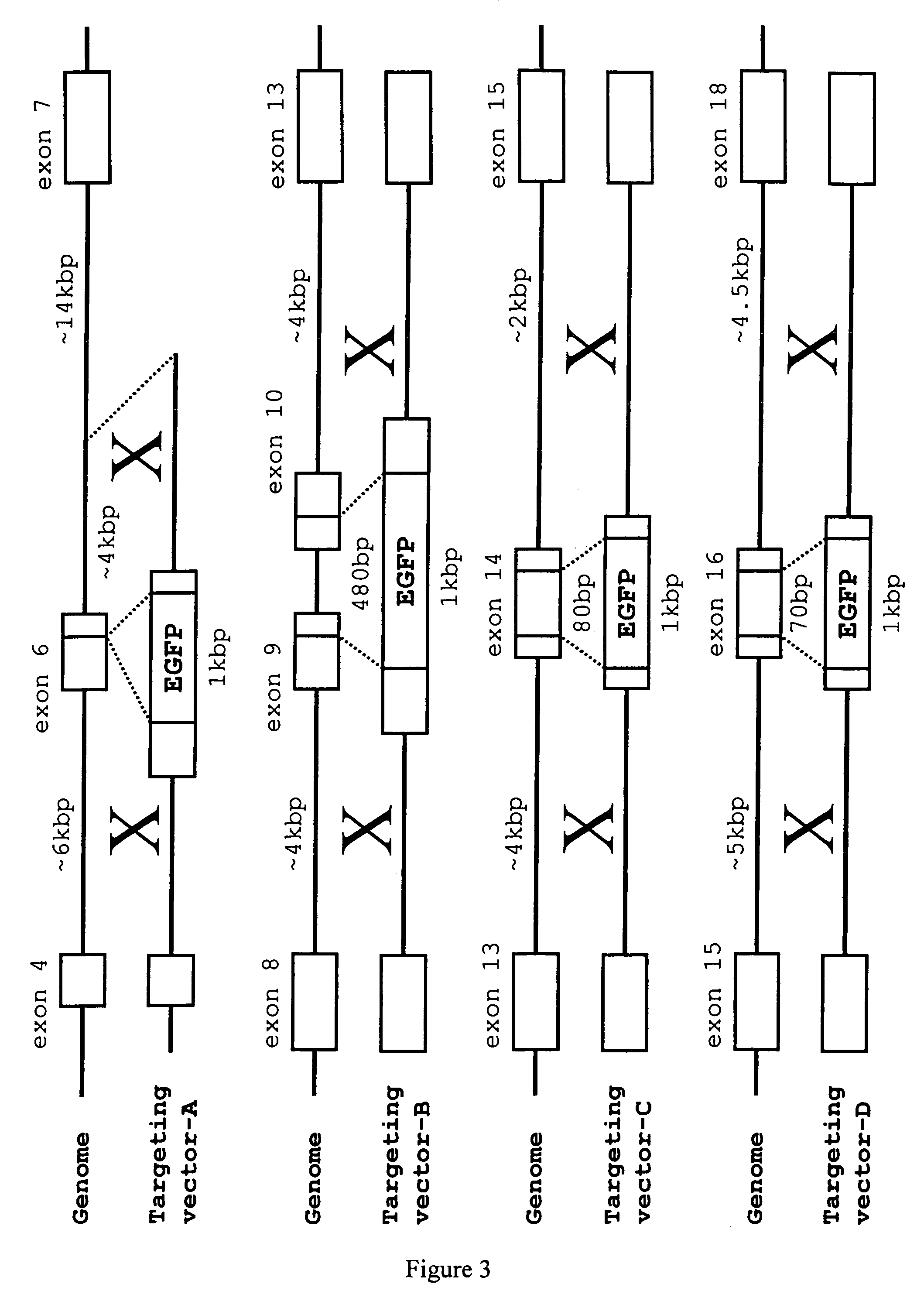
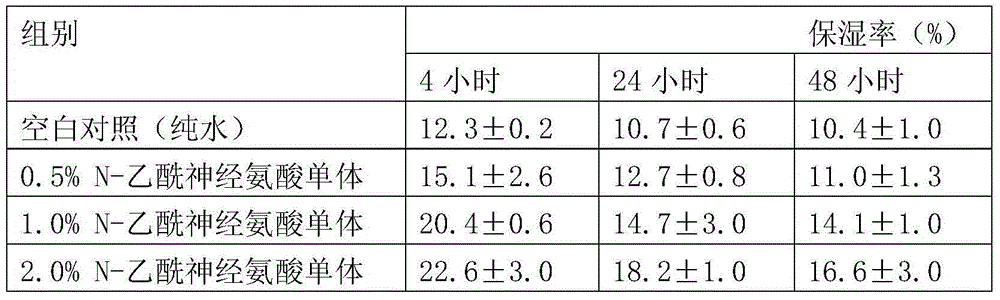
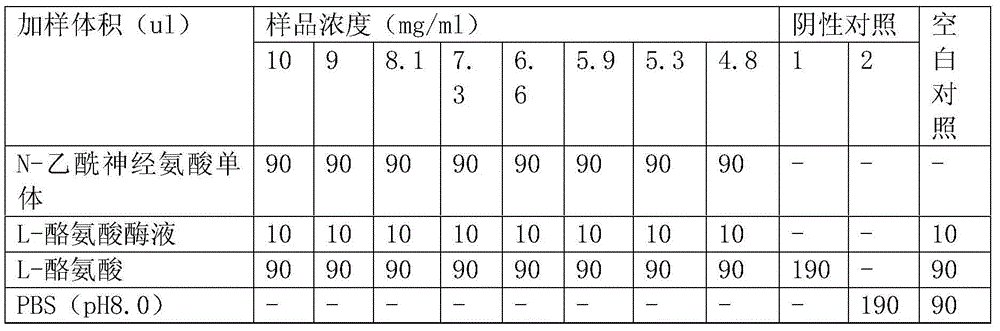
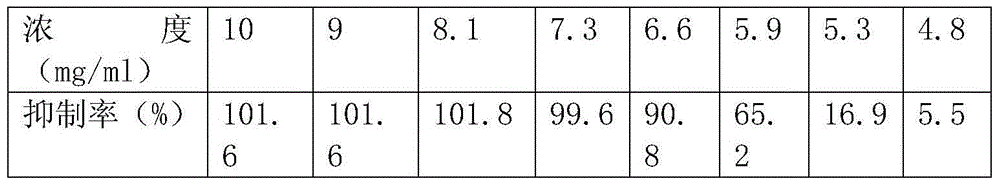
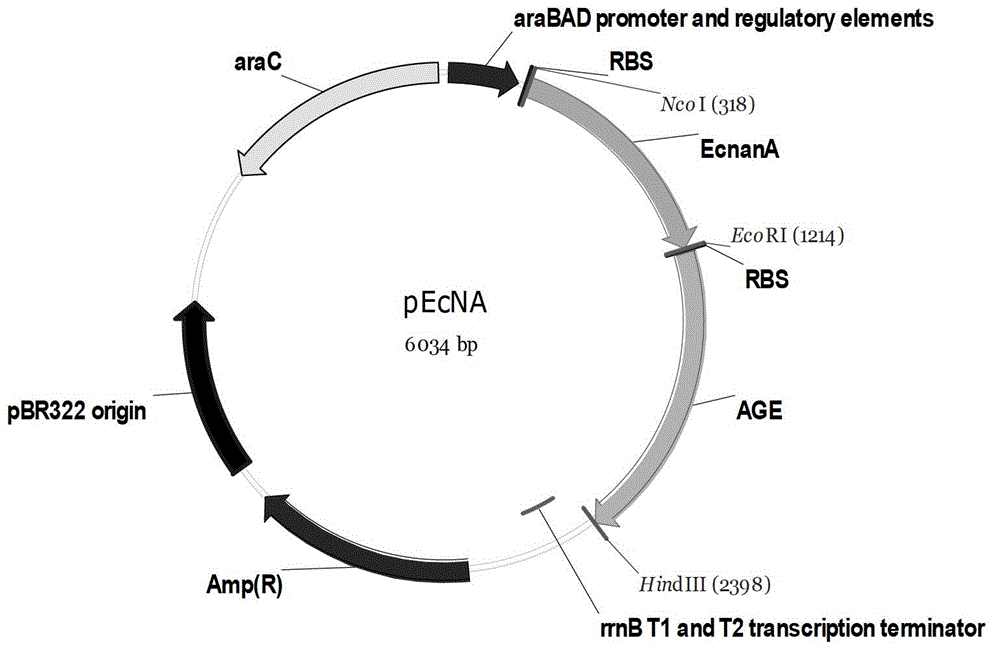
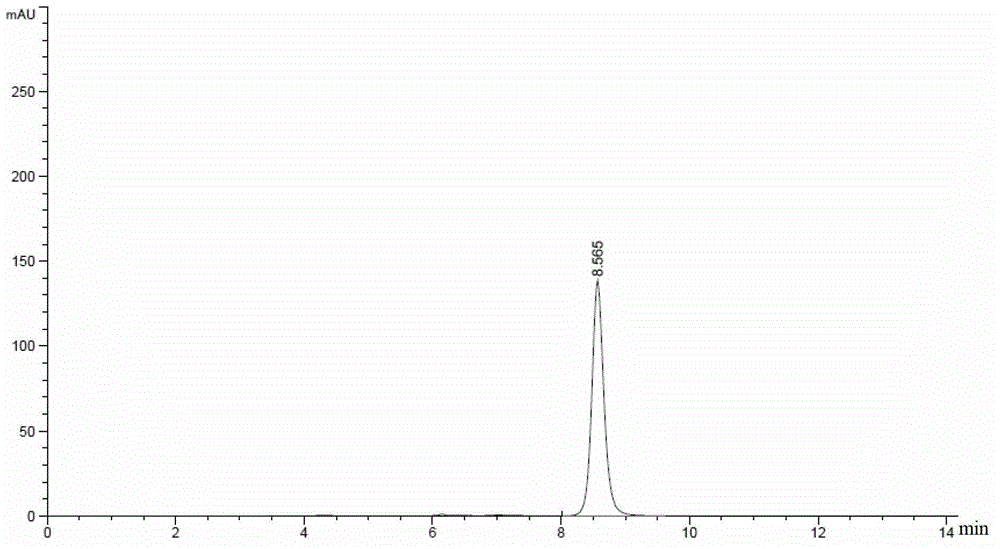
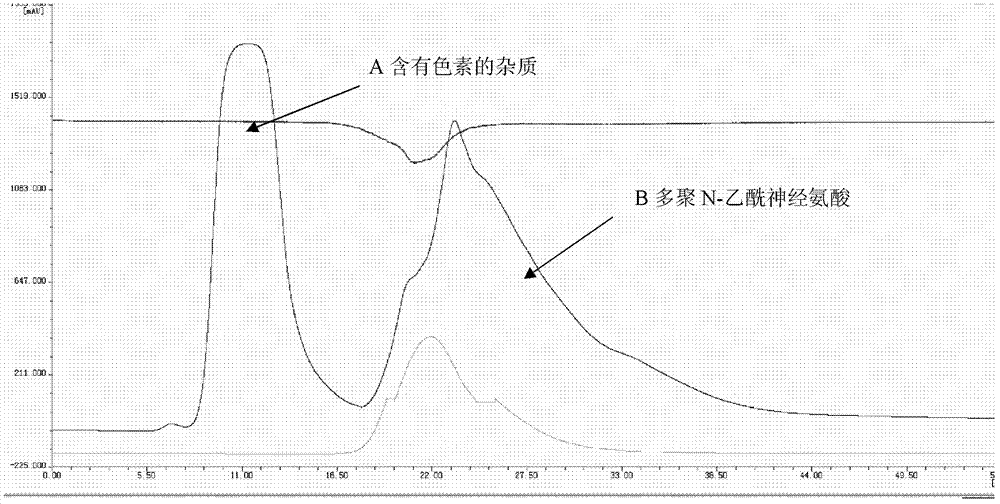
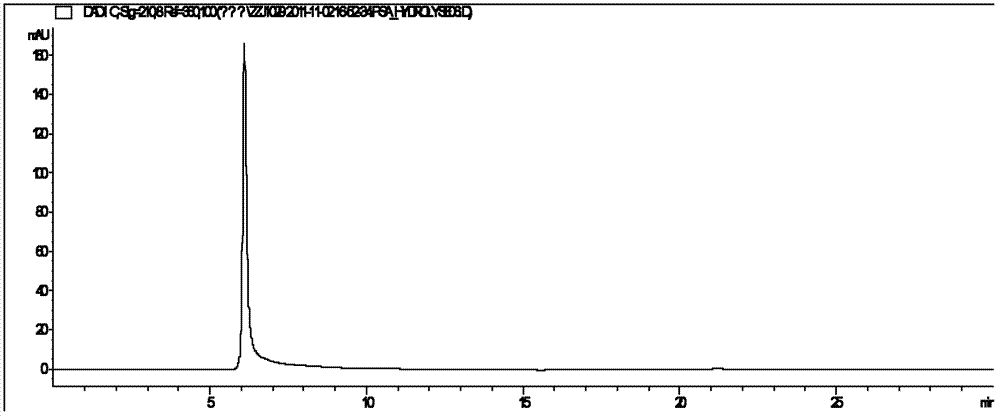
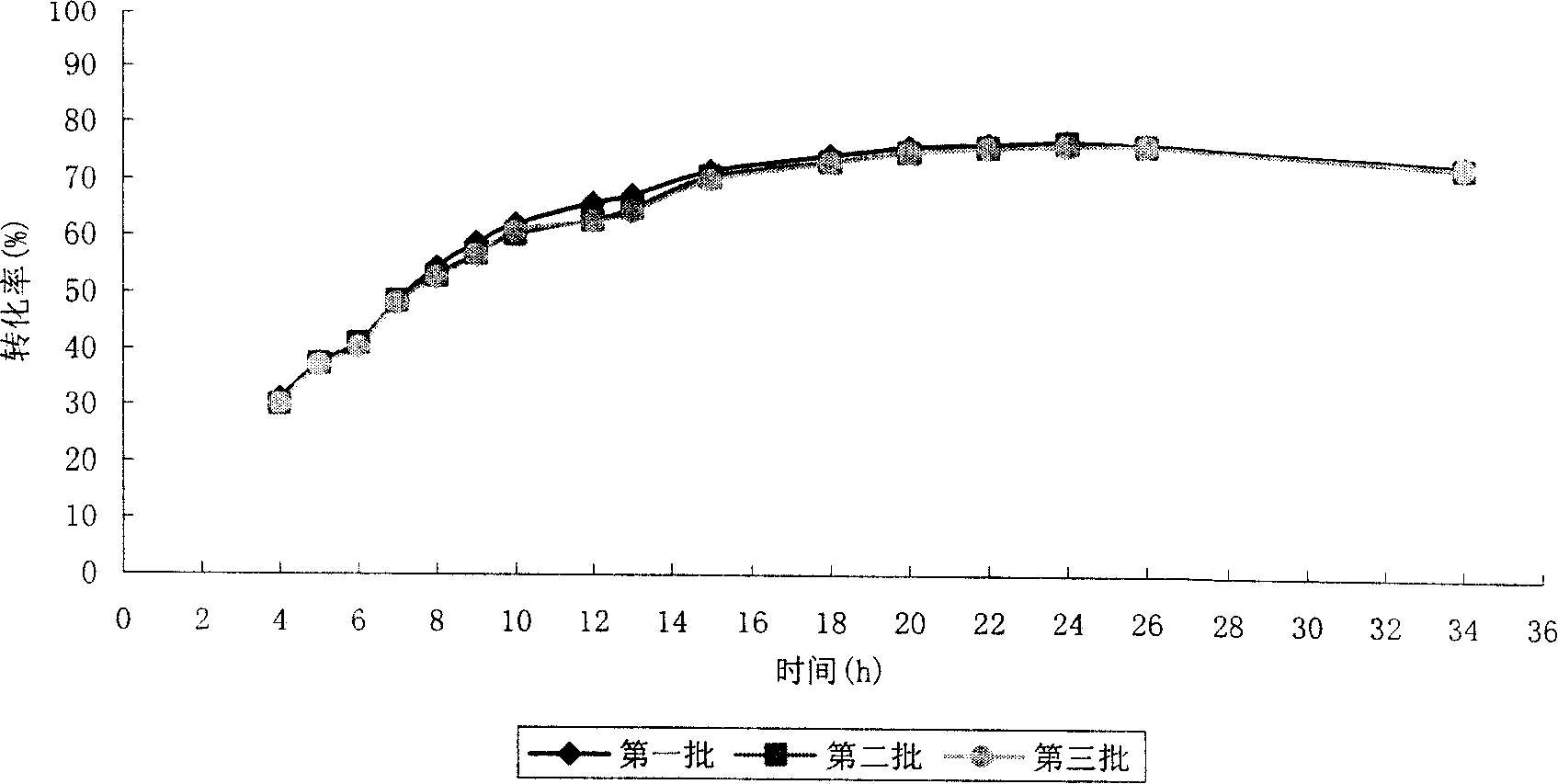
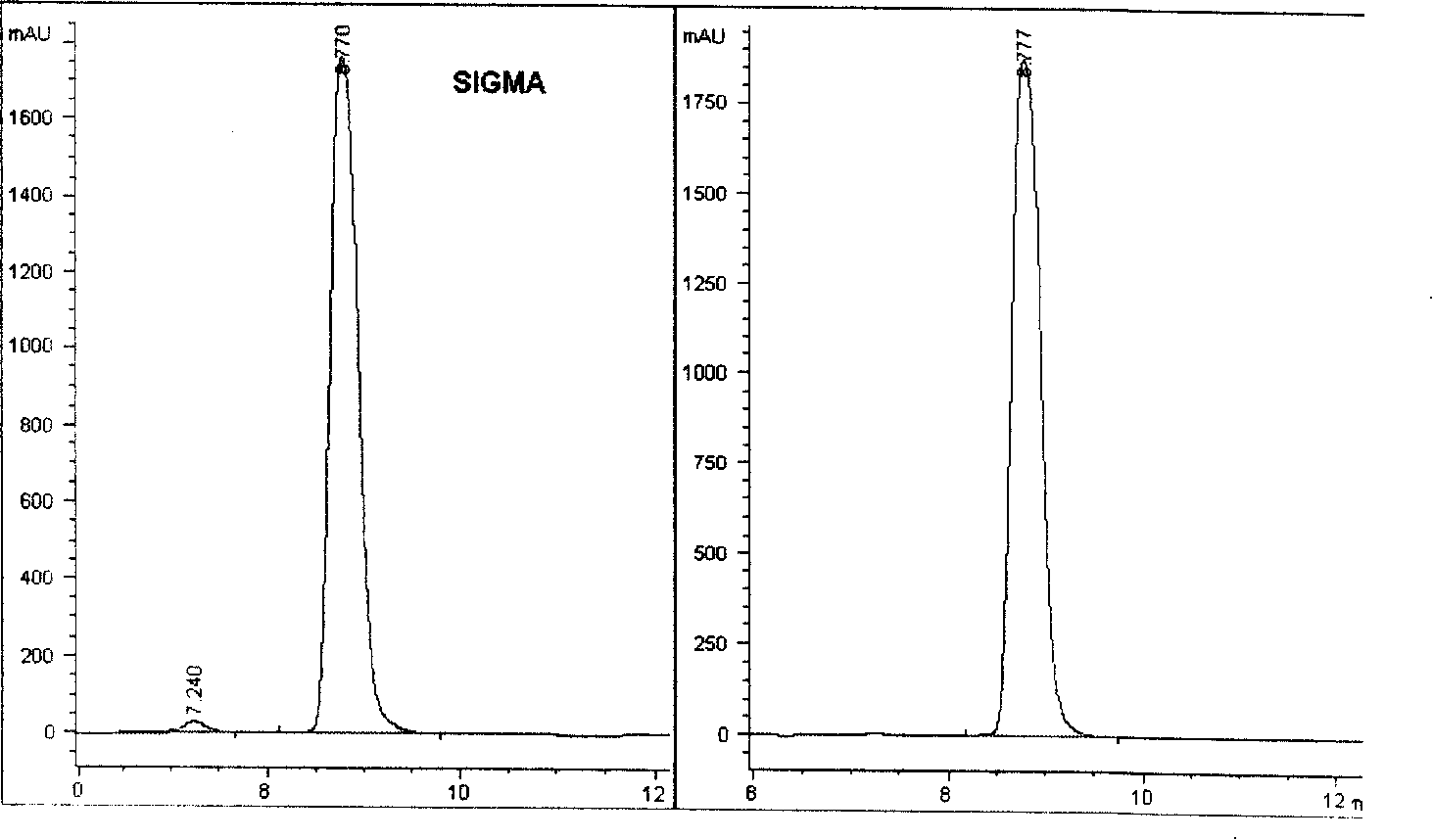
