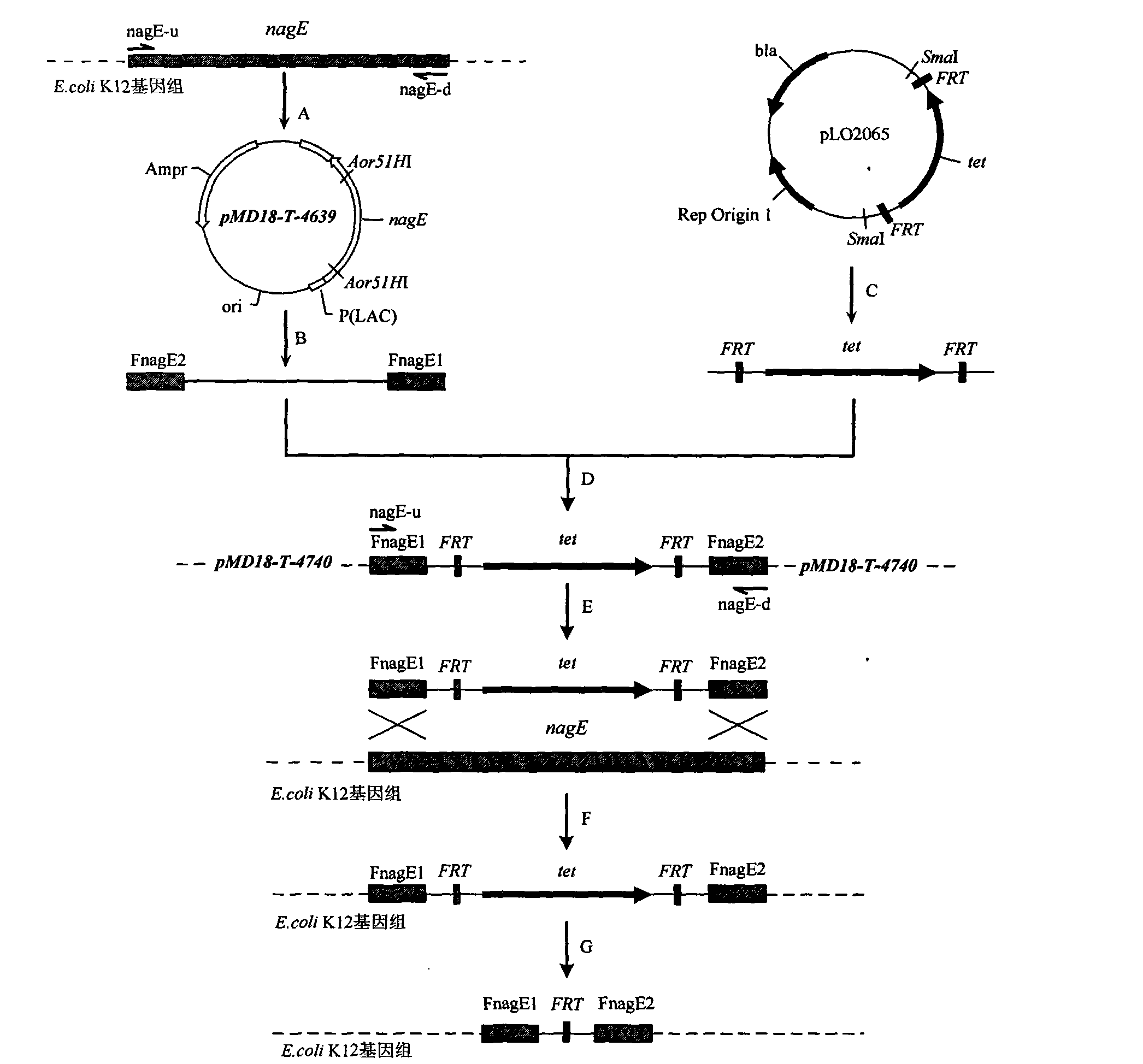
Recombinant escherichia coli of temperature-control coexpression exogenous gene and application thereof
A technology for recombining Escherichia coli and exogenous genes, applied in microorganism-based methods, bacteria, microorganisms, etc., can solve the problems of low conversion rate of whole cells, toxic substances, and unsuitable large-scale preparation of recombinant catalysts.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
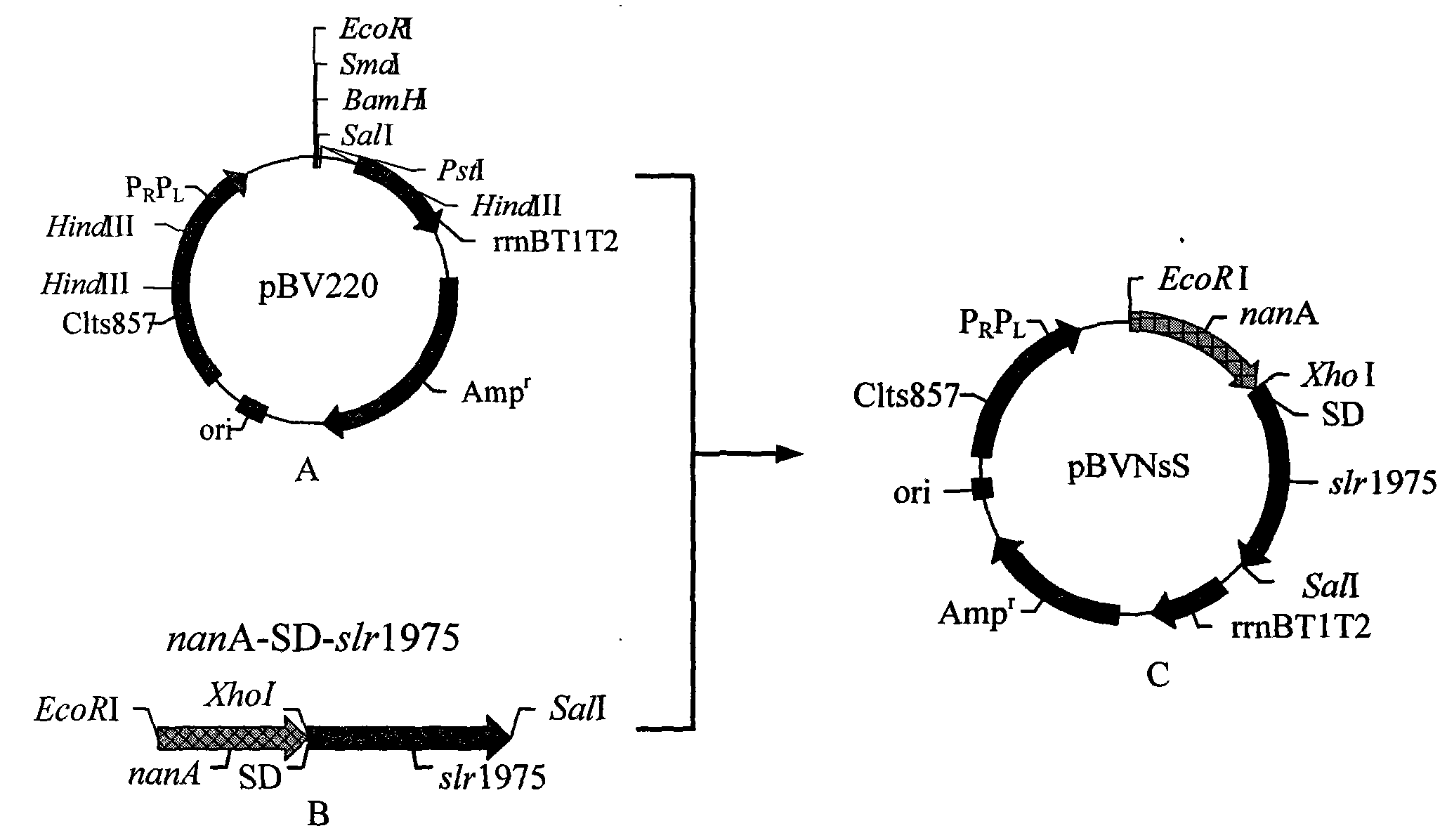
[0075] Example 1: Recombinant genetic engineering strain Escherichia coli DT26 (pBVNsS) CCTCCNO: M 209018 construction
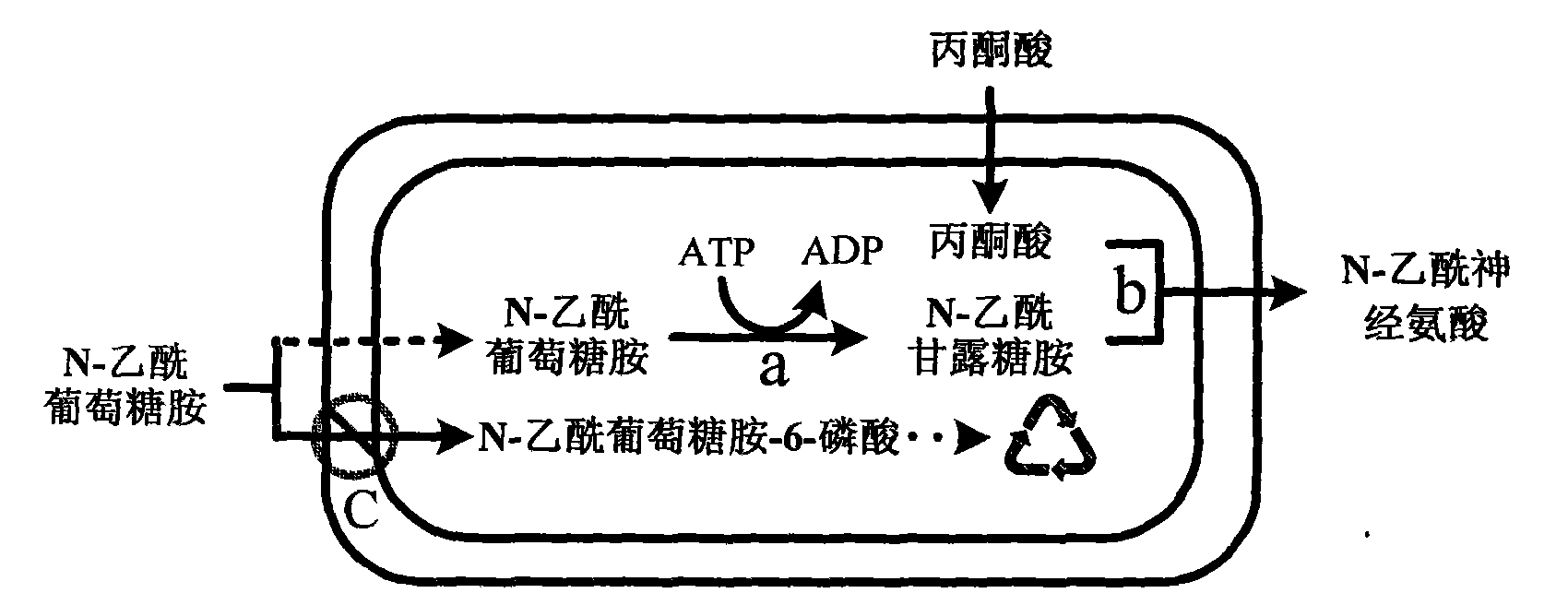
[0076] 1. Cloning of N-acetylneuraminic acid aldolase gene (nanA)
[0077] The genomic DNA of strain Escherichia coli K12 ATCC 25404 was prepared by conventional methods. For this process, please refer to the method of small-scale preparation of bacterial genome in the "Refined Molecular Biology Guide" published by Science Press; use synthetic primers from Escherichia coli K12 The N-acetylneuraminidase gene nanA was obtained by PCR amplification from the genomic DNA. The fragment was digested with EcoRI and PstI and recovered, and then ligated to the plasmid pBV220 treated with the same enzyme and recovered (see Acta Virology, Vol. 6, No. 2, pages 111-116).
