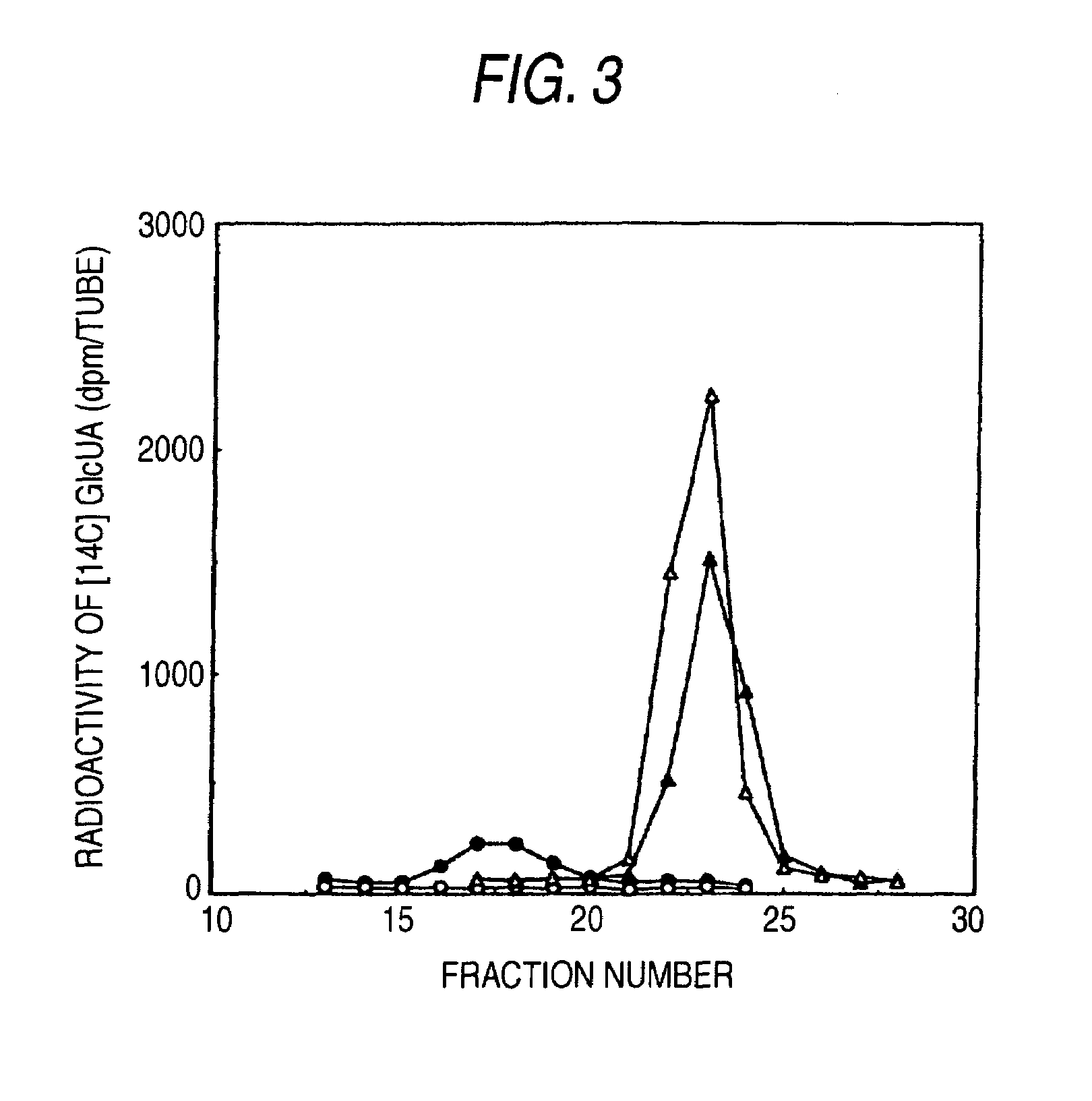
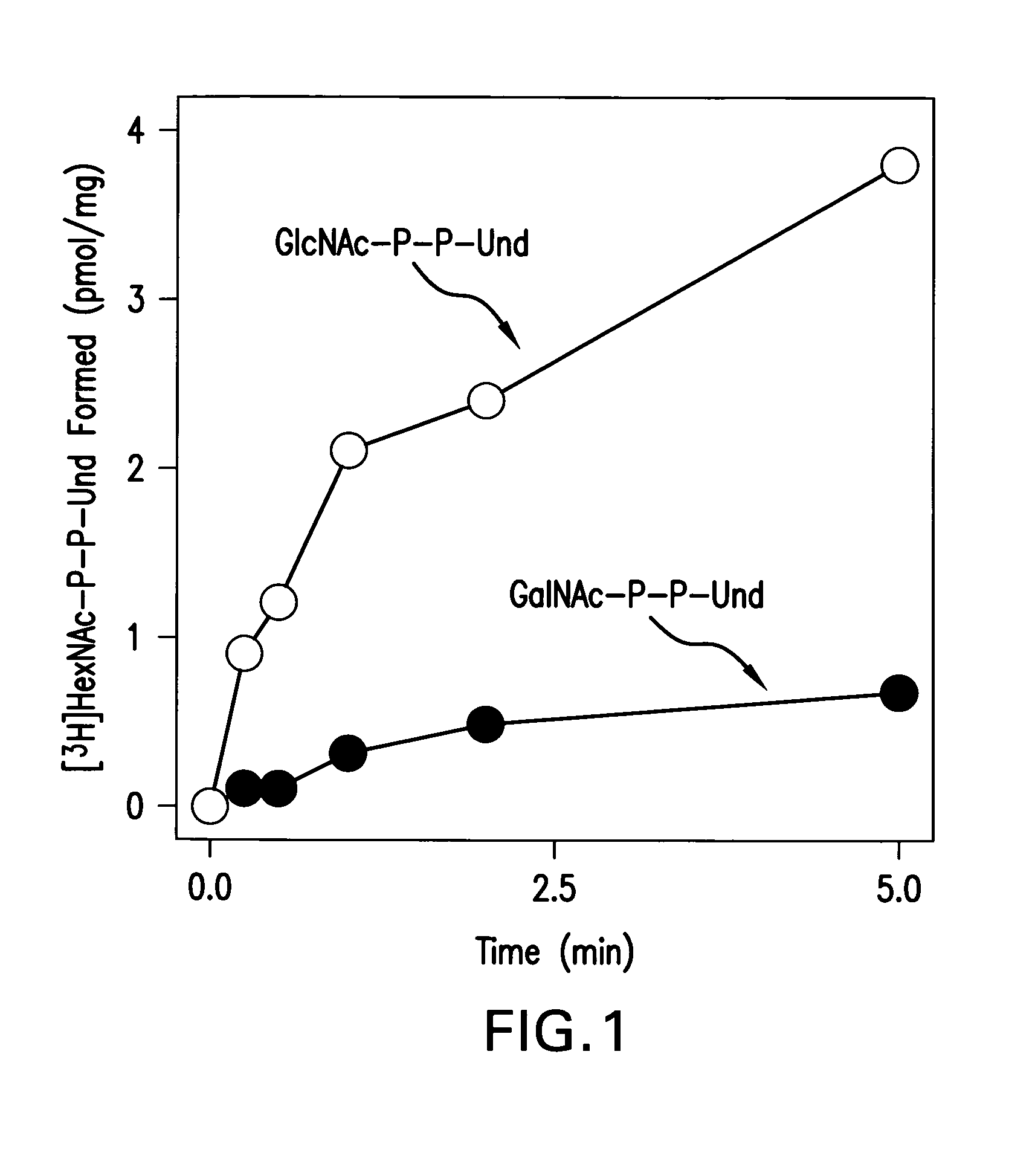
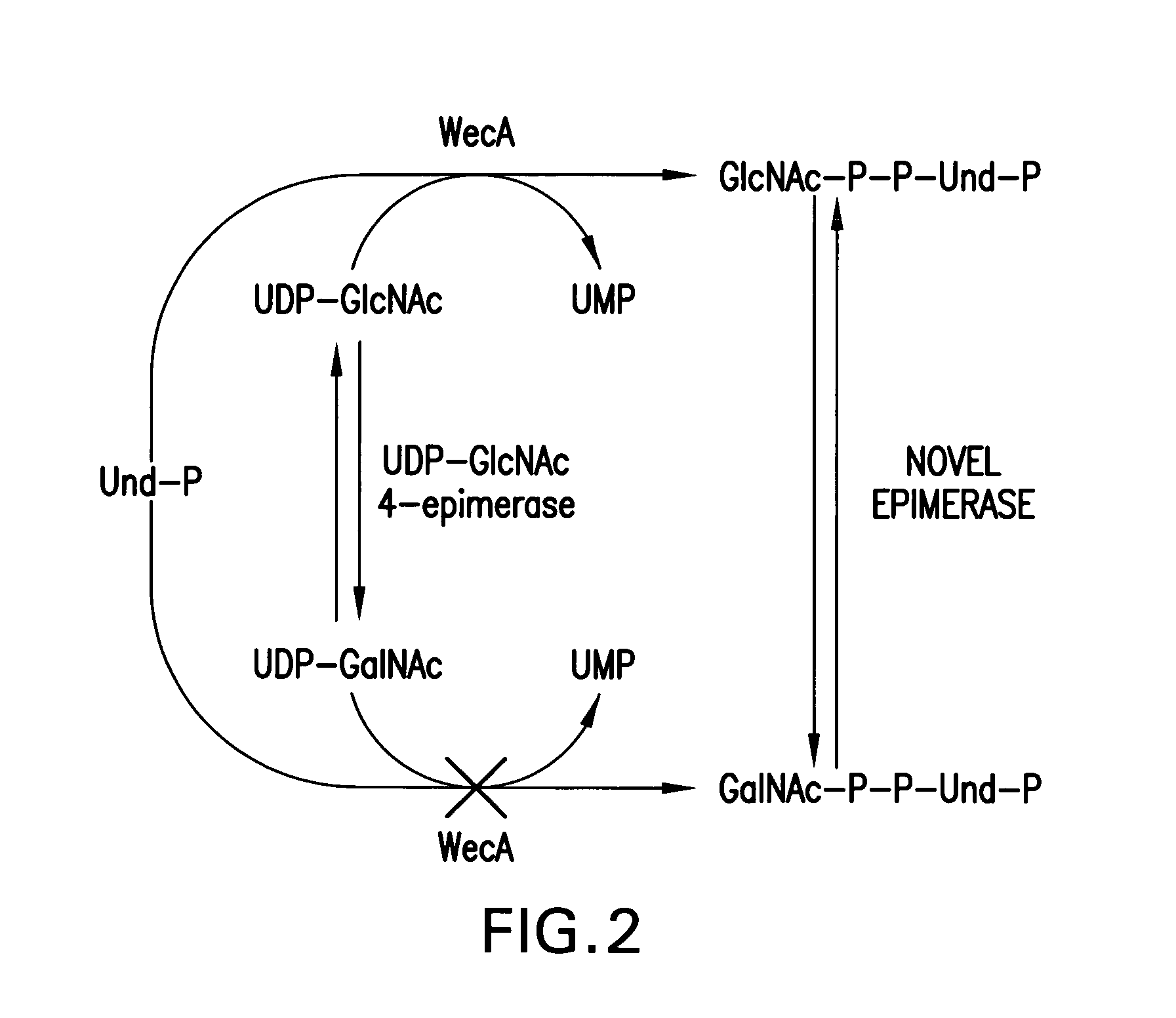
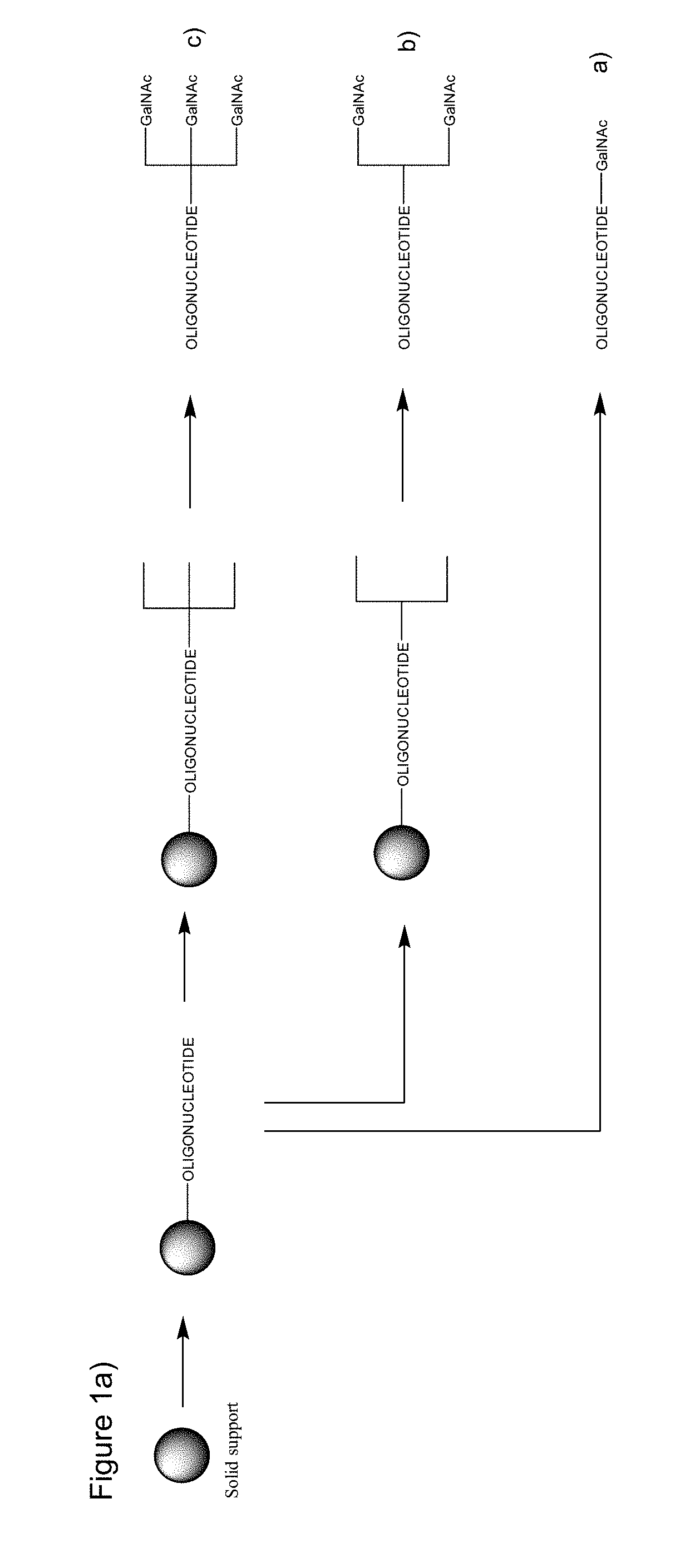
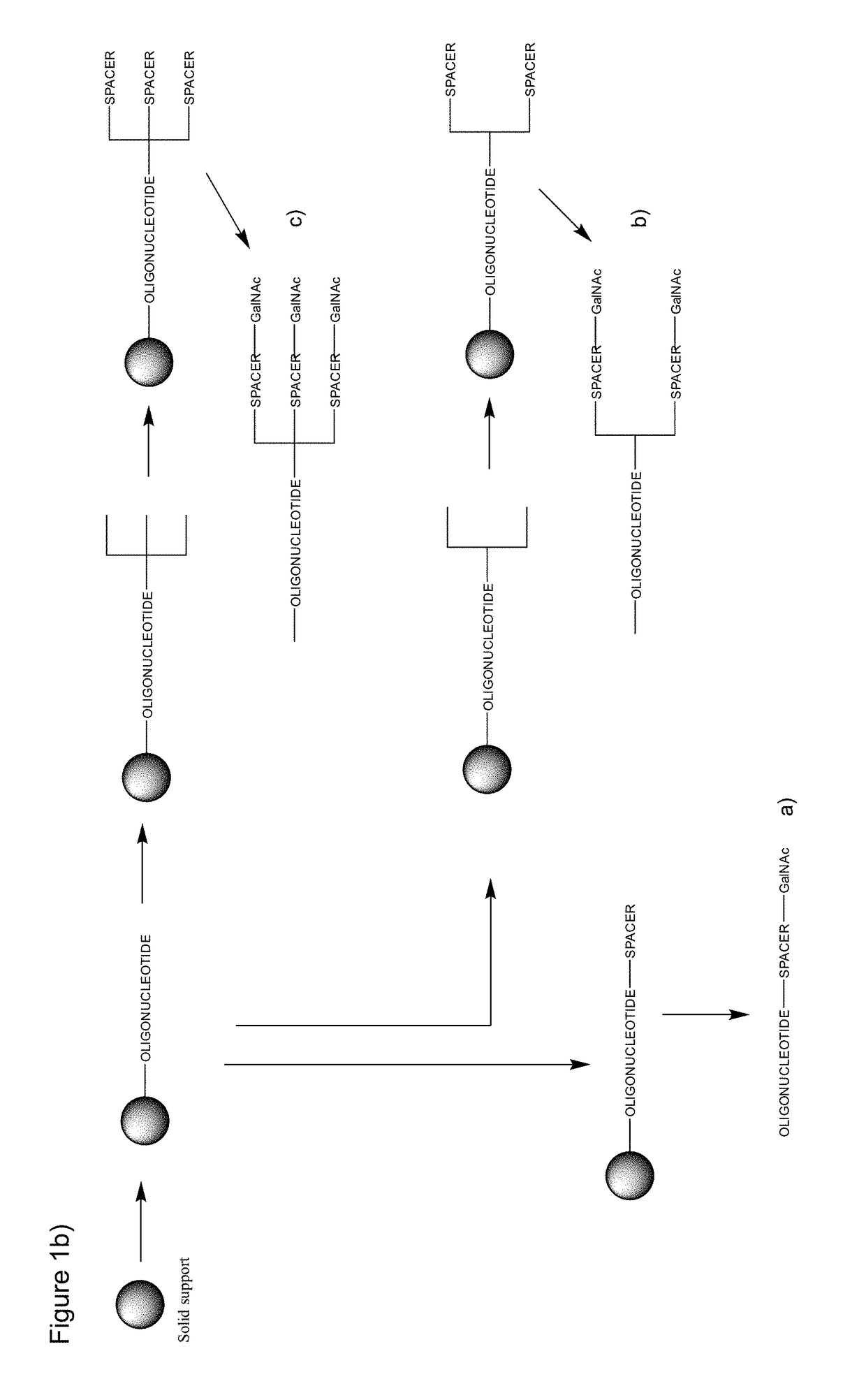
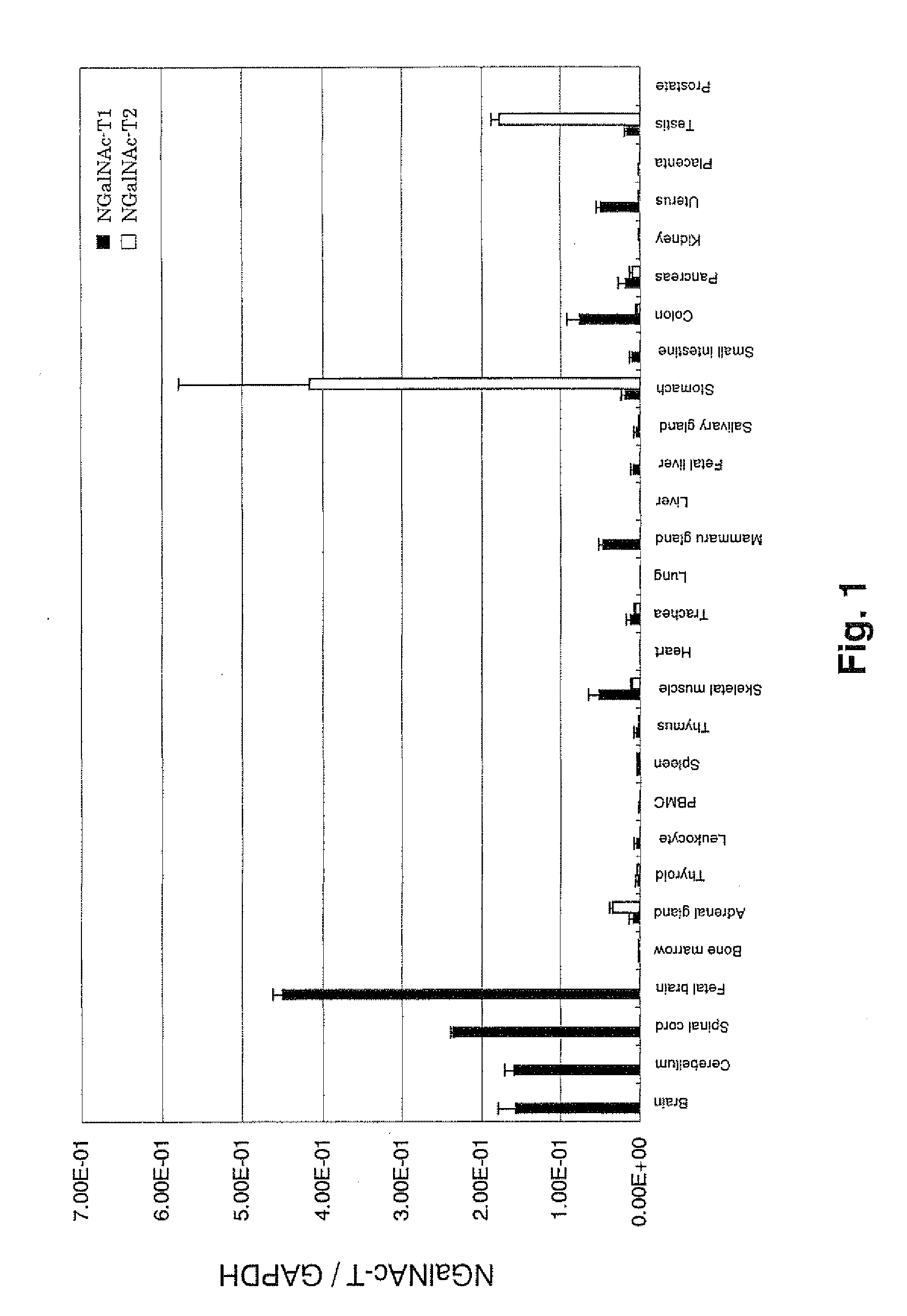
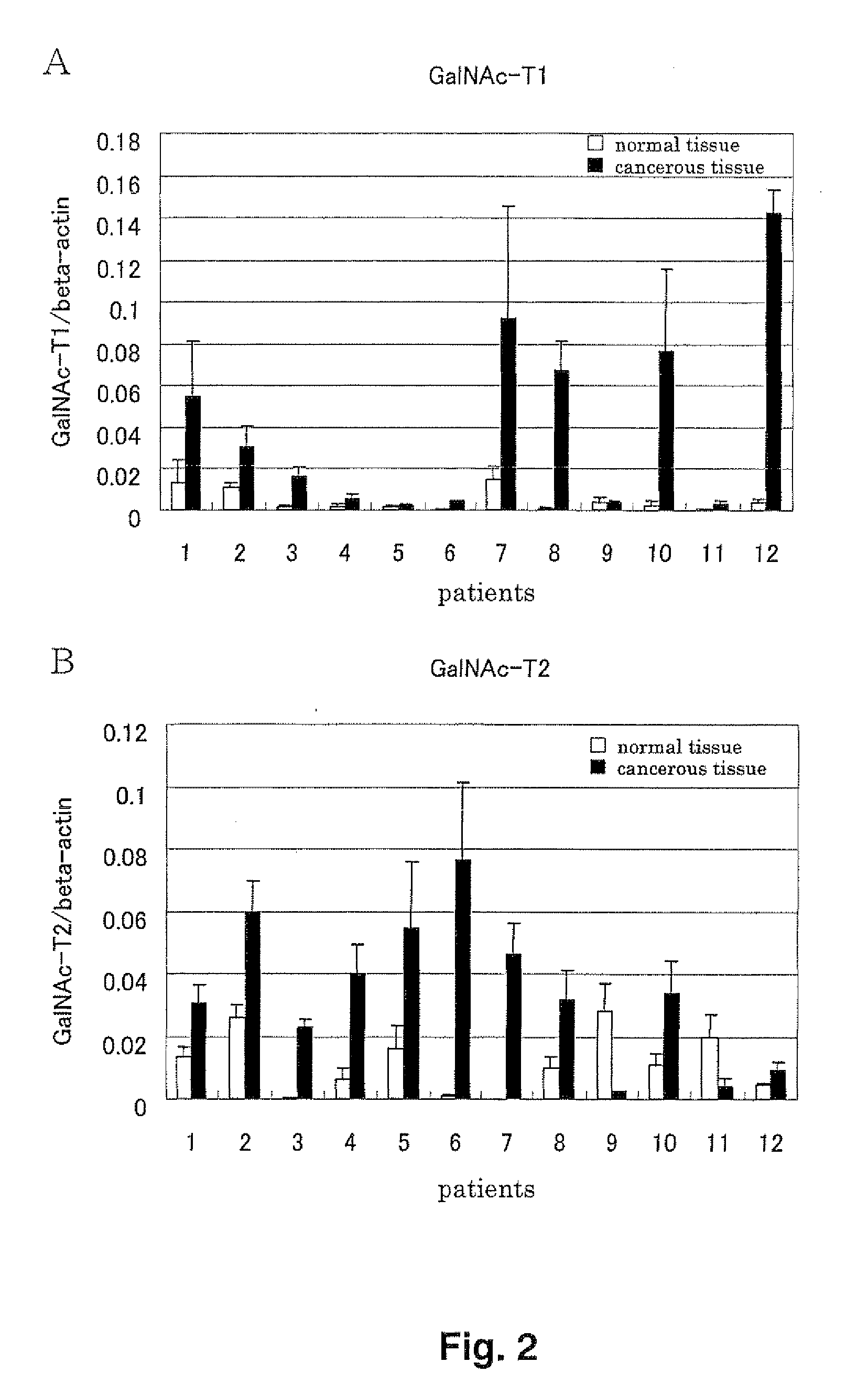
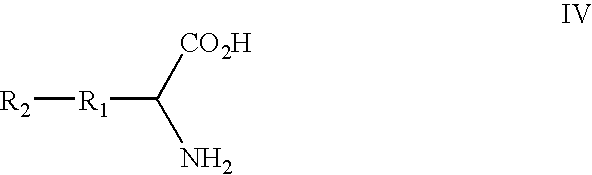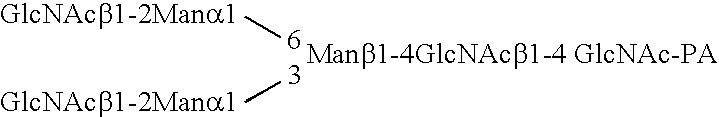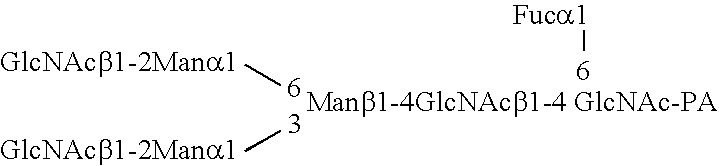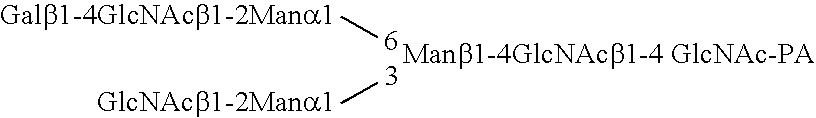Patents
Literature
85 results about "N-Acetylgalactosamine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
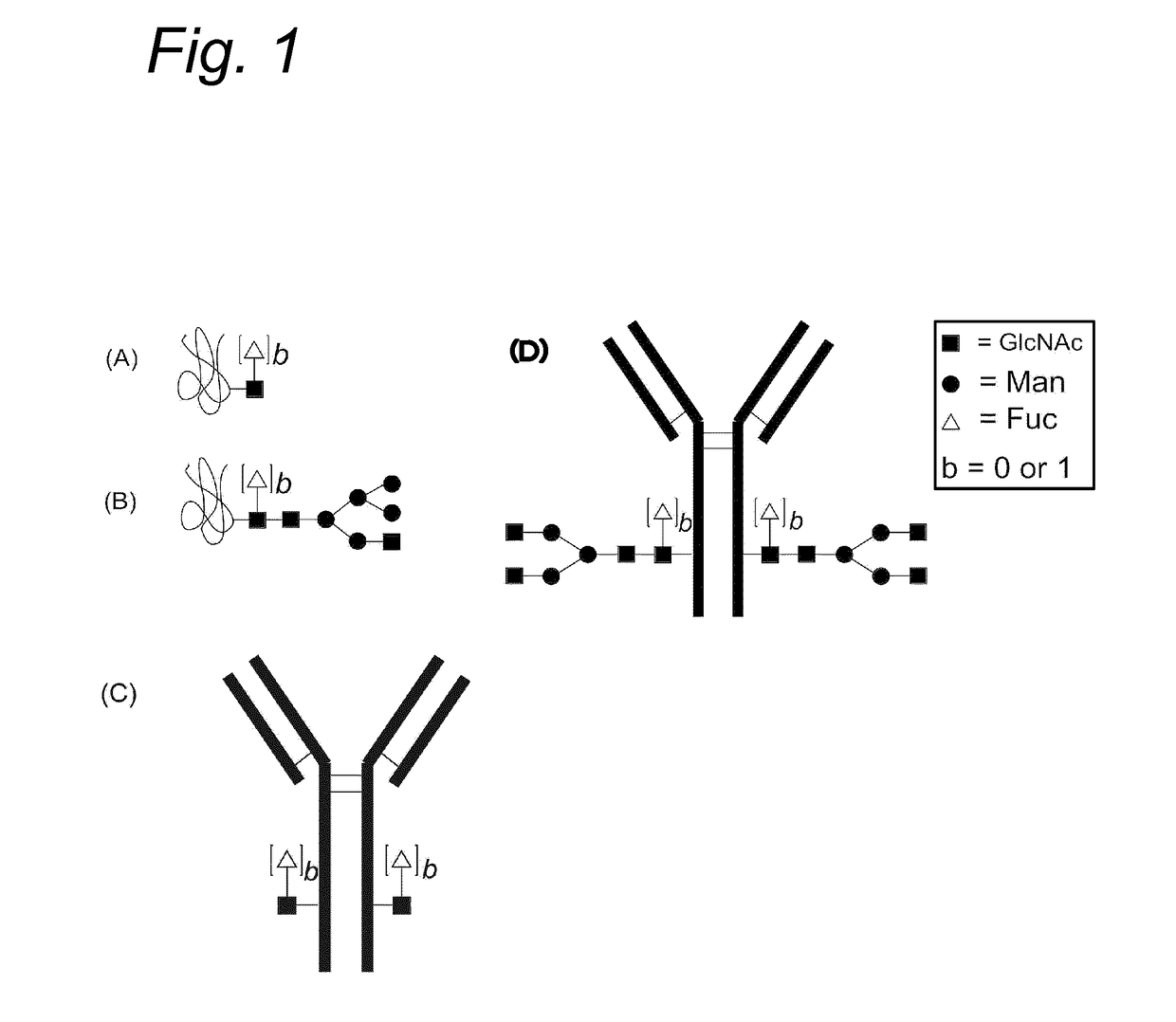
N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), is an amino sugar derivative of galactose.