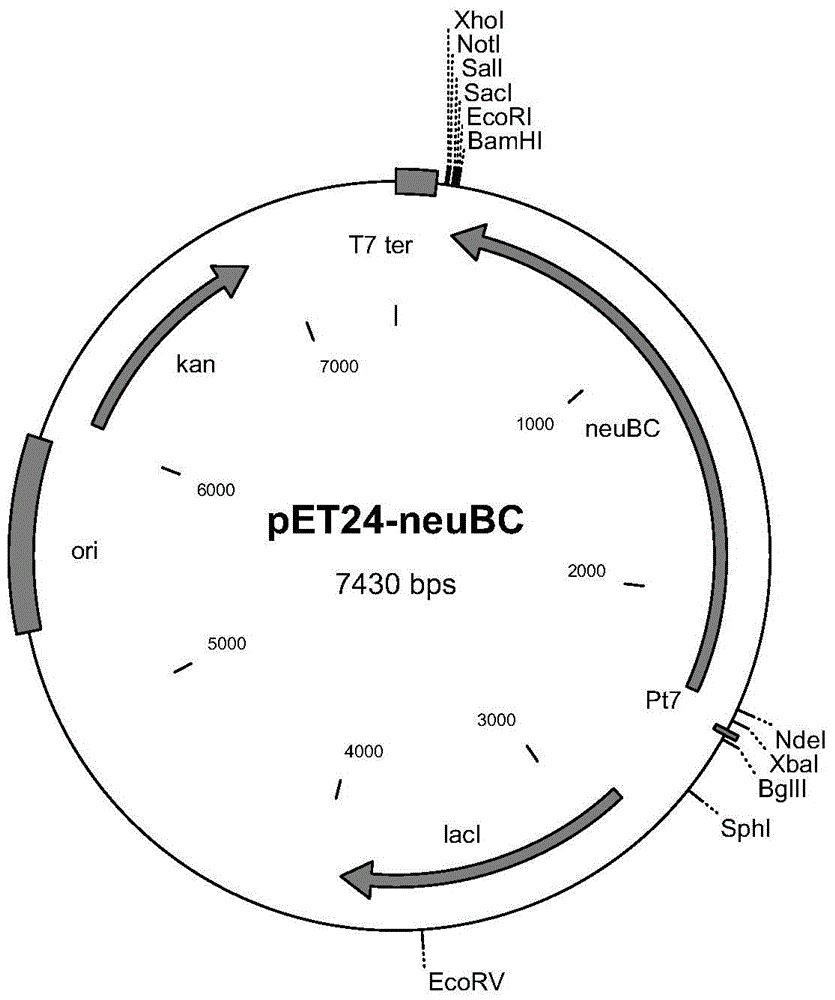
Patents
Literature
147 results about "N acetylneuraminate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
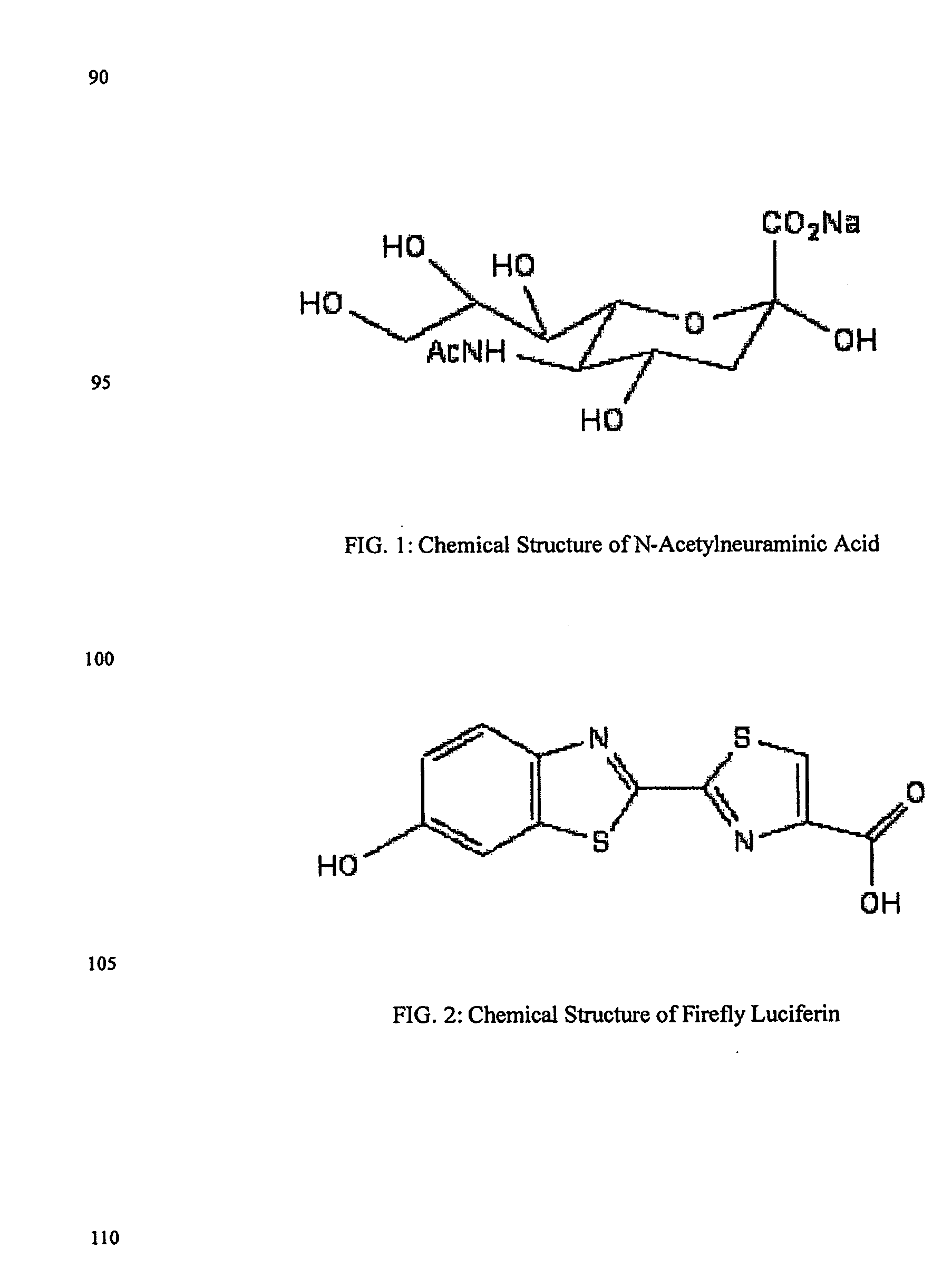
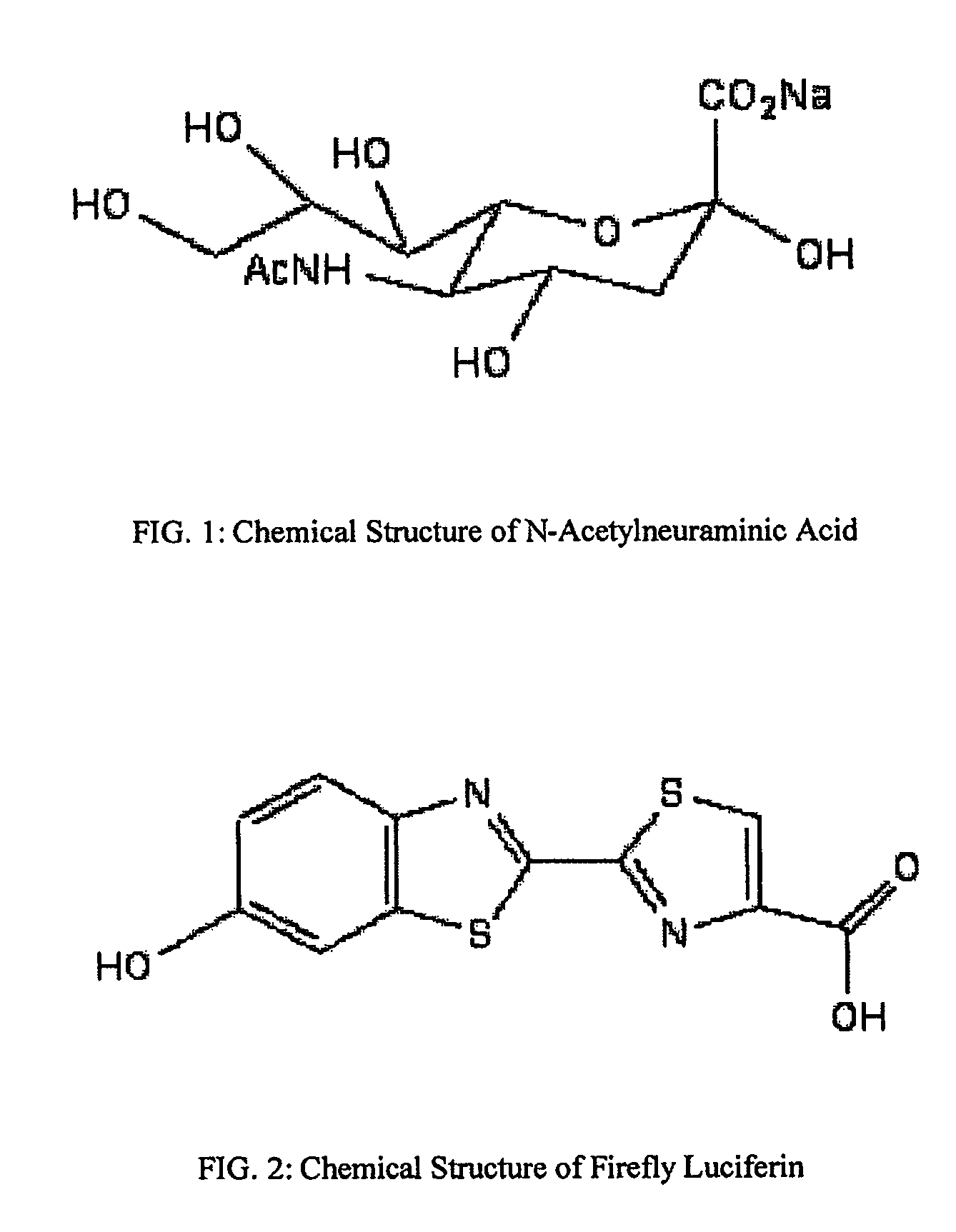
N-acetyl derivative of the amino sugar neuraminic acid; the most common of the sialic acids; occurs in many polysaccharides, glycoproteins, and glycolipids in animals and bacteria.
