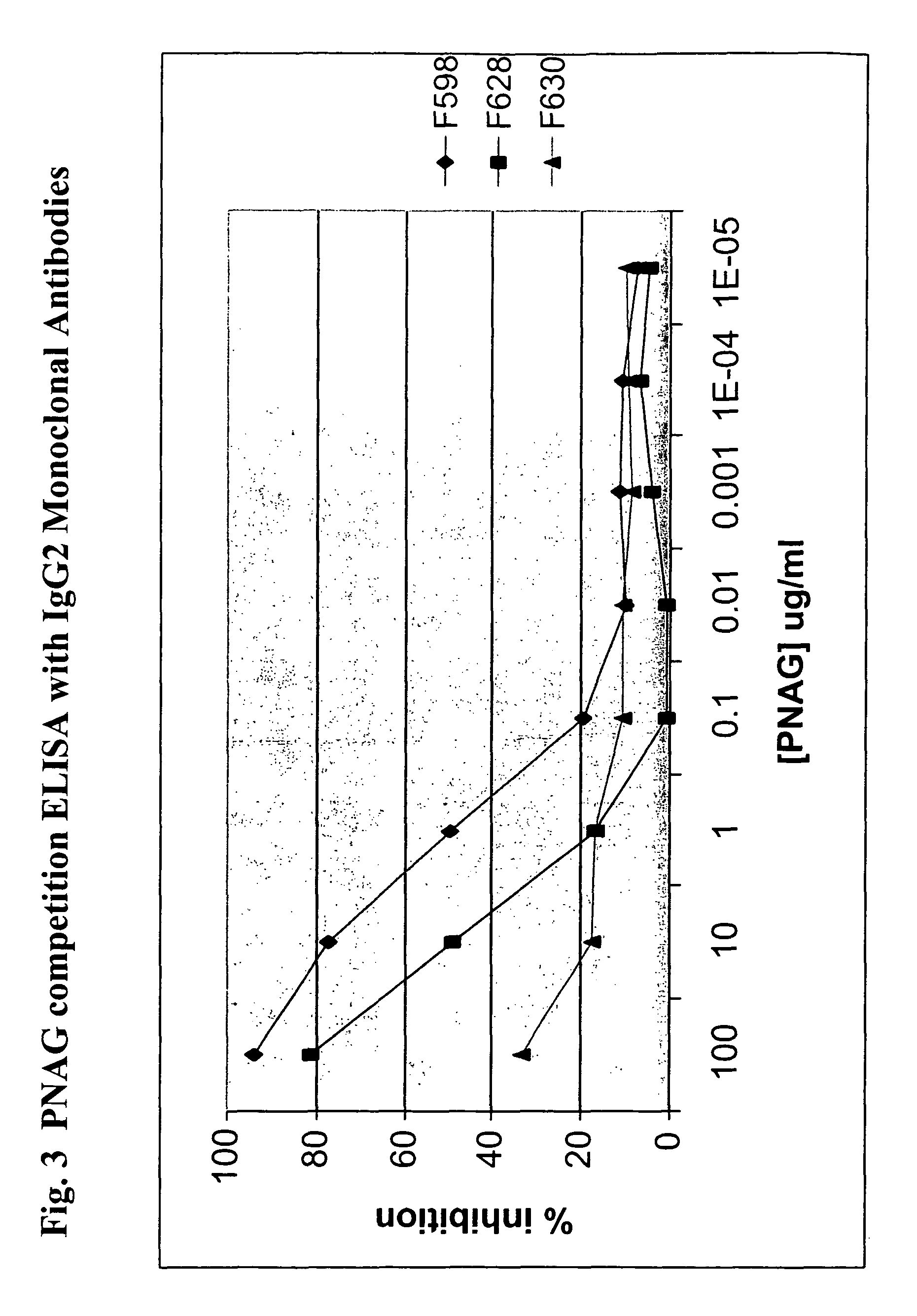
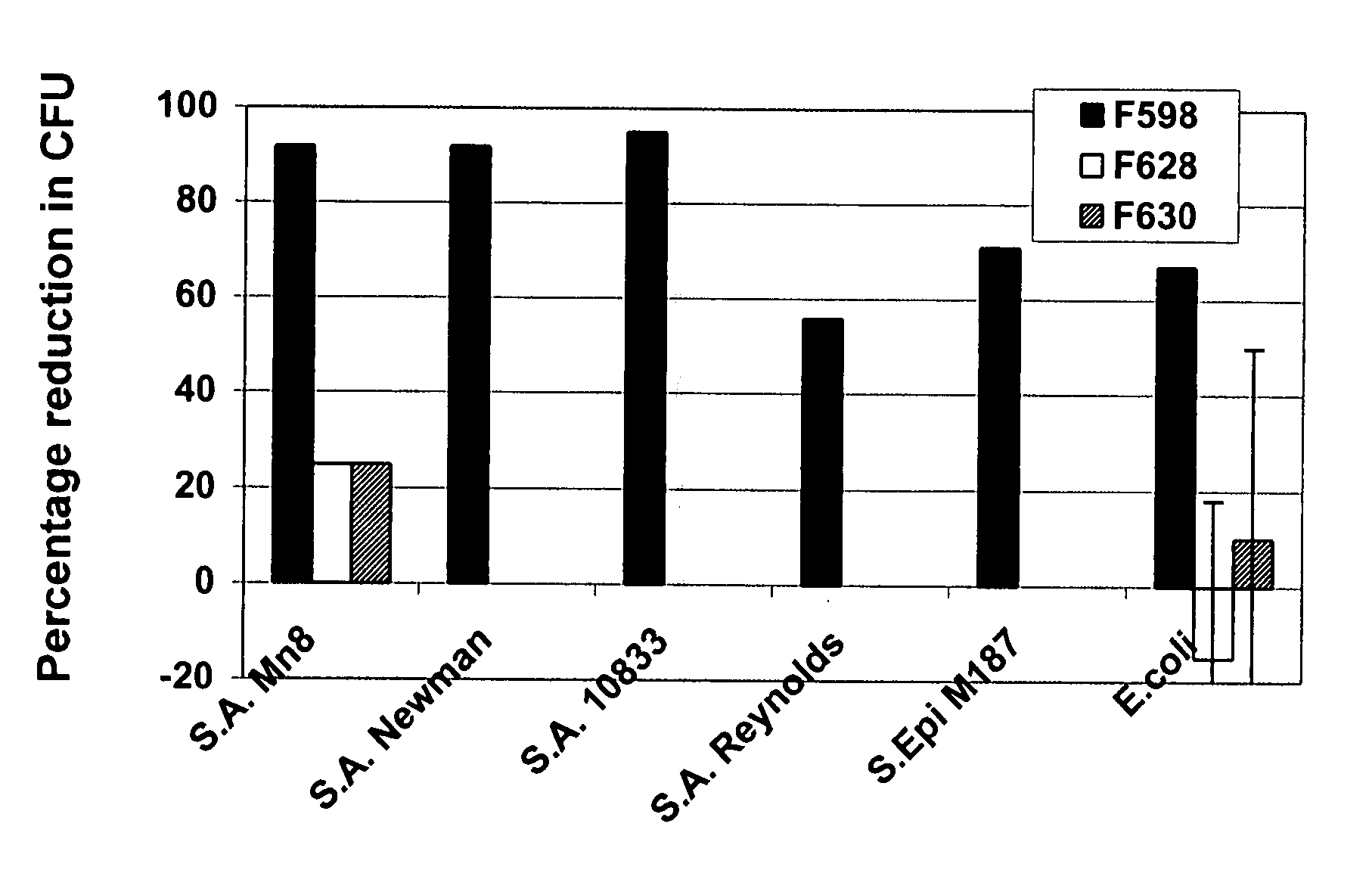
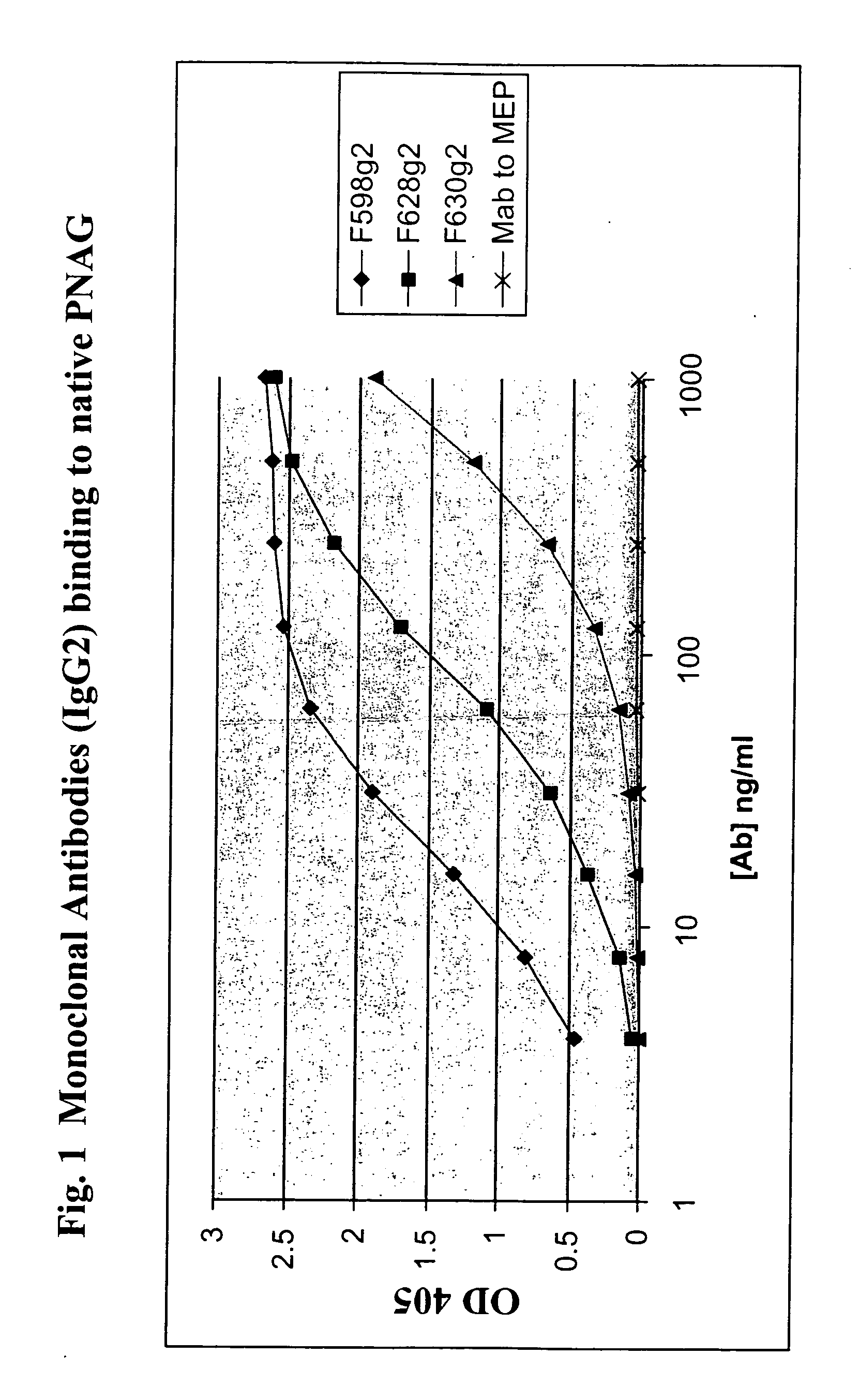
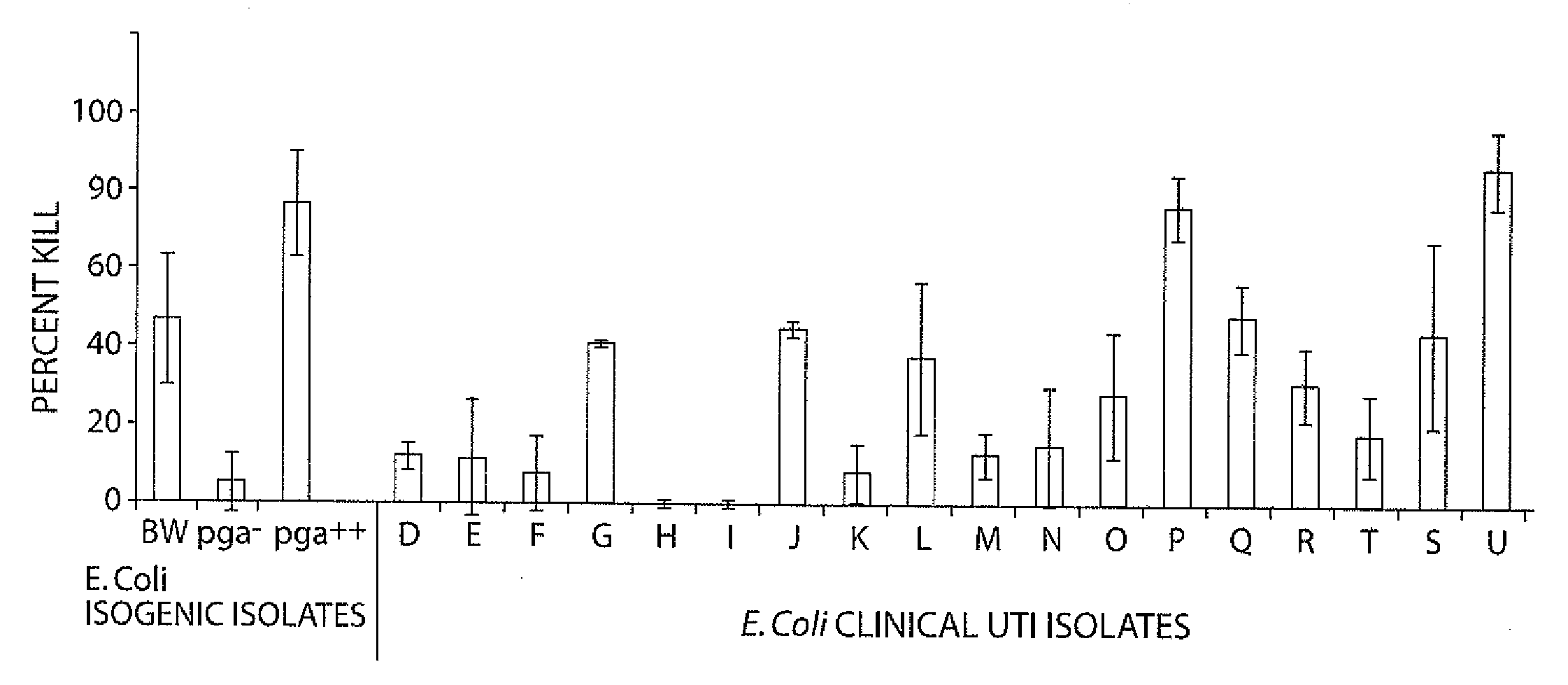
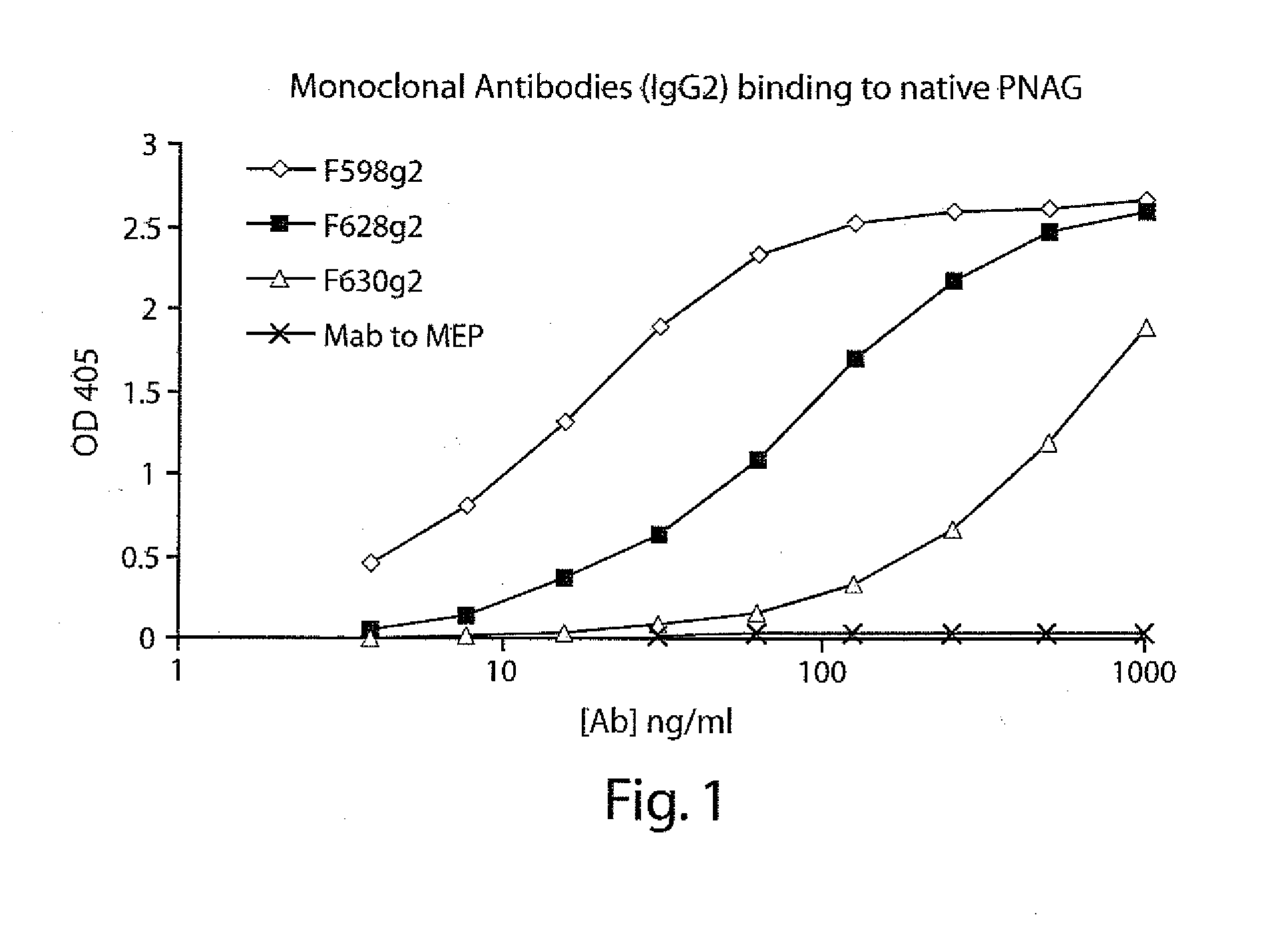
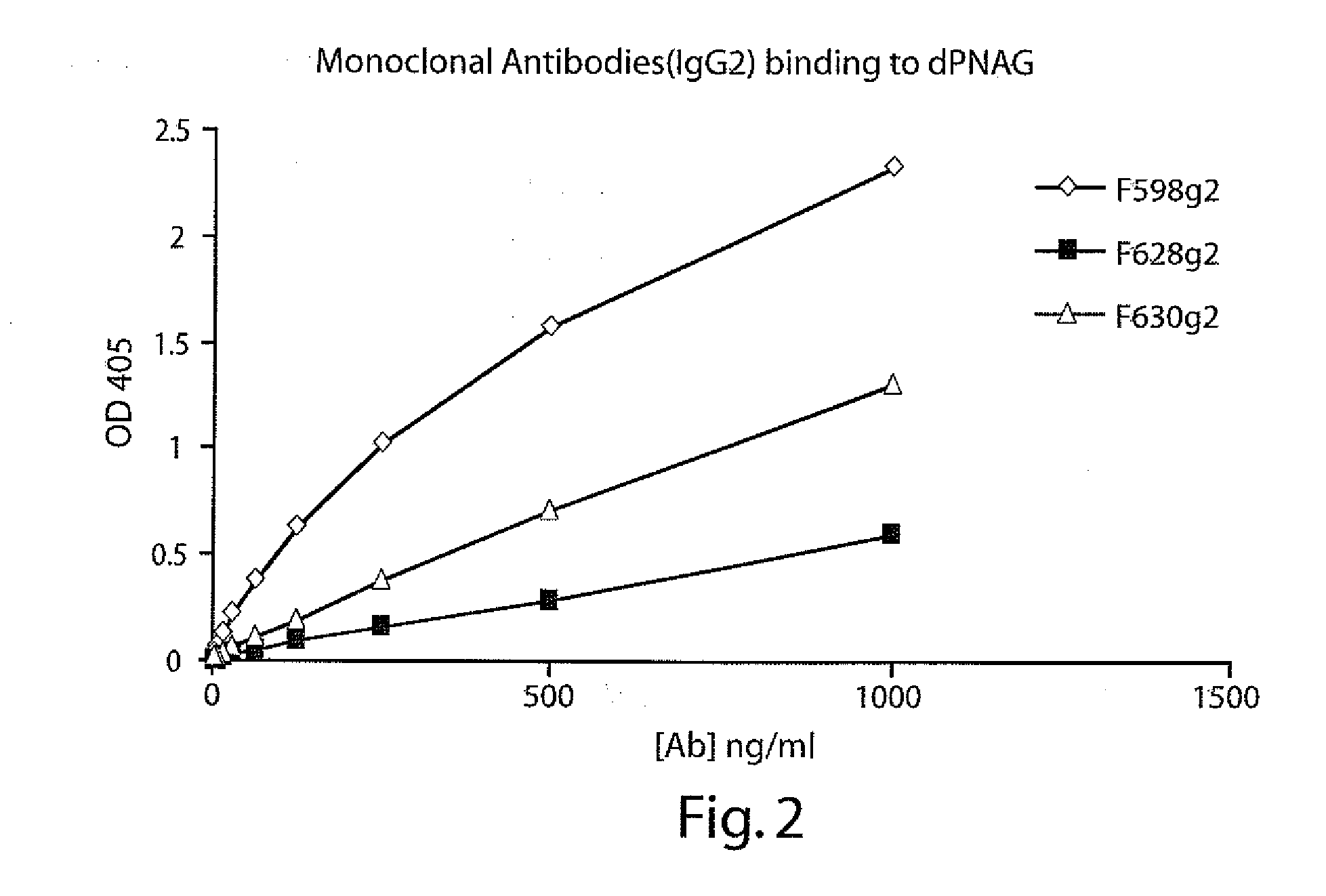
Poly-N-acetyl glucosamine (PNAG/dPNAG)-binding peptides and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS7786255B2Bacterial load in subjectReduce bacterial loadAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliBacteroides
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Poly-N-acetyl glucosamine (PNAG/dPNAG)-binding peptides and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS20060115486A1Bacterial load in subjectReduce bacterial loadAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliStaphylococcus
The present invention relates to peptides, particularly human monoclonal antibodies, that bind specifically to poly-N-acetyl glucosamine (PNAG), such as Staphylococcal PNAG, in acetylated, partially acetylated and / or fully deacetylated form. The invention further provides methods for using these peptides in the diagnosis, prophylaxis and therapy of infections by bacteria that express PNAG such as but not limited to Staphylococci and E. coli. Some antibodies of the invention enhance opsonophagocytic killing and in vivo protection against bacteria that express PNAG such as but not limited to Staphylococci and E. coli. Compositions of these peptides, including pharmaceutical compositions, are also provided, as are functionally equivalent variants of such peptides.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
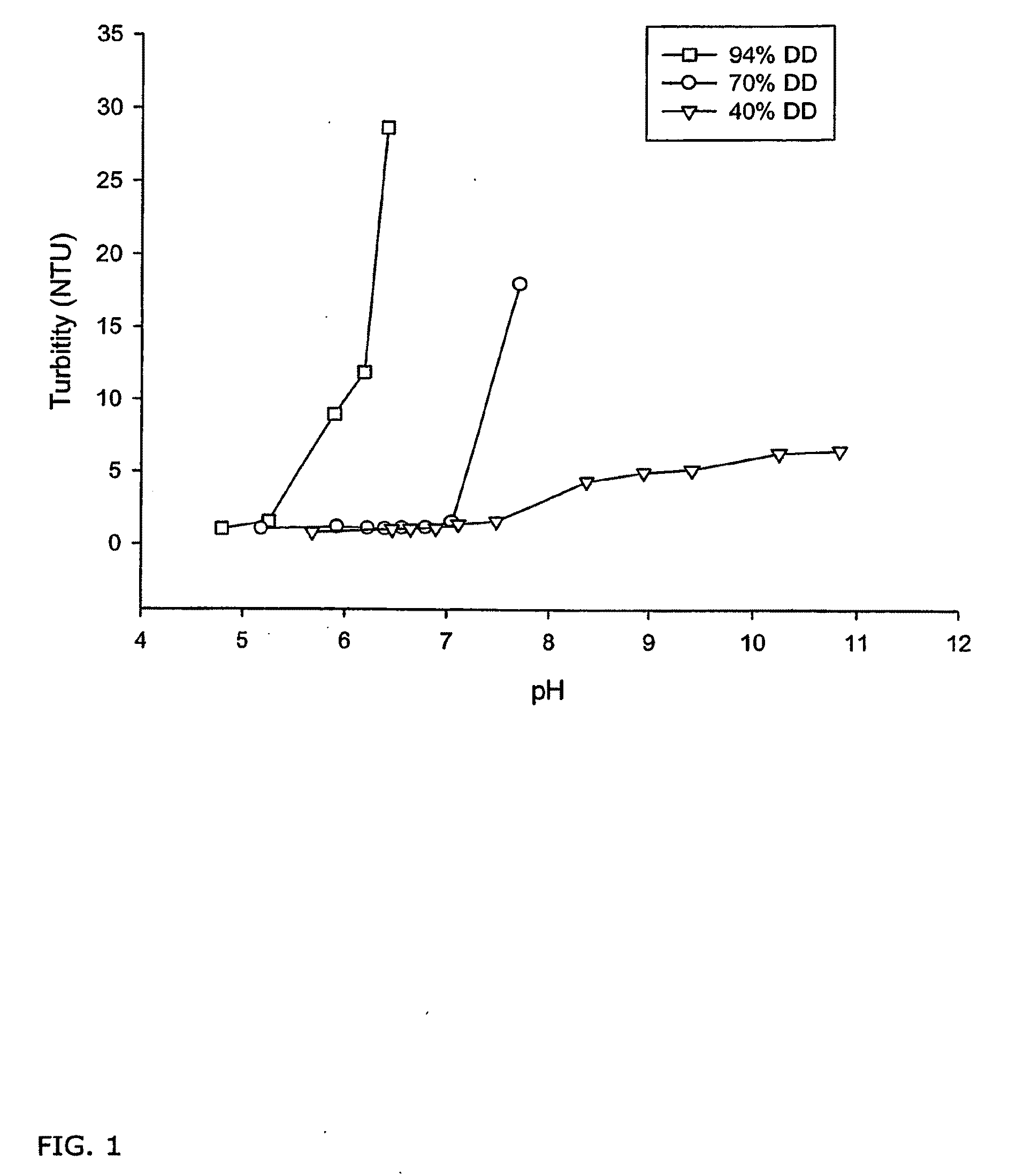
Compositions of partially deacetylated chitin derivatives
ActiveUS20090281058A1Modulate water activityPromote degradationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSaxitoxinBiological materials
