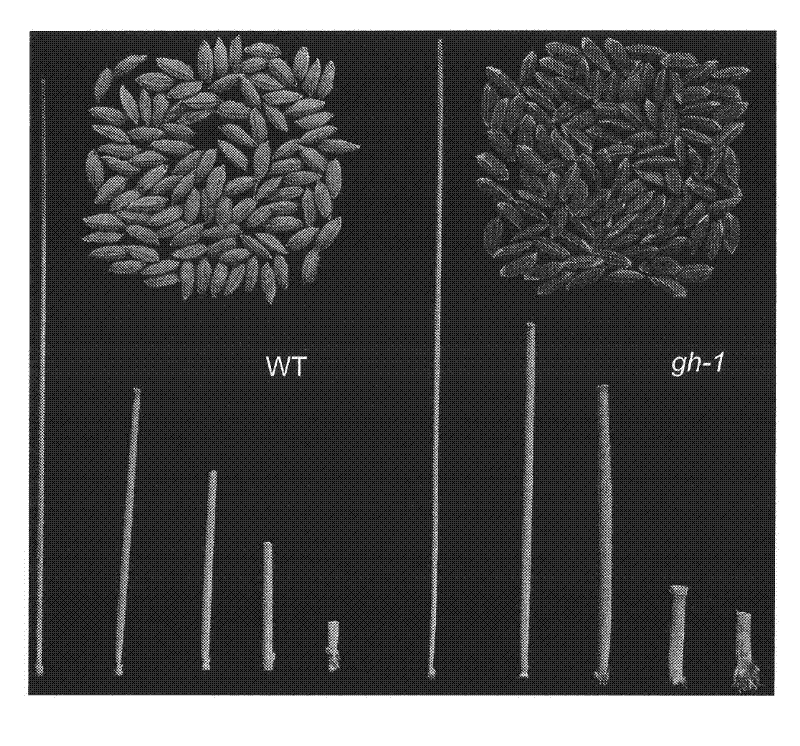
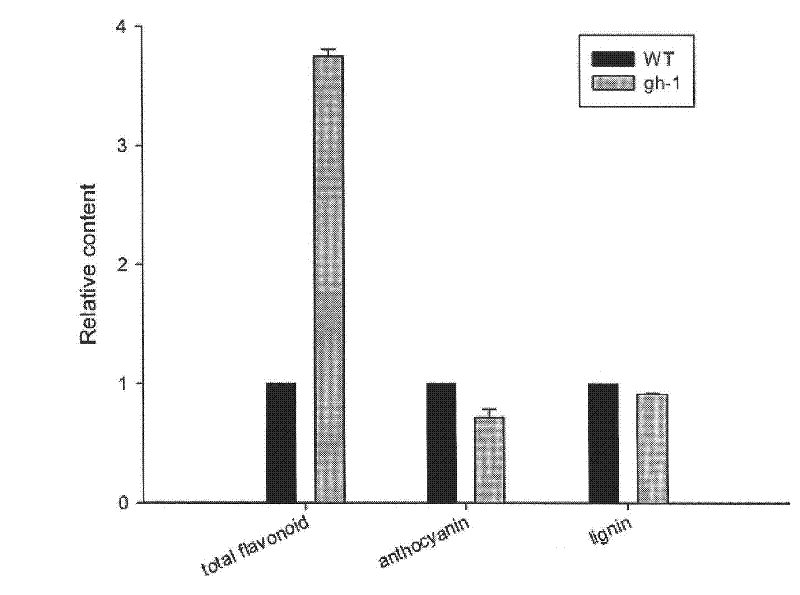
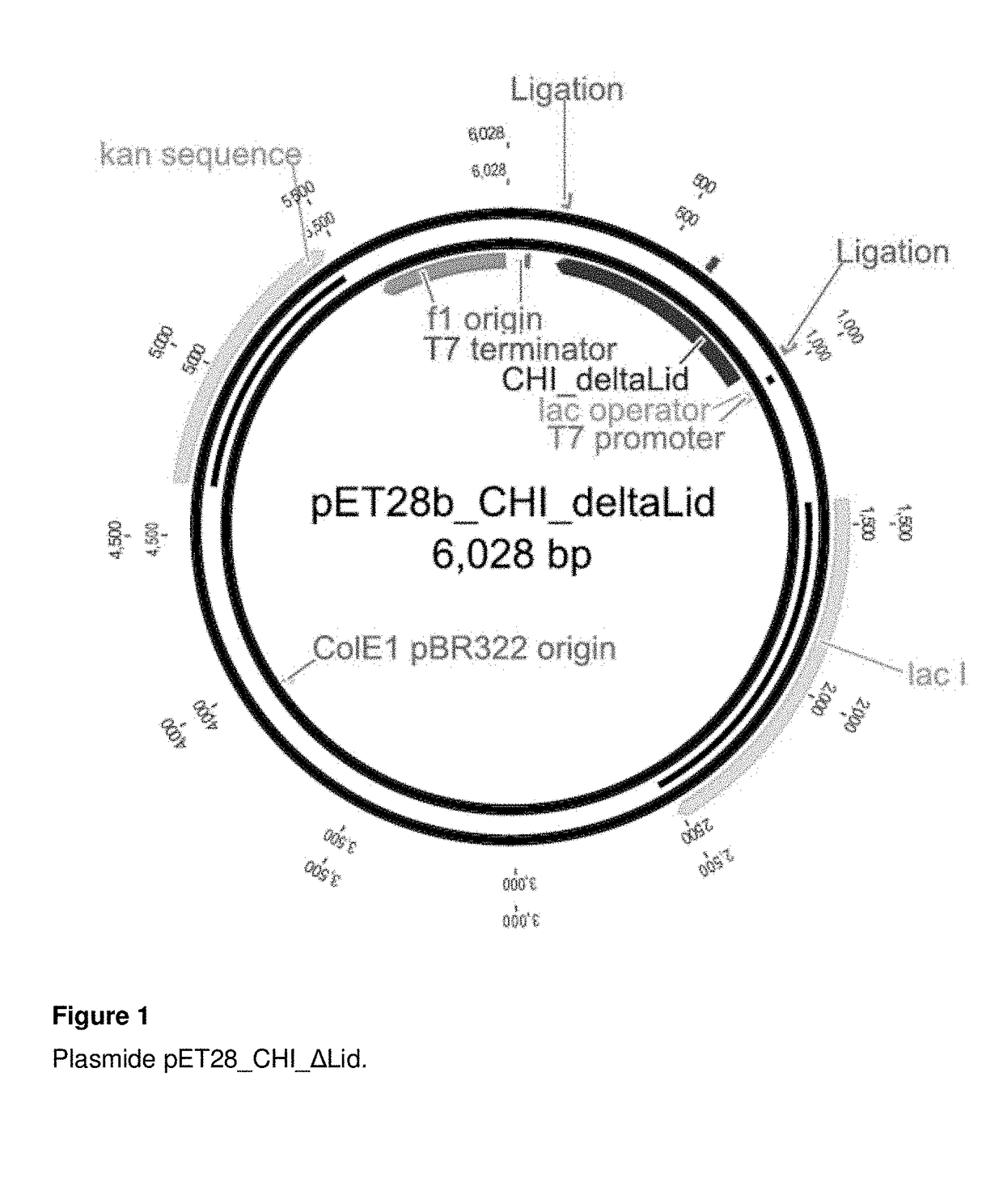
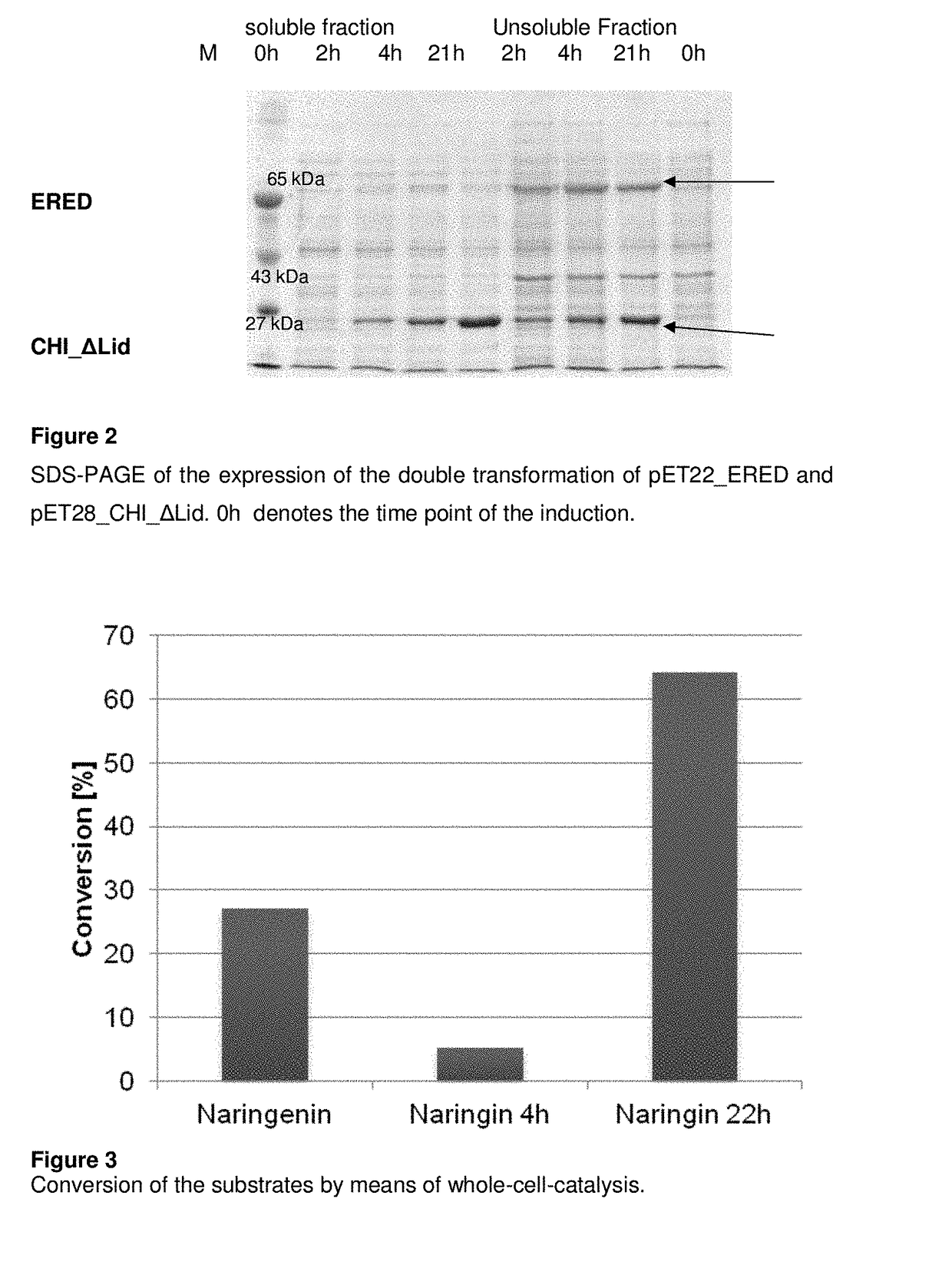
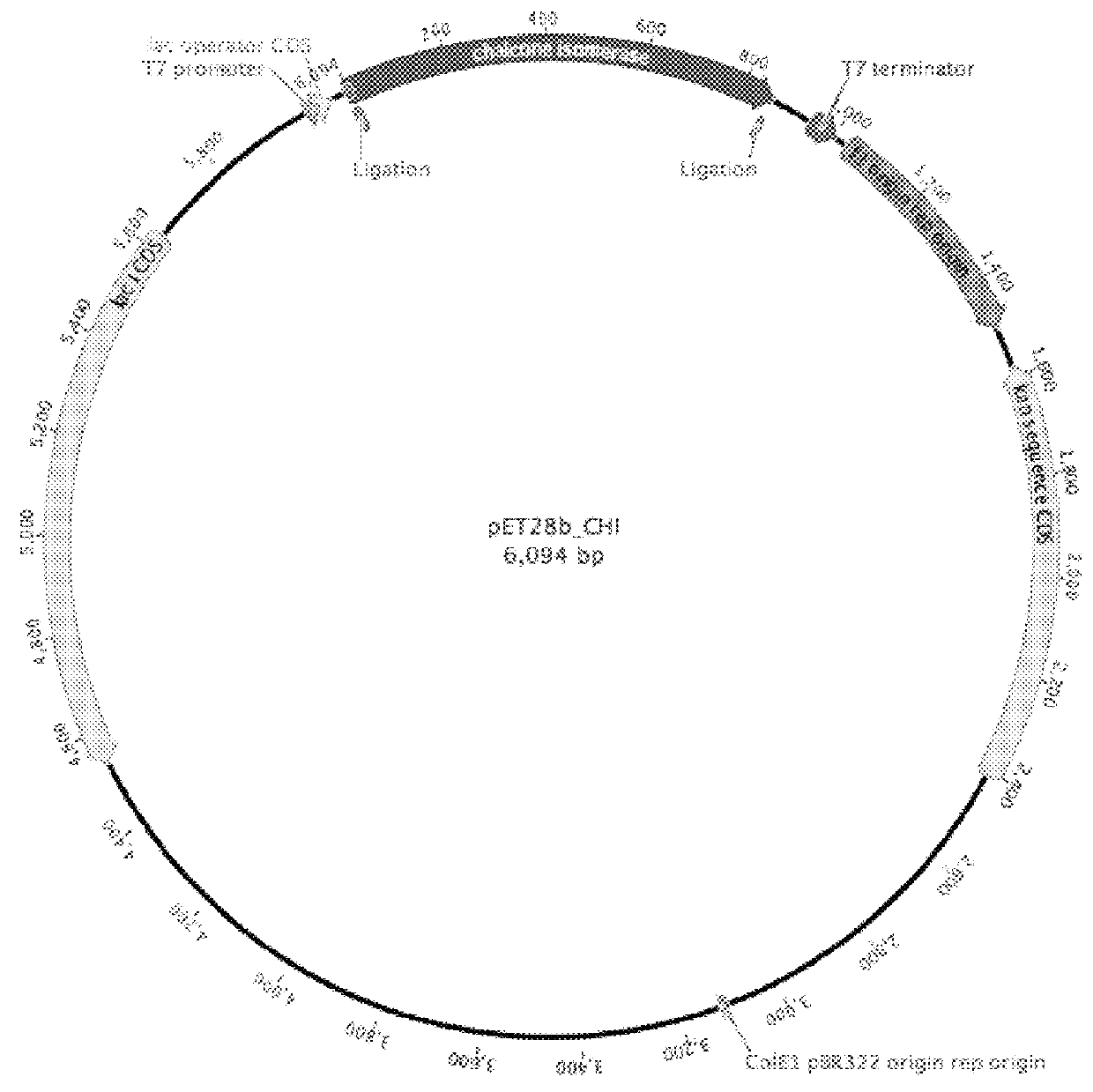
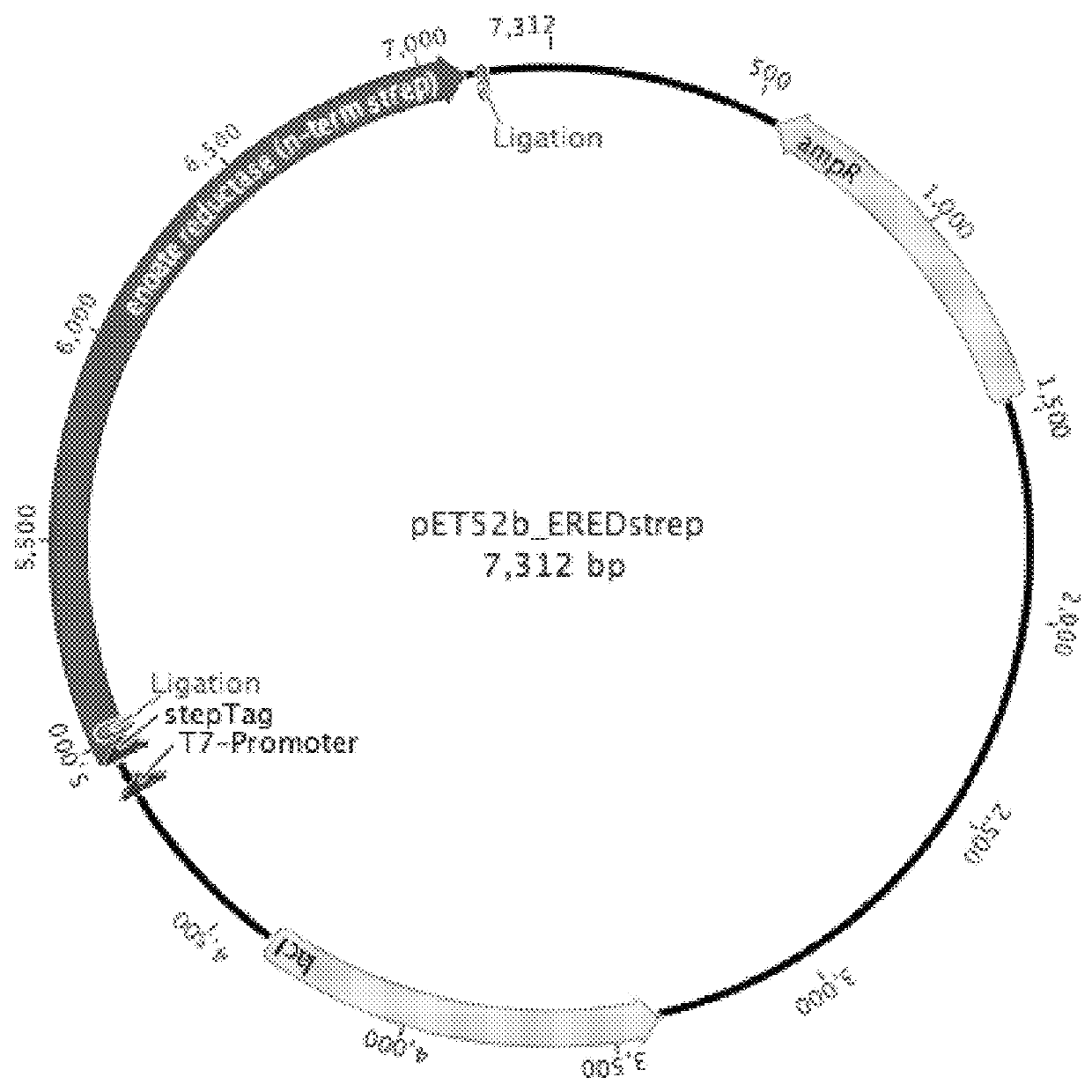
Patents
Literature
41 results about "Chalcone isomerase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
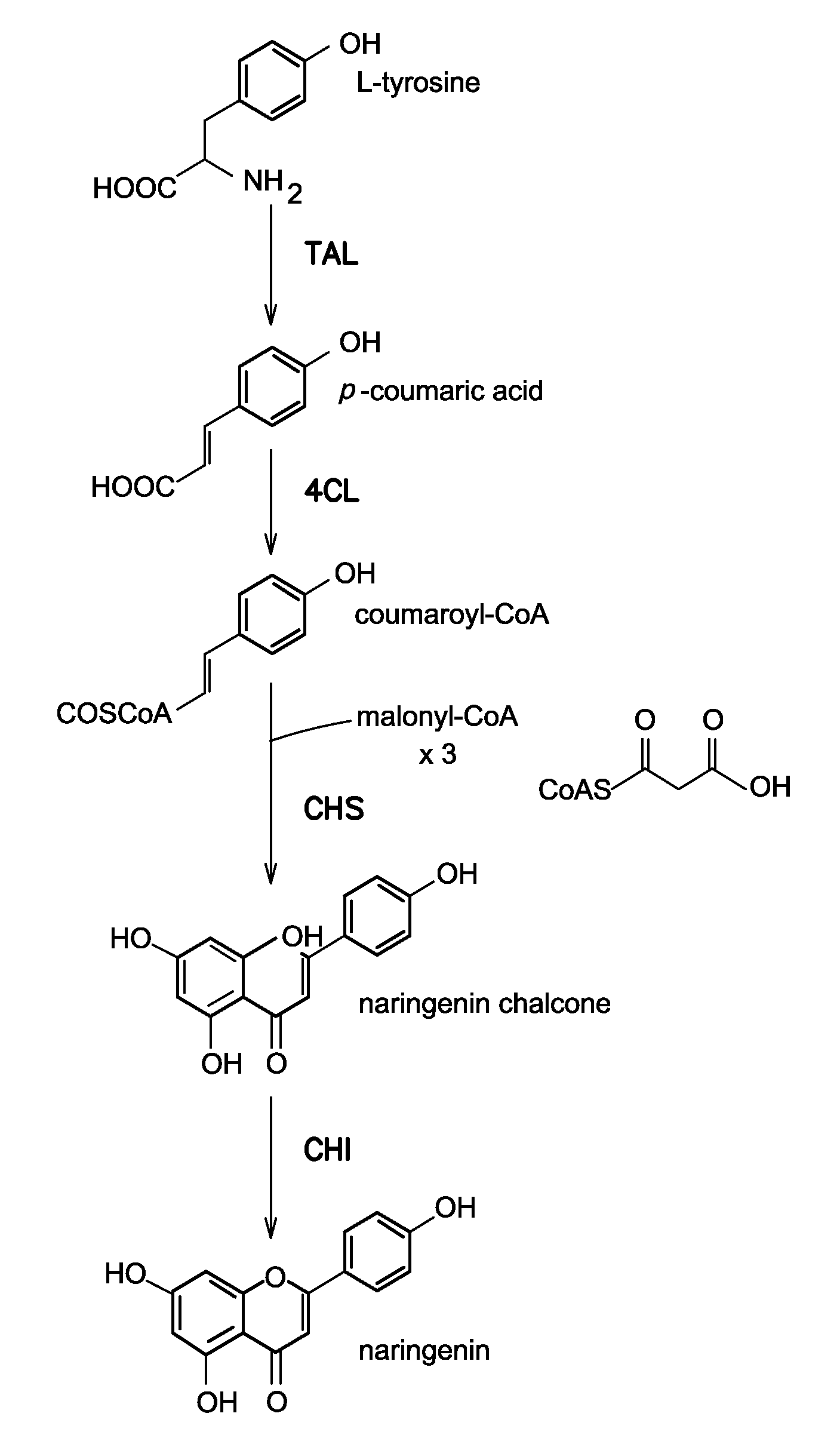
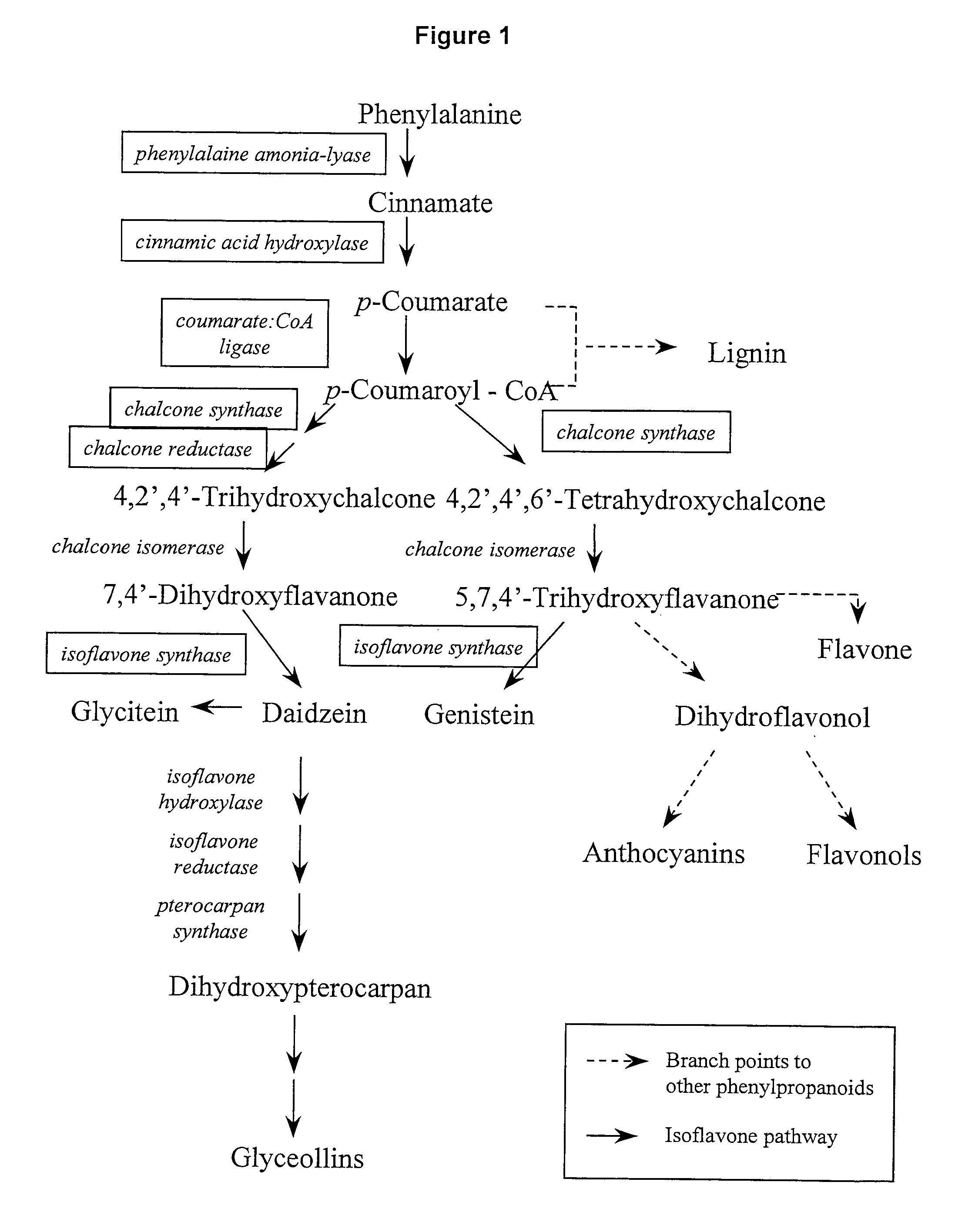
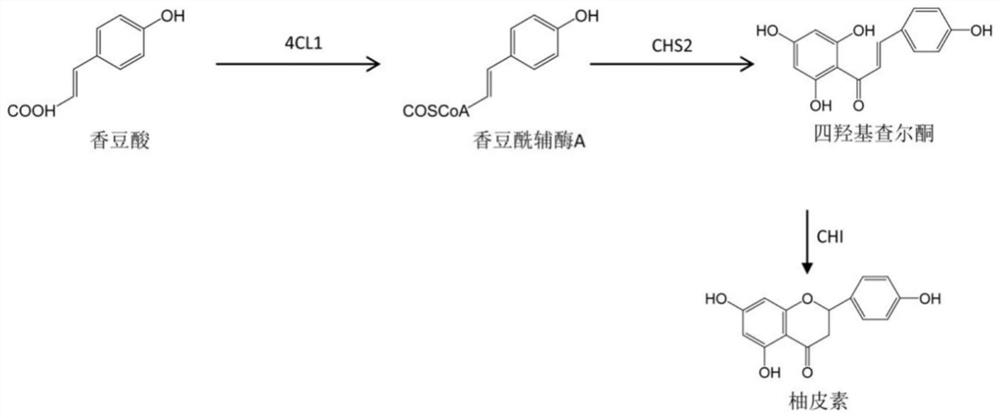
In enzymology, a chalcone isomerase (EC 5.5.1.6) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction a chalcone ⇌ a flavanone Hence, this enzyme has one substrate, a chalcone, and one product, a flavanone. This enzyme belongs to the family of isomerases, specifically the class of intramolecular lyases. The systematic name of this enzyme class is flavanone lyase (decyclizing). This enzyme is also called chalcone-flavanone isomerase.