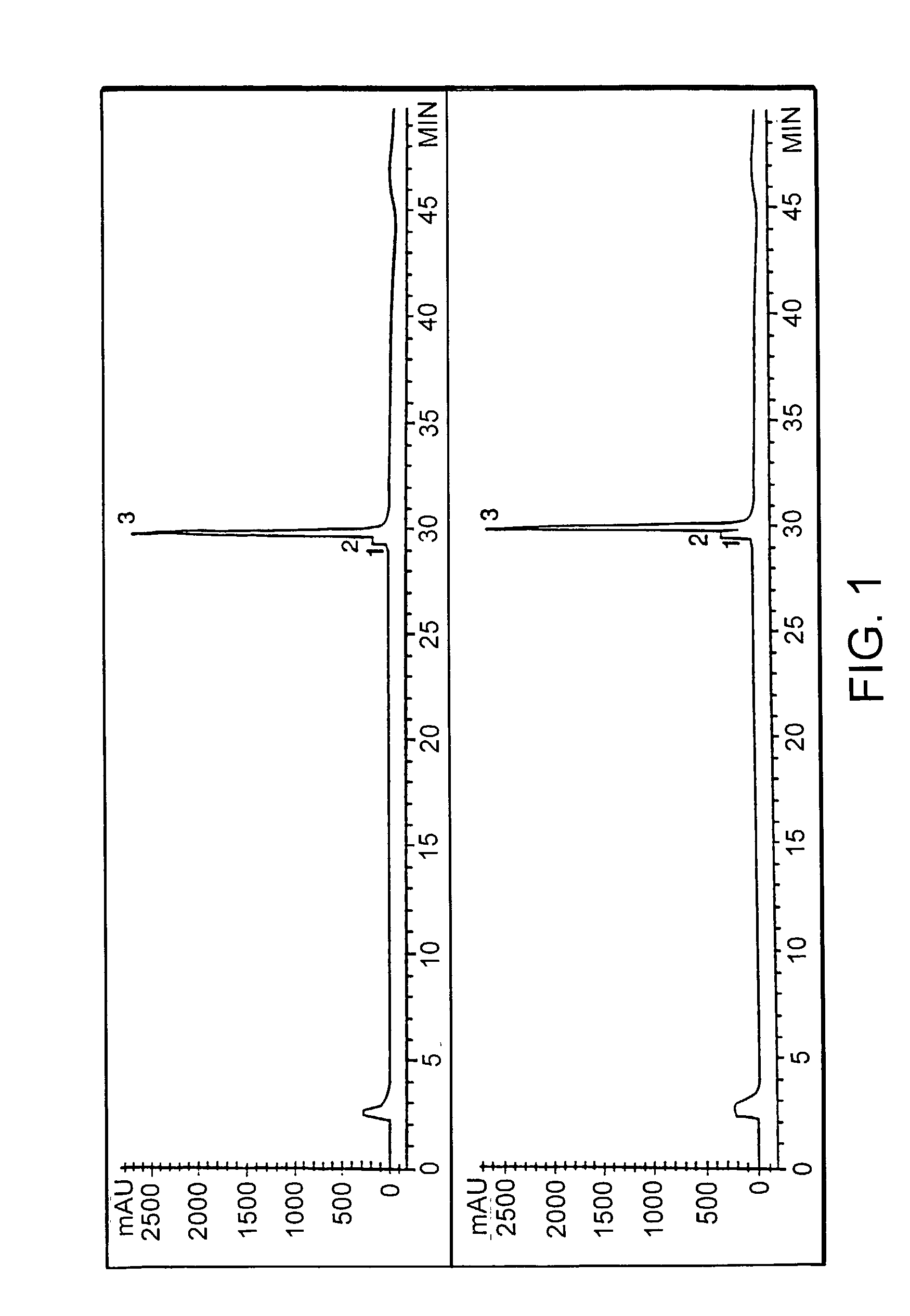
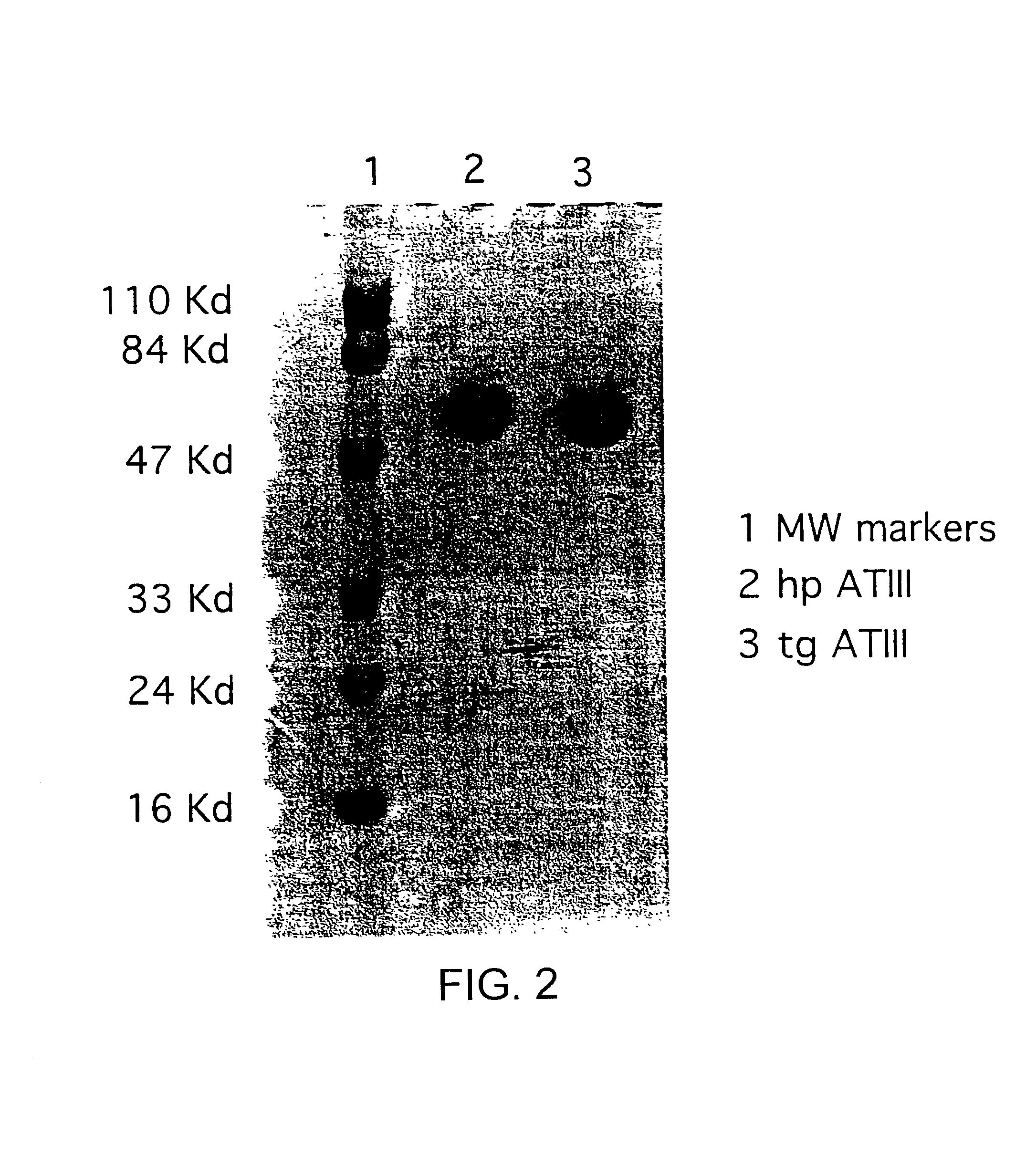
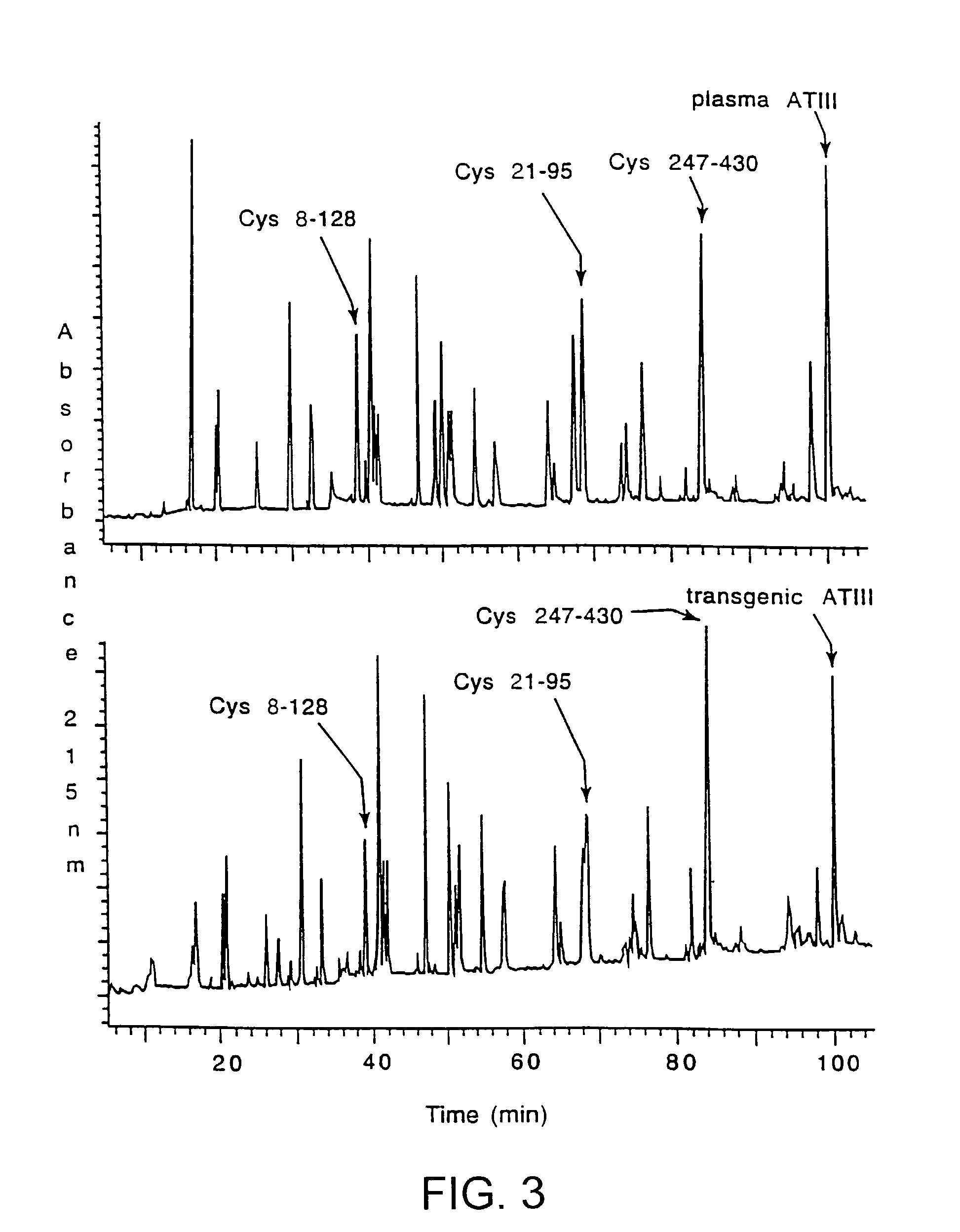
Treatments using transgenic goat produced antithrombin III
InactiveUS7019193B2Improve clearance ratePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPlasma derivedMonosaccharide composition
This invention relates to transgenically produced human Antithrombin III (tgATIII). The human ATIII produced by the transgenic process of the present invention has a monosaccharide composition which comprises N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) along with fucose, N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, mannose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid / N-glycolyneuraminic acid. The monosaccharide composition differs with that of plasma derived ATIII (phATIII). It has been found that tgATIII has an increased clearance rate when compared to phATIII.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
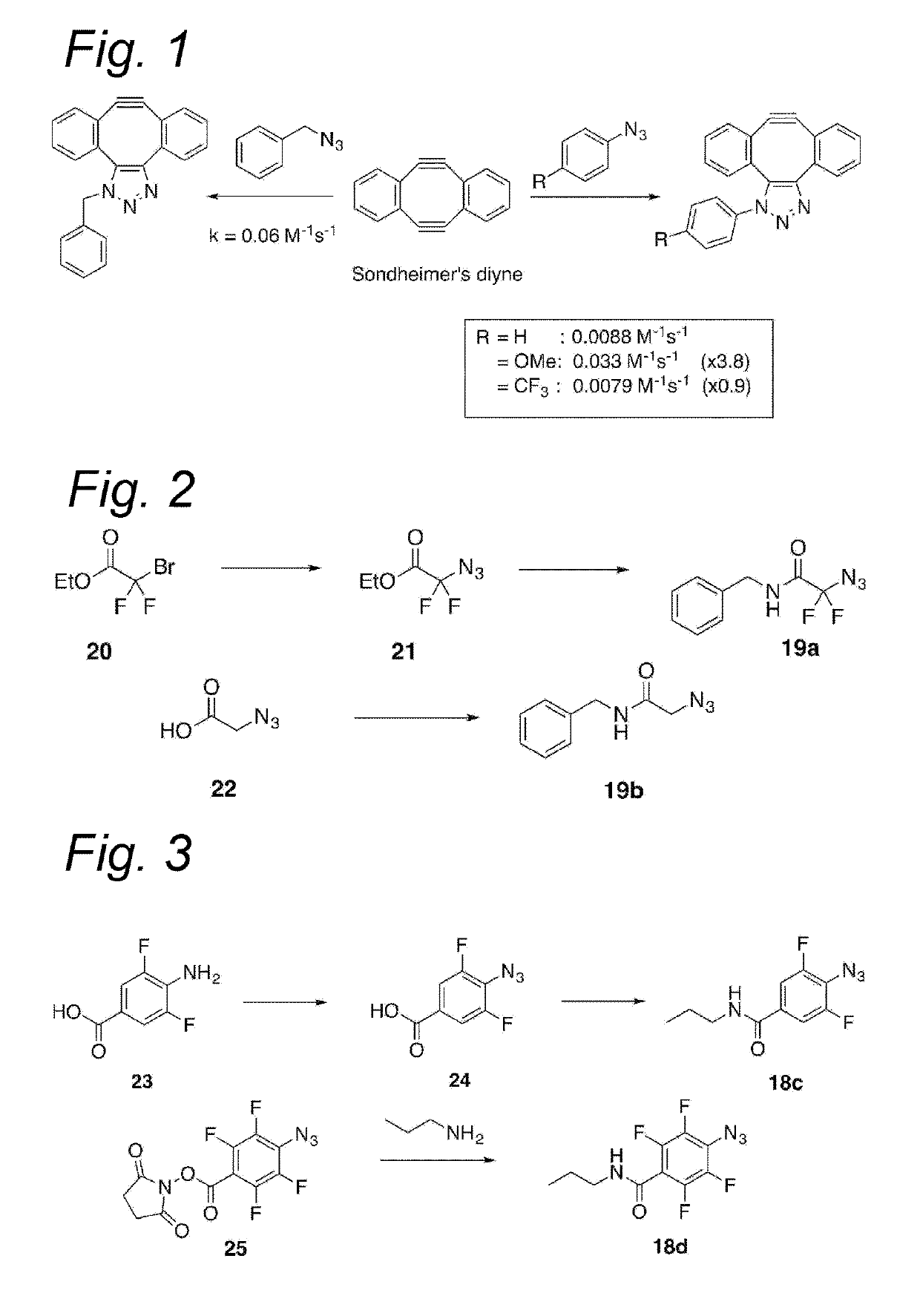
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS10266502B2Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Porcine CMP-N-Acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase gene
InactiveUS7368284B2Reduce immune rejectionNervous disorderSugar derivativesGenomic DNACMP-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase
The present invention provides porcine CMP-N-Acetylneuraminic-Acid Hydroxylase (CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase) protein, cDNA, and genomic DNA regulatory sequences. Furthermore, the present invention includes porcine animals, tissues, and organs, as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissues, and organs, which lack expression of functional CMP-Neu5Ac hydroxylase. Such animals, tissues, organs, and cells can be used in research and in medical therapy, including in xenotransplantation, and in industrial livestock farming operations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Application of N-acetylneuraminic acid monomer or its hydrate in cosmetics
InactiveCN104083291AHas moisturizing effectHas whitening effectCosmetic preparationsMake-upCell membraneMelanin