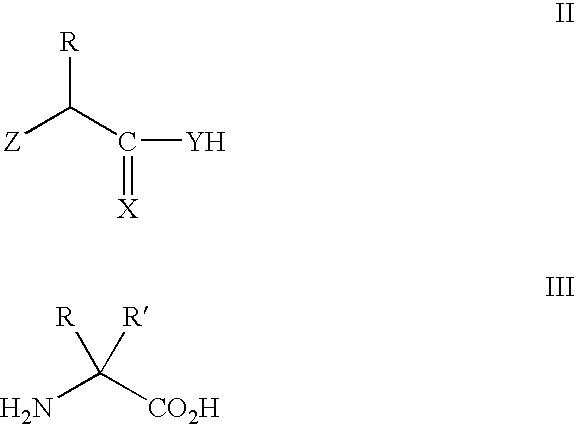
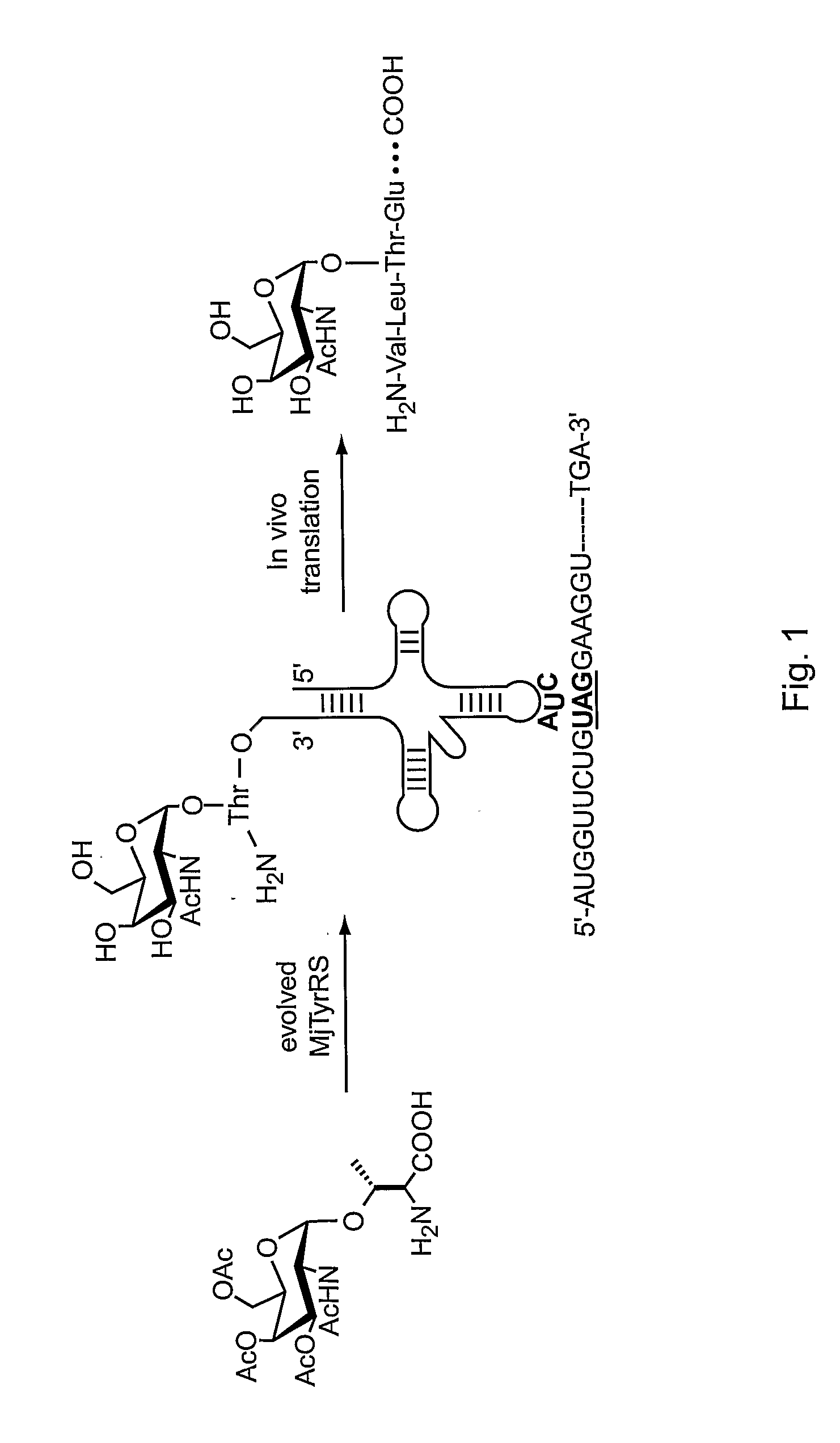
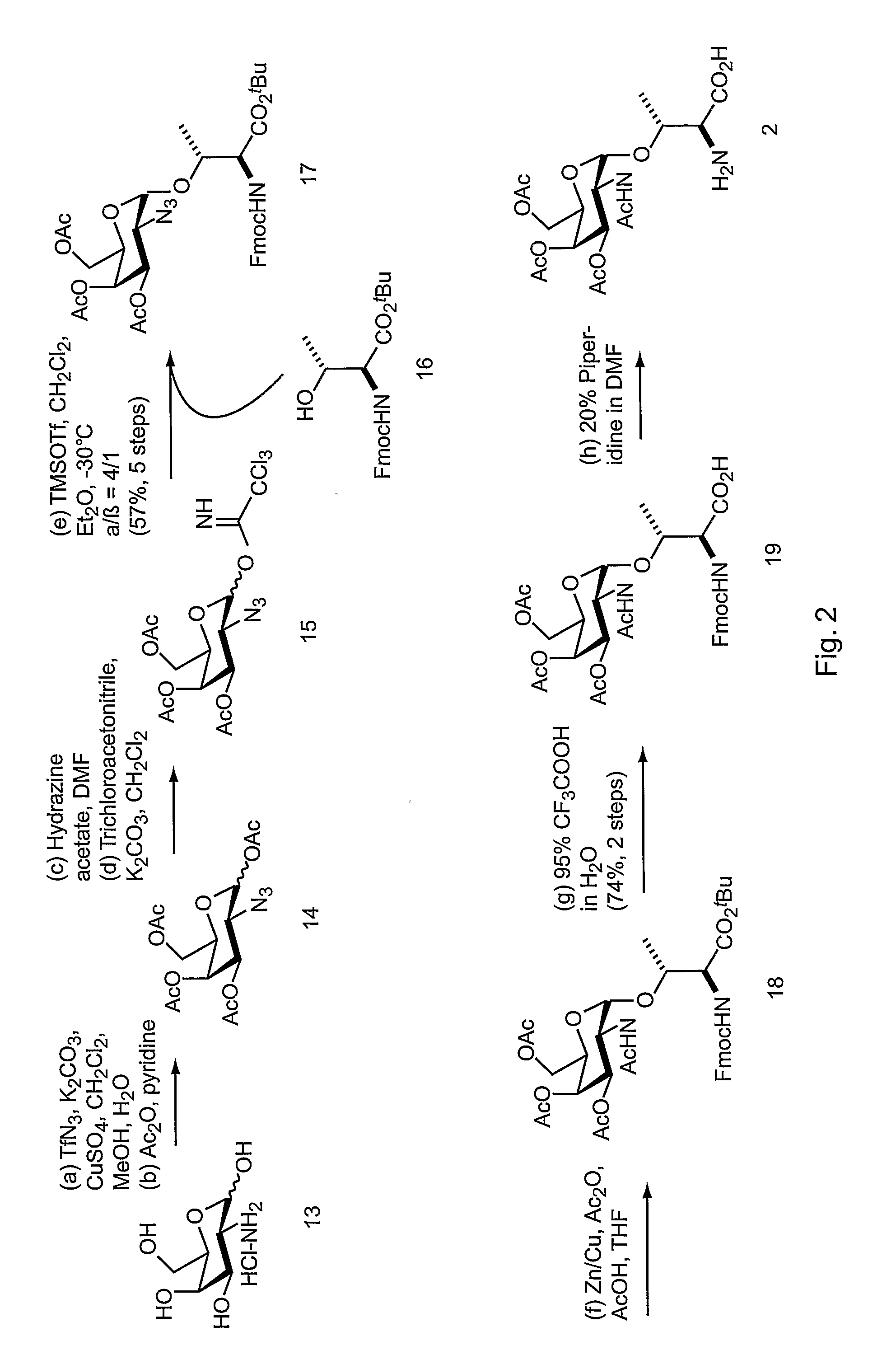
In vivo site-specific incorporation of N-acetyl-galactosamine amino acids in eubacteria
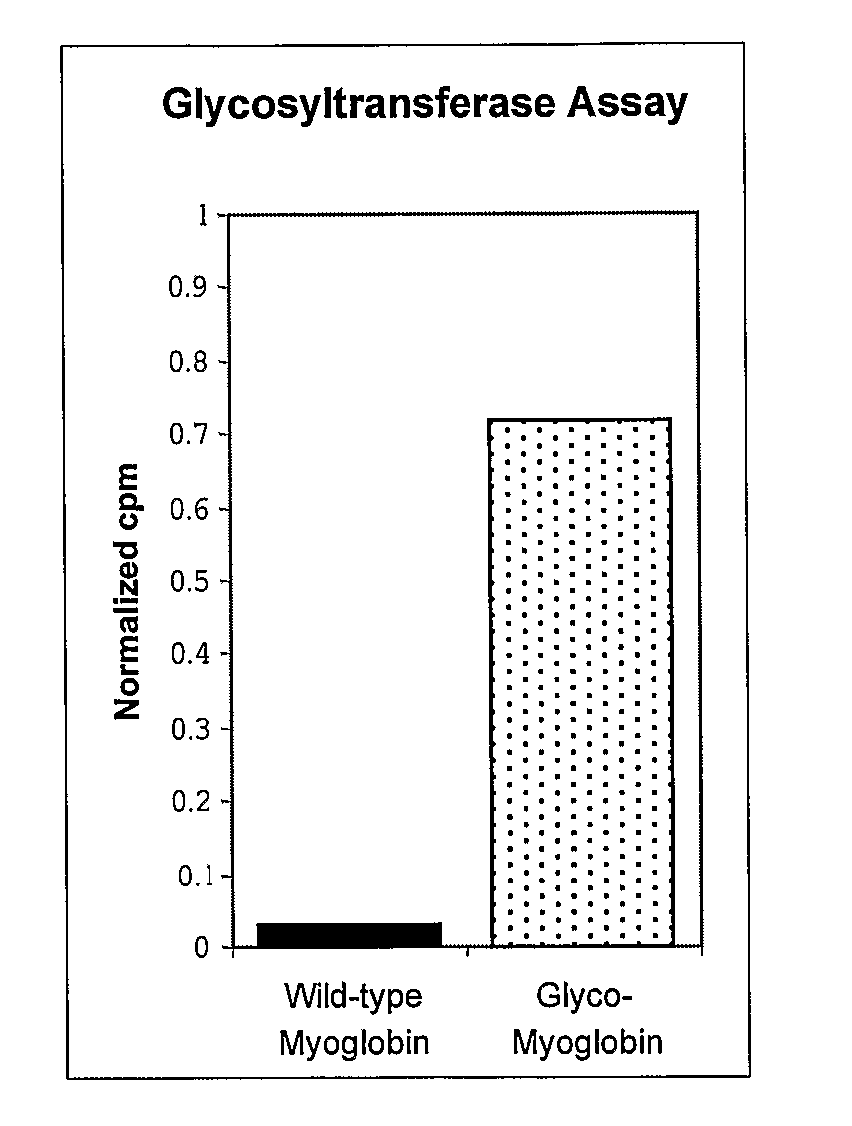
Methods and compositions for making glycoproteins, both in vitro and in vivo, are provided. One method involves incorporating an unnatural amino acid having a N-acetylgalactosamine moiety into a protein; optionally, the N-acetylgalactosamine-containing unnatural amino acid can be further modified with additional sugars.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
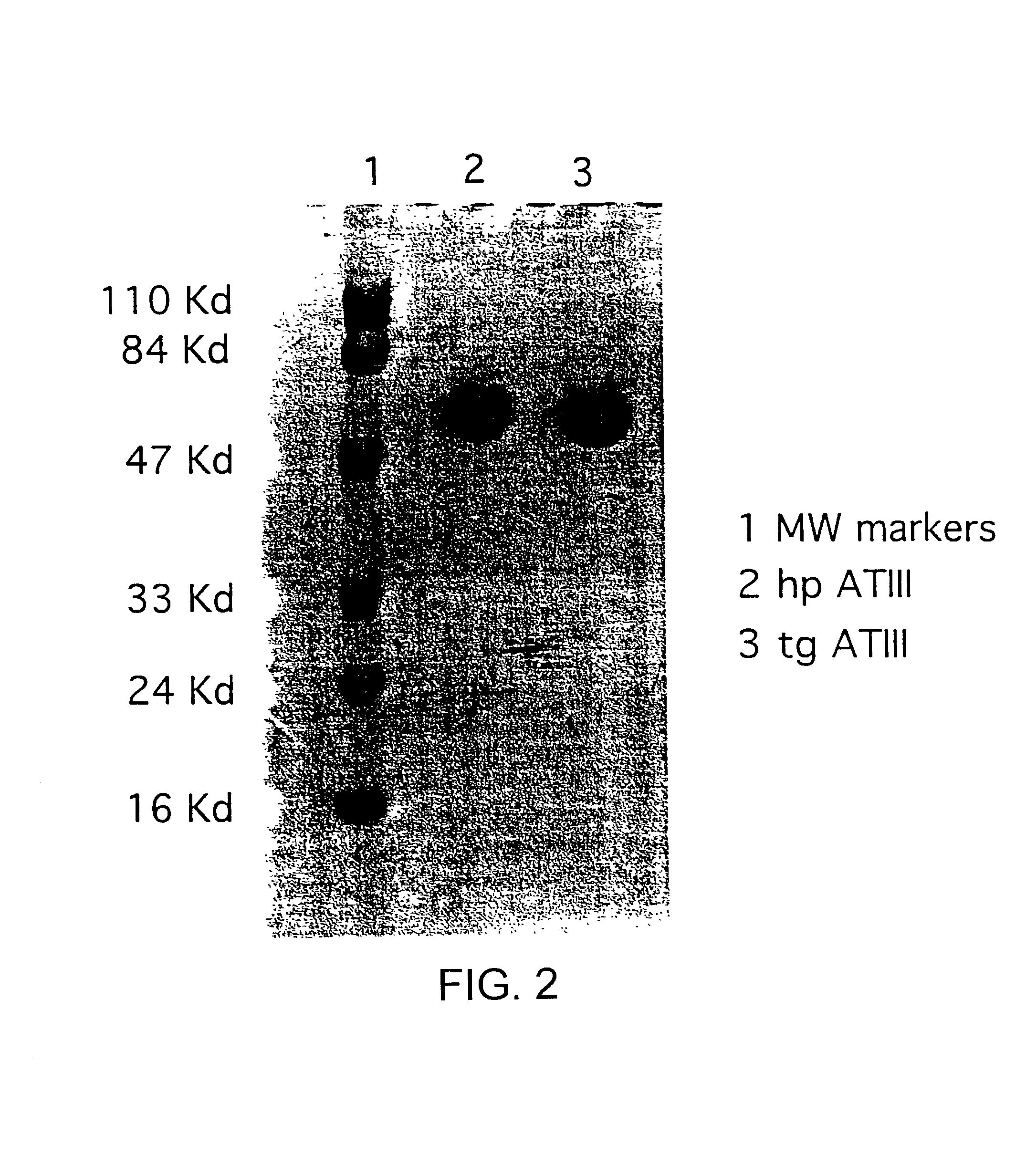
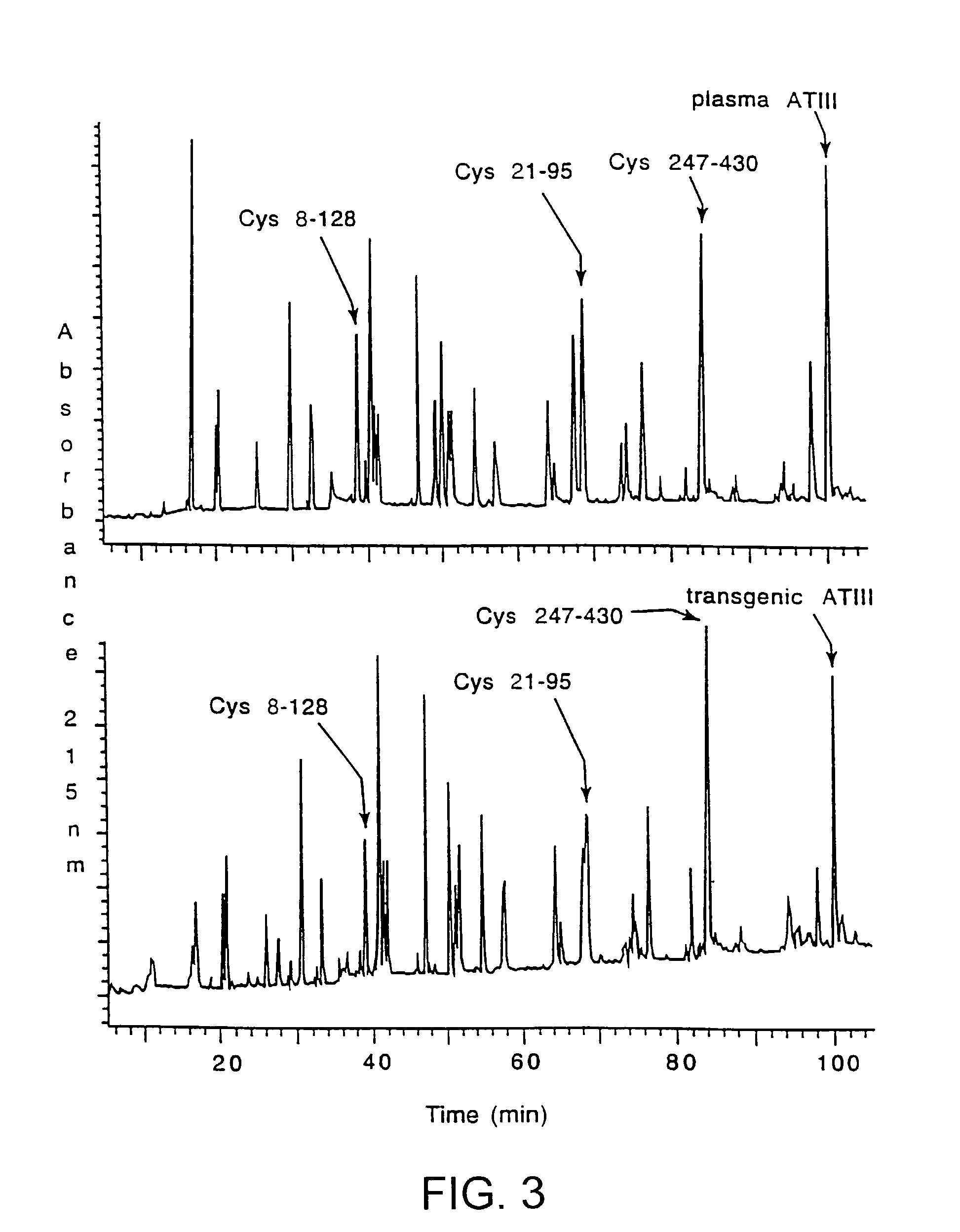
Treatments using transgenic goat produced antithrombin III
InactiveUS7019193B2Improve clearance ratePeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesPlasma derivedMonosaccharide composition
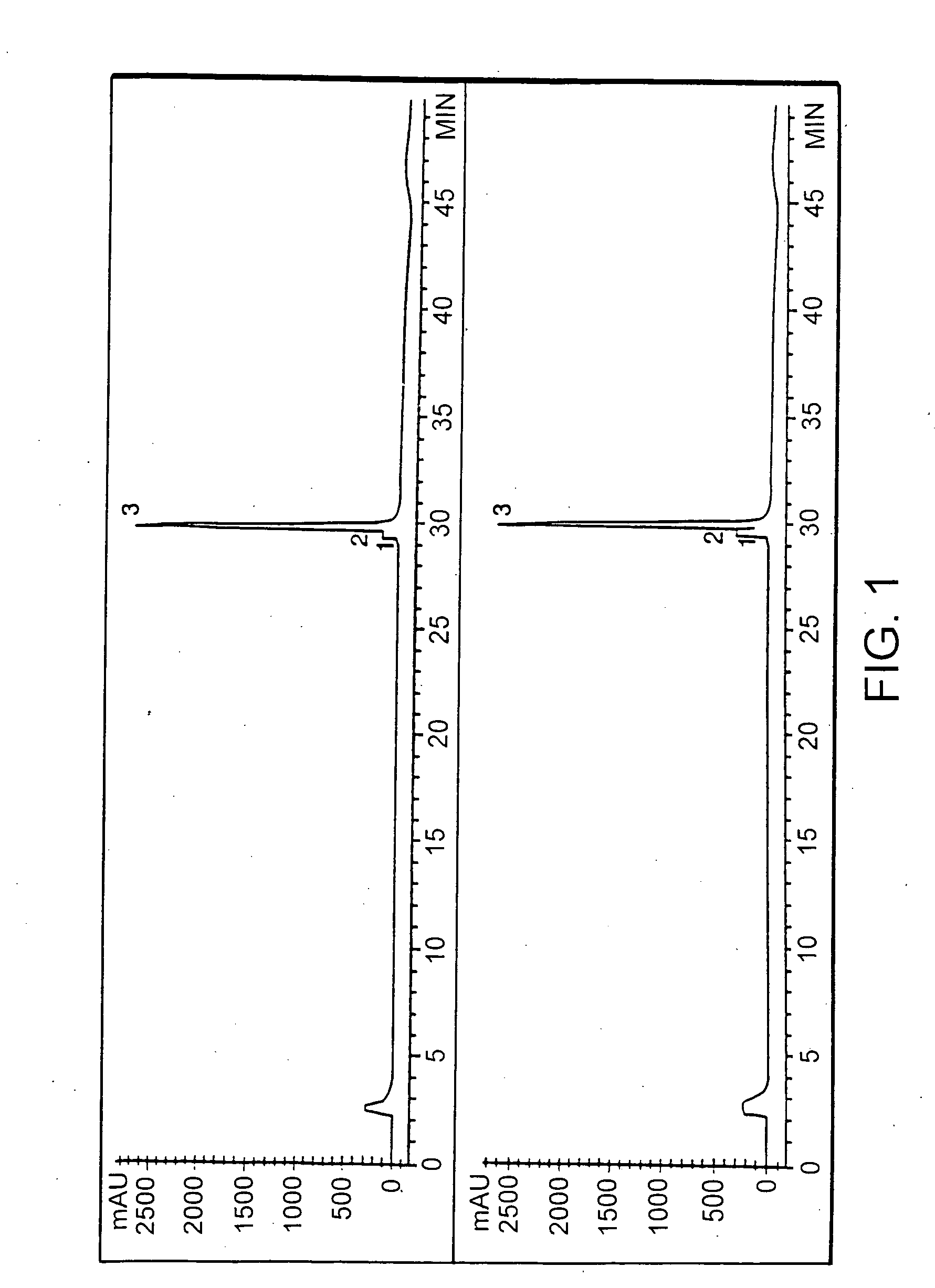
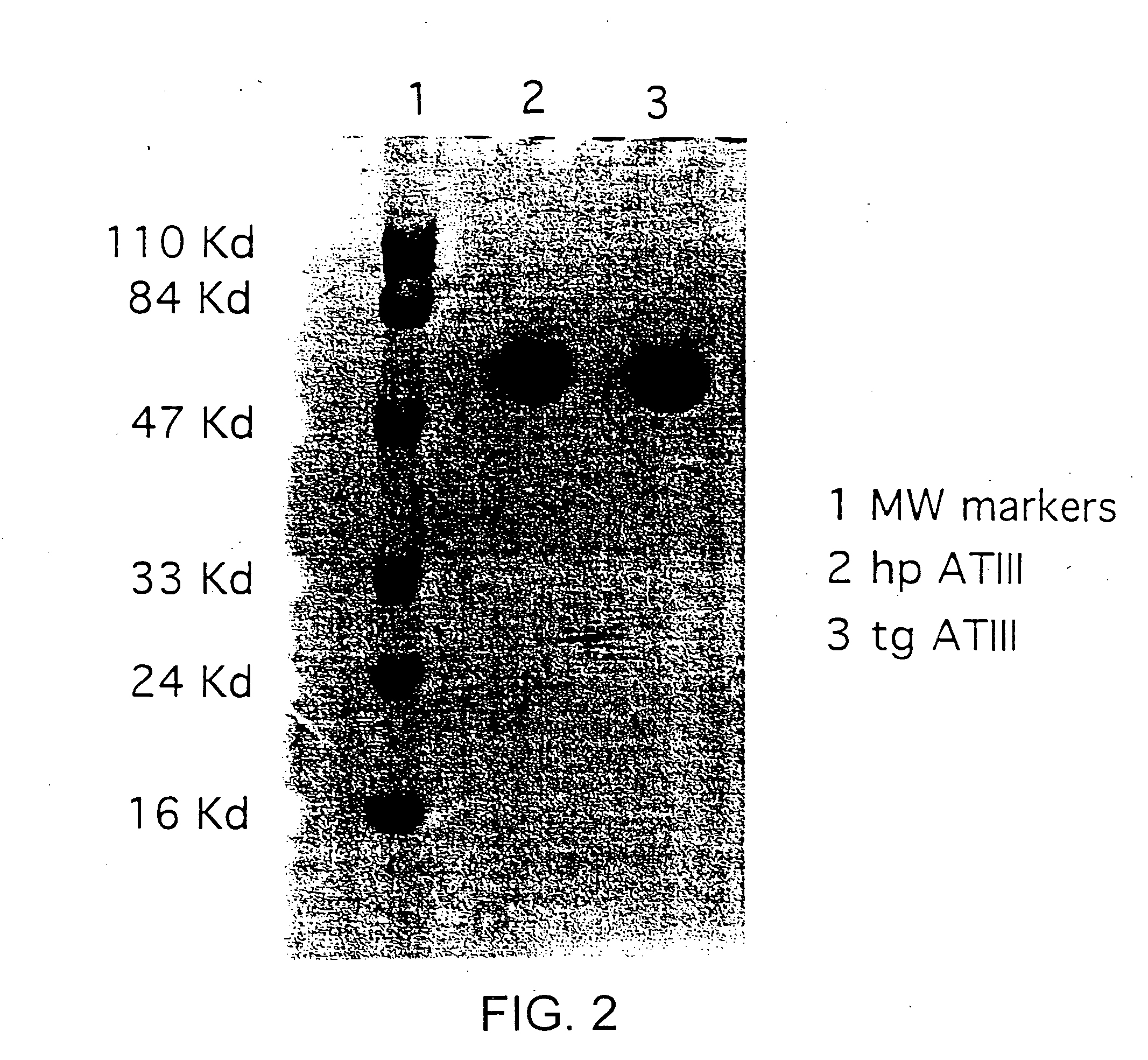
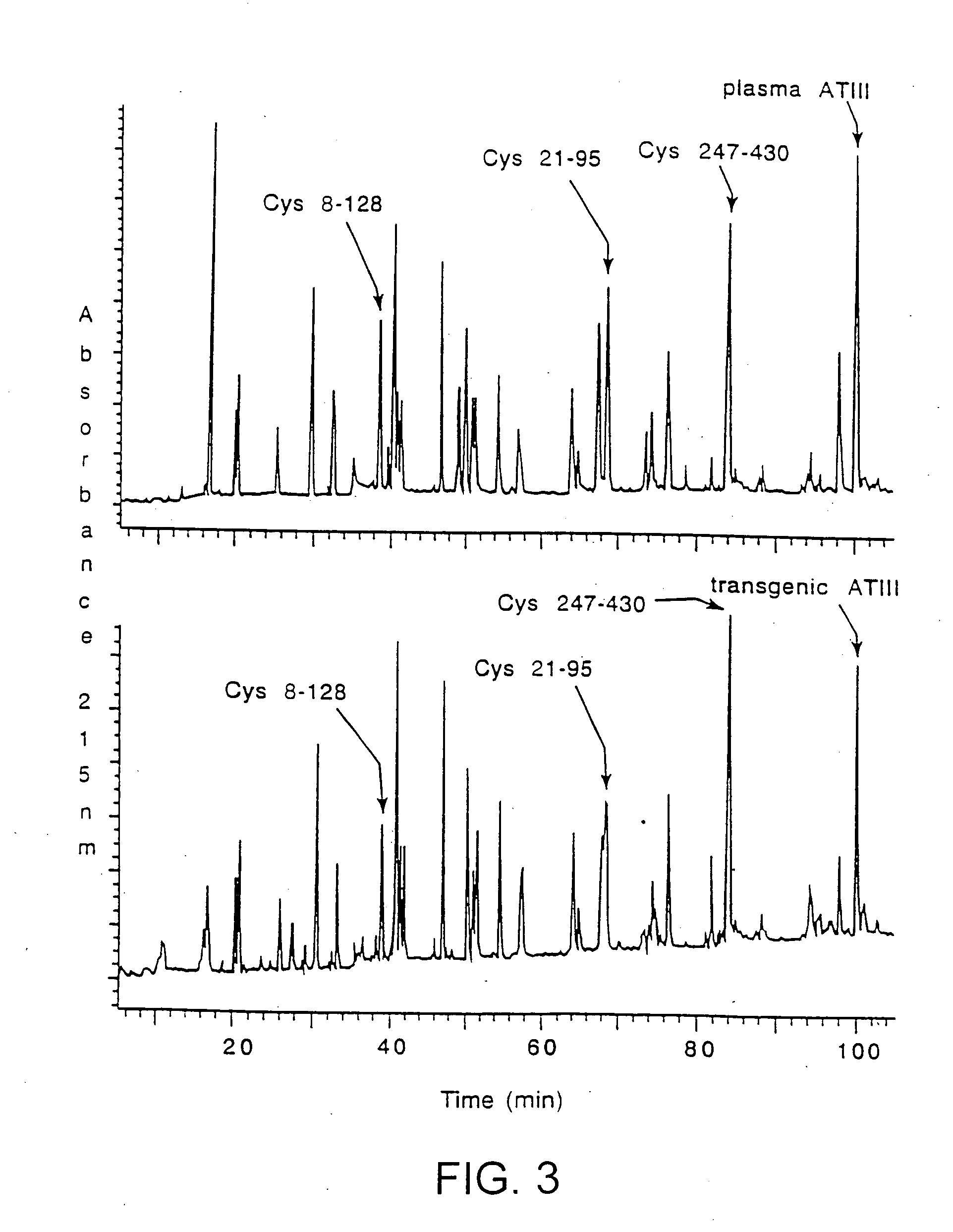
This invention relates to transgenically produced human Antithrombin III (tgATIII). The human ATIII produced by the transgenic process of the present invention has a monosaccharide composition which comprises N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) along with fucose, N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, mannose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid / N-glycolyneuraminic acid. The monosaccharide composition differs with that of plasma derived ATIII (phATIII). It has been found that tgATIII has an increased clearance rate when compared to phATIII.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
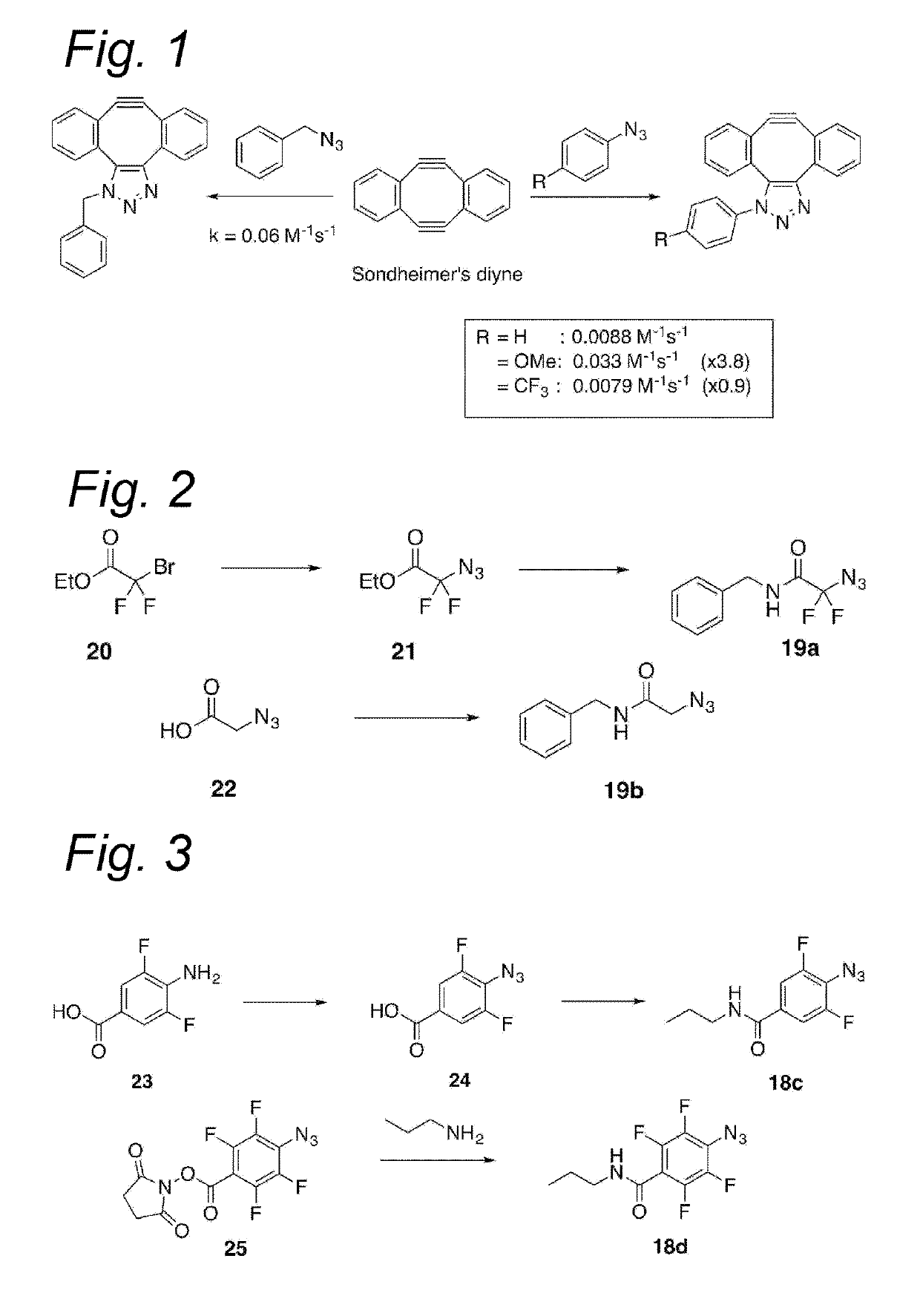
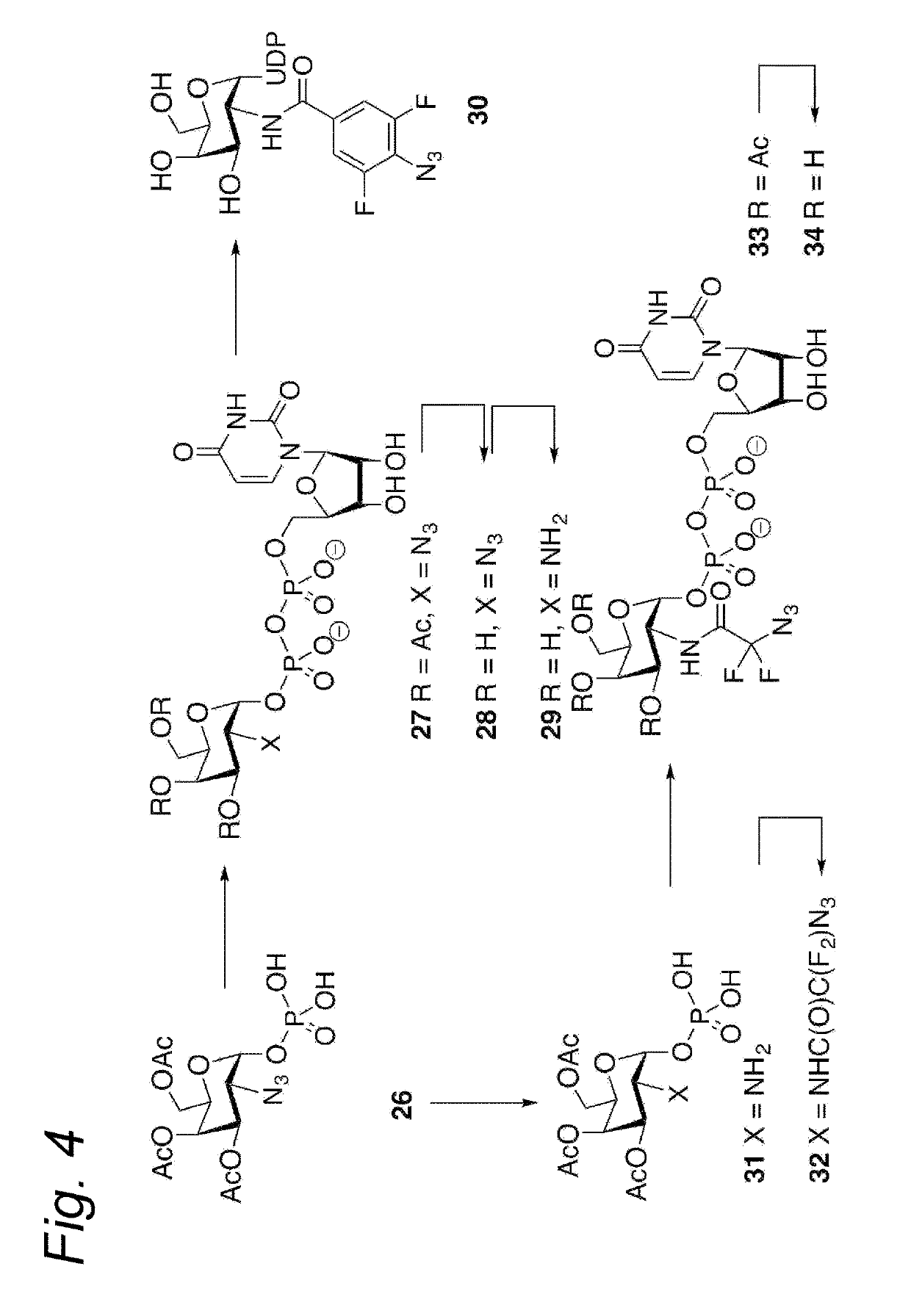
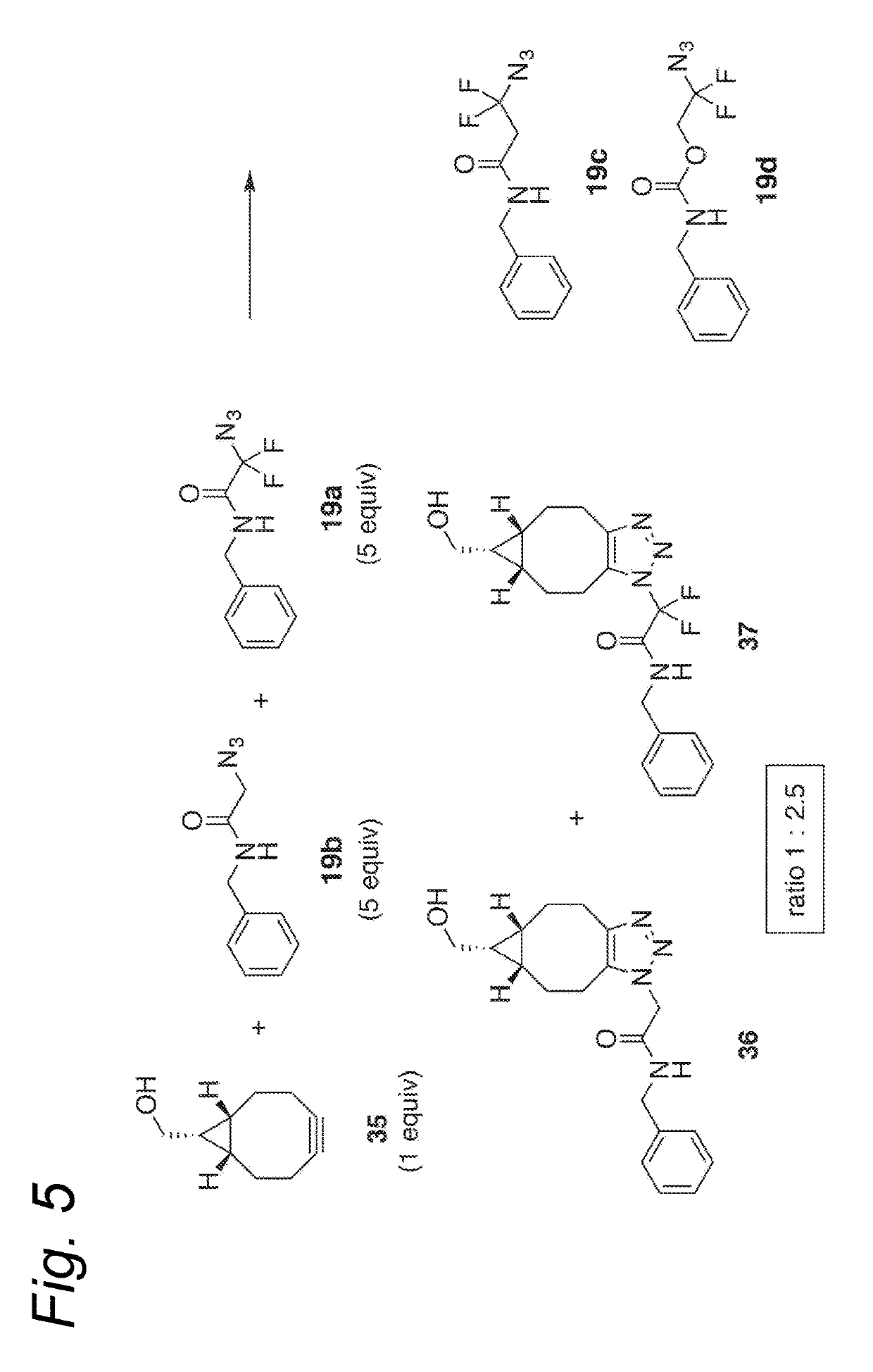
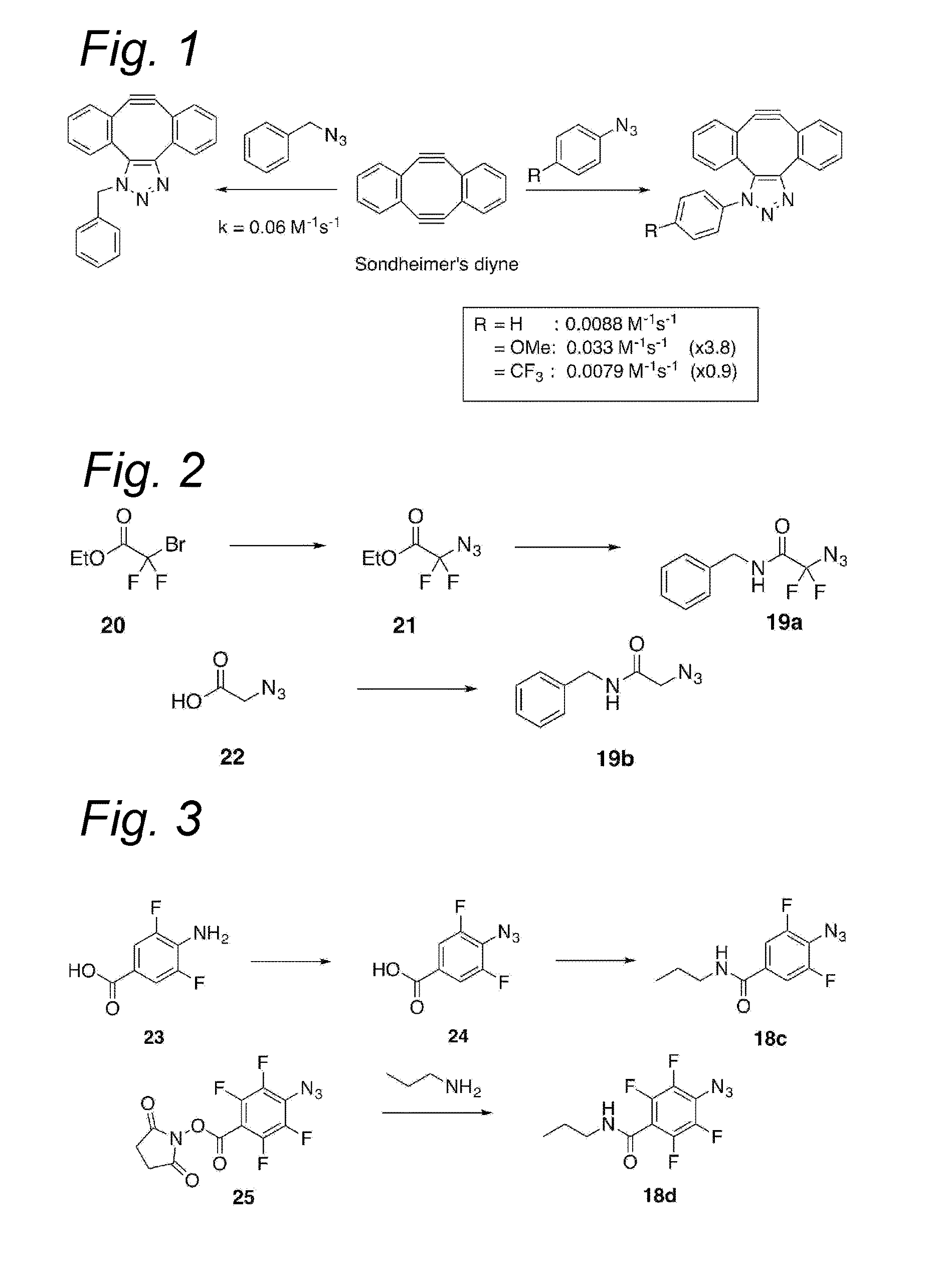
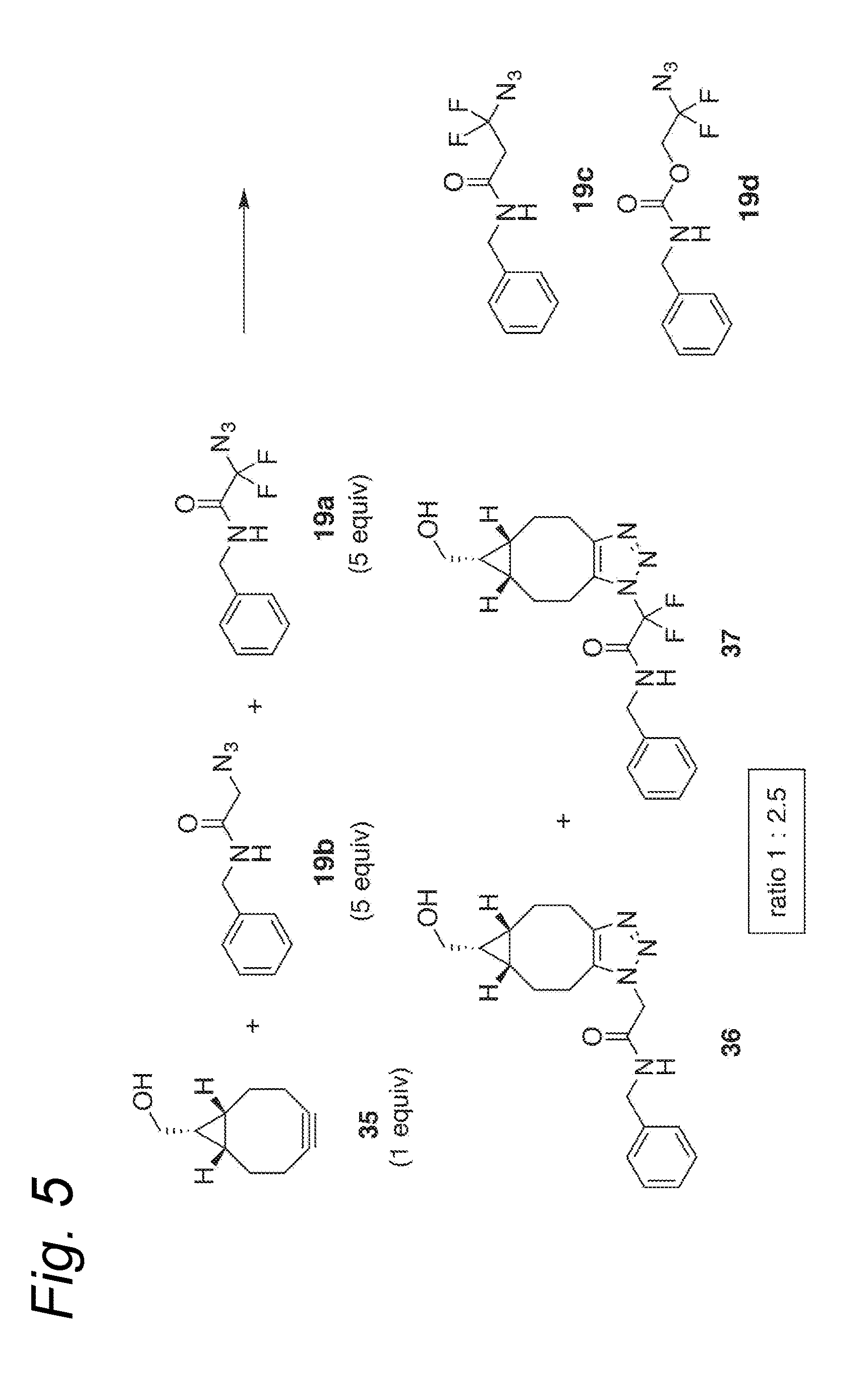
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS10266502B2Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
Owner:SYNAFFIX
Pharmaceutical composition for enzyme replacement therapy
ActiveUS20100291059A1Increase doseEffective absorptionSenses disorderSugar derivativesSide effectWild type
Owner:ALTIF LAB +1
In Vivo Site-Specific Incorporation of N-Acetyl-Galactosamine Amino Acids in Eubacteria
Methods and compositions for making glycoproteins, both in vitro and in vivo, are provided. One method involves incorporating an unnatural amino acid having a N-acetylgalactosamine moiety into a protein; optionally, the N-acetylgalactosamine-containing unnatural amino acid can be further modified with additional sugars.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST
Long-chain chondroitin sugar chain and method for producing the same and method for promoting synthesis of chondroitin
ActiveUS20090263867A1Efficient productionEasy to produceBacteriaSugar derivativesFiltrationChondroitinase ABC
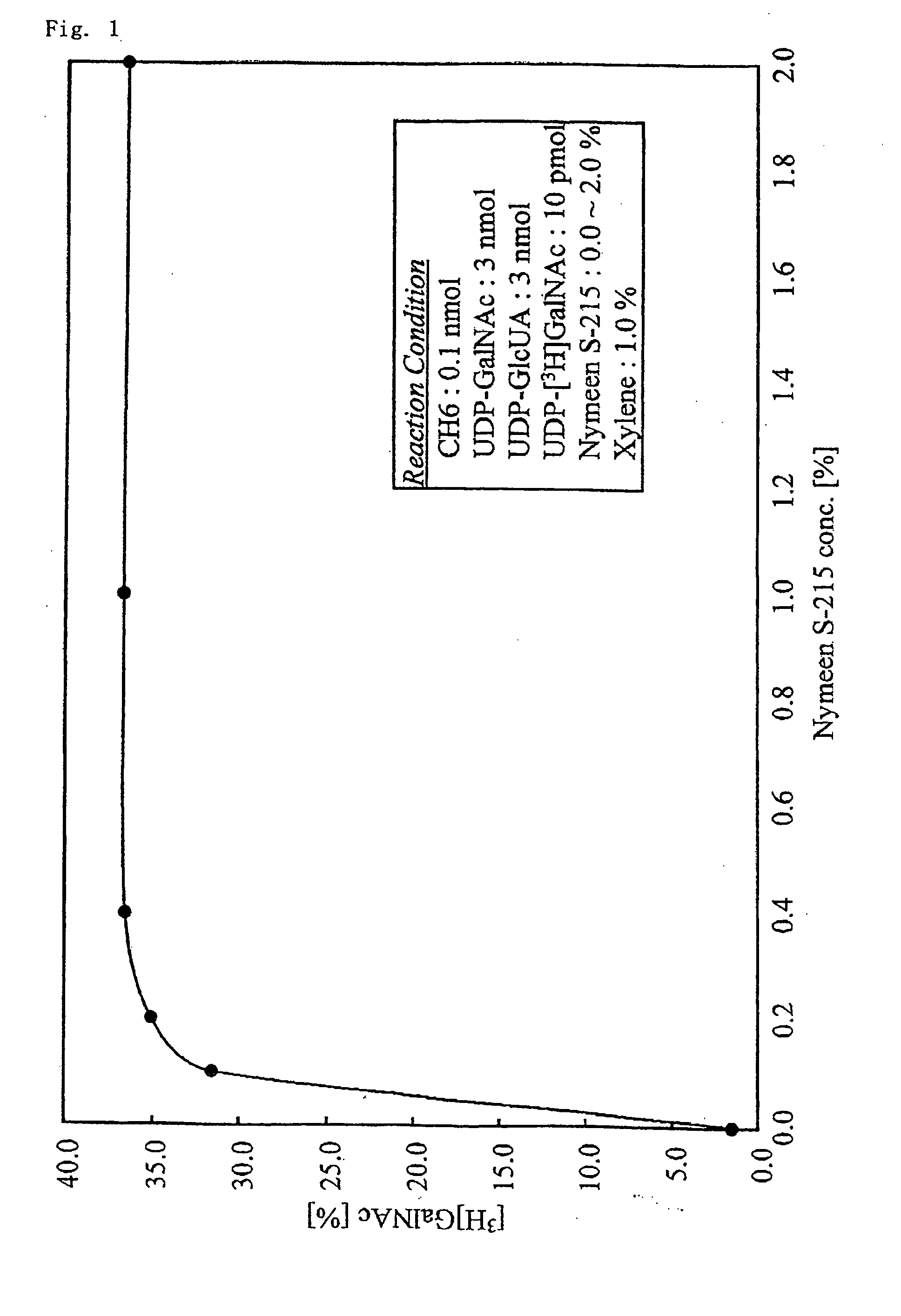
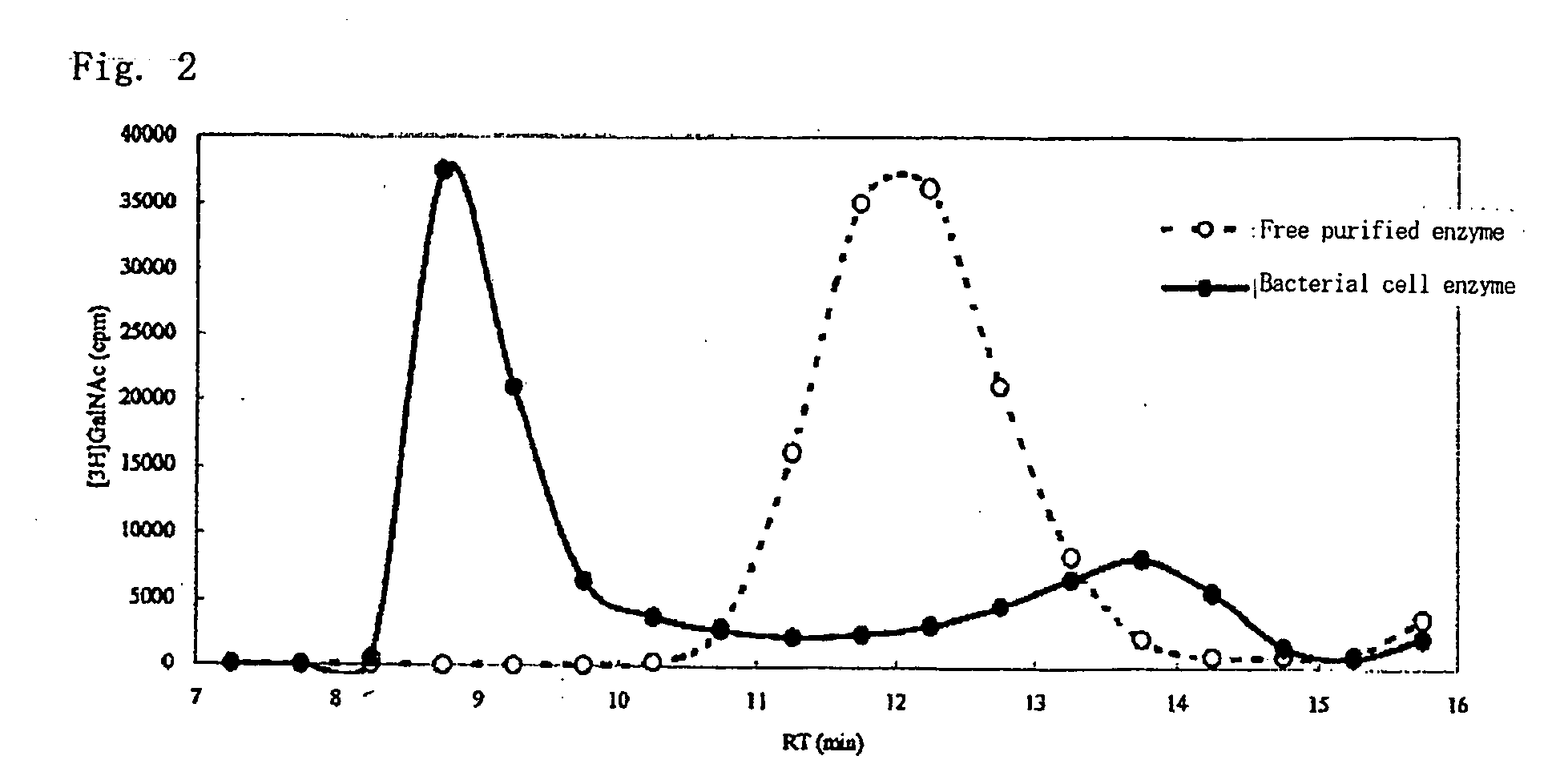
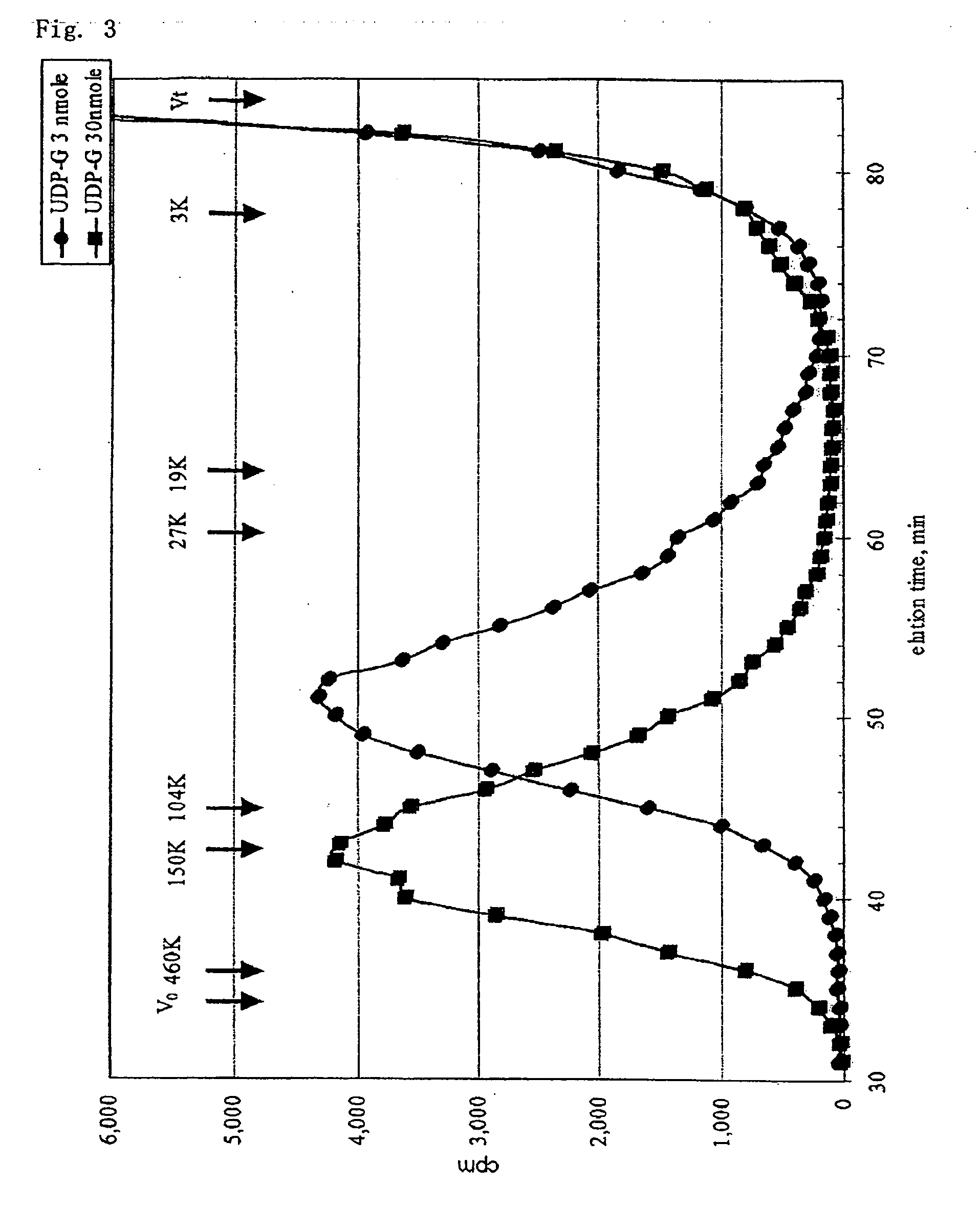
A method for producing a chondroitin sugar chain comprises at least the following step: a step of allowing “a glucuronic acid donor”, “an N-acetyl galactosamine donor”, “a sugar receptor” and “a bacterial cell enzyme which synthesizes chondroitin” to coexist in a reaction system in the presence of a surfactant. Here, the surfactant is preferably selected from n-nonyl-β-D-thiomaltopyranoside, sucrose monocaproate and sucrose monolaurate. The chondroitin sugar chain has all the following properties 1) to 3): 1) a weight average molecular weight: 50,000 or more when it is measured by gel filtration chromatography, 2) it is completely degraded to disaccharides with chondroitinase ABC, 3) when the sugar chain is decomposed with chondroitinase ABC and the decomposed products are subjected to a disaccharide analysis, substantially all of them correspond to an unsaturated disaccharide unit of chondroitin.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Chondroitin synthetase and dna encoding the enzyme
A human-derived novel chondroitin synthase, which is an enzyme for synthesizing a fundamental backbone of chondroitin and has both glucuronic acid transferase activity and N-acetylgalactosamine transferase activity.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD +1
Process for the cycloaddition of a halogenated 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne
ActiveUS20170008858A1Esterified saccharide compoundsSugar derivativesNeuraminic acidN-Acetylglucosamine
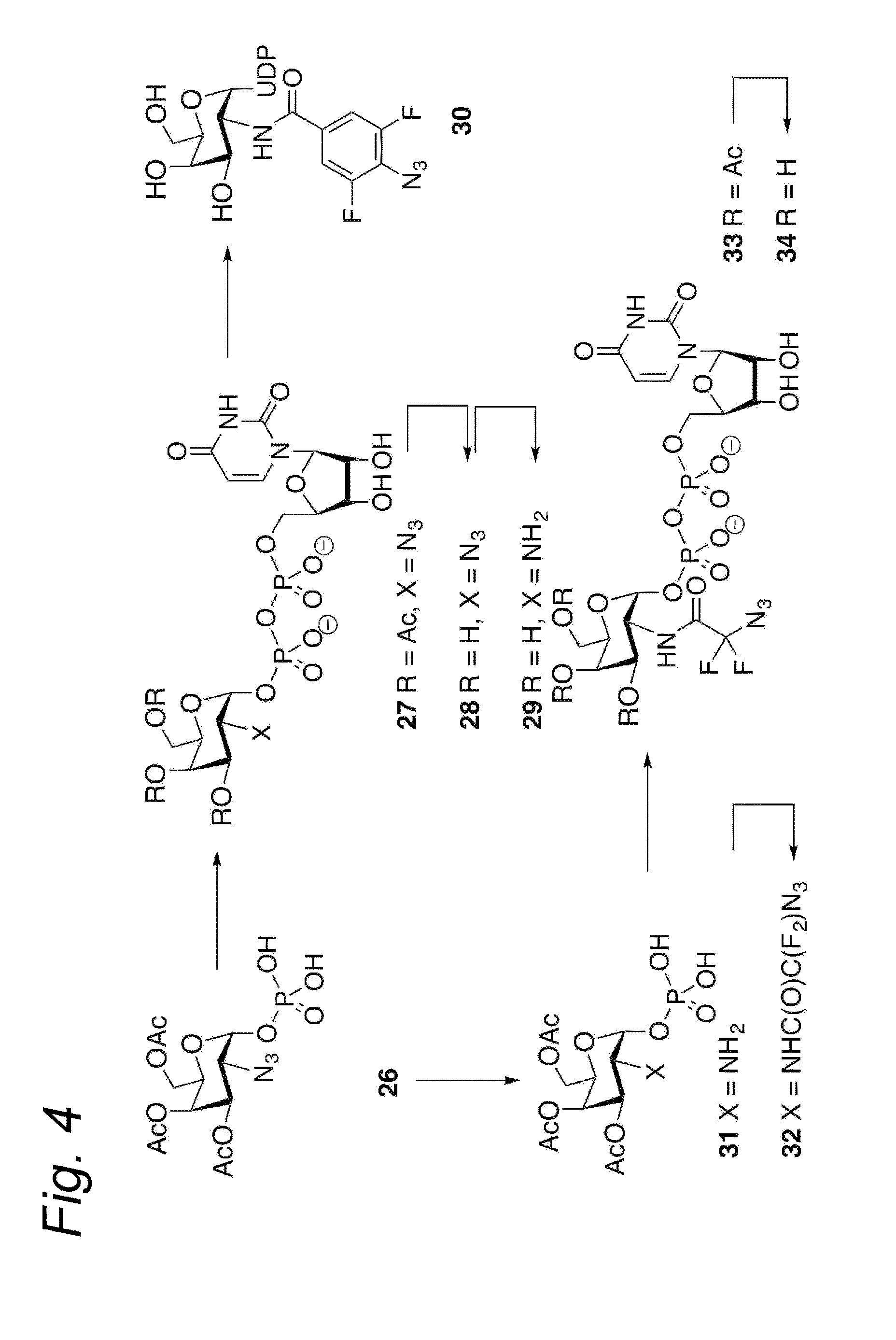
The present invention relates to a cycloaddition process comprising the step of reacting a halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compound with a (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1): Preferably, the (hetero)cycloalkyne according to Formula (1) is a (hetero)cyclooctyne. The invention also relates to the cycloaddition products obtainable by the process according to the invention. The invention further relates to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds, in particular to halogenated aliphatic 1,3-dipole compounds comprising N-acetylgalactosamine-UDP (GalNAc-UDP), and to halogenated 1,3-dipole compounds comprising (peracylated) N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc), N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc), N-acetylmannosamine (ManNAc) and N-acetyl neuraminic acid (NeuNAc).