Method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering
ActiveCN103865864AReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
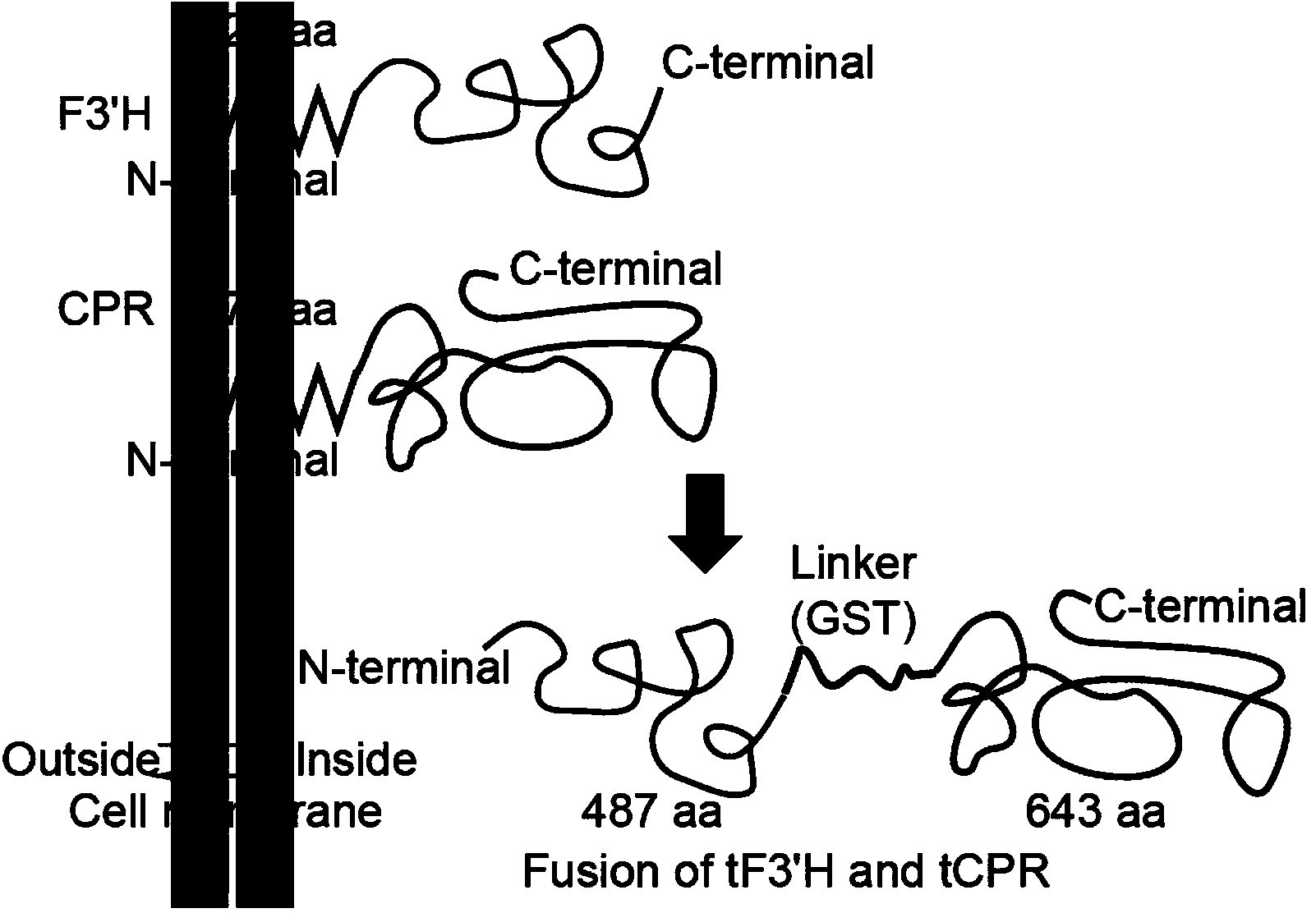
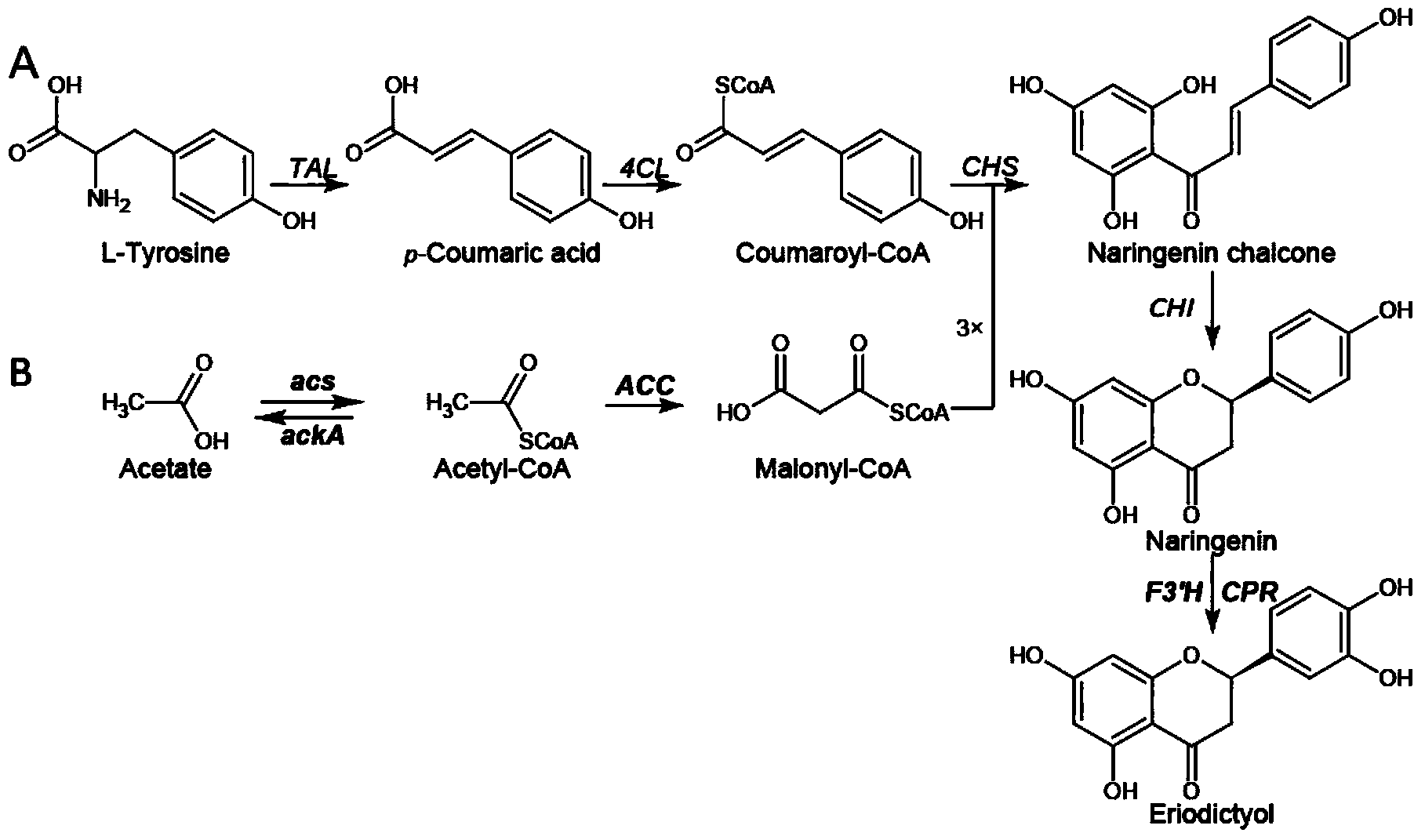
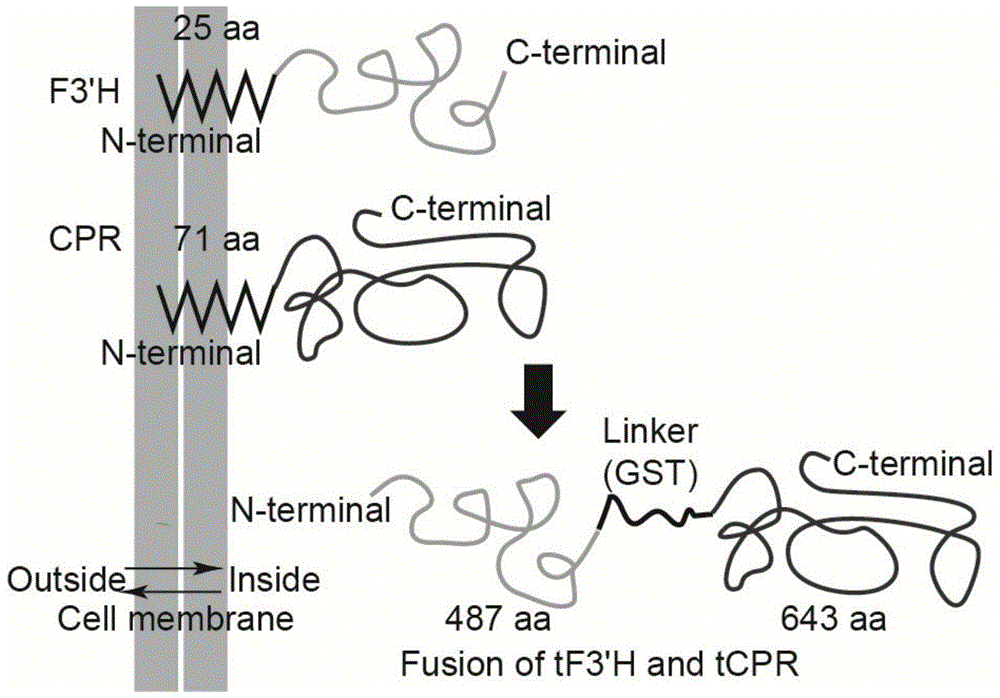
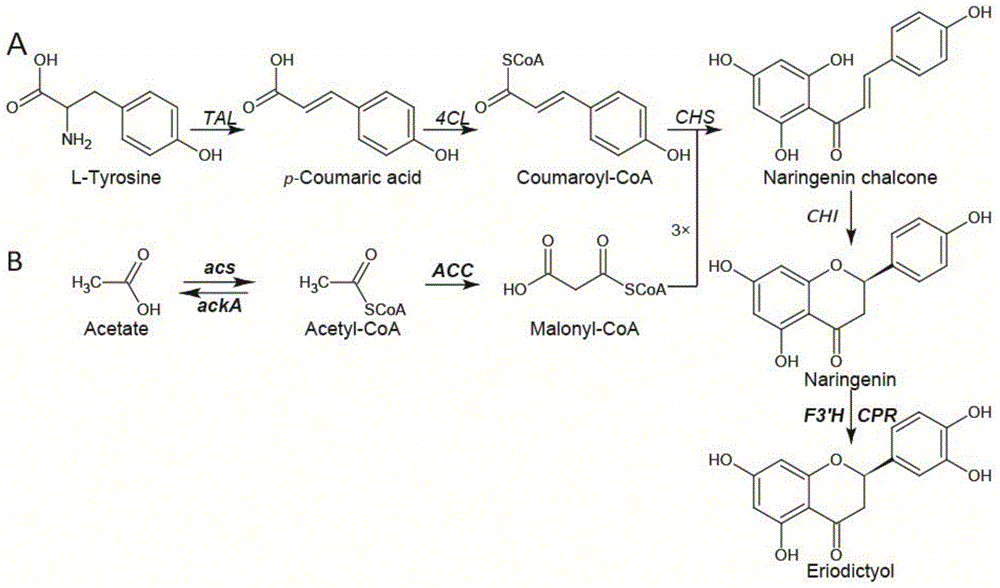
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetic engineering strain taking tyrosine as substrate to synthesize naringenin and construction method thereof
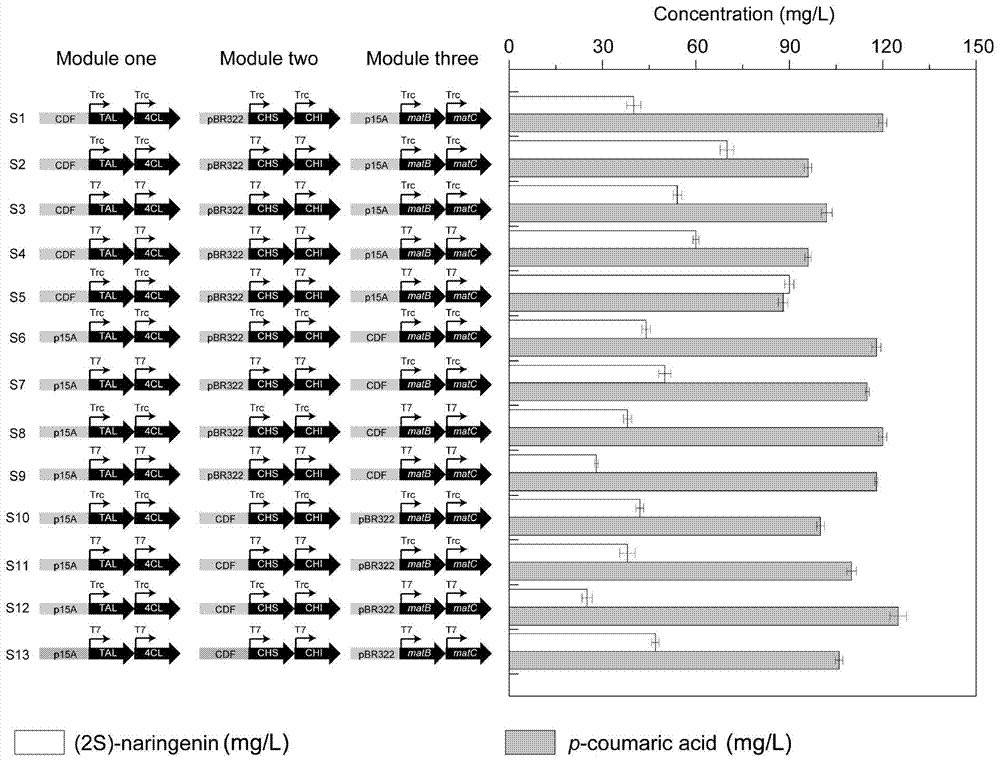
The invention discloses a genetic engineering stain taking tyrosine as a substrate to synthesize naringenin and a construction method thereof, belonging to the field of synthetic biology or metabolic engineering. According to the construction method disclosed by the invention, a synthesis route constituted by six genes, namely a gene matB encoding a malonic acid transporting enzyme, a gene matC encoding a malonic acid absorption route, a gene encoding a tyrosine ammonialyase (TAL), the gene encoding a 4-cinnamic acid: coenzyme A ligase (4CL), the gene encoding a chalcone synthase (CHS) and the gene encoding a chalcone isomerase (CHI) is introduced into Escherichia coli BL21 to obtain a recombinant strain capable of taking the tyrosine as the substrate to synthesize the naringenin, the synthesis route is further optimized through a modular transformation theory, the strain is finally fermented in a shaking flask for 72 hours by taking the tyrosine as the substrate, and the yield of the naringenin achieves 90mg / L. A strategy adopted by the construction method disclosed by the invention provides certain reference significance for future production of natural small molecular substances by a microbiological method.