The invention relates to an application of an N-acetylneuraminic acid monomer or its hydrate in cosmetics. The N-acetylneuraminic acid monomer or its hydrate has the efficacies of moisture retention, whitening, inflammation eliminating, acne eliminating and ageing resisting. The N-acetylneuraminic acid monomer having a moisture retention efficacy can maintain water in skins; the N-acetylneuraminic acid monomer having a whitening efficacy can effectively inhibit the generation of melanin in skin cells; the N-acetylneuraminic acid monomer having inflammation and acne eliminating efficacies can accelerate the elimination of inflammations and acnes; and the N-acetylneuraminic acid monomer having an ageing resisting efficacy is an important component of glycoprotein on the cell membrane, and has substantial effects on intercellular adhesion and cell elasticity guaranteeing.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103602627AEnhanced rate-limiting enzyme gene expressionPrevent backflowBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPhosphate
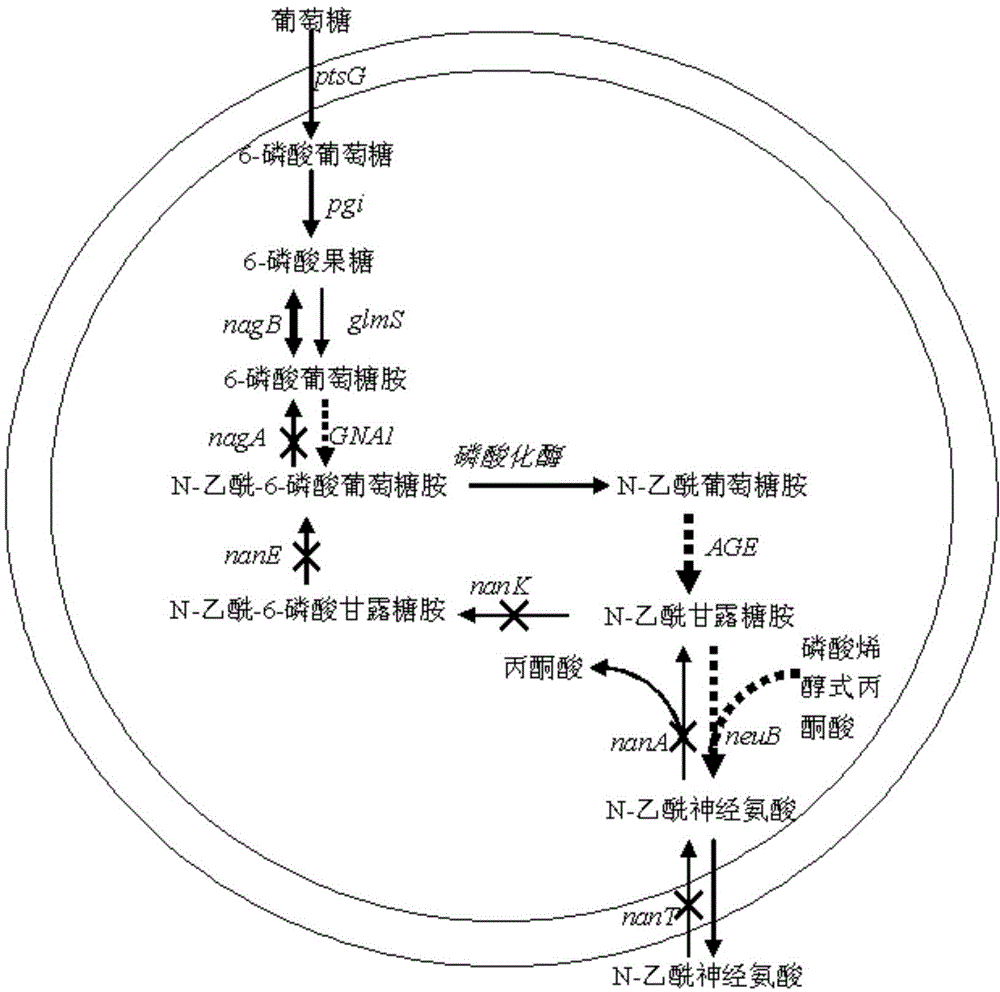
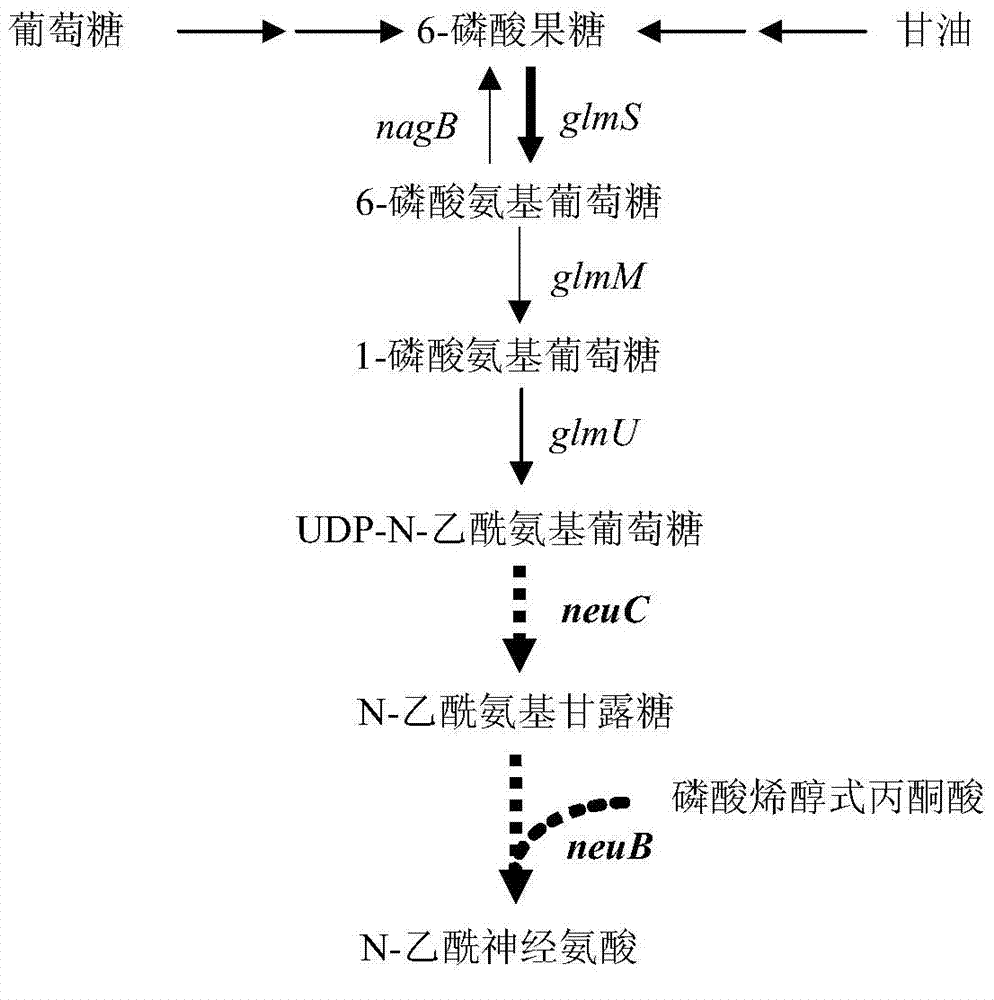
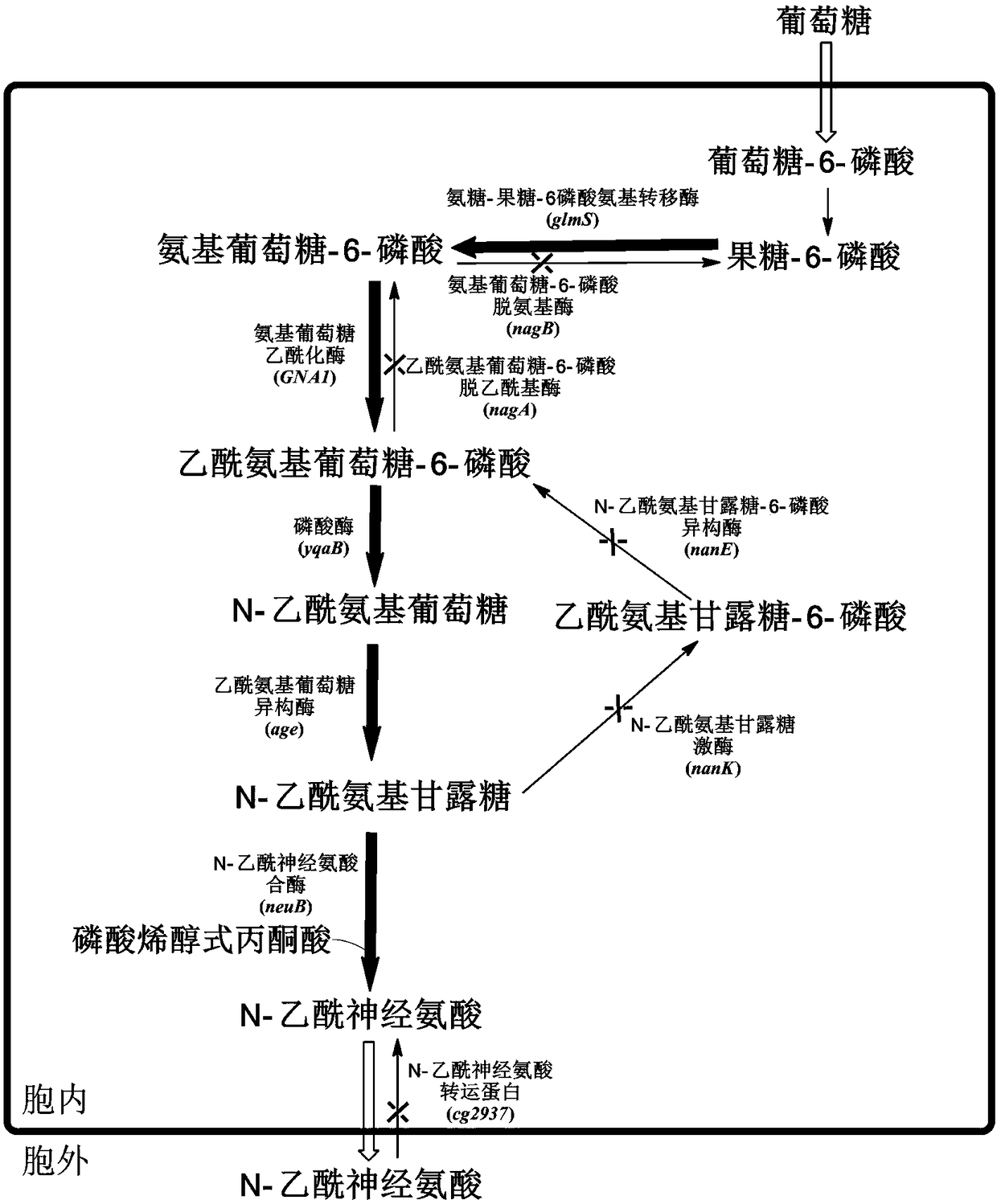
The invention discloses novel N-acetylneuraminic acid-producing escherichia coli engineering bacteria as well as a construction method and application thereof. The engineering bacterial is constructed by introducing an encoded 6-glucosamine phosphate acetylase gene, an N-acetyl glucosamine-2-isomerase gene and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene into escherichia coli to express, carrying out strengthened expression on 6-glucosamine phosphate deaminase gene contained in the escherichia coli per se and knocking off genes, for decomposing and utilizing enzyme in metabolic pathways, of the N-acetylneuraminic acid in the engineering bacteria. The engineering bacteria disclosed by the invention can be used for fermentation culture to synthesize the N-acetylneuraminic acid by using glucose or glycerinum as a substrate.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid
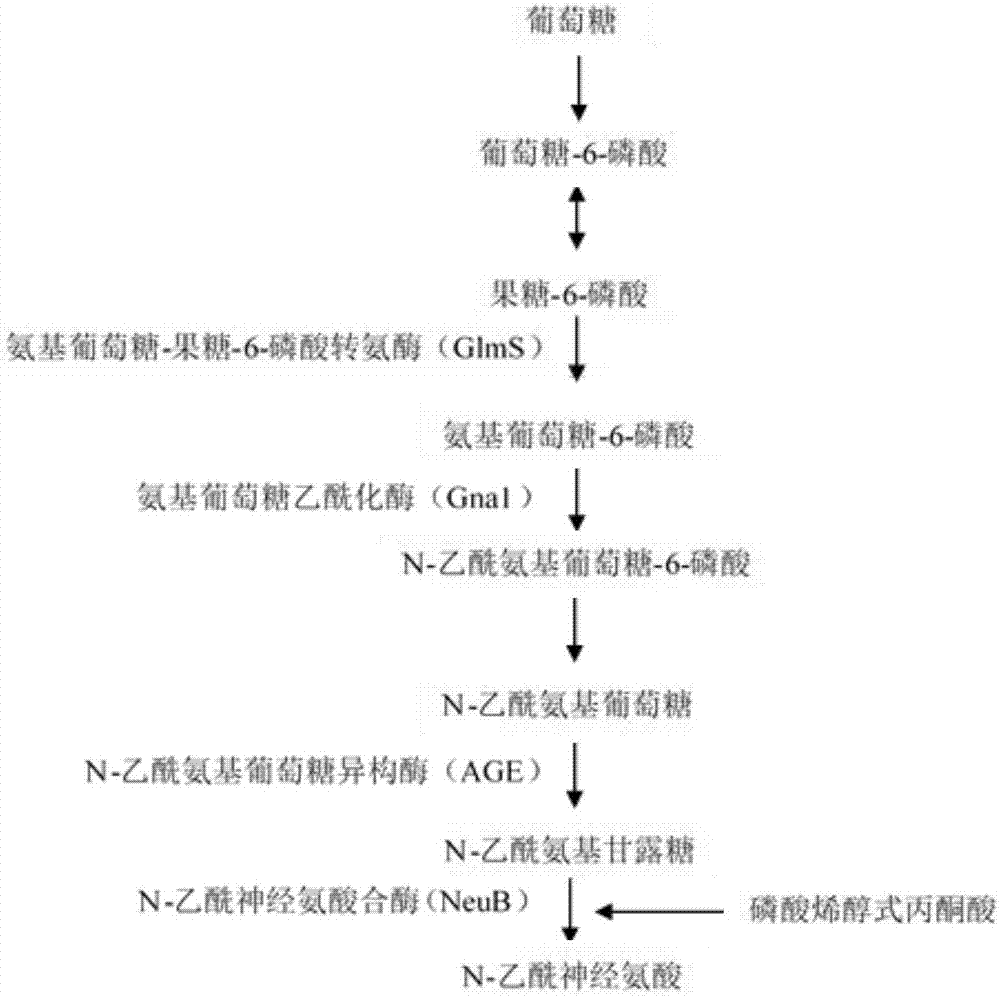
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis capable of increasing the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. Supply of phosphoenolpyruvic acid in the synthesis pathway of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased by taking bacillus subtilis (bacillus subtilis 168 delta nagP delta nagP delta gamP delta gamA delta nagA delta nagB delta 1dh delta pta::lox72; delta ctc::p43-Gna1, pP43NMK-AGE-NeuB) as