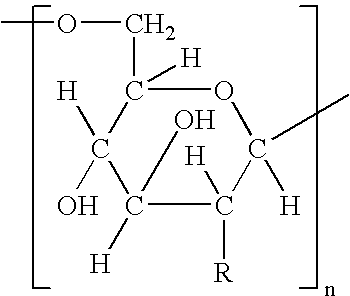
The present invention relates to compositions comprising biologically active chitinous oligomers and their endotoxin purified and partially deacetylated chitin polymer precursors, and their use in pharmaceutical compositions, biomaterial compositions, medical devices, and processes to produce the said oligomers. More specifically the present invention relates to novel compositions and processes to produce such compositions. The compositions include therapeutic hetero polymer and hetero oligomer compositions comprising specific sequences of N-acetyl glucosamine and glucosamine, developed to optimize chemical and structural features which are important for the therapeutic activity of these compositions. In addition, the present invention provides methods to use degree of deacetylation of a partially deacetylated chitin polymer in order to modulate physical and biological parameters in a calcium phosphate composite for bone implant applications.
Owner:GENIS EHF
Pharmaceutical composition comprising chito-oligomers
ActiveUS20050004073A1Good results in alleviating the symptoms of joint disordersReduce inflammationEsterified saccharide compoundsBiocideDiseaseOligomer
Compositions are provided comprising chito-oligomers obtainable from chitin, comprising oligomers of N-acetyl glucosamine (NAG) and glucosamine, wherein at least 50% of the oligomers have a chain length of about 2-50, and the degree of deacetylation of the oligomers is in the range of about 0-70%, preferably about 30-50%. The compositions are highly useful as pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of joint disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Also provided are methods for treatment of joint disorders and treatment against inflammatory activity.
