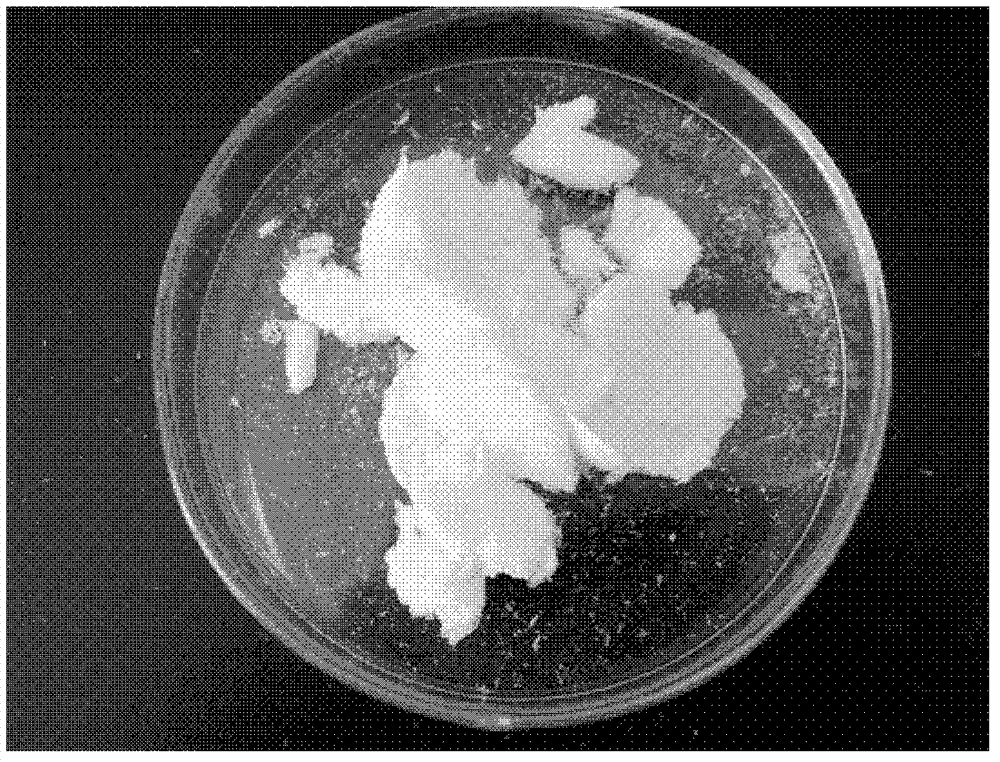
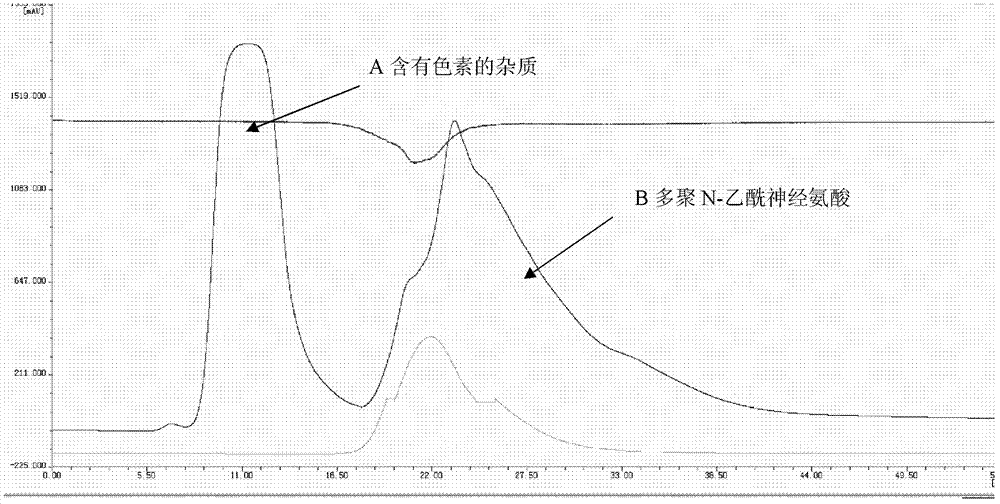
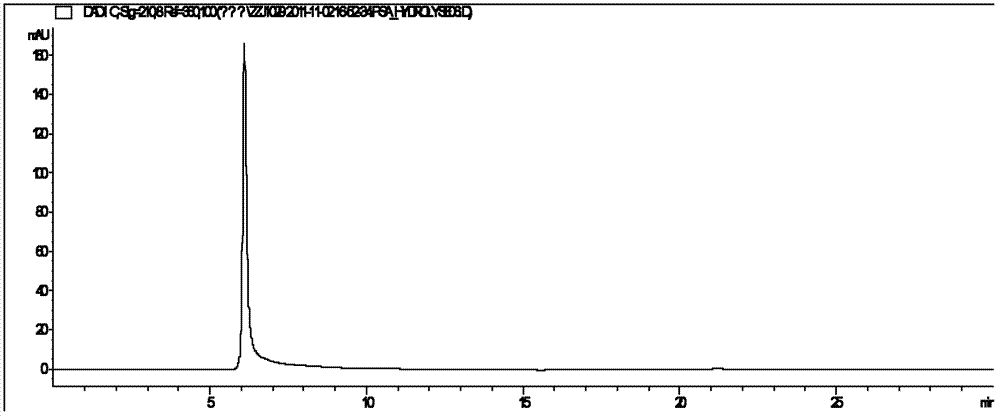
Method for producing poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid by microbial fermentation and purification method thereof
A technology of acetylneuraminic acid and microbial fermentation method, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of high cost, unable to meet the requirements of various indicators, limiting the application of poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid, etc. quantity and difficulty, and the effect of reducing production costs
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Embodiment 1 microbial fermentation method produces poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid
[0048]The fermentation strain is Escherichia coli CGMCC NO.5585, which was screened by mutagenesis in the Industrial Microbiology Laboratory of the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Seed tanks are fermented in 5 liters. The basal medium used is glucose 25g / L, ammonium sulfate 5g / L, casein peptone 15g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 20g / L, magnesium sulfate 0.4g / L, after mixing evenly, steam sterilization. After reaching 121°C, maintain the tank pressure at 0.09MPa and sterilize for 30 minutes. The sterilization process requires continuous stirring at 200rpm. After cooling, inoculate 9 liters of bacterial culture solution. Cultivate at 37°C for 12 hours to obtain seed culture solution.
[0049] The fermenter adopts 200 liters of fermentation. The basal medium is glucose 25g / L, ammonium sulfate 5g / L, casein peptone 15g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 20g / L, ma...
Embodiment 2
[0051] The separation and purification of embodiment 2 poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid
[0052] The fermentation broth obtained in Example 1 was used. Carry out the separation and purification of poly-N-acetylneuraminic acid according to the following steps:
[0053] 1. Separation of bacteria liquid
[0054] The 0.1 micron ceramic membrane tangential microfiltration method is used to separate the bacteria (microfiltration device) and the fermentation liquid. The filtrate volume is 7 / 8 of the original volume. Then wash the thalline with 3 / 8 of the original volume of water, microfilter the thalline washing liquid, and combine with the aforementioned filtrate.
[0055] 2. Remove small molecule impurities
[0056] The supernatant separated from step 2 was ultrafiltered with a 70,000 Dalton ultrafilter to concentrate macromolecules. The filtered waste was discarded. This step can concentrate the above supernatant at least 20 times the volume. The concentrated solution was washe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com