Owner:SYNAFFIX
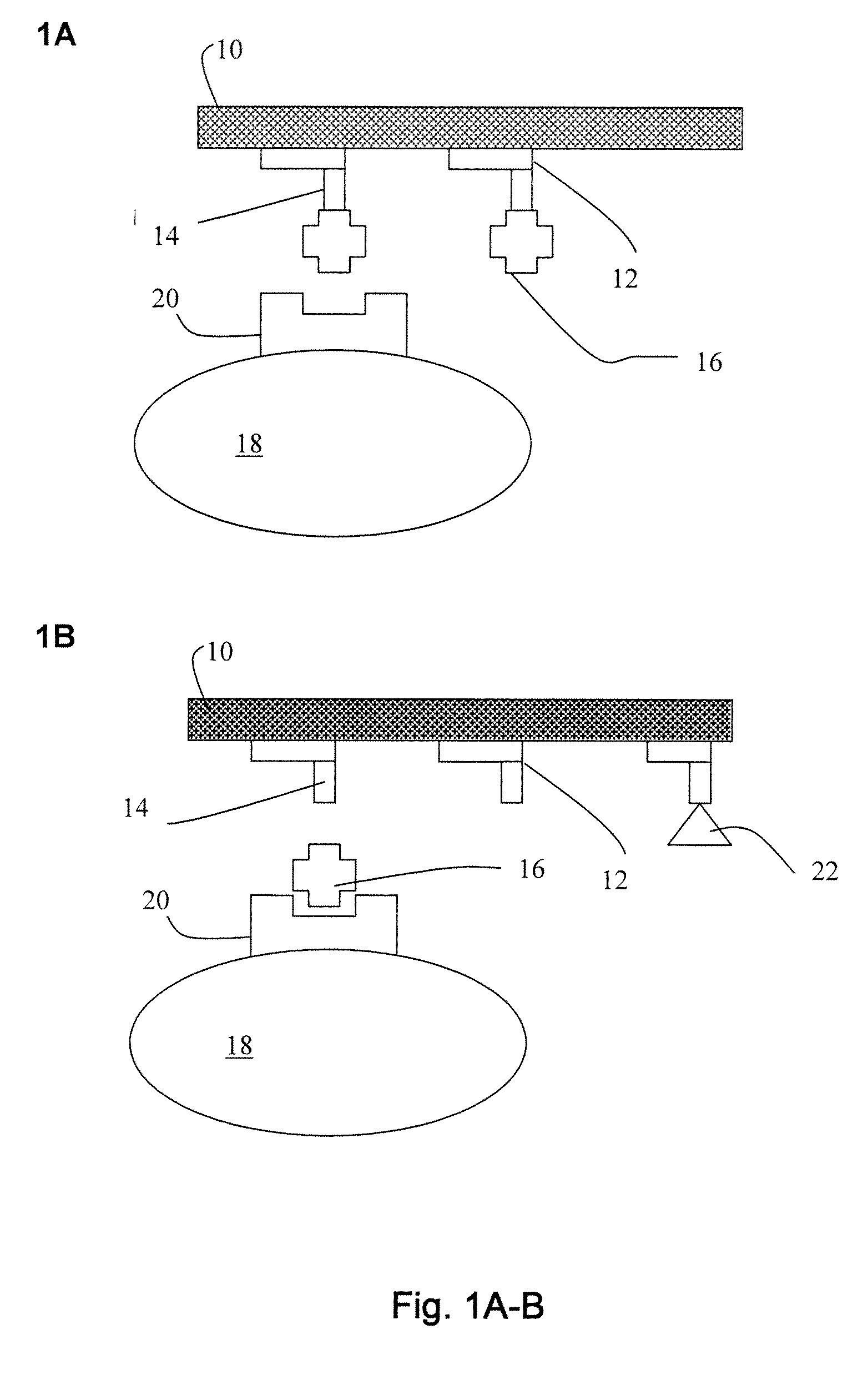
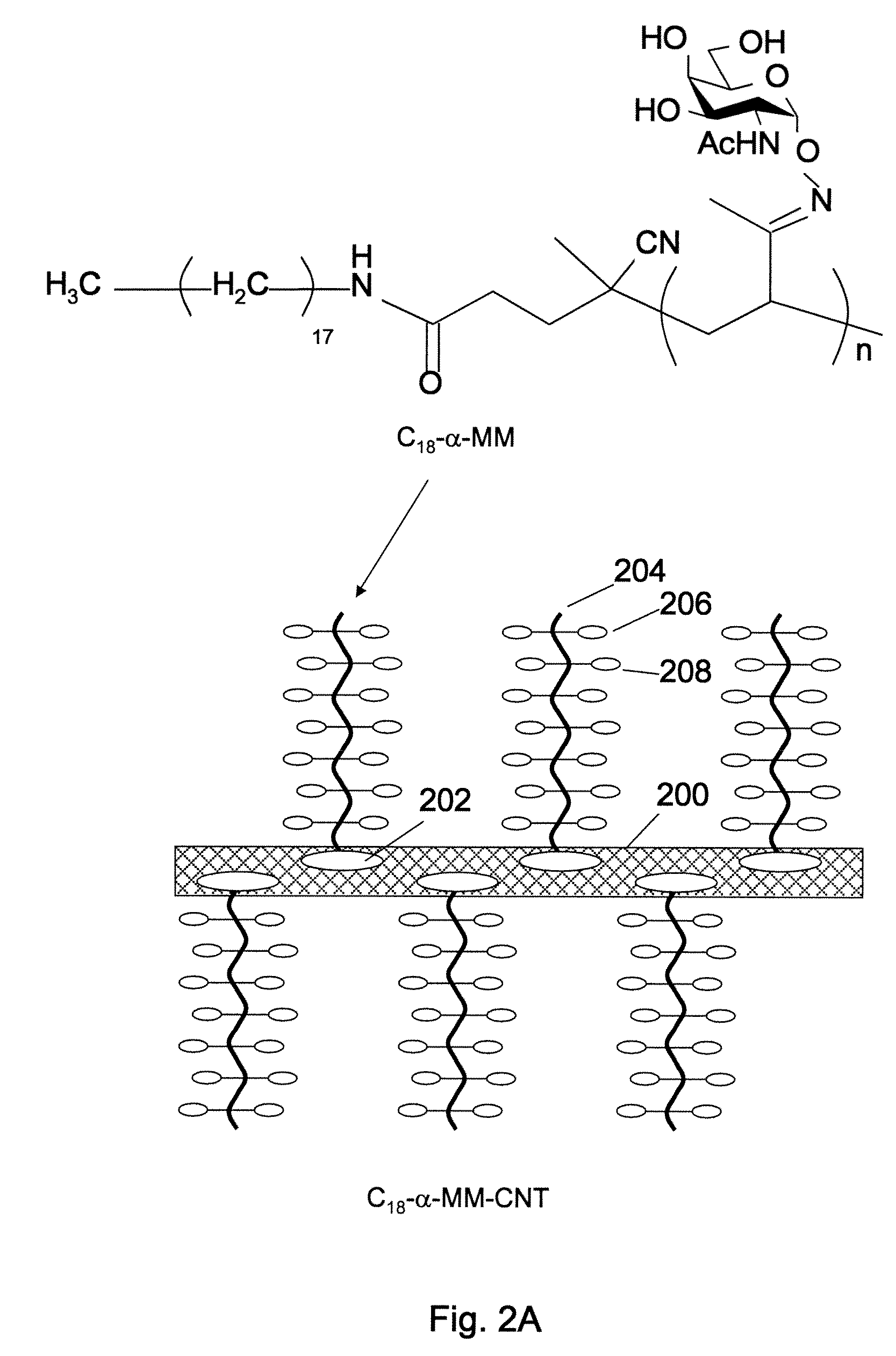
Interfacing Nanostructures to Biological Cells
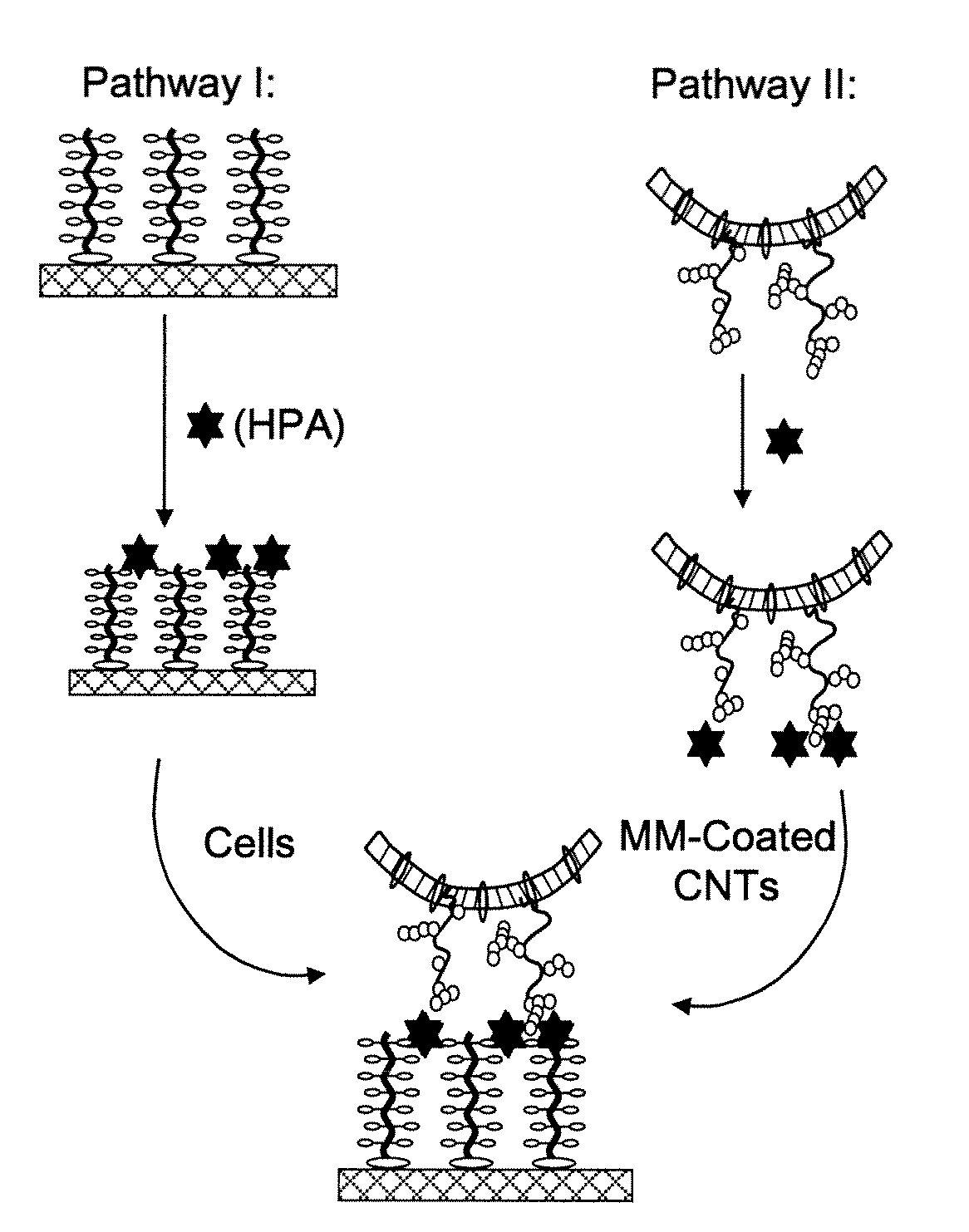
Disclosed herein are methods and materials by which nanostructures such as carbon nanotubes, nanorods, etc. are bound to lectins and / or polysaccharides and prepared for administration to cells. Also disclosed are complexes comprising glycosylated nanostructures, which bind selectively to cells expressing glycosylated surface molecules recognized by the lectin. Exemplified is a complex comprising a carbon nanotube functionalized with a lipid-like alkane, linked to a polymer bearing repeated α-N-acetylgalactosamine sugar groups. This complex is shown to selectively adhere to the surface of living cells, without toxicity. In the exemplified embodiment, adherence is mediated by a multivalent lectin, which binds both to the cells and the α-N-acetylgalactosamine groups on the nanostructure.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Cholesterol Sulfate And Amino Sugar Compositions For Enhancement Of Stratum Corneum Function
InactiveUS20100247692A1Enhances protective barrierImprove skinCosmetic preparationsBiocideWrinkle skinSkin barrier function
The present invention provides compositions containing a mixture of cholesterol sulfate and an exfoliant. The exfoliant can be N-acetyl-D-glucosamine, N-acetylgalactosamine, or a combination thereof. The combination of cholesterol sulfate with the exfoliant surprisingly enhances the skin barrier even though the activity of each of the components is opposite the other. In addition, because of the ability to enhance or repair the skin barrier function, methods of maintaining or improving a healthy skin barrier are included in the present invention by apply to the skin an effective amount of the mixture of cholesterol sulfate with the exfoliant. The mixture can also be useful in treating or preventing damage to the skin, where the damage is caused by a comprised skin barrier function. As a result of improved skin barrier function, the appearance of lines and wrinkles is generally reduced; rough and dry skin conditions are also improved.