Owner:GENIS EHF
Probiotics and prebiotic compound preparation
PendingCN106617091ARapid stimulation of reproductionIncrease vitalityFood ingredient functionsOligosaccharide food ingredientsSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHENGDANGNIAN BIO TECH CO LTD
Bacillus subtilis for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid to recombine and application thereof
ActiveCN106929462AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus aryabhattaiGenetic engineering
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid to recombine and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the bacillus subtilis, bacillus subtilis 168-delta-nagP delta-nagP delta-gamP delta-gamA delta-nagA delta-nagB delta-1dh delta-pta:: lox72 are taken as expression hosts, through the over-expression of glucosamine acetylase coding geneS GNA 1 which are derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C, N-acetyl-glucosamine epimerase (AGE) which is derived from anabaena sp. CH1 and N-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase (NeuB) which is derived from escherichia coli K1, genetically engineered bacteria of the bacillus subtilis for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid are obtained, the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid reaches 190mg / L, and bacillus subtilis further lays a foundation for the process that the bacillus subtilis is transformed by metabolic engineering to produce the N-acetylneuraminic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for continuously separating sialic acid
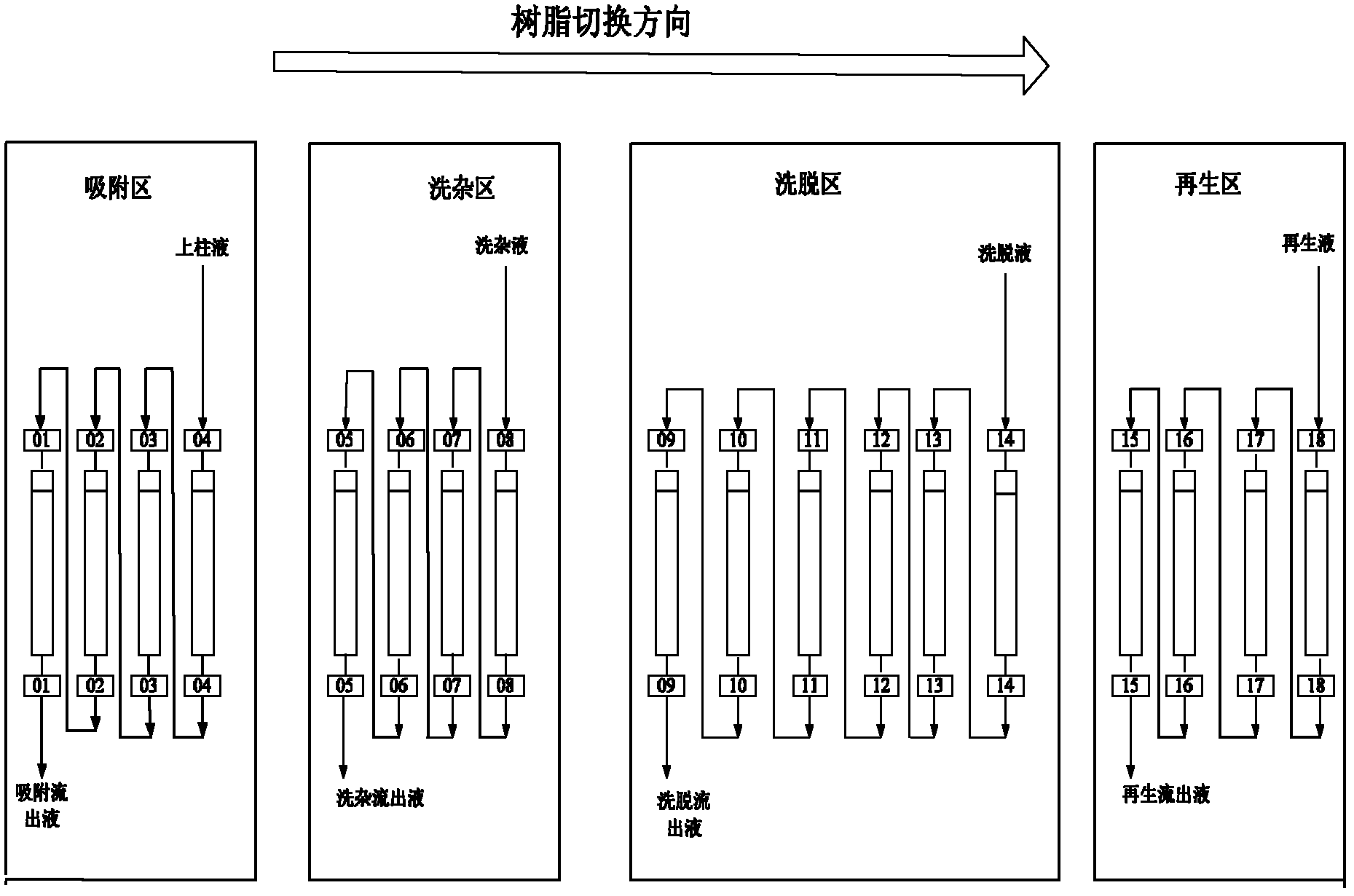
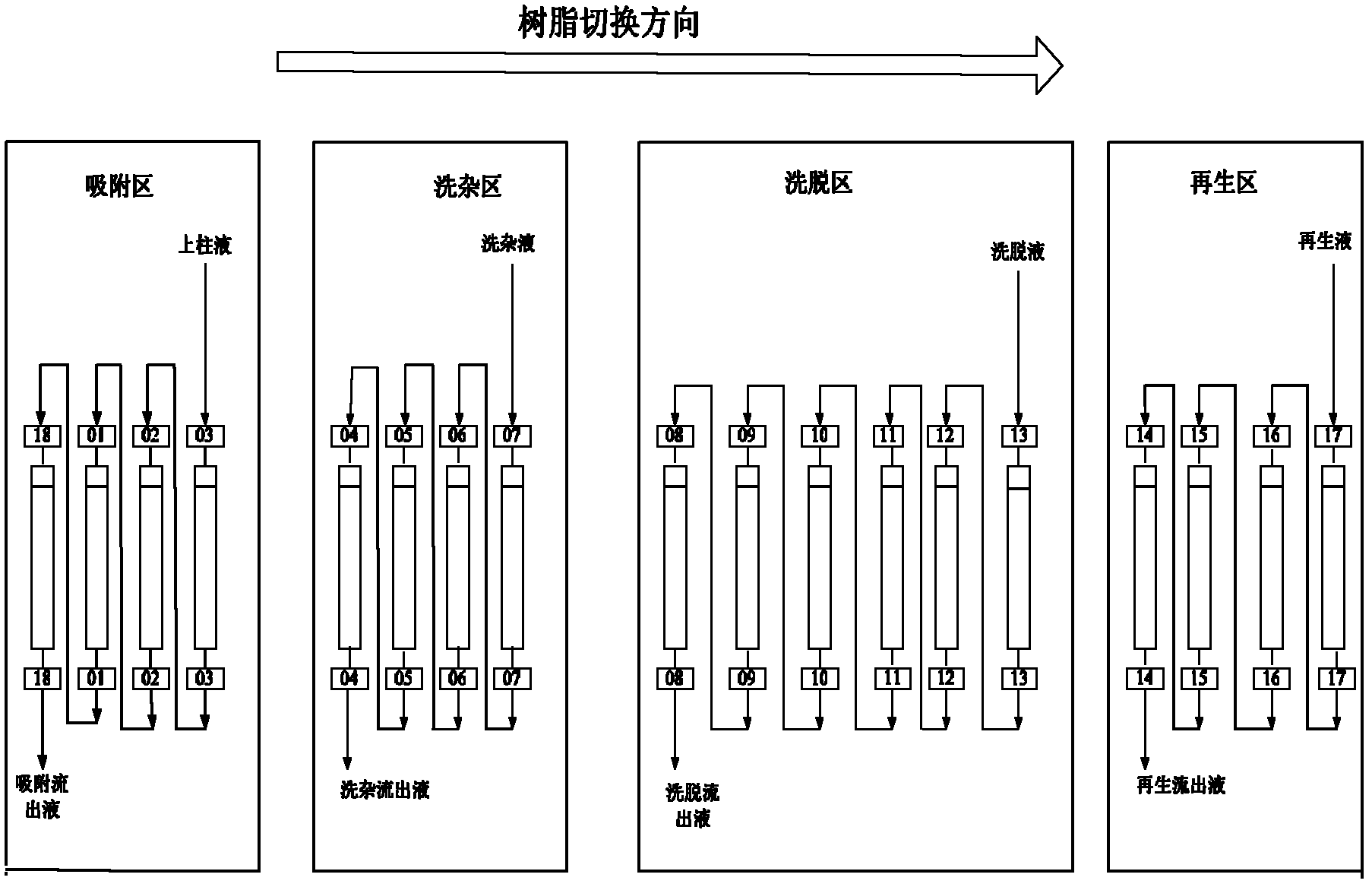
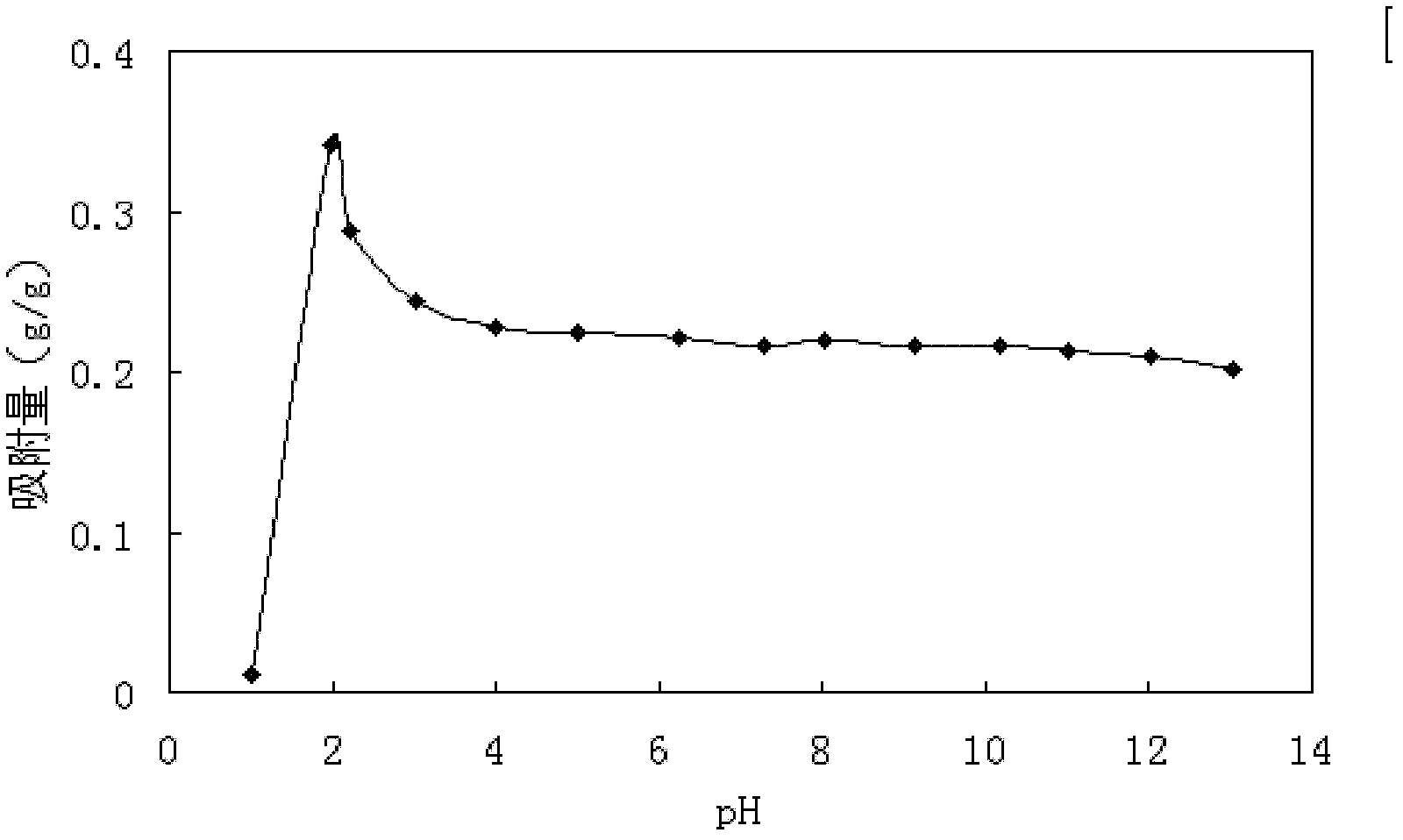
ActiveCN102532208ASave pipesSmall footprintSugar derivativesSaccharide compounds with non-saccharide radicalsPurification methodsUltrafiltration
The invention discloses a method for continuously separating sialic acid, wherein sialic acid is prepared through microbial fermentation by taking N-acetyl glucosamine and sodium pyruvate as substrates; fermentation liquor is processed through filtration and ultrafiltration so as to obtain sialic acid clear liquid; sialic acid clear liquid is pumped in a continuous ion exchange system provided with OH-type anion exchange resin for adsorption; deionized water is adopted for leaching; a sodium chloride solution is adopted for elution; a sodium hydroxide solution is adopted for resin regeneration; eluent containing sialic acid is collected, is leached through an ethanol water solution, and then is added with ethyl acetate for dilution crystallization; and crystals are dried under reduced pressure, so that pure sialic acid is obtained. The separation and purification method is simple, convenient and feasible, achieves good effect and low running cost, and can implement the separation from kilogram class to ton class according to the separation amount; and in addition, products that are obtained by adopting the method gain excellent results on yield coefficient and product quality, and the product quality is ensured..
Owner:NANJING HIGH TECH UNIV BIOLOGICAL TECH RES INST CO LTD
Synthetic nutritional formulations
InactiveUS20070048354A1Improve developmentIncreasing tissue repairBiocideVitamin food ingredientsTissue repairPhysiology
The present invention provides a synthetic nutritional formulation comprising a substantially pure free N-acetyl glucosamine in concentrations effective for enhancing organ development, enhancing an immune response, or increasing tissue repair or healing in a subject. A synthetic nutritional formulation of the invention may optionally comprise one or both of substantially pure free sialic acid and / or substantially pure free fucose.
Owner:WASSENAAR WILLEM
Bacillus subtilis gene engineering bacterial producing Neu5Ac, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103923869AWith industrial productionSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood industryGlycerol
The present invention discloses Bacillus subtilis gene engineering bacterial producing Neu5Ac, a construction method and an application thereof. According to the present invention, according to the gene engineering bacterial, genes for coding UDP-N-acetyl glucosamine epimerase and Neu5Ac synthetase are introduced into Bacillus subtilis so as to be expressed, and expression of glucosamine 6-phosphate synthetase of the Bacillus subtilis is enhanced to construct the complete metabolic pathway from glucose or glycerol to Neu5Ac in the Bacillus subtilis so as to utilize glucose or glycerol as a substrate to carry out fermentation culture so as to produce Neu5Ac; and the adopted Bacillus subtilis is widely used in the food industry, is safe and harmless, and is suitable for production of Neu5Ac required by food and health products.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Beverage and additive for wellness
InactiveUS6979458B1Improve mobilityReduce inflammationBiocideDispersion deliverySulfonateGlucosamine Sulfate
The invention is an ingestible wellness one time daily dosage made of a large quantity of rapid absorbing glucosamine sulfate, glucosamine hydrochloride, and an n-acetyl glucosamine and combinations thereof, a large quantity of chondroitin sulfate, chondroitin hydrochloride and combinations thereof, a vasodialating sulfonate with at least one methyl group, and a buffer to reduce adverse symptoms from large amounts of glucosamine and chondroitin selected from the family of araliaceae and a B3 vitamin, wherein the invention is also a wellness beverage that involves a fluid combined with the ingestible wellness dosage.