an expression host and knocking out ptsG of a glucose specific enzyme EIICBA component of a phosphotransferase system, and therefore the synthesis passway is enhanced; compared with an original strain, the recombinant bacillus subtilis has the advantages that the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid is increased to 660 mg / L from 190 mg / L, and a foundation is laid for improving N-acetylneuraminic acid production from bacillus subtilis in metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for separating and purifying N-acetylneuraminic acid produced by microbiological fermentation
ActiveCN104628794AEasy to separatePromote flocculationEsterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesEscherichia coliMicroorganism
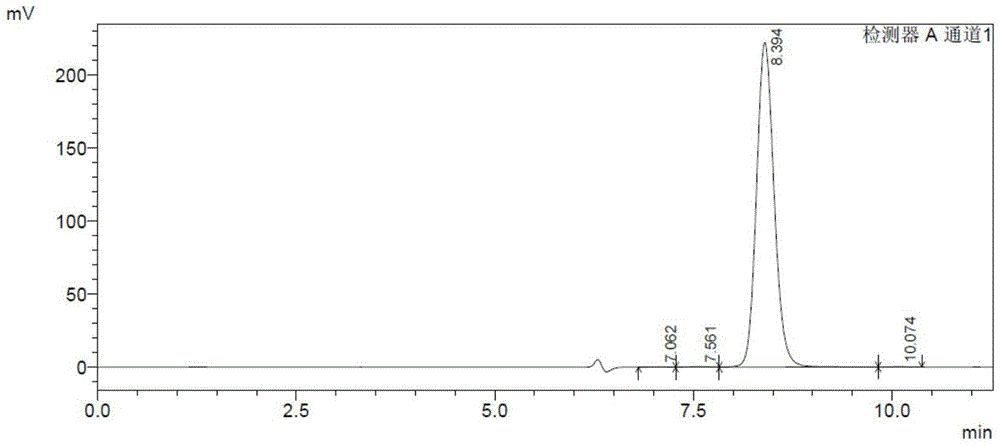
The invention provides a method for separating and purifying N-acetylneuraminic acid produced by microbiological fermentation. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: by taking fermentation liquid in fermenting production of N-acetylneuraminic acid by escherichia coli as a raw material, sterilizing; removing proteins; decoloring; desalting; crystallizing and the like to obtain a high purity N-acetylneuraminic acid product. Through tests, the product purity is at least 98%, and the requirements in the fields of foods, healthcare, medicines, cosmetics and the like can be satisfied. Moreover, the method is simple and easy to operate and is particularly suitable for industrial fermentation production of N-acetylneuraminic acid.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Reagents and kits for detection of influenza virus and the like
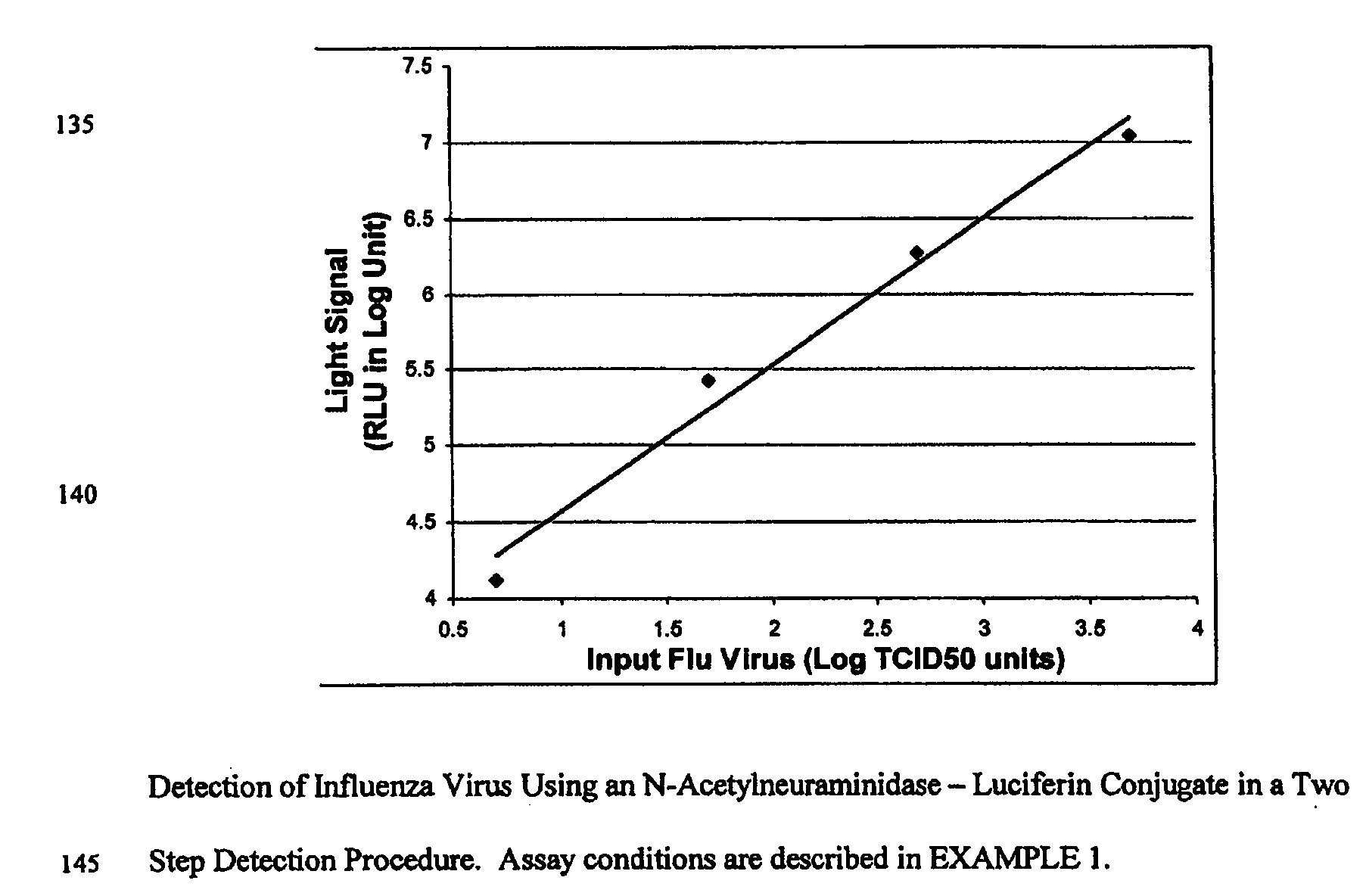
ActiveUS20080286758A1Simple and rapid and specific and sensitive detectionHigh detection sensitivityOrganic chemistryMicrobiological testing/measurementNeuraminidaseFluorescein
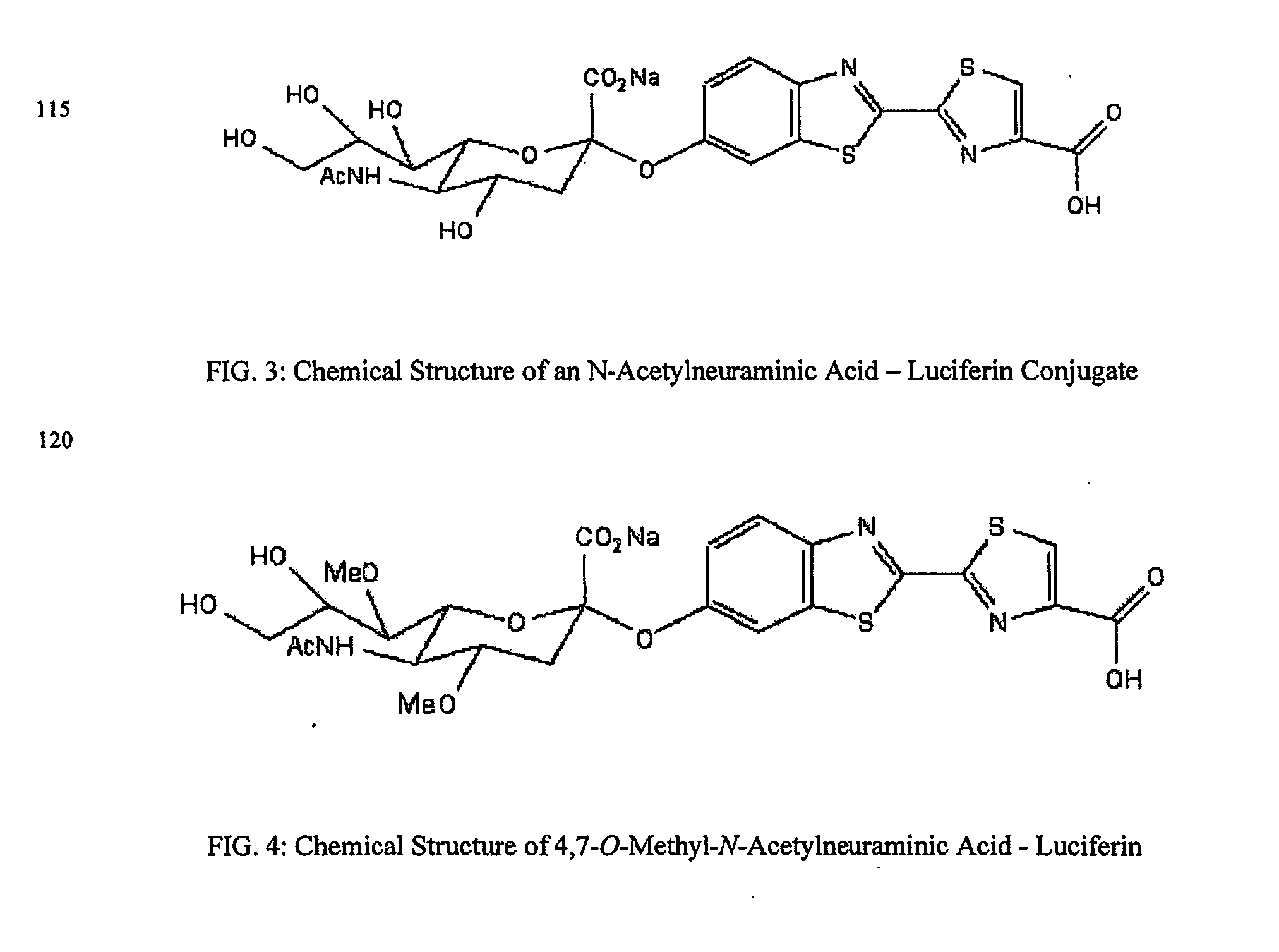
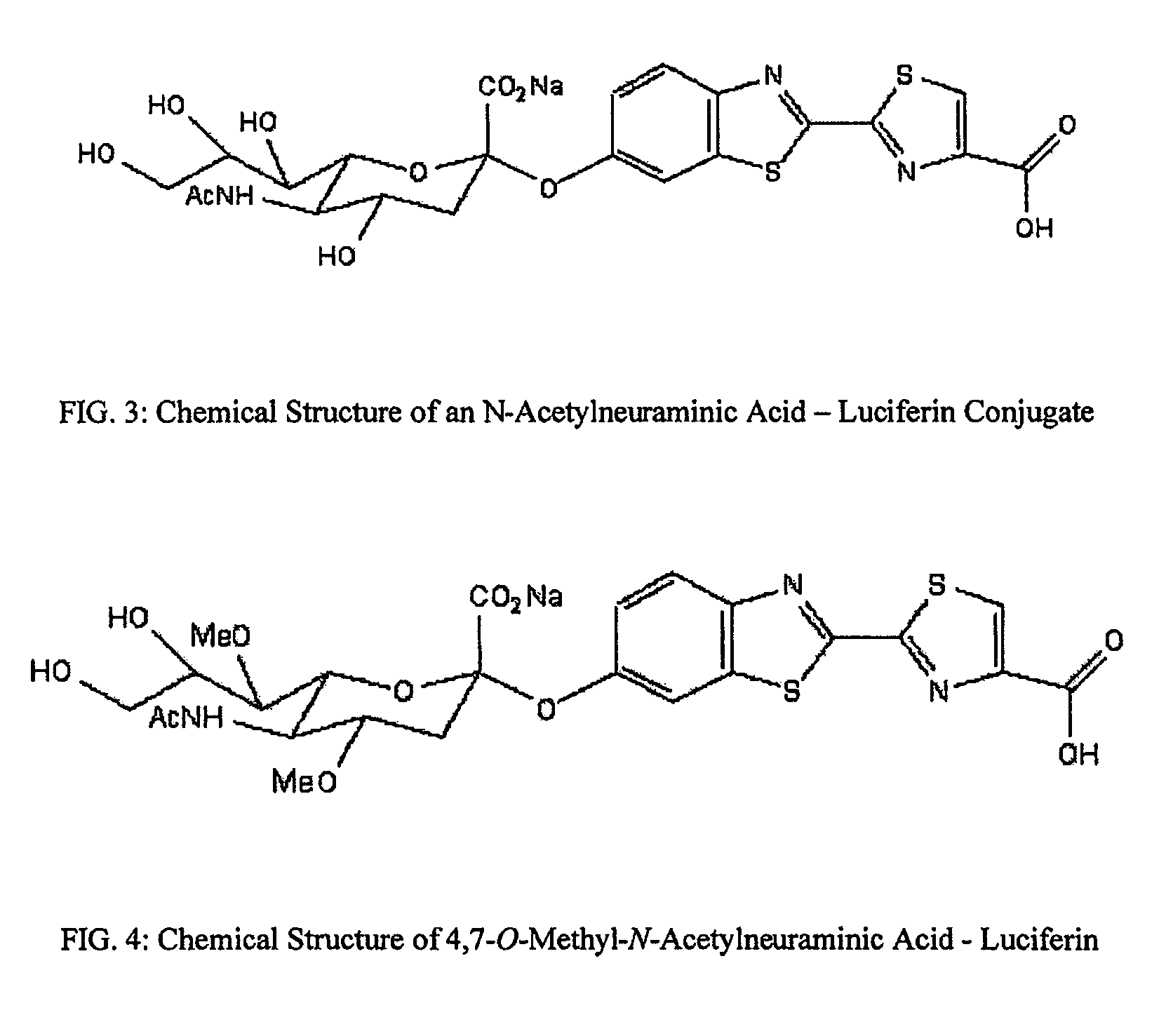
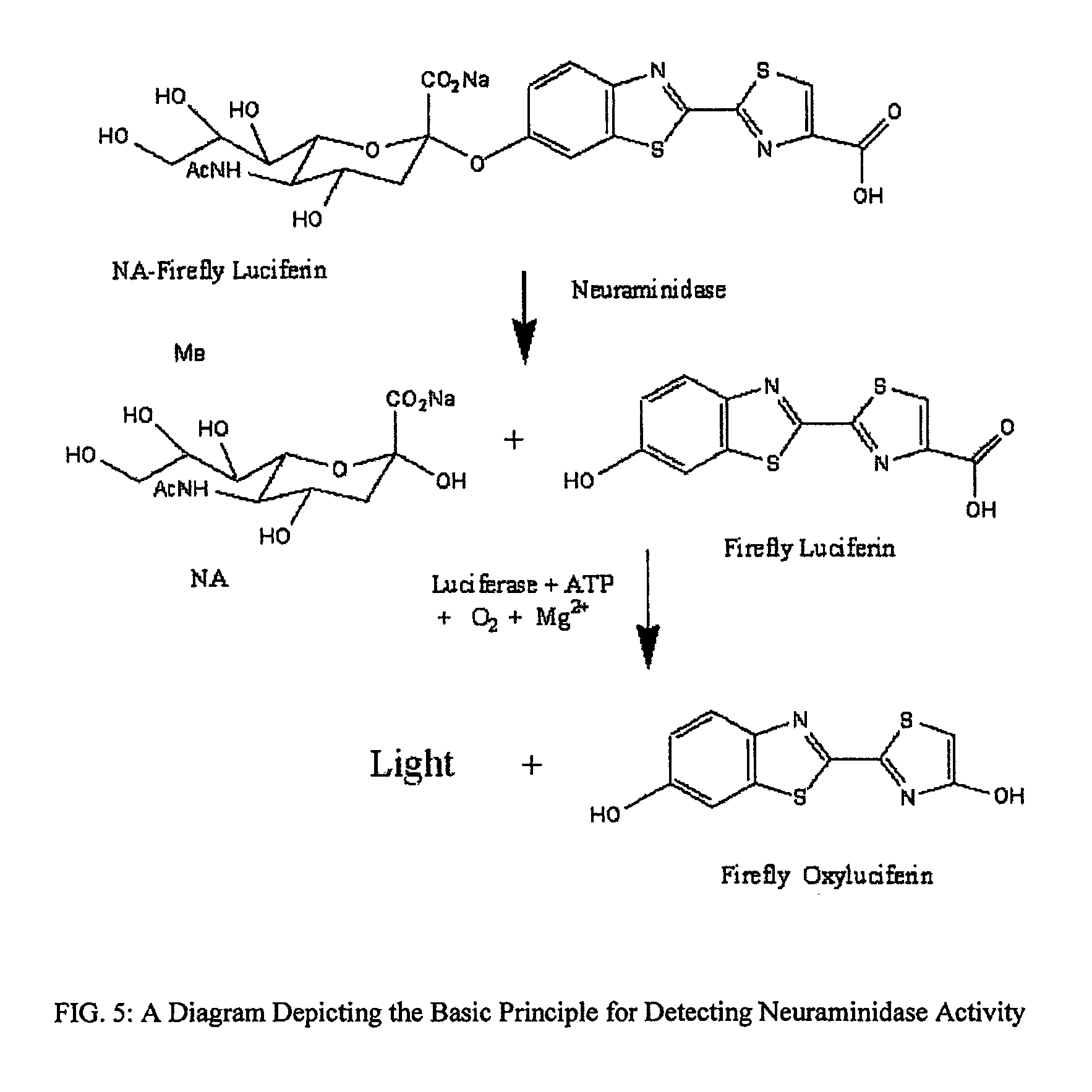
The present invention relates to reagents and methods for influenza virus detection. These reagents and methods disclosed in the present invention enable simple, rapid, specific and sensitive detection of influenza virus types A and B. These reagents are N-acetylneuraminic acid-firefly luciferin conjugates which can be cleaved by influenza virus neuraminidase.