Owner:MAES DANIEL H +1
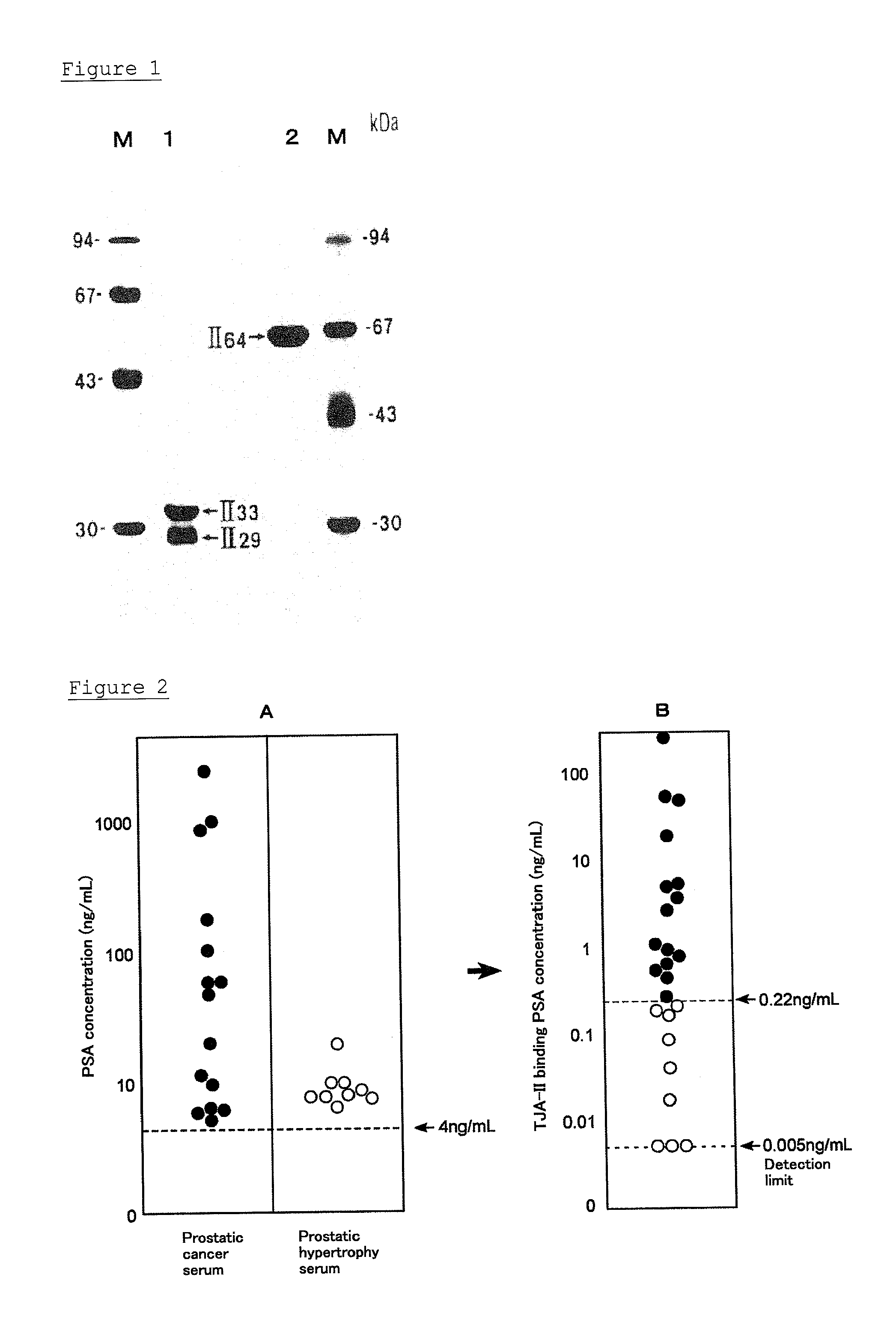
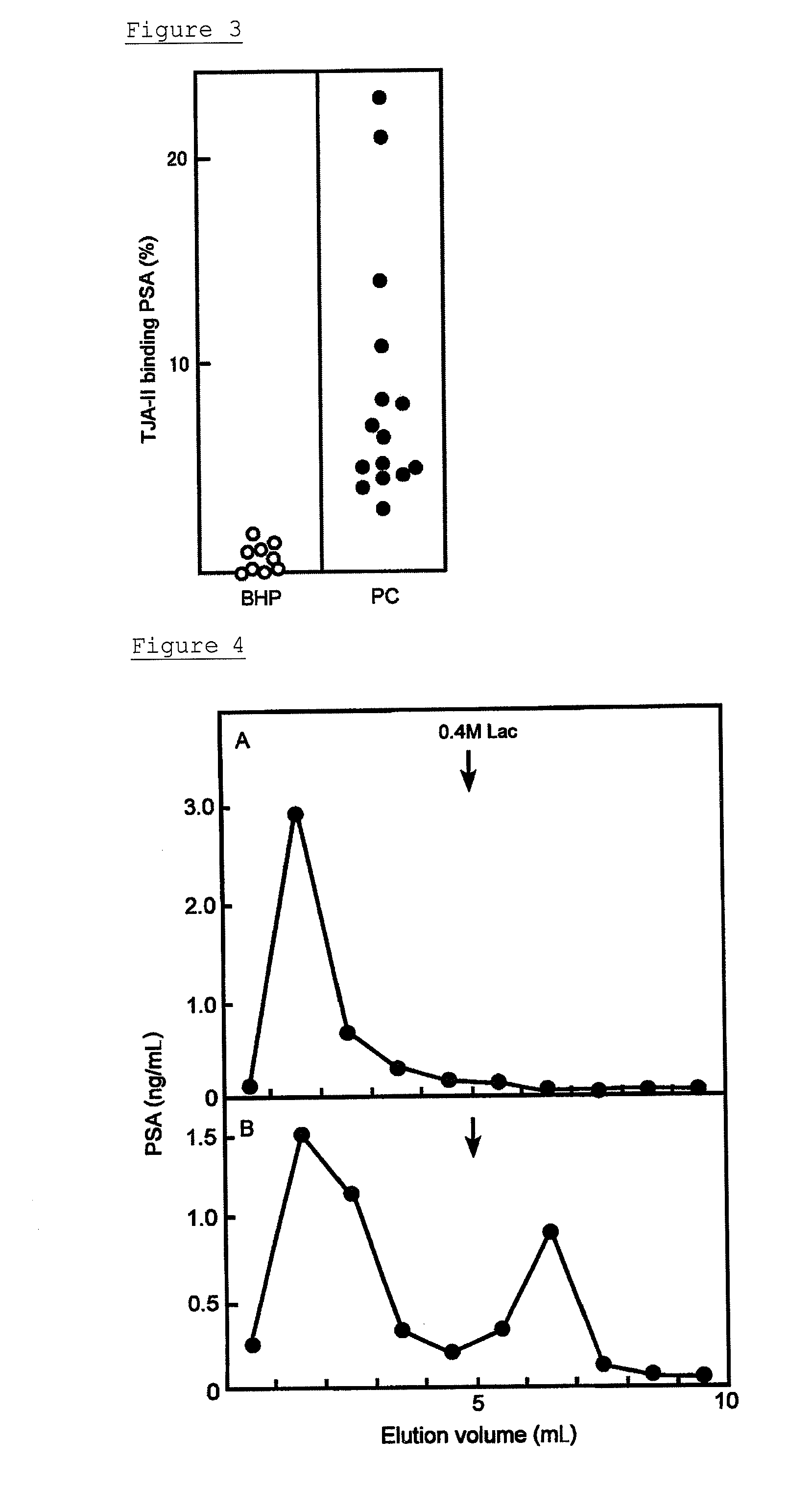
Method for analyzing psa and method for distinguishing prostate cancer from prostatic hypertrophy using that method for analyzing psa
ActiveUS20110294141A1Distinguish clearlyAccurate measurementHydrolasesDisease diagnosisEccentric hypertrophyMedicine
A method for distinguishing prostate cancer from prostatic hypertrophy using the method for analyzing PSA and an analysis kit of PSA are provided.An object of the present invention can be solved by being brought into contact a lectin having an affinity for β-N-acetylgalactosamine residues and / or a lectin having an affinity for fucose α(1, 2) galactose residues with a sample possibly containing PSA, to determine an amount of PSA having an affinity for the lectin. A method for distinguishing prostate cancer from prostatic hypertrophy can be provided by this method.
Owner:OTSUKA PHARM CO LTD
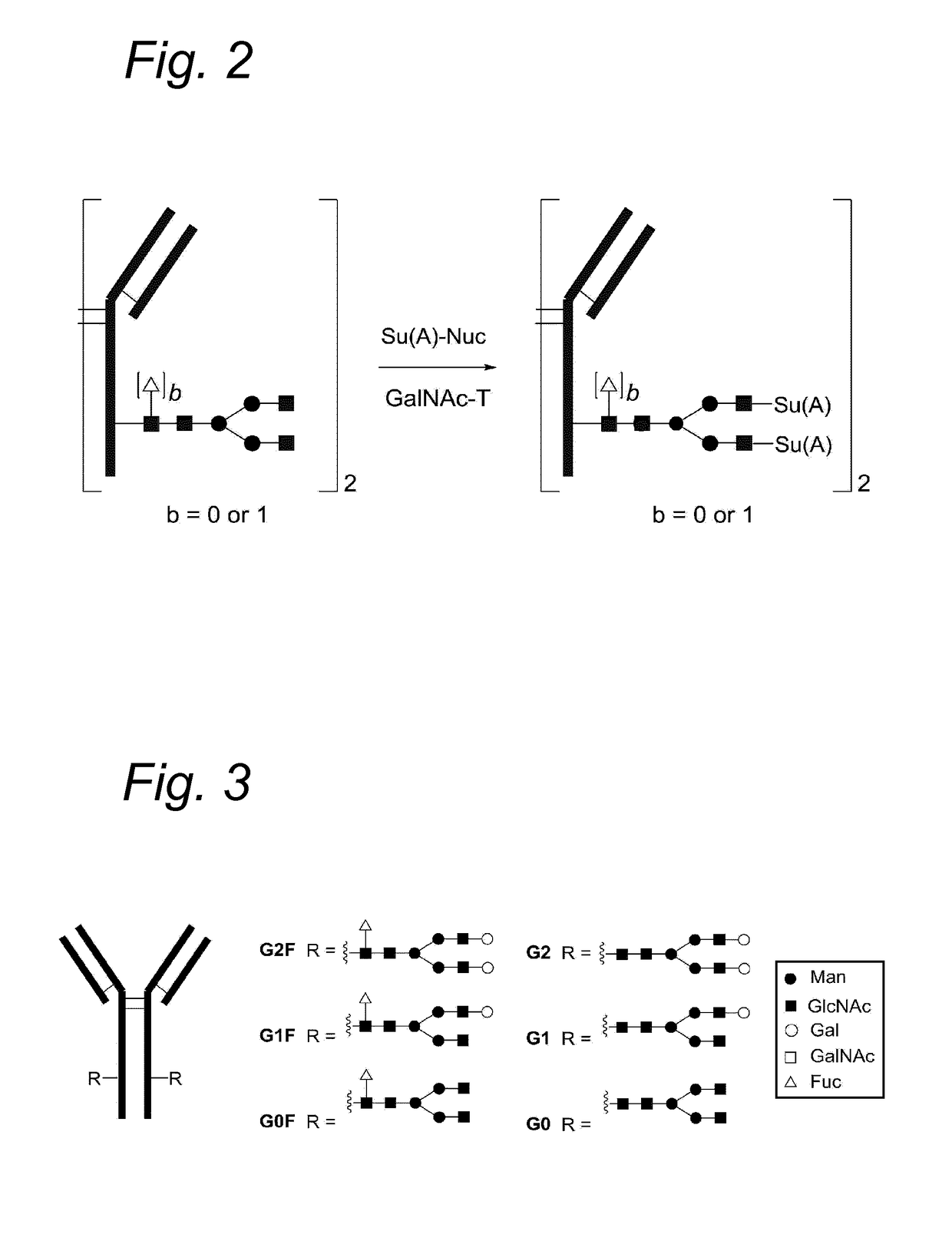
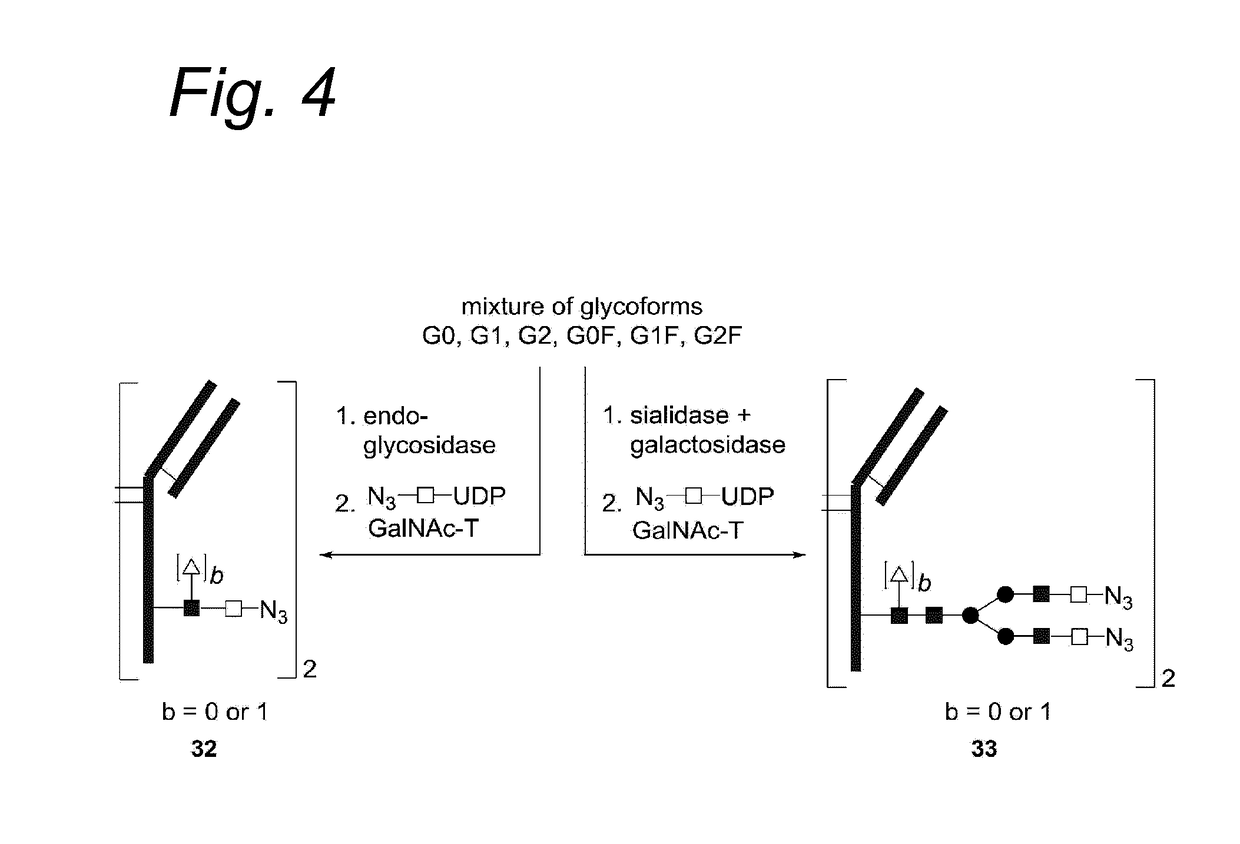
Process for the modification of a glycoprotein using a glycosyltransferase that is or is derived from a ß(1,4)-n-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase
ActiveUS20170130256A1Immunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsN-AcetylgalactosaminyltransferasesN-Acetylgalactosamine
The present invention relates to a process for the enzymatic modification of a glycoprotein. The process comprises the step of contacting a glycoprotein comprising a glycan comprising a terminal GlcNAc-moiety, in the presence of glycosyltransferase that is, or is derived from, a β-(1,4)-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase, with a non-natural sugar-derivative nucleotide. The non-natural sugar-derivative nucleotide is according to formula (3): wherein A is selected from the group consisting of —N3, —C(O)R3, —(CH2)iC≡C—R4, —SH, —SC(O)R8, —SC(0)OR8, —SC(S)OR8, —F, —CI, —Br —I, —OS(O)2R5, terminal C2-C24 alkenyl groups, C3-C5 cycloalkenyl groups, C4-C8 alkadienyl groups, terminal C3-C24 allenyl groups and amino groups. The invention further relates to a glycoprotein obtainable by the process according to the invention, to a bioconjugate that can be obtained by conjugating the glycoprotein with a linker-conjugate, and to β-(1,4)-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferases that can be used in preparing the the glycoprotein according to the invention.
Owner:SYNAFFIX
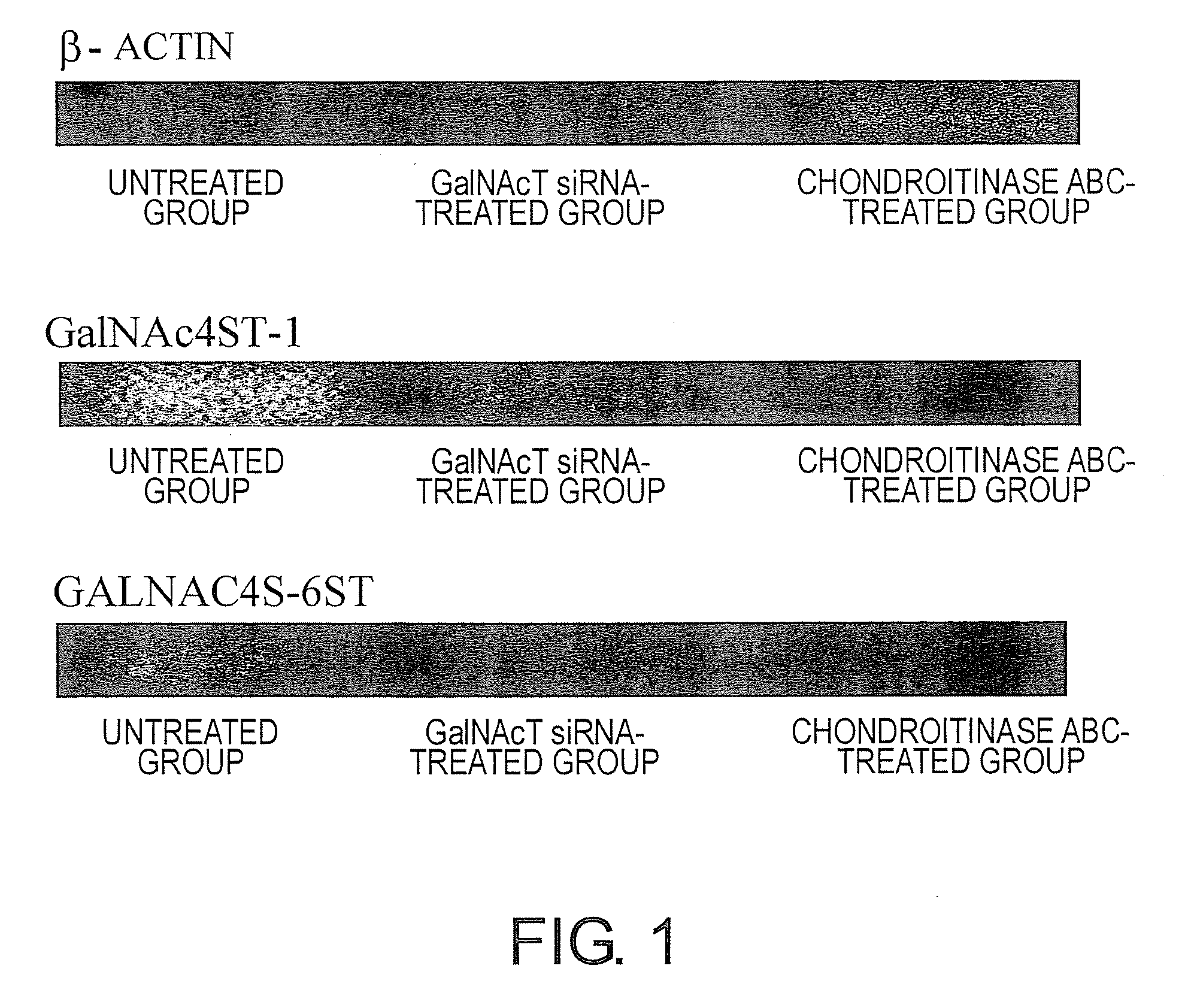
Agents for suppressing neural fibrotic degeneration
InactiveUS20090202515A1Suppress neural fibrotic degenerationGreat medical and industrial significanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSide chainNeural cell
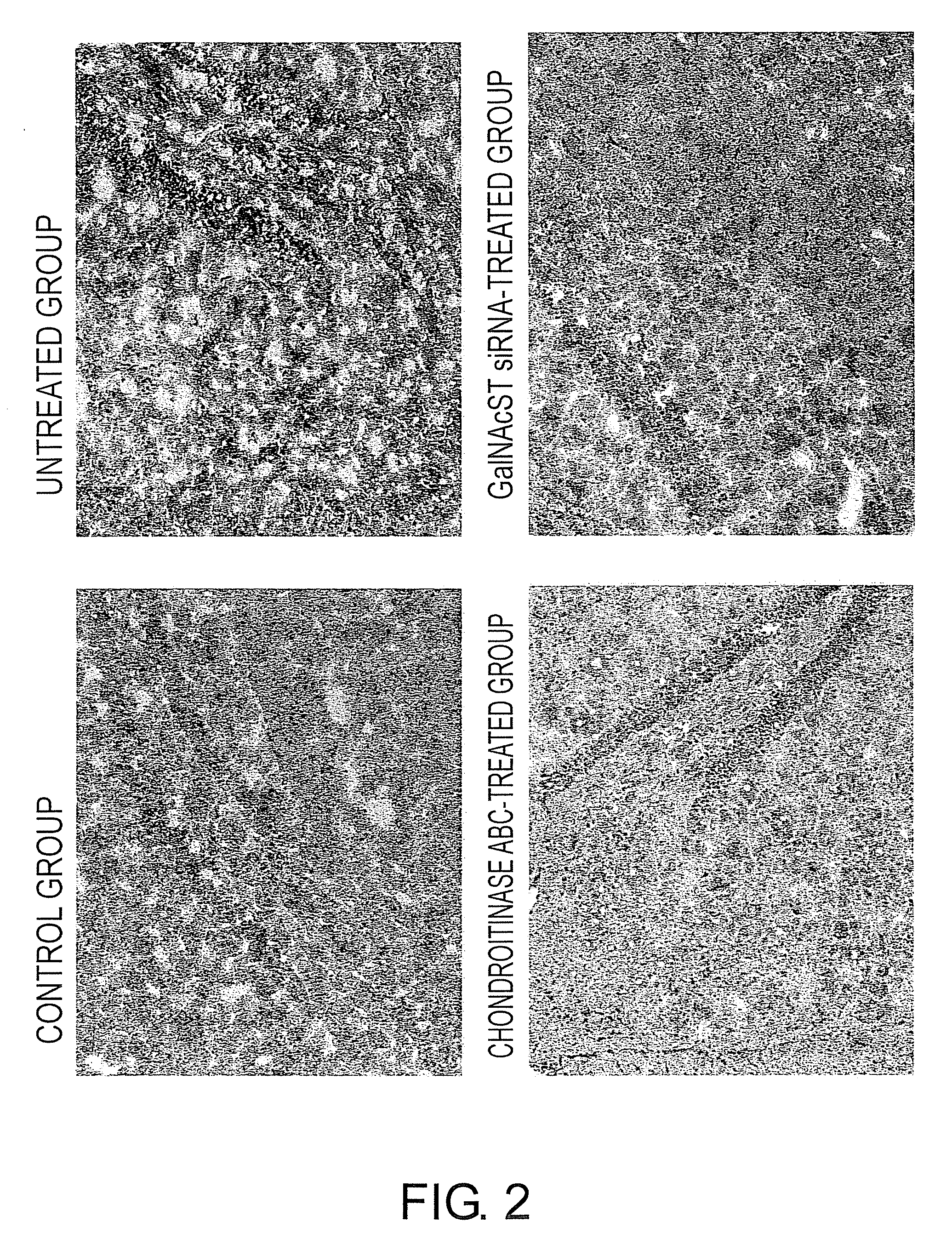
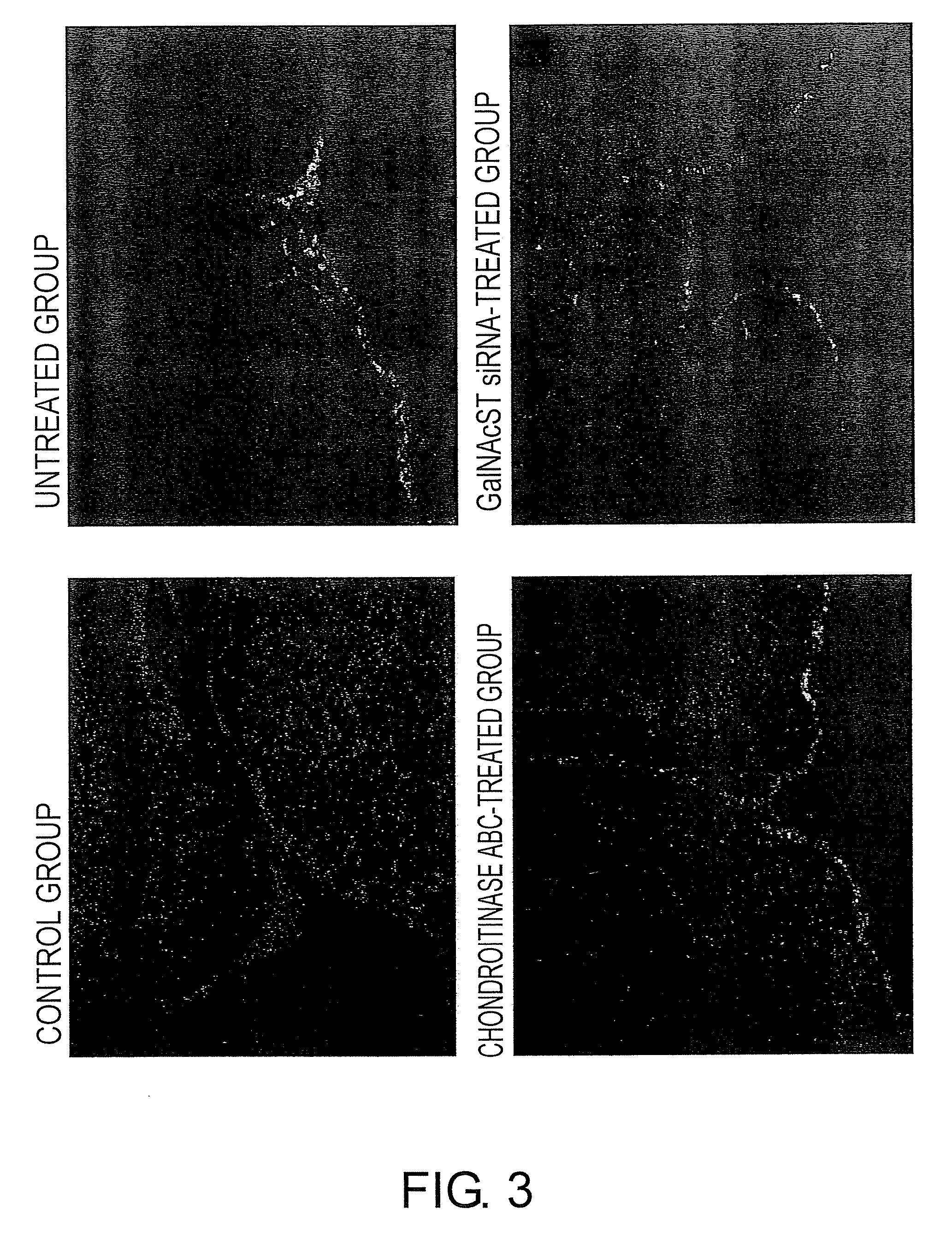
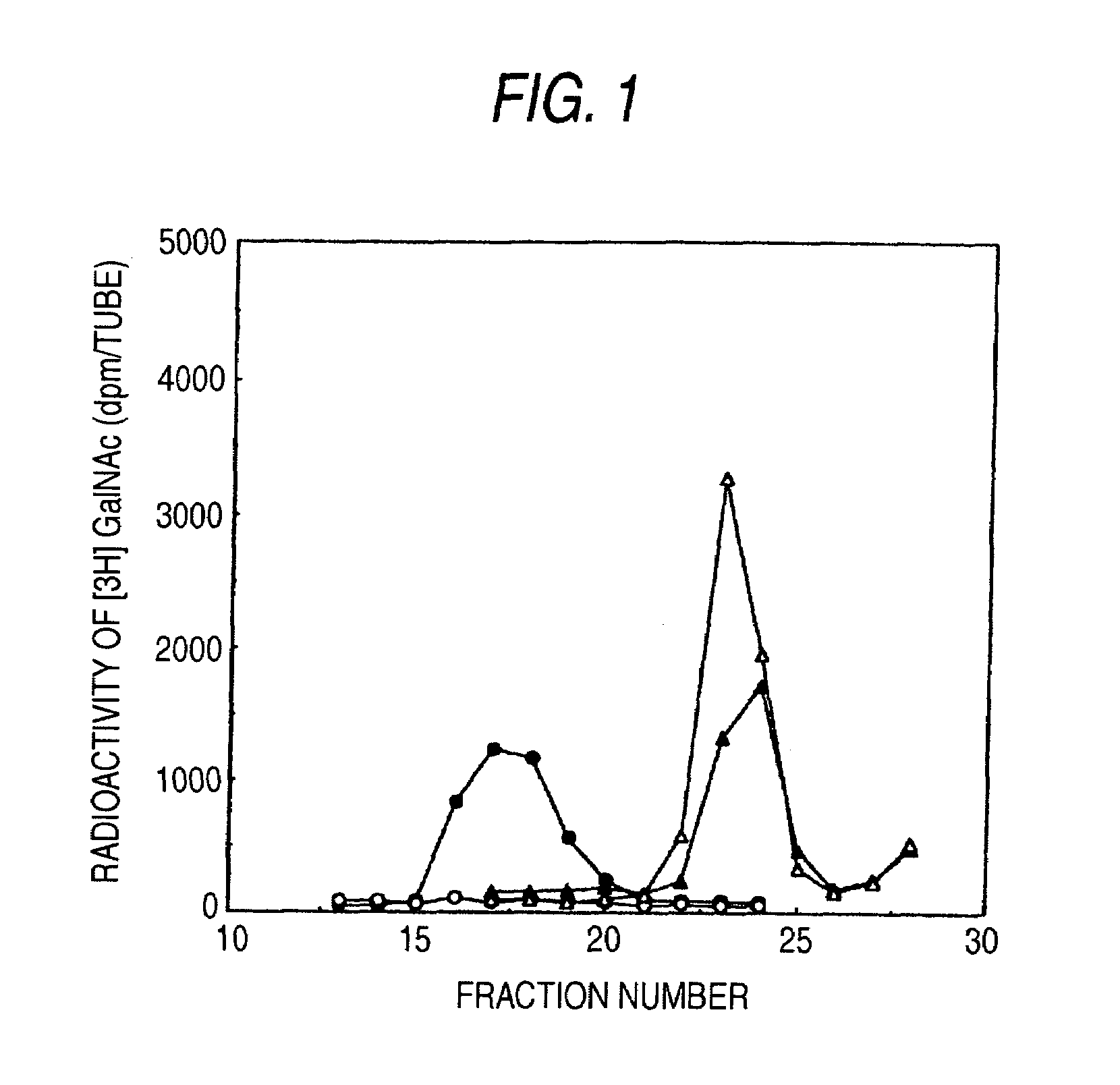
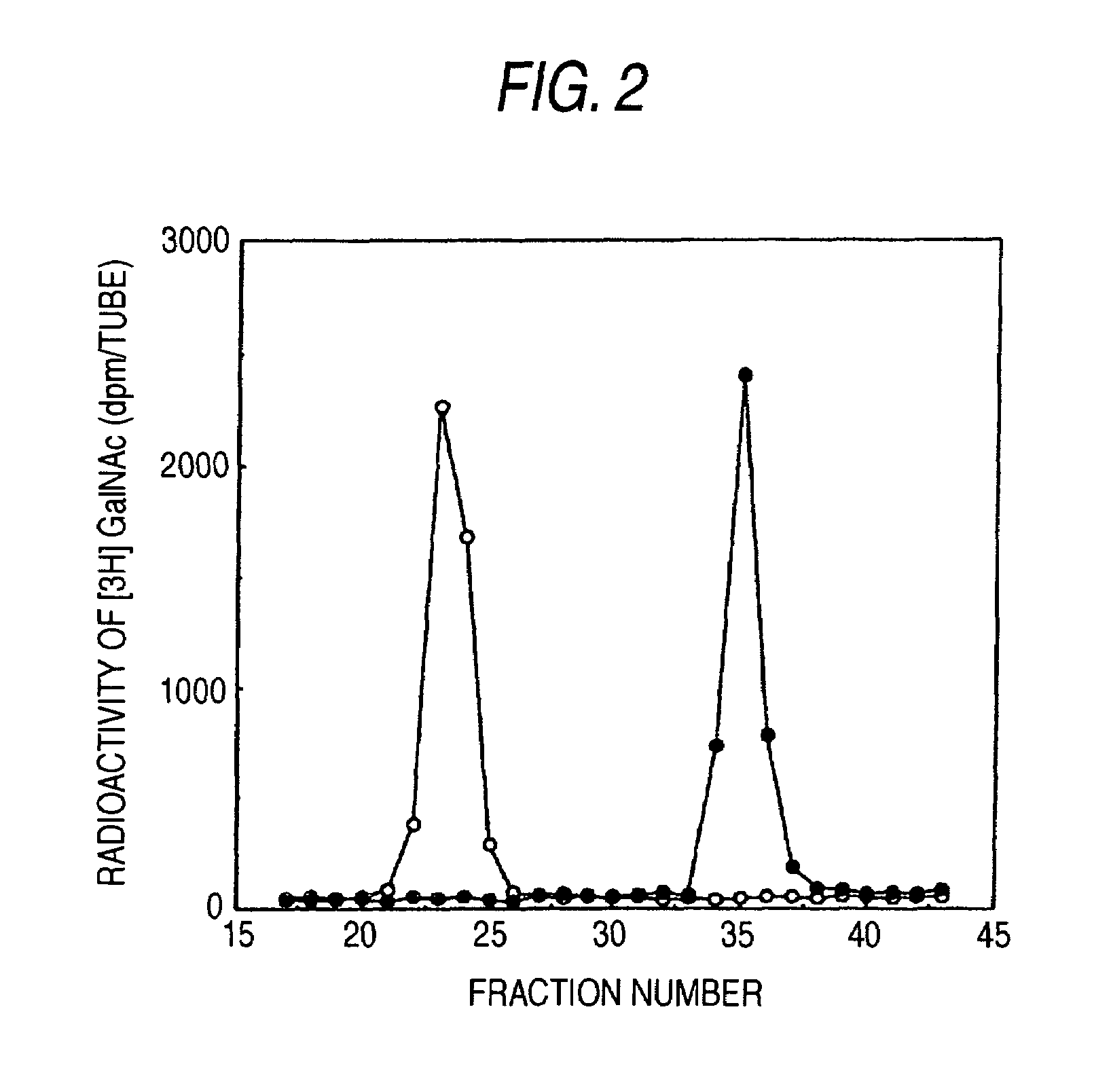
The present invention examined the accumulation of chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs). The present invention relates to neurodegeneration-suppressing agents that are suitable for gene therapy or prevention of neural fibrotic degenerative diseases which induce neural cell death due to an accumulation of abnormal proteins, where the therapies are based on siRNAs against N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferases (N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferase-1, N-acetylgalactosamine-4-O-sulfotransferase-2, and N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfate 6-O-sulfotransferase (GalNAc4ST-1, GalNAc4ST-2, and GALNAC4S-6ST, respectively)), which are sulfotransferases for acetylgalactosamine, a CSPG side chain, and chondroitinase ABC, an enzyme that degrades chondroitin sulfate, another CSPG side chain.