Owner:MARTIN KENNETH A
Antimicrobial solution and methods of making and using the same
ActiveUS9132296B2Promote absorptionHigh immediate and short-term effectivenessBiocideCosmetic preparationsCarboxylic acidEthylene Homopolymers
A chitosan solution is formed from chitin, which is a homopolymer of beta (1-4)-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Rinsed, dried and ground chitin undergoes a process of deacetylation to convert some N-acetyl glucosamine to glucosamine, a primary component of chitosan. The chitosan solution is prepared by mixing 5chitosan with an alpha-hydroxy acid such as glycolic acid. An aqueous chelated silver solution is prepared by mixing silver oxide with a carboxylic acid such as citric acid. The chitosan solution can then be mixed with the silver solution resulting in a cationic complex. The cationic complex of the present invention may then be electrostatically bonded with generally negatively charged surfaces. In use, citrate promotes uptake of the silver by microbes. The antimicrobial complex can be applied via several methods of application, including an impregnated wipe, a foam, a gel, a spray, a lotion and an ointment.
Owner:AG TECH LLC
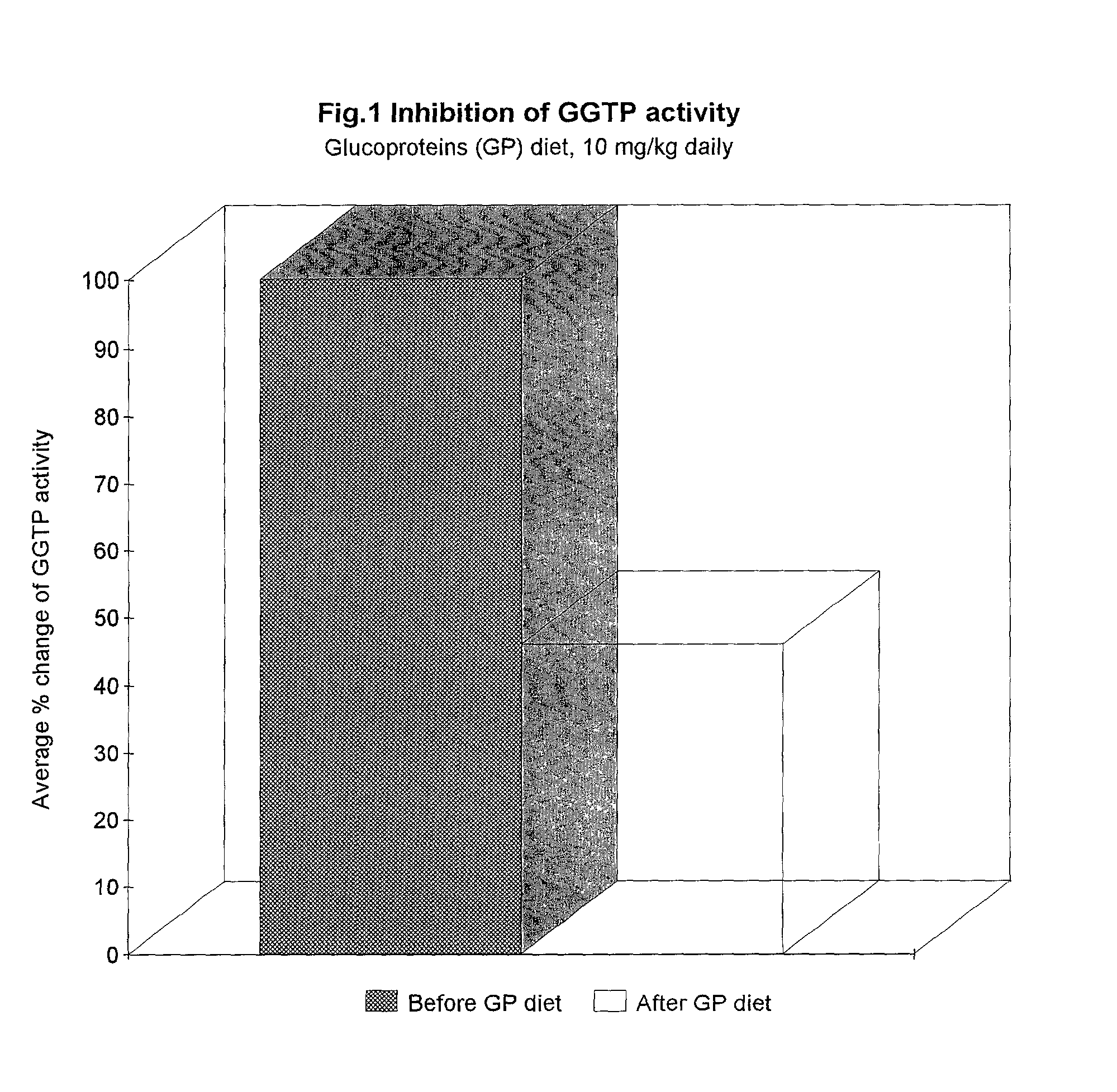
Dietary modulators of gamma glutamyl transpeptidase
InactiveUS20010034325A1Easy to solveEasy to adjustSenses disorderNervous disorderGamma-glutamyltransferaseBiology
The invention relates to the new compositions comprising probiotic glucoproteins and isolated soy proteins for lowering upregulated gamma glutamyl transpeptidase humans or domestic animals. Their synergetic effects with N-acetyl glucosamine is disclosed.
Owner:SLESAREV VLADIMIR I
Method of modulating release of saccharides and uses thereof
The present invention relates to a method of controlled release of saccharides and oligosaccharides in human and animal. Polysaccharides are digested in a manner to provide oligomers having desired numbers of units of saccharides or monosaccharides, most particularly glucosamine and N-acetyl-glucosamine and derivatives thereof. The rate of release of monosaccharides is proportional to the length of the oligomers administered to an organism, and has targeted physiological effects depending on the length of the oligomers used.
Owner:ISM BIOPOLYMER
Conjugation of streptococcal capsular saccharides
ActiveUS8513392B2Avoid disruptionImproving immunogenicityAntibacterial agentsImmunoglobulinsStreptococcus agalactiaeLactose oxidase
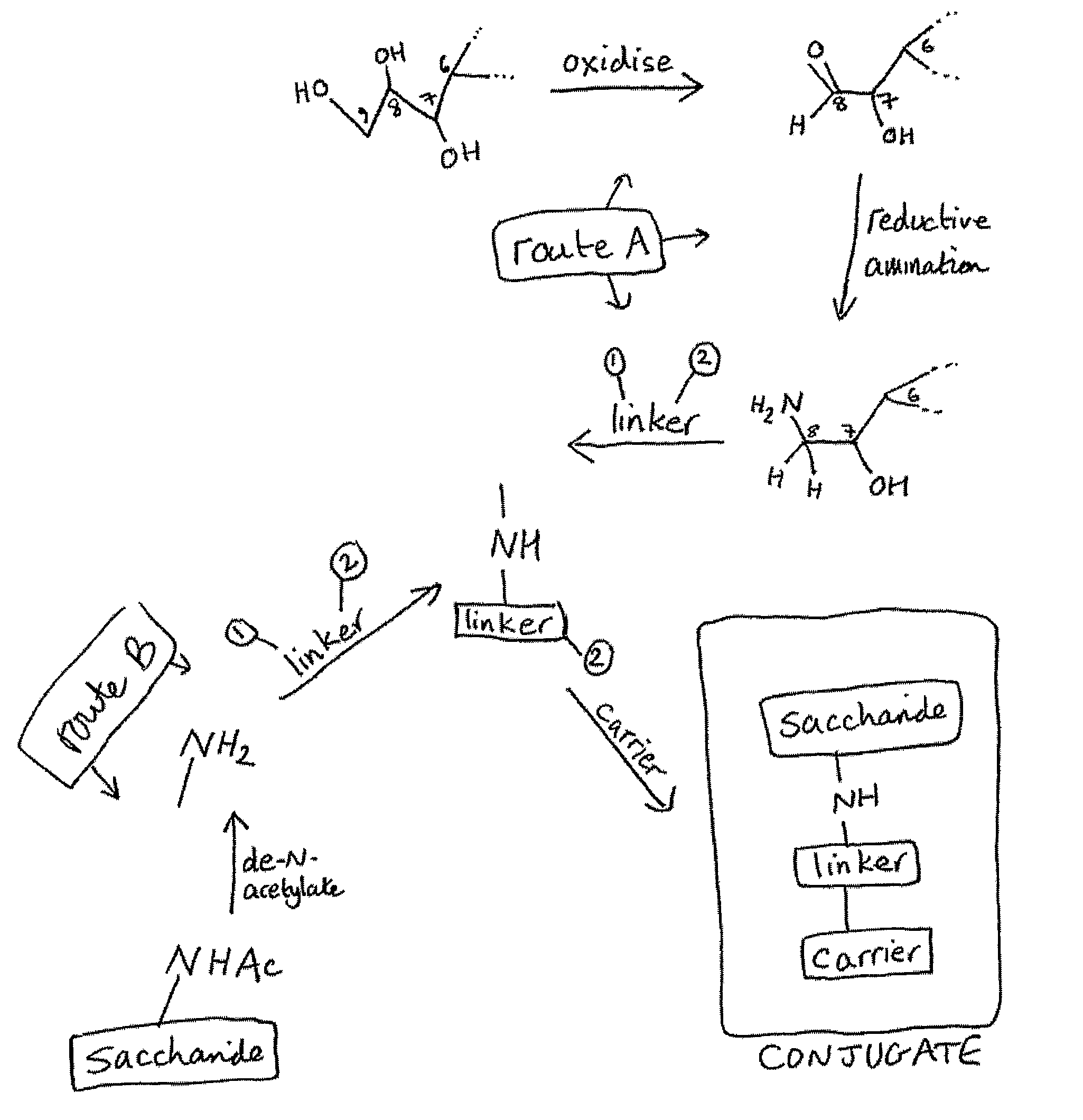
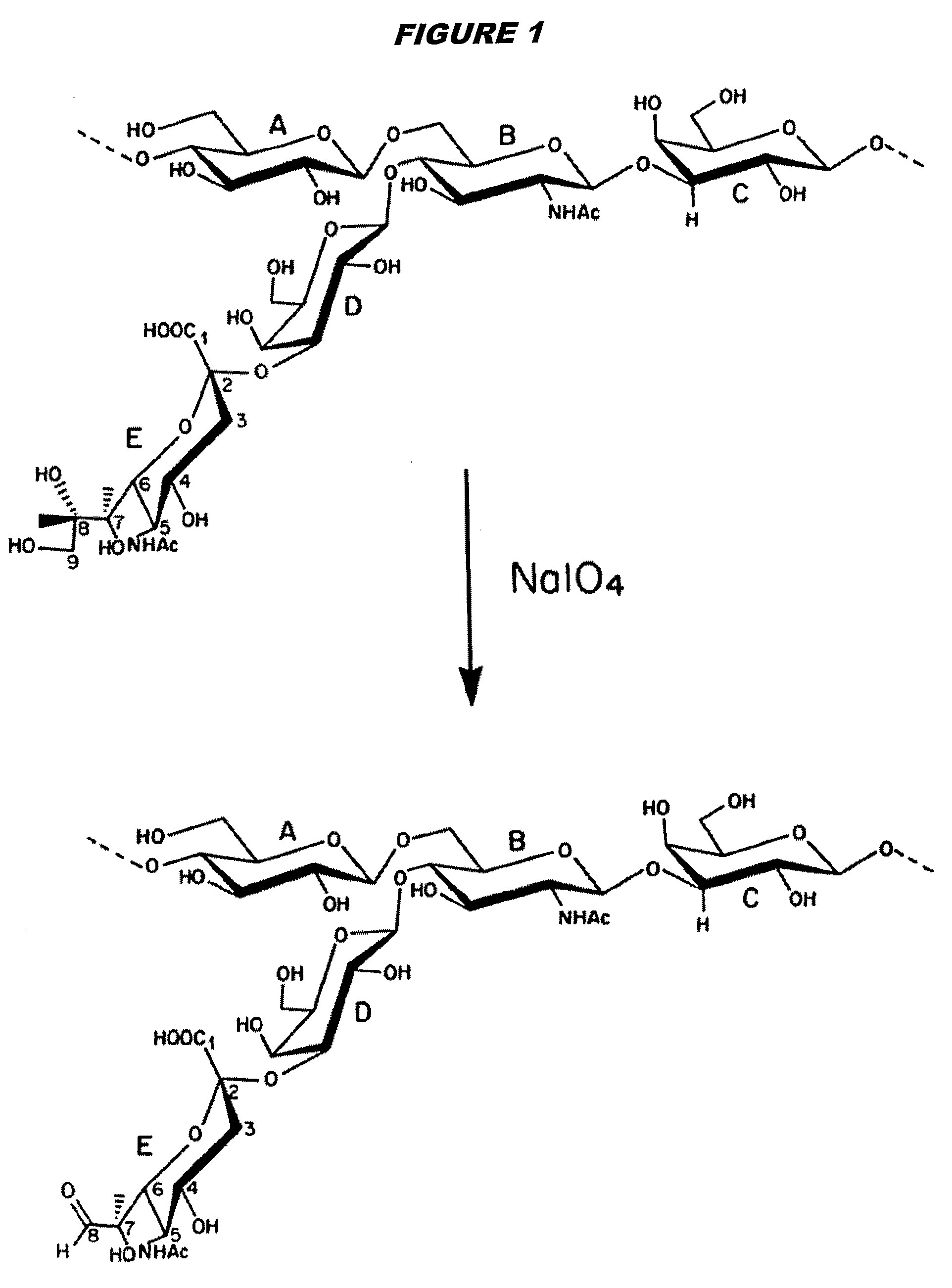
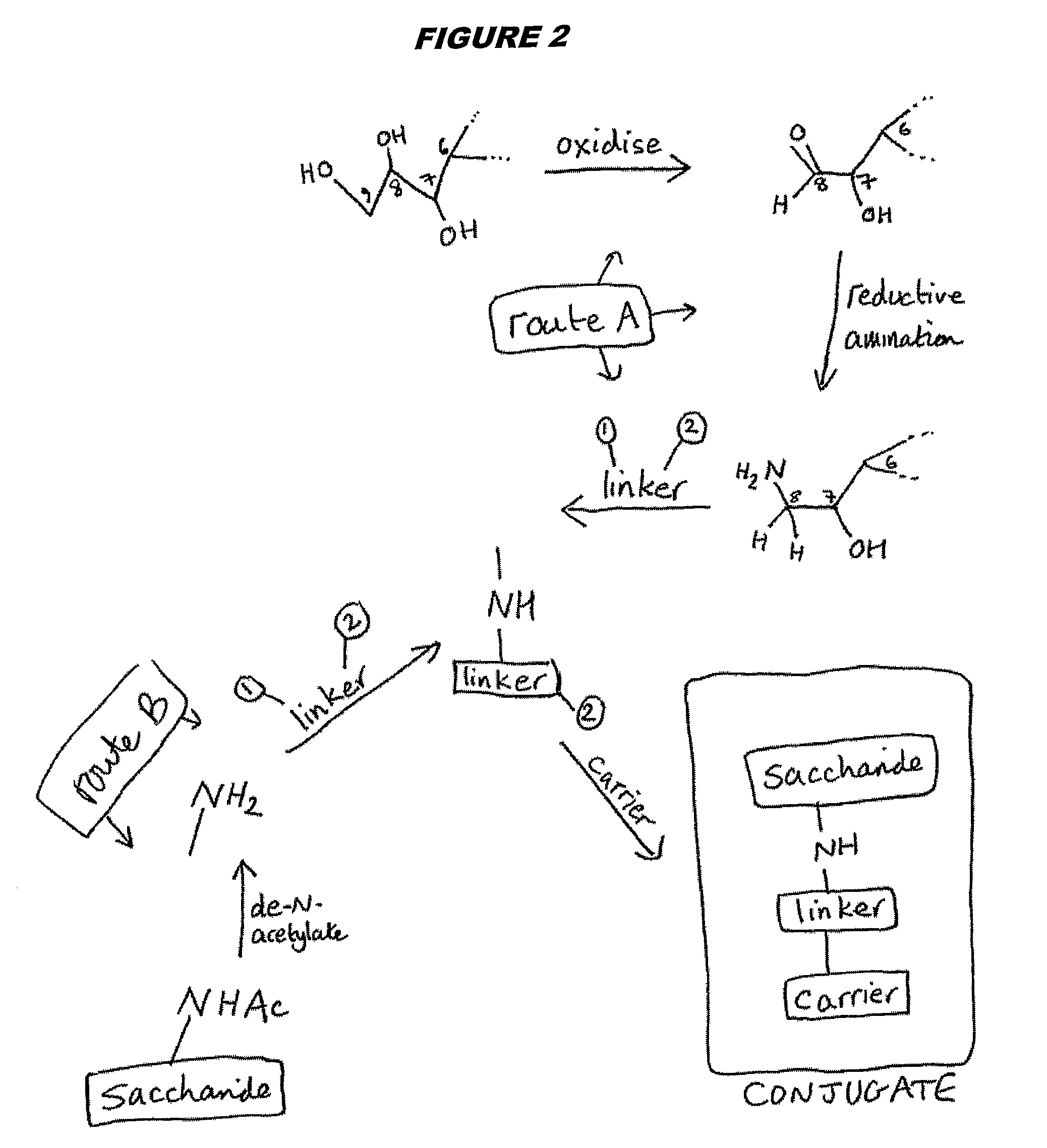
Three conjugation methods for use with the capsular saccharide of Streptococcus agalactiae. In the first method, reductive animation of oxidized sialic acid residue side chains is used, but the aldehyde groups are first aminated, and then the amine is coupled to a carrier via a linker. In the second method, sialic acid residues and / or N-acetyl-glucosamine residues are de-N-acetylated to give amine groups, and the amine groups are coupled to a carrier protein via a linker. In the third method, linkage is via galactose residues in the capsular saccharide rather than sialic acid residues, which can conveniently be achieved using galactose oxidase.