Owner:CELLEX BIOLOGICAL TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS20170008858A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
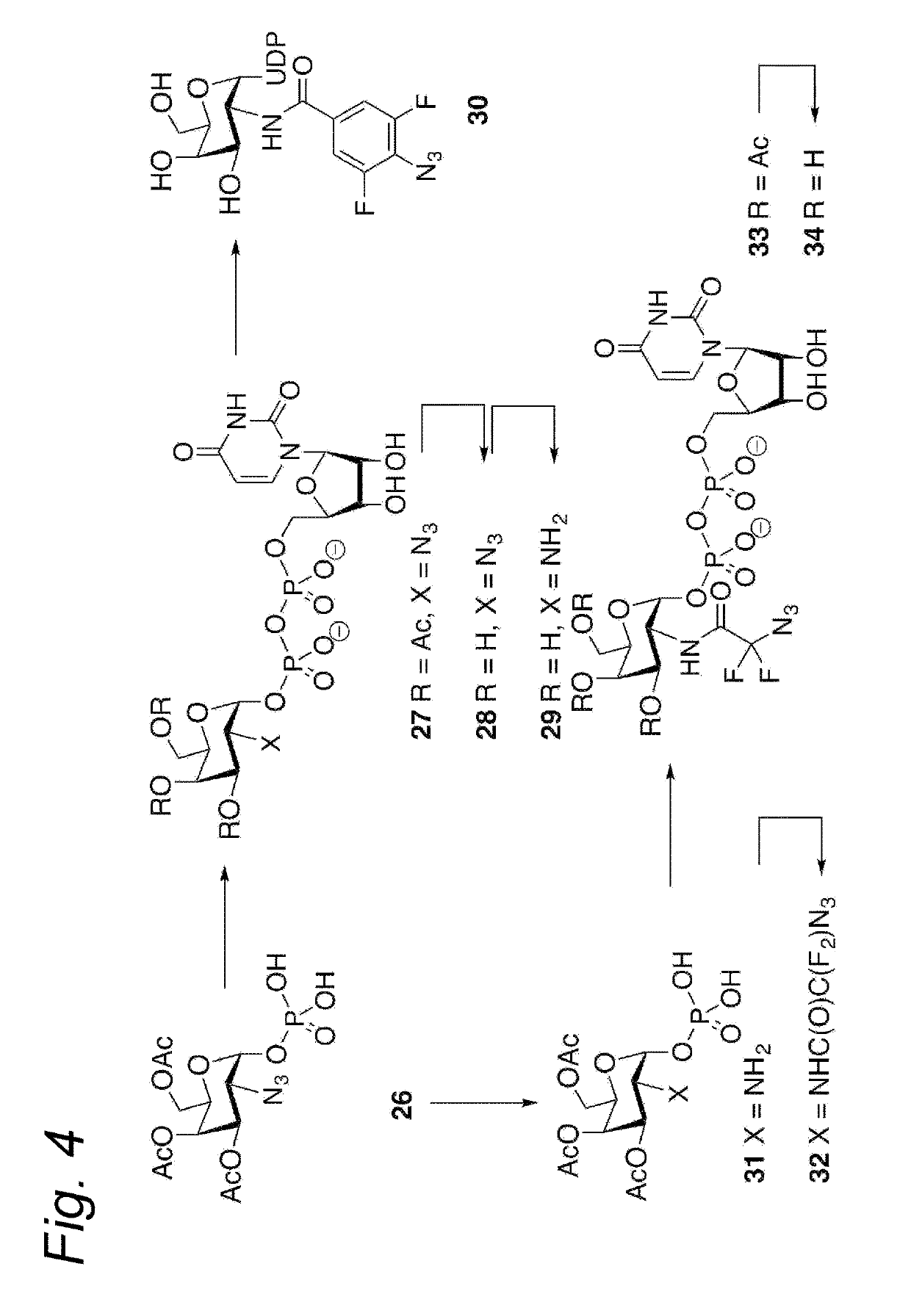
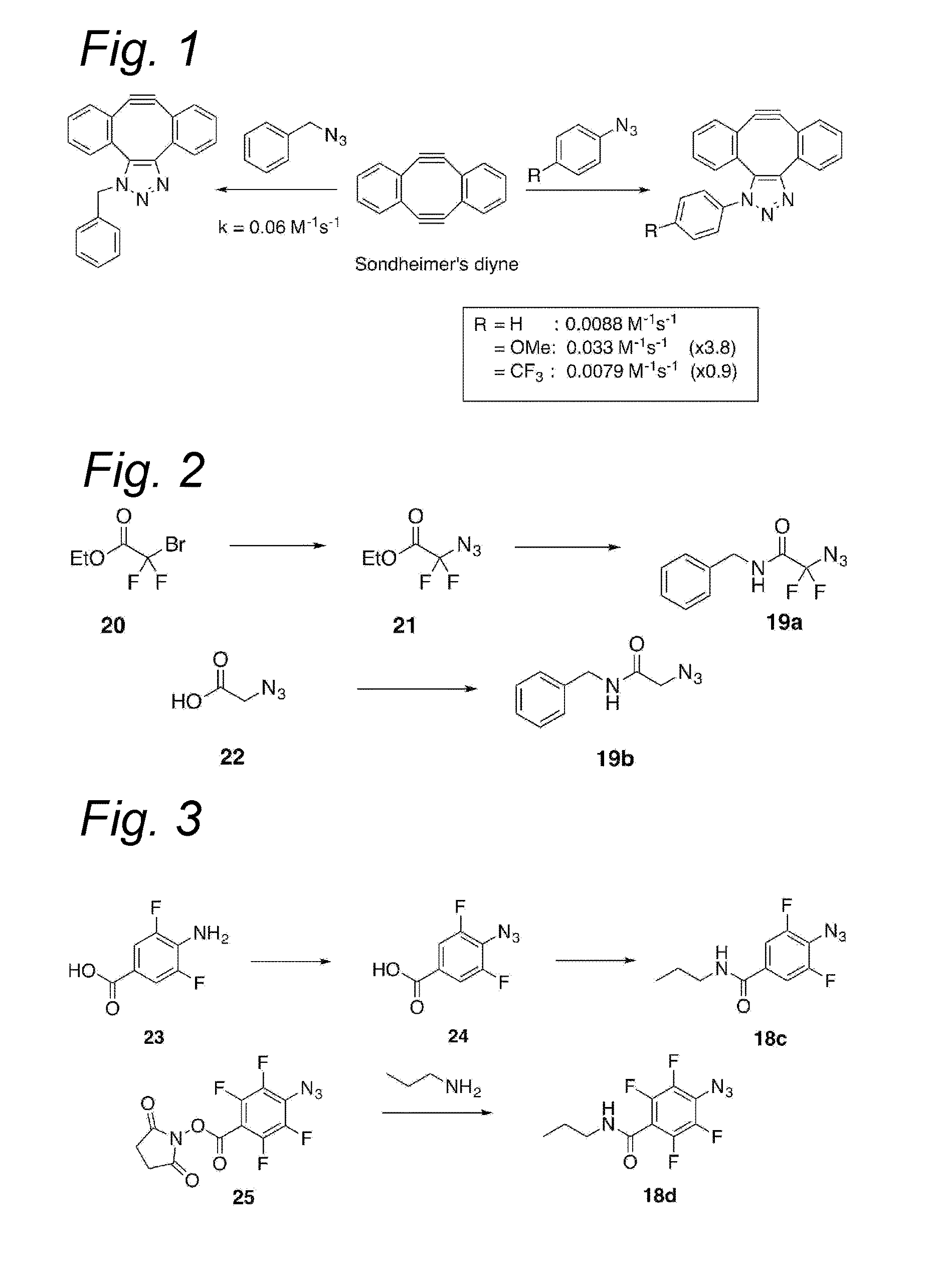
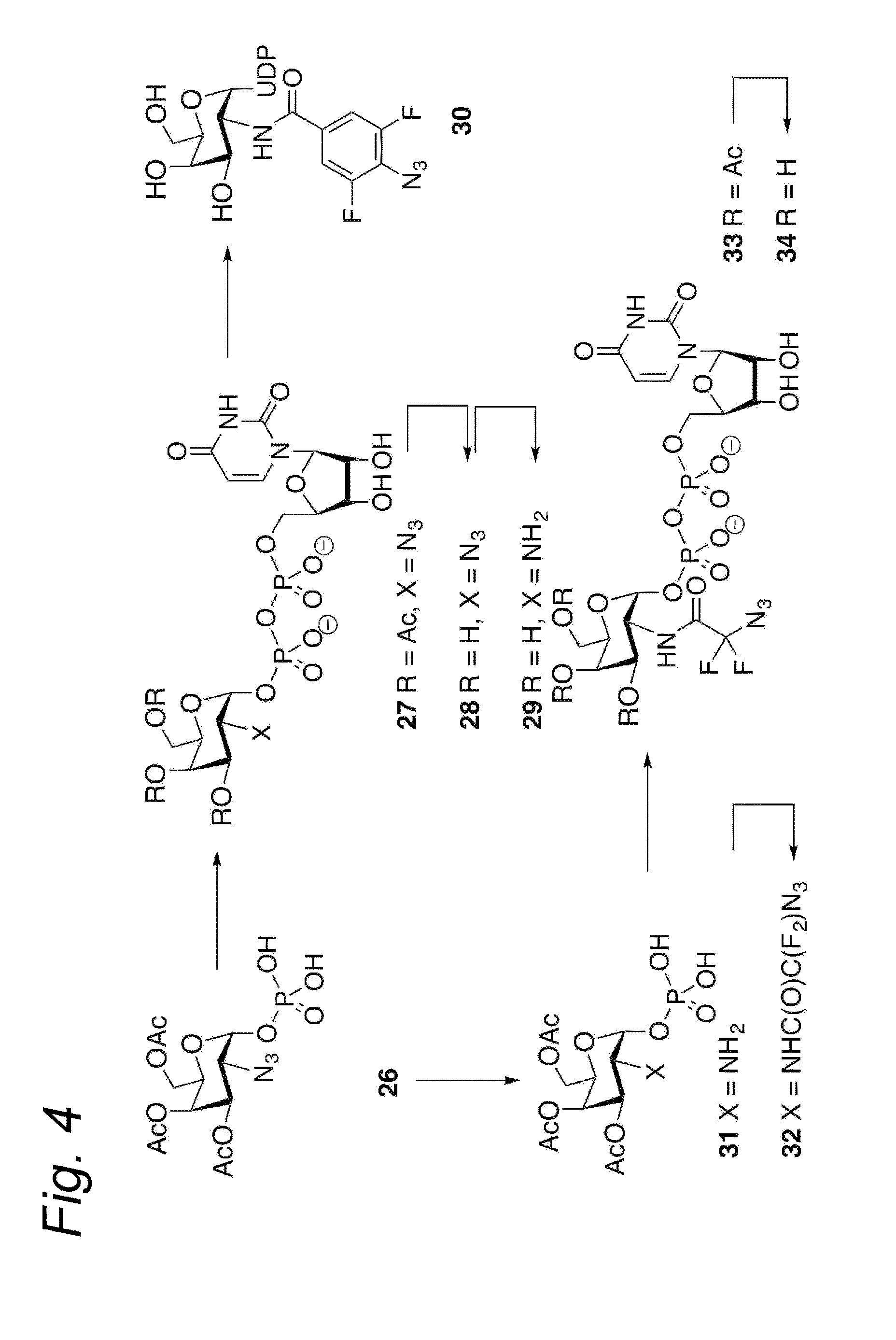
The present invention relates to a cycloaddition process comprising the step of reacting a halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1): Preferably, the (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1) is a (hetero)cyclooctyne. The invention also relates to the cycloaddition products obtainable by the process according to the invention. The invention further relates to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds, in particular to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds comprising N-acetylgalactosamine-UDP (GalNAc-UDP), and to halogenated 1,3-dipole compounds comprising (peracylated) N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuNAc).
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Crystal forms of sialic acid or salt or solvate thereof
Owner:ULTRAGENYX PHARMA
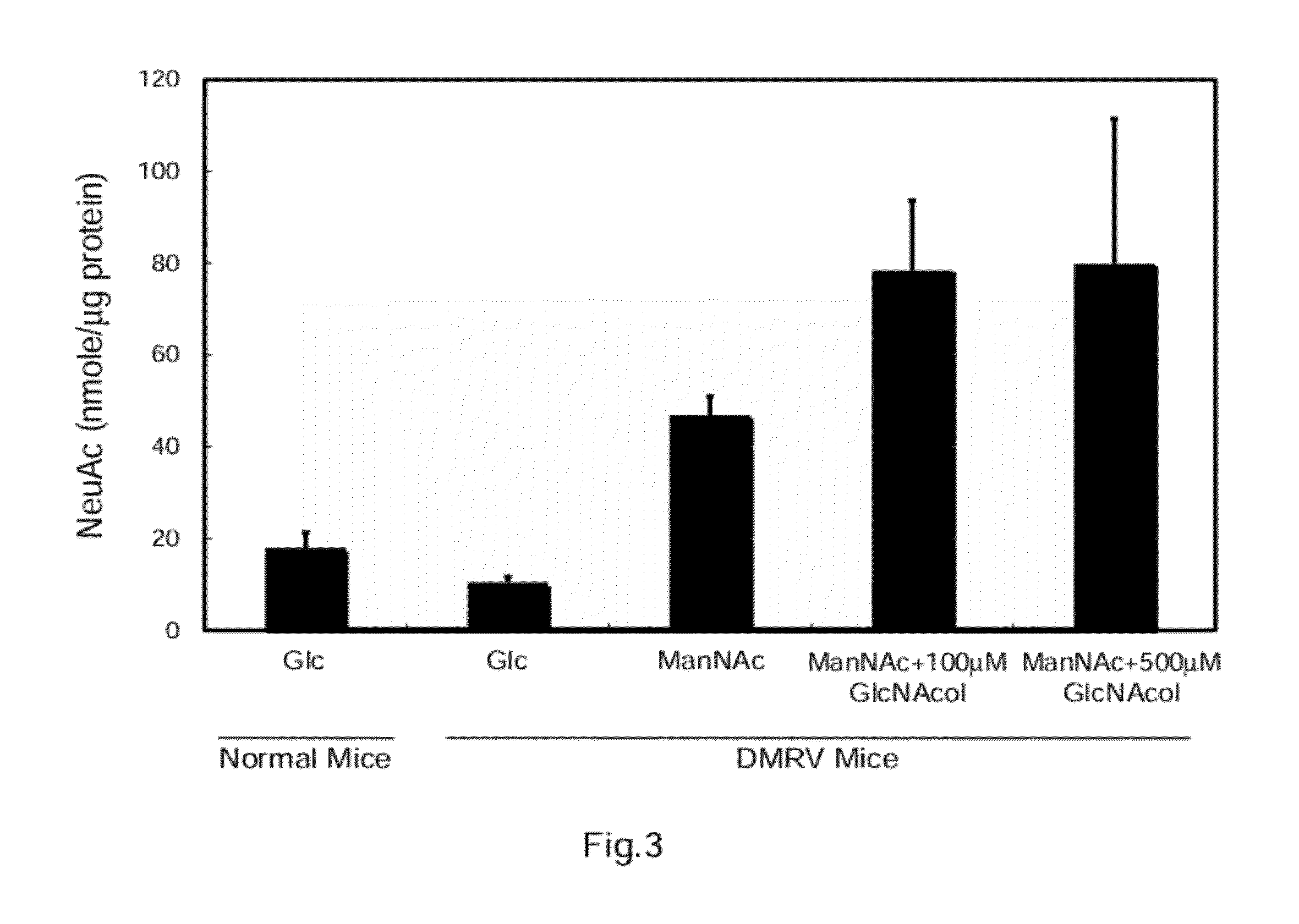
Therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with decrease in function of gne protein, food composition, and food additive
InactiveUS20120264928A1Easily embodiedEsterified saccharide compoundsOrganic active ingredientsDiseaseFood additive
Disclosed are a therapeutic pharmaceutical agent for diseases associated with the decrease in the function of GNE protein, a food composition, and a food additive. The therapeutic pharmaceutical agent is characterized by comprising a compound capable of increasing the quantity of N-acetylneuraminic acid in cells. Examples of the compound to be contained in the therapeutic pharmaceutical agent include N-acetylneuraminic acid, an intermediate produced downstream from N-acetylmannosamine in an N-acetylneuraminic acid biosynthesis pathway, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative, an N-acetylneuraminic acid-containing compound, an N-acetylneuraminic acid derivative-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine-containing compound, an N-acetylmannosamine derivative-containing compound, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylneuraminic acid, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for N-acetylmannosamine, an inhibitor of a degrading enzyme for the intermediate, and others.
Owner:HEALTH SCI TECH TRANSFER CENT JAPAN HEALTH SCI FOUND
Insulin secretion promoter
InactiveUS6946451B2Promote insulin secretionSuppress elevation of blood glucose levelBiocideDough treatmentLevel insulinGlycemic
Provided are a method for promoting insulin secretion, a method for suppressing the elevation of a blood glucose level, a method for ameliorating diabetes mellitus, a method for promoting growth of an animal, and a method for increasing an insulin level in breast milk. These methods comprising administering at least one member selected from the group consisting of a di- or a higher saccharide containing galactose, a derivative thereof, a saccharide containing N-acetylneuraminic acid, and a derivative thereof, to a patient in need thereof or an animal.