Owner:STELIC INST OF REGENERATIVE MEDICINE STELIC INST
N-Acetylglucosamine transferase, nucleic acid encoding the same, antibody against the same and use thereof for diagnosing cancer or tumor
Described are an enzyme having an activity to transfer N-acetylglucosamine to N-acetylgalactosaminyl group through a β1,3-linkage; nucleic acid coding for the enzyme; and method for diagnosis of a cancer and / or tumor, especially a cancer and / or tumor of a digestive organ using the expression amount of the gene of the enzyme as an index. A gene coding for a novel enzyme having an activity to transfer N-acetylglucosamine to N-acetylgalactosaminyl group through the β1,3-linkage was cloned from human colon and stomach cells, and the gene was sequenced. The enzyme was expressed, and a monoclonal antibody to the enzyme was prepared. Since this enzyme is not produced substantially or at all in cancer and / or tumor cells, especially in cancer or tumor cells of a digestive organ, the cancer and / or tumor may be diagnosed using the expression of the gene of the enzyme as an index.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Chondroitin synthase and nucleic acid encoding the enzyme
A human-derived novel chondroitin synthase, which is an enzyme for synthesizing a fundamental backbone of chondroitin and has both glucuronic acid transferring activity and N-acetylgalactosamine transferring activity.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD +1
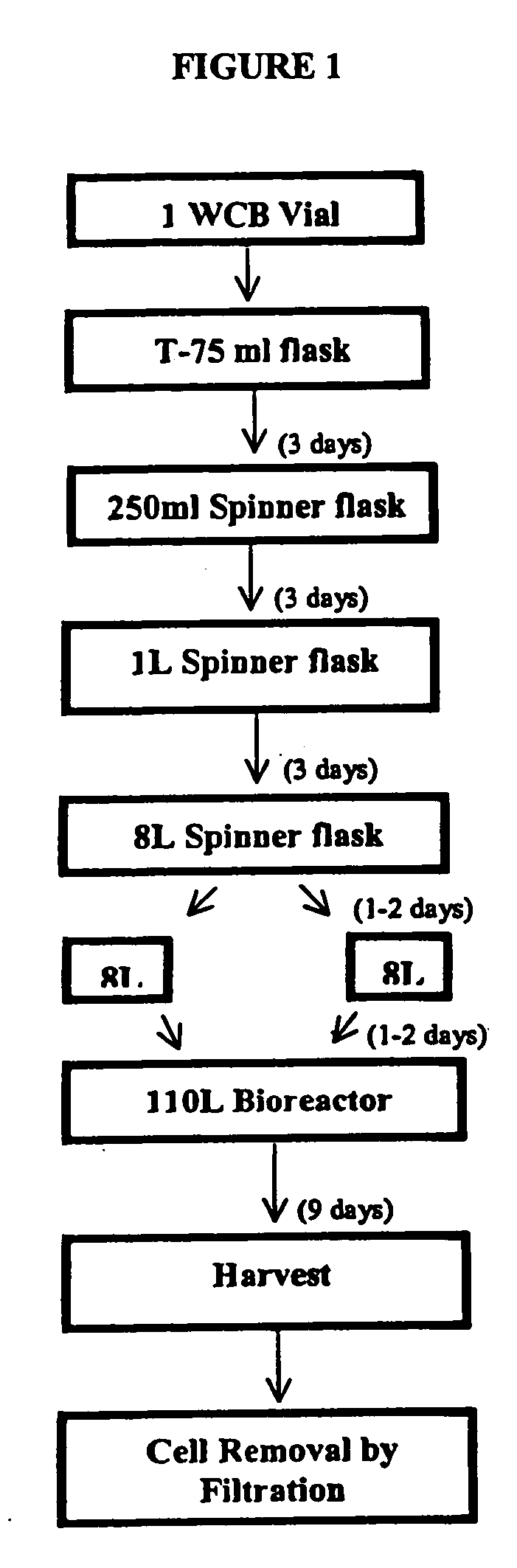
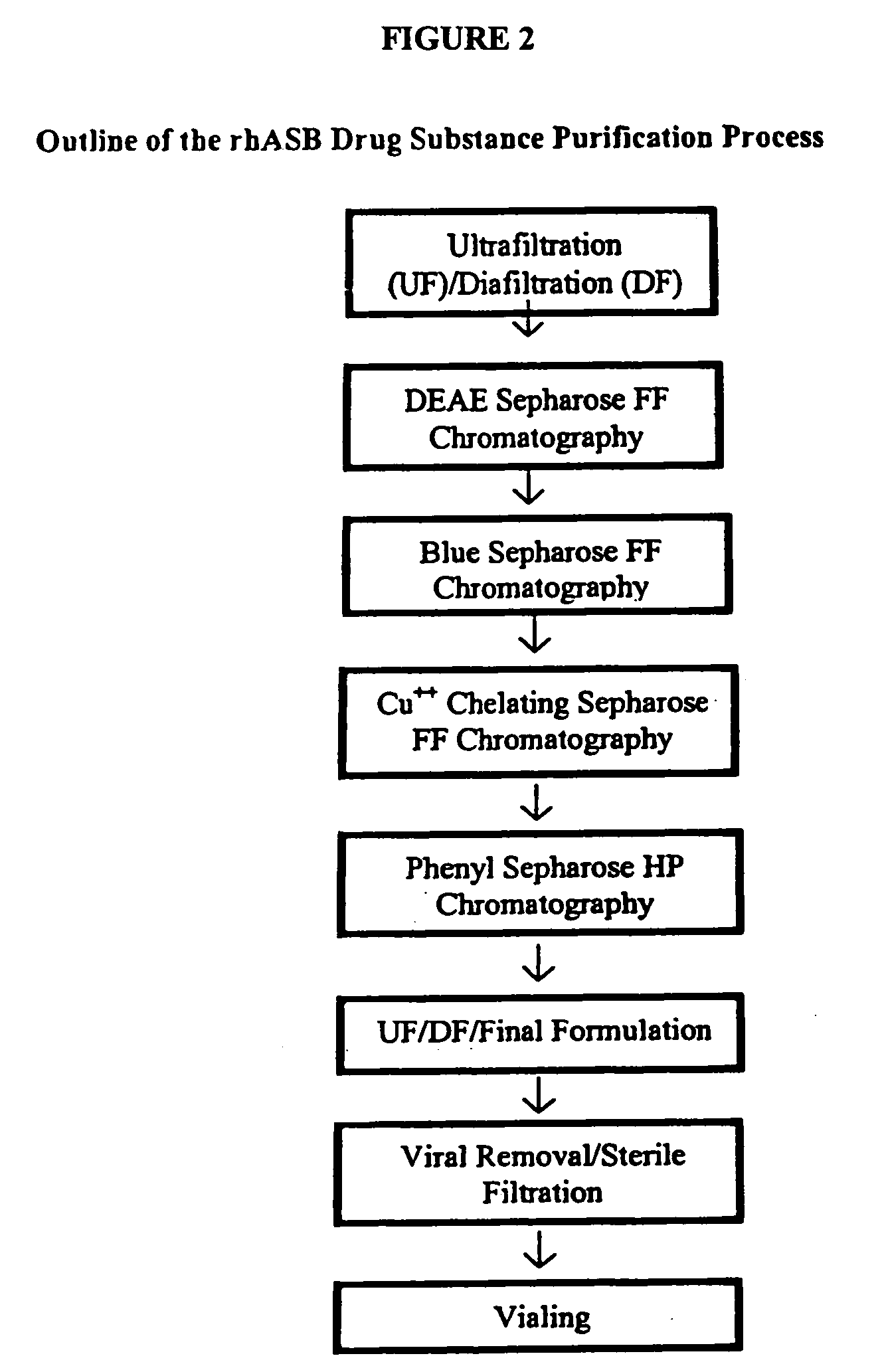
Precursor of N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase, methods of treatment using said enzyme and methods for producing and purifying said enzyme
InactiveUS6972124B2High puritySufficient amountBacteriaHydrolasesN-Acetylgalactosamine-4-SulfataseMutant
The present invention provides a highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase and biologically active mutants, fragments and analogs thereof as well as pharmaceutical formulations comprising highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase. The invention also provides methods for treating diseases caused all or in part by deficiencies in human N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase including MPS VI and methods for producing and purifying the recombinant precursor enzyme to a highly purified form.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
Method for determining prostate cancer
InactiveUS20110236995A1Accurately determineImprove accuracyComponent separationIsotope separationGlycanN-Acetylglucosamine
The present invention provides a method for detecting a glycan structure of a prostate specific antigen (PSA) rapidly and with high sensitivity and determining prostate carcinoma based on the difference in the structure, in particular, a method for determining between prostate carcinoma and benign prostatic hyperplasia accurately. A method for determining prostate carcinoma, wherein the method includes a step of analyzing a PSA glycan structure in a sample derived from a test subject, and prostate carcinoma is determined in the case that amount of a glycan having LacdiNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(+)) is more than 30% of amount of a glycan not having LacdiNAc but having LacNAc (galacotose-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(−)). Especially, a method for determining prostate carcinoma, wherein prostate carcinoma is determined in the case that amount of a glycan having LacdiNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(+)) is more than 30% of amount of a glycan not having LacdiNAc but having LacNAc (galacotose-N-acetylglucosamine) (LacdiNAc(−)), and benign prostatic hyperplasia is determined in the case of 30% or less.
Owner:NOGUCHI INST
Biosynthetic system that produces immunogenic polysaccharides in prokaryotic cells
ActiveUS8846342B2Efficient productionAntibacterial agentsBacterial antigen ingredientsProkaryote organismsIsomerase
Owner:GLAXOSMITHKLINE BIOLOGICALS SA
Novel n-acetylgalactosamine transferases and nucleic acids encoding the same
An enzyme which transfers N-acetylgalactosamine to N-acetylglucosamine via a β1-4 linkage was isolated and the structure of its gene was explained. This led to the production of said enzyme or the like by genetic engineering techniques, the production of oligosaccharides using said enzyme, and the diagnosis of diseases on the basis of said gene or the like. The present invention uses a protein having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 26 or 27 in the Sequence Listing or a variant of said amino acid sequence wherein one or more acids are substituted or deleted, or one or more acids are inserted or added and having the activity of transferring N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) to N-acetylglucosamine serving as a substrate via a β1-4 linkage and nucleic acids encoding said protein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Transgenically produced antithrombin III
InactiveUS20080176786A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntipyreticMonosaccharide compositionPlasma derived
This invention relates to transgenically produced human Antithrombin III (tgATIII). The human ATIII produced by the transgenic process of the present invention has a monosaccharide composition which comprises N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) along with fucose, N-acetylglucosamine, galactose, mannose, and N-acetylneuraminic acid / N-glycolyneuraminic acid. The monosaccharide composition differs with that of plasma derived ATIII (phATIII). It has been found that tgATIII has an increased clearance rate when compared to phATIII.
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
Precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4 sulfatase, methods of treatment using said enzyme and methods for producing and purifying said enzyme
The present invention provides a highly purified recombinant, human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase and biologically active mutants, fragments and analogs thereof as well as pharmaceutical formulations comprising highly purified recombinant human precursor N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase. The invention also provides methods for treating diseases caused all or in part by deficiencies in human N-acetylgalactosamine-4-sulfatase including MPS VI and methods for producing and purifying the recombinant precursor enzyme to a highly purified form.
Owner:BIOMARIN PHARMA INC
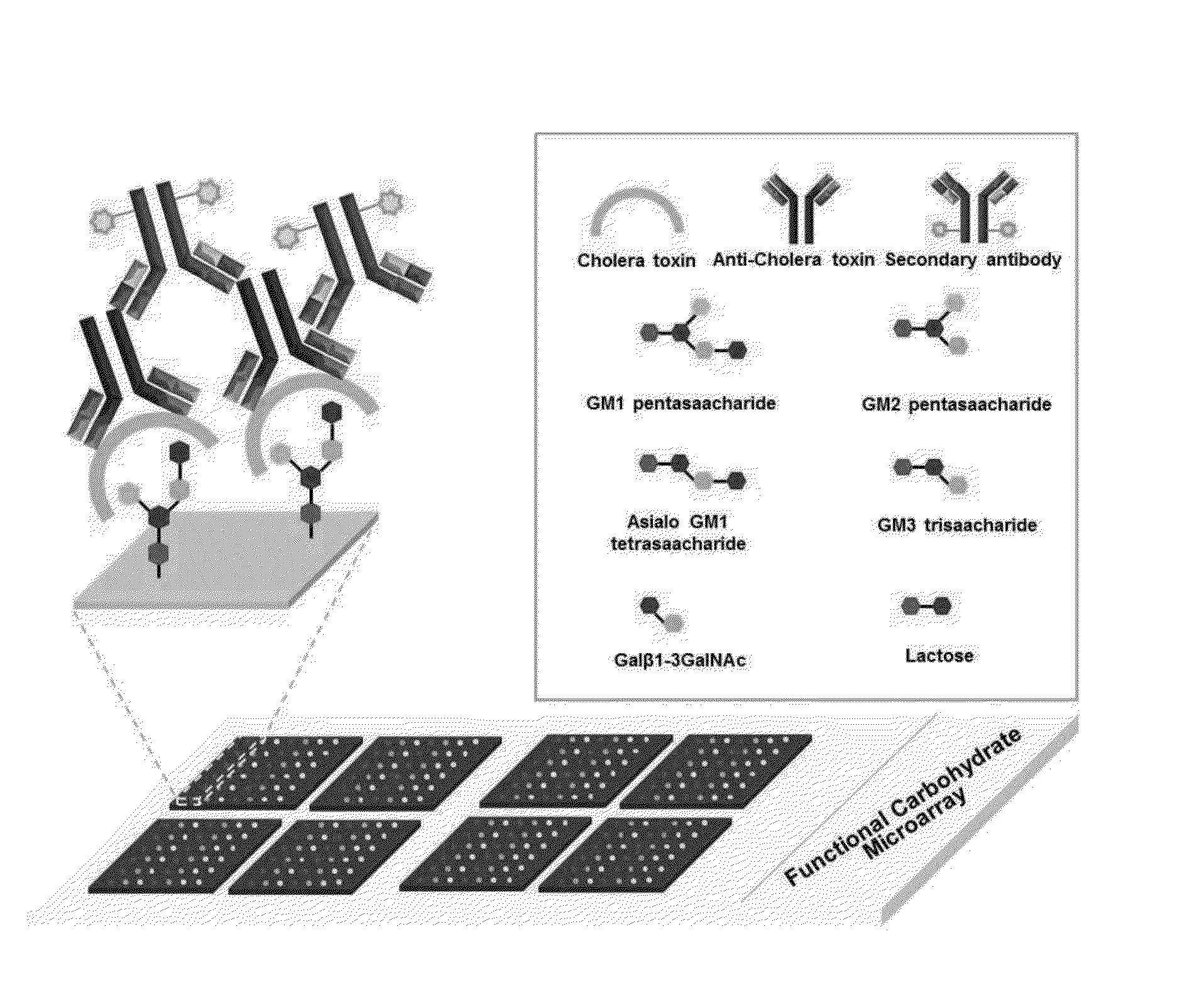
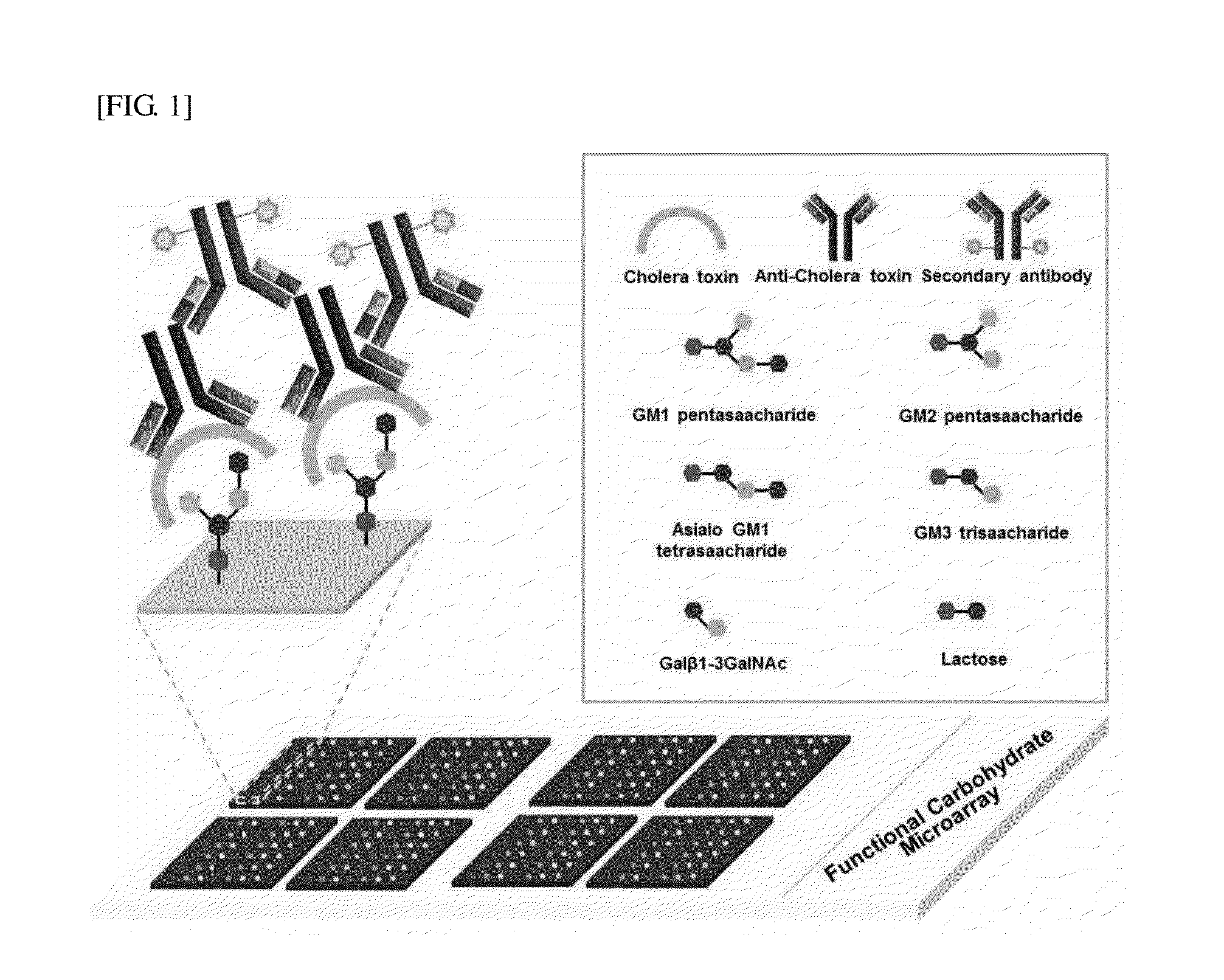
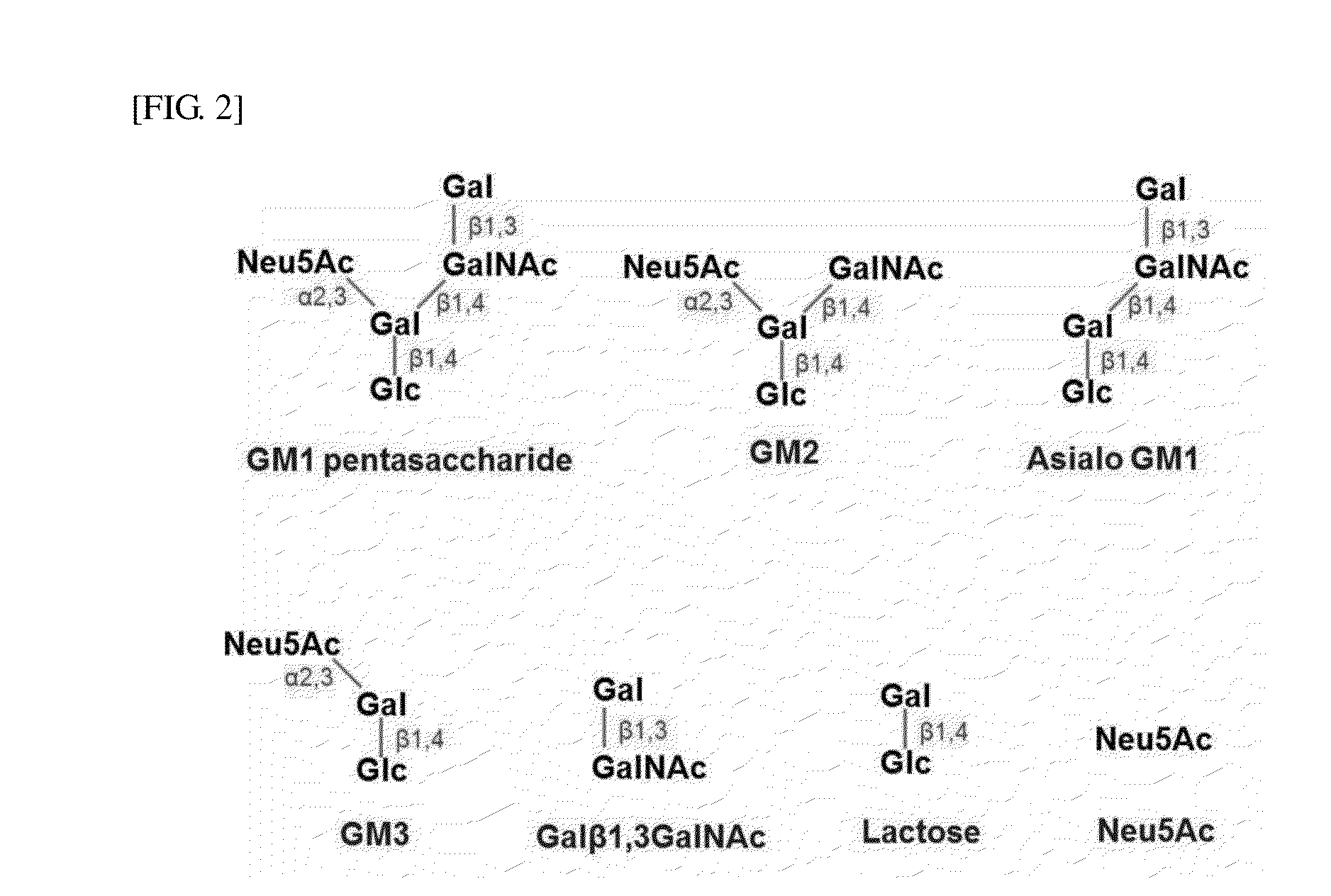
Carbohydrate Chip for Detection of Pathogen Vibrio Cholerae and Method of Preparing the Same
InactiveUS20130267433A1Microbiological testing/measurementSaccharide librariesSolid substrateBiology
The present invention related to a saccharide-based cholera toxin detection sensor for detection of Vibrio cholerae and its use. More specifically, the present invention relates to a carbohydrate chip for detection of Vibrio cholerae, a method for detecting Vibrio cholerae using the same, and a method for preparing the same, where the carbohydrate chip comprises GM1 pentasaccharide, GM2 tetrasaccharide, asialo GM1 tetrasaccharide, GM3 trisaccharide, galactose-β 1,3-N-acetylgalactosamine, lactose, and sialic acid that are immobilized on the surface of a solid substrate.