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Recombinant microorganisms and uses thereof
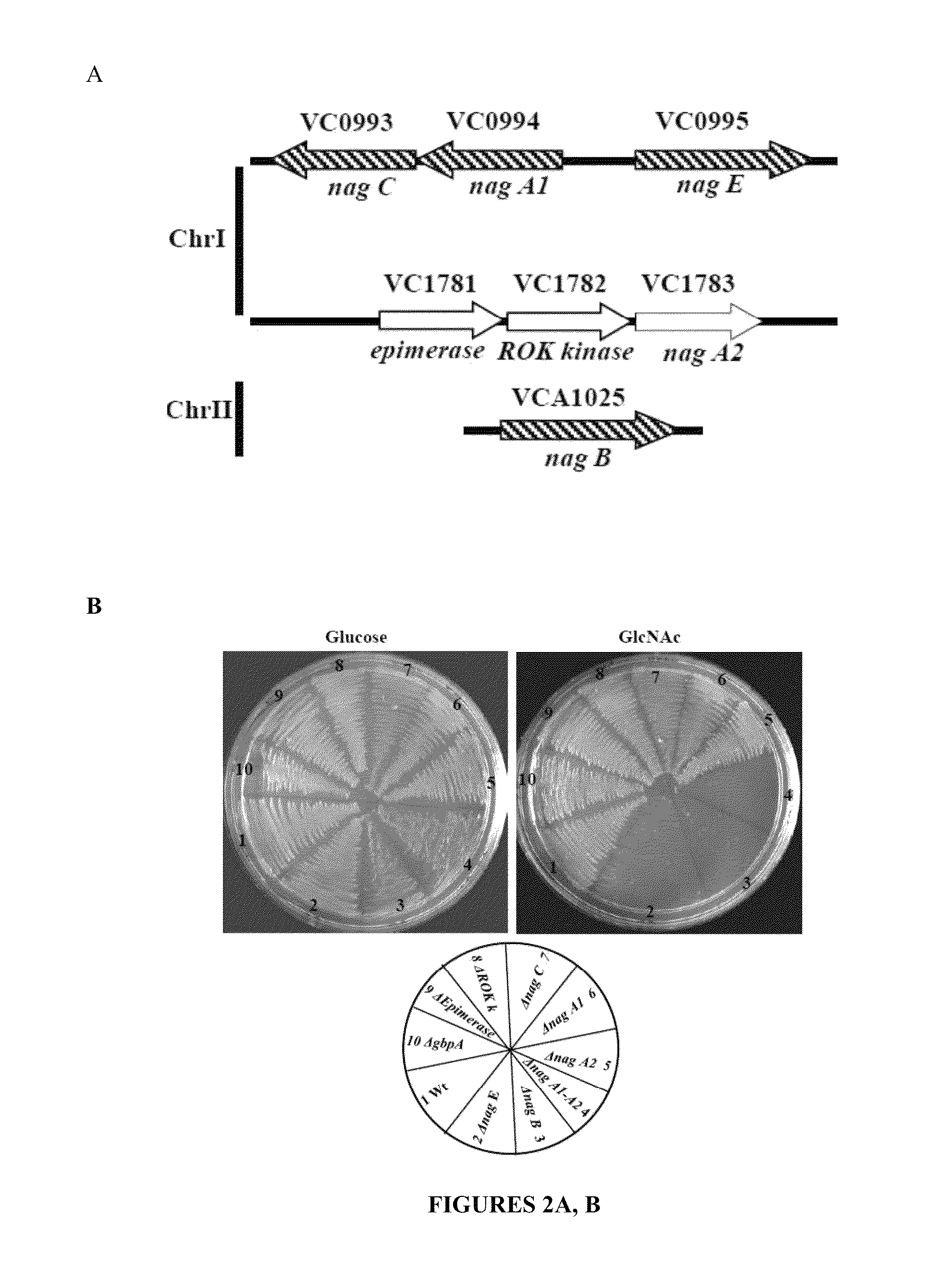
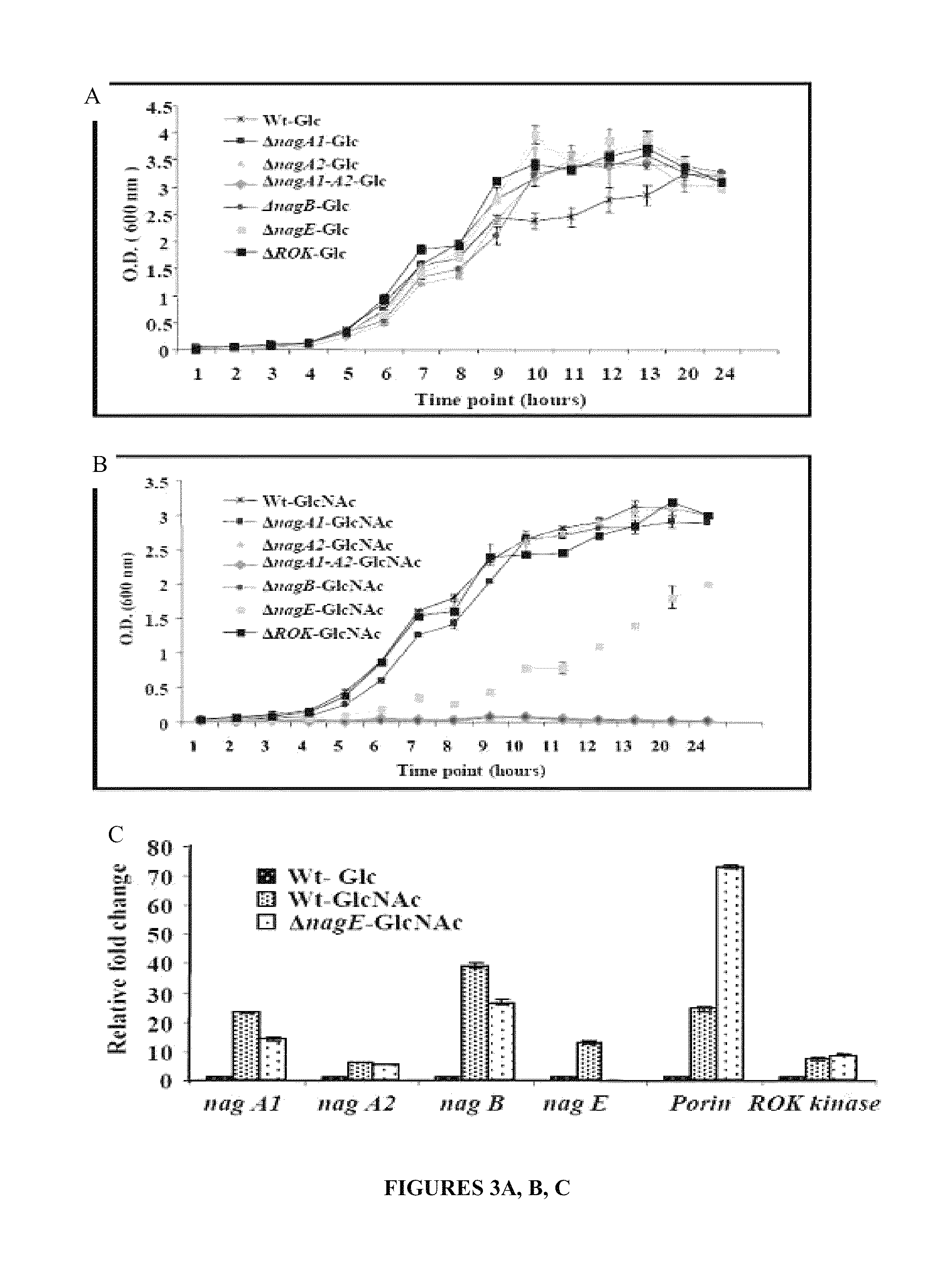
The present invention relates to recombinant strains of Vibrio spp, which are unable to utilize the amino sugar N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) as a sole carbon source. This inability to utilize GlcNAc severely impairs the colonization property of the recombinants. The present invention also provides compositions comprising these recombinant strains for use in pharmaceuticals and in providing immunity.
Owner:NAT INST OF PLANT GENOME RES ORG
Method for preparing fondaparinux sodium intermediate
ActiveCN102942601AThe synthesis process is simpleReduce manufacturing costSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationRaw materialN acetyl glucosamine
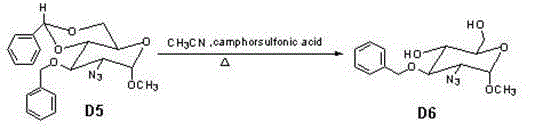
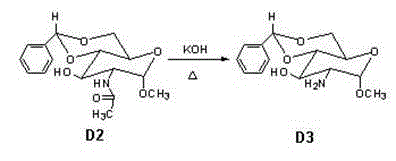
The invention provides a method for preparing a fondaparinux sodium intermediate. N-acetyl glucosamine is taken as a raw material, and through a plurality of steps of reaction, a compound D7 with the formula shown in the specification is synthesized, therefore, a technology for synthesizing fondaparinux sodium is simplified, and the production cost is lowered.