Owner:KYOWA HAKKO KOGYO CO LTD
Immobilization method using chitosan as carrier
ActiveCN101993867AMicroorganism based processesCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesCitrullineDiethyl glutarate
The invention discloses an immobilization method using chitosan as a carrier, which comprises the following steps of: directly mixing and crosslinking a chitosan solution with a solution or suspension of enzyme, cells, thallus, fermentation liquor or protein, and other substances to be immobilized; and immobilizing and dispersing under the alkaline condition to obtain granular crosslinking chitosan. An immobilized particle formed by the invention has the advantages of porous structure, high mechanical strength, high filter performance and no need of complex equipment. The invention can be used for large-scale cell immobilization, enzyme immobilization and direct immobilization of fermentation liquor without solid-liquid separation, such as 2,000L scale fermentation liquor direct immobilization in citrulline production and conversion reaction for preparing S-2,2-dimethylcyclopropylformamide, R-flurbiprofen, N-acetylneuraminic acid or R-3-hydroxyl-diethyl glutarate. The invention can be also used for the degerming or clarifying of a solution.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HISUN PHARMA CO LTD
Double reagent for detecting sialic acid liquid by stable enzyme method and use thereof
ActiveCN101469344AEasy to useLittle difference between bottlesMicrobiological testing/measurementLactate dehydrogenaseNeuraminidase
The invention relates to a double reagent, in particular to a liquid double reagent for determining sialic acid by an enzyme method and application thereof. The technical proposal of the liquid double reagent comprises: the steady liquid double reagent for determining the sialic acid by the enzyme method consists of a reagent 1 and a reagent 2, wherein the reagent 1 comprises 0.01 to 50KU / L of neuraminidase, 0.1 to 50KU / L of lactate dehydrogenase, and 25 to 100mmol / L of buffer liquid; and the reagent 2 comprises 0.1 to 50KU / L of N-acetyleuraminic acid aldolase, 0.05 to 5mmol / L of reducing coenzyme NADH, 0.1 to 10000U / L of glucose dehydrogenase, 0.1 to 500mmol / L of glucose, and 5 to 100mmol / L of the buffer liquid. The liquid double reagent has the advantages that the liquid double reagent has convenient use, does not need a dissolving solution to redissolve, has small difference among bottles, ensures that the packaging of the liquid double reagent can adapt to various automatic biochemical analyzers, can avoid secondary pollution, and simplify a production technology method.
Owner:上海微鸿企业管理有限公司
Bacillus subtilis for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid to recombine and application thereof
ActiveCN106929462AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacillus aryabhattaiGenetic engineering
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid to recombine and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the bacillus subtilis, bacillus subtilis 168-delta-nagP delta-nagP delta-gamP delta-gamA delta-nagA delta-nagB delta-1dh delta-pta:: lox72 are taken as expression hosts, through the over-expression of glucosamine acetylase coding geneS GNA 1 which are derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C, N-acetyl-glucosamine epimerase (AGE) which is derived from anabaena sp. CH1 and N-N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase (NeuB) which is derived from escherichia coli K1, genetically engineered bacteria of the bacillus subtilis for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid are obtained, the yield of N-acetylneuraminic acid reaches 190mg / L, and bacillus subtilis further lays a foundation for the process that the bacillus subtilis is transformed by metabolic engineering to produce the N-acetylneuraminic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method and kit for stably detecting sialic acid by enzyme method
The invention relates to a method and a kit for stably detecting sialic acid by an enzyme method. The method comprises the following steps of: generating N-acetylneuraminic acid from bound sialic acid under the catalysis of neuraminic acid aldolase; transforming the N-acetylneuraminic acid into N-acetylmannosamine under the catalysis of neuraminidase; reacting the product with mannosamine dehydrogenase and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) to generate reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH); and measuring the sialic acid content by detecting the amount of the generated NADH. The invention also relates to the kit prepared according to the method. The method and the kit are conveniently and quickly used, the sialic acid is not required to be redissolved by dissolving liquid, is stable for a long time and has small inter-bottle variation, the method and the kit are suitable for various biochemical analyzers, secondary pollution is avoided, and a production process method is simplified.
Owner:BEIJING STRONG BIOTECH INC
Reagents and kits for detection of influenza virus and the like
ActiveUS7893272B2Simple and rapid and specific and sensitive detectionHigh detection sensitivityOrganic active ingredientsBiocideNeuraminidaseFluorescein
The present invention relates to reagents and methods for influenza virus detection. These reagents and methods disclosed in the present invention enable simple, rapid, specific and sensitive detection of influenza virus types A and B. These reagents are N-acetylneuraminic acid-firefly luciferin conjugates which can be cleaved by influenza virus neuraminidase.
Owner:CELLEX BIOLOGICAL TECH SUZHOU CO LTD
Bacillus subtilis gene engineering bacterial producing Neu5Ac, construction method and application thereof
InactiveCN103923869AWith industrial productionSimple production processBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFood industryGlycerol
The present invention discloses Bacillus subtilis gene engineering bacterial producing Neu5Ac, a construction method and an application thereof. According to the present invention, according to the gene engineering bacterial, genes for coding UDP-N-acetyl glucosamine epimerase and Neu5Ac synthetase are introduced into Bacillus subtilis so as to be expressed, and expression of glucosamine 6-phosphate synthetase of the Bacillus subtilis is enhanced to construct the complete metabolic pathway from glucose or glycerol to Neu5Ac in the Bacillus subtilis so as to utilize glucose or glycerol as a substrate to carry out fermentation culture so as to produce Neu5Ac; and the adopted Bacillus subtilis is widely used in the food industry, is safe and harmless, and is suitable for production of Neu5Ac required by food and health products.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Child formula milk powder beneficial to eye protecting and brain intelligence development helping
The invention relates to child formula milk powder beneficial to eye protecting and brain intelligence development helping. The child formula milk powder is prepared from docosahexaenoic acid, arachidonic acid, lutein, N-acetylneuraminic acid, phosphatidylserine (PS), (3R,3'R)-dihydroxy-beta-carotene, phospholipid, vitamins, folic acid, taurine, choline chloride, ferrous sulfate and zinc sulfate.Through three major nutritional systems of an intelligence and vision core nutrition system, a vision BLZ system and an intelligence NPC system, a formula not only provides basic nutrition elements for the development of brains and eyes, but also protects the eyes through the vision BLZ system and reduces loss of the eyes; necessary nutrition is provided for the connection of cerebral nerve cellsthrough the intelligence NPC system.
Owner:上海育博营养食品有限公司
Modified organs and cells for xenotransplantation
InactiveUS7166278B2Maintain integrityMaintaining viabilityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsHeterograftsEngineered genetic
It has been discovered that there are at least two significant antigens present on the cells of animal species such as pigs that elicit an immune or inflammatory response immediately upon implantation into humans or contact with human serum. The first is an α-galactosyl (Gal) epitope, for example, Galα(1->3)Galβ(1->4)GlcNac (linear B type 2) or Galα(1->3) Galβ(1->4)Glc (linear B type 6). The second is an N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc) structure. By eliminating these epitopes, preferably by genetically engineering the animal so that the epitope is either not produced or is greatly reduced, or by chemical or enzymatic treatment of the animal's cells to remove the epitopes, it is possible to produce organs, tissues and cells suitable for xenotransplantation into humans. Cells can be rendered even more compatible by genetically engineering the animal to express a human complement regulatory protein (inhibitor), such as CD59, on its cells, or to express an excess of a pig complement regulatory protein.
Owner:RBC BIOTECH
Synthesis of new fucose-containing carbohydrate derivatives
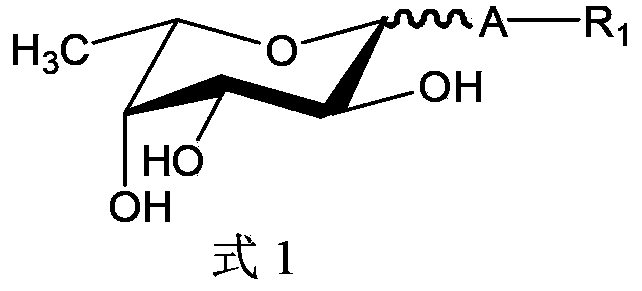
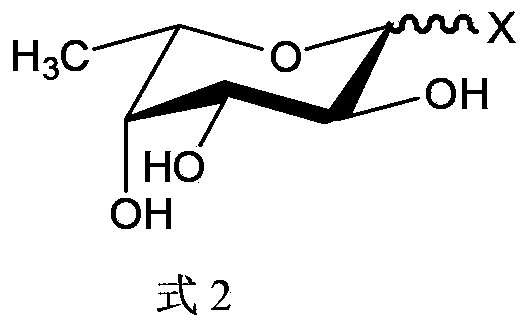
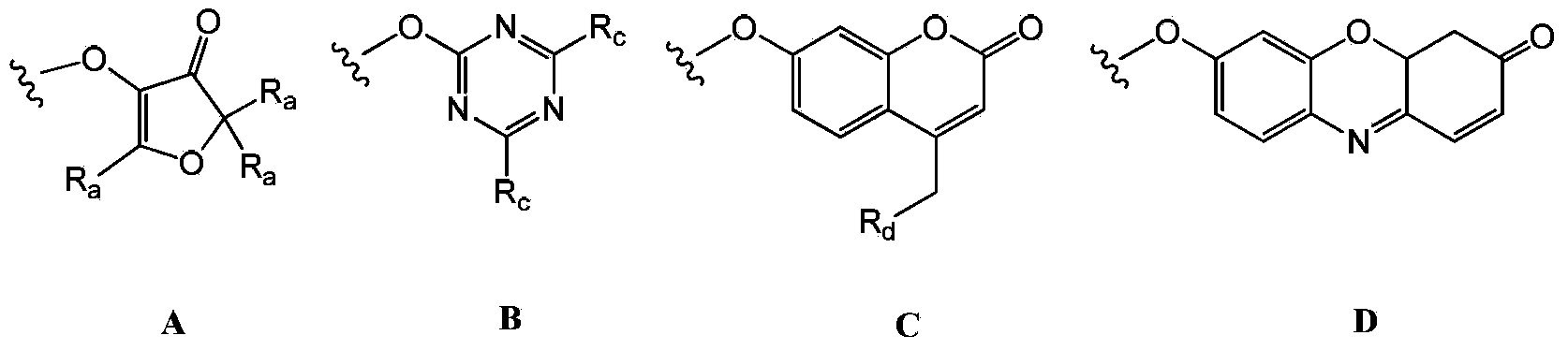
A method for the synthesis of a compound of formula (1) or a salt thereof, wherein A is a carbohydrate linker which is a lactosyl moiety or which consists of a lactosyl moiety and at least one monosaccharide unit selected from the group consisting of: glucose, galactose, N-acetylglucosamine, fucose and N-acetyl neuraminic acid; and wherein R1 is one of the following anomeric protecting groups: a) -OR2, wherein R2 is a protecting group removable by catalytic hydrogenolysis; b) -SR3, wherein R3 is an optionally substituted alkyl, an optionally substituted aryl or an optionally substituted benzyl; c) -NH- C(R")=C(R')2, wherein each R' independently is one of the following electron withdrawing groups: -CN, -COOH, -COO-alkyl, -CO-alkyl, -CONH2, -CONH- alkyl or -CON(alkyl)2, or wherein the two R'-groups are linked together and form -CO-(CH2)2-4-CO- and thus form, together with the carbon atom to which they are attached, a 5-7 membered cycloalkan-1,3-dione, in which dione any of the methylene groups is optionally substituted with 1 or 2 alkyl groups, and R" is H or alkyl, in which a fucosyl donor of formula (2) wherein X is selected from the group consisting of: a guanosine diphosphatyl moiety, a lactose moiety, azide, fluoride, optionally substituted phenoxy-, optionally substituted pyridinyloxy-, optionally substituted 3-oxo-furanyloxy- of formula (A), optionally substituted 1,3,5-triazinyloxy- of formula (B), 4-methylumbelliferyloxy-group of formula (C), and a group of formula (D) wherein Ra is independently H or alkyl, or two vicinal Ra groups represent a=C(Rb)2 group, wherein Rb is independently H or alkyl, Rc is independently selected from the group consisting of alkoxy, amino, alkylamino and dialkylamino, Rd is selected from the group consisting of H, alkyl and -C(=O)Re, wherein Re is OH, alkoxy, amino, alkylamino, dialkylamino, hydrazino, alkylhydrazino, dialkylhydrazino or trialkylhydrazino, is reacted with an acceptor of formula H-A-R1 or a salt thereof, wherein A and R1 are as defined above, under the catalysis of an enzyme capable of transferring fucose. A compound of formula 1', its use in manufacture of human milk oligosaccharides, a method of manufacture of human milk oligosaccharides, and a fucosyl donor are also provided.
Owner:GLYCOM AS (DK)
Recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid and application thereof
The invention discloses recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum for accumulating N-acetylneuraminic acid and application thereof and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. The recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum takes corynebacterium glutamicum as an expression host, and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis way is reinforced through over-expression of a glucosamine-fructose-6 phosphate aminotransferase gene, a glucosamine acetylase encoding gene, a phosphatase encoding gene, an acetylglucosamine isomerase encoding agene and an N-acetylneuraminic acid synthase encoding gene; an N-acetylneuraminic acid transport protein encoding gene in the corynebacterium glutamicum and a related gene in an intracellular N-acetylneuraminic acid decomposition, utilization and metabolism are knocked off to obtain corynebacterium glutamicum genetically engineered bacteria for extracellularly accumulating the N-acetylneuraminic acid and the yield reaches 110mg / L; a foundation is laid for further modifying corynebacterium glutamicum through metabolic engineering to produce the N-acetylneuraminic acid.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103060358AEliminate degradation pathwaysPromote accumulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyN-Acetylglucosamine
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid as well as a construction method and application thereof. A method for preparing the genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid comprises the following step of: introducing genes associated with the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis into host bacteria so as to obtain recombinant bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid, wherein the genes associated with the N-acetylneuraminic acid synthesis are coding genes of N-acetylglucosamine and 2-isomerase and a coding gene of N-nacetylneuraminic acid aldolase. The genetically engineered bacteria for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid constructed by the invention have the following advantages that the used raw materials are relatively cheap and liable to realize industrial mass product, so that the genetically engineered bacteria play an important role in the production of N-acetylneuraminic acid in the future.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid by spore surface display system
InactiveCN101906449ASafe, simple and efficient preparationImprove efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSurface displayN-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase
The invention discloses a method for producing N-acetylneuraminic acid by a spore surface display system. The method comprises the following step of: after recombining with a spore coating protein gene and an N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase gene by utilizing a high-copy shuttle vector, constructing a surface display expression carrier; and converting the surface display expression carrier into bacillus subtilis to obtain a recombined strain, wherein a spore of the recombined strain can catalyze the synthesis of the N-acetylneuraminic acid. Compared with other methods in the field, the invention can finish the expression, purification and immobilization of enzyme at one step and has concise and efficient operating process. In addition, by utilizing the characteristics of stable spore, easy separation and stress resistance of the bacillus subtilis, the following separating process is simplified, the stability of N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase is improved, and the safety of the whole catalyzing process is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Sialidase detection reagent
InactiveCN1405562AImprove stabilityImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingNeuraminateSialidase
This invention discloses a sialic acid enzyme test reagent for testing sialic acid enzyme activity in vagina secreta outside the body, containing substrate on the carrier named N-acetyl neuraminate and its salt which can be its derivant or thymolphthaleic N-acetyl neuraminate and its salt, 5-Br-4-Cl-3-indolyl-alpha-D-N-acytylneuraminate and its salt. We can diagnose the bacteriogenic vagina deseases quickly and simple by testing sialic acid enzyme to vagina searate with this sialic acid ester reagent which can be used as an independent diagnosis target with good stability, extremely excellent accuracy and simple operation (one step test).