Owner:湖南鸿健生物科技有限公司
Strains for the production of flavonoids from glucose
ActiveUS20120034661A1Simple and economical processIncrease productionFungiBacteriaGlucose polymersD-Glucose
Owner:THE RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
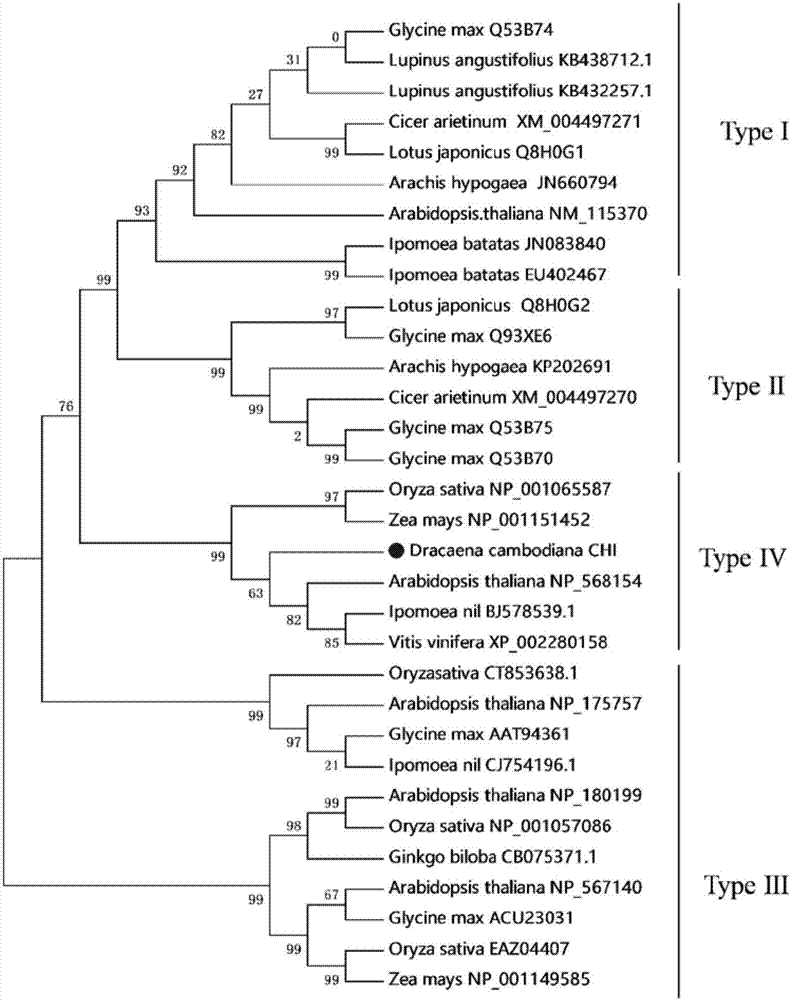
Dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1, encoding gene thereof and application
InactiveCN107190016AIncrease productionHigh economic valueBacteriaMicroorganism based processesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention discloses dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1, an encoding gene thereof and an application. The nucleotide sequence of the gene comprises: (a) a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; or (b) a nucleotide sequence formed by substituting, deleting and / or increasing one or a plurality of proteins expressing the same function of the nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1; or (c) a nucleotide sequence with 90% or more homologous proteins expressing the same function of the nucleotide sequence (a) or (b). The amino acid sequence of the dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, or is an amino acid sequence formed by substituting, deleting or increasing one or a plurality of amino acids of SEQ ID NO: 2 and has the same function. The dracaena cambodiana chalcone isomerase DcCHIL1 gene is obtained by cloning for the first time, the obtained DcCHIL1 proteins have chalcone isomerase activity, the gene is transferred into dracaena cambodiana by biotechnology, so that dracaena cambodiana flavone accumulation and the yield of dragon's blood can be improved, and the gene has a wide application prospect and great economic values.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Protein used for controlling anthocyanidin content, coding gene thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN102477092AHigh in anthocyaninsHigh nutritional valueViruses/bacteriophagesPlant peptidesOrganic chemistryChalcone isomerase
The invention discloses a protein used for controlling the content of anthocyanidin, a coding gene thereof, and an application thereof. The invention discloses a paddy rice chalcone isomerase (CHI), a coding gene thereof, and an application thereof. The protein is represented by the following (1) or (2): (1) a protein composed of an amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence list; (2) a protein with a same activity as that of the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2, wherein the protein is derived from the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2 through substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues. The paddy rice CHI gene provided by the invention can be used as a molecular marker and assists in paddy rice seed breeding. The paddy rice CHI gene also has an important value on the study of reasonable utilization of rice hulls.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Tulip chalcone isomerase TfCHI protein and encoding gene thereof
The invention relates to a tulip chalcone isomerase TfCHI protein and an encoding gene thereof. The protein is composed of amino acid sequences represented by the SEQ ID No.4, or the protein is composed of amino acid sequences represented by the SEQ ID No.4 which have been processed by replacing, removing, or adding one or several amino acids, and has a tulip chalcone isomerase activity. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence which encodes the protein mentioned above and is represented by the SEQ ID No.3. By utilizing the tulip chalcone isomerase gene provided by the invention and various screening method, substances, acceptors, inhibitors or antagonists which can interact with the chalcone isomerase TfCHI can be screened out. By utilizing the tulip chalcone isomerase gene provided by the invention, people can change the flower color through a gene engineering method, and a novel way is provided for creating new flower colors.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Safflower chalcone isomerase (CHI) gene and application thereof
InactiveCN103820478AEasy to synthesizeReduce flavonoid contentGenetic engineeringFermentationComplementary deoxyribonucleic acidTransgene
The invention discloses a safflower chalcone isomerase (CHI) gene. The RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of safflower pedals is reversely transcribed into a cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid), the cDNA is used as a template to carry out 3' and 5' race cloning, the 3' and 5' end sequences of the safflower CHI gene are respectively obtained, a safflower CHI sequence is obtained through splicing of the 3' and 5' end sequences, the whole gene length is 1161bp, and the length of an opening reading frame is 654bp. The safflower CHI gene is named ct-(i)CHI( / i), and the result of the sequence comparison and analysis of the safflower CHI gene on ncbi (National Center for Biotechnology Information) shows that the homology of the gene with a dutchmanspipe root CHI gene reaches 82%. Experiments show that the synthesis of flavone can be promoted by the over-expression ct-(i)CHI( / i) gene, the flavone content can be lowered after the ct-(i)CHI( / i) gene is inhibited, and the safflower CHI gene has wide prospects in the aspect of cultivating high-content flavonoids transgenic plants.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Lonicera japonica chalcone isomerase (LjCHI) gene, LjCHI gene coded protein and their application