Owner:CUREGEN JIANGSU PHARMA
Lecanicillium psalliotae strain
InactiveCN102417886AIncrease enzyme activityIncreased parasitic abilityBiocideFungiDegradative enzymeLife stage
The invention discloses a lecanicillium psalliotae strain with the preservation number of CGMCC NO: 5329. The strain can colonise spawns, two-year-old larvae and female adults at different life stages of rootknot nematode. Activations of chitinous substance degradative enzyme and excisionenzyme generated by the strain can be respectively determined through an N-acetyl glucosamine method and a p-nitrobenzene method, the enzymatic activities thereof can reach 3.98 U / h.mL and 0.38 U / h.mL, and higher activity of the produced chitinous substance enzyme can be detected at different temperature (27 DEG C-75 DEG C) and different pH (3.0-7.0); and the influence of chitinous substance enzyme extract produced by the strain on eclosion of rootknot nematode spawns is determined in vitro, and the inhibition ratio and the destruction ratio of enzyme solution on relative eclosion of the spawns are respectively 94.52 percent and 84.32 percent. The lecanicillium psalliotae strain disclosed by the invention is applied to biological control of crop rootknot nematodiasis, provides an effective way for protecting sweet potatoes, fruits, vegetables in north China and particularly controlling destructiverootknot nematodiasis, and has obvious ecological benefit, economic value and social value.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase of Paenibacillus barungensis, encode gene thereof and application of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase
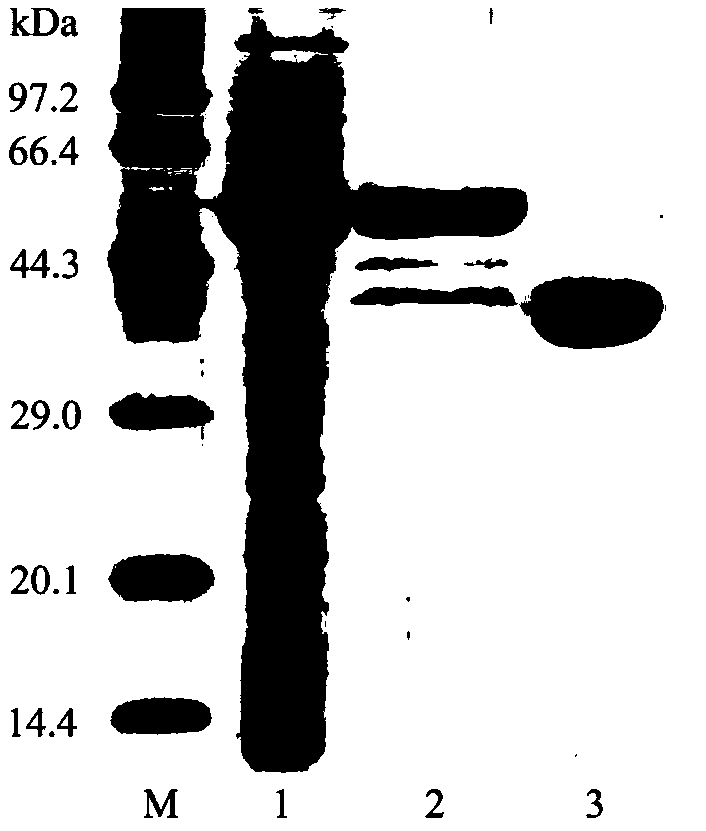
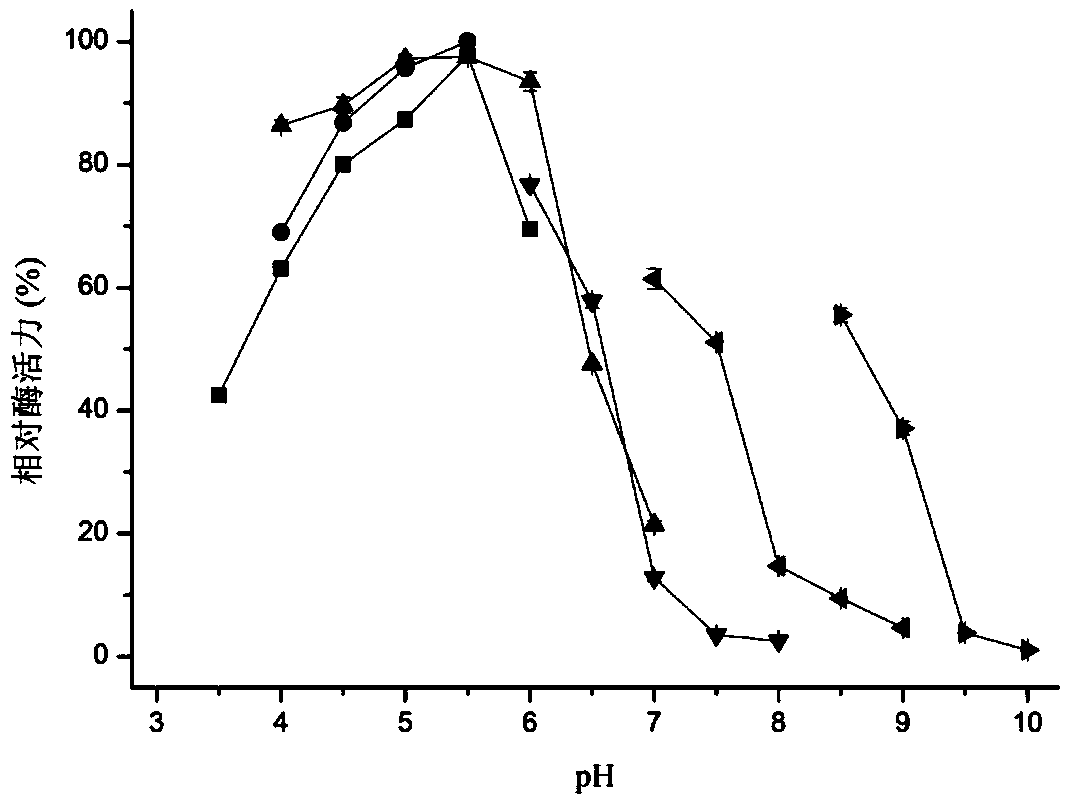
ActiveCN109182303AGood enzymatic propertiesIncreased specific enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChitinaseThermal stability
The invention discloses a Beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase of Paenibacillus barungensis, an encode gene thereof and an application of beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase. The provided Beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase PbNag39 is excellent in the enzymatic property, and has a specific activity against chitosan is 28.3 U / mg, and the final products of hydrolysis of chitosan oligosaccharides are N-Acetyl glucosamine.The Beta-N-Acetylglucosaminidase and chitinase can hydrolyze chitin powder synergistically and obtain N-Acetyl glucosamine. The Beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase PbNag39 has the characteristics of high specific activity, good thermal stability and excellent hydrolysis characteristics. It can stabilize and play a catalytic role in a wide range of pH, and has important application value in chitin conversion.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Antimicrobial Solution and Methods of Making and Using the Same
ActiveUS20140314820A1Promote absorptionHigh immediate and short-term effectivenessCosmetic preparationsBiocideCarboxylic acidEthylene Homopolymers
A chitosan solution is formed from chitin, which is a homopolymer of beta (1-4)-linked N-acetyl-D-glucosamine. Rinsed, dried and ground chitin undergoes a process of deacetylation to convert some N-acetyl glucosamine to glucosamine, a primary component of chitosan. The chitosan solution is prepared by mixing 5 chitosan with an alpha-hydroxy acid such as glycolic acid. An aqueous chelated silver solution is prepared by mixing silver oxide with a carboxylic acid such as citric acid. The chitosan solution can then be mixed with the silver solution resulting in a cationic complex. The cationic complex of the present invention may then be electrostatically bonded with generally negatively charged surfaces. In use, citrate promotes uptake of the silver by microbes. The antimicrobial complex can be applied via several methods of application, including an impregnated wipe, a foam, a gel, a spray, a lotion and an ointment.
Owner:AG TECH LLC
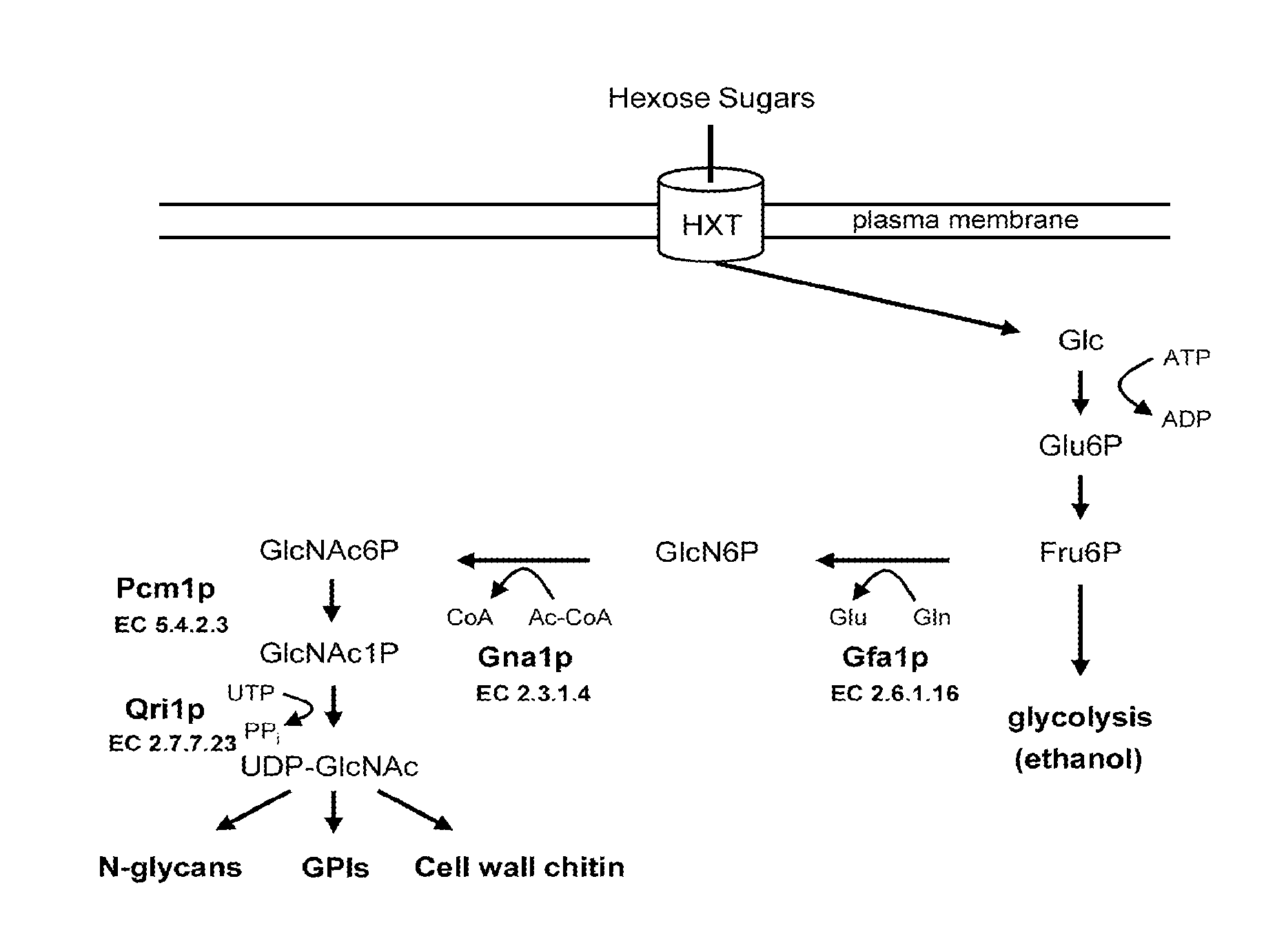
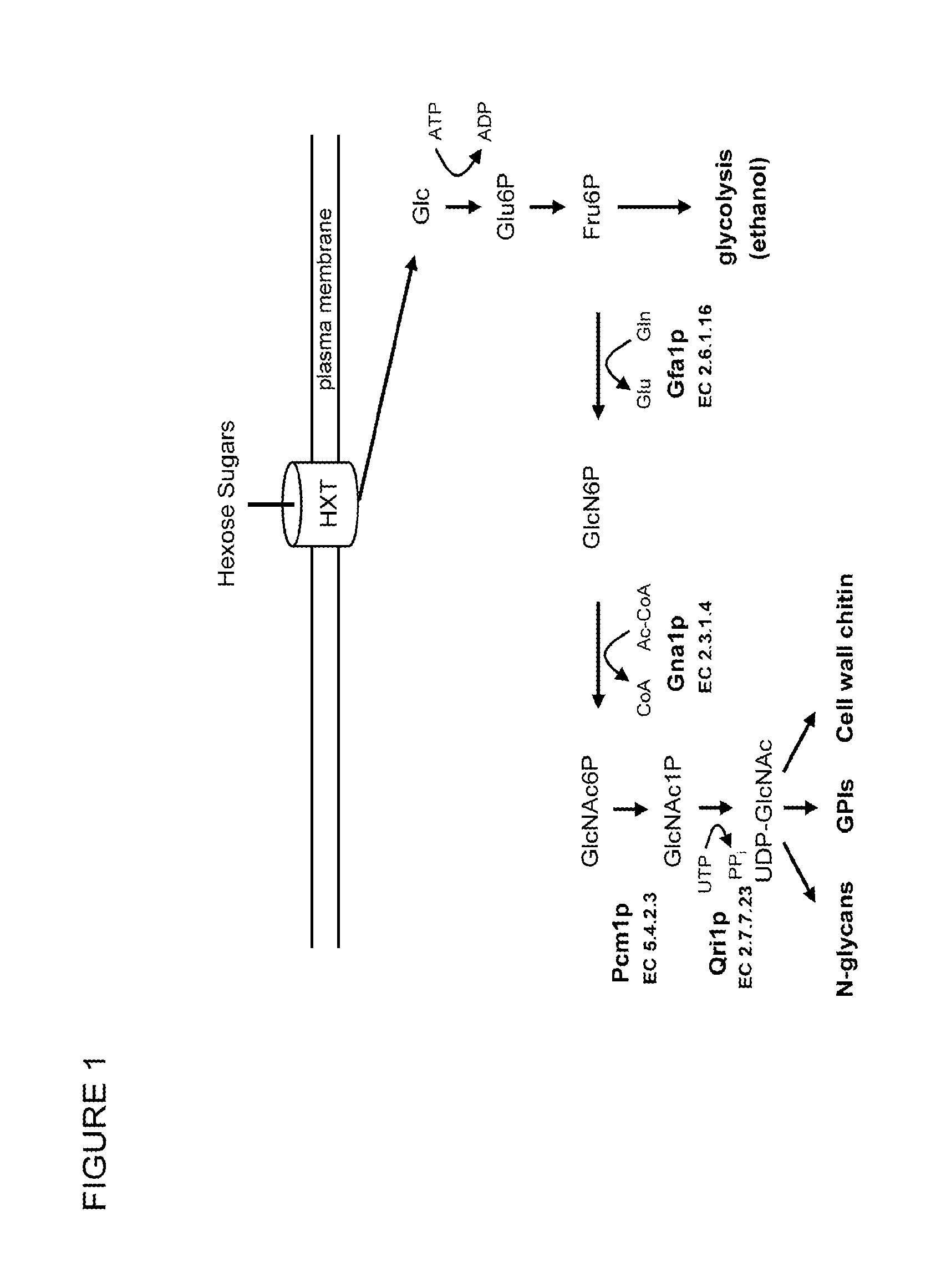
Genetically Engineered Yeast for the Production of Biofuels
Compositions and methods are provided for generating biofuels by fermentation from carbon sources other than glucose using genetically engineered yeast strains. For example, a Saccharomyces strain which is capable of converting glucose to ethanol but not of metabolizing N-acetyl glucosamine is genetically engineered to utilize N-acetyl glucosamine as a nutrient carbon source.
