Bacillus subtilis for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid to recombine and application thereof
A technology of Bacillus subtilis and acetylneuraminic acid, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as insufficient metabolic flow strength, and achieve good application prospects, easy to use, and simple construction methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Construction of embodiment 1 recombinant fragment
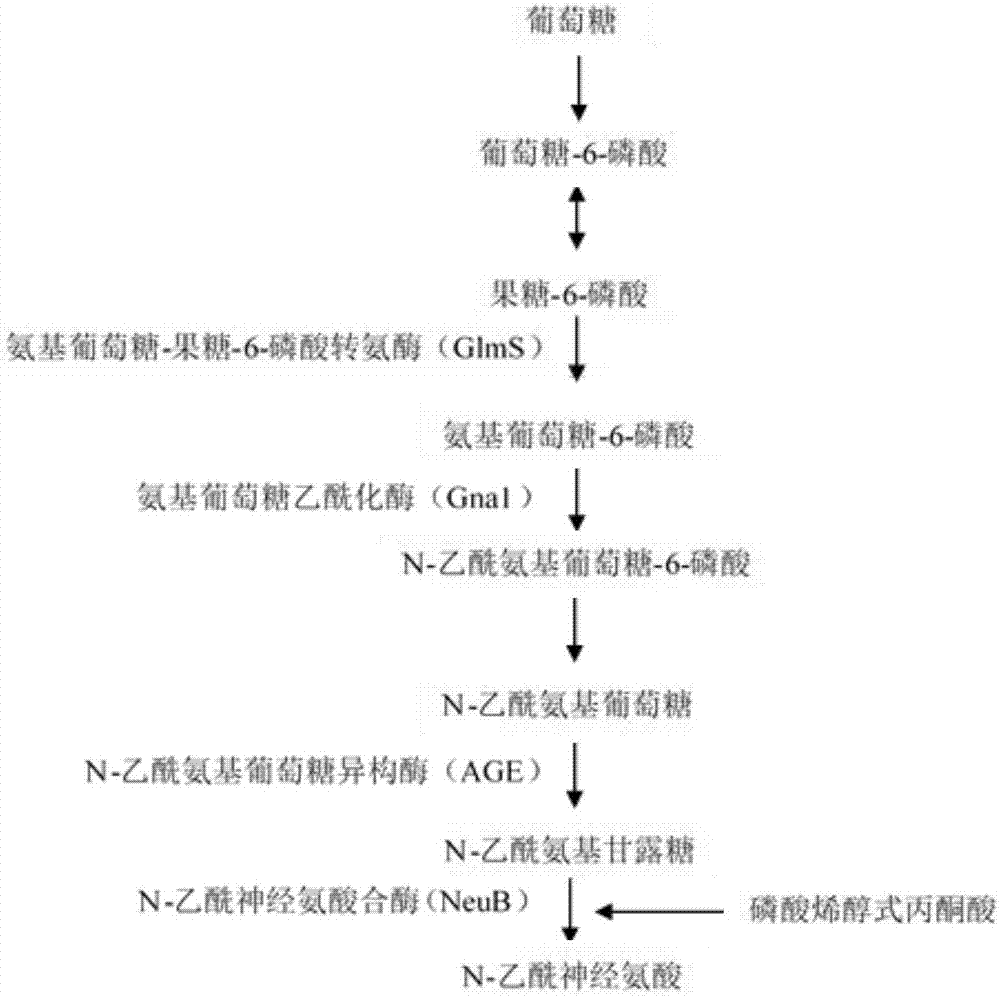
[0032]According to the sequence information of plasmid p43NMK-Cegna1 (constructed earlier in this experiment), primers with sequences such as SEQ ID NO.4 and SEQ ID NO.5 were designed GNA1-F: 5'-AACGACAAGAGGATGGTGCTGAATTGATAGGTGGTATGTTTTCGCTTGAAC-3', GNA1-R: 5'-CCTGTGTGAAATTGTTATCCGCTCTTAAAAGCGCTGGGTCATAAAATTACAG -3', use the above primers and use the plasmid pP43NMK-Cegna1 as a template to amplify the glucosamine acetylase encoding gene GNA1 containing the P43 promoter; according to the Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis 168) genome as a template, according to the 50S published on NCBI Ribosomal protein L25 gene (CTC, GenBank: NC_000964.3), design both sides of the homology arm primers, the sequences are as SEQ ID NO.6 and SEQ ID NO.7 left homology arm primer: ctc-1F: 5' -ACGGGGAAGTCCAAATTAATATCG-3', ctc-1R:5'-TTCAAGCGAAAACATACCACCTATCAATTCAGCACCATCCTCTTGTCGTT-3', the sequence is respectively the right homology arm ...
Embodiment 2
[0033] The construction of embodiment 2 recombinant plasmids
[0034] According to the N-acetylglucosamine isomerase gene AGE in Nostoc algae (Anabaena sp.CH1, GenBank: DQ661858.1) published on NCBI, the gene was synthesized after optimizing the preferred codon of Bacillus subtilis, and the designed sequences were SEQ The primers of ID NO.12 and SEQ ID NO.13: AGE-F: 5'-ATAAAGTGATAGCGGTACCATTATAGGTAAGAGAGGAATGTACACATGGGCAAAAACTACAAGCTCTG-3', AGE-R: 5'-ACGATGTAGATGTTAGACATGTGTACATTCCTCTTACCCCGGGTTATGAAAGTGCTTCAAACTGTTGCC-3', using the above primers to synthesize isomeric N-acetylglucose The enzyme gene was used as a template to amplify the AGE gene fragment; according to the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase gene NeuB of Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli K1, GenBank: U05248.1) published on NCBI, after optimizing the preferred codon of Bacillus subtilis, Gene synthesis, primers designed with sequences of SEQ ID NO.14 and SEQ ID NO.15: NeuB-F: 5'-ATGTCTAACATCATCGTGGCAGAAAT-3', Neu...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Embodiment 3 Construction of recombinant CPZC fragment Bacillus subtilis
[0036] The constructed recombinant fragment CPZC was transformed into Bacillus subtilis (Bacillus subtilis 168ΔnagPΔnagPΔgamPΔgamAΔnagAΔnagBΔ1dhΔpta::lox72). GNA1-F and GNA1-R primers were used to select transformants for colony PCR, and a band of 864bp appeared, verifying that the recombinant Bacillus subtilis B6C was successfully constructed.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com