The invention discloses a lonicera japonica chalcone isomerase (LjCHI) gene, a LjCHI gene coded protein and their application. The LjCHI gene is obtained from a lonicera japonica cDNA library for the first time and thus in China, separation and cloning of a chalcone isomerase gene from a traditional Chinese medicine lonicera japonica are realized. The LjCHI gene provided by the invention has a nucleotide sequence of SEG ID NO.1, a homologous nucleotide sequence prepared from the nucleotide sequence of SEG ID NO.1 through addition, replacement, insertion or deletion of one or more nucleotides,or a nucleotide sequence of an allele or an allele derivative. The LjCHI gene coded protein has an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.2, or a homologous amino acid sequence prepared from the amino acidsequence of SEQ ID NO.2 through addition, replacement, insertion or deletion of one or more amino acids. The LjCHI gene can improve lonicera japonica flavonoid content of lonicera japonica flavonoid active components through the biotechnology, is conducive to lonicera japonica medicinal material quality improvement, realizes selective breeding, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Method for Biotechnological Production of Dihydrochalcones
A method for production of a dihydrochalcone, especially of phloretin, using a transgenic microorganism, containing a nucleic acid section (a), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial chalcone isomerase, and / or a nucleic acid section (a′), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a plant chalcone isomerase, and a nucleic acid section (b), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial enoate reductase, corresponding transgenic microorganisms, containing a nucleic acid section (a), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial chalcone isomerase, and / or a nucleic acid section (a′), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a plant chalcone isomerase, and / or a nucleic acid section (b), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial enoate reductase, and host cells, containing one or more identical or different such vectors.
Owner:SYMRISE GMBH & CO KG
Chalcone isomerase
InactiveUS7202398B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationDNA construct
An isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a chalcone isomerase is disclosed. Also of concern is the synthesis of a recombinant DNA construct encoding all or a portion of the chalcone isomerase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels of the chalcone isomerase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
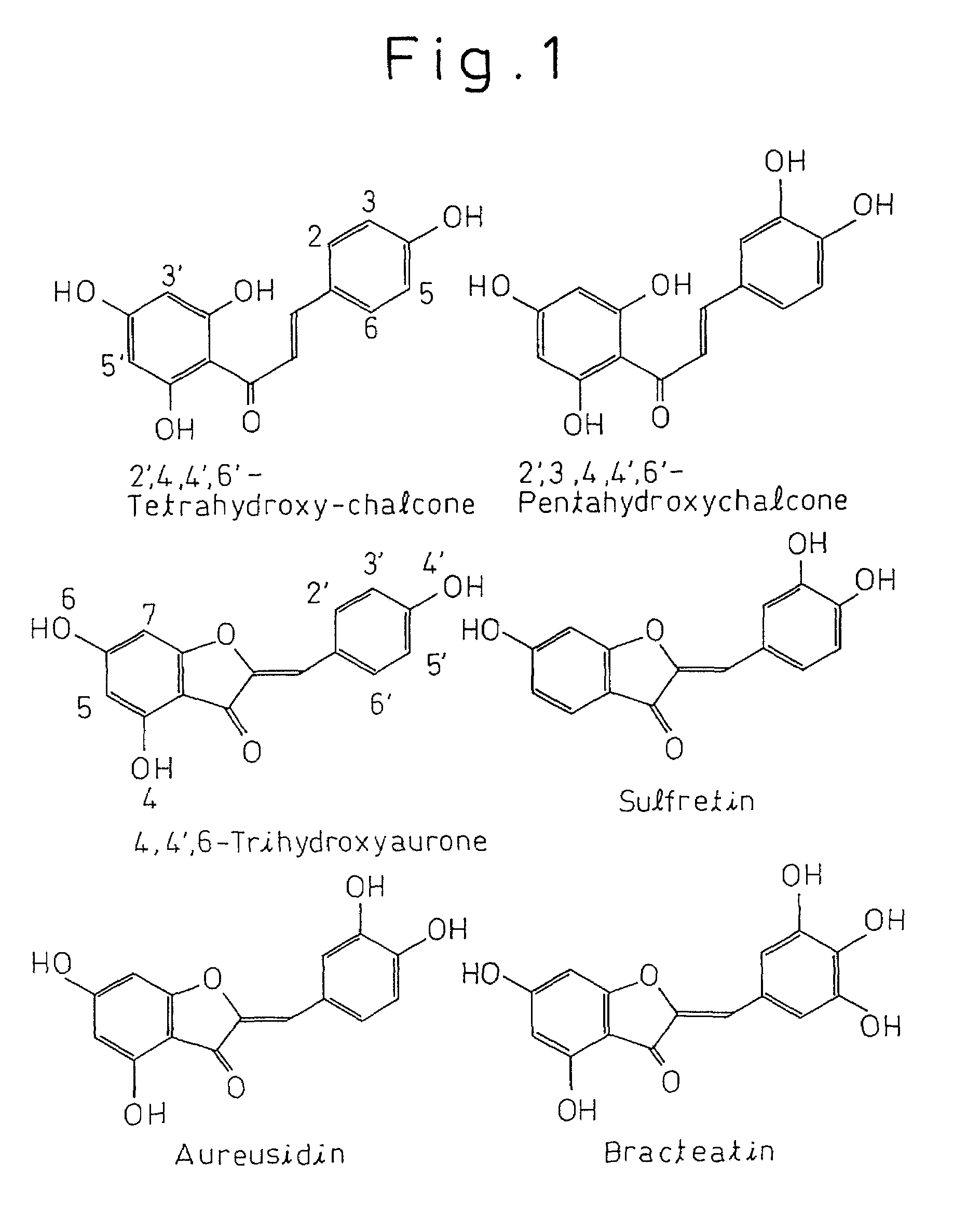
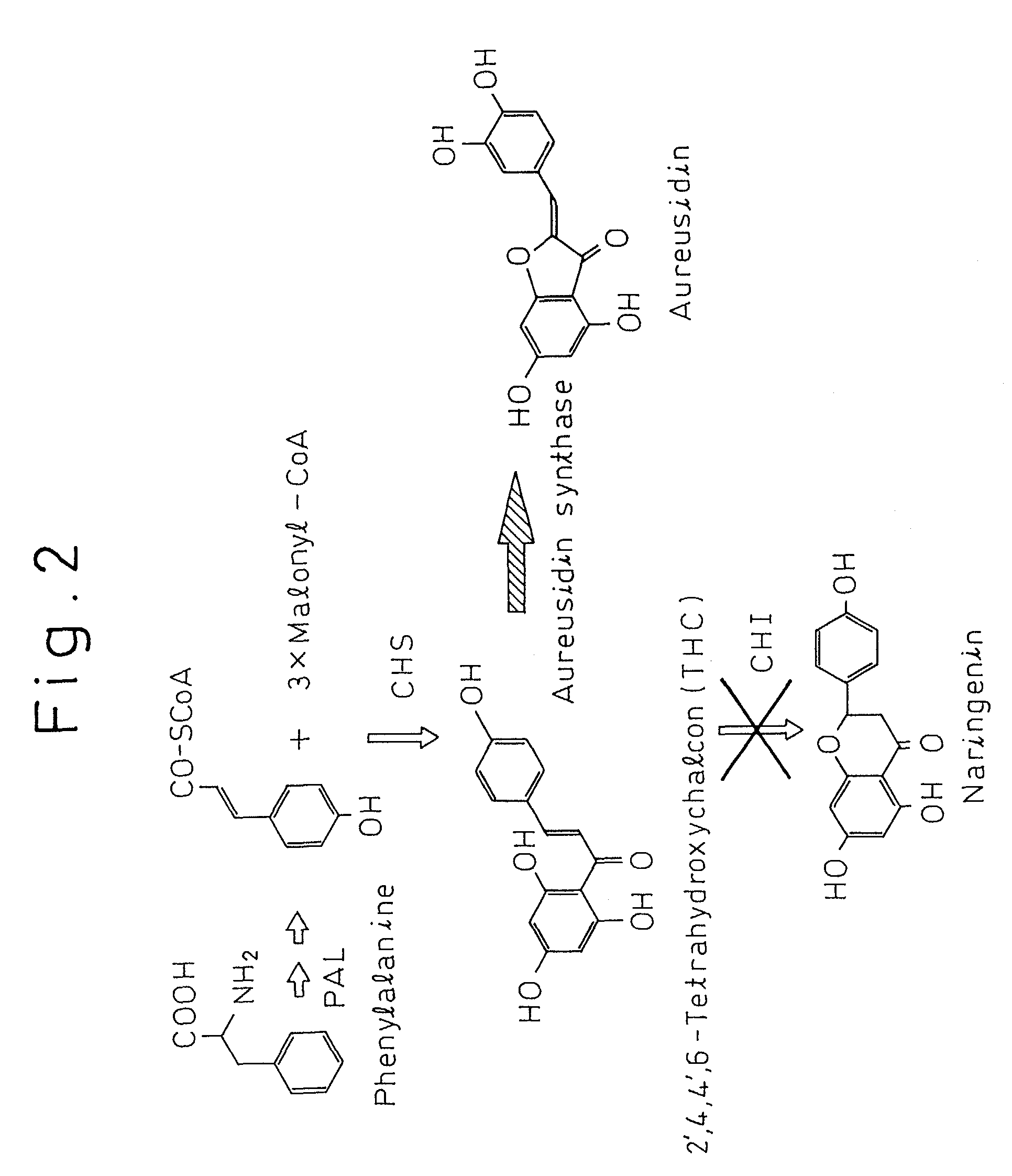
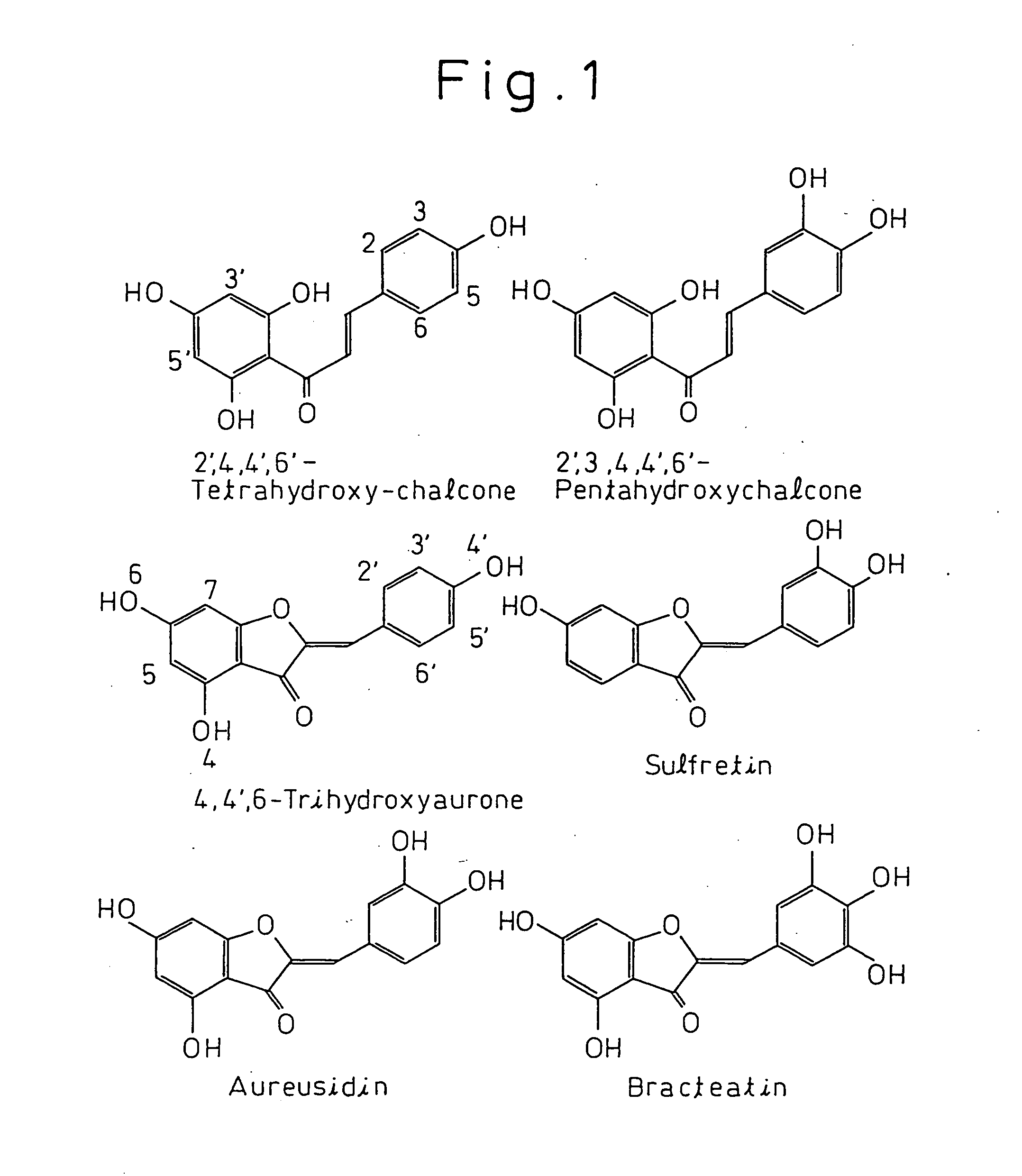
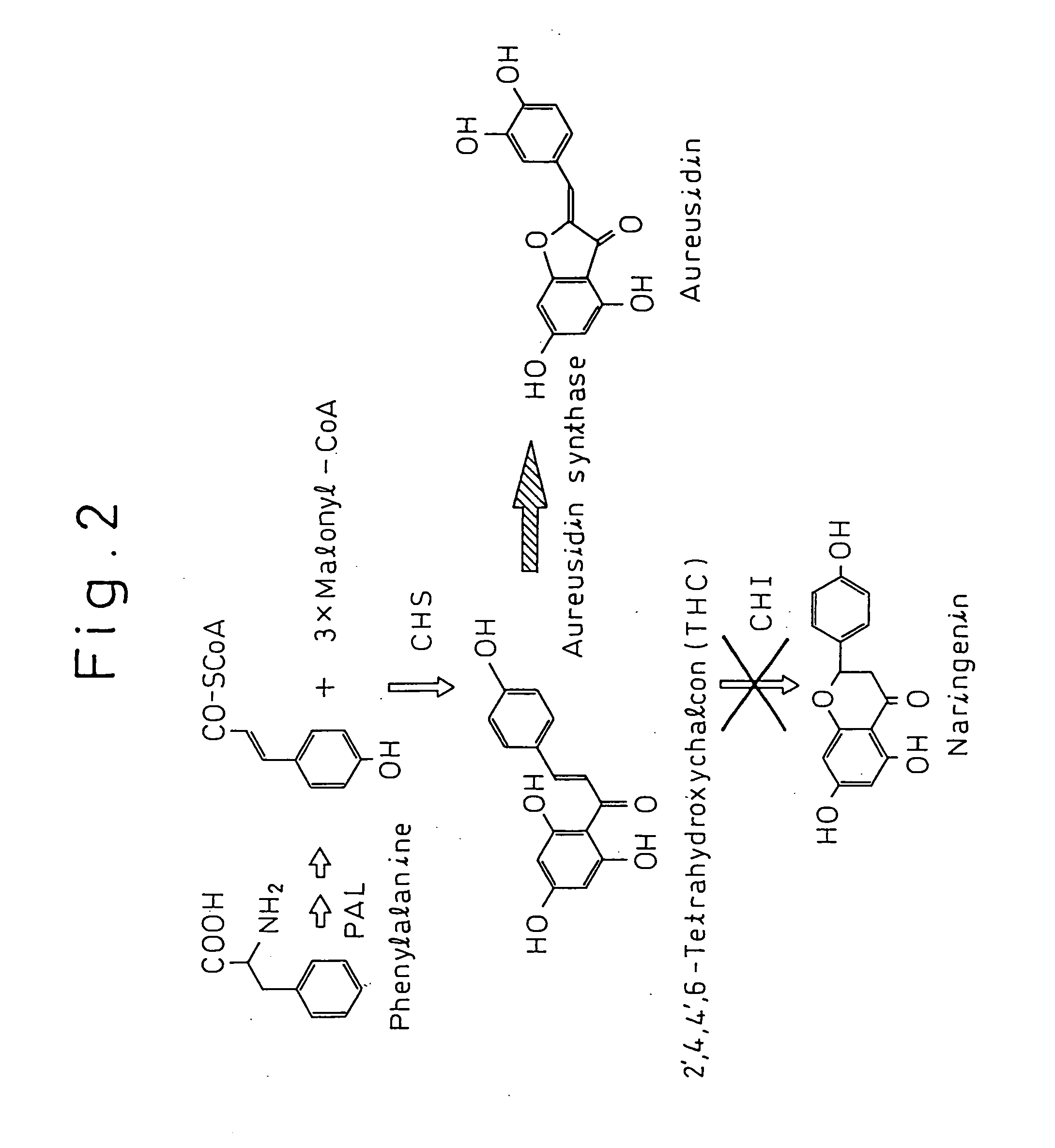
Gene encoding protein having aurone synthesizing activity
The present invention provides a protein having aurone synthase activity involved in the color of flowers such as snapdragons, a gene that encodes it, cDNA in particular, and its applications. This gene can give yellow color to the flowers of plants by introducing into plants deficient in chalcone isomerase and so forth and expressing.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
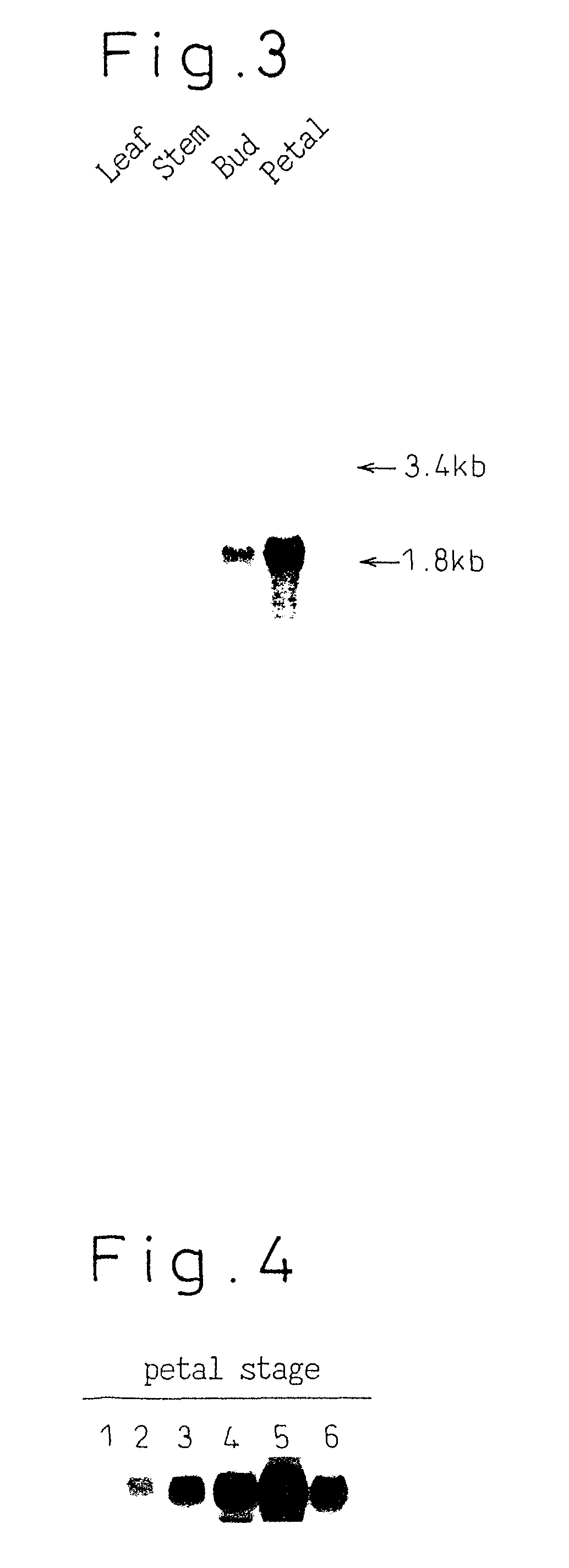
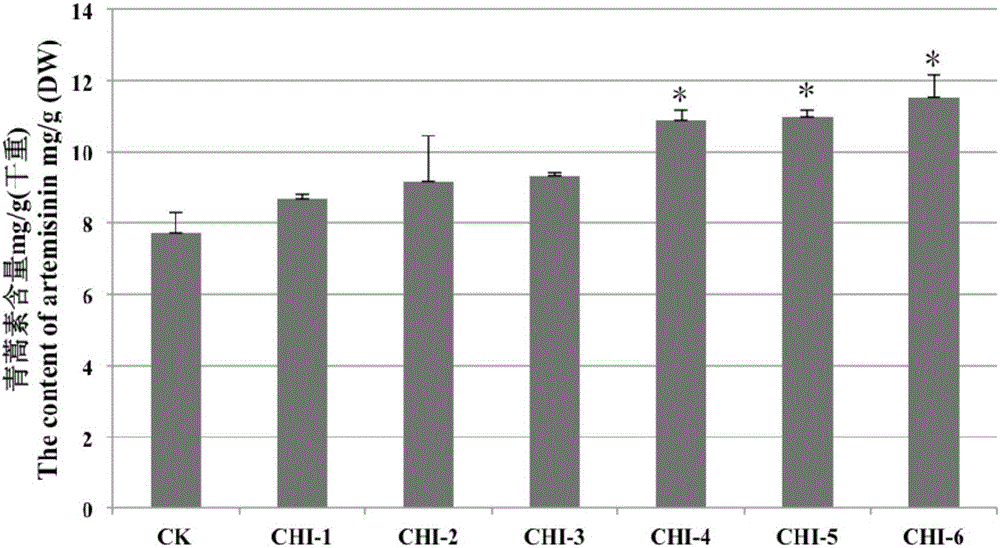
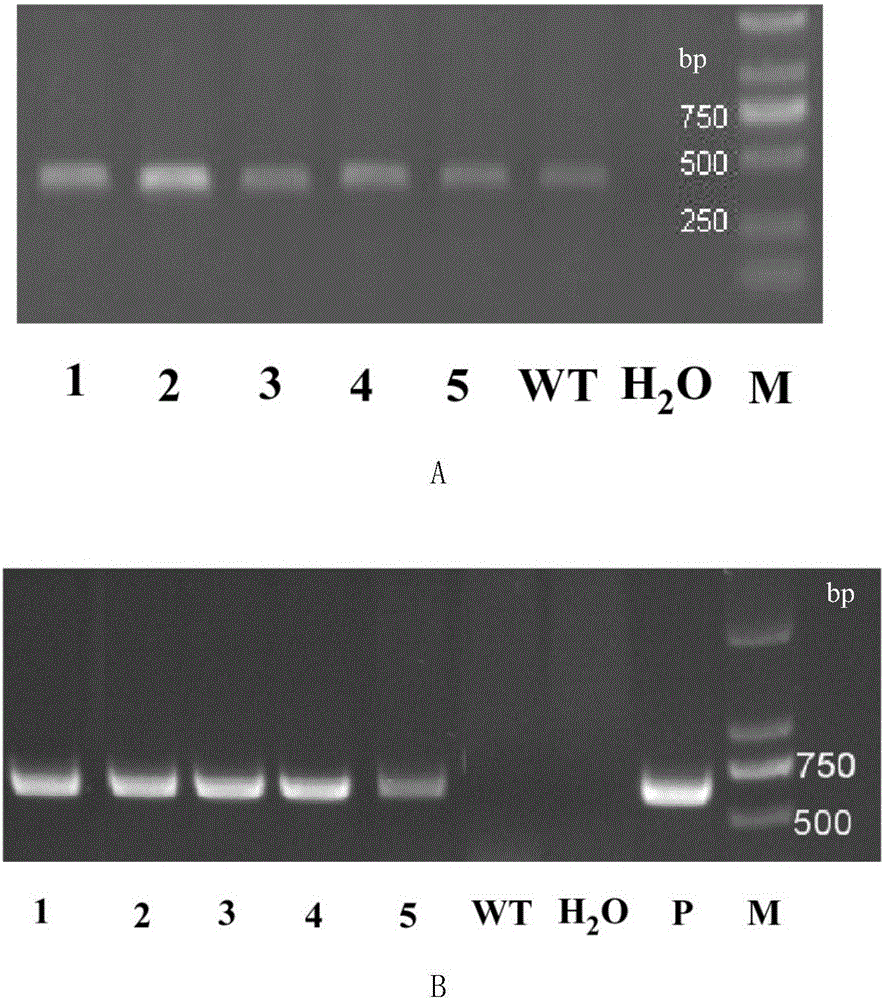
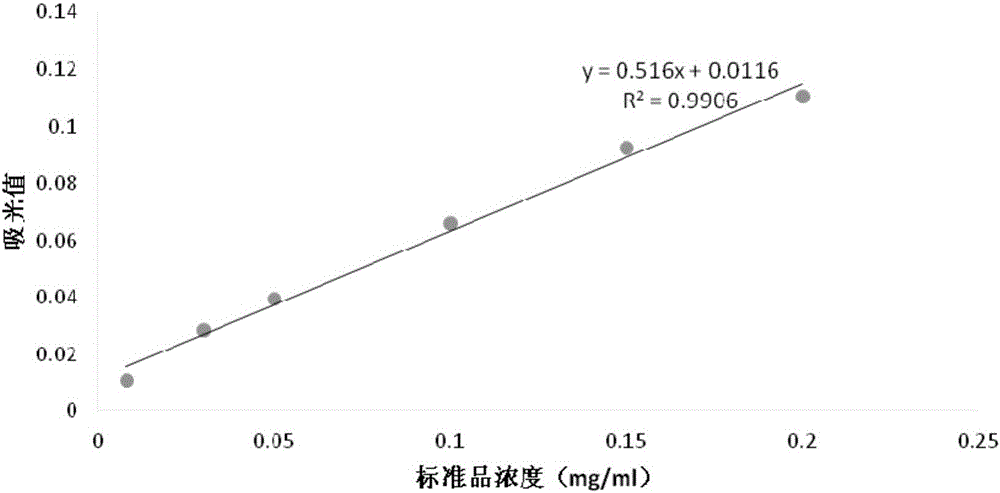
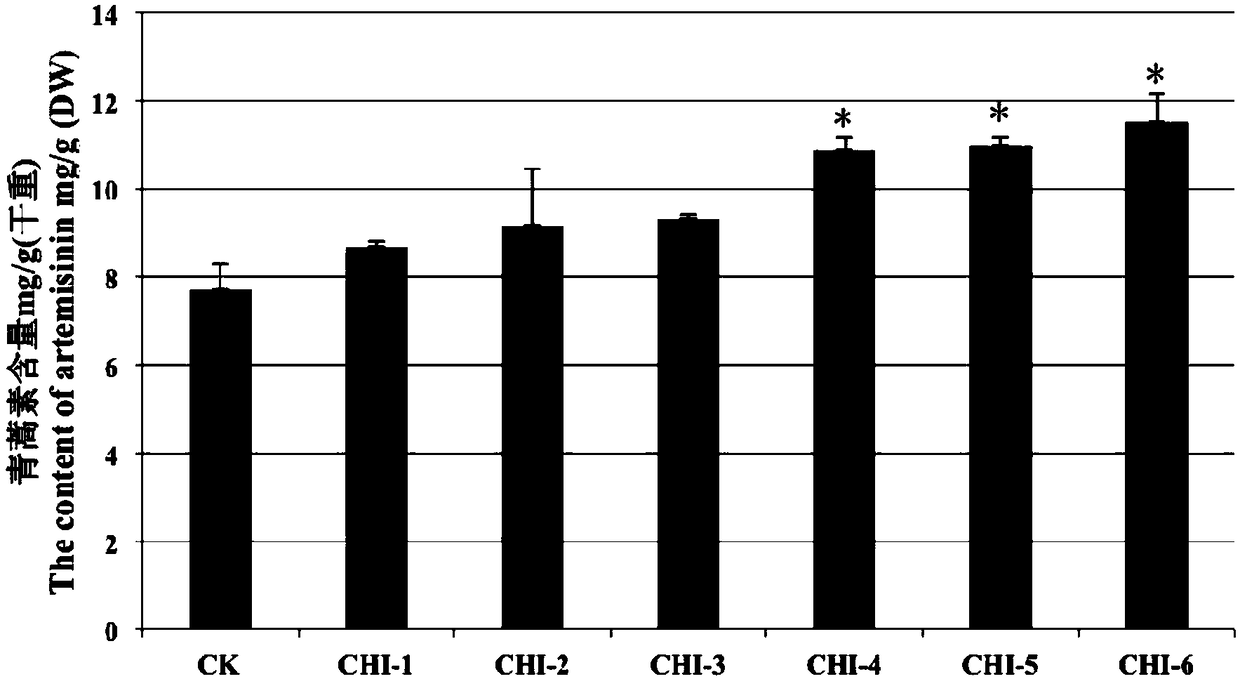
Method for increasing content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. by genetic modification with CHI (chalcone Isomerase) genes
The invention relates to the field of biological technologies and provides a method for increasing content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. by genetic modification with CHI (chalcone Isomerase) genes. According to the method, the CHI genes are cloned from Artemisia annua L., a plant expression carrier containing the CHI genes is established, the CHI genes are mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens to be transferred into Artemisia annua L. for regeneration of a plant, the integration condition of an exogenous target gene CHI is detected through the PCR (polymerase chain reaction), the content of artemisinin in transgenic Artemisia annua L. is detected through an HPLC-ELSD (high performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector), and the transgenic Artemisia annua L. plant with the content of artemisinin increased is screened out. The content of artemisinin in transgenic Artemisia annua L. is increased and is 1.5 times that of a non-transgenic contrast plant in the highest level, and the method for increasing the content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. is provided and lays a foundation for large-scale production of artemisinin from transgenic Artemisia annua L..
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for improving content of bioactive substance quercetin of buckwheat sprouts through magnetic field induction treatment
InactiveCN102640596AHigh activityIncrease contentSeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationPolygonum fagopyrumBiochemistry