Owner:NEW ENGLAND BIOLABS
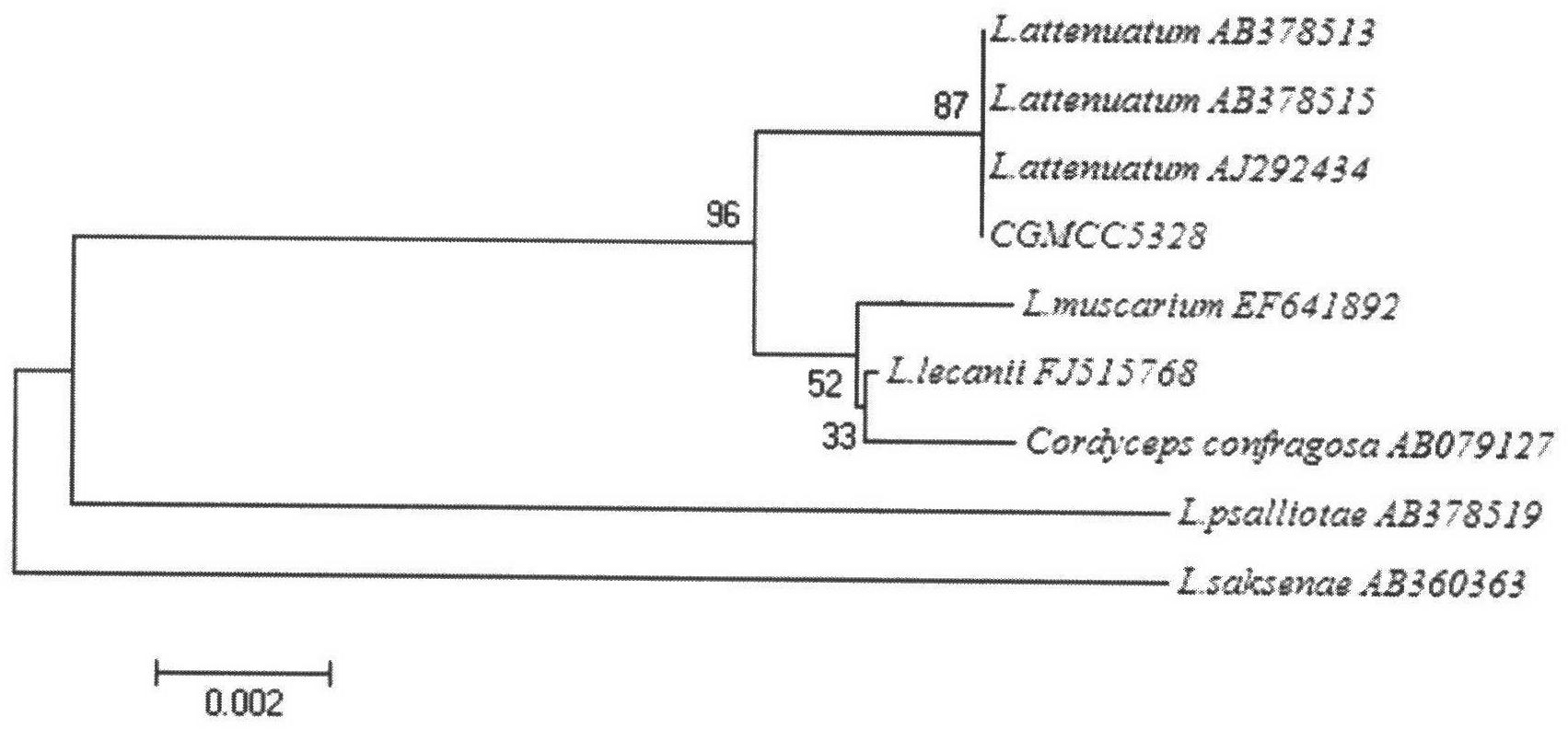
Lecanicillium attenuatum strain
InactiveCN102433264AIncrease enzyme activityIncrease hatch inhibition rateBiocideFungiDiseaseDegradative enzyme
The invention discloses a lecanicillium attenuatum strain with the preservation number of CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection) NO.5328. The strain can allow meloidogyne ova and female ova to parasitize in the strain. The activities of chitin degradative enzyme and excision enzyme are respectively measured by applying an N-acetyl glucosamine method and a paranitrobenzene methodto be 16.34U / h ml and 0.59U / h ml respectively; and higher activities of the generated chitin degradative enzyme system at different temperatures of 27-50DEG C and different pH values of 3.5-6.0 can be respectively detected. According to the measurement of the activity of chitin enzyme by electrophoresis, five bands are measured with the molecular weights of 79.6kDa, 65.6kDa, 54.1kDa, 42.1kDa and 32.9kDa respectively. The relative hatching inhibition rate of chitin enzyme coarse liquid generated by the lecanicillium attenuatum to the meloidogyne ova is measured to be 83.17 percent under the invitro condition. The lecanicillium attenuatum is applied to biological control over meloidogyne diseases of crops, particularly provides an effective path for controlling the meloidogyne diseases seriously harming melon and fruit vegetables in protected land in northern area of China as well as has remarkable biological benefit, economic value and social value.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
POLY-N-ACETYL GLUCOSAMINE (PNAG/dPNAG)-BINDING PEPTIDES AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF
InactiveUS20110002932A1Bacterial load in subjectReduce bacterial loadAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliBinding peptide
The present invention relates to peptides, particularly human monoclonal antibodies, that bind specifically to poly-N-acetyl glucosamine (PNAG), such as Staphylococcal PNAG, in acetylated, partially acetylated and / or fully deacetylated form. The invention further provides methods for using these peptides in the diagnosis, prophylaxis and therapy of infections by bacteria that express PNAG such as but not limited to Staphylococci and E. coli. Some antibodies of the invention enhance opsonophagocytic killing and in vivo protection against bacteria that express PNAG such as but not limited to Staphylococci and E. coli. Compositions of these peptides, including pharmaceutical compositions, are also provided, as are functionally equivalent variants of such peptides.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC +1
Preparation of N-aceto-D-neuraminic acid by N-aceto-D-neuraminic acid aldonase immobilizing method
The invention relates to produce the N-acetyl neuraminic acid by the N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid aldolase immobilized enzyme. The process immobilizes the N-acetyl-D-neuraminic acid aldolaseby the affinity carrier using the N-acetyl glucosamine and the pyruvic sodium as the substrate.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for producing N-acetyl-glucosamine by using insect chitinase to degrade solid chitin
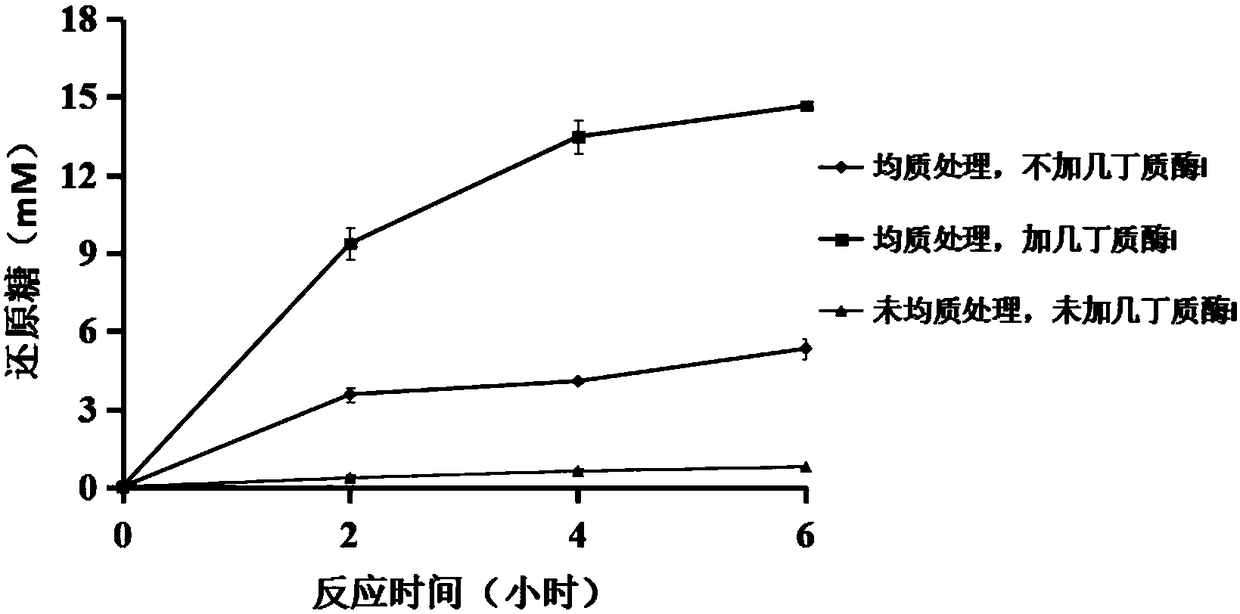
ActiveCN108085353APromote hydrolysisIncrease the areaFermentationBiotechnologyPotassium ferricyanide
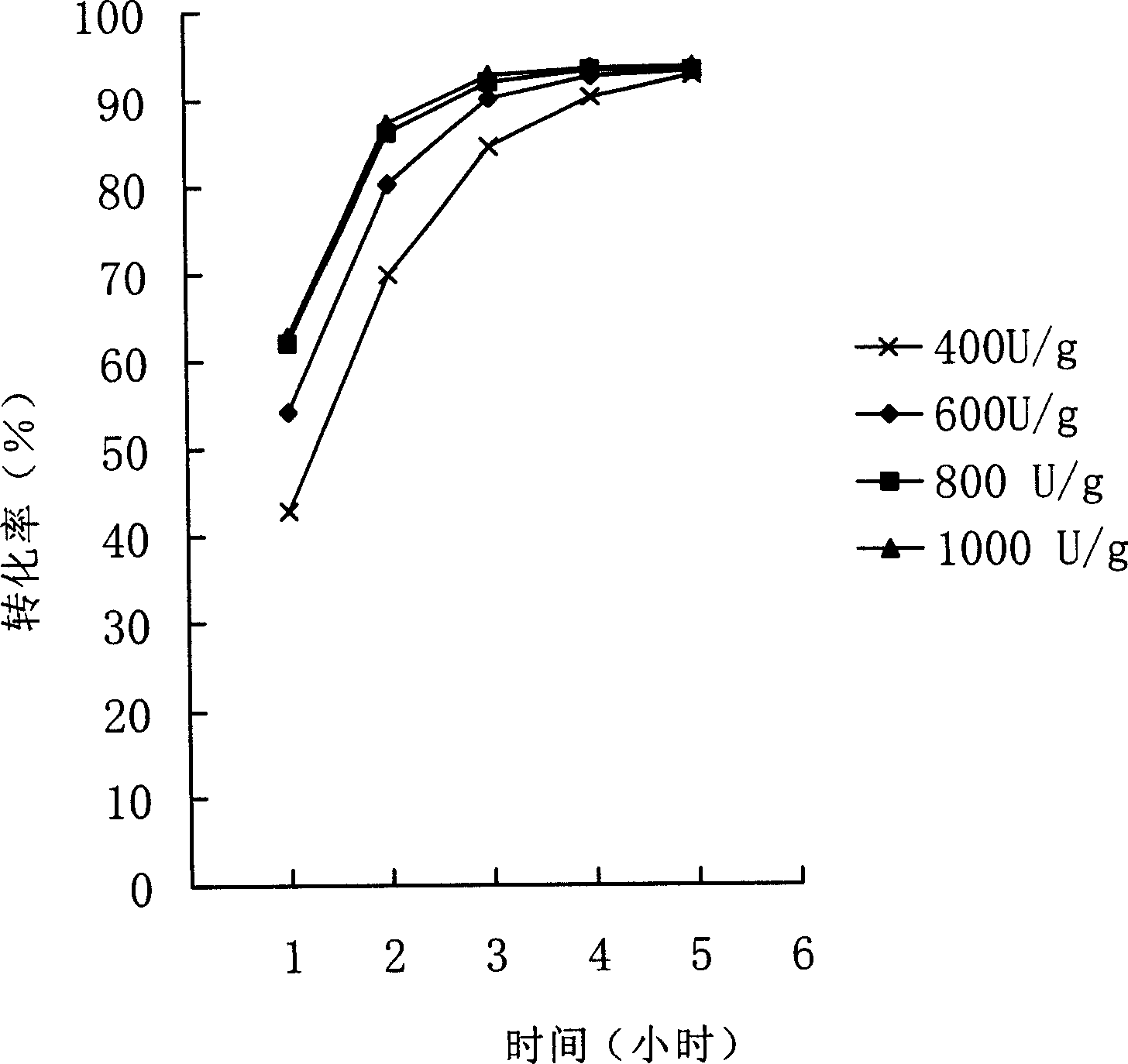
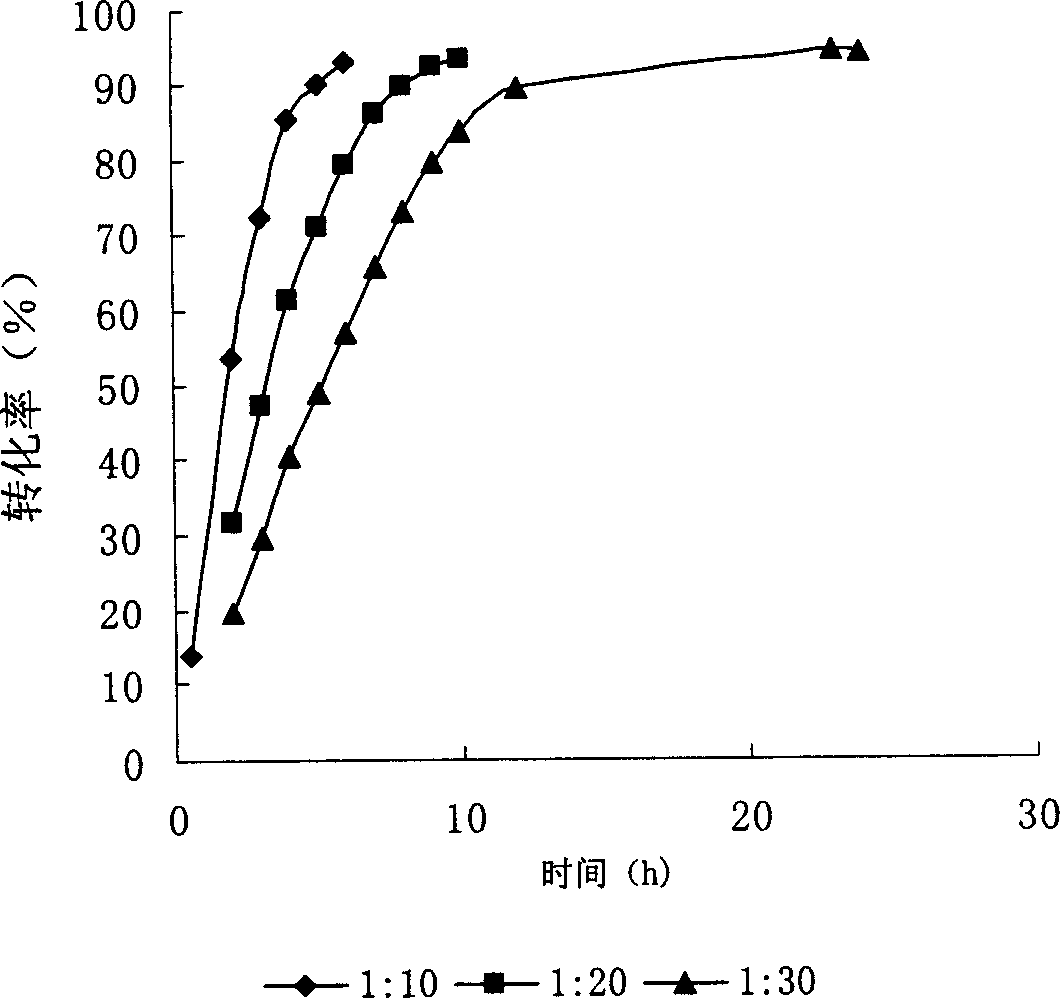
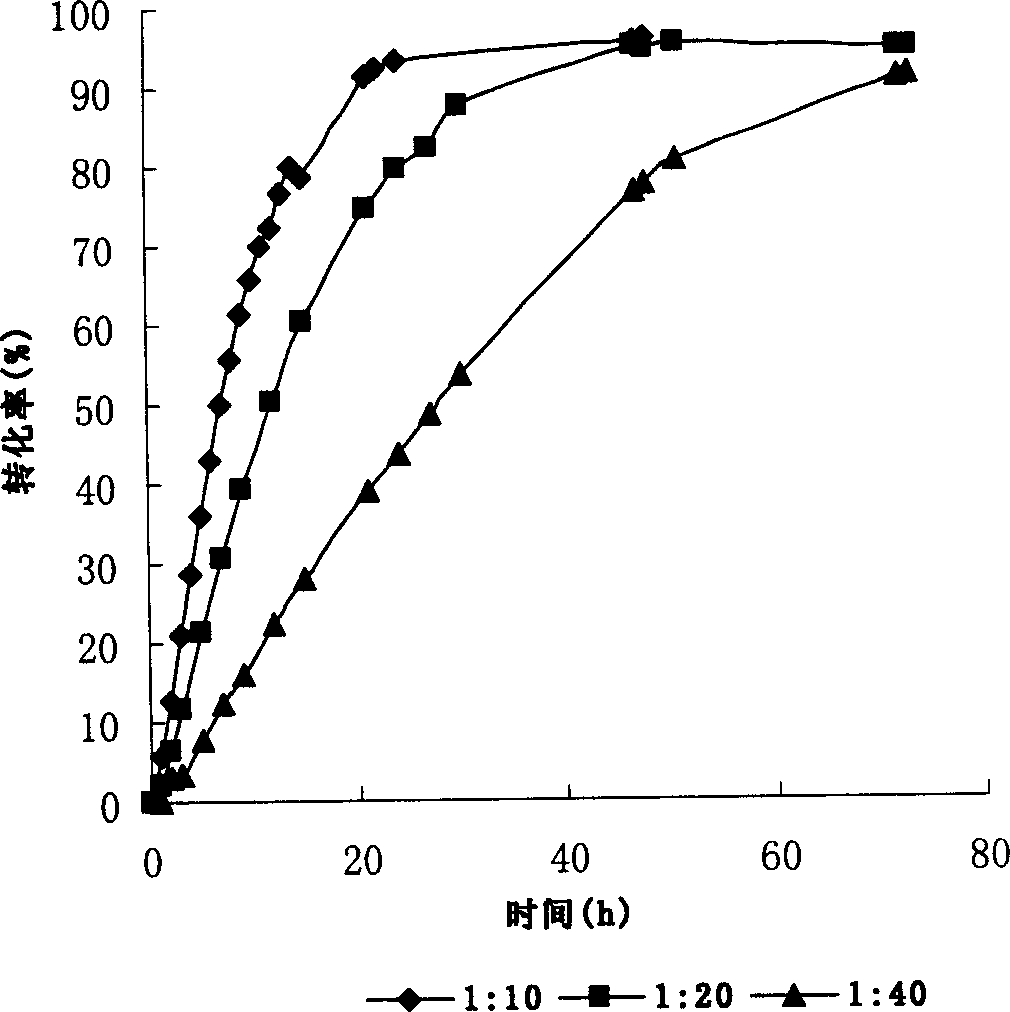