[0078] Among them, the above-mentioned Escherichia coli K12ATCC 25404 is used as the source strain of the nanA gene, and the primer is designed according to the sequenced genome sequence of the strain: the ...
Embodiment 2
[0116] Example 2: Application of whole-cell catalyst in the synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid
[0117](1) Plate culture: Streak the above-mentioned Escherichia coli DT26(pBVNsS)CCTCC NO:M 209018 strain onto an LB plate containing 1.5% agar by mass and volume and containing 100μg / ml of ampicillin, culture at 37℃ 12 hours.
[0118] (2) First-level seeds: Under aseptic conditions, use a sterile toothpick to pick a single colony on the plate in step (1), and then inoculate it into 5ml of liquid medium containing 100μg / ml ampicillin, 30 Incubate with shaking at ℃ for 12 hours.
[0119] (3) Shake flask culture: Under aseptic conditions, take the culture solution cultured in step (2) at a volume ratio of 1% and inoculate 30ml of LB liquid medium containing 100μg / ml of ampicillin. Incubate for 2 hours on a rotary shaker at 30°C at 200 rpm.
[0120] (4) Induction: Move the shaker to a 45°C shaker and induce at 180 rpm for 4 hours.
[0121] Wherein: the LB medium formula described in the...
Embodiment 3
[0131] Example 3: Application of whole cell catalyst in the synthesis of N-acetylneuraminic acid
[0132] (1) Plate culture: Streak Escherichia coli DT26 (pBVNsS) CCTCC NO:M 209018 strain onto an LB plate containing 1.5% agar by mass and volume and containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin, culture at 37°C for 12 hour.
[0133] (2) First-grade seeds: Under aseptic conditions, use a sterile toothpick to pick a single colony on the plate in step (1), and then inoculate it into 5ml of liquid medium containing 100μg / ml ampicillin, 37 Incubate with shaking at ℃ for 12 hours.
[0134] (3)Secondary seed: Under aseptic conditions, take the culture solution cultivated in step (2) with a volume ratio of 1%, and inoculate 500ml of LB inorganic salt liquid medium containing 100μg / ml of ampicillin Incubate with shaking at 30°C for 12 hours.
[0135] (4) Fermenter culture: Under aseptic conditions, take the culture solution obtained in step (3) to inoculate 5 L of the above LB inorganic salt liquid mediu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com