The invention discloses a method for improving the content of the bioactive substance quercetin of buckwheat sprouts through magnetic field induction treatment. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly performing induction treatment on buckwheat grains by means of a magnetic field; and then sprouting the induced buckwheat grains for 7 days, thereby obtaining the buckwheat sprouts containing high content of the bioactive substance quercetin. The method for improving the content of the bioactive substance quercetin of the buckwheat sprouts through the magnetic field induction treatment provided by the invention is capable of obviously improving the activity of phenylalnine ammonialyase (PAL) and chalcone isomerase (CHI) in the sprouting process of the buckwheat while improving the sprouting percentage and germinative force of the buckwheat grains, thereby obviously improving the content of the bioactive substance quercetin in the buckwheat.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF TECH
Chalcone isomerase gene of asparaguses, protein encoded by chalcone isomerase gene and application of chalcone isomerase gene
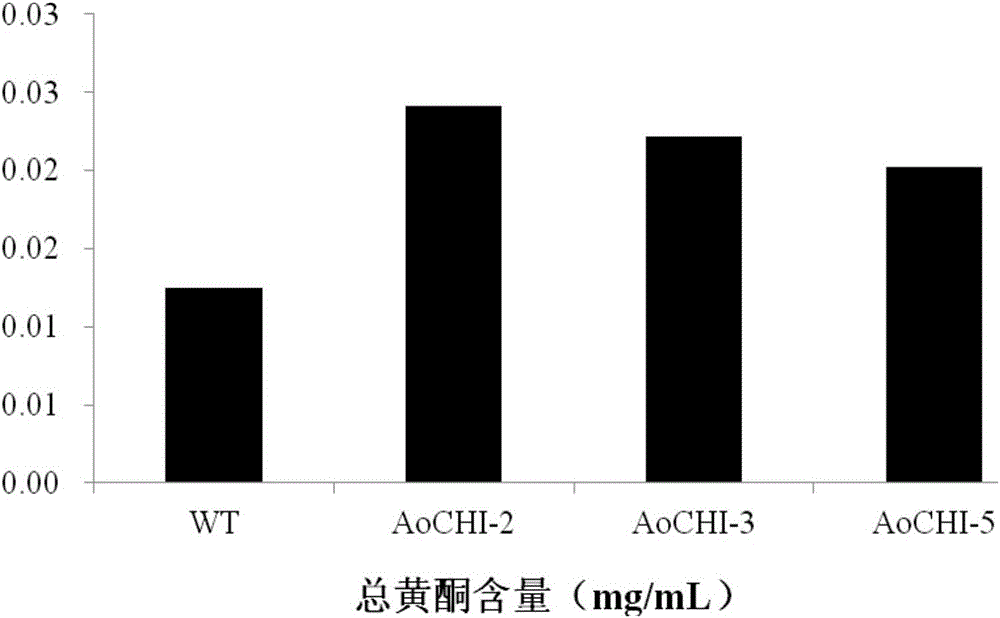
The invention provides a chalcone isomerase gene of asparaguses, a protein encoded by the chalcone isomerase gene and application of the chalcone isomerase gene. The CDS sequence of the chalcone isomerase gene AoCHI1 is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1; the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by the gene is represented by SEQ ID NO: 2. The chalcone isomerase gene AoCHI1 is cloned from the asparagus for the first time, and is one of key genes for synthesizing plant flavonoids; by the adoption of a method of gene engineering, the gene AoCHI1 is transferred into a target plant, so that the total flavonoids content of a transgenic plant can be increased, to improve the plant quality by using a gene engineering technology in the future; furthermore, an important theoretical basis is provided for obtaining medicines or food with high oxidization resistance, and the chalcone isomerase gene has a wide application prospect and high economic value.
Owner:VEGETABLE & FLOWER INST JIANGXI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Chalcone isomerase
InactiveUS20040172674A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesAntisense OrientationIsomerase
An isolated nucleic acid fragment encoding a chalcone isomerase is disclosed. Also of concern is the synthesis of a recombinant DNA construct encoding all or a portion of the chalcone isomerase, in sense or antisense orientation, wherein expression of the recombinant DNA construct results in production of altered levels of the chalcone isomerase in a transformed host cell.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Tulip chalcone isomerase TfCHI protein and coding gene thereof and probe
InactiveCN102978194AImprove viewing valueMicrobiological testing/measurementIsomerasesNucleic acid sequencingGene engineering
The invention relates to a tulip chalcone isomerase TfCHI protein and a coding gene thereof and a probe. The protein is one selected from (a) and (b), wherein (a) is a protein composed of an amino acid sequence as represented by SEQ ID No. 4, and (b) is a protein derived from (a), obtained through replacement, deletion or addition of one or more amino acids of the amino acid sequence as represented by SEQ ID No. 4 and having activity of tulip chalcone isomerase. The invention also provides a nucleic acid sequence coding the protein and the probe for detection of the nucleic acid sequence. According to the invention, the tulip chalcone isomerase TfCHI protein and the coding gene thereof provide theoretical bases for changing flower colors and creating new flower colors through regulation and control of temporal-spatial expression characteristics of the tulip chalcone isomerase TfCHI protein by using gene engineering technology, and have a significant application value.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
A method for metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli to produce eriodictyol
ActiveCN103865864BReduce manufacturing costLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAcetyl Coenzyme A SynthetaseTyrosine
The invention discloses a method for producing eriodictyol by reforming escherichia coli in metabolic engineering, belonging to the field of metabolic engineering. The step of transforming naringenin into the eriodictyol is successfully realized through a gene engineering technology by carrying out fusion expression on two genes, namely a flavone 3' hydroxylase gene tF3'H with a membrane binding sequence cut and a P450 reductase gene tCPR, in escherichia coli. A tyrosine ammonia lyase gene TAL from R.glutinis, 4-coumarate:coenzyme A ligase gene 4CL from P.crispum, a chalcone synthase gene CHS from P.hybrida and a chalcone isomerase gene CHI from M.sativa are simultaneously expressed to realize that naringenin is directly produced through tyrosine, so that an engineered strain for directly producing eriodictyol through tyrosine is established. According to the method, in order to increase the output of eriodictyol, an acetokinase ackA gene contained in an escherichia coli genome is removed by being knocked, an acetyl coenzyme A synthetase gene acs and an acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase gene ACC are excessively expressed, and the output of eriodictyol can finally reach 106.7 mg / L.