The invention discloses a method for producing N-acetyl-glucosamine by using insect chitinase to degrade solid chitin. According to the method, the solid chitin in a crystal state is used as a substrate to perform hydrolysis, and a composite enzyme used in the hydrolysis is chitinase H with a final concentration greater than 0.3mg / mL and chitinase I with a final concentration greater than 0.06mg / mL; and beta-N acetylhexosaminidase 1 with a final concentration greater than 0.06mg / mL can also be added. The method of the invention also comprises a pretreatment step of solid chitin, i.e., the solid chitin is crushed to serve as a substrate for producing the N-acetyl-glucosamine, the amount of a monosaccharide product is determined by virtue of a potassium ferricyanide method, the composite enzyme is used for degrading the solid chitin substrate, so that the conversion of more than 81 percent of substrate can be realized in 5 hours, and the industrialized application prospect is good.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Technology for preparing N-acetyl glucosamine through enzymatic hydrolysis chitin
InactiveCN109628525AEasy to operateImprove production efficiencyFermentationGlucose preparationsAlcohol
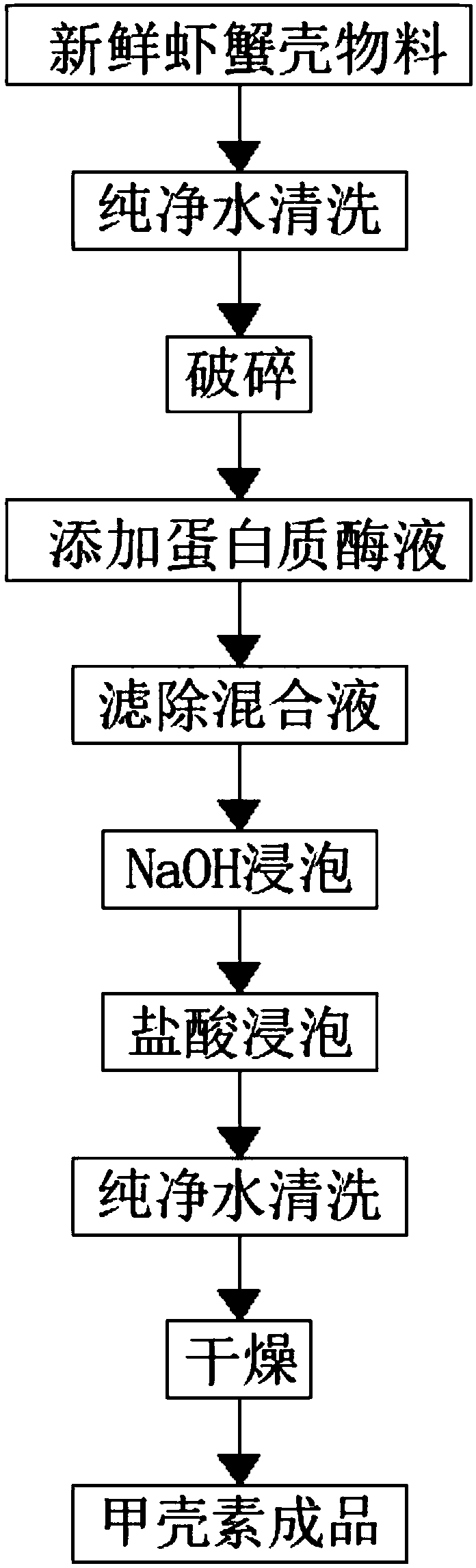
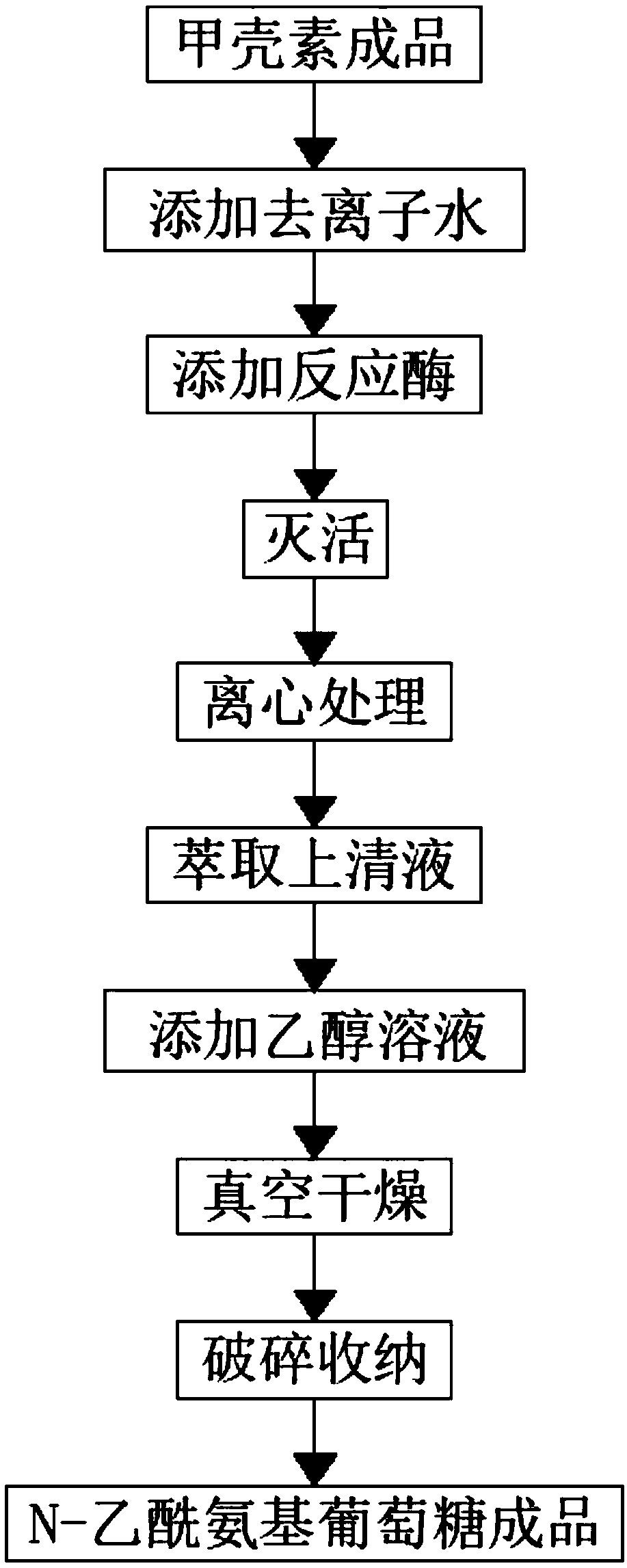
The invention relates to the technical field of glucose preparation technologies, and discloses a technology for preparing N-acetyl glucosamine through enzymatic hydrolysis chitin. The technology comprises the steps that a fresh shrimp and crab shell material is taken to be cleaned and crushed, a proteineous enzyme liquid is poured for enzymolysis treatment, a filter is adopted to filter the mixedliquid, soaking is carried out through 5%-8% of NaOH and 5%-8% of hydrochloric acid, drying is carried out after cleaning, a finished chitin product is obtained, 5000 L of deionized water is used forswelling, reaction enzyme is added, inactivation is carried out, centrifugal treatment is carried out, a liquid supernatant is extracted and mixed with an ethyl alcohol solution for precipitation, vacuum drying is carried out, the crushed material is packaged and stored, and the finished N-acetyl glucosamine product is obtained. The technology for preparing the N-acetyl glucosamine through the enzymatic hydrolysis chitin has the advantages that the common fresh shrimp and crab shell material is adopted for preparing the chitin, the operation is simple, the preparation efficiency is high, andthe product quality is high; the mixed enzyme liquid is adopted for the enzymolysis of the chitin in combination with auxiliary oscillation of ultrasonic wave, so that the preparation efficiency is improved, the technological process is simplified, the material is easy to obtain, and the product quality is higher.
Owner:ACERCHEM INT
Mass-spectrum-based analysis method of oxygen-connected N-acetyl-glucosamine-modified sugar protein
ActiveCN105445358AEnhanced MS signalEasy to analyzeMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGlycopeptideOxygen
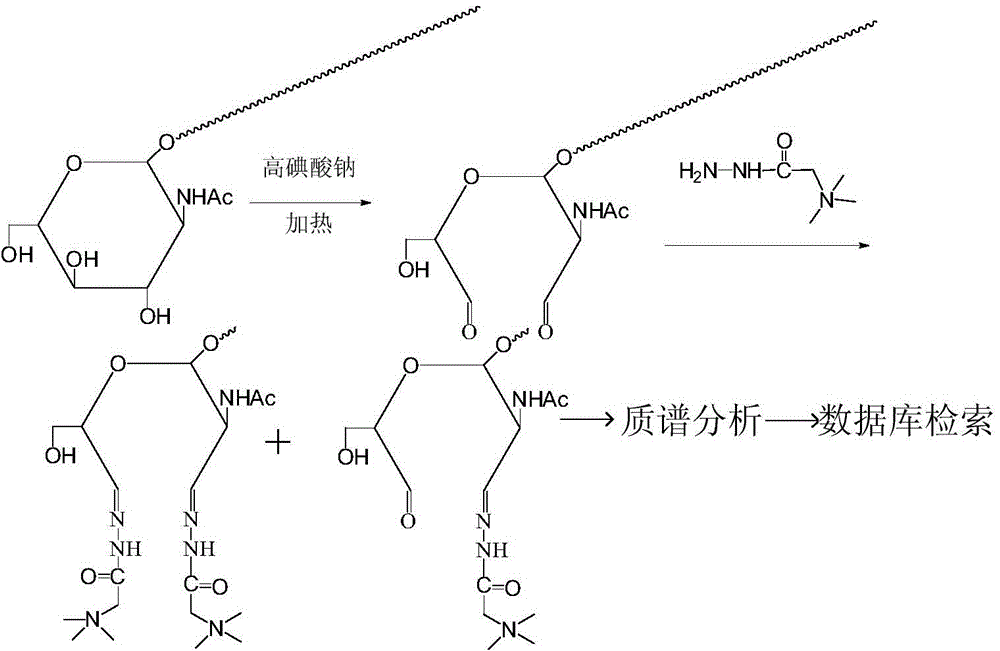
The present invention relates to a mass-spectrum-based analysis method of an oxygen-connected N-acetyl-glucosamine (O-GlcNAc)-modified sugar protein. After enzymolysis of the O-GlcNAc-modified sugar protein by protease, peptide sections are generated, sodium periodate is used for oxidation for modifying para-position hydroxyl groups on group N-acetyl-glucosamine to form two aldehyde groups by ring-opening reaction, and acylhydrazine on Girard reagent T is reacted with the newly formed aldehyde group, so that a quaternary ammonium salt group is chemically derived on the O-GlcNAc-modified glycopeptide. The presence of the quaternary ammonium salt group can effectively enhance a mass response signal of the peptide sections, and the derived glycopeptide can keep certain raw sugar modified groups, subsequent mass spectrometry is performed, and the sugar-based modified sugar protein can be analyzed and identified by database search and other analysis means.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com