Owner:POSTECH ACAD IND FOUND
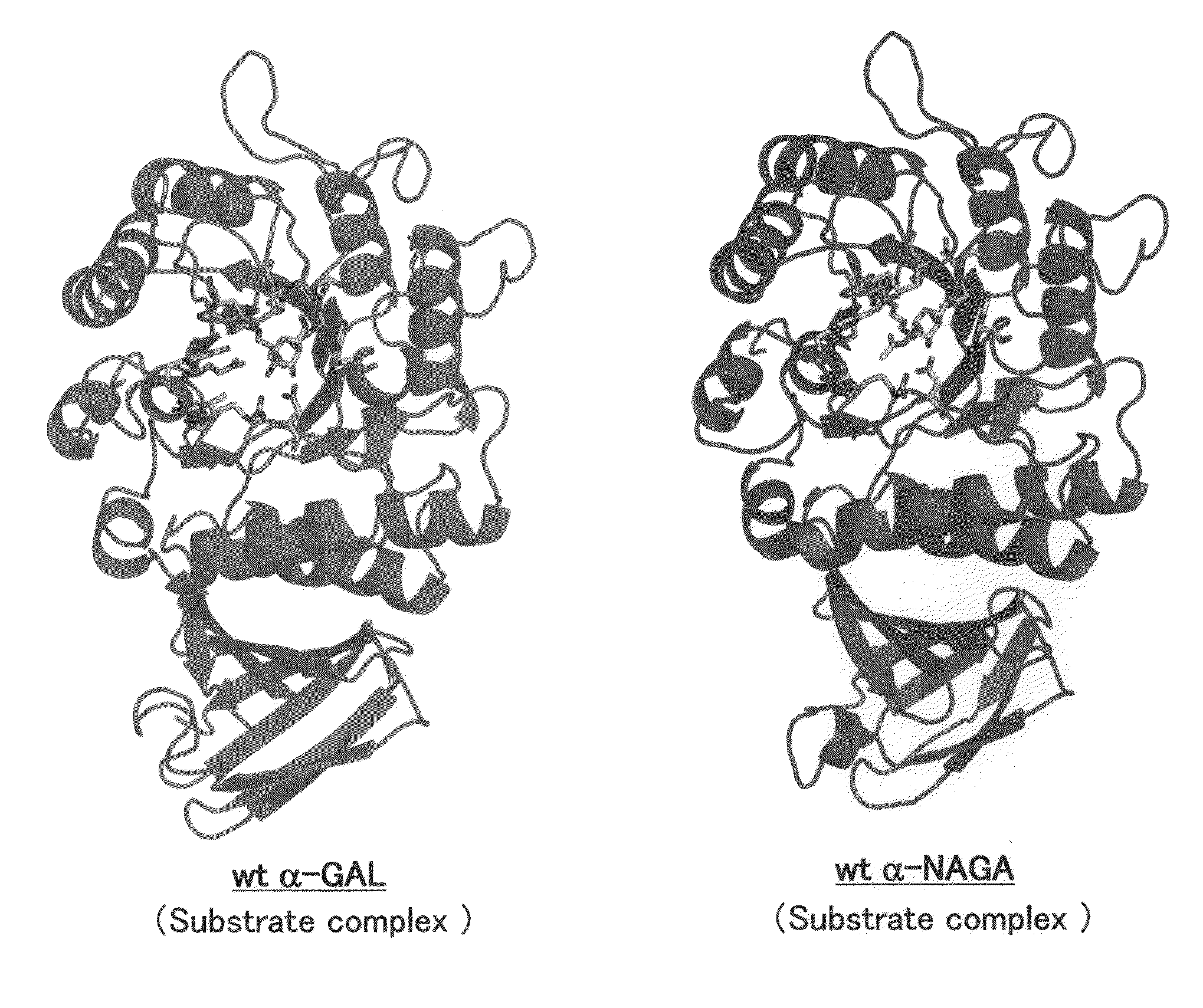
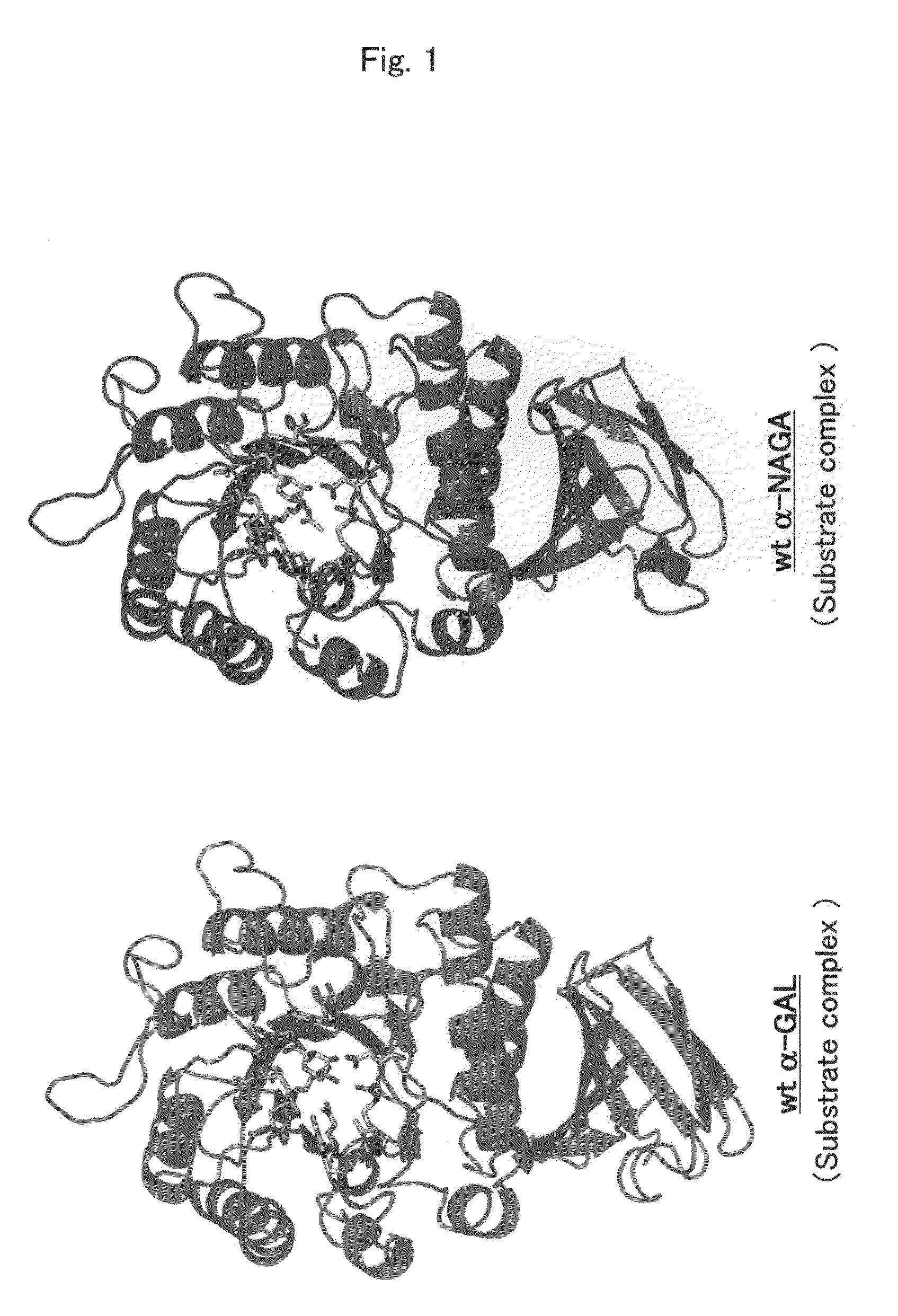
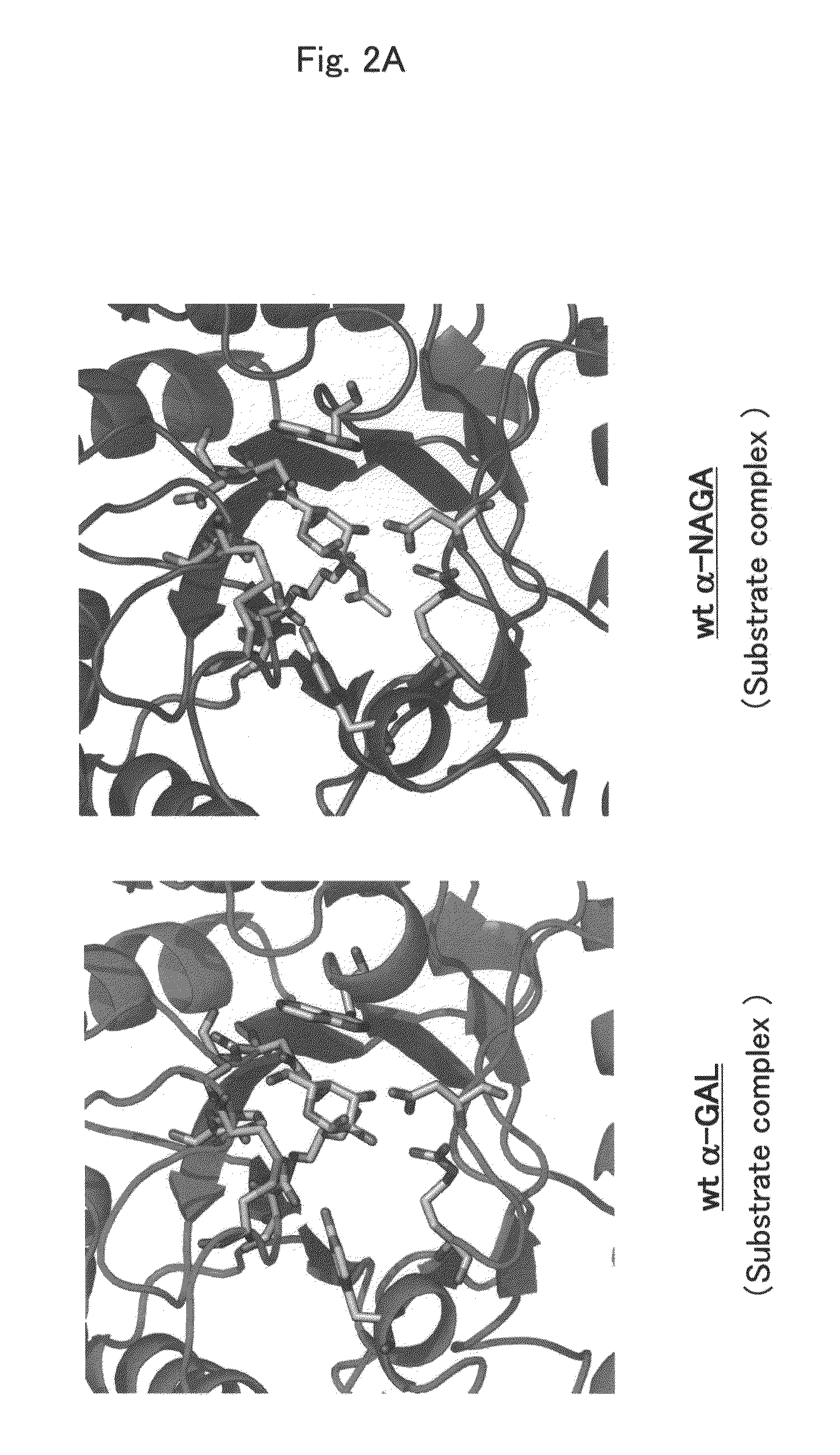
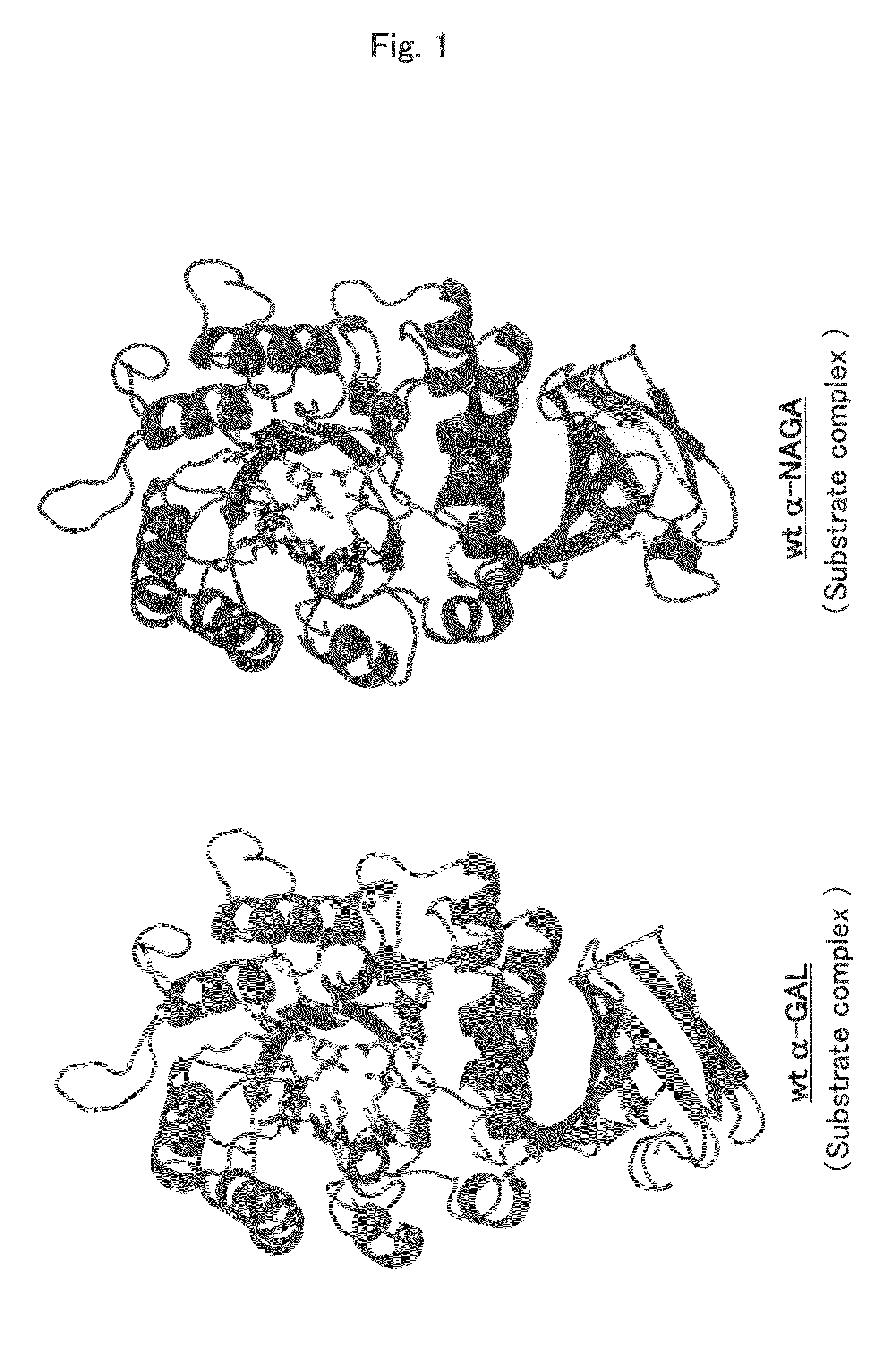
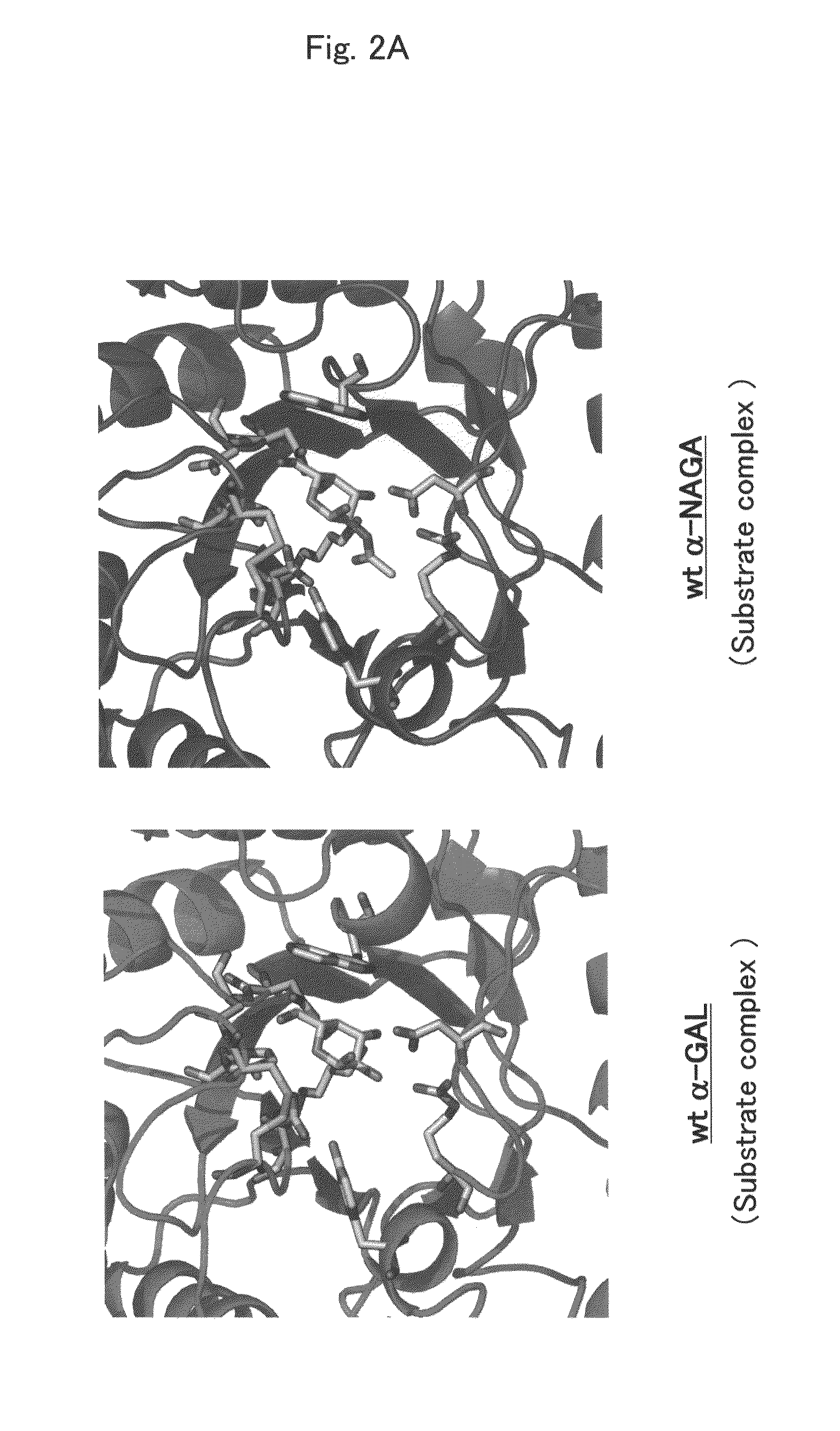
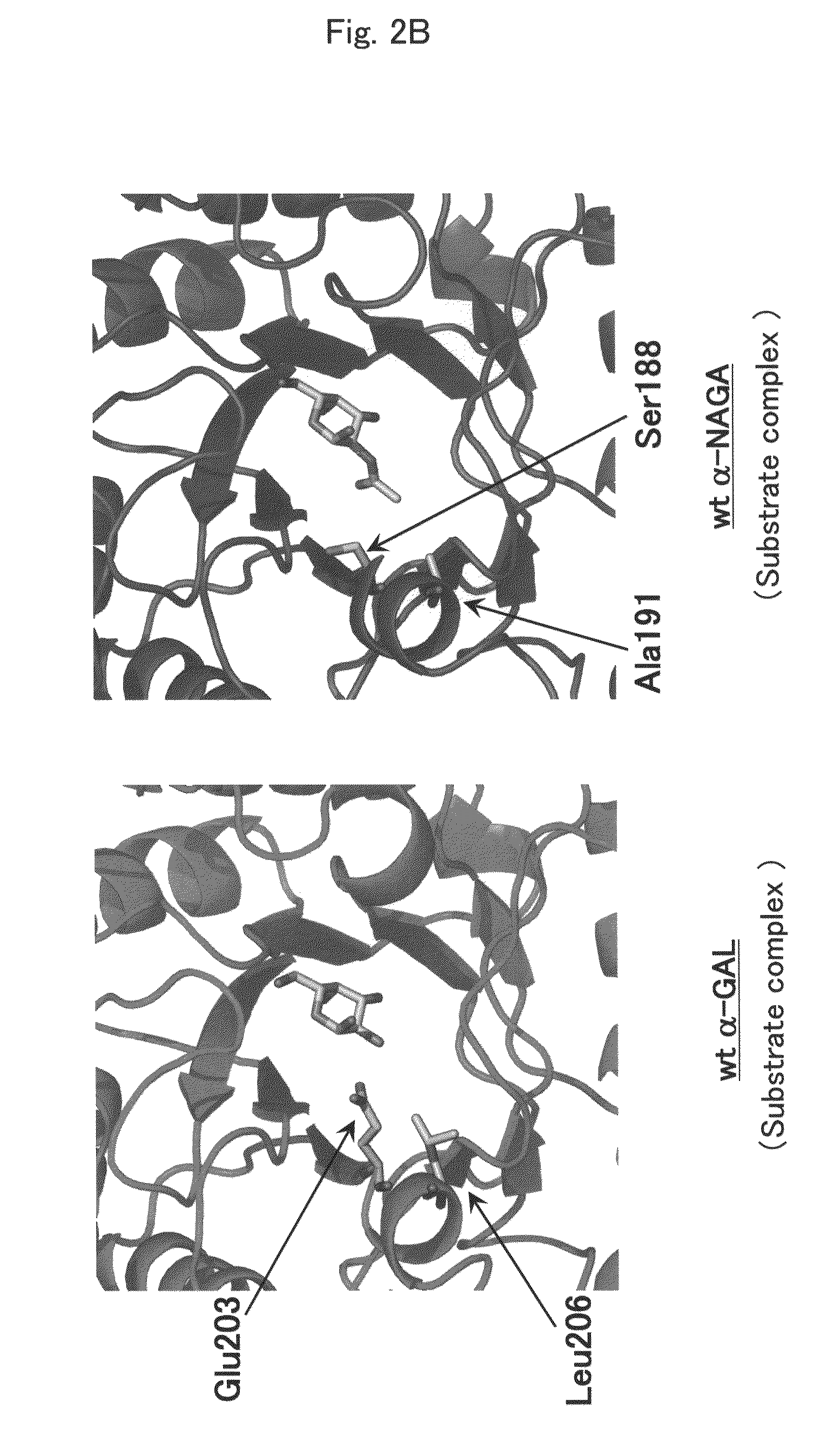
Proteins having acquired A-galactosidase activity
ActiveUS8569032B2Easy to carryAltered substrate specificitySenses disorderSugar derivativesSide effectWild type
The present invention provides a pharmaceutical composition comprising a protein having α-galactosidase activity for treating Fabry disease, which causes no allergic side effect, which is highly stable in blood (plasma) and which can readily be taken up by a cell of an affected organ. The pharmaceutical composition for treating Fabry disease of the invention comprises, for example, a protein which acquires an α-galactosidase activity through alteration of the structure of the active site of wild-type human α-N-acetylgalactosaminidase.