Owner:湖南鸿健生物科技有限公司
Protein used for controlling anthocyanidin content, coding gene thereof, and application thereof
ActiveCN102477092BHigh in anthocyaninsHigh nutritional valueViruses/bacteriophagesPlant peptidesBiotechnologyChalcone isomerase
The invention discloses a protein used for controlling the content of anthocyanidin, a coding gene thereof, and an application thereof. The invention discloses a paddy rice chalcone isomerase (CHI), a coding gene thereof, and an application thereof. The protein is represented by the following (1) or (2): (1) a protein composed of an amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2 in a sequence list; (2) a protein with a same activity as that of the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2, wherein the protein is derived from the amino acid residue sequence of SEQ ID No.2 through substitution and / or deletion and / or addition of one or more amino acid residues. The paddy rice CHI gene provided by the invention can be used as a molecular marker and assists in paddy rice seed breeding. The paddy rice CHI gene also has an important value on the study of reasonable utilization of rice hulls.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gene encoding a protein having aurone synthesis activity
InactiveUS20060020123A1Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesGeneChalcone isomerase
The present invention provides a protein having aurone synthase activity involved in the color of flowers such as snapdragons, a gene that encodes it, cDNA in particular, and its applications. This gene can give yellow color to the flowers of plants by introducing into plants deficient in chalcone isomerase and so forth and expressing.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Method for the biotechnological production of flavone glycoside dihydrochalcones
The invention relates to a method for producing flavone glycoside dihydrochalcones, having the following steps: (a) providing a transgenic microorganism containing (i) a first nucleic acid portion (A) containing a gene which codes for a bacterial chalcone isomerase and (ii) a second nucleic acid portion (B) containing a gene which codes for a bacterial enoate reductase, (b) adding one or more flavone glycosides to the transgenic microorganism under conditions which allow the simultaneous isomerization and reduction of the flavone glycoside into the flavone glycoside dihydrochalcone, and optionally (d) isolating and purifying the final product, wherein the nucleic acid portion (A) (1) is a nucleotide sequence according to SEQ ID NO:1, in which the nucleic acid portion (A′) according to SEQ ID NO:3 has been cut out, or (2) is an amino acid sequence according to SEQ ID NO:2, in which the amino acid portion (A′) according to SEQ ID NO:4 has been cut out.
Owner:SYMRISE GMBH & CO KG
Method for biotechnological production of dihydrochalcones
A method for production of a dihydrochalcone, especially of phloretin, using a transgenic microorganism, containing a nucleic acid section (a), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial chalcone isomerase, and / or a nucleic acid section (a′), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a plant chalcone isomerase, and a nucleic acid section (b), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial enoate reductase, corresponding transgenic microorganisms, containing a nucleic acid section (a), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial chalcone isomerase, and / or a nucleic acid section (a′), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a plant chalcone isomerase, and / or a nucleic acid section (b), comprising or consisting of a gene coding for a bacterial enoate reductase, and host cells, containing one or more identical or different such vectors.
Owner:SYMRISE GMBH & CO KG
Chalcone isomerase and coding gene, expression vector, host bacteria and application thereof
The invention provides chalcone isomerase and a coding gene, an expression vector, host bacteria and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The chalcone isomerase provided by the invention is obtained by expression of a chalcone isomerase coding gene obtained by cloning ophiorrhiza japonica for the first time, and the coding gene is connected to the expression vector and transferred to the host bacteria. When the chalcone isomerase coding gene is applied to regulation and control of plant anthocyanin or seed color, regulation and control effects are better, and actual application values are realized.
Owner:GUIZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of ISR mechanism based disease-resistant inductive agent in preventing and treating turfgrass disease
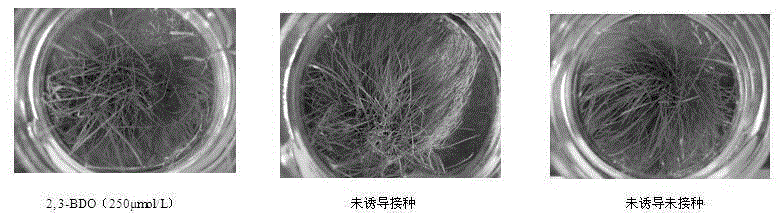
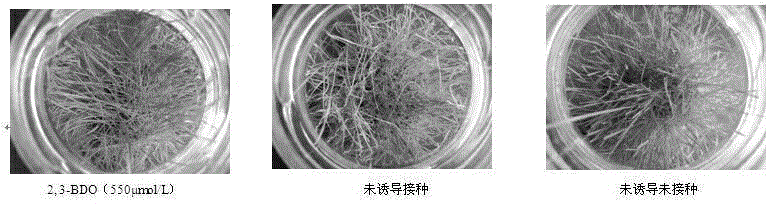
InactiveCN104686512AImprove the immunityAgainst infectionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsDisease2,3-Butanediol
The invention discloses application of an ISR mechanism based disease-resistant inductive agent in preventing and treating turfgrass disease. The inductive agent is a 2, 3-butanediol stereisomer mixture, and can induce the original herbal disease resistance of turfgrass, and has obvious preventing and treating effects on agrostis stolonifera, meadow grass, brown blotch of perennial ryegrass and festuca arundinacea and fusarium blight by applying to the root part with the most proper concentrations (250, 550, 450 and 250 mu mol / L), and the effect of resisting brown blotch can respectively reach 86, 68.5, 73.2 and 81%. When the inductive agent is affected to agrostis stolonifera, the activities of phenylalnine ammonialyase, chalcone isomerase and 4-coumarate coenzyme A ligase are all improved obviously. The inductive agent can obviously increase the content of secondary metabolism products relevant to the agrostis stolonifera resistance, such as total hydroxybenzene, flavones, lignin, can be applied to the prevention and treatment of turfgrass disease, can reduce the use of chemical bactericides, protect the environment, and reduce the turfgrass maintenance expense.
Owner:马晖玲
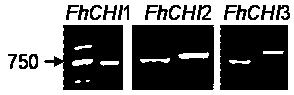
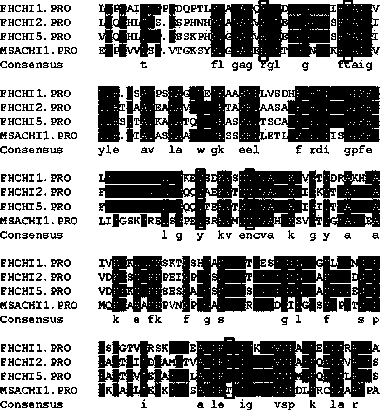
cDNA of chalcone isomerase that controls anthocyanin synthesis in Cymbidium japonica
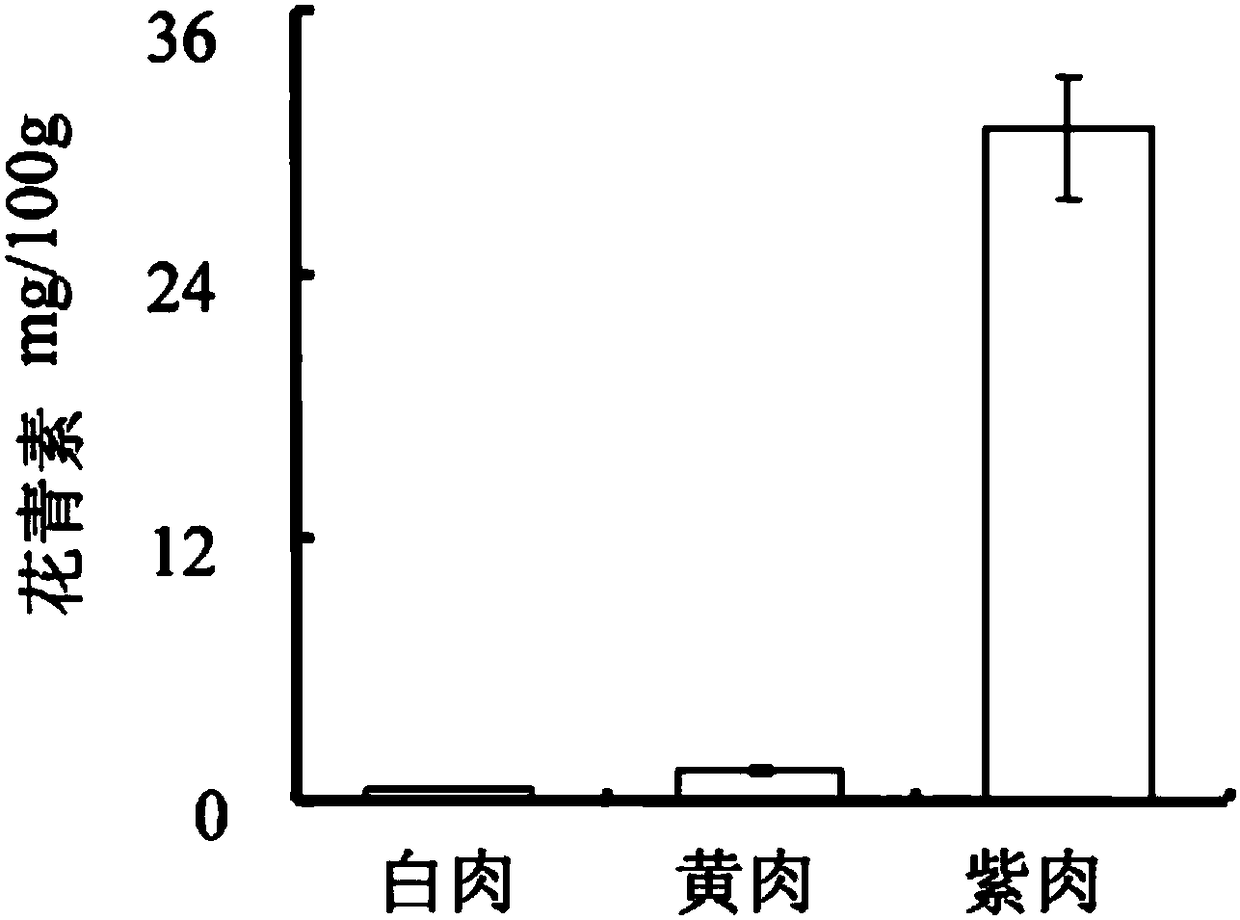
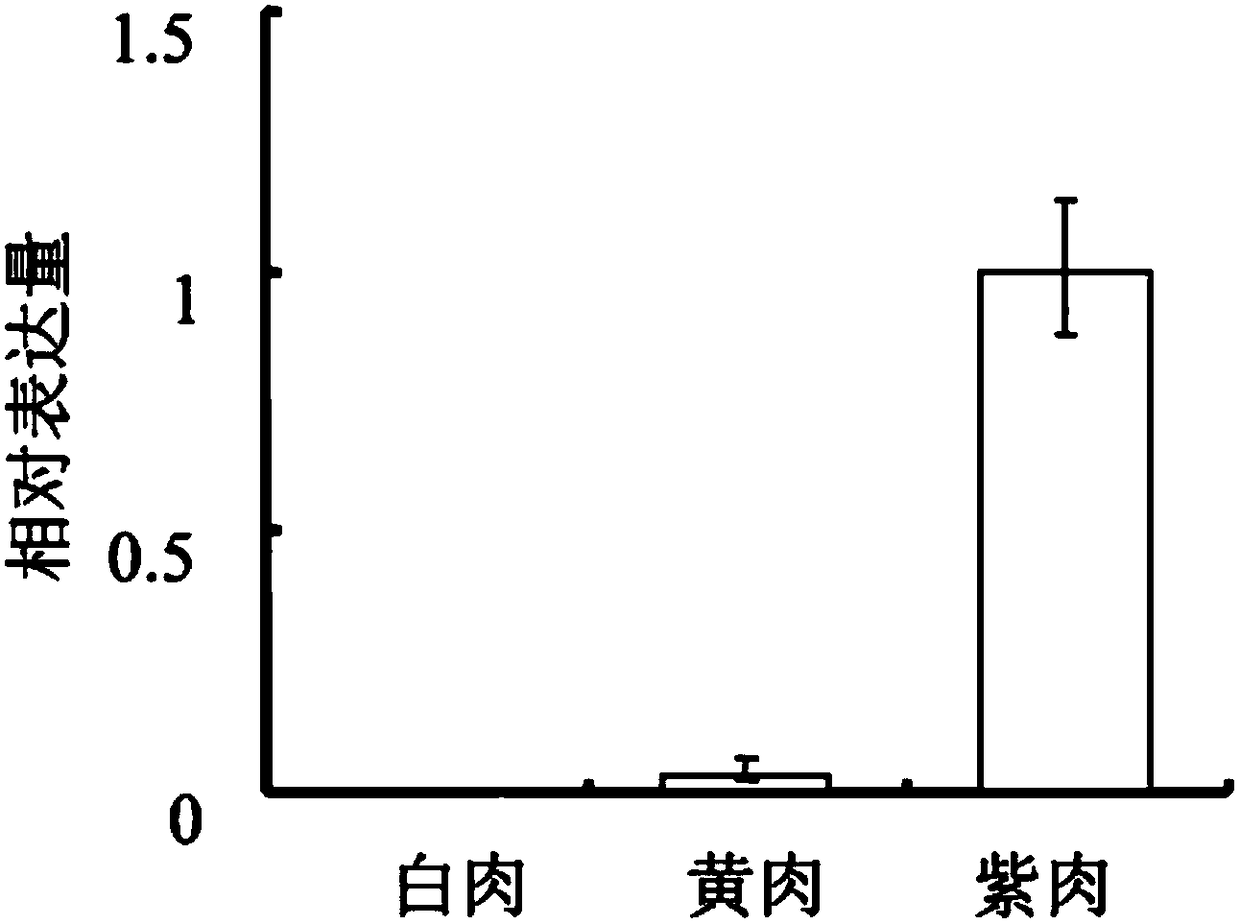
The present invention clones three chalcone isomerase (CHI) cDNAs for the first time from the petals of safflower safflower, and determines its nucleotide sequence and the resulting amino acid sequence. During the flower coloring process of Cymbidium thaliana, the expression of the three genes and the synthesis of anthocyanins showed an obvious correlation. In addition, the three eukaryotic expression vectors of FhCHI were transfected into the CHI mutant of Arabidopsis thaliana, and the seedlings and seed coats of the three FhCHI mutants were both The phenotype was restored.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Eggplant chalcone isomerase smchi protein and its coding gene
ActiveCN104745561BGood anti-oxidant health effectImprove qualityIsomerasesFermentationIsomerase activityPlant quality
