Method for producing N-acetyl-glucosamine by using insect chitinase to degrade solid chitin
A technology for chitinase and acetamido, which is applied in the field of producing N-acetylglucosamine, can solve the problems of low efficiency of chitin, limited chitin, complex composition and the like, achieves fast reaction speed, facilitates purification and simple composition Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0024] Step 1, pretreatment of chitin
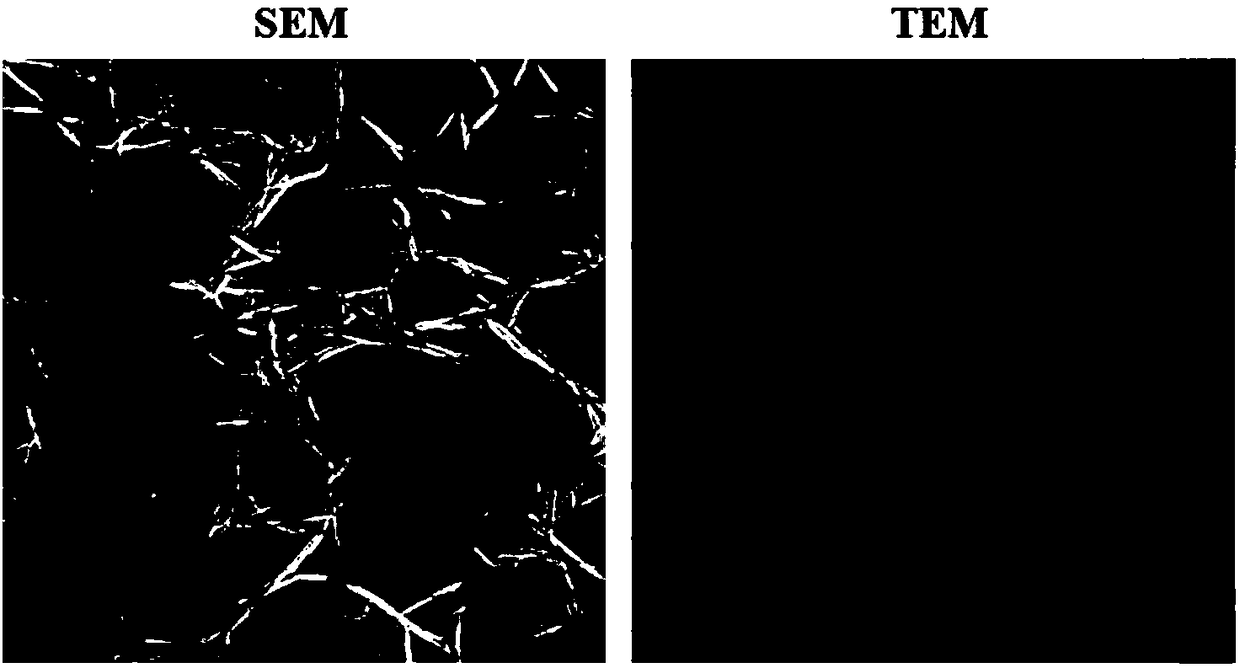
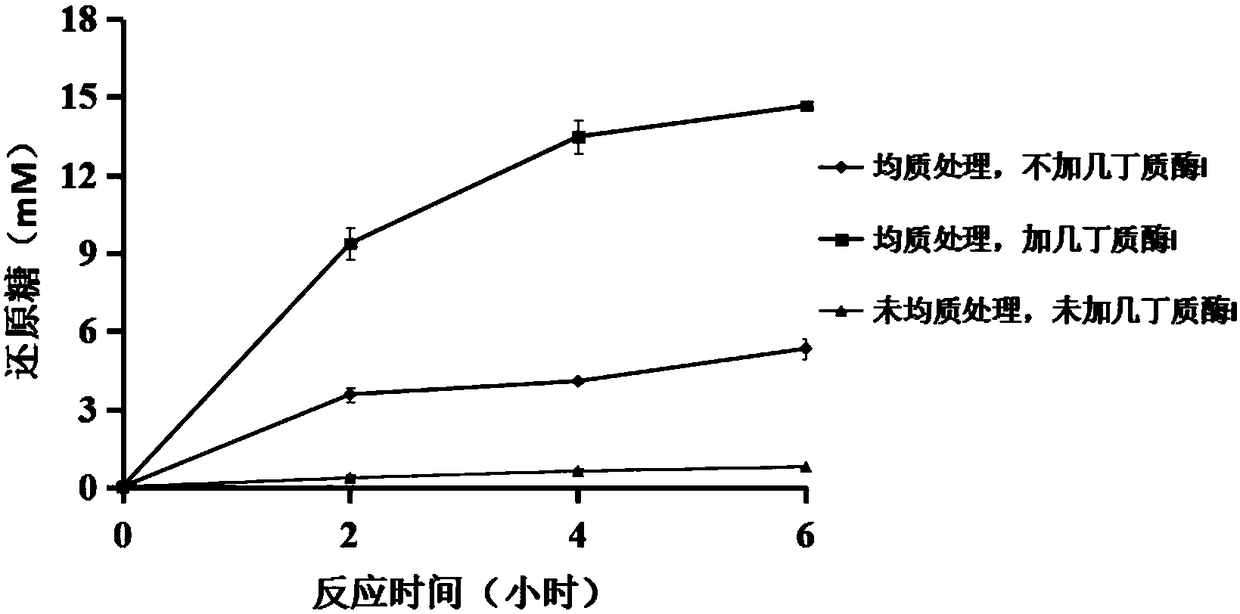
[0025] Get solid chitin (TCI company) to be dissolved in water and be configured into 1% solution, adopt high-pressure homogenizer, solid chitin is broken under 90mPa condition, time 10 minutes, obtain such as figure 1 Nanoscale chitin microfilaments shown.
[0026] Step 2, Pichia pastoris engineered bacteria express chitin hydrolase
[0027] According to the reports in the known literature, the insect chitinase H gene (GeneBank ID: AB201281, Liu et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry. 2016, 292, 2080-2088), chitinase I gene (GeneBank ID: DQ294305, Chen et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry.2014, 289, 17932–17940) and β-N acetylhexosaminidase 1 gene (GeneBank ID: DQ887769, Liu et al., Journal of Biological Chemistry .2011,286,4049–4058) Pichia strain GS115 of pPIC9 was used as a seed and inoculated into medium BMGY (1% yeast extract, 2% peptone, 0.34% yeast nitrogen base, 1% glycerol, 100mM KH 2 PO4, pH 6.0), cultured at 30°C and 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com