Owner:ALTIF LAB +1
Formulation of complex carbohydrate for fodder
ActiveUS20160295885A1Reduce impactImprove the level ofOrganic active ingredientsFood processingSialic acidWheat middlings
A formulation of complex carbohydrates for fodder, fodder comprising the same, and application, the fodder comprising of the following ingredients: corn, bean pulp, whey powder, fish meal, soymilk, wheat middling, piglet premix, glucose and a formulation of complex carbohydrates, and the formulation of complex carbohydrates consisting of flucose, galactose, N-acetylgalactosamine, glucosamine, acetylglucosamine, glucuronic acid, mannose, sialic acid and xylose.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
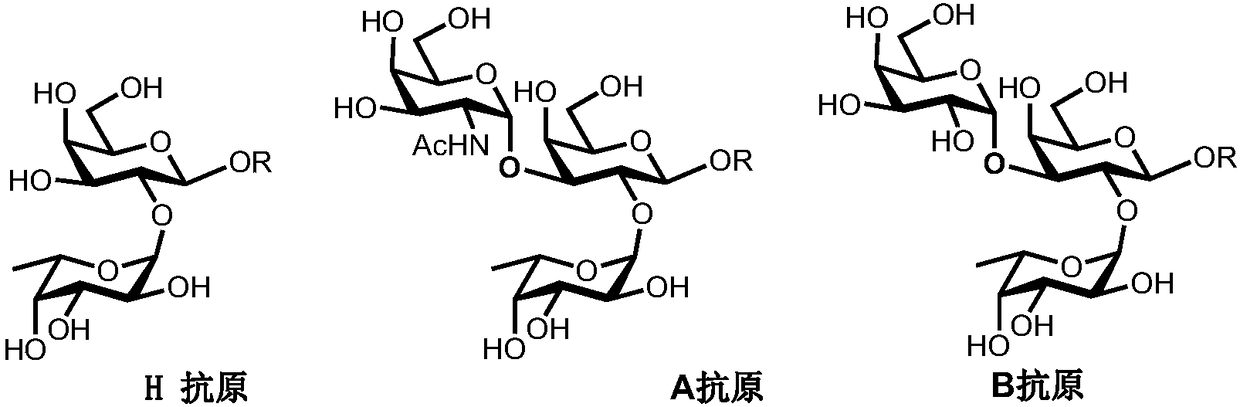
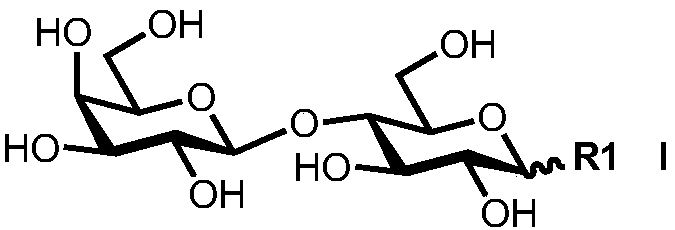
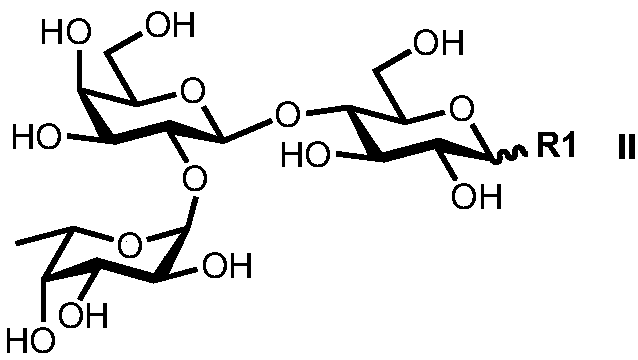
Synthesis method of human ABH blood group antigen
InactiveCN108251474AGenerate noneHigh synthesis efficiencyFermentationTrisaccharideSynthesis methods
The invention relates to a synthesis method of saccharides, in particular to synthesis of ABH blood group antigen. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: through a one-pot and multi-enzyme system, coupling fucose to disaccharide shown as a formula (I) by using an alpha1-2 glucosidic bond to synthesize trisaccharide shown as a formula (II); through the one-pot and multi-enzyme system,coupling galactose to the trisaccharide shown as the formula (II) by using an alpha1-3 glycosidic bond to synthesize tetrasaccharide shown as a formula (III); through the one-pot and multi-enzyme system, coupling N-acetylgalactosamine to the trisaccharide shown as the formula (II) by using the alpha1-3 glycosidic bond to synthesize tetrasaccharide shown as a formula (IV). Through utilization of enzymatic modular assembly and full utilization of the high efficiency of various enzymes and the specificity of a substrate, the synthesis of the ABH blood group antigen is completed.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
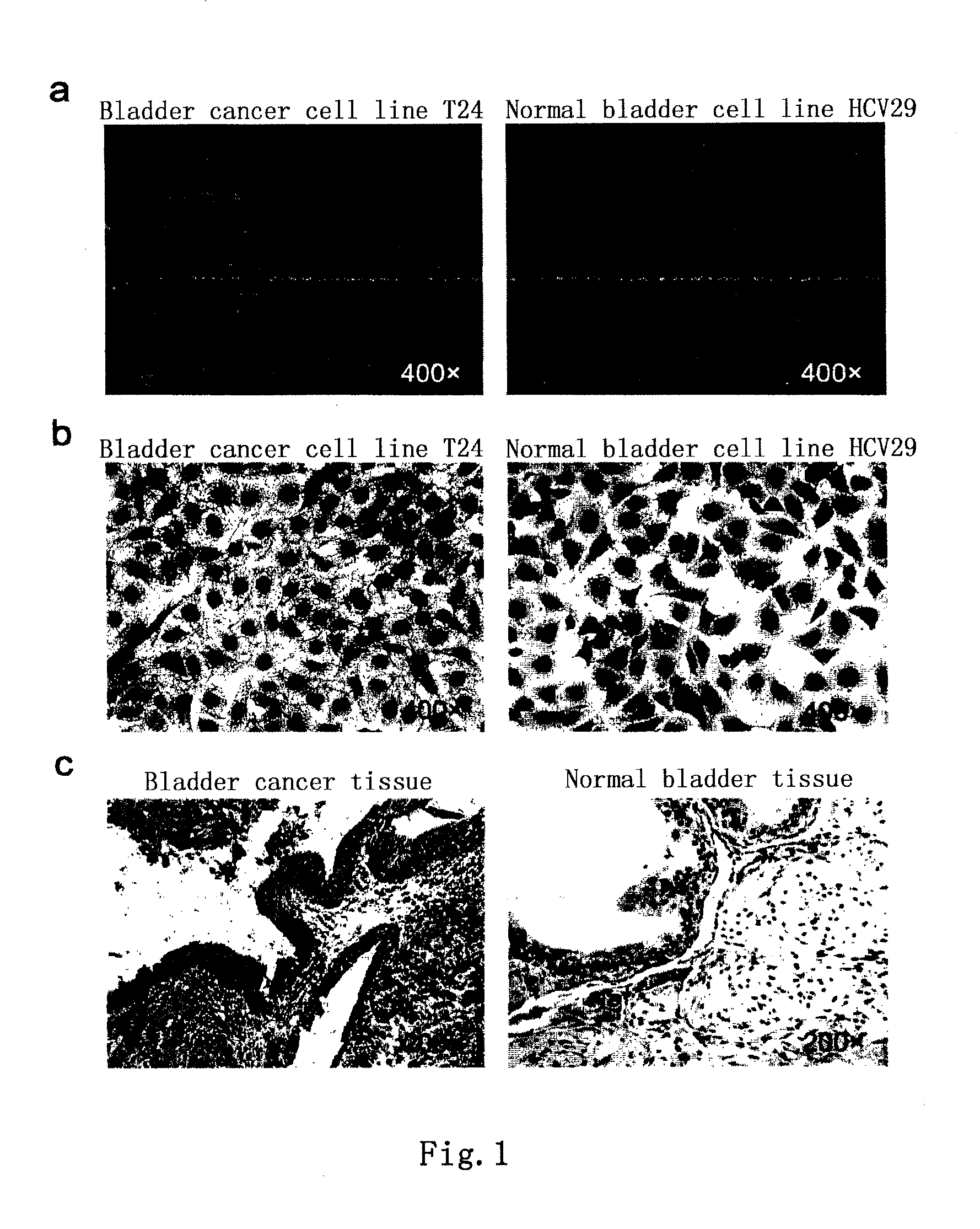
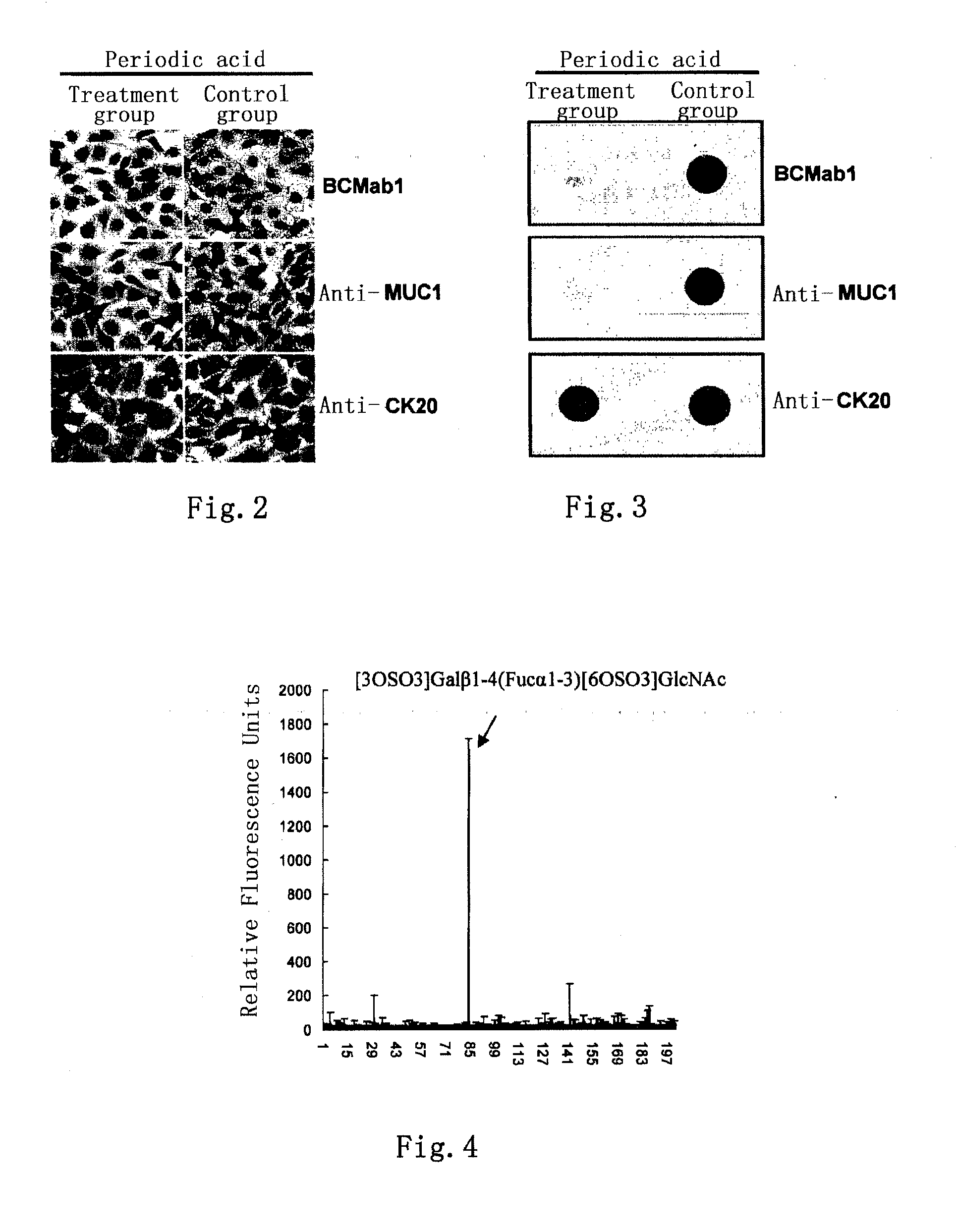
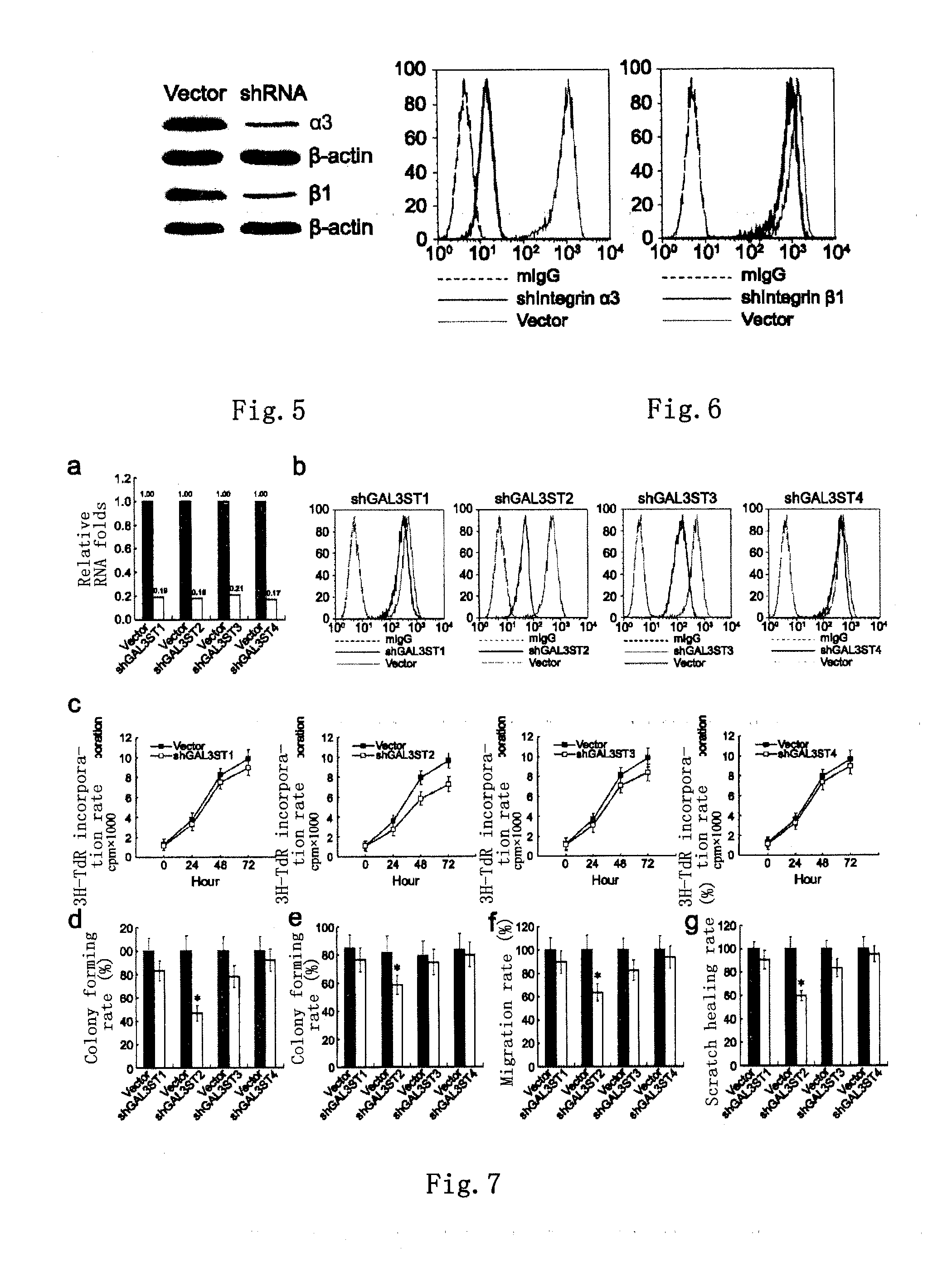
Bladder cancer tumor marker, antibody and use thereof
ActiveUS20130164216A1Facilitates malignant transformationGrowth inhibitionLibrary screeningTransferasesBladder cancerAbnormal glycosylation
Provided in the present invention are an aberrantly glycosylated integrin, AG-α3β1, and use thereof as a bladder cancer marker. Also provided in the present invention are a hybridoma cell generating an anti-AG-α3β1 monoclonal antibody, a monoclonal antibody BCMab1 secreted by the same, and use of BCMab1 in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of bladder cancer. Also provided in the present invention is use of inhibitors of GAL3ST2 and N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 in the preparation of a medicament for the treatment of bladder cancer.
Owner:INSITUTE OF BIOPHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
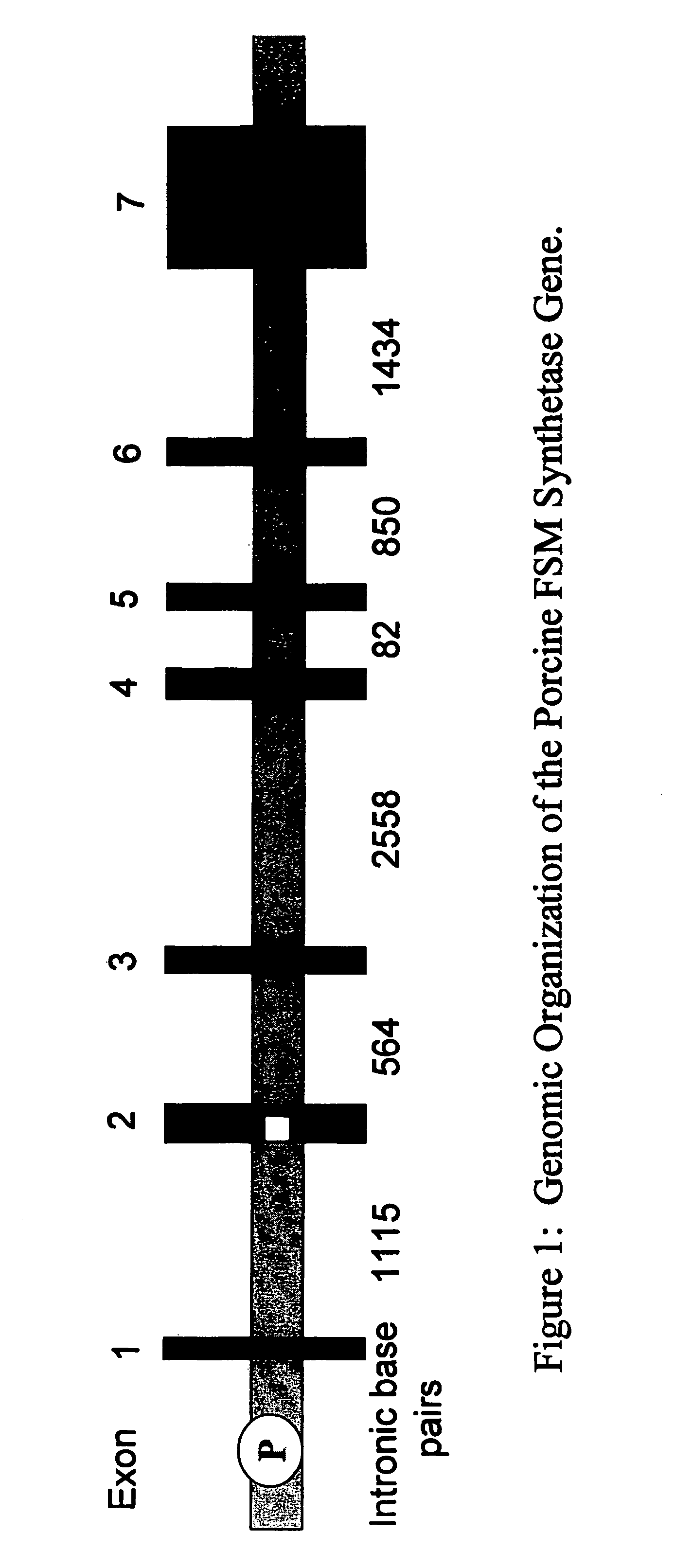
Porcine Forssman synthetase protein, cDNA, genomic organization, and regulatory region
The present invention provides porcine Forssman synthetase (FSM synthase) (Globoside α-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase) protein, cDNA, and genomic DNA sequence. Furthermore, the present invention includes porcine animals, tissue and organs as well as cells and cell lines derived from such animals, tissue and organs, which lack expression of functional FSM synthetase. Such animals, tissues, organs and cells can be used in research and in medical therapy, including in xenotransplantation. In addition, methods are provided to prepare organs, tissues, and cells lacking the porcine FSM synthetase gene for use in xenotransplantation.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF PITTSBURGH
Method of producing uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine
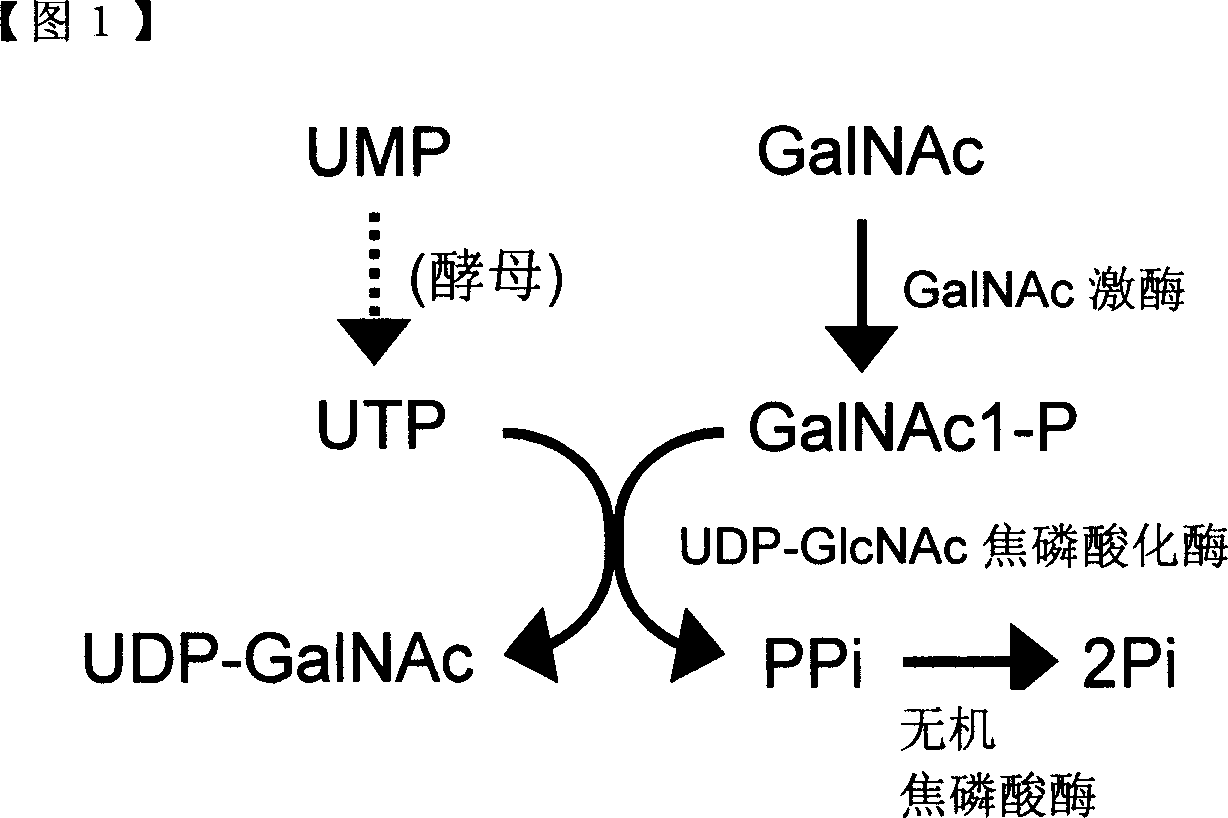
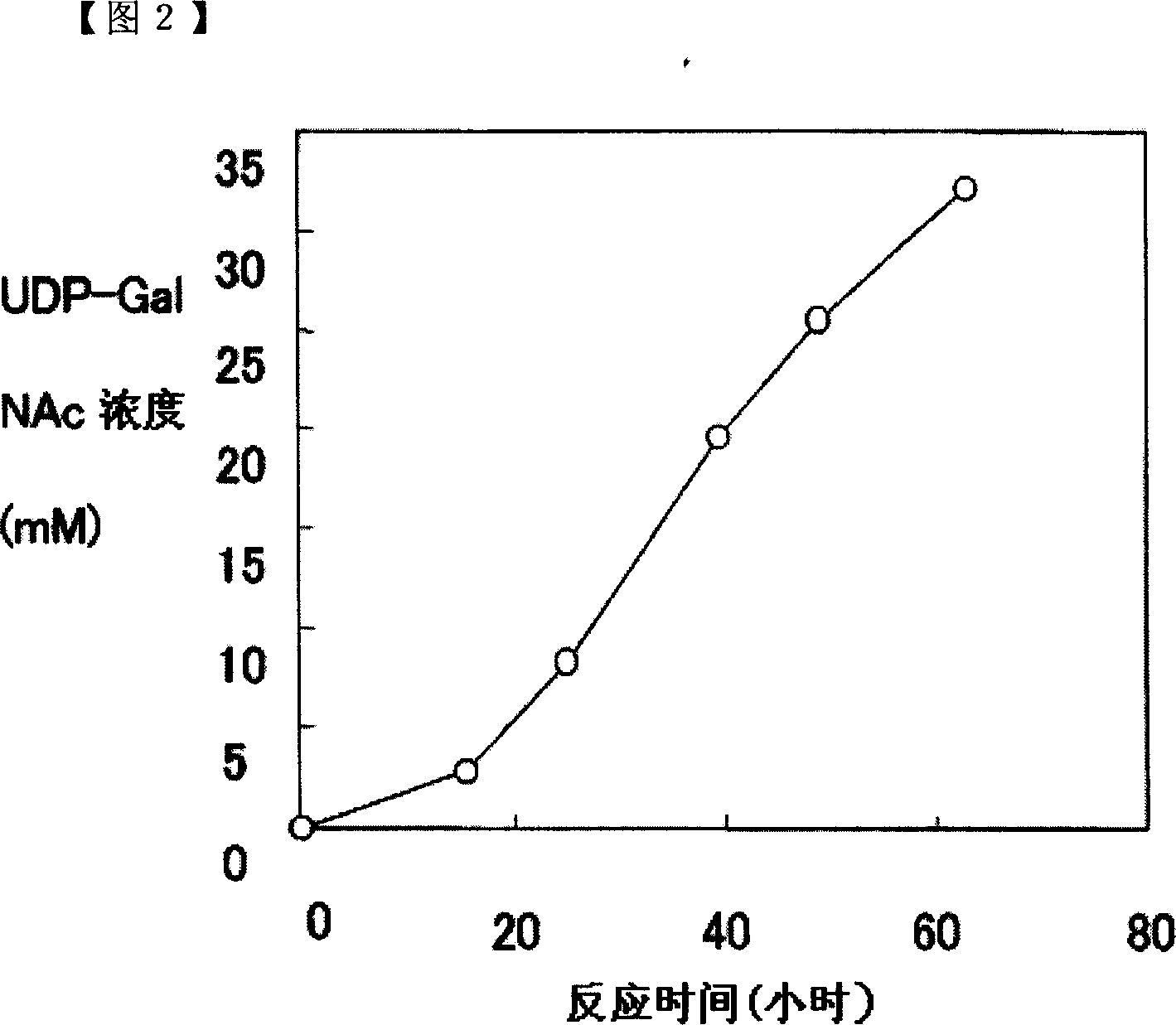
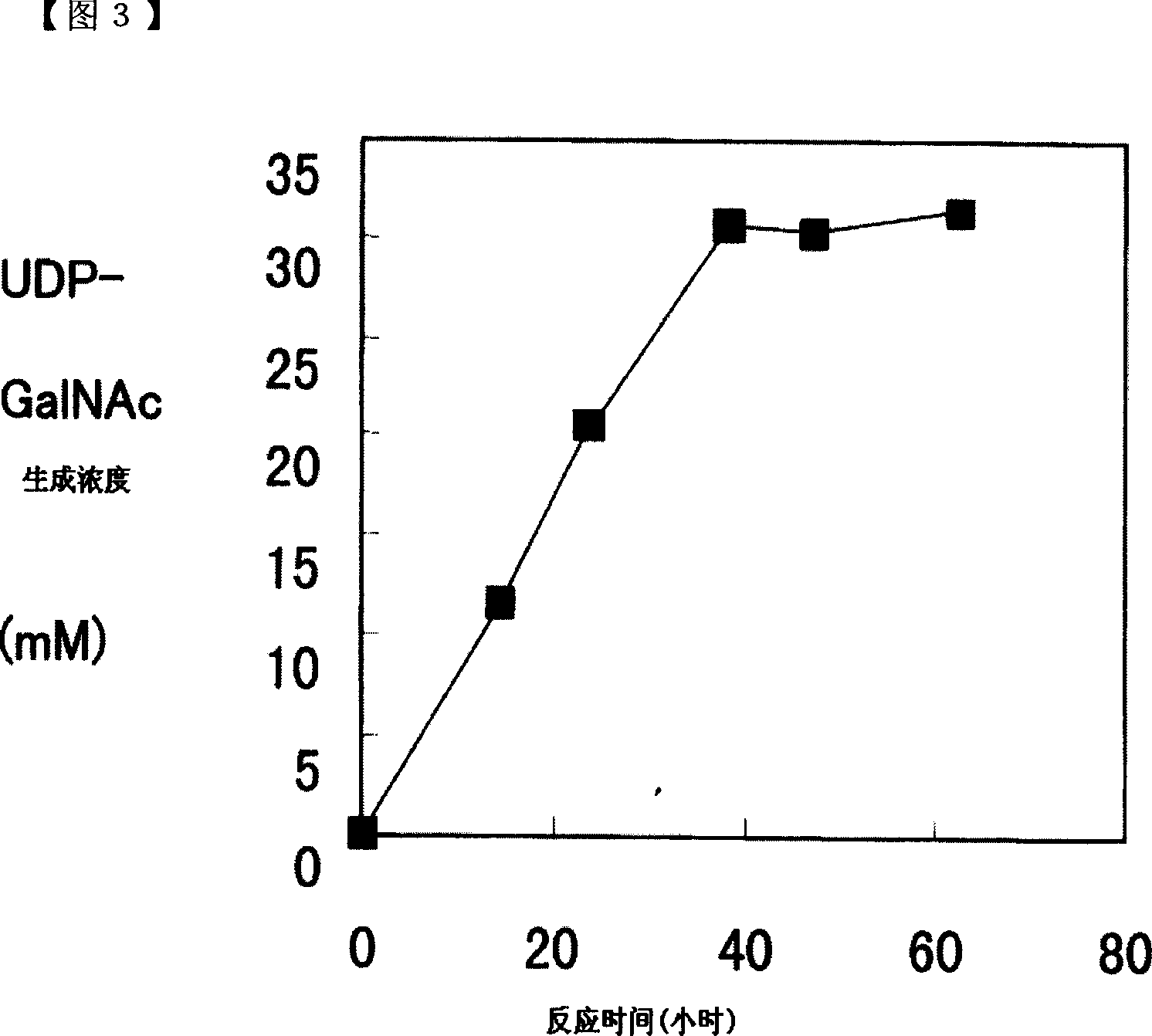
ActiveCN101052724AEfficient manufacturingEasy to manufactureTransferasesFermentationUDP-GalNAcPhosphate
A method of producing uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine (UDP-GalNAc), which is an important substrate in synthesizing an oligosaccharide, characterized in that in enzymatically producing uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine from uridine 5'-triphosphate (UTP) and N-acetylgalactosamine-1-phosphate (GalNAc1-P), uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine pyrophosphorylase (UDP-GlcNAc pyrophosphorylase) originating in a microorganism (excluding pathogenic ones) is used as an enzyme. In this method, it is also possible to use, as GalNAc-1P, a product prepared from N-acetylgalactosamine and a phosphate donor in a reaction system with the use of N-acetylgalactosamine kinase. According to this method, uridine 5'-diphospho-N-acetylgalactosamine can be efficiently produced by using a relatively inexpensive substrate.
Owner:YAMASA SHOYU CO LTD
Galnac phosphoramidites, nucleic acid conjugates thereof and their use
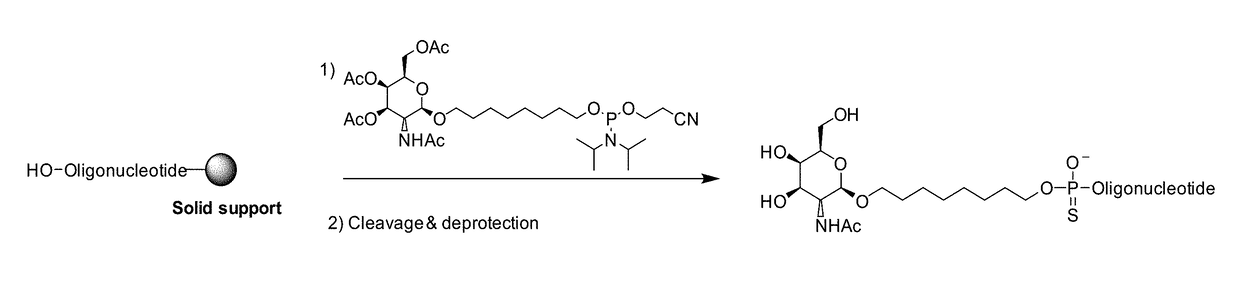
InactiveUS20170327524A1Easy to produceFew operationSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderN-AcetylgalactosaminePhosphoramidite
This invention generally relates to the field of phosphoramidite derivatives. In particular, the invention relates to N-Acetylgalactosamine phosphoramidite molecules and to conjugates of nucleic acid molecules with N-Acetylgalactosamine containing molecules. Also provided are methods for preparation of these molecules and possible uses thereof, in particular in medicine.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Novel n-acetylgalactosamine transferases and nucleic acids encoding the same
An enzyme which transfers N-acetylgalactosamine to N-acetylglucosamine via a β1-4 linkage was isolated and the structure of its gene was explained. This led to the production of said enzyme or the like by genetic engineering techniques, the production of oligosaccharides using said enzyme, and the diagnosis of diseases on the basis of said gene or the like.The present invention uses a protein having the amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, 3, 26 or 27 in the Sequence Listing or a variant of said amino acid sequence wherein one or more acids are substituted or deleted, or one or more acids are inserted or added and having the activity of transferring N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) to N-acetylglucosamine serving as a substrate via a β1-4 linkage and nucleic acids encoding said protein.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com