The invention discloses eggplant chalcone isomerase SmCHI protein and a coding gene thereof. The protein comprises (a) protein consisting of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.3; or (b) protein derived from the amino acid sequence in (a), which is substituted, lost or added by one or more amino acids and has the activity of eggplant chalcone isomerase. The cDNA and gDNA of the coding gene respectively have base sequences as shown in SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2; and the gene is expressed in roots, stems, leaves, flowers, peels and pulp, and has the expression quantity in peels remarkably higher than that in other tissues. Under stress of low temperature, the expression quantity of the gene reaches the maximal value in 48 hours, which is 3.65 times that of an unprocessed gene. The eggplant chalcone isomerase SmCHI protein and the coding gene thereof provide a theoretical basis for improving plant quality by utilizing the genetic engineering technology to obtain high oxidation resistance medicines or foods in the future, thereby having great application values.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
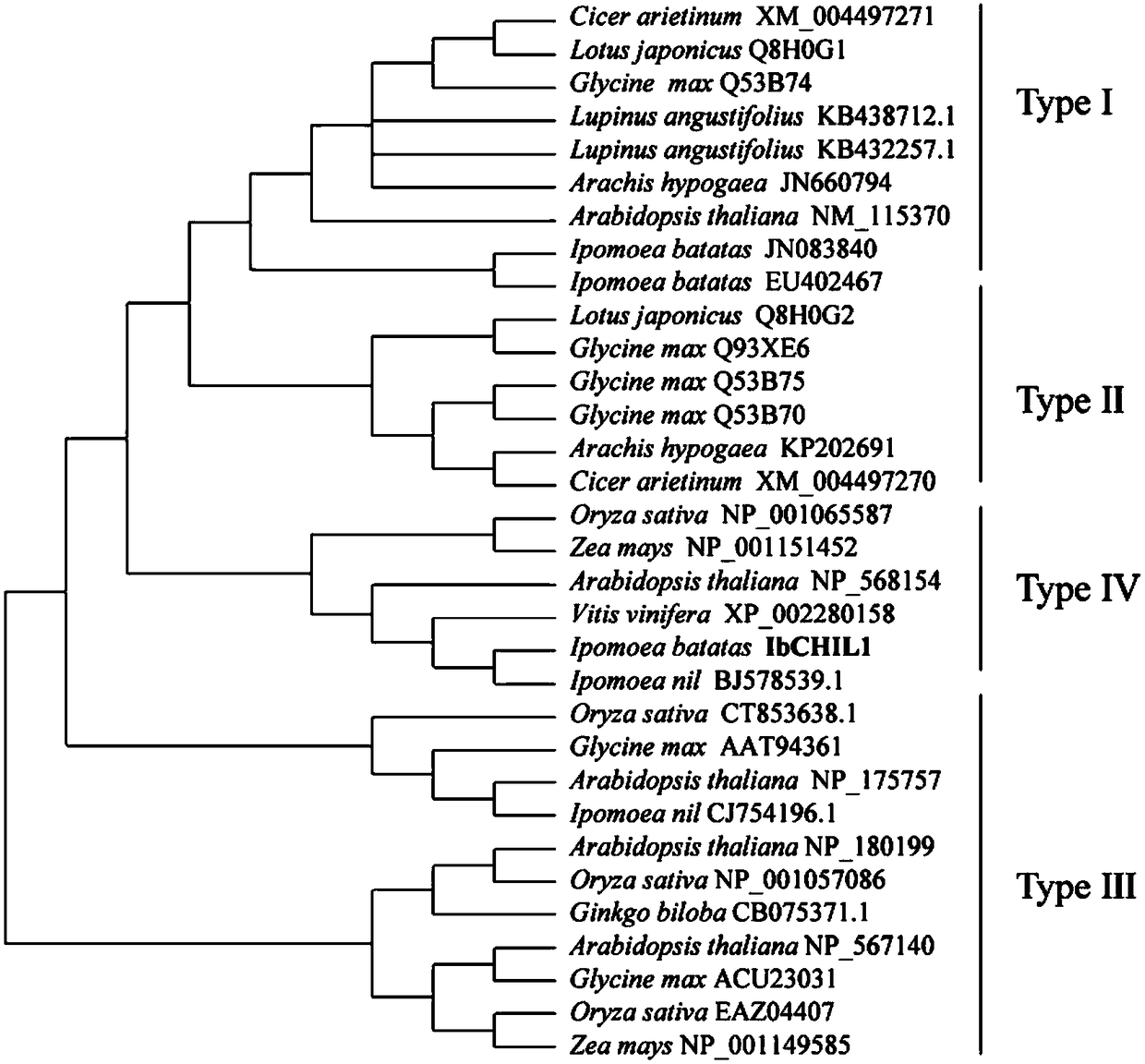
Sweet potato chalcone isomerase IbCHIL1, as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108239650AIncrease content of anthocyaninsHigh economic valueMicrobiological testing/measurementIsomerasesNucleotideNucleotide sequencing
The invention relates to the technical field of plant biology, and particularly relates to sweet potato chalcone isomerase IbCHIL1, as well as a coding gent and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the gene comprises a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO:1, or a nucleotide sequence which is the nucleotide sequence as shown in the SEQ ID NO:1 substituted, lost and / or added with oneor more proteins expressing the same function; or a nucleotide sequence which has more than 90 percent of homology with the nucleotide sequence of (a) or (b) and proteins expressing the same function; the amino acid sequence of the chalcone isomerase IbCHIL1 is as shown in SEQ ID NO:2, or is the amino acid sequence as shown in the SEQ ID NO:2, which is formed by substituting, losing or adding oneor more amino acids and has the same function. The chalcone isomerase gene is transferred into sweet potatoes by a biological technology, or expression of the gene is regulated, so that the content of anthocyanin of sweet potatoes can be increased, and the gene has a wide application prospect and a great economical value.
Owner:海南省农业科学院粮食作物研究所
Trifunctional enzyme for de novo synthesis of flavanone as well as synthesis method and application of trifunctional enzyme
ActiveCN113528471ASimple and fast operationEasy to separateAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid vectorEscherichia coliEnzymatic synthesis
The invention discloses a trifunctional enzyme for de novo synthesis of flavanone, wherein 4-coumaroyl-coenzyme A ligase genes, chalcone isomerase genes and chalcone synthase genes are cloned to a prokaryotic expression vector to construct recombinant plasmids, then escherichia coli is converted to induce expression of recombinase; and then purified recombinase is utilized to establish a cell-free synthesis system, and in-vitro enzymatic synthesis of flavanone is realized. According to the invention, the problems of low yield and low substrate conversion rate in an in-vitro multi-enzyme synthesis system of flavanone are solved, and an in-vitro enzymatic synthesis system with simple components is established at the same time. The system does not have a complex regulation effect in engineering bacteria cells, the reaction process is easy to accurately control, byproducts are few, product separation is relatively simple, the production period is obviously shortened, and the production cost is obviously reduced.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Method for increasing artemisinin content in Artemisia annua by transgenic chi gene
The invention relates to the field of biological technologies and provides a method for increasing content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. by genetic modification with CHI (chalcone Isomerase) genes. According to the method, the CHI genes are cloned from Artemisia annua L., a plant expression carrier containing the CHI genes is established, the CHI genes are mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens to be transferred into Artemisia annua L. for regeneration of a plant, the integration condition of an exogenous target gene CHI is detected through the PCR (polymerase chain reaction), the content of artemisinin in transgenic Artemisia annua L. is detected through an HPLC-ELSD (high performance liquid chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector), and the transgenic Artemisia annua L. plant with the content of artemisinin increased is screened out. The content of artemisinin in transgenic Artemisia annua L. is increased and is 1.5 times that of a non-transgenic contrast plant in the highest level, and the method for increasing the content of artemisinin in Artemisia annua L. is provided and lays a foundation for large-scale production of artemisinin from transgenic Artemisia annua L..
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Safflower Chalcone Isomerase Chi Gene and Its Application
InactiveCN103820478BEasy to synthesizeReduce flavonoid contentFermentationGenetic engineeringBiotechnologyComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention discloses a safflower chalcone isomerase (CHI) gene. The RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of safflower pedals is reversely transcribed into a cDNA (Complementary Deoxyribonucleic Acid), the cDNA is used as a template to carry out 3' and 5' race cloning, the 3' and 5' end sequences of the safflower CHI gene are respectively obtained, a safflower CHI sequence is obtained through splicing of the 3' and 5' end sequences, the whole gene length is 1161bp, and the length of an opening reading frame is 654bp. The safflower CHI gene is named ct-(i)CHI( / i), and the result of the sequence comparison and analysis of the safflower CHI gene on ncbi (National Center for Biotechnology Information) shows that the homology of the gene with a dutchmanspipe root CHI gene reaches 82%. Experiments show that the synthesis of flavone can be promoted by the over-expression ct-(i)CHI( / i) gene, the flavone content can be lowered after the ct-(i)CHI( / i) gene is inhibited, and the safflower CHI gene has wide prospects in the aspect of cultivating high-content flavonoids transgenic plants.
Owner:JILIN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
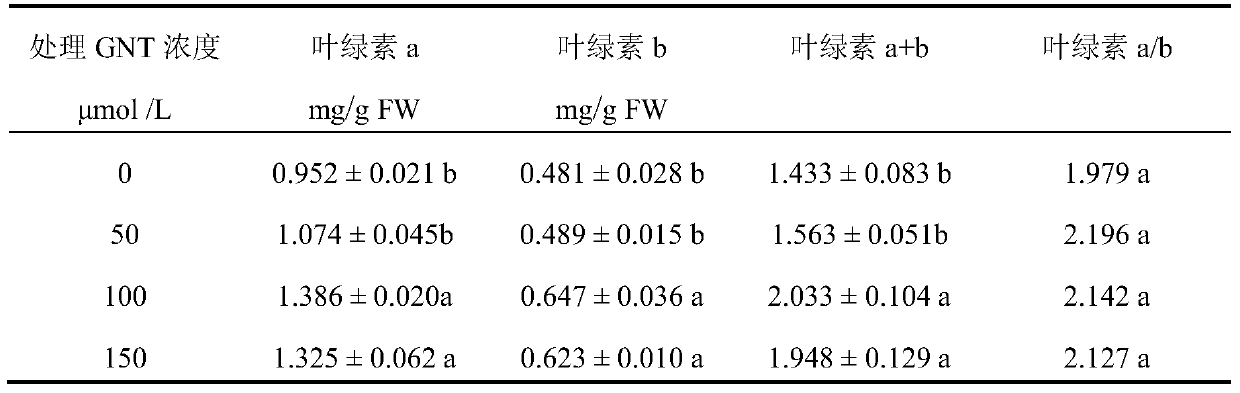
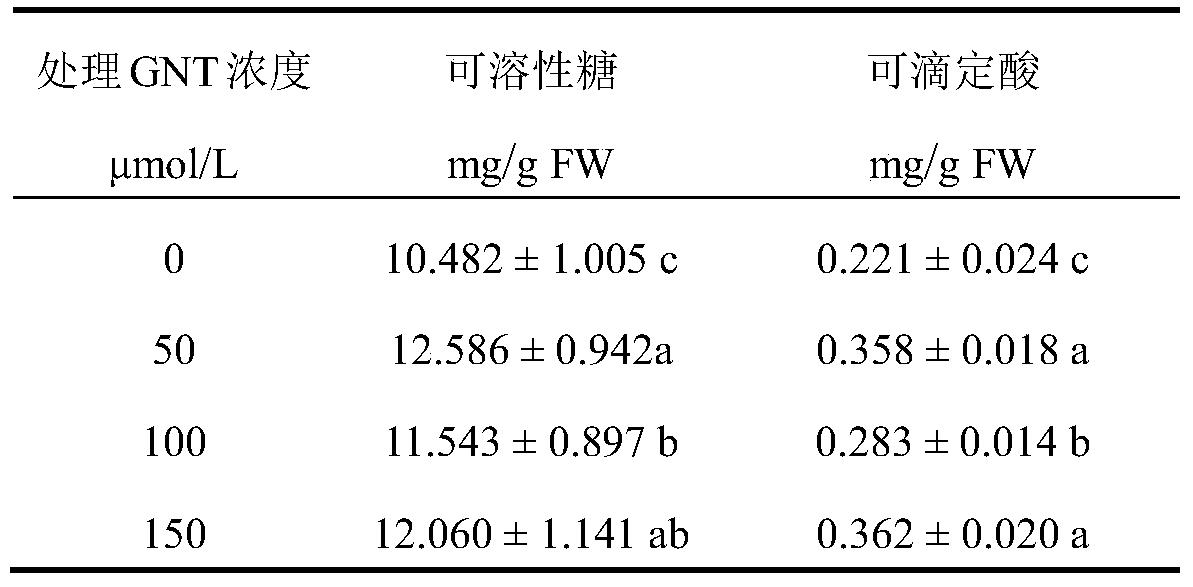
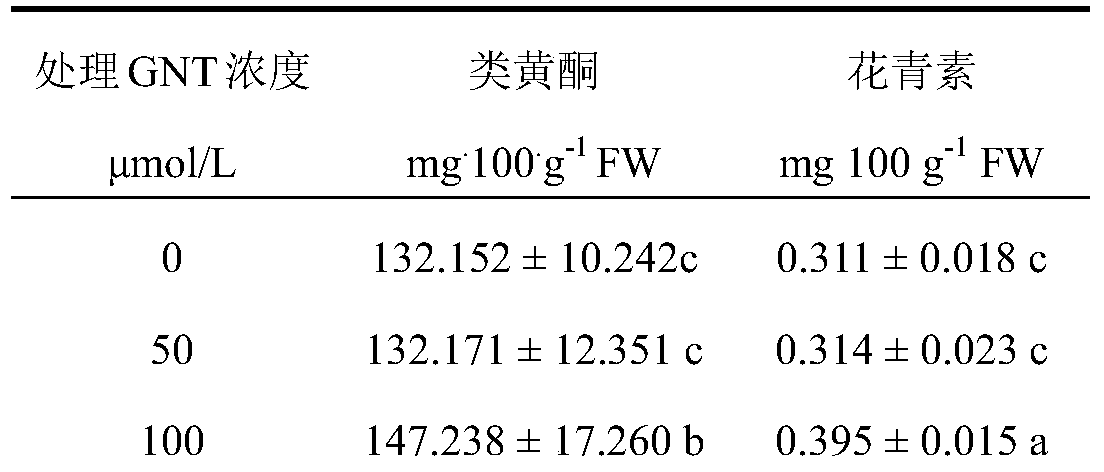
A method for increasing ginkgo flavonoid content and application of genistein
InactiveCN105432343BChanges in physiological metabolismPromote photosynthesisHorticulture methodsGinkgo bilobaGenistein
Owner:YANGTZE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com