Owner:肖洪武
Method for producing poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid by microbial fermentation and purification method thereof
InactiveCN103361283AReduce manufacturing costHigh degree of polymerizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPurification methods
The invention provides a method for producing poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid by fermentation of escherichia coli CGMCC NO.5585 and a purification method of the poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid. The high-purity poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid without endotoxins is further obtained and can meet the production requirements of foods, cosmetics and medicaments. According to the methods provided by the invention, the fermentation raw material uses cheap glucose to replace more expensive sorbitol, the yield of 5-6g / L can be still obtained during the fermentation stage, and the methods are particularly suitable for industrial fermentation production of PSA (polysialic acid); and finally, through the follow-up purification step, the high-purity PSA with the polymerization degree of at least above 70000Da, the purity of at least more than 95% (HPLC(high performance liquid chromatography)) and the yield of 4-4.5g / L can be obtained.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
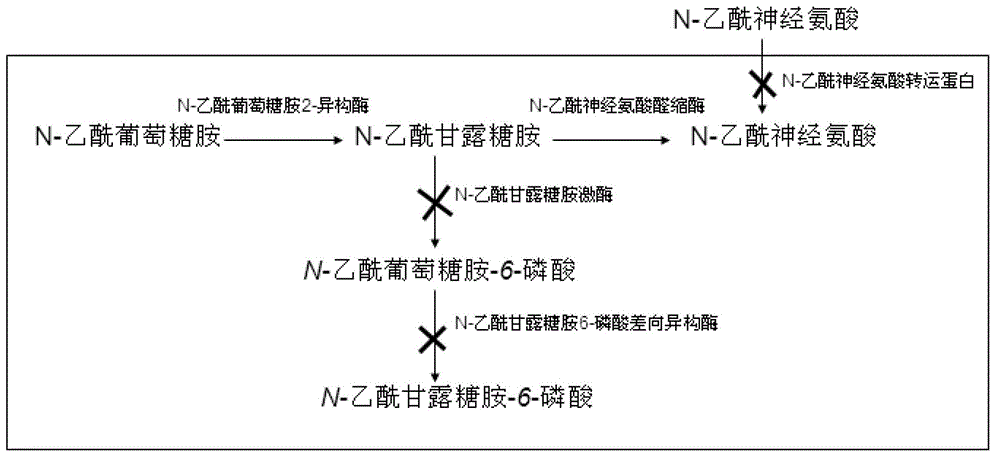
Preparation for N-acetylneuraminic acid by immobilization double-enzyme method
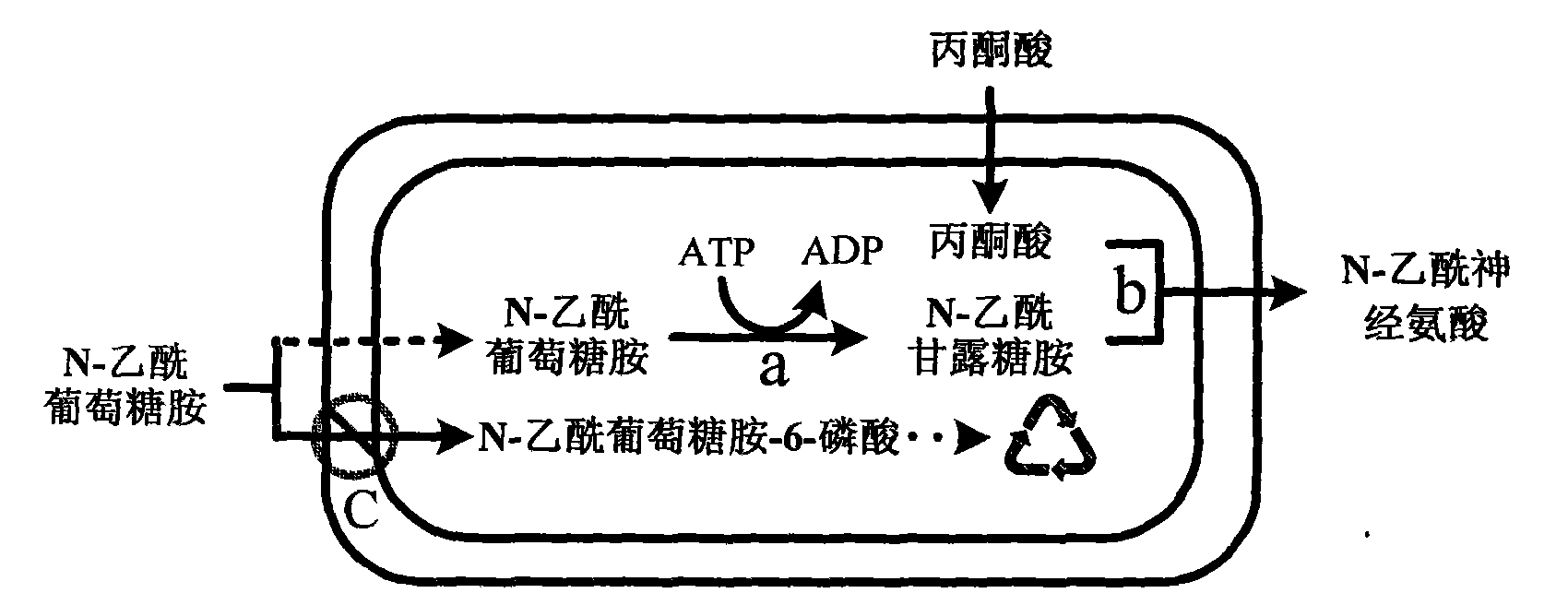
The present invention discloses a process of producing N-acetylneuraminic acid with two kinds of immobilized enzyme. In the process, immobilized N-acetylglucosamine-2-epimerase (E.C.5.1.3.8) in the concentration of 0.6-10 U / ml and immobilized N-acetylneuraminate aldolase (E.C.4.1.3.3) in the concentration of1.2-10 U / ml are utilized in the identical reactor to convert N-acetylglucosamine and pyruvic acid or its salt into N-acetylneuraminic acid. The process can reach N-acetylglucosamine converting rate up to 77 %, and has a conversion reaction period within 20 hr, repeated use of enzyme source and great industrial significance.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
High-yield N-acetylneuraminic acid metabolic engineering bacterium and construction method and application
InactiveCN104988108AHigh synthesis efficiencyAvoid consumptionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliGlycerol
The invention discloses a high-yield N-acetylneuraminic acid metabolic engineering bacterium and a construction method and application. According to the engineering bacterium, the activity of coded UDP-N-acetylglucosamine epimerase and N-acetylneuraminic acid synthetase gene enzyme is enhanced by expressing the two enzymes in Escherichia coli through a T7 strong promoter, and the recombinant Escherichia coli is constructed by removing genes of an N-acetylneuraminic acid decomposition pathway enzyme in the Escherichia coli; and a constructed engineered strain utilizes glucose or glycerinum as a substrate for fermentation cultivation to generate N-acetylneuraminic acid. The engineering bacterium utilizes glucose or glycerinum for synthesizing the N-acetylneuraminic acid, so that the fermentation level is high, the accumulated by-products are few, and the engineering bacterium has the industrial potential.
Owner:武汉中科光谷绿色生物技术有限公司
Drop, tablet and powder type N-acetylneuraminic acid anti-virus composition
The invention discloses a drop, tablet and powder type N-acetylneuraminic acid anti-virus composition which comprises a drop agent, a tablet agent or a powder agent, wherein the drop agent comprises 0.6-12% of lactoferrin, 5-12% of N-acetylneuraminic acid, 3-6% of immune globulin, 5-10% of glycerinum, 10.1-40% of fructo-oligosaccharide and 10.1-40% of concentrated elderberry juice; the tablet agent comprises 0.2-6% of lactoferrin, 1.5-6% of N-acetylneuraminic acid, 1-45% of immune globulin and 5-15% of elderberry fruit powder; the powder agent comprises 2-20% of immune globulin, 0.1-10% of lactoferrin, 0.5-6% of N-acetylneuraminic acid, 0.01-0.5% of lactobacillus fermenti CECT5716, 0.05-0.25% of lactalbumin, 0.1-0.25% of yolk globulin and 0.02-0.1% of a food nutritive fortifier; the lactoferrin is derived from whey protein or lactoferrin; the immune globulin is derived from bovine colostrum powder or whey protein. The composition is long in respiratory tract retention time and virus combination time, and is remarkable in anti-virus effect.
Owner:浙江索契壹营养科技有限公司
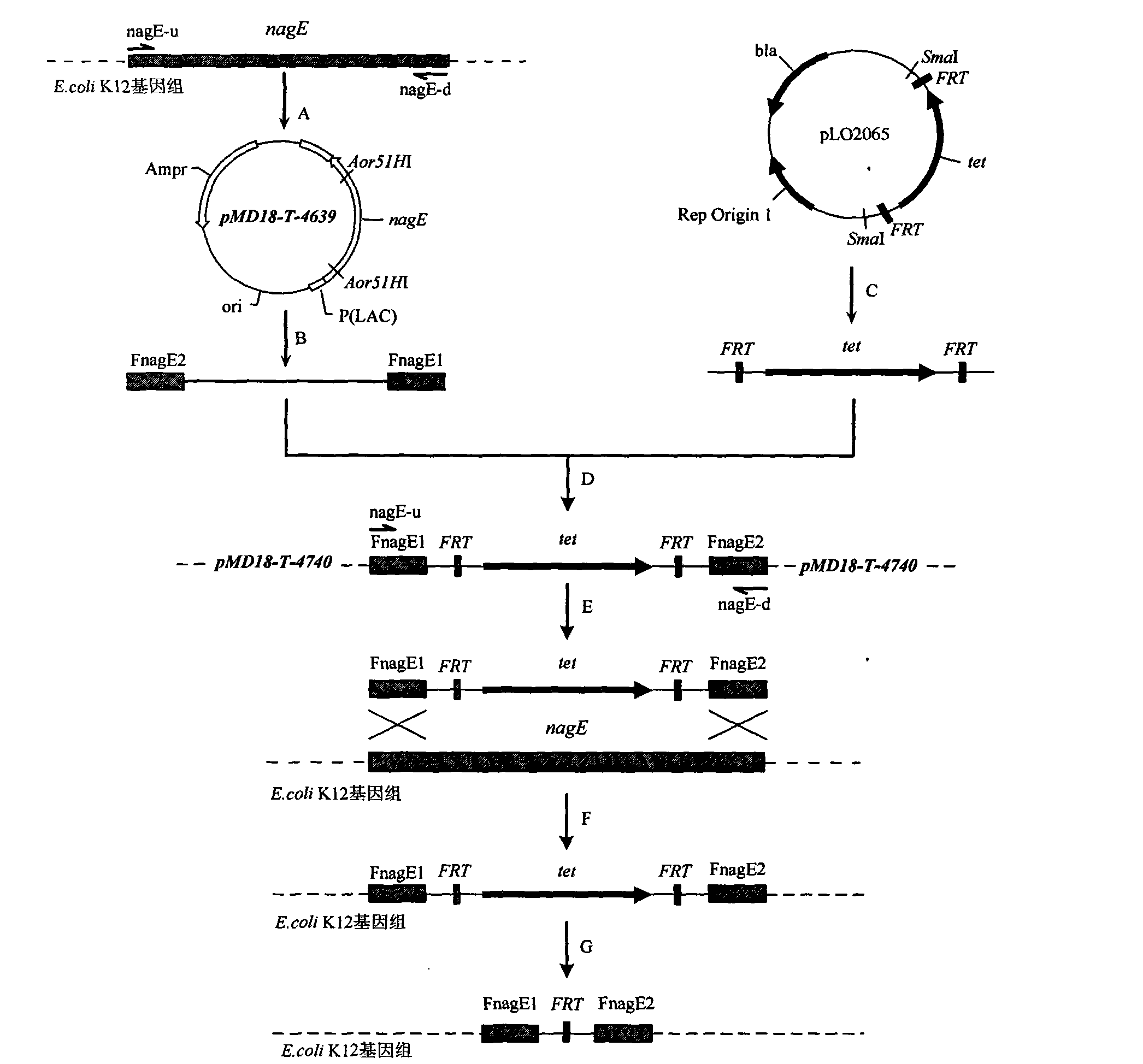
Recombinant escherichia coli of temperature-control coexpression exogenous gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101603023ASuitable for repeated usePost-processing is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliTemperature control
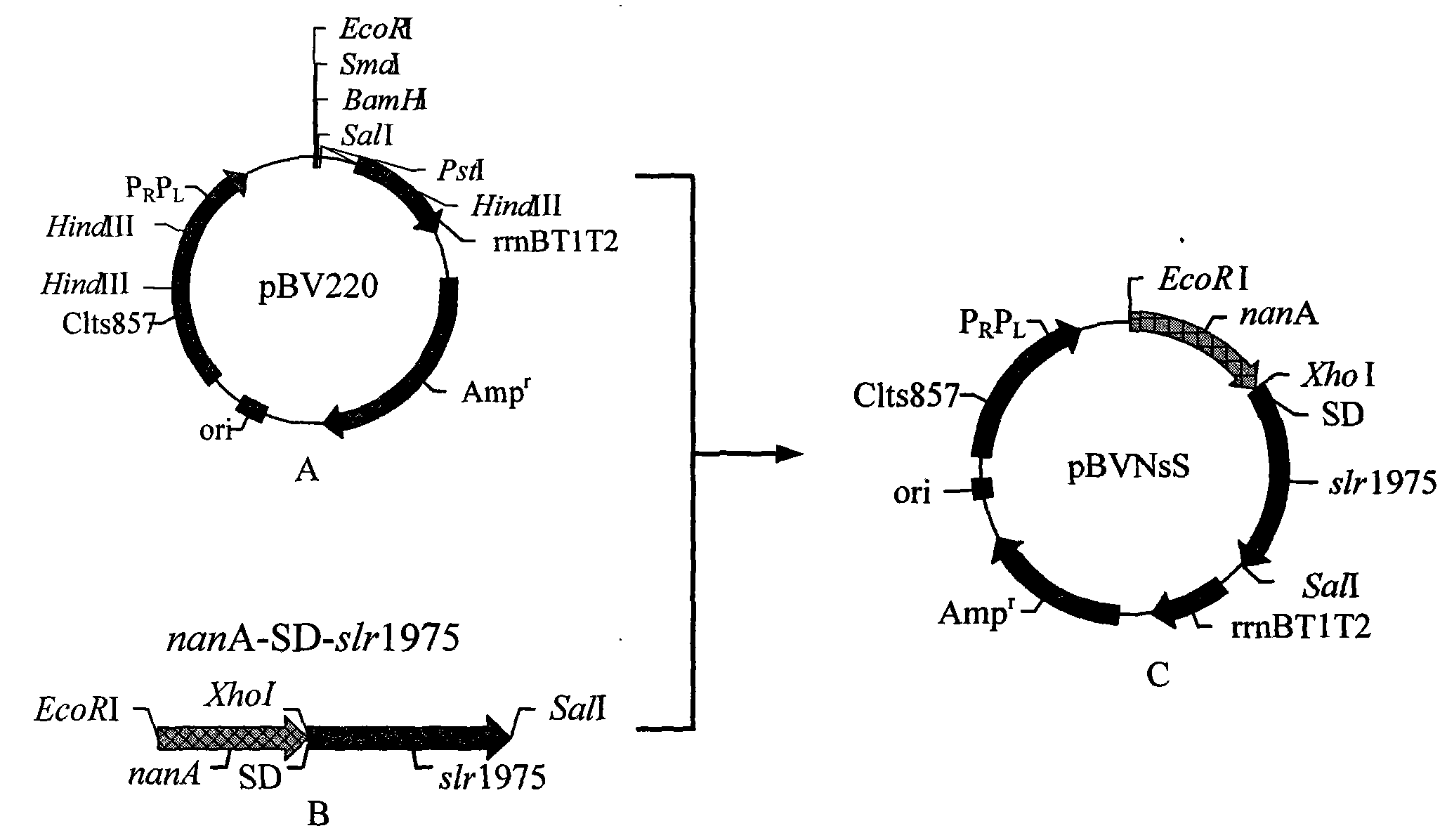
The invention discloses recombinant escherichia coli of a temperature-control coexpression exogenous gene, which is named as Escherichia coli DT26 (pBVNsS) CCTCC NO:M 209018. The genotype of the recombinant escherichia coli is delta nagE::FRT; and the recombinant escherichia coli contain a temperature-control coexpression carrier pBVNsS. Simultaneously, the invention also discloses the application of the recombinant escherichia coli used as a catalyst for the complete cell catalytic preparation of N-acetylneuraminic acid. In the process of the large-scale catalytic production of the N-acetylneuraminic acid, the recombinant escherichia coli of the temperature-control coexpression exogenous gene has the characteristics of safe and convenient preparation of the catalyst, simple operation of the catalytic process, cheap price, higher efficiency, easy extraction and the like.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com